Patents
Literature
163results about How to "Reduced flow separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Redundancies and flows in vehicles
InactiveUS20100270419A1Efficient flightReduce suctionSynchronous generatorsAircraft navigation controlControl powerIn vehicle
A control system for a vehicle having plural control elements actuated at a single actuation point including a redundant electric actuator assembly including a control rod moveable linearly in two opposite directions mounting n electric motors, each motor having a controller and a feedback sensor for controlling linear movement of said rod, each motor contributing approximately 1 / n of total control power required for adjusting one or more of said plural control elements, such that failure of any of said motors controllers or feedback sensors leaves sufficient predetermined minimum control power available for operating said control system.
Owner:URBAN AERONAUTICS
Vane or blade for an axial flow compressor
ActiveUS20110081252A1Losses have been minimisedExpand flow rangePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTrailing edge
A compressor vane or compressor blade is provided. The axial flow compressor includes an axial direction, a radial direction, a compressor hub and a compressor casing. The vane or blade includes an airfoil with airfoil sections having a span, a chamber line and a leading edge at which the chamber line includes a leading edge blade angle with the axial direction of the compressor and a trailing edge at which the chamber line includes a trailing edge blade angle with the axial direction of the compressor. The airfoil sections are stacked at the leading edge on a straight line extending along a radial direction of the compressor from the compressor hub towards a compressor casing and in that the leading edge angles of the airfoil sections vary along the span and are larger for airfoil sections close to the hub and close to the wall than for mid-span airfoil sections.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
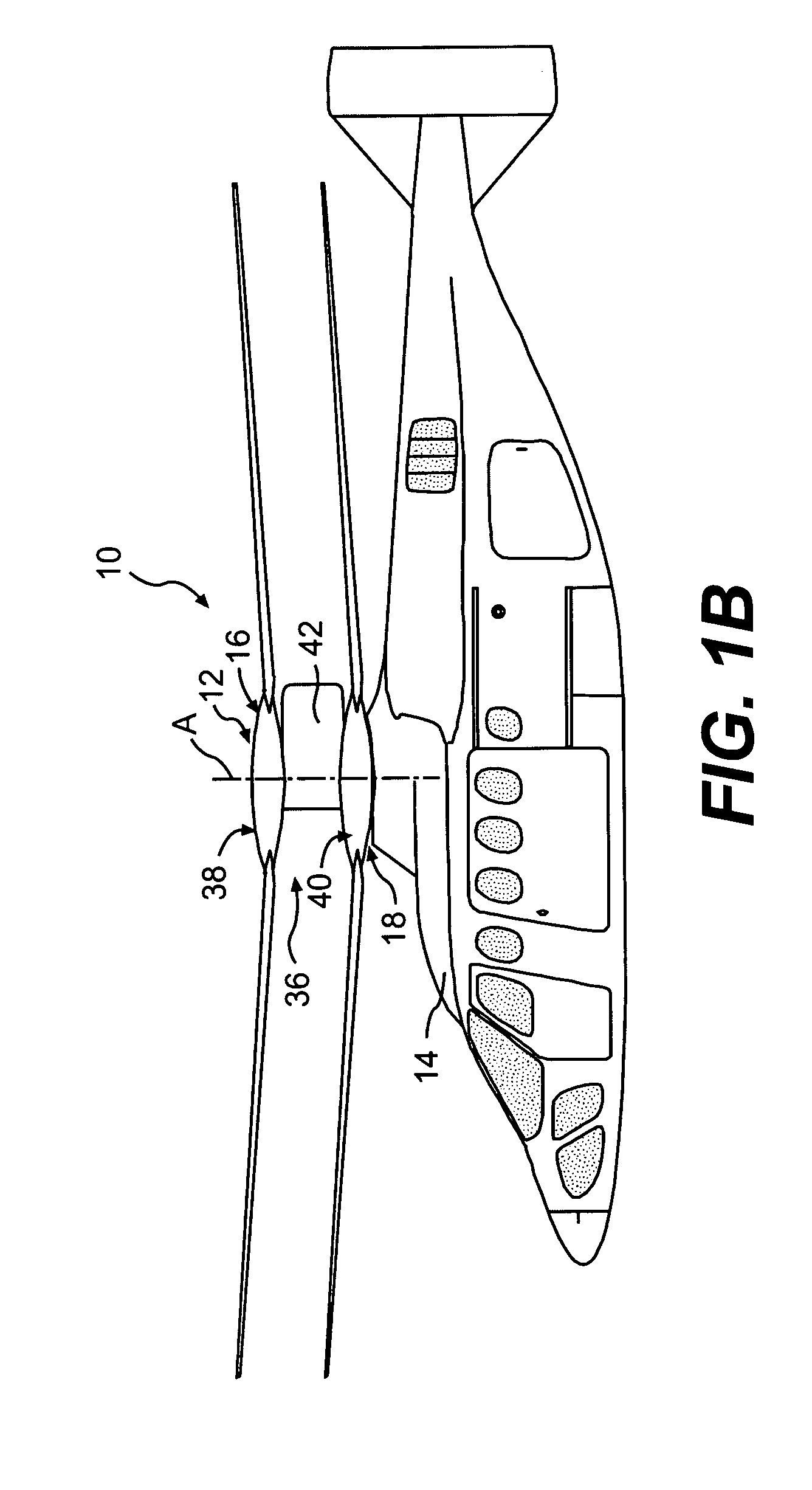
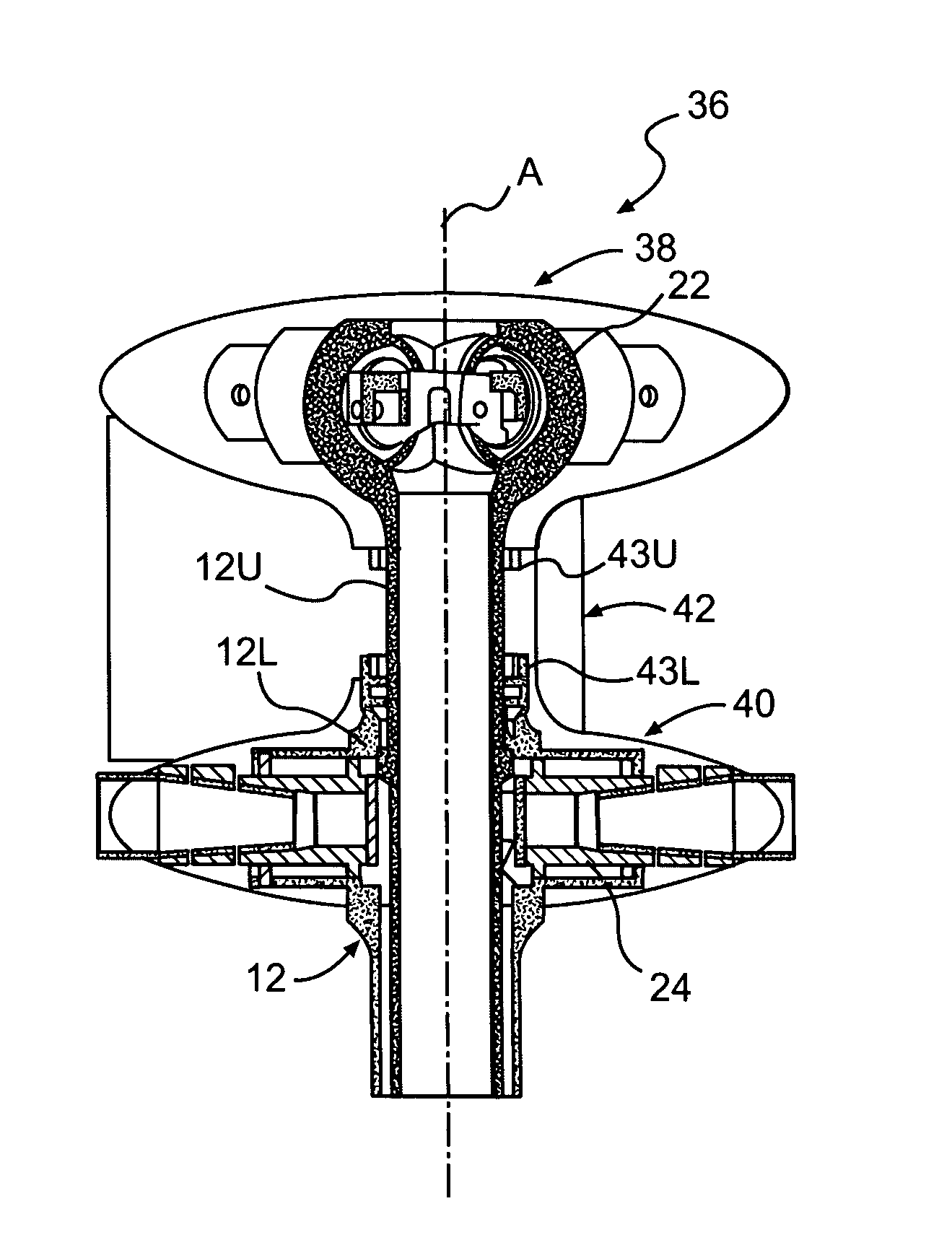
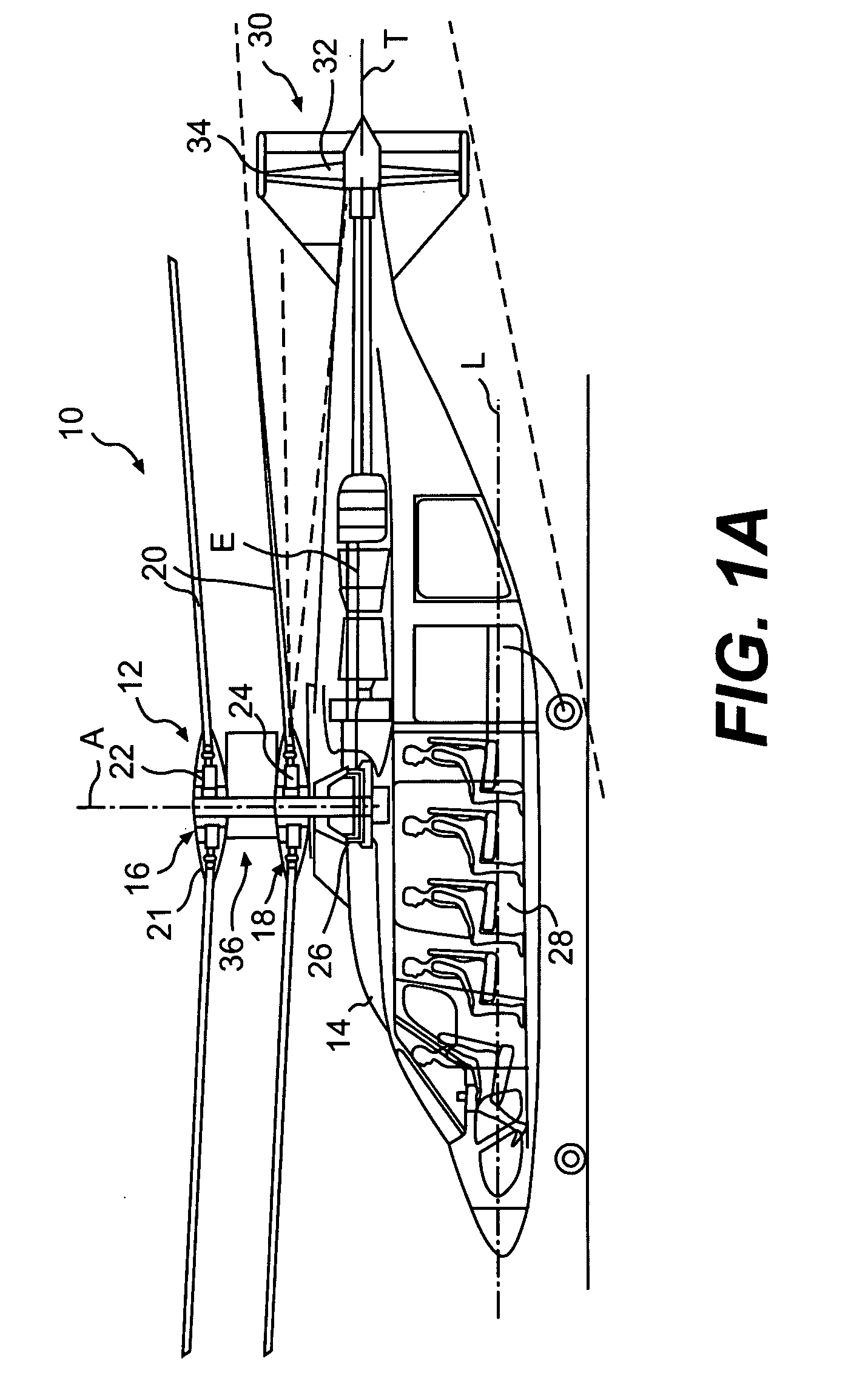
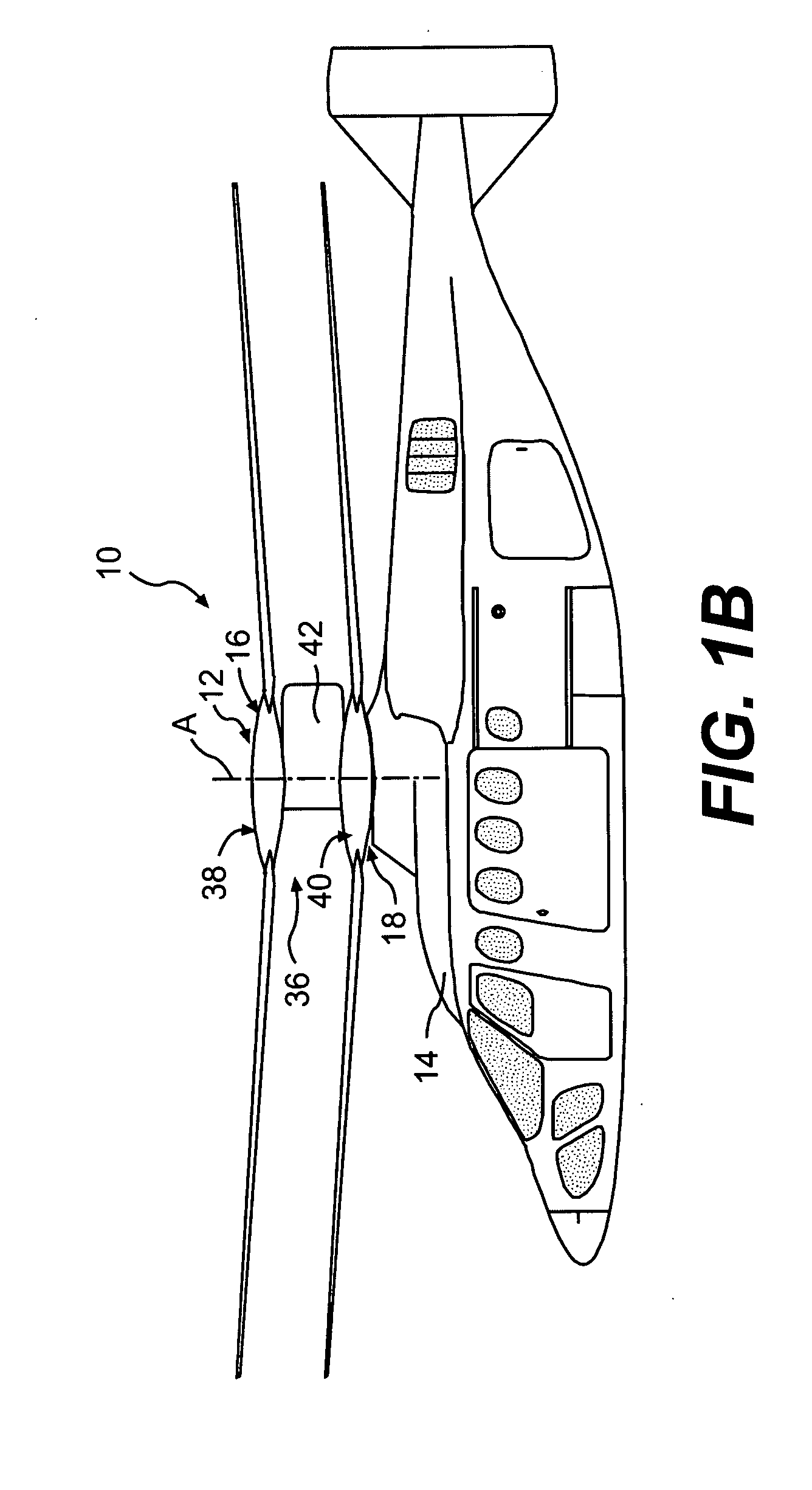
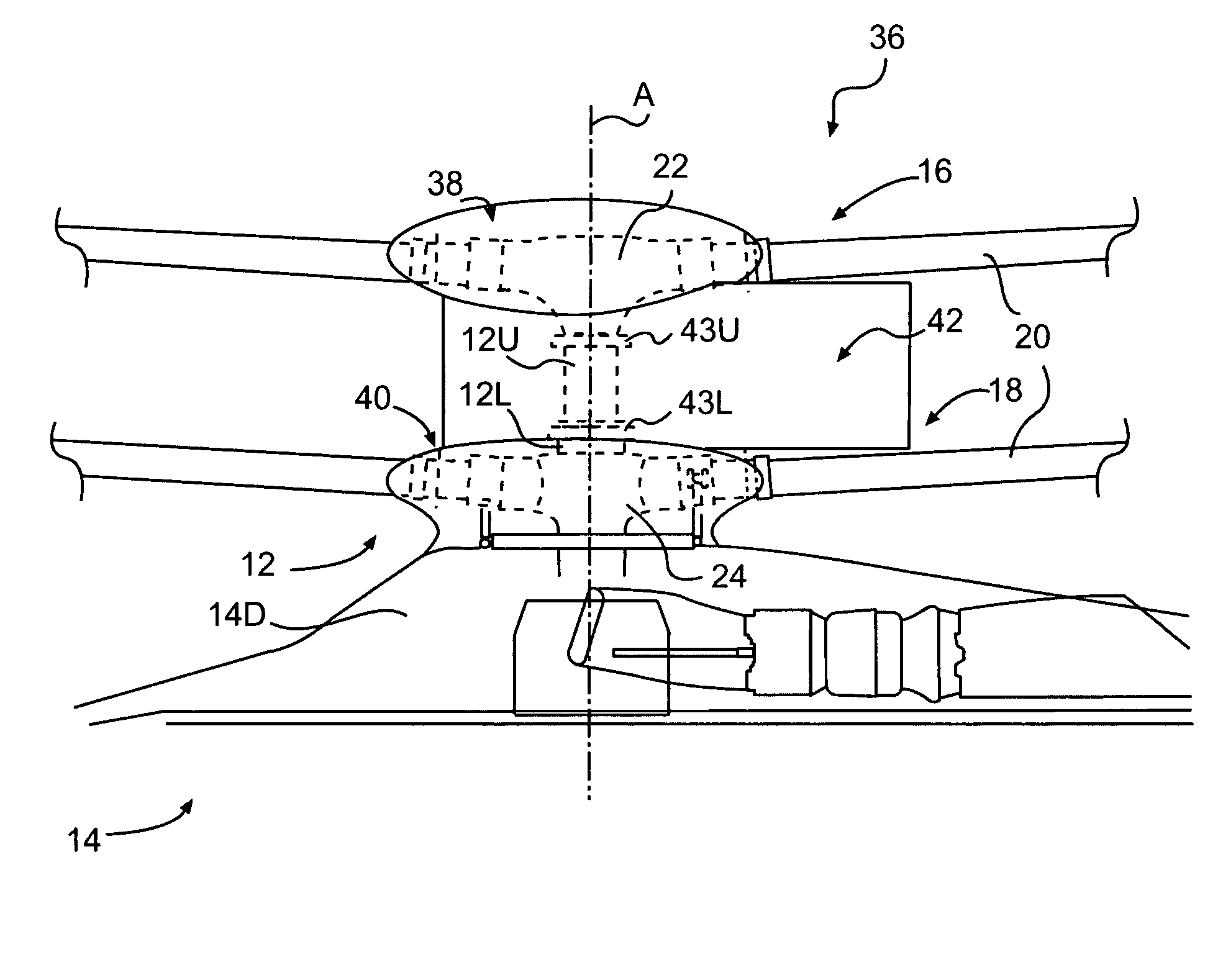
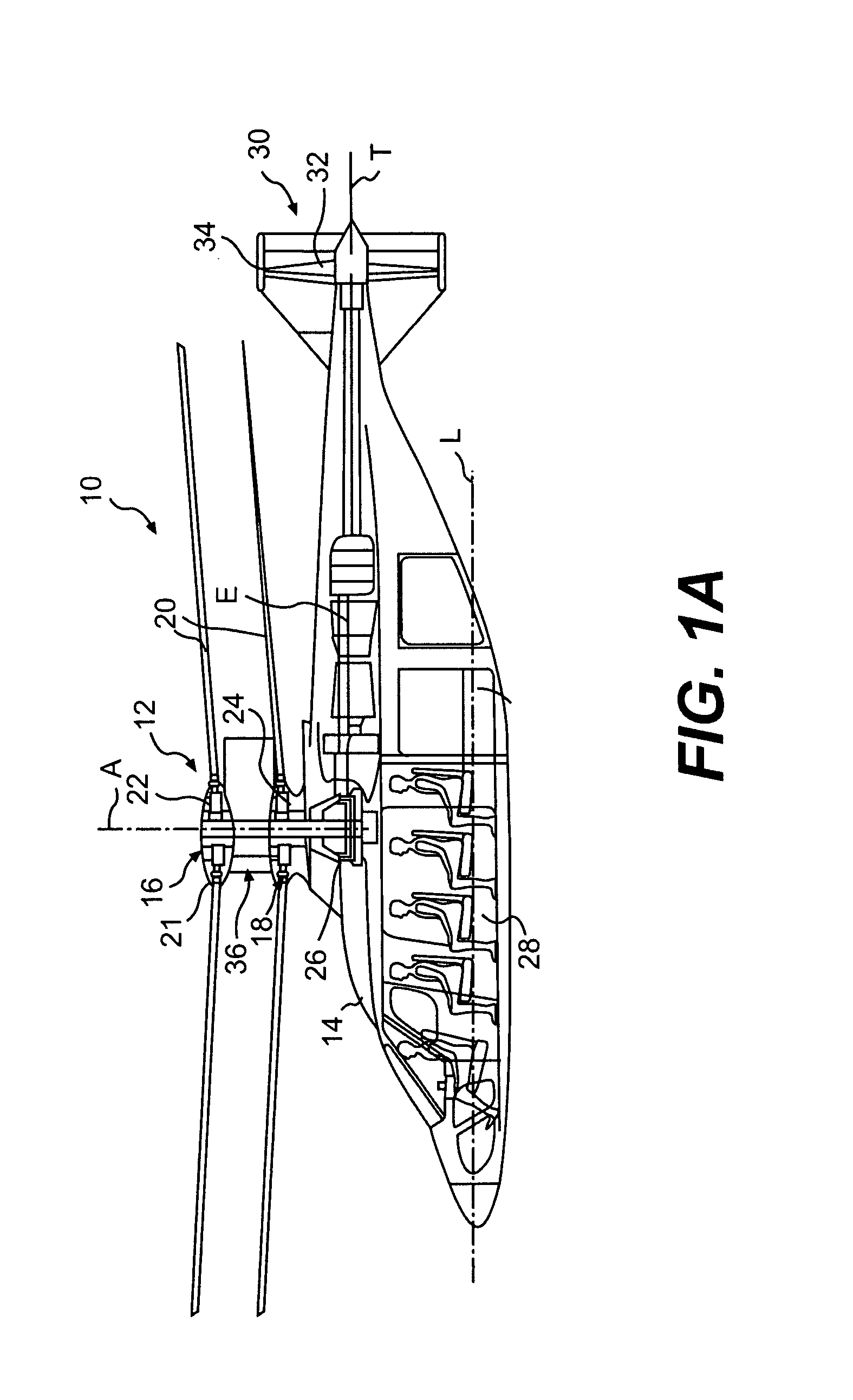
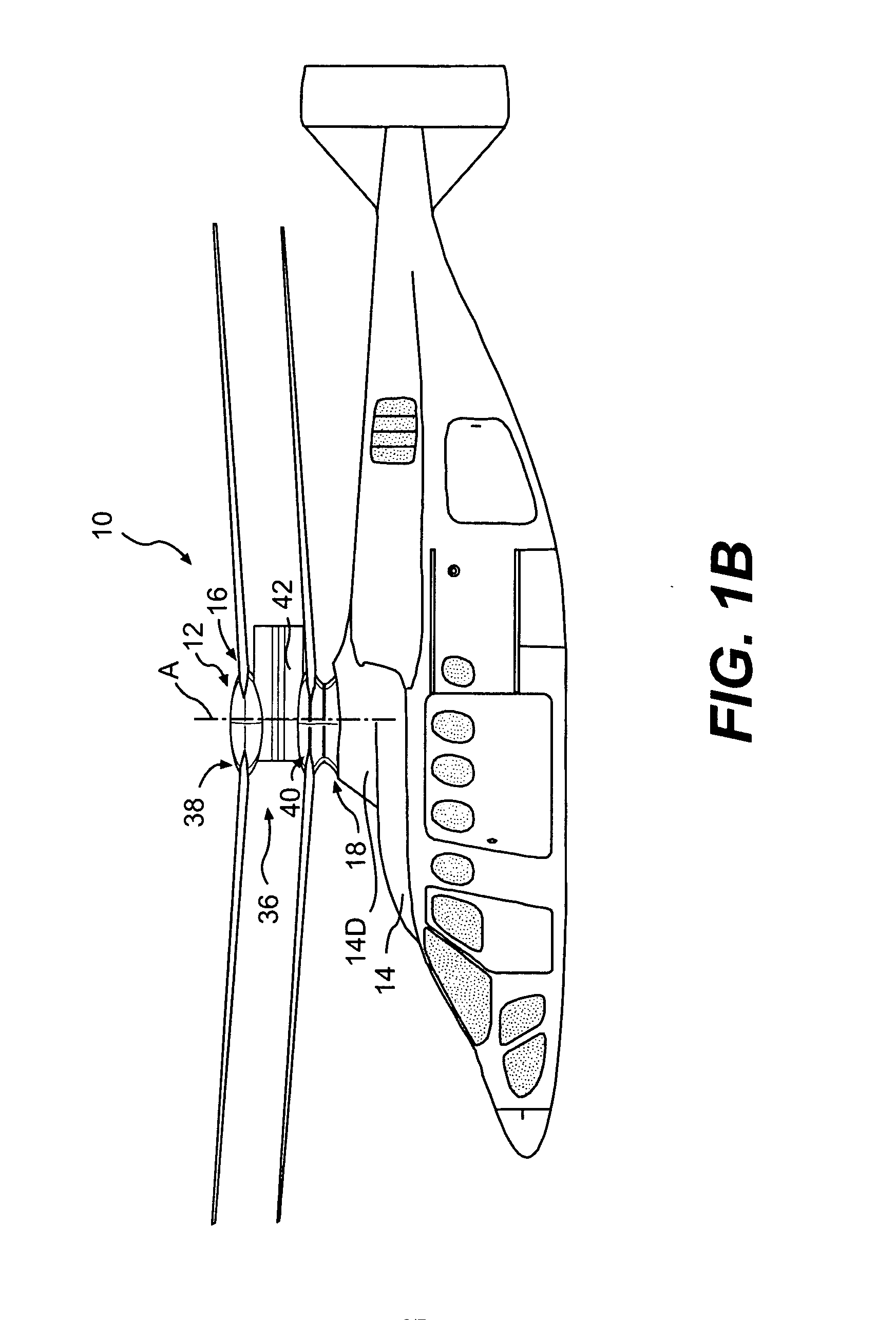
ActiveUS7229251B2Reduce the overall drag on the rotor systemMinimizing excessive separationPropellersPump componentsCowlingAerodynamics
