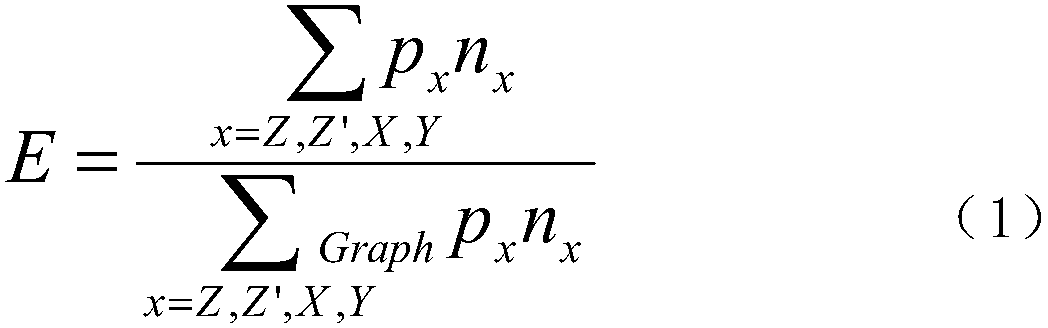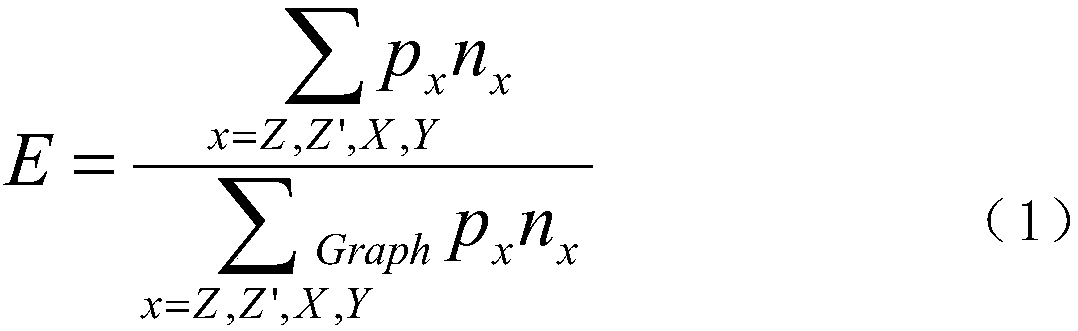Patents
Literature
31 results about "Intrusion detection and prevention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method, system and computer-readable media for reducing undesired intrusion alarms in electronic communications systems and networks
InactiveUS20080295172A1Reduce probabilityHigh speed detectionMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCommunications systemElectronic communication
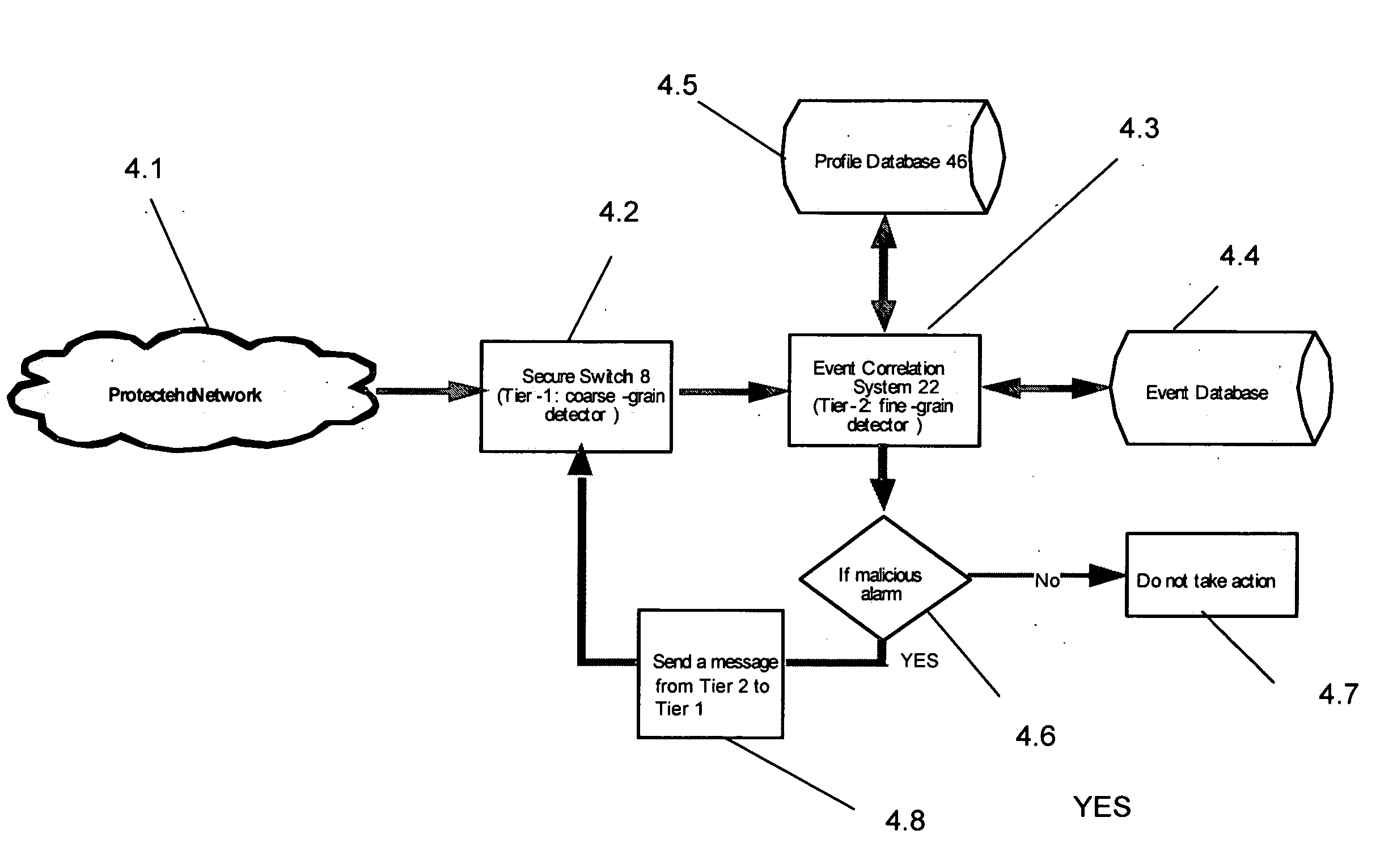
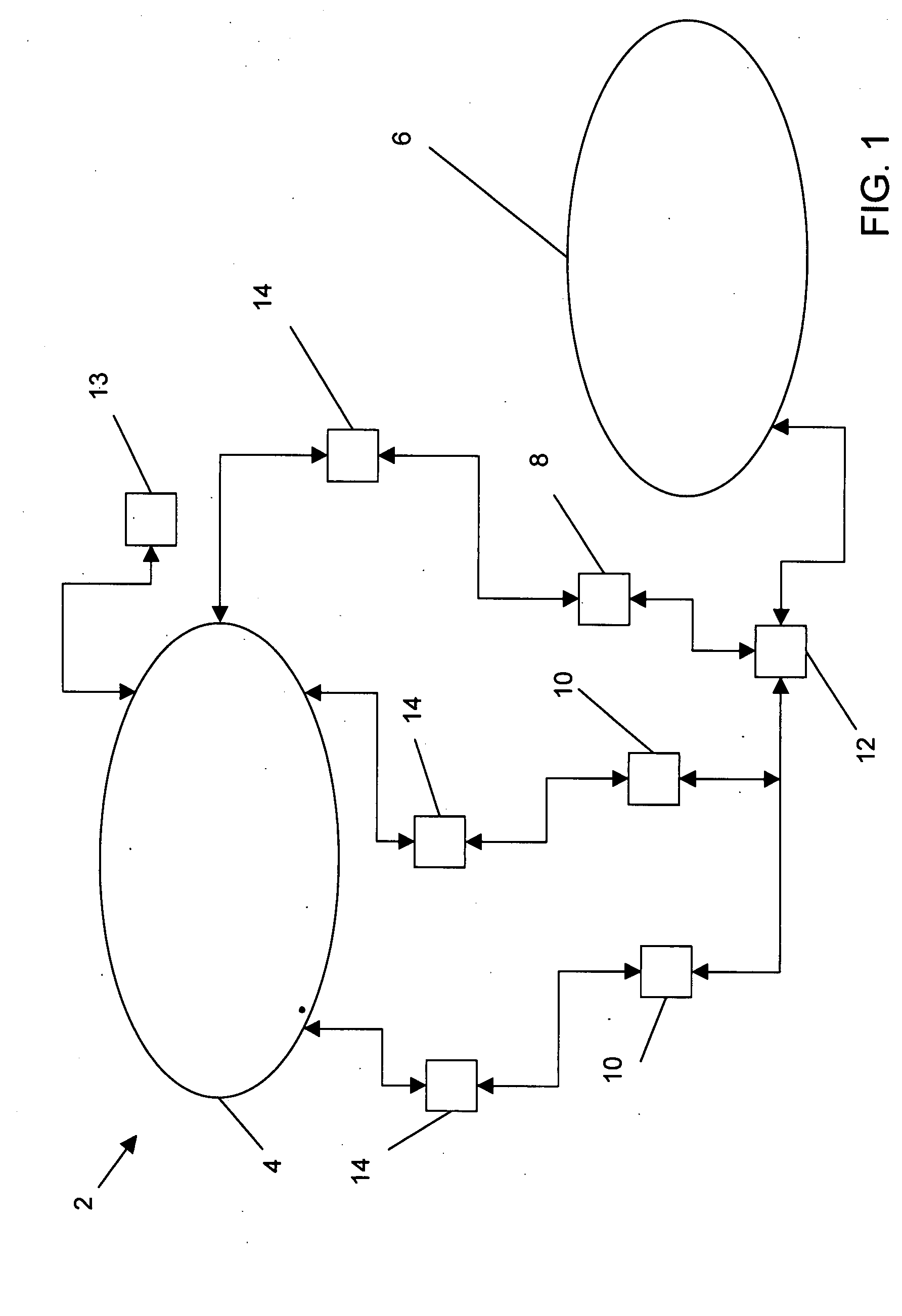
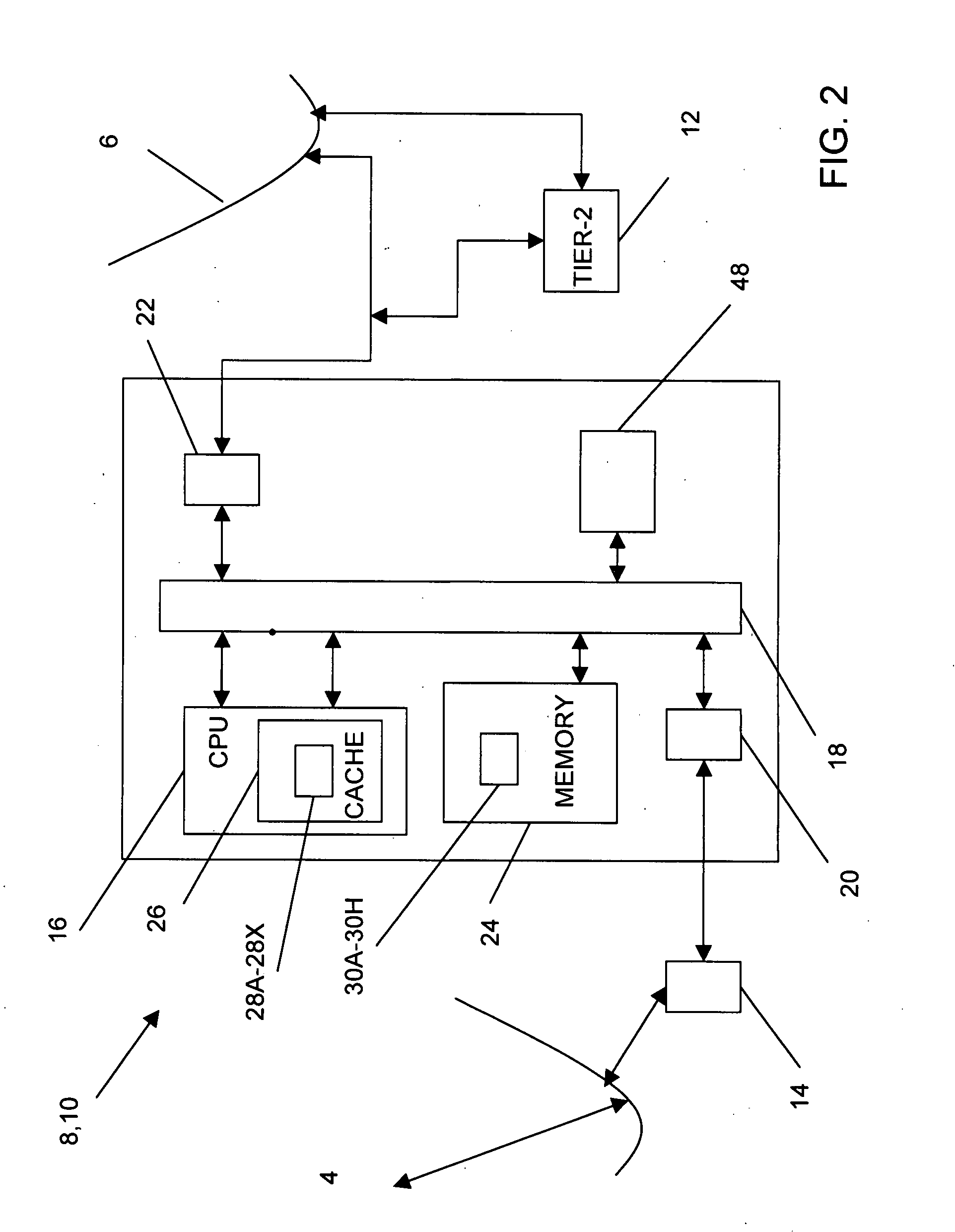
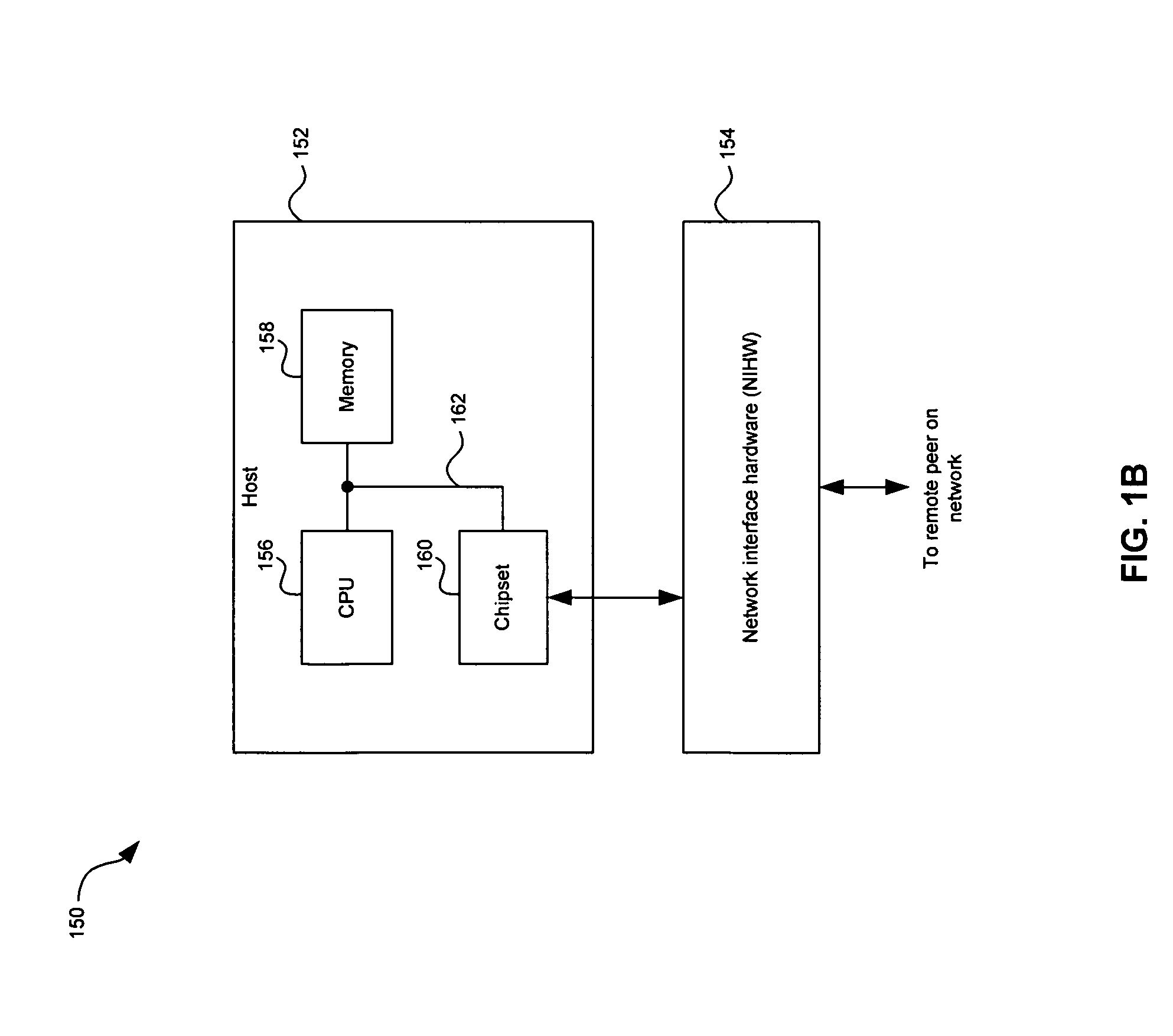
A method, system and computer-readable media that enable the employment of an intrusion detection process are provided. This present invention is able to differentiate between certain malicious and benign incidents by means of a two-stage anomaly-based intrusion detection and prevention system. The invented system works at high-speed and with low-memory resources requirements. In particular, the invented method is implemented in a two-stage detector that performs coarse grain detection using sub-profiles 30A-30H (key features extracted from a profile) at one stage and fine grain (detailed behavioral profile) detection at another stage to eliminate unwanted attacks and false positives. Furthermore, in order to suppress specific alarms, the invented system allows the administrator to specify detailed profiles 32A-32H. By using a sub-profile extractor, a sub-profile is extracted, which is then downloaded into the coarse grain detector.
Owner:NEVIS NETWORLS INC
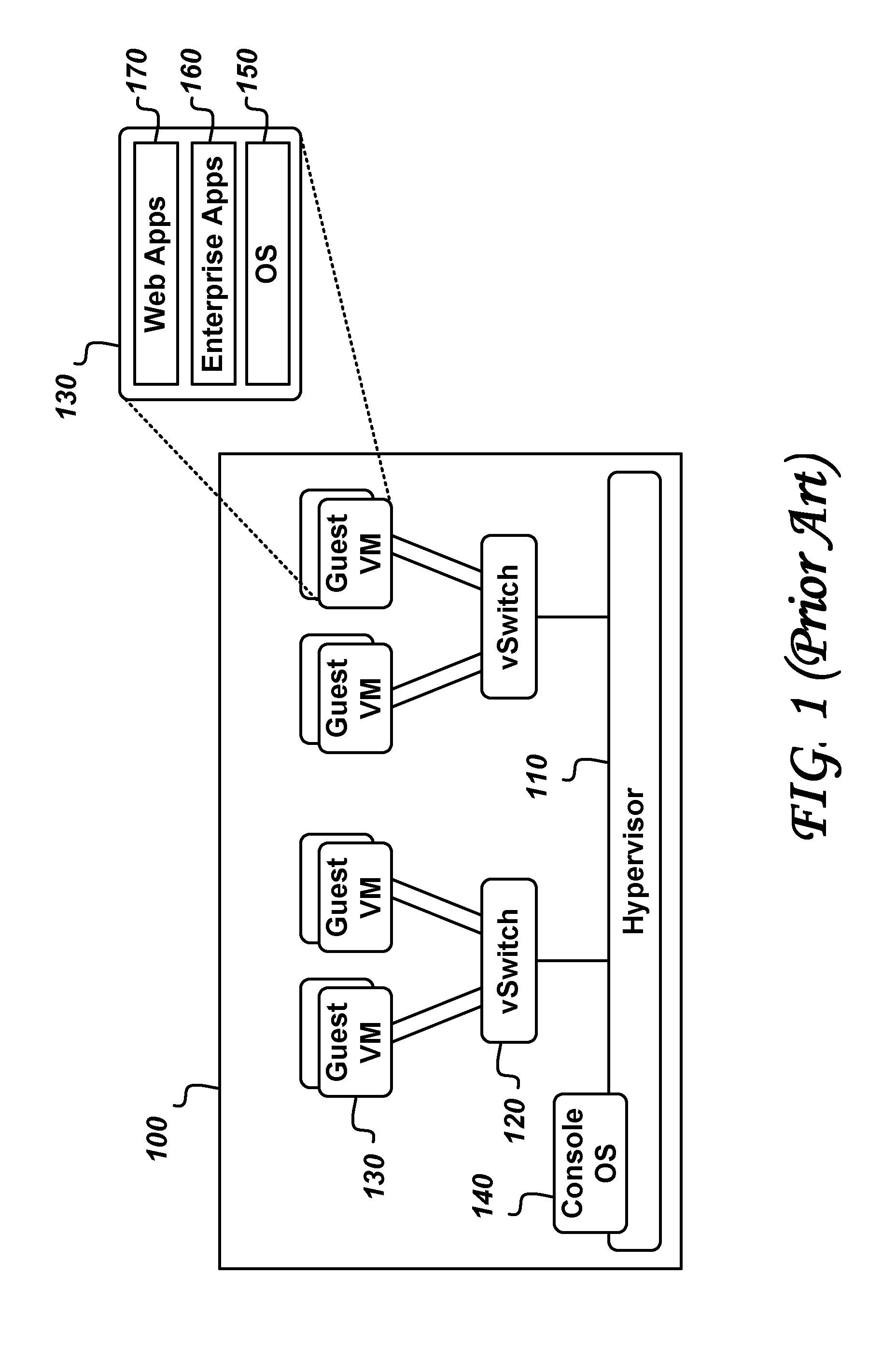
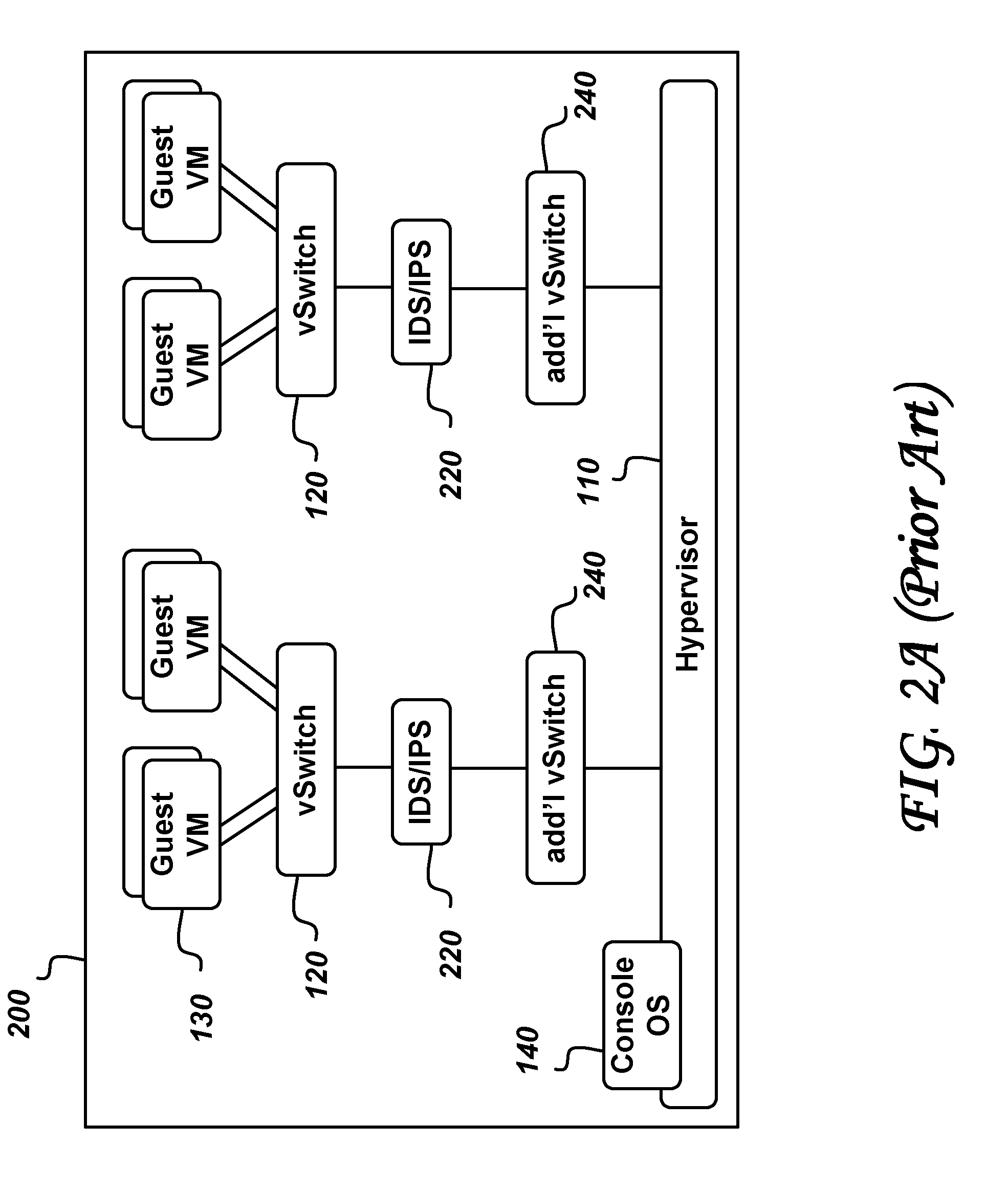
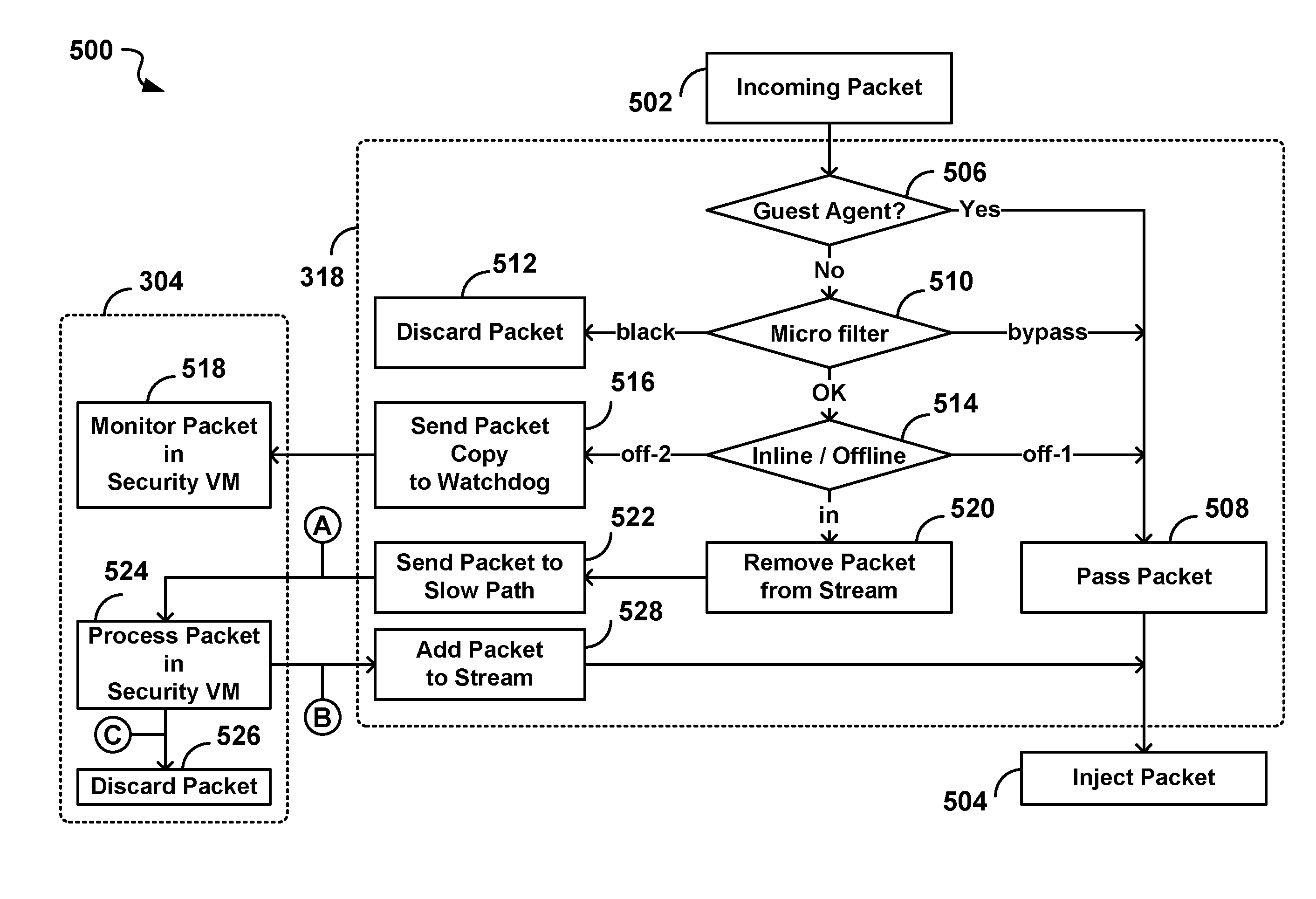
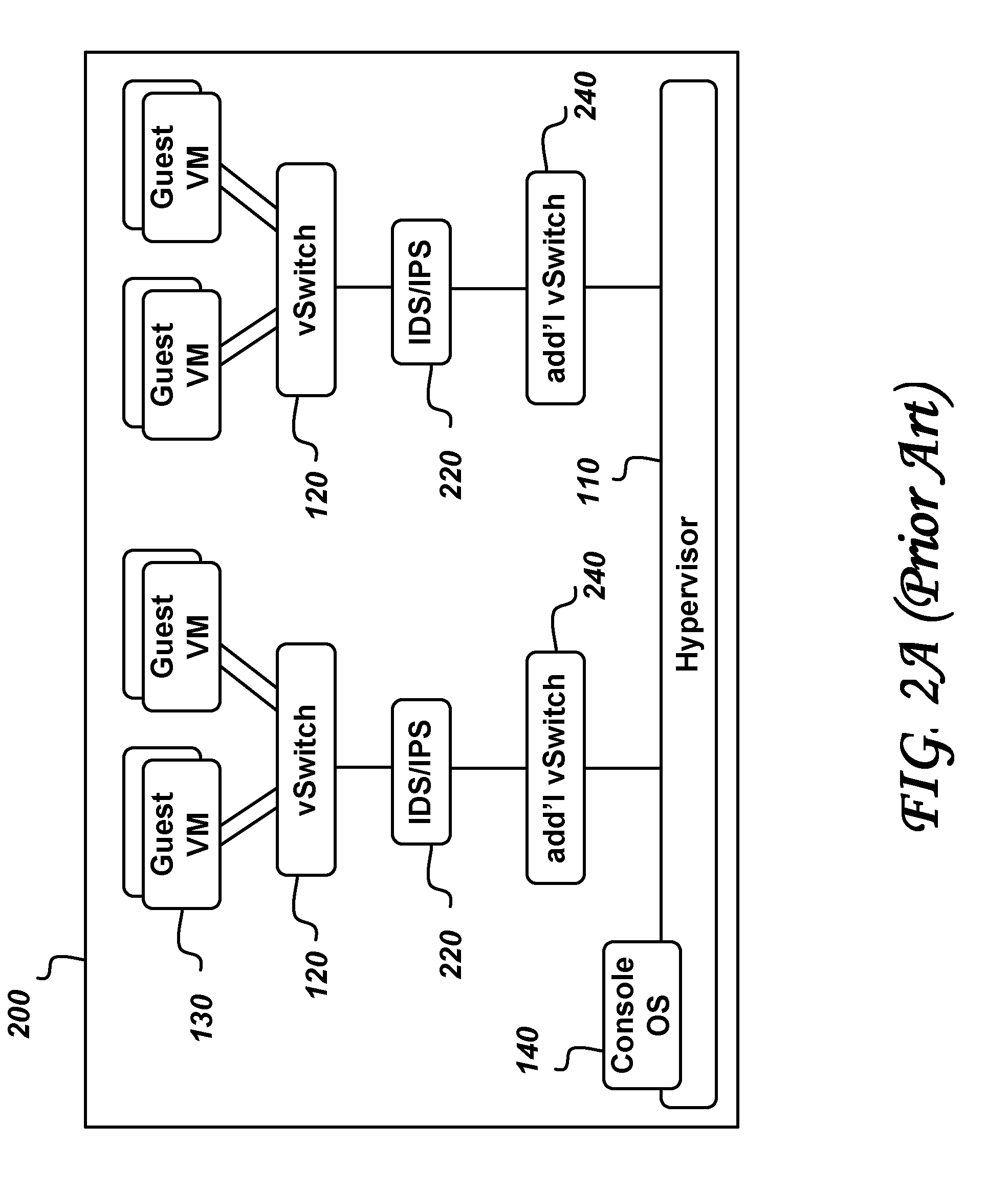
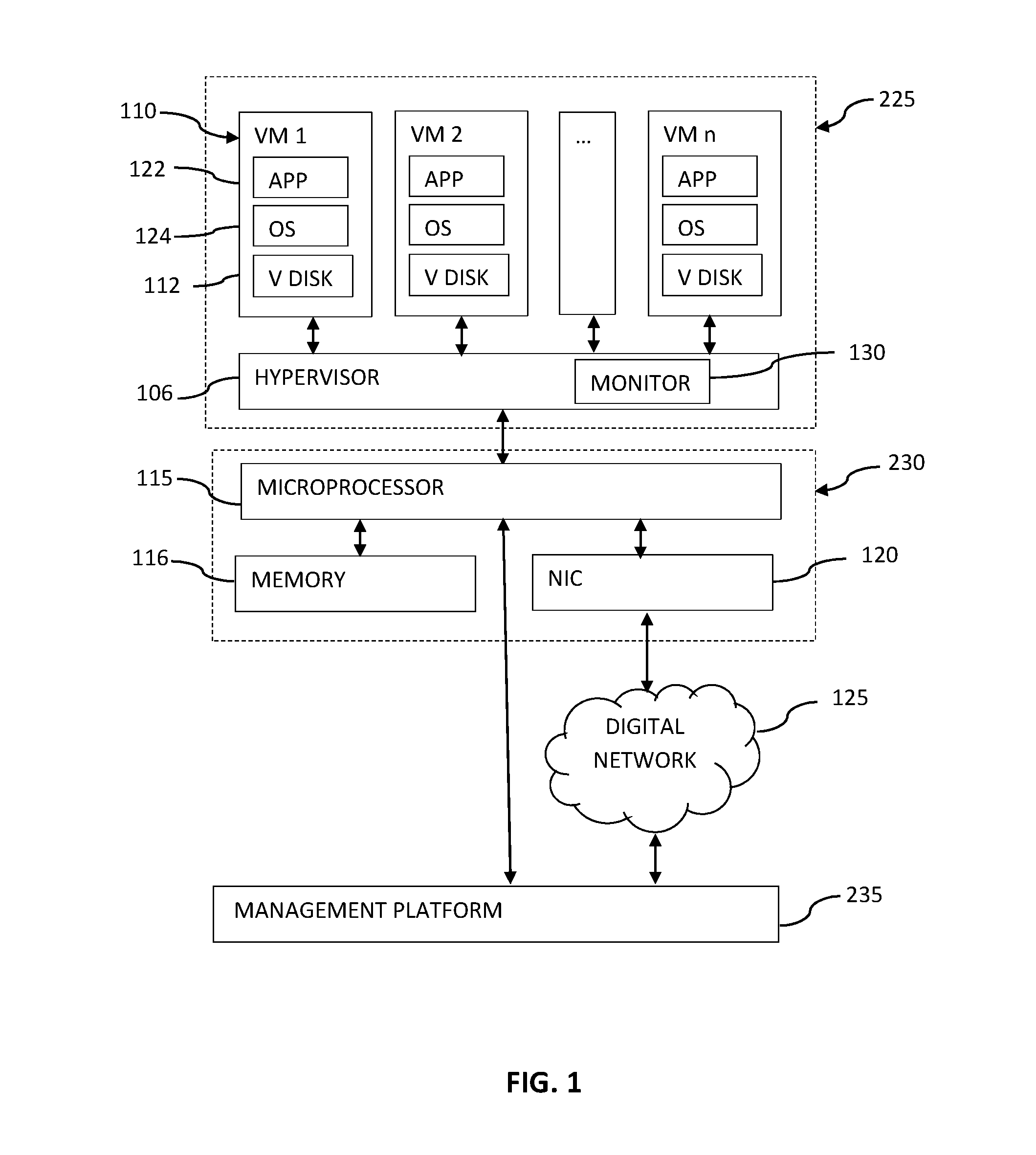
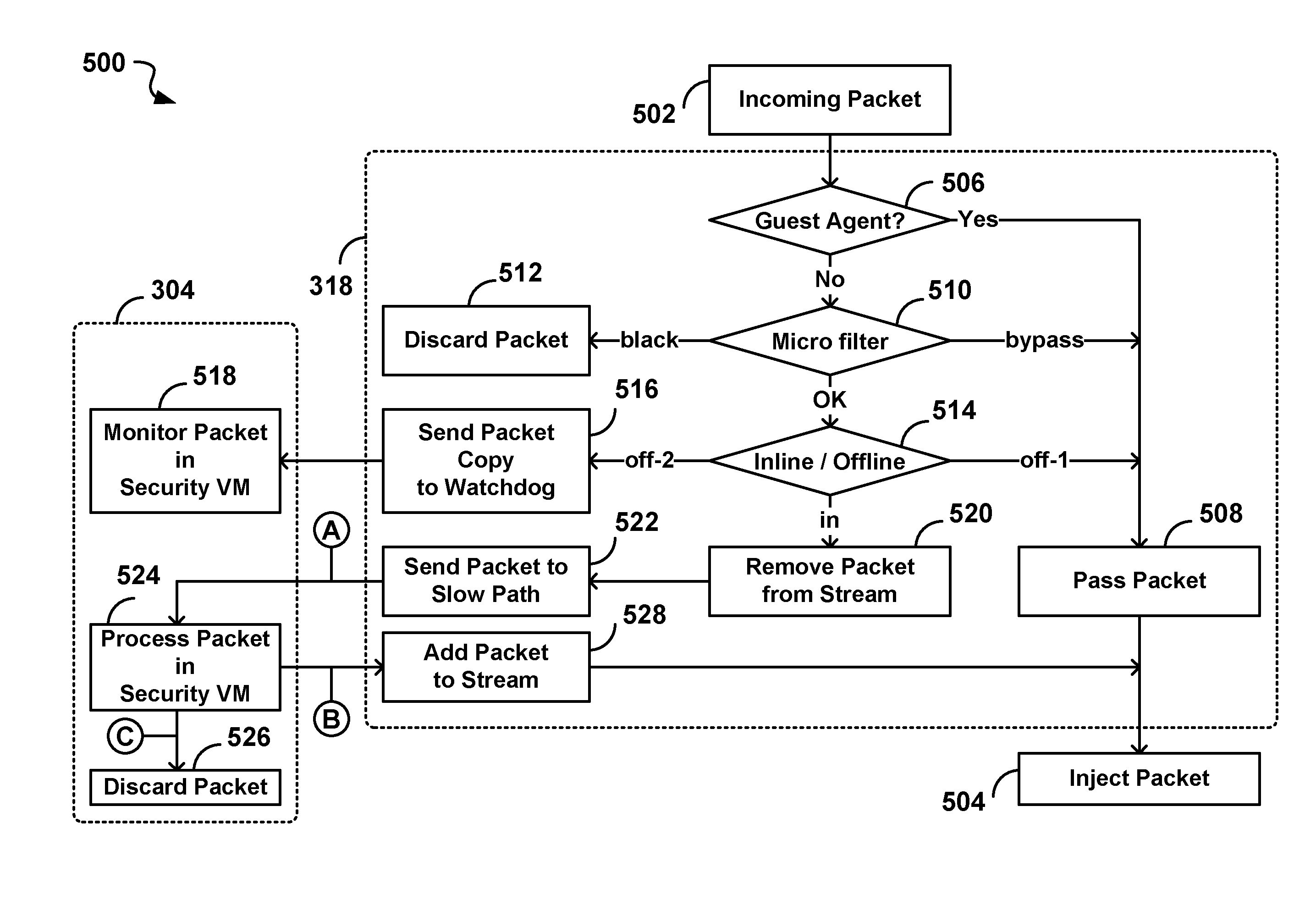
