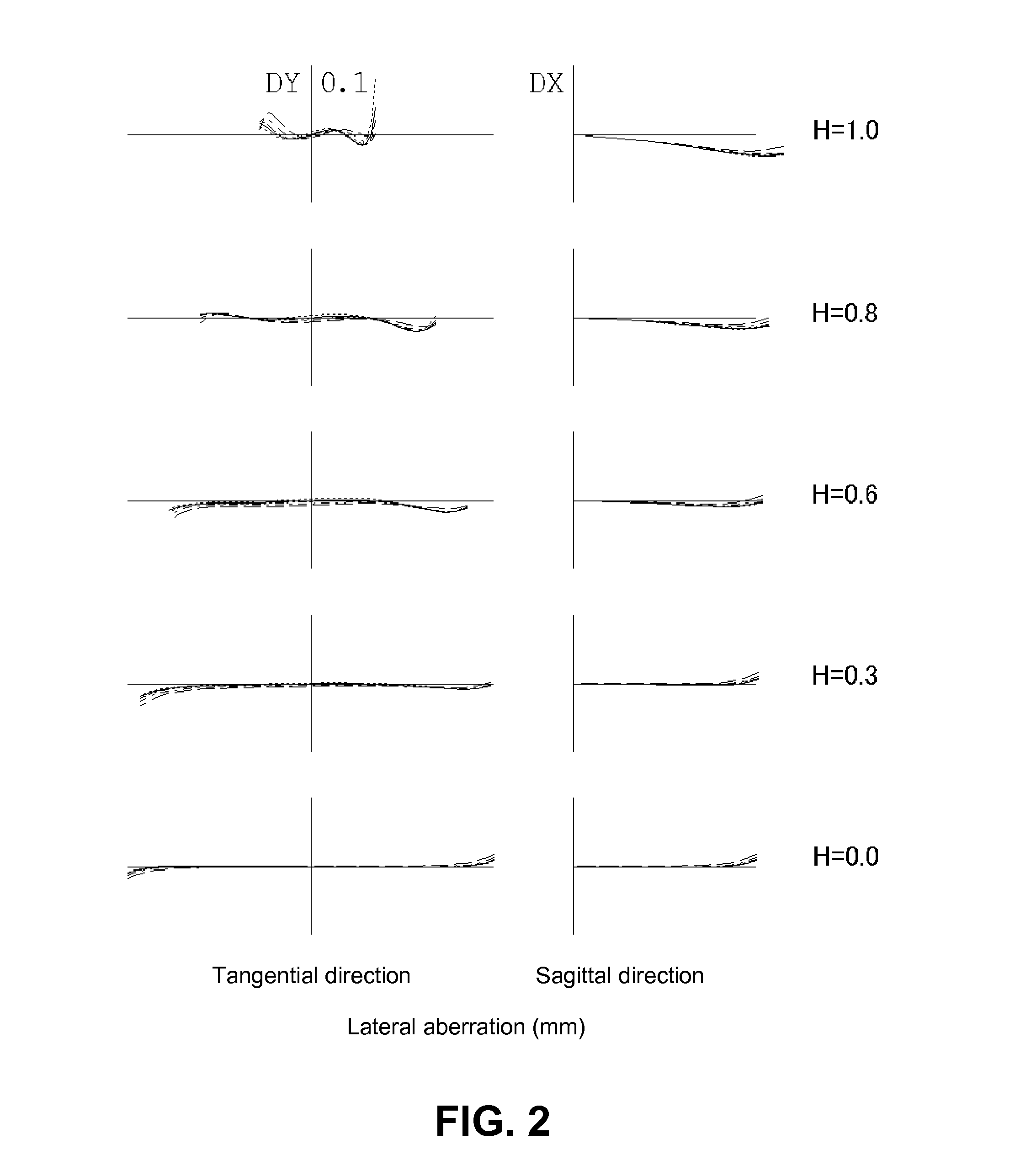
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Broad imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
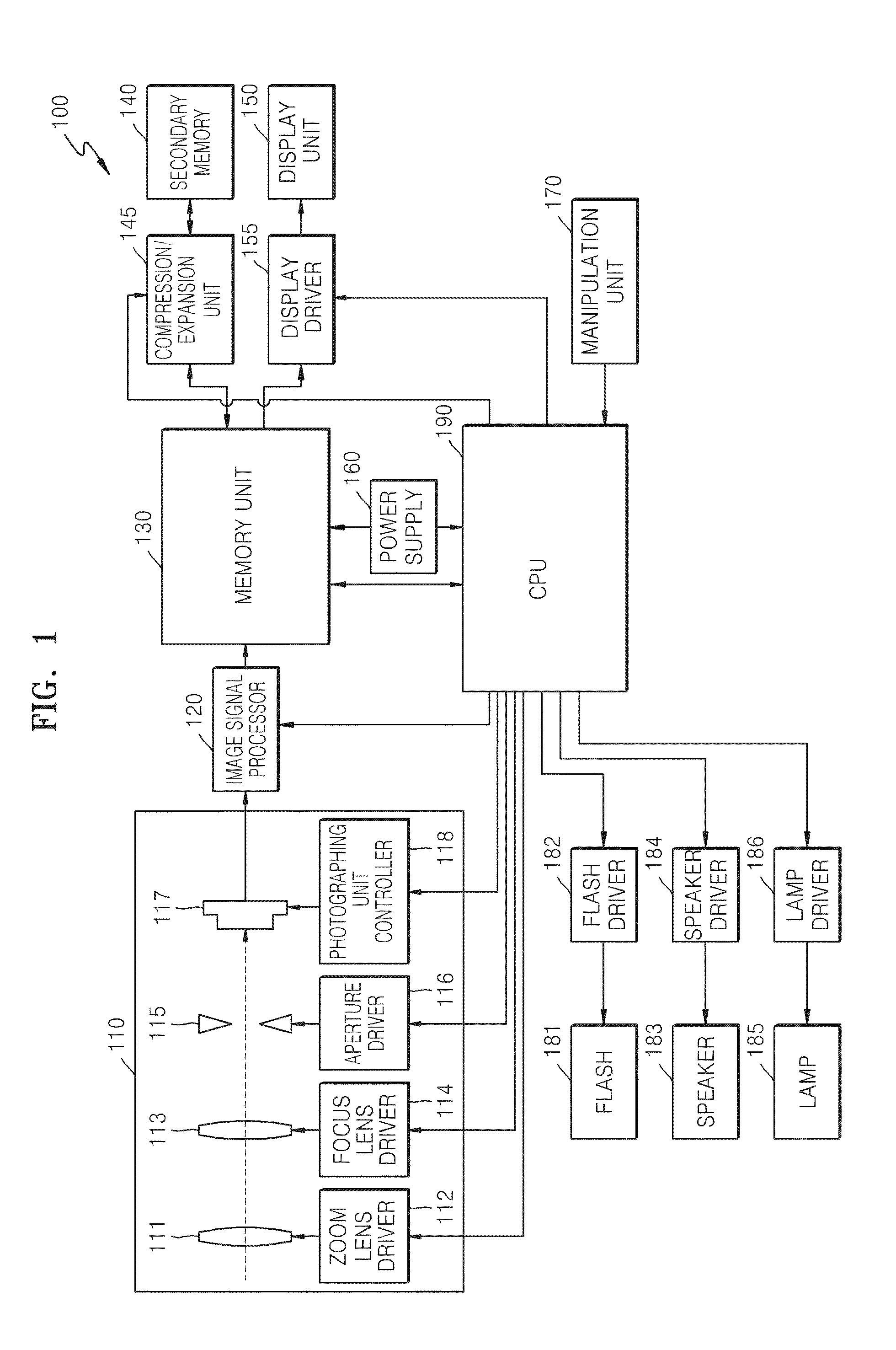
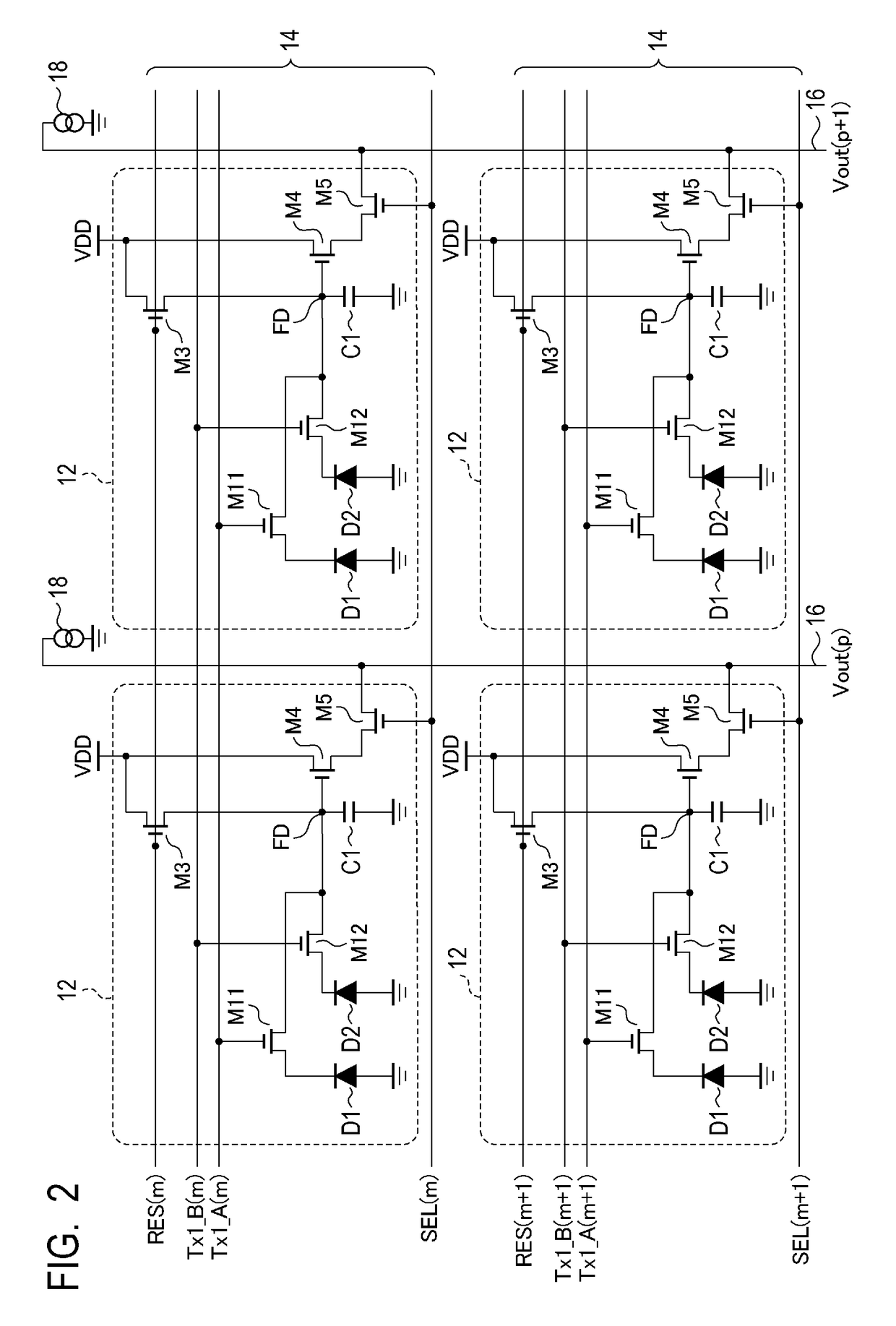
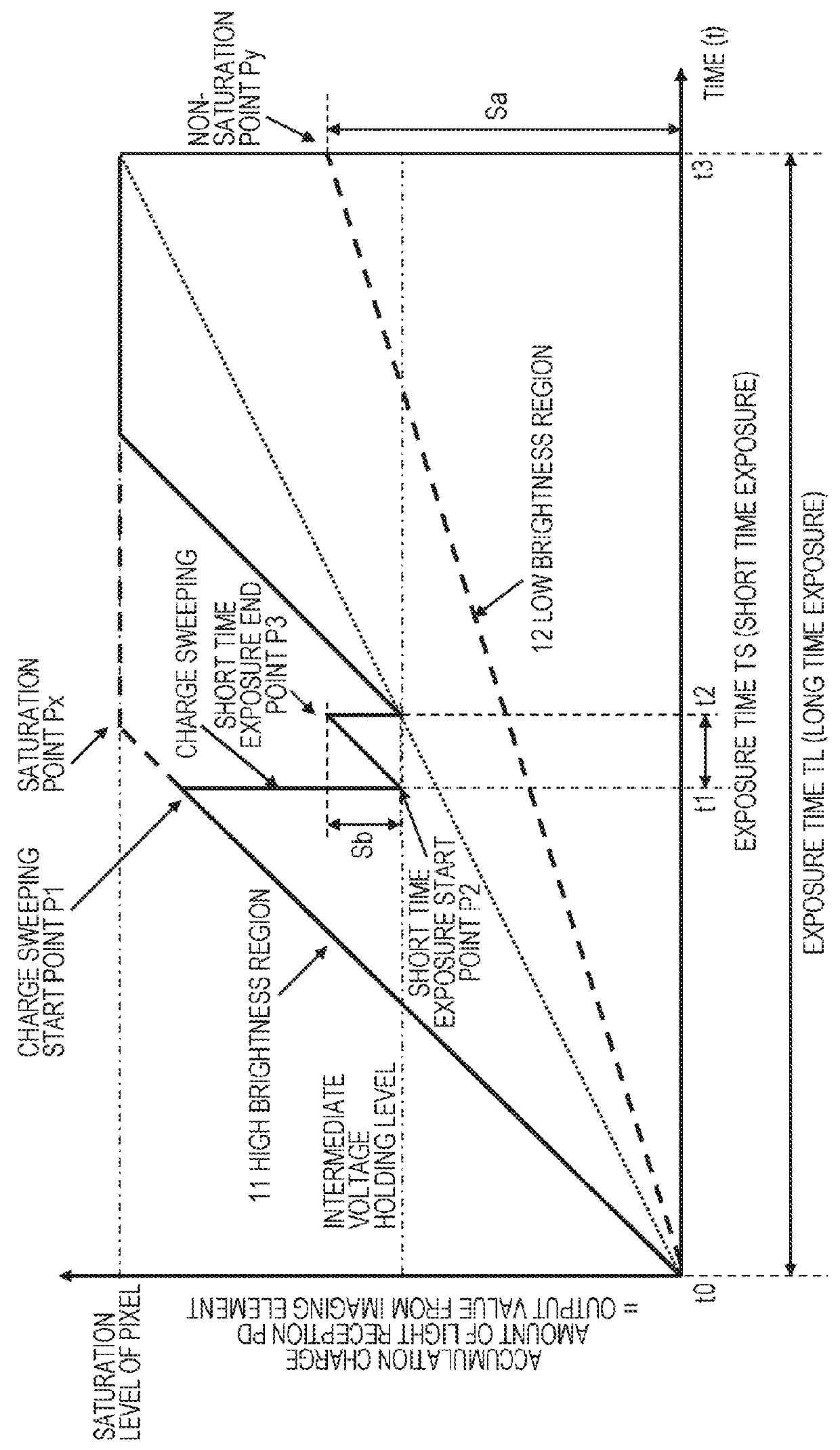
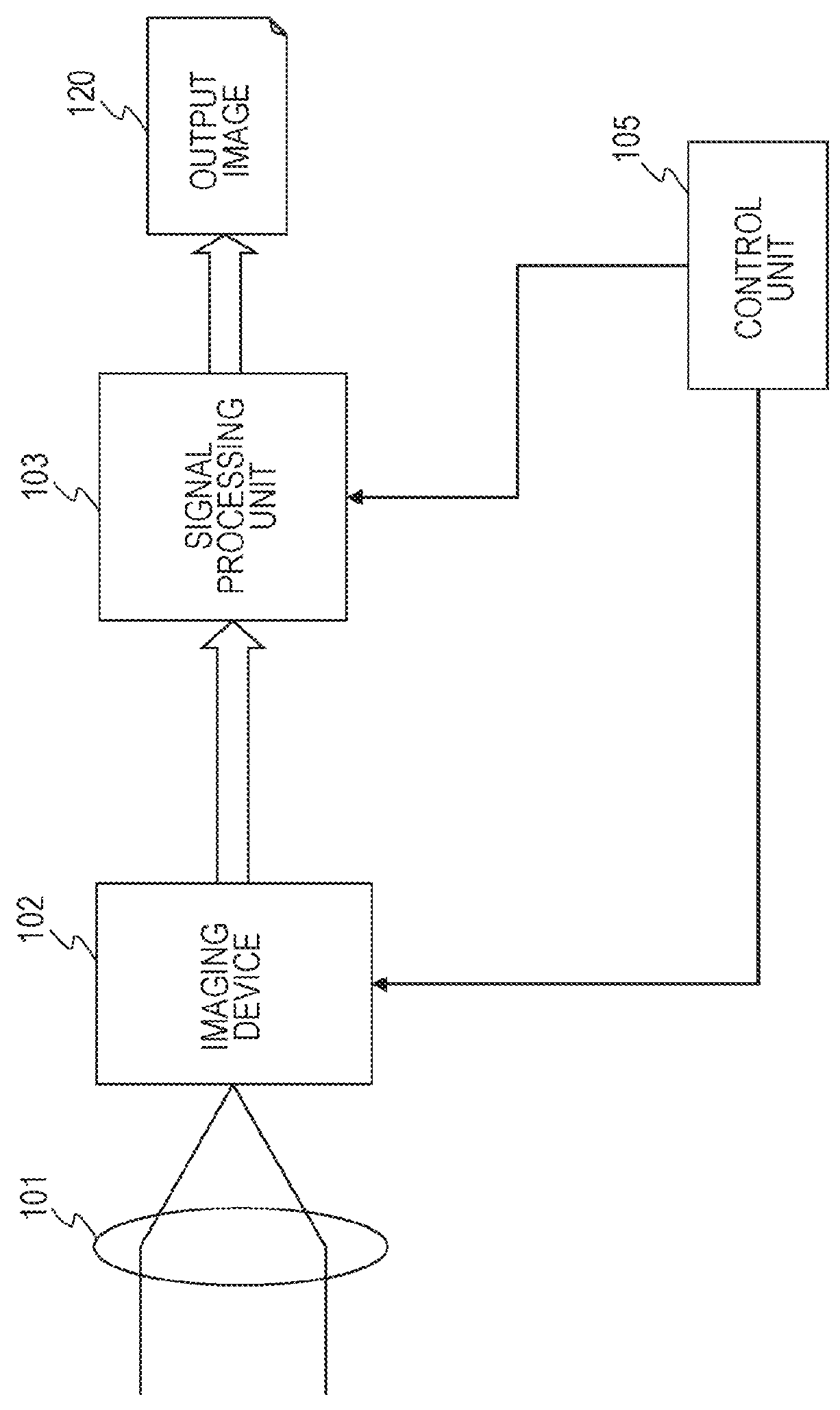
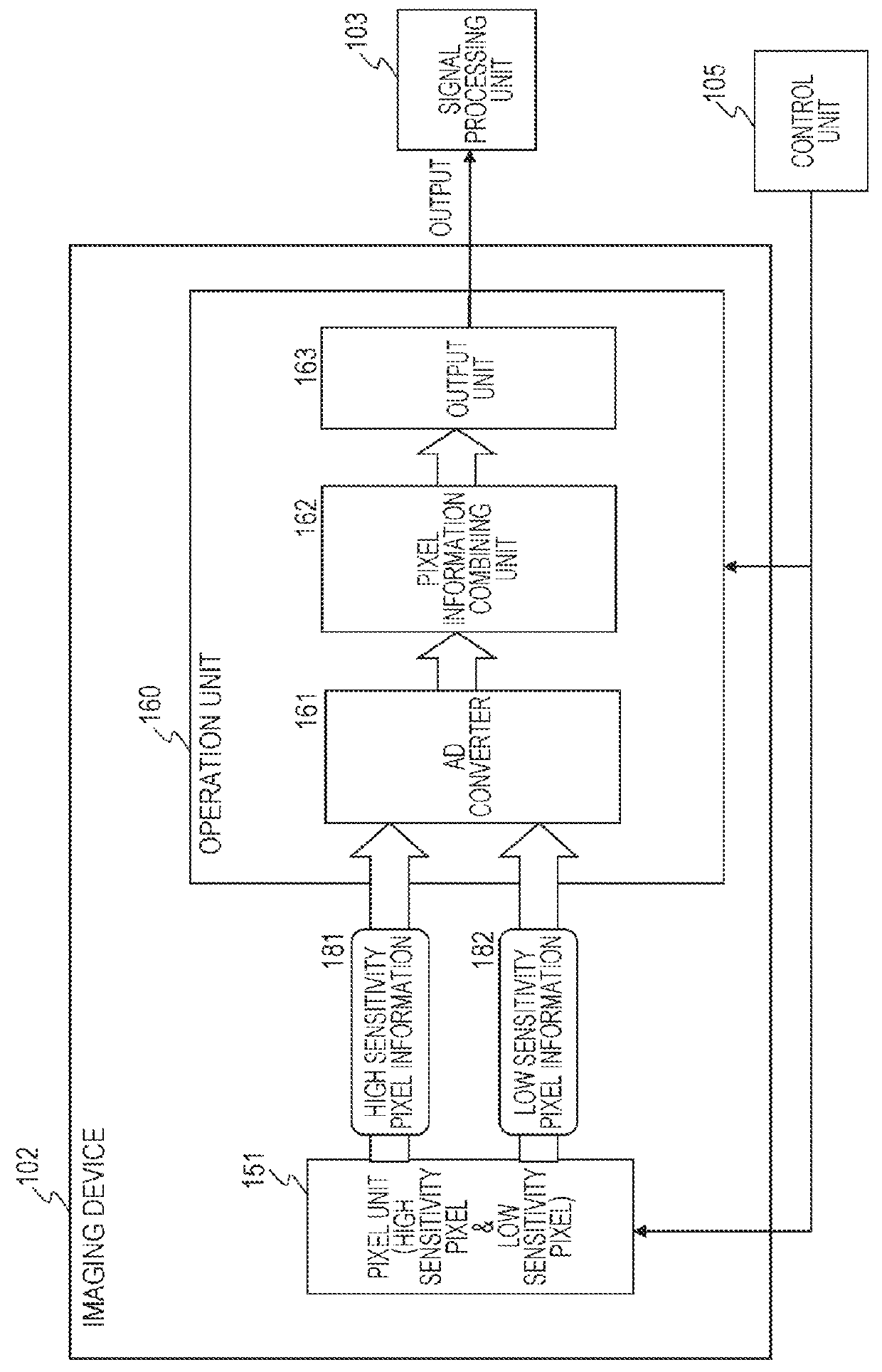
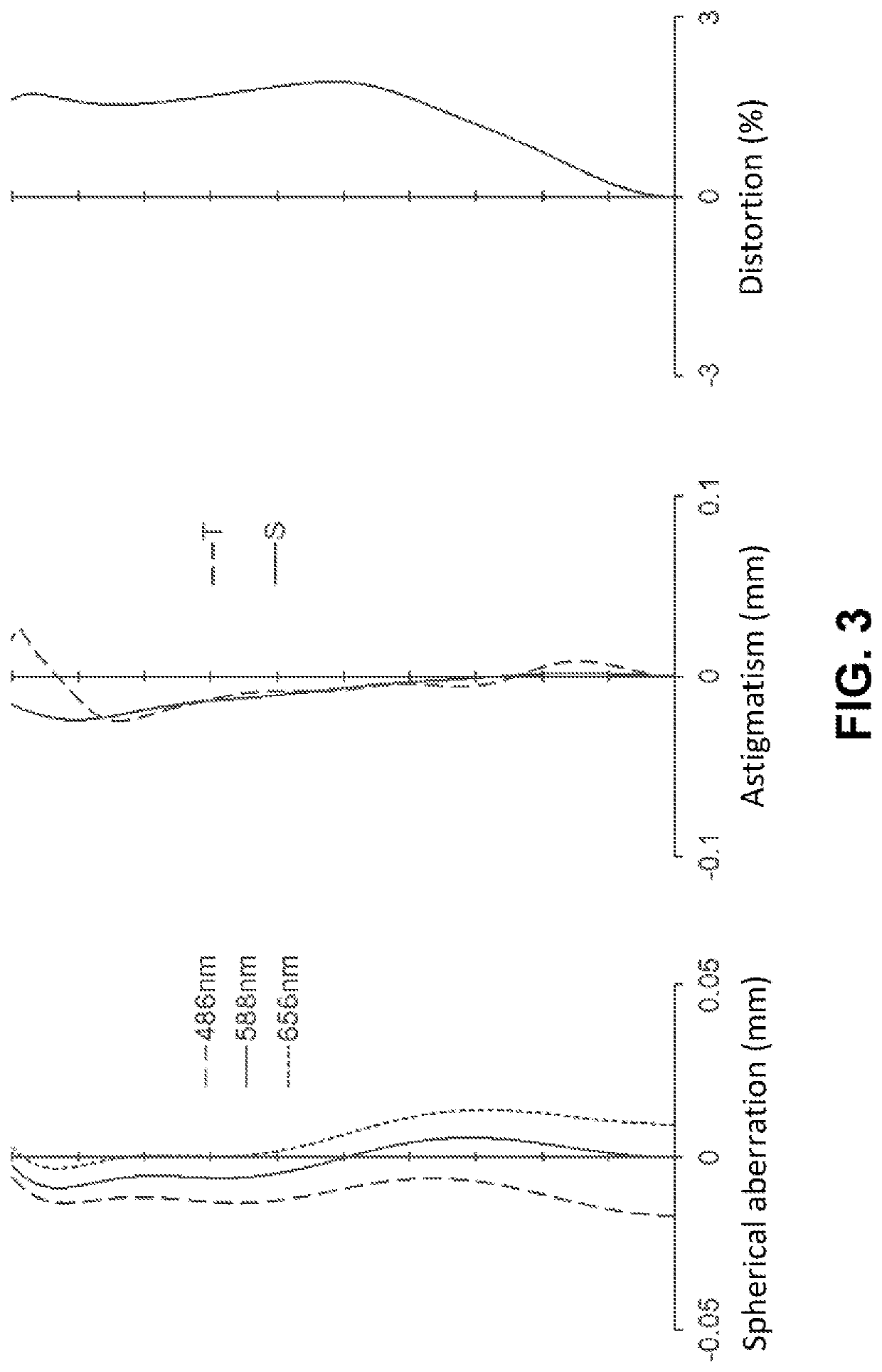
Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, image processing method, and program
ActiveUS20140267828A1Generate efficientlyHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesWide dynamic rangeImaging equipment
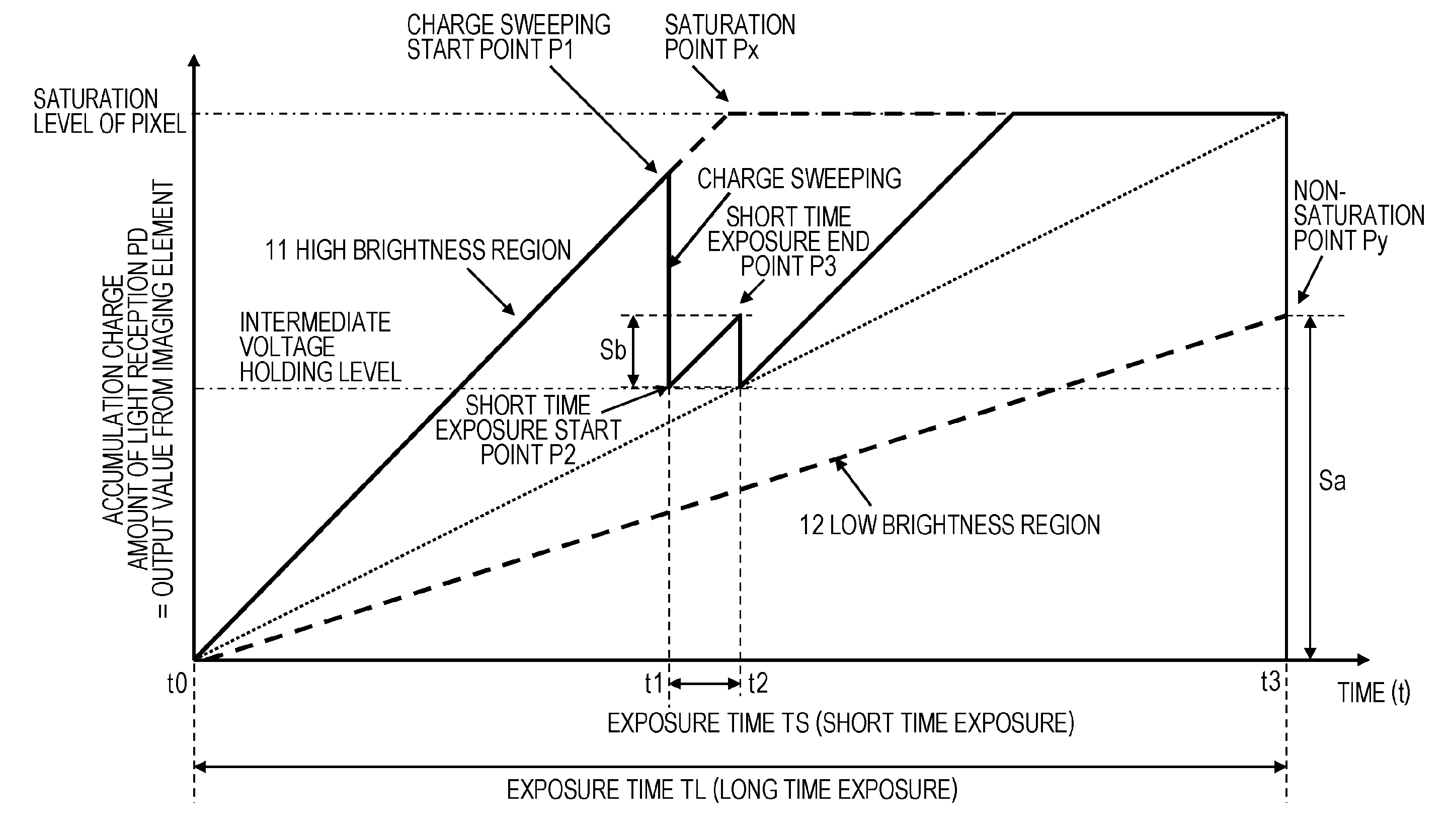
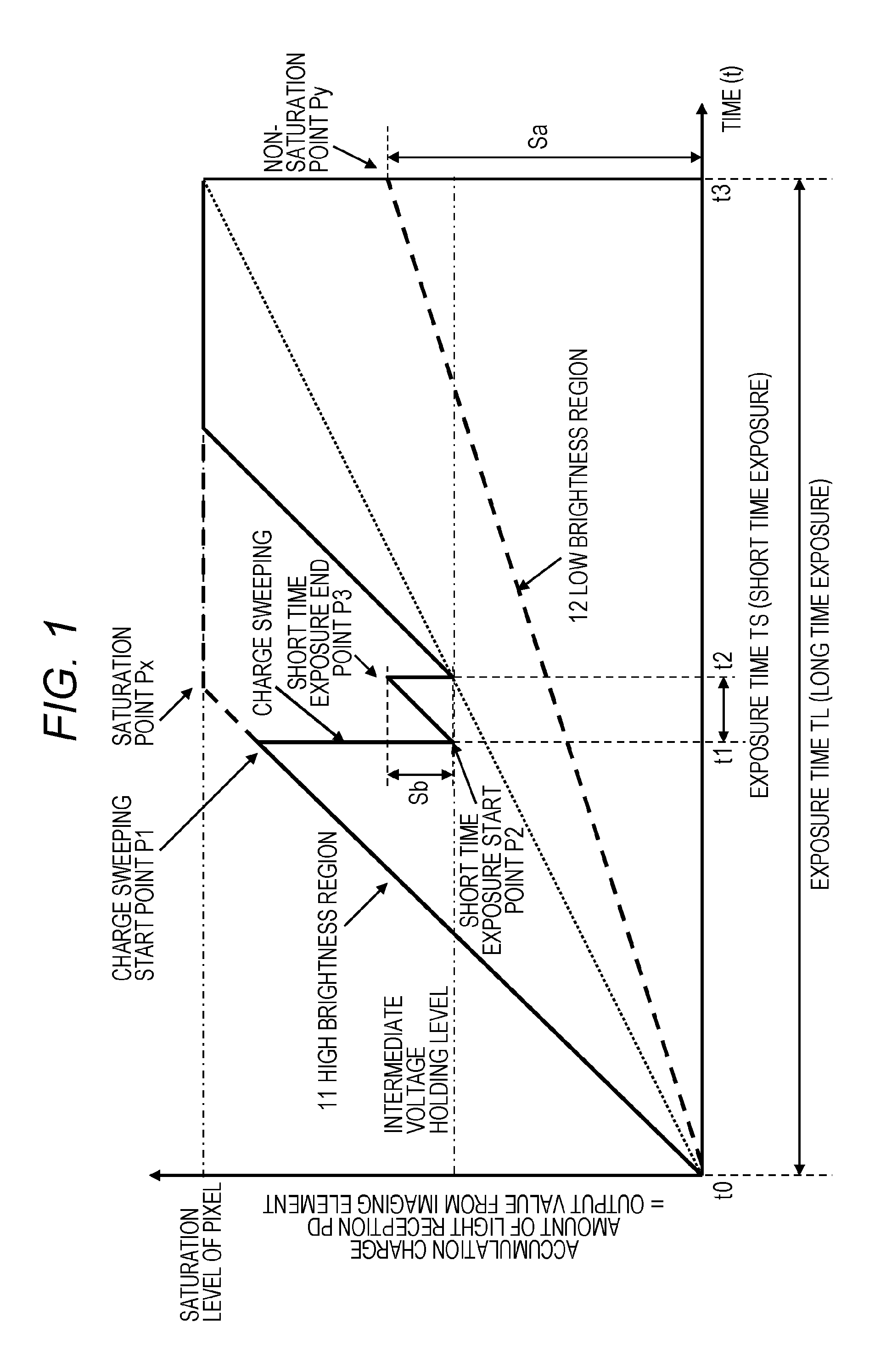
An apparatus and a method that can efficiently generate a wide dynamic range image to which each piece of pixel information of a high sensitivity pixel and a low sensitivity pixel is applied are realized. High sensitivity pixel information obtained by adding pixel values of a plurality of high sensitivity pixels and low sensitivity pixel information obtained by adding pixel values of a plurality of low sensitivity pixels are output as output pixel signals from pixels of different sensitivities from a pixel unit, these pixel information are combined in a pixel information combining unit, an output pixel value is determined, and an output image of a wide dynamic range is output. In the pixel information combining unit, a weight for the high sensitivity pixel information or the low sensitivity pixel information is changed according to brightness of a subject, weight addition of the high sensitivity pixel information and the low sensitivity pixel information is performed, a pixel value of an output image is determined, and the pixel value is output.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
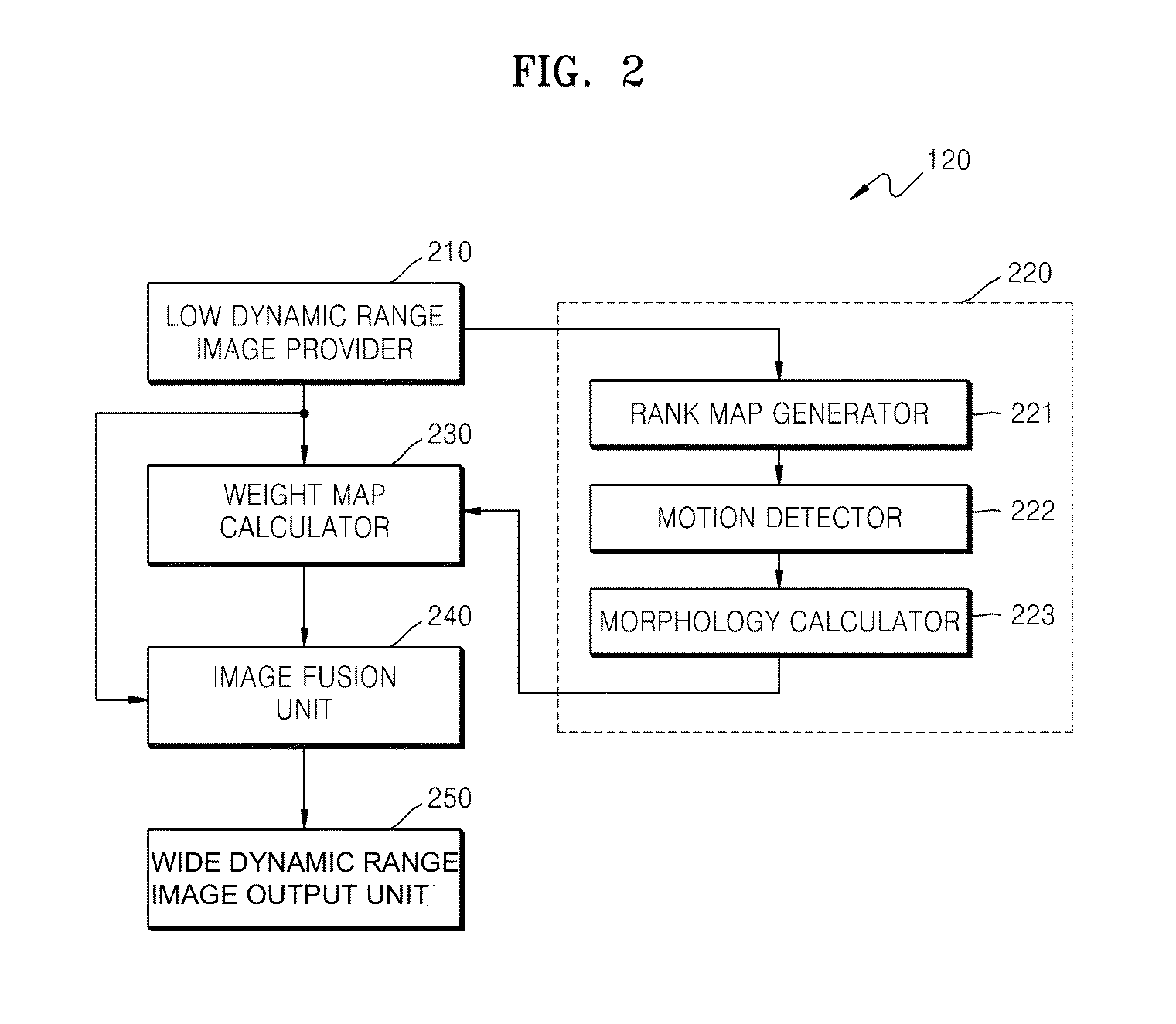
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20130070965A1Accurately detect motion areaIncrease computing speedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTone mappingImaging processing
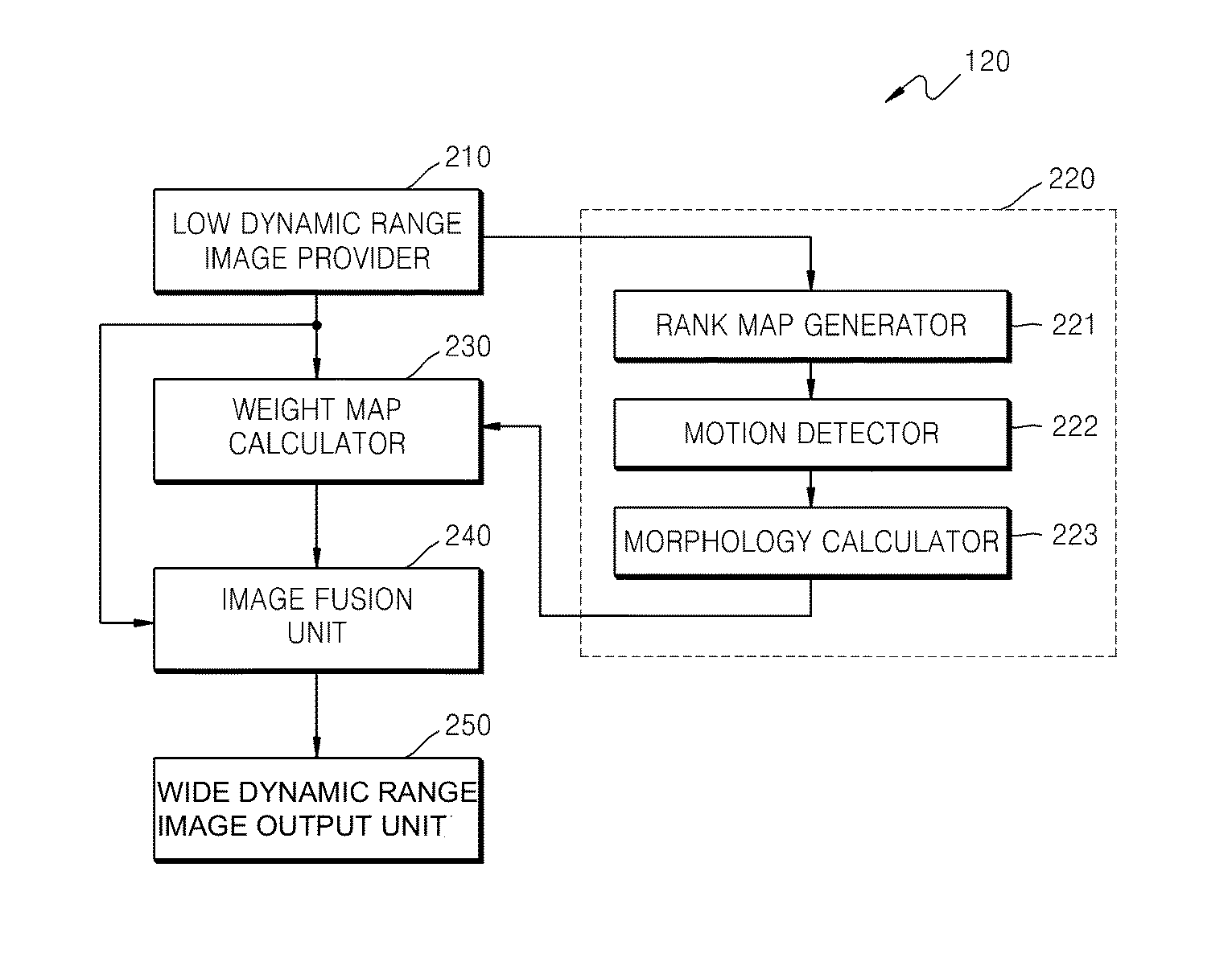
