Patents
Literature
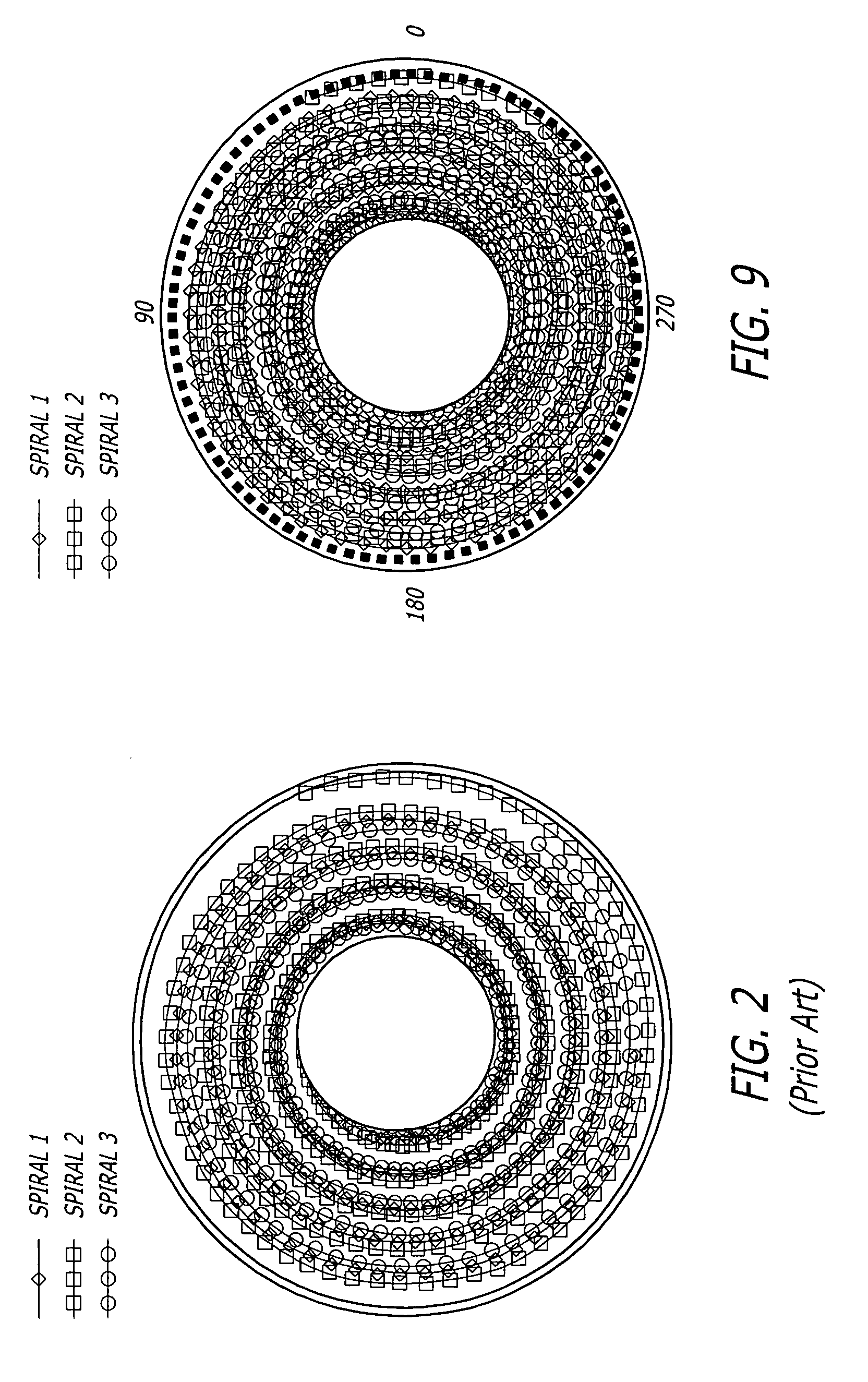
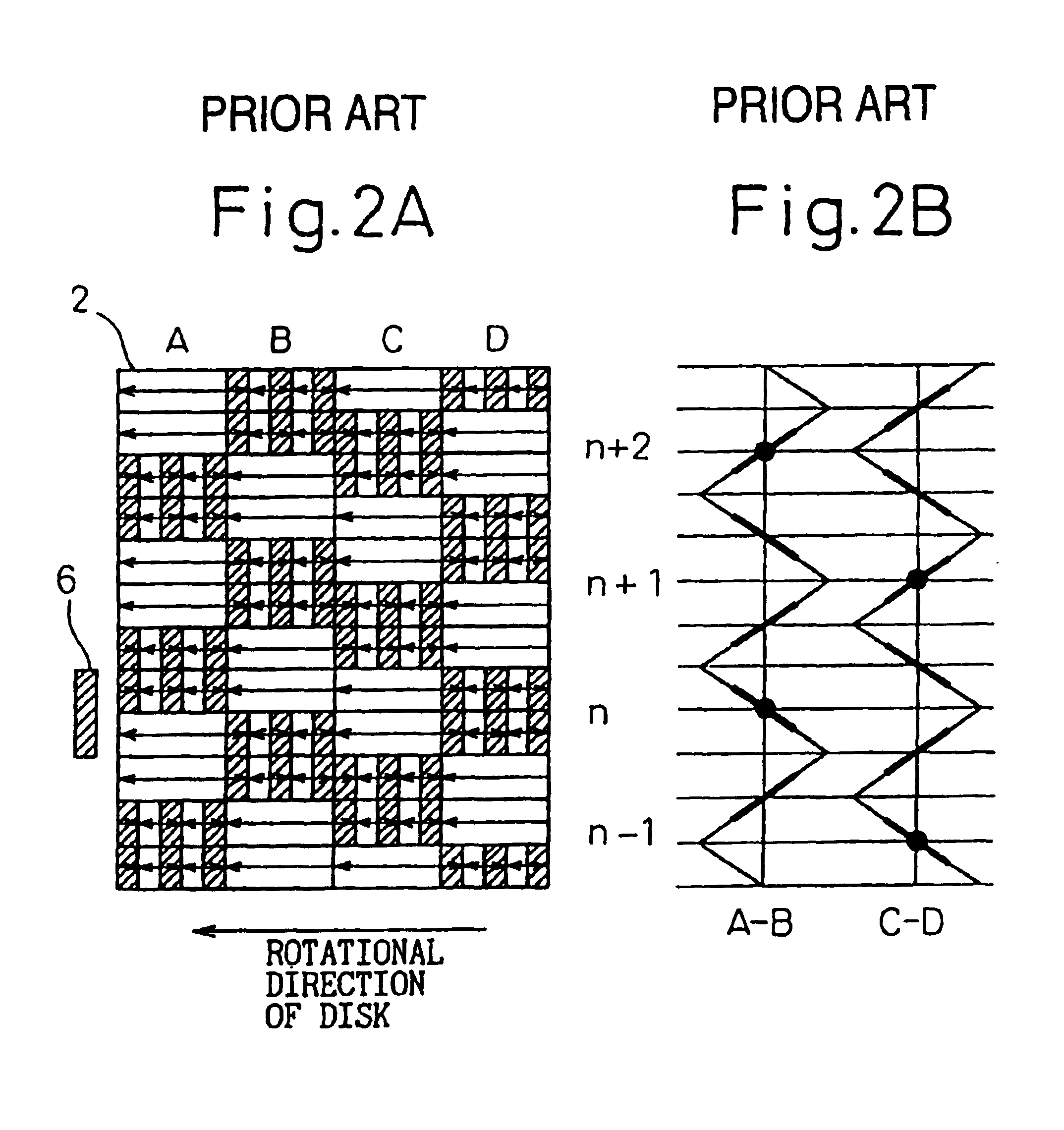
90 results about "Servo track writing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
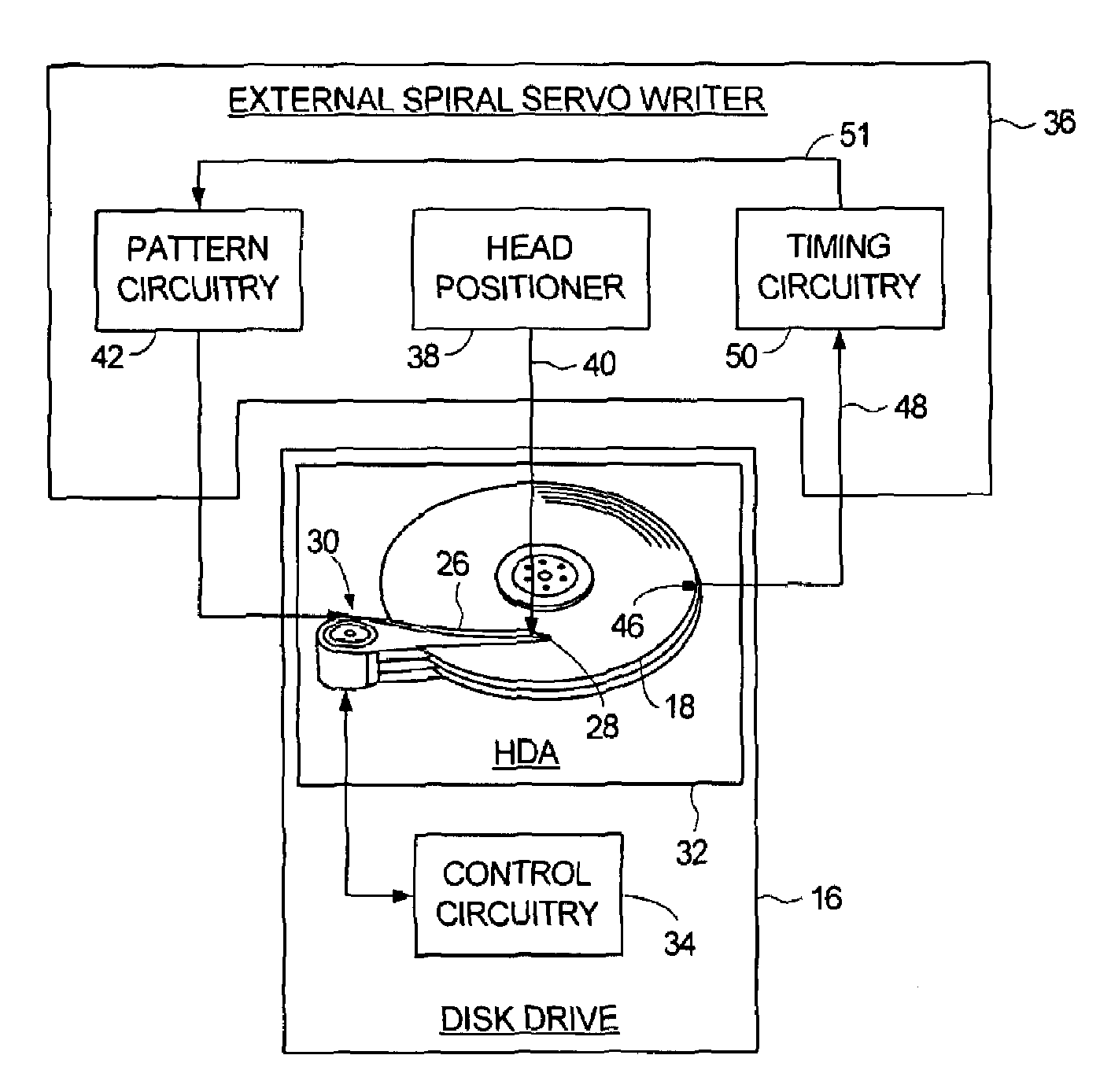
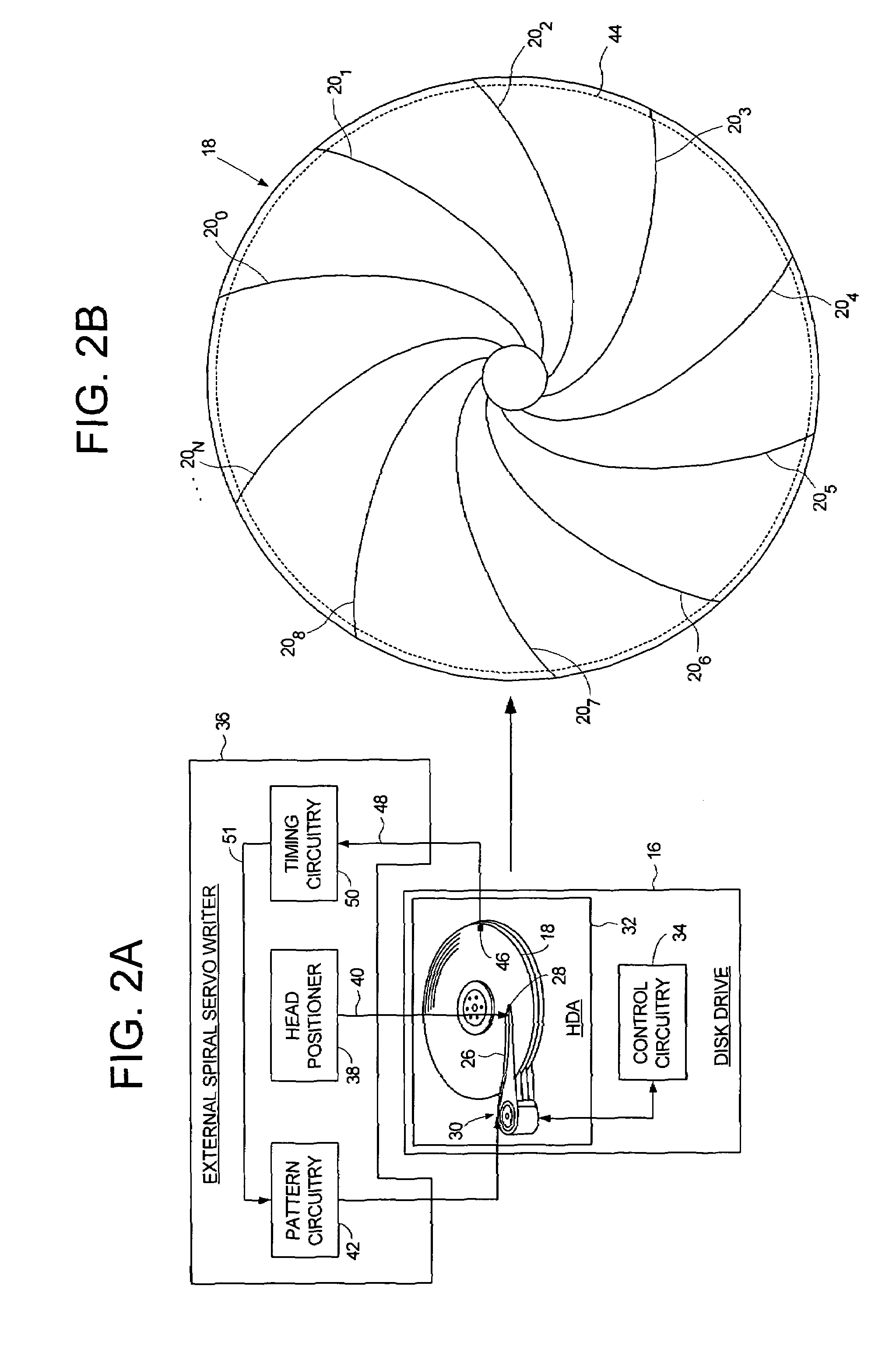
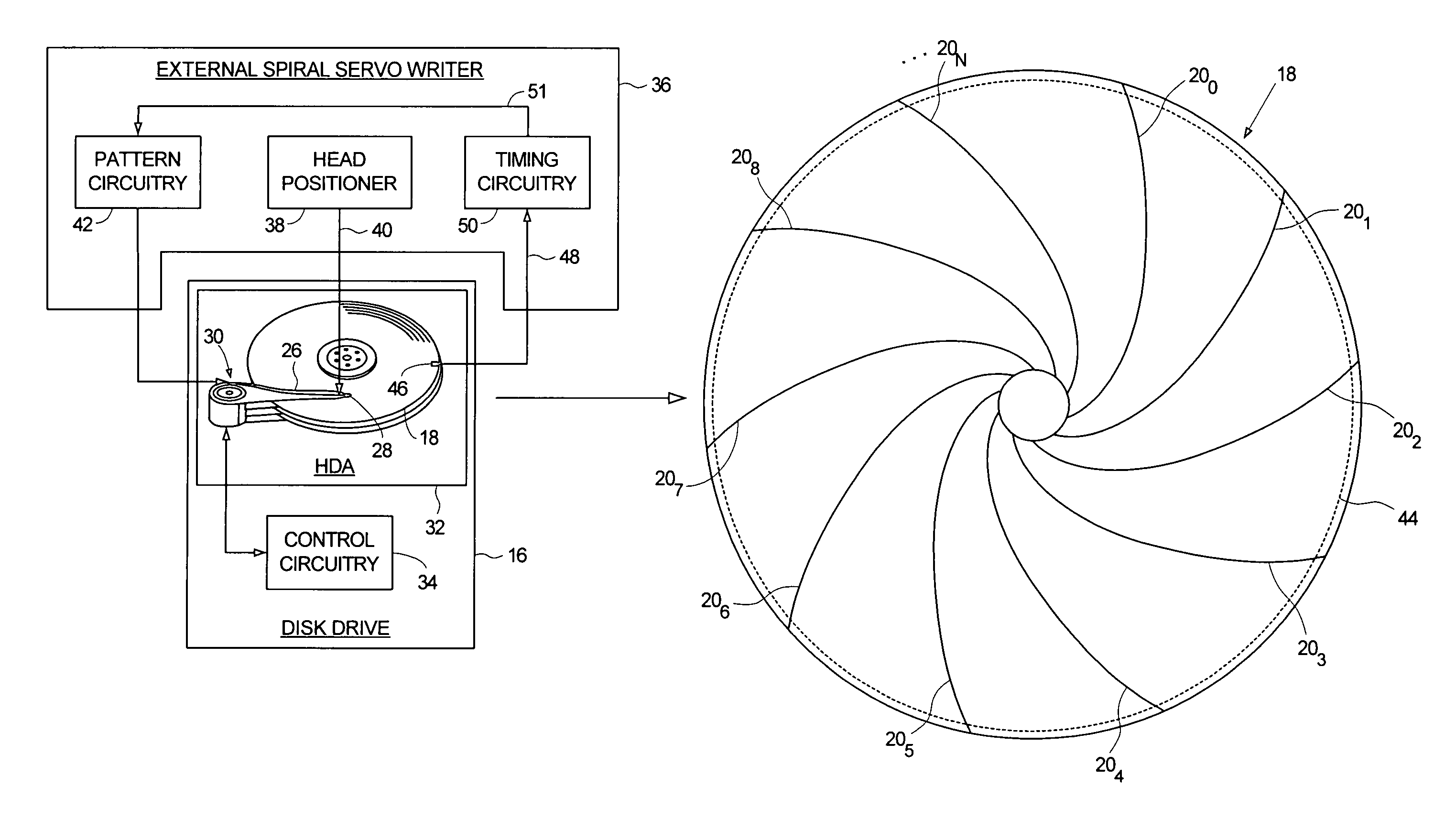
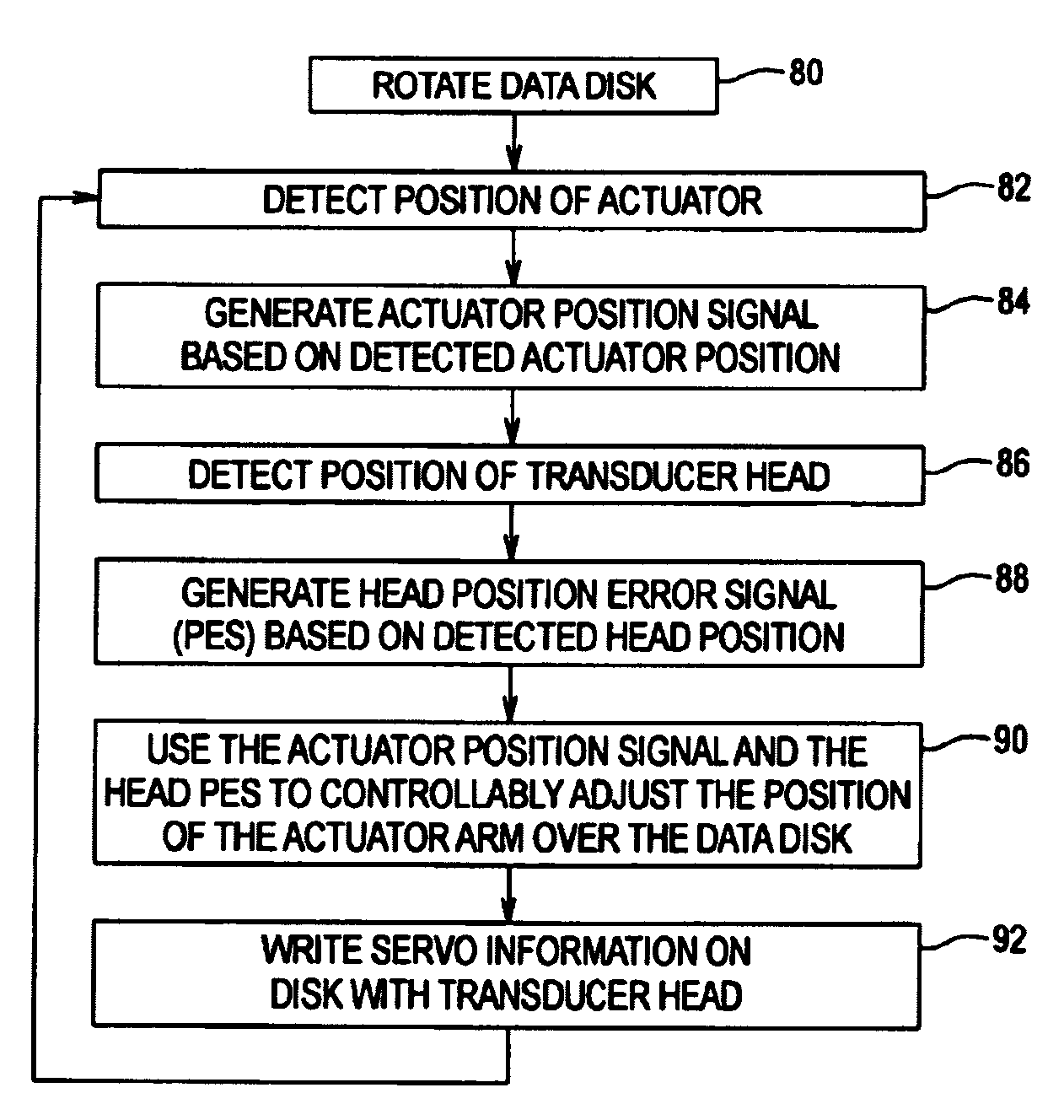
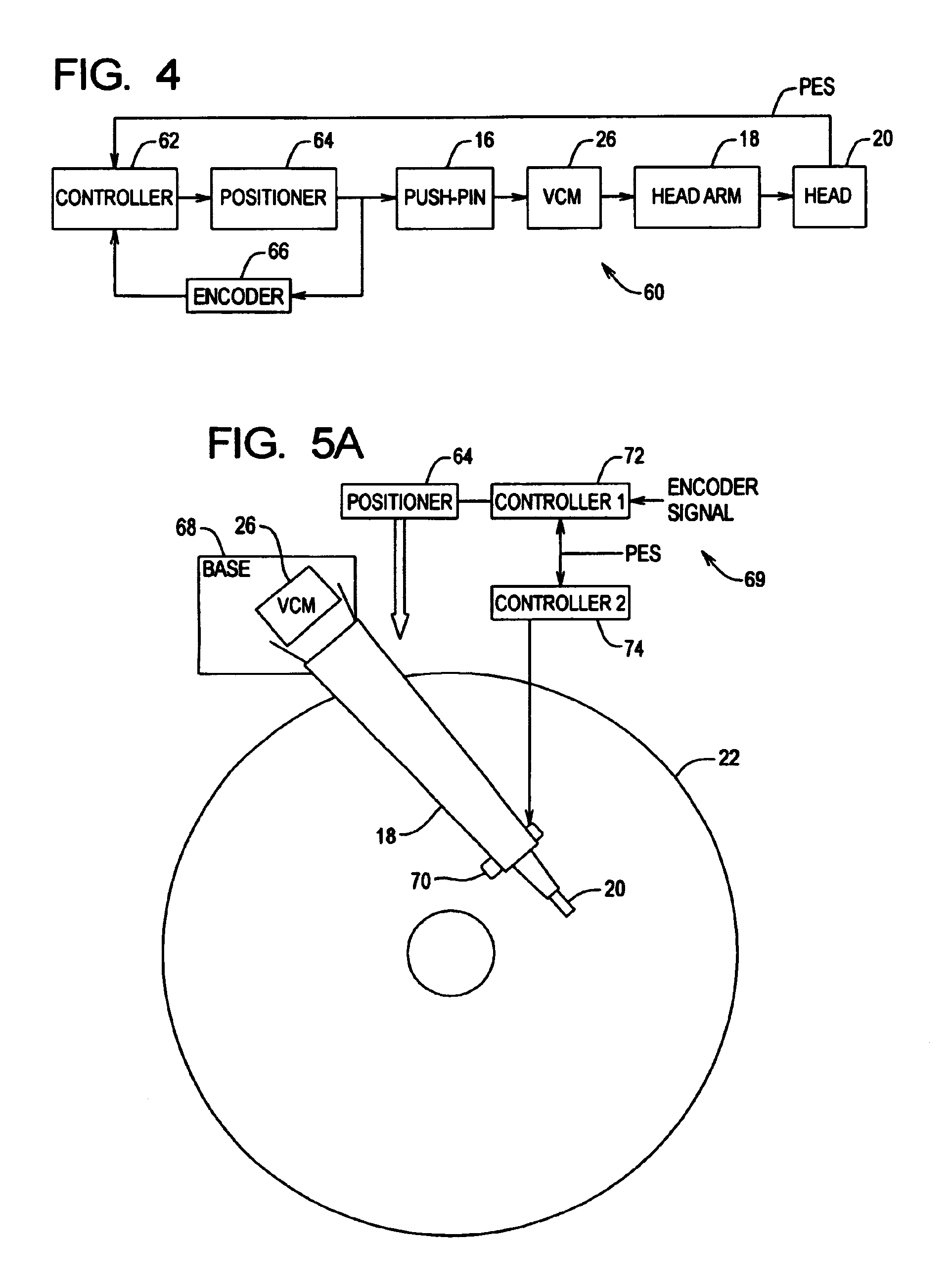
Servo writing a disk drive by integrating a spiral track read signal
InactiveUS7301717B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl theoryPosition error signal
A method of writing product servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive is disclosed. The disk comprises a plurality of spiral tracks, wherein each spiral track comprises a high frequency signal interrupted by a sync mark at a sync mark interval. The head internal to the disk drive is used to read the spiral tracks to generate a read signal. The read signal is integrated to generate a ramp signal, wherein a position error signal is generated from the ramp signal. The position error signal is used to maintain the head internal to the disk drive along a servo track while writing product servo sectors along the servo track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Adjusting track density by changing PES algorithm when servo writing a disk drive from spiral tracks
InactiveUS7068459B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityControl theory
A method and apparatus is disclosed for writing product servo sectors to a disk of a disk drive to define a plurality of data tracks. The disk drive comprises the disk and a head actuated over the disk. The disk comprises a plurality of spiral tracks which are read using the head to synchronize a write clock and to generate a position error signal (PES) according to a PES algorithm used to maintain the head along a first servo track while writing product servo sectors along the first servo track. The PES algorithm is adjusted to seek the head to a second servo track, and the head is used to write product servo sectors along the second servo track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Servo writing a disk drive by writing spiral tracks using a mechanical position sensor
InactiveUS7495857B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl signalEngineering
A disk drive is disclosed including a disk, an actuator arm, a head attached to a distal end of the actuator arm, a mechanical position sensor operable to generate a position signal representing a position of the head relative to the disk, and a voice coil motor for rotating the actuator arm about a pivot. The disk is rotated at a predetermined velocity, a control signal is generated in response to the position signal generated by the mechanical position sensor, and the control signal is applied to the voice coil motor in order to seek the head radially over the disk while writing a spiral track to the disk. The spiral track is then processed to maintain the head along a servo track while writing product servo sectors along the servo track.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
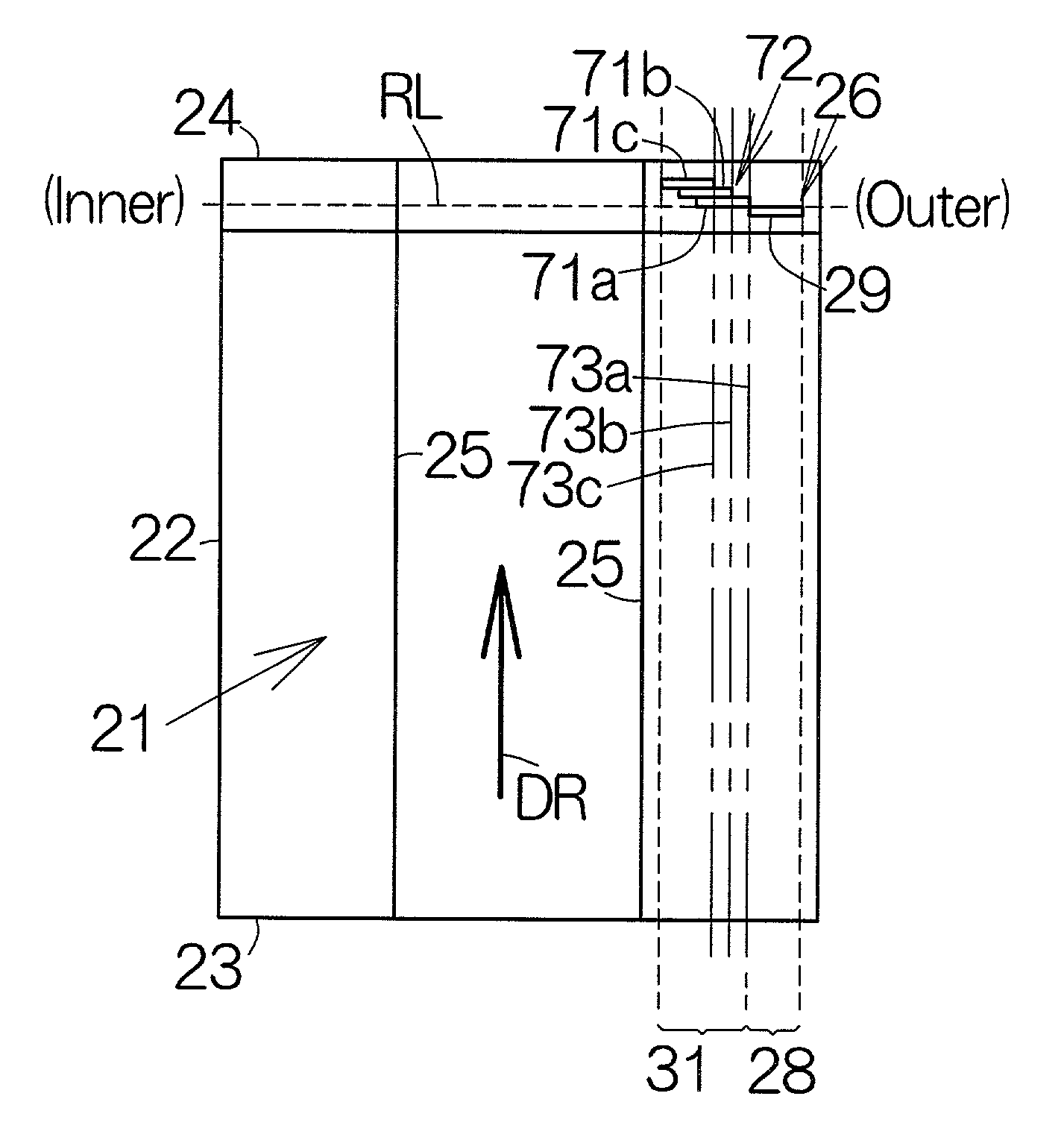
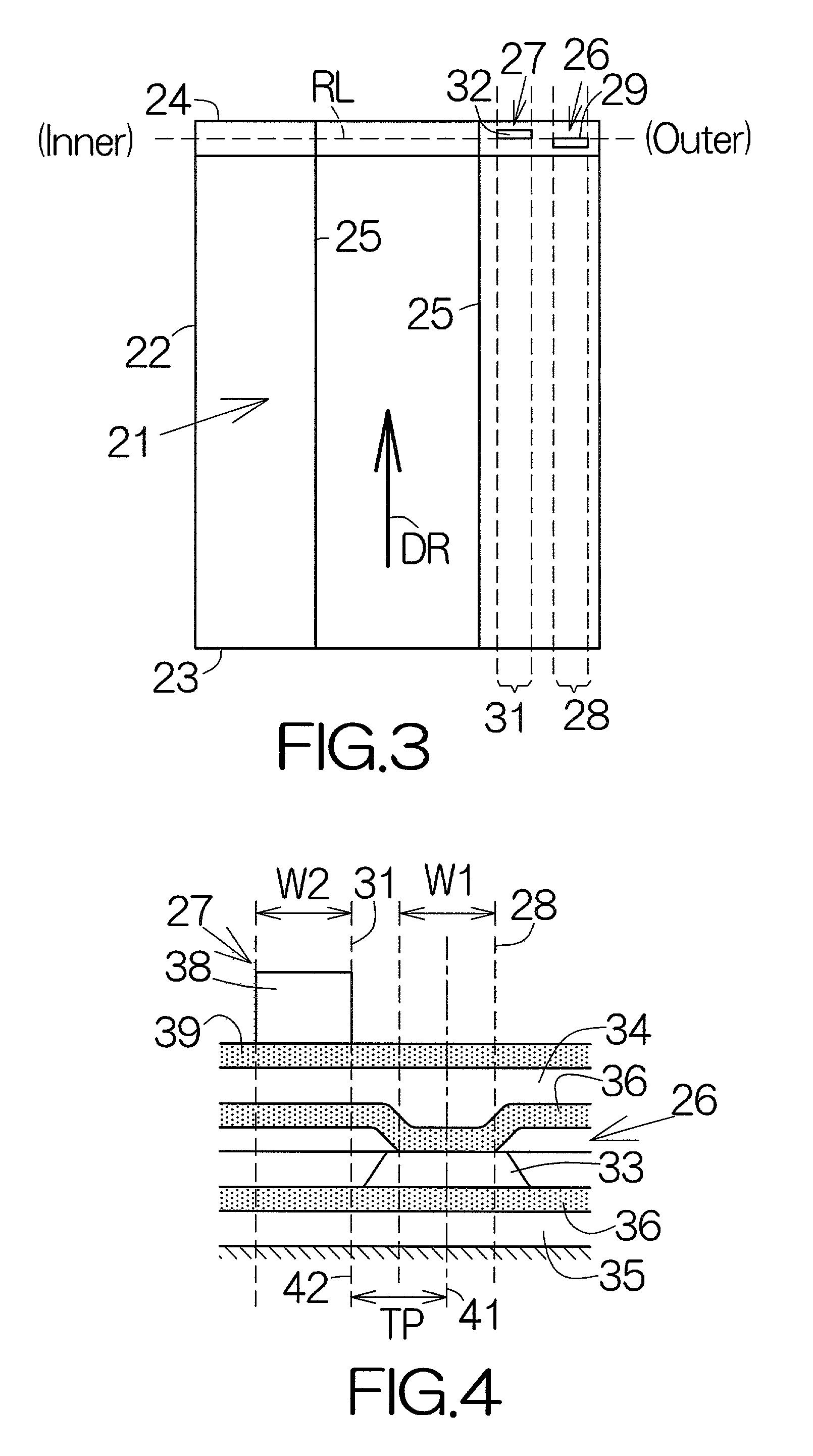
System and method for writing servo sectors in a perpendicular media recording environment
InactiveUS7388728B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksControl theoryServo track writing
A perpendicular media recording (PMR) servo track writer (STW) system and method for writing servo sectors onto a disk is disclosed. The servo writer includes a head positioner to position a head of a head disk assembly (HDA) relative to a disk, wherein the head writes servo sectors onto the disk with a perpendicular flux. The servo writer includes a controller to control the head positioner such that the head writes servo sectors onto the disk from one of an inner diameter (ID) or an outer diameter (OD) of the disk to a middle diameter (MD) of the disk, respectively, followed by writing servo sectors between the other of the OD or the ID of the disk to the MD of the disk, respectively.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus for performing a self-servo write operation in a disk drive using spiral servo information