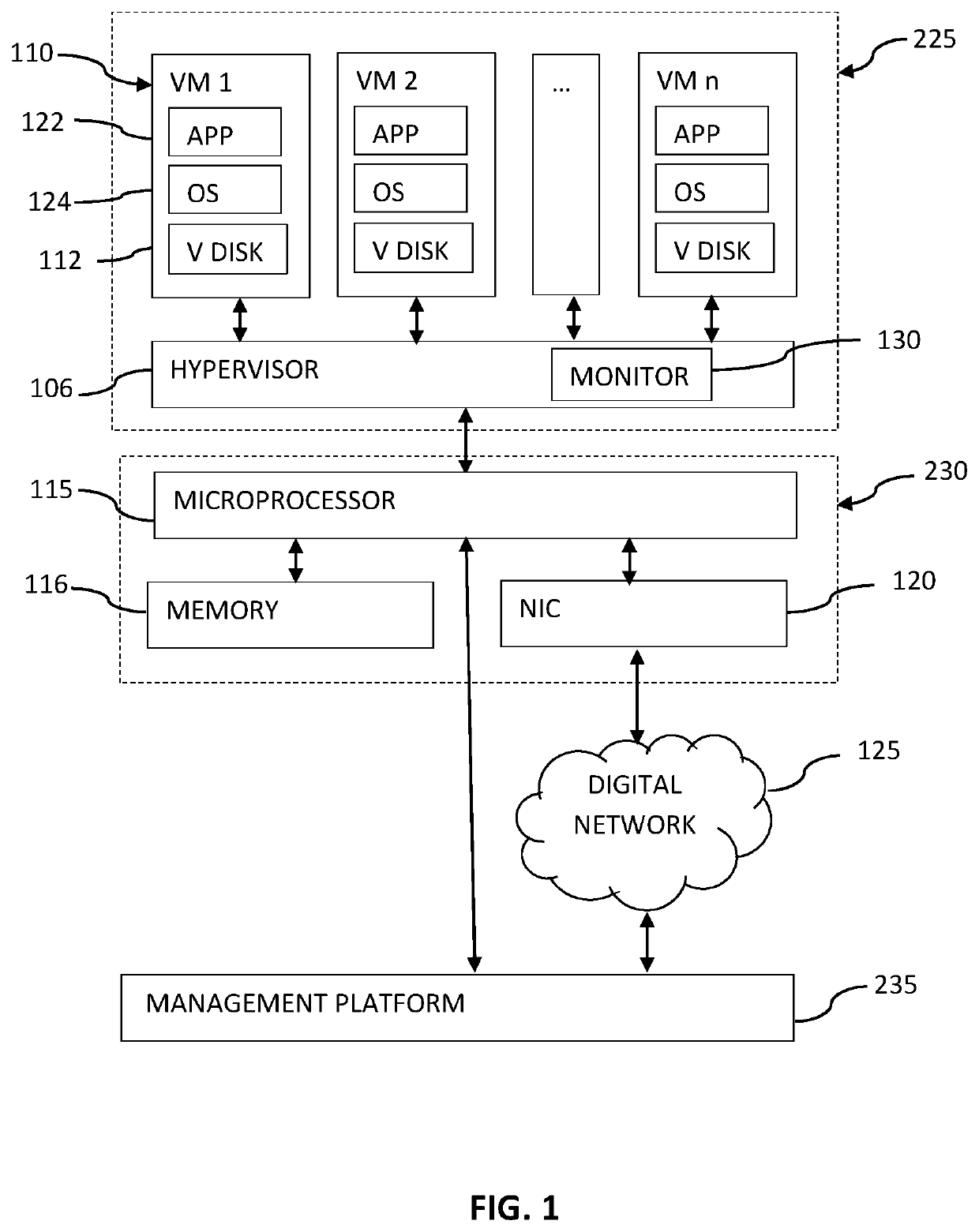
System and method for intelligent coordination of host and guest intrusion prevention in virtualized environment
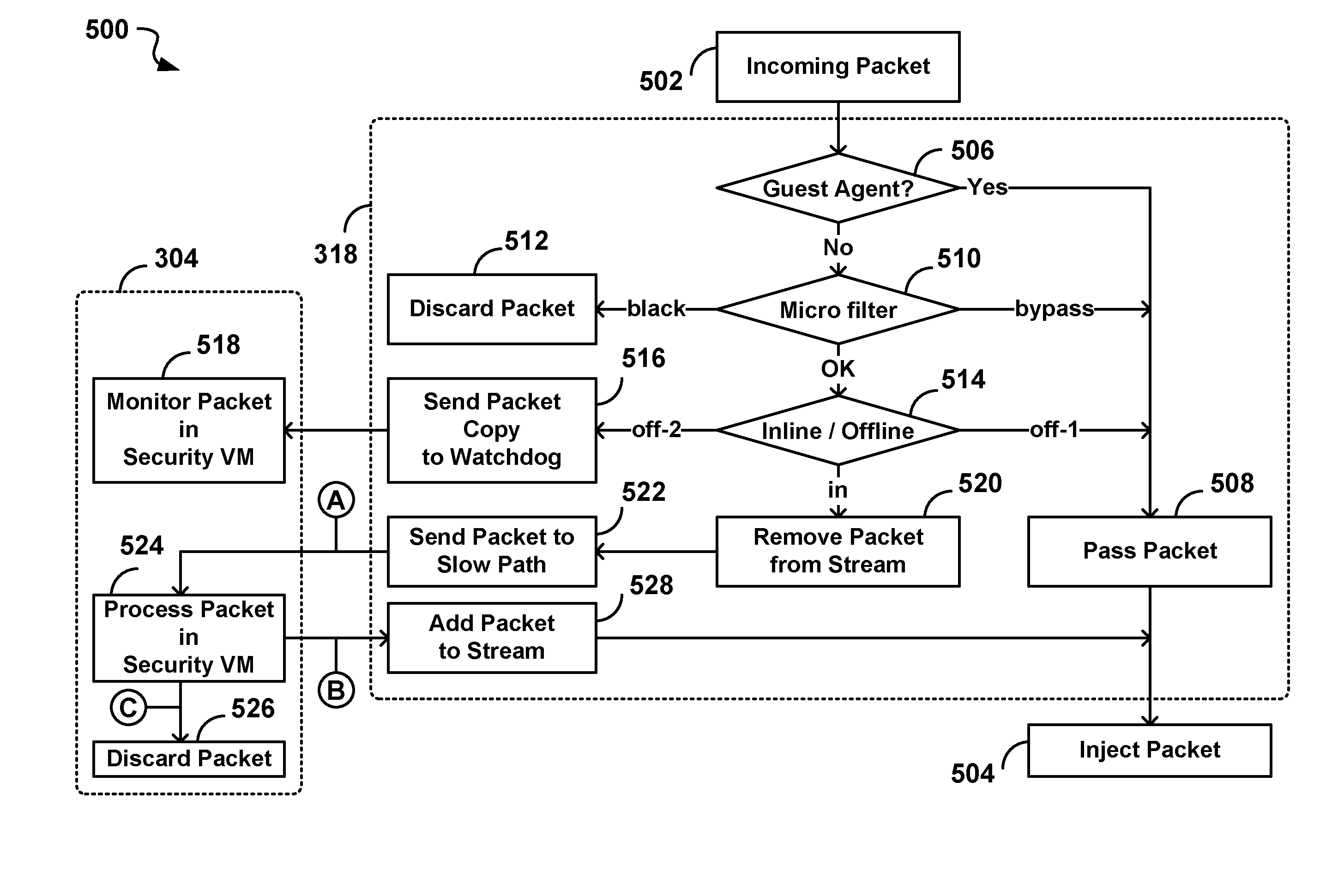
A distributed and coordinated security system providing intrusion-detection and intrusion-prevention for the virtual machines (VMs) in a virtual server is described. The virtualization platform of the virtual server is enhanced with networking drivers that provide a “fast path” firewall function for pre-configured guest VMs that already have dedicated deep packet inspection security agents installed. A separate security VM is deployed to provide virtual security agents providing deep packet inspection for non pre-configured guest VMs. The network drivers are then configured to intercept the data traffic of these guest VMs and route it through their corresponding virtual security agents, thus providing a “slow-path” for intrusion detection and prevention.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
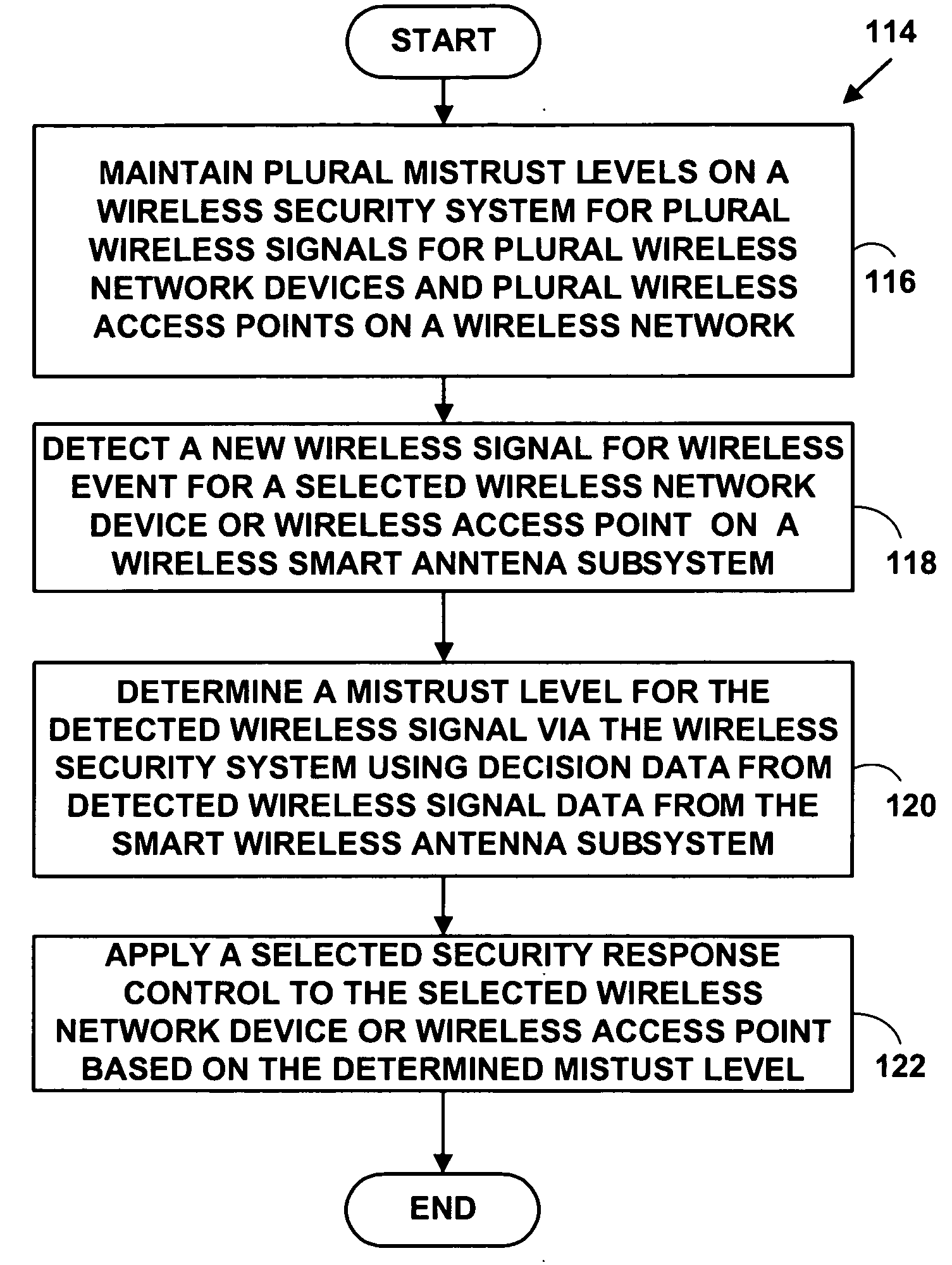
Method and system for wireless intrusion detection prevention and security management
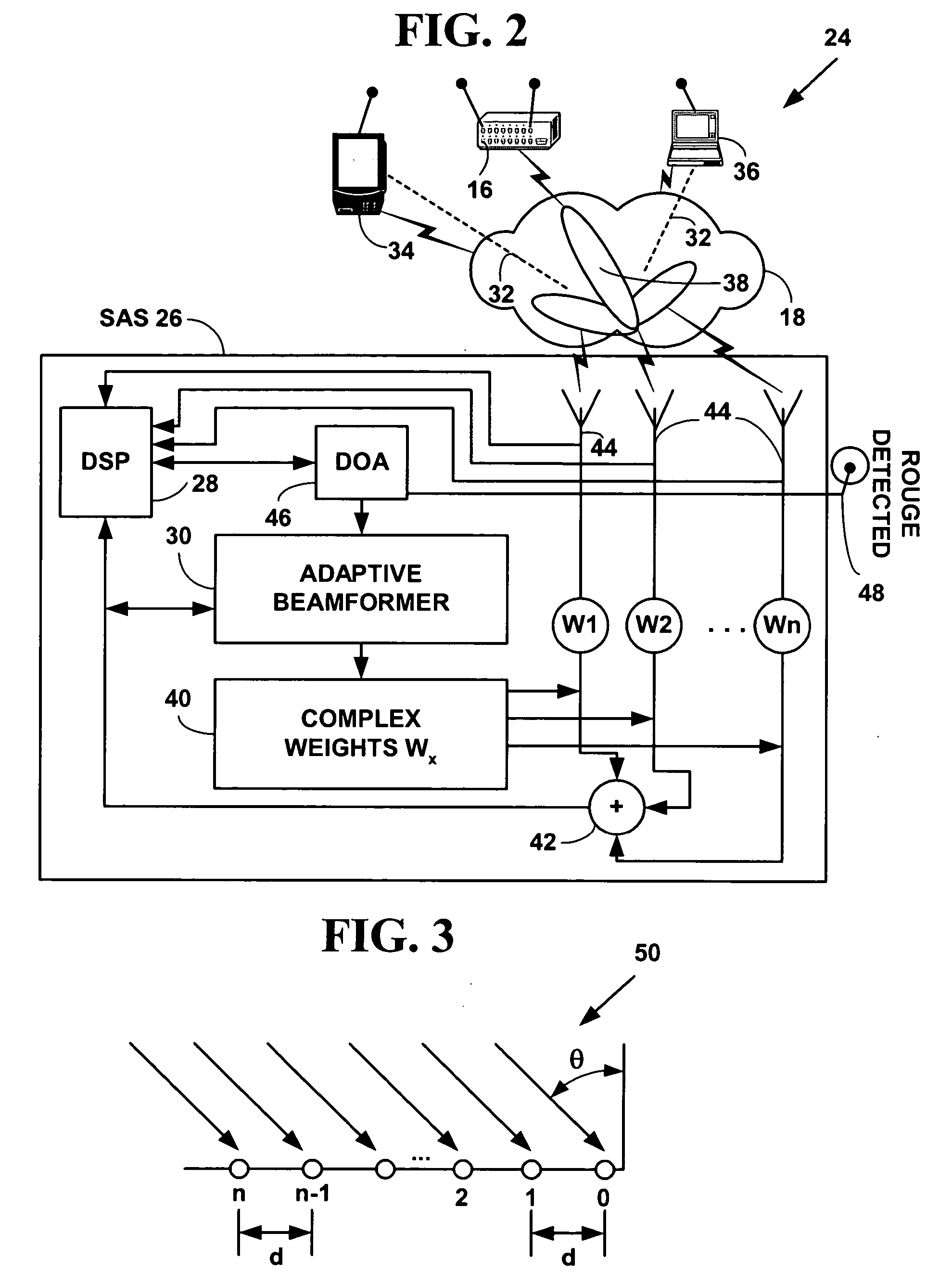
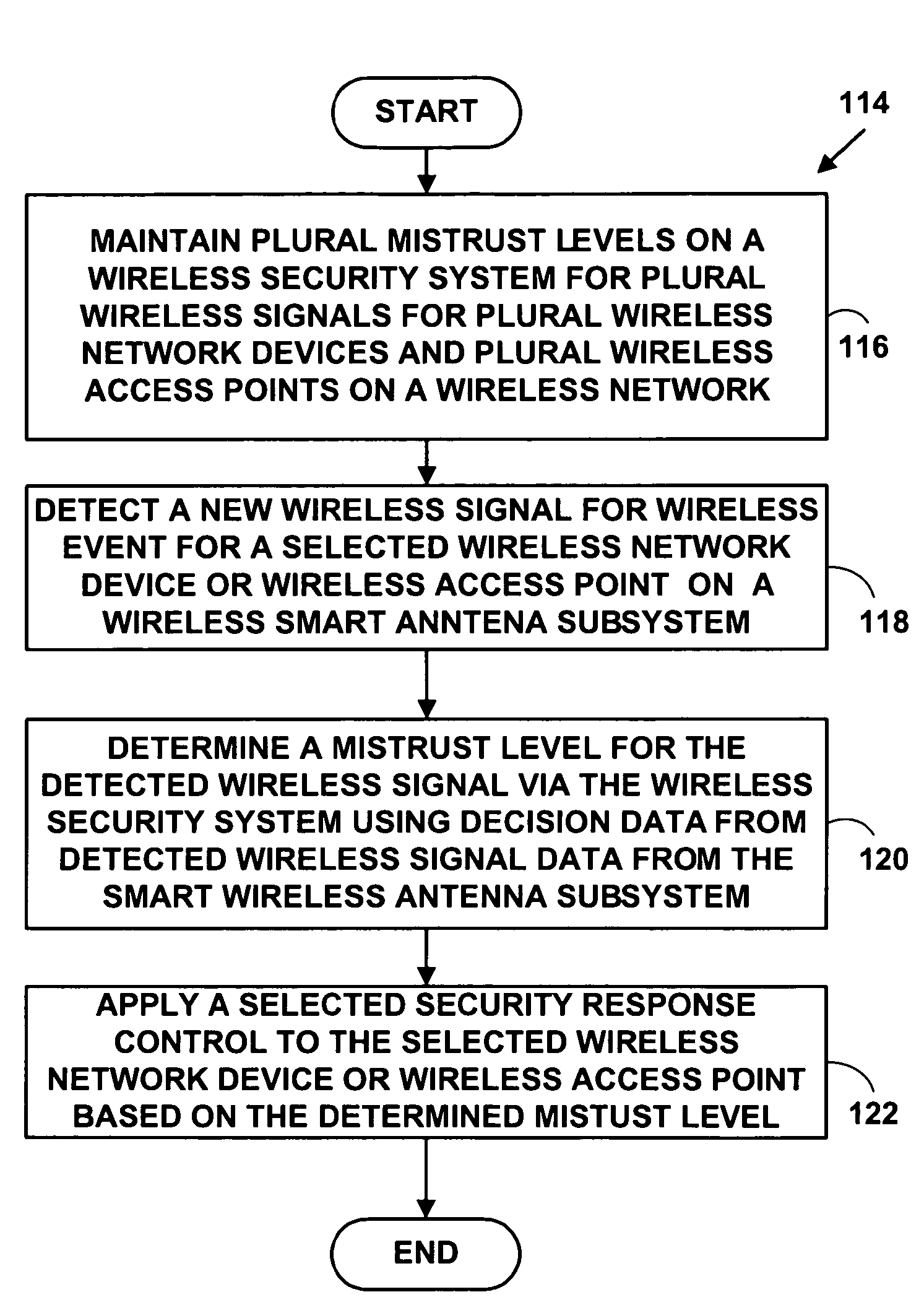
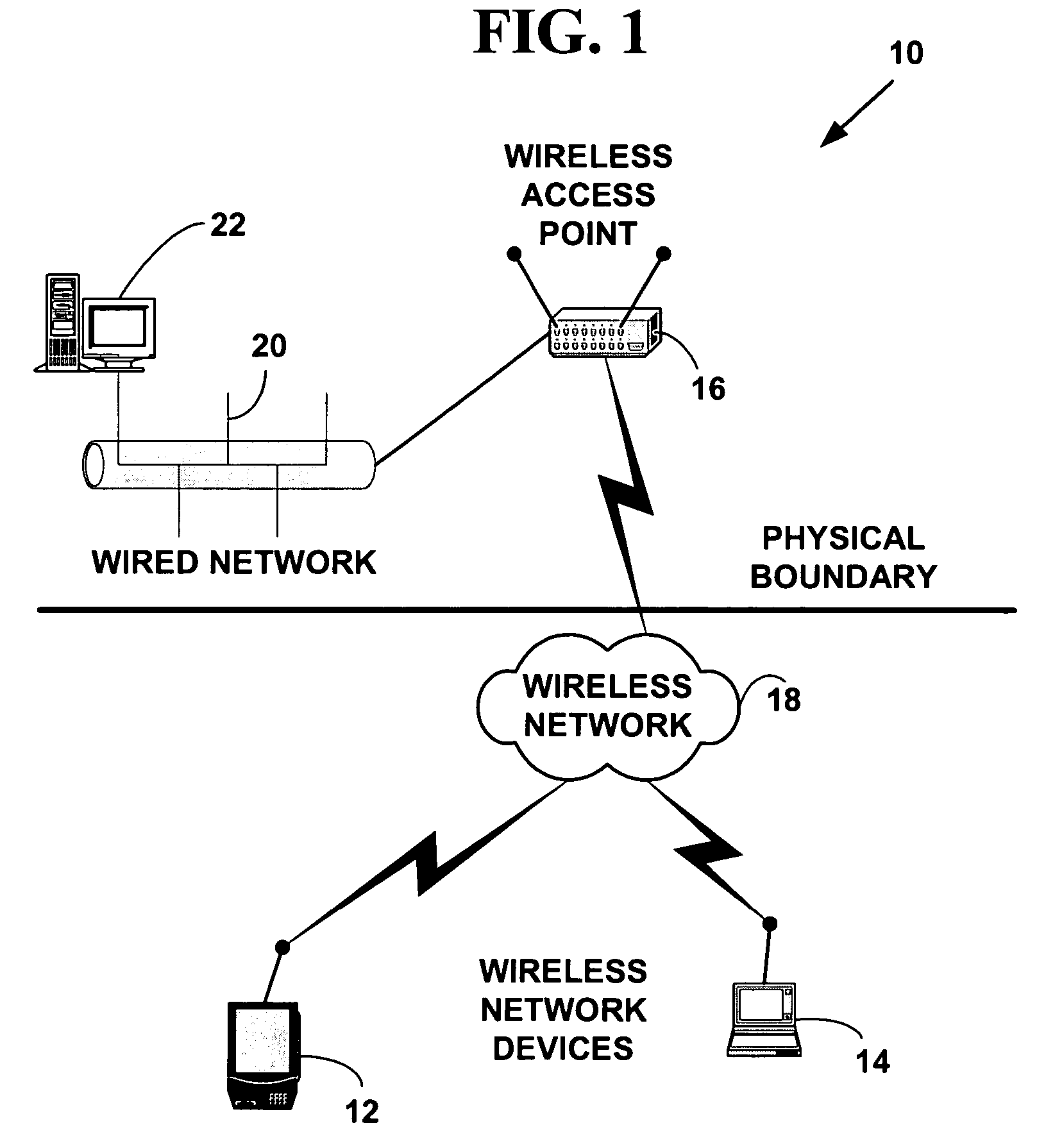
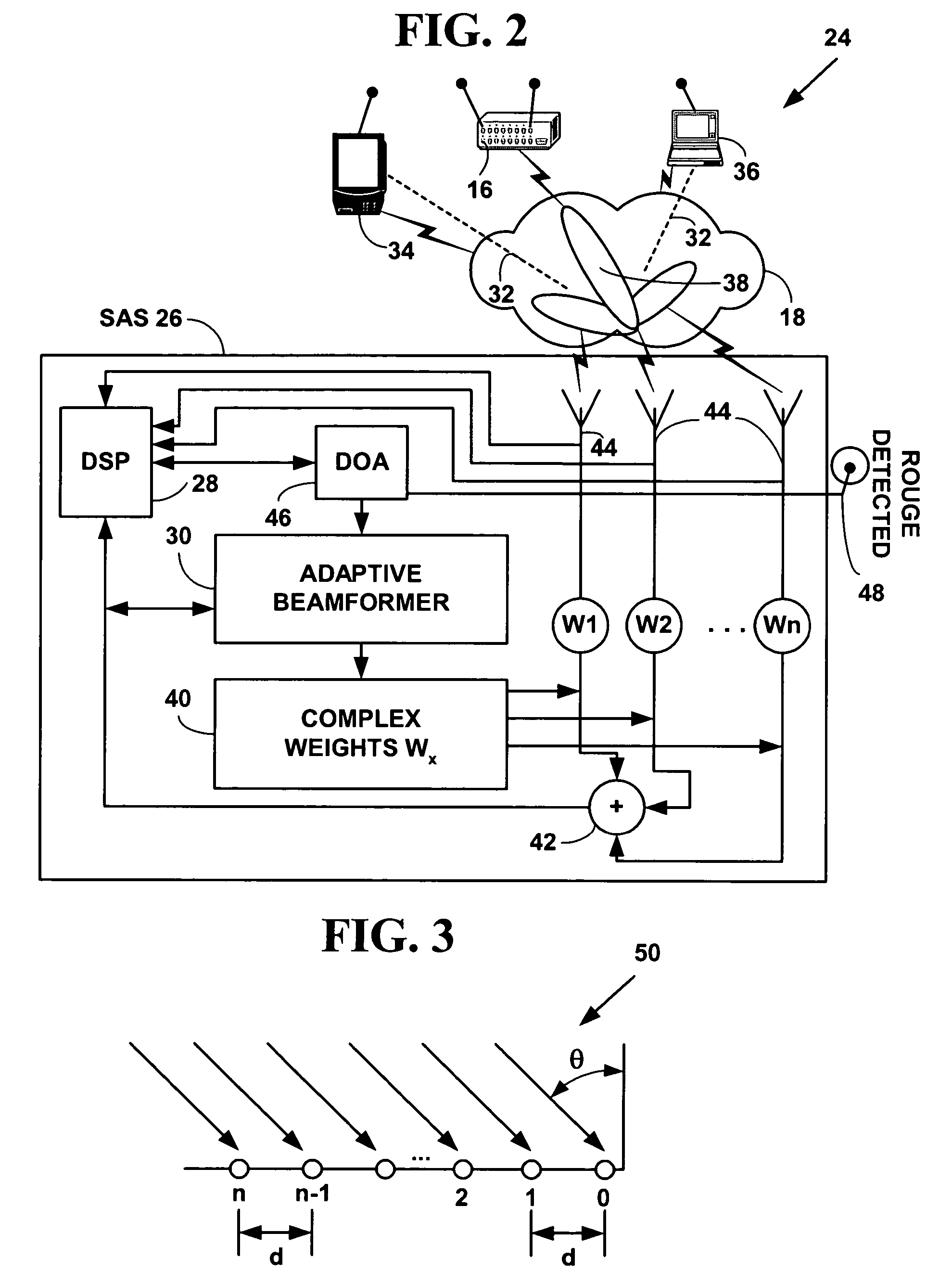
ActiveUS20050037733A1Spatial transmit diversityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSystems managementIntrusion detection and prevention
A method and system for wireless intrusion detection, prevention and security management. The method and system provides autonomous wireless intrusion detection and prevention, with minimal or no operator intervention. The method and system integrates a physical layer (e.g., OSI layer 1) a smart wireless radio frequency (RF) antenna subsystem with a data-link layer (e.g., OSI layer 2) wireless security system management platform.
