Patents
Literature
236 results about "Strake" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
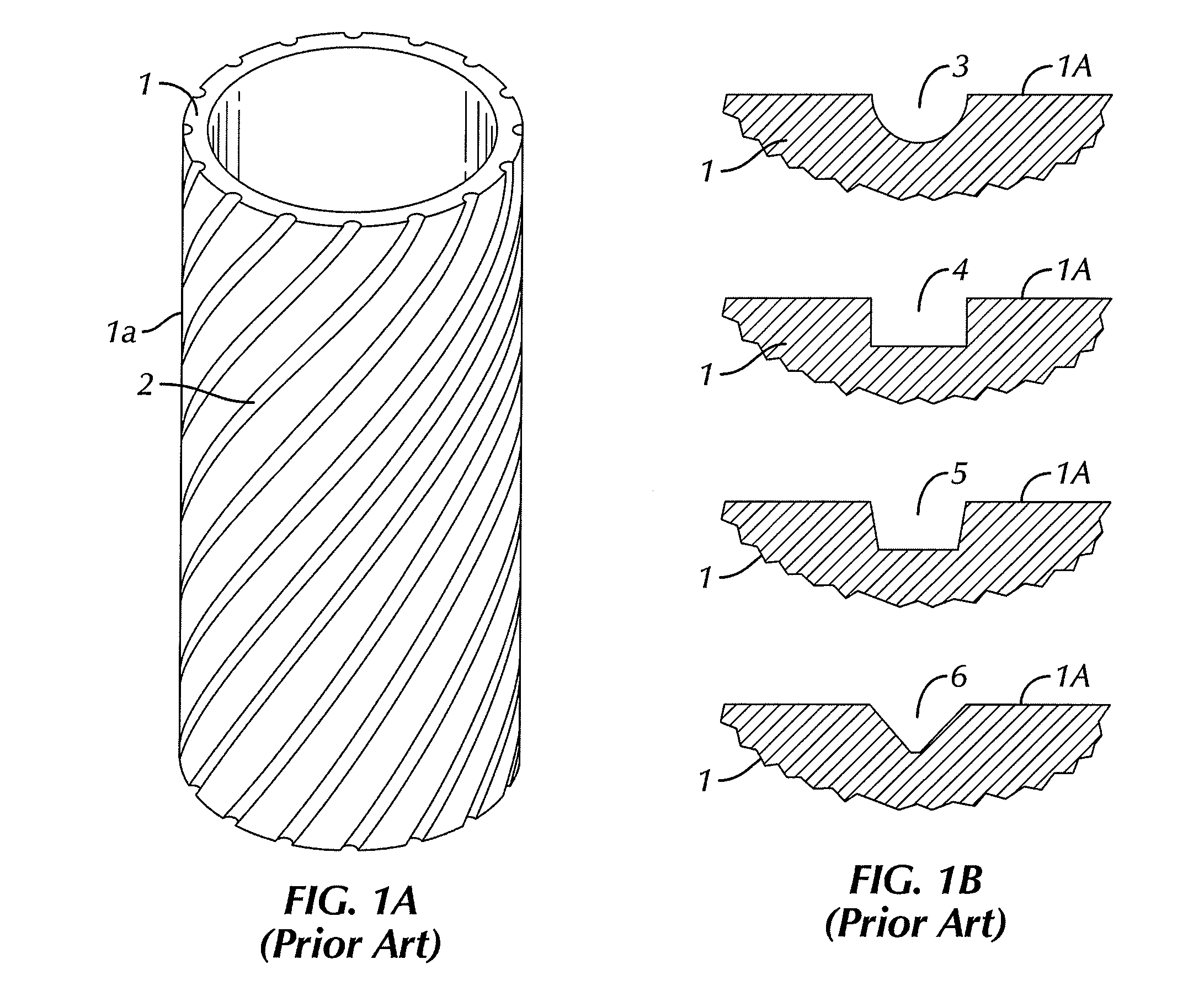
A strake is a course of the planking or plating of the hull of a vessel. In a wooden construction it is a strip of planking (or multiple planks combined into one) running longitudinally along the vessel's bottom and sides. In a metal ship it is a course of plating.
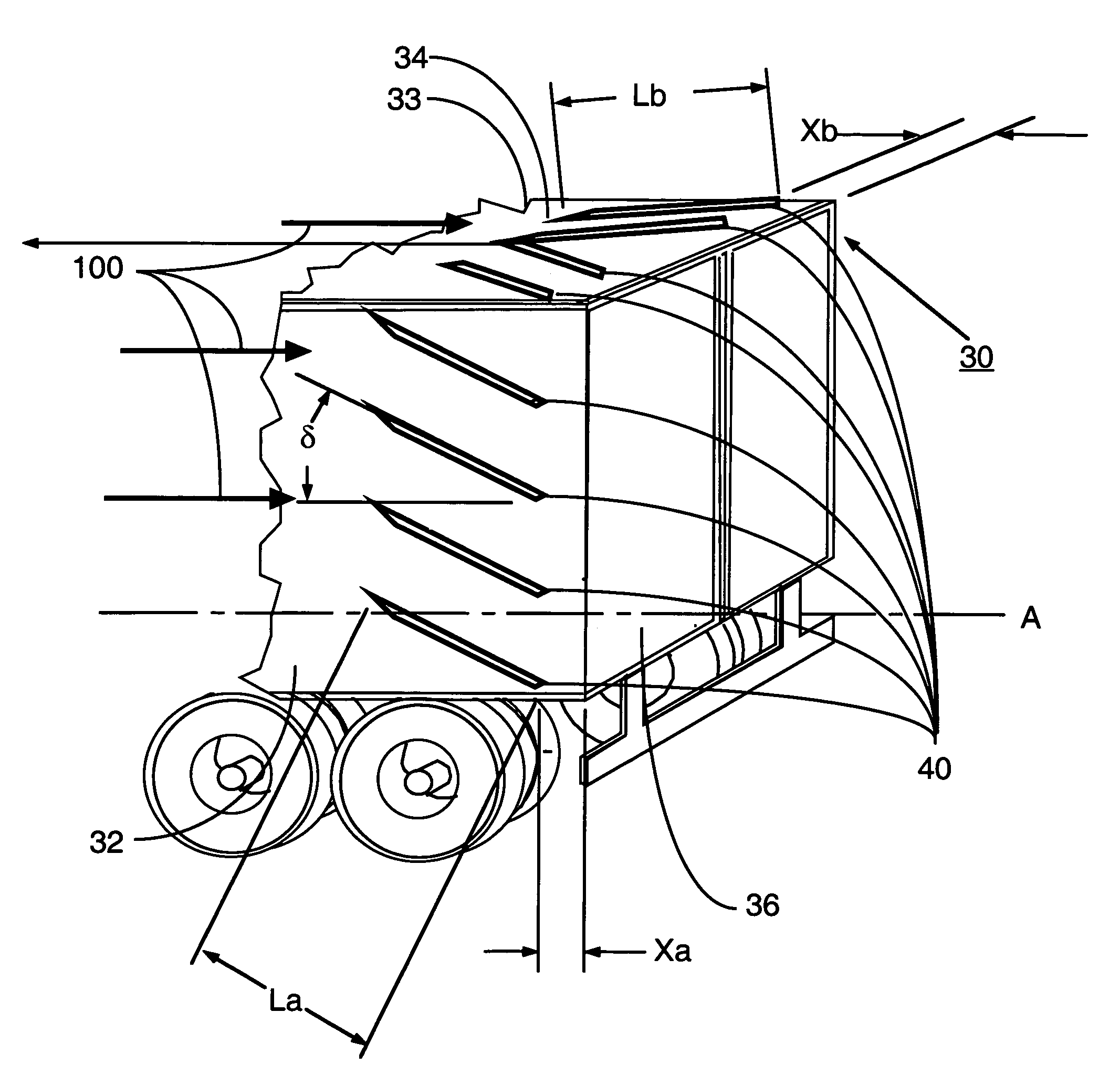
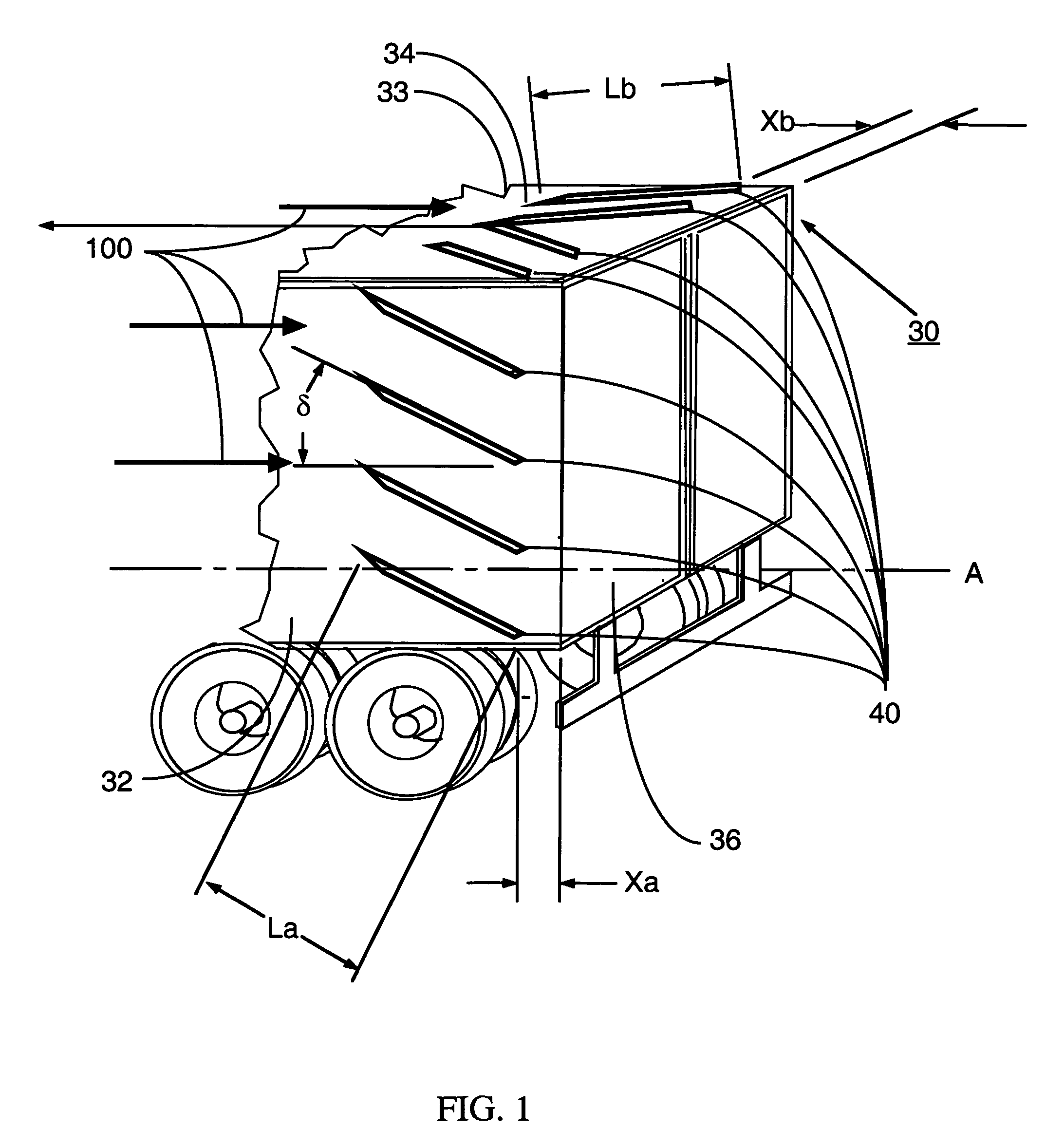
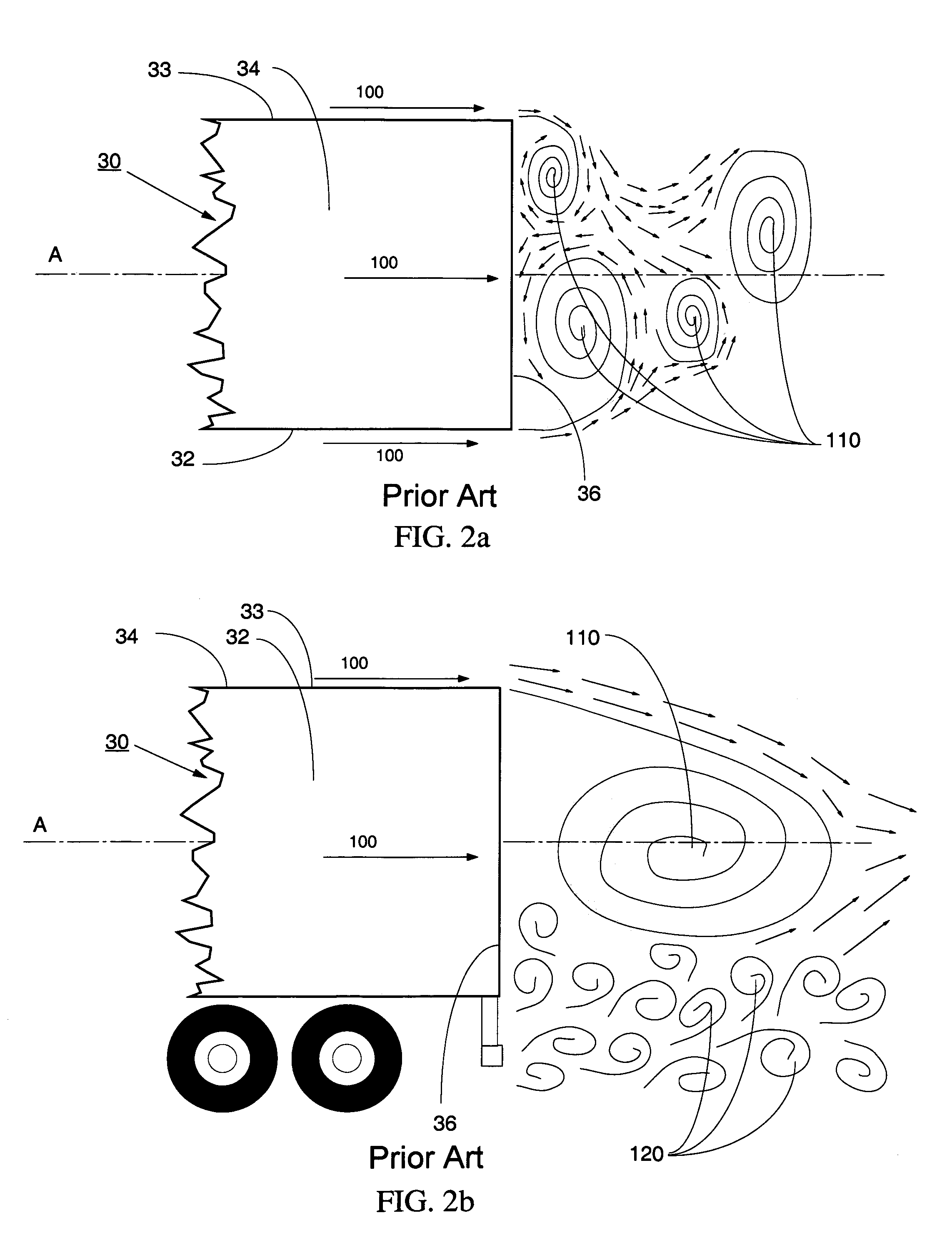
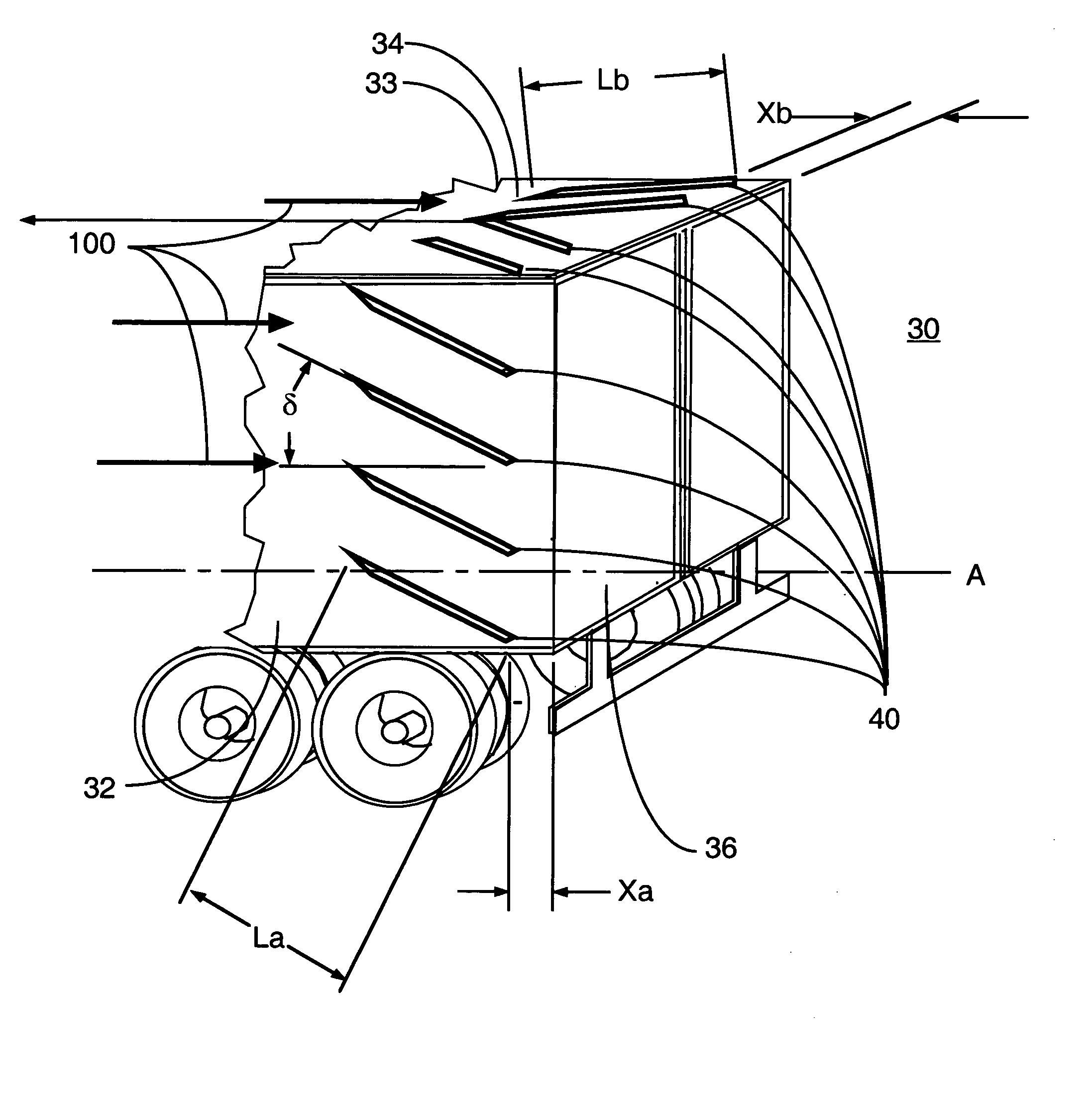
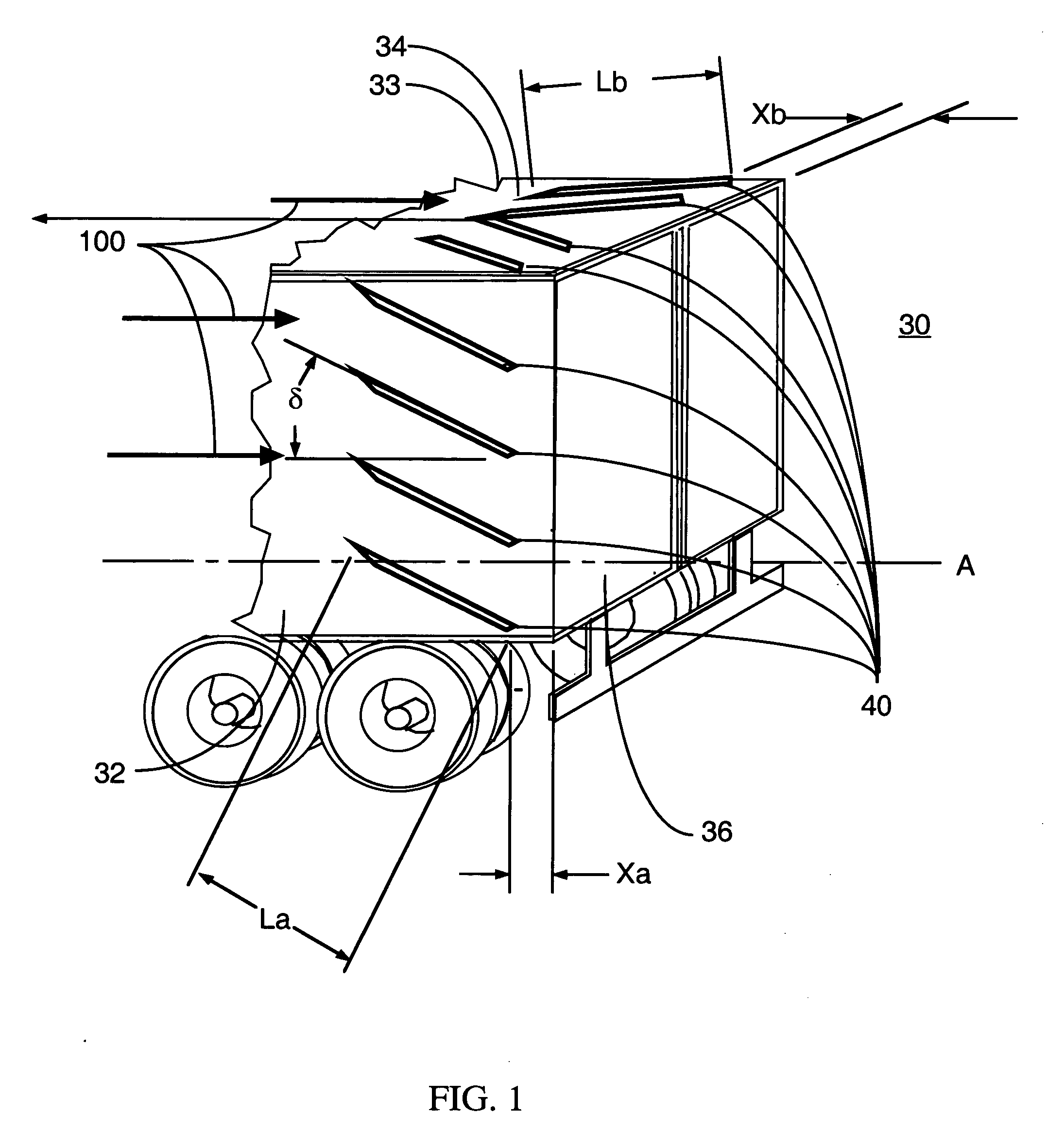
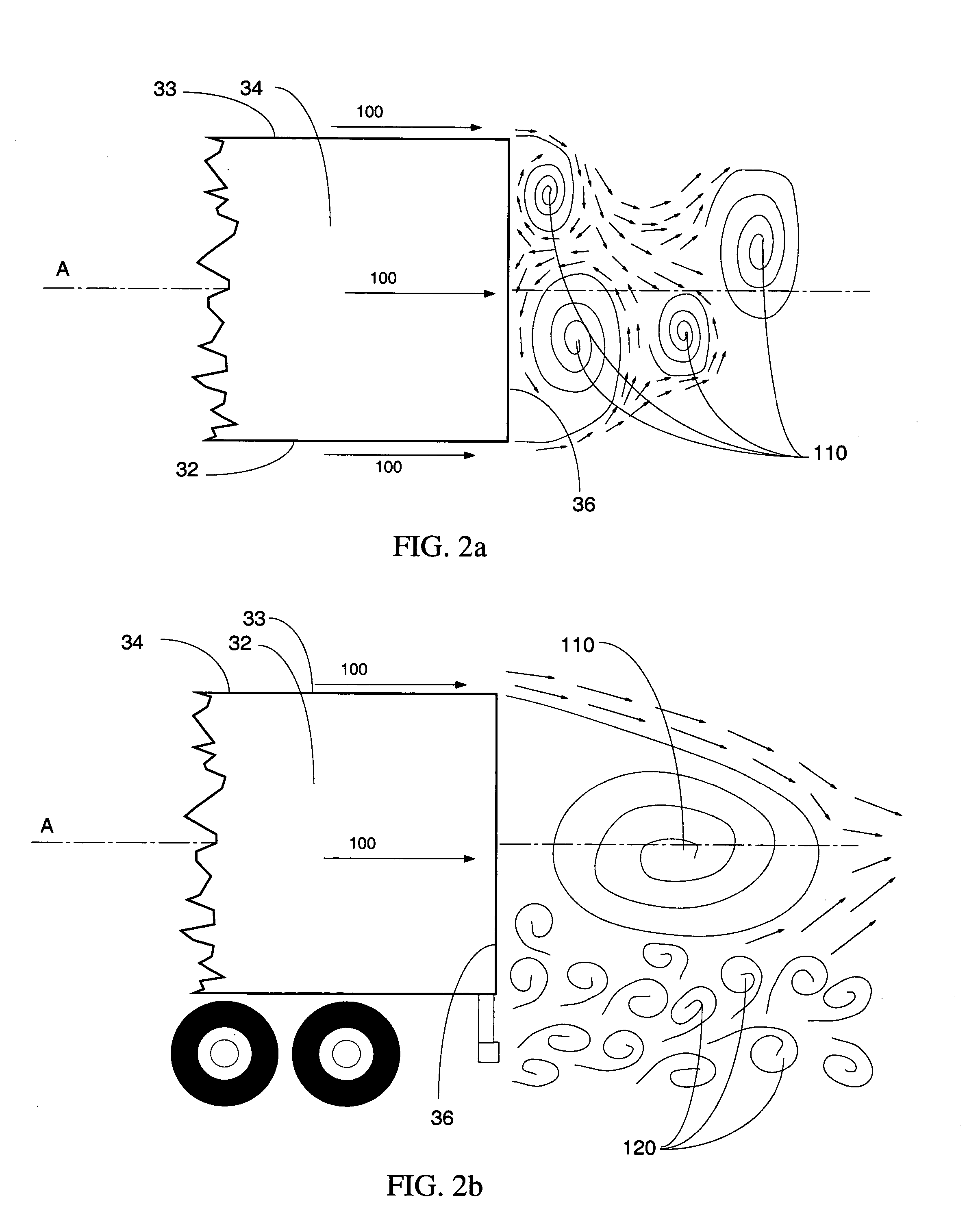
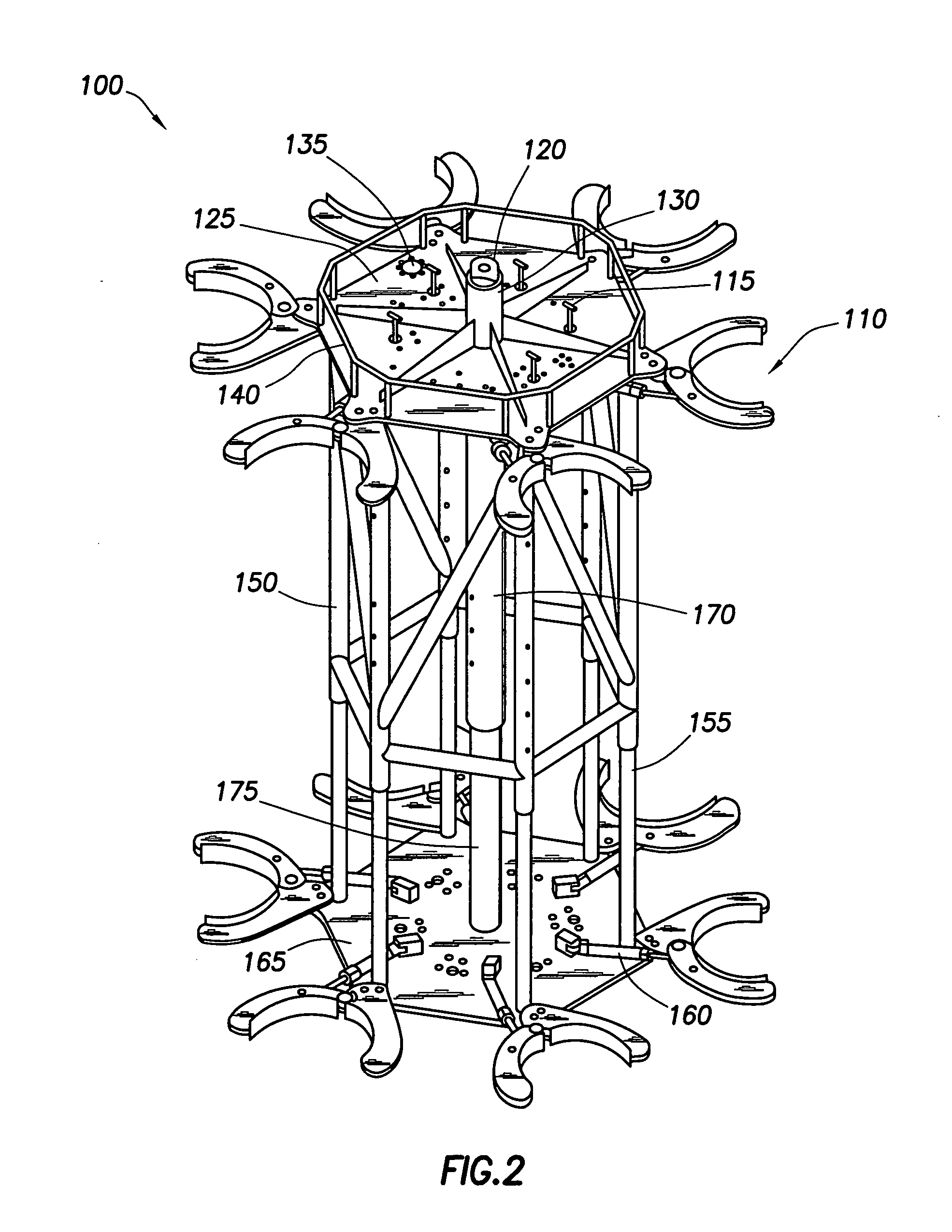
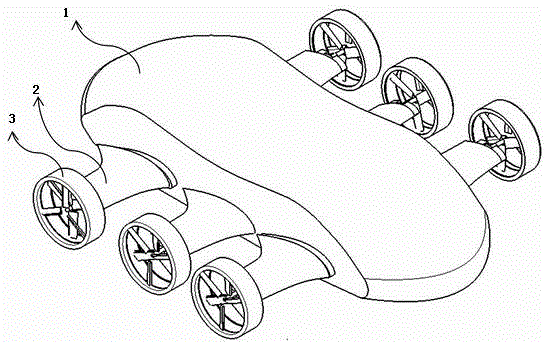
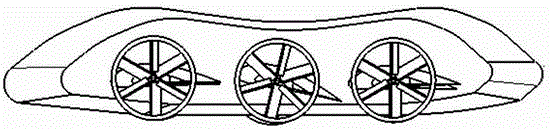
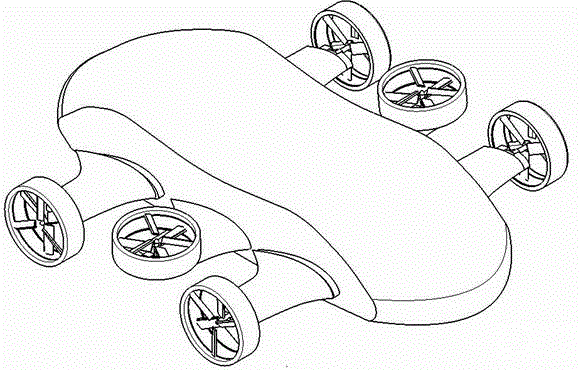
Vortex strake device and method for reducing the aerodynamic drag of ground vehicles
An improved method and device for the reduction of aerodynamic drag and for increased fuel economy of ground vehicles by increasing the pressure on the rear surface of the vehicle with a plurality of vortices generated along the top and side surfaces of the ground vehicle that flow in to the base wake region of the vehicle. The invention is comprised of a minimum number of small surfaces that attach to the side and top exterior surfaces of a ground vehicle. The spacing and orientation of the small surfaces, comprising the device, are dependent upon the vehicle geometry and vehicle operating conditions. The plurality of small surfaces are located forward of the vehicle base area. The plurality of adjacent small surfaces and are distributed circumferentially over the side and top surfaces of the ground vehicle.
