Patents
Literature
327 results about "Physical Exertions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exertion is the physical or perceived use of energy. Exertion traditionally connotes a strenuous or costly effort,resulting in generation of force, initiation of motion, or in the performance of work.
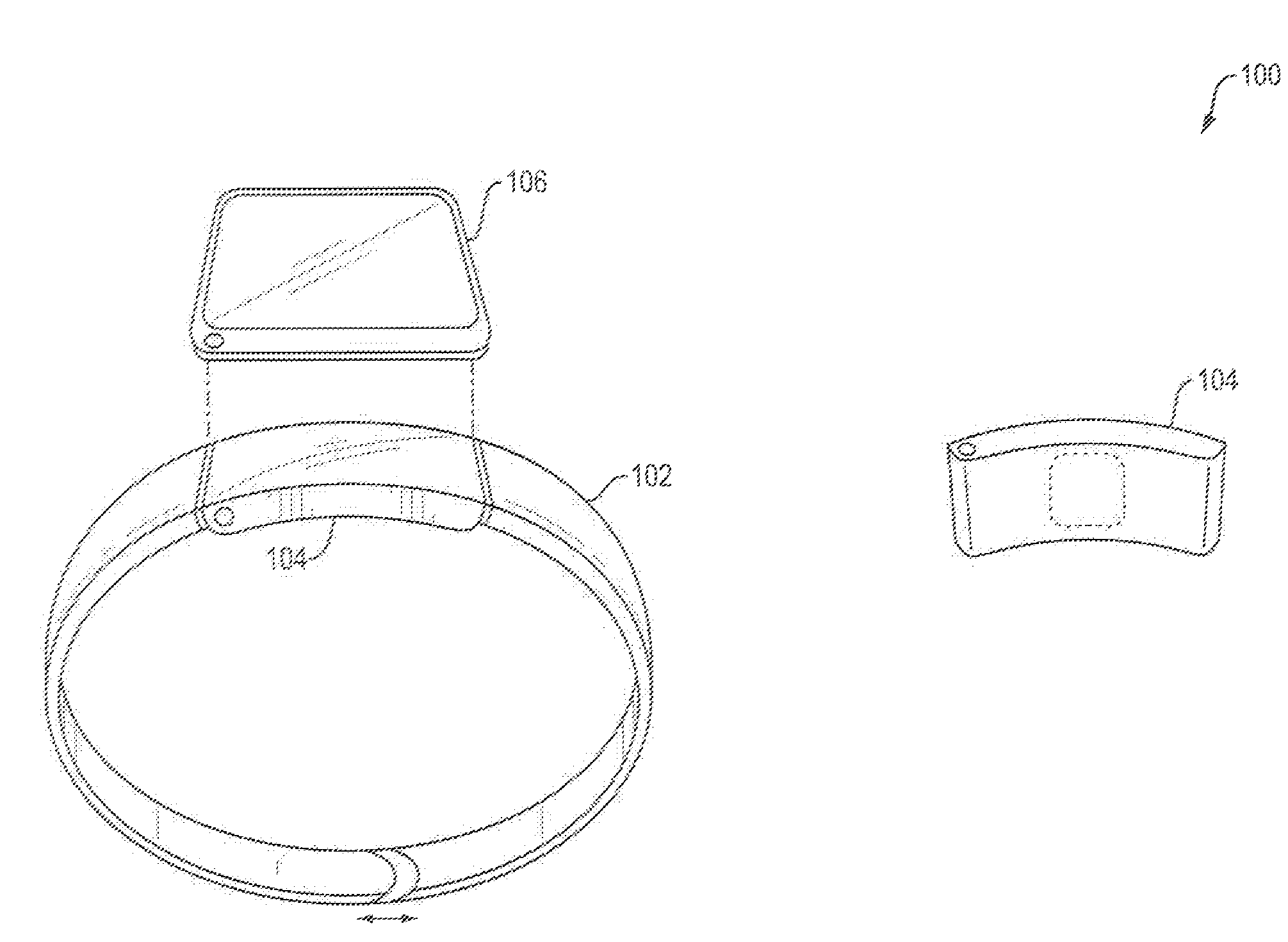
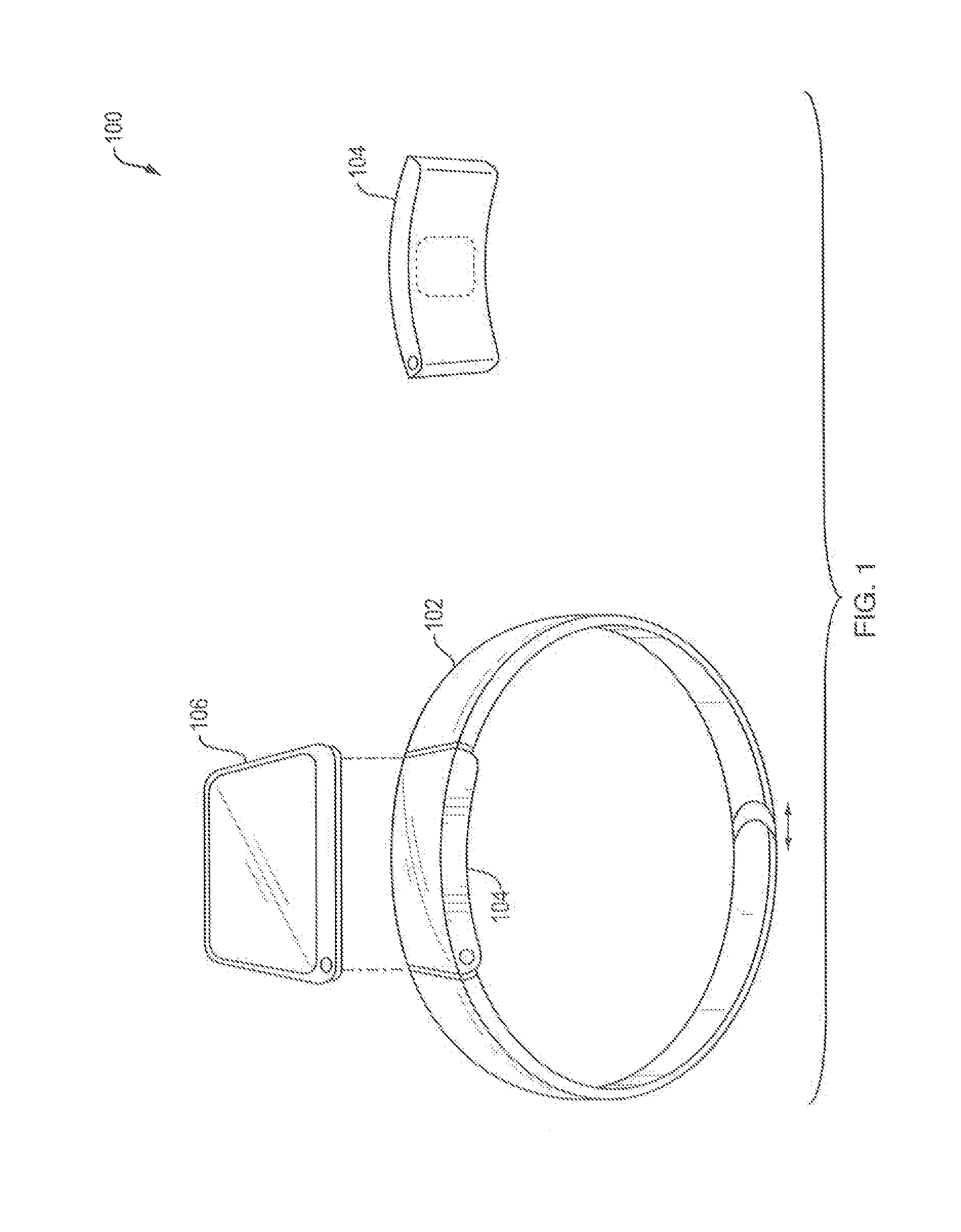
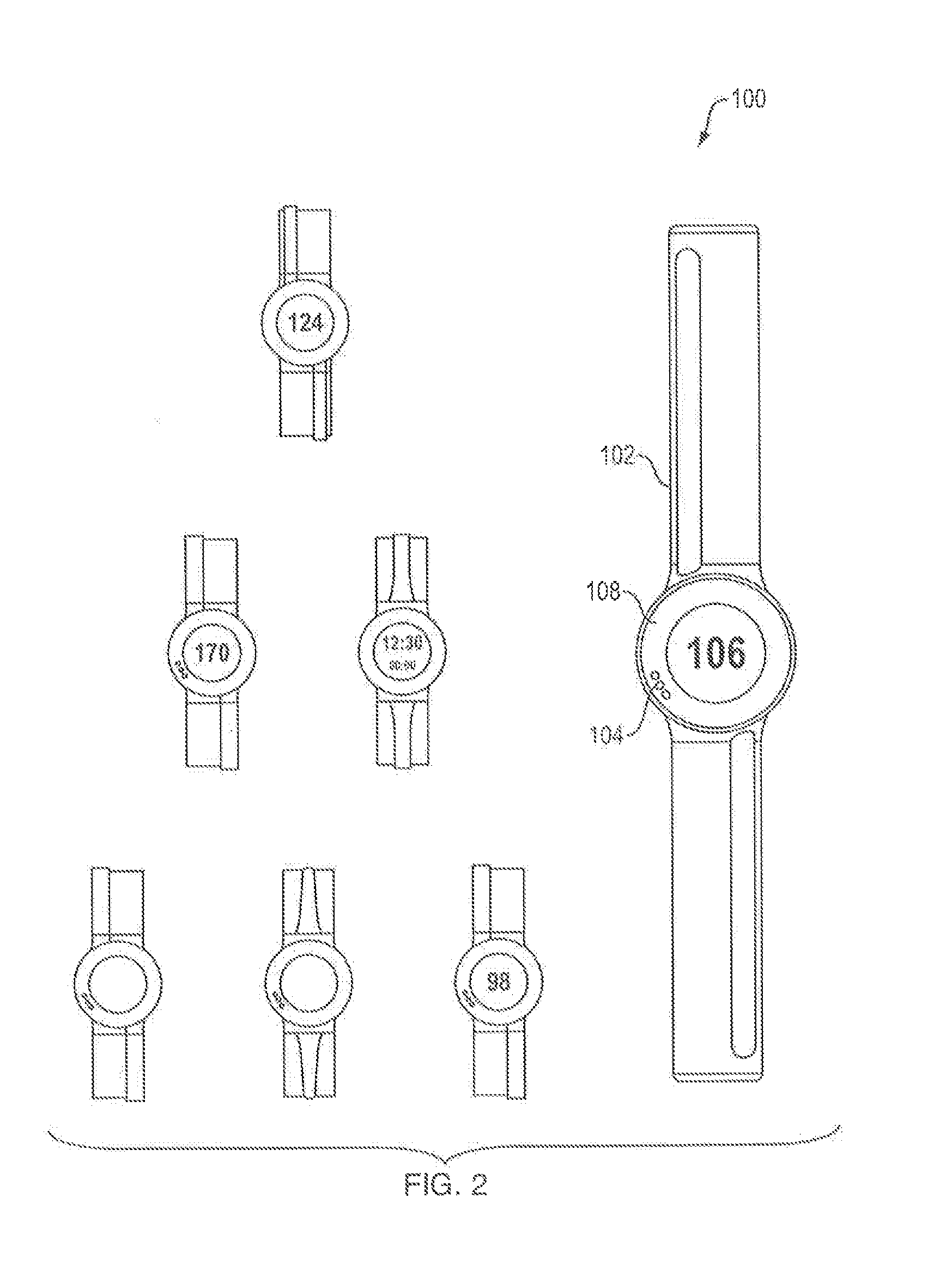
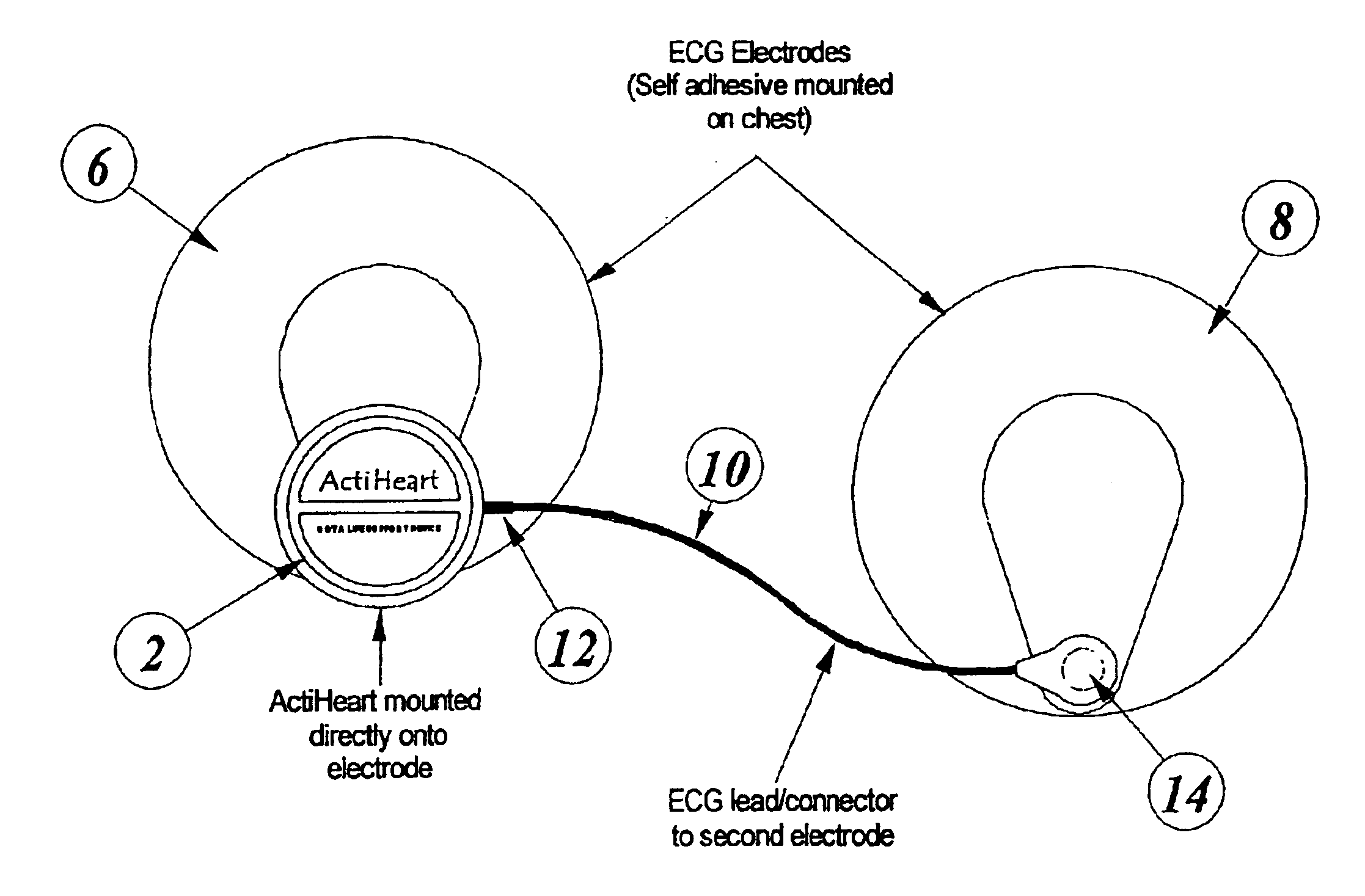
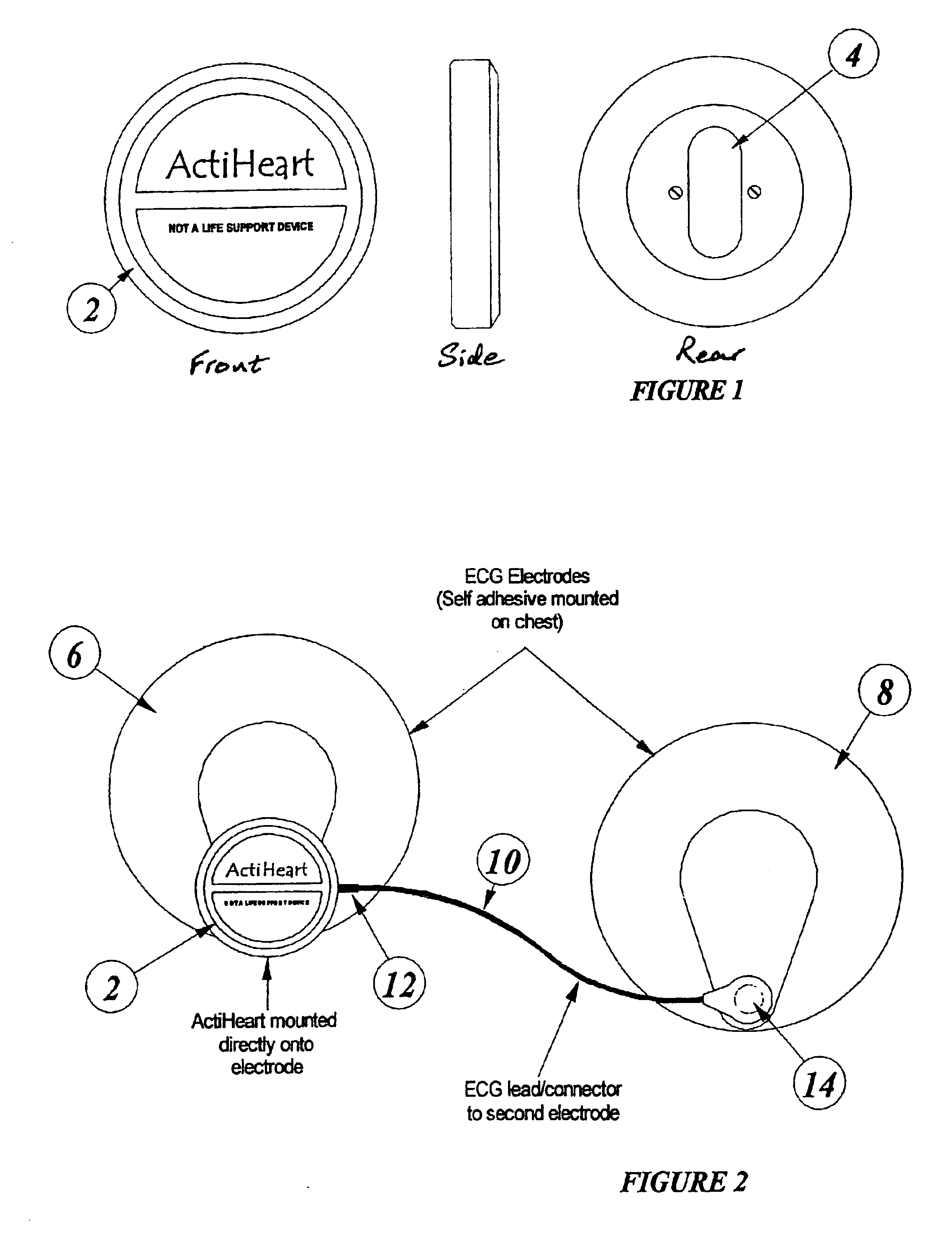
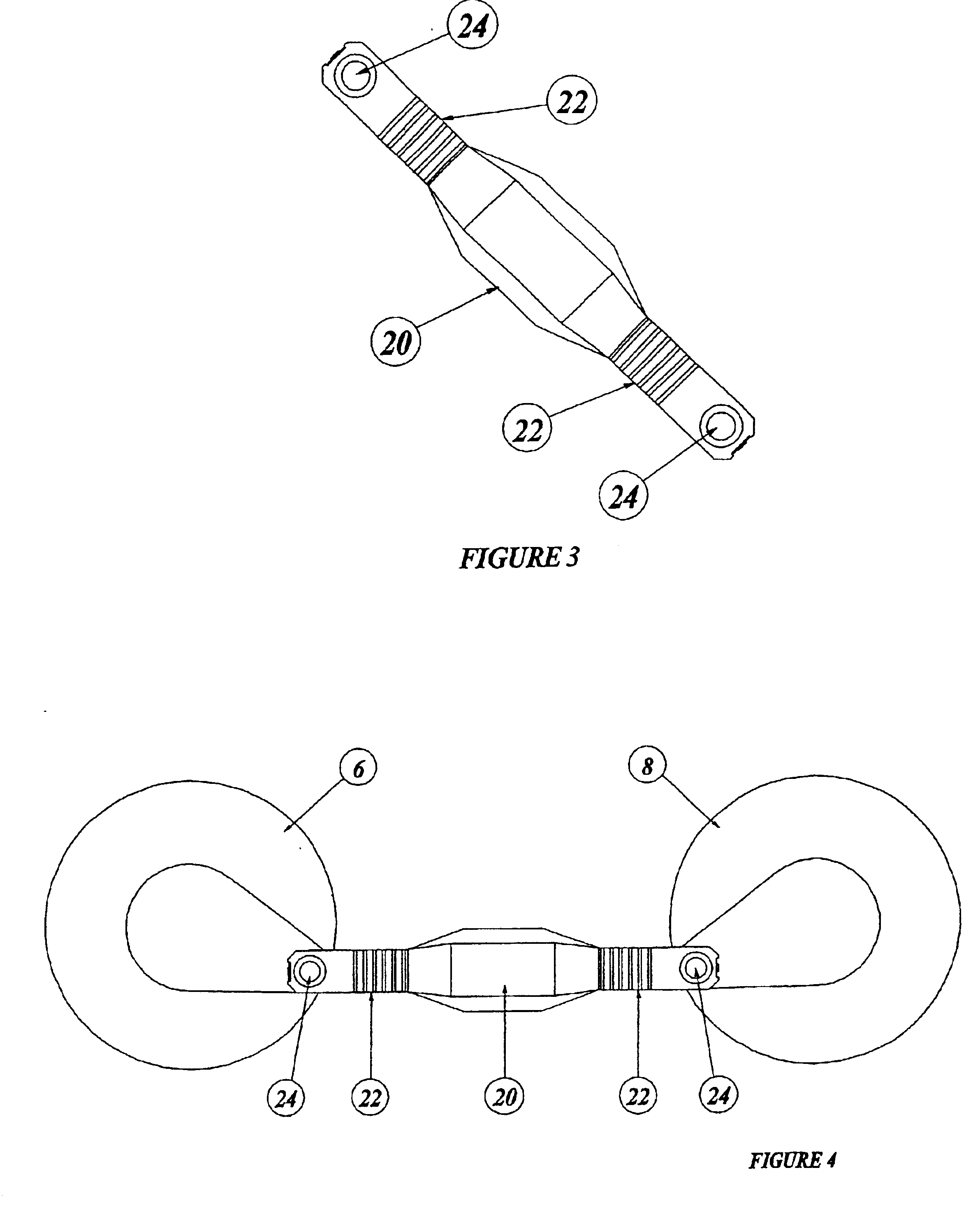
Systems, devices and methods for continuous heart rate monitoring and interpretation
InactiveUS20140073486A1Reduce consumptionPhysical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPhysical ExertionsPhysical strength
Embodiments provide physiological measurement systems, devices and methods for continuous health and fitness monitoring. A lightweight wearable system is provided to collect various physiological data continuously from a wearer without the need for a chest strap. The system also enables monitoring of one or more physiological parameters in addition to heart rate including, but not limited to, body temperature, heart rate variability, motion, sleep, stress, fitness level, recovery level, effect of a workout routine on health, caloric expenditure. Embodiments also include computer-executable instructions that, when executed, enable automatic interpretation of one or more physiological parameters to assess the cardiovascular intensity experienced by a user (embodied in an intensity score or indicator) and the user's recovery after physical exertion (embodied in a recovery score). These indicators or scores may be displayed to assist a user in managing the user's health and exercise regimen.
