Patents
Literature
103results about "Clear air turbulence detection/forecasting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Storm top detection
ActiveUS7307577B1Efficient detectionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionReflectivityStorm
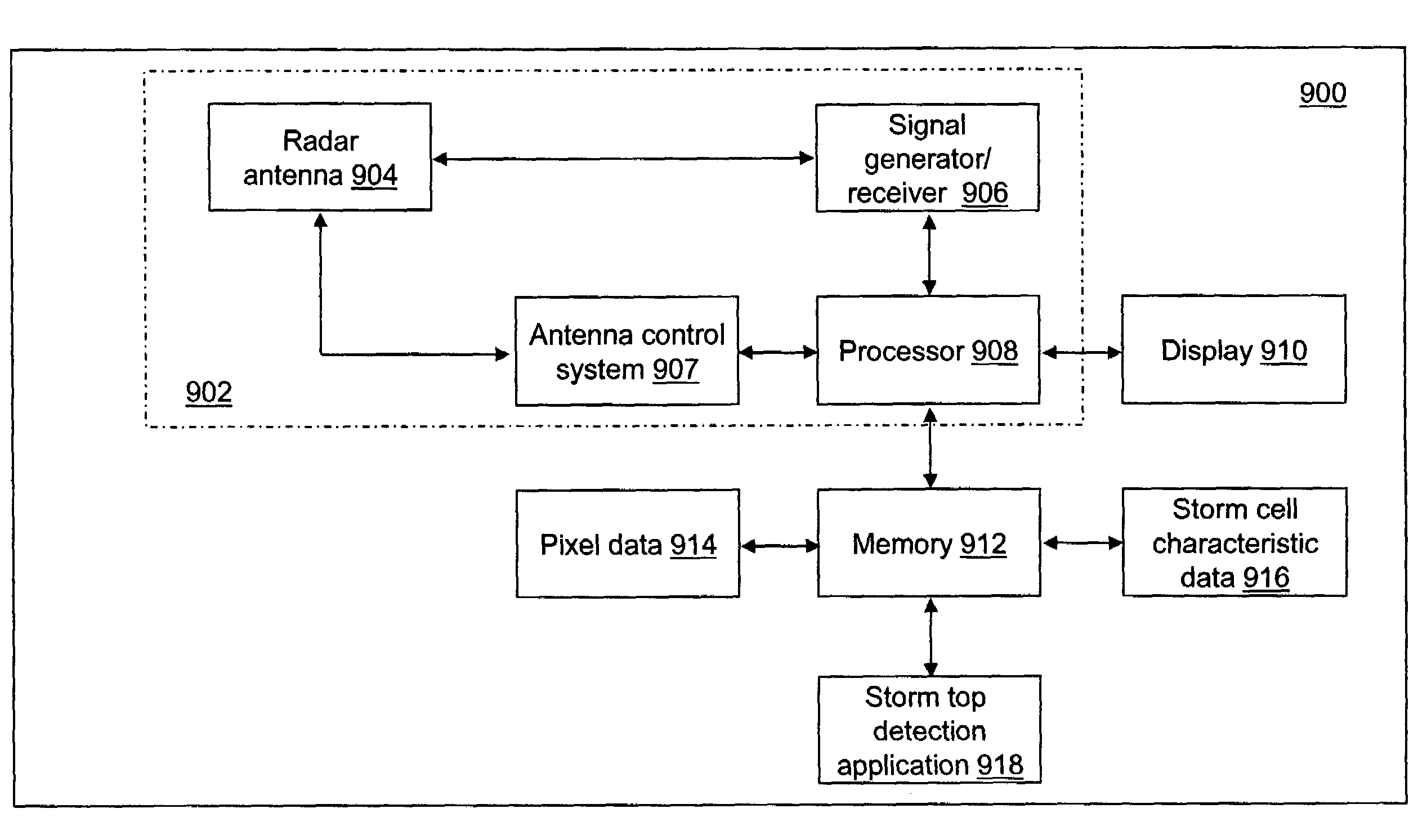
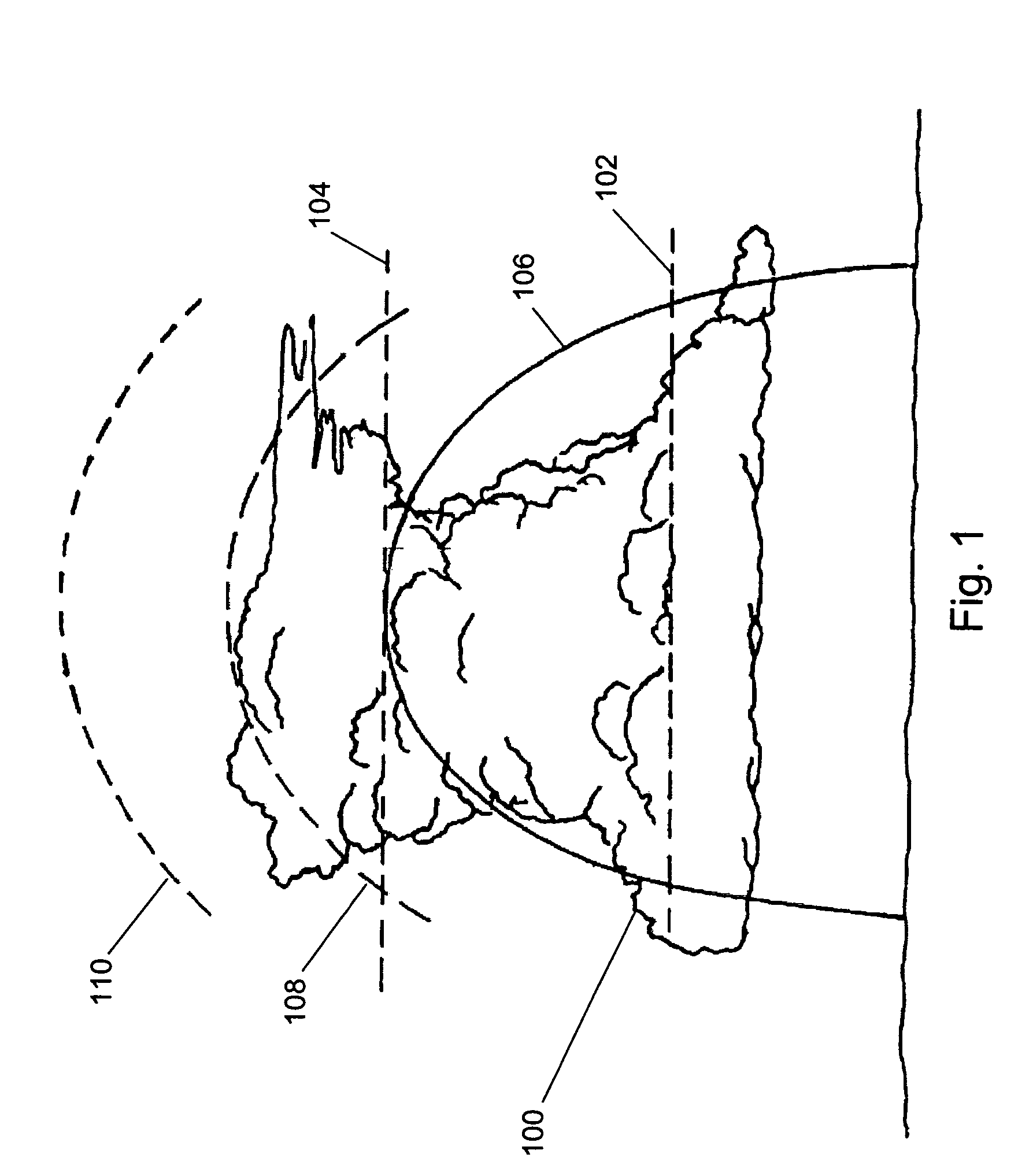
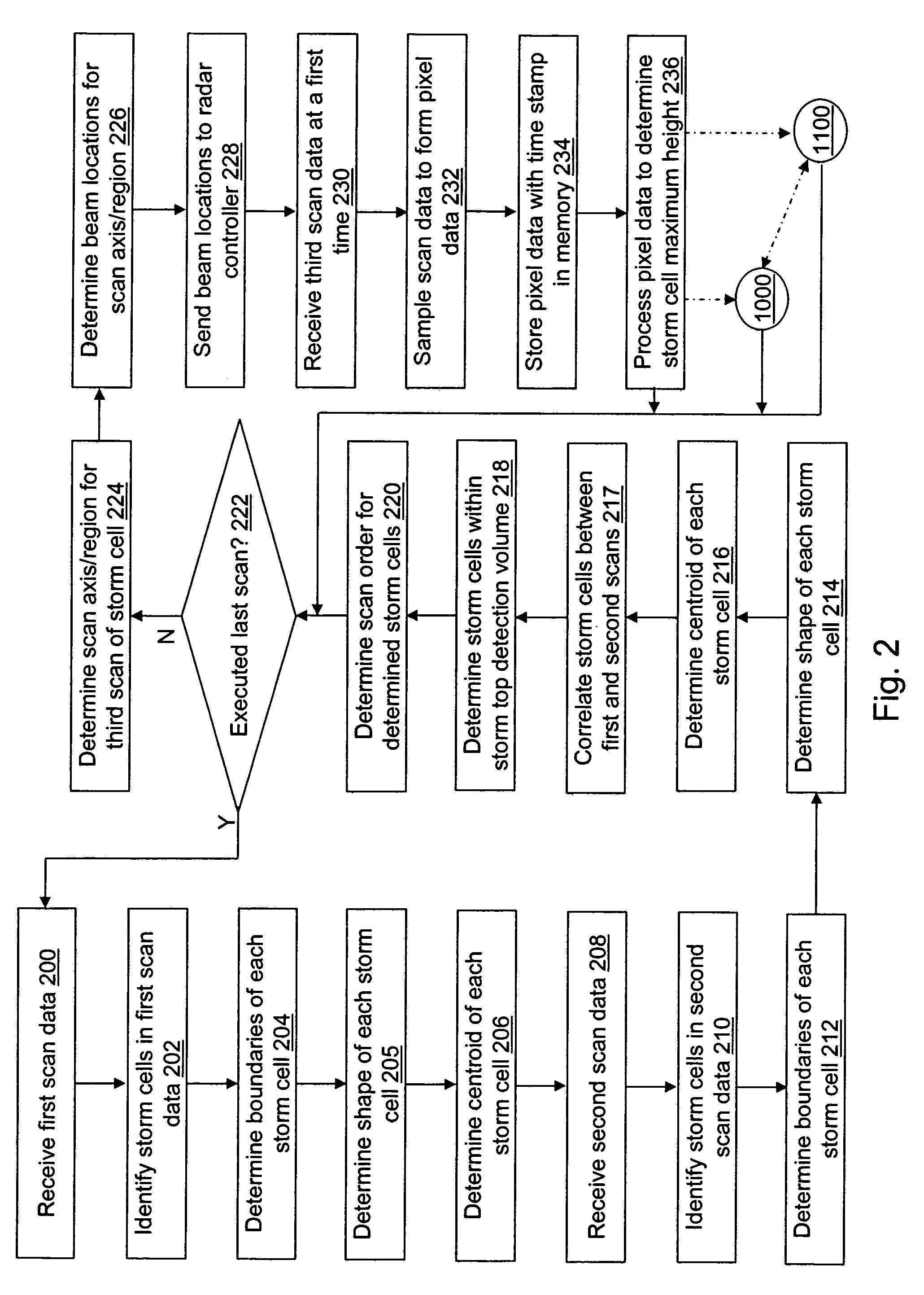
A method of characterizing a maximum height of a storm cell for an aircraft is provided. First reflectivity data formed from a first scan of a storm cell by a radar is received and a first centroid of the storm cell is identified. Second reflectivity data formed from a second scan of the storm cell by the radar is received and a second centroid of the storm cell is identified. A scan axis for a third scan of the storm cell based on the first centroid and the second centroid is determined. Third reflectivity data formed from the third scan of the storm cell by the radar at a first time is received. The third reflectivity data is sampled to form pixel data that includes a reflectivity indicator determined for each pixel formed from the third reflectivity data. A maximum height of the storm cell is determined by processing the pixel data.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
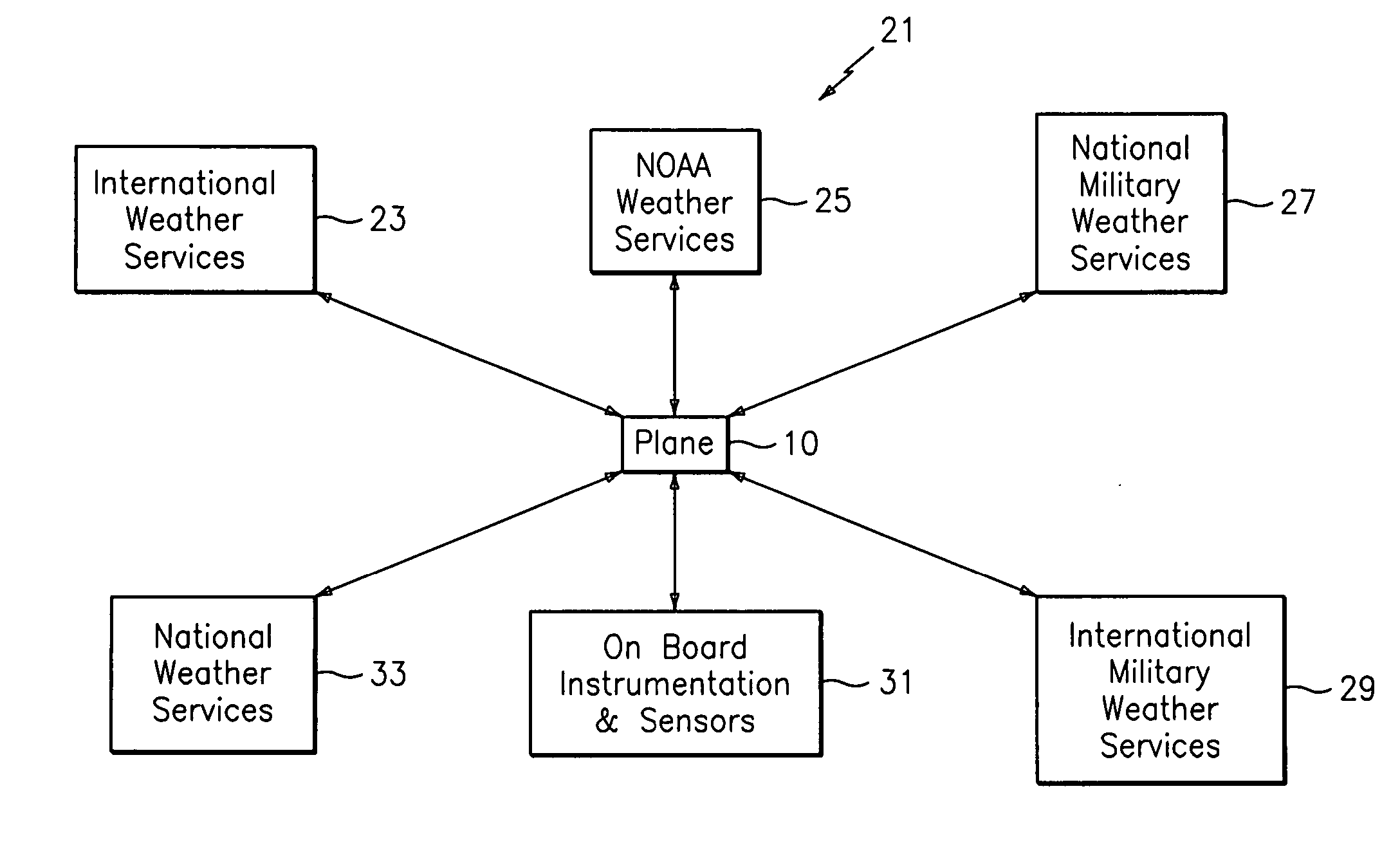
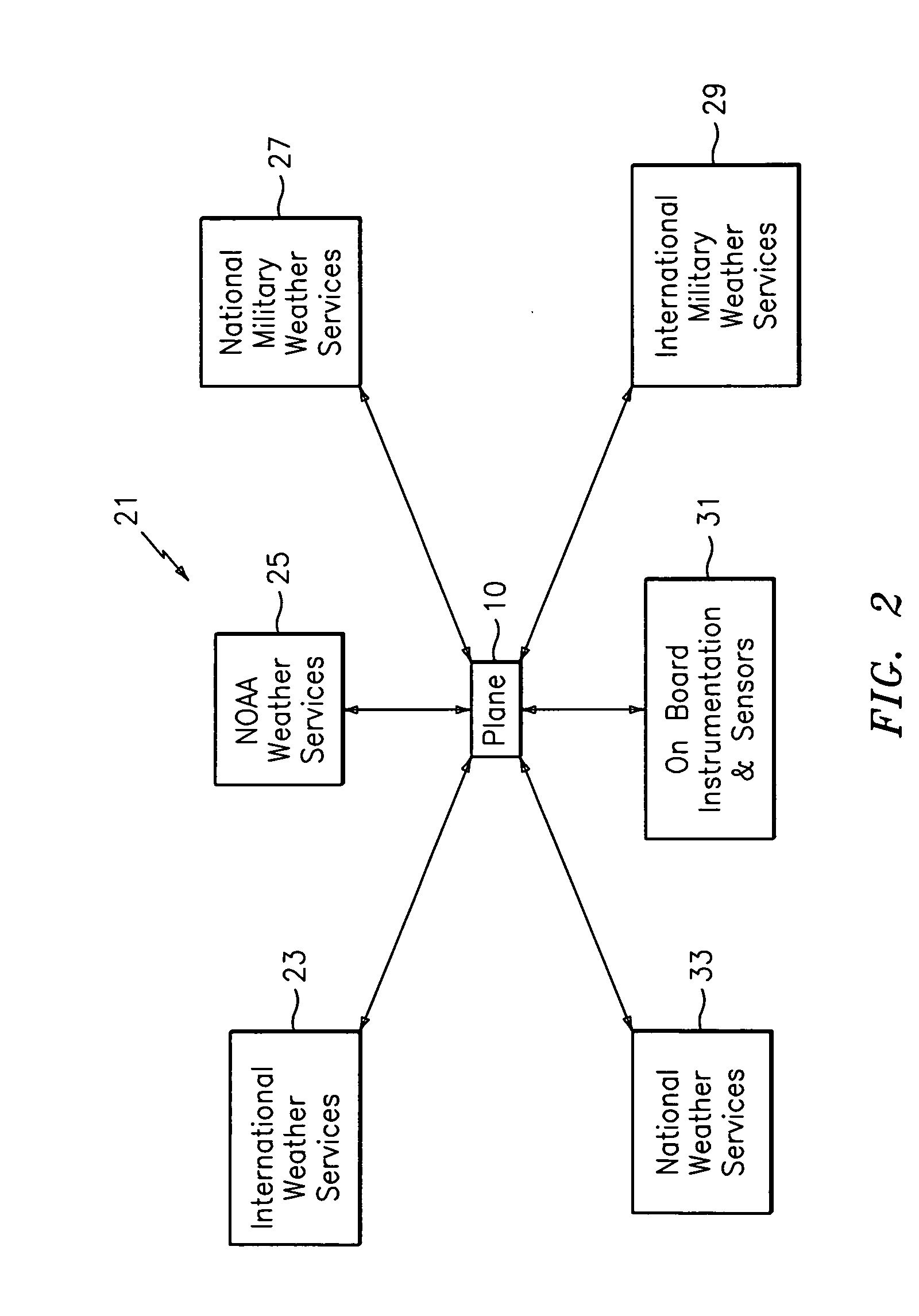
Weather information network including graphical display
InactiveUS7027898B1More informed and intelligent decisionEnhanced Situational AwarenessAircraft componentsAnalogue computers for trafficGraphicsGraphical user interface
An apparatus for providing weather information onboard an aircraft includes a processor unit and a graphical user interface. The processor unit processes weather information after it is received onboard the aircraft from a ground-based source, and the graphical user interface provides a graphical presentation of the weather information to a user onboard the aircraft. Preferably, the graphical user interface includes one or more user-selectable options for graphically displaying at least one of convection information, turbulence information, icing information, weather satellite information, SIGMET information, significant weather prognosis information, and winds aloft information.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Weather avoidance tool system
ActiveUS20130226452A1Instruments for road network navigationClear air turbulence detection/forecastingAviationWeather risk
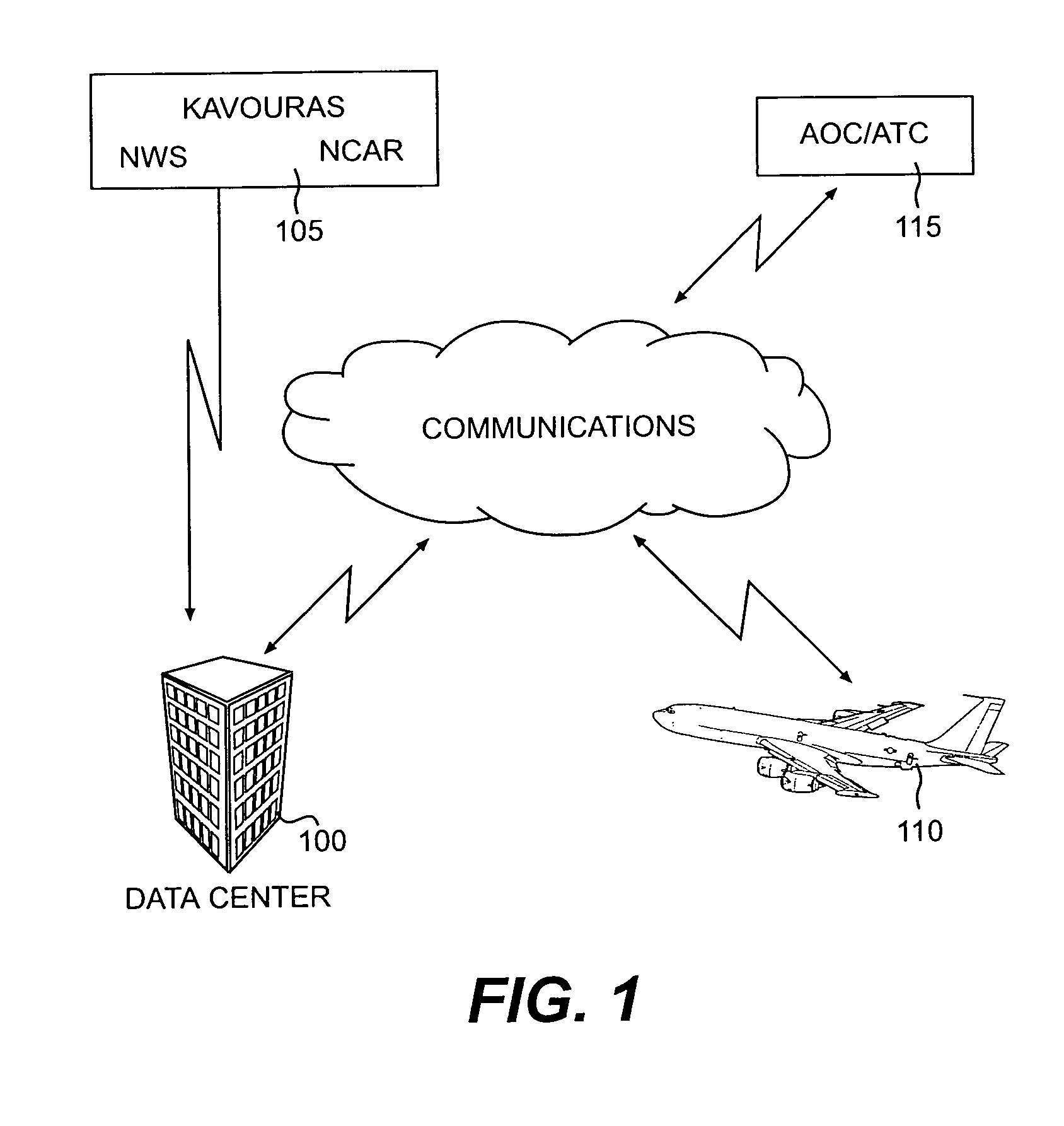
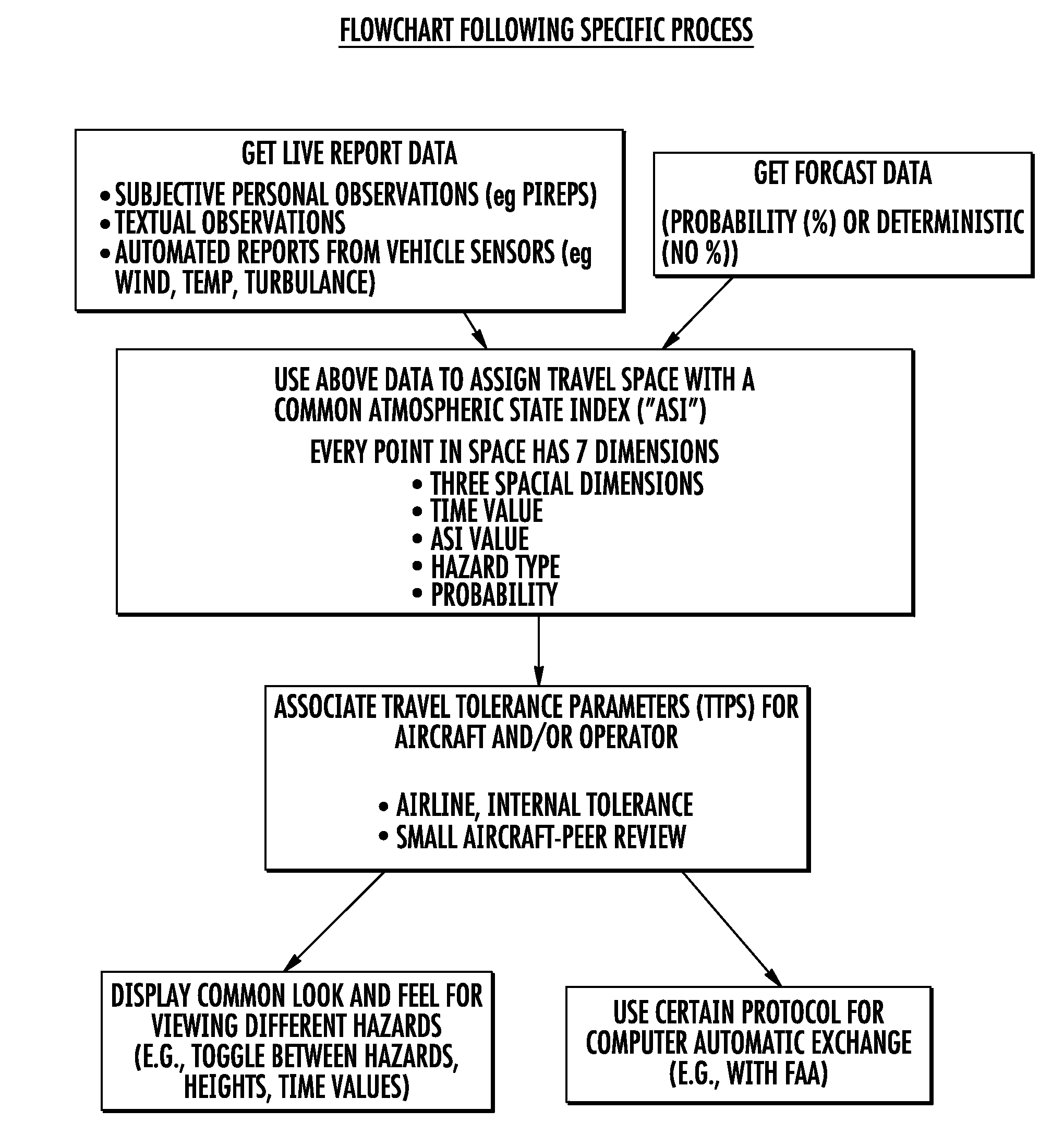
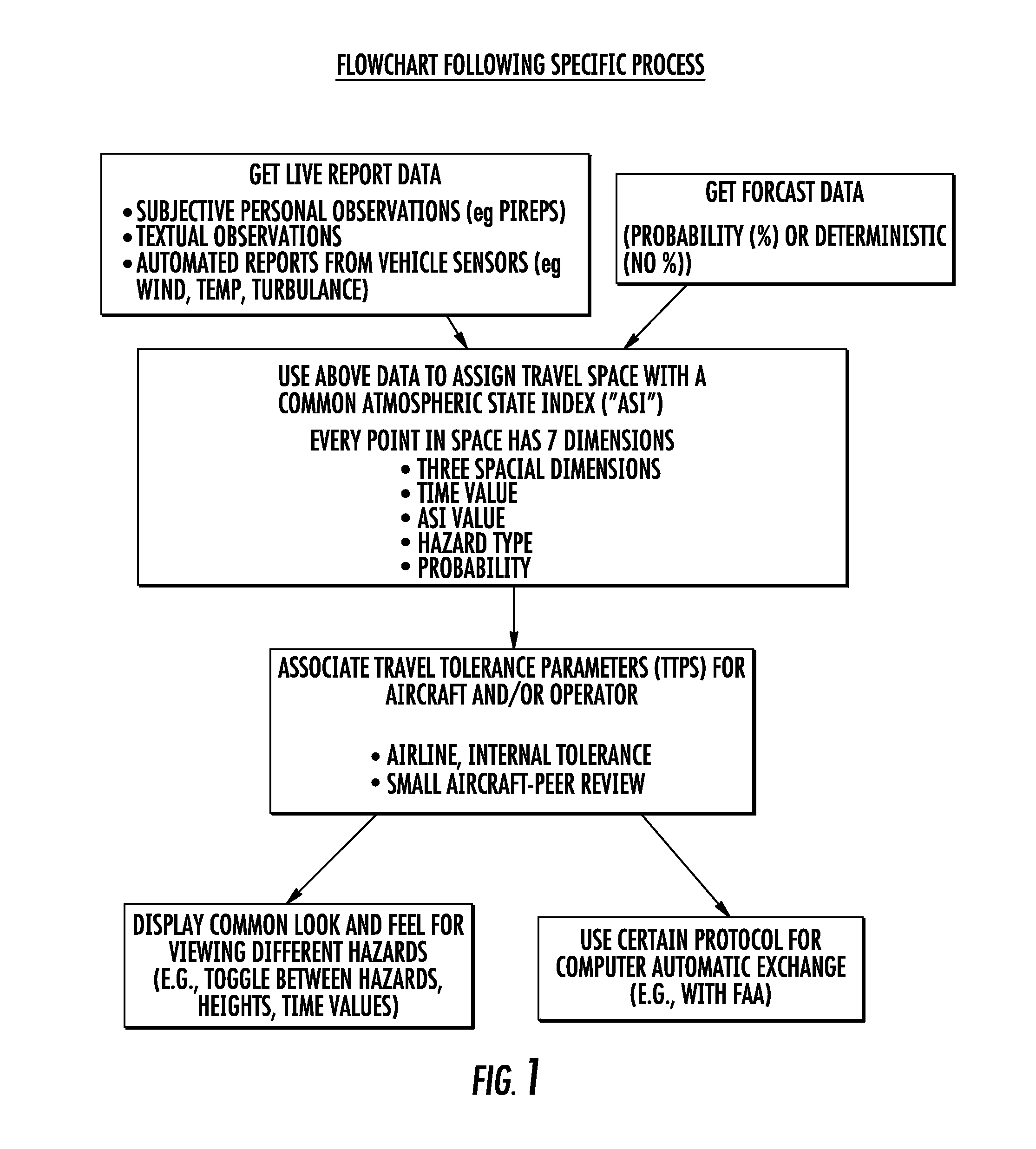
This invention relates to a method of providing a simplified practice for dealing with aviation turbulence and other weather hazards that allows the end users to better communicate turbulence as a state of the atmosphere metric and the additional weather threats affecting the flight. The invention will provide an Atmospheric State Index (ASI) that will allow all the users to work with a standardized metric that describes the turbulence as the state of the atmosphere and a similar scale for other weather risks to the flight. This system will make the correlation between the forecast and aircraft reports for turbulence easier to interpret for the end users. This approach would concentrate on turbulence as one of the weather hazards with a more objective and easier to use metric. This invention would provide a transition for moving from a system based on turbulence PIREPS to a more objective data driven process in the future air traffic environment. This invention would provide an end solution for the future air traffic system commonly referred to as NextGen for both turbulence and other weather hazards.