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is sized and configured to reduce the overall drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Preferably, the rotor hub fairing is fully integrated. The shaft fairing preferably includes a minimal thickness at the midsection to reduce drag with an increasing thickness adjacent the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce the flow separation on the hub fairing surfaces without overly excessive drag. Other aerodynamic structures, such as a horizontal splitter and / or a plurality of turning vanes may be mounted to the shaft fairing to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system is sized and configured to reduce the overall drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Preferably, the rotor hub fairing is fully integrated. The shaft fairing preferably includes a minimal thickness at the midsection to reduce drag with an increasing thickness adjacent the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce the flow separation on the hub fairing surfaces without overly excessive drag. Other aerodynamic structures, such as a horizontal splitter and / or a plurality of turning vanes may be mounted to the shaft fairing to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Implantable centrifugal blood pump with hybrid magnetic bearings
InactiveUS20080240947A1Reduce heatLess attractivePump componentsHeart valvesImpellerMagnetic bearing
A pump for pumping sensitive fluids, such as blood, has no mechanical contact between the impeller and any other structure.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
Compressed gas cooling apparatus
InactiveUS20140000841A1Lower overall pressure dropReduced flow separationReinforcing meansPump componentsEngineeringGas cooling
A compressed gas cooling apparatus in which gas from an upstream compression stage enters an inlet section from an inlet opening and flows to a heat exchanger that cools the gas. The cooled gas then flows from the heat exchanger to the outlet section where the gas is discharged from an outlet opening. Pressure drop within the apparatus is decreased by providing the inlet and outlet sections with ever increasing and decreasing cross-sectional flow areas. In order to further decrease pressure drop due to a swirl within the gas flow imparted from the upstream compression stage, the inlet section is provided with first and second subsections wherein the cross-sectional flow area of the first subsection increases at lesser rate than the second subjection. Alternatively, or in addition, the inlet section can be provided with partitions to divide the gas flow into subflows in order to lessen pressure drop from swirl.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
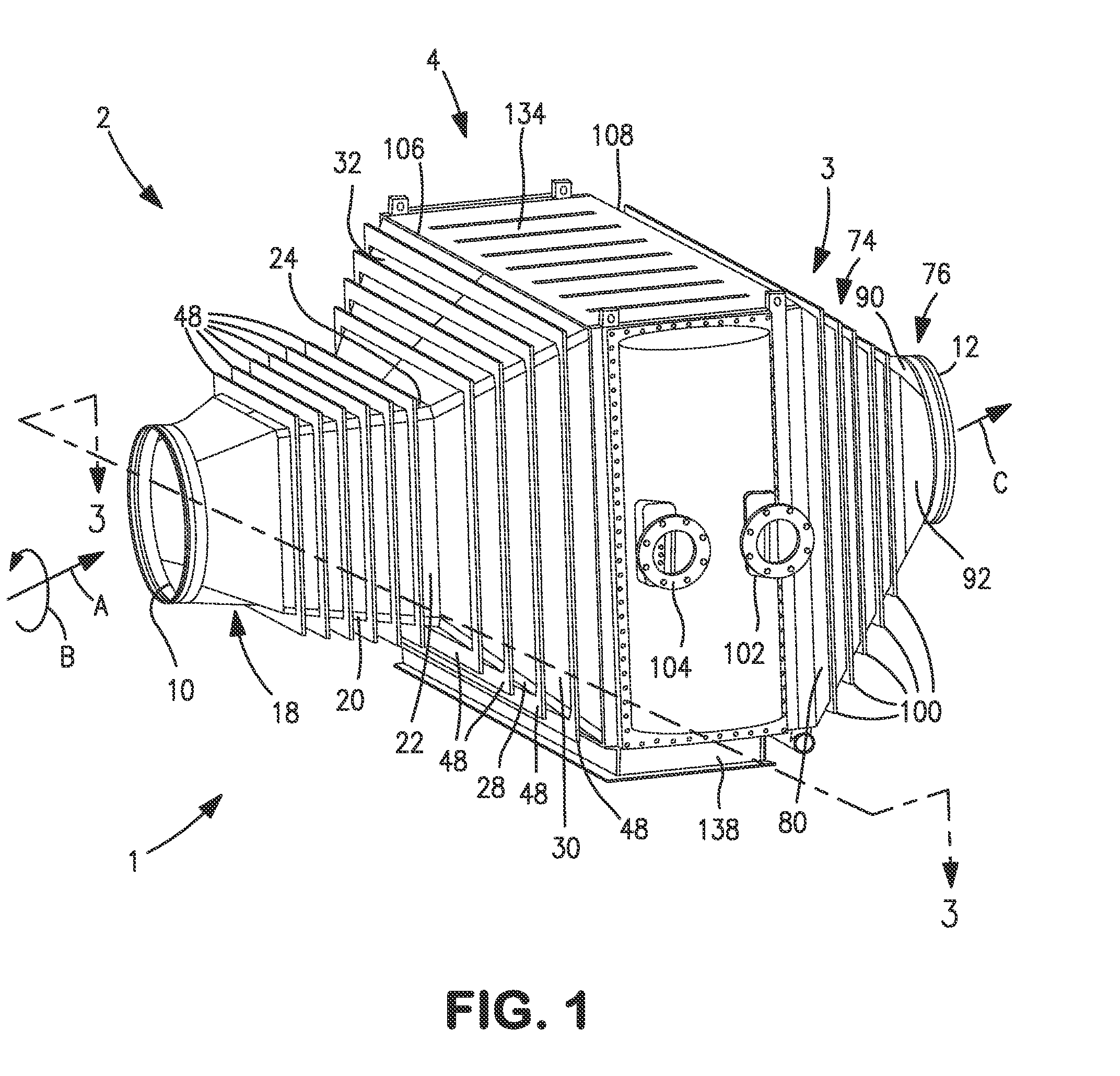
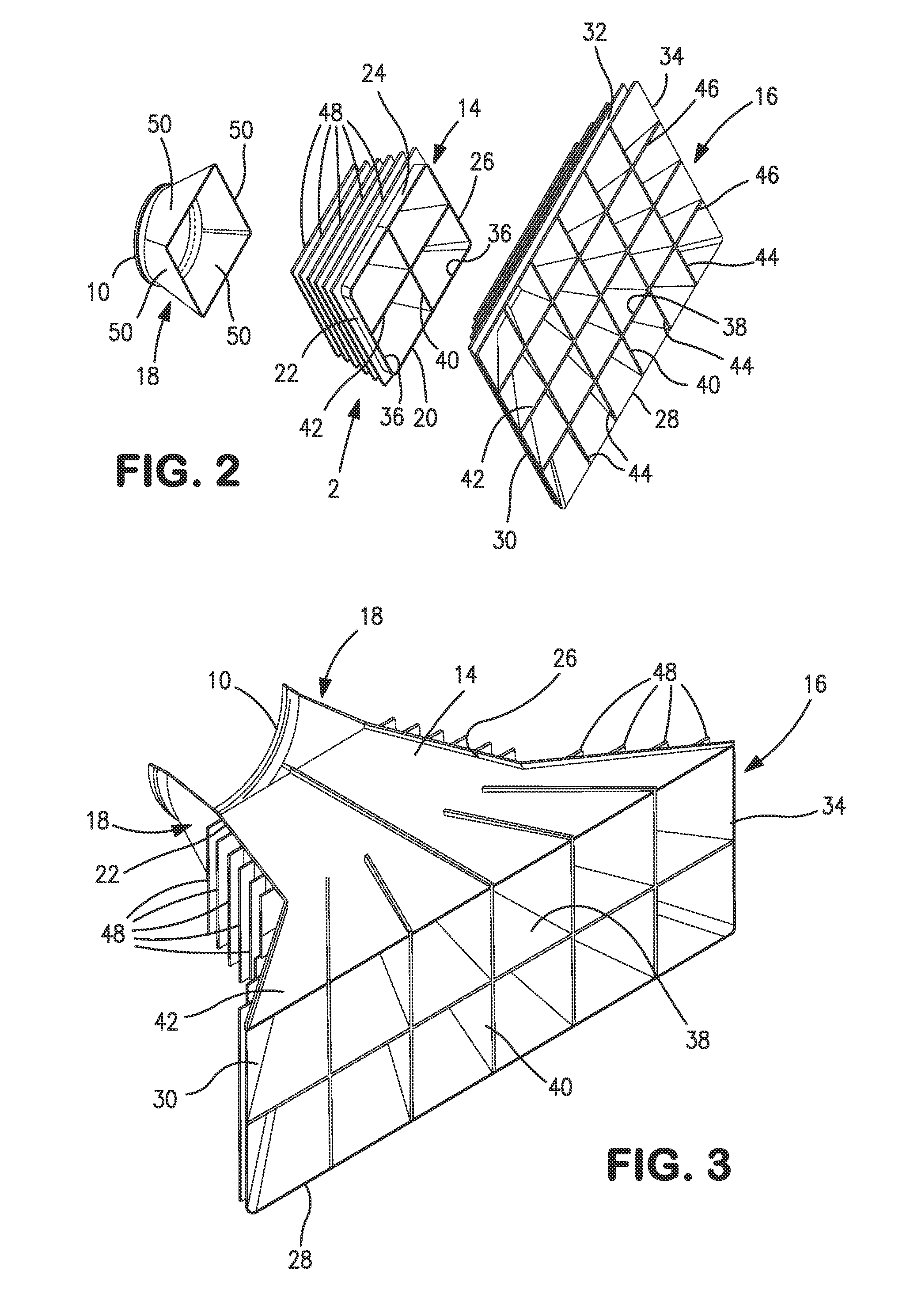
Method and apparatus for enhancing engine-powered lift in an aircraft
InactiveUS7878458B2Restricting span-wise movementIncrease volumeBoundary layer controlsWing adjustmentsExit planeEngine power
