Patents
Literature
63 results about "Streaking Artifact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An artifact resulting from an inconsistency in a single measurement.
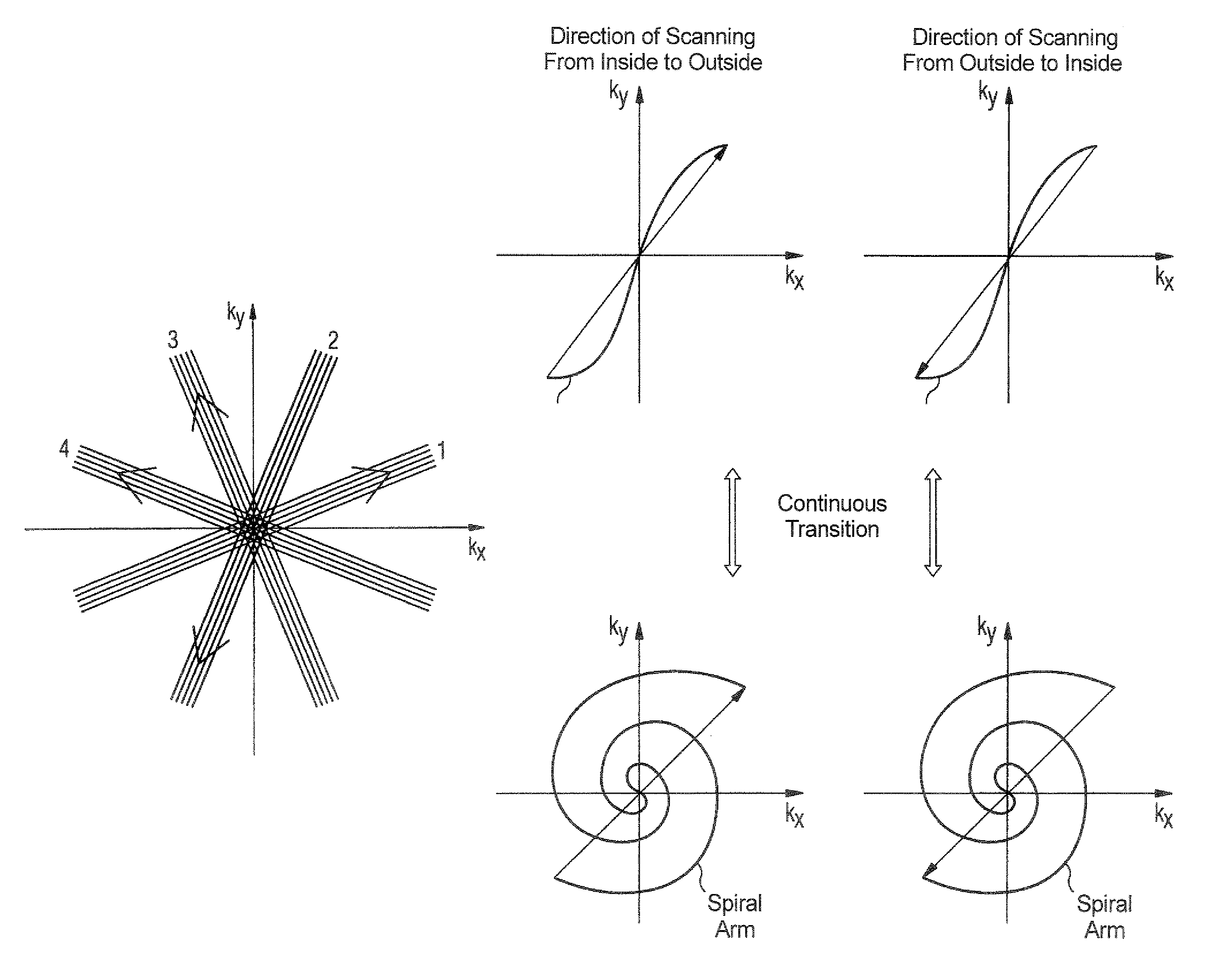
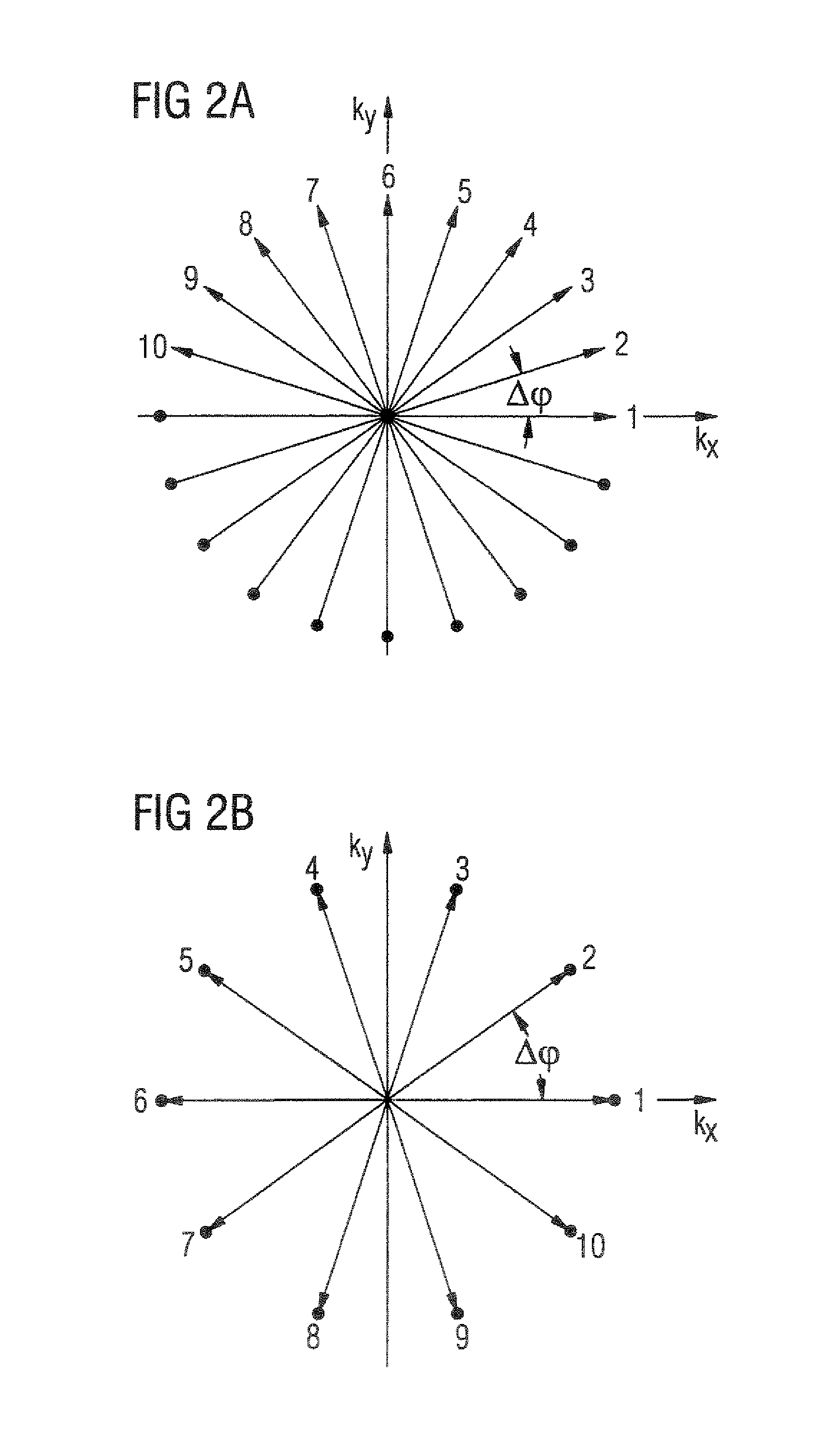
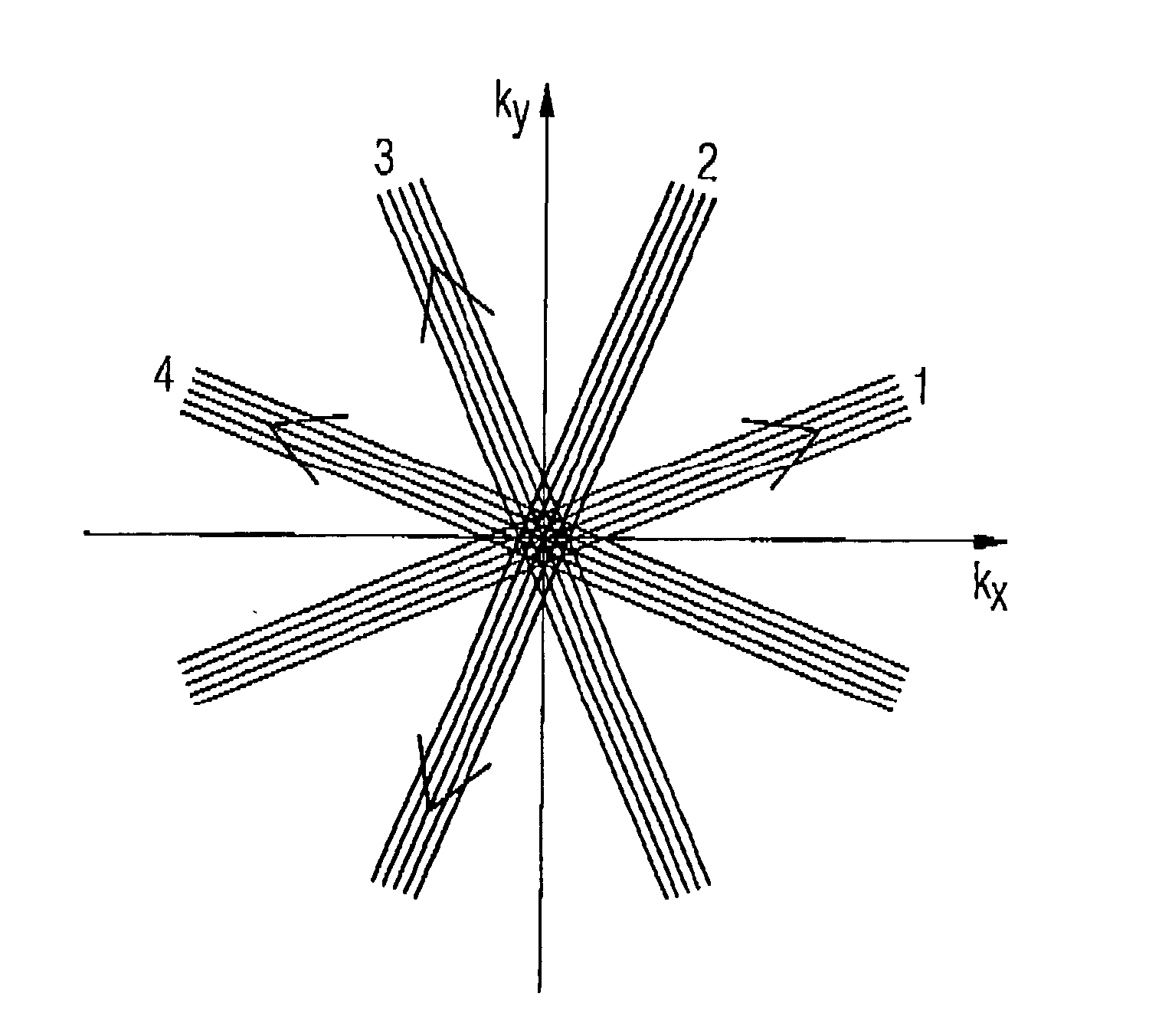
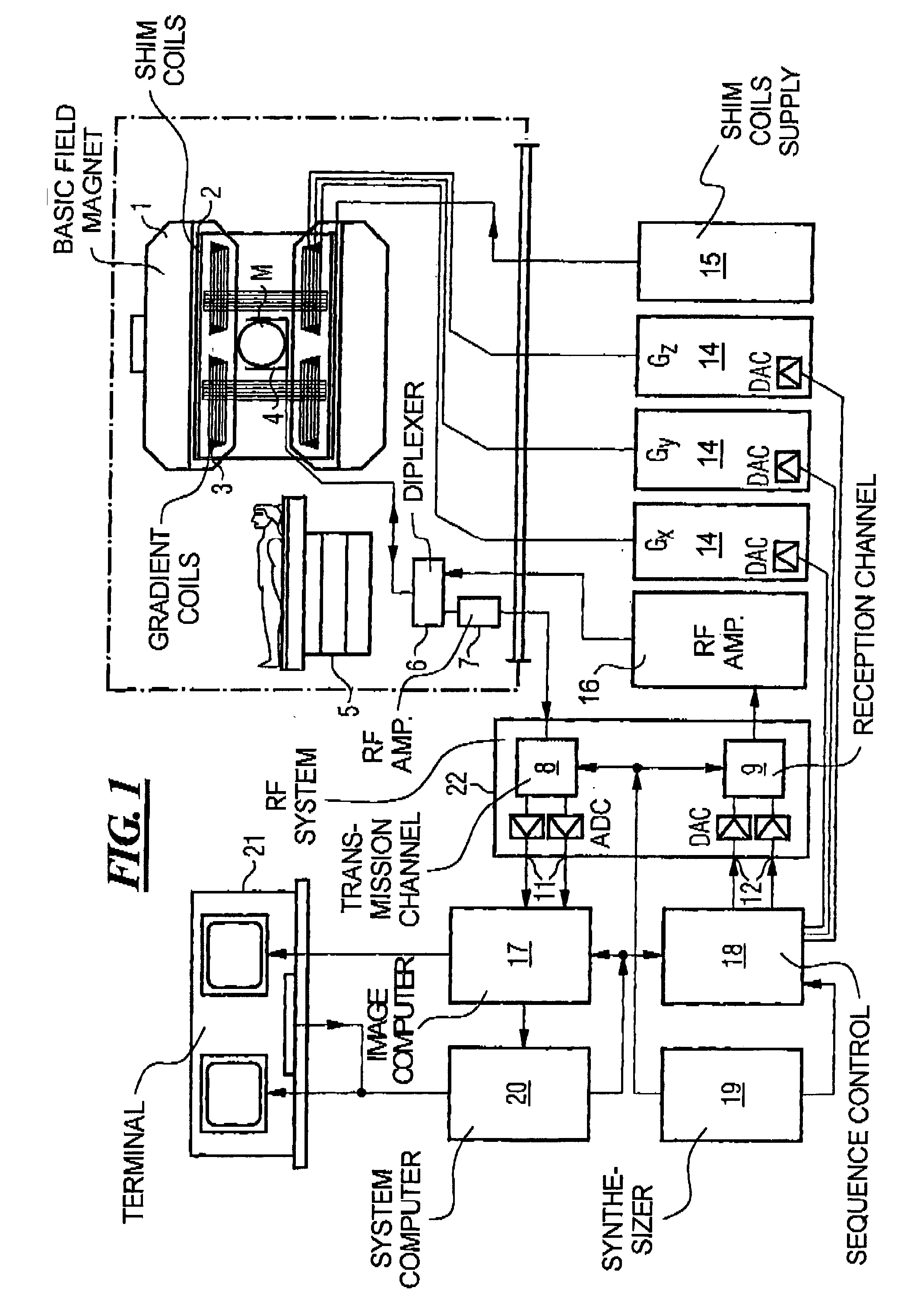
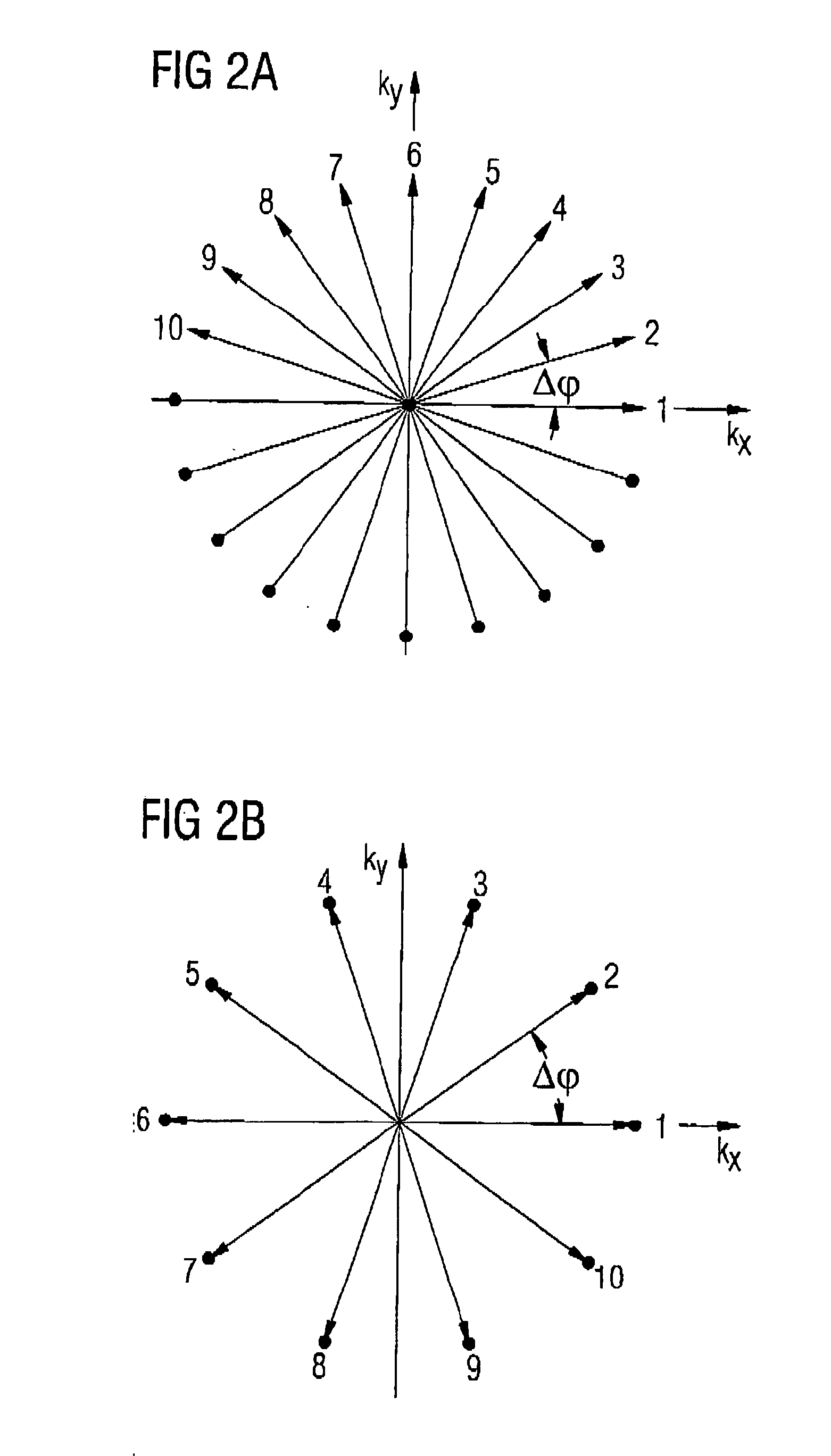
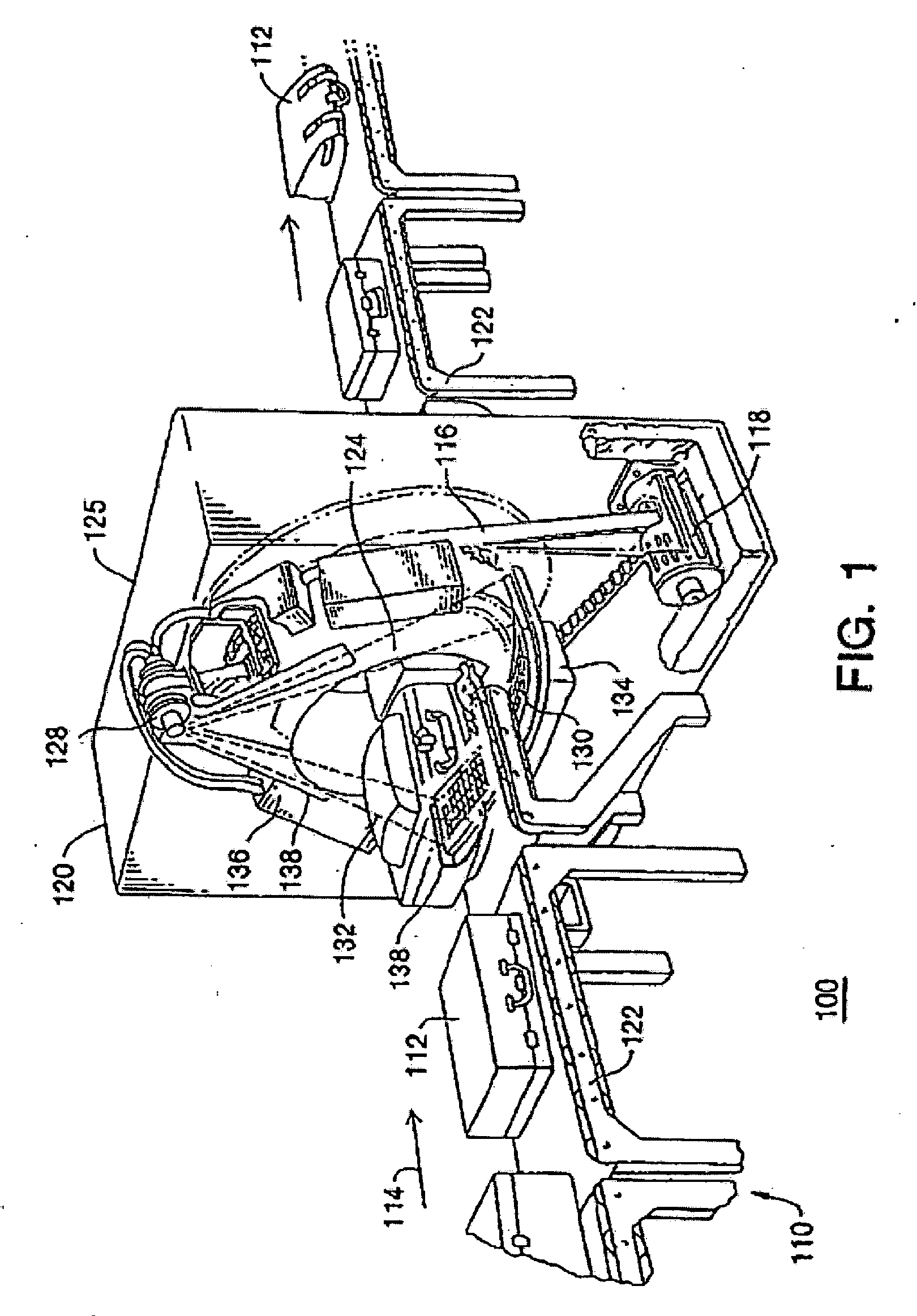
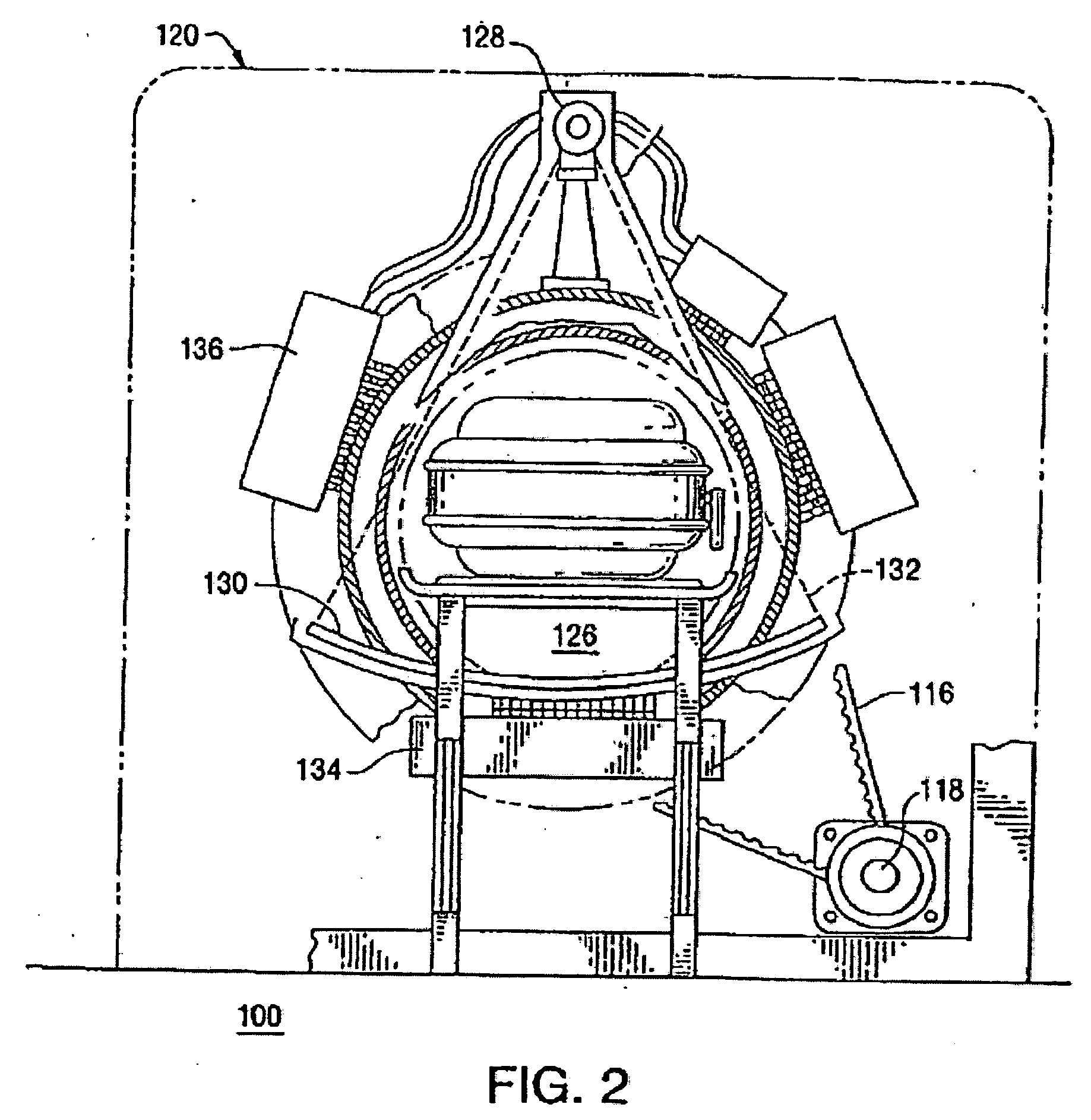
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method wherein streak artifacts are minimized in modular k-space scanning
ActiveUS7245125B2Increase influenceQuicker procedureMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceModularity
In a method and MRI apparatus for the minimization of streak artifacts in modular k-space scanning in magnetic resonance imaging, an odd integer k-space scanning module number Nφ=2n+1 is defined that defines the number of incrementally rotated repeated modules of the k-space scanning process, a slice selection gradient selects any slice in the range of the object to be examined, and data for all Nφ angle-oriented k-space scanning modules in the selected slice acquired such that each k-space scanning module has an azmuthal distance ofΔφ2=360°2Nφfrom both adjacent projections, with the direction of the scanning of the adjacent k-space scanning modules alternating.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method wherein streak artifacts are minimized in modular k-space scanning
ActiveUS20050073303A1Easy accessStreak artifactMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceComputer science
In a method and MRI apparatus for the minimization of streak artifacts in modular k-space scanning in magnetic resonance imaging, an odd integer k-space scanning module number Nφ=2n+1 is defined that defines the number of incrementally rotated repeated modules of the k-space scanning process, a slice selection gradient selects any slice in the range of the object to be examined, and data for all Nφ angle-oriented k-space scanning modules in the selected slice acquired such that each k-space scanning module has an azmuthal distance of Δ φ2=360°2 Nφfrom both adjacent projections, with the direction of the scanning of the adjacent k-space scanning modules alternating.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
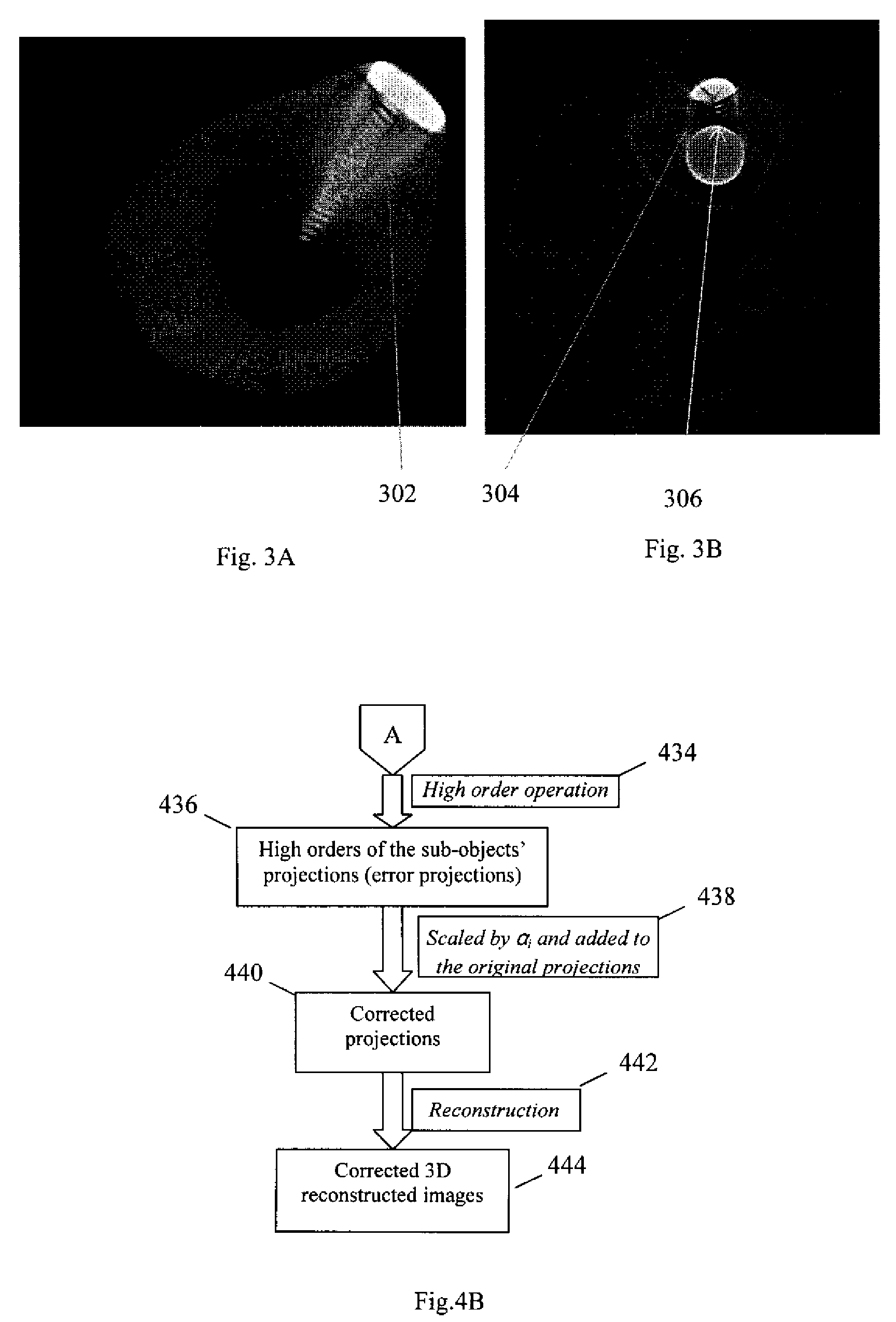
Method and apparatus for 3D metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam CT imaging
ActiveUS8023767B1Correction of artifactAccurate reconstruction imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
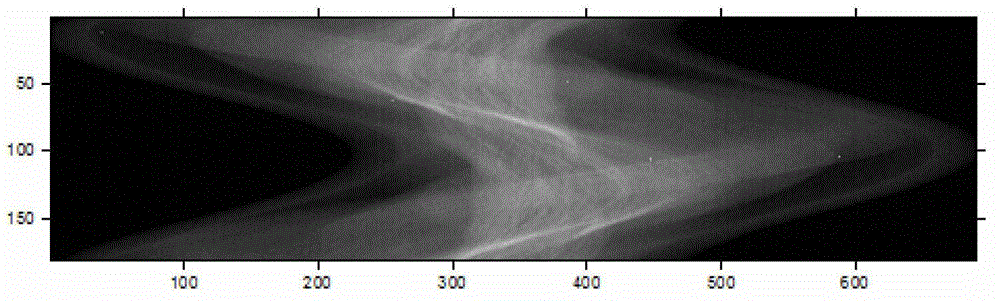
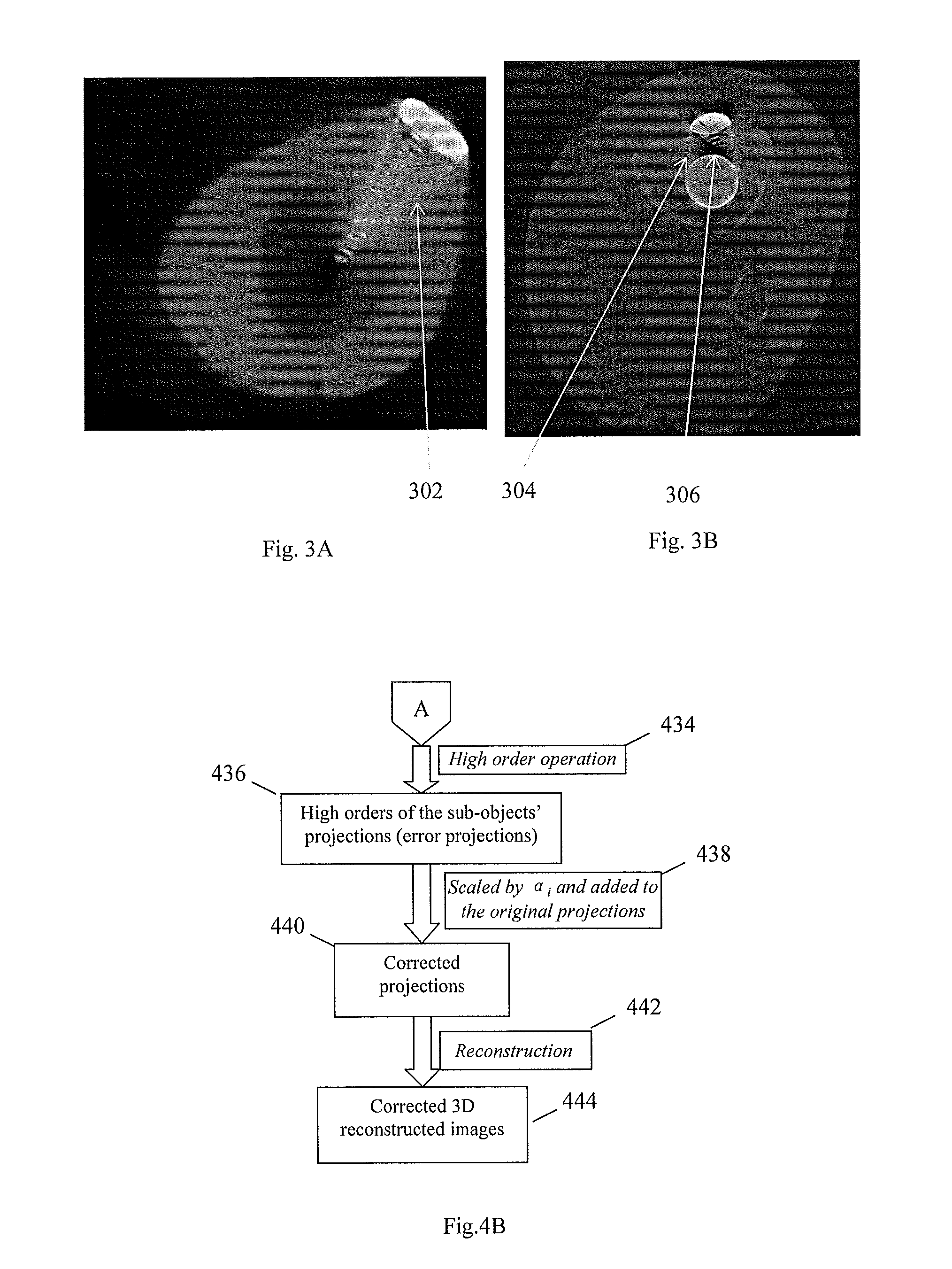
