Patents
Literature
88 results about "Cell growth inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mesothelioma therapeutic agent
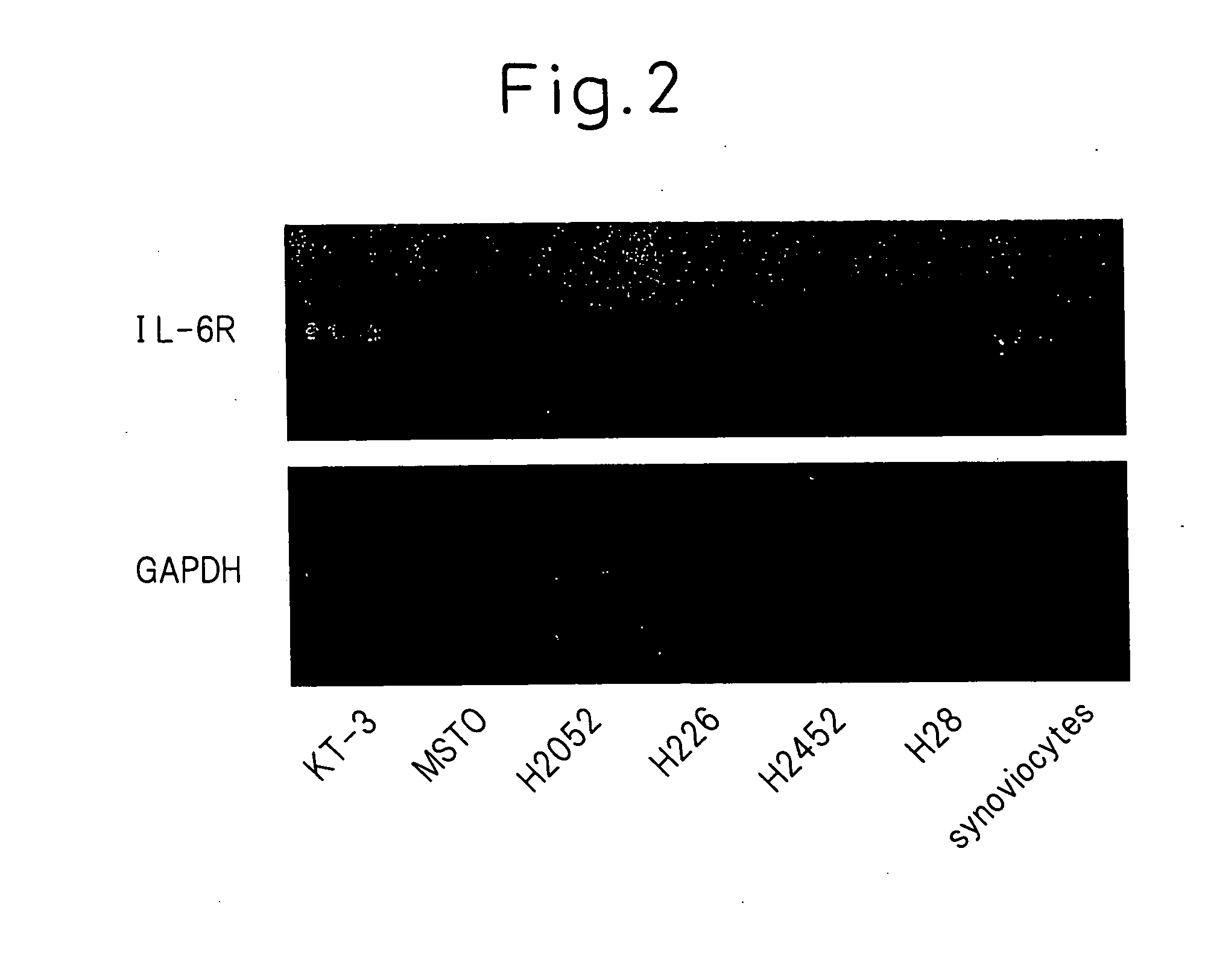
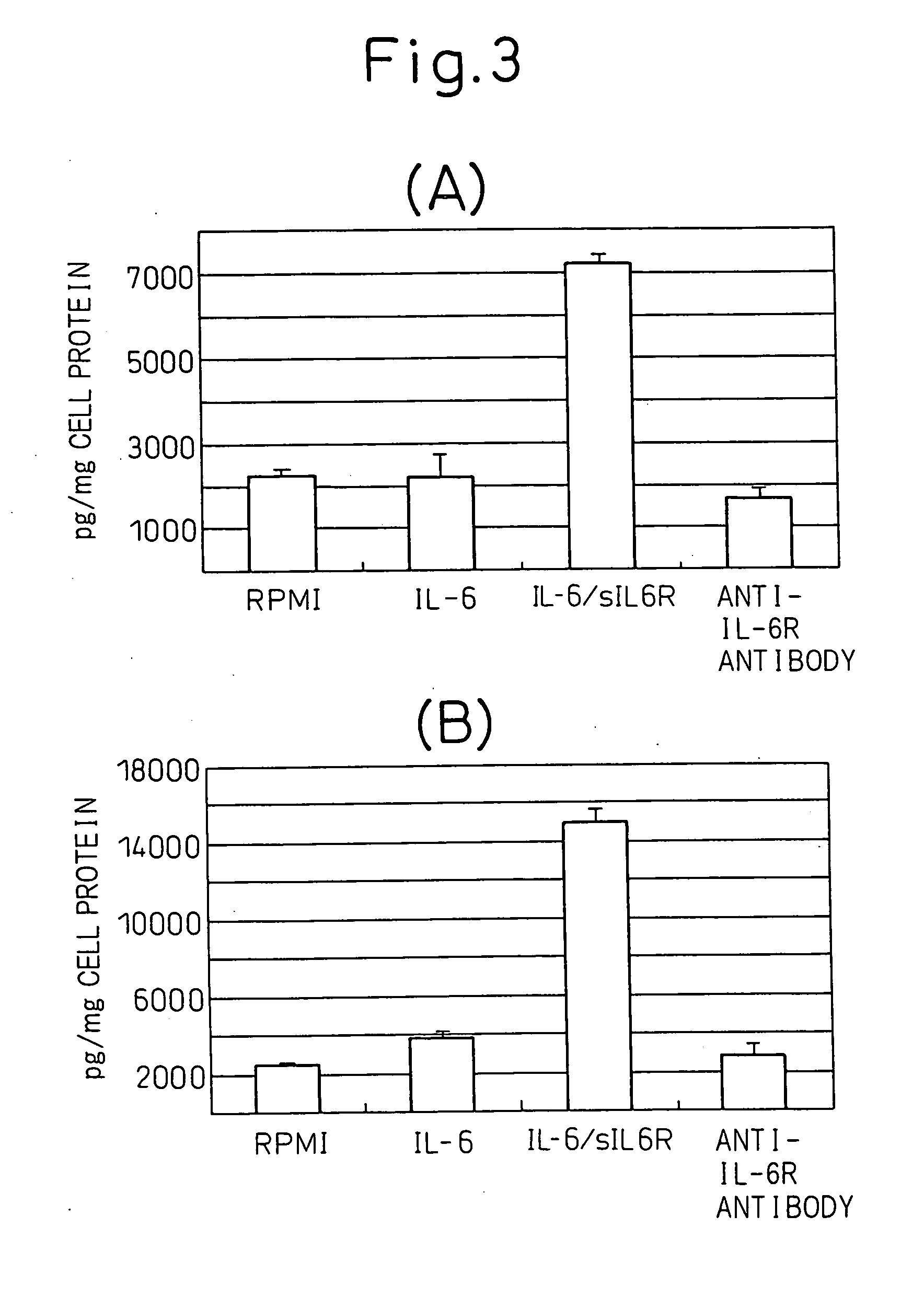
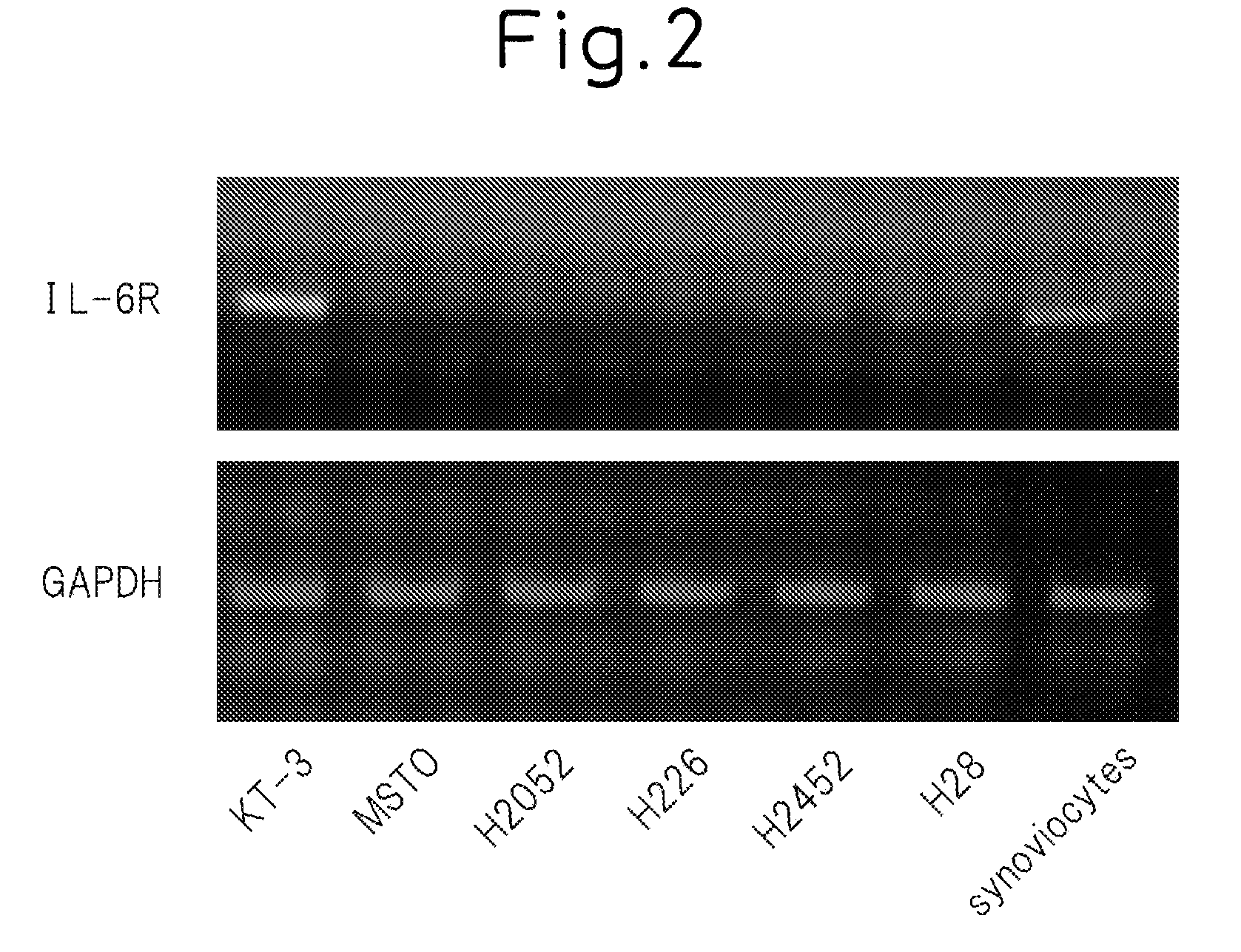
InactiveUS20070134242A1Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsInterleukin 6Mesothelioma
The present invention provides a mesothelioma therapeutic agent containing an interleukin-6 (IL-6) antagonist such as antibody to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), and a mesothelioma cell growth inhibitor containing an IL-6 antagonist such as antibody to IL-6R.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
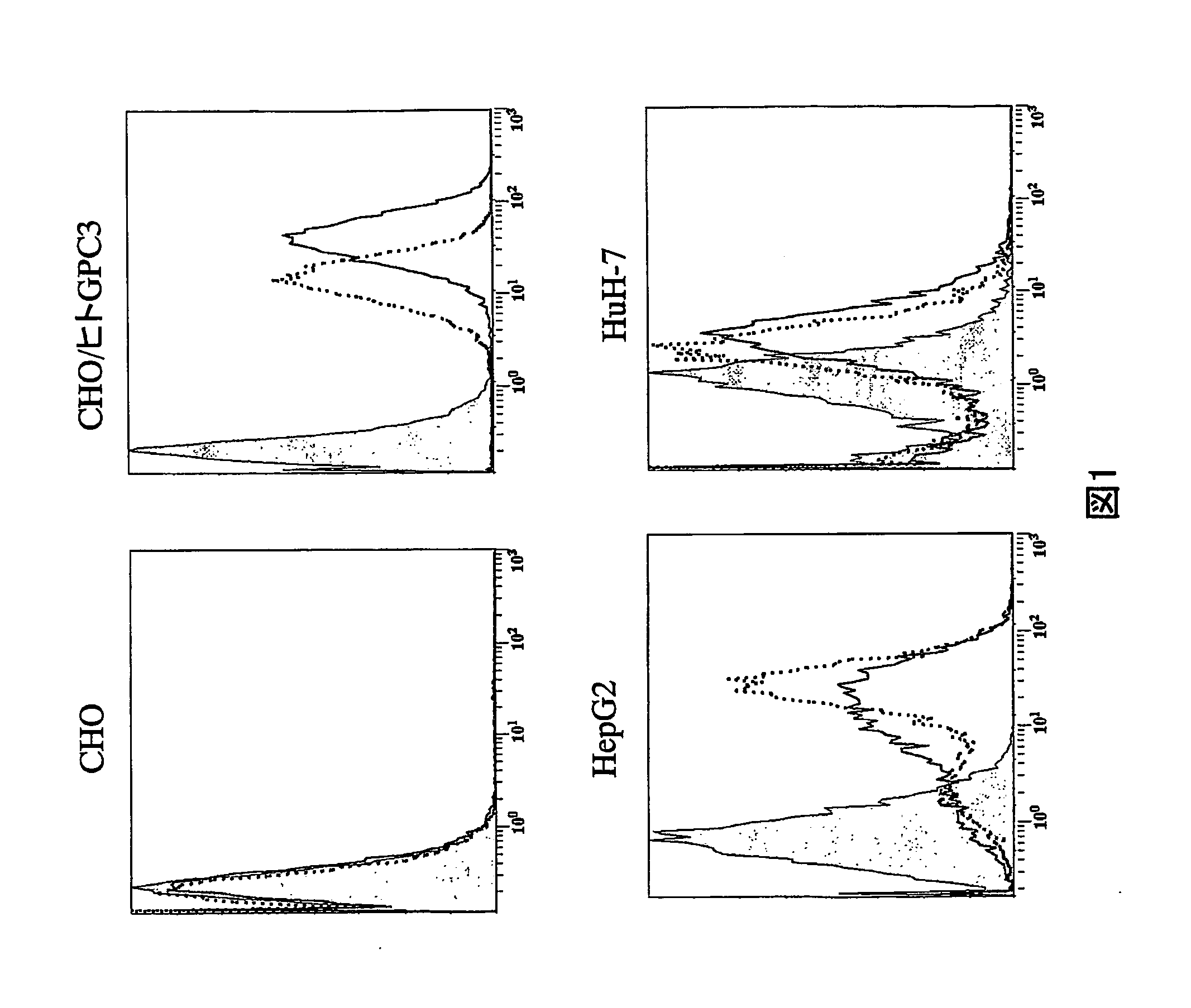
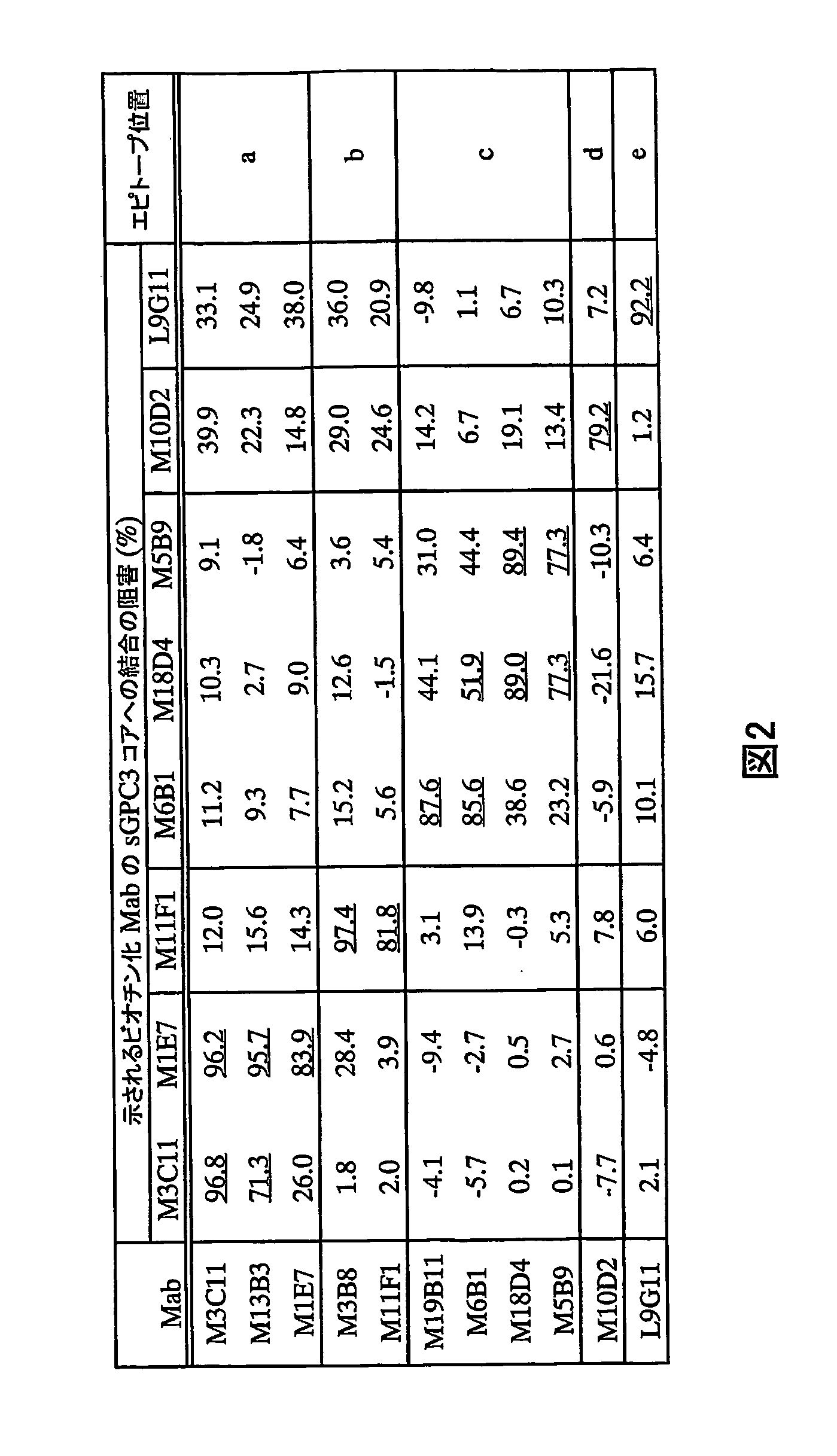
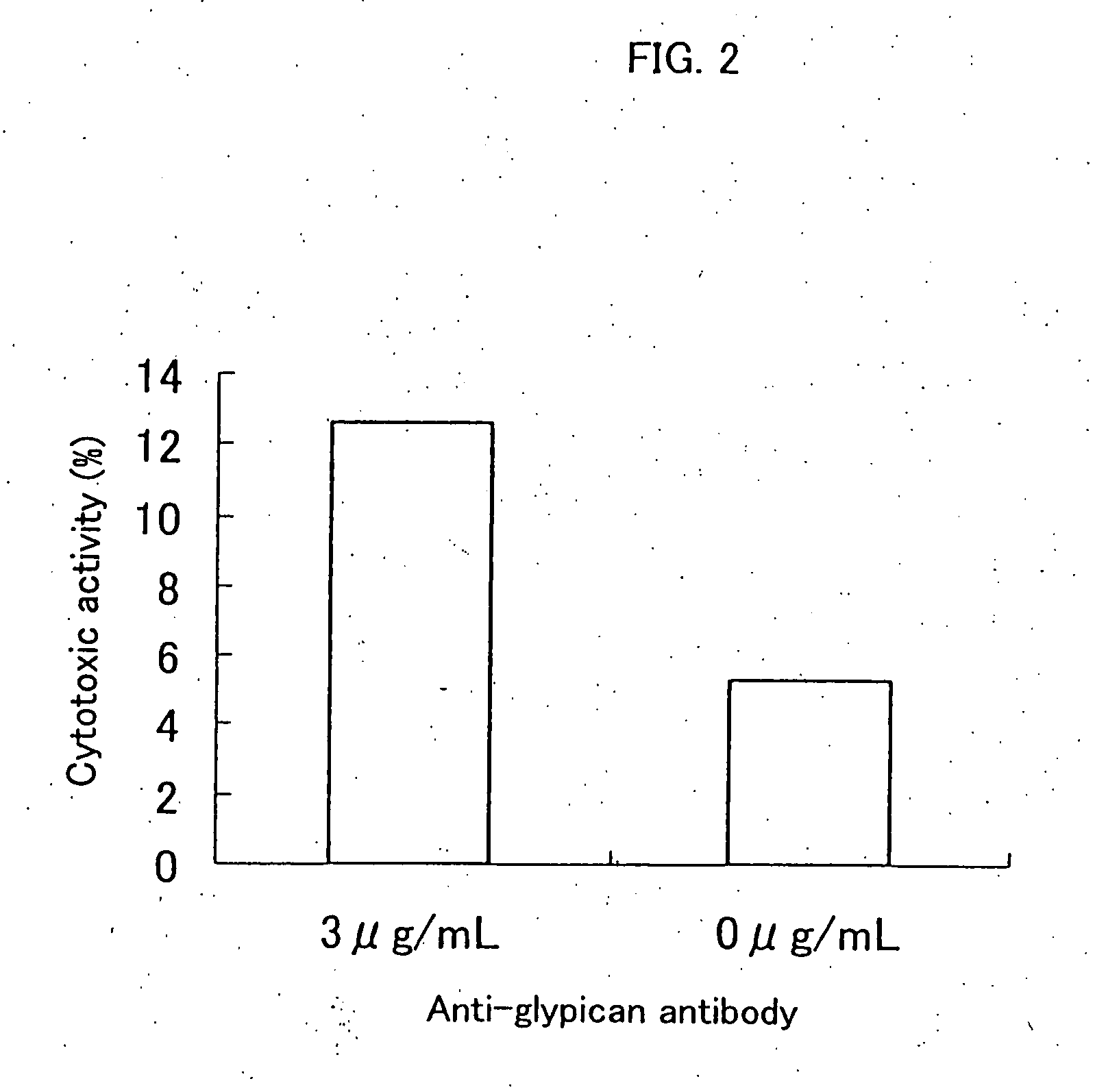
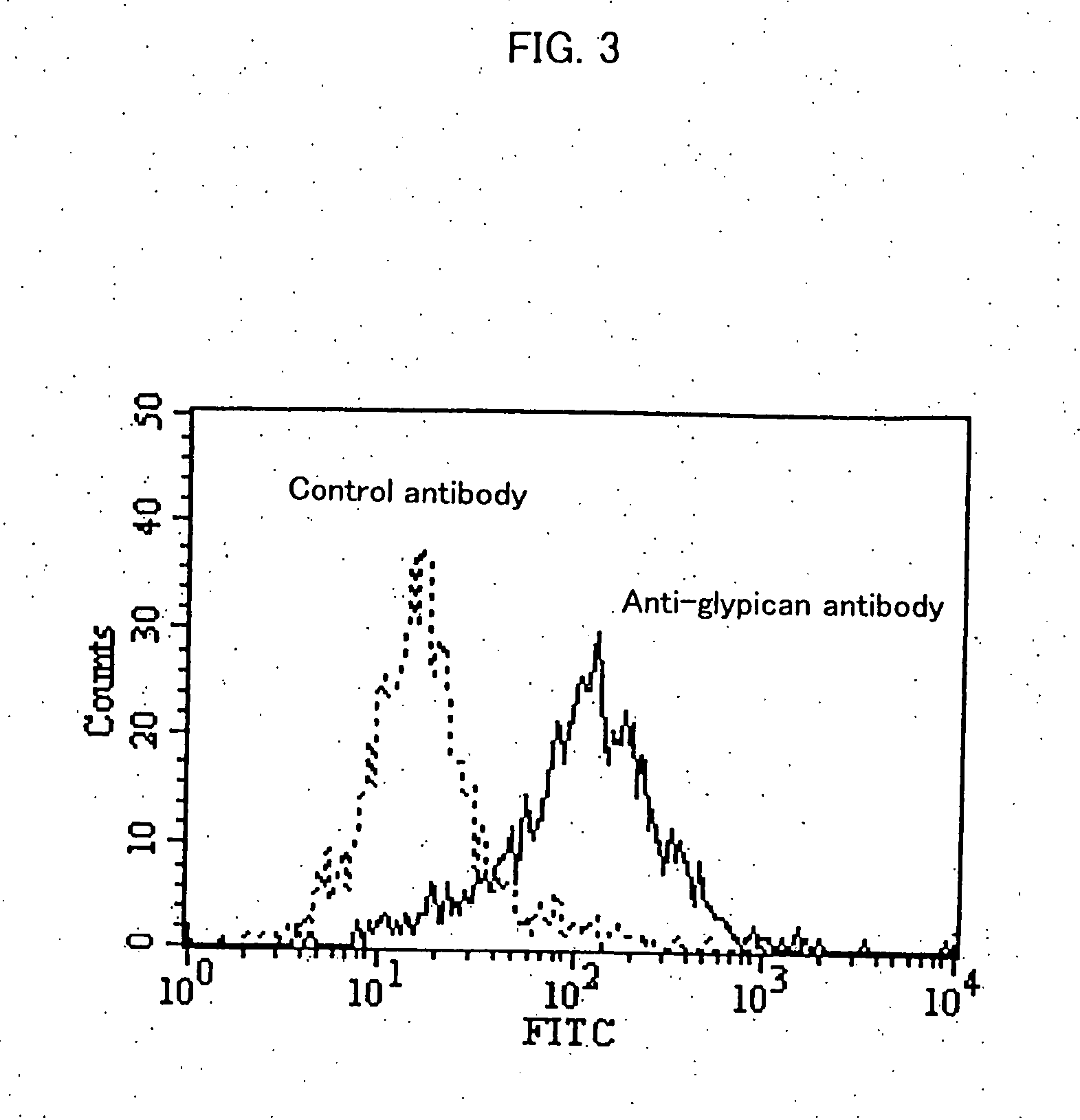
Anti-glypican 3 antibody
ActiveUS20070190599A1High cytotoxic activityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAnticarcinogenHumanized antibody
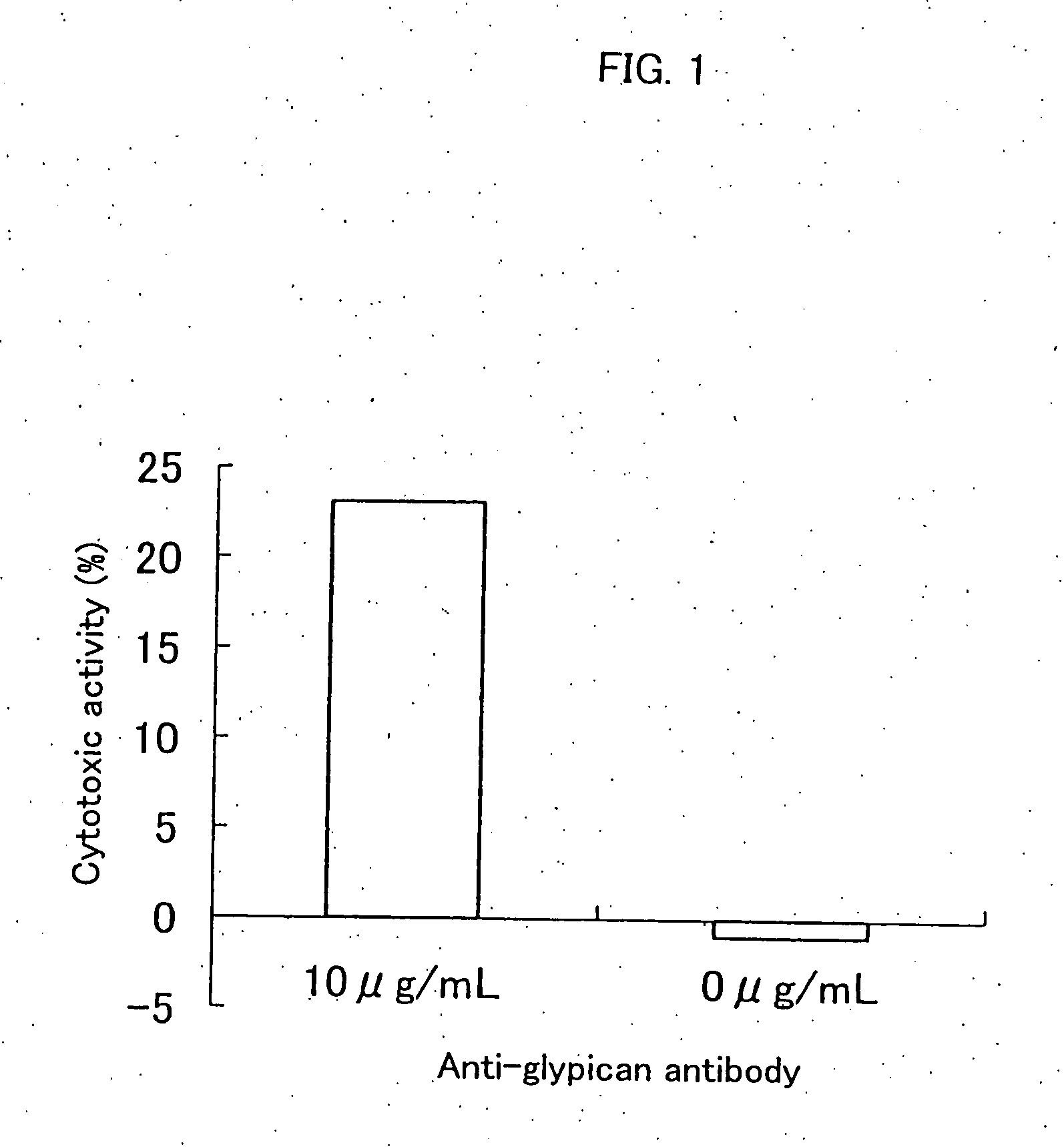
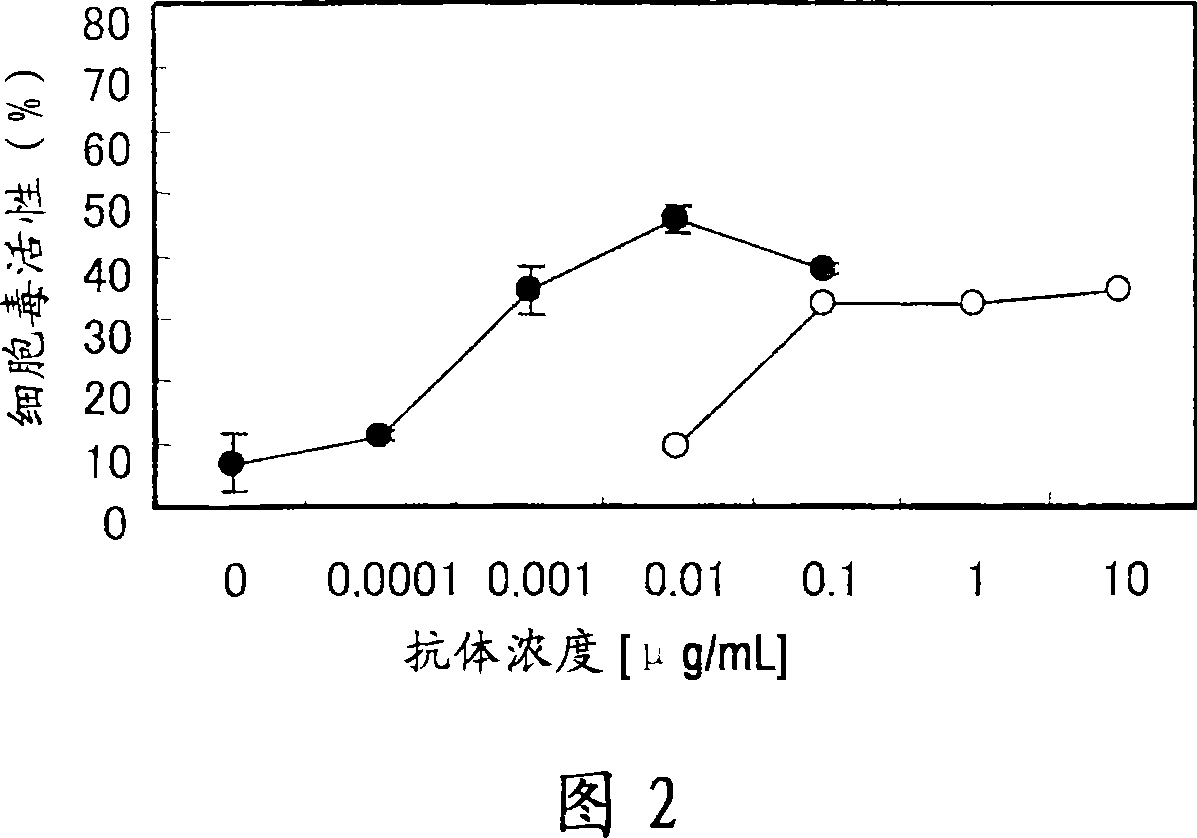
An antibody capable of binding to a specific region of glypican 3, as well as a humanized antibody created based on that antibody are disclosed. The anti-GPC3 antibody of the invention has a higher ADCC activity and CDC activity compared with those of a conventional antibody. The antibody of the present invention is useful as a cell growth inhibitor, an anticancer agent and an agent for diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-glypican 3 antibody
An antibody capable of binding to a specific region of glypican 3, as well as a humanized antibody created based on that antibody are disclosed. The anti-GPC3 antibody of the invention has a higher ADCC activity and CDC activity compared with those of a conventional antibody. The antibody of the present invention is useful as a cell growth inhibitor, an anticancer agent and an agent for diagnosis of cancers.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Biodegradable vascular support
ActiveCN101636187AAvoid decompositionAvoid breakingSurgeryCoatingsBiodegradable coatingMetal framework
The invention relates to biodegradable vascular supports consisting of an inner biodegradable metal skeleton and an outer polymeric coating. The biodegradable coating preferably consists of biodegradable polymers and can also contain at least one pharmacologically active substance such as an anti-inflammatory, cytostatic, cytotoxic, anti-proliferative, anti-microtubule, anti-angiogenic, anti-restenotic (anti-restenosis), anti-fungicidal, anti-neoplastic, anti-migrative, athrombogenic and / or antithrombogenic active ingredient.