Owner:SOLUS SOLUTIONS & TECH
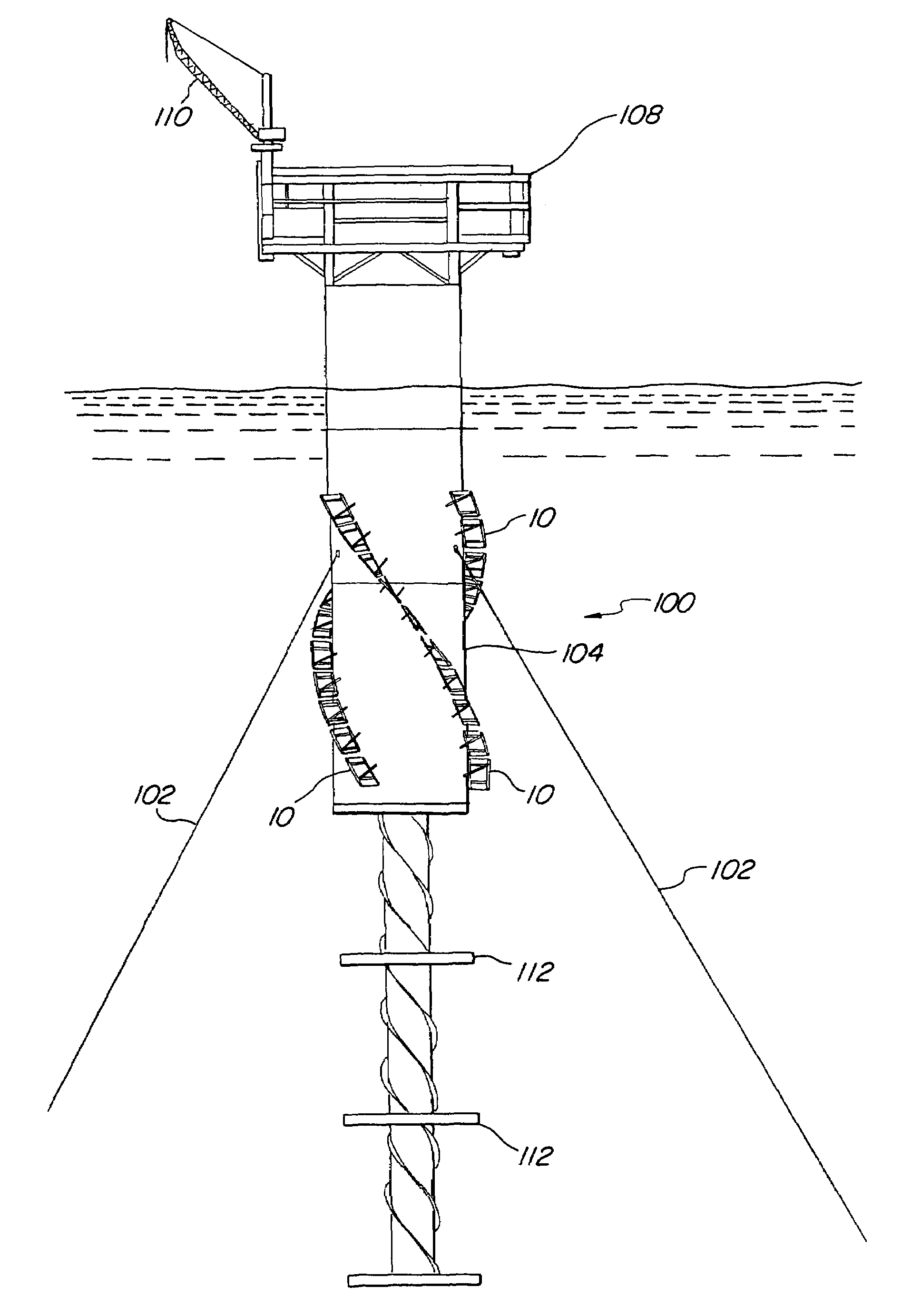
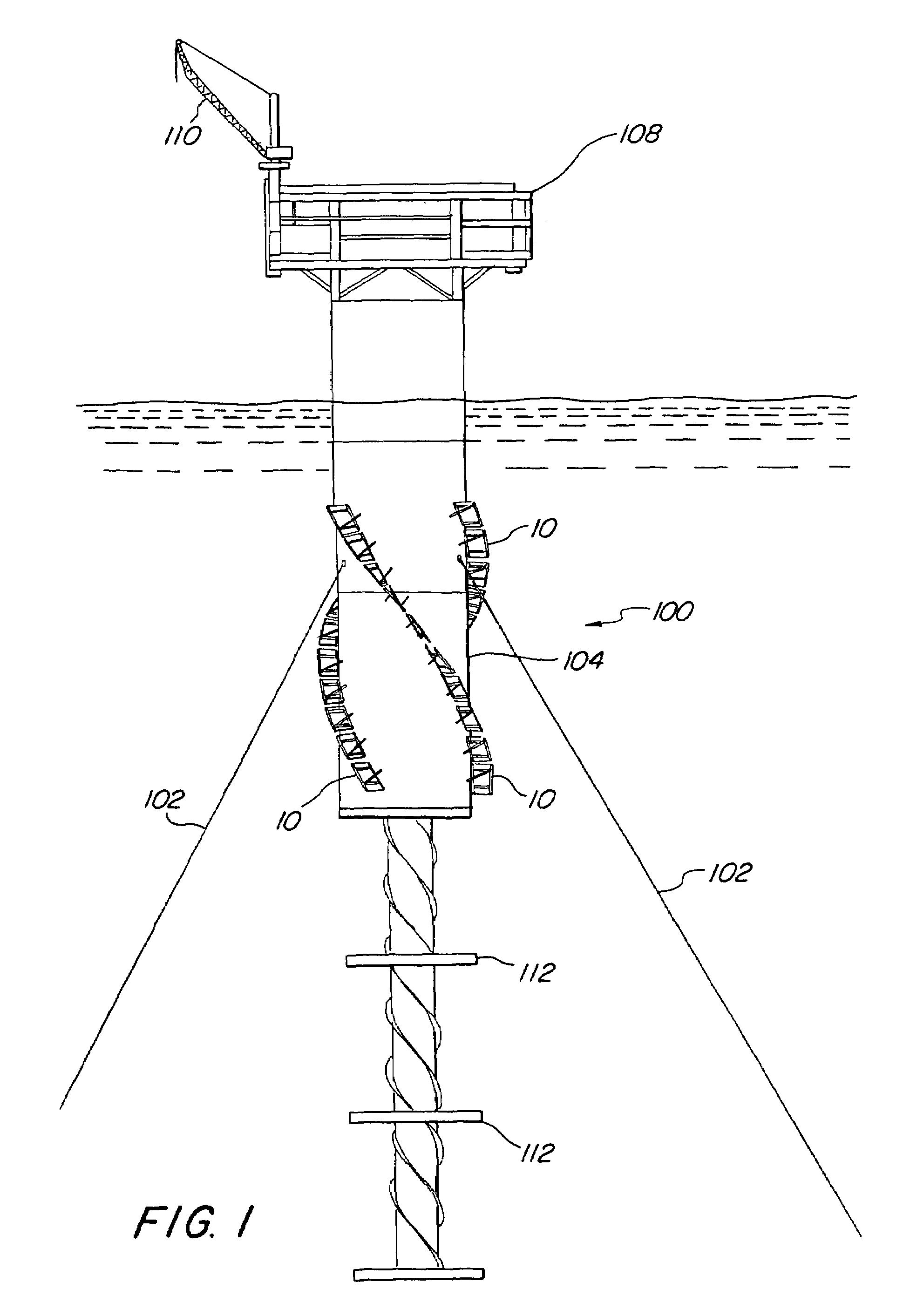
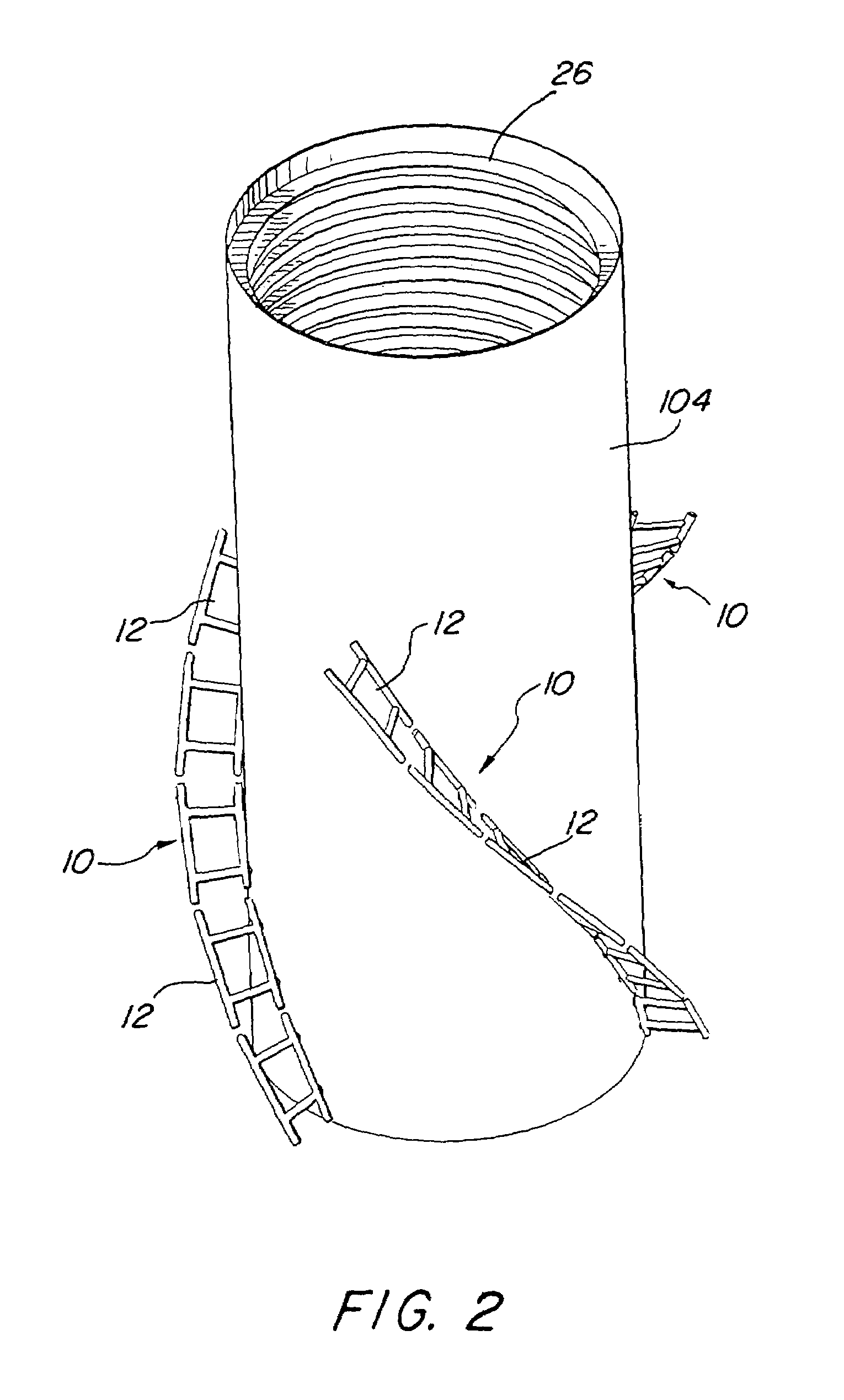
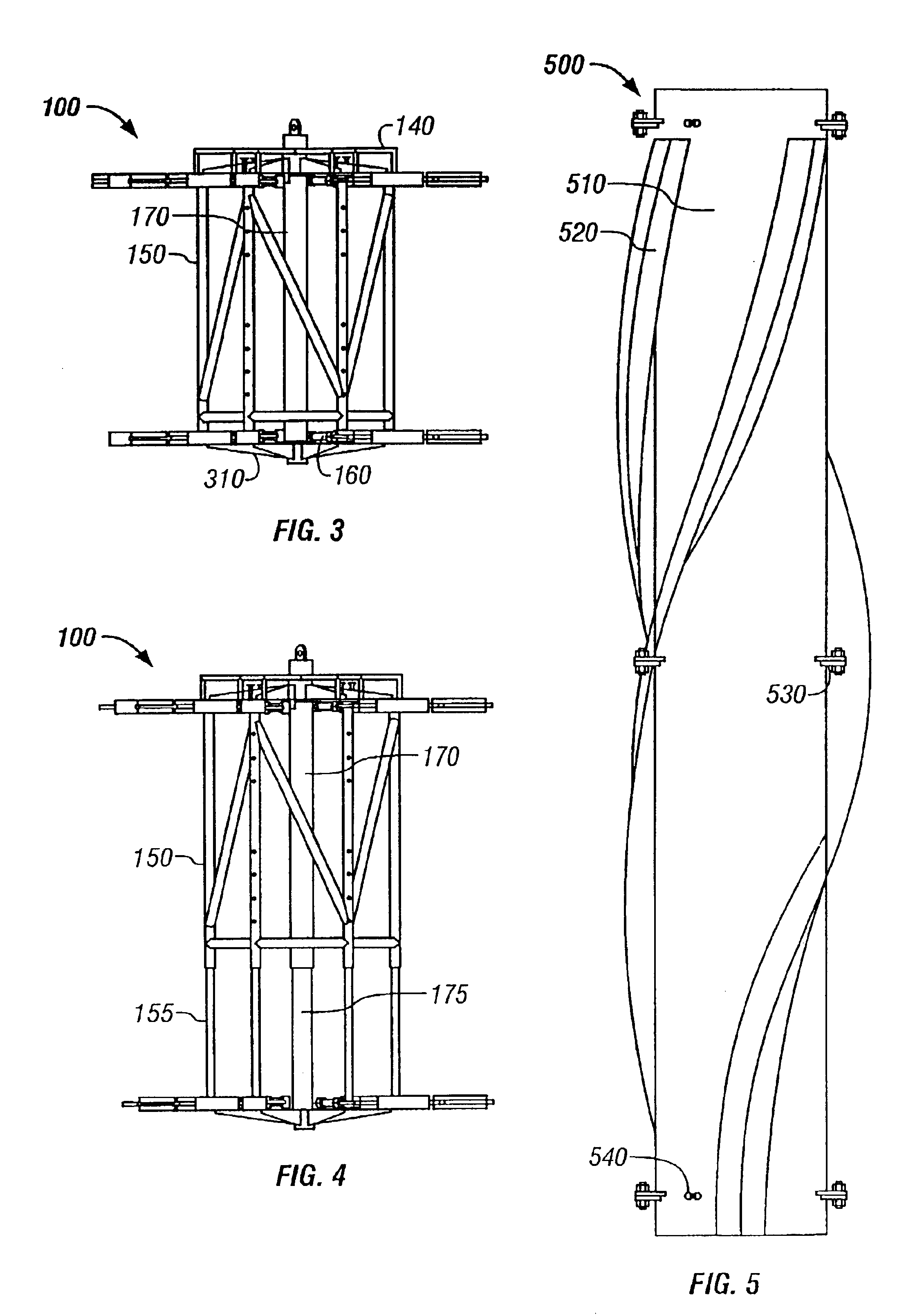
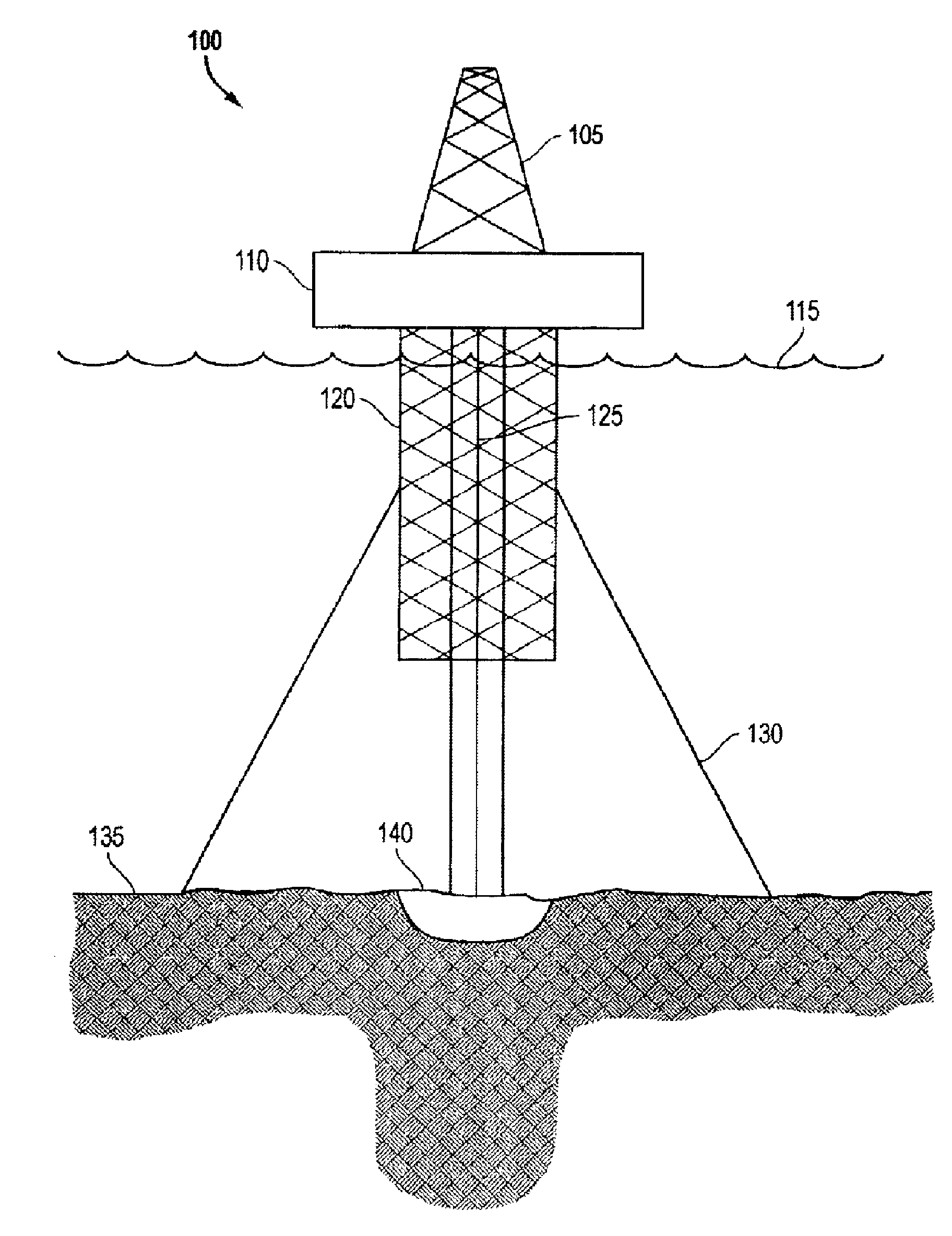
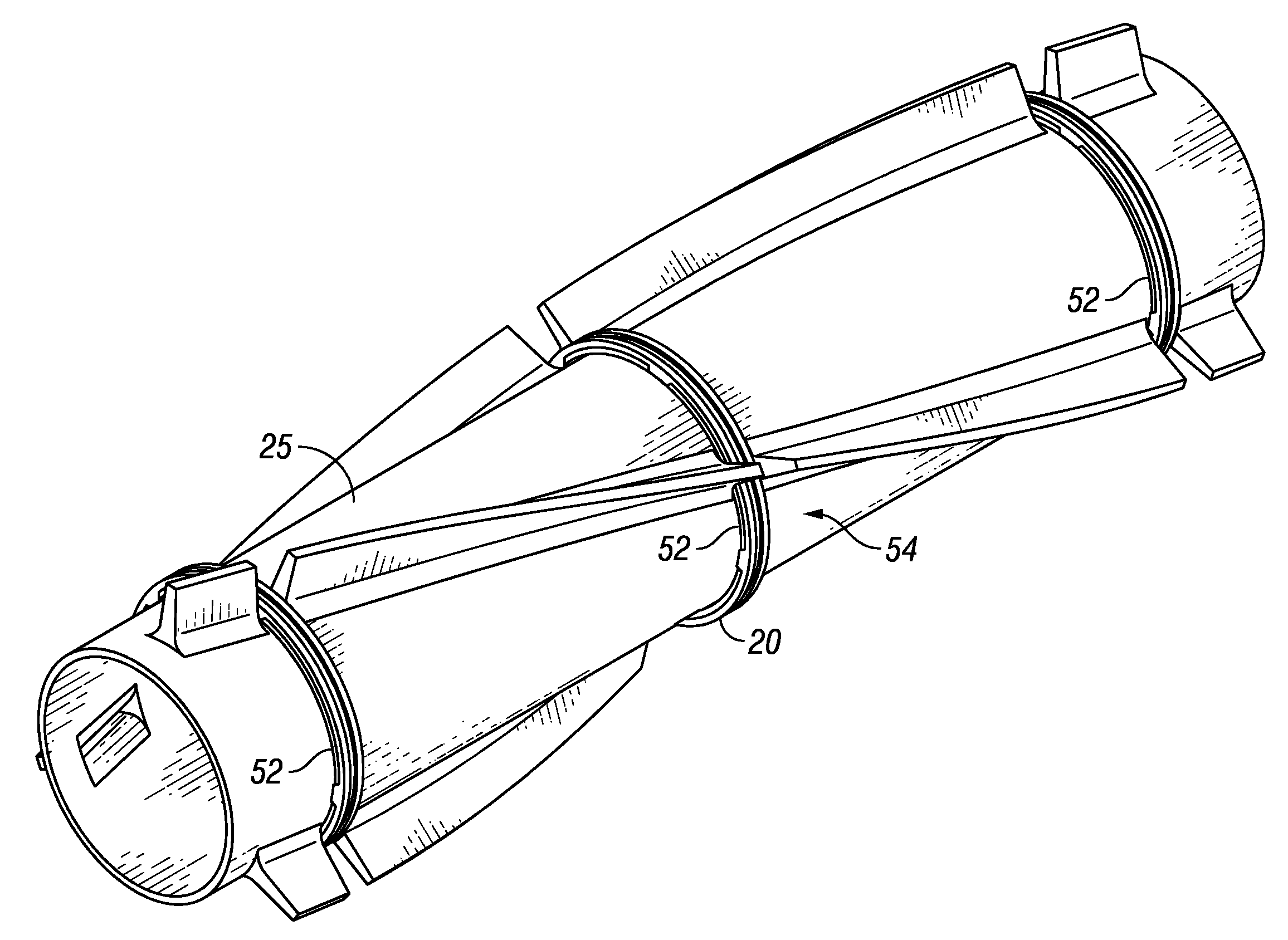
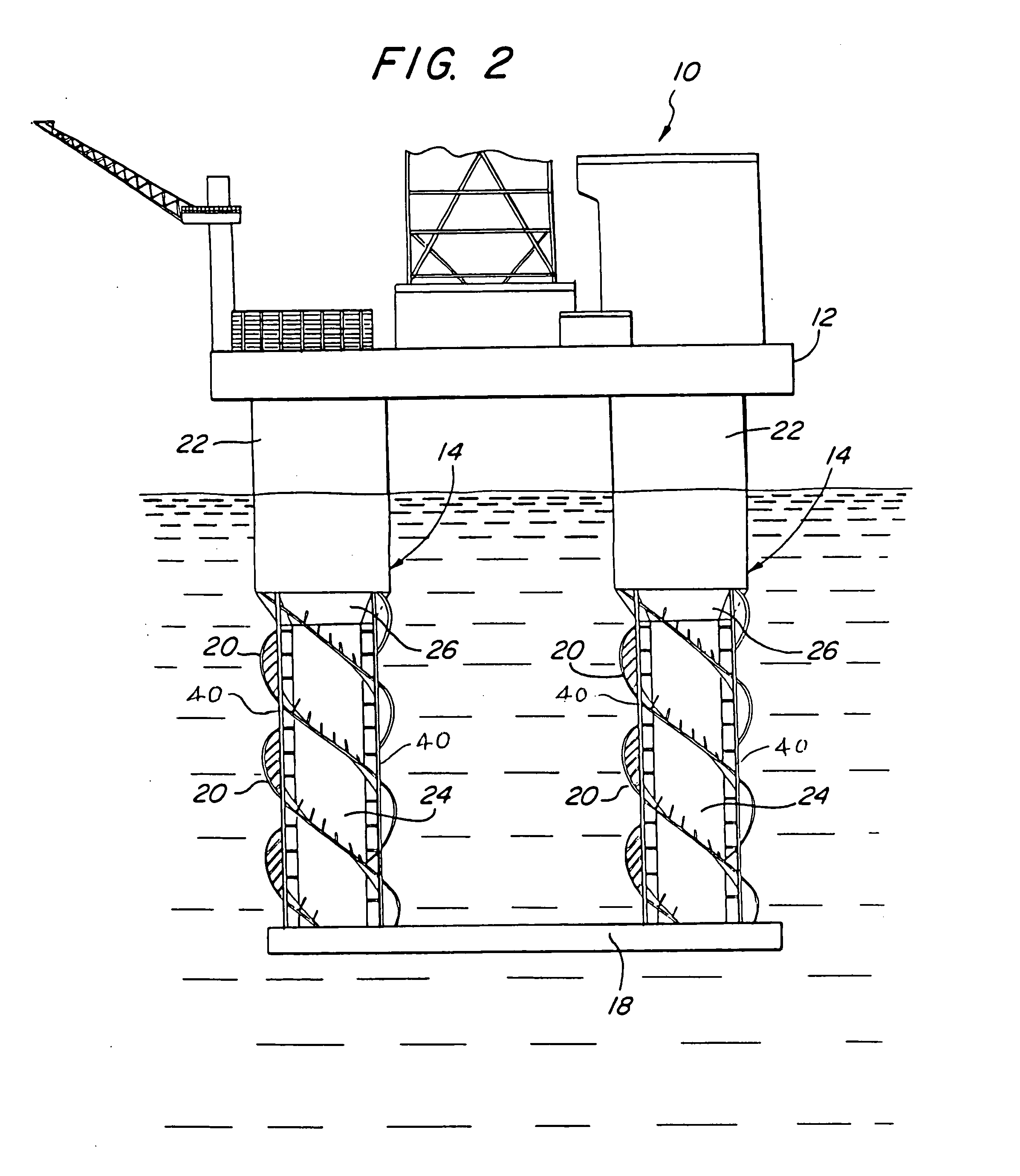
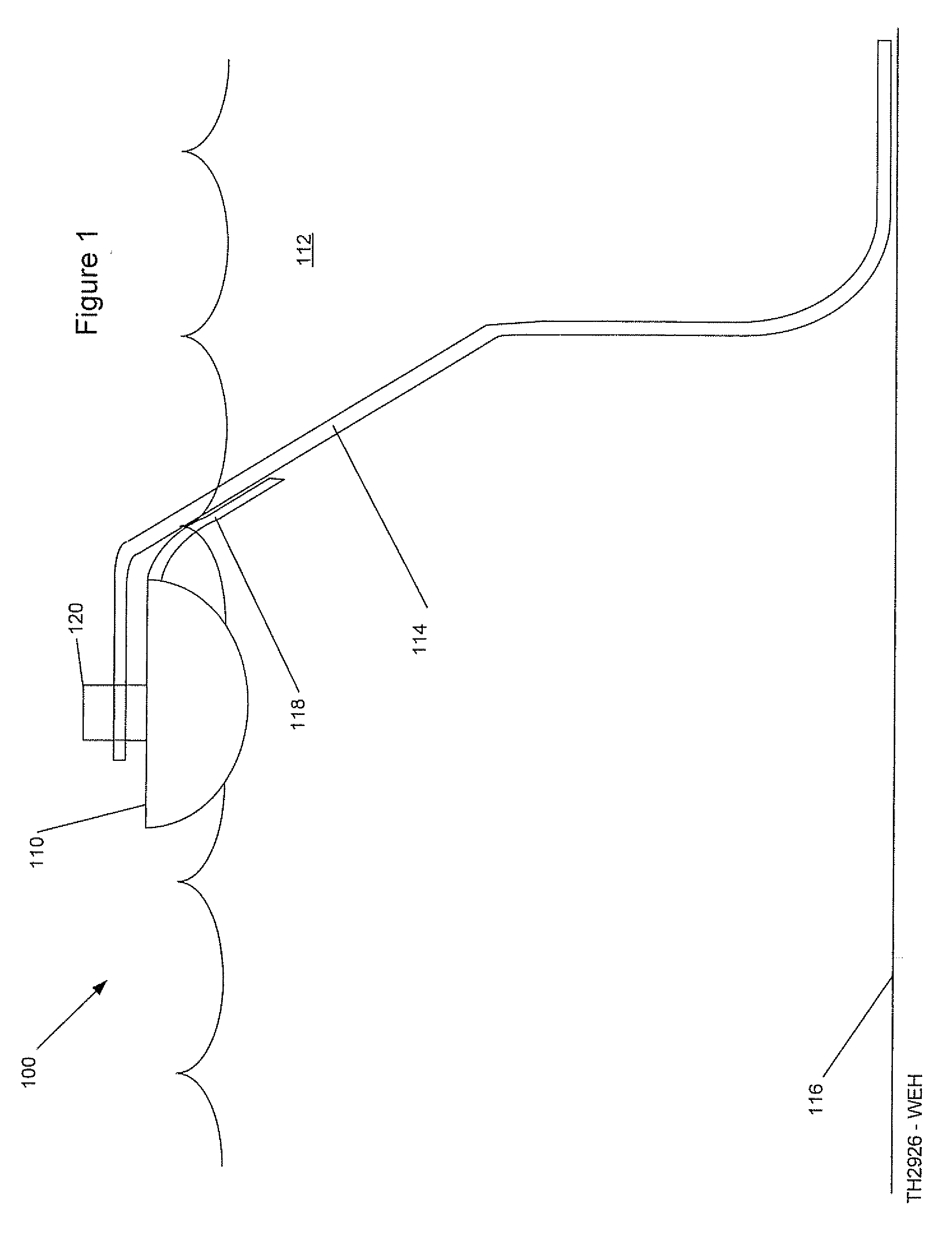
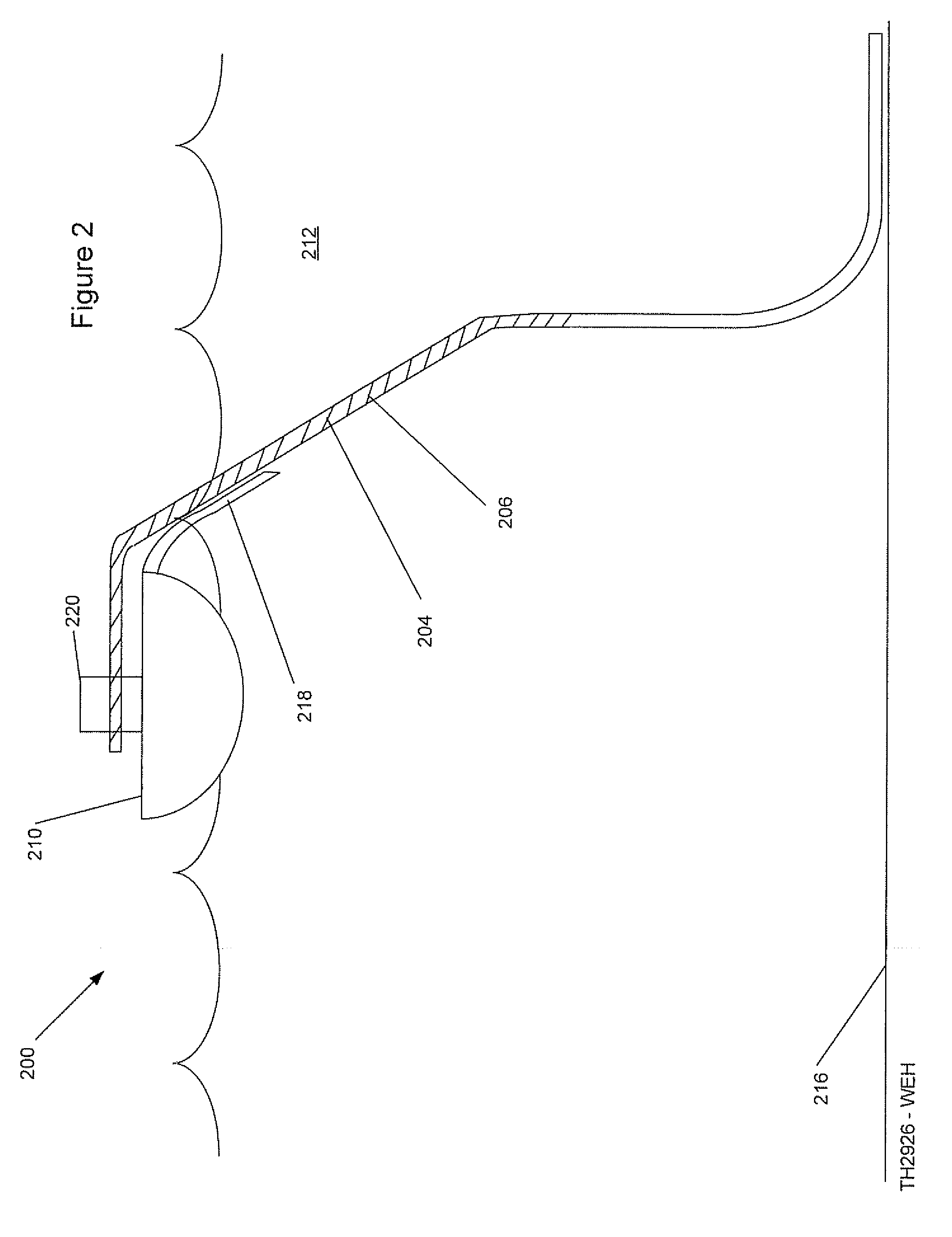
Offshore platform stabilizing strakes
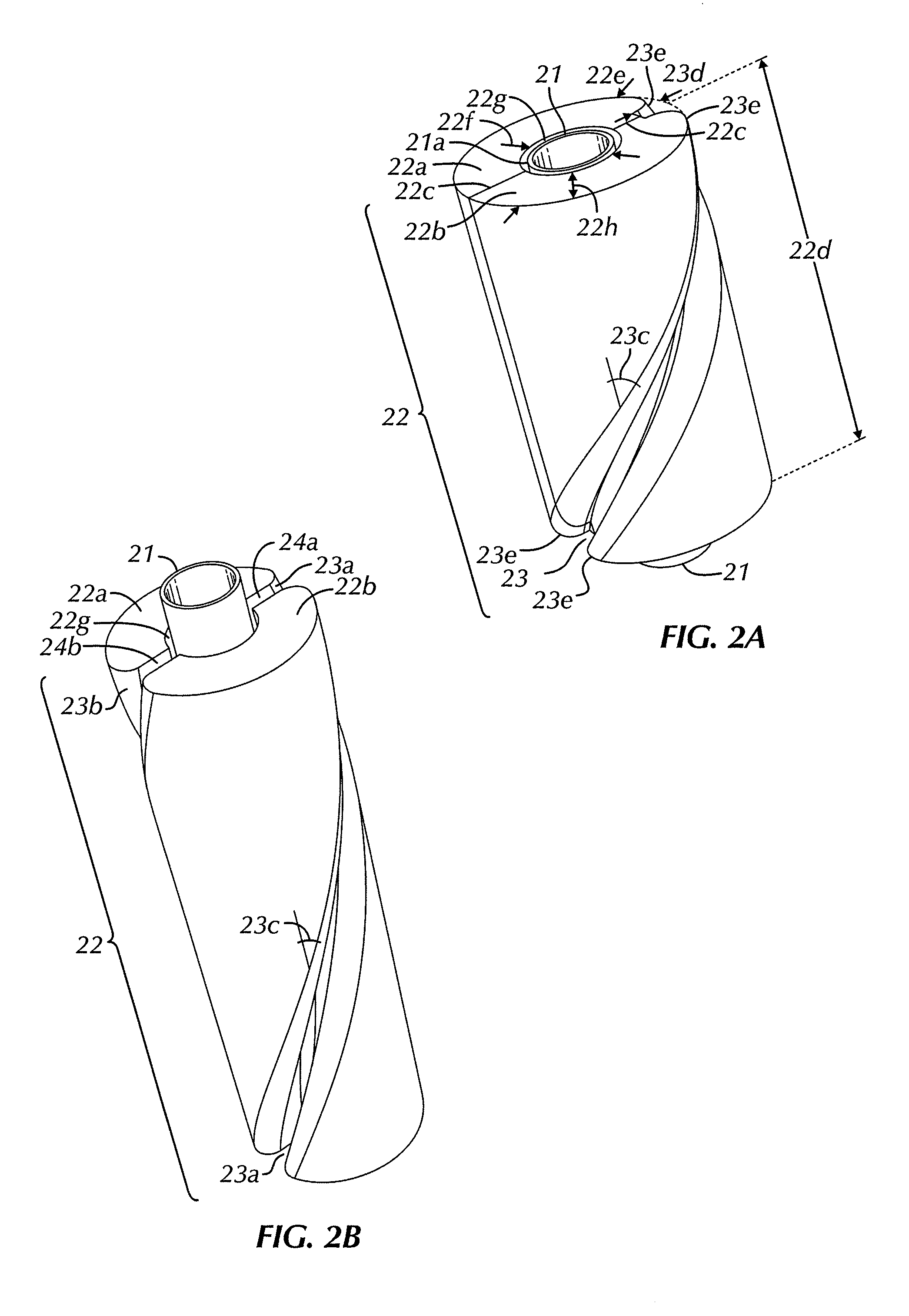
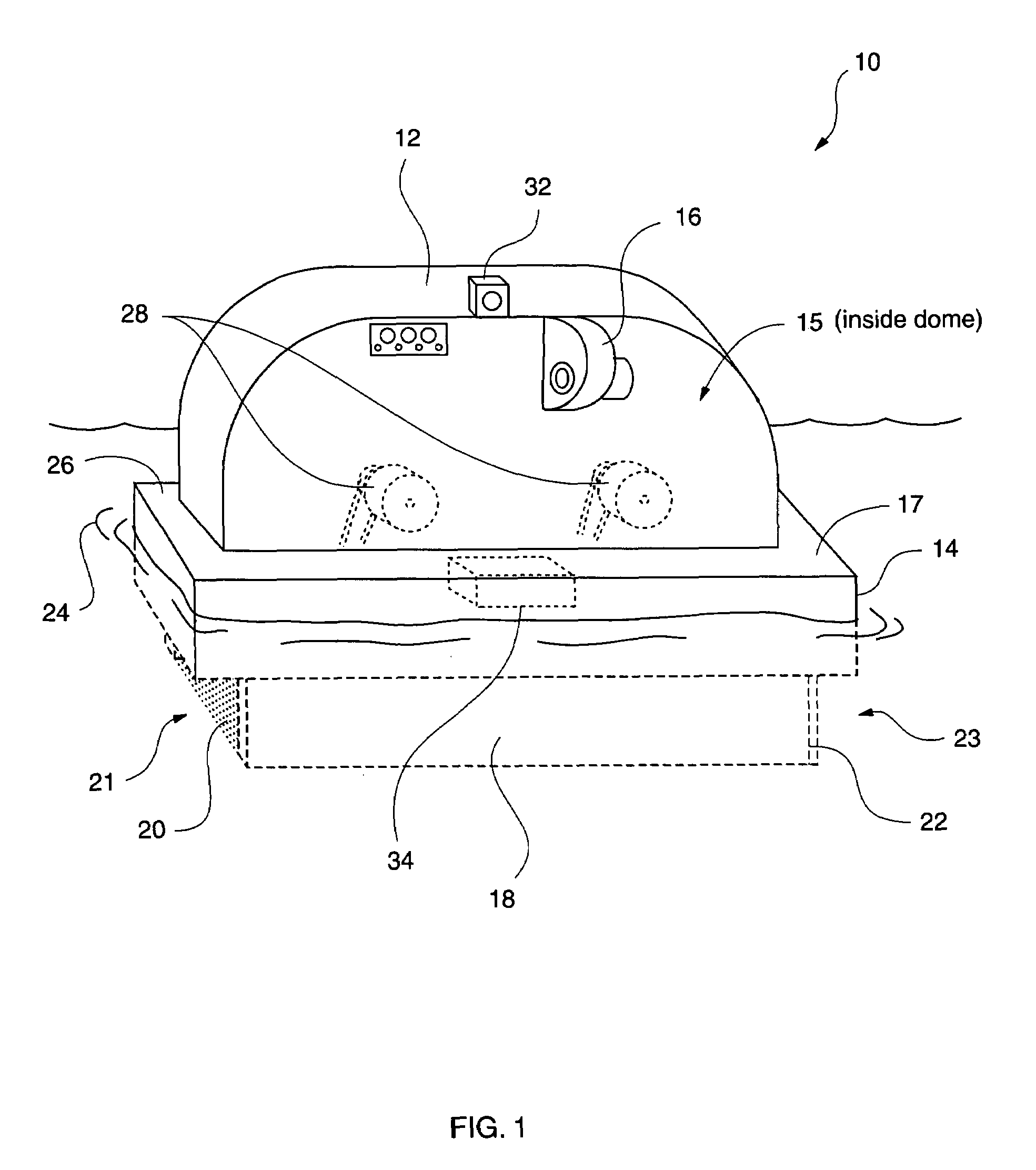
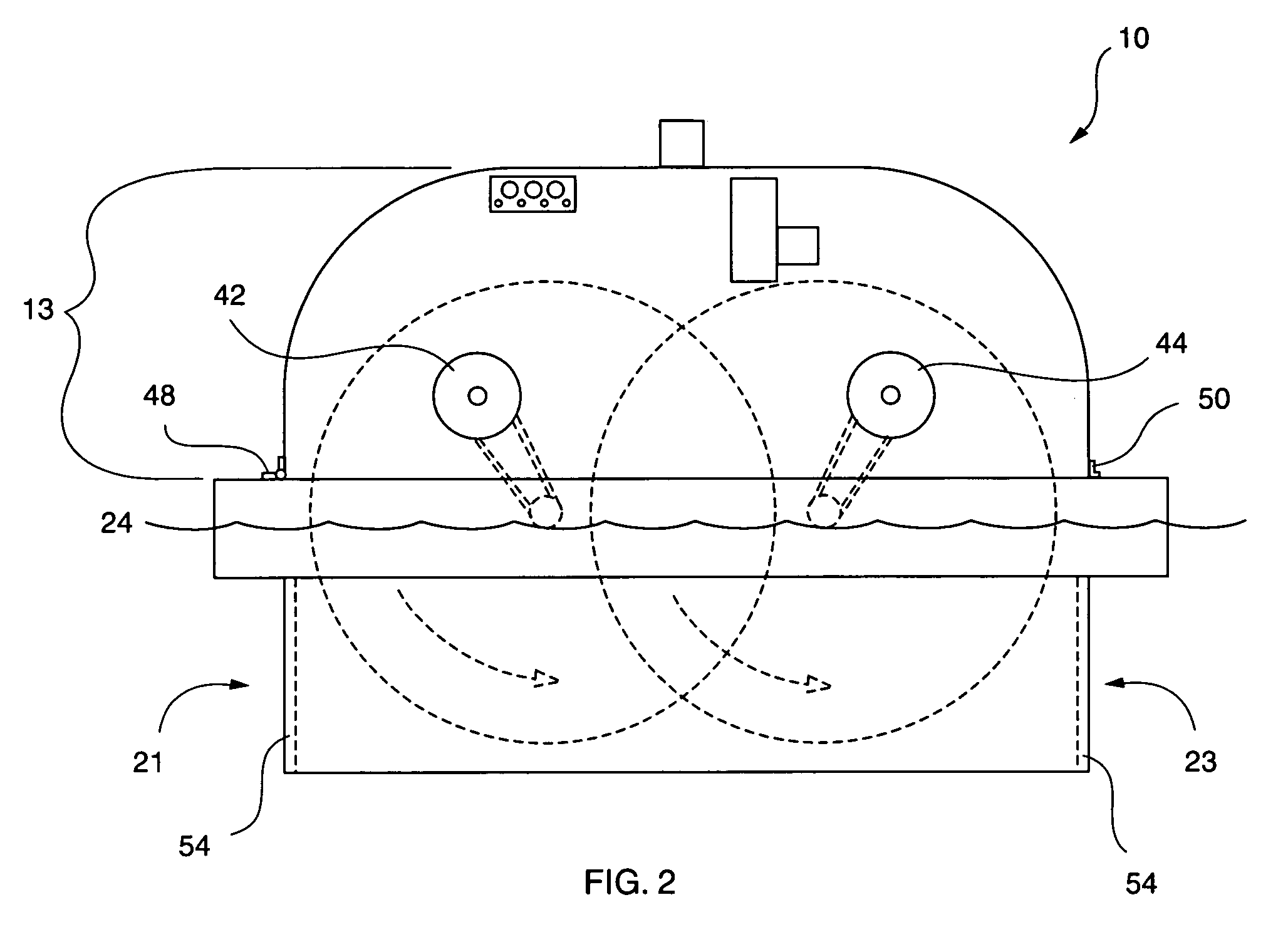
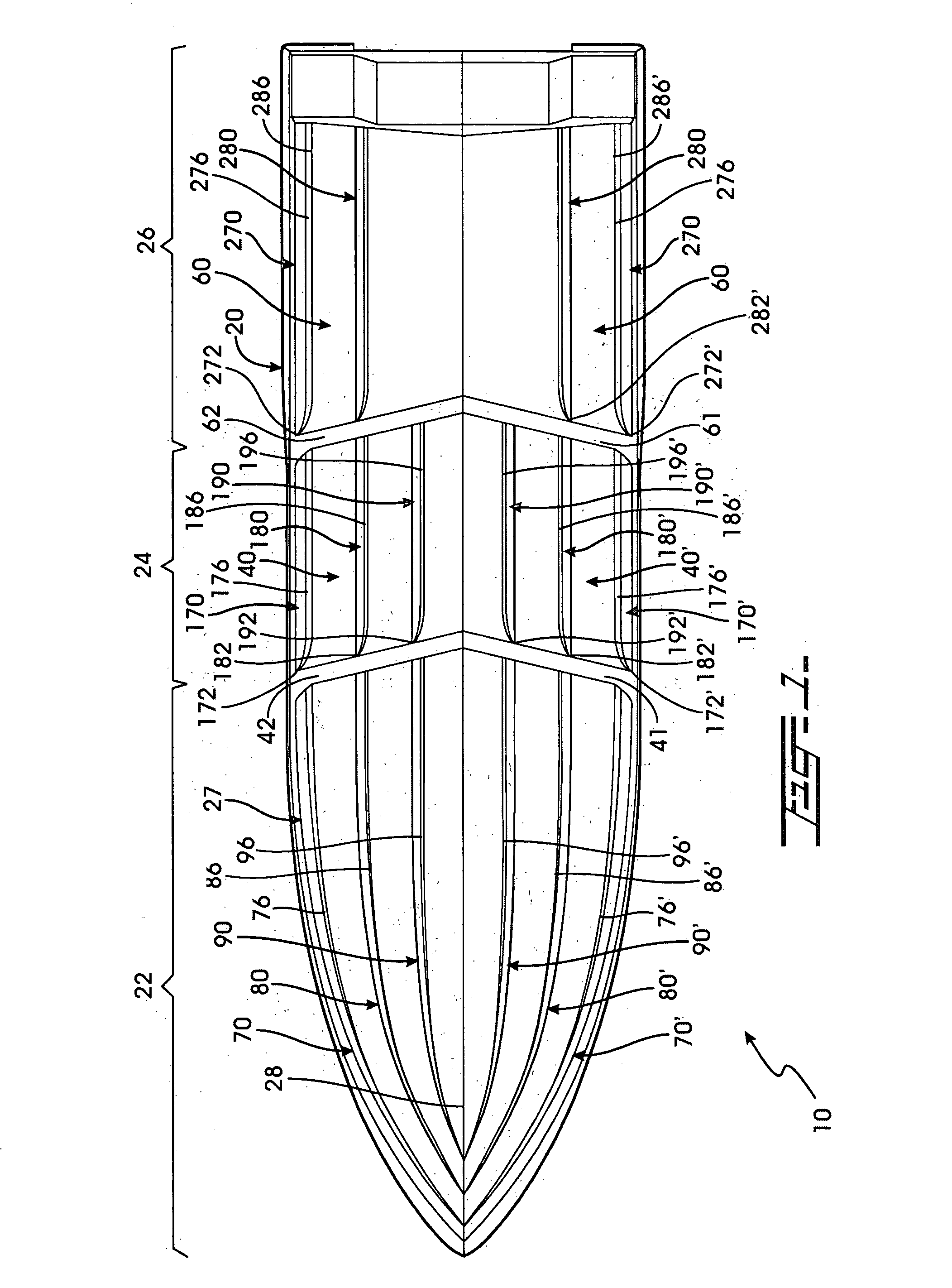
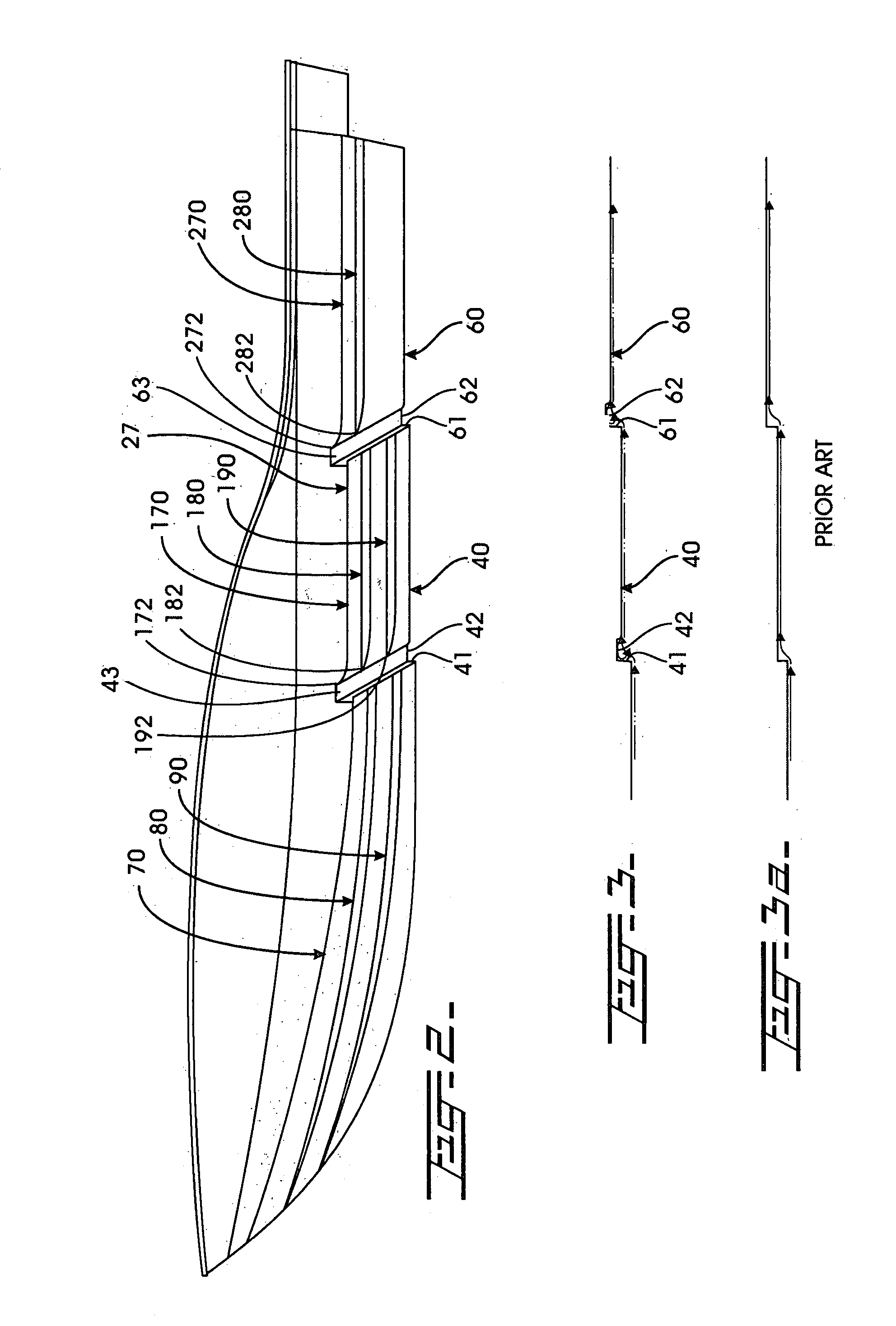
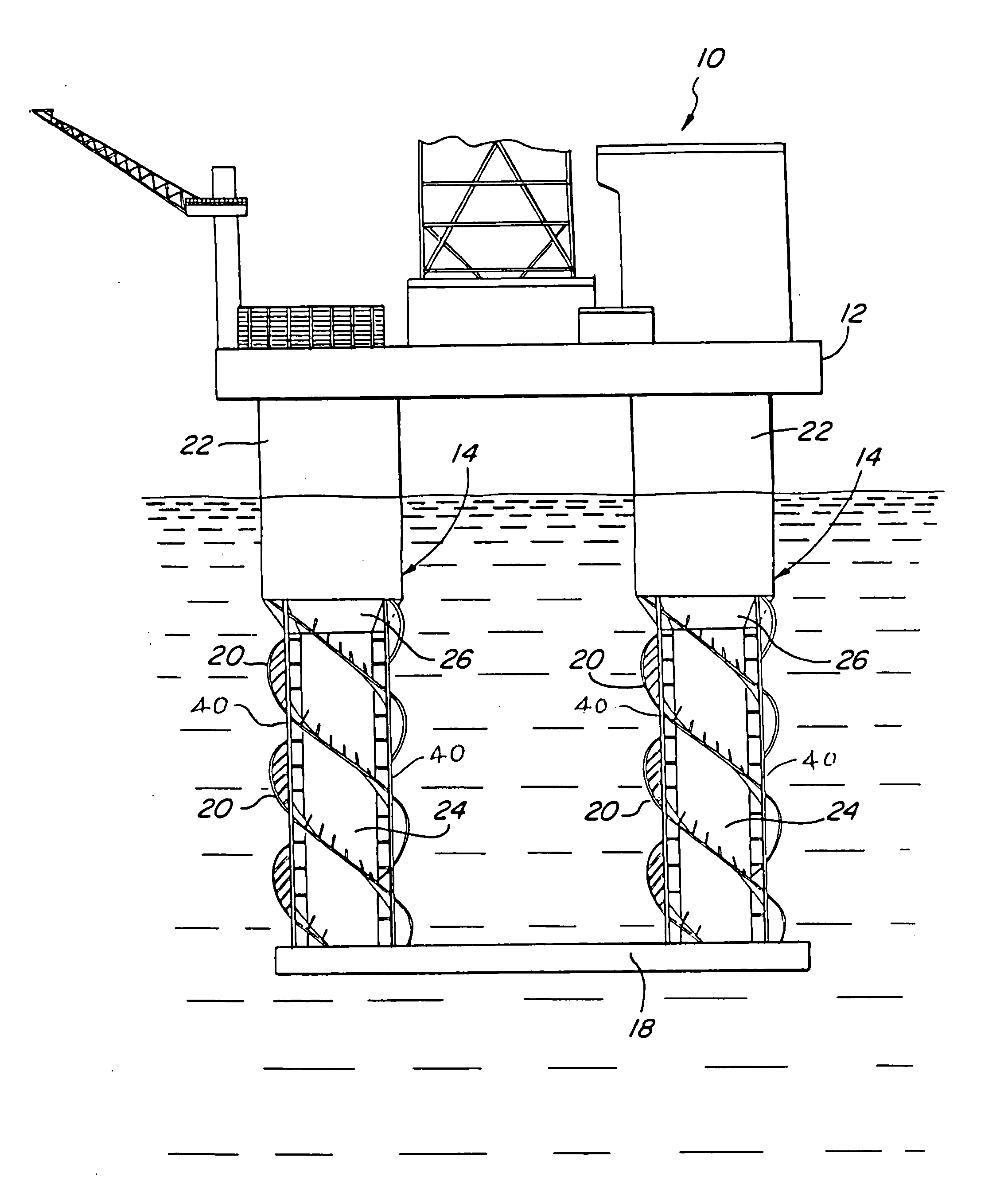
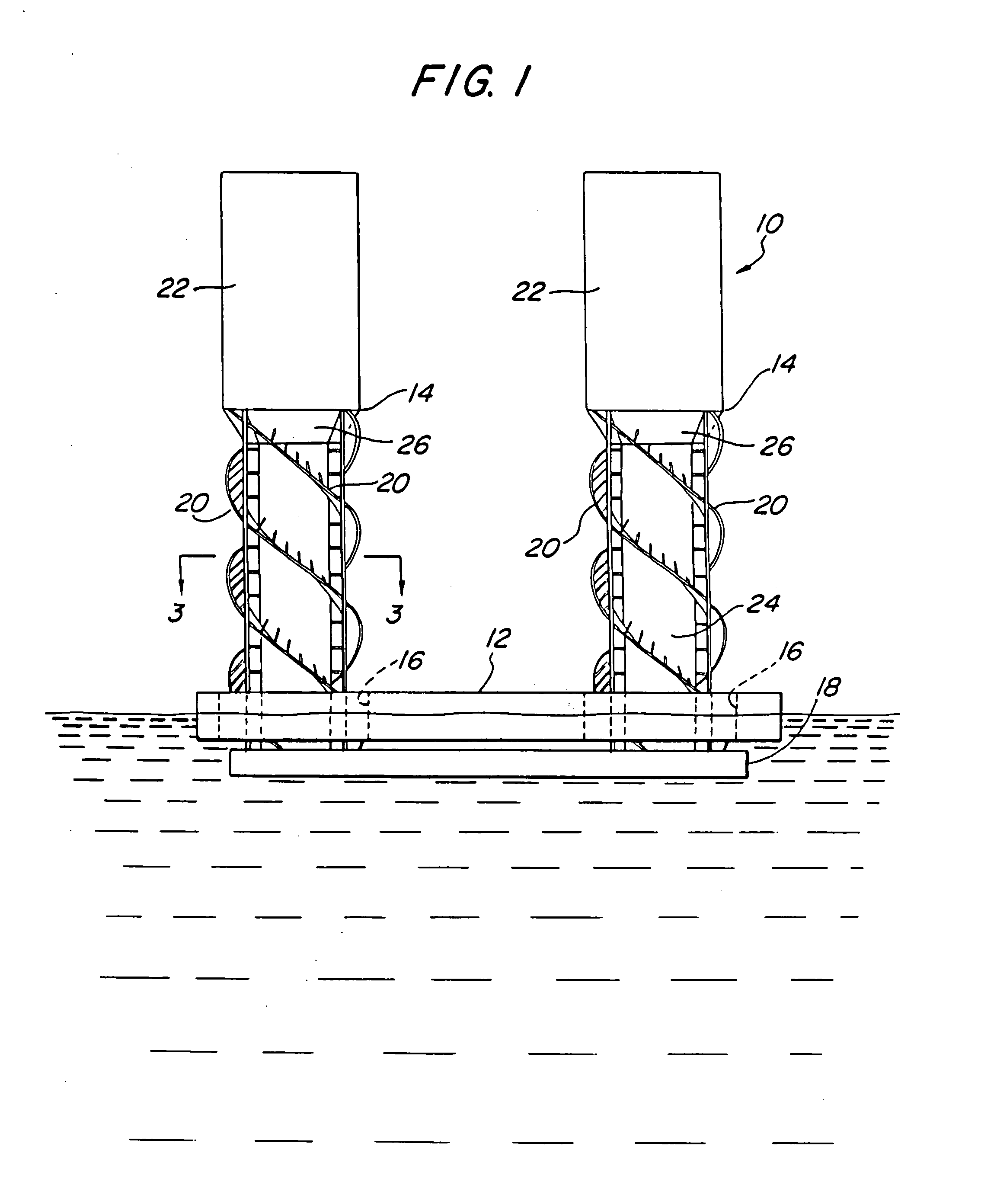
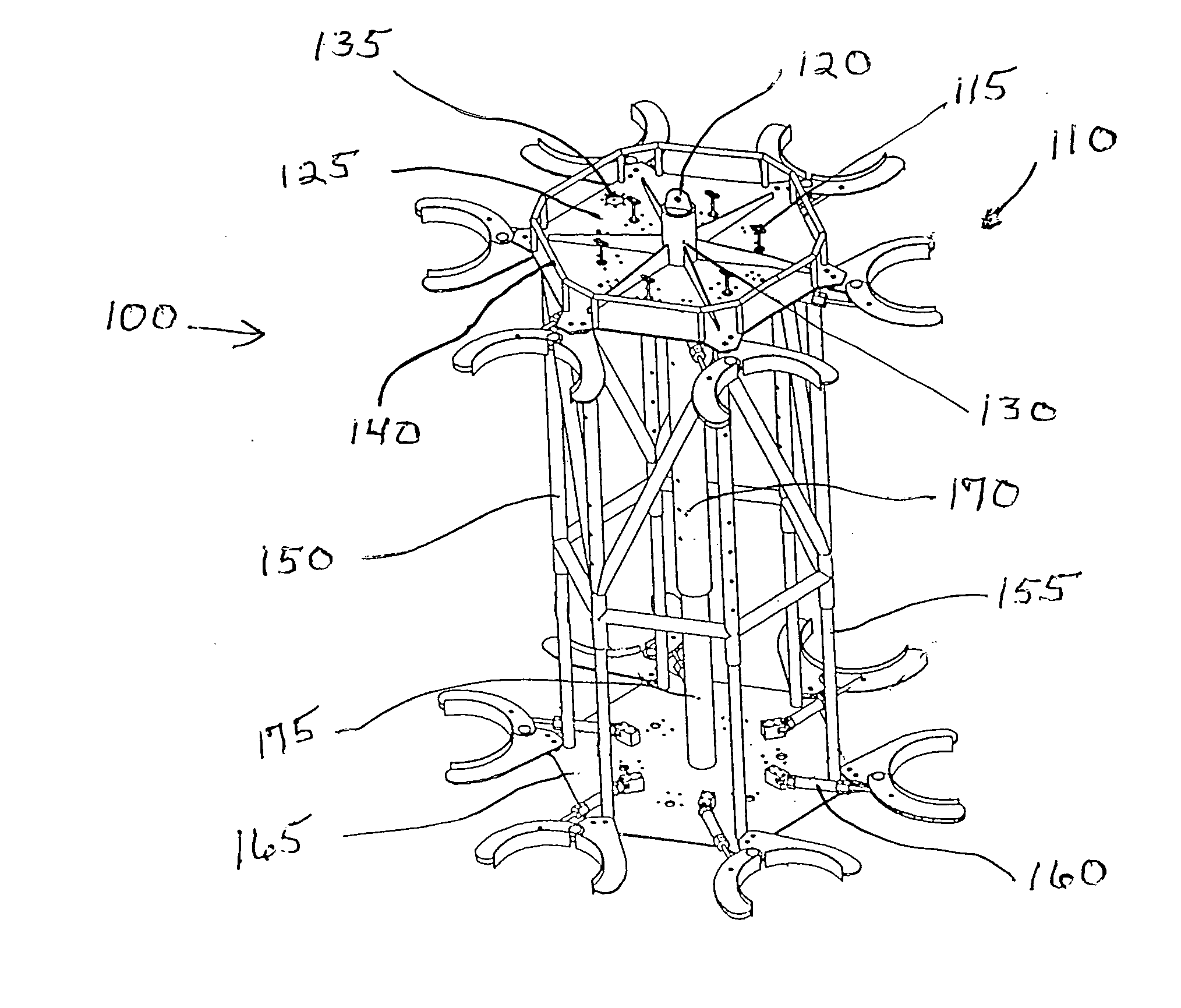
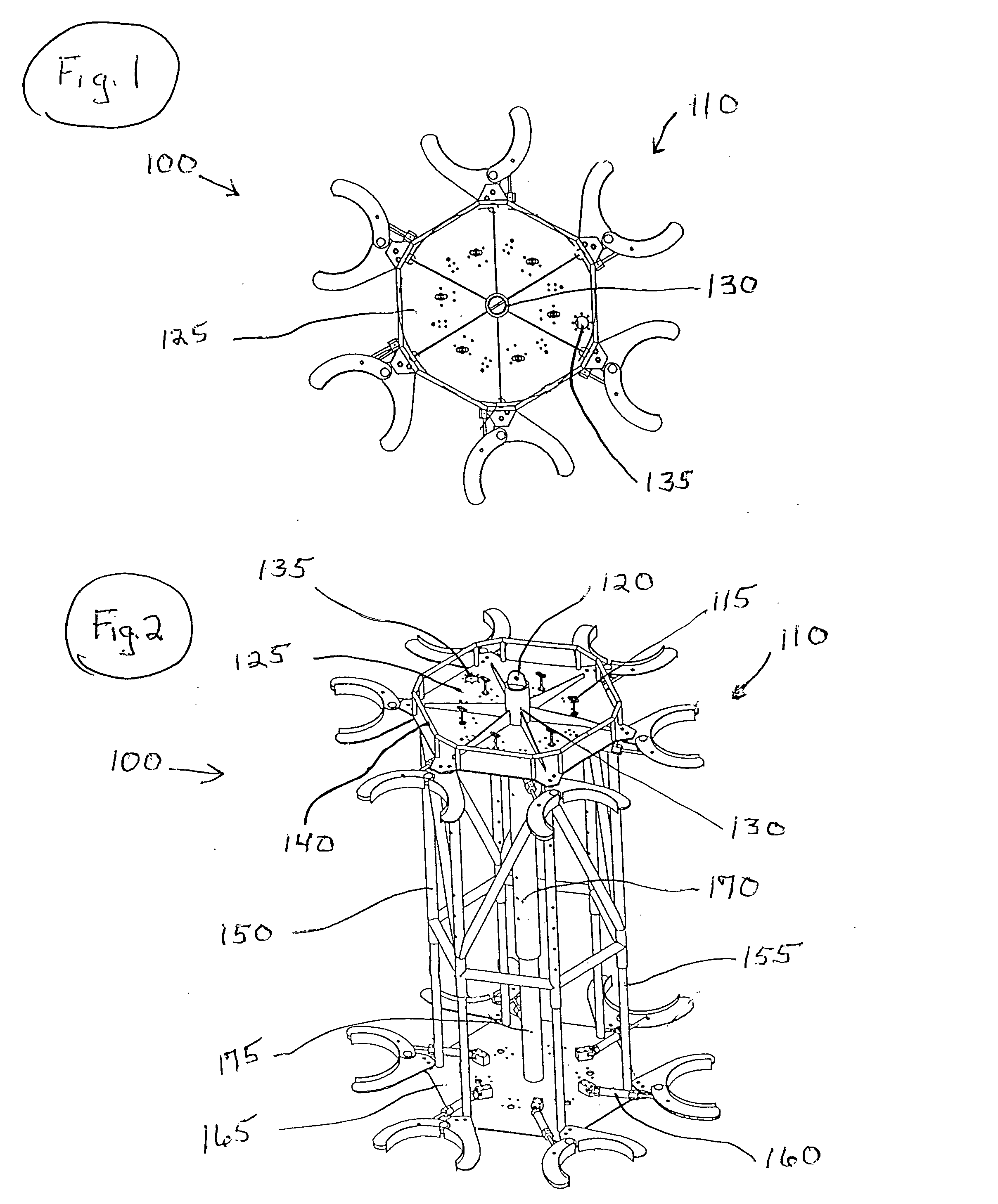
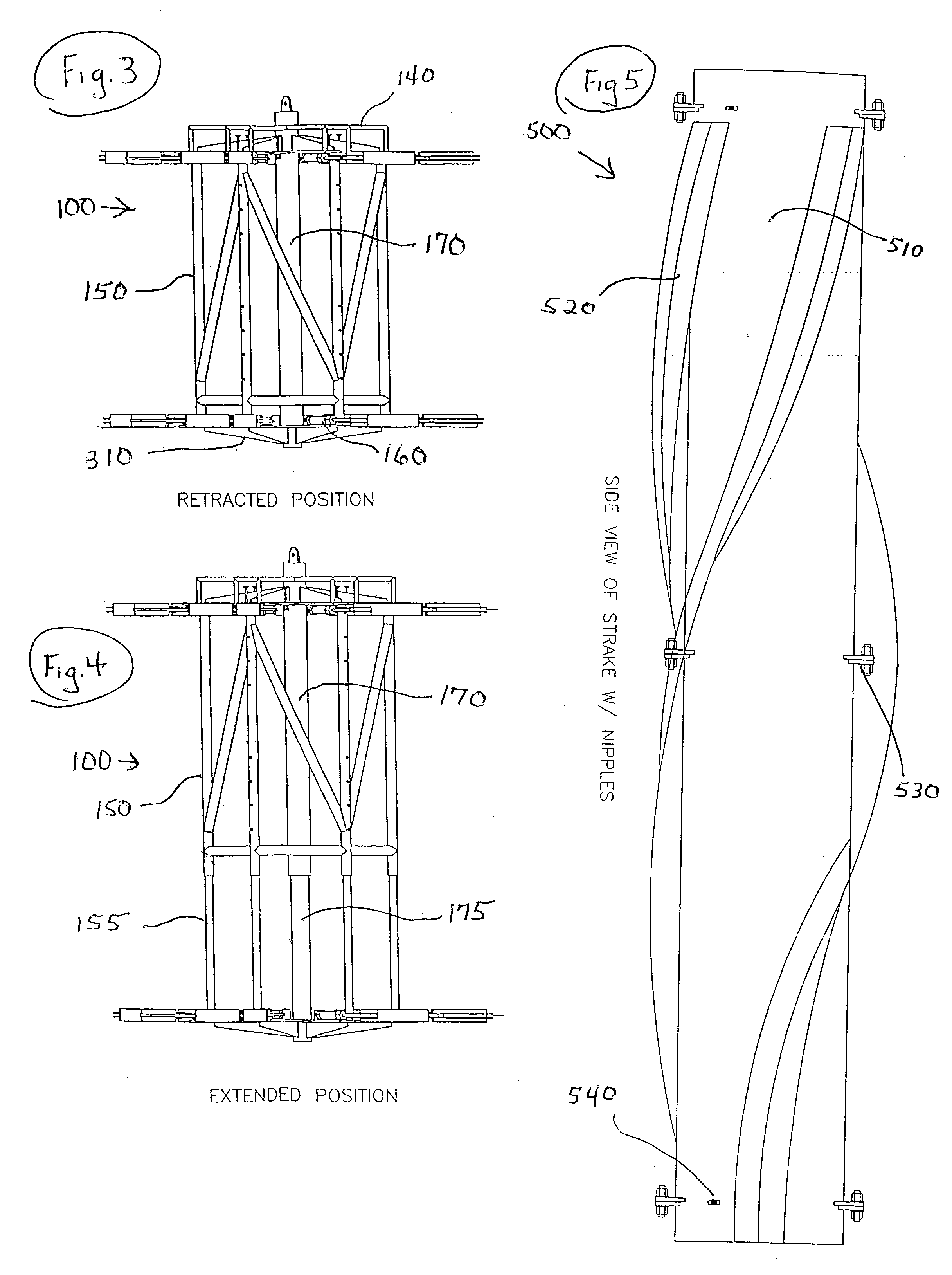
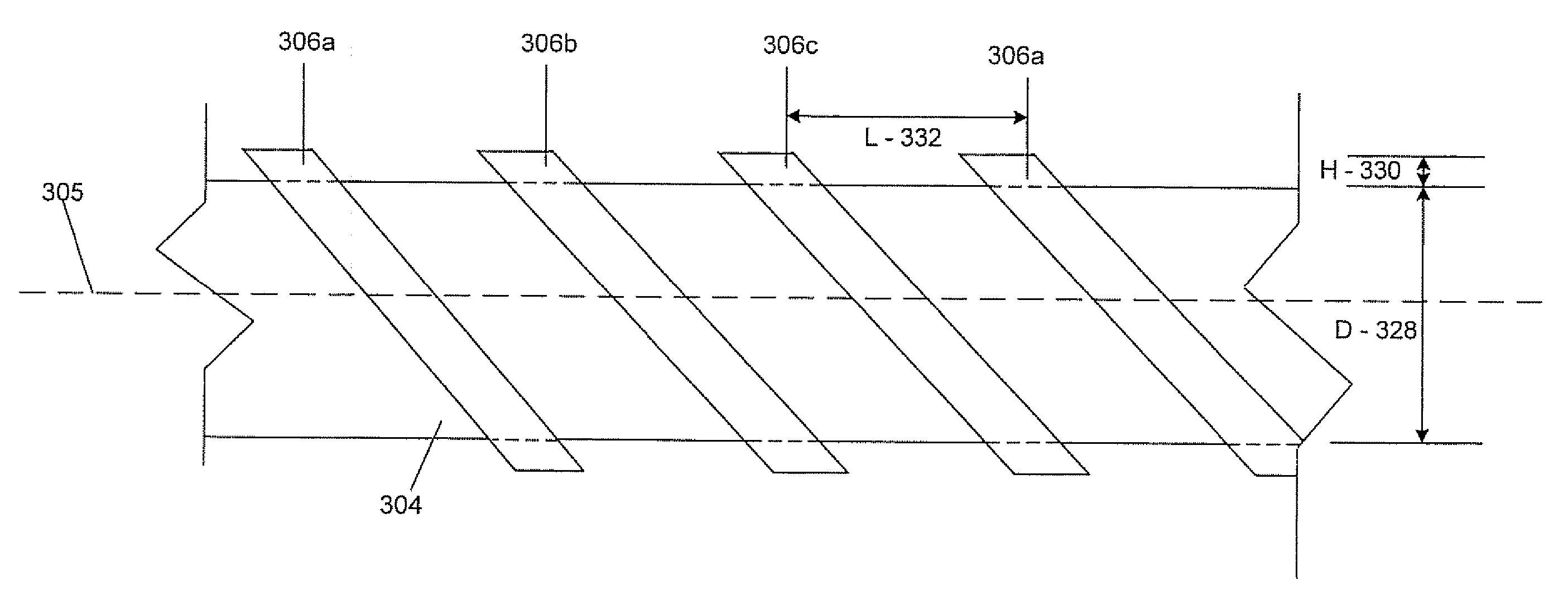
An elongated, annular hull of a floating offshore platform includes one or more segmented, helical strakes disposed on an outer peripheral surface of the hull to reduce vortex-induced vibrations resulting from water currents. The hull may comprise a single annular hull or a plurality of parallel, adjacent hulls. Each strake includes a plurality of generally rectangular segments extending substantially radially outward from the hull. Each of the segments includes a pair of spaced-apart radial stanchions supporting a generally rectangular frame to which a corresponding panel is attached. The panels have a radial width that is about 13 percent of the effective diameter of the hull. The segments are arranged in a spaced-apart, end-to-end relationship that defines a discontinuous, but generally helical band extending around the circumference of the hull from about 35 feet (11.7 m) below the mean water line of the hull to its lowermost end.