InactiveUS7230789B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageComputer scienceServo track writing
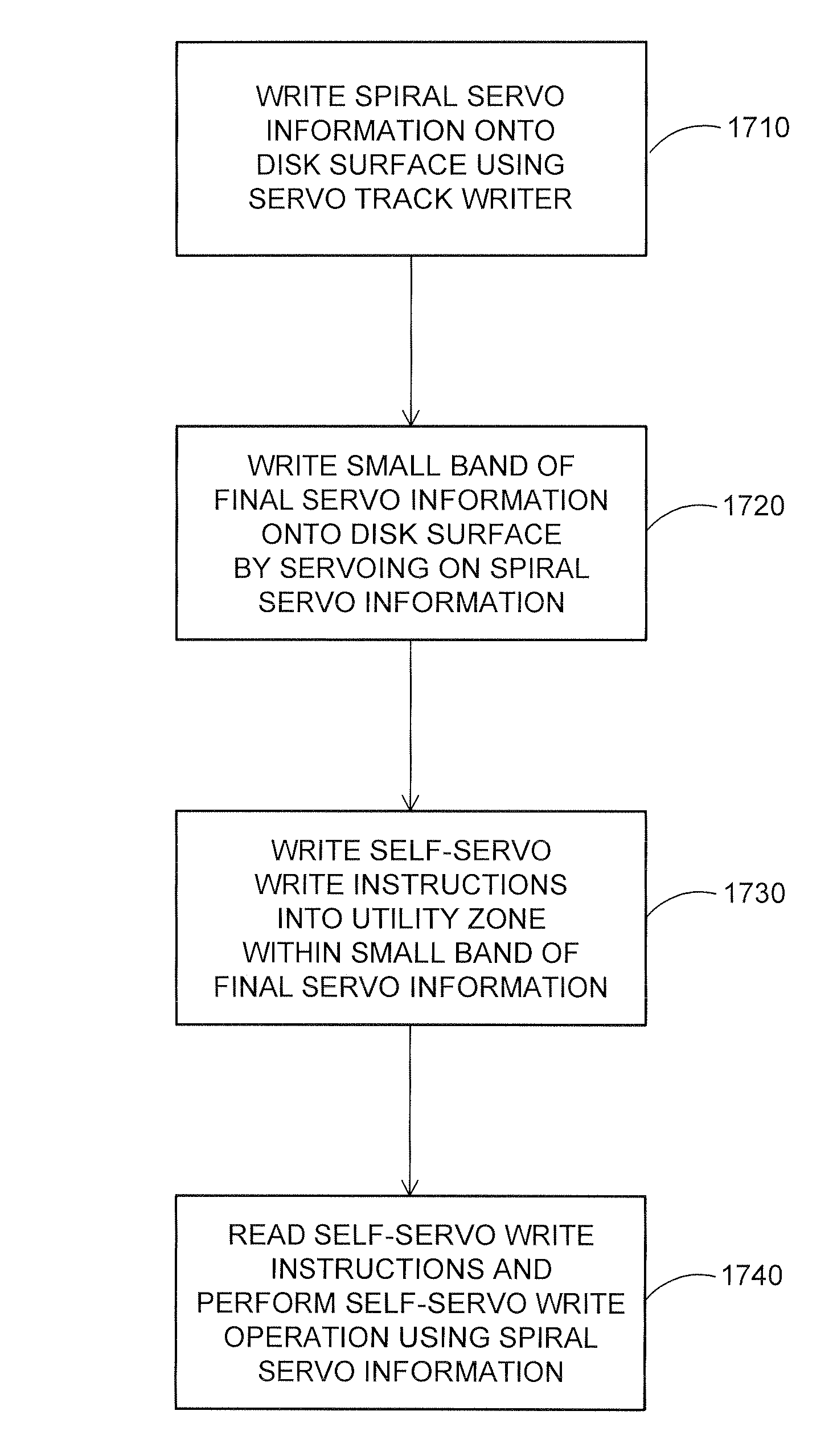
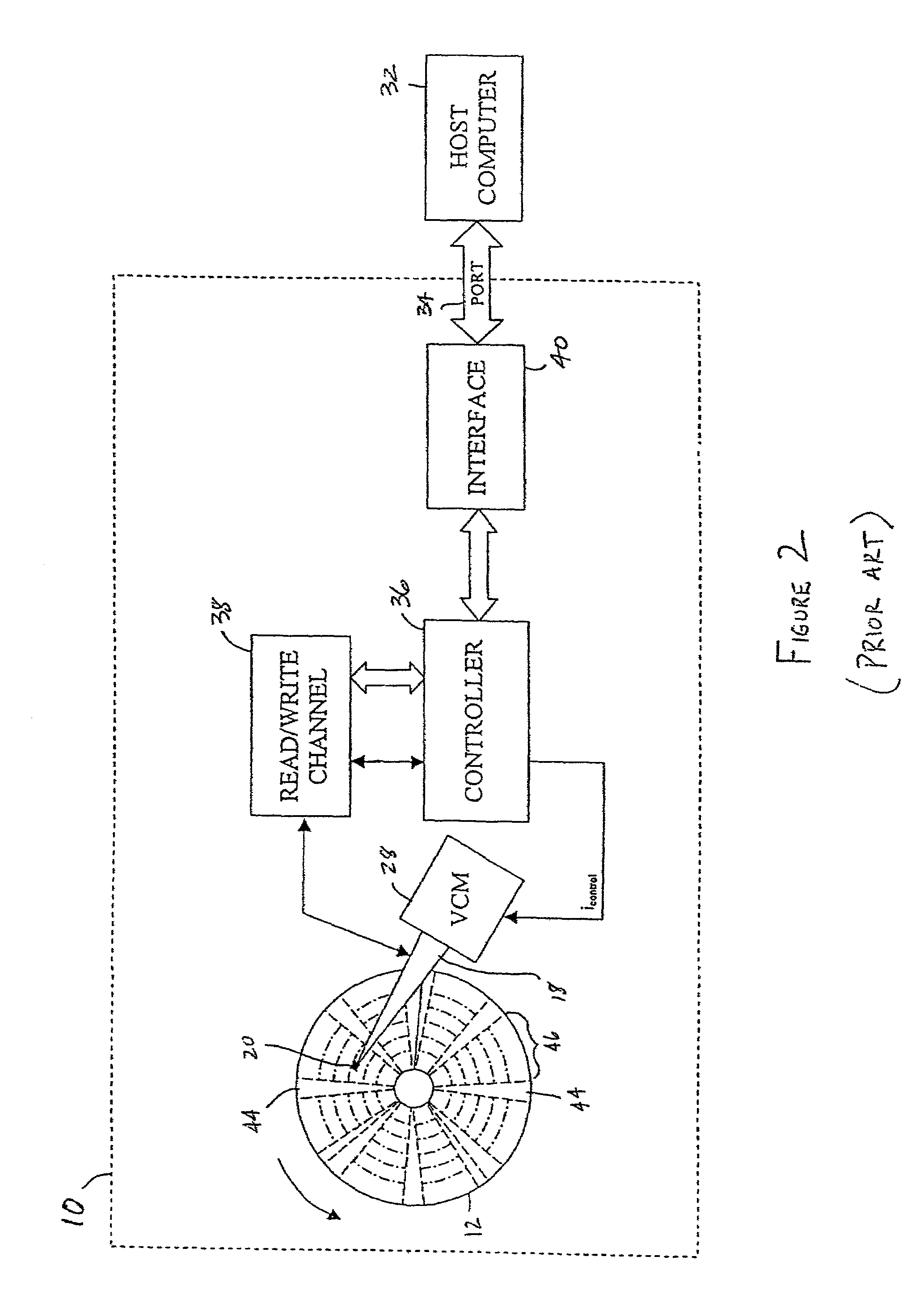
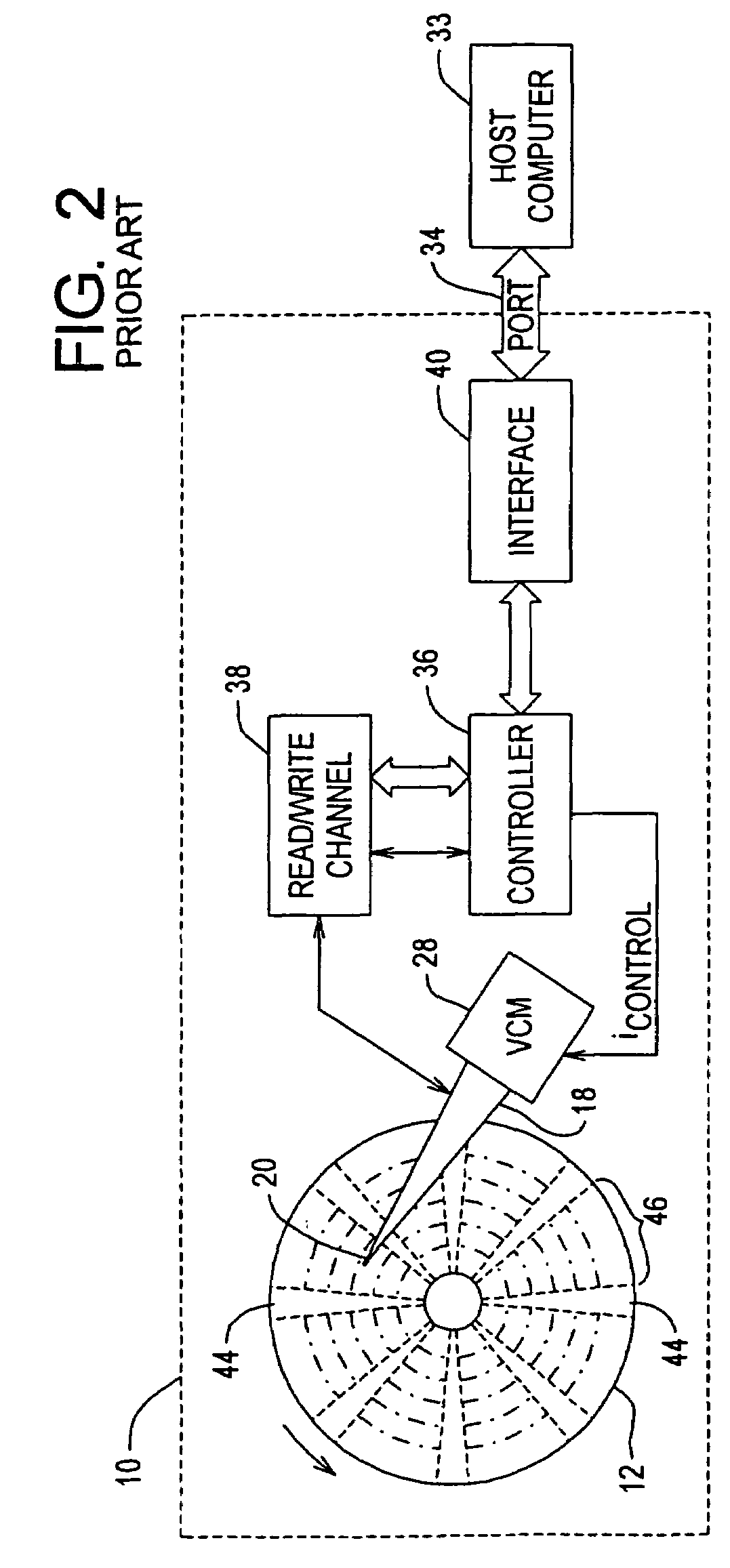
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for performing a self-servo write operation in a disk drive. In one embodiment, the disk drive includes a disk surface having a read head and a write head associated therewith. Spiral servo information is written onto the disk surface using a servo track writer. The read head reads the spiral servo information and is used to position the write head, which writes a small band of final servo information onto the disk surface. The small band of final servo information may be embedded servo information. Importantly, the small band of final servo information is not written using the servo track writer. The write head is also used to write self-servo write instructions into the small band of final servo information. Subsequently, the self-servo write instructions are read and a self-servo write operation is performed using the spiral servo information.
Owner:MAXTOR
Method of self servo write with low density gas
InactiveUS20060023339A1Track pitch is reducedImprove accuracyElectrical transducersDriving/moving recording headsVolumetric Mass DensityLow density
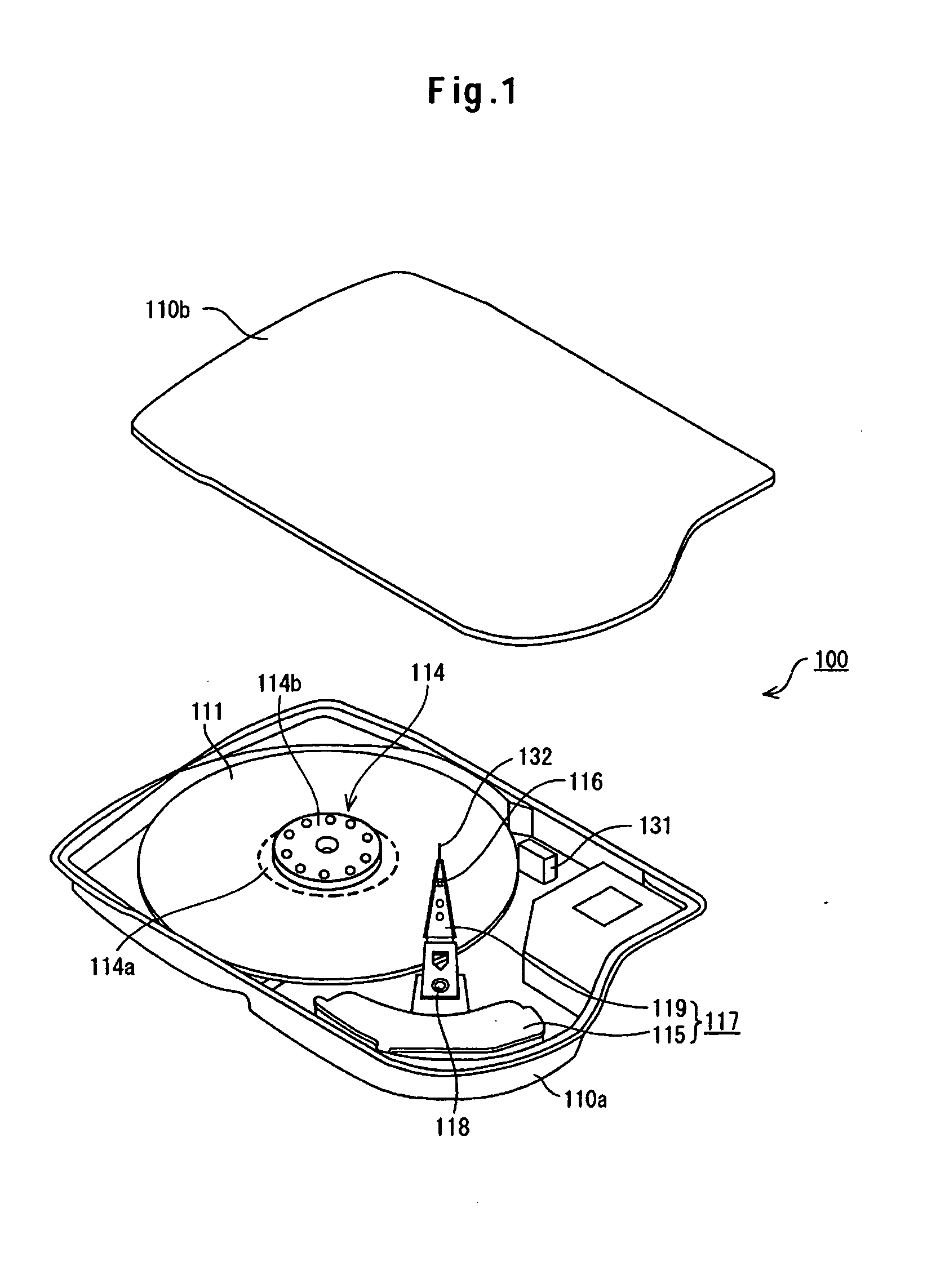
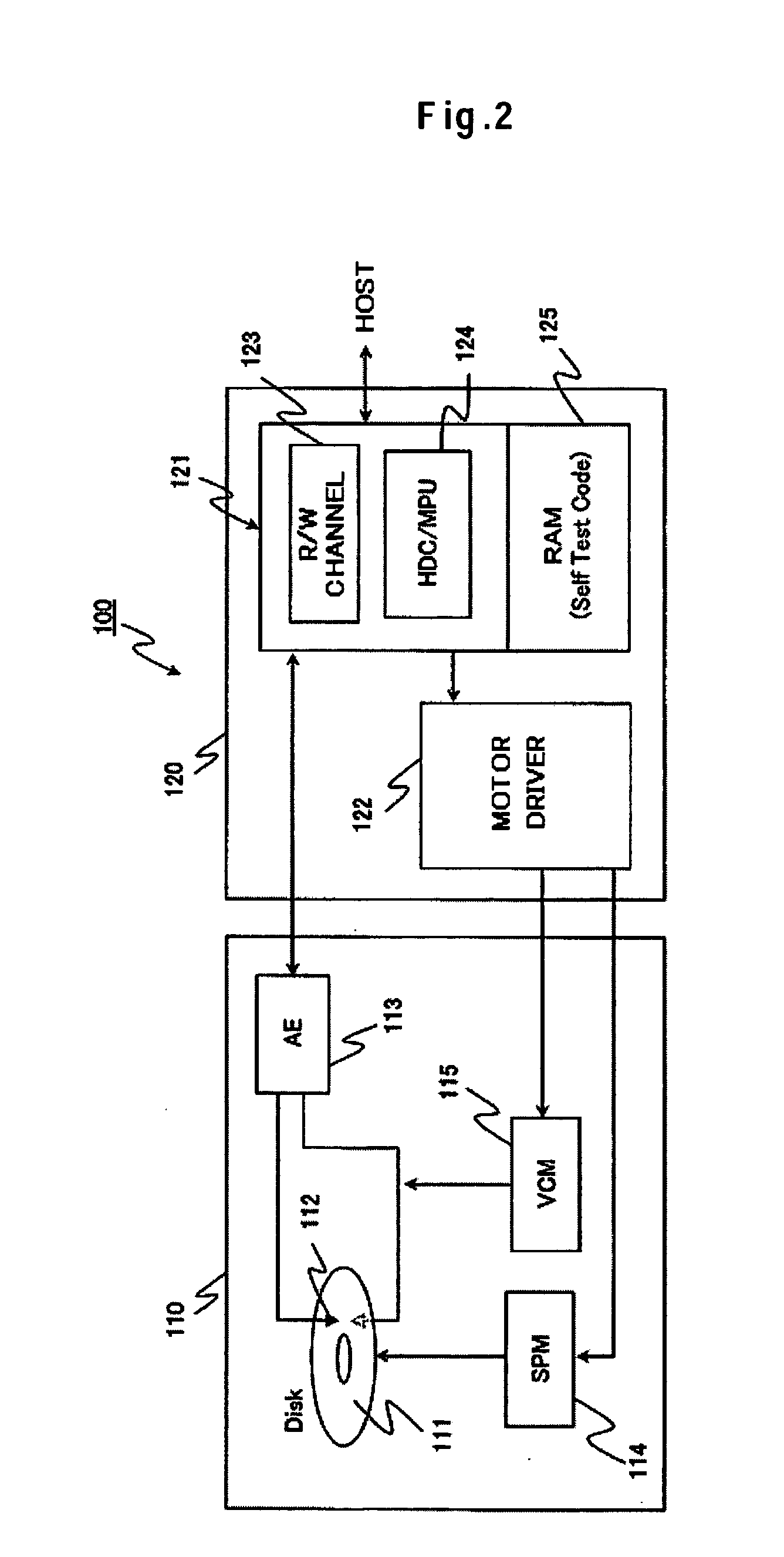
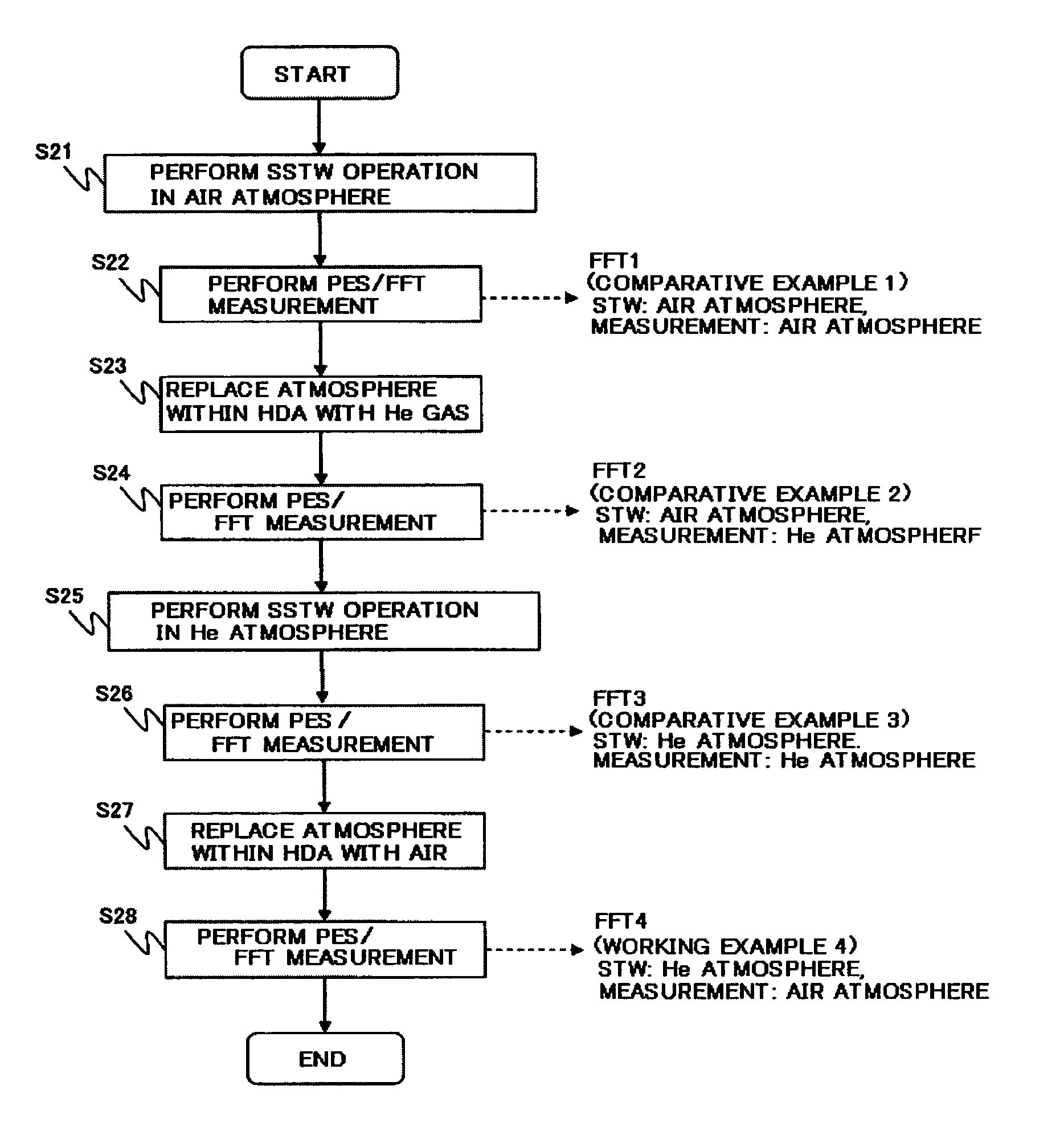
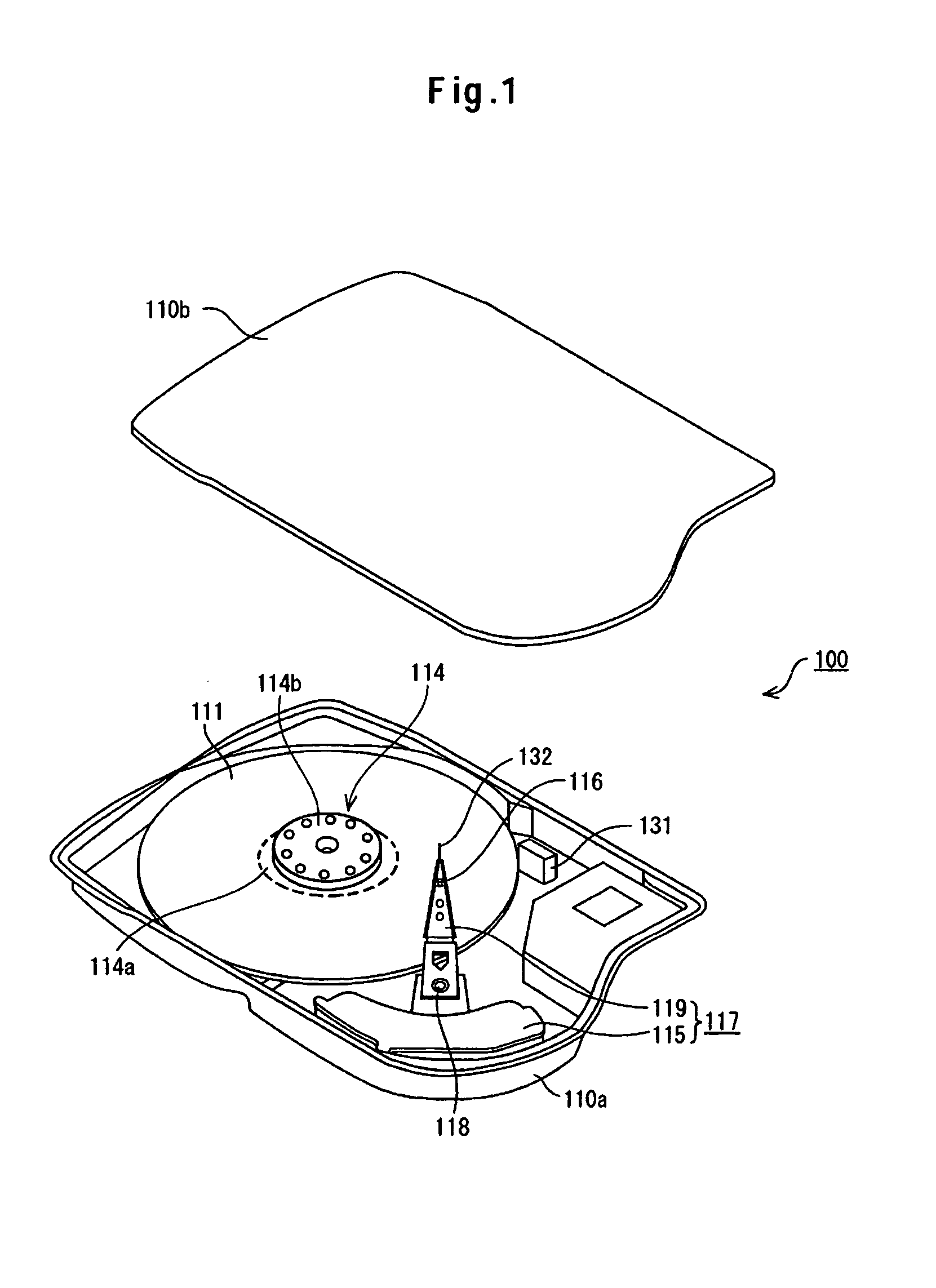
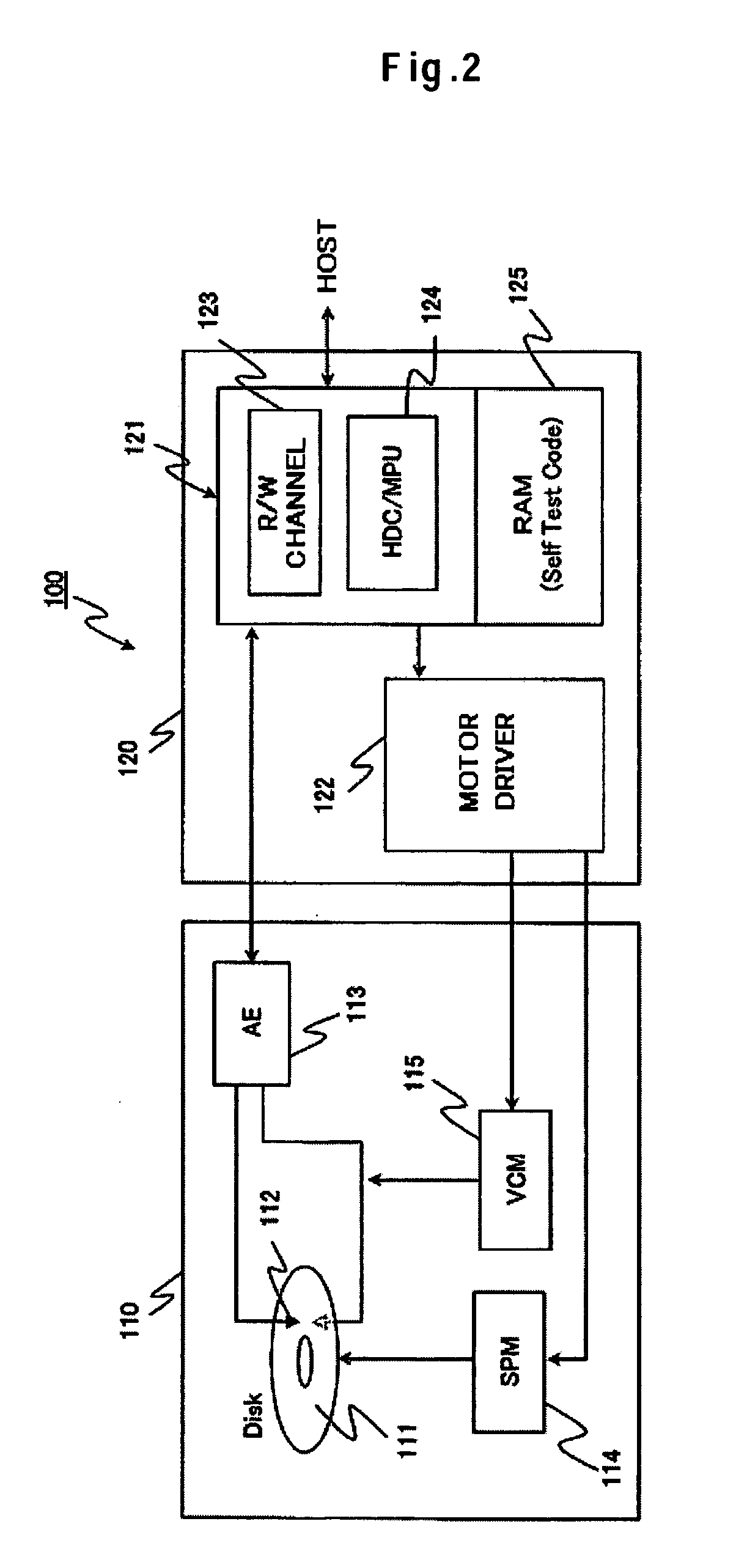
Embodiments of the invention provide a disk device capable of writing highly accurate servo data using an extremely simple technique, and a manufacturing method therefor. According to one embodiment, a method for manufacturing a disk device includes: mounting a magnetic disk and each assembly for driving the magnetic disk, such as an SPM and a VCM, in a base and attaching a top cover so as to seal the enclosure (made up of the base and the top cover) with each assembly of the HDD therein; replacing the air within the hard disk assembly (HDA) with a gas having a lower density than air, such as He; writing servo data to the magnetic disk in a self servo track write operation; and replacing the gas within the HDA with air.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus for writing and reading servo information written in a spiral fashion
InactiveUS7167333B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringServo track writing
A method and apparatus for writing spiral servo information onto one or more disk surfaces at a variable velocity using a servo track writer (STW) is provided. In one embodiment, a variable velocity profile is chosen so that spiral crossing angles across the disk surface are set to be equal. In another embodiment, a variable velocity profile is chosen so that spiral crossing angles across groups of tracks (i.e., two or more tracks) are set to be equal. In yet another embodiment, a variable velocity profile is chosen to adjust the number of tracks per inch (TPI) across the disk surface.
Owner:MAXTOR
Method and apparatus for performing a self-servo write operation in a disk drive
InactiveUS7623313B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageClosed loopComputer science