Owner:HEMOTEQ AG
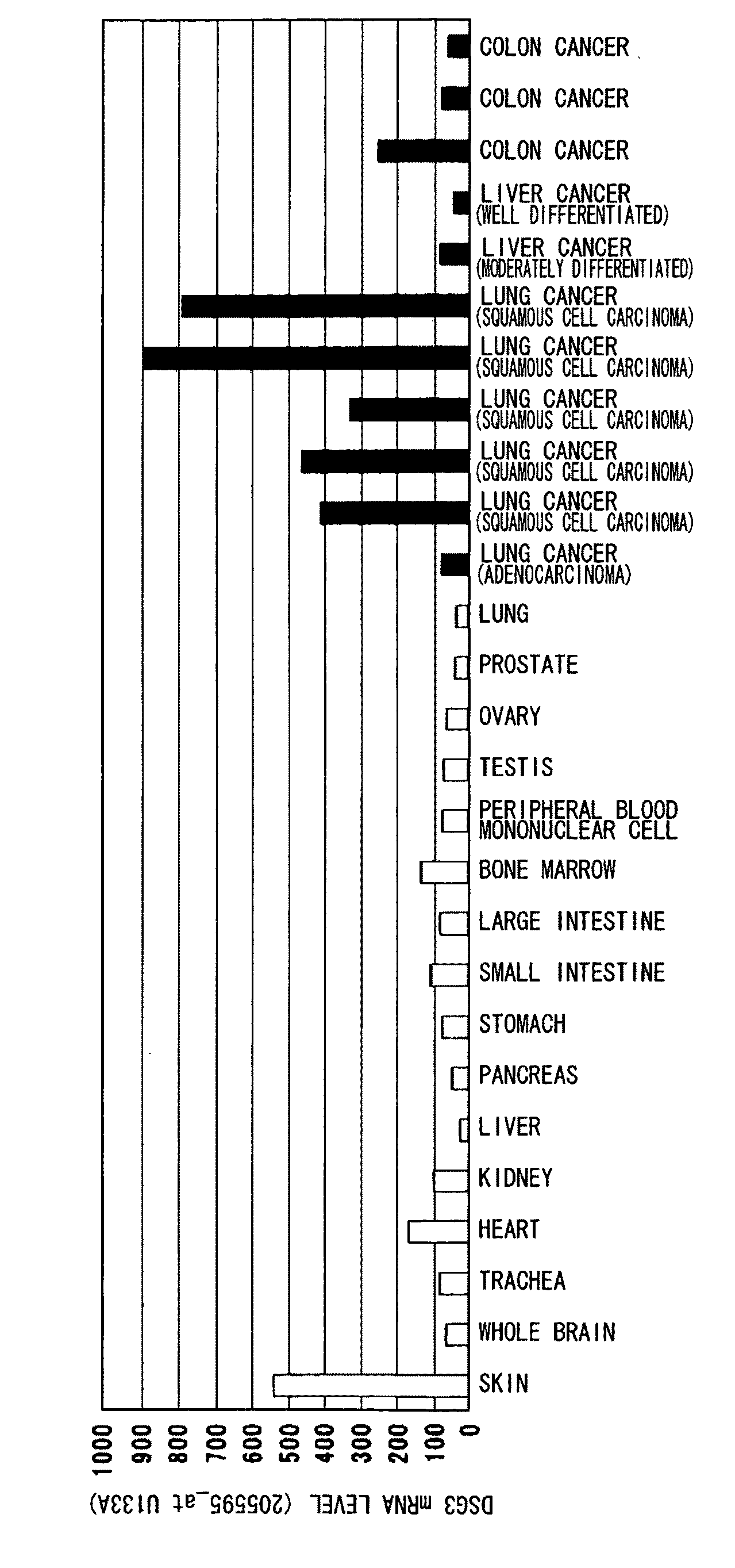
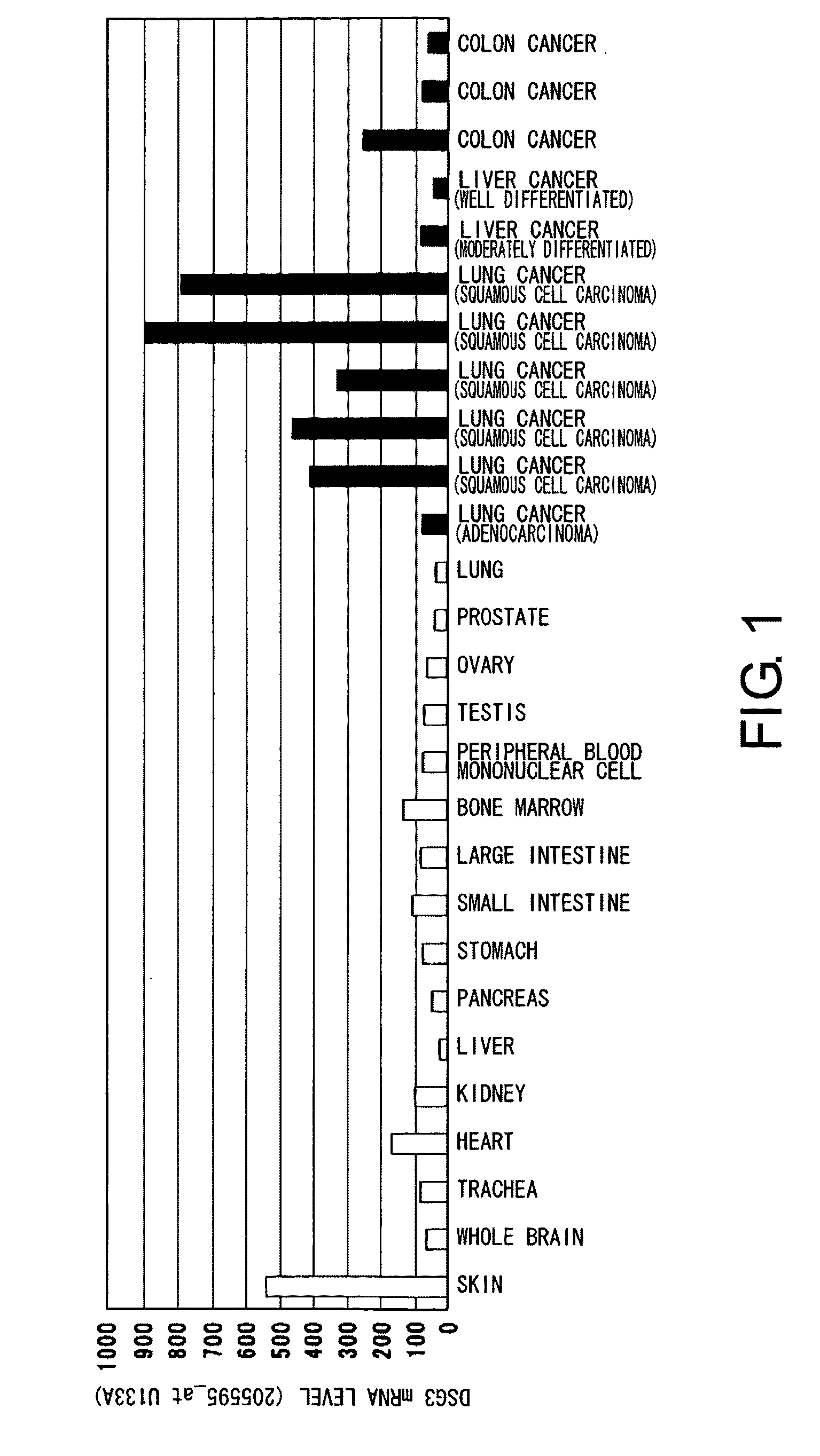
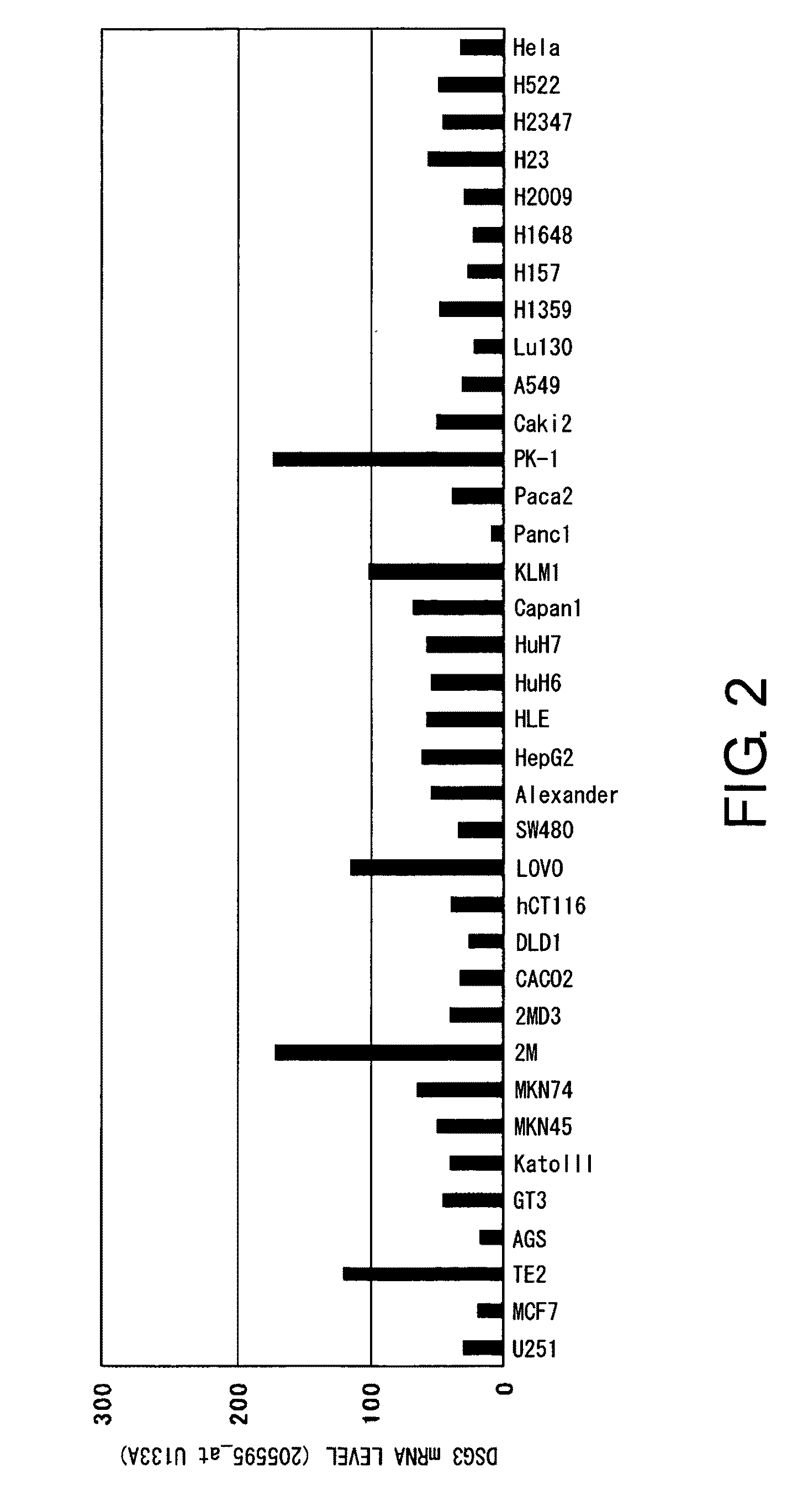
Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancer Using Anti-Desmoglein-3 Antibodies
InactiveUS20100092457A1High expressionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Methods that involve detection of a DSG3 protein for diagnosing cancer are disclosed. In lung cancer, the expression of DSG3 was found to be enhanced at very high frequency at the gene level and protein level. Methods of the present invention can be carried out using an antibody that recognizes a DSG3 protein. Pharmaceutical compositions, cell growth inhibitors, and anticancer agents containing a DSG3-binding antibody as an active ingredient are also disclosed. Methods of inducing cell damage in DSG3-expressing cells and methods of suppressing proliferation of DSG3-expressing cells by contacting the DSG3-expressing cells with DSG3-binding antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Mesothelioma therapeutic agent
ActiveUS20080274106A1Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsInterleukin 6Growth retardant
The present invention provides a mesothelioma therapeutic agent containing an interleukin-6 (IL-6) antagonist such as antibody to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), and a mesothelioma cell growth inhibitor containing an IL-6 antagonist such as antibody to IL-6R.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Use of rpn2 gene expression inhibitor
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD +3
Pharmaceutical composition comprising Anti-grp78 antibody as active ingredient
ActiveUS20100041074A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntitumor antibodyAnticarcinogen
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-Glypican 3 Antibody Having Modified Sugar Chain
InactiveUS20080124330A1Improve the level ofImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAnticarcinogenSugar
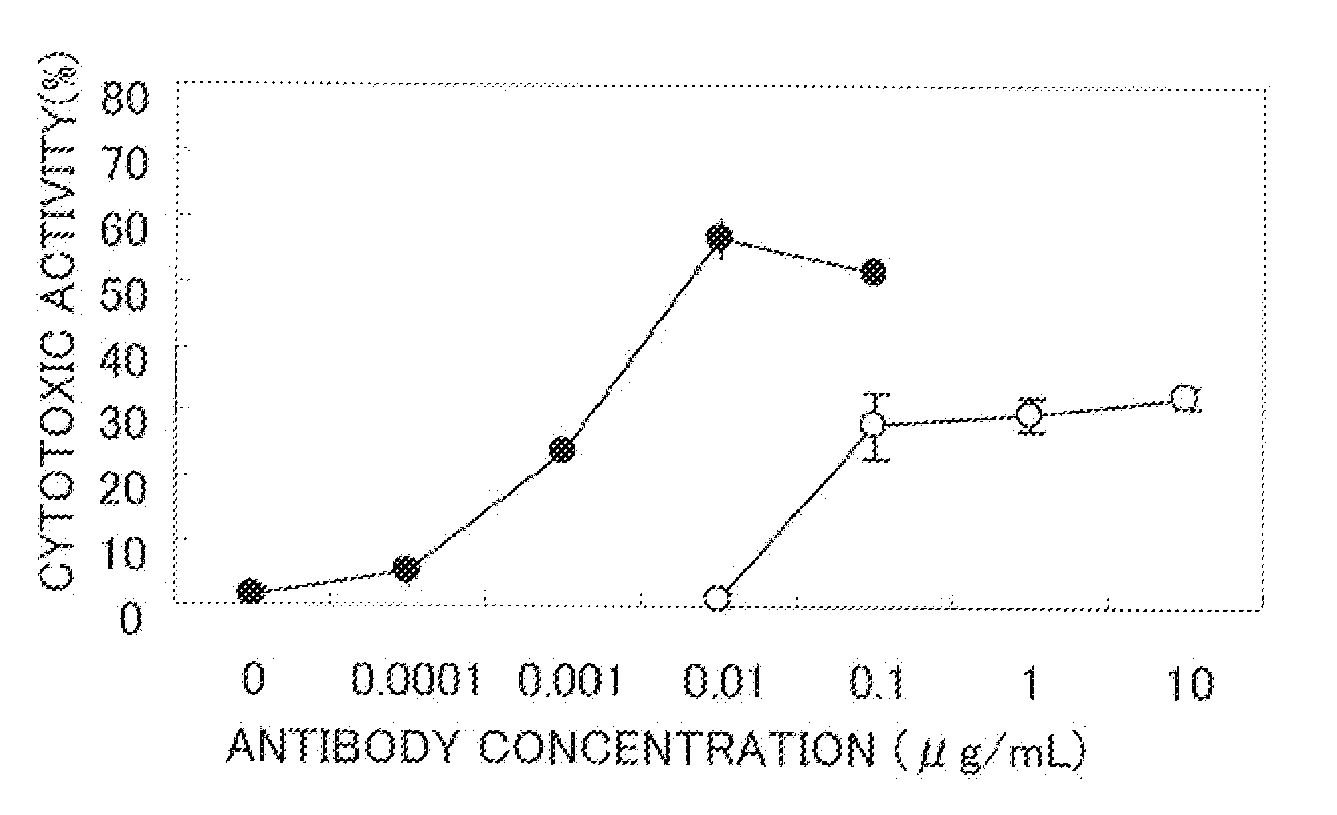
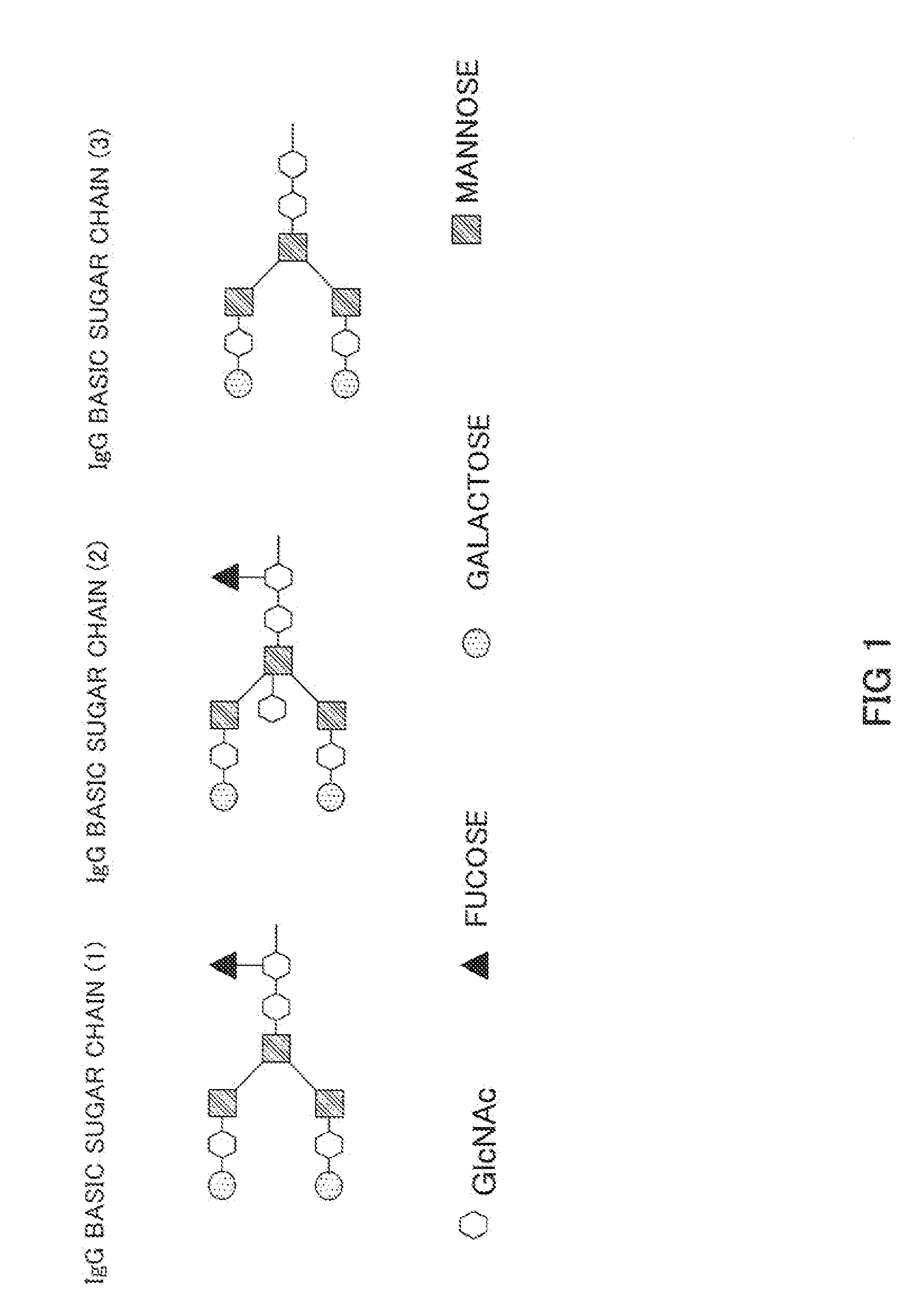
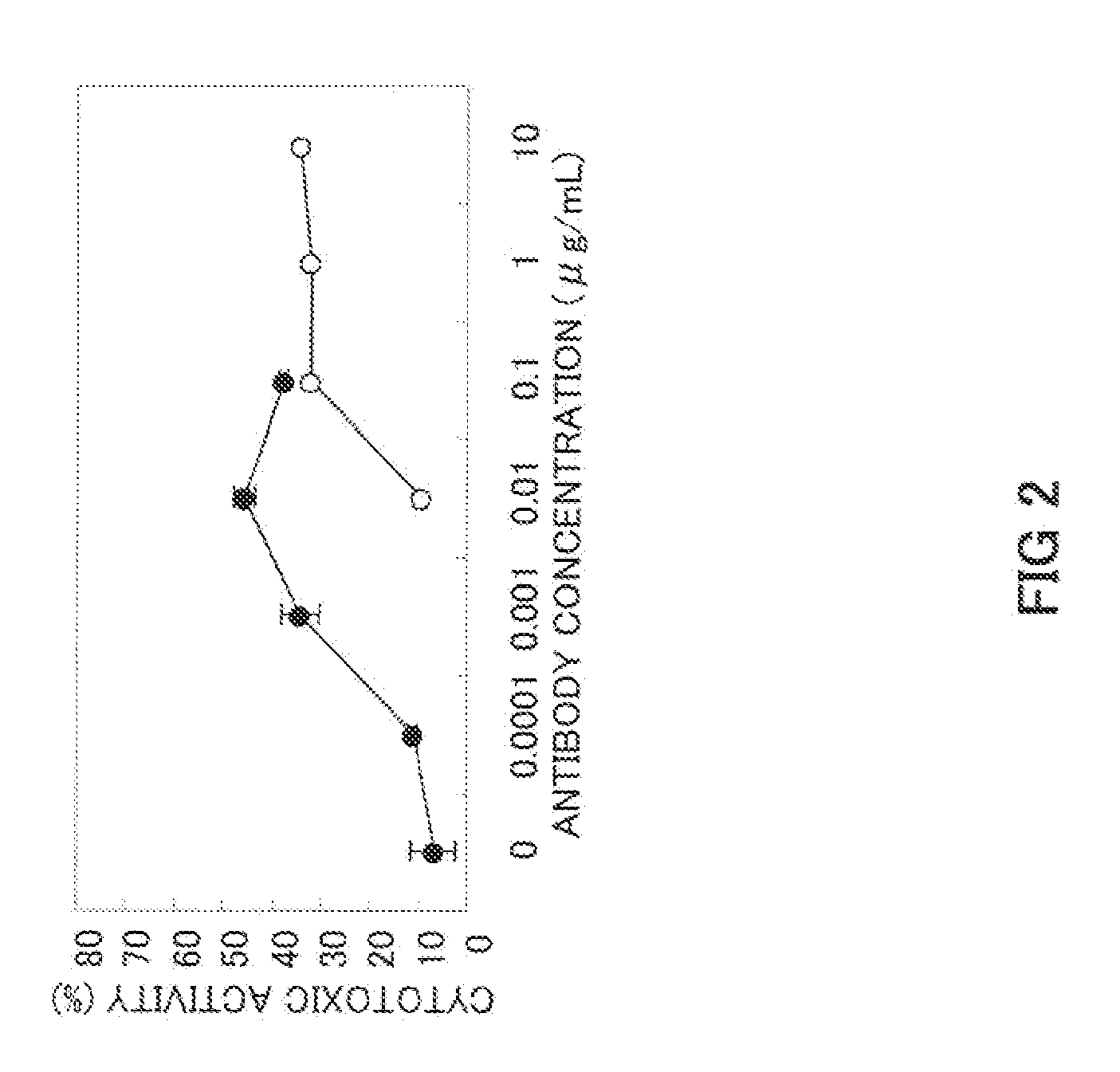
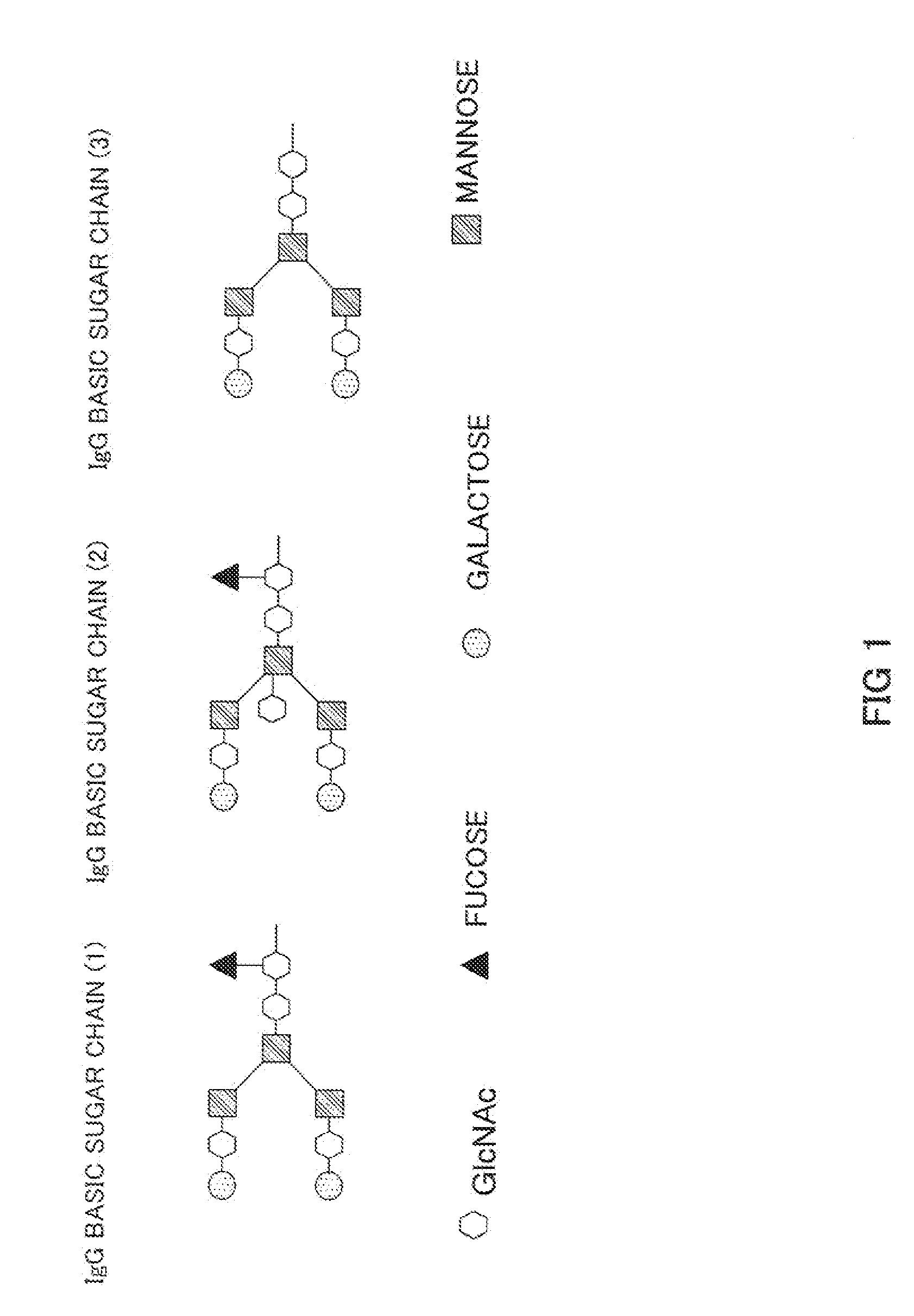
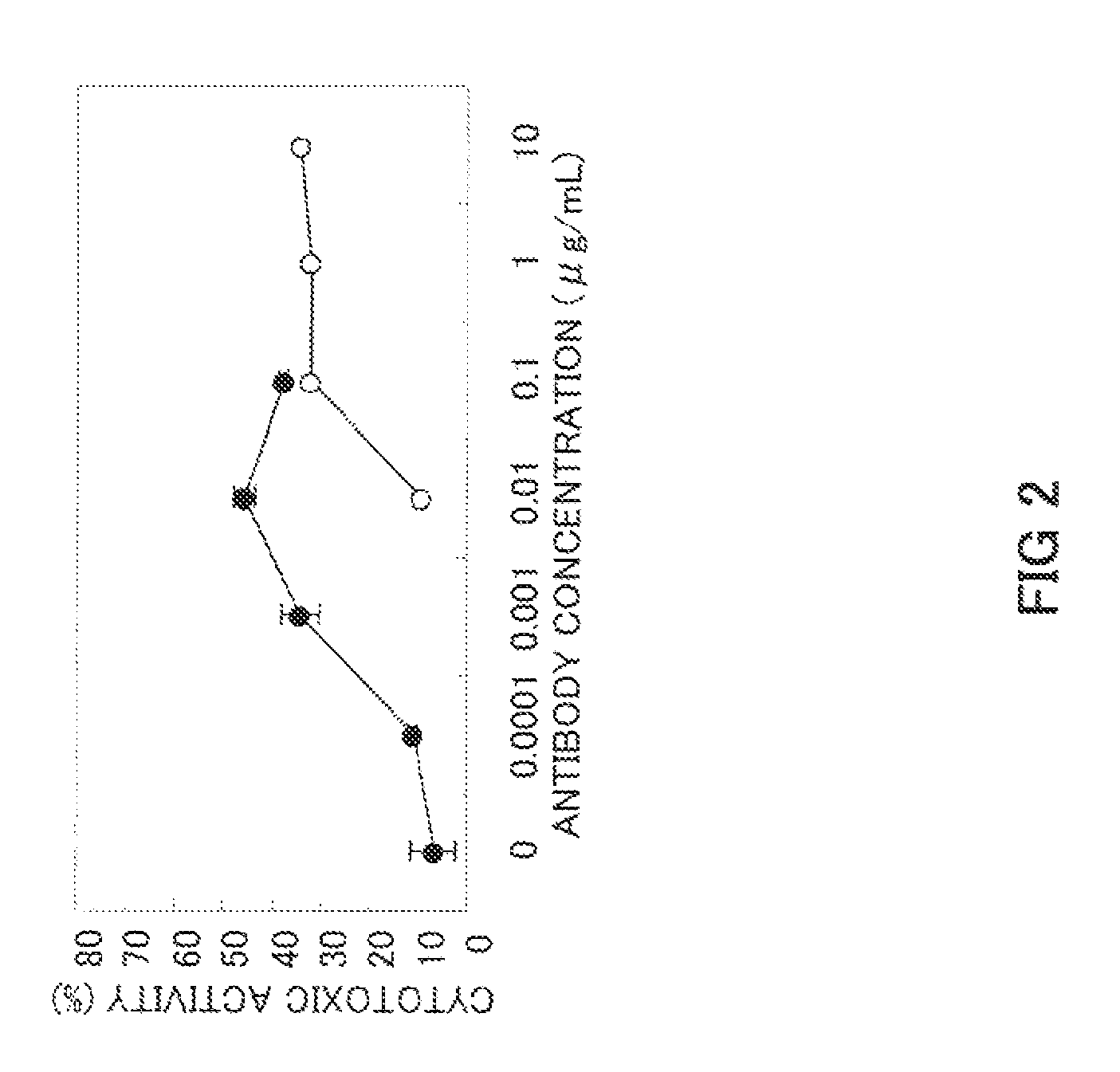
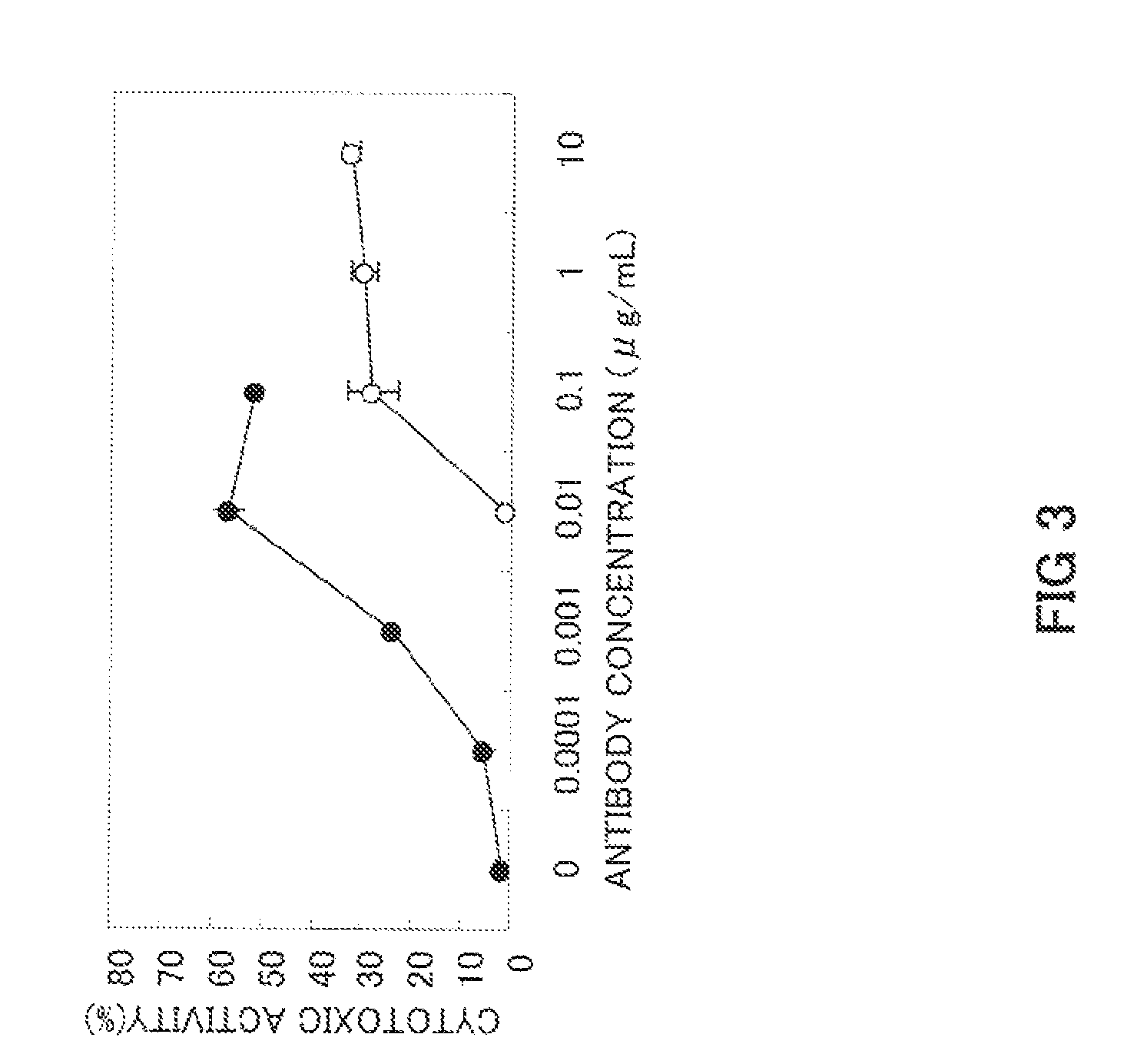
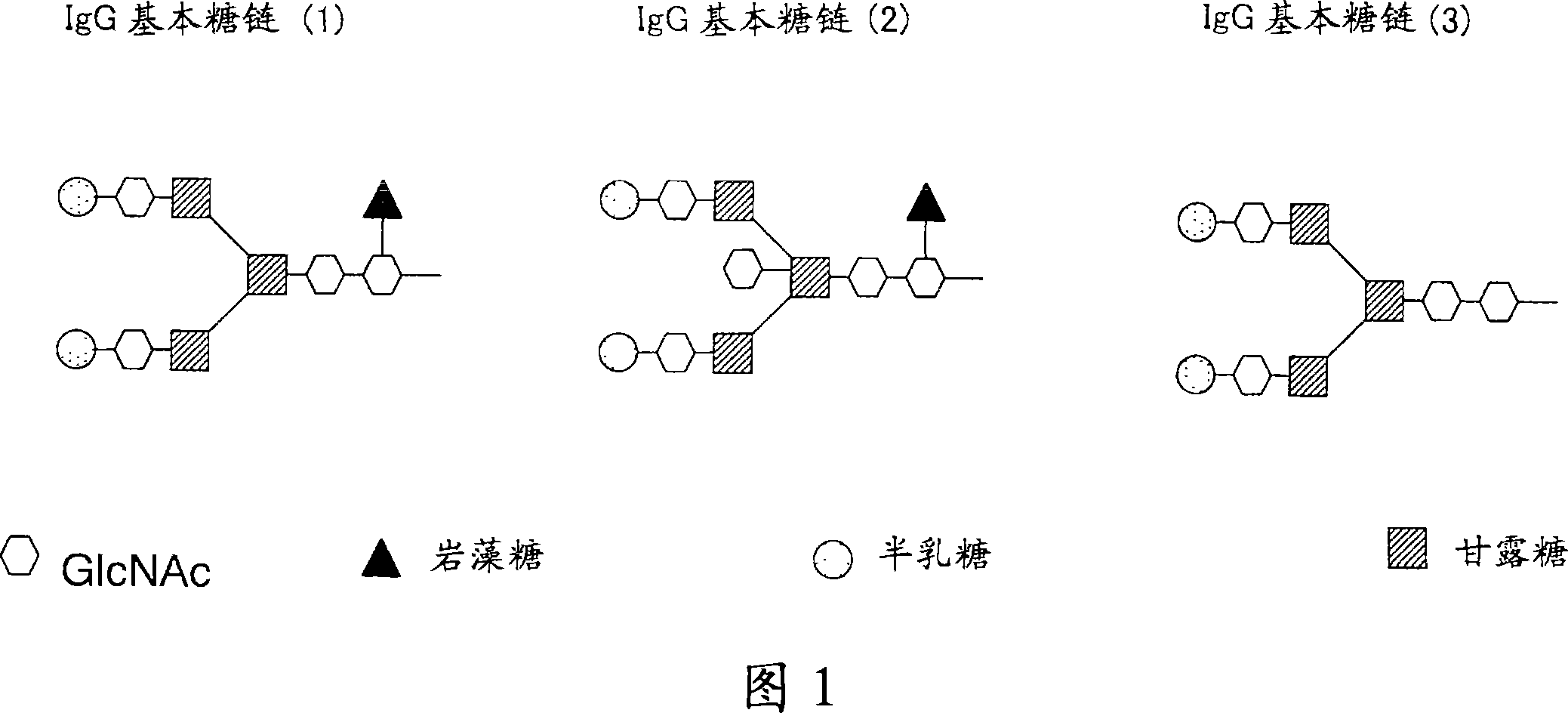
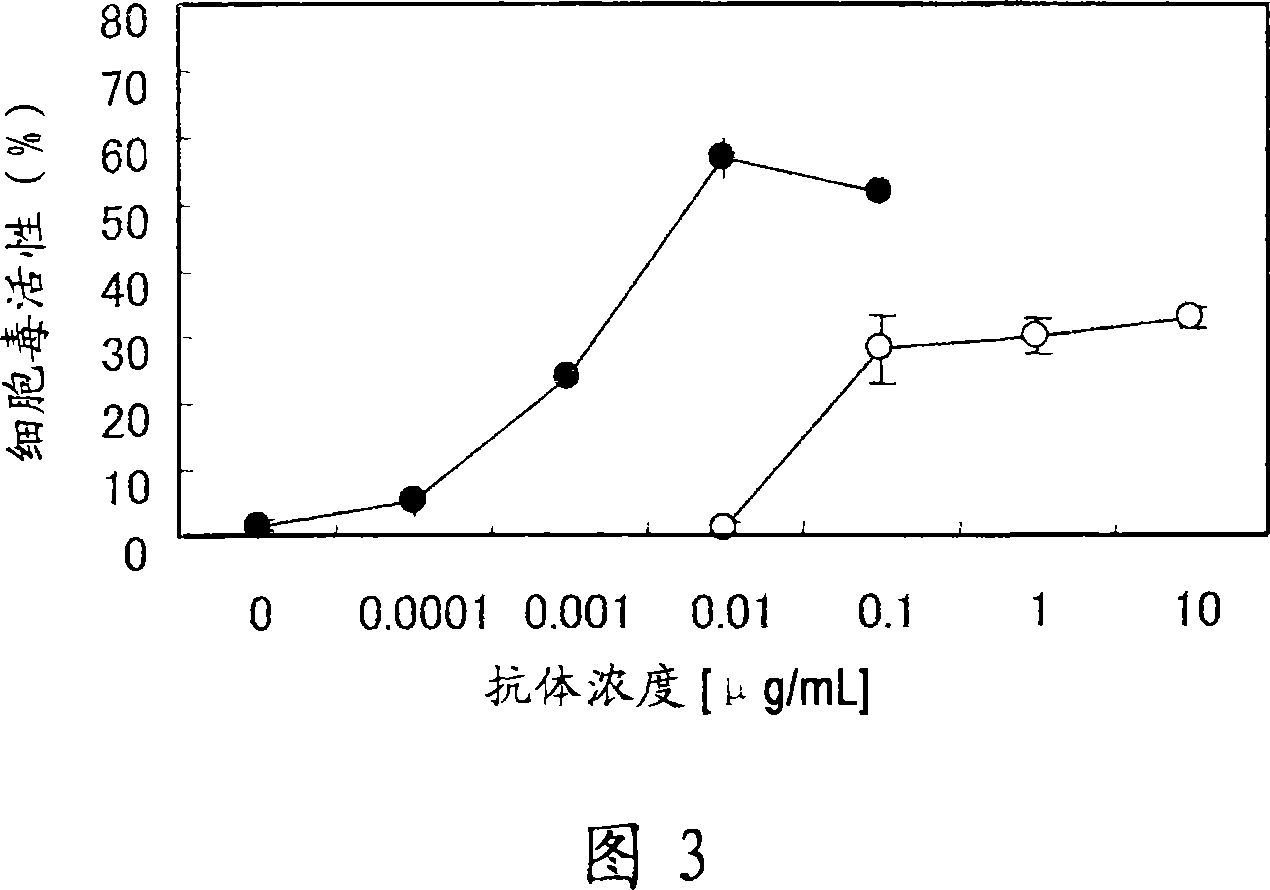
An anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains, more specifically, an anti-glypican 3 antibody lacking fucose is provided. The anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains of the present invention may be produced by a process comprising introducing a nucleic acid encoding an anti-glypican 3 antibody into host cells with reduced fucose addition capability, such as YB2 / 0 cells and cells lacking a fucose transporter. The anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains of the present invention has a high level of cytotoxic activity and therefore is useful as a cell growth inhibitor such as an anticancer agent.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-glypican 3 antibody having modified sugar chain
An anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains, more specifically, an anti-glypican 3 antibody lacking fucose is provided. The anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains of the present invention may be produced by a process comprising introducing a nucleic acid encoding an anti-glypican 3 antibody into host cells with reduced fucose addition capability, such as YB2 / 0 cells and cells lacking a fucose transporter. The anti-glypican 3 antibody with modified sugar chains of the present invention has a high level of cytotoxic activity and therefore is useful as a cell growth inhibitor such as an anticancer agent.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
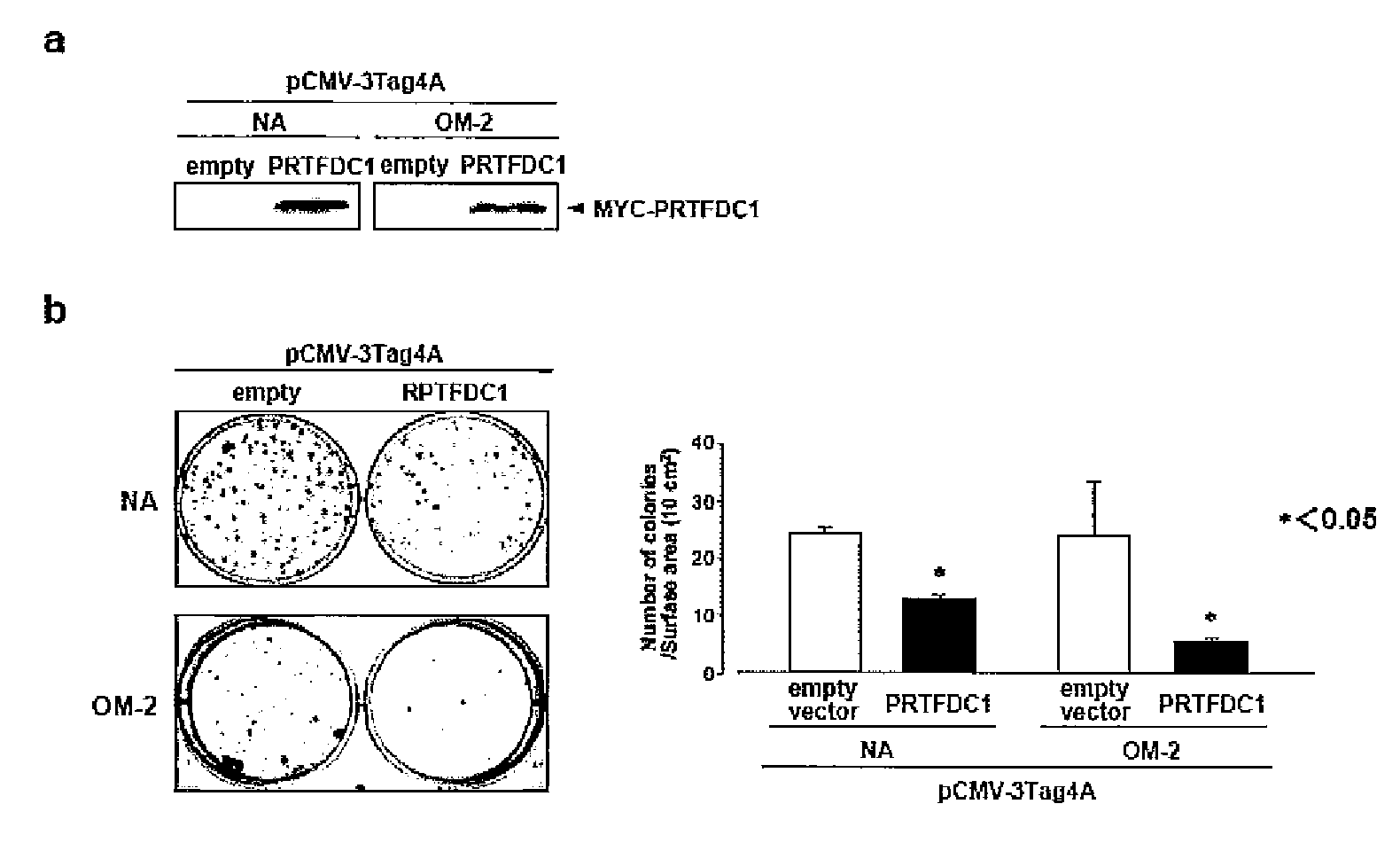
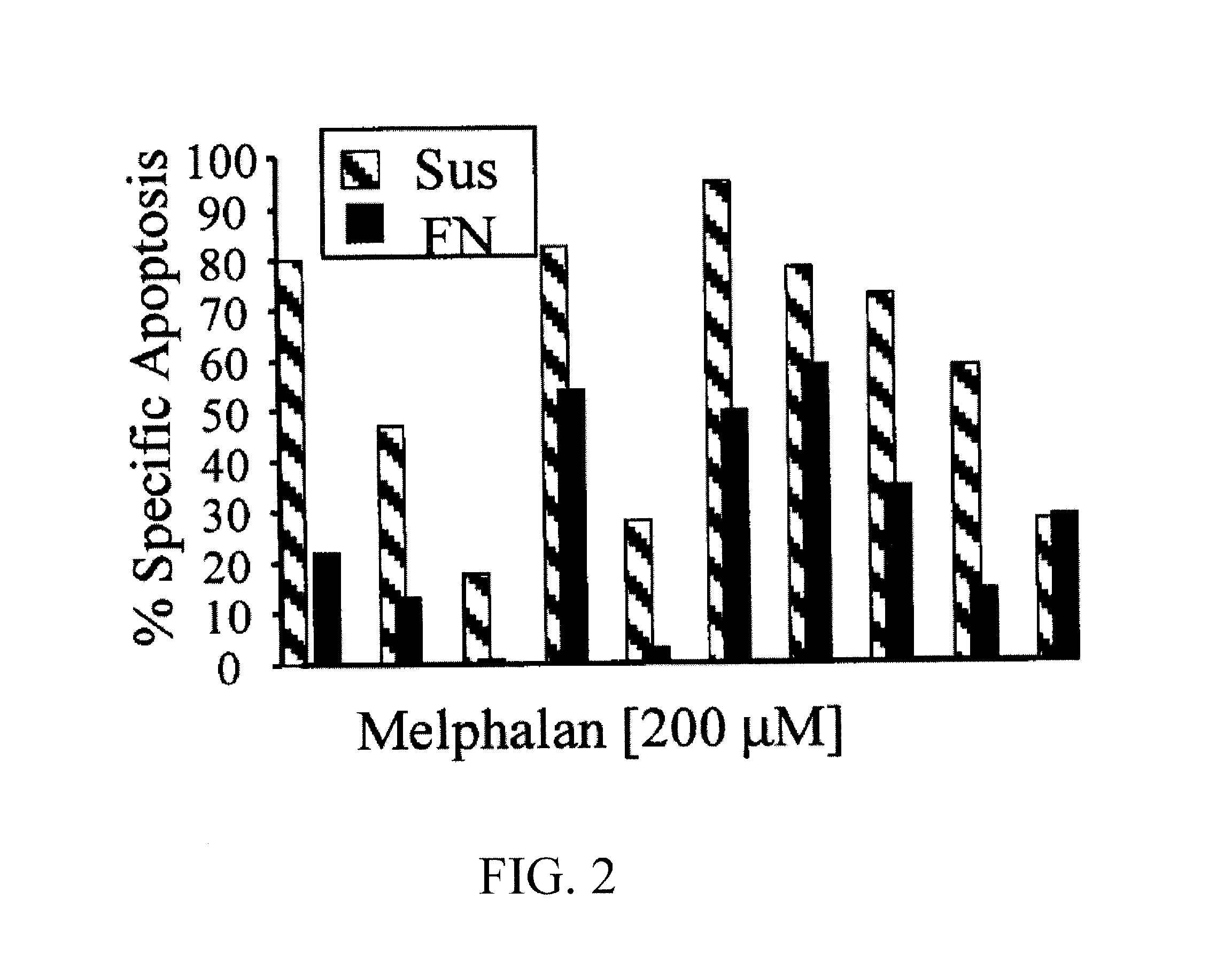
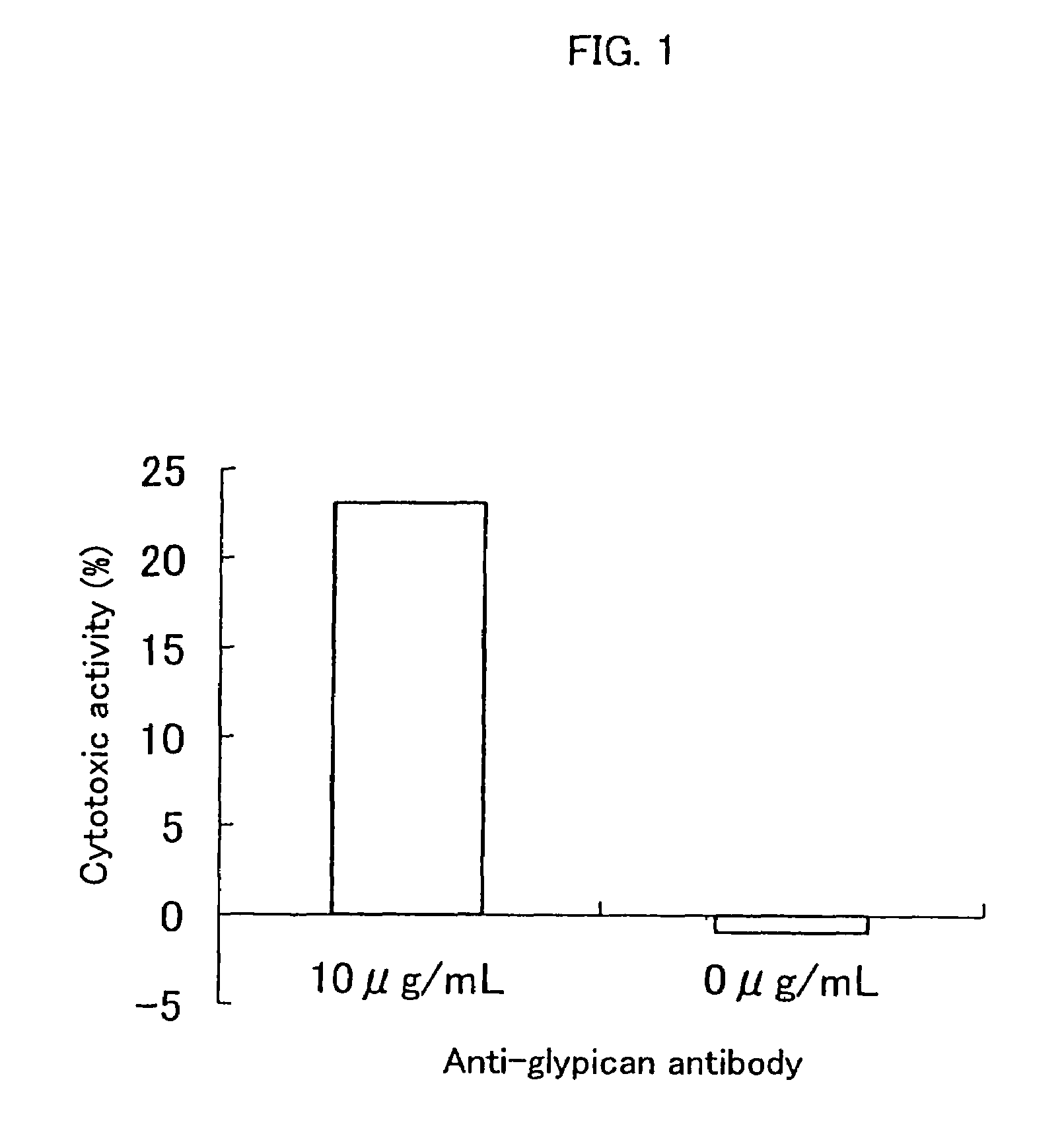
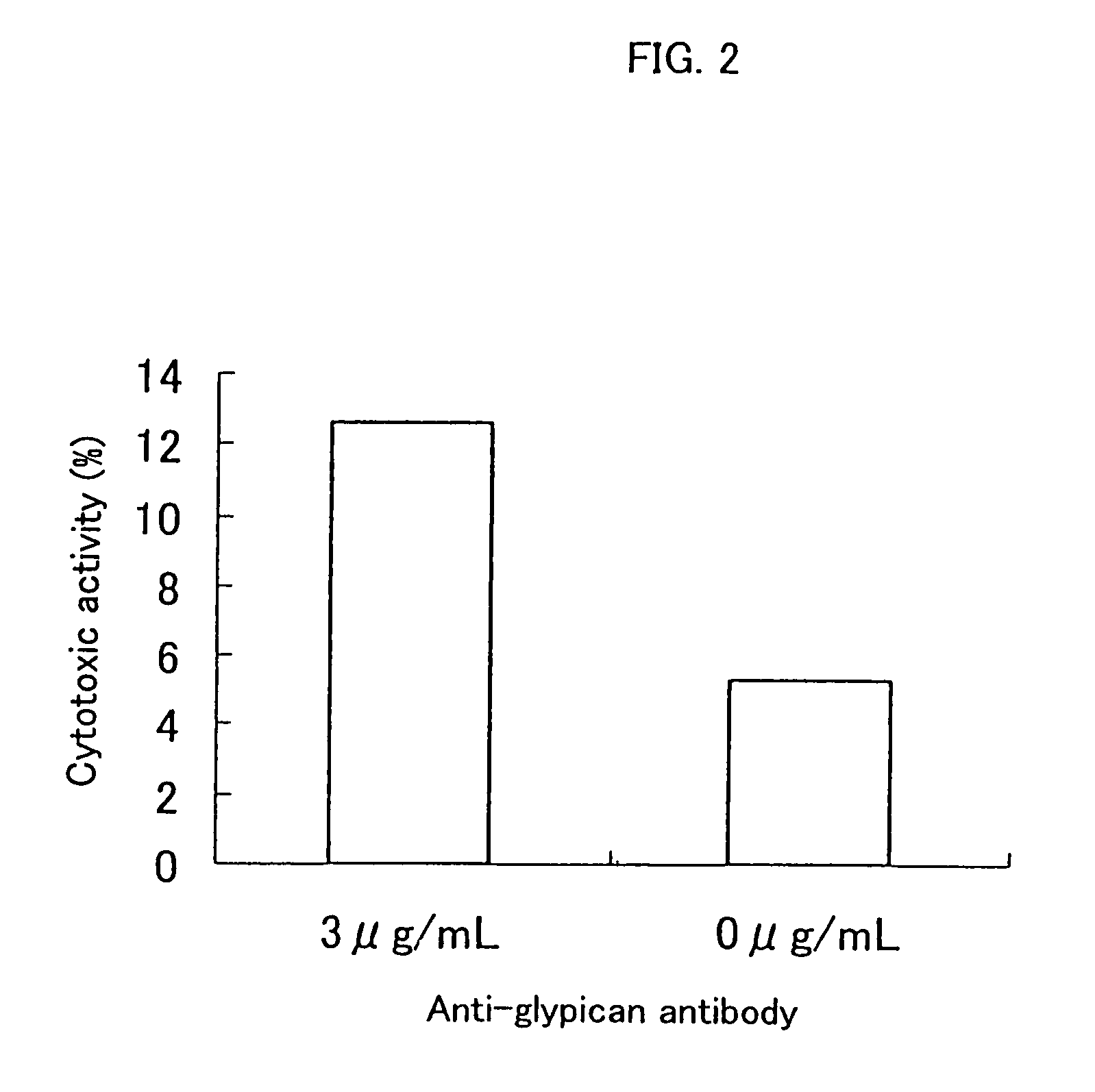
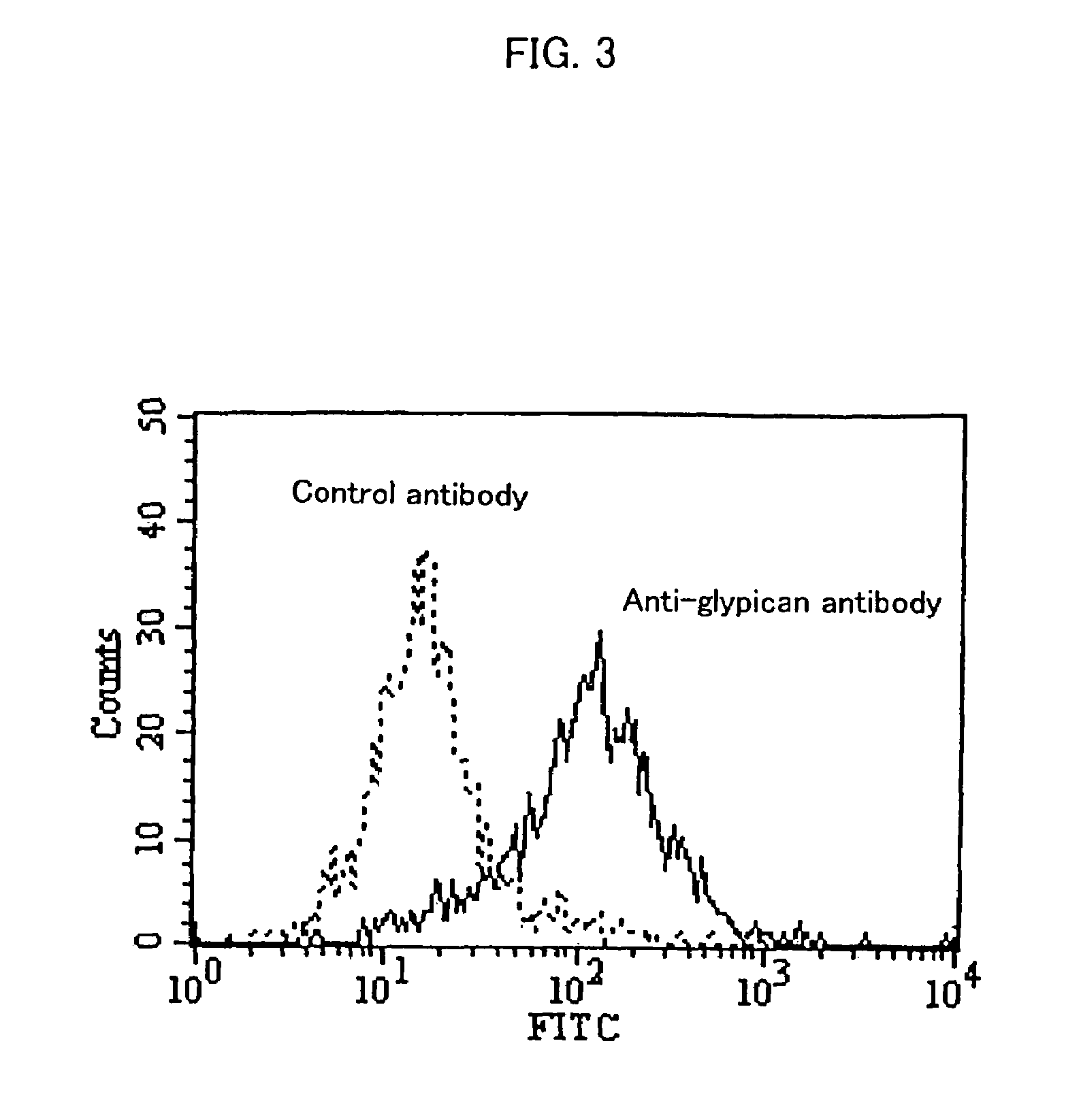
Cell growth inhibitors containing anti-glypican 3 antibody
InactiveUS20070172488A1Easy to implementImprove fusion efficiencyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseDepressant
Provided is a cell growth inhibitor that can be used for treating diseases based on abnormal cell proliferation, and in particular cancer. The cell growth inhibitor contains an anti-glypican 3 antibody as an active ingredient.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Induction of differential stress resistance and uses thereof
ActiveUS8211700B2Improve efficiencyImprove the immunityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose intakeSide effect
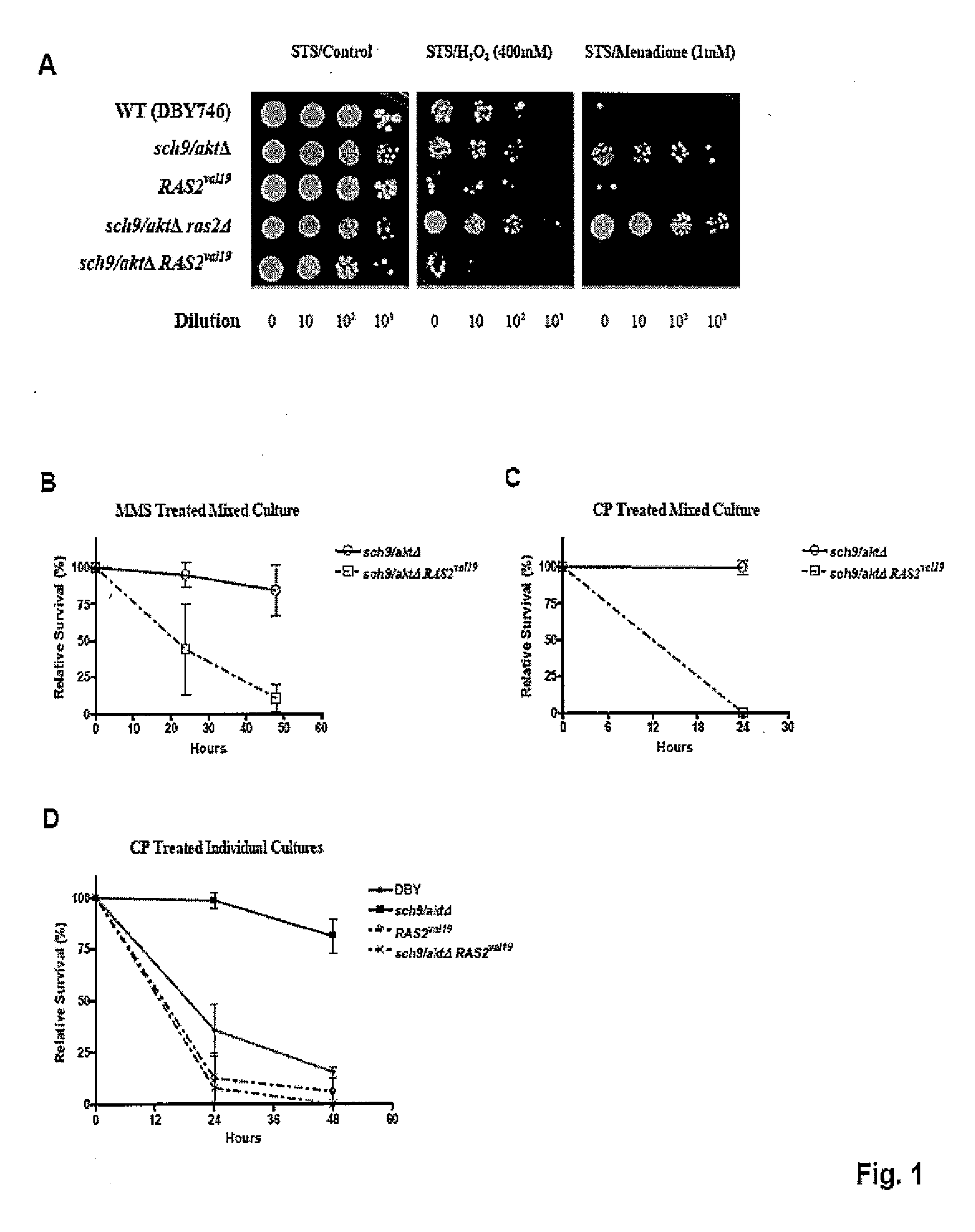
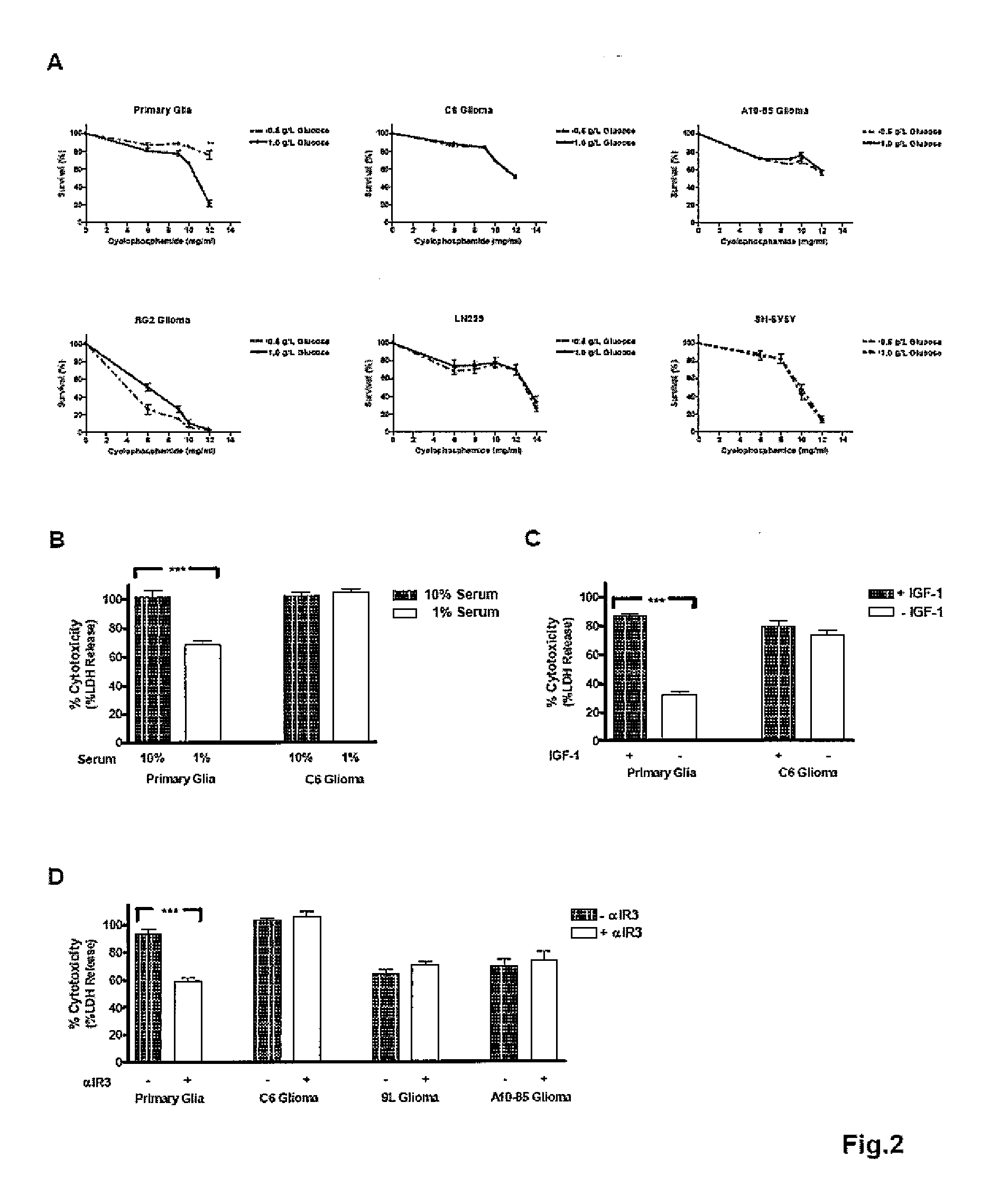