Owner:3E TECH INT
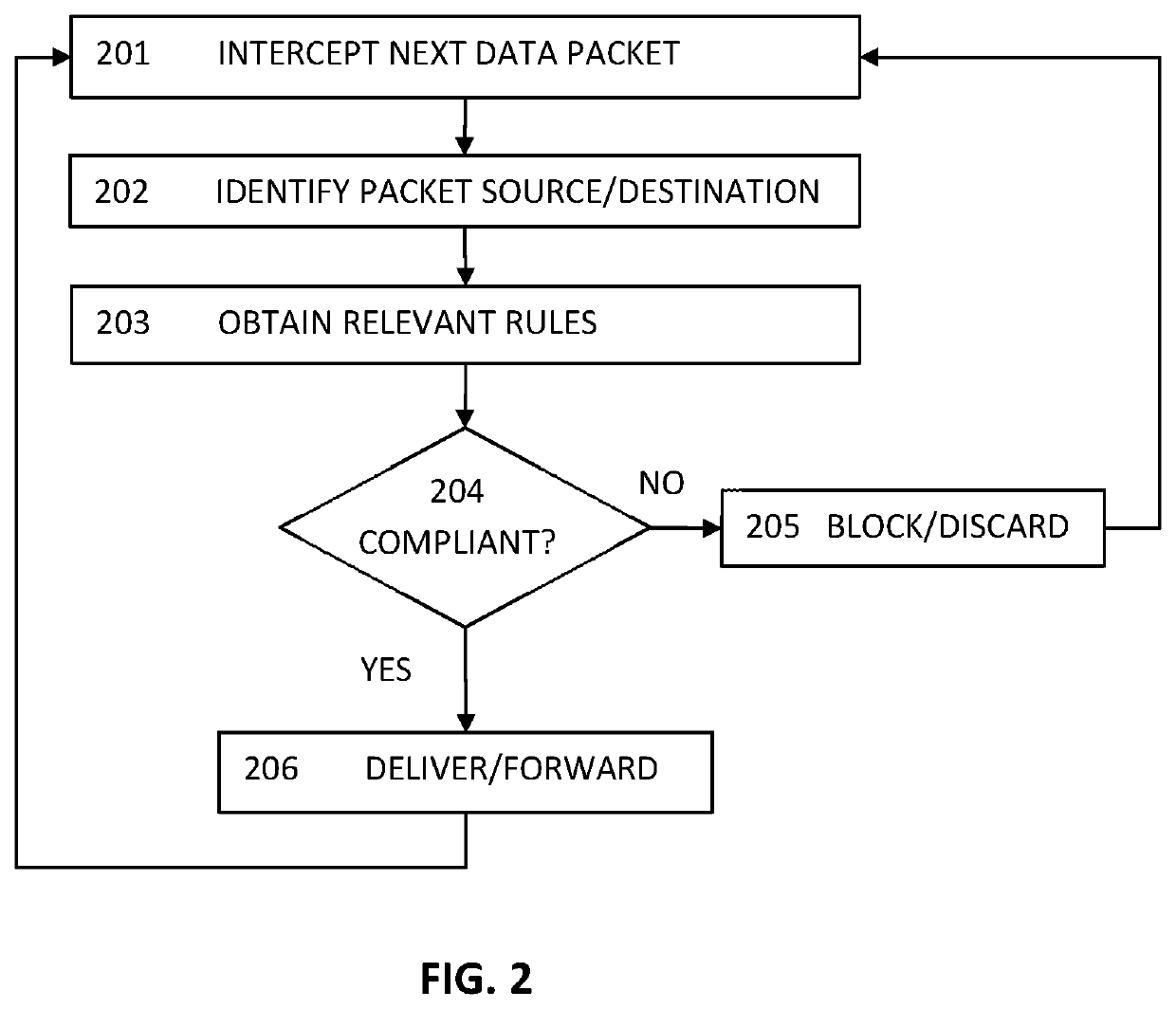
Methods and apparatus for computer network security using intrusion detection and prevention
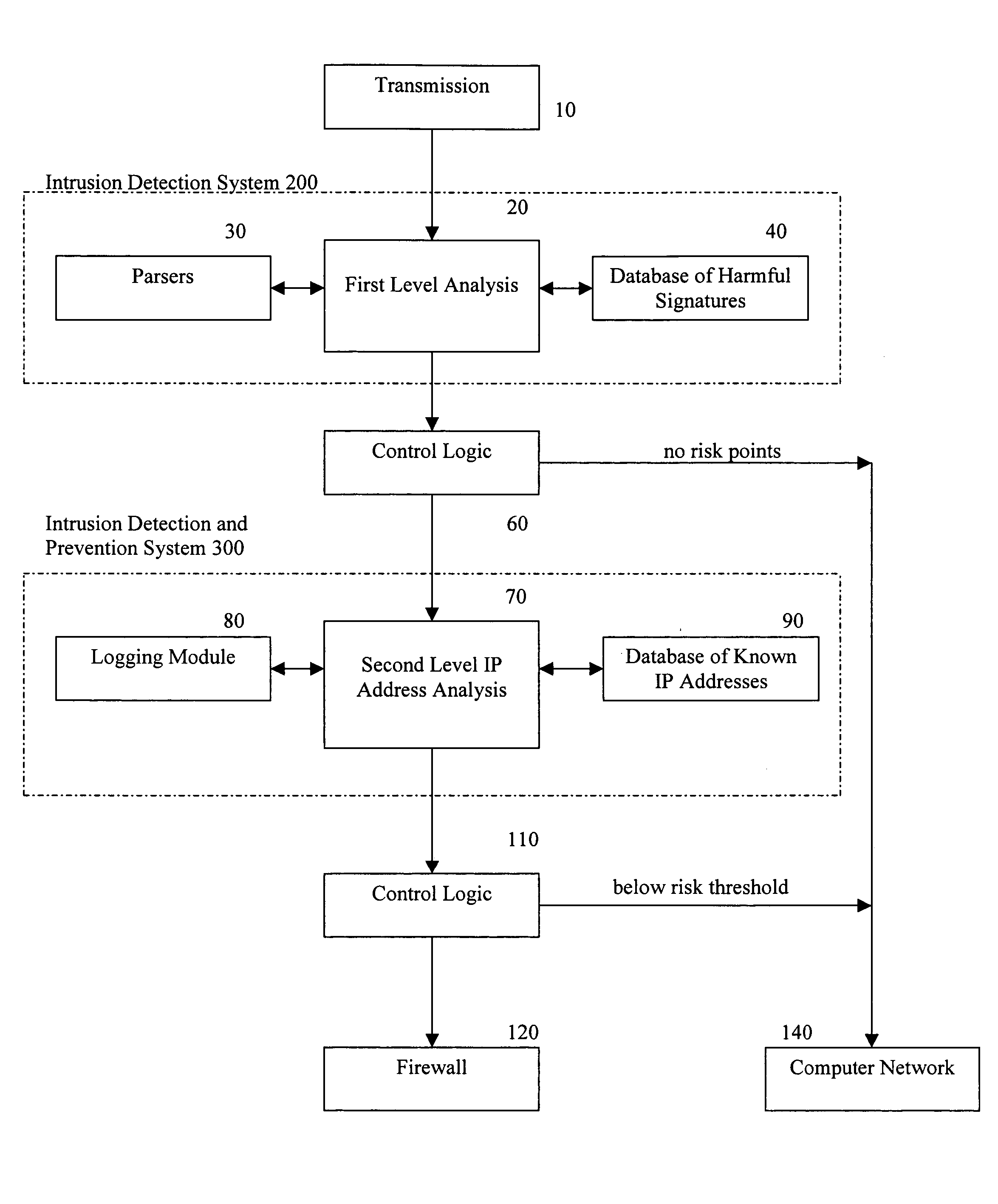
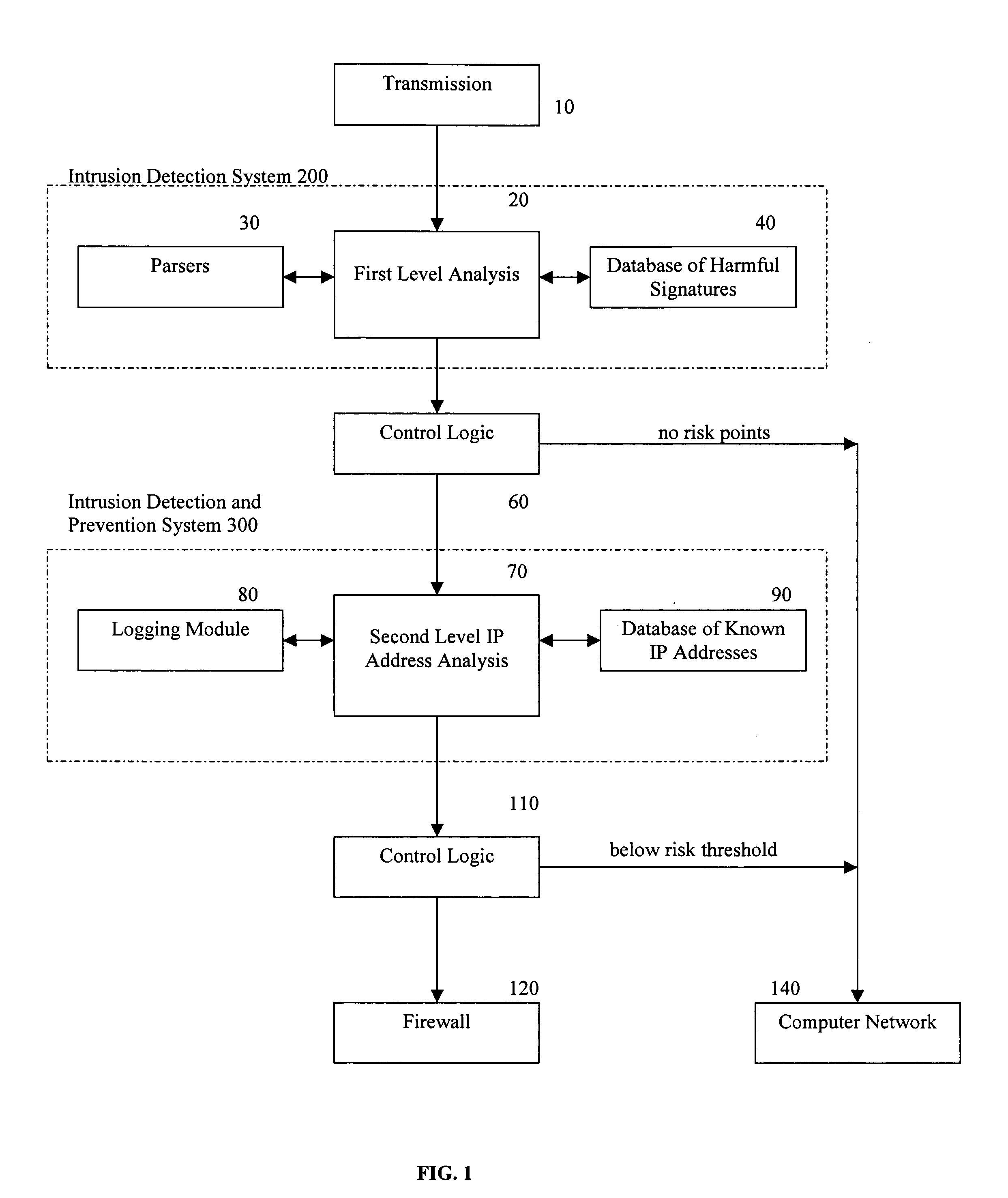
InactiveUS20050262556A1Overcome disadvantagesMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsIp addressIntrusion detection and prevention
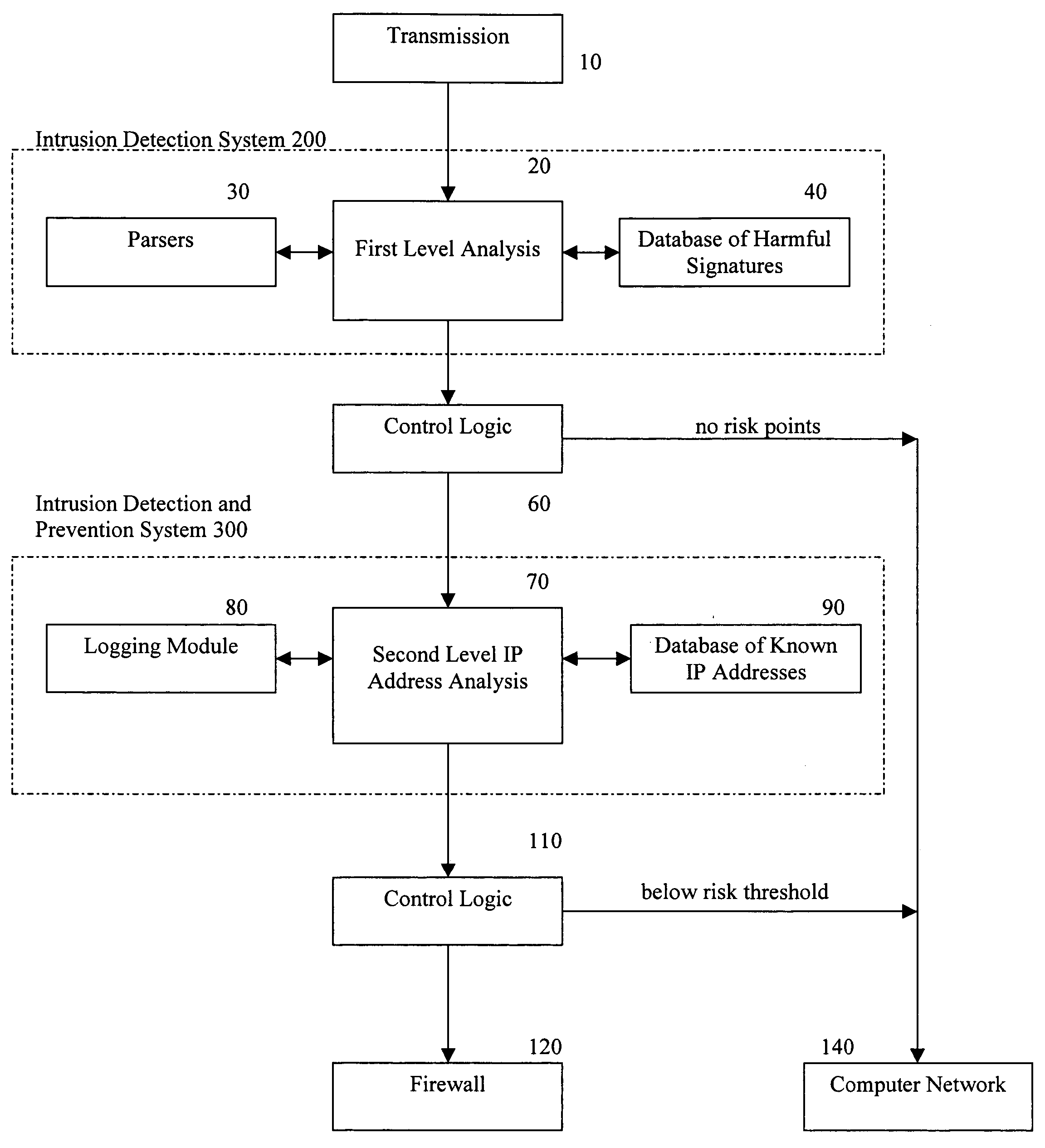
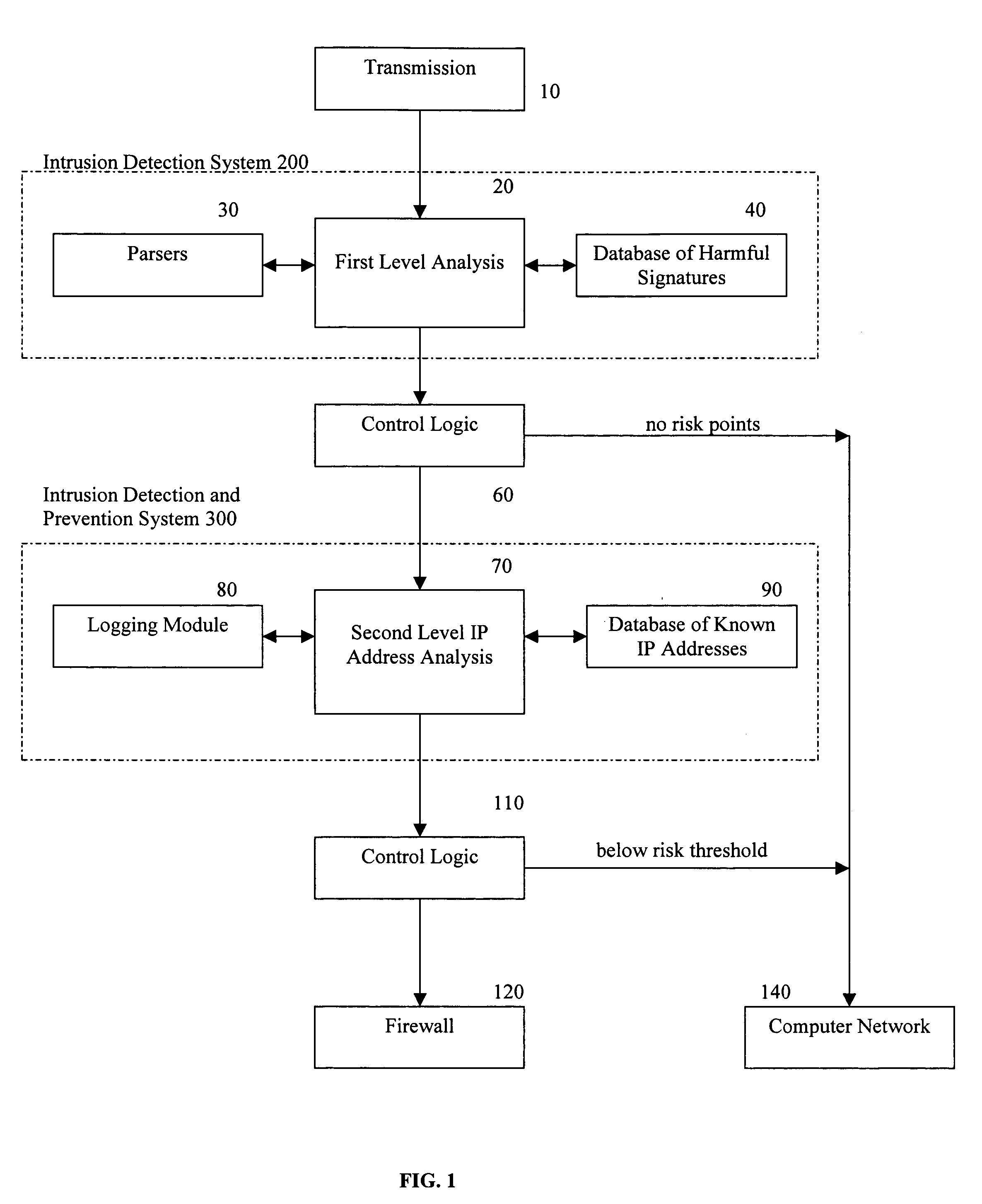
A method for providing security to a computer network by selectively blocking network transmissions from selected IP addresses comprising the steps of: establishing a risk threshold whereby transmissions from IP addresses exceeding said risk threshold are selectively blocked; receiving a network transmission having an originating IP address and payload; analyzing the payload of said transmission and assigning a current risk rating to said IP address on the basis of said analysis; comparing the originating IP address of said transmission to a database of known IP addresses, each of said said previous cumulative assigned risk rating being based on at least one previous transmission from a known IP address; known IP addresses having a previous cumulative assigned risk rating, assigning a new cumulative risk rating to said originating IP address, said new cumulative risk rating being the sum of said current risk rating and said previous cumulative assigned risk rating for said originating IP address, with the proviso that where said originating IP address is not contained in said database of known IP addresses, the new cumulative risk rating will equal the current risk rating; logging the new cumulative risk rating for said originating IP address in said database of known IP addresses, with the proviso that where the originating IP address of said transmission is not contained in said database of known IP addresses, a new record is created for the originating IP address and said new cumulative risk rating in said database of known IP addresses; comparing said new cumulative risk rating to said risk threshold; and automatically blocking said transmission if said new cumulative risk rating exceeds said risk threshold.
Owner:DIGITAL SECURITY NETWORK
Methods and apparatus for computer network security using intrusion detection and prevention
InactiveUS7225468B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsIp addressIntrusion detection and prevention
A method provides security to a computer network by selectively blocking network transmissions from selected IP addresses. The method includes the steps of: establishing a risk threshold whereby transmissions from IP addresses exceeding said risk threshold are selectively blocked; receiving a network transmission having an originating IP address and payload; analyzing the payload of said transmission and assigning a current risk rating to said IP address on the basis of said analysis; comparing the originating IP address of said transmission to a database of known IP addresses, each of said known IP addresses having a previous cumulative assigned risk rating, said previous cumulative assigned risk rating being based on at least one previous transmission from a known IP address; assigning a new cumulative risk rating to said originating IP address; logging the new cumulative risk rating for said originating IP address in said database of known IP addresses. The new cumulative risk rating is compared to said risk threshold and the transmission is blocked if said new cumulative risk rating exceeds said risk threshold.
Owner:DIGITAL SECURITY NETWORK
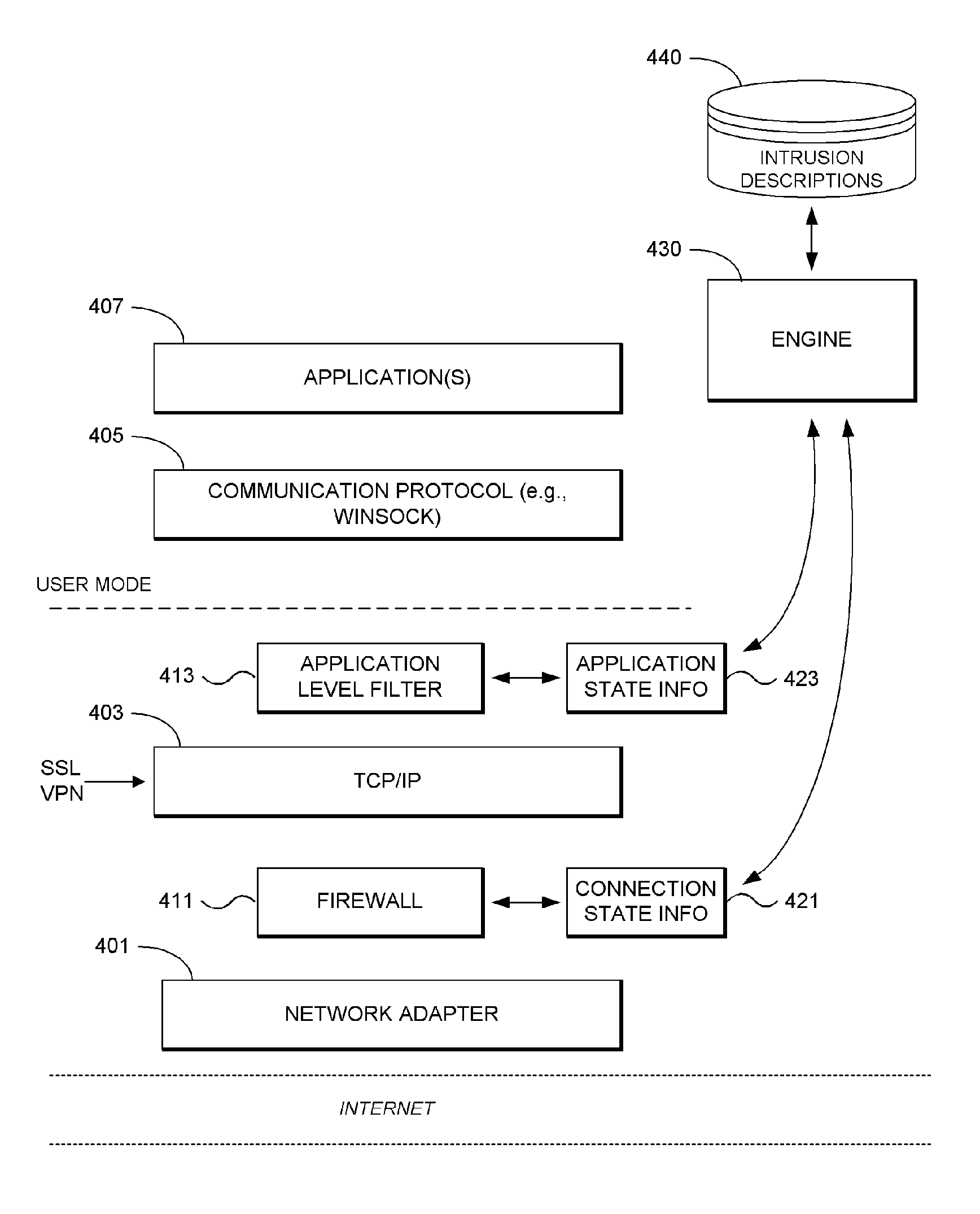
System and Methodology for Intrusion Detection and Prevention
ActiveUS20050273857A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInternet trafficIntrusion detection and prevention
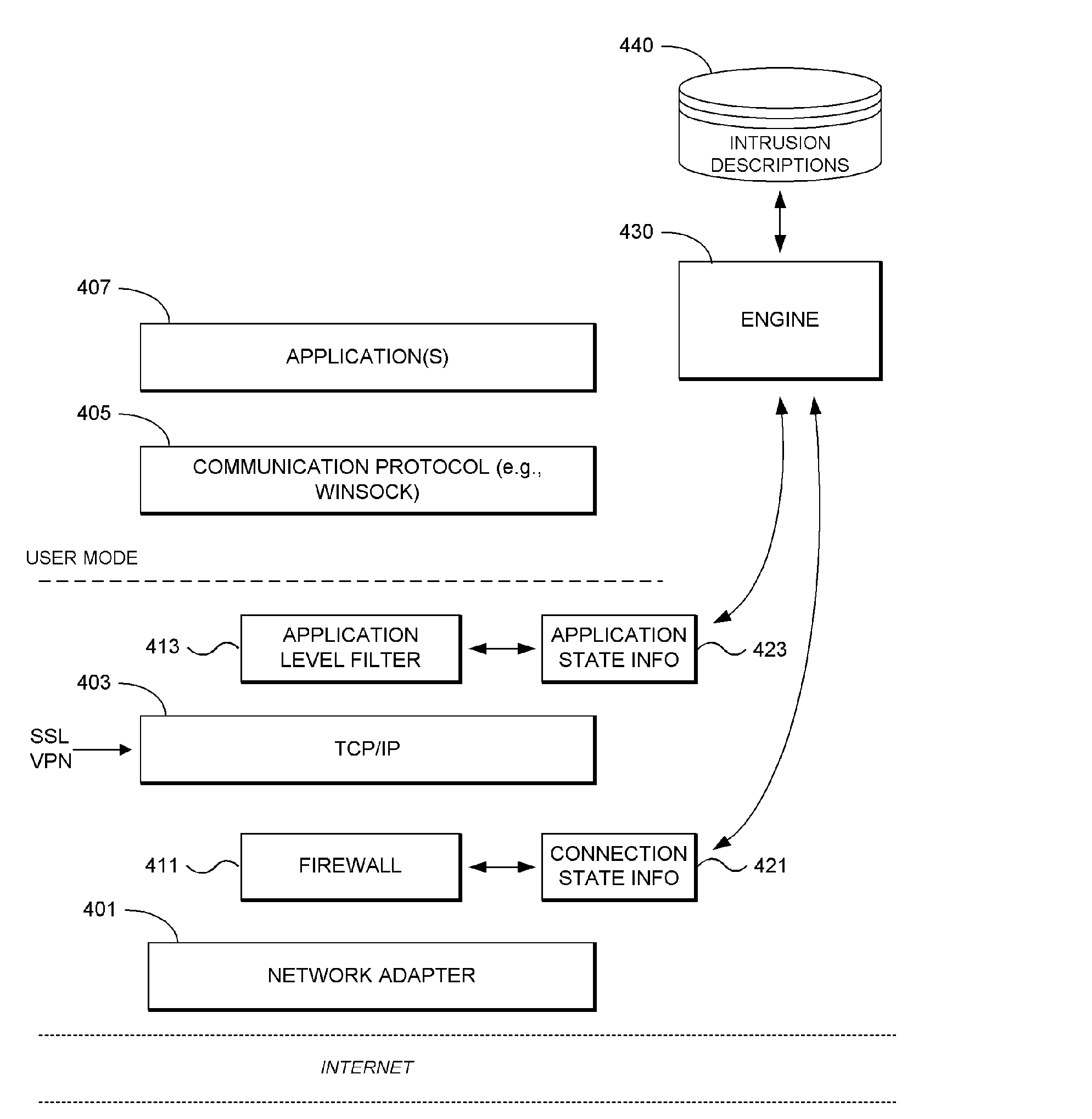