Owner:WHOOP
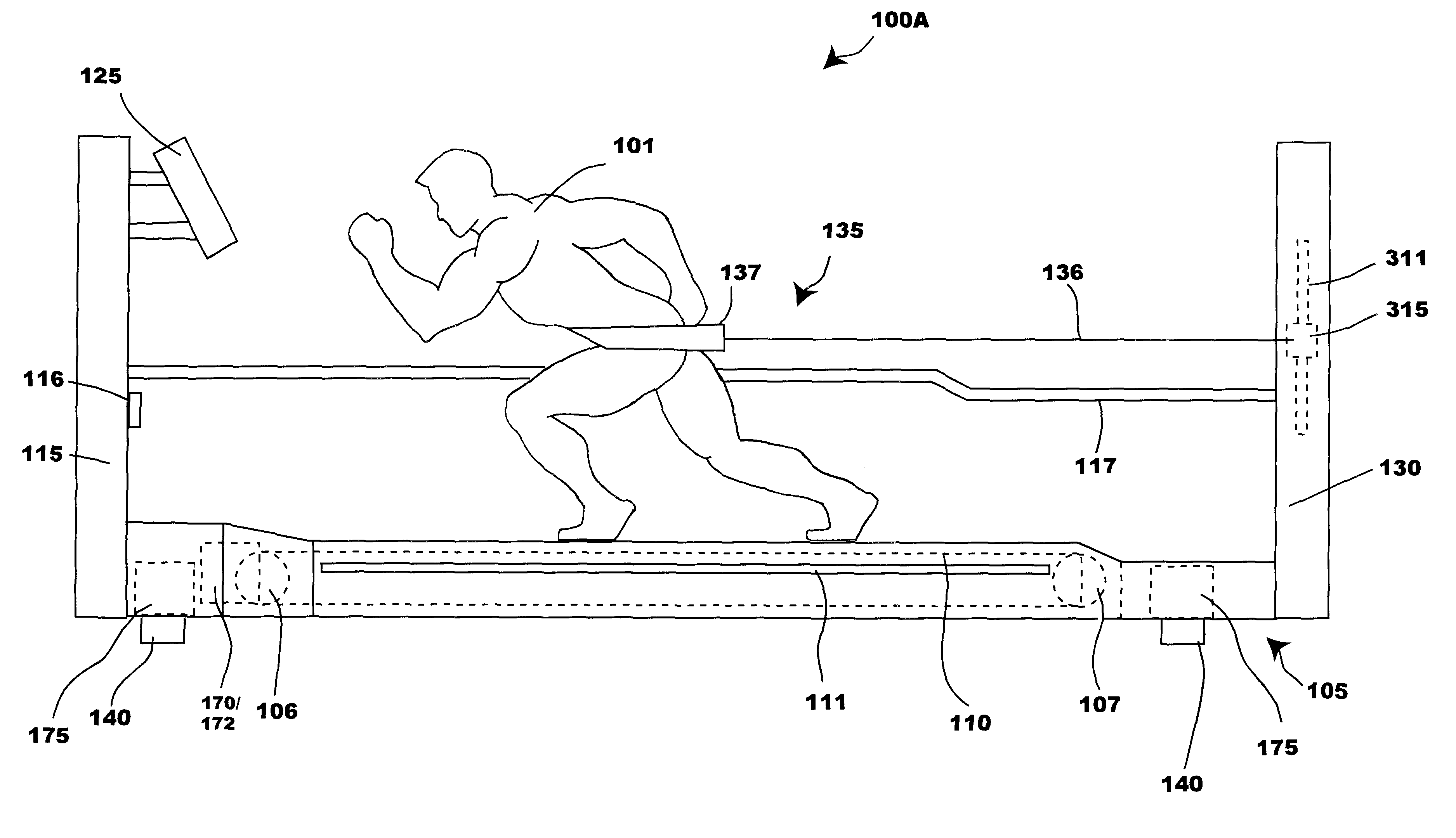
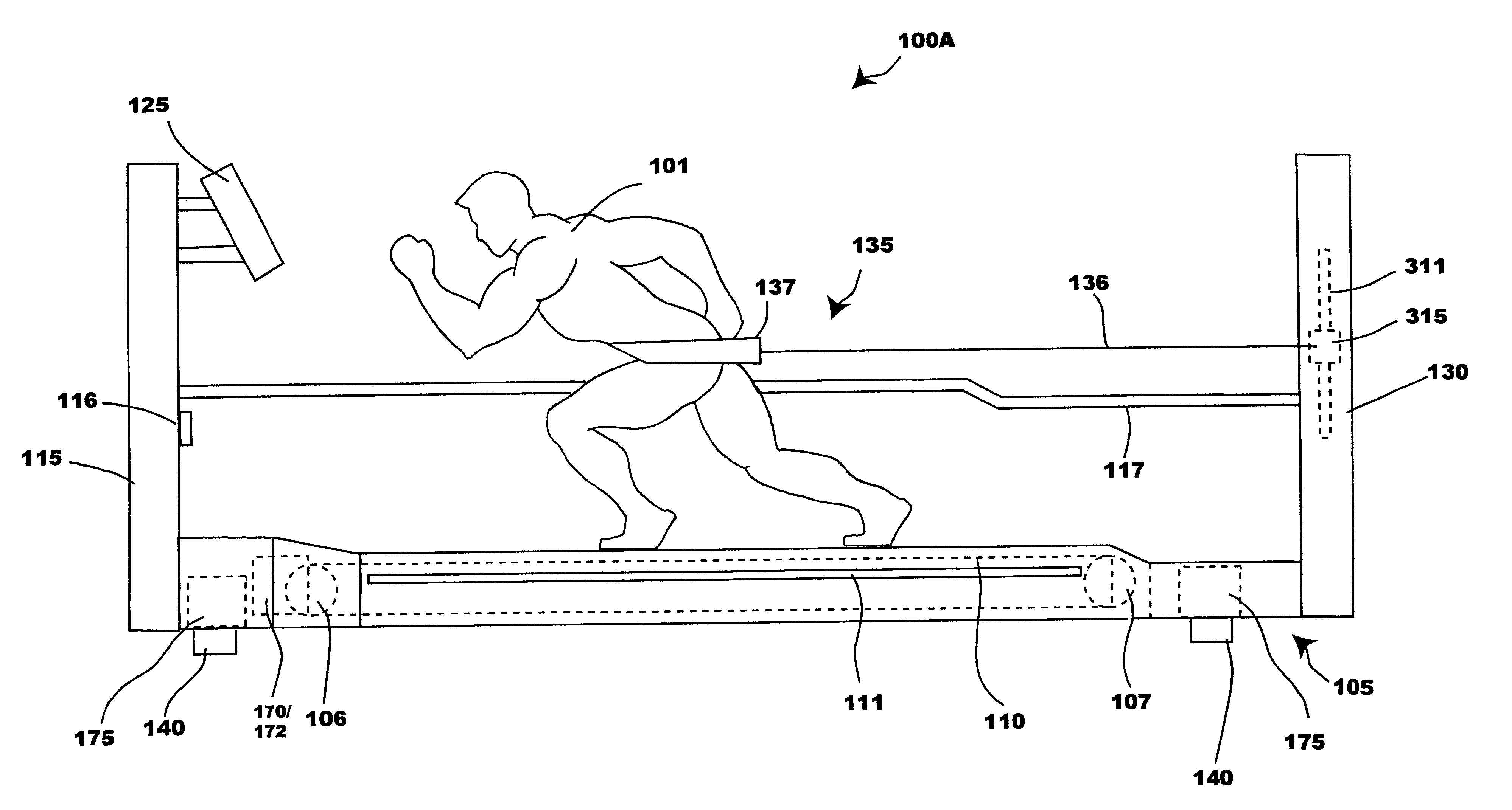
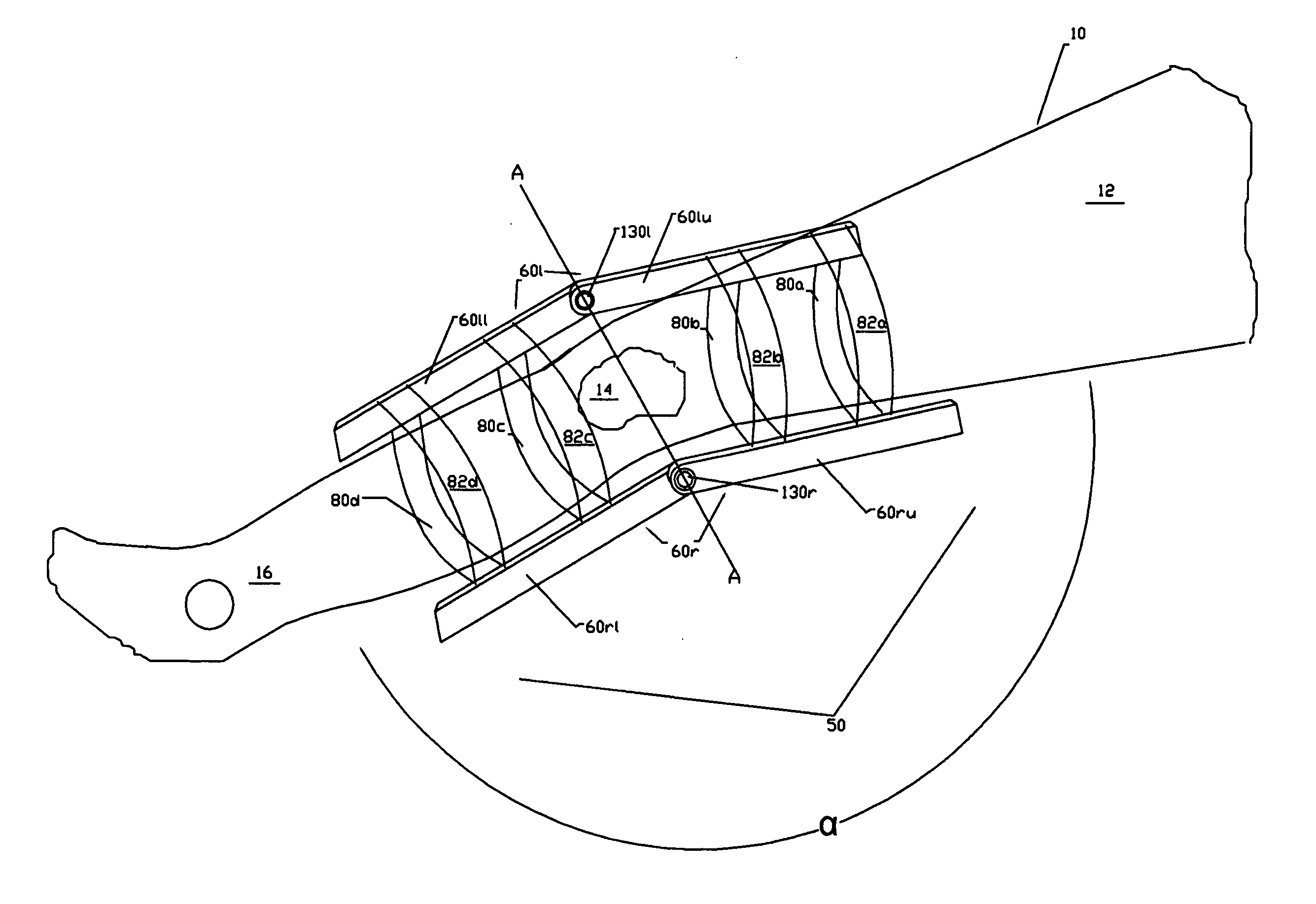
Bipedal locomotion training and performance evaluation device and method
InactiveUS6454679B1Effective mass reductionTherapy exerciseMovement coordination devicesExercise performanceForce velocity
A bipedal locomotion exercise and performance evaluation apparatus including a revolving belt, a harness for securing the position of a subject on the belt, a harness-force measuring means, and a belt volocity monitoring and controlling means. The harness may be secured on various points of a subject and includes push / pull engagement means. An overhead harness may be used to reduce effective body mass. The velocity of the belt may be controlled by a unidirectional or bidirectional motor / brake system. Velocity of the belt may also be controlled by a brake only. A digital processor may be used to control the motor and / or brake as a function of the forces applied allowing multiple operating modes. Recording of velocity and force as functions of time facilitates analysis of exercise performance. The apparatus allows exertions throughout the first quadrant of a force-velocity-duration space, and outside that first quadrant.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT BRIAN
Method, performance monitor and computer program for determining performance
ActiveUS20070082789A1Monitor performanceElectromyographyEvaluation of blood vesselsExertionComputer science
The invention relates to a method, a user-specific performance monitor and a computer program for determining the user's performance. In the method, the performance power of a physical exercise is determined by means of user movement data registered by the user-specific performance monitor. Further, the exertion level corresponding to the performance power of the physical exercise is determined by means of physiological information measured from the user, the physiological information being registered by the user-specific performance monitor; and the user's performance is estimated by means of the performance power of the physical exercise and the exertion level corresponding to the performance power of the physical exercise.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
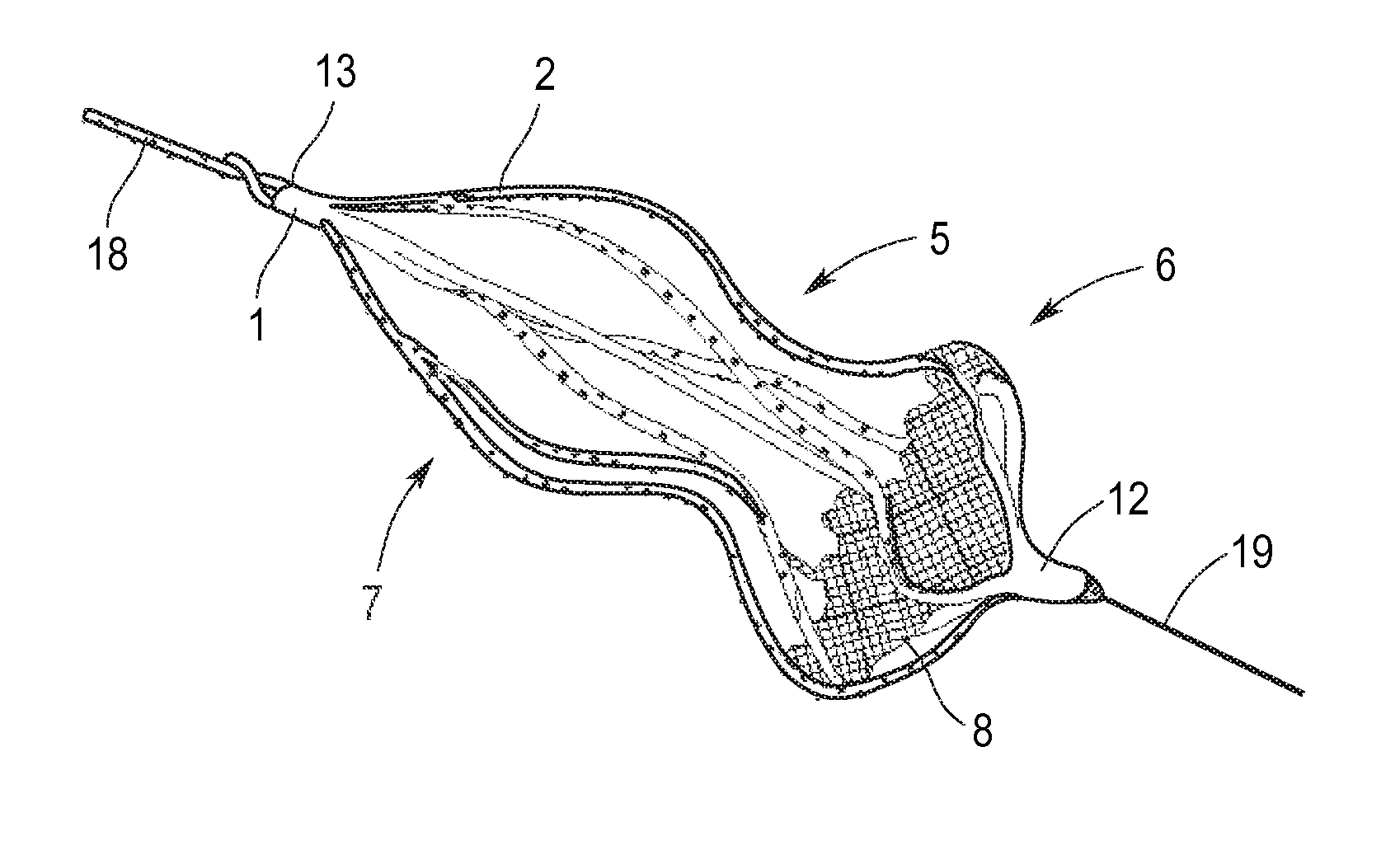
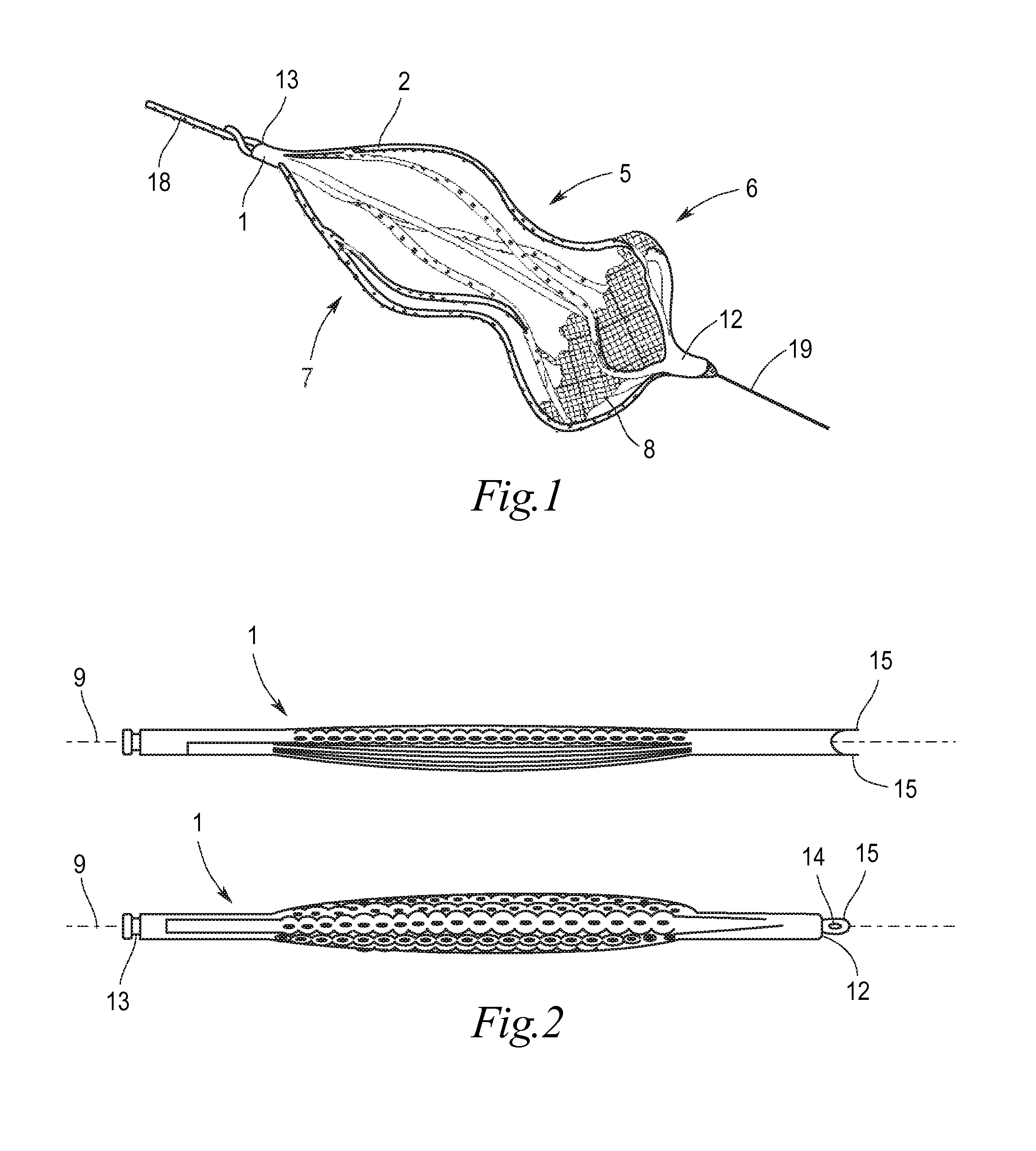
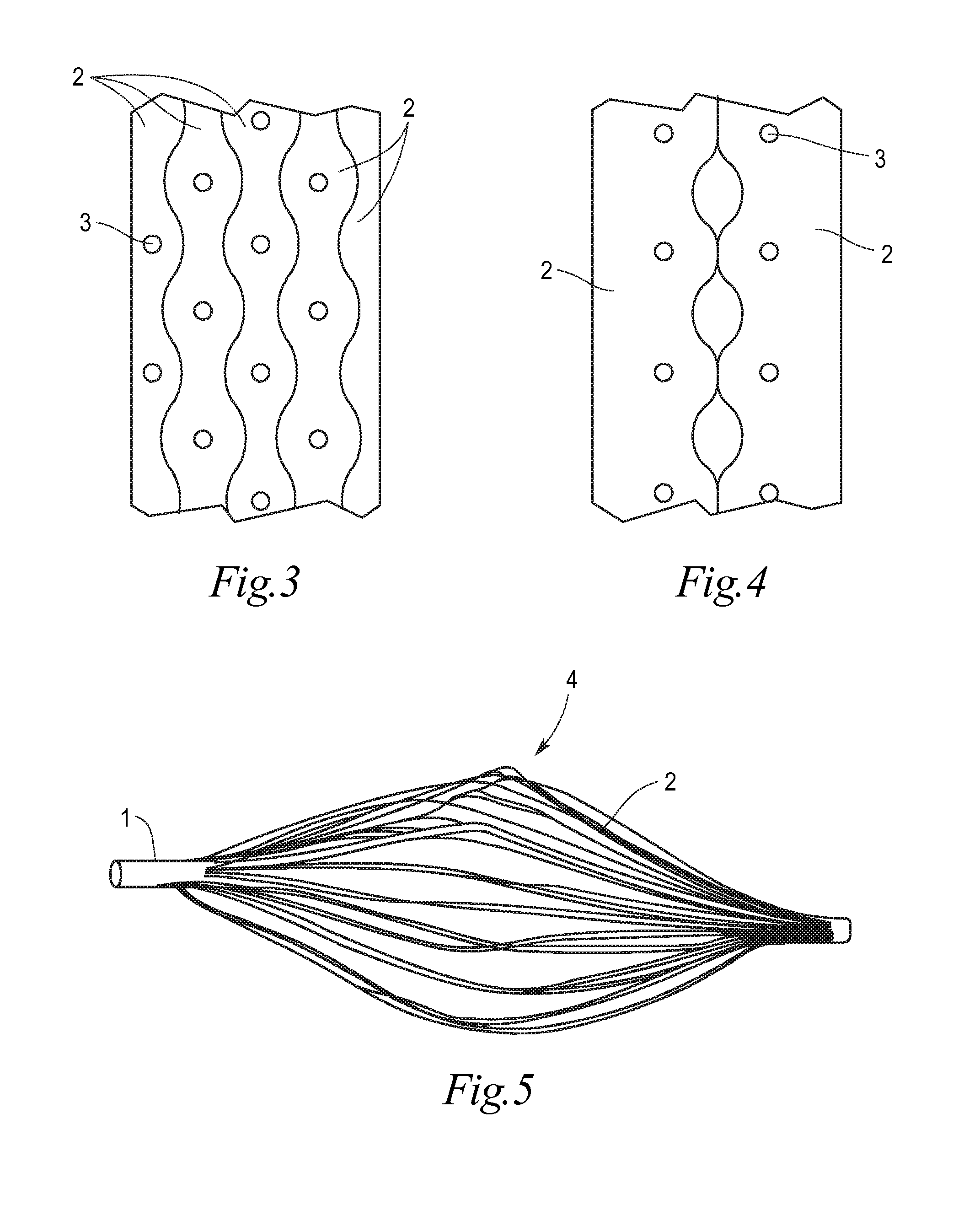
Implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal and a system for the placement of such an implant
InactiveUS7097653B2Quick upgradeReduce effortDilatorsSurgical veterinaryExertionBiomedical engineering
An implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal is proposed, with a load-bearing structure which, in a first operating state (primary form), has a great ratio of length to transverse extent along an axis (9) and, at least in a further operating state (secondary form), has a much smaller ratio of length to transverse extent along the axis (9), the load-bearing structure (1) being capable of being reversibly transformed from the secondary form into the primary form by exertion of a force against elastic material forces, the secondary form assuming approximately the form of a double disc with a proximal disc element (7) and a distal disc element (6) for receiving the surroundings of the defect opening between the disc elements, and the load-bearing structure (1) being formed essentially in one piece without joining connections, and a placement system.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
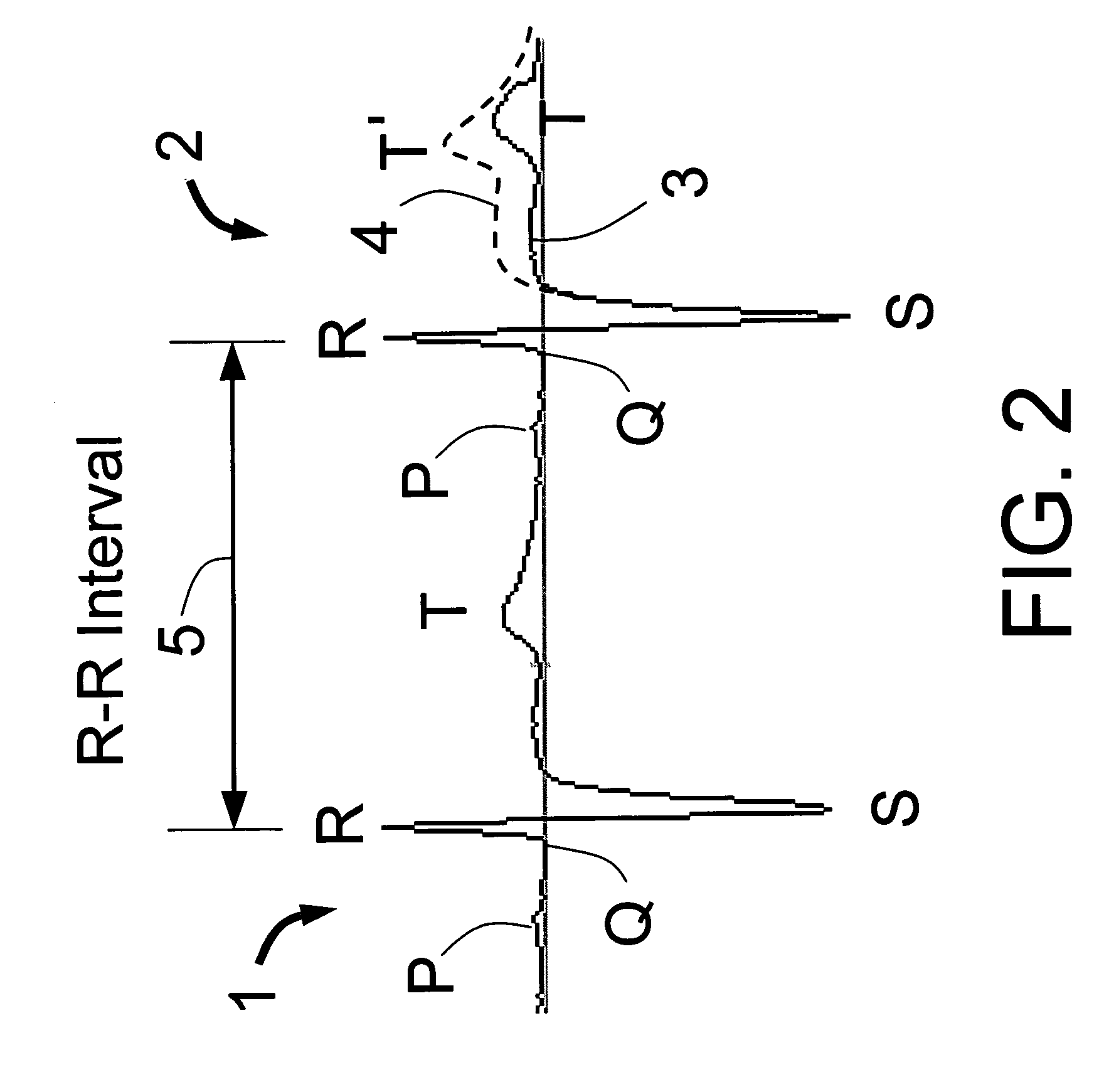
Cardiac monitoring apparatus and method
InactiveUS6881191B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to cleanElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsPulse rateCardiac monitoring
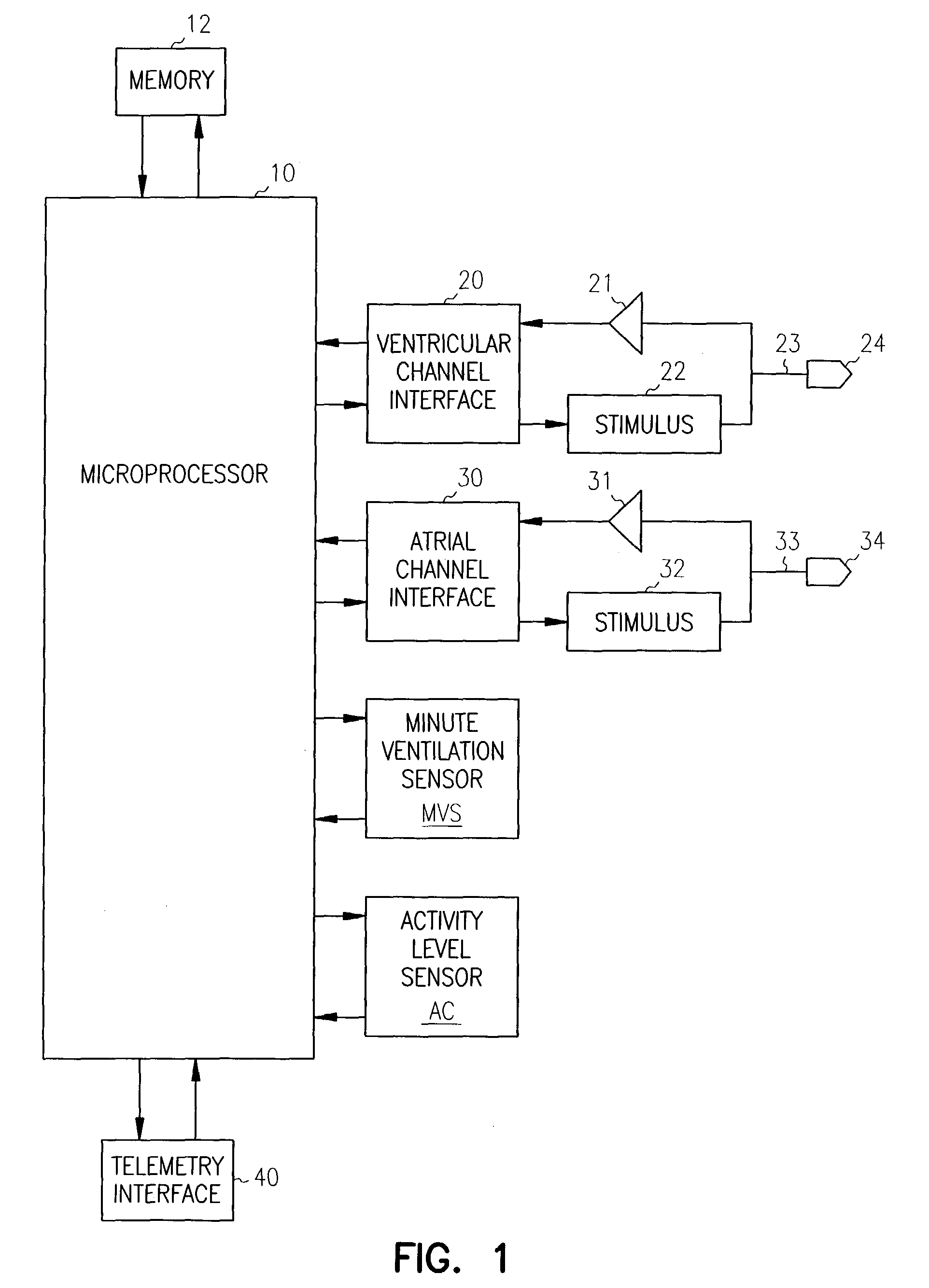
A monitor includes cardiac and movement sensors 36, 34 responsive to a user's heart beat and a user's movement. The monitor includes a processor coupled to the sensors for generating heart-rate or other cardiac data and user movement or activity data. These data can be stored in a memory and used to analyse the relationship between heart rate and physical exertion.
