Application of blumea balsamifera leaf total flavone
A technology of the total flavonoids of the leaves and the flavonoids of the leaves of Aina, which is applied in the field of the total flavonoids of the leaves of Aina, to achieve the effects of reducing the expression, increasing the water content, reducing epidermal hyperplasia and the generation of sunburn cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1-a kind of preparation method of total flavonoids of leaves of Aina radix, comprises the steps:
[0026] (1) Weigh 400 g of Aina japonica leaf powder passed through a 40-mesh sieve, add 4000 mL of ethanol solution with a mass concentration of 75-85% and cold-soak for 24 hours;
[0027] (2) Heating to reflux at 75-85°C for 1 hour, rotary steaming until alcohol-free, adding distilled water to dissolve, and obtaining a crude extract;
[0028] (3) After the crude extract is extracted with petroleum ether, it is purified by polyamide resin, concentrated under reduced pressure, and evaporated to dryness to obtain an extract;
[0029] (4) The extract was dissolved in an ethanol solution with a mass concentration of 85%, and the total flavonoids of the leaves of Aina japonica with a concentration of 100 mg / mL and 200 mg / mL were prepared respectively.
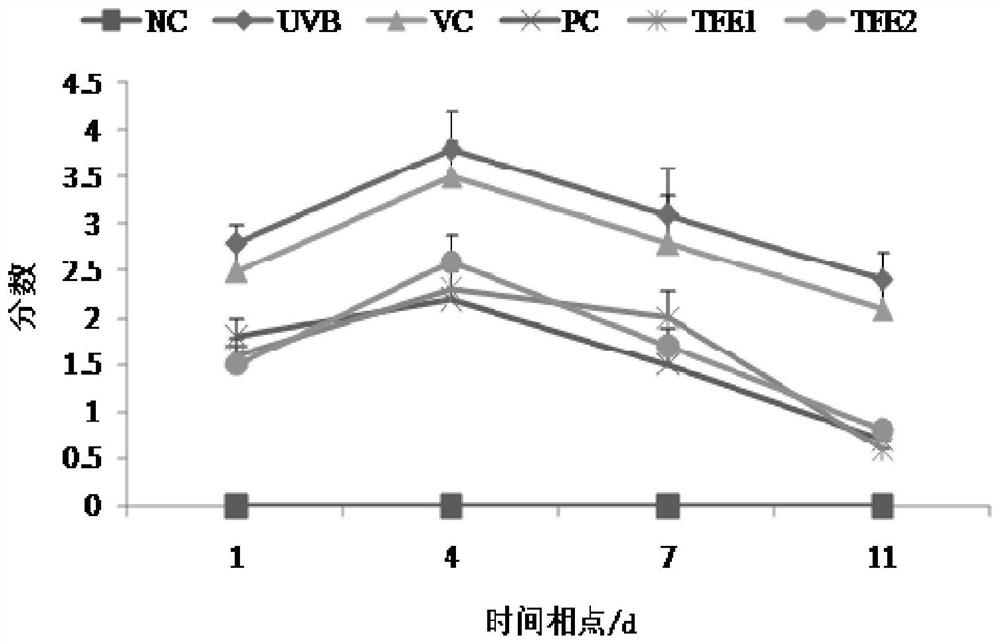
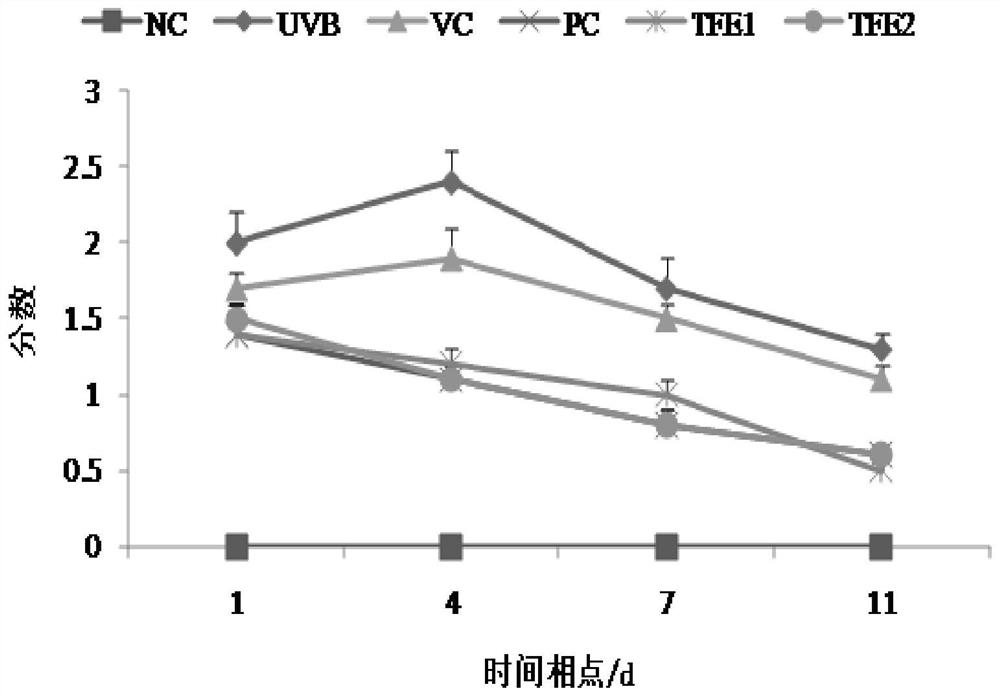
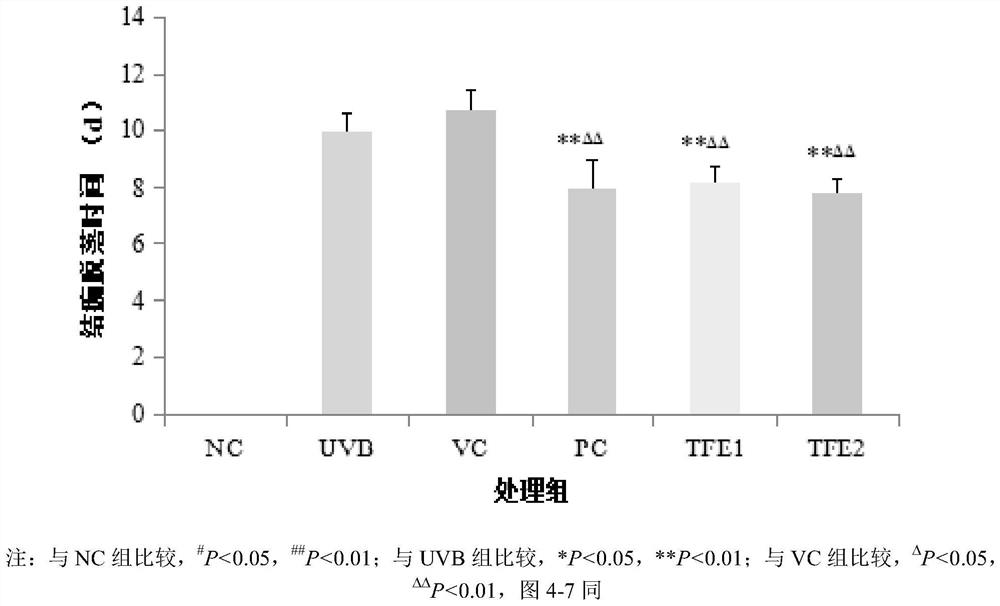
[0030] In order to confirm the effect of the total flavonoids of the leaves of Ainaspermia on skin photodamage tre...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2-The effect experiment of the total flavonoids of Ai Naxiang leaves on the photodamage of mouse skin caused by UVB radiation
[0032] 1. Experimental method
[0033] (1) Experimental animals and groups