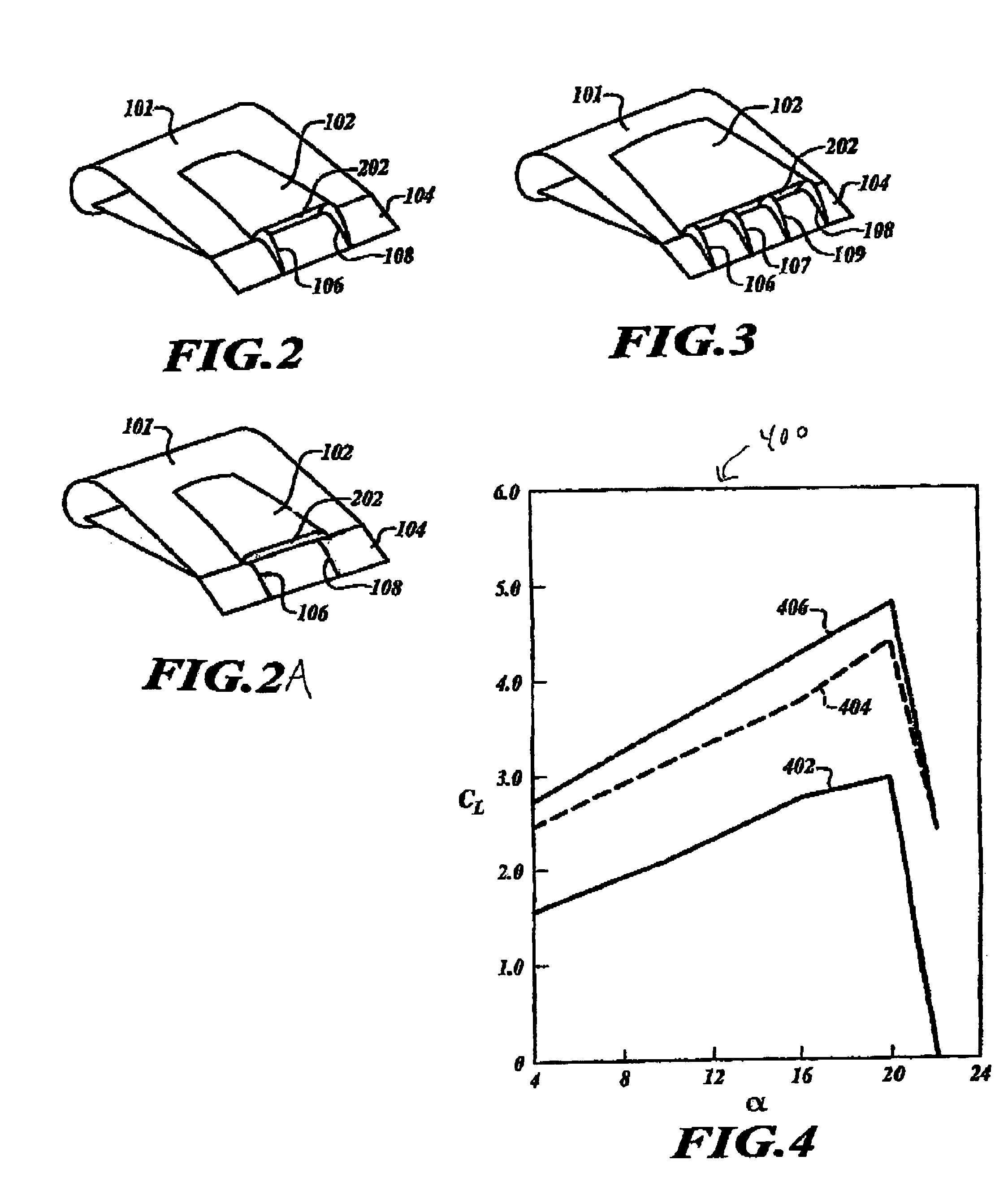
Lift produced by an airfoil of an aircraft is increased by suppressing fluid detachment from the surface of the airfoil. An engine cowling extends outwardly from the surface of the airfoil that has an exit plane configured for directing exhaust gases toward a rear of the aircraft. Fences extending outwardly from the surface and proximate to the exit plane of the engine cowling are configured to guide the exhaust gases along at least a portion of the airfoil surface, thereby restricting spanwise movement of the gases and increasing the Coanda Effect exhibited by the gases, thereby increasing the amount of lift produced along the surface of the airfoil. Such techniques may be used in short take-off and landing (STOL) aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
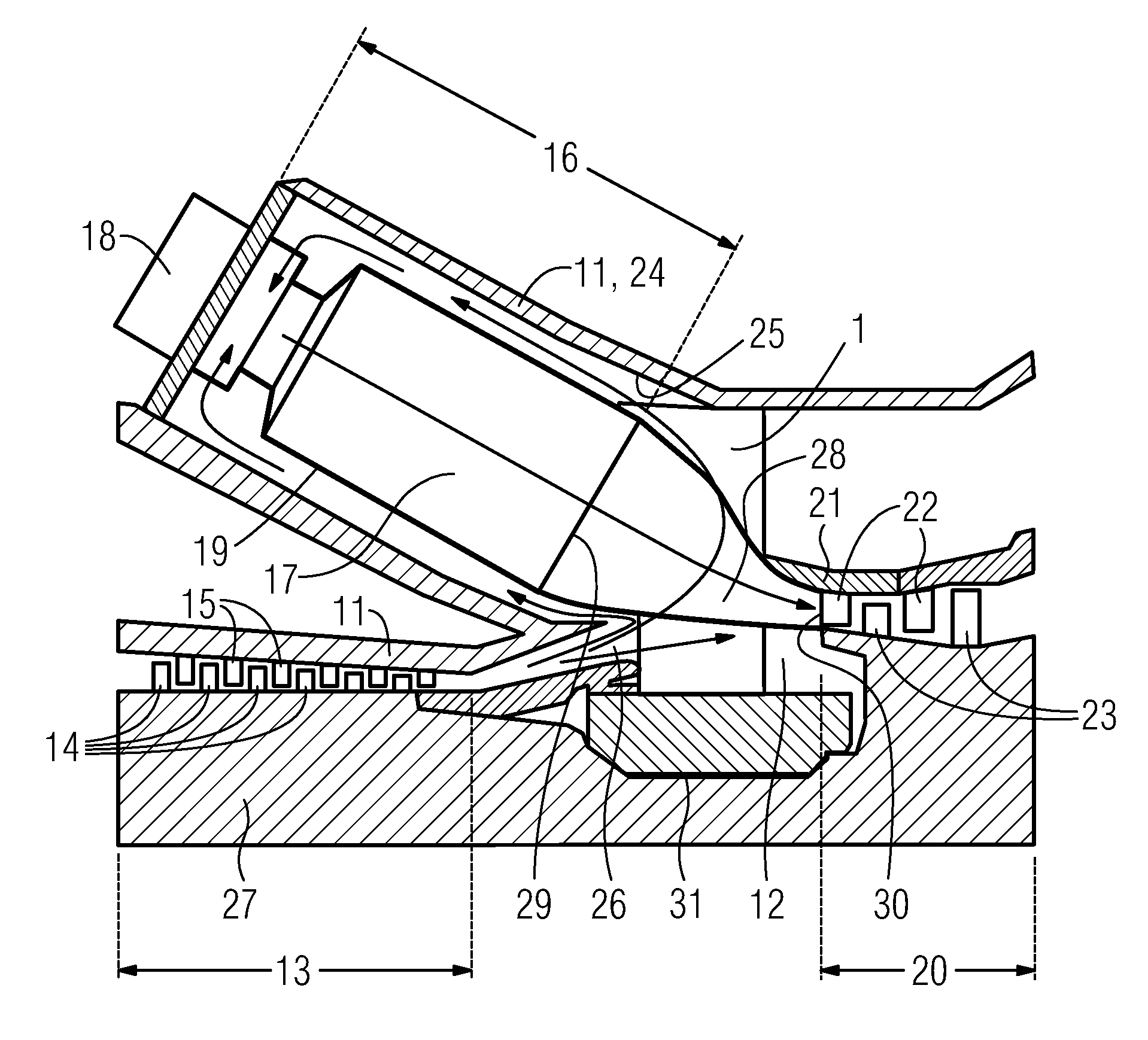
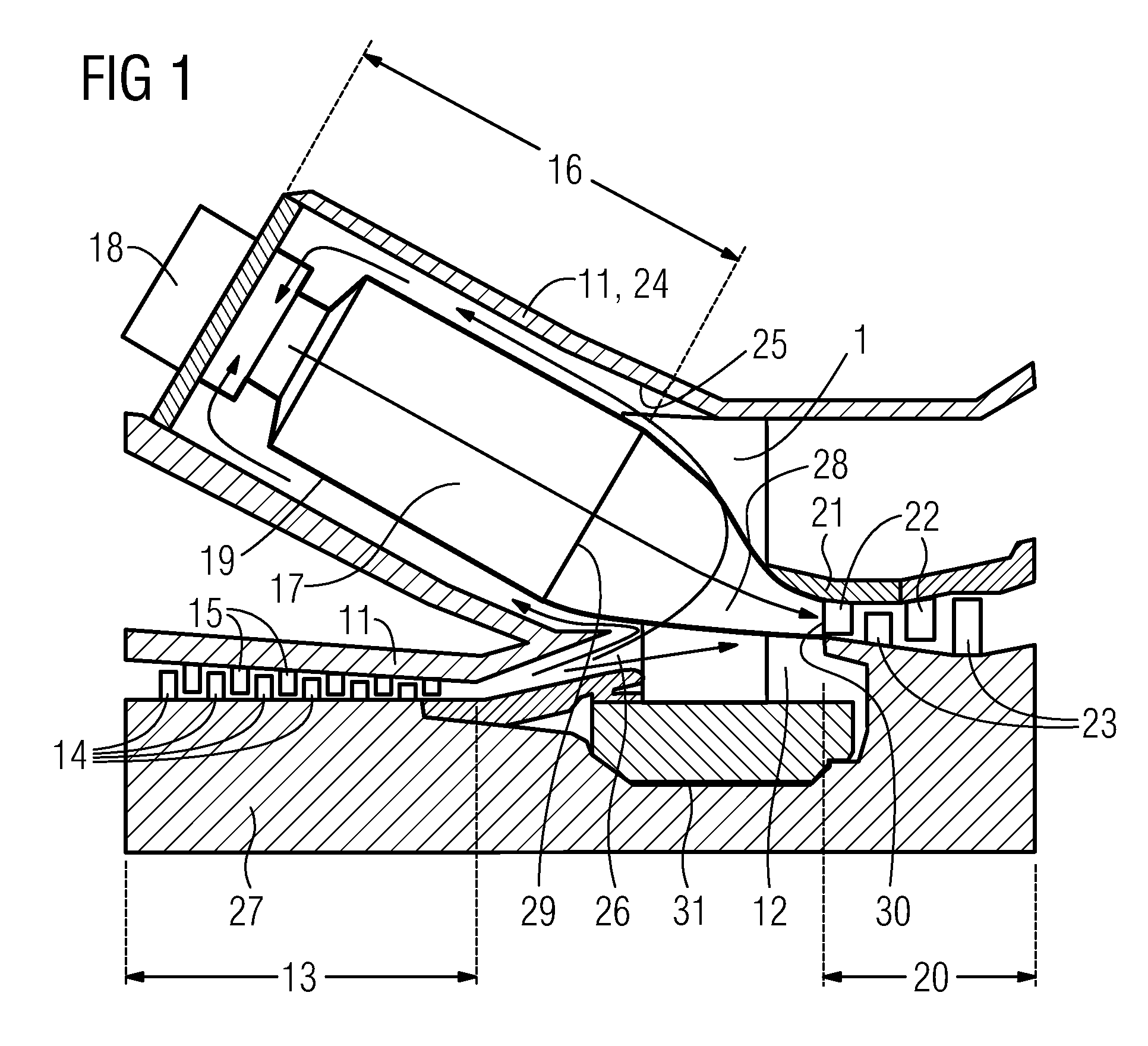
Low pressure steam turbine exhaust hood
InactiveUS6971842B2Reduced flow separationProvide supportEngine manufacturePump componentsTurbineAirflow
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotor hub fairing system for a counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system
A rotor hub fairing system includes an upper hub fairing, a lower hub fairing and a shaft fairing therebetween. The rotor hub fairing system reduces the total drag on a dual, counter-rotating, coaxial rotor system. Other aerodynamic structures may be mounted to the shaft fairing, hub fairings and airframe to facilitate flow around the upper and lower hub fairings to reduce flow separation and drag.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
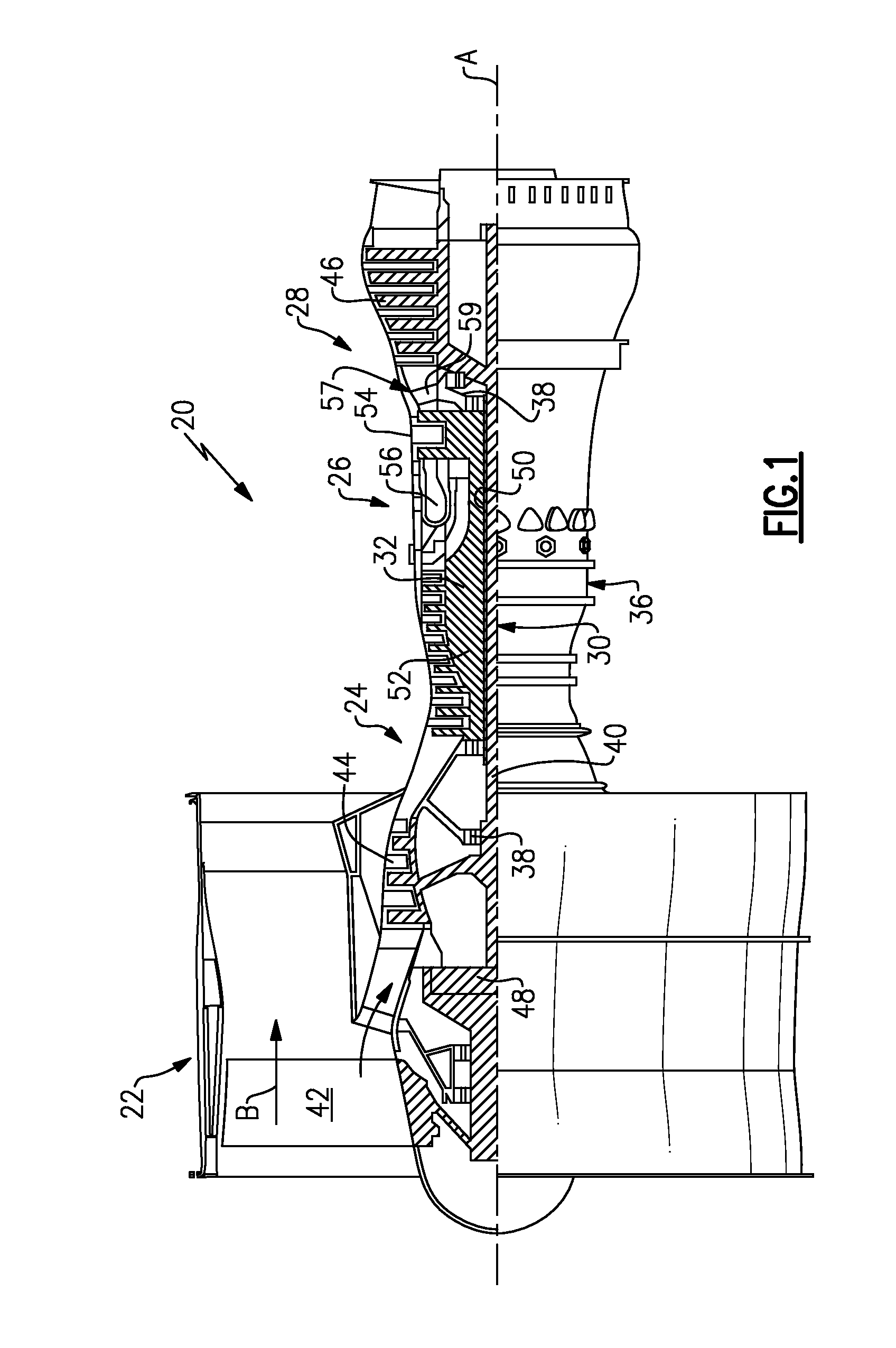
Compressor flowpath
InactiveUS20130192198A1Reduce clearanceReduced flow separationPump componentsEngine fuctionsSlope angleEngineering
A core flowpath through a low pressure compressor section of a gas turbine engine includes an outer diameter, which has a slope angle relative to an axis defined by the core flowpath. The slope angle is a slope angle that is operable to prevent flow separation of a fluid passing through the core flowpath.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
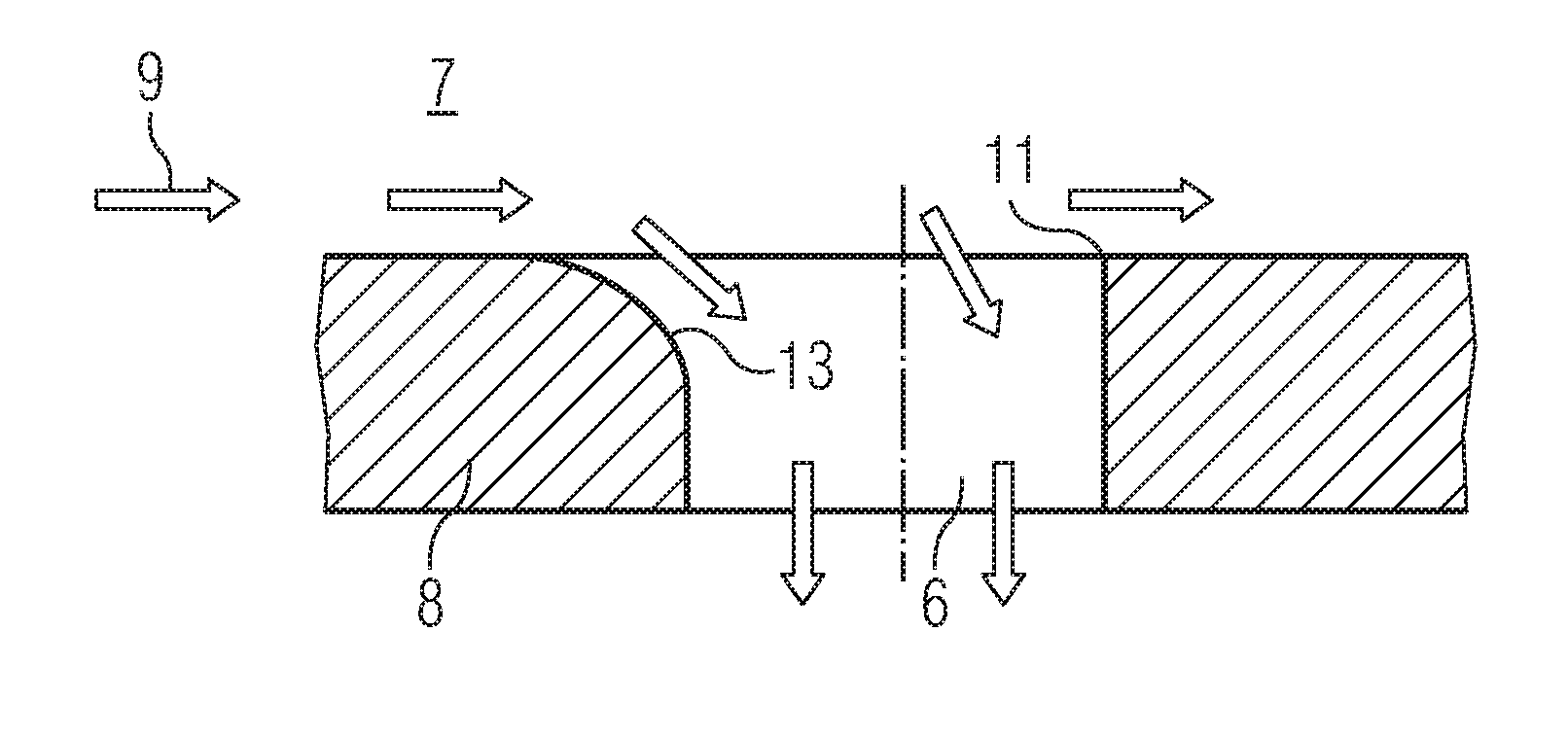
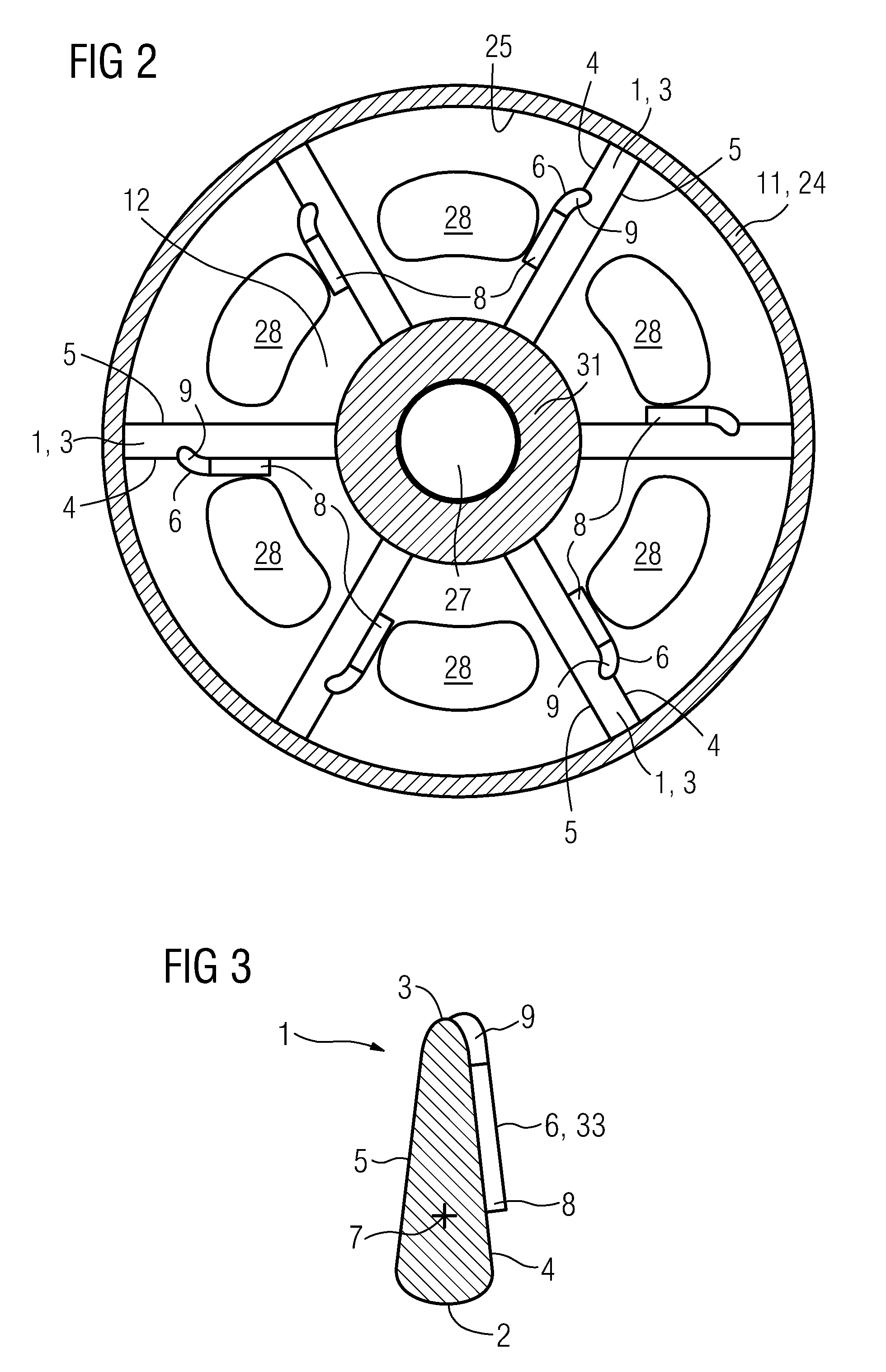
Eccentric chamfer at inlet of branches in a flow channel
ActiveUS20100115967A1Avoid pressure lossIncrease in heat transfer coefficientEngine manufacturePump componentsMain channelEngineering
A flow channel with a branch channel perpendicular to a main channel including an edge defining an inlet opening of the branch channel is provided. A chamfer is disposed at the upstream edge of the inlet opening and a straight edge is disposed at the downstream edge of the inlet opening, perpendicular to the main channel.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus for enhancing engine-powered lift in an aircraft