An image processing method and apparatus for obtaining a wide dynamic range image, the method including: obtaining a plurality of low dynamic range images having different exposure levels for a same scene; generating motion map representing whether motion occurred, depending on brightness ranks of the plurality of low dynamic range images; obtaining weights for the plurality of low dynamic range images; generating a weight map by combining the weights and the motion map; and generating a wide dynamic range image by fusing the plurality of low dynamic range images and the weight map. According to the image processing method and apparatus, it is possible to accurately detect motion area using a rank map, obtain a wide dynamic range image at a higher operation speed, and reduce a possibility that a phenomenon such as color warping occurs by directly combining images without using a tone mapping process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
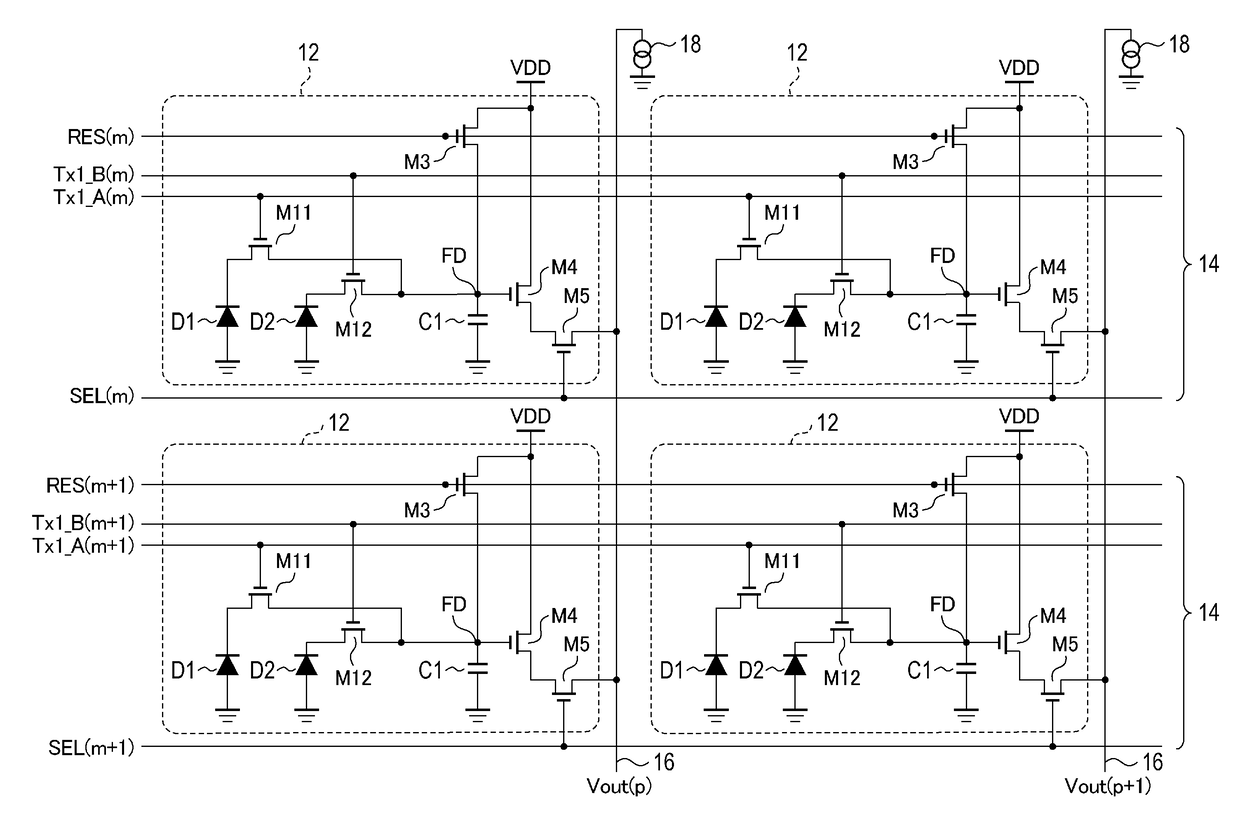
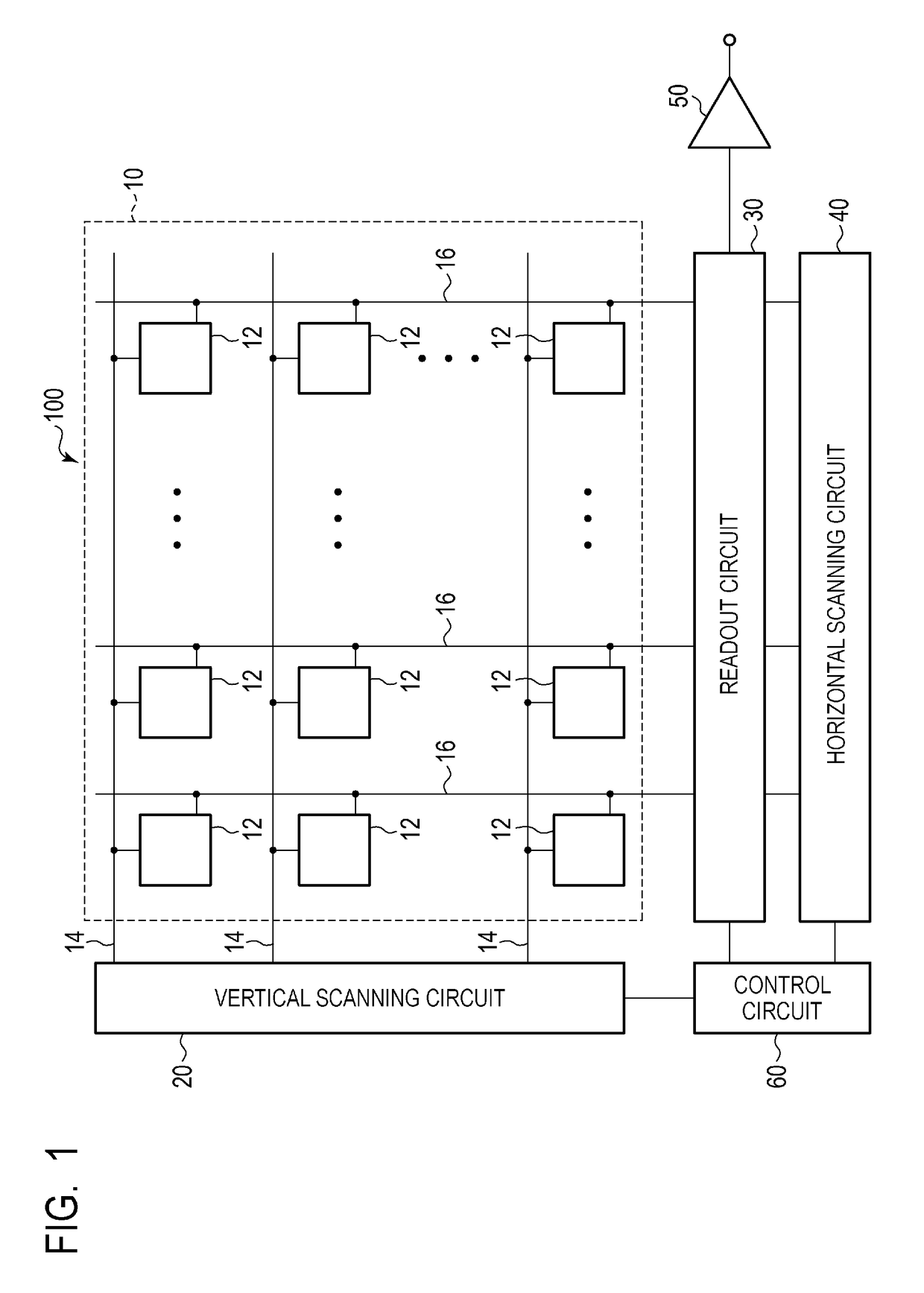
Imaging device and imaging system
ActiveUS20170359539A1Broad imagingHigh-performance autofocusTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringPupil
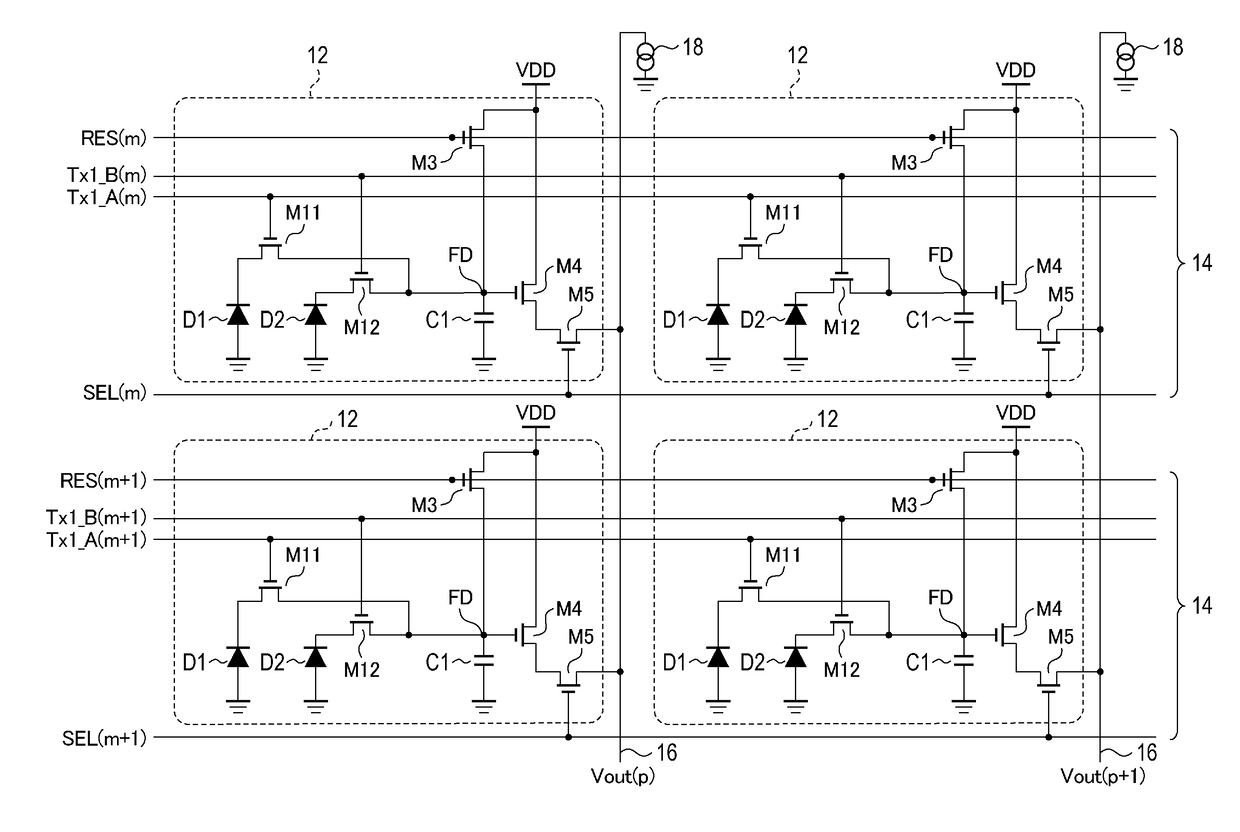
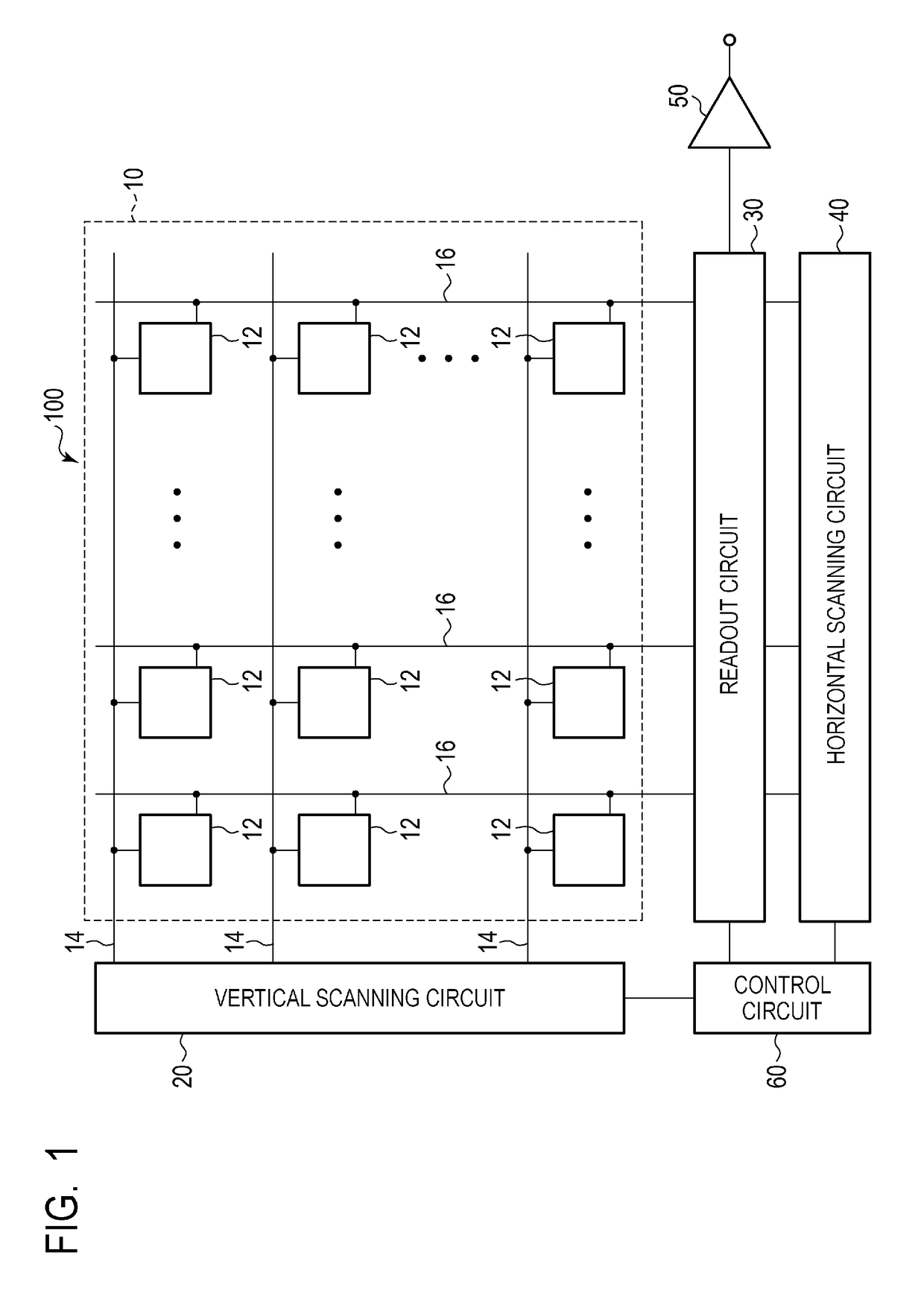
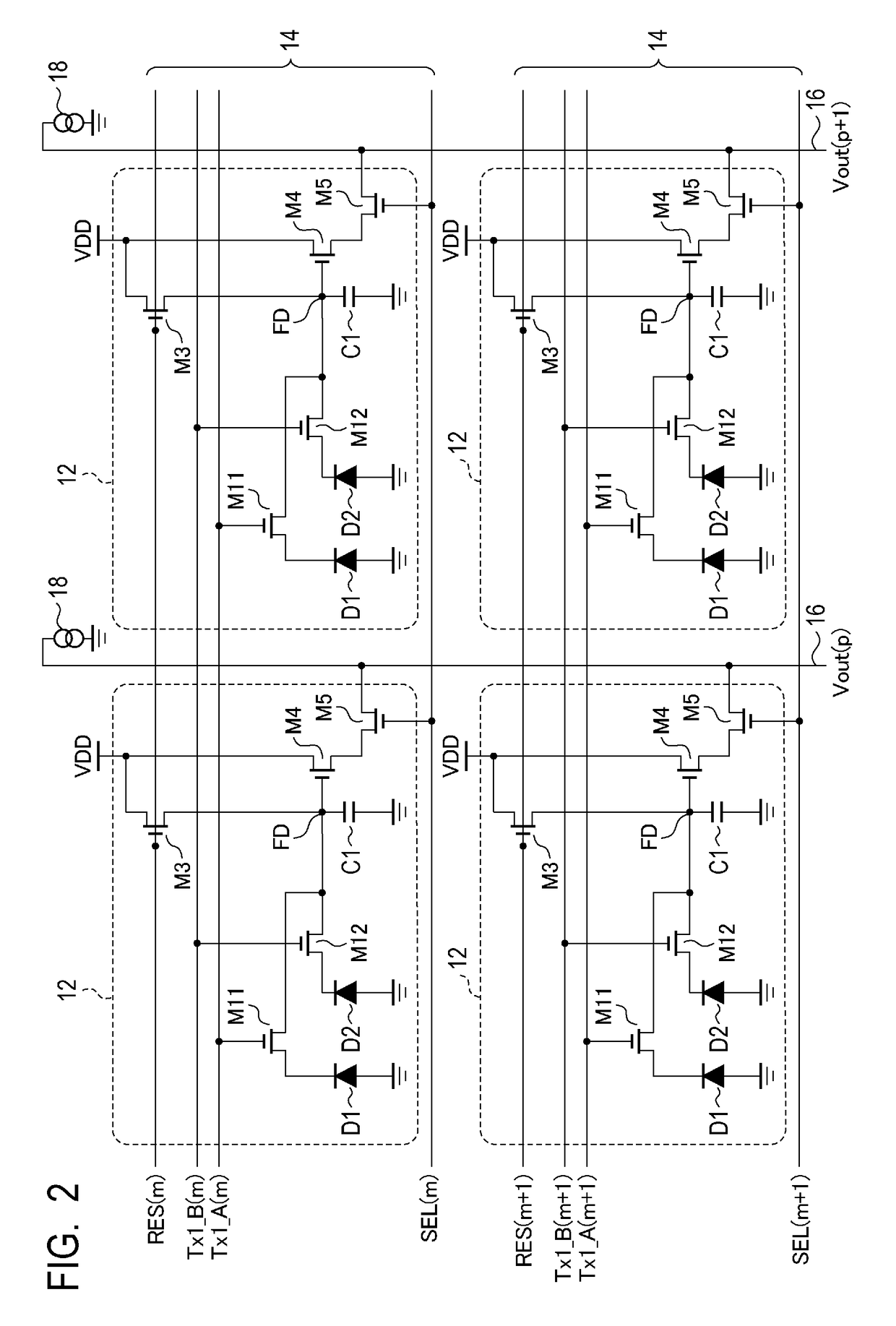
An imaging device includes pixels each including first and second photoelectric conversion units on which pupil-divided parts of incident light are incident and a holding unit that holds charges transferred from the first and second photoelectric conversion units, and outputting signals based on amounts of charges held by the holding unit. Each pixel outputs a first signal and a second signal based on amounts of charges generated by the first photoelectric conversion unit and by the first and second photoelectric conversion units, respectively, during a first exposure time, and a third signal and a fourth signal based on amounts of charges generated by the first photoelectric conversion unit and by the first and second photoelectric conversion units, respectively, during a second exposure time. The first and second signals are output before the third and fourth signals in one frame and after the third and fourth signals in another frame.
