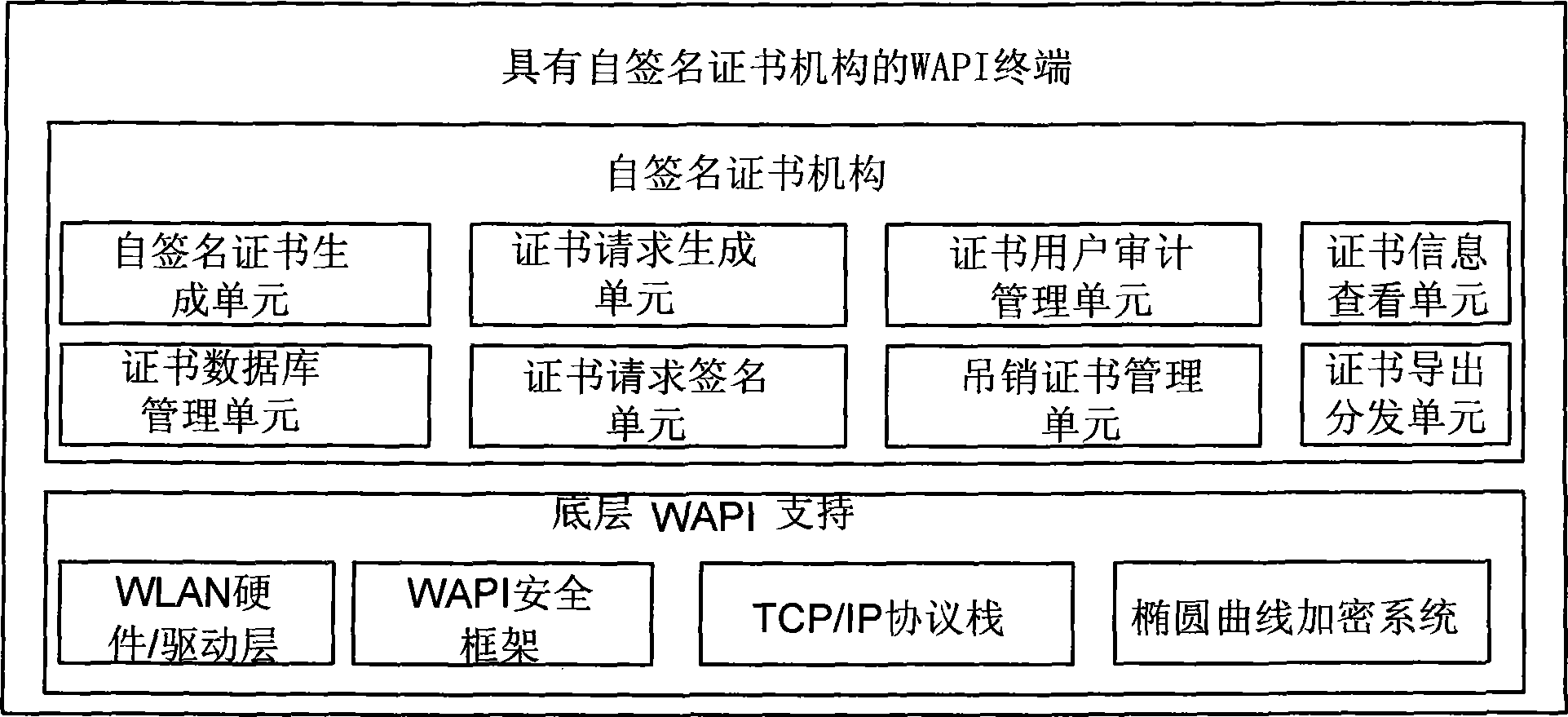
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Self-signed certificate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography and computer security, a self-signed certificate is a certificate that is not signed by a certificate authority (CA). These certificates are easy to make and do not cost money. However, they do not provide all of the security properties that certificates signed by a CA aim to provide. For instance, when a website owner uses a self-signed certificate to provide HTTPS services, people who visit that website will see a warning in their browser. Website visitors who bypass such warnings are exposed to a risk that a third party could intercept traffic to the website using the third-party's own self-signed certificate. This is a type of man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack, and it allows the third party to read and modify all data sent to or from the website by the target user.
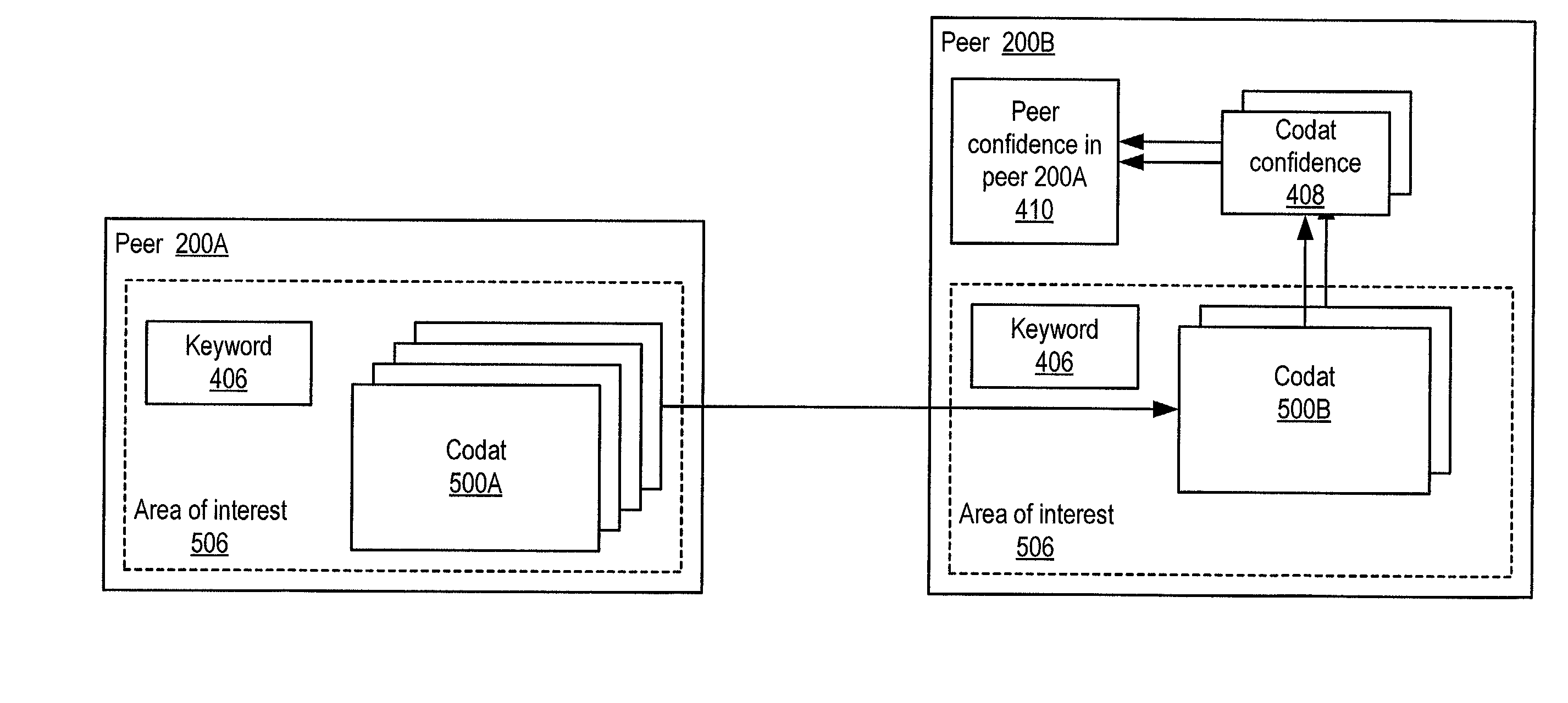
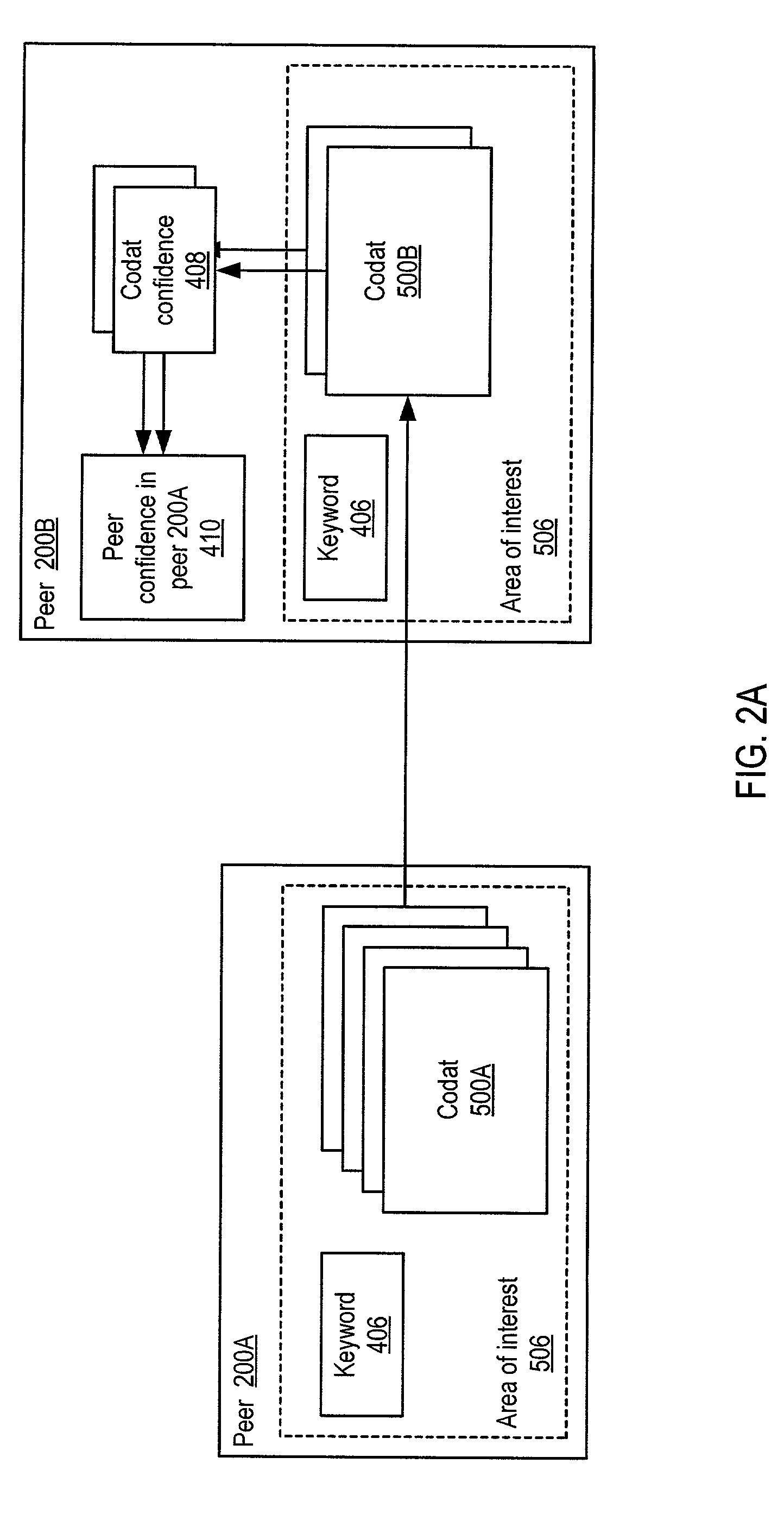
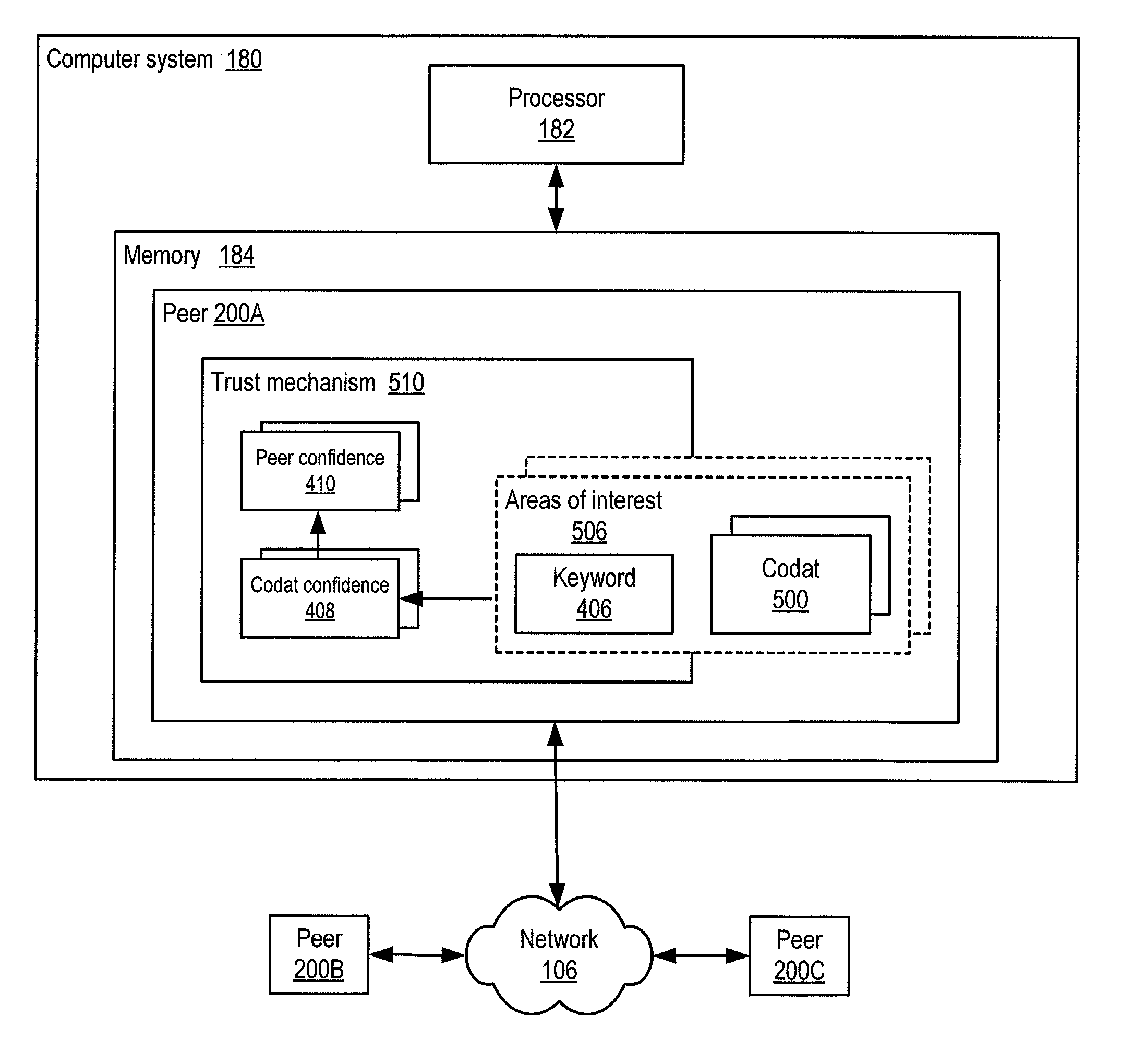
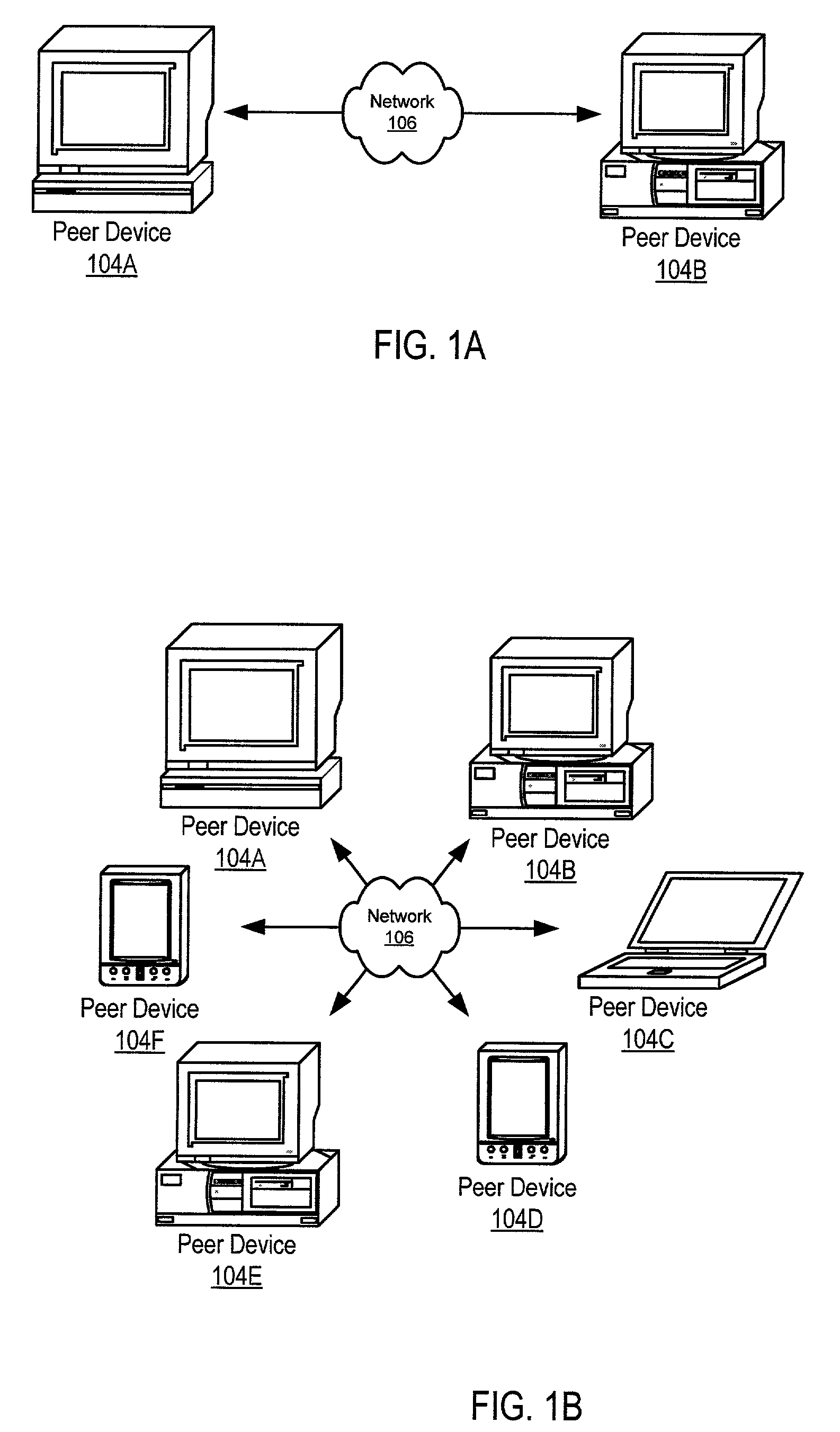
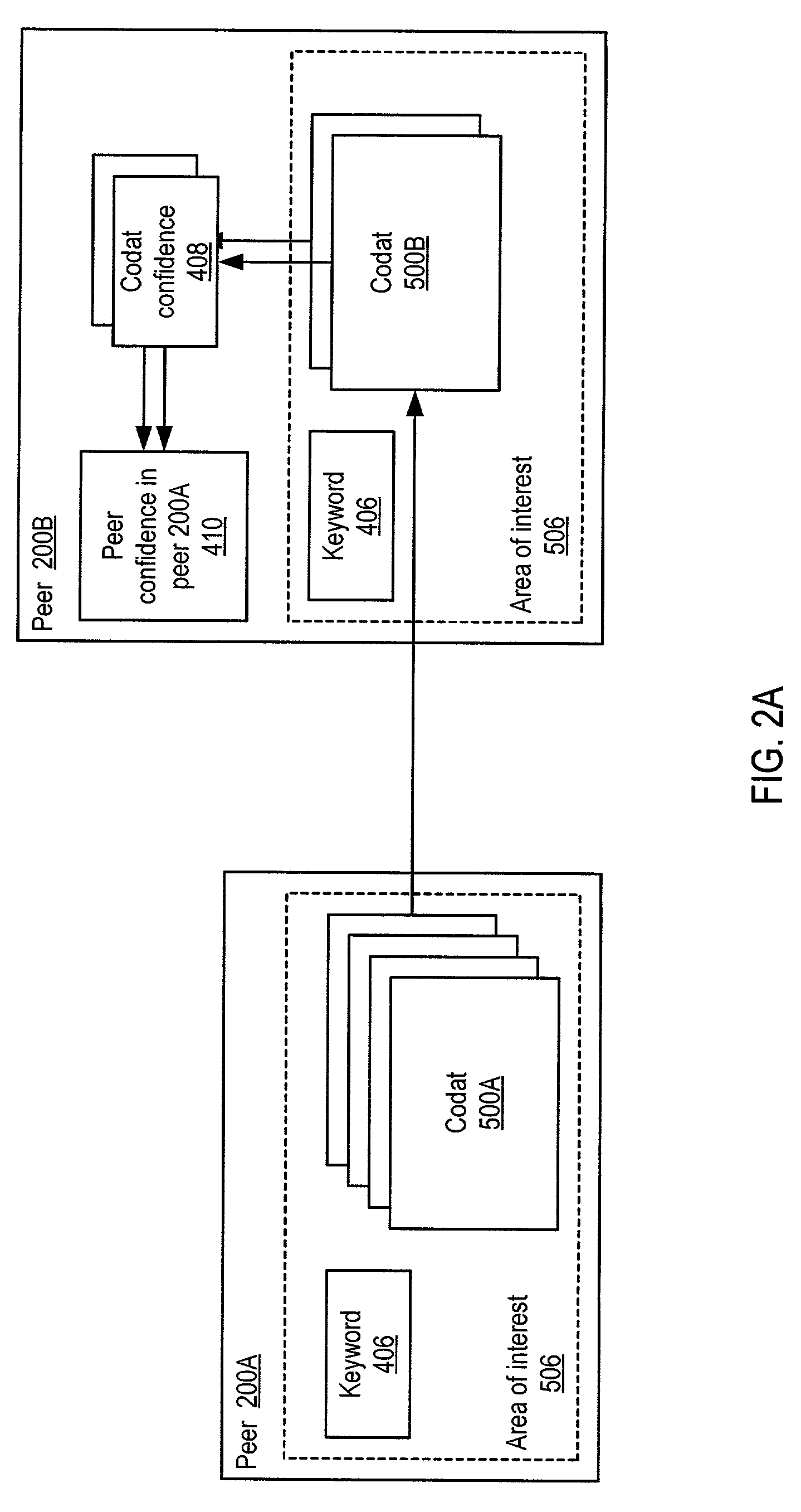
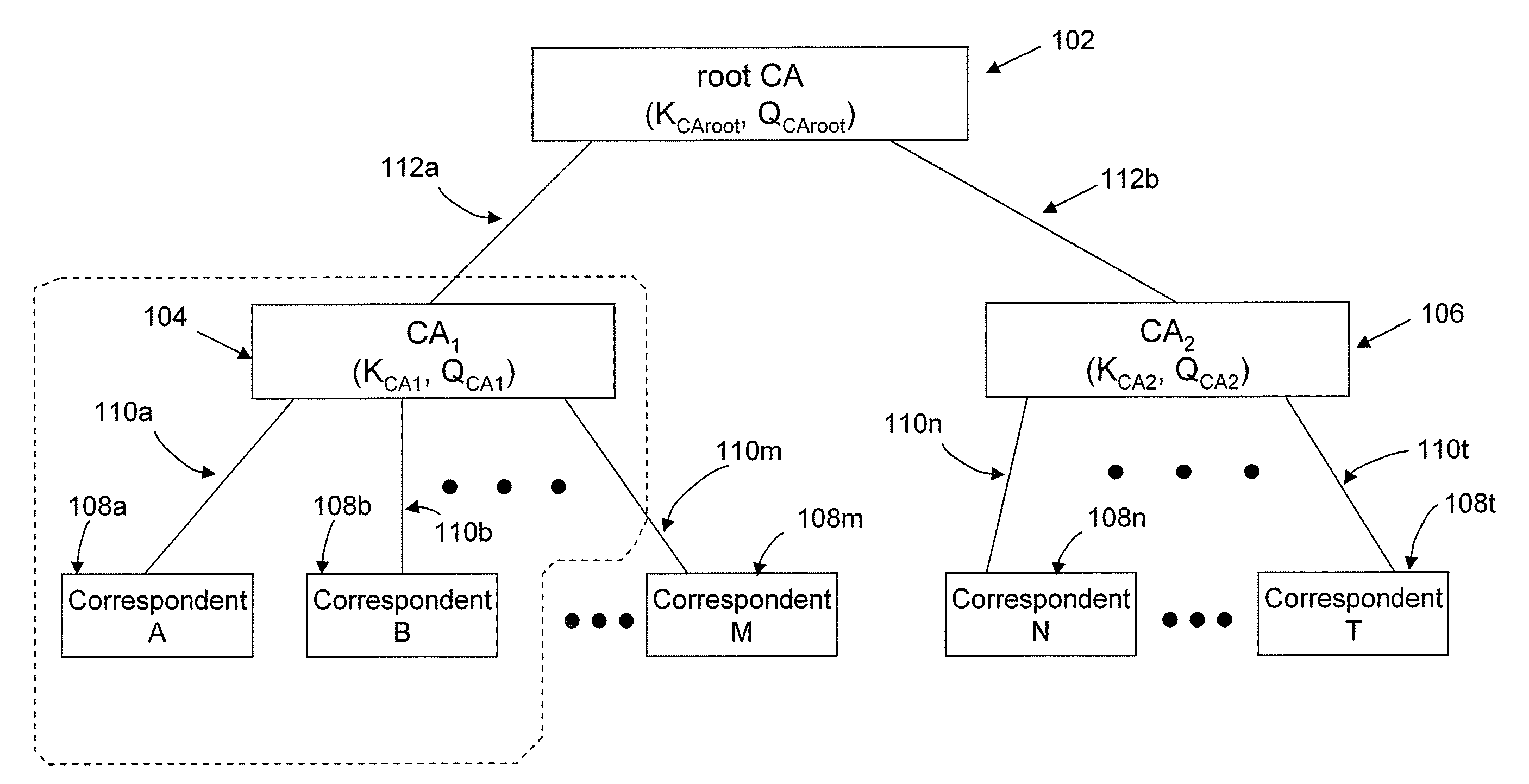
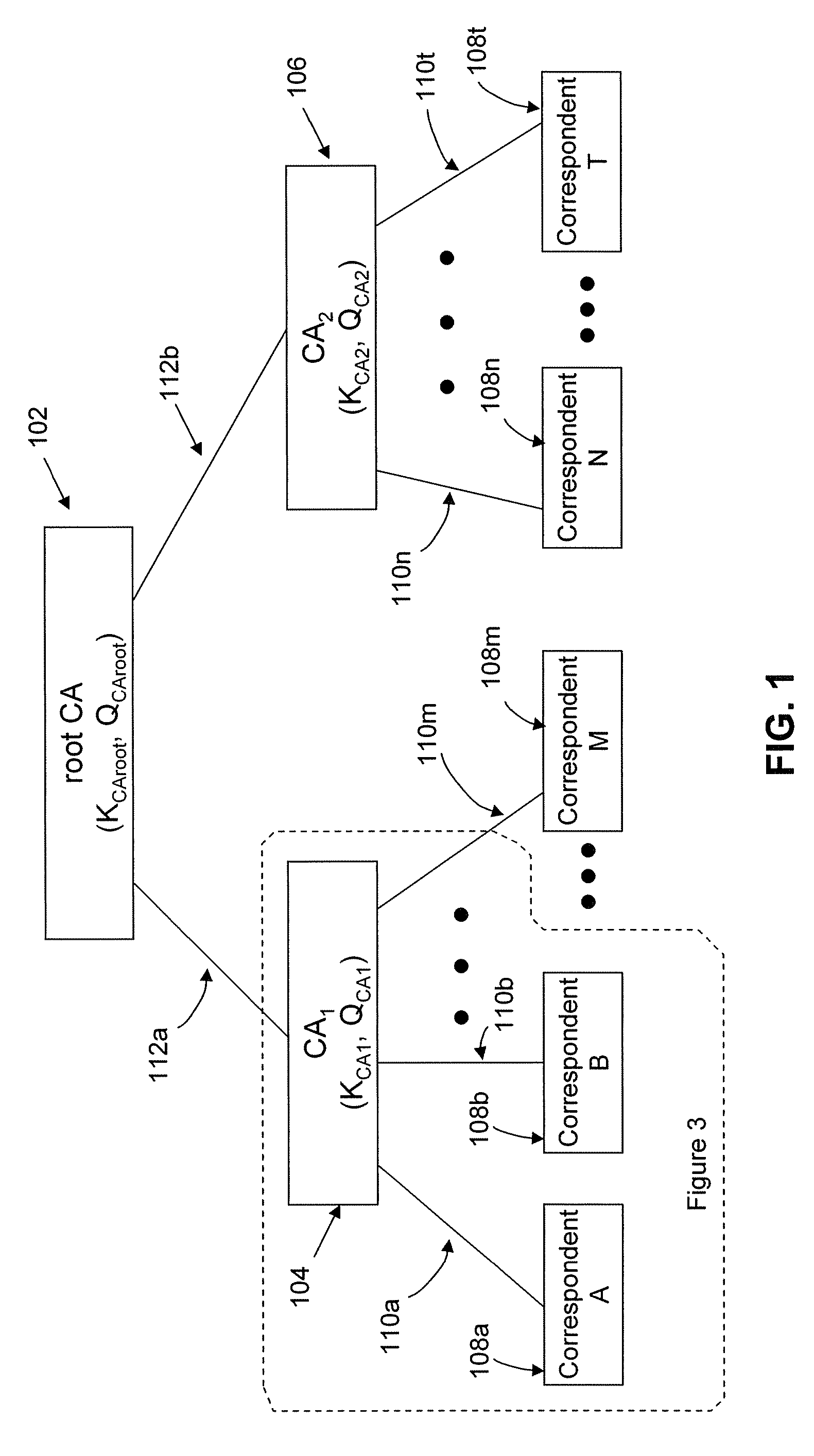
Trust spectrum for certificate distribution in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS20030070070A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsFrequency spectrumMaximum level
Embodiments of a decentralized, distributed trust mechanism that may be used in peer-to-peer platforms, to implement trust relationships based on data relevance between peers on a network and to implement trust relationships between peers and content and data (codat). In one embodiment, the trust mechanism may provide a trust spectrum of multiple levels wherein unique peer identities may be established to enable authentication and the assignment of the peers' associated access policies within a peer group. In one embodiment, the trust spectrum may have Certificate Authority signed certificates as a maximum level of security, and self-signed certificates as a minimum level of security. Since a certificate is one form of codat, in one embodiment the trust mechanism may be applied to a peer group member's collection of signed certificates for a given peer group.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Trust spectrum for certificate distribution in distributed peer-to-peer networks
ActiveUS7383433B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsMaximum levelSelf-signed certificate
Embodiments of a decentralized, distributed trust mechanism that may be used in peer-to-peer platforms, to implement trust relationships based on data relevance between peers on a network and to implement trust relationships between peers and content and data (codat). In one embodiment, the trust mechanism may provide a trust spectrum of multiple levels wherein unique peer identities may be established to enable authentication and the assignment of the peers' associated access policies within a peer group. In one embodiment, the trust spectrum may have Certificate Authority signed certificates as a maximum level of security, and self-signed certificates as a minimum level of security. Since a certificate is one form of codat, in one embodiment the trust mechanism may be applied to a peer group member's collection of signed certificates for a given peer group.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
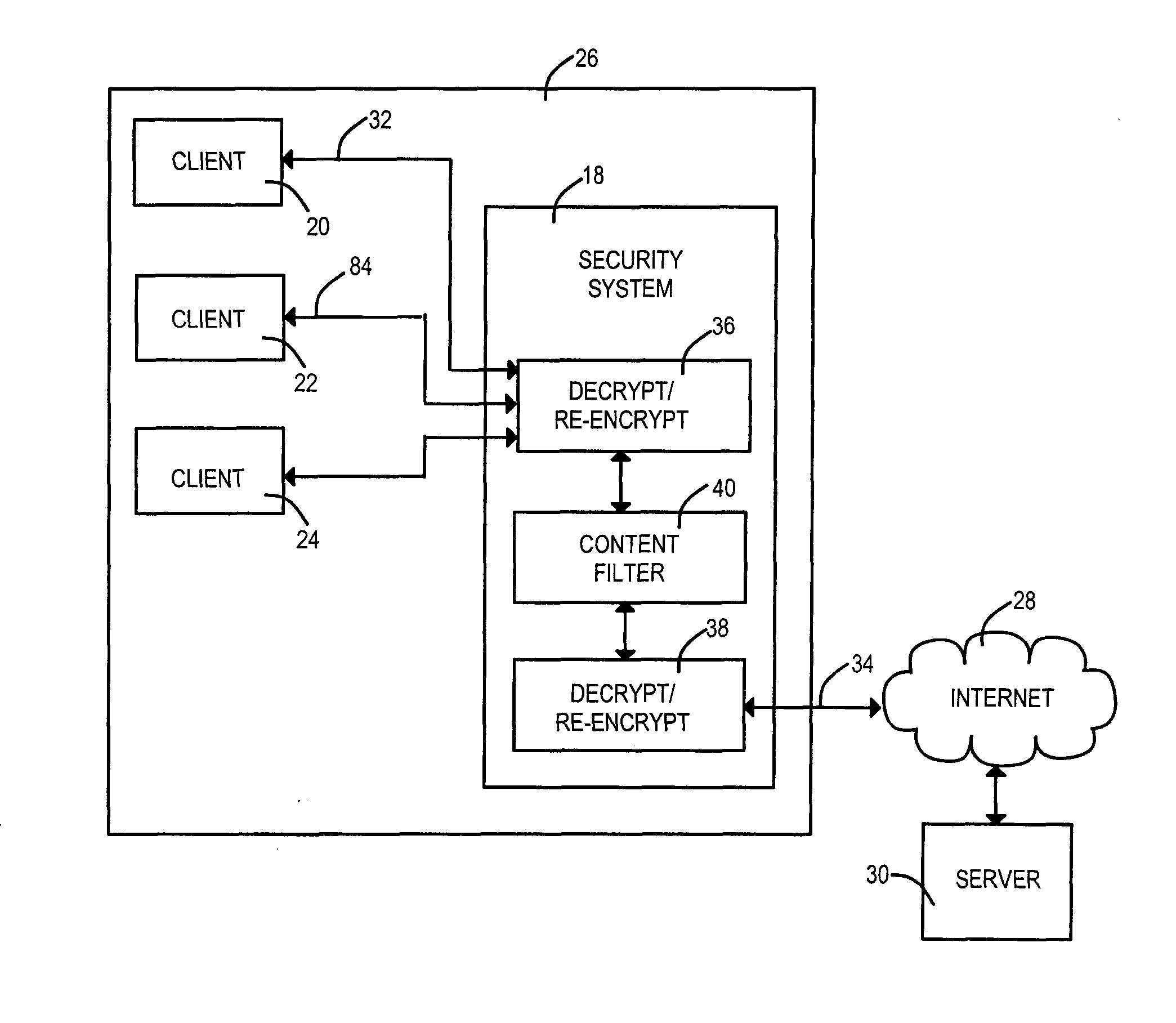
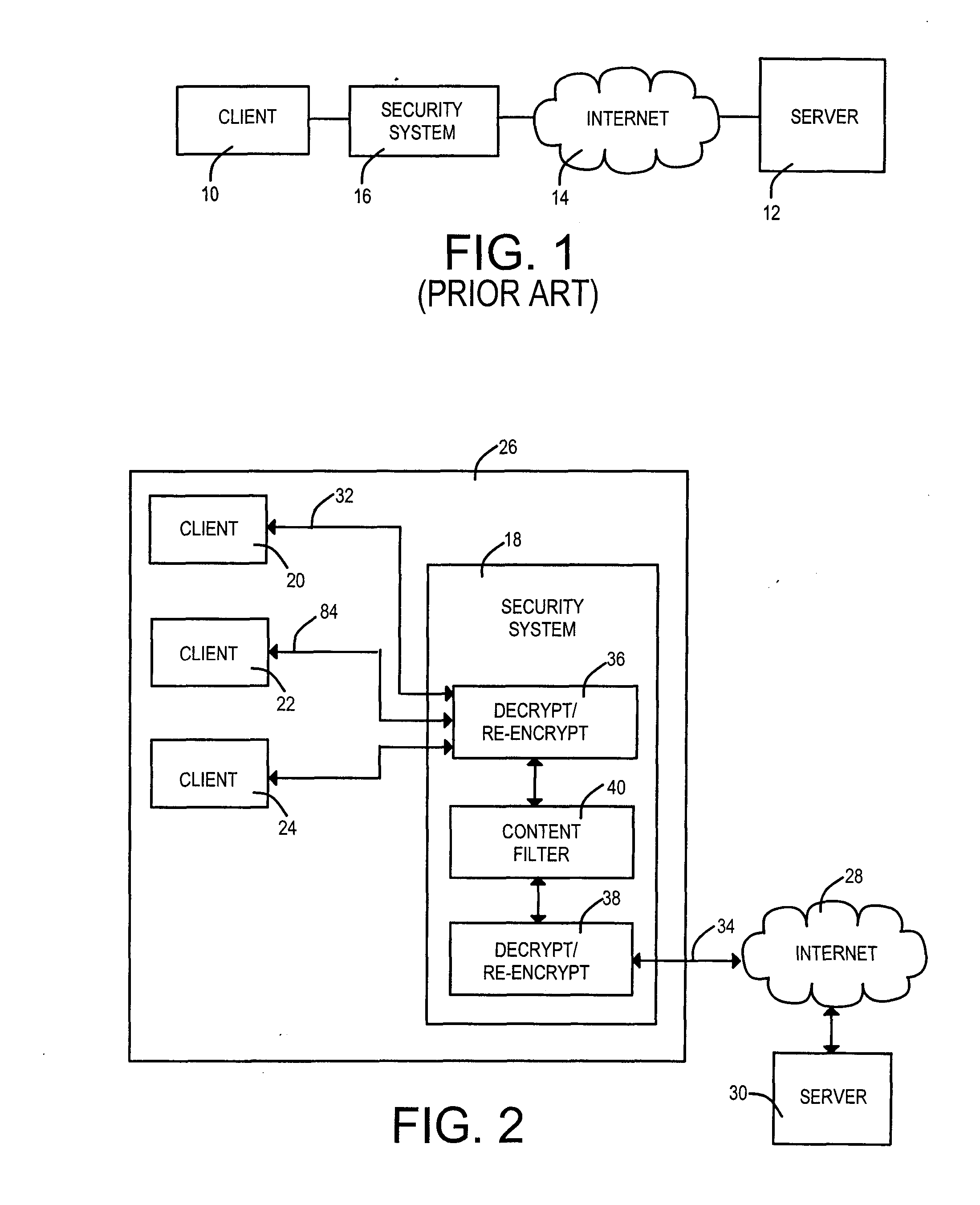
Tandem encryption connections to provide network traffic security method and apparatus
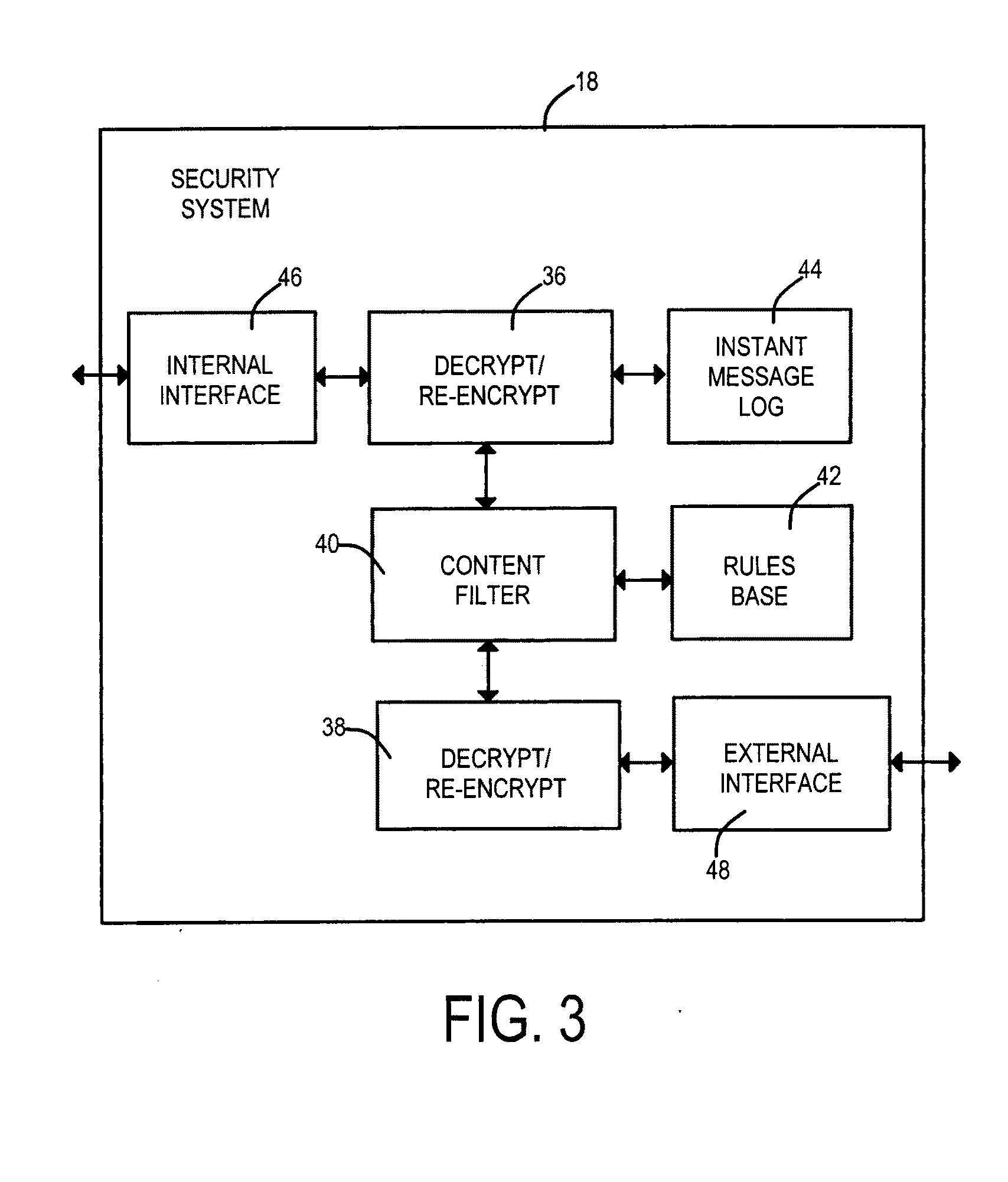
