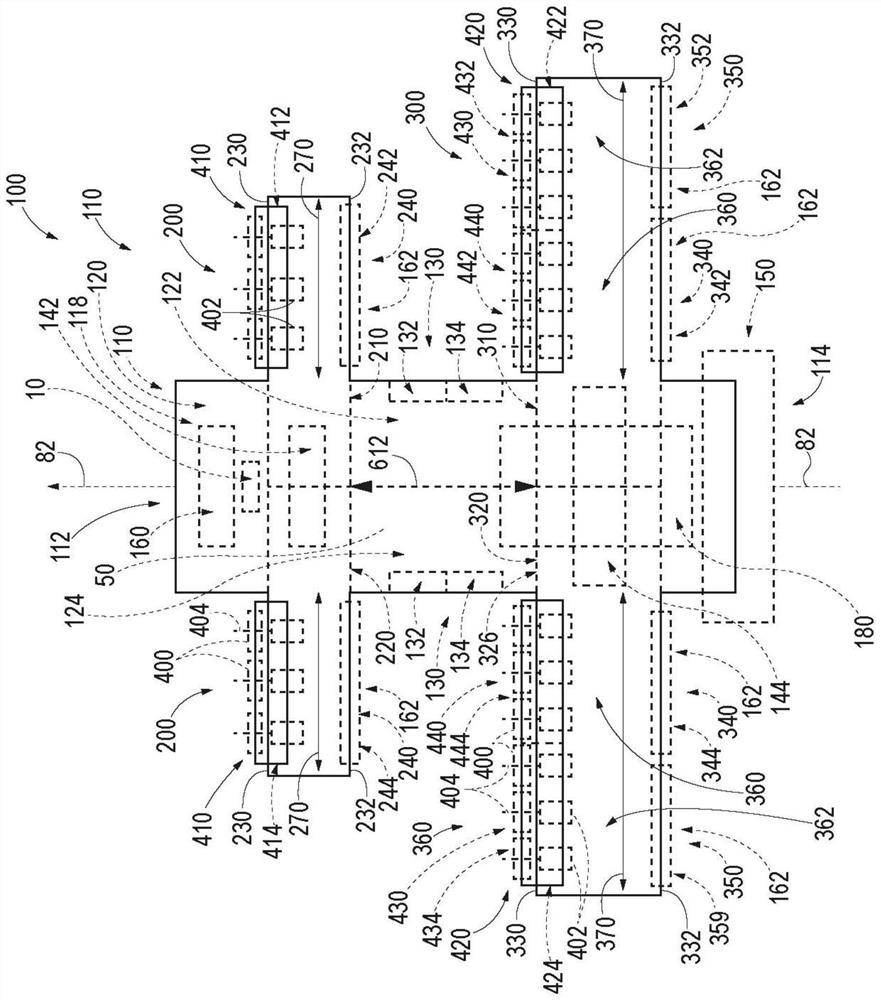
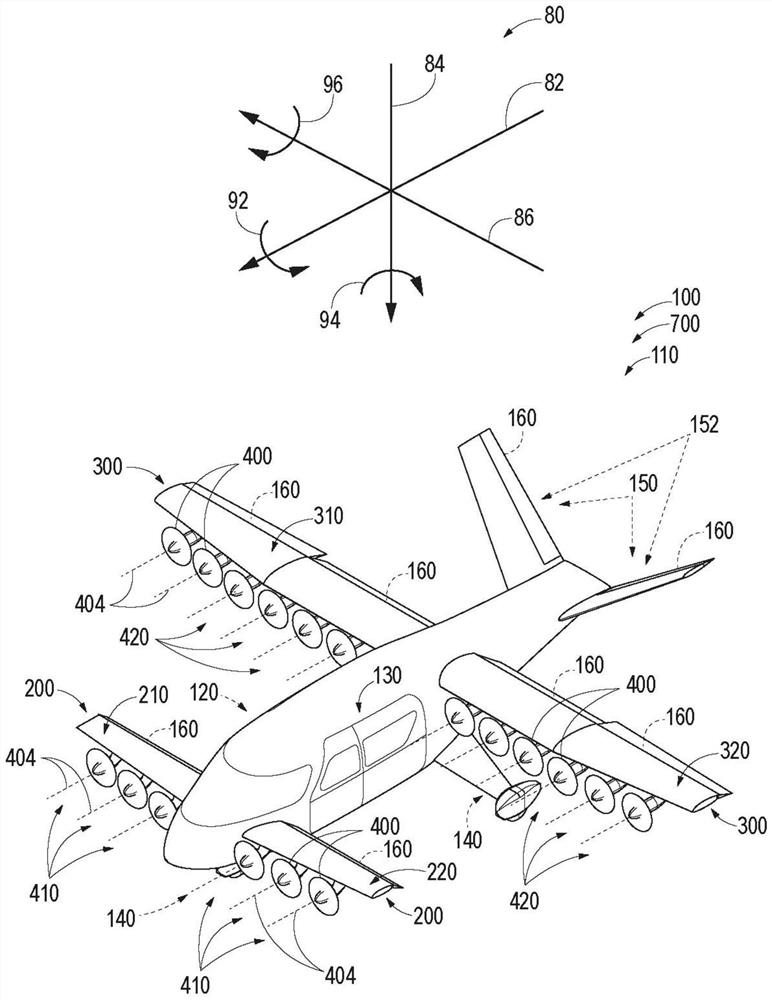
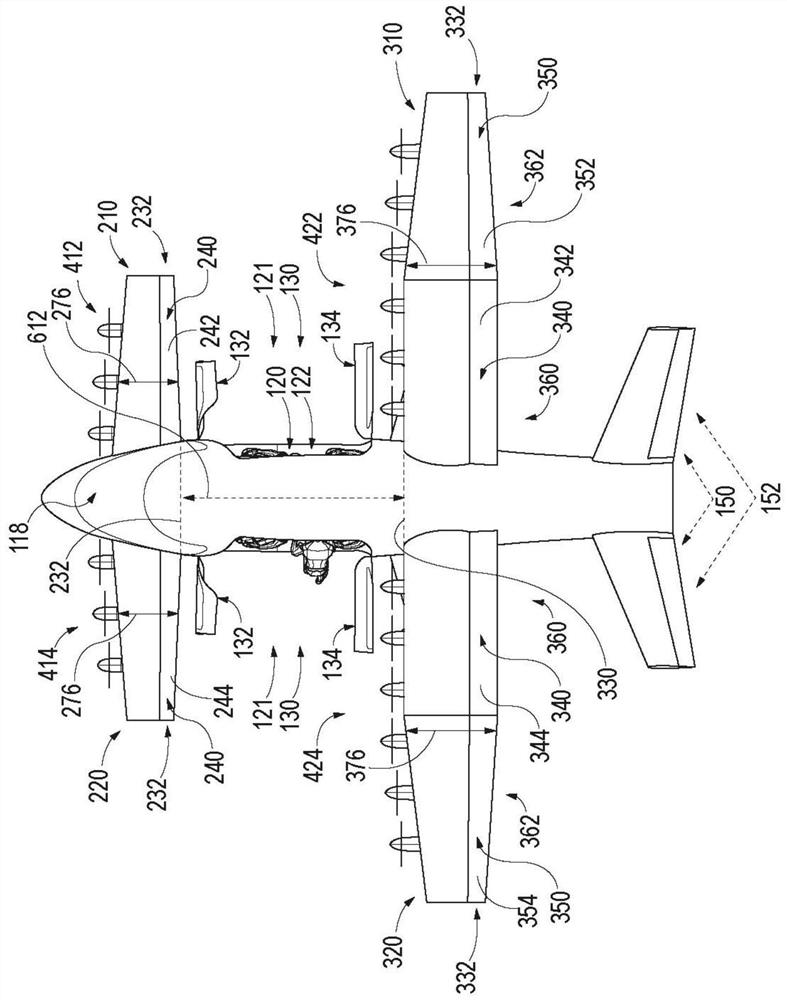
Patents
Literature
42results about "Influencers using rotating members" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
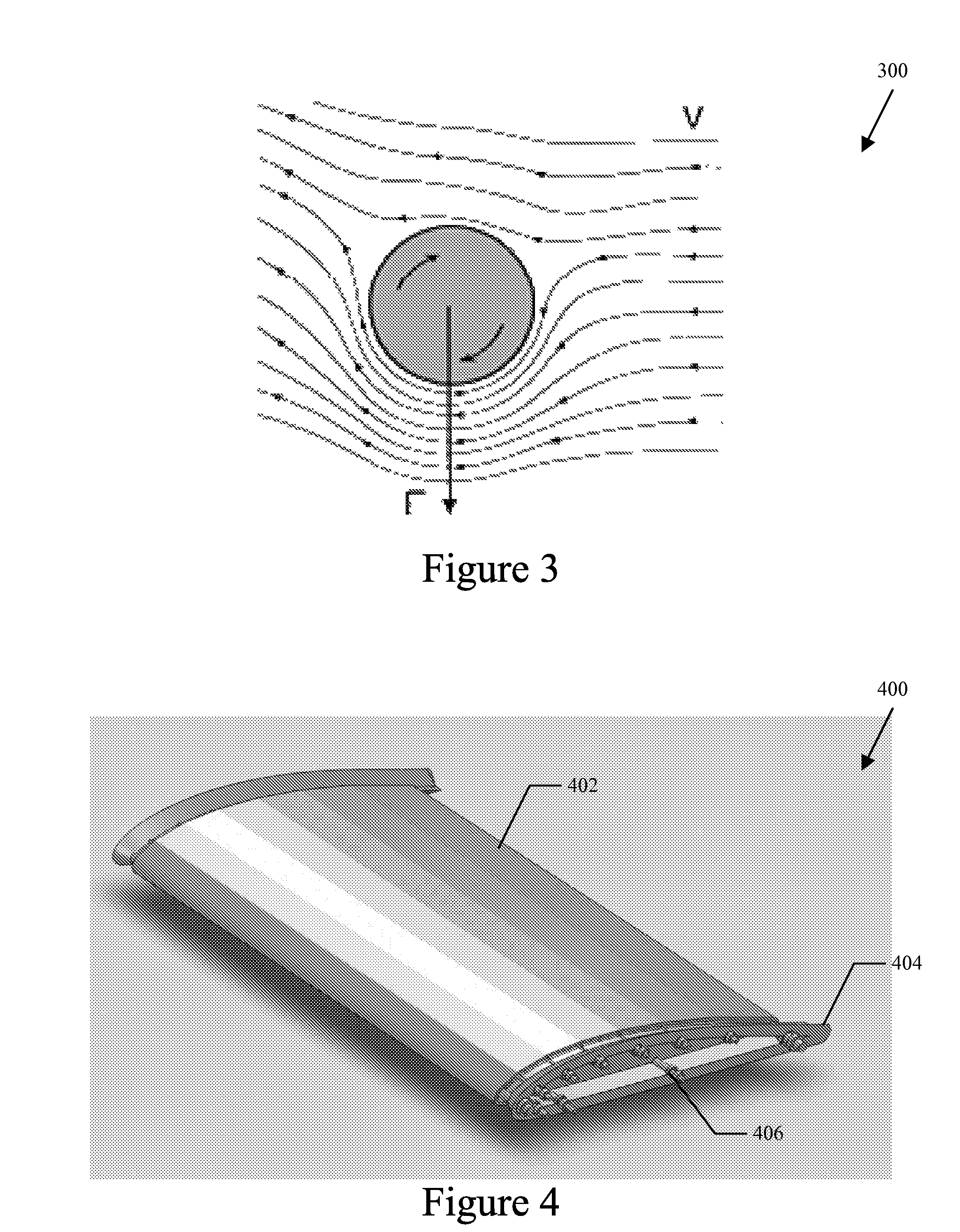
Turbulent flow drag reduction
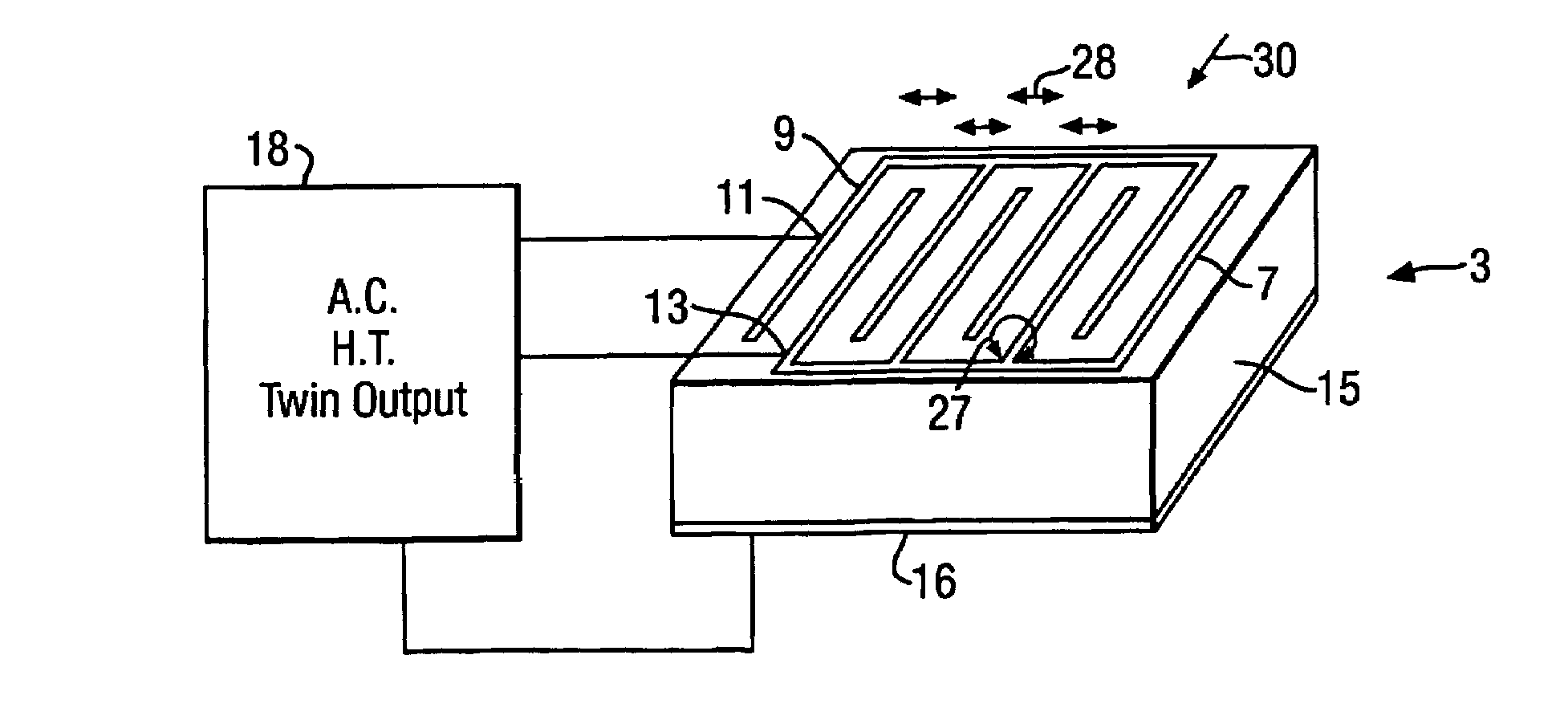
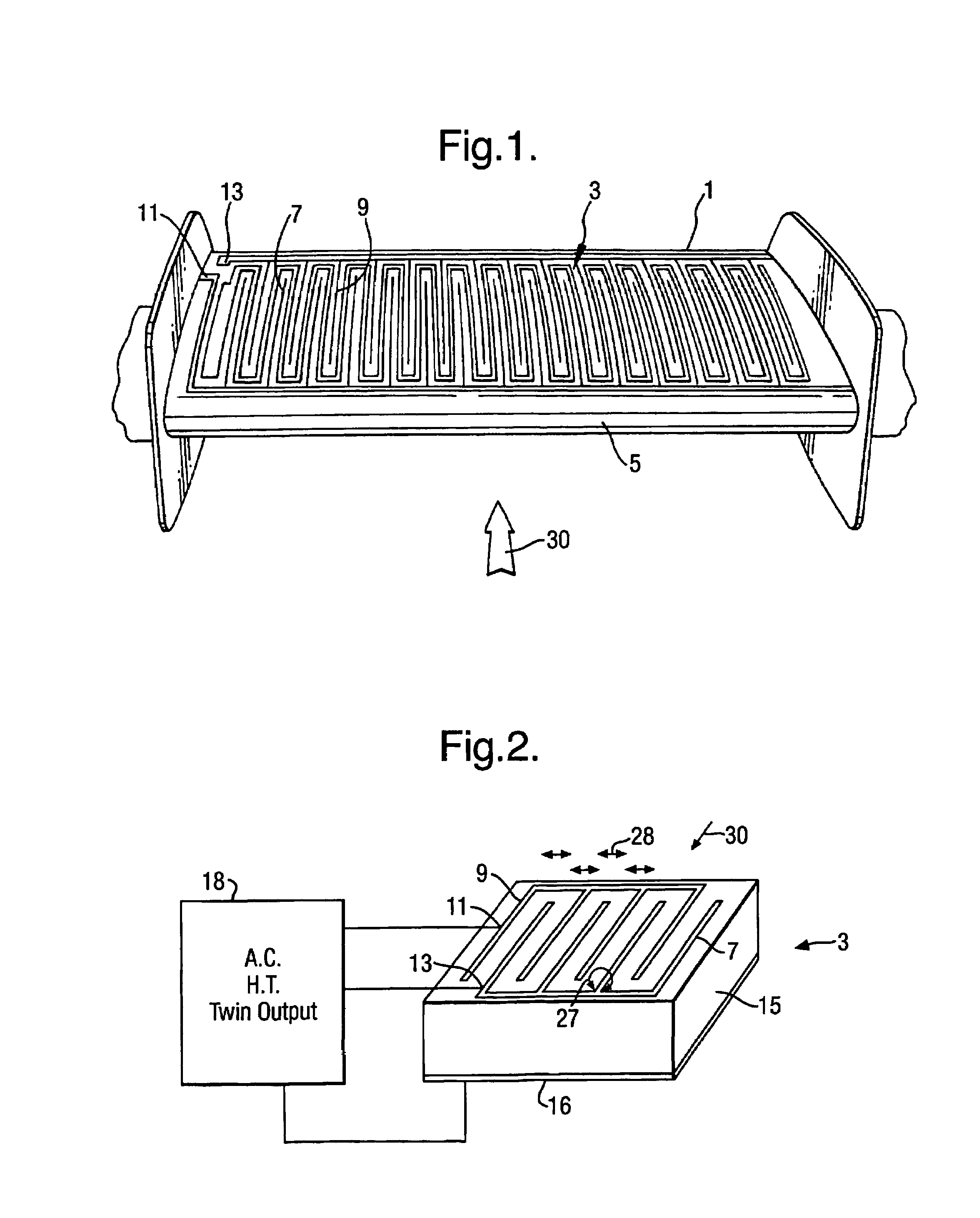
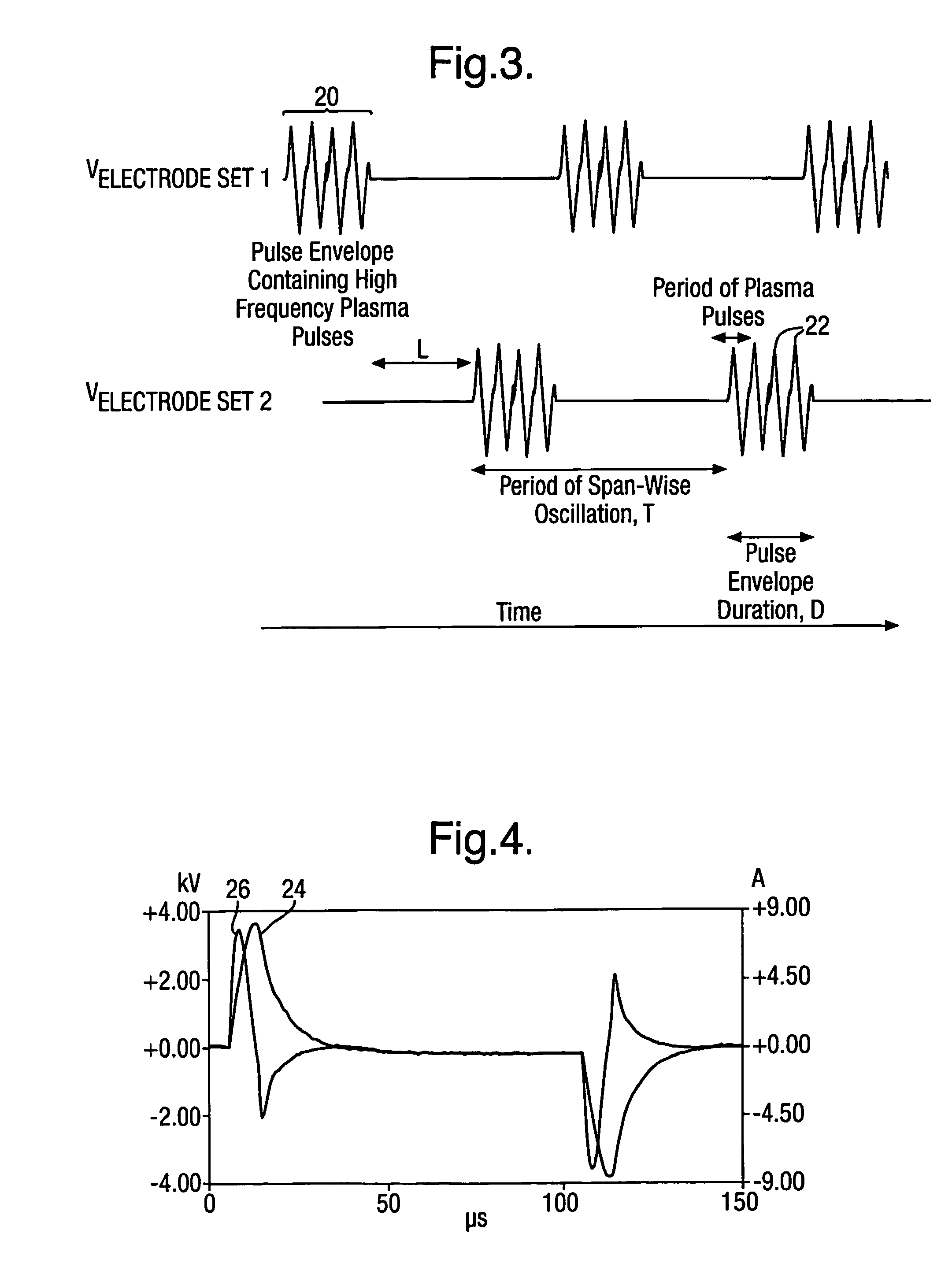
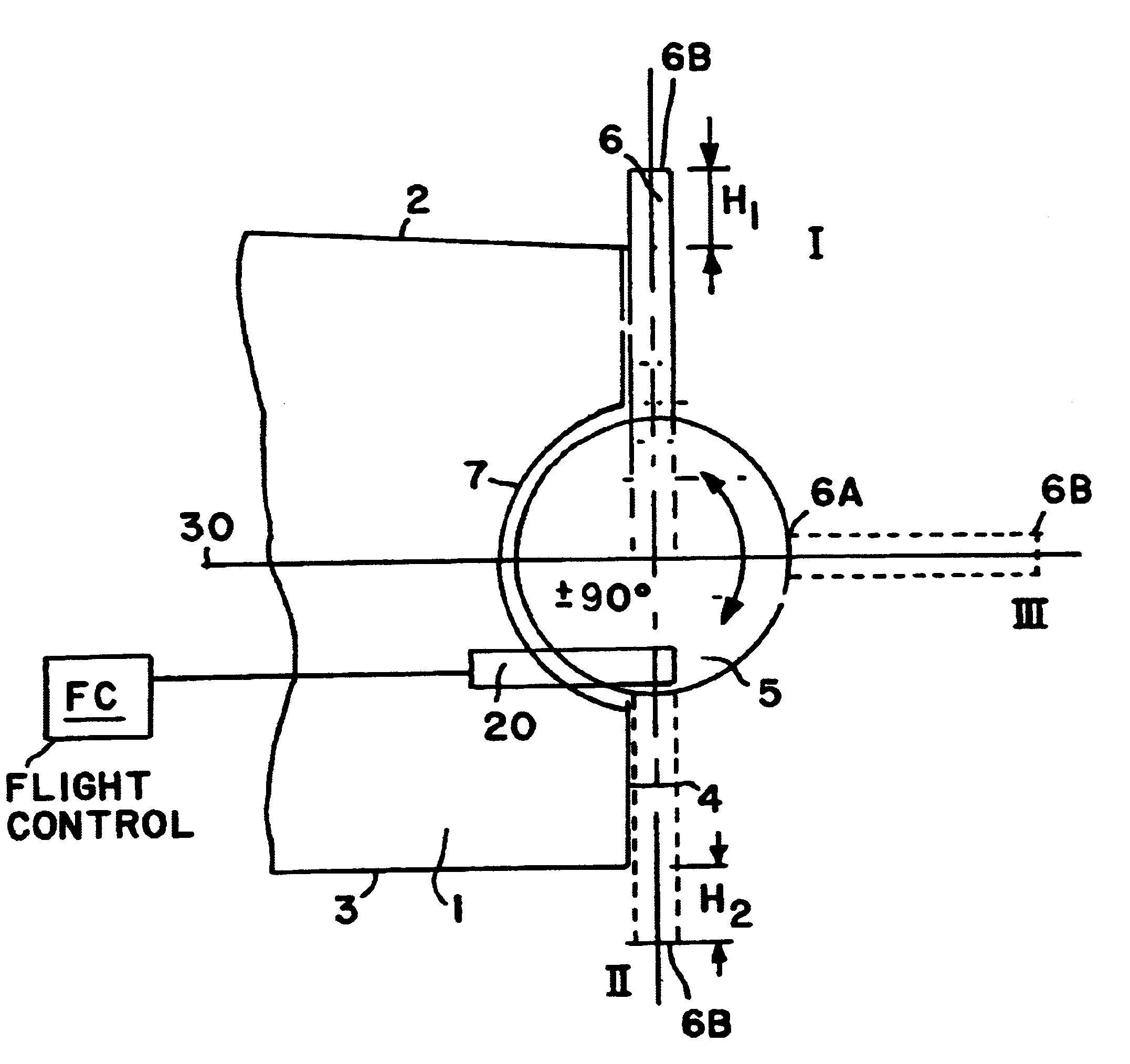
InactiveUS7017863B2Reduce resistanceObject's drag can be reducedBoundary layer controlsWingsPlasma generatorEngineering
The present invention relates to apparatus for influencing fluid flow over a surface, and more particularly, but not exclusively, to turbulent boundary layer flow drag reduction for an aircraft. The present invention provides such apparatus including a plasma generator comprising first and second spaced-apart independently controllable electrodes operable to cause a change in direction of the flow of the fluid over the surface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Flap arrangement for varying the aerodynamic lift generated by an aerodynamic element of an aircraft
InactiveUS6641089B2Easy to adjustEasily variedAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyFree edgeTrailing edge
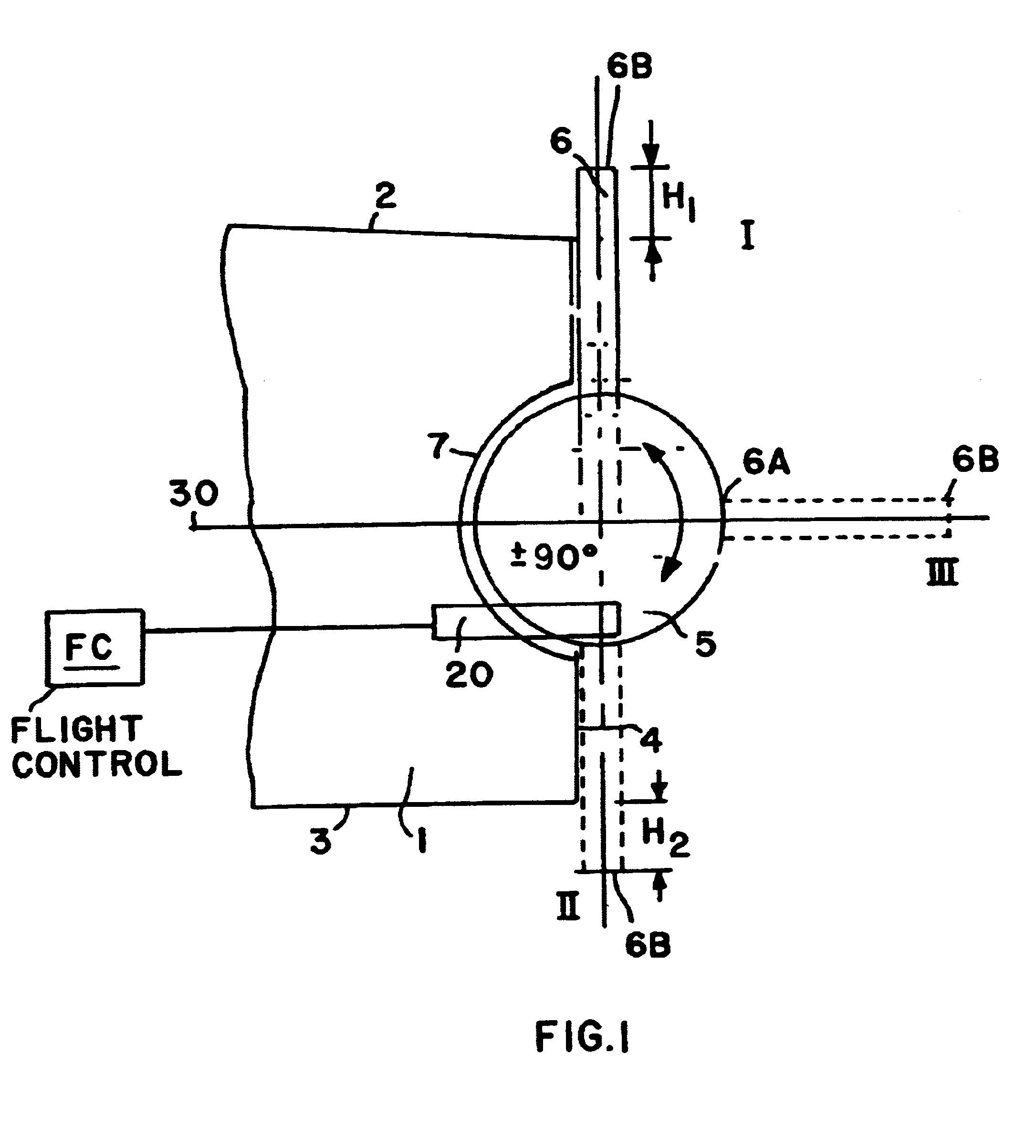
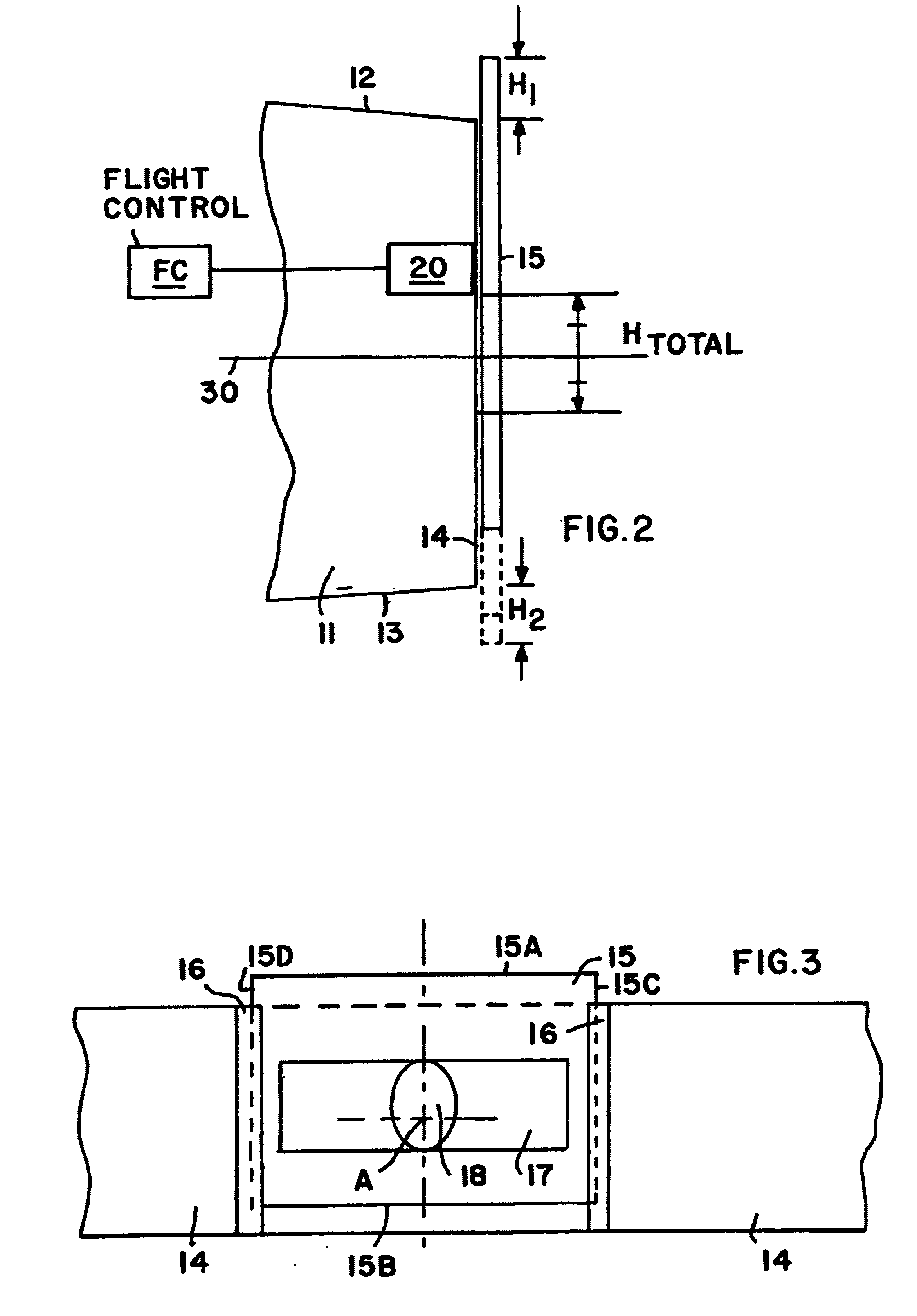
An auxiliary flap is movably arranged on a planar trailing edge of an aerodynamic element such as a wing, rudder, stabilizer, or flap. The auxiliary flap is rotatable and / or slidable relative to the aerodynamic element, to move selectively into three positions. In a first position, a free edge of the auxiliary flap protrudes into an airflow boundary layer on one side of the aerodynamic element, to decrease lift. In a second position, a free edge of the aerodynamic element protrudes into an airflow boundary layer on the other side of the aerodynamic element, to increase lift. In a third neutral position, the auxiliary element does not protrude into either boundary layer, so as not to influence lift. The auxiliary flap is simple and rapidly acting. The flap protrudes substantially perpendicularly into the boundary layer flow. The auxiliary flap has a planar plate shape.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Cross-flow fan propulsion system
ActiveUS7641144B2Improve efficiencyLow parasite dragAircraft navigation controlPropellersAirplaneAirflow
A cross-flow propulsion mechanism for use in providing propulsion to an aircraft, includes a housing defining an inlet, a rotor compartment, and an outlet. The inlet is adapted to receive an inflow of air along a first longitudinal axis. The rotor is mounted within the rotor compartment and adapted to receive the airflow introduced into the housing through the inlet and rotate about a second longitudinal axis that is substantially perpendicular to the first longitudinal axis. The outlet is adapted to receive the airflow processed through the rotor and exhaust air along a third longitudinal axis that is substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis. The propulsion mechanism can be applied in a personal aircraft, an STOL aircraft, and a hybrid automobile and aircraft.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Cross-flow fan propulsion system
ActiveUS20060266882A1Reduced flow separationImprove efficiencyAircraft navigation controlPropellersFlight vehicleAirflow
A cross-flow propulsion mechanism for use in providing propulsion to an aircraft, includes a housing defining an inlet, a rotor compartment, and an outlet. The inlet is adapted to receive an inflow of air along a first longitudinal axis. The rotor is mounted within the rotor compartment and adapted to receive the airflow introduced into said housing through the inlet and rotate about a second longitudinal axis that is substantially perpendicular to the first longitudinal axis. The outlet is adapted to receive the airflow processed through the rotor and exhaust air along a third longitudinal axis that is substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis. The propulsion mechanism can be applied in a personal aircraft, an STOL aircraft, and a hybrid automobile and aircraft.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Aerodynamic fan control effector