This invention relates to methods of inducing differential stress resistance in a subject with cancer by starving the subject for a short term, administering a cell growth inhibitor to the subject, or reducing the caloric or glucose intake by the subject. The induced differential stress resistance results in improved resistance to cytotoxicity in normal cells, which, in turn, reduces cytotoxic side-effects due to chemotherapy, as well as improved effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
HYD1 peptides as anti-cancer agents
The present invention concerns fragments and variants of the HYD1 peptide; polynucleotides encoding the peptides; host cells genetically modified with the polynucleotides; vectors comprising the polynucleotides; compositions containing these peptides, polynucleotides, vectors, or host cells; and methods of using the peptides, polynucleotides, vectors, and host cells as inhibitors of aberrant cell growth in vitro or in vivo, e.g., as anti-cancer agents for treatment of cancer, such as myeloma. The present invention further includes a method of increasing the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, comprising administering an agent that binds β1 integrin to a patient in need thereof. In one embodiment, the β1 integrin binding agent is the HYD1 peptide, or a functional fragment or variant thereof. In another aspect, the invention pertains to a composition (an adhesion trap) comprising a substrate (also referred to as a surface or support) with a HYD1 peptide, or fragment or variant thereof, immobilized to the substrate, and a method of removing circulating tumor cells (CTC) from blood by contacting a subject's blood with the immobilized peptide. Another aspect of the invention concerns a method of identifying modulators of peptide binding. Another aspect of the invention concerns a method for detecting CTC.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +3
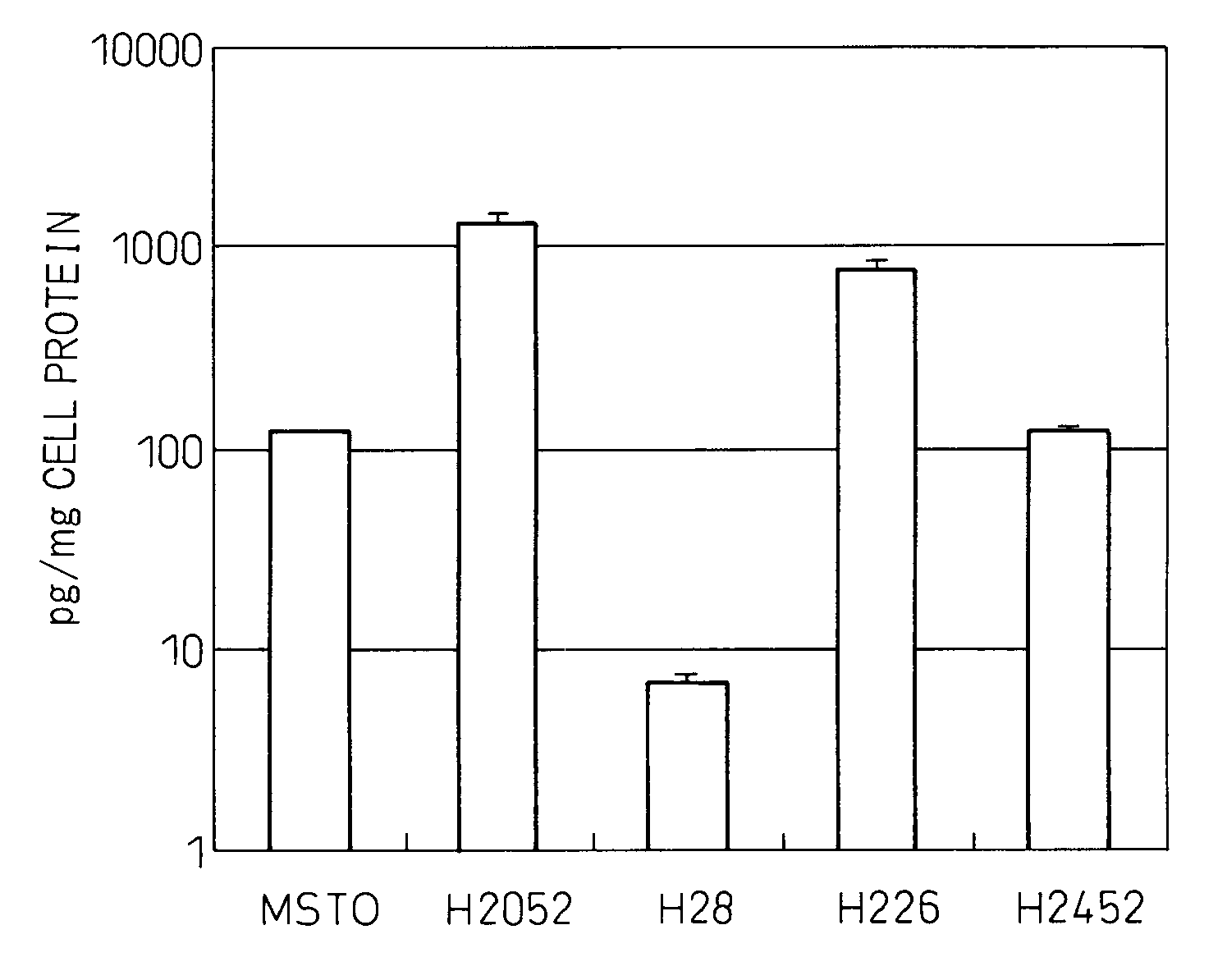
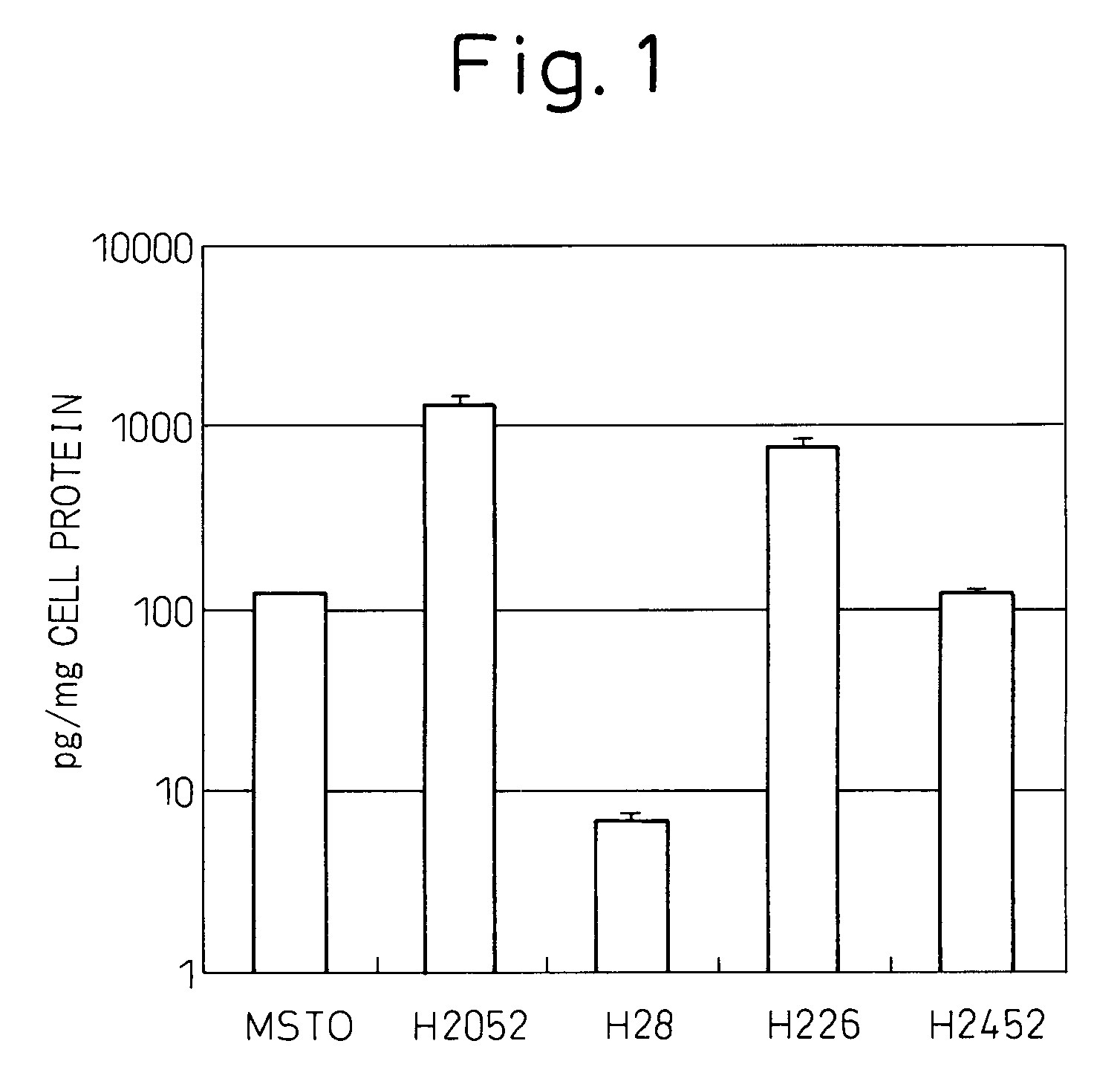
Therapeutic Agent And Diagnostic Agent For Cholangiocarcinoma
InactiveUS20080008710A1Easy to reachDifficult to reachDigestive systemImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsGrowth retardantDiagnostic agent
Disclosed is a cholangiocarcinoma cell growth inhibitor comprising an anti-glypican-3 antibody as an active ingredient. Preferably, the anti-glypican-3 antibody has a cytotoxic activity such as an antibody-dependent cytotoxic (ADCC) activity and a complement-dependent cytotoxic (CDC) activity. Also disclosed is a diagnostic agent for diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma comprising an anti-glypican-3 antibody.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +3
HYD1 Peptides as Anti-Cancer Agents
