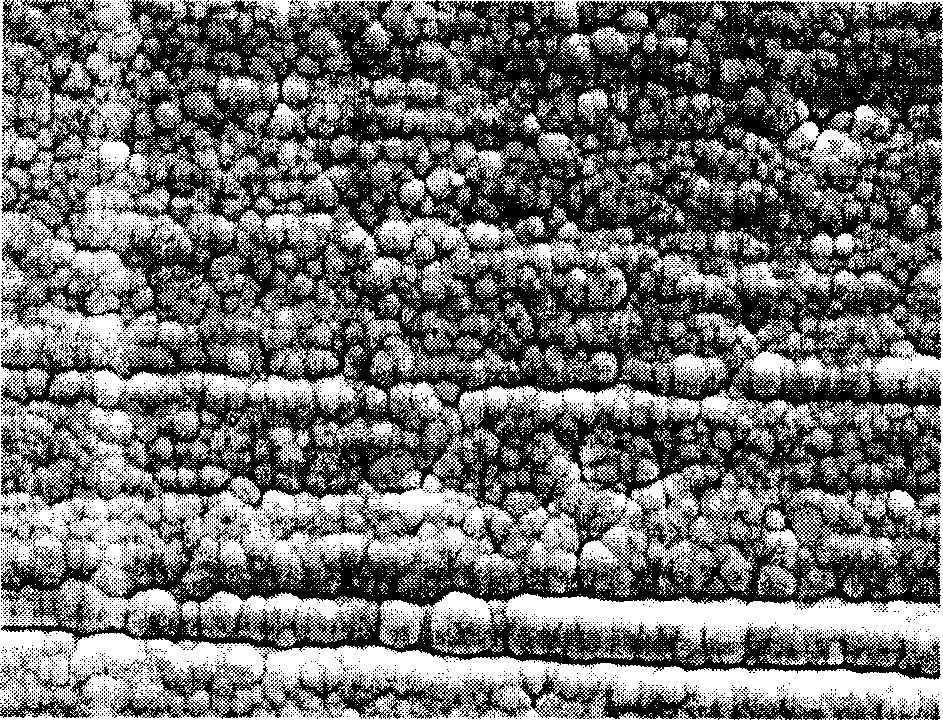Method for chemical plating nickel-boron alloy on magnesium alloy surface
A surface chemical and magnesium alloy technology, applied in liquid chemical plating, metal material coating process, coating, etc., can solve the problems of chemical plating cost increase, environmental pollution, and nickel cannot be replenished, and achieve good practical application prospects. Good deposition effect, avoiding the effect of base alkali corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
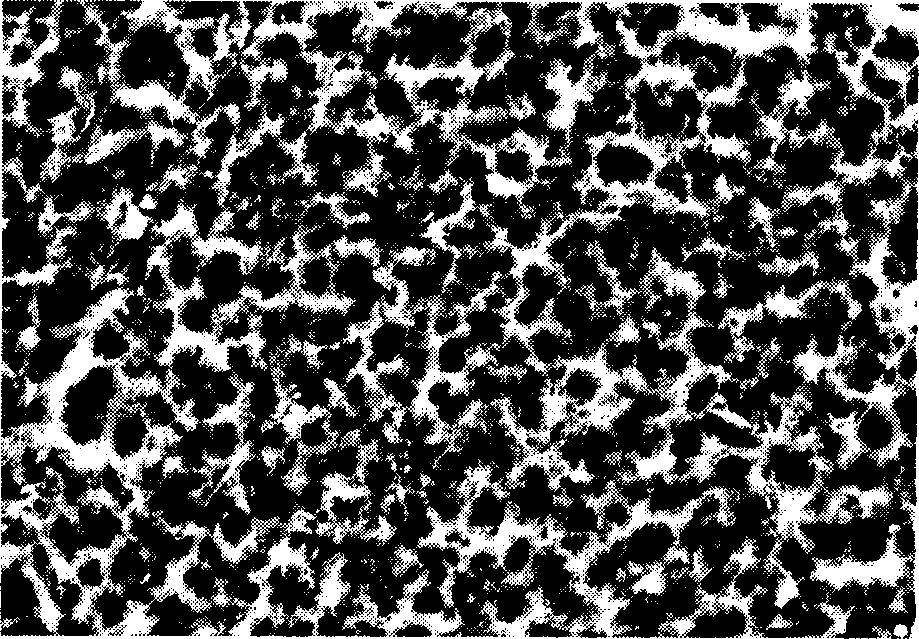
[0028] 1) Alkali washing, at room temperature, add sodium carbonate (15g), sodium phosphate (15g), OP-10 (5mL) to deionized water (1L) in turn, heat to 75°C after the dissolution is complete, and process it into 10mm× AZ91D magnesium alloy samples with a size of 10mm×2mm were placed in the alkaline cleaning solution and continuously stirred by ultrasonic waves, and were taken out after 15 minutes of treatment. At room temperature, wash in flowing deionized water for 2 min and then take it out. The surface morphology of the treated AZ91D magnesium alloy sample is shown in figure 1 , indicating that a clean mechanically polished surface of the AZ91D magnesium alloy was obtained after alkaline washing.
[0029] 2) Pickling, at room temperature, add 36% glacial acetic acid (18mL) and sodium nitrate (36g) in sequence to deionized water (1L), put the AZ91D magnesium alloy after alkali washing into the pickling solution and continue ultrasonic Stir, process for 75 seconds and remov...
Embodiment 2
[0044] 1) Alkali washing, at room temperature, add sodium carbonate (20g), sodium phosphate (20g), OP-10 (10mL) in sequence to deionized water (1L), and heat to 60°C after the dissolution is complete, AZ91D magnesium alloy sample Put it into the alkaline cleaning solution and continue ultrasonic stirring, take it out after 10 minutes of treatment. At room temperature, put the treated AZ91D magnesium alloy into flowing deionized water and wash it for 4 minutes before taking it out.
[0045] 2) pickling, with embodiment 1.
[0046] 3) Electroless Ni-B plating, at room temperature, add nickel acetate (38g) into deionized water (700mL) to dissolve completely, then add ethylenediamine (52mL) under stirring, and add composite additives under stirring after cooling to room temperature , followed by: sodium p-benzenesulfonate (6g), malonic acid (3g), sulfosalicylic acid (50mg), after the dissolution is complete, add sodium hydroxide (28g) under stirring, and after the dissolution is ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] 1) alkali washing, with embodiment 1.
[0059] 2) Pickling, at room temperature, add 36% glacial acetic acid (22mL) and sodium nitrate (45g) to deionized water (1L) successively, put the treated AZ91D magnesium alloy into this solution and continue ultrasonic stirring for 30 seconds Take it out and wash it with deionized water.
[0060] 3) Electroless Ni-B plating, at room temperature, add nickel acetate (40g) in deionized water (700mL), after the dissolution is complete, add ethylenediamine (55mL) while stirring, and add the composite additive while stirring after cooling to room temperature , followed by: sodium p-benzenesulfonate (8g), malonic acid (6g), sulfosalicylic acid (60mg), add sodium hydroxide (48g) under stirring after the dissolution is complete, add boron after the dissolution is complete Sodium hydride (0.6g), finally add deionized water to 1L, heat to a constant temperature of 80°C, put the treated AZ91D magnesium alloy into this constant temperature s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com