Owner:CAMNTECH
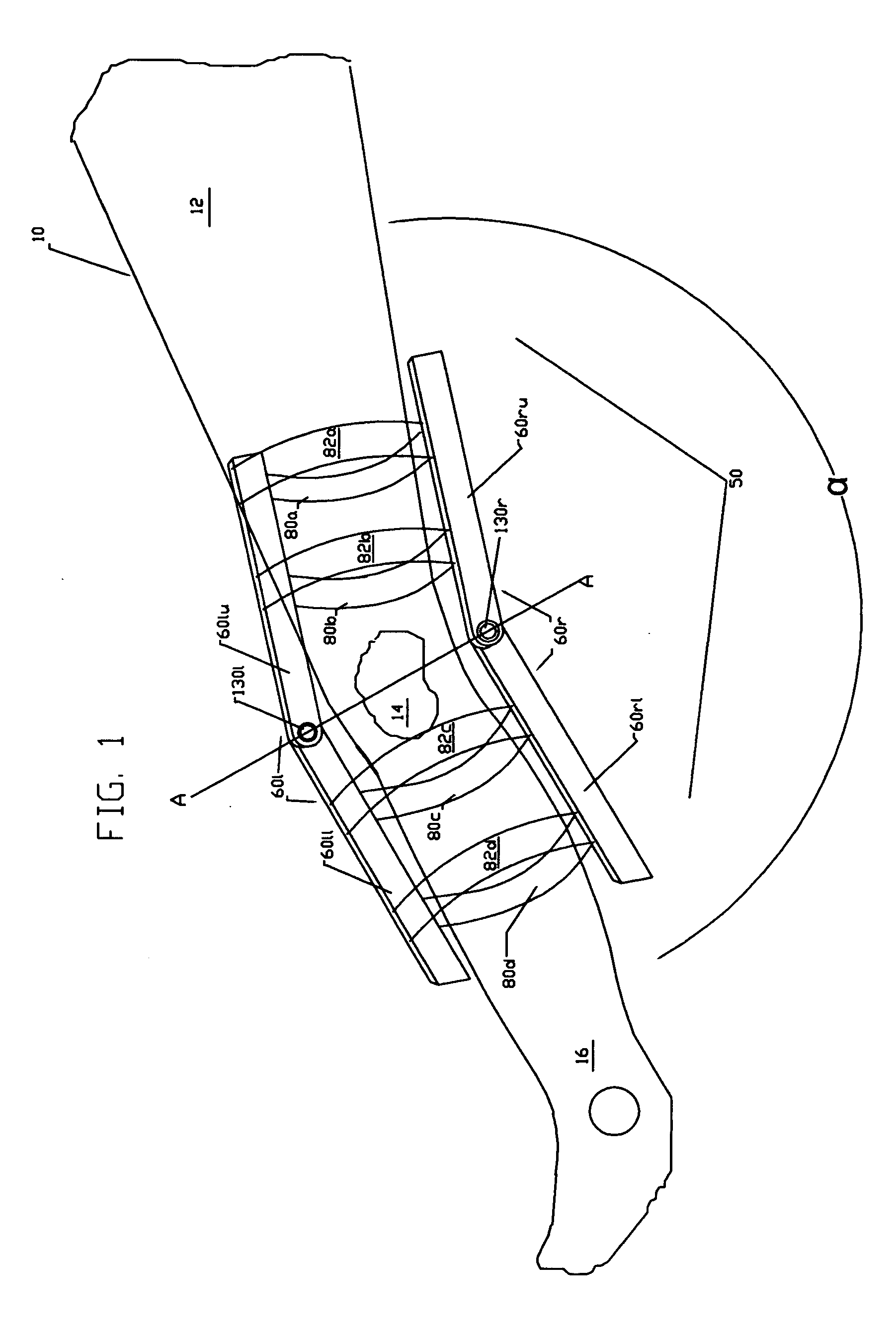
Bipedal locomotion training and performance evaluation device and method
InactiveUS6676569B1Effective mass reductionTherapy exerciseMovement coordination devicesForce velocityEngineering
An exercise and performance evaluation apparatus including a revolving belt or other engagement surface on which a subject can perform forward, backward, or sideways bipedal locomotion or other exercise movement, a means for securing the position of the subject relative to the frame of the apparatus, a means for measuring the force applied by the subject to the engagement surface, and a means for monitoring and / or controlling the velocity of the engagement surface. Securing the subject relative to the frame of the apparatus facilitates monitoring velocity as a function of time. Processing of velocity and force as a function of time allows for recording and analysis of data such as the maximal exertion force-velocity curve. Force-velocity-duration data for exertions is analyzed in terms of an intensity function. The apparatus allows exertions to be performed throughout, and outside, the first quadrant of a force-velocity-duration space.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT BRIAN
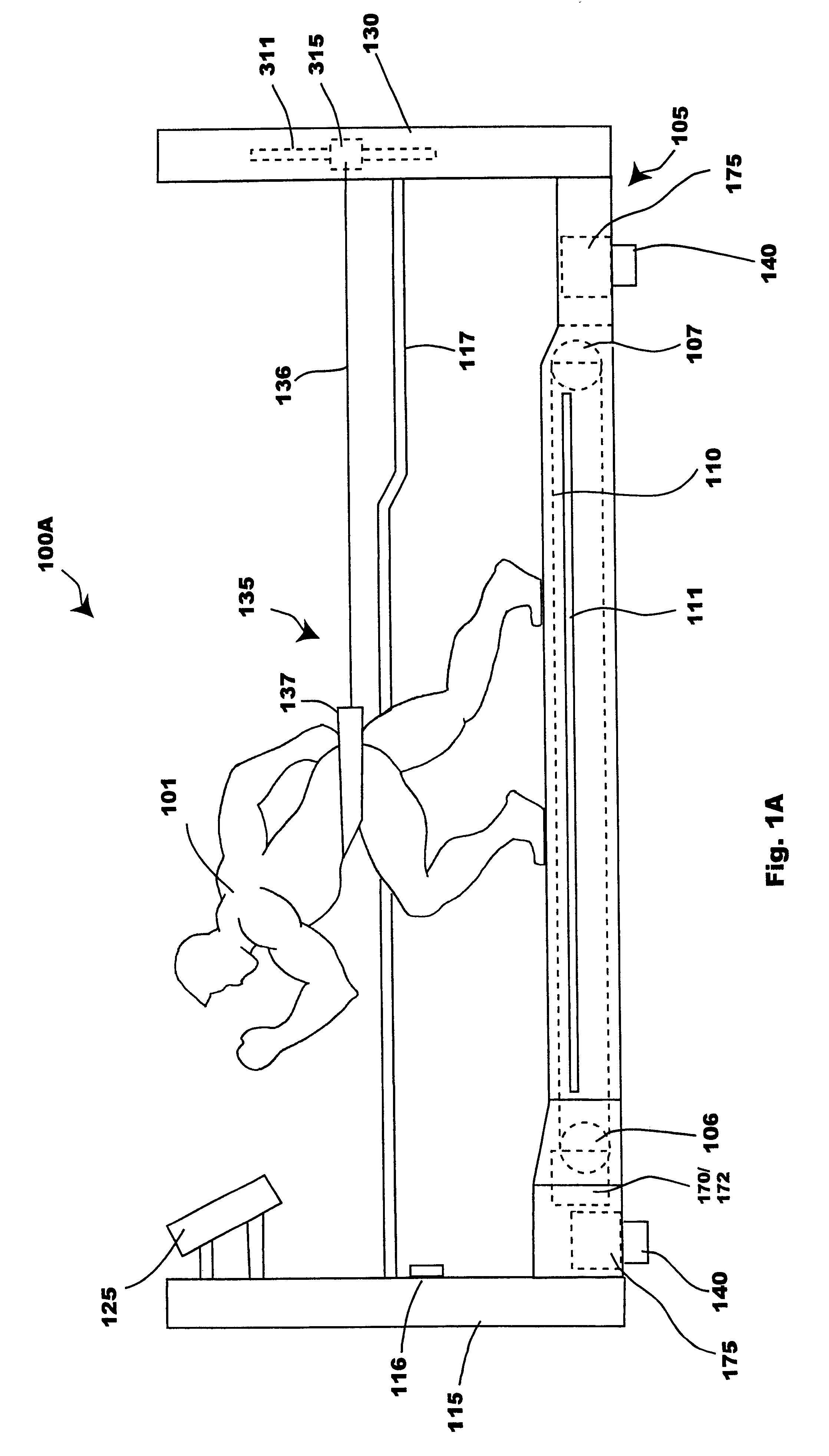
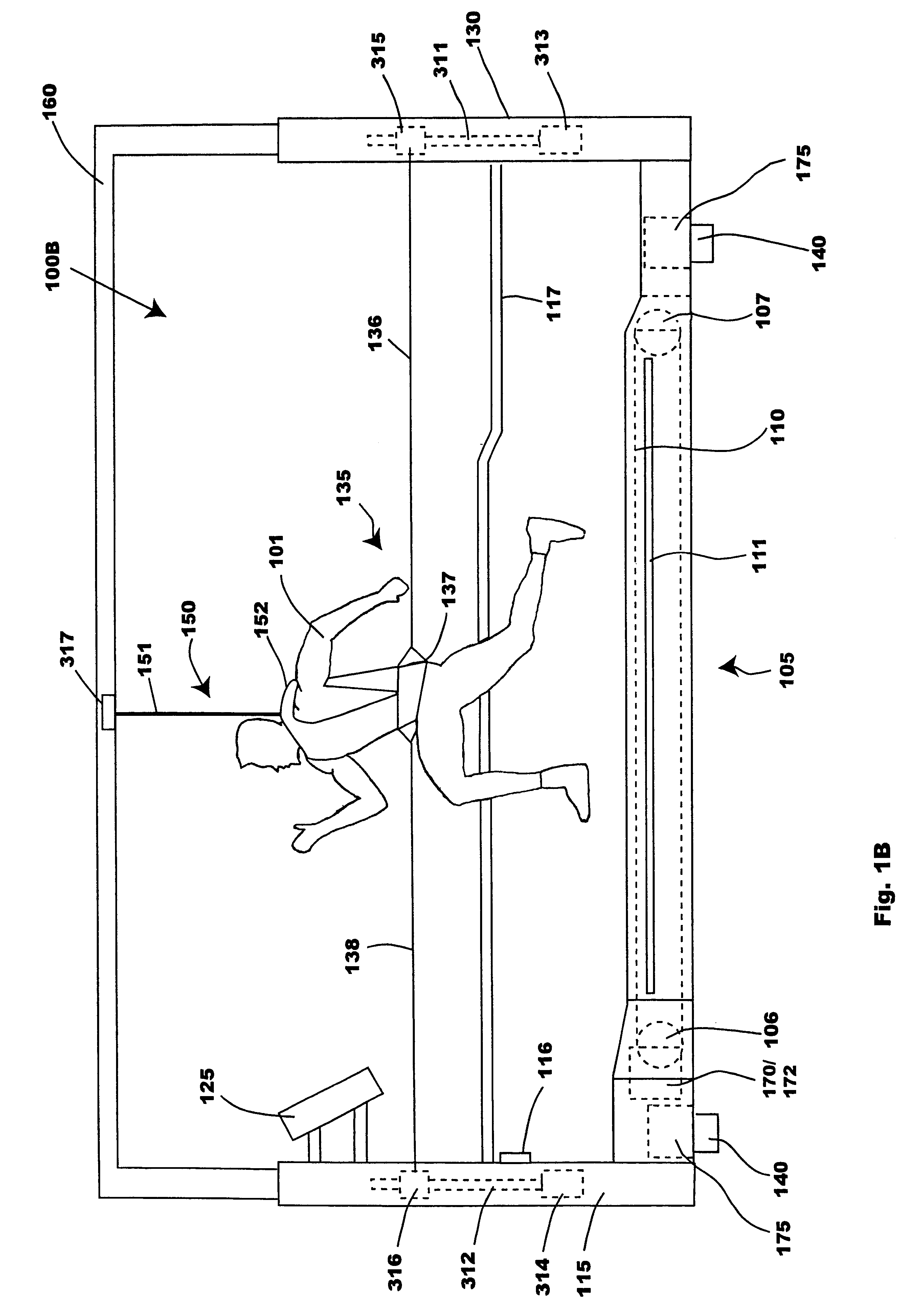
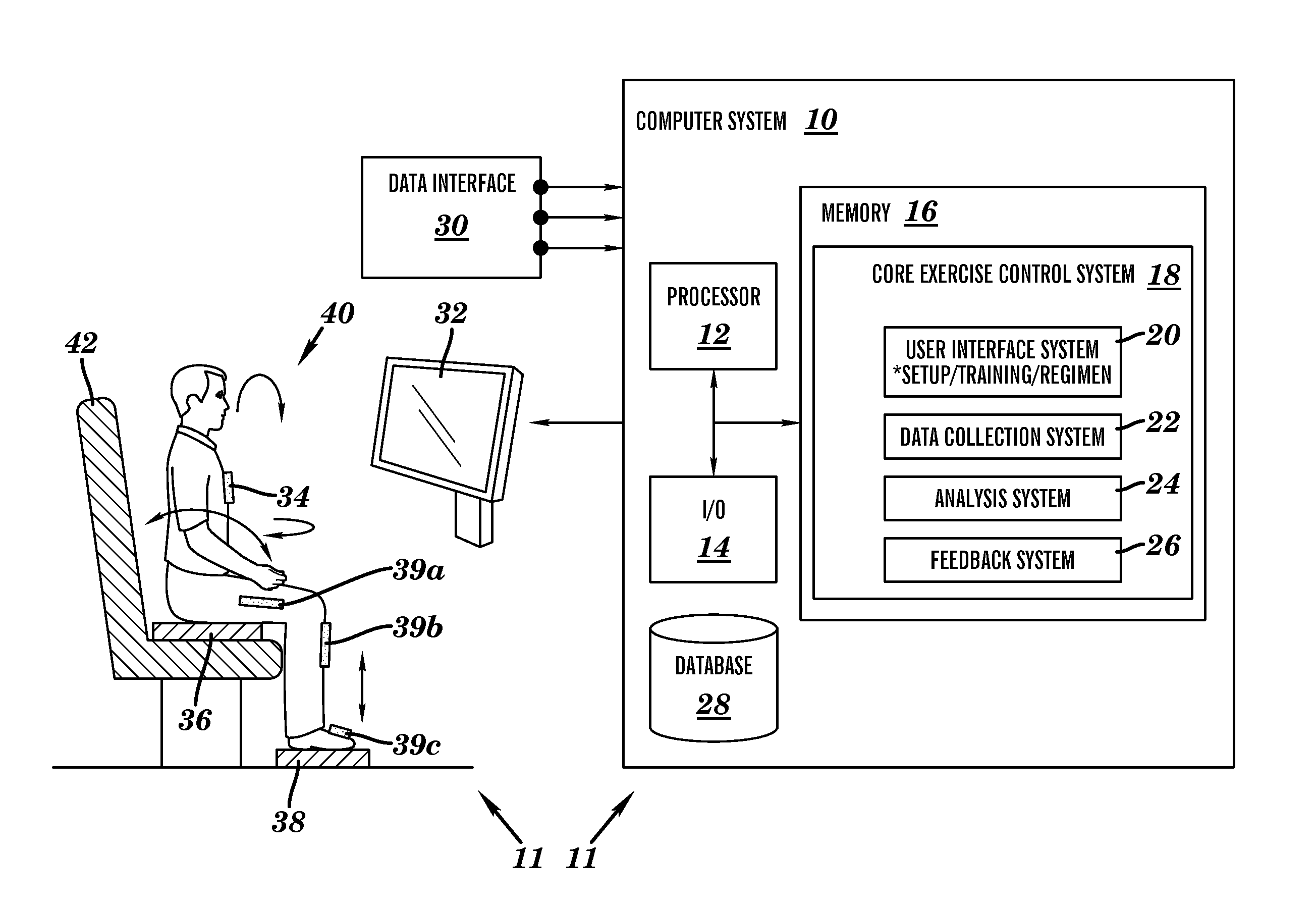
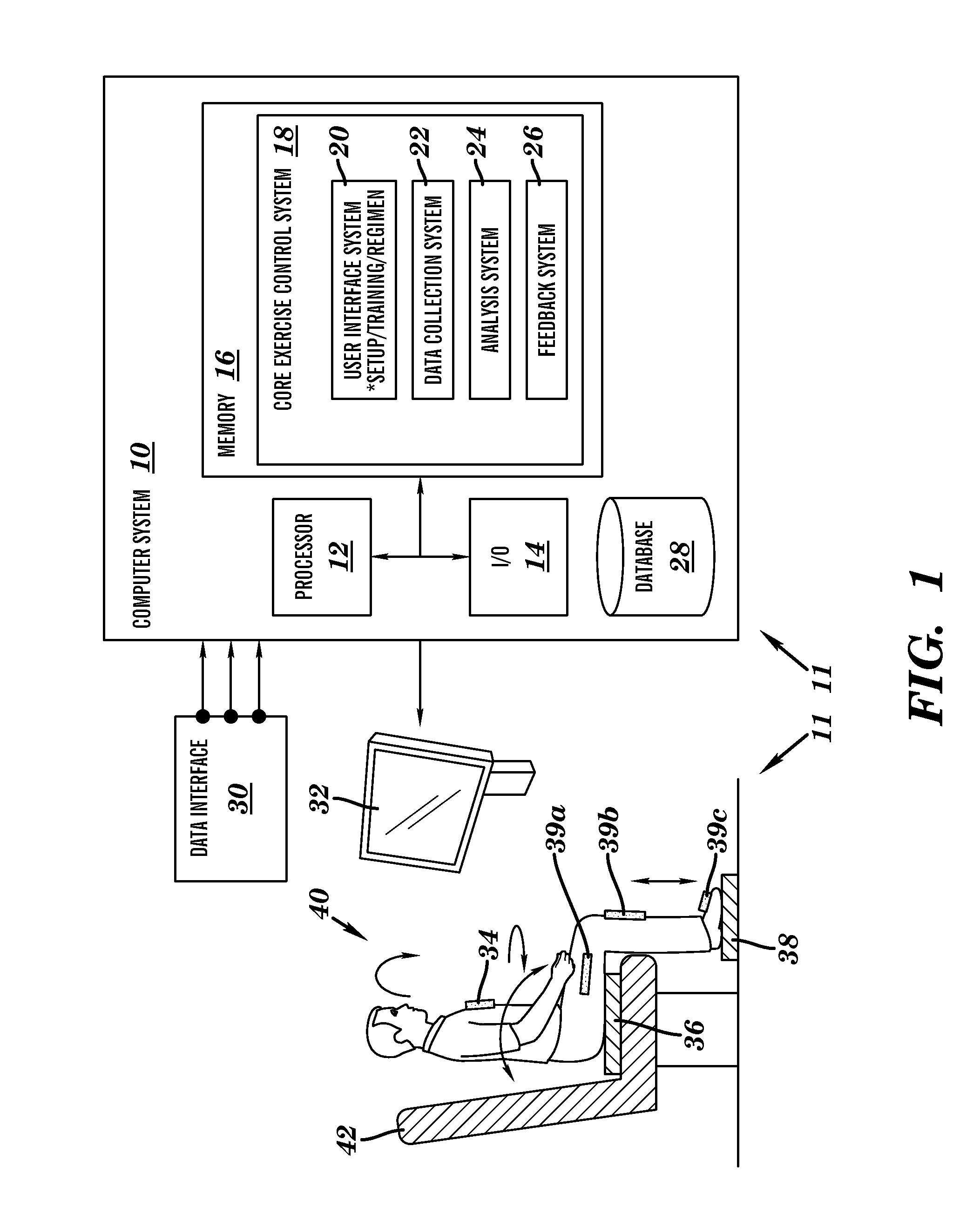
Sensor based exercise control system
InactiveUS20110269601A1Promote sportsStrengthen core musclesGymnastic exercisingPosition fixationControl systemExertion
A system and method for exercising core muscles, particularly the lumbar intrinsic musculature, including the multifidi. A system is disclosed that includes: a first sensor for detecting upper body exertions of a user engaged in an exercise; a second sensor for detecting lower torso exertions for the user engaged in the exercise; a third sensor for detecting lower extremity exertions for the user engaged in the exercise; a control system for processing sensor data from the first, second and third sensor, said control system including: a user interface system for communicating information with the user; a data collection system for collecting sensor data; an analysis system for analyzing the sensor data and determining if the user is performing the exercise in a technically correct manner; and a feedback system for alerting the user when the exercise is not being performed in the technically correct manner.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
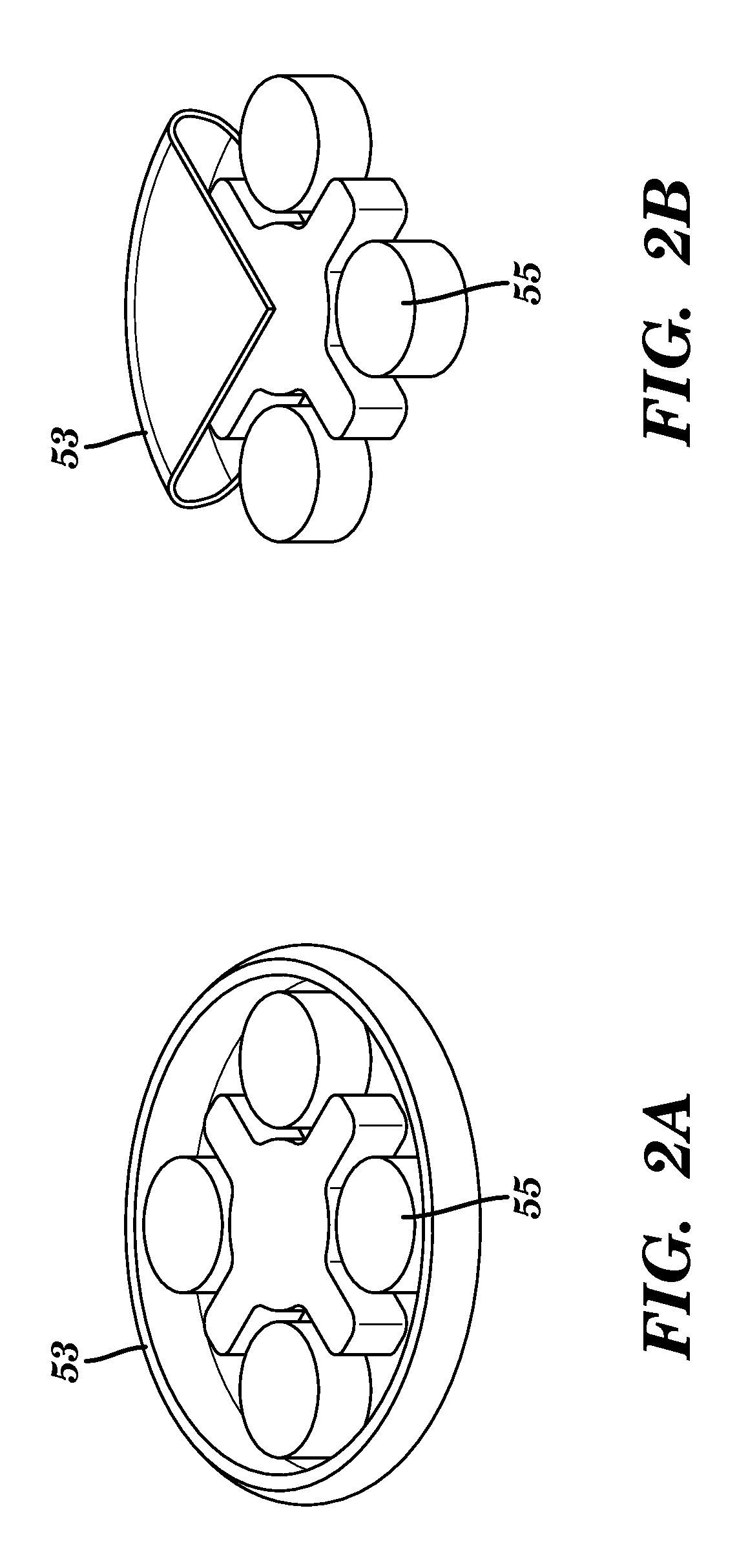
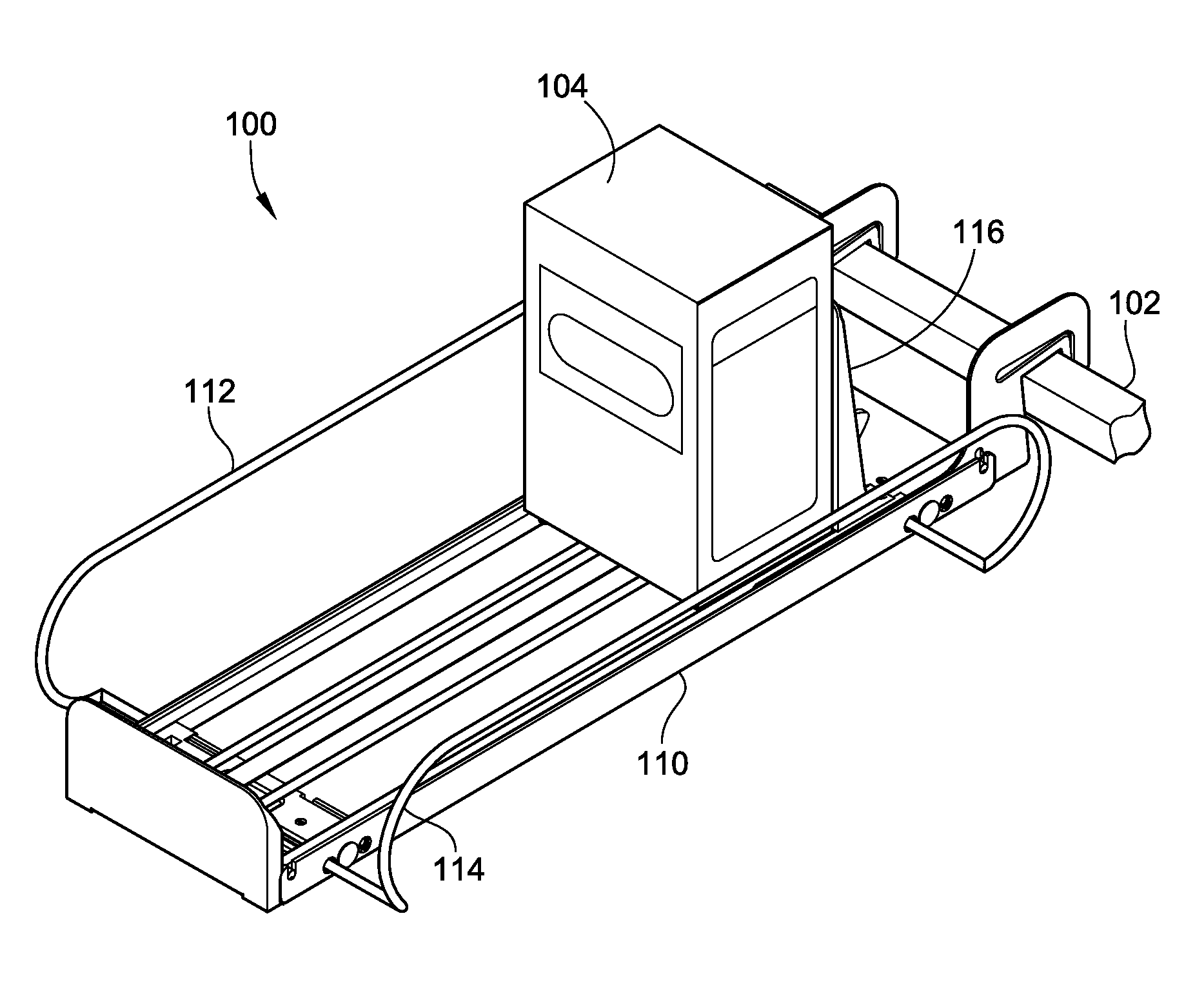
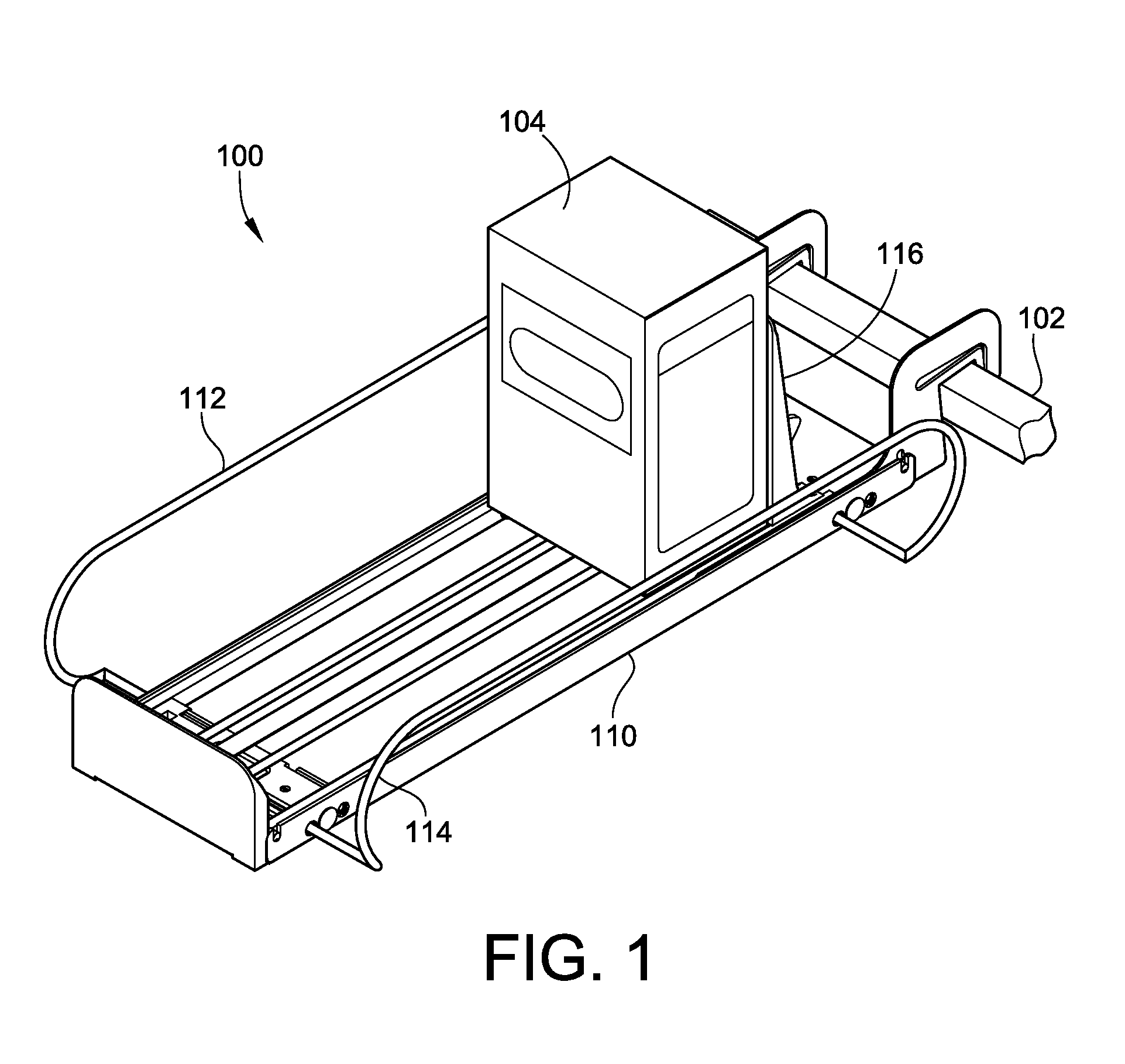
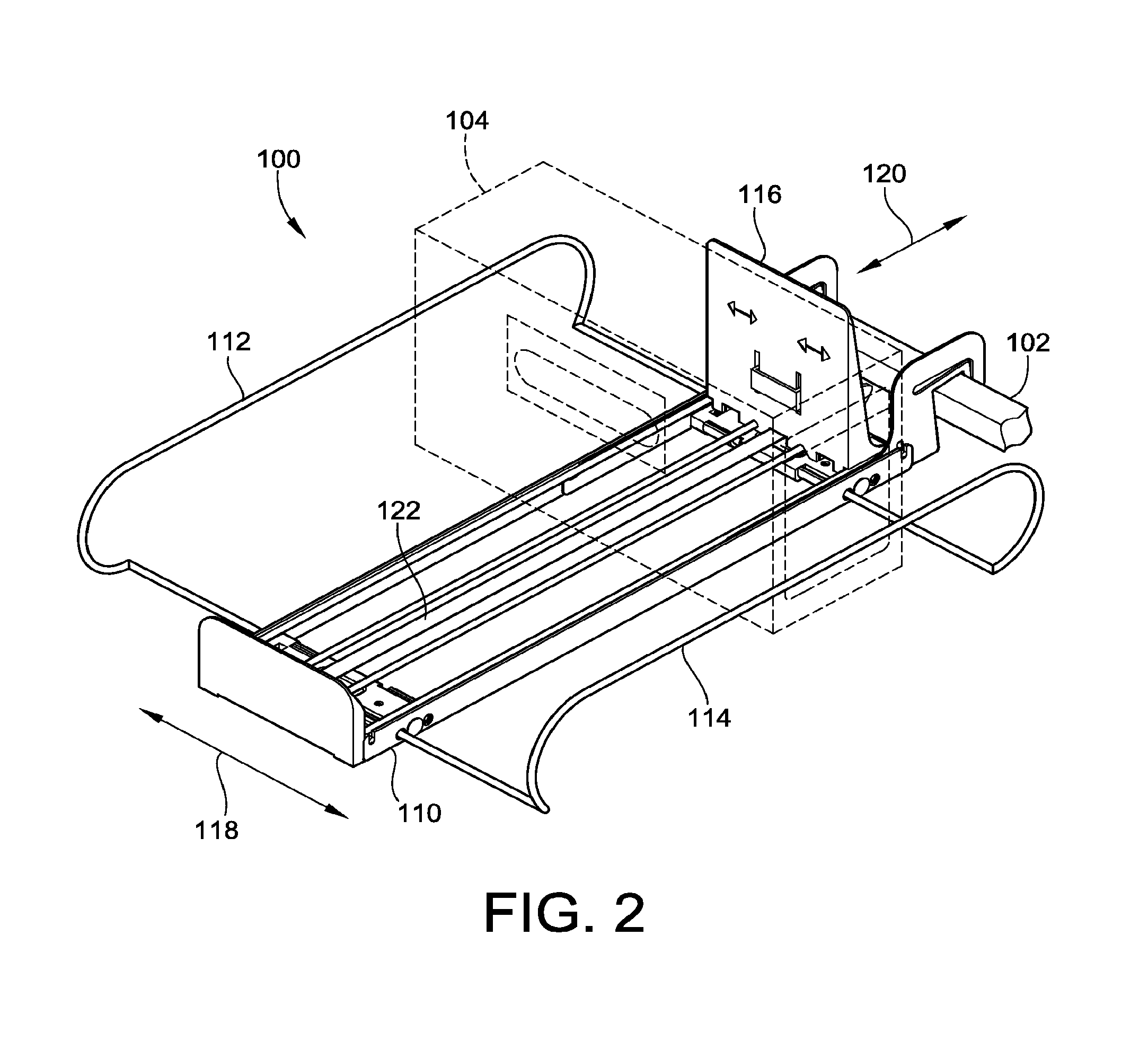
Merchandise pusher tray with adjustable side barriers
A merchandise pusher tray is provided. The merchandise pusher tray includes a base structure. The base structure is configurable for bar or shelf mounting. The base structure includes a pair of load bearing members for supporting a floor of the base structure. The merchandise pusher tray also includes at least one divider mounted to and adjustable in a first direction relative to the base structure. The merchandise pusher tray also includes a pusher mounted to and movable in a second direction relative to the base structure. A locking arm is provided for locking the pusher in a locked position and automatically unlocking the pusher from the locked position upon the exertion of an actuation force against the locking arm.