InactiveUS20090108141A1Easy to liftRestricting span-wise movementBoundary layer controlsWing adjustmentsExit planeFlight vehicle
Lift produced by an airfoil of an aircraft is increased by suppressing fluid detachment from the surface of the airfoil. An engine cowling extends outwardly from the surface of the airfoil that has an exit plane configured for directing exhaust gases toward a rear of the aircraft. Fences extending outwardly from the surface and proximate to the exit plane of the engine cowling are configured to guide the exhaust gases along at least a portion of the airfoil surface, thereby restricting spanwise movement of the gases and increasing the Coanda Effect exhibited by the gases, thereby increasing the amount of lift produced along the surface of the airfoil. Such techniques may be used in short take-off and landing (STOL) aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Implantable centrifugal blood pump with hybrid magnetic bearings
InactiveUS20140314597A1Reduce heatLess attractivePump componentsHeart valvesImpellerMagnetic bearing
Owner:WORLD HEART
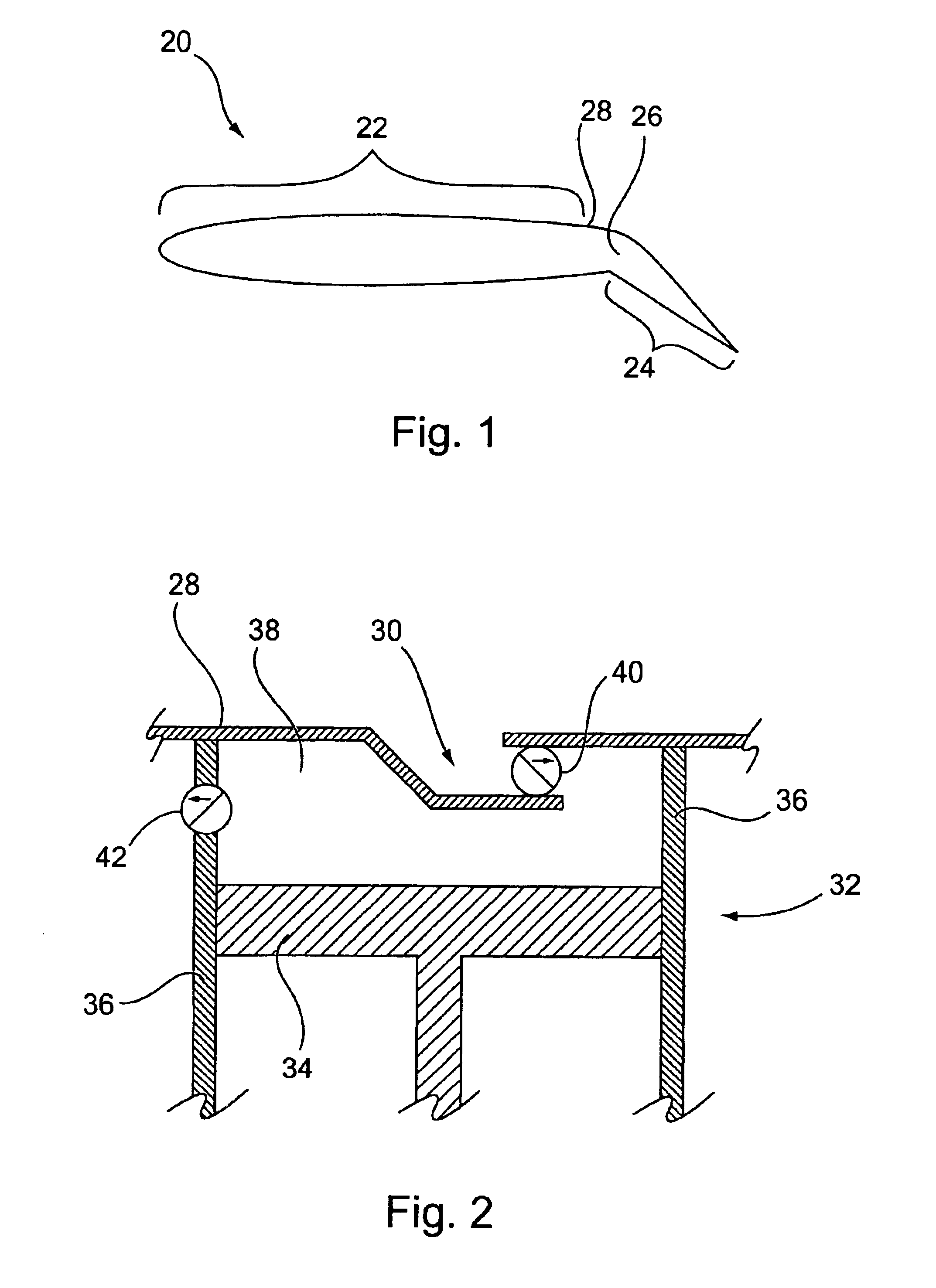
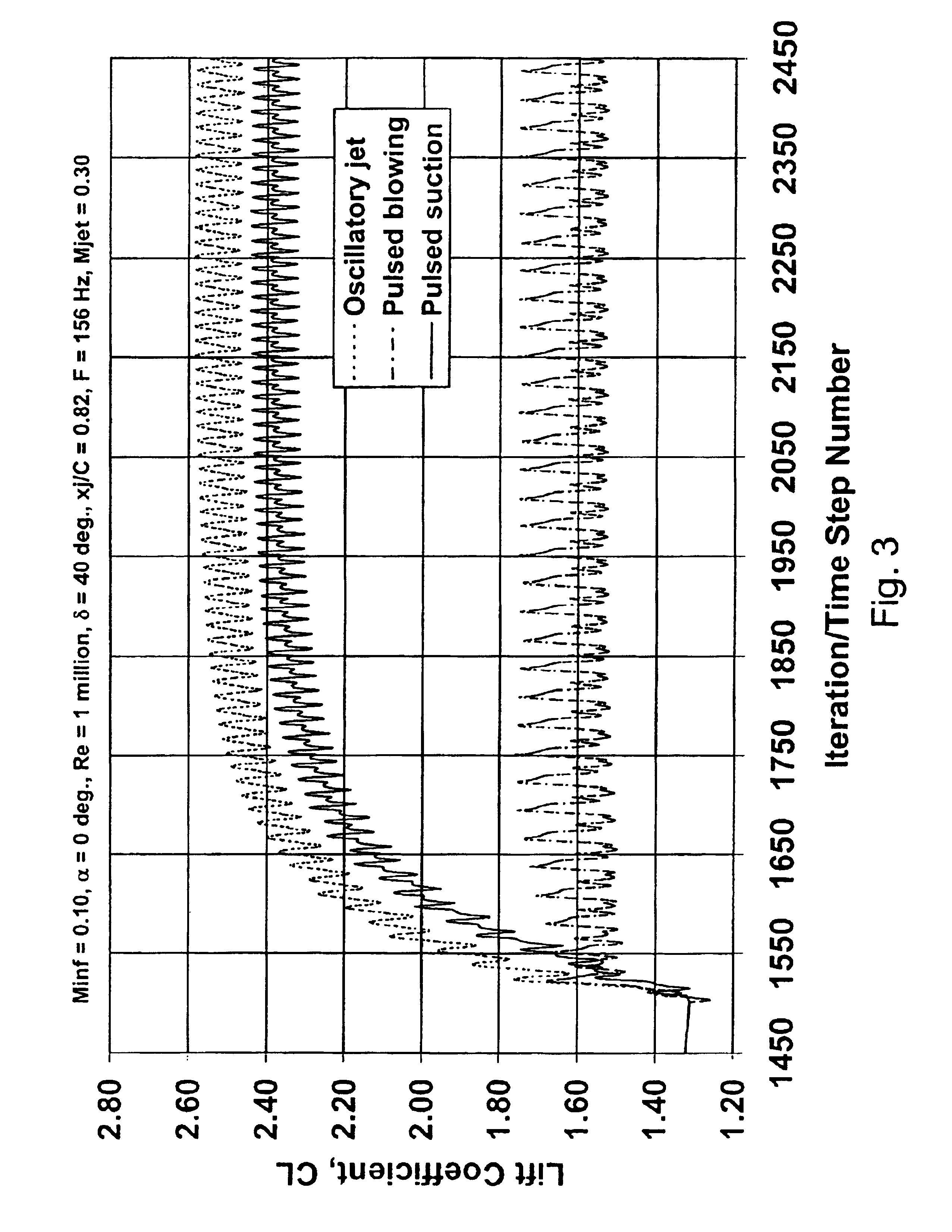
Method and device for altering the separation characteristics of air-flow over an aerodynamic surface via intermittent suction
InactiveUS6866234B1Reduced flow separationLess powerPump componentsBlade accessoriesEngineeringAirflow
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Low pressure steam turbine exhaust hood
ActiveUS20050063821A1Reduced flow separationProvide supportEngine manufacturePump componentsTurbineAirflow
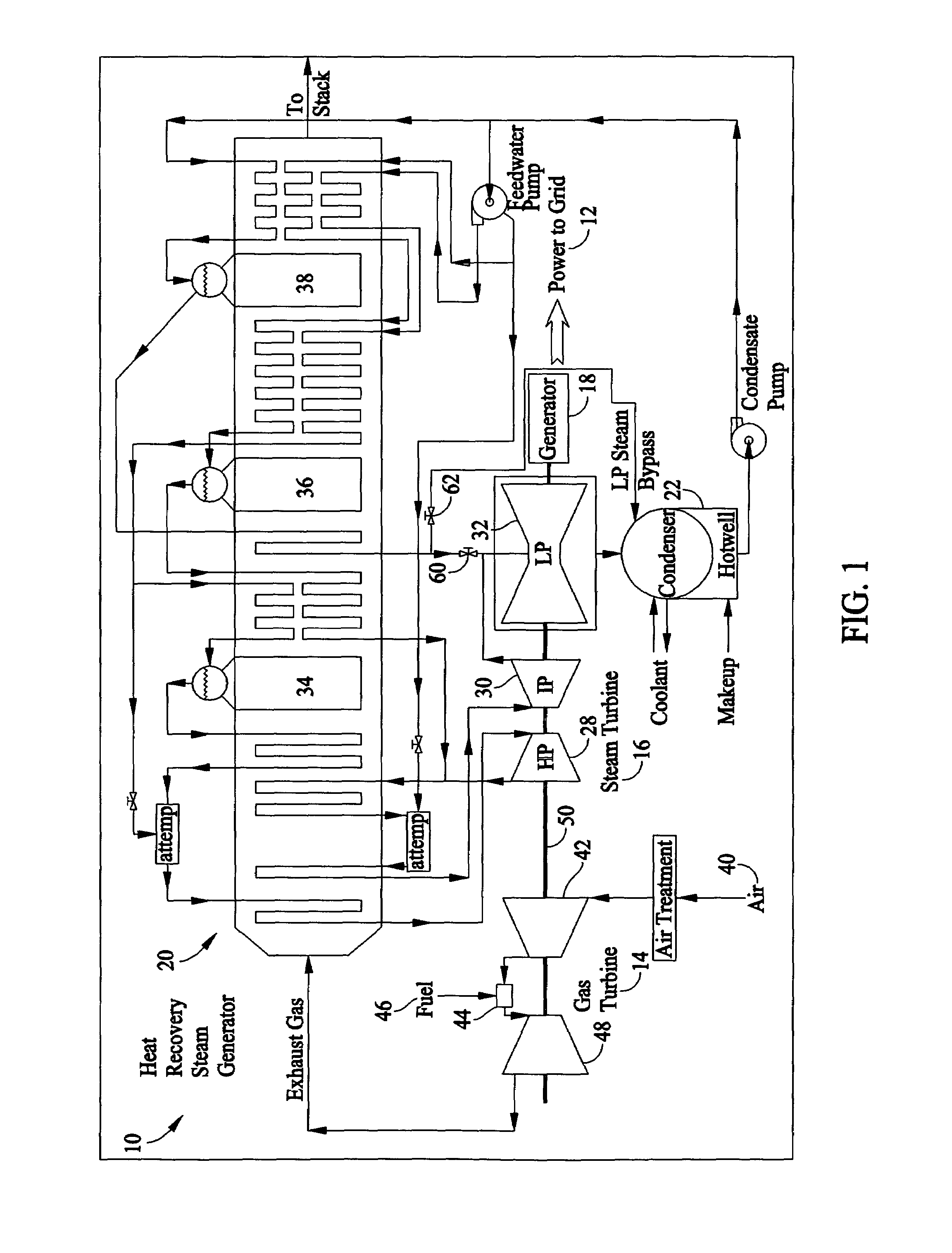
An exhaust hood for a turbine includes a shell casing, an external support structure, conical corner plates, and a butterfly plate. The shell casing includes an inner surface and an outer surface. The external support structure is coupled to the shell casing outer surface, and provides structural support to said shell casing. The butterfly plate is coupled to the shell casing inner surface for channeling flow into the exhaust hood and subsequently into the condenser. The butterfly plate has a substantially elliptically-shaped cross-sectional profile that facilitates reducing flow separation losses of steam flowing therethrough into the exhaust hood.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cross-flow fan propulsion system
ActiveUS7641144B2Improve efficiencyLow parasite dragAircraft navigation controlPropellersAirplaneAirflow