InactiveUS20080108552A1Good curative effectAvoid stickingPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderAnticarcinogenIn vivo
The present invention concerns fragments and variants of the HYD1 peptide; polynucleotides encoding the peptides; host cells genetically modified with the polynucleotides; vectors comprising the polynucleotides; compositions containing these peptides, polynucleotides, vectors, or host cells; and methods of using the peptides, polynucleotides, vectors, and host cells as inhibitors of aberrant cell growth in vitro or in vivo, e.g., as anti-cancer agents for treatment of cancer, such as myeloma. The present invention further includes a method of increasing the efficacy of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, comprising administering an agent that binds β1 integrin to a patient in need thereof. In one embodiment, the β1 integrin binding agent is the HYD1 peptide, or a functional fragment or variant thereof. In another aspect, the invention pertains to a composition (an adhesion trap) comprising a substrate (also referred to as a surface or support) with a HYD1 peptide, or fragment or variant thereof, immobilized to the substrate, and a method of removing circulating tumor cells (CTC) from blood by contacting a subject's blood with the immobilized peptide. Another aspect of the invention concerns a method of identifying modulators of peptide binding. Another aspect of the invention concerns a method for detecting CTC.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +3
Cell growth inhibitors containing anti-glypican 3 antibody
InactiveUS7744880B2Improve fusion efficiencyImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Provided is a cell growth inhibitor that can be used for treating diseases based on abnormal cell proliferation, and in particular cancer. The cell growth inhibitor contains an anti-glypican 3 antibody as an active ingredient.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Dolastatin 15 derivatives
Compounds of the present invention include cell growth inhibitors which are peptides of Formula I,A-B-D-E-F-(G)r-(K)s-L, (I)and acid salts thereof, wherein A, B, D, E, F, G and K are α-amino acid residues, and s and r are each, independently, 0 or 1. L is a monovalent radical, such as, for example, an amino group, an N-substituted amino group, a β-hydroxylamino group, a hydrazido group, an alkoxy group, a thioalkoxy group, an aminoxy group, or an oximato group. The present invention also includes a method for treating cancer in a mammal, such as a human, comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of a compound of Formula I in a pharmaceutically acceptable composition.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