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for performing a self-servo write operation in a disk drive. In one embodiment, the disk drive includes a disk surface having a read head and a write head associated therewith. Spiral servo information is written onto the disk surface in a closed-loop fashion through use of a servo track writer. The read head reads the spiral servo information and is used to position the write head, which writes final servo information onto the disk surface. The final servo information may be embedded servo information. The final servo information that has been written onto the disk surface looks substantially identical to a disk surface that has had its final servo patterns written using a servo track writer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Servo track writing for ultra-high TPI disk drive in low density medium condition
InactiveUS6999262B2Track finding/aligningFilamentary/web record carriersMedia controlsHard disc drive
Owner:SEAGATE TECH INT
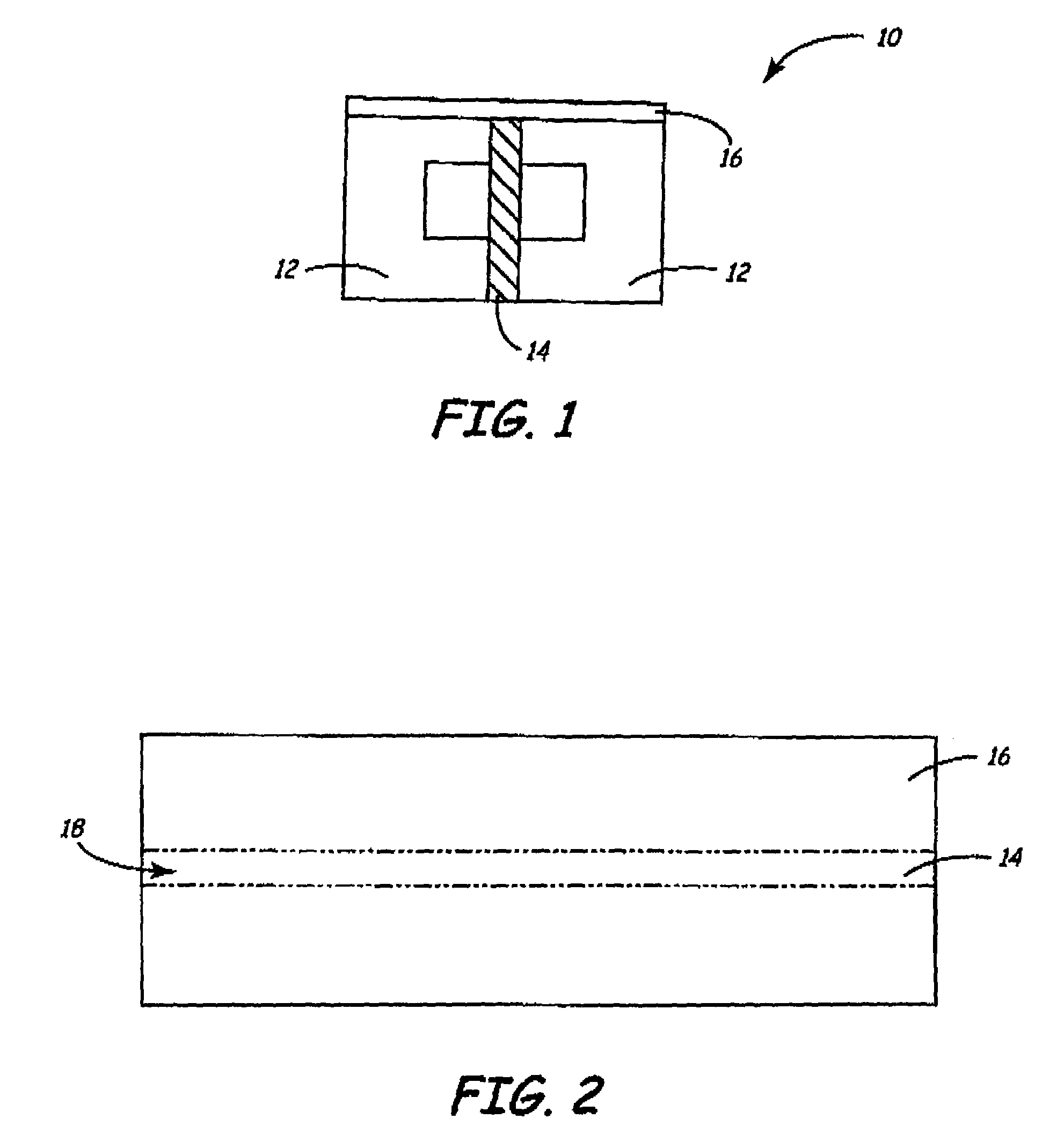
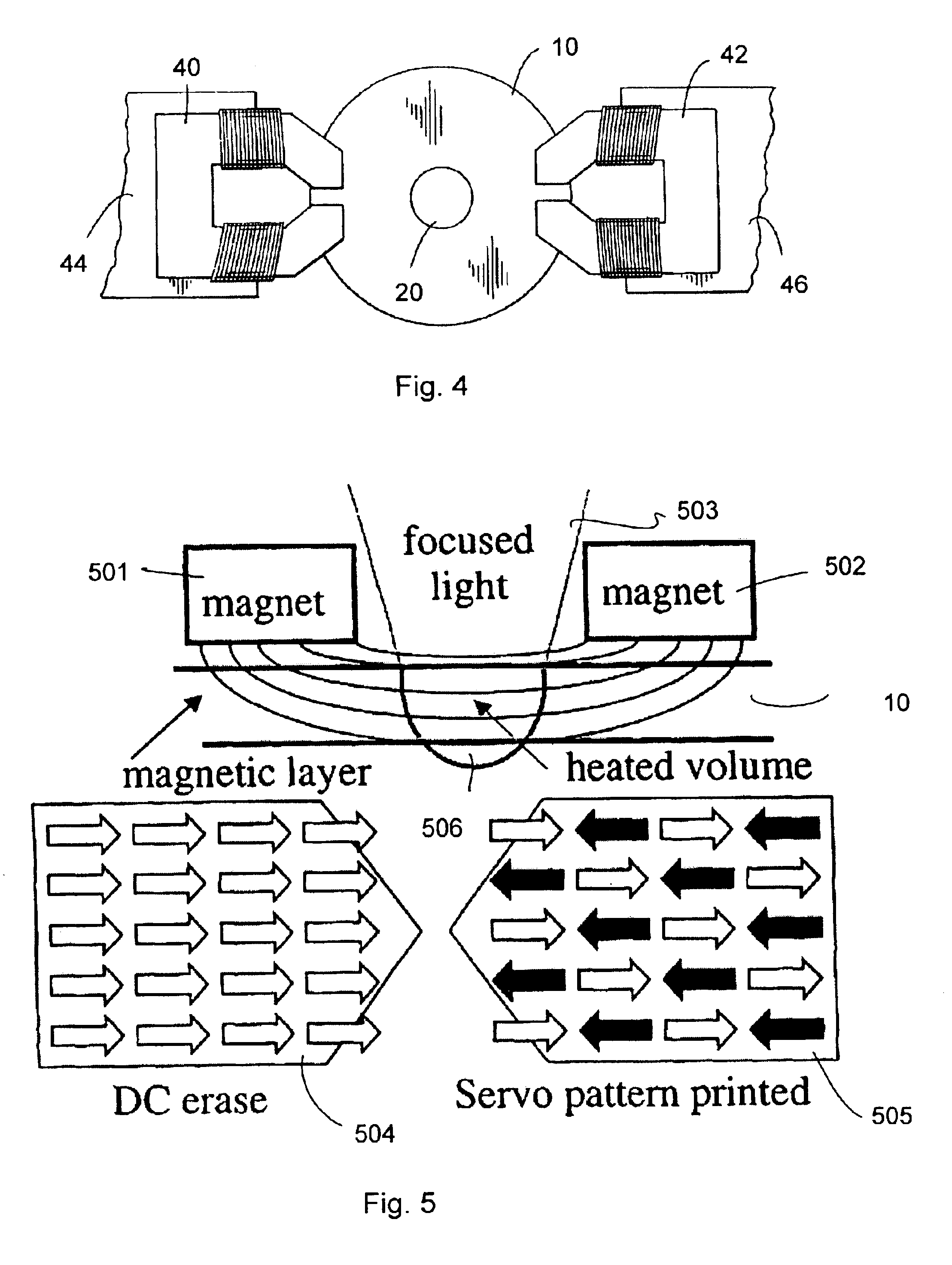
Thin-film magnetic recording head having a timing-based gap pattern for writing a servo track on magnetic media
A thin film magnetic recording head utilizing a timing based servo pattern is fabricated using a focused ion beam (FIB). The recording head is fabricated by sputtering a magnetically permeable thin film onto a substrate. A gap pattern, preferably a timing based pattern, is defined on the thin film and the FIB cuts a gap through the thin film based on that pattern. Once completed, the recording head is used to write a servo track onto magnetic tape. The timing based servo track then allows for the precise alignment of data read heads based on the positional information obtained by a servo read head which scans the continuously variable servo track.
Owner:ADVANCED RES
Self-servo writing using recording head micropositioner
InactiveUS7218471B2Reduce manufacturing costDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageIndependent motionContinuous use
Servo tracks are written onto different disk surfaces using multiple recording heads within a disk drive without requiring a servo writing machine or clean room conditions. Microactuators in the reference heads in the disk drive are capable of independent motion with respect to one another, which allows the servo tracks to be written to the disk surfaces. The process begins as the recording heads are biased against a crash stop, and then moved to an adjacent track. One of the heads writes a reference track at this adjacent track position when a microactuator of the head is centered. This reference head then follows the reference track with its microactuator centered, while the other recording heads move in the radial direction to write servo information on their respective tracks. Reference tracks are then successively used to write the servo information as the recording heads move in a direction away from the crash stop.
Owner:MEYER DALLAS W
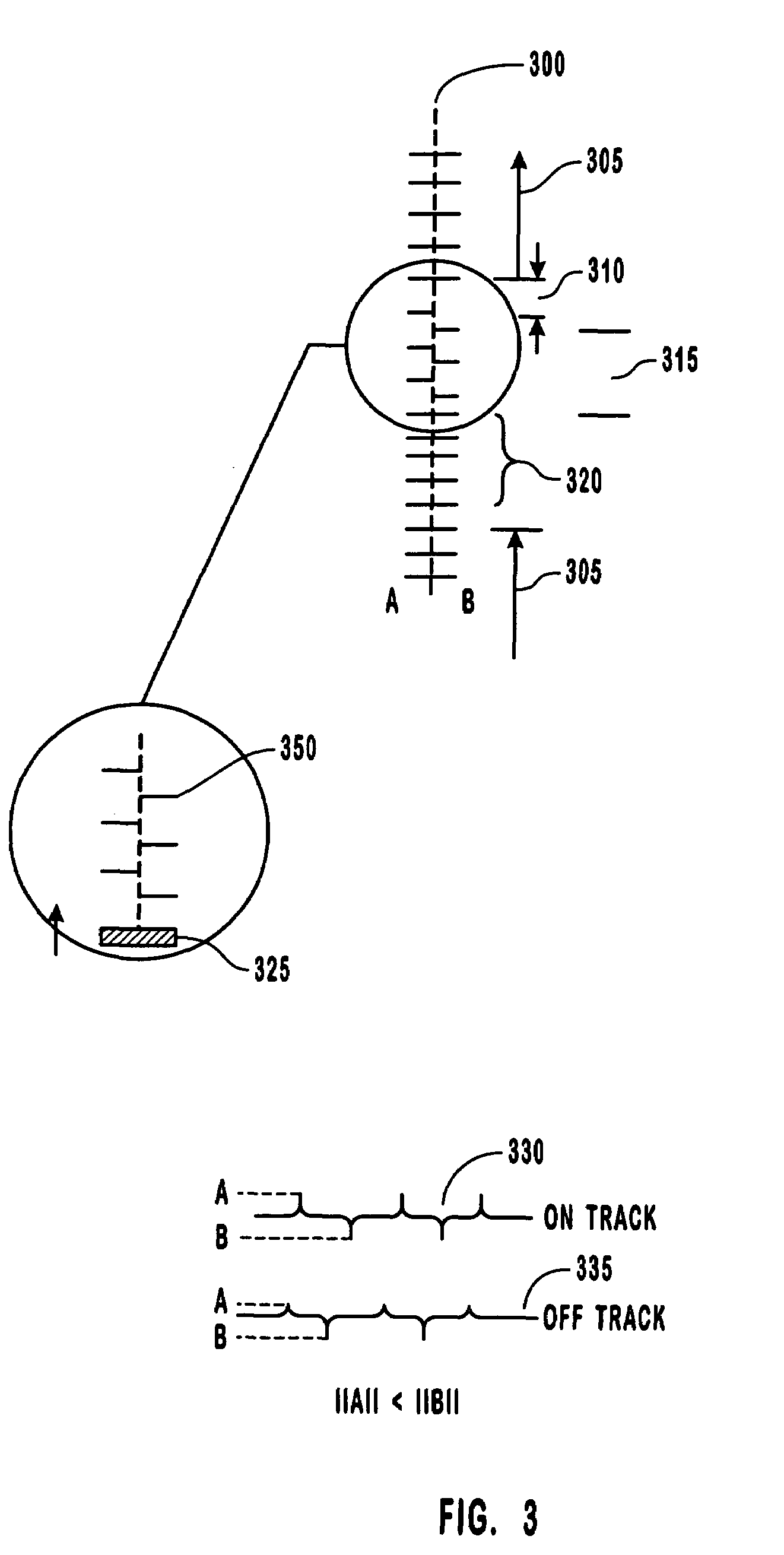
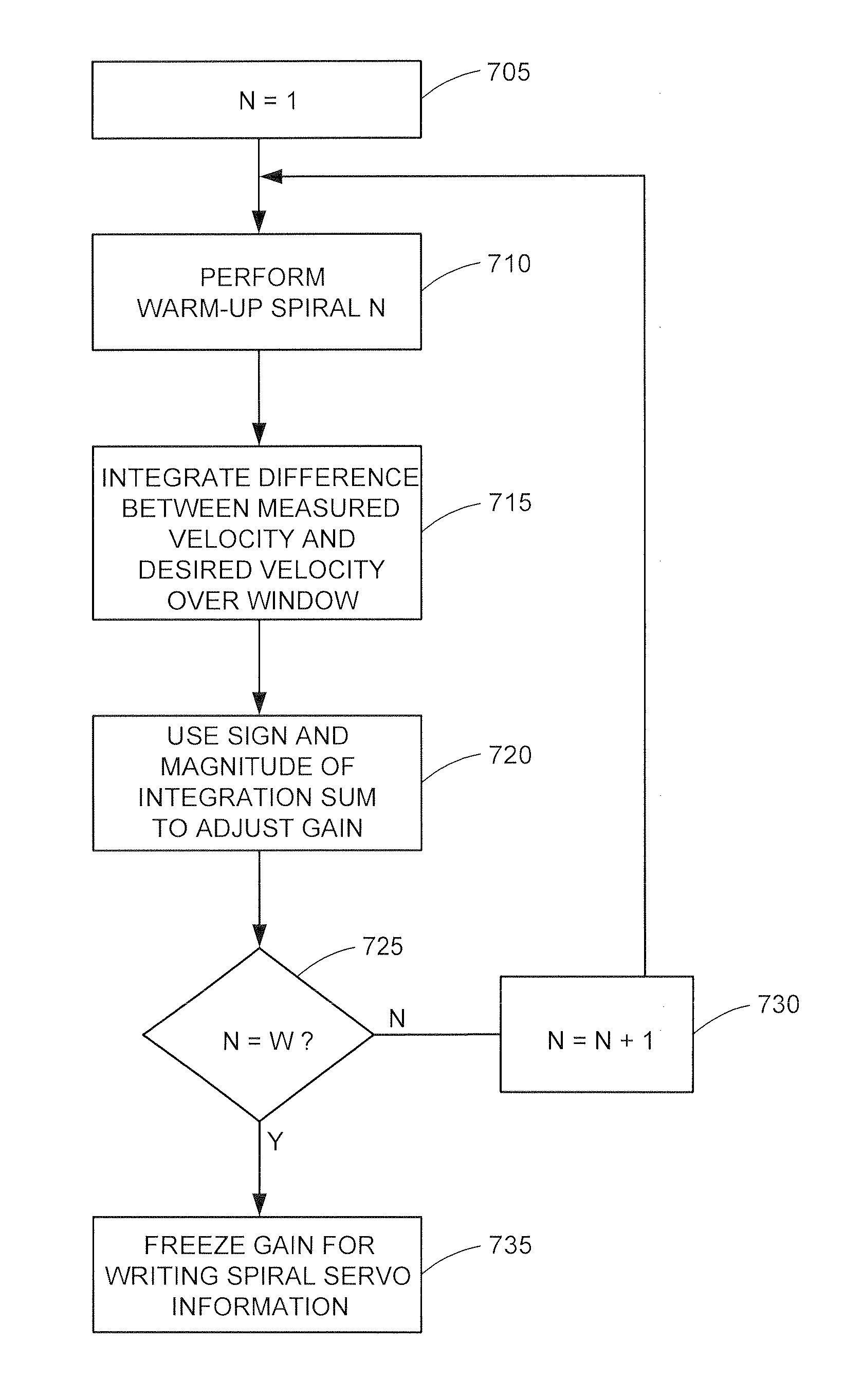
Method and apparatus for reducing velocity errors when writing spiral servo information onto a disk surface
InactiveUS7248427B1Reduction in velocity errorReduce the average velocityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringControl theory
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for reducing velocity errors when writing spiral servo information onto a disk surface of a disk drive. In one embodiment, a servo track writer is provided for moving a write head at a controlled velocity. The write head is used to write spiral servo information onto a disk surface. The write head is moved, using the servo track writer, at an actual velocity trajectory to simulate writing one spiral of spiral servo information. Differences between the actual velocity trajectory and a desired velocity trajectory are measured on a control sample by control sample basis over a window of control samples. The differences are integrated over the window. A gain, associated with the servo track writer controlling the velocity of the write head, is adjusted using the integrated differences.