System and methodology for intrusion detection and prevention is described. In one embodiment, for example, a method is described for detecting and preventing network intrusion, the method comprises steps of: defining intrusion descriptions specifying exploits that may be attempted by malicious network traffic, the intrusion descriptions indicating specific applications that may be targeted by individual exploits; for a particular application participating in network communication, deriving a subset of the intrusion descriptions specifically applicable to that particular application; using the subset of the intrusion descriptions specifically applicable to that application, monitoring network traffic destined for the particular application for detecting an attempted network intrusion; and if a network intrusion is detected, blocking network traffic destined for the particular application determined to comprise an exploit.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
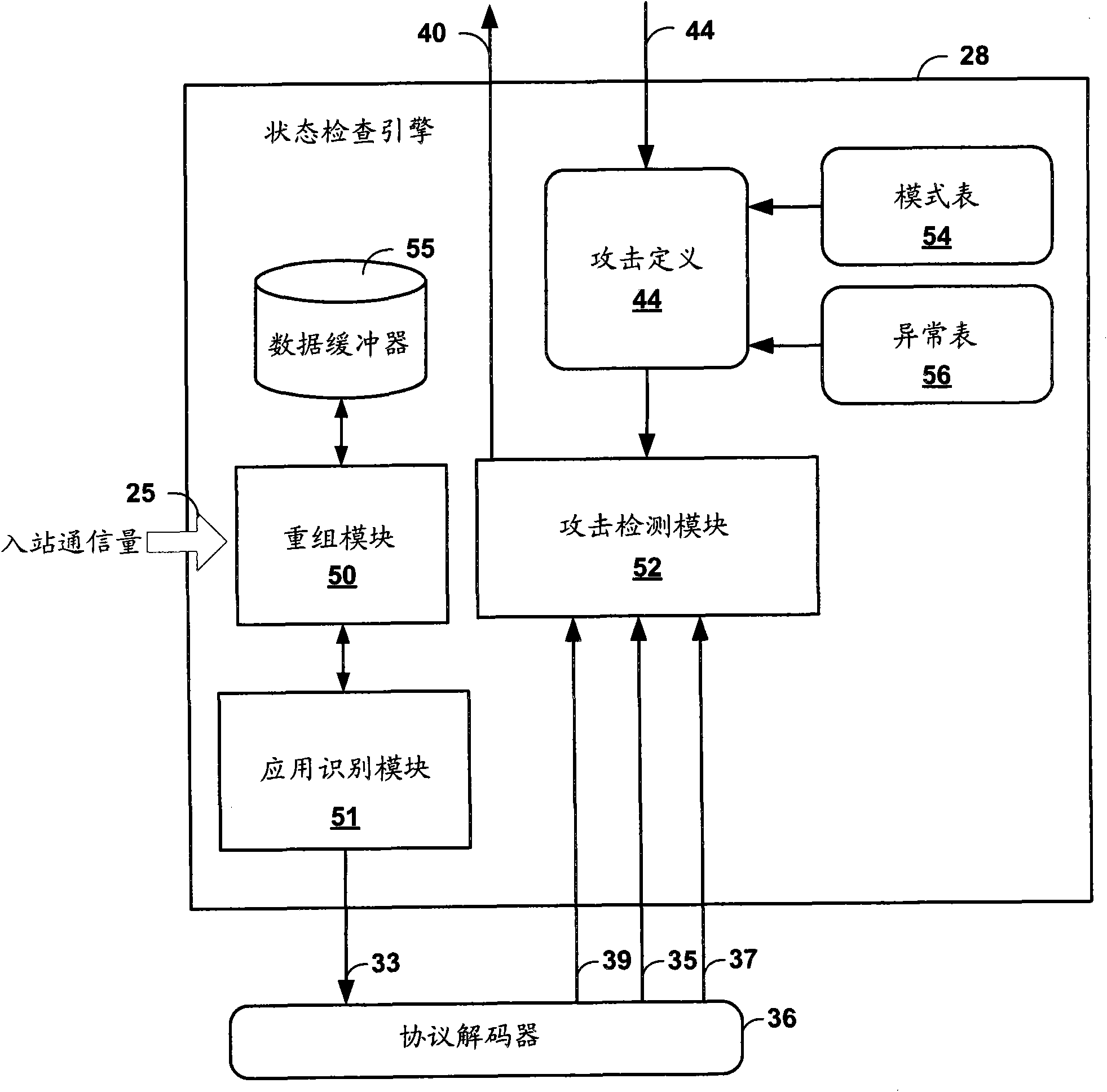
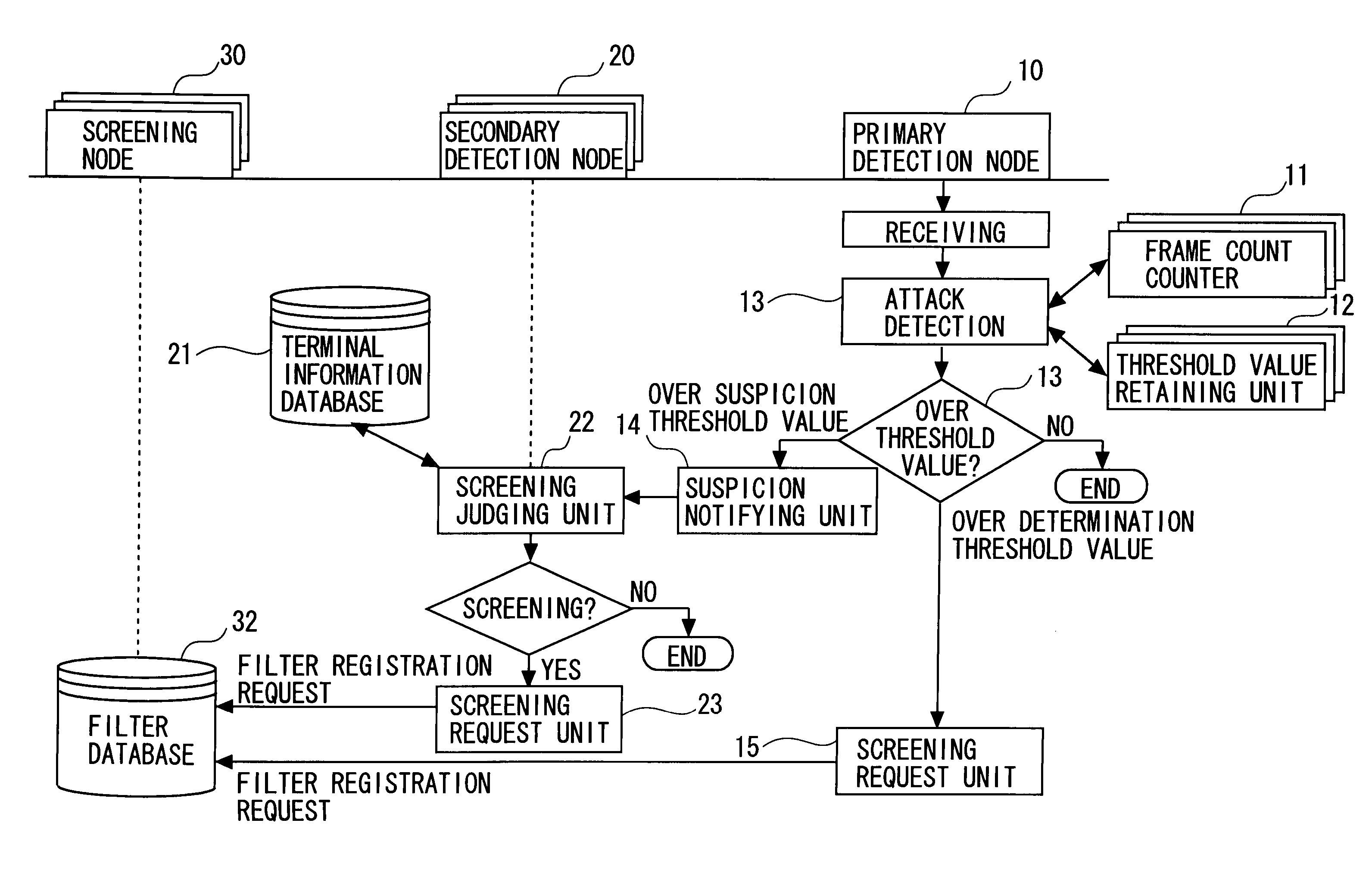
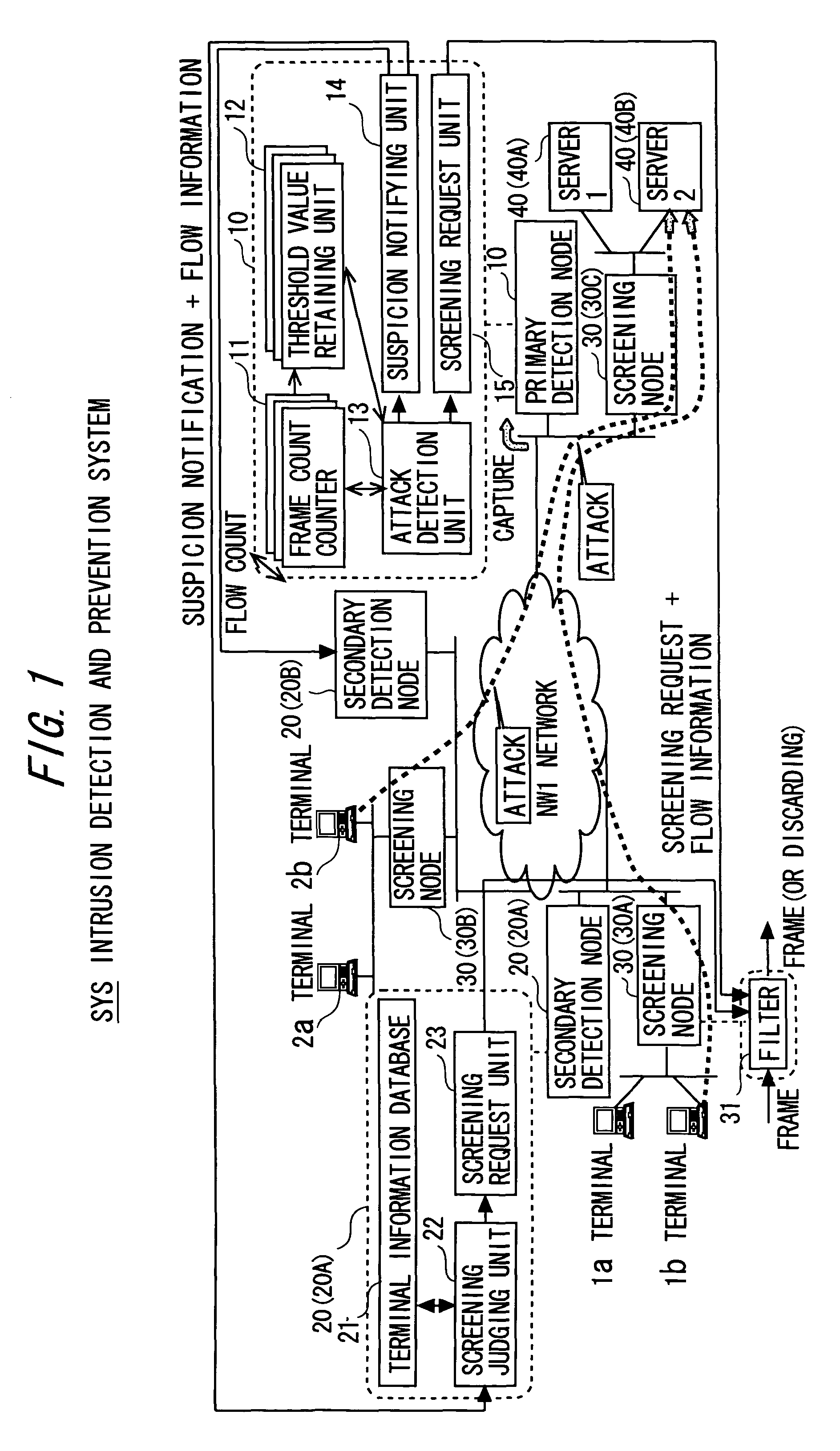
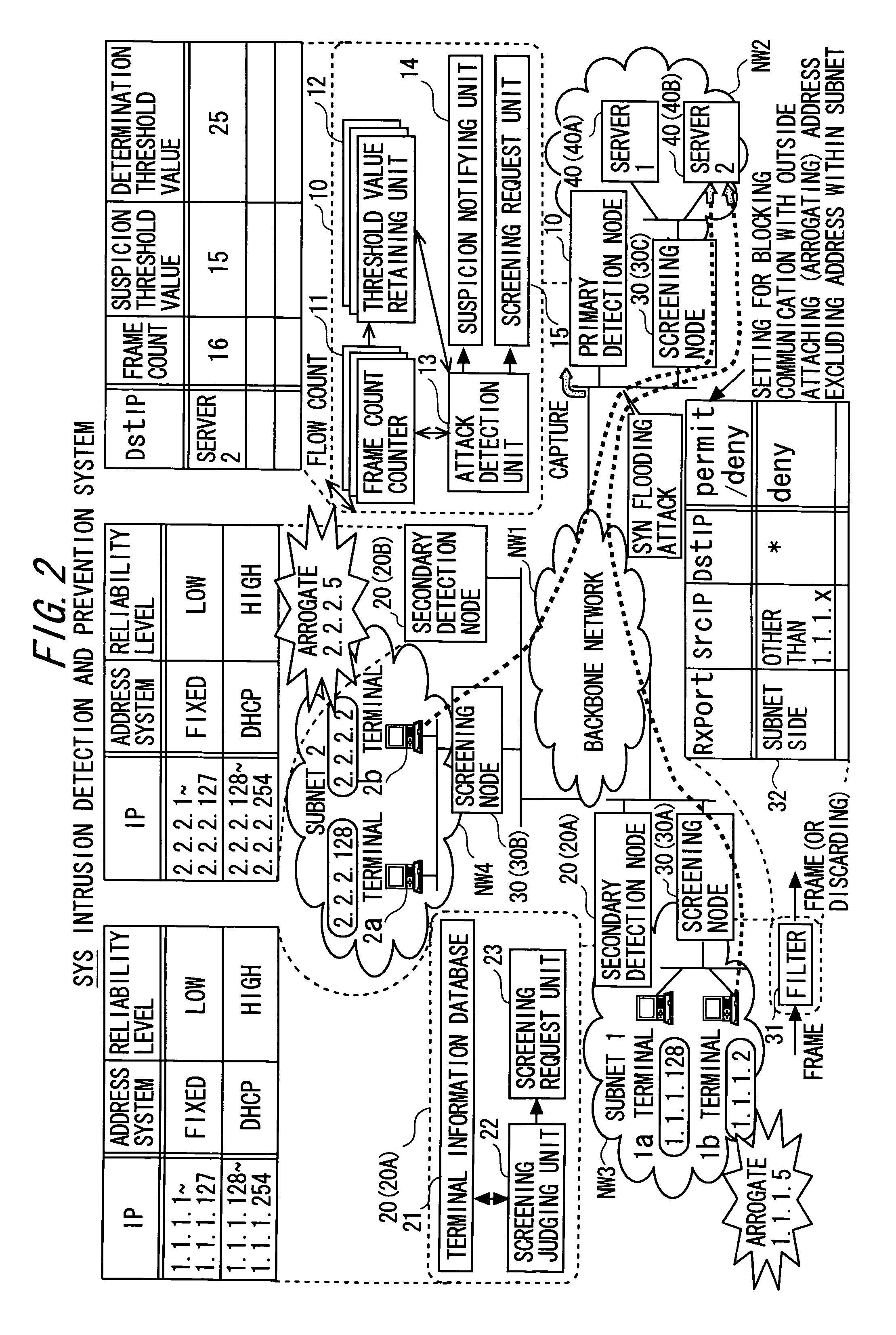
Intrusion detection and prevention system
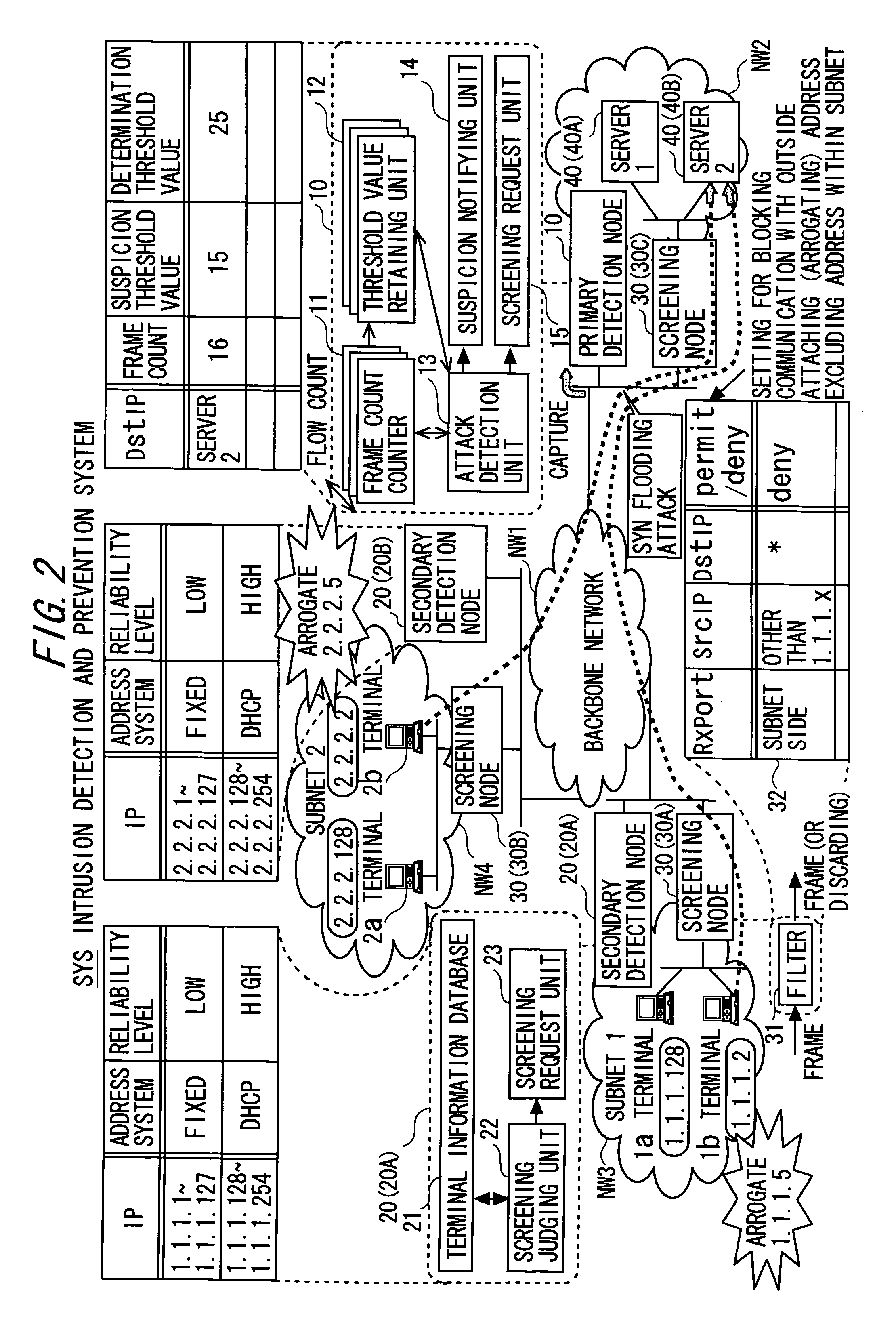
InactiveUS20060288413A1Efficient detectionImprove accuracyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionIntrusion detection and preventionEngineering
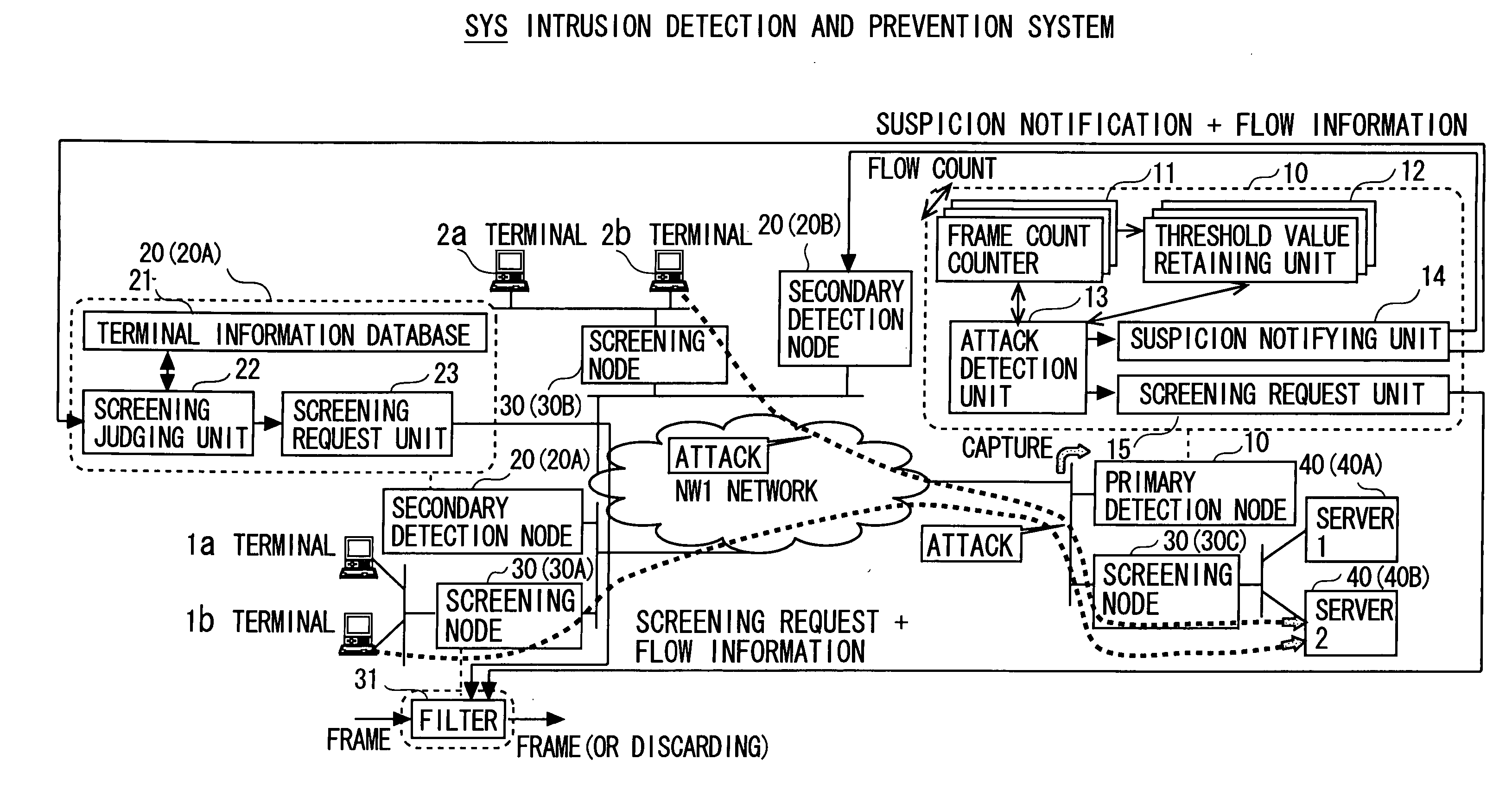
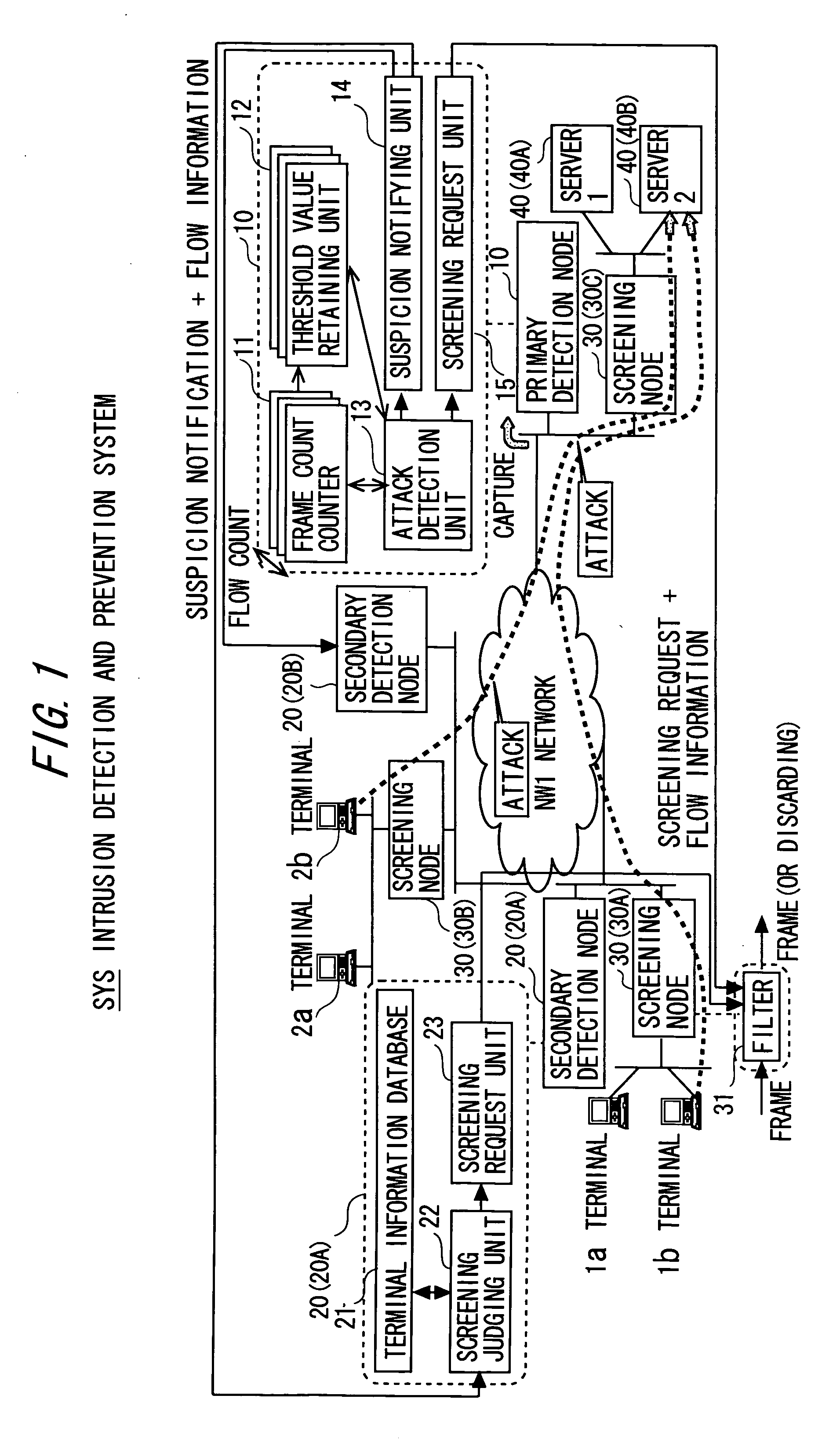
An intrusion detection and prevention device includes a retaining unit retaining at least one of attack suspicion threshold values of which levels are different from each other in order to detect a denial-of-service attack, and an attack determination threshold value, a detecting unit detecting an attack suspicion state when a frame count in the attack detection target flow exceeds the attack suspicion threshold value, and detecting an attack determination state when the frame count exceeds the attack determination threshold value, a notifying unit notifying of the attack suspicion state together with the corresponding flow information when the attack suspicion state is detected, a judging unit judging, based on a reliability level of at least one of the frame source terminal and the flow, whether the flow is blocked or not when notified of the attack suspicion state, and a requesting unit making a screening request together with notification of the corresponding flow information when the attack determination state is detected.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for wireless intrusion detection prevention and security management
ActiveUS7295831B2Spatial transmit diversityUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSystems managementIntrusion detection and prevention
Owner:3E TECH INT
Accelerated threat mitigation system
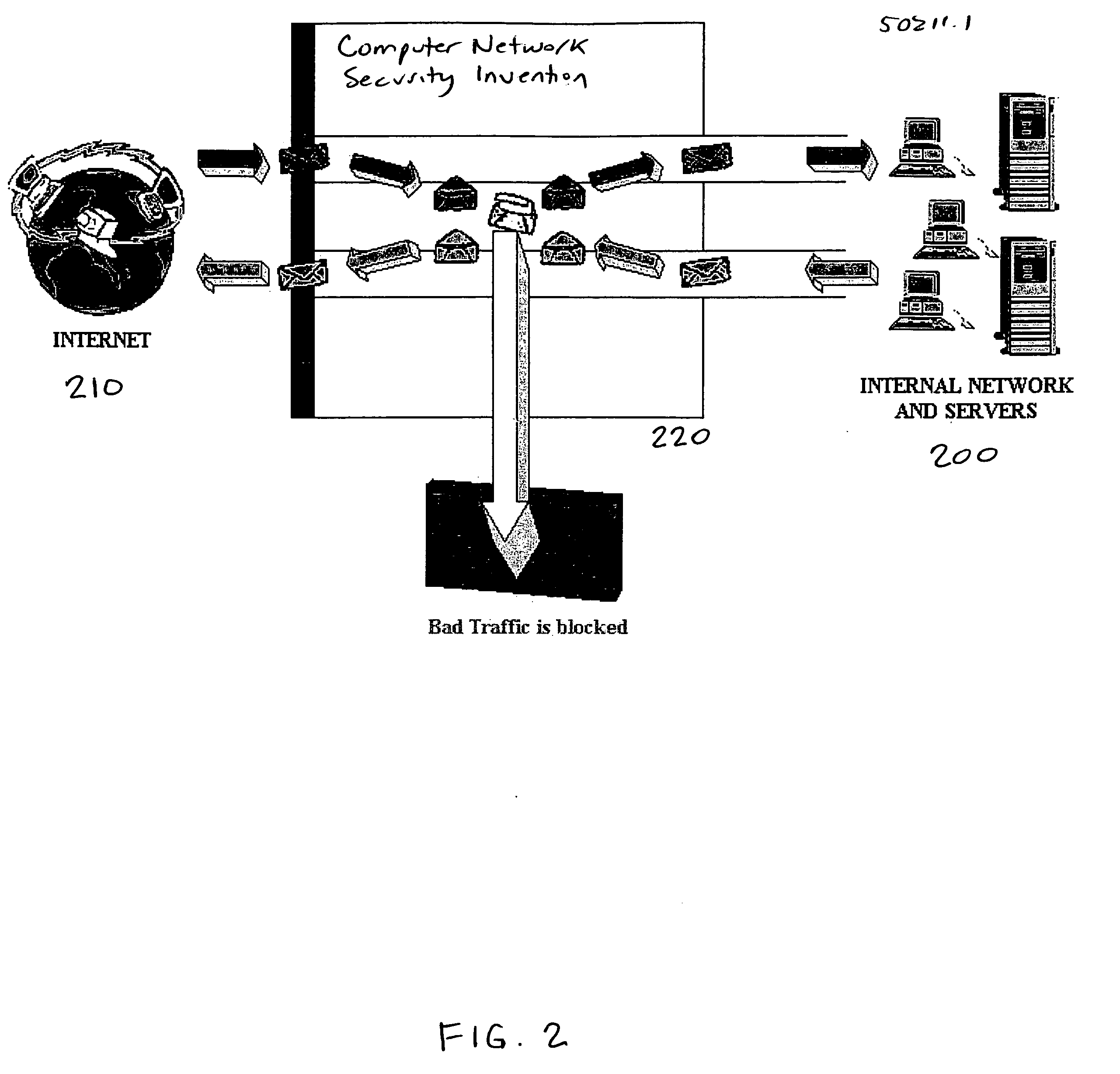
InactiveUS20160191558A1Increase speedImprove performanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionFirst pathwayInternet traffic
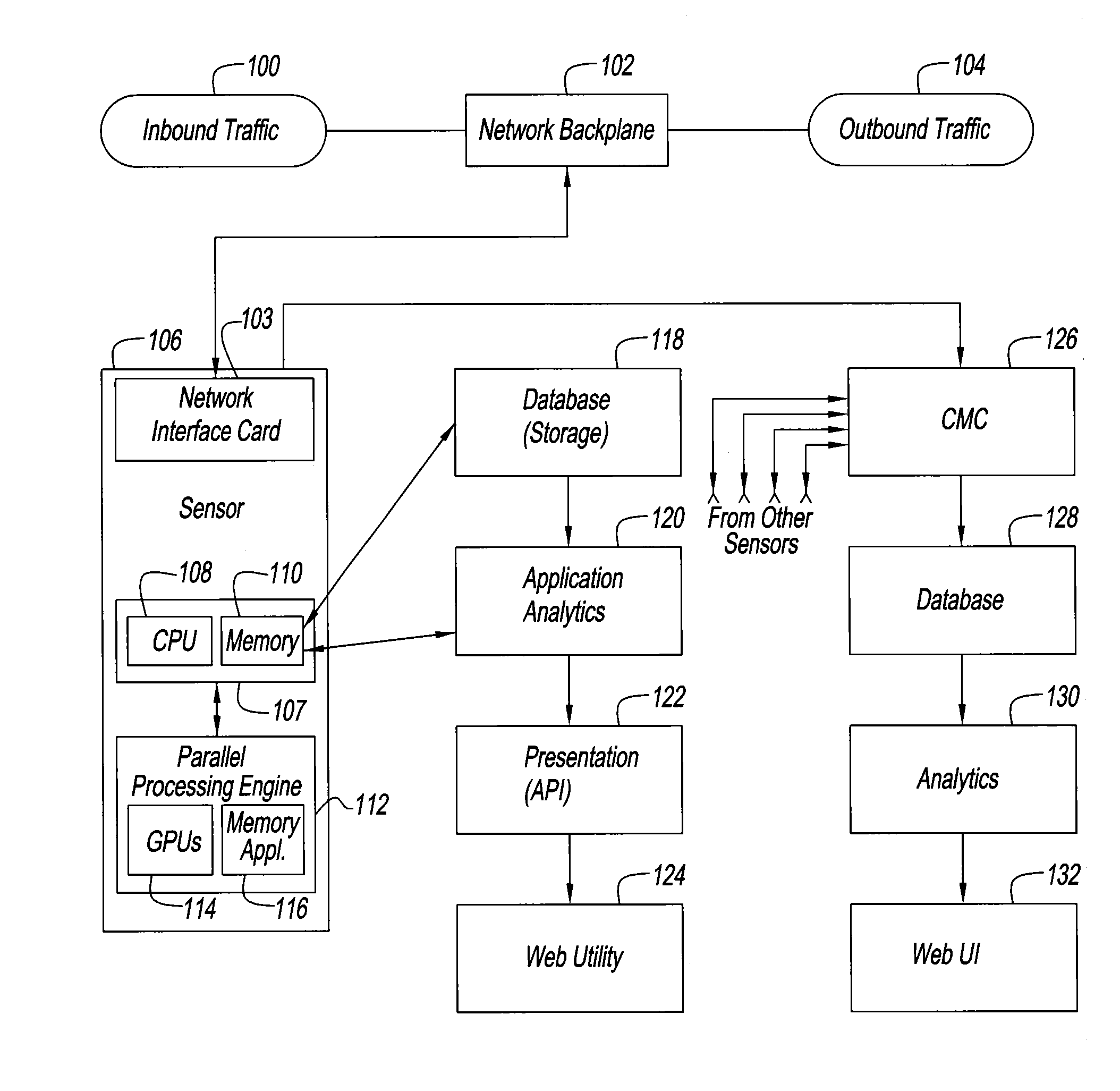
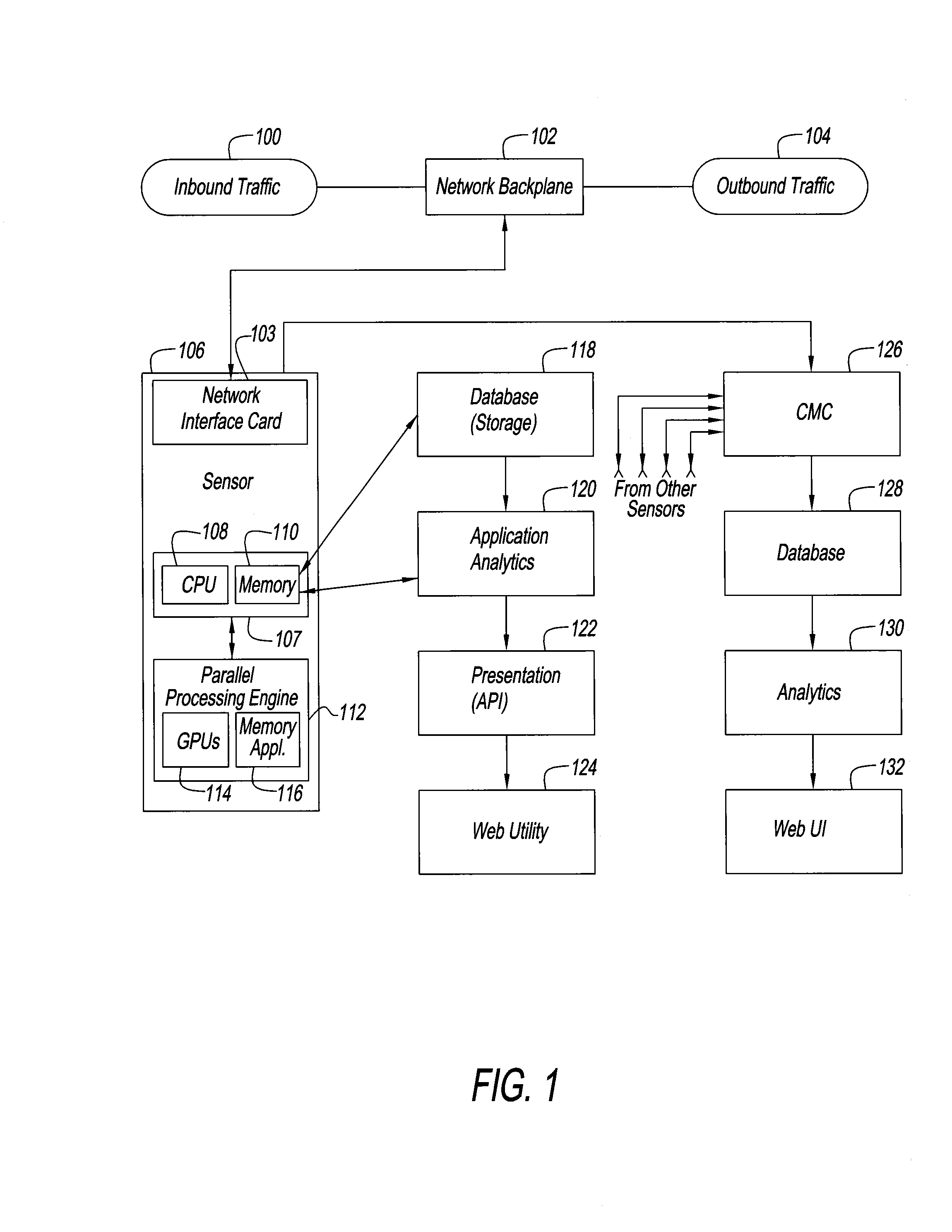
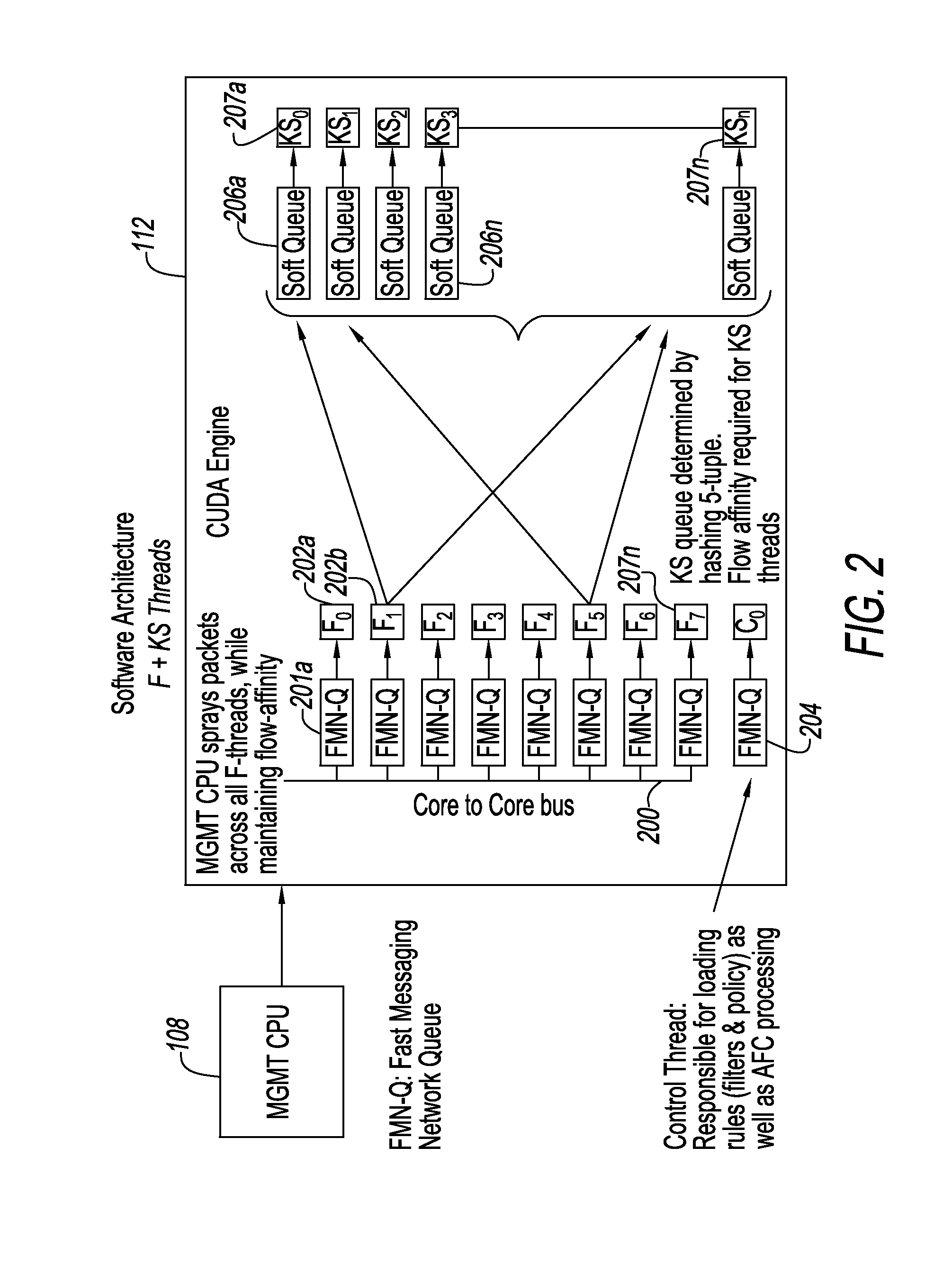
An intrusion detection and prevention system and method for dealing with threats to computers and computer networks, and in particular to computers and networks connected to the Internet, is disclosed. A sensor receives network traffic. The sensor includes a first processor for managing the network traffic that is received, a first path for the traffic that is received for storing the traffic in a memory for subsequent use, a second path for analyzing the traffic that is received, and for processing the traffic at a speed that is at least as fast as speed of the first path. The second processor is associated with the second path so that some of the traffic is allowed along the first path and other of the traffic is rate limited or not allowed along the first path. The system and method use four tiers of threat detection to successively mitigate a large variety of threats.