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
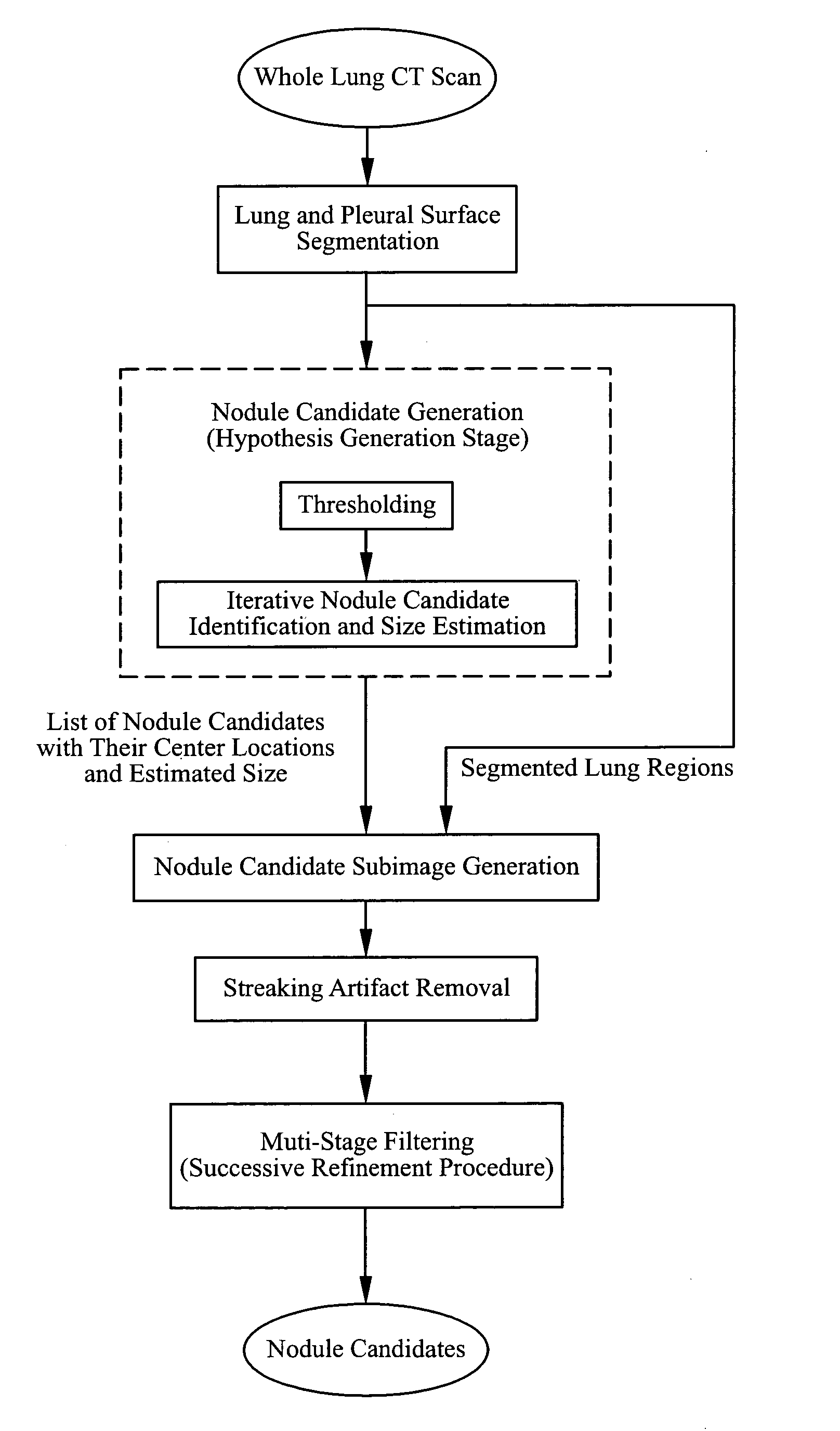
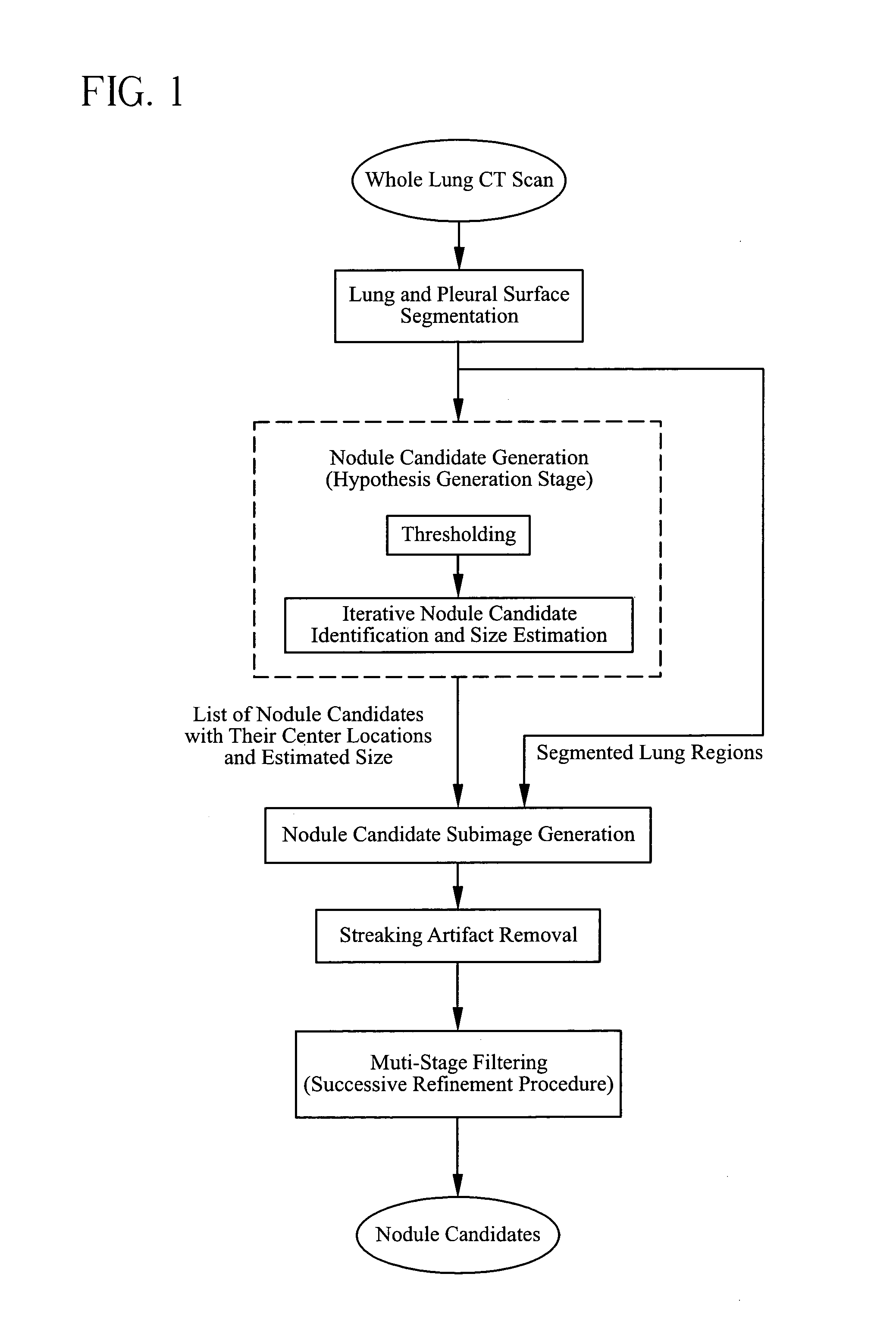
System, method and apparatus for small pulmonary nodule computer aided diagnosis from computed tomography scans
ActiveUS7499578B2Improve consistencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleVoxel
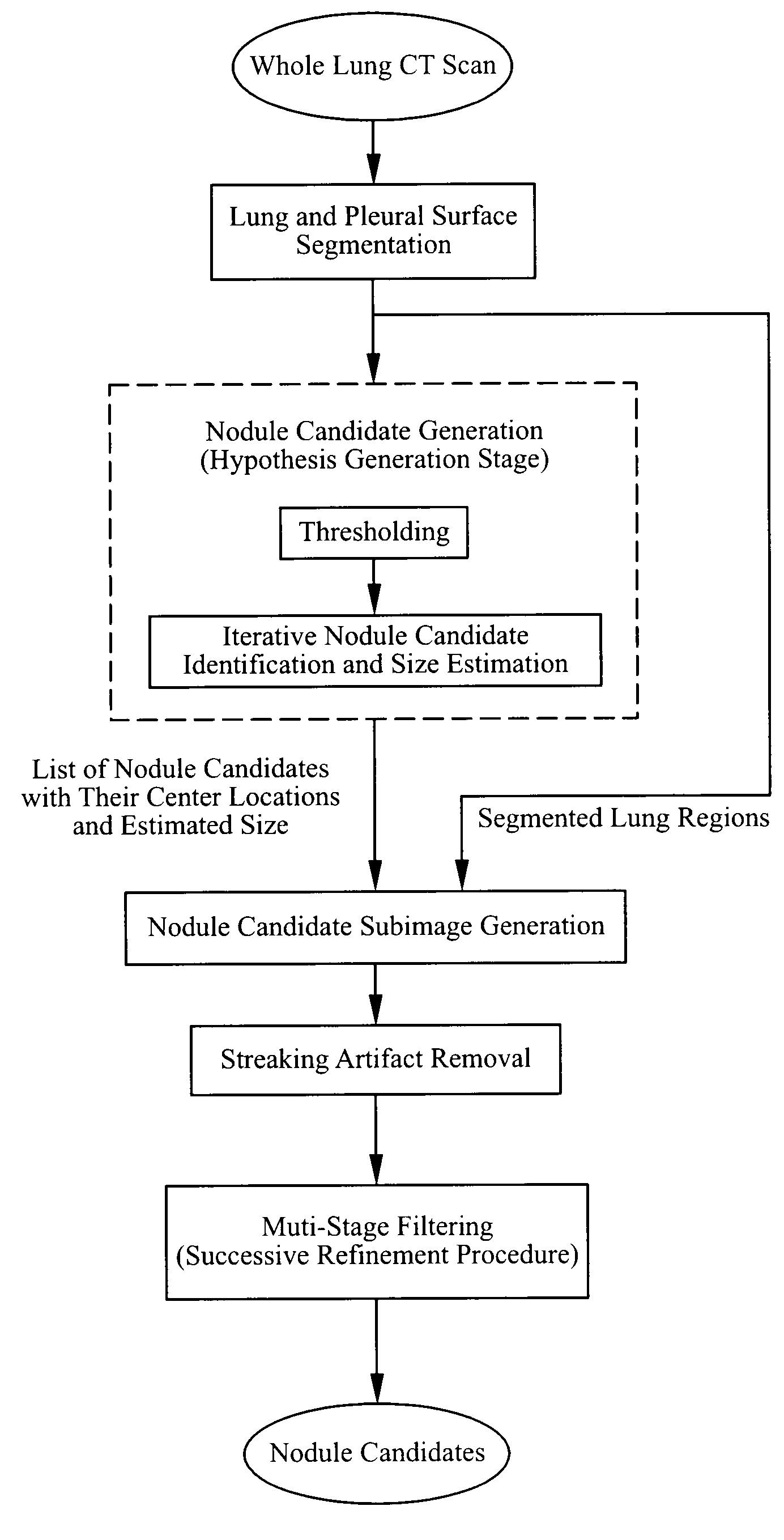
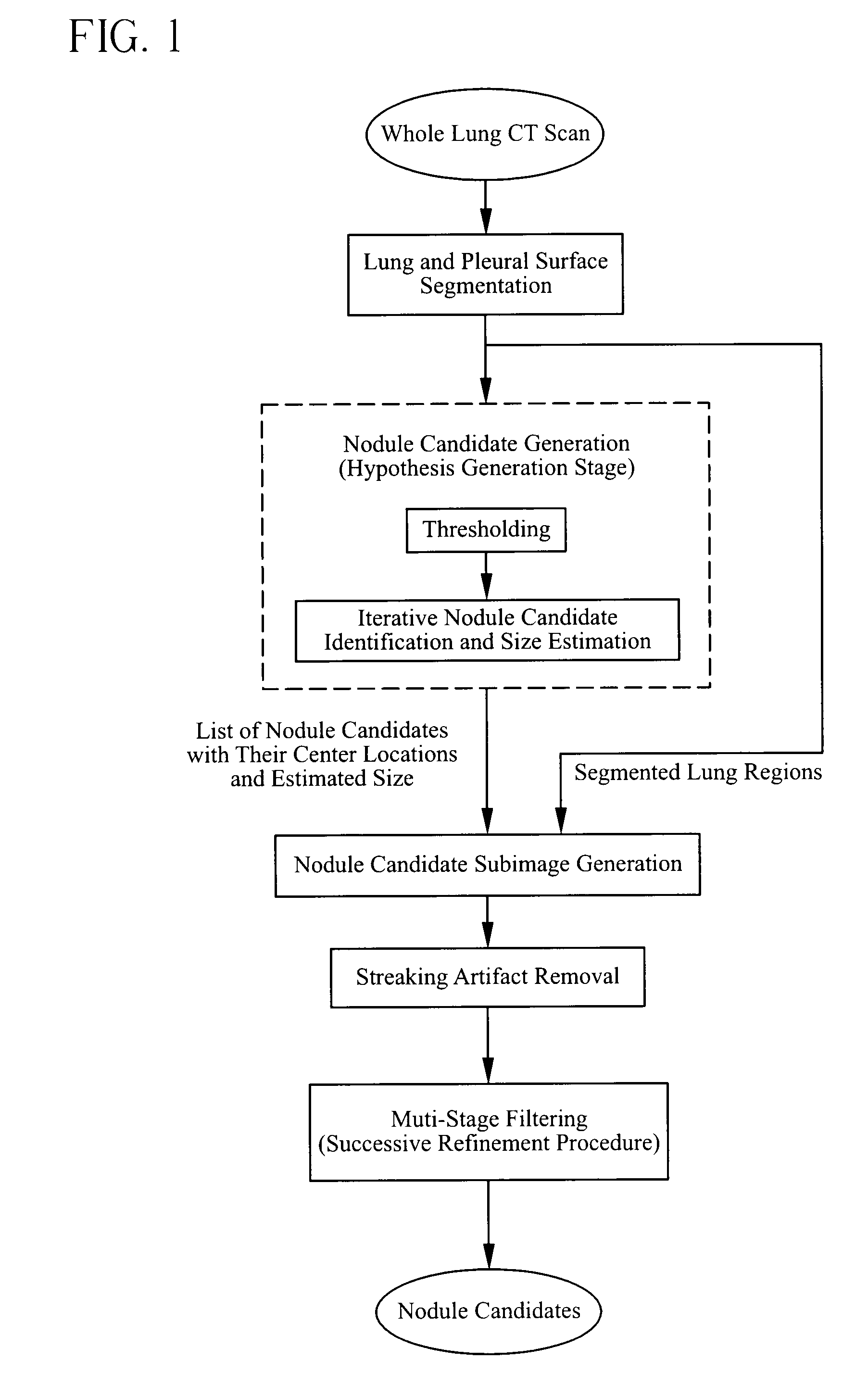
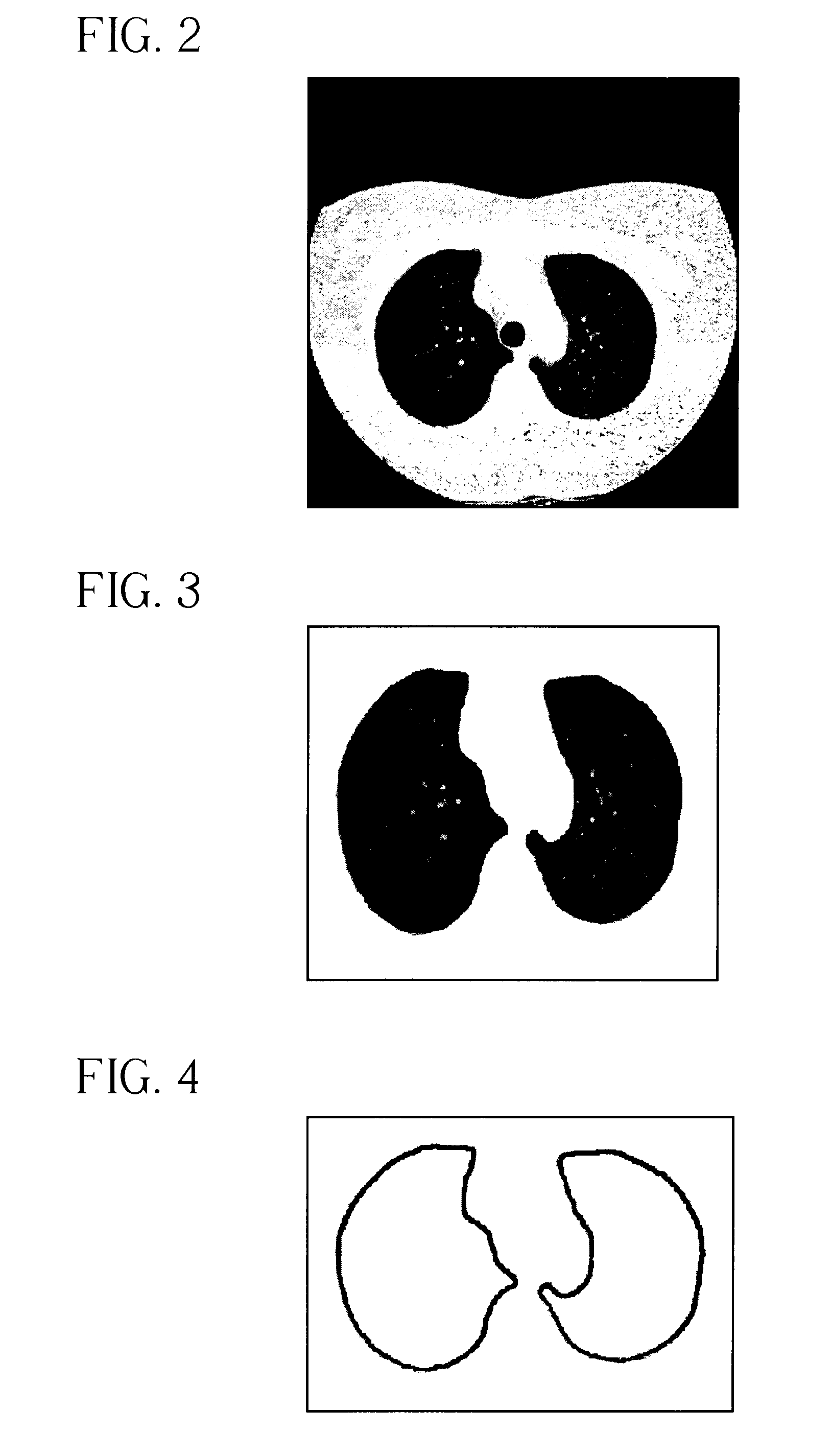
The present invention is a multi-stage detection algorithm using a successive nodule candidate refinement approach. The detection algorithm involves four major steps. First, the lung region is segmented from a whole lung CT scan. This is followed by a hypothesis generation stage in which nodule candidate locations are identified from the lung region. In the third stage, nodule candidate sub-images pass through a streaking artifact removal process. The nodule candidates are then successively refined using a sequence of filters of increasing complexity. A first filter uses attachment area information to remove vessels and large vessel bifurcation points from the nodule candidate list. A second filter removes small bifurcation points. The invention also improves the consistency of nodule segmentations. This invention uses rigid-body registration, histogram-matching, and a rule-based adjustment system to remove missegmented voxels between two segmentations of the same nodule at different times.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
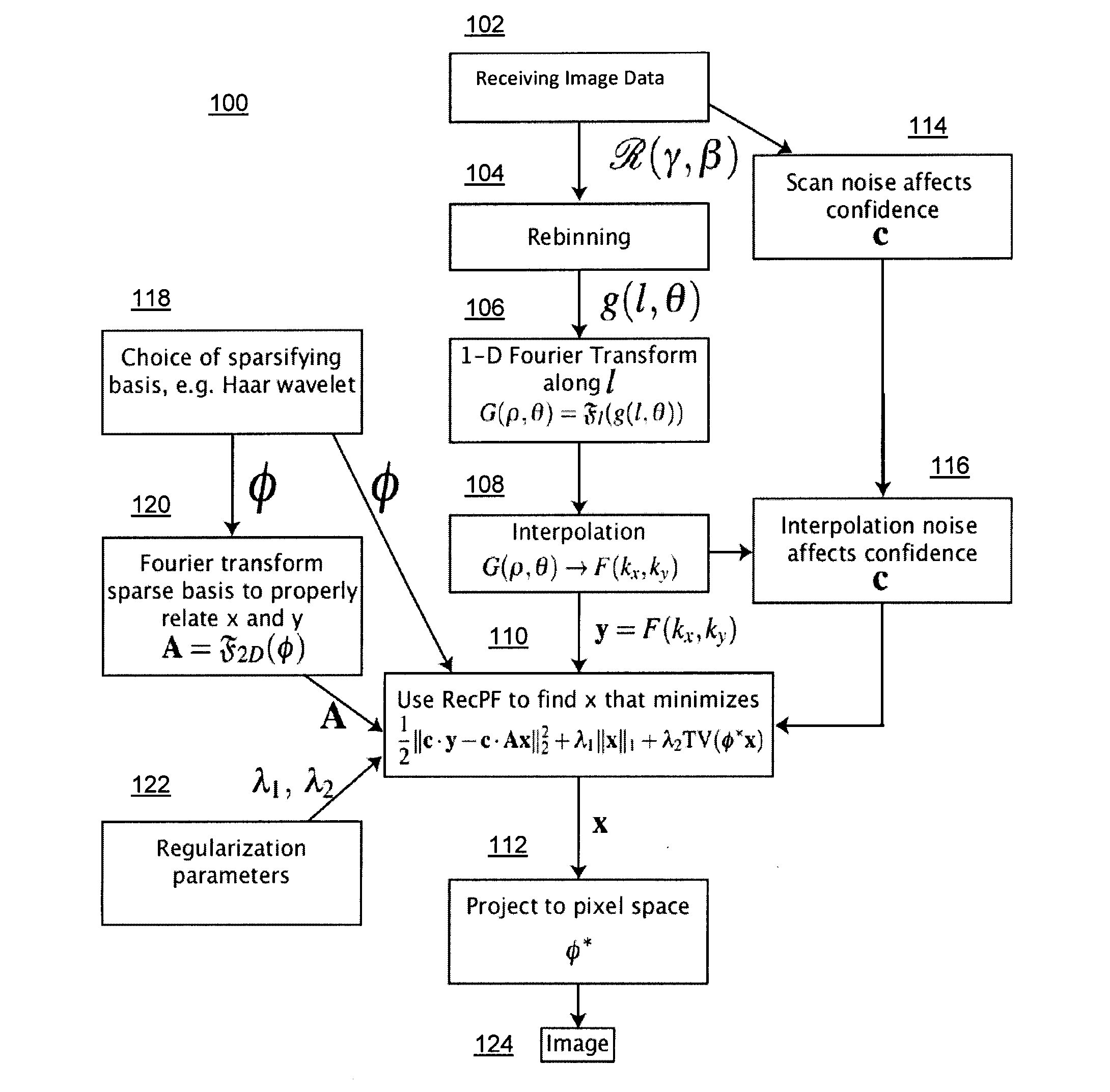
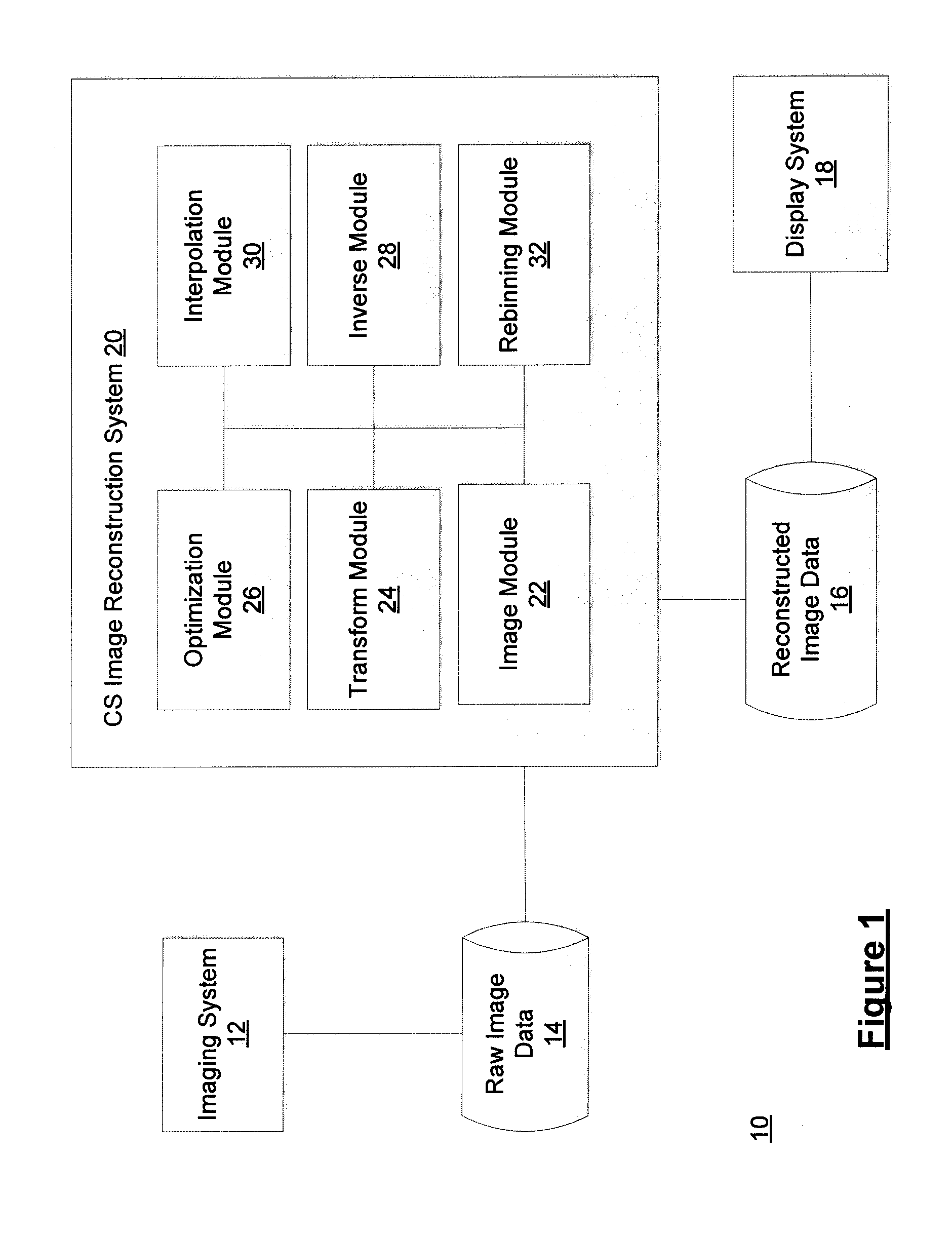
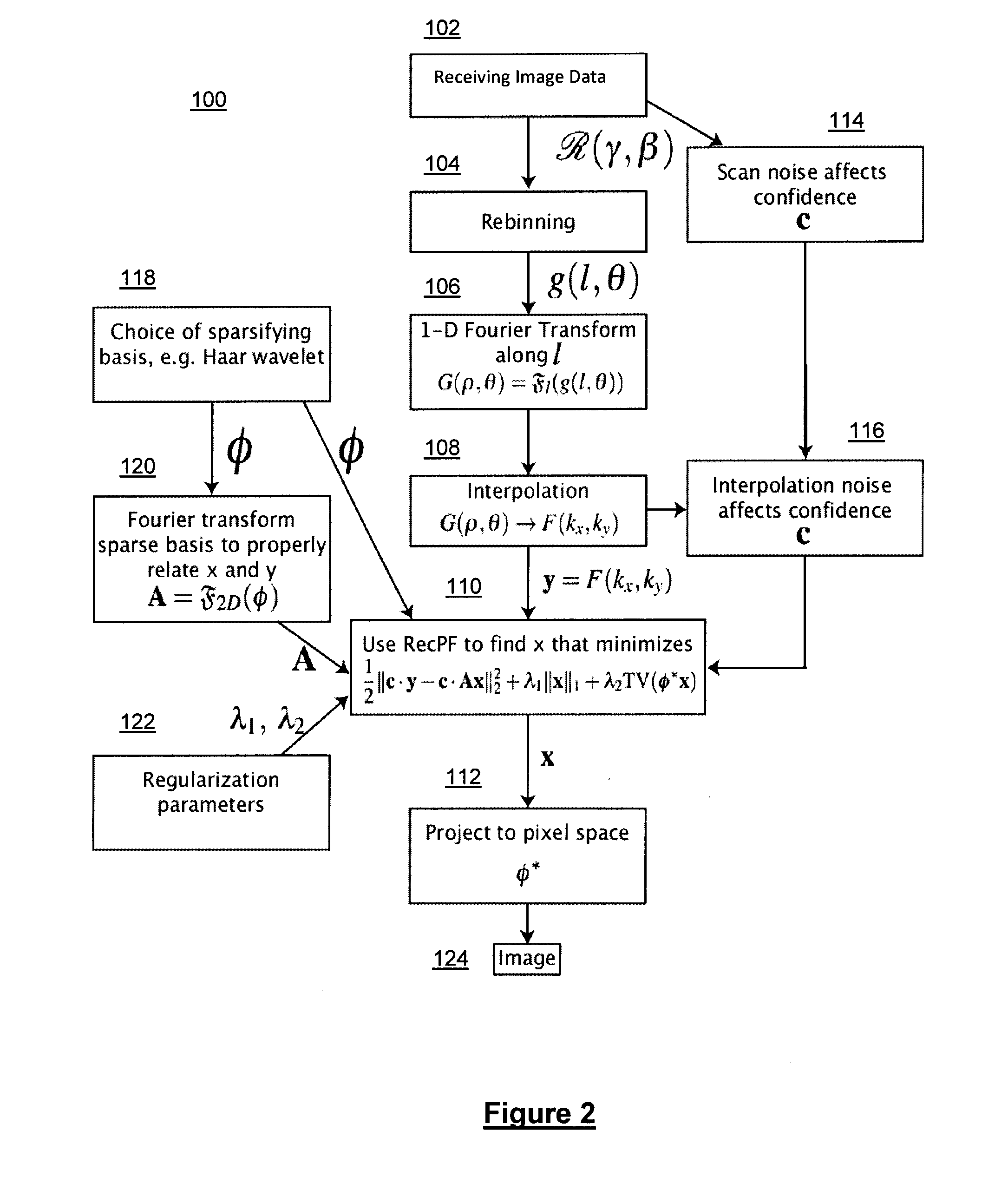
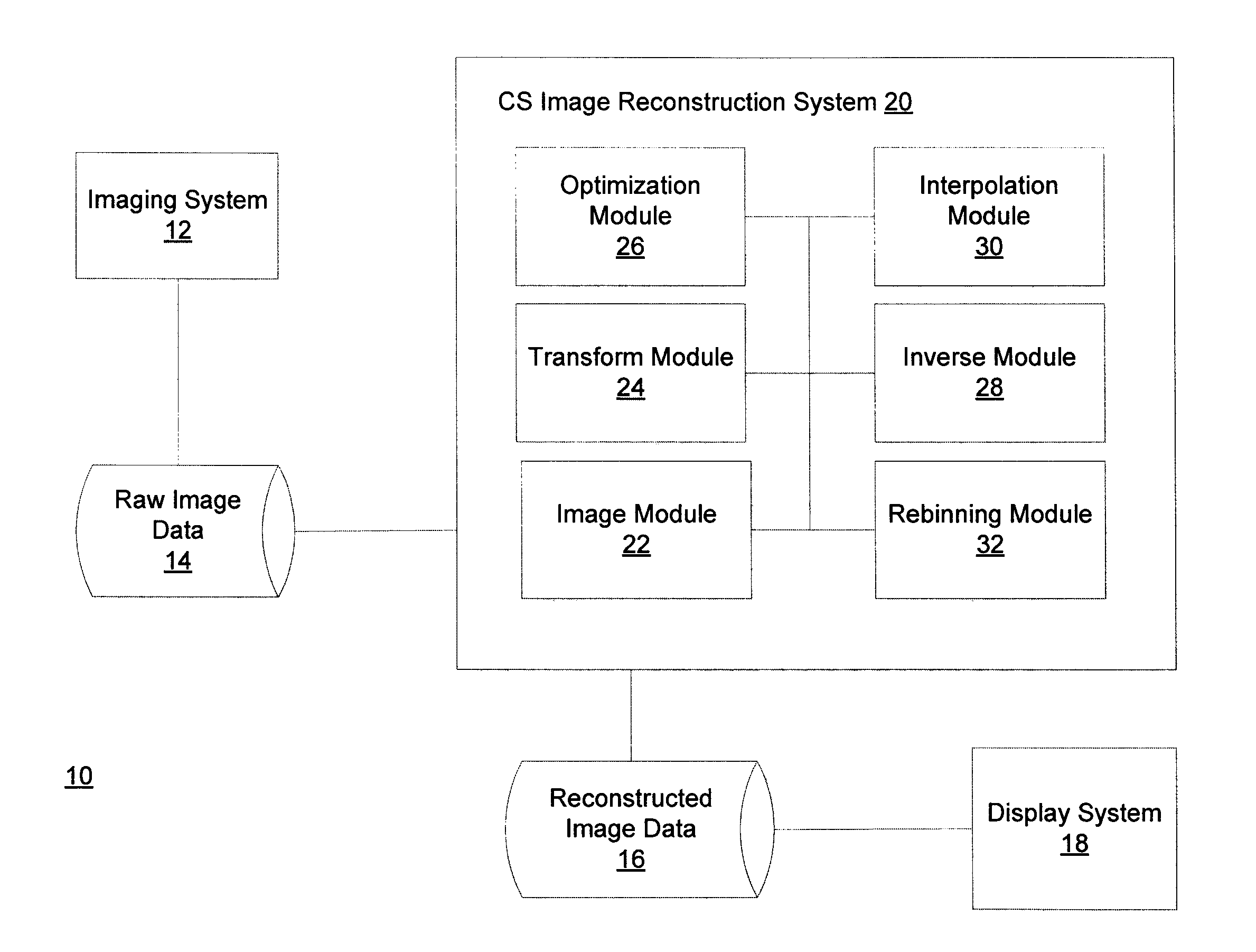
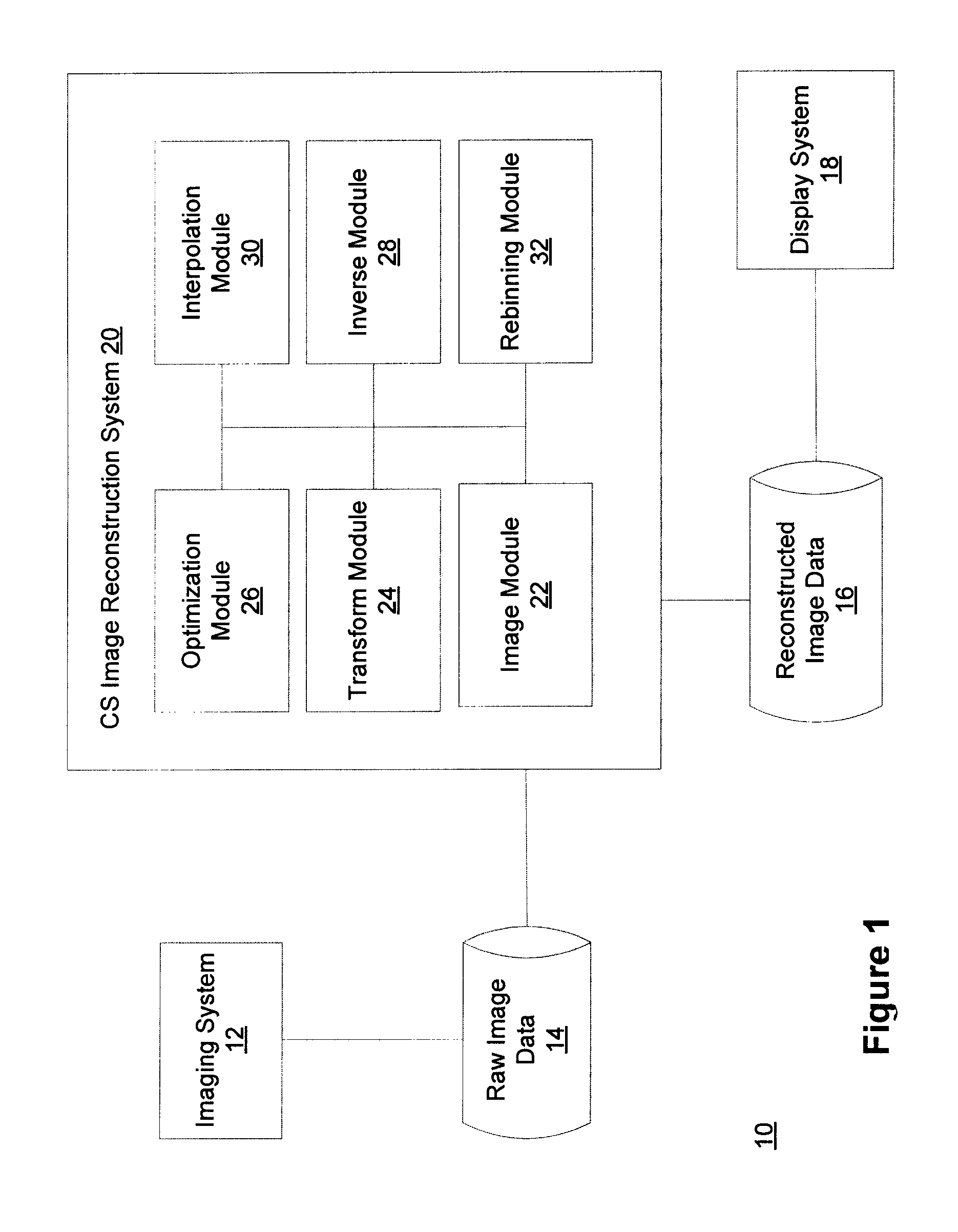
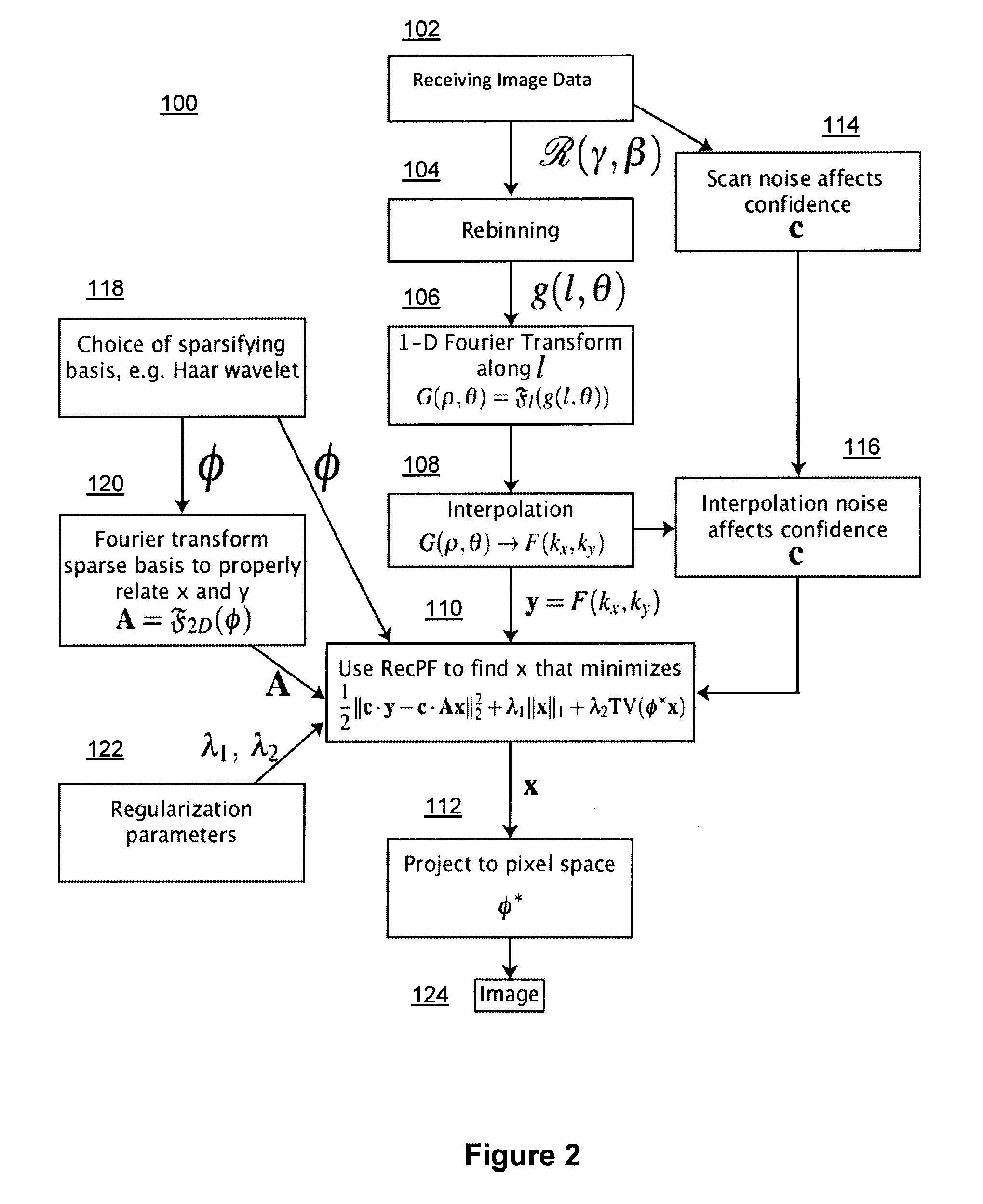
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150187052A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
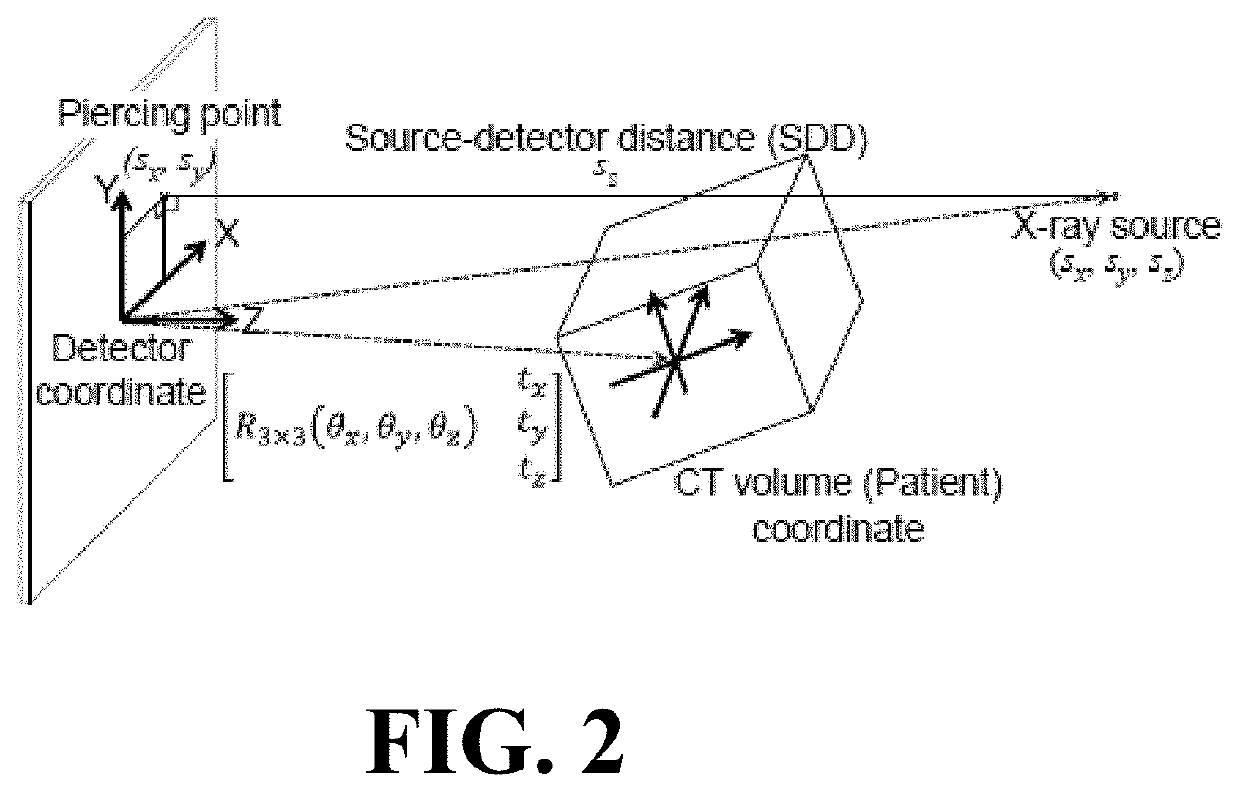
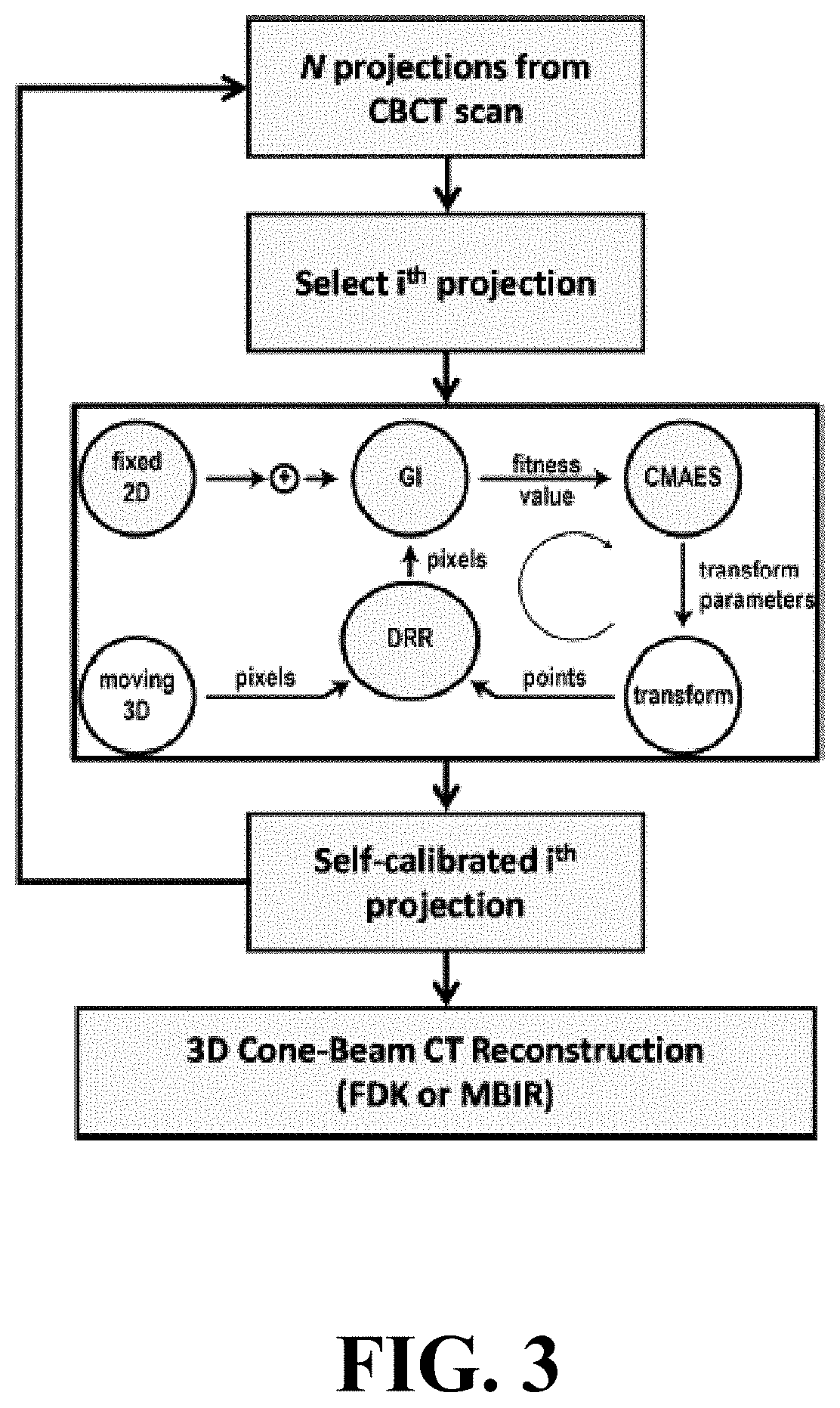
Self-calibrating projection geometry for volumetric image reconstruction
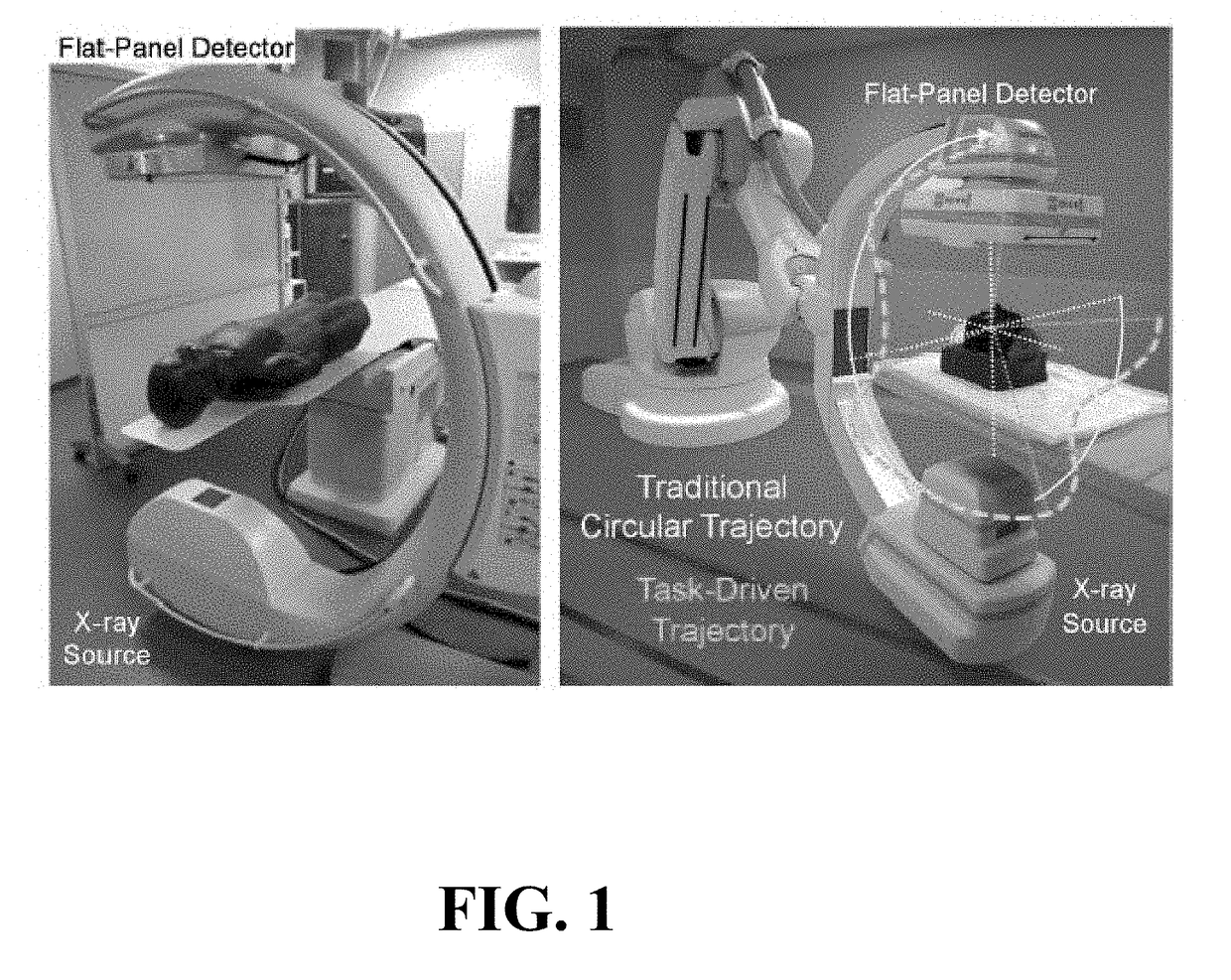
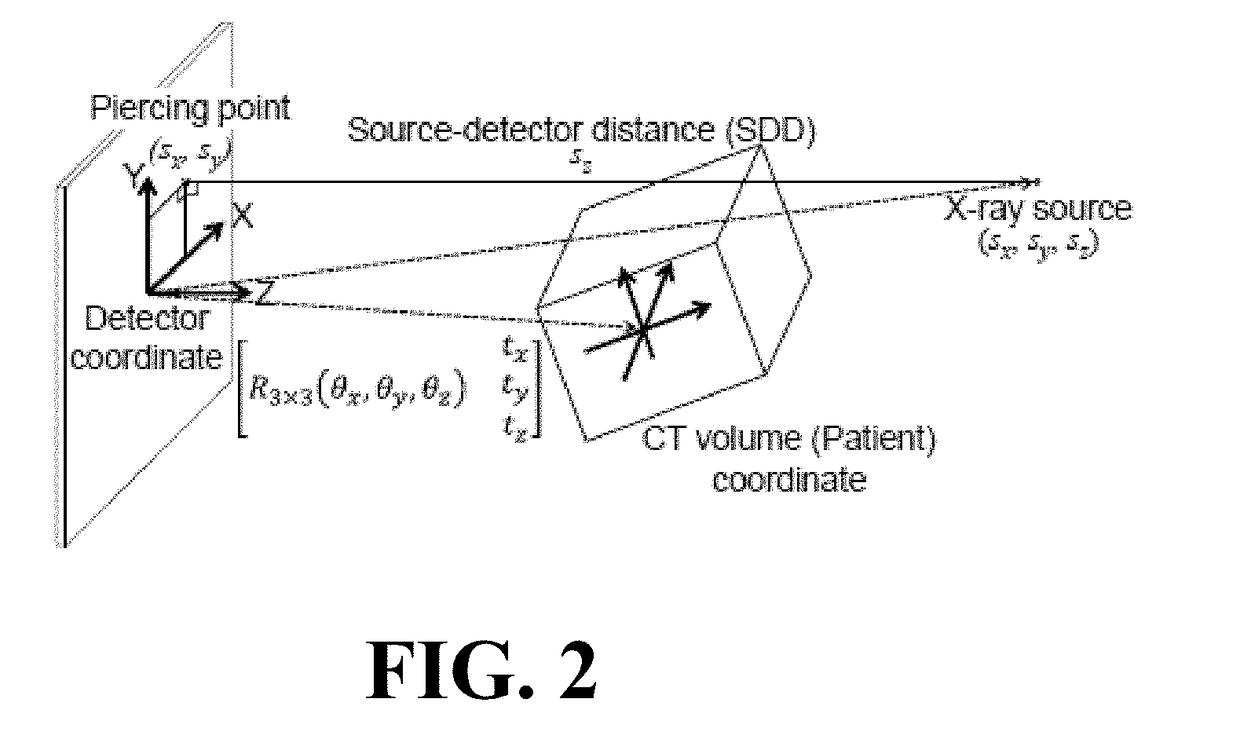
The present invention is directed to a method for enabling volumetric image reconstruction from unknown projection geometry of tomographic imaging systems, including CT, cone-beam CT (CBCT), and tomosynthesis systems. The invention enables image reconstruction in cases where it was not previously possible (e.g., custom-designed trajectories on robotic C-arms, or systems using uncalibrated geometries), and more broadly offers improved image quality (e.g., improved spatial resolution and reduced streak artifact) and robustness to patient motion (e.g., inherent compensation for rigid motion) in a manner that does not alter the patient setup or imaging workflow. The method provides a means for accurately estimating the complete geometric description of each projection acquired during a scan by simulating various poses of the x-ray source and detector to determine their unique, scan-specific positions relative to the patient, which is often unknown or inexactly known (e.g., a custom-designed trajectory, or scan-to-scan variability in source and detector position).
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
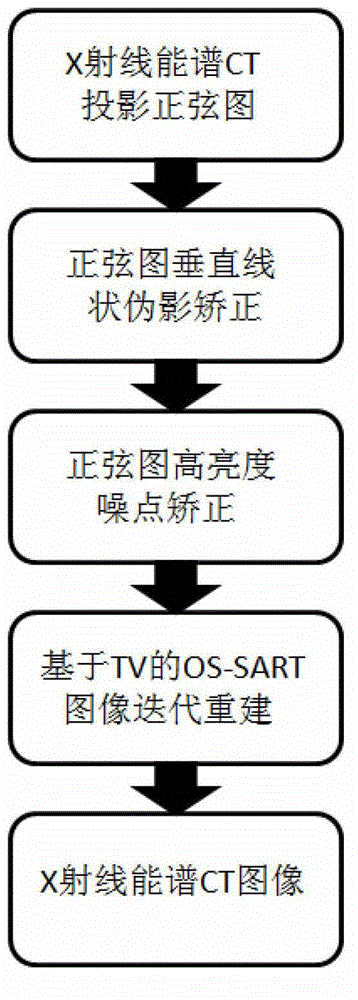
X-ray multi-energy spectrum computed tomography (CT) projection data processing and image reconstruction method
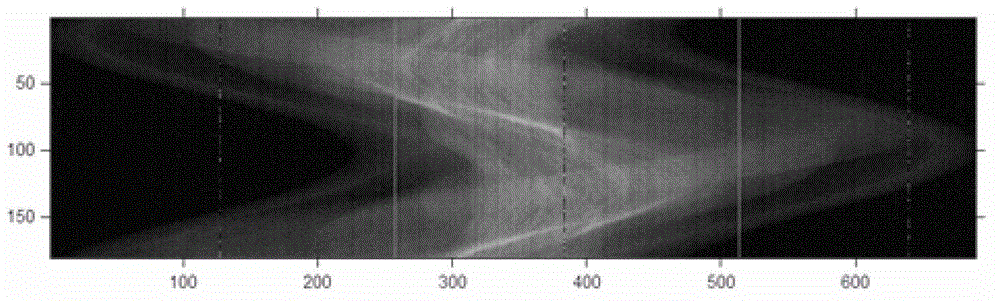
InactiveCN103150744ASuppresses vertical line artifactsEfficient removal2D-image generationReconstruction methodX-ray
The invention discloses an X-ray multi-energy spectrum computed tomography (CT) projection data processing and image reconstruction method, which mainly comprises an X-ray energy spectrum CT projection sinogram processing method and a compressed sensing-based accelerated iterative convergent reconstruction algorithm. The X-ray energy spectrum CT projection sinogram processing method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) restraining vertical streaking artifacts in a projection sinogram; (2) removing high-brightness noisy points in the projection sinogram. The compressed sensing-based accelerated iterative convergent reconstruction algorithm refers to that image total variation (TV) minimization-based optimal constraint conditions and the ordered-subset simultaneous algebraic reconstruction techniques (OS-SART) are combined. As a number of defects still exist in a traditional X-ray energy spectrum CT detection system (X-ray energy resolution photon counting detector), more noise and artifacts exist in acquired projection data. According to the X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT projection data processing and image reconstruction method, X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT projection data are effectively preprocessed by utilizing a preprocessing means, and meanwhile, a TV-based OS-SART algorithm is introduced into X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT image reconstruction, and therefore, image iterative convergence is accelerated, and the noise and the artifacts in a reconstructed image is well restrained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and apparatus for 3d metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam ct imaging