Owner:MAXTOR
Use of offline servo track writer together with single pass servo writing process
InactiveUS20050174679A1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveControl theory
A method for writing servo information onto a disk of a hard disk drive. The method includes writing a reference servo pattern onto a track of a disk with an off-line servo track writer. The reference servo pattern has less servo bits than the final pattern allowing the off-line writer to write in a single pass. The disk is then assembled into a hard disk drive assembly and a final servo pattern is written onto the track. The final pattern can also be written with two passes. The single pass writing process reduces the time required to write the servo information. Additionally, the off-line servo track writer can write servo on a plurality of disk at the same time, further reducing the process time for writing servo and mass producing hard disk drives.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of self servo write with low density gas
InactiveUS7271974B2Highly accurate servo dataAccurate dataDriving/moving recording headsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionLow densityControl theory
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method to control spiral start point during ammonite servo track writer process using reference servo track band
InactiveUS20060171058A1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveControl theory
a method for writing servo information onto a disk of a hard disk drive with a servo writer. The method includes writing a reference servo pattern onto a track of a disk. A head is then positioned relative to the reference servo pattern and a spiral servo track is written onto the disk. The process of positioning the head relative to the reference servo pattern and writing a spiral servo track can be repeated to create a plurality of spiral servo tracks on the disk. The spiral tracks are used to write radial servo patterns that are utilized during normal operation of the drive. The reference servo pattern allows each spiral track to start at a point with the same radial distance from the center of the disk. This improves the accuracy of the spiral tracks and the resultant final servo patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
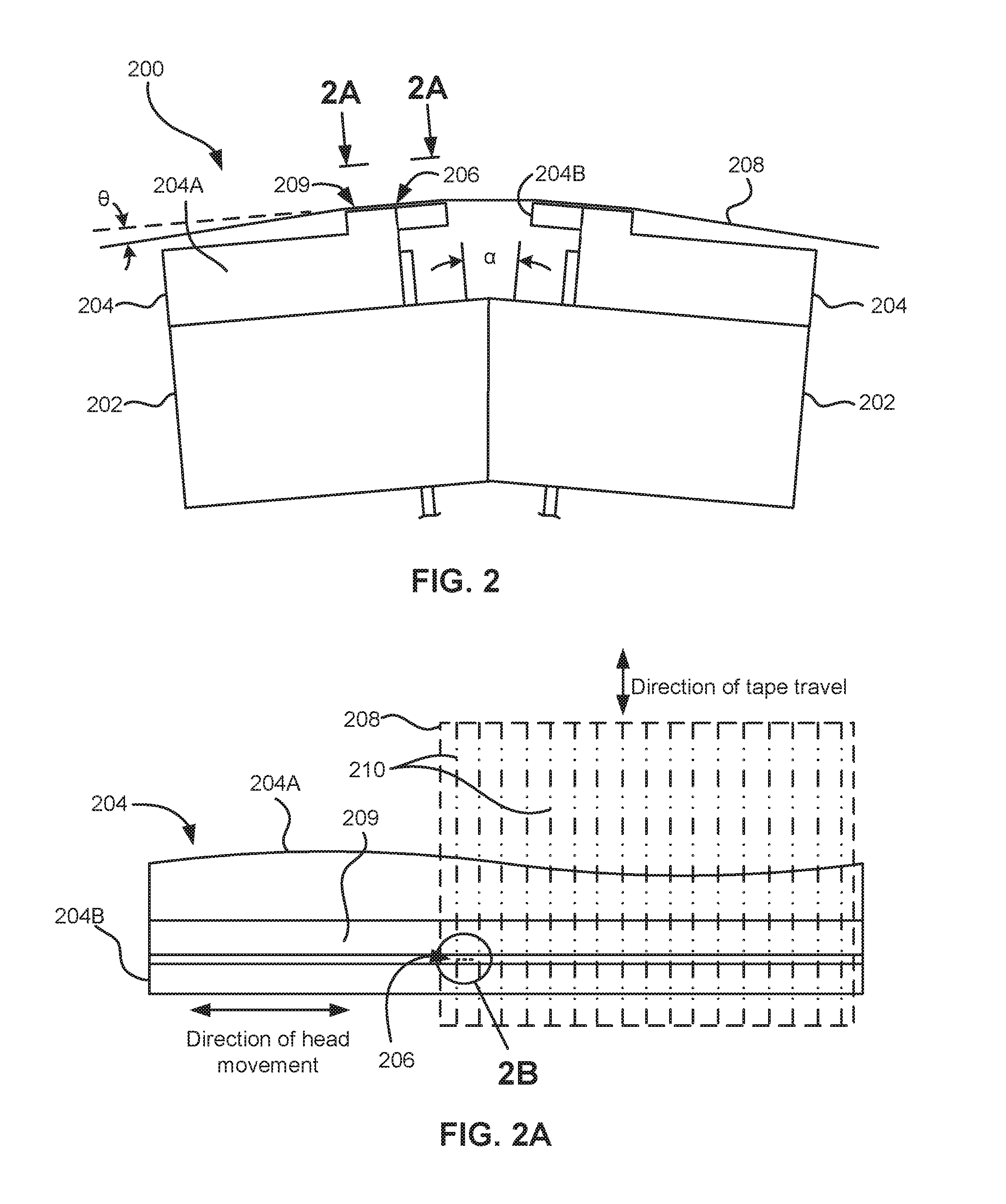
Method of writing servo tracks for disk file apparatus using write start or stop sectors
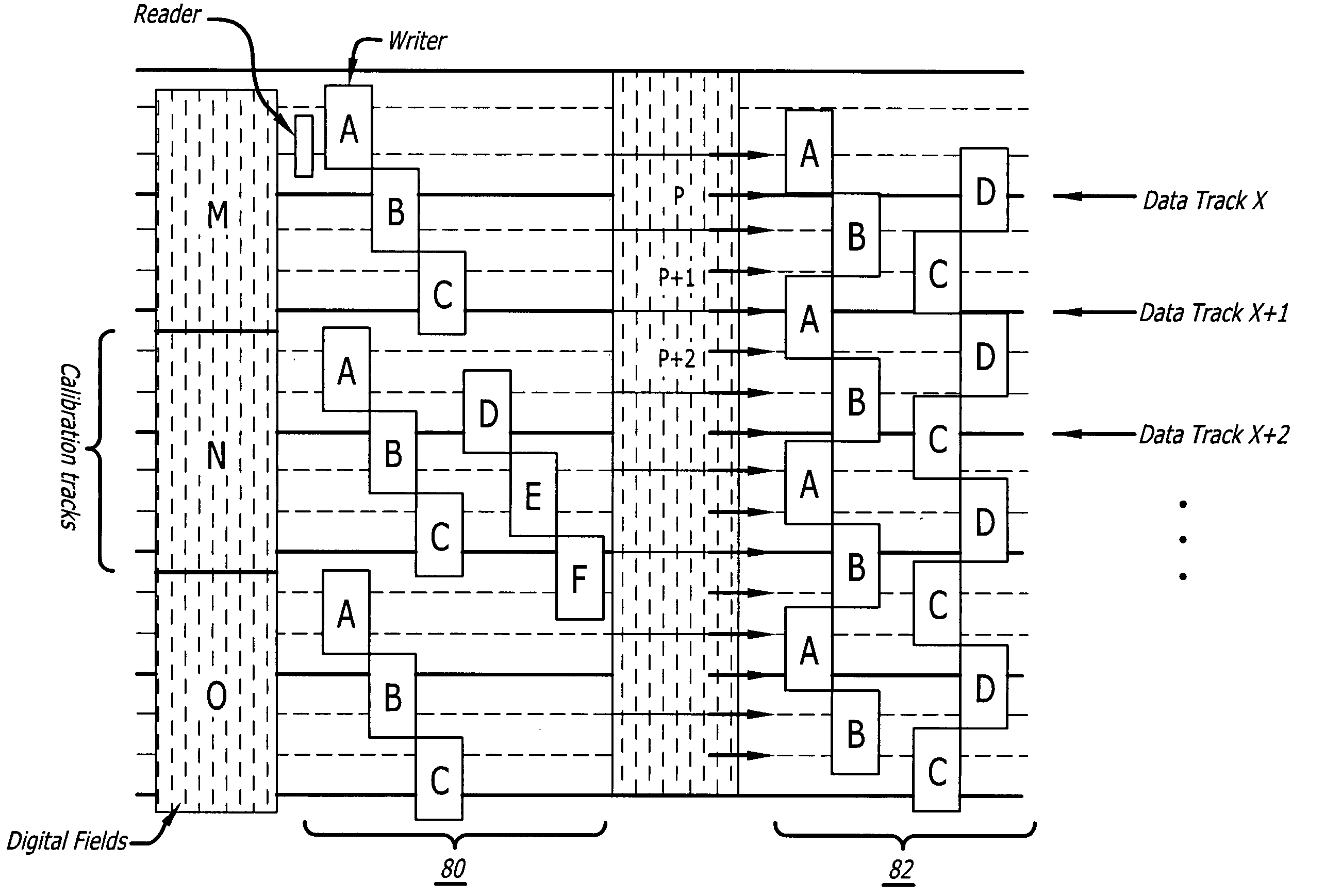
InactiveUS6904010B1Quality improvementCombination recordingTrack finding/aligningStart timeEngineering
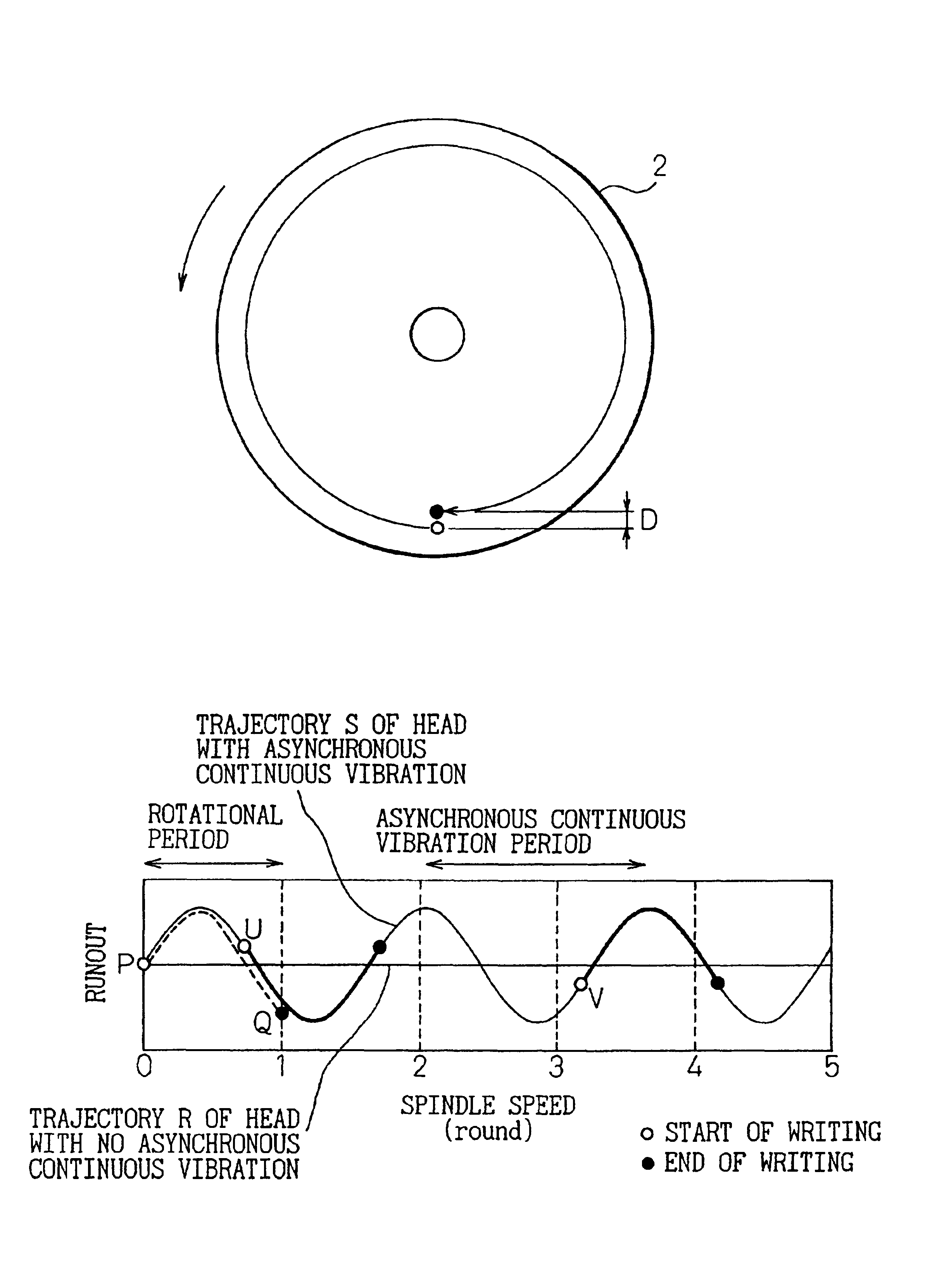
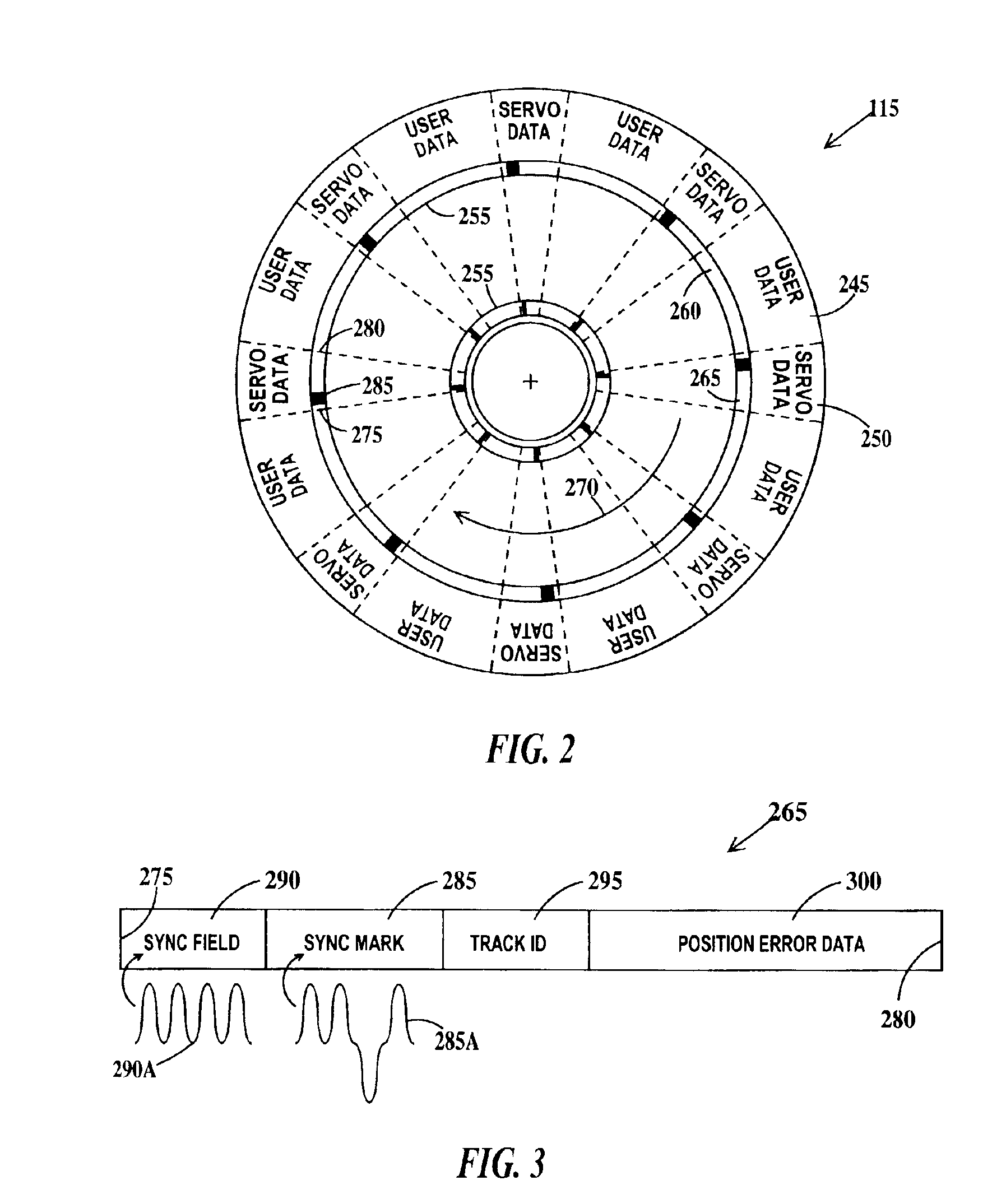
A method of STW (servo track write) for improving the quality of the servo tracks by suppressing the misalignment of the write start position caused by the asynchronous continuous vibration of a disk drive is disclosed. The disk drive includes a spindle motor, a disk medium, a write / read head and a head moving mechanism for carrying out the sector servo operation. The STW method comprises the steps of detecting the continuous vibration asynchronous with the rotational frequency of the spindle motor, detecting the phase of the asynchronous continuous vibration detected, determining the write start sector of each servo track based on the detected phase of the asynchronous continuous vibration, determining the write start time of each servo track in accordance with the clock signal, and moving the head onto the servo track where the head positioning information is written, by the head moving mechanism and writing the information in the servo track based on the write start time.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
