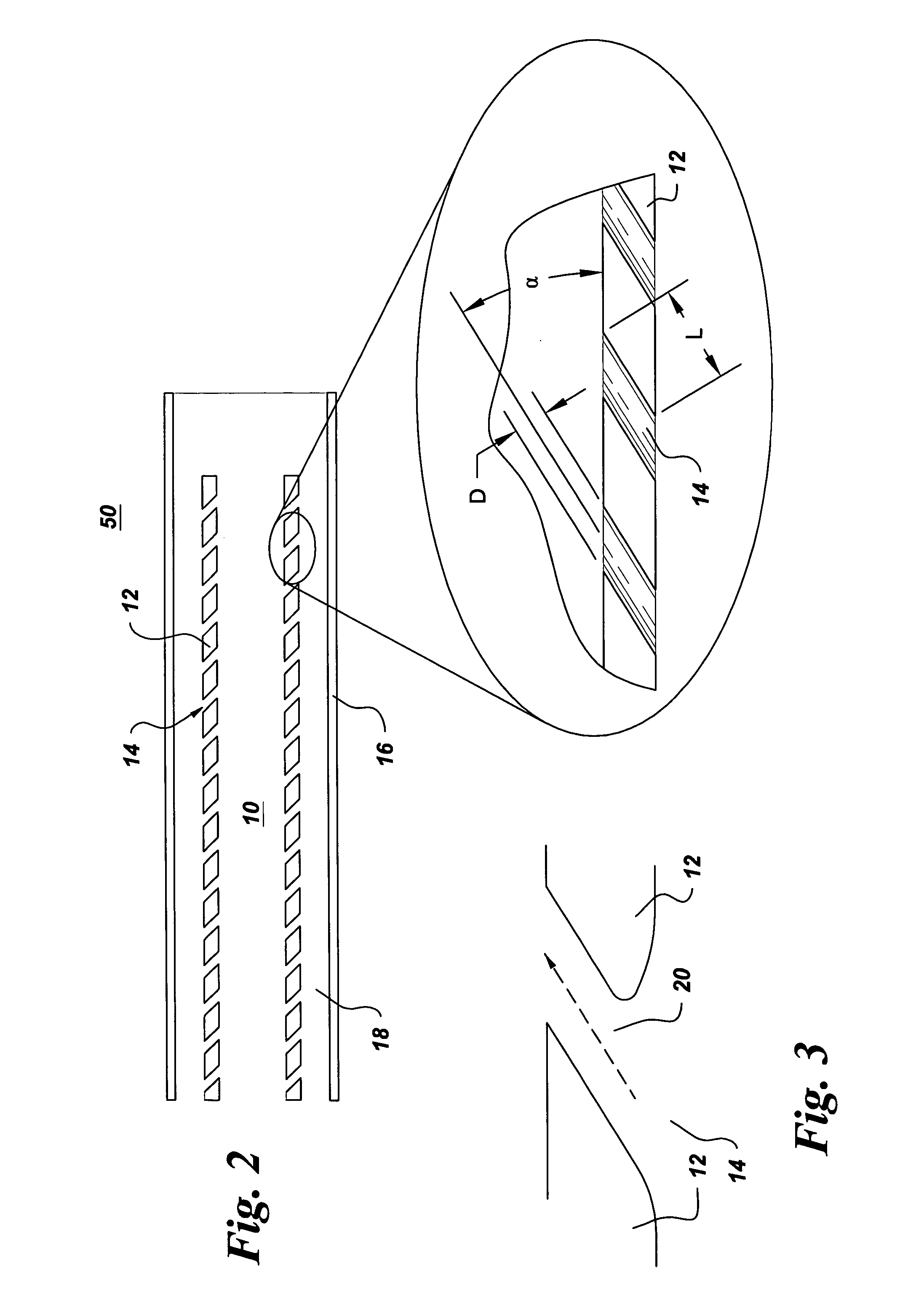
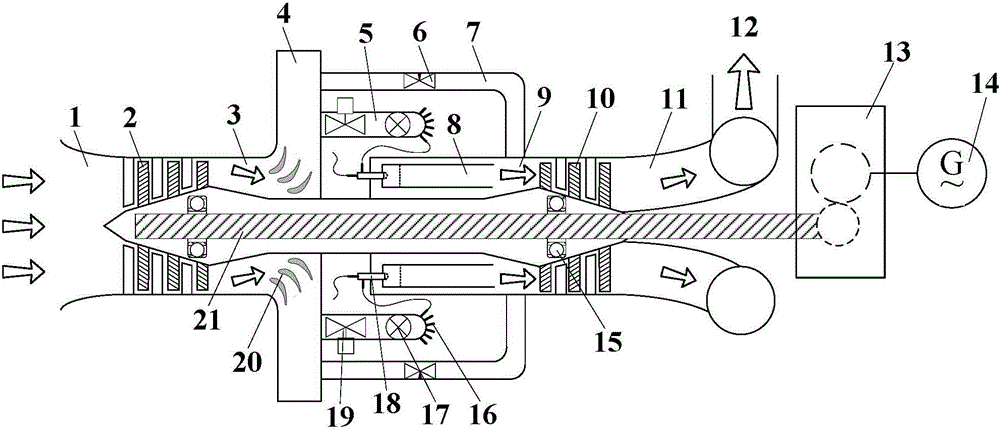
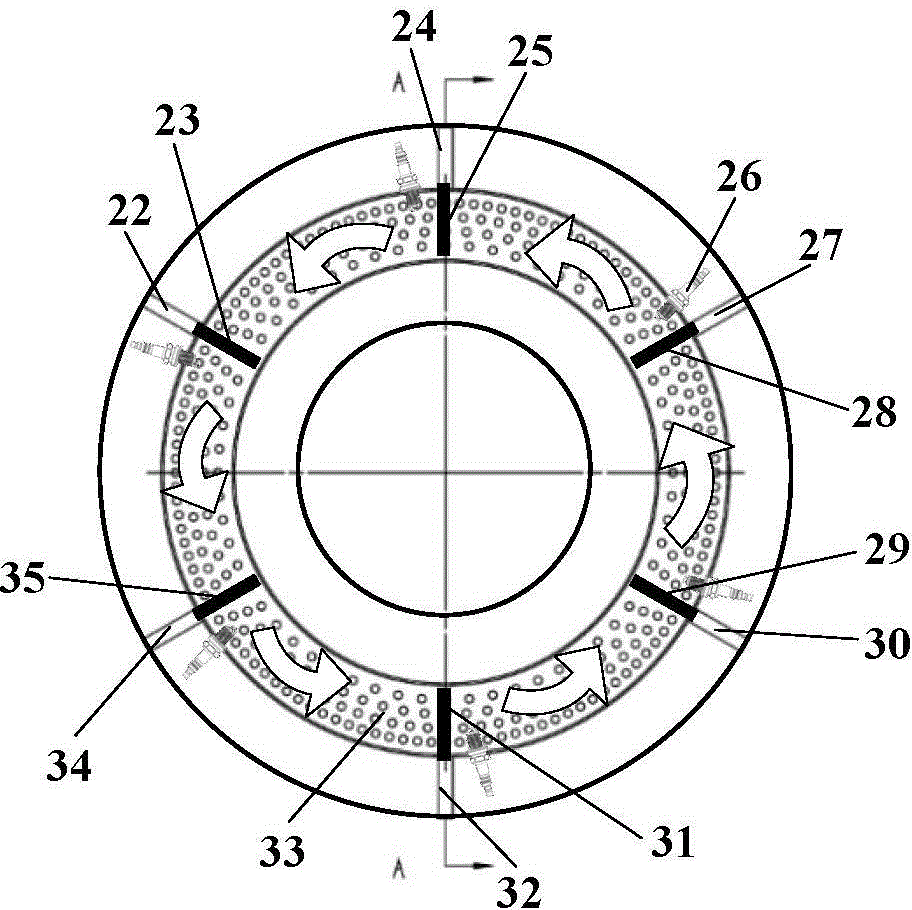
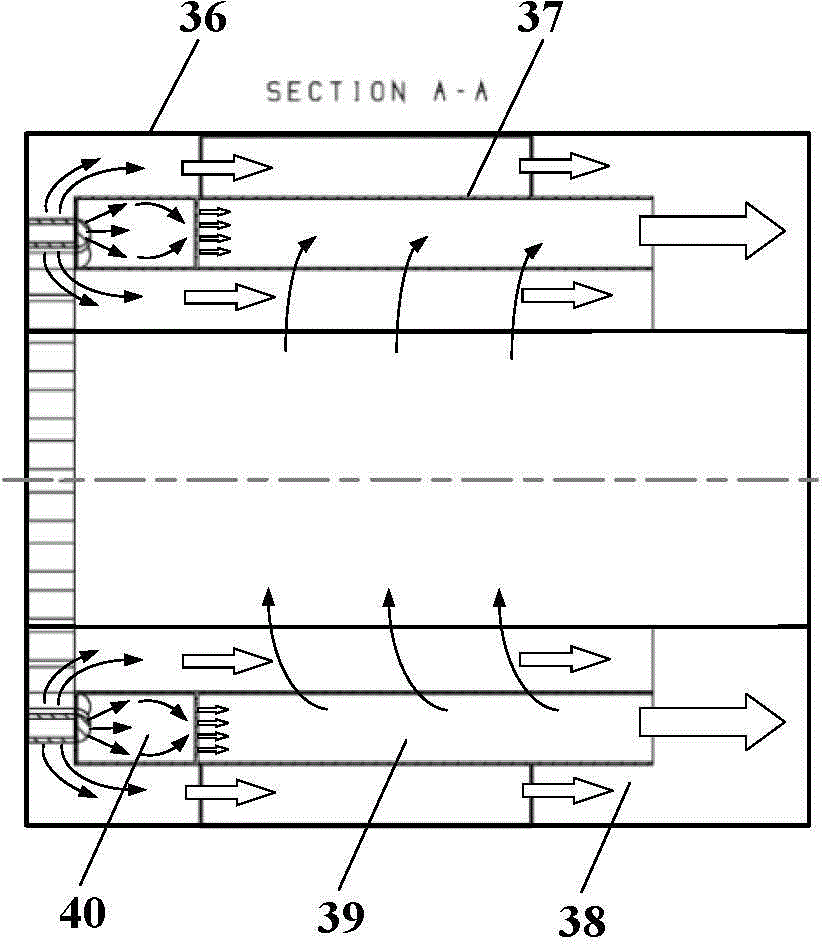
Patents
Literature
300results about "Explosive combustion chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
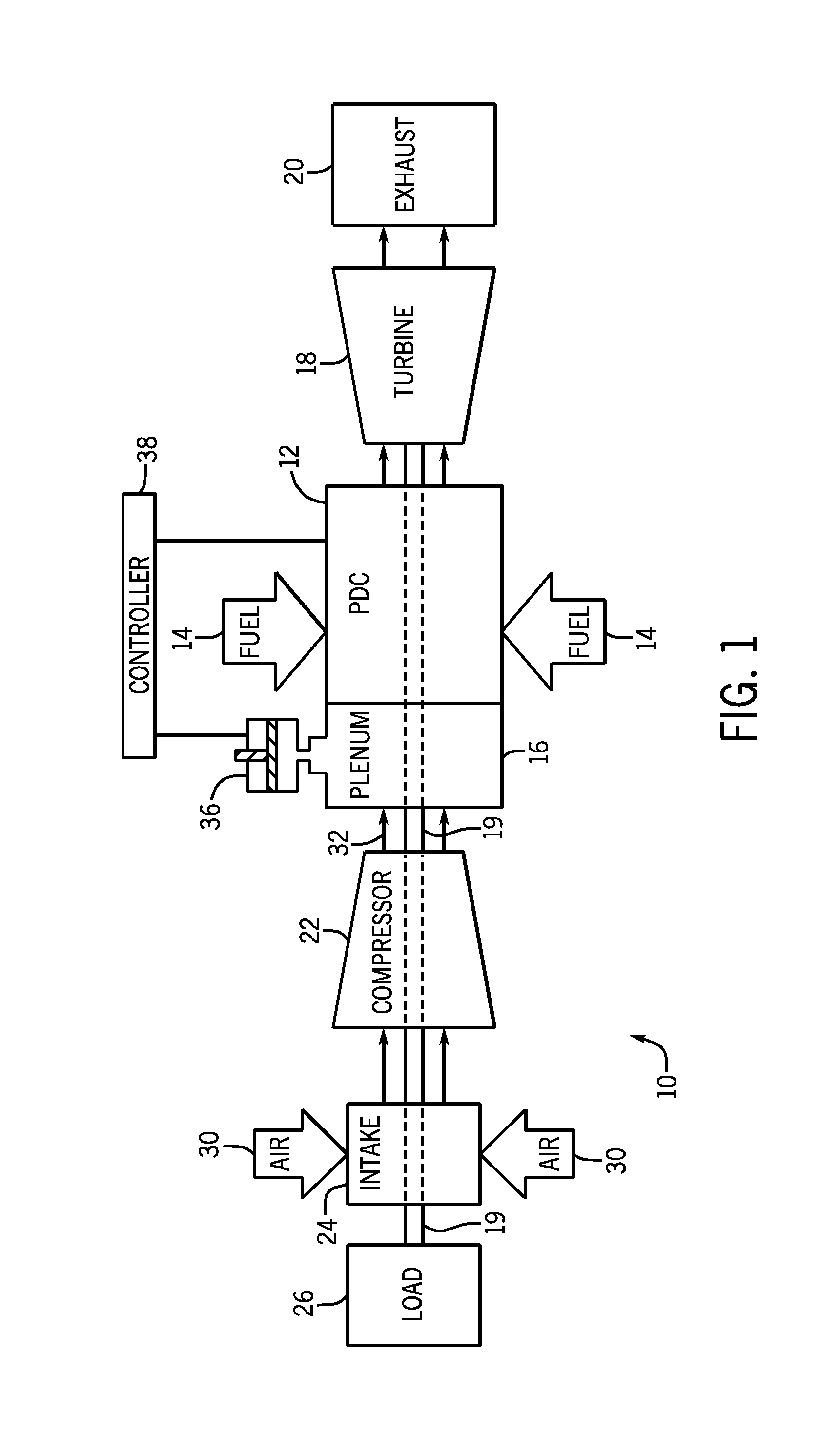
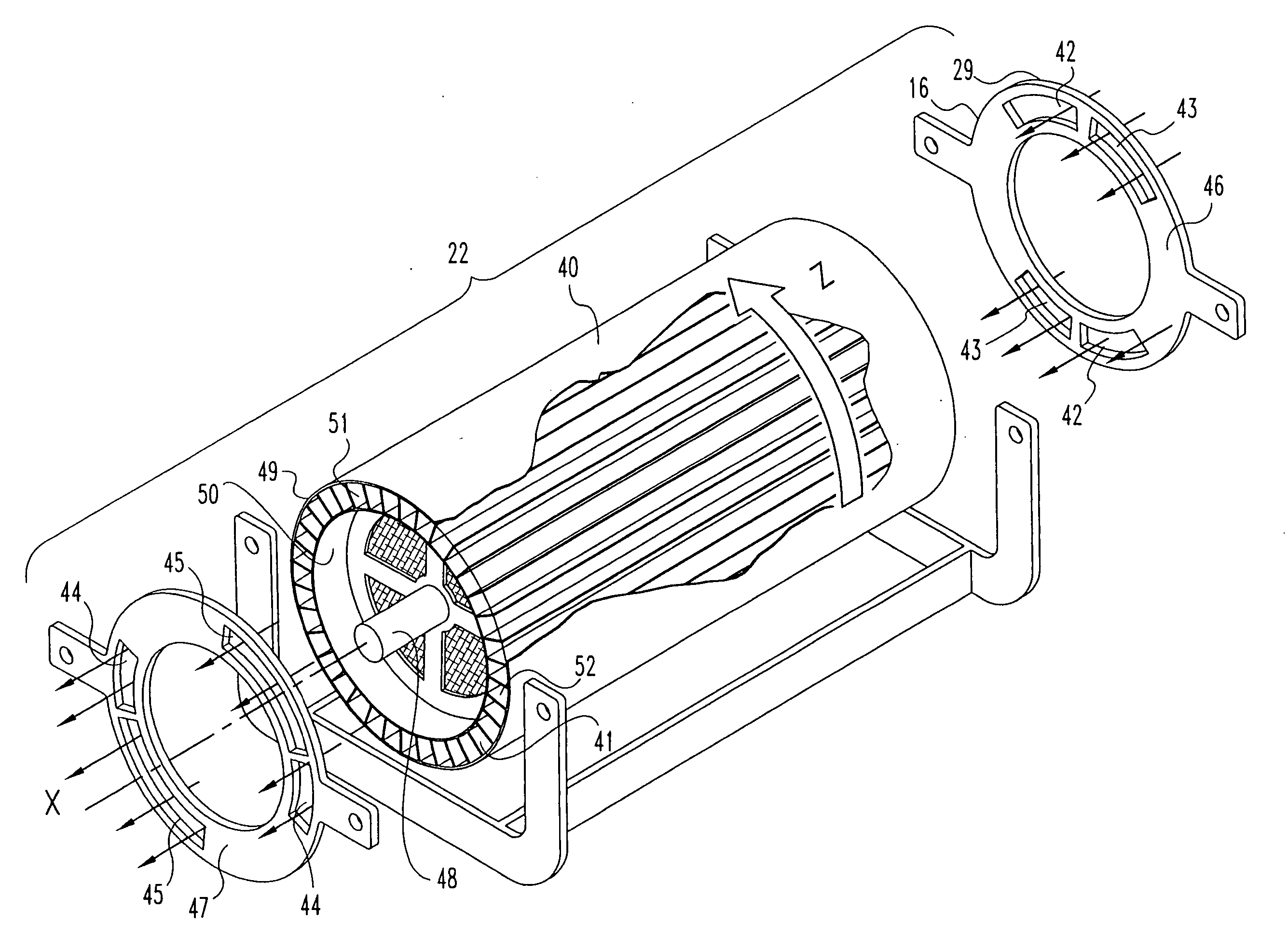
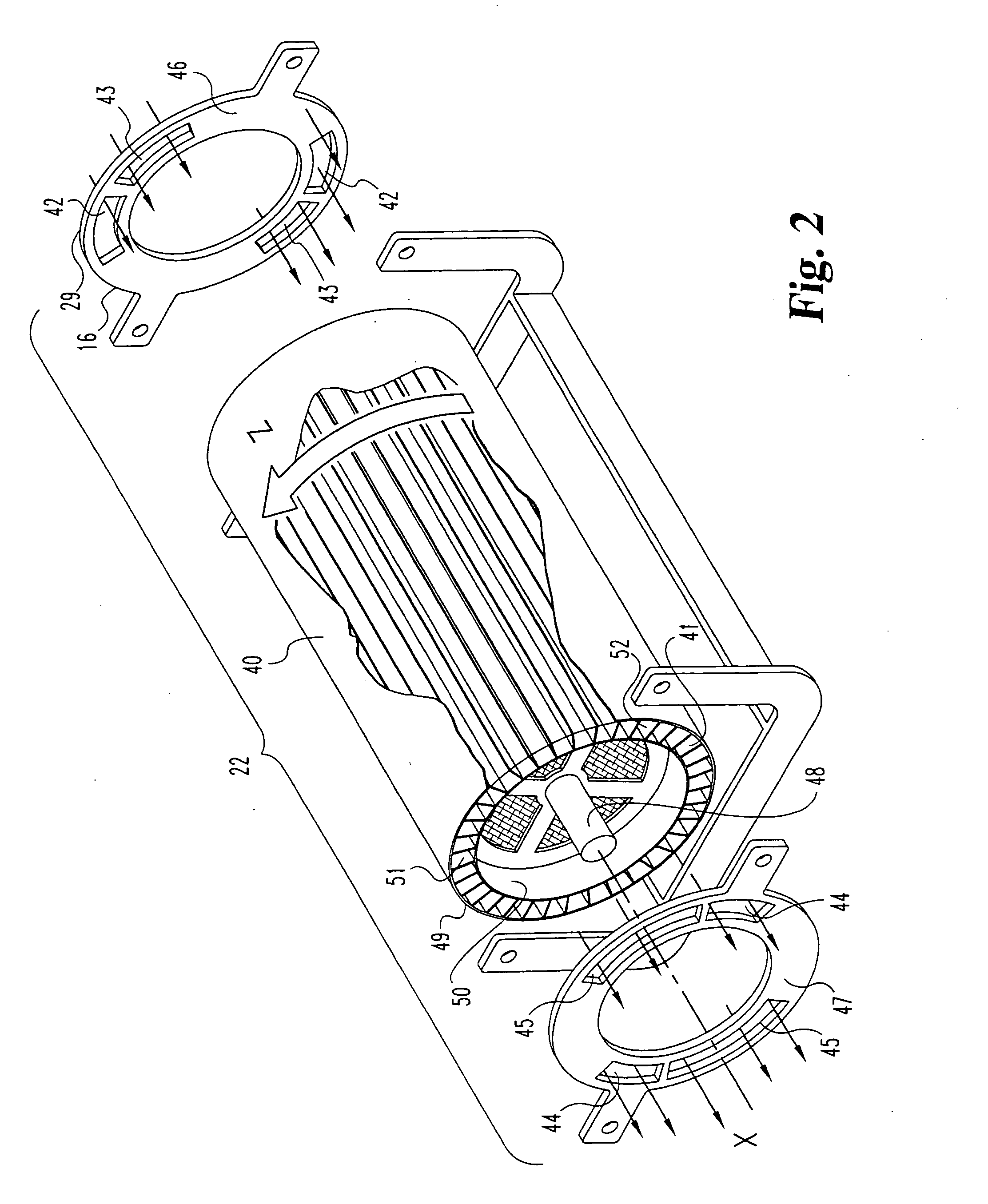
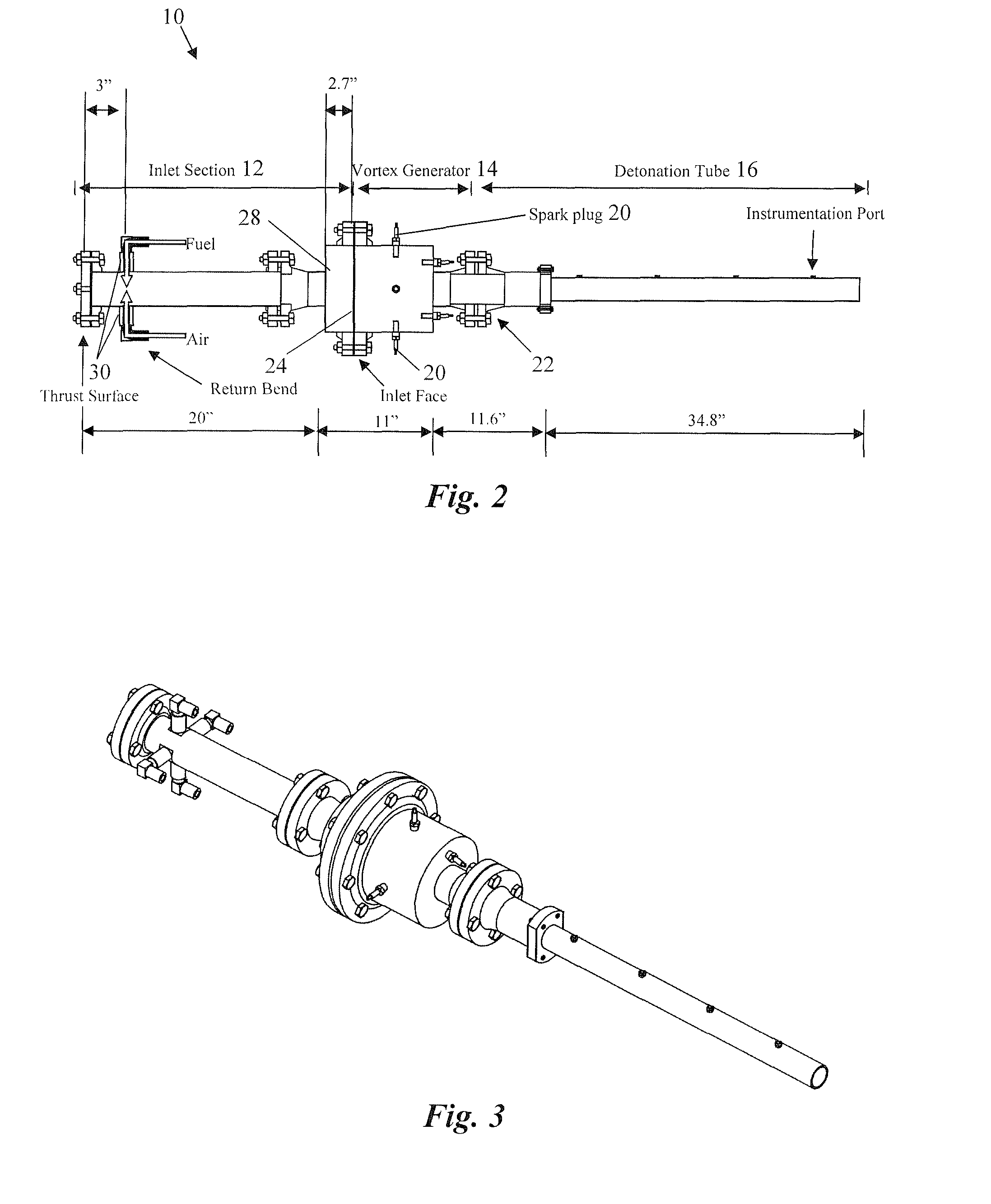
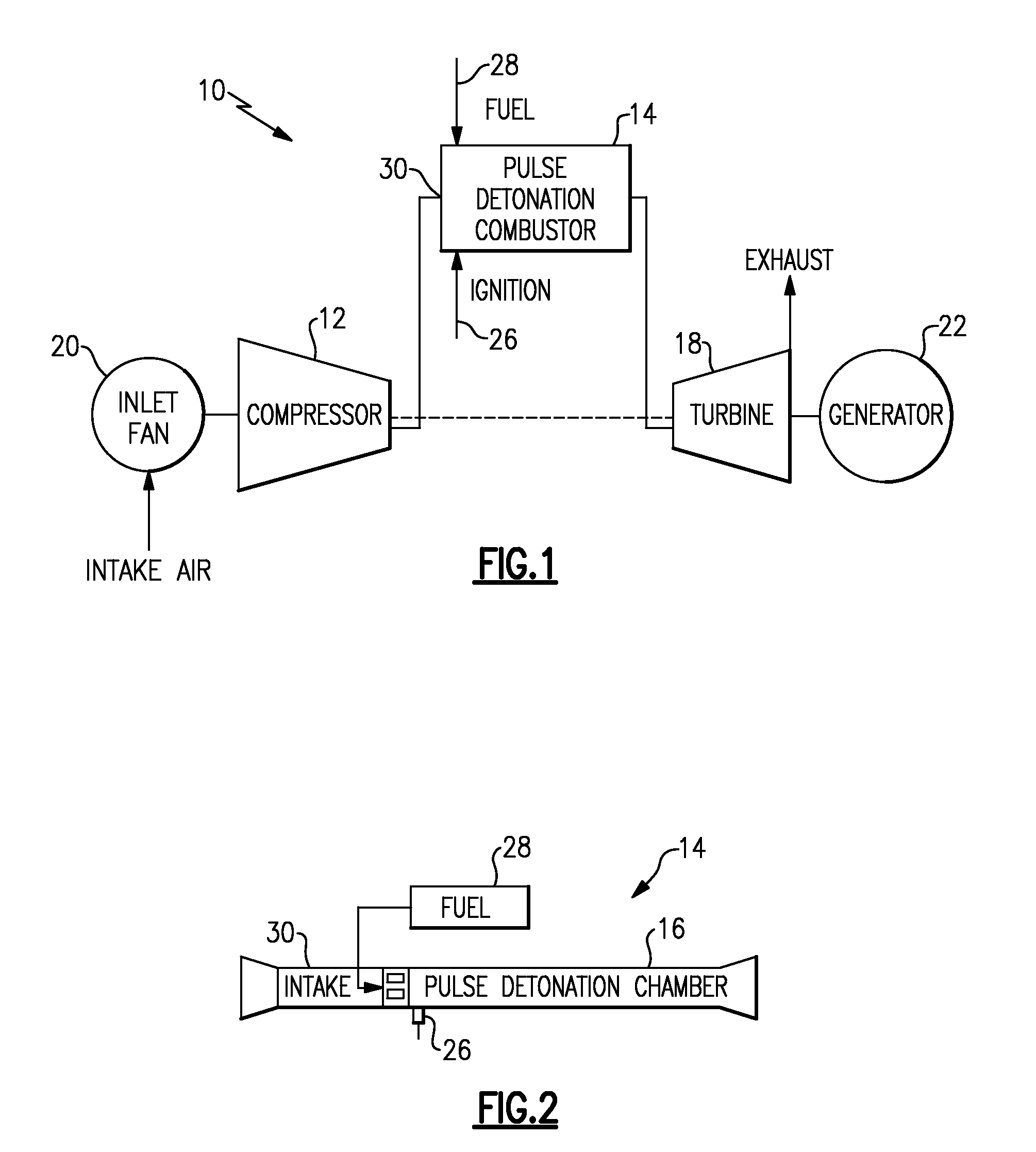
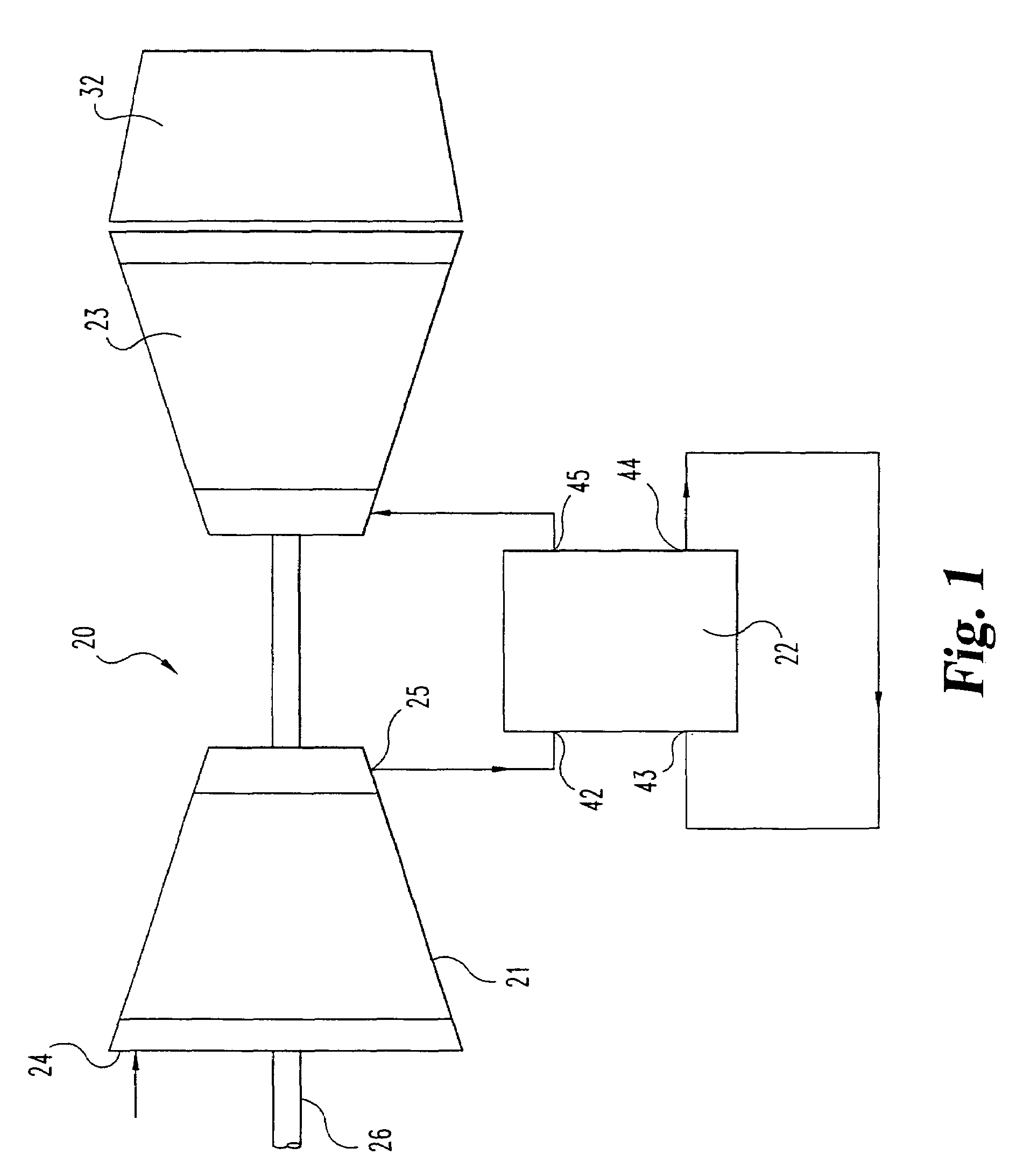
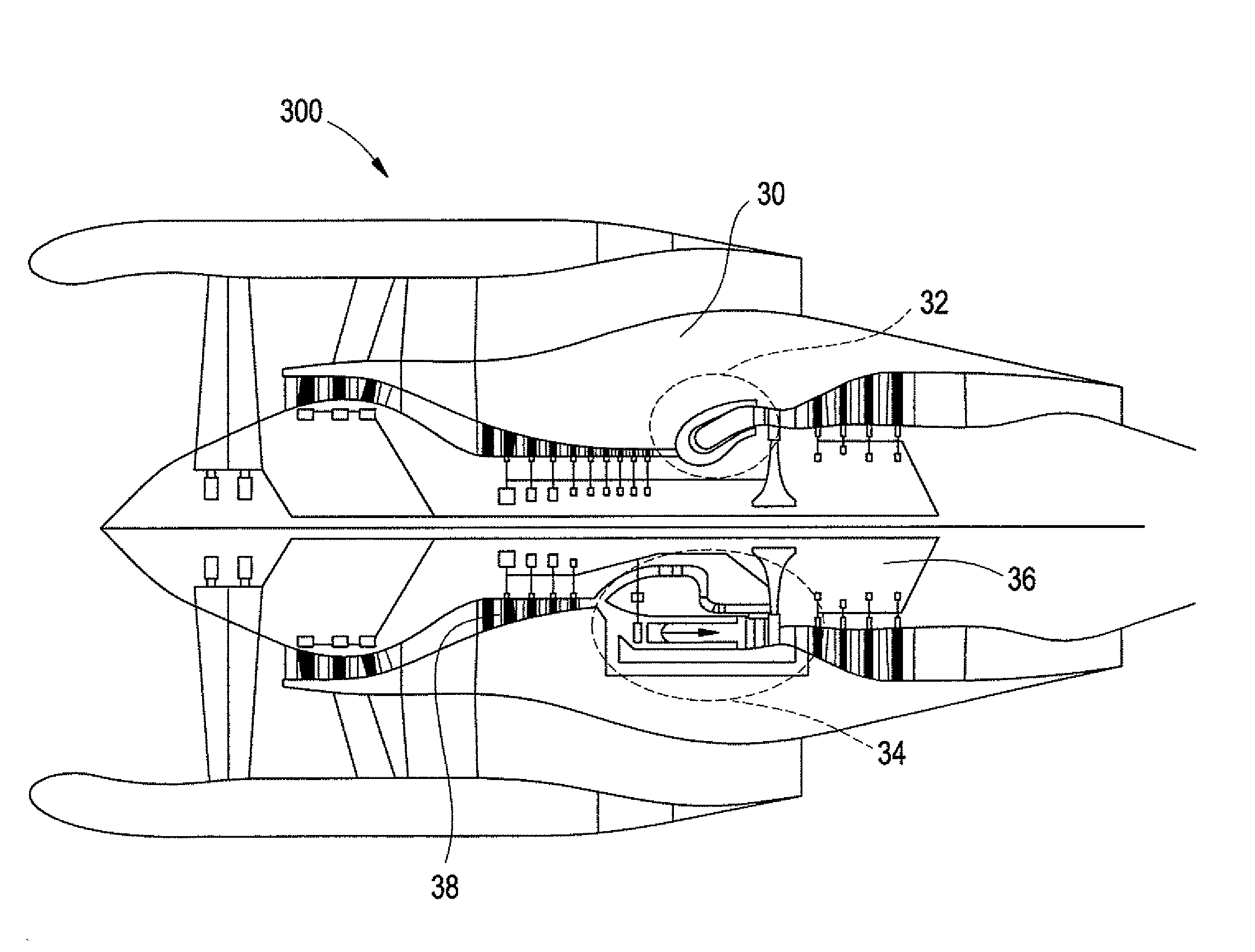
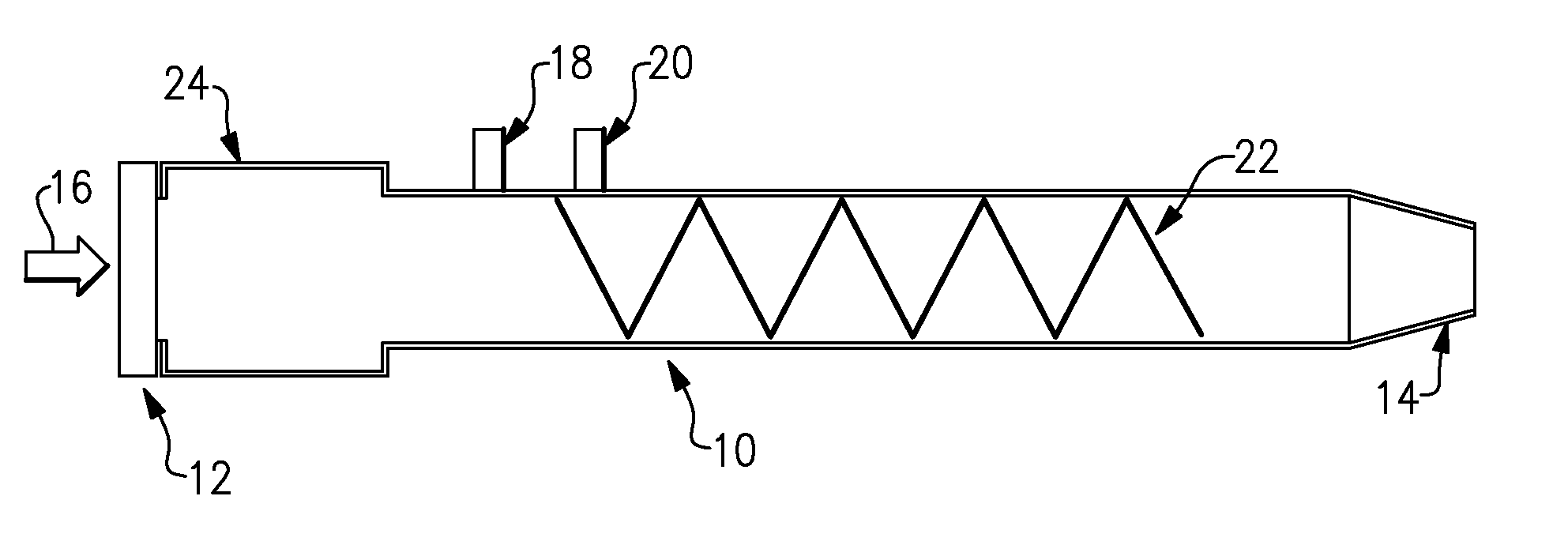
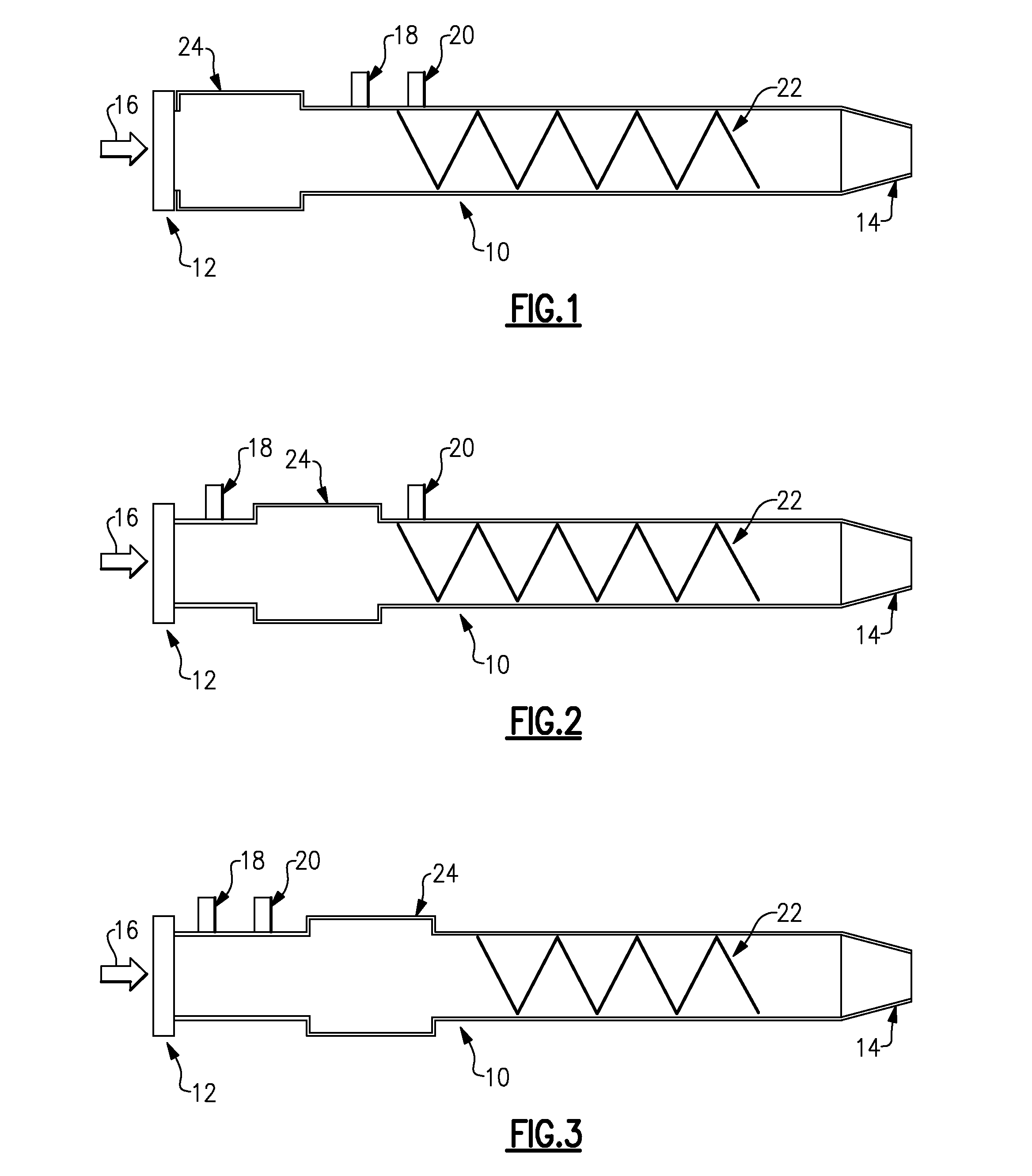
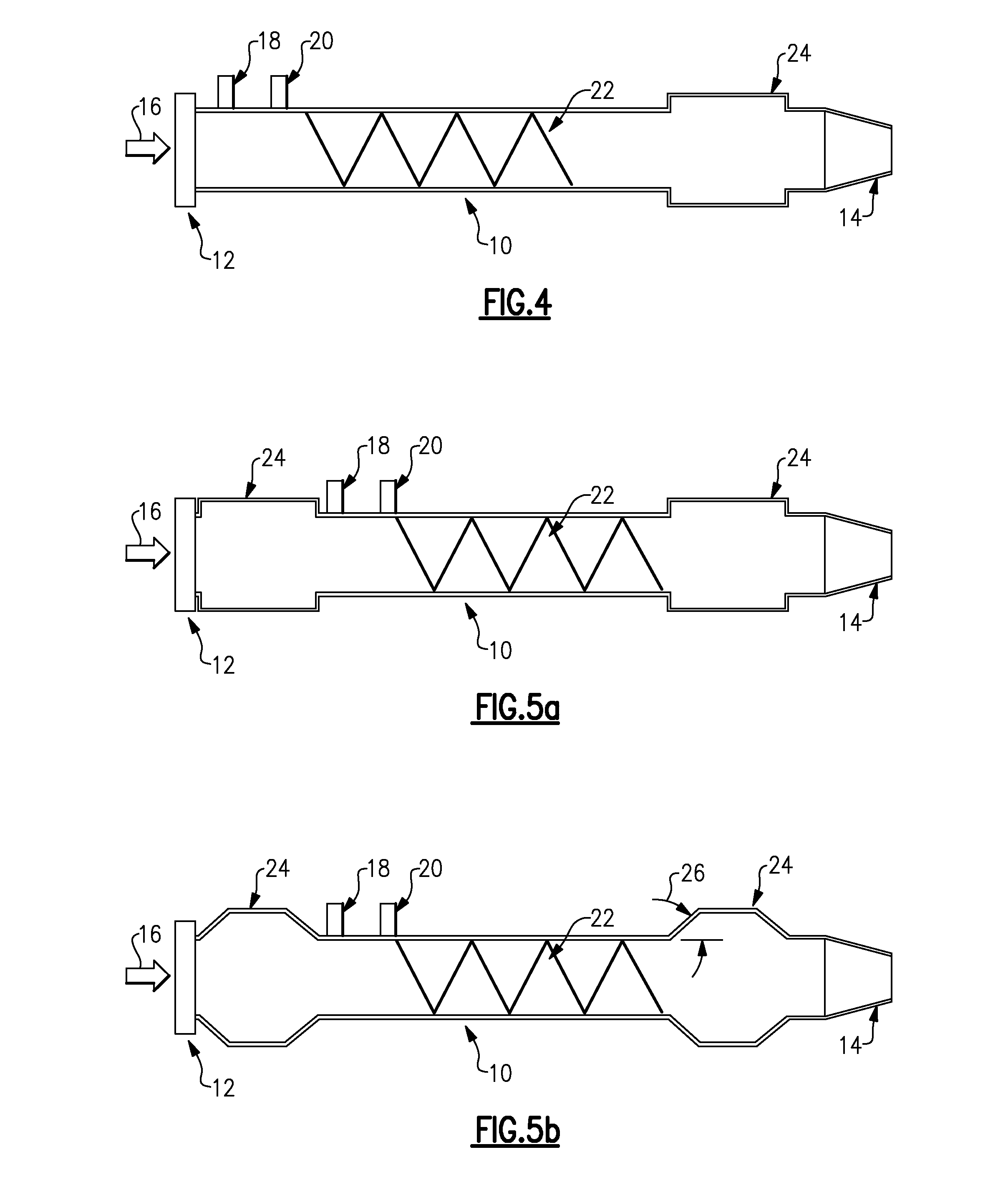
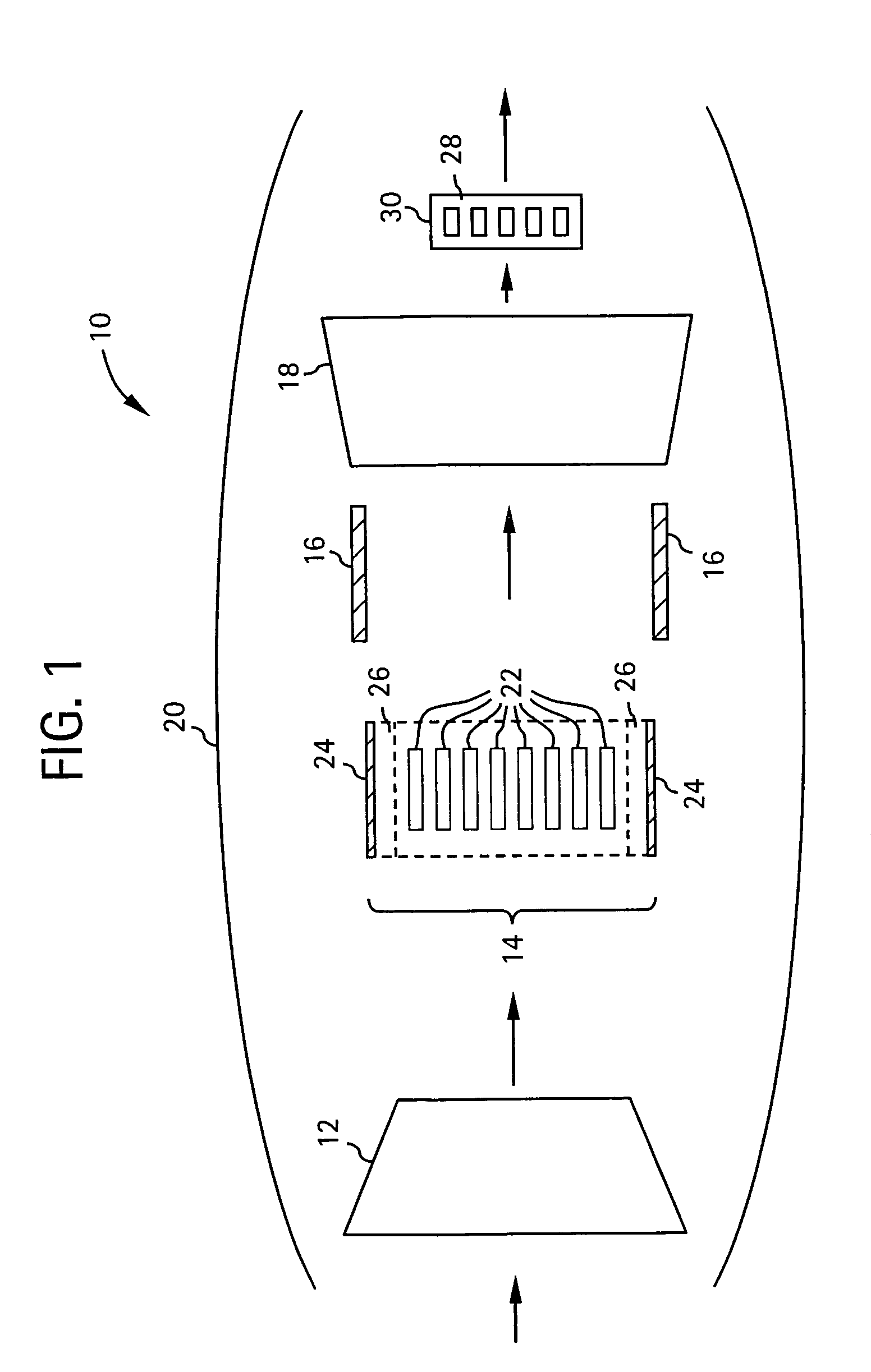
Pulse detonation combustor with folded flow path
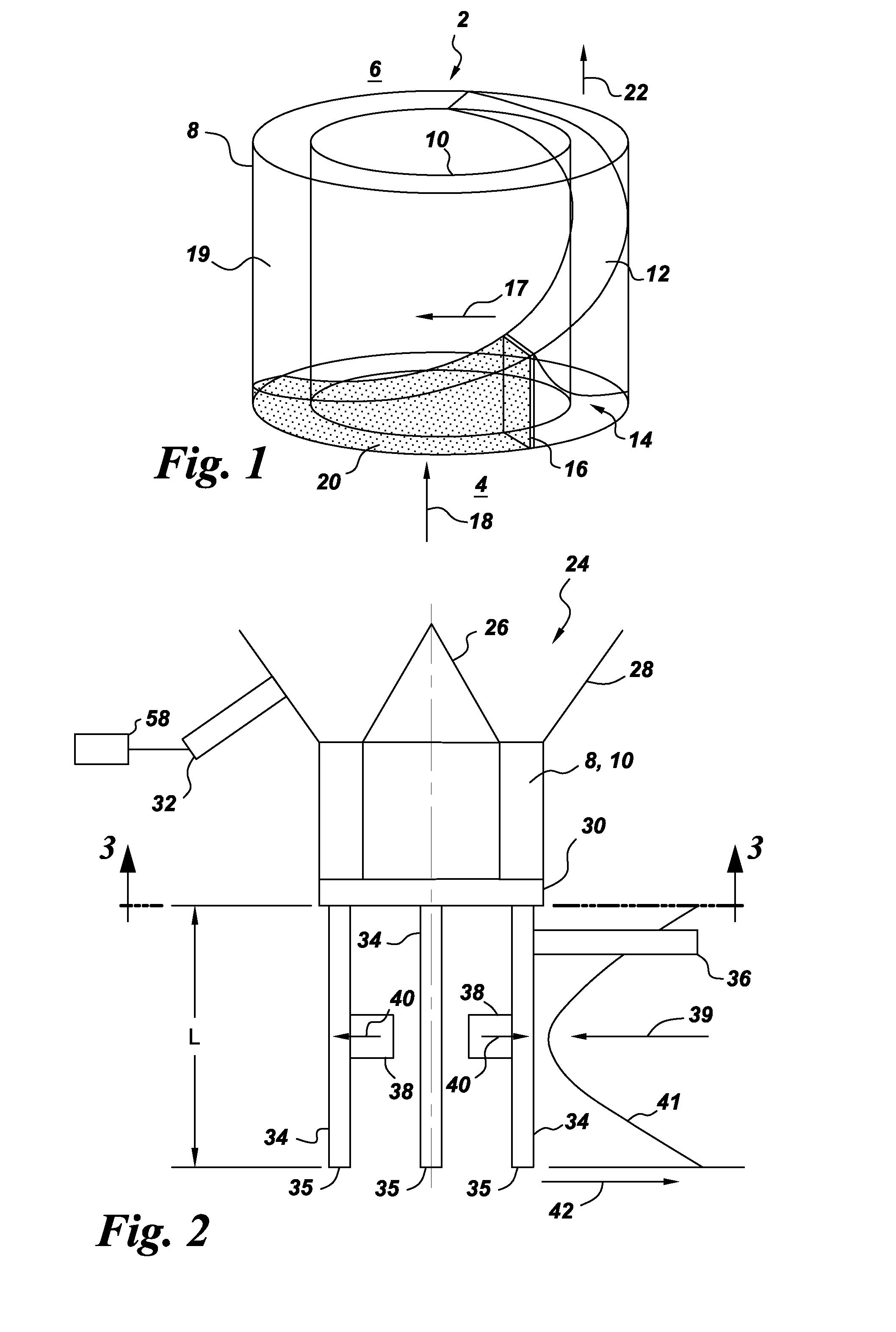
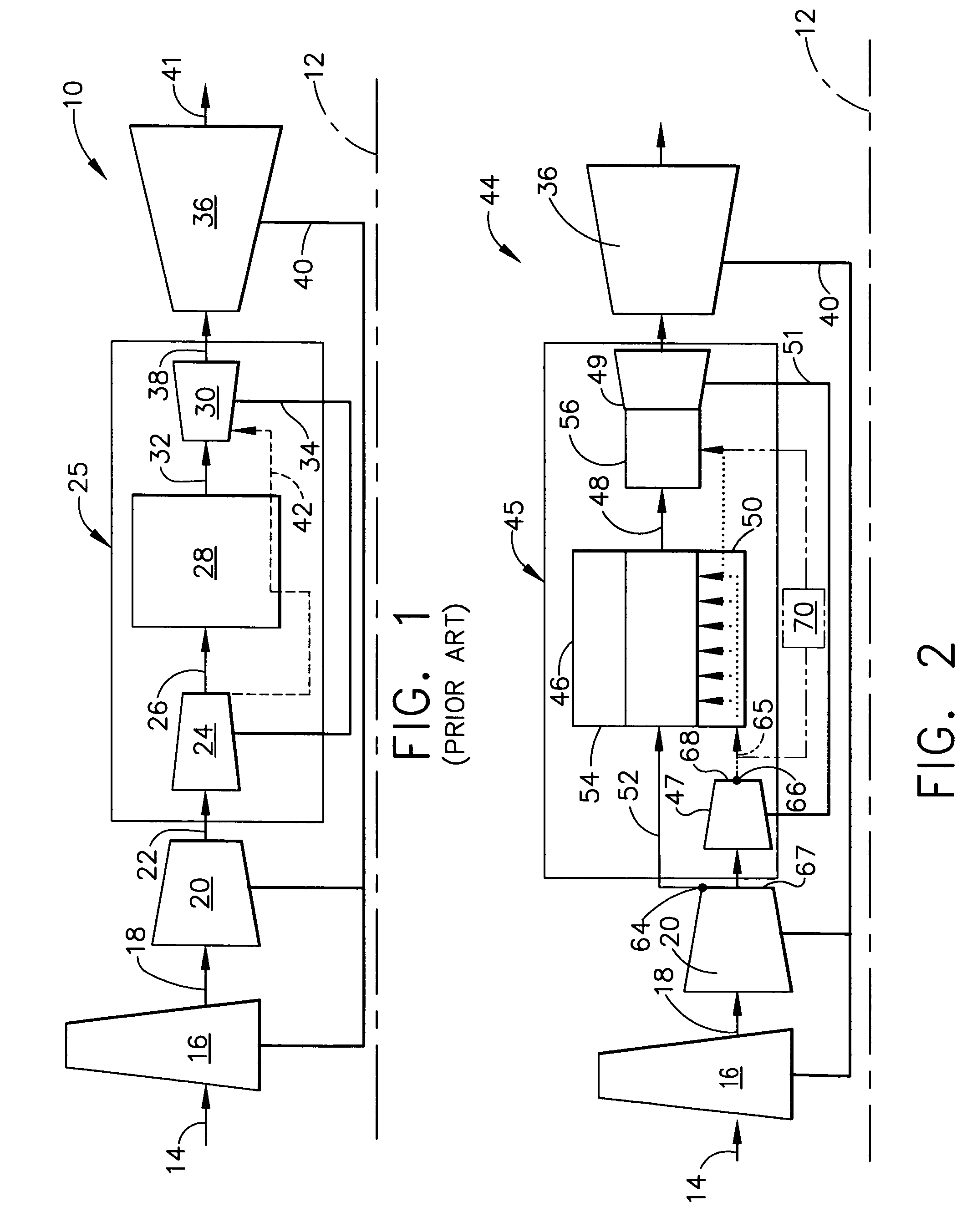
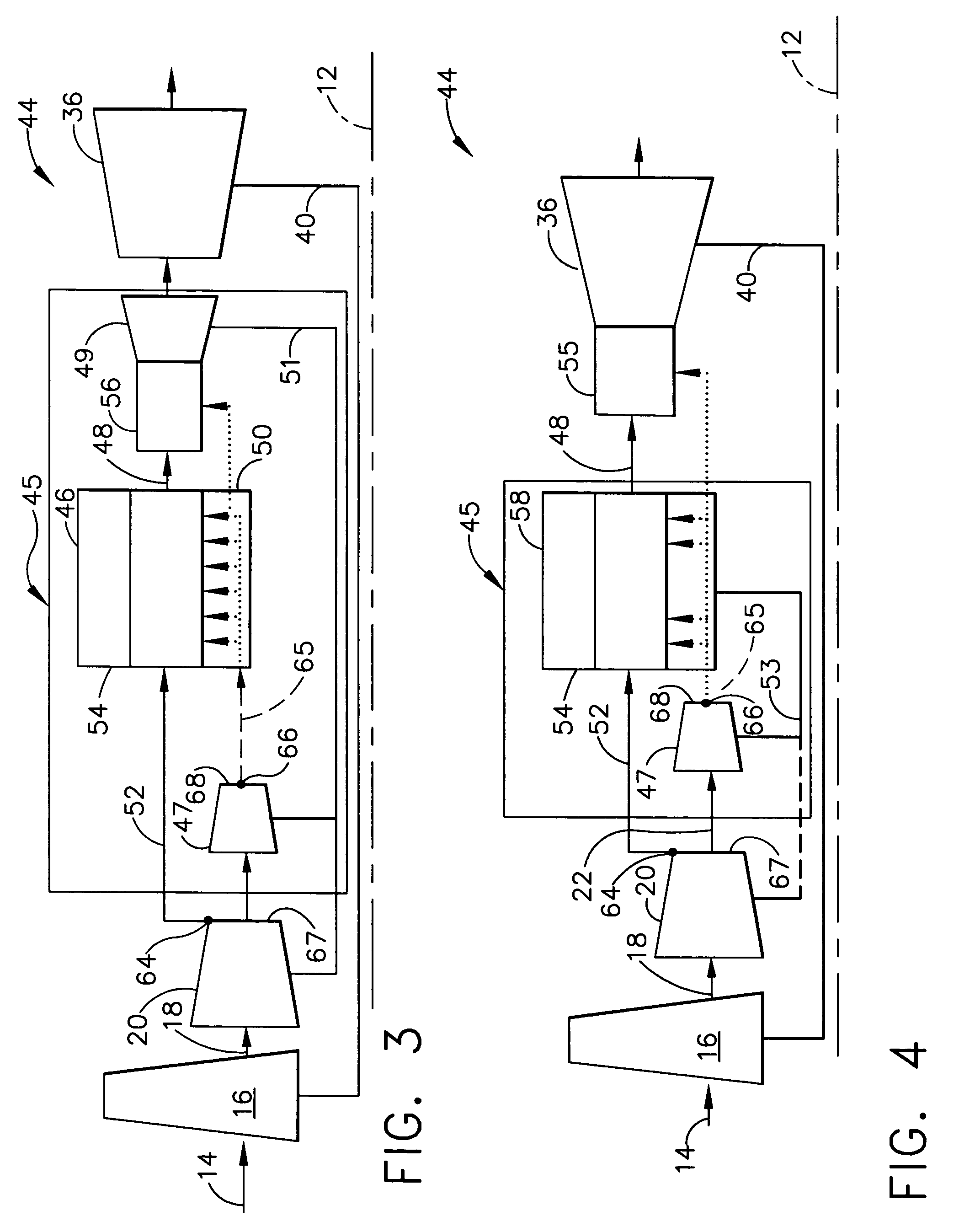
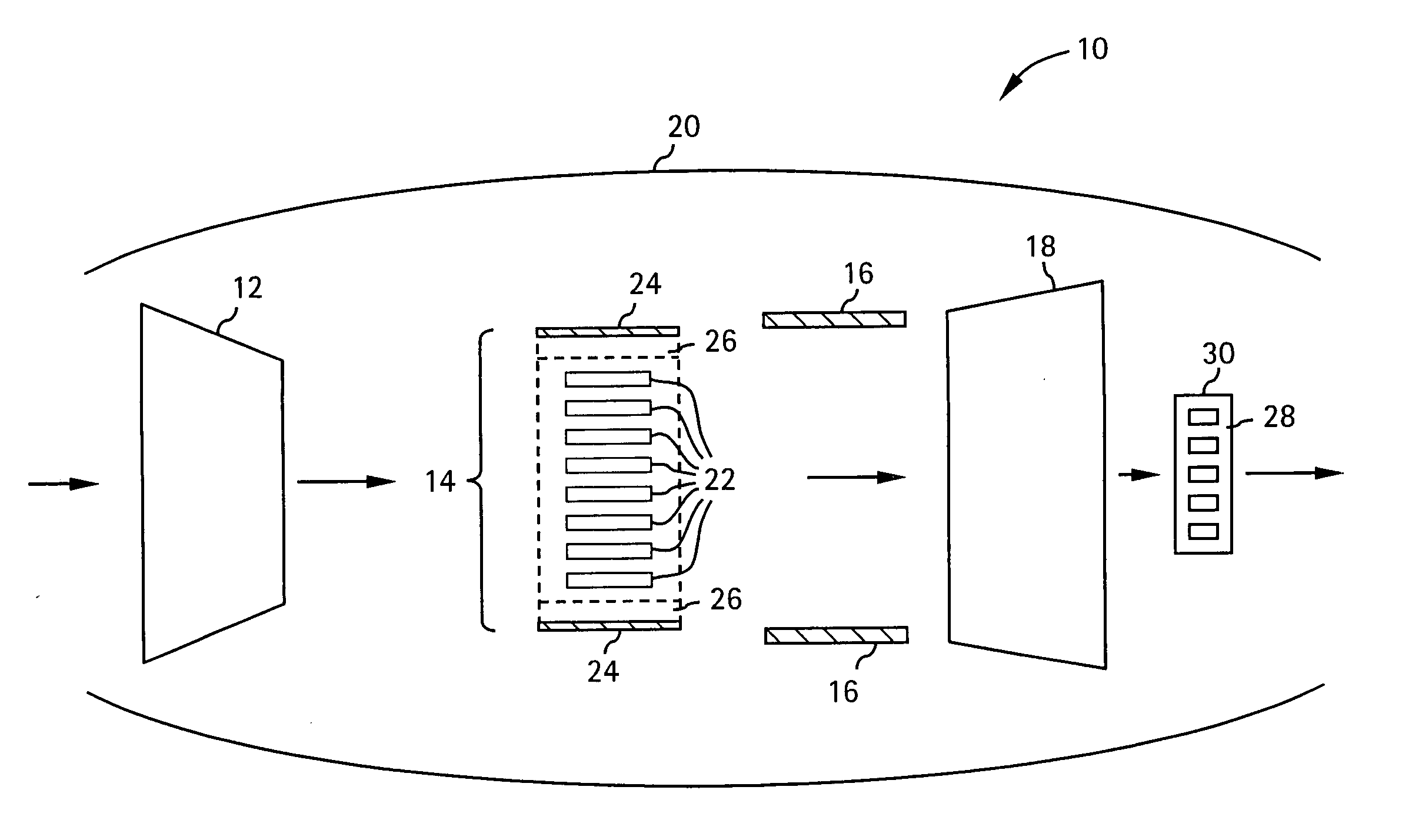
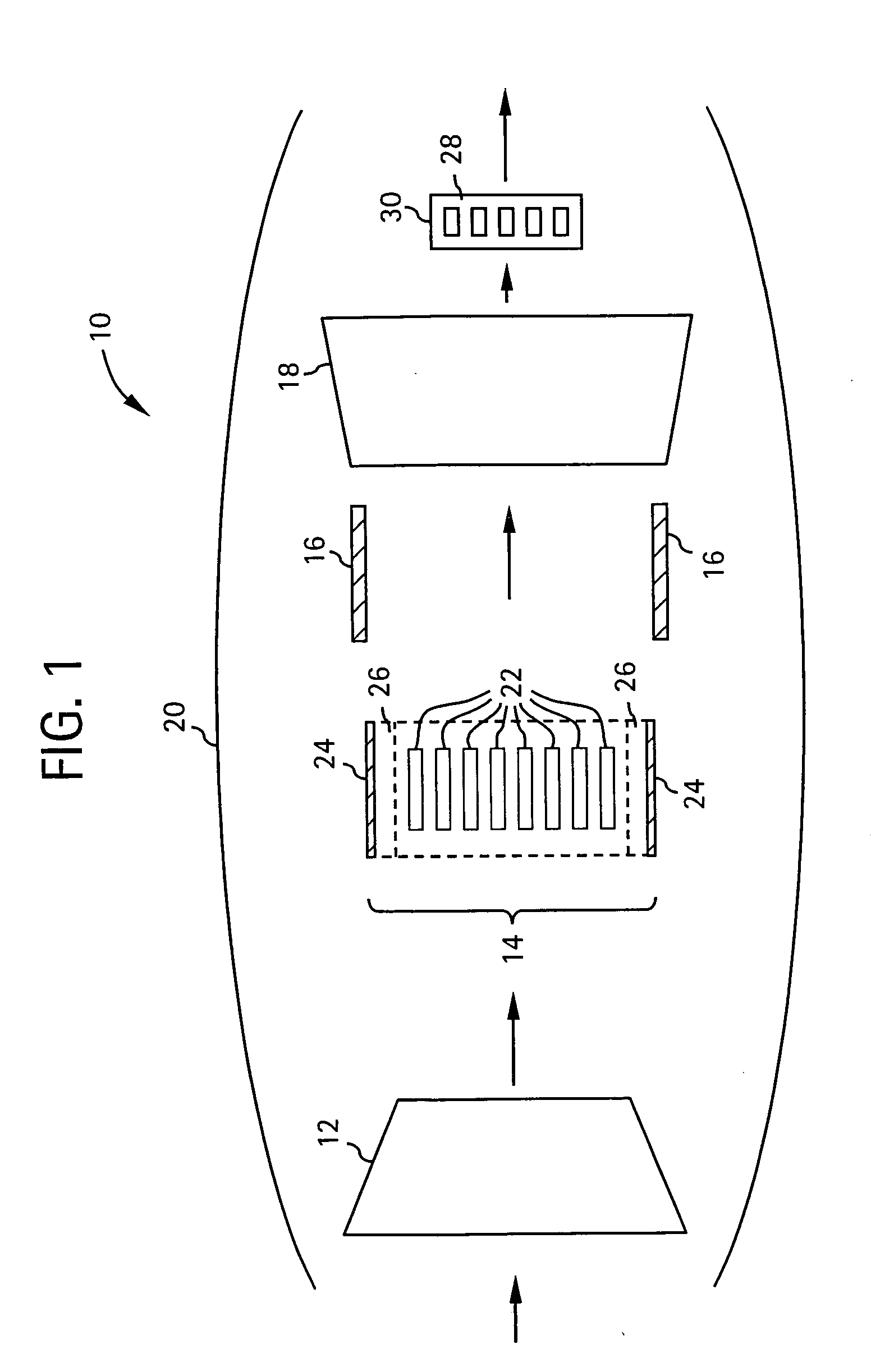
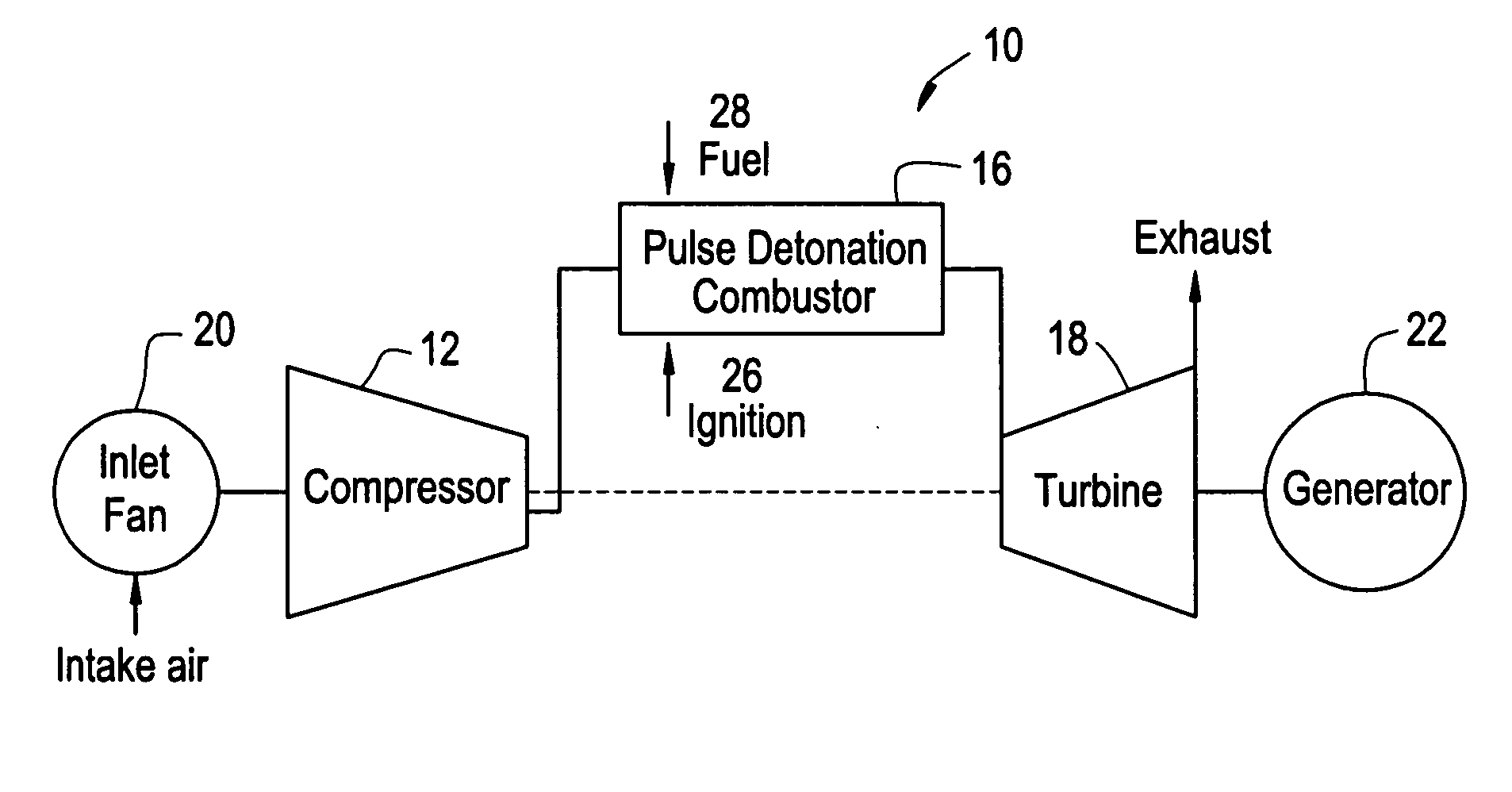
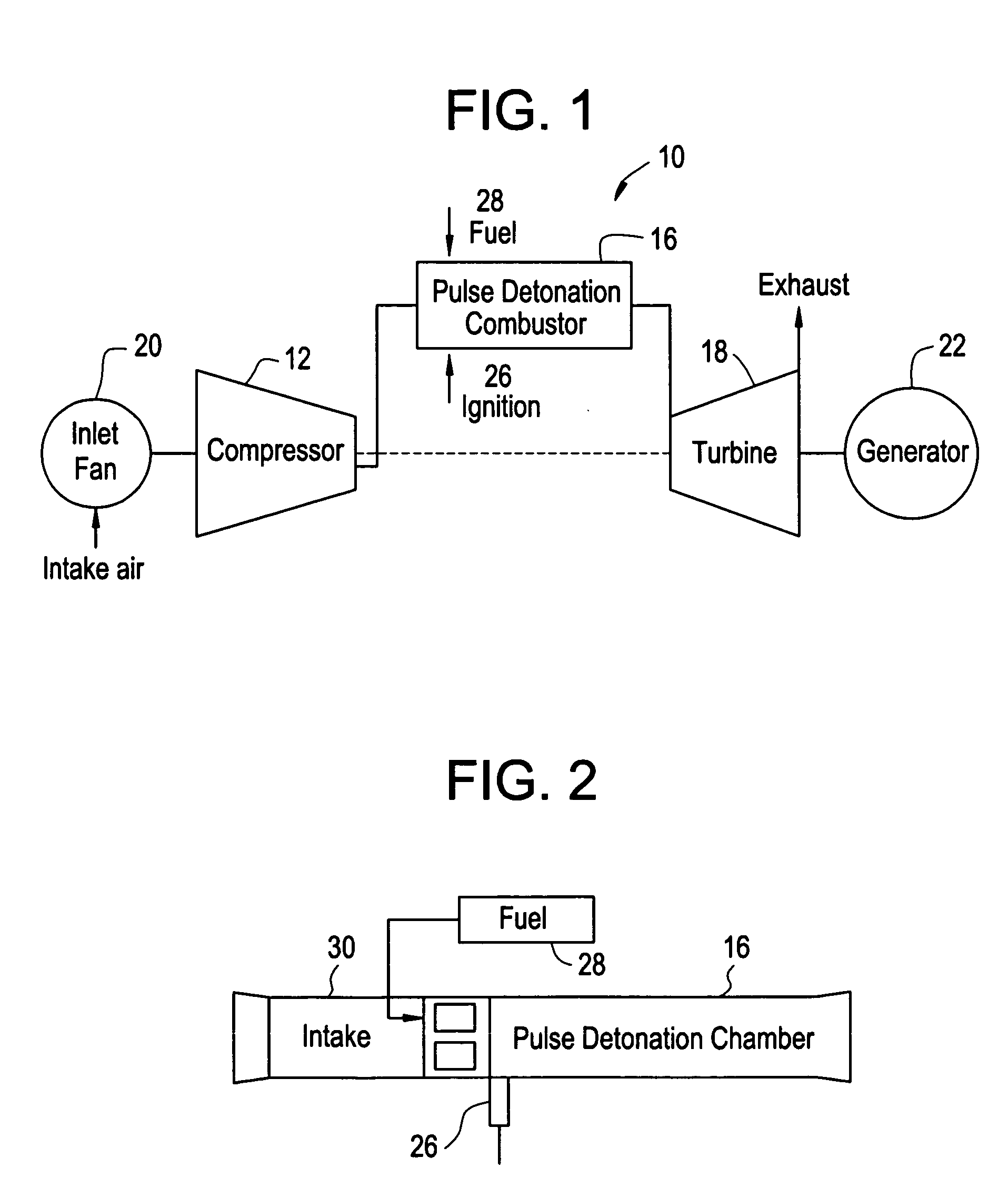
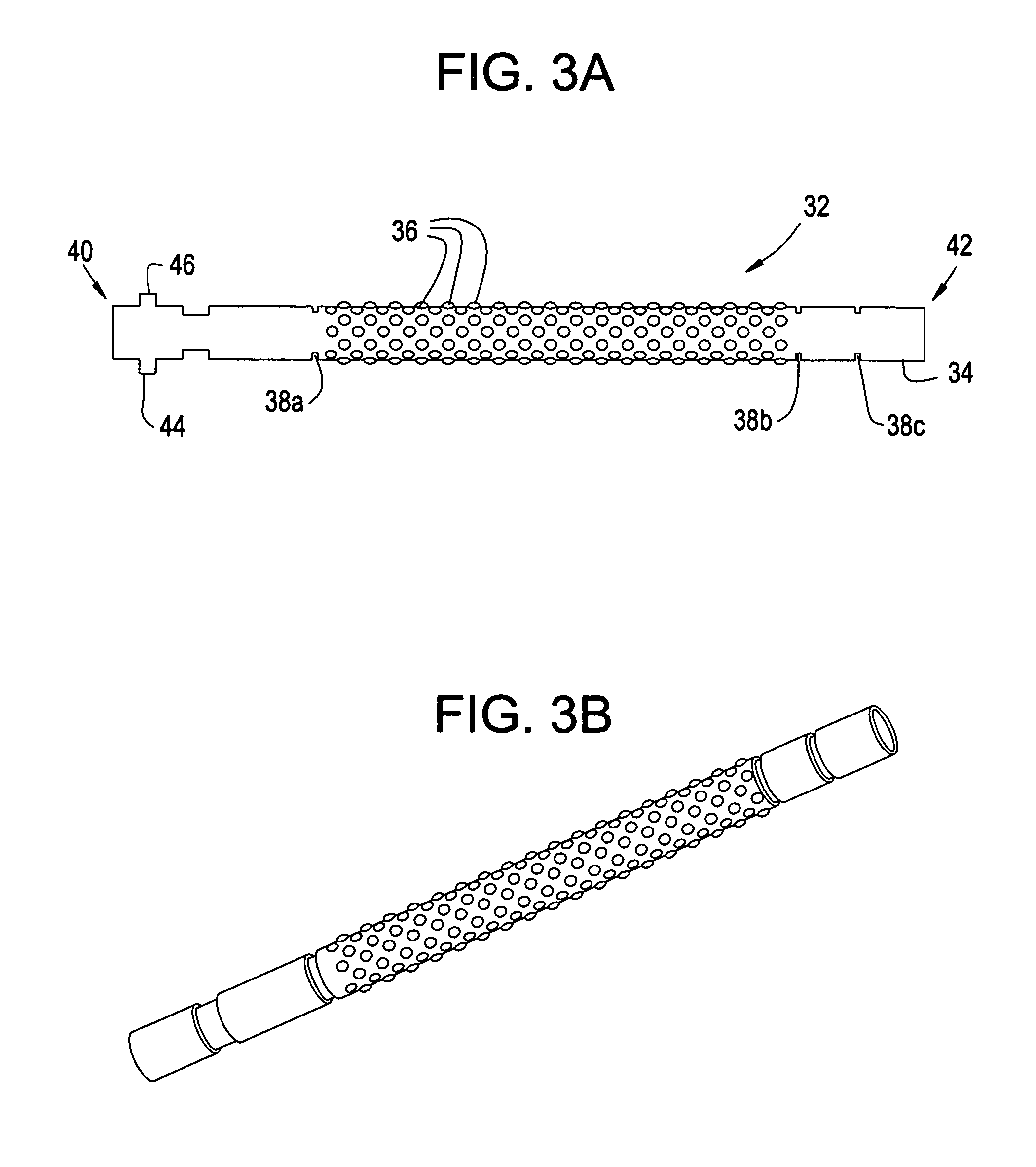
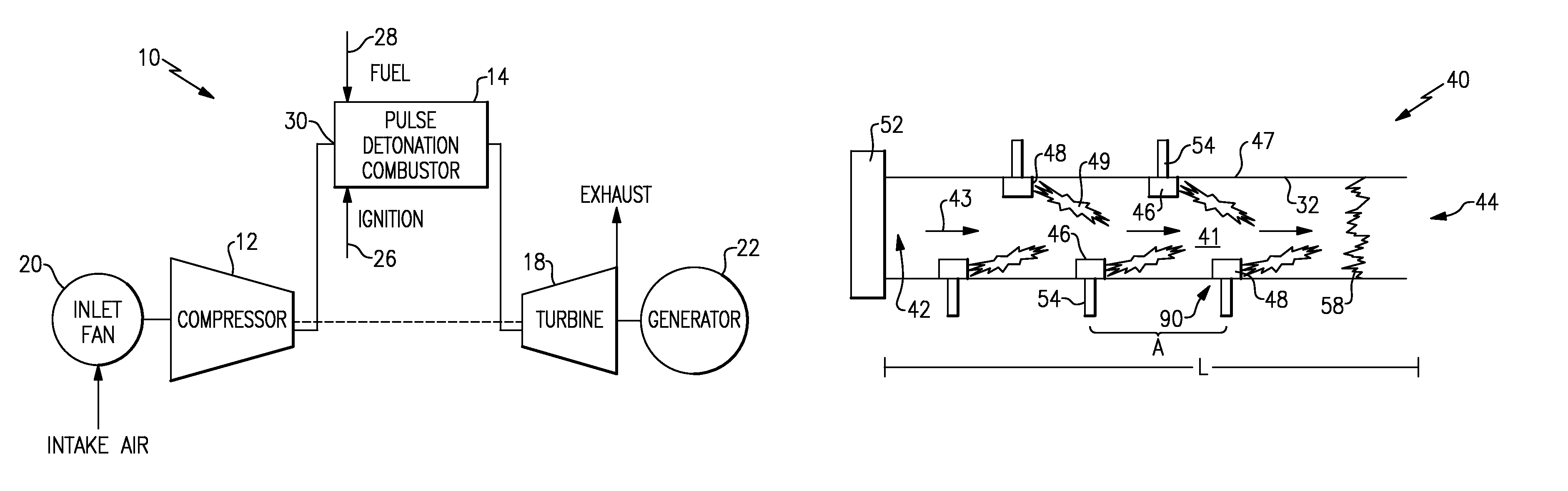
A pulsed detonation combustor (PDC) is described. The PDC includes an outer casing defining a first hollow chamber configured to receive a flow and an inner liner. The inner liner includes at least one portion positioned within the first hollow chamber and configured to receive the flow from a plenum formed between the outer casing and inner liner. The PDC further includes a flow turning device with geometric features configured to direct the flow from the plenum to a second hollow chamber defined within the inner liner. The PDC also includes at least one fuel injection port located downstream of an inlet to the outer casing and an ignition device located downstream of the at least one fuel injection port and configured to periodically ignite fuel.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gas turbine with improved part load emissions behavior