A cross-flow propulsion mechanism for use in providing propulsion to an aircraft, includes a housing defining an inlet, a rotor compartment, and an outlet. The inlet is adapted to receive an inflow of air along a first longitudinal axis. The rotor is mounted within the rotor compartment and adapted to receive the airflow introduced into the housing through the inlet and rotate about a second longitudinal axis that is substantially perpendicular to the first longitudinal axis. The outlet is adapted to receive the airflow processed through the rotor and exhaust air along a third longitudinal axis that is substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis. The propulsion mechanism can be applied in a personal aircraft, an STOL aircraft, and a hybrid automobile and aircraft.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
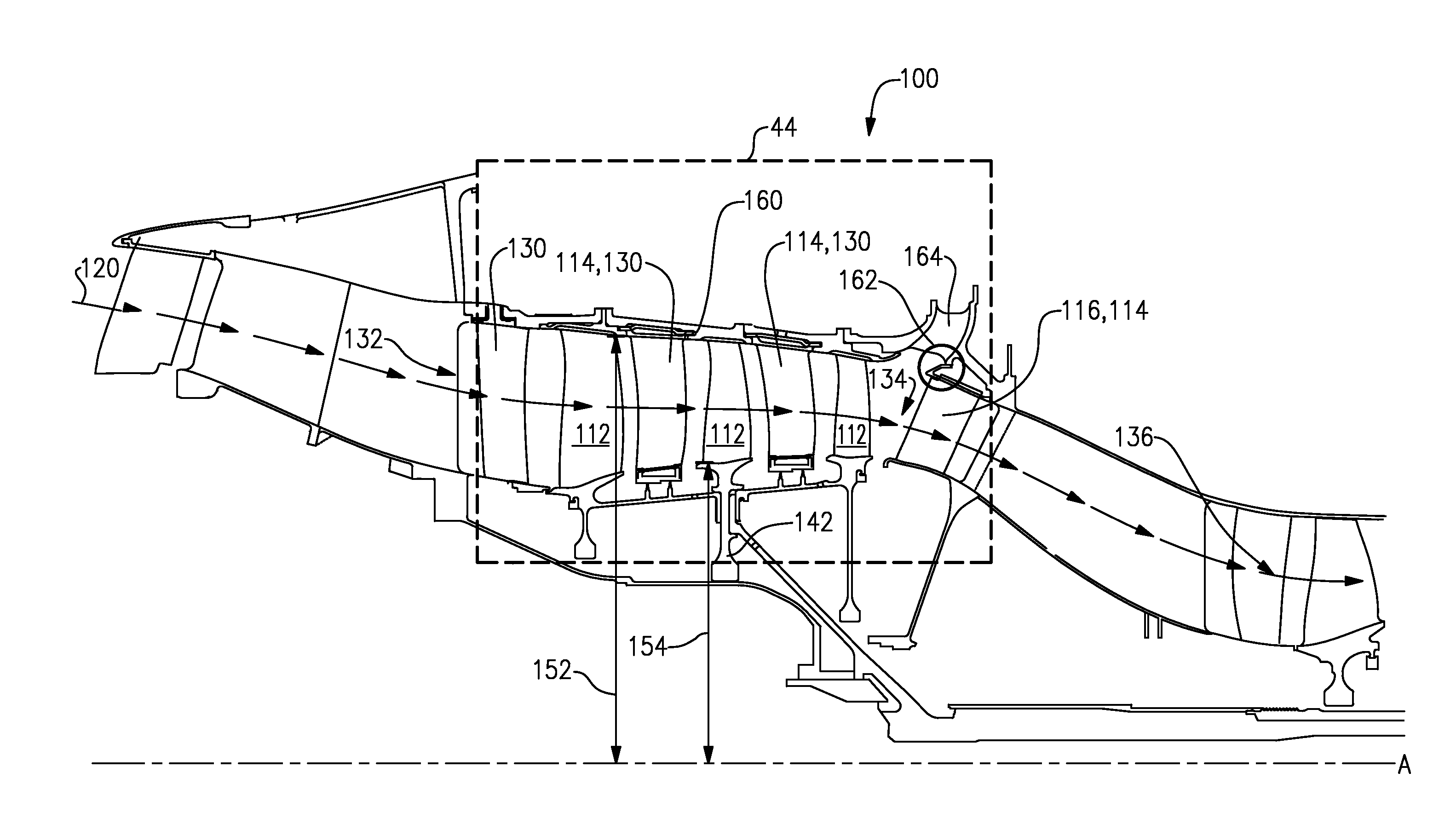
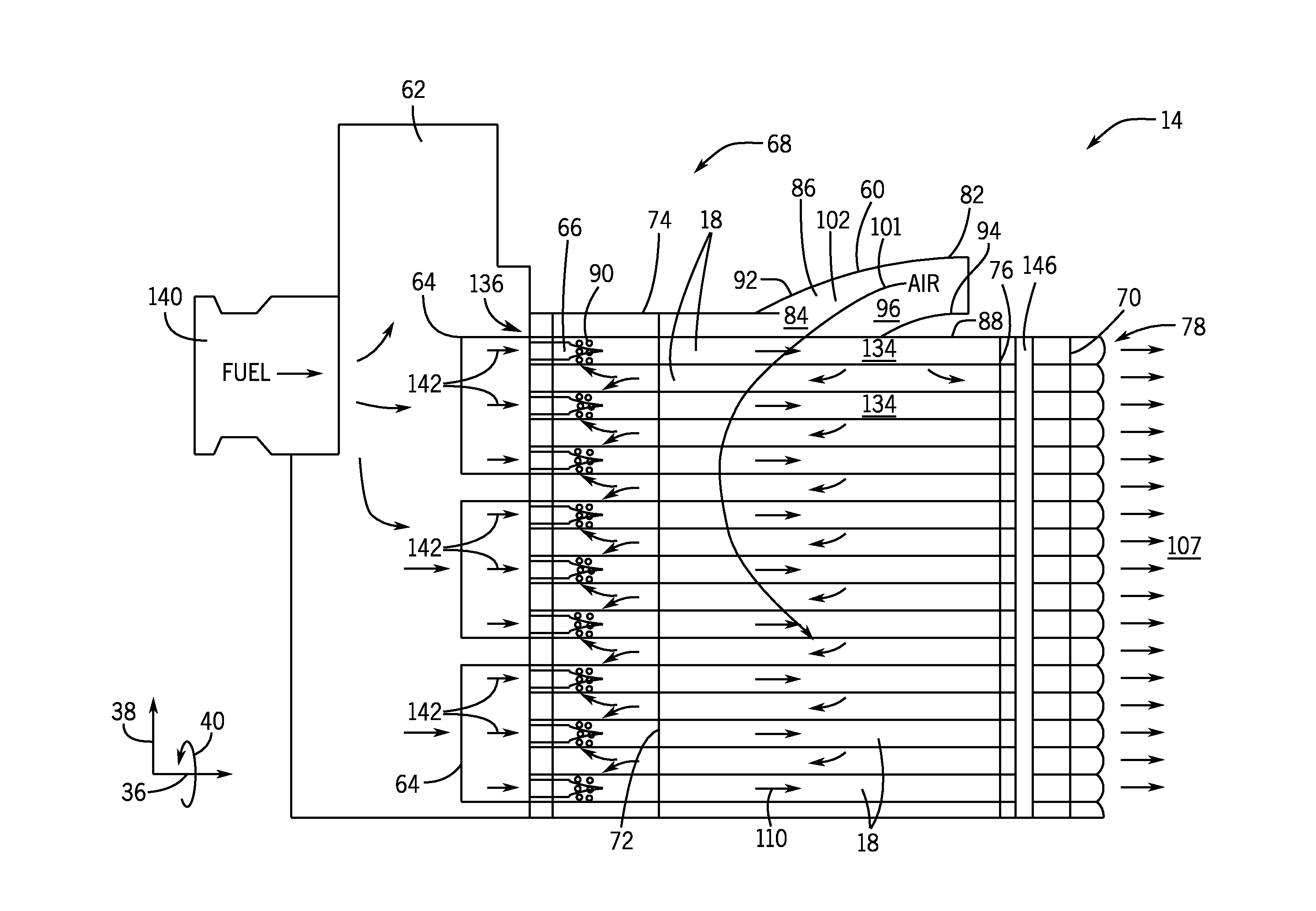
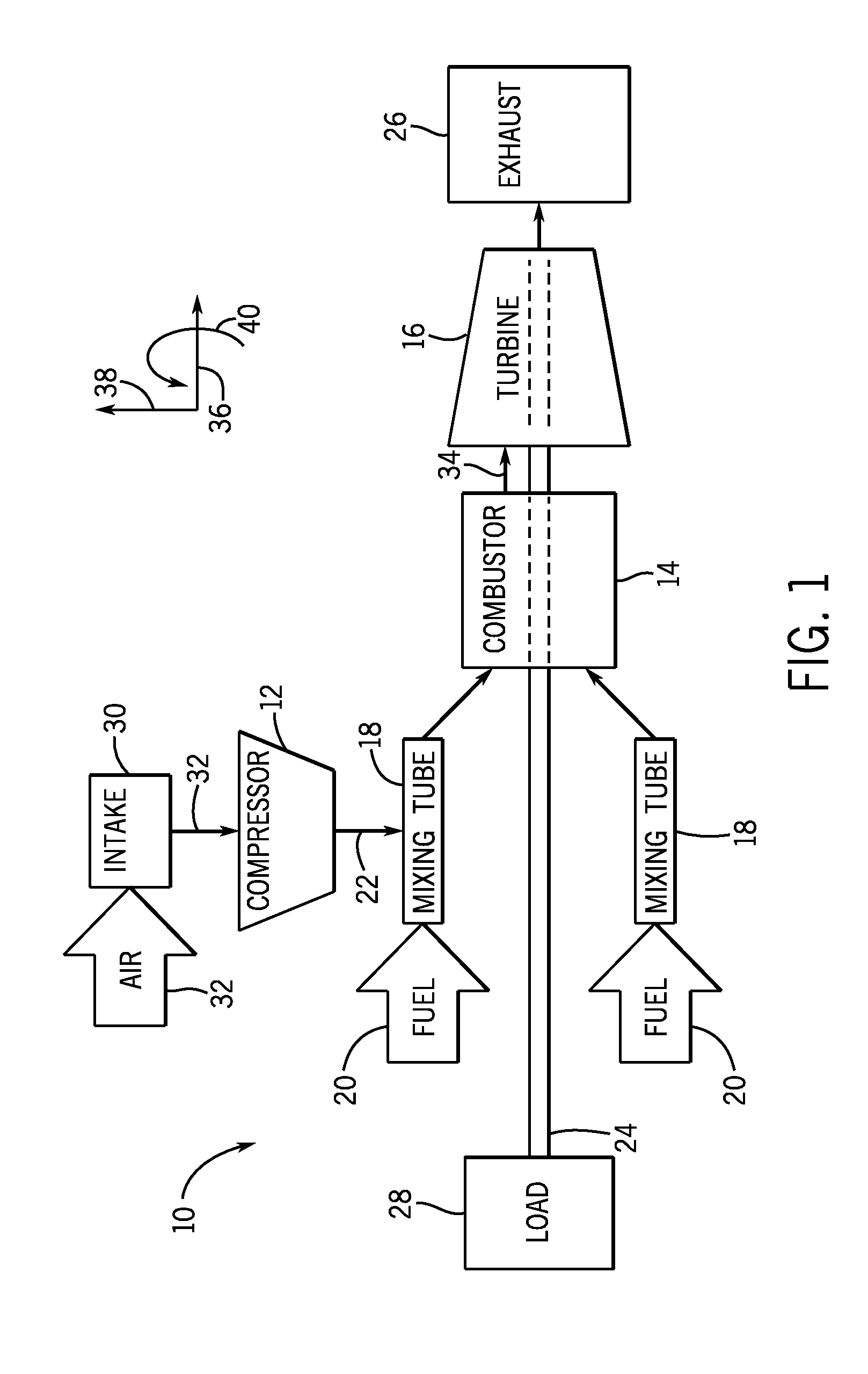
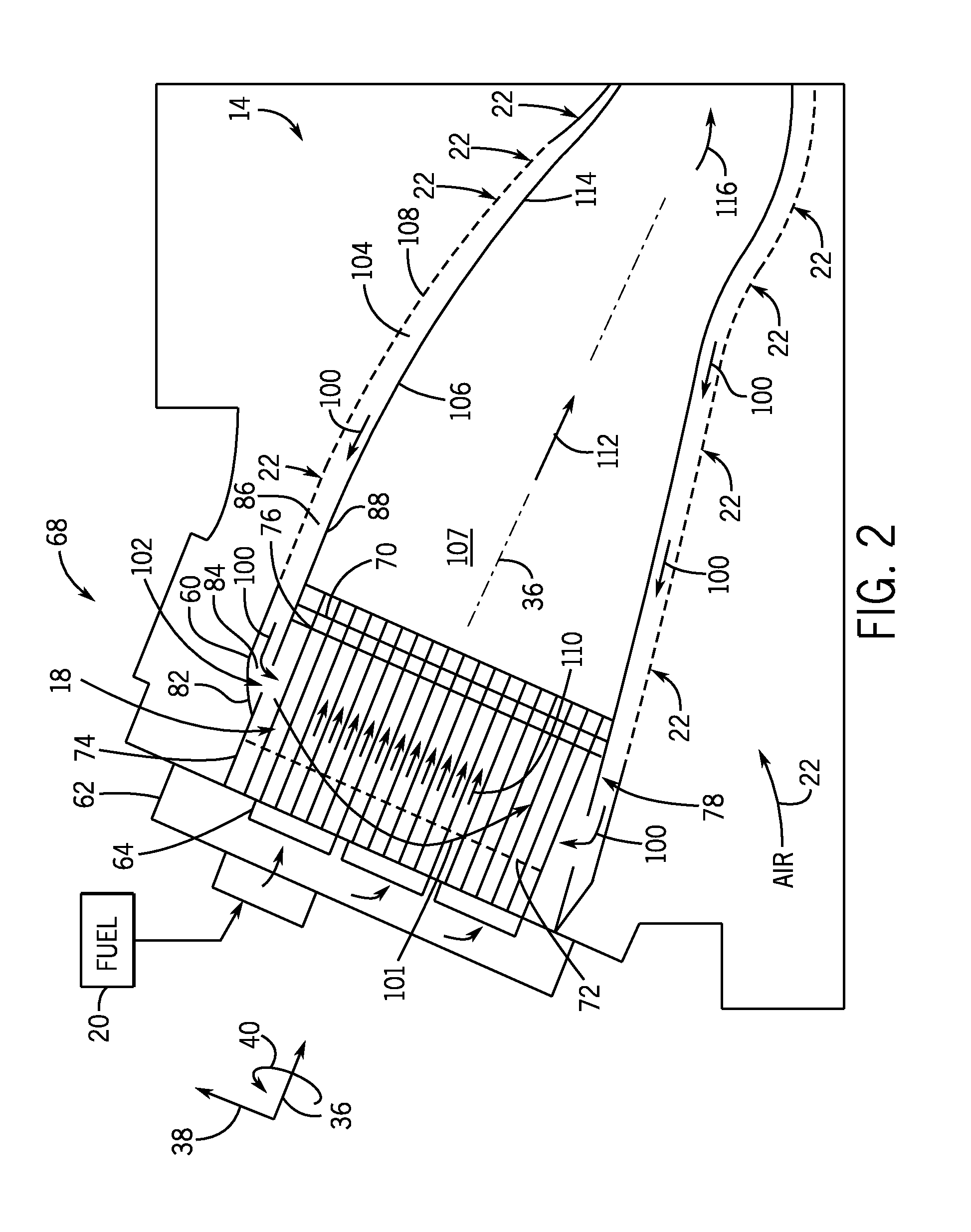
Air diffuser for combustor
ActiveUS20140260300A1Reduced flow separationReduce manufacturing costContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsInjectorInterior space
A system includes a multi-tube fuel nozzle of a turbine combustor. The multi-tube fuel nozzle includes a support structure defining an interior volume configured to receive an air flow; a plurality of mixing tubes disposed within the interior volume, wherein each of the plurality of mixing tubes comprises a respective fuel injector; and an outer annular wall configured to direct an air flow from an annulus between a liner and a flow sleeve of the turbine combustor at least partially radially inward into the interior volume through an air inlet and toward the plurality of mixing tubes, wherein the outer annular wall at least partially defines an air flow passage extending from the annulus to the interior volume.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Football with a modified surface conferring altered aerodynamic properties
InactiveUS20060105866A1Reduce air resistanceReduce loss rateHollow inflatable ballsEngineeringAerodynamics
A generally prolate-spheroidal, inflatable game ball with a plurality of air-turbulence-producing depressions distributed over a majority of the outer surface of the skin. The depressions produce a preferably circular surface shape, with a breadth of less than about one-quarter inch and preferably having a breadth to depth ratio of about 2 to about 6. The game ball of the present invention is preferably an American-style football, wherein the depressions are distributed substantially uniformly over the majority of the outer surface. A method for providing the game ball with altered aerodynamic performance may include forming depressions by embossing the skin or molding depressions therein.