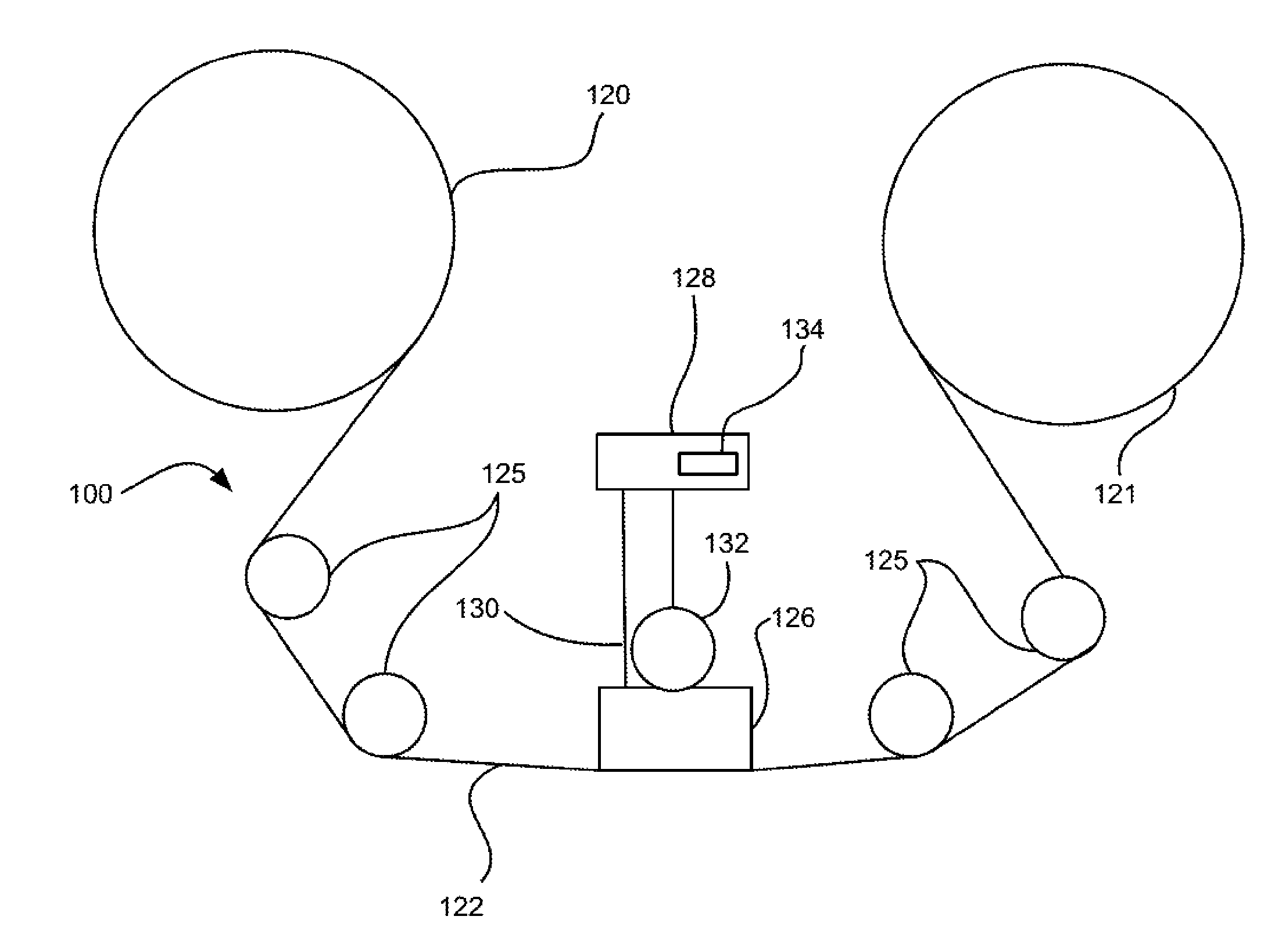
Writer for head positioning information over recording medium
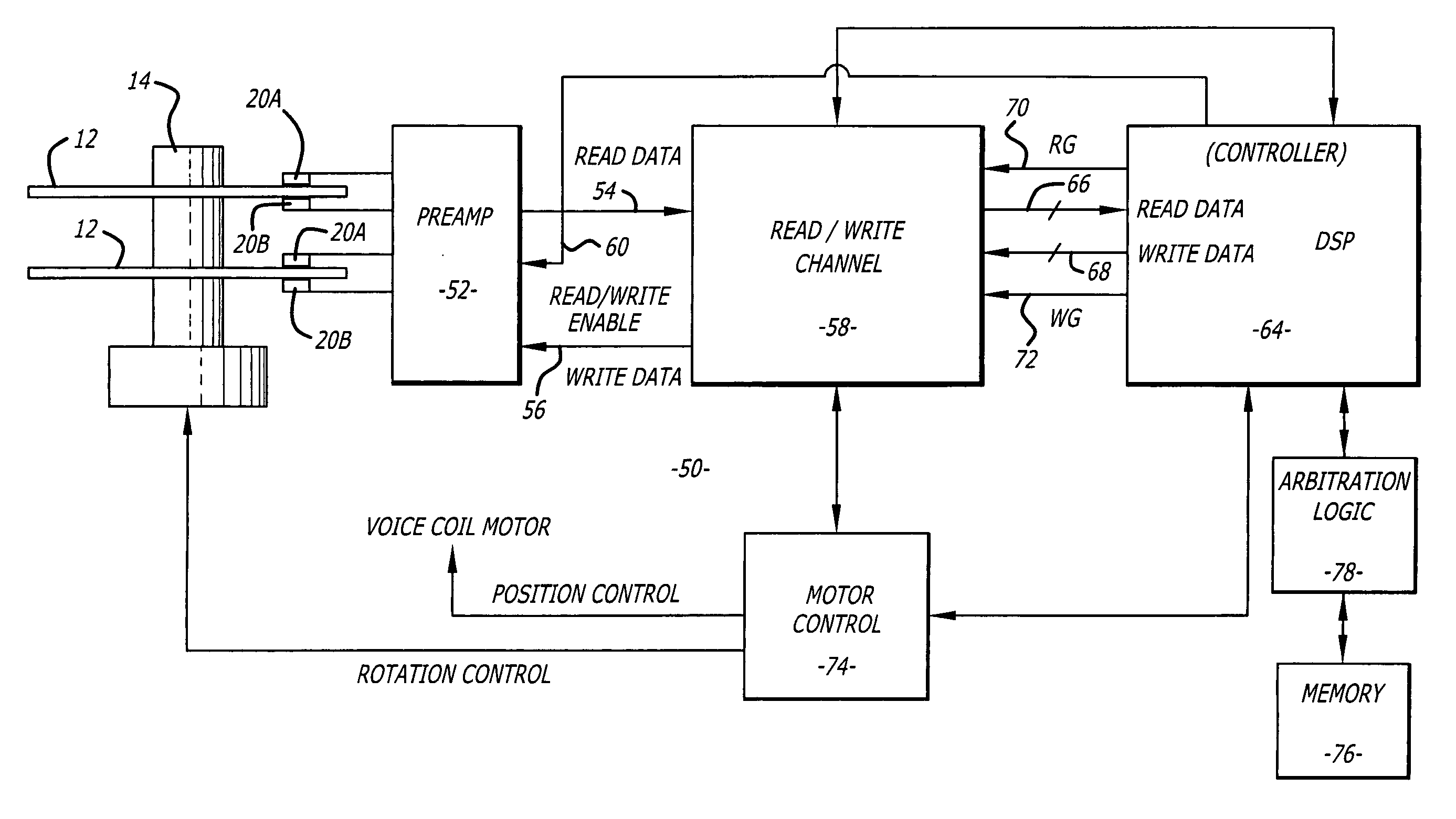
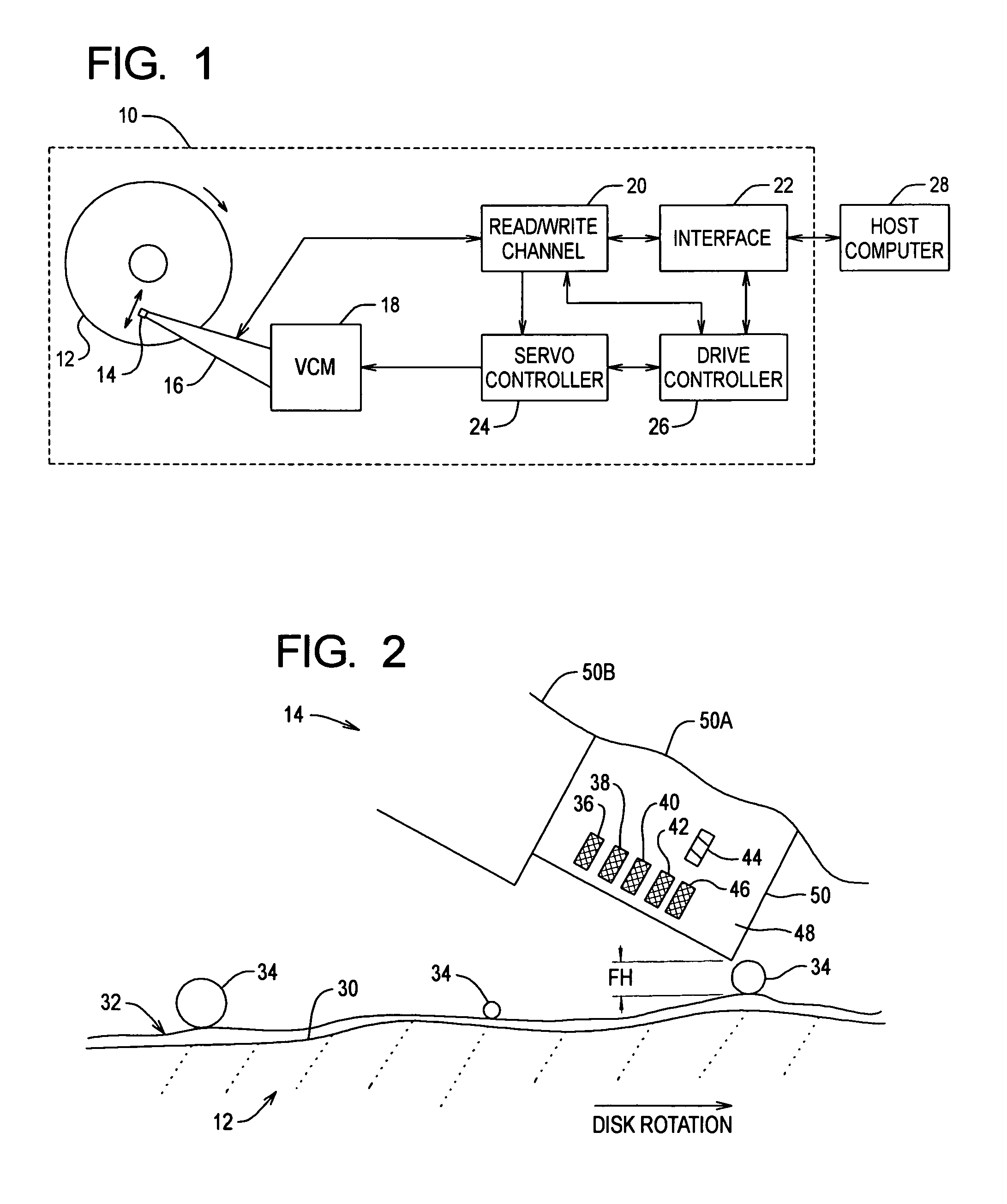
InactiveUS7012775B2Write reliablyHigh positioning accuracyTrack finding/aligningFilamentary/web carriers operation controlEngineeringRecording media
A writer for head positioning information, or a so-called servo track writer allows the read gap to follow a track which has been established on a recording medium or disk. As long as the read gap keeps following the existing track, the write gap is allowed to move along a path extending in parallel with the existing track. The write gap is utilized to write head positioning or servo information into the recording medium along the path. Even when the recording medium suffers from vibration or the like, the read gap can follow the track. The head positioning information can thus be written into the recording medium so as to establish a head positioning pattern at a higher positional accuracy.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
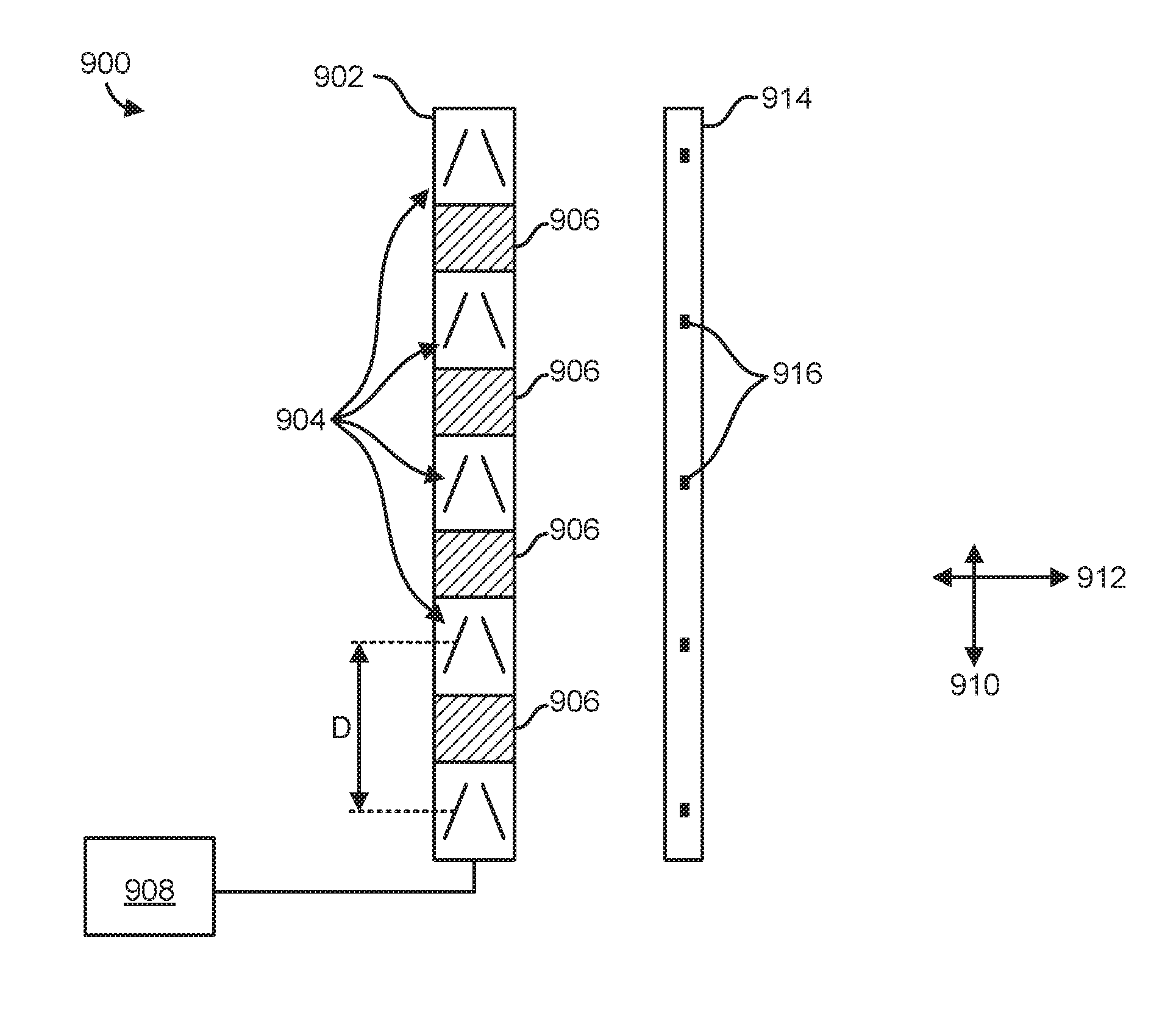
Tape servo track write compensation
InactiveUS8937786B1Alignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeControl theory
Setting a servo write head spacing for writing servo tracks on a magnetic tape in a manufacturing environment. One or more processors receive one or more environmental condition measurements of the manufacturing environment. The processors determine a spacing for a pair of servo write heads based at least on a nominal spacing for the pair of servo tracks, and a product of a difference between the nominal environmental conditions associated with the nominal spacing and the corresponding environmental condition measurements of the manufacturing environment, and coefficients of expansion for the magnetic tape. Spacing for the pair of servo write heads is set to the determined spacing, such that the spacing of the pair of servo write heads is substantially the nominal spacing when the one or more manufacturing environment environmental condition measurements are the one or more nominal environmental conditions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
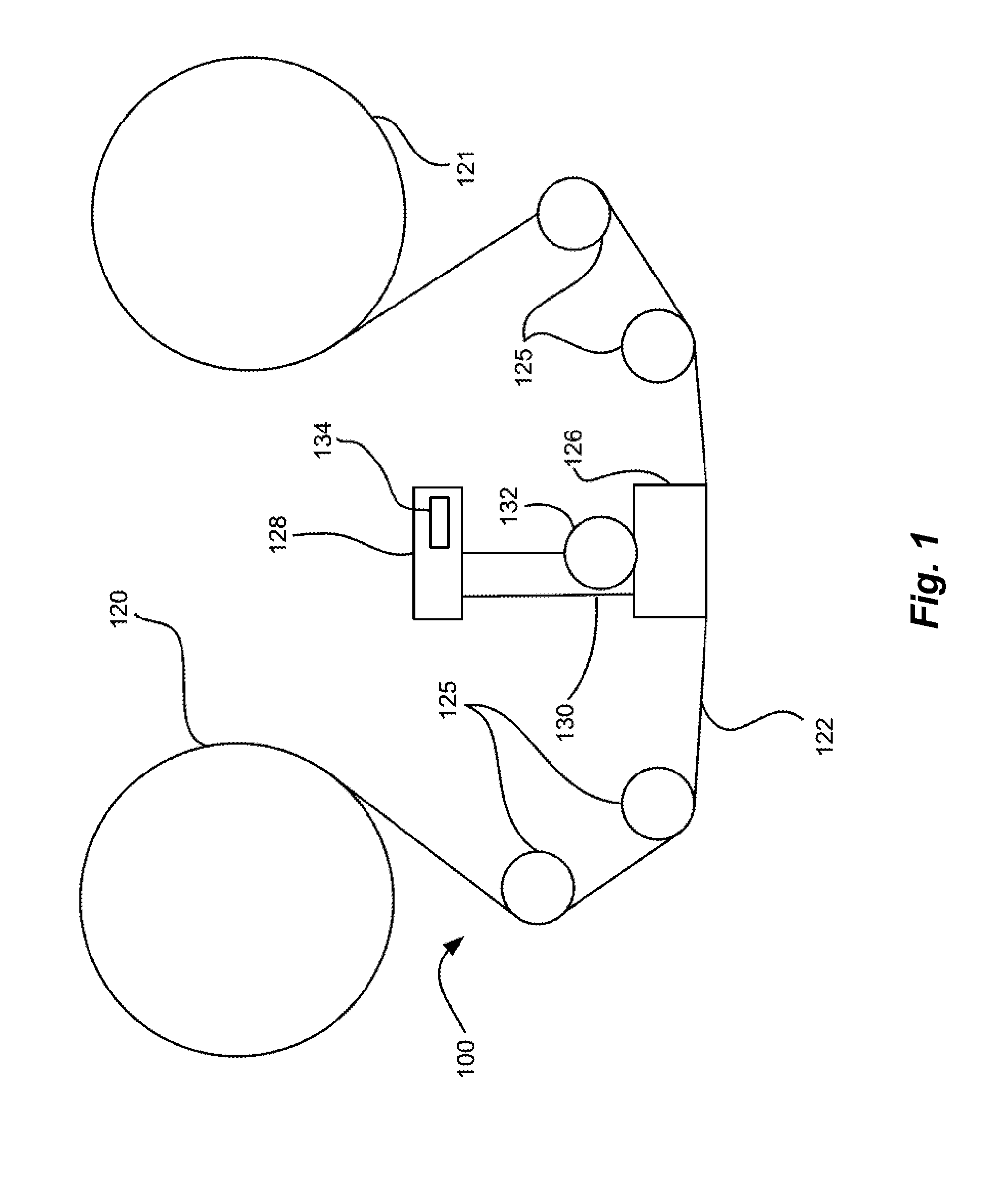
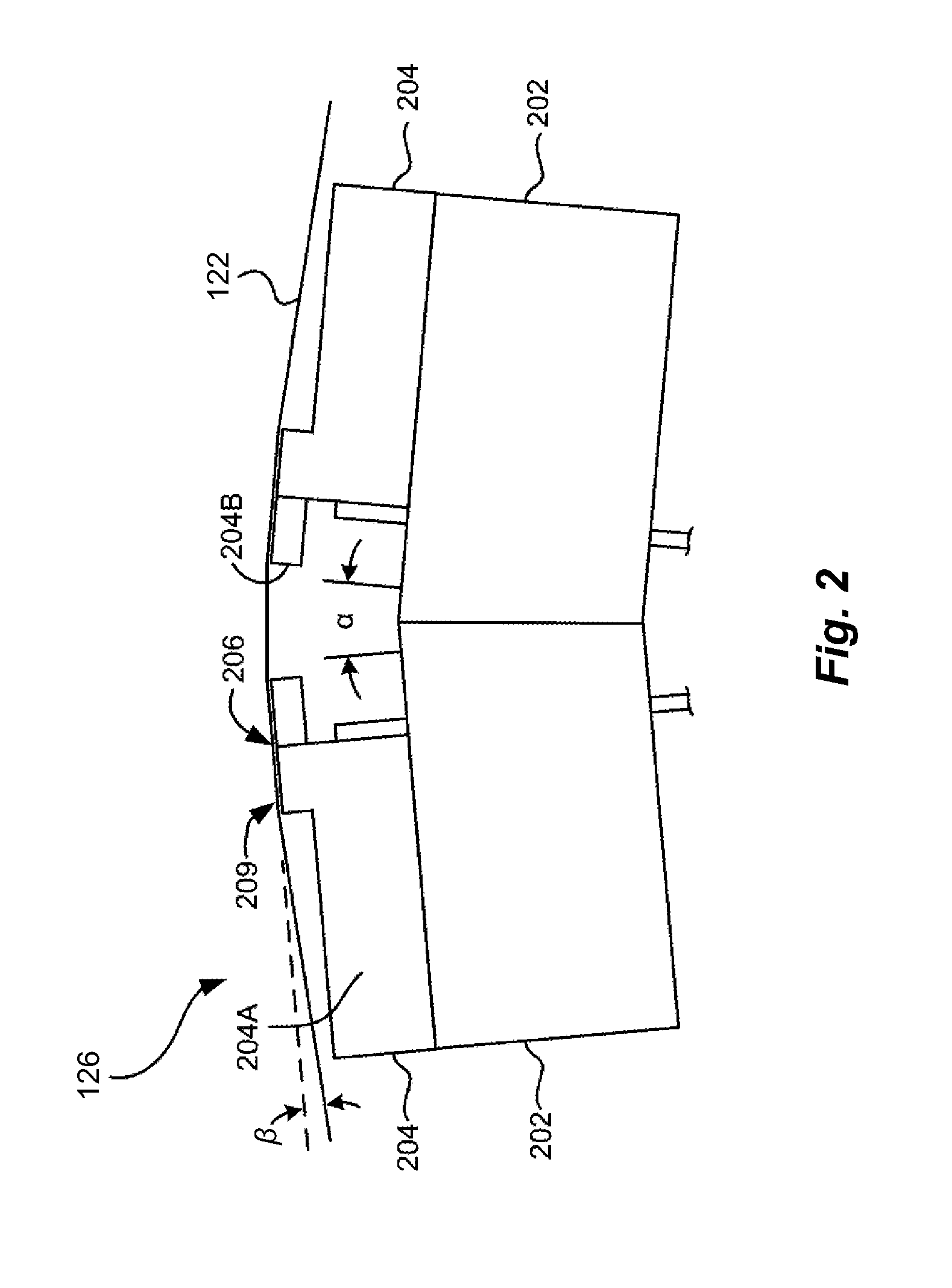
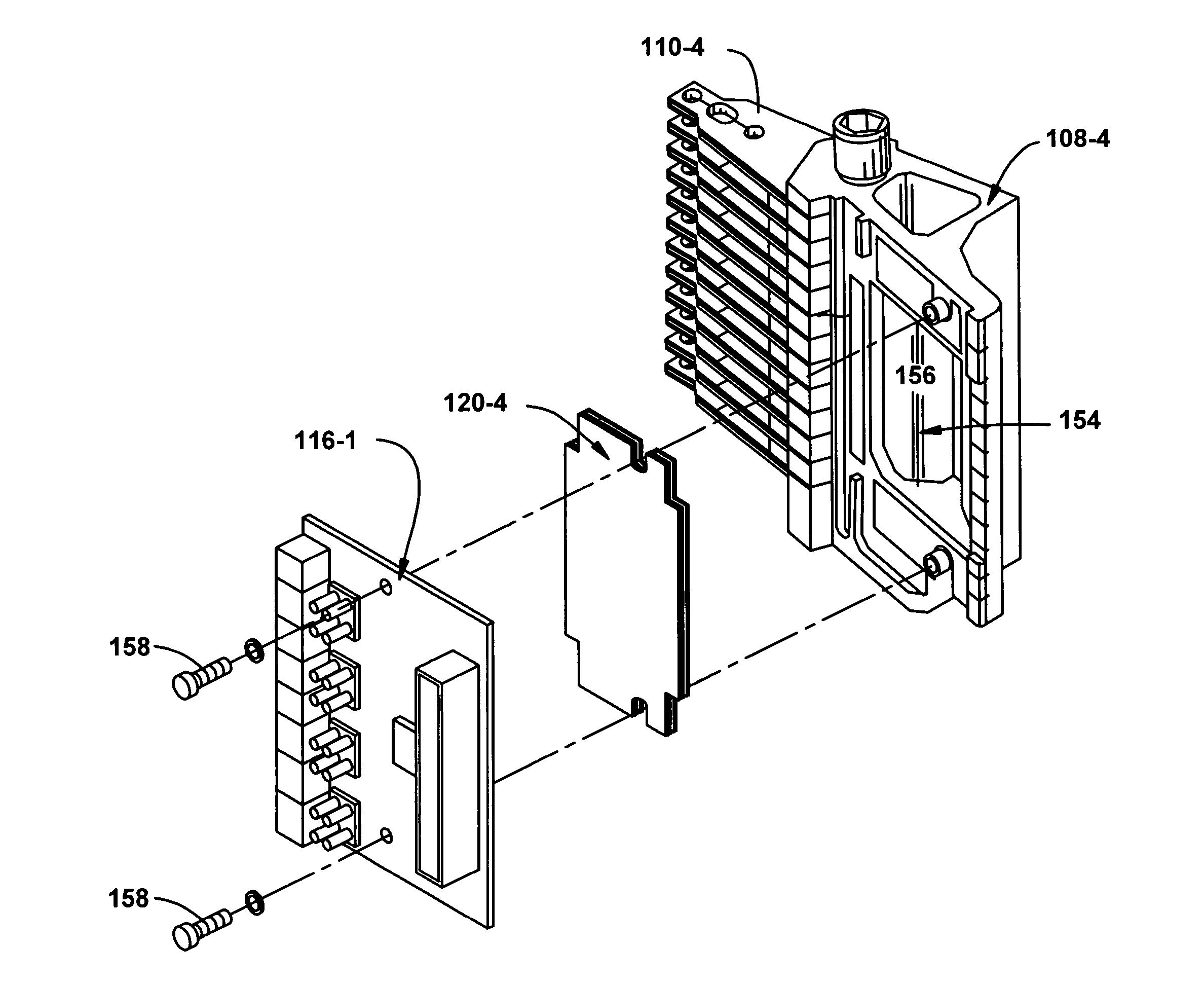
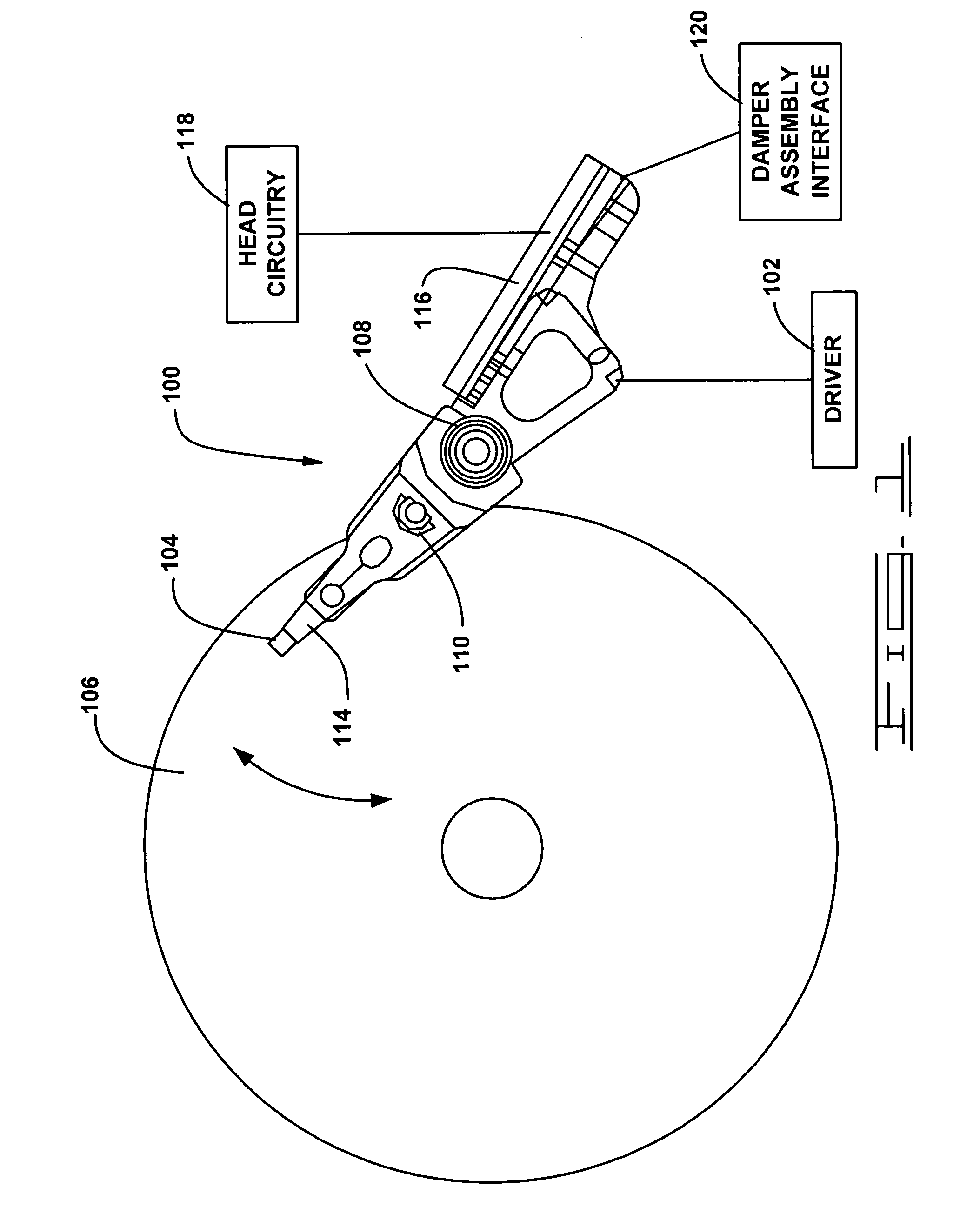
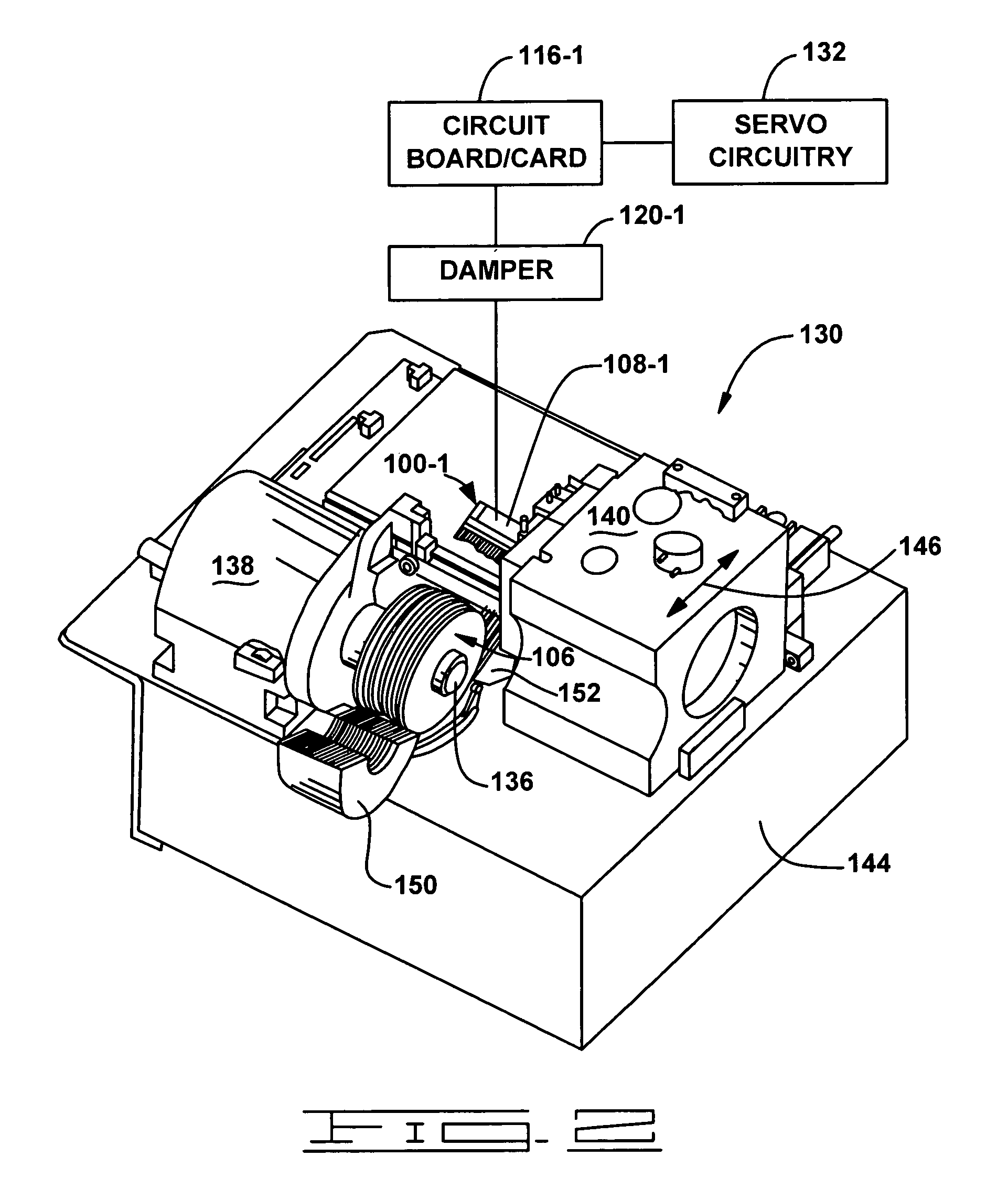
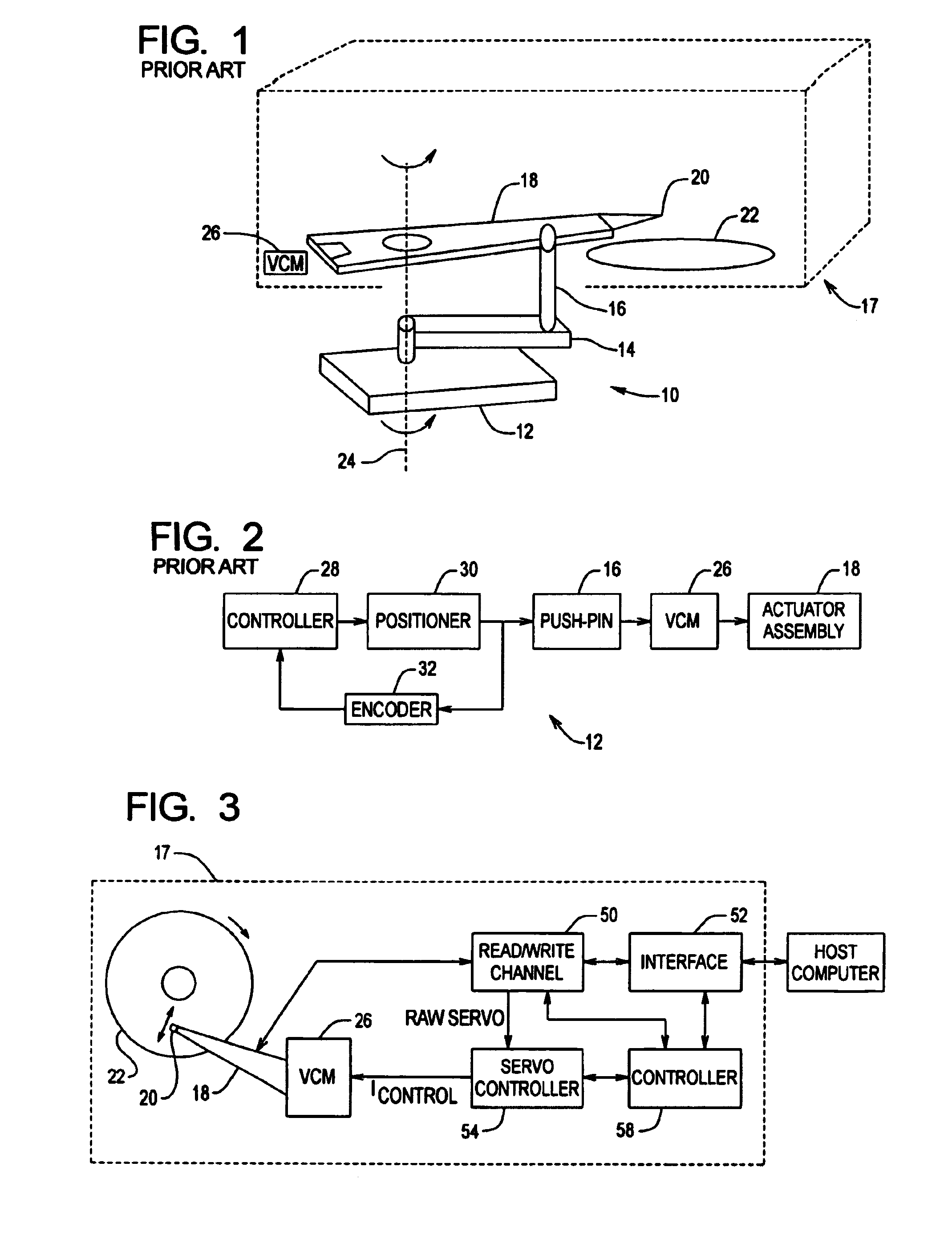
Actuator assembly including a circuit assembly and a damper therefor
Apparatus and method for damping operational vibration modes of an actuator assembly. The actuator assembly preferably supports a data transducing head adjacent a storage medium in a servo track writing environment. The actuator assembly further supports a circuit assembly comprising circuit board, card or other circuit portion to facilitate electrical communication with the data transducing head. A damping assembly is interposed between the circuit assembly and the actuator assembly to mechanically decouple the circuit assembly from the actuator assembly. Preferably, the damper assembly comprises one or more rigid damper plates and one or more viscoelastic layers therebetween to provide constrain layer damping. As desired, the plates can be provided with progressively larger thickness dimensions in a direction away from the actuator assembly.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
