Electrolyte for high-capacity lithium ion battery, preparation method and lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and electrolyte technology, applied in the field of electrolyte, can solve problems such as increased internal resistance of batteries, potential safety hazards of batteries, instability of surface SEI films, etc., achieve improved cycle performance and high temperature performance, and improve the structural stability of negative electrode materials Sexuality, the effect of alleviating the deterioration of battery performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
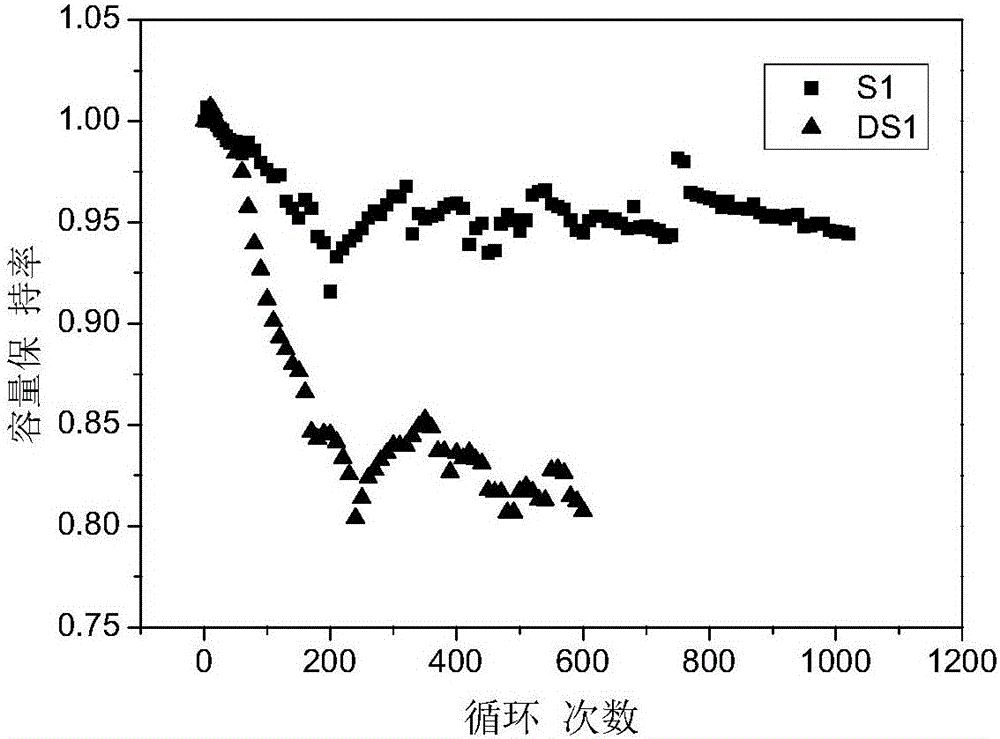
Embodiment 1
[0047] Battery production:
[0048] Positive electrode preparation: The ratio of positive electrode materials is: LiNi 0.6 co 0.2 mn 0.2 o 2 (lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide), acetylene black (conductive agent), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF, binder) mass ratio is 95:2.5:2.5. Add PVDF to N-methyl-pyrrolidone (NMP), stir evenly at a high speed, add acetylene black to the solution, stir evenly, then add lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxygen and stir evenly to form a positive electrode slurry, and coat the positive electrode slurry with On the aluminum foil, the positive electrode sheet is baked, compacted, cut, and welded.
[0049] Negative electrode preparation: The ratio of negative electrode materials is silicon-carbon composite material, acetylene black, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and propylene butyl rubber (SBR), with a mass ratio of 95:1.0:1.5:2.5. Add CMC into water, stir at high speed to dissolve completely, then add acetylene black, continue to stir unti...