Owner:DEEPWATER TECH
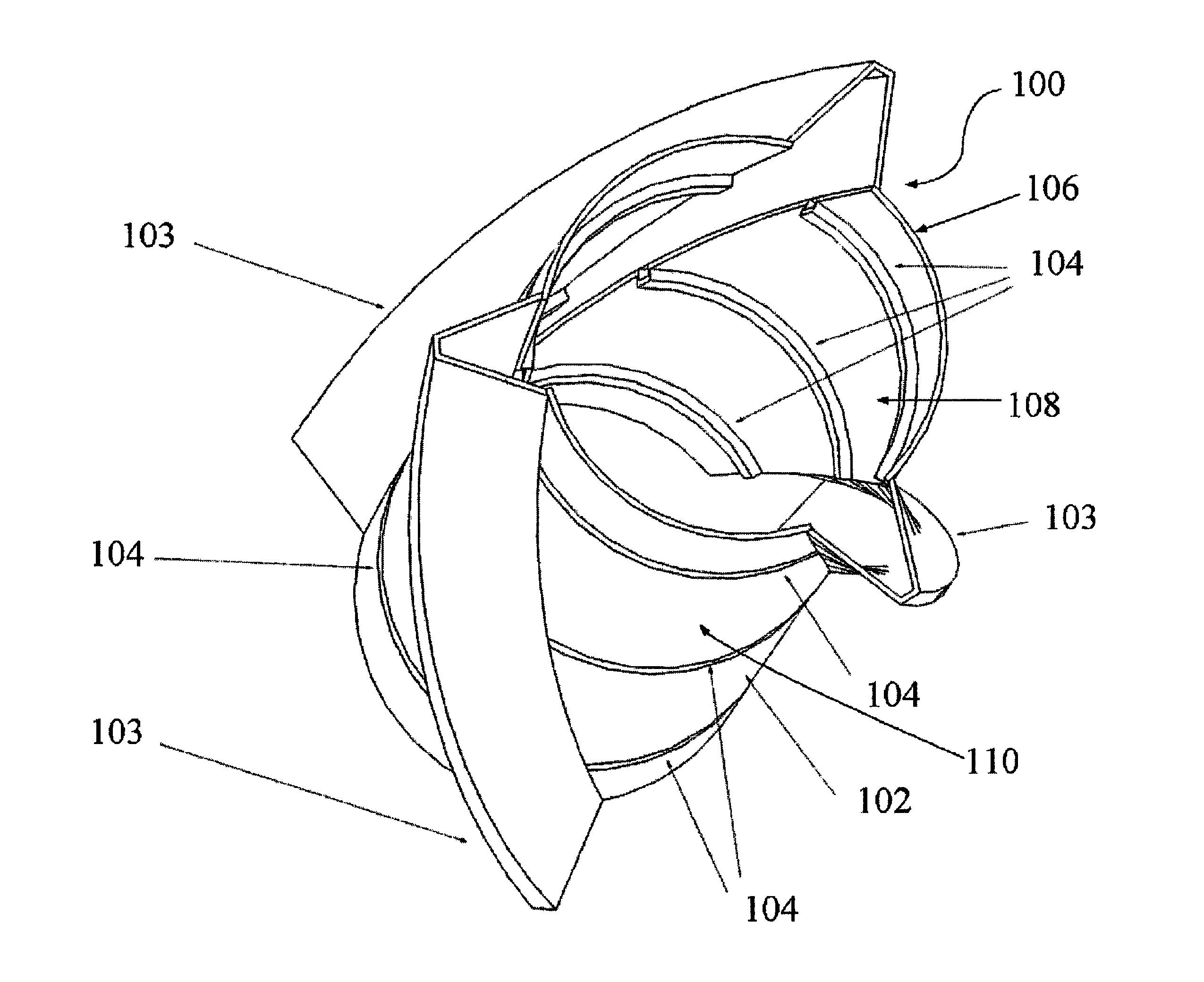
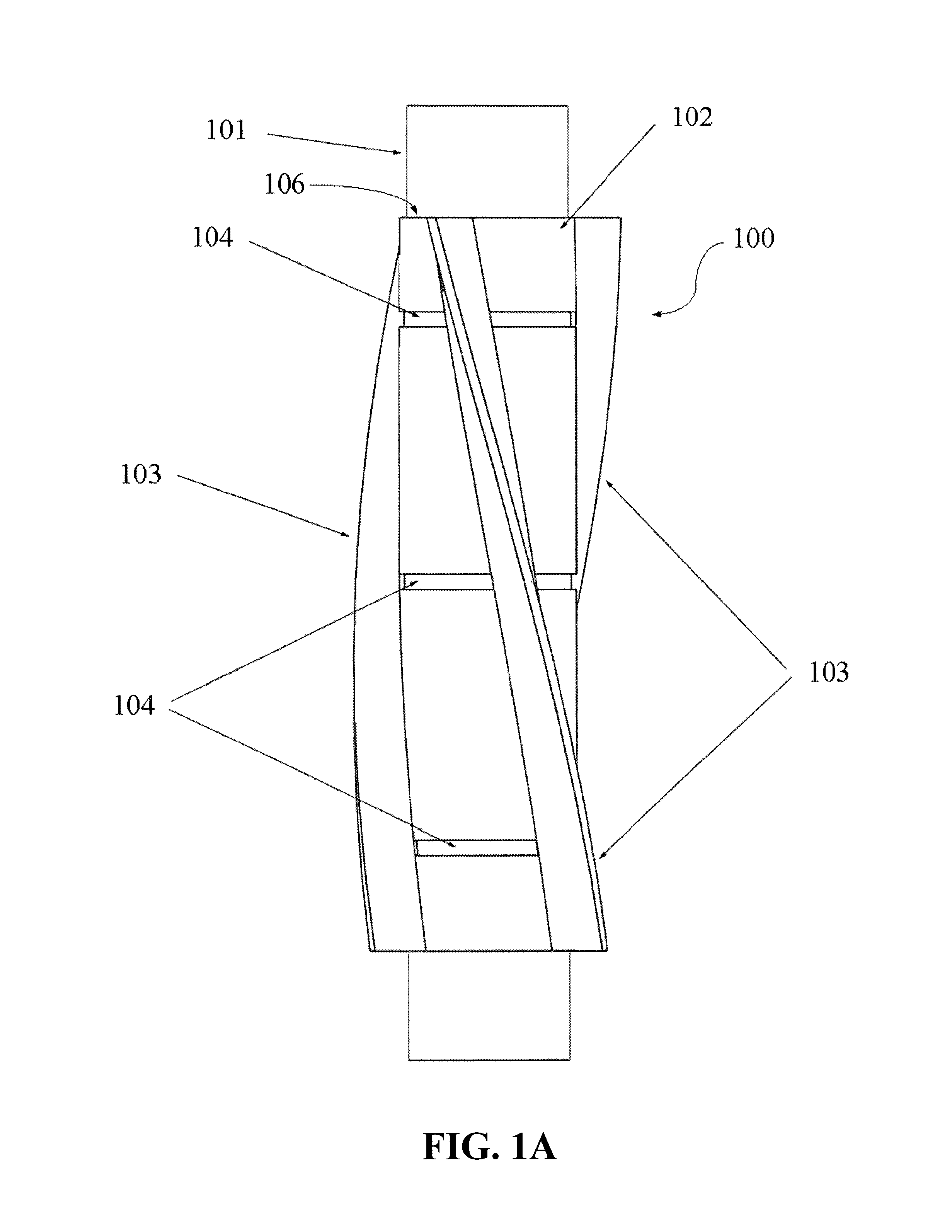
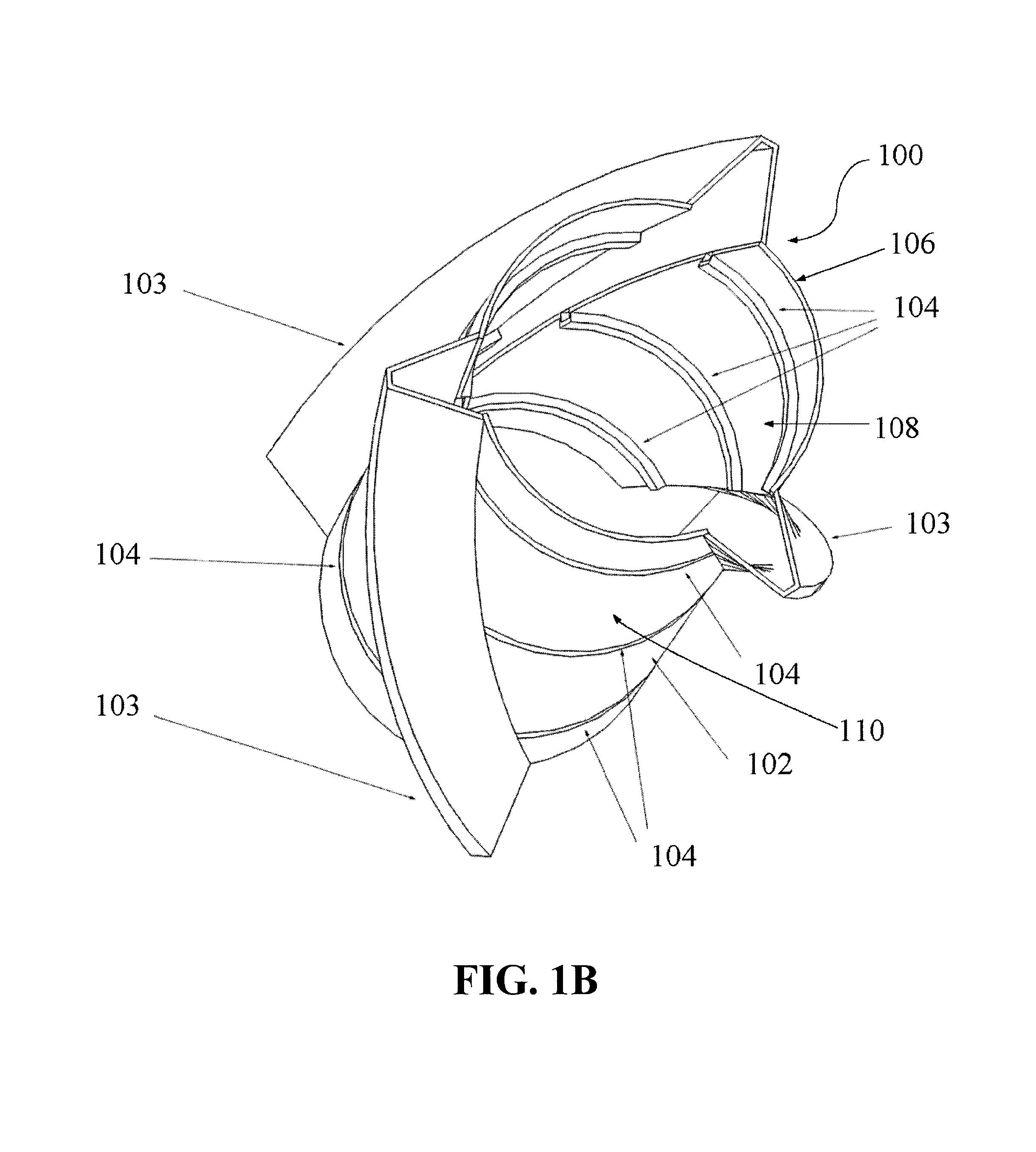
Apparatus for remote installation of devices for reducing drag and vortex induced vibration
Apparatus and methods for remotely installing vortex-induced vibration (VIV) reduction and drag reduction devices on elongated structures in flowing fluid environments. The apparatus is a tool for transporting and installing the devices. The devices installed can include clamshell-shaped strakes, shrouds, fairings, sleeves and flotation modules.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Polyurethane elastomer composition and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyurethane elastomer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing polyurethane prepolymer with curing agent, removing foam, casting and curing to obtain the polyurethane elastomer, wherein the curing agent is composed of at least one of chain extender and cross-linking agent, catalyst and other additives. The Shaw hardness Aof the polyurethane elastomer prepared by the invention is 70-90A, the tensile strength thereof is not less than 14MPa, and the elongation at break thereof is not less than 360%; and the polyurethaneelastomer can resist hydrolysis, meets performance requirements for the spiral strake material in the deep-sea riser vortex-excited oscillation suppression device, and has important application value.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
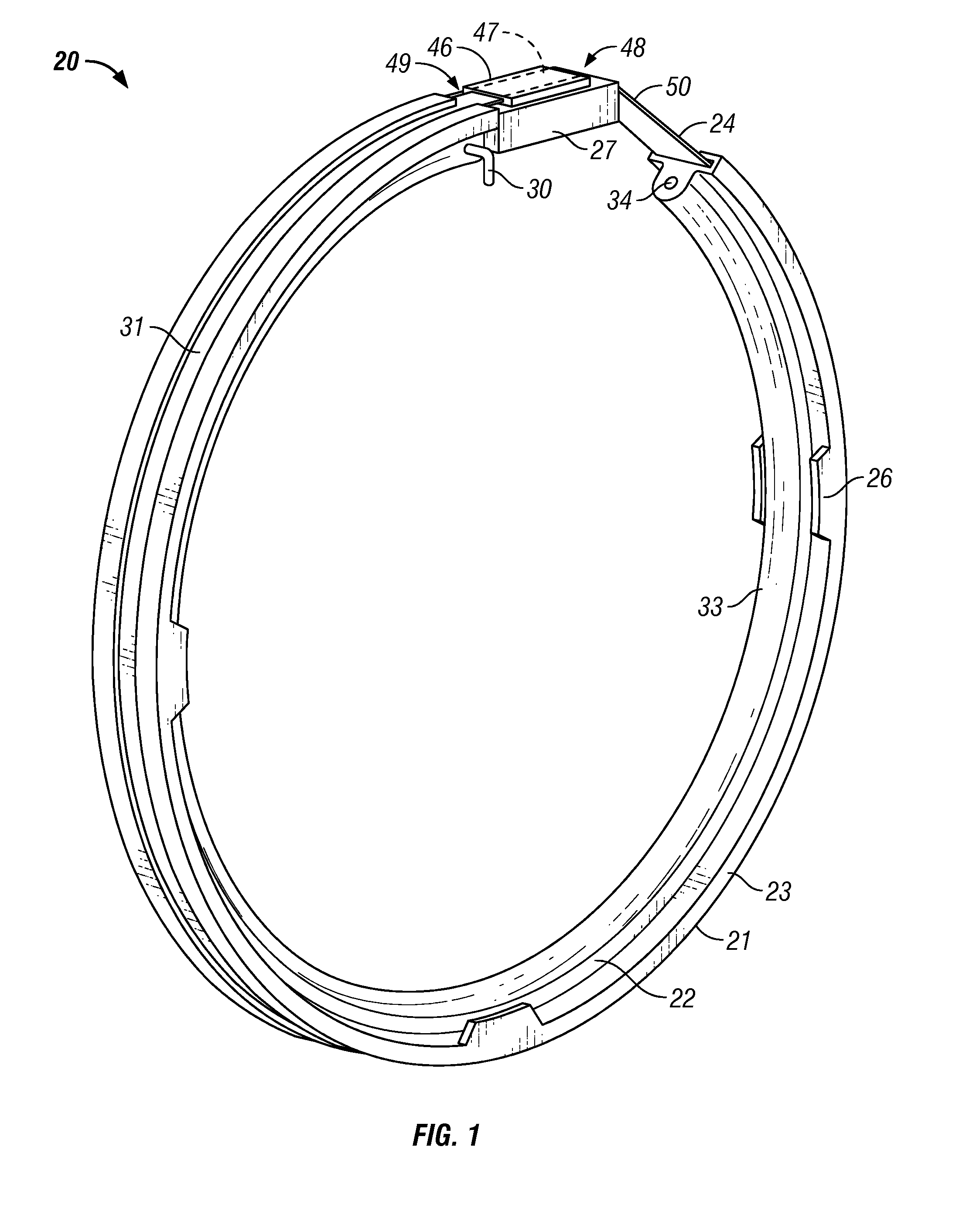
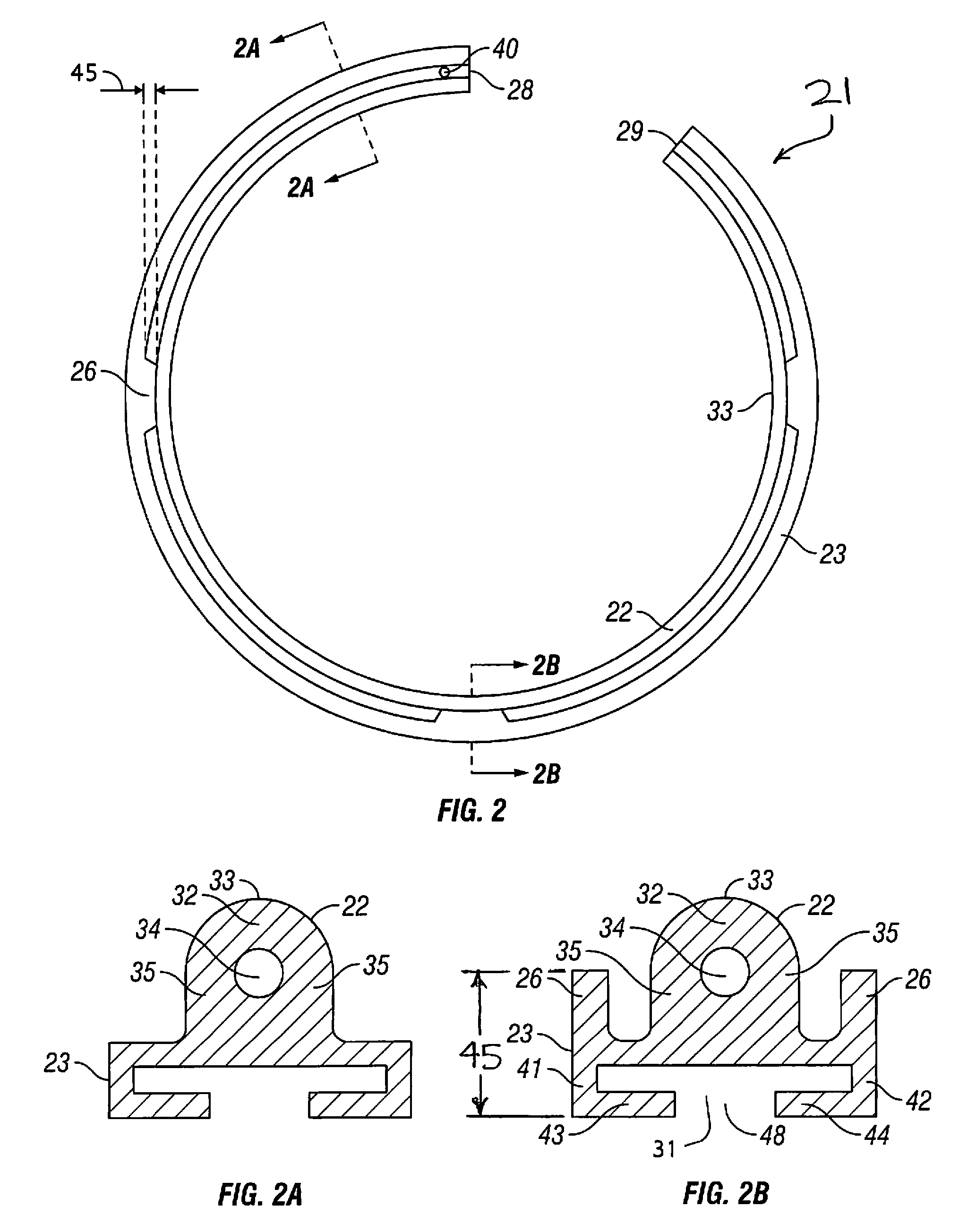
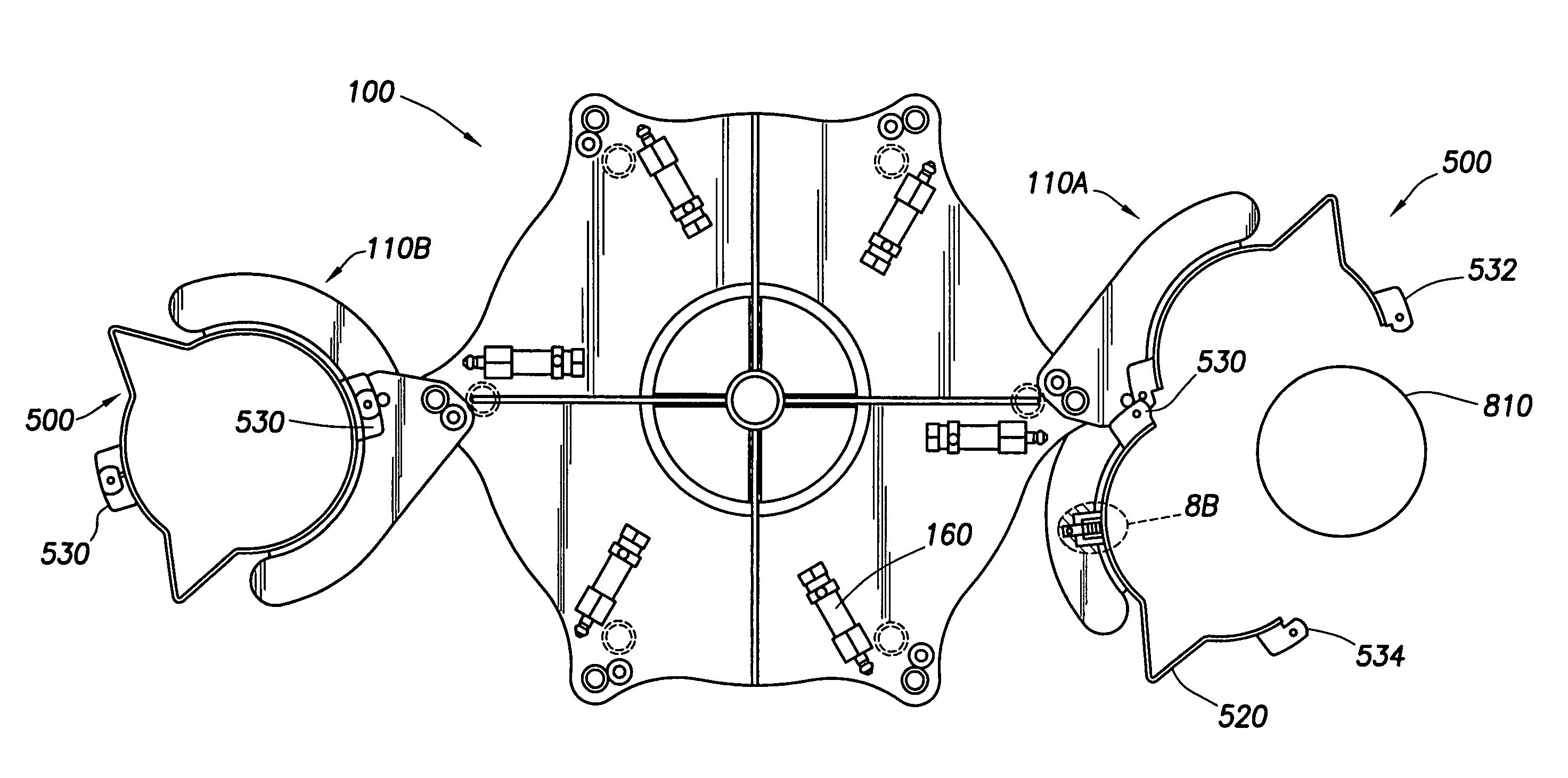
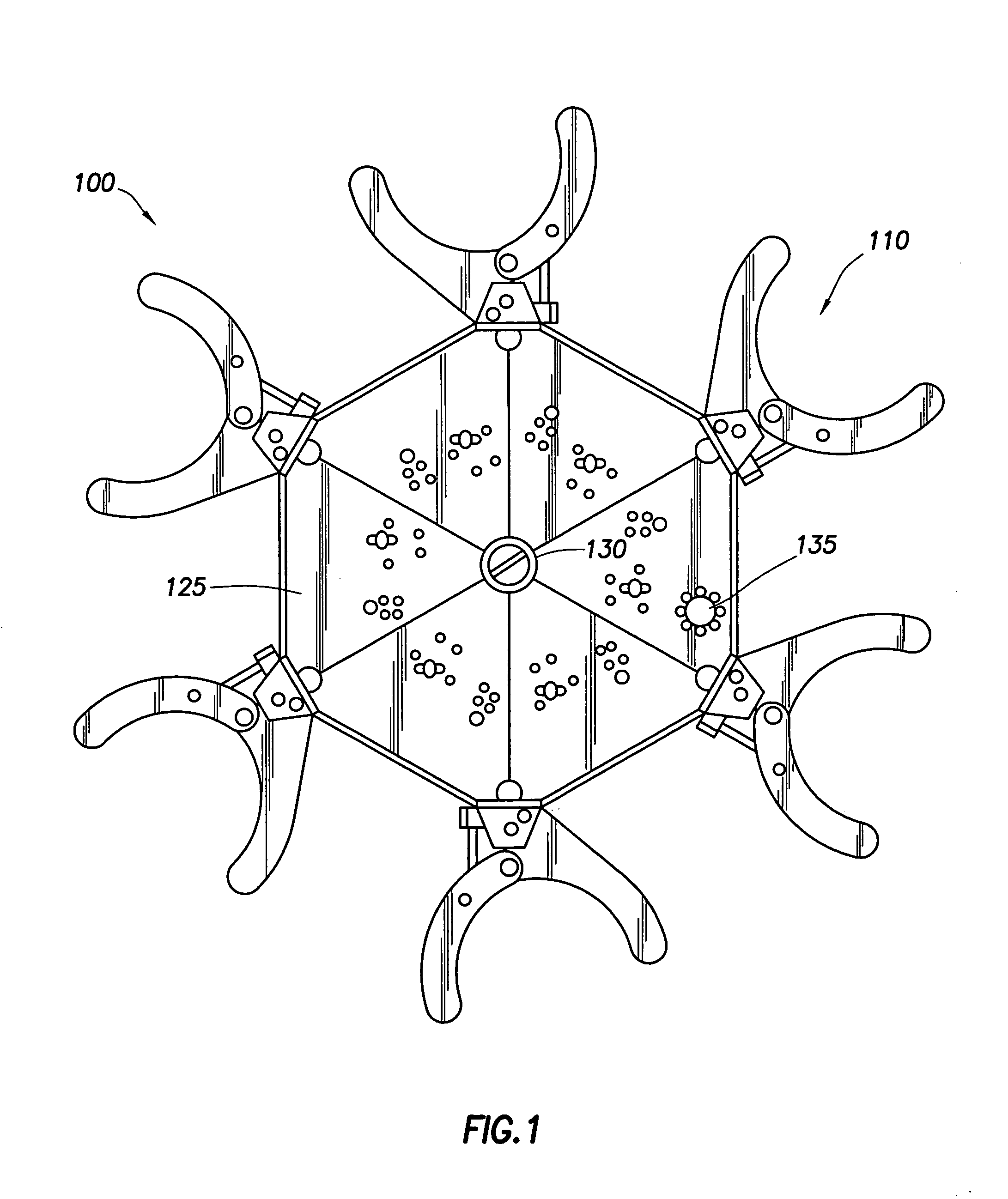
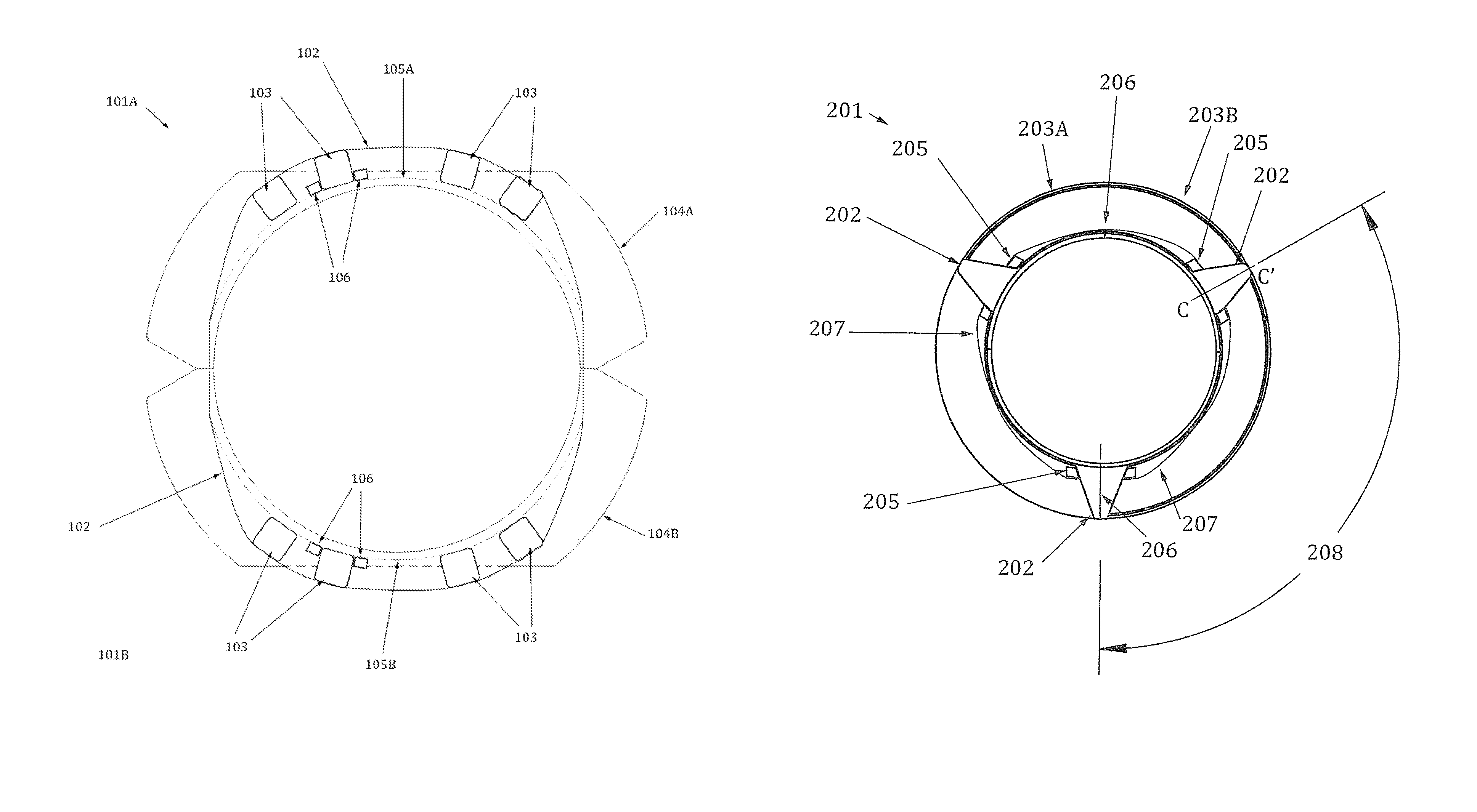
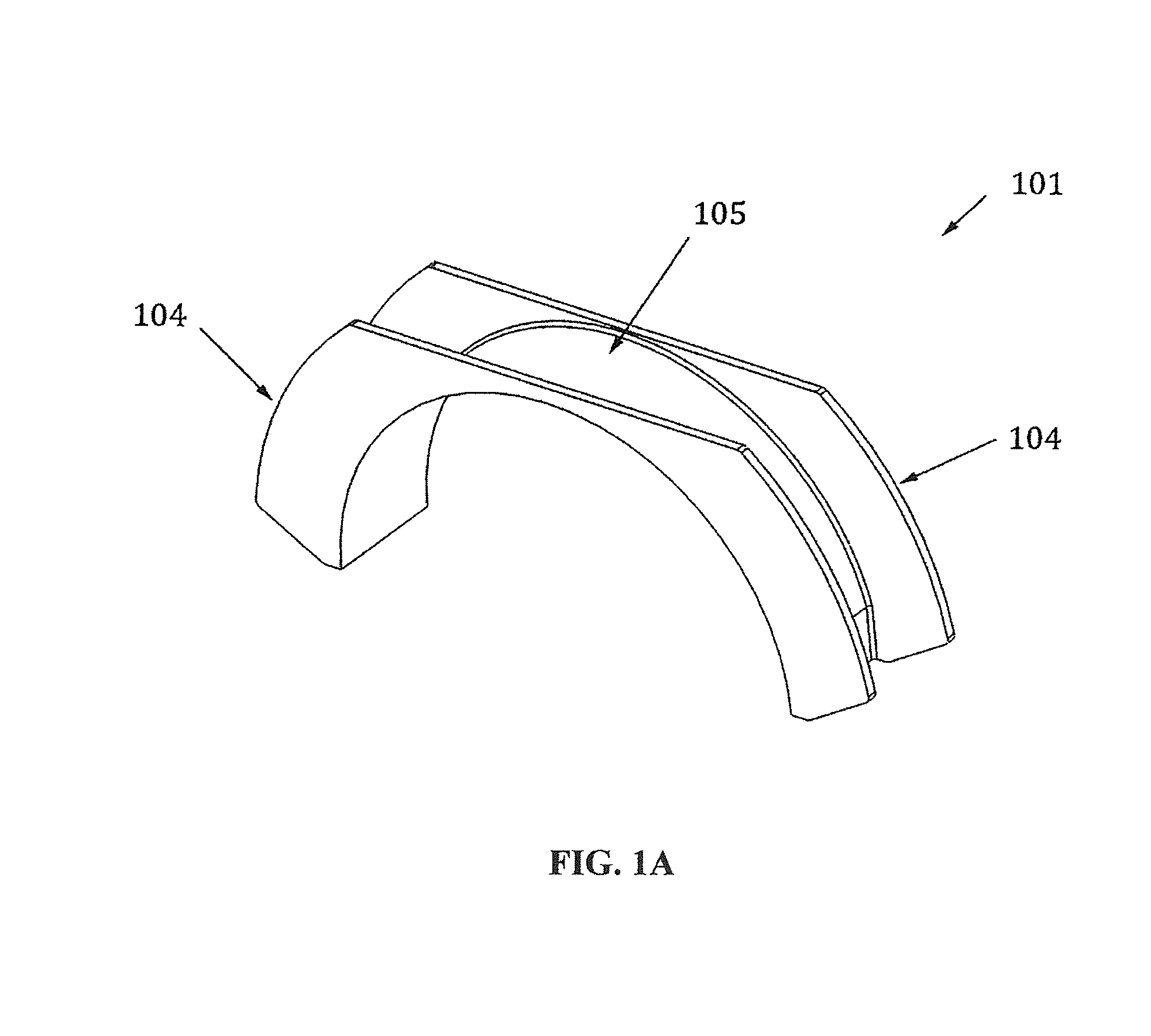
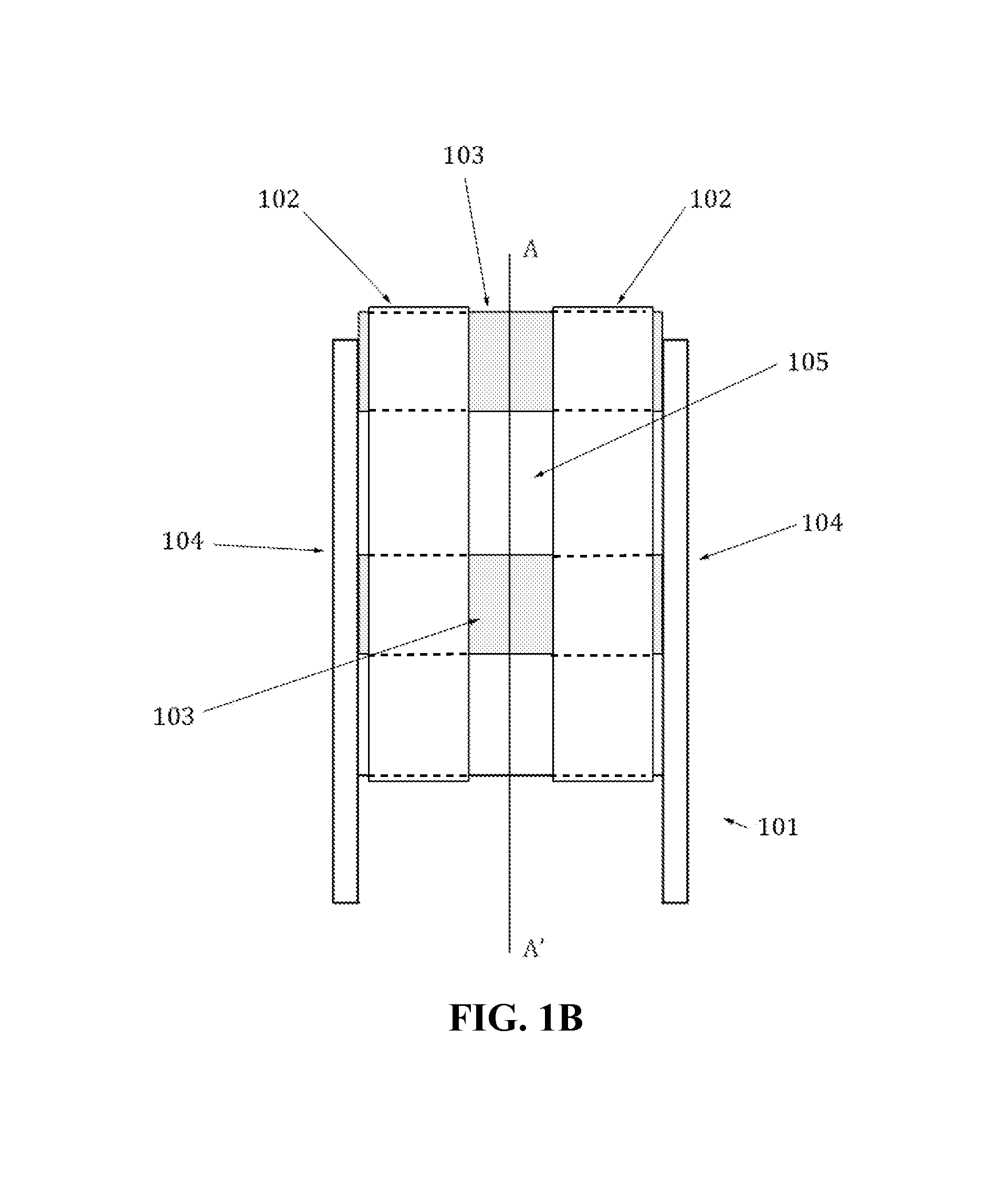
Apparatus with strake elements and methods for installing strake elements
InactiveUS20060280559A1Efficient methodEasy to installPipe laying and repairWaterborne vesselsStrakeEngineering
There is disclosed an apparatus comprising a plurality of strake elements, each strake element adapted to cover an arc-angle about a circumference of a structural element; and a mechanism adapted to attach the strake elements to each other to cover at least a portion of the circumference of the structural element.