ActiveUS20120008845A1Accurate reconstruction imageHigh artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
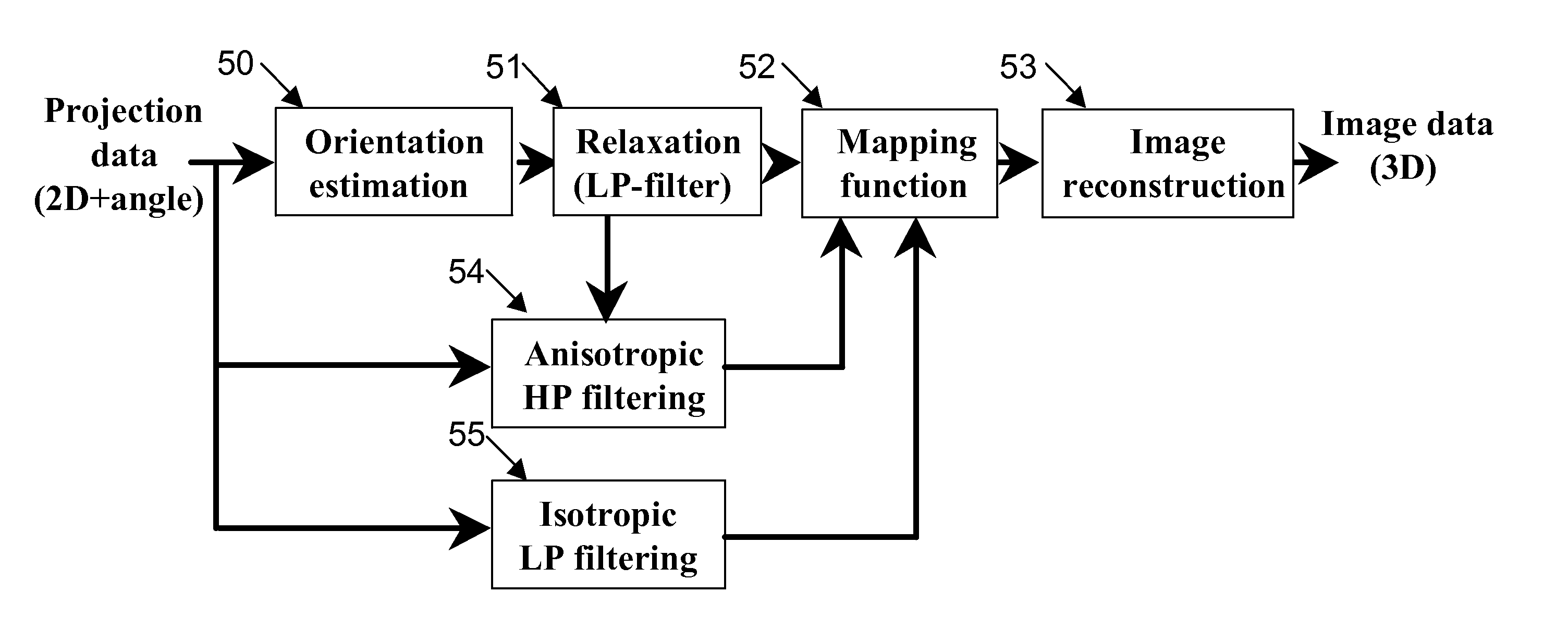
Adaptive anisotropic filtering of projection data for computed tomography
ActiveUS20080069294A1Reduce high frequency noiseReduce radiation doseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLow-pass filterImaging quality
CT imaging is enhanced by adaptively filtering x-ray attenuation data prior to image reconstruction. Detected x-ray projection data are adaptively and anisotropically filtered based on the locally estimated orientation of structures within the projection data from an object being imaged at a plurality of rotation positions. The detected x-ray data are uniformly low pass filtered to preserve the local mean values in the data, while the high pass filtering is controlled based on the estimated orientations. The resulting filtered data provide projection data with smoothing along the structures while maintaining sharpness along edges. Image noise and noise induced streak artifacts are reduced without increased blurring along edges in the reconstructed images. The enhanced image allows reduced x-ray dose while maintaining image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
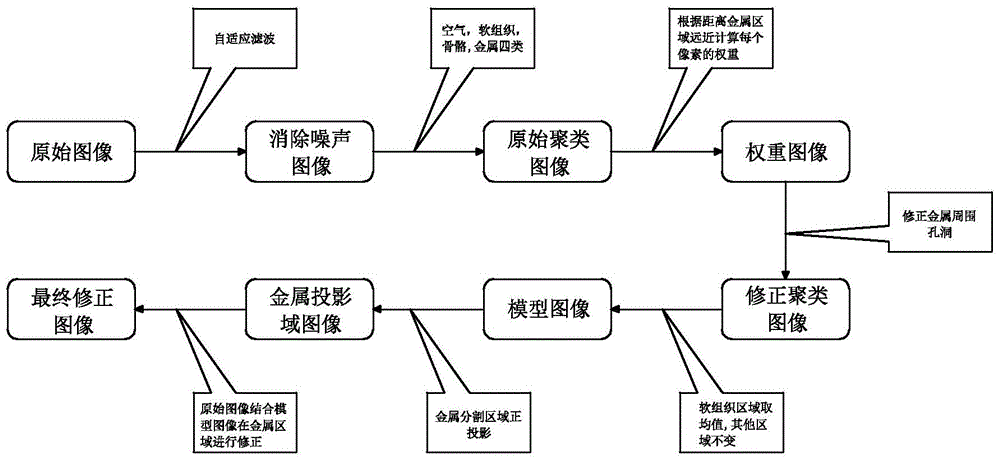
Method of removing metal artifact from CT image
ActiveCN105701778APrecisely correct imagesEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMetal Artifact
The present invention relates to a method of removing metal artifact from a CT image. The method comprises the steps of firstly carrying out the pre-processing via the image adaptive filtering to obtain an original reconstruction image from which the noise and a part of streak artifact are removed; then segmenting the original reconstruction image via a clustering method to obtain the areas of different tissues, establishing a model image, at the same time, carrying out the orthographic projection on a segmented metal area to obtain the position of the metal area in a projection domain; and then carrying out the orthographic projection on the model image to obtain the projection data of the model image, and then using the projection domain data of the model image to substitute for the projection domain data of the original reconstruction image according to the previously obtained position of the metal area in the projection domain; finally carrying out the filtering back projection on the repaired projection domain data to obtain a final corrected image. The method of the present invention reduces a real image accurately, enables the metal artifact to be removed effectively, and helps doctors to judge the states of illnesses accurately.
