Method for producing single-cell protein by microbial fermentation
A single-cell protein and microbial fermentation technology, applied in the methods of using microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as loss of active nitrogen, reduce the level of active nitrogen, achieve resource recovery, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] A method for acclimating microorganisms that can be used to produce single-cell proteins, the specific steps are as follows:
[0086] 1) configure the basal medium, add 15g / L agar after sterilization; the formula of the basal medium is to contain the following amount of substances in every liter of solution: potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2.3g, disodium hydrogen phosphate 2.9g, chloride Ammonium 1g, magnesium sulfate 0.5g, sodium carbonate 0.5g, calcium chloride 0.01g, ferric ammonium citrate 0.05g, boric acid 0.6mg, cobalt chloride 0.4mg, zinc sulfate 0.2mg, manganese chloride 0.06mg, sodium molybdate 0.06mg, nickel chloride 0.04mg, copper sulfate 0.02mg;
[0087] 2) inoculation of anaerobic microorganisms and aerobic microorganisms;
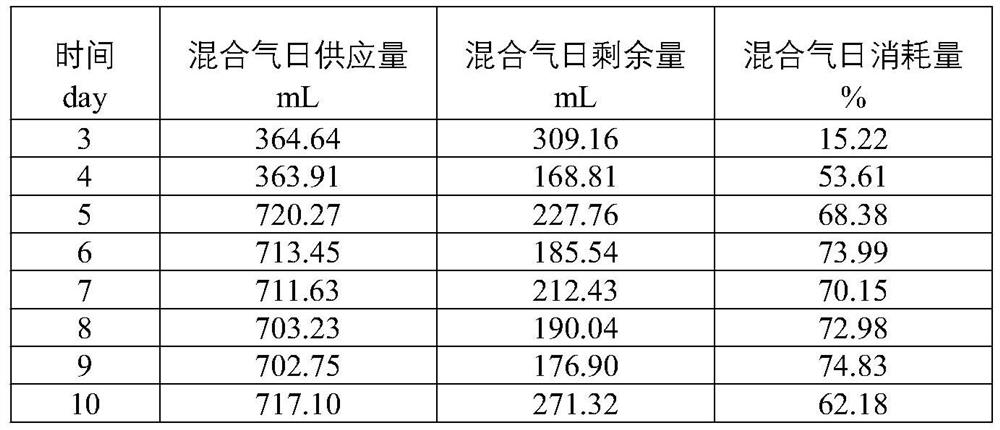
[0088] 3) Adjust the temperature and pH of the domestication system, and the volume ratio of the feed is H 2 :O 2 :CO 2 = 60:25:15 mixed gas, reacted in the shaker reactor;
[0089] 4) Supplement the mixed gas to the reaction system t...
Embodiment 2
[0097] A method for efficiently producing single-cell protein by microbial fermentation, the specific steps are as follows:
[0098] 1) Configure the basal medium, add NH after sterilization 4 Cl to the initial nitrogen content in the system is 1000mgN / L; The formula of described basal medium is to contain the following amount of material in every liter of solution: Potassium dihydrogen phosphate 2.3g, disodium hydrogen phosphate 2.9g, ammonium chloride 1g, sulfuric acid Magnesium 0.5g, sodium carbonate 0.5g, calcium chloride 0.01g, ferric ammonium citrate 0.05g, boric acid 0.6mg, cobalt chloride 0.4mg, zinc sulfate 0.2mg, manganese chloride 0.06mg, sodium molybdate 0.06mg, chlorine Nickel 0.04mg, copper sulfate 0.02mg;
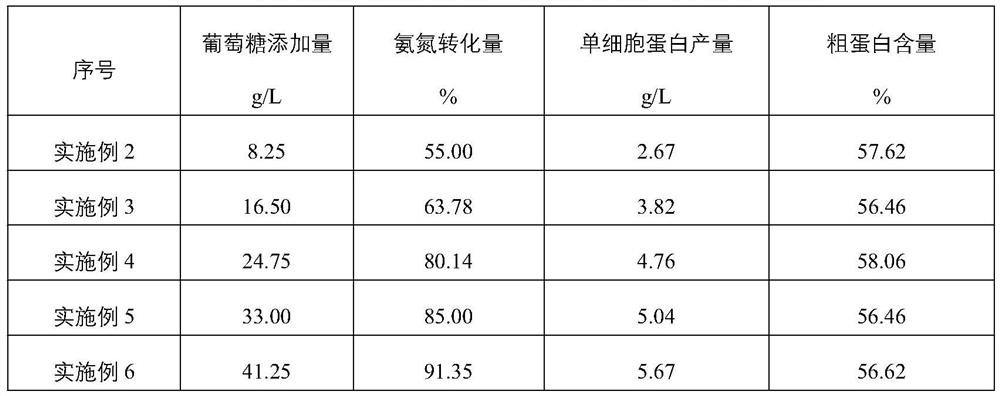
[0099] 2) Add glucose to the medium, and the amount of glucose added is 8.25g / L;
[0100] 3) Regulate temperature and pH, feed volume ratio is H 2 :O 2 :CO 2 = 60: 25: 15 mixed gas, reacted in the shaker reactor;
[0101] 4) Supplement the mixed gas to ...
Embodiment 3
[0108] Repeat Example 2, the difference is only: in step 2), the added amount of glucose is 16.50g / L.
[0109] The amount of ammonia nitrogen conversion and the yield of single-cell protein of microorganisms in the fermentation system of this example are shown in Table 2. As can be seen from Table 2, the amount of ammonia nitrogen conversion and single-cell protein production in the fermentation system of this embodiment are higher than that of Example 2, and the crude protein content in the product is close to that of Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com