ActiveUS20090230240A1Maximize net area of bladeFacilitate packaging and stowageInfluencers by generating vorticesAir braking surfacesActuatorAirplane
A fan control effector for an aircraft comprises at least one blade configured to be pivotably deployable in a radially outward direction from a retracted position to a deployed position such that the blade extends out of the aircraft. The fan control effector may be mounted in a symmetrical arrangement about a longitudinal axis on opposing wings of the aircraft. Furthermore, the fan control effector may comprise any number of blades for independent deployment outwardly from the wing. The blades are configured to be angularly deployable along a direction that is non-parallel to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The blades may be configured to be deployable sequentially from the wing starting with an initial deployment of an aft-most one of the blades.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Flap arrangement for varying the aerodynamic lift generated by an aerodynamic element of an aircraft
InactiveUS20030057332A1Easy to adjustEasily variedAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyFree edgeTrailing edge
An auxiliary flap is movably arranged on a planar trailing edge of an aerodynamic element such as a wing, rudder, stabilizer, or flap. The auxiliary flap is rotatable and / or slidable relative to the aerodynamic element, to move selectively into three positions. In a first position, a free edge of the auxiliary flap protrudes into an airflow boundary layer on one side of the aerodynamic element, to decrease lift. In a second position, a free edge of the aerodynamic element protrudes into an airflow boundary layer on the other side of the aerodynamic element, to increase lift. In a third neutral position, the auxiliary element does not protrude into either boundary layer, so as not to influence lift. The auxiliary flap is simple and rapidly acting. The flap protrudes substantially perpendicularly into the boundary layer flow. The auxiliary flap has a planar plate shape.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Aerodynamic properties of ground vehicles
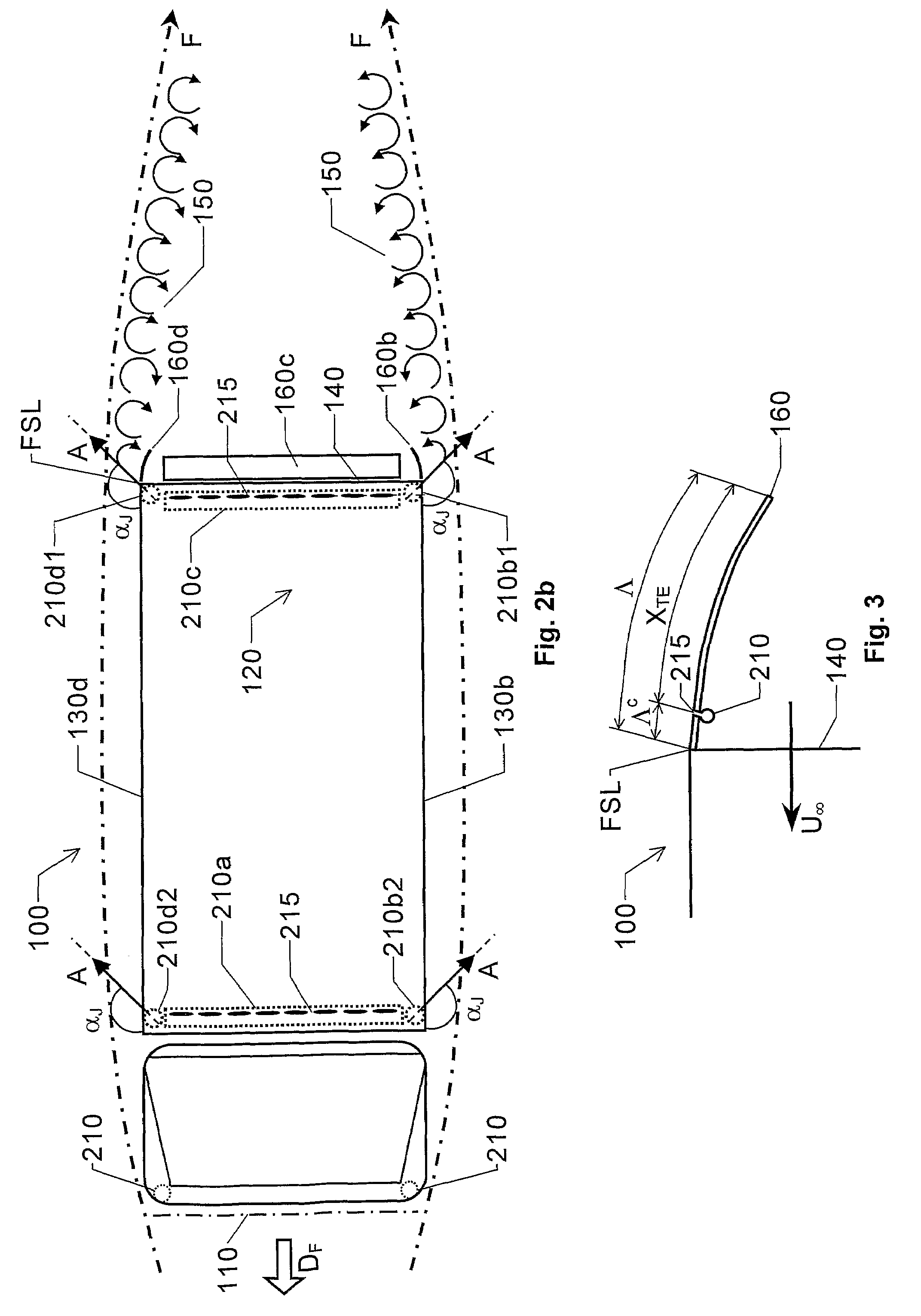
The present invention relates to the improvement of the aerodynamic properties of bluff-body shaped ground vehicles. A least one air modulator is assembled on the vehicle to modify an air flow around the vehicle, such that the drag on the vehicle is decreased. Each air modulator has an array of openings including a number of openings, which are arranged next to one another along an essentially straight line. A control unit controls the at least one air modulator output oscillating air from each opening such that air vortices are formed outside the opening. The at least one air modulator is arranged on the vehicle, such that these air vortices have axes that, in proximity to the opening, are essentially perpendicular to a forward driving direction of the vehicle.
Owner:SEMCON CARAN
Apparatus and method for directing thrust from tilting cross-flow fan wings on an aircraft
A variable thrust cross-flow fan system for an aircraft including a rotatable wing member having a first housing member; an actuator assembly operably coupled to the first housing member; and a variable thrust cross-flow fan assembly including a first and second driver plates having a plurality of blades rotatably mounted therebetween. The plurality of blades has a circular path of travel when rotating and includes a control assembly coupled to the plurality of blades to generate a variable thrust force. The control assembly includes a control cam that is substantially non-rotatable relative to the first and second driver plates and a hinge member that is fixedly connected to the control cam and to the first housing member at a hinge axis. Rotation of the first housing member by the actuator assembly imparts rotation of the control cam about the hinge axis, thereby changing the direction of the variable thrust force.