Security measures are applied to encrypted data exchanges by enabling content decryption, rule application, and content re-encryption at a network location. A certificate, self-signed or authenticated by an official Certificate Authority is obtained for and installed within the secure proxy apparatus. A link to a secure page is replaced with a link to a page having a fully qualified domain name of the proxy apparatus as the suffix. An encrypted session between the client is established between the client and the proxy apparatus without deceit in the later case. A first encryption-enabled connection is established from the first node to a content filter, while a second encryption-enabled connection is established from the content filter to the second node. Following decryption, a determination is made as to whether the content includes Undesired Data. Restricted material is blocked, while unrestricted material is re-encrypted and delivered to the destination node. For a self-signed certificate, the destination node comprises a private security system-signed root certificate installed in the destination node's Trusted Root Certification Authorities certificate store. In another aspect of the invention, at least one of encrypted Instant Messages, e-mail messages and web pages are decrypted and recorded at a location between sources and destinations of the transmissions. The look and feel is maintained of a single encrypted link between the requestor and the external source by the inventive use of a wildcard certificate within the network local to the requestor.
Owner:BARRACUDA NETWORKS
Computer system and program to update SSL certificates
InactiveUS20060075219A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationProgram instructionSelf-signed certificate
System and computer program product for updating an SSL certificate for a server. First program instructions detect when a change has been made to a name, domain or IP address of the server and detect that the server is using an SSL certificate based on a name, domain or IP address applicable before the change. In response, the first program instructions notify an administrator that a change is required to the SSL certificate to reflect the change to the name, domain or IP address. Second program instructions respond to a request by the administrator, to automatically create a new SSL certificate signing request. The new SSL certificate signing request is a form which can be sent to an SSL certificate authority. Third program instructions respond to another request by the administrator, to send the new SSL certificate signing request to the SSL certificate authority. Fourth program instructions respond to receipt of a new SSL certificate from the SSL certificate authority and another request by the administrator, to substitute the new SSL certificate for the existing SSL certificate. Fourth program instructions query the administrator if the administrator wants to use a new self-signed SSL certificate reflecting the change to the name, domain or IP address of the server, until the new SSL certificate signed by the SSL certificate authority is received from the SSL certificate authority, and if so, generate the new SSL self-signed certificate. Other program instructions respond to a request by the administrator, to create a self-signed SSL certificate and substitute the self-signed SSL certificate for the existing SSL certificate.
Owner:IBM CORP
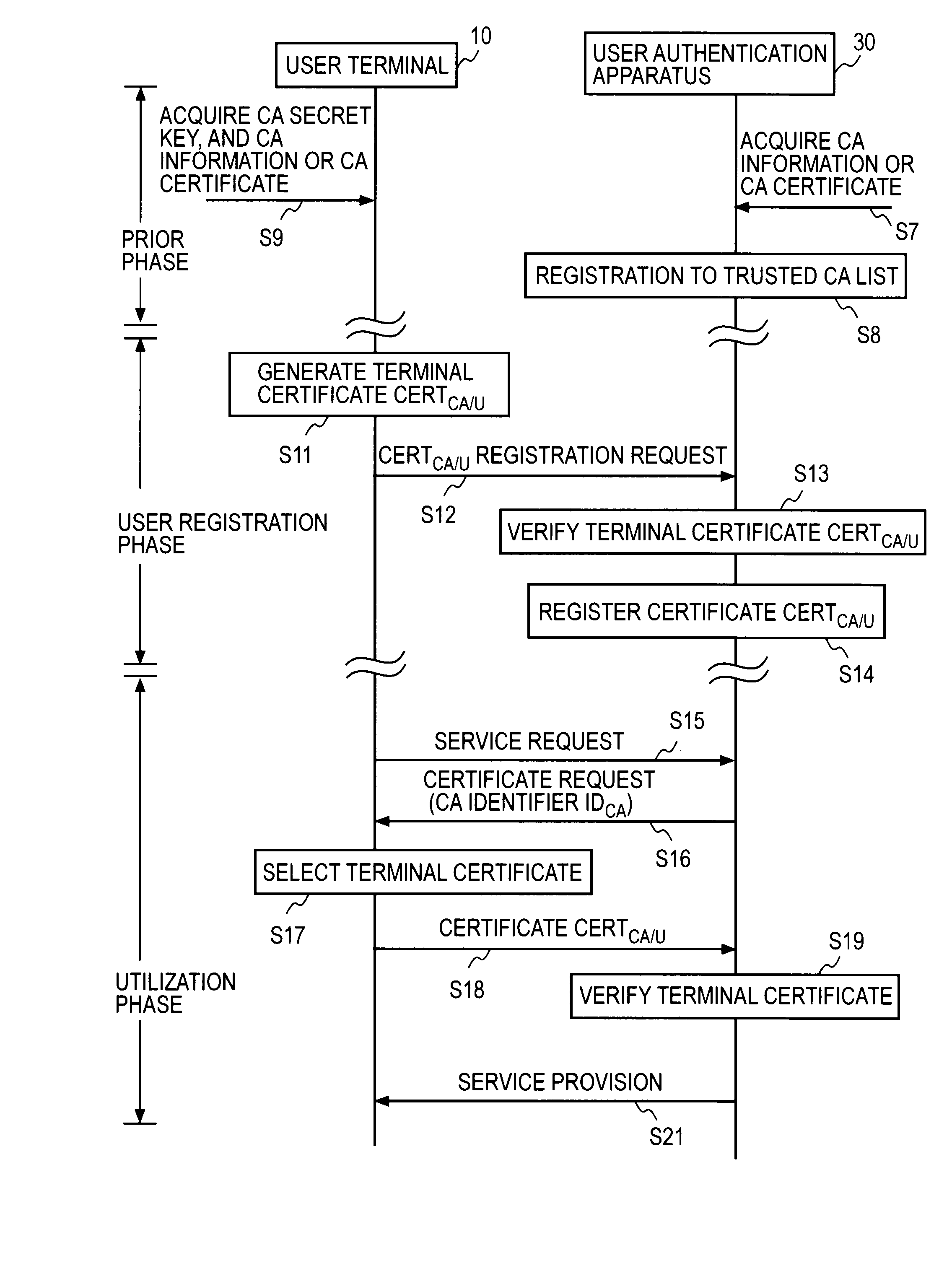
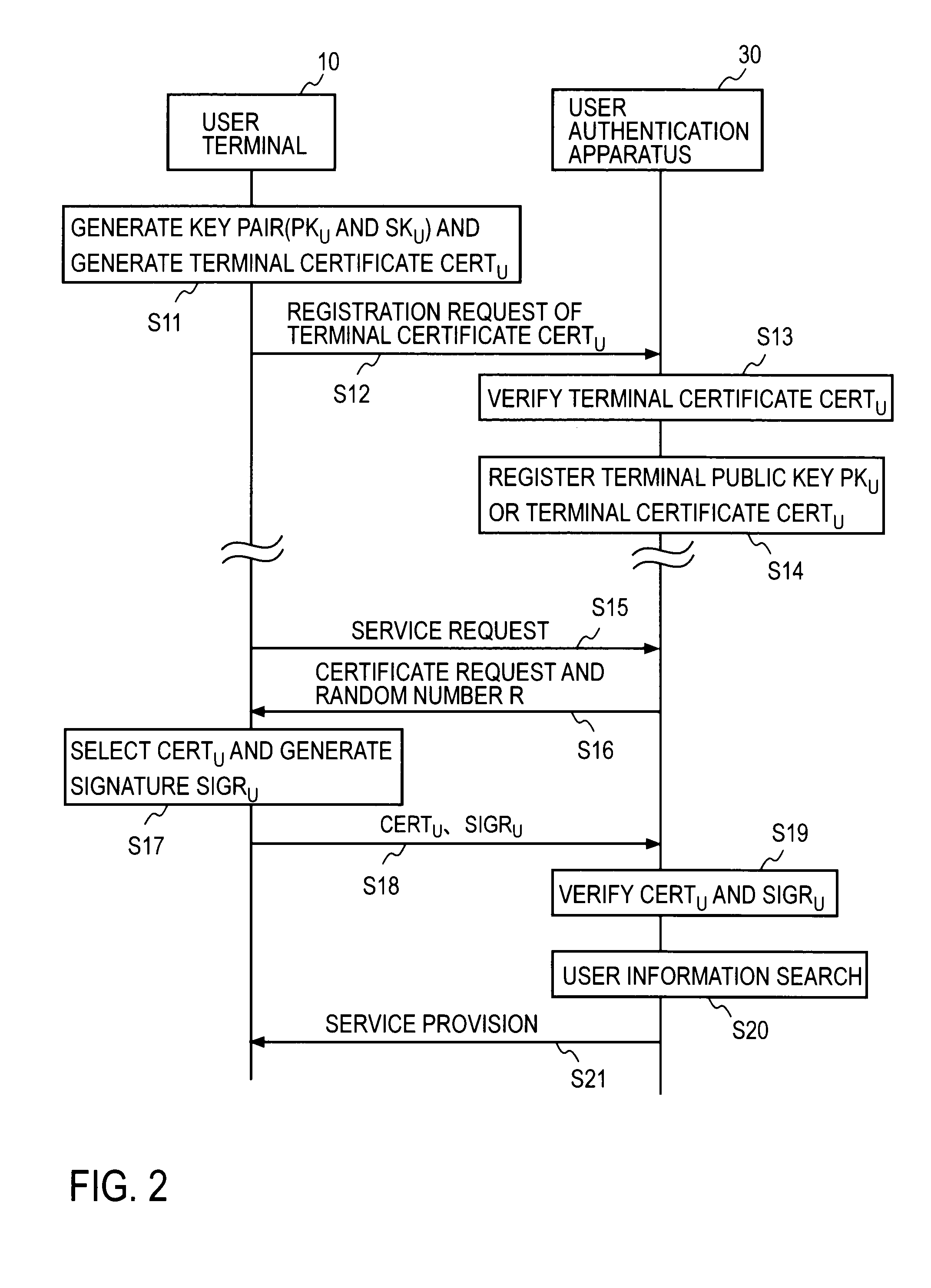
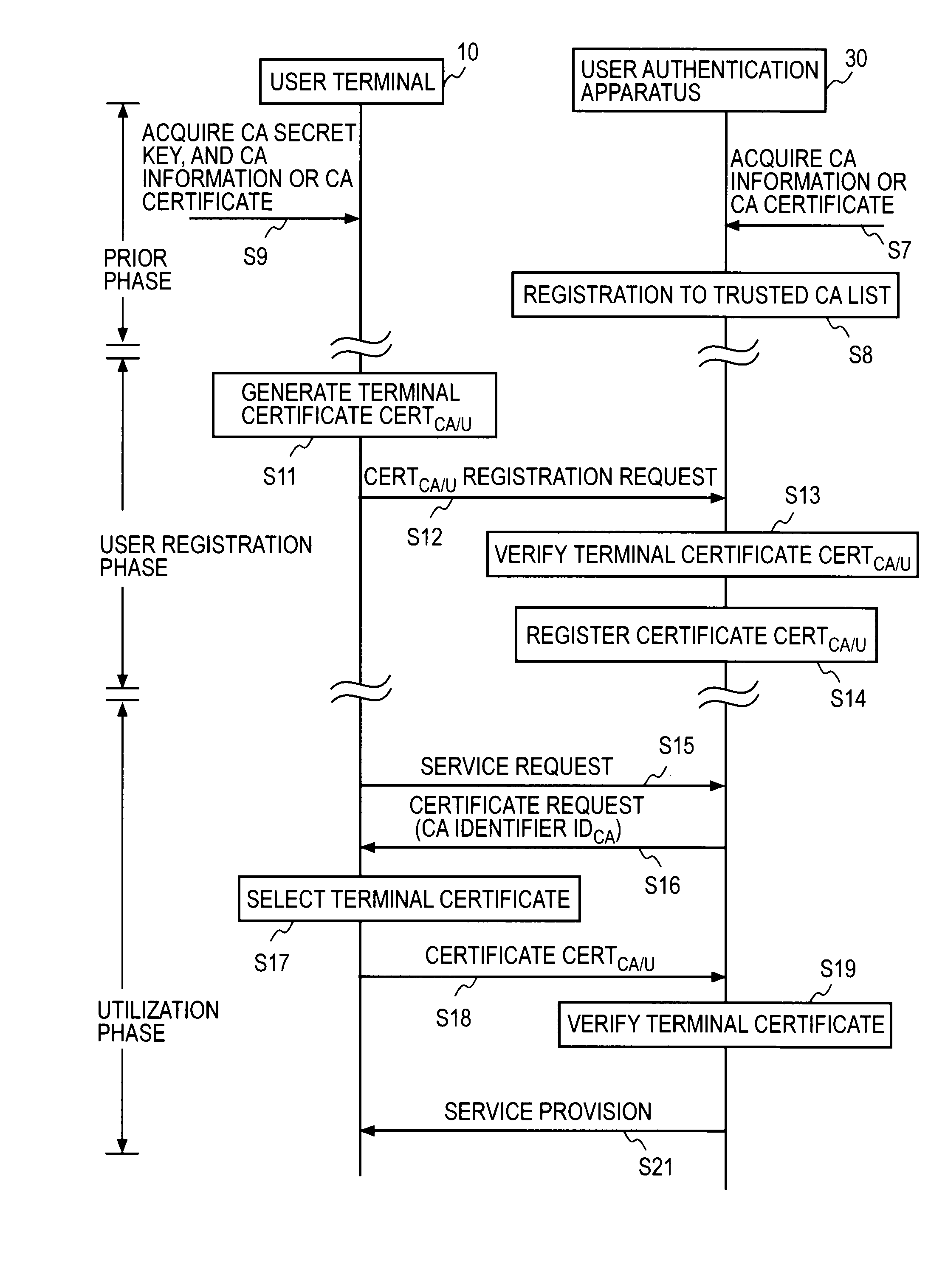
User authentication system and method for the same
InactiveUS20110047373A1Removal costEliminate operationKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSelf-signed certificateUser authentication
At the user authentication apparatus 30, an identifier of a certification authority (CA) certificate that a CA information disclosure server 20 discloses in advance is registered in an identifier list of the CA. At the user terminal 10, a key pair consisting of a terminal public key and a terminal secret key is generated, the terminal signature is generated for information containing the terminal public key using the CA secret key acquired in advance, and a self-signed certificate of the same form as the certificate issued from CA, that is, a terminal certificate containing at least a terminal public key, a terminal signature, and a CA identifier, is created and stored, and registered in the user authentication apparatus 30. The terminal certificate having the same issuer information as the CA identifier in the identifier list of the CA notified from the user authentication apparatus 30 at the time of the service request is selected, and user authentication in accordance with a well-known user authentication protocol is executed using the terminal certificate.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
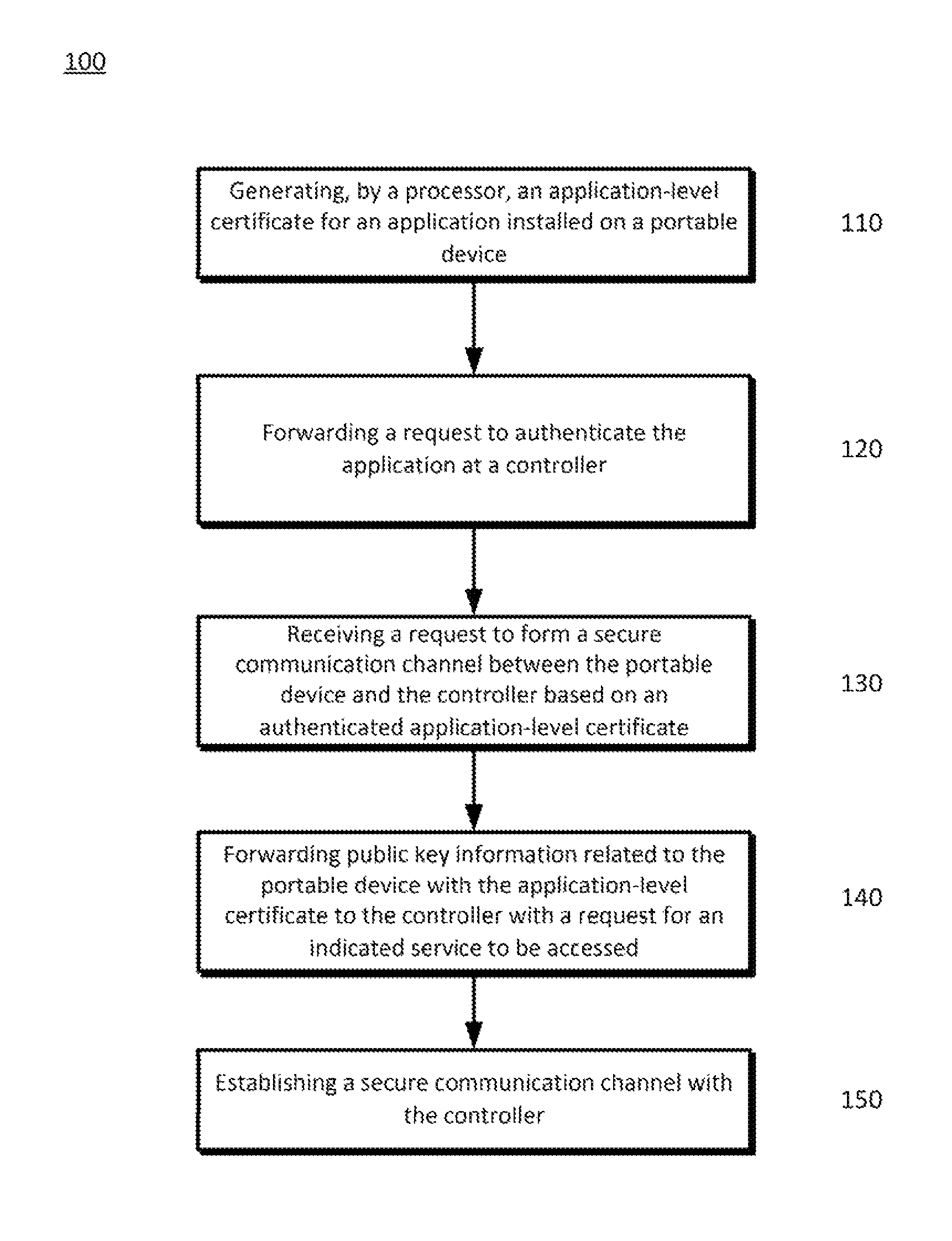
Application-level certificates for identity and authorization