InactiveUS20120017601A1Reduce flow rateHigh fuel flow rateFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
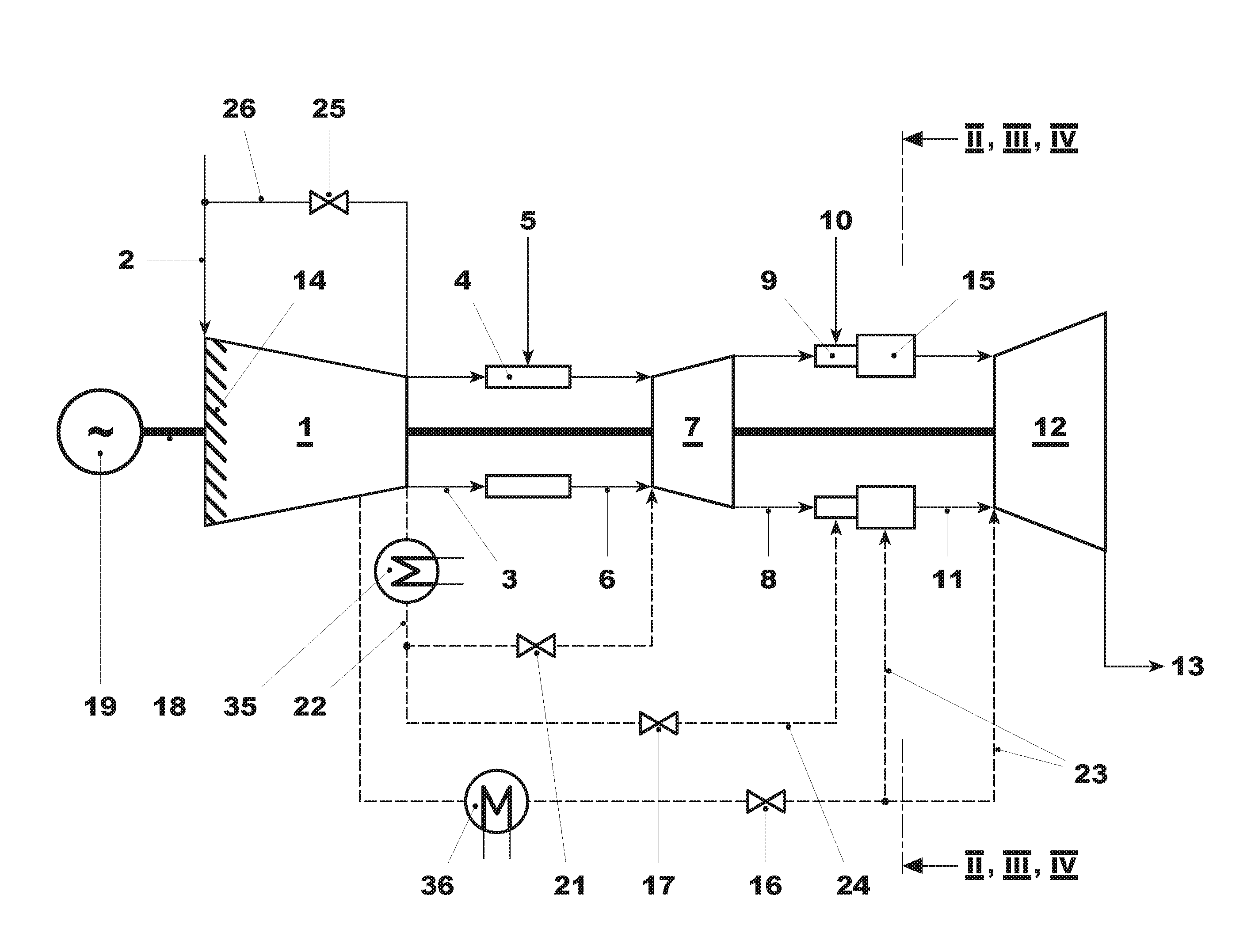
In a method for the low-CO emissions part load operation of a gas turbine with sequential combustion, the air ratio (λ) of the operative burners (9) of the second combustor (15) is kept below a maximum air ratio (λmax) at part load In order to reduce the maximum air ratio (λ), a series of modifications in the operating concept of the gas turbine are carried out individually or in combination. One modification is an opening of the row of variable compressor inlet guide vanes (14) before engaging the second combustor (15). For engaging the second combustor, the row of variable compressor inlet guide vanes (14) is quickly closed and fuel is introduced in a synchronized manner into the burner (9) of the second combustor (15). A further modification is the deactivating of individual burners (9) at part load.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
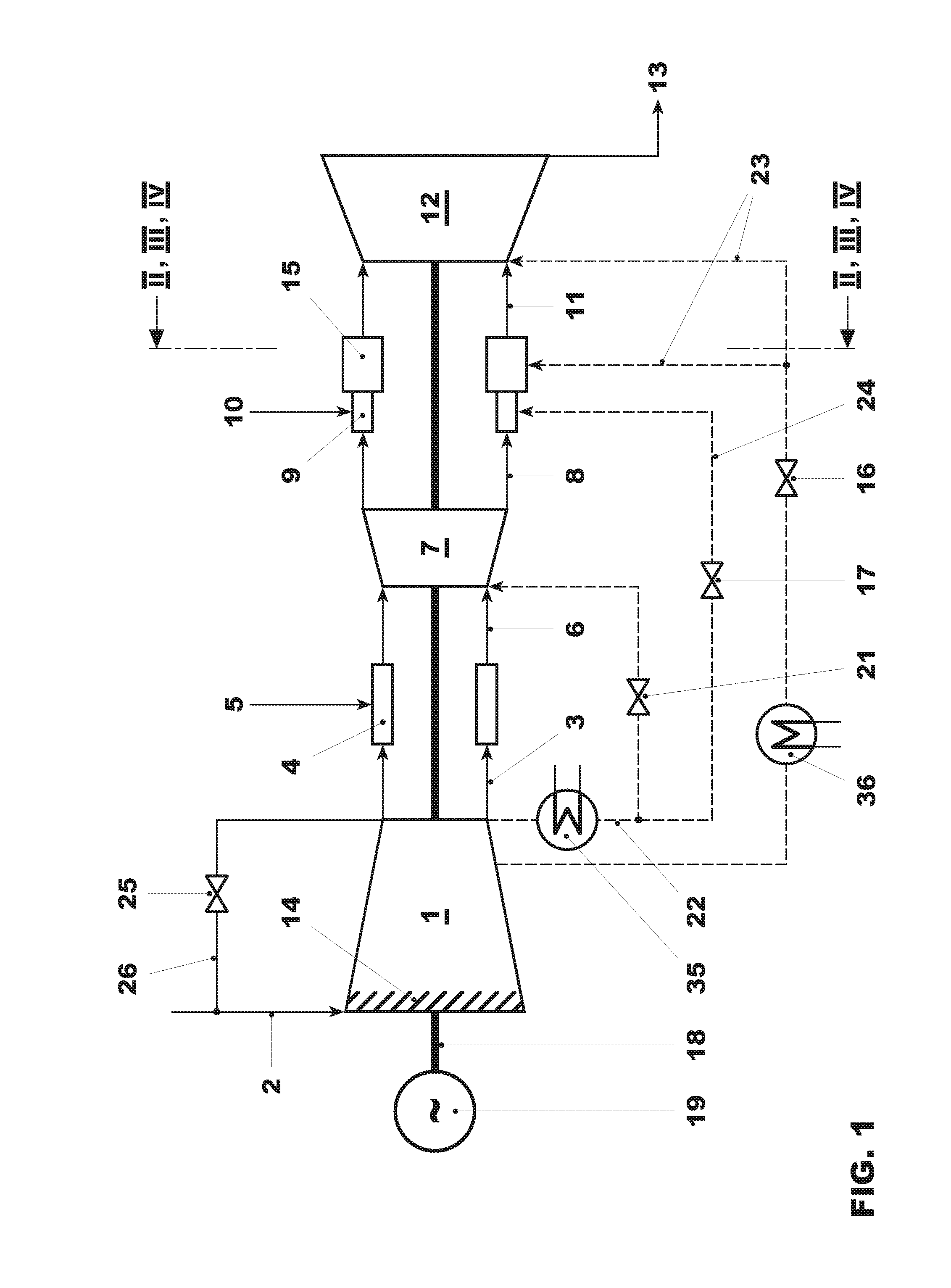
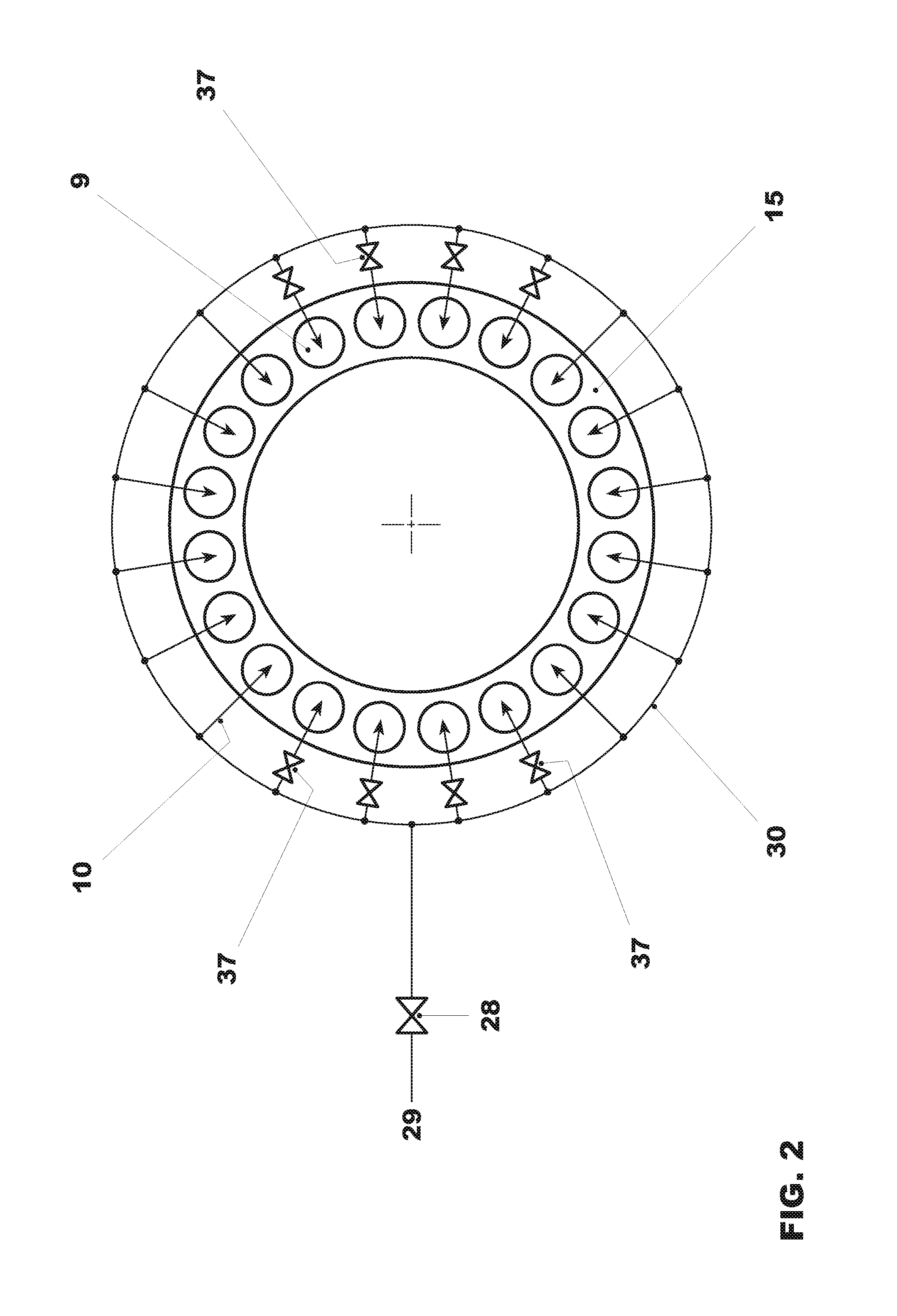
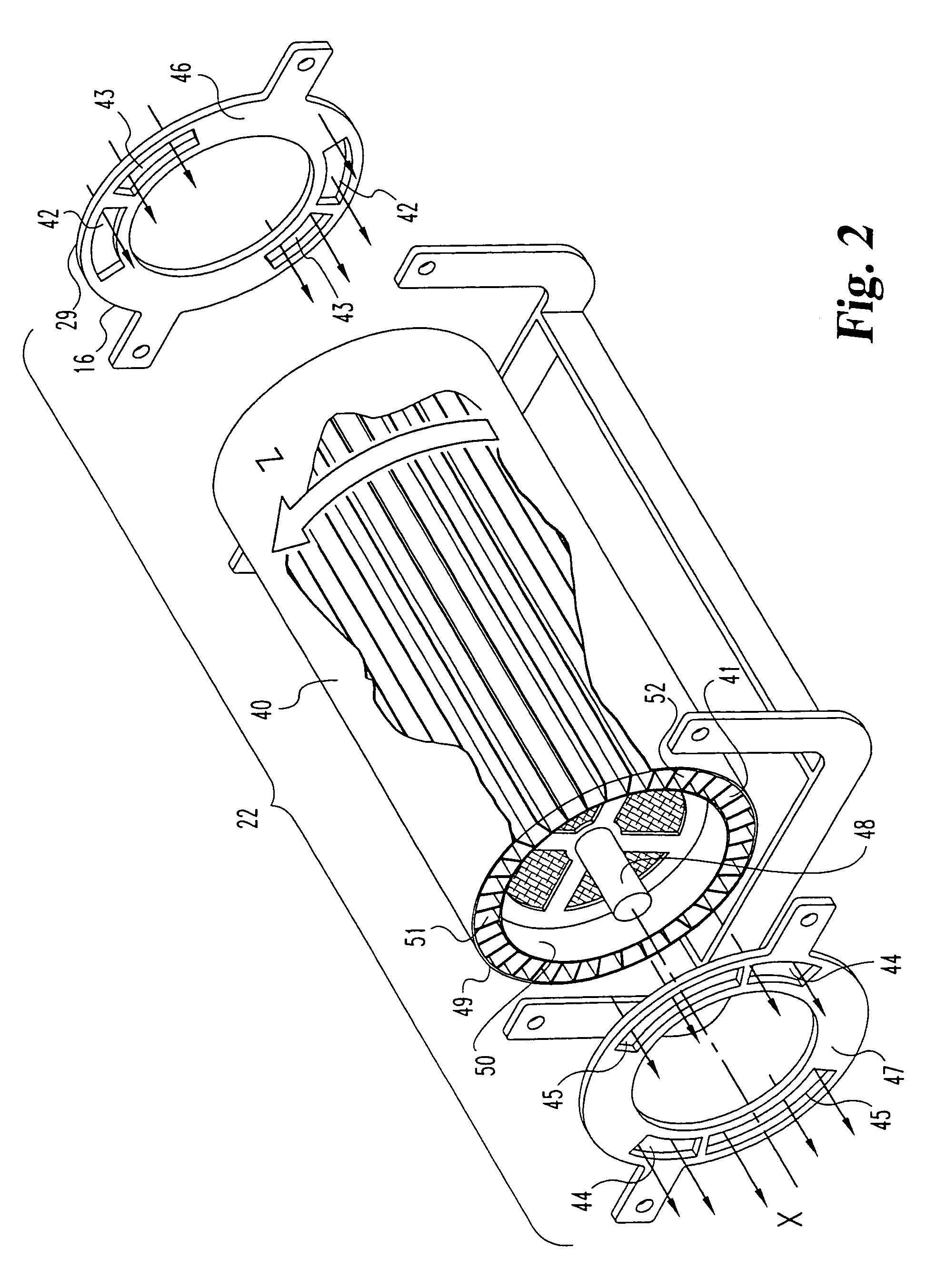
Pulse detonation assembly with cooling enhancements
A pulse detonation (PD) assembly includes at least one PD chamber having a wall, which defines cooling holes arranged along at least a portion of the PD chamber. A manifold extends around the PD chamber. The manifold and PD chamber are separated by a bypass region. A PD assembly with reverse flow cooling includes at least one PD chamber. A sleeve extends around the PD chamber. The sleeve and PD chamber are separated by a reverse flow cooling passage configured to receive a flow of air and to flow the air in a reverse direction to supply the PD chamber. A PD assembly with bypass flow cooling includes at least one PD chamber and a manifold extending around the PD chamber(s), which are separated by a bypass region. The PD assembly further includes a mixing plenum configured to receive and mix the bypass flow from the bypass region and the detonation by-products from the PD chamber(s).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotary knocking gas turbine