Owner:CANON KK
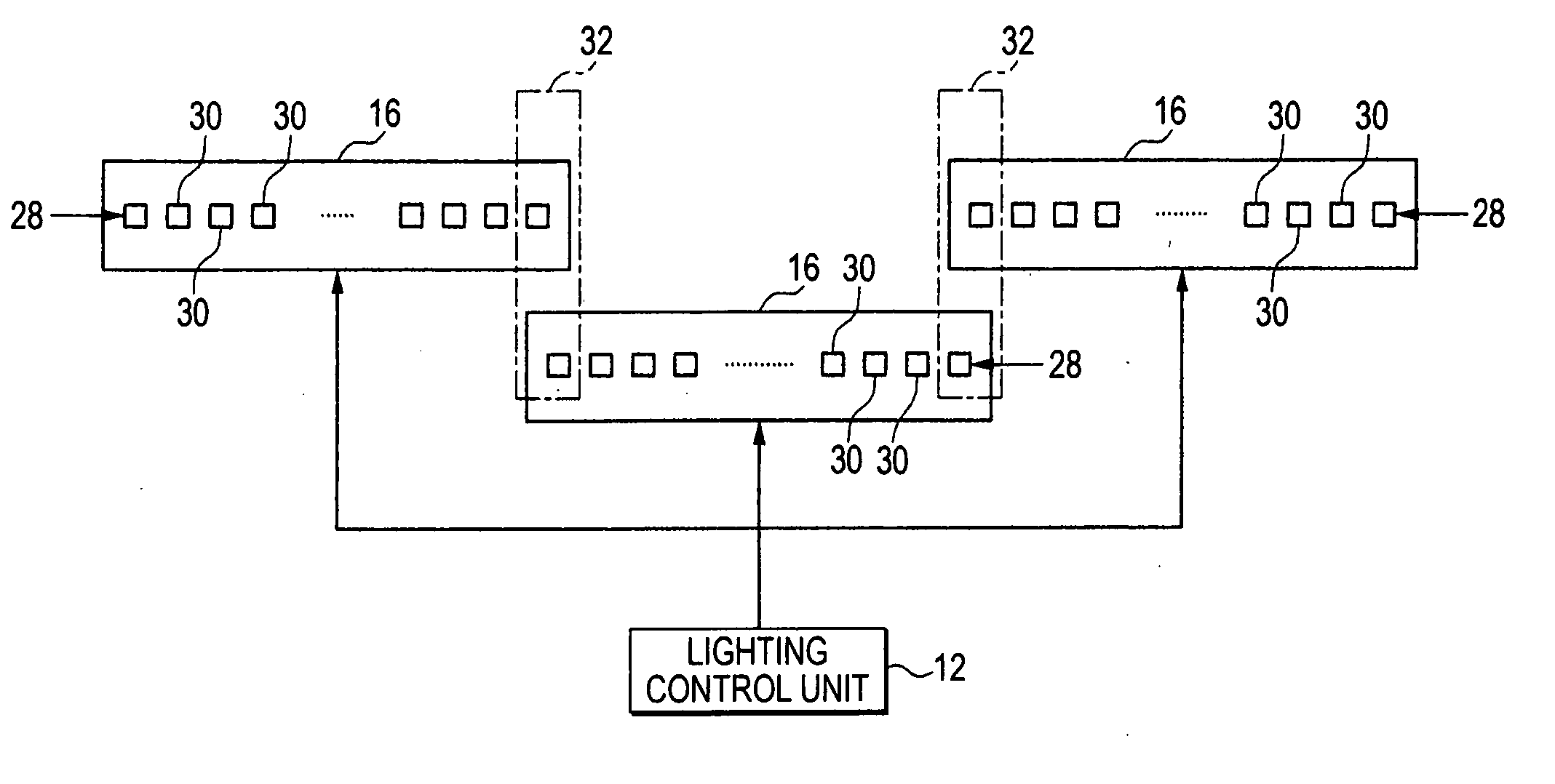
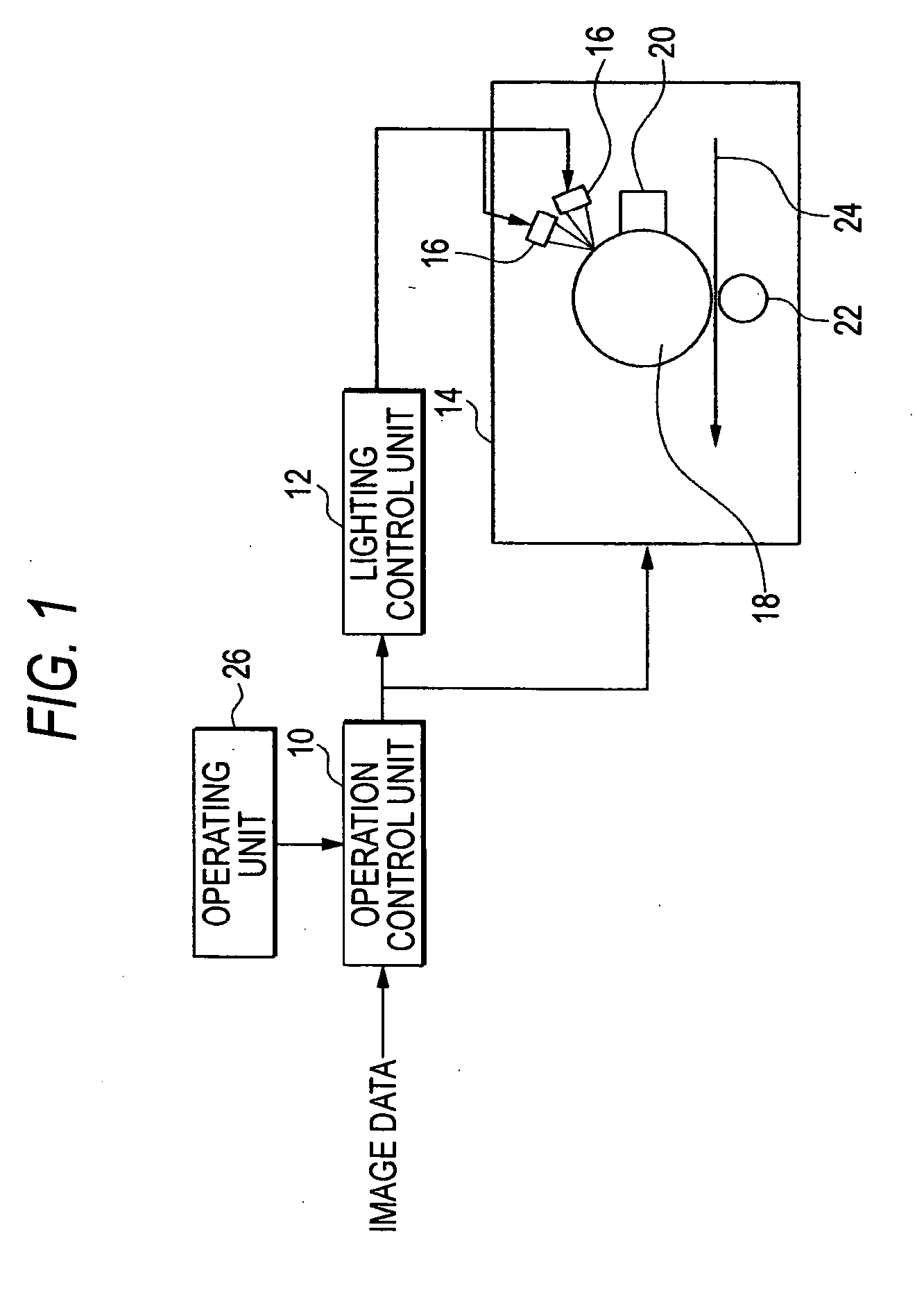
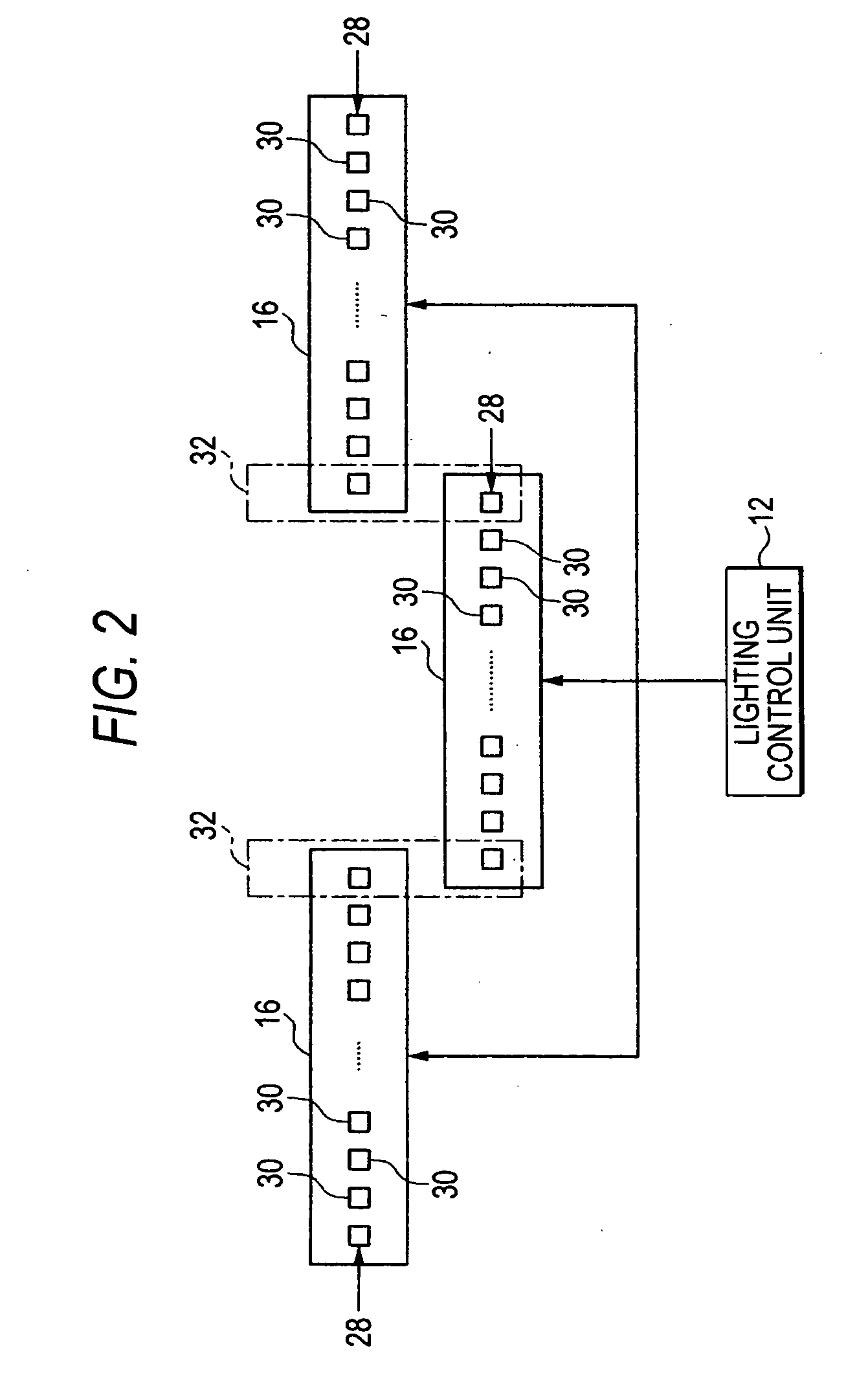
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20070070166A1Small size errorImprove accuracyElectrographic processes using charge patternPrintingImage resolutionImage formation
An image forming apparatus capable of forming wide images, includes: an exposing unit having a plurality of LED (light-emitting diode) heads arranged alternately in a main scanning direction, in which the resolution of an LED row formed in at least one of the plurality of LED heads is higher than the resolution of image data in a main scanning direction; and a lighting control unit that controls to turn on or turn off dots in the LED row such that the exposing position of a photoconductive drum is moved in the unit of dots of the high resolution LED row.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
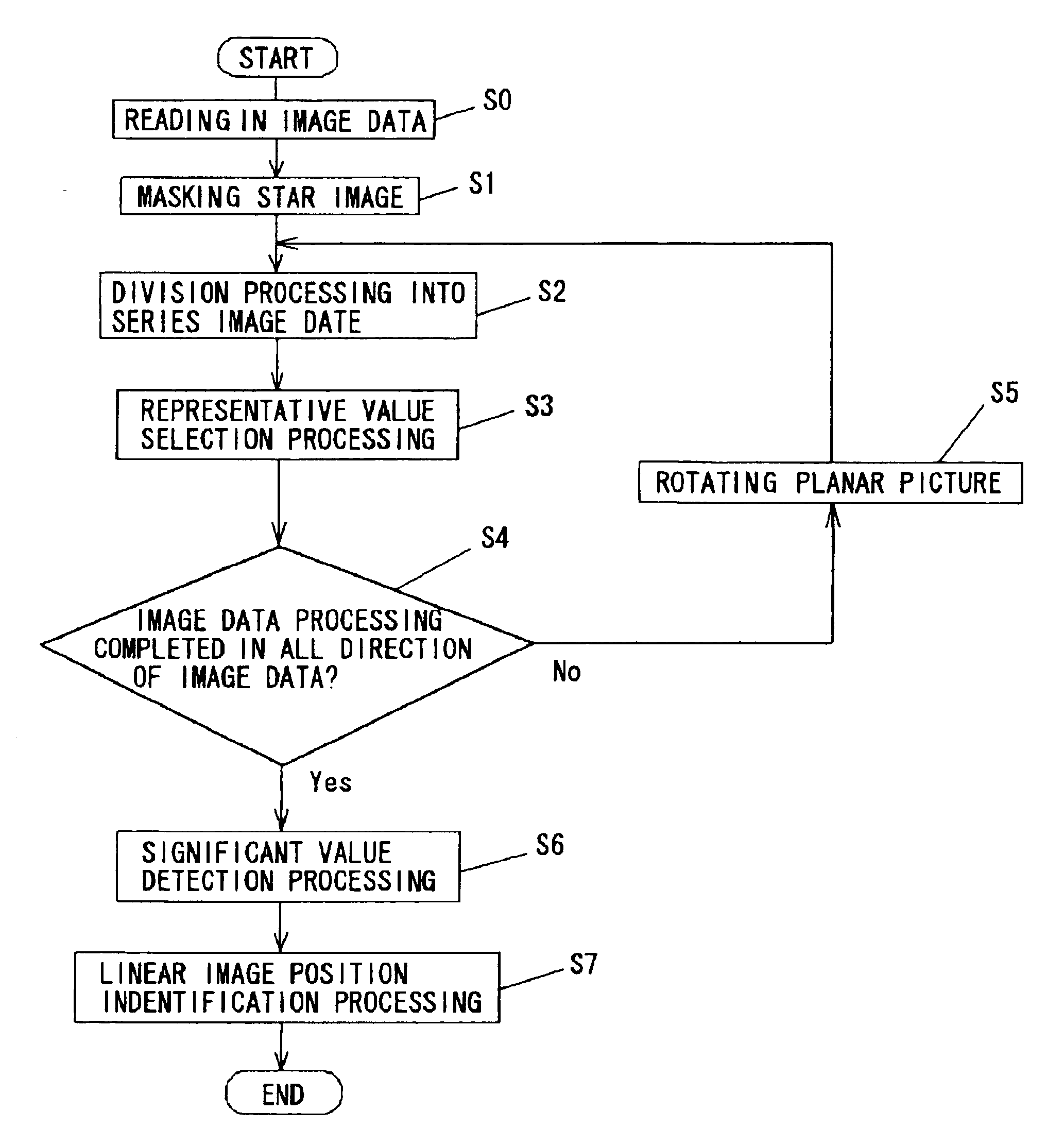
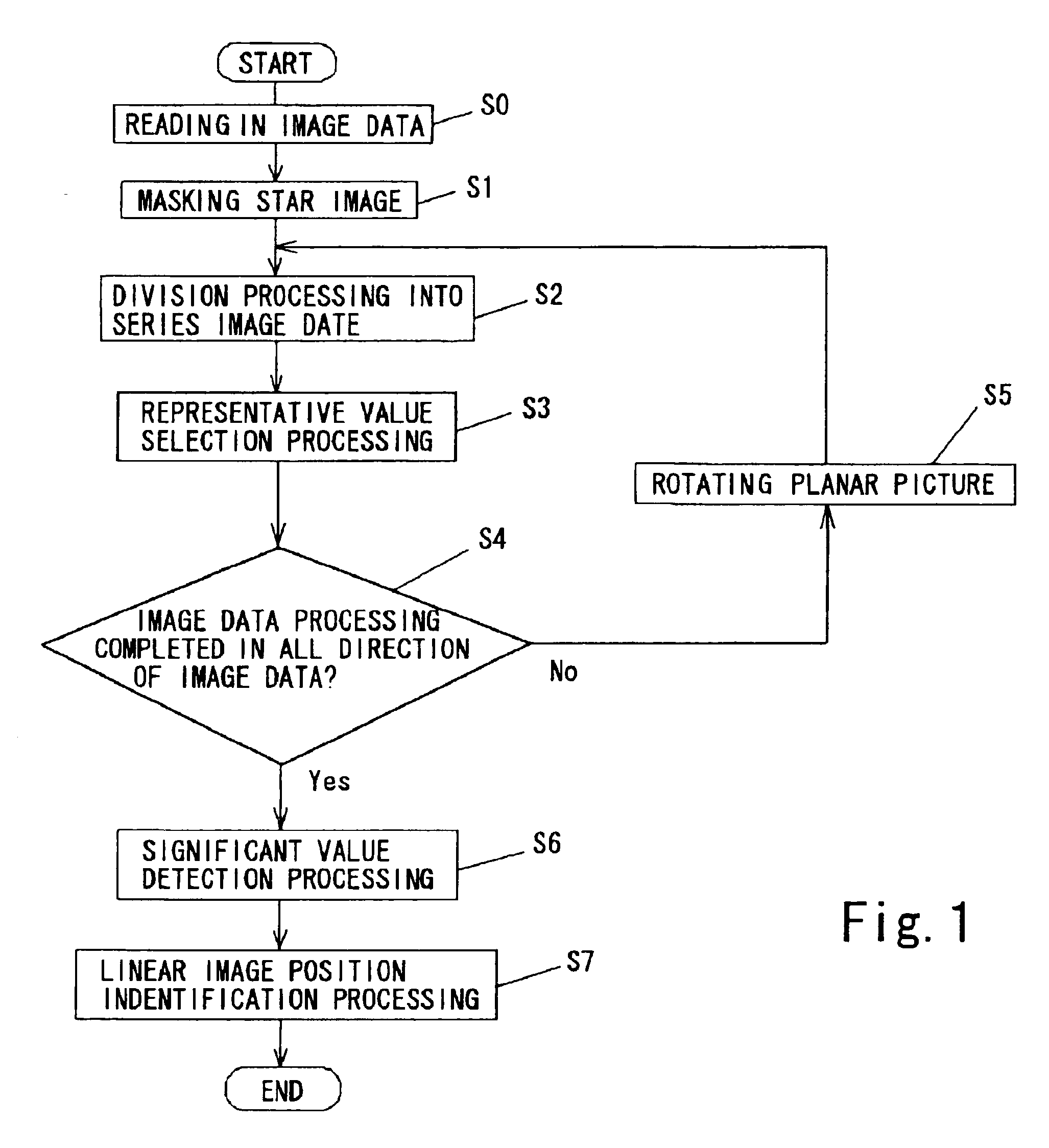
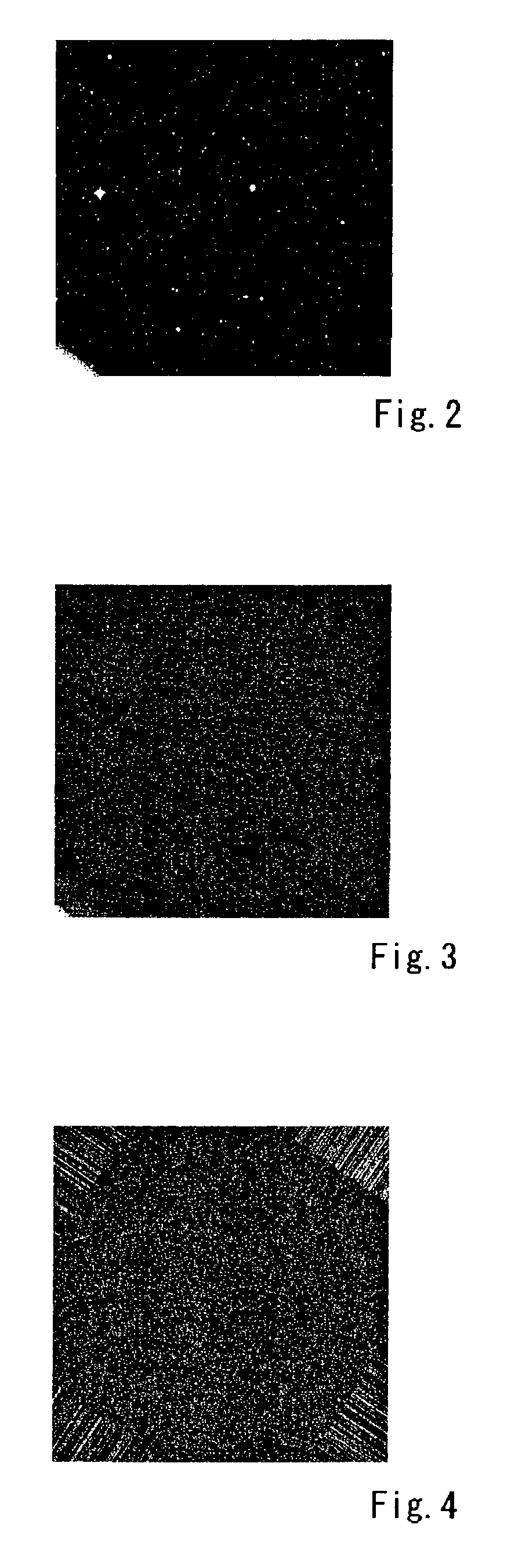
Method for detecting linear image in planar picture
InactiveUS20060110007A1Short exposure timeSatisfactory imageImage analysisCosmonautic vehiclesPattern recognitionLinearity
A method for detecting a linear image in a planar picture is provided whereby the positions of a linear image can be determined by devising suitable processing of image data, even if a linear image traced by a moving object, such as space debris, a meteor, or the like, does not appear clearly on a picture. Image data processing, consisting of division processing (S2) for dividing image data of a planar picture captured by an imaging element into a plurality of mutually parallel columnar image data and representative value selection processing (S3) for taking the median value determined for each of the columnar image data as a representative value for the corresponding columnar image data, is performed in every direction of said planar picture, whereupon analysis processing consisting of significant value detection processing (S6) for detecting whether or not said representative value of each of said columnar image data is a significant value, and linear image position identification processing (S7) for identifying the linear position of columnar image data having a representative value indicating a significant value as the position of a linear image resulting from the passage of the moving object or the like, is performed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
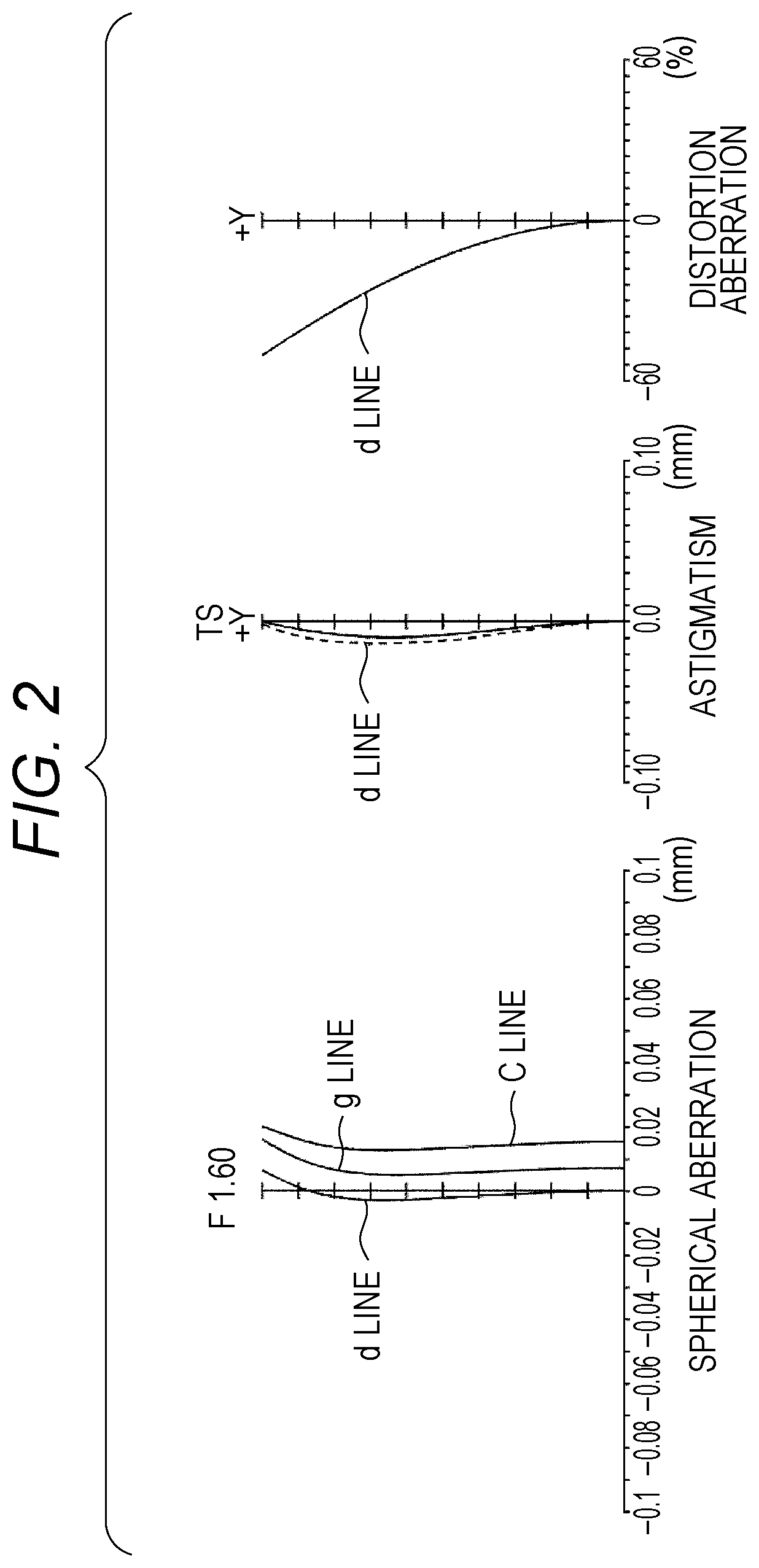
Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, image processing method, and program
ActiveUS9344637B2Generate efficientlyBroad imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging processingImaging equipment
An apparatus and a method that can efficiently generate a wide dynamic range image to which each piece of pixel information of a high sensitivity pixel and a low sensitivity pixel is applied are realized. High sensitivity pixel information obtained by adding pixel values of a plurality of high sensitivity pixels and low sensitivity pixel information obtained by adding pixel values of a plurality of low sensitivity pixels are output as output pixel signals from pixels of different sensitivities from a pixel unit, these pixel information are combined in a pixel information combining unit, an output pixel value is determined, and an output image of a wide dynamic range is output. In the pixel information combining unit, a weight for the high sensitivity pixel information or the low sensitivity pixel information is changed according to brightness of a subject, weight addition of the high sensitivity pixel information and the low sensitivity pixel information is performed, a pixel value of an output image is determined, and the pixel value is output.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Imaging lens and camera apparatus