Owner:BLUE EAGLE FUND
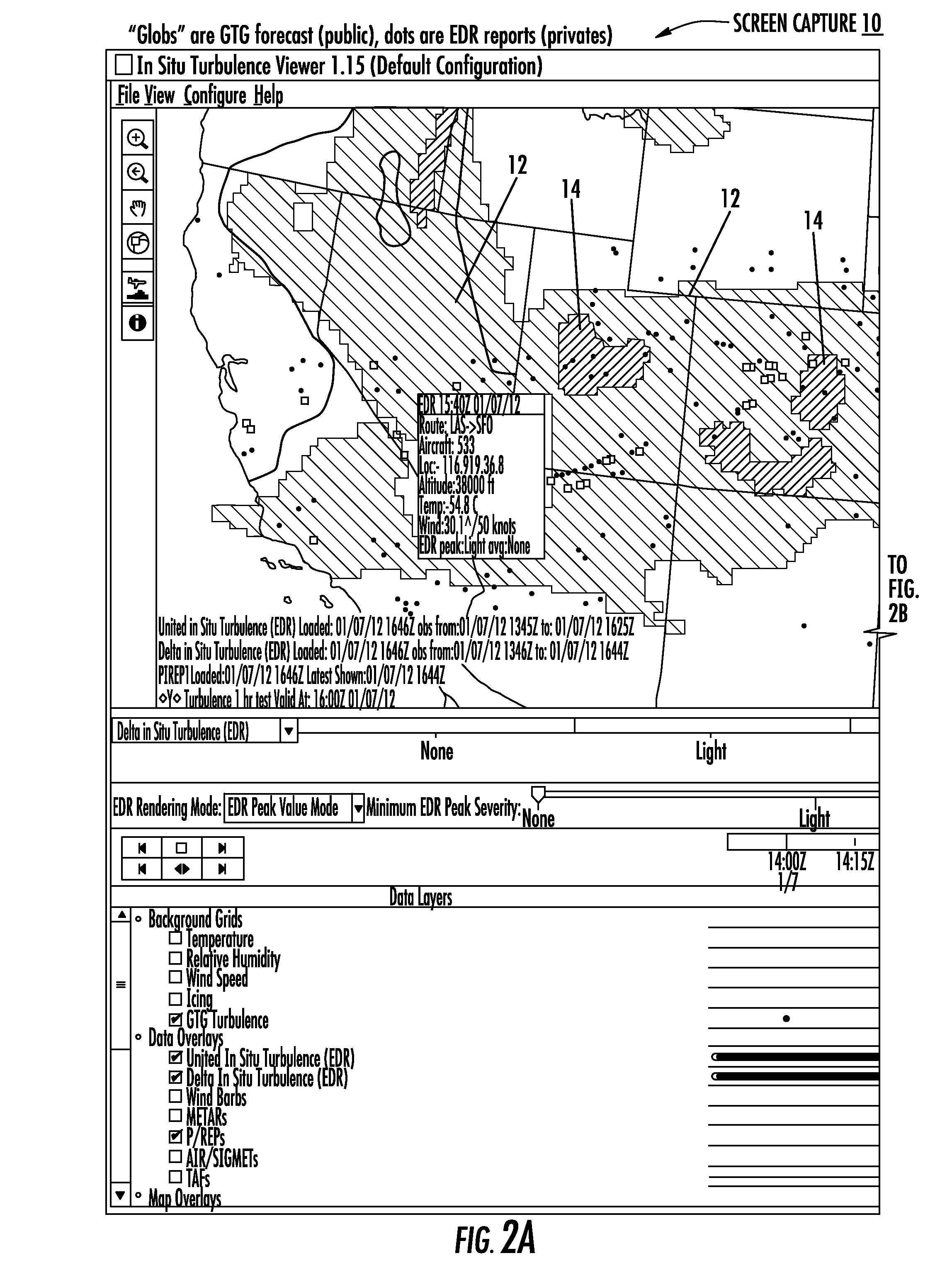
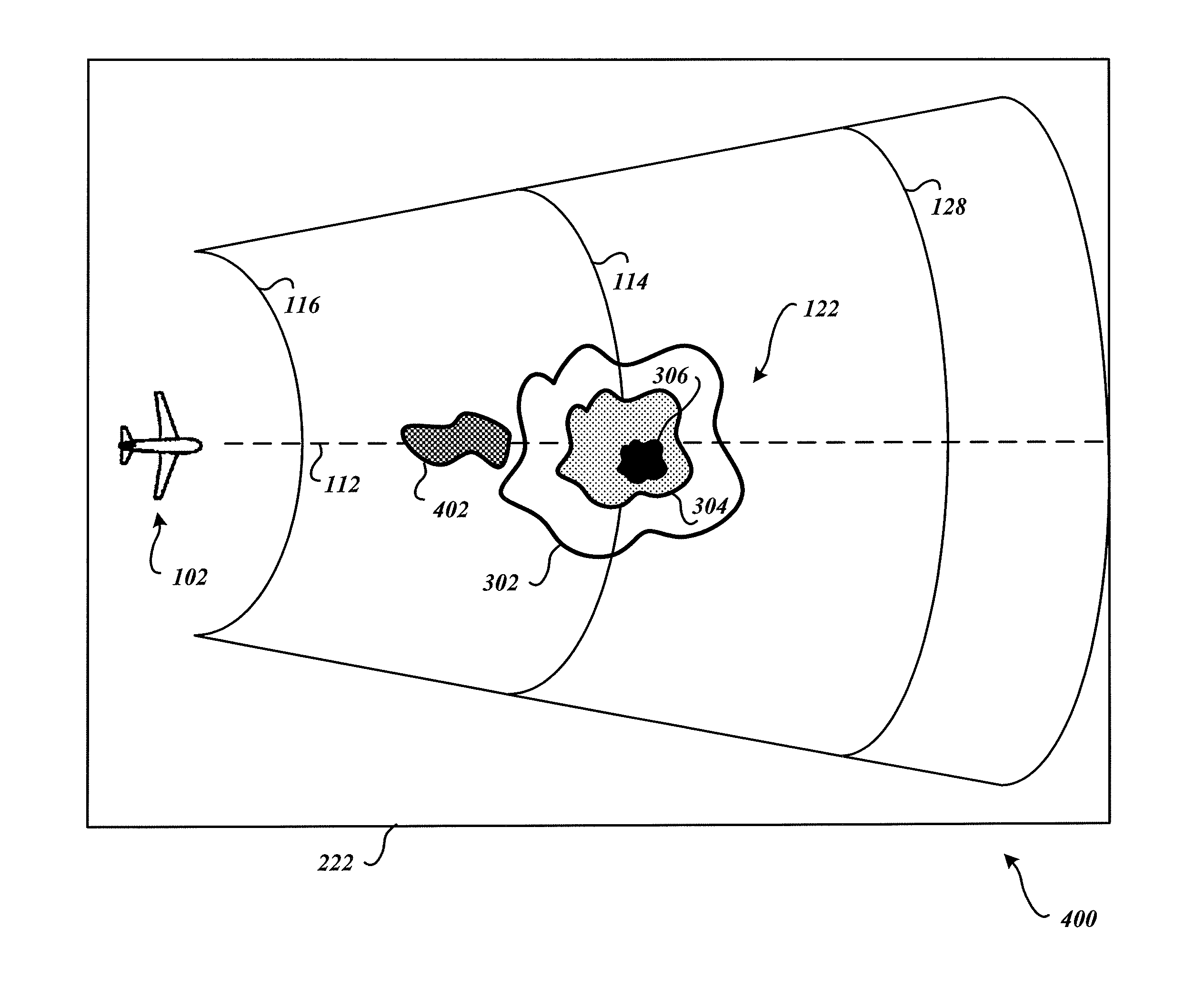
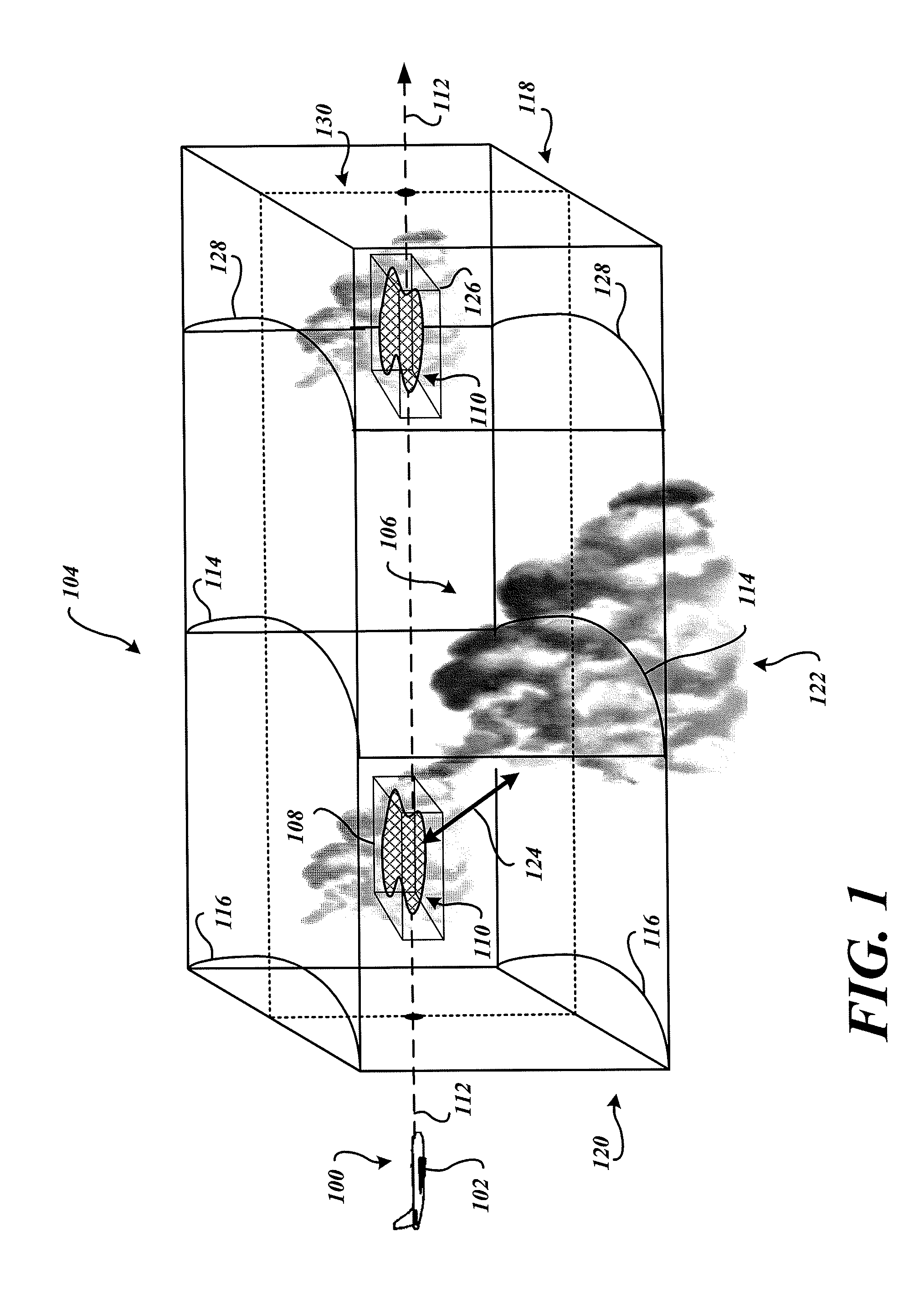
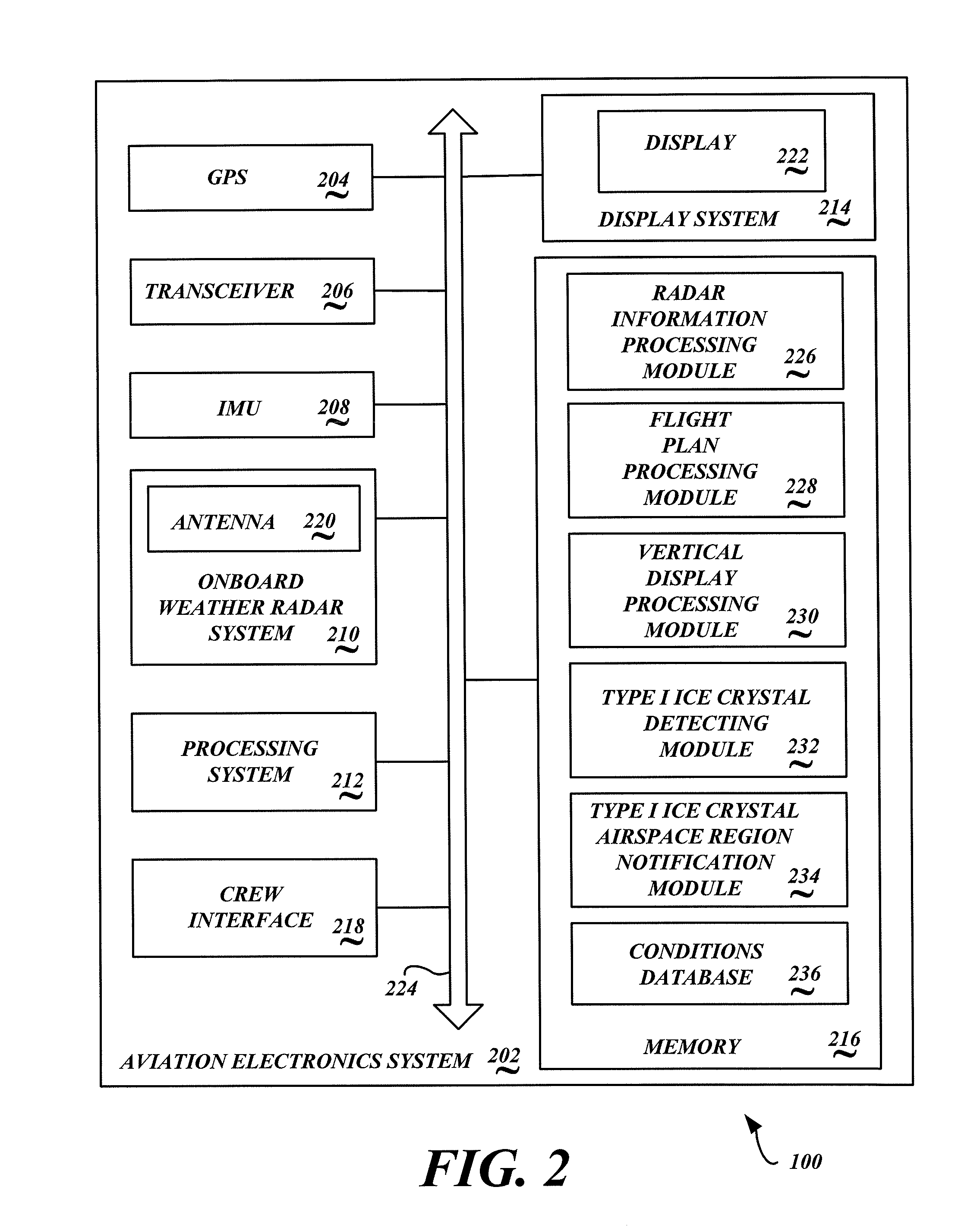
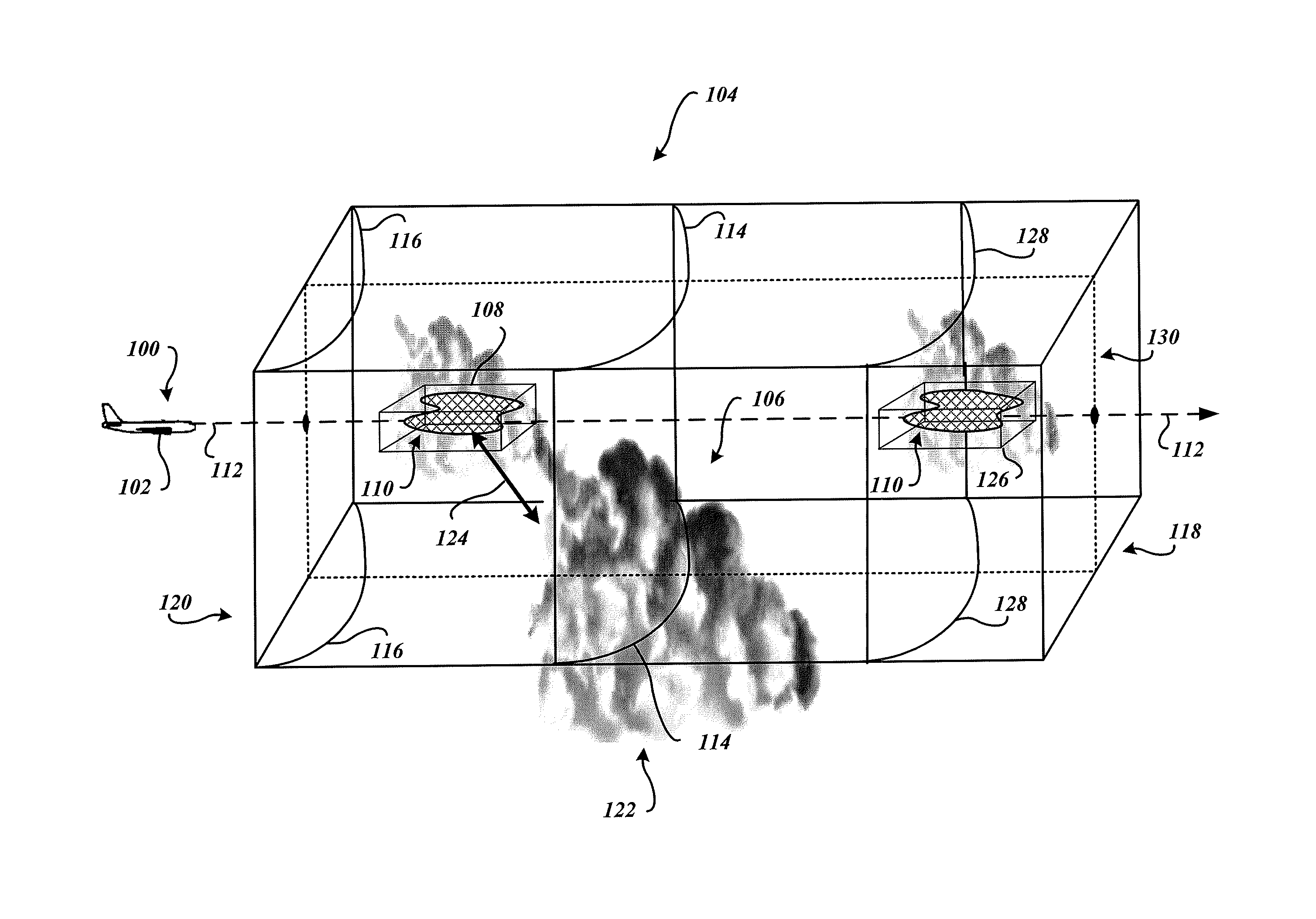
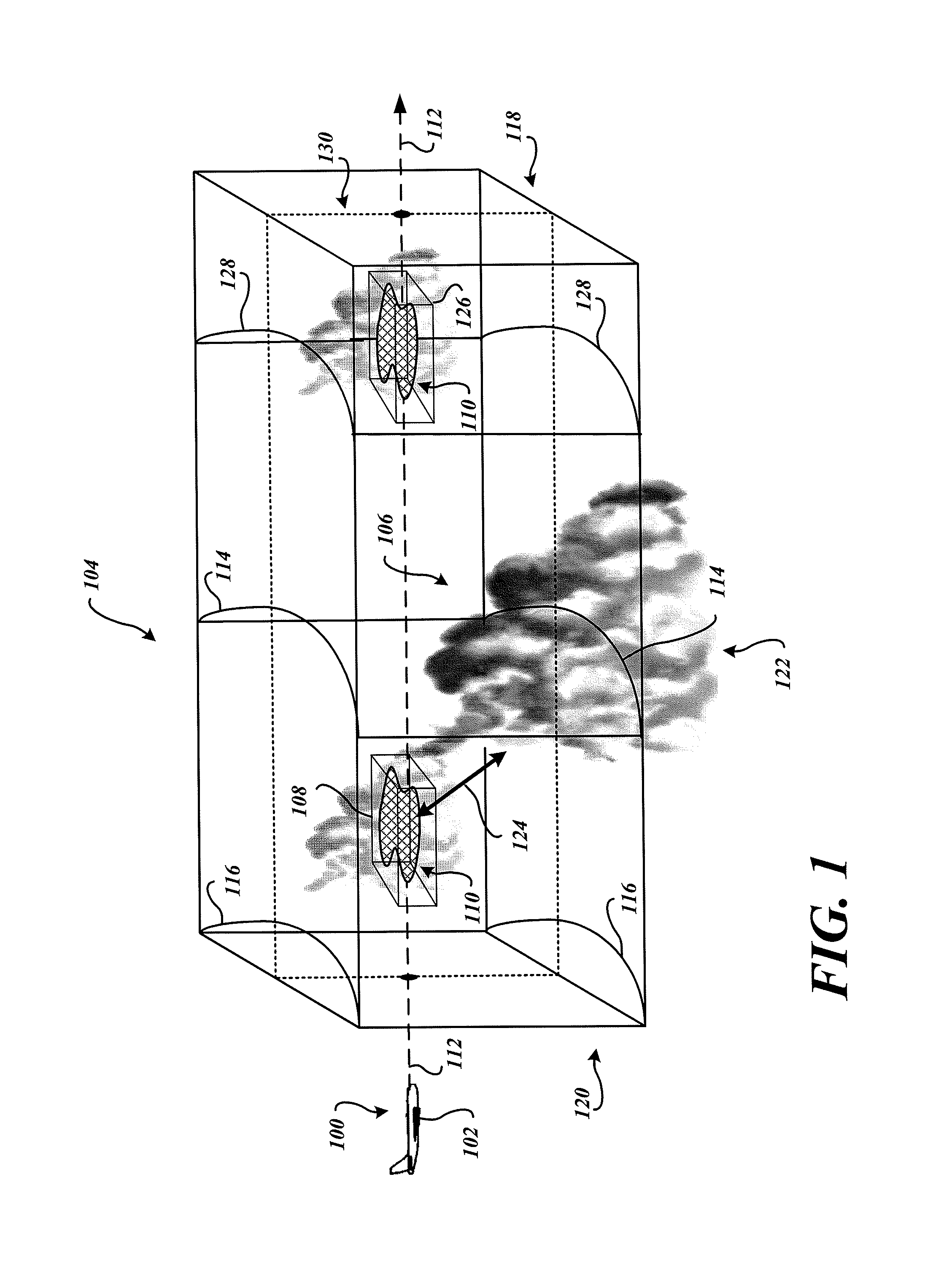
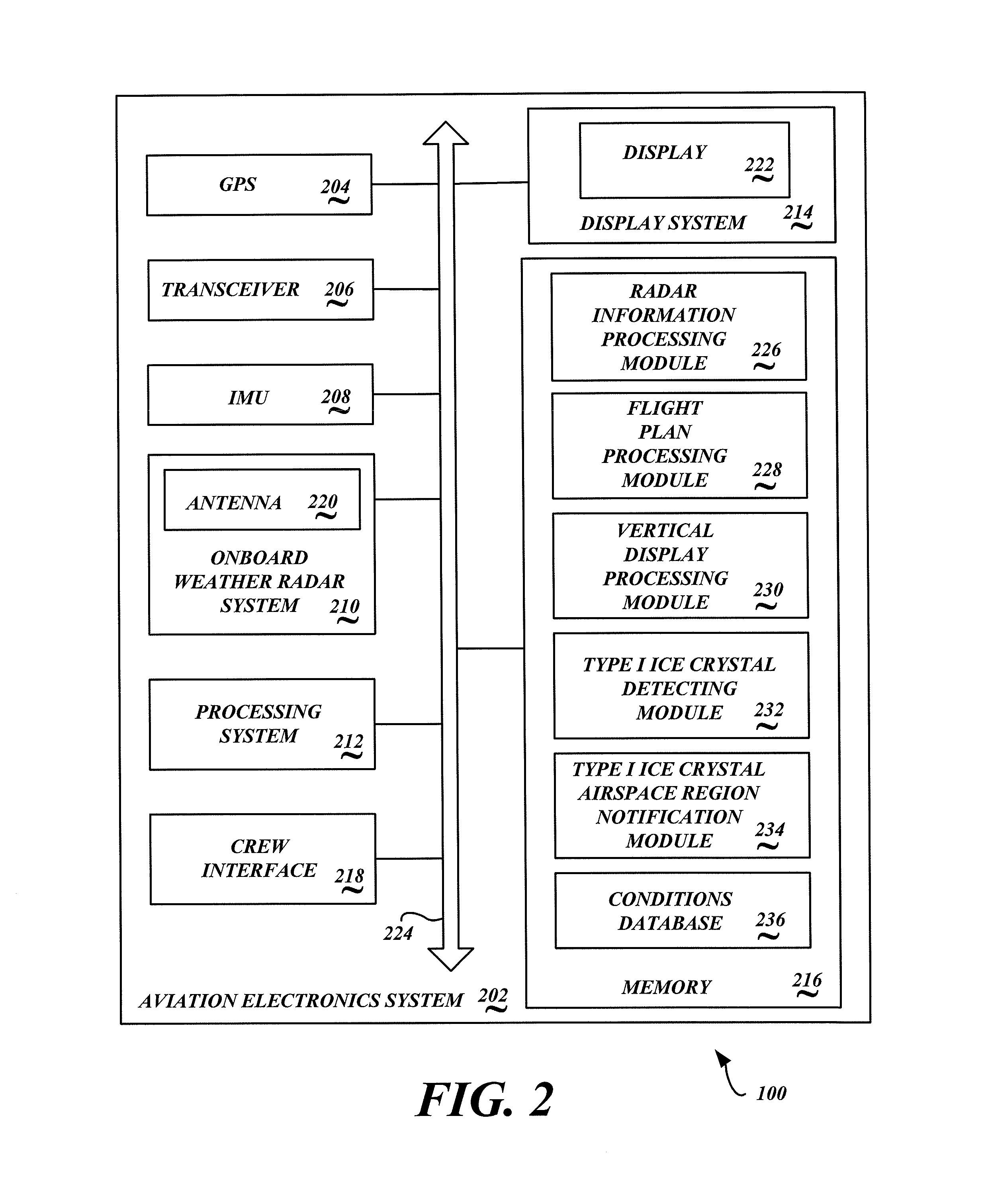
System and method to identify regions of airspace having ice crystals using an onboard weather radar system
ActiveUS20130234884A1Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingDe-icing equipmentsWeather radarAtmospheric sciences
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Methods and systems for monitoring atmospheric conditions, predicting turbulent atmospheric conditions and optimizing flight paths of aircraft
InactiveUS20060155432A1Energy saving arrangementsNavigational calculation instrumentsInformation dataAirplane
A method for optimizing the flight path of an aircraft is performed by collecting atmospheric information data from one or more sensors mounted on an aircraft; processing the collected atmospheric information; predicting an atmospheric condition in a flight path of the aircraft based upon the collected atmospheric information; and modifying the flight path in anticipation of the atmospheric condition.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Airborne based monitoring
InactiveUS6937937B1Improve weather forecastsOptimize aircraft routingWeather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingAir traffic controlEngineering
A weather monitoring and prediction system that uses a fleet of aircraft to obtain data. Each aircraft has a local air data system that facilitates the measurement, recordation, and transmittal of local atmospheric data such as barometric pressure, and the corresponding temporal, positional, and altitudinal data. The data is electronically transmitted from each aircraft to a ground based processing system where it is stored. The data may then be transmitted to subscribing users such as aircraft, other weather data systems or to air traffic control centers in either a compiled form or in a raw form. Another embodiment also provides for measuring barometric pressure as a function of altitude at an in-flight aircraft.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
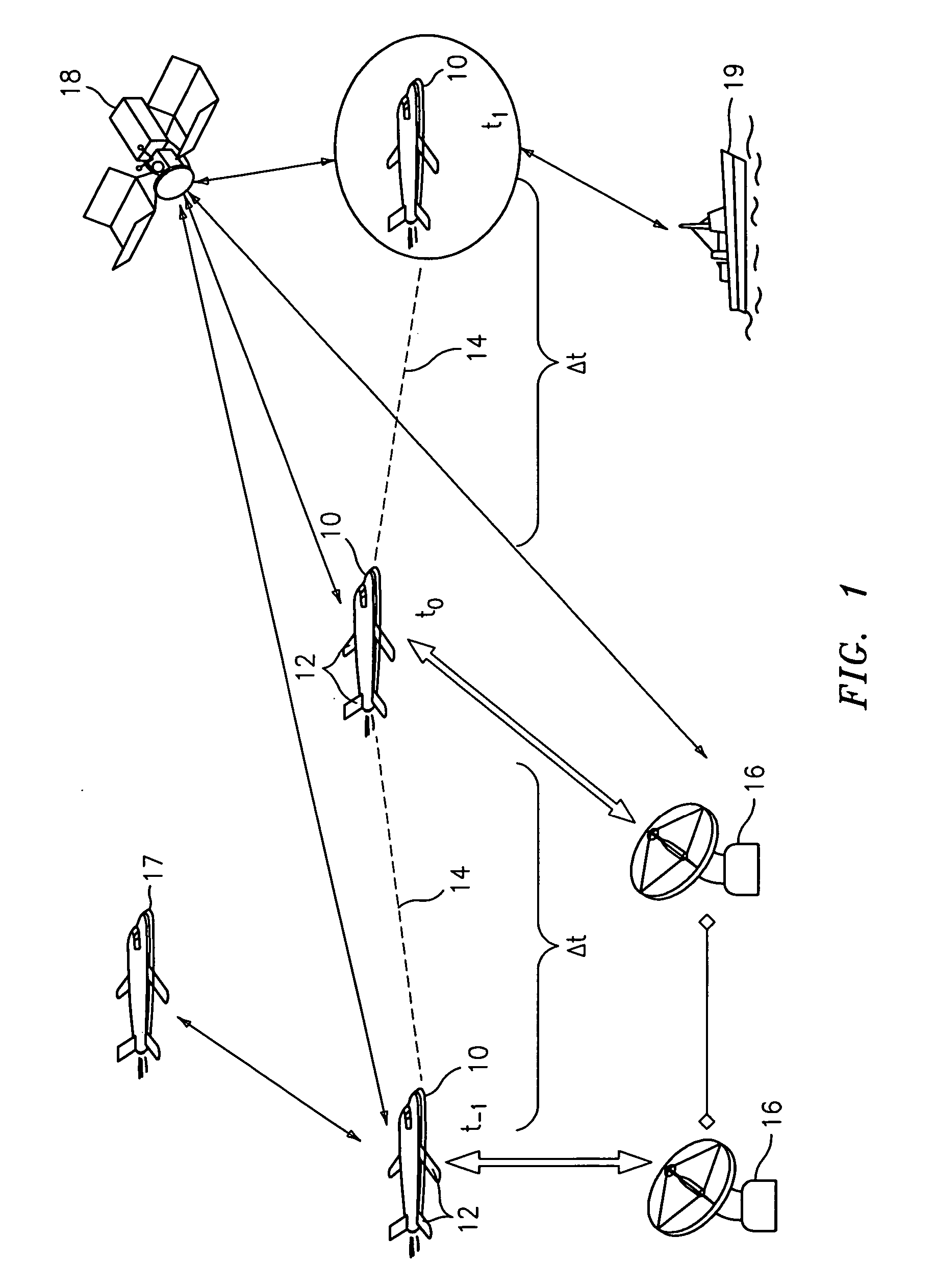
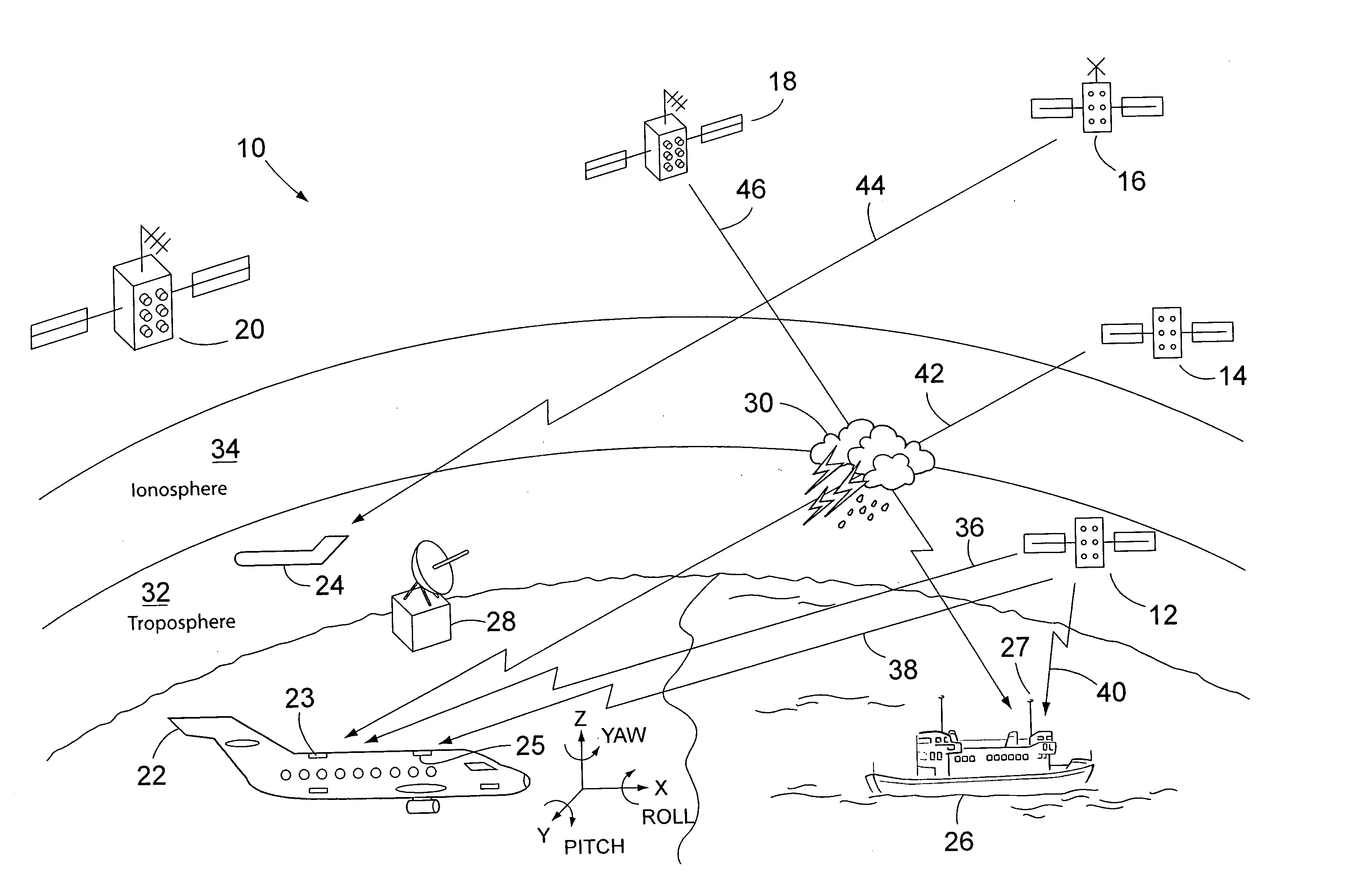
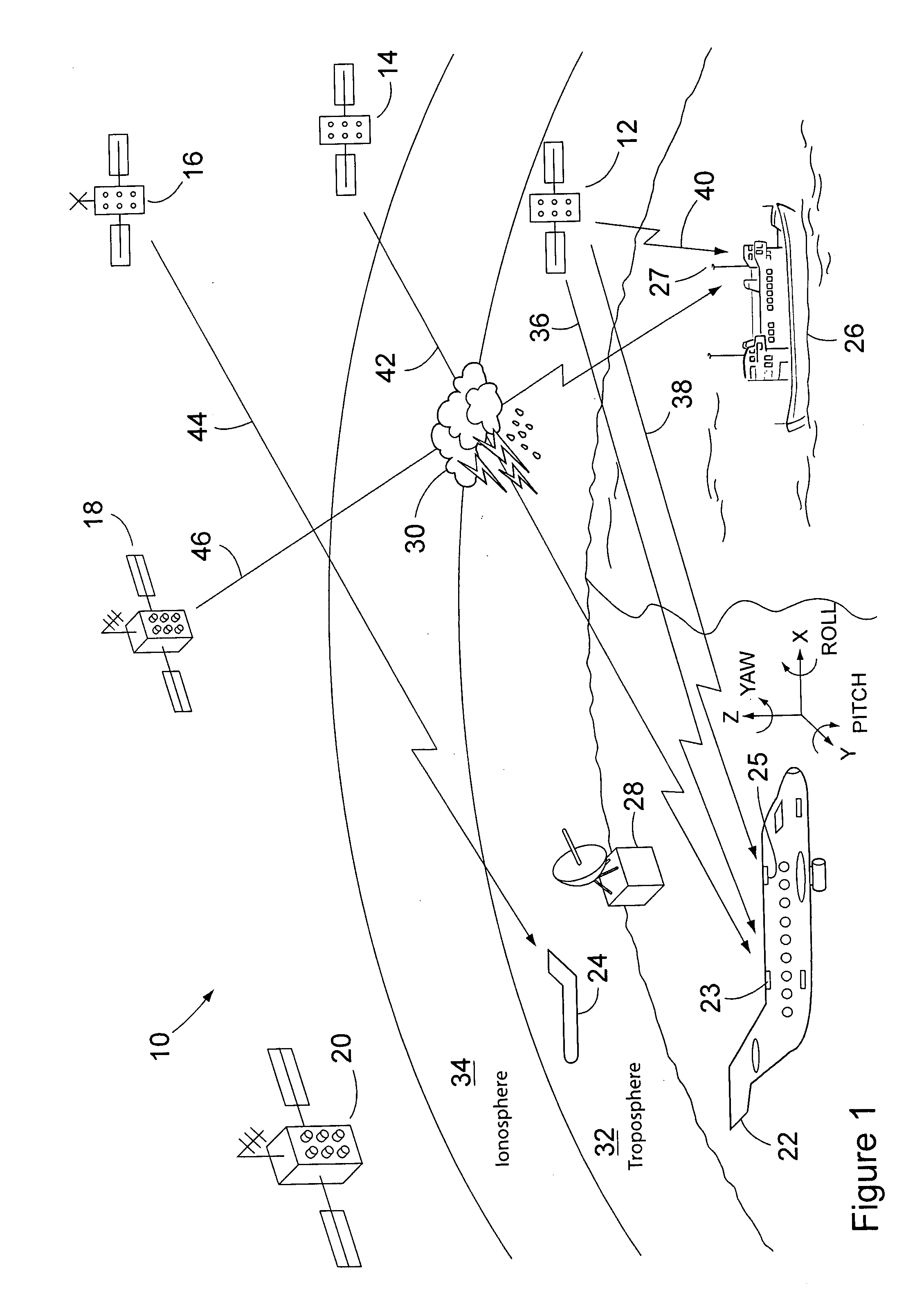
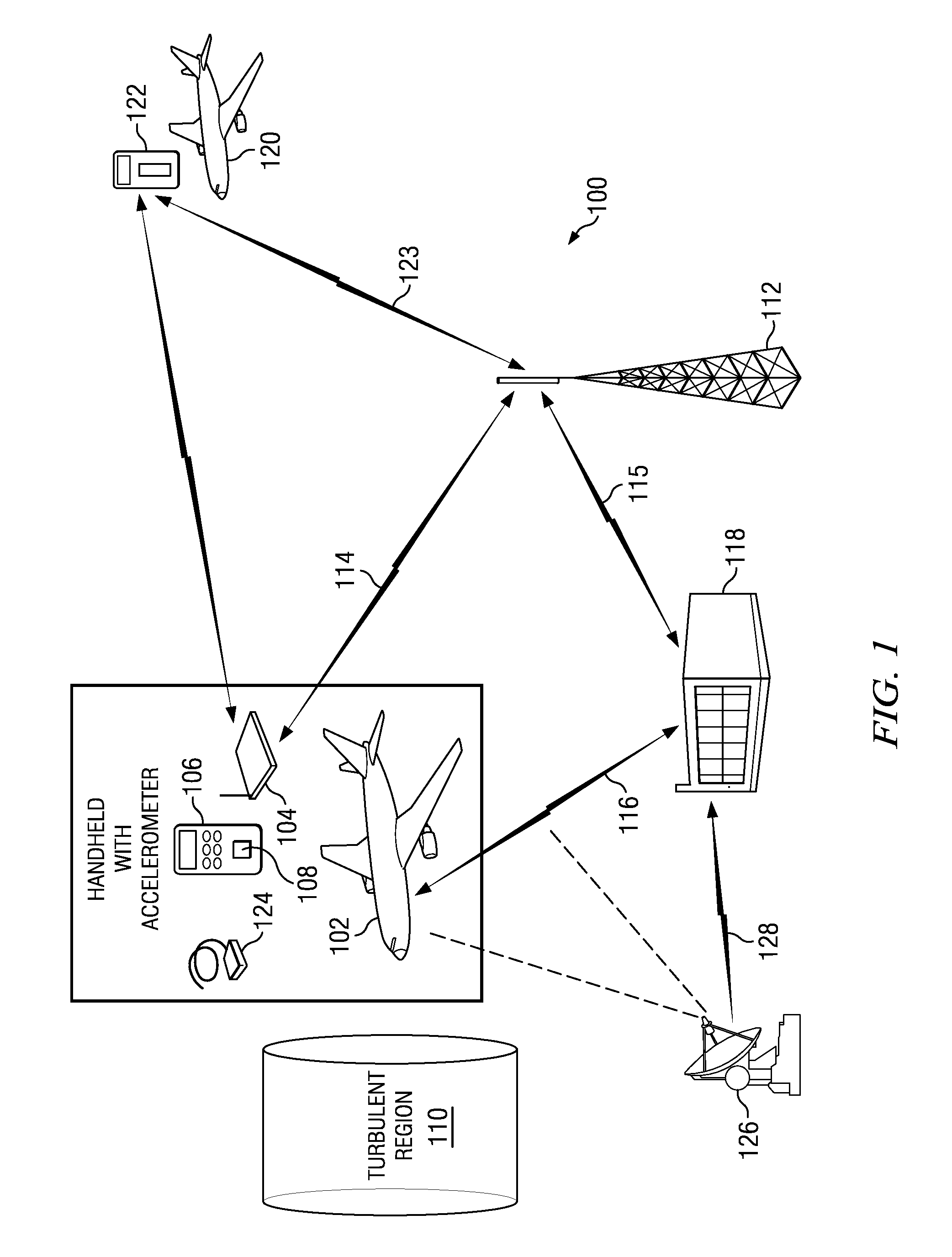
System for measuring turbulence remotely
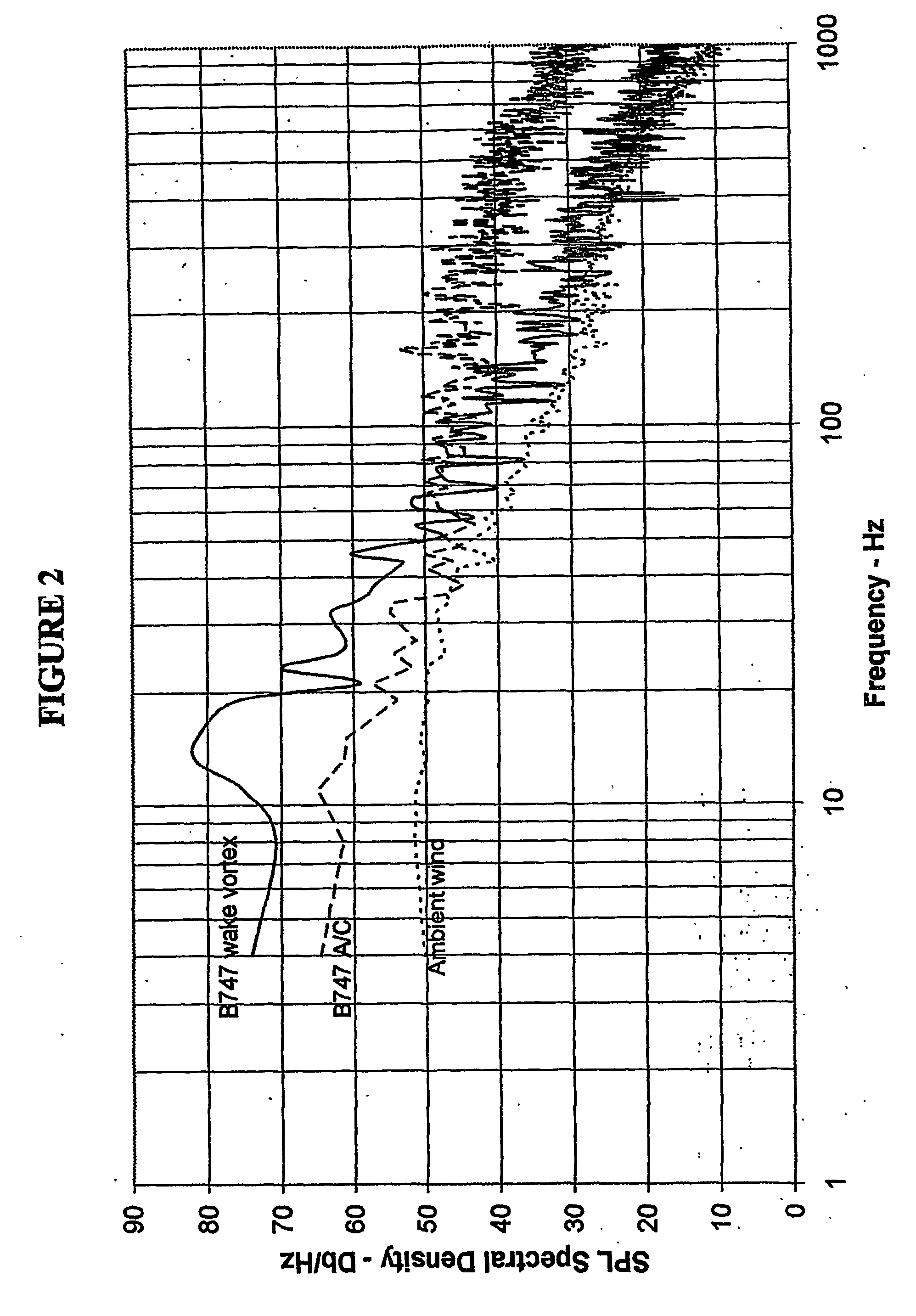
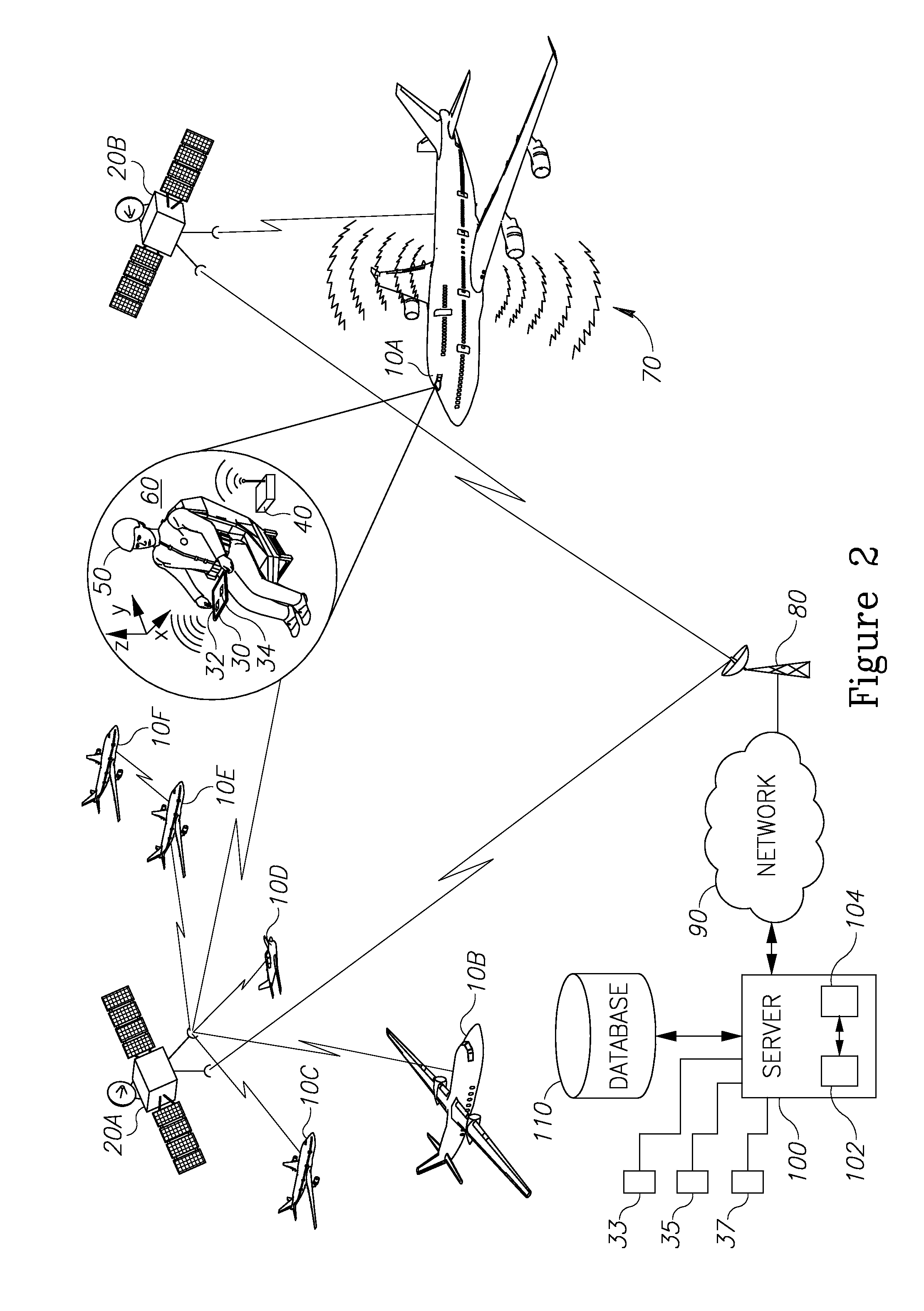
ActiveUS7598901B2Improve usabilityIncrease coverageBeacon systems using radio wavesClear air turbulence detection/forecastingEnergy variationEngineering