Owner:BRICATA
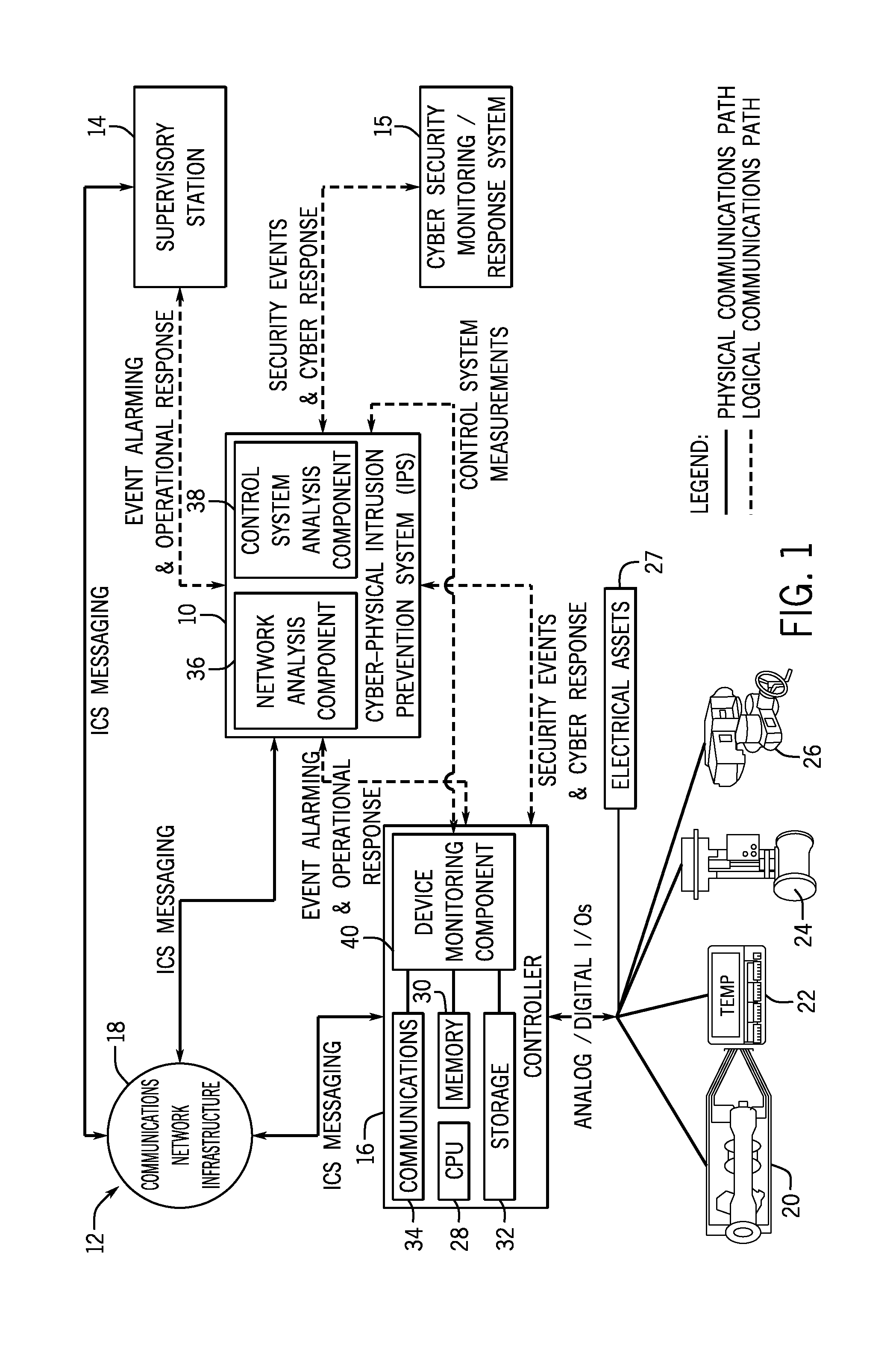
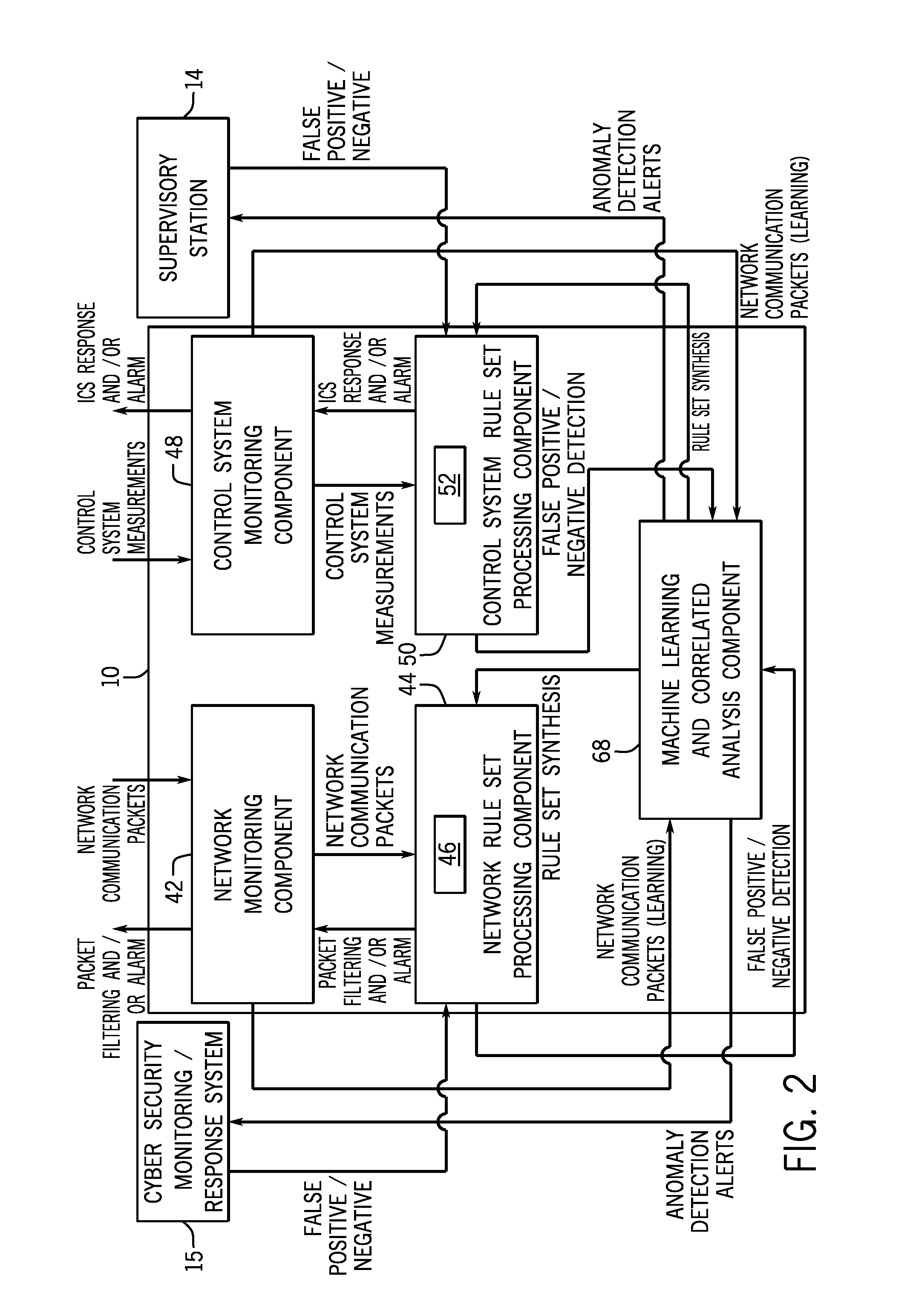
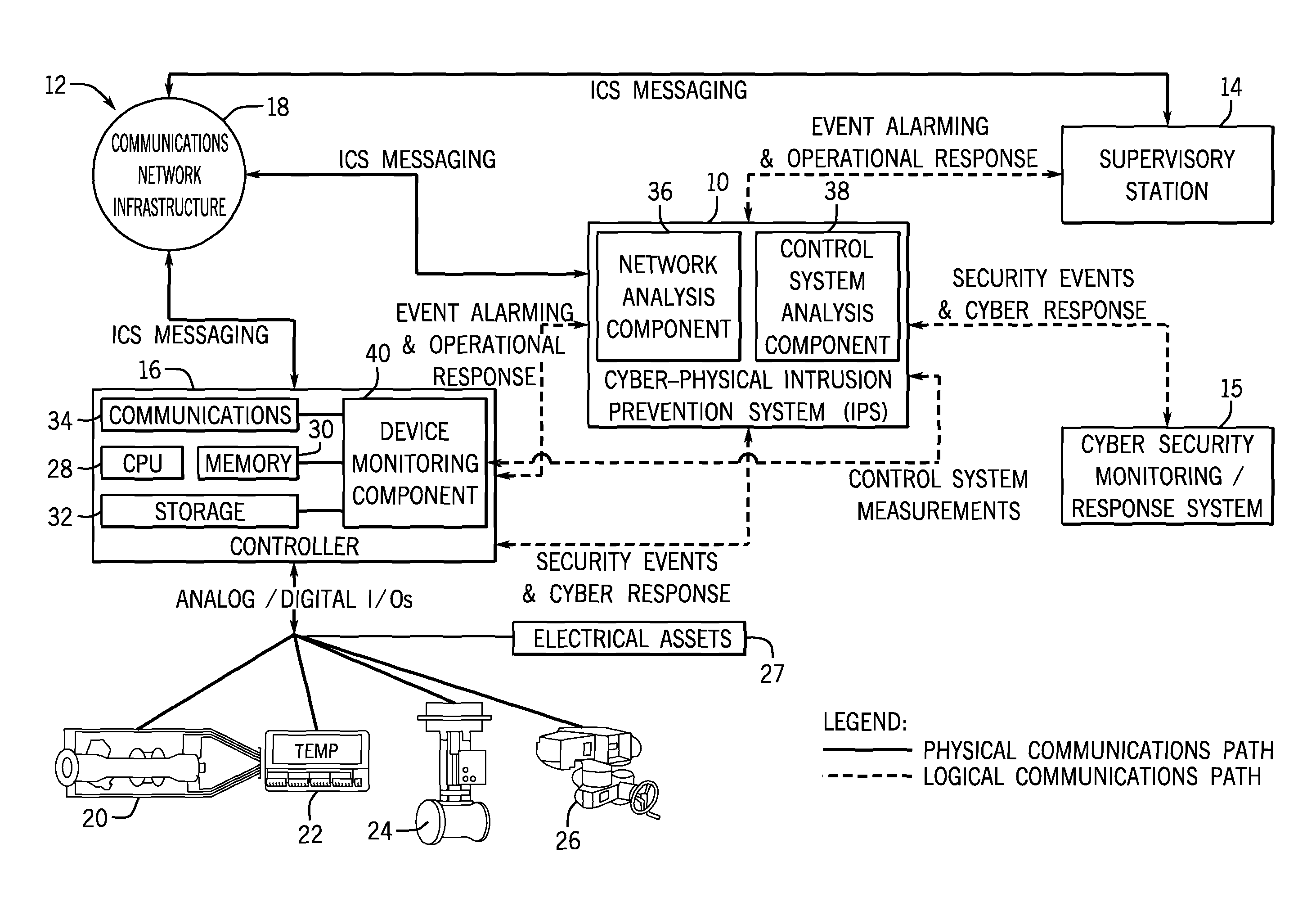
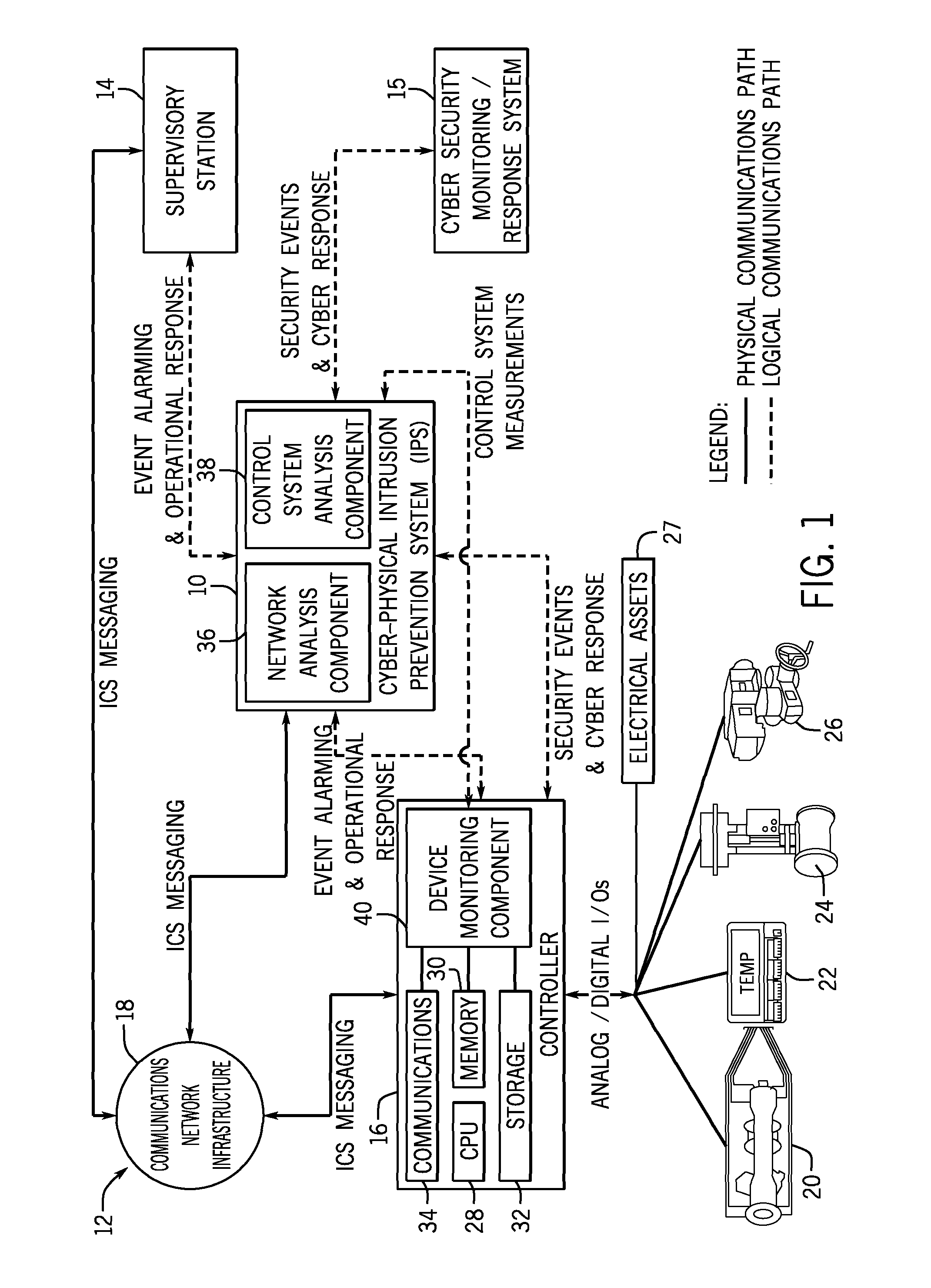
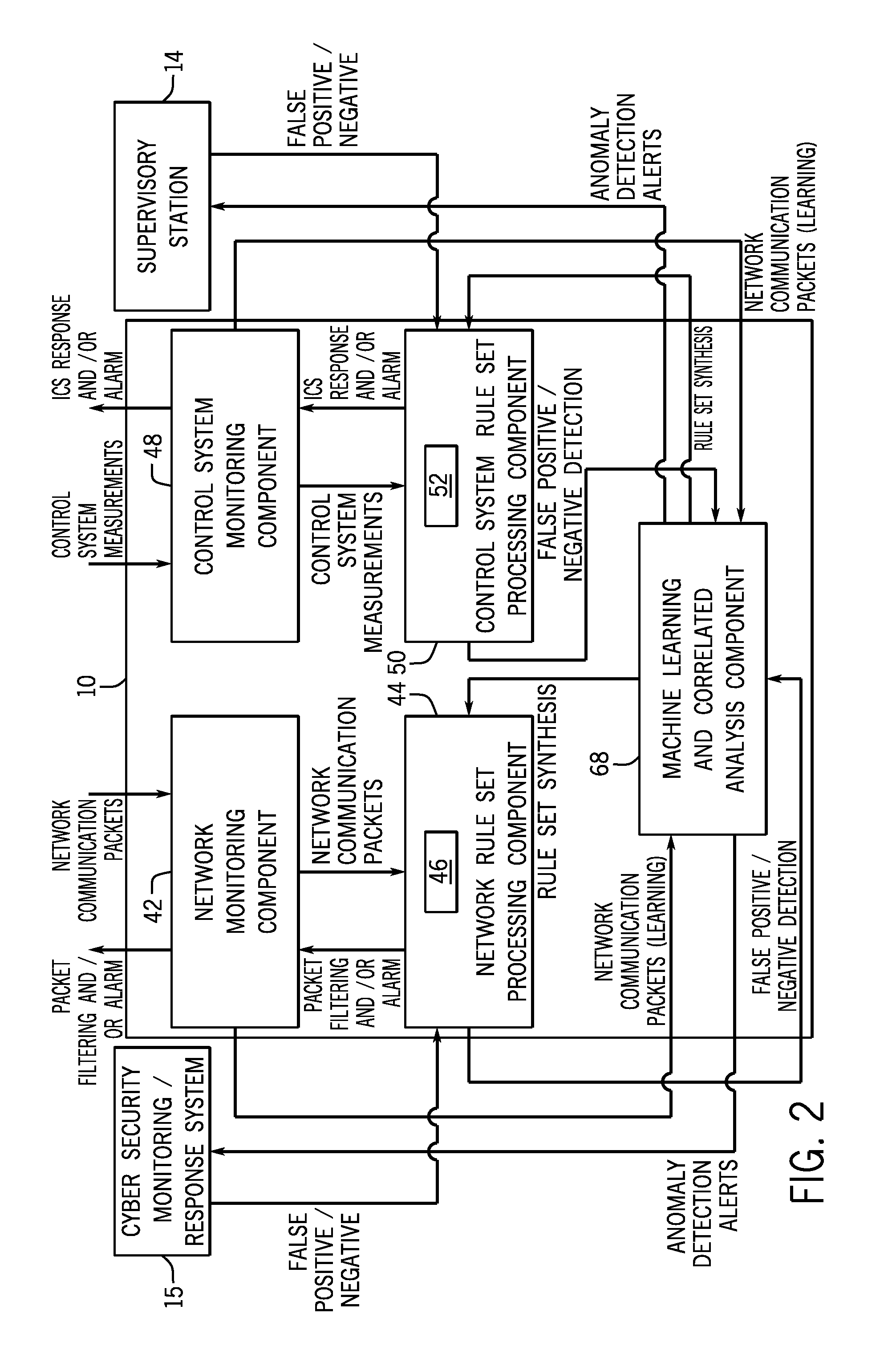
Intelligent cyberphysical intrusion detection and prevention systems and methods for industrial control systems
ActiveUS20140283047A1Memory loss protectionPower network operation systems integrationIntrusion detection and preventionIndustrial control system
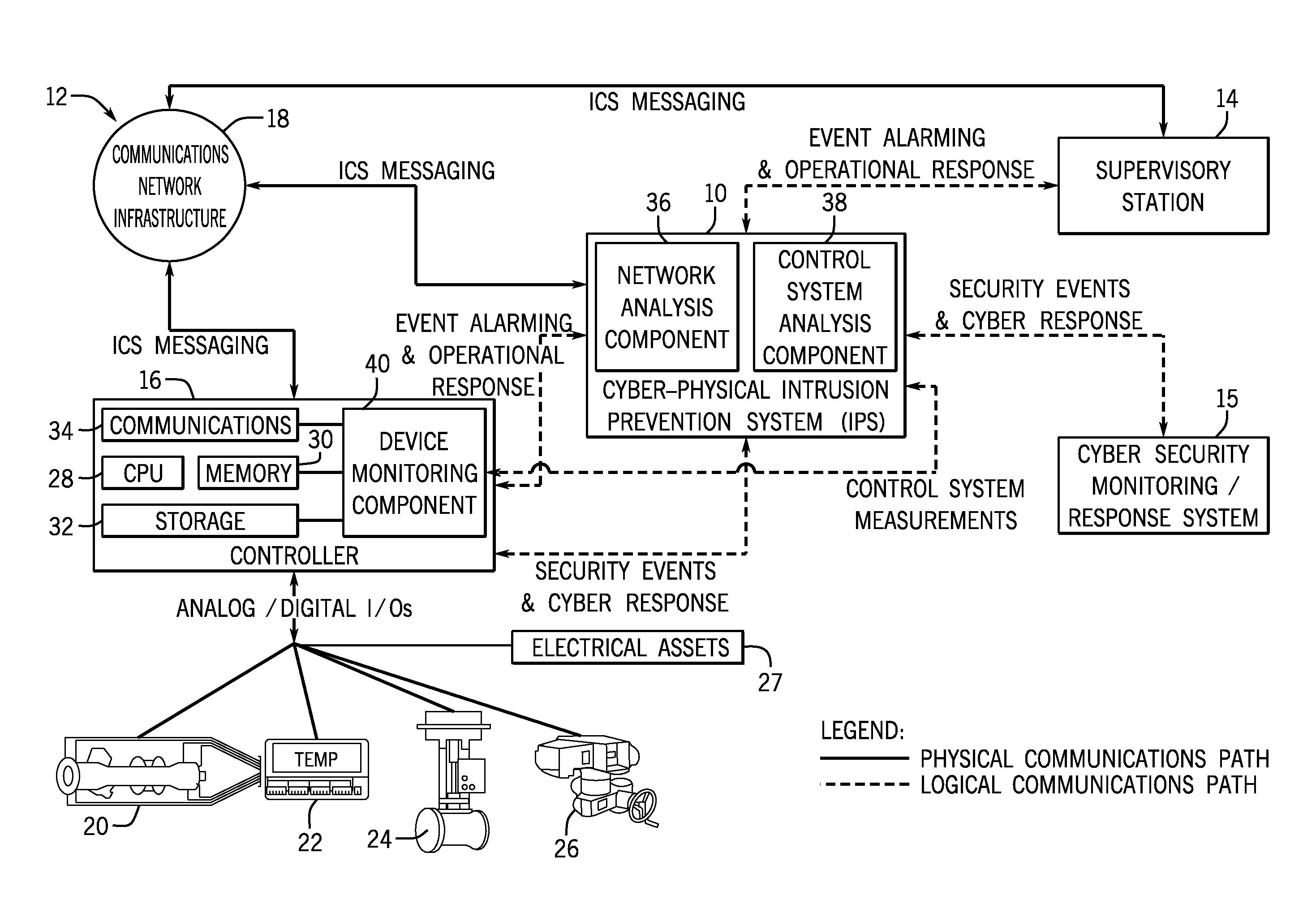
The embodiments described herein include a system and a method. In one embodiment, a system includes a device monitoring component configured to measure control system behavior and an intrusion prevention system communicatively coupled to the device monitoring component and a communications network. The intrusion prevention system includes a control system analysis component configured to analyze the control system behavior measured by the device monitoring component against a first rule set to determine whether an anomaly, an intrusion, or both are present.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for intelligent coordination of host and guest intrusion prevention in virtualized environment
A distributed and coordinated security system providing intrusion-detection and intrusion-prevention for the virtual machines (VMs) in a virtual server is described. The virtualization platform of the virtual server is enhanced with networking drivers that provide a “fast path” firewall function for pre-configured guest VMs that already have dedicated deep packet inspection security agents installed. A separate security VM is deployed to provide virtual security agents providing deep packet inspection for non pre-configured guest VMs. The network drivers are then configured to intercept the data traffic of these guest VMs and route it through their corresponding virtual security agents, thus providing a “slow-path” for intrusion detection and prevention.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
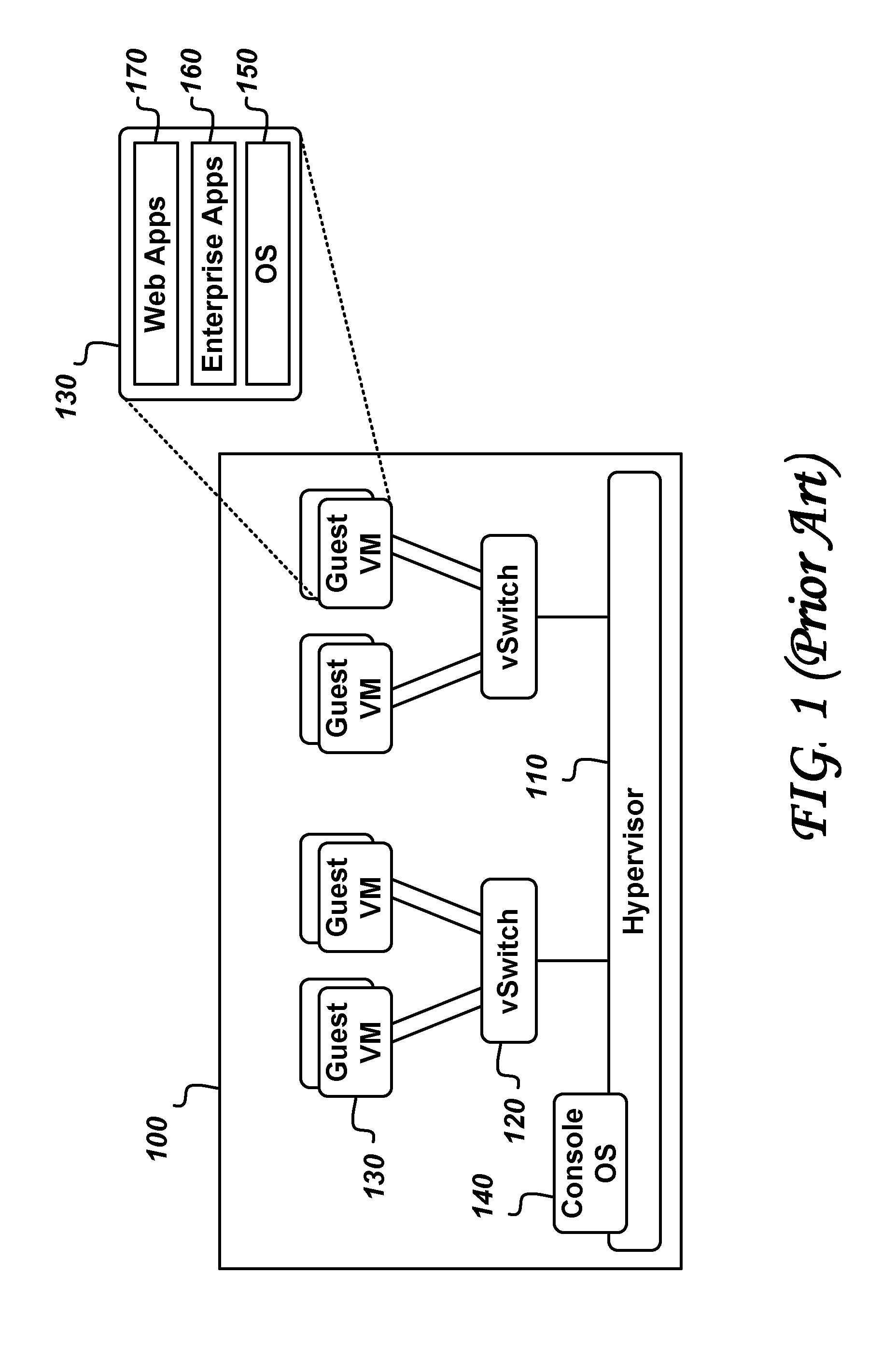
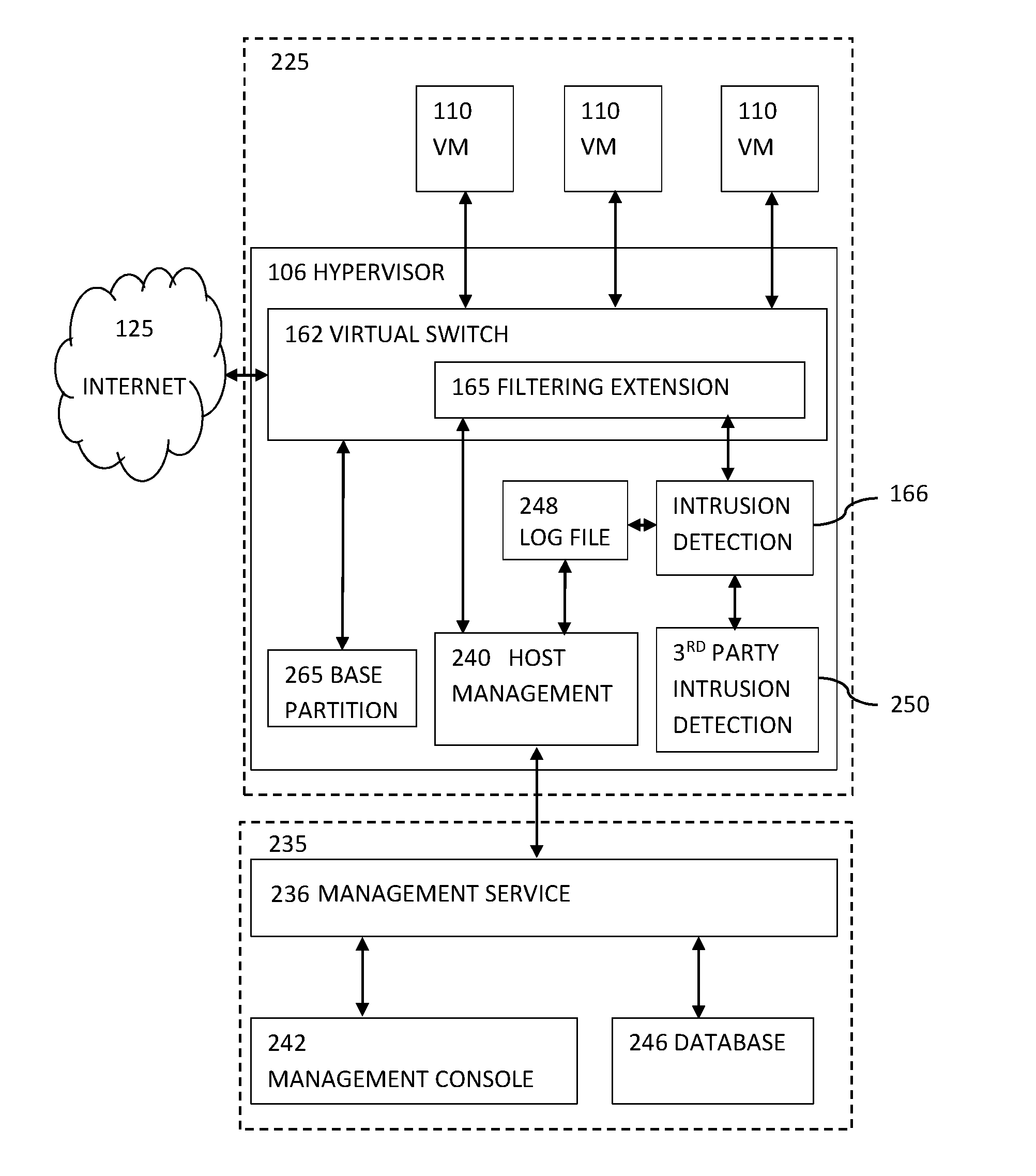
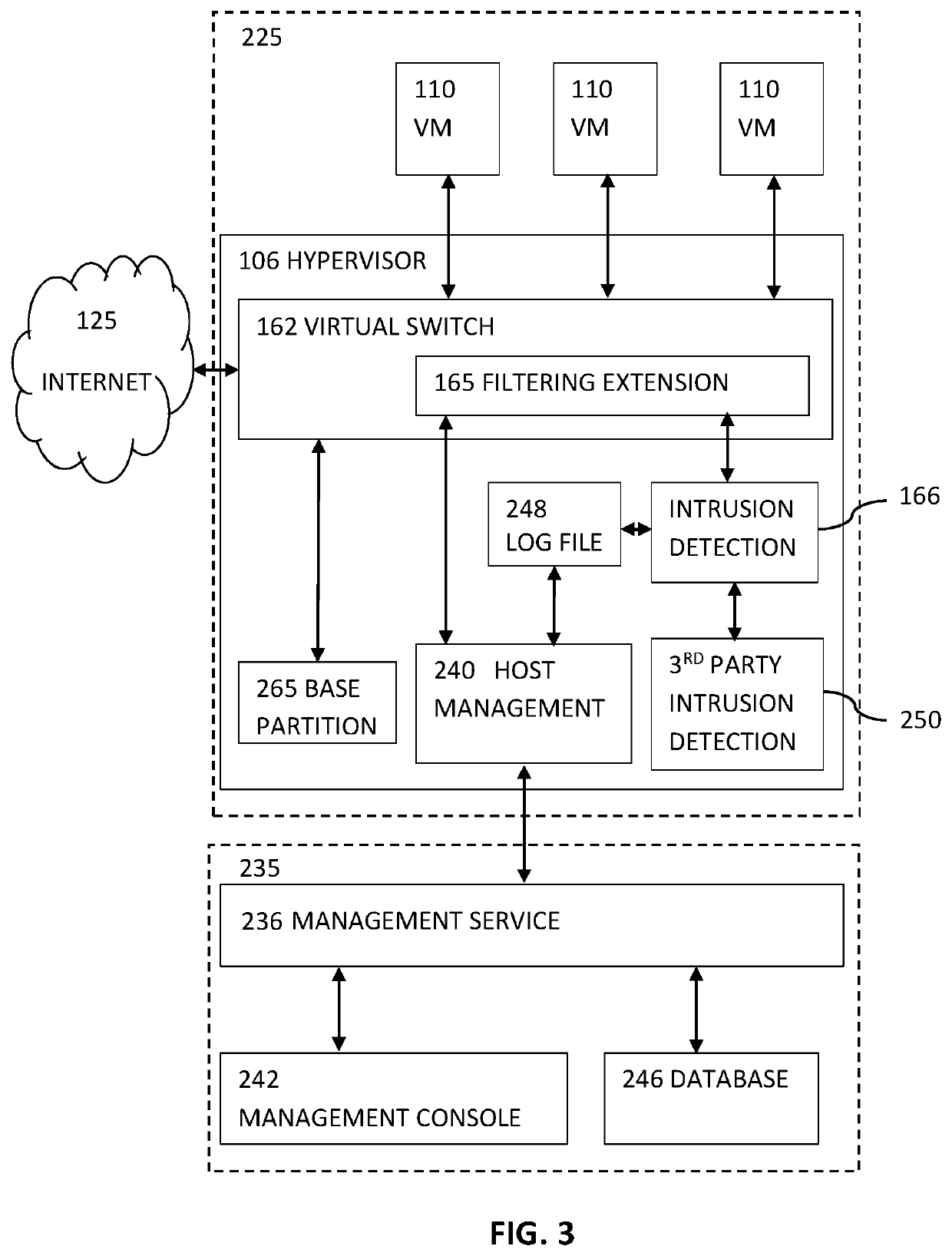
Agentless Security of Virtual Machines using a Filtering Platform
An agentless intrusion detection and prevention digital processing system and environment, or virtual firewall is disclosed. The agentless, virtual firewall monitors and controls digital data communications between a digital communications network and one or more virtual digital processing machines. The virtual digital processing machines, or virtual machines (VMs), are operative on a host digital processor under the supervision of a hypervisor software module. The agentless, virtual firewall is implemented as part of a virtual switch filtering extension to an extensible virtual switch running in a kernel mode as part of the hypervisor software module.