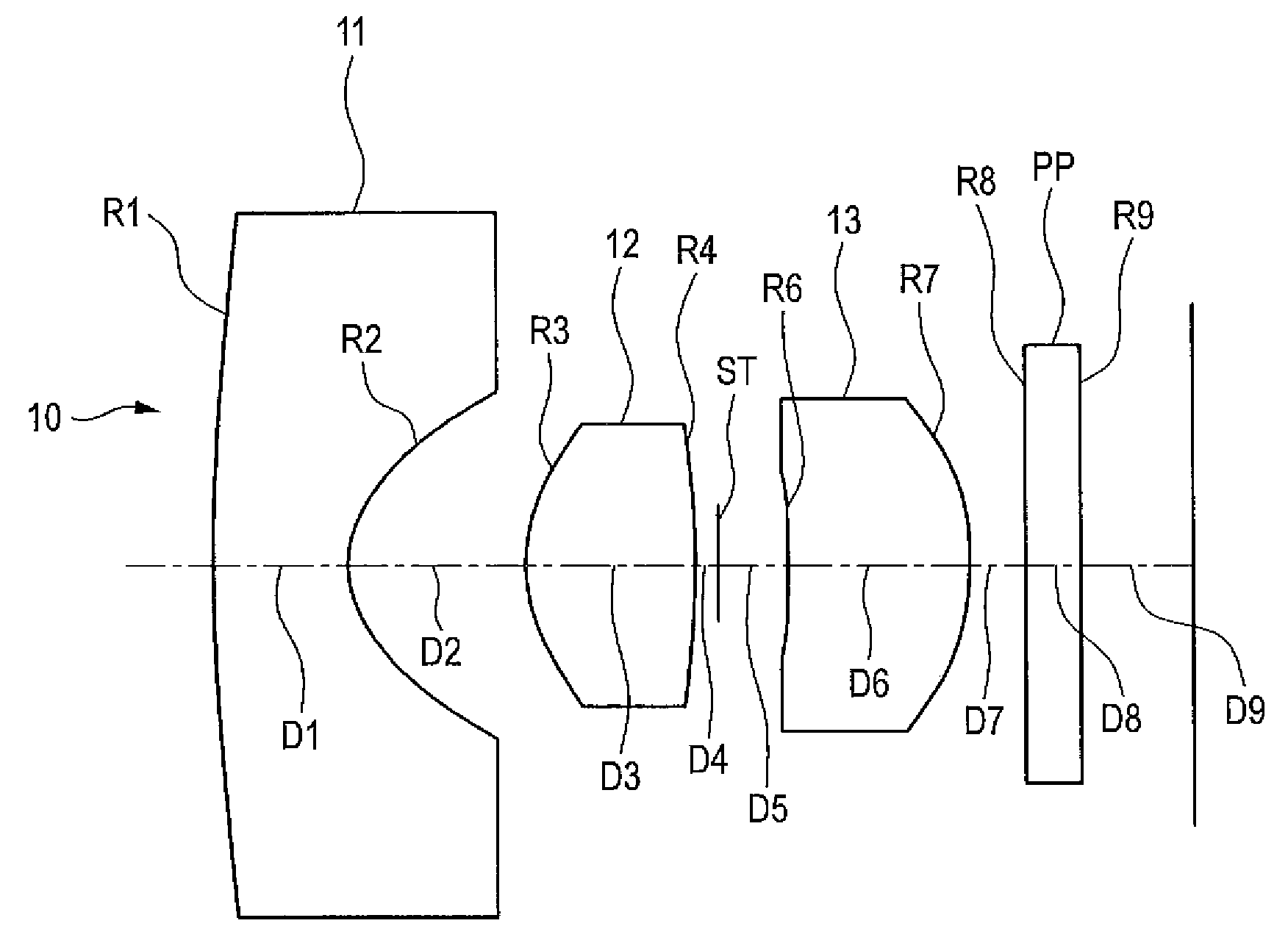
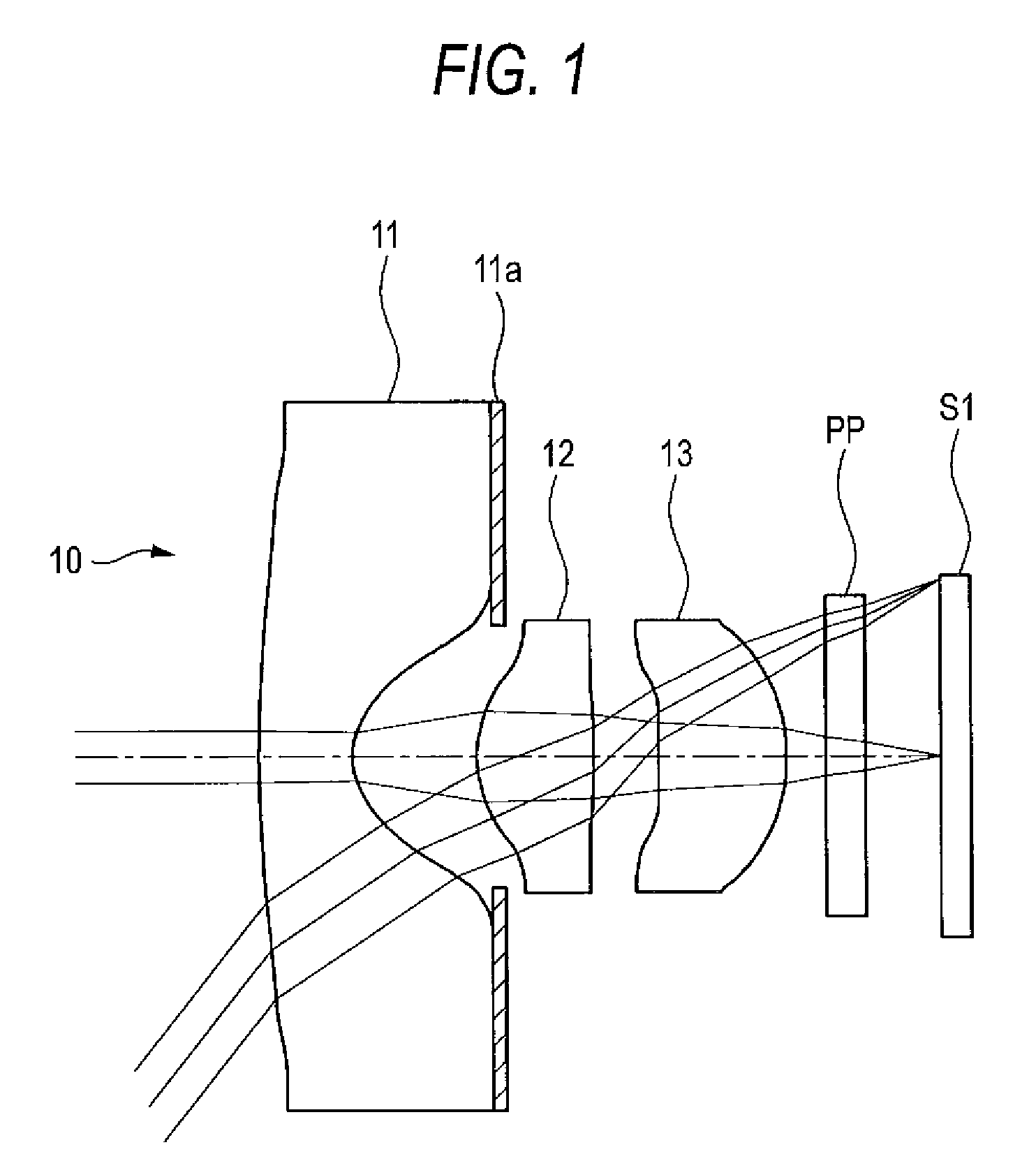
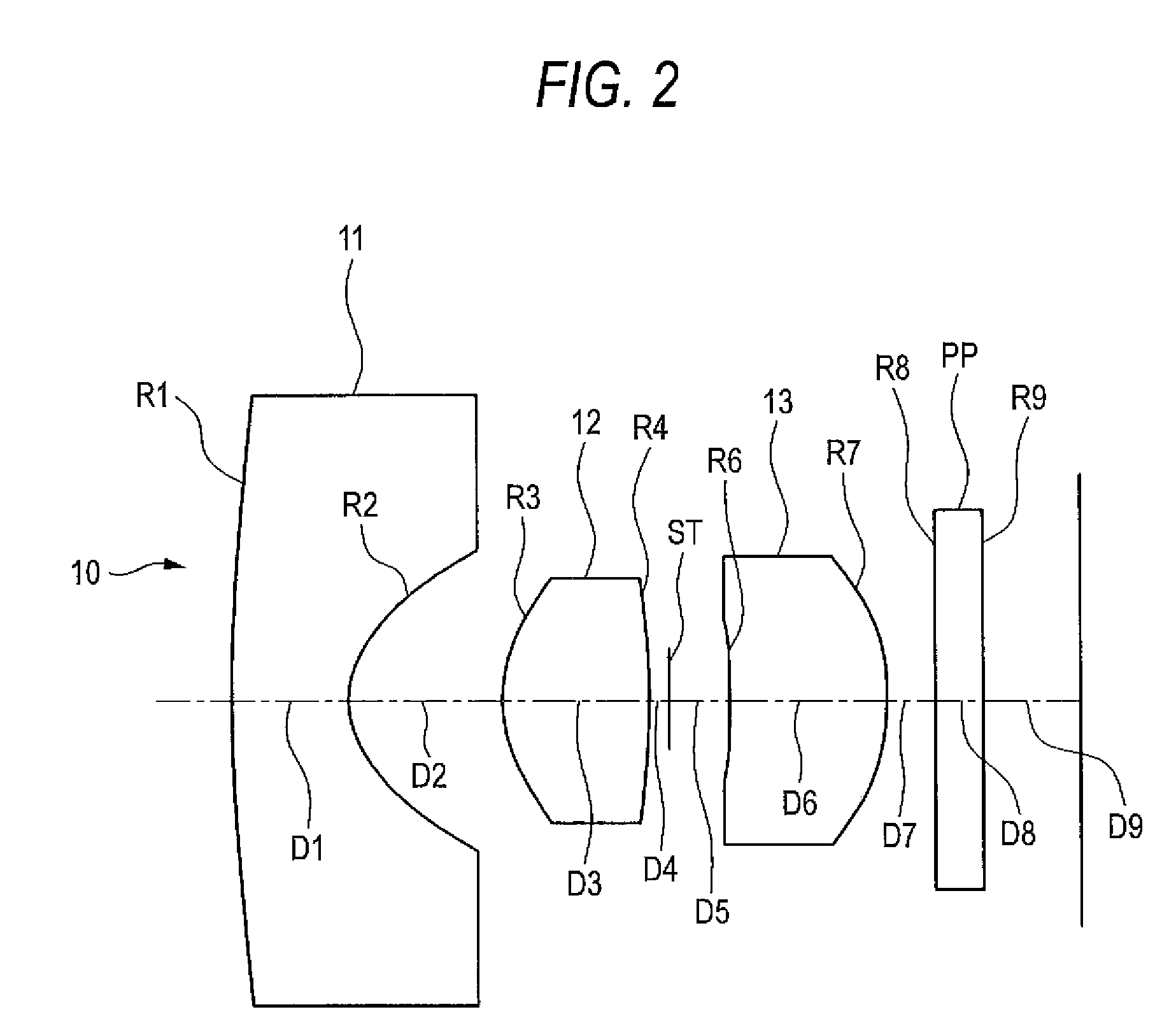
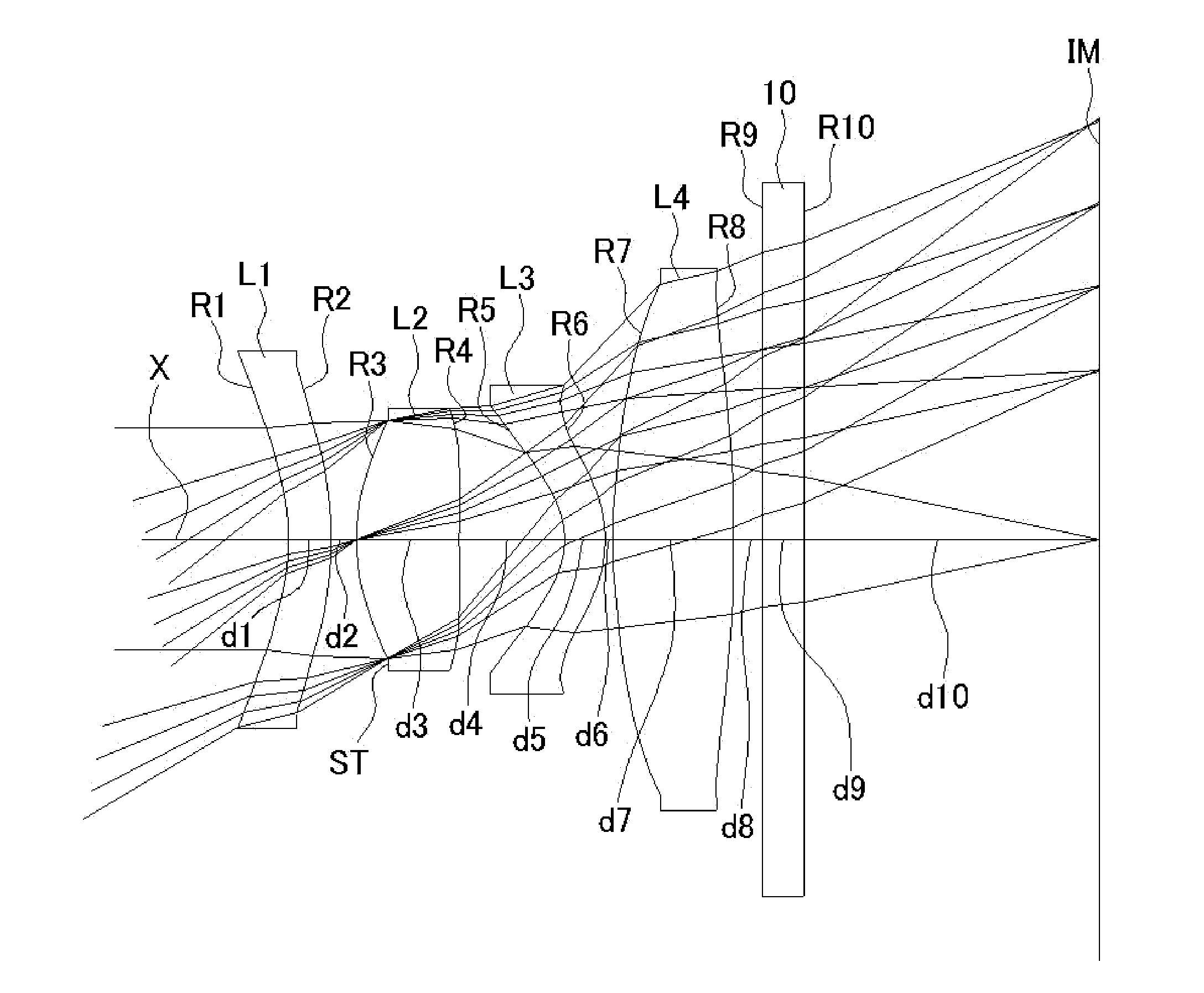
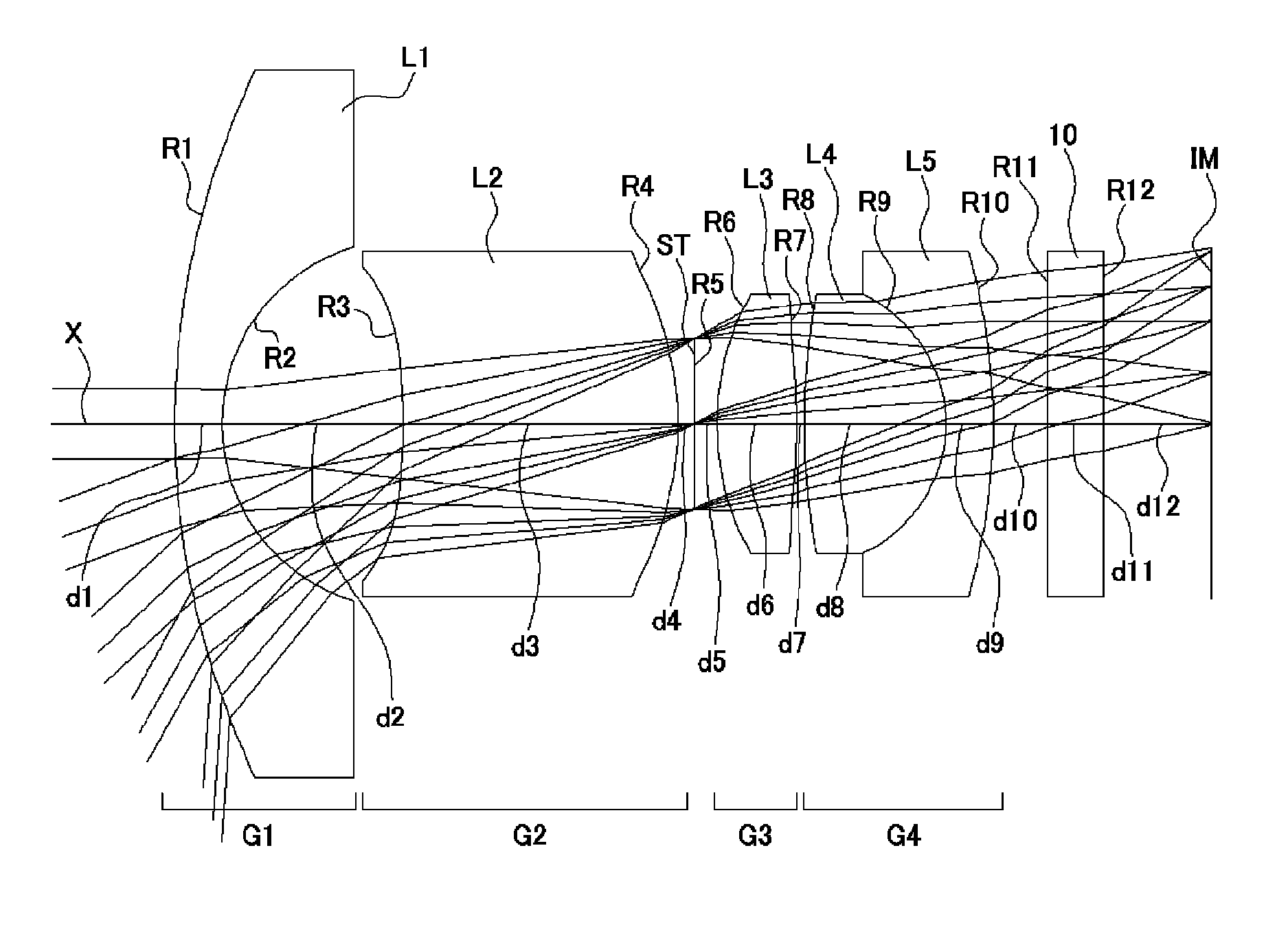
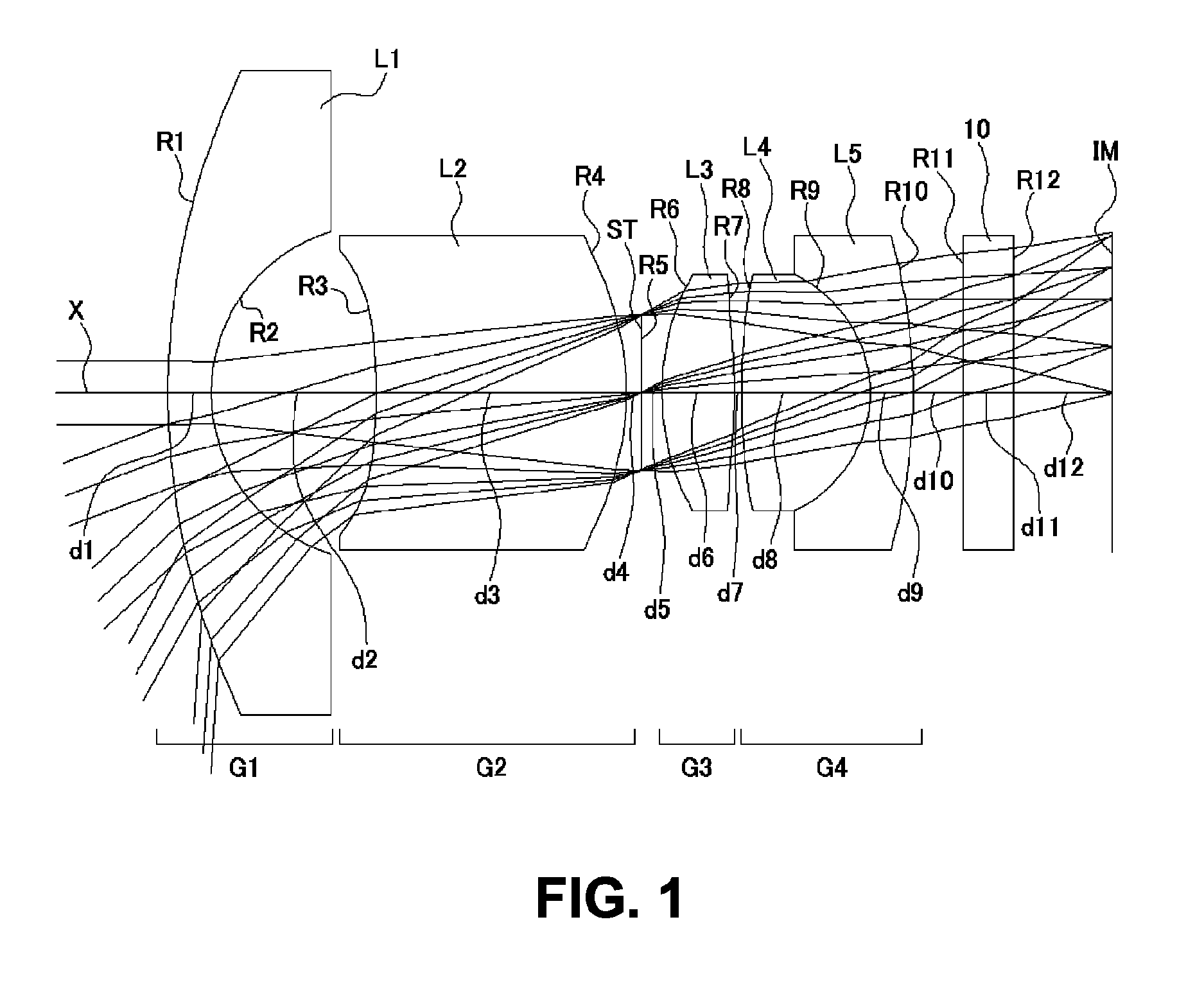
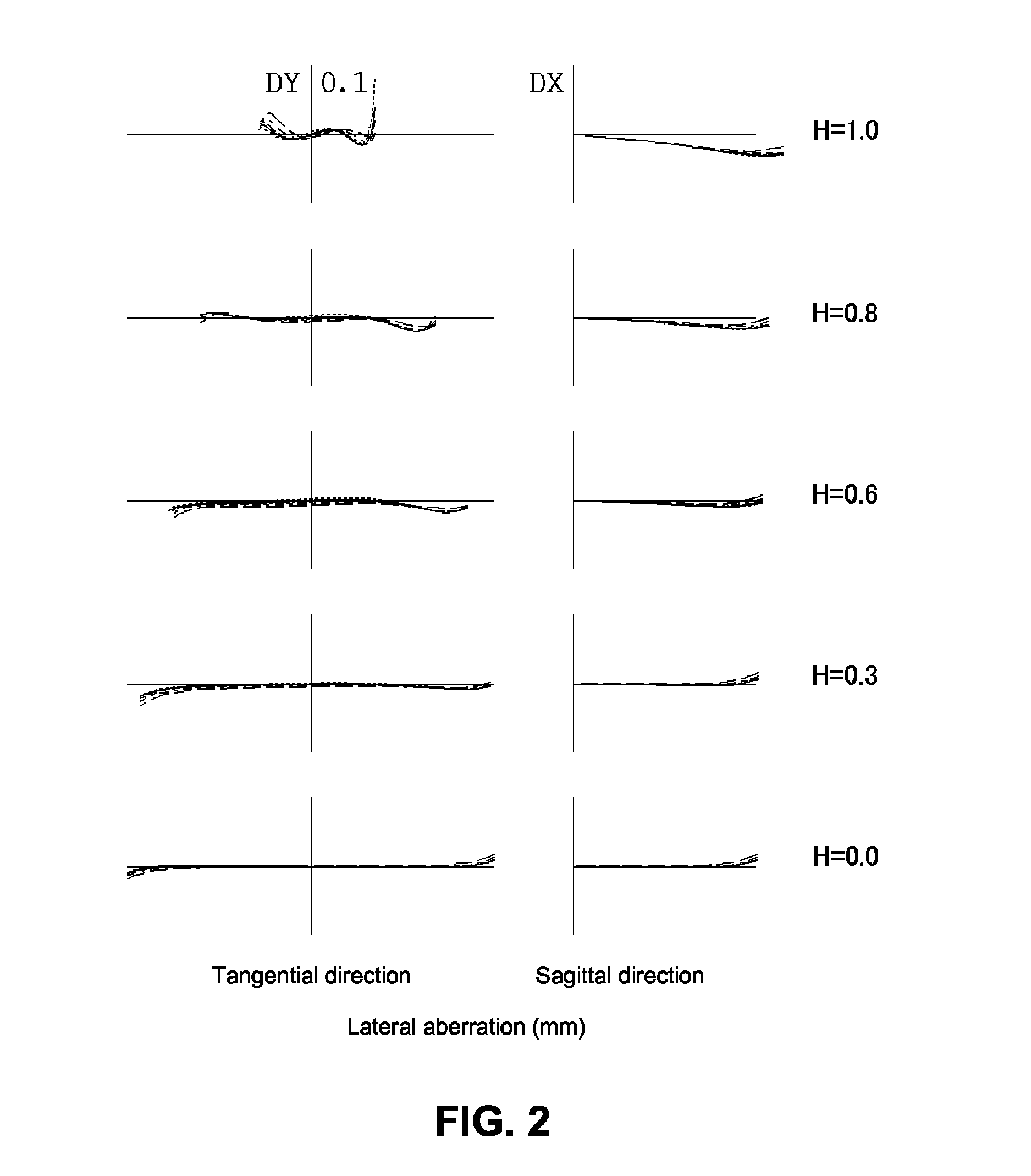
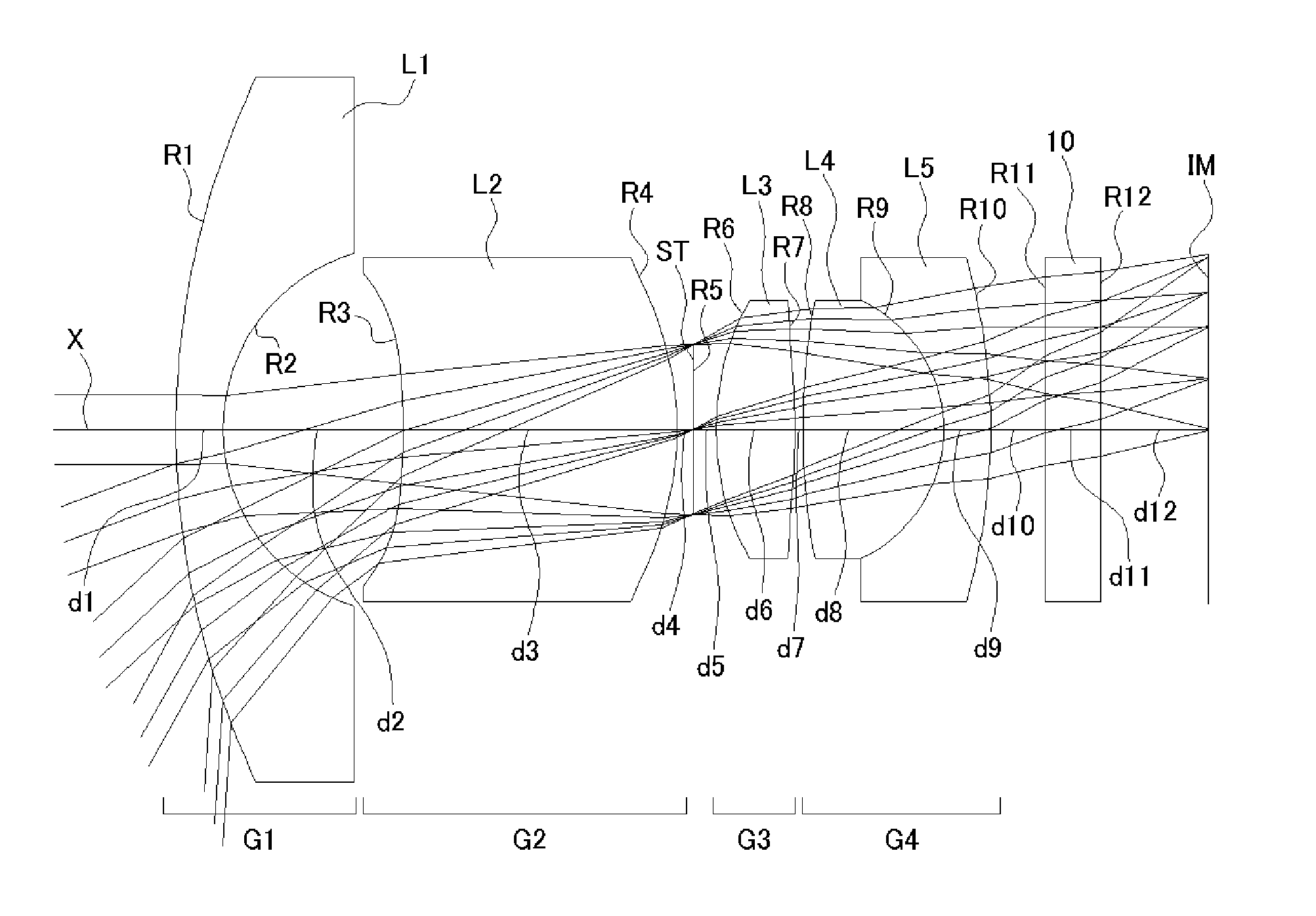
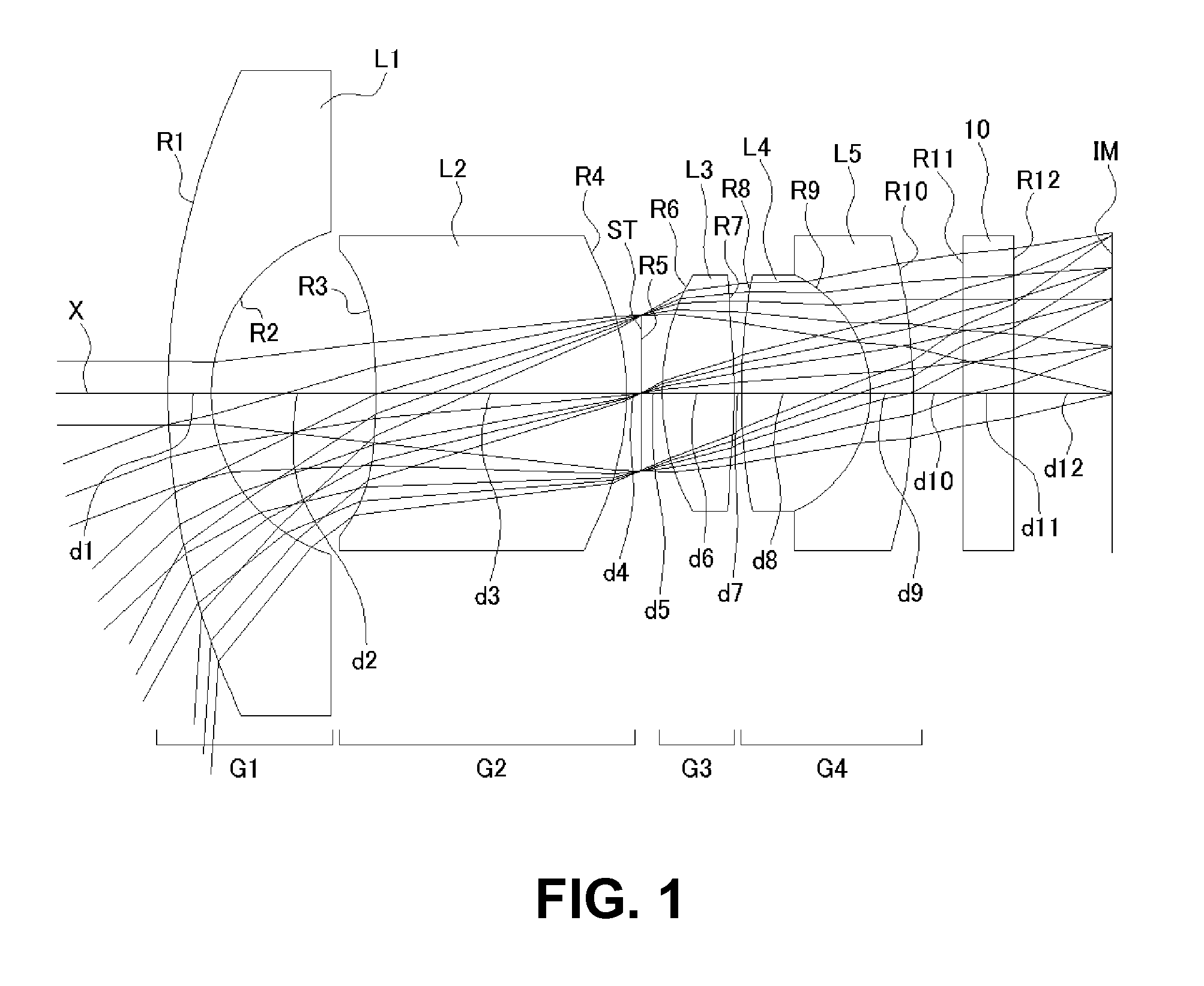
ActiveUS7436605B2Good optical performanceReduced in size and weight and costLensCamera lensImaging lens
An imaging lens is configured sequentially from the object side by: a first lens having a meniscus shape where a convex surface is directed to the object side; a second lens; and a positive third lens in which an image-side surface is a convex surface. The first lens, the second lens, and the third lens are configured by a bi-aspherical plastic lens. The second lens is configured by a bi-convex lens in which the absolute value of the radius of curvature of the object-side surface is smaller than that of the image-side surface. The third lens is a positive lens and a meniscus lens in which a concave surface is directed to the object side, and a convex surface is directed to the image side.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
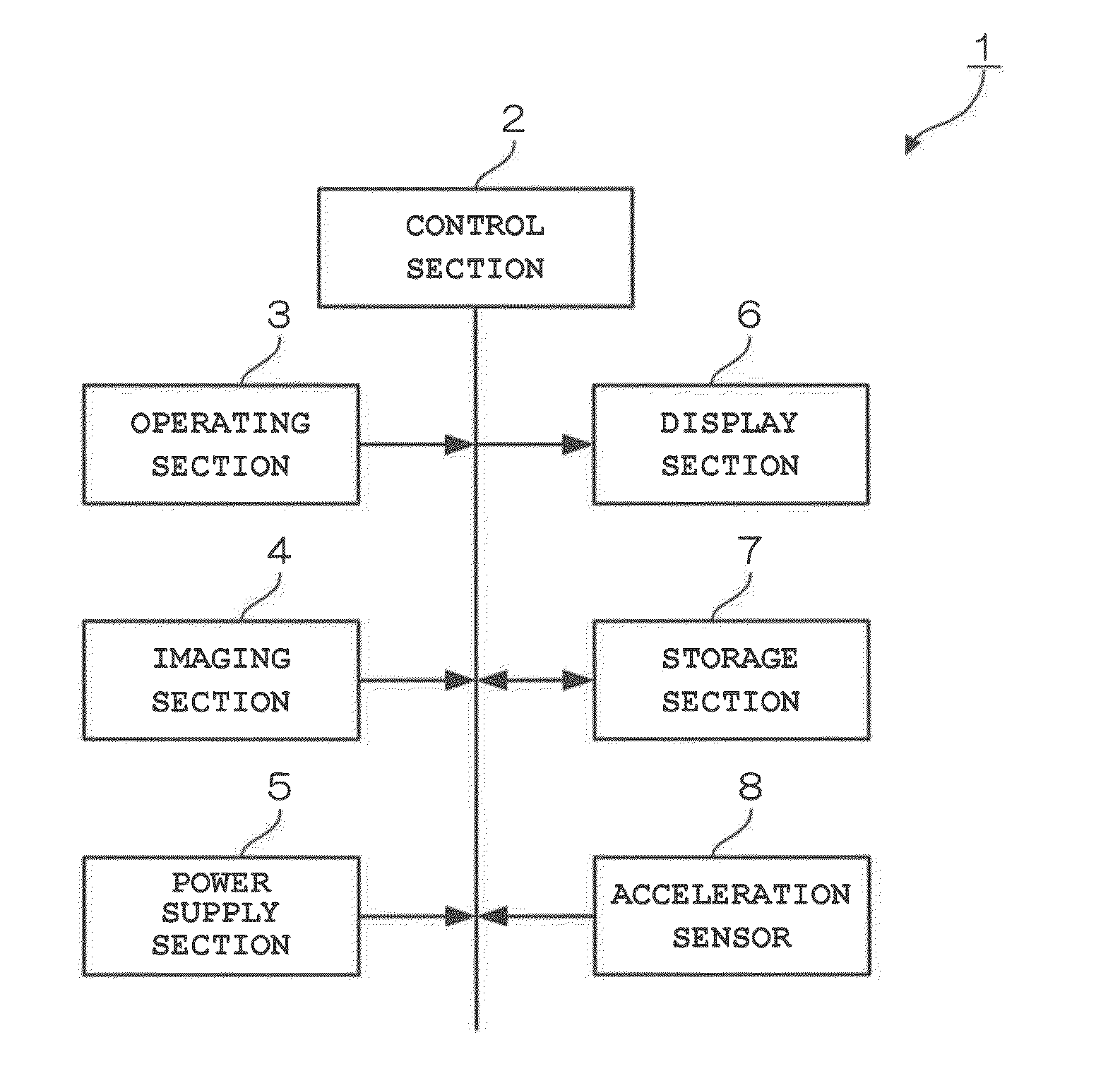
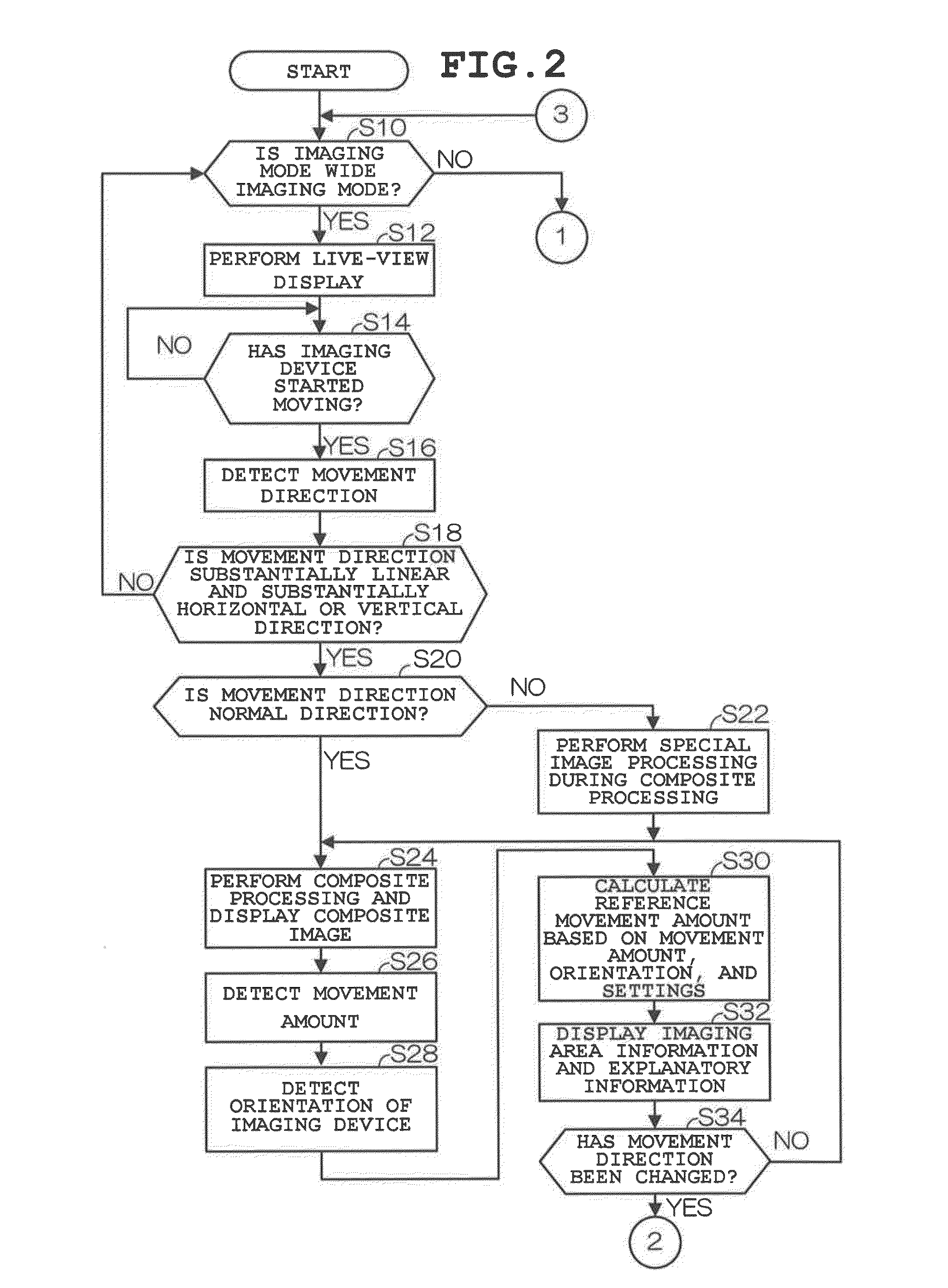
Imaging device, imaging method and storage medium
ActiveUS20130093840A1Broad imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAspect ratioEngineering
The present invention can easily acquire images having a uniform aspect ratio. In an imaging device of the invention, a control section detects the movement amount and the movement direction of the imaging device based on output from an acceleration sensor. Then, when the movement direction of the imaging device in its initial movement started at the beginning of imaging is substantially linear and a substantially horizontal or vertical direction, the control section calculates a reference movement amount by which a composite image having a predetermined aspect ratio can be generated, based on the movement amount of the imaging device, and controls the display section to display imaging area information (guide) indicating the final imaging area having the predetermined aspect ratio based on the reference movement amount.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Imaging lens and camera apparatus
An imaging lens is configured sequentially from the object side by: a first lens having a meniscus shape where a convex surface is directed to the object side; a second lens; and a positive third lens in which an image-side surface is a convex surface. The first lens, the second lens, and the third lens are configured by a bi-aspherical plastic lens. The second lens is configured by a bi-convex lens in which the absolute value of the radius of curvature of the object-side surface is smaller than that of the image-side surface. The third lens is a positive lens and a meniscus lens in which a concave surface is directed to the object side, and a convex surface is directed to the image side.