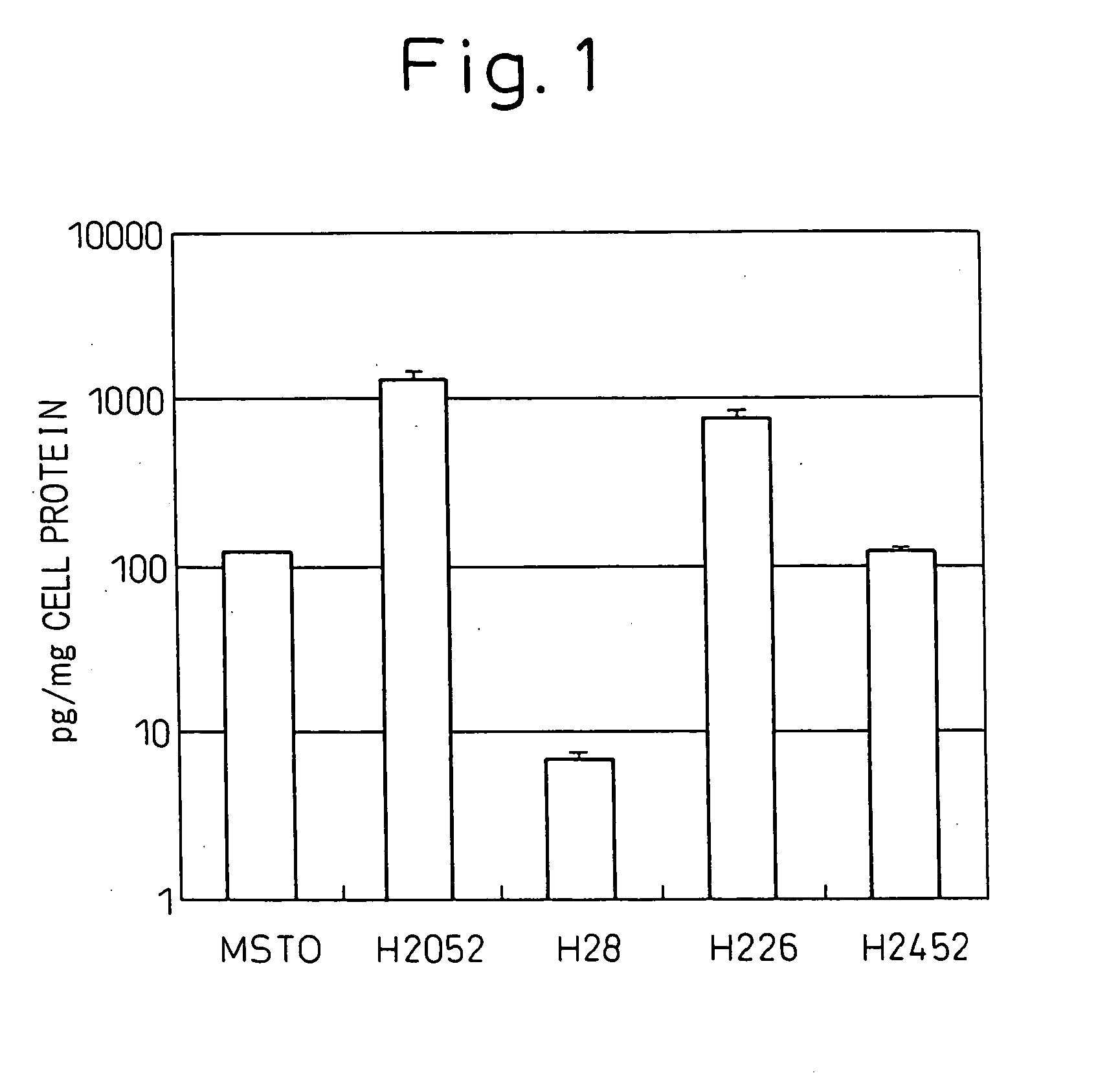
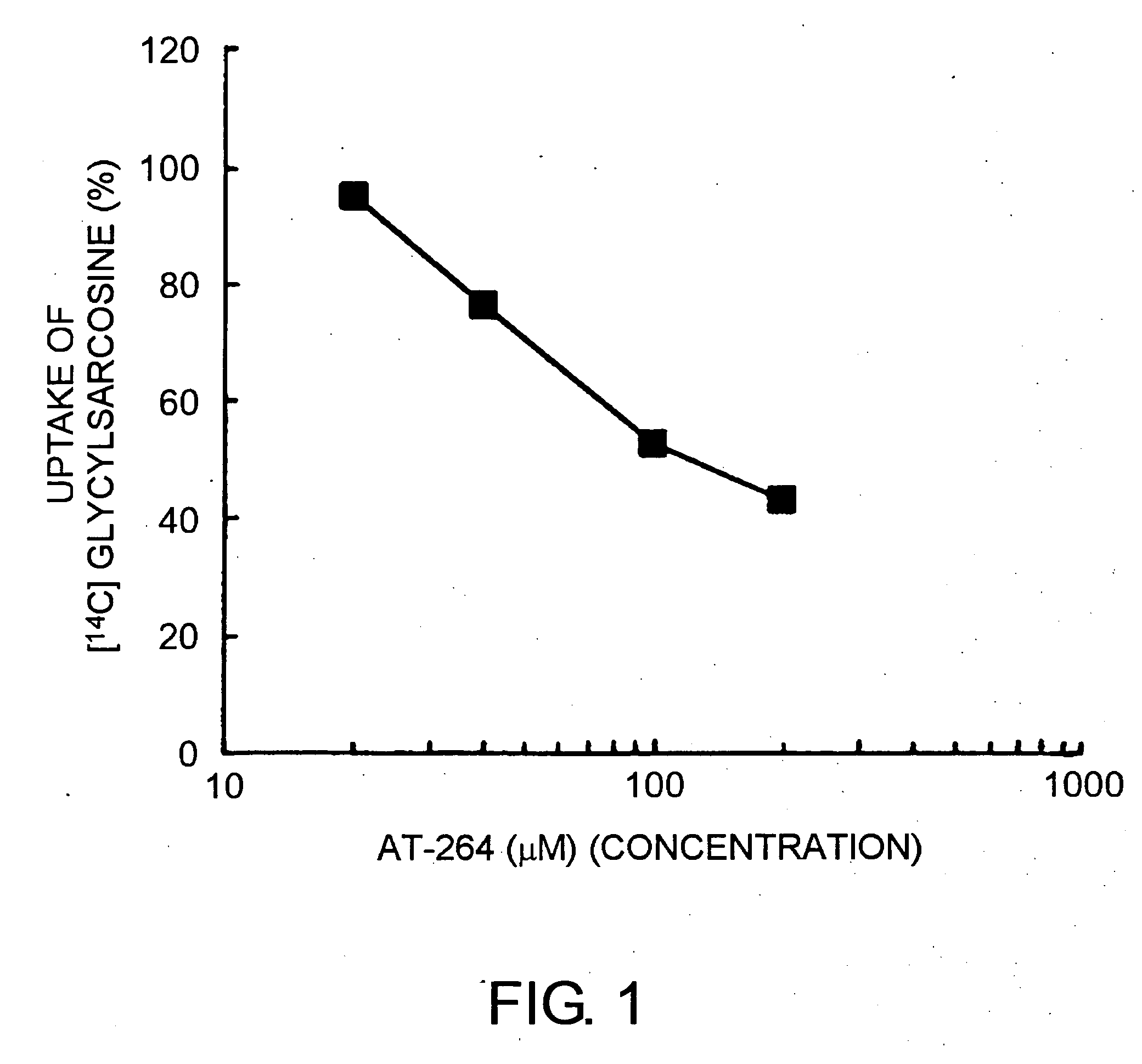
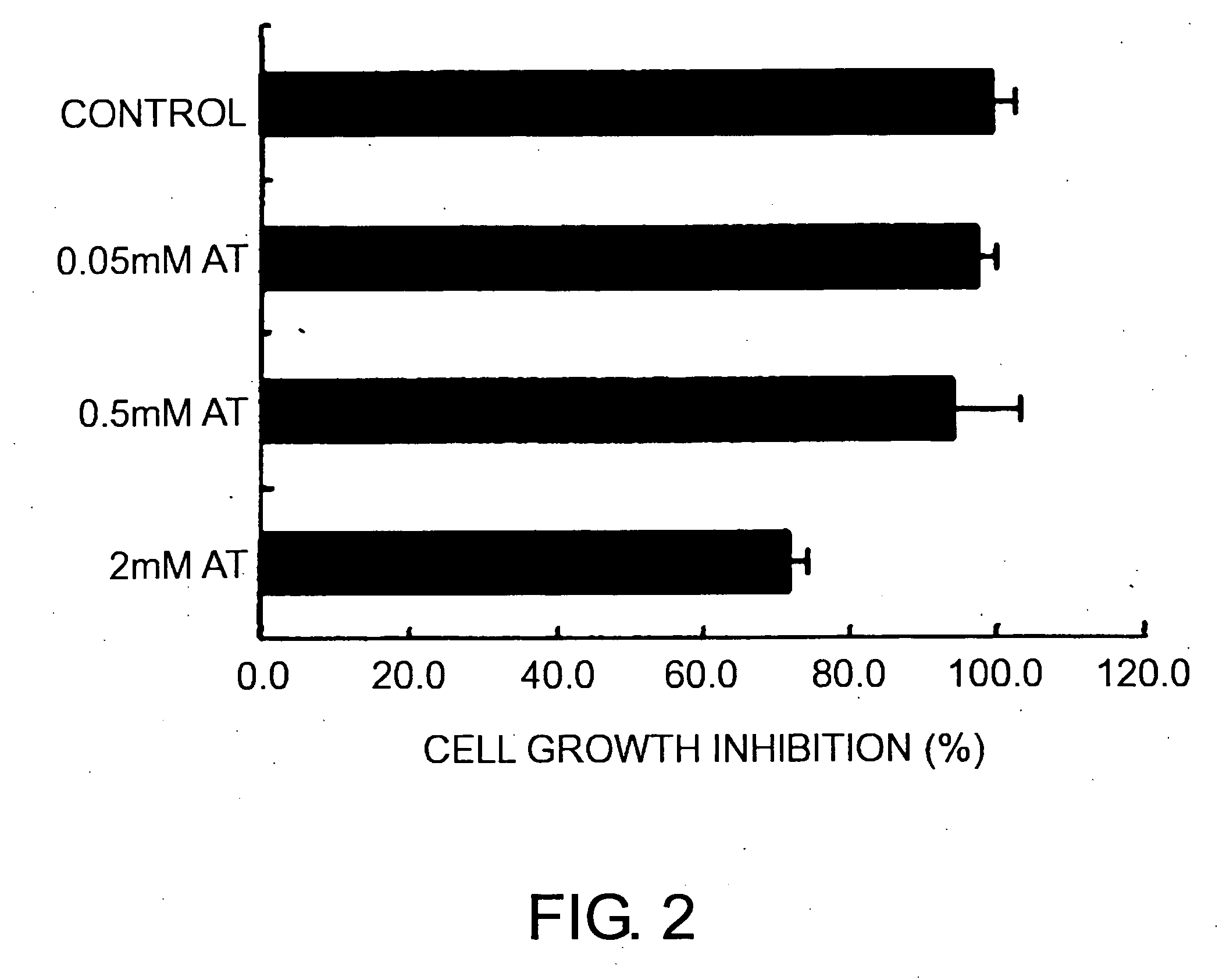
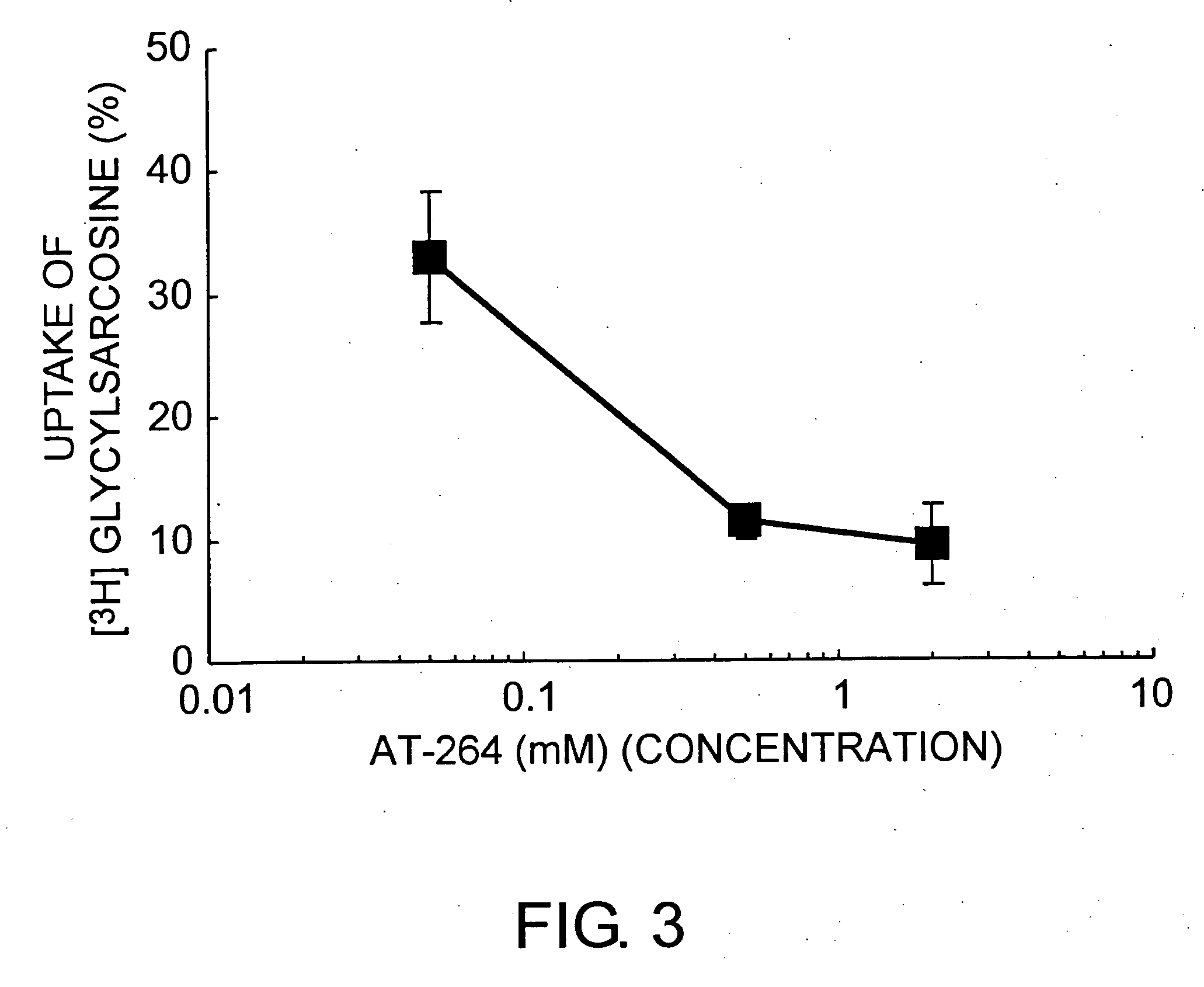
Cell growth inhibitor
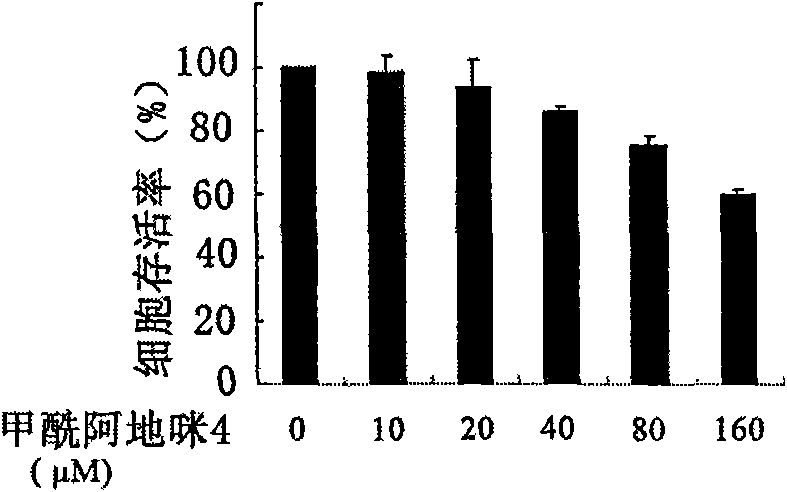
The present invention revealed that AT-264 suppresses cell growth through its inhibitory effect on PepT1 activity. Furthermore, as a result of examining whether AT-264 comprises the effect of inhibiting the cell growth of human pancreatic cancer cell line AsPC-1, the present invention revealed that cell growth is similarly suppressed. These findings show that cell growth can be suppressed by inhibiting the activity of peptide transporters. Suppression of peptide transporter activity can be considered to be an important indicator in the development of growth inhibitors for cancer cells and such.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
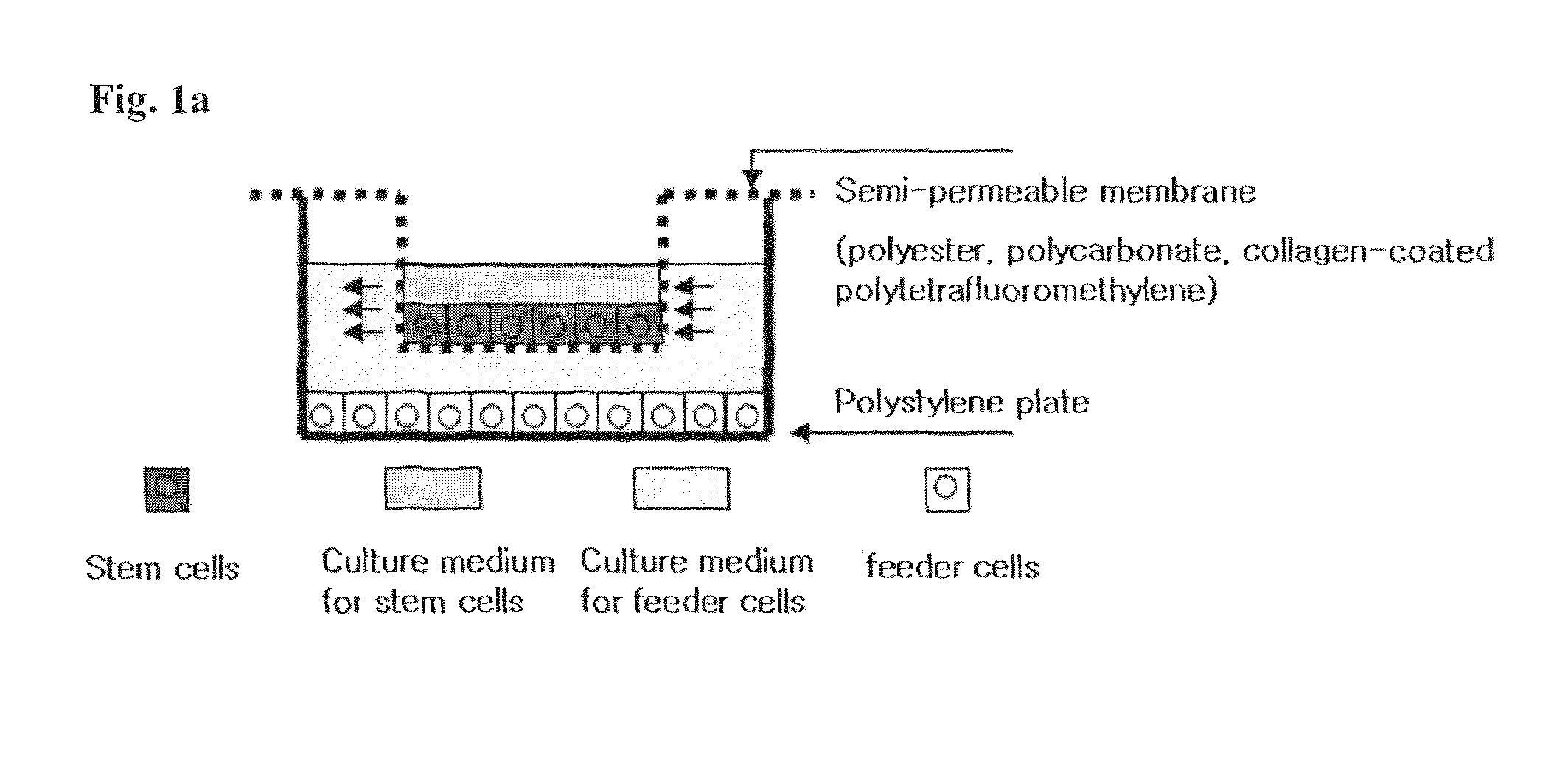
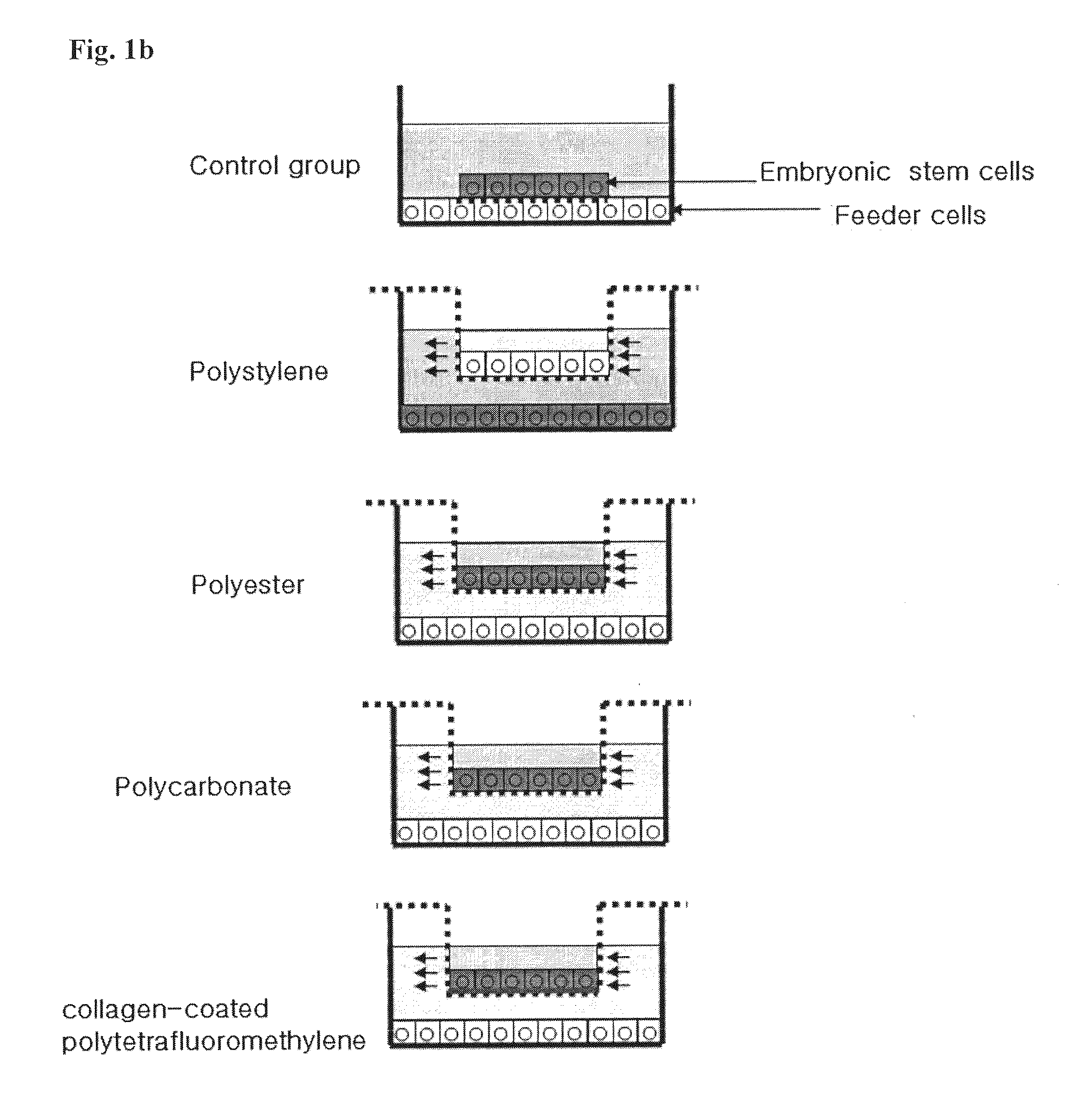
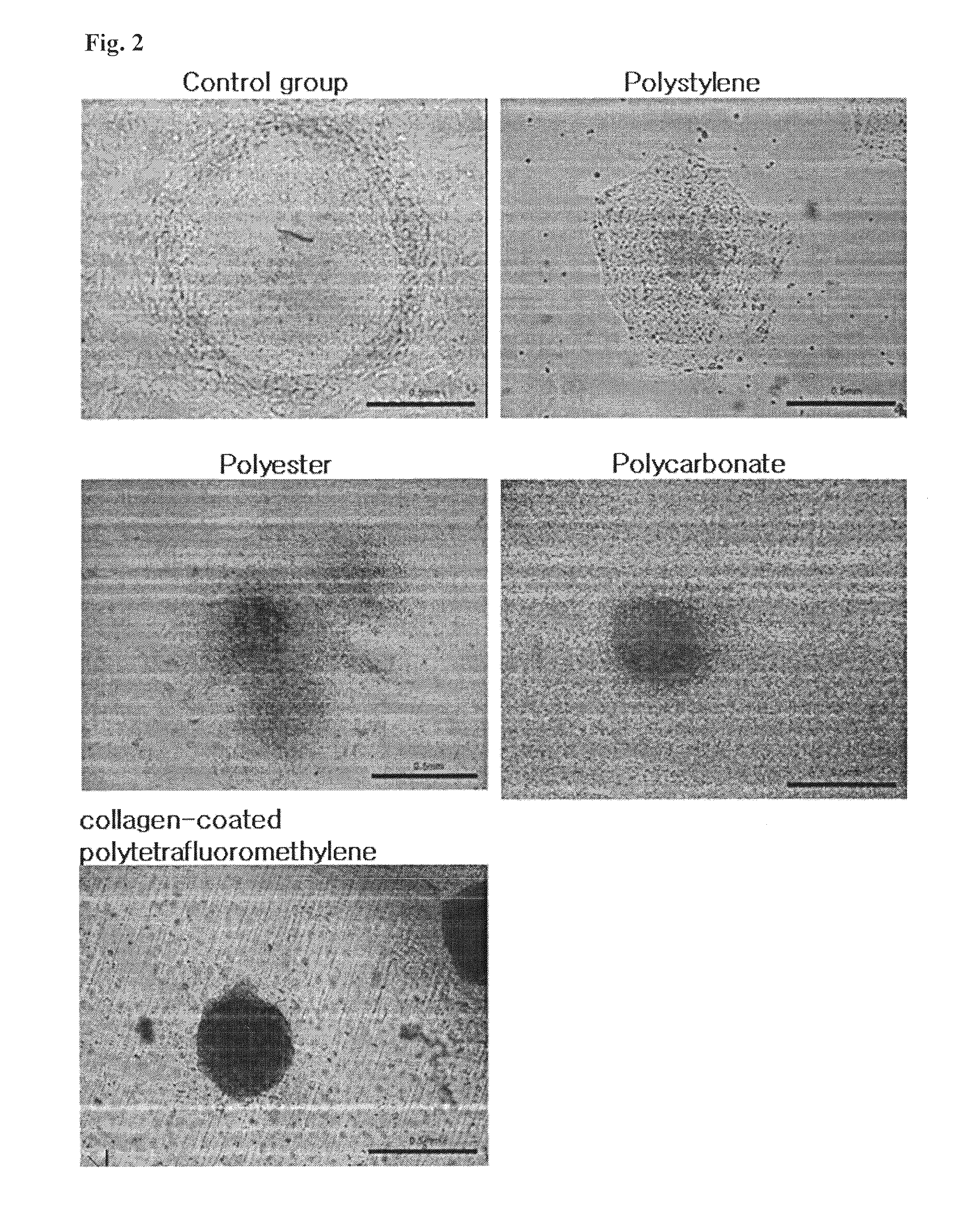
Method for co-culture of human embryonic stem cells and fibroblast feeder cells using a polyester membrane
Owner:MODERN CELL & TISSUE TECH
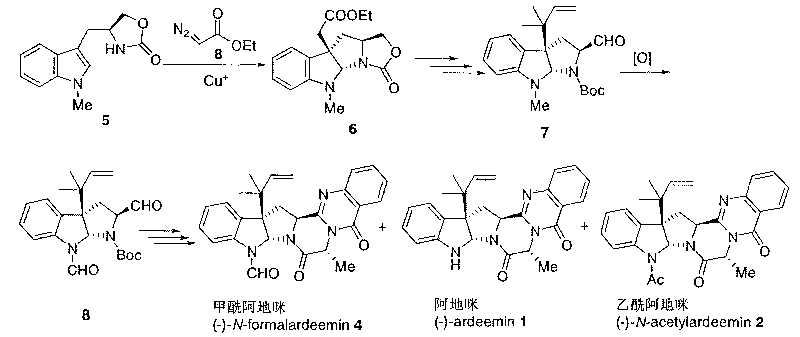
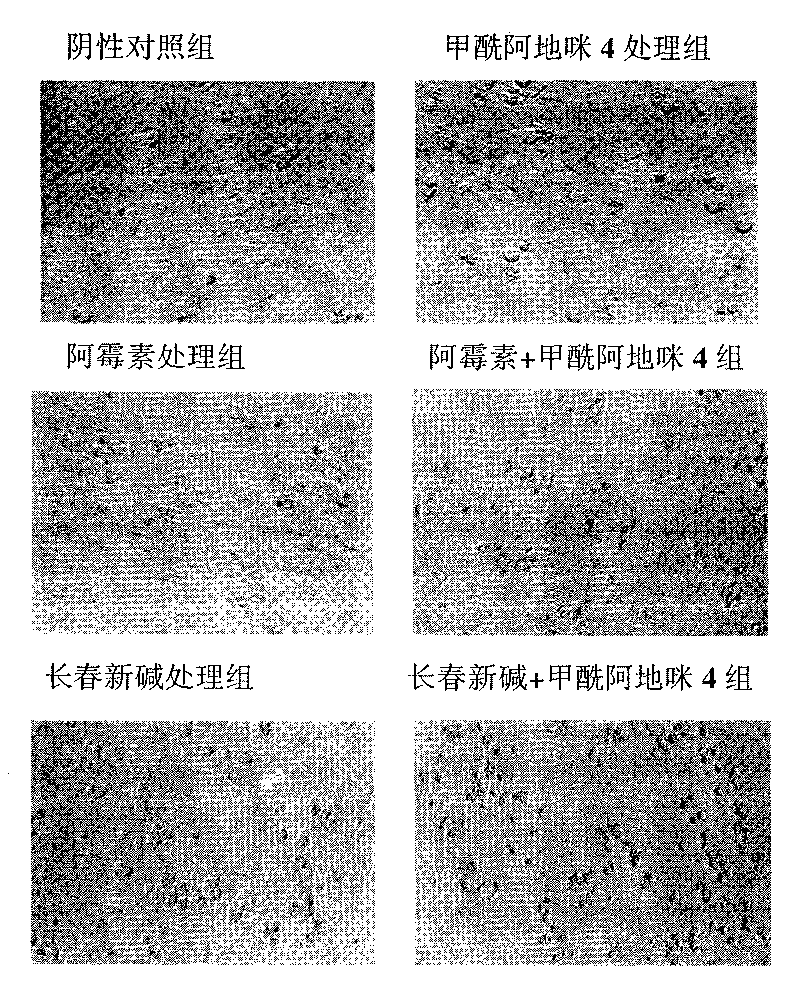
High-activity anti-caner new medicament formalardeemin for inhibiting multi-drug resistance of tumor cells
The invention relates to indole alkaloid formalardeemin shown in a chemical structural formula ((-)-5-N-formalardeemin), pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the same, and application of the indole alkaloid formalardeemin serving as an anti-tumor medicament in curing malignant tumors of human beings. The indole alkaloid formalardeemin serving as an anti-tumor medicament can not only inhibit the growth of malignant tumors directly, but also can be used as a chemosensitizer when used together with other anti-tumor medicaments such as doxorubicine, vincristine and the like to achieve the effect of effectively killing tumor cells by reversing the multi-drug resistance of the tumor cells. More significantly, compared with the indole alkaloid formalardeemin serving as a tumor cell growth inhibitor directly, the indole alkaloid formalardeemin serving as the chemosensitizer has a better effect, so the indole alkaloid formalardeemin has important clinical application prospect.