A system and method for detecting turbulence includes several mobile platforms, a mobile platform velocity sensor, and several electromagnetic energy transmitters and receivers. The receivers receive the energy transmitted by the transmitter(s) after it has traveled along a path subject to the turbulence. The receivers detect alterations of the energy caused by the turbulence and filter the alterations for effects of the mobile platform velocity (on which either a transmitter or receiver is located). Additionally, the system may create a three-dimensional model of the. In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a method of detecting turbulence using a mobile platform. The method includes receiving electromagnetic energy that has traveled along a path subject to the turbulence and determining the alteration to the energy caused by the turbulence. The alterations are filtered of the effects of the velocity of the mobile platform on which the receivers are preferably located.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System for measuring turbulence remotely
ActiveUS20060121893A1Improve usabilityReduce fuel consumptionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEnergy variationEngineering
A system and method for detecting turbulence includes several mobile platforms, a mobile platform velocity sensor, and several electromagnetic energy transmitters and receivers. The receivers receive the energy transmitted by the transmitter(s) after it has traveled along a path subject to the turbulence. The receivers detect alterations of the energy caused by the turbulence and filter the alterations for effects of the mobile platform velocity (on which either a transmitter or receiver is located). Additionally, the system may create a three-dimensional model of the. In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a method of detecting turbulence using a mobile platform. The method includes receiving electromagnetic energy that has traveled along a path subject to the turbulence and determining the alteration to the energy caused by the turbulence. The alterations are filtered of the effects of the velocity of the mobile platform on which the receivers are preferably located.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
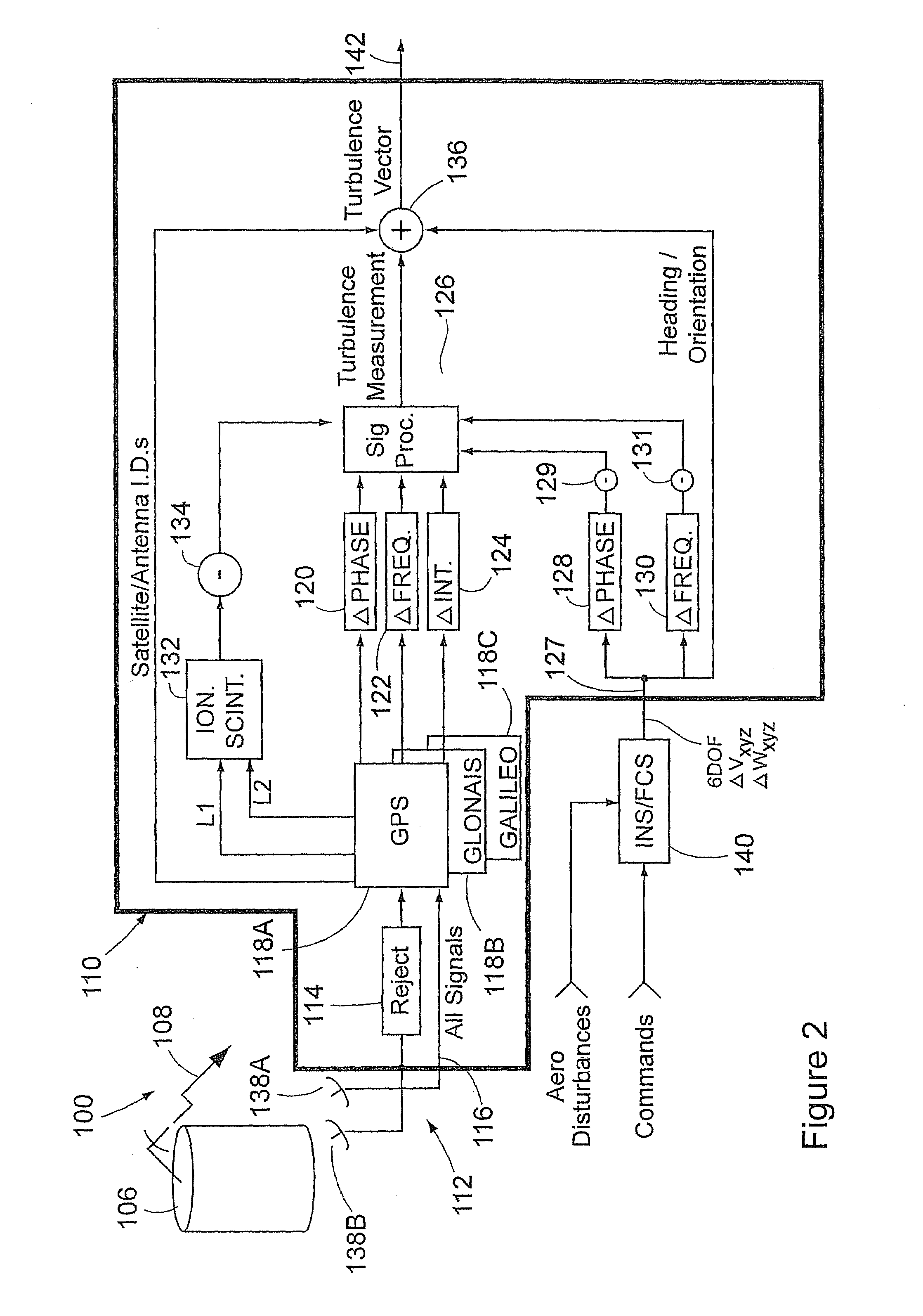
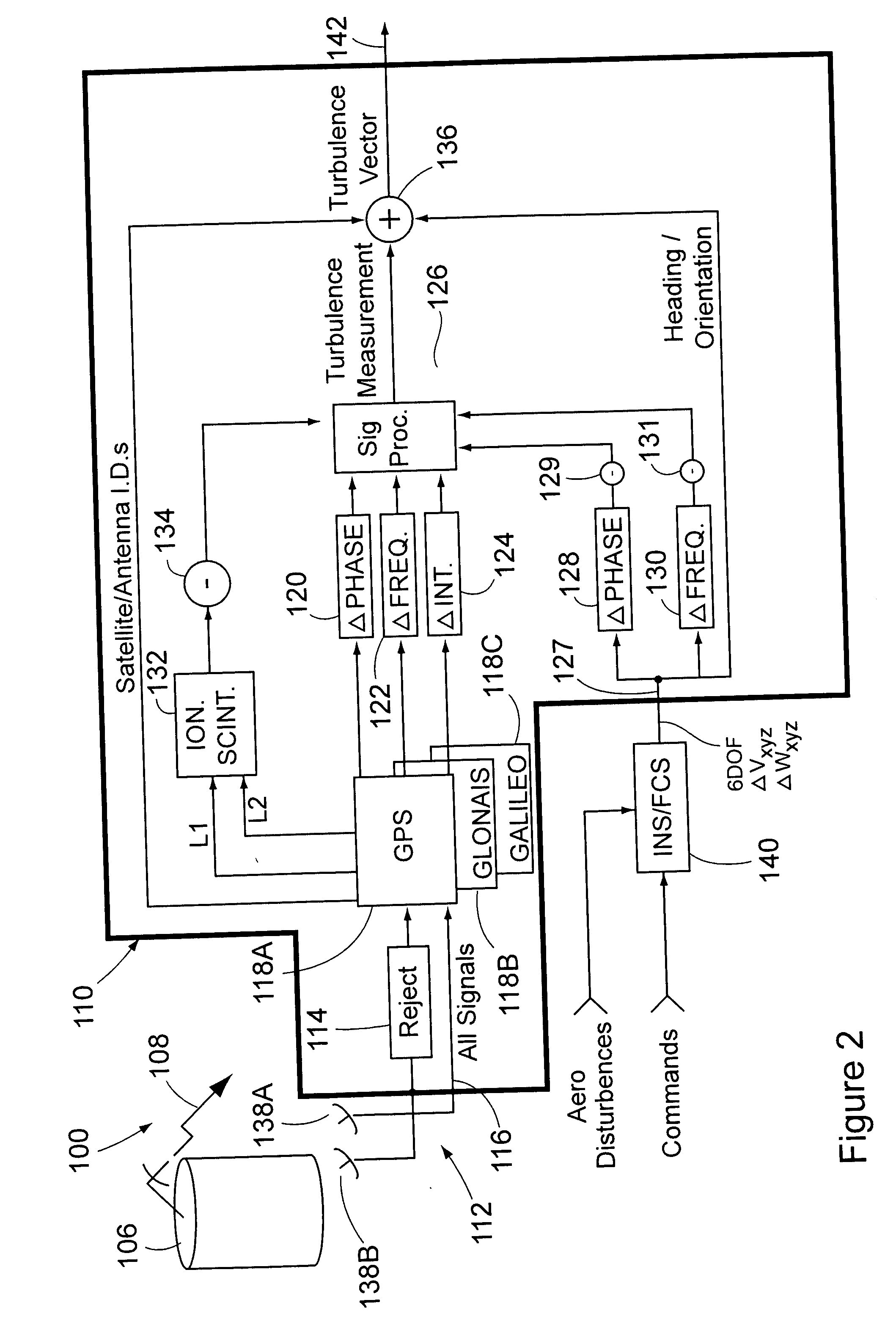
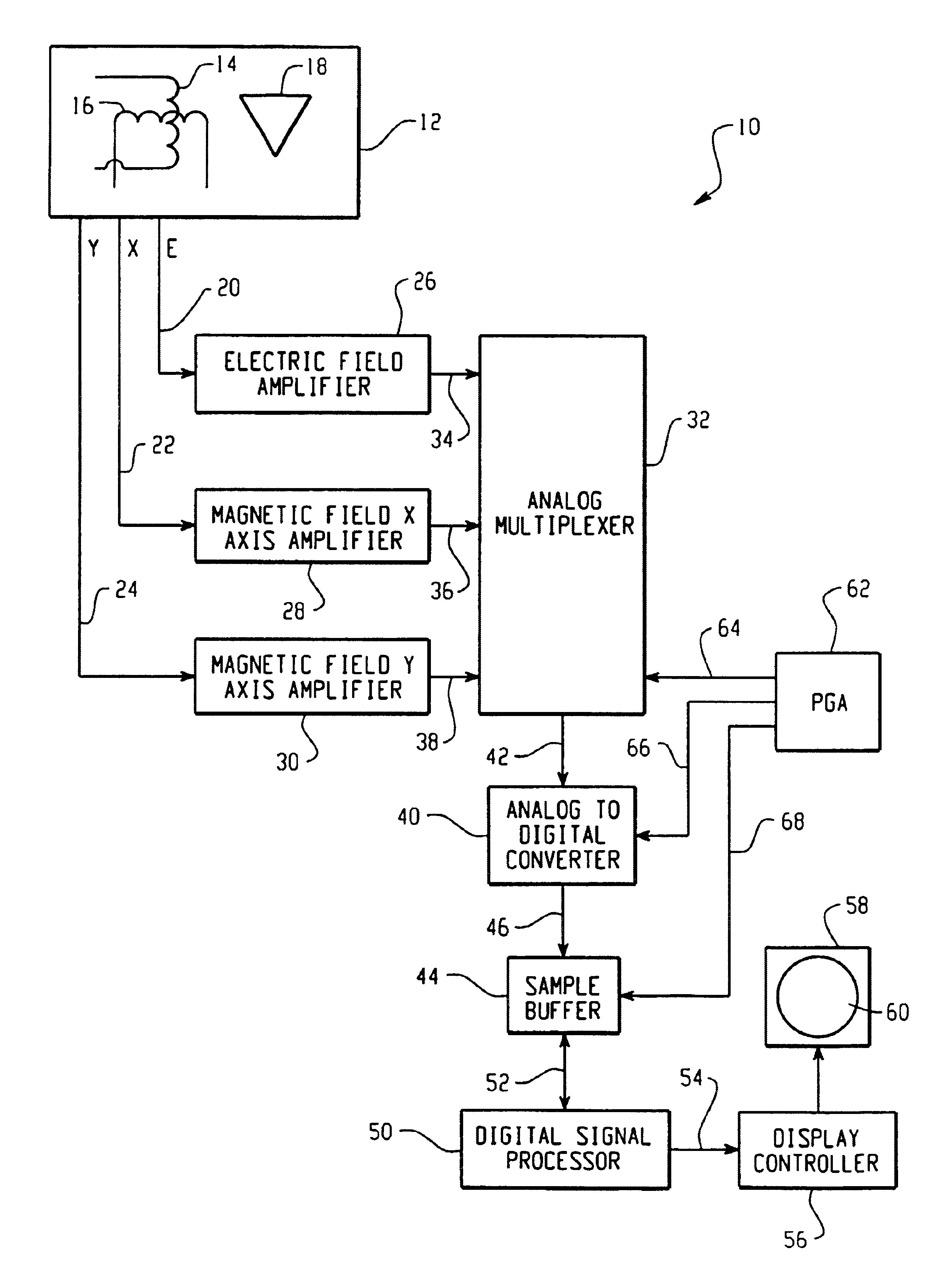
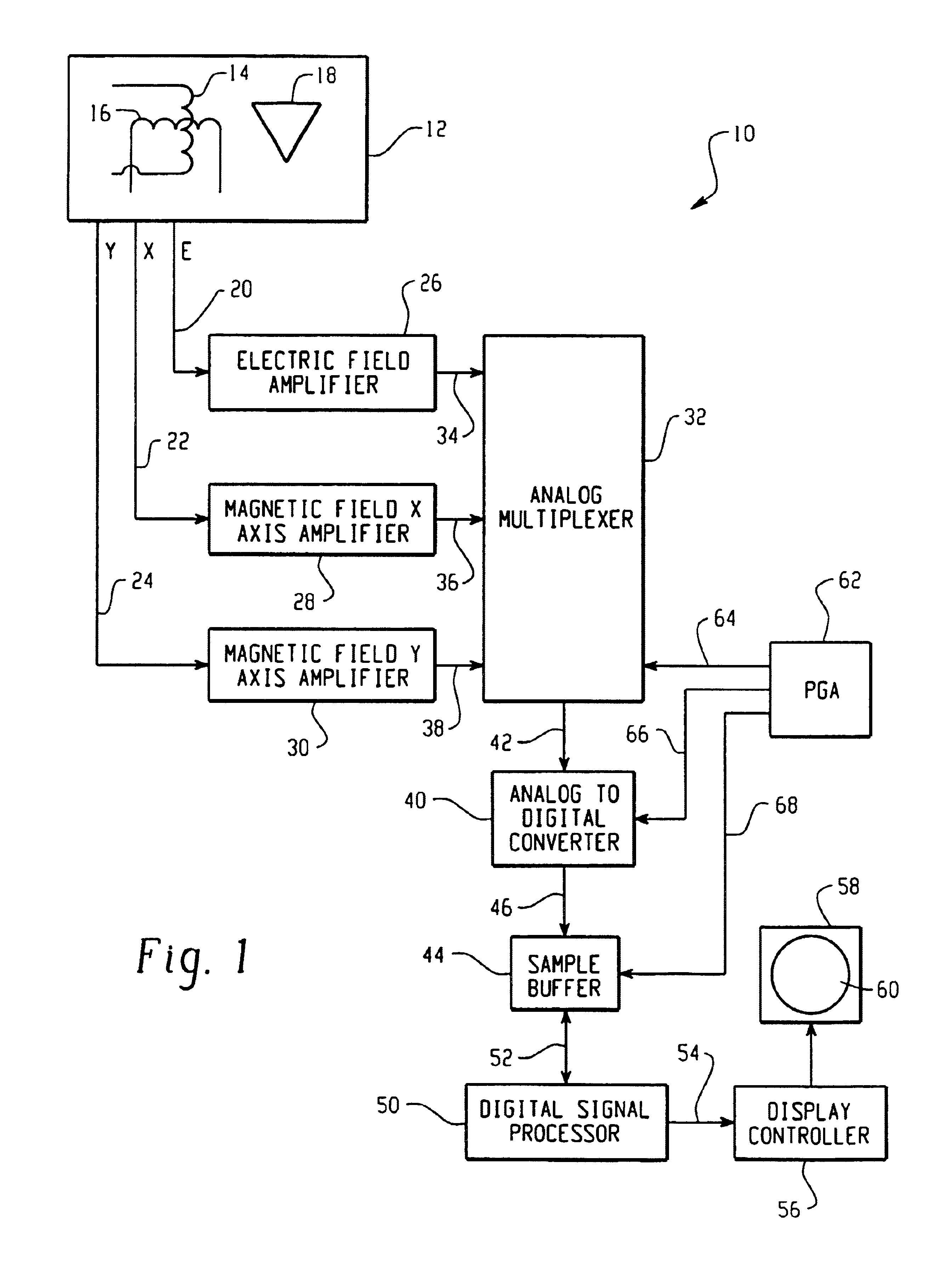
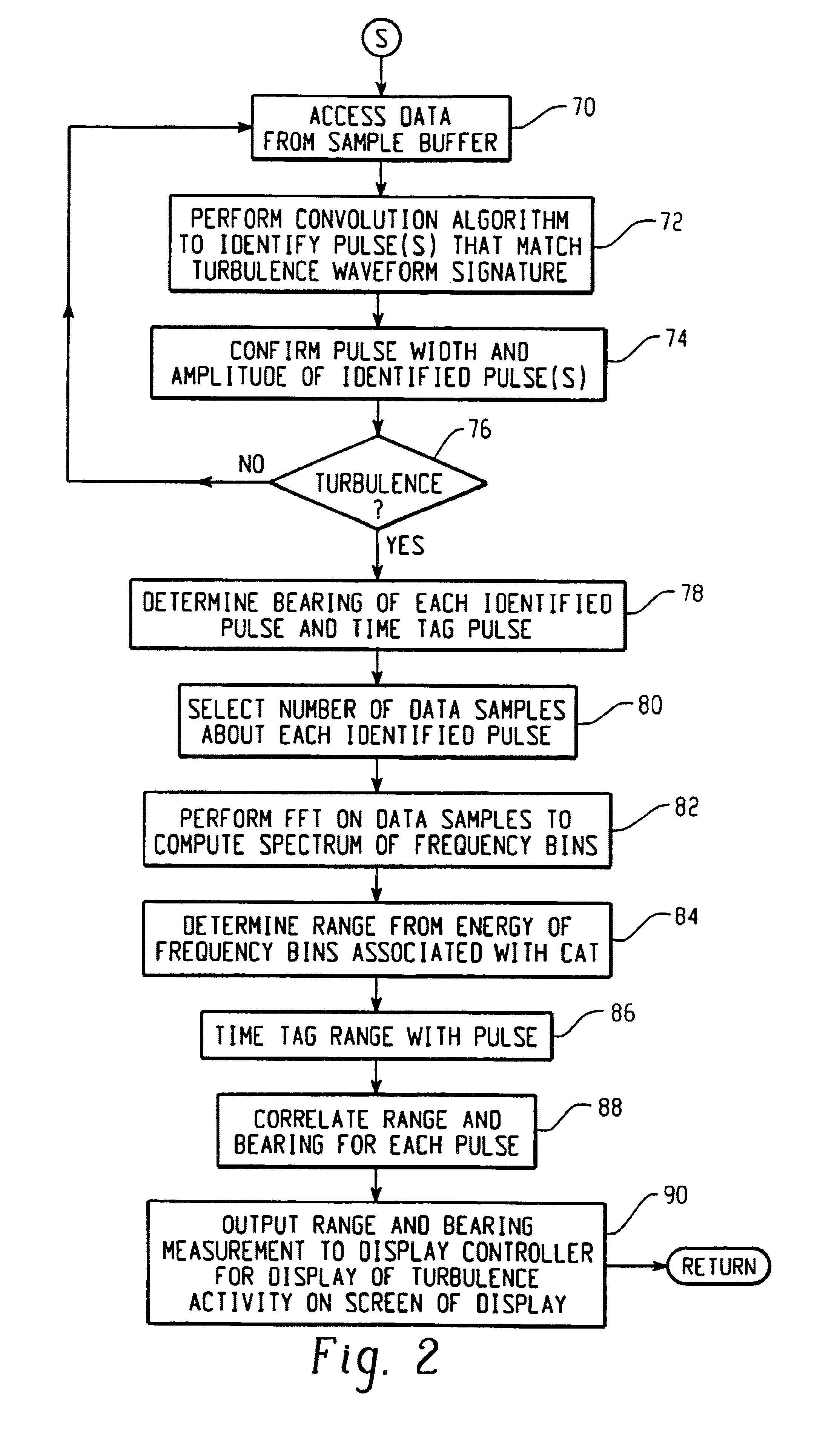
Passive clear air turbulence detection avionics system and method
InactiveUS6856908B2Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingSpecial data processing applicationsAviationOn board
A passive clear turbulence (CAT) detection system for use on-board an aircraft comprises: an antenna for receiving electromagnetic radiation and for generating electrical signals representative thereof; and a processor for processing the electrical signals with at least one CAT waveform signature to detect CAT activity in relation to the aircraft. Also disclosed is a method of detecting clear air turbulence (CAT) from an aircraft, the method comprising the steps of: receiving electromagnetic radiation and generating electrical signals representative thereof; and processing the electrical signals with at least one CAT waveform signature to detect CAT activity in relation to the aircraft.
