Ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) derived from Klebsiella oxytoca, and coding gene and application thereof
A technology of ribitol dehydrogenase and Klebsiella, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of poor bacterial substrate specificity, no involvement in the production of allicitol, etc., and achieve low pollution, The effect of small amount of NAD and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1, expression of ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH)
[0049] The expression method of ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) of the present invention may comprise the following steps:
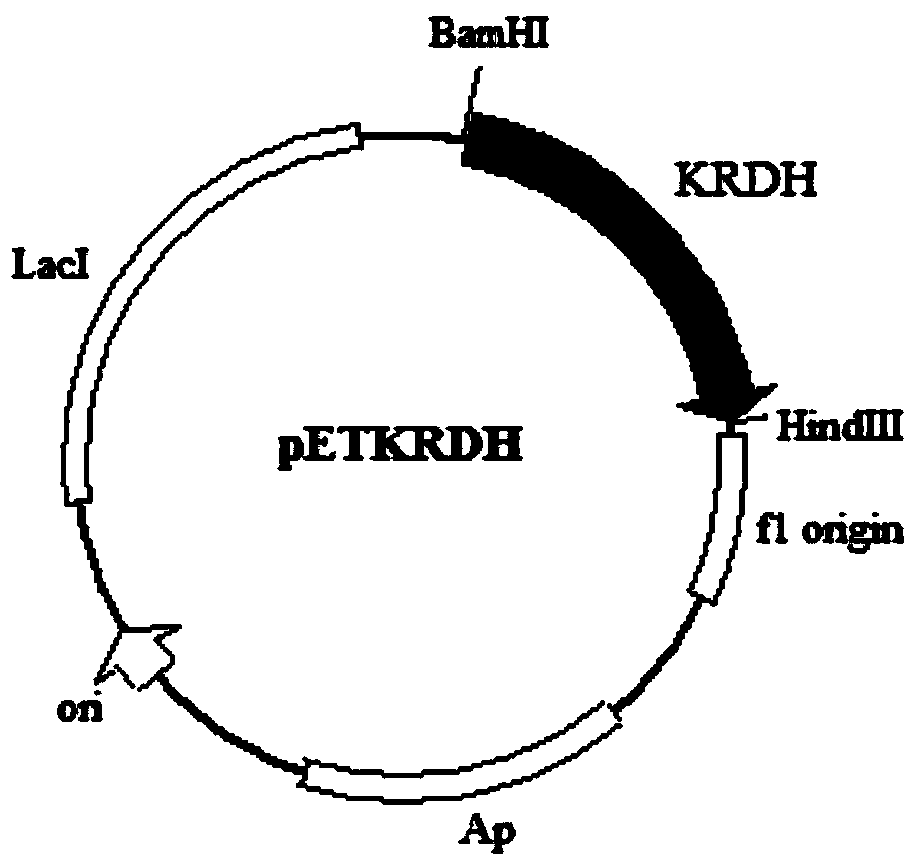
[0050] 1) Obtaining the ribitol dehydrogenase gene (RDH): using the genomic DNA of Klebsiella oxytoca G4A4 with the deposit number CGMCC No.7662 as a template, in primer 1:
[0051] 5'-CG GGATCC ATGAATACTTCCCCTTAGC-3' (sequence 3 in the sequence listing, the underlined base is the BamH I restriction site) and primer 2: 5'-CCC AAGCTT Under the guidance of GAGATCCACGCTGTTCG-3' (sequence 4 in the sequence listing, the underlined base is the Hind III restriction site), the ribitol dehydrogenase gene (RDH) was amplified by PCR, and the PCR reaction system was: acid-producing Klebsiella Bacteria (Klebsiella oxytoca) G4A4CGMCC No.7662 genomic DNA 1μl, 10×PCR buffer 5μl, 2mM dNTP 5μl, 10mM primer 11μl, 10mM primer 21μl, high-fidelity DNA polymerase 0.5μl, add water to make up to a total volume of 50...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, using ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) to convert and produce allicitol
[0056] 1) Collect the bacteria in Example 1 by centrifugation, and use 50mL pH8.0, 50mM Tris-HCl buffer solution (recipe: 50mM Tris aqueous solution, adjust the pH to 8.0 with hydrochloric acid) [phosphate buffer solution (recipe: 50mM hydrogen phosphate Aqueous solution of disodium and sodium dihydrogen phosphate, pH 8.0) or HEPES buffer solution (recipe: 50mM HEPES aqueous solution, pH 8.0 adjusted with sodium hydroxide) can also be] resuspended bacteria, sonicated, centrifuged at 15000rpm for 30min to collect The clear liquid is the crude enzyme liquid. The crude enzyme solution is purified by affinity chromatography and ion exchange chromatography to obtain pure enzyme (purity over 95%).