Owner:SAINUO WEISHENG SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method and system for reducing localized artifacts in imaging data
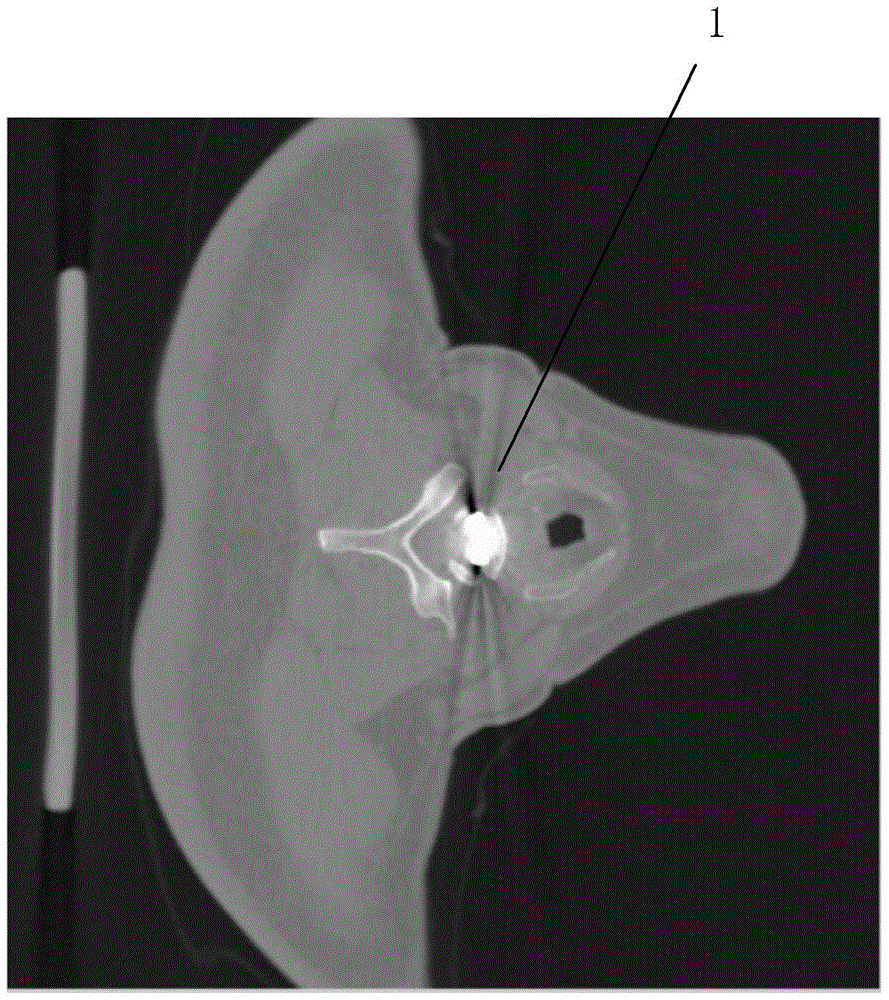
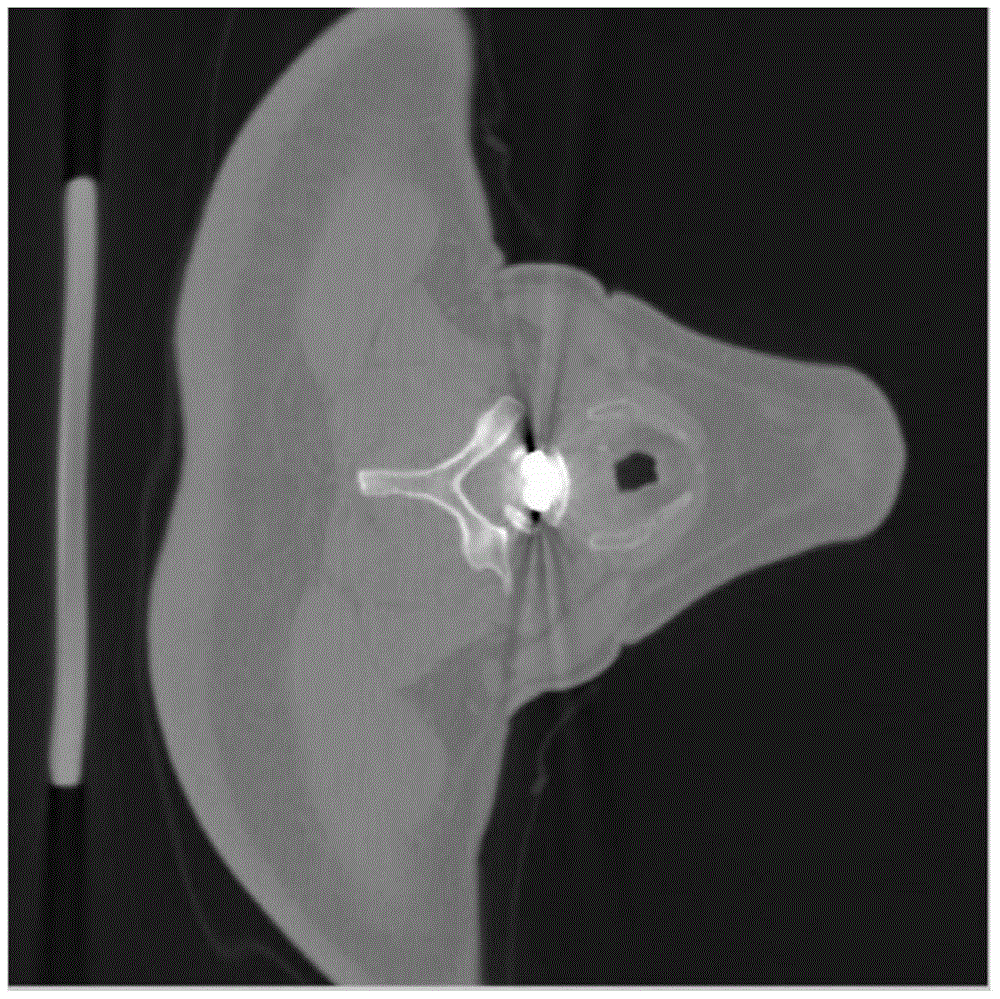
A method and system for reducing localized artifacts in imaging data, such as motion artifacts and bone streak artifacts, are provided. The method includes segmenting the imaging data to identify one or more suspect regions in the imaging data near which localized artifacts are expected to occur, defining an artifact-containing region of interest in the imaging data around each suspect region, and applying a local bias field within the artifact-containing regions to correct for the localized artifacts.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
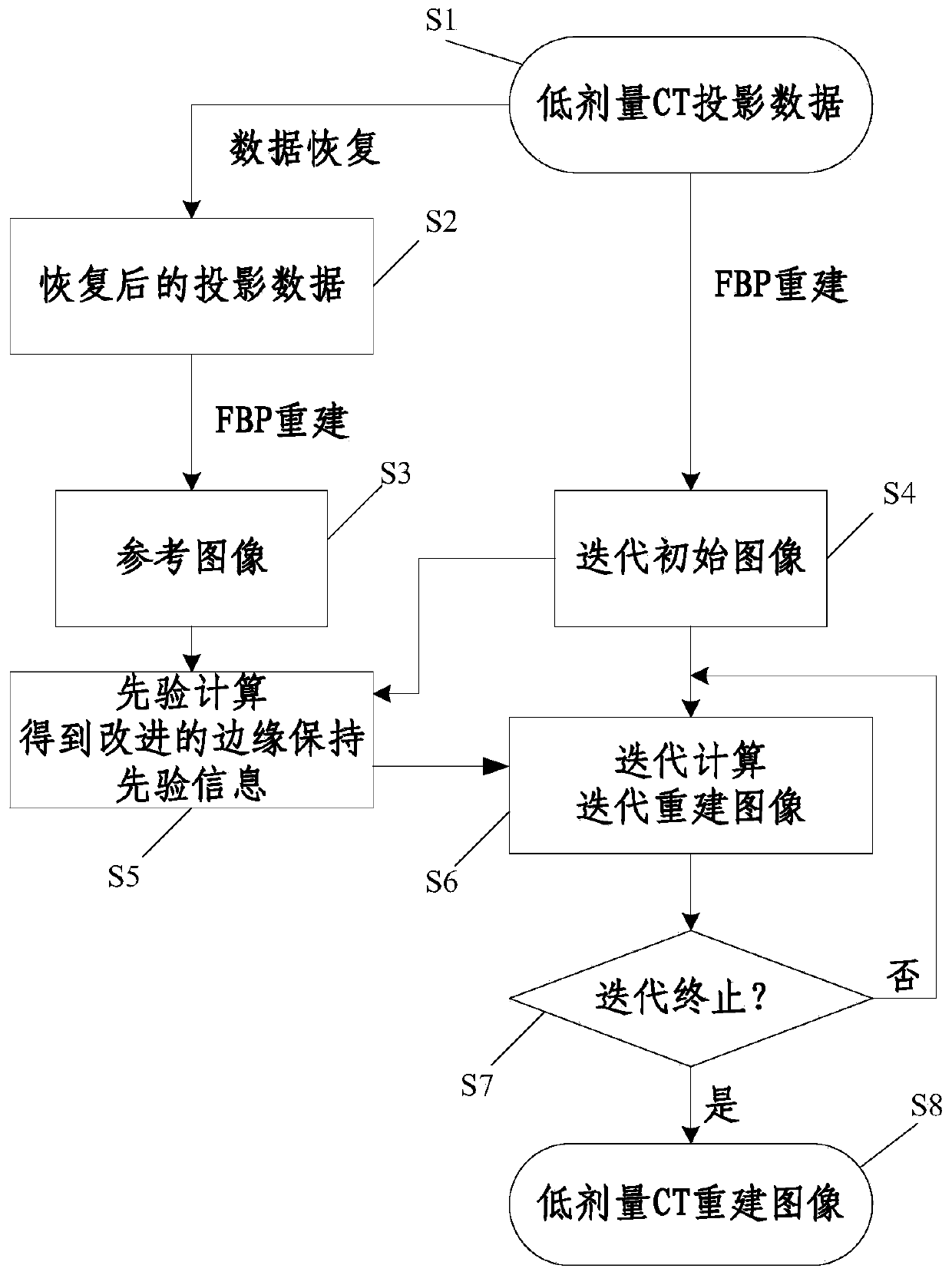
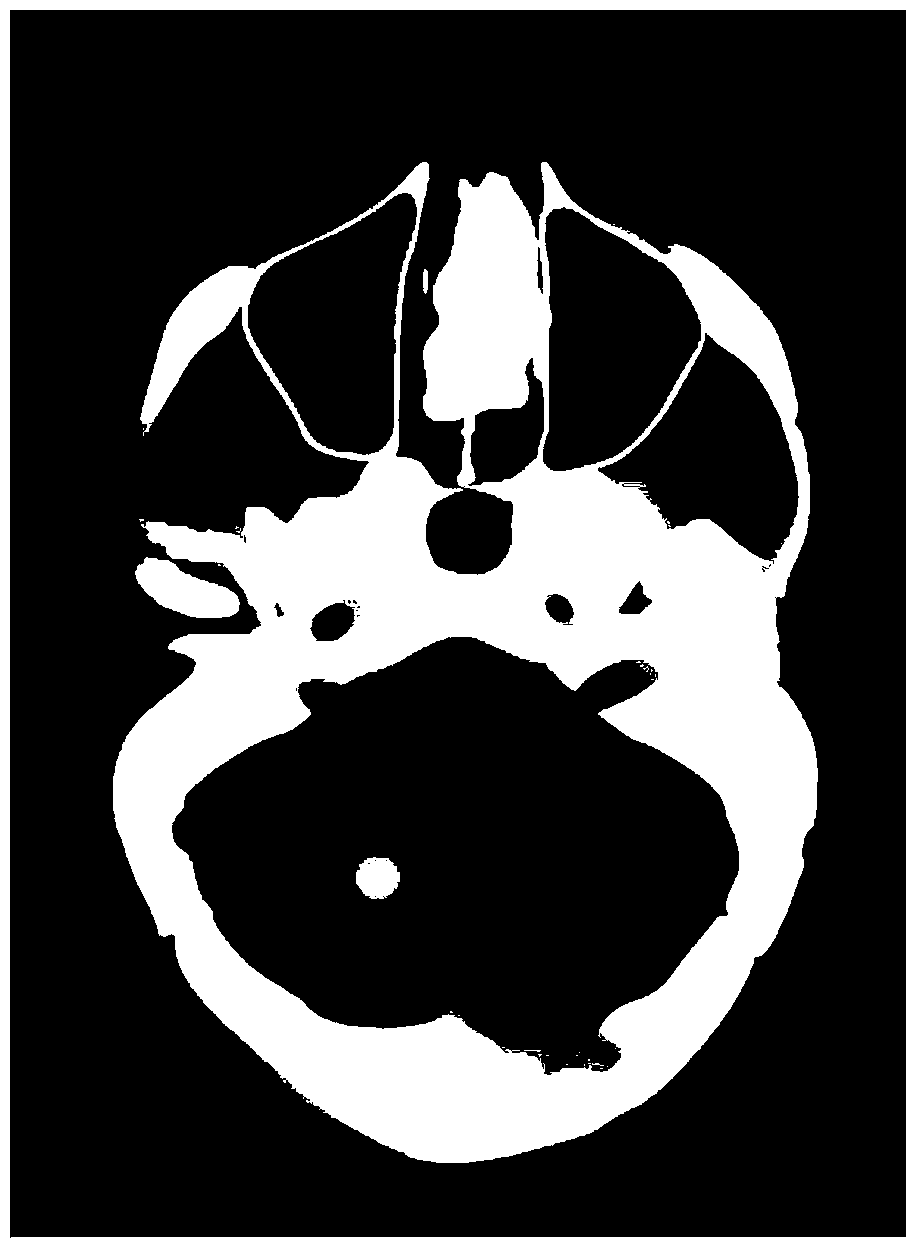
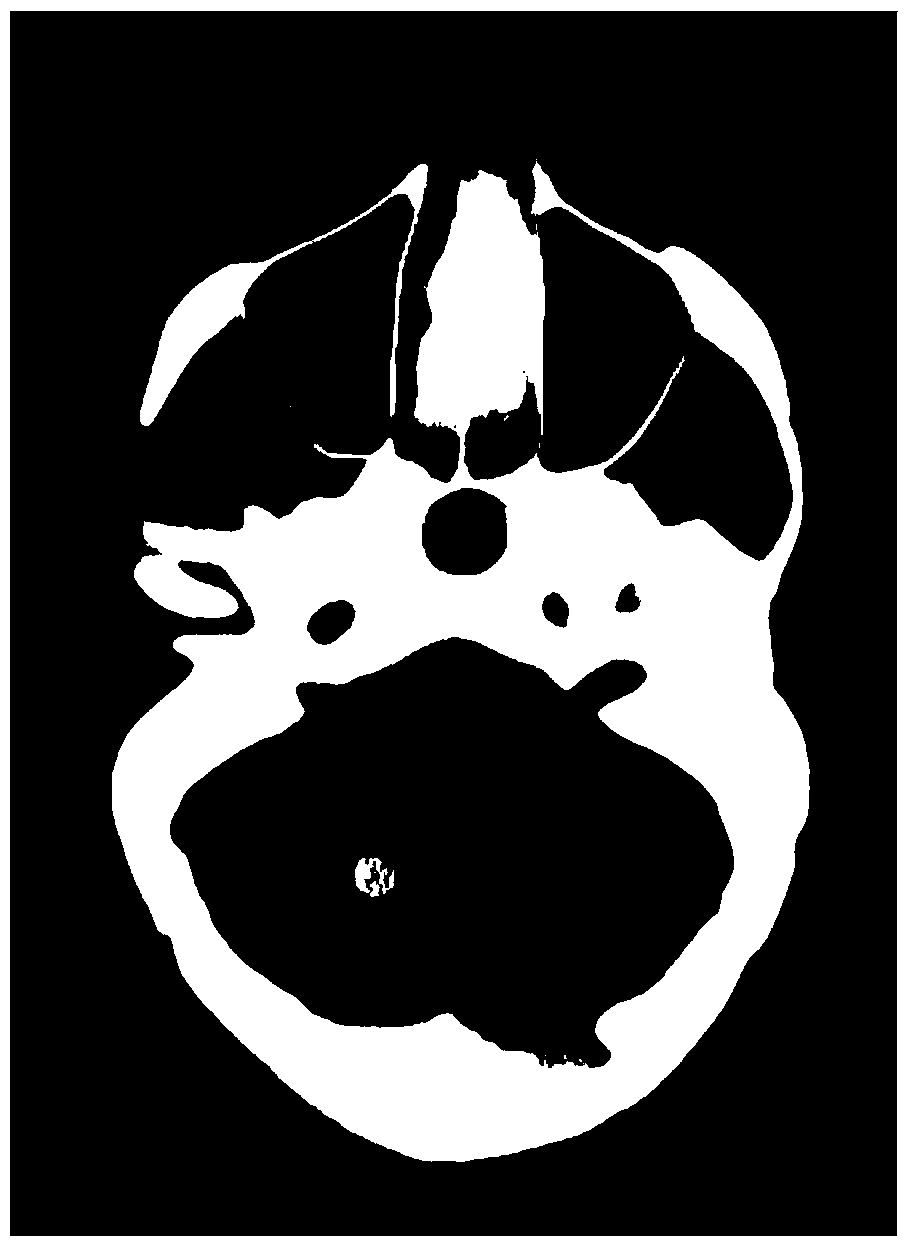
Statistical iterative reconstructing method for low-dose X-ray CT image
InactiveCN103810735ARemove image noiseStreak suppressionImage enhancement2D-image generationReference imageX-ray
The invention discloses a statistical iterative reconstructing method for a low-dose X-ray CT image. The statistical iterative reconstructing method includes reconstructing an image for projection data y<raw> of the low-dose X-ray image of CT equipment to obtain an initial iterative image mu<init>; restoring the projection data y<raw> to obtain the restored projection data y<restored>, reconstructing an image for the restored projection data y<restored> to obtain a reference image mu<ref>; based on the reference image mu<ref> and the initial iterative image mu<init>, constructing an edge-preserving prior R (mu<init>) according to FORMULA (shown in the description), wherein phi () is an energy potential function, and SRNLM (mu<init>) is non-local mean filtering led by the reference image mu<ref>; performing iterative computation according to the edge-preserving prior R (mu<init>) of the initial iterative image mu<init> by means of a statistical iterative formula to obtain an iterative reconstructed image mu<iter>; when the iterative result of the reconstructed image mu<iter> satisfies the iteration stopping condition, stopping iterating, and obtaining the final reconstructed image of the low-dose X-ray CT image. The statistical iterative reconstructing method for the low-dose X-ray CT image is capable of effectively eliminating the image noise, inhibiting the streak artifact and well keeping the detail information of the image.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
System, Method and Apparatus for Small Pulmonary Nodule Computer Aided Diagnosis from Computed Tomography Scans
InactiveUS20090080748A1Improve consistencyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleVoxel
The present invention is a multi-stage detection algorithm using a successive nodule candidate refinement approach. The detection algorithm involves four major steps. First, the lung region is segmented from a whole lung CT scan. This is followed by a hypothesis generation stage in which nodule candidate locations are identified from the lung region. In the third stage, nodule candidate sub-images pass through a streaking artifact removal process. The nodule candidates are then successively refined using a sequence of filters of increasing complexity. A first filter uses attachment area information to remove vessels and large vessel bifurcation points from the nodule candidate list. A second filter removes small bifurcation points. The invention also improves the consistency of nodule segmentations. This invention uses rigid-body registration, histogram-matching, and a rule-based adjustment system to remove missegmented voxels between two segmentations of the same nodule at different times.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