Owner:MALKOV KONSTANTIN +1
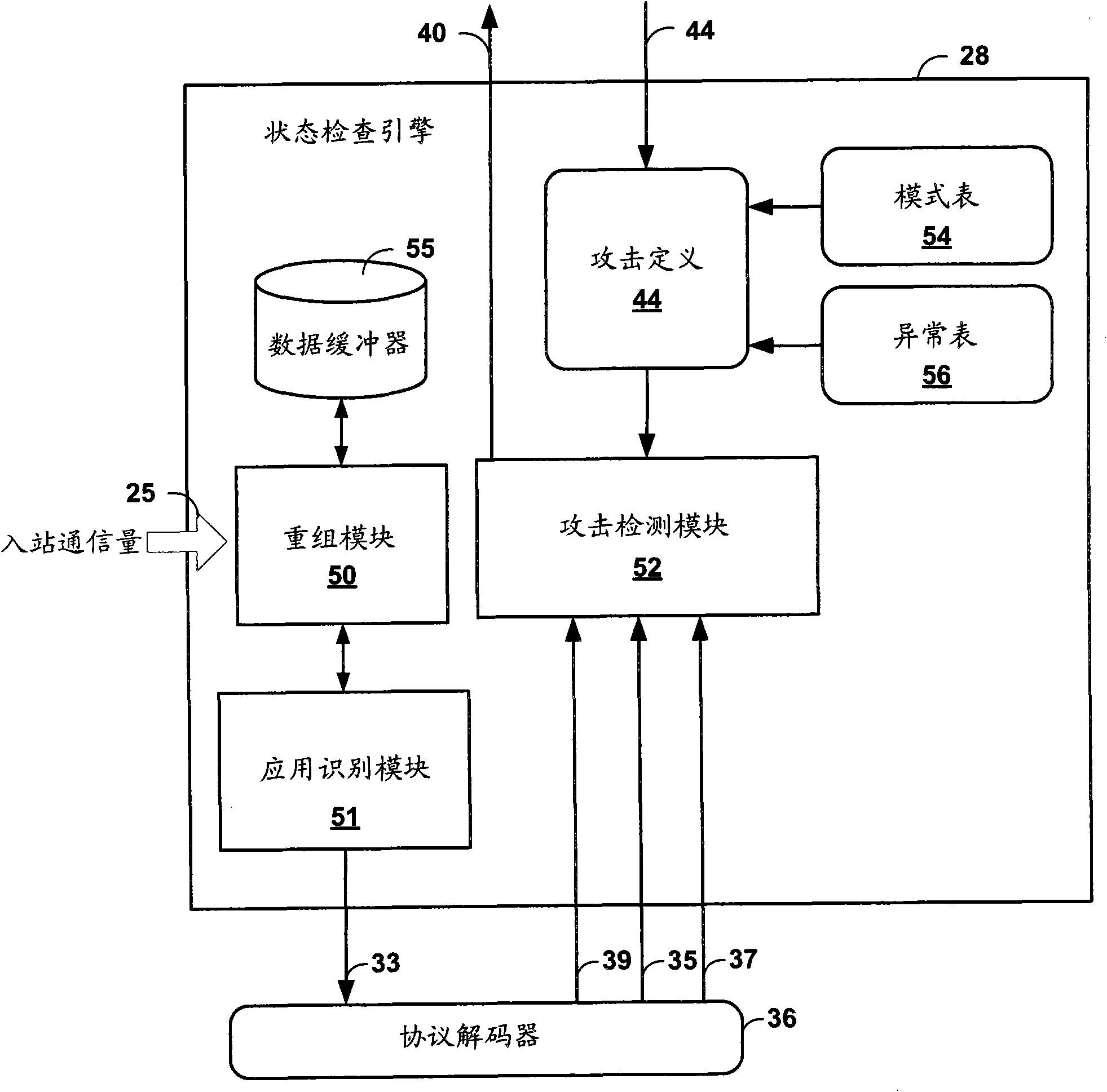
Application-layer monitoring and profiling network traffic
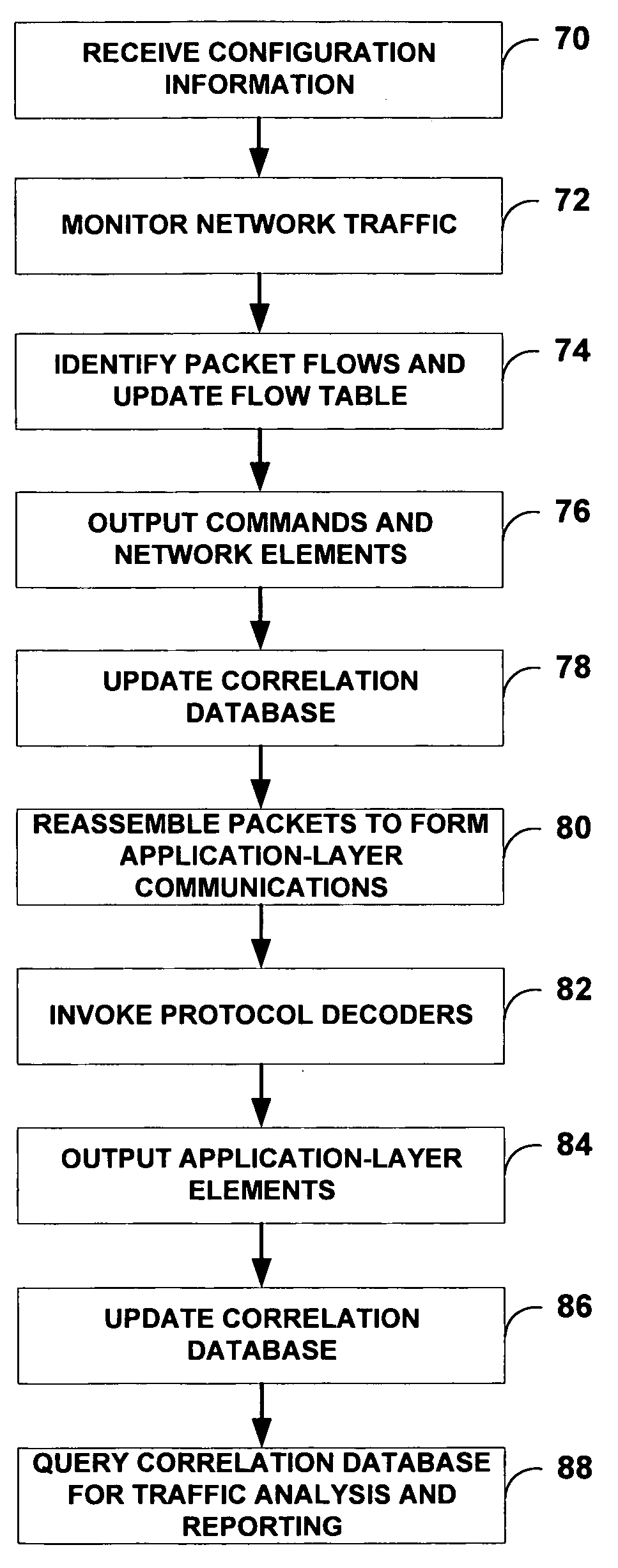
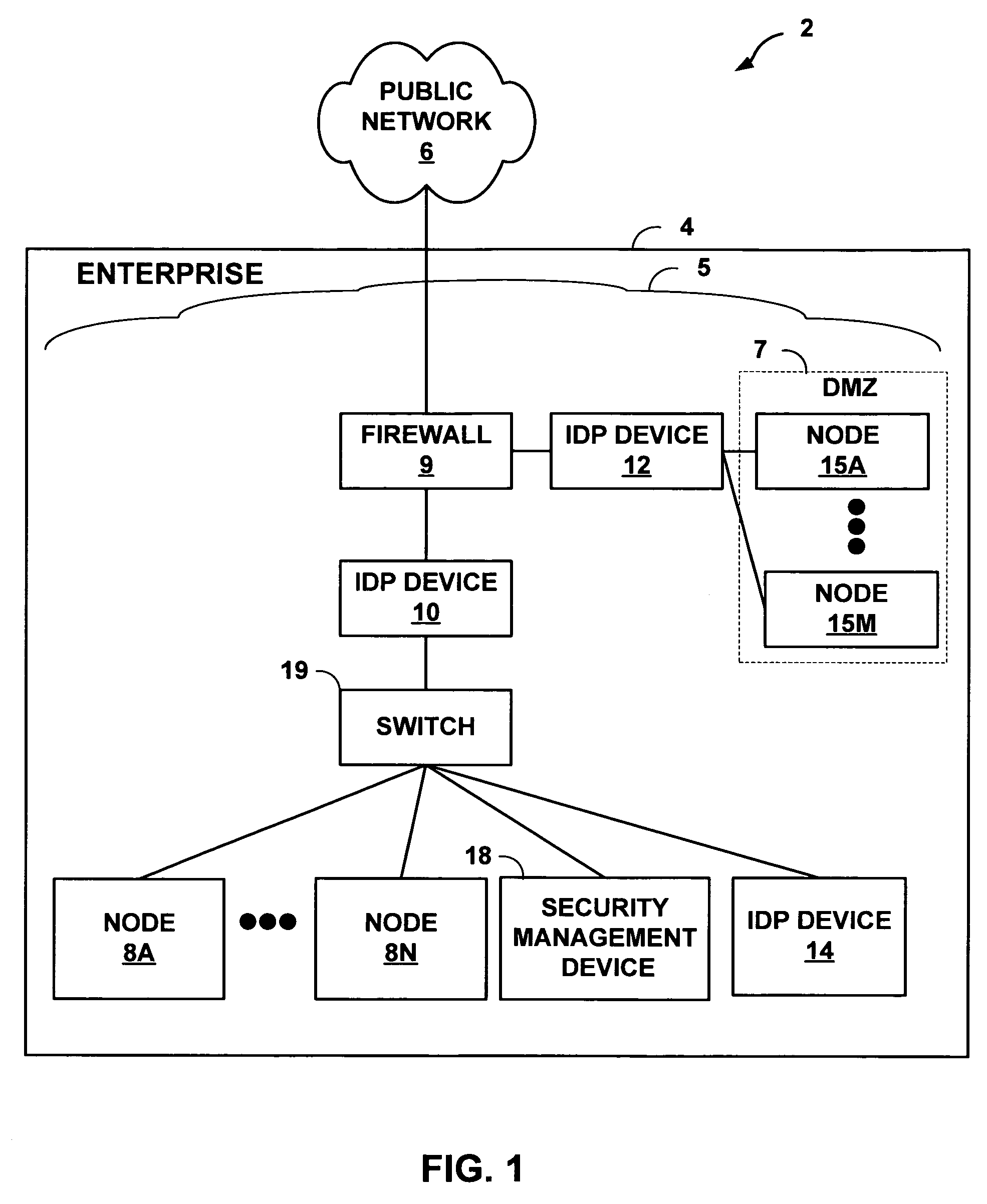
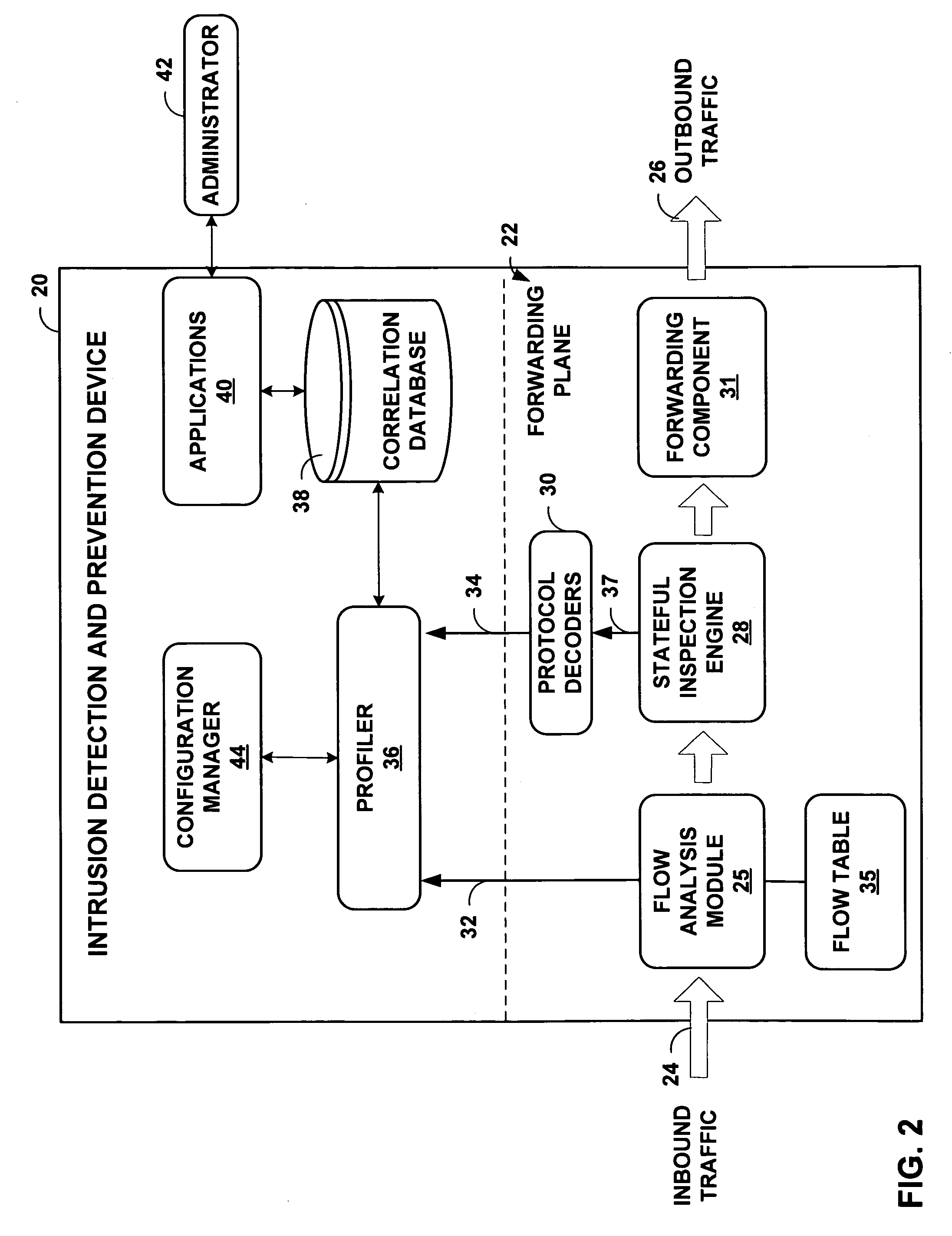
ActiveUS7769851B1Efficient communicationPreserve security postureMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTraffic capacityIntrusion detection and prevention
An intrusion detection and prevention (IDP) device includes a flow analysis module, an analysis engine, a plurality of protocol-specific decoders and a profiler. The flow analysis module processes packet flows in a network to identify network elements associated with the packet flows. The analysis engine forms application-layer communications from the packet flows. The plurality of protocol-specific decoders processes the application-layer communications to generate application-layer elements. The profiler correlates the application-layer elements of the application-layer communications with the network elements of the packet flows of the computer network.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for intrusion detection and prevention based on packet type recognition in a network
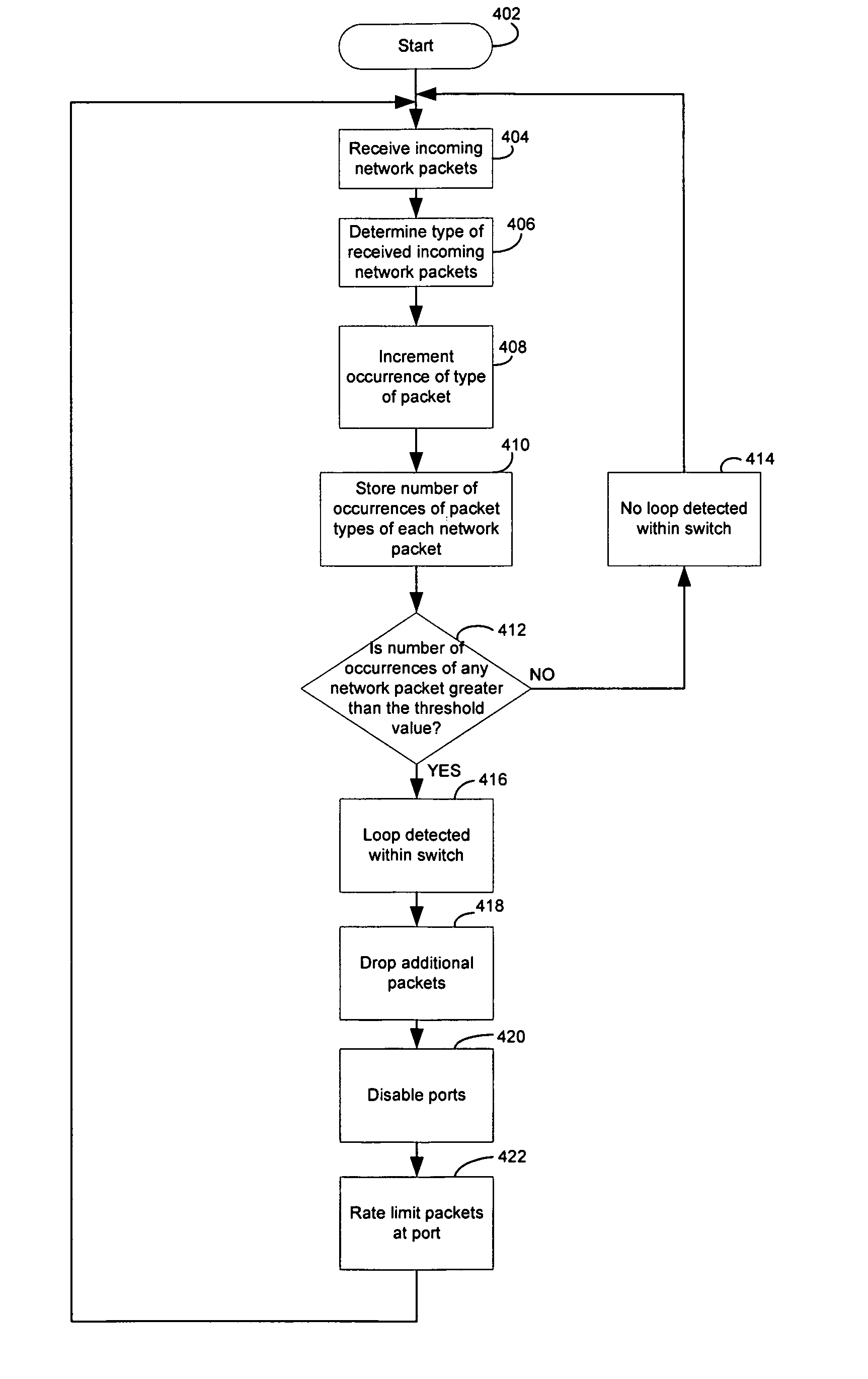
ActiveUS20070280106A1Error preventionTransmission systemsNetwork packetIntrusion detection and prevention
Certain aspects of a method and system for intrusion detection and prevention based on packet type recognition in a network are disclosed. Aspects of one method may include determining a packet type for each of a plurality of received network packets based on at least one of: a header and content of each of the plurality of received network packets. The rate at which the plurality of received network packets are handled at a port in the network switching device may be regulated based on a number of occurrences of the determined packet type of the plurality of received network packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
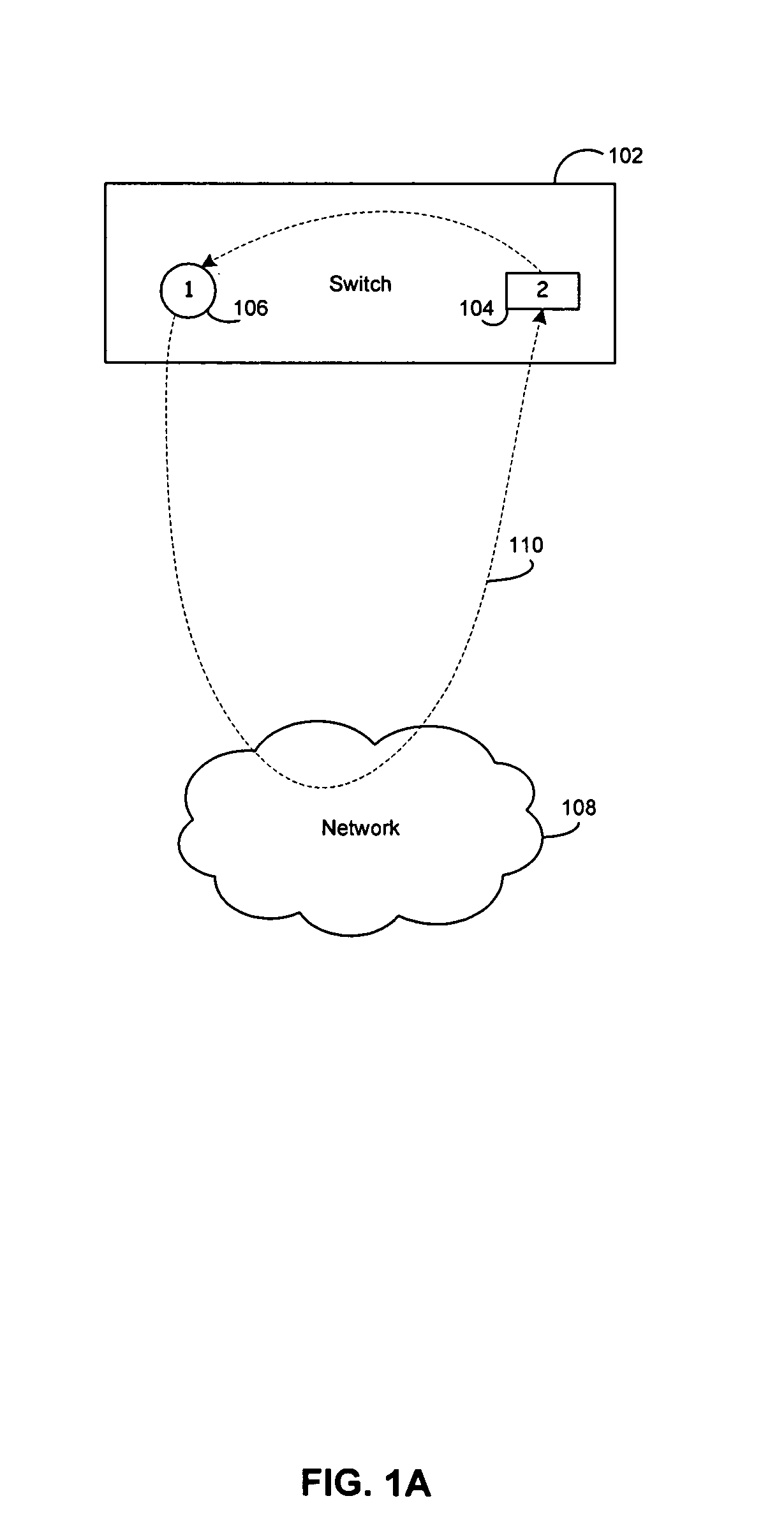
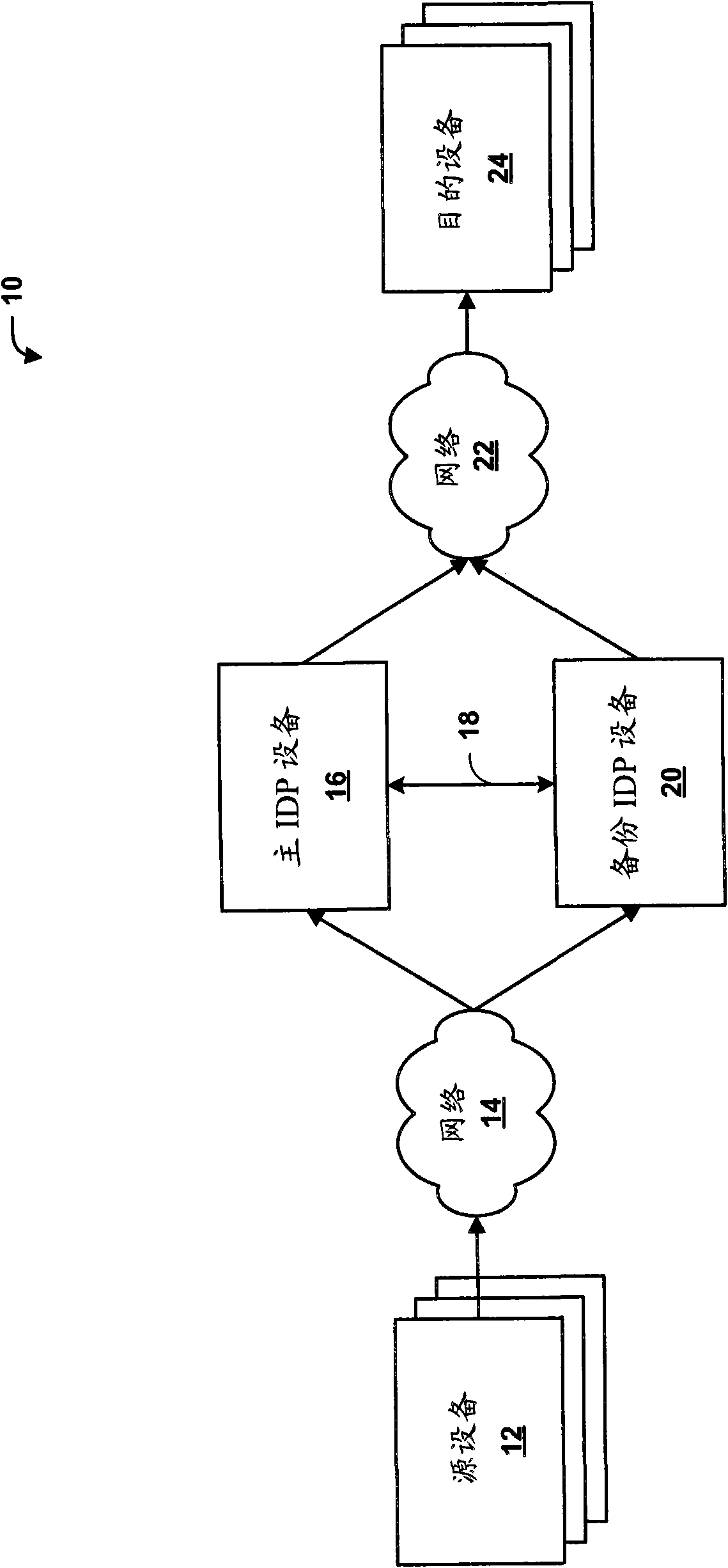
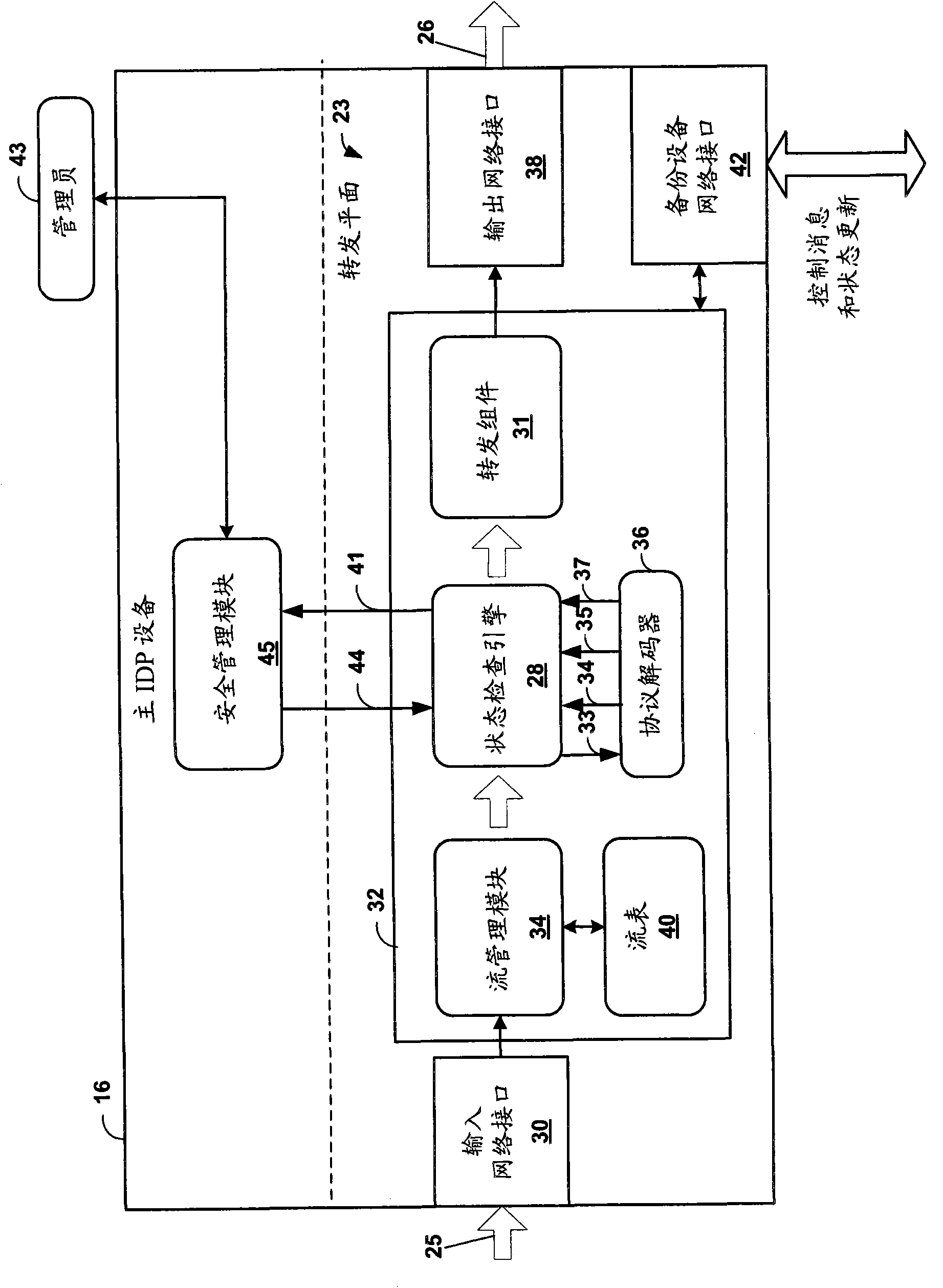
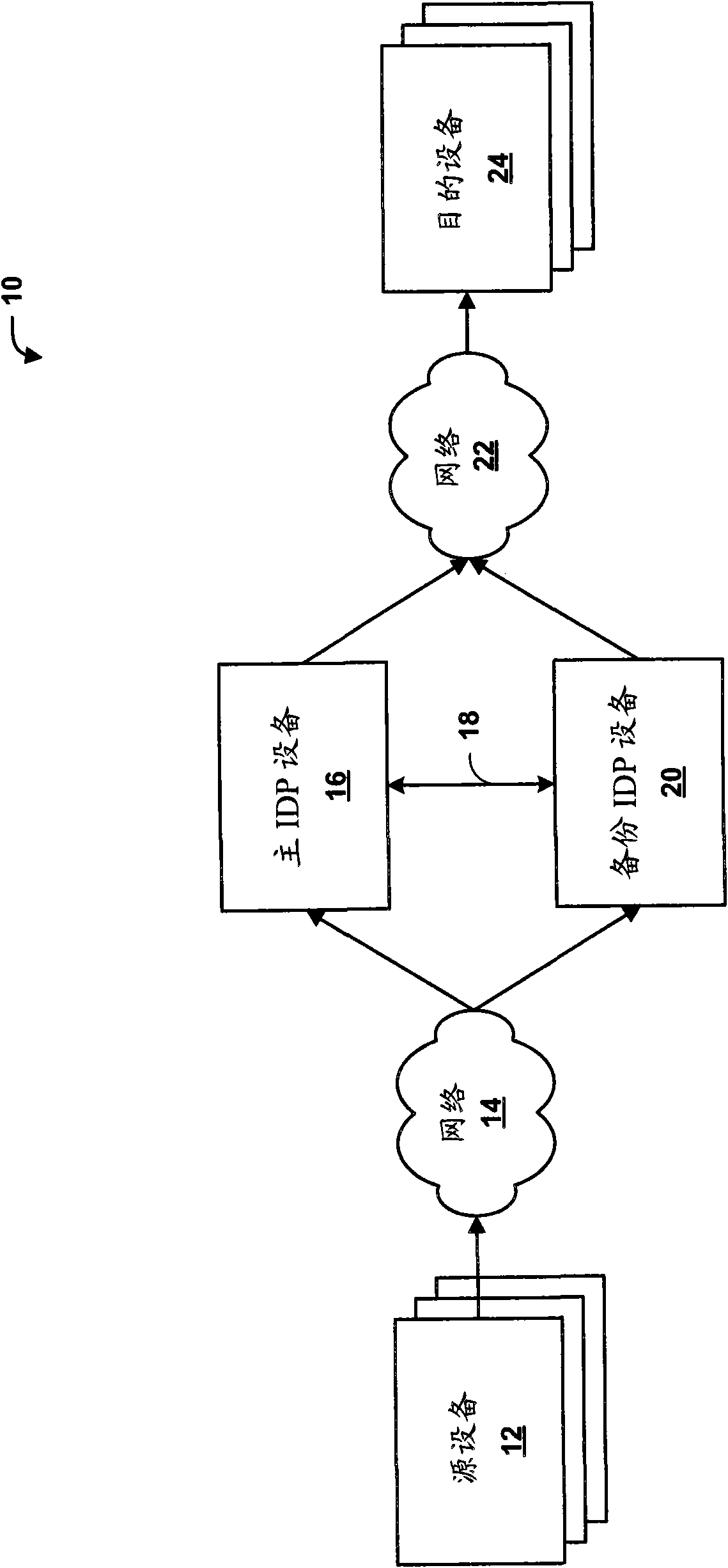
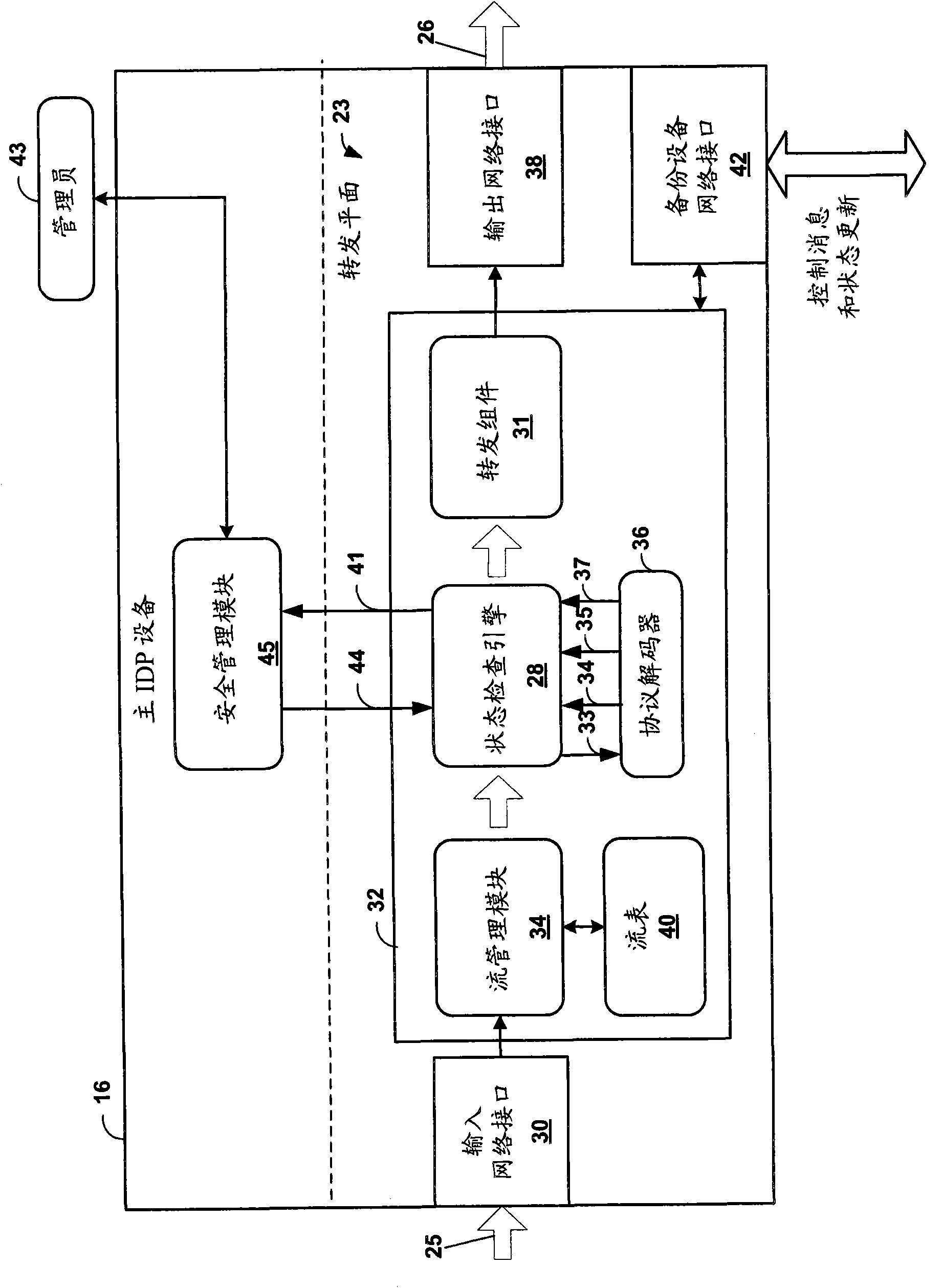
High availability for network security devices
ActiveCN102123076AError preventionData switching networksNetwork packetIntrusion detection and prevention
The invention provides methods, devices and systems of high availability for network security devices. In one example, a backup intrusion detection and prevention (IDP) device includes one or more network interfaces to receive a state update message from a primary IDP device, wherein the state update message indicates a network session being inspected by the primary IDP device and an identified application-layer protocol for the device, to receive an indication that the primary device has switched over or failed over to the backup device, and to receive a plurality of packets of the network session after receiving the indication, each of the plurality of packets comprising a respective payload including application-layer data, a protocol decoder to detect a beginning of a new transaction from the application-layer data of one of the plurality of packets, and a control unit to statefully process only the application-layer data of the network session that include and follow the beginning of the new transaction.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Intrusion detection and prevention system
InactiveUS7757285B2Efficient detectionImprove accuracyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionIntrusion detection and preventionEngineering
An intrusion detection and prevention device includes a retaining unit retaining at least one of attack suspicion threshold values of which levels are different from each other in order to detect a denial-of-service attack, and an attack determination threshold value, a detecting unit detecting an attack suspicion state when a frame count in the attack detection target flow exceeds the attack suspicion threshold value, and detecting an attack determination state when the frame count exceeds the attack determination threshold value, a notifying unit notifying of the attack suspicion state together with the corresponding flow information when the attack suspicion state is detected, a judging unit judging, based on a reliability level of at least one of the frame source terminal and the flow, whether the flow is blocked or not when notified of the attack suspicion state, and a requesting unit making a screening request together with notification of the corresponding flow information when the attack determination state is detected.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Intelligent cyberphysical intrusion detection and prevention systems and methods for industrial control systems
ActiveUS9405900B2Power network operation systems integrationPlatform integrity maintainanceIntrusion detection and preventionIndustrial control system
The embodiments described herein include a system and a method. In one embodiment, a system includes a device monitoring component configured to measure control system behavior and an intrusion prevention system communicatively coupled to the device monitoring component and a communications network. The intrusion prevention system includes a control system analysis component configured to analyze the control system behavior measured by the device monitoring component against a first rule set to determine whether an anomaly, an intrusion, or both are present.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Agentless Security of Virtual Machines Using a Network Interface Controller