Owner:FASTENERS FOR RETAIL
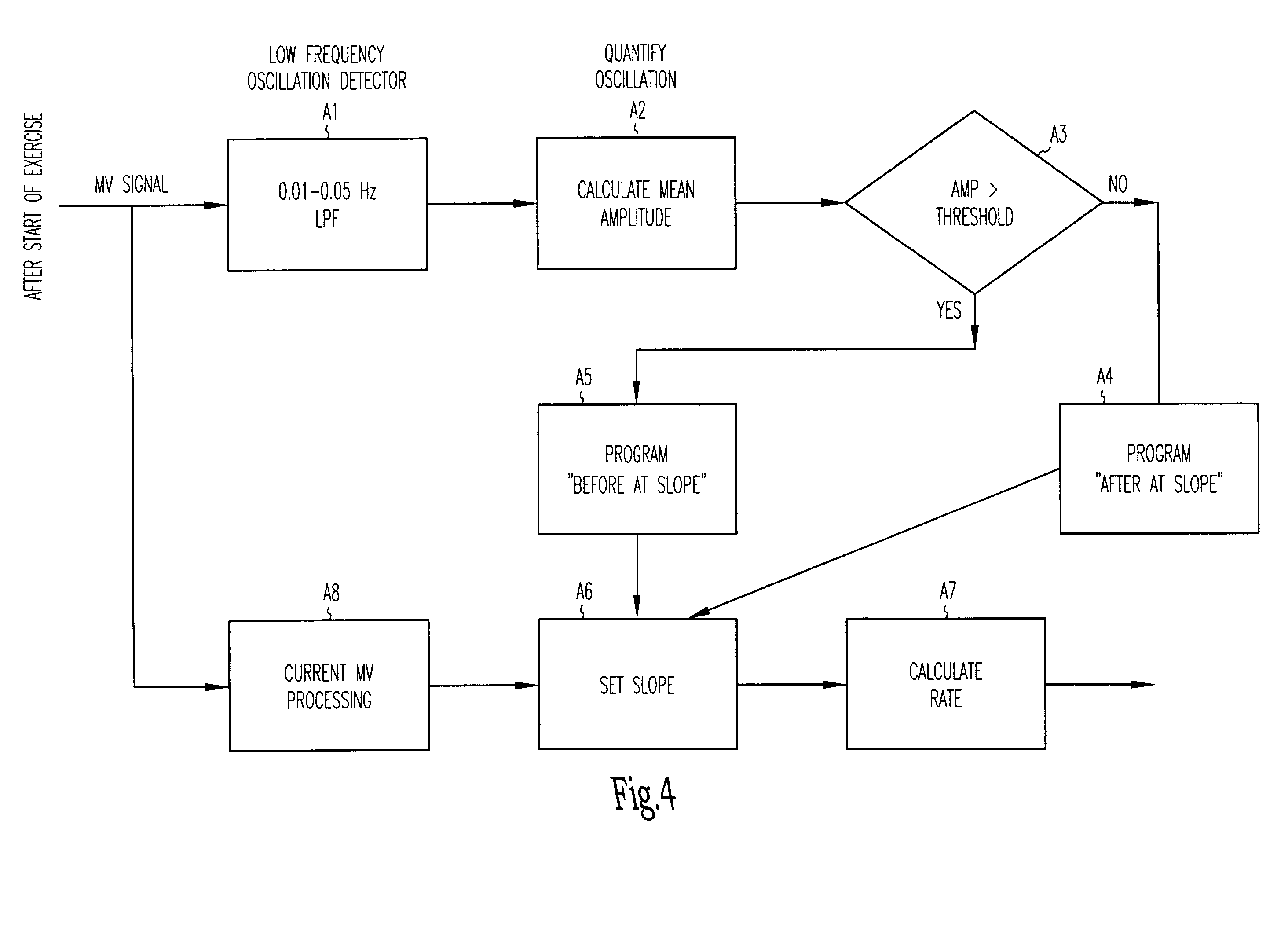
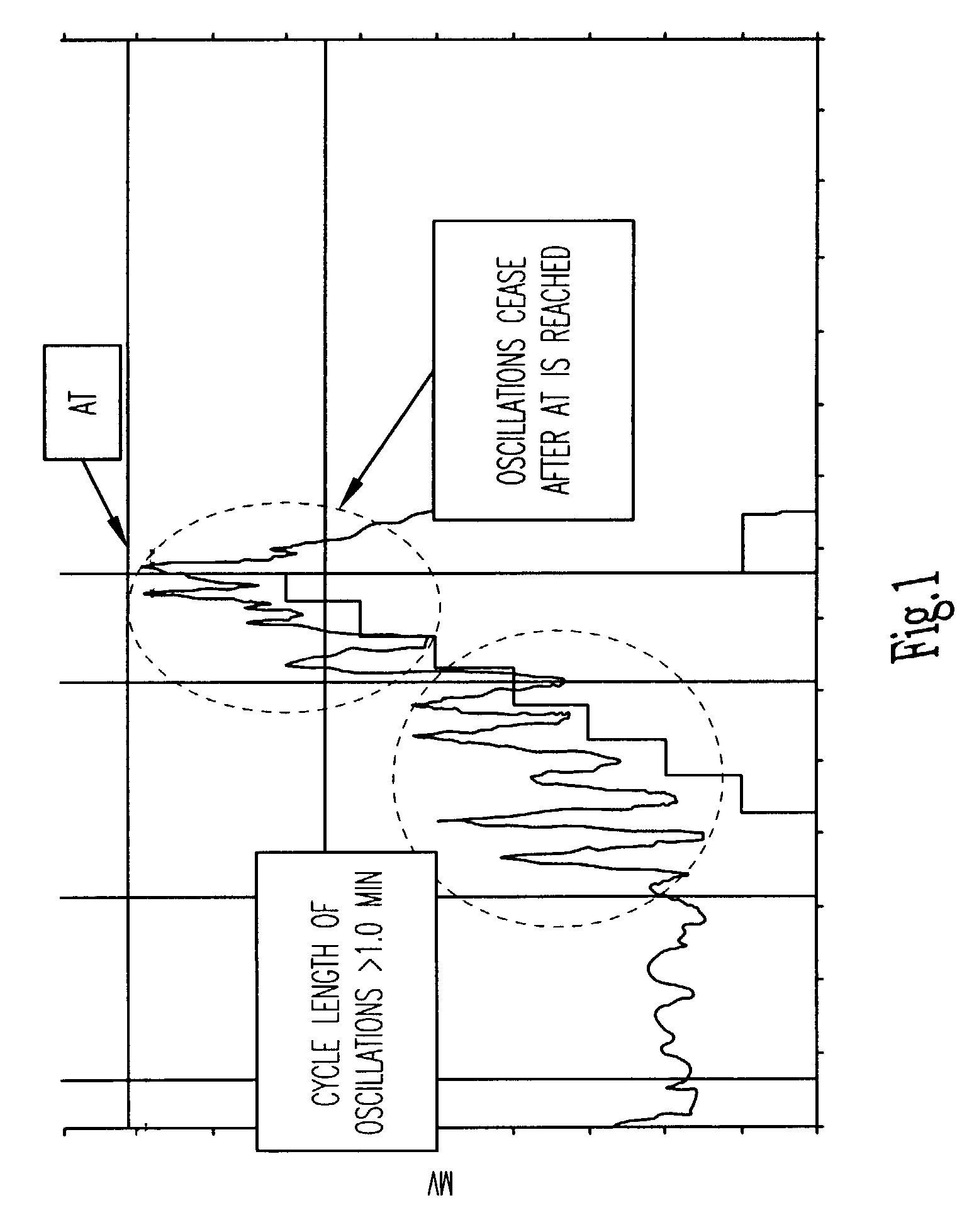
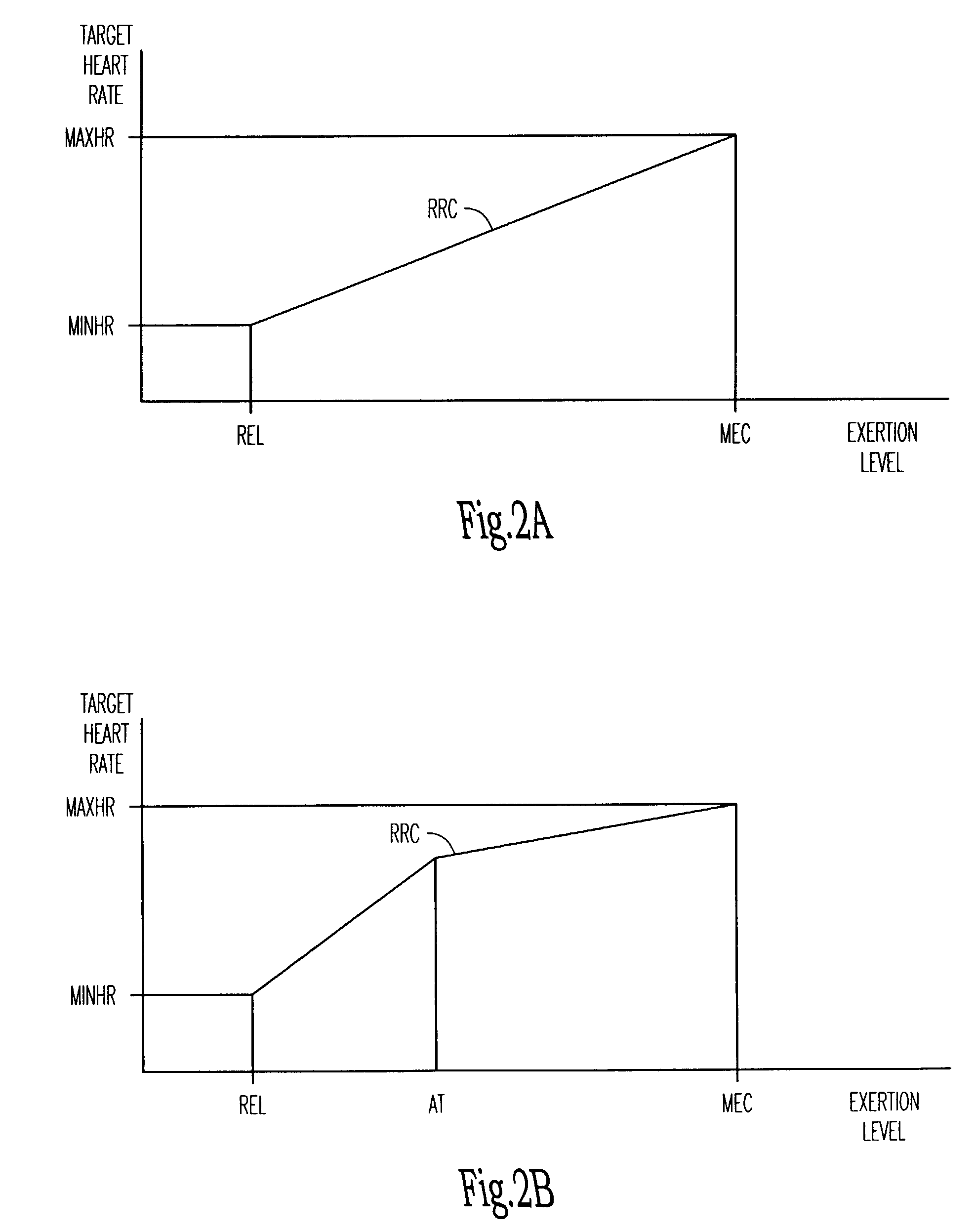
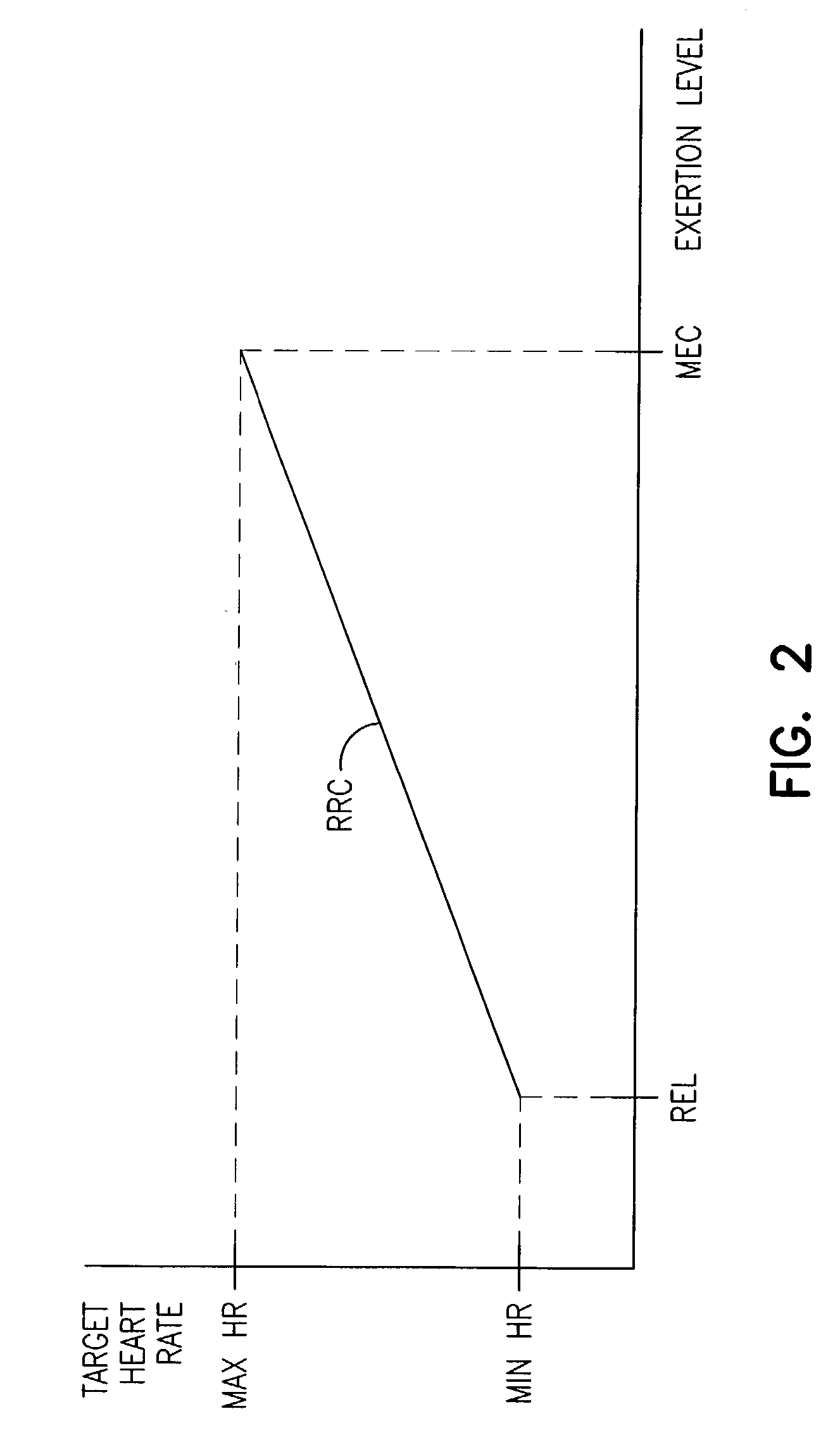
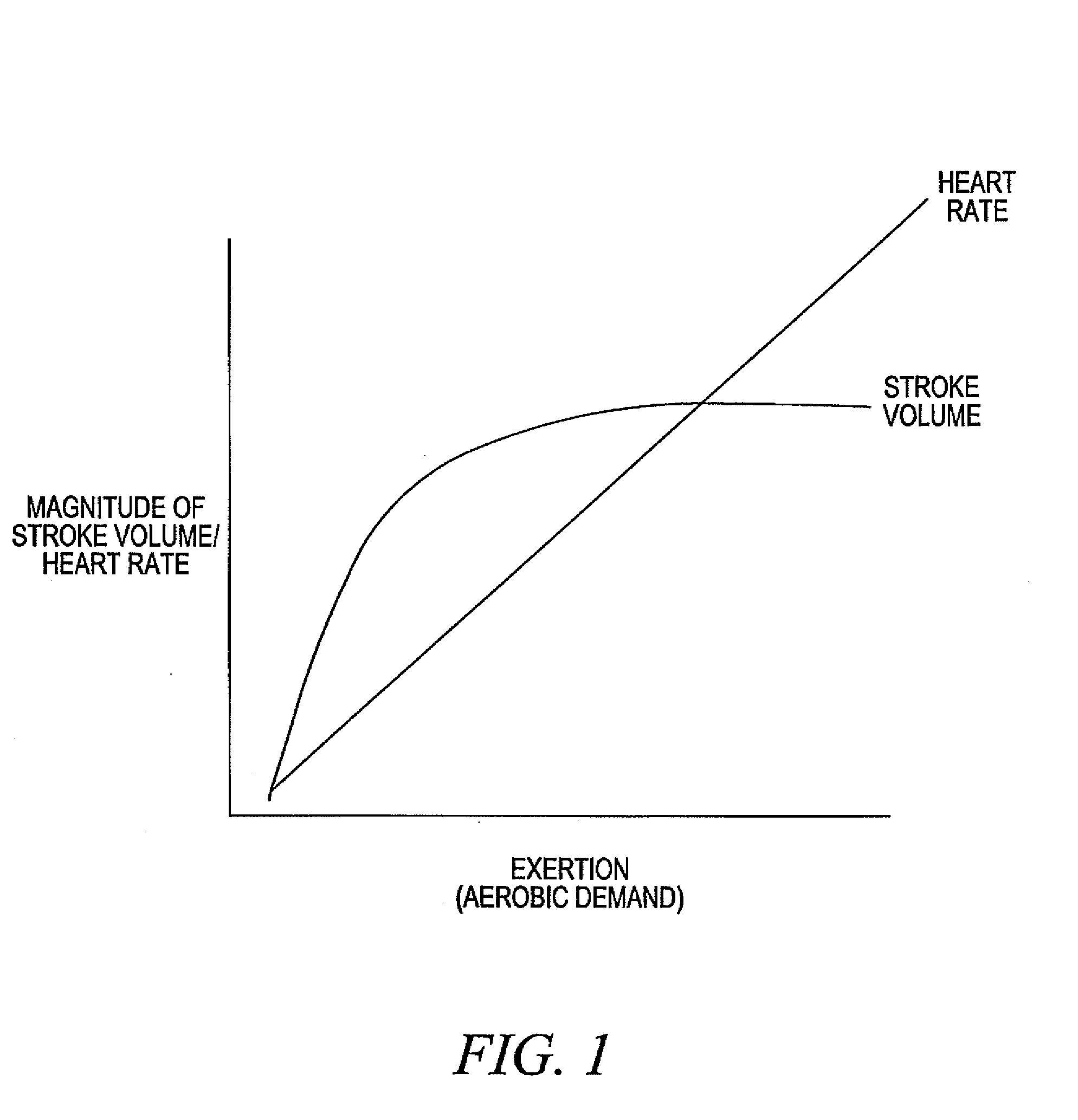
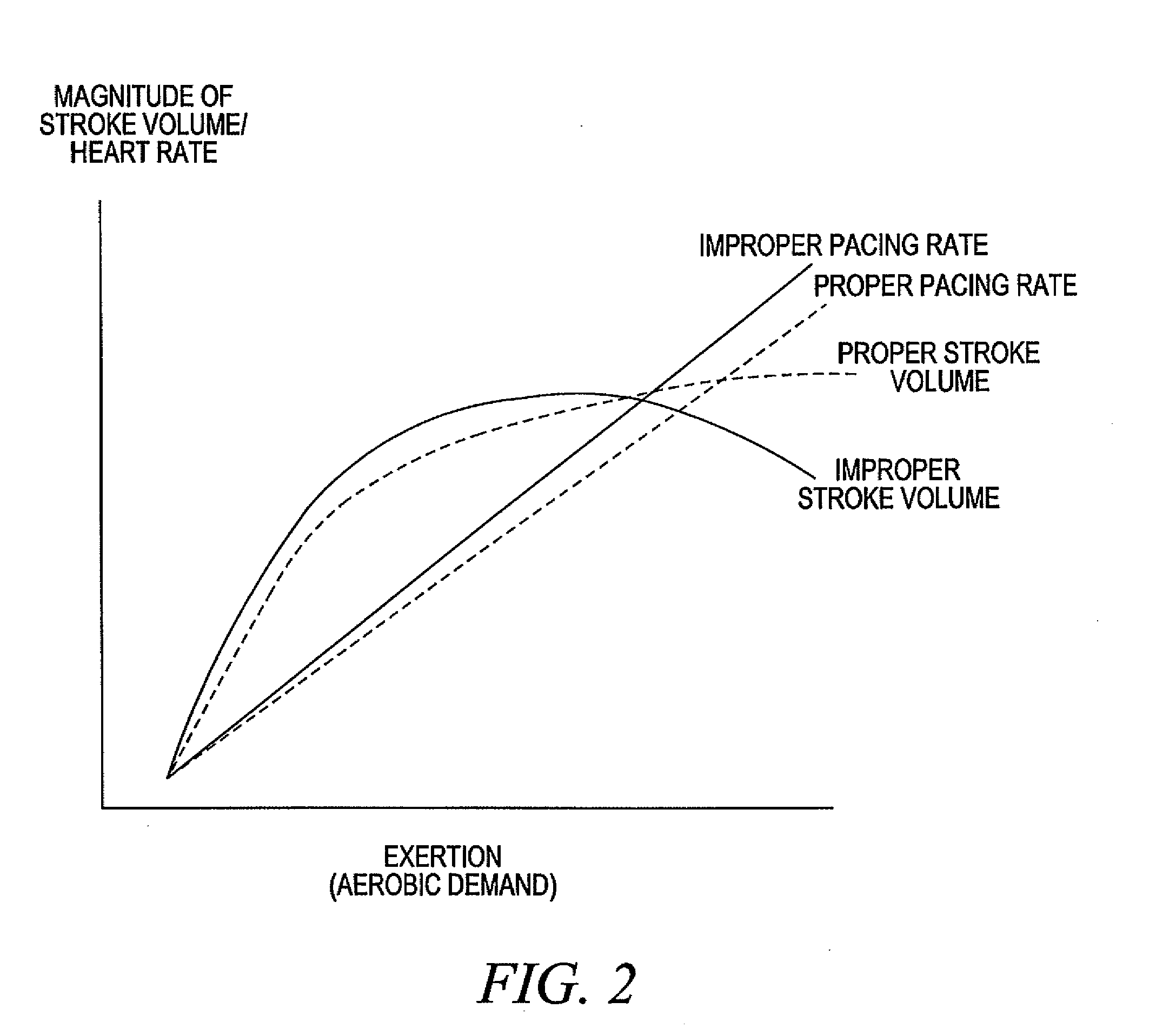
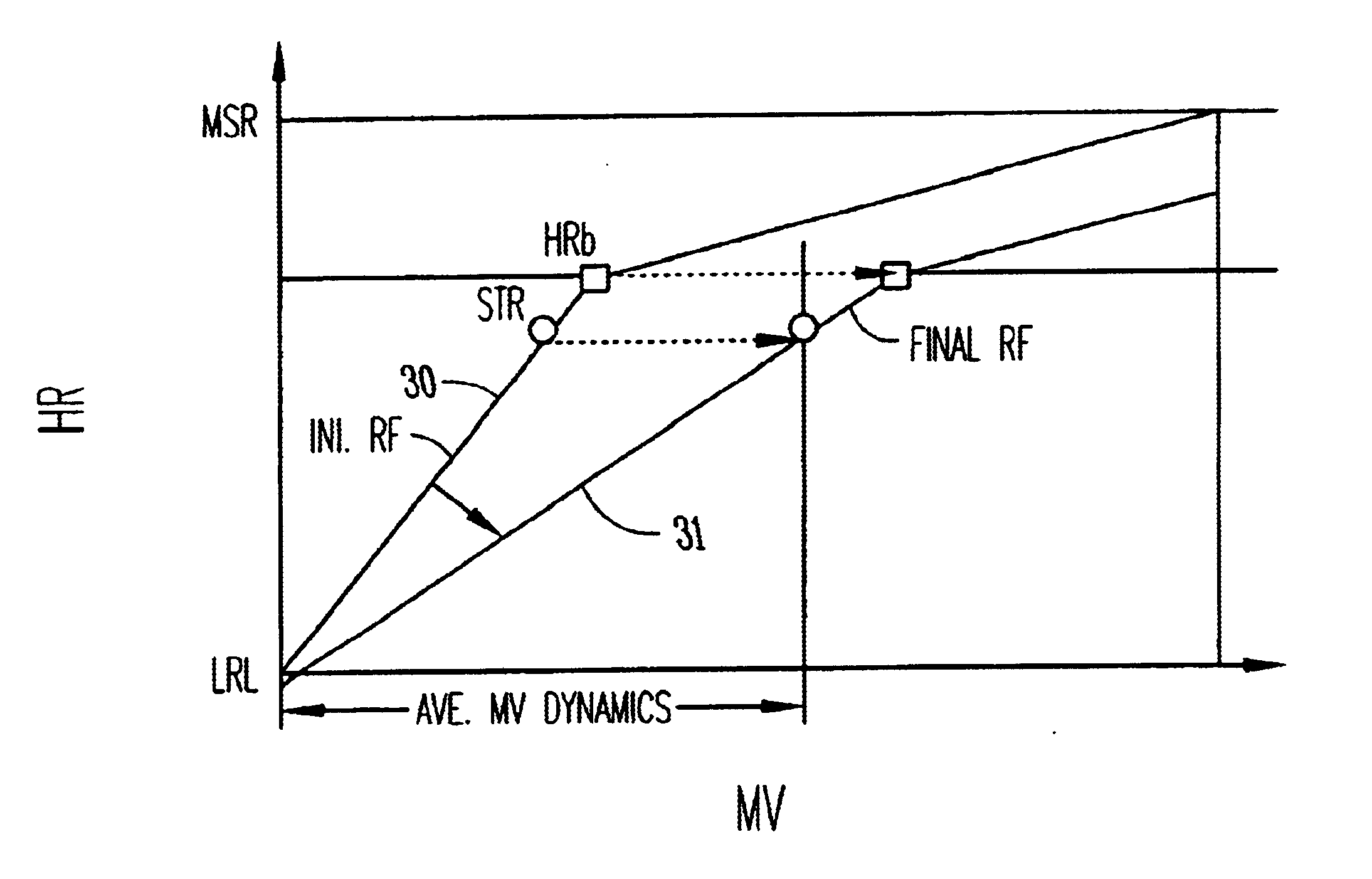
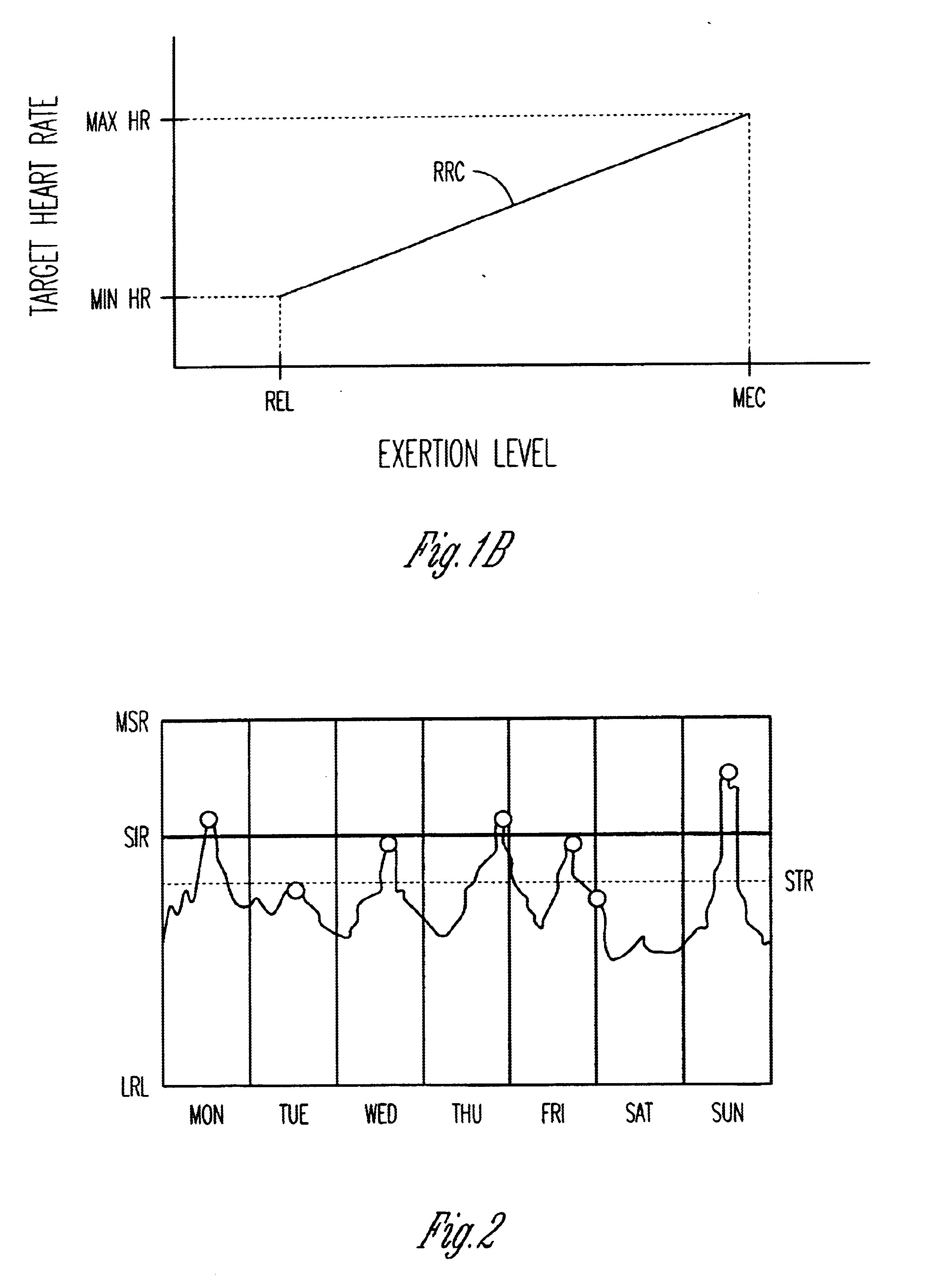
Adjustment of the breakpoint of the rate response curve based on minute ventilation values
A method and system for operating a rate-adaptive pacemaker utilizing minute ventilation to measure exertion level. The method is applicable to heart failure patients who exhibit an oscillatory minute ventilation pattern.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
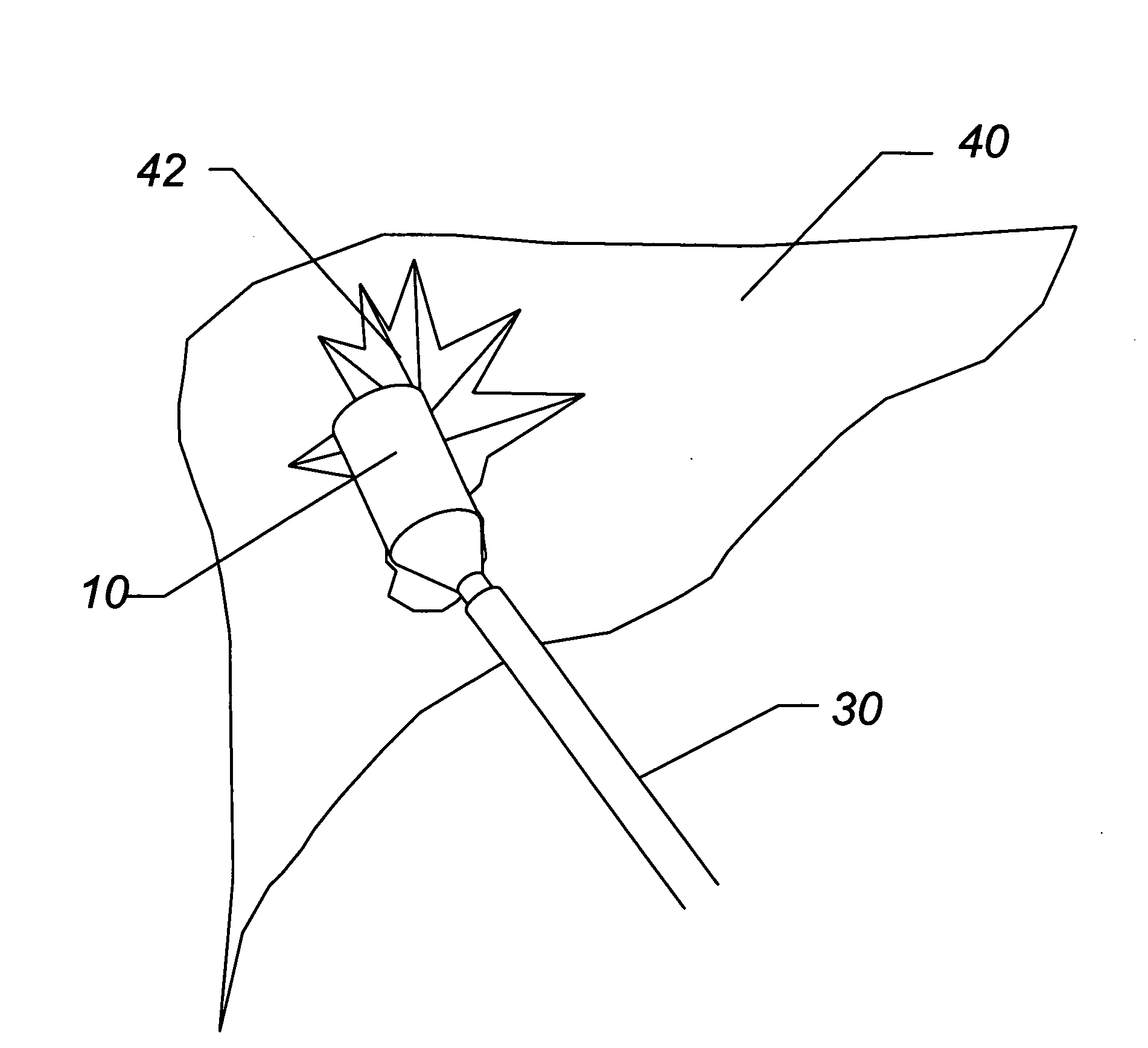
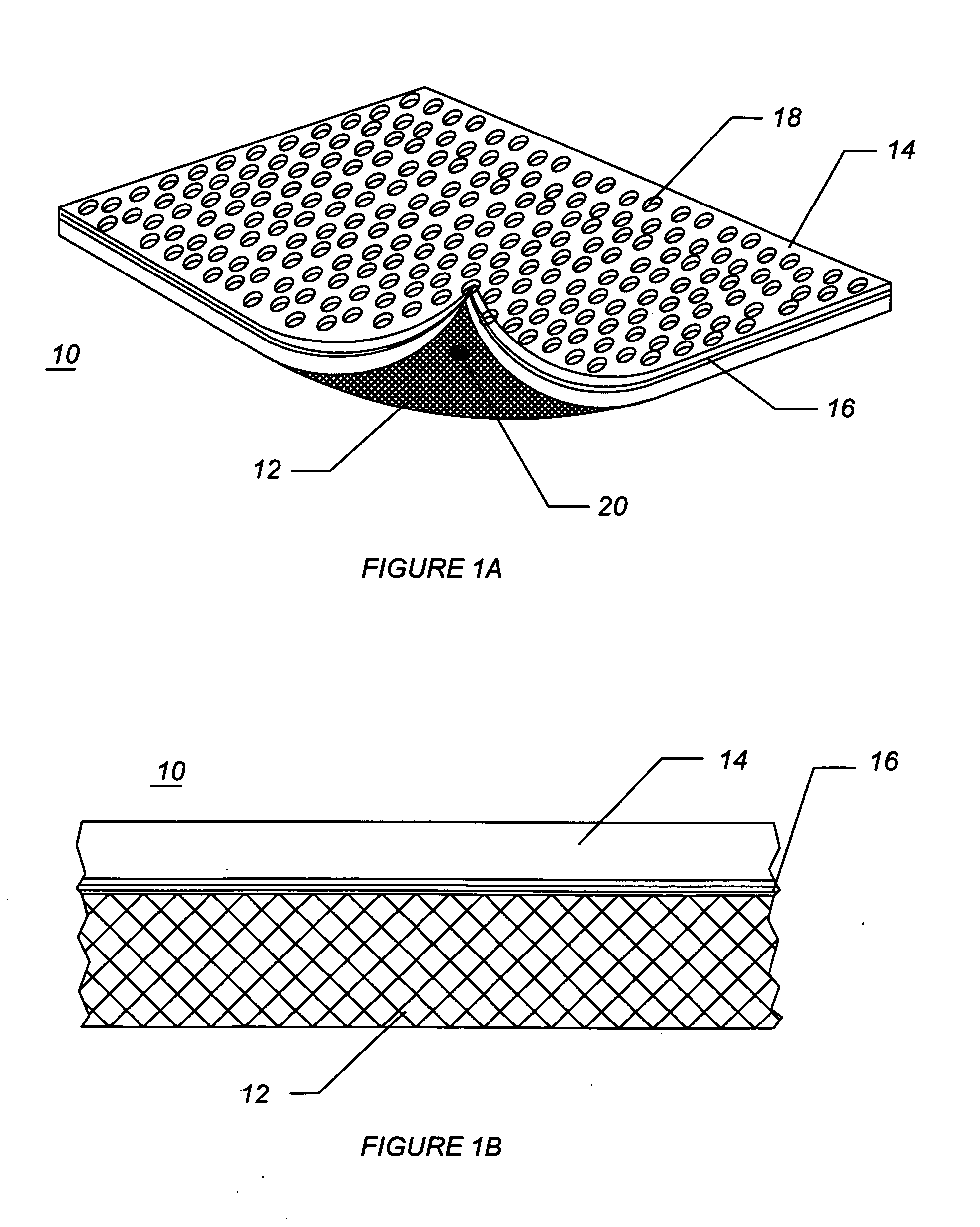
Method and apparatus for improved hemostasis and damage control operations
InactiveUS6998510B2Improved hemostatic packing in trauma careGood hemostasisPlastersBaby linensTamponadePERITONEOSCOPE
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in traumatized patients. The devices utilize fluid impermeable outer surfaces and distributed pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of pressure. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for throabogenic or antipathogenic agents. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to cover the entire wound area over the hemostatic pack. The hemostatic packing devices may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access without generating excessive re-bleeding, and may further comprise antimicrobial or thrombogenic regions.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
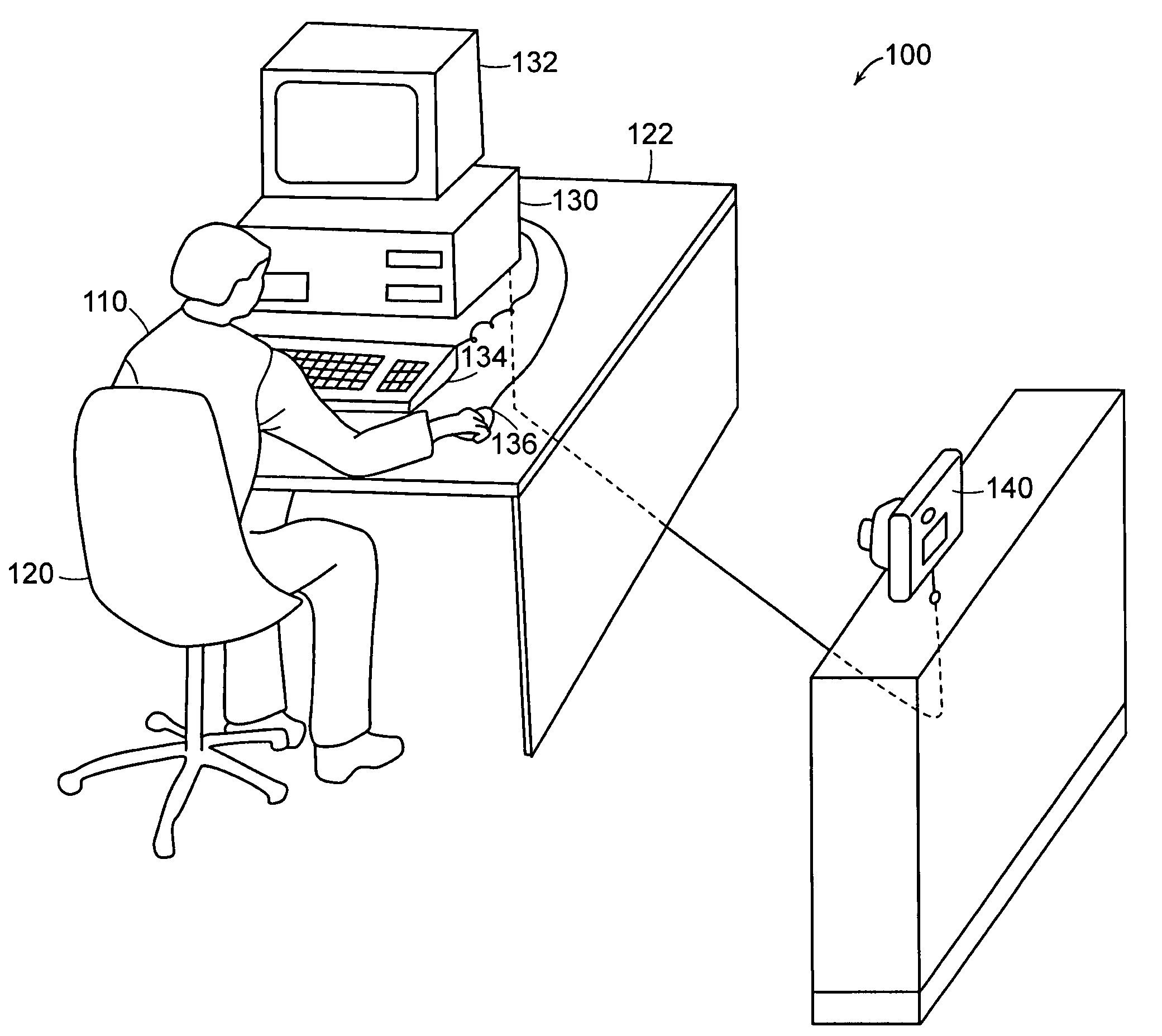
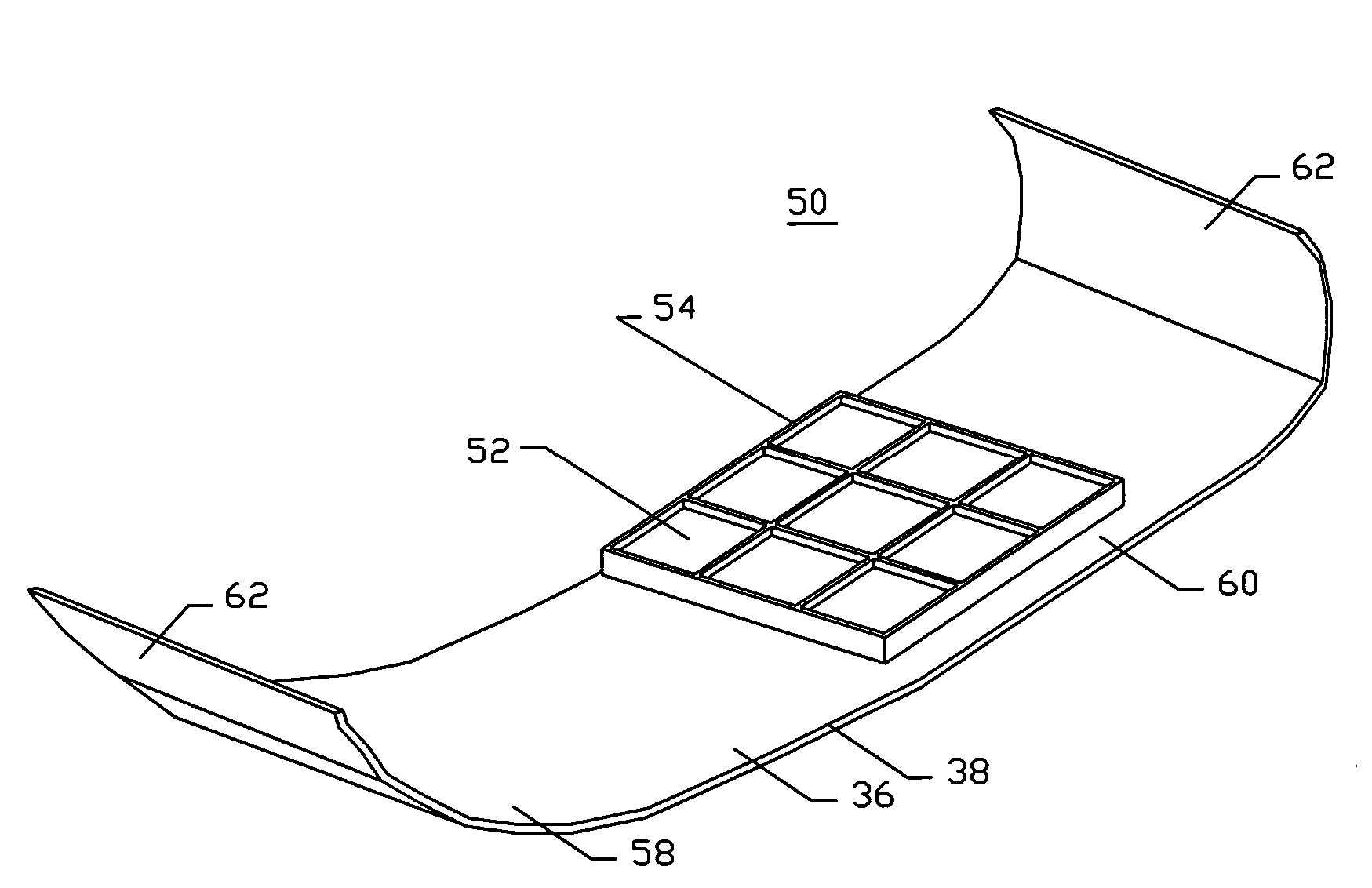
System and method for ergonomic tracking for individual physical exertion
ActiveUS7315249B2Low costPreventing various kinds of incapacitating traumaSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomechanicsComputer module
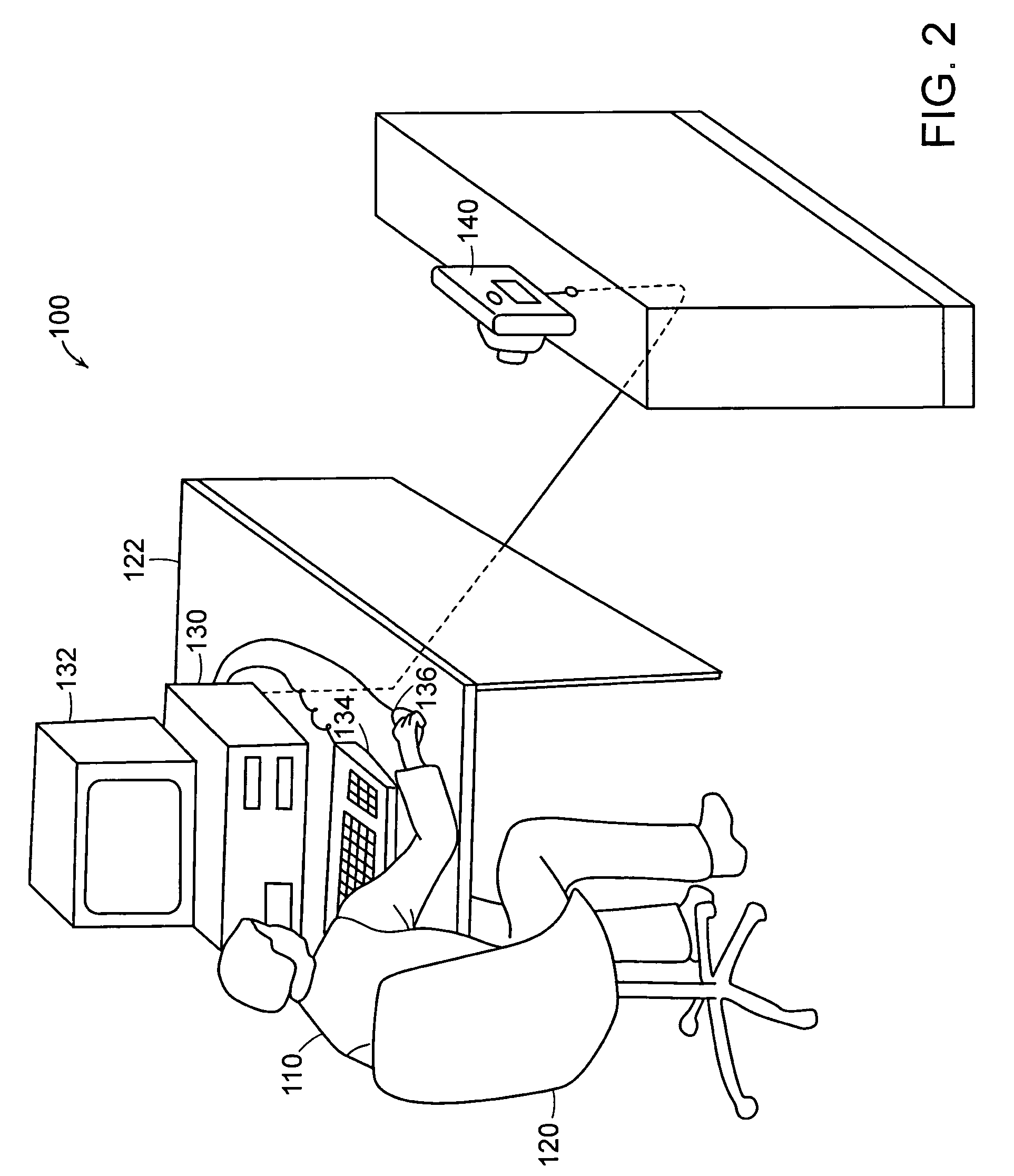
A system and method are provided for tracking a user's posture. The system and method include an environmental module for determining the user's physical environment, a biomechanical module for determining at least a user's posture in the user's physical environment, and an output module for outputting to the user an indication of at least the user's posture relative to at least a target correct posture. The physical environment can include a computer workstation environment, a manufacturing environment, a gaming environment, and / or a keypadding environment.