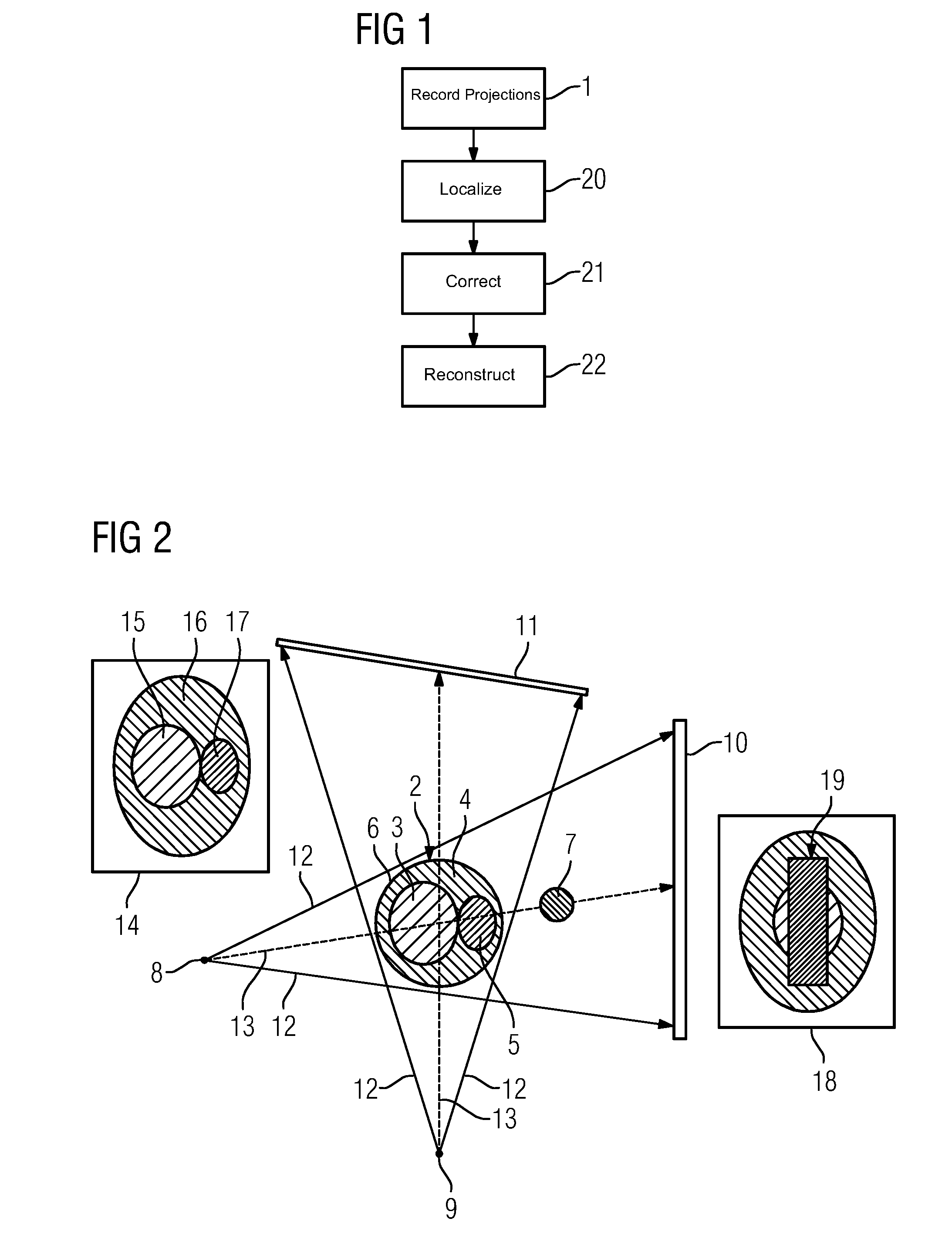
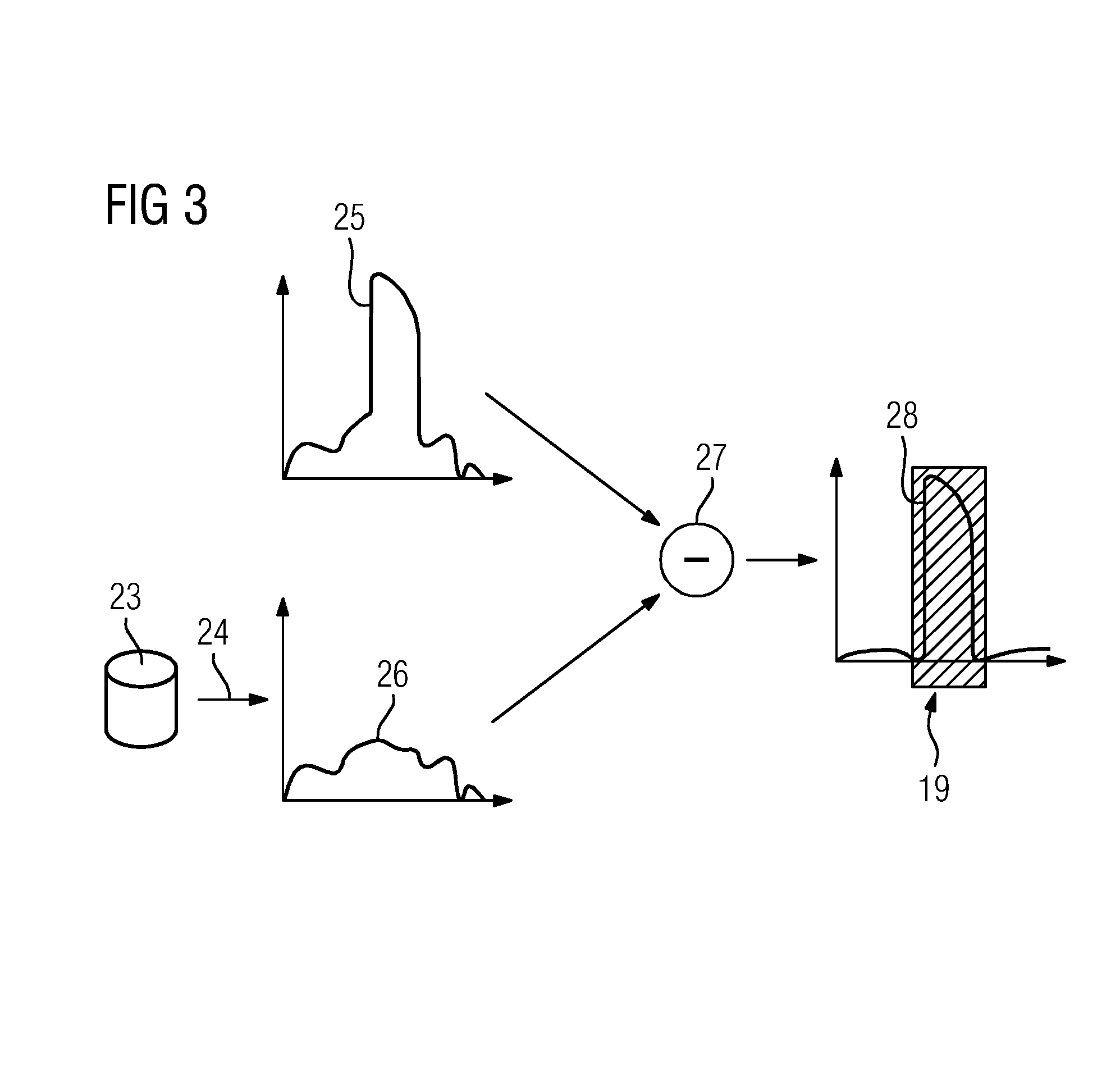
Reducing Artifacts in an Image Data Set and X-Ray Device
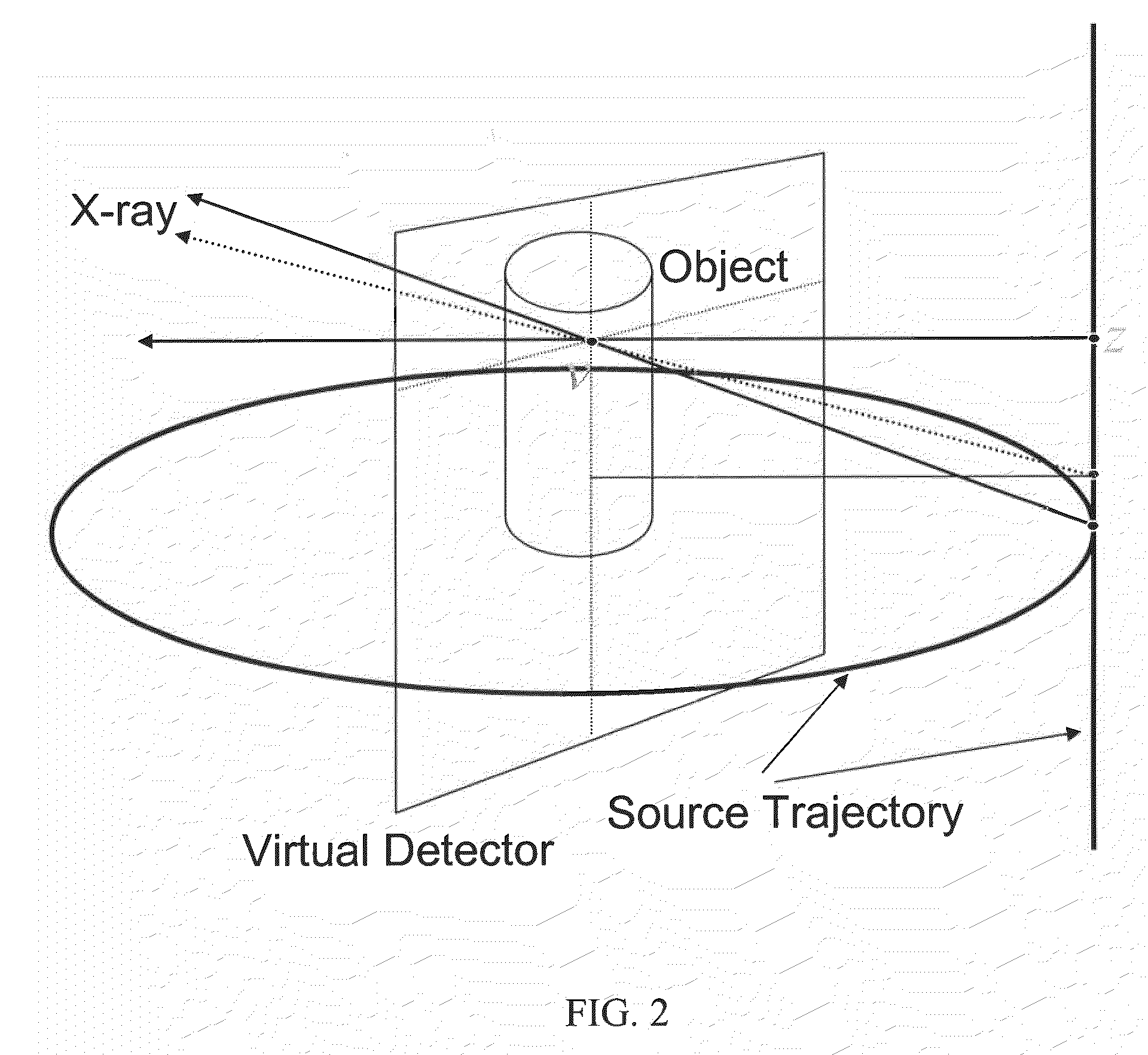
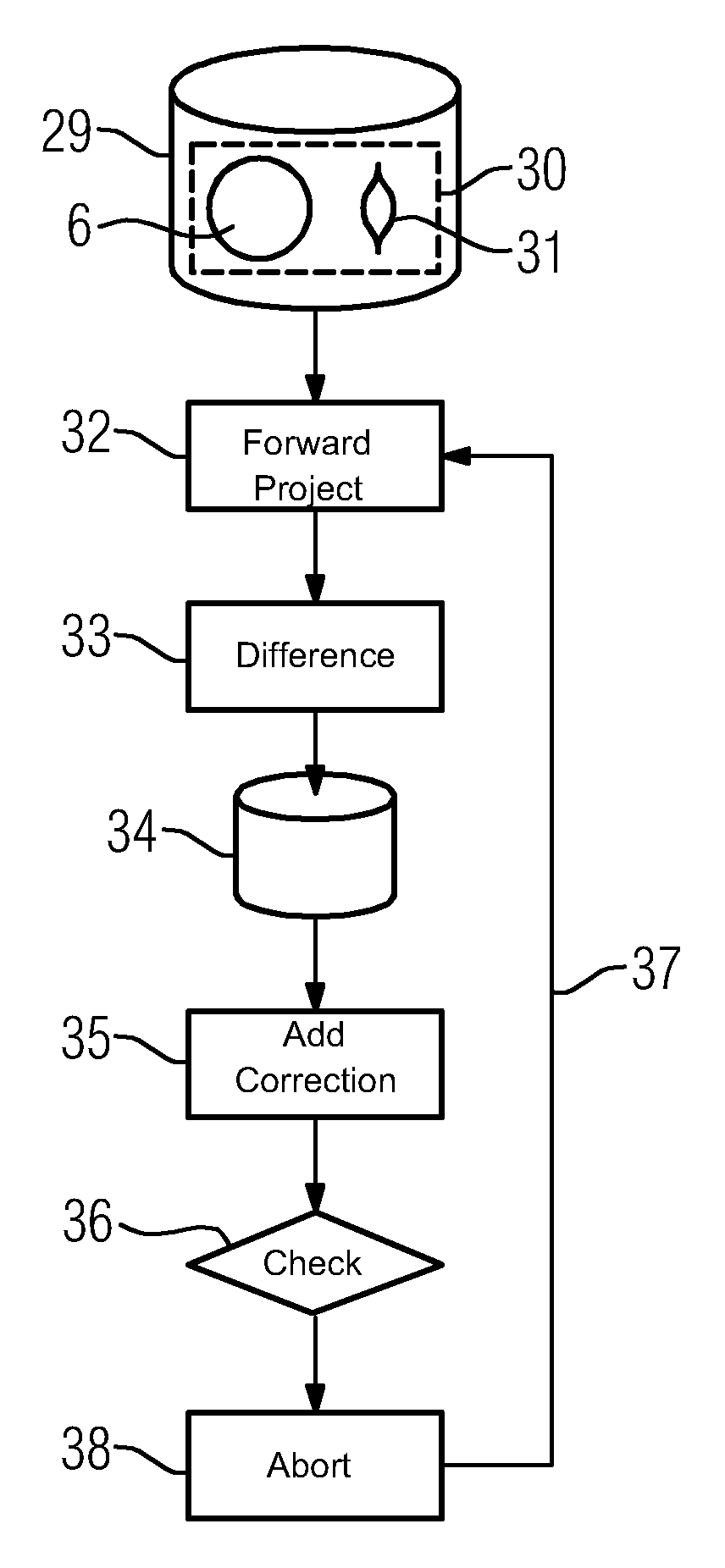
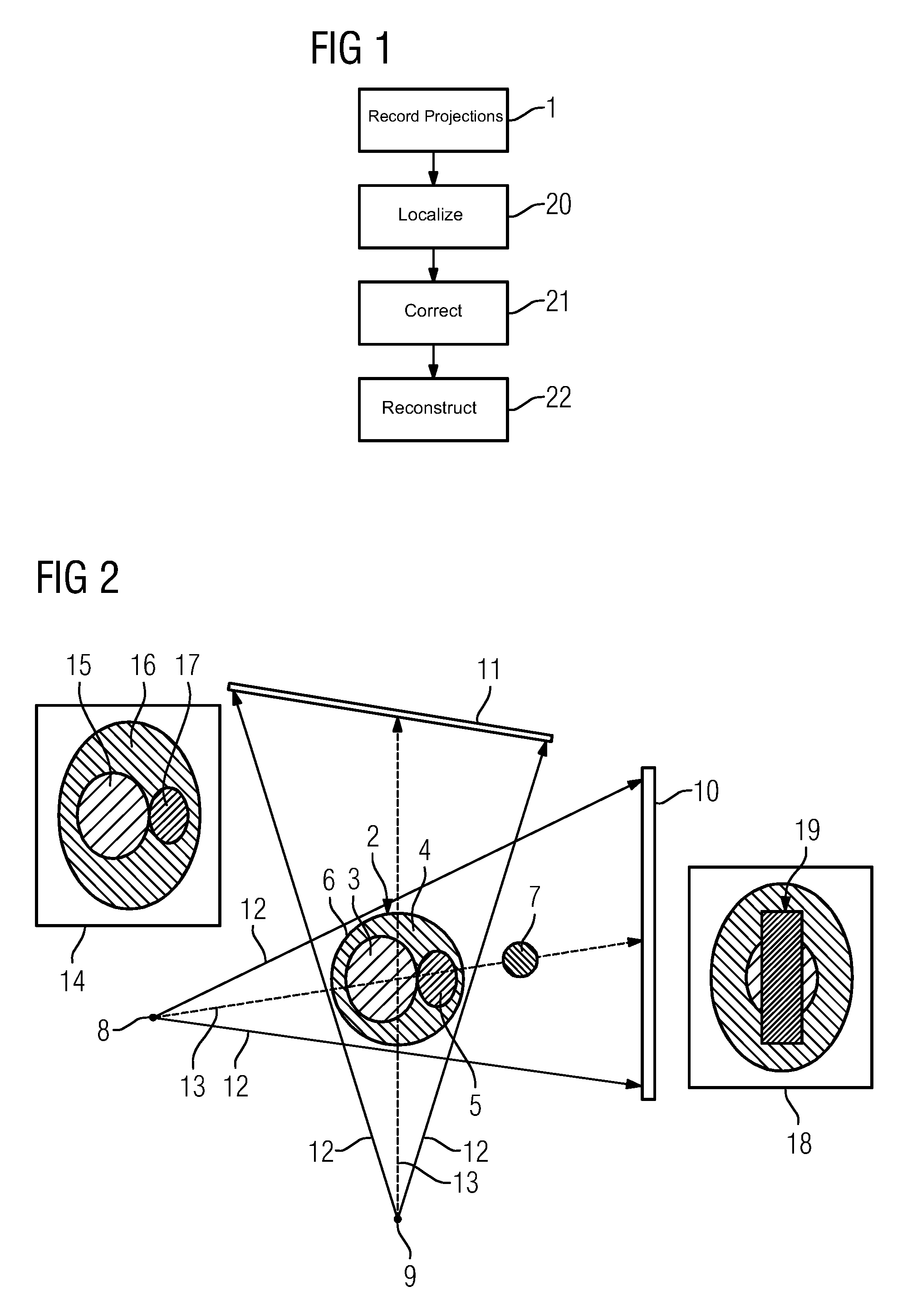
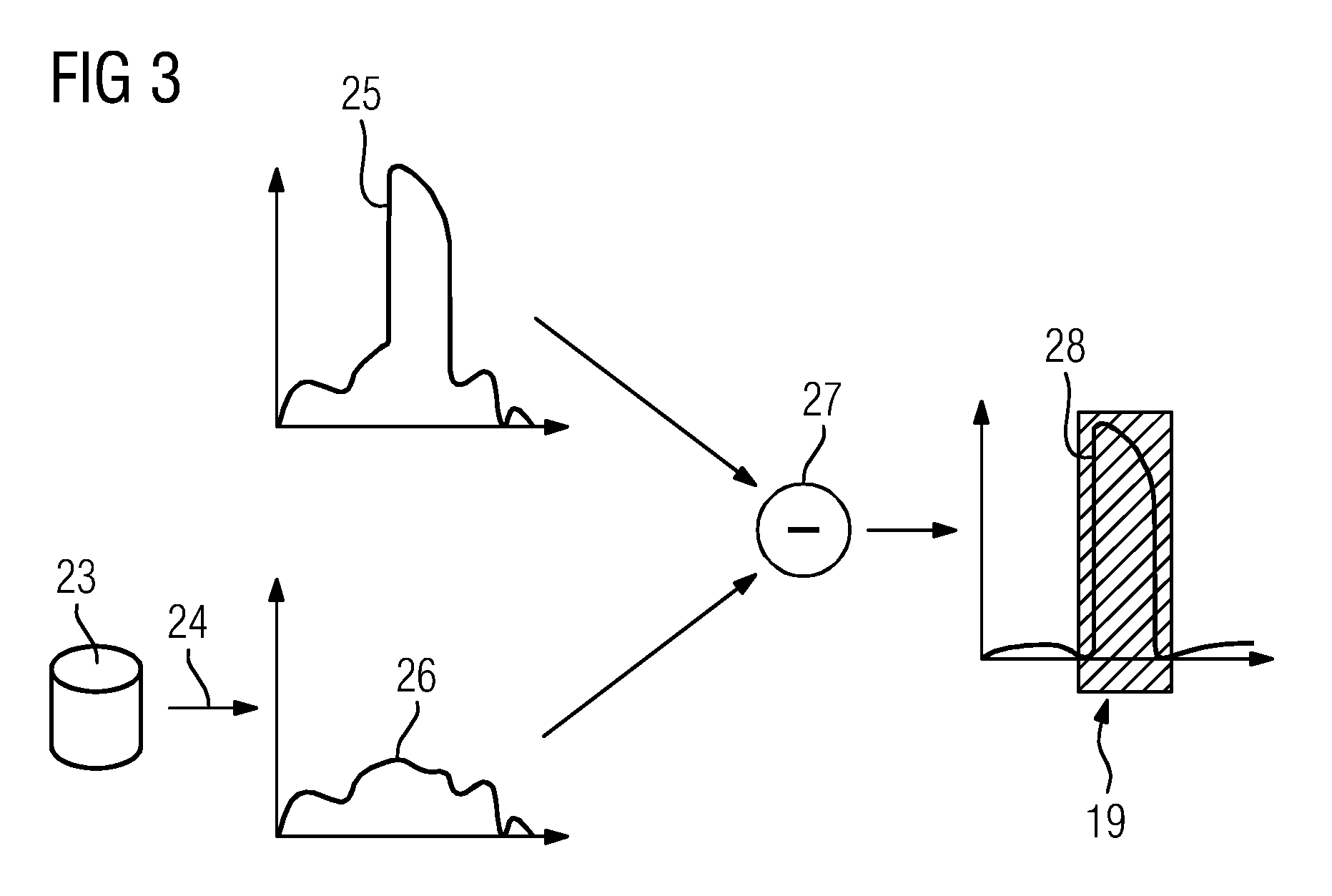
ActiveUS20150078507A1Describe wellMinimize the differenceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setProjection image
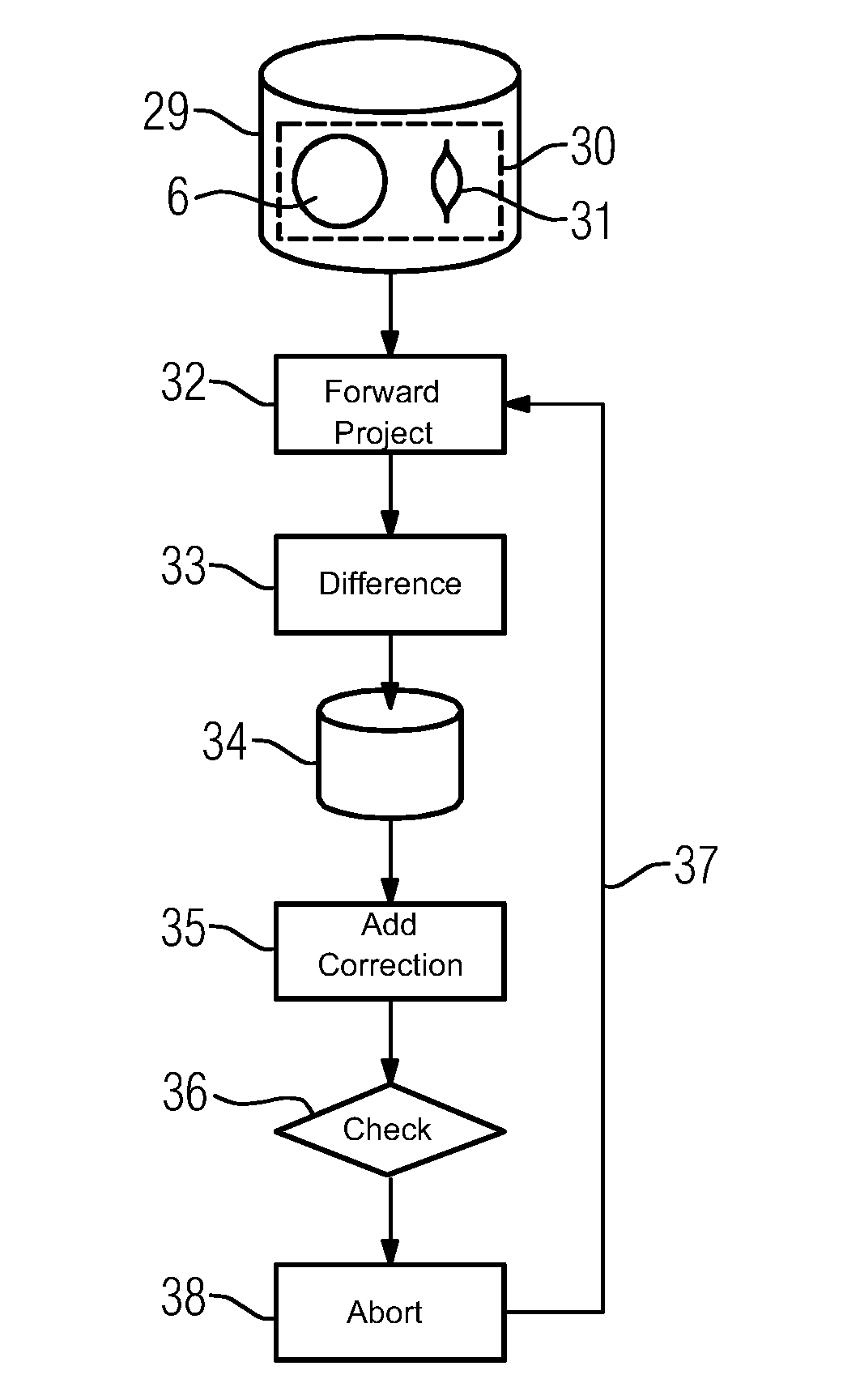
Streak artifacts generated by at least one X-ray attenuating object arranged outside a reconstruction volume in a three-dimensional image data set showing the reconstruction volume are reduced. The reconstruction volume is reconstructed from two-dimensional projection images recorded from different projection directions. The object is localized in the projection images showing the object. To determine corrected projection images for the reconstruction of the image data set, the image data of the area of each projection image showing the object is corrected to remove the object. The localization of the object is performed taking into account difference images of the measured projection images and from a reconstruction data set of forward-projected comparative images reconstructed from the measured projection images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
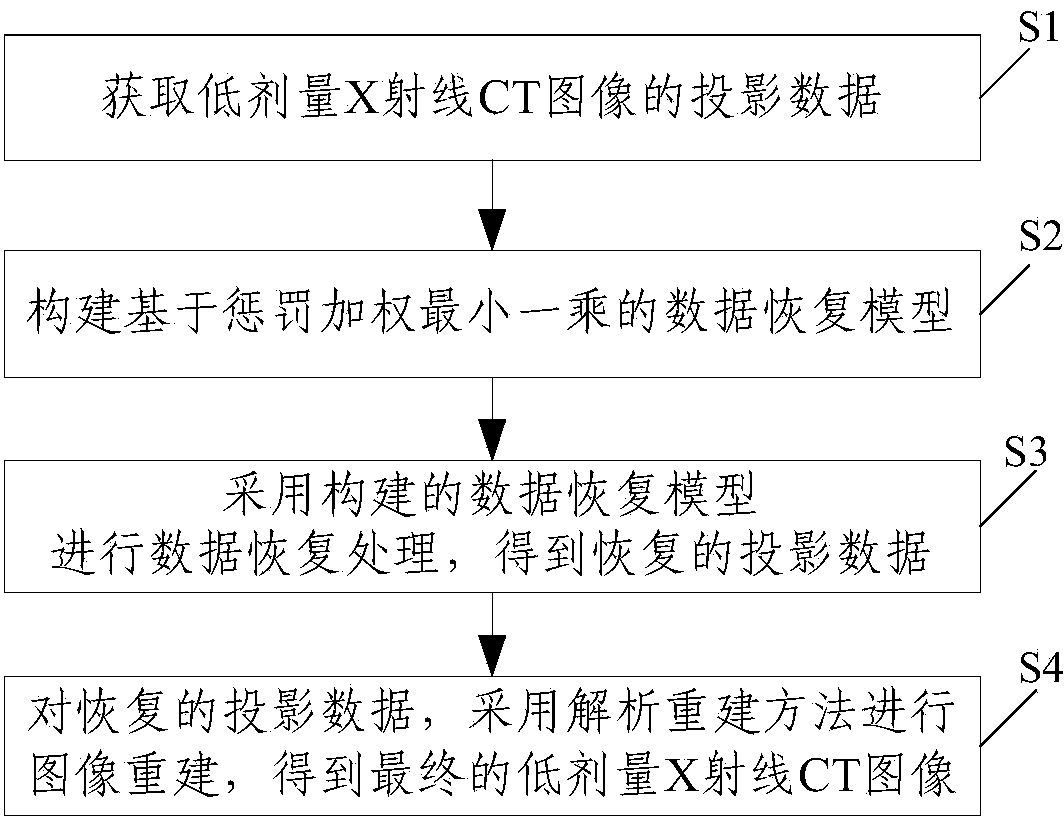
Low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method
ActiveCN103810734AQuality rebuildSolve the noiseImage enhancement2D-image generationX-rayComputer science
The invention discloses a low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method. The low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method includes acquiring projection data y<raw> of a low-dose X-ray CT image; setting up a data restoring model (shown in the description) based on penalized weighted least absolute for the projection data y raw, restoring the projection data y<raw> to obtain restored projection data y<restored>, wherein p is ideal projection data to be calculated, the parameter lambda is a non-negative real number, w is a weight factor (shown in the description), wherein both the parameters beta and epsilon are non-negative real numbers, and (shown in the description) is variance of the projection data y<raw>; reconstructing an image for the restored projection data y<restored> by means of an analyzing and reconstructing method to obtain the final low-dose X-ray CT image. The low-dose X-ray CT projection data restoring method is capable of restoring the low-dose CT projection data which is capable of reducing the tube current and scanning time and reconstructing the image through the analyzing and reconstructing method, the image noise is eliminated effectively, the streak artifact is inhibited, and the detail information of the image is well kept.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Reduction of Streak Artifacts In Low Dose CT Imaging through Multi Image Compounding
InactiveUS20070140407A1Improve reconstruction qualityImprove image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMulti-imageBack projection
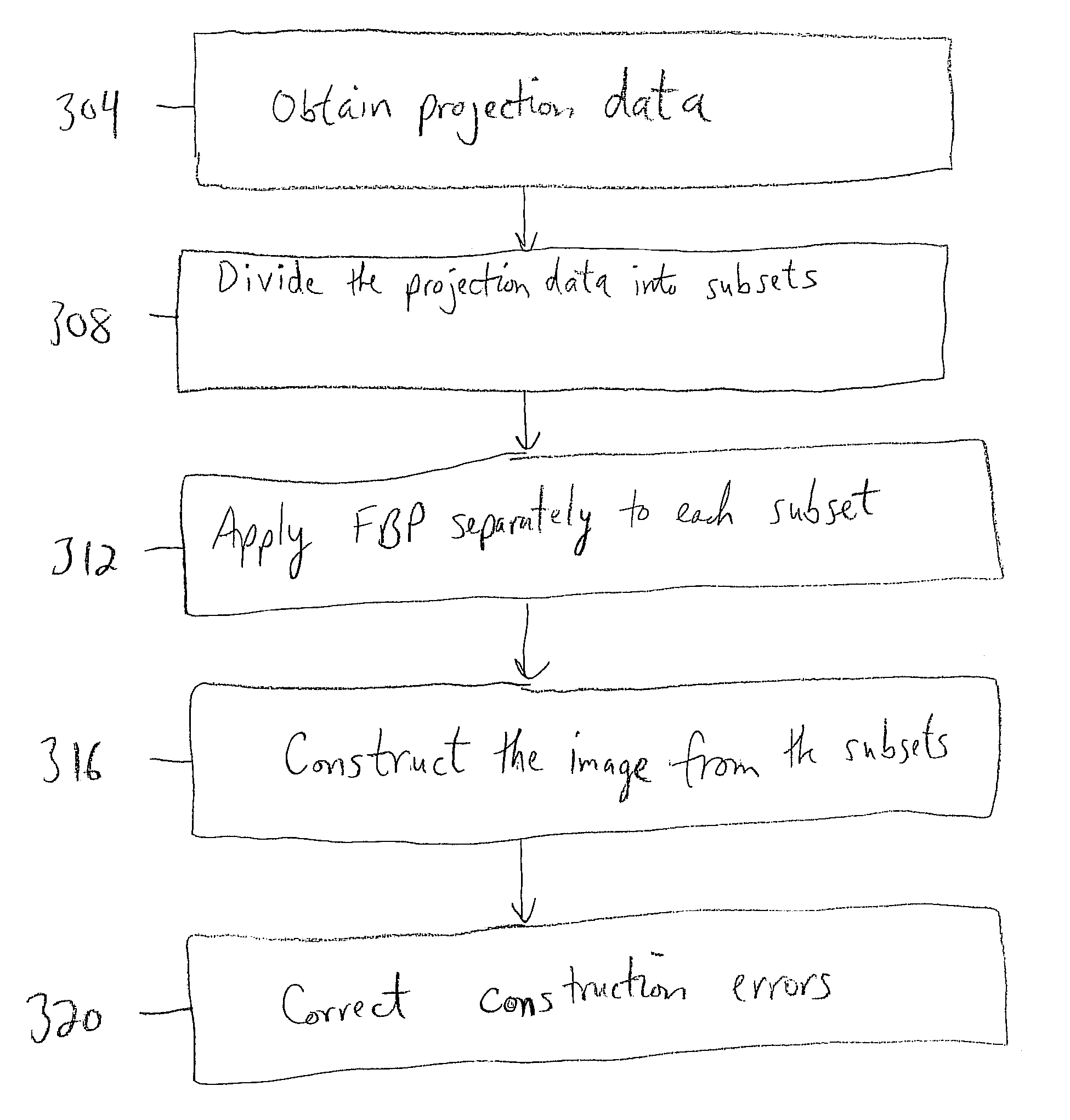
Disclosed is a method and system for constructing, from a computerized tomography (CT) scan, an image relating to a physical structure. Projection data associated with the image is obtained and divided into a plurality of subsets. Filtered back projection (FBP) is then applied to each subset in the plurality of subsets. The image is constructed based on the application of the FBP to each subset in the plurality of subsets.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Reduction of streak artifacts in low dose CT imaging through multi image compounding