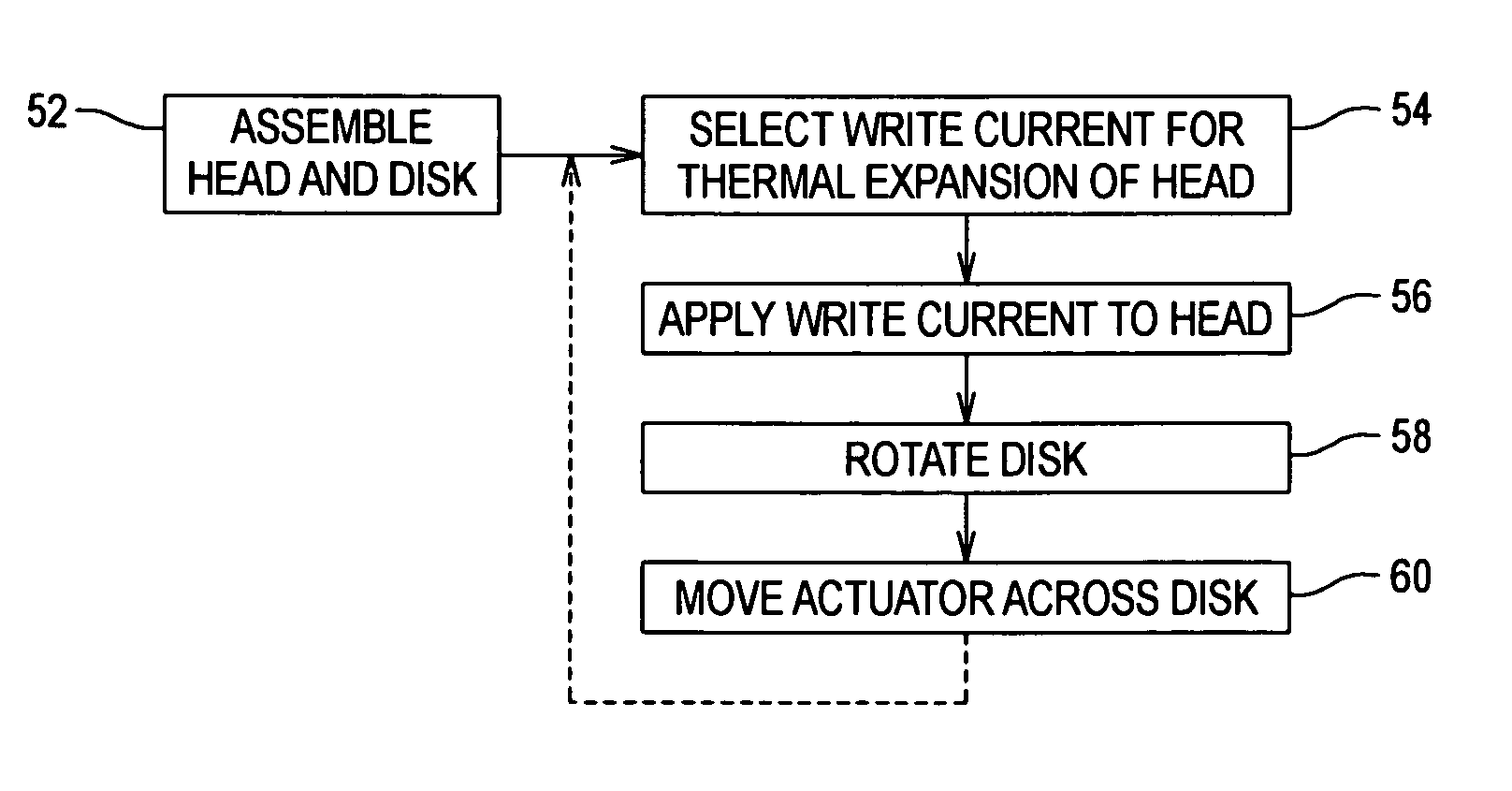
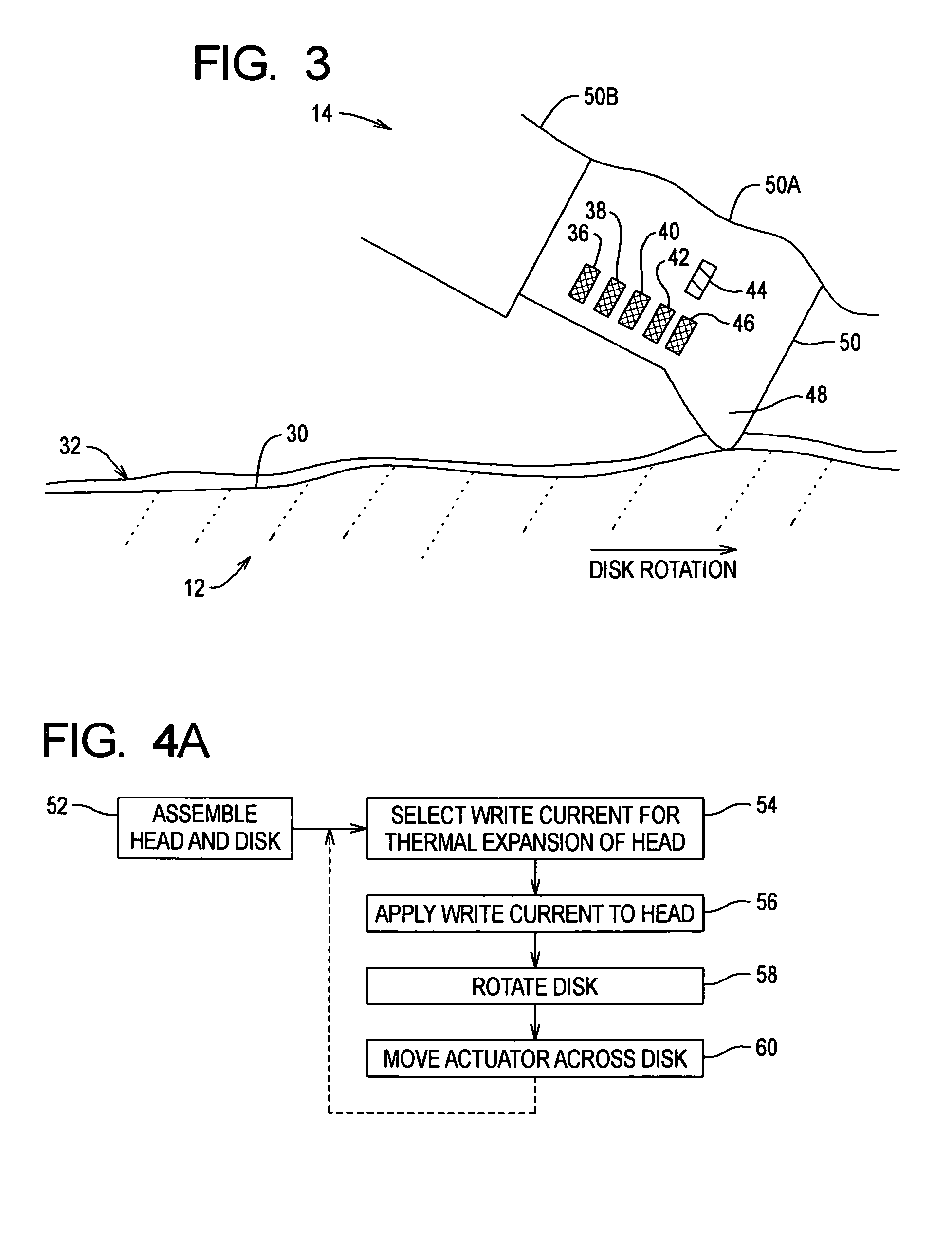
Head-disk interface preconditioning using write current before servo track write
InactiveUS7088532B1Smooth connectionReduce and eliminate interferenceDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringFlying height
Disk drive preconditioning allows the head-disk interface to be burnished or worn so that head-disk interference is reduced or eliminated before servo track writing. The head is positioned closer to the disk than the normal fly height during a preconditioning sweep and then returns to the normal fly height during servo track writing.
Owner:MAXTOR
Adjustable spacing formatter head
ActiveUS9472221B1Alignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageProgram instructionMagnetic tape
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Magnetic alignment marking of hard disks
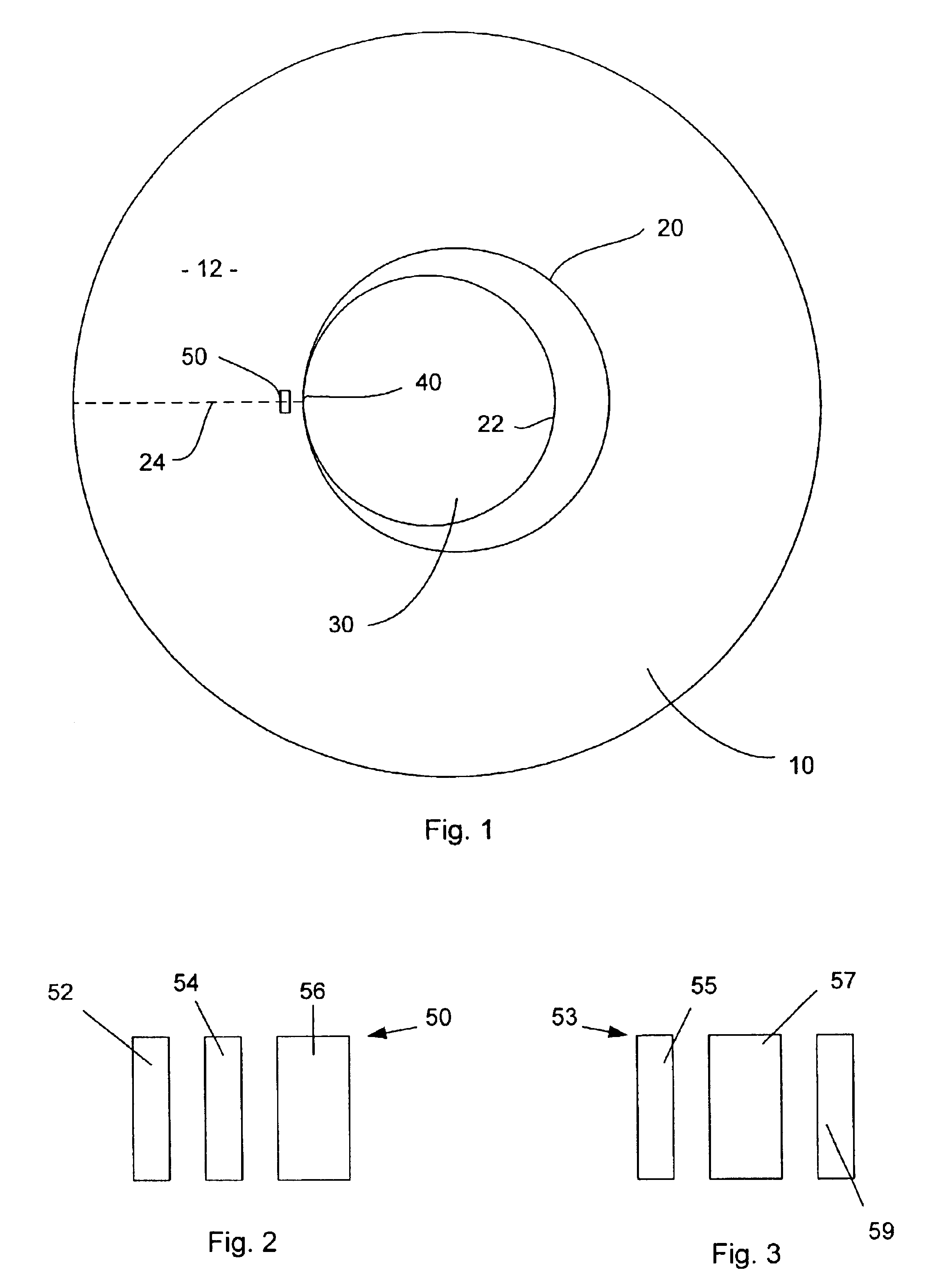
InactiveUS6940678B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageEngineeringServo track writing
Magnetic alignment marks are recorded on a recording surface of a magnetic hard disk to mark the location where the disk is abutted against the hub of the spindle of a multiple-disk servo-writer. The alignment marks for each recording surface may be different so as to distinguish between top and bottom disk surfaces so that when the discs are assembled onto the spindle of a disk drive they may be assembled with the proper orientation, i.e., the top surface is mounted “up.” The marks may be large, low frequency patterns that are both written and detected by non contact means other than the servo-track writer's or the disk drive's heads.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
High precision servo track writing with position error signal feedback
InactiveUS7050259B1High bandwidthServo writing time can be reducedDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageMagnetic transducersEngineering
A servo writer system for a disk drive uses the reader element of a magnetic transducer head in the disk drive to read head position information during servo writing of the disk drive. A positioning system in the servo writer uses both the head position information and actuator position information, as feedback signals to accurately position the transducer during servo writing, resulting in high quality servo tracks.
Owner:MAXTOR
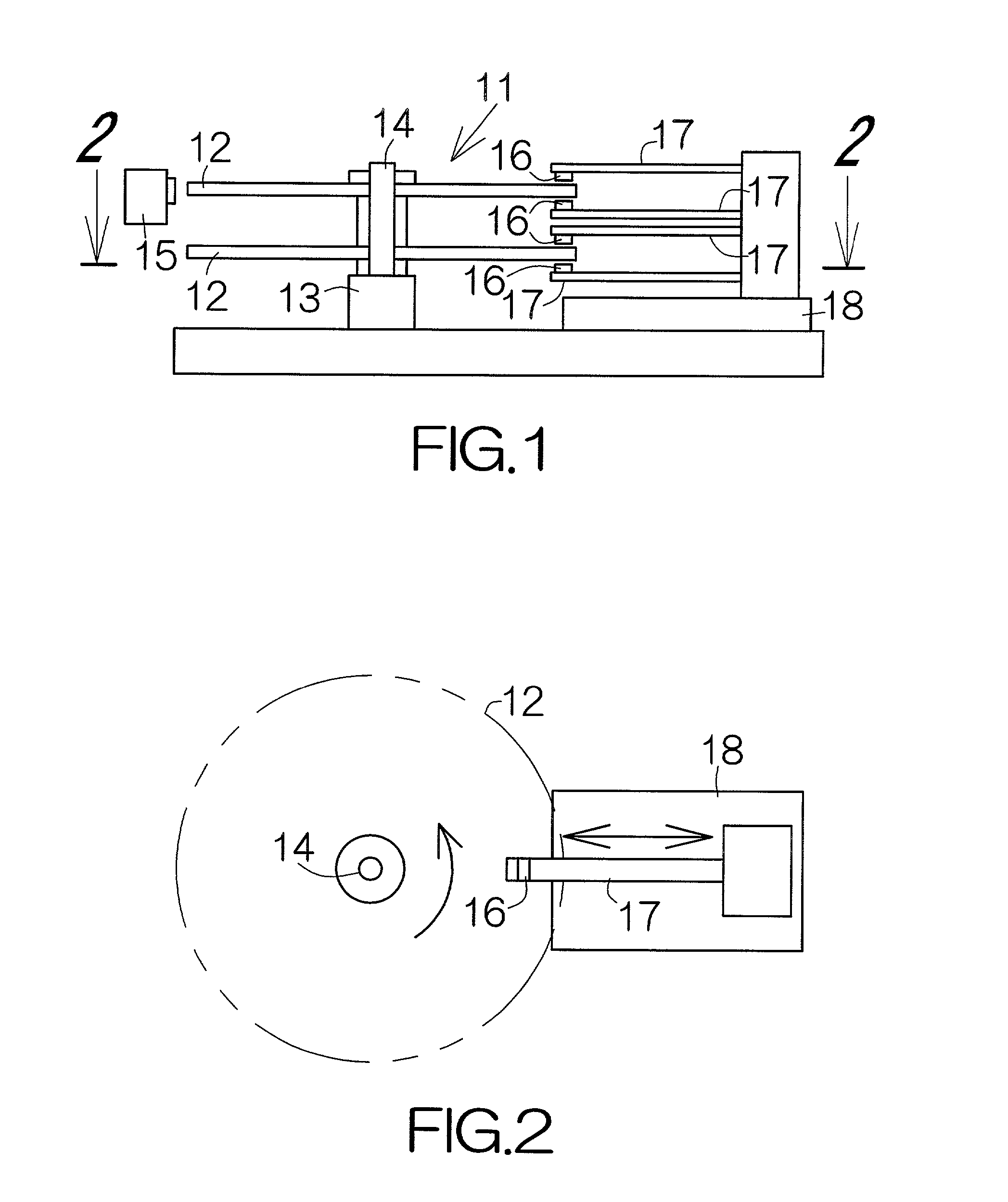
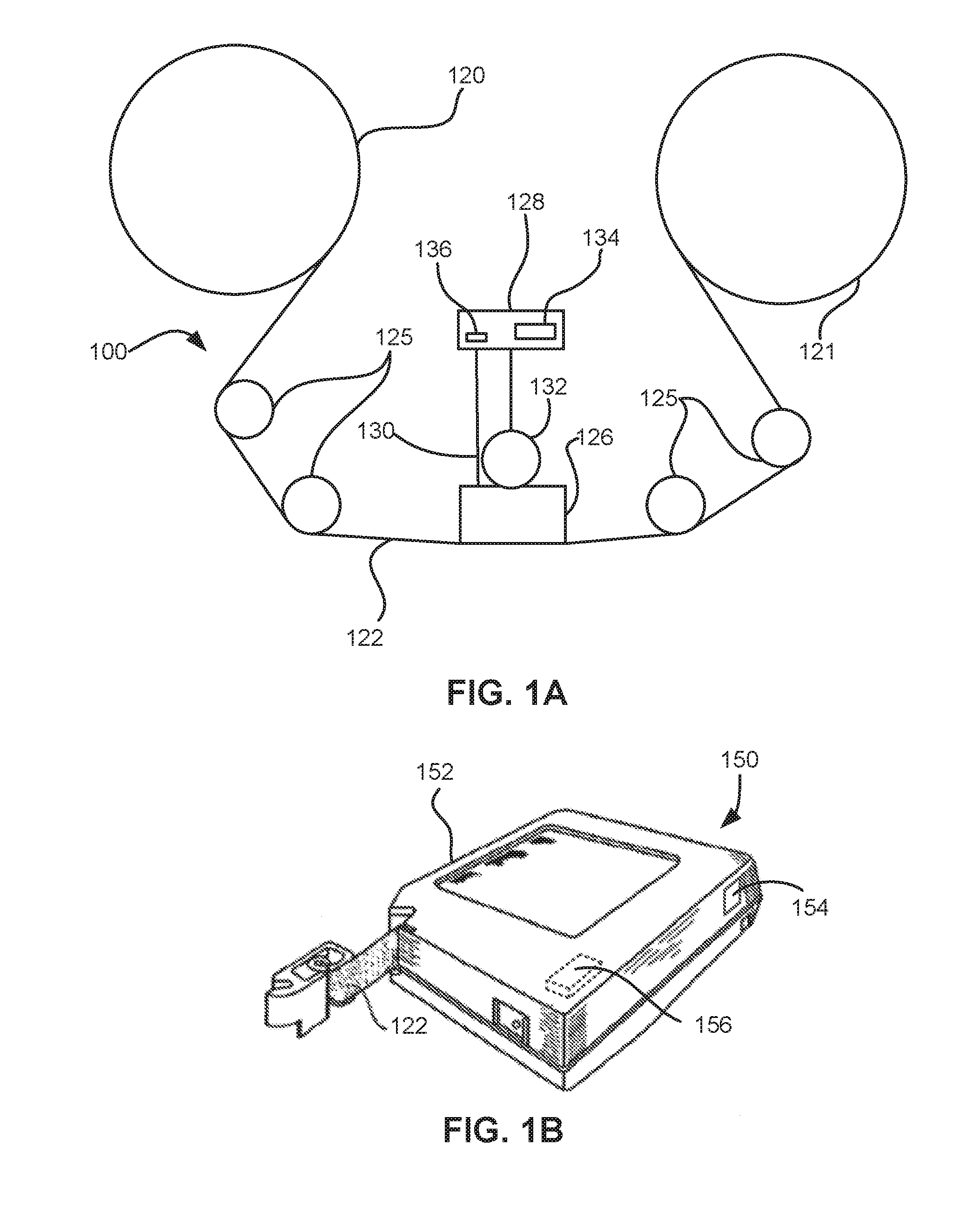
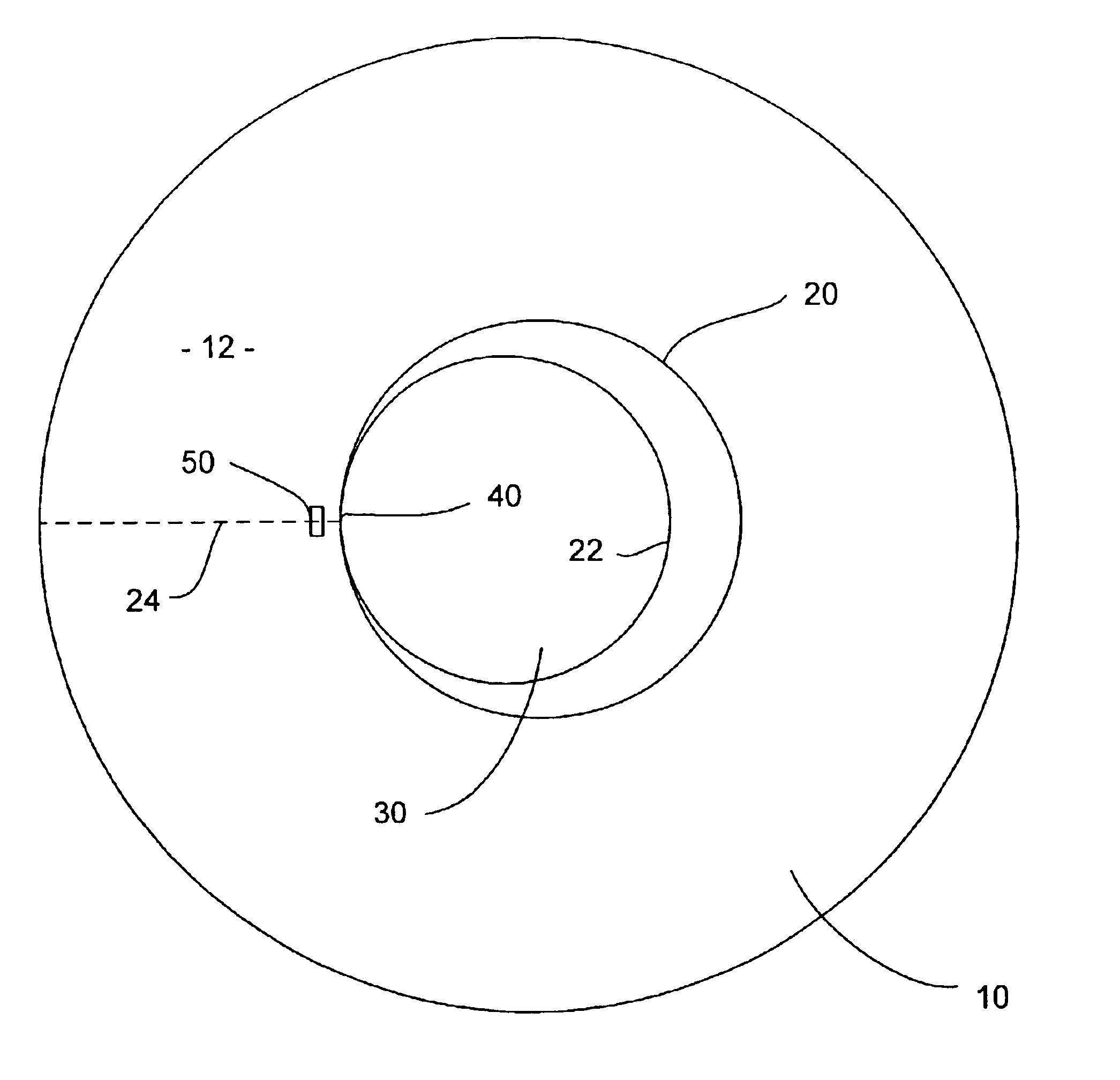
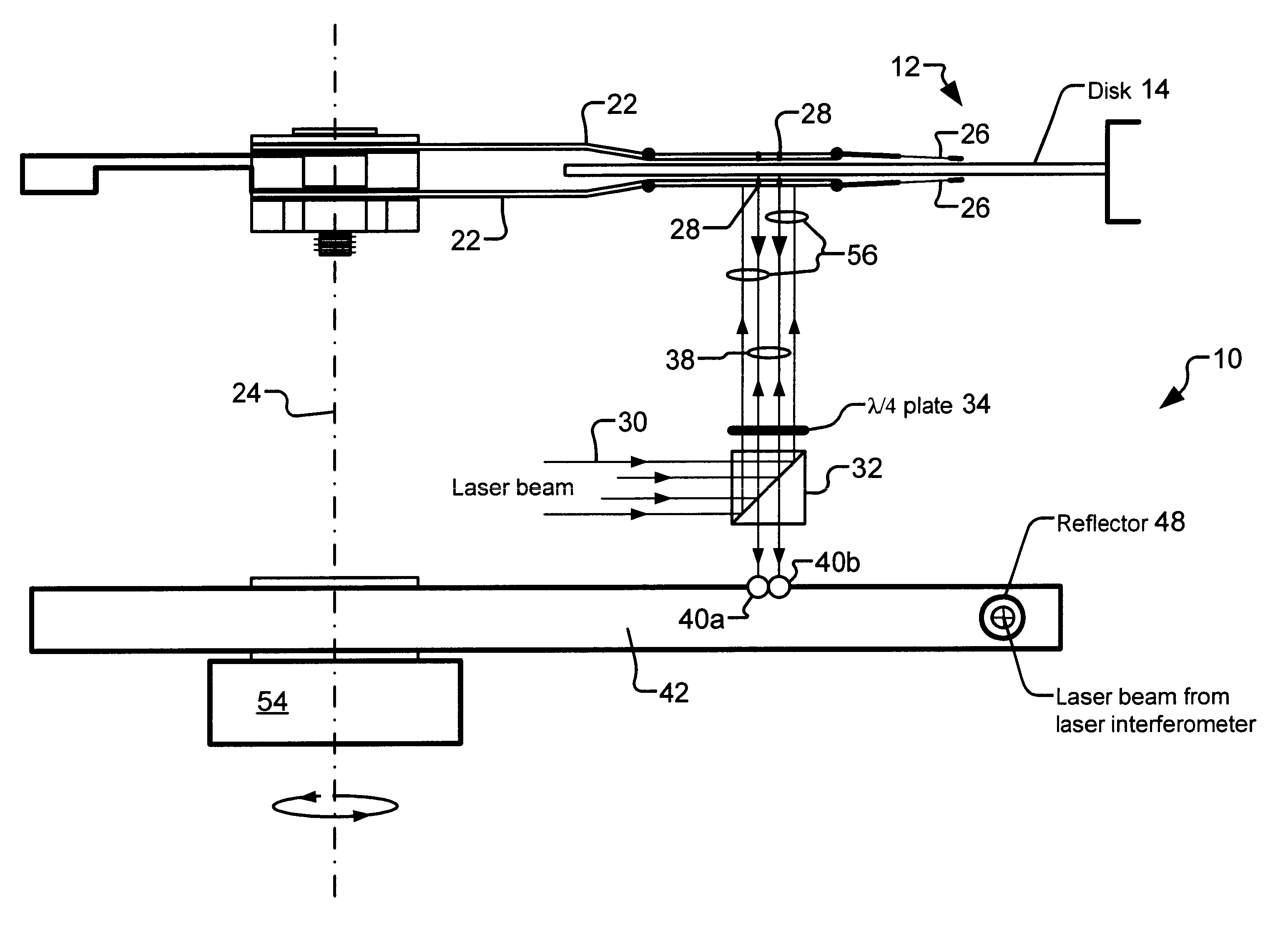
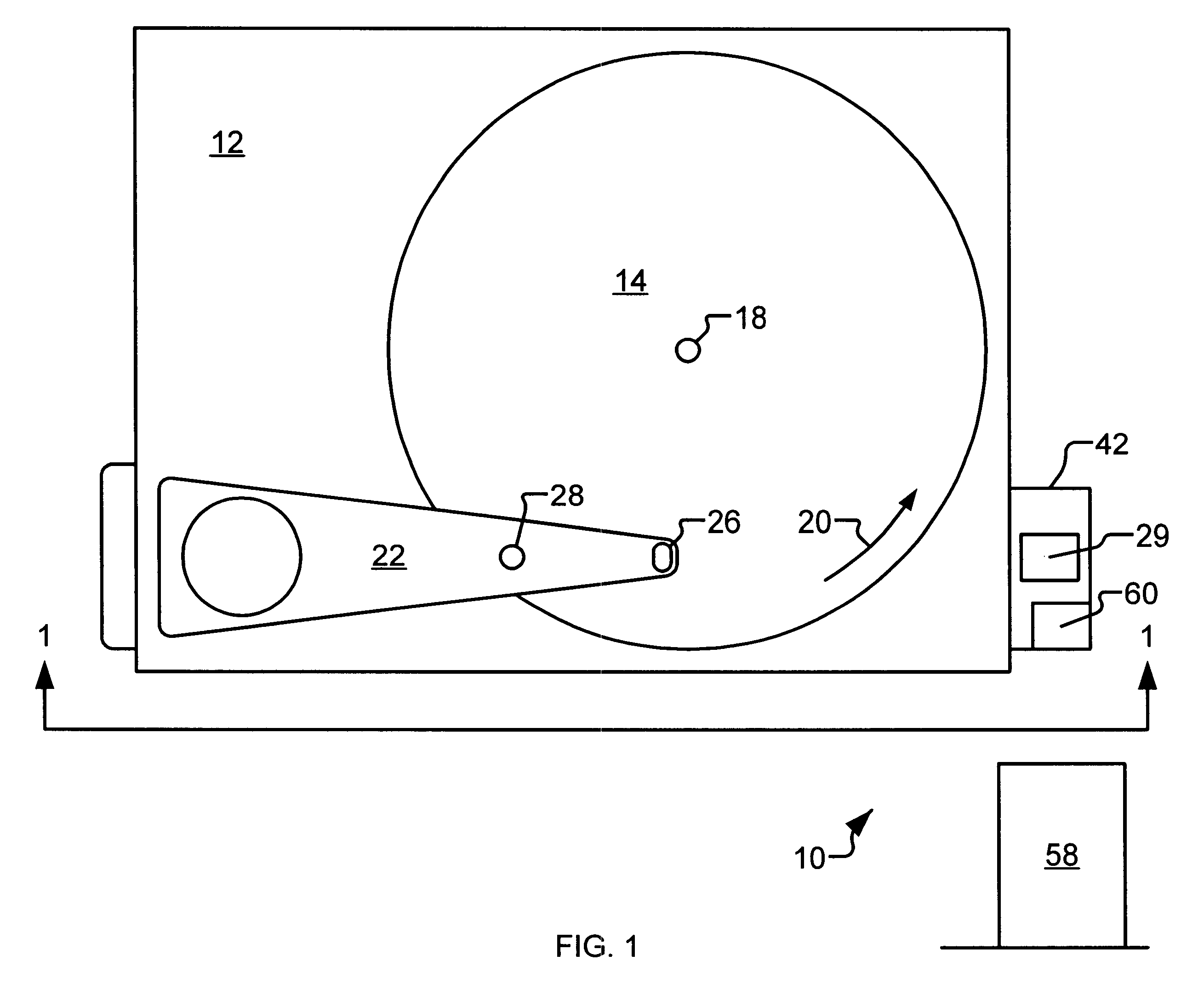
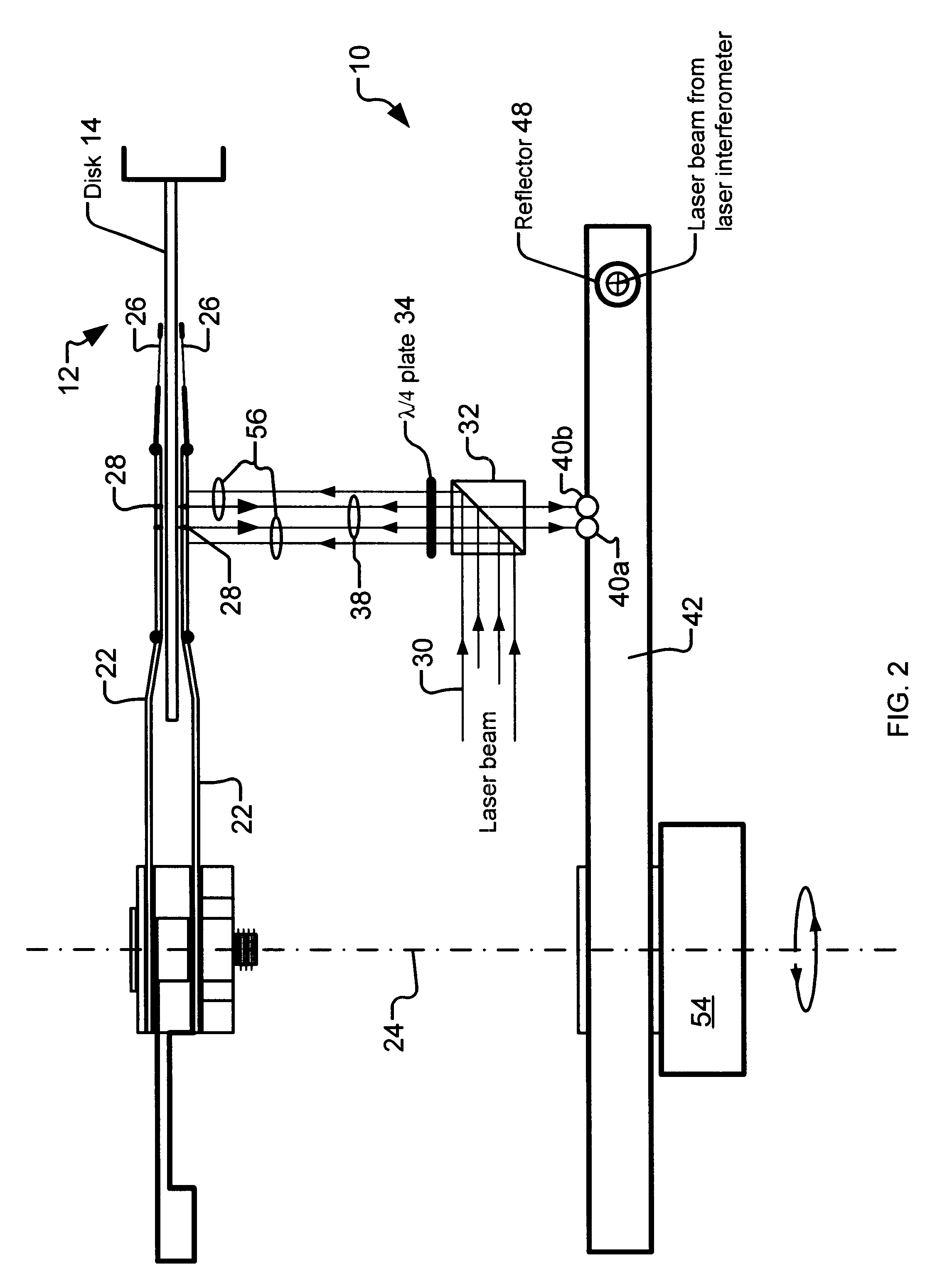
Non-contact servo track writing apparatus and method
InactiveUS6603629B1Maintain precisionLow production costTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageBeam splitterPolarization beam splitter