Owner:L3 AVIATION PROD INC
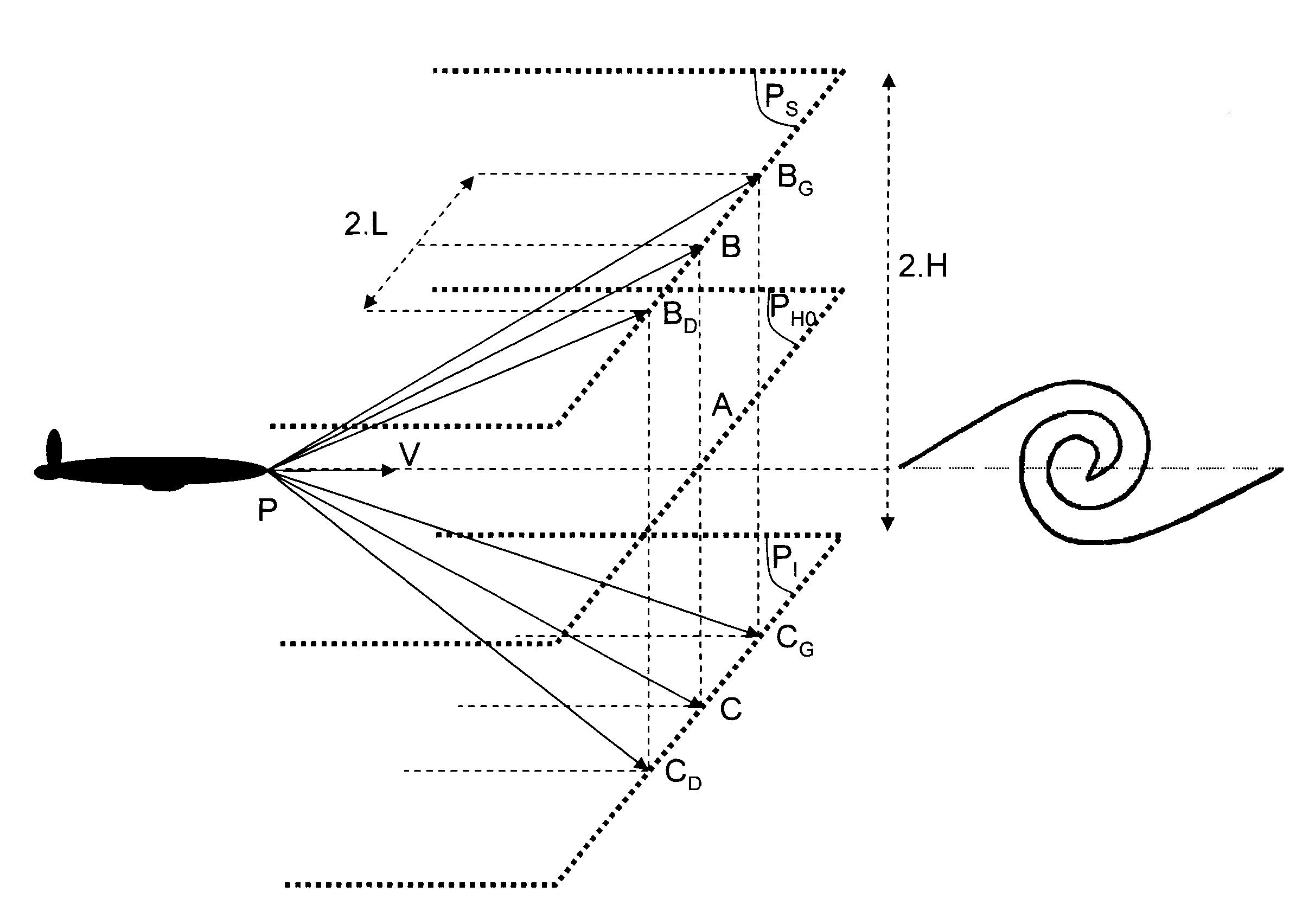
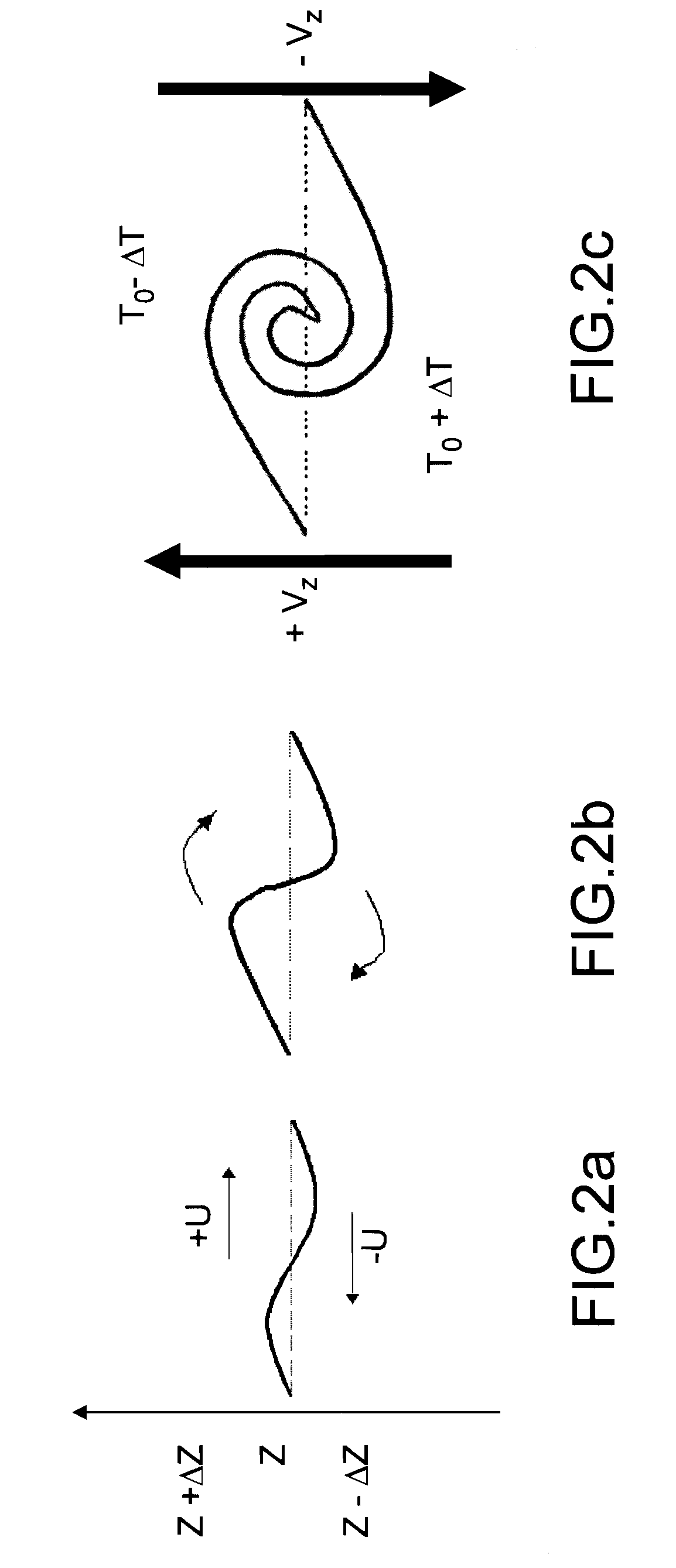
Method and device for protecting an aircraft against clear air turbulence
InactiveUS7581441B2Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingVolume measurement and fluid deliveryAir temperatureAirplane
The invention relates to a method of protecting aircraft in flight against clear air turbulence (CAT). Consider an aircraft occupying a position P and moving horizontally at a speed V, a plane PH0 being the horizontal plane passing through P. According to the invention, the method includes performing at least one pair of evaluations of air temperature TB, TC at two points B, C which have positions that are symmetrical relative to the plane PH0. At least one pair of horizontal air speed evaluations are performed VHB, VHC at the two points B, C; An air temperature gradient is determined; A horizontal air speed gradient is determined; An index signifying a presence of CAT is determined; The preceding steps are repeated; A trend is analyzed over time of the index.
Owner:THALES SA
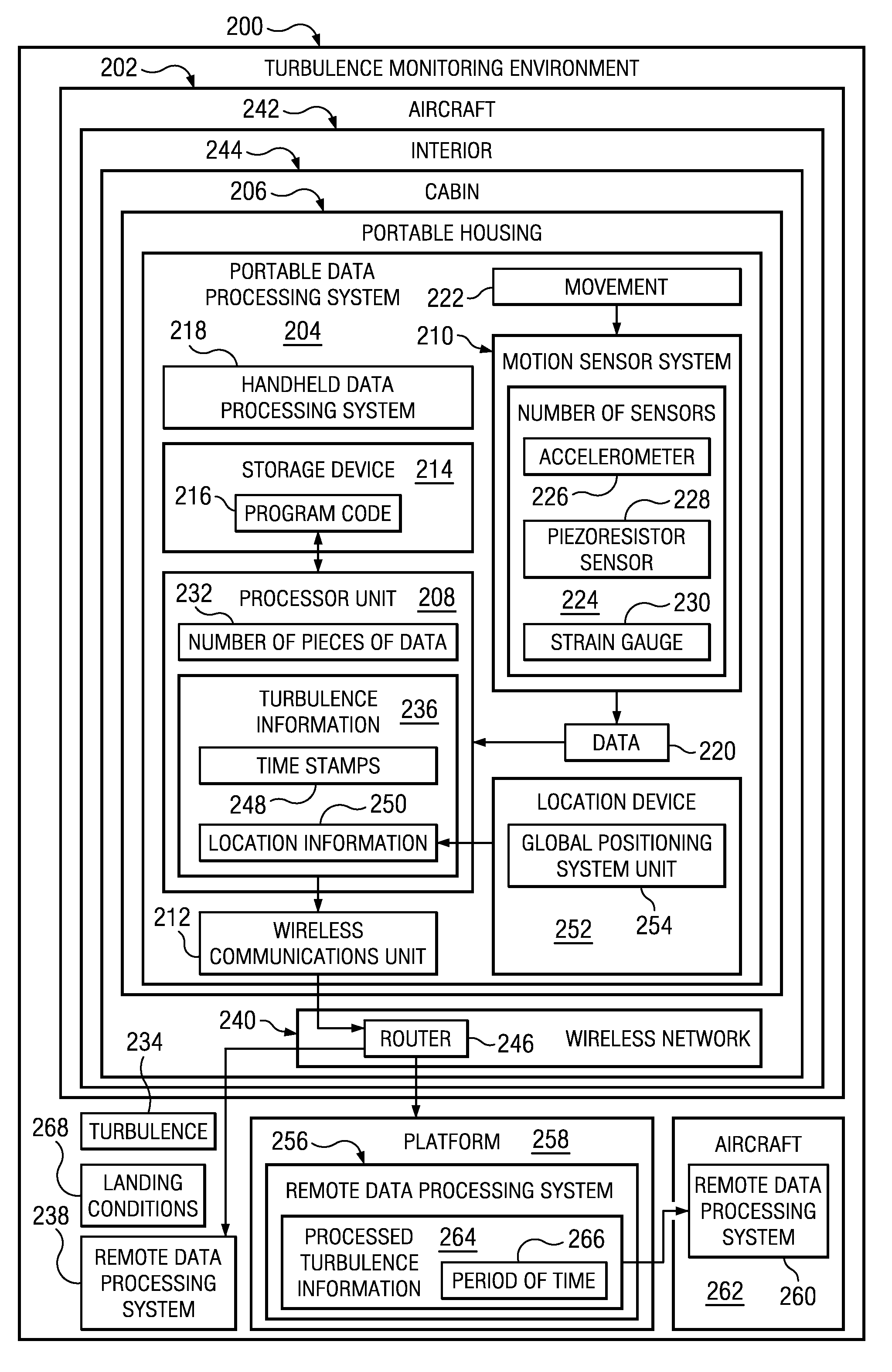
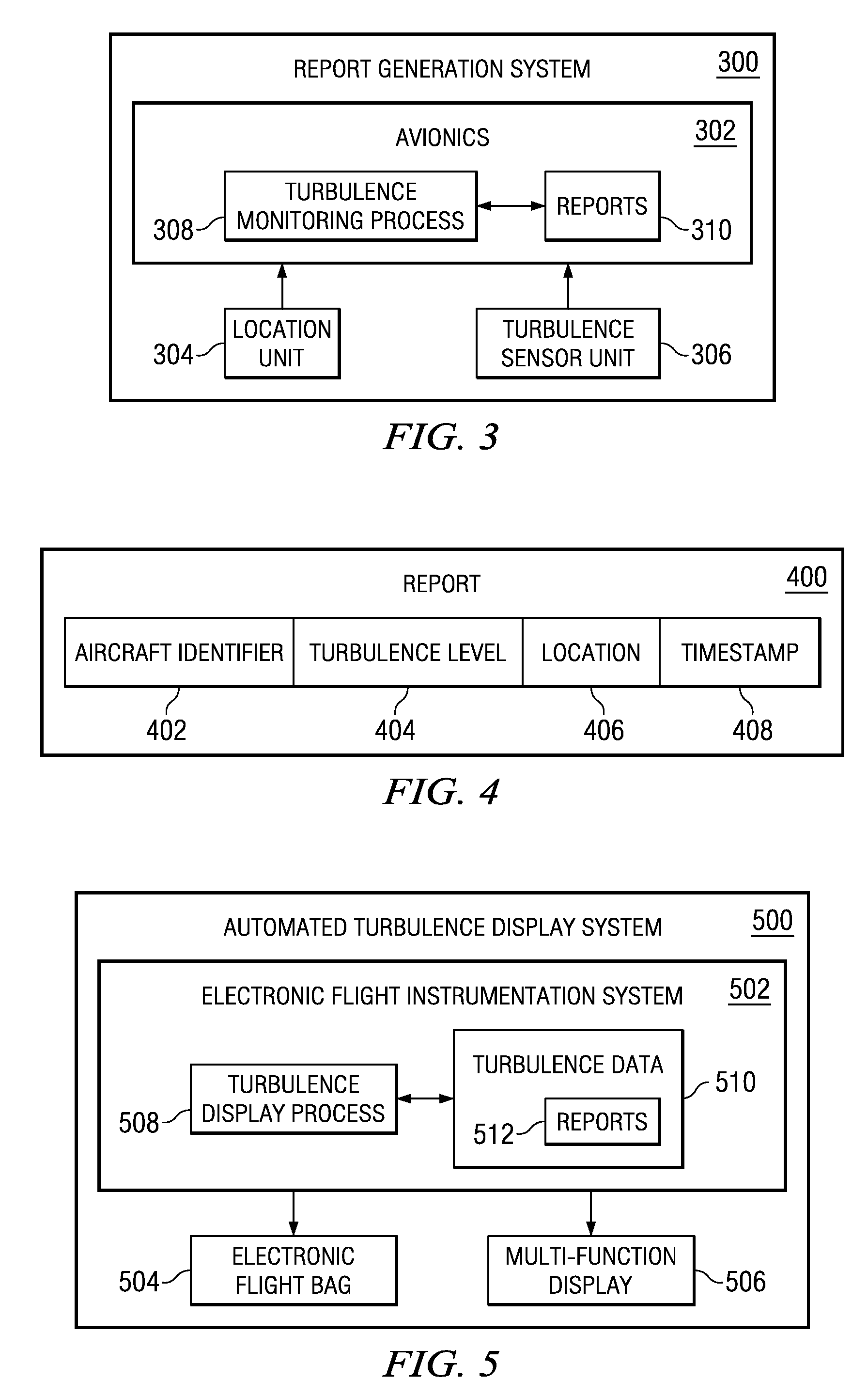
Dynamically Monitoring Airborne Turbulence
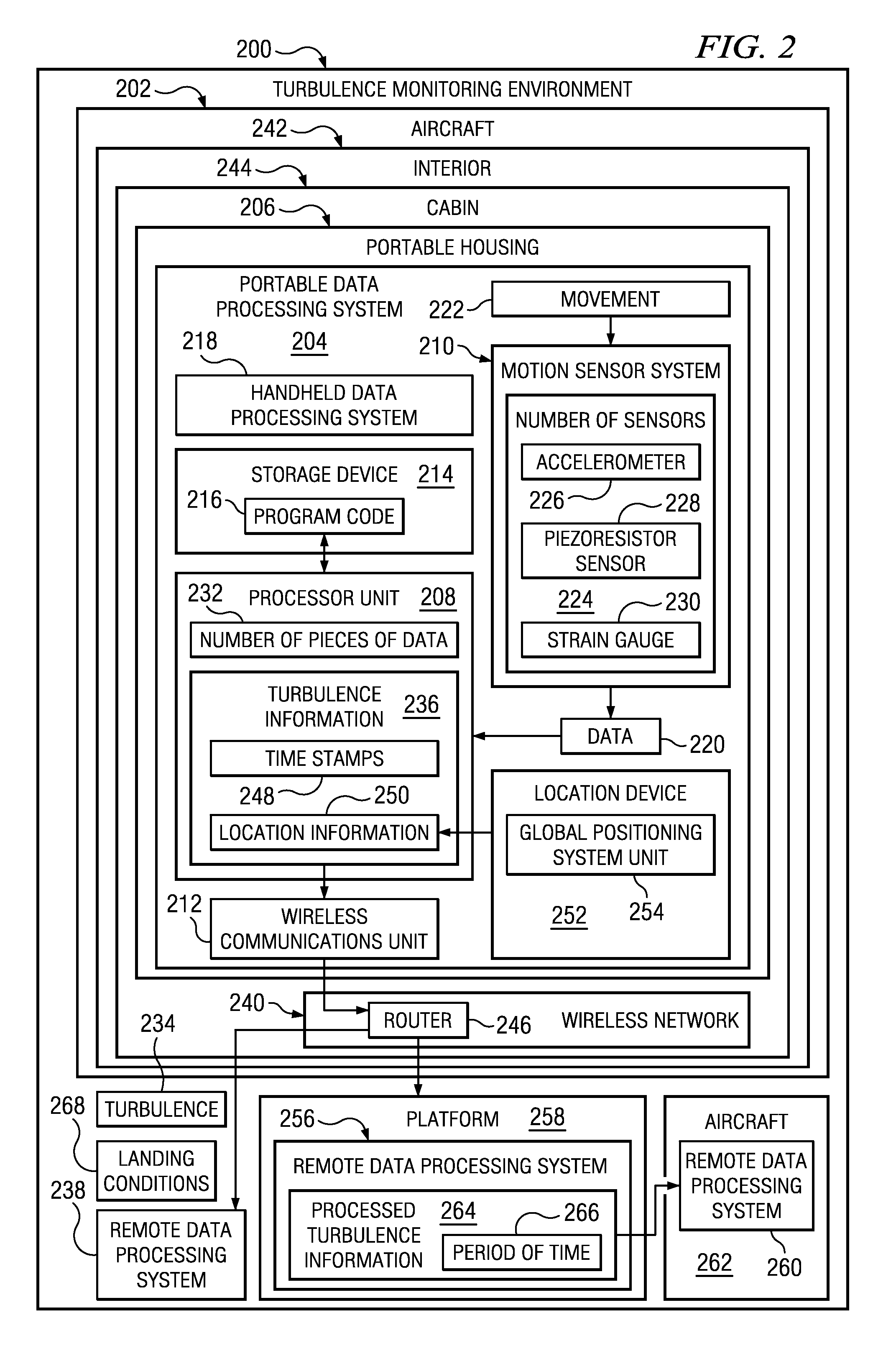
InactiveUS20110257818A1Analogue computers for trafficClear air turbulence detection/forecastingData processing systemMotion sensors
A method for monitoring for turbulence. Data is received from a motion sensor system in a portable data processing system in an aircraft while the aircraft is in operation. The portable data processing system is configured to be moved by a single person. A number of pieces of data is identified in the data received from the motion sensor system in which the number of pieces of data indicates a presence of turbulence encountered. Turbulence information is generated using the number of pieces of data. The turbulence information identified is sent to a remote data processing system outside of the aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Remote Wind Turbulence Sensing
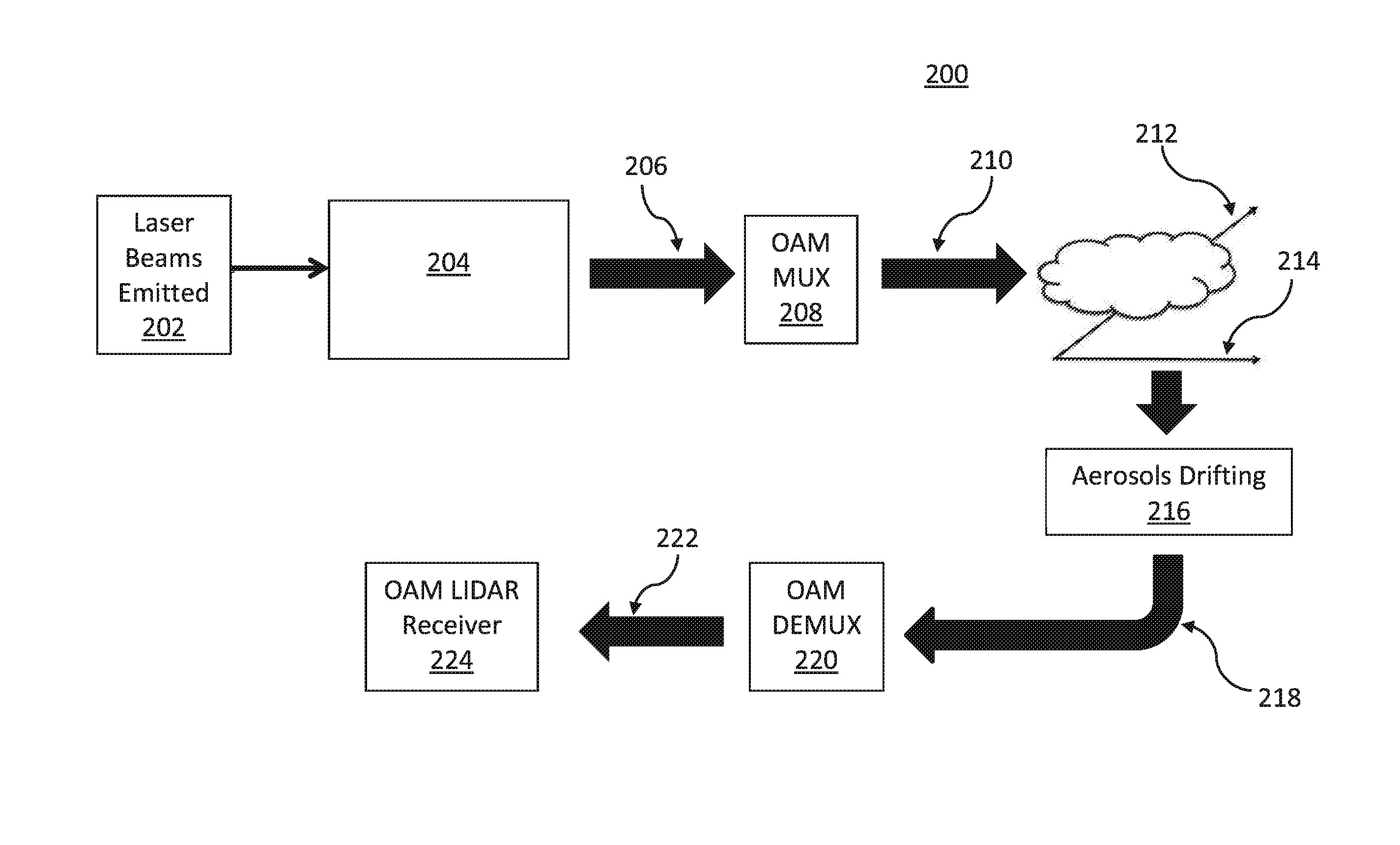
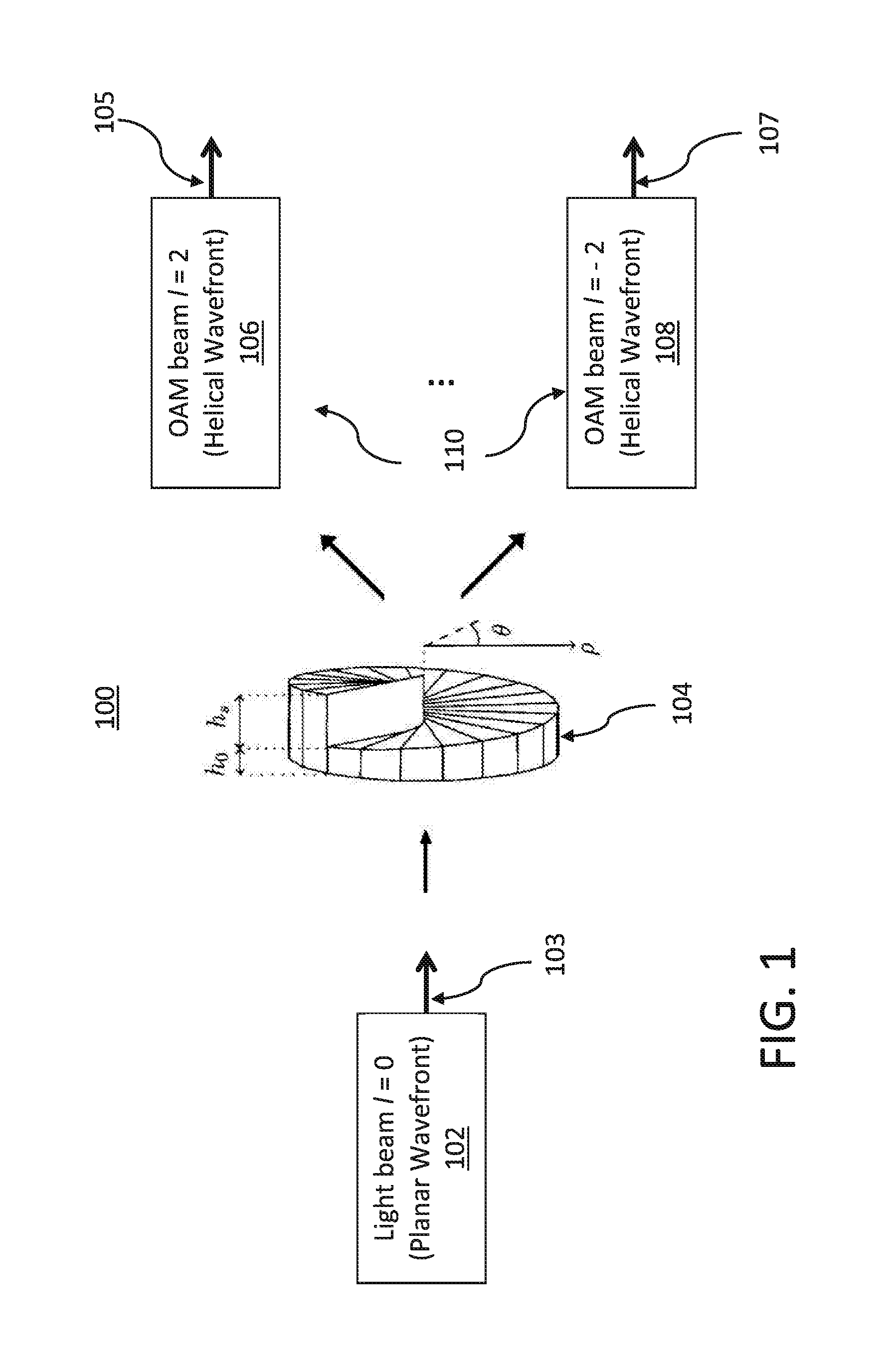
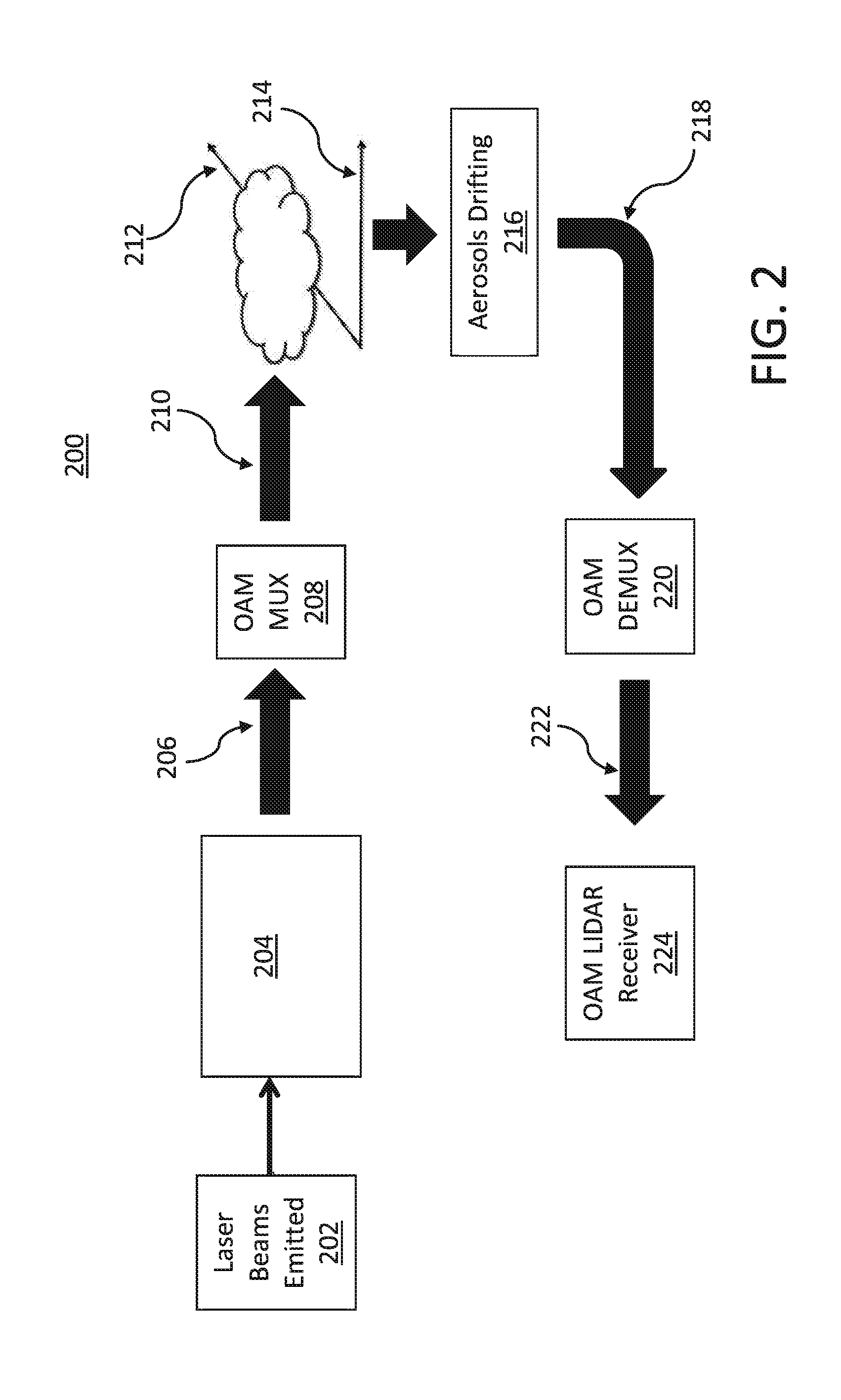
ActiveUS20160202283A1Weather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingLight beamAngular momentum
Systems and methods for detection of atmospheric conditions using optical orbital angular momentum (OAM)-based spectroscopy include applying OAM states to a light beam to generate an OAM spectrum, transmitting OAM light beams into an atmosphere, and determining degradation of the generated OAM light beams passing through atmospheric turbulence. A rotation rate of aerosols in the atmosphere is determined by analyzing different frequency shifts in OAM states of OAM light beams. A reflected OAM spectrum including a plurality of OAM light beams associated with the aerosols in the atmosphere may be received, and Doppler frequency shifts caused by reflection off the aerosols in the atmosphere may be measured. Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) modes of the received light beams may be detected and sorted based on the OAM states of the LG modes, and wind turbulence values are predicted by analyzing a difference in the Doppler frequency shifts for the received OAM light beams.