Owner:成都常春藤生物科技有限公司
Pharmaceutical composition comprising anti-GRP78 antibody as active ingredient
ActiveUS8192740B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntitumor antibodyAnticarcinogen
An object of the present invention is to provide novel pharmaceutical compositions using anti-GRP78 antibodies. More particularly, the present invention provides a novel method of cancer treatment using anti-GRP78 antibodies, novel cell growth inhibitors and anticancer agents that contain anti-GRP78 antibodies, as well as novel anti-GRP78 antibodies. The present inventor prepared antitumor antibodies to target GRP78, the localization of which in cancer cells changed to the cell membrane. The inventor successfully obtained an anti-GRP78 antibody that would bind specifically to the cell surface of cancer cells, leading to the accomplishment of the above-mentioned objects.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-glypican 3 antibody having modified sugar chain
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Diagnosis and treatment of cancer by using Anti-prg-3 antibody
InactiveUS20100111851A1LevelImprove the level ofIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnticarcinogenCancer type
The present invention discloses an antibody capable of binding to the PRG-3 protein and inhibiting the growth of cells expressing the PRG-3 protein. The growth inhibitory activity is cytotoxic activity, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. The present invention also discloses a pharmaceutical composition, cell growth inhibitor, and an anticancer agent comprising the antibody of the present invention as an active ingredient. Examples of the type of cancer include hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, colon cancer, and glioblastoma. In addition, the present invention discloses a method for diagnosing cancer by detecting expression of the PRG-3 protein or the gene encoding the PRG-3 protein, as well as a diagnostic agent and kit for use in the method.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
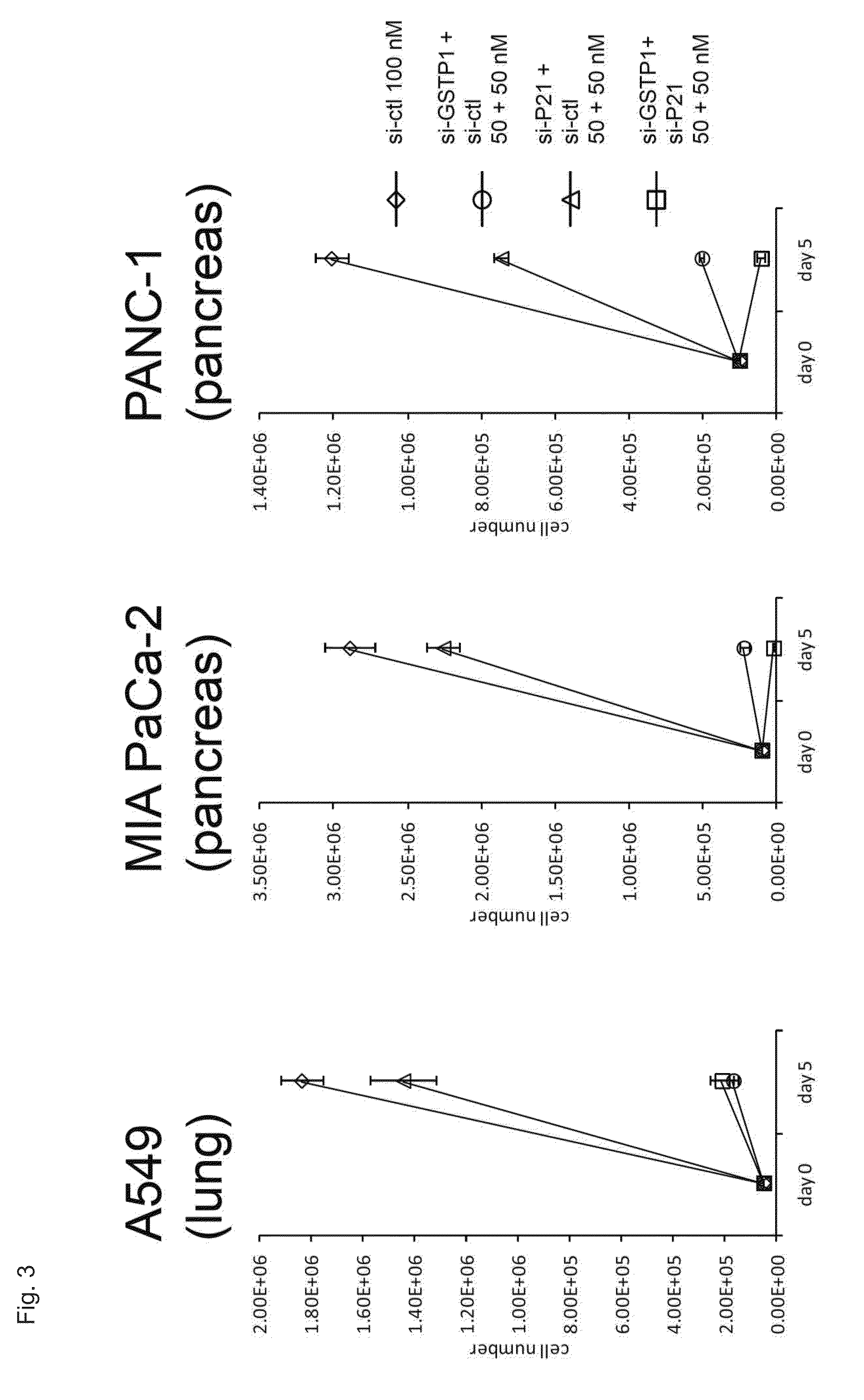
Cell death-inducing agent, cell growth-inhibiting agent, and pharmaceutical composition for treatment of disease caused by abnormal cell growth
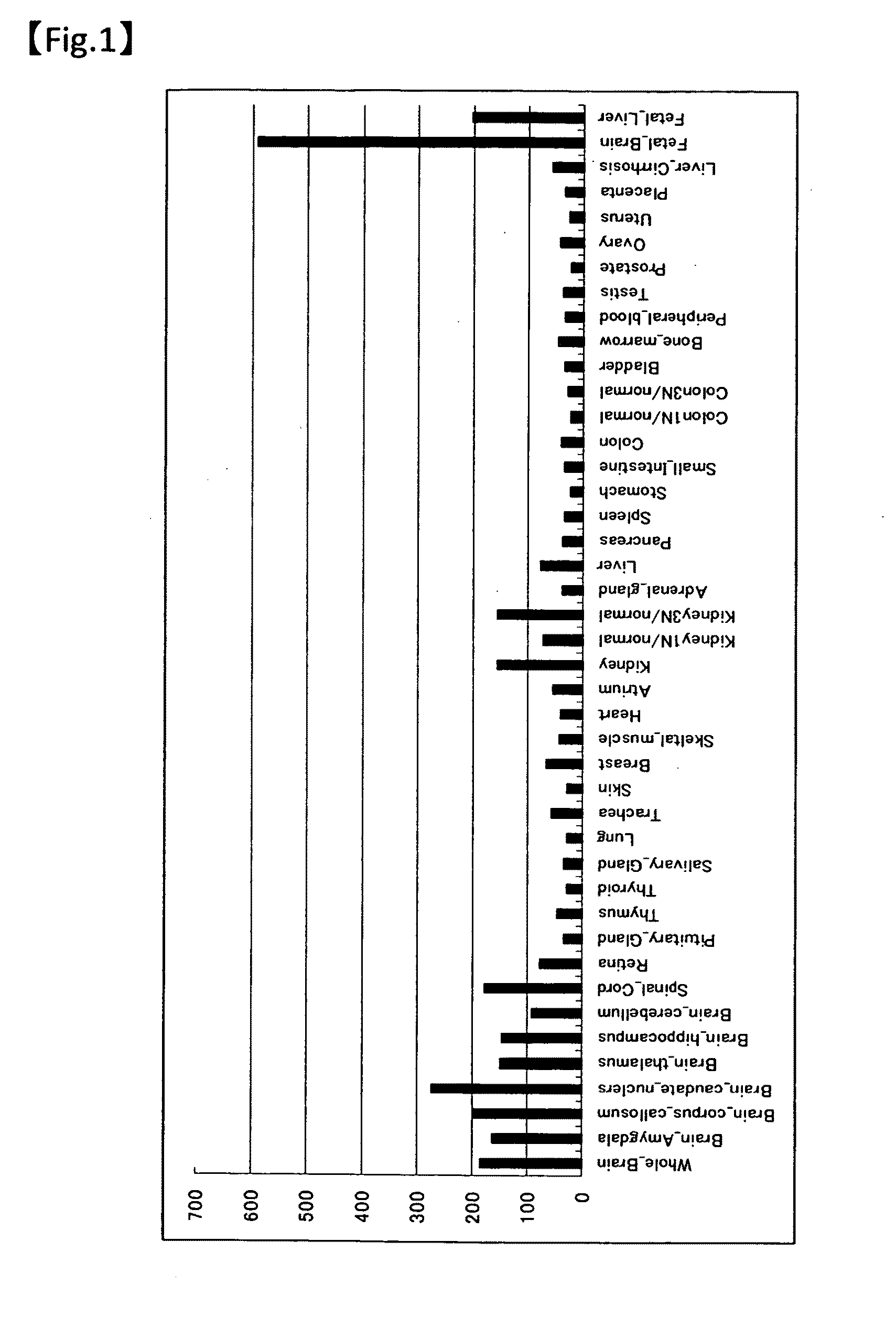
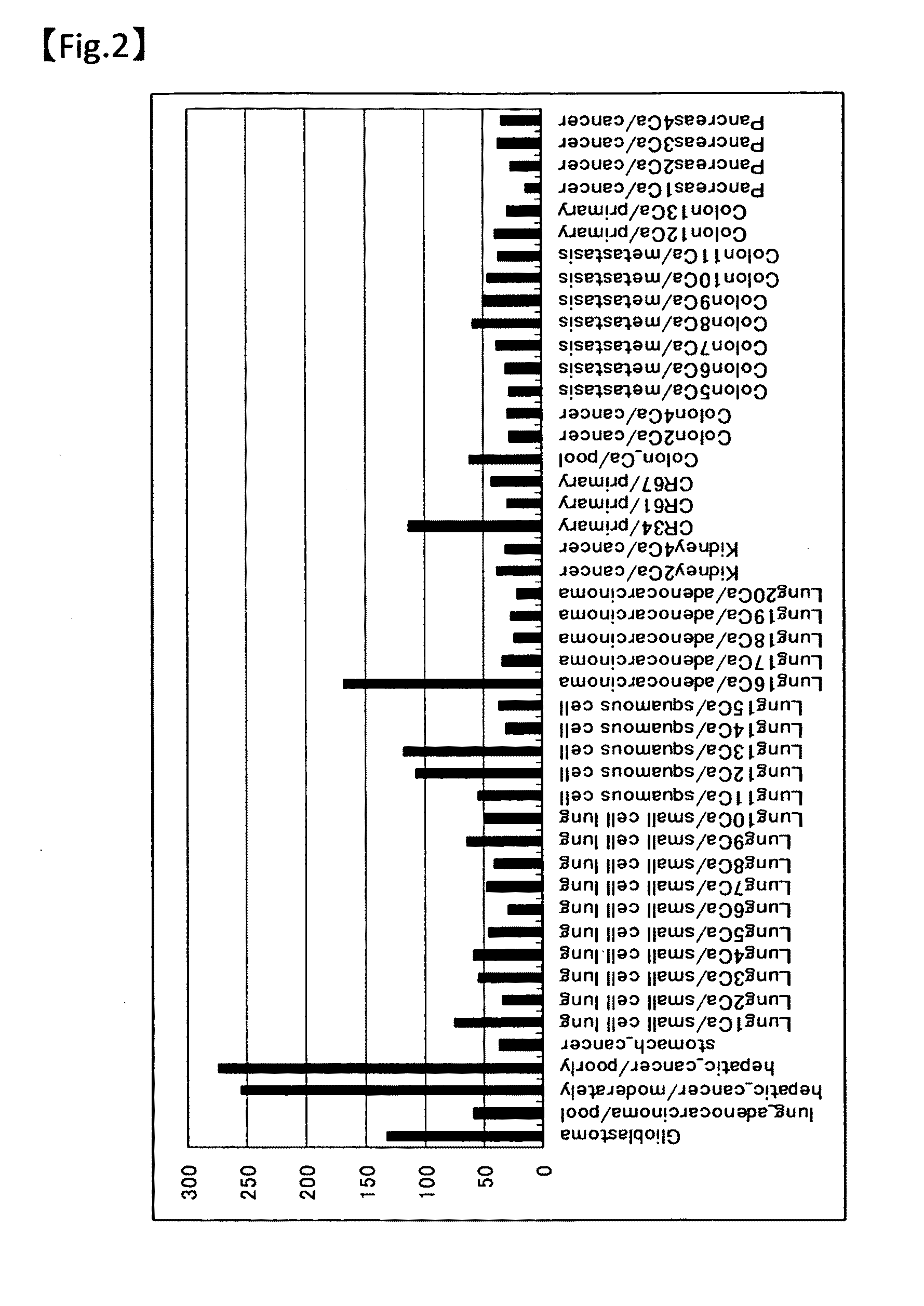
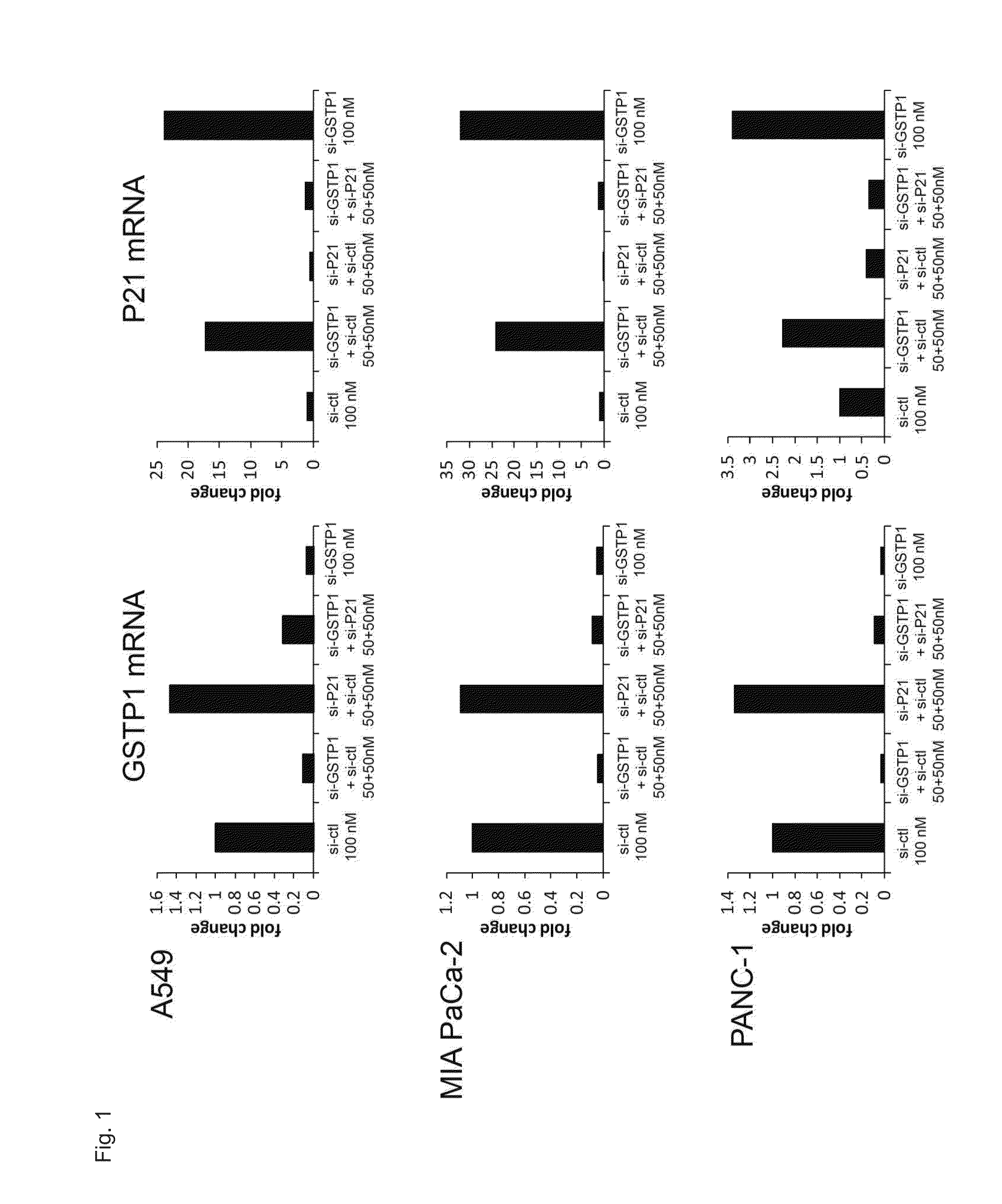
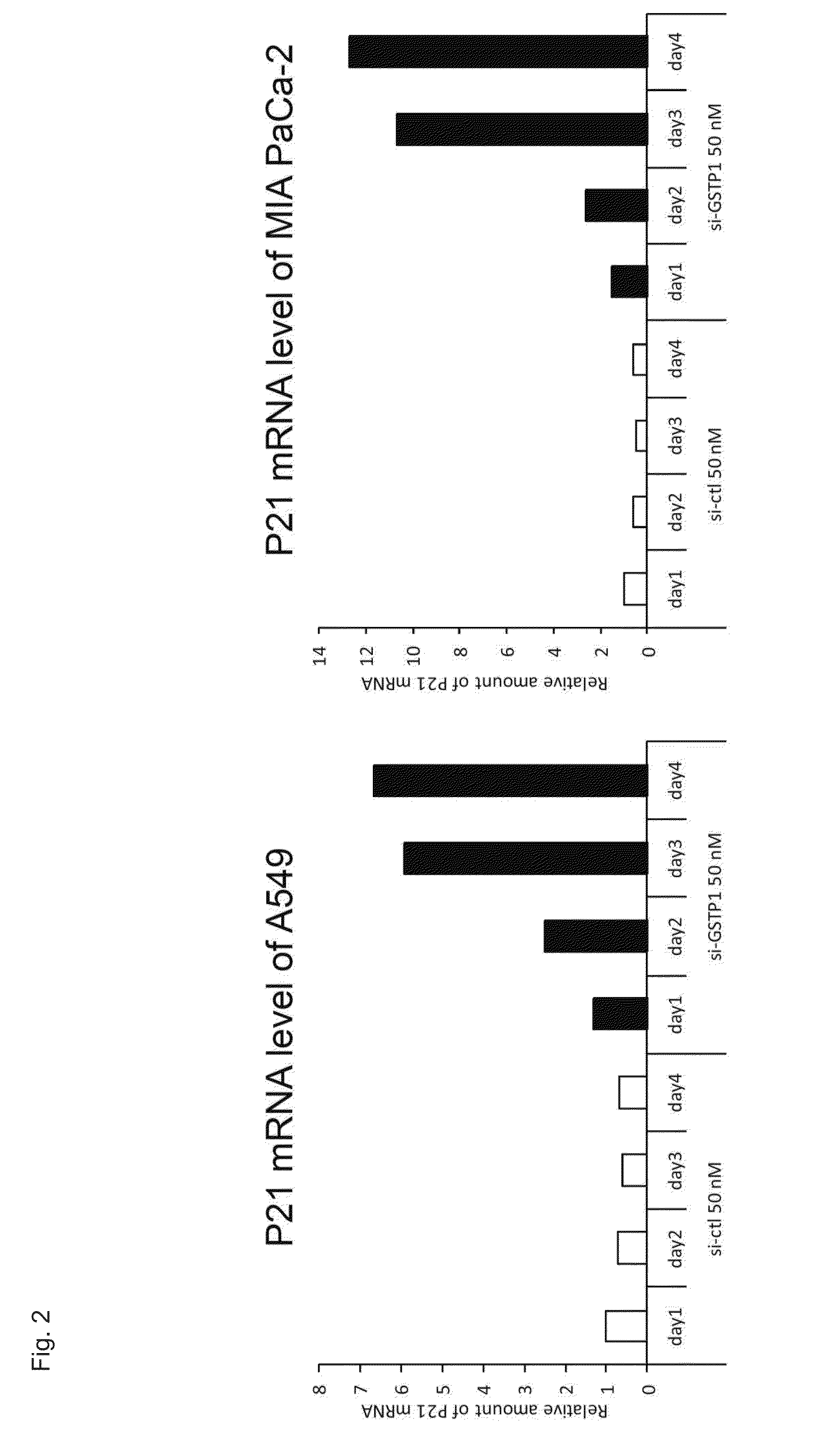
InactiveUS20160187319A1Induce cell deathImprove efficacyOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic lethalityCancer cell
An agent for inducing cell death and / or inhibiting cell growth for cancer cells. The agents of the present invention comprise, as active ingredients, a drug inhibiting GST-π and a drug inhibiting a homeostasis-related protein that exhibits synthetic lethality when inhibited together with GST-π. The homeostasis-related protein can be a cell cycle-regulating protein or an anti-apoptosis-related protein.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
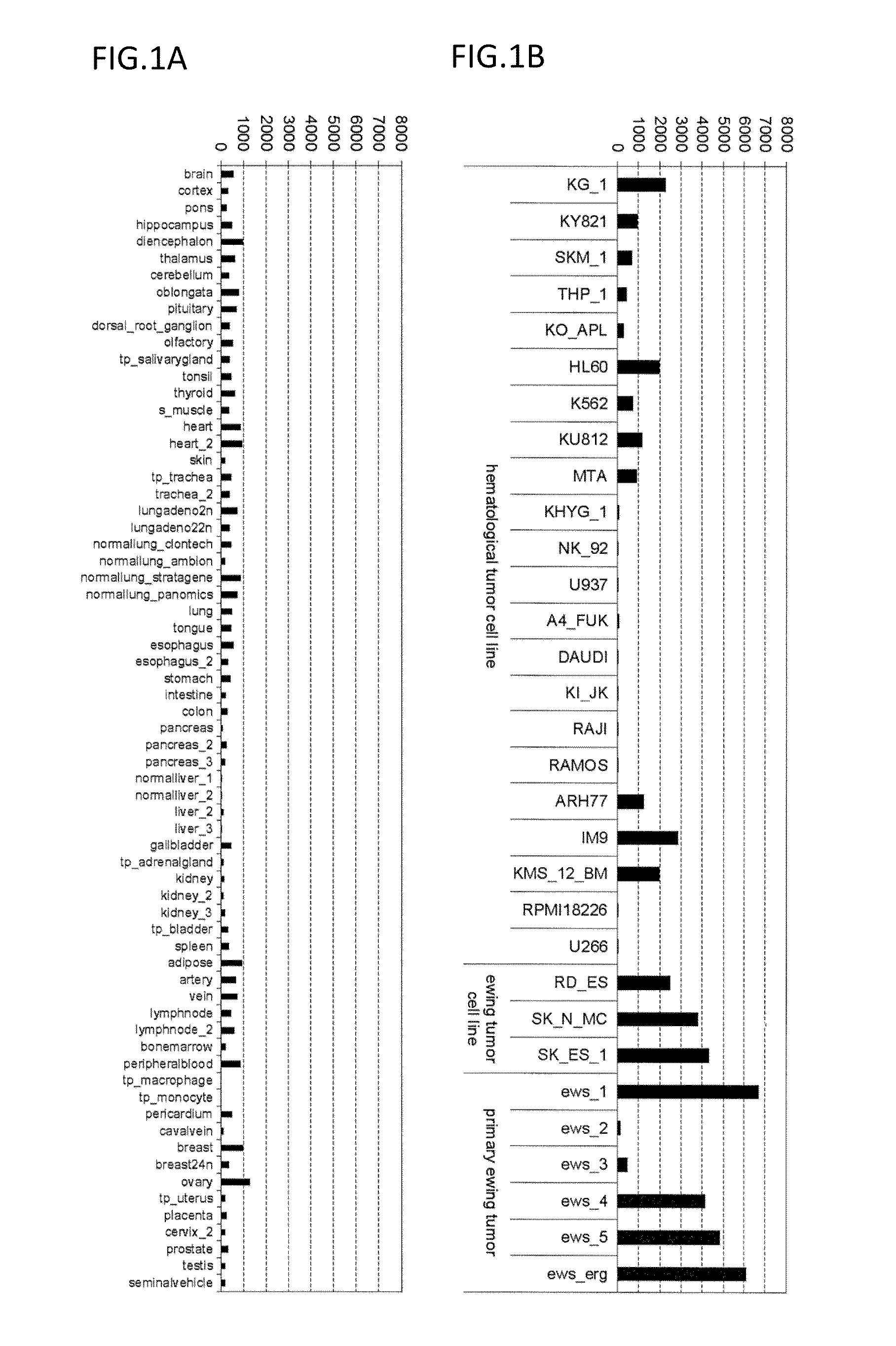
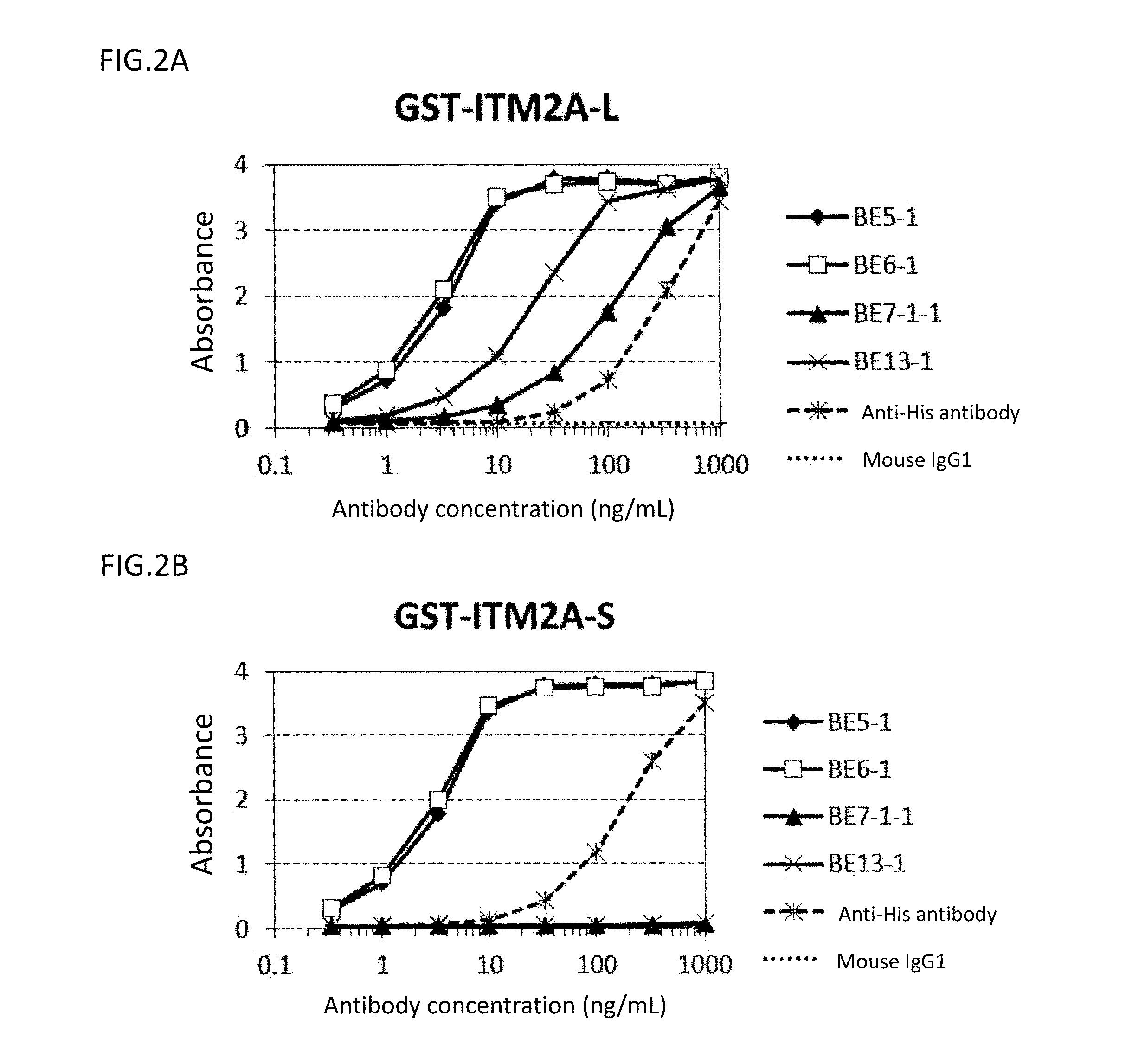
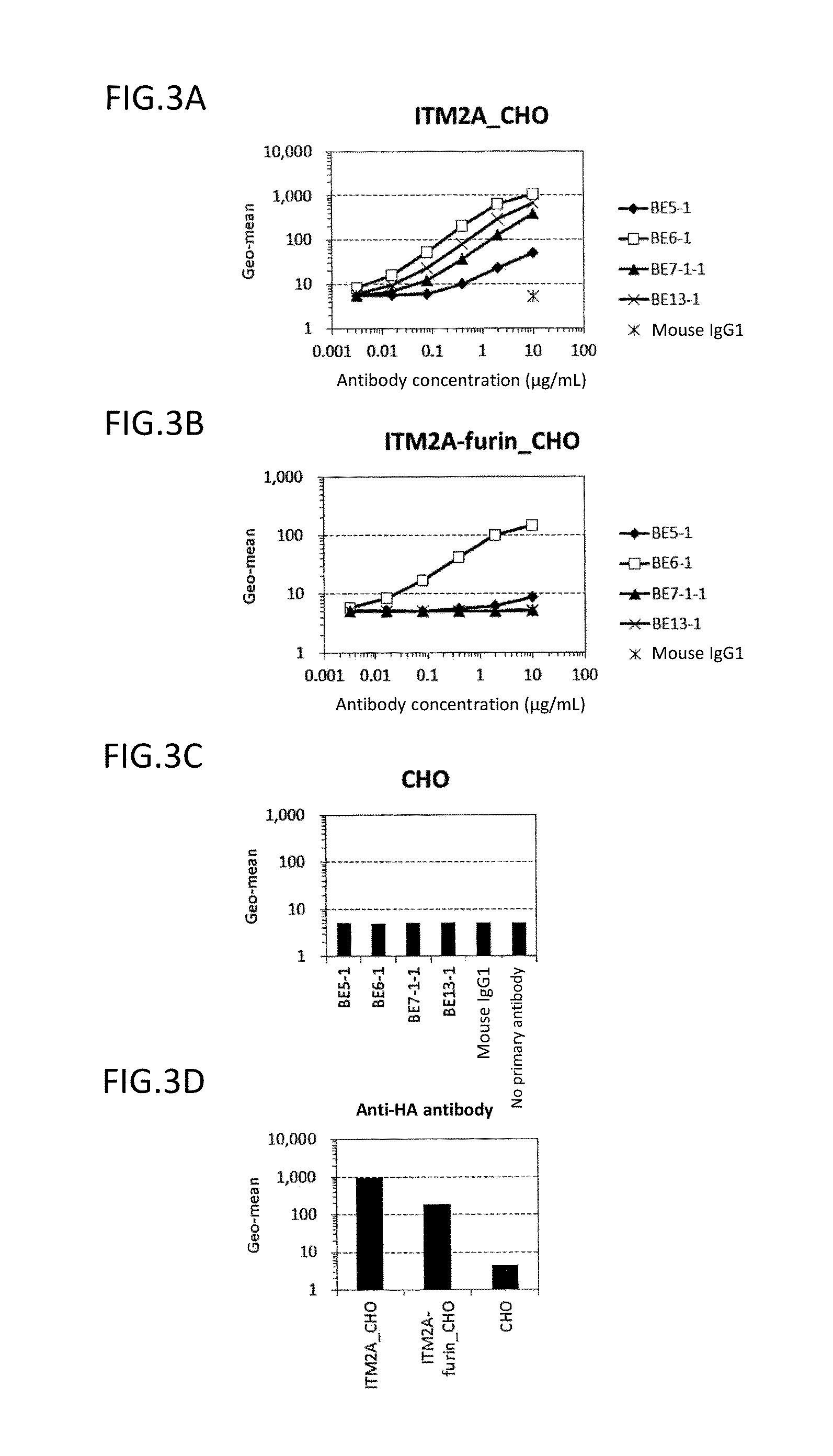
Diagnosis and treatment of cancer using Anti-itm2a antibody
InactiveUS20140193420A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDisease diagnosisAnticarcinogenAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed is a monoclonal antibody binding to an ITM2A protein. This antibody is useful in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of cancer such as Ewing's sarcoma, T cell leukemia, T cell lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, B cell tumor, and multiple myeloma. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition, a cell growth inhibitor, and an anticancer agent containing the antibody as an active ingredient, and a method for treating cancer, a method for predicting the efficacy of cancer treatment, and a method for determining the presence of cancer in a test subject using the antibody.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Novel polyamine analog conjugates and quinone conjugates as therapies for cancers and prostate diseases