InactiveUS9294468B1Reduce needKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSelf-signed certificateApplication software
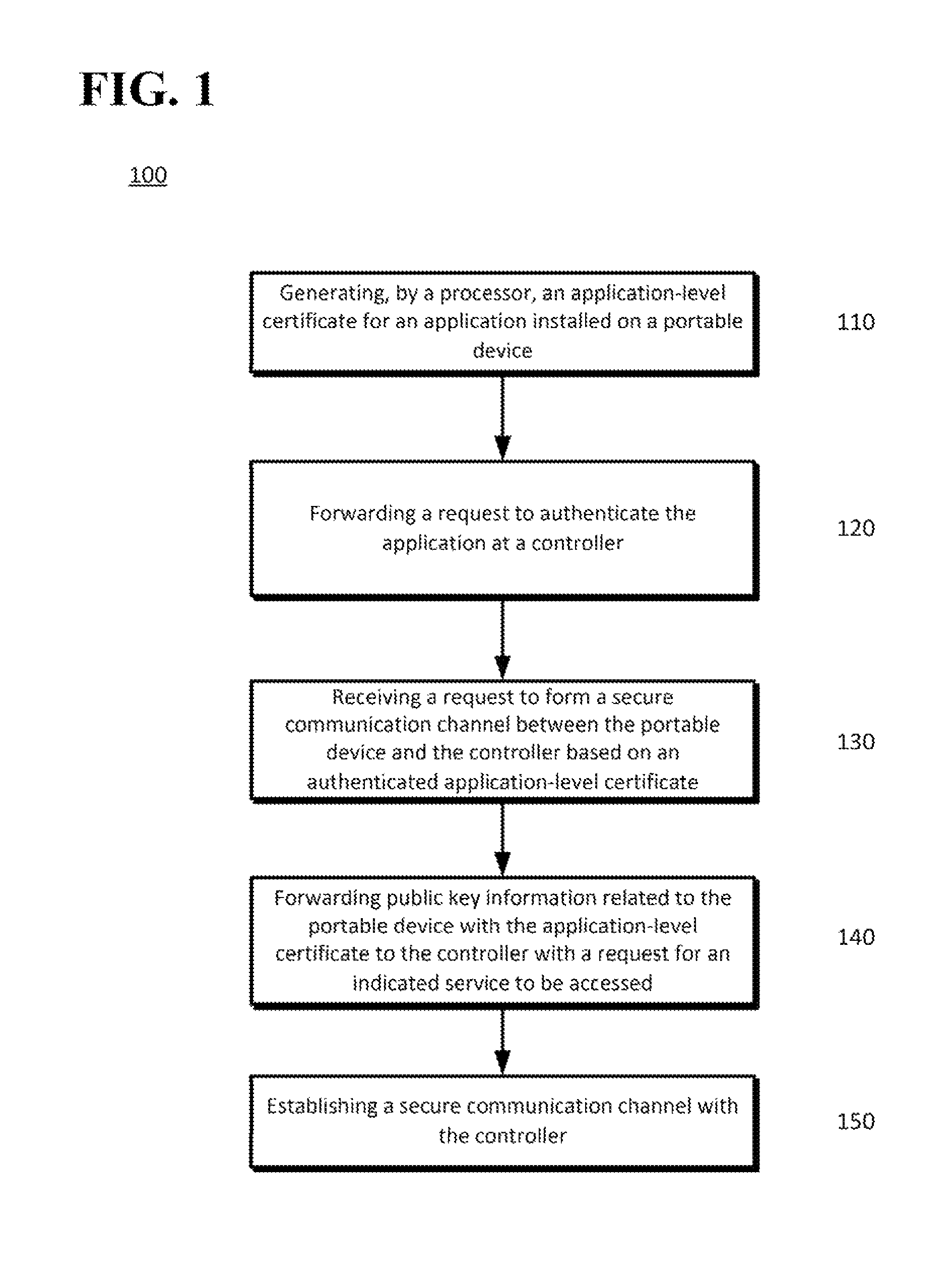
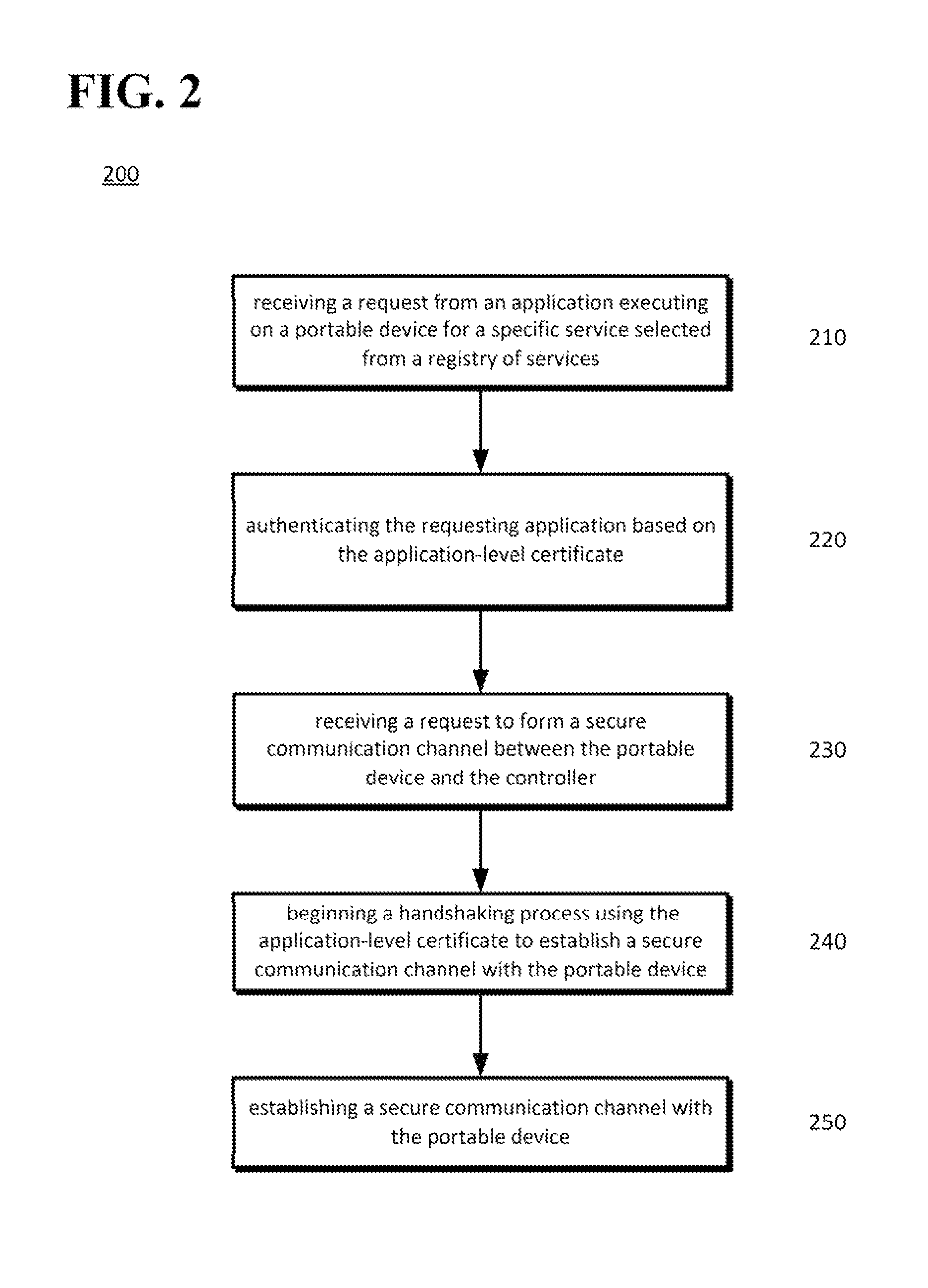
Disclosed is a method in which a portable device processor may generate an application-level certificate for an application installed on the portable device. The processor may, for example, insert an application name in a package name field of a self-signed device-level certificate of the portable device to generate an application-level self-signed certificate. A request to authenticate the application may be forwarded to the controller. The request may include the application-level certificate. The portable device processor may receive a request to form a secure communication channel between the portable device and the controller based on the authenticated application-level certificate. A controller may respond to a portable device request for services by authenticating an application-level certificate provided by the portable device so requested services may be securely provided to the portable device.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
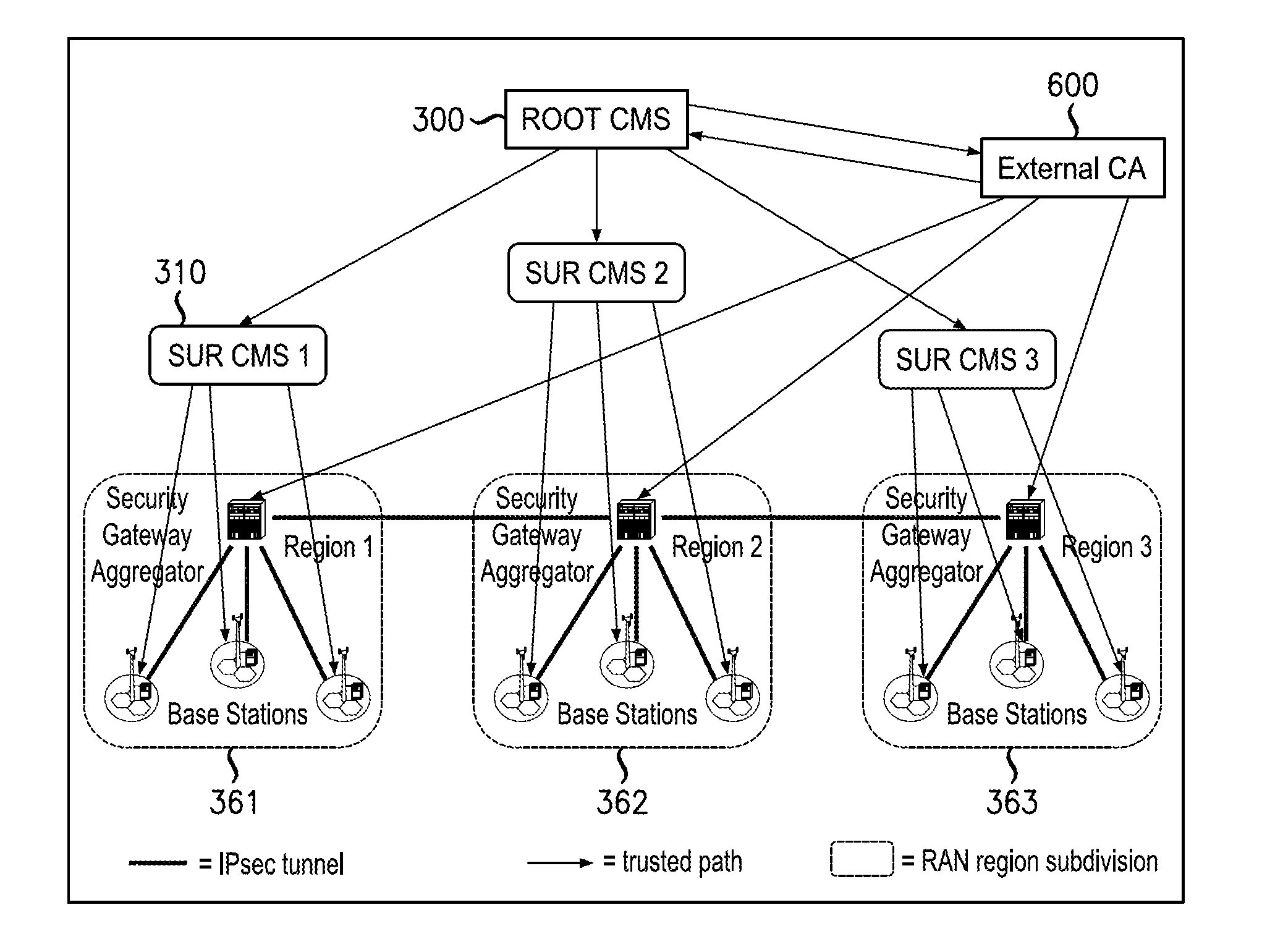
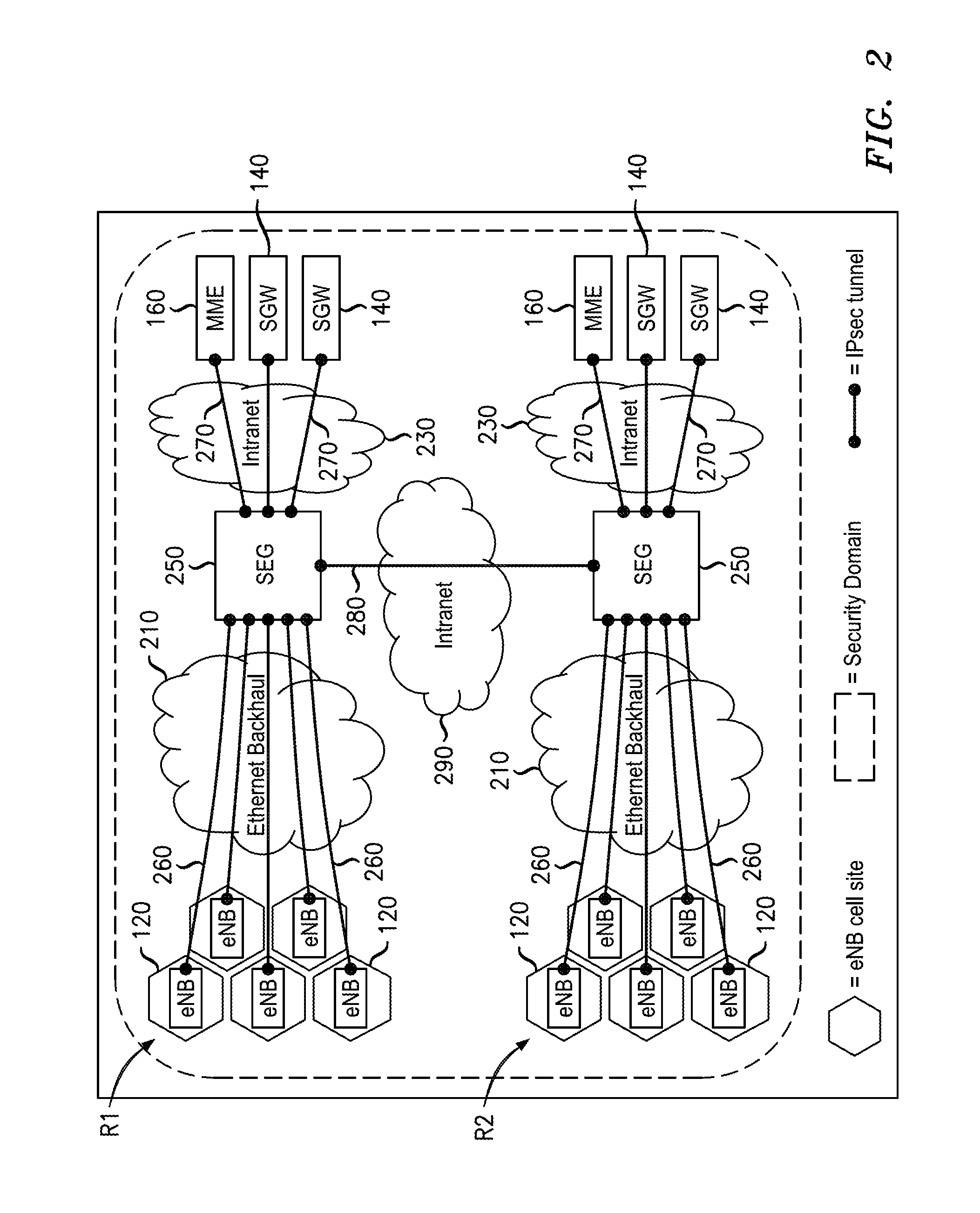
Flexible System And Method To Manage Digital Certificates In A Wireless Network
InactiveUS20120246466A1User identity/authority verificationPublic key infrastructure trust modelsRoot certificateWireless mesh network
An infrastructure is provided for managing the distribution of digital certificates for network security in wireless backhaul networks. In embodiments, a root certificate management system (root CMS) processes requests for digital certificates, issues root certificates, automatically authenticates surrogate certificate management systems (sur-CMSs), and automatically processes certificate requests and issues certificate bundles to sur-CMSs that are successfully authenticated. The infrastructure includes sur-CMSs to which are assigned base stations within respective regions. Each sur-CMS automatically authenticates its own base stations and automatically processes certificate requests and issues certificate bundles to base stations that are successfully authenticated. A certificate bundle issued to a base station includes a digital certificate, signed by the issuing sur-CMS, of a public key of such base station, and at least one further digital certificate, including a self-signed certificate of the root CMS.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Secure mobile communication architecture with dynamic two-way authentication and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN105337977ASecurity APP businessEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationMan-in-the-middle attackSelf-signed certificate
The invention provides a secure mobile communication architecture with dynamic two-way authentication and an implementation method thereof. In the secure mobile communication architecture, a client terminal and a server-side implement two-way authentication, the server-side adopts an SSL self-signed certificate, and the authentication to the server-side by the client terminal is finished through authentication to the SSL certificate of the server; the authentication to the client terminal by the server-side is finished through management of identity access authority provided by an asymmetric key pair and a PKI technology; and communication between the client terminal and the server-side adopts an SSL security authentication protocol so as to guarantee the data security in the communication process. By adopting the secure mobile communication architecture with dynamic two-way authentication for carrying out mobile communication, the implementation way is simple, counterfeiting, hacker attack and man-in-the-middle attack threats in the common mobile communication mechanism are eliminated, and the security of communication between the mobile client terminal and the server-side is greatly increased.
Owner:JIANGSU PAYEGIS TECH CO LTD
Computer system and program to update SSL certificates
InactiveUS7512974B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationProgram instructionSelf-signed certificate