Owner:NEC CORP
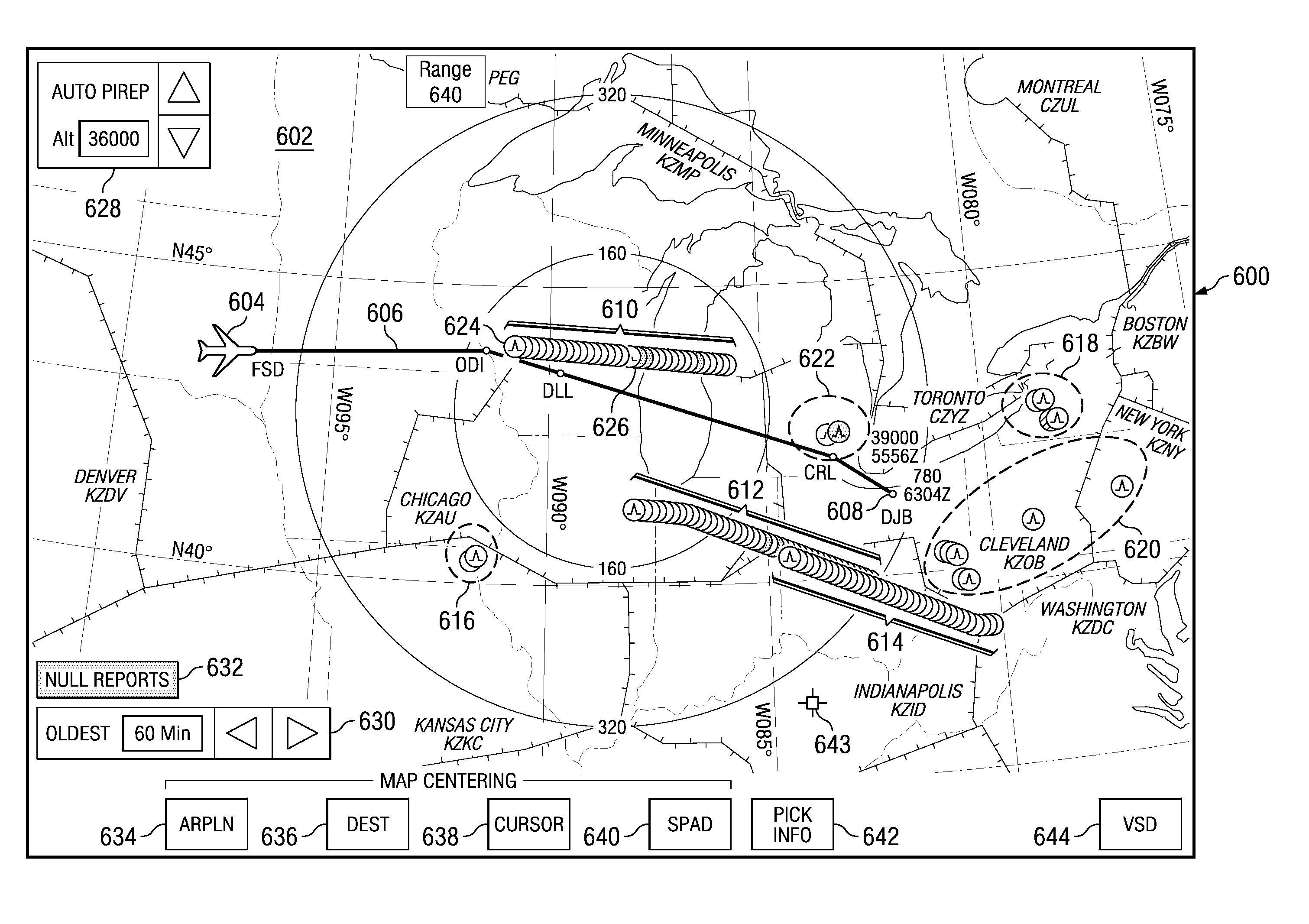
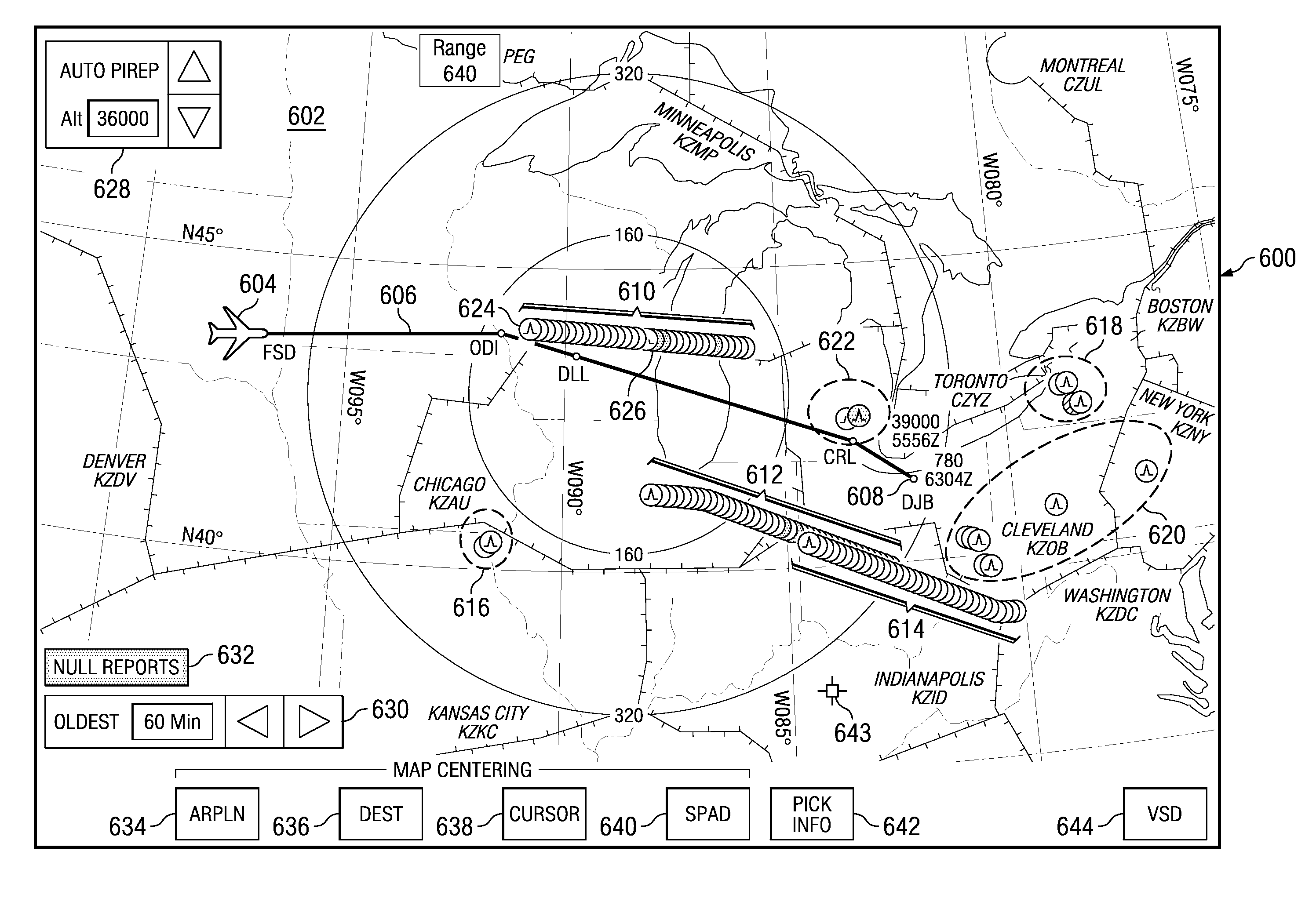
Automated turbulence display system
ActiveUS8130121B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDisplay deviceComputer science
A method identifies turbulence information from turbulence data generated by a set of remote aircraft based on a request to form identified turbulence information. The turbulence information is identified in response to the request received at an aircraft to view the turbulence information. The identified turbulence information is displayed on a display device in the aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Turbulence detection and monitoring
ActiveUS20160133137A1Navigational calculation instrumentsClear air turbulence detection/forecastingData processing systemMonitoring system
A turbulence detection and monitoring system may include a data processing system configured to collect and analyze motion-related sensor data from a plurality of personal electronic devices onboard an aircraft in flight. The personal electronic devices may communicate with the data processing system at least in part via an onboard wireless network.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
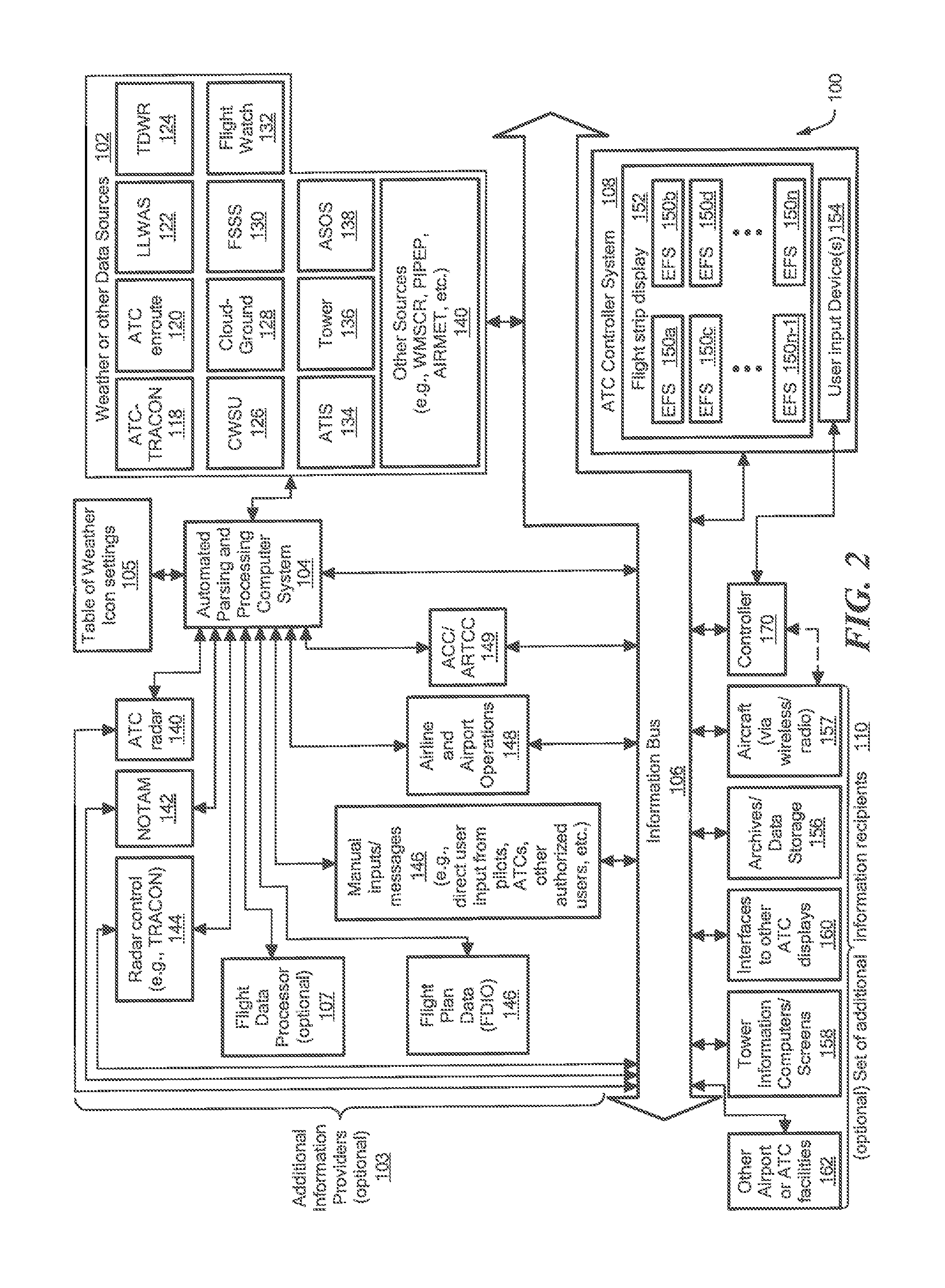
Adding weather icon to electronic flight strips
ActiveUS8874288B1Improve performanceImprove securityAnalogue computers for trafficClear air turbulence detection/forecastingDisplay deviceComputerized system
A method is provided, for displaying dynamically updated weather information for a vehicle using a computer system comprising a processor and a memory. A table is stored in the memory, the table defining, for a predetermined plurality of different weather conditions, a corresponding predetermined plurality of sets of visually distinguishable icon settings, wherein each weather condition corresponds to a corresponding respective set of icon settings, the respective set of icon settings defining the appearance of a first weather icon configured to appear on a display in operable communication with the processor, wherein the appearance of the weather icon, by itself, is sufficient to convey at least one weather condition. The appearance of the first icon is dynamically updated, during at least a portion of the travel by the vehicle along its travel path, to correspond to changes in the first set of weather data.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Automated turbulence display system
ActiveUS20100315265A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDisplay deviceComputer science
A method identifies turbulence information from turbulence data generated by a set of remote aircraft based on a request to form identified turbulence information. The turbulence information is identified in response to the request received at an aircraft to view the turbulence information. The identified turbulence information is displayed on a display device in the aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Measurement of air characteristics in the lower atmosphere
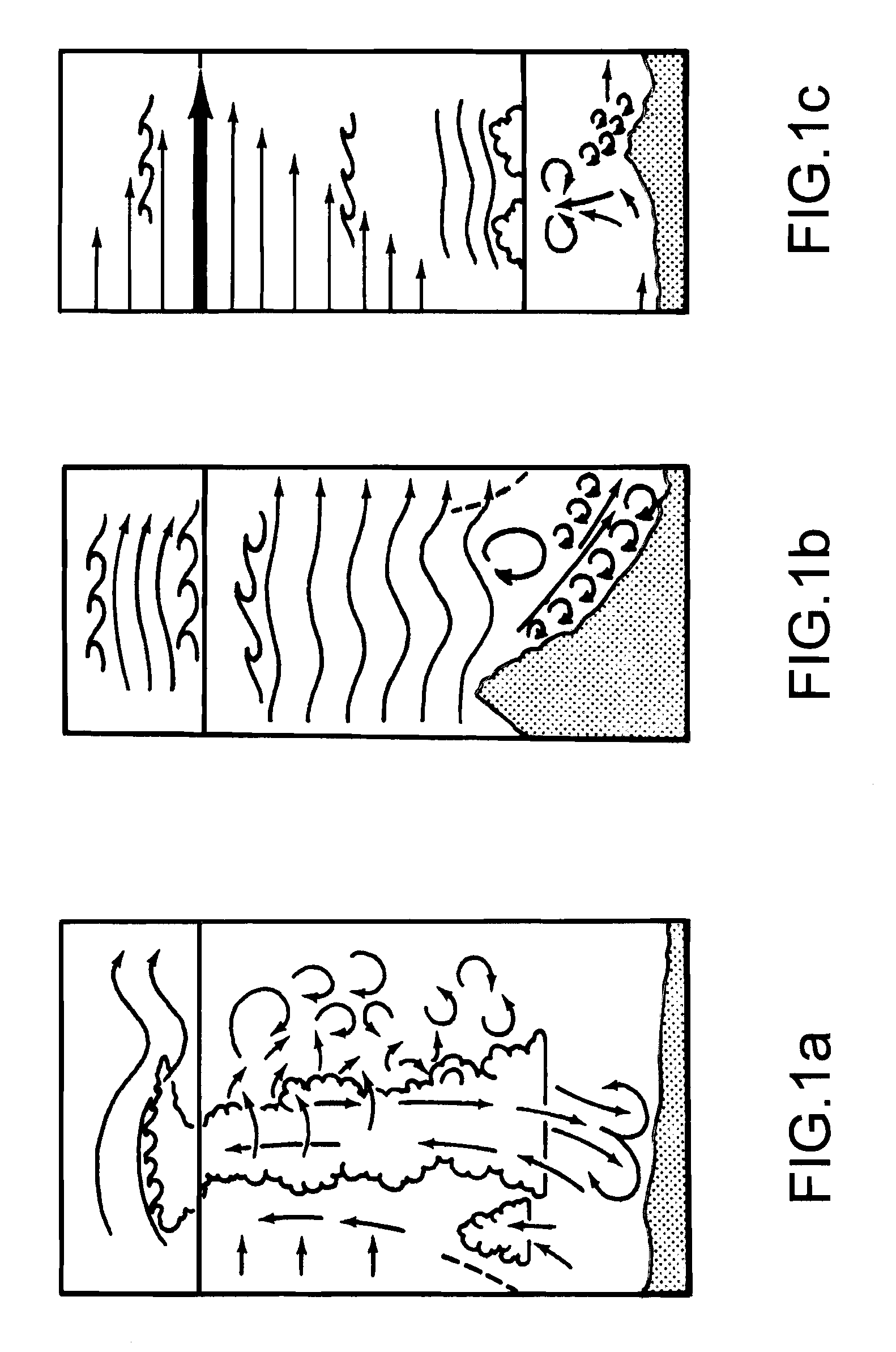
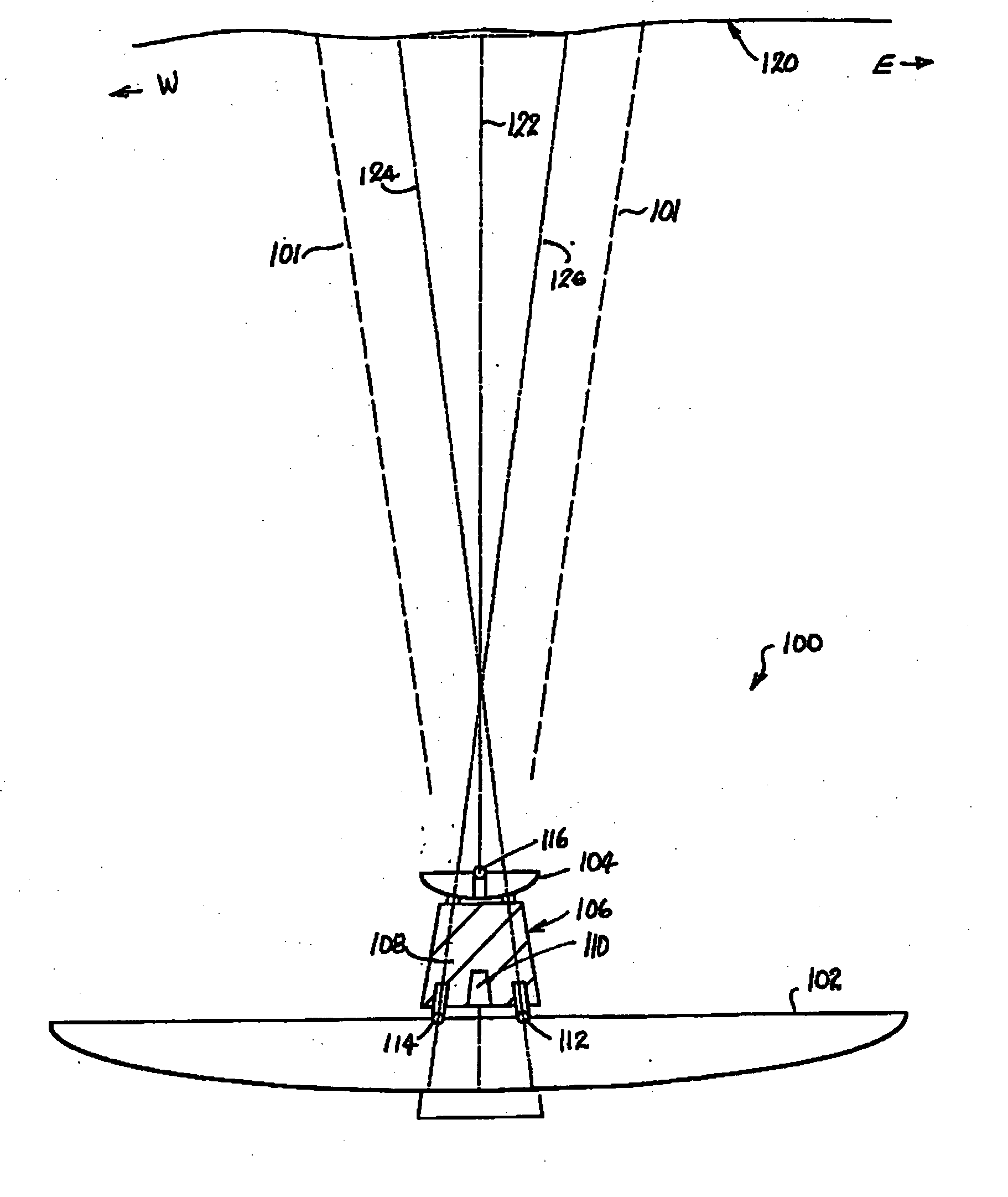
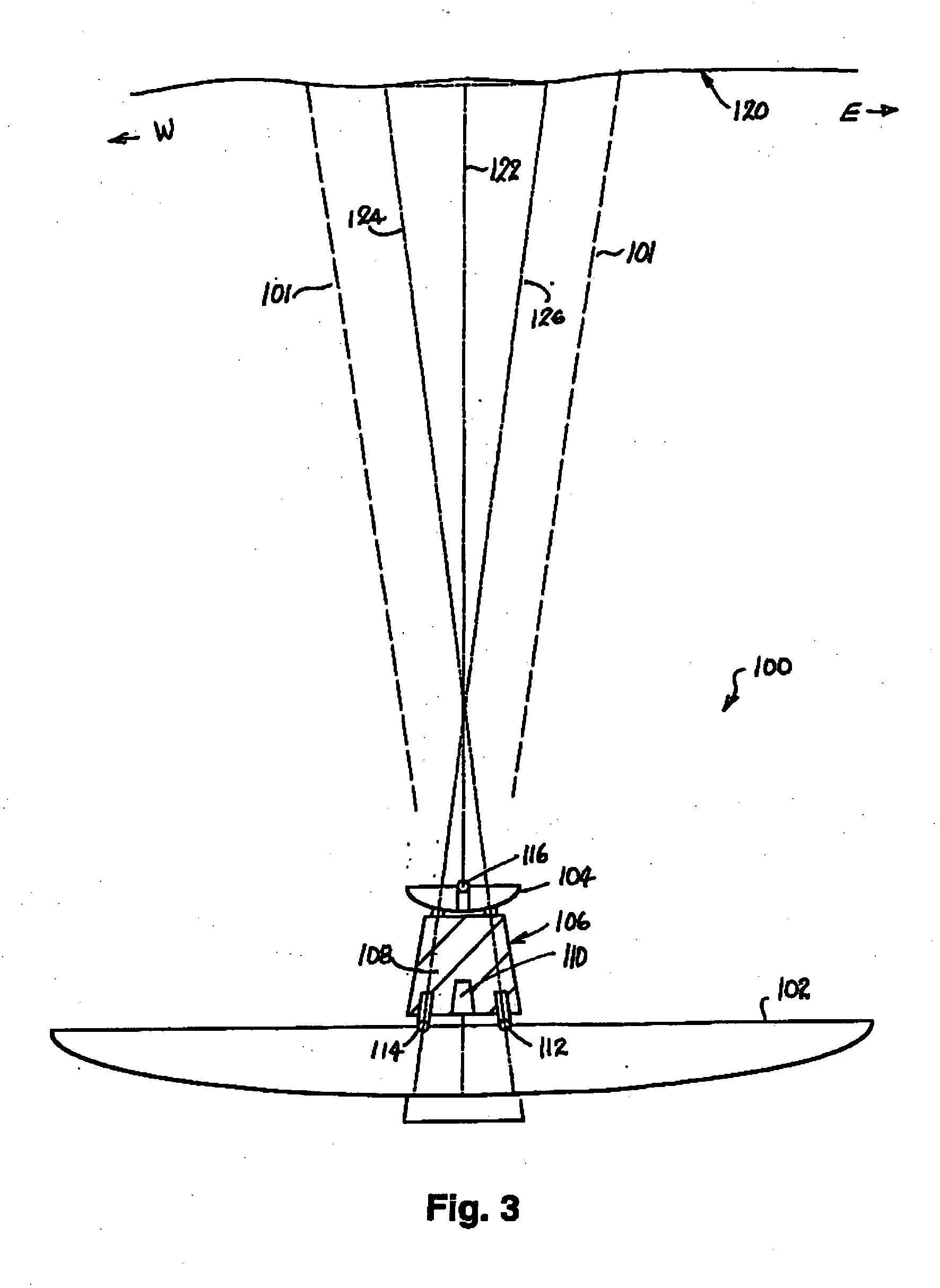
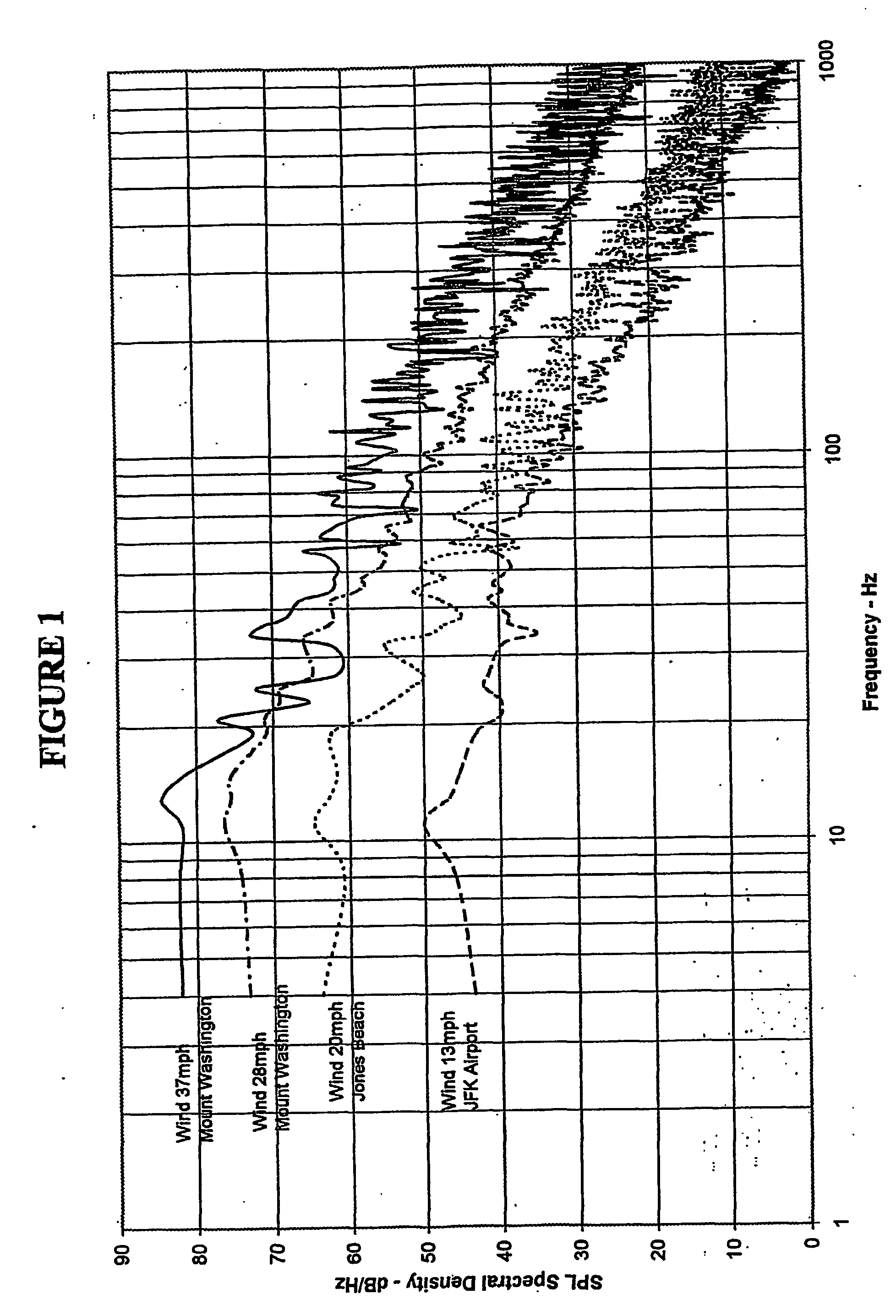
InactiveUS20040252586A1Control lengthAvoid the needAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesClear air turbulence detection/forecastingAtmospheric airDifferential signaling
Sodar systems and methods for acoustically sounding air are disclosed in which chirps longer than 300 ms-and preferably with durations of tens of seconds-are used along with matched filter and / or Fourier processing methods to derive phase signals indicative of air characteristics in range. A listen-while-transmit strategy is preferred, the direct signal being removed by subtracting the phase signals from two or more receivers located near the transmitter so as to be in the same noise environment. The resultant differential signals can be related to cross-range wind with range distance. In one example, apparatus (100) is employed comprising a reflector dish (102) over which one central loudspeaker (110) and four microphones (112, 114, 130 and 132) are mounted, the microphones preferably being located on cardinal compass points and having their axes (124, 126) slightly angled with respect to the vertical transmission axis (122).