ActiveUS20170054685A1TransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDigital dataVirtual firewall
An agentless intrusion detection and prevention digital processing system and environment, or virtual firewall is disclosed. The agentless, virtual firewall monitors and controls digital data communications between a digital communications network and one or more virtual digital processing machines. The virtual digital processing machines, or virtual machines (VMs), are operative on a host digital processor under the supervision of a hypervisor software module. The agentless, virtual firewall is implemented as part of a virtual switch filtering extension to an extensible virtual switch running in a kernel mode as part of the hypervisor software module.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
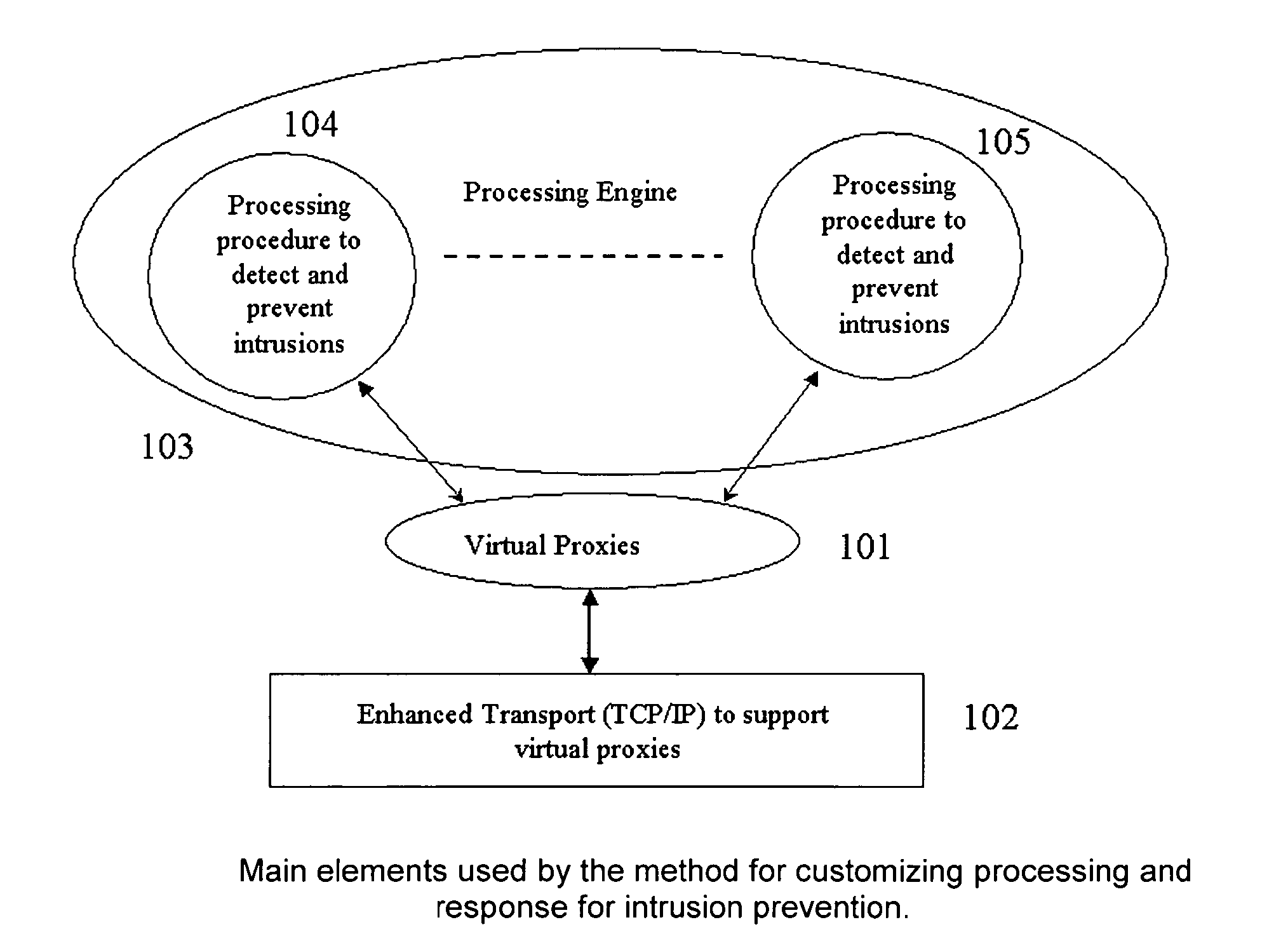
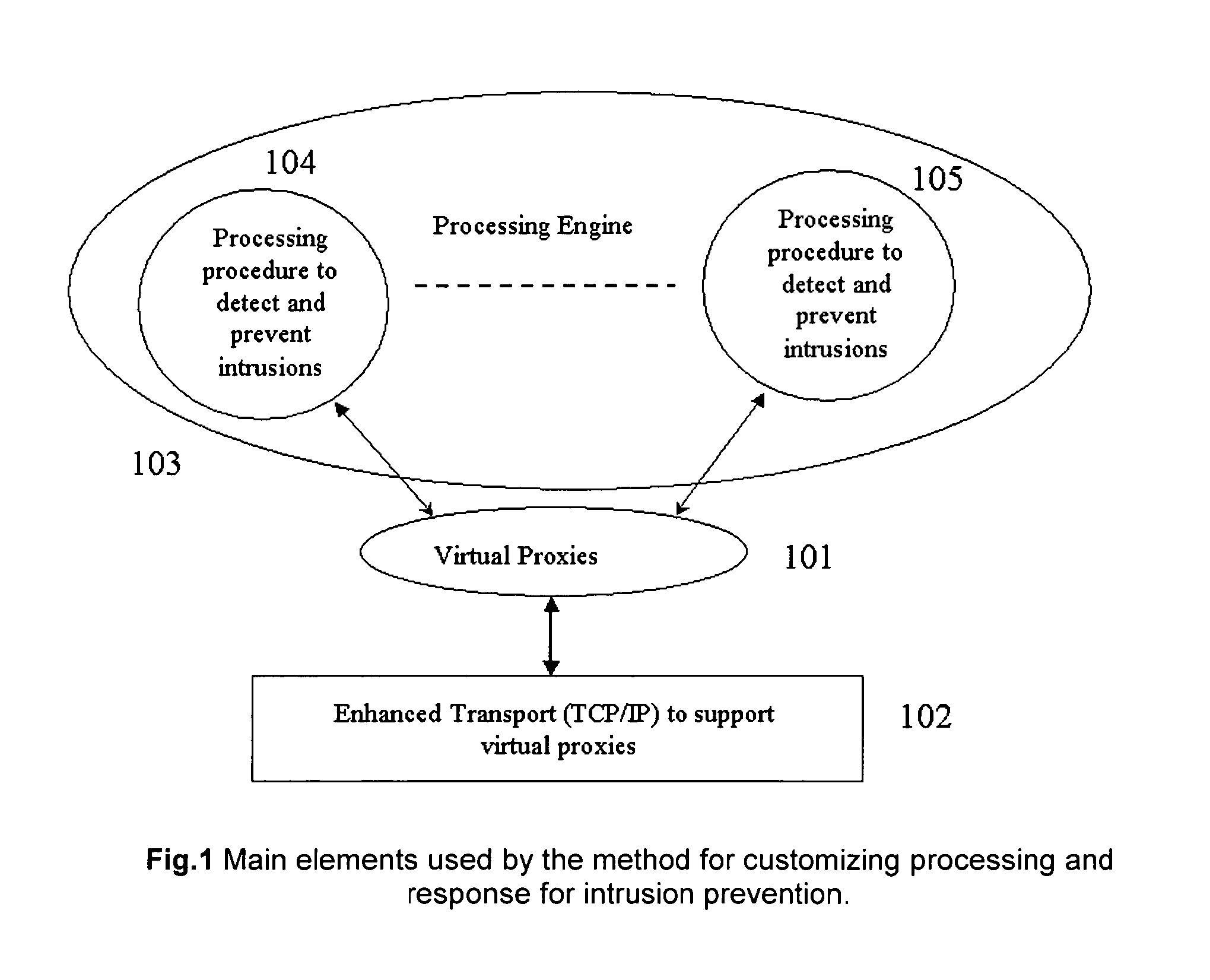
Method for customizing processing and response for intrusion prevention
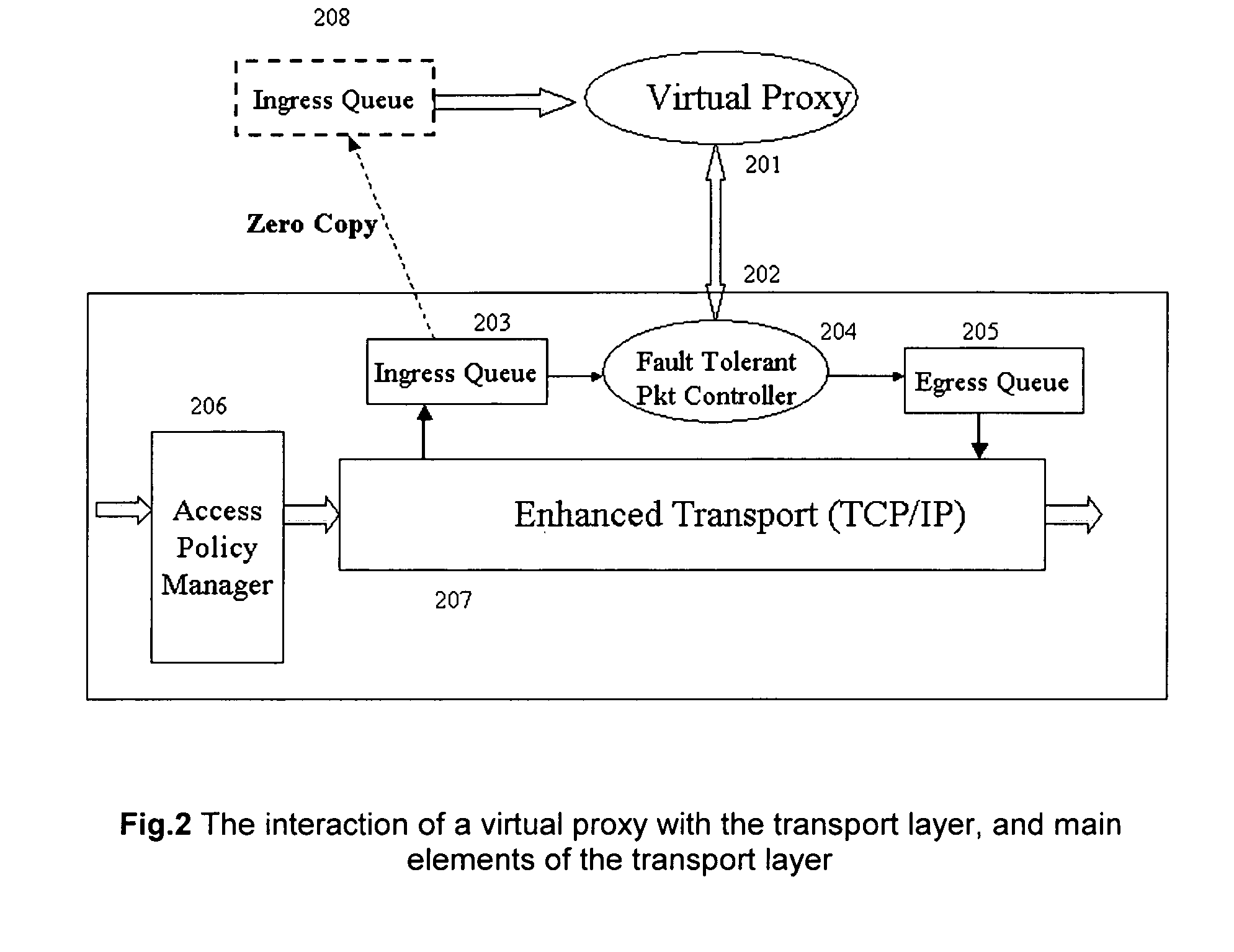
ActiveUS7657937B1Improve performanceFully captureMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionTransport layerIntrusion detection and prevention
A method for customizing the response for network based intrusion prevention comprising of: 1) virtual proxying the application data to enable custom response 2) enhancing transport layer (TCP / IP) to enable selective processing and selective modification of the stream for intrusion prevention. The invention also discloses a method for customizing the processing for both network or host based intrusion prevention comprising of: 1) loading externally defined processing procedures for the detection and prevention of intrusions 2) combining multiple of these processing procedures to form a unified processing engine that can be used for intrusion detection and prevention 3) unloading processing procedures that are not needed any more 4) loading new processing procedures that improve the intrusion detection and prevention.
Owner:VMWARE INC
System and method for intelligent coordination of host and guest intrusion prevention in virtualized environment
A distributed and coordinated security system providing intrusion-detection and intrusion-prevention for the virtual machines (VMs) in a virtual server is described. The virtualization platform of the virtual server is enhanced with networking drivers that provide a “fast path” firewall function for pre-configured guest VMs that already have dedicated deep packet inspection security agents installed. A separate security VM is deployed to provide virtual security agents providing deep packet inspection for non pre-configured guest VMs. The network drivers are then configured to intercept the data traffic of these guest VMs and route it through their corresponding virtual security agents, thus providing a “slow-path” for intrusion detection and prevention.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Overlay automata approach to regular expression matching for intrusion detection and prevention system
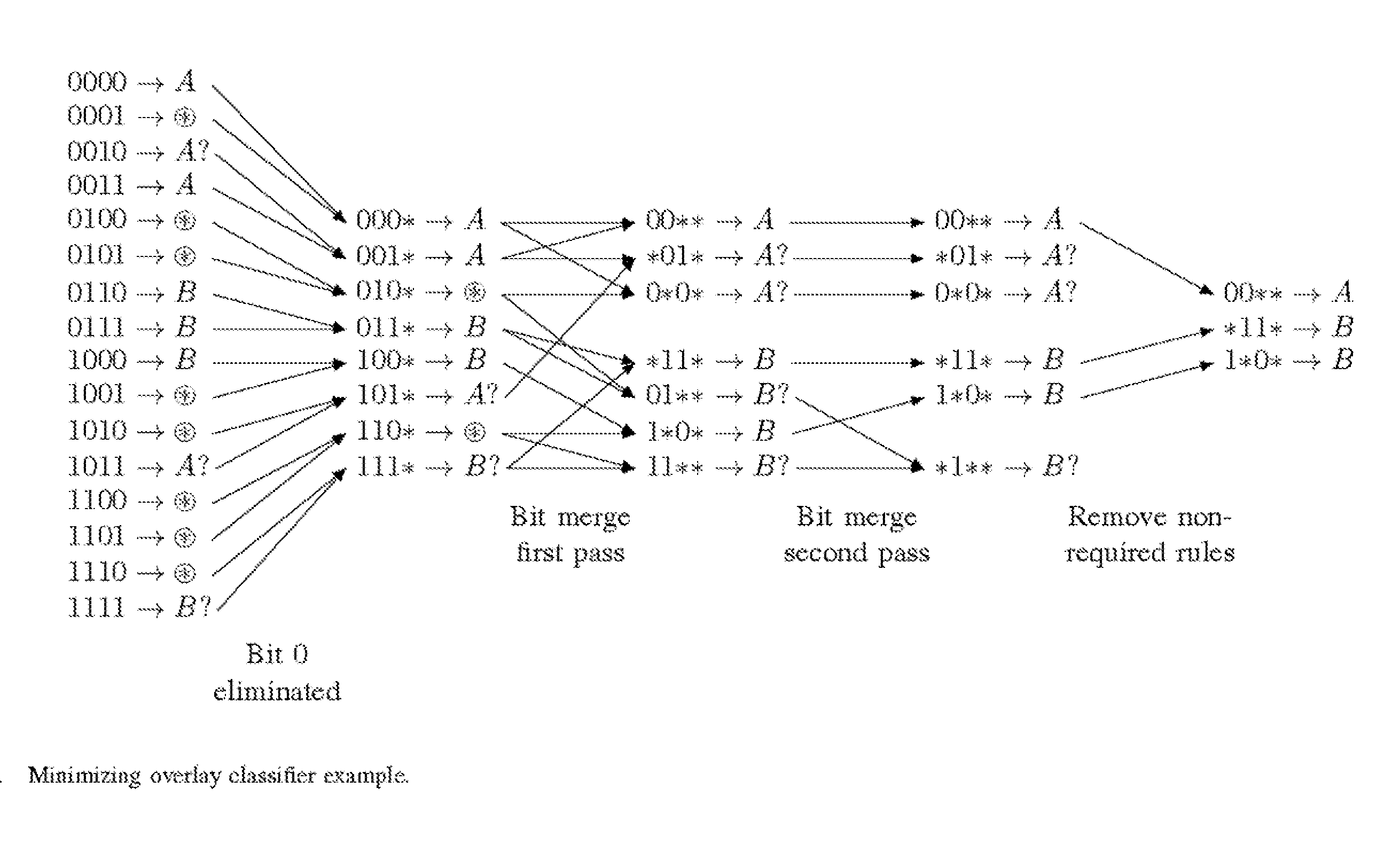
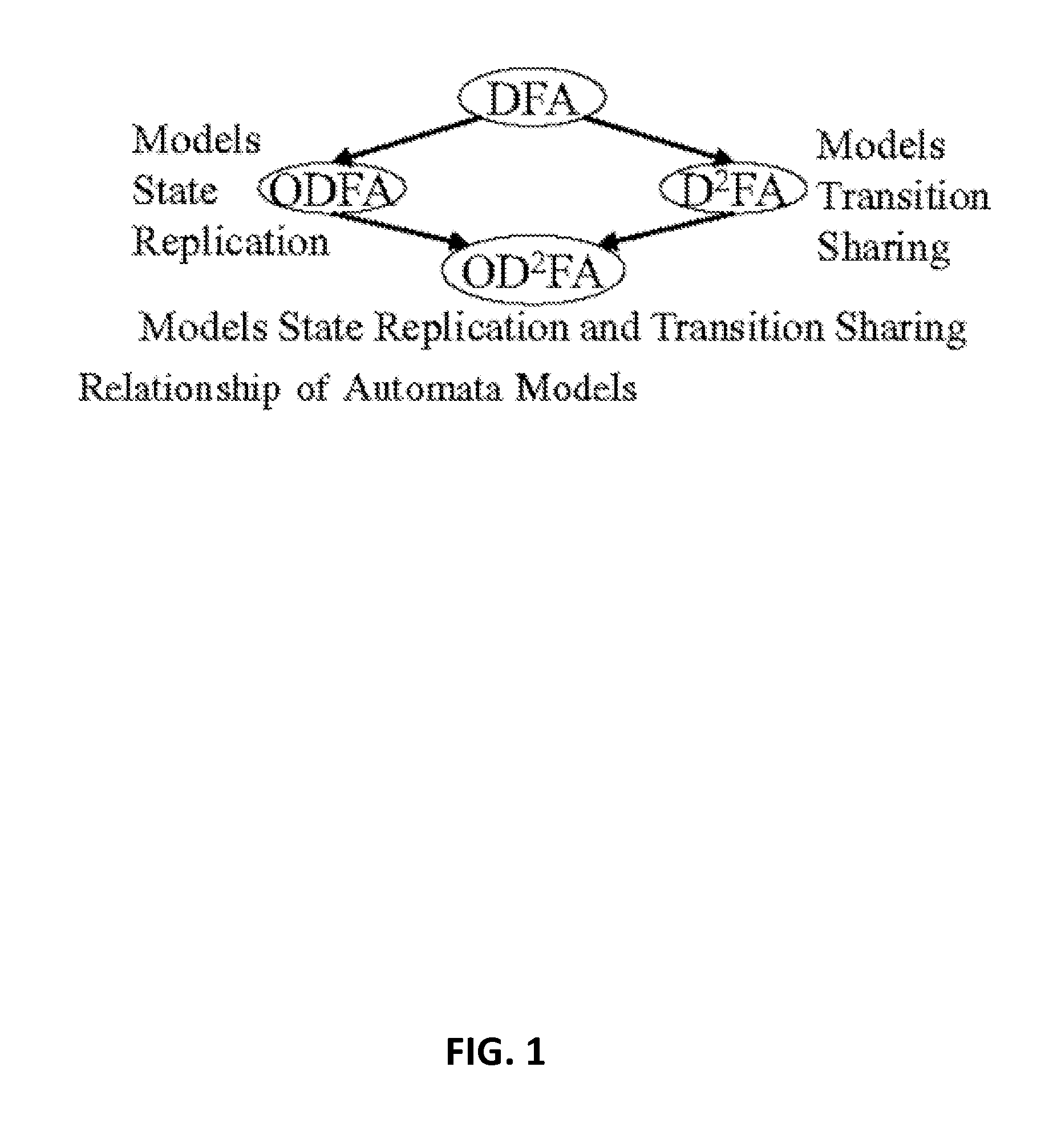
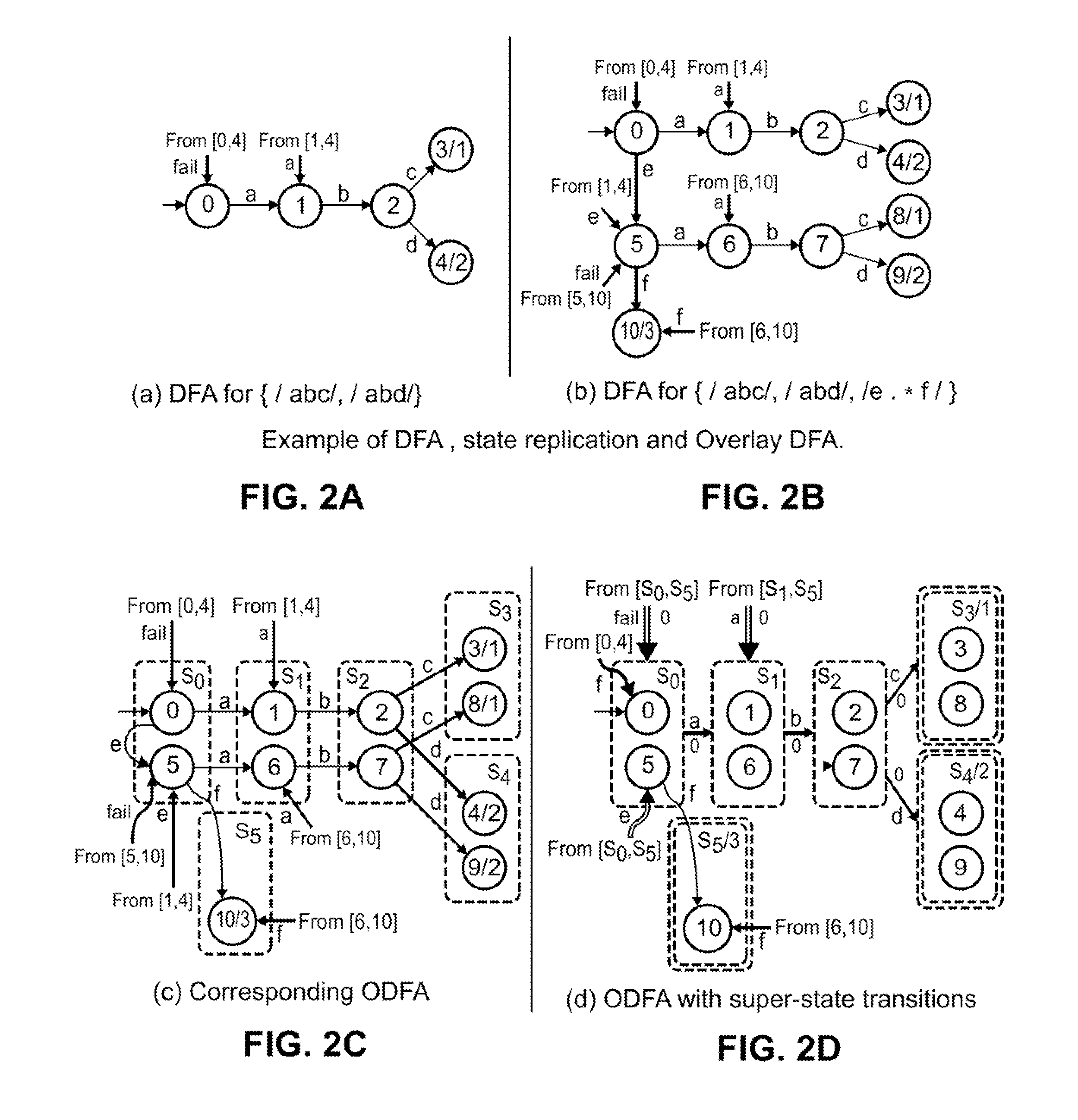
InactiveUS20150310342A1Efficient constructionProgram controlMachine learningIntrusion detection and preventionTernary content addressable memory
Embodiments are described for automata models for use in deep packet inspection. Various embodiments are described for a new automata model, Overlay DFA (ODFA), which captures state replication in DFAs. Additional embodiments include combining the ODFA model with a D2FA model to provide an Overlay Delayed Input DFA (OD2FA). As the DFA model captures transition sharing, the OD2FA model captures both state replication and transition sharing. Algorithms are disclosed for efficiently constructing the OD2FA model and for implementing the OD2FA model in Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM).
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
System and methodology for intrusion detection and prevention
ActiveUS8074277B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsIntrusion detection and preventionNetwork communication
System and methodology for intrusion detection and prevention is described. In one embodiment, for example, a method is described for detecting and preventing network intrusion, the method comprises steps of: defining intrusion descriptions specifying exploits that may be attempted by malicious network traffic, the intrusion descriptions indicating specific applications that may be targeted by individual exploits; for a particular application participating in network communication, deriving a subset of the intrusion descriptions specifically applicable to that particular application; using the subset of the intrusion descriptions specifically applicable to that application, monitoring network traffic destined for the particular application for detecting an attempted network intrusion; and if a network intrusion is detected, blocking network traffic destined for the particular application determined to comprise an exploit.