InactiveCN104153884AImprove cycle thermal efficiencyLower Burn Control SystemGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsCombustion chamberGas compressor
The invention discloses a rotary knocking gas turbine. The rotary knocking gas turbine comprises a gas inlet passage, a diffusion section and a gas storage chamber which are connected in sequence from left to right, wherein a gas compressor is arranged at the downstream of the gas inlet passage; a rotary knocking combustion chamber is positioned at the right end of the gas storage chamber, the right end of the rotary knocking combustion chamber is connected with a mixing chamber, a turbine and an exhaust pipe in sequence, a plurality of nozzles are annularly arranged on the left end face of the rotary knocking combustion chamber at equal intervals, and six ignition plugs are uniformly arranged on the circumference of the rotary knocking combustion chamber; an air passage and a combustion passage are arranged on each nozzle, the gas storage chamber is communicated with the rotary knocking combustion chamber through a gas supply passage and the air passages of the nozzles, and the mixing chamber is communicated with the gas storage chamber through a gas escape bypass; a rotor is arranged between the gas compressor and the turbine, the gas compressor of a rotating component of the gas turbine and the turbine are connected with a casing of a static bearing component of the gas turbine through two bearings, and one end of the rotor is led out from the gas exhaust pipe. When the rotary knocking gas turbine is used, the leading-out end of the rotor is connected with a generator assembly through a speed changer.