Owner:TIANJIN OFILM OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
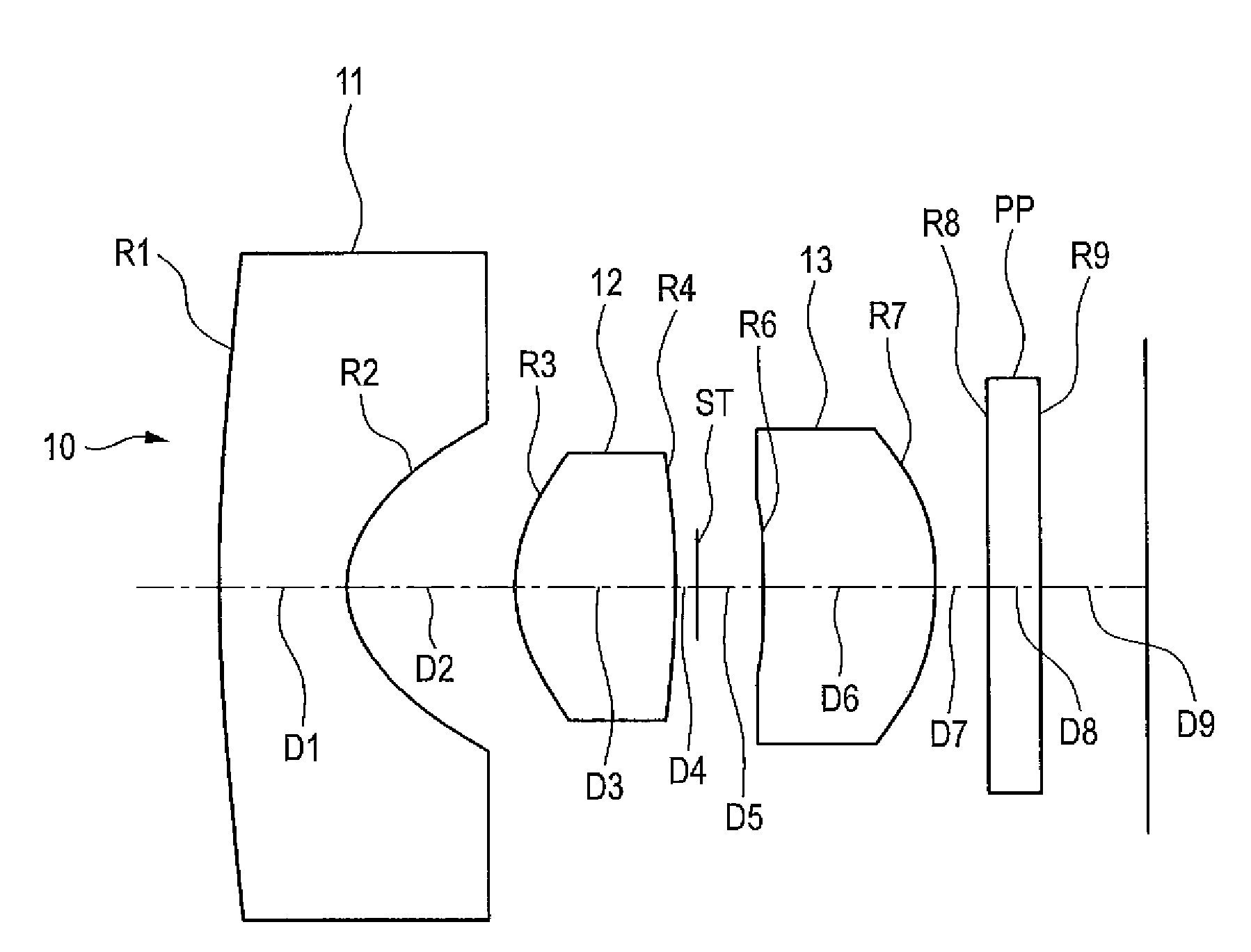
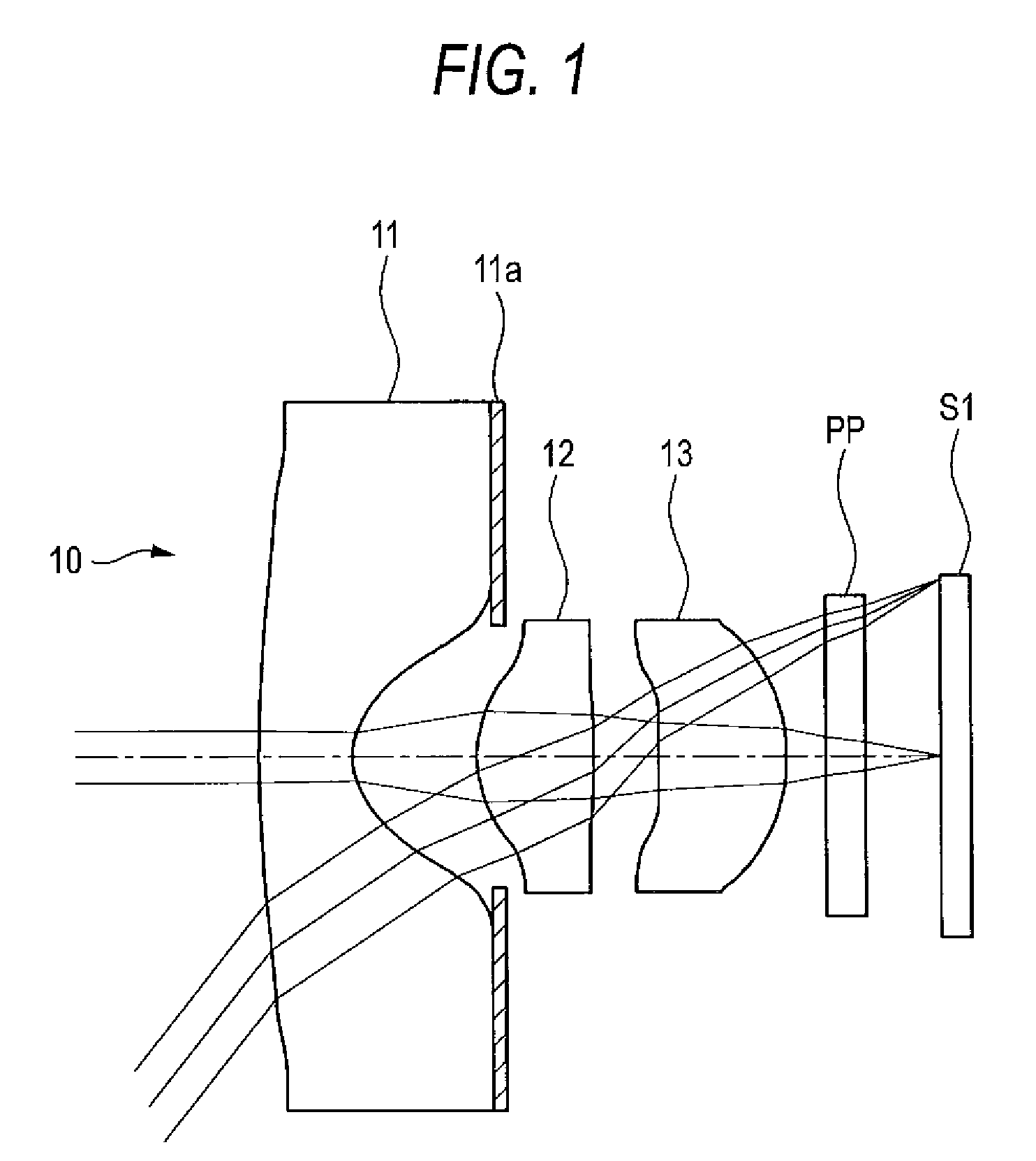
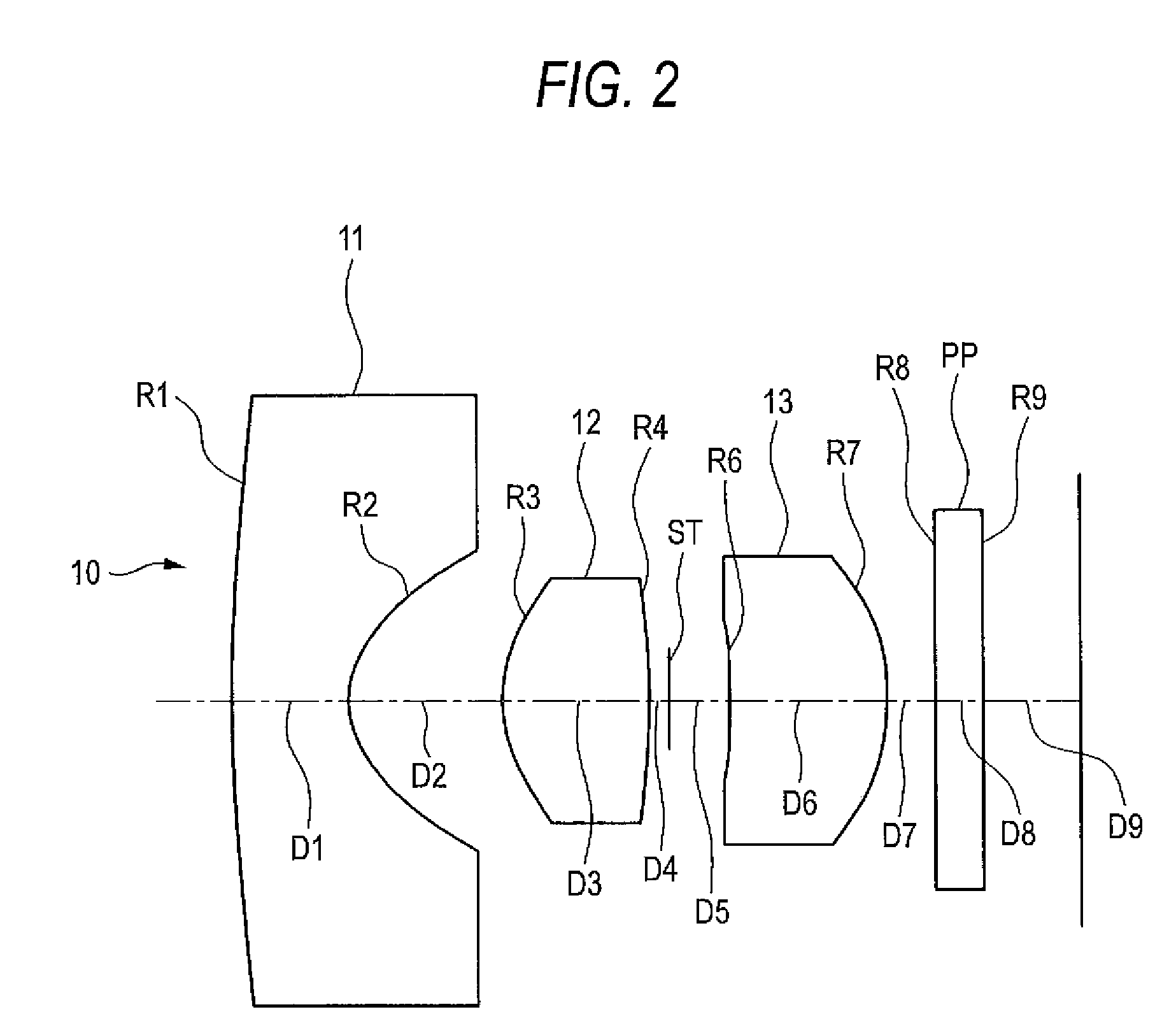
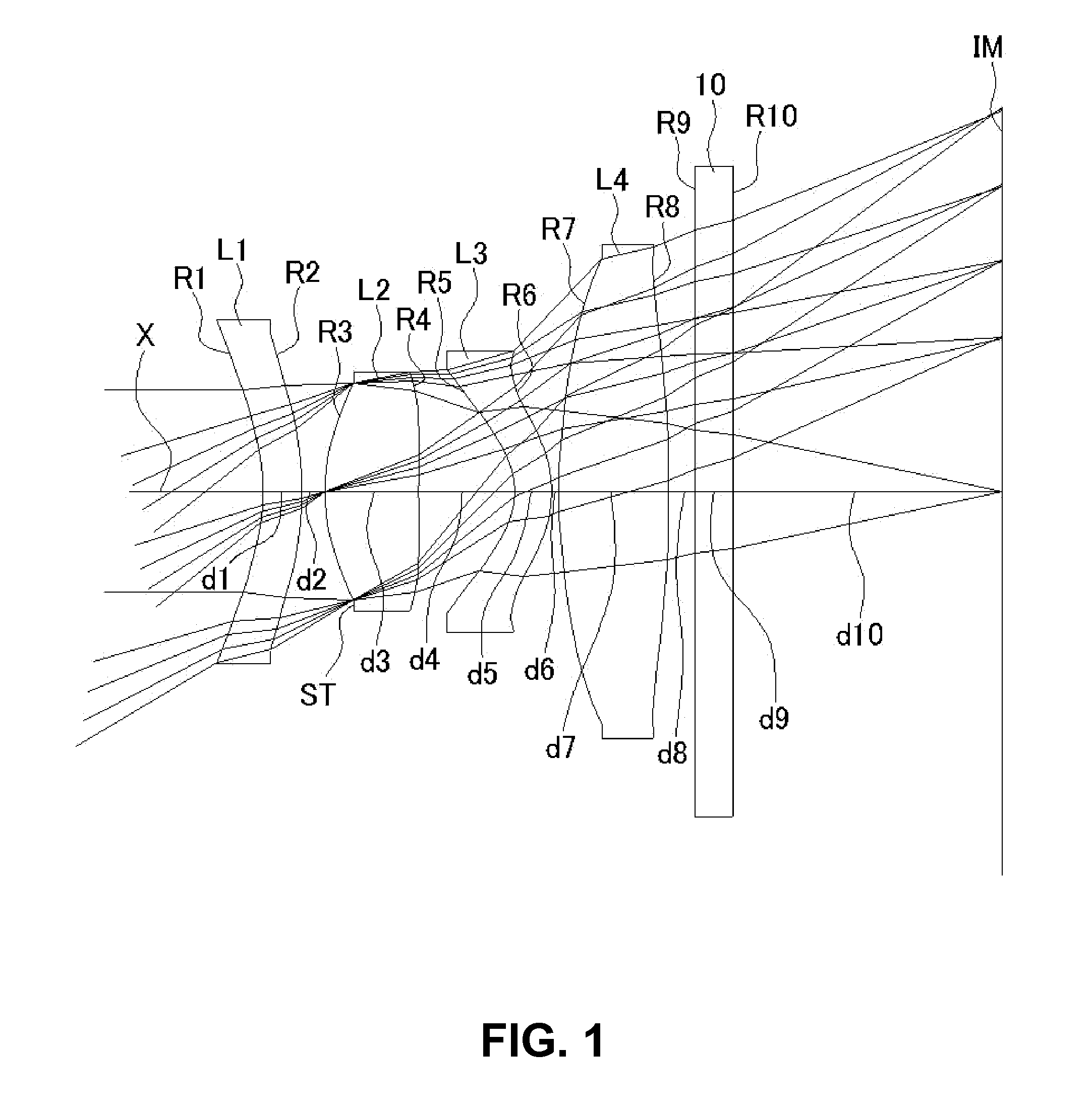
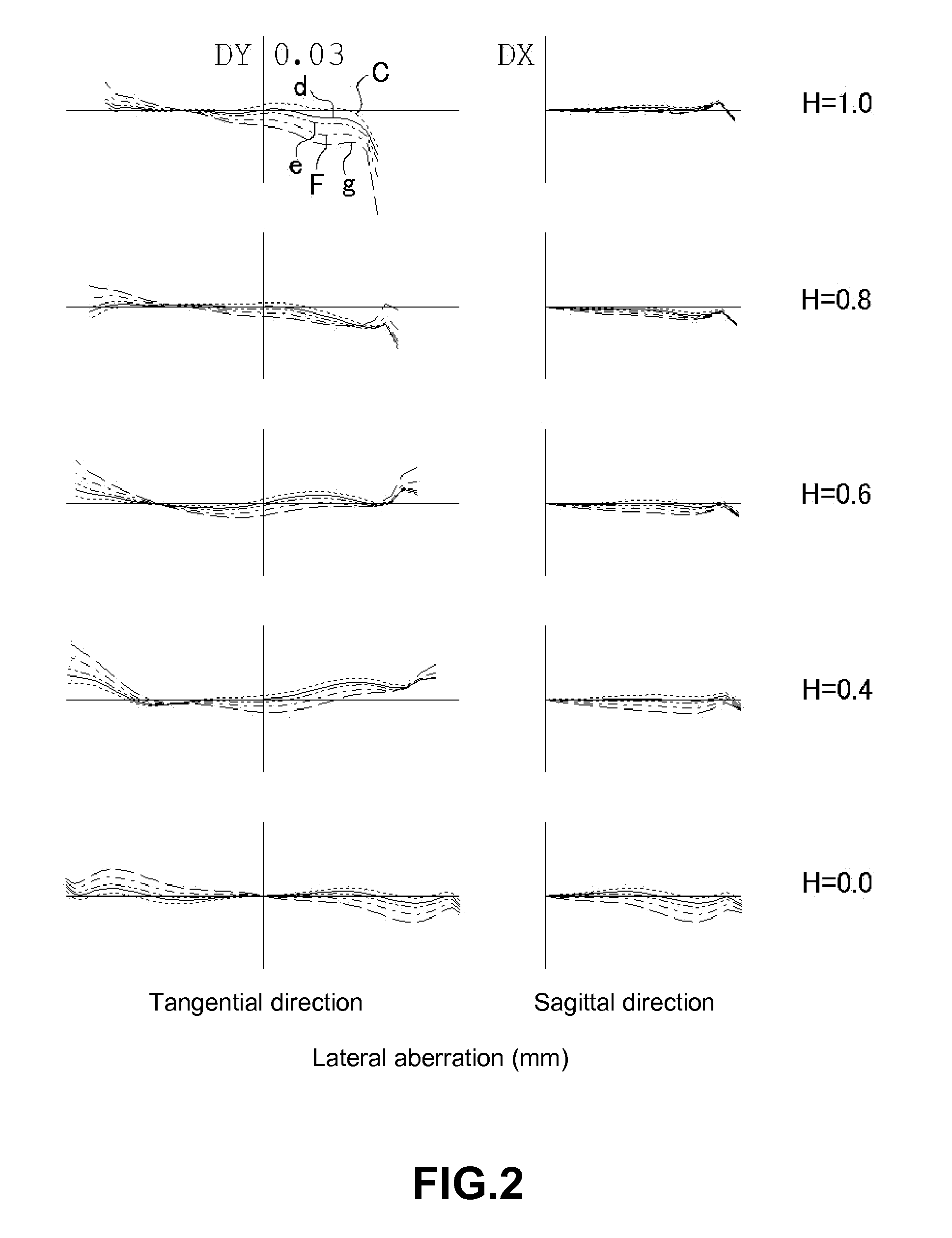
Imaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having negative refractive power; a second lens having positive refractive power; a third lens having positive refractive power; a stop; and a fourth lens having positive refractive power arranged in the order from an object side to an image plane side. The first lens has an image plane-side surface having a positive curvature radius. The second lens has an image plane-side surface having negative curvature radius. The third lens has an image plane-side surface having a negative curvature radius. The fourth lens has an object-side surface having a positive curvature radius and an image plane-side surface having a negative curvature radius. The first lens has a specific focal length and a specific Abbe's number to satisfy specific conditional expressions.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having positive refractive power; a second lens having negative refractive power; a third lens having negative refractive power; a fourth lens having negative refractive power; a fifth lens; a sixth lens; a seventh lens; an eighth lens; and a ninth lens having negative refractive power, arranged in this order from an object side to an image plane side. The ninth lens is formed in a shape so that a surface thereof on the image plane side has an aspherical shape having an inflection point.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Zoom lens
A zoom lens includes, sequentially from an object side, a first lens group having a negative refractive power; and a second lens group having a positive refractive power, where focal length is varied by changing a distance between the first lens group and the second lens group, and a first conditional expression 0.8<|f1 / f2|<1.0 is satisfied, f1 being the focal length of the first lens group and f2 being the focal length of the second lens group.
Owner:TAMRON
Imaging device and imaging system
ActiveUS10021321B2Broad imagingHigh-performance autofocusTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionPupil
An imaging device includes pixels each including first and second photoelectric conversion units on which pupil-divided parts of incident light are incident and a holding unit that holds charges transferred from the first and second photoelectric conversion units, and outputting signals based on amounts of charges held by the holding unit. Each pixel outputs a first signal and a second signal based on amounts of charges generated by the first photoelectric conversion unit and by the first and second photoelectric conversion units, respectively, during a first exposure time, and a third signal and a fourth signal based on amounts of charges generated by the first photoelectric conversion unit and by the first and second photoelectric conversion units, respectively, during a second exposure time. The first and second signals are output before the third and fourth signals in one frame and after the third and fourth signals in another frame.
Owner:CANON KK
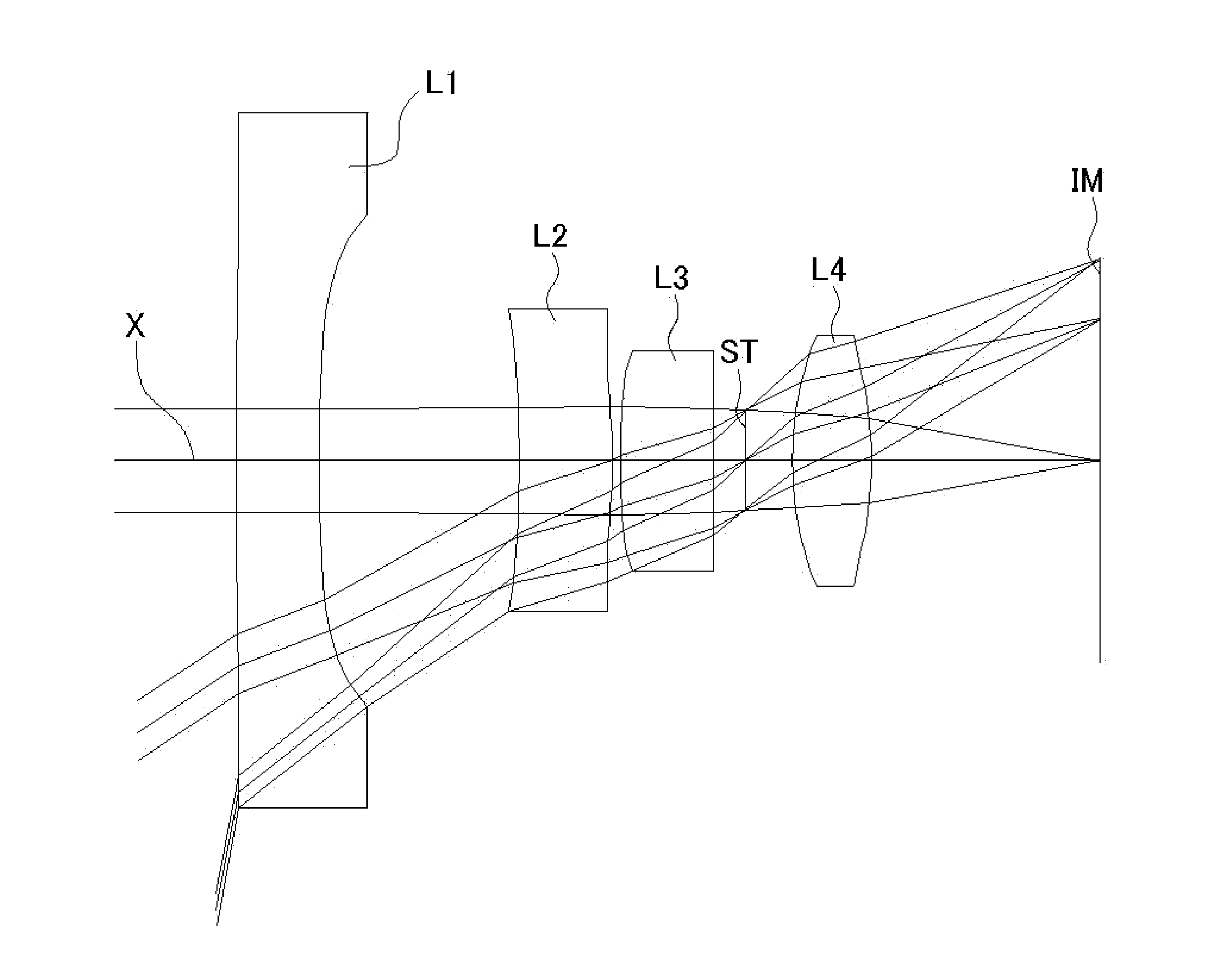
Imaging lens
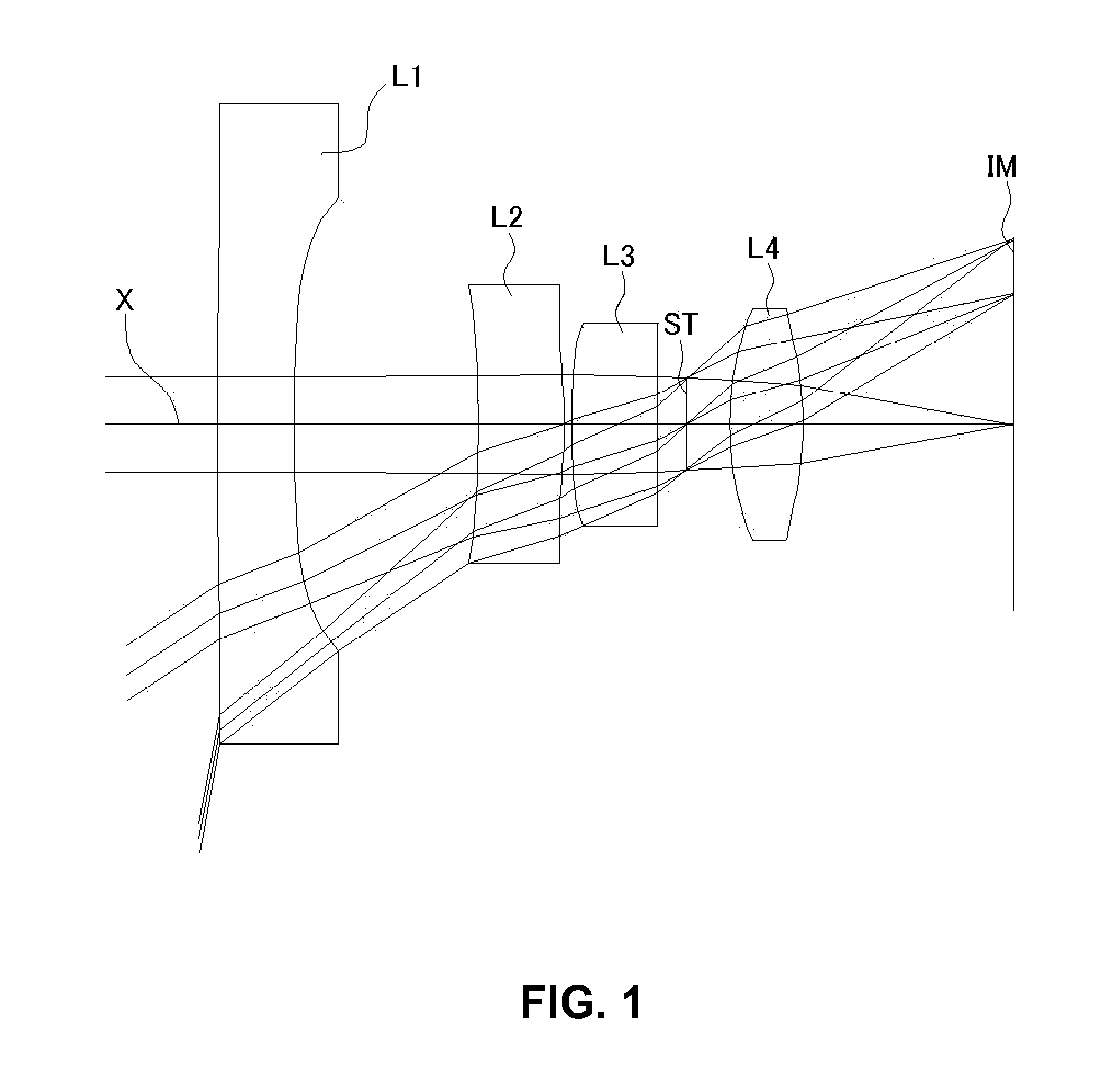
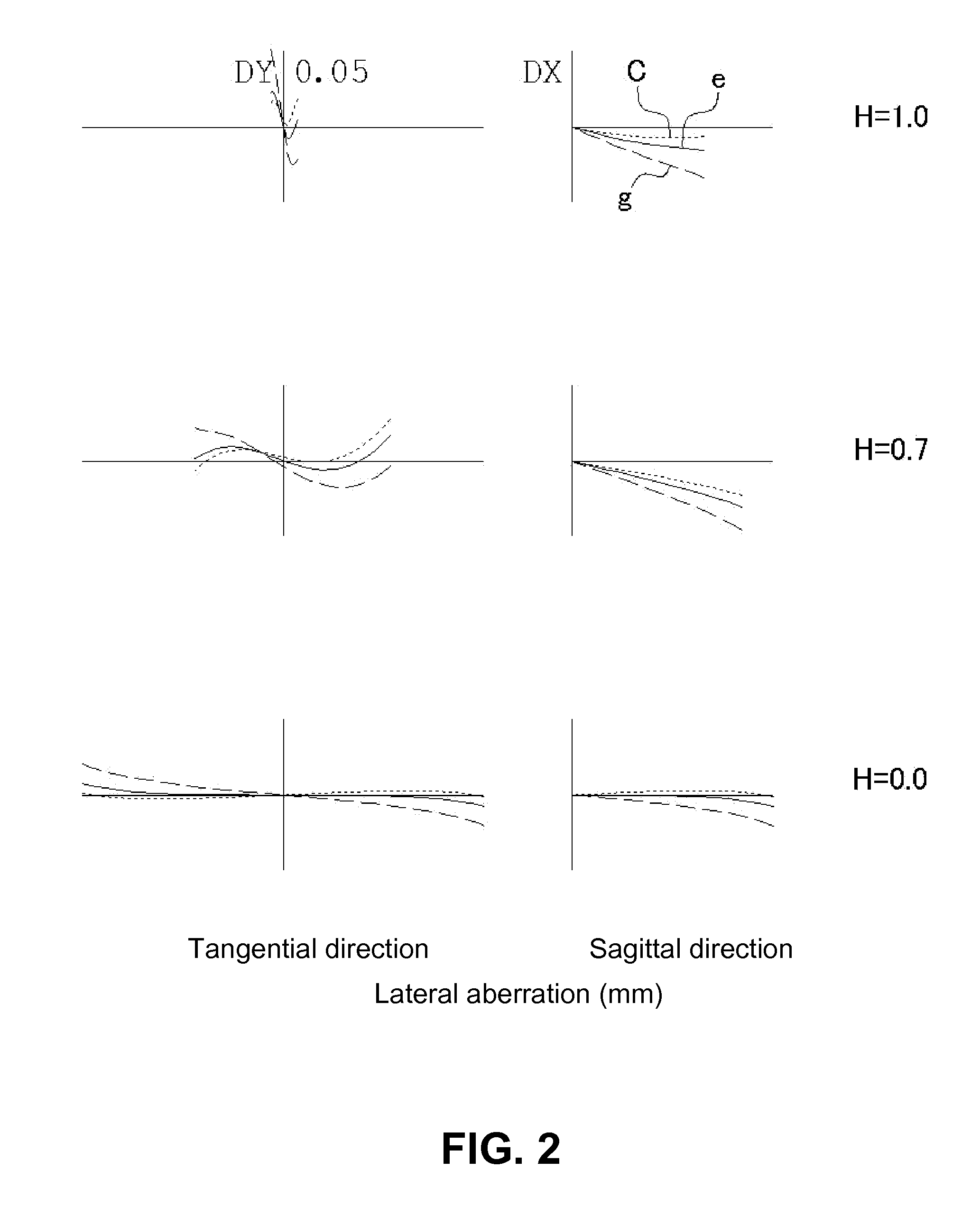
An imaging lens includes a first lens having negative refractive power; a stop; a second lens having positive refractive power; a third lens having negative refractive power; and a fourth lens having positive refractive power, arranged in the order from an object side to an image plane side. The first lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both negative. The second lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both positive. The third lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both negative. The fourth lens has an object-side surface, a curvature of which is positive.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Zoom lens
A zoom lens includes, sequentially from an object side, a first lens group having a negative refractive power; and a second lens group having a positive refractive power, where focal length is varied by changing a distance between the first lens group and the second lens group, and a first conditional expression 0.8<|f1 / f2|<1.0 is satisfied, f1 being the focal length of the first lens group and f2 being the focal length of the second lens group.