InactiveUS7672421B2Improve image qualityImprove reconstruction qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMulti-imageBack projection
Disclosed is a method and system for constructing, from a computerized tomography (CT) scan, an image relating to a physical structure. Projection data associated with the image is obtained and divided into a plurality of subsets. Filtered back projection (FBP) is then applied to each subset in the plurality of subsets. The image is constructed based on the application of the FBP to each subset in the plurality of subsets.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method of and system for detecting anomalies in projection images generated by computed tomography scanners
InactiveUS20060039599A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersProjection image
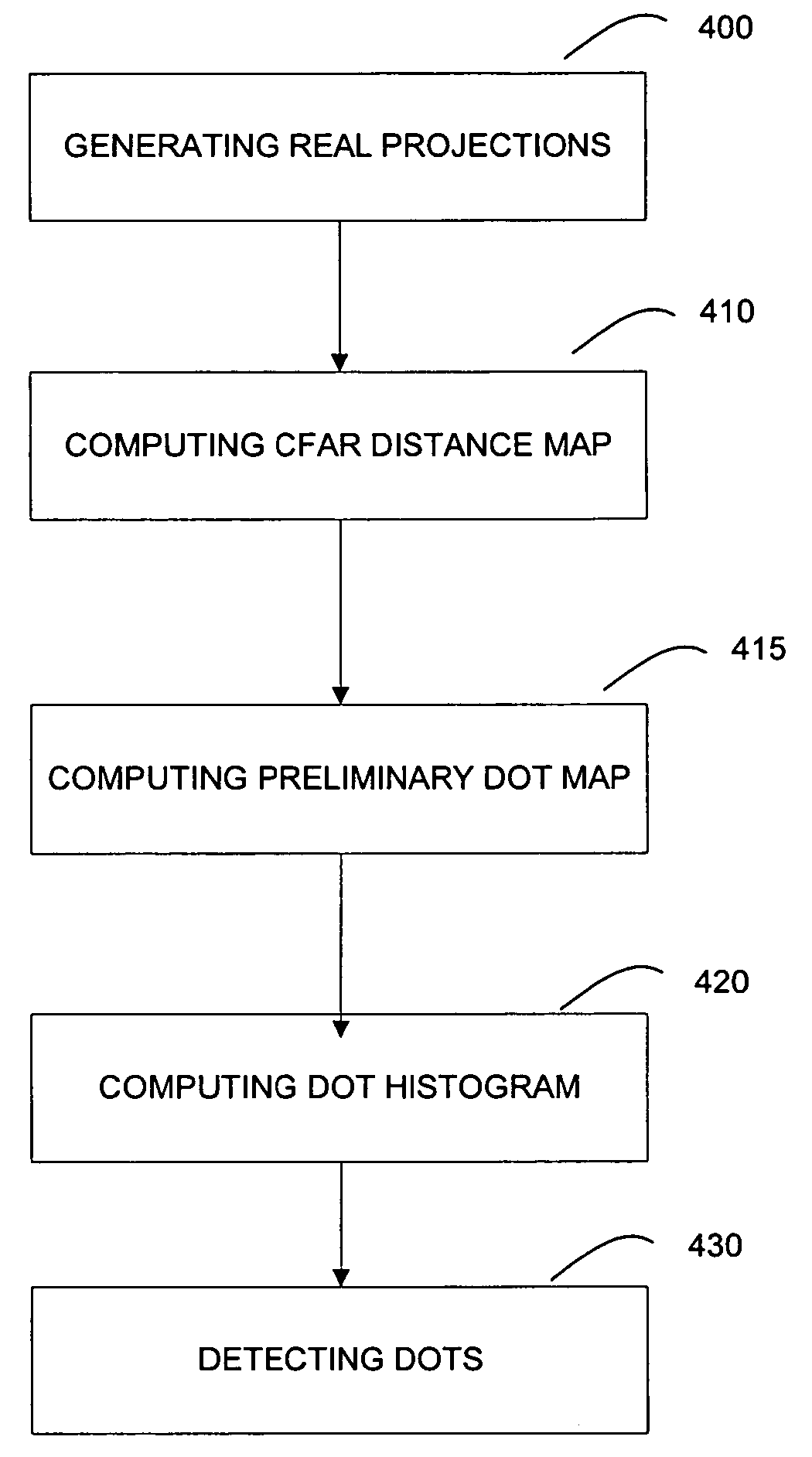
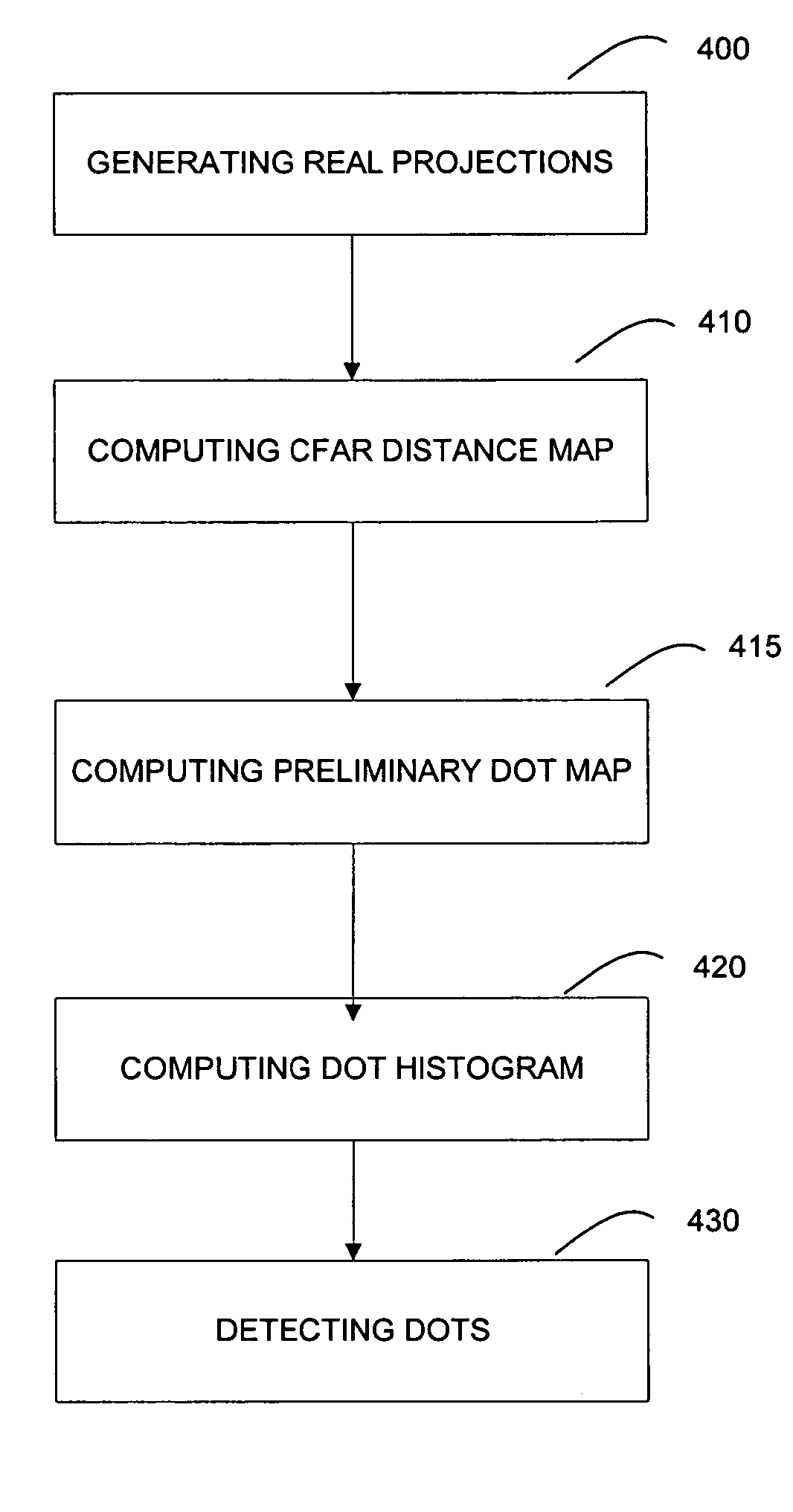
A method of and a system for detecting anomalies in projection images generated by CT scanners are provided. One type of anomaly of particular interest is bright or / and dark dots in projection images, which correspond to streak artifacts in the CT images. The method for detecting such bright or / and dark dots in projection images comprises: generating projection images; computing a CFAR distance map; computing a preliminary dot map; generating dot histograms; and detecting bright dots or / and dark dots based on the generated histograms.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS9373159B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
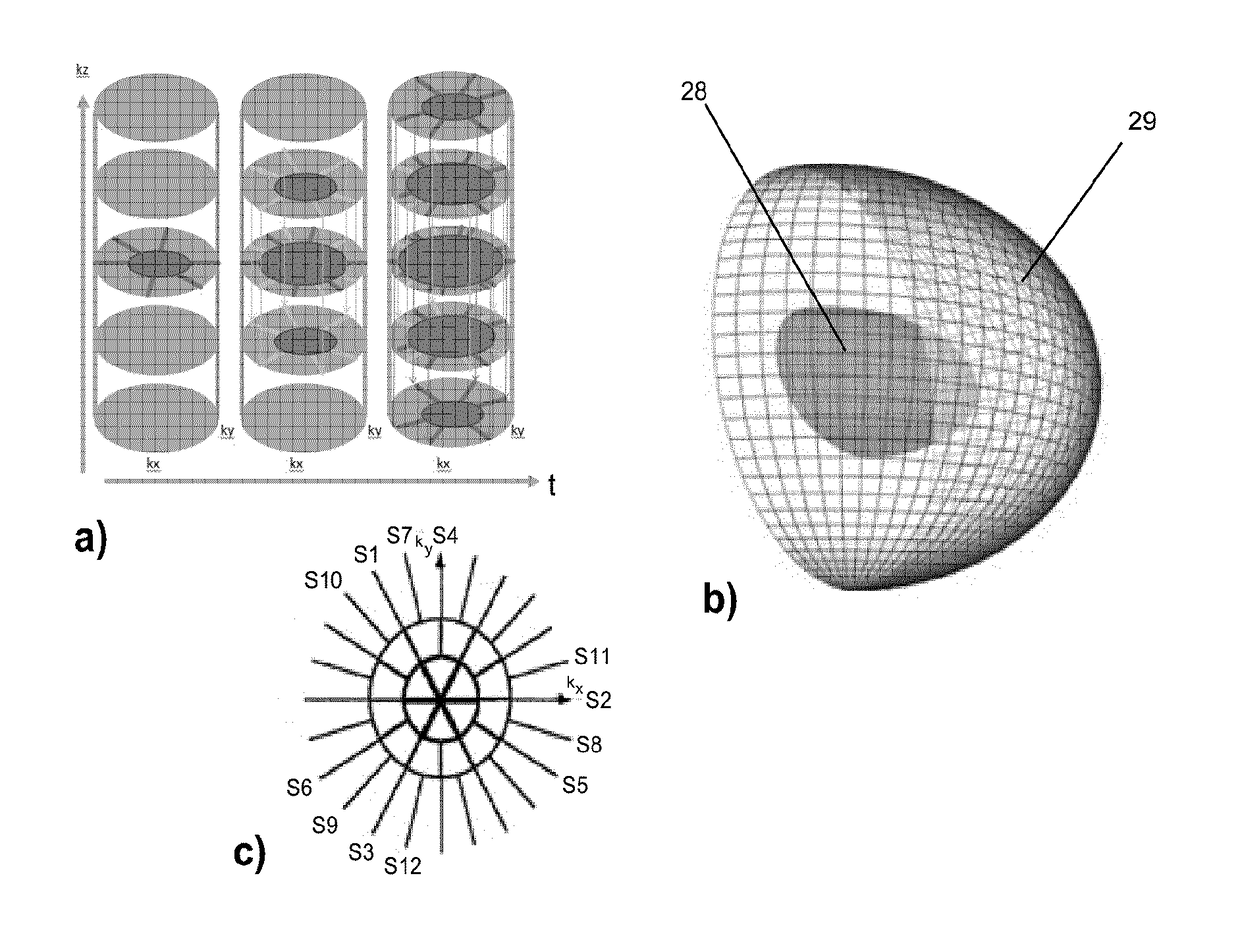
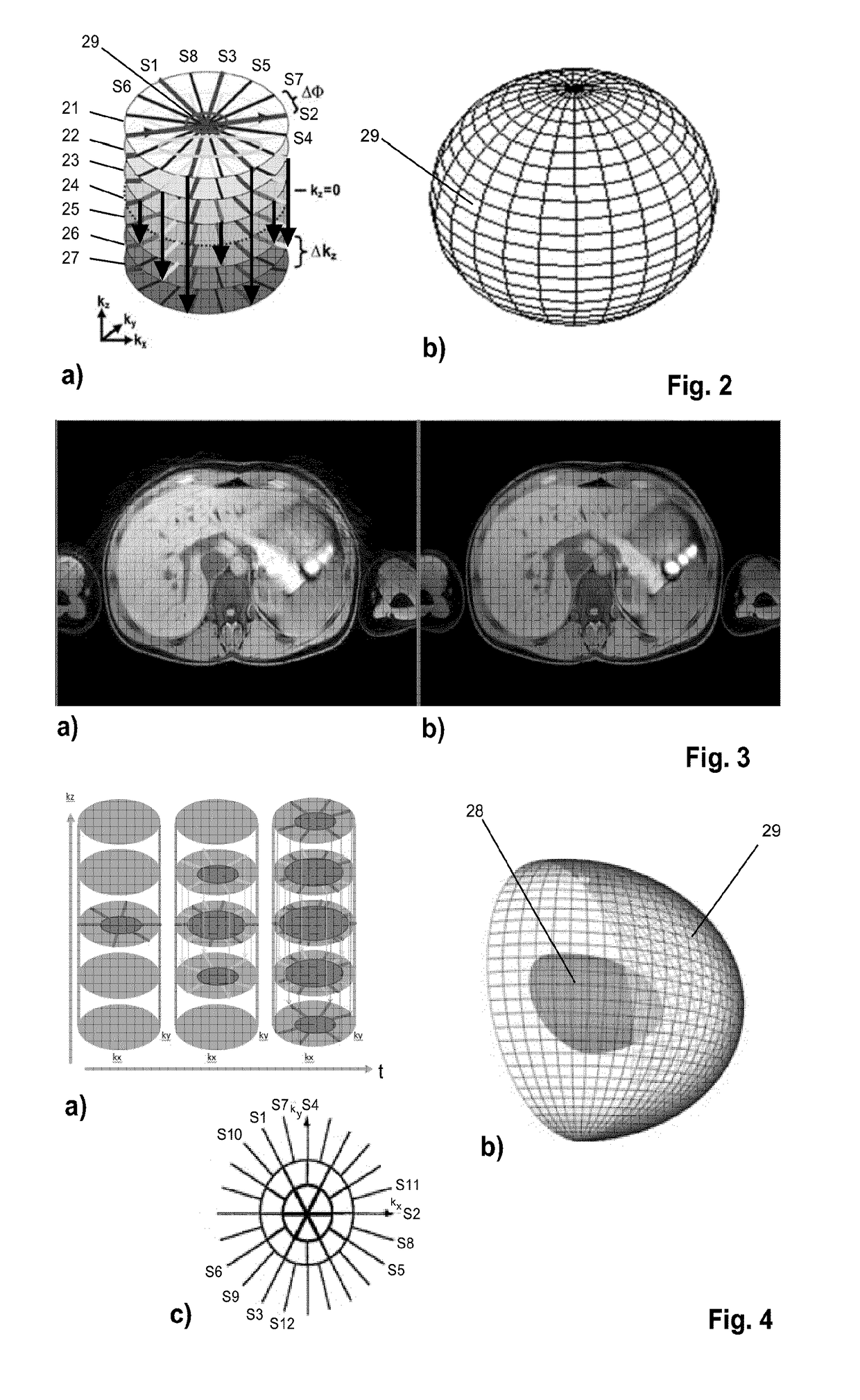
Mr imaging using a stack-of stars acquisition
ActiveUS20180149721A1Improve time resolutionLower Level RequirementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientAcquisition Scheme
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least an object (10) placed in an examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to enable fast MR imaging using the stack-of-stars acquisition scheme with a reduced level of streaking artifacts. The method of the invention comprises: —subjecting the object (10) to an imaging sequence of at least one RF pulse and switched magnetic field gradients, —acquiring MR signals according to a stack-of-stars scheme, wherein the MR signals are acquired as radial k-space profiles (S 1-S 12) from a number of parallel slices (21-27) arranged at different positions along a slice direction, wherein the radial density of the k-space profiles (SI-SI2) varies as a function of the slice position, wherein the radial density is higher at more central k-space positions and lower at more peripheral k-space positions and wherein k-space profiles are acquired at a higher temporal density from slices at more central positions than from slices at more peripheral k-space positions, and —reconstructing a MR image from the MR signals.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
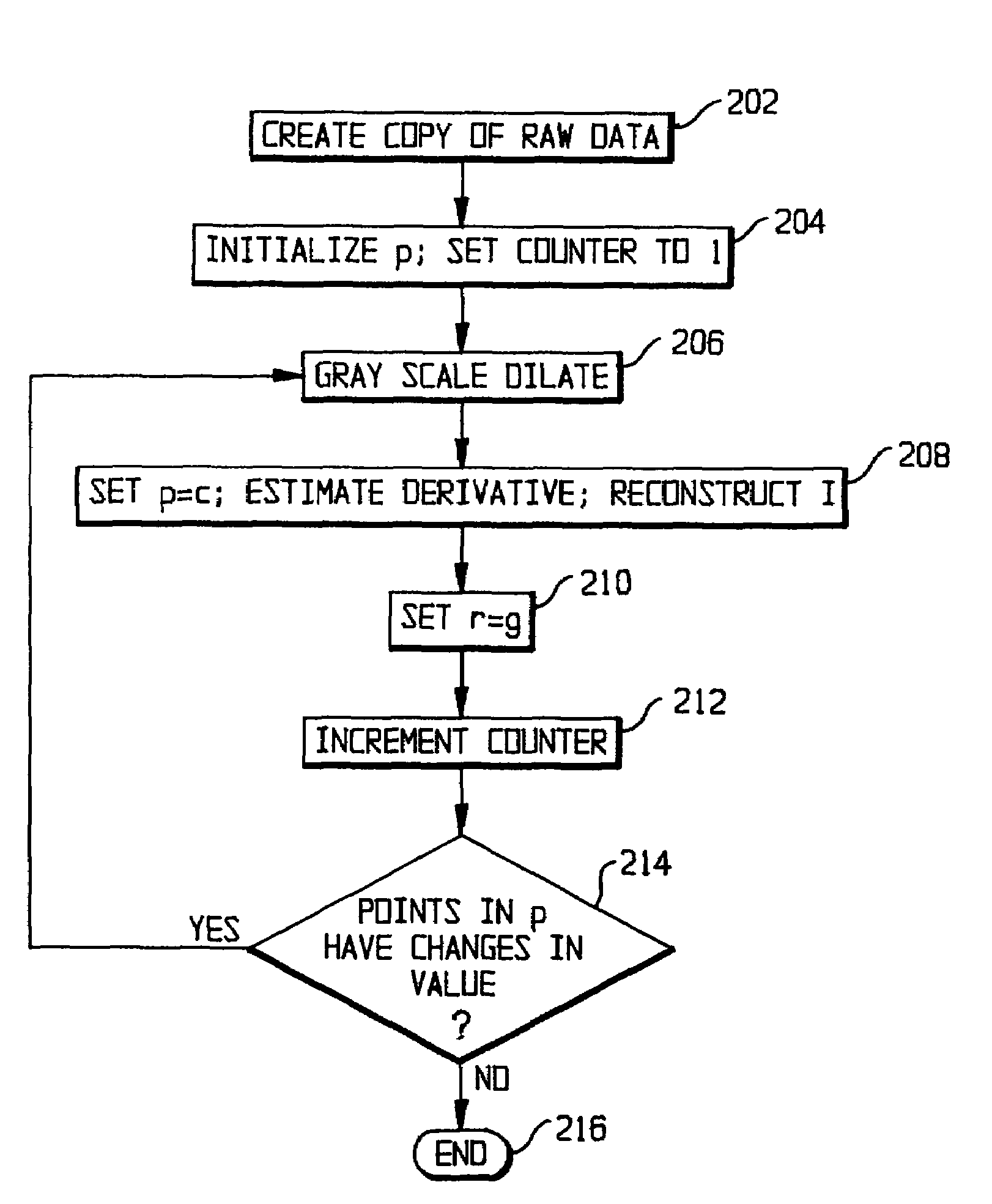
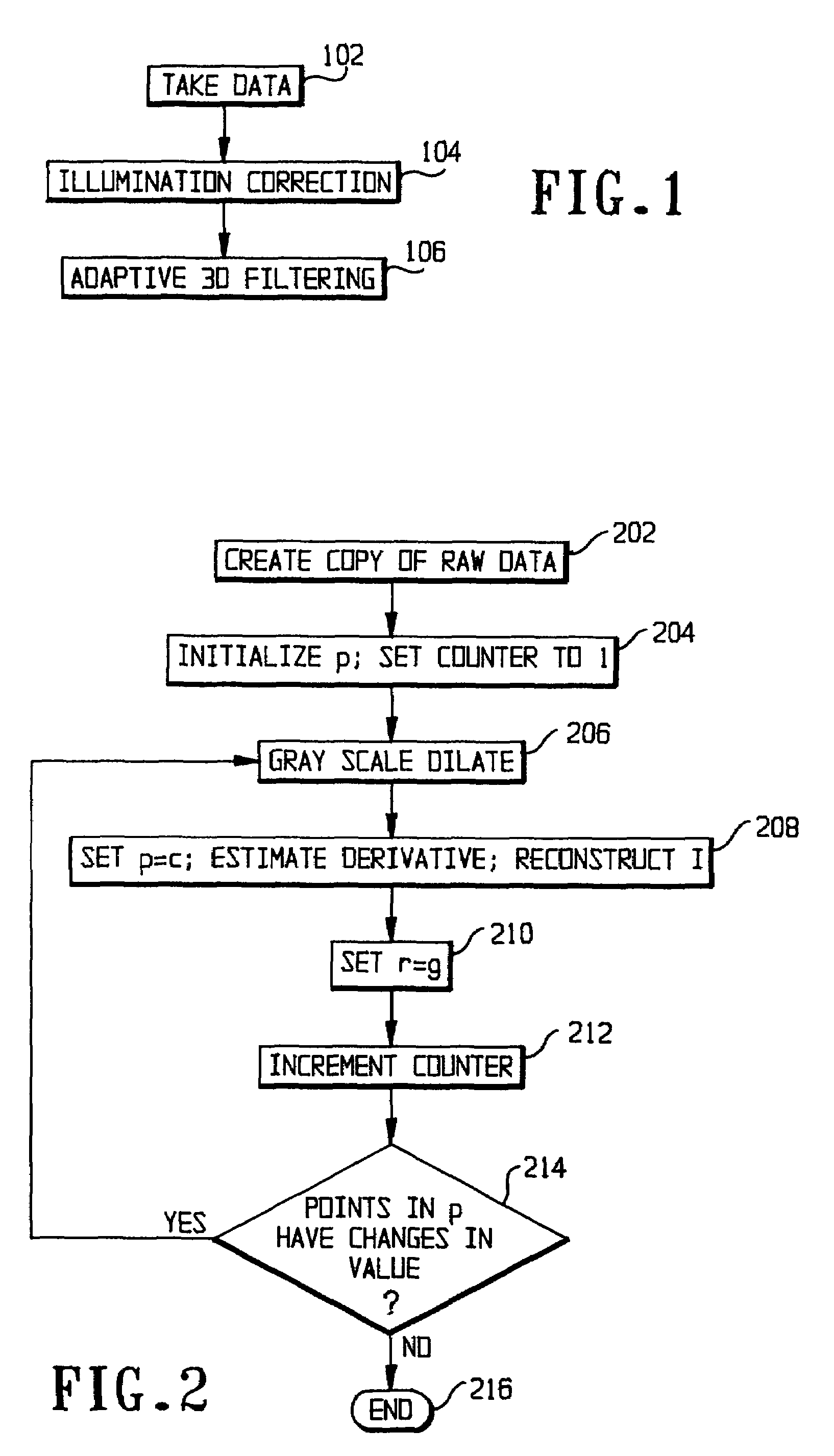
System and method for reducing or eliminating streak artifacts and illumination inhomogeneity in CT imaging
InactiveUS7406211B2Reduce and eliminate streak artifactImage enhancementImage analysisImage contrastGray scale morphology
In CT (computed tomography) images, streak artifacts caused by the presence of metal implants and inhomogeneous estimation of tissue density are reduced or eliminated. The algorithm has two basic steps: 1) illumination correction and 2) adaptive 3D filtering. The algorithm starts by estimating the direction of the streak and the degree of inhomogeneous densities by gray scale morphology dilatation. Then, it proceeds to estimate the correct densities based on the estimations and to reduce the streak by an adaptive 3D filtering whose parameters depend on the streak direction and the local image contrast.