System and computer program product for updating an SSL certificate for a server. First program instructions detect when a change has been made to a name, domain or IP address of the server and detect that the server is using an SSL certificate based on a name, domain or IP address applicable before the change. In response, the first program instructions notify an administrator that a change is required to the SSL certificate to reflect the change to the name, domain or IP address. Second program instructions respond to a request by the administrator, to automatically create a new SSL certificate signing request. The new SSL certificate signing request is a form which can be sent to an SSL certificate authority. Third program instructions respond to another request by the administrator, to send the new SSL certificate signing request to the SSL certificate authority. Fourth program instructions respond to receipt of a new SSL certificate from the SSL certificate authority and another request by the administrator, to substitute the new SSL certificate for the existing SSL certificate. Fourth program instructions query the administrator if the administrator wants to use a new self-signed SSL certificate reflecting the change to the name, domain or IP address of the server, until the new SSL certificate signed by the SSL certificate authority is received from the SSL certificate authority, and if so, generate the new SSL self-signed certificate. Other program instructions respond to a request by the administrator, to create a self-signed SSL certificate and substitute the self-signed SSL certificate for the existing SSL certificate.
Owner:IBM CORP
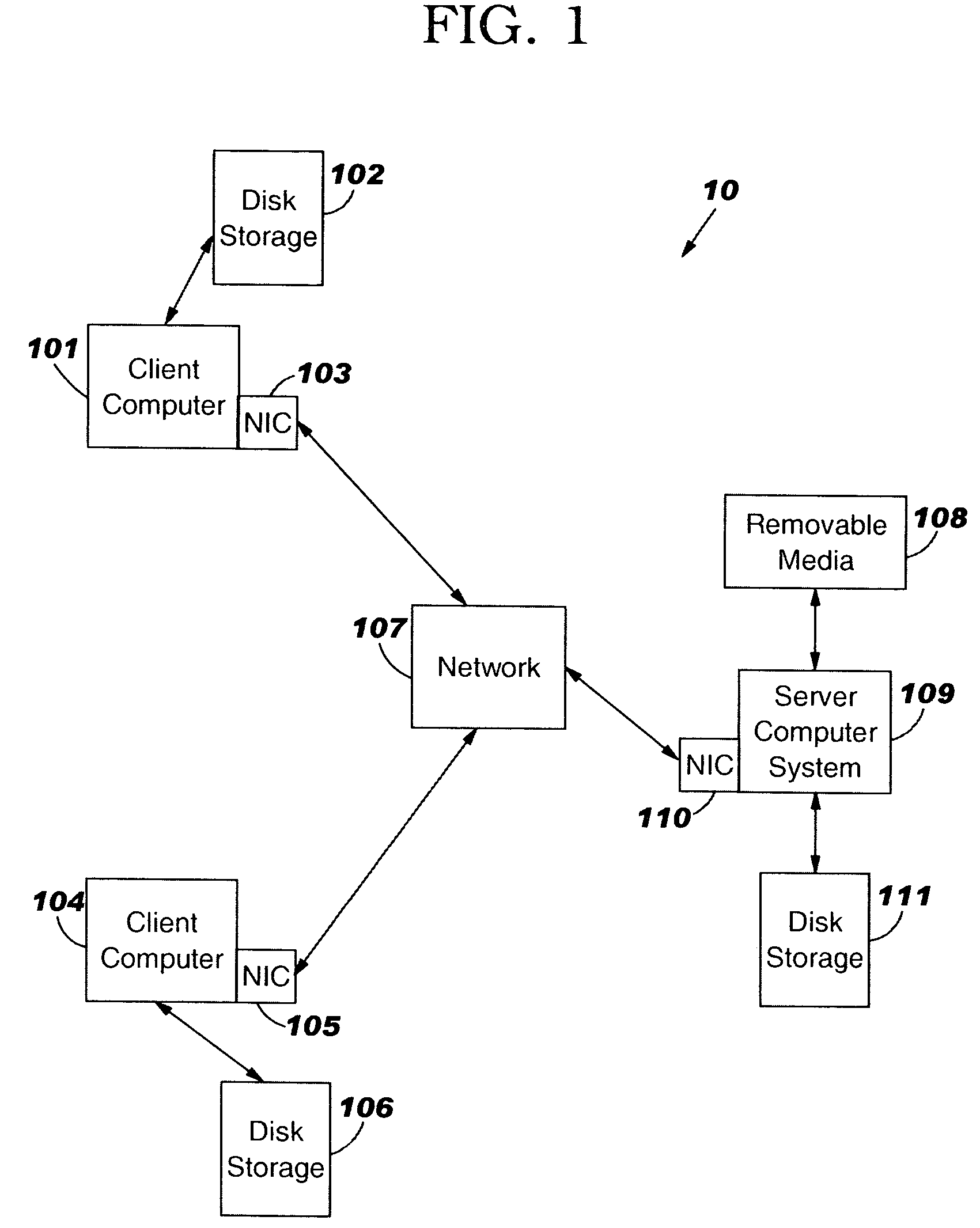
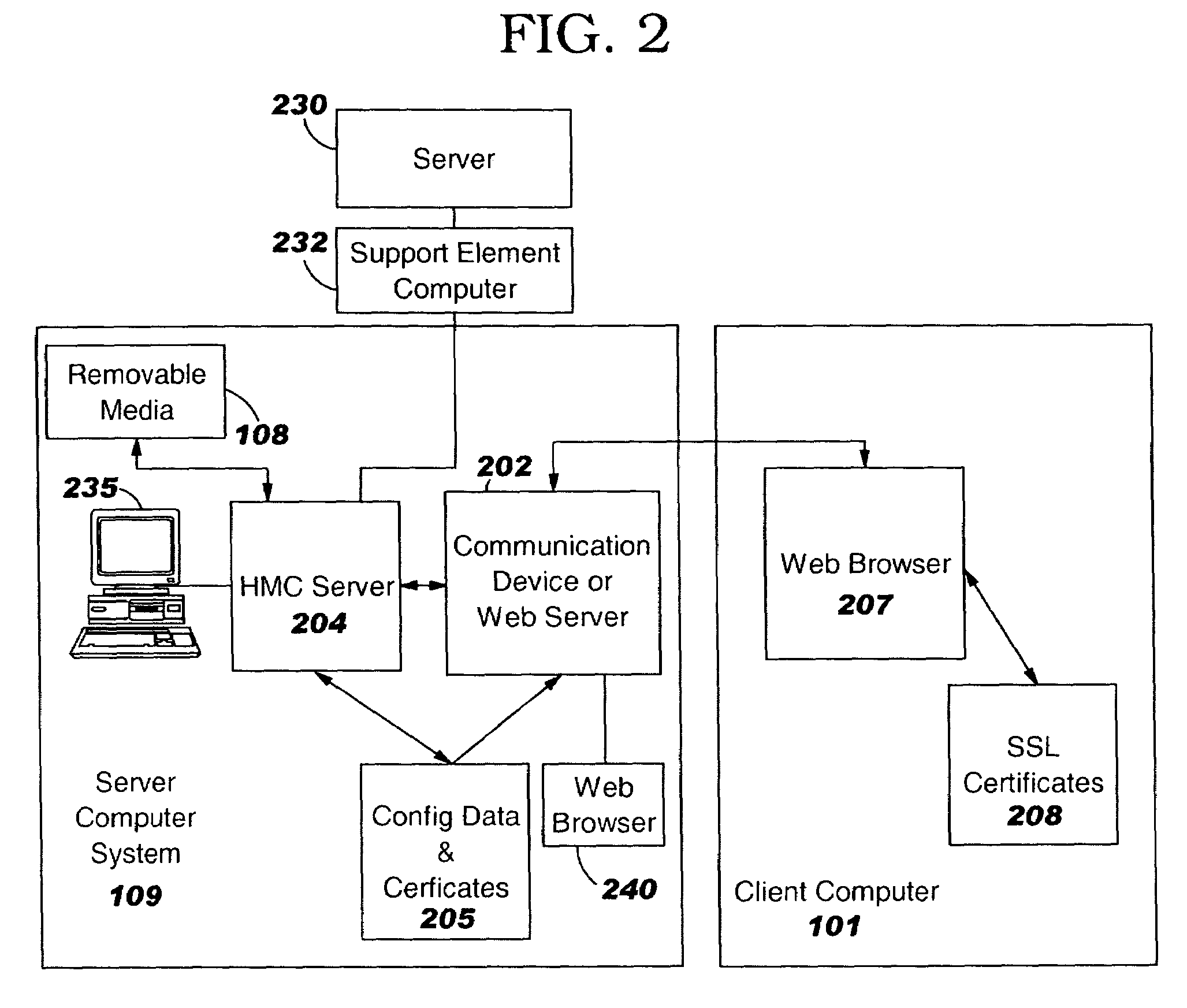
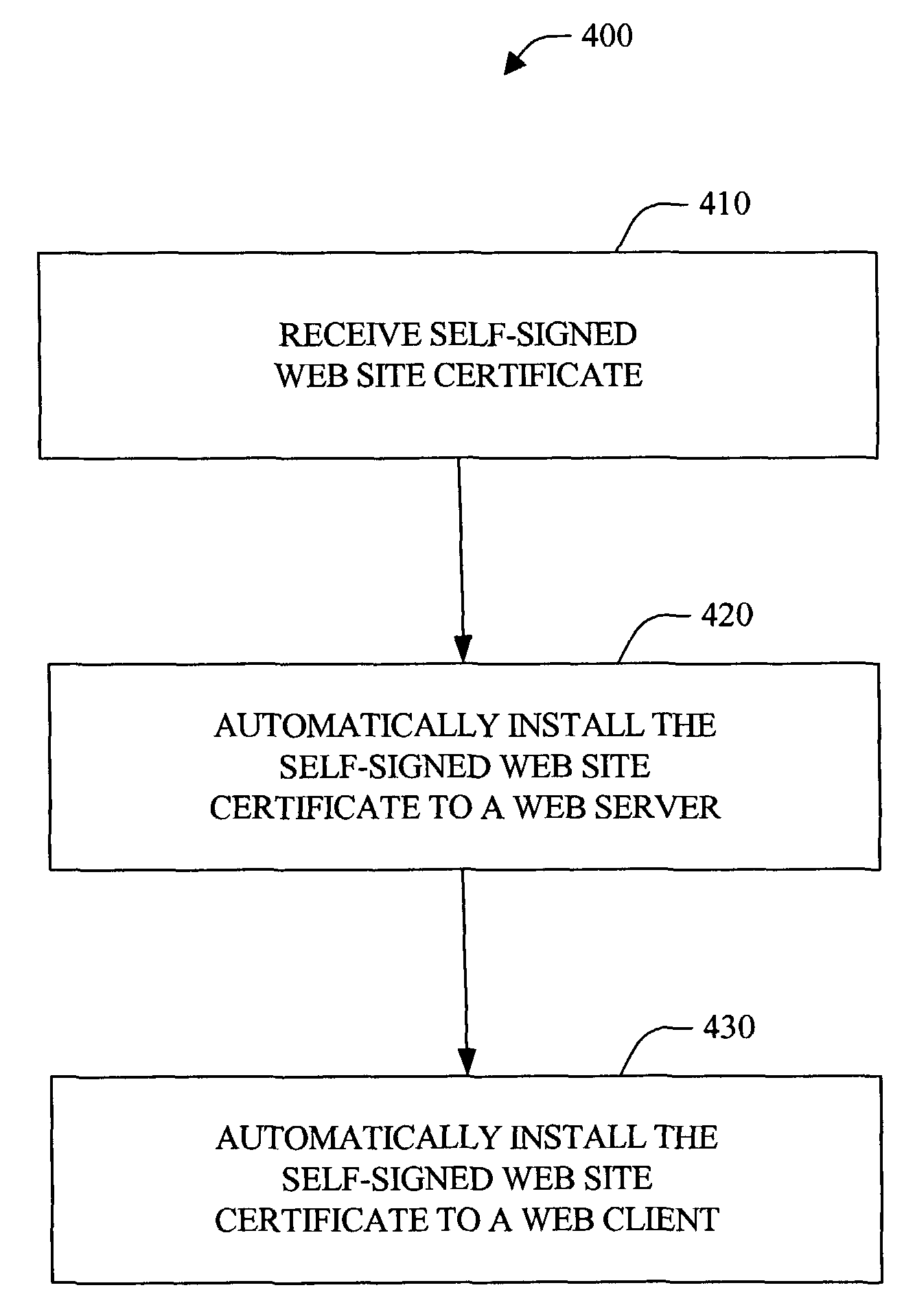
Systems and methods for automated configuration of secure web site publishing
ActiveUS7788495B2Easy to optimizeEasy to installDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationWeb siteSelf-signed certificate
The present invention provides systems and methods to automatically install and trust a self-signed (e.g., untrusted) web site certificate on one or more web clients local to the network. In addition, the systems and methods provide for automatic installation of the self-signed certificate and / or a signed (e.g., trusted) certificate on a web server, and automatic configuration to enable an authentication and / or encryption mechanism (e.g., SSL encryption) with at least a portion of the web site. Conventionally, certificate installation, configuration and trusting are achieved manually, which can be time consuming and prone to errors such as trusting a fictitious certificate, for example. The systems and methods of the present invention provide a novel approach to mitigate manual web site certificate installation (e.g., trusted and untrusted) and trusting, web client interruption via untrusted web site warning notifications, and domain web site redirection to a fictitious web site.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
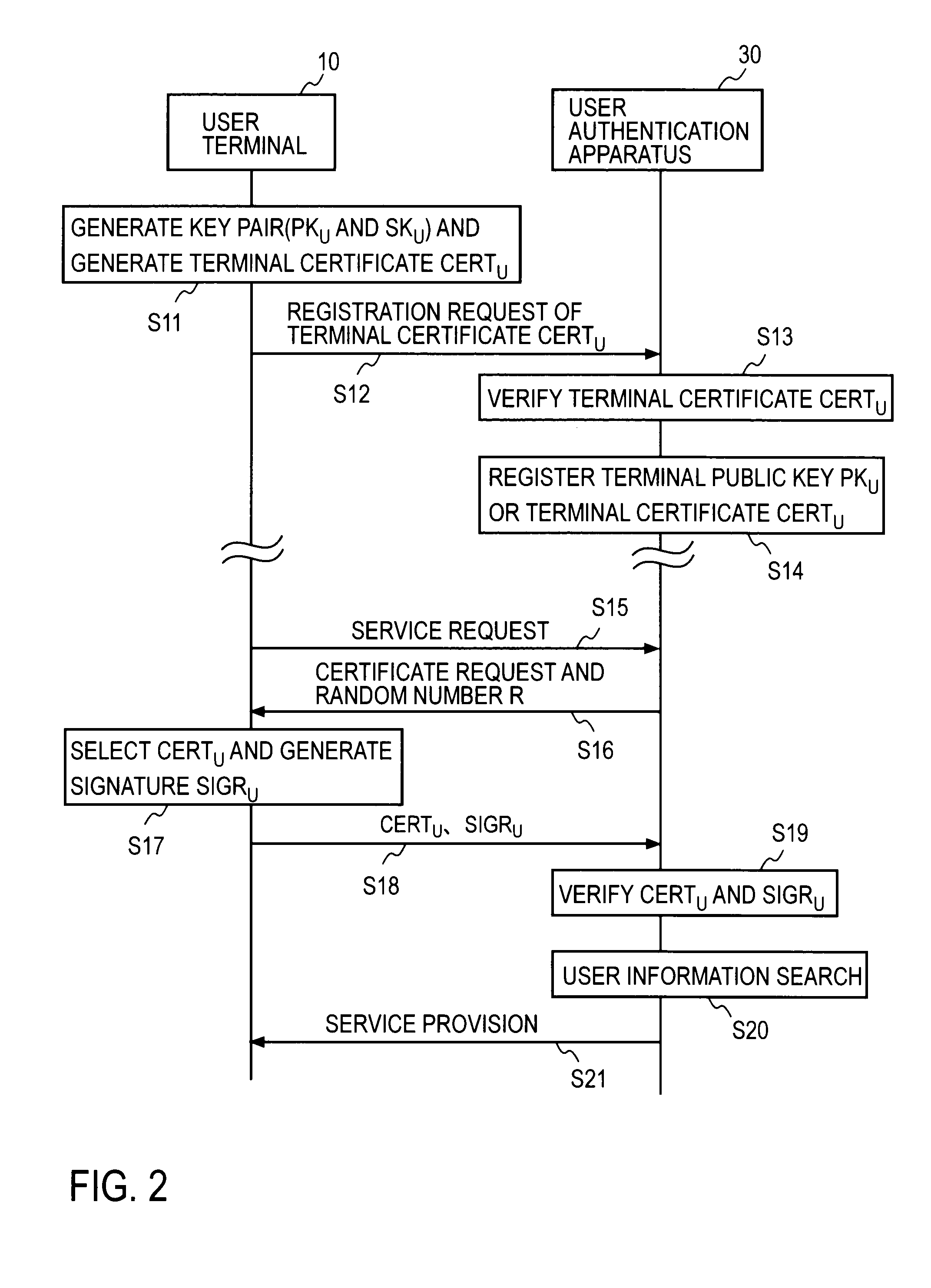
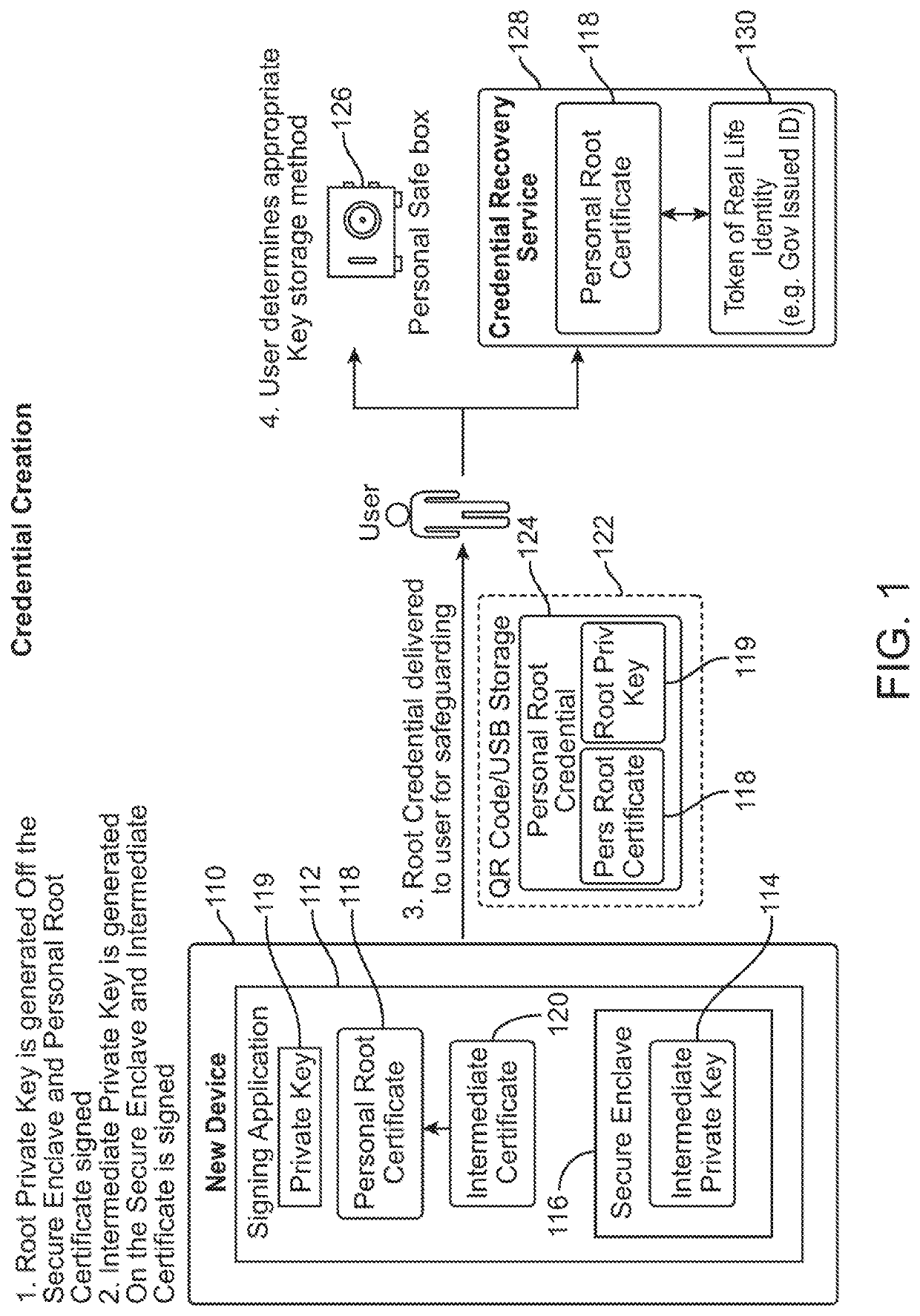
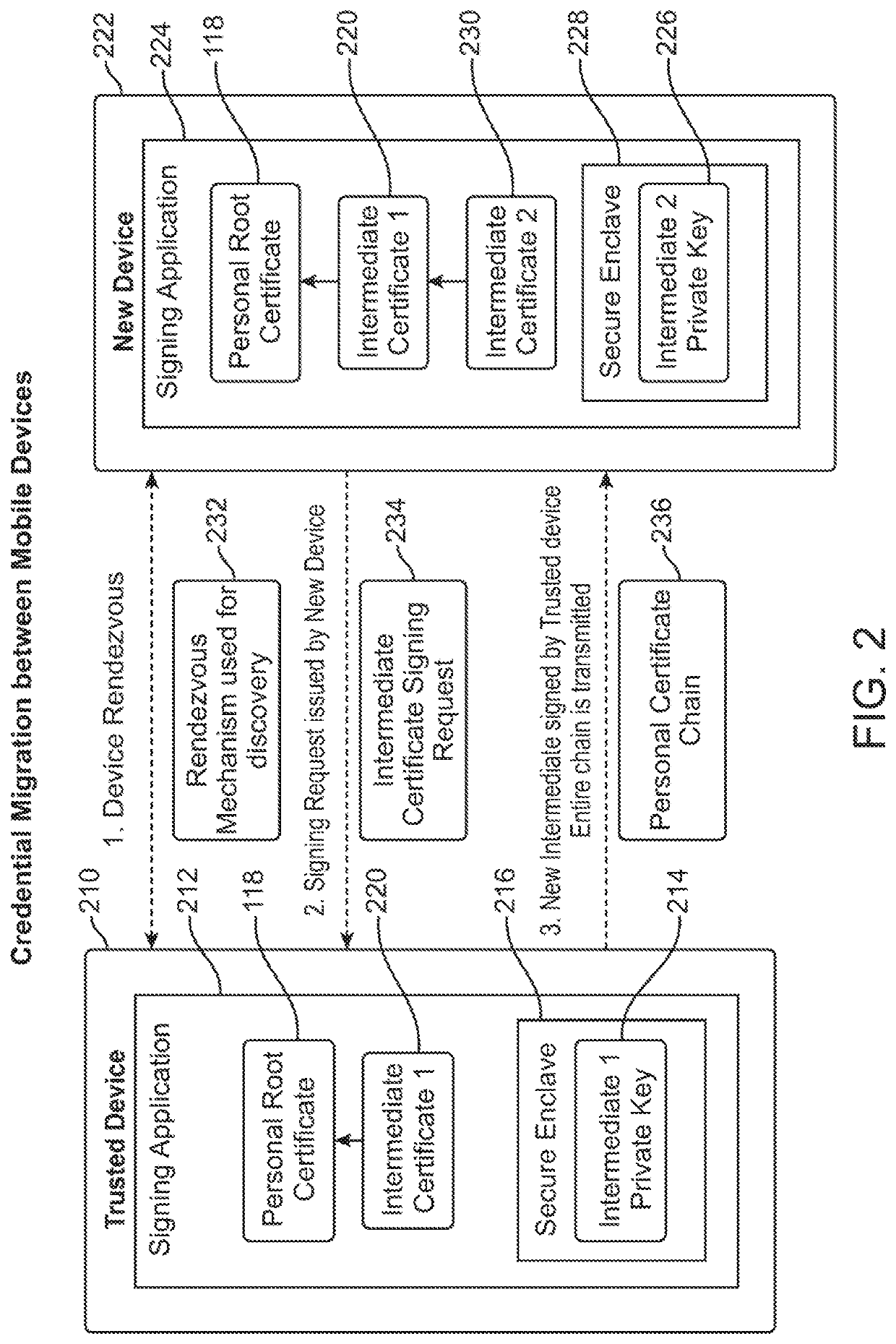
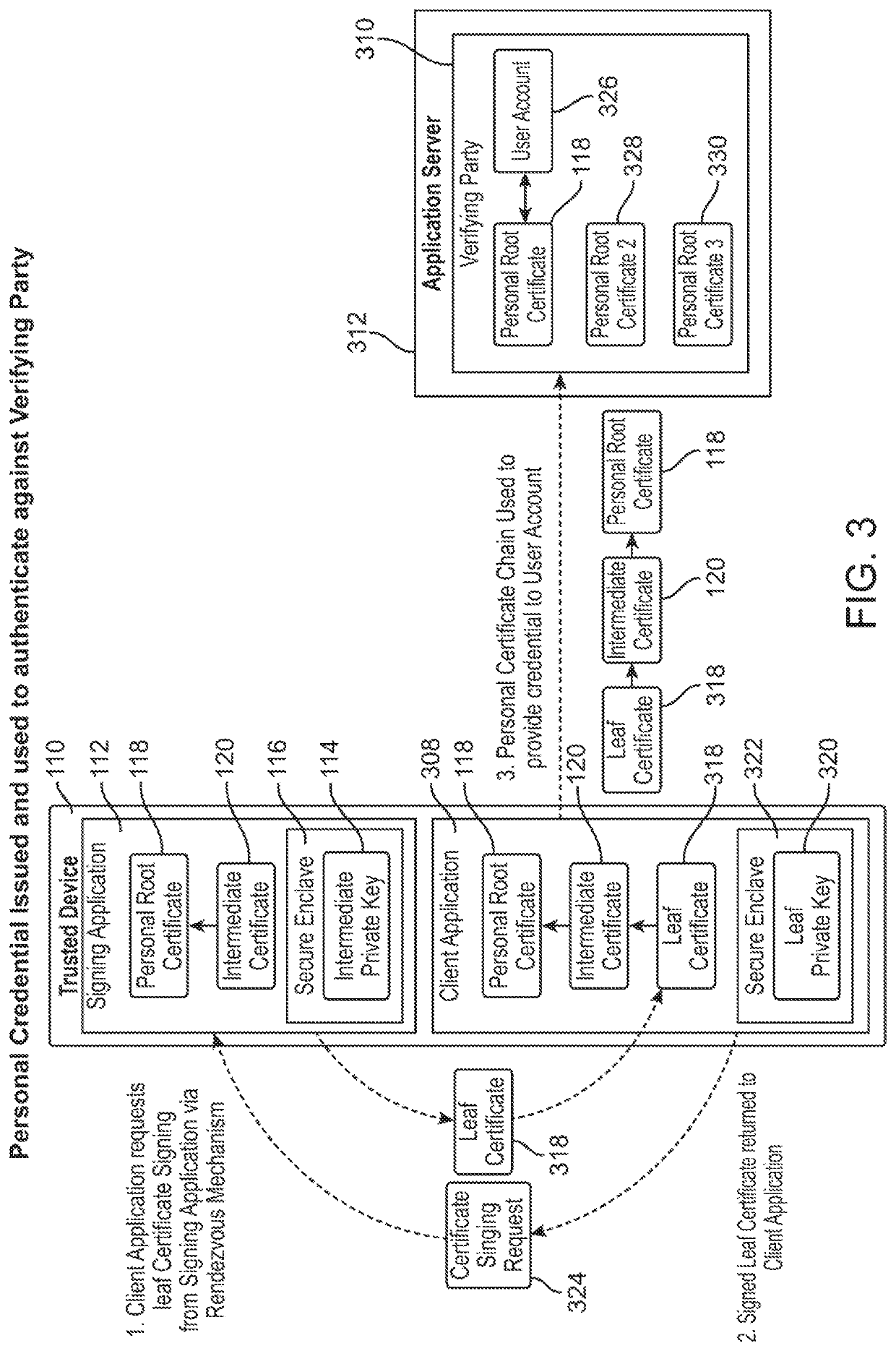
User authentication with self-signed certificate and identity verification and migration
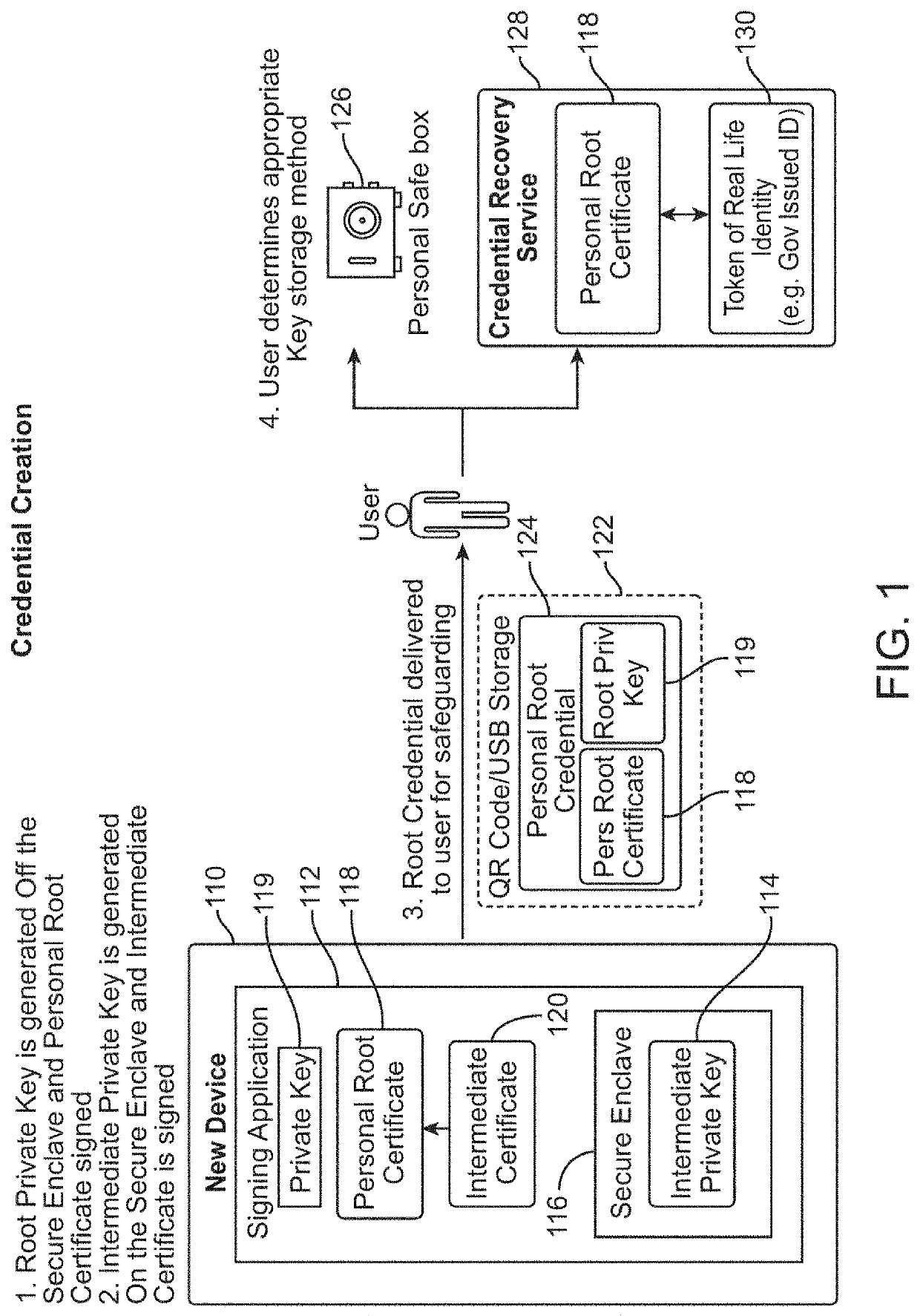
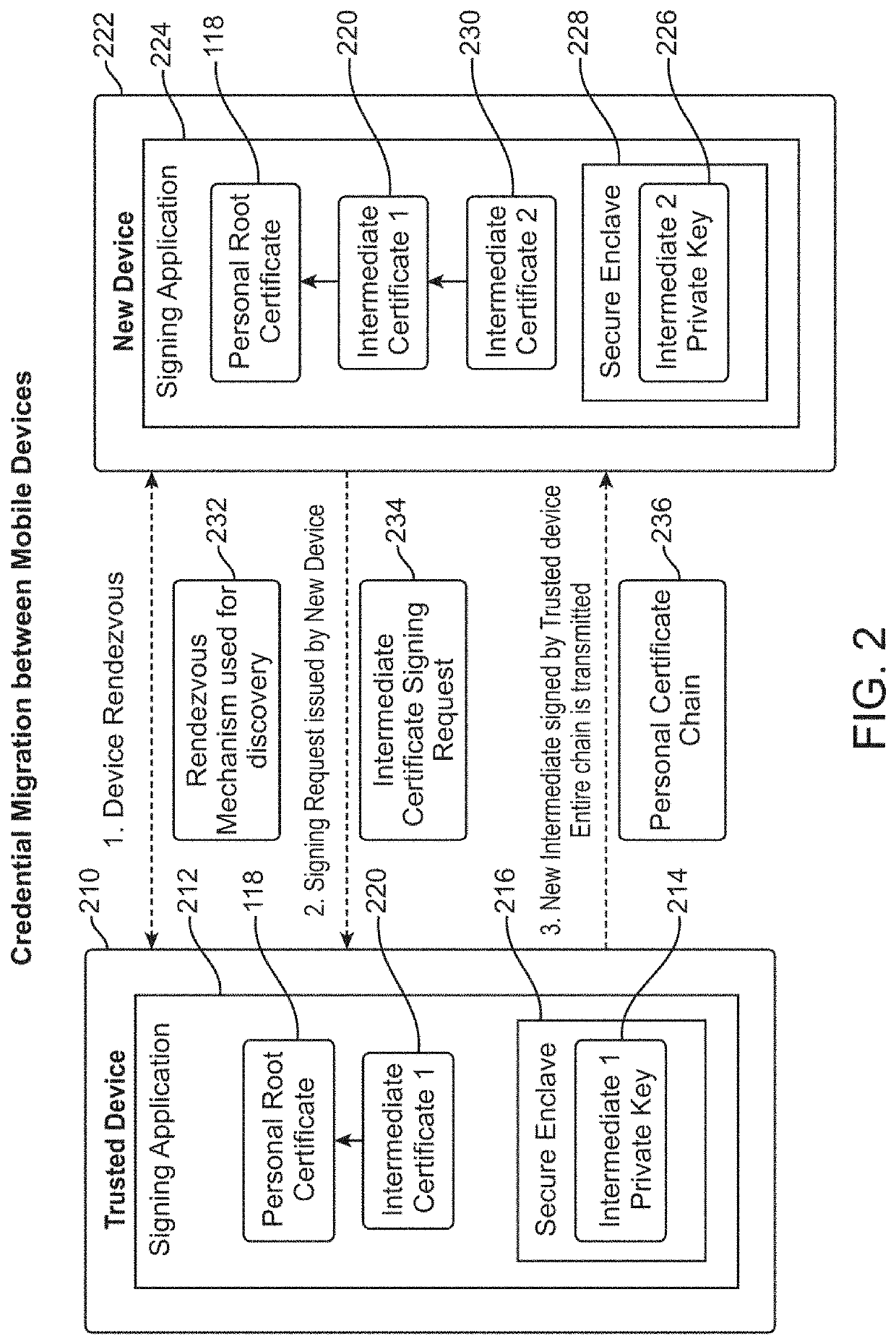
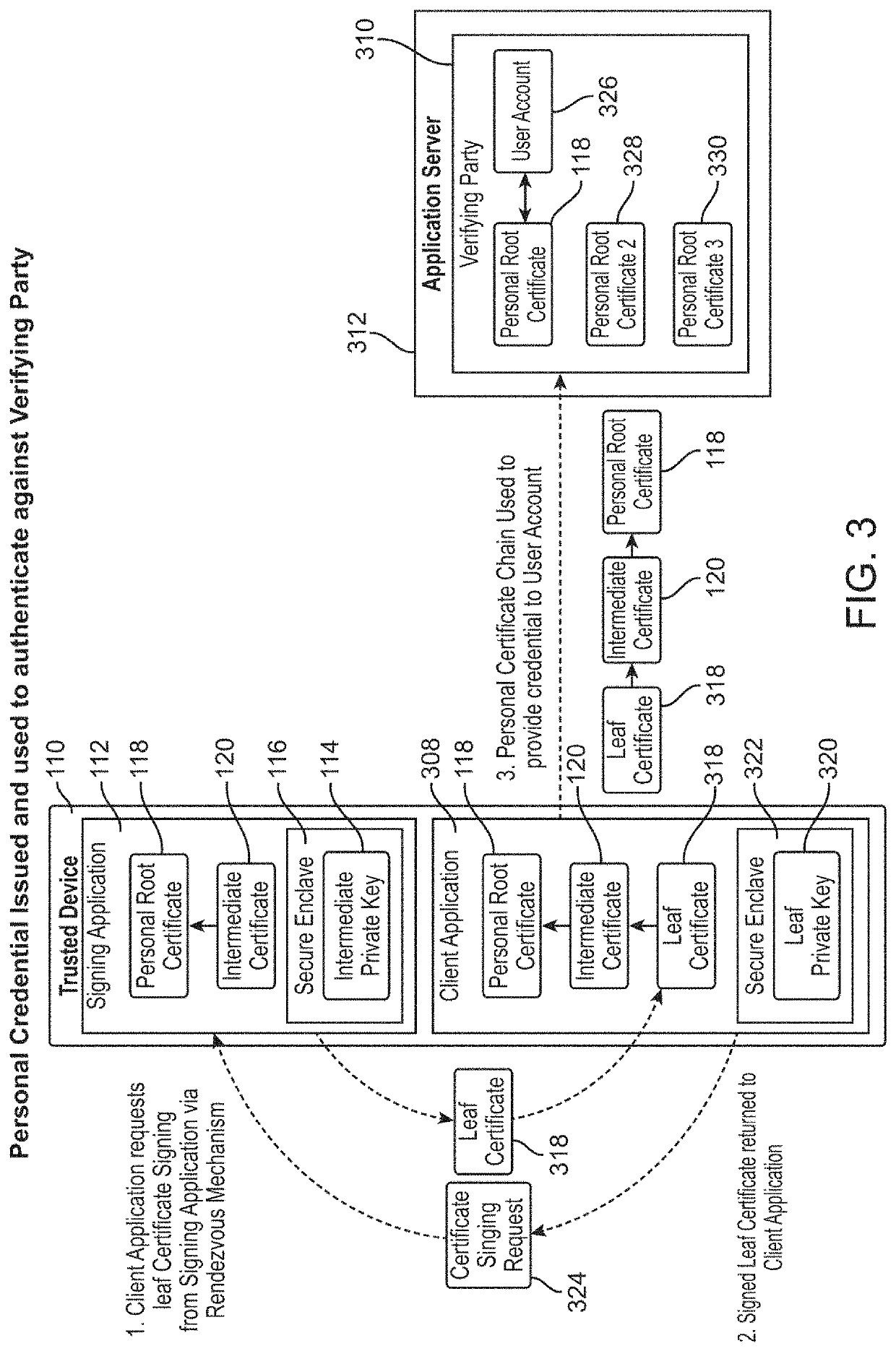
ActiveUS10728044B1Recovery lossEasily migrate trustMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationRoot certificateUser device
In embodiments, an authentication server interfaces between a user device with a self-signed certificate and a verifying computer that accepts a user name and password. The user device generates a self-signed certificate signed by a private key on the user device. The self-signed certificate is transmitted to a verifying party computer over a network. The verifying party stores the self-signed certificate with user identification data. The user migrates trust to another device by providing the root certificate and intermediate certificate as a certificate chain to a second device, which then adds a new intermediate certificate to create a longer certificate chain with the same root certificate. In subsequent communications, the verifying party receives a certificate chain including the self-signed certificate from the second user device, and matches that with the user identification data stored in a database.
