Method for preparing glucaric acid through whole-cell transformation
A technology for whole-cell transformation and glucaric acid, which is applied in the field of whole-cell transformation to prepare glucaric acid, can solve the problems of expensive catalyst, high nitric acid oxidation process cost, low yield, etc. Single ingredient and mild production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0031] The Udh genomes derived from Pseudomonas synxantha strain KENGFT3 (Pseudomonas synxantha strain KENGFT3) and Pseudomonas fragilis P121 (Pseudomonas fragi strain P121) were respectively used as templates for PCR amplification reactions, and the amplified fragments were used with SalI, NotI and NdeI, XholI endonuclease was connected to the expression vector pETDuet-1 to construct the plasmid pETDuet-2×Udh, primers F1, R1, F2, R2, the primers are as follows
[0032] F1: 5'-ATGCGTCCGGCGTAGA-3'
[0033] R1: 5'-GATTATGCGGCCGTGTACAA-3'
[0034] F2: 5'-TTGTACACGGCCGCATAATC-3'
[0035] R2: 5'GCTAGTTATTGCTCAGCGG3'
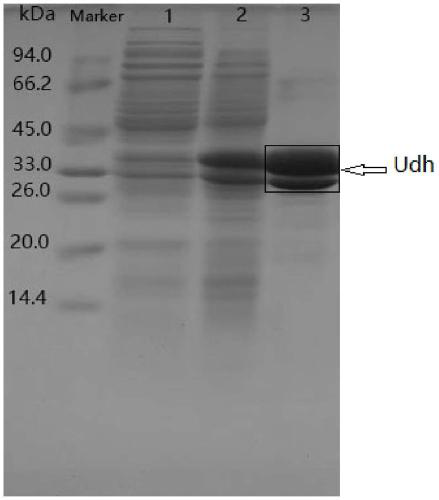
[0036] ①Transform the expression vector into the host strain E.coli BL21(DE3), smear / streak the recombinant strain on a plate containing ampicillin resistance, select positive clones, and verify by extracting the plasmid for enzyme digestion and electrophoresis , to obtain the recombinant Esc...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: High-density fermentation culture of recombinant Escherichia coli pETDuet-2×Udh
[0040] Seed medium (LB): yeast extract powder 5g / L, tryptone 10g / L, sodium chloride 10g / L.
[0041] Fermentation medium: glucose 25g / L, tryptone 7g / L, ammonium sulfate 3.5g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.55g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 3.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 3.5g / L.