Owner:BELL HELICOPTER TEXTRON INC
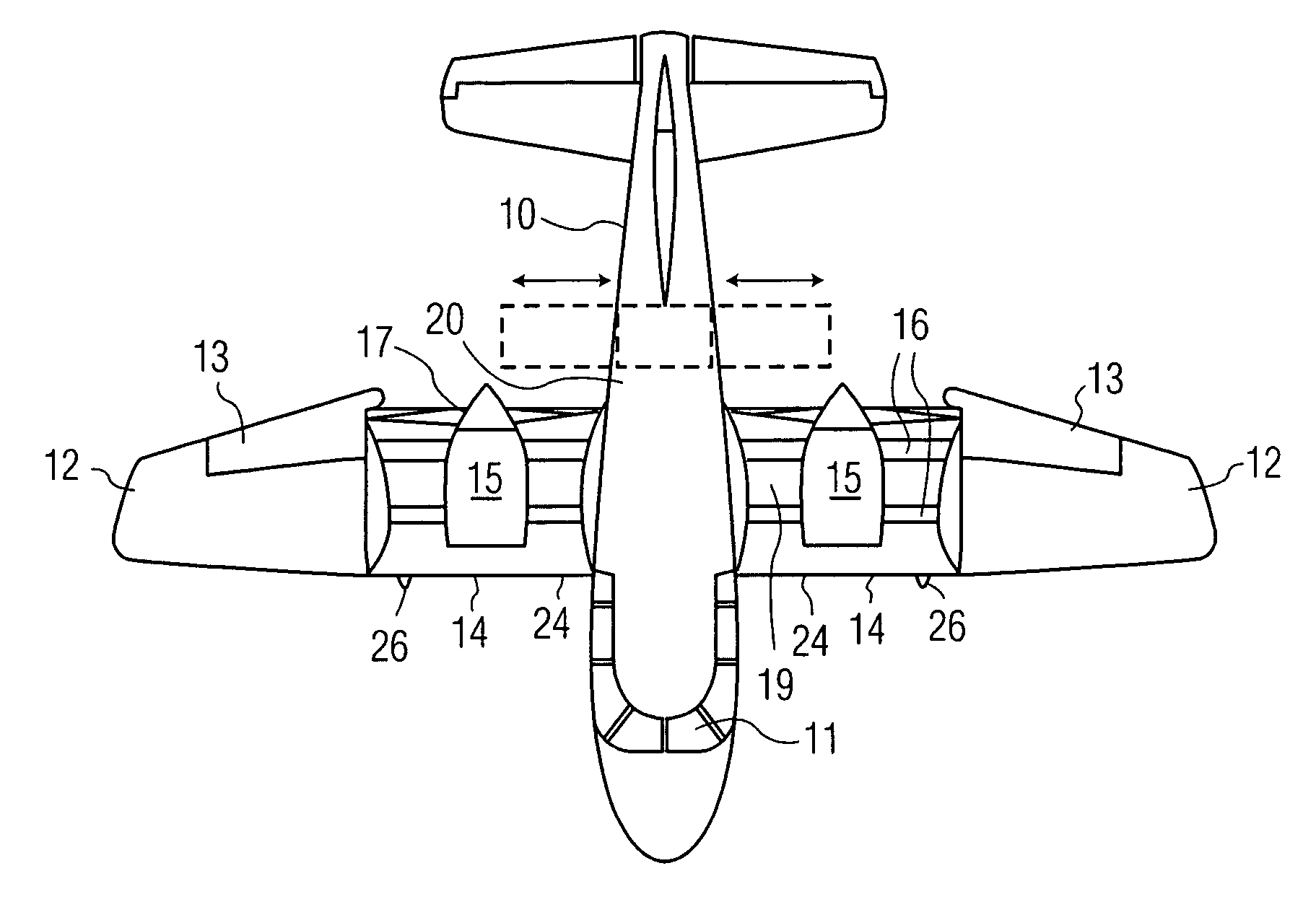
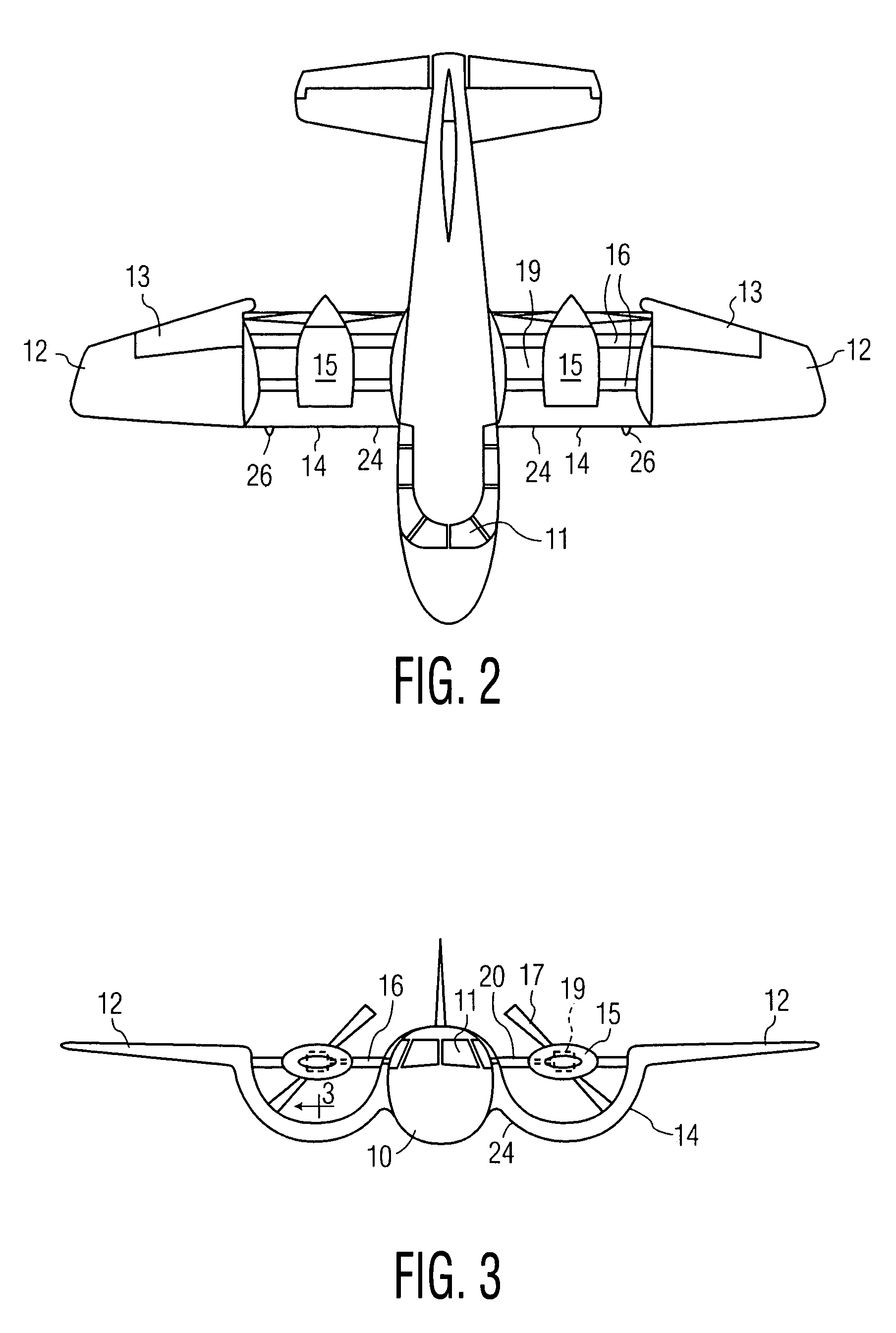
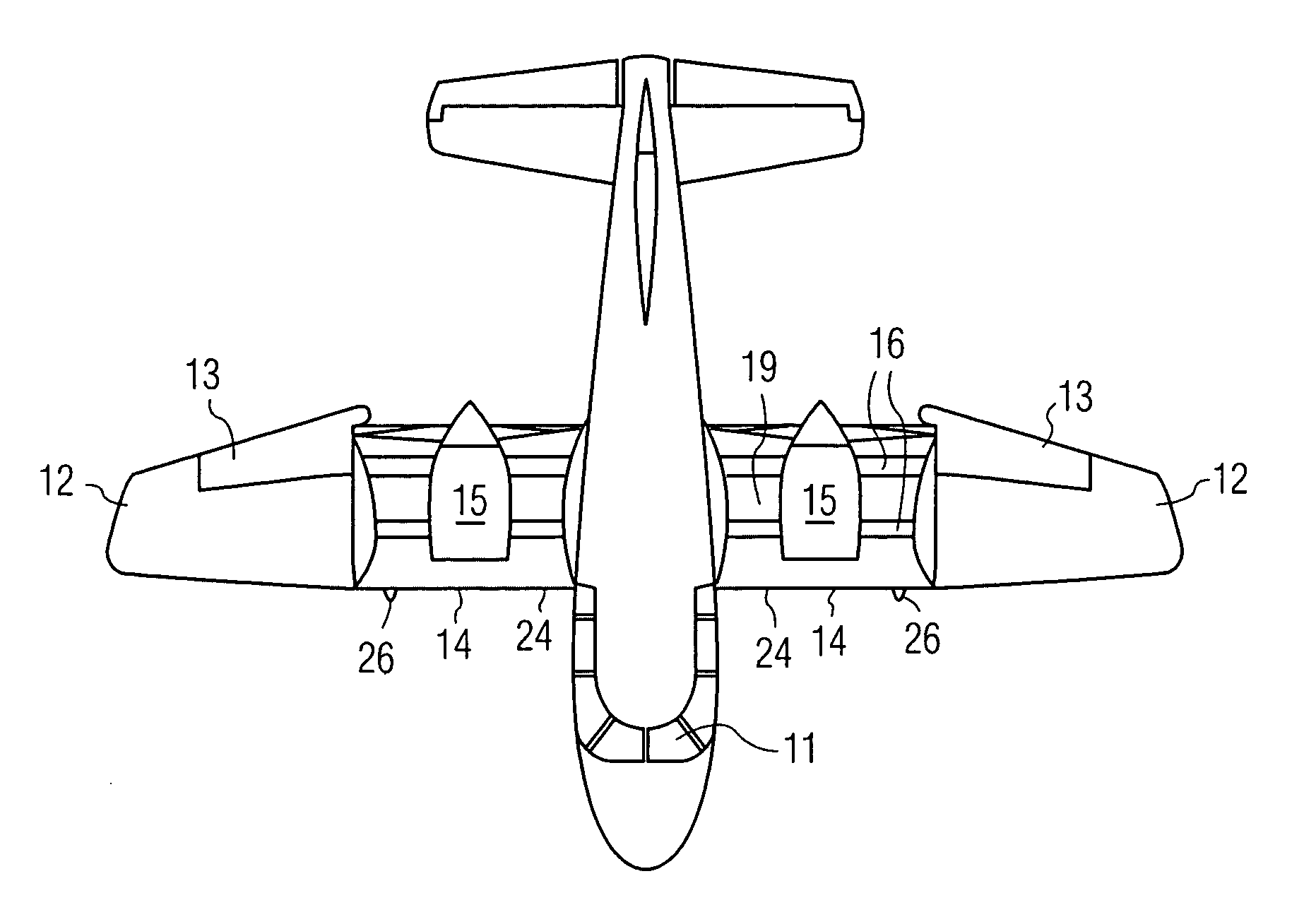
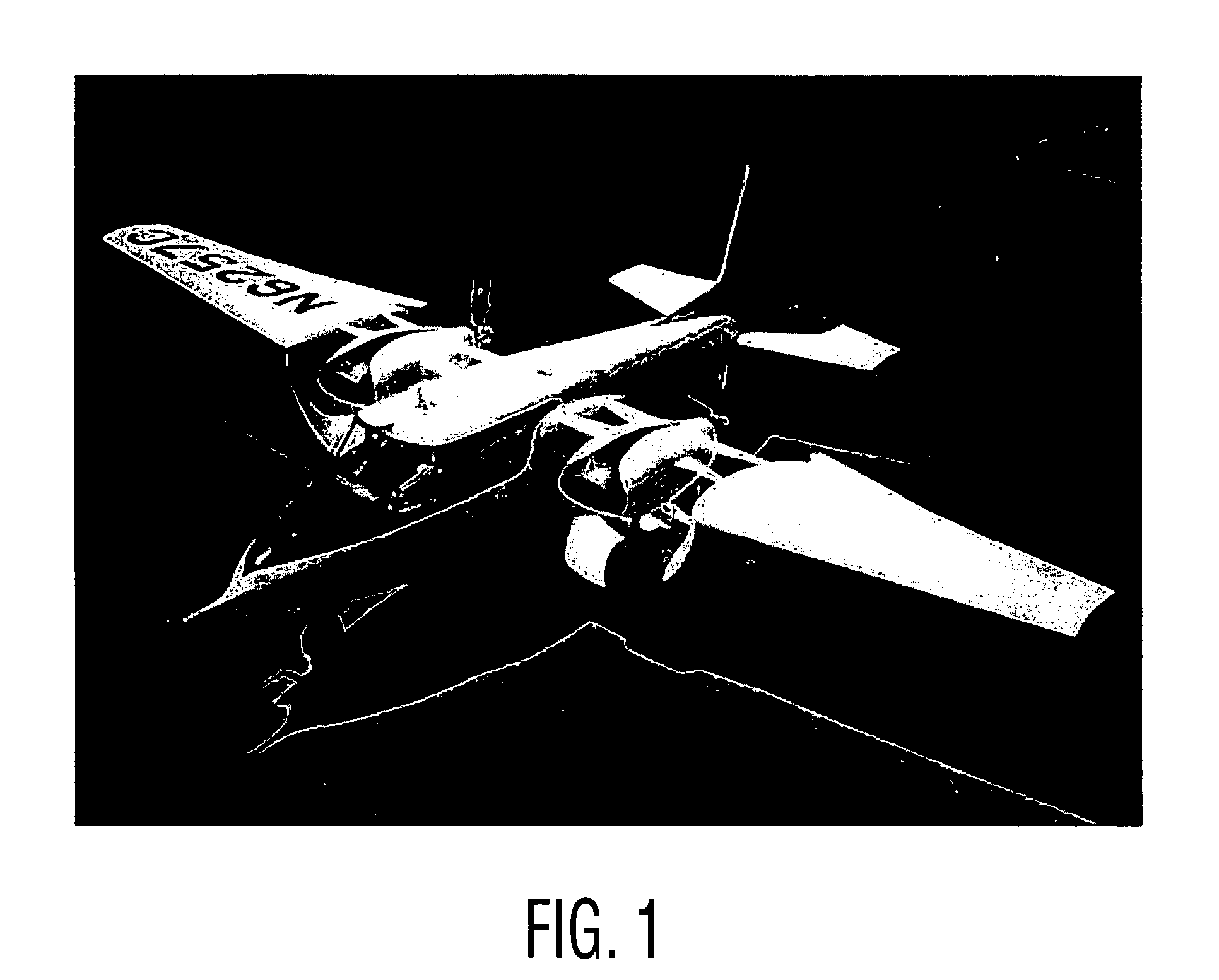
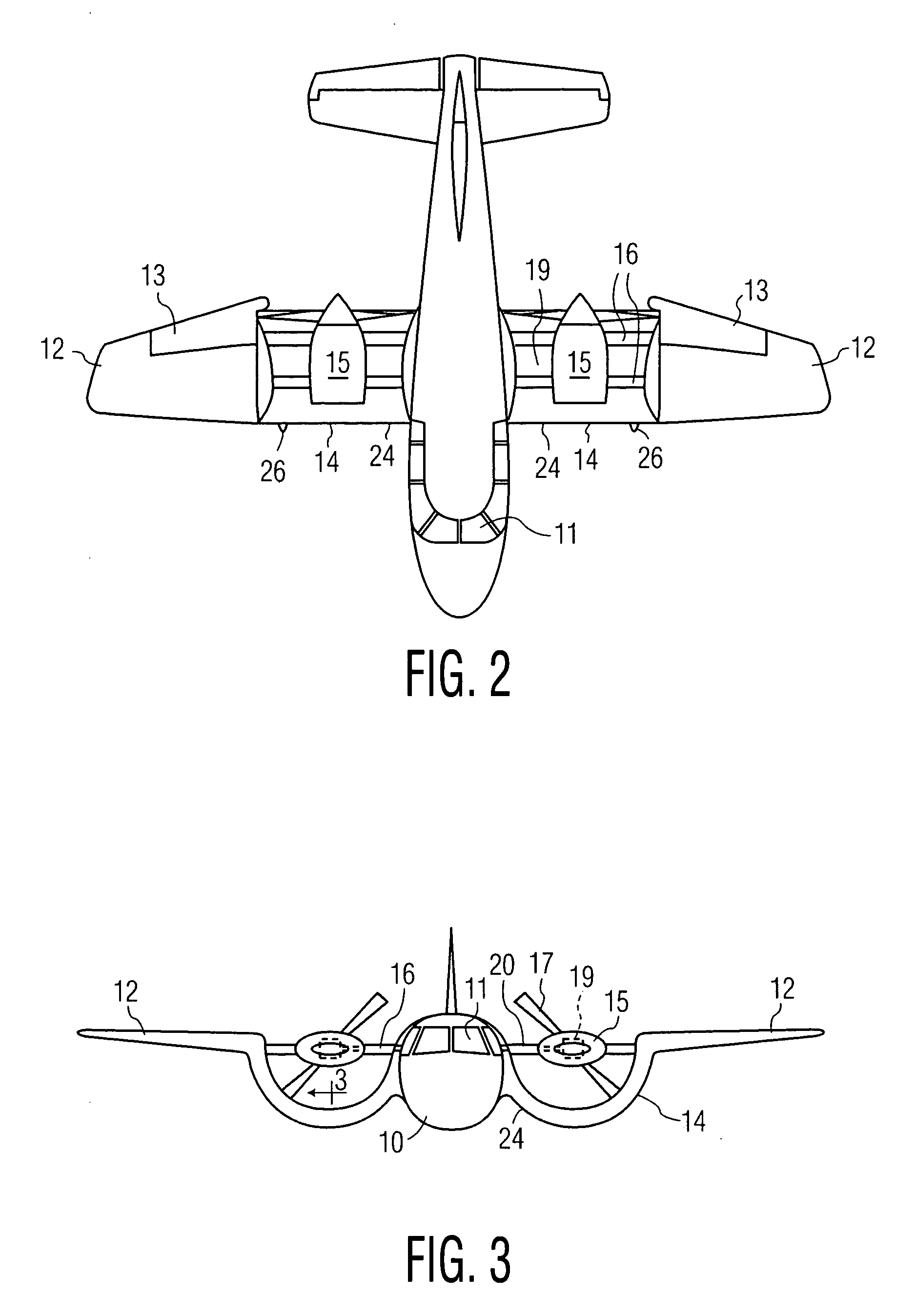
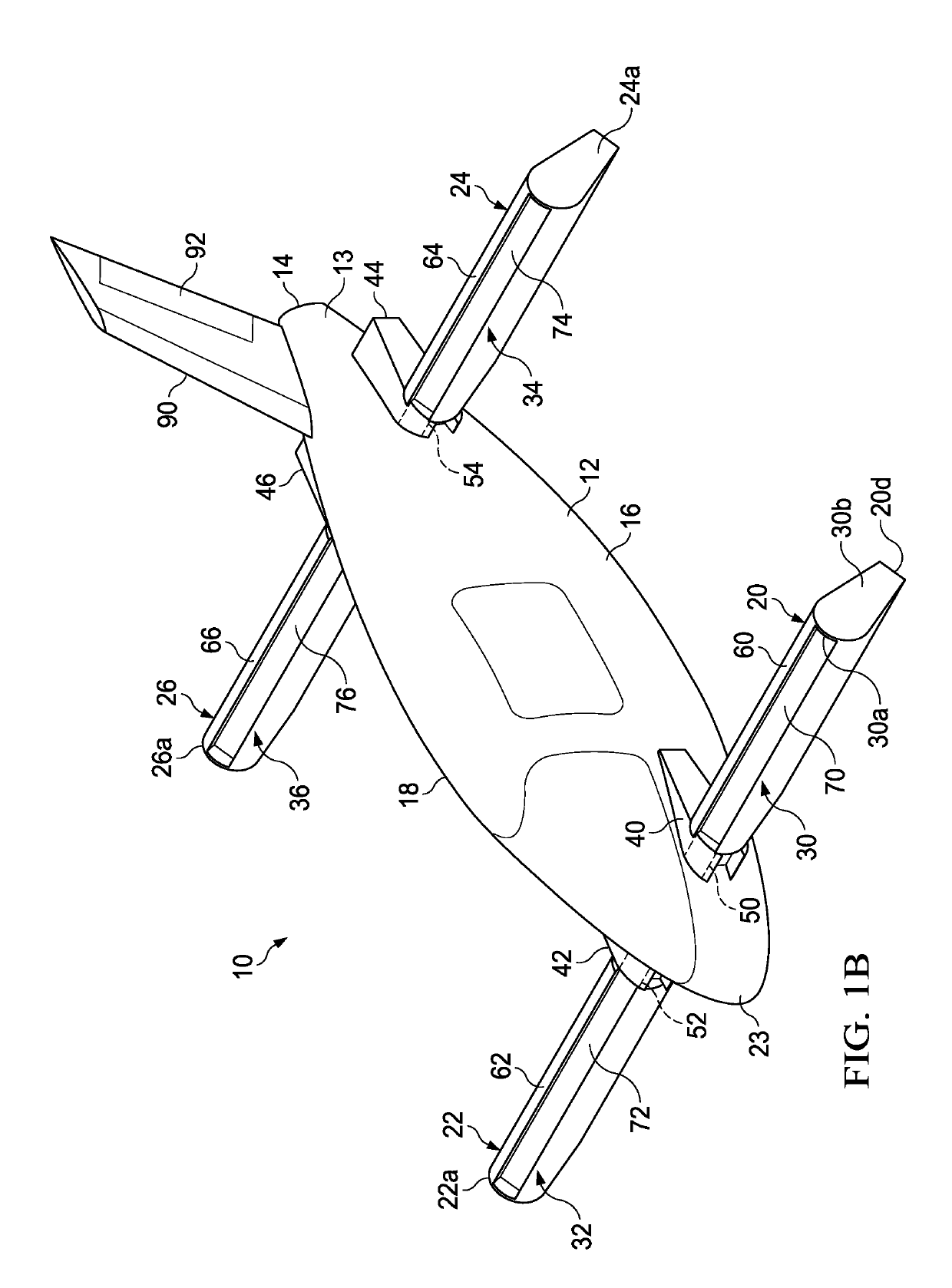
VTOL personal aircraft
InactiveUS7568657B2Increase air velocityReliable executionPower plant arrangements/mountingAircraft stabilisationJet aeroplaneFront edge
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft comprises (1) a fuselage having a front end, a rear end and two lateral sides, the fuselage defining a substantially horizontal central longitudinal axis of the aircraft; (2) an aircraft tail arranged at the rear end of the fuselage and including a rudder and an elevator on each side of the fuselage with movable surfaces for controlling the aircraft; and (3) a wing on each side of the fuselage having a front edge, a trailing edge and an upper surface extending from the front edge to the trailing edge. According to the invention, means are provided for increasing the speed of an airstream flowing over the upper surface of each wing, and an air deflector is disposed on each side of the fuselage between the trailing edge of each wing and the aircraft tail. These deflectors each have a deflection surface to deflect downward the airstream flowing over the upper surface of the wing to act as a “brake” to the forward motion of the aircraft and to provide additional lift so that the aircraft may hover.