Owner:BEYOND IDENTITY INC
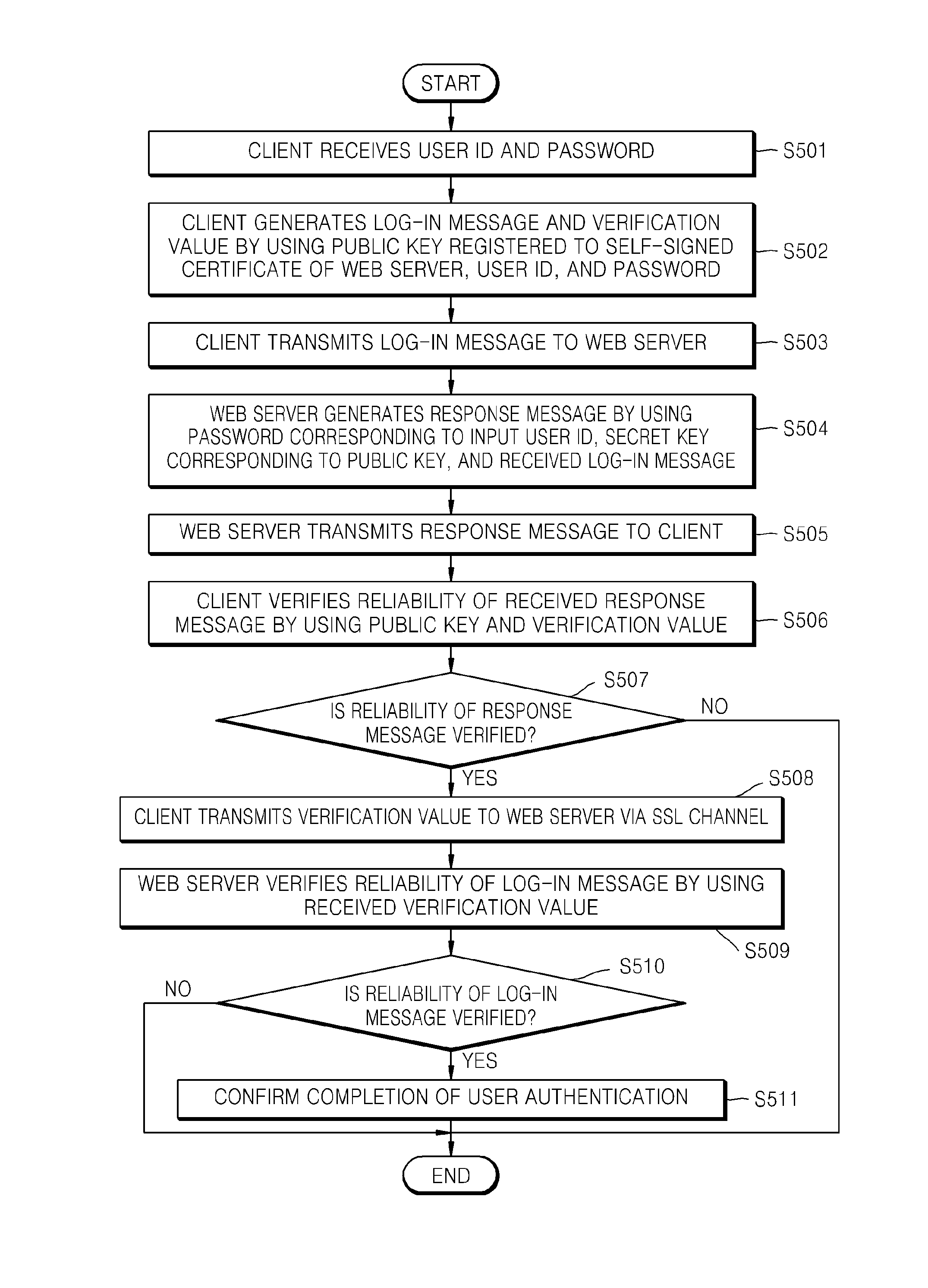
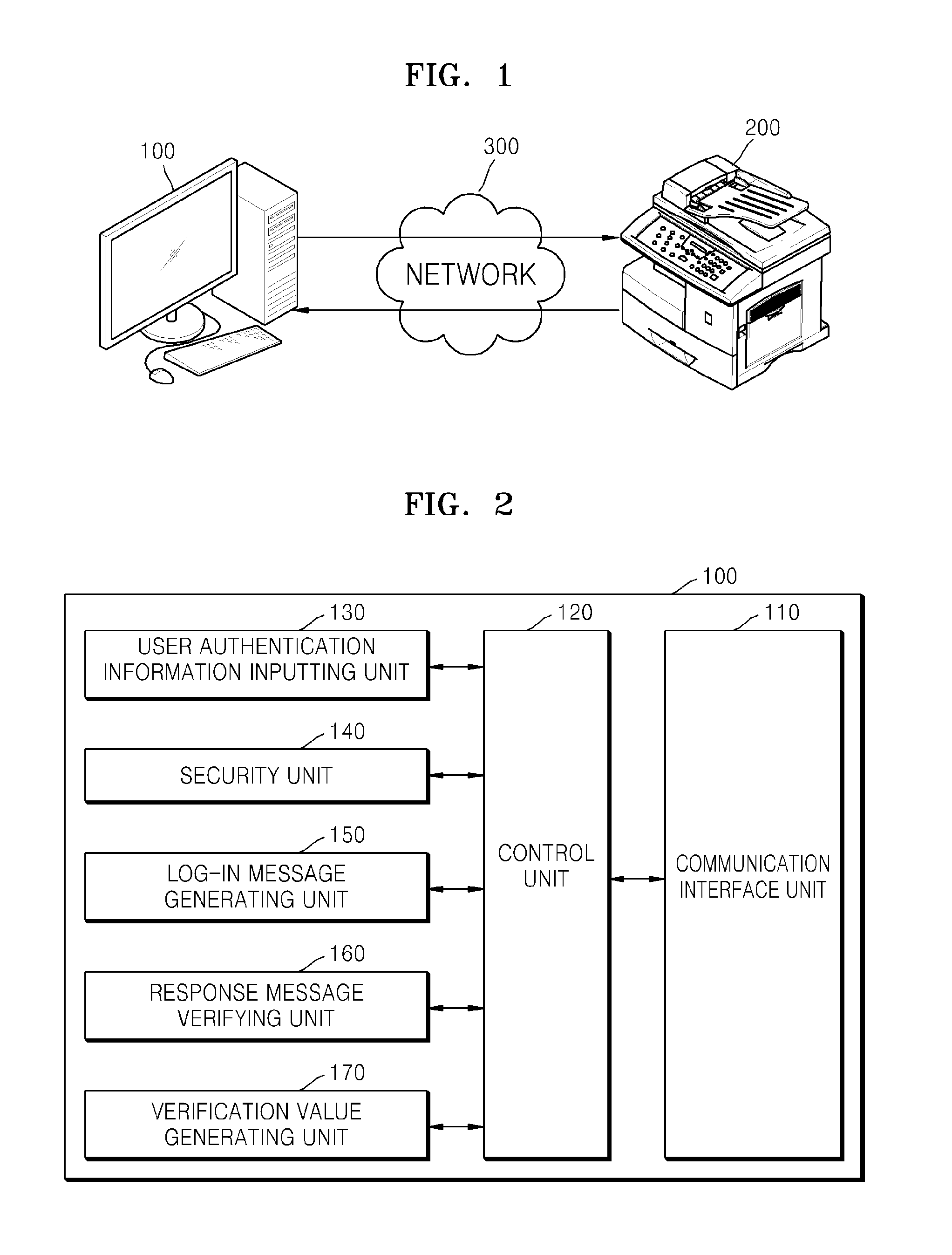
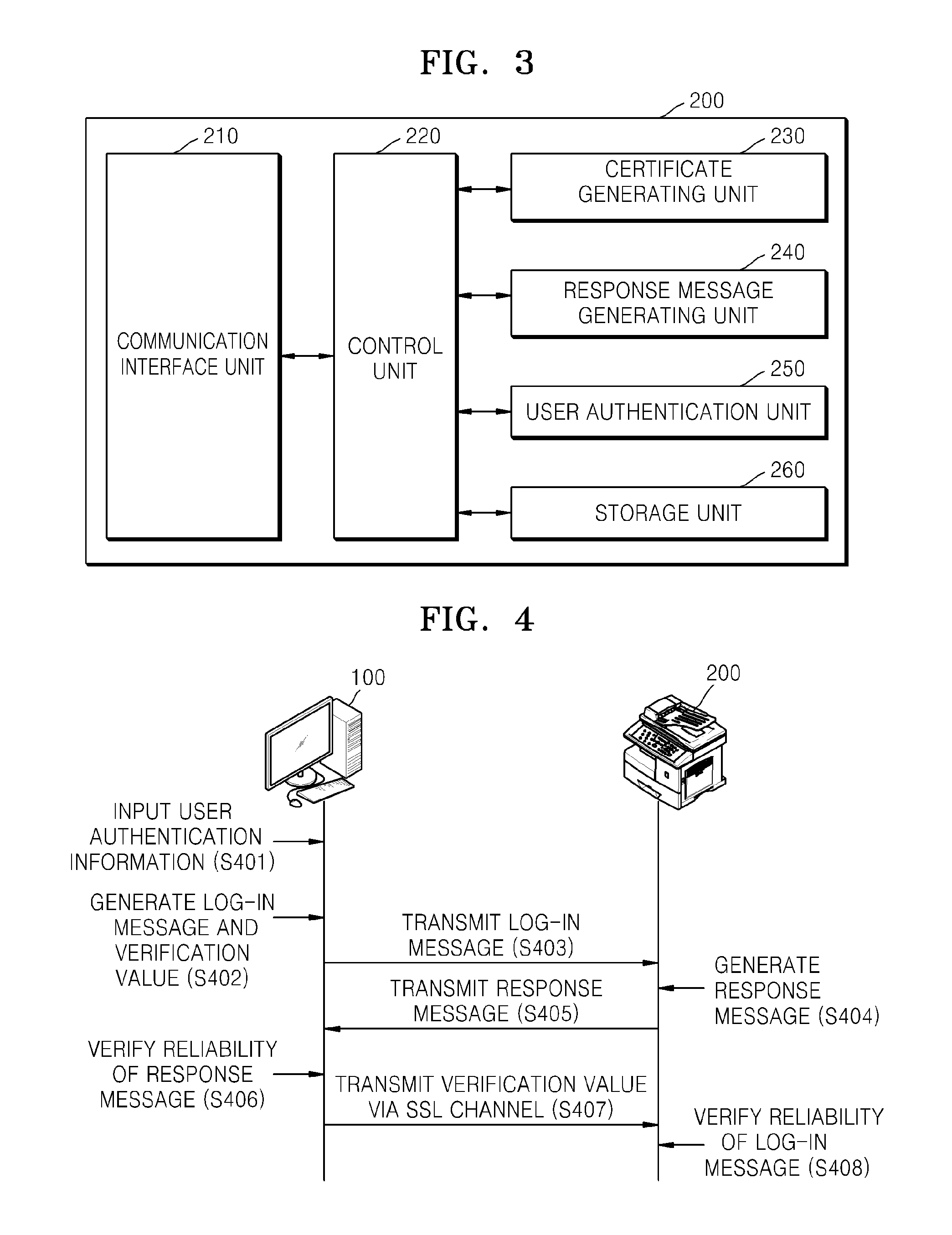
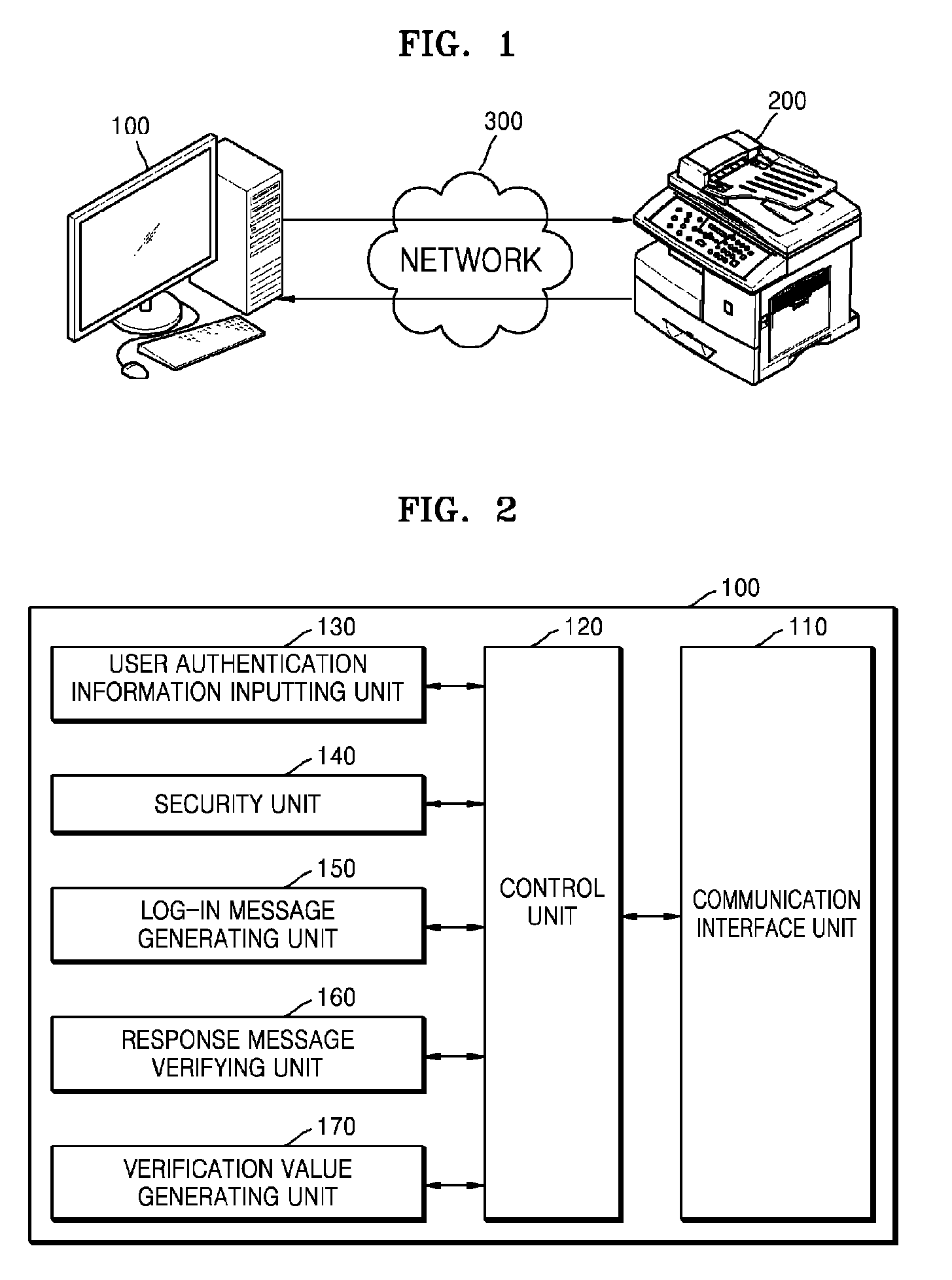
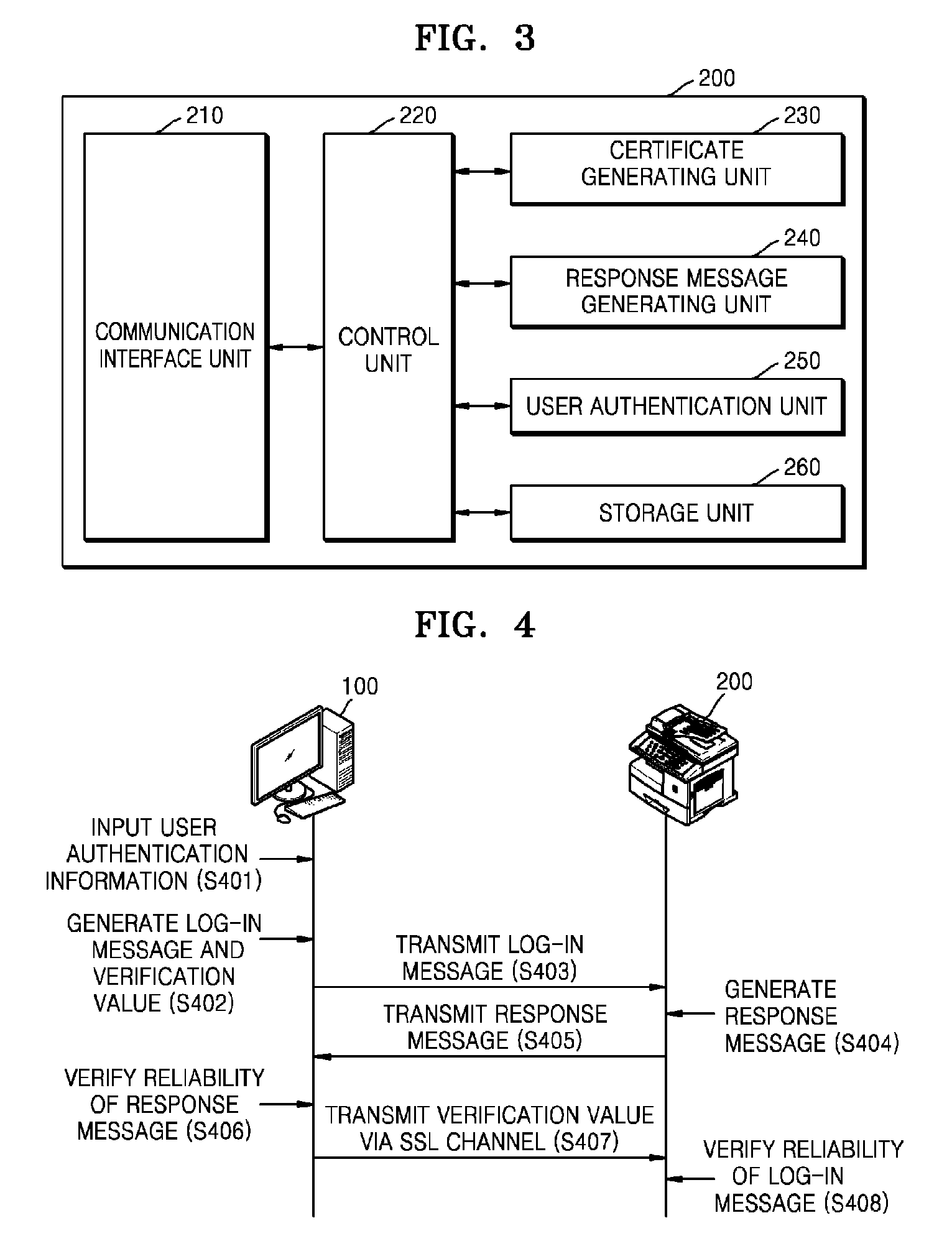
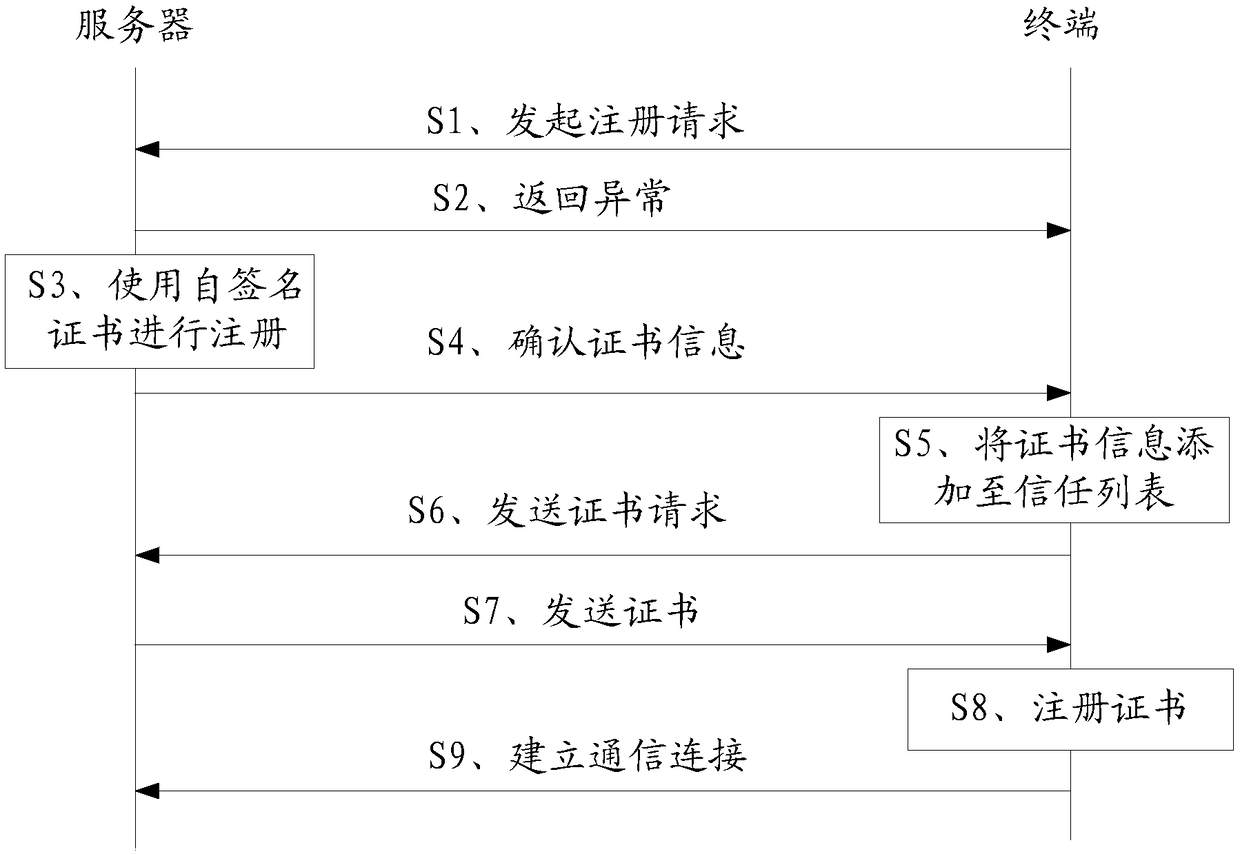
User authentication method using self-signed certificate of web server, client device and electronic device including web server performing the same
ActiveUS20140129828A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSelf-signed certificateWeb service
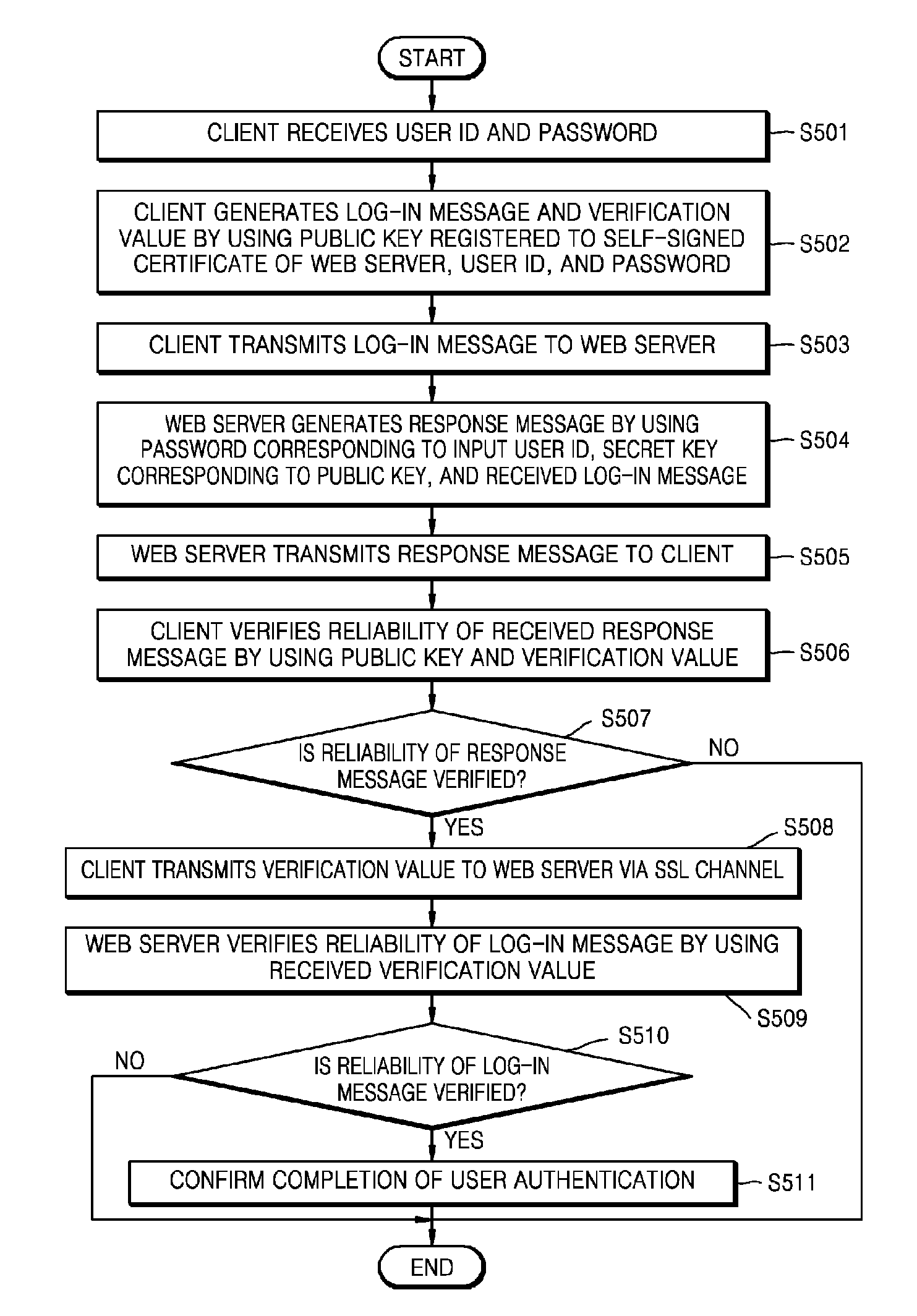
A user authentication method using a self-signed certificate of a web server includes: receiving a log-in message generated by using a public key registered to the self-signed certificate of the web server from a client device; generating a response message by using the log-in message and a secret key corresponding to the public key; transmitting the generated response message to the client device; receiving a verification value from the client device via a secure socket layer (SSL) channel connected by using the self-signed certificate of the web server from the client device when a reliability of the response message is verified at the client device; verifying a reliability of the log-in message by using the received verification value; and confirming completion of user authentication if the reliability of the log-in message is verified.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
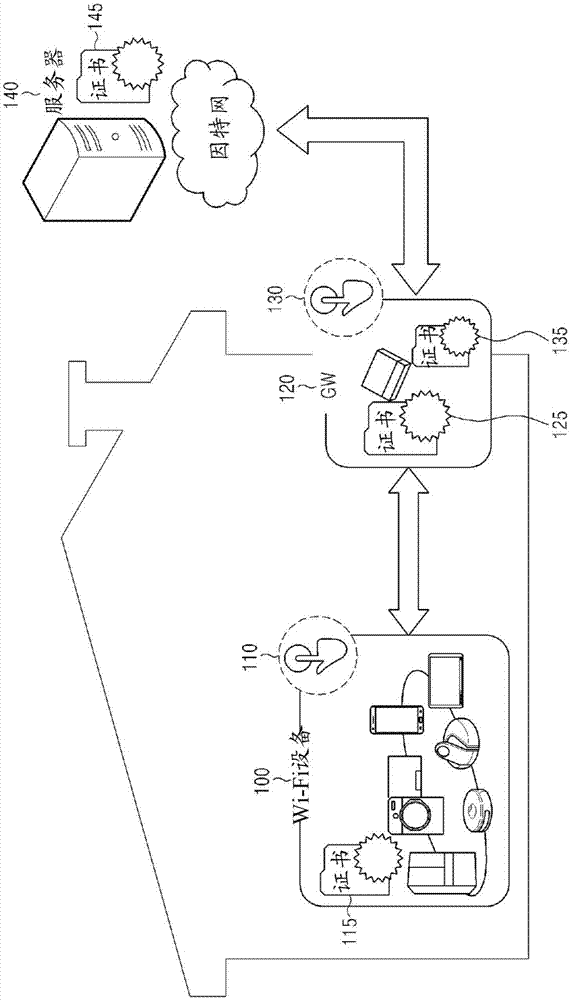
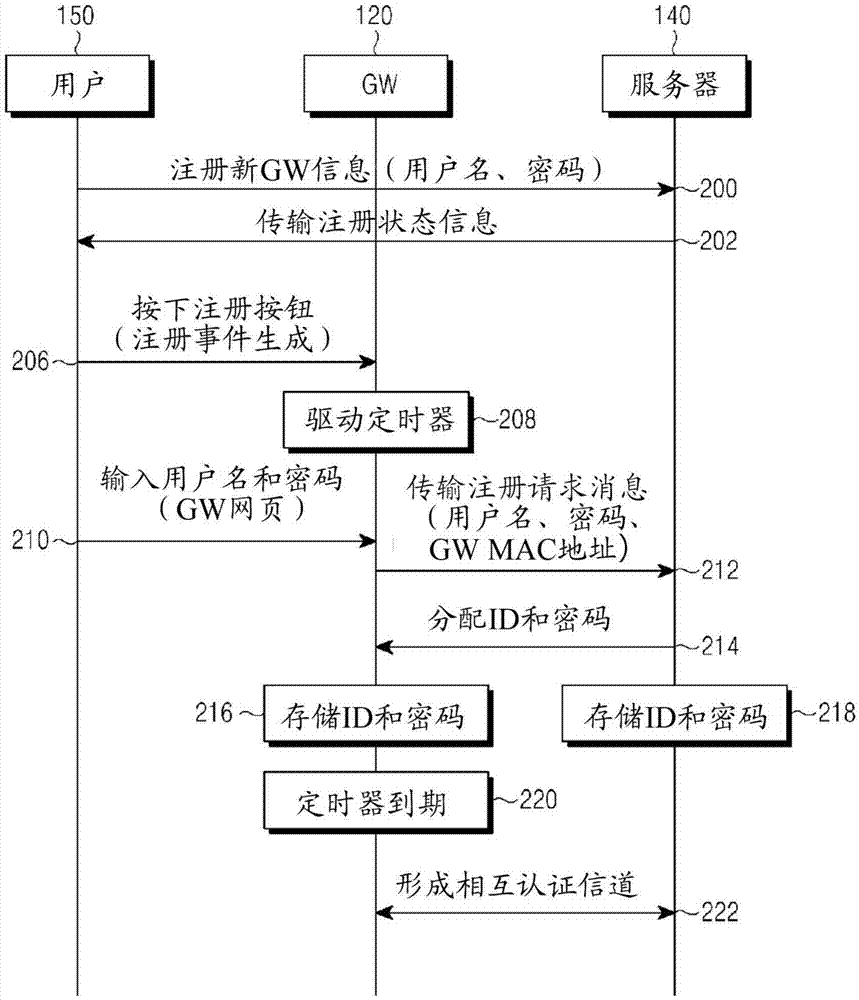
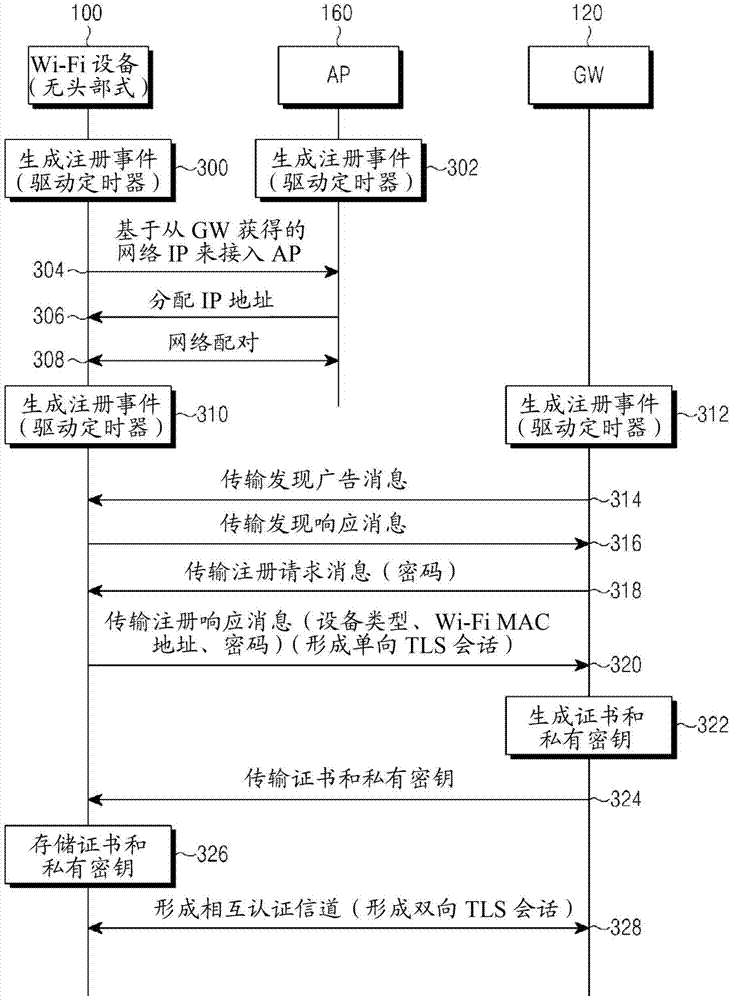
Method and device for registering and certifying device in wireless communication system
InactiveCN105453621AShorten the time intervalImprove securityNetwork topologiesConnection managementCommunications systemSelf-signed certificate
A gateway (GW) in a wireless communication system, according to the present invention, generates self-signed certificate information, allocates the self-signed certificate information to at least one device, transmits a registration request message for requesting registration of the at least one device to a server if a certificate channel with the at least one device is generated on the basis of the self-signed certificate information, and transmits certificate information for the at least one device to the at least one device if the certificate information for the at least one device is received from the server.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flexible system and method to manage digital certificates in a wireless network
InactiveUS8627064B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationRoot certificateSelf-signed certificate
An infrastructure is provided for managing the distribution of digital certificates for network security in wireless backhaul networks. In embodiments, a root certificate management system (root CMS) processes requests for digital certificates, issues root certificates, automatically authenticates surrogate certificate management systems (sur-CMSs), and automatically processes certificate requests and issues certificate bundles to sur-CMSs that are successfully authenticated. The infrastructure includes sur-CMSs to which are assigned base stations within respective regions. Each sur-CMS automatically authenticates its own base stations and automatically processes certificate requests and issues certificate bundles to base stations that are successfully authenticated. A certificate bundle issued to a base station includes a digital certificate, signed by the issuing sur-CMS, of a public key of such base station, and at least one further digital certificate, including a self-signed certificate of the root CMS.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
User authentication system and method for the same
InactiveUS8595816B2Removal costEliminate operationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSelf-signed certificateUser authentication
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
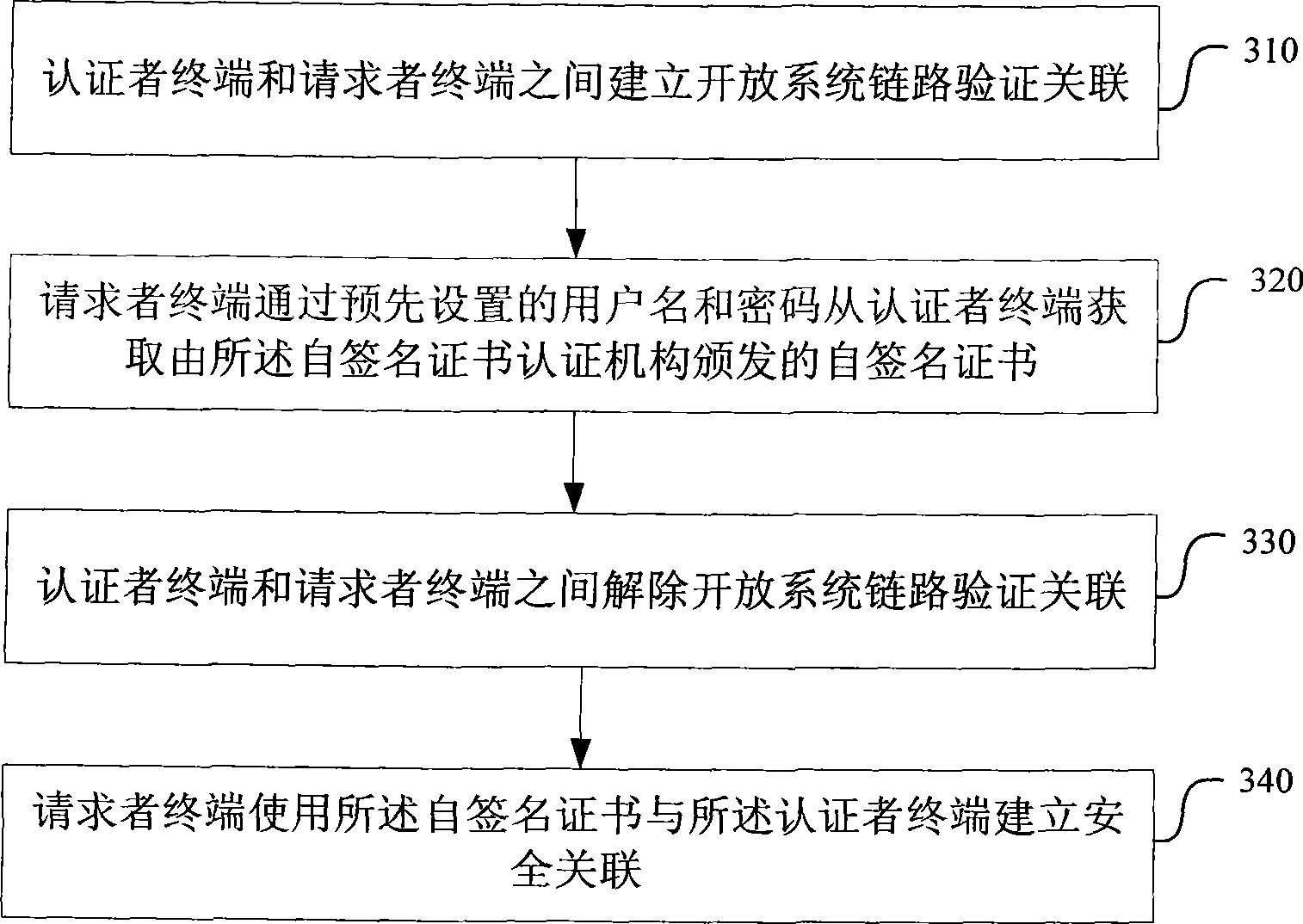
Terminal and security association establishment method under ad hoc network mode and
InactiveCN101521884AReduce power consumptionReduce the handshake processEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementSelf-signed certificatePassword
The invention provides an ad hoc network mode security association establishment method which is applied to a requester terminal and an authenticator terminal containing a self-signed certification authority. The method comprises the following steps: the requester terminal obtains a self-signed certificate issued by the self-signed certification authority from the authenticator terminal through an open system link established between the requester terminal and the authenticator and the preset name and password of a user; and the requester terminal uses the self-signed certificate to establish security association with the authenticator terminal. The invention further provides a terminal containing a self-signed certification authority. The invention does not need two rounds of five-time handshake processes to negotiate two groups of unicast keys and multicast keys, reduces the handshake processes of establishing security association, accelerates the security association establishment speed and reduces the terminal power consumption.