A servo track writing apparatus (10) for writing servo tracks (16) on a media disk (14) of a disk drive assembly (12) having a Positioning arm (22) with a through hole (28) therein. The writing apparatus (10) has a laser source (29) which directs a source beam (30) through a polarizing beam splitter (32) and a quarter-wave plate (34) to either pass through the through hole (28) and reflect off of the media disk (14) as a reflected beam (38), or to be reflected from regions of the positioning arm (22) proximate to the through hole (28) as a reflected beam (56). The writing apparatus (10) further has a remote tracking arm (42) with two photodiodes (40a, 40b) suitably mounted thereon to receive the reflected beams (38, 56). The tracking arm (42) is caused by a motive means (54) to precisely track the positioning arm (22) of the disk drive assembly (12). A laser interferometer (58) is then used to detect an optical target (60) mounted on the tracking arm (42) and determine positioning for writing of the servo track (16).
Owner:EXCEL PRECISION
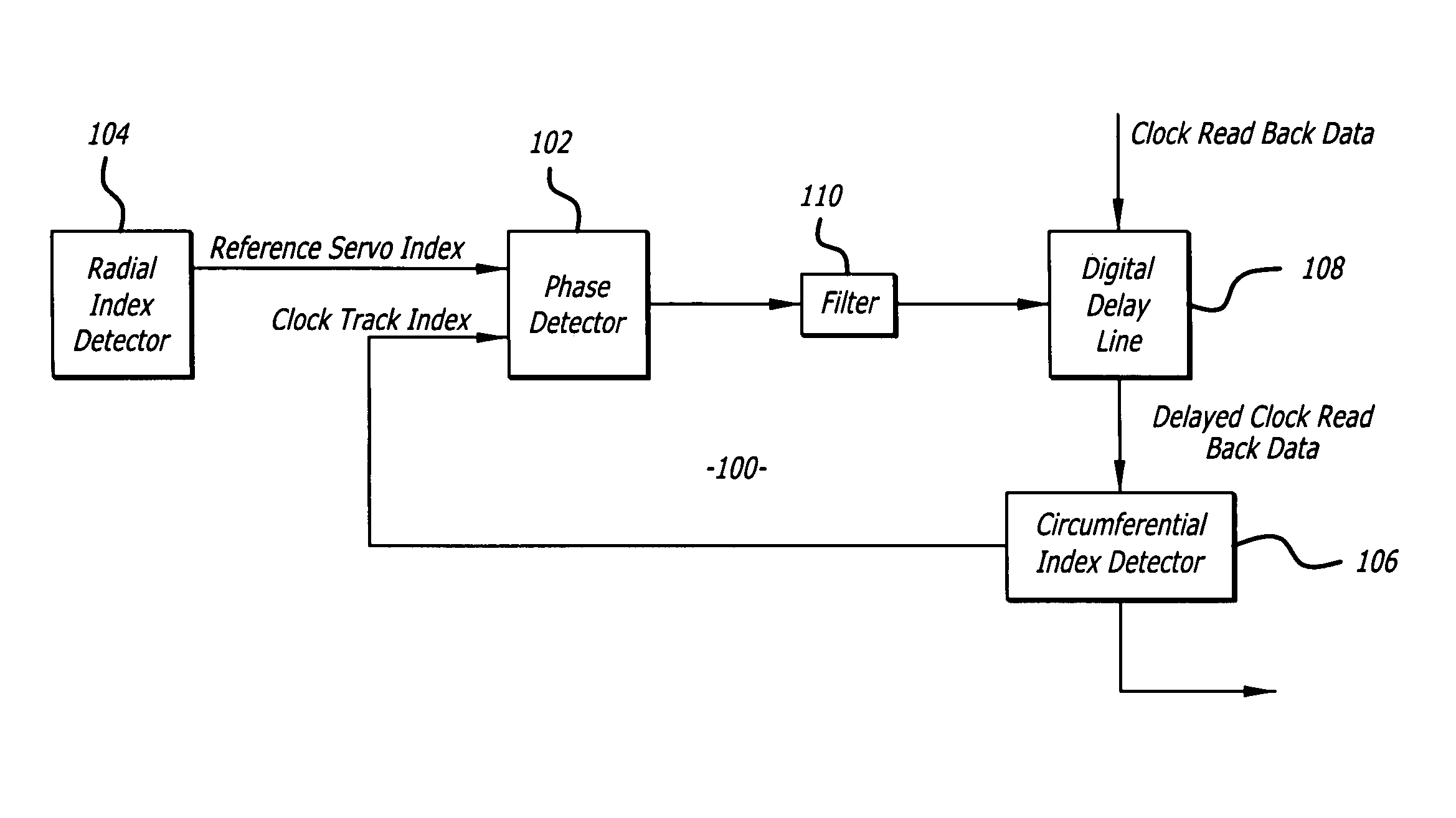
Delay clock track read back data to compensate time variance due to disk thermal expansion in spiral servo track writing
A method for writing servo information onto a disk of a hard disk drive with a servo writer. The disk has a circumferential index and a band of servo reference tracks. The circumferential index is detected from a clock signal generated from a clock track of the disk. The reference tracks include radial indices. A spiral servo pattern is written upon the detection of the circumferential index and a radial index. The servo writer includes a phase detector that detects changes in the relative position of the circumferential and radial indices and a delay circuit that delays the clock signal to offset such changes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
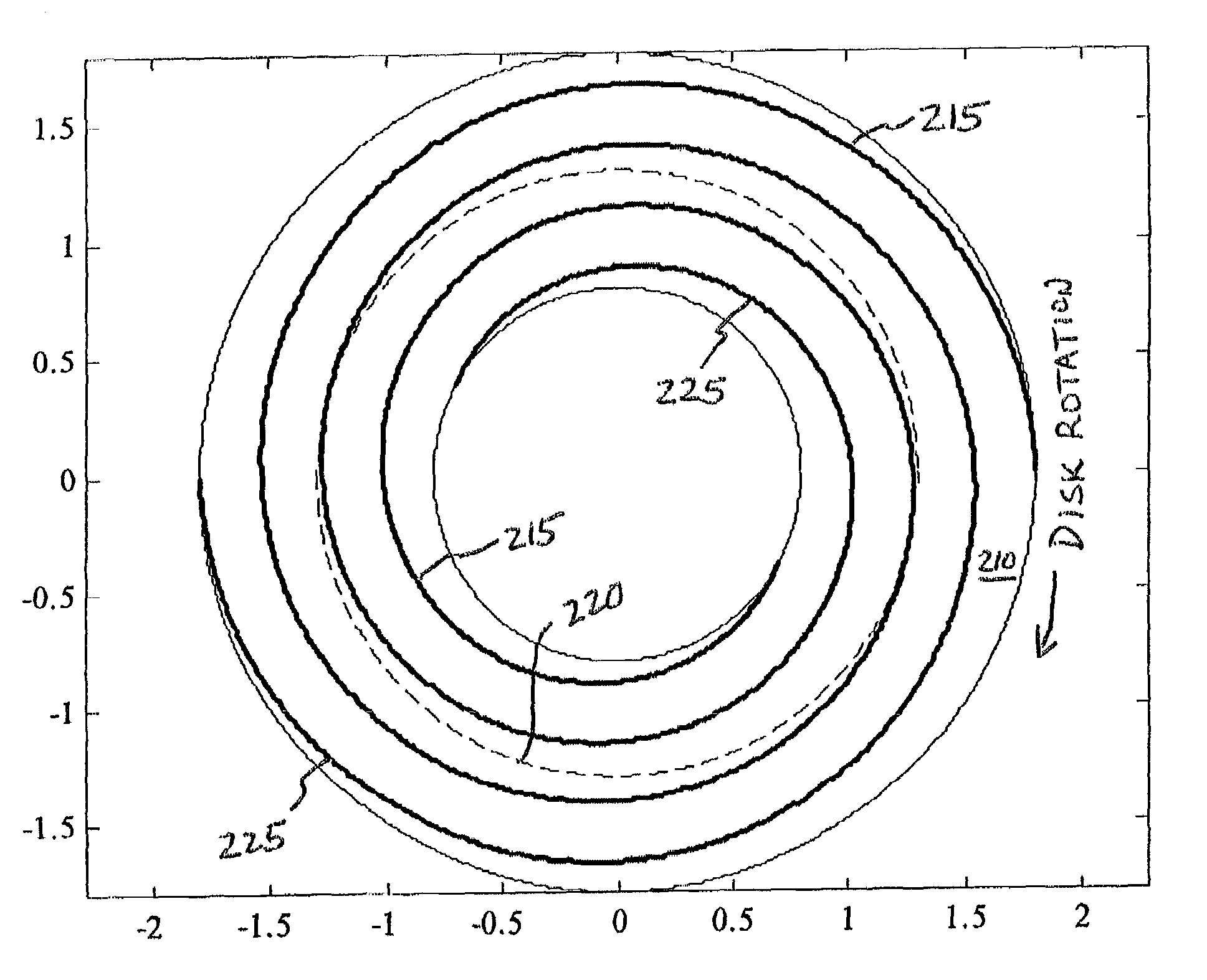
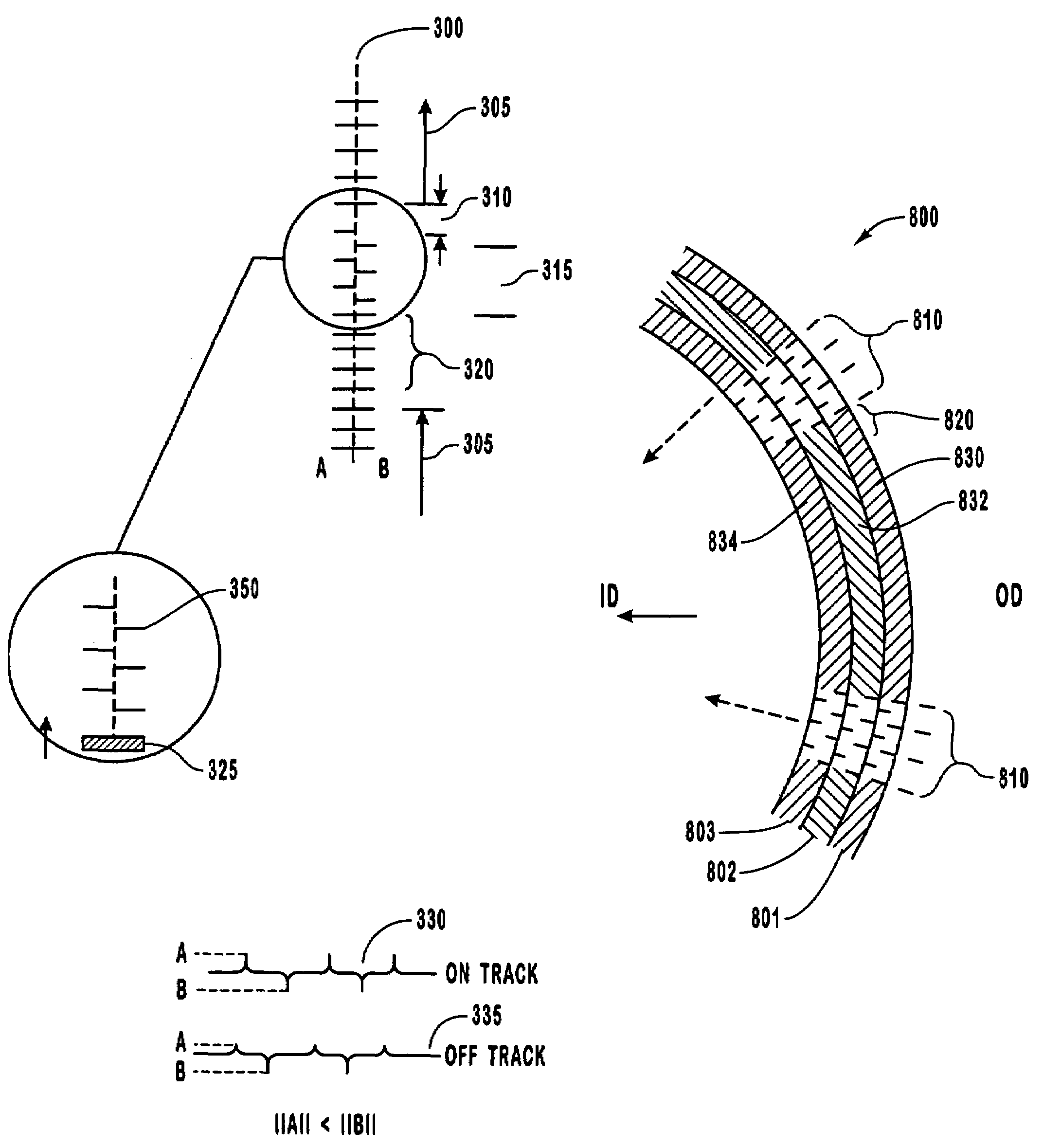
Spiral servo patterns with absolute reference point
InactiveUS7561359B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksNon symmetricComputer science
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for providing an absolute reference point on a disk surface of a disk drive. A write head associated with the disk surface is used to write spirals of servo information thereon, for example, under control of a servo track writer. The spirals of servo information include standard spirals and special spirals. In one embodiment, the special spirals are shorter than the standard spirals and the special spirals are rotationally non-symmetric. For example, an unequal number of standard spirals are interposed between one pair of adjacent special spirals relative to the number of standard spirals interposed between other pairs of adjacent special spirals. The special spirals may take a variety of other forms to distinguish themselves from standard spirals.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
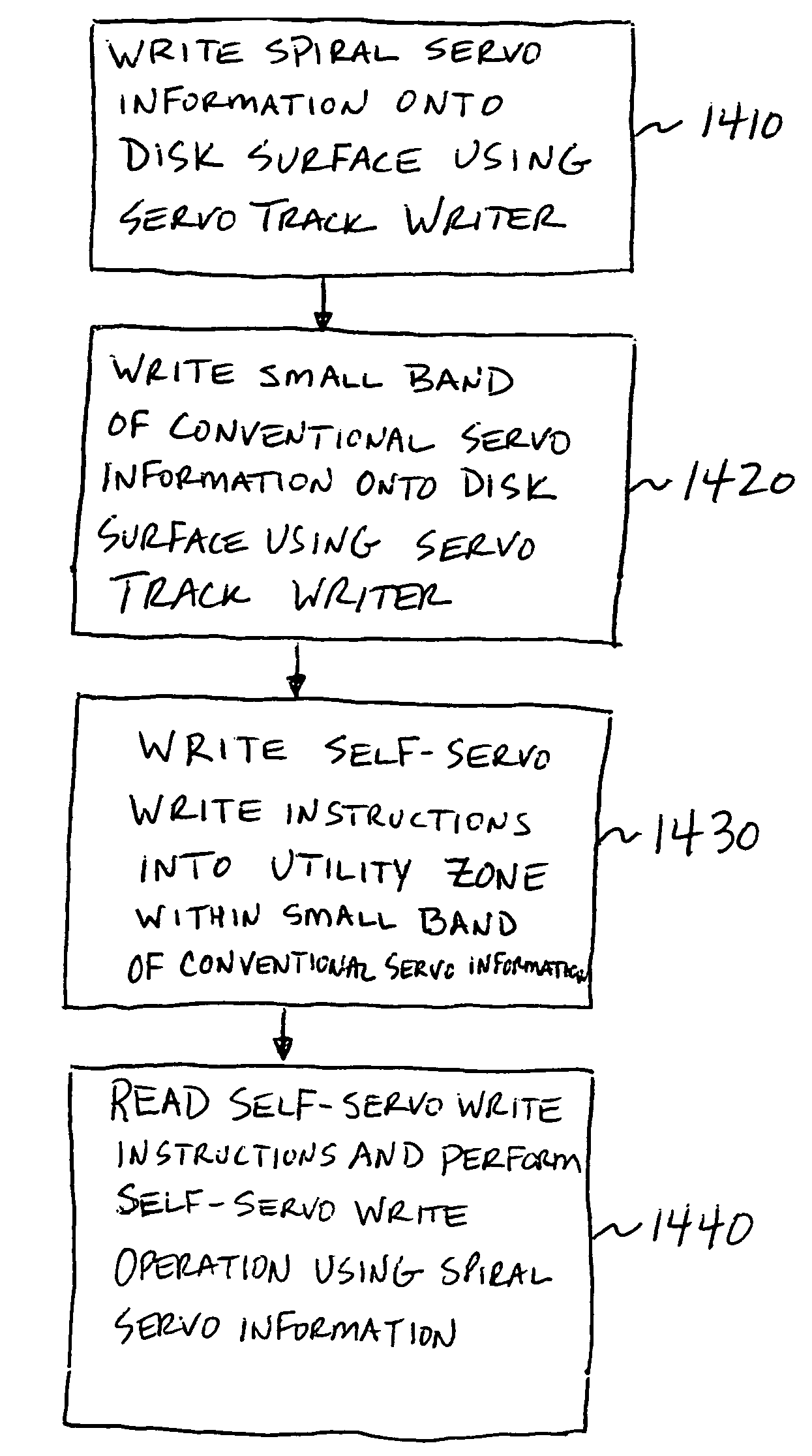
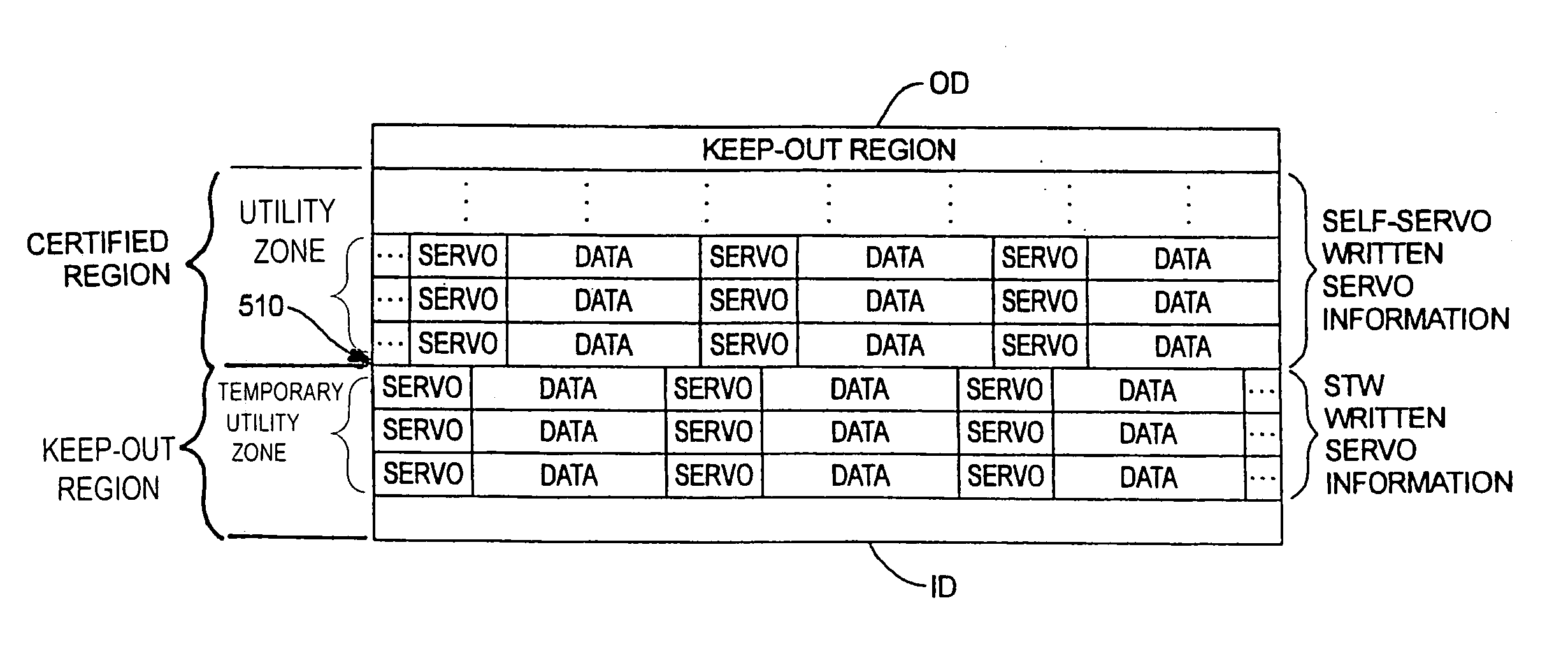
Method and apparatus for providing a temporary utility zone in a disk drive
A disk surface has a keep-out region and a certified region. A transducer associated with the disk surface writes servo information in the keep-out region under control of a servo track writer. The transducer then writes data in a temporary utility zone in the keep-out region. Next, a self-servo write operation uses data in the temporary utility zone to write servo information in the certified region. Thereafter, data is transferred from the temporary utility zone to a final utility zone in the certified region.