Owner:MA HANSAN
Vane or blade for an axial flow compressor
ActiveUS8678757B2Losses have been minimisedExpand flow rangePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTrailing edge
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Casing of a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20100031673A1Reduced flow separationHigh heat transfer coefficientPump componentsGas turbine plantsRadial spokeGas turbines
A section of a gas turbine engine including a radial spoke is provided. The spoke includes an aerodynamic shape with a leading side and a trailing side and, extending from the leading side to the trailing side, a first side and a second side, opposite the first side. The spoke also includes at least one flow guiding element arranged on at least the first side.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
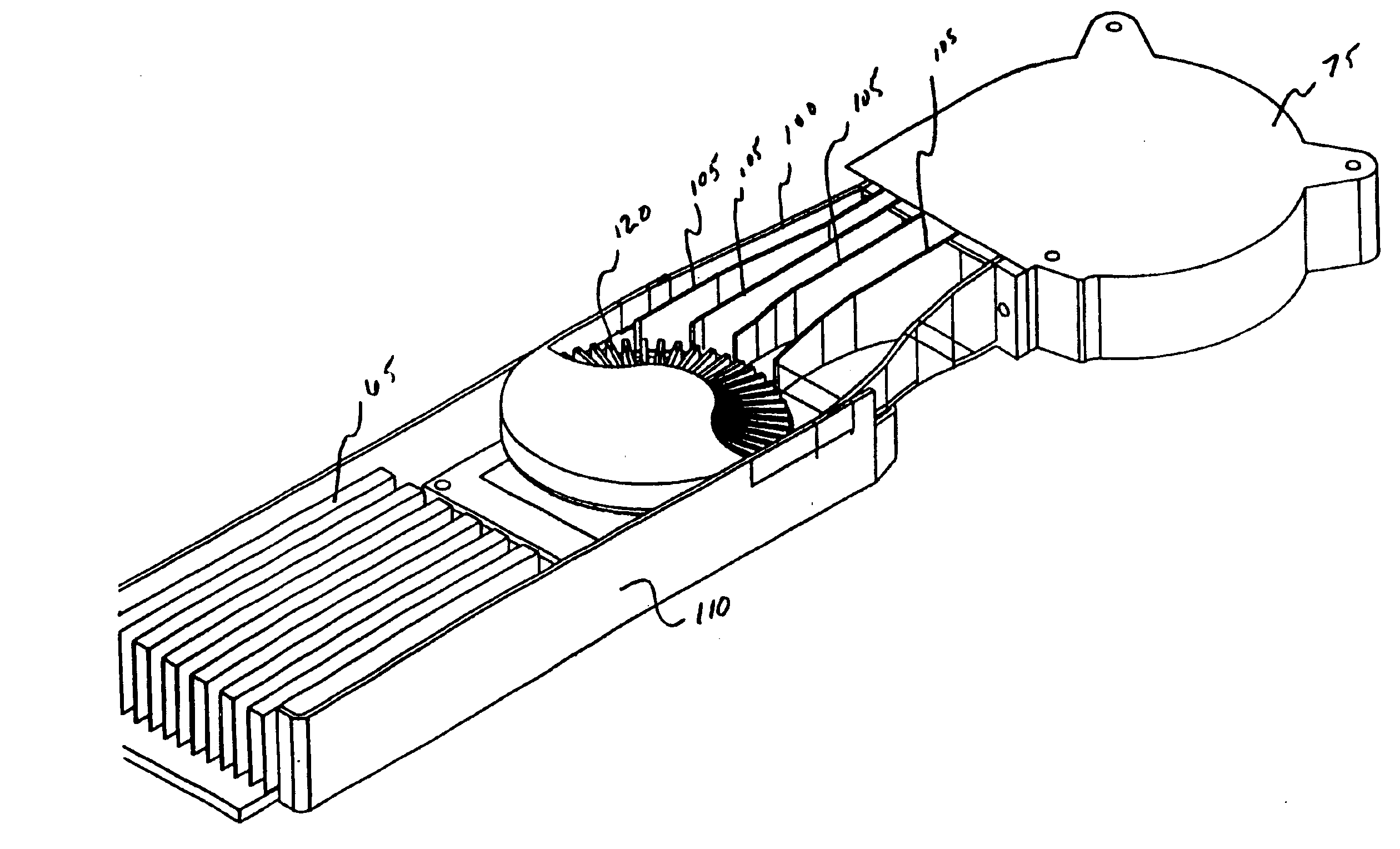
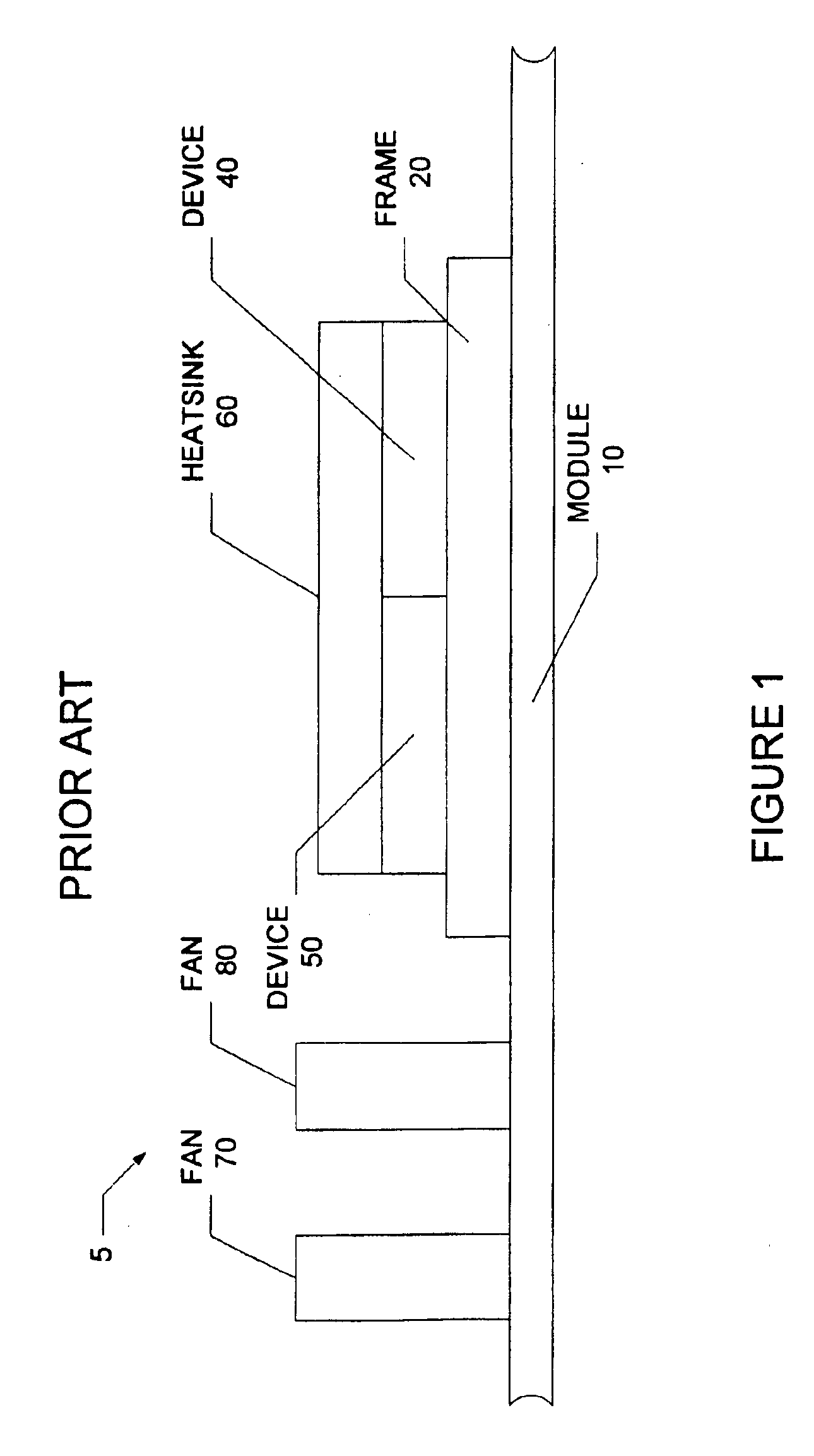
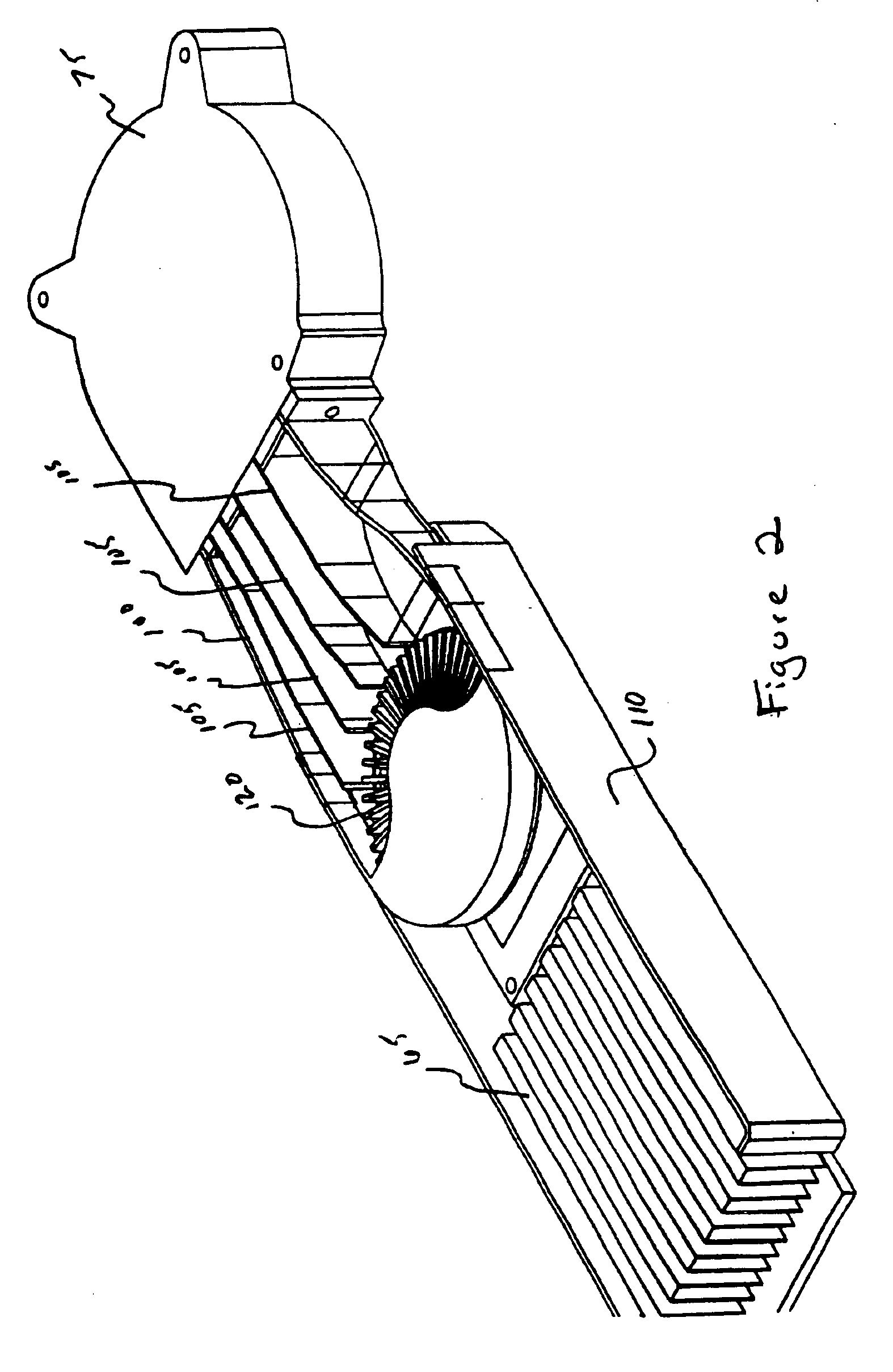
Electronics cooling subassembly
InactiveUS6912128B2Reduce turbulenceReducing air boundary separationDomestic stoves or rangesMagnetic/electric field screeningElectronics coolingEngineering
A thermo-electro sub-assembly comprises a gas supply, a first duct, a first heatsink adjacent a first device, a second duct, and a second heat sink adjacent a second device. The gas supply may be realized as a fan, a blower, or a compressed gas source. The first duct provides a passageway for delivering pressurized gas from the gas supply to the first heat sink. The duct may include a plurality of vanes for reducing the turbulence and air boundary separation within the duct. The first heatsink is in thermal communication with a first heat-producing device such as a microprocessor. In a preferred embodiment the heatsink comprises an axial shaped folded fin heatsink. The second duct is used to provide a pathway for the air leaving the first heatsink and delivers the air to the second heatsink. The second duct may also include a plurality of vanes for reducing turbulence and boundary flow separation within the second duct.
Owner:CELESTICA INT INC
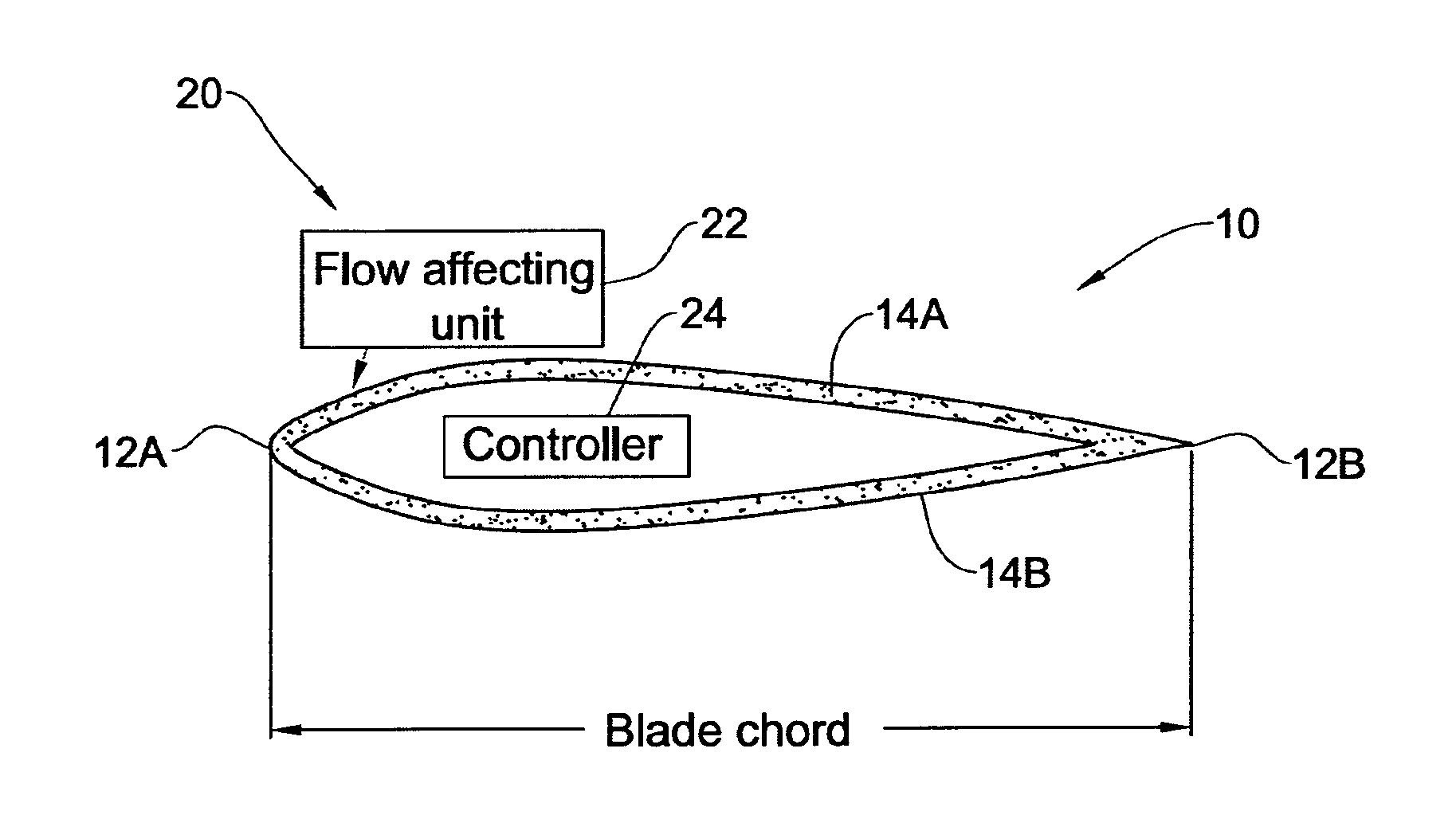
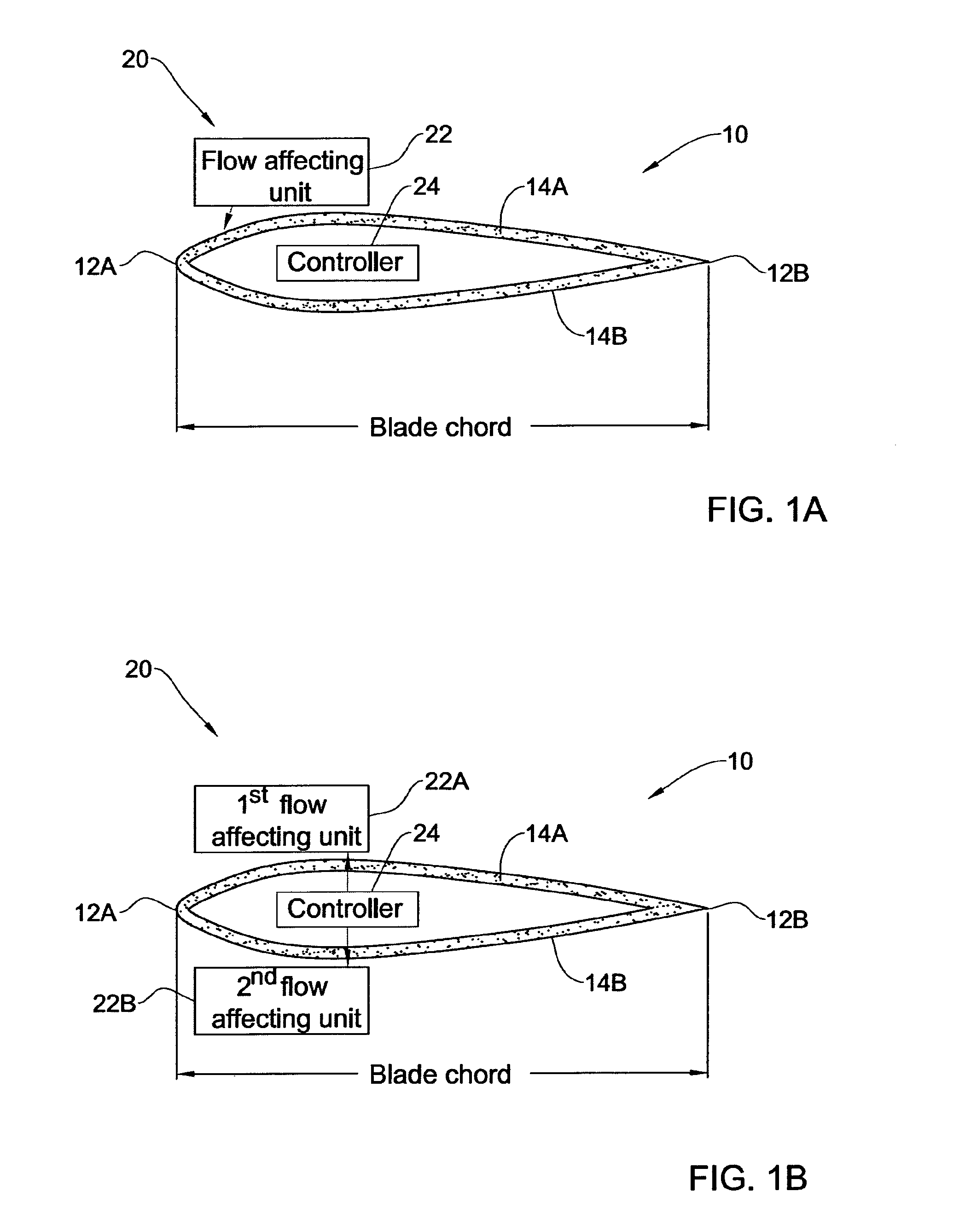
Flow control on a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT)
ActiveUS20120301296A1Improve performanceReducing dynamic stallPropellersWind motor controlLeading edgeMomentum
A control system is presented for controlling operation of a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) for generating energy from an incoming fluid flow. The control system comprises at least one flow affecting arrangement associated with at least one blade of the VAWT and a control unit connected to said flow affecting arrangement, the flow affecting arrangement comprising two flow affecting units located in two opposite sides of the blade respectively at a leading edge thereof, each flow affecting unit being operable for creating a blowing jet at the respective side of the blade thereby inducing an increase in a fluid flow momentum, the control unit being configured and operable for selectively activating the flow affecting units in alternating fashion according to a predetermined time pattern to oscillate the blowing jet at the opposite sides of the blade.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Blade or vane for a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20190101002A1Increase roughnessRaise the possibilityEngine manufacturePump componentsGas turbinesSuction surface