Owner:ZTE CORP
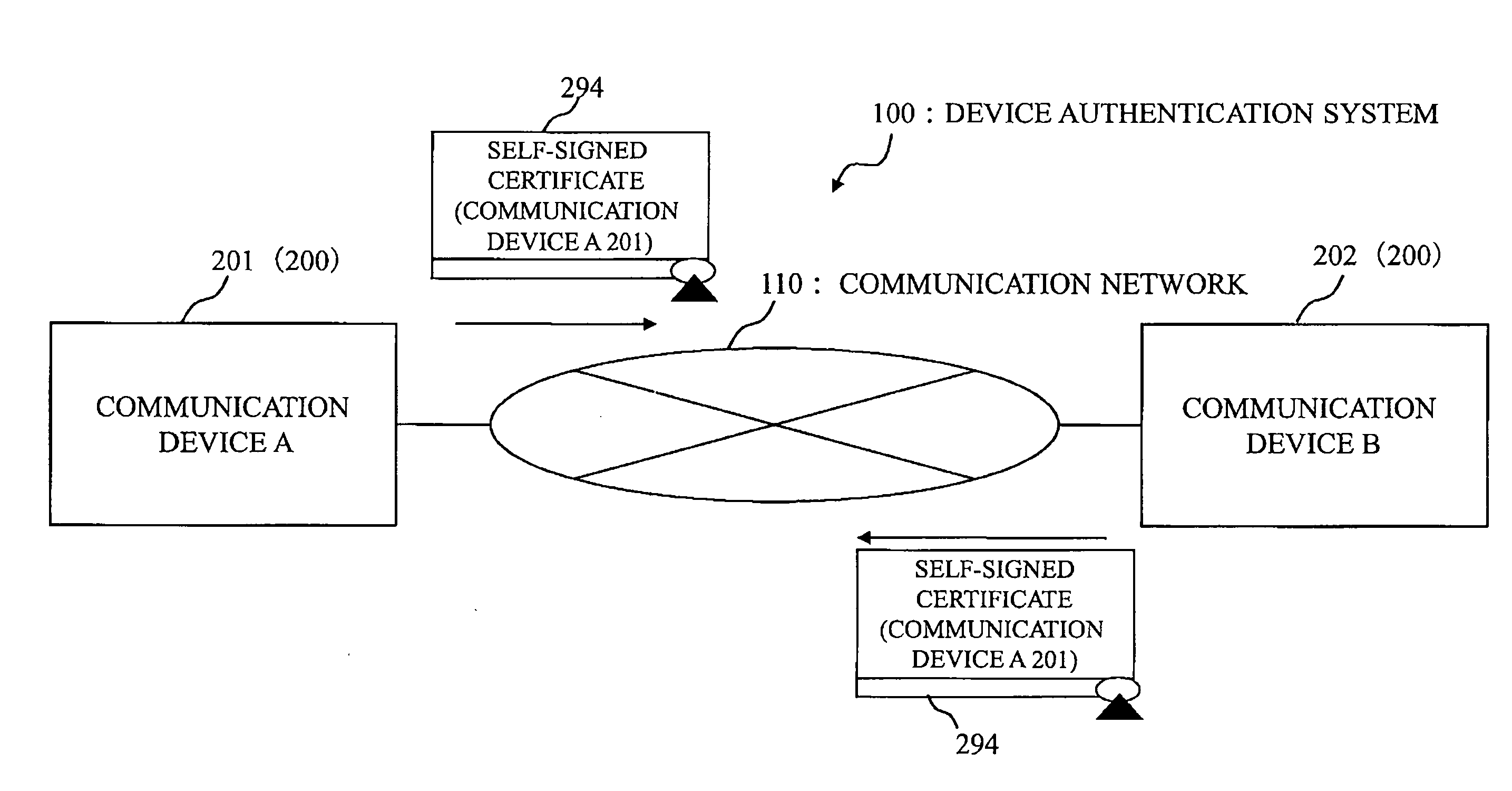
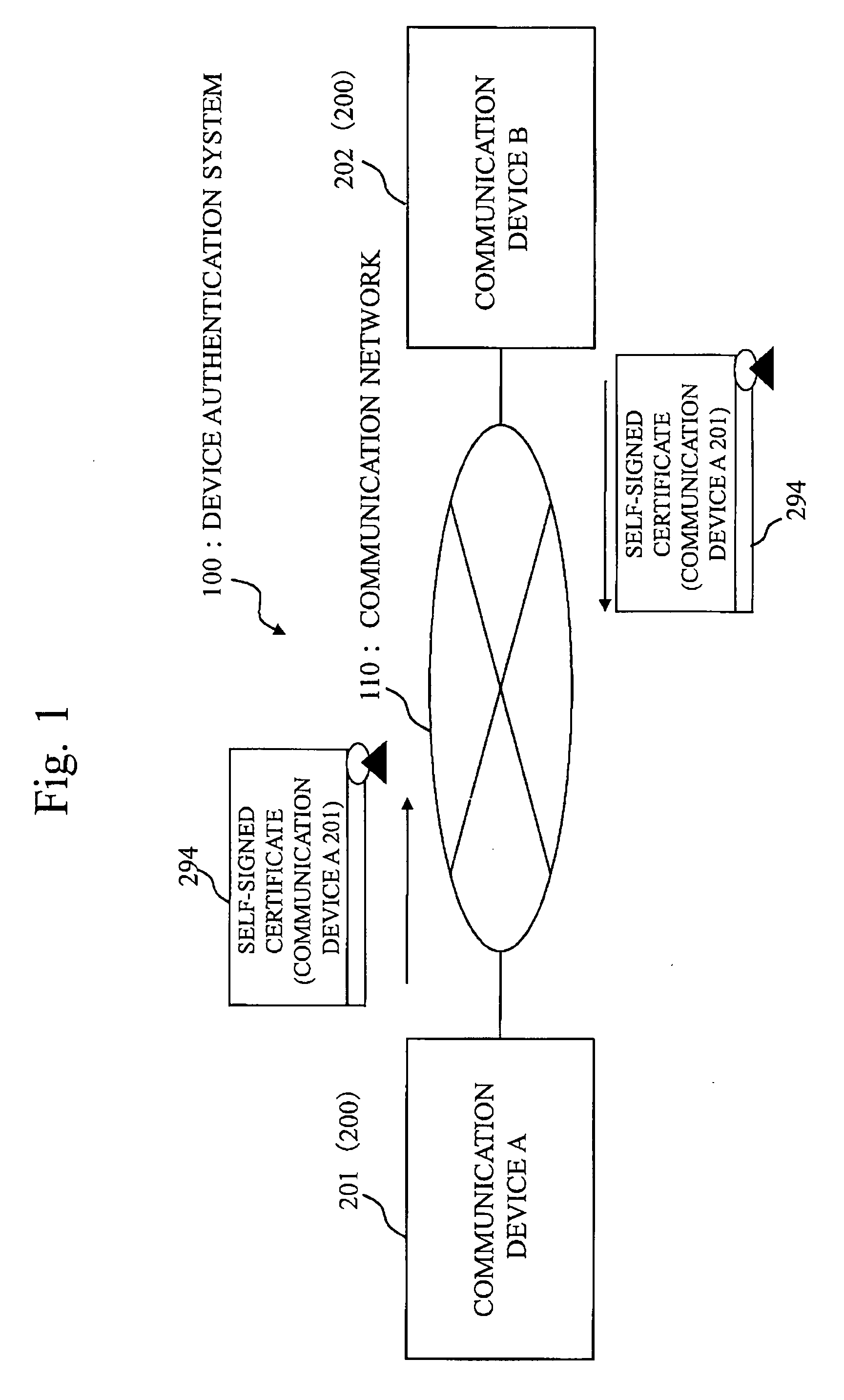
Self-authentication communication device and device authentication system
InactiveUS8479001B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationID-based encryptionSecure communication
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Self-signed implicit certificates
There are disclosed systems and methods for creating a self-signed implicit certificate. In one embodiment, the self-signed implicit certificate is generated and operated upon using transformations of a nature similar to the transformations used in the ECQV protocol. In such a system, a root CA or other computing device avoids having to generate an explicit self-signed certificate by instead generating a self-signed implicit certificate.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
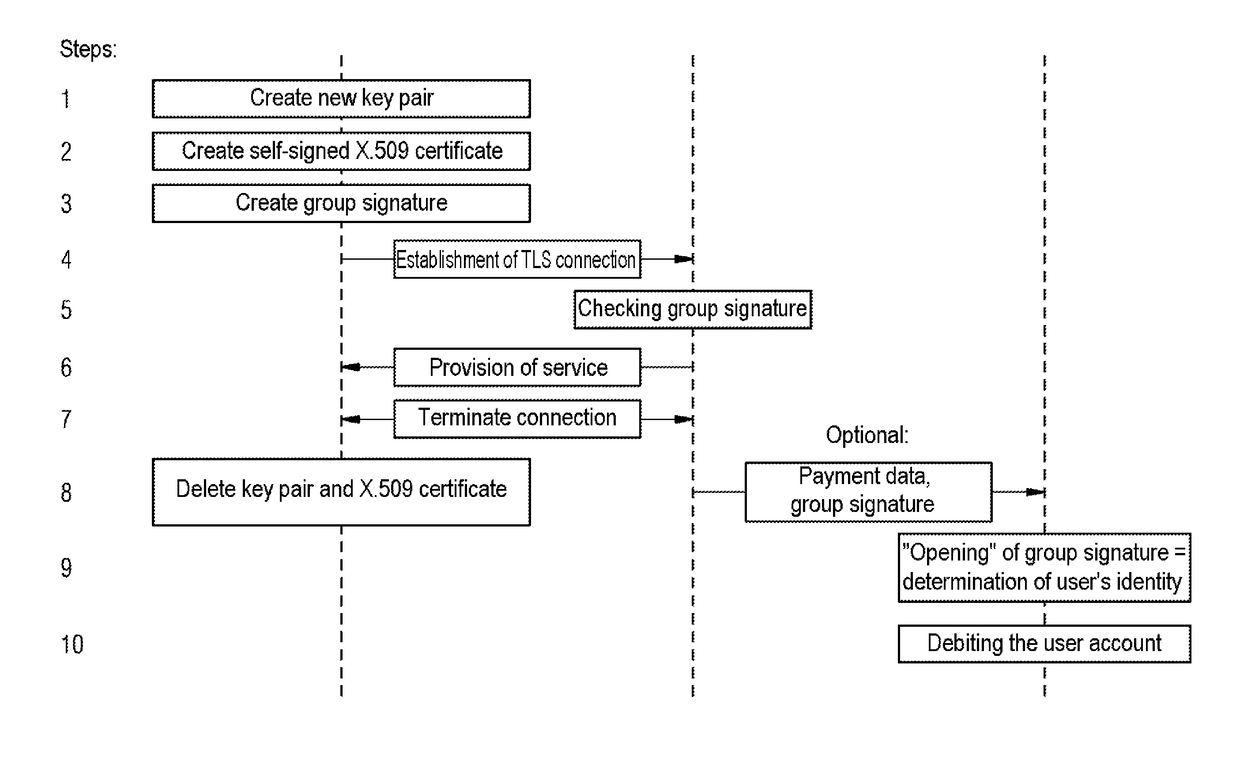
Method and apparatus for authenticating a service user for a service that is to be provided
InactiveUS20180205559A1User identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionSelf-signed certificateService provision
A method and an apparatus for authenticating a service user for a service that is to be provided. The method has the following steps: a) provision of an anonymous and self-signed certificate, produced by a service use means of the service user, for set-up of a connection, protected by the use of a security protocol, for data transmission between the service use device which is for example, a mobile device or a PC, via his anonymous, self-signed certificate and a service provision device, for example, a server, at the application level using the group signature, and b) verification of the provided anonymous and self-signed certificate by means of a group signature, assigned to a group, for detecting the authorization of the service user to use the service, in order to establish whether the service user providing the certificate through his service use device is a member of the group.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
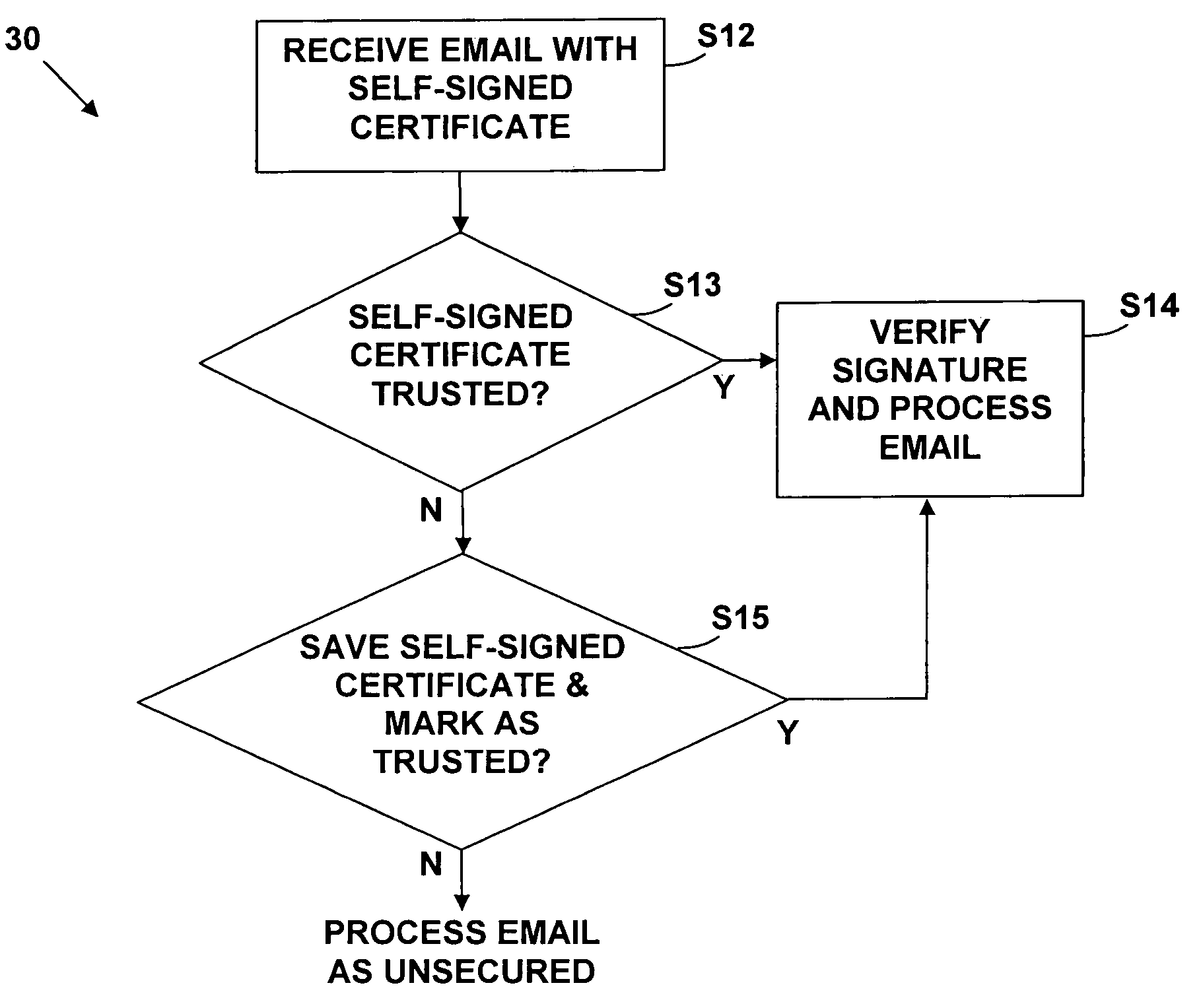
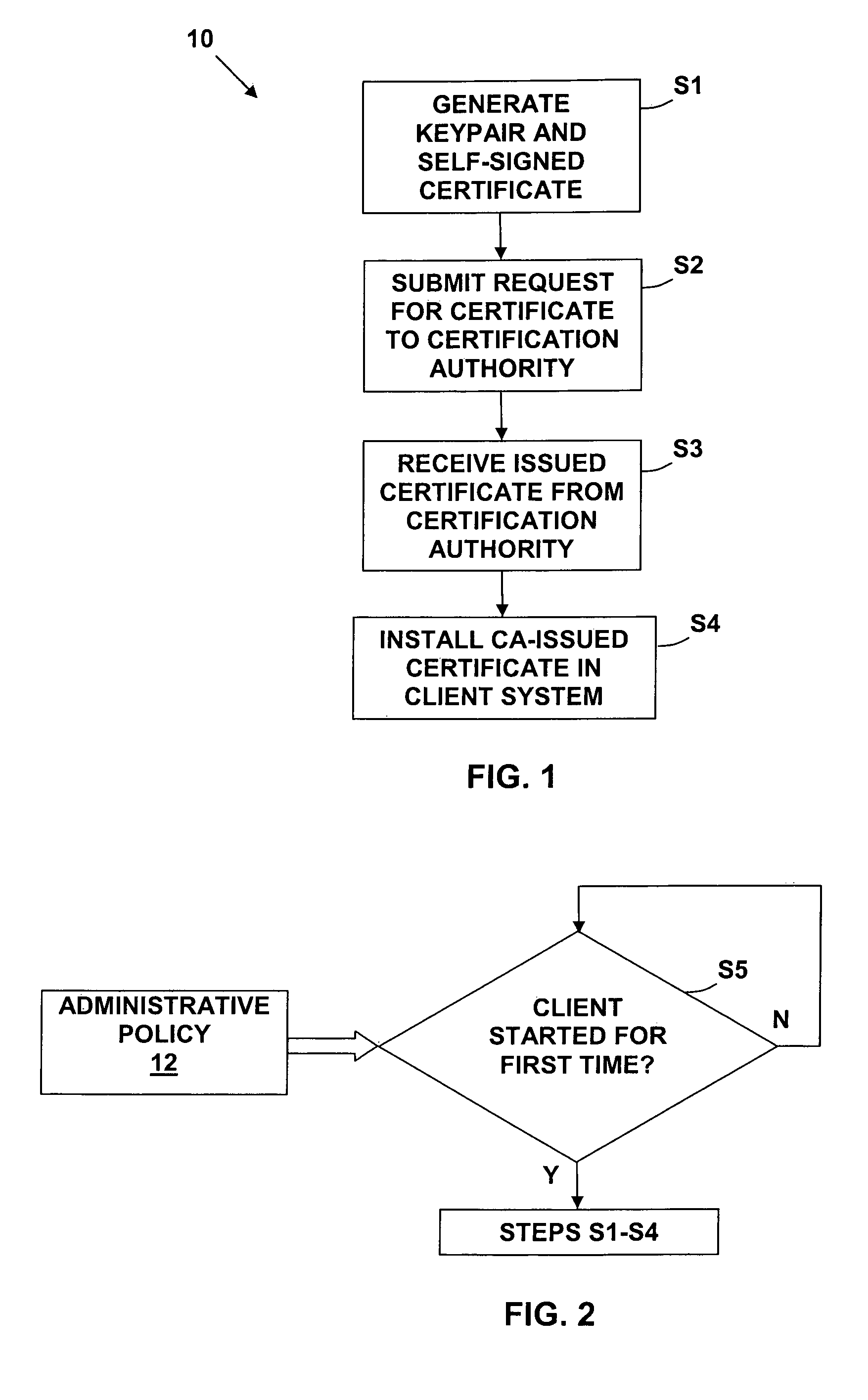
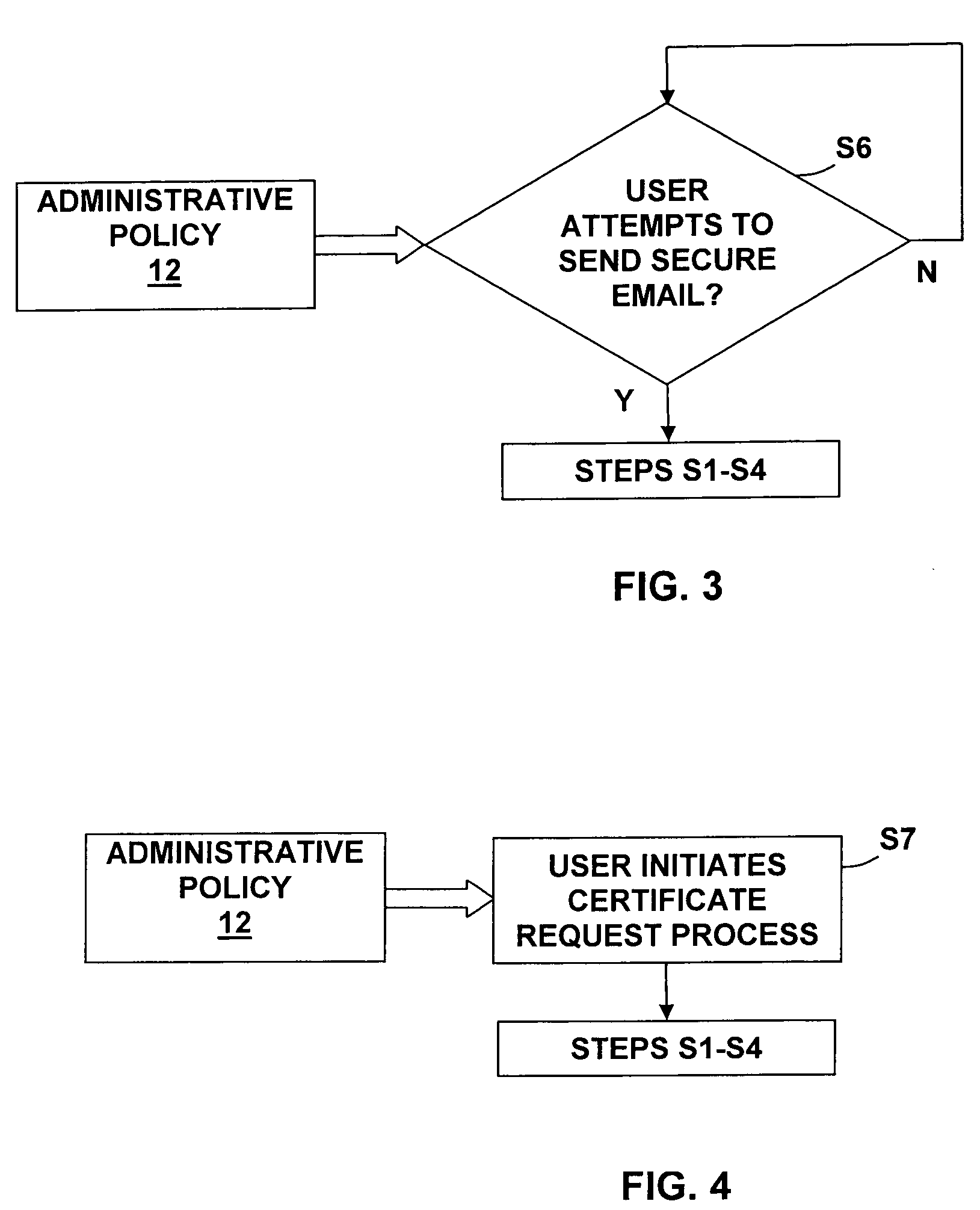
Transparent on-demand certificate provisioning for secure email
The present invention provides a method, system, and computer program product for transparent on-demand certificate provisioning for secure email. The method comprises: generating a keypair and a self-signed certificate; requesting a certificate from a certification authority; temporarily securing email using the self-signed certificate; and securing email using the requested certificate, after receipt of the requested certificate from the certification authority. The present inventions uses self-signed certificates as an initial, interim security mechanism, provides automatic submission of certificate requests and renewal requests, provides an administrative policy to specify when keypairs and self-signed certificates are generated by a user's client system, and when certificate requests are submitted, and provides automatic transition from end-user defined trust to delegated trust based upon CA-issued certificates.