Owner:XIAN THERMAL POWER RES INST CO LTD
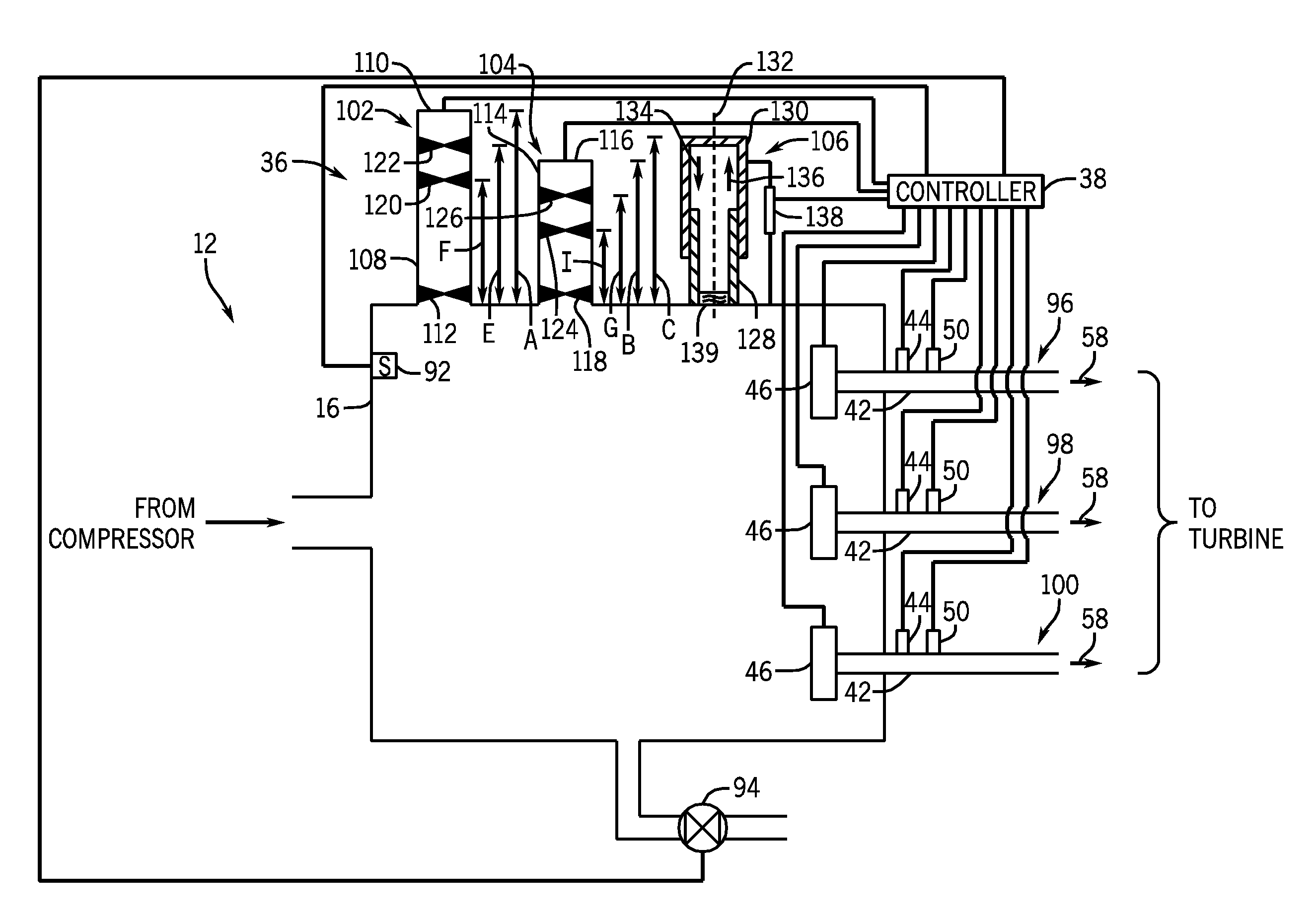
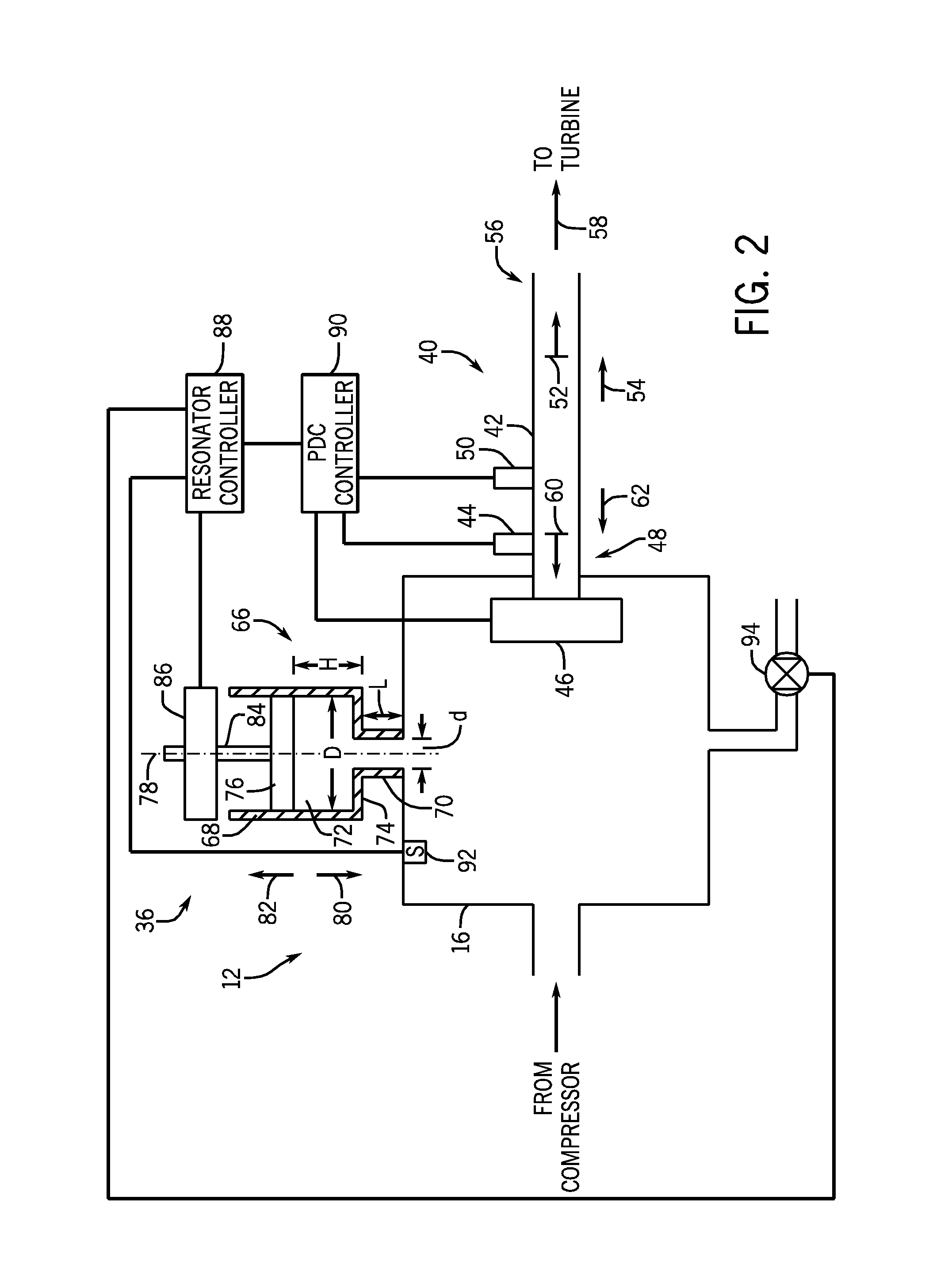
System and method for damping pressure oscillations within a pulse detonation engine
InactiveUS20120204534A1Continuous combustion chamberCosmonautic vehiclesOperating frequencyResonator
In one embodiment, a pulse detonation engine includes a resonator configured to fluidly couple to an air flow path upstream of a pulse detonation tube. The pulse detonation engine also includes a controller configured to receive signals indicative of an operating frequency of an air valve disposed at an upstream end of the pulse detonation tube, and to adjust a geometric configuration of the resonator in response to the signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
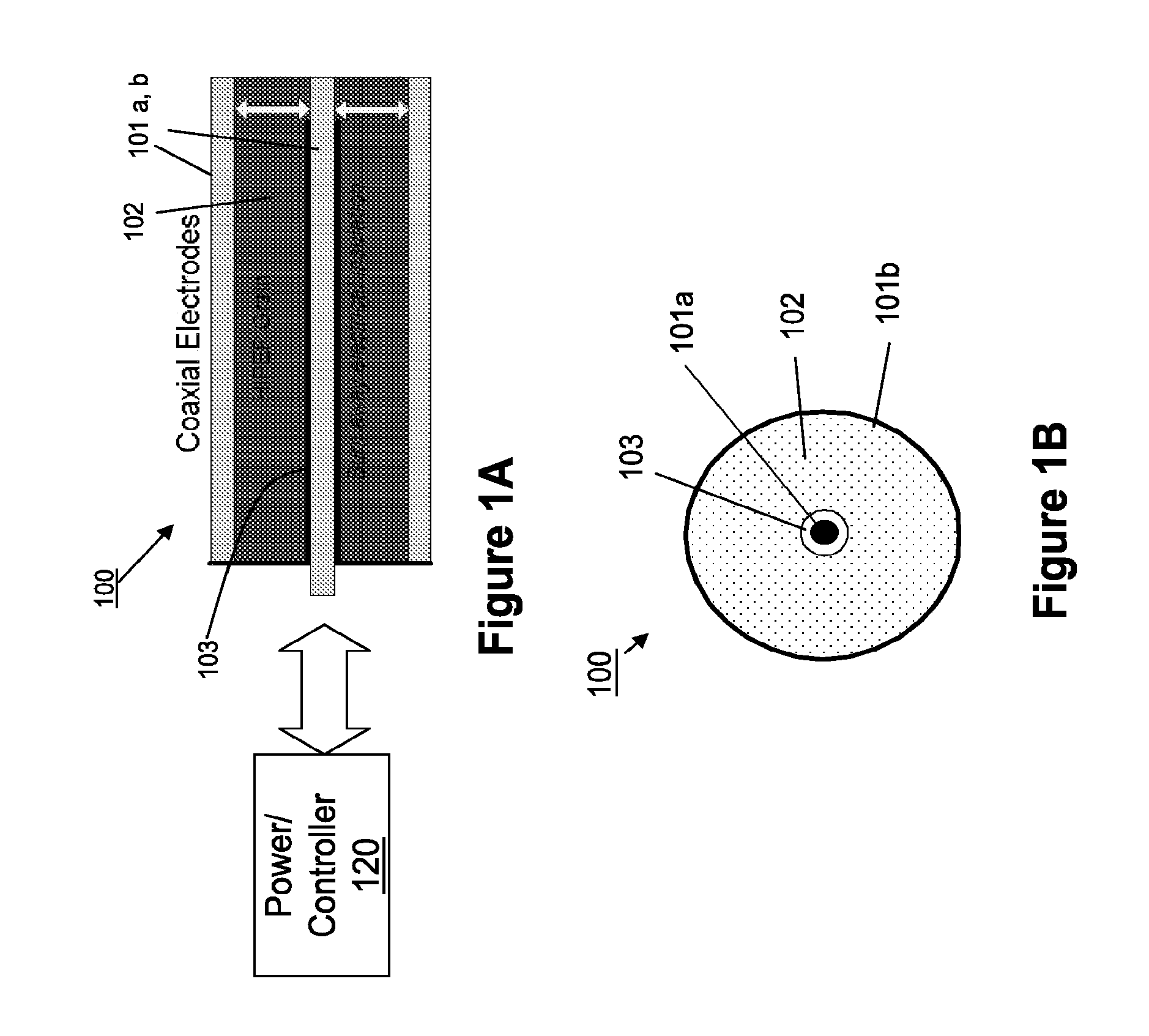
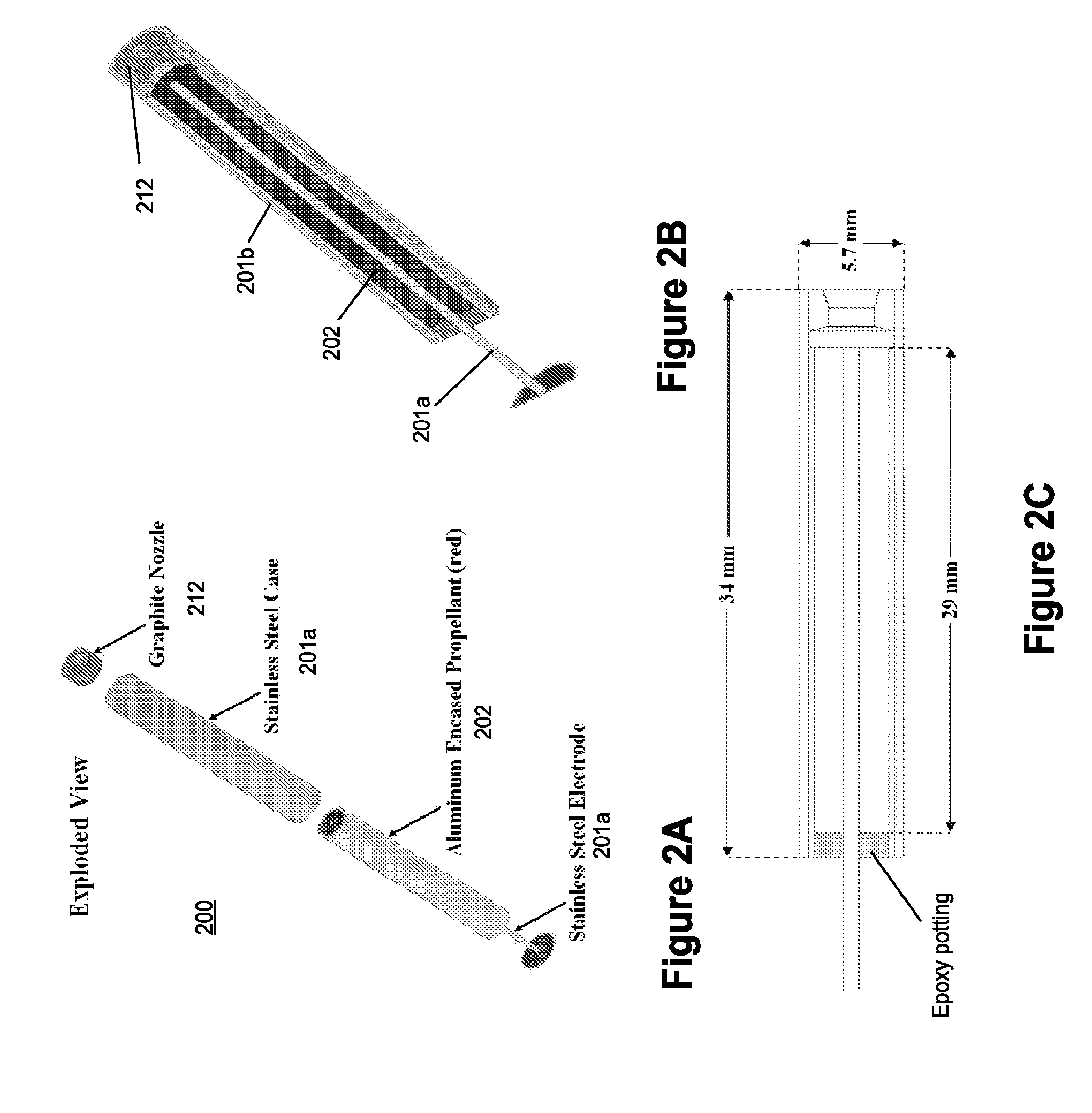
Electrode ignition and control of electrically ignitable materials
Apparatus for providing electrically initiated and / or controlled combustion of electrically ignitable propellants is provided. In one example, the apparatus includes a volume of electrically ignitable propellant (liquid and / or gas) capable of self sustaining combustion, and electrodes operable to ignite the propellant. The apparatus may further include a power supply and controller in electrical communication with the electrodes for supplying a potential across the electrodes to initiate combustion of the propellant and / or control the rate of combustion of the propellant. Various configurations and geometries of the propellant, electrodes, and apparatus are possible. In one example, the electrodes are supplied a direct current, which causes combustion of the propellant at the positive electrode. In another example, the electrodes are supplied an alternating current, which initiates combustion of the propellant at both electrodes.
Owner:DIGITAL SOLID STATE PROPULSION
Methods and apparatus for generating gas turbine engine thrust with a pulse detonation thrust augmenter
InactiveUS6883302B2Increase temperatureIncrease pressureCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusDetonationGas turbines
A method enables thrust to be generated from a gas turbine engine using a pulse detonation system is provided. The engine includes an inlet portion and an exhaust portion, and the pulse detonation system includes a multi-staged pulse detonation augmentor including predetonator. The method comprises supplying a less than stoichiometric fuel / air mixture to the pulse detonation system during a first operating stage, detonating the fuel / air mixture with the predetonator to increase the temperature and pressure within the engine and to generate engine thrust, and supplying additional fuel and air to the pulse detonation system during a second operating stage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
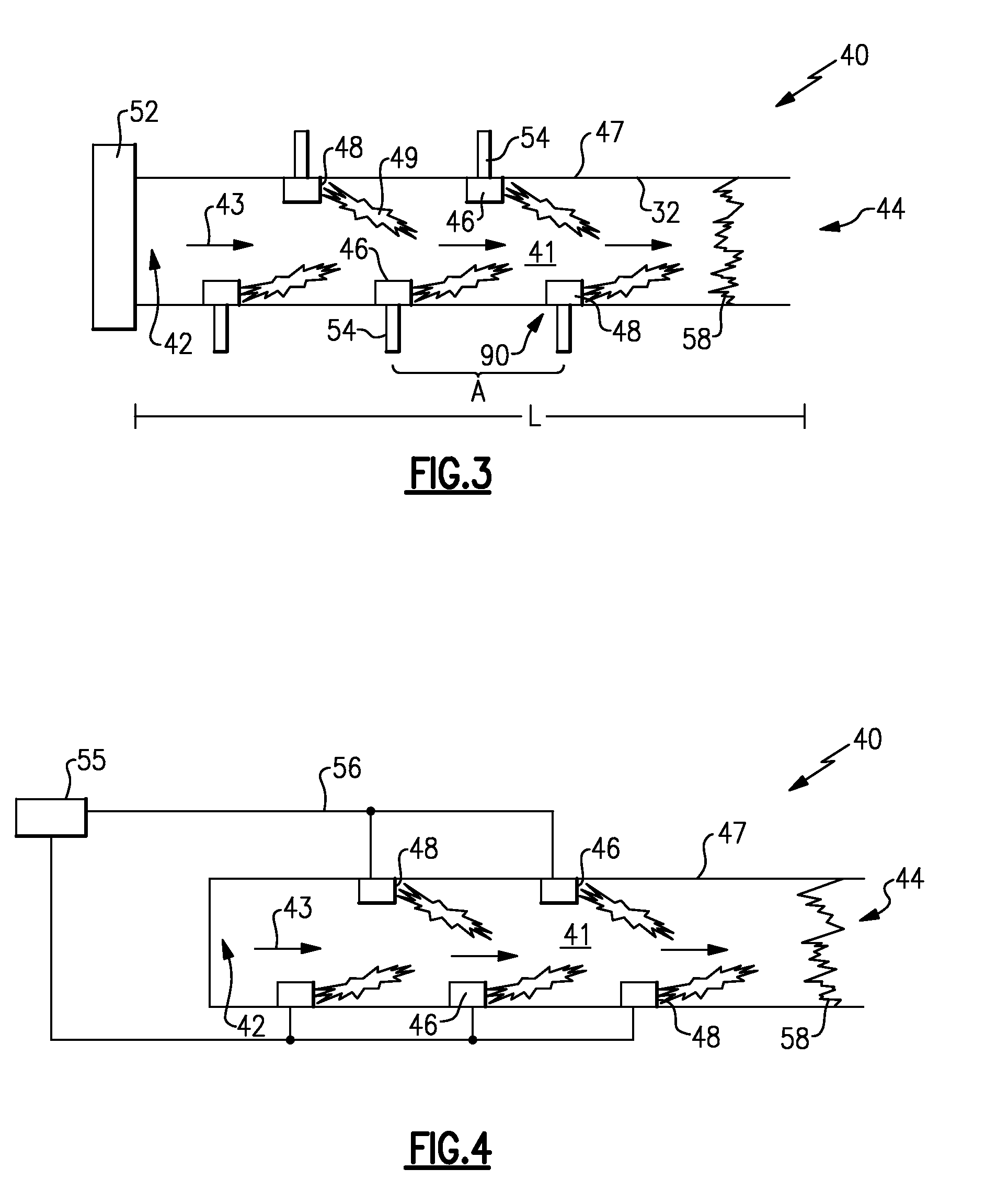
Pulse detonation assembly and hybrid engine
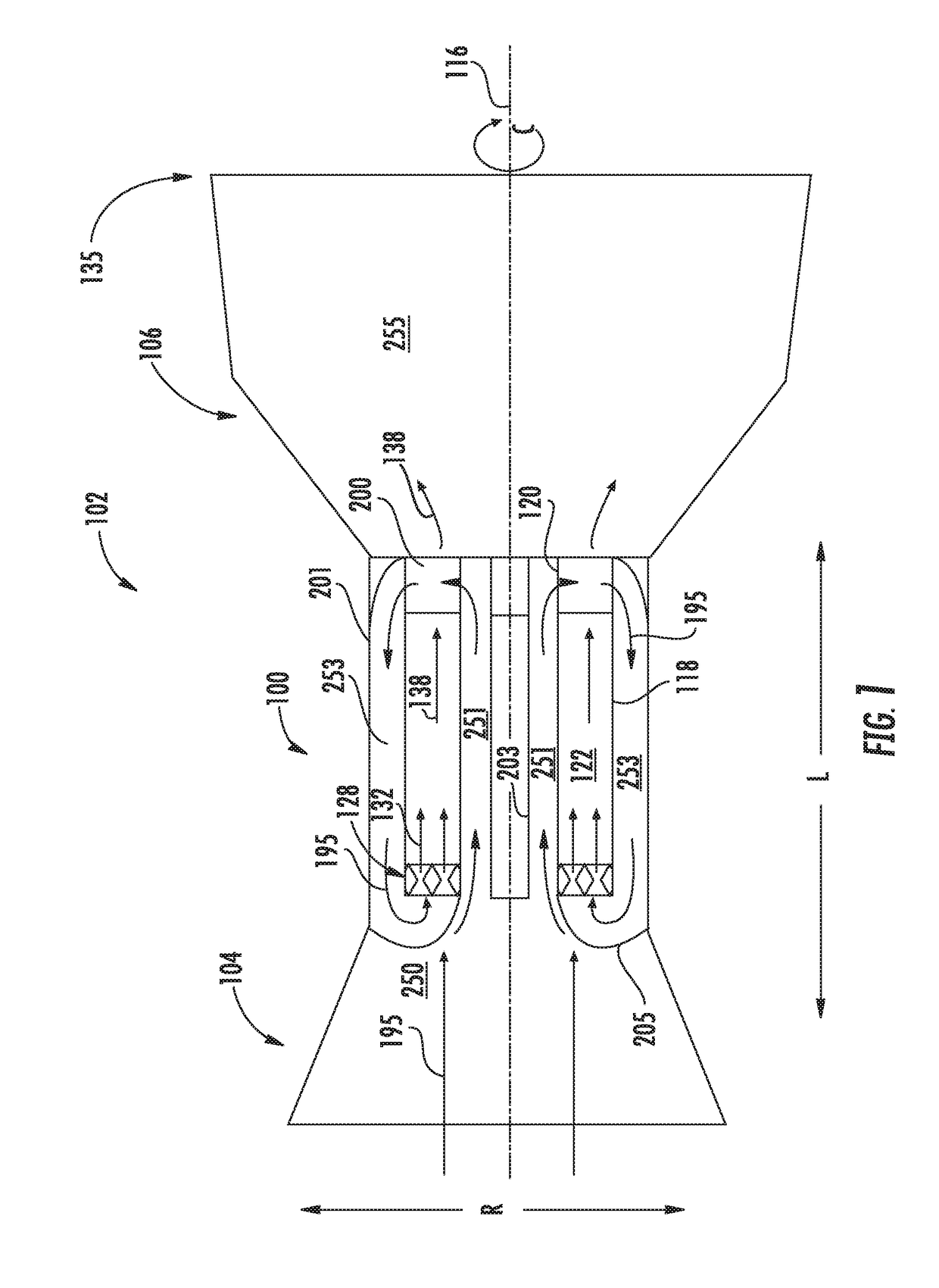
ActiveUS20060254252A1Reducing undesirable interactionReduce the overall heightPulsating combustionGas turbine plantsDetonationTurbine
A pulse detonation (PD) assembly includes a number of PD chambers adapted to expel respective detonation product streams and a number of barriers disposed between respective pairs of PD chambers. The barriers define, at least in part, a number of sectors that contain at least one PD chamber. A hybrid engine includes a number of PD chambers and barriers. The hybrid engine further includes a turbine assembly having at least one turbine stage, being in flow communication with the PD chambers and being configured to be at least partially driven by the detonation product streams. A segmented hybrid engine includes a number of PD chambers and segments configured to receive and direct the detonation product streams from respective PD chambers. The segmented hybrid engine further includes a turbine assembly configured to be at least partially driven by the detonation product streams.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Constant volume combustor
InactiveUS20070157625A1Increase pressureContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustorMagnetic bearing
A constant volume combustor device includes detonative combustion. In one form the wave rotor of the constant volume combustor is supported by magnetic bearings.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE NORTH AMERICAN TECH
Tuned cavity rotating detonation combustion system
ActiveUS20150167544A1Continuous combustion chamberInternal combustion piston enginesFlame arresterCombustion system
A tuned cavity rotating detonation combustion system includes a an annular chamber having an inlet and an outlet; a valve plate at the inlet of the annular chamber and comprising a plurality of openings spaced circumferentially around the inlet; a plurality of tubes each having an open end in communication with a corresponding opening of the valve plate and a closed end forming a tuned cavity, and a first opening between the open end and the closed end for injection of air; and a plurality of fuel injectors corresponding to the plurality of tubes, each fuel injector being configured to inject fuel into the tube between the first opening and the open end. Each of the tuned cavities has a length sized to resonate at a same frequency as a continuous detonation frequency of at least one detonation wave in the annular chamber. Alternately, or additionally, a plurality of flame arresters corresponding to the plurality of tubes are configured to arrest the at least one detonation wave generated in the detonation chamber from travelling into the tube.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Valveless pulsed detonation combustor
Pulse detonation combustors of valveless construction. One valveless pulse detonation combustor, having a tube with a closed end and an open end, is constructed with a flame accelerator within the tube, adjacent the open end. A valveless, apertured flow restrictor is positioned between the flame accelerator and the closed end of the tube. A sparking device is positioned within the tube, between the flow restrictor and the flame accelerator. Valveless fuel and air ports are positioned between the flow restrictor and the closed end of the tube. Substantially right-angle manifold passageways are in communication with each of the ports.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Controllable combustion method and device
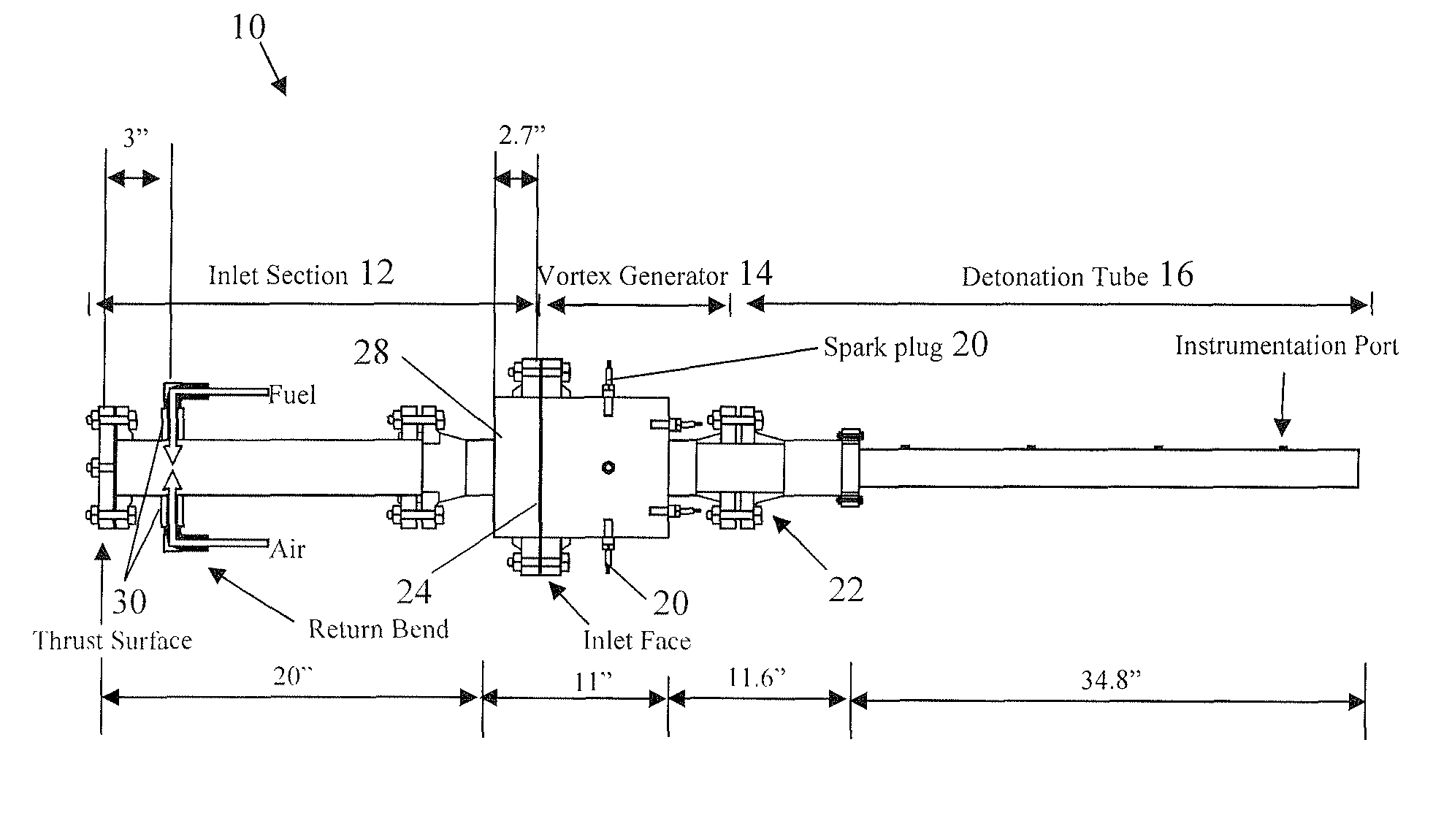
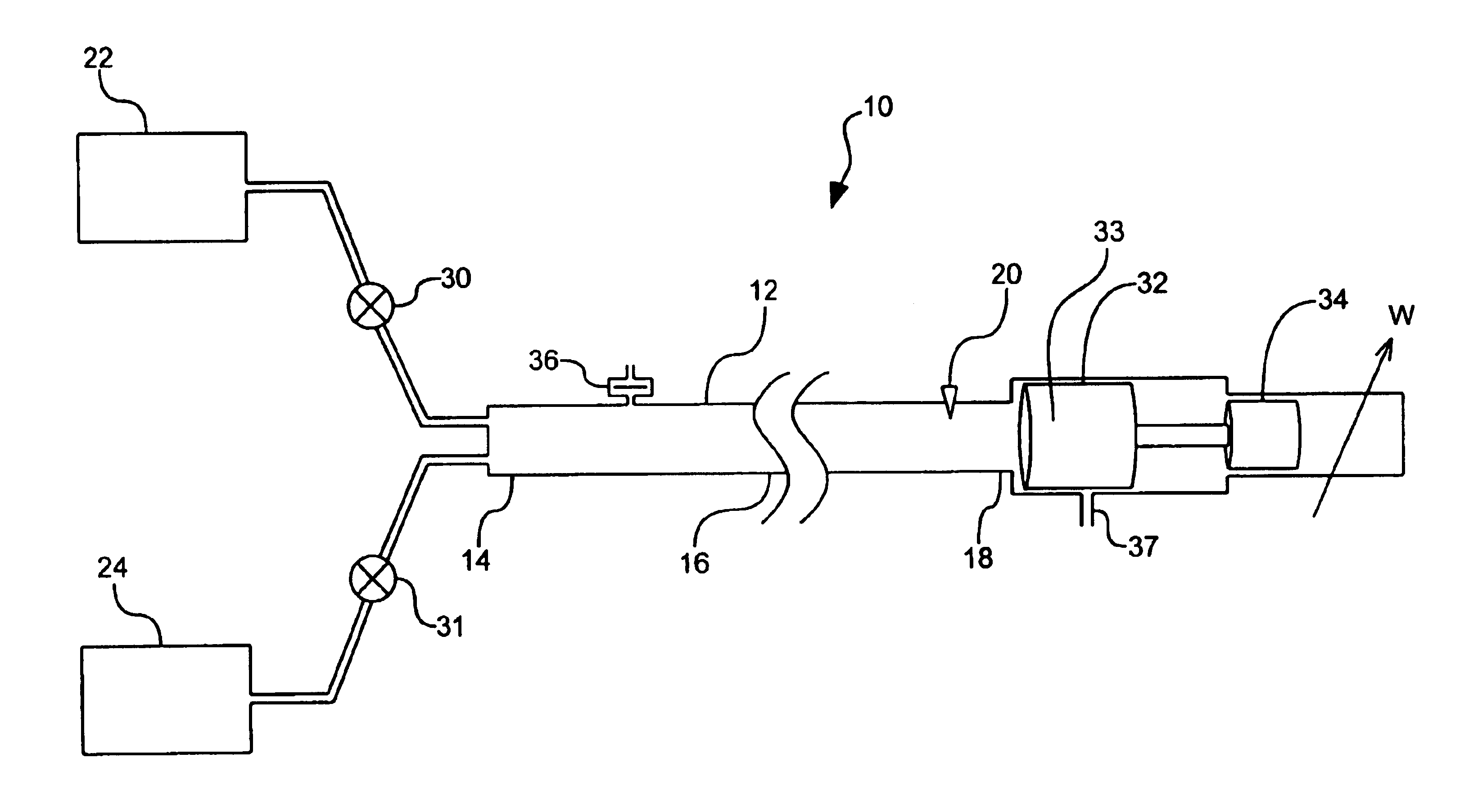
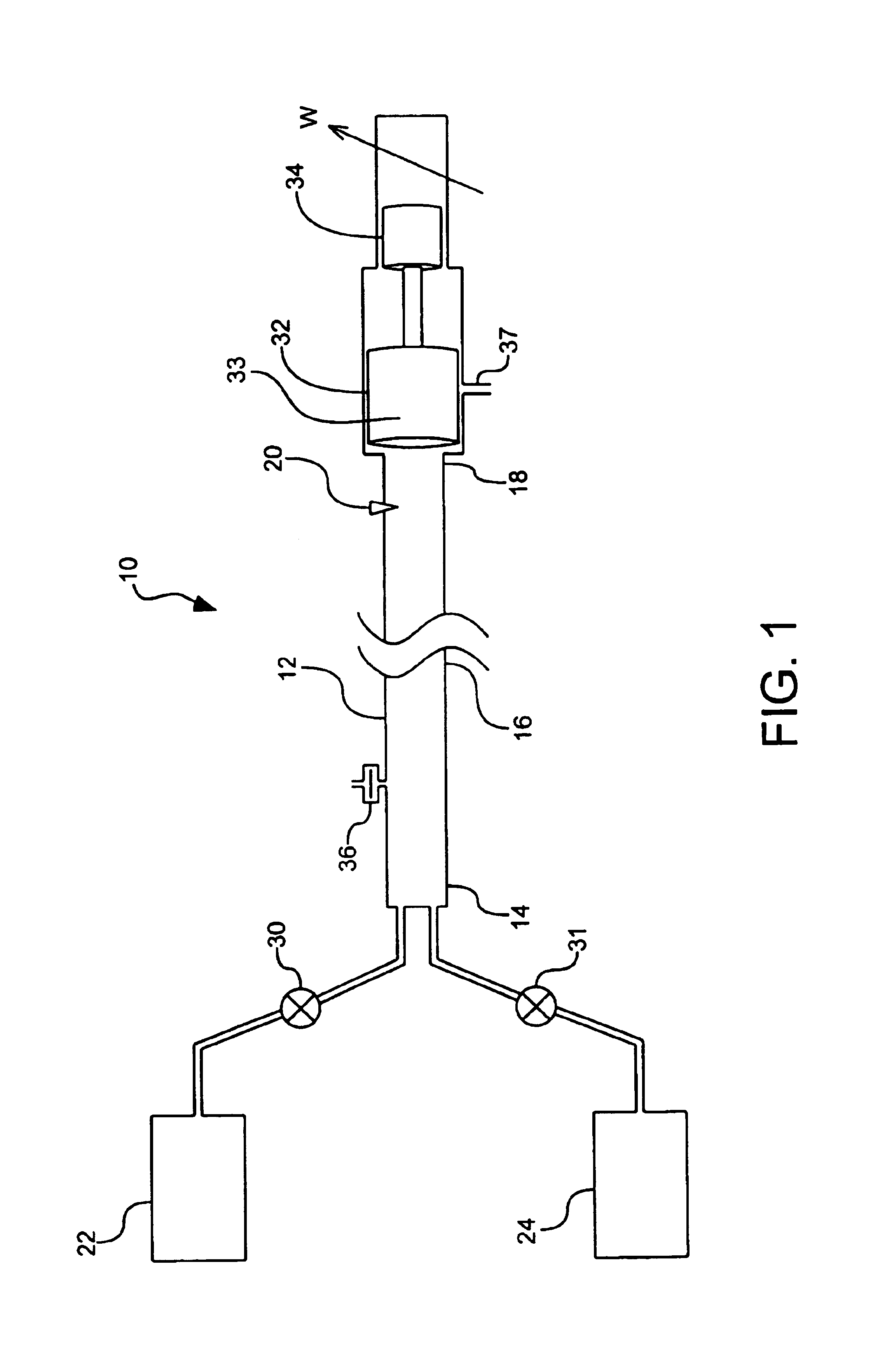
InactiveUS6938588B2High bandwidthFast energy extractionPulsating combustionFuel-injection pumpsCombustionEngineering
A method and device for controllably combusting combustible material, including a combustion device comprising an elongate combustion tube having an inlet section including an inlet for combustible material, an ignition section, including an igniter displaced along a length of the tube from the inlet section to ignite the combustible material, and at least one energy extraction device operatively coupled to the combustion tube and configured to extract energy from combustion of the combustible mixture.