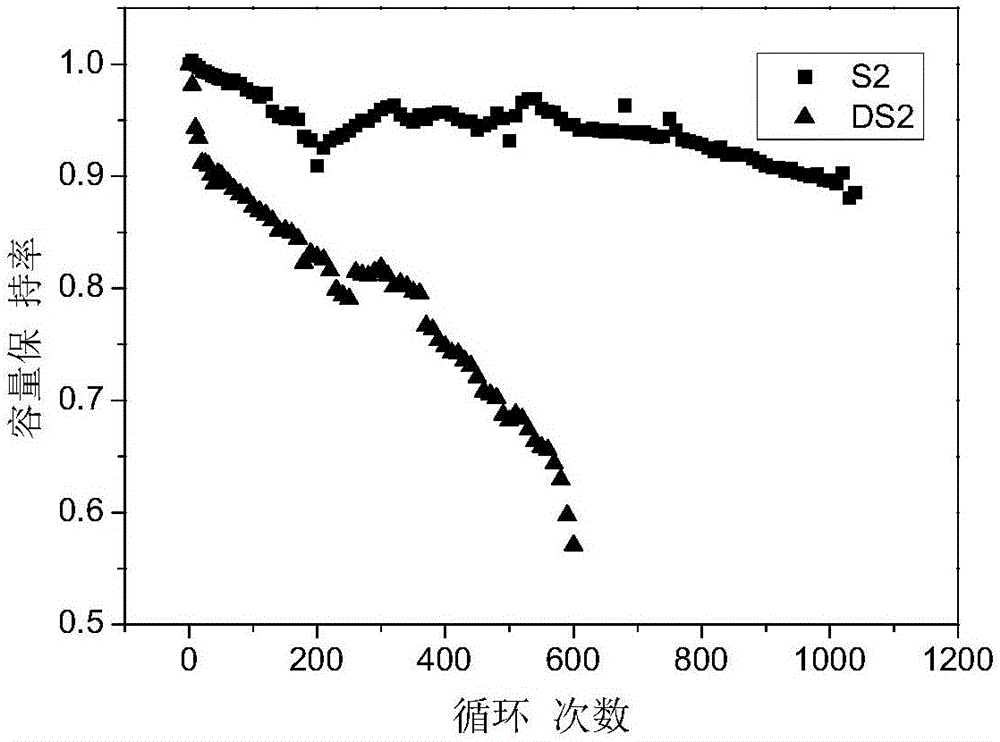
Embodiment 2
[0053] The preparation method of the electrolyte solution in Example 1 is used to prepare the electrolyte solution A2. The difference is that the additives added are fluoroethylene carbonate, 1,3-propene sultone, lithium bisoxalate borate, and triphenyl phosphite. The amounts accounted for 12.0%, 1.0%, 0.5%, 0.5%, respectively, of the total mass. Lithium hexafluorophosphate accounts for 17.5% (about 1.40mol / L) of the total mass of the electrolyte, and the remaining components are non-aqueous solvents, the proportion of which is the same as in Example 1, accounting for 68.5% of the total electrolyte.
[0054] S2 was prepared according to the method of Example 1 using the above electrolyte. The difference is that the cathode material is LiNi 0.8 co 0.15 Al 0.05 o 2 (lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxygen), negative electrode material is silicon carbon composite material (silicon content is 11%); All the other are the same as embodiment 1.
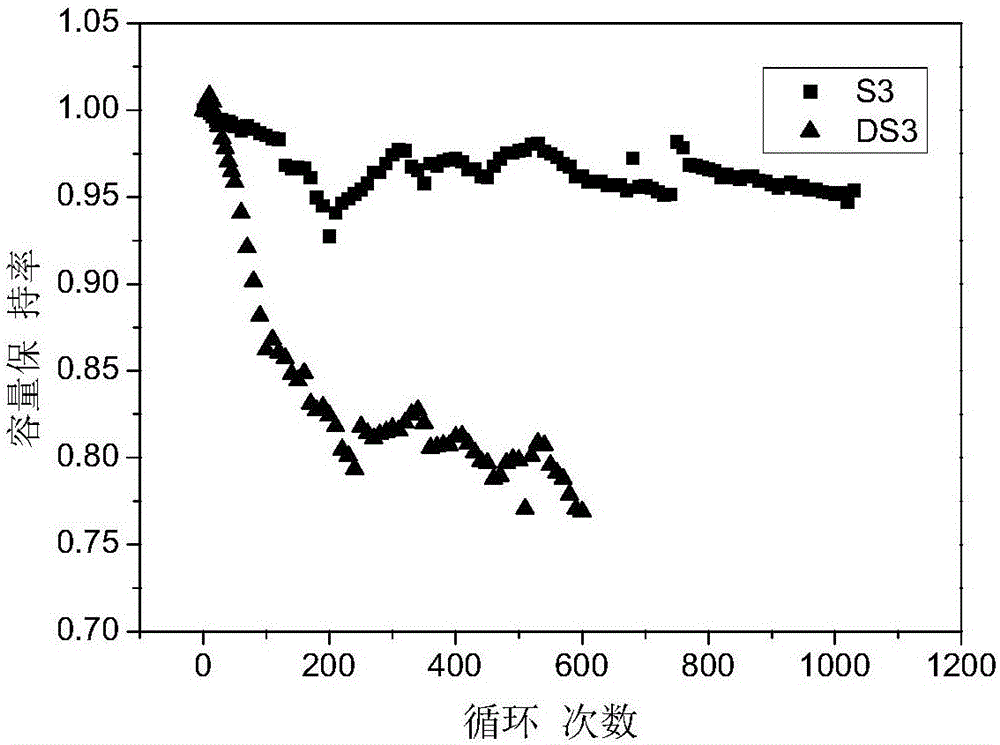
Embodiment 3
[0056] Electrolyte A3 was prepared using the preparation method of the electrolyte in Example 1, except that the additives added were vinylene carbonate, 1,3-propane sultone, lithium difluorooxalate borate, lithium bisoxalate borate, phosphorous acid Triphenyl ester and triphenyl phosphate are added in amounts of 2.0%, 3.0%, 1.5%, 1.0%, 0.1%, and 0.1% of the total mass, respectively. Among them, lithium hexafluorophosphate accounts for 10.0% (about 0.80mol / L) of the total mass of the electrolyte, and the remaining components are non-aqueous solvents, which are composed of ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, ethyl acetate mixture, ethylene carbonate, dicarbonate The mass ratio of methyl ester to ethyl acetate is 1:1:1.
[0057] S3 was prepared according to the method of Example 1 using the above electrolyte. The difference is that the cathode material is LiNi 0.5 co 0.2 mn 0.3 o 2 (lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide), the negative electrode material is silicon carbo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com