Owner:TELE IP
Acoustic sounding
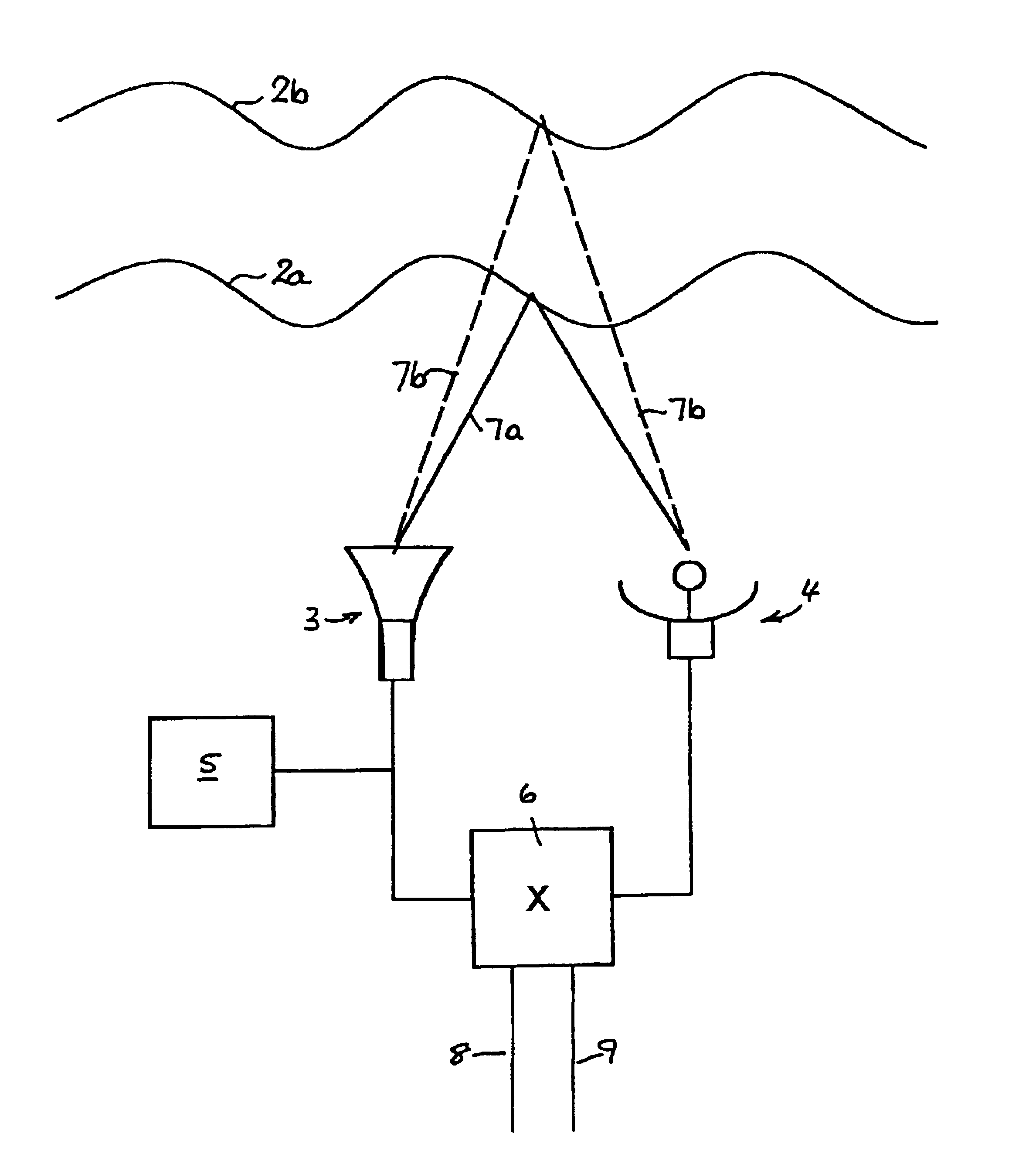
InactiveUS6755080B2Improve efficiencyReliable detectionVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhase shiftedMicrowave
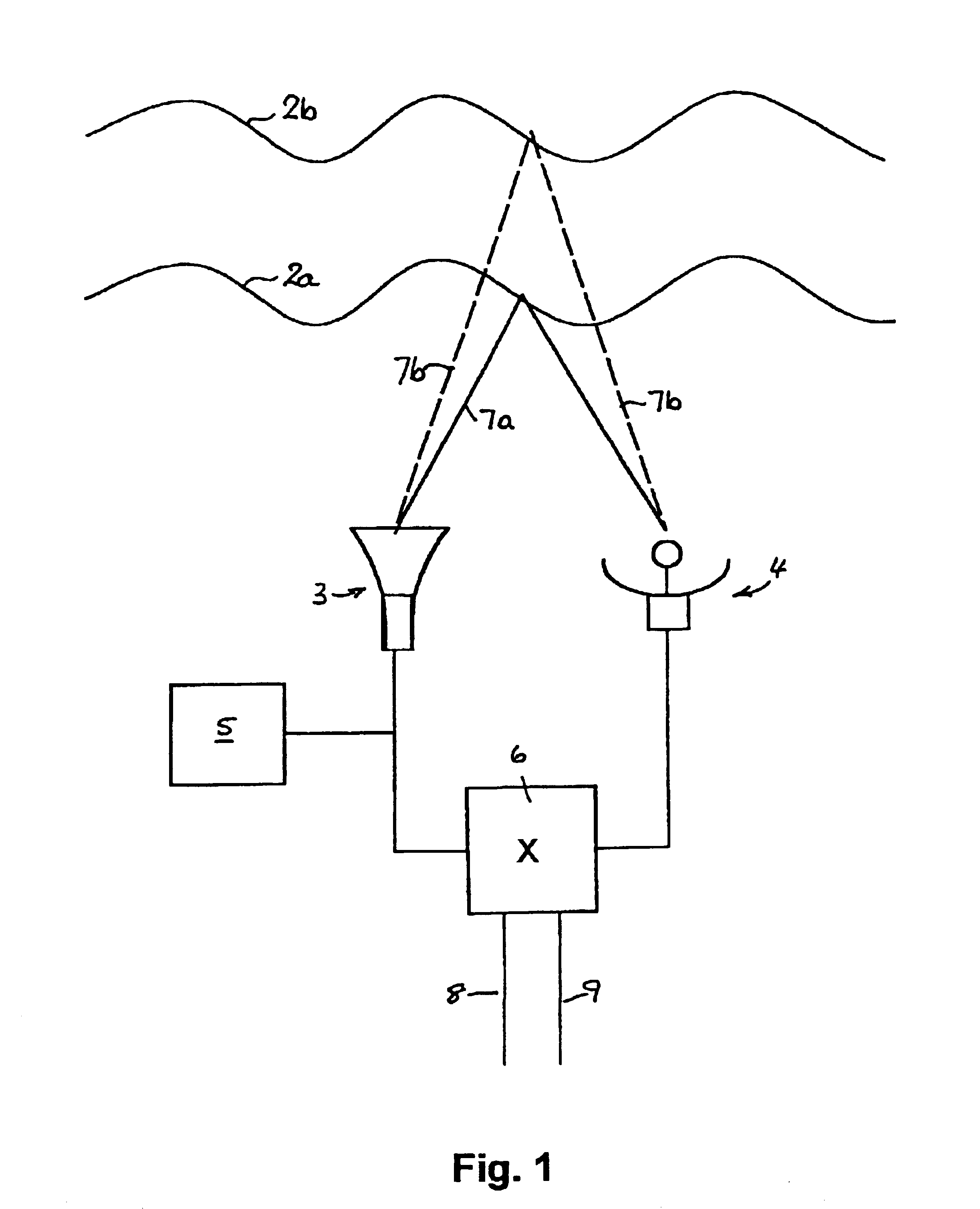
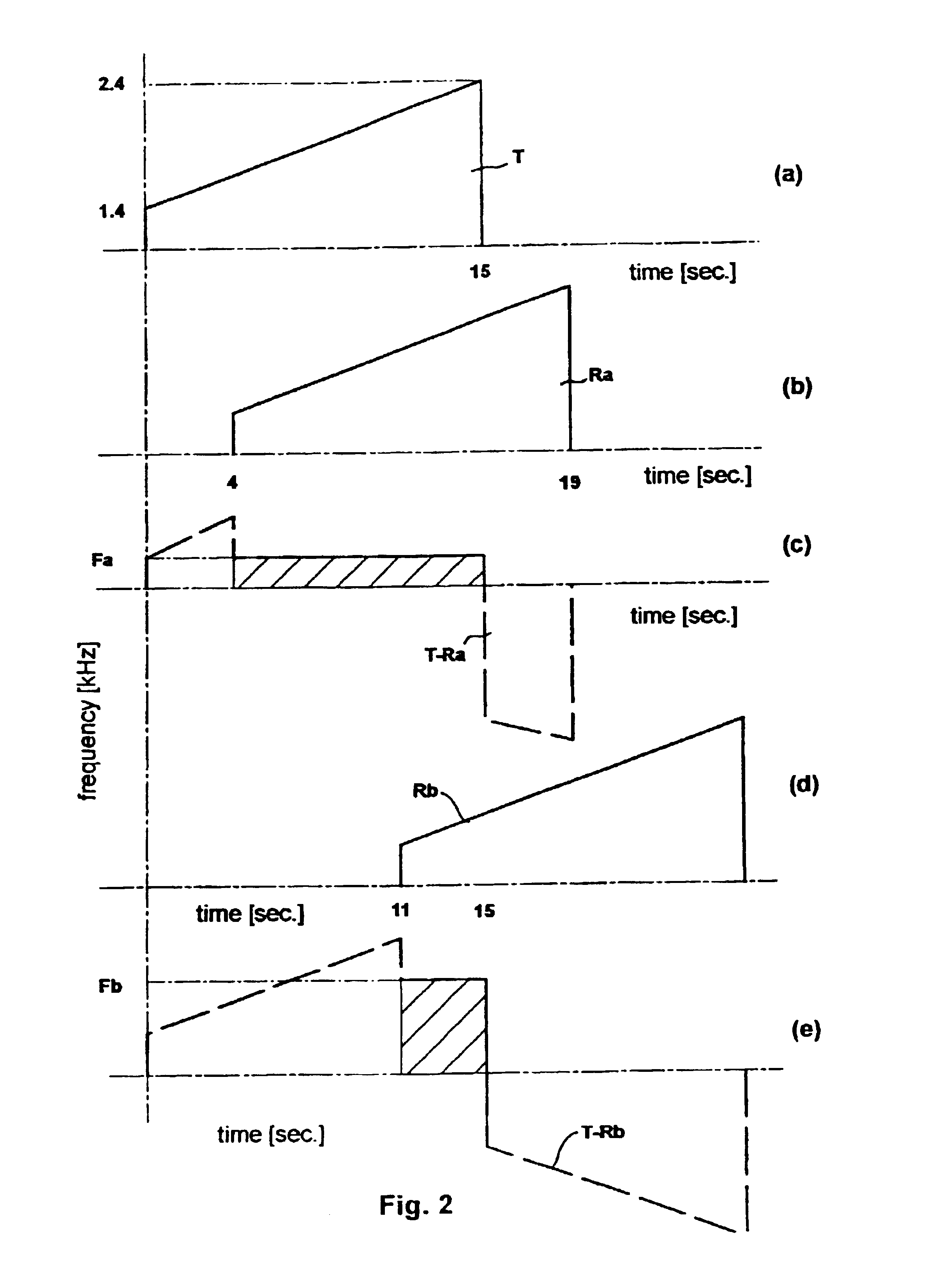
Methods and apparatus for atmospheric sounding using acoustic chirps are disclosed, the transmitted and echo chirps being compared in a mixer that yields frequency sums and differences. Preferably, the mixing is performed as a complex multiplication in the Fourier domain. In one system (1) a signal generator (5) such as a PC sound card drives a loudspeaker (3) that serves as a transmitter and echo pulses are detedcted by a microphone (4) that serves as a receiver. Chirps transmitted by the loudspeaker (3) travel by different paths (7a and 7b) due to reflection from TILS or thermal inversion layers (2a and 2b) at different altitudes. The transmitted and echo chirp signals are compared in a mixer (6) from which various outputs (8 and 9) can be generated. One output (8) might be the magnitude of the difference between the transmitted and echo chirp tones, instant by instant, which is indicative of the altitudes of the respective TILs. The other output (9) might be the phase shift in an echo tone with transit time, which is indicative of vertical wind velocity at different altitudes. Such sounding methods and apparatus are useful for weather research, prediction of plume dispersal and the design of microwave links to minimize multipath fading.
Owner:WINDBIDCO
Method of determining a turbulent condition in an aircraft
InactiveUS20140074326A1Analogue computers for trafficClear air turbulence detection/forecastingGyroscopeAccelerometer
A method of determining a turbulent condition in an aircraft with a handheld device where the handheld device has at least one of a gyroscope, seismometer, and an accelerometer where the method includes receiving an output from the at least one of the gyroscope, seismometer, and accelerometer while the handheld device is located within the aircraft and providing an indication of a turbulent condition.
Owner:GE AVIATION SYST LLC
Improved real-time weather forecasting for transportation systems
ActiveUS20190340940A1Reduce probabilityWeather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingVisibilityAtmospheric air
Improved mechanisms for collecting information from a diverse suite of sensors and systems, calculating the current precipitation, atmospheric water vapor, atmospheric liquid water content, or precipitable water and other atmospheric-based phenomena, for example presence and intensity of fog, based upon these sensor readings, predicting future precipitation and atmospheric-based phenomena, and estimating effects of the atmospheric-based phenomena on visibility, for example by calculating runway visible range (RVR) estimates and forecasts based on the atmospheric-based phenomena.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING SOLUTIONS INC
Atmospheric turbulence hazard detector
InactiveUS7394723B2Weather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingLocation detectionAtmospheric sciences
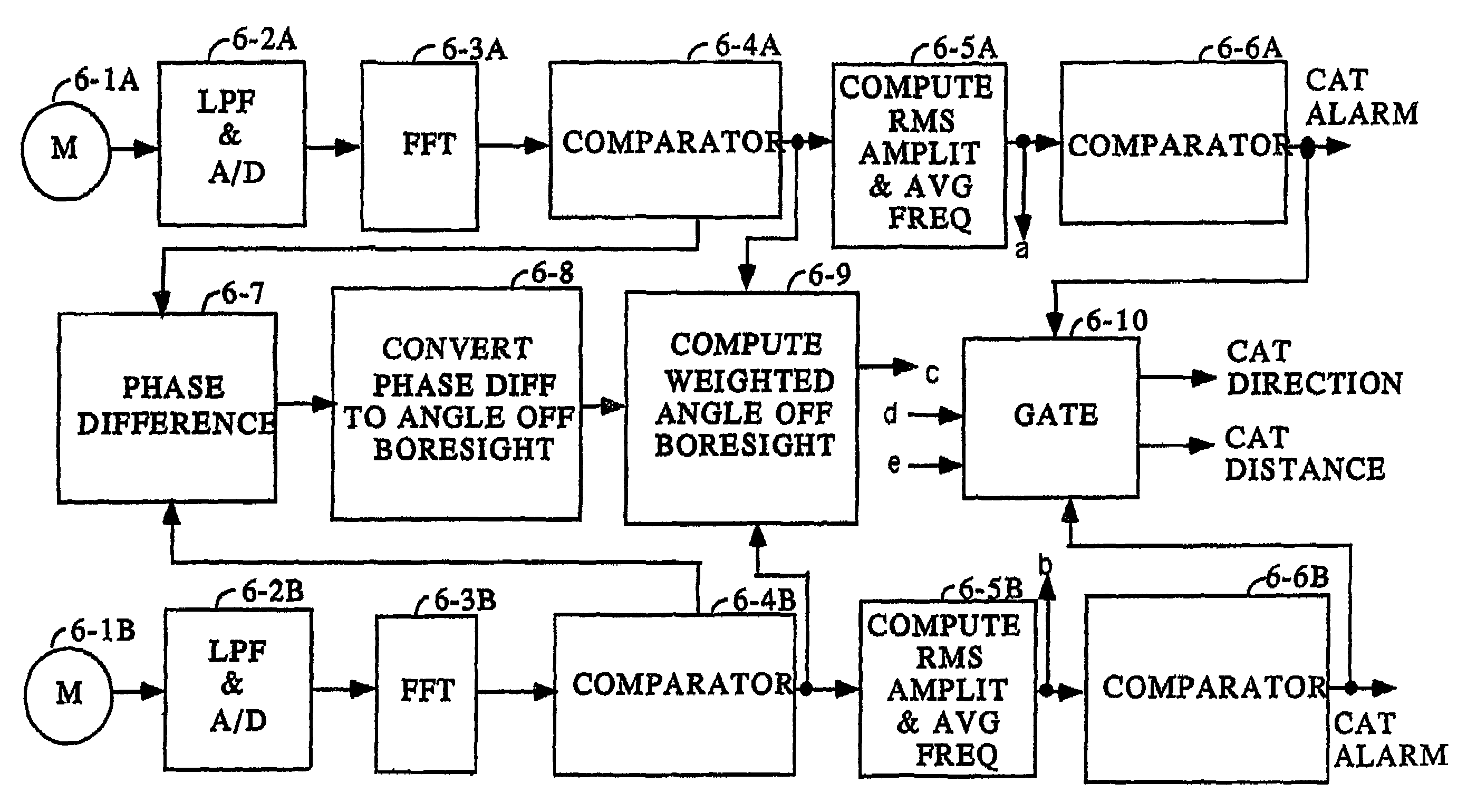
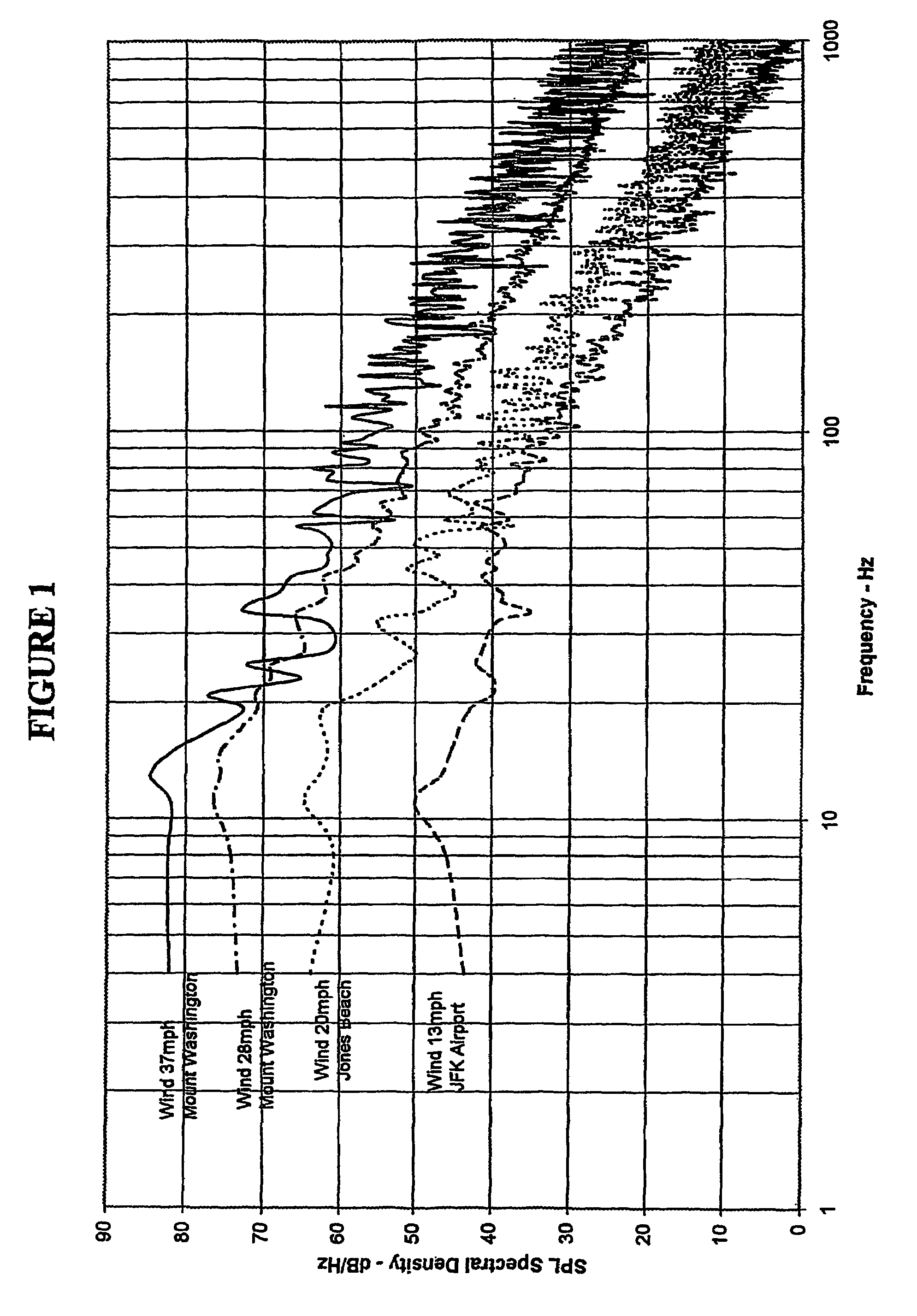
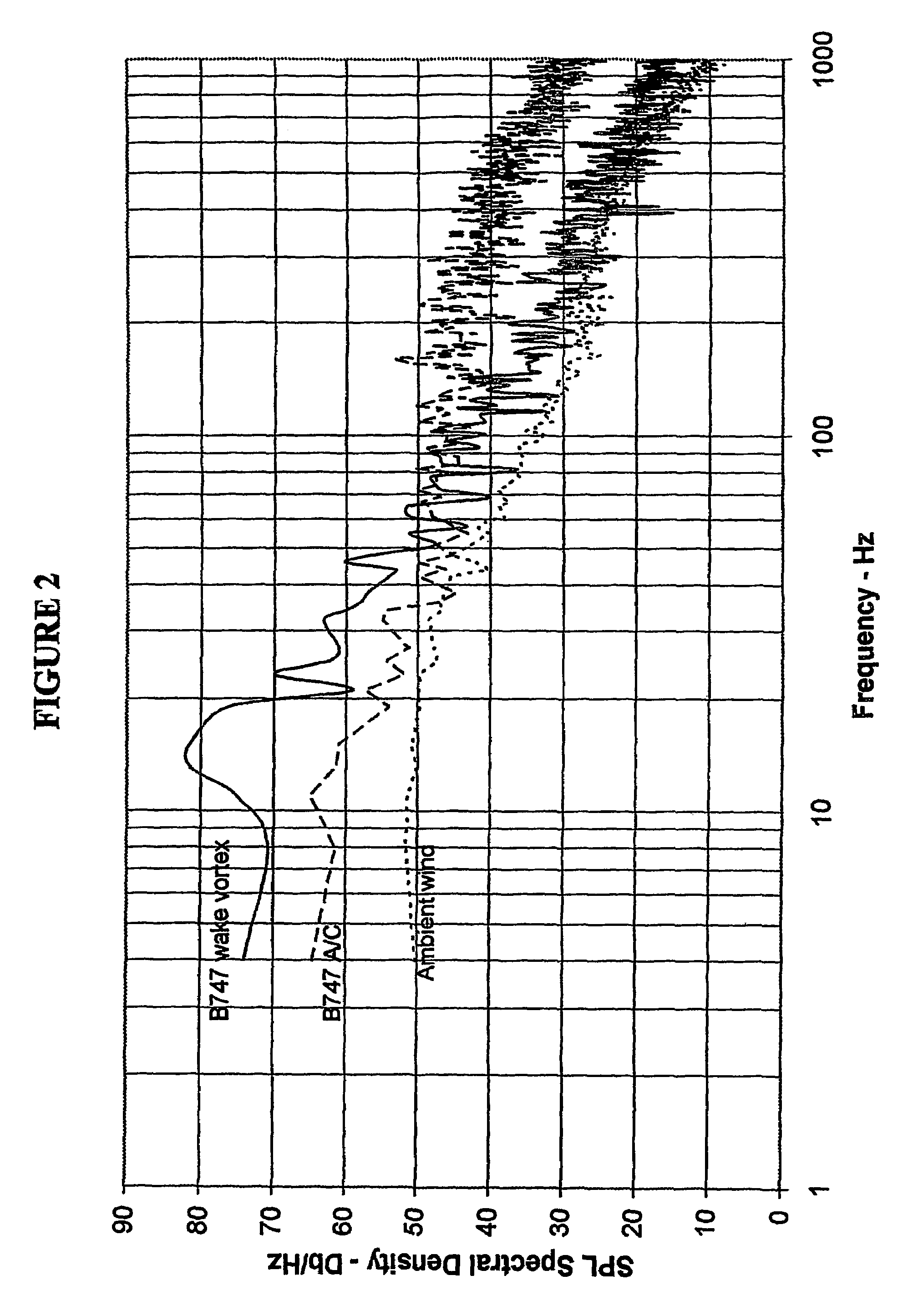
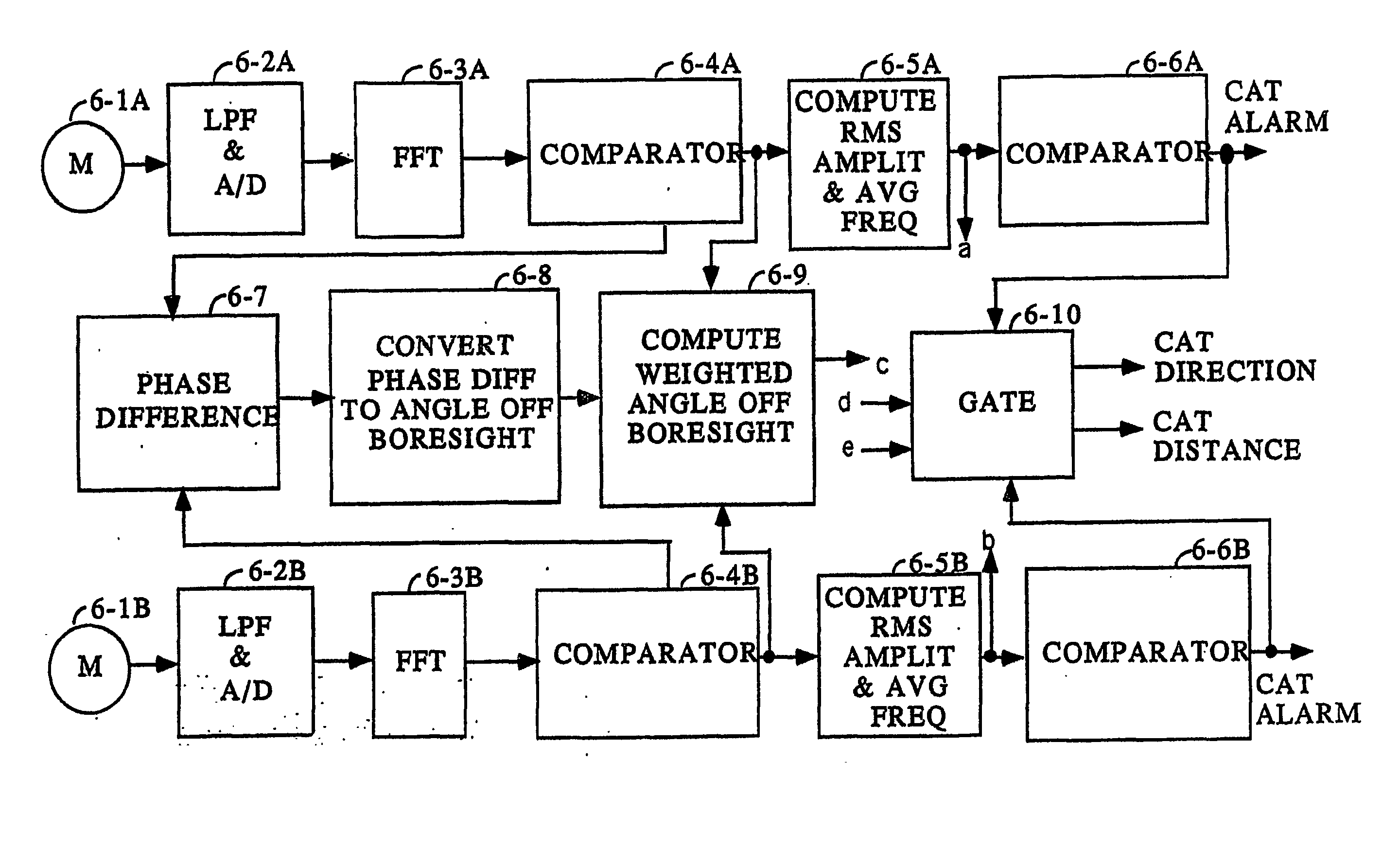
An Atmospheric Turbulence Detector utilizes a sensor to detect noise and extracts infrasound having frequencies below a specified infrasound frequency. A threshold is computed from the detection of infrasound in the vicinity of the sensor prior to the arrival of infrasound from the turbulence and an alarm is given when the infrasound from the turbulence are determined with the utilization of two sensors (6-1A, 6-1B), measuring amplitude differences of the infrasound detected at two seperate locations.