Owner:SARCOS LC
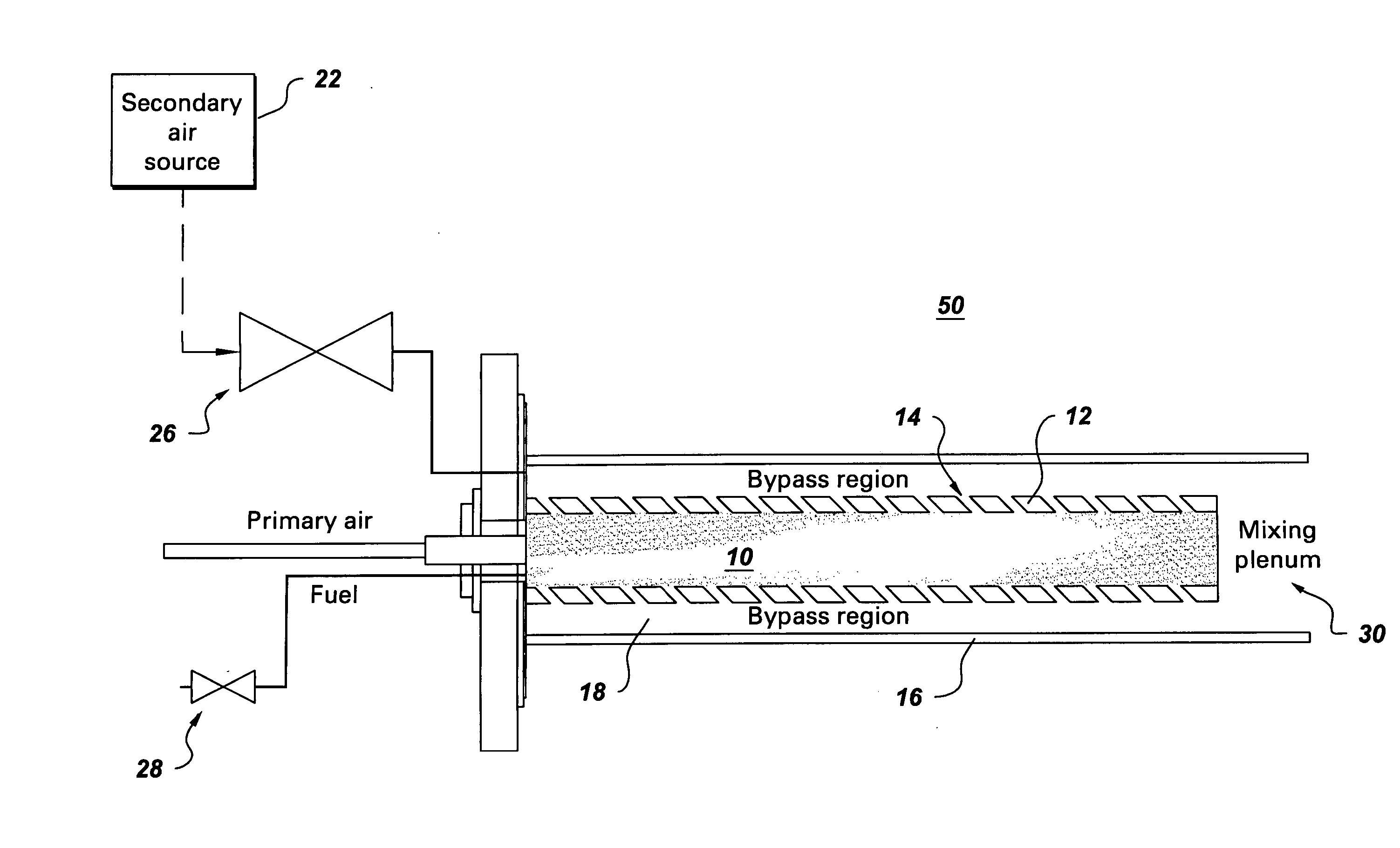
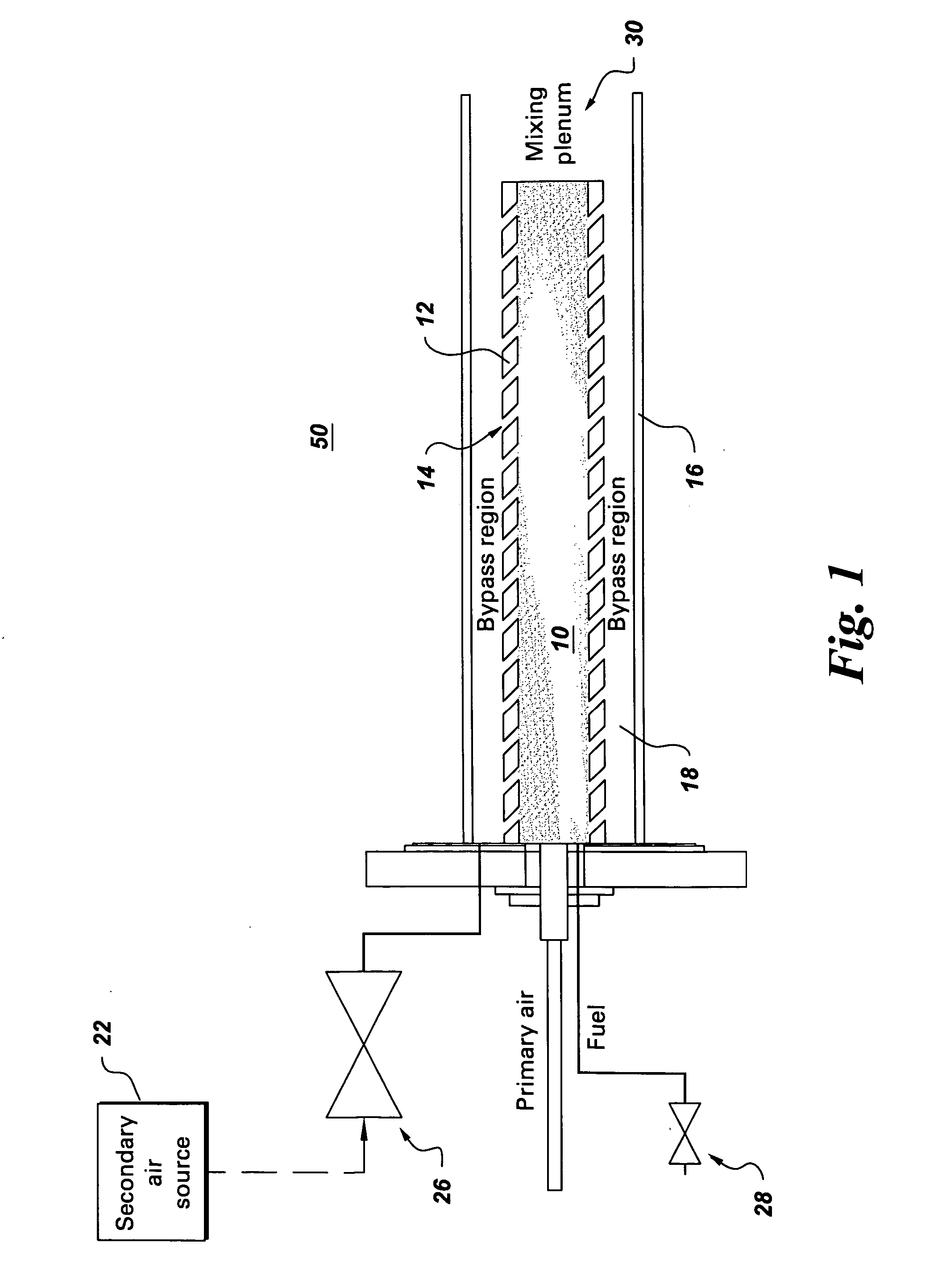
Pulse detonation engines and components thereof
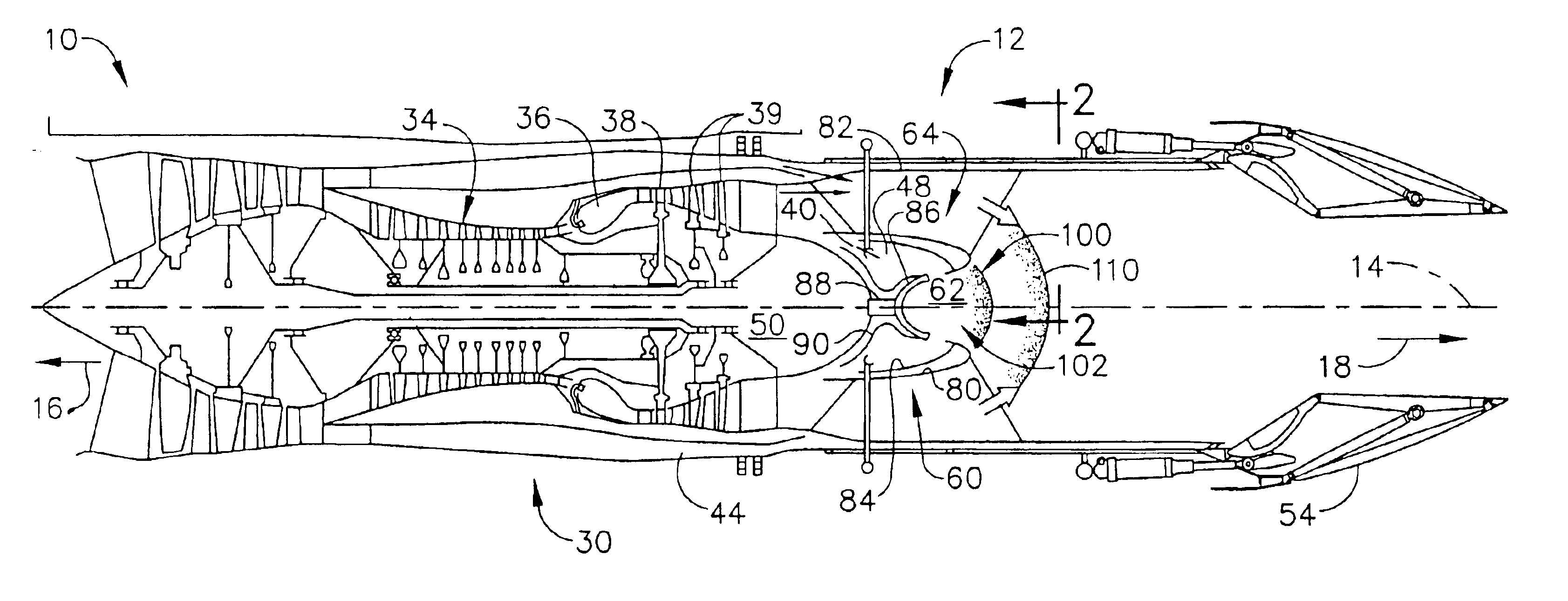
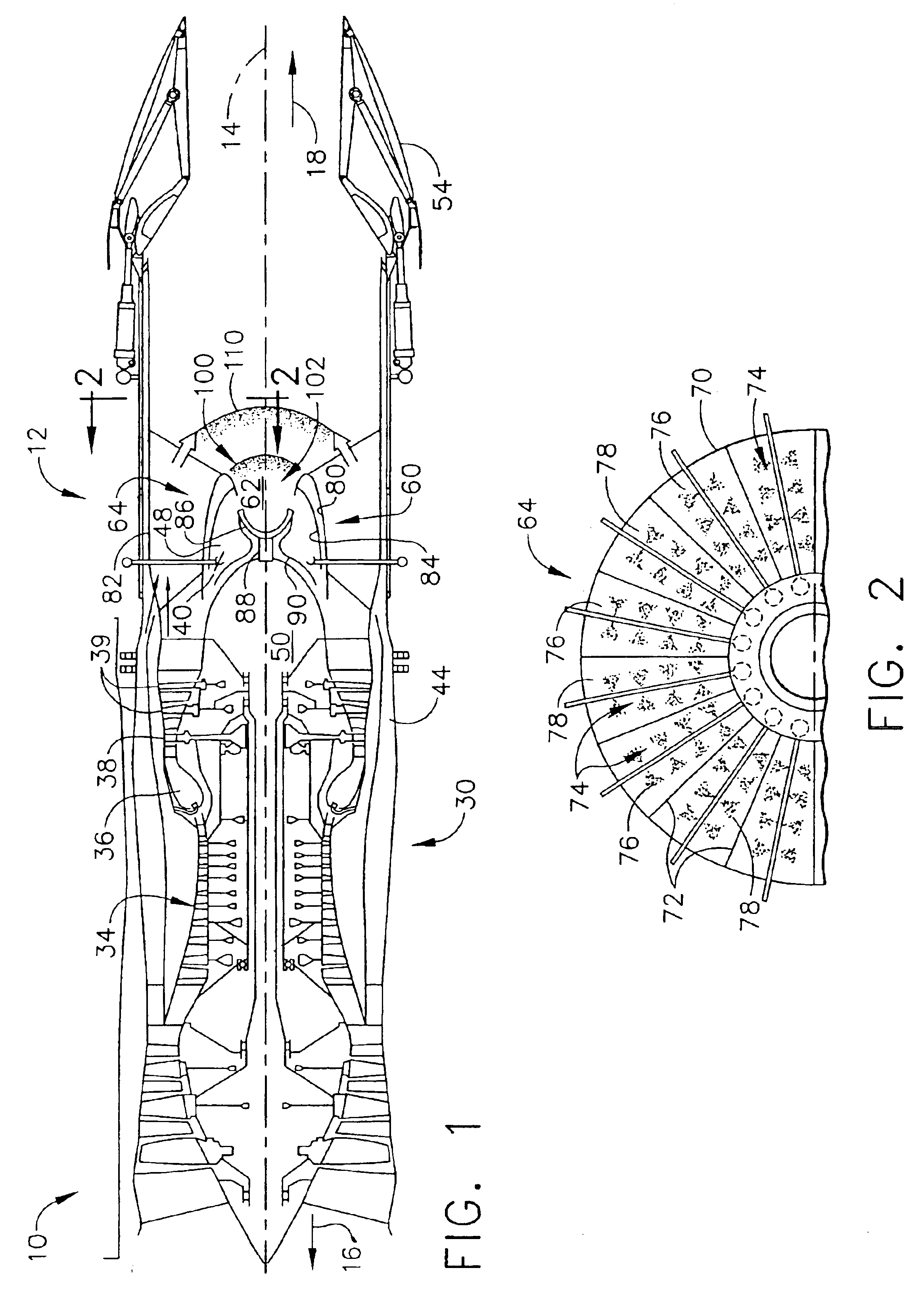
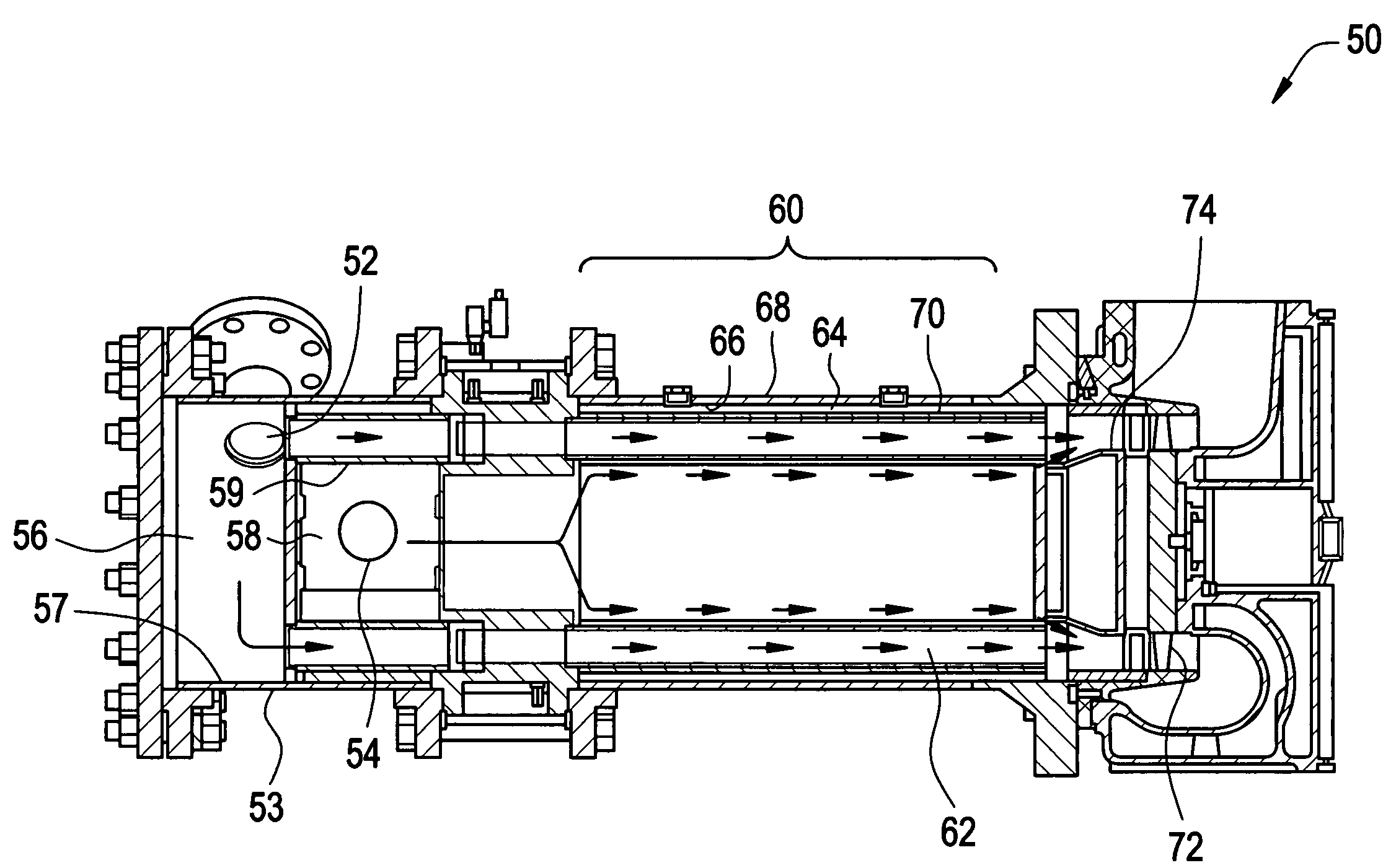
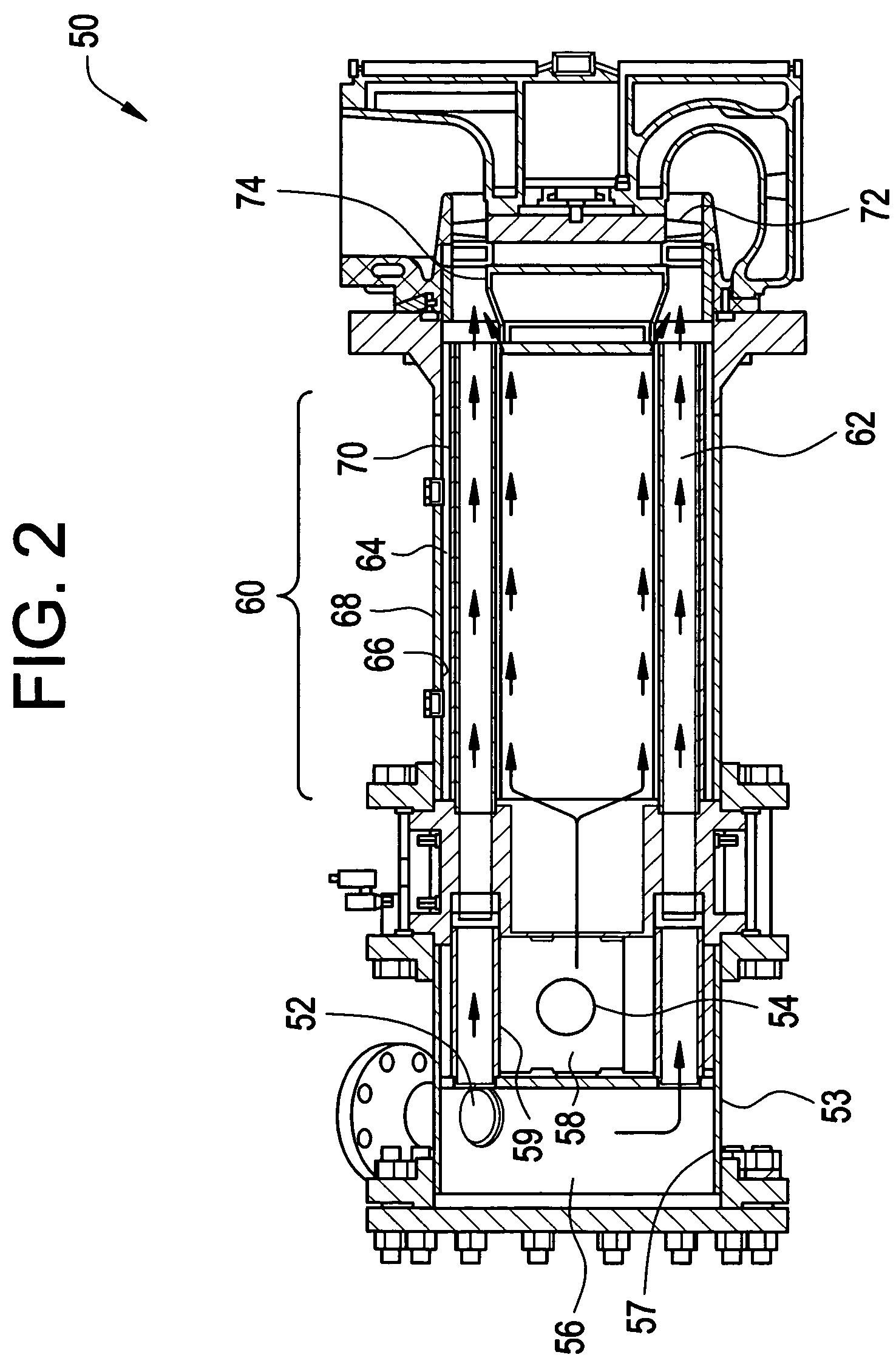
A pulse detonation engine comprises a primary air inlet; a primary air plenum located in fluid communication with the primary air inlet; a secondary air inlet; a secondary air plenum located in fluid communication with the secondary air inlet, wherein the secondary air plenum is substantially isolated from the primary air plenum; a pulse detonation combustor comprising a pulse detonation chamber, wherein the pulse detonation chamber is located downstream of and in fluid communication with the primary air plenum; a coaxial liner surrounding the pulse detonation combustor defining a cooling plenum, wherein the cooling plenum is in fluid communication with the secondary air plenum; an axial turbine assembly located downstream of and in fluid communication with the pulse detonation combustor and the cooling plenum; and a housing encasing the primary air plenum, the secondary air plenum, the pulse detonation combustor, the coaxial liner, and the axial turbine assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High thrust gas turbine engine with improved core system
InactiveUS7096674B2Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingWorking fluidEngineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
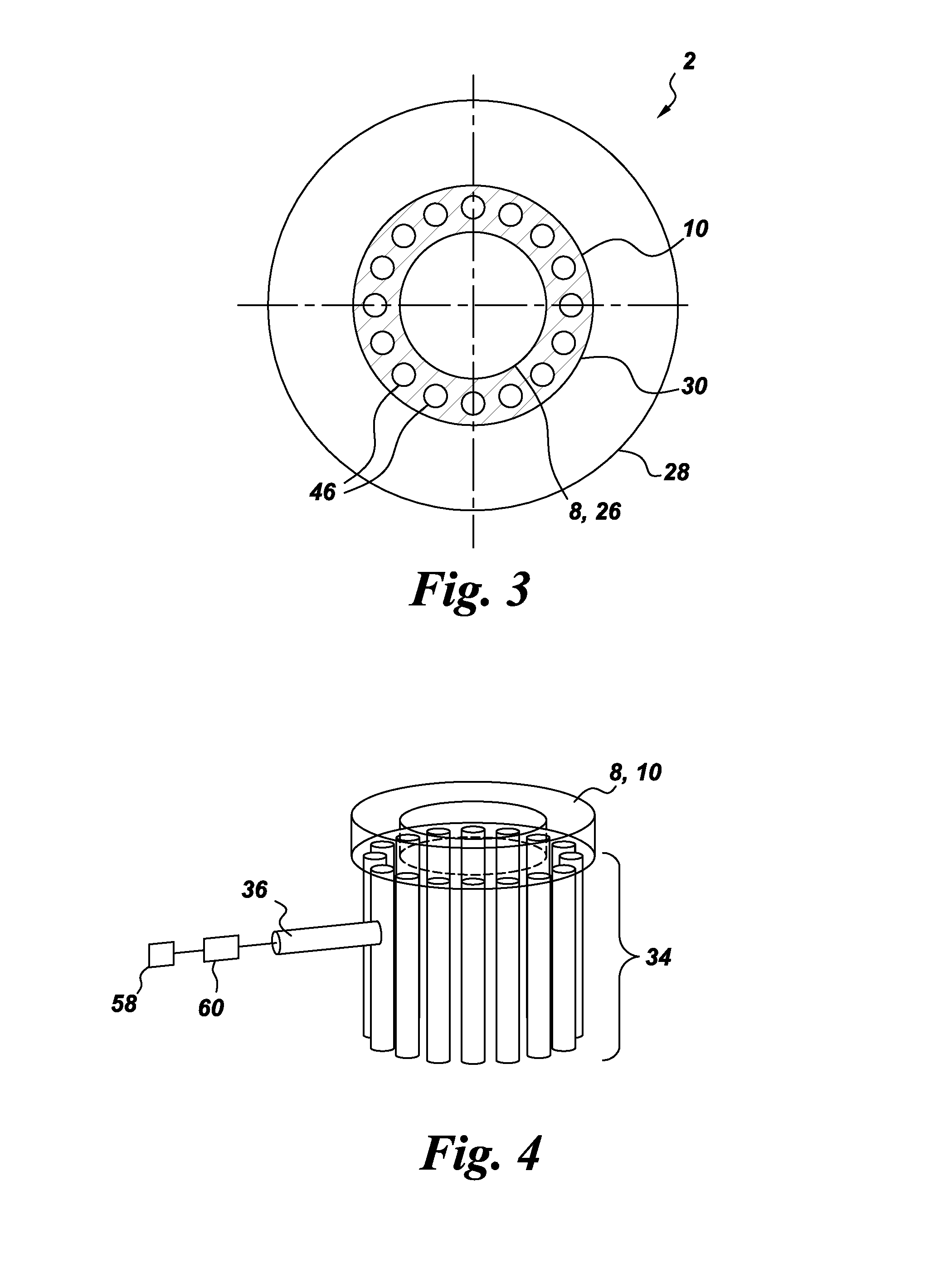
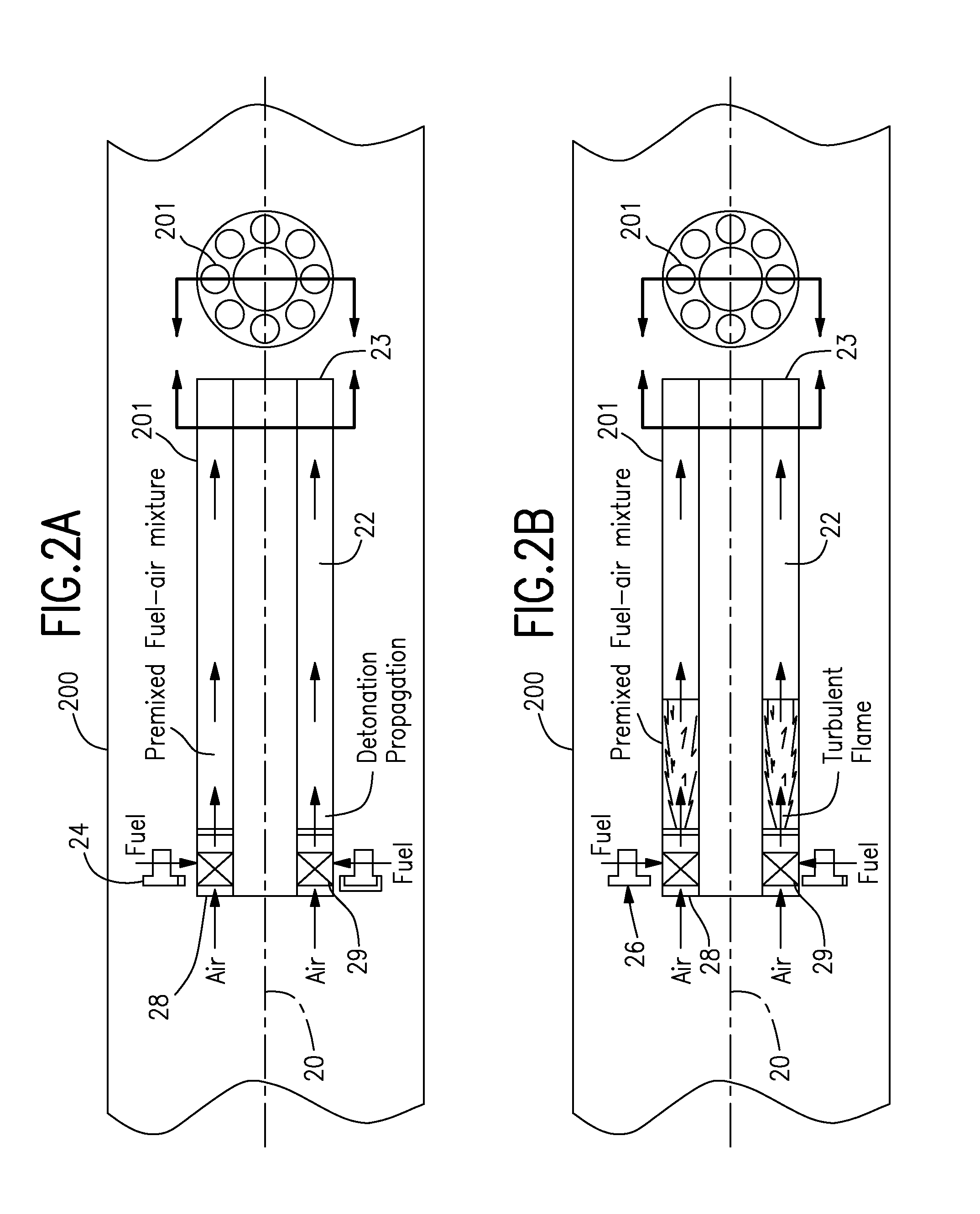
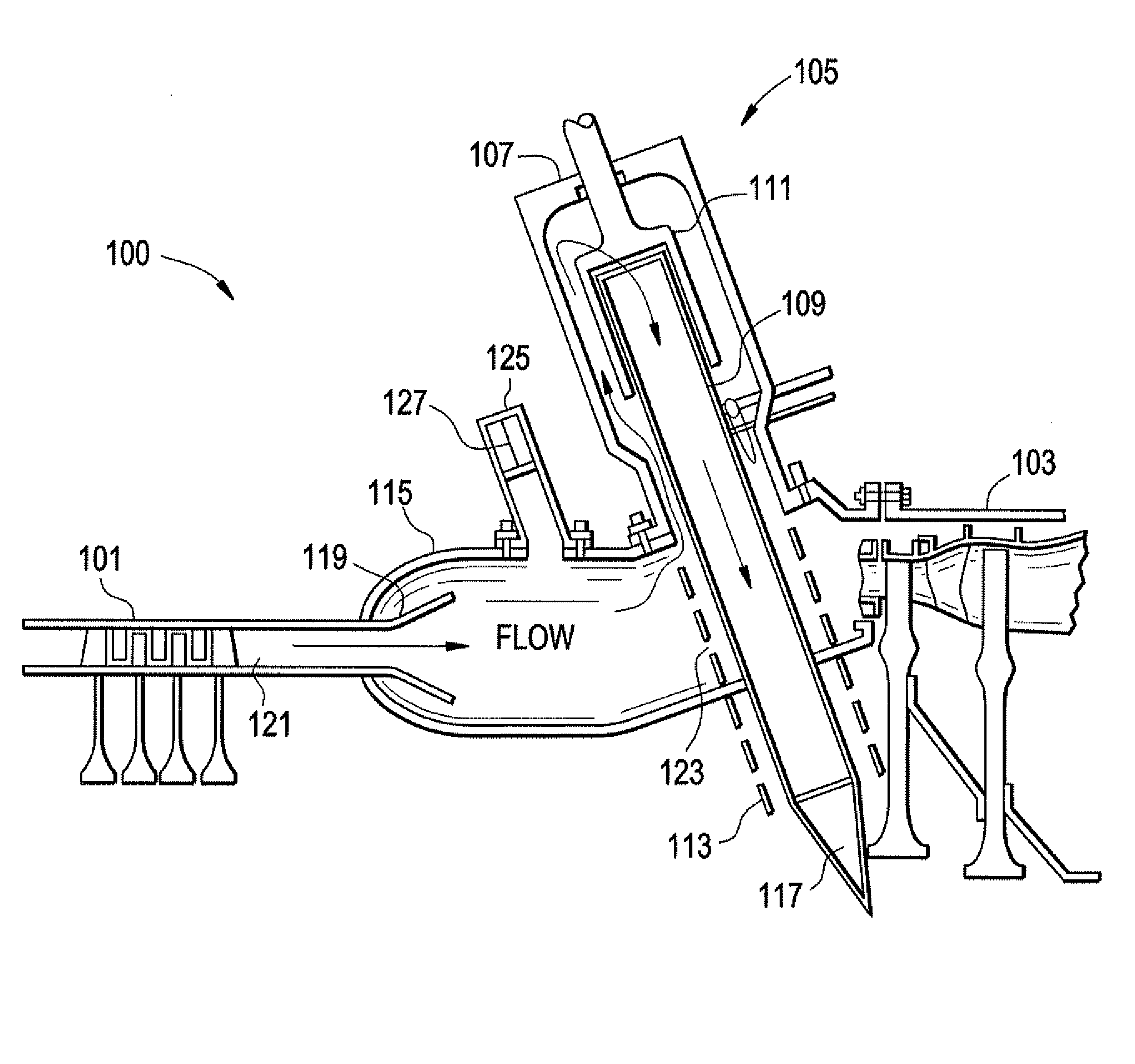
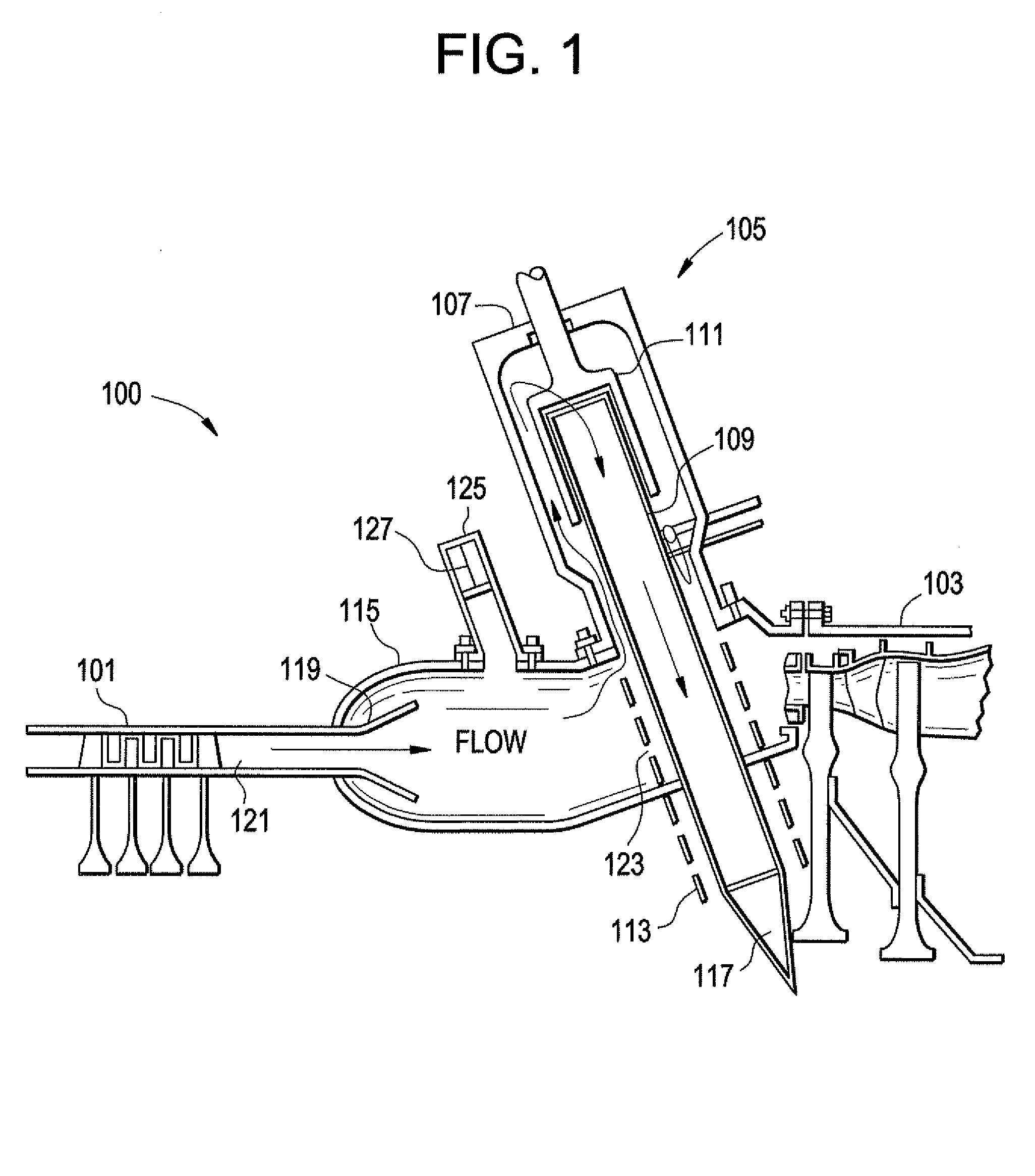
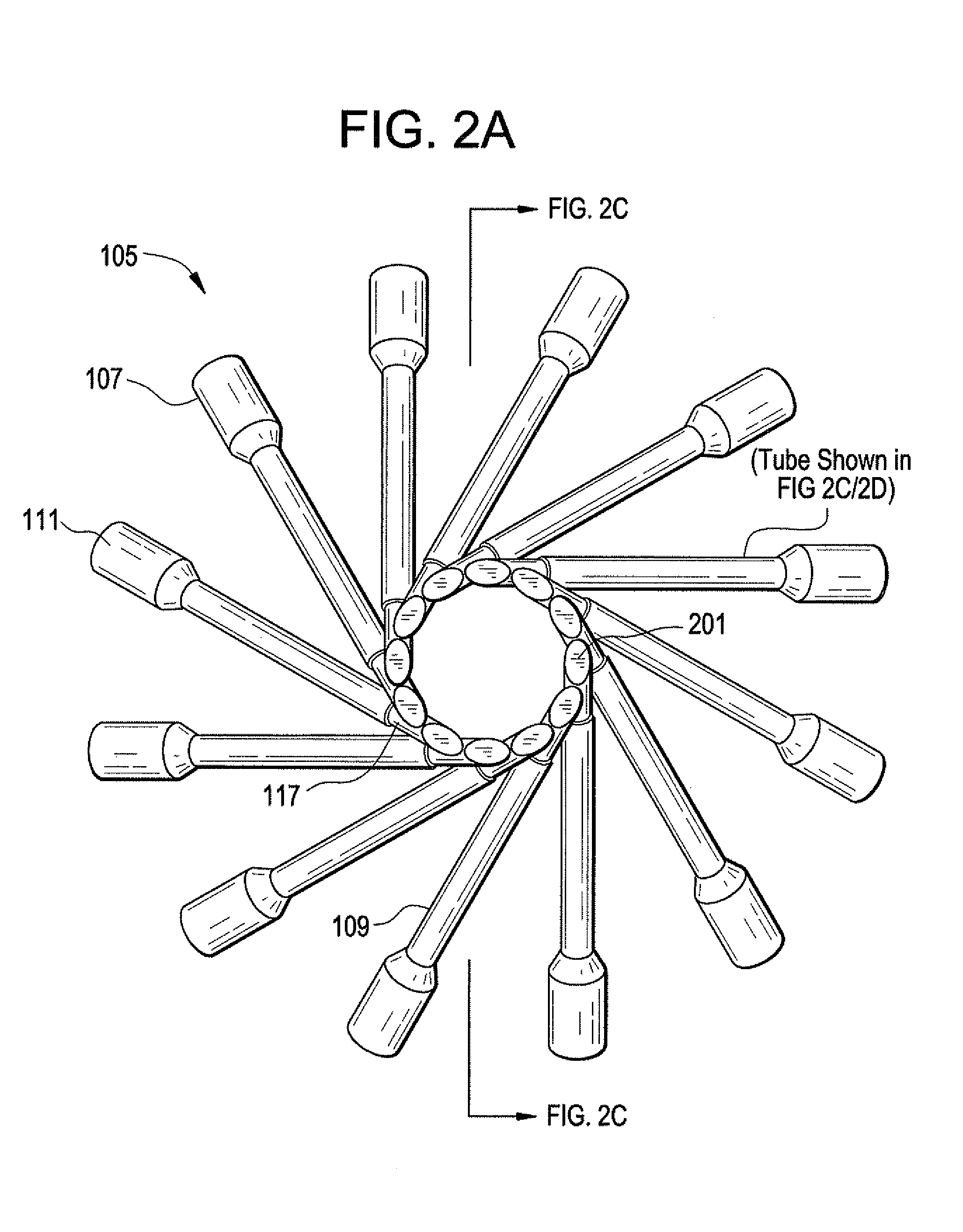
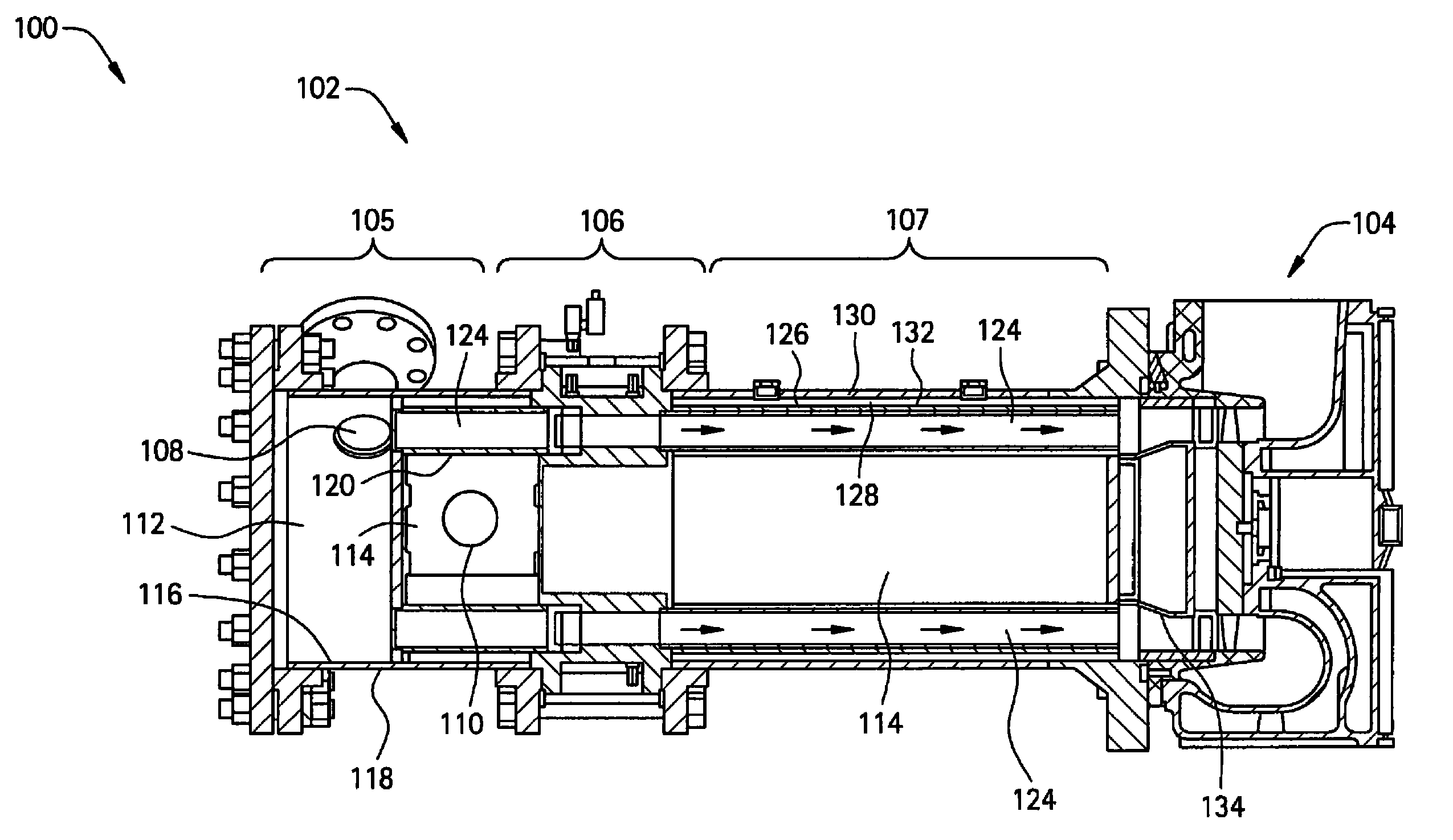
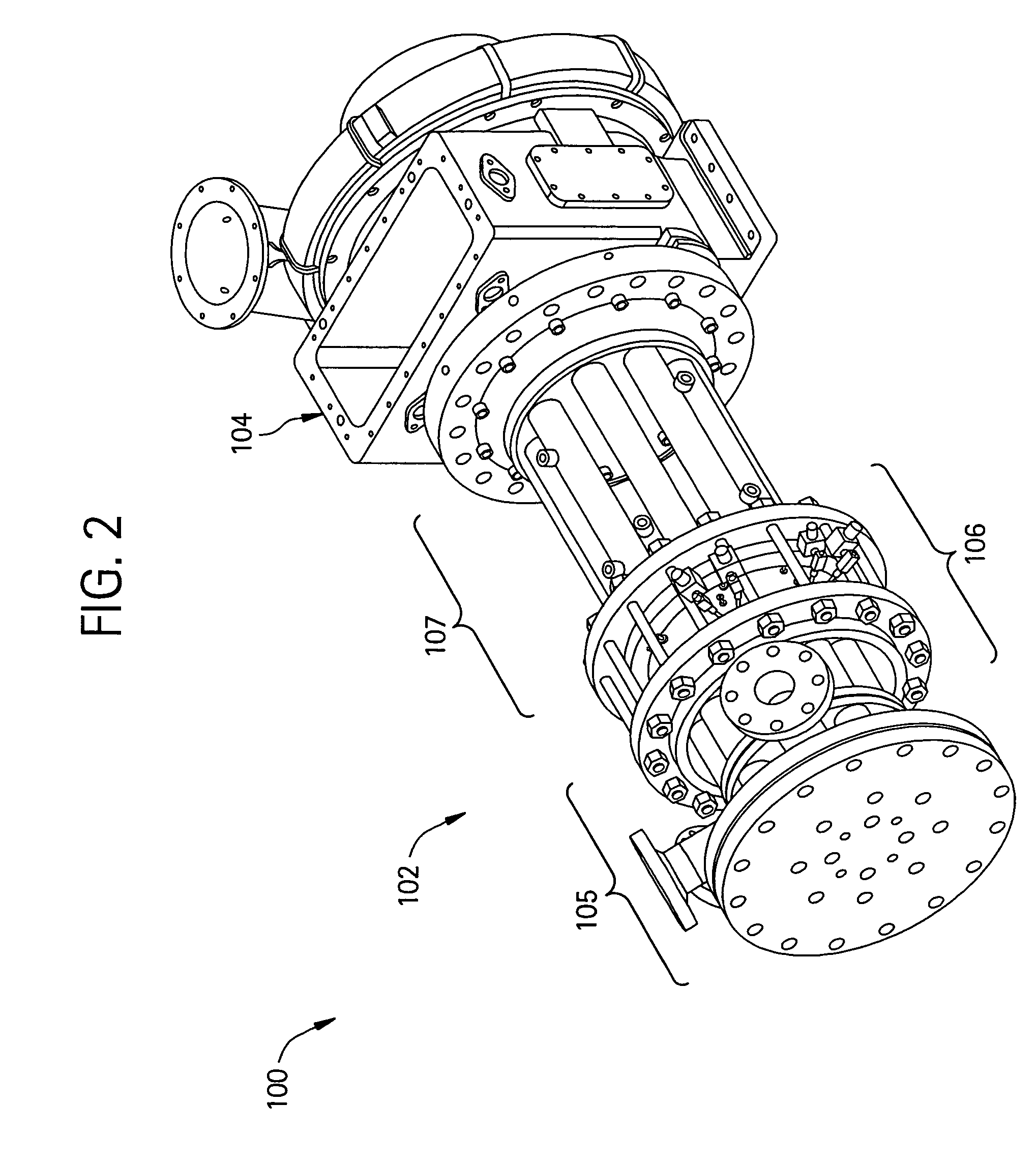
Multiple tube pulse detonation engine turbine apparatus and system
ActiveUS20070180811A1Facilitate fuel injectionEasy to igniteGas turbine plantsExplosive combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
A pulse detonation combustor (PDC) assembly includes an upstream chamber forming an inlet plenum, a downstream chamber including a downstream portion of at least one PDC tube, and an integrated PDC head coupled to the upstream chamber and the downstream chamber. The integrated PDC head is configured to facilitate fuel injection and ignition within the PDC tube. The PDC tube includes an inner seal surface and an outer seal surface configured to mate with the inner seal surface, wherein the inner seal surface includes an elevated section thereon that engages with the outer seal surface such that the PDC tube is free to partially pivot about a longitudinal axis thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pulse detonation engine and valve
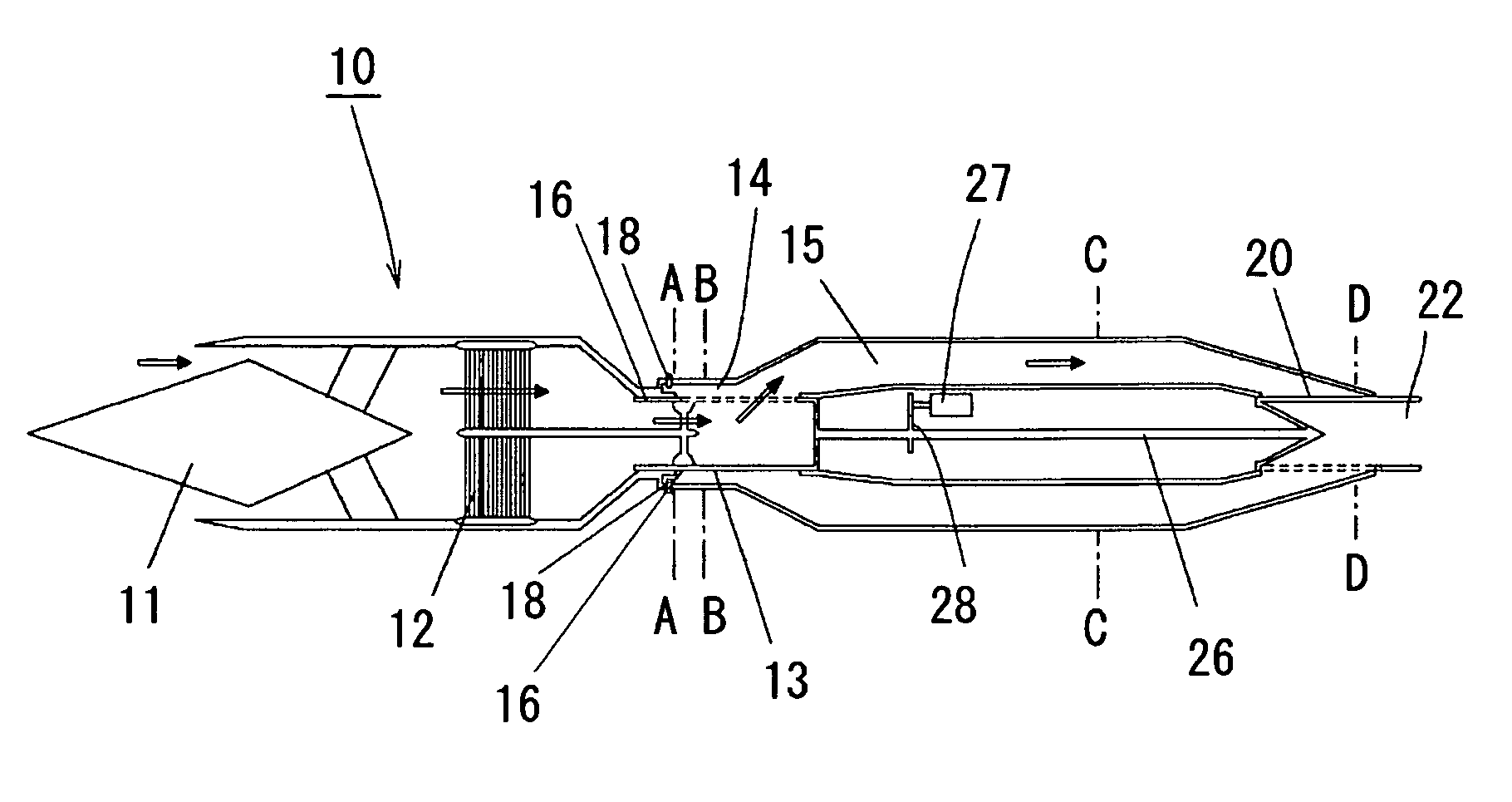
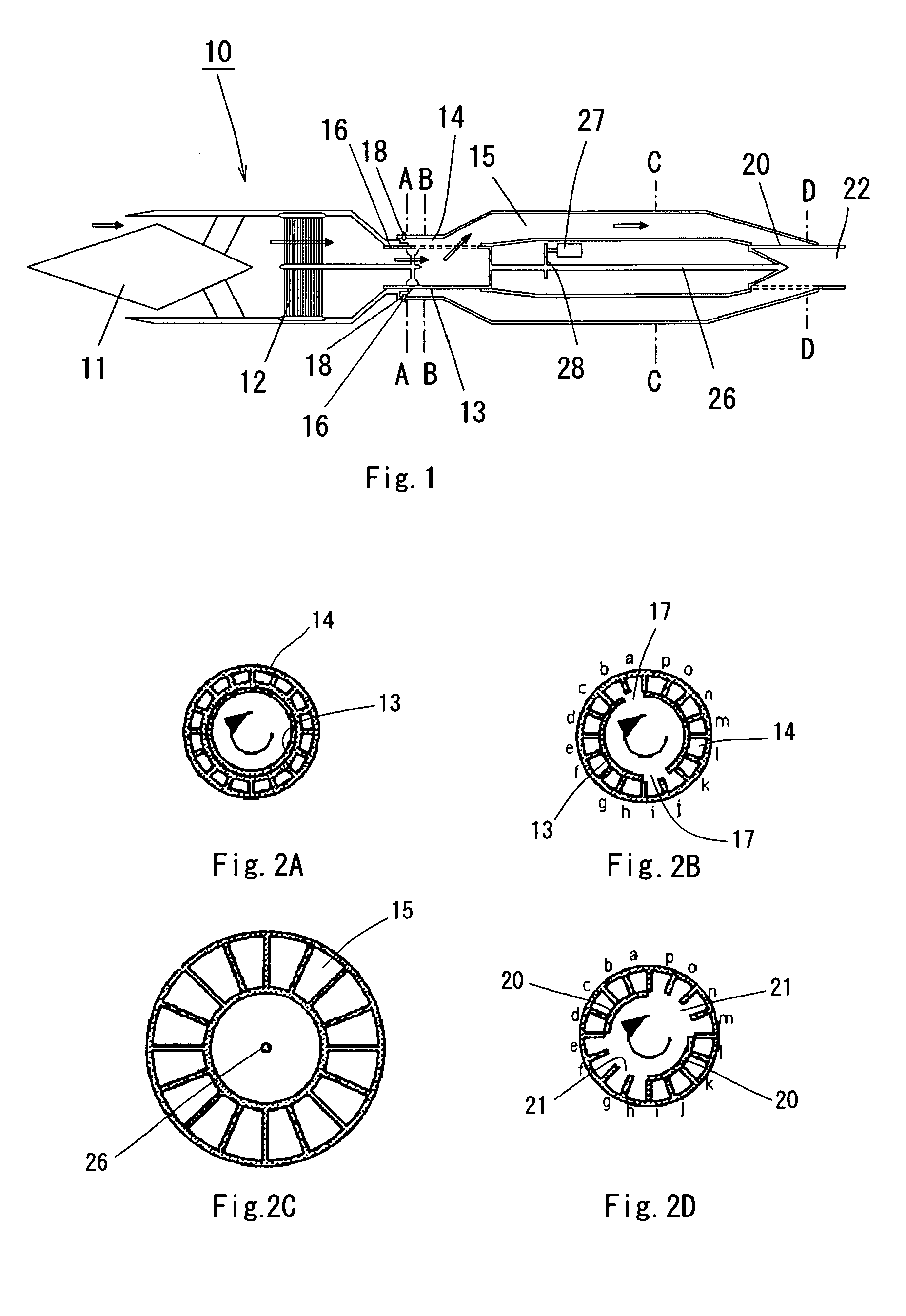
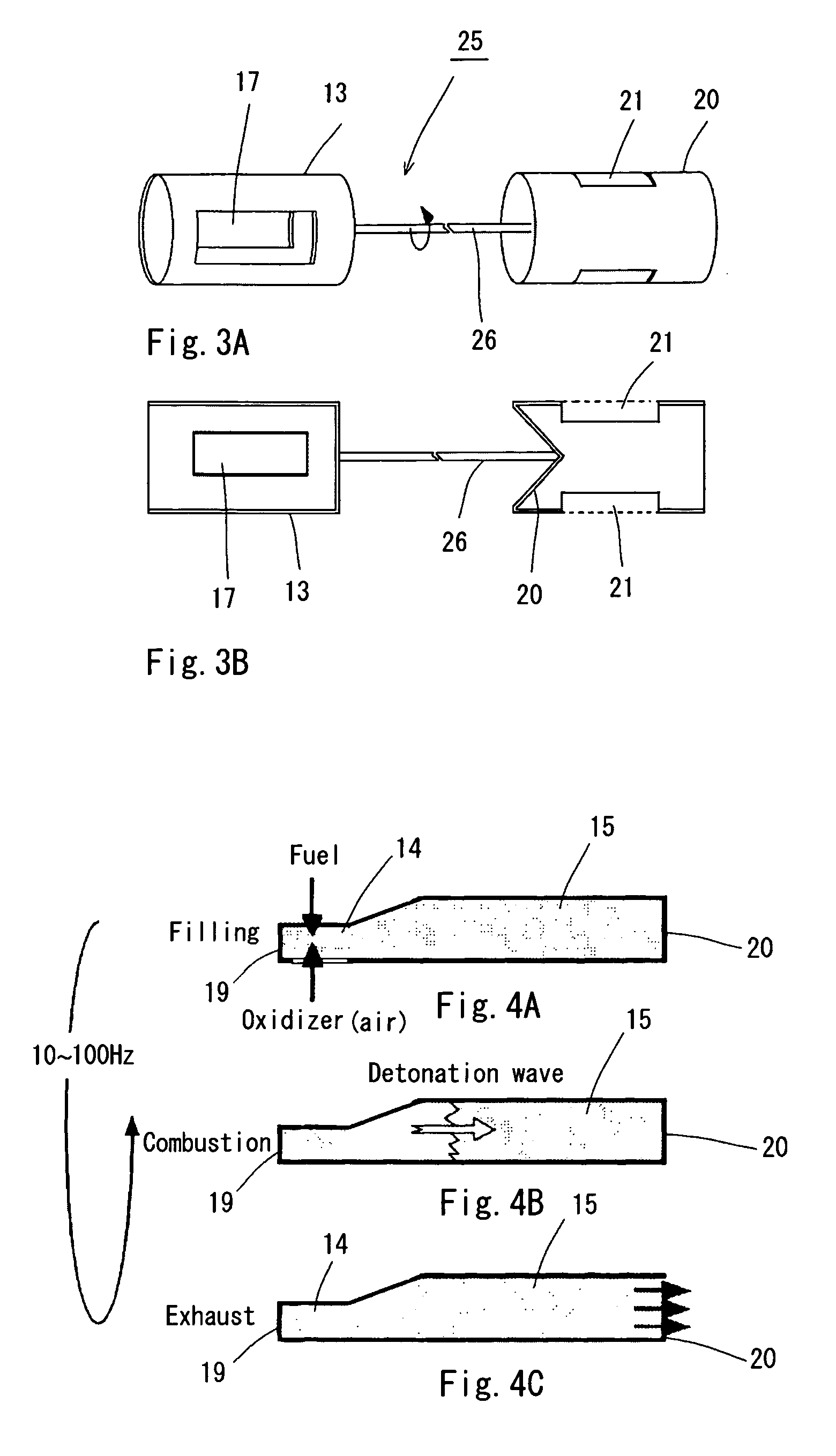
InactiveUS20050183413A1Accurate timingIncrease air densityPulsating combustionTurbine/propulsion fuel heatingCombustion chamberCombustor
Pressure and density of a gaseous mixture are increased in the process of introducing the gaseous mixture into the combustor of an air-breathing pulse detonation engine employing atmospheric oxygen as an oxidizer. The exit valve 20 able to be opened and closed is provided at the outlet of the combustor 15, an air cooler 12 is provided in the exit of the intake, and density is increased by exchange of heat of the air received at the intake with a coolant in the air cooler 12. Furthermore, by closing the exit valve 20 provided in the outlet of the combustor during the process of loading the gaseous mixture, transition to the detonation process is possible without expansion of the high-pressure high density air obtained by ram-compression at the intake.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