Owner:DROPBOX
Seamless authentication mechanism for user processes and web services residing on common host
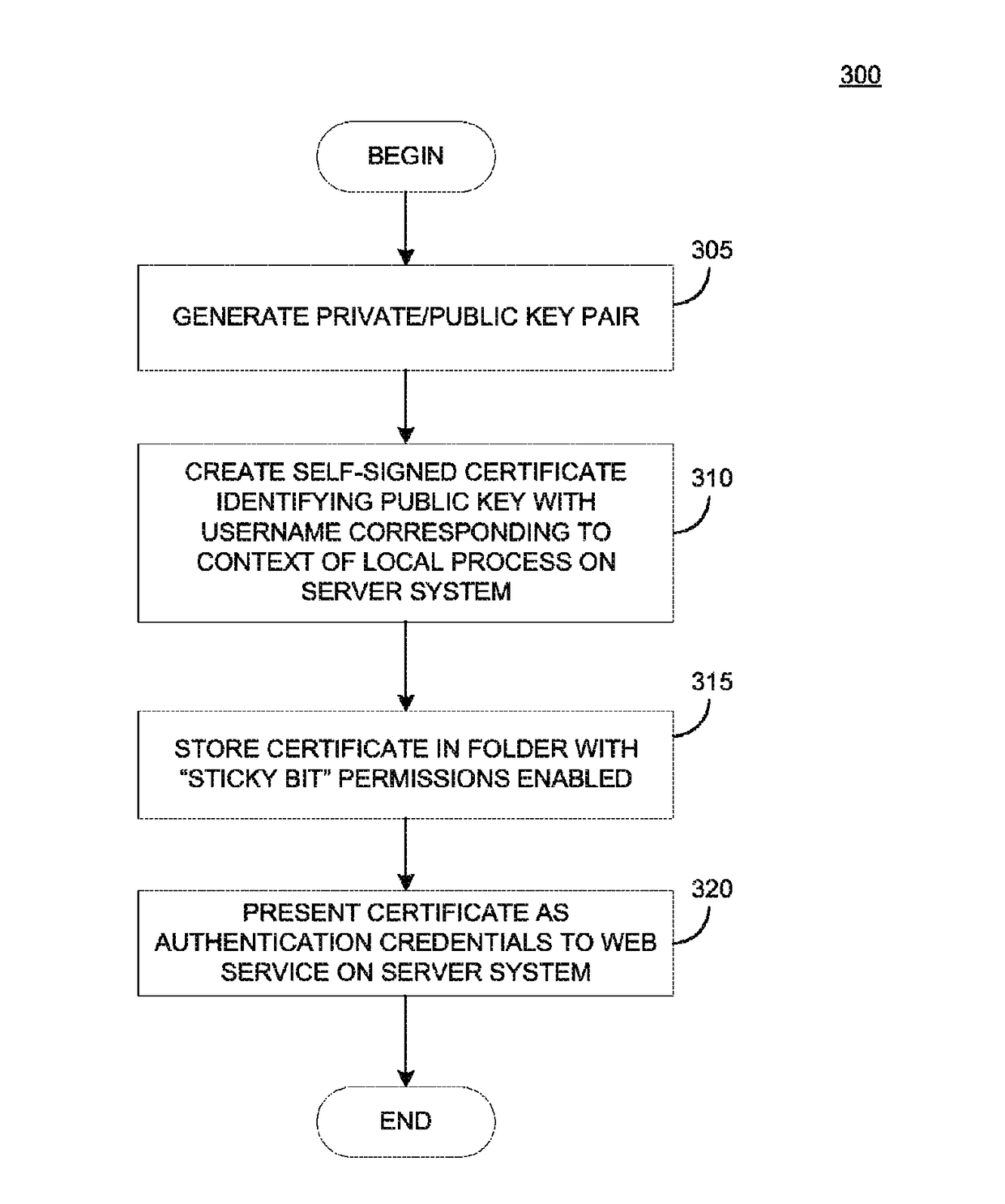
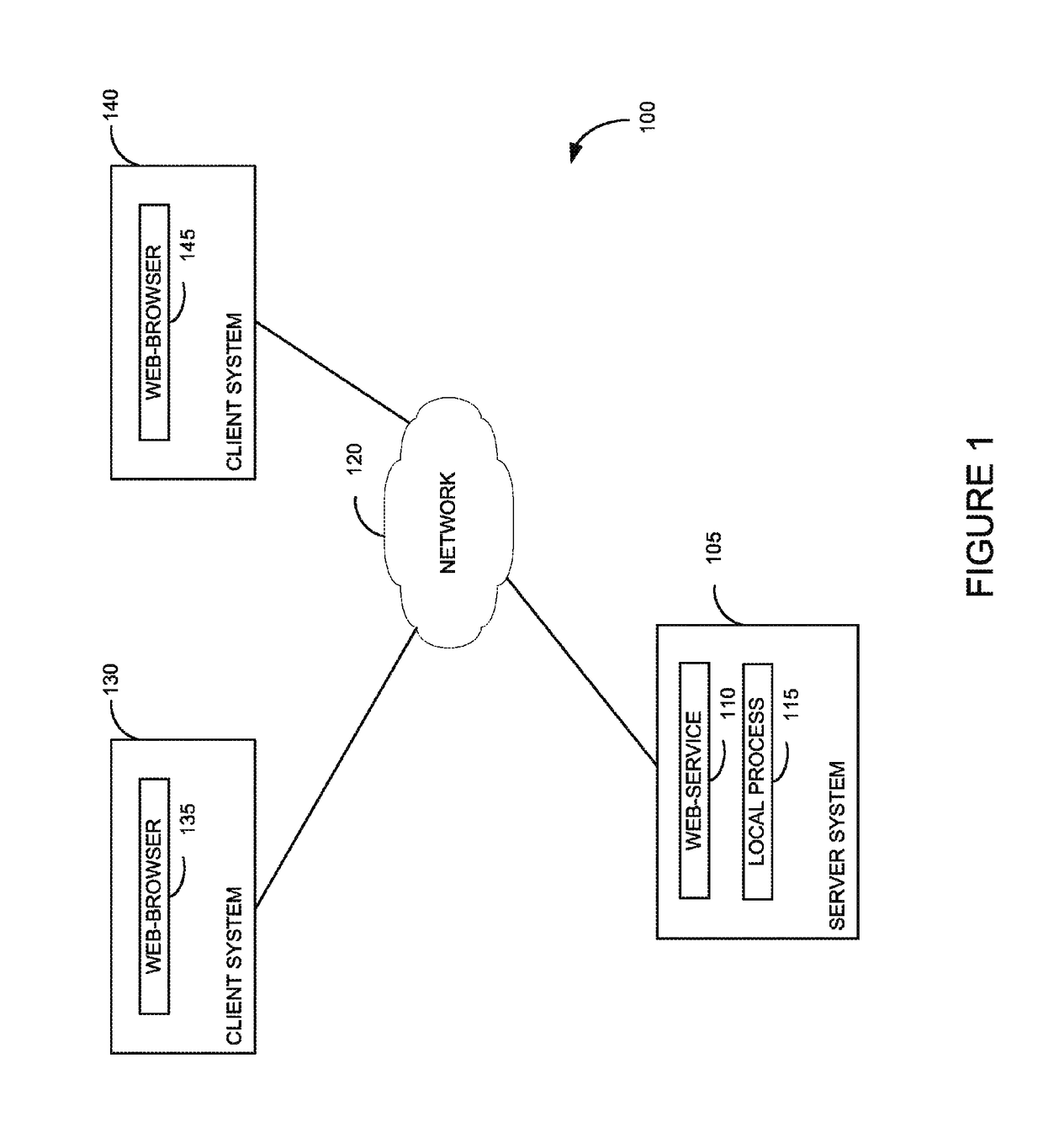
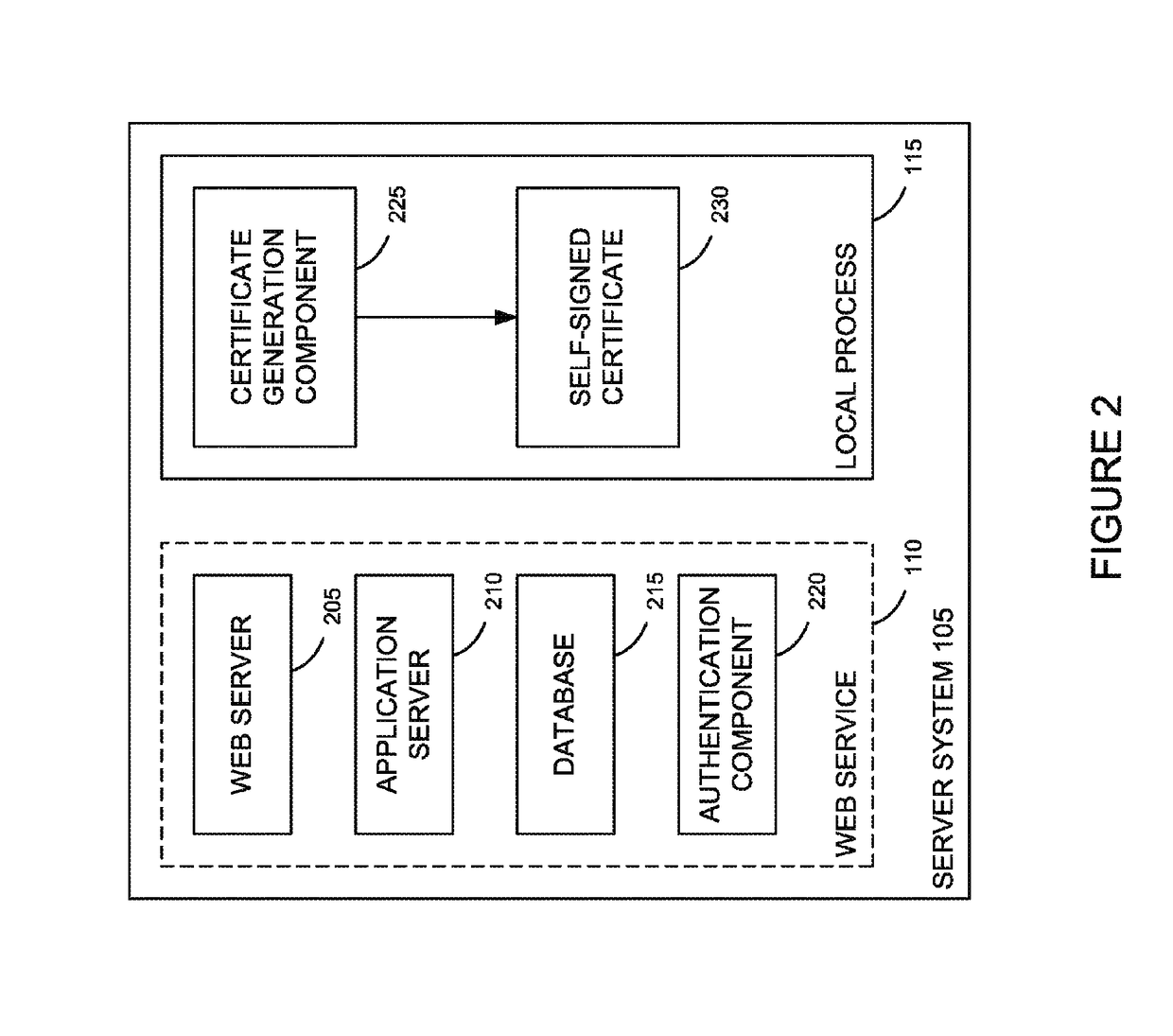
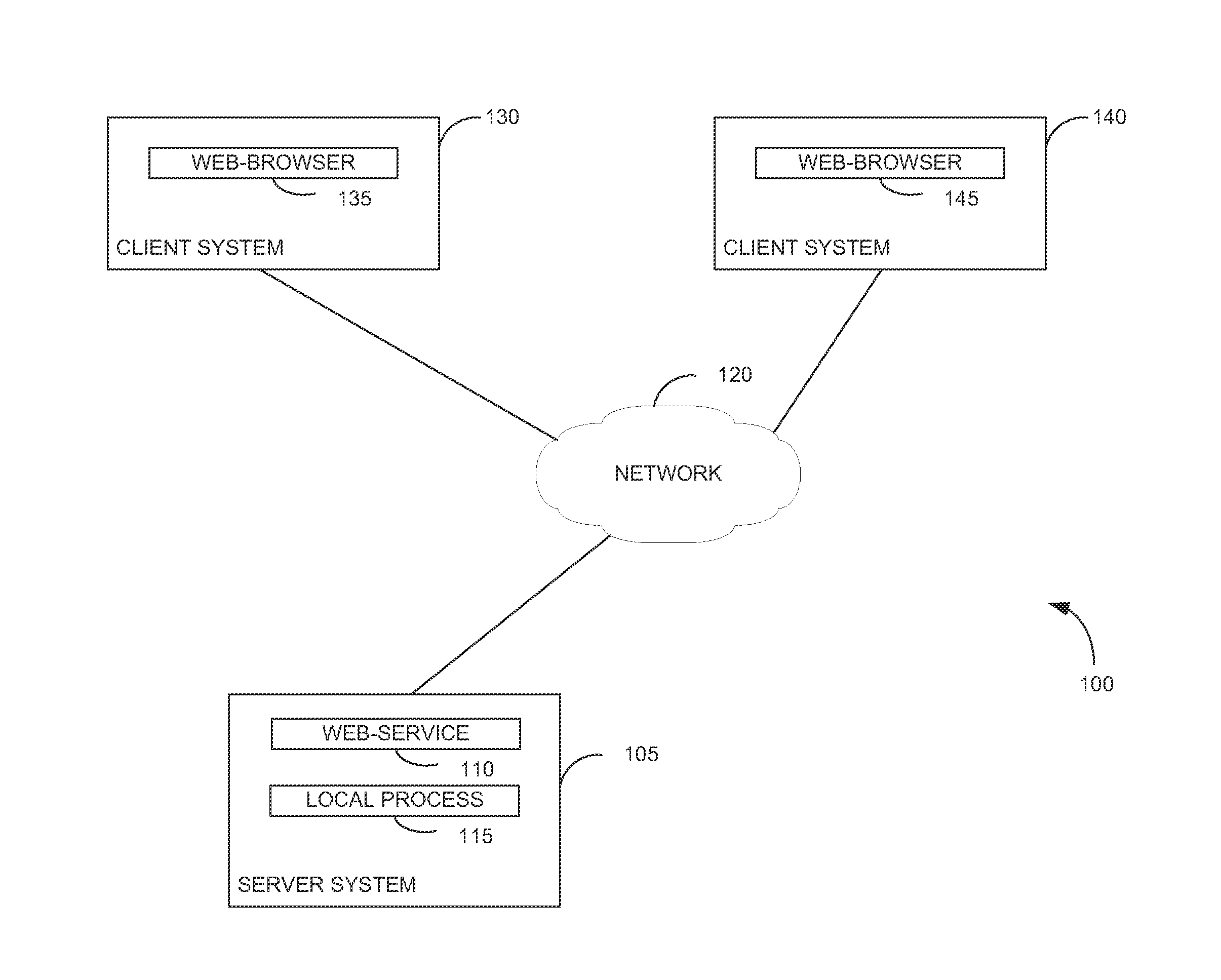
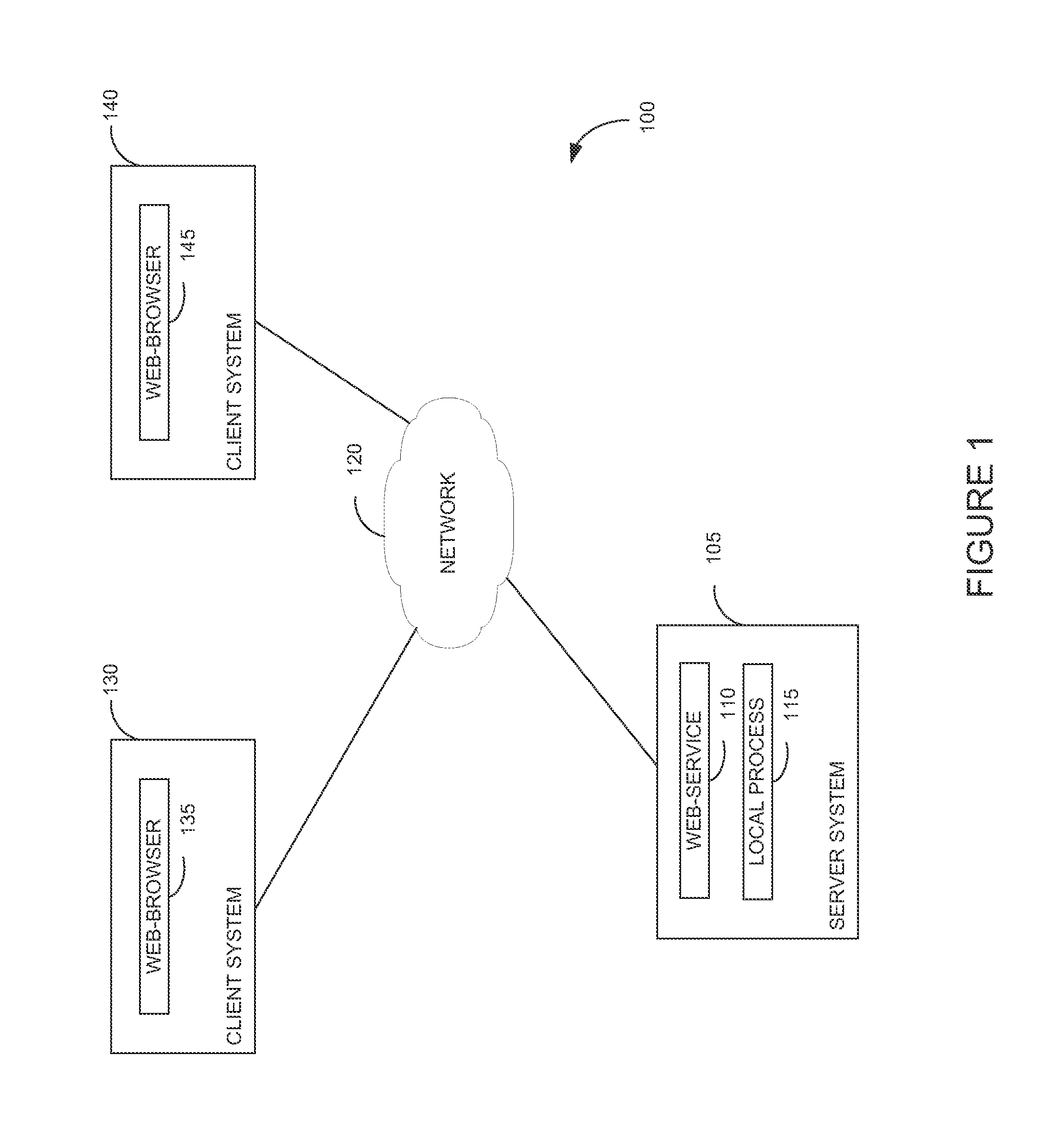
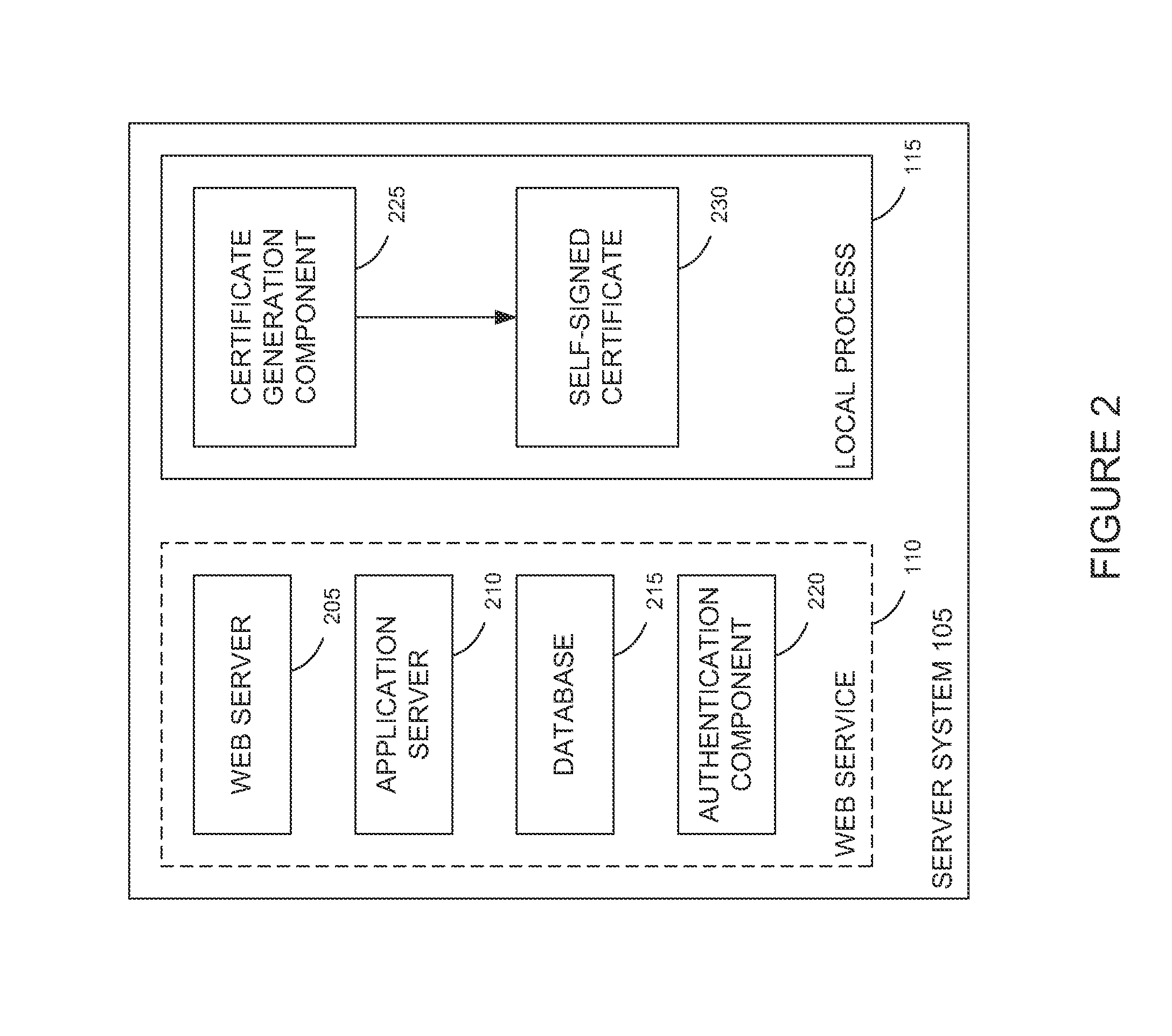
ActiveUS9742759B2User identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationData matchingSelf-signed certificate
Techniques are presented herein for authenticating local process to a web service, both executing on a common host computer server. The local process may present a self-signed certificate to the web service. In response, the web service may identify a file system directory on the first computer server containing a file storing the self-signed certificate. If the subject information identifying the owner of the process matches file system metadata indicating an owner of the file, then the web service may consider the process as being authenticated to the web service.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method of managing secure communications
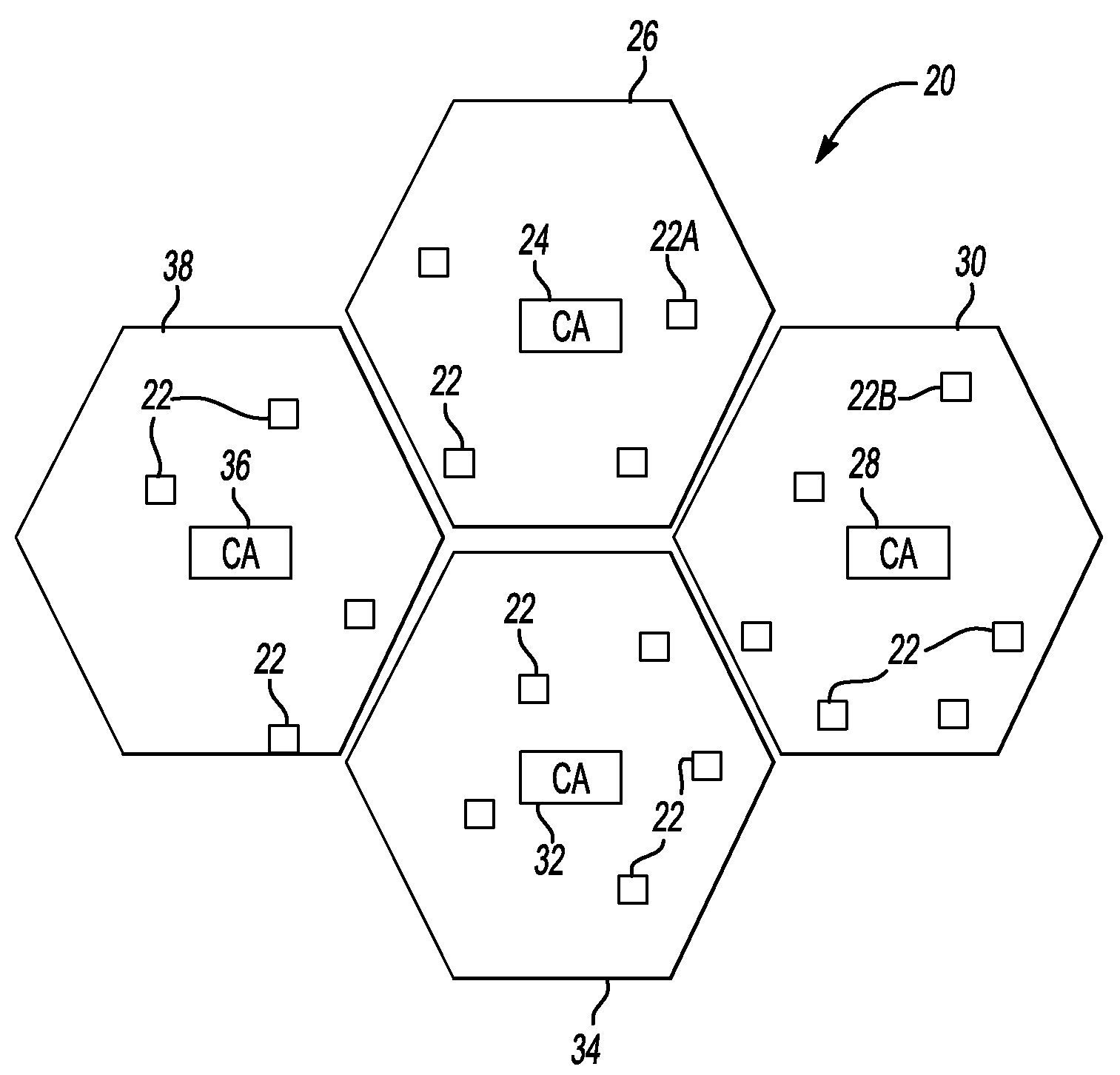
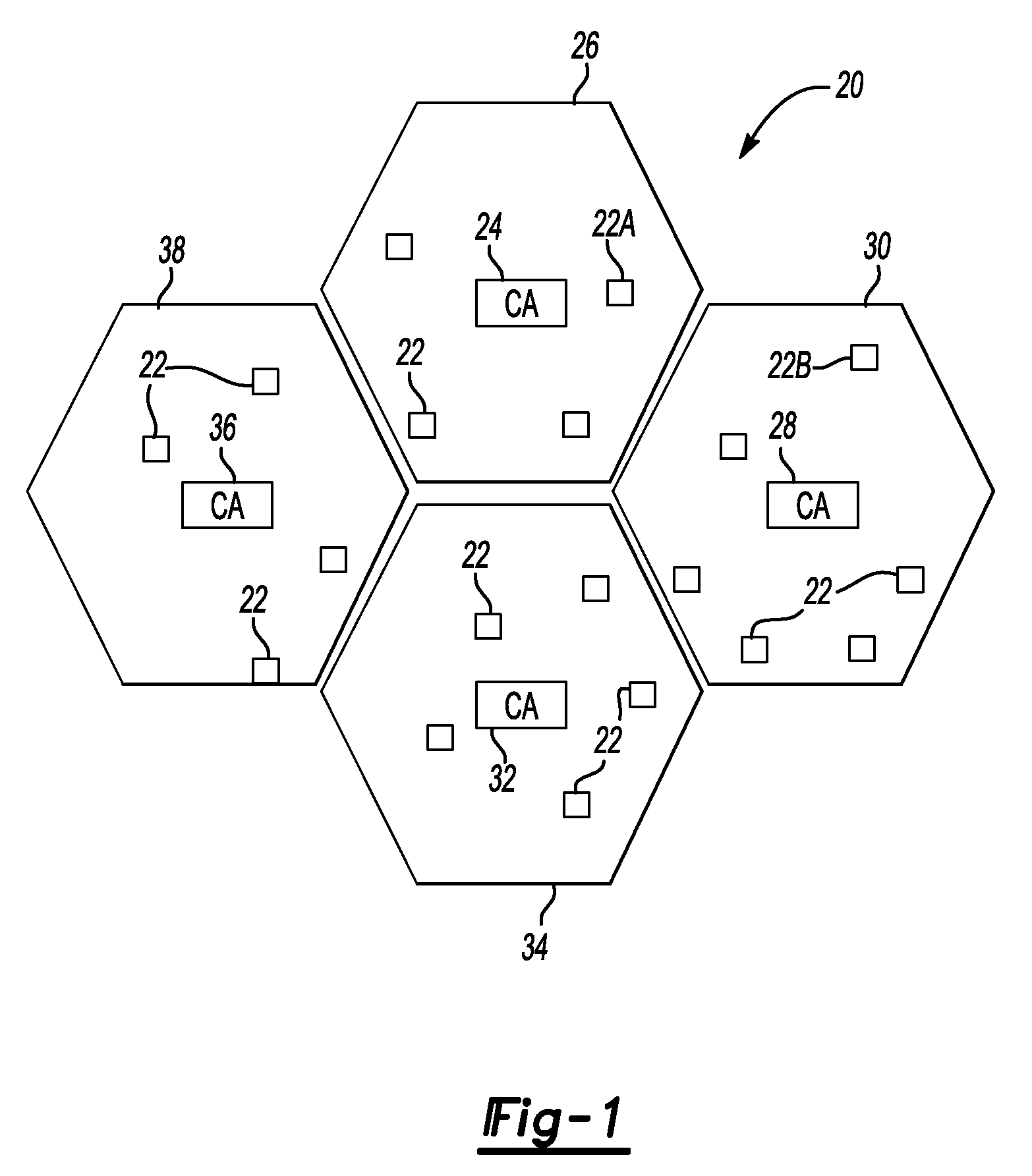
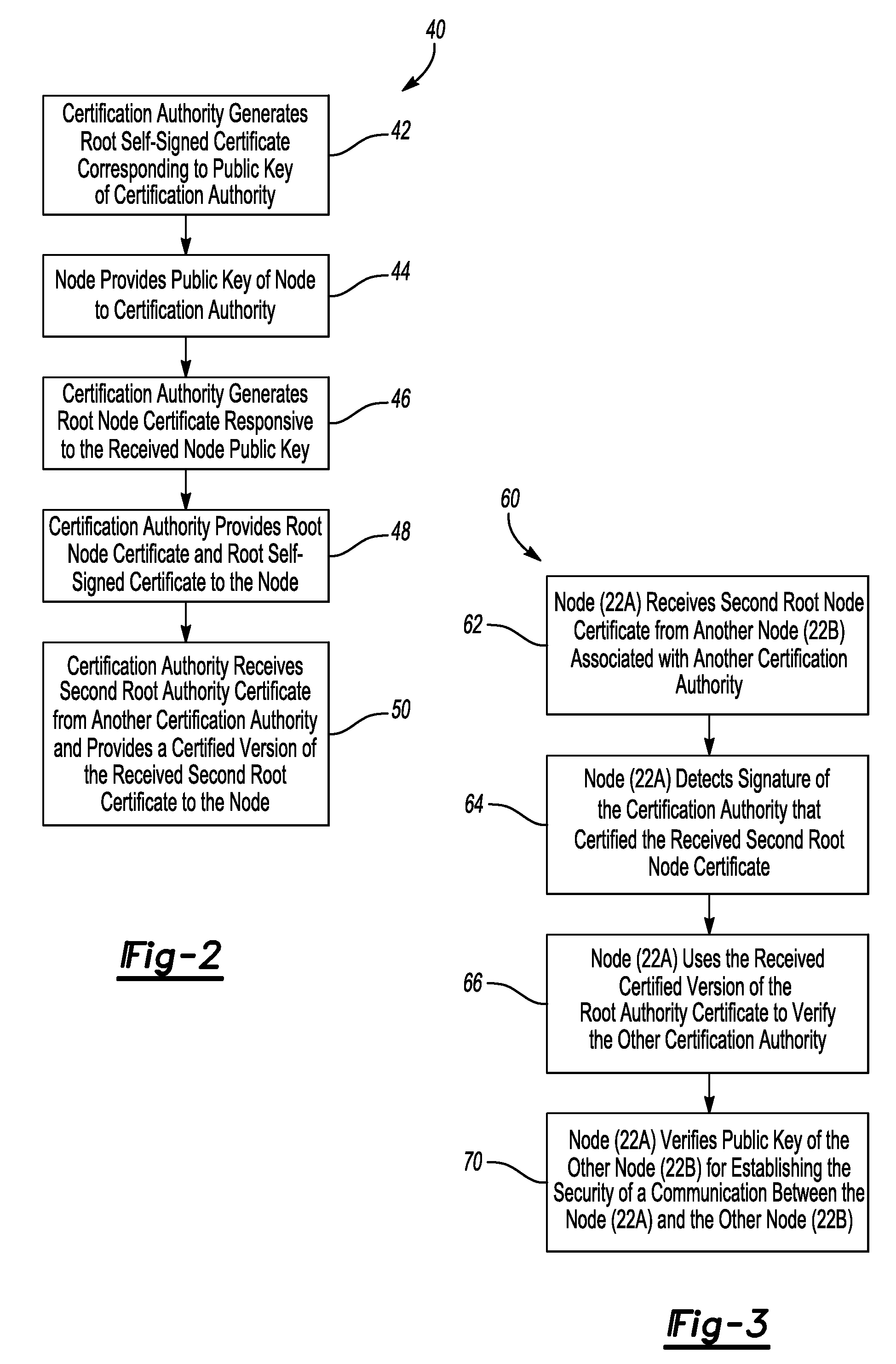
InactiveUS20100318788A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationSelf-signed certificate
An exemplary method of managing secure communications between nodes includes receiving a public key of a node associated with a certification authority. A root node certificate is provided to the node responsive to the received public key. The root node certificate indicates that the received public key belongs to the node. A root self-signed certificate corresponding to a public key of the certification authority is also provided to the node.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
User authentication method using self-signed certificate of web server, client device and electronic device including web server performing the same
ActiveUS9178870B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSelf-signed certificateWeb service
A user authentication method using a self-signed certificate of a web server includes: receiving a log-in message generated by using a public key registered to the self-signed certificate of the web server from a client device; generating a response message by using the log-in message and a secret key corresponding to the public key; transmitting the generated response message to the client device; receiving a verification value from the client device via a secure socket layer (SSL) channel connected by using the self-signed certificate of the web server from the client device when a reliability of the response message is verified at the client device; verifying a reliability of the log-in message by using the received verification value; and confirming completion of user authentication if the reliability of the log-in message is verified.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Identity calibration method and related device
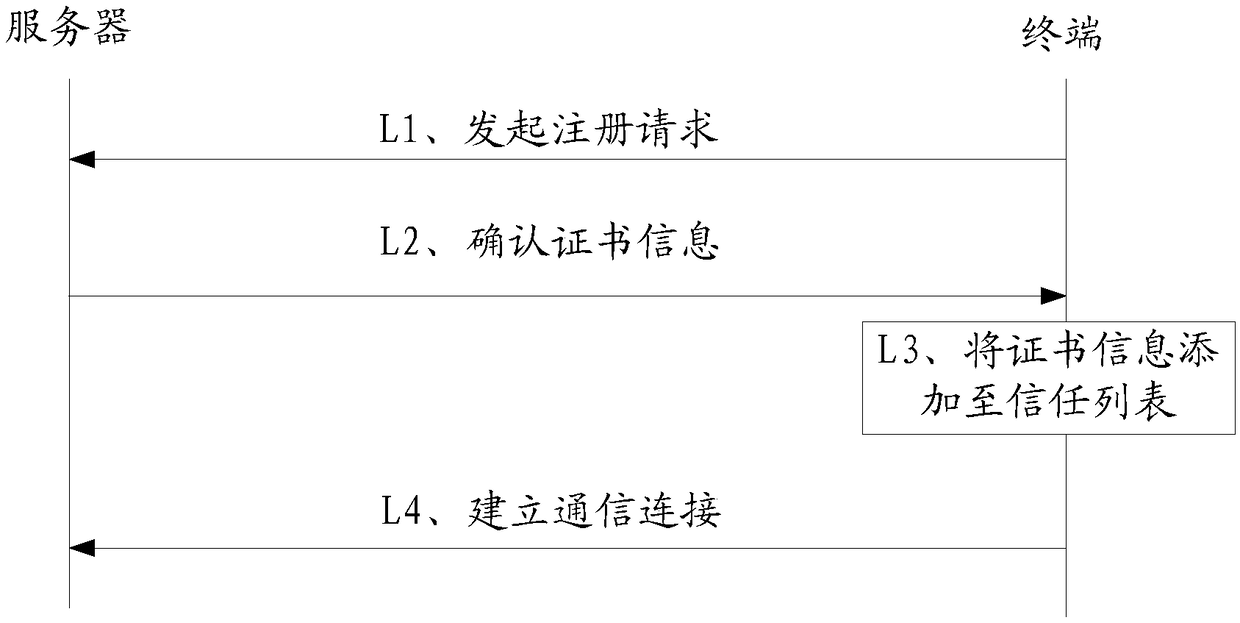
InactiveCN109194631AImprove securityReduce risk of leakageUser identity/authority verificationSelf-signed certificateServer authentication
The embodiment of the invention discloses an identity calibration method. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a first certificate of a terminal by a server, and performing identity calibration for the first certificate, wherein the first certificate is a self-signature certificate of the terminal; when the identity calibration for the first certificate is failed by the server, sending certificate information to the terminal by the server; generating a second certificate by the server; establishing communication connection between the second certificate and the terminal by the server.The embodiment of the invention further discloses an identity calibration device. The embodiment of the invention provides the method, when the terminal employs the self-signature certificate to perform identity calibration, a new signature certificate passing the authentication of the server is sent to the terminal, and the terminal and the server can use the new signature certificate for communication so as to improve the safety of the identity calibration and reduce the risk of information leakage.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Seamless authentication mechanism for user processes and web services residing on common host
ActiveUS20150350195A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsSelf-signed certificateFile system
Techniques are presented herein for authenticating local process to a web service, both executing on a common host computer server. The local process may present a self-signed certificate to the web service. In response, the web service may identify a file system directory on the first computer server containing a file storing the self-signed certificate. If the subject information identifying the owner of the process matches file system metadata indicating an owner of the file, then the web service may consider the process as being authenticated to the web service.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Device and method certificate generation