Owner:LITTELL STEPHANIE
Rate-adaptive therapy with sensor cross-checking
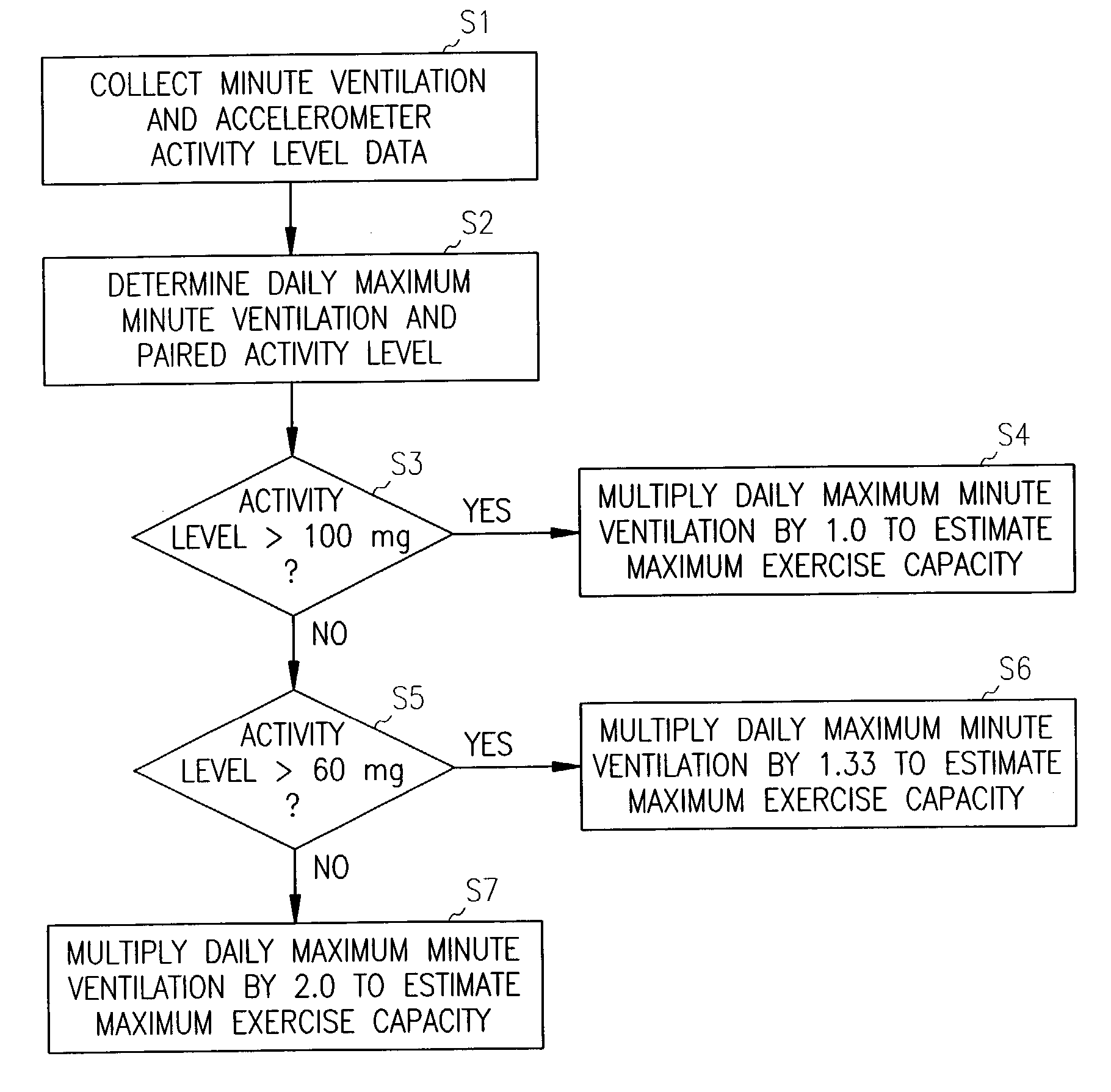
A method and system for automatically adjusting the operating parameters of a rate-adaptive cardiac pacemaker in which maximum exertion levels attained by the patient are measured at periodic intervals and stored in order to compute or update a maximum exercise capacity. The slope of the rate-response curve is then adjusted to map an exertion level corresponding to the updated maximum exercise capacity to a maximum allowable pacing rate. In accordance with the invention, a maximum exercise capacity is determined by cross-checking periodic maximum exertion level sensor values with a motion-level sensor value.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
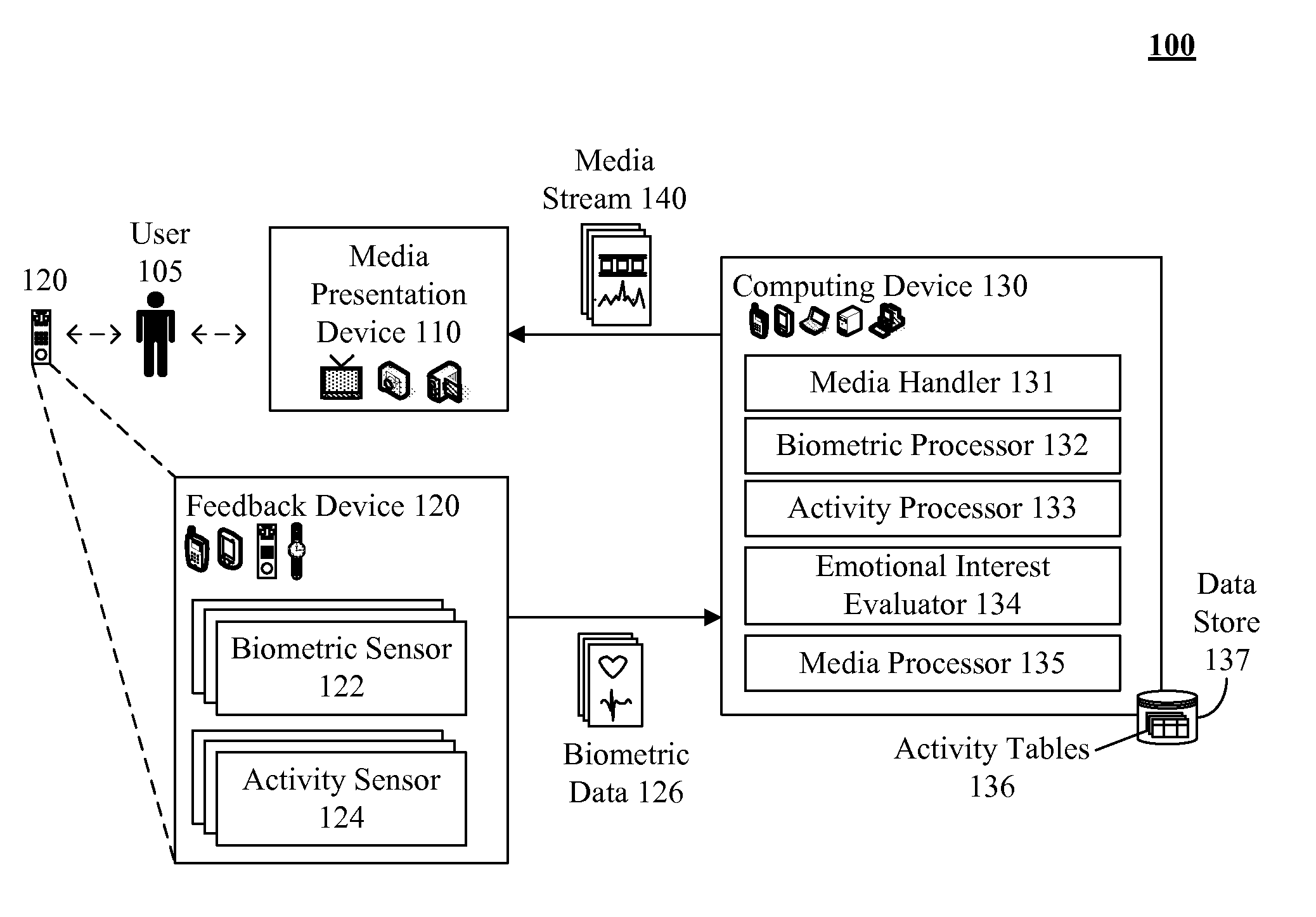
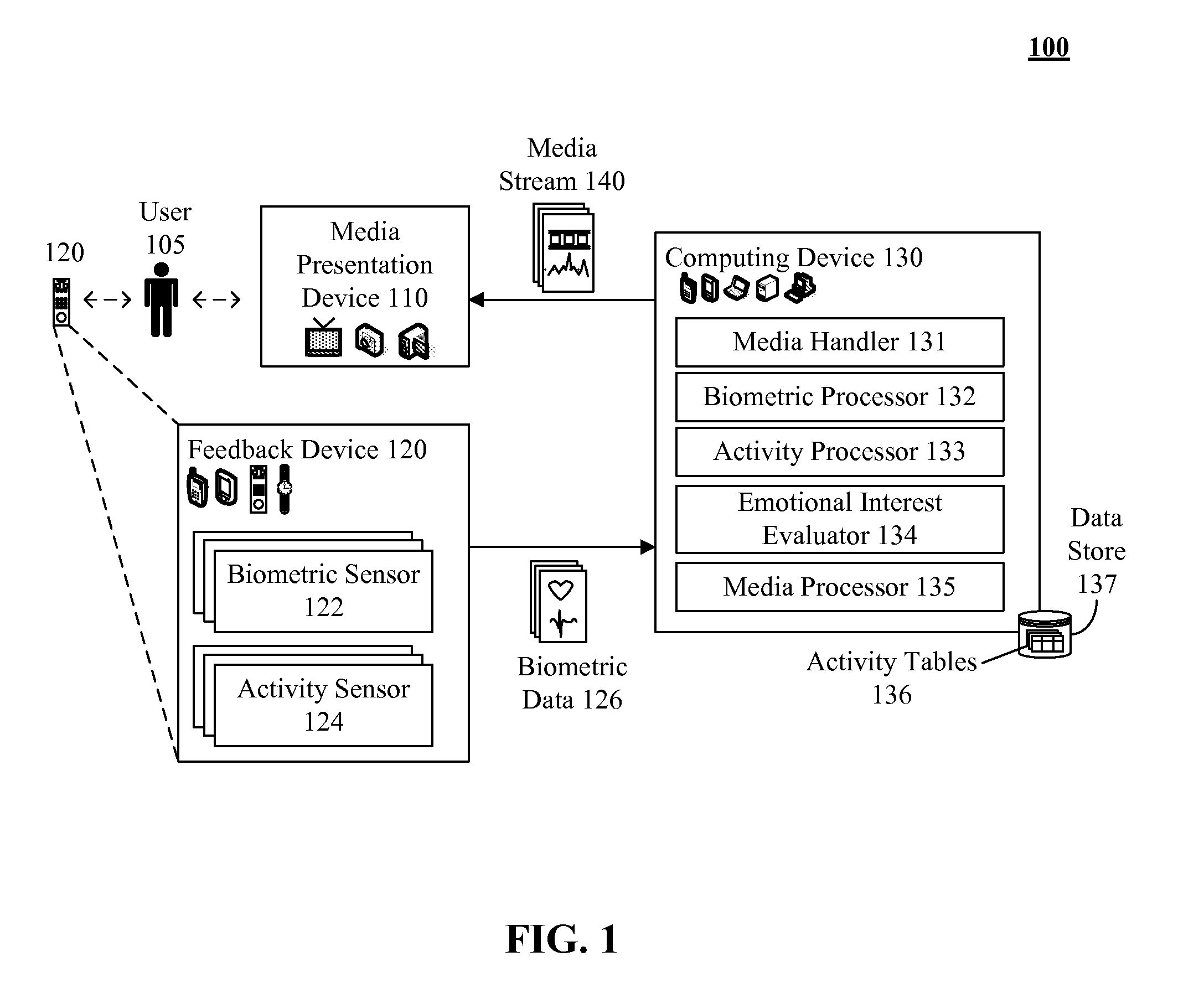
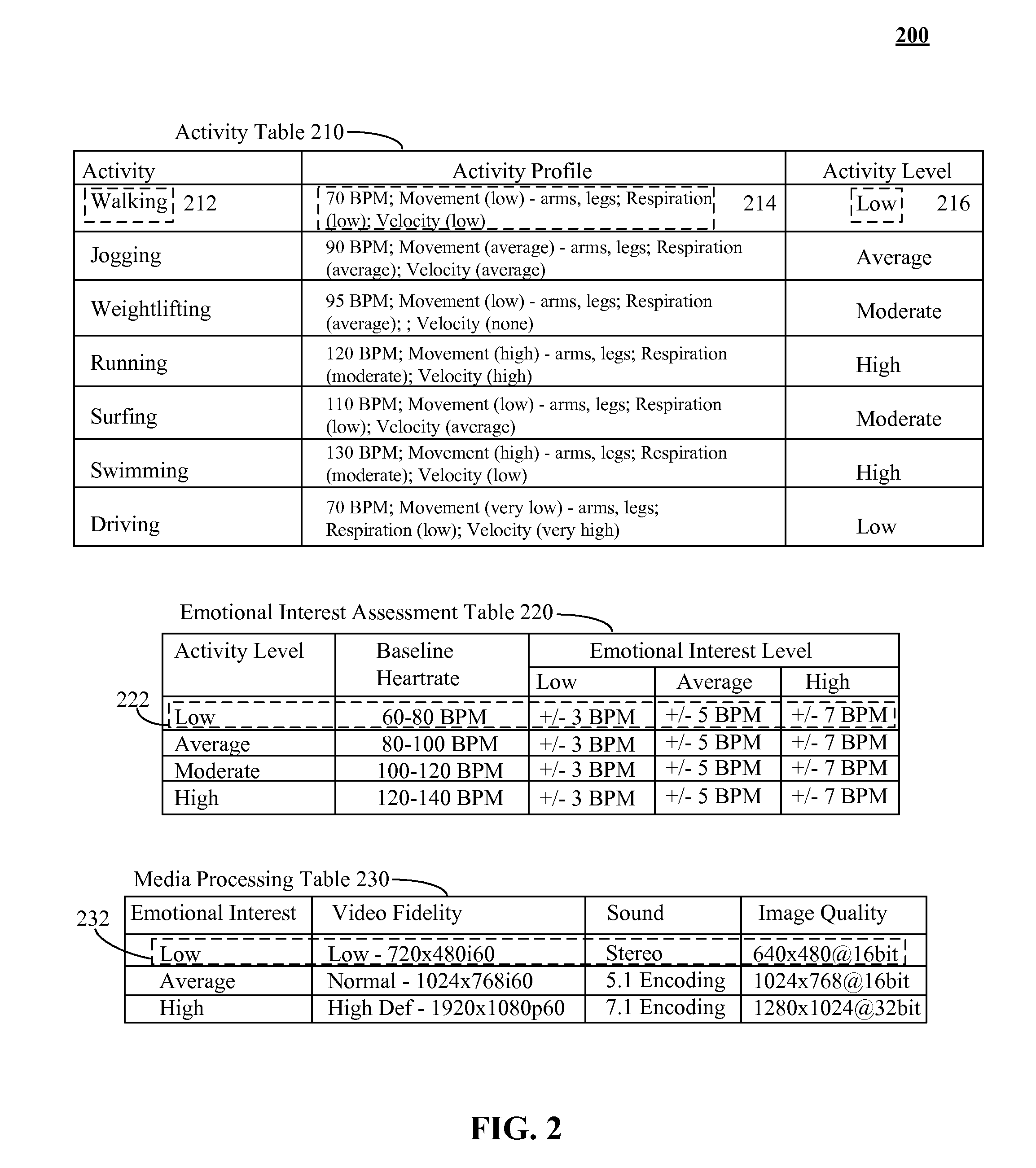
Distinguishing between user physical exertion biometric feedback and user emotional interest in a media stream
ActiveUS20110169603A1Electric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usagePhysical exhaustionBiometric data
The present invention discloses a method, system, and computer program product for determining user interest in media. The invention can select one of a set of different activity profiles specified within a data store. Each activity profile can include biometric attributes and associated baseline attribute values specific to an activity state. A media stream can be manipulated (e.g., created from environmental inputs and / or played upon a presentation device). Biometric data can be received from a user in proximity to the media stream. The received biometric data can be compared values in the selected activity profile. An interest level in the media stream can be determined based on comparison differences. A programmatic action can be performed relating to the media stream based upon the determined interest level. For example, a bitrate of the media and / or a marker in the media can be modified based on interest level.