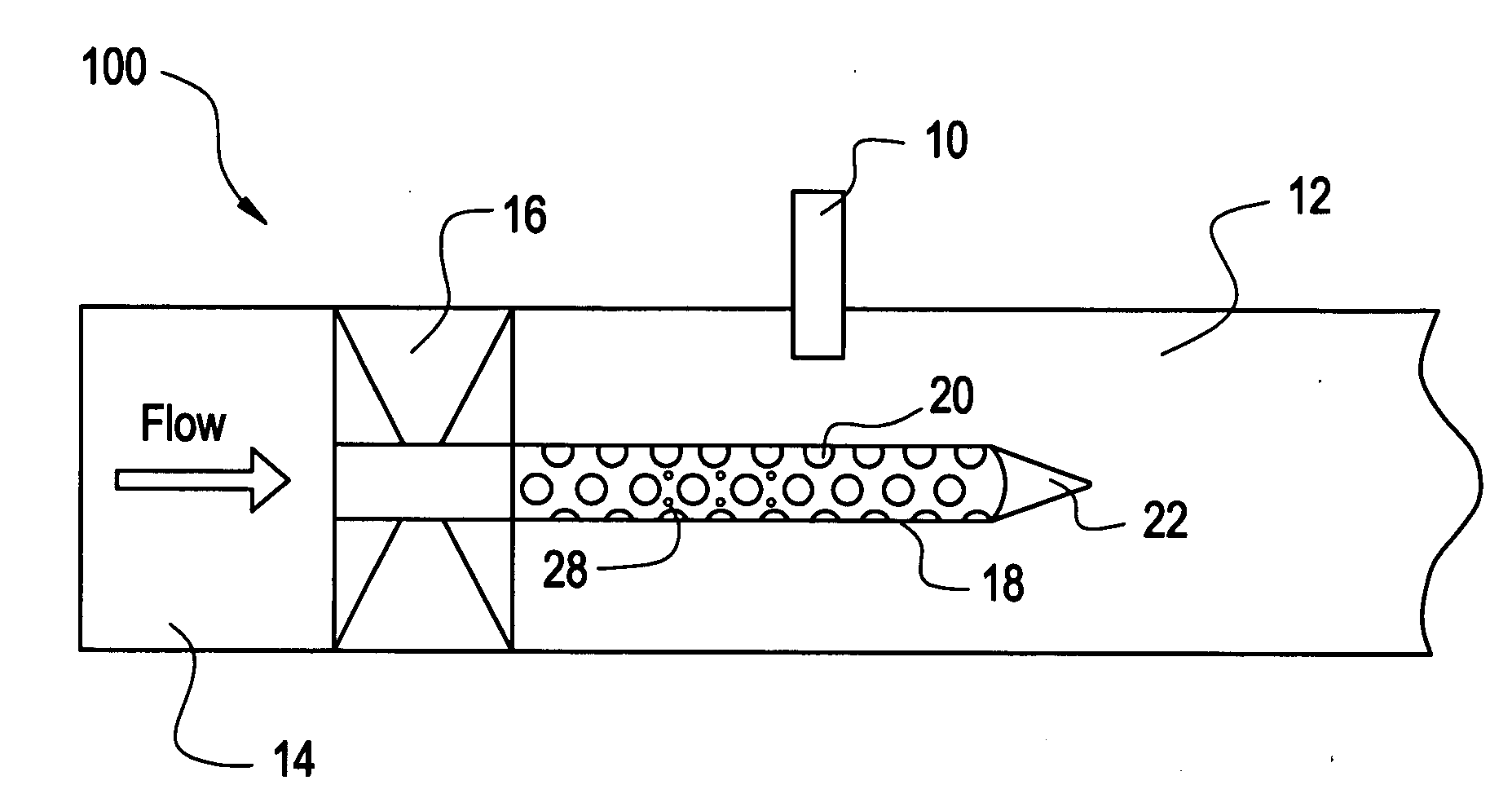
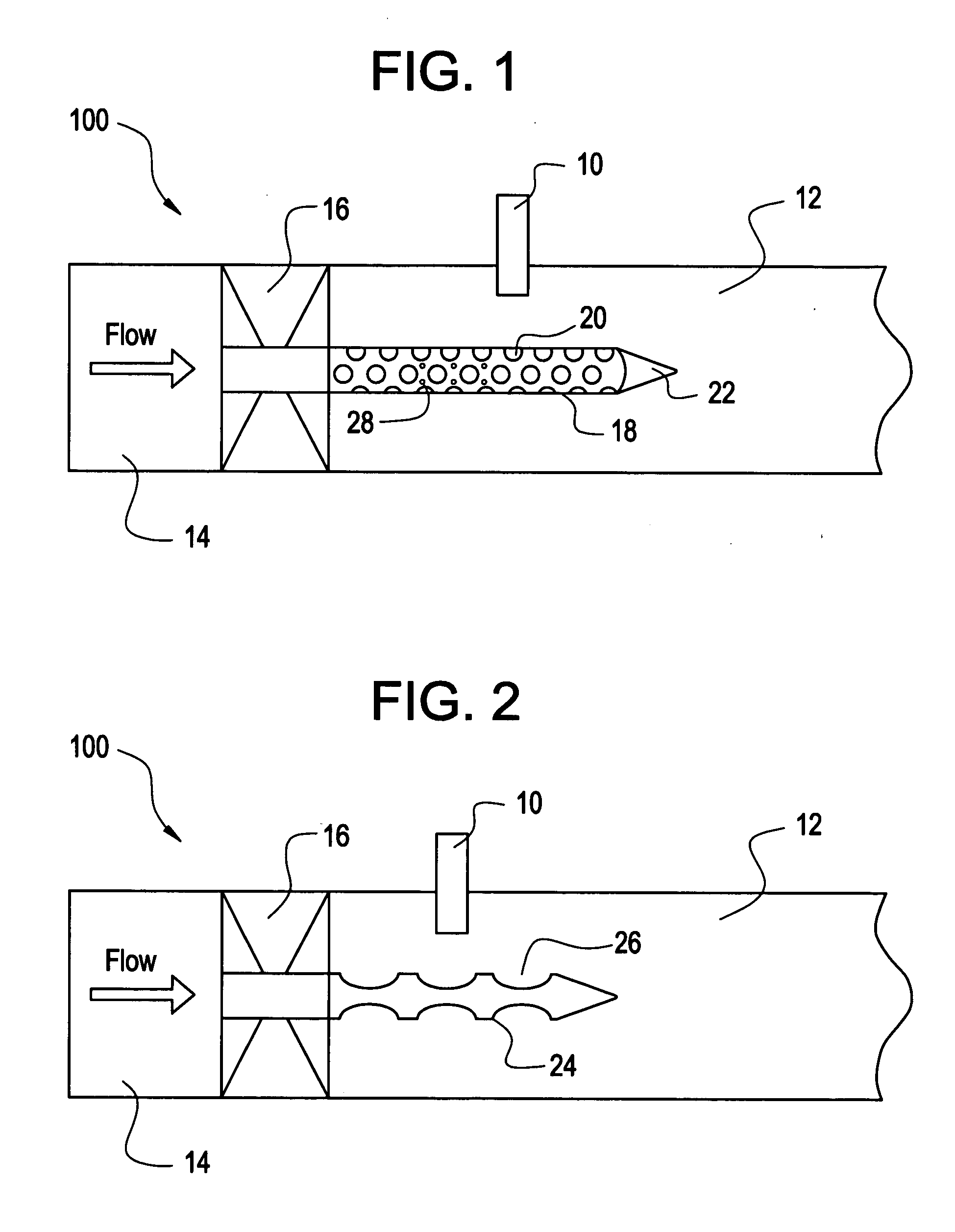
Shaped walls for enhancement of deflagration-to-detonation transition
ActiveUS20070144179A1Increased turbulenceIncrease turbulent kinetic energyTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustorCombustion chamber
A detonation chamber for a pulse detonation combustor including: a plurality of dimples disposed on at least a portion of an inner surface of the detonation chamber wherein the plurality of dimples enhance a turbulence of a fluid flow through the detonation chamber
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Integrated deflagration-to-detonation obstacles and cooling fluid flow
A detonation chamber and a pulse detonation combustor including a detonation chamber, wherein the detonation chamber includes a plurality of initiation obstacles and at least one injector in fluid flow communication with each of the plurality of initiation obstacles. The plurality of initiation obstacles are disposed on at least a portion of an inner surface of the detonation chamber with each of the plurality of initiation obstacles defining a low pressure region at a trailing edge. The plurality of initiation obstacles are configured to enhance a turbulence of a fluid flow and flame acceleration through the detonation chamber. The at least one injector in provides a cooling fluid flow to each of the plurality of initiation obstacles, wherein the cooling fluid flow is one of a fuel, a combination of fuels, air, or a fuel / air mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
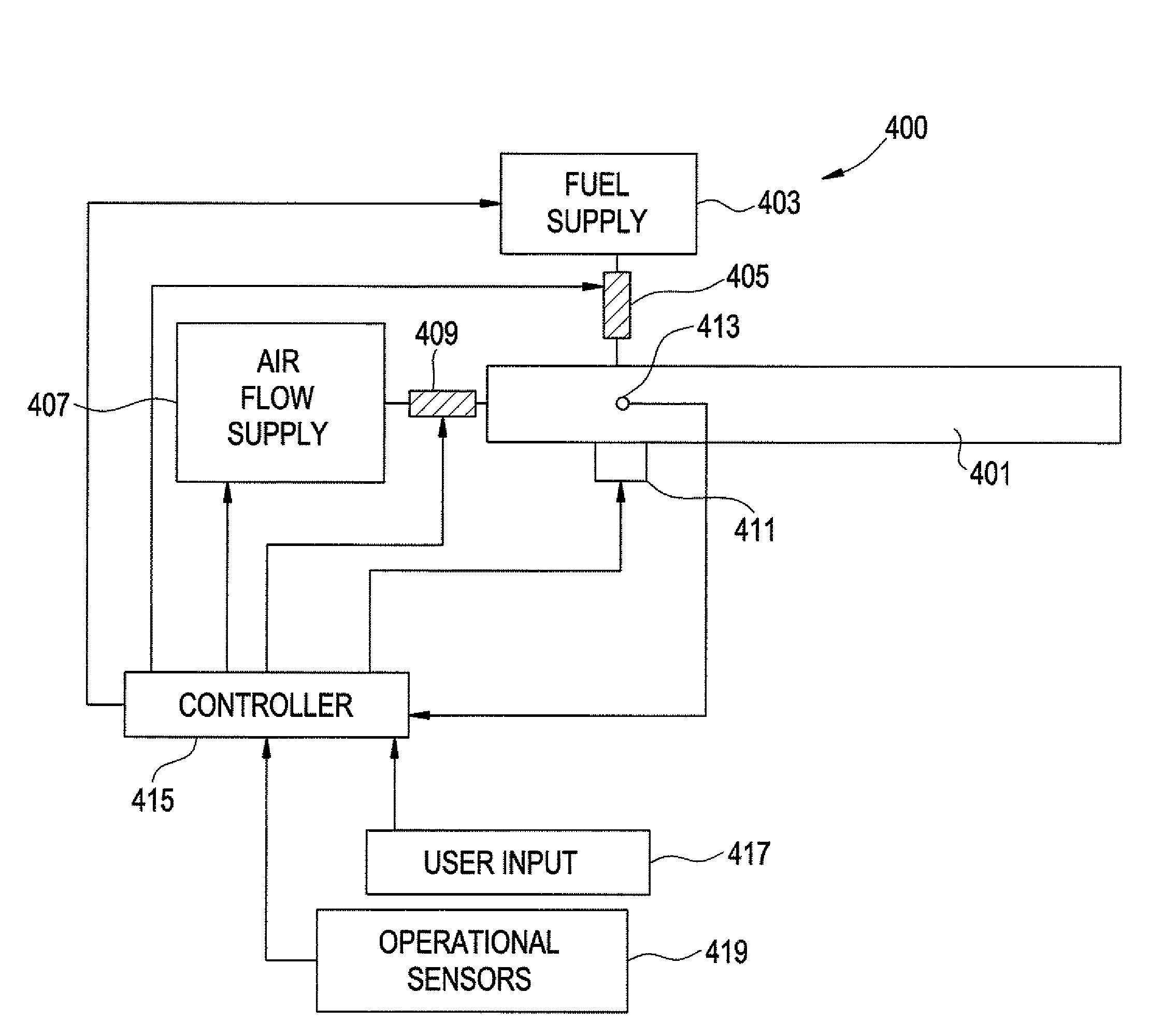
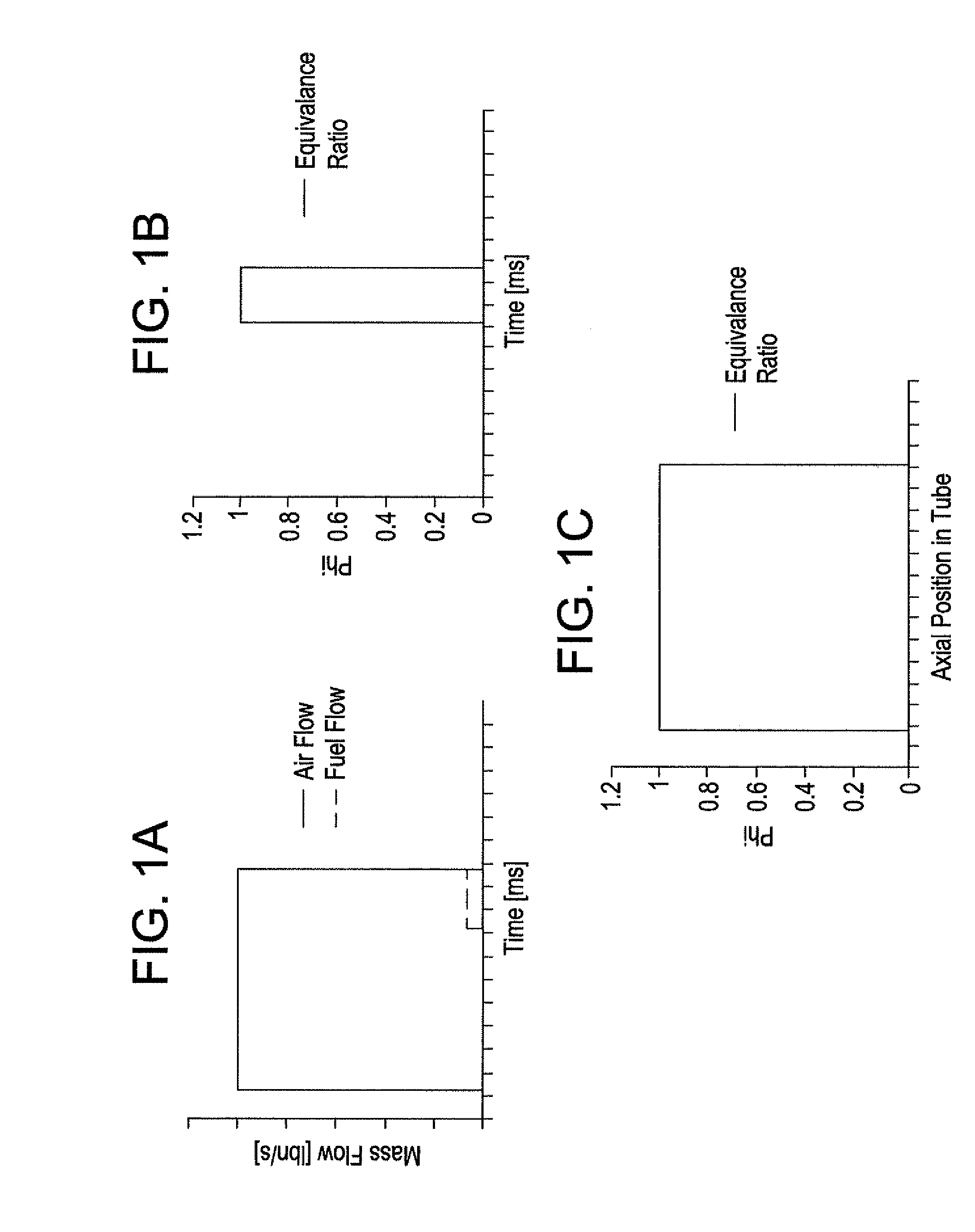
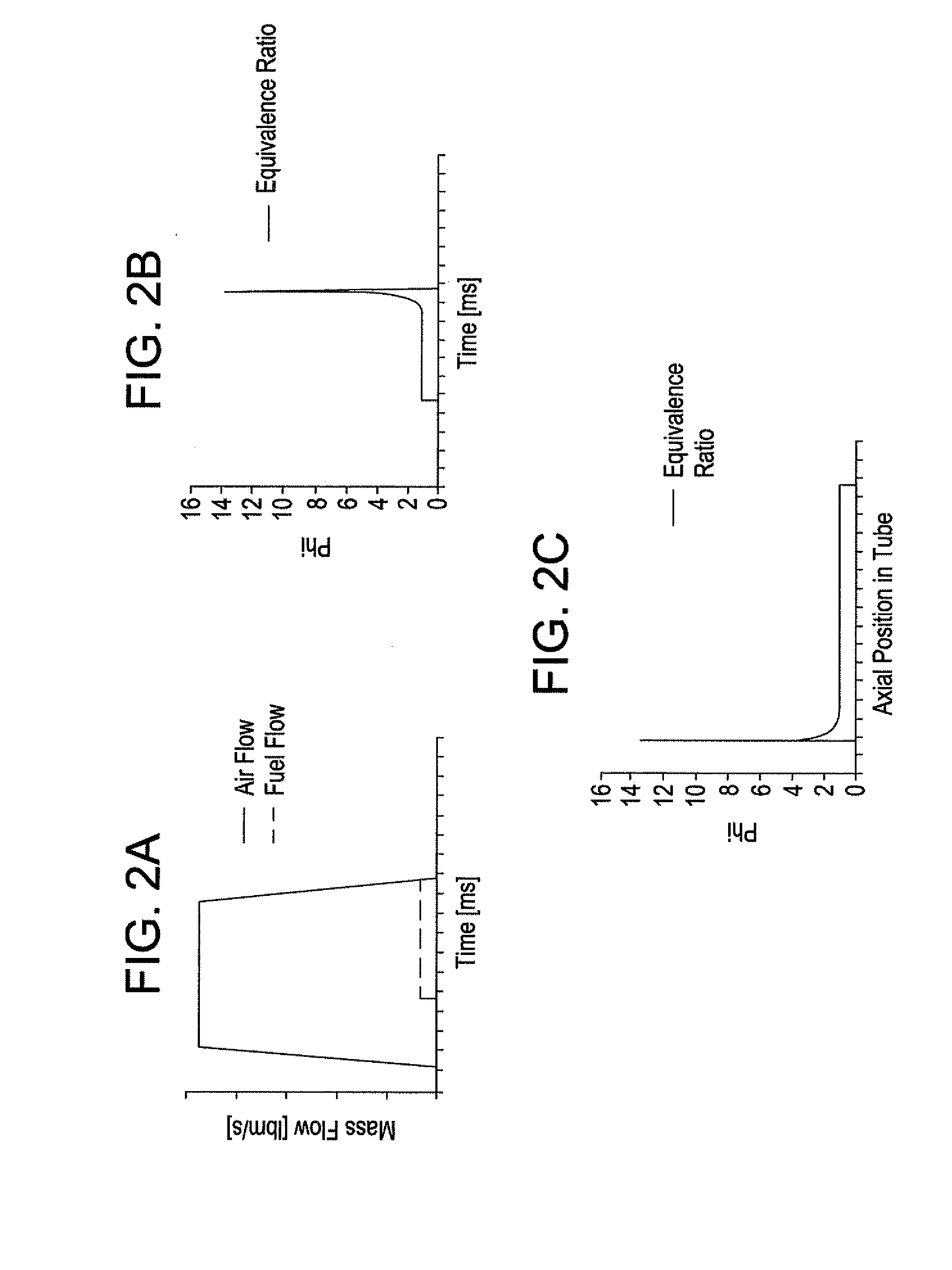
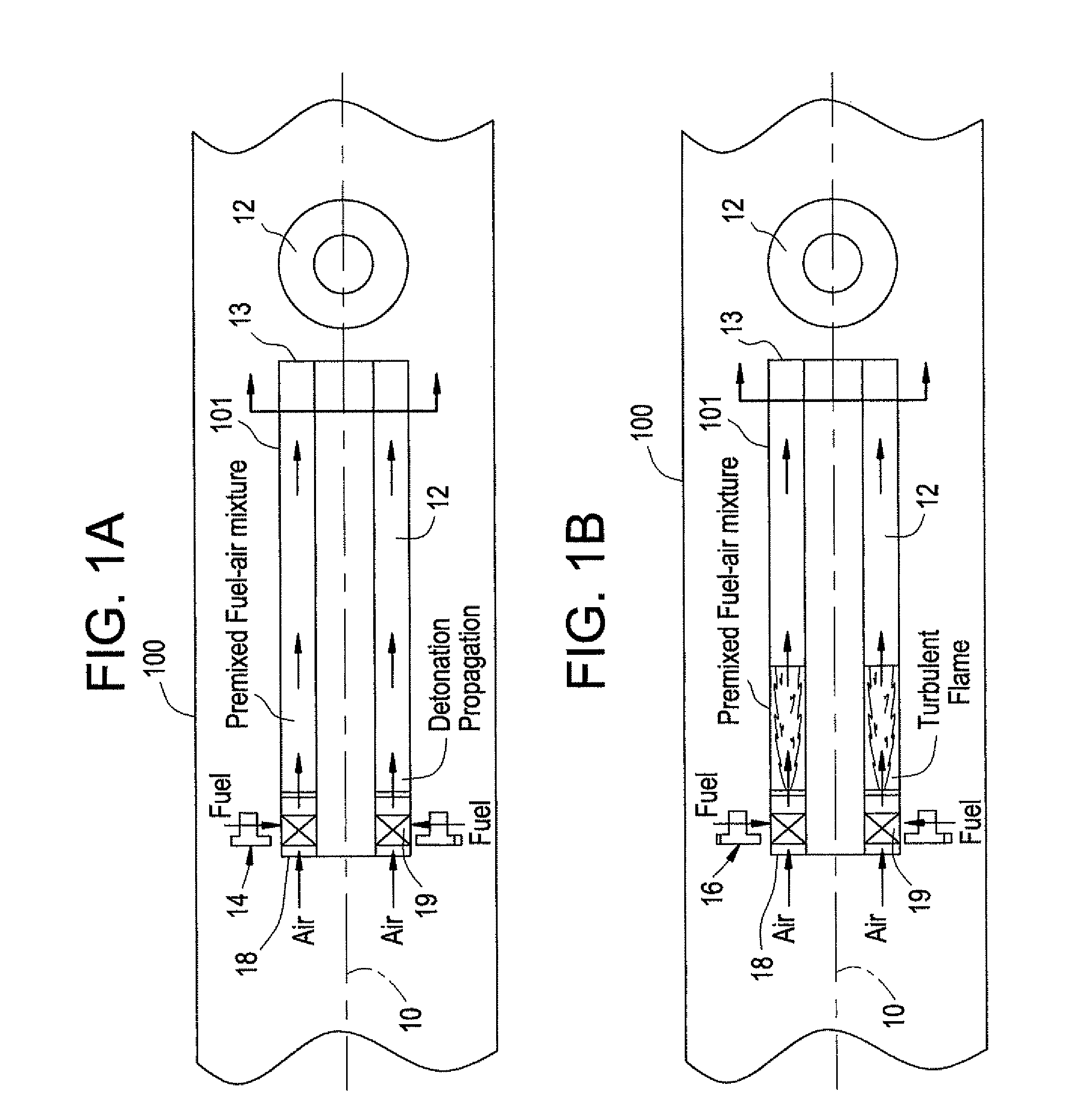
Method and apparatus for tailoring the equivalence ratio in a valved pulse detonation combustor
A pulse detonation combustor assembly contains at least one PDC tube, a mechanical air flow valve which directs an air flow into the PDC tube, where the mechanical air flow assembly changes a rate of the air flow into the PDC tube during a fill stage of the PDC tube. The assembly also contains a fuel flow control valve which directs fuel to the PDC tube and changes the rate of the fuel flow into PDC tube. By controlling the flow of the fuel and air into the PDC tube the equivalence ratio profile of the PDC tube can be tailored and controlled.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Constant volume combustor having a rotating wave rotor
InactiveUS7621118B2Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorMagnetic bearing
A constant volume combustor device includes, in one form, a detonative combustion. In one form the wave rotor of the constant volume combustor is supported by magnetic bearings. The constant volume combustor device includes a rotor having a number of fluid passageways that rotate about an axis. End plates having at least one inlet port and at least one outlet port are located on either end of the rotor. Relatively compressed air enters the rotor through the at least one inlet port, is burned with fuel in a pulsed combustion process, and exits at least one exit port. The pulsed combustion process can be a pulsed detonation combustion process or a pulsed deflagration combustion process.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE NORTH AMERICAN TECH