Peptide conjugates in which cytostatic and cytostatic agents, such as polyamine analogs or naphthoquinones, are conjugated to a polypeptide recognized and cleaved by enzymes such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and cathepsin B are provided, as well as compositions comprising these conjugates. Methods of using these conjugates in the treatment of prostate diseases are also provided.
Owner:PROGEN PHARMA INC
Induction of differential stress resistance and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080242638A1Improve efficiencyImprove the immunityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGlucose intakeSide effect
This invention relates to methods of inducing differential stress resistance in a subject with cancer by starving the subject for a short term, administering a cell growth inhibitor to the subject, or reducing the caloric or glucose intake by the subject. The induced differential stress resistance results in improved resistance to cytotoxicity in normal cells, which, in turn, reduces cytotoxic side-effects due to chemotherapy, as well as improved effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof
The present invention provides a compound of the following formula (1) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein X is an oxygen atom and the like; Y is -CO-, -S02-and the like; R1 is an optionally-substituted C1-6 alkyl group, an optionally-substituted C1-6 alkylcarbonyl group and the like; R2 is an optionally-substituted C1-6 alkyl group, an optionally-substituted C1-6 alkoxy group, an optionally-substituted amino group, an optionally-substituted 5-to 12-membered monocyclic or polycyclic saturated heterocyclic group and the like; R3, R4, R5, and R6 are independently a hydrogen atom and the like which exhibits excellent effects in suppressing the proliferation and sphere-forming ability of cancer cells, and can be useful as an antitumor drug or cell growth inhibitor.
Owner:1GLOBE BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
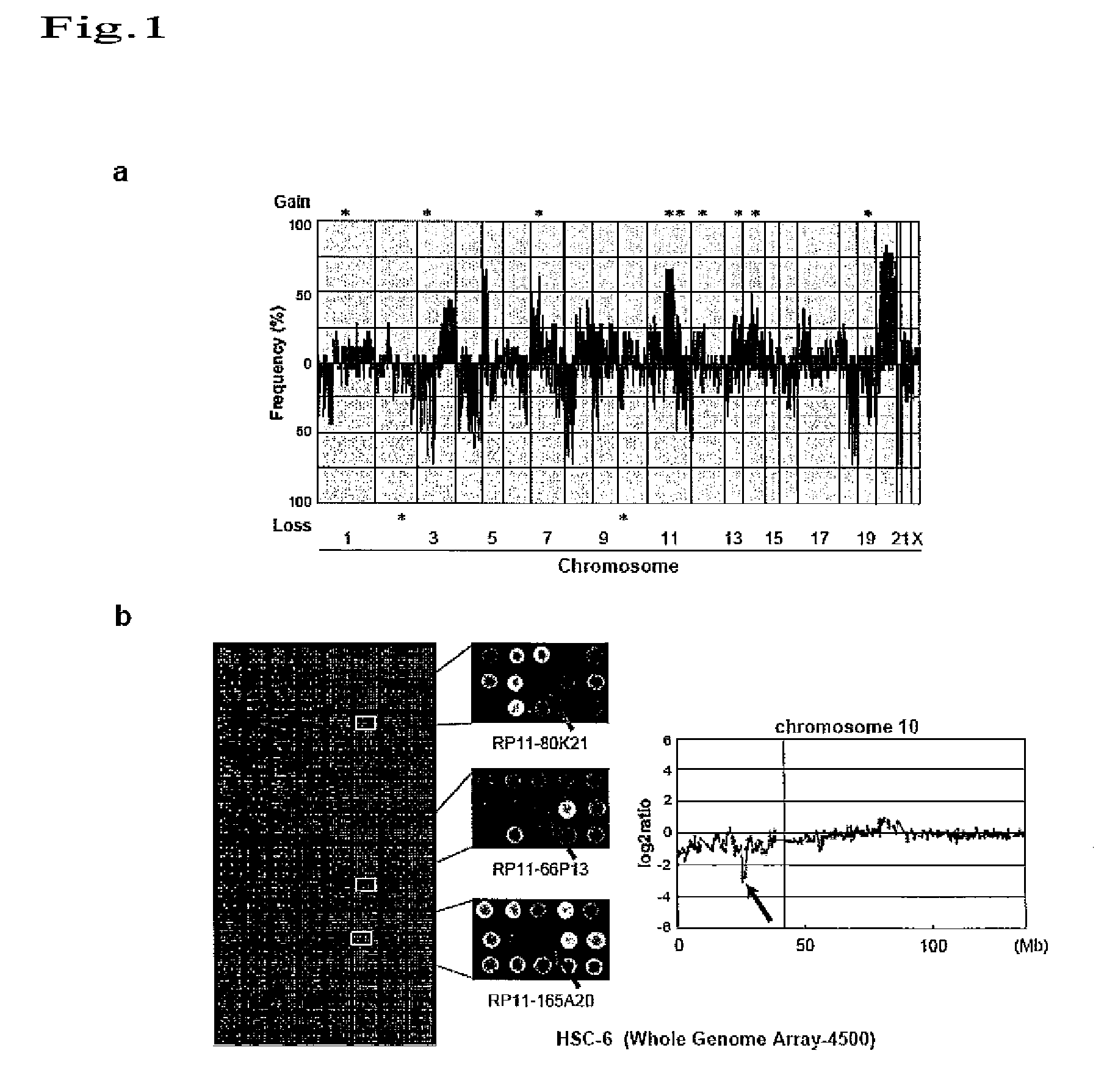
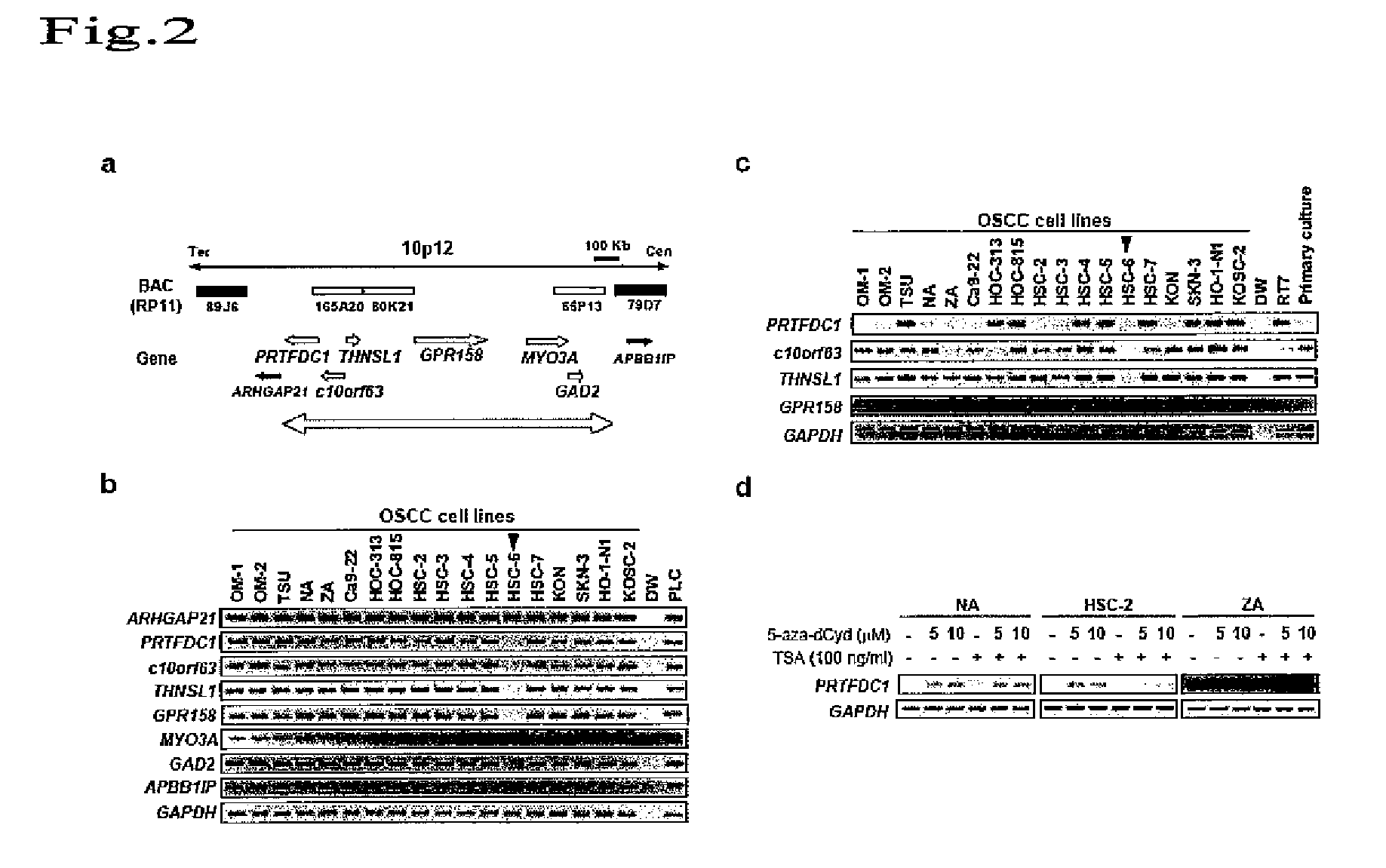
Method for detecting oral squamous-cell carcinoma and method for suppressing the same
InactiveUS20090011950A1Conveniently and rapidly analyzingPromotes cancerationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSmall-cell carcinomaSquamous Carcinomas
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for detecting cancer through identification of genes exhibiting characteristic behavior in the cases of cancer such as oral squamous-cell carcinoma, and a cell growth inhibitor. The present invention provides a method for detecting cancer, which comprises detecting canceration including malignancy of a specimen through detection of at least one alteration of a gene existing in a chromosomal region 1q21, 2q24. 1-q24.2, 3p13, 7p11.2, 10p12.1, 11p5.4, 11p15.2, 11p13.3, 11q22, 11q23.3, 12p13, 12q24.31, 13q33.3-q34, 12q24.1, 19q13, or 22q12.1 in the specimen.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Medicine composition with carbazole alkaloid in clausena plants as antineoplastic activity ingredient and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102988356AReduce lossesLow costOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCarbazoleBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Provided is a medicine composition with carbazole alkaloid clausine D(1), 6-methoxyheptaphylline (2) and mafaicheenamine C (3) or claulansine G (4) as active ingredients. The invention further provides a preparation method of the medicine composition, application of the composition in preparation of tumor cell growth inhibitor and application of the composition in preparation of antineoplastic medicine.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com














![3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof 3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e165219-82b3-4561-b3ea-40a04fe42863/BDA0001069261980000021.PNG)
![3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof 3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e165219-82b3-4561-b3ea-40a04fe42863/BDA0001069261980000022.PNG)
![3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof 3-substituted carbonyl-naphtho[2,3-b]furane derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2e165219-82b3-4561-b3ea-40a04fe42863/BDA0001069261980000023.PNG)