[0057] 2) Add ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) crude enzyme solution or purified ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) to pH 8.0, 50mM Tris-HCl buffer (phosphate buffer or HEPES buffer is also acceptable) , the ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3, using ribitol dehydrogenase (RDH) to convert and produce allicitol
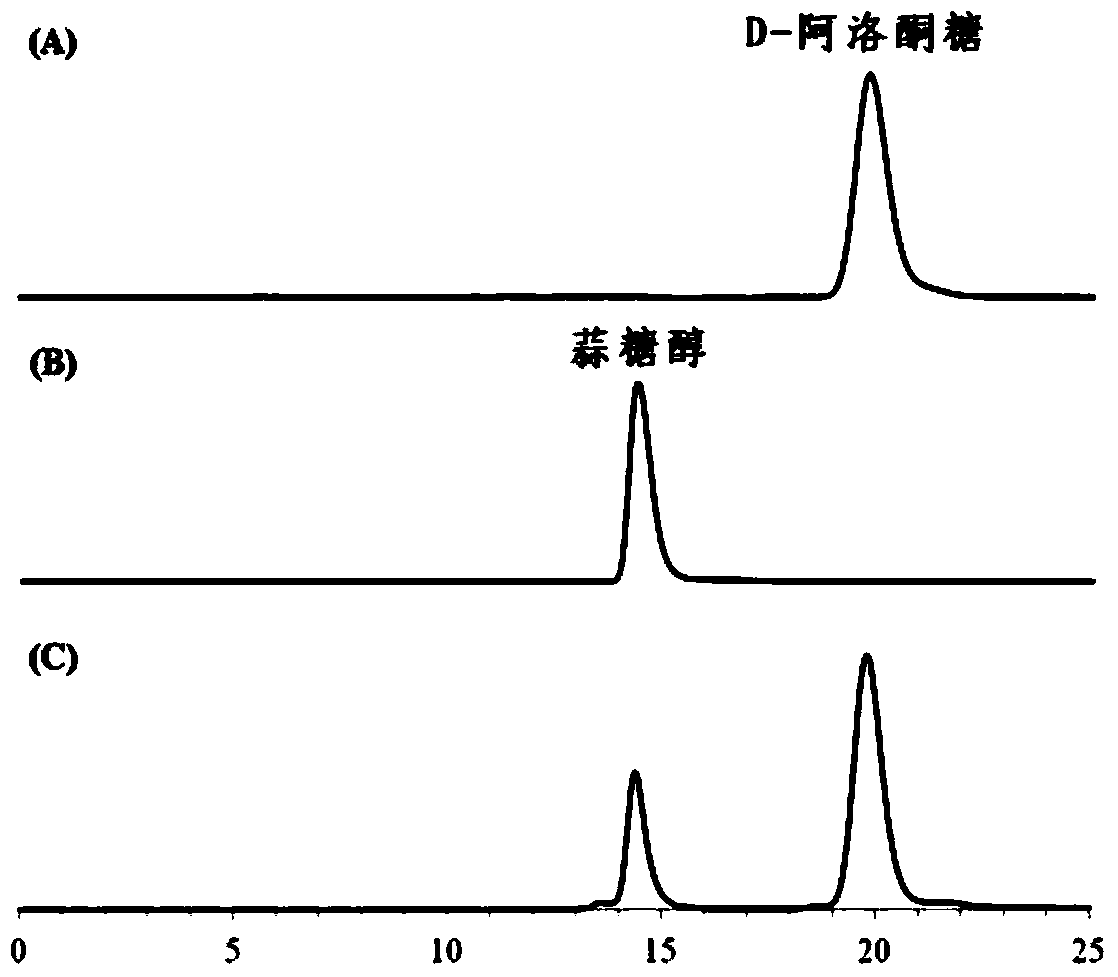
[0062] The method is the same as in Example 2, except that the concentration of D-psicose in the allicitol conversion reaction system is 3% (mass / volume percent concentration, g / 100ml), and the concentration of sodium formate in the NADH regeneration system is 200mM.
[0063] The reaction process curve of ribitol dehydrogenase purified protein and concentration of 3% substrate D-psicose and 200mM sodium formate is as follows Figure 4 As shown, after 48 hours of reaction, the conversion rate of allicitol reached 90.1%, and the conversion rate continued to prolong the reaction time, and the conversion rate did not change, indicating that the reaction had reached equilibrium.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com