Dual mode combustion operation of a pulse detonation combustor in a hybrid engine
InactiveUS7950219B2Easy to operateEfficient combustionContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberSolenoid valve
A dual mode combustor of a gas turbine engine contains at least one dual mode combustor device having a combustion chamber, a fuel air mixing element, a high frequency solenoid valve and a fuel injector. During a first mode of operation the dual mode combustor device operates in a steady, constant pressure deflagration mode, receiving its fuel from the fuel injector. In a second mode of operation the dual mode combustor device operates in a pulse detonation mode, receiving its fuel from the high frequency solenoid valve.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combustion Section Heat Transfer System for a Propulsion System
ActiveUS20180363555A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustion chamberTurbine
The present disclosure is directed to a propulsion system including an annular inner wall and an annular outer wall, a nozzle assembly, a turbine nozzle, and an inner casing and an outer casing. The inner wall and outer wall together extend at least partially along a longitudinal direction and together define a combustion chamber inlet, a combustion chamber outlet, and a combustion chamber therebetween. The nozzle assembly is disposed at the combustion inlet and provides a mixture of fuel and oxidizer to the combustion chamber. The turbine nozzle defines a plurality of airfoils in adjacent circumferential arrangement disposed at the combustion chamber outlet. The turbine nozzle is coupled to the outer wall and the inner wall. The inner casing is disposed inward of the inner wall and the outer casing is disposed outward of the outer wall. Each of the inner casing and the outer casing are coupled to the turbine nozzle. A primary flowpath is defined between the inner casing and the inner wall, through the turbine nozzle, and between the outer casing and the outer wall, and in fluid communication with the combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
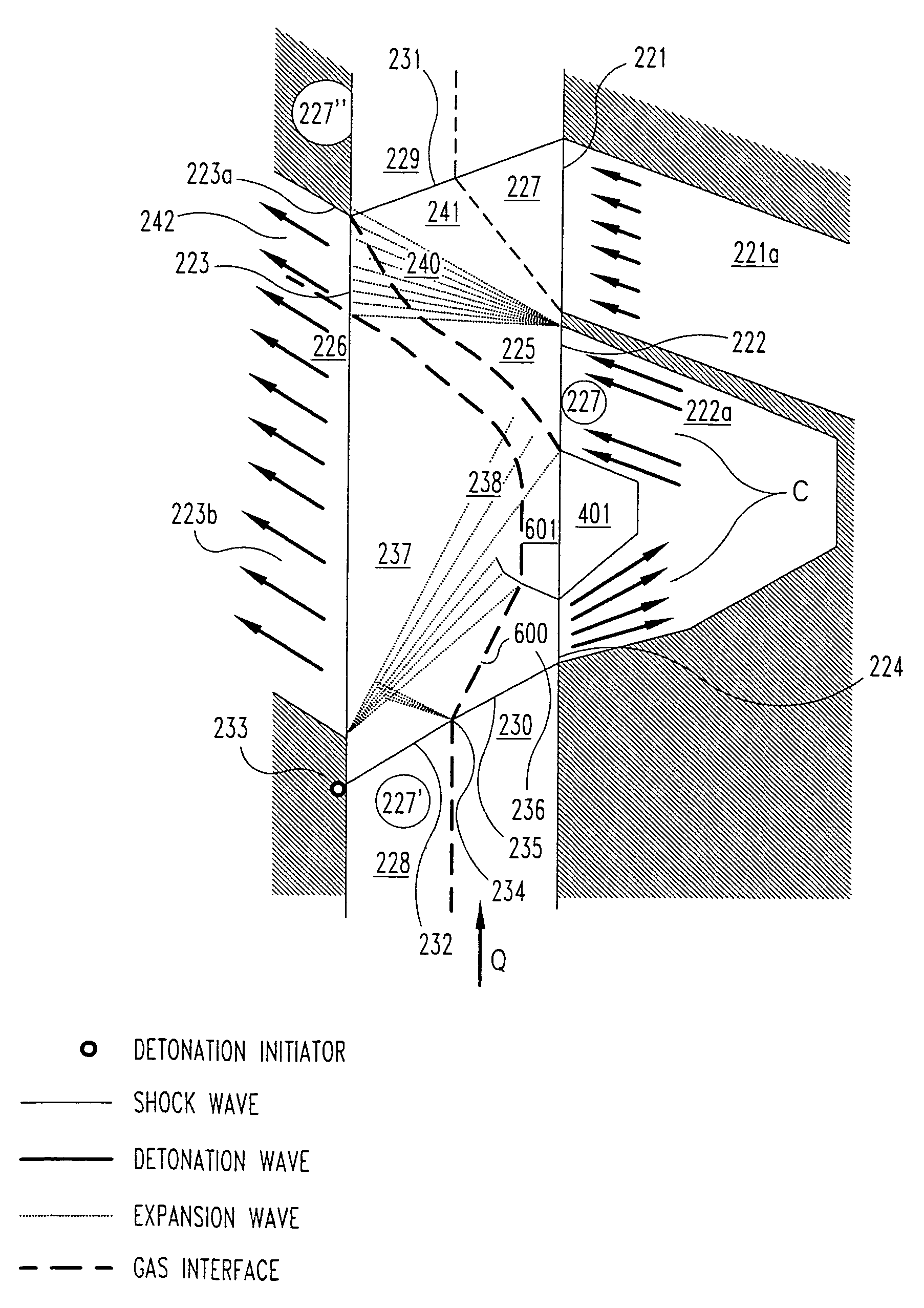
Geometric configuration and confinement for deflagration to detonation transition enhancement
InactiveUS20070137172A1Increase elasticityWell mixedContinuous combustion chamberEfficient propulsion technologiesCombustorDeflagration to detonation transition
A pulse detonation combustor is provided with a fuel-air mixer located upstream from a detonation chamber. A fuel-air mixture exits the fuel-air mixer and enters the detonation chamber, where it is ignited by an ignition source. The flow from the fuel-air mixer passes over the surface of a center body, which extends downstream from the fuel-air mixer. The surface of the center body contains at least one turbulence generator, which imparts additional turbulence in the fuel-air mixture passing through the chamber. The turbulence generator aids in the mixing of the fuel and air of the fuel-air mixture to enhance the deflagration to detonation transition within the pulse detonation combustor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-tube, can-annular pulse detonation combustor based engine with tangentially and longitudinally angled pulse detonation combustors