[0034] A total of 120 SPF-grade healthy female Balb / C mice (4-6 weeks), weighing 18-22 g, were provided by the Hubei Experimental Animal Research Center (production license: SCXK (E) 2015-0018).
[0035]Animals were kept in separate cages according to the standard conditions of clean animals, and adaptively fed for 7 days. Afterwards, they were randomly divided into 6 groups according to body weight, 20 animals in each group, which were blank control group (Normal Control, NC) and UVB radiation model group (UVB-irradiation, UVB), 85% ethanol solvent control group (Vehicle Control, VC), compound menthol ointment positive control group (PositiveControl, PC), the 100mg / mL Ainaxiang leaf total flavonoids treatment group (Total Flavonoids 1 , TFE1), the 200mg / mL t...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3-The effect of total flavonoids from the leaves of Aina japonica on oxidative stress and DNA damage in the skin of mice with UVB radiation-induced photodamage
[0071] 1. Experimental method
[0072] Take 100 mg of tissue pieces from each group (take the skin from the sunburned model on the back of the mice after cervical dislocation) and rinse them in ice-cold saline to remove the blood on the tissue pieces, dry them with filter paper, weigh them, and use ophthalmic scissors as soon as possible. Cut up the tissue block, and then prepare it with an internal cutting tissue homogenizer (homogenization time 10 seconds / time, interval 30s, continuous 3 to 5 times, in ice water; prepare 10% homogenate with low temperature and low speed centrifugation Centrifuge at about 3500r / min for 6-8min, leave the supernatant of the centrifuged homogenate and discard the sediment below, and store at -80°C. The mouse 8-OHdG ELISA kit was purchased from Beijing Xinfang Biotechnolog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com