A blade or vane for a gas turbine engine comprising a pressure surface and a suction surface. The pressure surface or the suction surface comprises a roughness zone which is configured to provide greater flow resistance in a direction along the blade or vane than in a direction across the blade or vane.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Casing based on self-circulation oscillation jet, compressor and stability enhancing method thereof
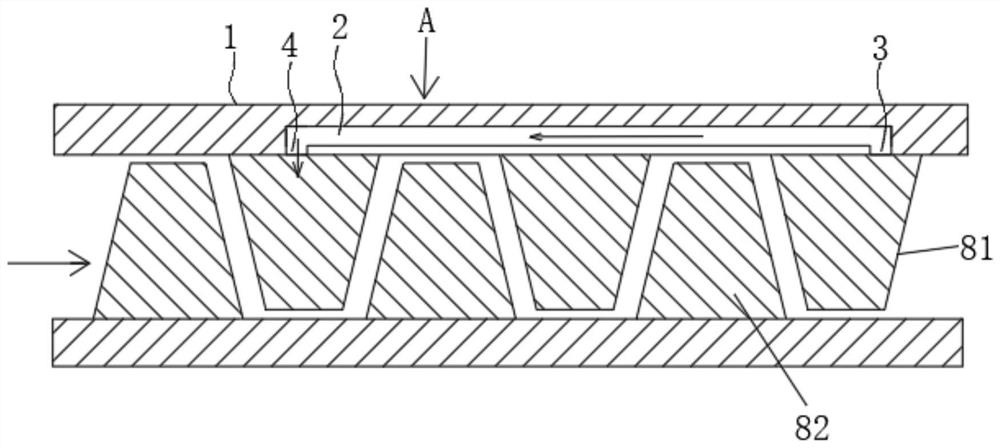
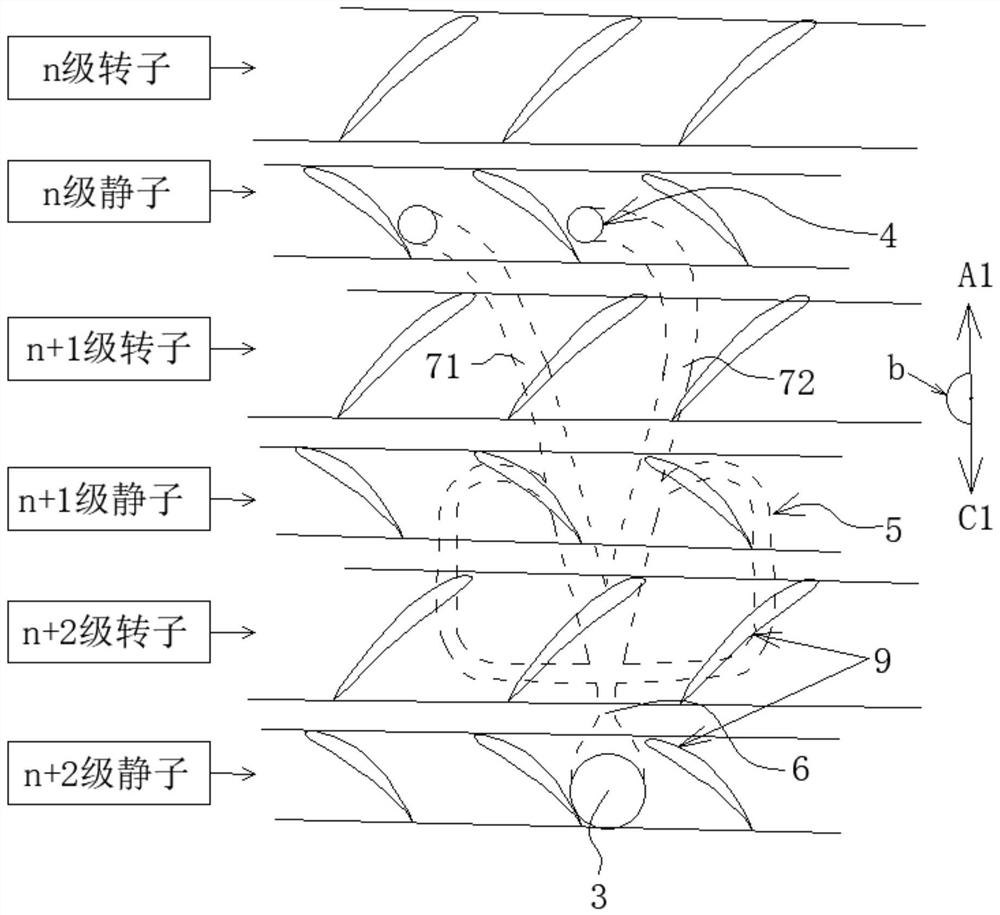
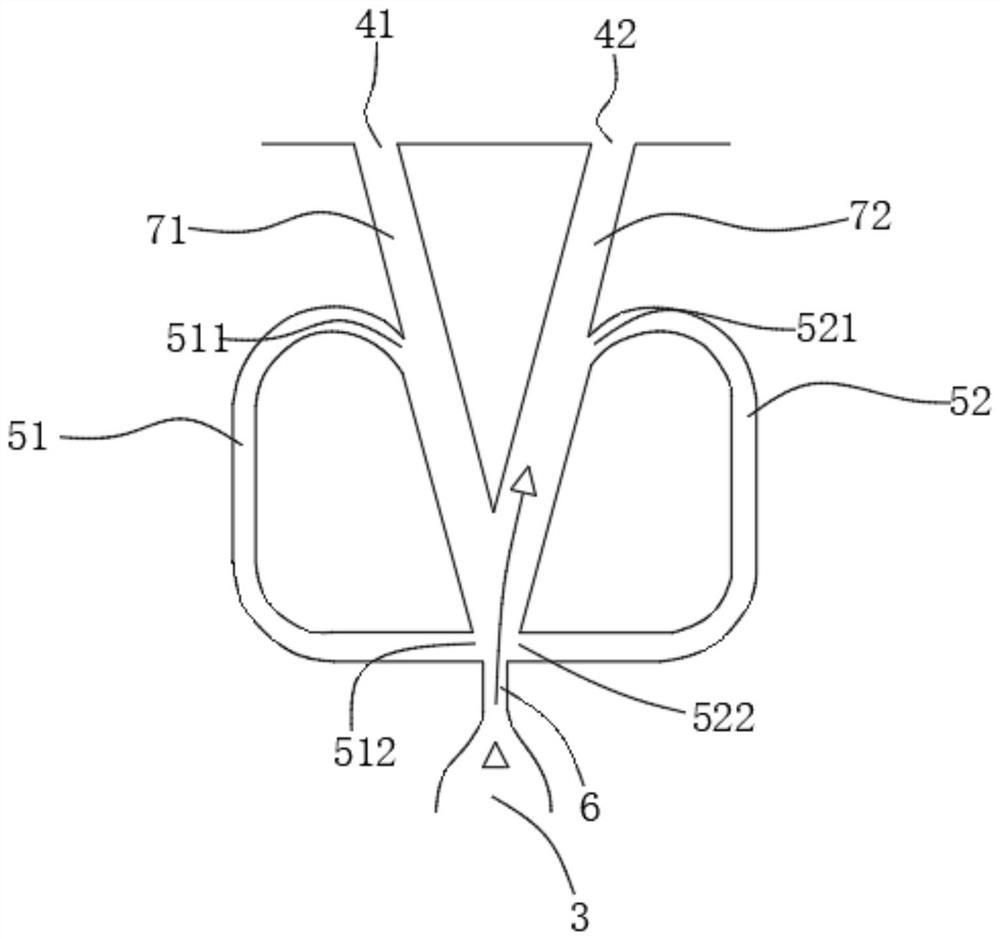
PendingCN111810454AImprove stable working marginIncrease working marginPump componentsGas turbine plantsSuction forceFluidic oscillator
The invention provides a casing based on self-circulation oscillation jet, a compressor and a stability enhancing method thereof. A fluid oscillator flow channel is arranged in the casing, and air flow enters the fluid oscillator flow channel from an oscillation jet air entraining inlet between (n+m) stage stators or rotors of the casing; the pressure of the oscillation jet air entraining inlet is greater than the pressure of an oscillation jet outlet between n stage stators or rotors, the air flow forms oscillation jet on the oscillation jet outlet between the stators after flowing through the fluid oscillator flow channel, and angle area flow separation and suction surface flow separation corresponding to the top ends of stator blade grids are reduced; or, the oscillation jet isformed on the oscillation jet outlet of the rotors, tip clearance secondary flow corresponding to rotor blades is reduced, and the stable work margin of the compressor is improved; and due to a pressure difference, when the oscillation jet air entraining inlet is located between the (n+m) stage stators or rotors, the fluid oscillator flow channel generate suction action on a top end boundary layer and the secondary flow of the (n+m) stage stators or rotors, the flow separation is reduced, and the stability enhancing effect is generated.
Owner:AERO ENGINE ACAD OF CHINA
Eccentric chamfer at inlet of branches in a flow channel
ActiveUS8628292B2Maintain validityOptimised cross flowPropellersEngine manufactureMain channelEngineering
A flow channel with a branch channel perpendicular to a main channel including an edge defining an inlet opening of the branch channel is provided. A chamfer is disposed at the upstream edge of the inlet opening and a straight edge is disposed at the downstream edge of the inlet opening, perpendicular to the main channel.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
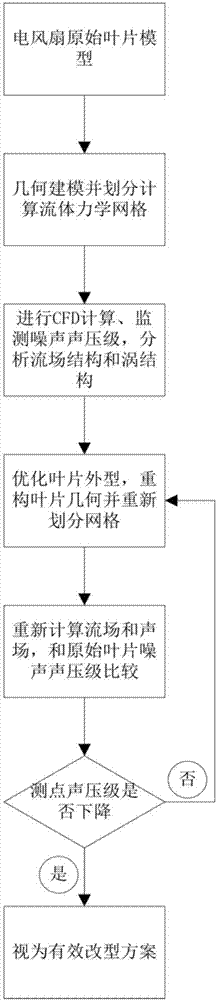
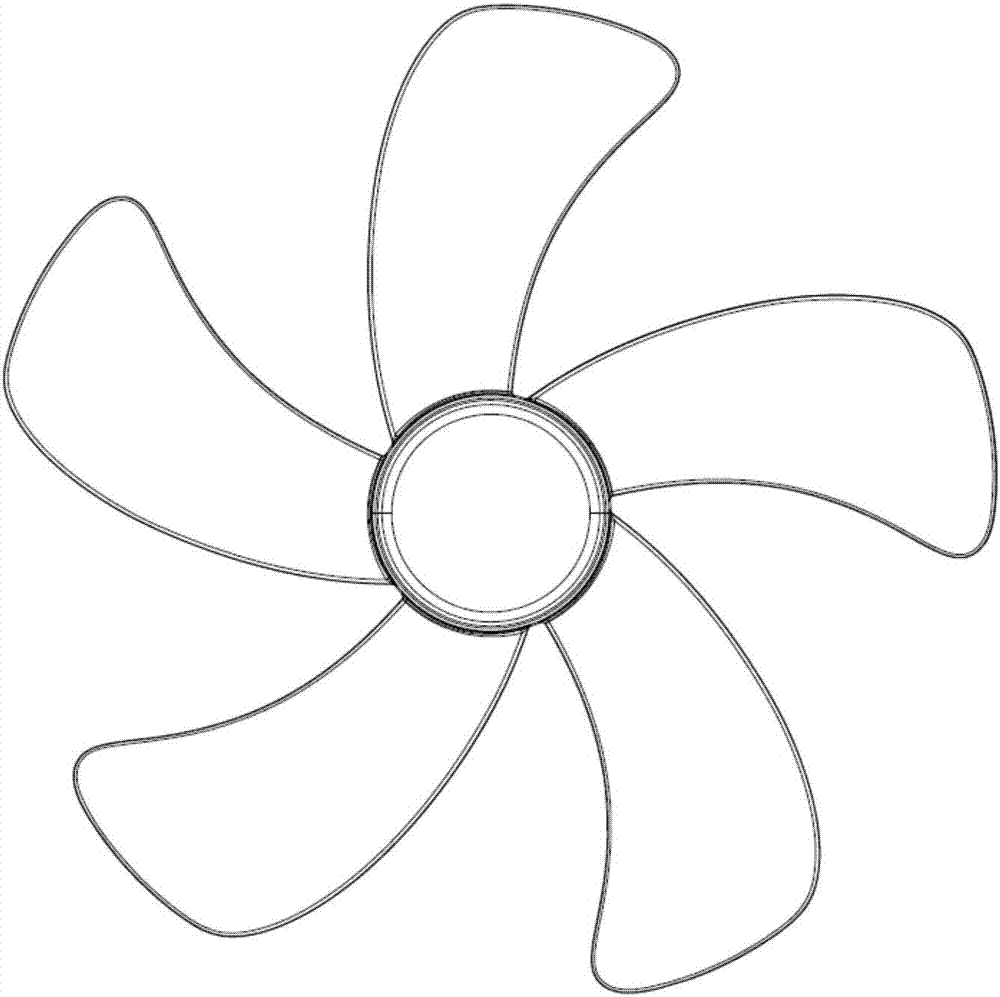
Noise-reducing method for electric fan based on blade modification and improved blade structure of electric fan
InactiveCN107489658AReduce aerodynamic noiseRealize noise reduction of the whole machineGeometric CADPump componentsEngineeringOperability