An engine contains a compressor stage, a pulse detonation combustion stage and a turbine stage. The pulse detonation combustion stage contains at least one pulse detonation combustor which has an inlet portion. The pulse detonation combustor is oriented longitudinally and / or tangentially with respect to a centerline of the engine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Adiabatic power generating system
Owner:PRIMLANI INDRU J
Valveless pulsed detonation combustor
Pulse detonation combustors of valveless construction. One valveless pulse detonation combustor, having a tube with a closed end and an open end, is constructed with a flame accelerator within the tube, adjacent the open end. A valveless, apertured flow restrictor is positioned between the flame accelerator and the closed end of the tube. A sparking device is positioned within the tube, between the flow restrictor and the flame accelerator. Valveless fuel and air ports are positioned between the flow restrictor and the closed end of the tube. Substantially right-angle manifold passageways are in communication with each of the ports.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
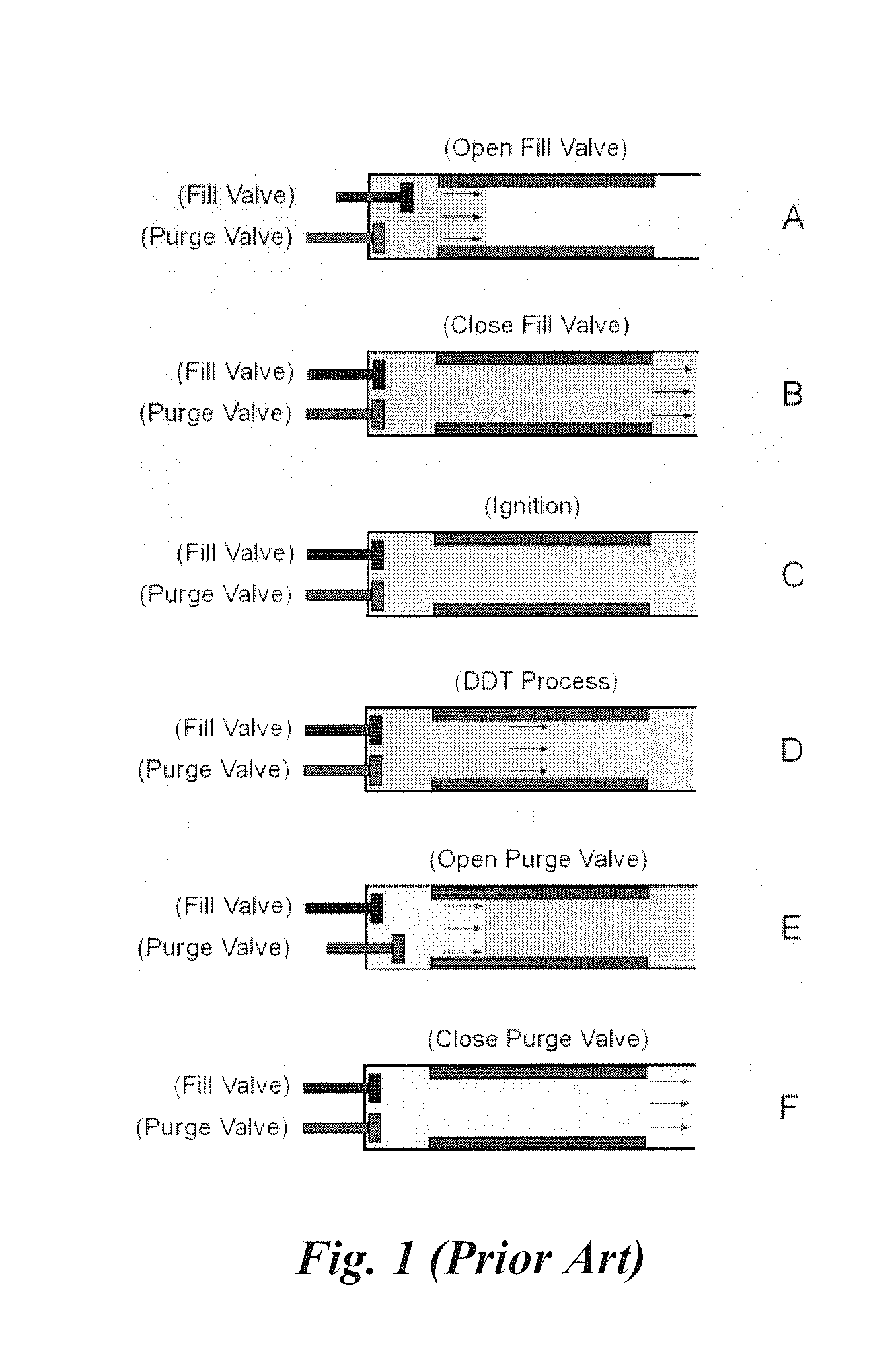
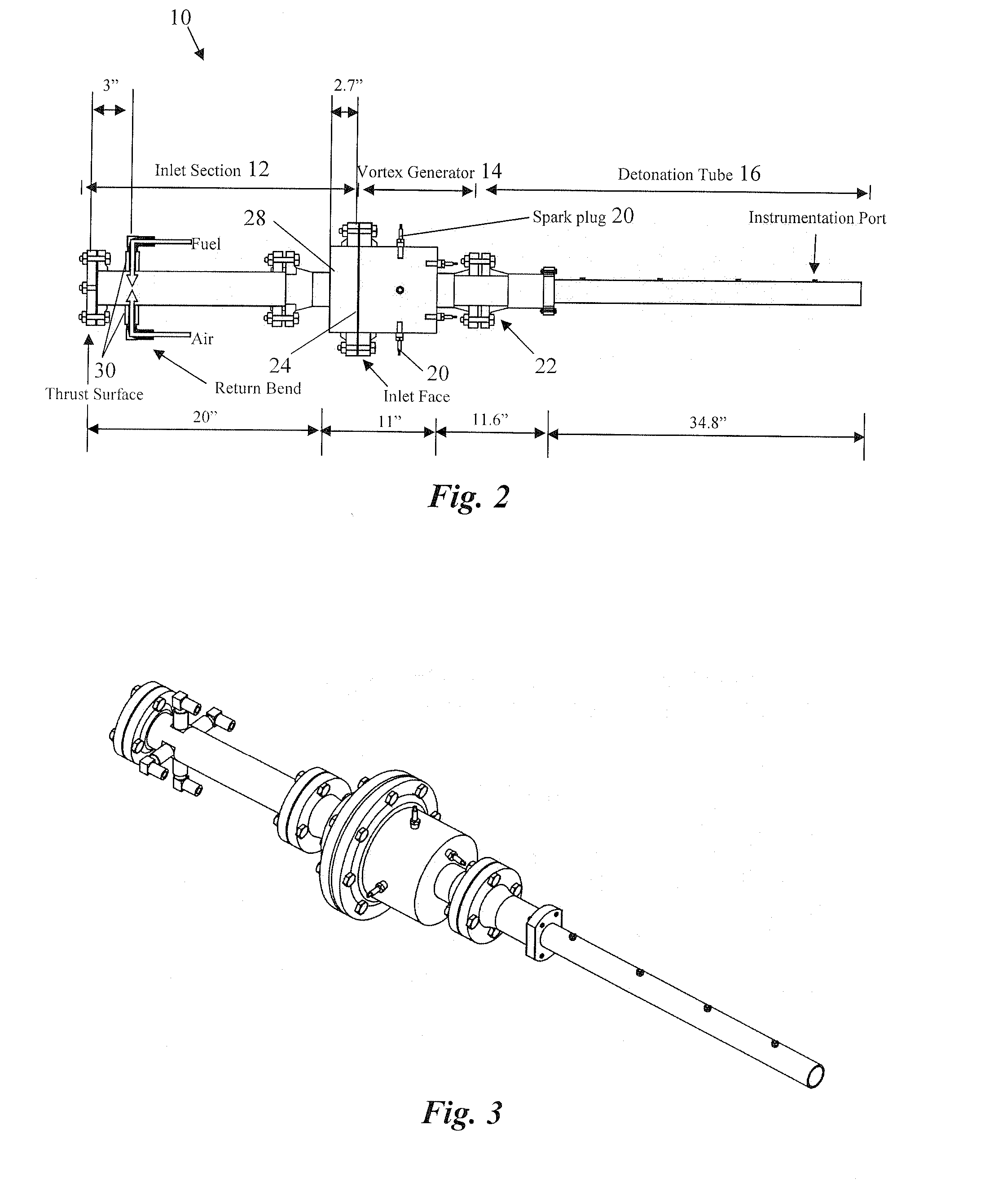
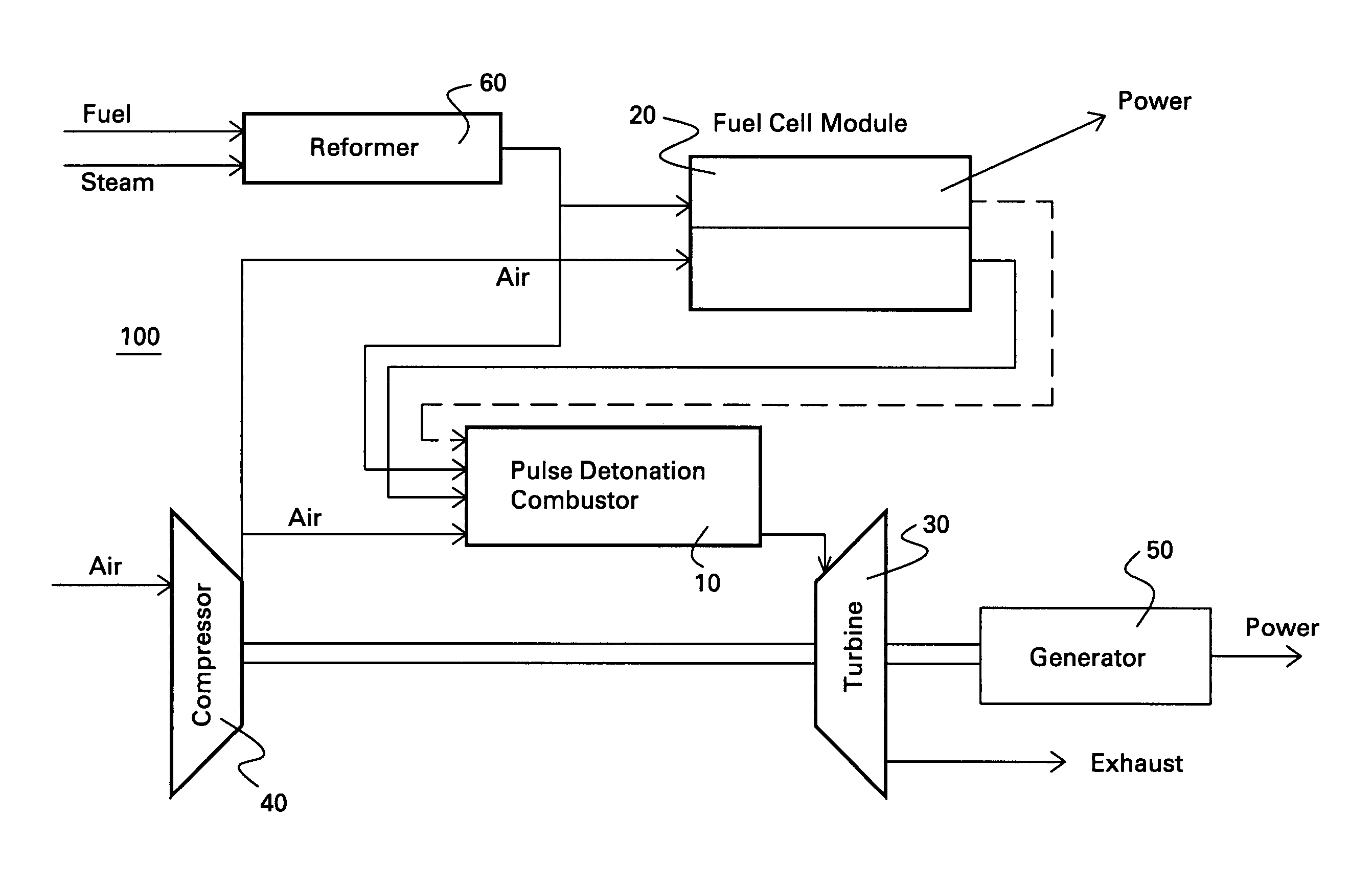
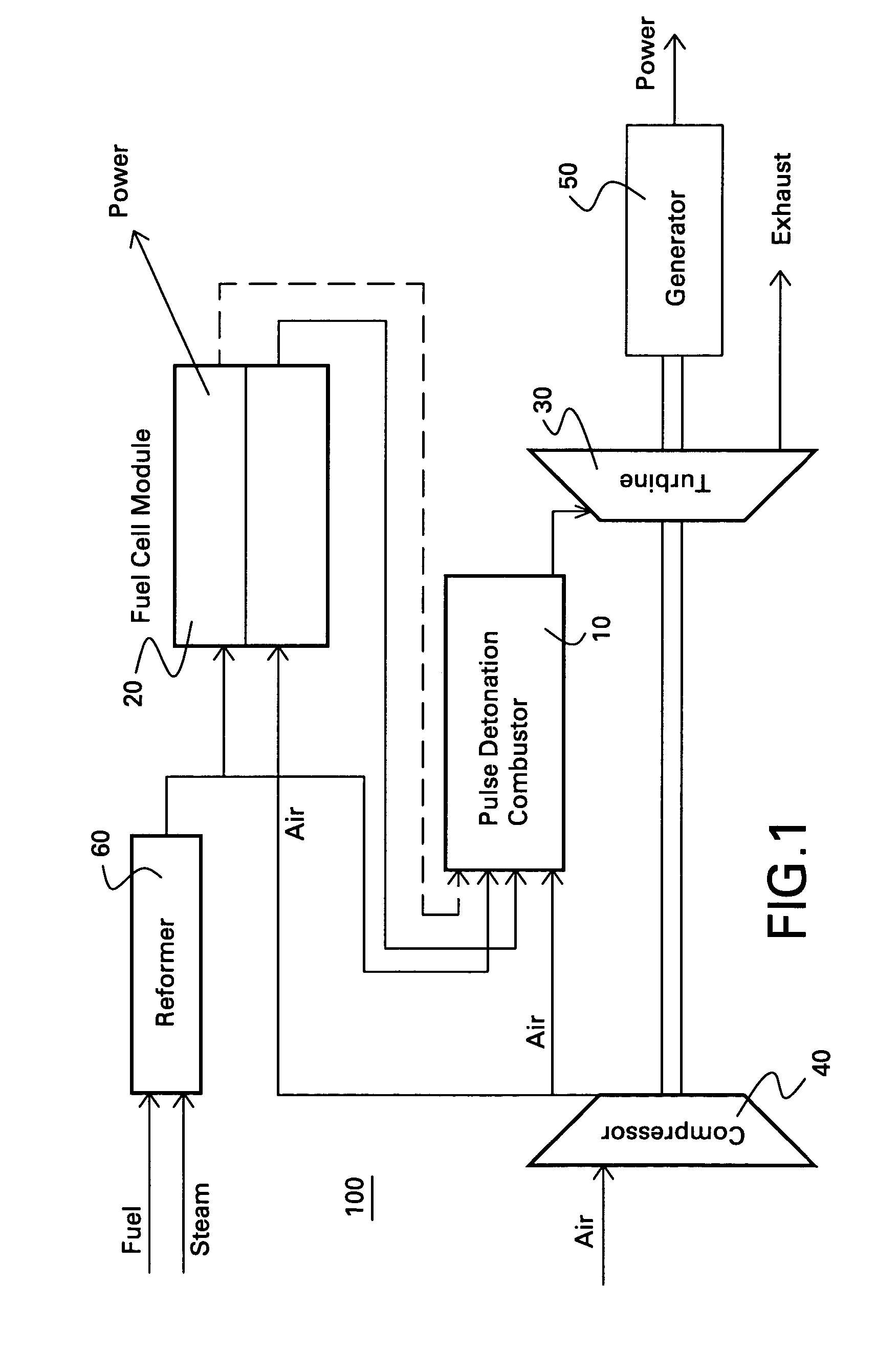
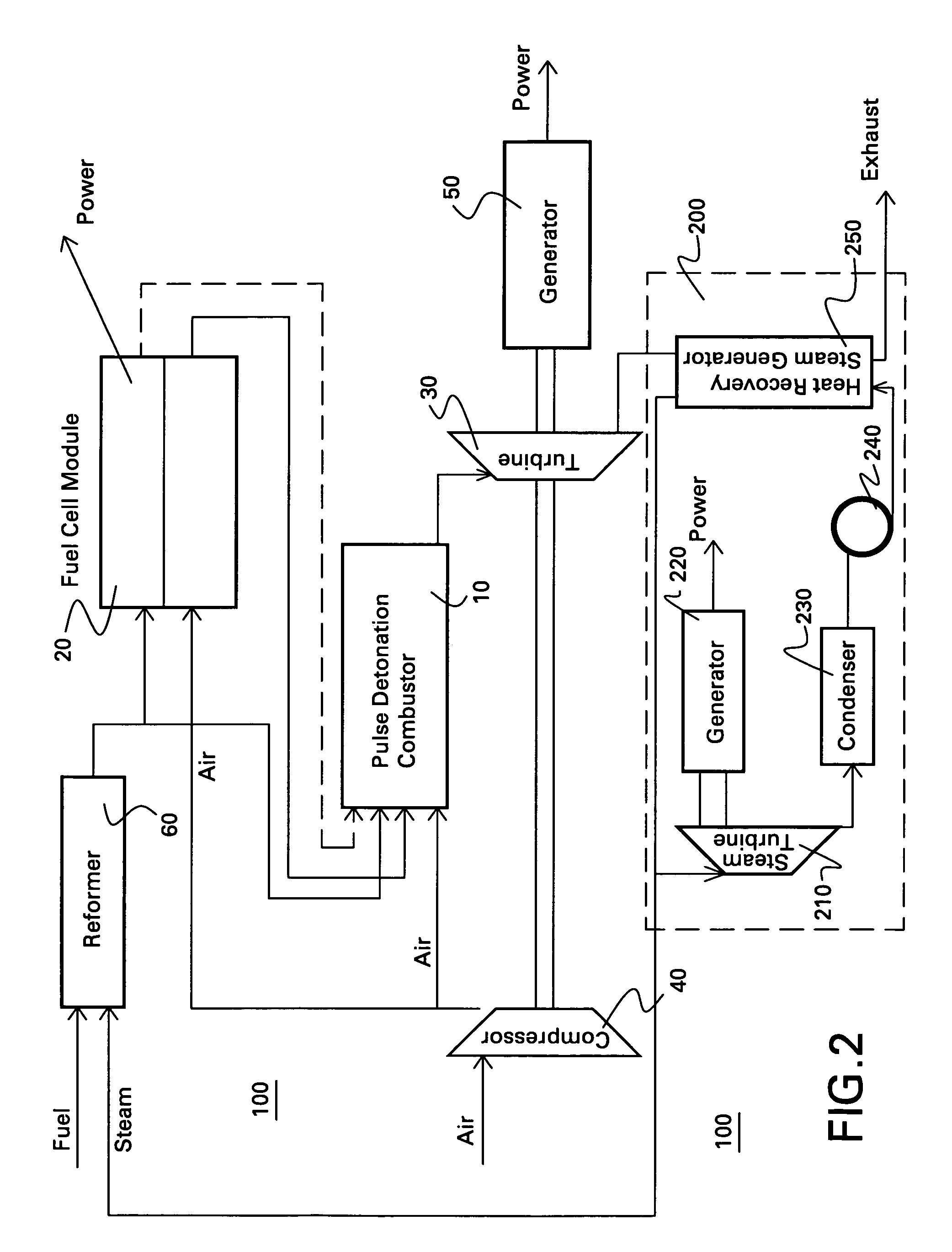
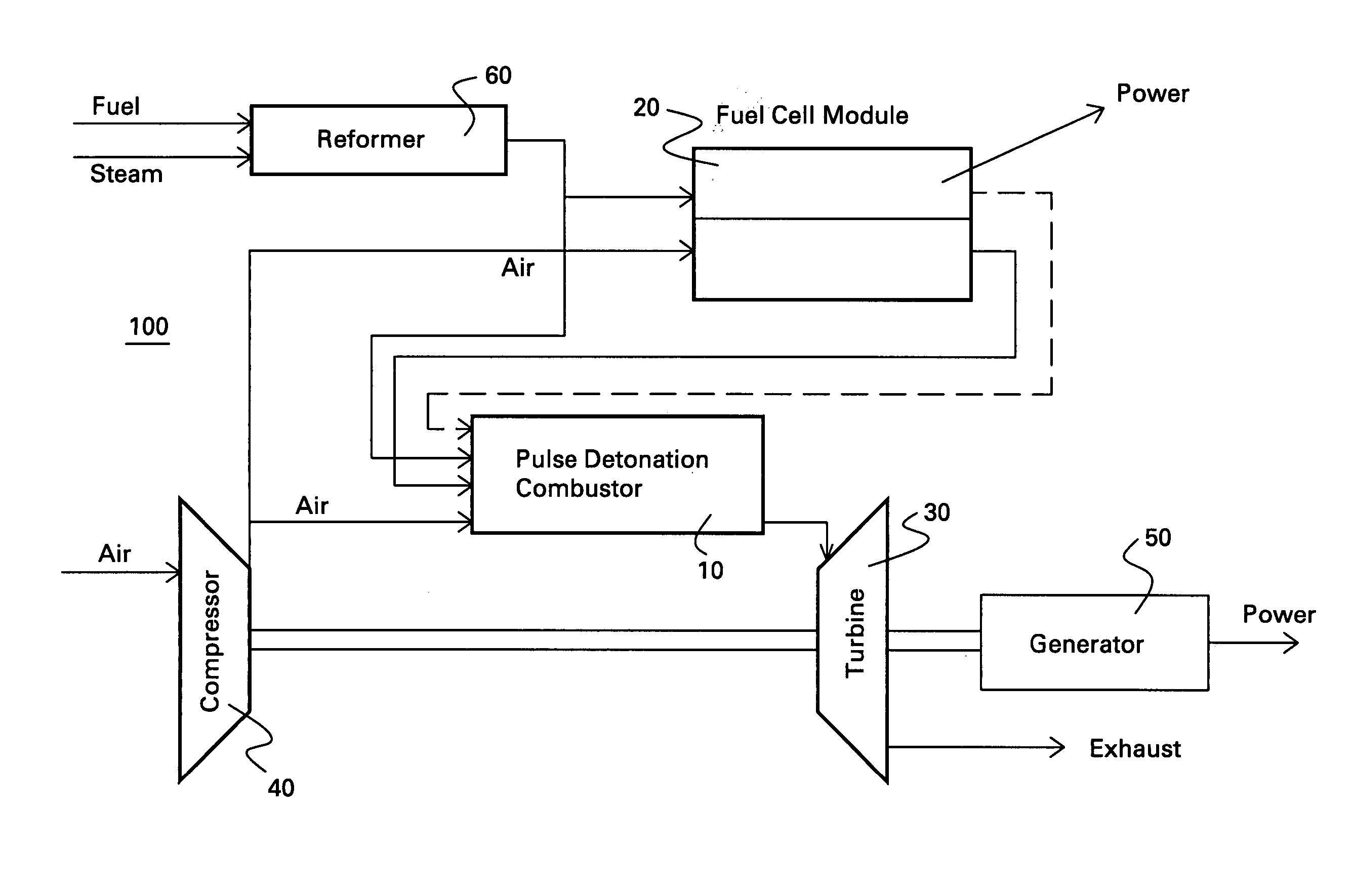
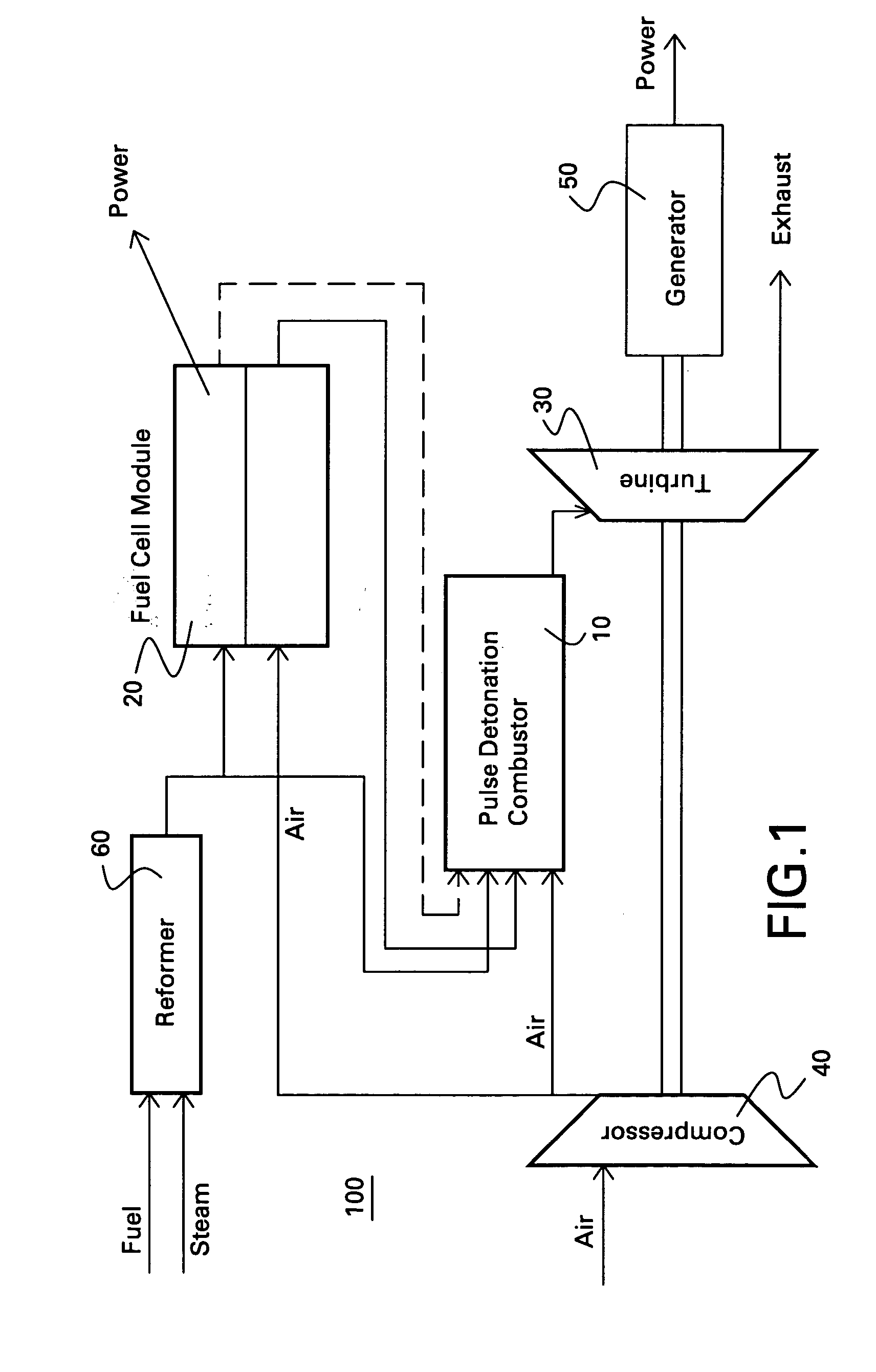
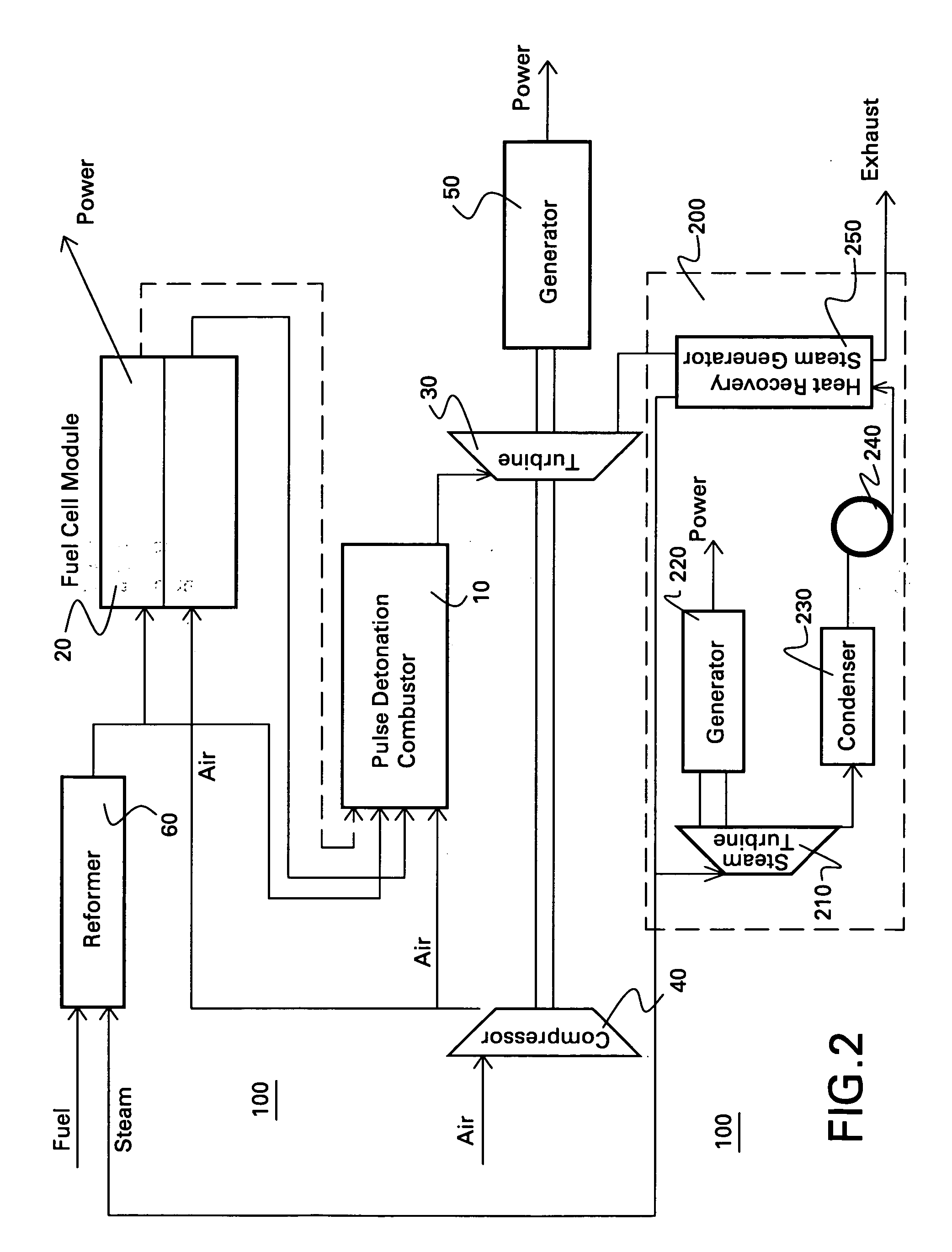
Hybrid fuel cell-pulse detonation power system
A power system includes a fuel cell module adapted to receive a first fuel and a pulse detonation combustor adapted to receive and detonate a second fuel and exhaust a number of detonation products to create thrust for propulsion, mechanical work extraction or electrical power production.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pulse detonation combustor with plenum
InactiveUS20130042595A1Extended durationExtension of timePulsating combustionIntermittent jet plantsCombustorDetonation
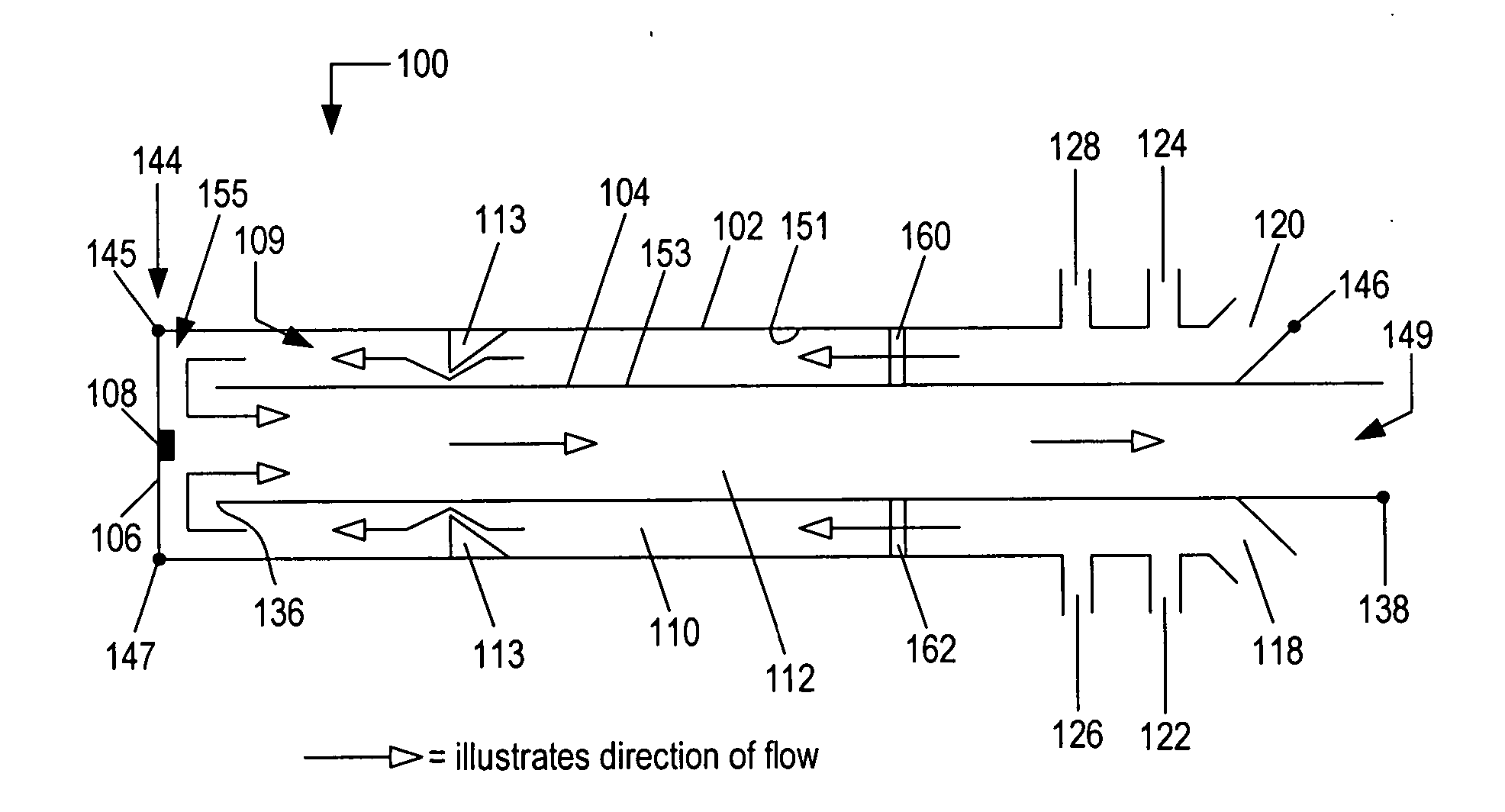
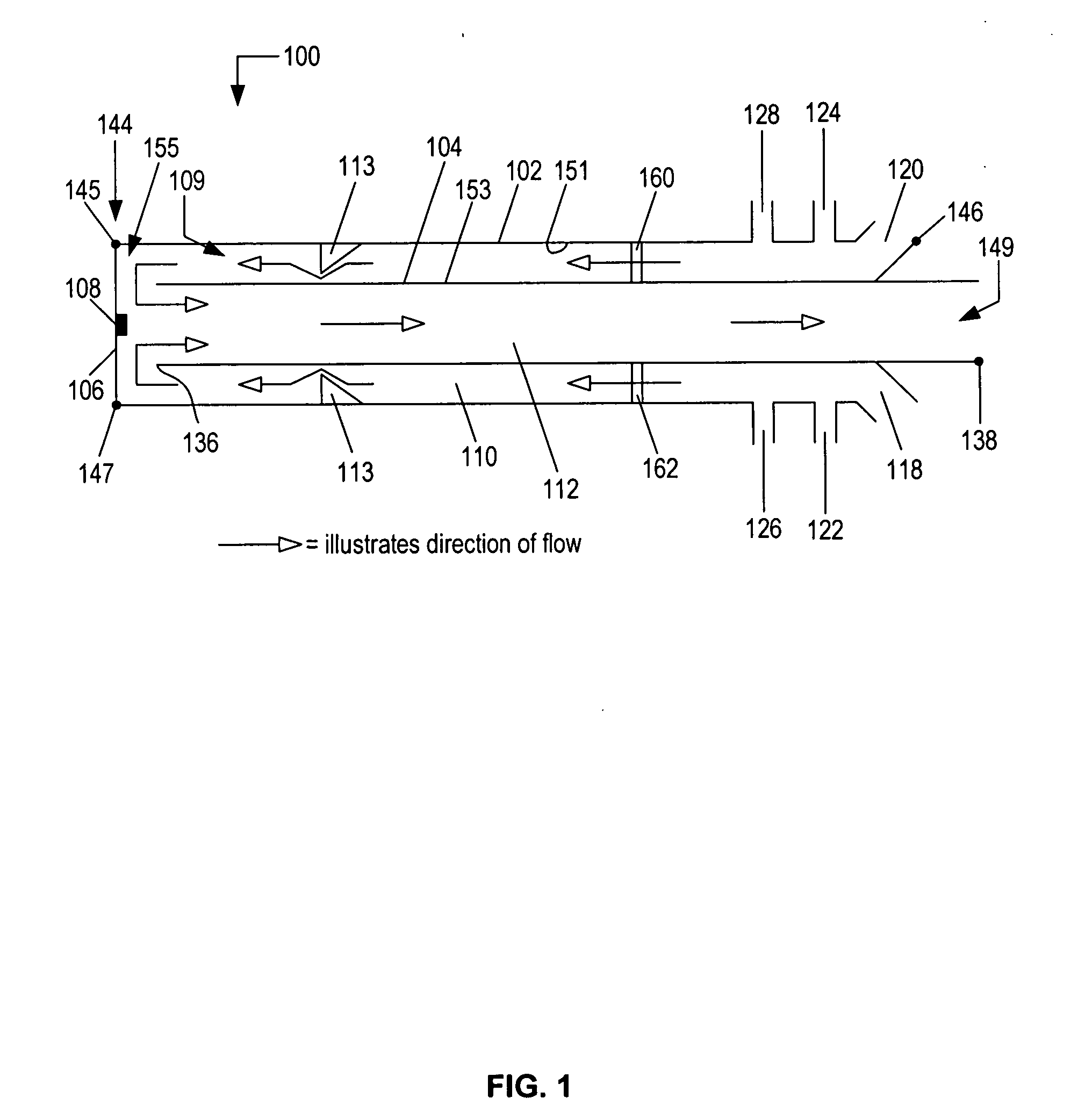
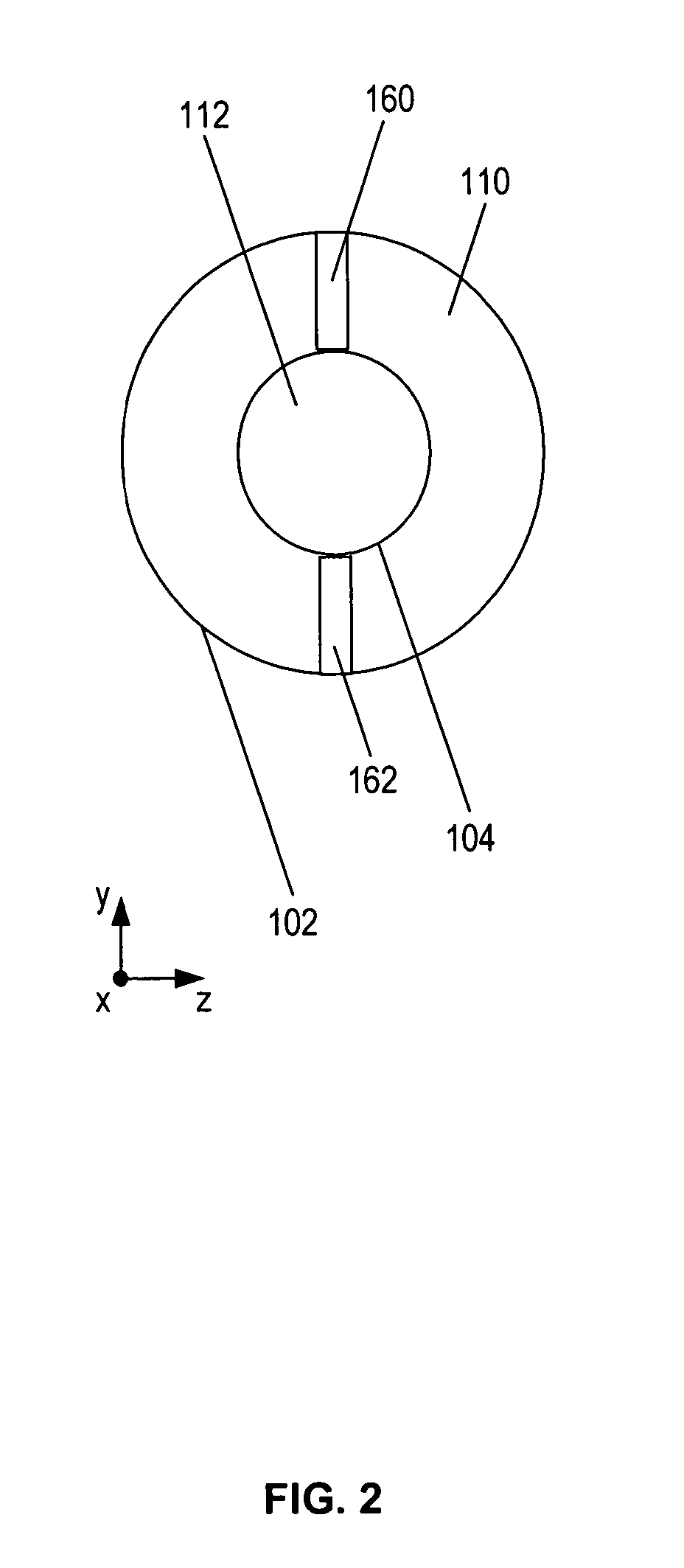
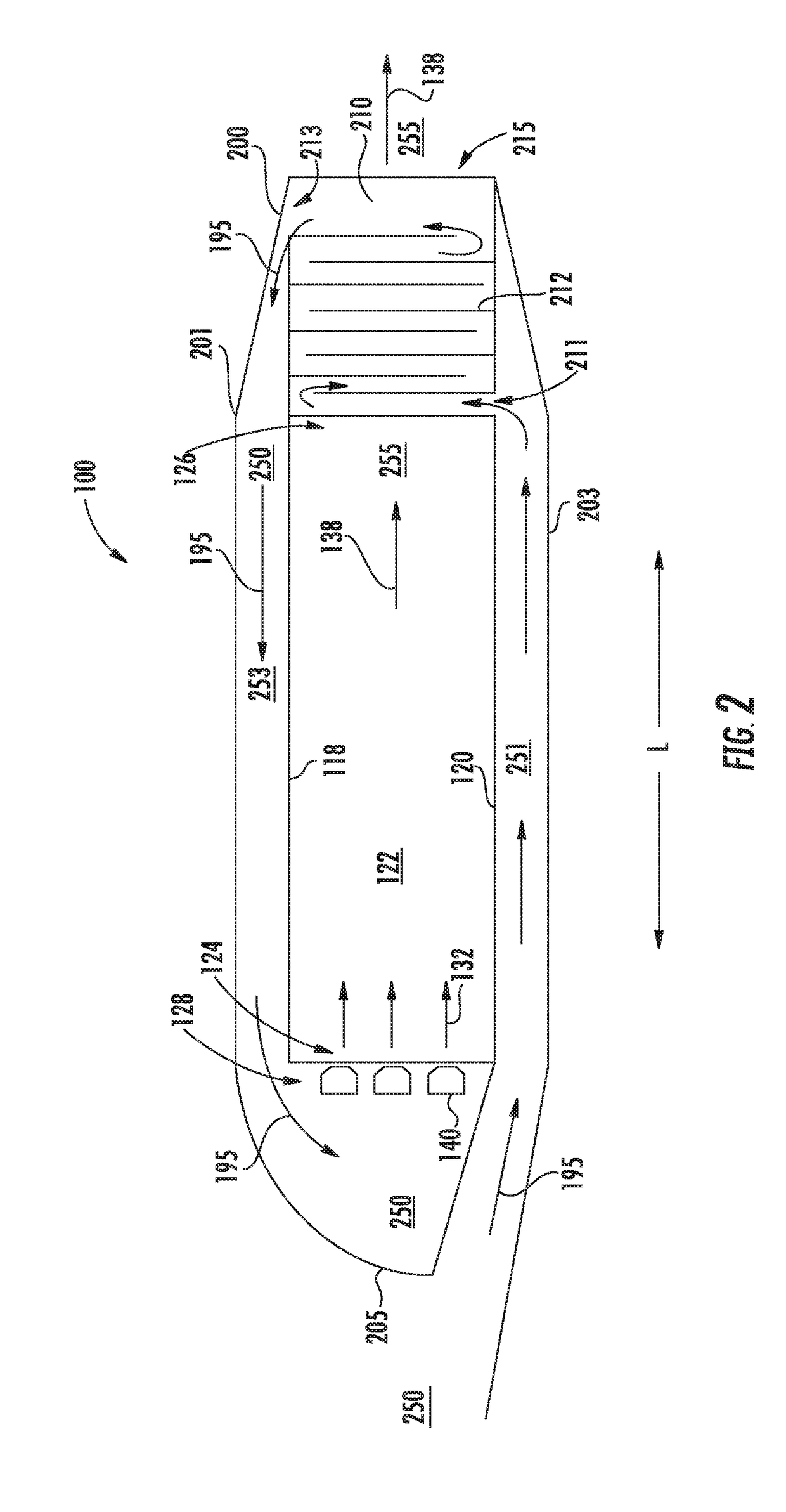
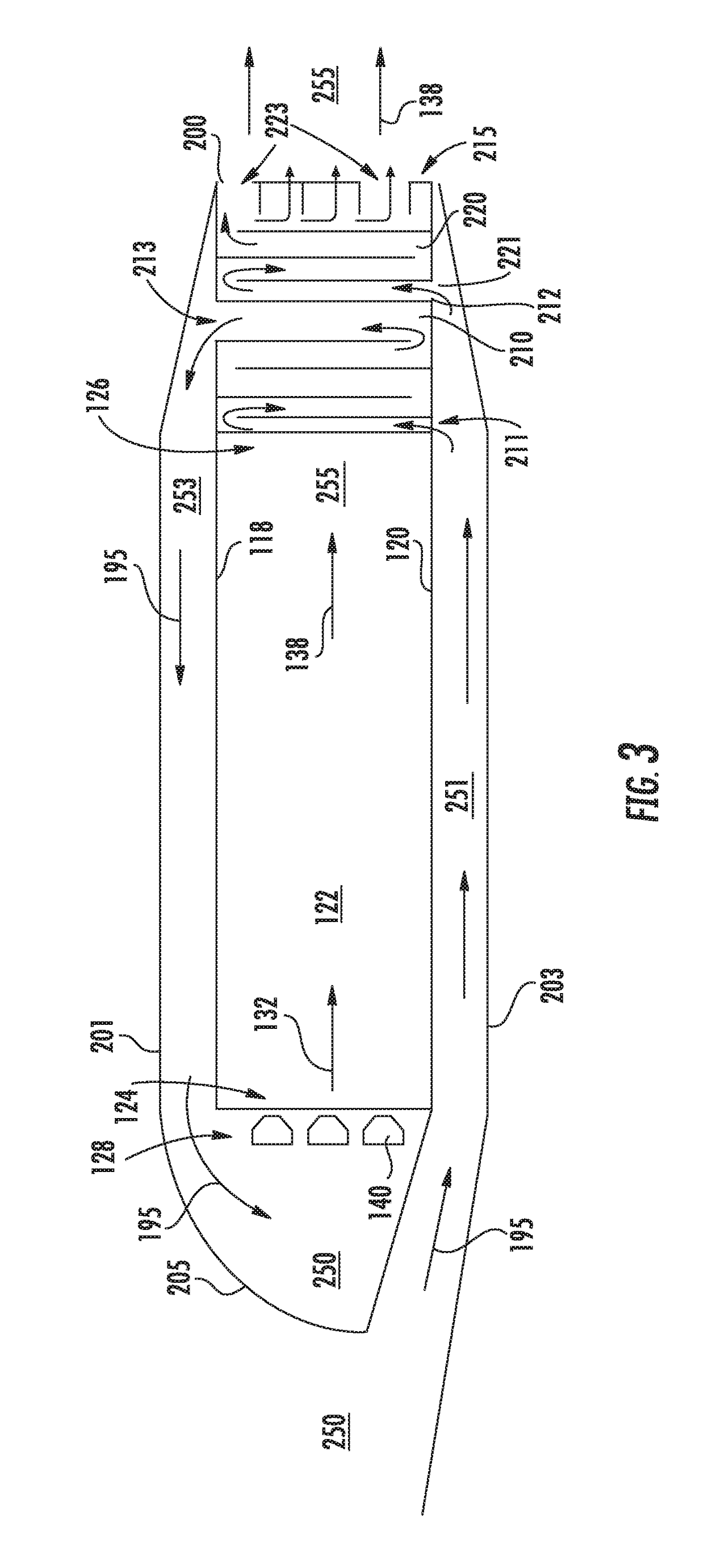
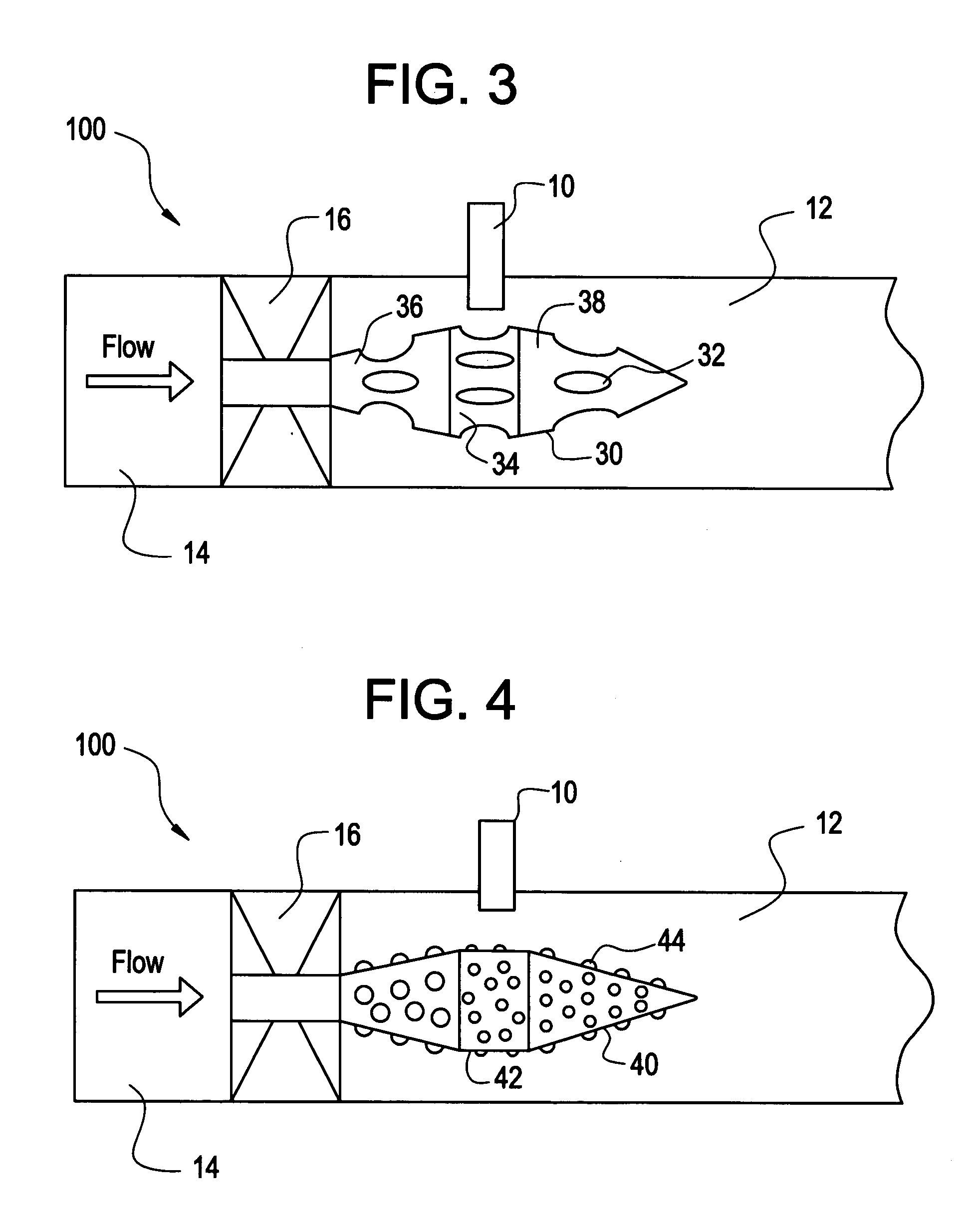
A pulse detonation combustor includes at least one plenum located along the length of the pulse detonation combustor. The plenum can be located: 1) proximate an air valve; 2) between a fuel injection port and an ignition source; 3) downstream of both the fuel injection port and the ignition source; and 4) proximate an exit nozzle of the pulse detonation combustor. In addition, the pulse detonation combustor can have multiple plenums, for example, proximate the air valve and proximate the exit nozzle. The location and dimensions of the plenum can be selectively adjusted to control mechanical loading on the wall, the velocity of fluid flowing within the combustor, and the pressure generated by the pulse detonation combustor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hybrid fuel cell-pulse detonation power system
A power system includes a fuel cell module adapted to receive a first fuel and a pulse detonation combustor adapted to receive and detonate a second fuel and exhaust a number of detonation products to create thrust for propulsion, mechanical work extraction or electrical power production.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple tube pulse detonation engine turbine apparatus and system
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com