Owner:MILDE JR KARL F
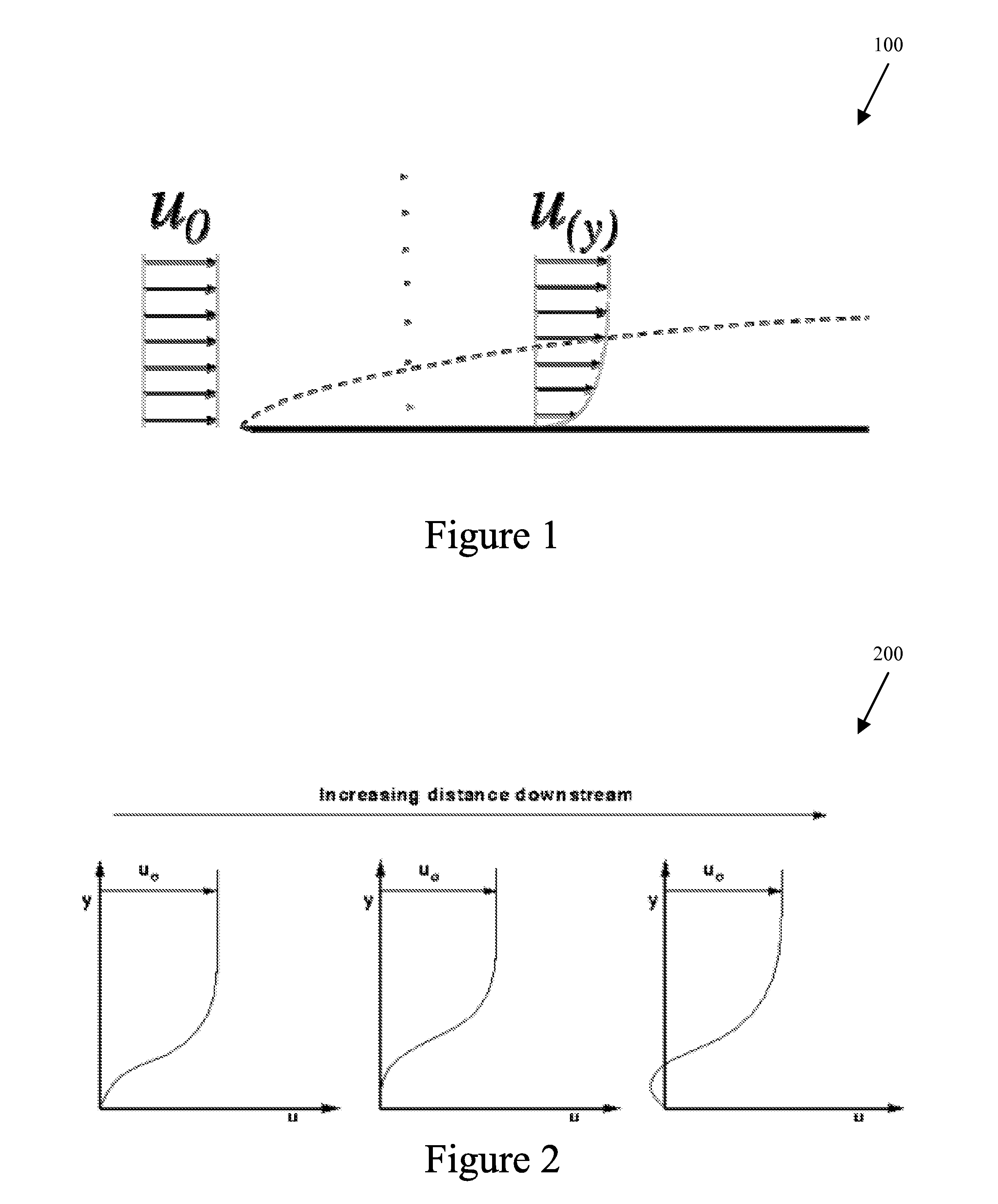
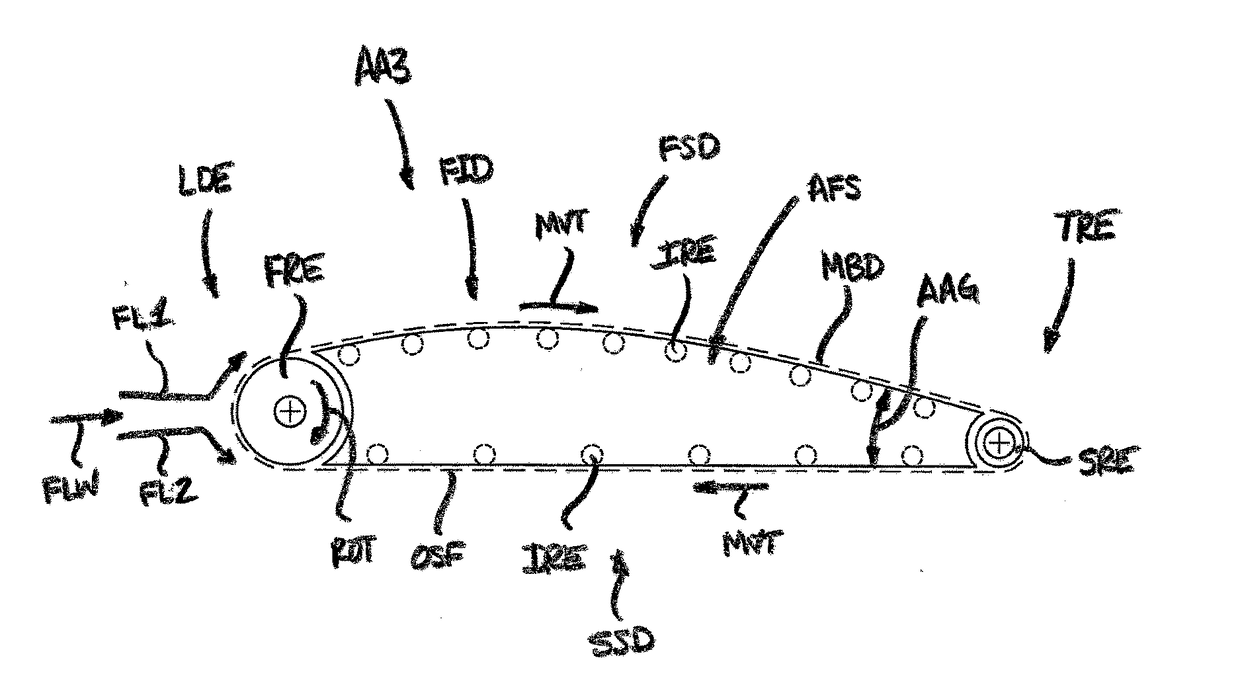
Fluid Boundary Layer Control
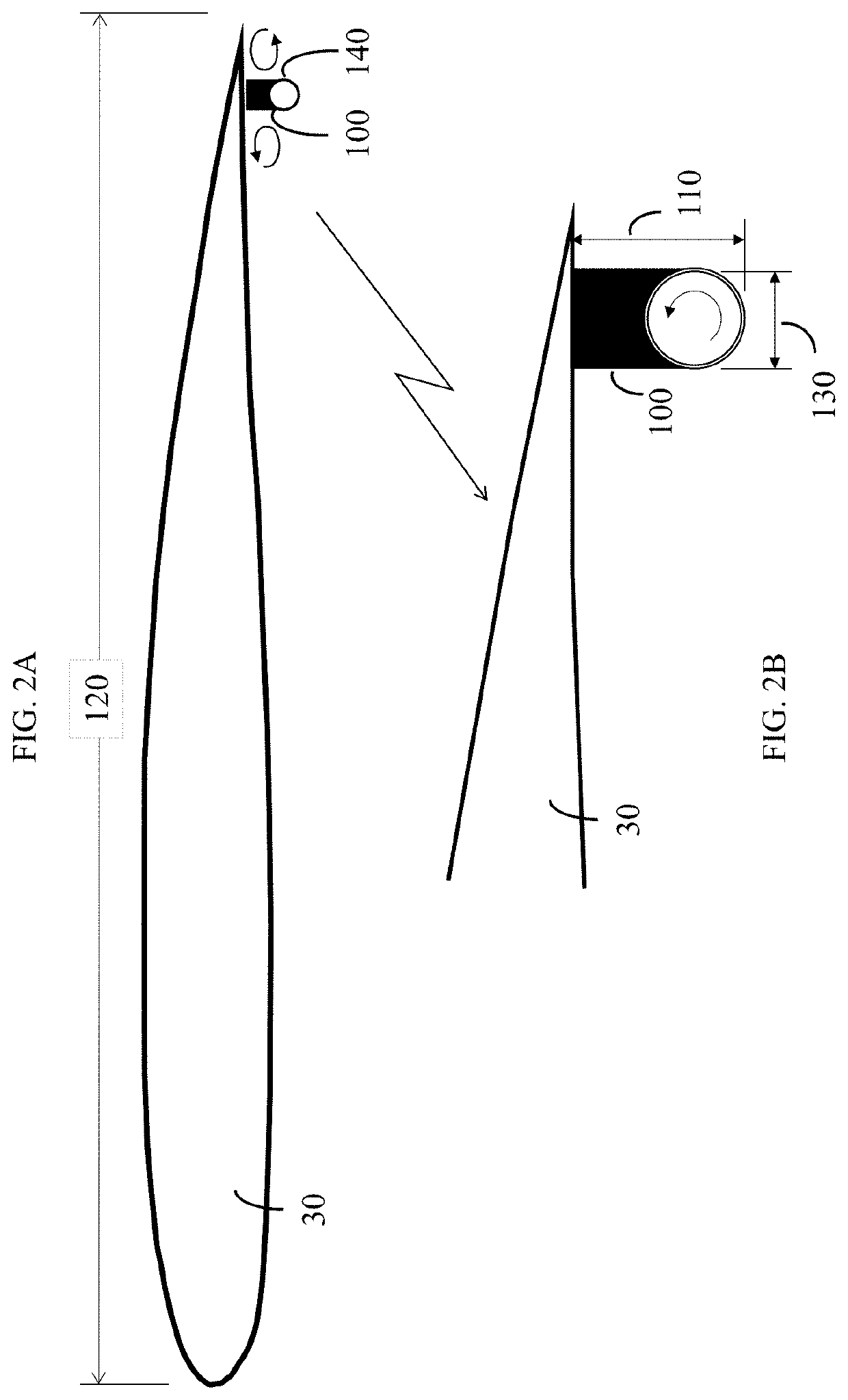
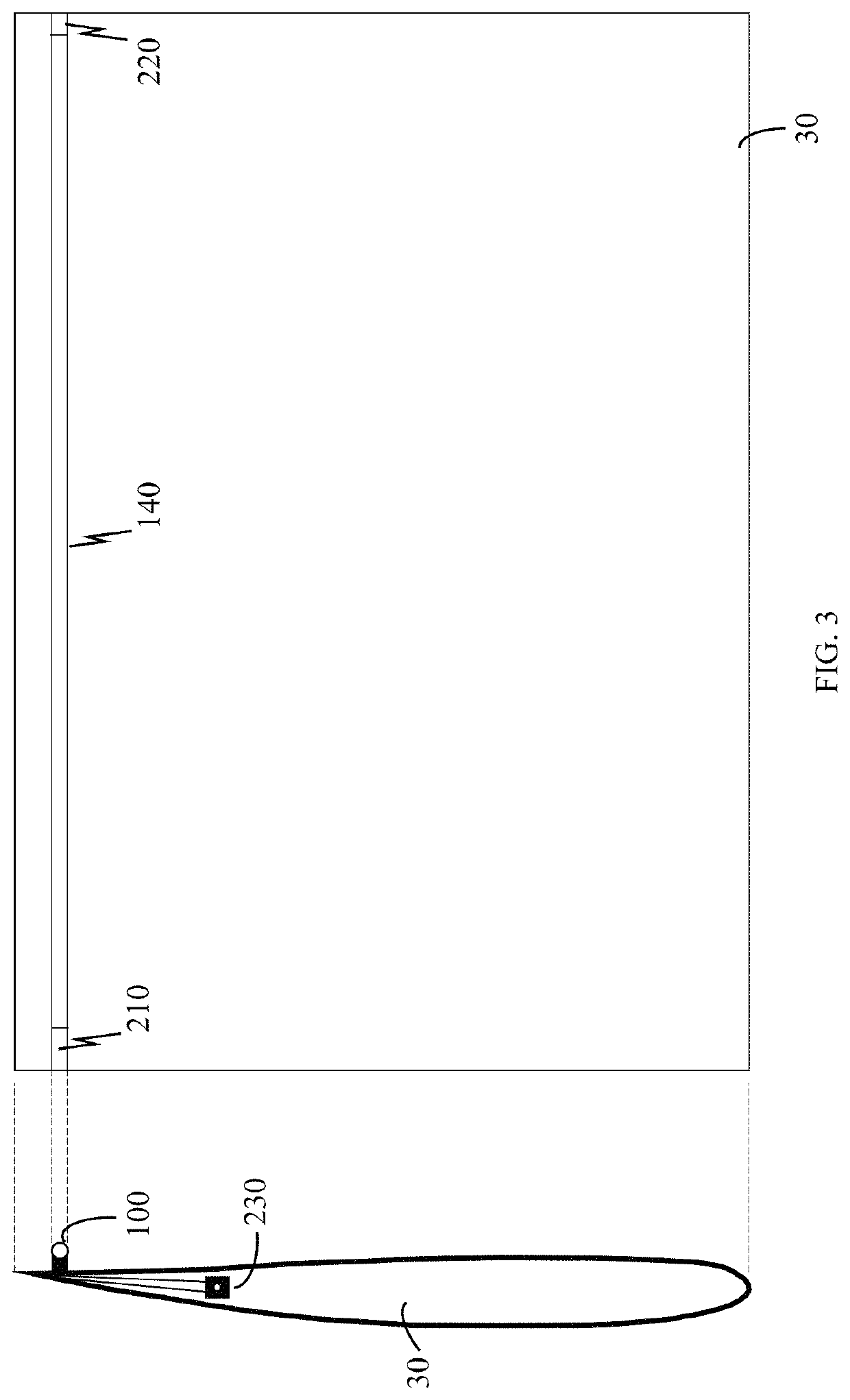
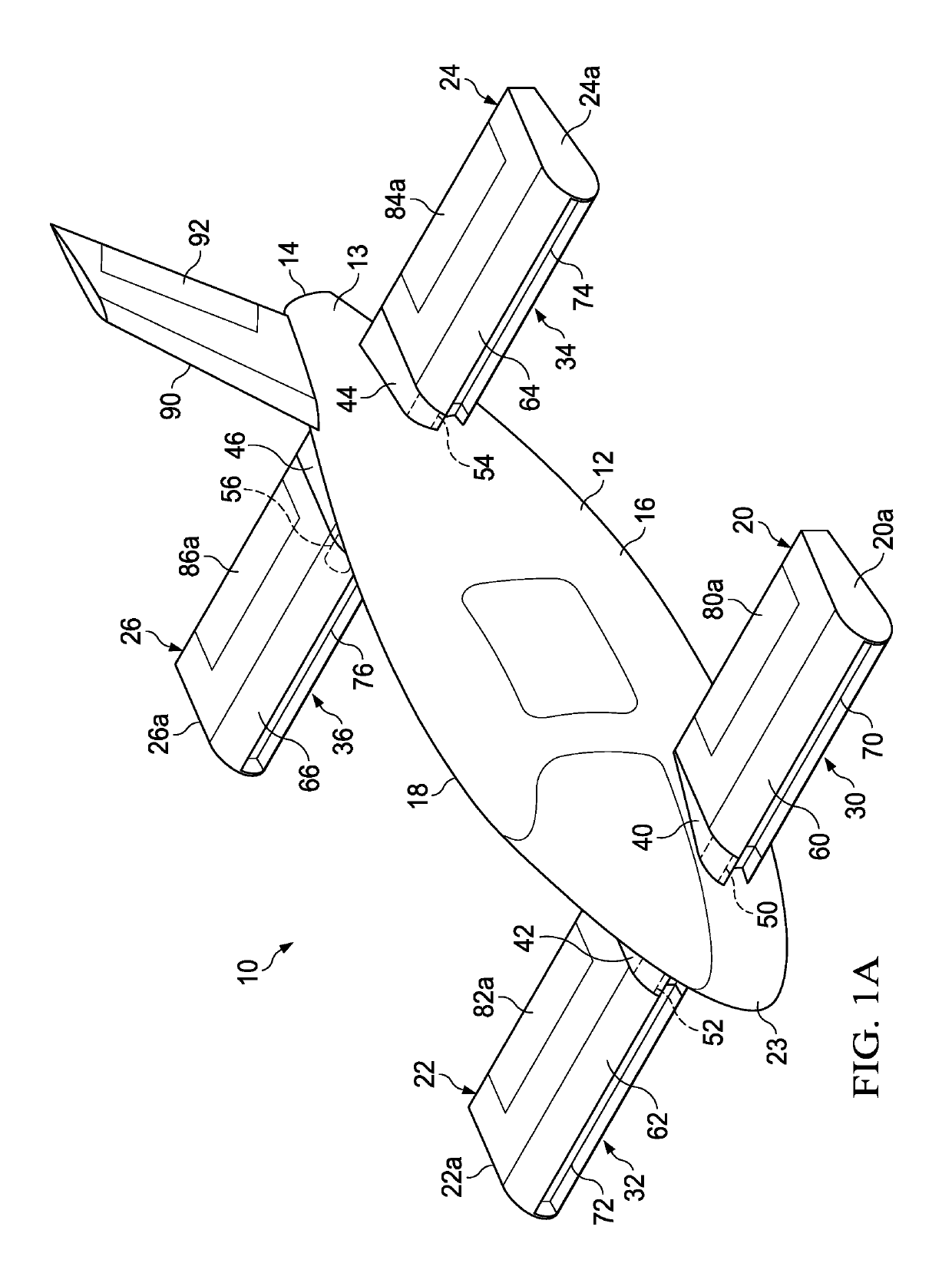
The lift and drag performance of all vehicles is strongly influenced by viscous effects, and in turn, laminar separation bubbles. This application employs an effective fluid boundary layer control strategy that reduces parasitic drag, allows for more usable angles of attack, and delays or stops separation. In the approach of this application, the control surface effectively uses the Magnus effect to delay or stop a separation bubble from forming, which can increase lift, reduce drag, and delay degrees of stall by directly manipulating the velocity gradient in the fluid boundary layer.
Owner:VIRES AERONAUTICS
VTOL personal aircraft
InactiveUS20060202083A1Increase air velocityReliable executionAircraft navigation controlPower plant arrangements/mountingFlight vehicleEngineering
A vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft comprises (1) a fuselage having a front end, a rear end and two lateral sides, the fuselage defining a substantially horizontal central longitudinal axis of the aircraft; (2) an aircraft tail arranged at the rear end of the fuselage and including a rudder and an elevator on each side of the fuselage with movable surfaces for controlling the aircraft; and (3) a wing on each side of the fuselage having a front edge, a trailing edge and an upper surface extending from the front edge to the trailing edge. According to the invention, means are provided for increasing the speed of an airstream flowing over the upper surface of each wing, and an air deflector is disposed on each side of the fuselage between the trailing edge of each wing and the aircraft tail. These deflectors each have a deflection surface to deflect downward the airstream flowing over the upper surface of the wing to act as a “brake” to the forward motion of the aircraft and to provide additional lift so that the aircraft may hover.