Owner:ALLEN DONALD WAYNE +5
Vortex strake device and method for reducing the aerodynamic drag of ground vehicles
InactiveUS20050040669A1Reduce air resistanceOperation efficiency can be improvedVehicle seatsWindowsIn planeStrake
An improved method and device for the reduction of aerodynamic drag and for improved performance of vehicles by increasing the pressure on the rear surface of the vehicle by generating a plurality of vortices along the top and side surfaces that flow in to the base wake region of the vehicle. An improved method and device for generating a reduction in the drag force on a moving object. The present invention is a simple device comprised of a minimum number of thin and slender small surfaces that are attached to or fabricated as part of the side and top exterior surfaces of a vehicle or vehicle component. The spacing and orientation of the small surfaces, comprising the device, are dependent upon the vehicle geometry and vehicle operating conditions. The plurality of adjacent small surfaces are located forward of the base area on the vehicle. The plurality of adjacent small surfaces and are distributed circumferentially over the side and top surfaces of the subject vehicle or vehicle component. To maximize the ability of each of the plurality of adjacent small surfaces to generate a vortex structure the small surfaces are aligned in planes that are perpendicular to the surface of the vehicle. Each of the plurality of adjacent small surfaces extends from the exterior top and side surfaces of the vehicle. The plurality of adjacent small surfaces is applied symmetrically to a vehicle, about a vertical plane passing through the centerline of the vehicle. Each of the plurality of adjacent small surfaces is orientated in a plane or surface that is at an angle to the local flow direction on the vehicle surface in the immediate vicinity of the present invention. The orientation and shape of the plurality of adjacent small surfaces are a function of the vehicle or vehicle component geometry.
Owner:SOLUS SOLUTIONS & TECH
Compliant banding system
InactiveUS20080236469A1Avoid displacementIncrease channel lengthPipe laying and repairWaterborne vesselsStrakeAerospace engineering
The present invention discloses a compliant banding system for use in a marine environment comprising a flexible compliant member and an abaxial relatively rigid strap, both constructed to extend circumferentially around an underlying structure such as a strake or fairing collar. The strap maintains a fixed circumference while the compliant member flexes intermediate the strap and an underlying.
Owner:VIV SUPPRESSION
Inflatable stand-up paddle board
A stand-up paddle board and nosecap are disclosed. The stand-up paddle board is made using drop-stitching and in inflatable. The nosecap is made using injection molding techniques and is relatively rigid. The nosecap is attached to the stand-up paddle board and provides the board with a displacement hull to more easily move through the water.
Owner:ADVANCED ELEMENTS
Watertight heat insualtion container with improved longitudinal stereo cross angle
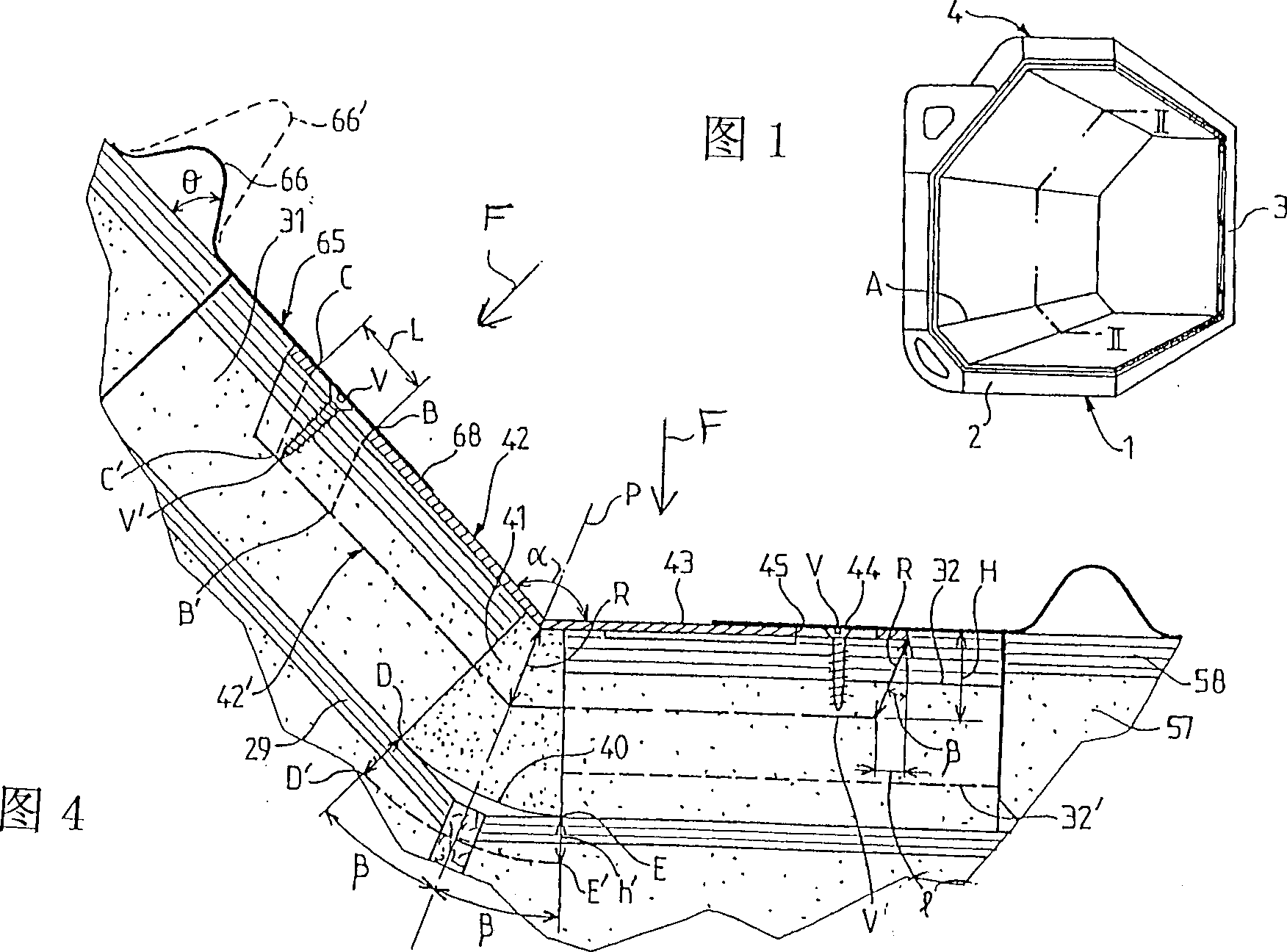
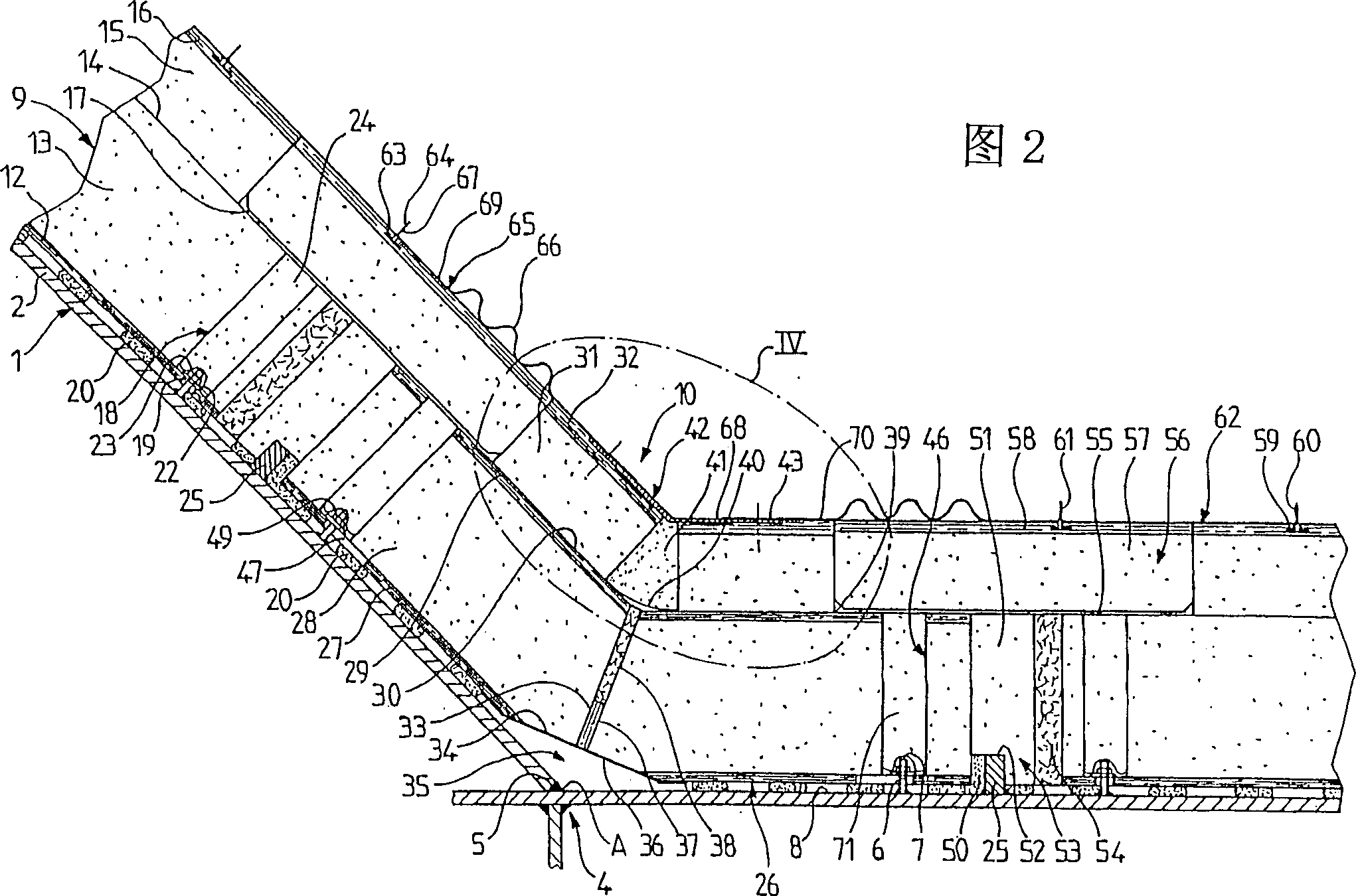
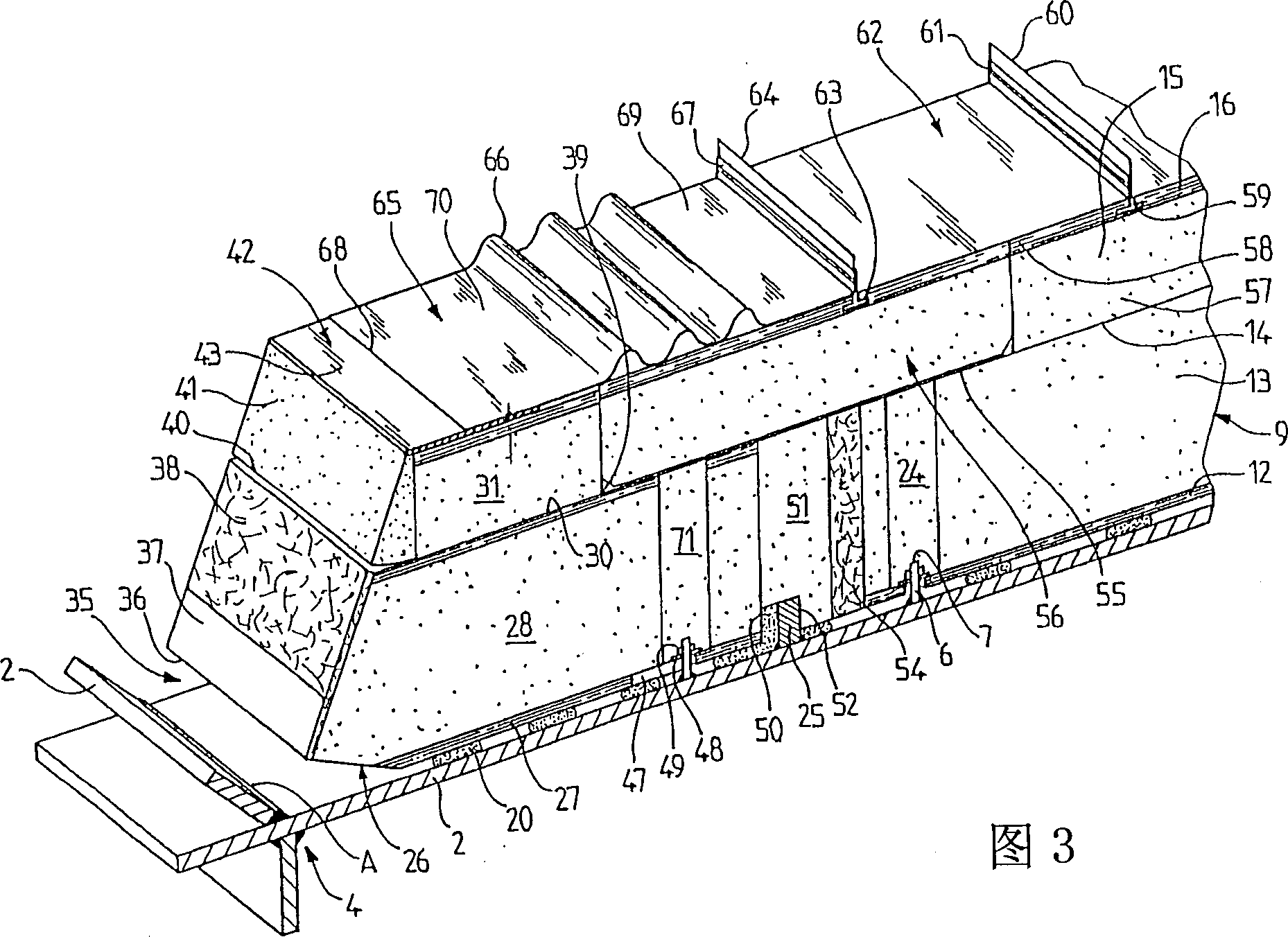
Watertight and thermally insulating tank intended for the transportation of liquefied gases by sea, said tank being built into a bearing structure (1) comprising longitudinally adjacent faces (2) forming a dihedron (4); said tank comprising two successive watertightness barriers, one of them a primary watertightness barrier in contact with the product contained in the tank and the other a secondary watertightness barrier (14,55,30,40) arranged between said primary watertightness barrier and the bearing structure, a primary thermally insulating barrier (12,13,24,27,28,29,37,38,51,54,71) being arranged between these two watertightness barriers and a secondary thermally insulating barrier (15,16,57,58,31,32,41) being arranged between said secondary watertightness barrier and the bearing structure; said primary watertightness barrier comprising substantially flat running metal strakes (62) and, on each side of the longitudinal solid angle of intersection (A) of at least one of said dihedra, a longitudinal row of corner strakes (65) which are corrugated so that they can deform transversely.
Owner:GAZTRANSPORT & TECHNIGAZ SA
Solar cell module and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101320760AEfficient outputTo achieve the purpose of lightweightFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationFiberStrake
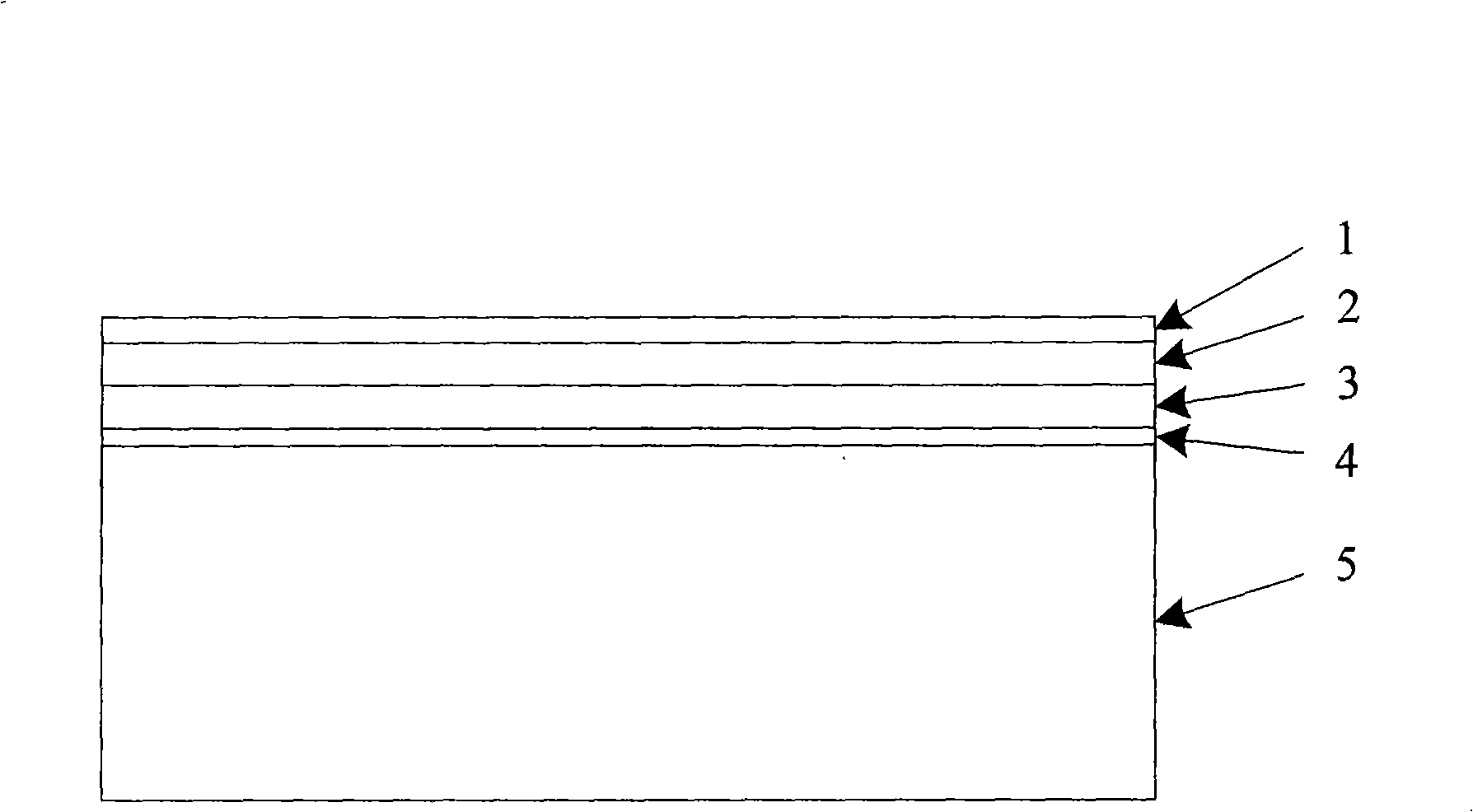
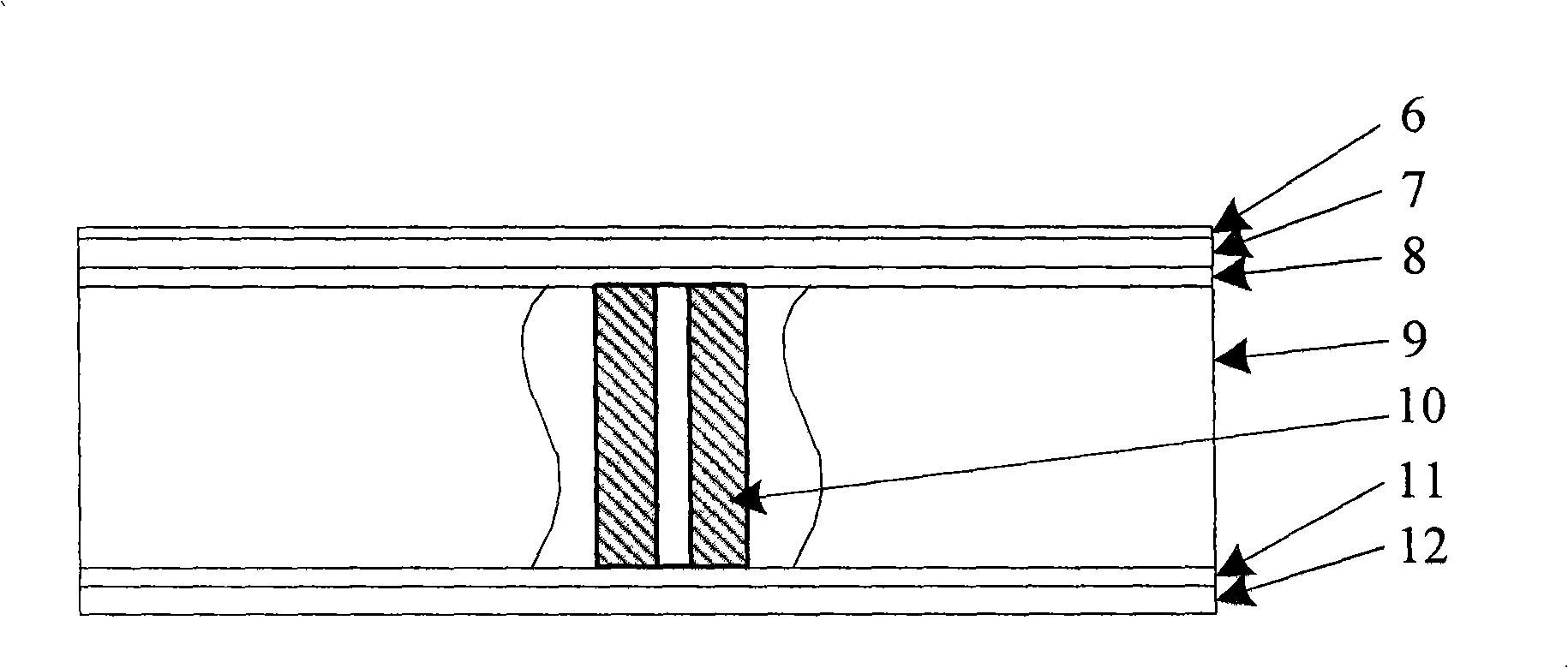
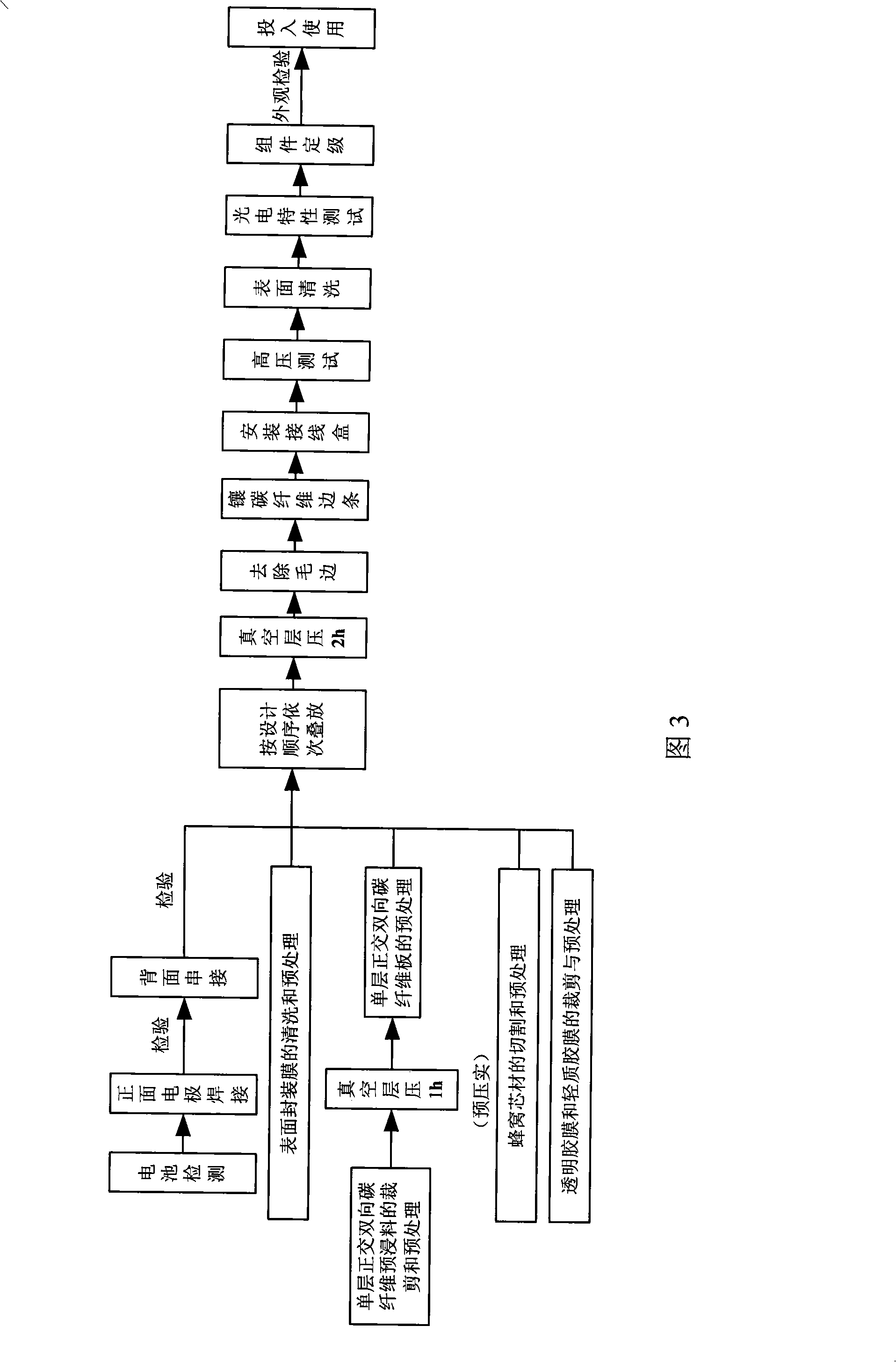