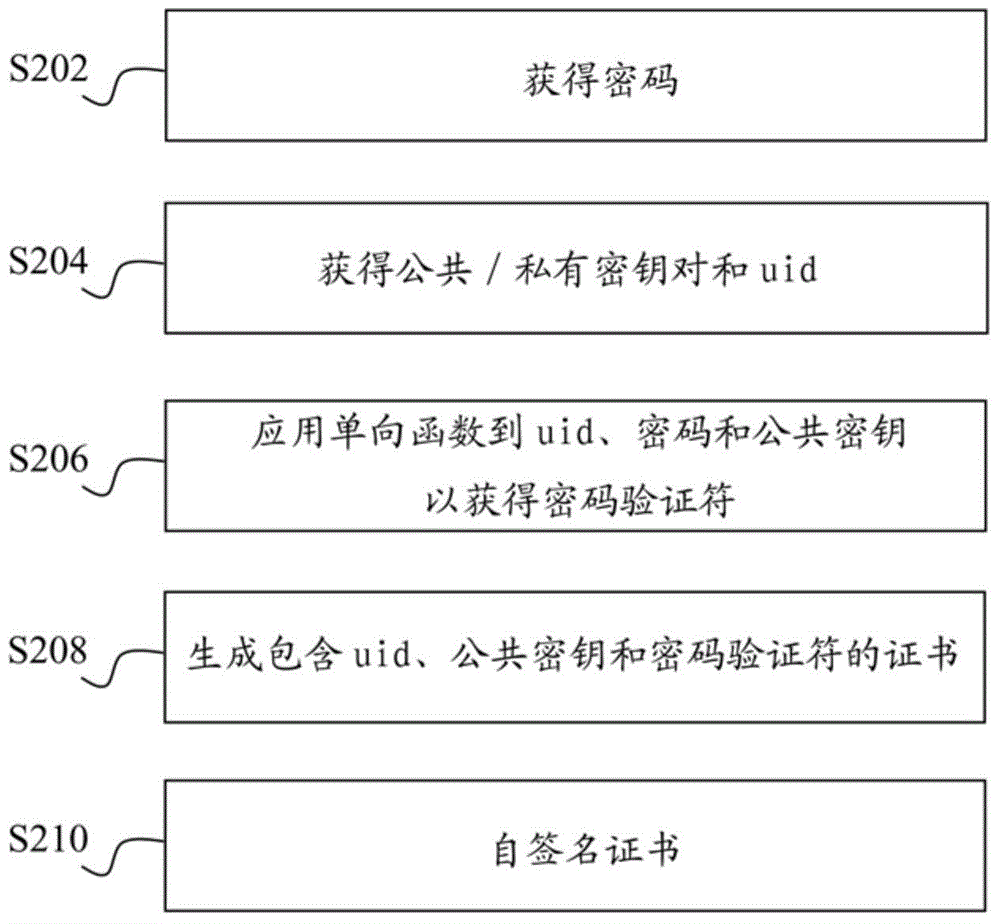
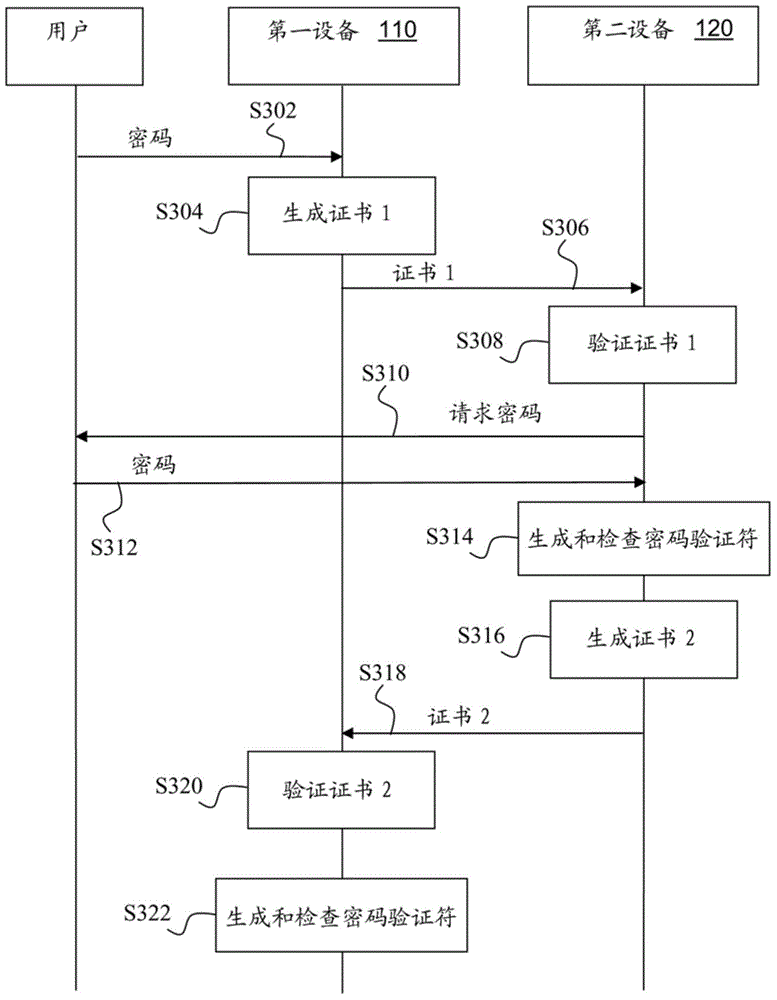
InactiveCN104821933AUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationSelf-signed certificatePassword
A device (110, 120) receives (S202) a password from a user, obtains (S204) a public key for a cryptographic algorithm for the device, obtains (S206) a password verifier by applying a one-way function to a combination of a unique identifier, the password and the public key, generates (S208) the certificate comprising the unique identifier, the public key and the password verifier, signs (S21 0) the certificate using a private key corresponding to the public key thereby obtaining a self-signed certificate, and outputs the self-signed certificate. Also provided is the device.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
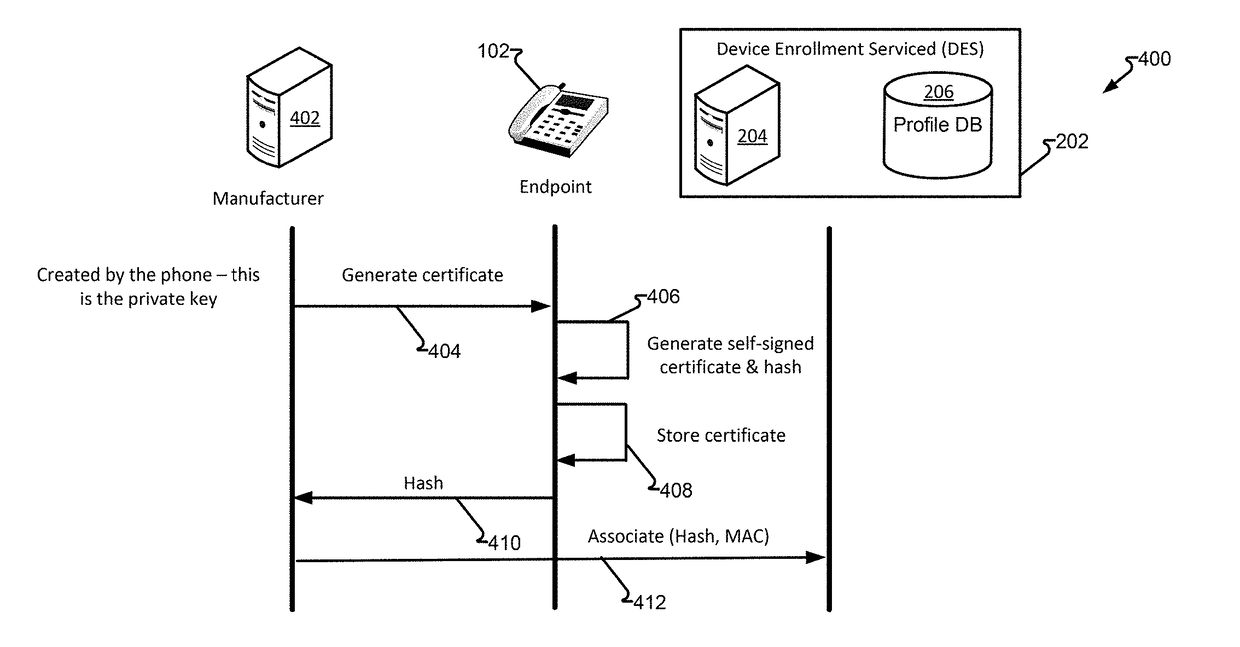
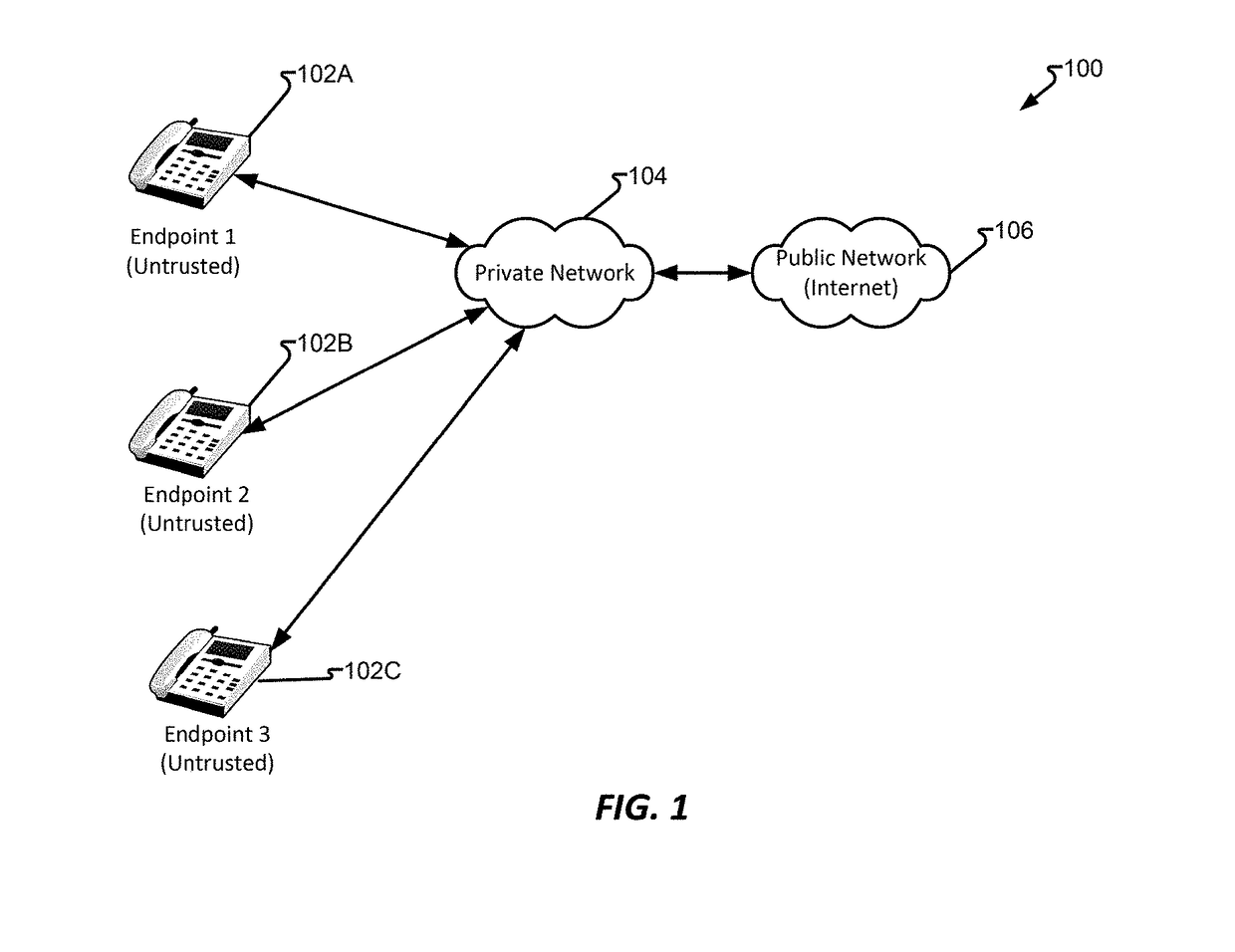
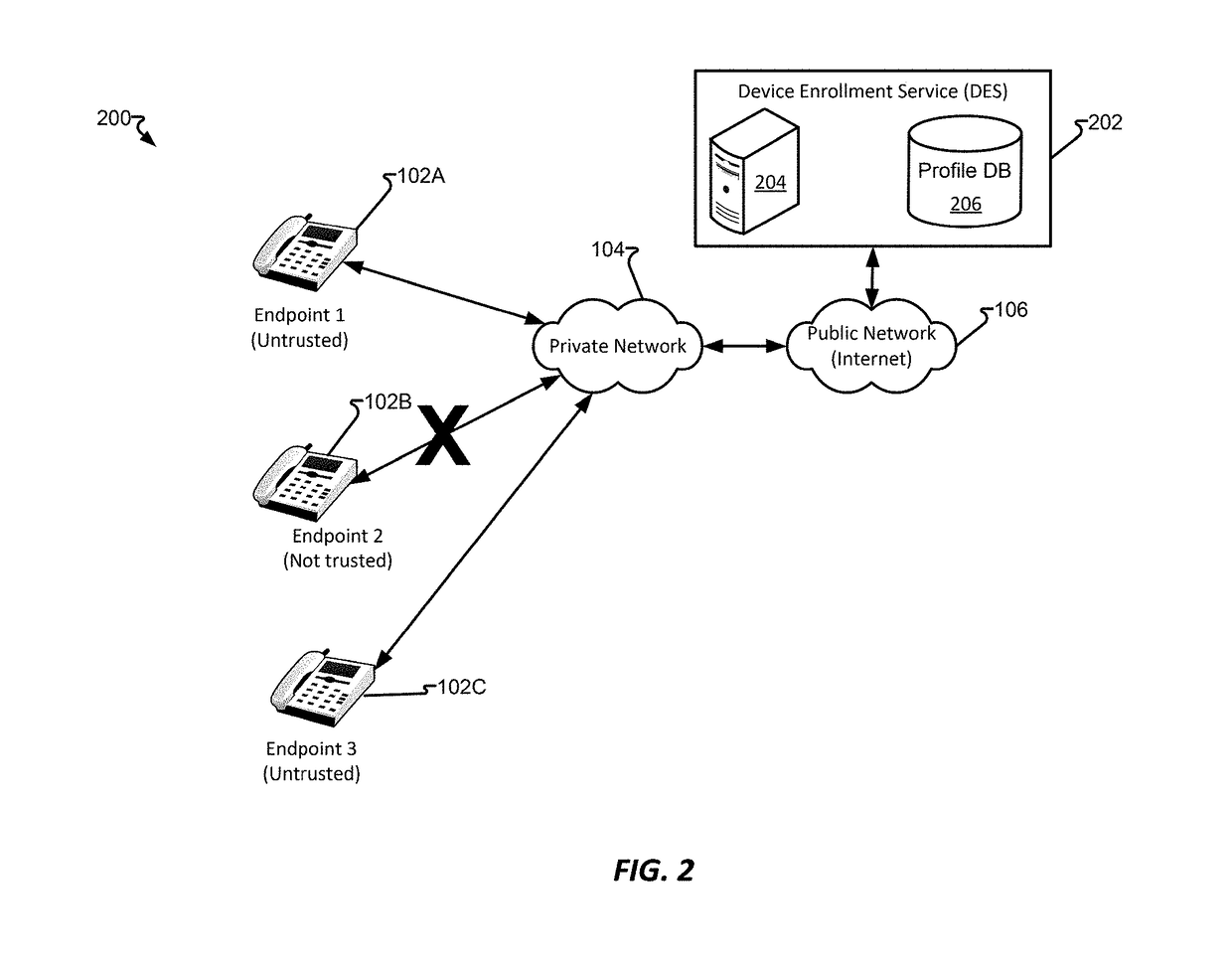
Device enrollment service system and method
InactiveUS20180288035A1Reducing and eliminating and potential for misuseAvoid the needDigital data information retrievalTransmissionSelf-signed certificatePrivate network
Endpoints, such as Session Initial Protocol enabled telephones, are capable of being public network (e.g., Internet) devices and, as such, require security measures to protect the endpoints and components on a private network they may be attached to, such as a call center. By providing a self-signed certificate into an endpoint with hardcoded certificate authorities (CAs) that enable the phone to call a trusted location, namely a Device Enrollment Service (DES) having a verifiable record of the endpoint that, on endpoint startup, authentication actions may be performed and, is successful, the endpoint is permitted to “point to” other services that may allow the endpoint to be redirected or otherwise use a particular private network, such as that of a customer.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Security authentication method for realizing multi-cloud management and control across public network
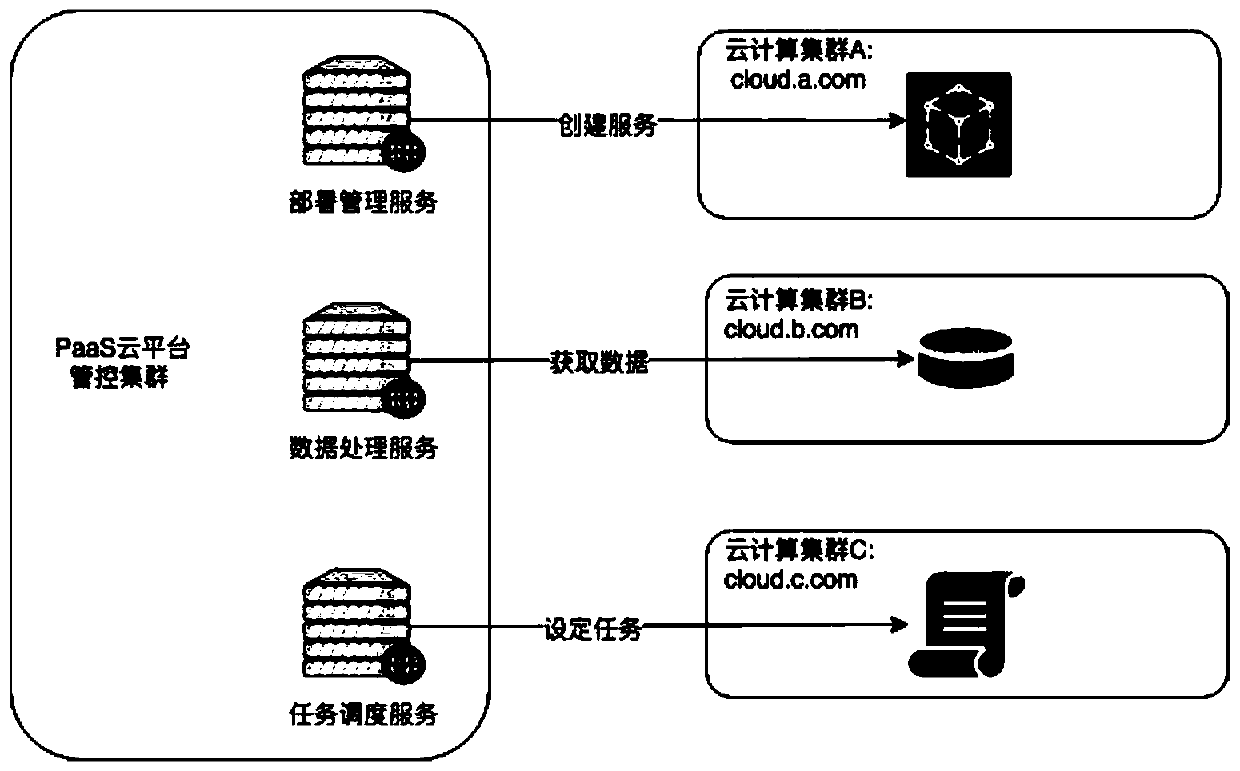
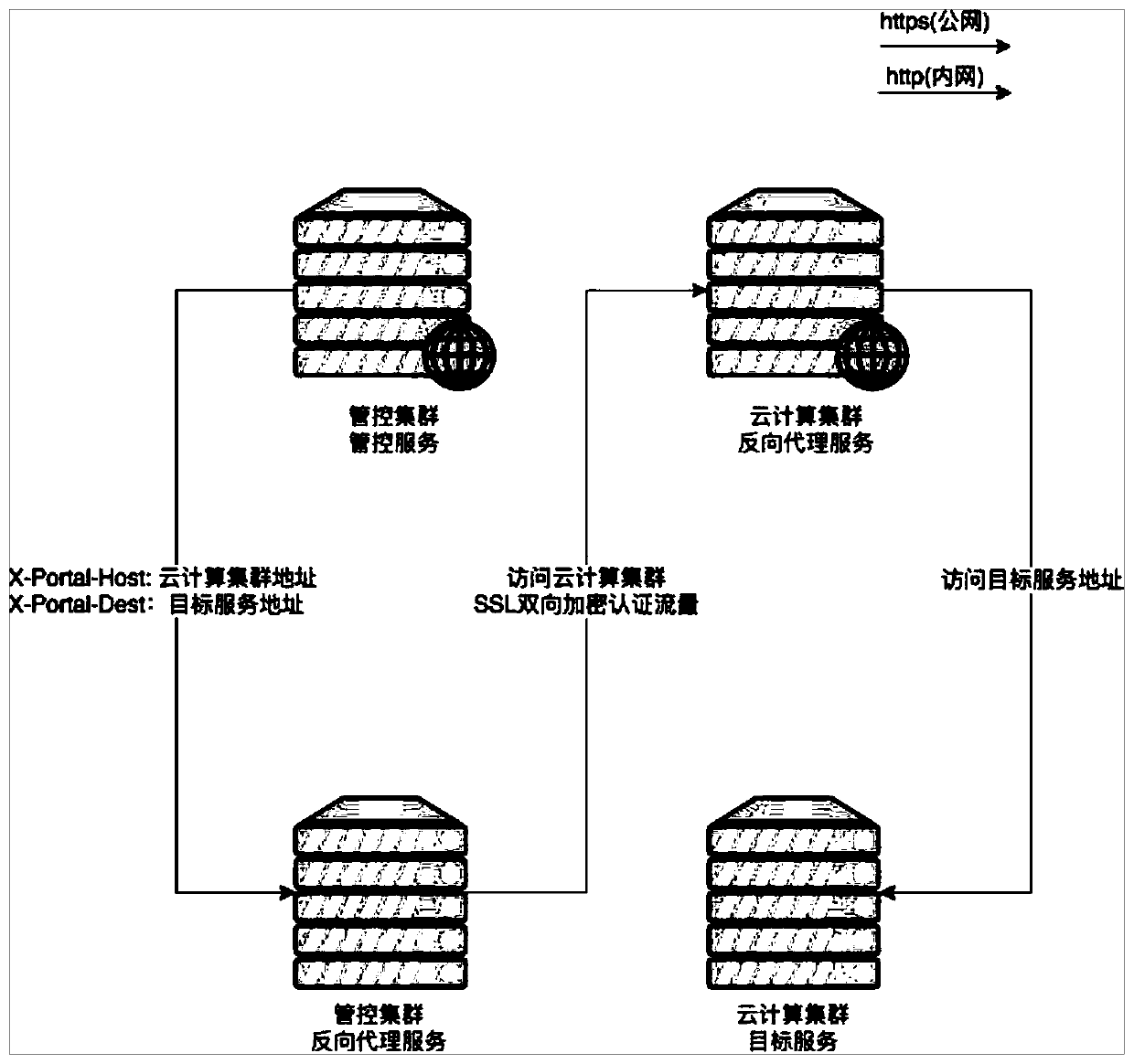
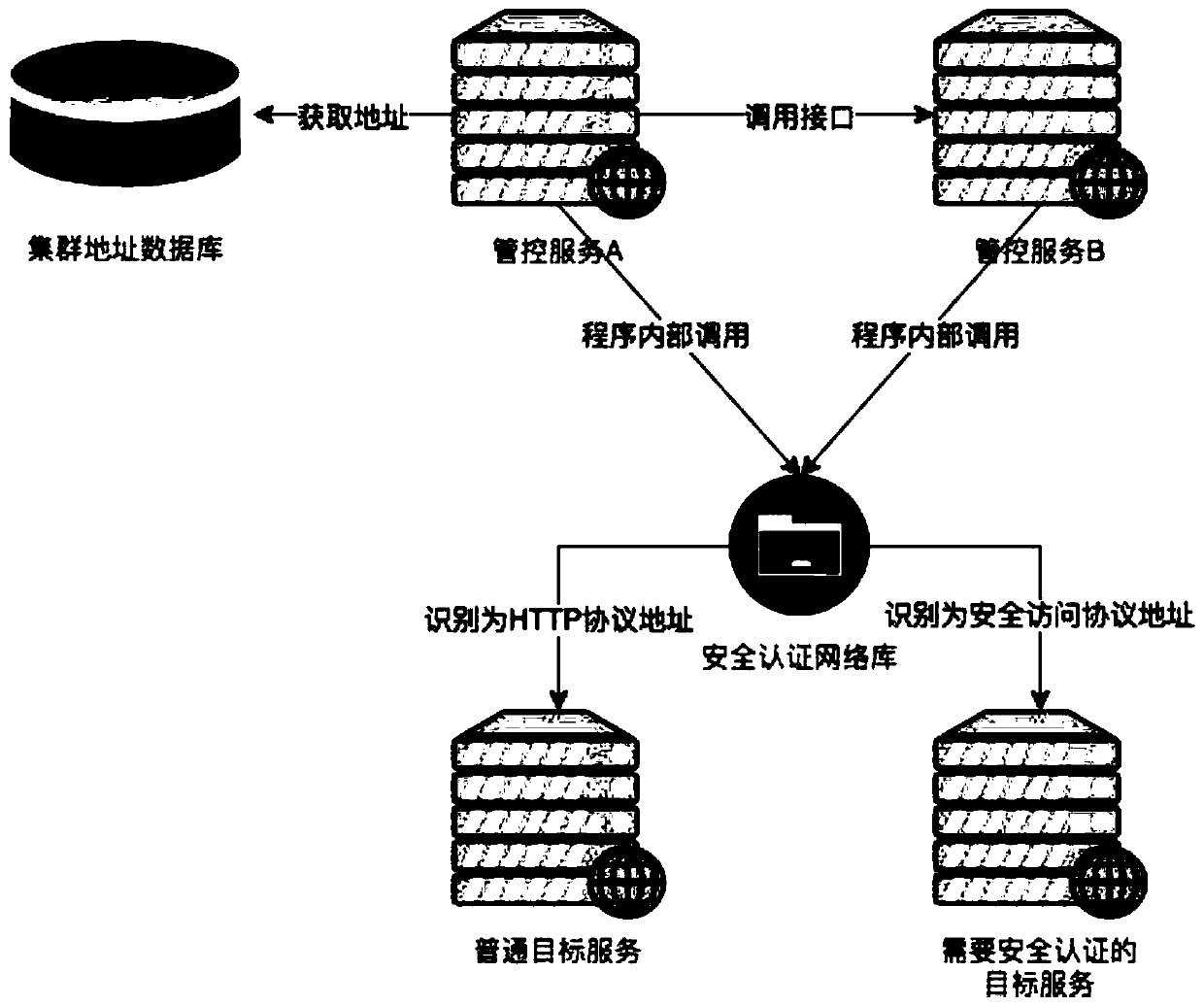
ActiveCN111147526AImplement security authenticationReduce risk of leakageTransmissionSelf-signed certificateReverse proxy
The invention discloses a security authentication method for realizing multi-cloud management and control across a public network. The method specifically comprises the following steps: a bidirectional authentication network channel between a management and control cluster and a cloud computing cluster is established through a group of reverse proxy servers; in the management and control cluster,a management and control service directly uses an HTTP protocol to access a reverse proxy service; after the reverse proxy server of the management and control cluster receives the request, a self-signed SSL client certificate is used to access the reverse proxy server of the cloud computing cluster through HTTPS to complete authentication of the management and control cluster; meanwhile, the cloud computing cluster returns the self-signed server certificate, and the management and control cluster also uses the same self-signed CA certificate to complete authentication of the cloud computing cluster; and after the bidirectional authentication is completed, the HTTPS protocol is uploaded by the cloud computing cluster reverse proxy service, and a target service is accessed by using the HTTPprotocol to realize security management and control. According to the method, manpower and financial resources can be saved, the method is safer, meanwhile, the control service can realize control bydirectly using the HTTP protocol to access the reverse proxy service, and the control is flexible and convenient.
Owner:杭州端点网络科技有限公司
User authentication with self-signed certificate and identity verification
ActiveUS10756908B1Recovery lossEasily migrate trustKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSelf-signed certificateUser device
In embodiments, an authentication server interfaces between a user device with a self-signed certificate and a verifying computer that accepts a user name and password. The user device generates a self-signed certificate signed by a private key on the user device. The self-signed certificate is transmitted to a verifying party computer over a network. The verifying party stores the self-signed certificate with user identification data, including at least one of a user name, user address, user email, user phone number, user tax identification (ID), user social security number and user financial account number. In subsequent communications, the verifying party receives a certificate chain including the self-signed certificate, and matches that with the user identification data stored in a database.
Owner:BEYOND IDENTITY INC
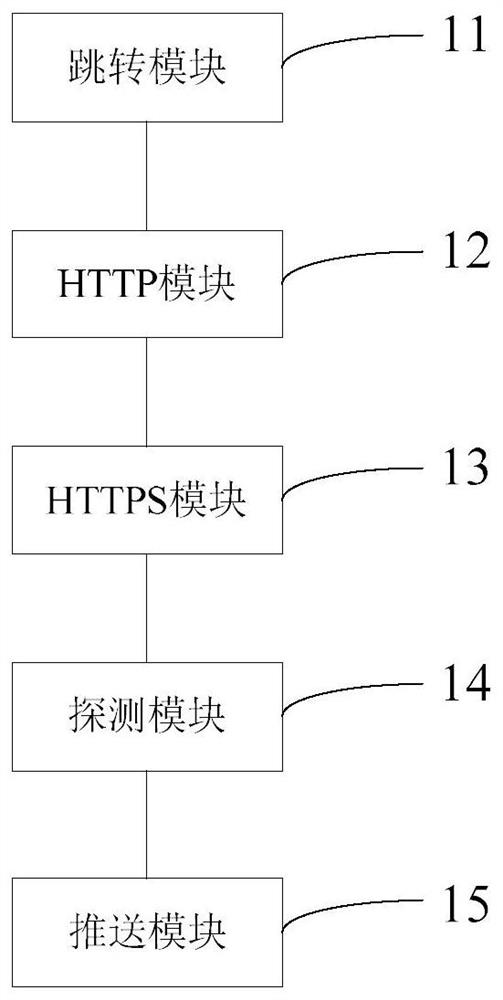
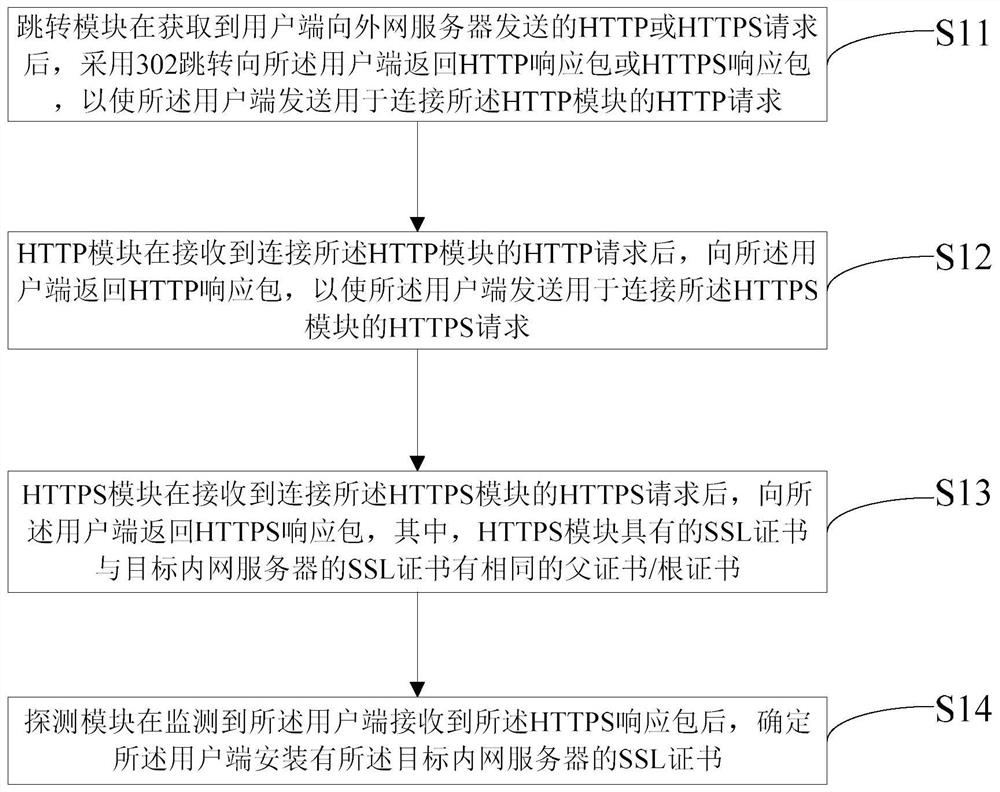
Self-signed ssl certificate processing system and method
Owner:BEIJING QIANXIN TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com