Owner:MILDE JR KARL F
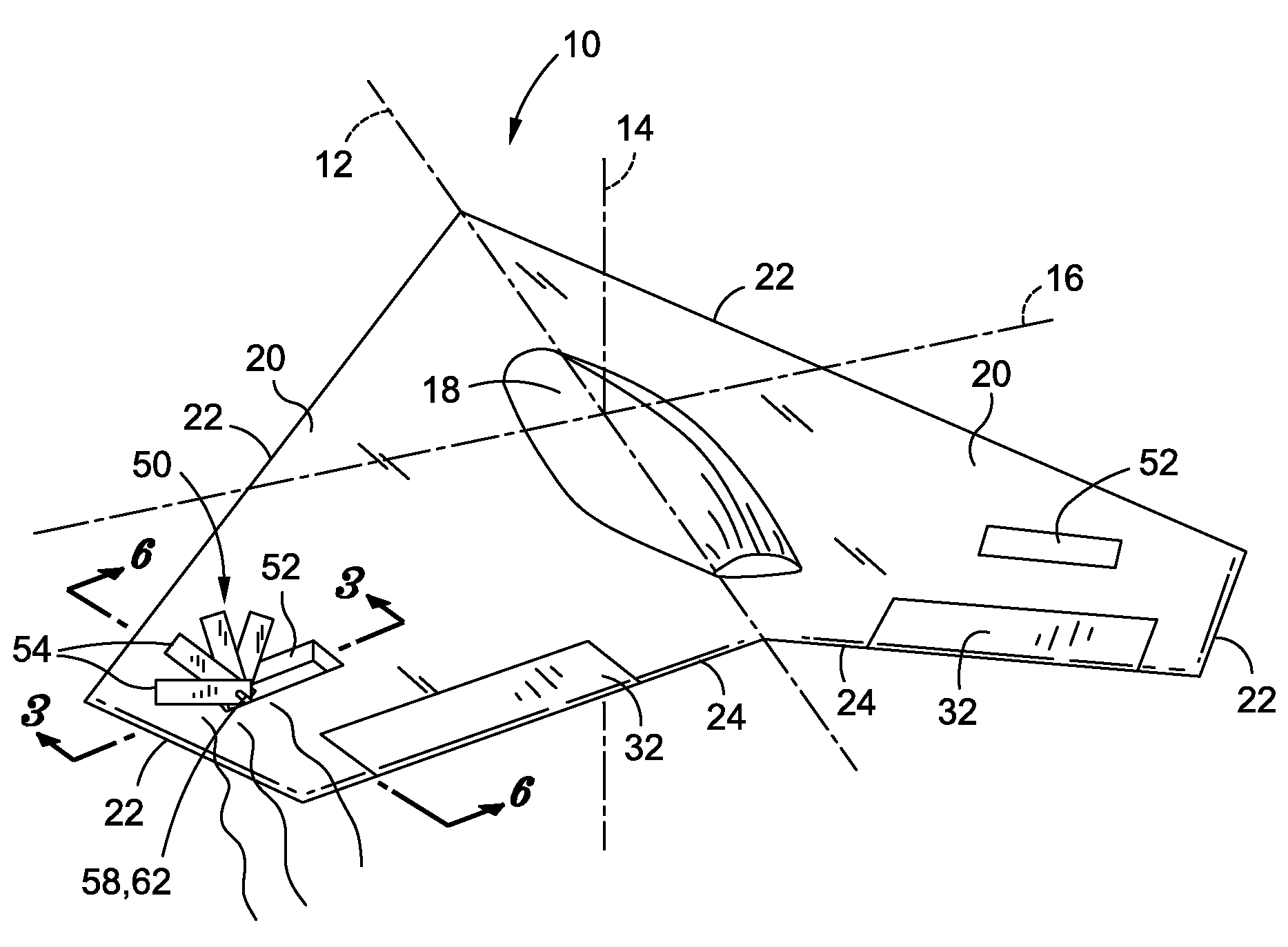
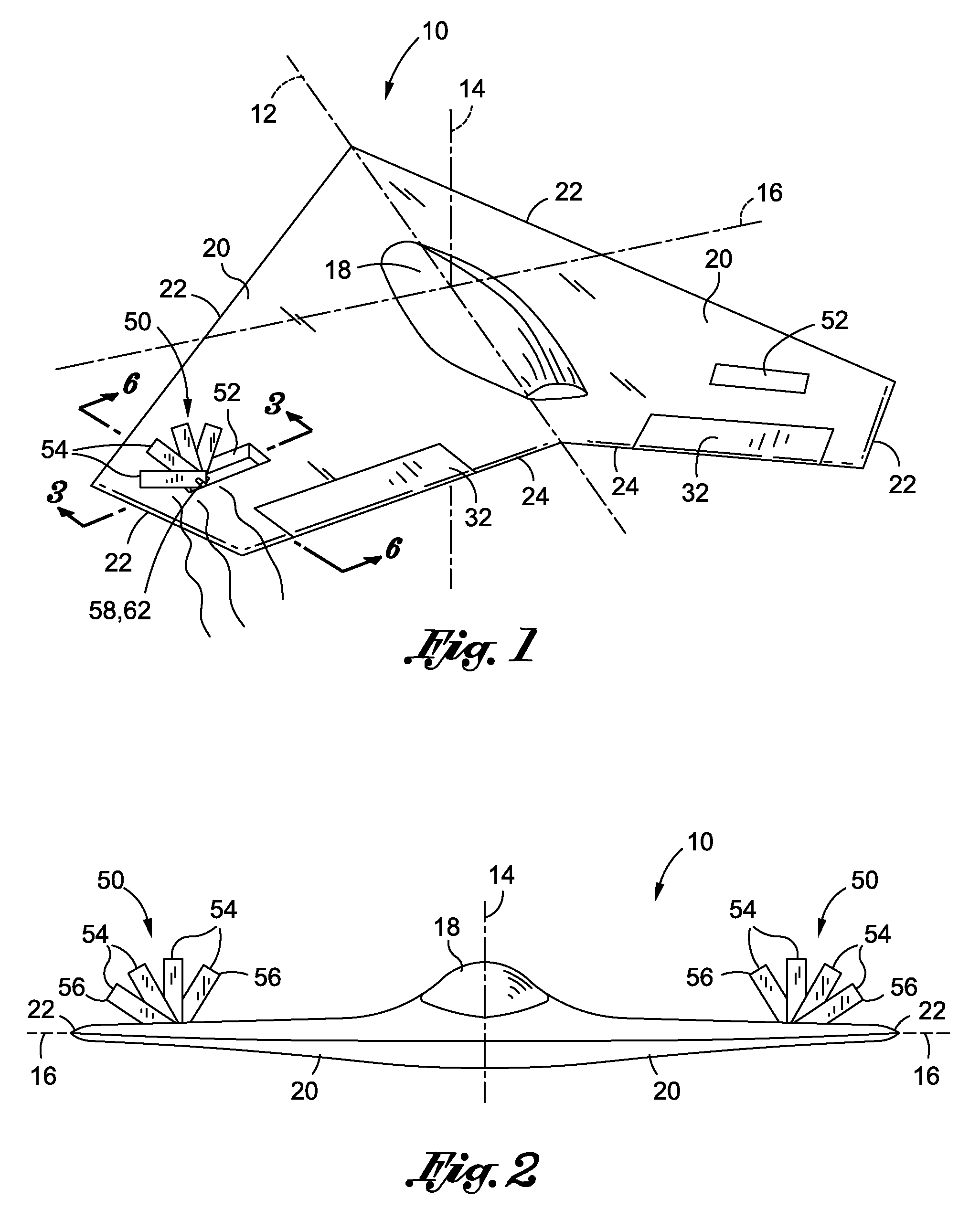
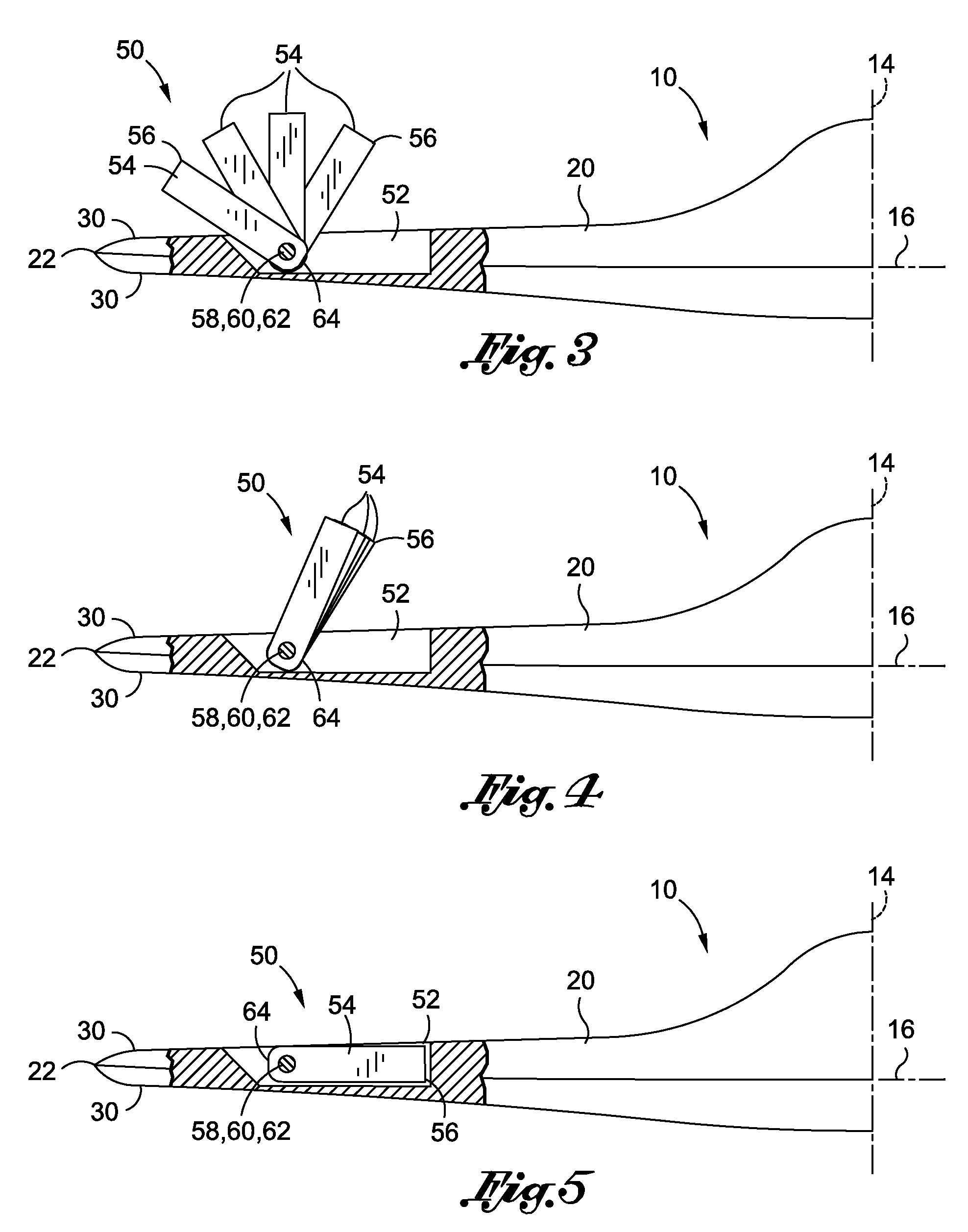
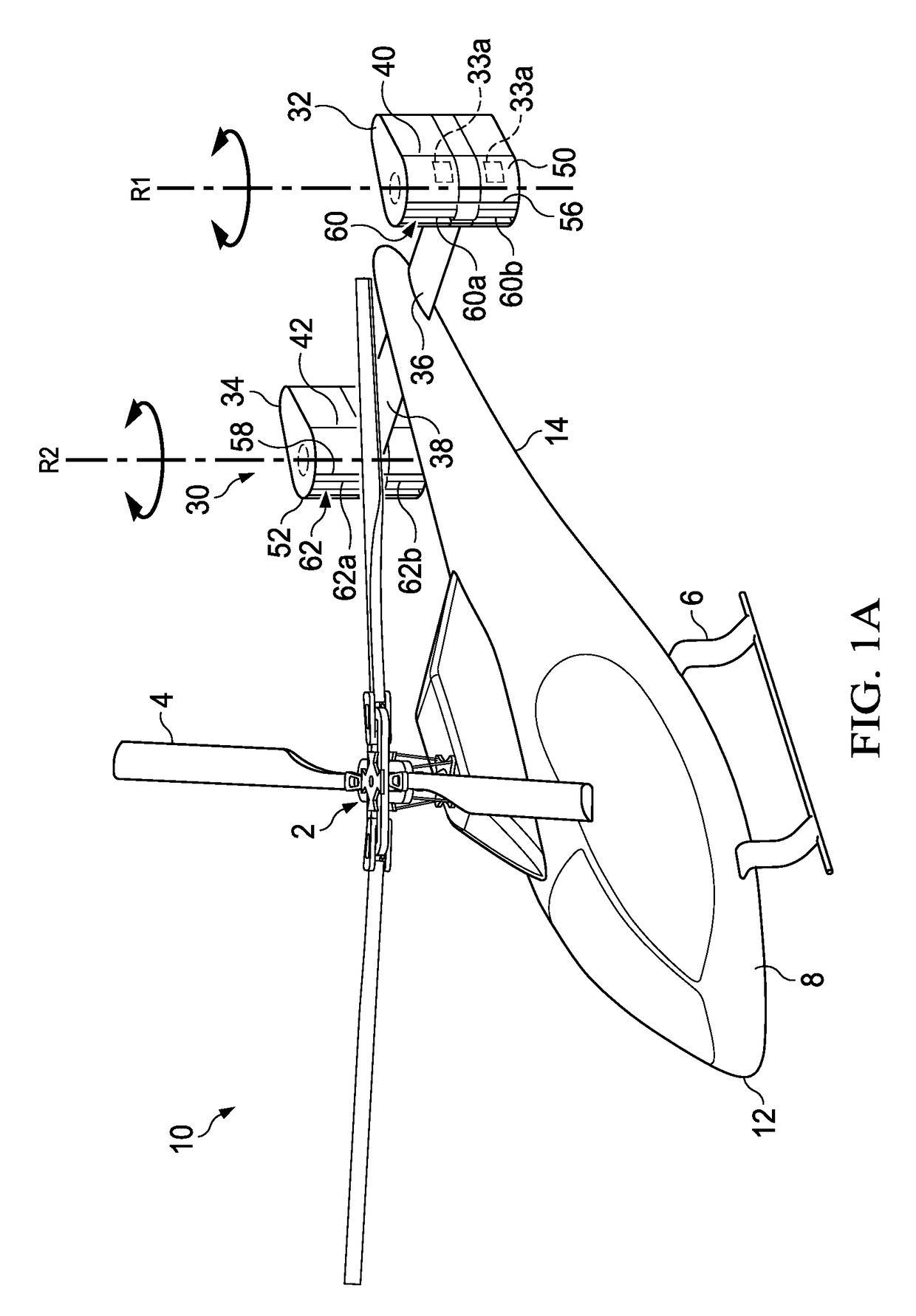
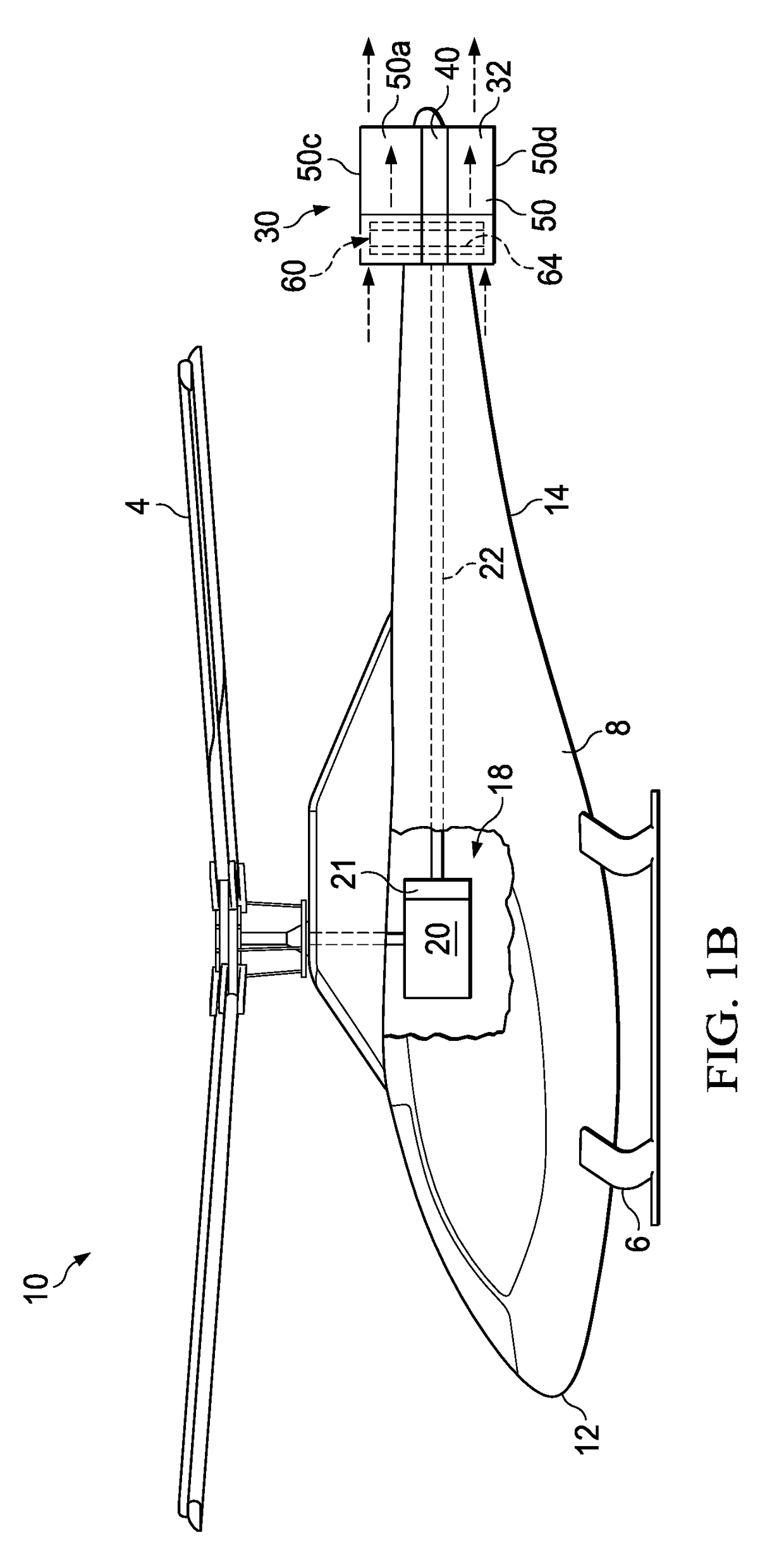
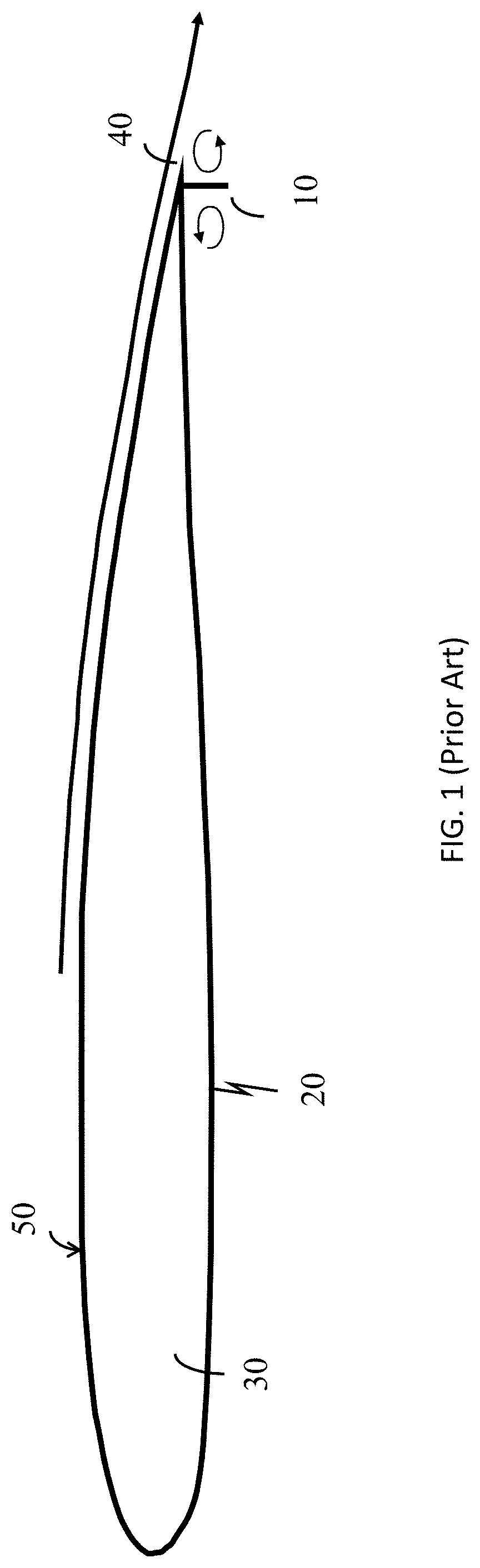
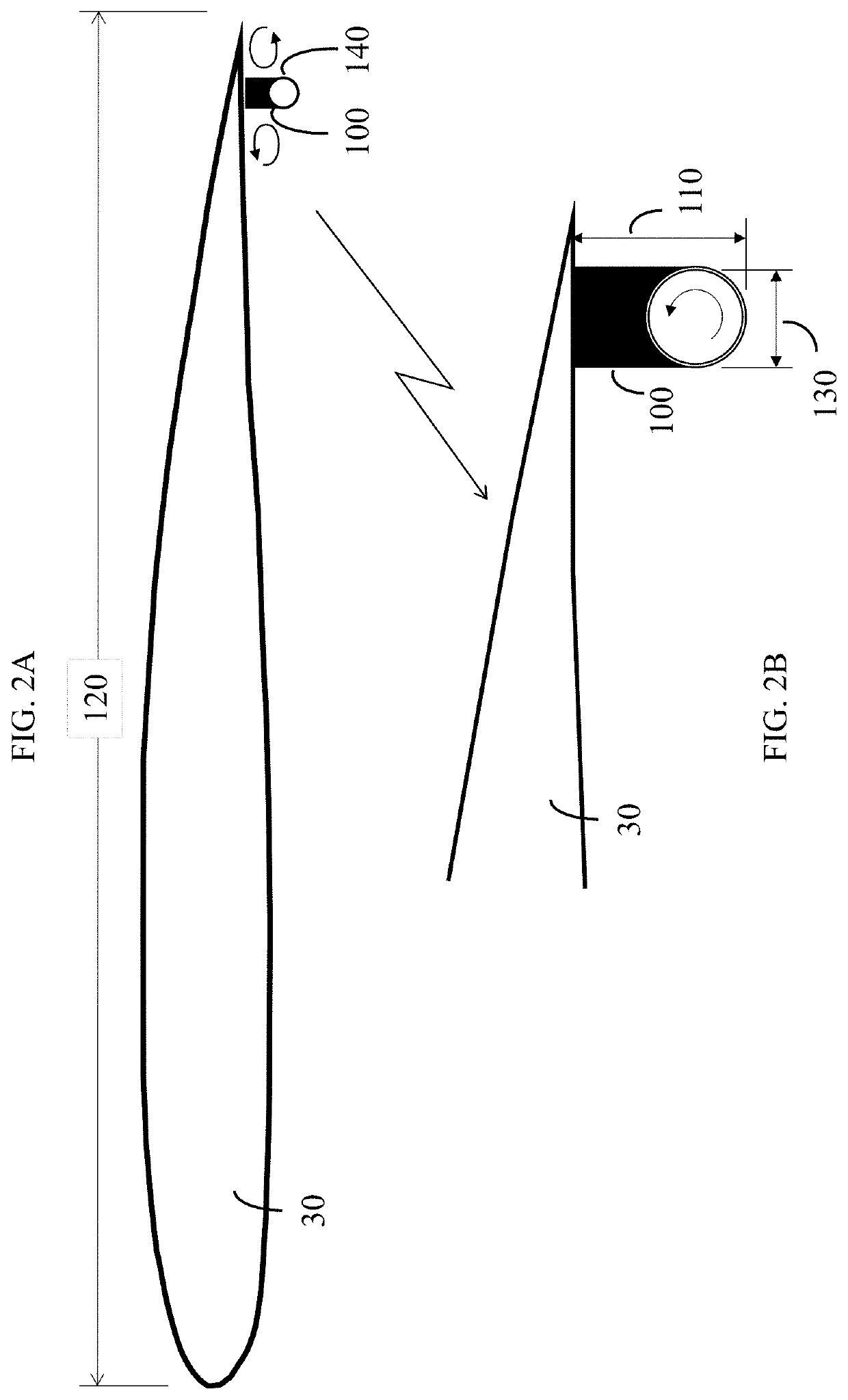
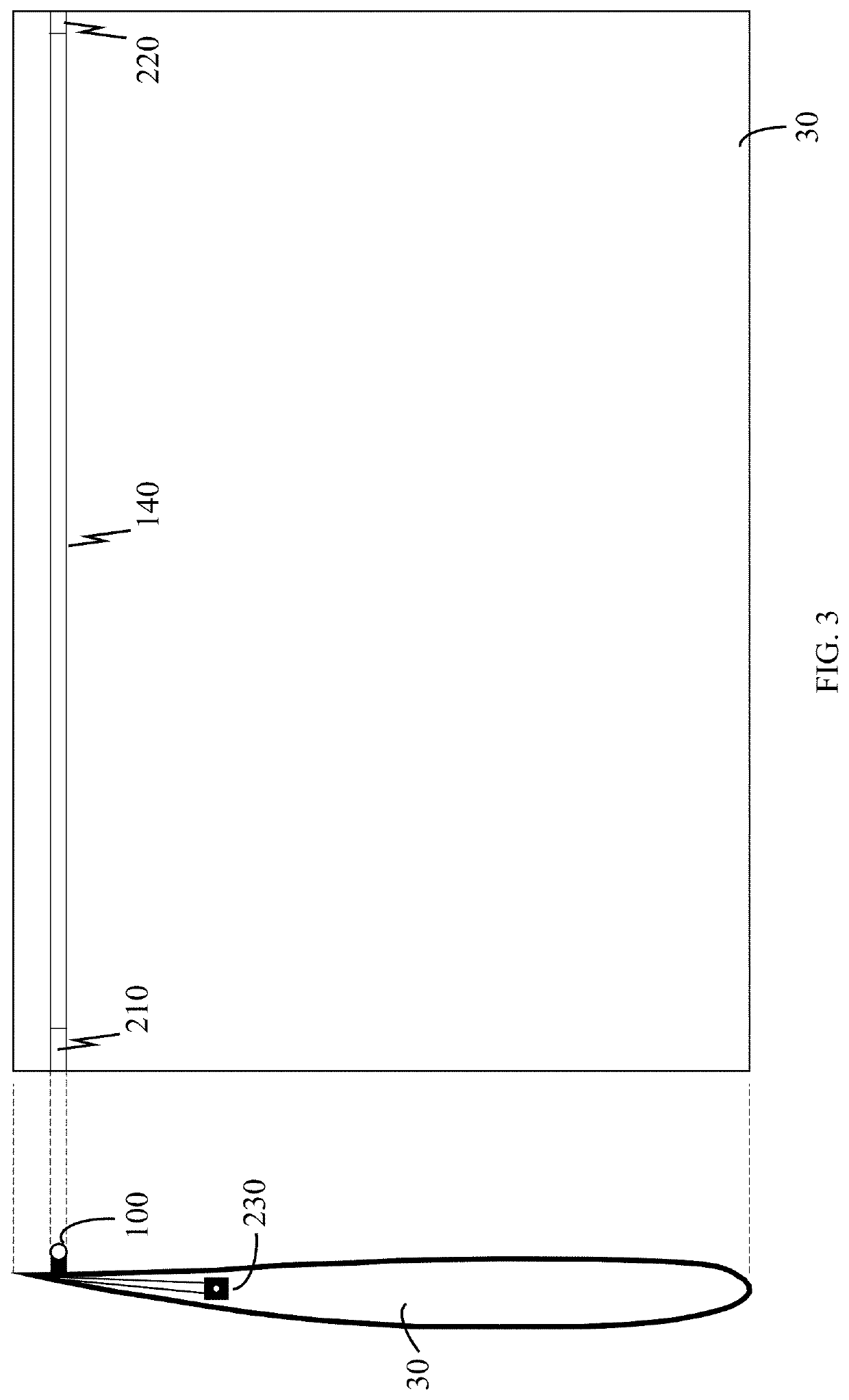
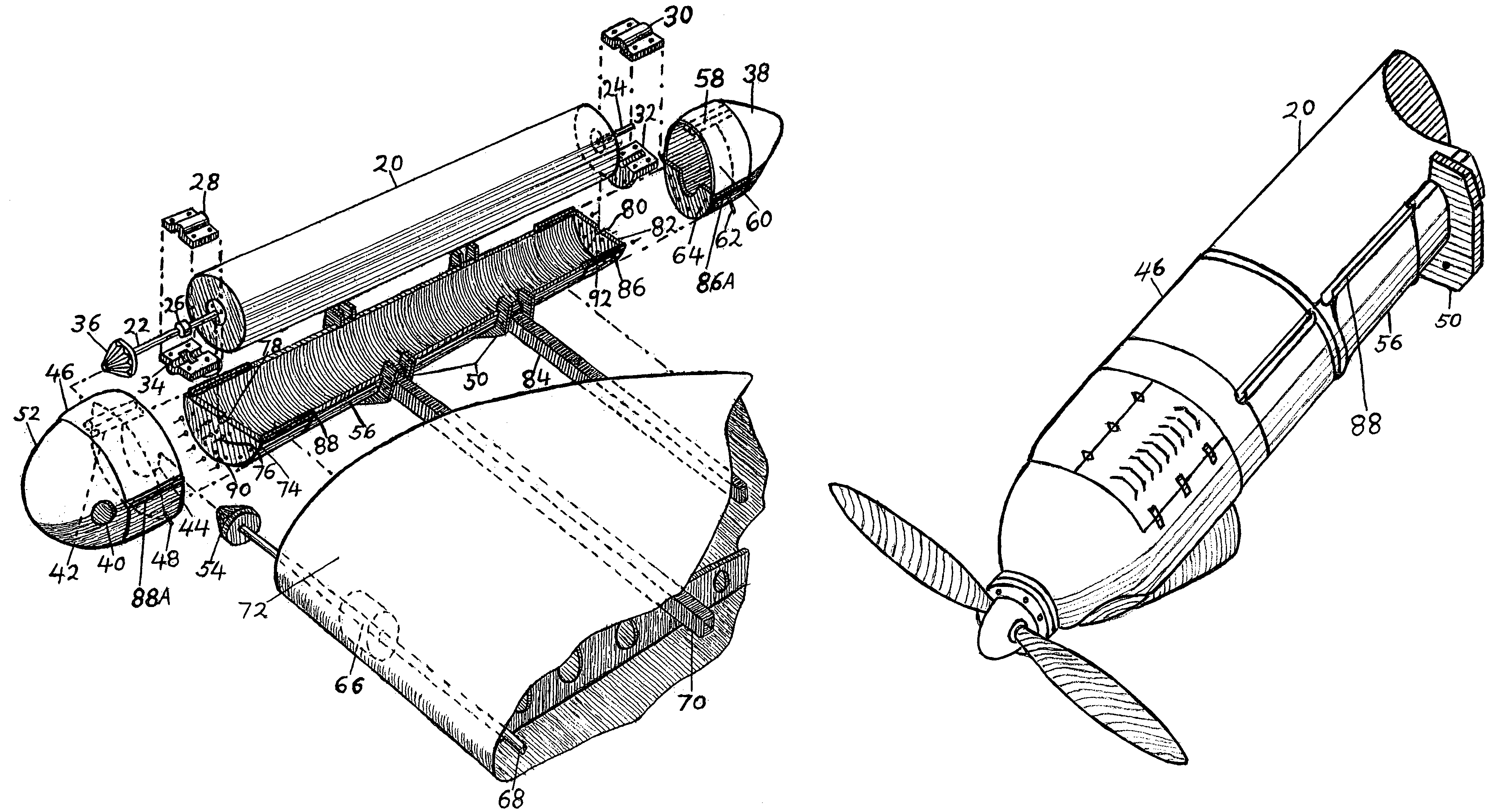
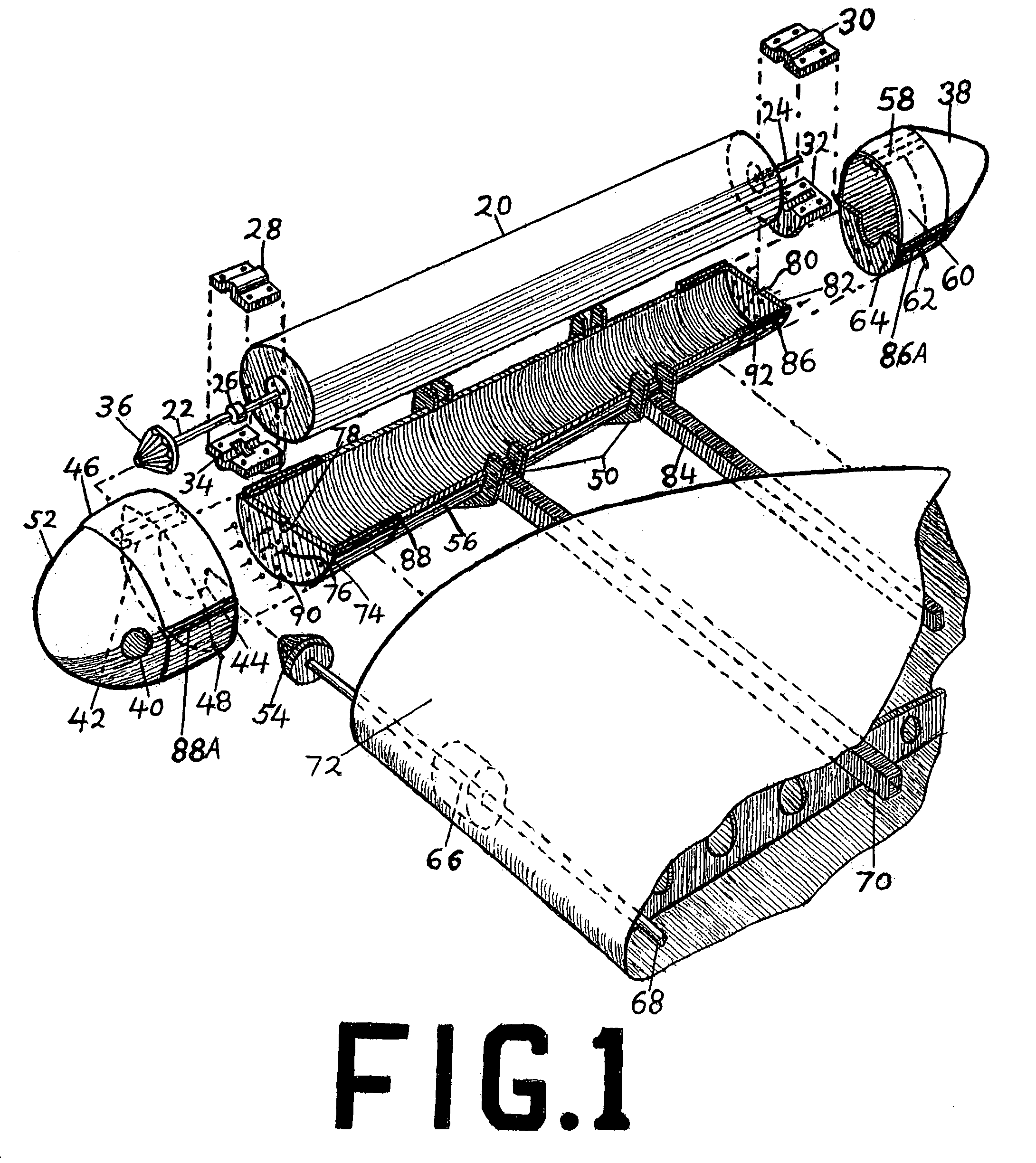
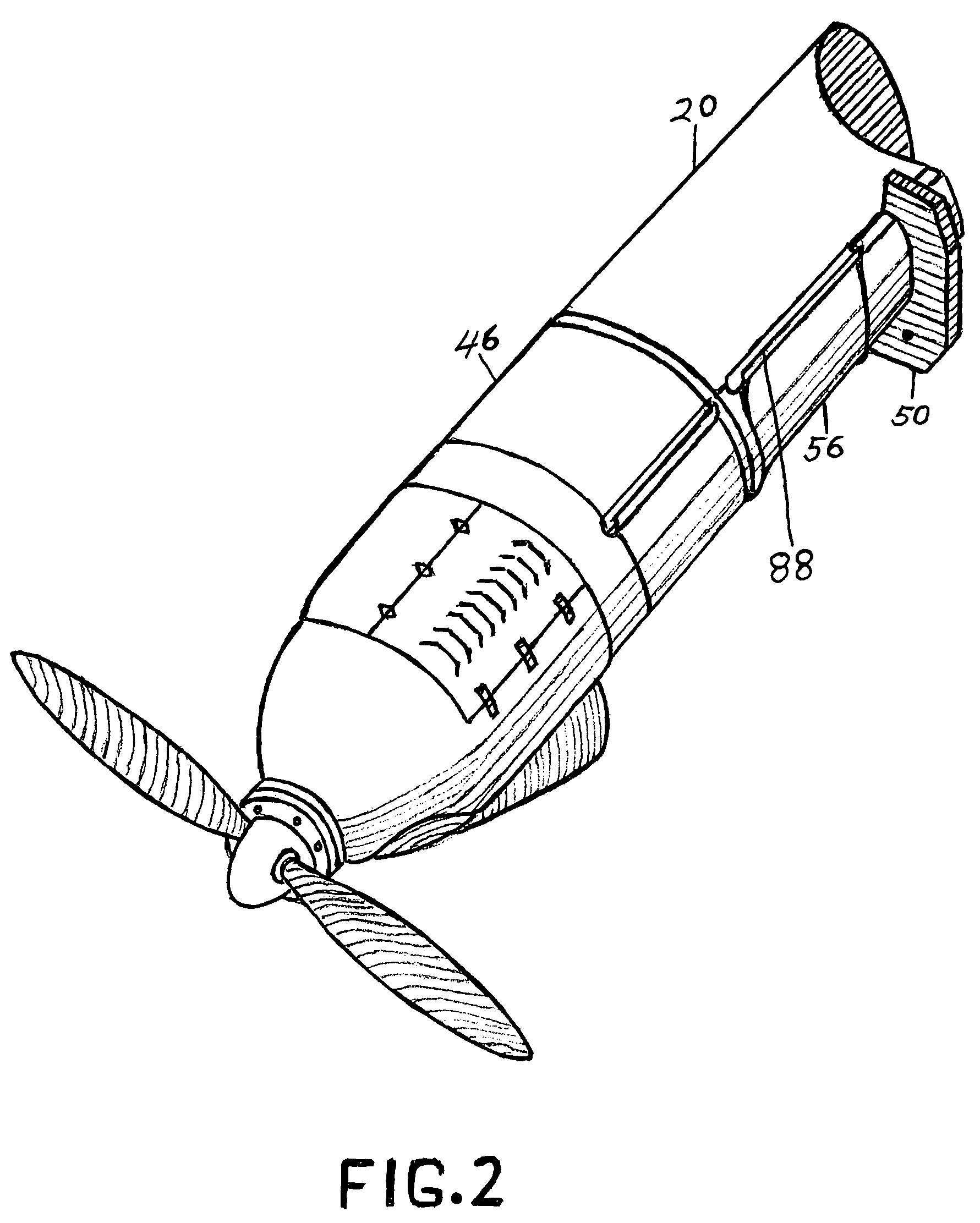
Powered aircraft including inflatable and rotatable bodies exhibiting a circular cross-section perpendicular to its rotation axis and in order to generate a lift force
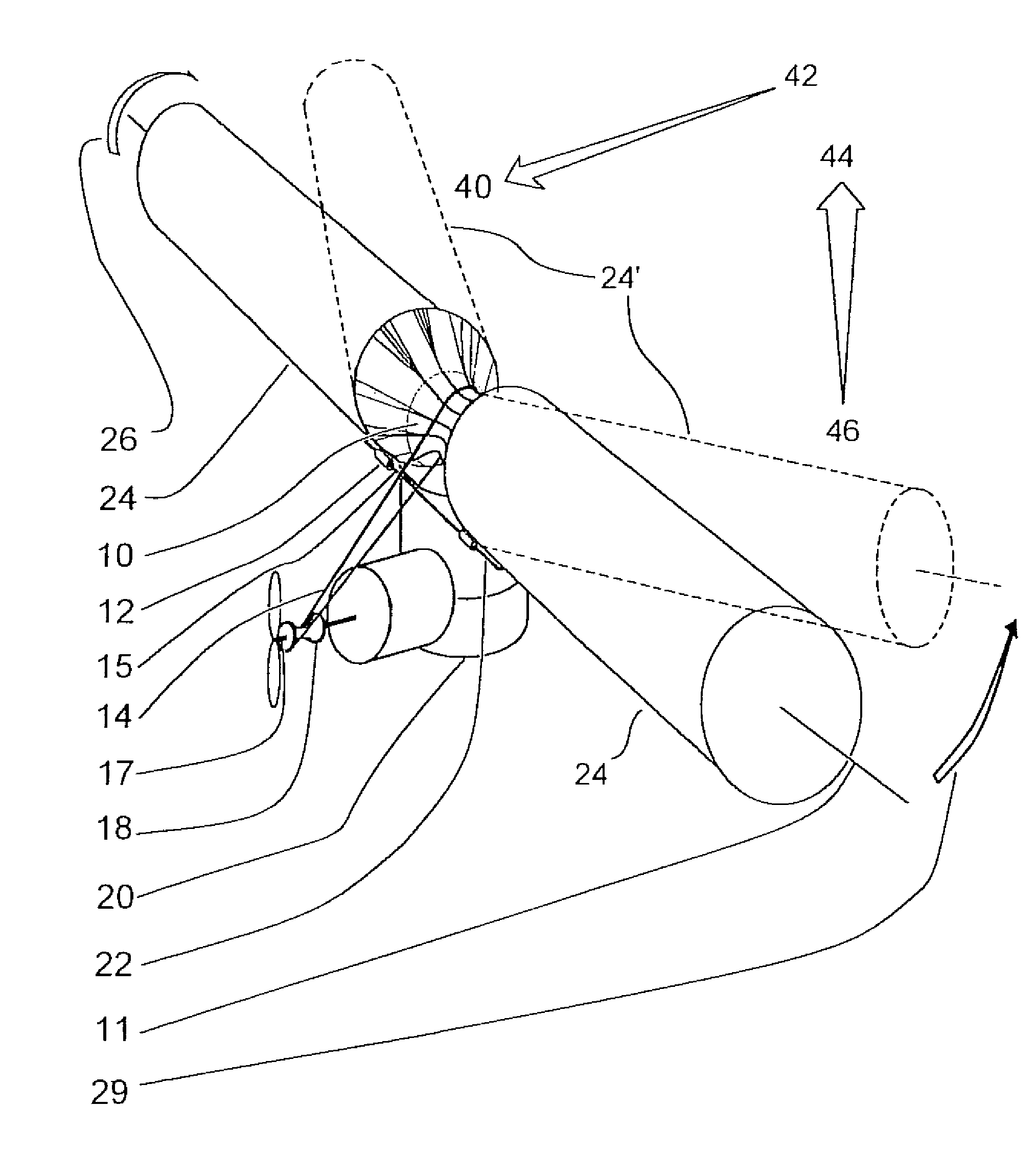
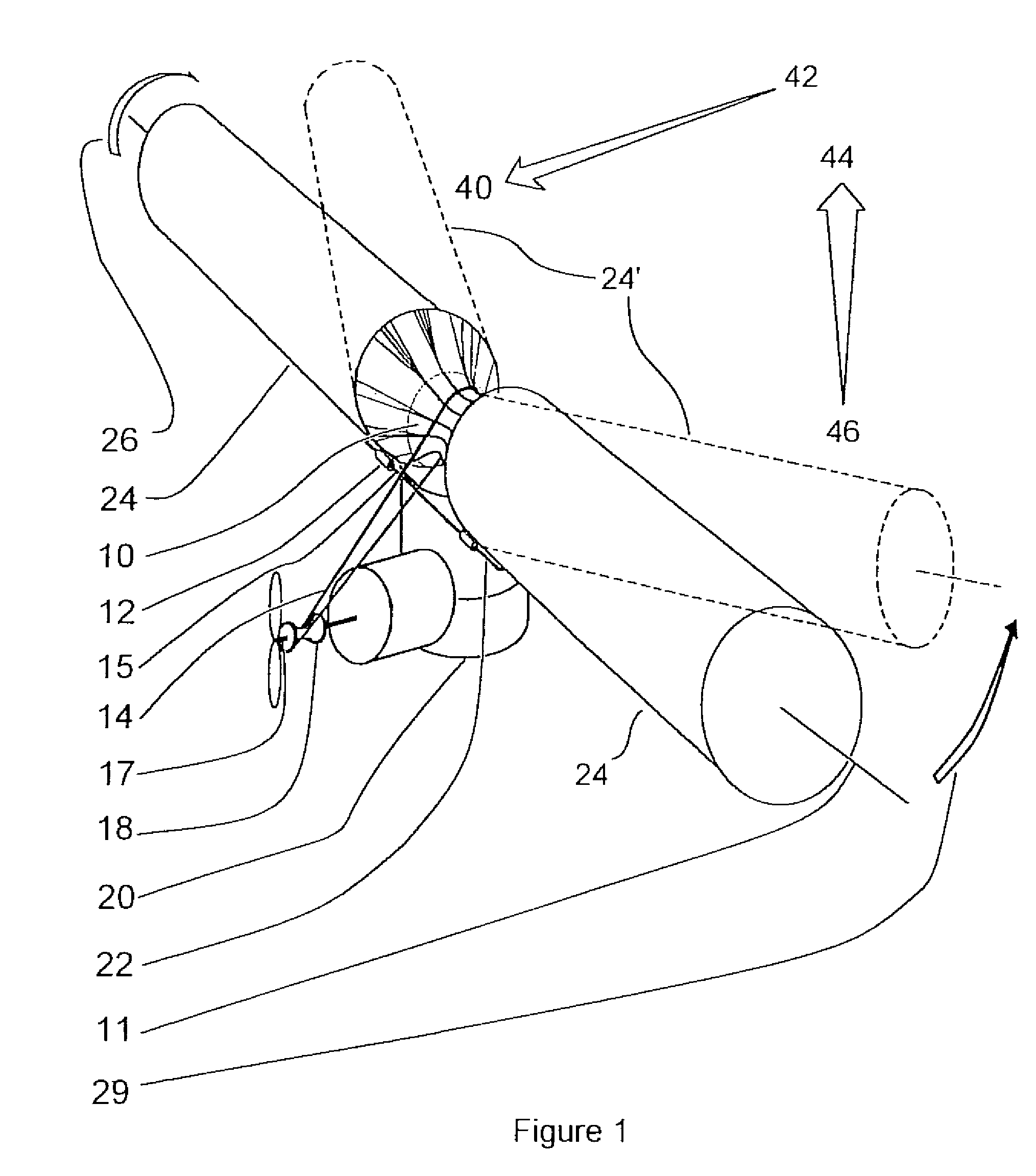
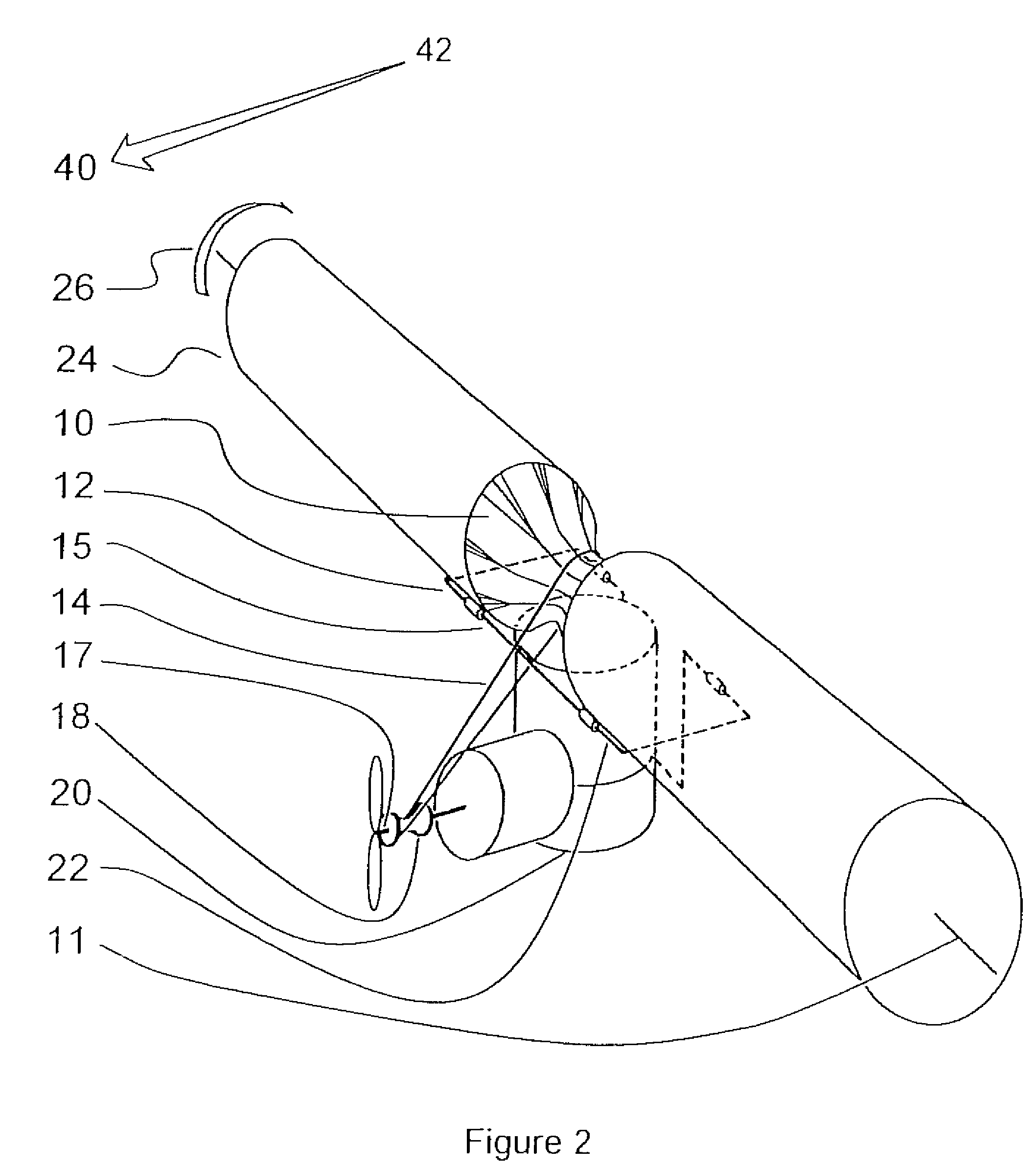
InactiveUS7427047B2Reduce air turbulenceReduce resistanceEfficient propulsion technologiesWing adjustmentsGravity centerCircular dichroism
A lift force generating aircraft having an engine and a thrust force producing device. A pair of elongated and rotating bodies, an axial centerline through the bodies extending in a direction substantially perpendicular to a fore to aft axis extending between the engine and thrust-producing device and at a location above a center of gravity associated with the engine and thrust-producing device. The rotating bodies being constructed of a material inflatable to a desired pressure. A rotary output associated with the engine rotating the bodies, causing them to deflect to angles lesser than the perpendicular with the fore to aft axis, and in response to air stream forces acting upon the bodies in order to reduce drag forces experienced on a rear side of the rotating bodies.
