Biological preparation method of mannitol
A technology of mannitol and derivatives, applied in the field of biological preparation of mannitol, can solve the problems of difficult metabolic transformation, metabolic by-products, low selectivity of chemical catalysis, single mannitol and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] Embodiment 1: Enzyme activity assay in the enzymatic synthesis pathway of mannitol
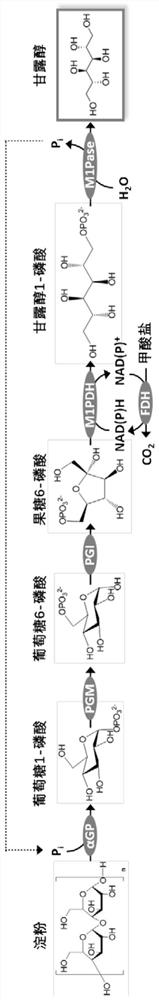
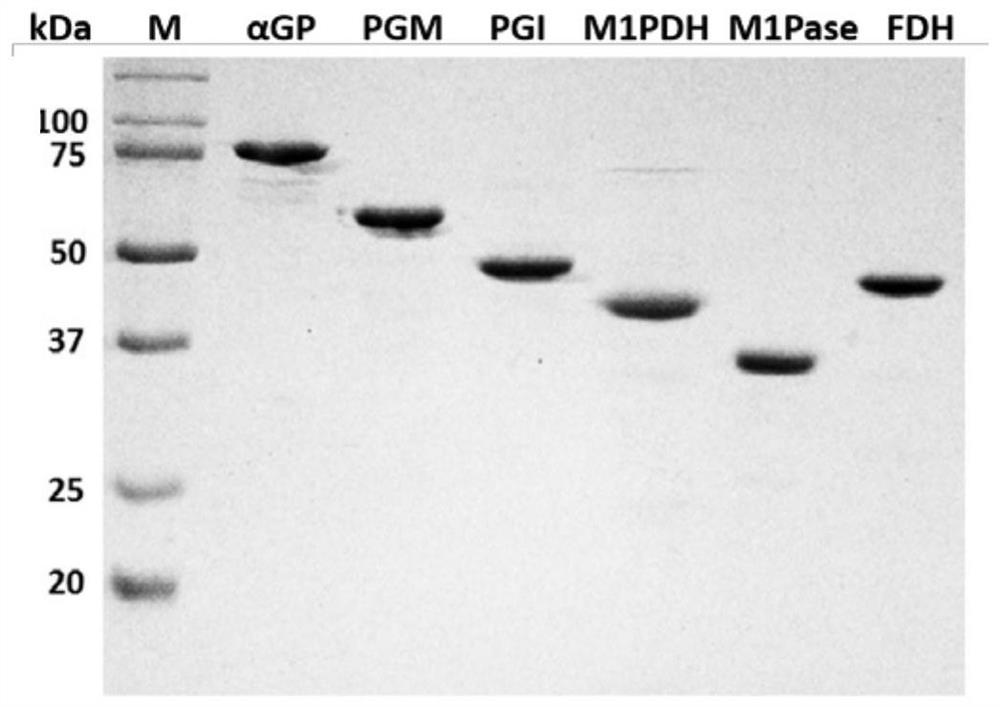
[0137] Catalytic pathway for the conversion of starch to mannitol by an in vitro multi-enzyme catalytic system see figure 2 . In this example, (1) starch phosphorylase (α-glucan phosphorylase, EC 2.4.1.1, αGP) is derived from Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli, UniProt number P00490); (2) glucose phosphomutase (phosphoglucomutase, EC 5.4.2.2, PGM) is derived from Clostridium thermocellum (Clostridium thermocellum, UniProt number A3DEW8); (3) phosphoglucose isomerase (phosphoglucose isomerase, EC 5.3.1.9, PGI) is derived from Clostridium thermocellum (Clostridium thermocellum , UniProt number A3DBX9); (4) Mannitol 1-phosphate 5-dehydrogenase (mannitol1-phosphate 5-dehydrogenase, EC 1.1.1.17, M1PDH) derived from Escherichia coli (Escherichiacoli, UniProt number P09424); (5) Mannitol 1 -Phosphatase (mannitol 1-phosphatase, EC 3.1.3.22, M1Pase) derived from Eimeria tenella (UniProt number...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Example 2: Synthesis of mannitol from soluble starch catalyzed by multiple enzymes in vitro
[0150] In this example, enzymes are used to catalyze the synthesis of mannitol from soluble starch in vitro. First, six kinds of enzymes were recombinantly expressed (Example 1): αGP derived from Escherichia coli, PGM derived from Clostridium thermocellum, PGI derived from Clostridium thermocellum, M1PDH derived from Escherichia coli, derived from A. tenenella M1Pase from Coccidia, FDH from Thiobacillus.
[0151] Mannitol was quantitatively analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The chromatographic column used was Bio-Rad Aminex HPX-87H, the mobile phase was 5mM sulfuric acid, the flow rate was 0.6mL / min, the column temperature was 60°C, and the detector used was a differential refractive index detector. Standard sample testing such as Figure 4 As shown in A, the retention time of mannitol is about 10.0 minutes. The concentration of mannitol is directly...
Embodiment 3
[0155] Example 3 In vitro multi-enzyme catalyzed synthesis of mannitol from soluble starch treated with isoamylase
[0156] Starch is a polysaccharide linked by α-1,4 and α-1,6 glycosidic bonds, which cannot be completely phosphorylated by starch phosphorylase. Isoamylase (IA, EC 3.2.1.68) can hydrolyze α-1,6 glycosidic bonds in starch, thereby helping starch phosphorylase to phosphorylate substrates and increasing the yield of mannitol.
[0157] In this example, the isoamylase is derived from Sulfolobus tokodaii (Sulfolobus tokodaii, UniProt number Q973H3). The expression vector pET20b-StIA reported in the literature (Cheng et al.2015. Scientific Reports 5:13184.) was introduced into E. coli BL21(DE3), and recombinant E. coli BL21(DE3) / pET20b-StIA, BL21 containing pET20b-StIA was obtained. (DE3) / pET20b-StIA can express the recombinant isoamylase StIA-his shown in sequence 7 in the sequence list. The protein expression of the recombinant isoamylase StIA-his was carried out a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com