Owner:TERRACE LICENSING LLC
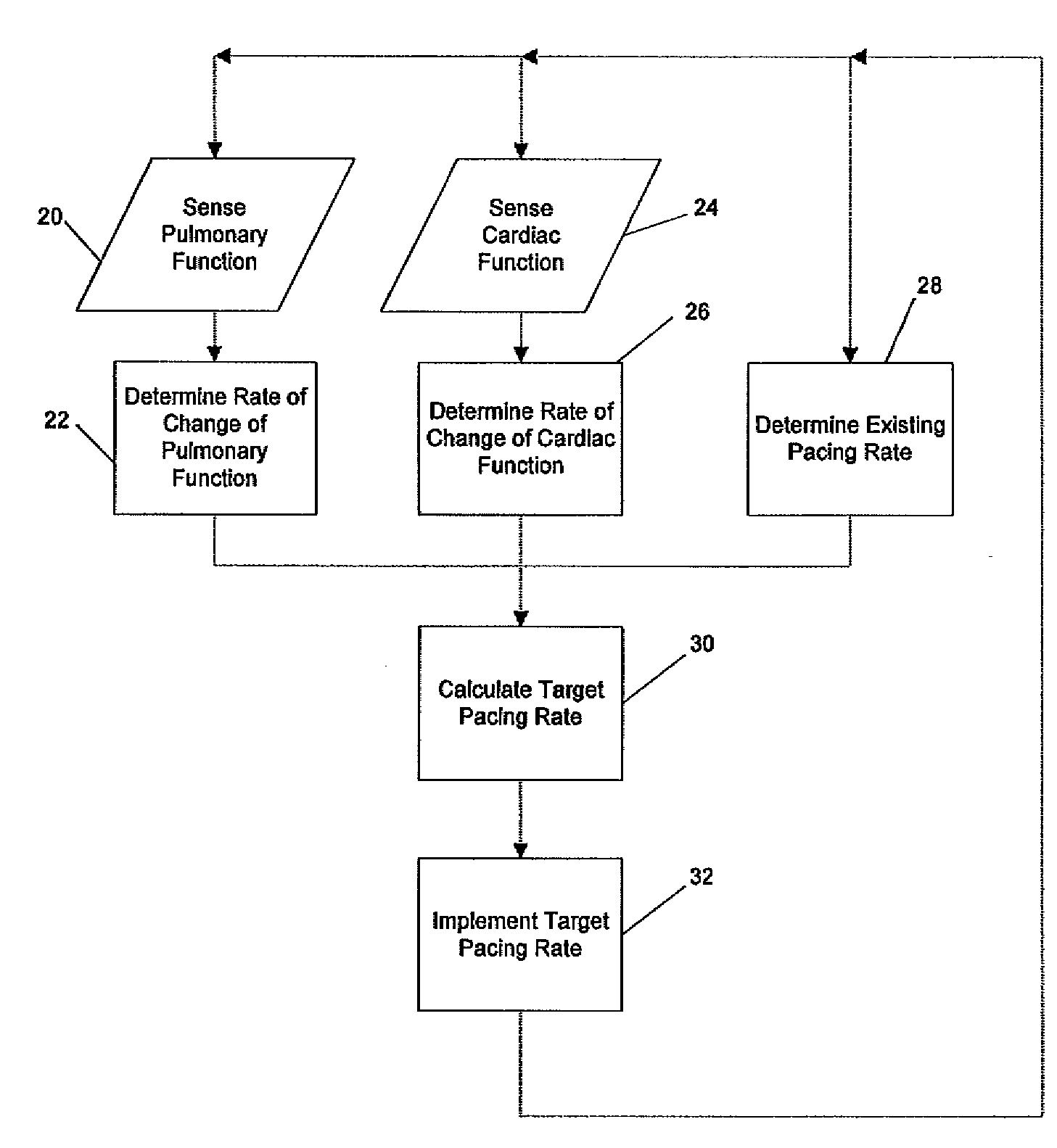
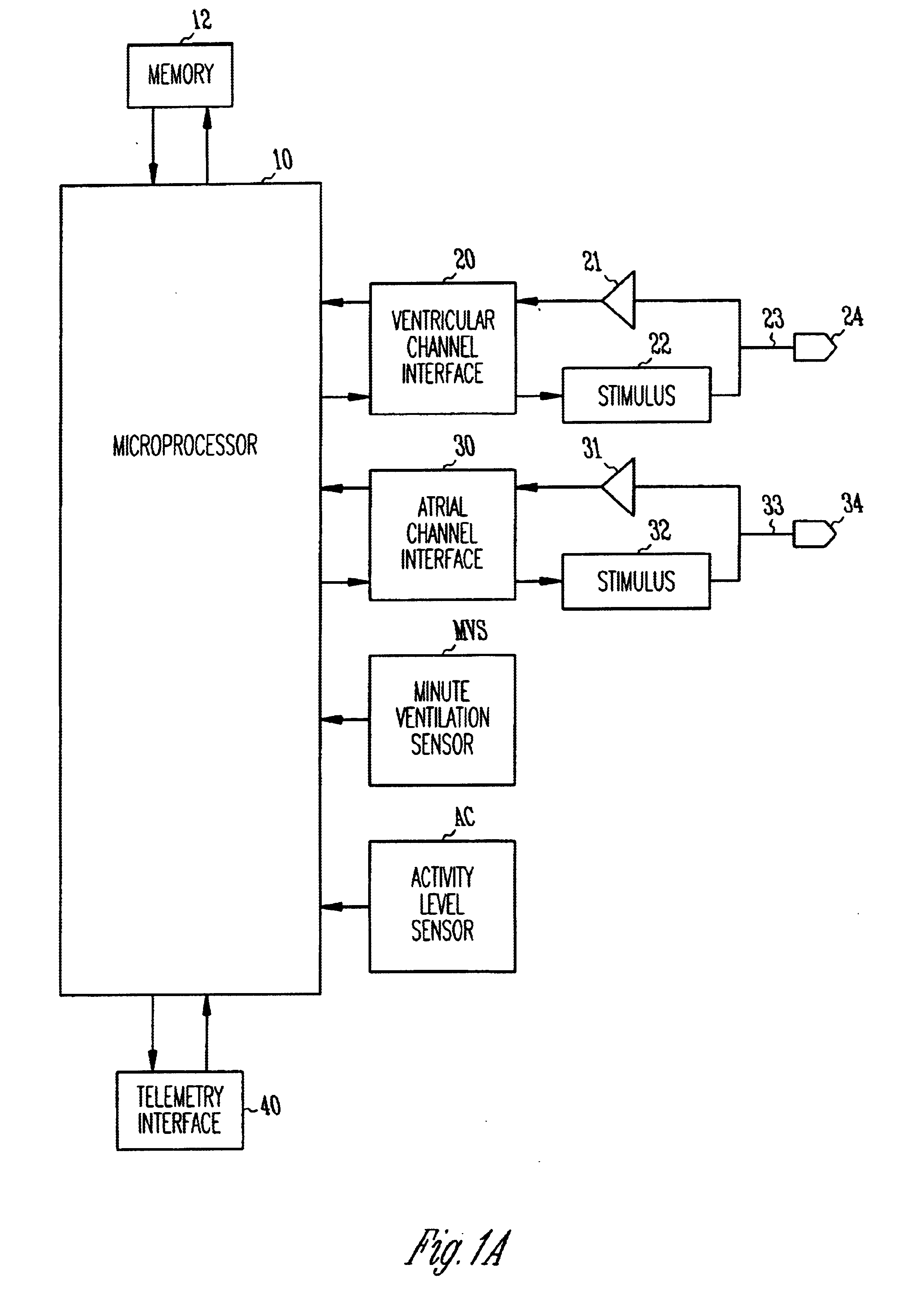
Rate Adaptive Cardiac Pacing Systems and Methods
The invention relates to cardiac rhythm management systems, and more particularly, to rate adaptive cardiac pacing systems and methods. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method for providing rate-adaptive cardiac pacing therapy from an implantable medical device, the method including sensing a pulmonary function of a patient; determining a rate of change in the pulmonary function; sensing a cardiac function of the patient; determining a rate of change in the cardiac function; and calculating a target pacing rate based on an existing pacing rate, the rate of change in the pulmonary function, and the rate of change in the cardiac function. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of controlling a cardiac rhythm management device in response to exertion of a patient, the method including sensing the patient's pulmonary function at a first time t1 and at a second time t2; calculating a rate of change of the pulmonary function between time t1 and time t2; sensing the patient's cardiac function at time t3 and t4; calculating a rate of change of the cardiac function between time t3 and time t4; and setting a desired pacing rate. Embodiments of the invention also include cardiac rhythm management devices.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
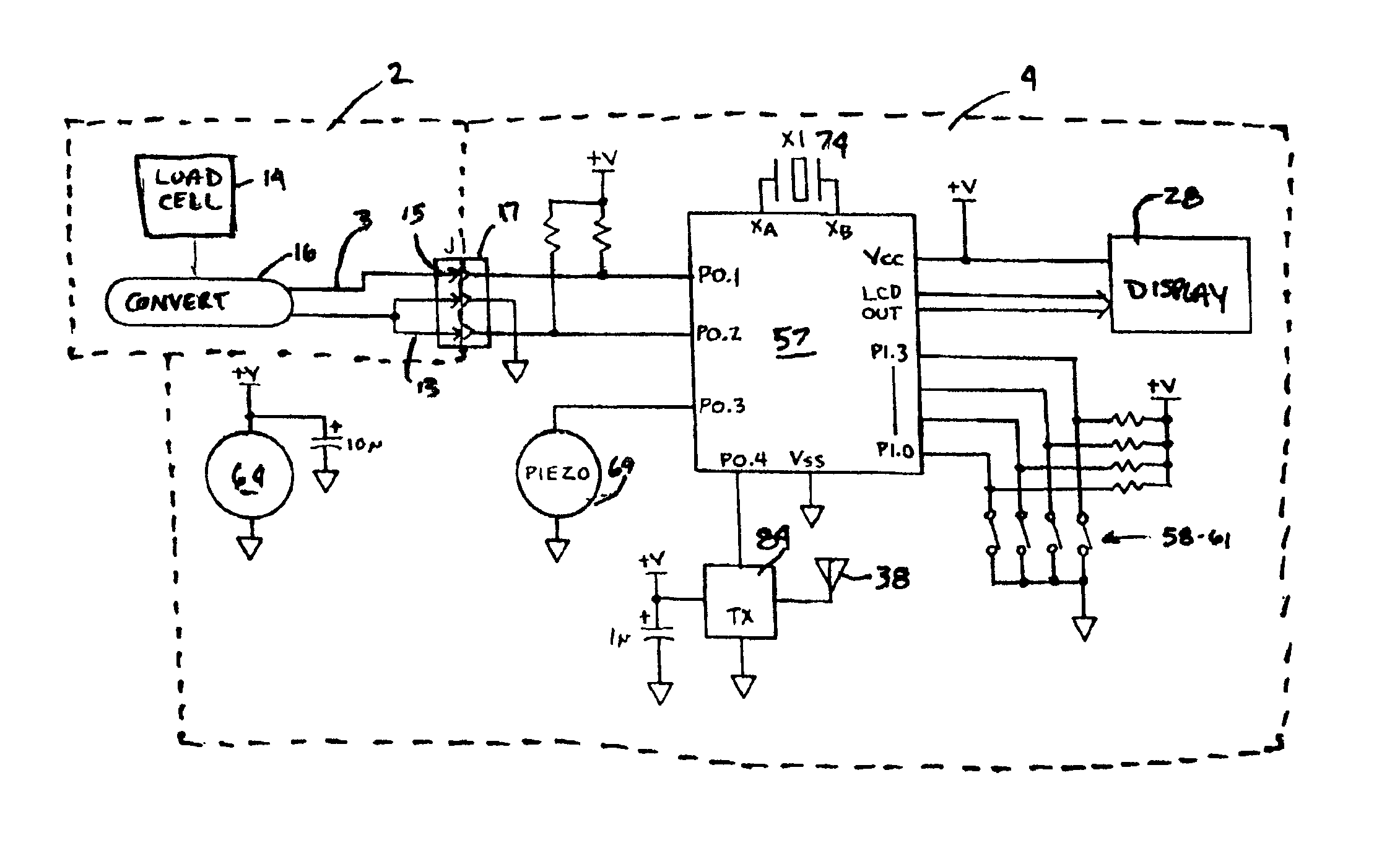
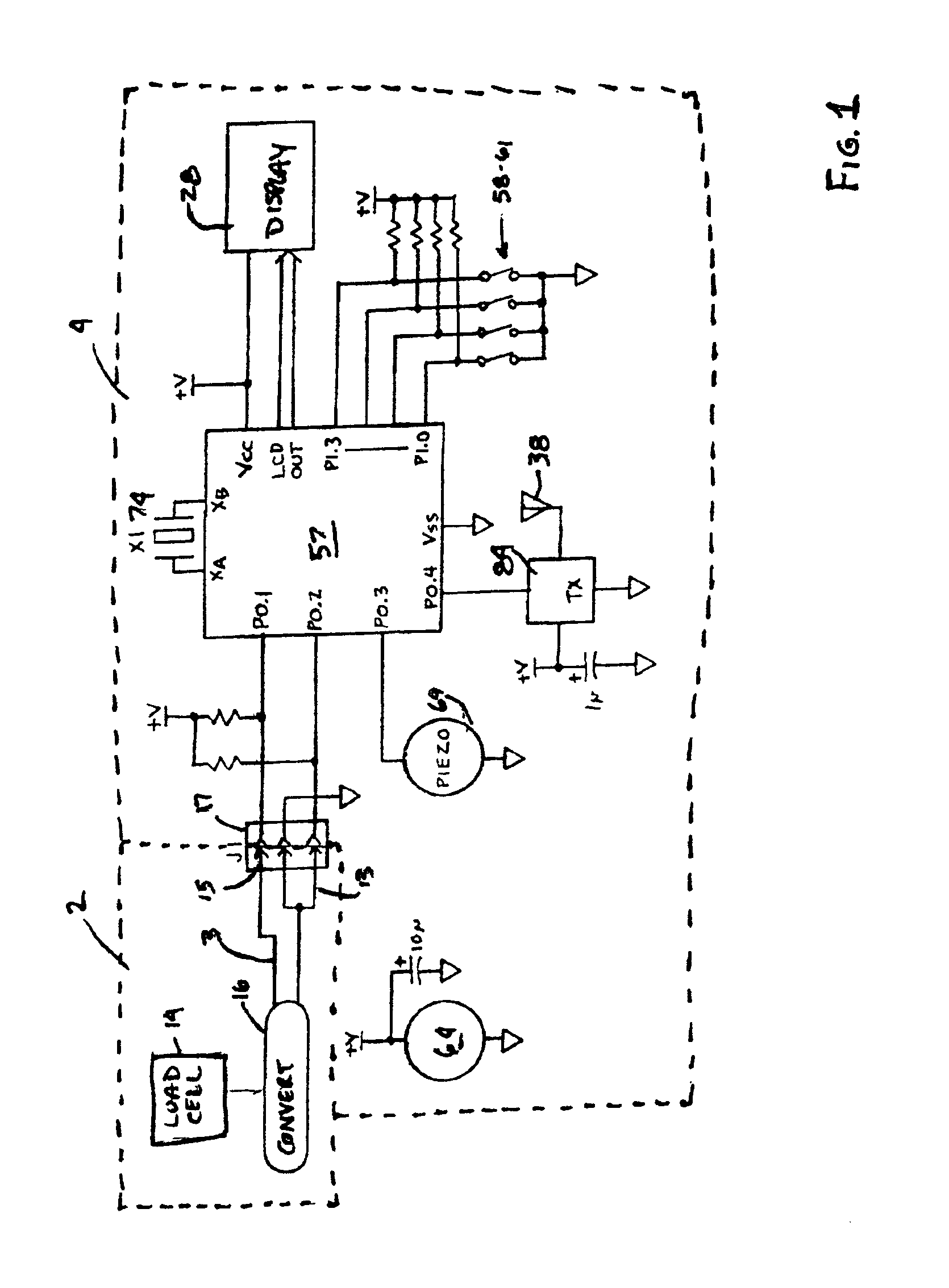
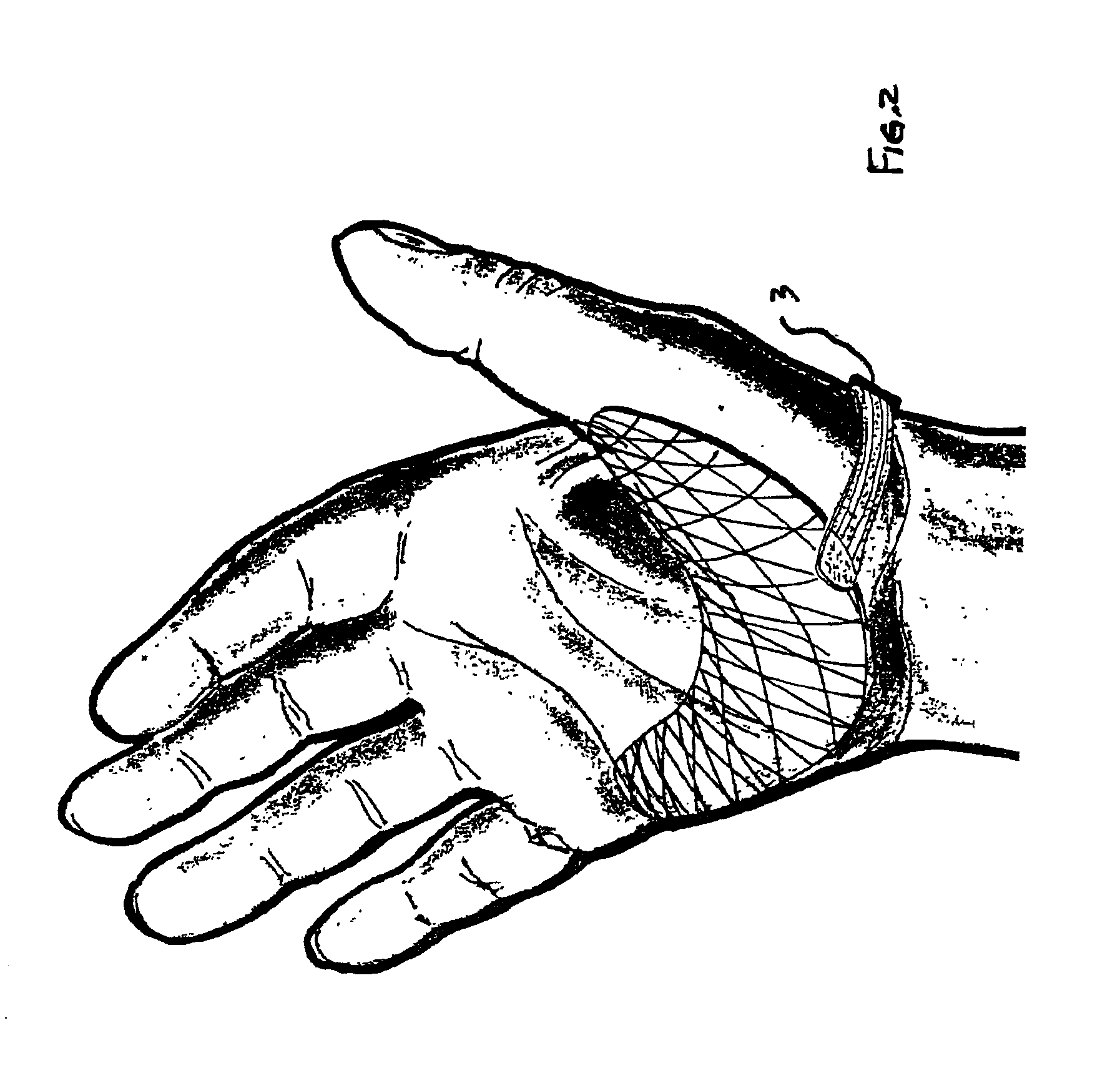
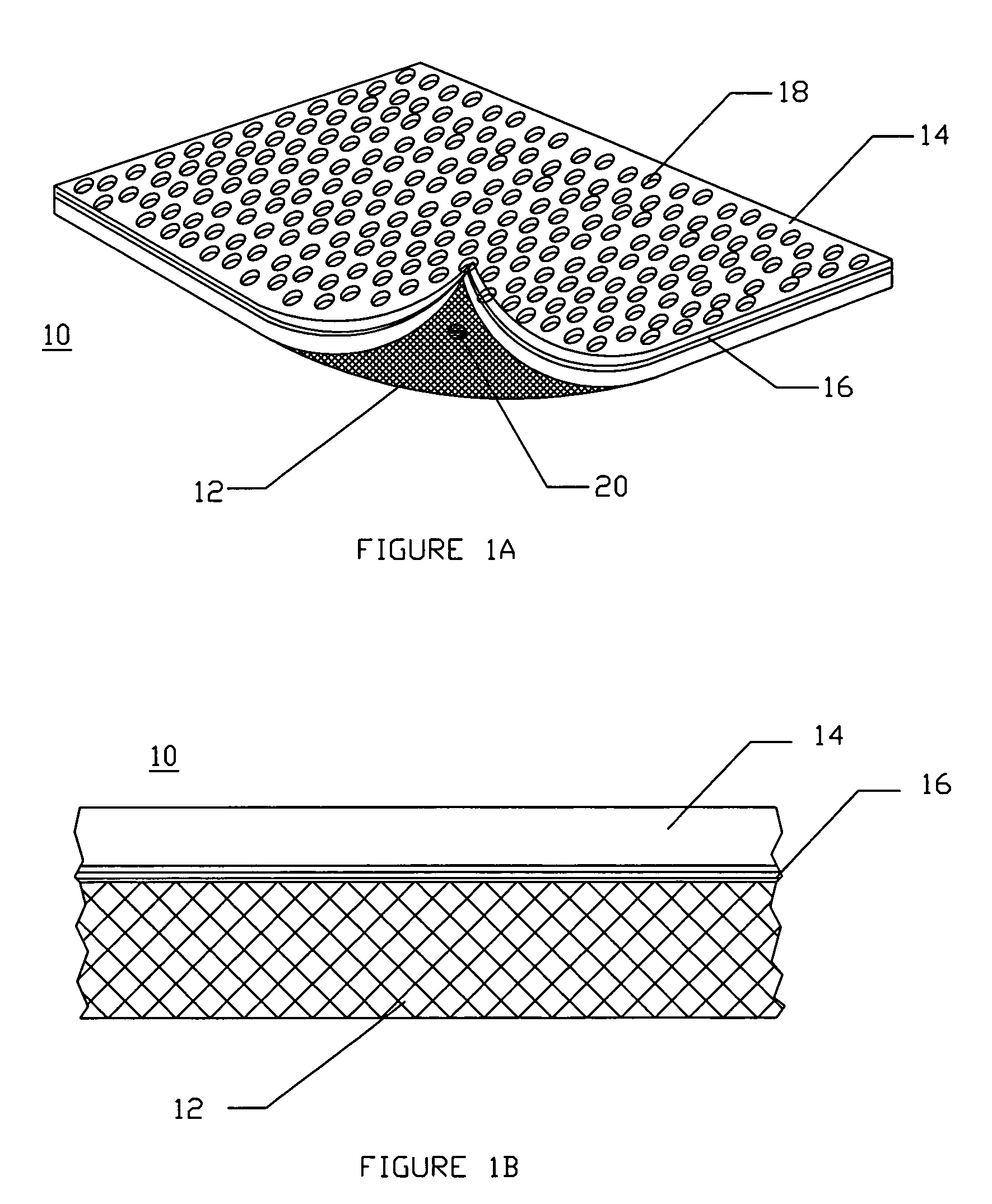
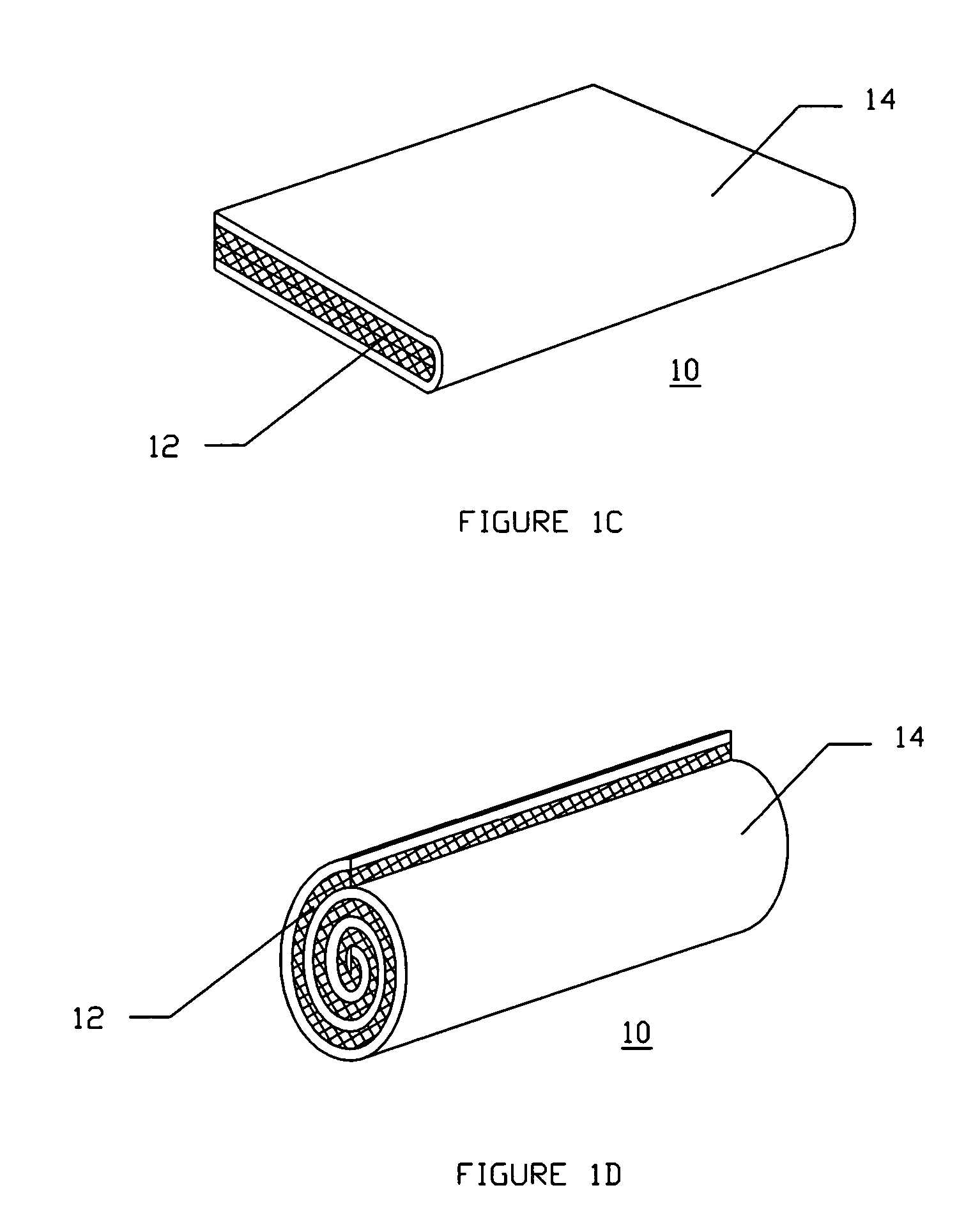
Apparatus for monitoring and displaying exertion data
An apparatus for monitoring and displaying information related to pressure exerted at a point of interest during an isometric exercise includes a fabric base, adapted to receive a body part. A sensor is attached to the fabric base and disposed at the point of interest during the isometric exercise, and measures a pressure magnitude at the point of interest and provides a pressure signal corresponding to the pressure magnitude. A processing unit is attached to the fabric base and receives the pressure signal, processes the pressure signal to derive information that is meaningful to a user, and generates a display corresponding to the information derived from the pressure signal.