Owner:SAEED TEHRANI OMID
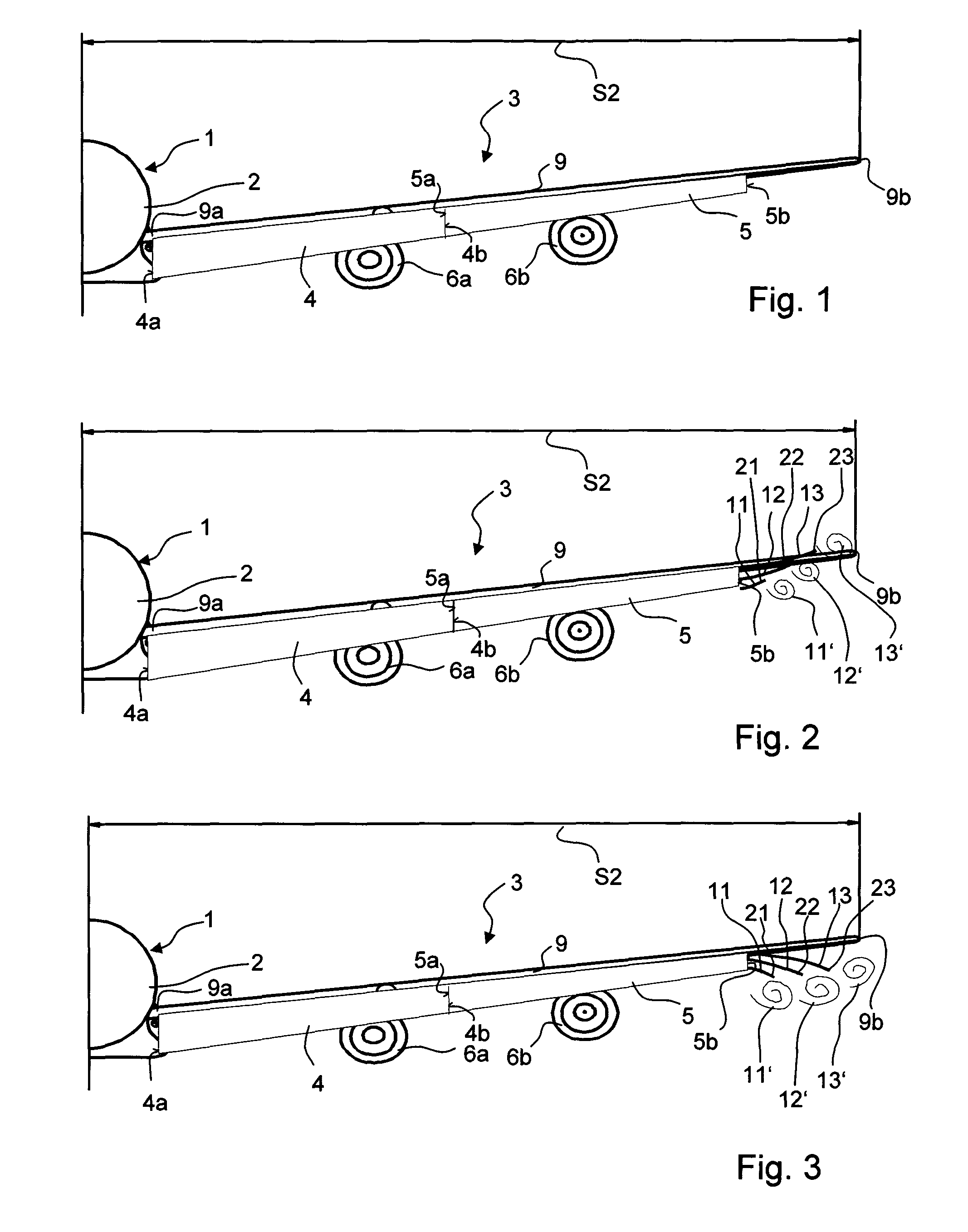
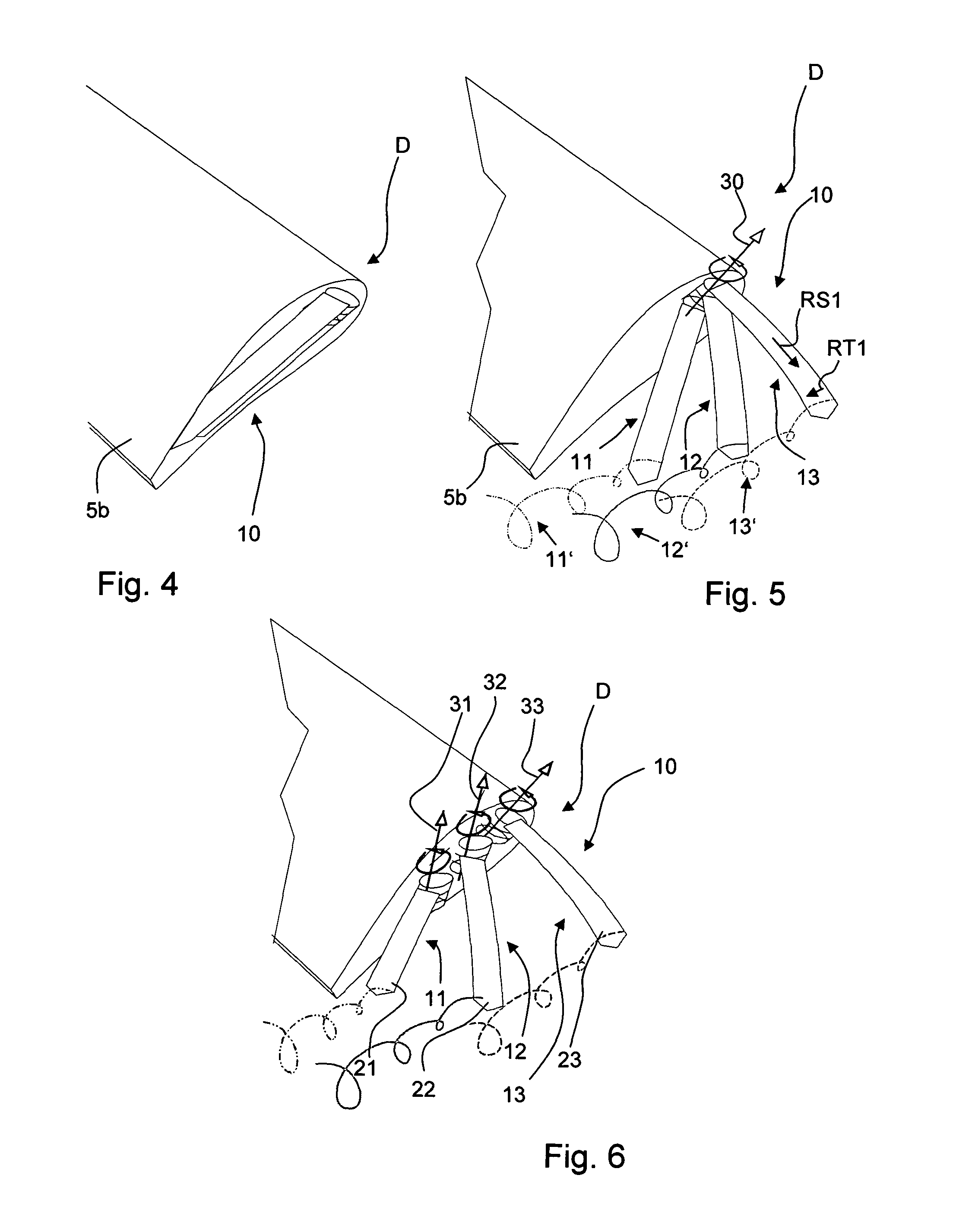
Device for the generation of aerodynamic vortices and also a regulating flap and wing with a device for the generation of aerodynamic vortices
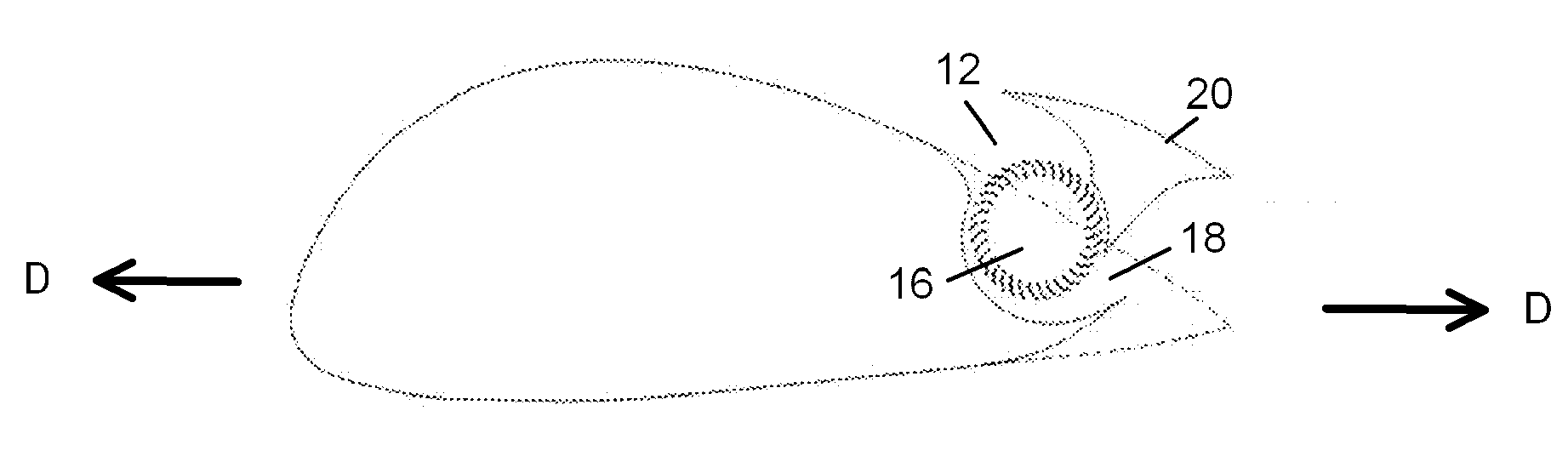
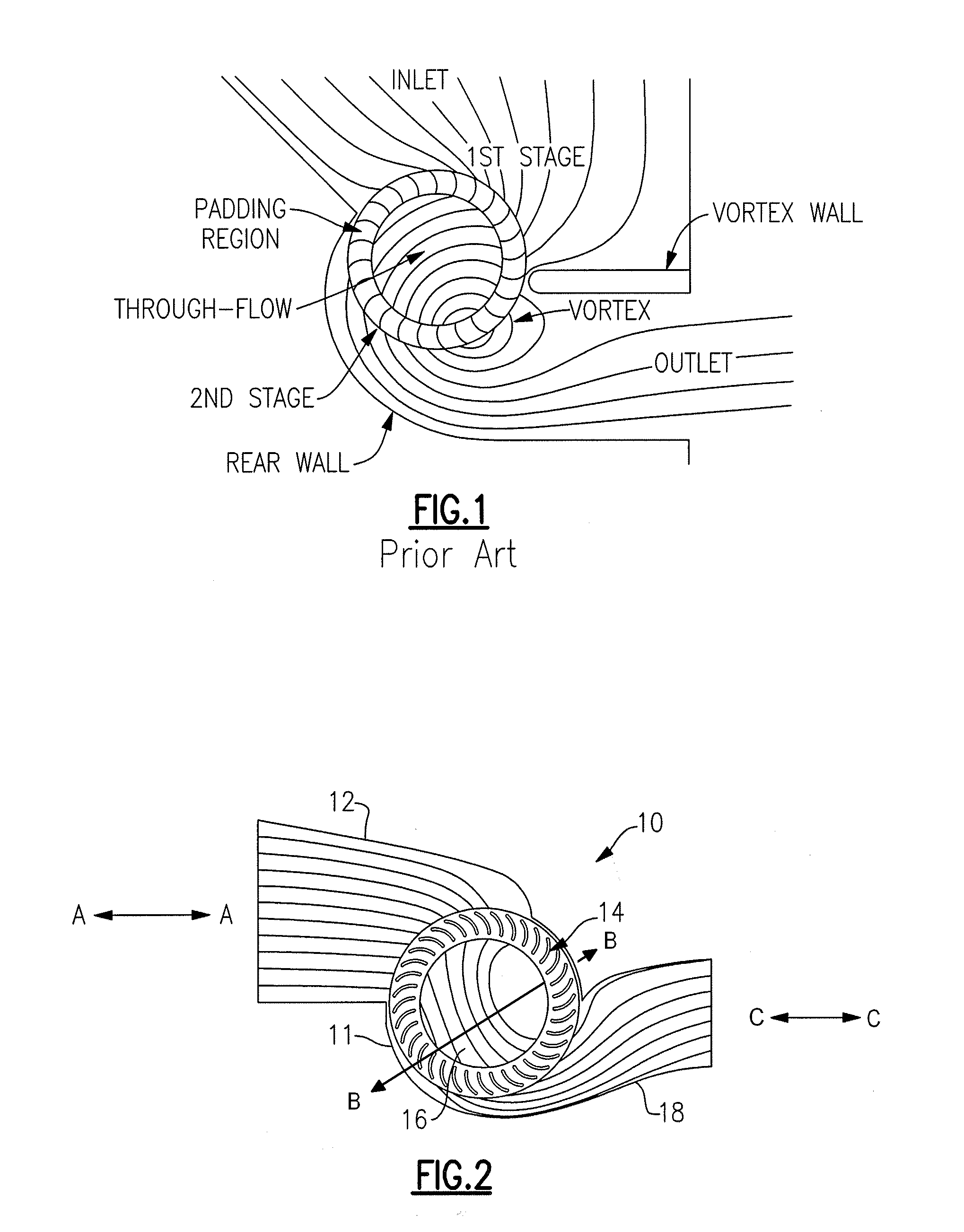
ActiveUS8783623B2Lower levelEasy to liftInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationAerodynamic forceAerospace engineering
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
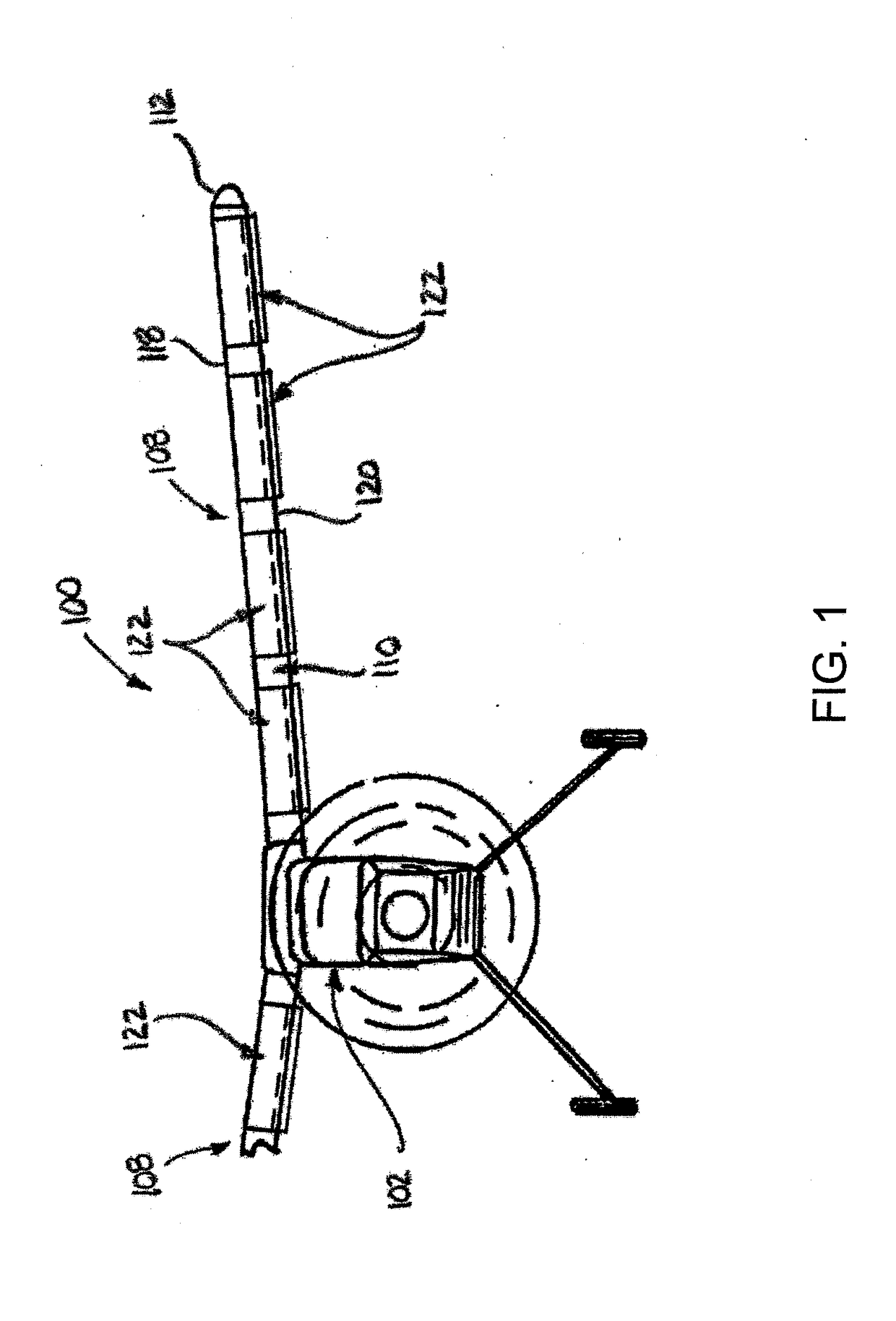
Fluid interface devices with stabilization features as well as airfoil assemblies including same
Fluid interface device, such as may be used in association with airfoil assemblies, can include at least one movable band oriented such that the band moves in a direction relative to an associated relative fluid flow. The at least one movable band can be supported such that at least a portion of an outer surface of the movable band is exposed to the associated relative fluid flow. Fluid interface devices can also include one or more lateral stabilization features operative to oppose lateral migration-inducing forces on the at least one movable band that may be experienced during use of the fluid interface device in the associated relative fluid flow. Airfoil assemblies including such fluid interface devices, as well as vehicles and a wind turbines including one or more of such airfoil assemblies are also included.
Owner:ECOLOGICAL ENERGY
Cross flow fan for wide aircraft fuselage
A cross flow fan to be incorporated into an aircraft fuselage comprises an ingestion fan rotor to be positioned in a tail section of an aircraft fuselage to reduce boundary layer air from a top surface of the fuselage and to drive the air away from the top surface, and a drive arrangement for the ingestion fan rotor. An aircraft is also disclosed.