The invention provides a solar module which is composed of a surface sealing film, a transparent adhesive film, a solar cell, a lightweight adhesive film A and an isolated substrate which are stacked from the top to the bottom in order; and the isolated substrate is composed of an isolated film, a carbon-fiber sheet, a lightweight adhesive film B, a honeycomb core, a lightweight adhesive film C and the carbon-fiber sheet which are stacked from the top to the bottom in order, wherein the honeycomb core inside also needs to be appropriately added embedded parts according to concrete operating requirements. The technical scheme of a preparation method of the solar module comprises following steps: (1) making use of an oven to match with a vacuum air pump to process a pre-compacting treatment for a carbon-fiber prepreg; (2) meanwhile, processing a welding sequence of the solar cell; (3) processing a cutting sequence; (4) processing a laminating technology treatment; (5) processing post treatment procedures which in order are: removing raw edges, embedding strakes, arranging a junction box, measuring high voltage, cleaning the surface, measuring photo-electrical output characteristics, classifying components, and examining the appearance. The solar module has the advantages of lightweight, high efficiency and good low-temperature characteristics, and being very suitable to being applied in the stratosphere.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
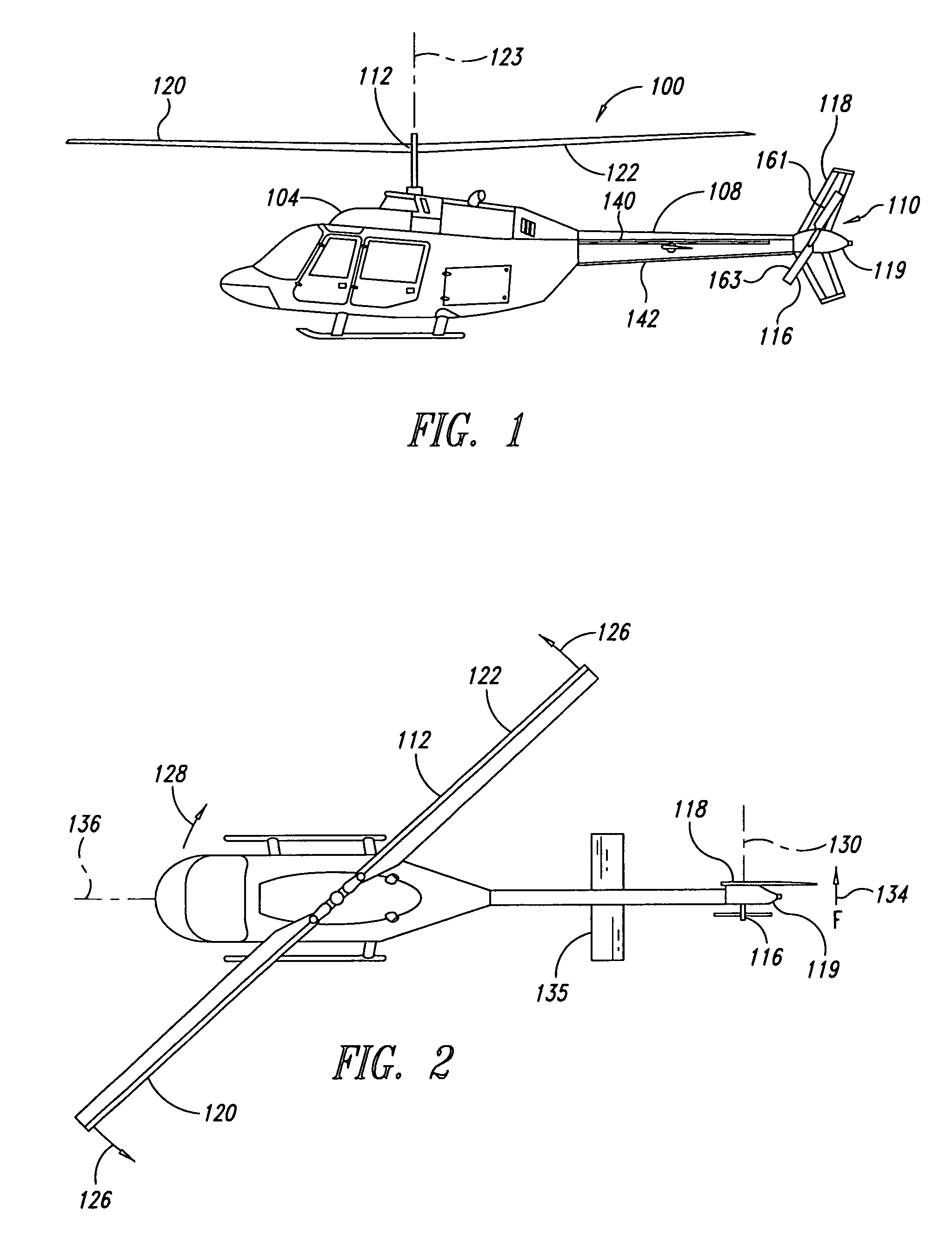
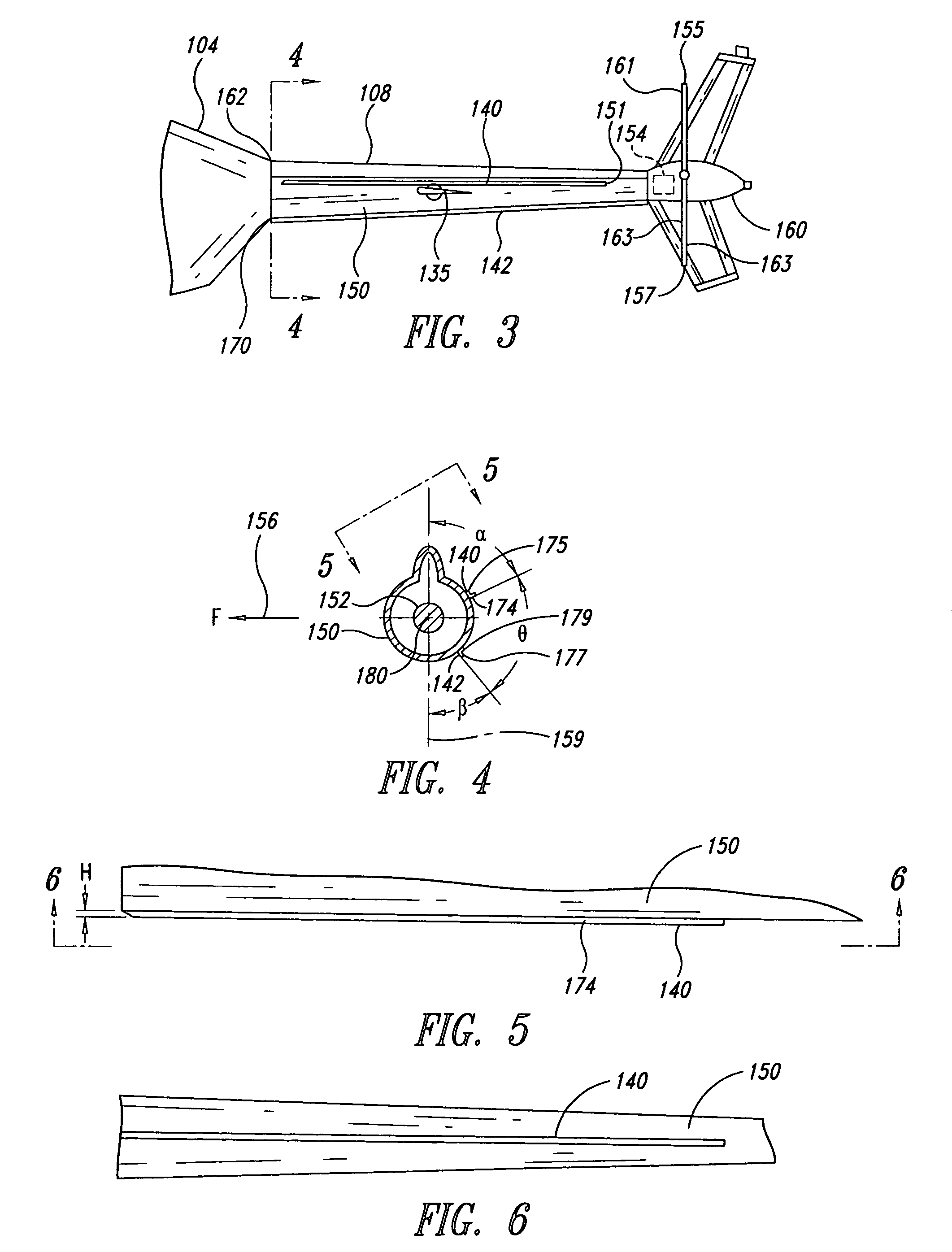
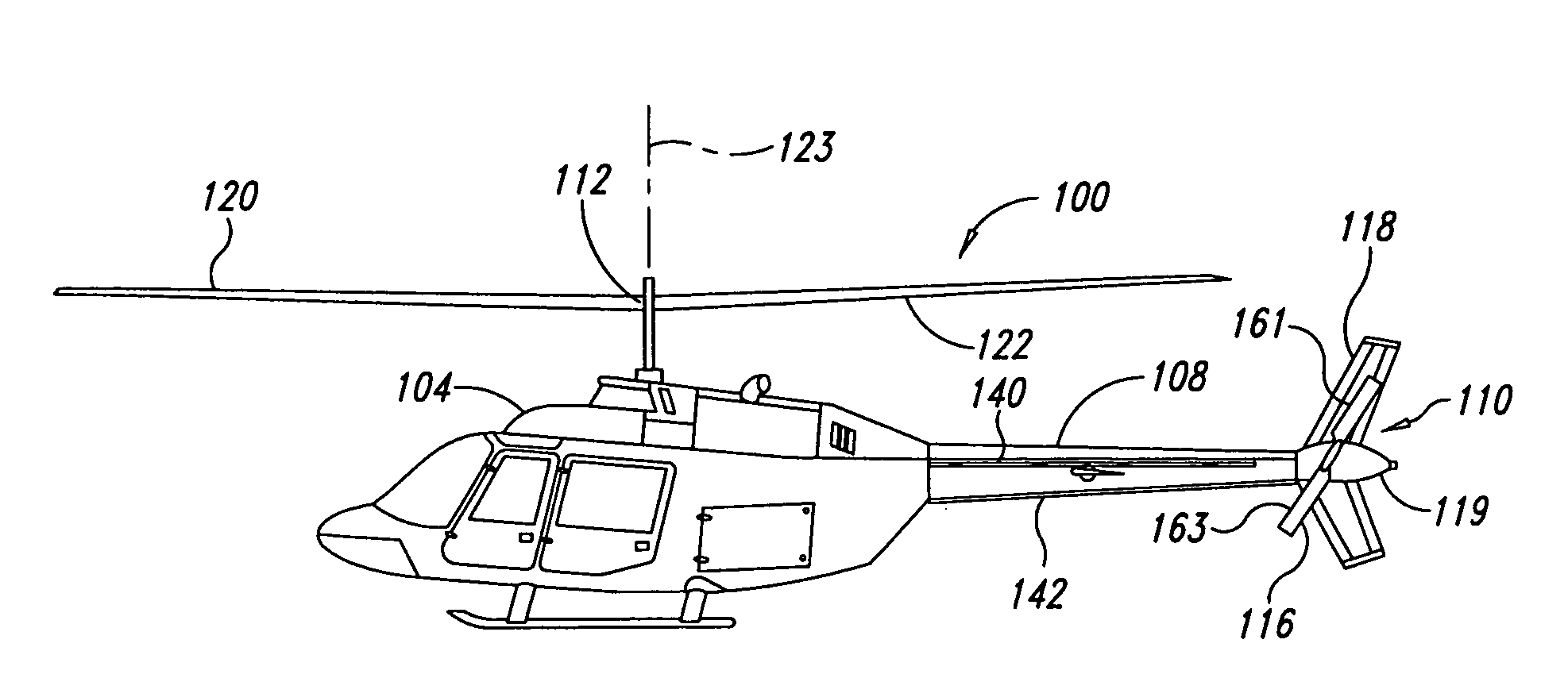
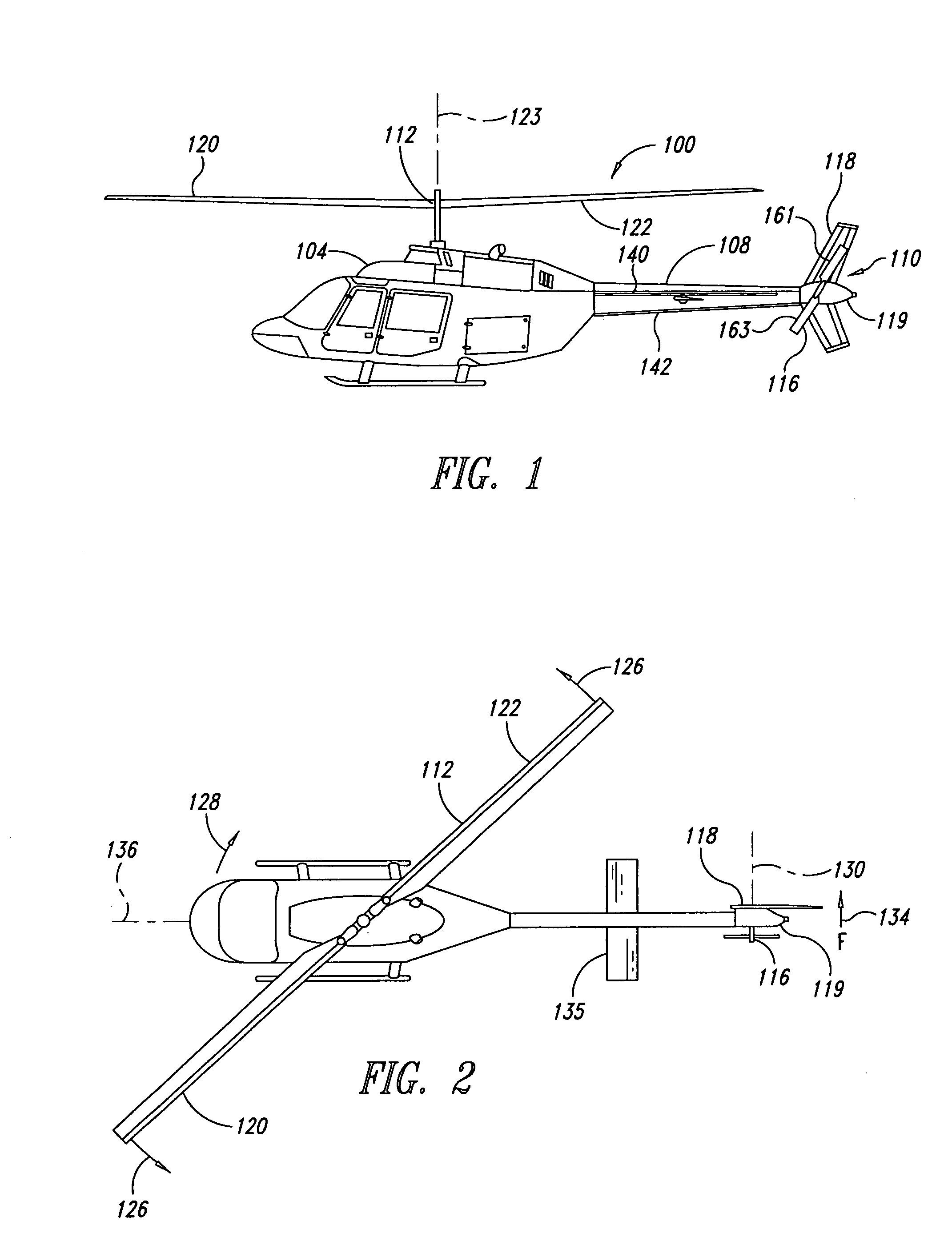
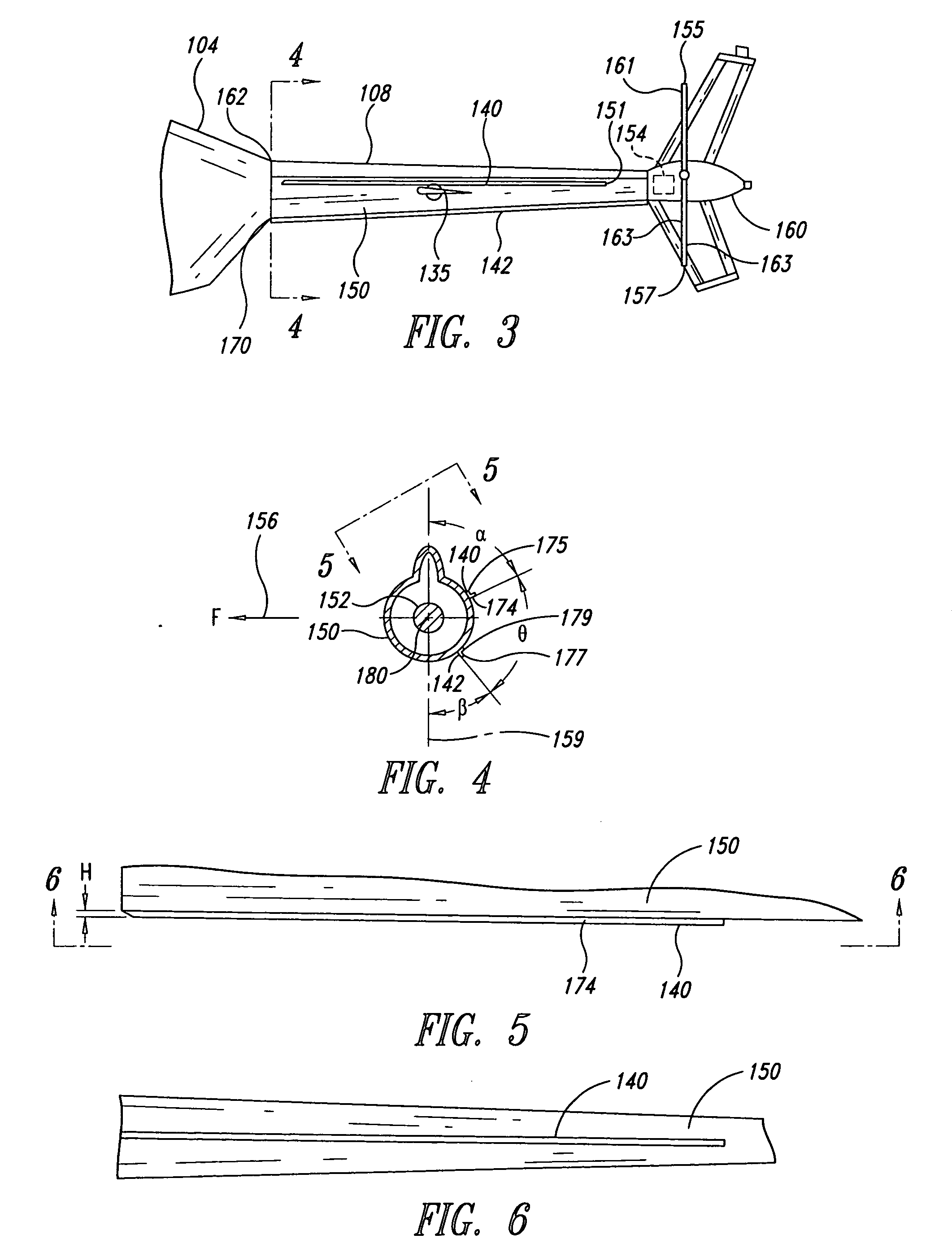
Aircraft stabilizer system and methods of using the same
ActiveUS8210468B2Improve performanceSmall shapeAircraft stabilisationOther manufacturing equipments/toolsStrakeTail rotor
Owner:BLR AEROSPACE
Section construction method of hatch coaming and ship side
ActiveCN105882891ARealize integrated constructionReduce the number of liftingVessel partsStrakeEconomic benefits
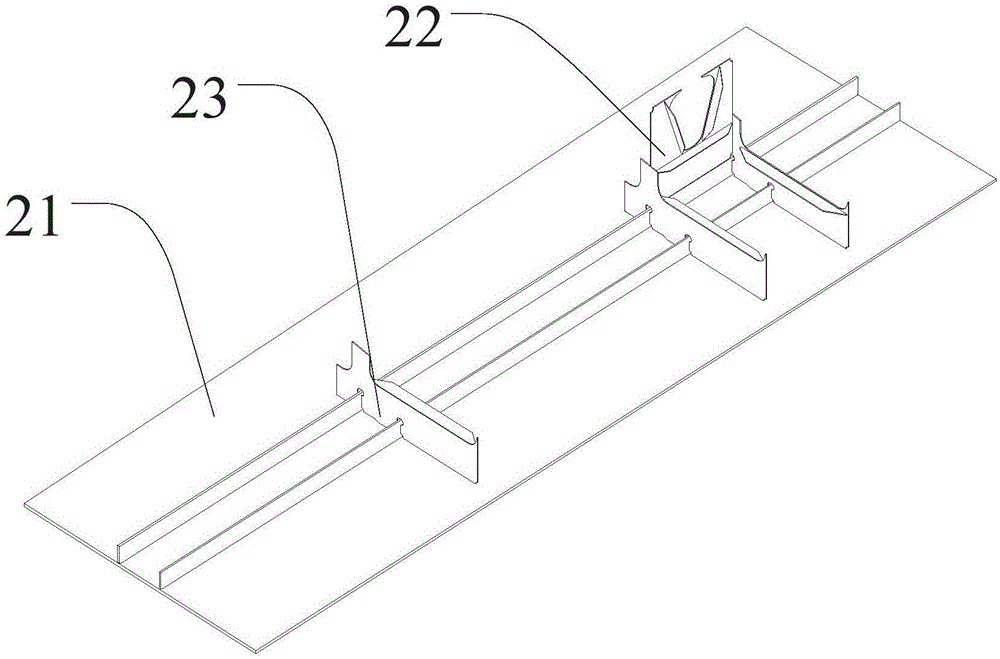
The invention discloses a section construction method of a hatch coaming and a ship side. A mounting structure at least comprises an outer plate component, a sheer strake component, a vertical wall component, an antitorsion box component, a vertical wall plate, a compartment component, a guide rail and a longitudinal framework, wherein the antitorsion box component comprises a hatch coaming component, and the hatch coaming component comprises upright columns. The section construction method further comprises the following steps: S1, fixing the outer plate component; S2, mounting the sheer strake component on one side of the outer plate component; S3, mounting the bottom of the vertical wall component on the outer plate component; S4, mounting the bottom of the antitorsion box component to the sheer strake component after mounting the hatch coaming component mounted with the upright columns to the antitorsion box component, and connecting one side of the antitorsion box component to the vertical wall component; S5, overlying and welding the vertical wall plate on the vertical wall component and the antitorsion box component; S6, mounting the compartment component and the guide rail on one side of the vertical wall plate far away from the outer plate component. The section construction method of the hatch coaming and the ship side disclosed by the invention realizes the integrated construction of ships, and provides necessary conditions for the batch ship building, and further lowers the requirements of the machining precision and brings about considerable economic benefits.
Owner:JIANGNAN SHIPYARD GRP CO LTD
Boat bottom hull design
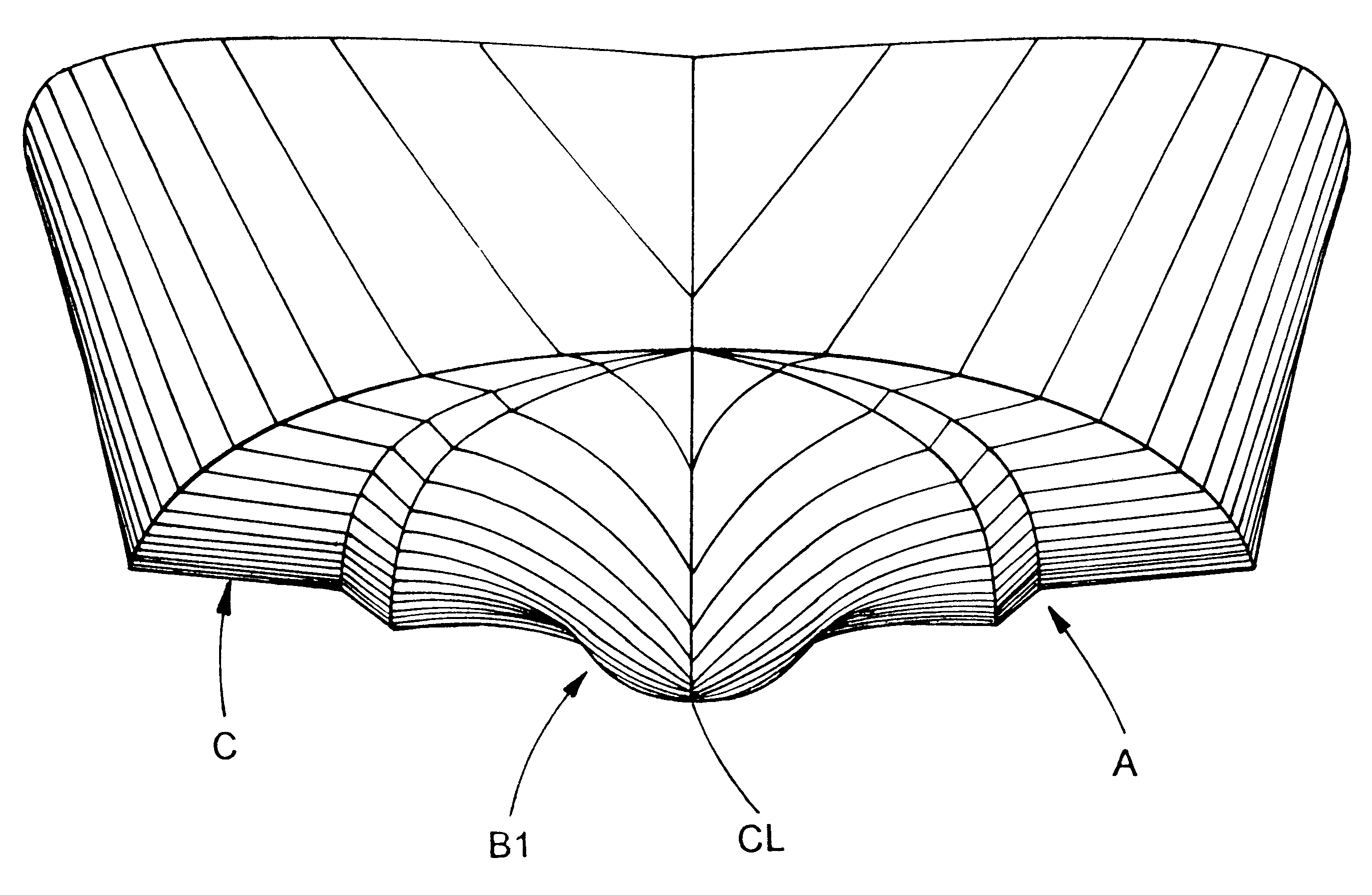
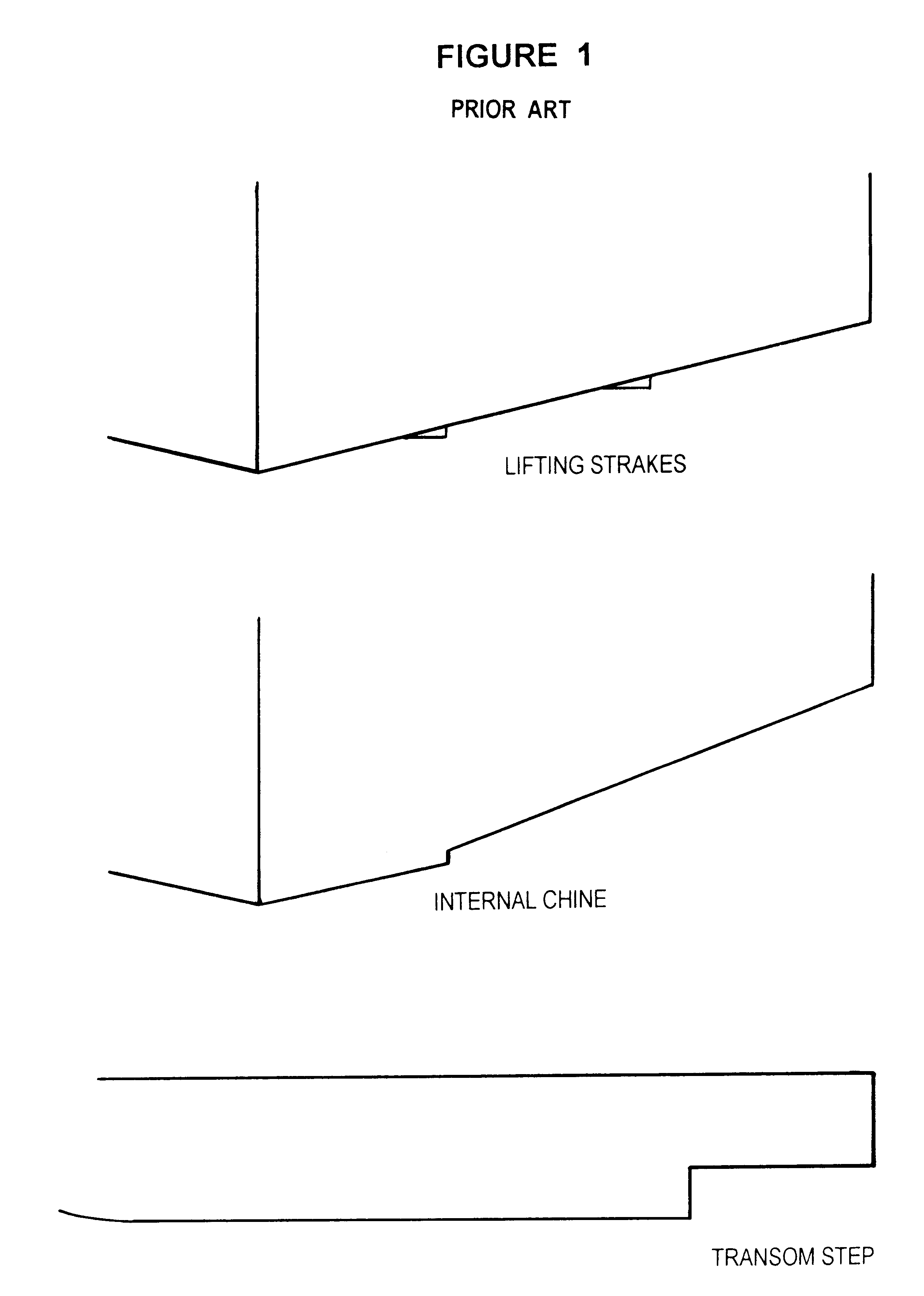
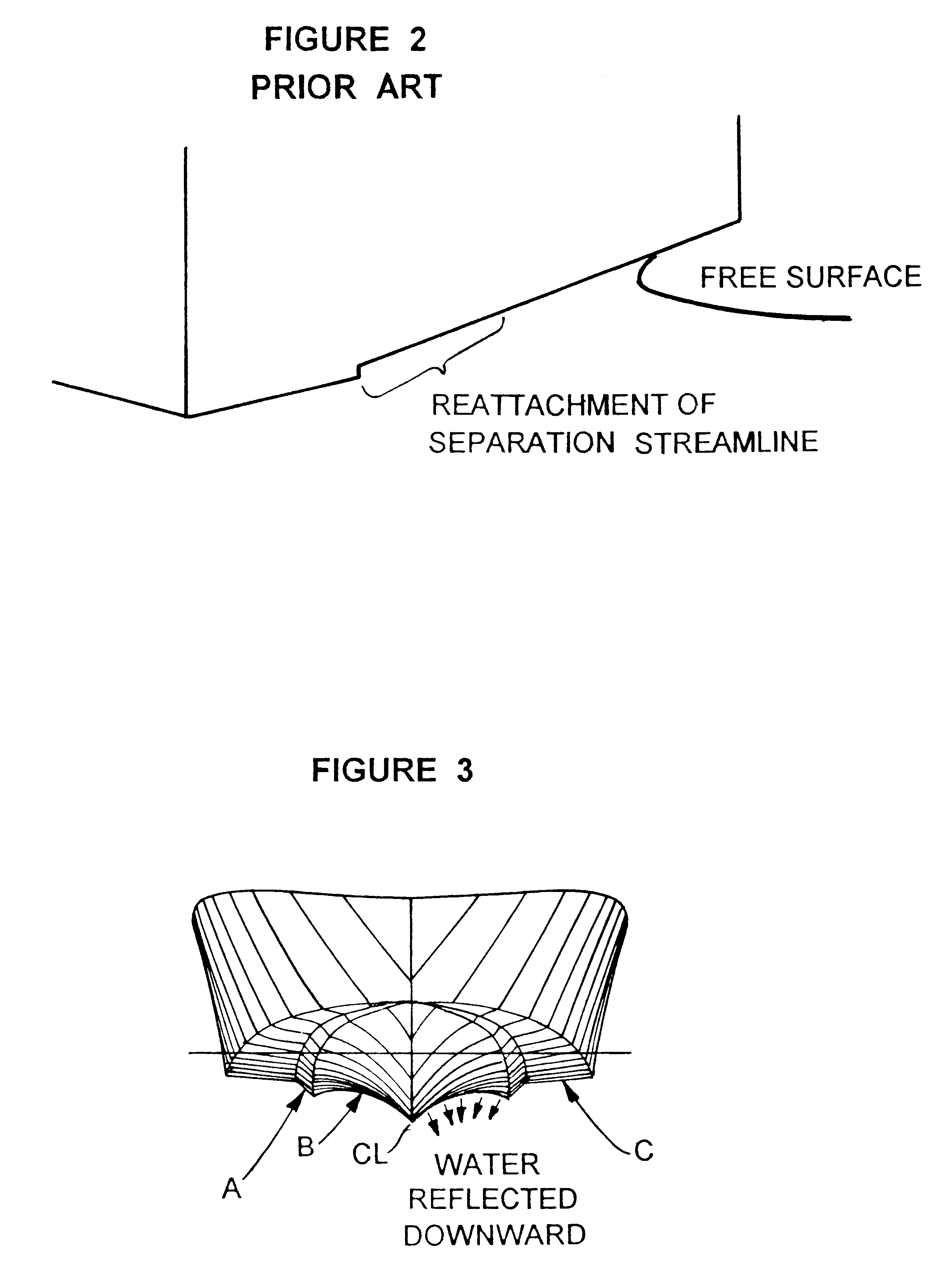
InactiveUS6176196B1Effectively exploit potential advantageFloating buildingsHydrodynamic/hydrostatic featuresStrakeBi modal
A hull design with a maximally narrowed lower hull comprised of a stepped inboard chine and a concave centerline section resulting in the center of buoyancy and center of gravity preferably being in the same longitudinal position. The narrow lower hull optimally reduces the wetted surface area required, thereby reducing power requirements, fuel costs, and increasing speed potential. Exemplary dimensions for a forty-five (45') foot hull are disclosed. The hull has a much deeper transverse step (note FIG. 3) to more effectively exploit the potential advantages of internal chines and lifting strakes, which deeper transverse step effectively achieves a bi-modal hull form-displacement and planing. The hull form consistently achieves and maintains the flow separation needed to assure the low surface area needed for minimum planing resistance and minimum sea wave impact acceleration. Additionally, the hull's convex curvature in the narrow planing region of the hull shifts the center of dynamic pressure forward, providing a more balanced acceleration, with less extreme boat attitudes, in the transition from displacement to planing mode, as well as when operating at steady speeds over the entire speed range.