Owner:TAMRON
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20150177488A1Wide viewing angleEfficient use ofCoatingsLensConditional expressionImaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having negative refractive power; a second lens having positive refractive power; a third lens; and a fourth lens arranged in the order from an object side to an image plane side. The first lens has an image plane-side surface having a positive curvature radius. The first lens has a specific focal length to satisfy a specific conditional expression.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
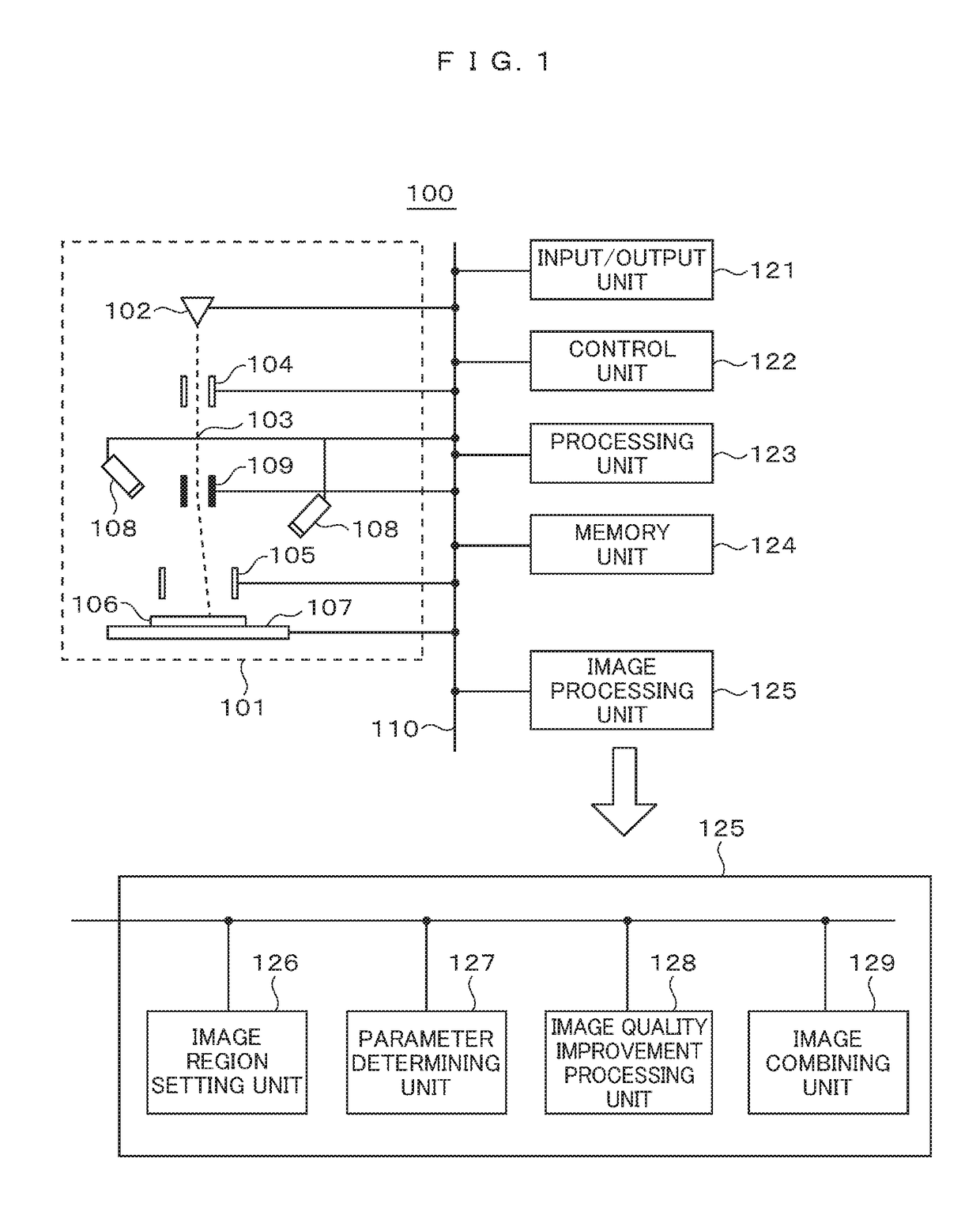
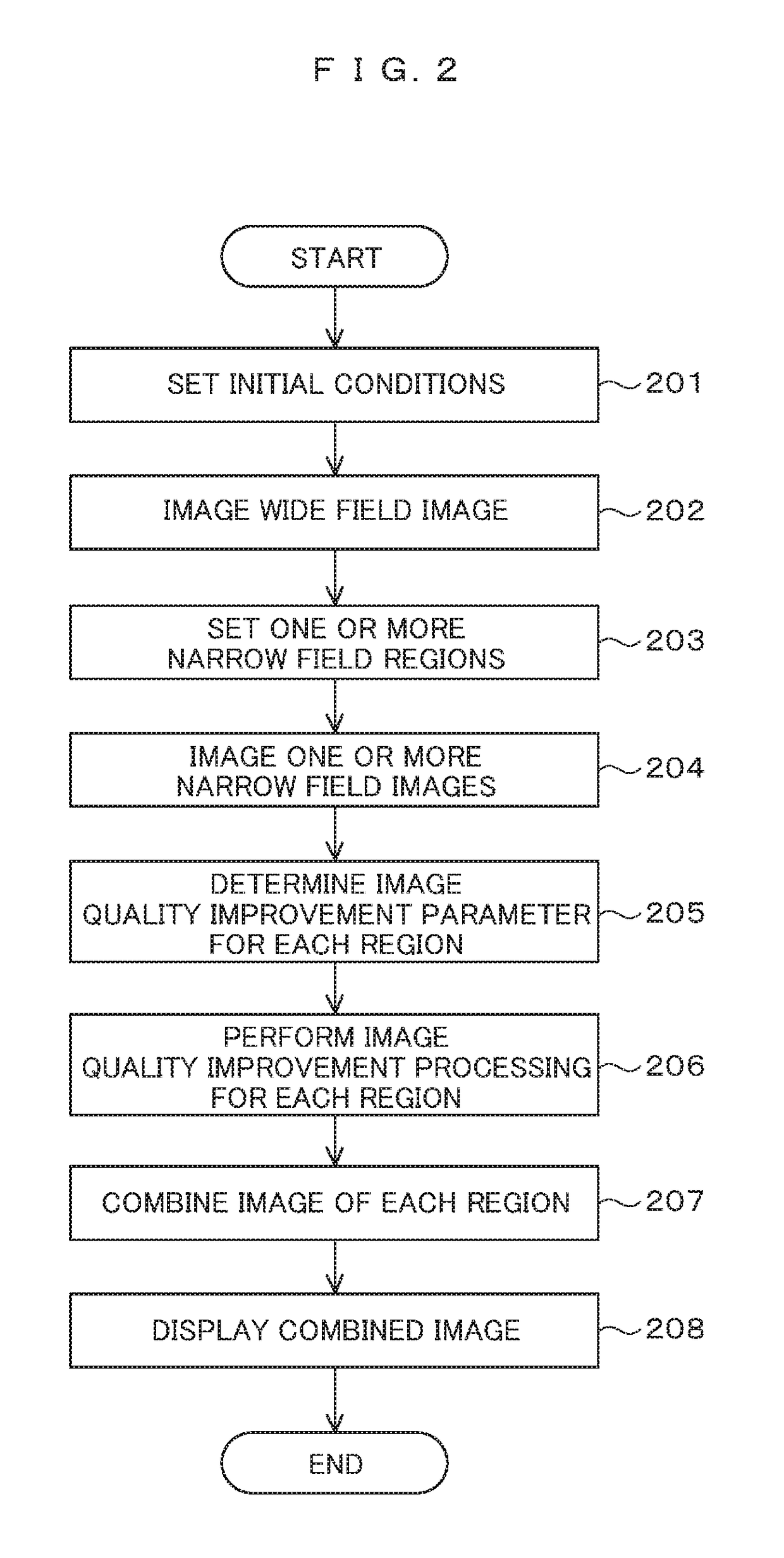
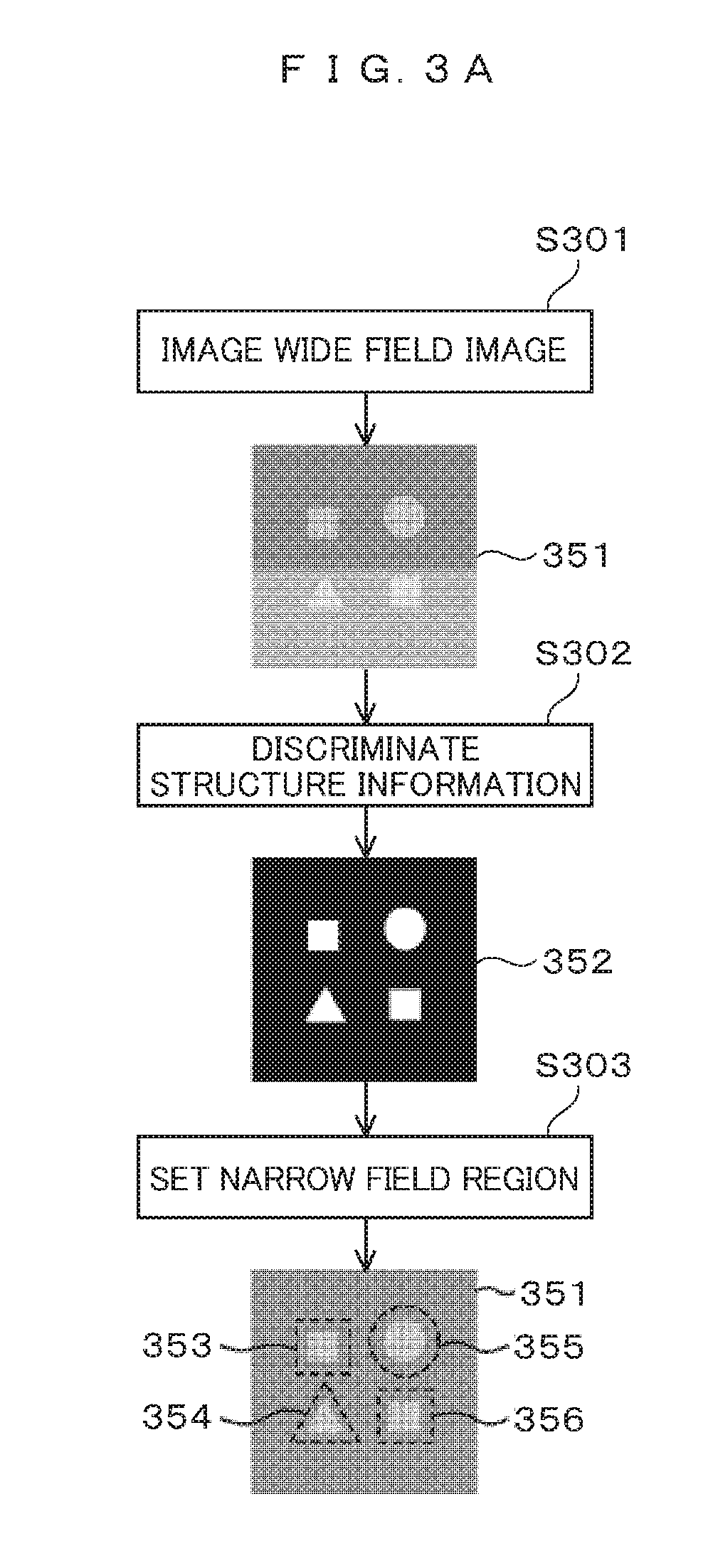
Electron microscope device and imaging method using same
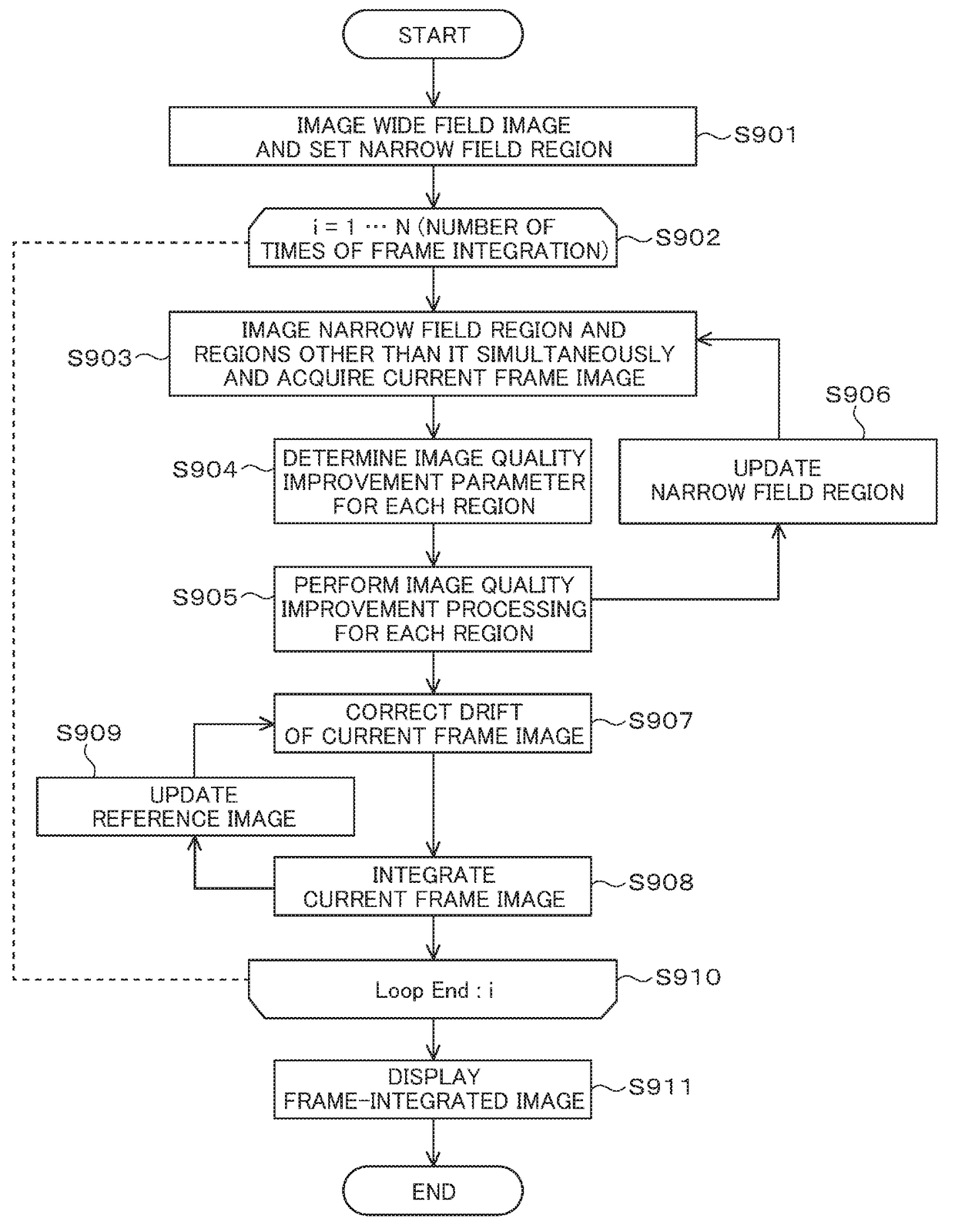
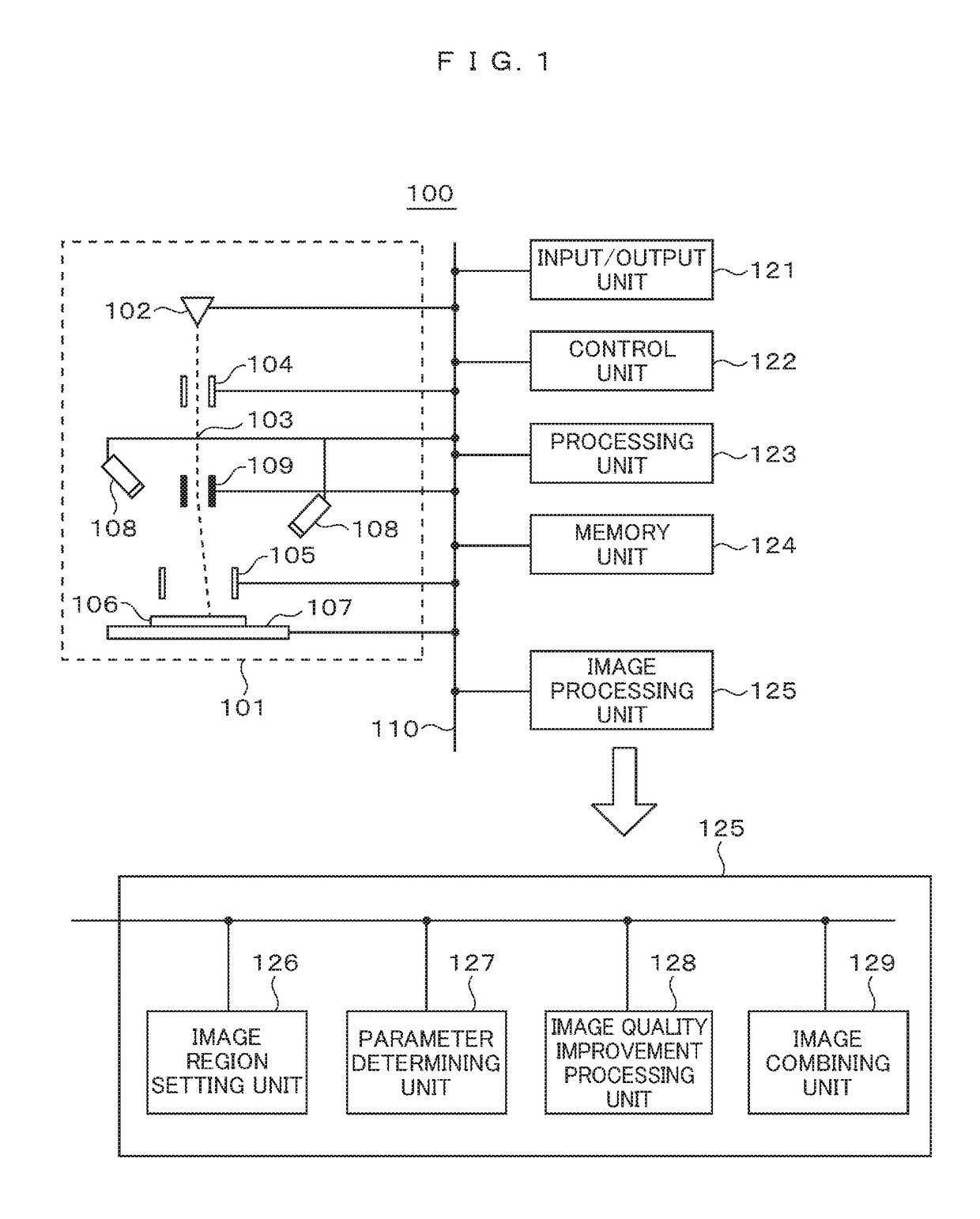
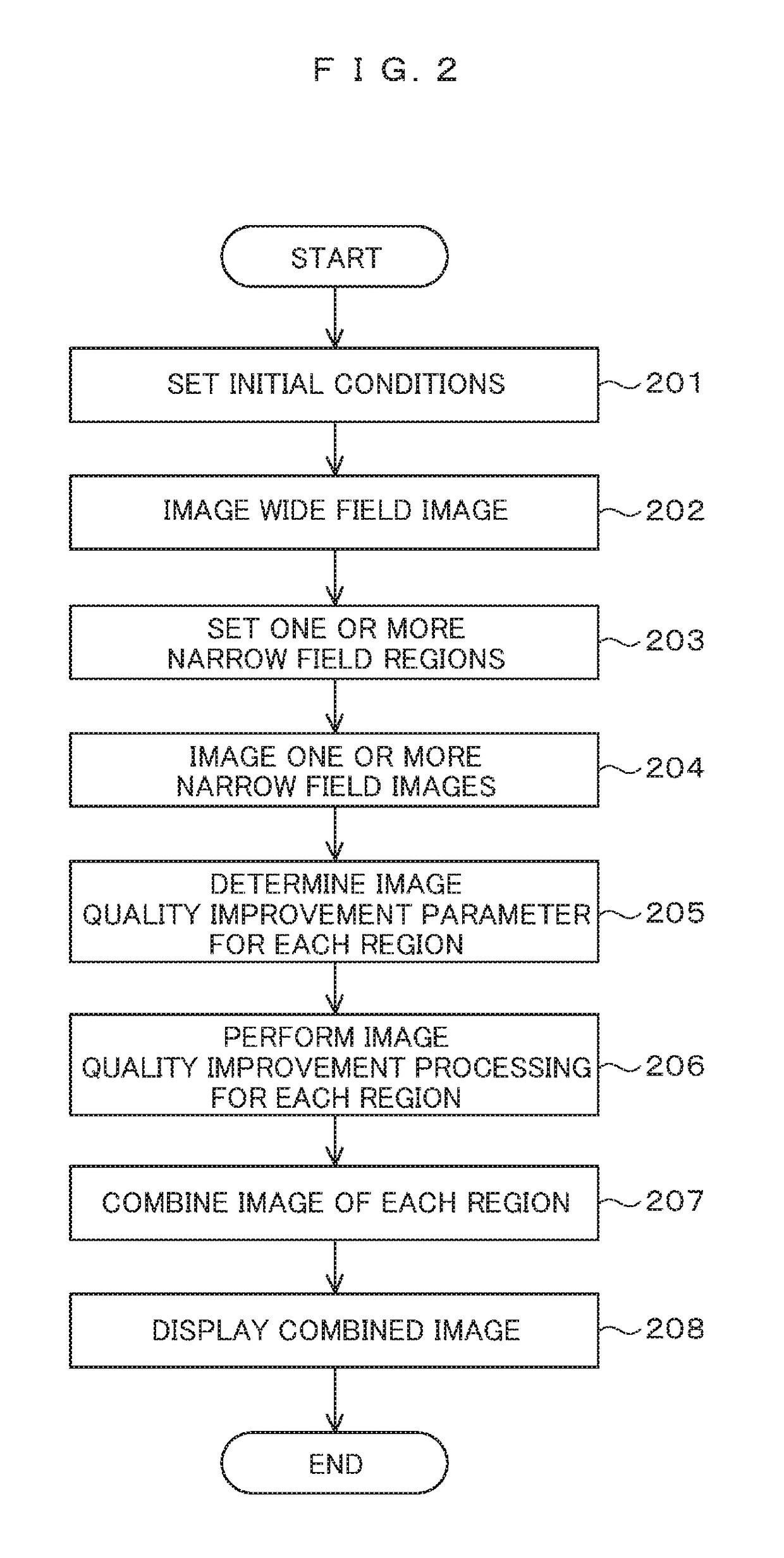
In order to enable high-speed imaging of a wide-field image, the imaging method using the electron microscope comprises: irradiating and scanning a wide-field region of the sample with a low-dose amount of electron beam, and acquiring a wide-field image of the sample; setting, from this wide-field image, a narrow-field region; irradiating and scanning this narrow-field region with a high-dose amount of the electron beam, and acquiring a narrow-field image of the sample; determining the noise-removal parameters for the acquired wide-field image and narrow-field image; performing image quality improvement processing on the wide-field image and the narrow-field image; performing drift correction on the narrow-field image undergone the image quality improvement processing; and combining the narrow-field image undergone this drift correction and the wide-field image in such a manner that the visibility of each is at the same level throughout the entirety of the combined image.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Imaging lens
InactiveUS8416510B2Enhance the imageRefractive power of becomes strongTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens group having a first lens that directs a concave surface to an image plane side and is negative; a second lens group having a second lens that directs a concave surface to an object side and is positive; an aperture; a third lens group having a third lens that is positive; and a fourth lens group having a joined lens that is composed of a fourth lens that is positive and a fifth lens that is negative. In the configuration, when the whole lens system has a focal length f and a composite focal length of the first lens group to the third lens group is Fa, the imaging lens satisfies the following relation:0.3<f / Fa<1.0.
Owner:OPTICAL LOGIC
Imaging lens
InactiveUS20120113533A1Enhance the imageRefractive power of becomes strongTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensImaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens group having a first lens that directs a concave surface to an image plane side and is negative; a second lens group having a second lens that directs a concave surface to an object side and is positive; an aperture; a third lens group having a third lens that is positive; and a fourth lens group having a joined lens that is composed of a fourth lens that is positive and a fifth lens that is negative. In the configuration, when the whole lens system has a focal length f and a composite focal length of the first lens group to the third lens group is Fa, the imaging lens satisfies the following relation:0.3<f / Fa<1.0
Owner:OPTICAL LOGIC
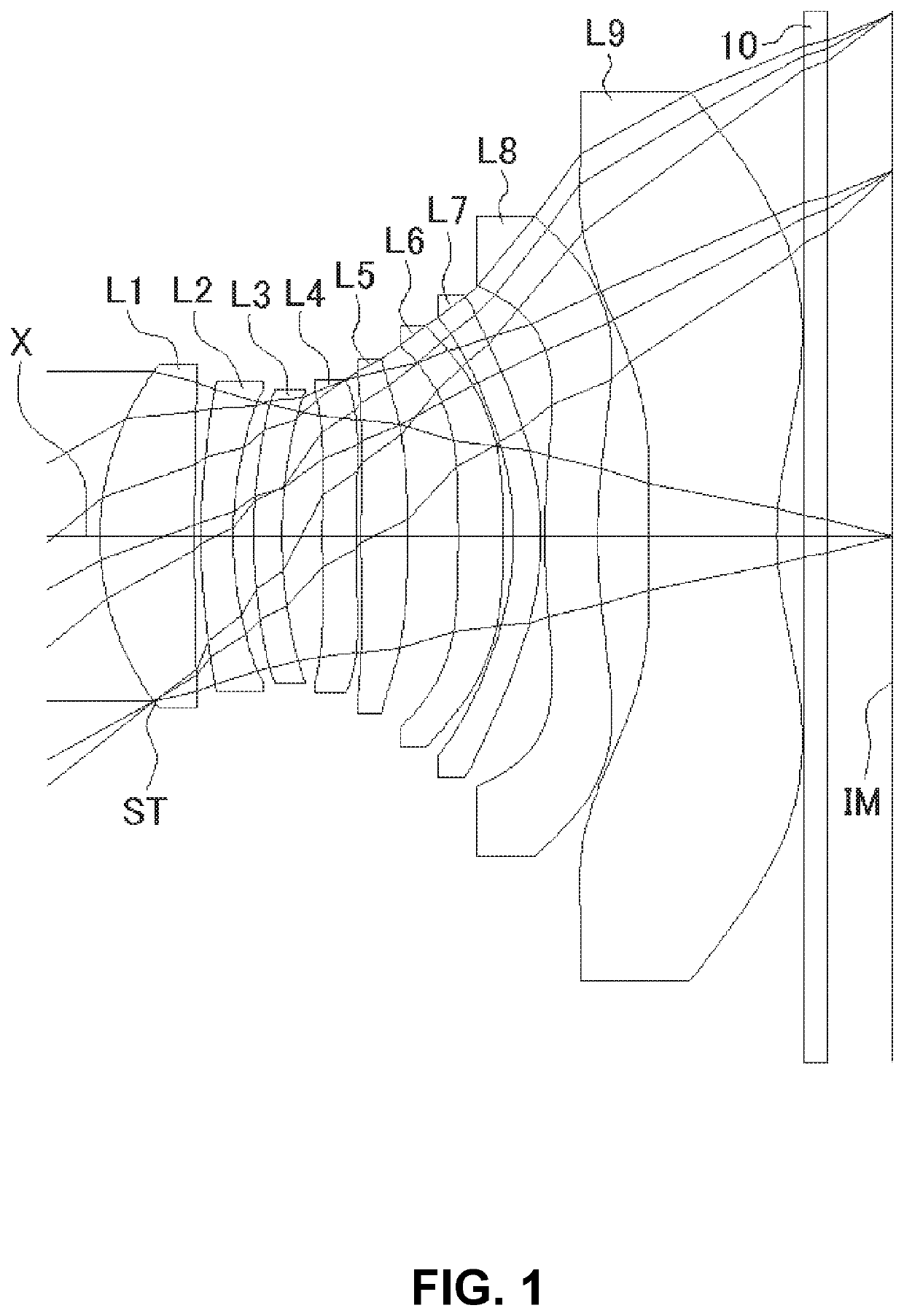
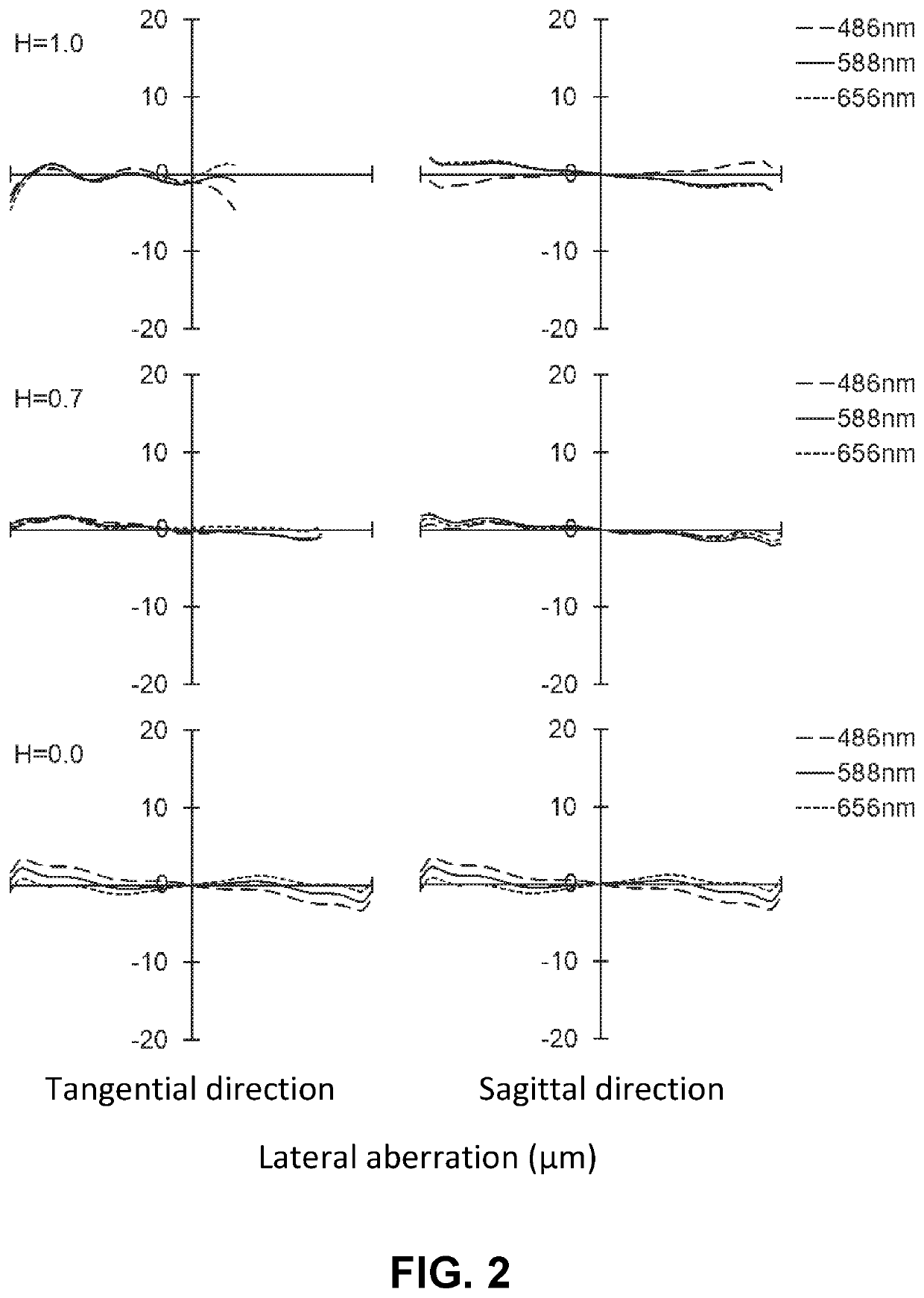
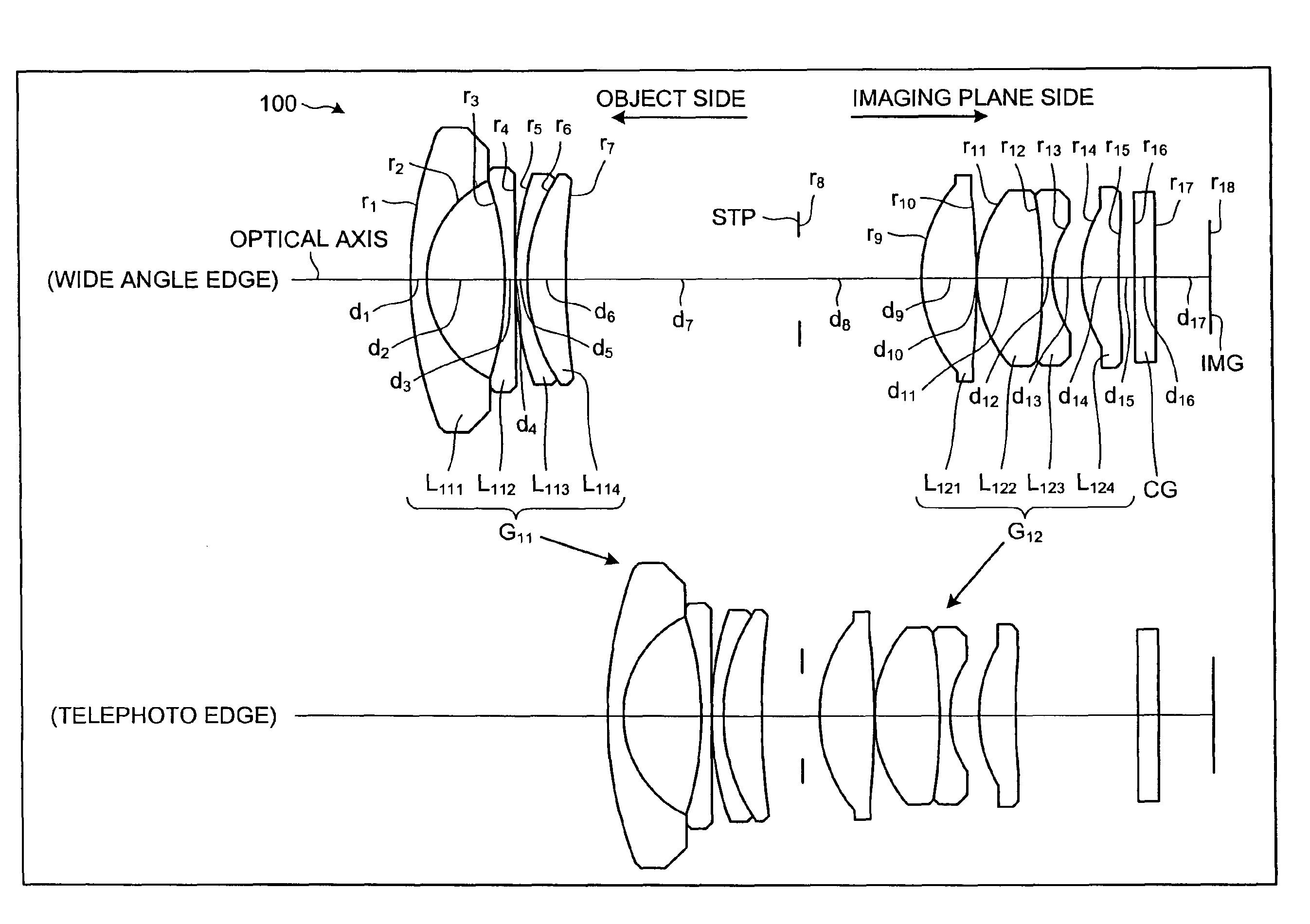
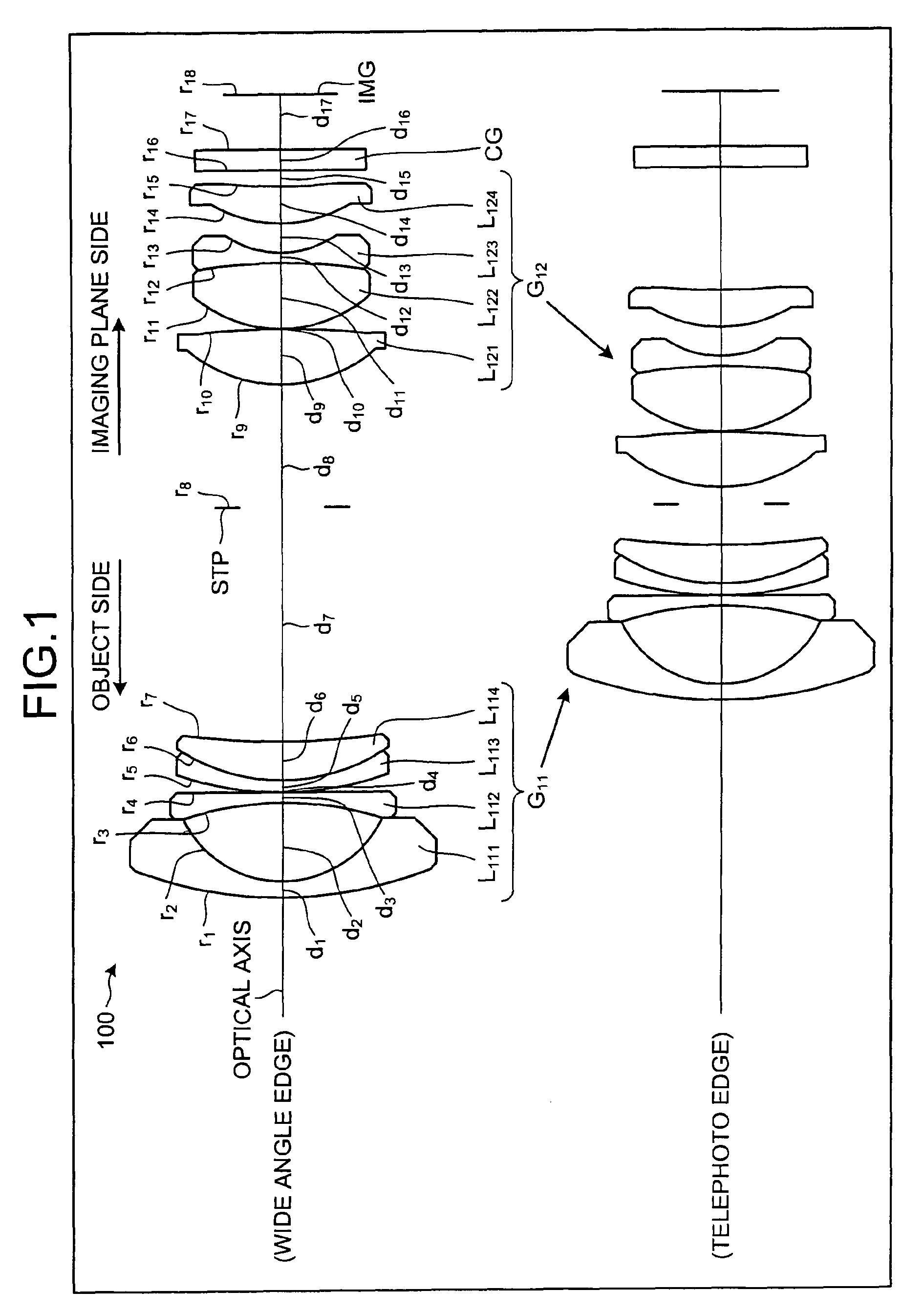
Imaging lens and imaging device
An imaging lens according to the present invention includes a negative first lens, a meniscus-shaped negative second lens having a concave surface facing to an object side, a positive third lens, a positive fourth lens having a convex surface on the object side, a positive fifth lens, a negative sixth lens, and a positive seventh lens arranged in order from the object side. Furthermore, an imaging device according to the present invention includes the imaging lens.