Owner:RTX CORP
Aerodynamic fan control effector
InactiveUS7997538B2Area maximizationReduced and minimized amountInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationAerodynamics
Owner:THE BOEING CO
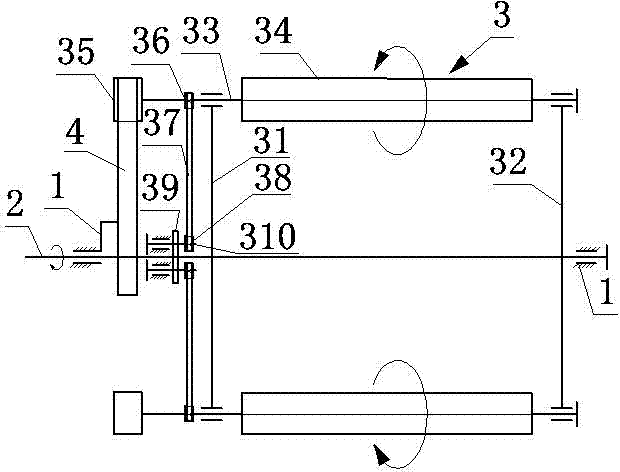
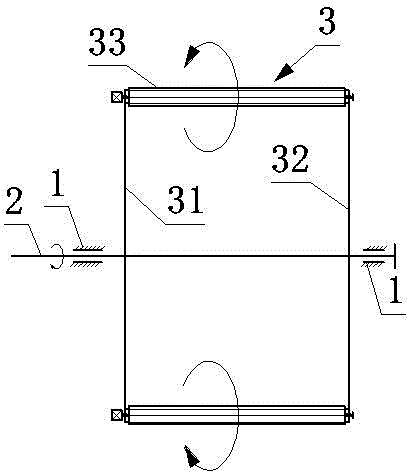
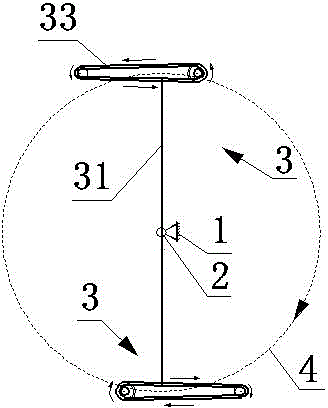
Mechanical transmission roller wing lift force generation device
The invention discloses a mechanical transmission roller wing lift force generation device, and belongs to the technical field of aviation. The mechanical transmission roller wing lift force generation device comprises a rack, a main shaft, an arc guide rail and two rotor wings which are symmetrically distributed on the periphery of the main shaft and are of the same structure. Each rotor wing comprises a left rotating arm, a right rotating arm, a roller shaft, a roller wing, a guide wheel, a driving synchronous wheel, a synchronous belt, a driven synchronous wheel, a gear and a gear shaft. The main shaft is horizontally installed on the rack through a bearing. The lower surface of the arc guide rail makes contact with the guide wheels higher than the horizontal plane of the main shaft. When the guide wheels above the horizontal plane of the main shaft revolve around the axis of the main shaft, the roller shafts connected with the guide wheels will be driven to rotate automatically and the roller wings connected with the roller shafts are driven to rotate automatically. The autorotation direction of the roller wings is opposite to the revolution direction of the roller wings around the main shaft. The guide wheels below the horizontal plane of the main shaft will rotate automatically in the direction opposite to the direction in which the guide wheels above the horizontal plane of the main shaft rotate. The mechanical transmission roller wing lift force generation device is applied to a vertical lift aircraft to be used as a lift force device.
Owner:董海宁
Aerofoil slot blowing
InactiveUS20110049304A1Improve performanceImprove lifting performanceWingsDrag reductionLeading edgeStagnation point
An aerofoil defining geometric upper and lower surfaces which together form a leading edge region and a trailing edge region, and comprising a blowing device having a slot in the lower geometric surface in the leading edge region for injecting fluid into the airflow over the aerofoil, wherein the slot is located forward of the leading edge stagnation point at the critical angle of incidence of the aerofoil, and wherein the blowing device is adapted to inject the fluid forwardly of the slot and substantially parallel to the lower surface. Also, a method of improving the performance of the aerofoil by injecting fluid into the airflow over the aerofoil from the slot. The upper surface of the aerofoil can be kept clean, giving the potential for laminar flow during cruise without significantly compromising the high lift performance of a blown leading edge at high incidence.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Aircraft tail with cross-flow fan systems
In one aspect, there is provided an aircraft, including a fuselage having a longitudinal axis extending from a front portion through an aft portion; first and second tail members extending from the aft portion; a first cross-flow fan system rotatably mounted to the first tail member; and a second cross-flow fan system rotatably mounted to the second tail member. The first and second cross-flow fan systems are configured to provide a forward thrust vector and an anti-torque vector on the aircraft. The first and second cross-flow fan systems can have a rotational axis oriented generally vertically. In another aspect, there is an aircraft including a fuselage having a front portion and a tail portion; and a cross-flow fan system supported by the tail portion. Embodiments include a cross-flow fan system retrofittable onto an aircraft and methods for retrofitting an aircraft with a cross-flow fan system.
Owner:BELL HELICOPTER TEXTRON INC
Active Lift Control Device and Method
ActiveUS20220009618A1Easy to liftIncrease pressureInfluencers using Magnus effectWind motor controlClassical mechanicsEngineering
A lift control device actively controls the lift force on a lifting surface. The device has a protuberance near a trailing edge of its lifting surface, which causes flow to separate from the lifting surface, generating regions of low pressure and high pressure which combine to increase the lift force on the lifting surface. The device further includes a means to keep the flow attached around the protuberance or to modify the position of the protuberance in response to a command from a central controller, so as to provide an active control of the lift between a maximum value and a minimum value.
Owner:ARCTURA INC
Lift unit for vertical take-off and landing aerial vehicle
A lift unit for a vertical take-off and landing type aerial vehicle. A smooth, cylindrical rotor, rotating at a high rate, as close as is practicable to the smooth, inside of a half-cylindrical, cradle-shaped stator, generates lift. While there is no up or down force within the very small space between the rotor and stator, there is reduced aerodynamic pressure on the exposed upper half of the rotor. Atmospheric pressure remains normal beneath the stator, producing considerable lift. Panels designed to slide over portions of the rotor, vary the lift, either uniformly or differentially to provide control. The streamlined unit is attached in a plurality to the wing of a conventionally configured, fixed-wing aircraft with the axis of the rotor aligned parallel to the thrust line of the vehicle. This lift unit is very efficient and produces no downward efflux, facilitating rescue operations.
Owner:MCKINNEY CHARLES CECIL
Aerofoil slot blowing
InactiveUS8573542B2Improve performanceImprove lifting performanceWingsDrag reductionLeading edgeStagnation point
An aerofoil defining geometric upper and lower surfaces which together form a leading edge region and a trailing edge region, and comprising a blowing device having a slot in the lower geometric surface in the leading edge region for injecting fluid into the airflow over the aerofoil, wherein the slot is located forward of the leading edge stagnation point at the critical angle of incidence of the aerofoil, and wherein the blowing device is adapted to inject the fluid forwardly of the slot and substantially parallel to the lower surface. Also, a method of improving the performance of the aerofoil by injecting fluid into the airflow over the aerofoil from the slot. The upper surface of the aerofoil can be kept clean, giving the potential for laminar flow during cruise without significantly compromising the high lift performance of a blown leading edge at high incidence.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
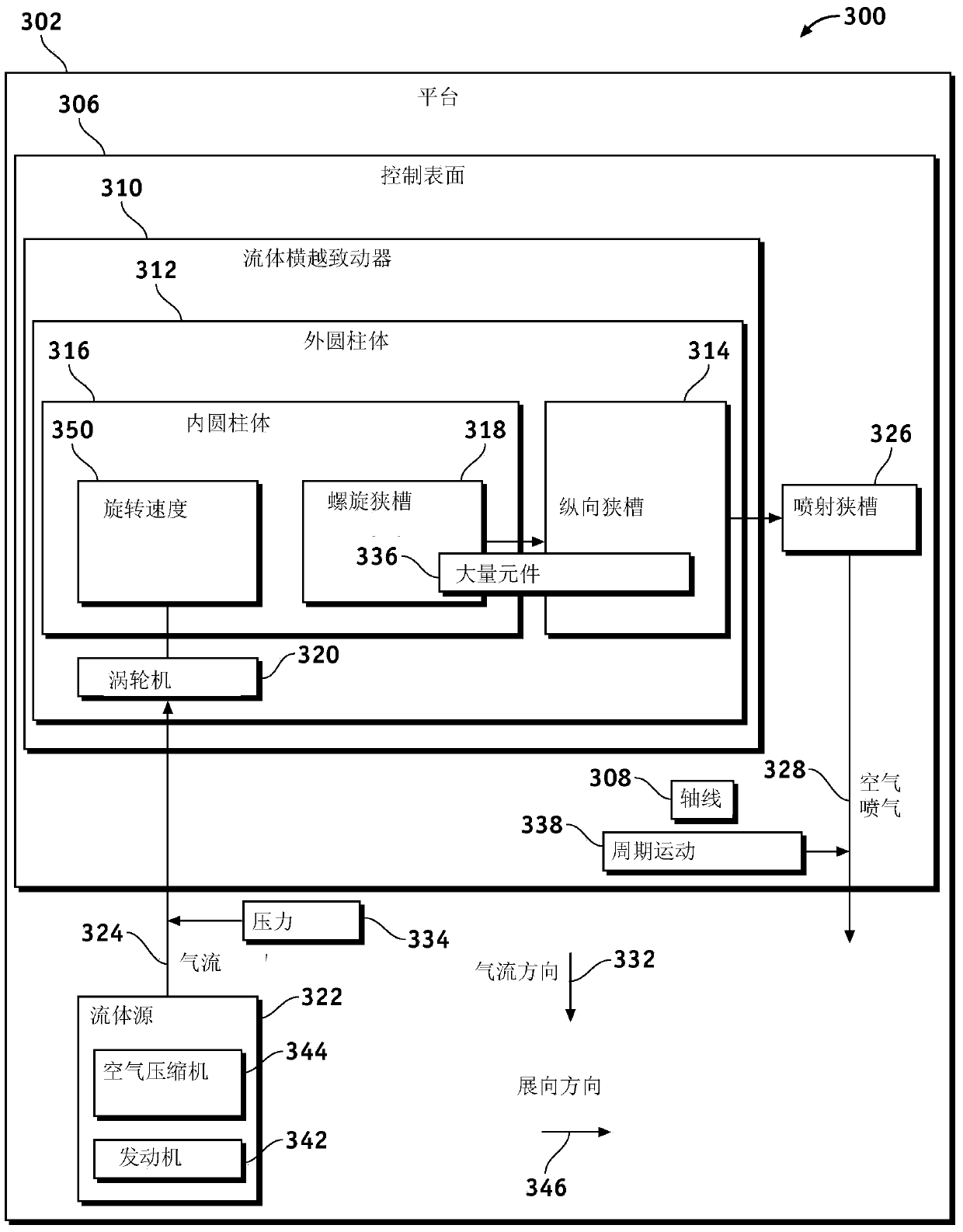
Fluidic traverse actuator
ActiveCN103786875AReduce implementation complexityReduce non-optimal lightning conditionsBoundary layer controlsDrag reductionEngineeringActuator
A system and method for a self-rotating fluidic traverse actuator are provided. A turbine rotates in response to a fluid flow, and an outer cylinder with a longitudinal slot that ejects the fluid flow. An inner cylinder rotates inside the outer cylinder in response to a rotation of the turbine and at least one helical slot of the inner cylinder ejects the fluid flow into the longitudinal slot.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Low drag surface
ActiveUS20200018333A1Lower resistanceAvoid icingFluid dynamicsMachines/enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A low drag surface is provided for a fluid washed object, the low drag surface comprising an aerodynamic surface comprising a cut-out region, and a continuously translatable surface comprising a surface portion. The surface portion is positioned in the cut-out region such that the aerodynamic surface and the surface portion form a fluidwash surface, and the surface portion is translatable relative to the aerodynamic surface.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Fixed-wing short-takeoff-and-landing aircraft and related methods
The title of the invention is fixed-wing short-takeoff-and-landing aircraft and related methods. The aircraft comprise an airframe comprising a rear wing assembly and a forward wing assembly positioned forward of the rear wing assembly, a rear plurality of blowing rotor assemblies operatively coupled to the rear wing assembly that are configured to blow air across the rear wing assembly to induce lift in the rear wing assembly, and a forward plurality of blowing rotor assemblies that are operatively coupled to the forward wing assembly and configured to blow air across the forward wing assembly to induce lift in the forward wing assembly. The methods comprise inducing lift in a forward wing assembly by blowing air across the forward wing assembly with a forward plurality of blowing rotor assemblies and inducing lift in a rear wing assembly by blowing air across a rear wing assembly with a rear plurality of blowing rotor assemblies.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
Active lift control device and method
ActiveUS11014652B1Easy to liftIncrease pressureInfluencers using Magnus effectWind motor controlEngineeringTrailing edge
A lift control device actively controls the lift force on a lifting surface. The device has a protuberance near a trailing edge of its lifting surface, which causes flow to separate from the lifting surface, generating regions of low pressure and high pressure which combine to increase the lift force on the lifting surface. The device further includes an arrangement to keep the flow attached around the protuberance or to modify the position of the protuberance in response to a command from a central controller, so as to provide an active control of the lift between a maximum value and a minimum value.
Owner:ARCTURA INC
Apparatus and method for directing thrust from tilting cross-flow fan wings on an aircraft
A variable thrust cross-flow fan system for an aircraft including a rotatable wing member having a first housing member; an actuator assembly operably coupled to the first housing member; and a variable thrust cross-flow fan assembly including a first and second driver plates having a plurality of blades rotatably mounted therebetween. The plurality of blades has a circular path of travel when rotating and includes a control assembly coupled to the plurality of blades to generate a variable thrust force. The control assembly includes a control cam that is substantially non-rotatable relative to the first and second driver plates and a hinge member that is fixedly connected to the control cam and to the first housing member at a hinge axis. Rotation of the first housing member by the actuator assembly imparts rotation of the control cam about the hinge axis, thereby changing the direction of the variable thrust force.
Owner:BELL HELICOPTER TEXTRON INC
Reciprocating linear movement roller airfoil lift force generating device
The invention provides a reciprocating linear movement roller airfoil lift force generating device and belongs to the technical field of aviation. The reciprocating linear movement roller airfoil lift force generating device comprises a spindle, a rack, a turntable, a slide block, a translation frame, a roller airfoil, a front press plate and a rear press plate. The turntable is horizontally installed at the upper end of the spindle. A front guide rod is installed on the rack through a front left linear bearing and a front right linear bearing. A rear guide rod is installed on the rack through a rear left linear bearing and a rear right linear bearing. A guide rail is connected with the slide block, and the slide block can flexibly slide along the guide rail back and forth. The translation frame with the roller airfoil can be driven by the turntable and the slide block to perform left-right reciprocating translation. The front press plate is attached to the front end of the roller airfoil and located at upper portion of the roller airfoil. The rear press plate is attached to the rear end of the roller airfoil and located at the upper portion of the roller airfoil. When the translation frame performs leftward movement, the roller airfoil rotates clockwise. When the translation frame performs rightward movement, the roller airfoil rotates anticlockwise. Under the driving of power, the reciprocating linear movement roller airfoil lift force generating device can produce thrust and can be applied to a vertical lifting aircraft to serve as a lift force device.
Owner:赵英
Circuit based unmanned aerial vehicle
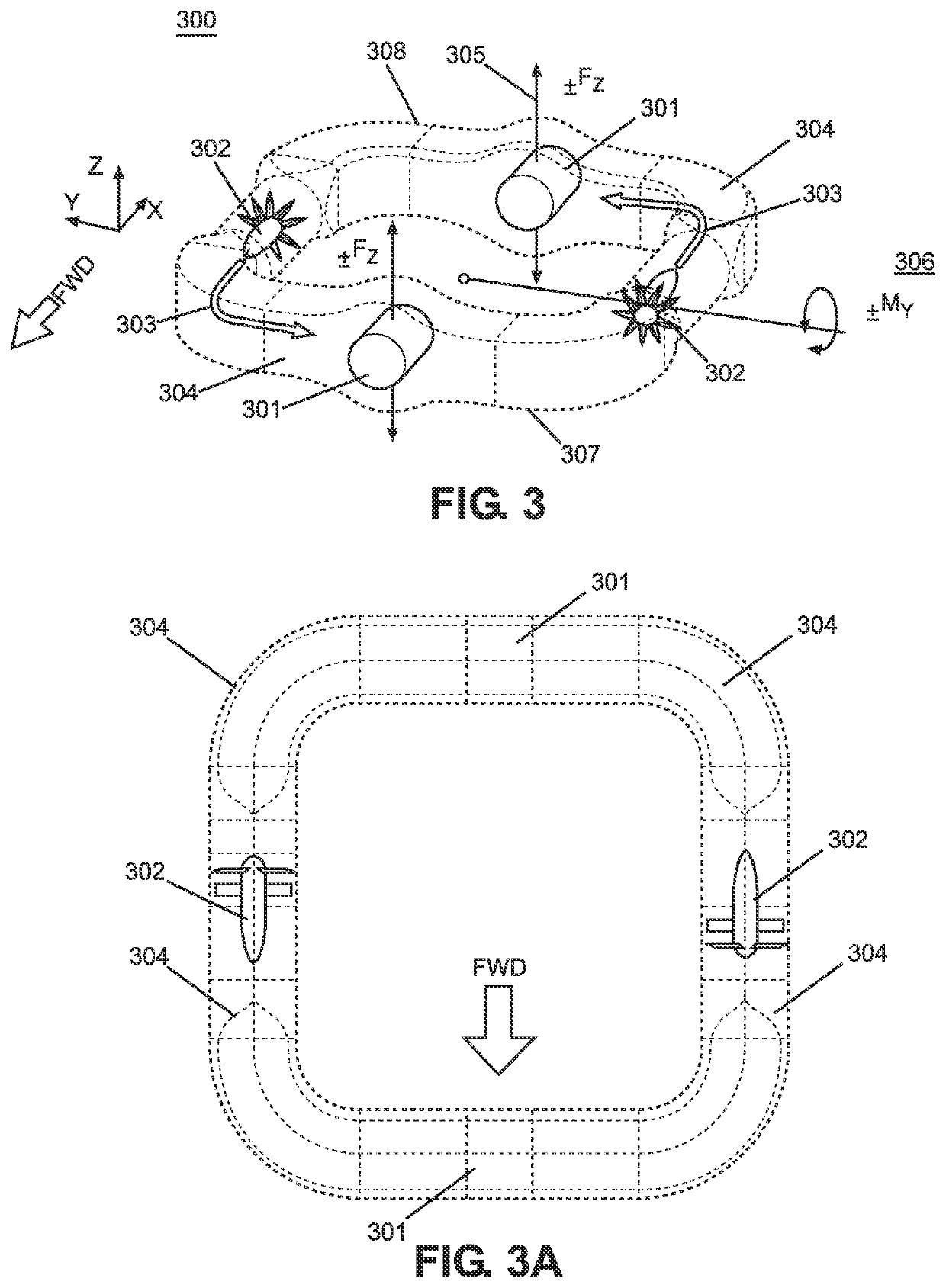
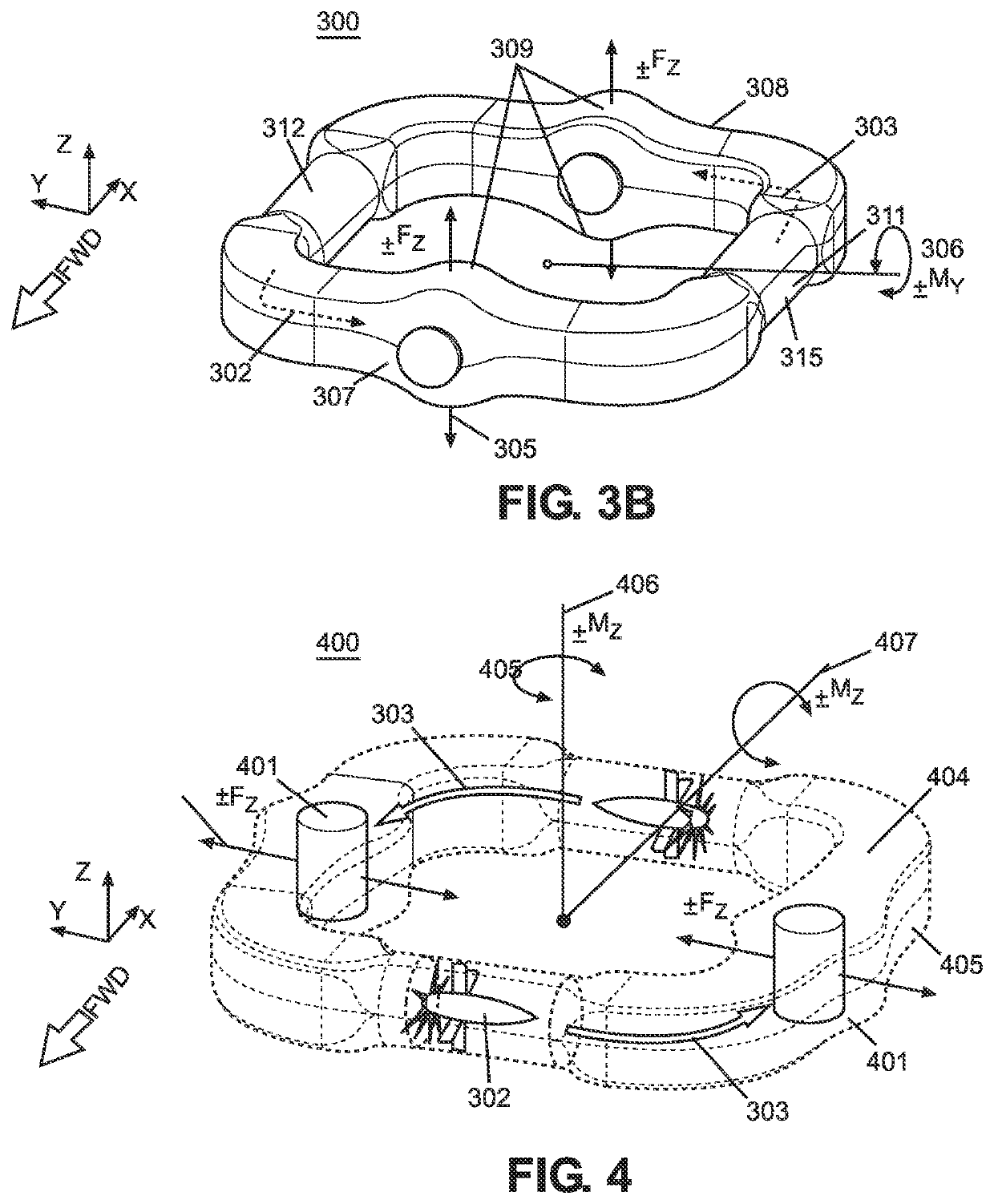
ActiveUS11414182B1Easy to navigateInfluencers using Magnus effectConvertible aircraftsFlight vehicleUncrewed vehicle
A first embodiment includes a circuit based unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) including at least one enclosed air duct vertical z-force circuit, at least one enclosed air duct lateral y-force circuit, and at least one enclosed air duct longitudinal x-force circuit whereby each circuit includes a plurality of fans within respective fan tunnels and a plurality of rotational cylinders within archways. The UAV utilizes a magnus effect at strategic points along each respective circuit to apply navigational force thereon.A second embodiment includes a circuit based unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) including a first and second air duct circuit joined at a medial trunk. Each circuit includes a plurality of fans within respective fan tunnels and a plurality of rotational cylinders within archways. The second embodiment also utilizes the magnus effect at strategic points along each respective circuit to apply navigational force thereon.
Owner:CARNEGIE CAMERON
Rotary movable side vane lift force generating device
Owner:FOSHAN SHENFENG AVIATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com