Owner:SMITH CARL M
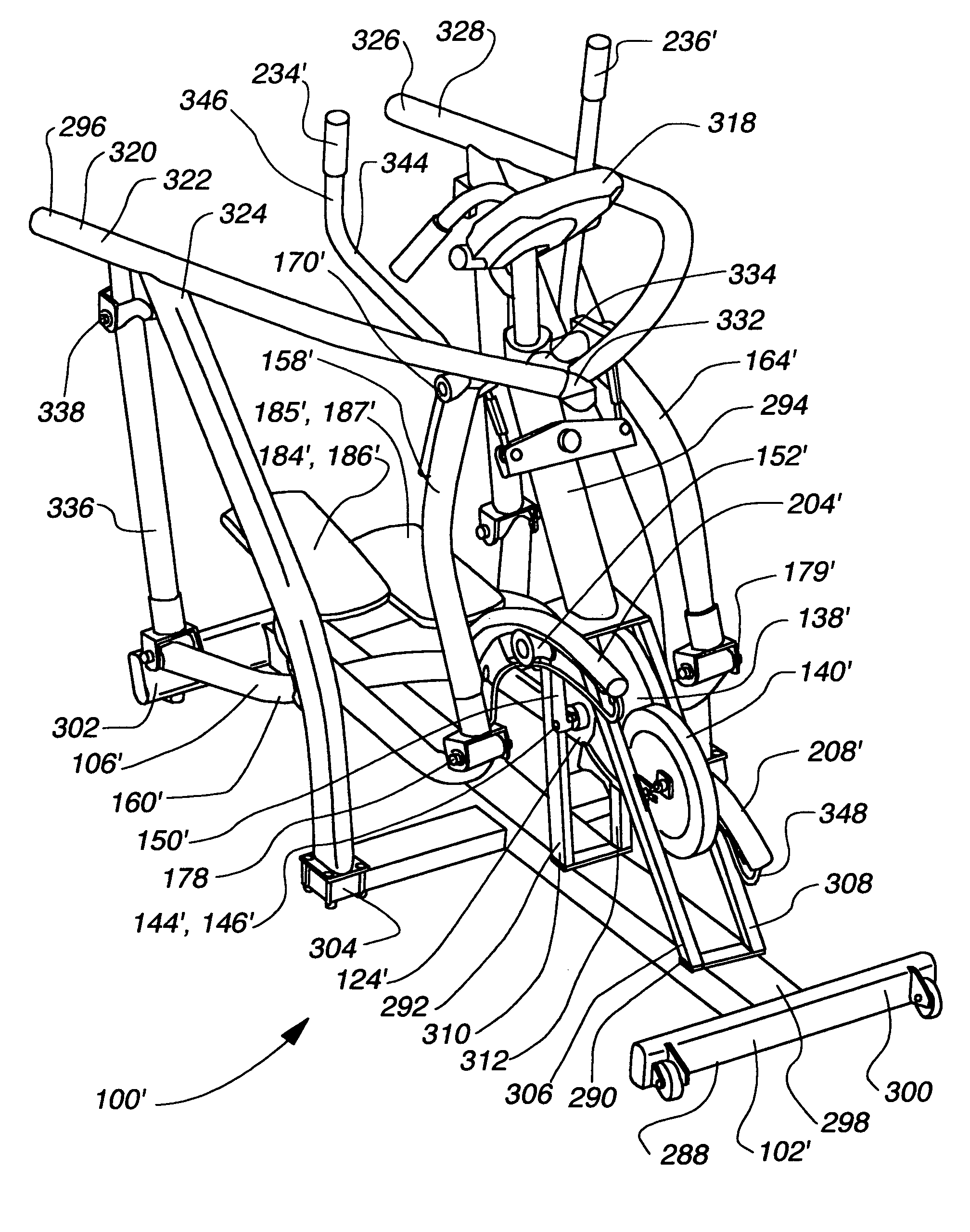
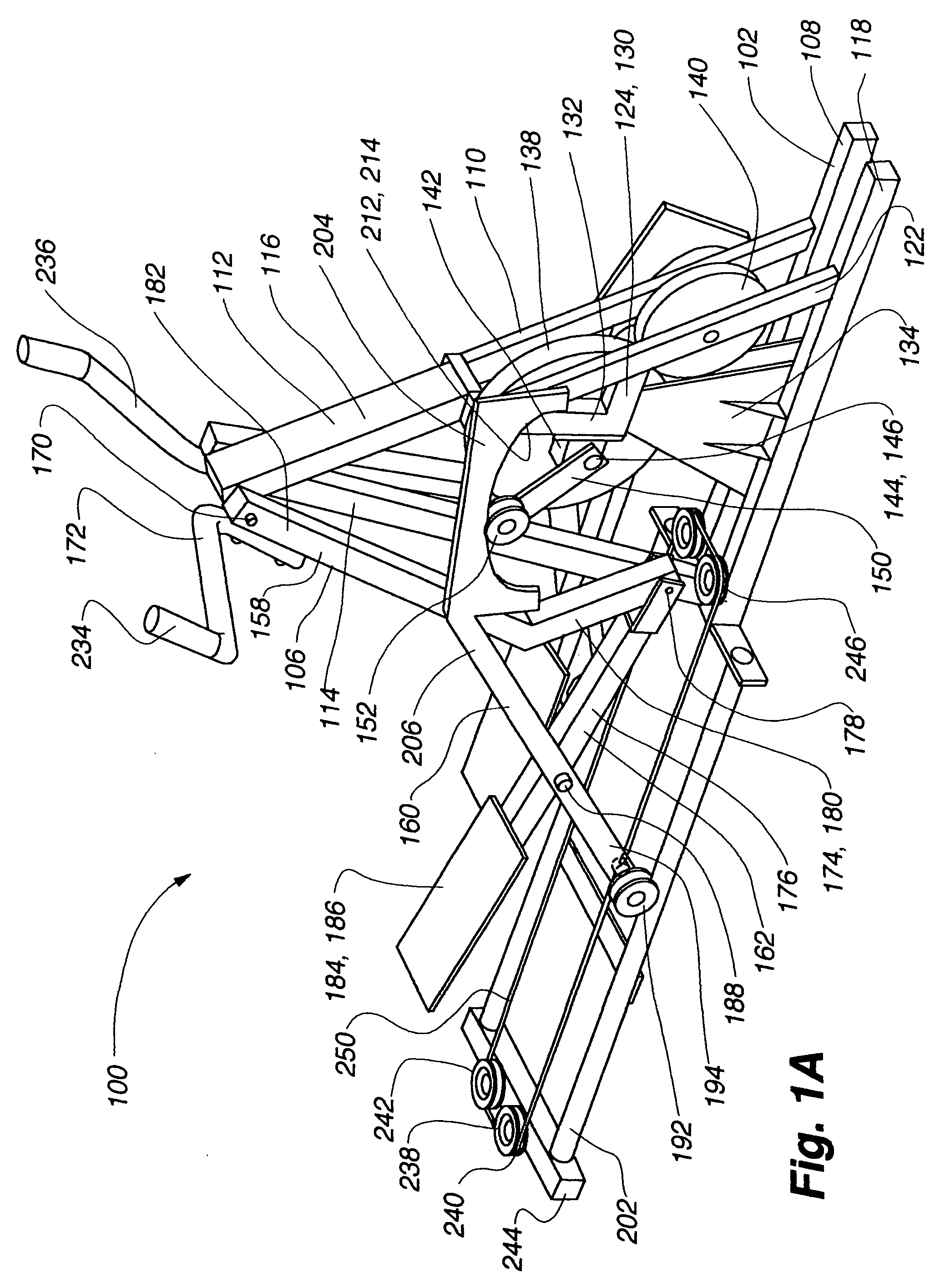
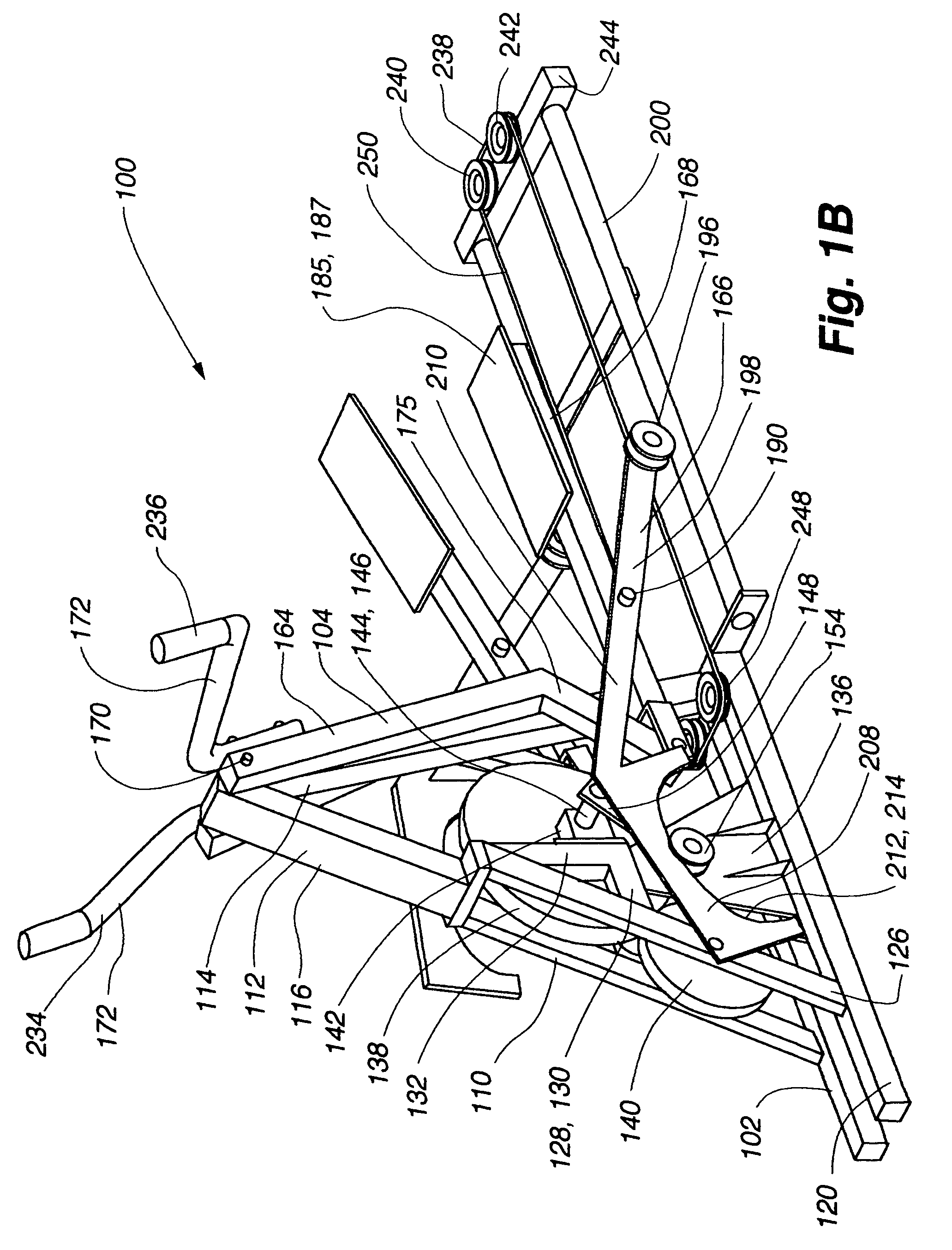
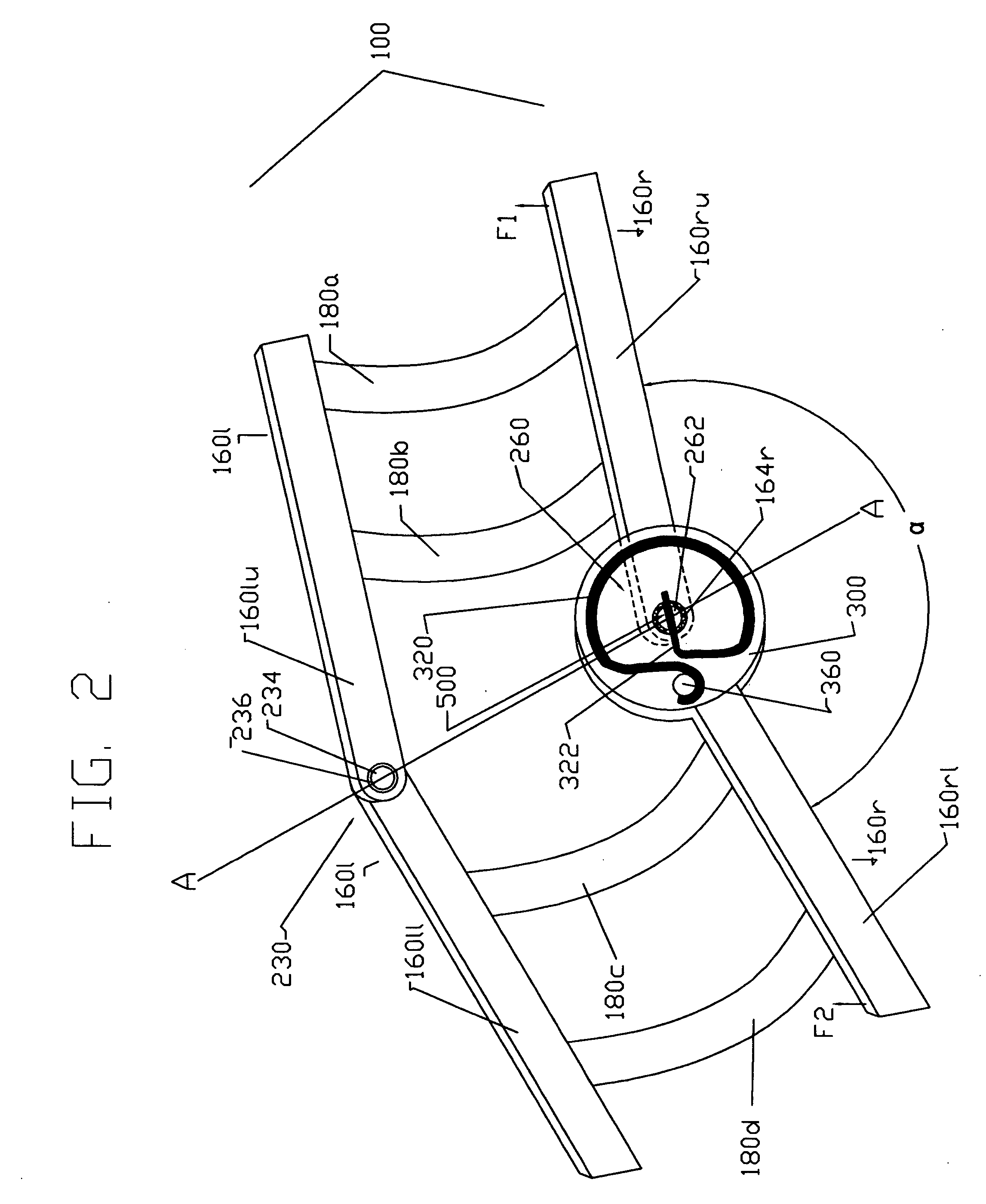
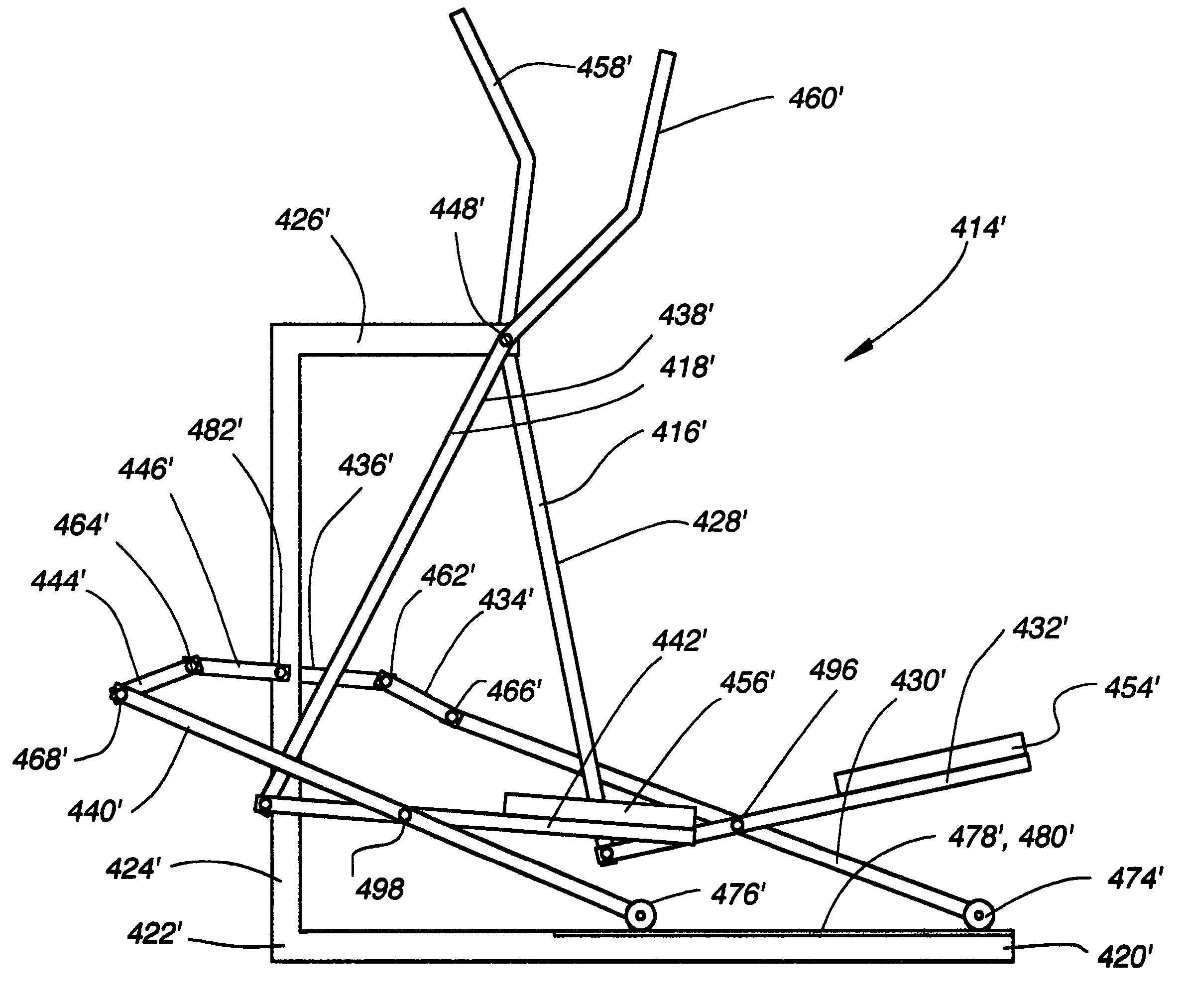
Variable stride exercise device
Owner:NAUTILUS INC
Method and apparatus for noninvasive physiologic monitoring
Intense environmental or working conditions can impede an individual's evaporative cooling mechanism normally responsible for thermoregulation during exercise or exertion. Non-invasive physiological monitoring capabilities are needed to more precisely define the cardiovascular responses and identify markers of impending failure of compensatory mechanisms prior to collapse or onset of irreversible pathology. The oxymetry method and system of the present invention provides non-invasive, continuous remote monitoring and analysis of cardiovascular and pulmonary function that overcomes accuracy and monitoring deficiencies of current oximetry systems.
Owner:SEKOS
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Ventilator to tracheotomy tube coupling
InactiveUS20070181130A1Avoid displacementMedical devicesPivotal connectionsTracheostomy tube insertionTracheotomy
A coupling for connecting a ventilator tube to a tracheotomy tube has a latching mechanism which prevents the coupling from axially displacing a tapered tubular extension of the tracheotomy tube after they have been mated in a pneumatically discrete path. For use with known adult tracheotomy tubes which have inner and outer cannulas, the latching mechanism engages the coupling with the leading end of the outer cannula collar with the inner cannula collar sandwiched therebetween. For use with known one piece children's tracheotomy tubes, the latching mechanism is a clamshell contoured to concentrically grip the tapered tubular extension of the tracheotomy tube. Interlocking the coupling and the tracheotomy tube prevents them from inadvertently axially displacing from each other. Non-axial force disengages the coupling from the tracheotomy tube so that the coupling can be axially displaced without exertion of excessive axial force on the system and the patient.
Owner:LAZARUS MEDICAL
360 degree rotator attachment for exercise equipment
InactiveUS20050085352A1Smooth rotationSmooth movementDumb-bellsMovement coordination devicesSports equipmentEngineering
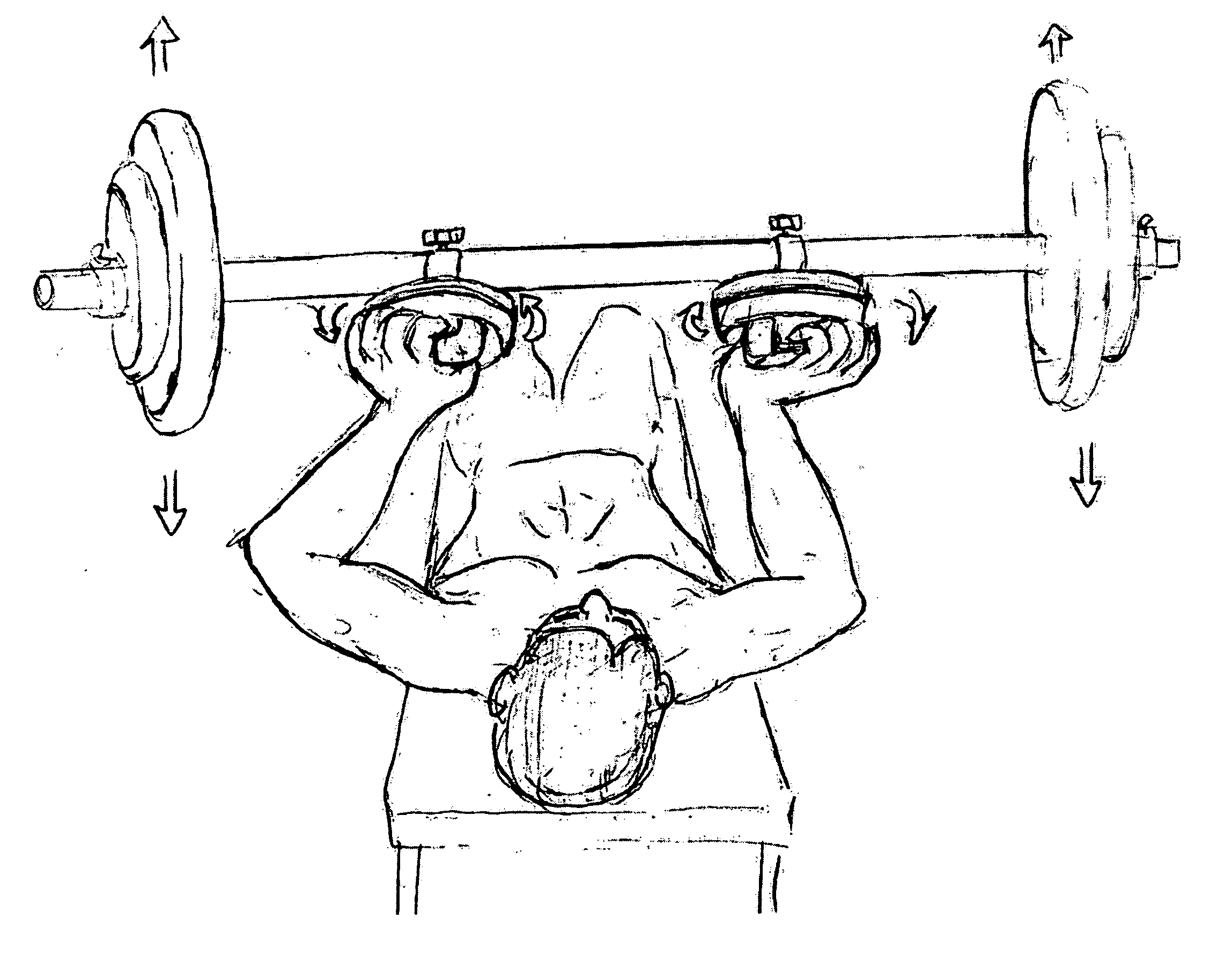
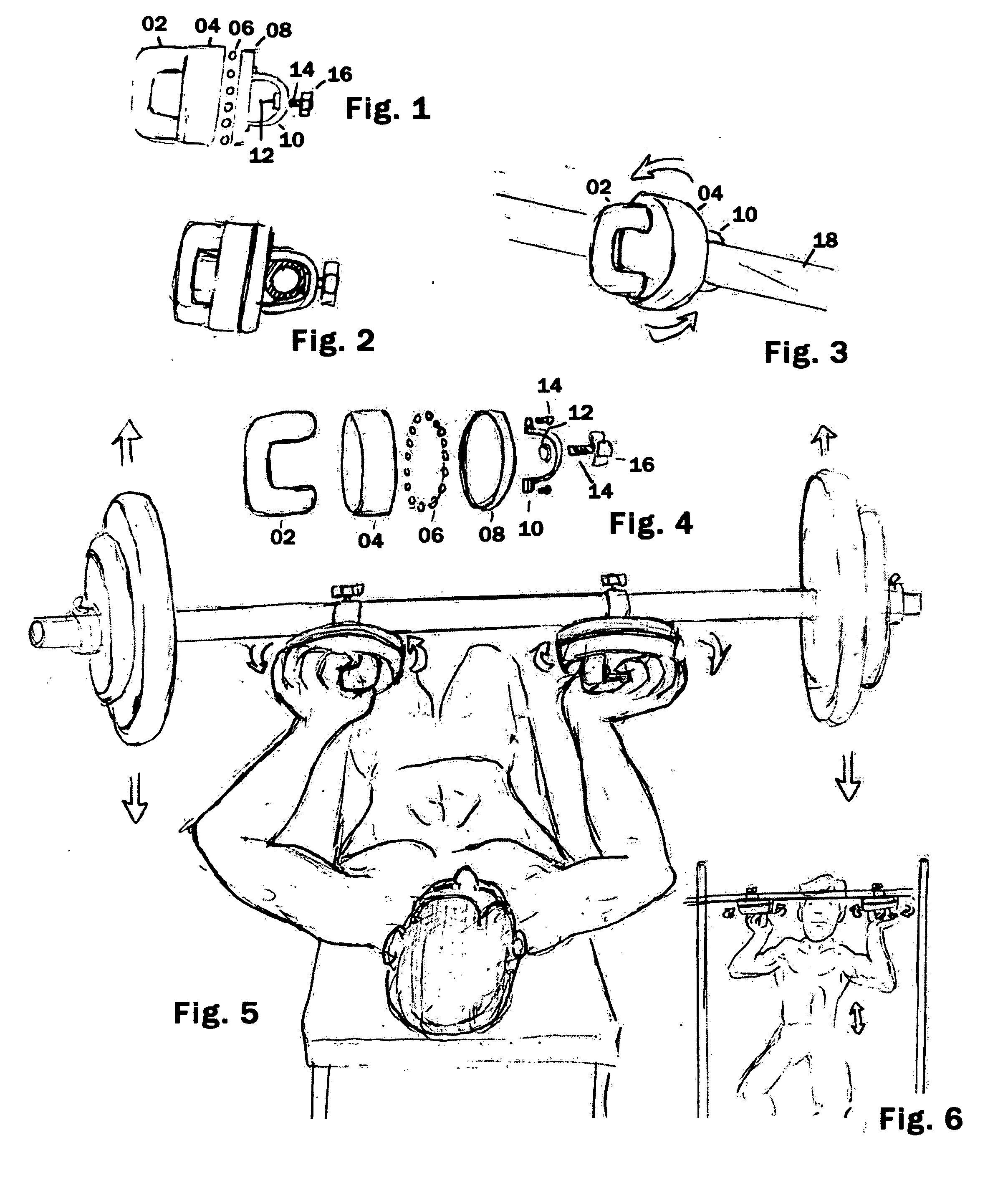
Disclosed is a weight lifting apparatus having mechanism for assisting in adding a rotational element to the traditional front / back (or flexion and extension) activities during the lifting of weights or other athletic resistance activitiesl. This invention to provides an attachment apparatus that provides a weight holding means that is able to offer 360 degrees of smooth movement which allows complete rotational positionability for use with any stationary or moving resistive weight apparatus. This invention also provids an apparatus wherein the weight holding means also provides a safety measure which can limit the speed of rotation or even stop this motion in the event that the weight is dropped or rotational exertion limits are reached.
Owner:BAXTER BRENT ALAN
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Rate-adaptive therapy with automatic limiting of maximum pacing rate
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Active assist for the ankle, knee and other human joints
InactiveUS20060142680A1Reduce the risk of injuryLower requirementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSports activityKnee Joint
A human joint assist device that applies a torque at the joint to assist physiological exertion forces, that is the load carrying task of the joint and surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The application of this device reduces the physiological exertion force requirement, and may be adjusted with respect to assist level, to suit the issue associated with joint motion and is useful for joint rehabilitation and sports activities. Among other things, this results in a reduction of physiological exertion force in a fashion that makes it easier to extend the levers (long bones) associated with extension against a given resistance. For example, standing from a squatted position with the assist of this device reduces the stress on physiological members associated with joint articulation.
Owner:IAROCCI MICHAEL ANTHONY
Device and method for radial pressure determination
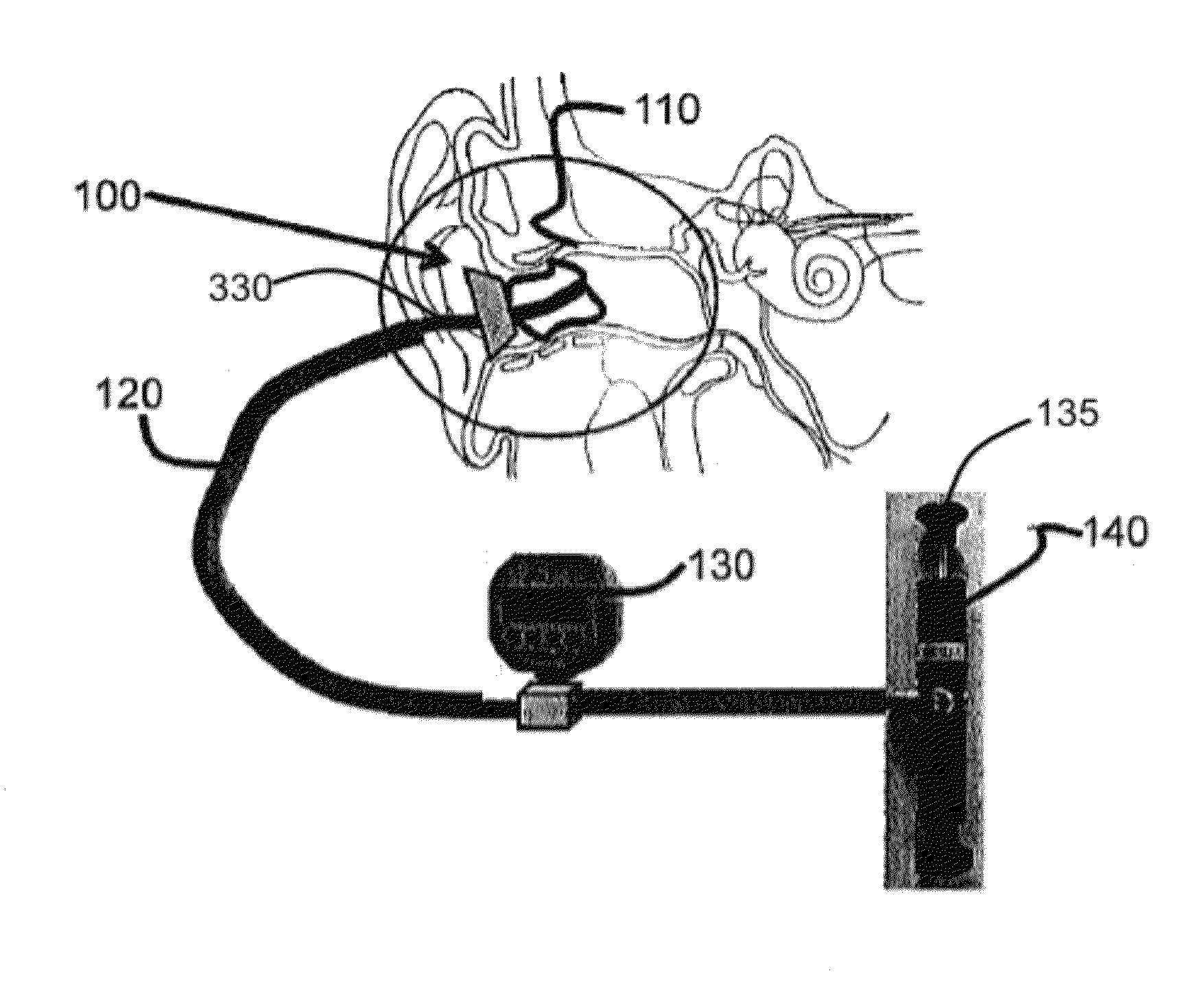
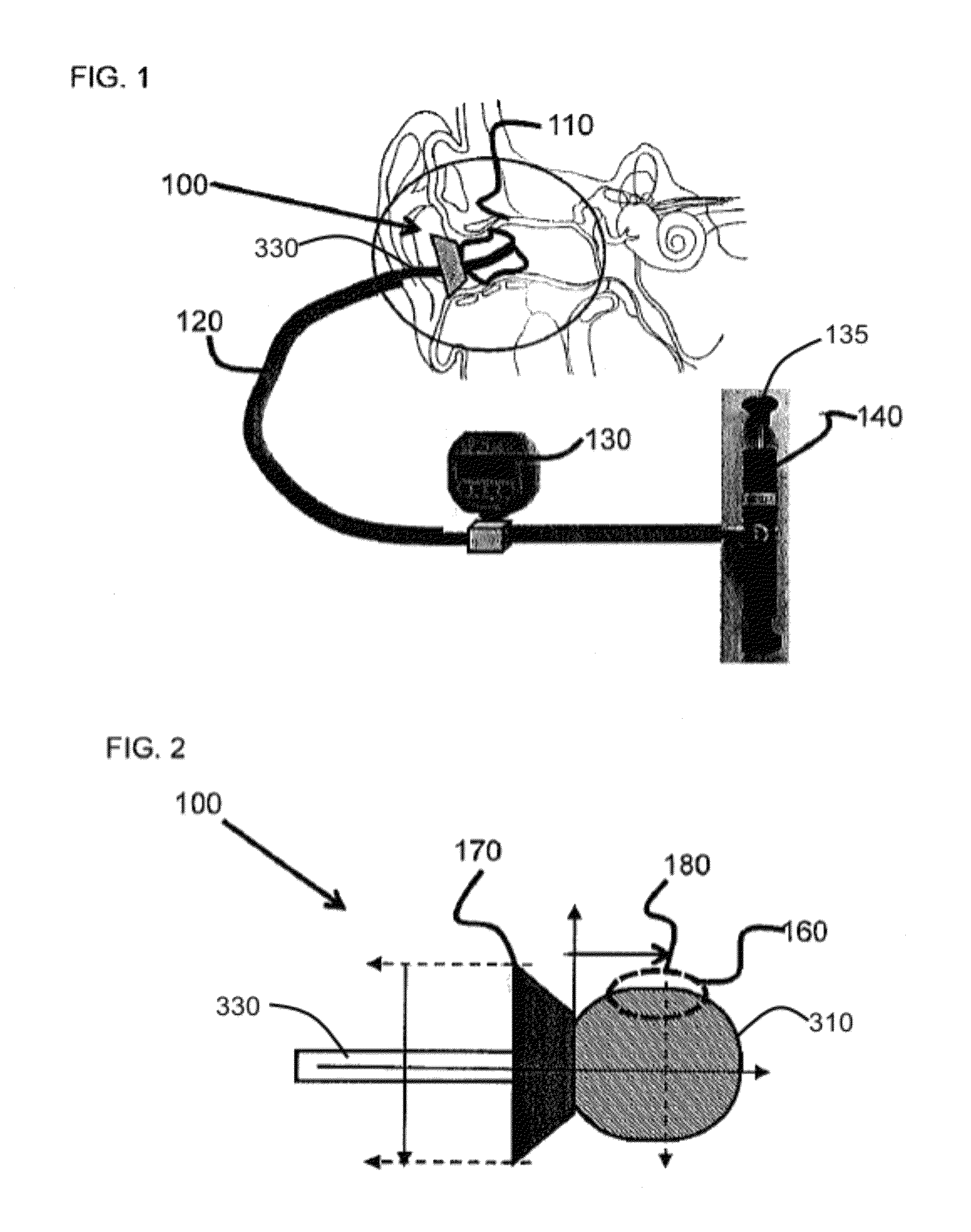
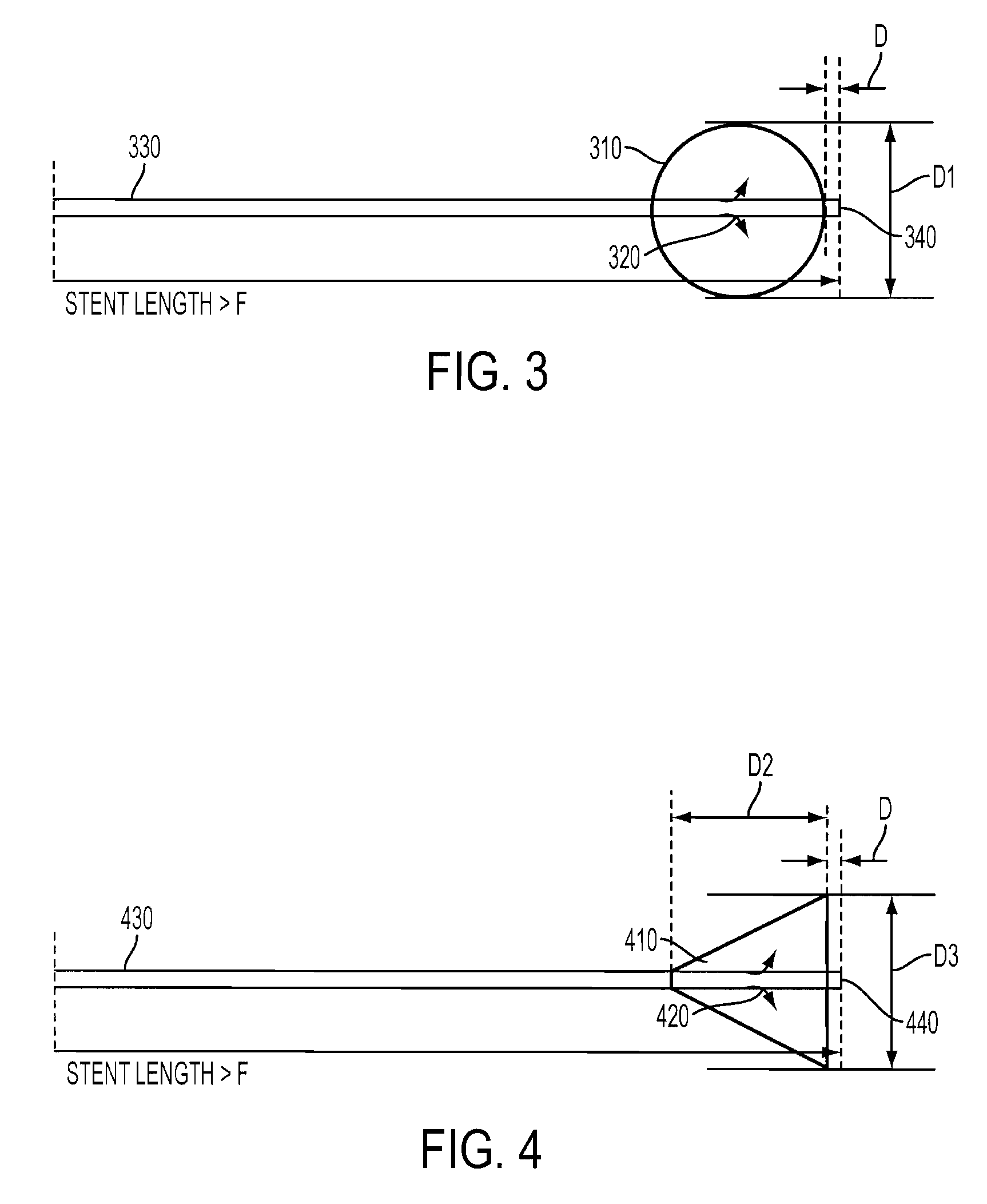
Methods and apparatus for measuring ear canal wall pressure comfort level are provided. An expandable pressure exertion device is inserted into an orifice. The device is expanded inside the orifice in increments of pressure. A threshold level is saved where a user indicates that the pressure exerted against the walls of the orifice is becoming at least one of uncomfortable, painful, and noticeable.