Owner:MAXTOR
Testing printed circuit boards of disk drives and servo track writers
InactiveUS20060145721A1Printed circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringPrinted circuit board
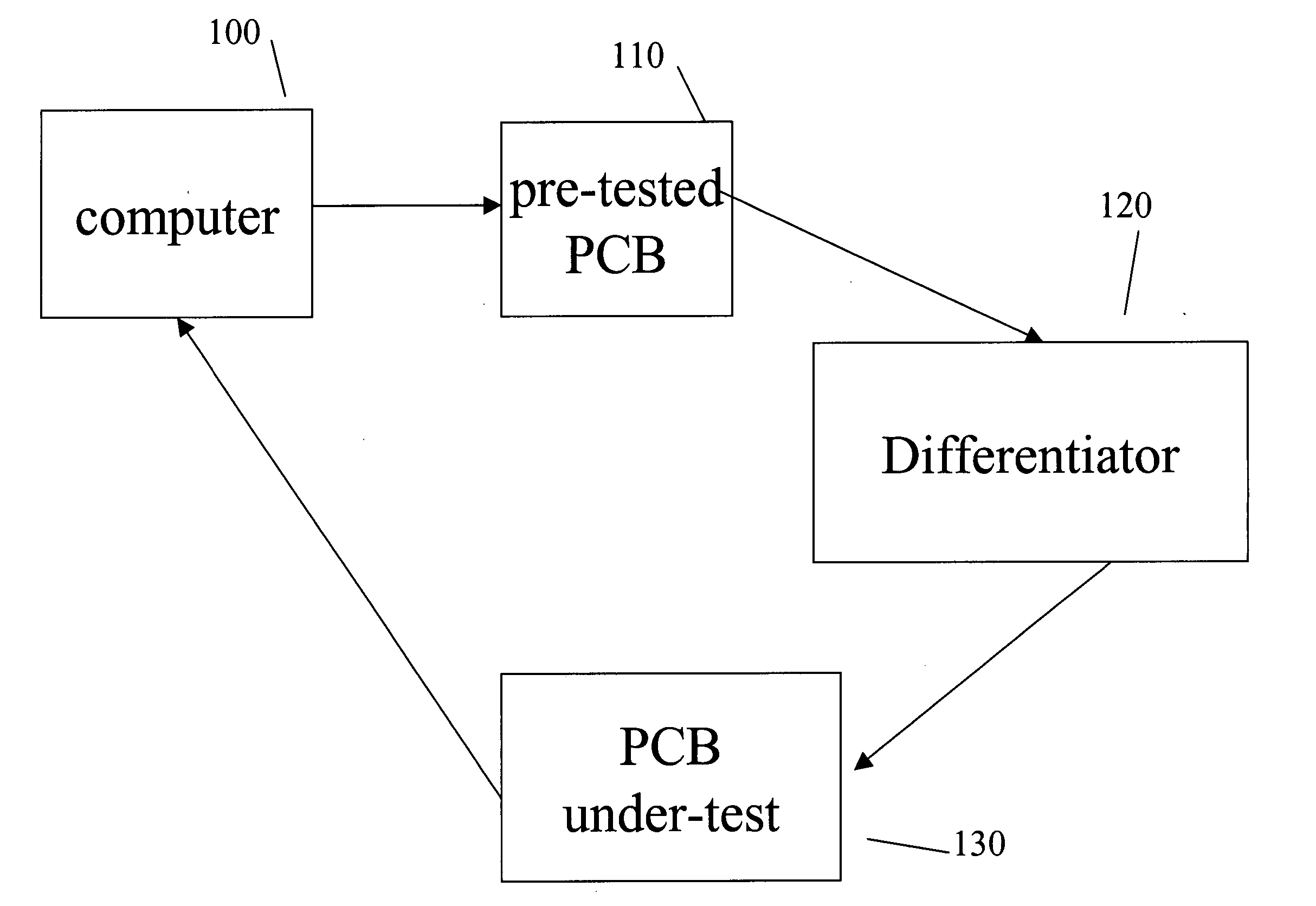
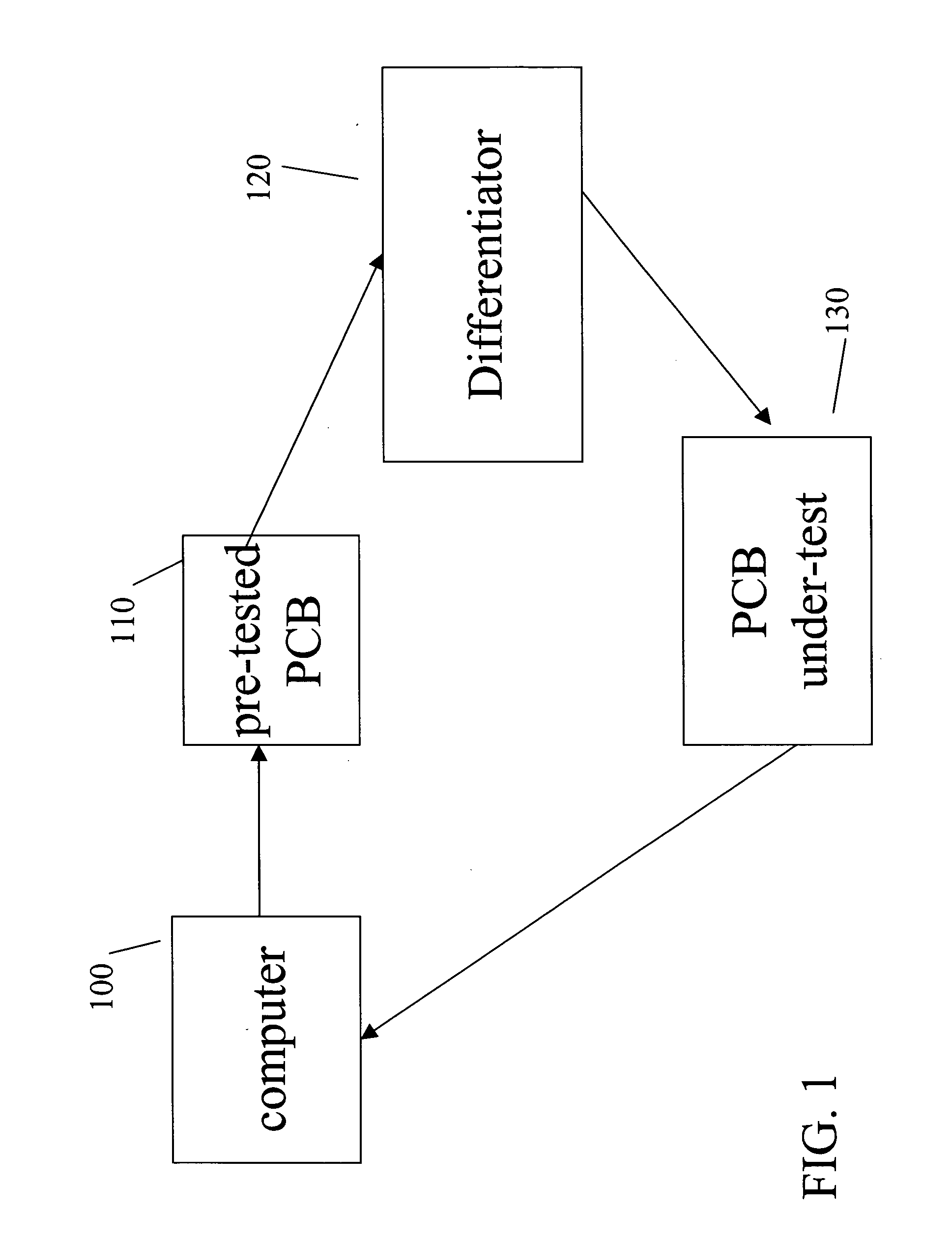
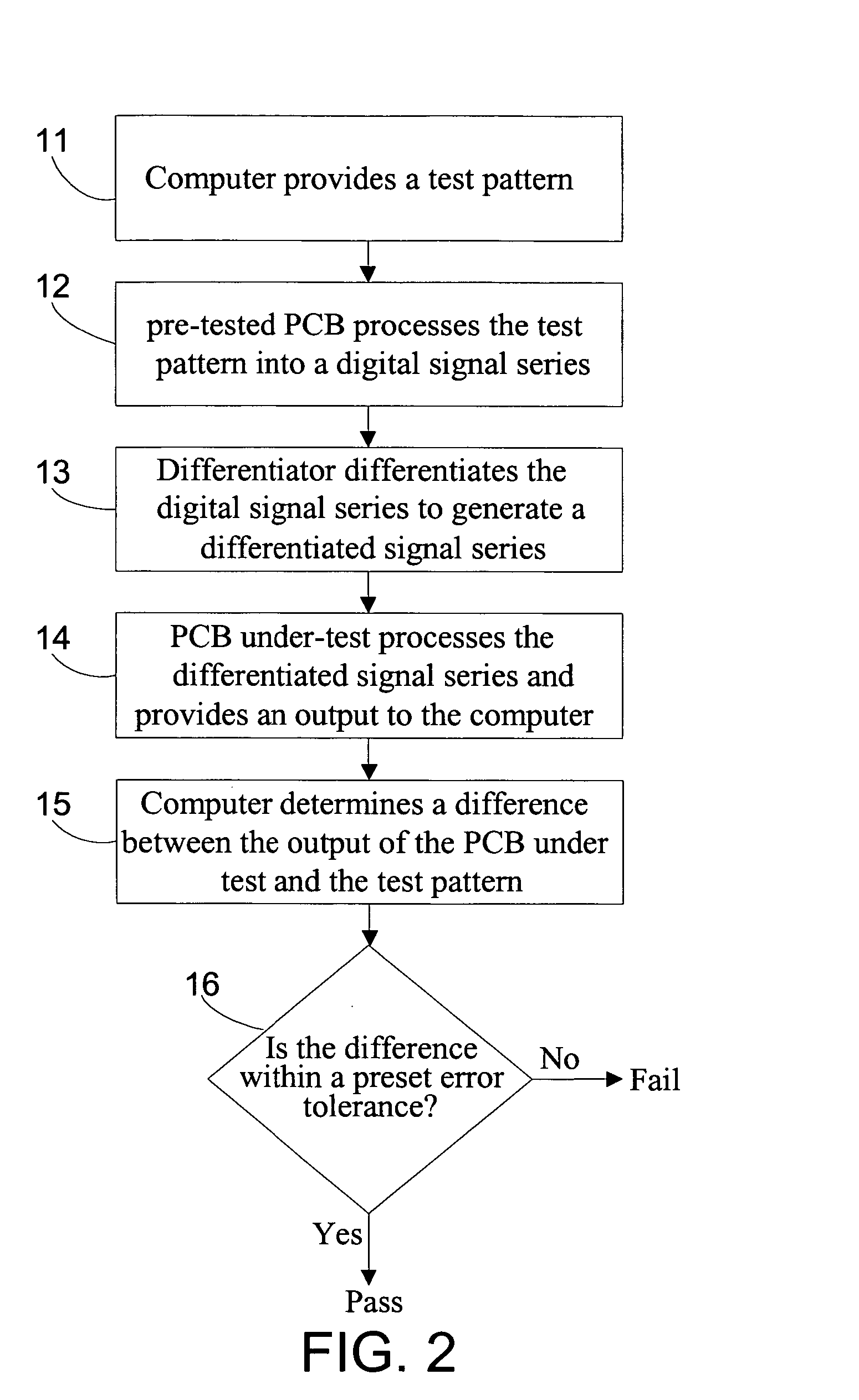
One embodiment of the present invention is method for testing a reading function of a printed circuit board of a disk drive or a servo track writer that includes: (a) providing a test pattern; (b) processing the test pattern to generate a digital signal series; (c) differentiating the digital signal series to provide a differentiated signal series; (d) applying the differentiated signal series as input to the printed circuit board; and (e) comparing an output from the printed circuit board with the test pattern.
Owner:GS MAGIC
Servo track writing for ultra-high tpi disk drive in low density medium condition
InactiveUS20050128628A1Track finding/aligningFilamentary/web record carriersMedia controlsHard disc drive
A servo writer that writes servo information onto a disk of a hard disk drive. The servo writer can write servo information onto a disk of a hard disk drive while the disk is within an inner chamber of a housing. The rotating disk creates a flow of fluid within the inner chamber. The disk is rotated during the servo writing process. The density of a fluid medium within the inner chamber is controlled by a medium control system so that the density of the medium is less than the density of air at one atmosphere. Lowering the density decreases the amplitude of vibrational forces created by the flow of fluid. Decreasing the amplitude reduces errors in the servo writing process. The density can be reduced by pulling a vacuum within the inner chamber. The density can also be reduced by filling the inner chamber with a gas such as helium that has a lower density than air.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH INT
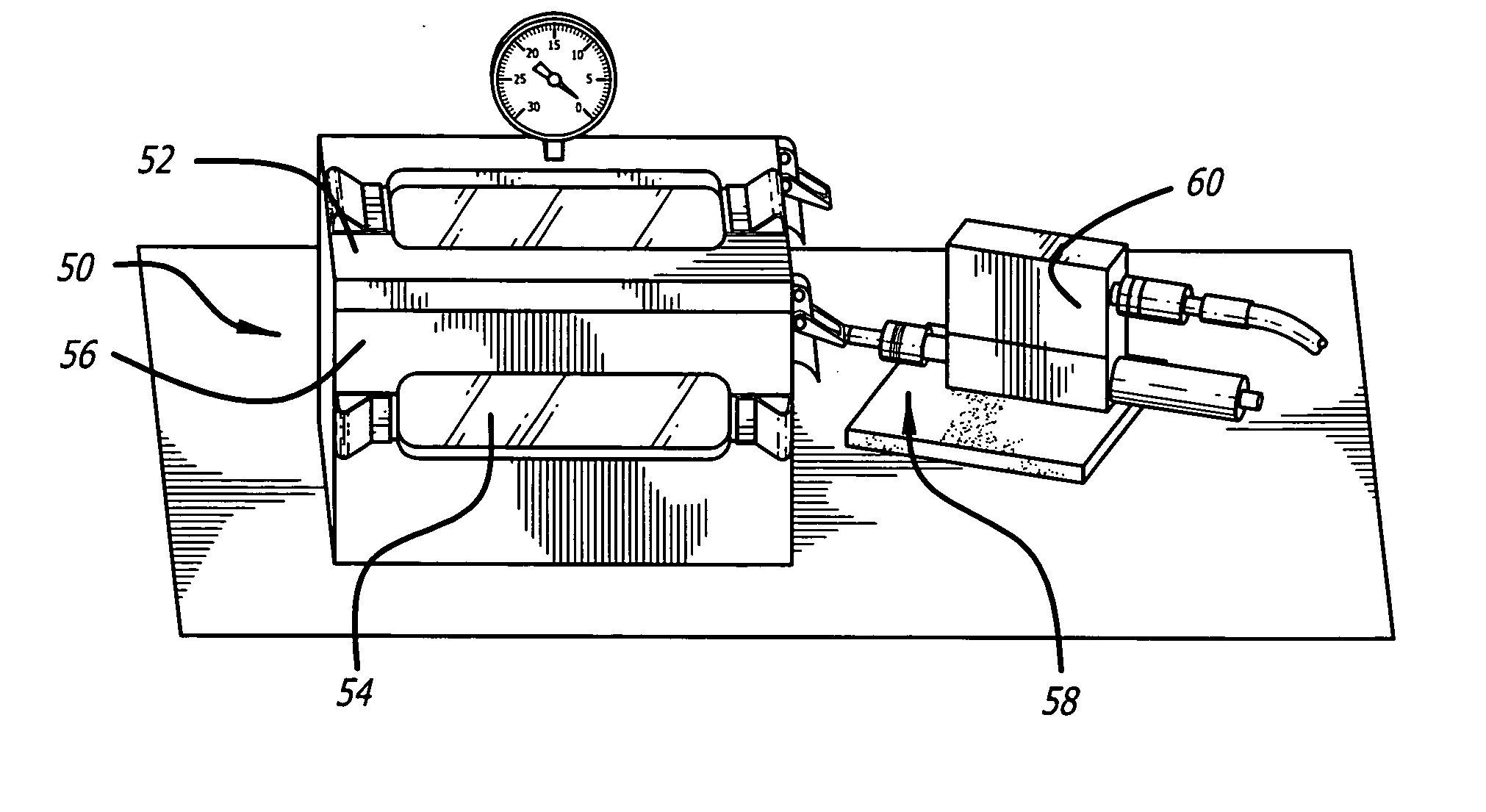
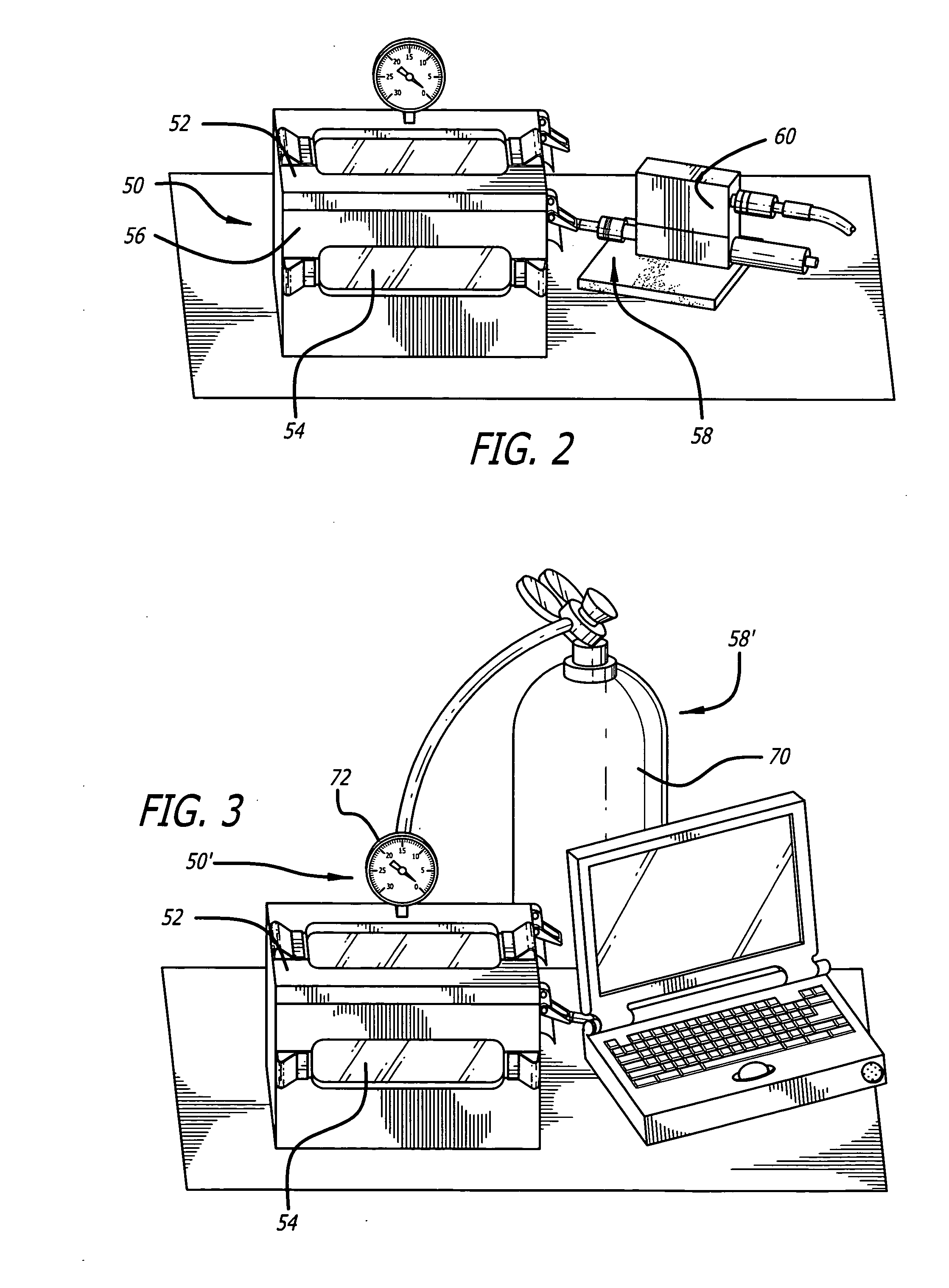
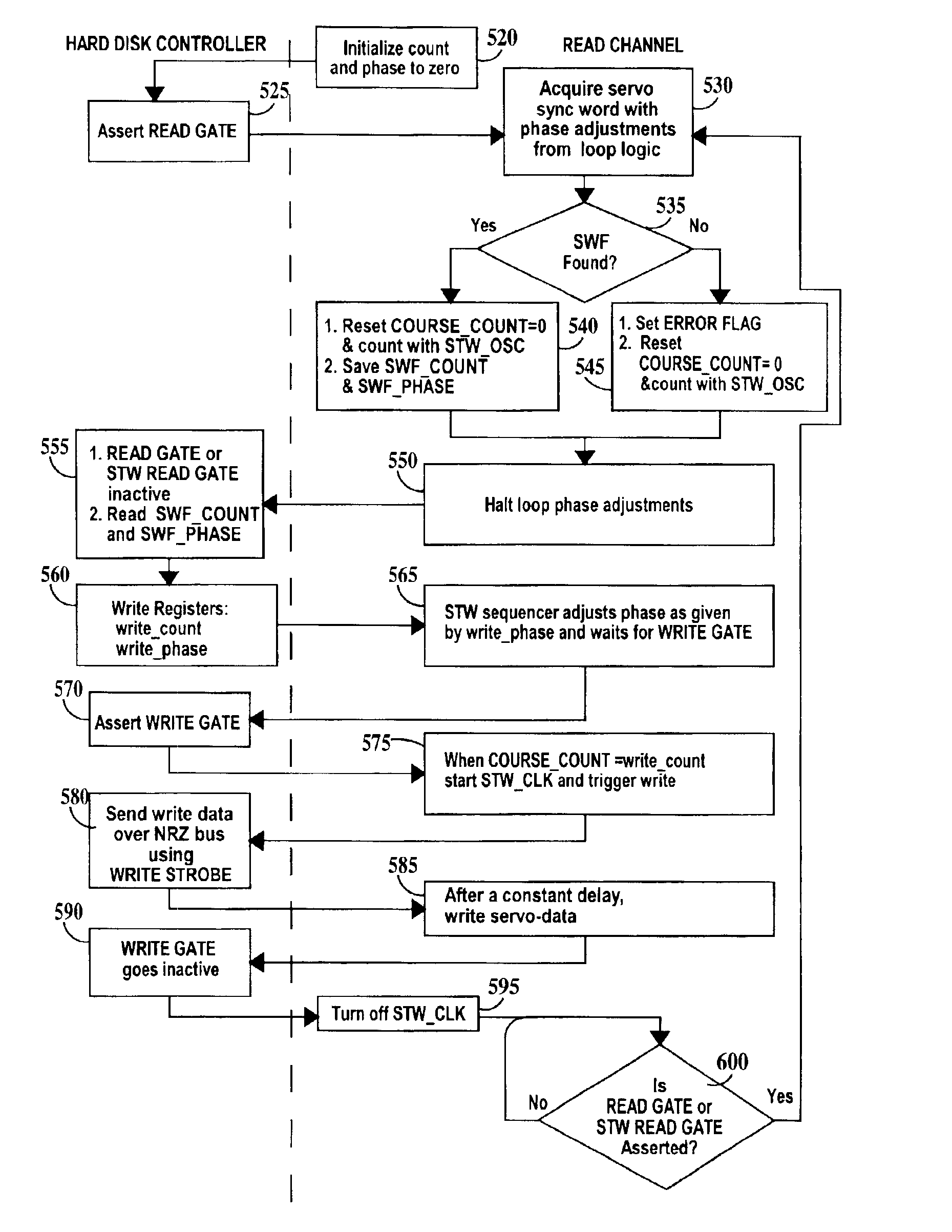
Read channel with automatic servo track writer
InactiveUS6934103B2Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDisk controllerComputer science
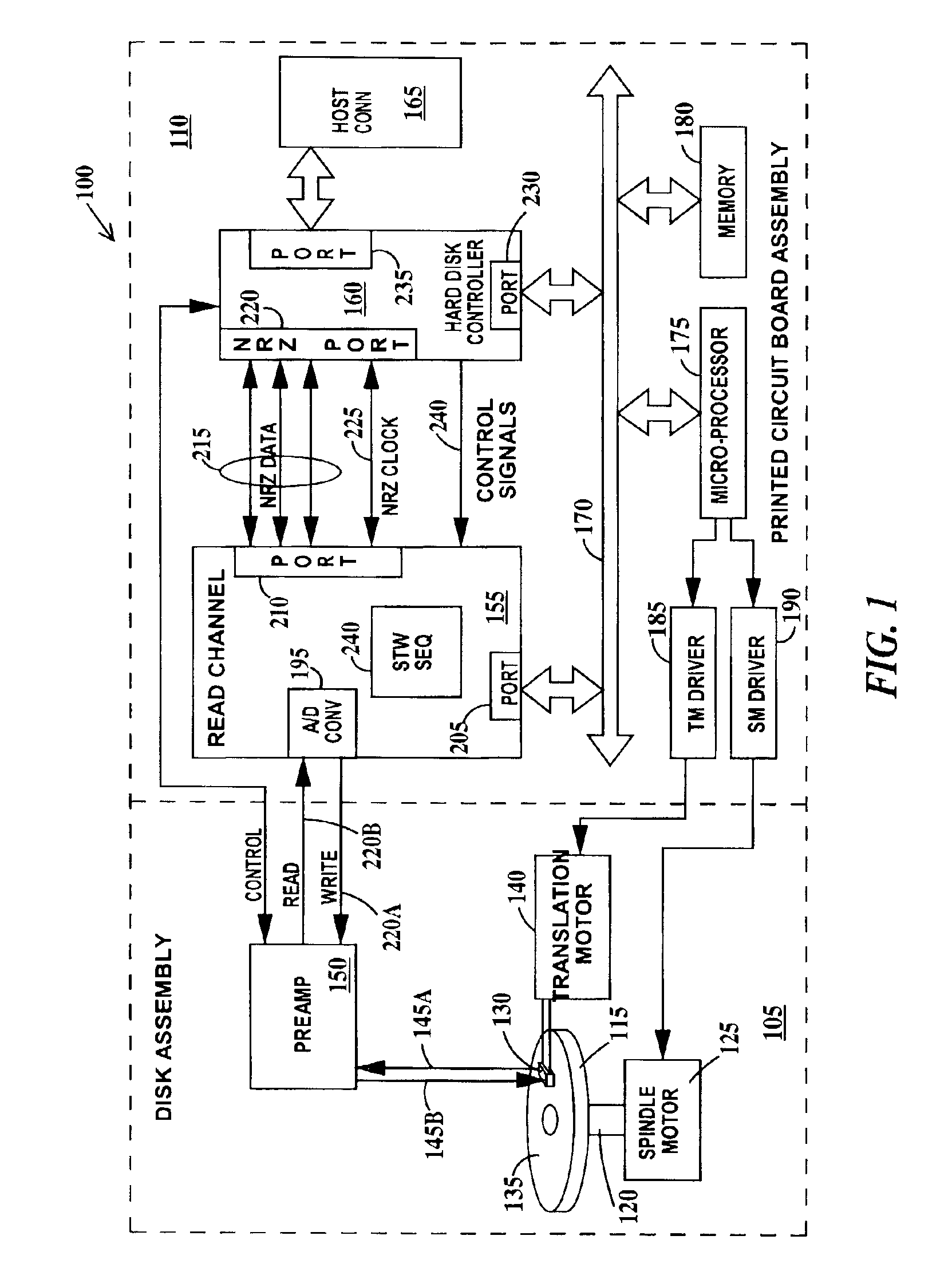
A read channel for a hard disk controller comprising: means for generating a sequence of start of write signals to individually control the start of writing of each of one or more servo sync words to a disk; and means for individually writing the one or more servo sync words to the disk.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com