Owner:CHECK POINT SOFTWARE TECH INC
Agentless security of virtual machines using a network interface controller
ActiveUS10701104B2TransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDigital dataVirtual firewall
An agentless intrusion detection and prevention digital processing system and environment, or virtual firewall is disclosed. The agentless, virtual firewall monitors and controls digital data communications between a digital communications network and one or more virtual digital processing machines. The virtual digital processing machines, or virtual machines (VMs), are operative on a host digital processor under the supervision of a hypervisor software module. The agentless, virtual firewall is implemented as part of a virtual switch filtering extension to an extensible virtual switch running in a kernel mode as part of the hypervisor software module.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
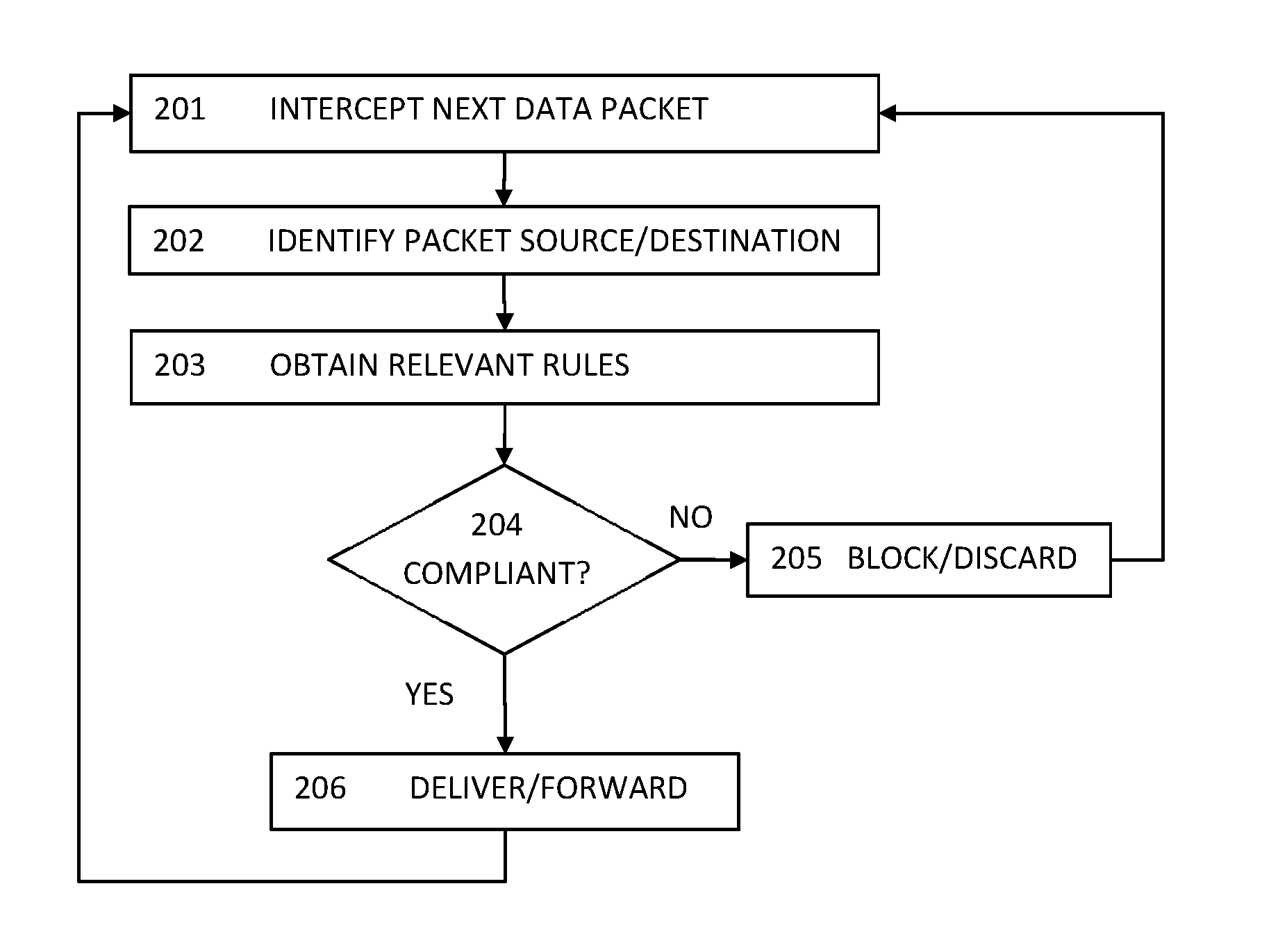
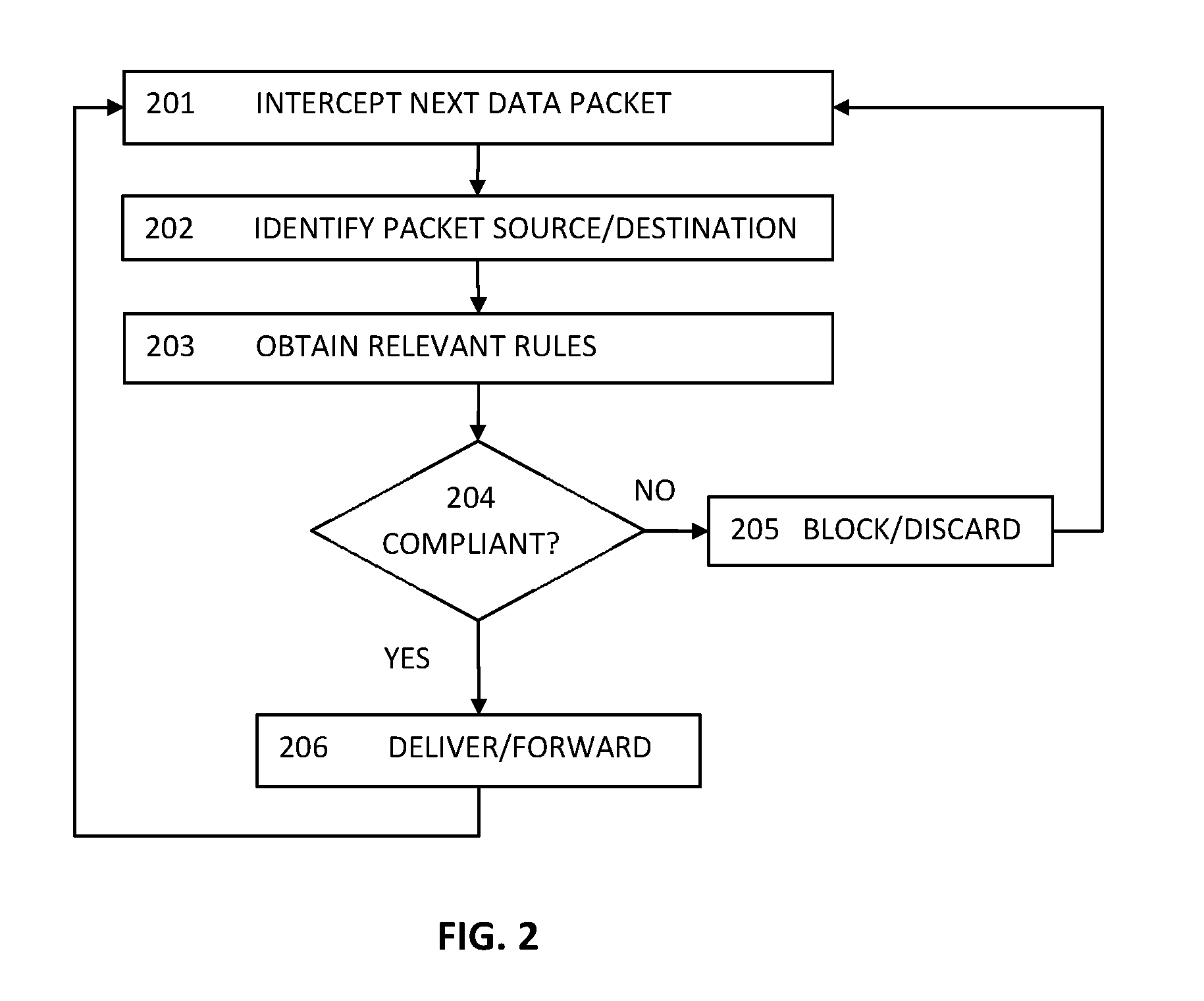
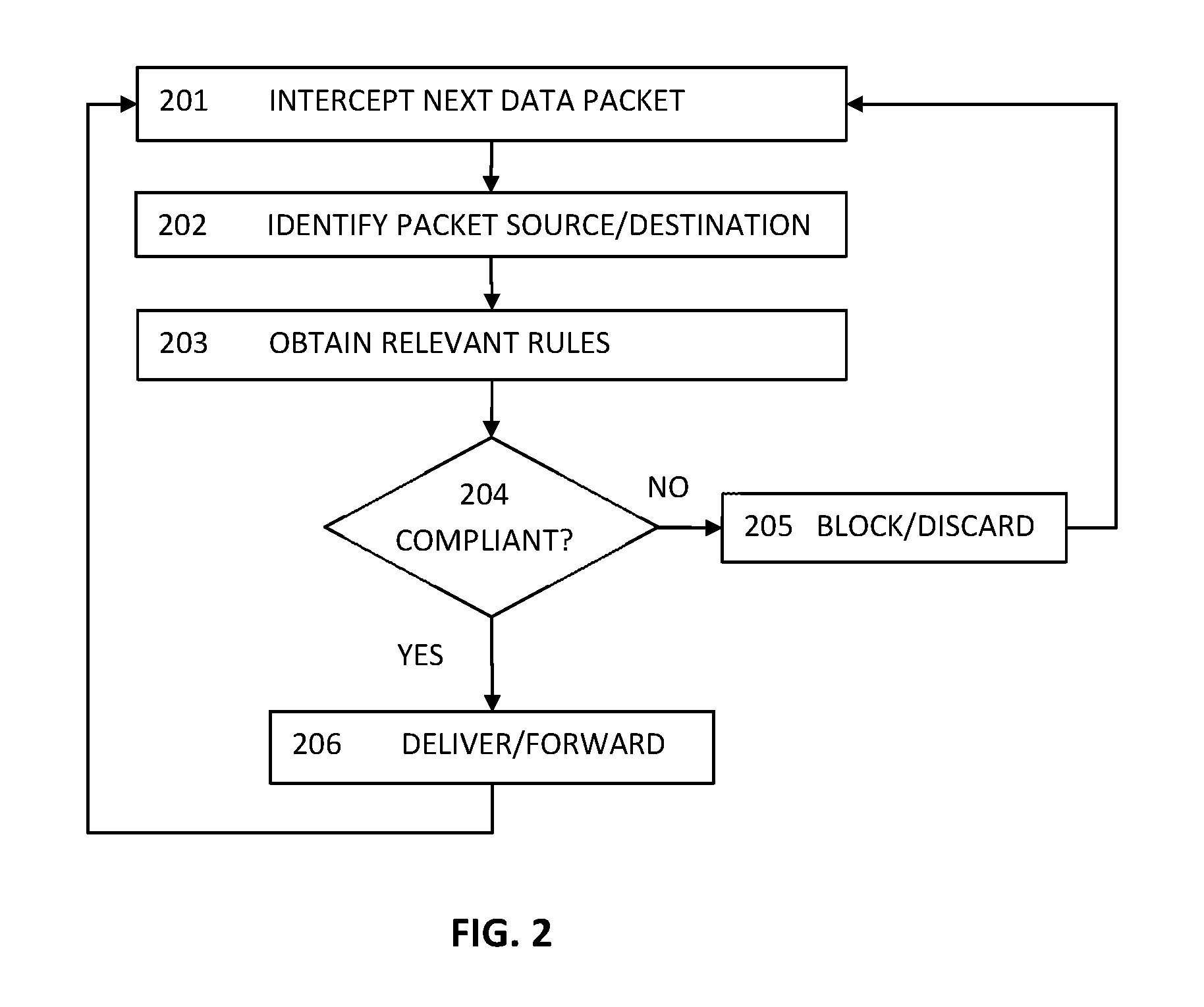
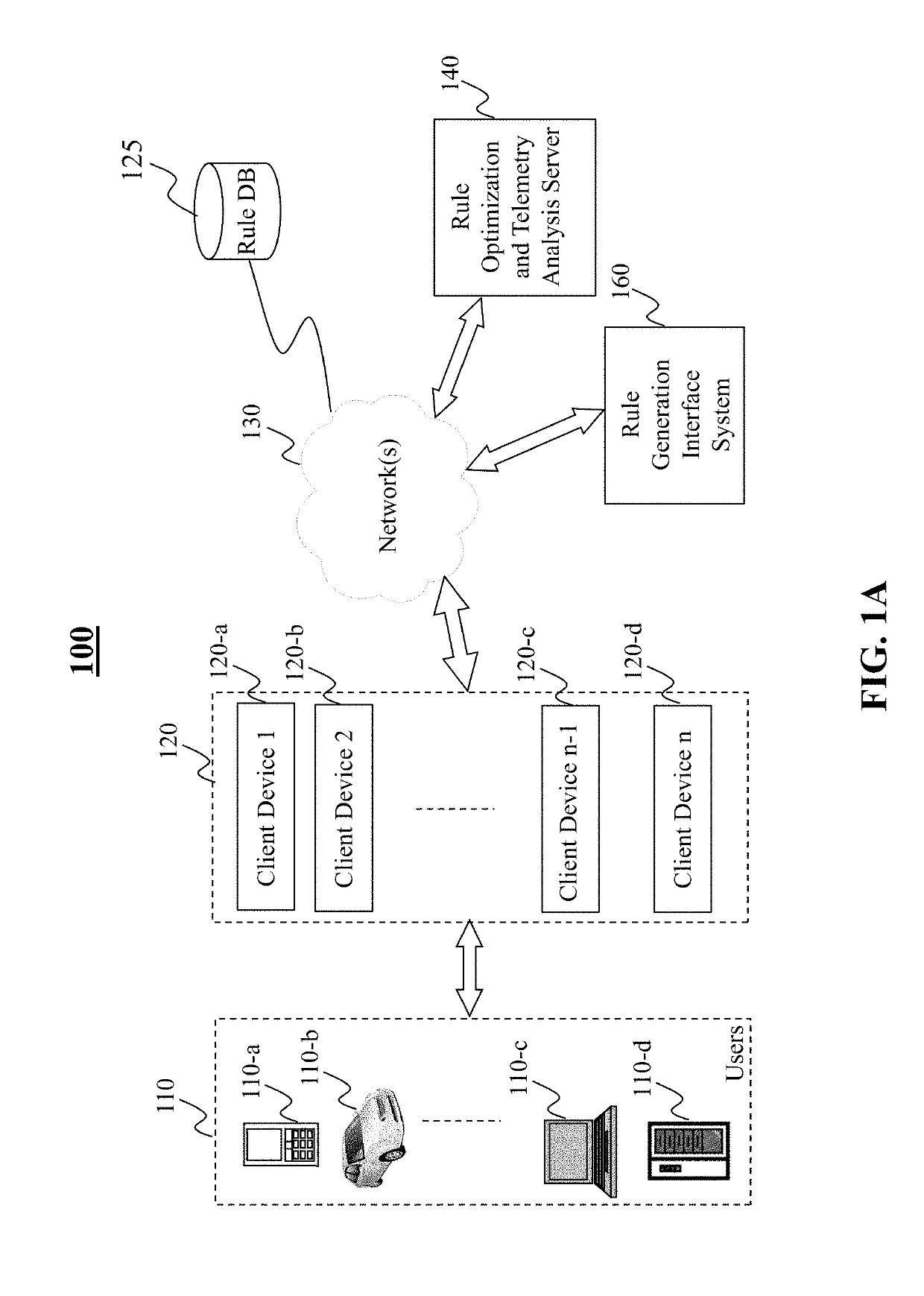
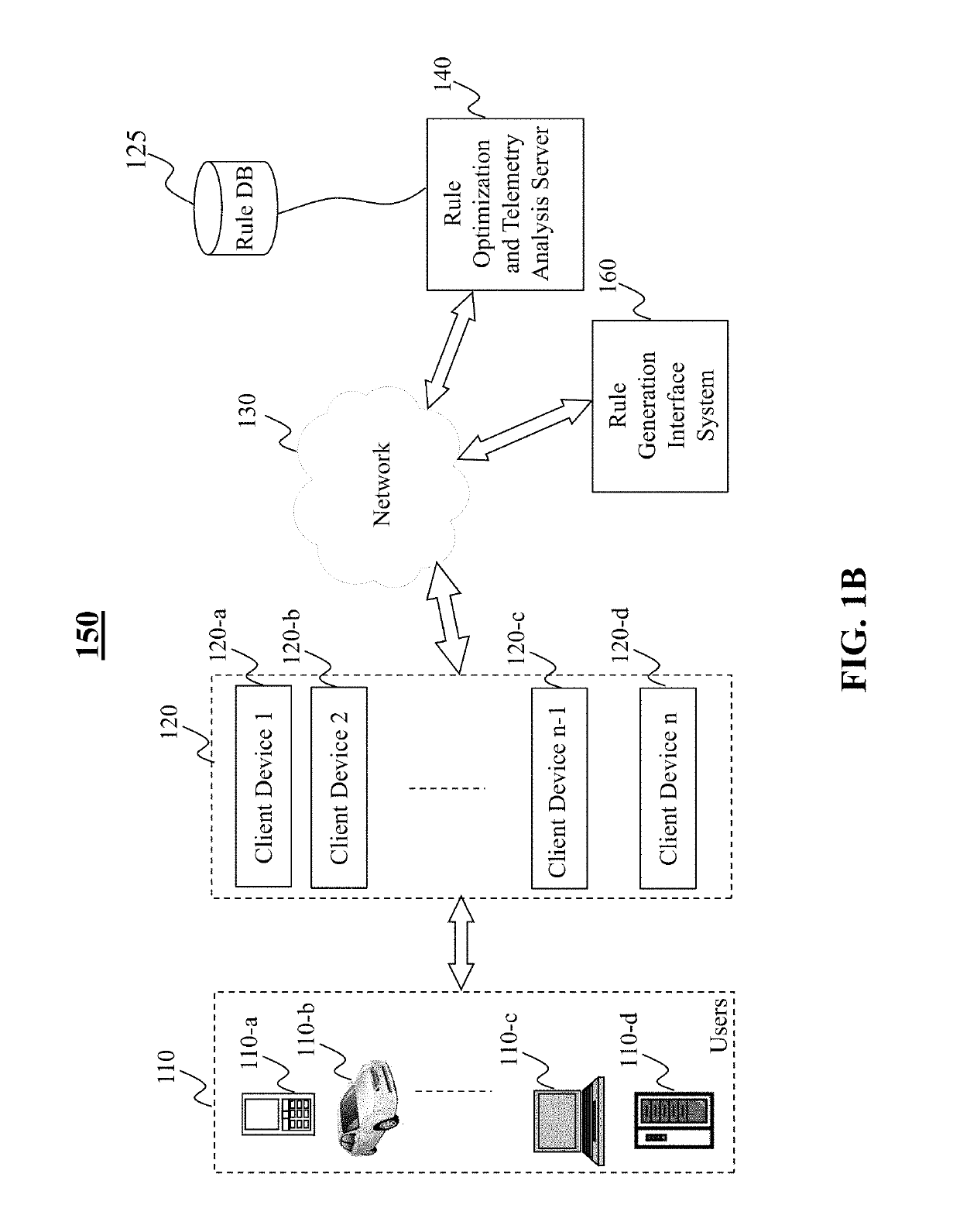
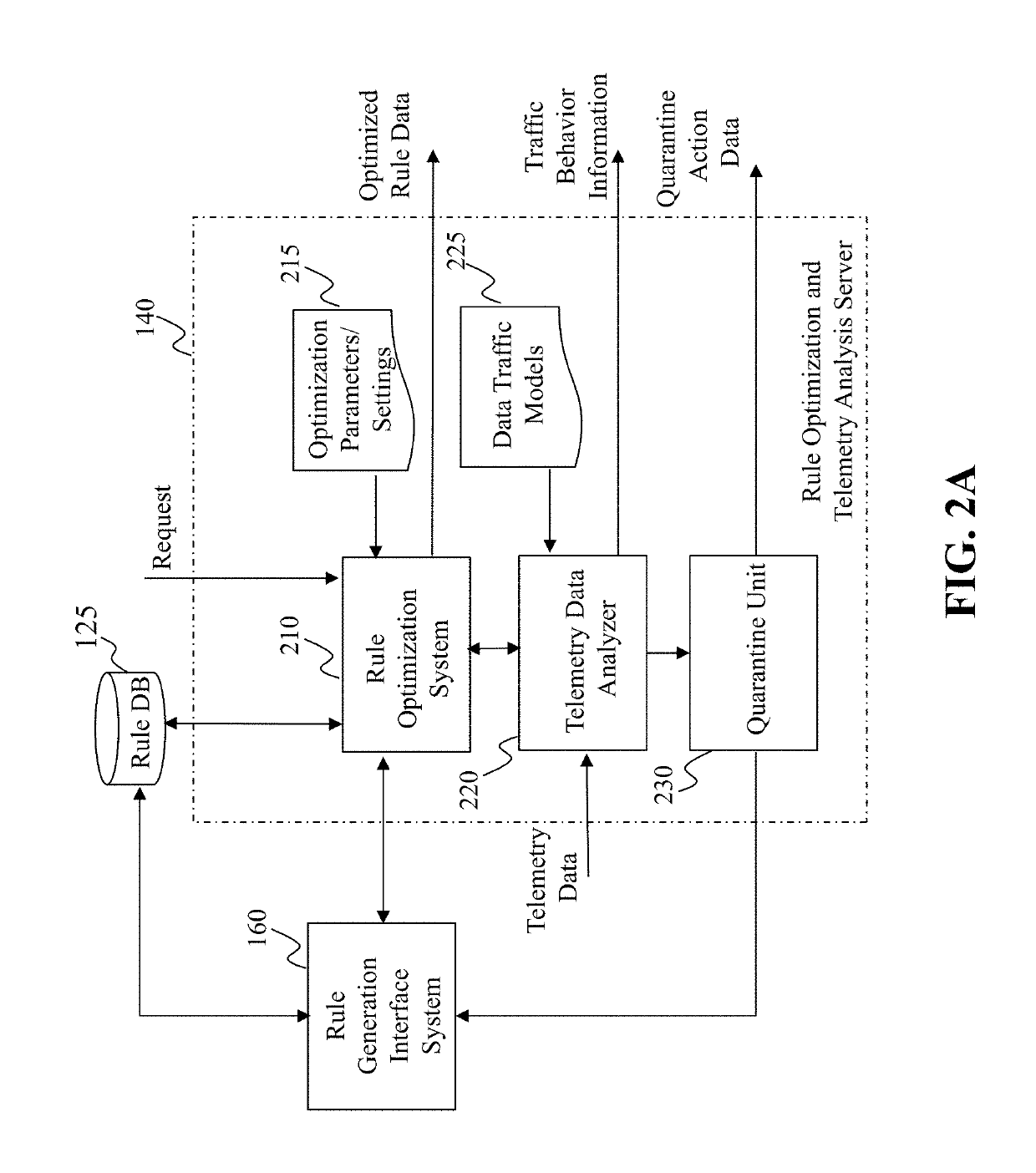
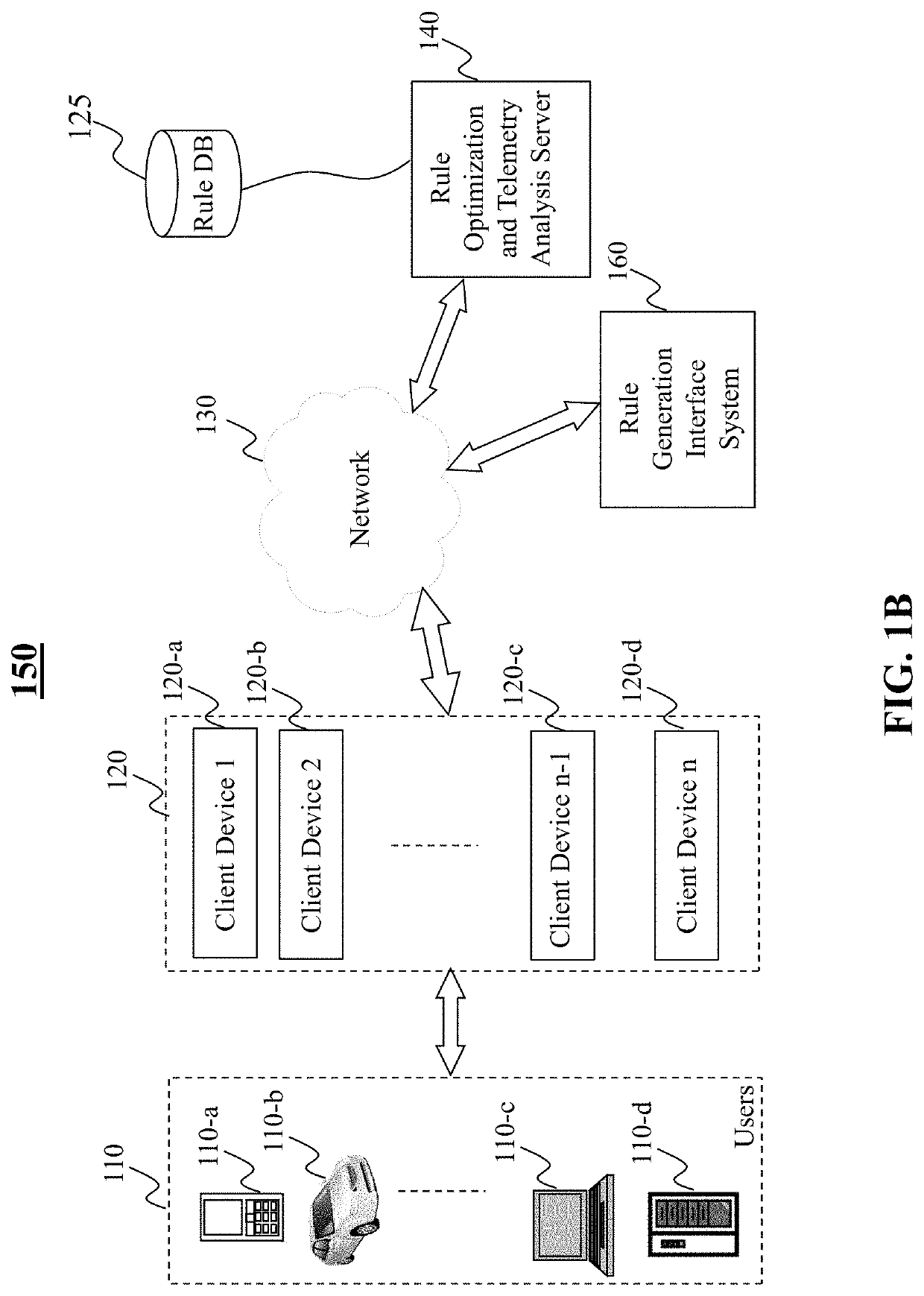
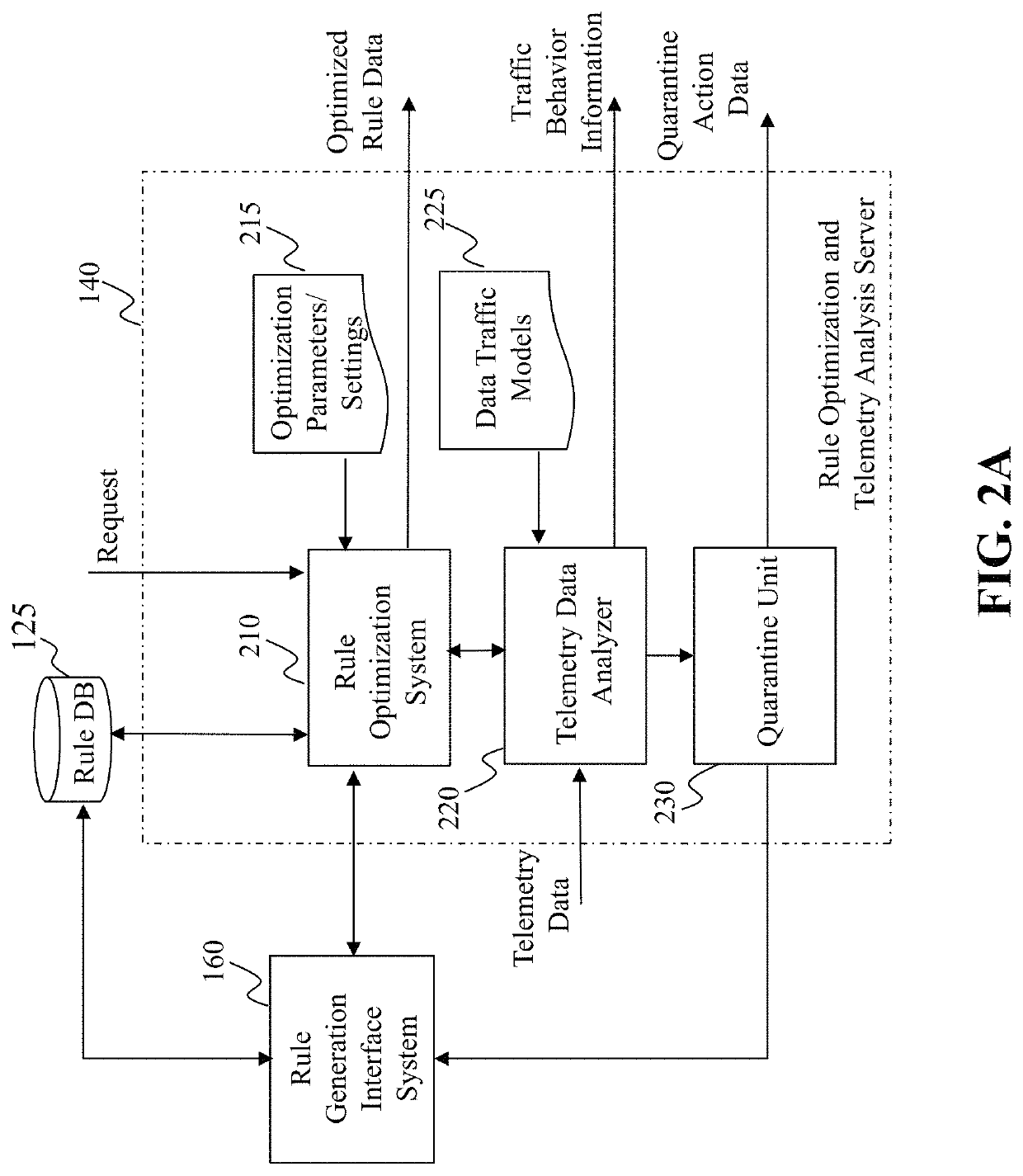
Method and system for intrusion detection and prevention
The present teaching generally relates to providing optimized access control rules. A request may be received from a client device. A determination may be made, based on the request, that an update is needed for access control rule information for the client device. Rule data may be generated. The rule data may include a plurality of data buckets each including one or more access control rules, each data bucket of the plurality being associated with a range of destination port numbers, and where each of the one or more access control rules comprise a set of tuples having a common source network and source port number, and one or more destination port numbers associated with the common source network and source port number. The rule data may be sent to the client device.
Owner:YAHOO ASSETS LLC
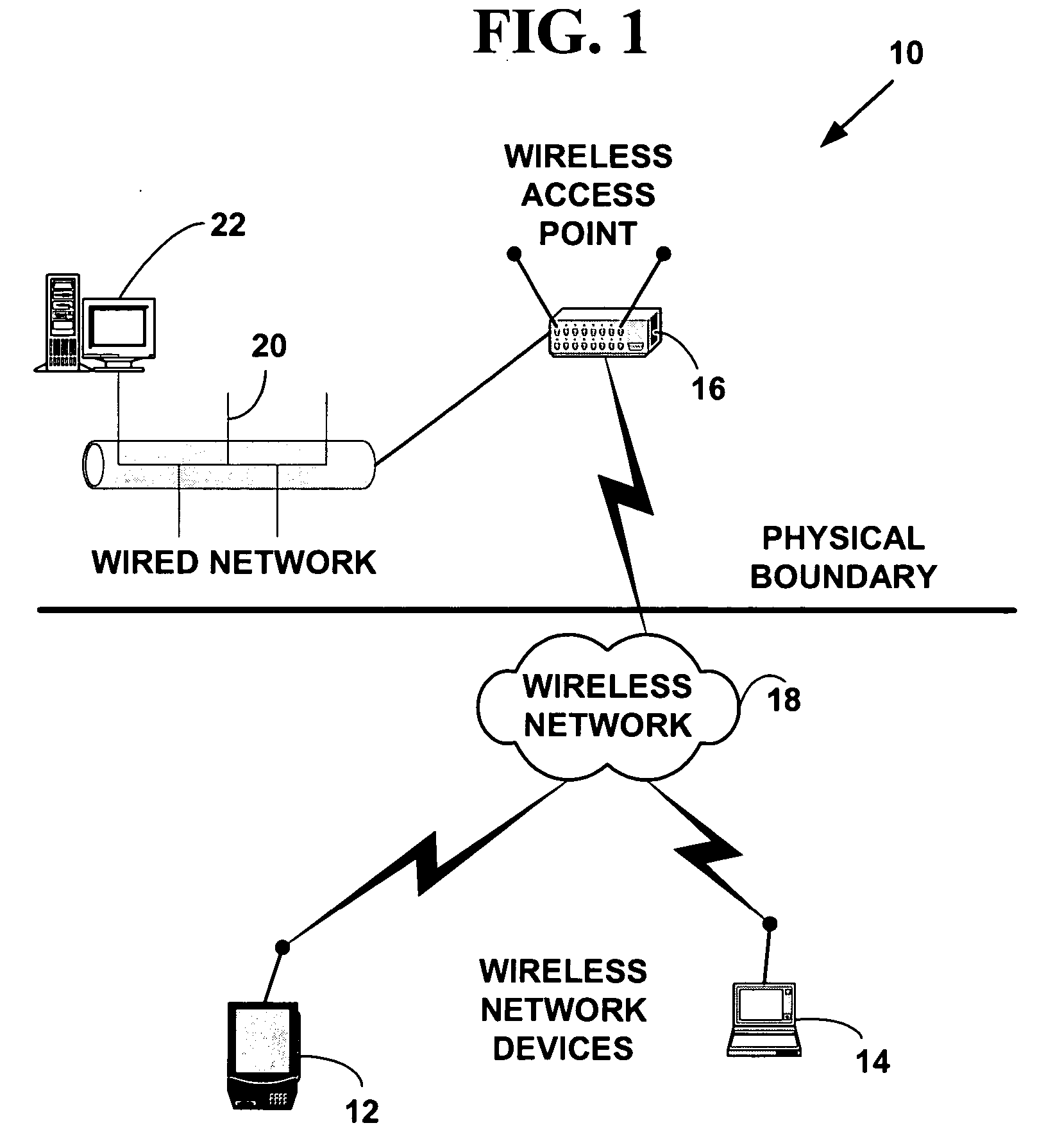
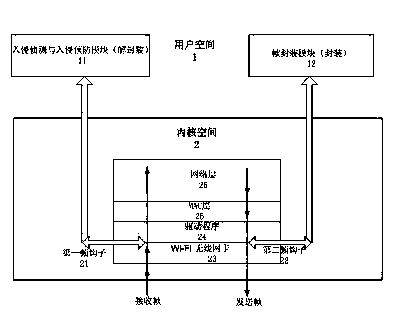
Network security method based on wireless firewall
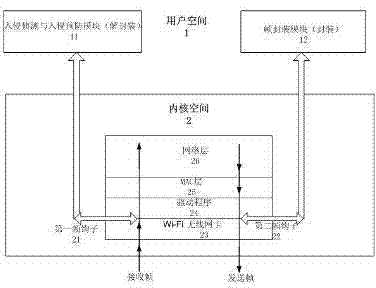
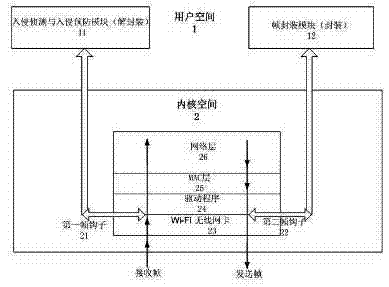
InactiveCN102378166AIncrease aggressivenessImprove usabilitySecurity arrangementOperational systemIntrusion detection and prevention
The invention relates to a network security method based on a wireless firewall. In the method, the wireless firewall acts on an MAC (Media Access Control) layer of OSI (Open System Interconnection) and comprises an intrusion detection and prevention module, a first frame hook and a second frame hook, wherein, the intrusion detection and prevention module is positioned in a user space of a system; the first frame hook is connected with a kernel space and the user space of the operating system, one end of the first frame hook is arranged in a wireless LAN (local area network) card driver in the kernel space of the operating system, the other end of the first frame hook is arranged in the user space and is connected with the intrusion detection and prevention module, the first frame hook transfers a frame received by the wireless LAN card driver to the intrusion detection and prevention module, and then the frame is sent back to the driver through the frame hook or is deleted after being processed by the module; and one end of the second frame hook is arranged in the wireless LAN card driver in the kernel space of the operating system, and the other end of the second frame hook is arranged in the user space and is connected with a frame encapsulation module. By adopting the network security method, the hacker attack resistance can be strengthened and the availability of the wireless network is improved.
Owner:周伯生
Method and system for intrusion detection and prevention based on packet type recognition in a network
ActiveUS8879388B2Error preventionTransmission systemsNetwork packetIntrusion detection and prevention
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
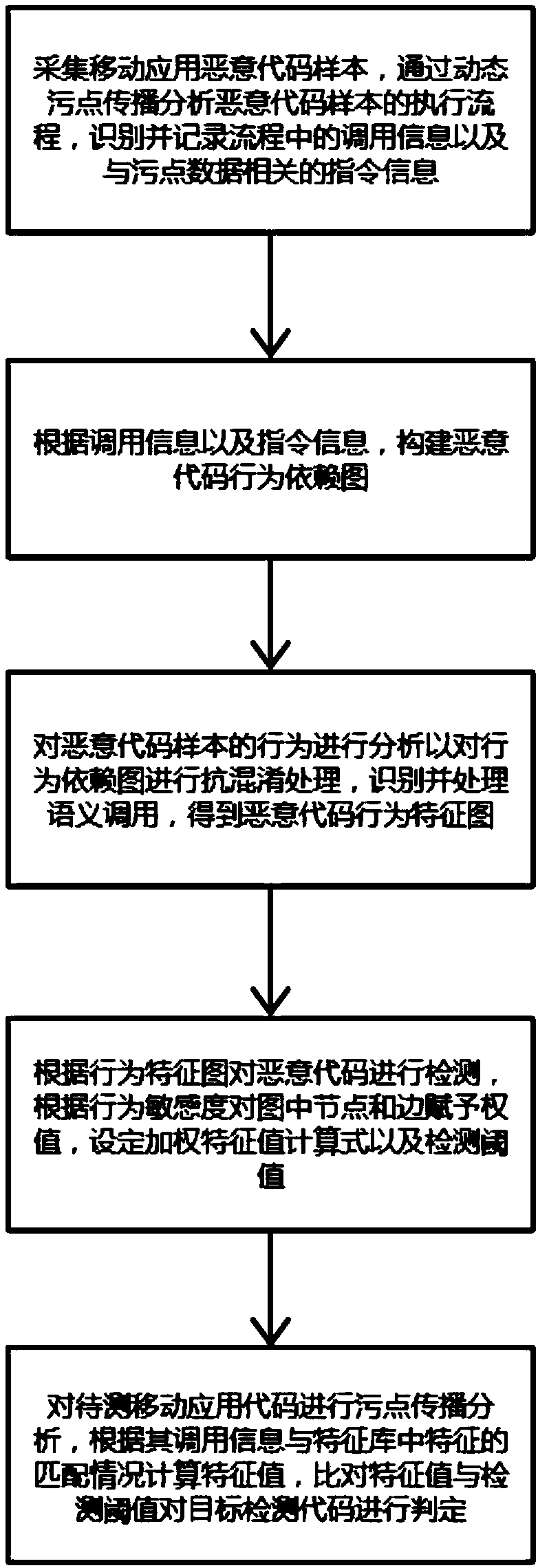
A malicious code intrusion detection and prevention method for a mobile application
InactiveCN109002716AImprove anti-interference abilityEasy to detectPlatform integrity maintainanceIntrusion detection and preventionDetection threshold
The invention discloses a malicious code intrusion detection and prevention method for a mobile application, which comprises the following steps: analyzing a malicious code sample execution flow through dynamic stain propagation, identifying and recording calling information in the flow and instruction information related to stain data; Constructing a malicious code behavior dependency graph according to the invocation information and the instruction information; analyzing the behavior of malicious code sample to deal with the behavior dependency graph, identifying and processing the semanticinvocation, and then obtaining the behavior characteristic graph of malicious code; detecting the malicious code according to the behavior characteristic graph, assigning value to nodes and edges in the graph according to behavior sensitivity, and setting weighted eigenvalue calculation mode and detection threshold; performing stain propagation analysis on the target detection code, calculating the feature value according to the matching condition of the called information and features and comparing the feature value and the detection threshold value to determine the malicious code. The methodcan detect the target to be tested from the sensitive behavior of the malicious code, and the detection accuracy is high, the performance is good, and the false alarm rate is low.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
High availability for network security devices
ActiveCN102123076BError preventionData switching networksIntrusion detection and preventionHigh availability
In one example, a backup intrusion detection and prevention (IDP) device includes one or more network interfaces to receive a state update message from a primary IDP device, wherein the state update message indicates a network session being inspected by the primary IDP device and an identified application-layer protocol for the device, to receive an indication that the primary device has switched over or failed over to the backup device, and to receive a plurality of packets of the network session after receiving the indication, each of the plurality of packets comprising a respective payload including application-layer data, a protocol decoder to detect a beginning of a new transaction from the application-layer data of one of the plurality of packets, and a control unit to statefully process only the application-layer data of the network session that include and follow the beginning of the new transaction.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for intrusion detection and prevention
ActiveUS10805271B2Computer security arrangementsData switching networksIntrusion detection and preventionEngineering
The present teaching generally relates to providing optimized access control rules. A request may be received from a client device. A determination may be made, based on the request, that an update is needed for access control rule information for the client device. Rule data may be generated. The rule data may include a plurality of data buckets each including one or more access control rules, each data bucket of the plurality being associated with a range of destination port numbers, and where each of the one or more access control rules comprise a set of tuples having a common source network and source port number, and one or more destination port numbers associated with the common source network and source port number. The rule data may be sent to the client device.
Owner:YAHOO ASSETS LLC
Network security method based on wireless firewall
InactiveCN102378166BIncrease aggressivenessImprove usabilitySecurity arrangementIntrusion detection and preventionOpen Systems Interconnection
The invention relates to a network security method based on a wireless firewall. In the method, the wireless firewall acts on an MAC (Media Access Control) layer of OSI (Open System Interconnection) and comprises an intrusion detection and prevention module, a first frame hook and a second frame hook, wherein, the intrusion detection and prevention module is positioned in a user space of a system; the first frame hook is connected with a kernel space and the user space of the operating system, one end of the first frame hook is arranged in a wireless LAN (local area network) card driver in the kernel space of the operating system, the other end of the first frame hook is arranged in the user space and is connected with the intrusion detection and prevention module, the first frame hook transfers a frame received by the wireless LAN card driver to the intrusion detection and prevention module, and then the frame is sent back to the driver through the frame hook or is deleted after being processed by the module; and one end of the second frame hook is arranged in the wireless LAN card driver in the kernel space of the operating system, and the other end of the second frame hook is arranged in the user space and is connected with a frame encapsulation module. By adopting the network security method, the hacker attack resistance can be strengthened and the availability of the wireless network is improved.
Owner:周伯生
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com