Owner:HALTER HAROLD P
Method and apparatus for aeration of liquid medium
InactiveUS7427058B2Efficient mixingIncrease the number ofCarburetting airLighting and heating apparatusStrakeLiquid medium
Owner:GALLETTA AERATOR
Apparatus and methods for remote installation of devices for reducing drag and vortex induced vibration
Apparatus and methods for remotely installing vortex-induced vibration (VIV) reduction and drag reduction devices on elongated structures in flowing fluid environments. The apparatus is a tool for transporting and installing the devices. The devices installed can include clamshell-shaped strakes, shrouds, fairings, sleeves and flotation modules.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Helical strakes with molded in stand-offs
Owner:VIV SOLUTIONS
Pontoon with integrated lifting strake and method for making the same
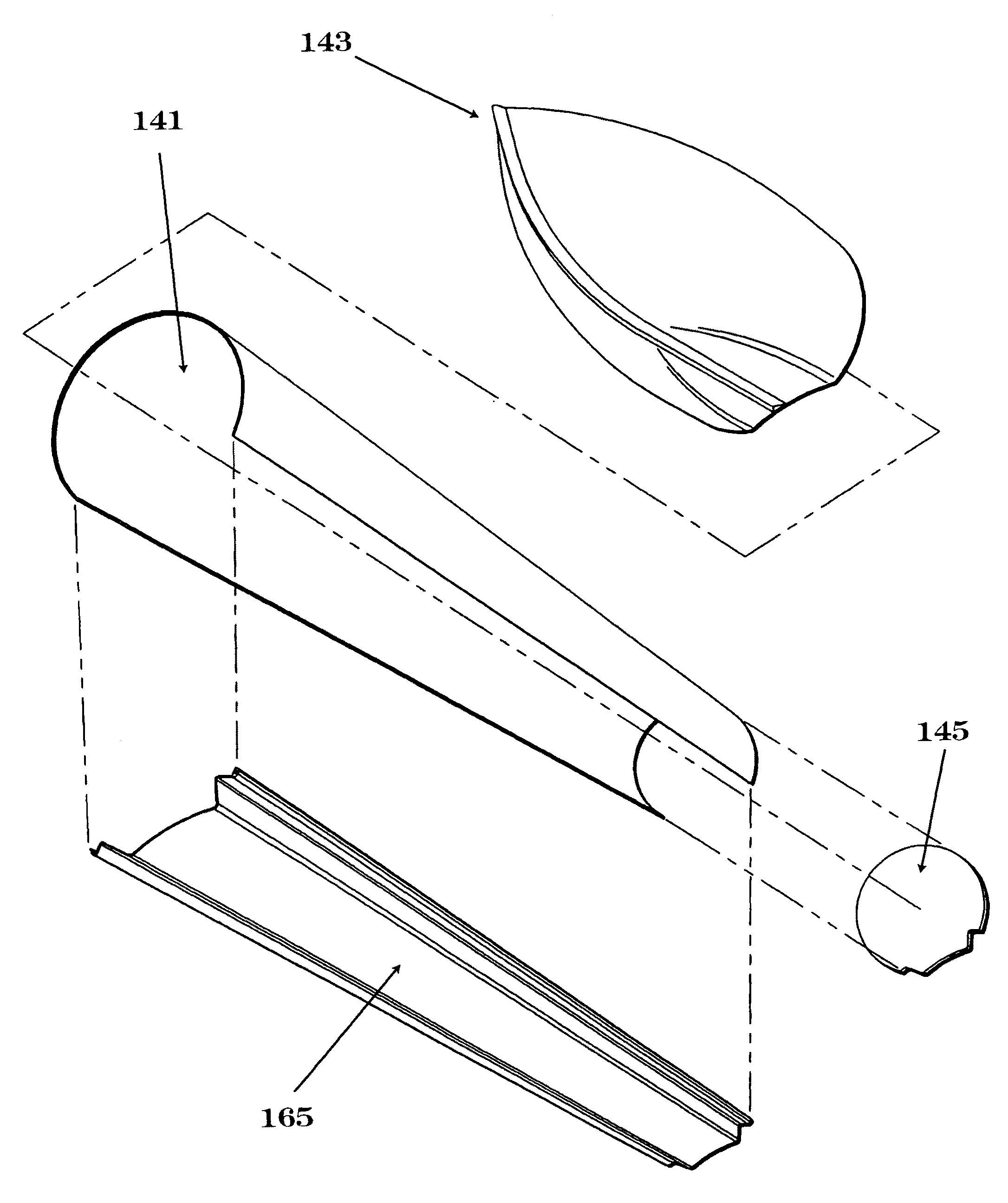
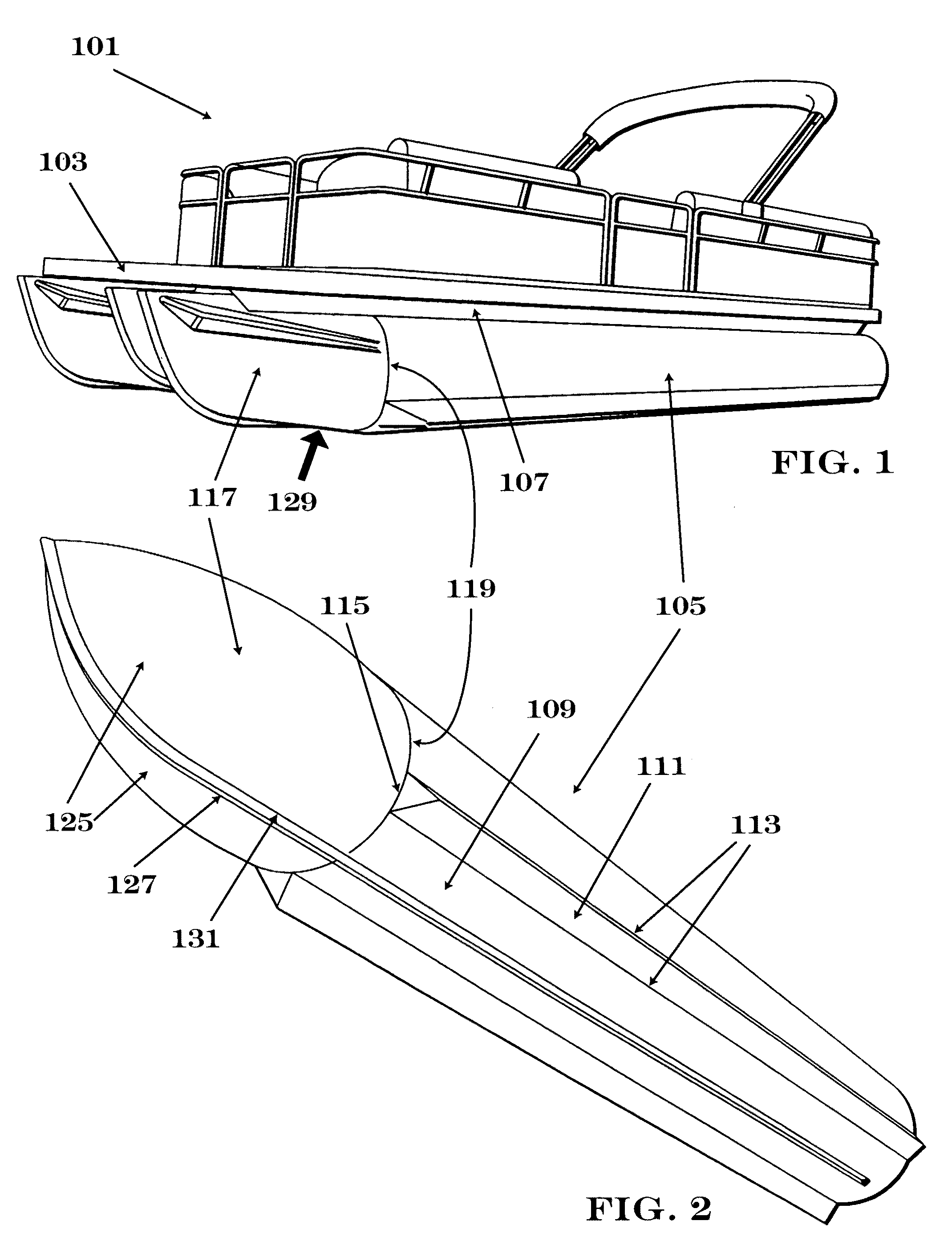
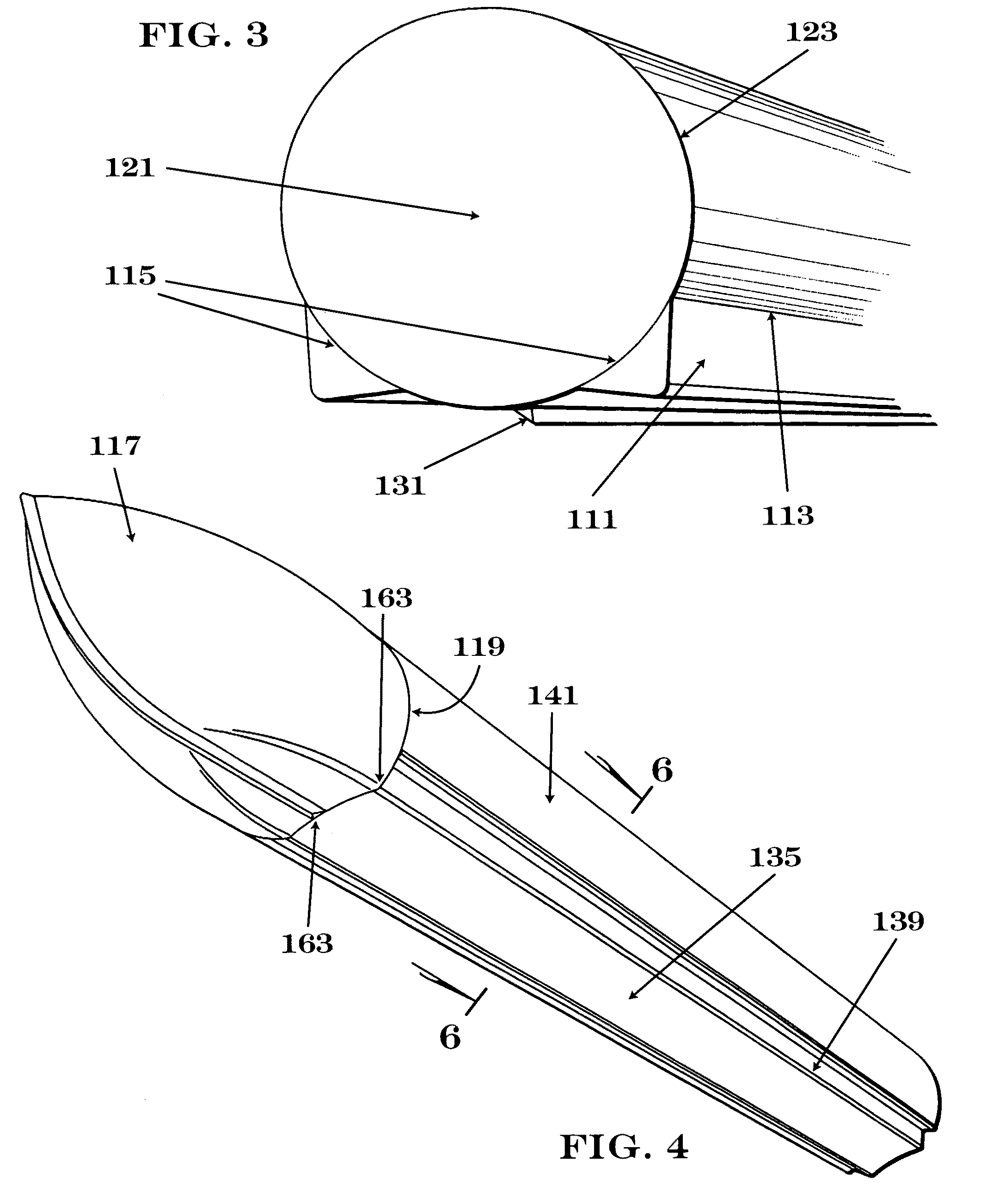
A pontoon with an improved running surface and methods for construction the same are provided. The pontoon comprises an interior concave main running surface formed along the longitudinal centerline of the pontoon which is bounded by two sponsons, which in turn are bounded by two distal concave surfaces, or integrated lifting strakes. The associated methods provide a process for retrofitting prior art pontoons or constructing the pontoon to avoid the need for welds below the waterline of the pontoon. The pontoon provides improved pontoon boat performance by maximizing lift and minimizing leakage. The pontoon also reduces construction costs by lowering the number of welds required to form a pontoon with lifting strakes.
Owner:ALUMA-WELD INC
Levitation and stabilizing hull system
InactiveUS6925953B1Optimal stabilization characteristicImprove performanceWatercraft hull designFloating buildingsChinLevitation
A hull system for boats that includes pairs of longitudinally extending strakes with a cross-section that includes a downwardly extending fin member with an adjacent flat horizontal section to provide running and idle stability. Steps with a projected V-shape pint forward and include air inlets with the distal ends. Channels run adjacent to the drop off wall of the steps to trap air forming an air cushion that tends to lift the moving hull. The resulting hull system provides optimal performance while running and still maintains good stability from oscillation when idle. A peripheral chin has a substantially triangular cross-section that extends vertically downwardly inside the body of water over which the boat floats.
Owner:CONQUEROR POWER BOATS
Extendable draft platform with buoyancy column strakes
ActiveUS20060067793A1Low costEasy to understandArtificial islandsProtective foundationStrakeMarine engineering
In an Extendable Draft Platform including a deck, a plurality of buoyancy columns installed in column wells in the deck for movement from a raised position to a submerged position, and a heave plate on the bottom of the columns, each of the columns has an upper portion and a lower portion. A helical strake having a radial height H is fixed to the lower portion of each column. The maximum width of the lower column portion is less than the maximum width of the upper column portion by at least 2H, so that the strake can pass through a column well having maximum width that is only slightly greater than that of the upper column portion. A plurality of guide rails is fixed to the lower portion of each column, each extending along the outer periphery of the strake from the upper column portion to the heave plate.
Owner:TECH FRANCE SA
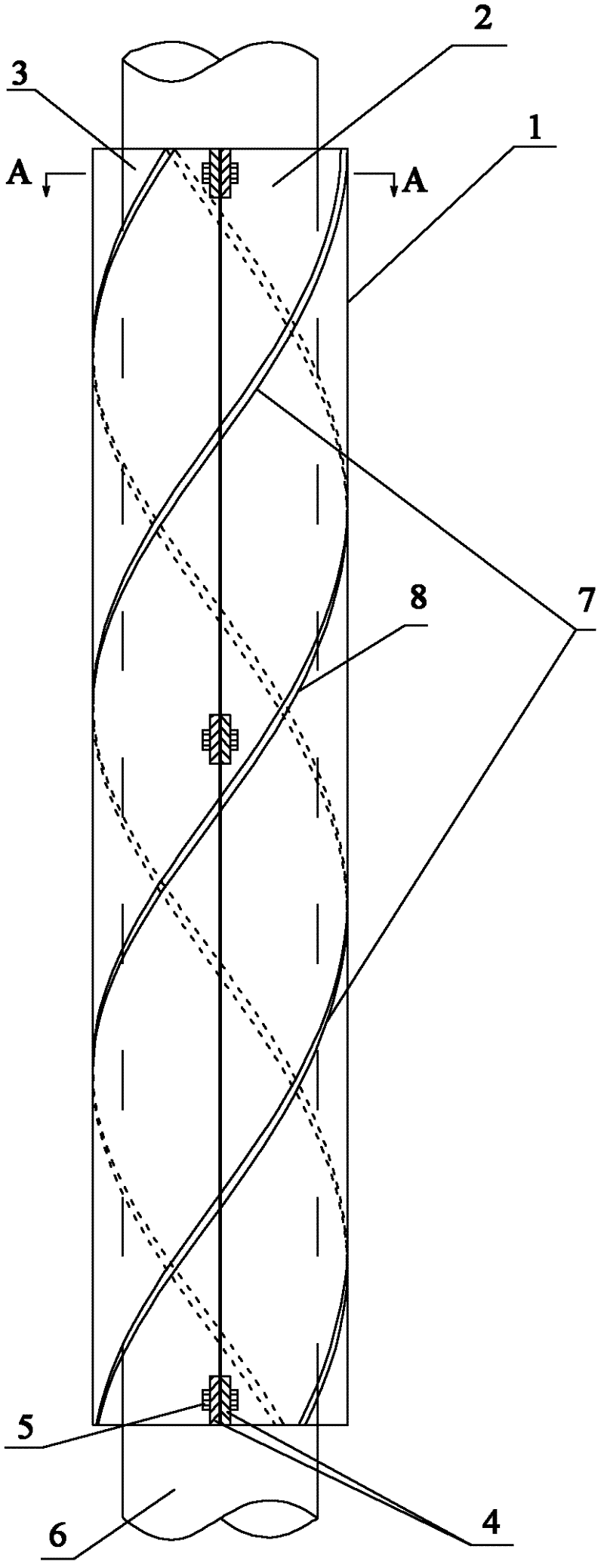
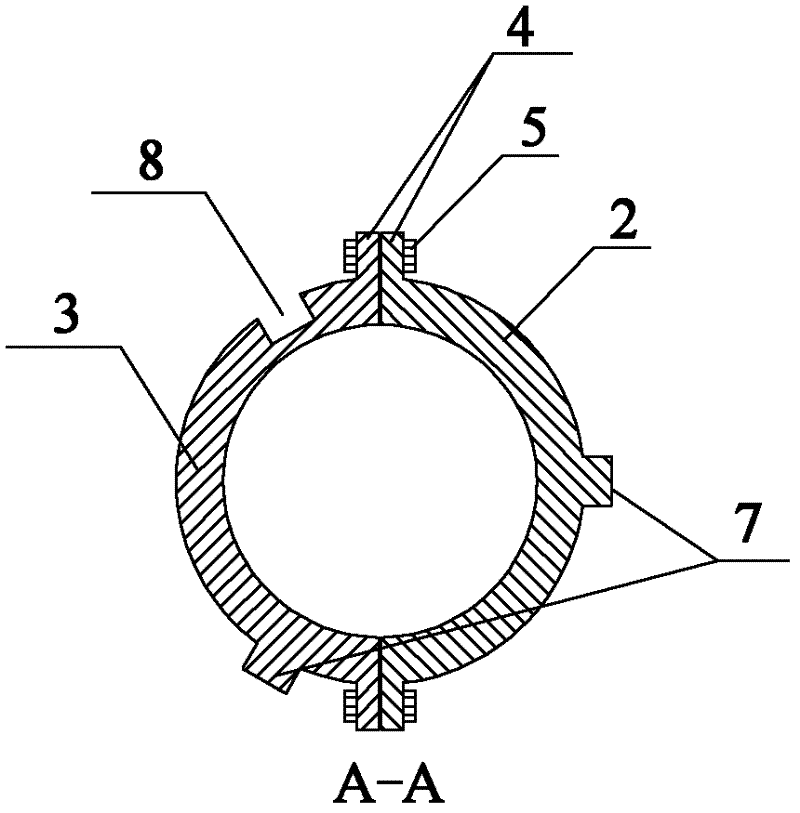
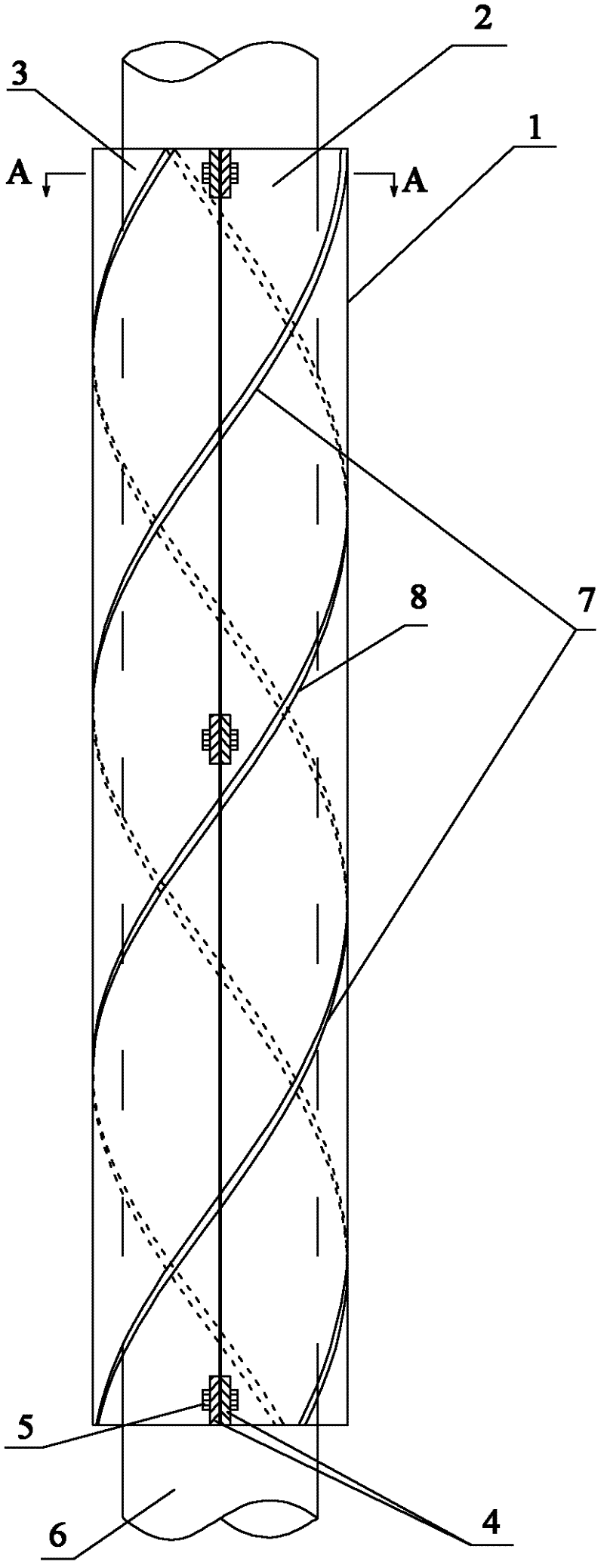
Helical strake vortex induced vibration inhibiting device
ActiveCN102121356AReduced Hydrodynamic DiameterReduce vibration amplitudeDrilling rodsFluid dynamicsVertical tubeStrake
The invention relates to a helical strake vortex induced vibration inhibiting device. The device is characterized by comprising a plurality of strip strakes, a plurality of chucks and a ligature, wherein the strakes are alternately arranged on the outer wall of a marine riser, and are helically arranged along the axial direction of the marine riser; the chucks are alternately fixed on the marine riser, and a plurality of grooves are formed on each chuck; and each strake is arranged in the groove of the chuck corresponding, and is fastened in the chuck through the ligature. The device has a simple structure, and the strakes can adopt a continuous structure to facilitate marine on-site assembly, thus the efficiency of marine on-site assembly is remarkably improved, and the device has remarkable economic benefits, and can be applied to the marine riser widely.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Apparatus and methods for remote installation of devices for reducing drag and vortex induced vibration
Apparatus and methods for remotely installing vortex-induced vibration (VIV) reduction and drag reduction devices on elongated structures in flowing fluid environments. The apparatus is a tool for transporting and installing the devices. The devices installed can include clamshell-shaped strakes, shrouds, fairings, sleeves and flotation modules.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Strake systems and methods
InactiveUS20070125546A1Reduce vibrationPipe laying and repairWaterborne vesselsStrakeBiomedical engineering
There is disclosed a system comprising a structural element, at least one helical strake about the structural element, and at least one ramp to provide a transition from the structural element to the helical strake.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
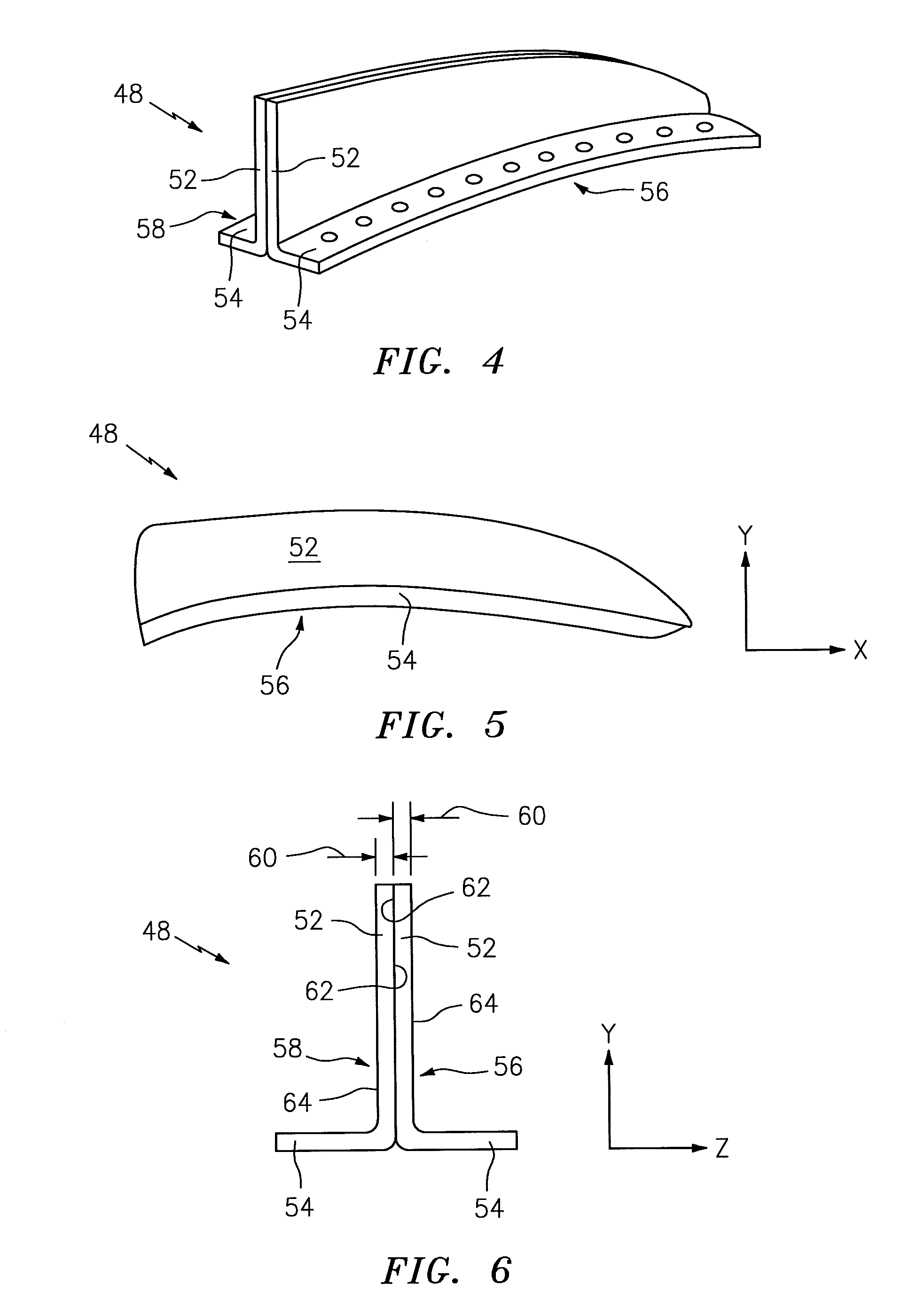
Method for manufacturing a nacelle strake
A method for manufacturing a strake is provided. The method includes: providing a first thermoplastic laminate panel; providing a second thermoplastic laminate panel; attaching the first thermoplastic laminate panel to the second thermoplastic laminate panel such that at least a portion of the attachment surface of the first thermoplastic laminate panel is attached to the attachment surface of a portion of the second thermoplastic laminate panel, which attached portions form a body of the strake; forming a first flange from a portion of the first thermoplastic laminate panel; and forming a second flange from a portion of the second thermoplastic laminate panel.