Owner:TAMRON
Electron microscope device and imaging method using same
In order to enable high-speed imaging of a wide-field image, the imaging method using the electron microscope comprises: irradiating and scanning a wide-field region of the sample with a low-dose amount of electron beam, and acquiring a wide-field image of the sample; setting, from this wide-field image, a narrow-field region; irradiating and scanning this narrow-field region with a high-dose amount of the electron beam, and acquiring a narrow-field image of the sample; determining the noise-removal parameters for the acquired wide-field image and narrow-field image; performing image quality improvement processing on the wide-field image and the narrow-field image; performing drift correction on the narrow-field image undergone the image quality improvement processing; and combining the narrow-field image undergone this drift correction and the wide-field image in such a manner that the visibility of each is at the same level throughout the entirety of the combined image.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
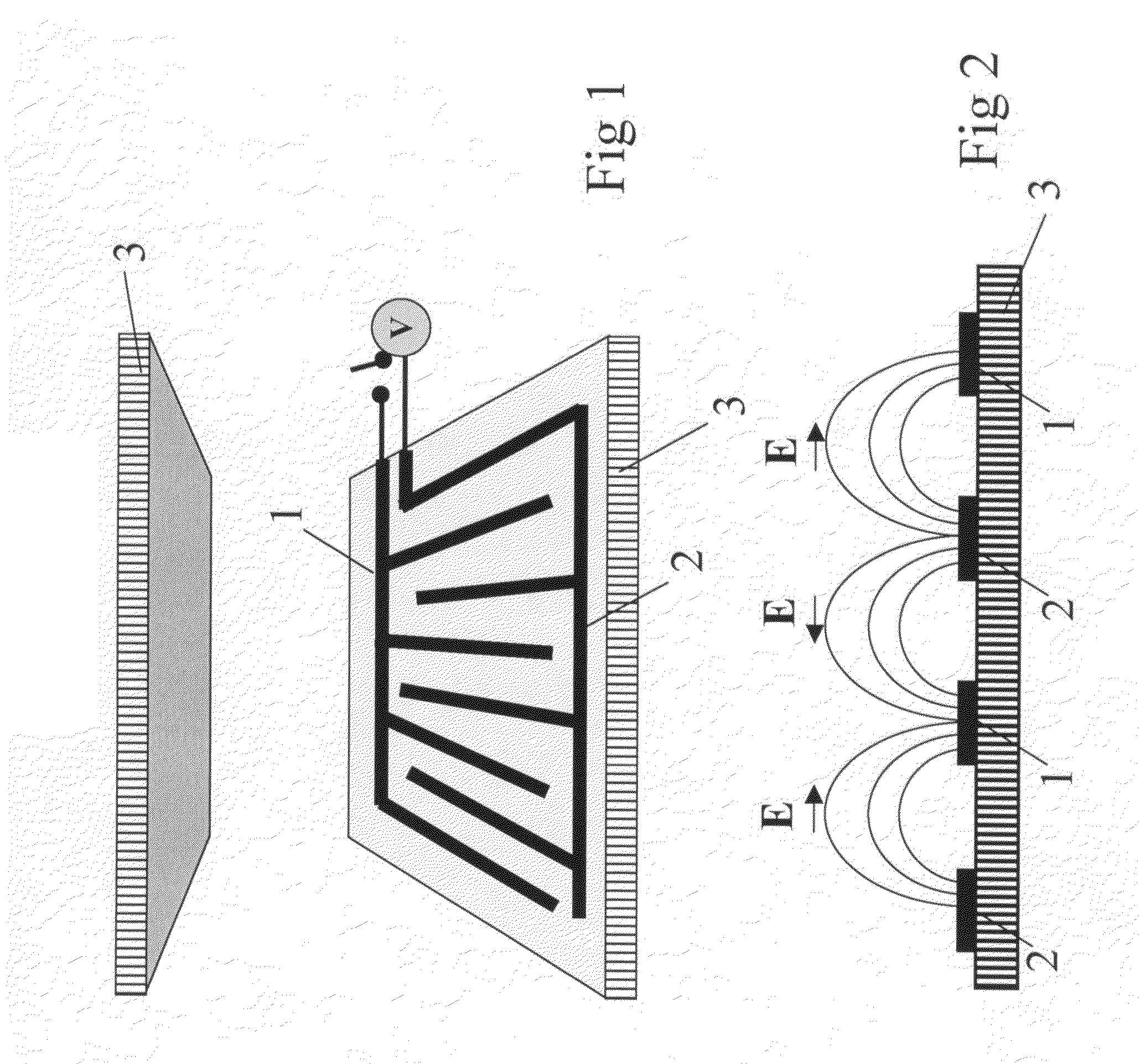
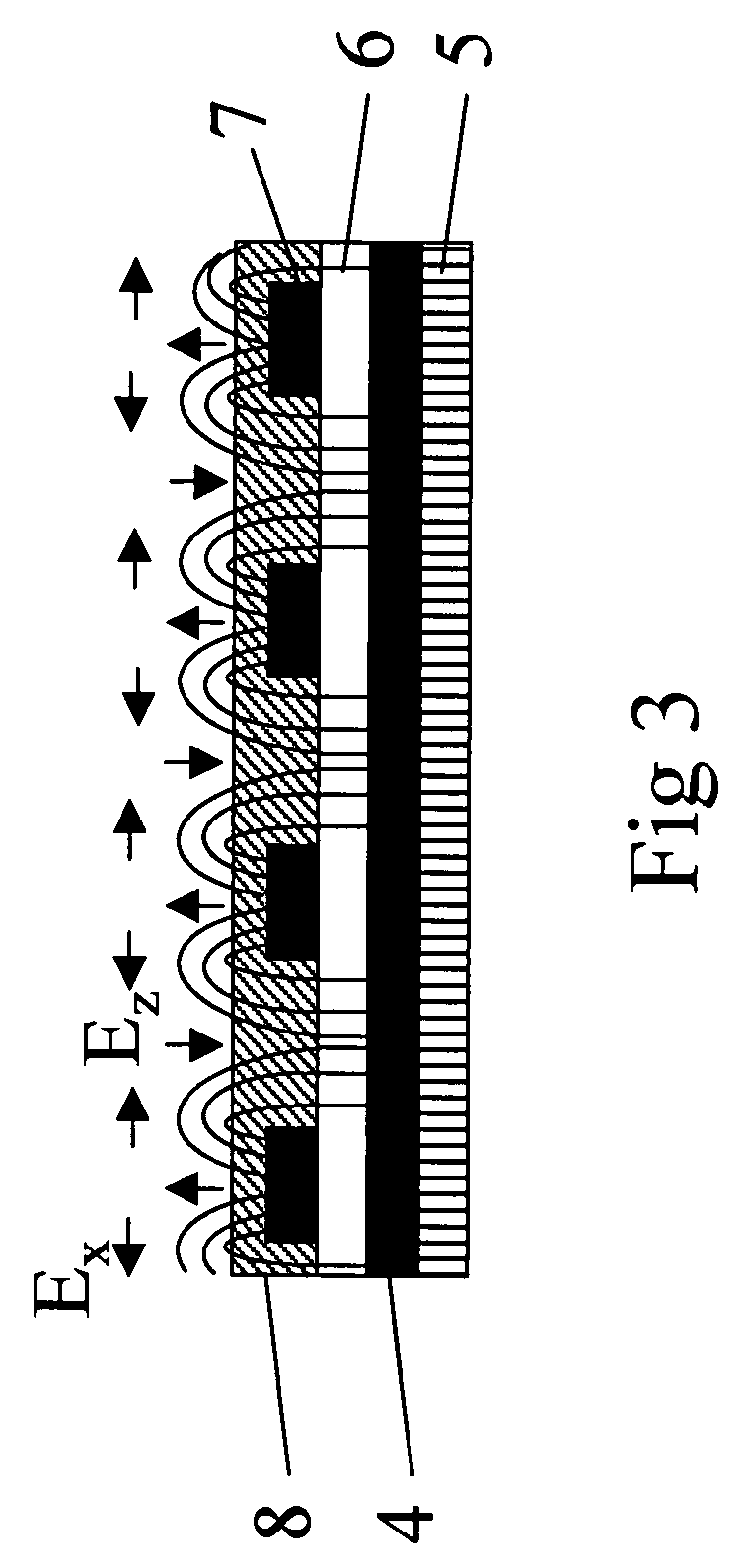
Liquid crystal device
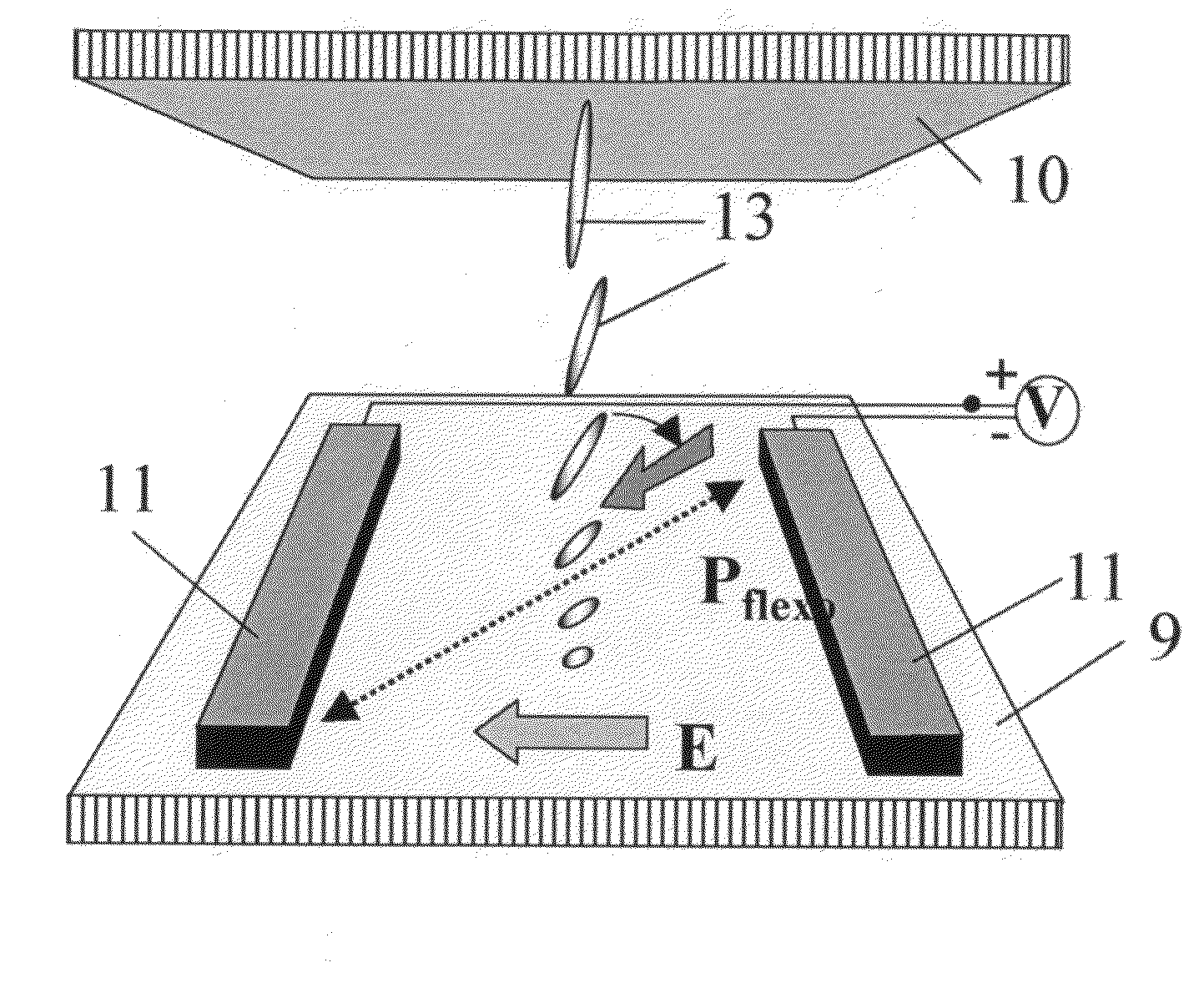
InactiveUS7876385B2Increase contrastFast in-plane switchingLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesIn planeElectric field
The present invention relates to a liquid crystal device driven by a linear coupling, such as ferroelectric and / or flexoelectric coupling, between an inhomogenous in-plane electric field generated by an electrode pattern over a first sub-volume of the bulk layer adjacent to said electrode pattern and liquid crystals in a polarized state comprised in said first sub-volume and / or in an optional alignment layer applied on said electrode pattern said polarization being stronger than any possible similar liquid crystal polarization of the bulk layer outside said first sub-volume, said alignment layer, and / or a second sub-volume of the bulk layer adjacent the inner surface of the other substrate, or an optional second alignment layer or an optional electrode pattern applied thereon.
Owner:KOMITOV LACHEZAR
Imaging lens
PendingUS20210356702A1Refractive power of becomes strongCorrected satisfactorilyOptical elementsOphthalmologyImaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having positive refractive power; a second lens having negative refractive power; a third lens having negative refractive power; a fourth lens having negative refractive power; a fifth lens; a sixth lens; a seventh lens; an eighth lens; and a ninth lens having negative refractive power, arranged in this order from an object side to an image plane side. The ninth lens is formed in a shape so that a surface thereof on the image plane side has an aspherical shape having an inflection point.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging lens and imaging device
An imaging lens according to the present invention includes a negative first lens, a meniscus-shaped negative second lens having a concave surface facing to an object side, a positive third lens, a positive fourth lens having a convex surface on the object side, a positive fifth lens, a negative sixth lens, and a positive seventh lens arranged in order from the object side. Furthermore, an imaging device according to the present invention includes the imaging lens.
Owner:TAMRON
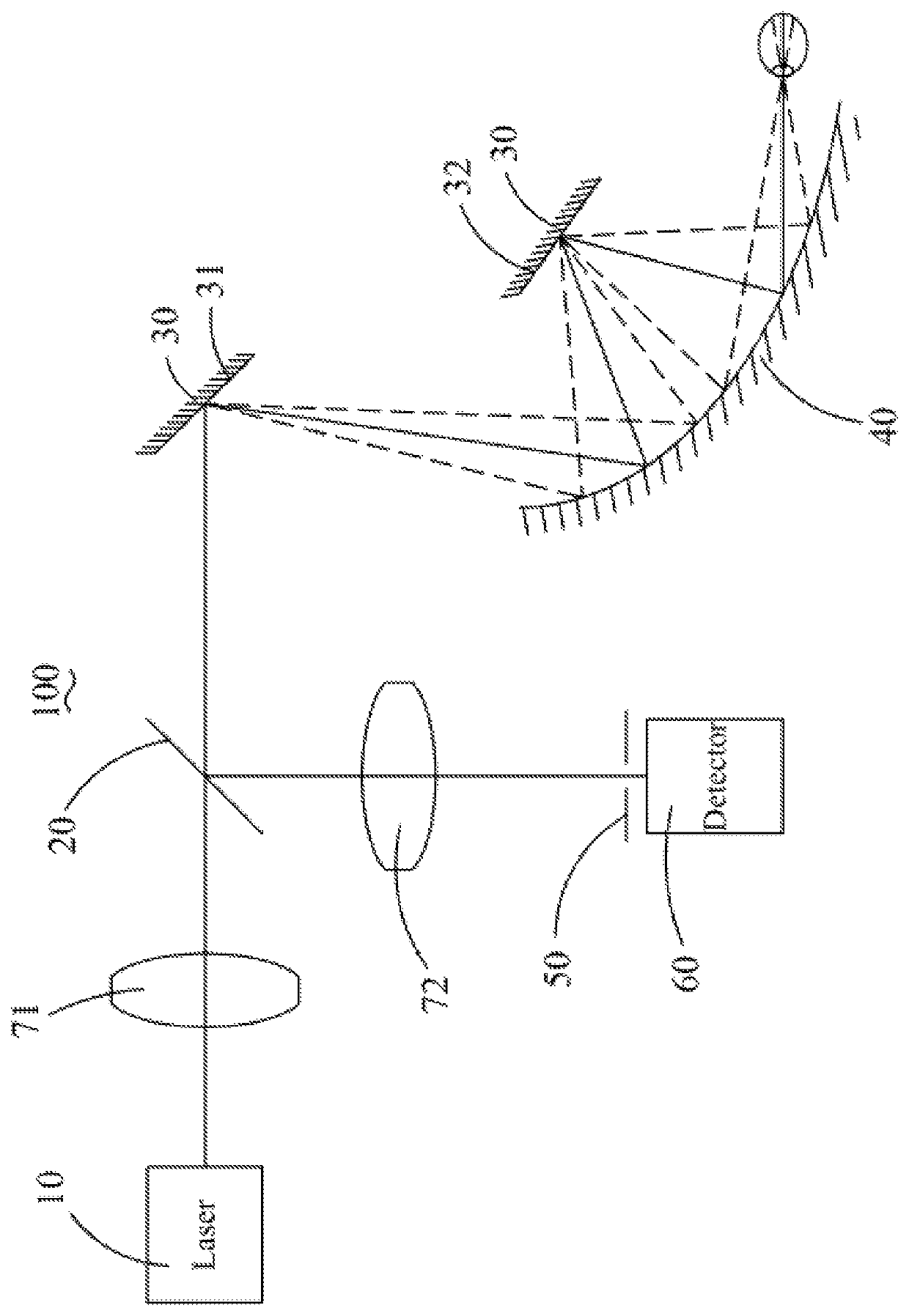
Ultra wide field fundus imaging system
ActiveUS10575730B2Avoid ghostingImprove image qualityMirrorsRefractometersAngle of incidenceOphthalmology
An ultra wide field fundus imaging system comprises a photosource, an optical splitter, a scanning assembly, a curved reflector, a probe pinhole and an imaging assembly. The scanning assembly includes a first scanning mirror scanning along a first direction and a second scanning mirror scanning along a second direction. The light emitted by the photosource passes through the optical splitter, then successively is reflected by the first scanning mirror, the curved reflector, the second scanning mirror and the curved reflector, and then enters in the fundus; the light entering the fundus is reflected by the retina and then successively is reflected by the curved reflector, the second scanning mirror, the curved reflector, the first scanning mirror and then returned to the optical splitter; the light is reflected by the optical splitter and passes through the probe pinhole, finally the light enters in the imaging assembly. Compared with the prior art, the ultra wide field fundus imaging system realizes fundus imaging by total reflection and can effectively avoid ghost images caused by lens module imaging to improve the imaging quality. Since the curvature of the curved reflector is gradually changed, so the light reflected by the curved reflector can enter in the fundus at a larger incident angle to achieve wide field imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
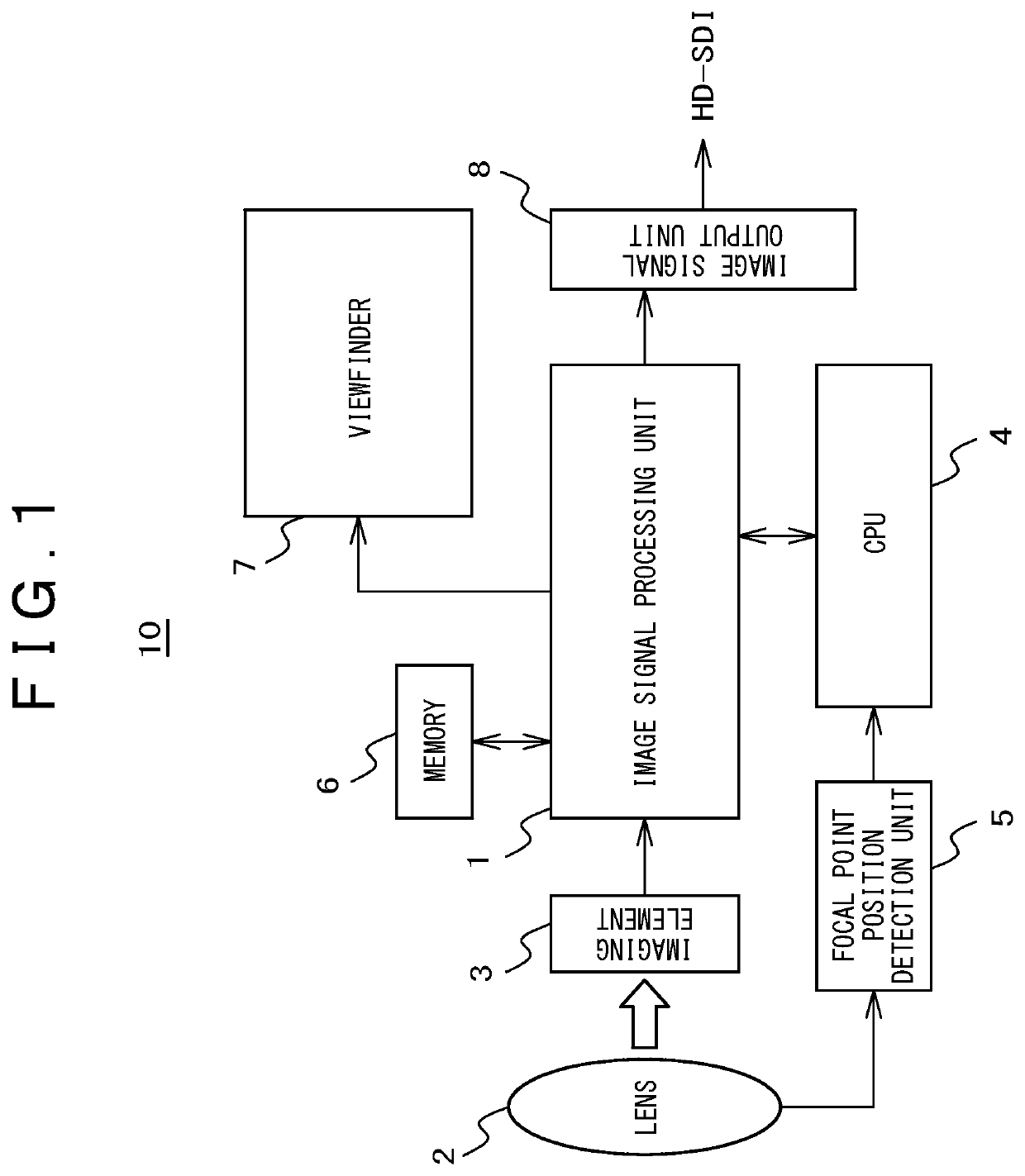
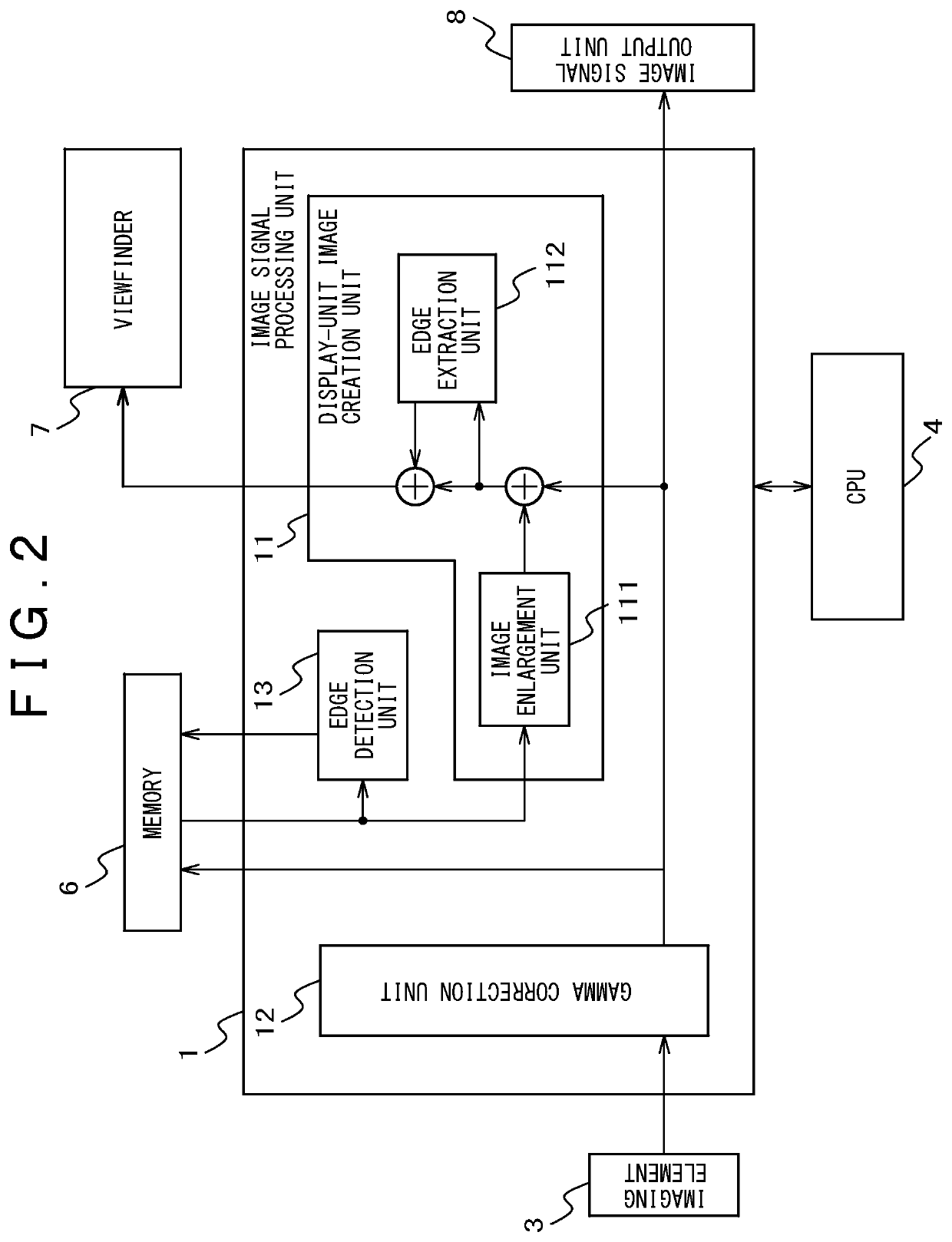
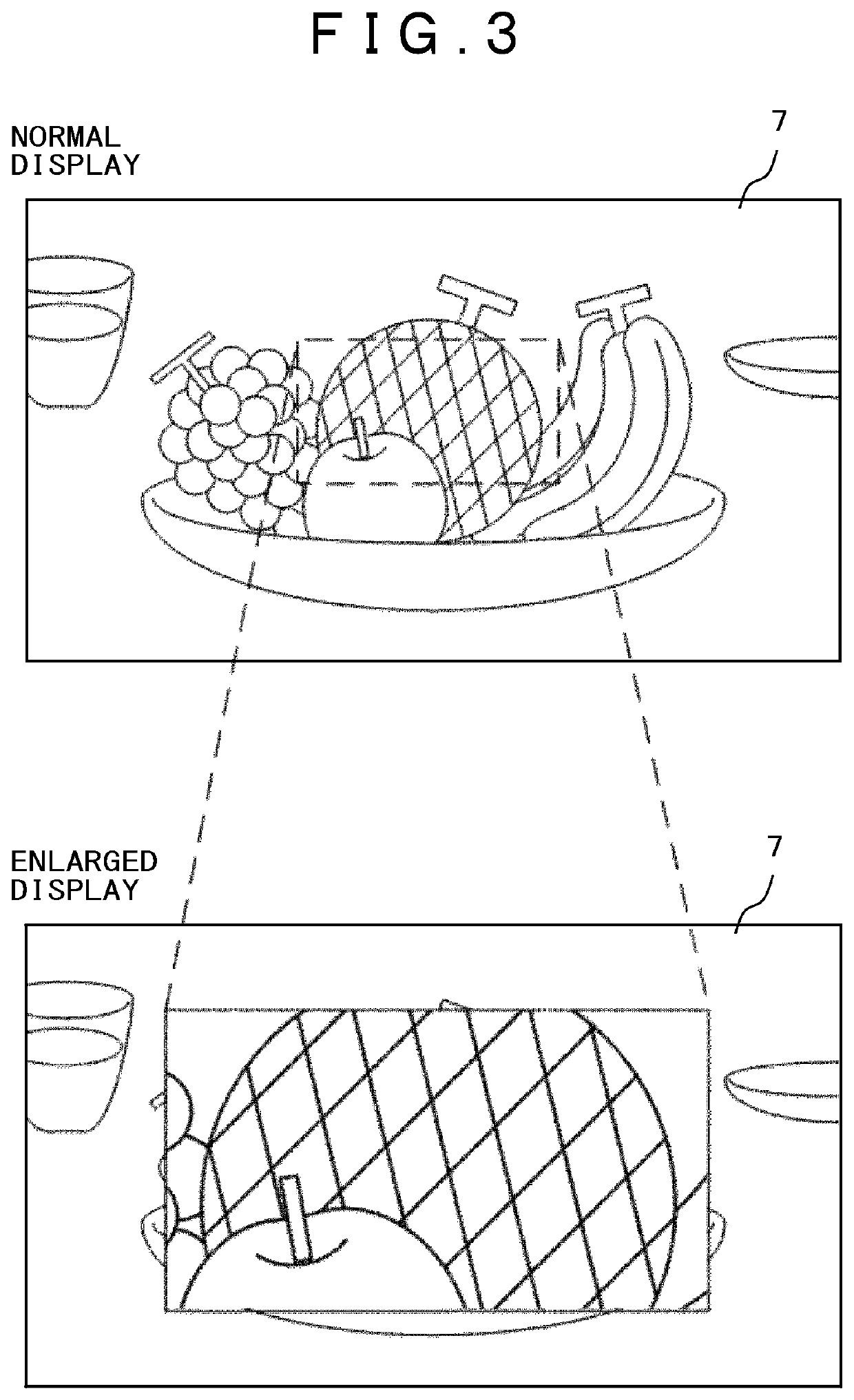
Imaging apparatus
ActiveUS11233945B2Comfortable focusing operationBroad imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadiologyFocal position
An object of the present invention is to provide an imaging apparatus that can comfortably be focused while an influence on a wide angle image is minimized. The imaging apparatus includes: a display unit for displaying an image being photographed; an enlarged image display function for displaying an image obtained by enlarging a part of an area being photographed in the display unit; an edge component detection function for detecting an edge component amount of an enlarged image area; and a focal point position detection function for detecting movement of a focal point operated by a photographer. Duration time of the enlarged image display displayed by the enlarged image display function is changed in conjunction with the edge component detected by the edge component detection function and the movement of the focal point detected by the focal point position detection function.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