Owner:RUBIN WILLIAM L
Atmospheric turbulence hazard detector
InactiveUS20070104026A1Weather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingPhase differenceAtmospheric sciences
An Atmospheric Turbulence Detector utilizes a sensor to detect noise and extracts infrasound having frequencies below a specified infrasound frequency. A threshold is computed from the detection of infrasound in the vicinity of the sensor prior to the arrival of infrasound from the turbulence and an alarm is given when the infrasound from the turbulence exceeds the computed threshold. Range and direction of atmospheric turbulence are determined with the utilization of two sensors, measuring the phase difference between the detected infrasound of the two sensors, measuring amplitude differences of the infrasound detected at two separate locations.
Owner:RUBIN WILLIAM L
Real-time data pipeline techniques for improving a fast weather forecasting system
ActiveUS20190339416A1Weather condition predictionClear air turbulence detection/forecastingReal-time dataHigh rate
The system as described collects and utilizes weather data sensor information in order to rapidly collect and update weather forecasts using real-time weather data collected at high rates of frequency, and use this collected high frequency weather data to rapidly correct and update the weather forecasts generated by the system.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING SOLUTIONS INC
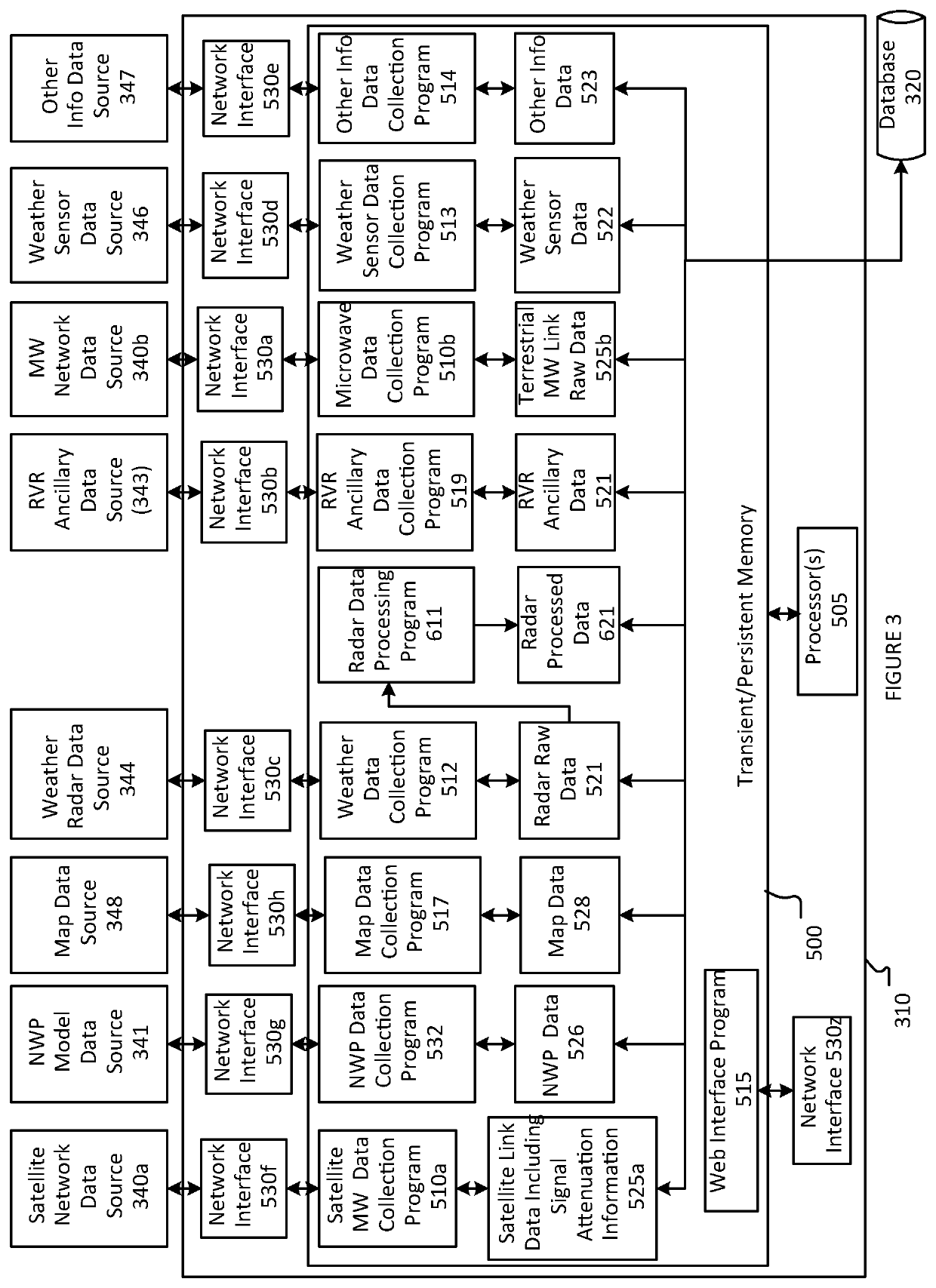
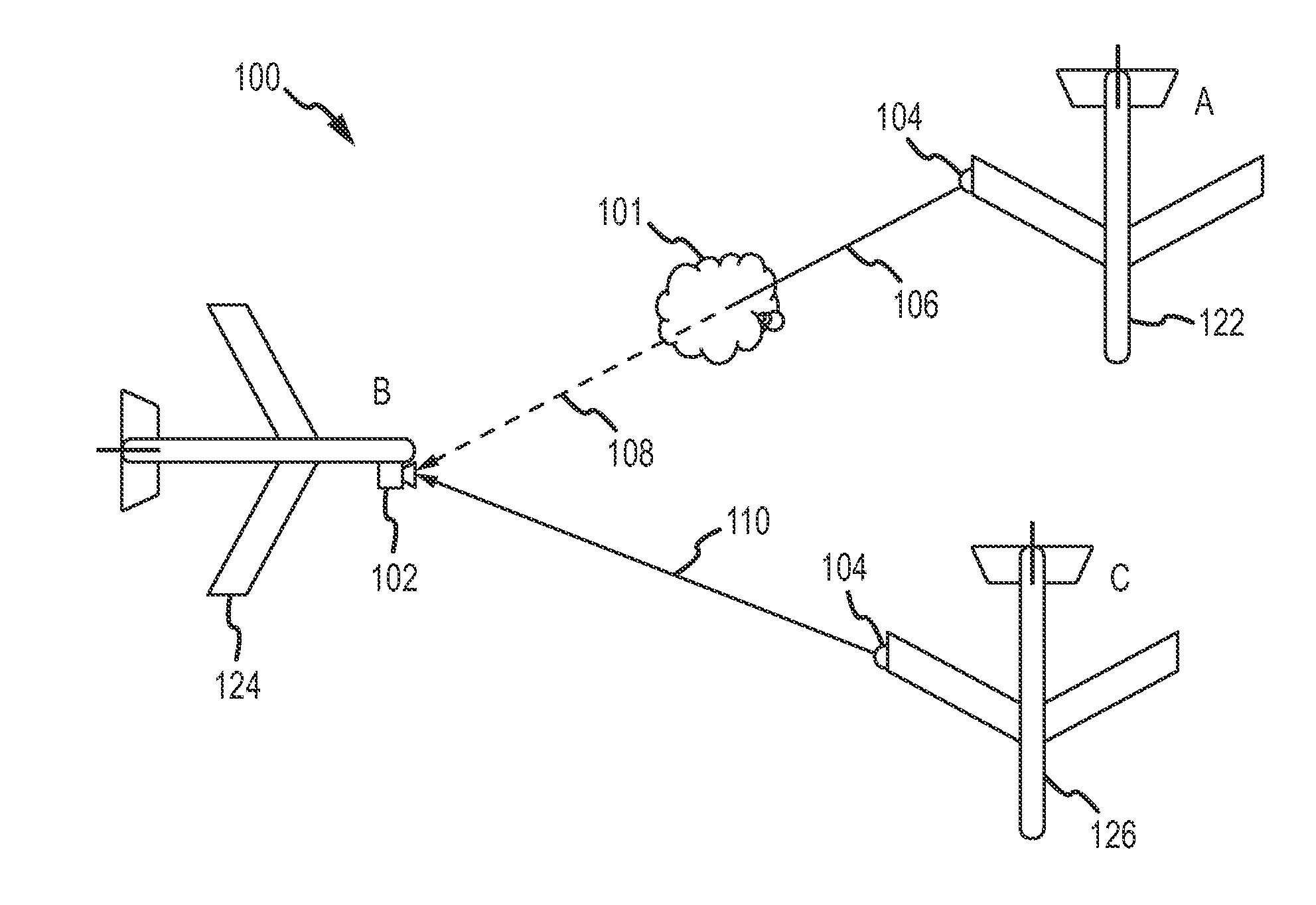
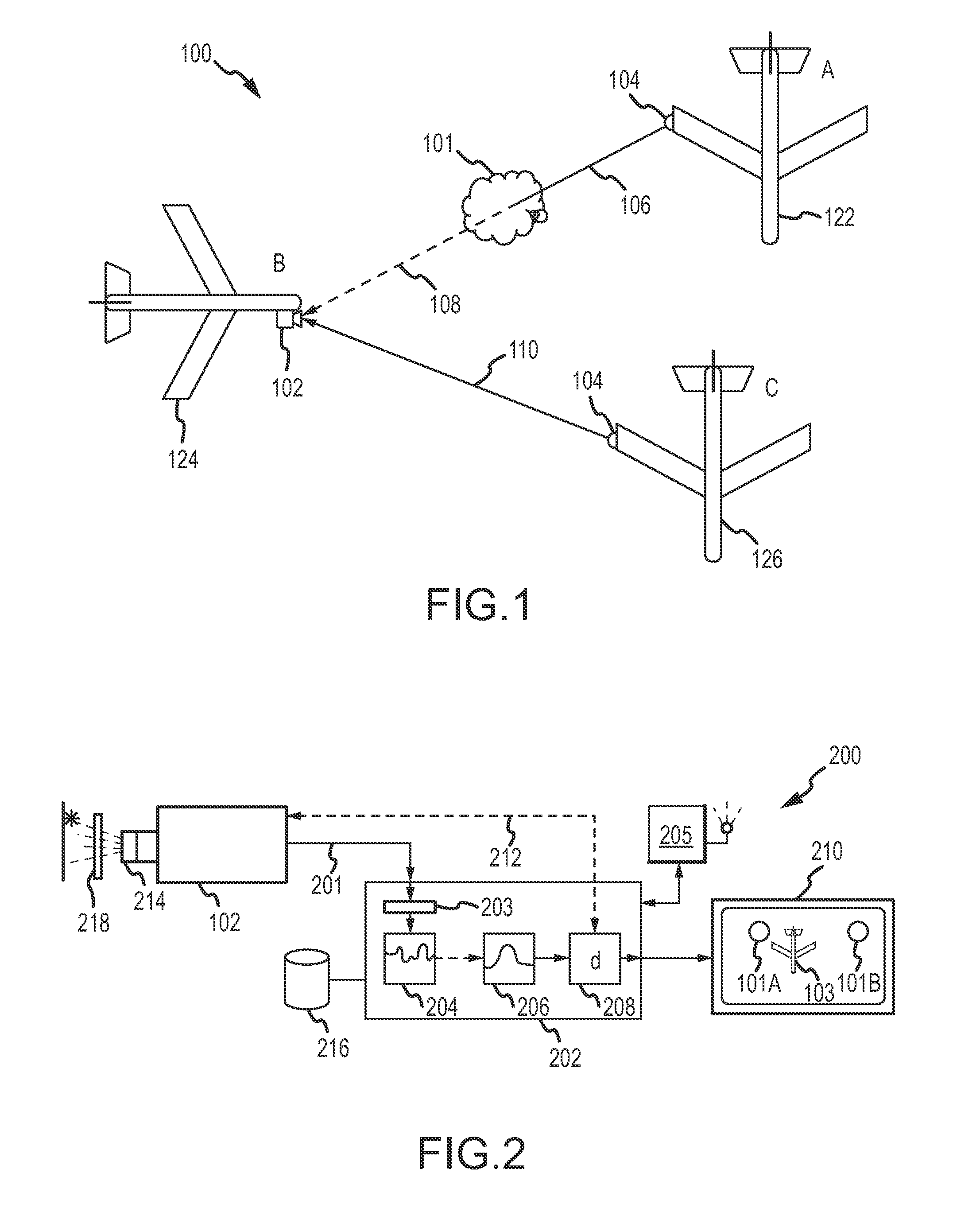
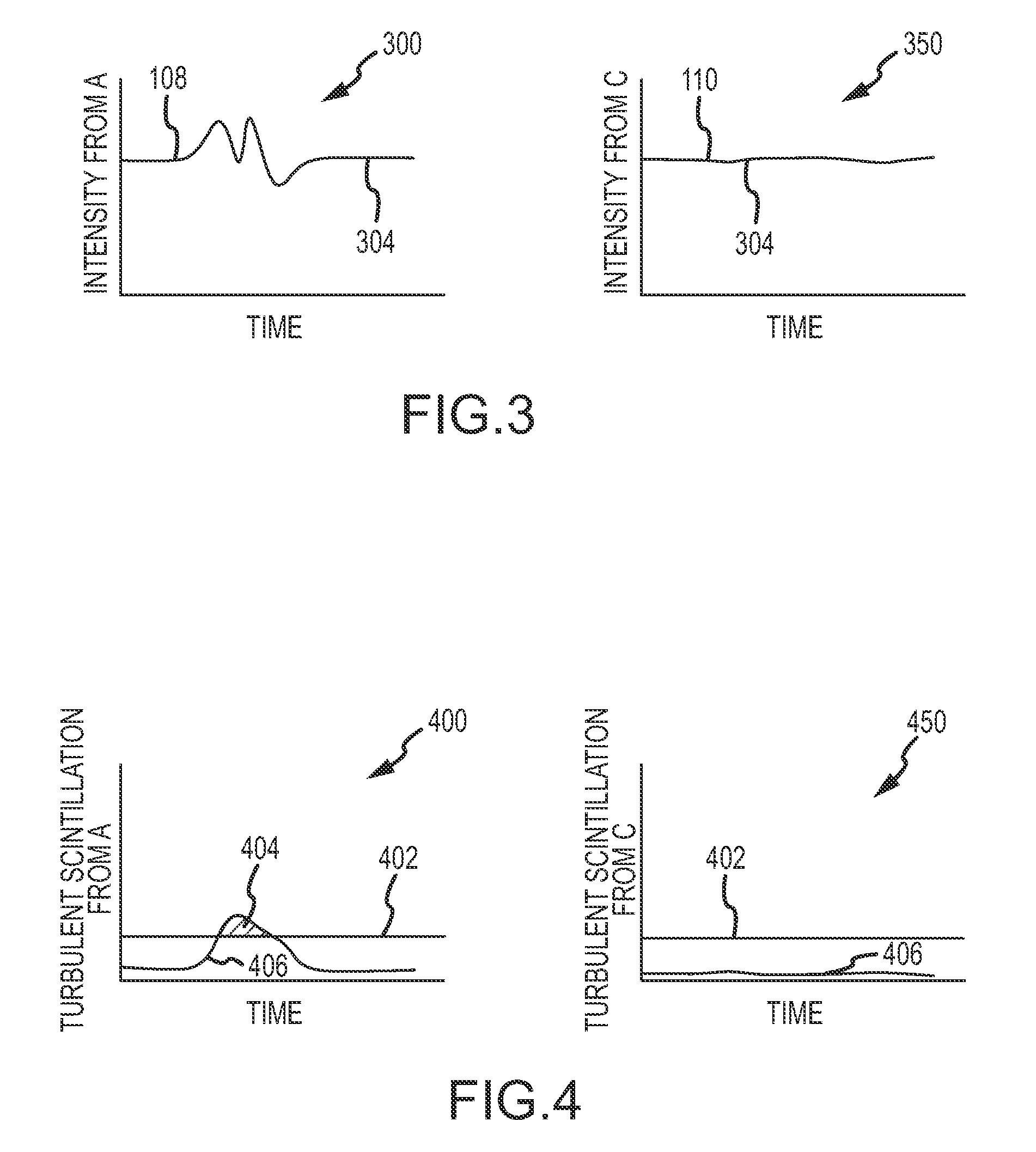
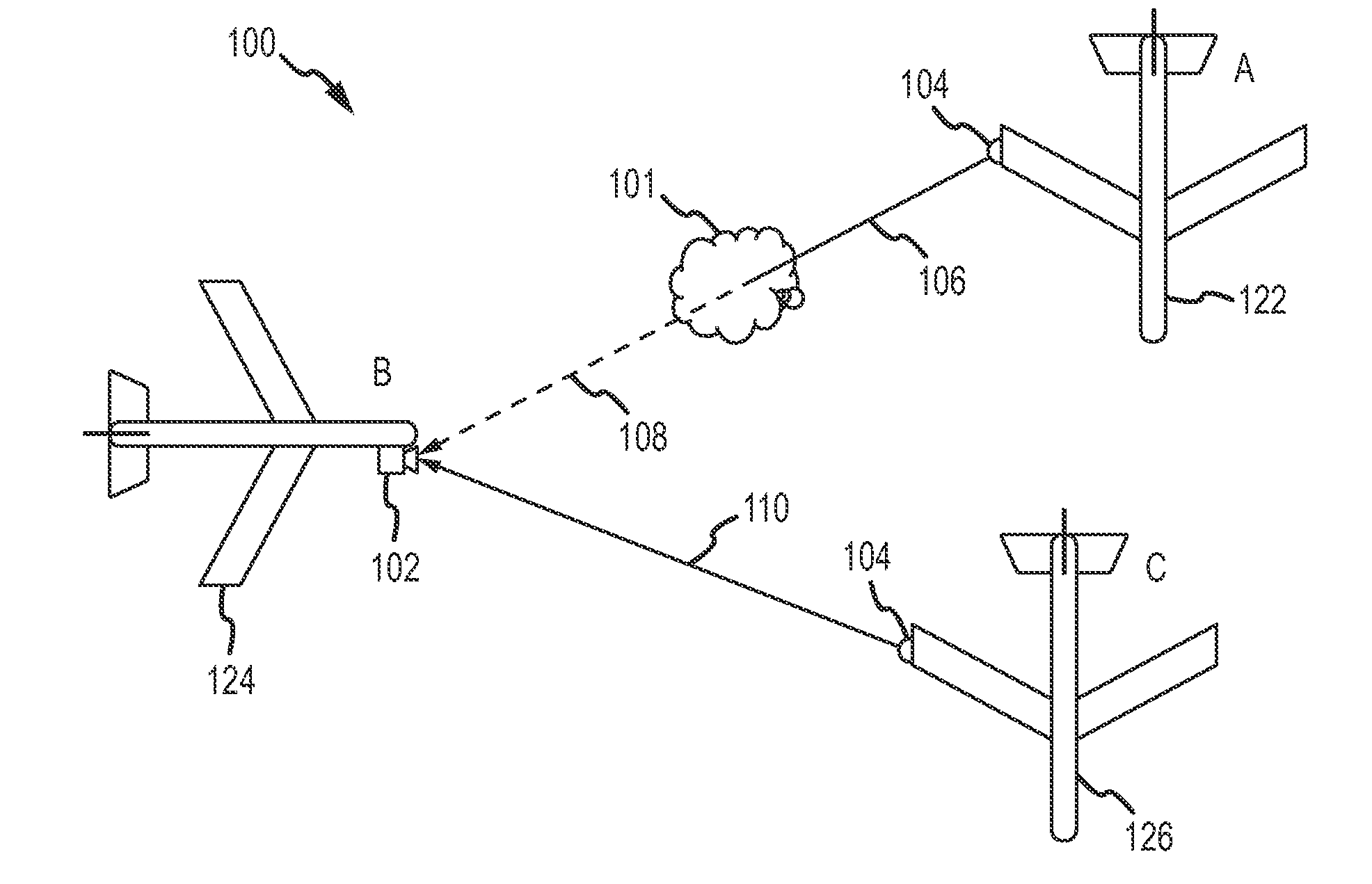
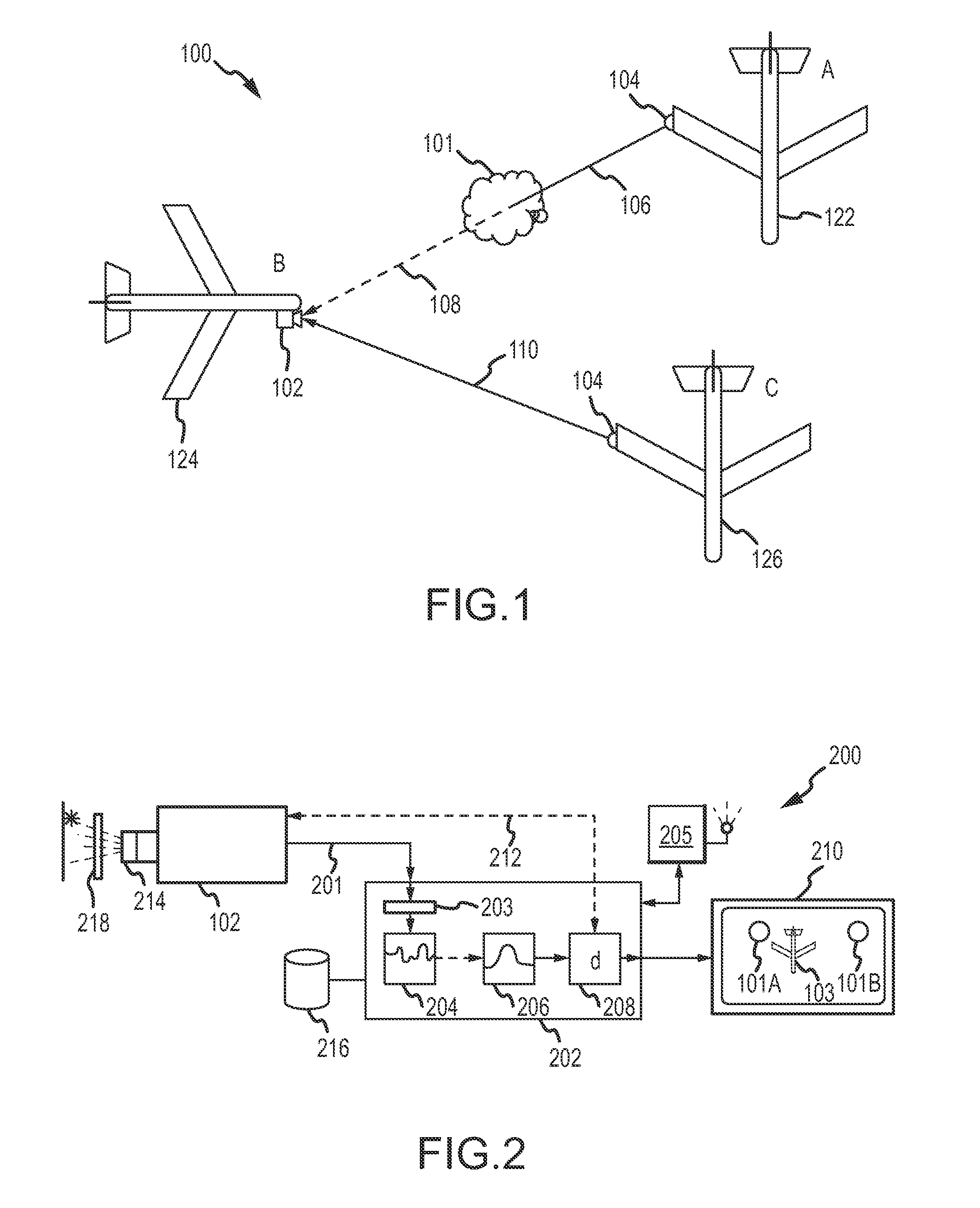
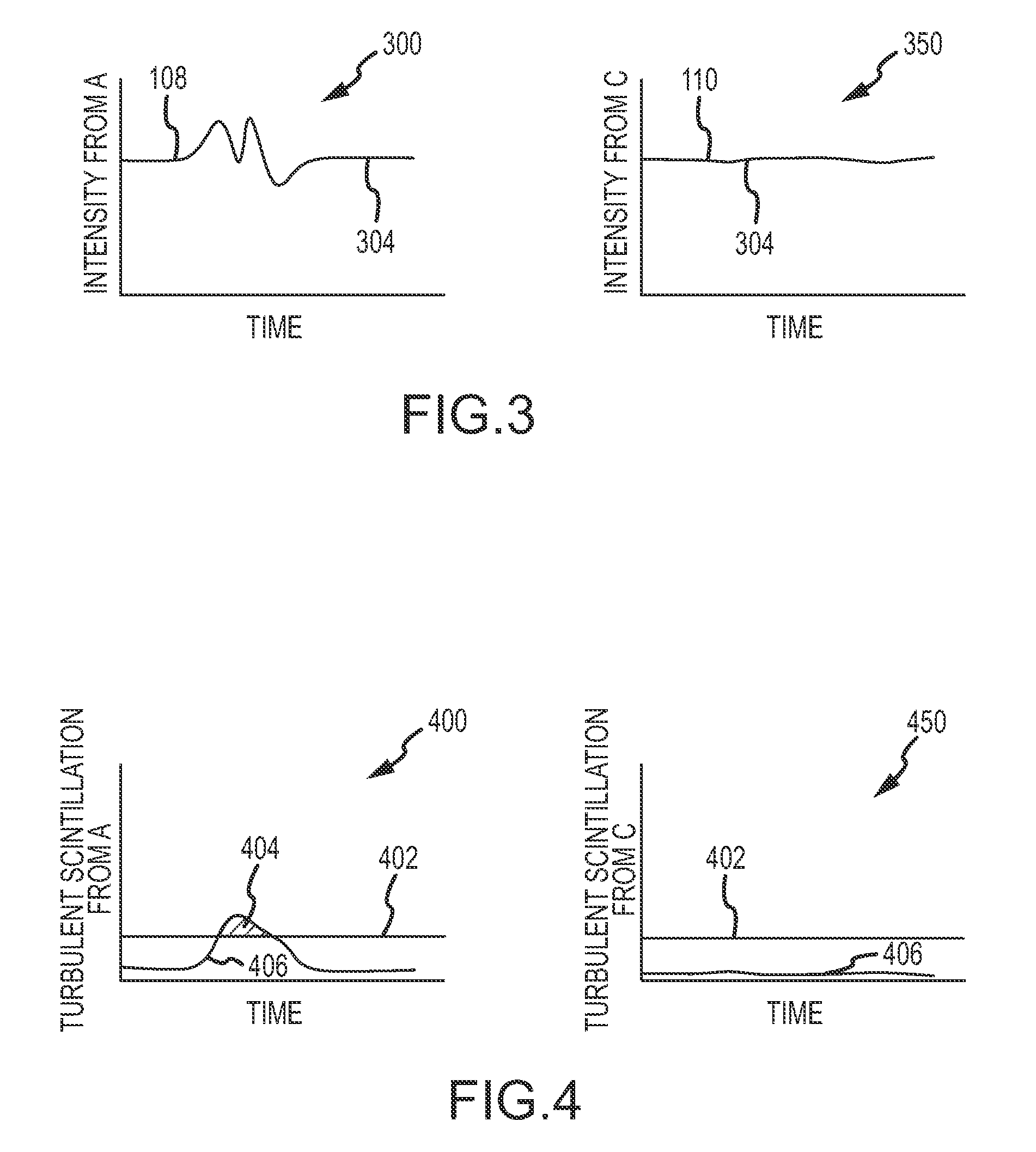
System and methods for detecting turbulence based upon observations of light scintillation
ActiveUS20090143988A1Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingMaterial analysis by optical meansObserver basedLight source
Systems and methods are provided for detecting turbulent air located between a light source and an observer based upon the scintillation of light produced by the light source. An optical sensor associated with the observer is configured to receive the light and to produce an indication of the light. A processor is configured to quantify scintillation in the light and to identify turbulent air between the light source and the optical sensor based upon the scintillation. A feedback device provides a notification when turbulent air is identified. Light sources and optical sensors may be located on airborne platforms or on the ground, and information may be transferred between multiple observers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
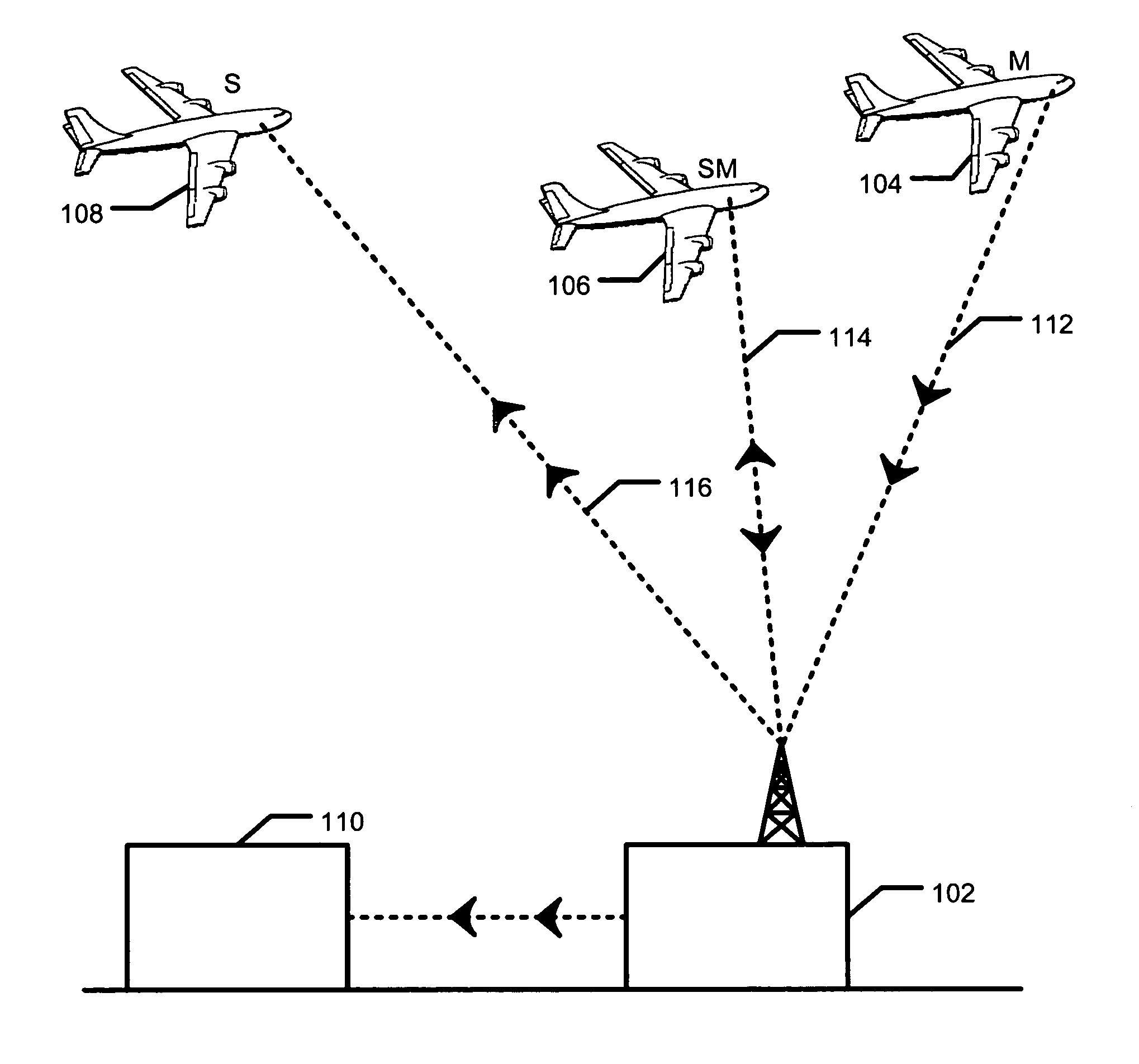
Method and system for obtaining and presenting turbulence data via communication devices located on airplanes
ActiveUS9126696B1Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingNavigation instrumentsOn boardData information
A method, device and system is provided for obtaining and processing turbulence data via communication devices located on-board airplanes. Turbulence data obtained by a plurality of communication devices may be received during flights on-board respective ones of a plurality of airplanes. Accumulated tempo-spatial turbulence information may be generated by super-positioning the turbulence data received from the plurality of communication devices onto a single tempo-spatial frame of reference. The accumulated tempo-spatial turbulence data information may be distributed to one or more of the communication devices. The plurality of communication devices may include one or more hand-held user communication device and / or embedded airplane communication device.