Owner:ROHR INC
Highly efficient supersonic laminar flow wing
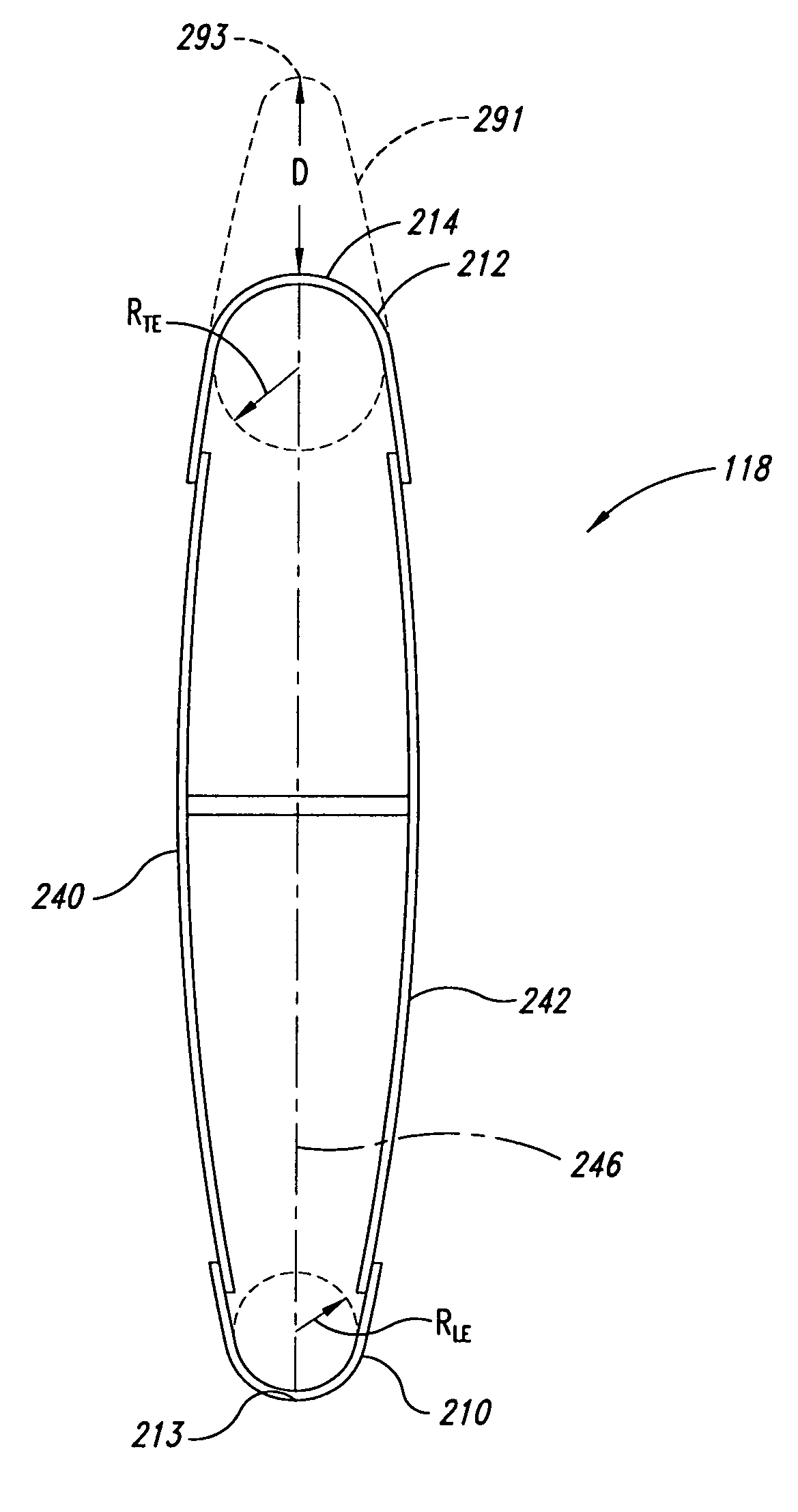
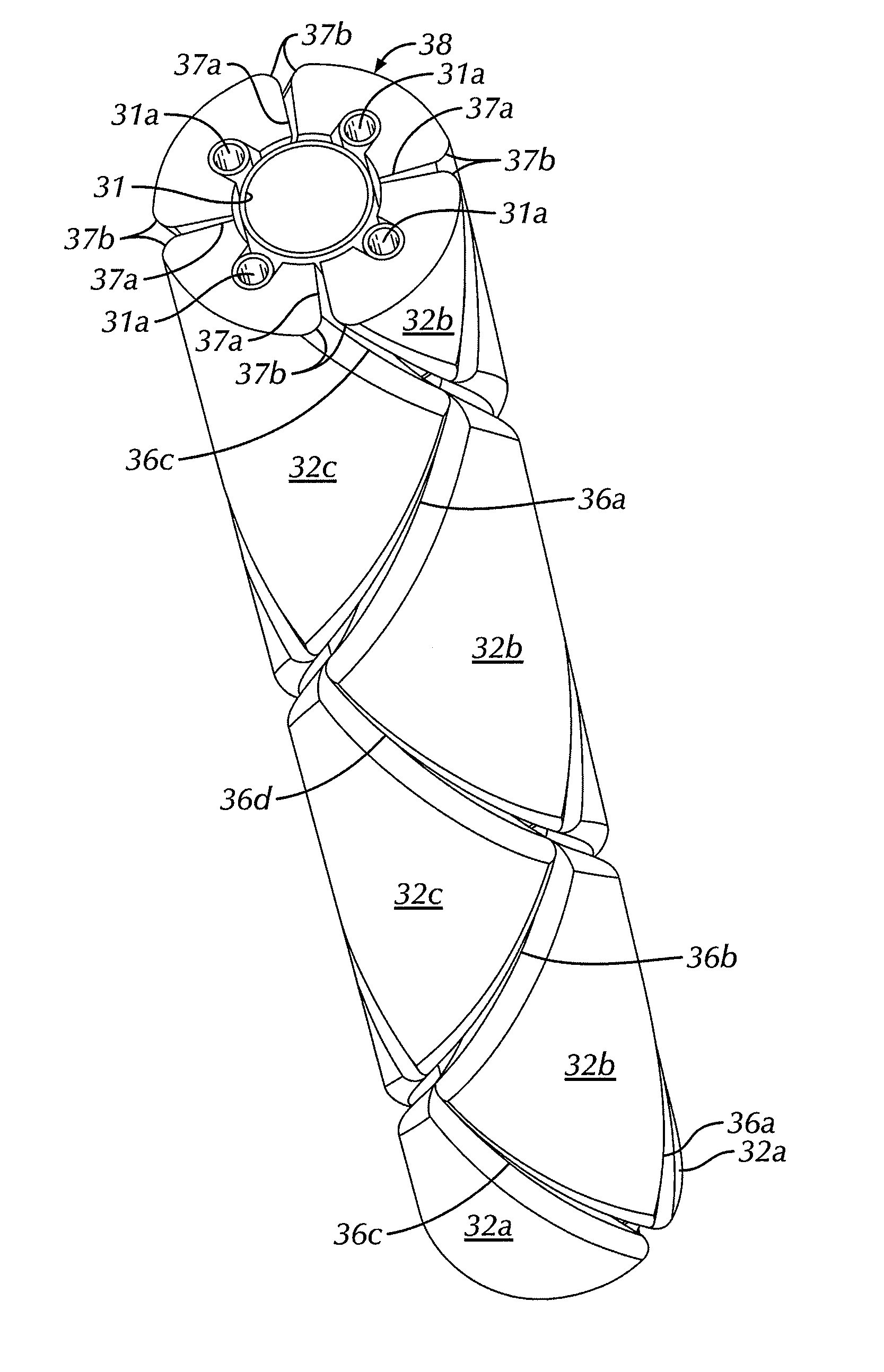
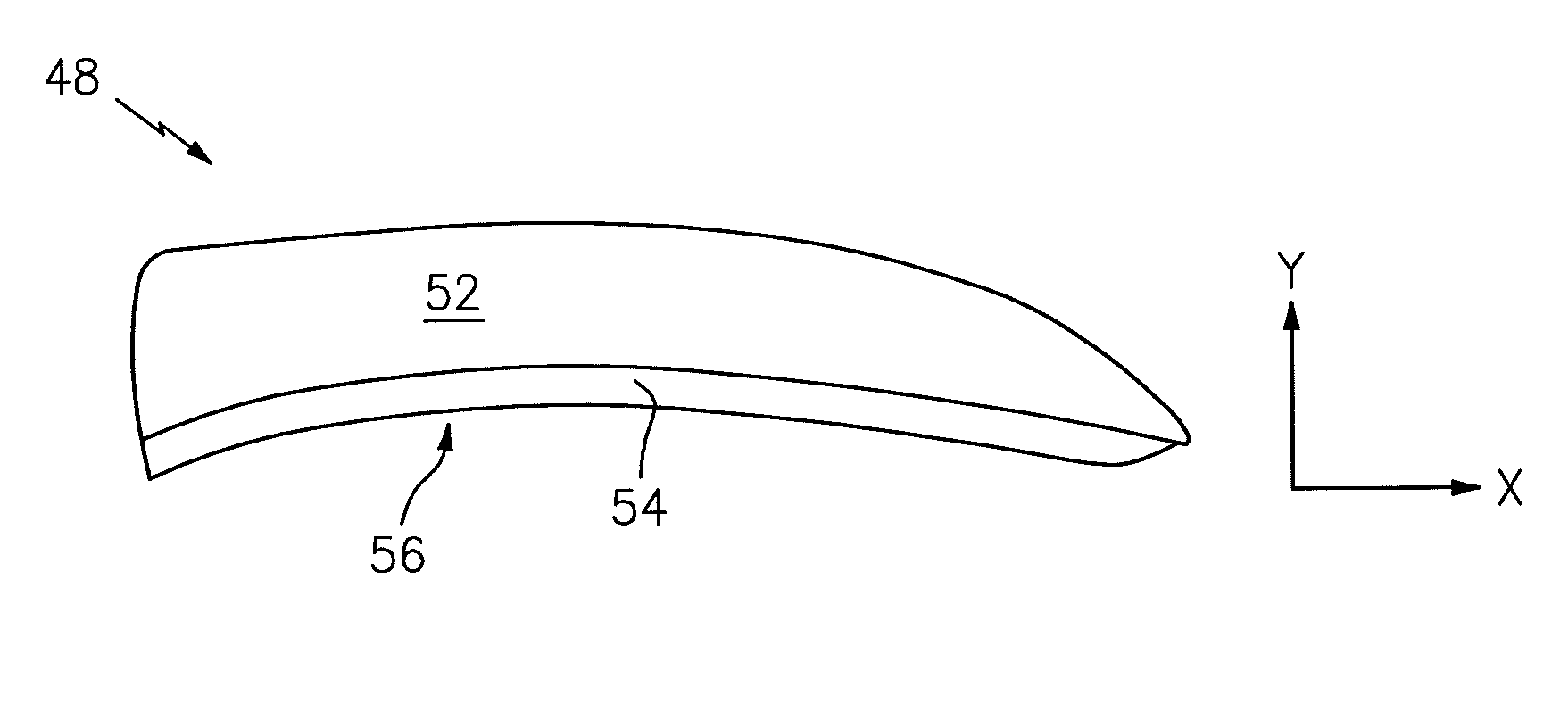
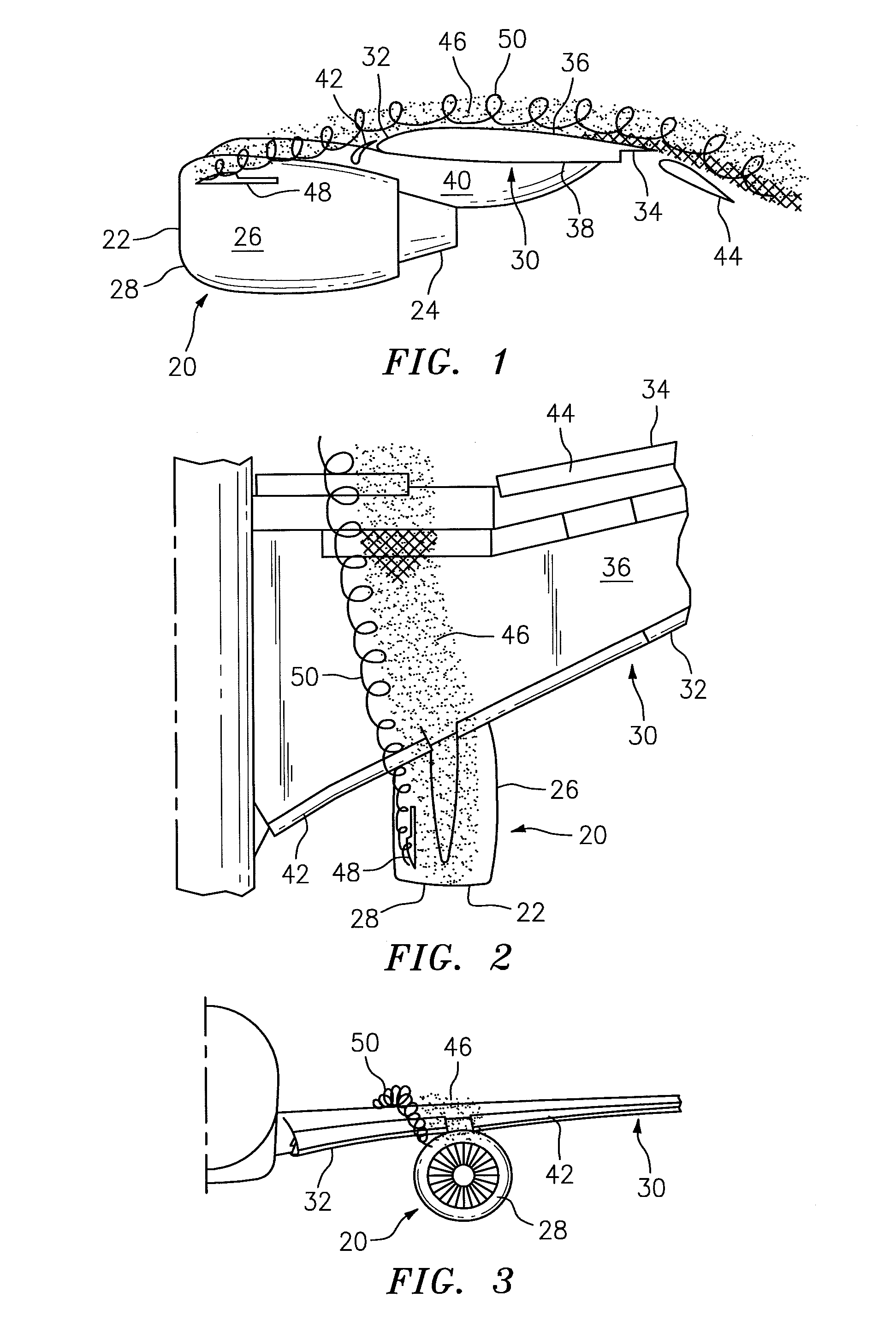
ActiveUS20090206206A1High gradientHigh skin friction dragInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationLeading edgeStrake
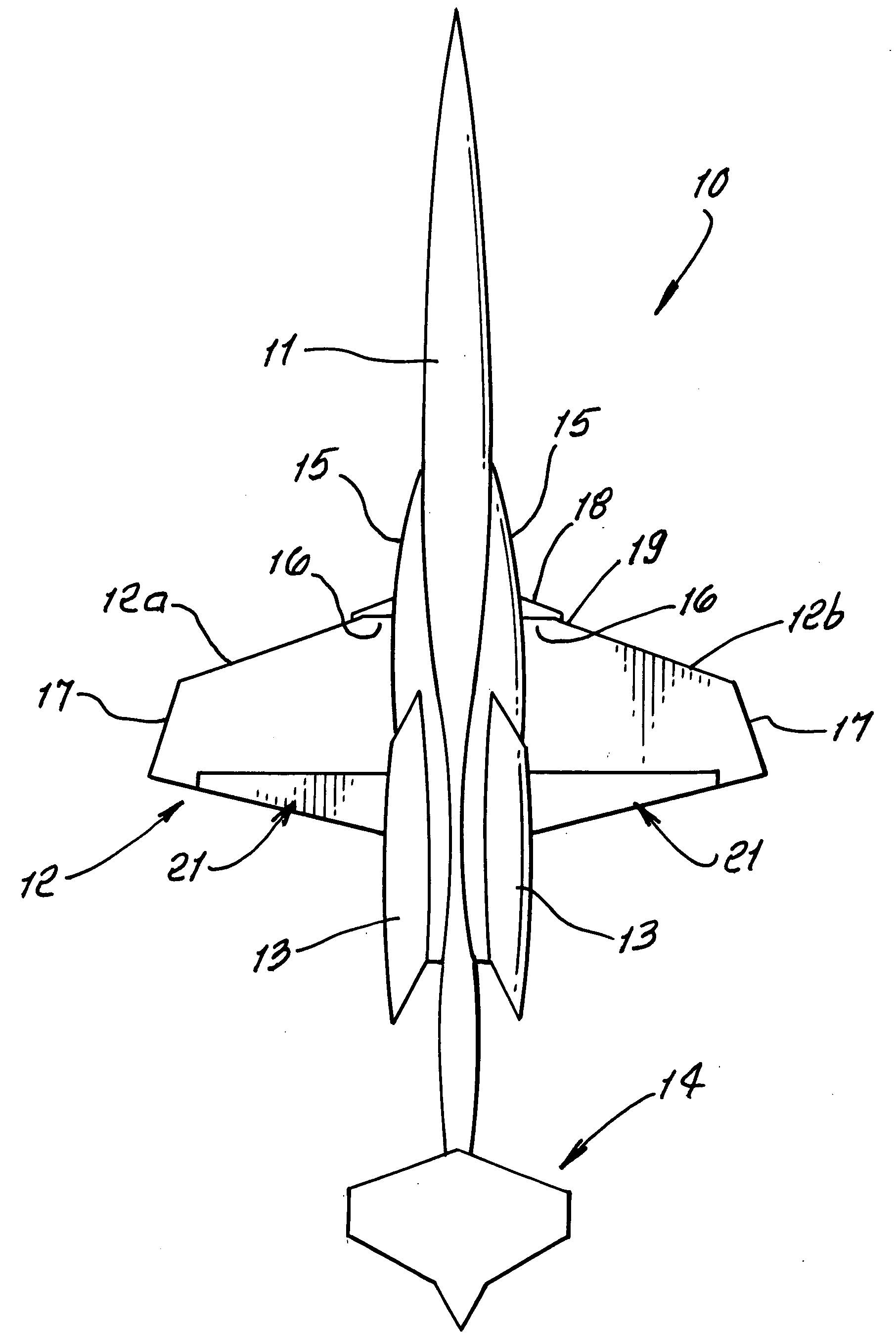
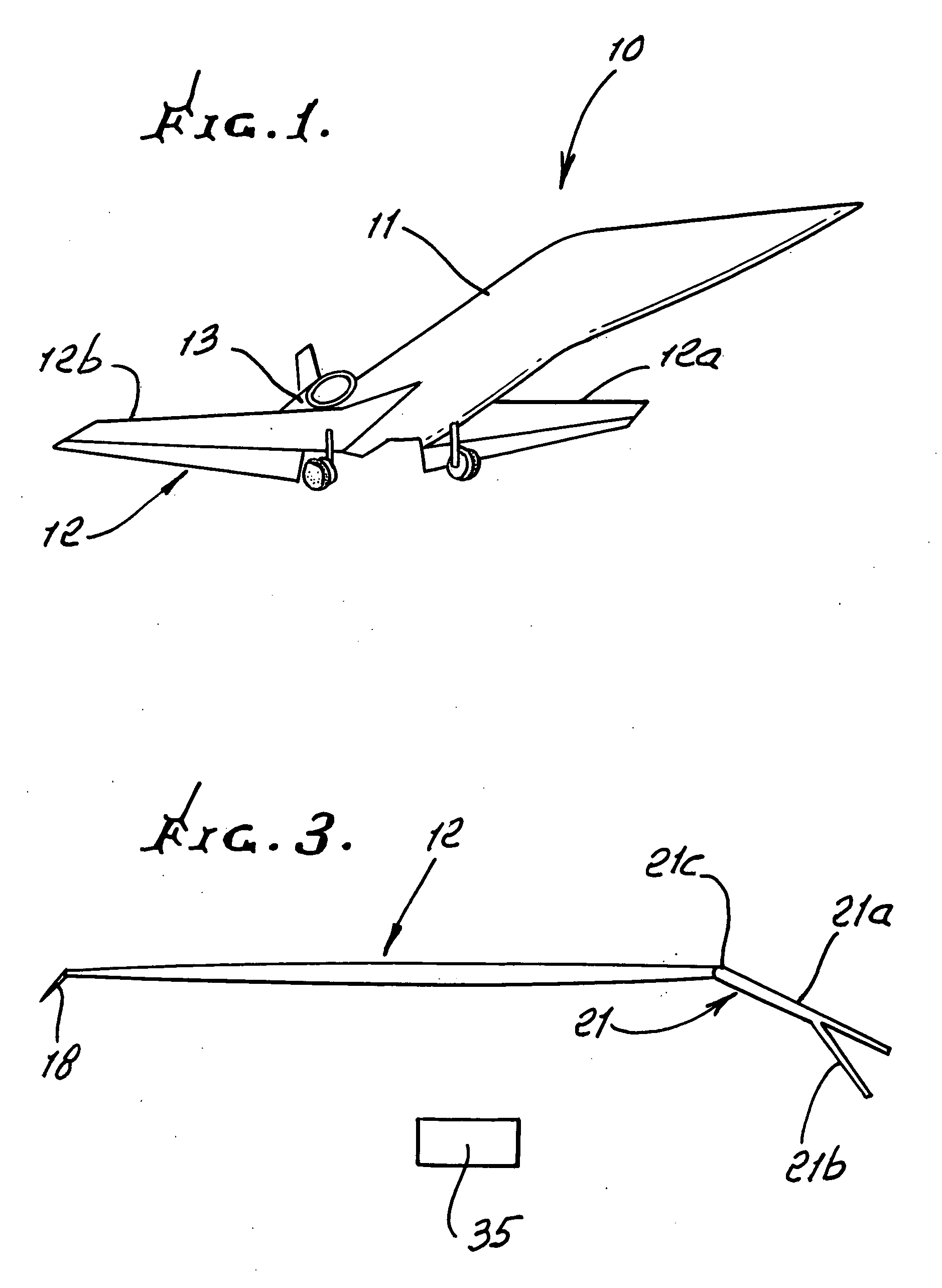
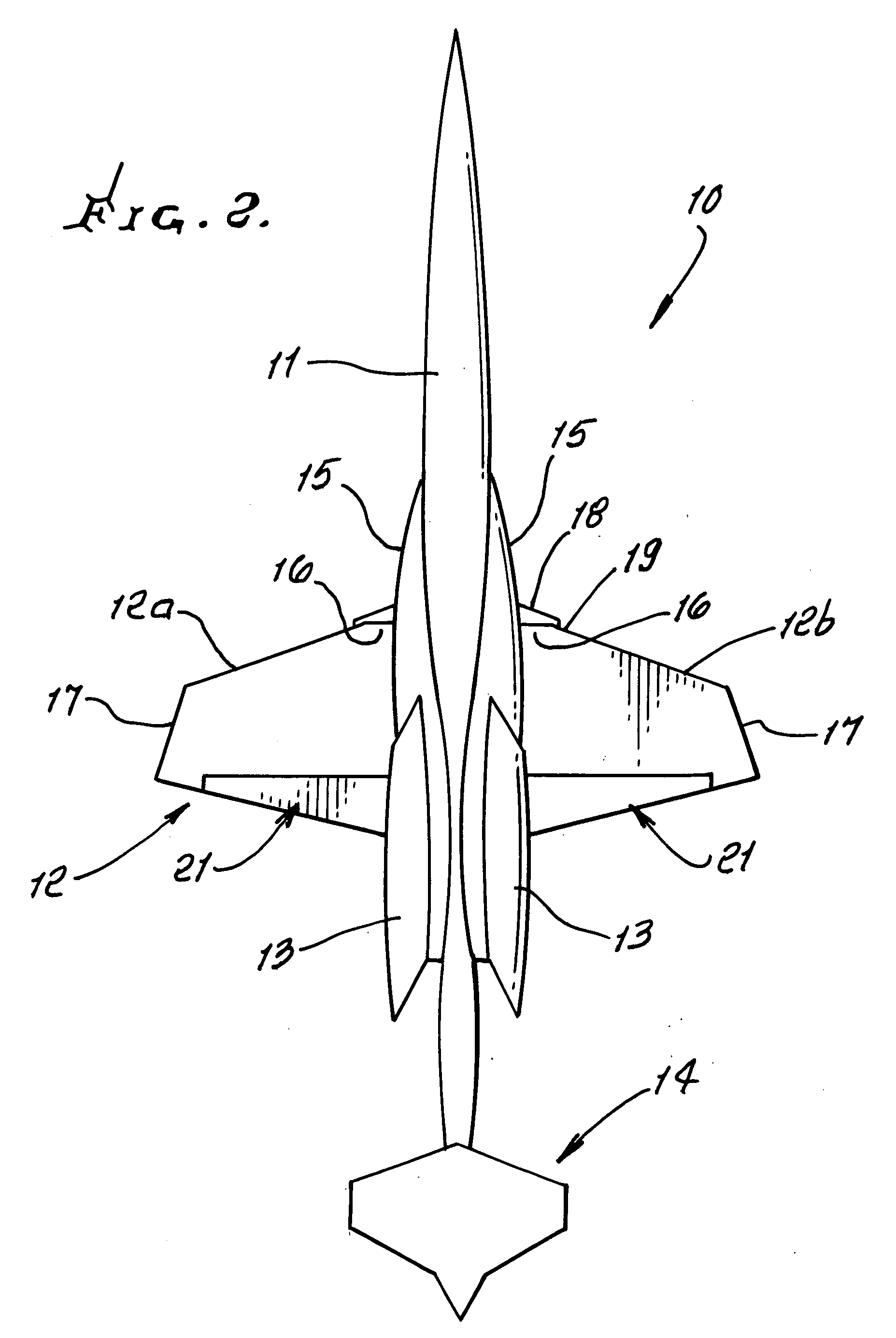
Improved supersonic laminar flow wing structure, on a supersonic aircraft, having one or more of the following:strake extending forwardly of the wing inboard extent,raked wing tip,reversed fillet at strake or fuselage junction,inboard leading edge flap extending over less than about 15% of the inboard wing panel span,hybrid plain-split flap having a lower surface portion deflectable downwardly relative to plain flap extent.
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
Spring systems for vortex suppression devices
A vortex-induced vibration (VIV) suppression system configured to accommodate a change in an underlying tubular diameter. The system including an encircling member dimensioned to at least partially encircle an underlying tubular. The encircling member may be, for example, a collar or a VIV suppression device such as a strake, or any other type of VIV suppression device. The system further including a band member dimensioned to encircle the encircling member and hold the encircling member around the underlying tubular at a desired axial position. A spring member may further be provided. The spring member may be positioned between the encircling member and the band member and dimensioned to contract in response to an increase in a diameter of the underlying tubular and expand in response to a decrease in a diameter of the underlying tubular such that the encircling member remains at the desired axial position.
Owner:VIV SOLUTIONS
Aircraft stabilizer system and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20090008498A1Improve performanceSmall shapeAircraft stabilisationMetal-working apparatusStrakeFlight vehicle
An aircraft can include a tail section and a stabilizing system coupled to the tail section. The stabilizing system has a vertical stabilizer and at least one strake that cooperate to generate forces that compensate for a reaction torque generated by a main lifting rotor that produces lifting forces when the aircraft is in flight. Methods for improving aircraft performance include installing the at least one strake and retrofitting of a vertical stabilizer to increase thrust forces produced by a tail rotor.
Owner:BLR AEROSPACE
Sleeve for marine riser
InactiveCN102226379ASuppression of vortex induced vibrationSimple manufacturing processDrilling rodsFluid dynamicsVertical tubeSurface ocean
The invention belongs to the technical field of laying of marine risers and relates to a sleeve for a marine riser. When in use, the sleeve for the marine riser is fixedly connected outside the marine riser, the sleeve for the marine riser comprises a pair of semi-circular ring-shaped shells which are manufactured according to the outer diameter of the marine riser and have the same size, spiral strakes and spiral grooves are arranged on the outer surfaces of the two semi-circular ring-shaped shells in a staggered manner, when the two shells are combined into an annular column, the spiral strakes or grooves distributed on the outer surfaces of the two shells are combined into a spiral structure. By adopting the sleeve for the marine riser, the cost can be reduced, the vortex-induced vibration of the marine riser can be effectively controlled, and the unification of economy and safety can be realized.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG +1
Vertical lifting aerodyne employing tiltable ducted wheels
InactiveCN104859392ASimple structureEasy to operateAircraft convertible vehiclesRotocraftStrakeControl power
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
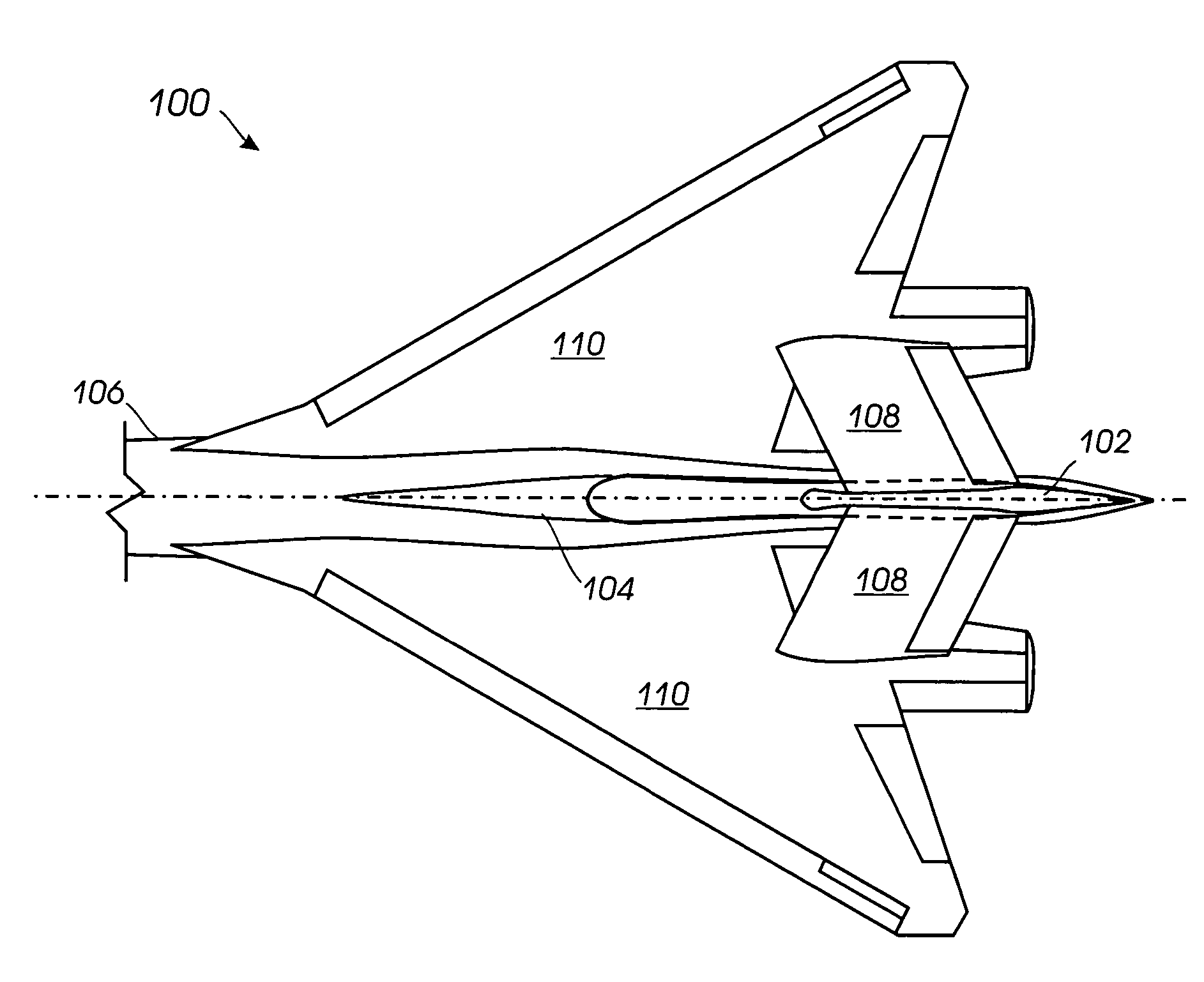
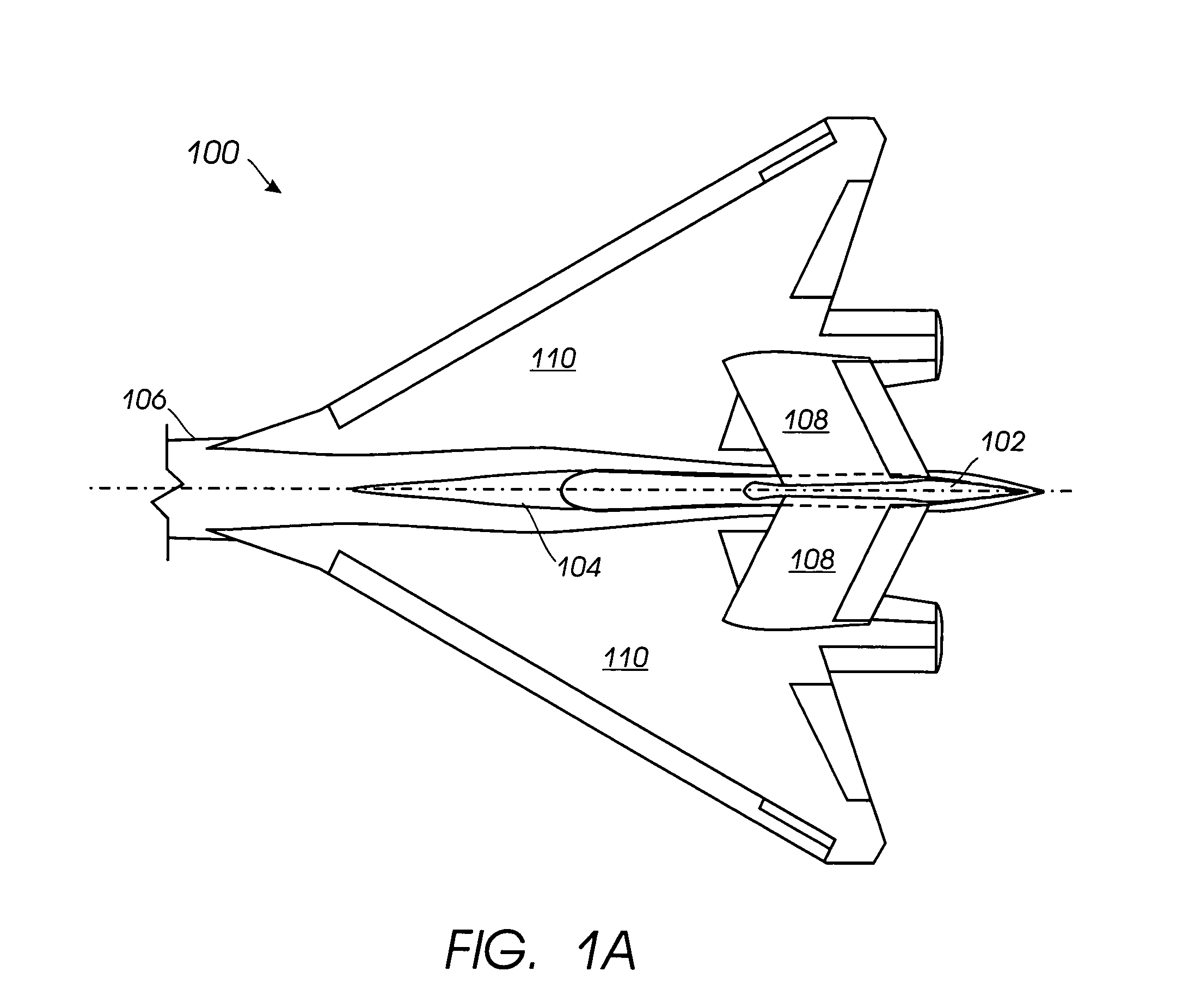
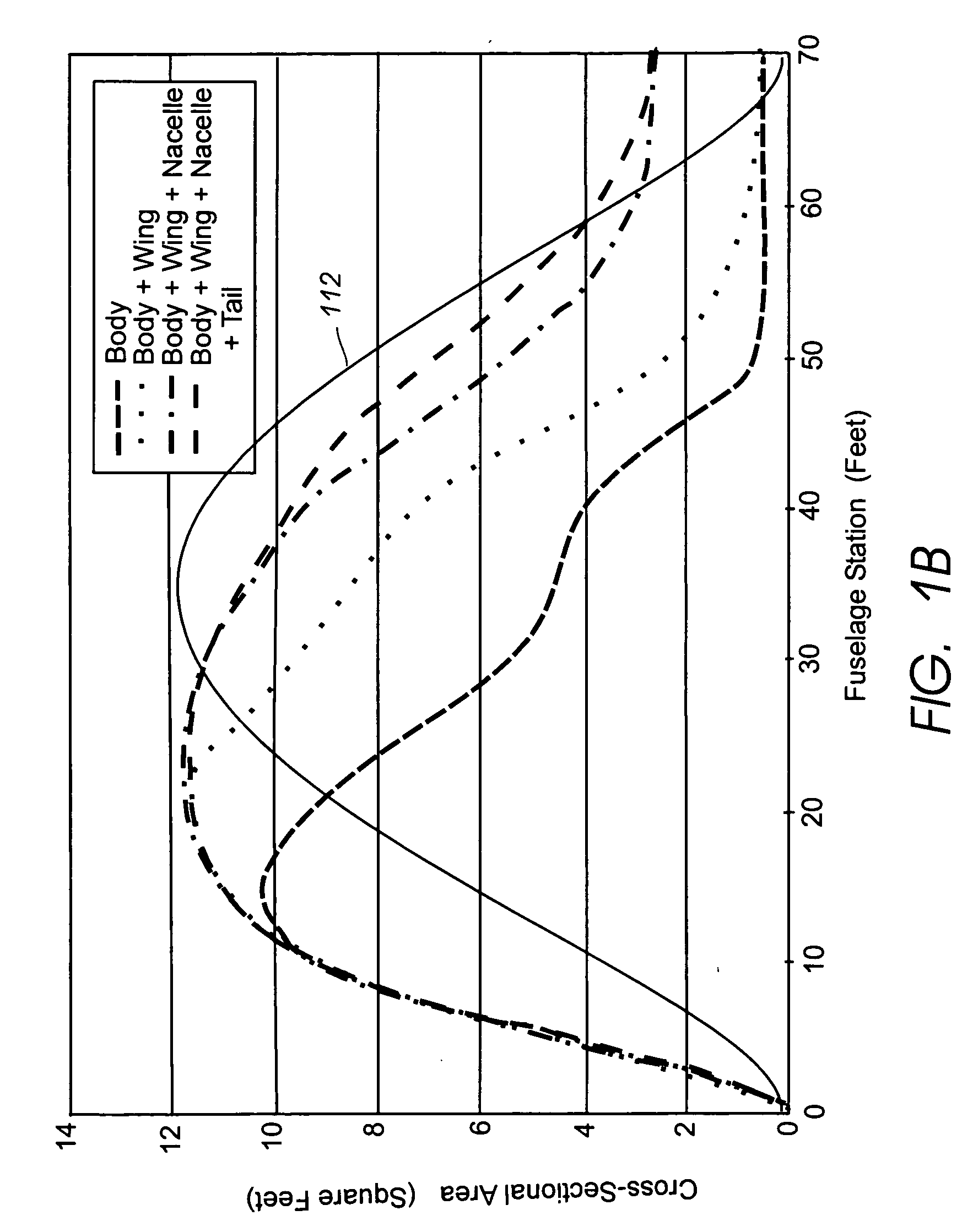
Area ruling for vertical stabilizers
InactiveUS20050116107A1Minimizes rate of changeReduce wave resistanceWing adjustmentsFuselagesStrakeVertical stabilizer
A vertical stabilizer is configured to minimize the rate of change of cross-sectional area of the vehicle or device to which the vertical stabilizer is mounted. One or more “waisted” areas can be included at the tip and / or the root of the vertical stabilizers, as well as over the distance from tip to root of the vertical stabilizer. In some situations, a strake is mounted on the vehicle or device, such as an aircraft, and the vertical stabilizer is mounted to the tip of the strake. The strake can also be area ruled with one or more “waisted” sections at the juncture of the vertical stabilizer. Applying area ruling to the vertical stabilizer helps to further reduce the drag of the vehicle or device.
Owner:SUPERSONIC AEROSPACE INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com