Owner:STATON TECHIYA LLC
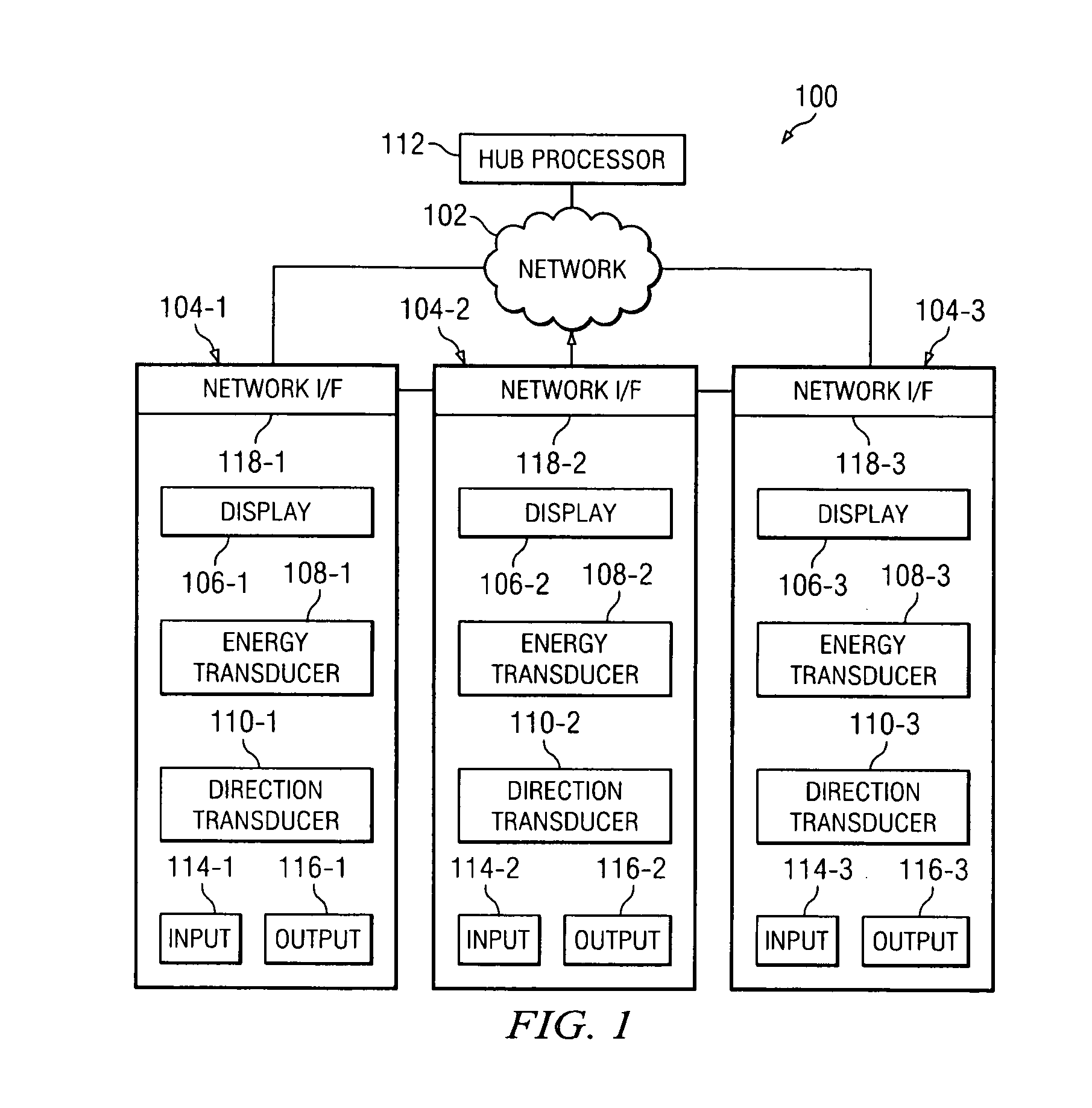
Networked exercise machine
Exercise machines are networked together to provide a user with an indication of the user's performance level compared to the performance levels of other users. Simulated characters corresponding to the users are shown on one or more displays viewable by the users. The simulated characters have a primary movement that may differ in type from the primary movement used in achieving the exercise by the corresponding user. Further, the primary movement used to achieve exercise by one user may differ from the primary movement used to achieve exercise by another user. Exertion transducers provide signals that are used in calculating parameters such as speed and acceleration. Biometric data may be measured from the users during exertion and displayed or uploaded onto the network.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
Resistance exercise method and system
InactiveUS20070093369A1Improves muscular strength and self-efficacyStiltsMovement coordination devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationExertion
A method for exercise by performing exercise sets in a sequence progressing from exertion of larger to smaller muscles, with the exercise movement performed using slow movements. Each exercise set is performed to a point of momentary failure. The slow movement is at a rate of less than about thirty degrees per second. The exercise sets are performed with as little rest between each exercise set as global or central fatigue will allow. Resistance is applied during each exercise set to produce muscle failure within a predefined time under tension parameter.
Owner:BOCCHICCHIO VINCENT J
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Variable stride exercise device
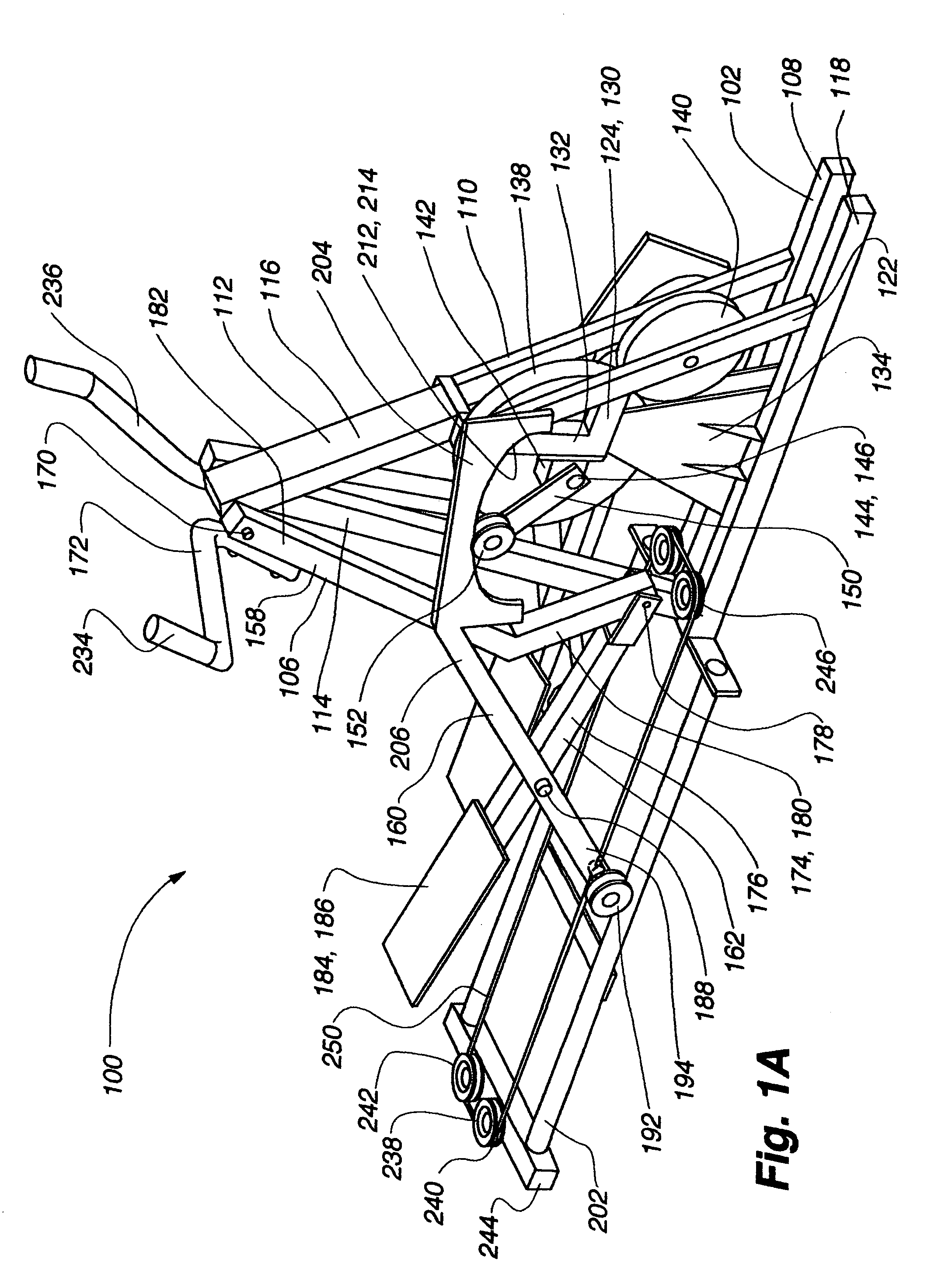
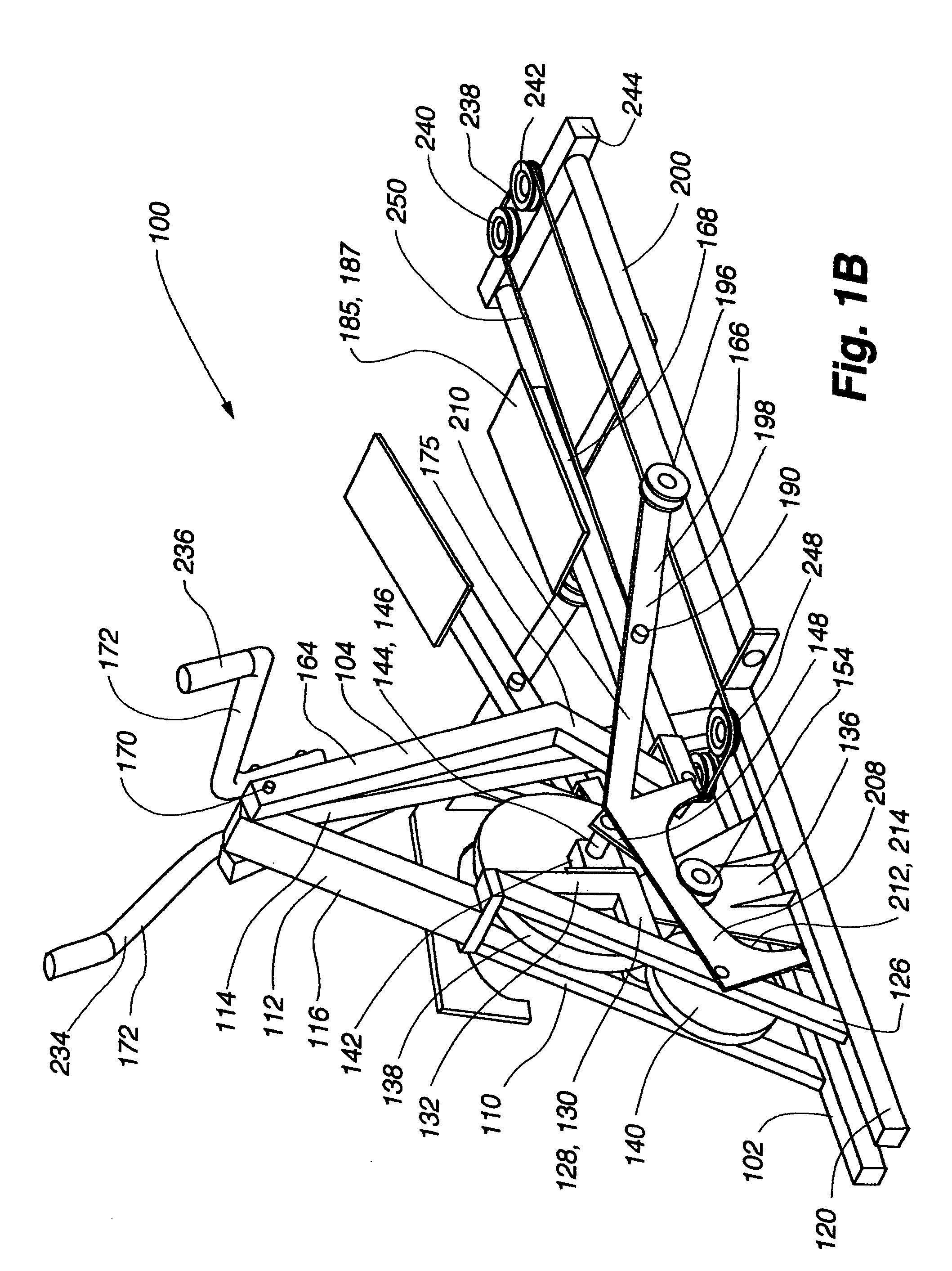
The present invention provides for a variable stride exercise device having a variable size close curved striding path during use. The exercise device described and depicted herein utilizes various configurations of linkage assemblies, cam members, and other components, connected with a frame to allow a user to dynamically vary his stride path during exercise. An exercise device conforming to aspects of the present invention provides a foot path that adapts to the change in stride length rather than forcing the user into a fixed size path. A user's exertion level may have several components impacting the stride length provided by the machine, such as leg power, torso power, and (in embodiments with arm supports or exercise components) arm power. Other embodiments of the exercise device include a lockout device that selectively eliminates the variable stride features of the exercise device and allows the user to exercise in a stepping motion.
Owner:NAUTILUS INC
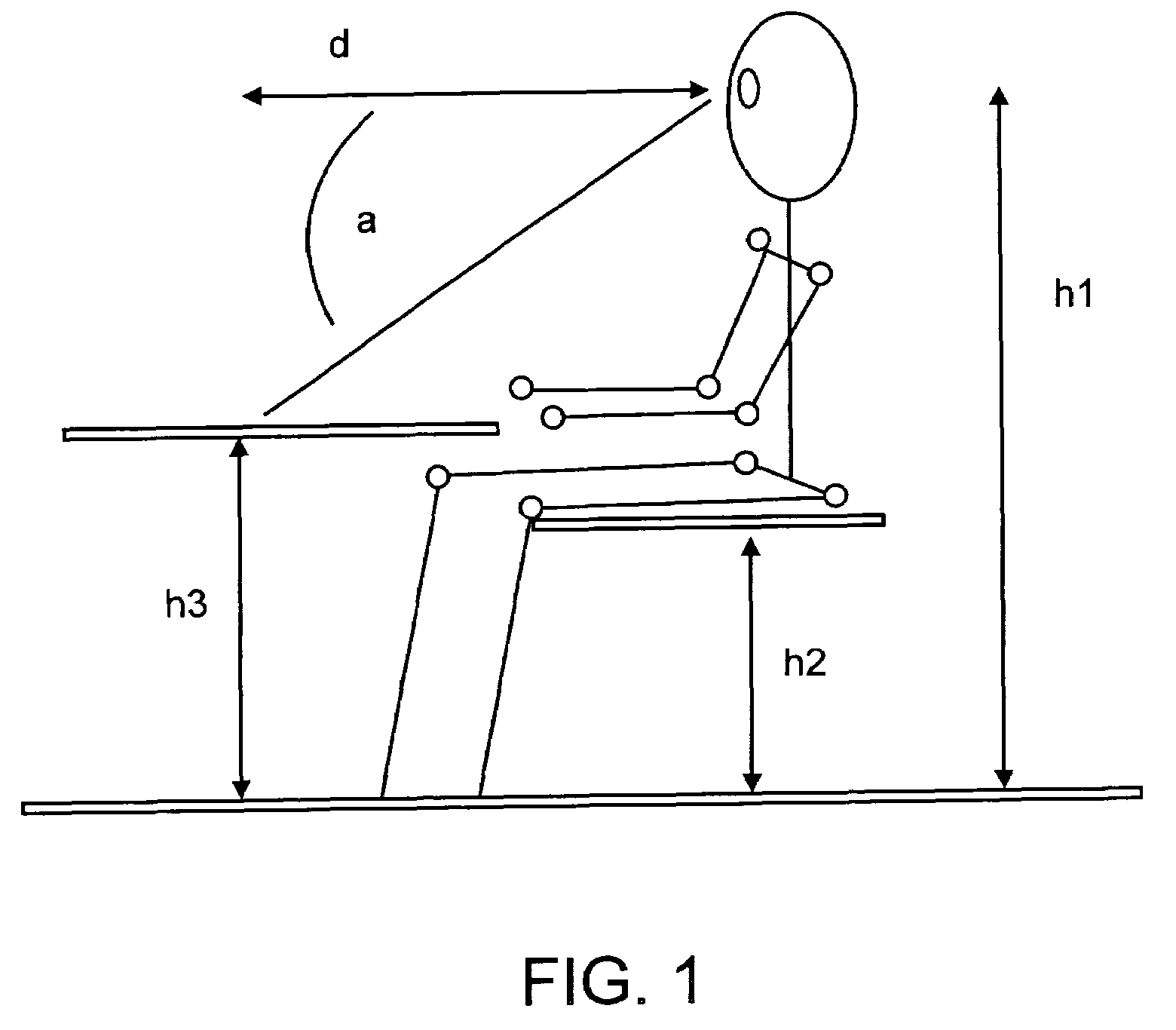
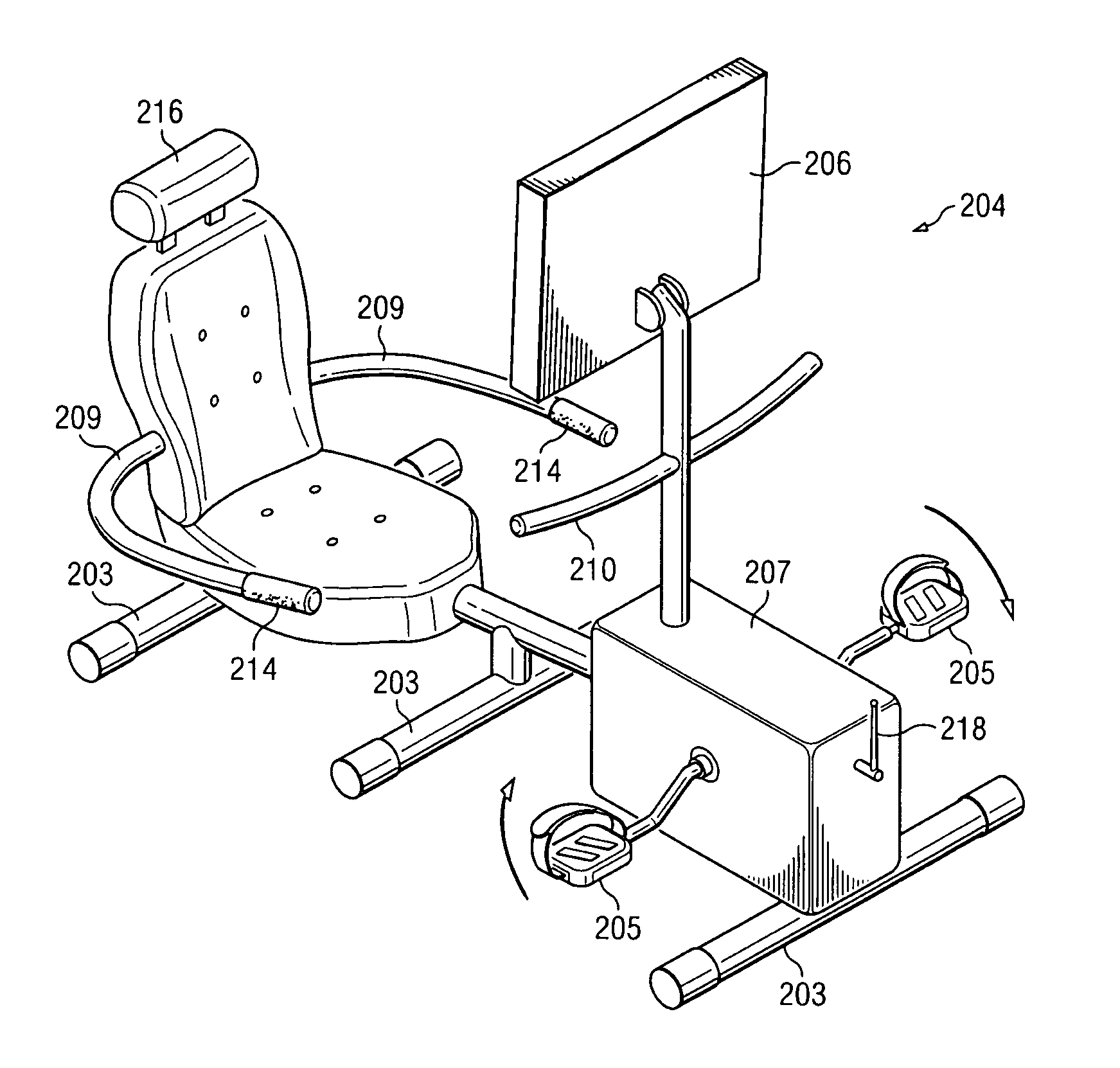
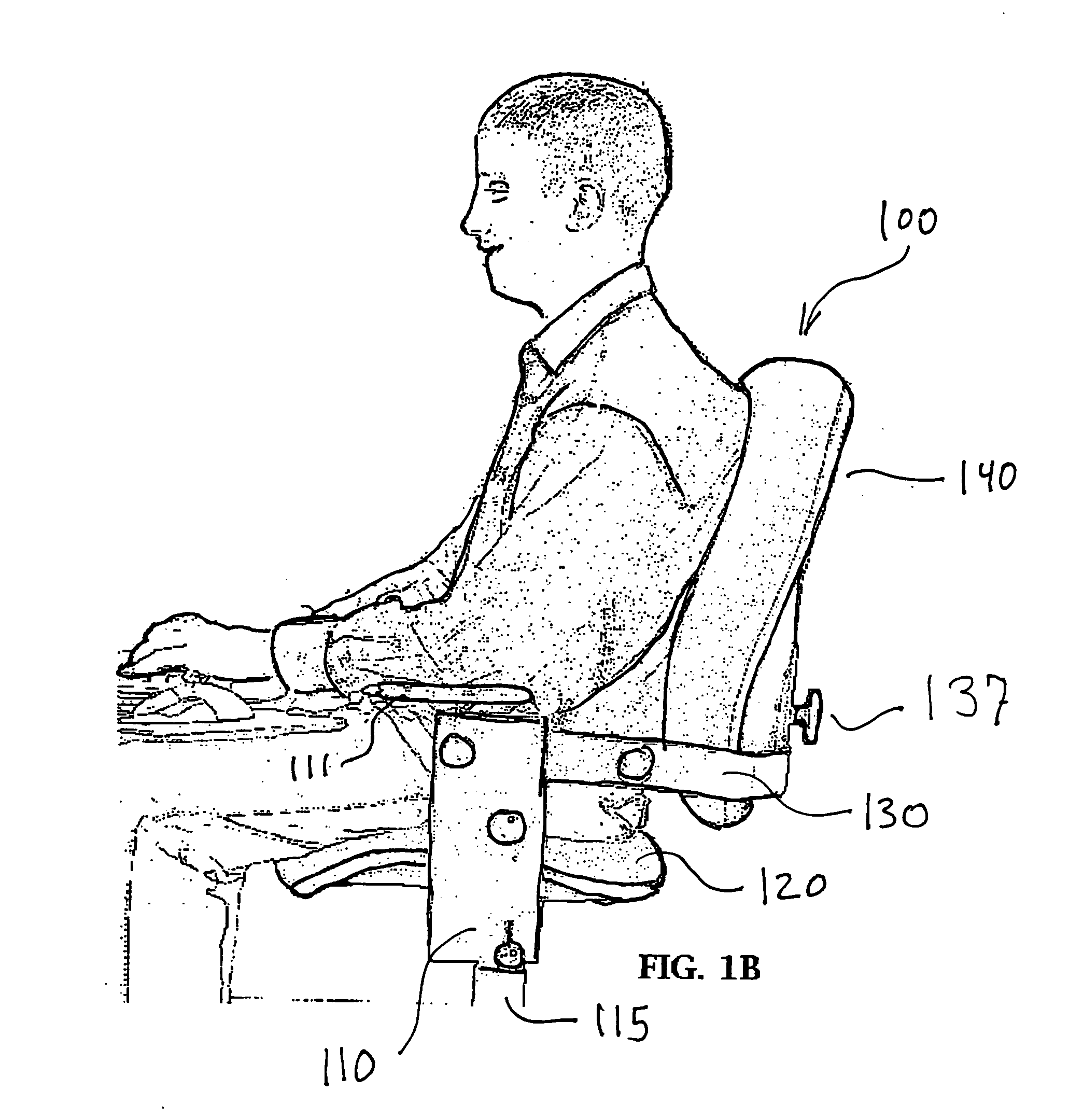
Ergonomic chair
InactiveUS20060103221A1Optimization rangeFirm supportStoolsAdjustable chairsFree rotationHorizontal axis
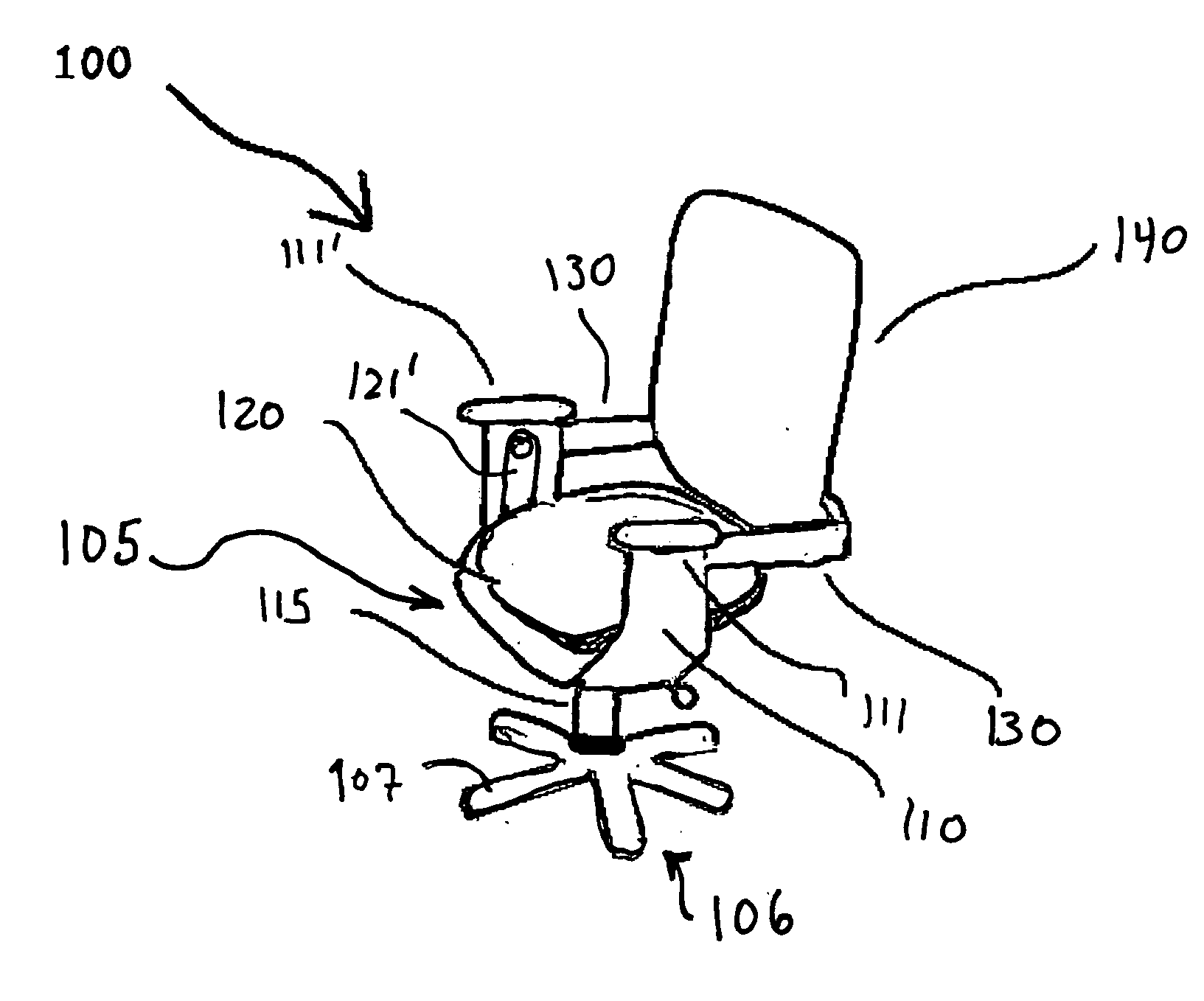
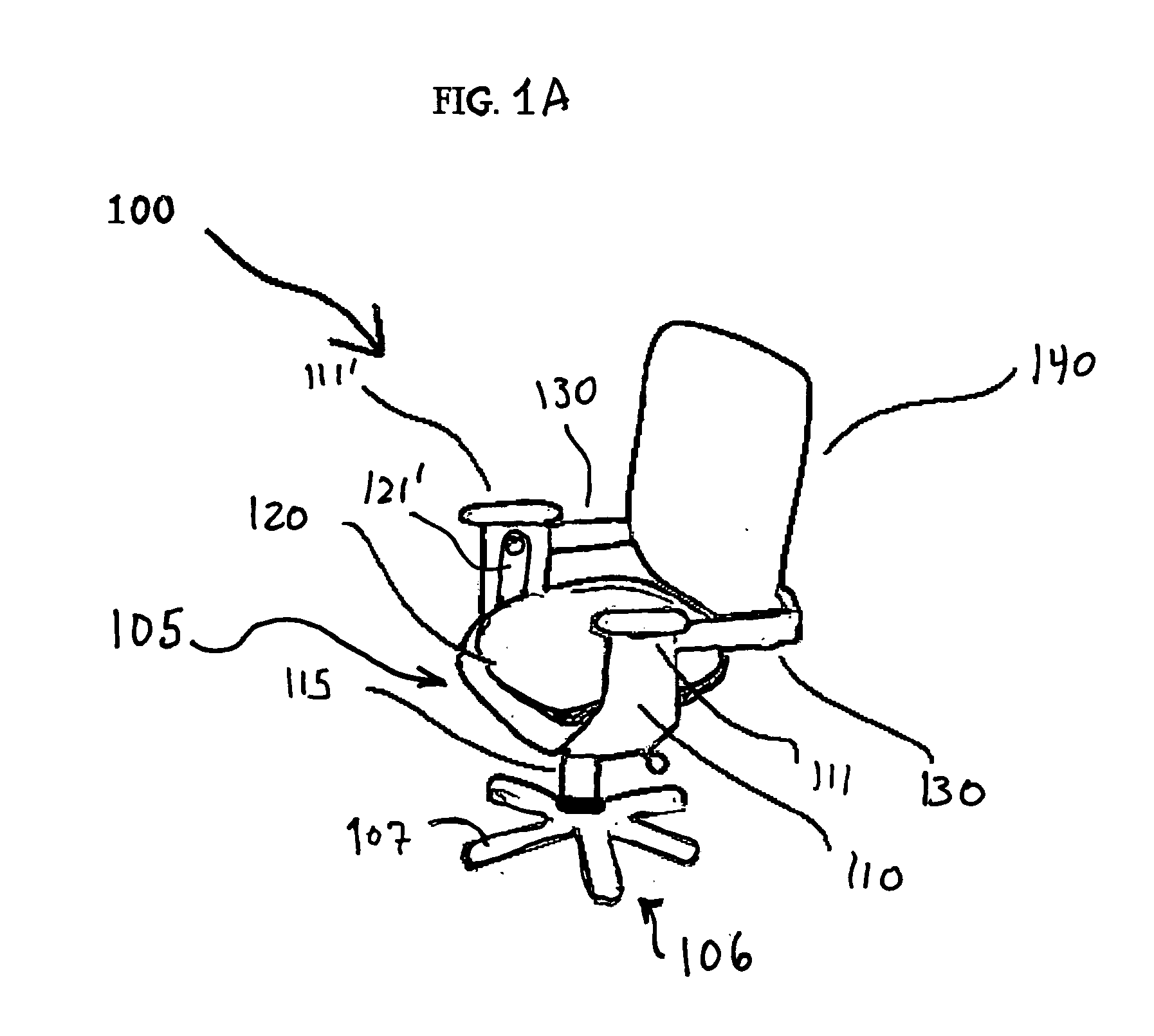
An ergonomic chair provides continuous support to the seated user throughout a broad range of postures by pivoting both the seat and back supporting cushions about a first or common axis disposed above the seat support cushion and in front of the back support cushion. The back supporting portion also independently pivots about a second horizontal axis proximate the lumbar region in a manner that allows the back supporting cushion to assume an angle that provides permanent contact with the seated user's back when said user is leaning back against the back support cushion. The springs that otherwise oppose the free rotation about the first and second axis are balanced such that the force inherently exerted by the user during movement through a range of seated postures is sufficient to initiate the coordinated rotation of the seat and back supporting element. No additional exertion is required once the user has reached the desired inclination, as the return springs are selected to counterbalance the redistributed weight of the user. Thus, full contact of the back supporting portion with the user's back is achieved over a full range of postures to provide proper ergonomic support, allowing the user to stay at task. In combination with such motion, which maintains the head at a level and angle such that the eyes can remain focused on their primary visual target without need to adjust the height, depth or angle of the target. The chair can offer armrests that support the forearms of the seated user to reduce the load carried by the arms, shoulders, neck and back and cooperate with the motion of the seat and back supporting elements to maintain ergonomically correct orientation of the hands to the keyboard or work surface.
Owner:KLEIST RONALD G
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com