[0042] In Example 1, single colonies were picked from the LB plate containing ampicillin antibiotic resistance, inoculated into a 25mL test tube containing 5mL of medium, 37°C, 220rpm, and cultivated for 12h to obtain the seed solution of recombinant Escherichia coli; by 1% The amount of inoculum inoculated the seed liquid into a 1L shake flask with 250mL of fermentation medium, the concentration of ampicillin finally reached 100μg / mL, adjusted the pH to 7, and continued to cultivate at 37°C and 220rpm until OD 600 When the value reaches 0.6, add IPTG to make the final concentration reach 0.4mM, cult...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: the method for preparing glucaric acid by transformation of whole cells
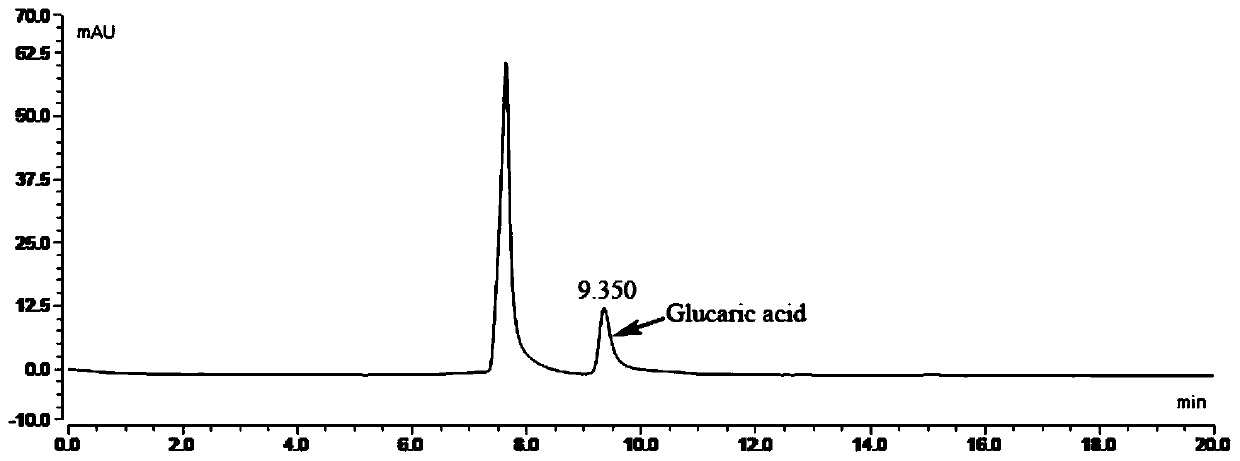
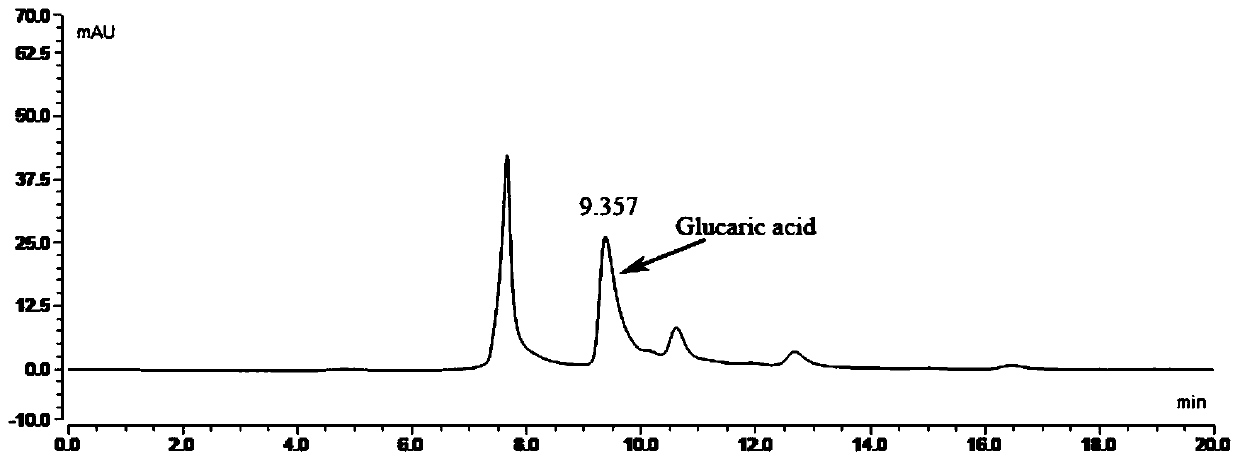
[0044] The recombinant Escherichia coli fermentation broth obtained in Example 2 was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 15 minutes to recover the Escherichia coli sludge I, resuspended the bacteria sludge I with the washing liquid and centrifuged again to obtain the bacteria sludge II; take 5-10 g of the bacteria sludge II and add 1000 mL The reaction solution (in the reaction solution, MOPS is 20.9g, and the initial amount of glucuronic acid is 2g) is placed in a 2.5L shake flask, and the reaction is stirred at a low speed at 37°C for 24 hours. During the reaction, the decrease of the substrate glucuronic acid is detected. Amount, after the reaction finishes, detect the content of glucaric acid in the conversion solution by MS and HPLC, the result is: the conversion solution containing glucaric acid is 1.5g / L.
[0045] The HPLC method for detecting glucaric acid in the conversion solution ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com