Owner:VIRTUALSCOPICS
Streak artifact prediction
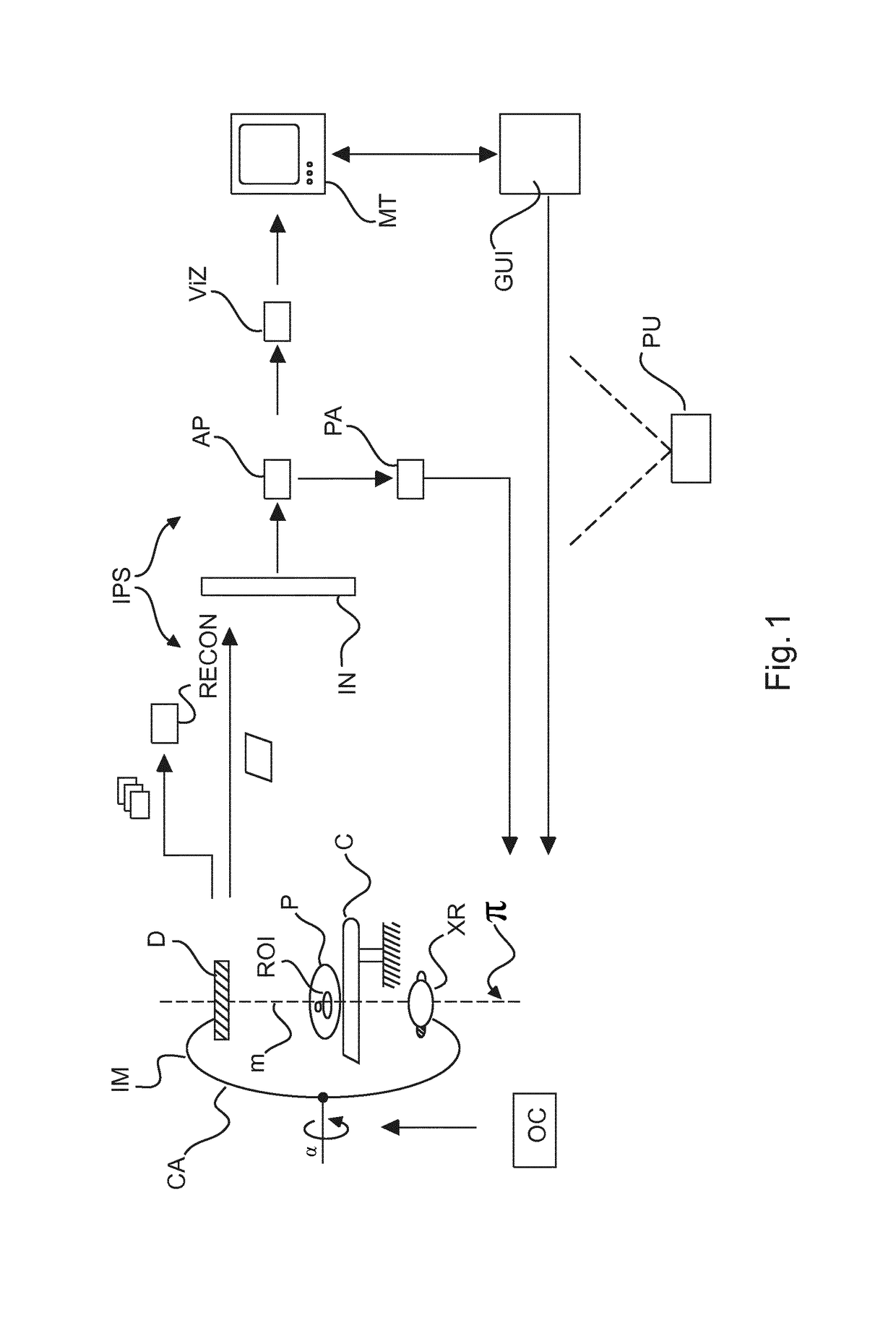
ActiveUS20180365869A1CollisionAvoid collisionReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsImaging processingProjection image
An image processing system, comprising an input port (IN) for receiving a projection image of an object. The image is acquired by a rotational image apparatus (IM) at a position on an imaging trajectory in an adjustable rotation plane (π) around an imaging region. An image artifact extent predictor (AP) of the system is configured to predict for said image a projection area of a reconstruction artifact. A visualizer (VIZ) is configured to visualize, on a display unit (MT), said image with a visual indication of the projection area.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for tomographic reconstruction utilizing circular trajectory and scanogram to reduce artifacts
InactiveUS20090213985A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomographic reconstructionComputer science
A computed tomography apparatus and method using line data estimated from circle data and scanogram data. An image of a subject is reconstructed using the circle data and the estimated line data. The circle data and scanogram data may be weighted in estimating the line data. The apparatus and method are useful in diminishing or eliminating streak artifacts in reconstructed images such as images including the spine.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Reducing artifacts in an image data set and X-ray device
ActiveUS9554766B2Improve image qualityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setProjection image
Streak artifacts generated by at least one X-ray attenuating object arranged outside a reconstruction volume in a three-dimensional image data set showing the reconstruction volume are reduced. The reconstruction volume is reconstructed from two-dimensional projection images recorded from different projection directions. The object is localized in the projection images showing the object. To determine corrected projection images for the reconstruction of the image data set, the image data of the area of each projection image showing the object is corrected to remove the object. The localization of the object is performed taking into account difference images of the measured projection images and from a reconstruction data set of forward-projected comparative images reconstructed from the measured projection images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of and system for detecting anomalies in projection images generated by computed tomography scanners
InactiveUS7388983B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersProjection image
A method of and a system for detecting anomalies in projection images generated by CT scanners are provided. One type of anomaly of particular interest is bright or / and dark dots in projection images, which correspond to streak artifacts in the CT images. The method for detecting such bright or / and dark dots in projection images comprises: generating projection images; computing a CFAR distance map; computing a preliminary dot map; generating dot histograms; and detecting bright dots or / and dark dots based on the generated histograms.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Image processing device and image processing method
ActiveUS20150010224A1Maintain edgeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImaging processingNon linear functions
In order to provide an image processing device and the like making it possible to generate a target image in which edges of a structure are upheld and from which streaking artifacts are removed, a computation device determines a shape of a non-linear function on the basis of feature amounts of an original image and a smoothed image (S101). Next, the computation device calculates a condition coefficient of the original image and the smoothed image by using the non-linear function for which the shape was determined in S101 (S102). Next, the computation device uses the condition coefficients calculated in S102 to calculate a weighting coefficient for each of the pixels of the original image and the smoothed image (S103). Next, the computation device adds weighting to the original image and the smoothed image to generate the target image (S104).
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Method for artifact reduction in a medical image data set, x-ray device, computer program and electronically readable data carrier
ActiveUS20200196974A1Suppress streak artifactWeaker weightingImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setLow-pass filter
A method for the reduction of streak artifacts in an image data set reconstructed from projection images of an X-ray device is provided. The method includes determining a first interim data set by applying a non-linear low-pass filter to pixels that satisfy a selection condition. A second non-linear, high-pass-filtered interim data set is determined by pixel-by-pixel subtraction of the first interim data set from the image data set. The second interim data set is Fourier transformed in order to obtain a spatial frequency data set. Frequency portions attributable to artifacts in the spatial frequency data set are removed, and the processed spatial frequency data set is inverse Fourier transformed, such that a third interim data set is obtained. An artifact-reduced result data set is determined by addition of the third interim data set and the first interim data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for artifact reduction in a medical image data set, X-ray device, computer program and electronically readable data carrier
ActiveUS11369331B2Suppress artifactsNot to damageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setLow-pass filter
A method for the reduction of streak artifacts in an image data set reconstructed from projection images of an X-ray device is provided. The method includes determining a first interim data set by applying a non-linear low-pass filter to pixels that satisfy a selection condition. A second non-linear, high-pass-filtered interim data set is determined by pixel-by-pixel subtraction of the first interim data set from the image data set. The second interim data set is Fourier transformed in order to obtain a spatial frequency data set. Frequency portions attributable to artifacts in the spatial frequency data set are removed, and the processed spatial frequency data set is inverse Fourier transformed, such that a third interim data set is obtained. An artifact-reduced result data set is determined by addition of the third interim data set and the first interim data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
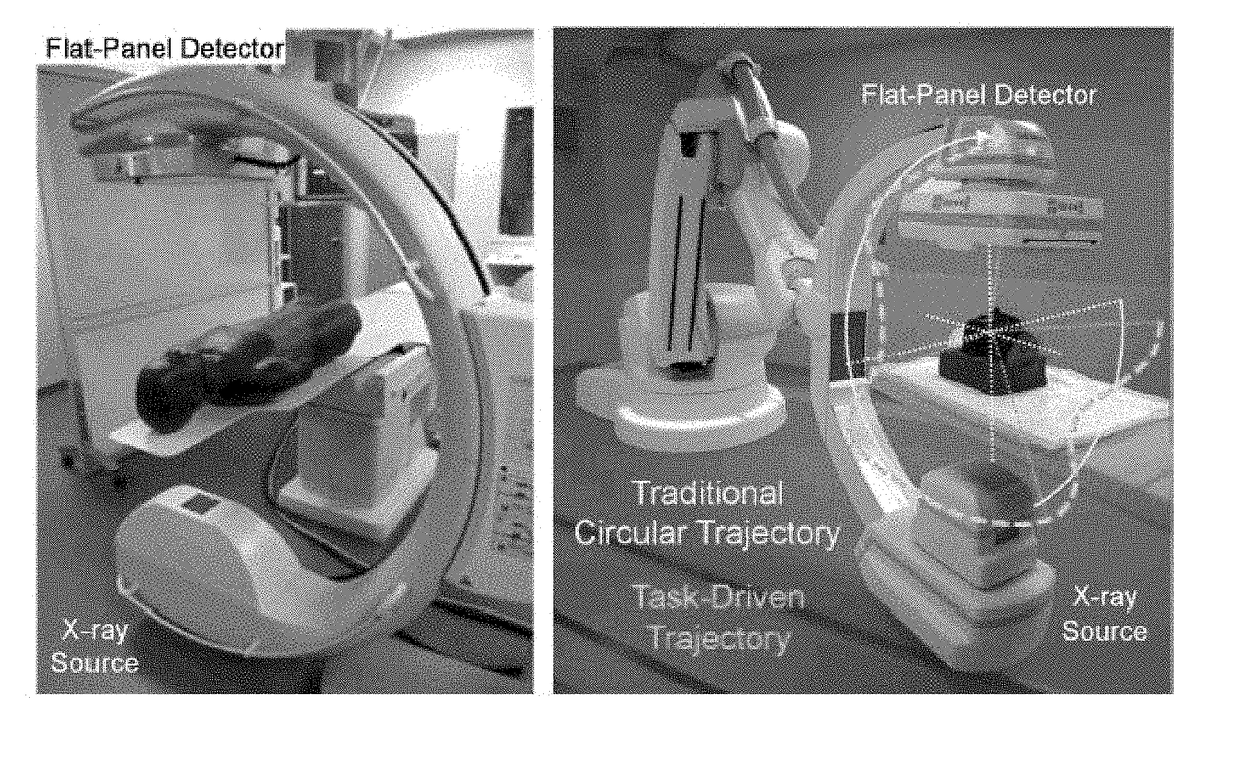
Self-calibrating projection geometry for volumetric image reconstruction
The present invention is directed to a method for enabling volumetric image reconstruction from unknown projection geometry of tomographic imaging systems, including CT, cone-beam CT (CBCT), and tomosynthesis systems. The invention enables image reconstruction in cases where it was not previously possible (e.g., custom-designed trajectories on robotic C-arms, or systems using uncalibrated geometries), and more broadly offers improved image quality (e.g., improved spatial resolution and reduced streak artifact) and robustness to patient motion (e.g., inherent compensation for rigid motion) in a manner that does not alter the patient setup or imaging workflow. The method provides a means for accurately estimating the complete geometric description of each projection acquired during a scan by simulating various poses of the x-ray source and detector to determine their unique, scan-specific positions relative to the patient, which is often unknown or inexactly known (e.g., a custom-designed trajectory, or scan-to-scan variability in source and detector position).
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
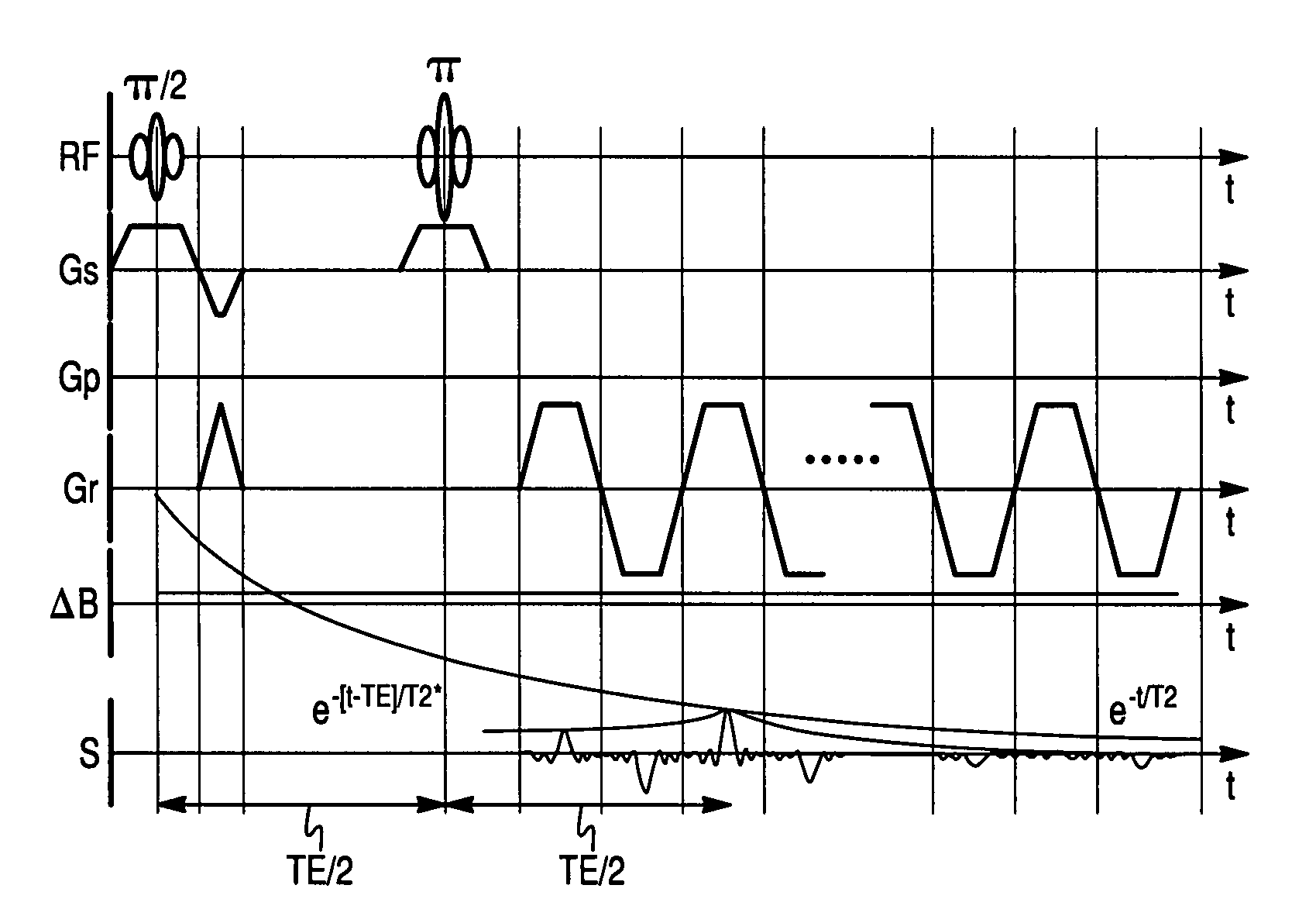
Method of obtaining a magnetic resonance image in which the streak artifacts are corrected using non-linear phase correction
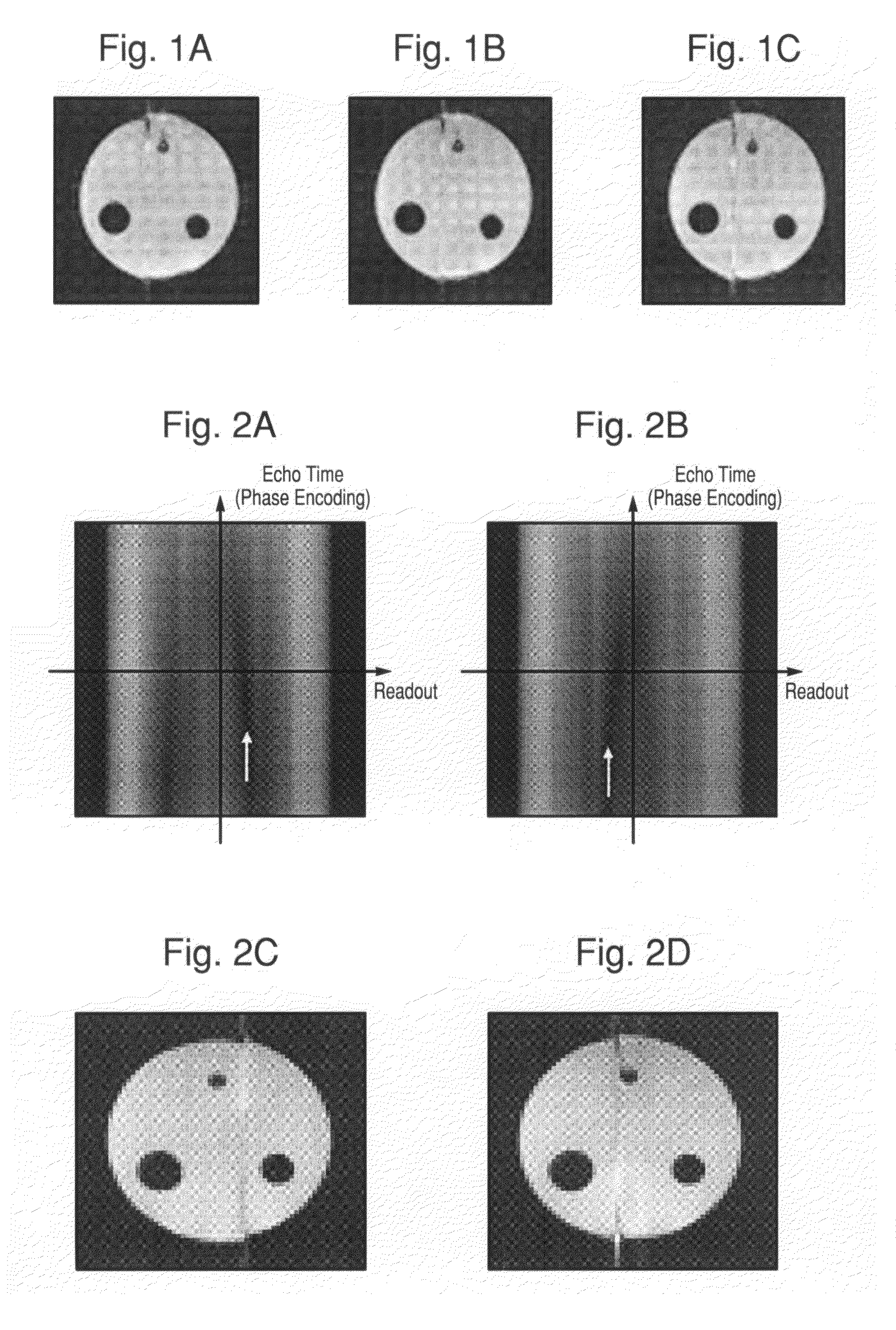
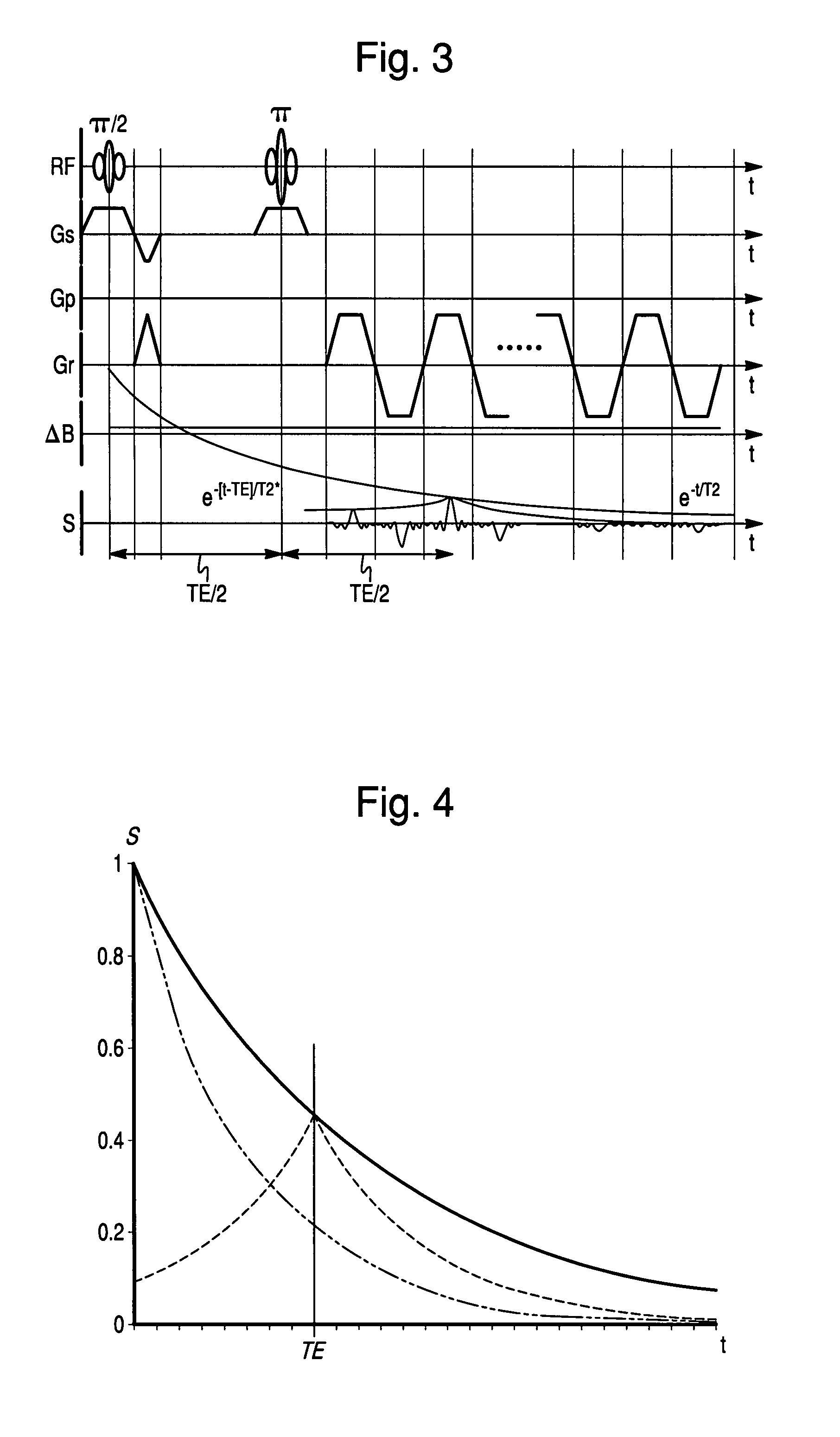
A non-linear phase correction method is provided. For the non-linear phase correction method, image information is acquired by gradient echo echo planar imaging (EPI). Reference information is acquired by spin echo EPI. The image information is corrected based on the reference information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com