Owner:YAMASEE
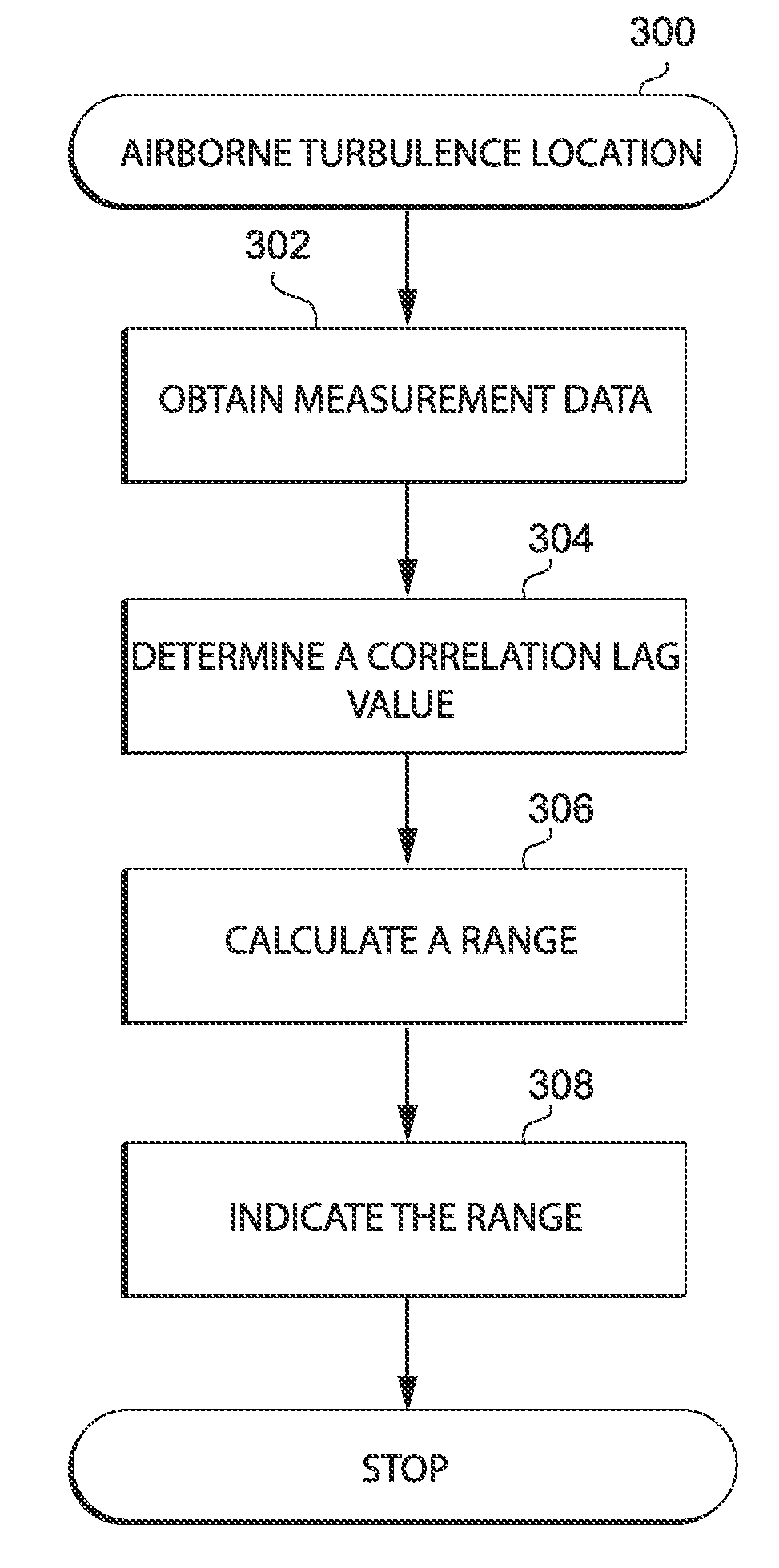
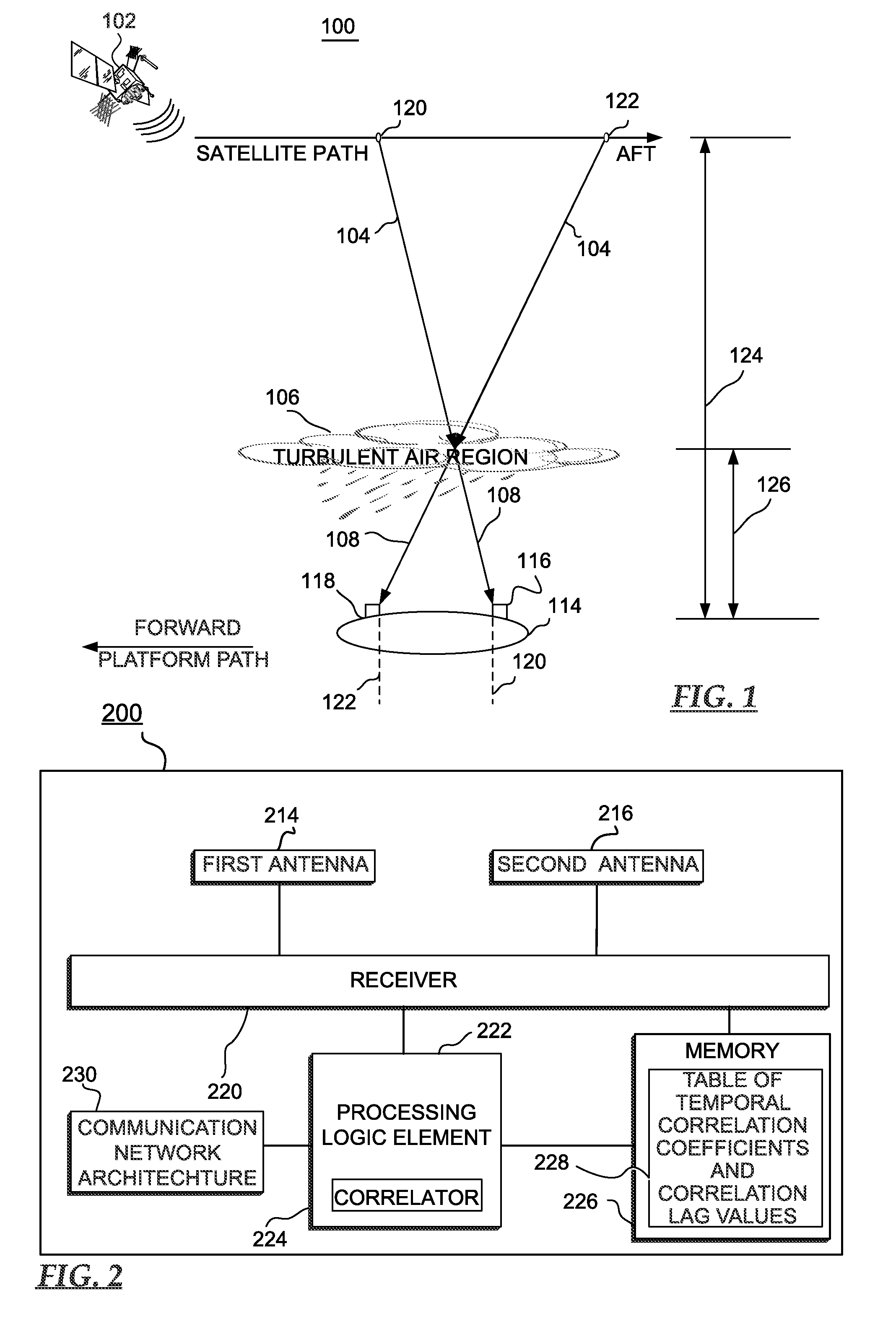
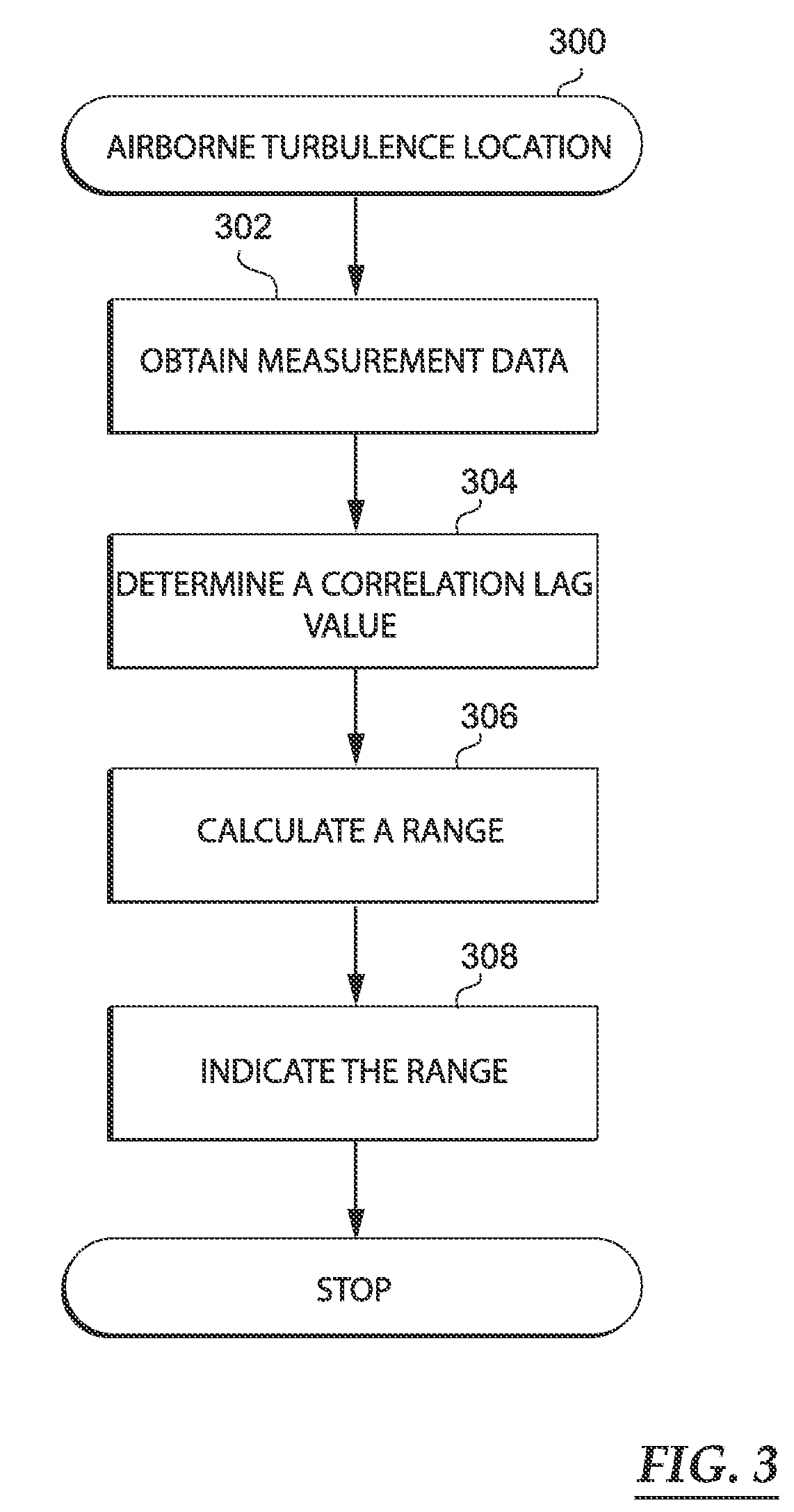
Airborne turbulence location system and methods
InactiveUS20090009393A1Increase air traffic system capacityIncrease system capacityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsClear air turbulence detection/forecastingLagTime shifting
A system and methods for calculating a range to a turbulent air region from an antenna platform is disclosed. The methods determine a correlation lag value corresponding to a time shift in receiving propagation of an interference pattern traveling along a path that is subject to the turbulent air region at antennas responsive to incident electromagnetic energy. Based upon the correlation lag value, the methods calculate the range to the turbulent air region from the antenna platform and issue a warning that indicate the range.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and methods for detecting turbulence based upon observations of light scintillation
ActiveUS7889328B2Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingMaterial analysis by optical meansObserver basedLight source
Systems and methods are provided for detecting turbulent air located between a light source and an observer based upon the scintillation of light produced by the light source. An optical sensor associated with the observer is configured to receive the light and to produce an indication of the light. A processor is configured to quantify scintillation in the light and to identify turbulent air between the light source and the optical sensor based upon the scintillation. A feedback device provides a notification when turbulent air is identified. Light sources and optical sensors may be located on airborne platforms or on the ground, and information may be transferred between multiple observers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method to identify regions of airspace having ice crystals using an onboard weather radar system
ActiveUS9188700B2Clear air turbulence detection/forecastingDe-icing equipmentsWeather radarAtmospheric sciences
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Automatic turbulence detection method
ActiveUS20080119971A1Analogue computers for trafficWeather condition predictionAirplaneInformation exchange
The invention relates to a method for automatic detection of turbulence by a second aircraft, by information exchange between the second aircraft and at least a first aircraft. The first aircraft has means for transmitting information and the second aircraft has means for receiving the information transmitted by the first aircraft. The method includes the identification of information about turbulence liable to be encountered by the second aircraft, by analyzing the information received from the first aircraft. An alarm is activated on the basis of the turbulence information.
Owner:THALES SA
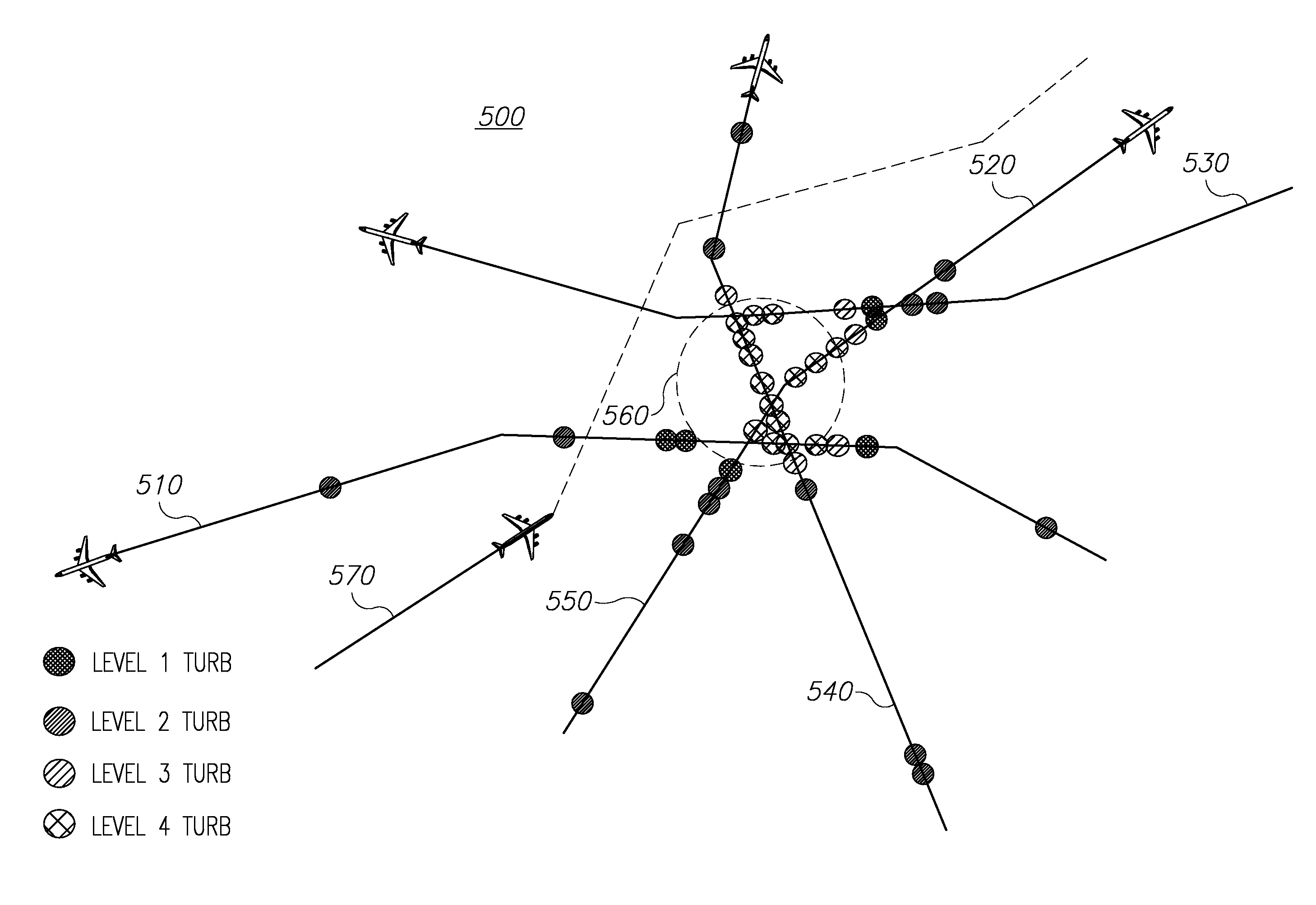
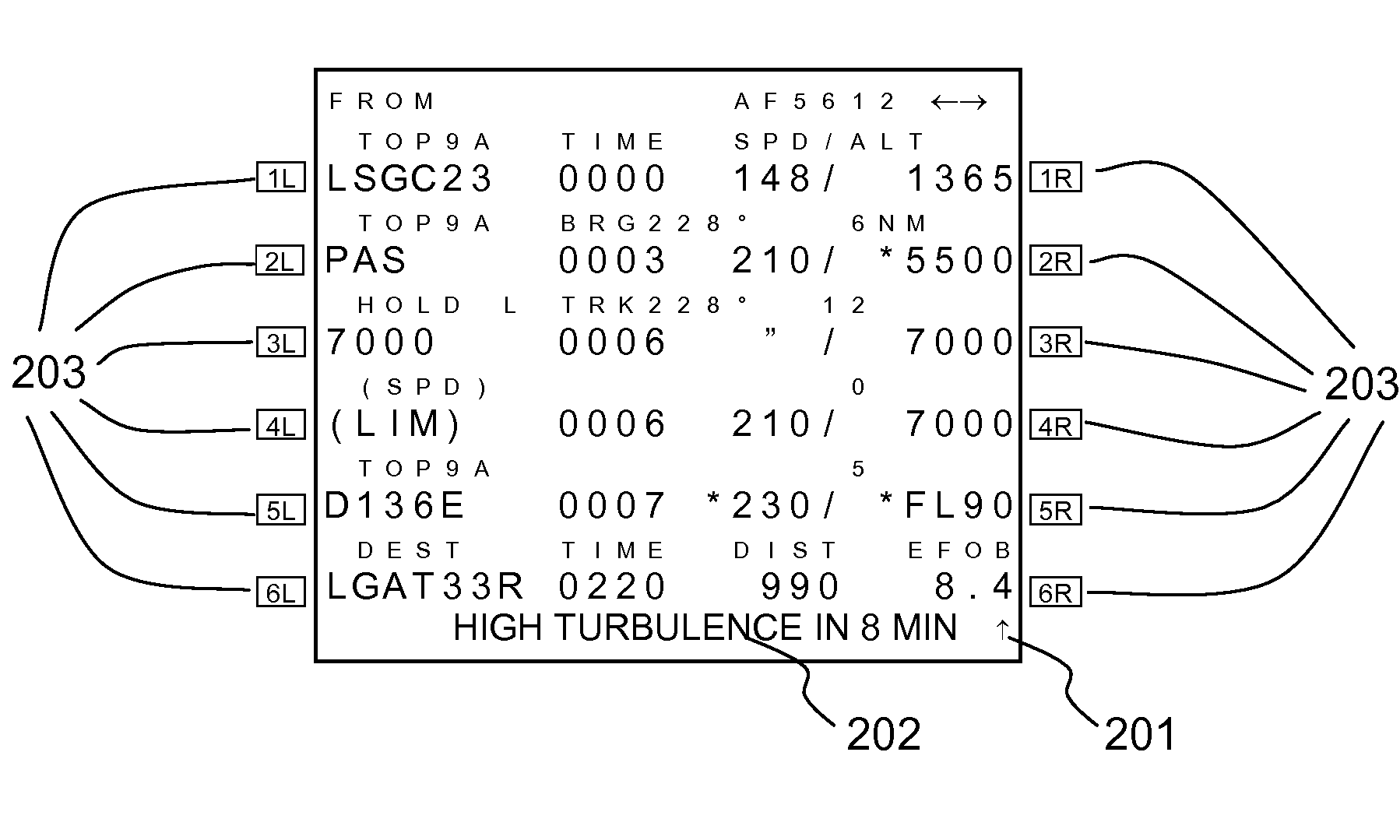
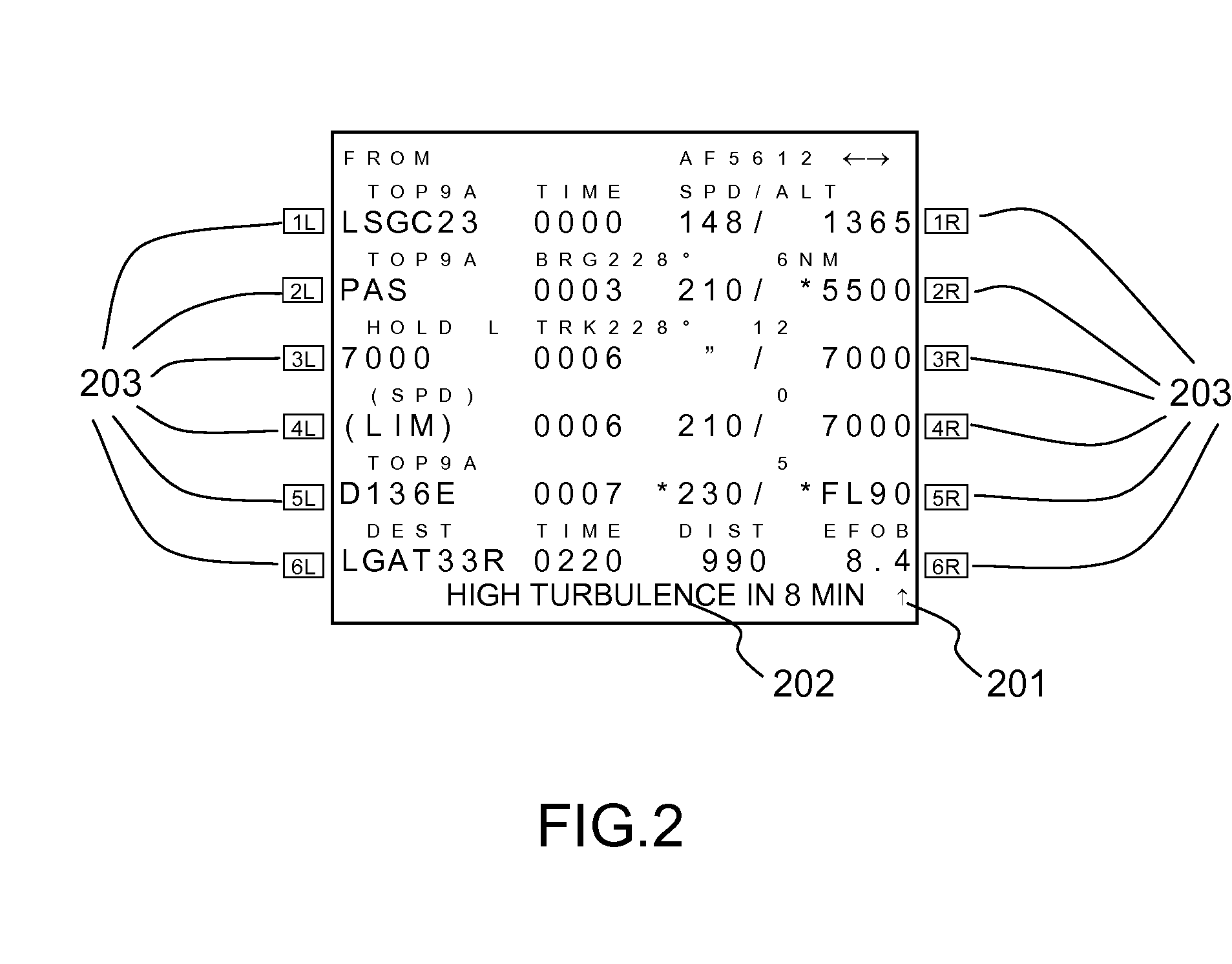
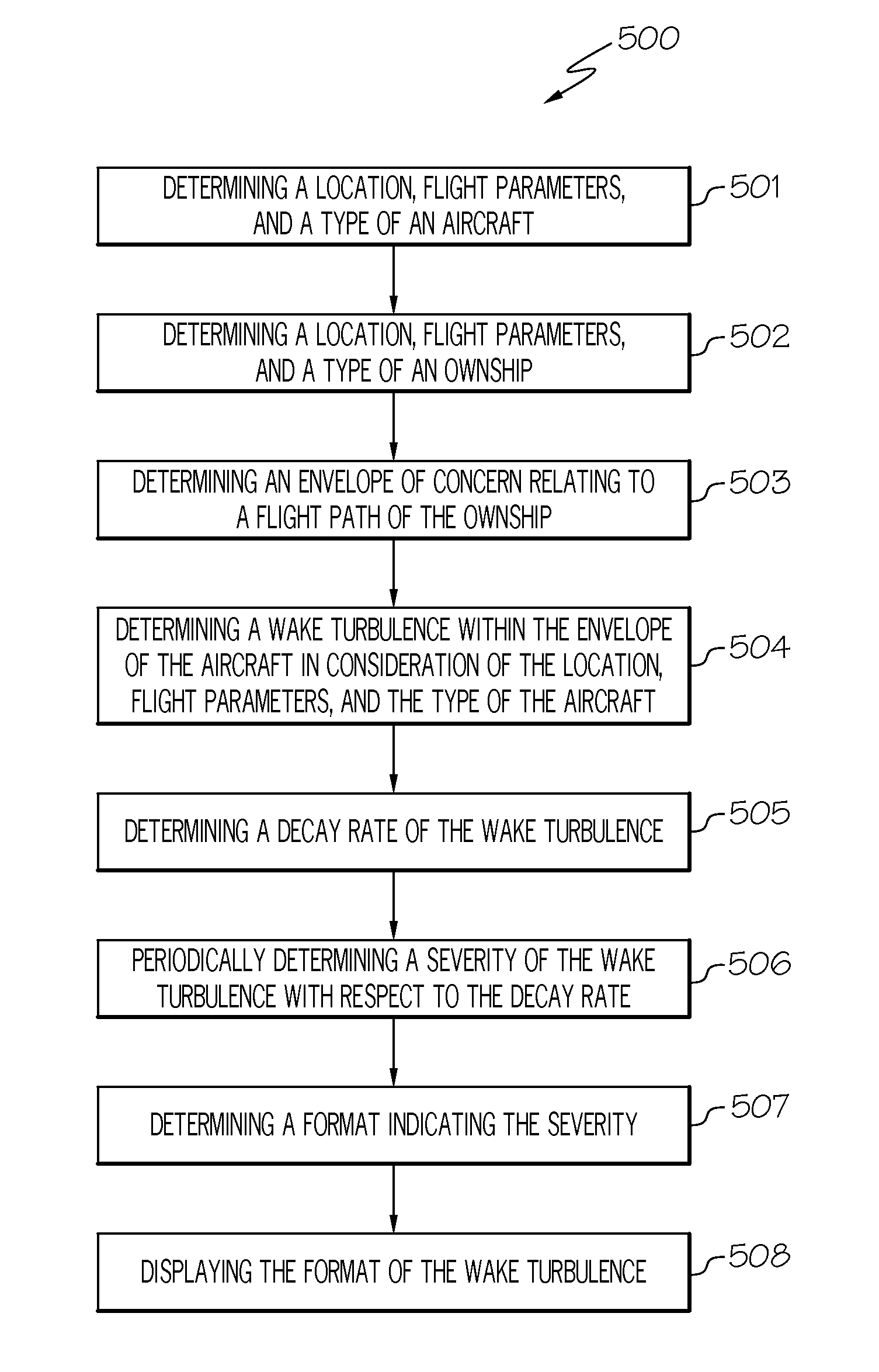
System and method for processing and displaying wake turbulence
A system and method to display, when within an envelope of an ownship's flight path, a symbol representing wake turbulence from another aircraft based on aircraft type and flight parameters received from the other aircraft, the symbol being formatted to indicate the severity of portions of the wake turbulence. The format is modified periodically in accordance with the aircraft's flight path and a decay rate of the wake turbulence.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com