The invention discloses a noise-reducing method for an electric fan based on blade modification and an improved blade structure of the electric fan. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a hydromechanic calculating model of an original blade structure of the electric fan; (2) performing kinetic analysis on the original blade structure of the electric fan to obtain fluid field data and monitoring the sound pressure level of noise of a preset measuring point, wherein the fluid field data comprises a blade surrounding vorticity value and vortex structure distribution; (3) performing a modified design on the fan blade structure of the electric fan continuously and performing kinetic analysis on the modified blade structure of the electric fan to obtain fluid field data and measured point noise data, and reducing the blade surrounding vorticity value and crushing large vortexes into small vortexes till the sound pressure level of noise of the preset measuring point is reduced on the premise that the blast capacity is invariable at same input power; and (4) manufacturing a fan model, measuring the blast capacity and the sound pressure level through experiments, and verifying the reducing effect of the sound pressure level of the noise of the measured point. By modified noise reduction on the blade of the fan by means of computational fluid mechanics, the method is high in pertinence and high in operability.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
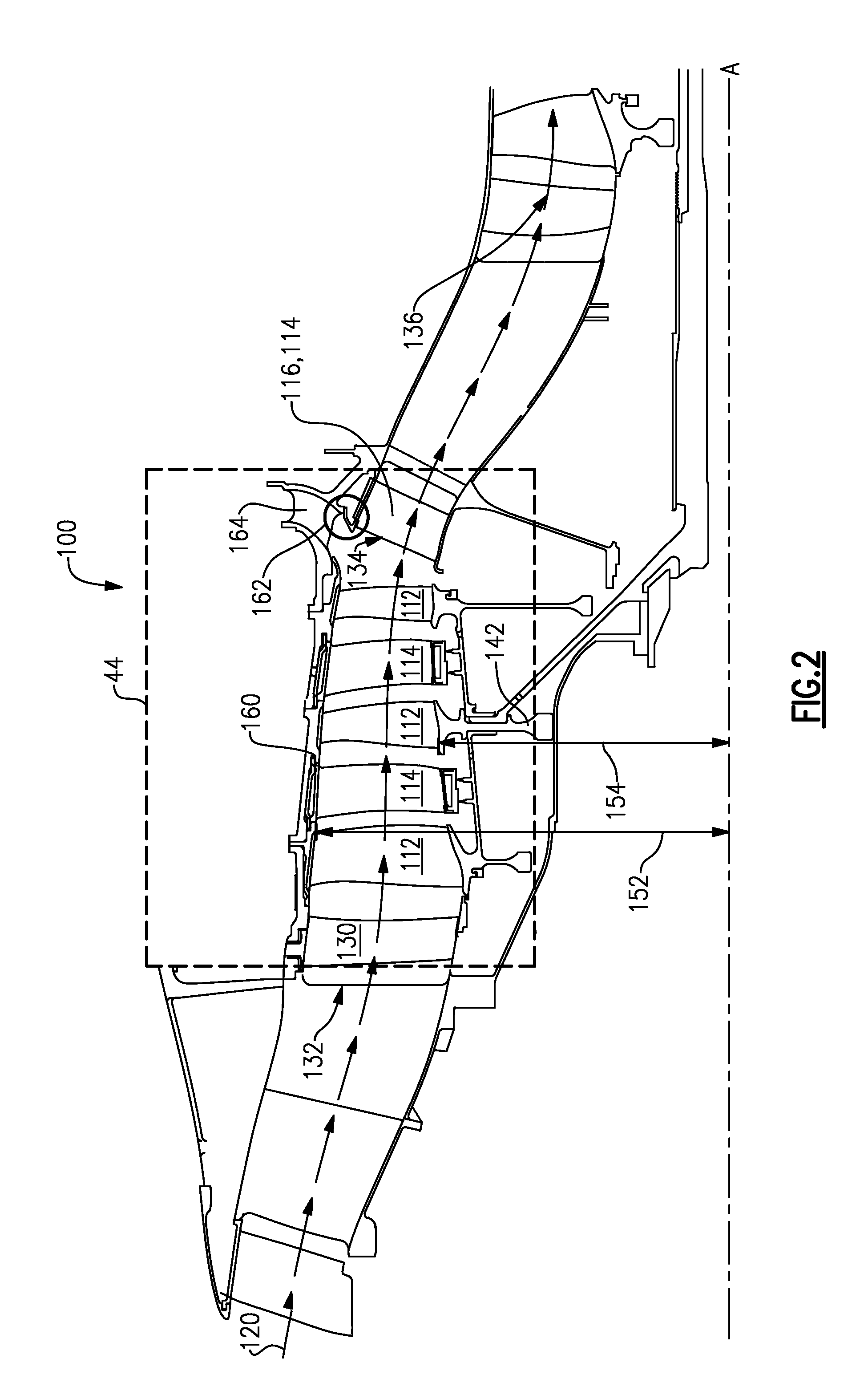
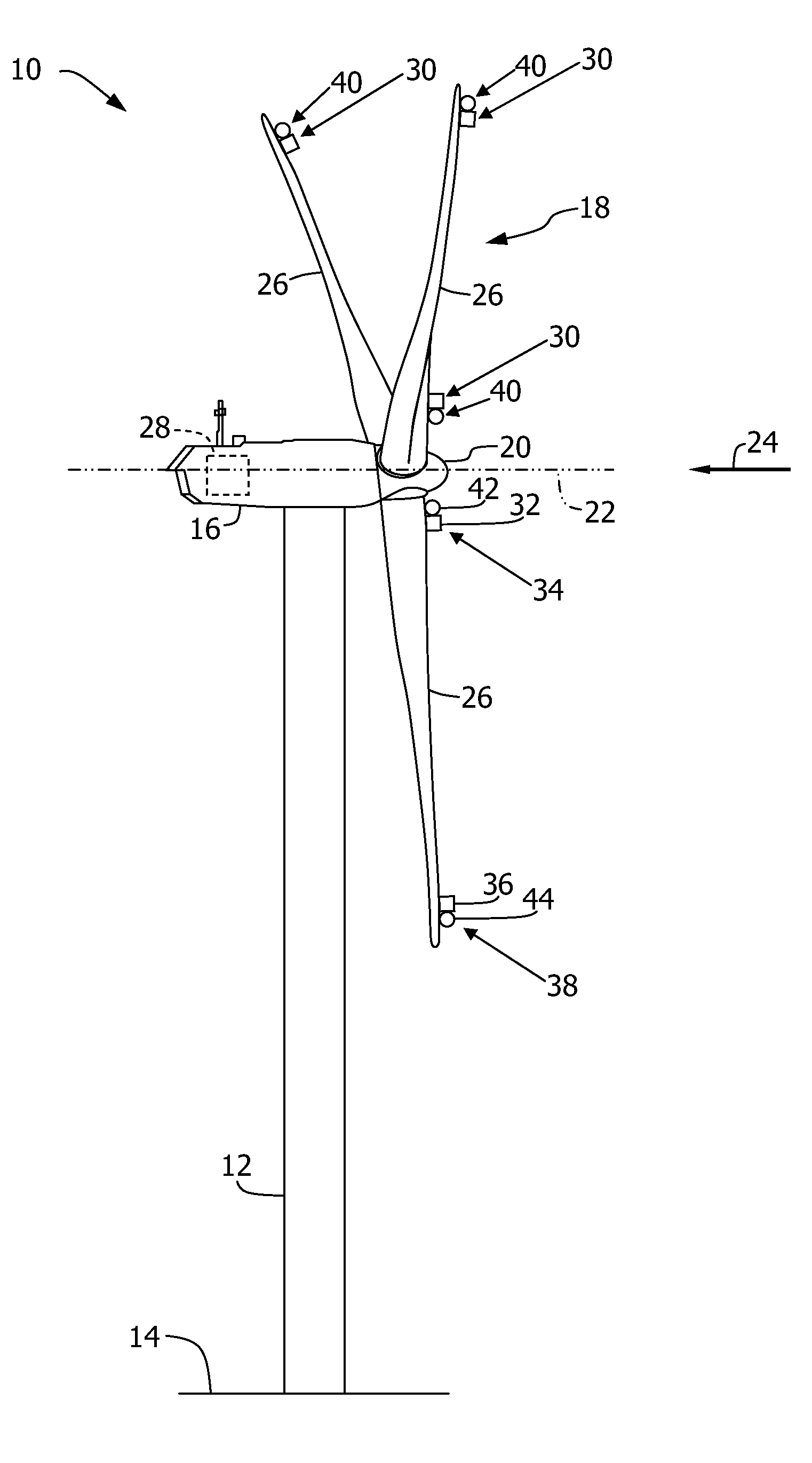
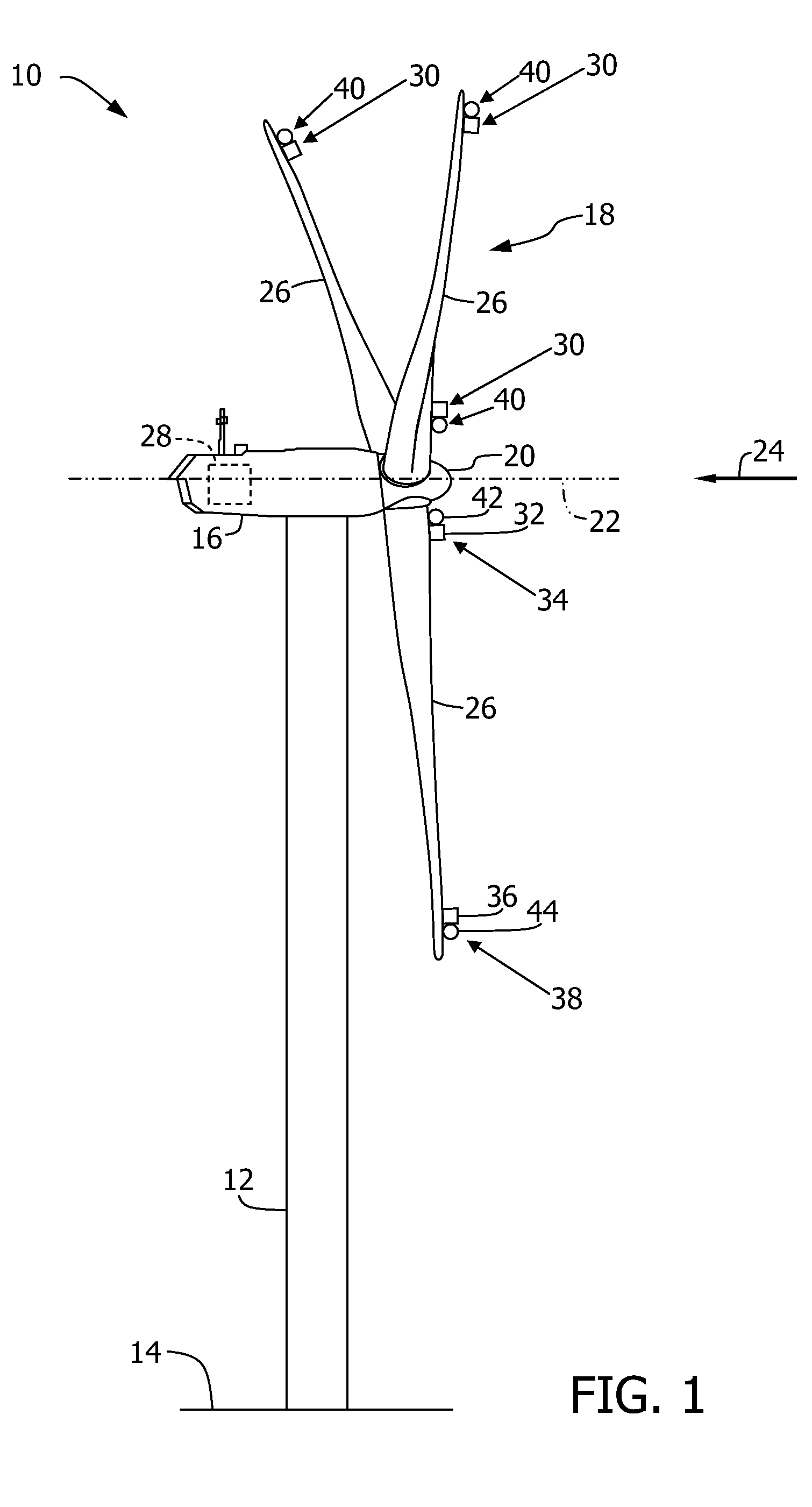
Active control of a wind turbine blade
ActiveUS8057175B2Increase power generationReduced flow separationPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeEngineering
A method and system for increasing power production of a wind turbine including a rotor, at least one rotor blade coupled to the rotor, at least one sensor, and a controller communicatively coupled to the sensor. A flow parameter of the rotor blade is detected, and operation of the wind turbine is controlled to reduce a flow separation at the rotor blade based at least partially on the flow parameter of the rotor blade.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Centrifugal fluid pump
InactiveCN101881282AConstant flow areaImprove pumping efficiencyPump componentsRadial flow pumpsImpellerHydraulic pump
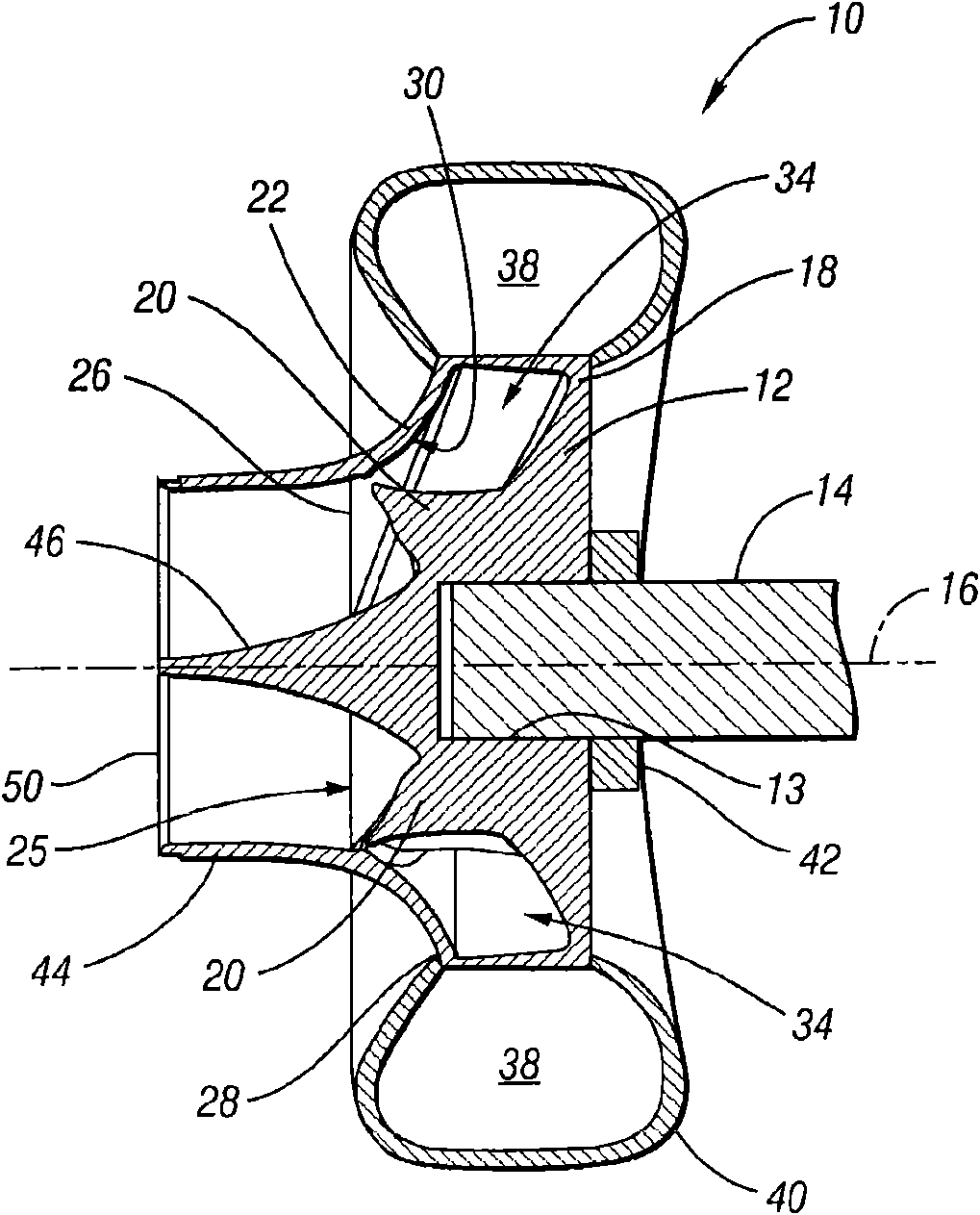
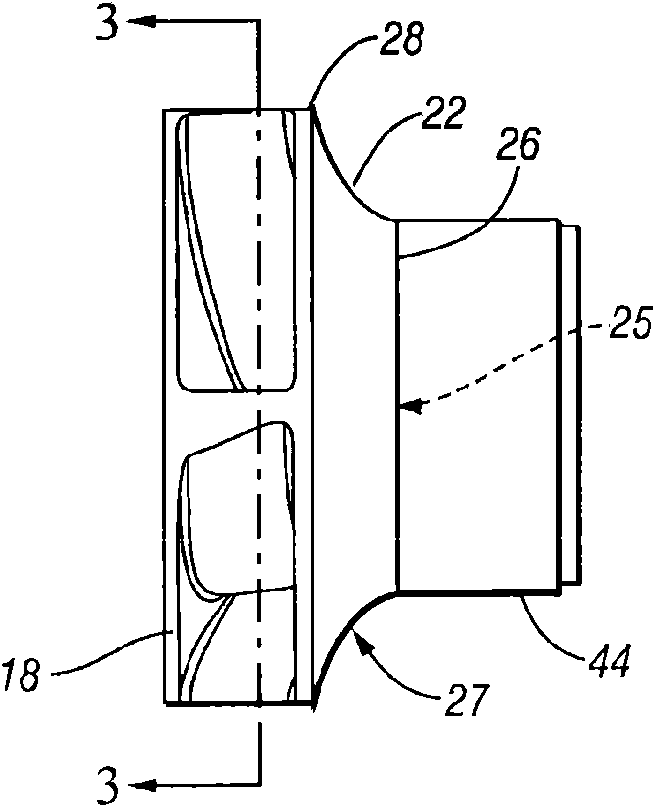
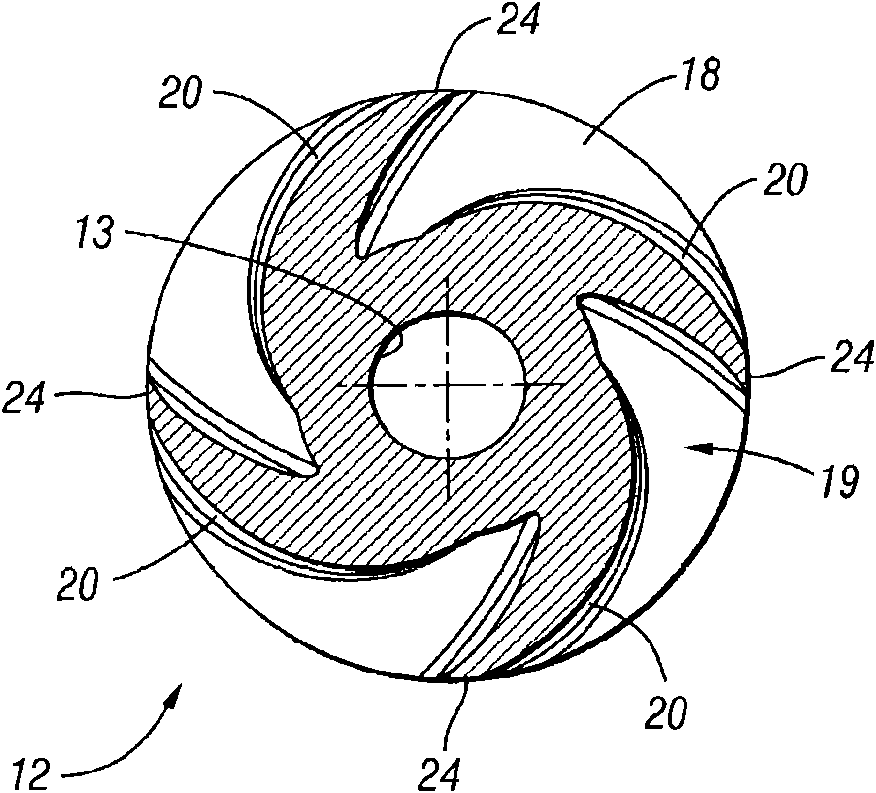
A centrifugal fluid pump has an impeller having a hub with vanes that may be airfoil shaped and may be twisted along their lengths. A shroud having an inlet is connected to the vanes to define with the impeller flow chambers between the vanes, at least a portion of each flow chamber having a substantially constant flow area to increase pump efficiency. An entrance feature may also be provided to improve entrance flow into the impeller, further enhancing pump efficiency.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
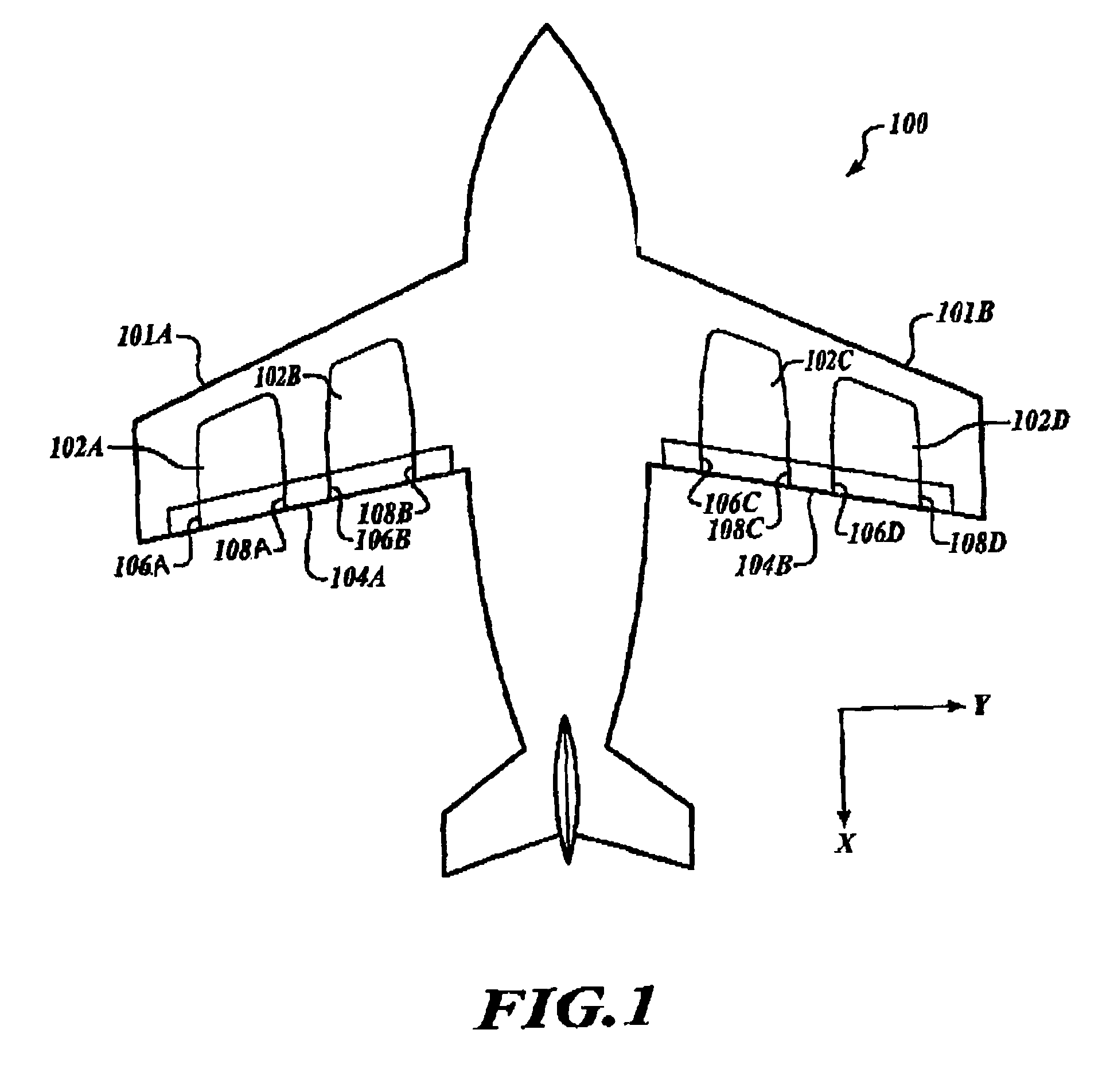
System and method for root loss reduction in wind turbine blades
InactiveUS20130156593A1Optimal angle of attackOptimal of lift generationPropellersPump componentsTrailing edgeWind force
A wind turbine blade includes a root region. A first extension (LEX) is attached to the leading edge side of the root region while a trailing edge strake (TES) is attached to the trailing edge side of the root region. The LEX and TES each include an outer profile that becomes more pronounced relative to their respective locations in the root region as the root region of the wind turbine blade morphs from a substantially cylindrical shape to a substantially airfoil shape. The LEX provides both optimal angle of attack and lift generation in the root region, while the TES mitigates airflow separation and enhances airfoil lift in the root region.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com