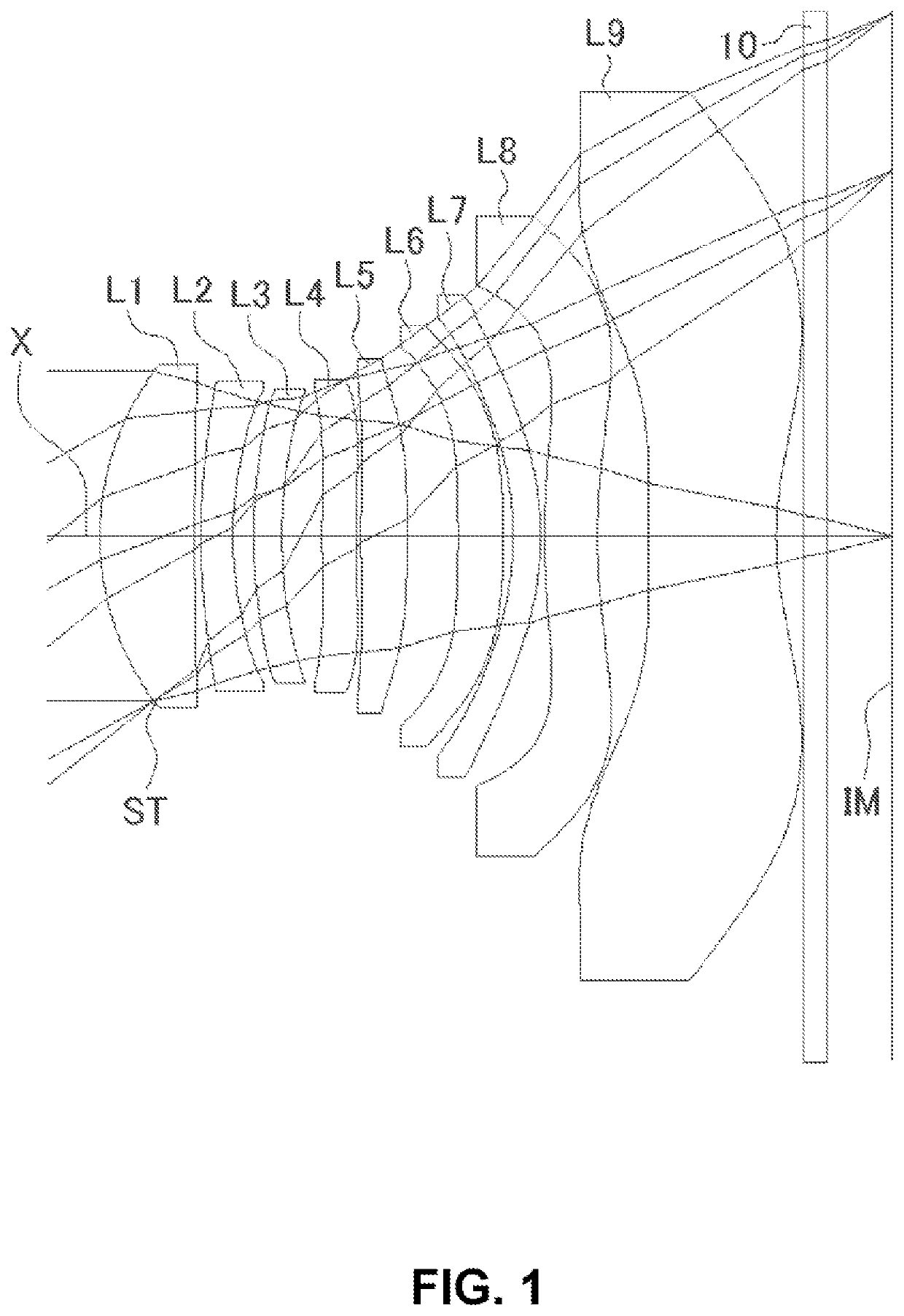
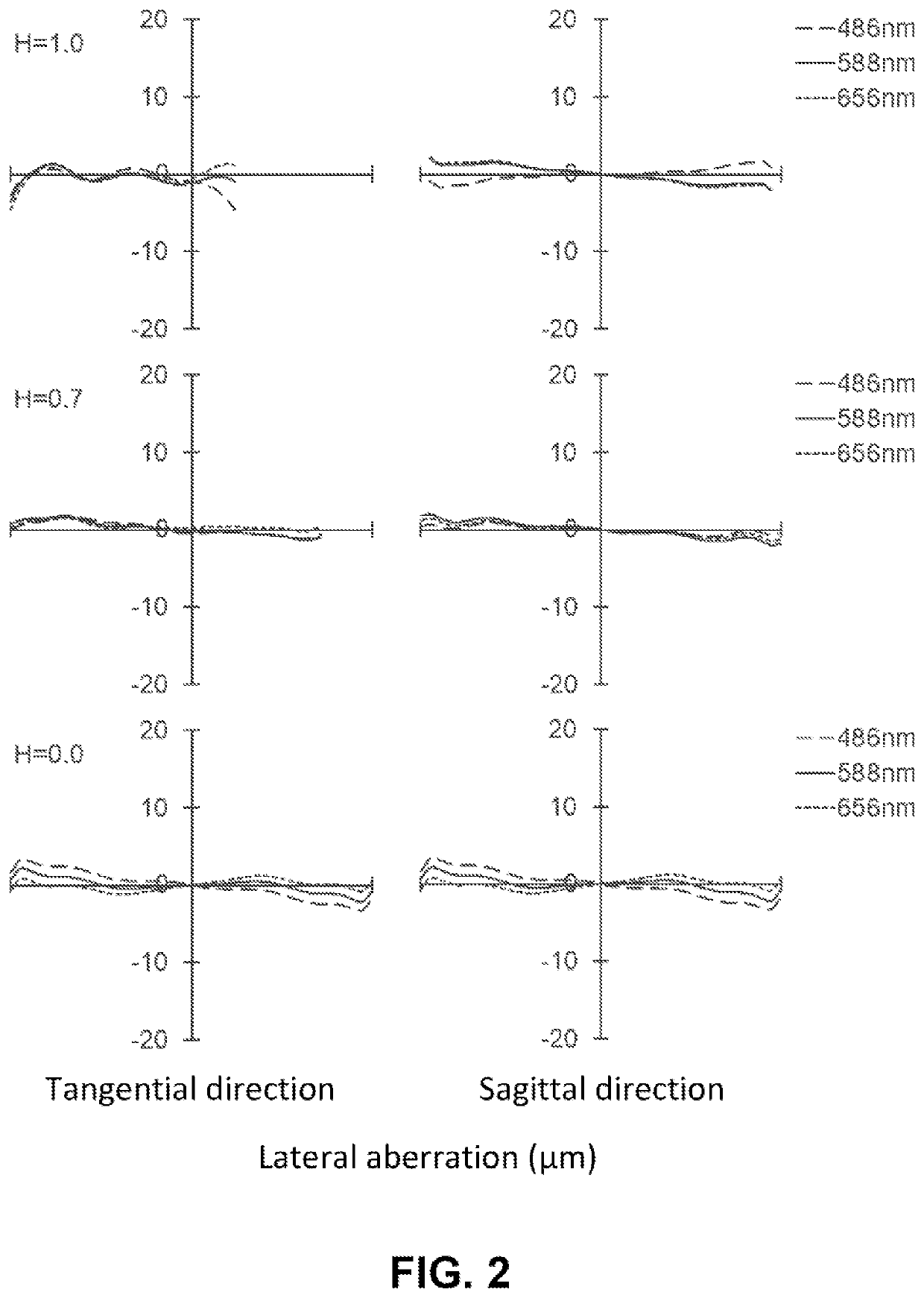
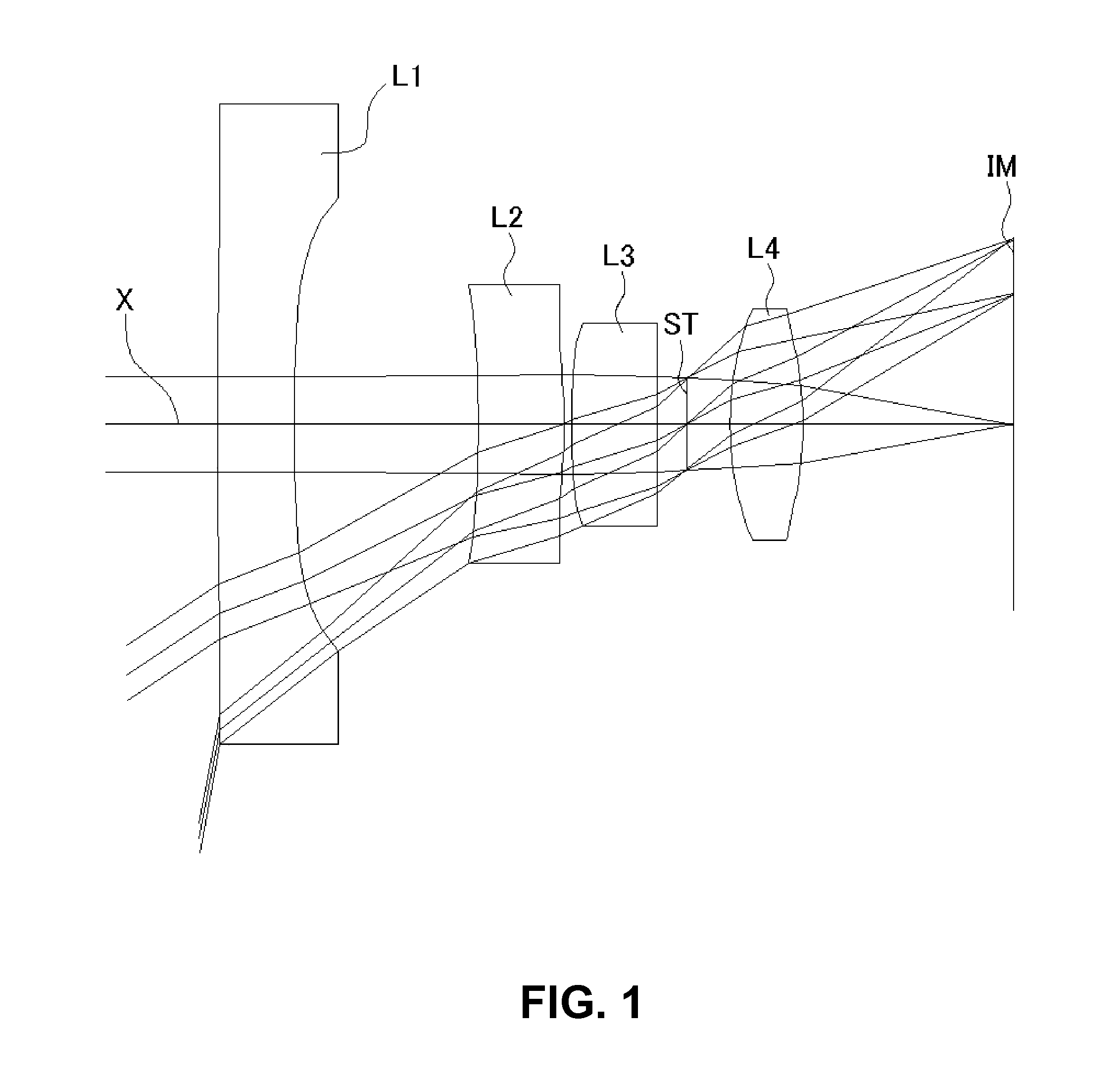
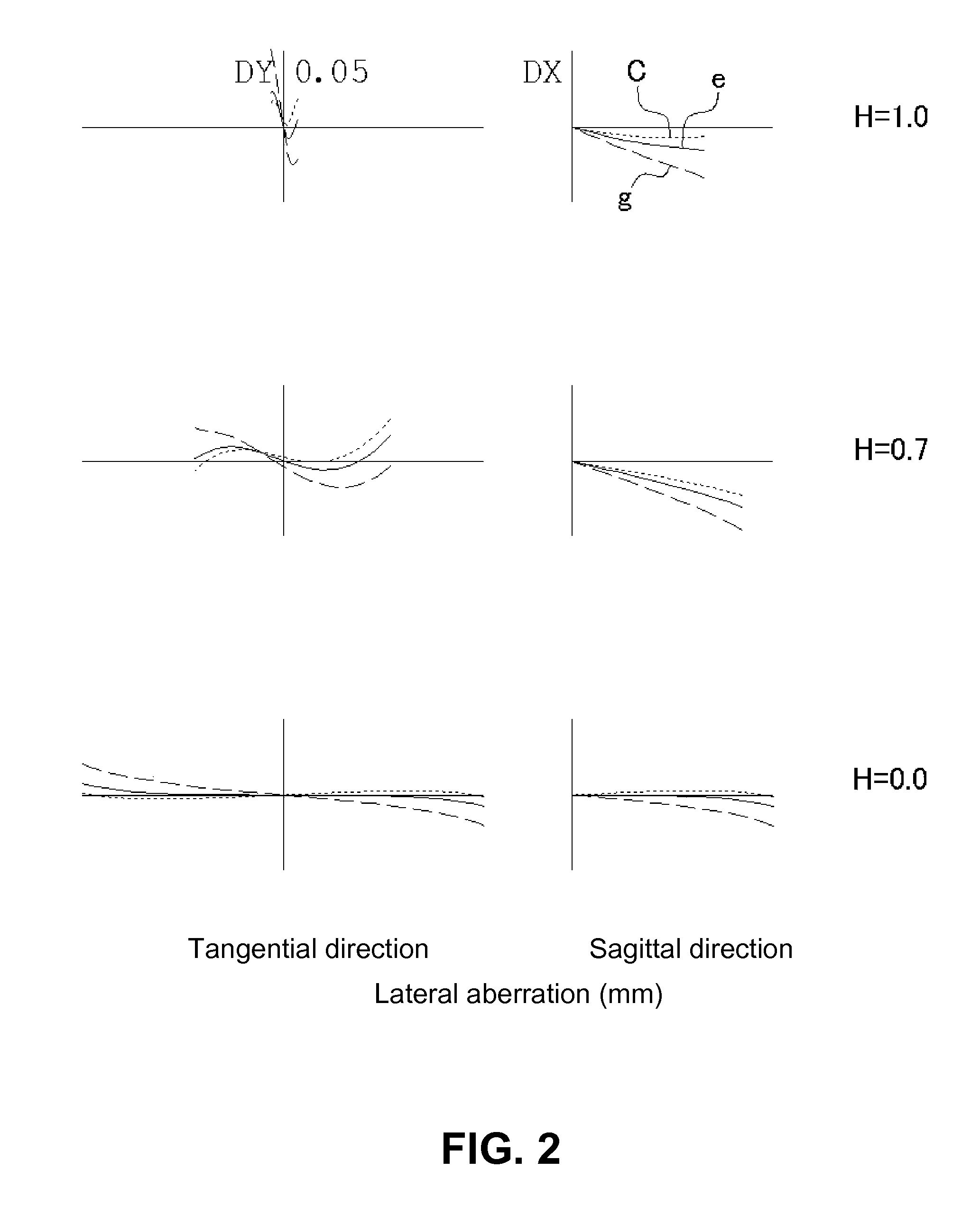
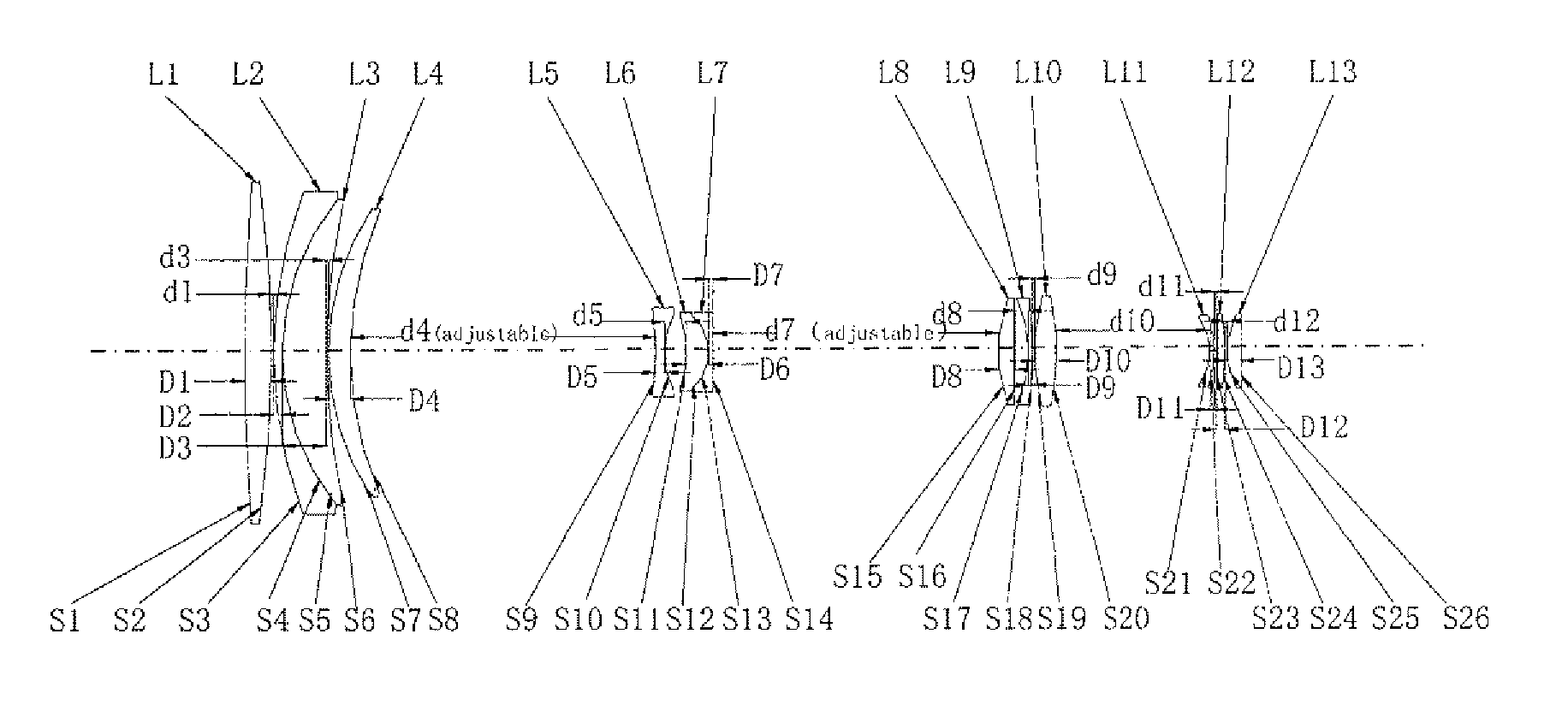
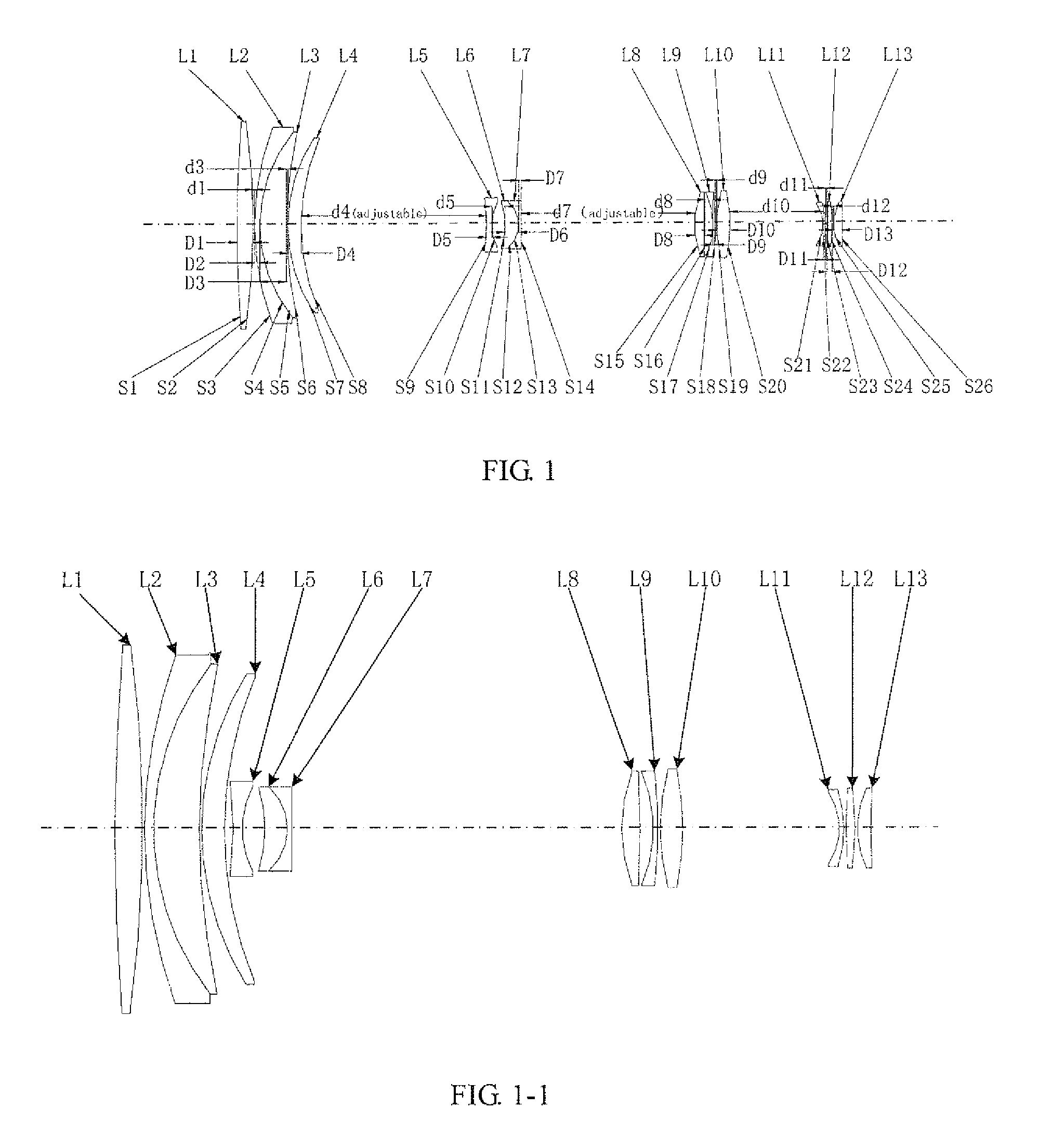
Variofocusing monitoring shot and monitoring device
ActiveUS20150293334A1Large fieldHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisMonitor equipment
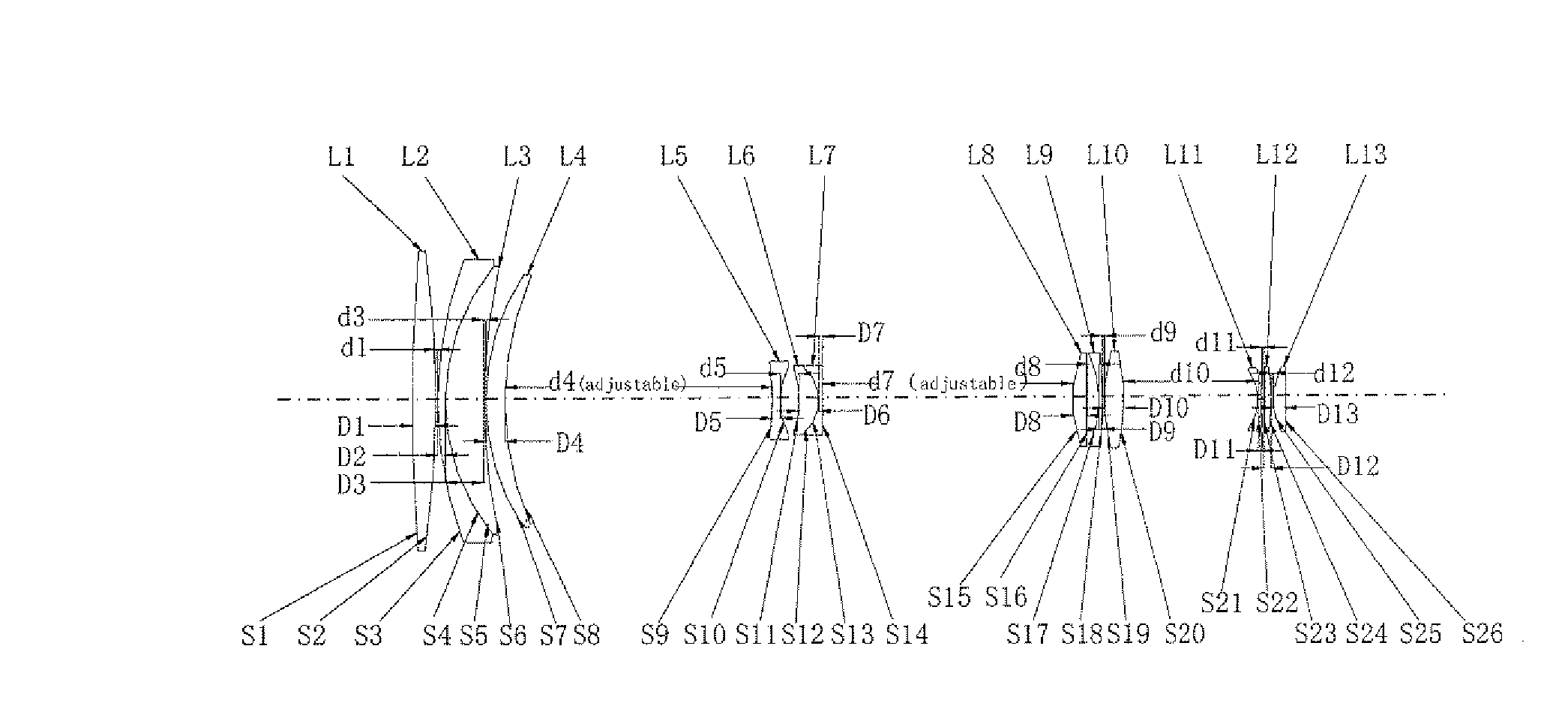
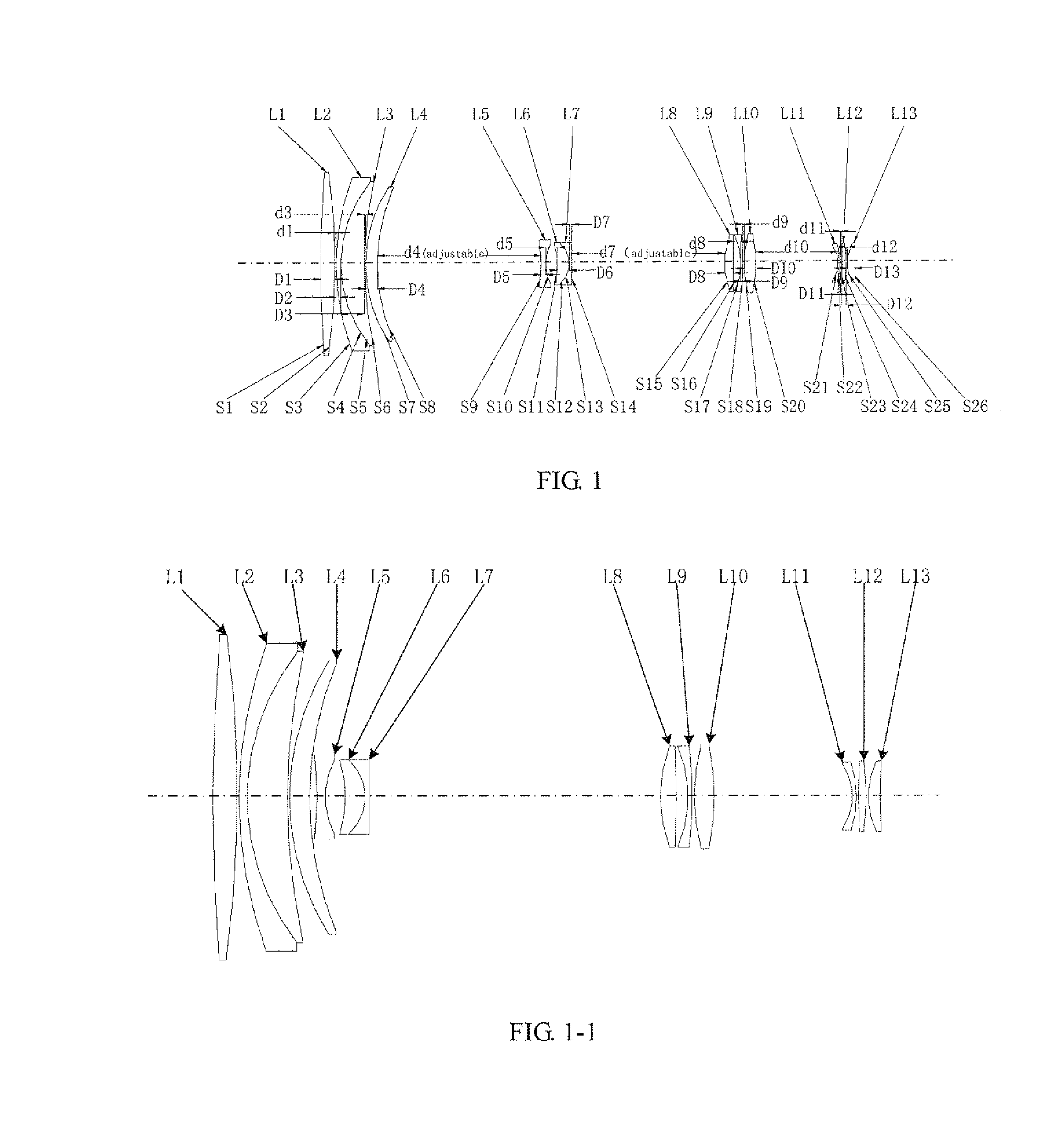
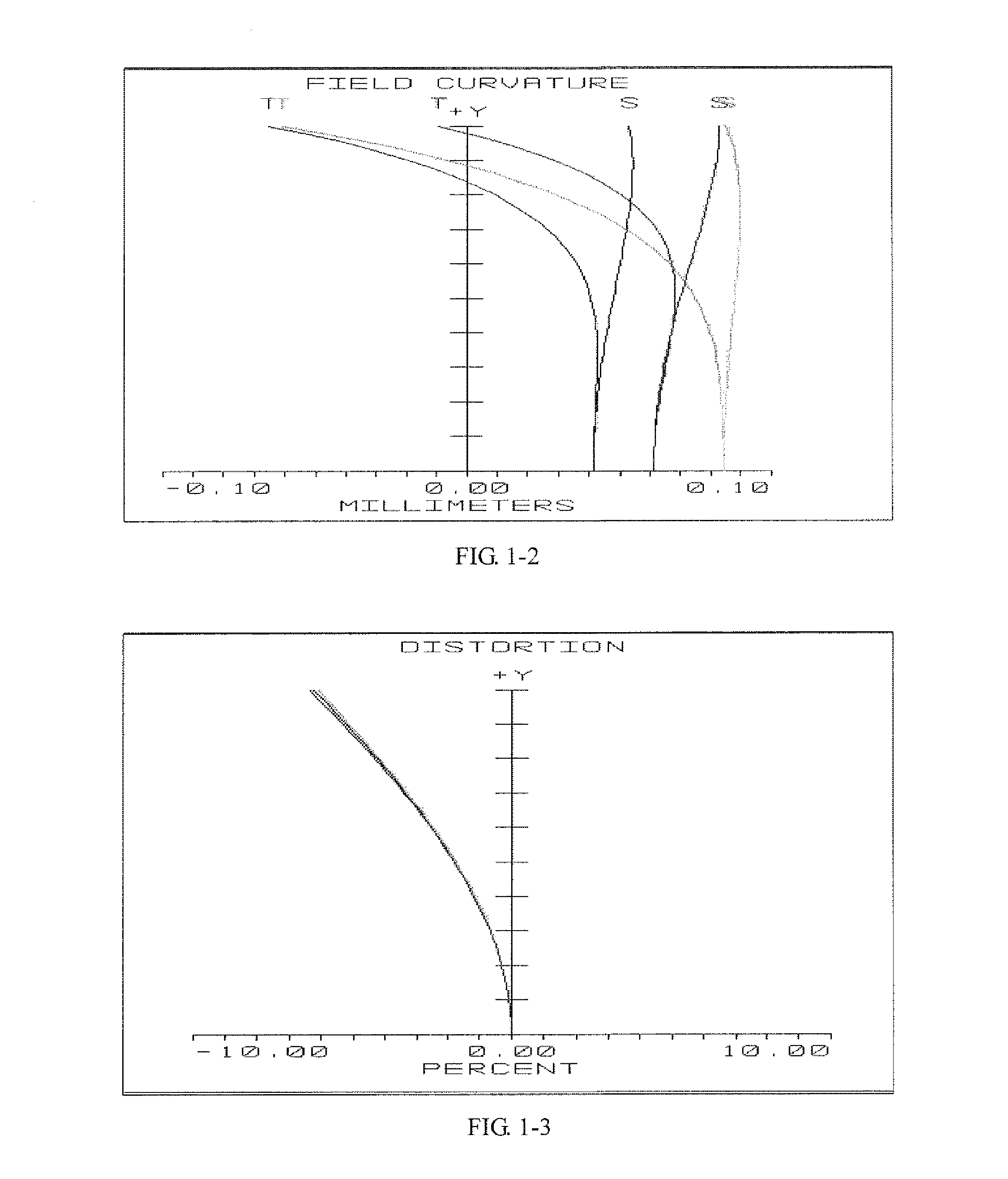
A zoom lens assembly for monitor and a monitoring device are provided. The lens assembly comprises a first to a thirteenth lenses (L1-L13) arranged successively coaxially along the transmission direction of an incident light beam. The first, the eighth, the tenth and the twelfth lenses (L1, L8, L10 and L12) are biconvex positive lenses; the second, the ninth and the eleventh lenses (L2, L9 and L11) are falcate negative lenses; the third, the fourth, the sixth and the thirteenth lenses (L3, L4, L6 and L13) are falcate positive lenses; the fifth lens (L5) is a biconcave negative lens; and the seventh lens (L7) is a plano-concave negative lens. The second and the third lenses (L2 and L3) are closely adhered to each other, and the sixth and the seventh lenses (L6 and L7) are closely adhered to each other. The intermediate parts of the second, the third, the fourth and the thirteenth lenses (L2, L3, L4 and L13) are all convex toward a direction reverse to the transmission direction an incident light beam; the intermediate parts of the sixth, the ninth and the eleventh lenses (L6, L9 and L11) are all convex toward the transmission direction of the incident light beam; and the fifth, the sixth and the seventh lenses (L5, L6 and L7) can move synchronously along a light axis direction. The shot can realize all-weather, wide-range and variofocusing monitoring. The shot has a high imaging sharpness and a simple structure; and the cost of the material is low, thus controlling the manufacturing cost effectively.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Imaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having negative refractive power; a second lens having positive refractive power; a third lens having positive refractive power; a stop; and a fourth lens having positive refractive power arranged in the order from an object side to an image plane side. The first lens has an image plane-side surface having a positive curvature radius. The second lens has an image plane-side surface having negative curvature radius. The third lens has an image plane-side surface having a negative curvature radius. The fourth lens has an object-side surface having a positive curvature radius and an image plane-side surface having a negative curvature radius. The first lens has a specific focal length and a specific Abbe's number to satisfy specific conditional expressions.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Variofocusing monitoring shot and monitoring device
ActiveUS9448391B2Large fieldHigh image resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsZoom lensIncident beam
A zoom lens assembly for monitor and a monitoring device are provided. The lens assembly comprises a first to a thirteenth lenses (L1-L13) arranged successively coaxially along the transmission direction of an incident light beam. The first, the eighth, the tenth and the twelfth lenses (L1, L8, L10 and L12) are biconvex positive lenses; the second, the ninth and the eleventh lenses (L2, L9 and L11) are falcate negative lenses; the third, the fourth, the sixth and the thirteenth lenses (L3, L4, L6 and L13) are falcate positive lenses; the fifth lens (L5) is a biconcave negative lens; and the seventh lens (L7) is a plano-concave negative lens. The second and the third lenses (L2 and L3) are closely adhered to each other, and the sixth and the seventh lenses (L6 and L7) are closely adhered to each other. The intermediate parts of the second, the third, the fourth and the thirteenth lenses (L2, L3, L4 and L13) are all convex toward a direction reverse to the transmission direction an incident light beam; the intermediate parts of the sixth, the ninth and the eleventh lenses (L6, L9 and L11) are all convex toward the transmission direction of the incident light beam; and the fifth, the sixth and the seventh lenses (L5, L6 and L7) can move synchronously along a light axis direction. The shot can realize all-weather, wide-range and variofocusing monitoring. The shot has a high imaging sharpness and a simple structure; and the cost of the material is low, thus controlling the manufacturing cost effectively.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Imaging lens
An imaging lens includes a first lens having negative refractive power; a stop; a second lens having positive refractive power; a third lens having negative refractive power; and a fourth lens having positive refractive power, arranged in the order from an object side to an image plane side. The first lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both negative. The second lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both positive. The third lens has an object-side surface and an image plane-side surface, curvature radii of which are both negative. The fourth lens has an object-side surface, a curvature of which is positive.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com