Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Luminance can be corrected" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
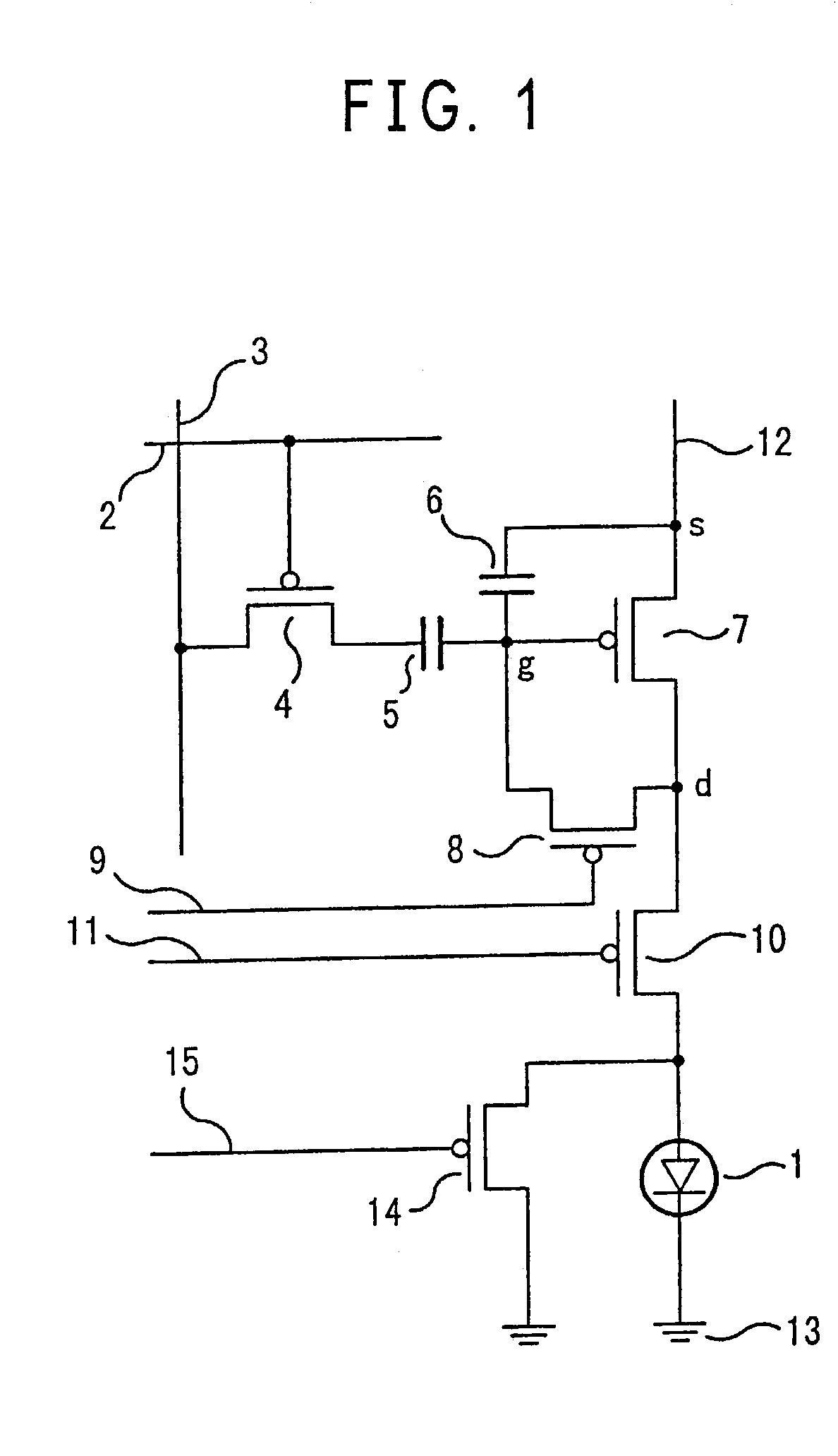
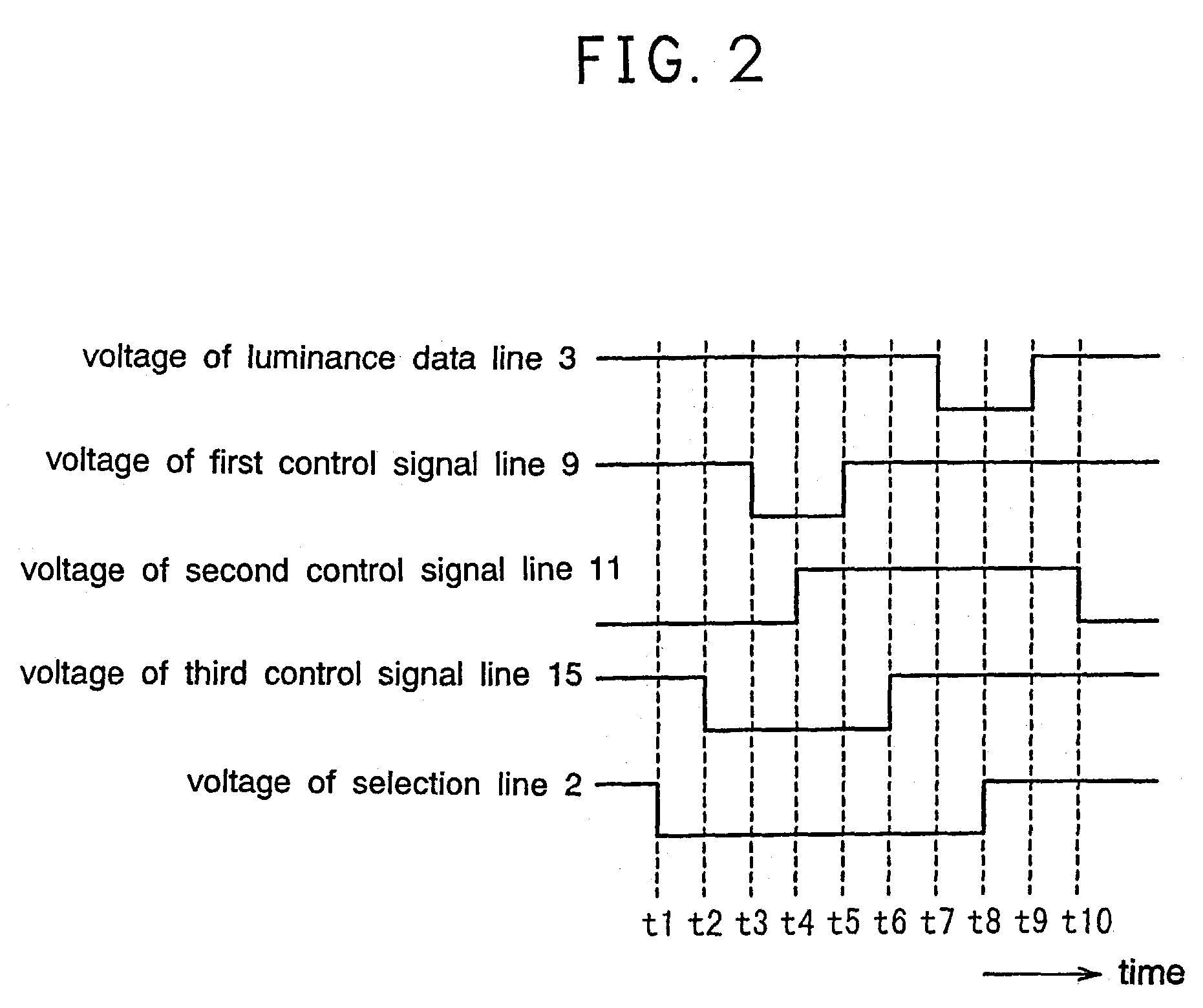
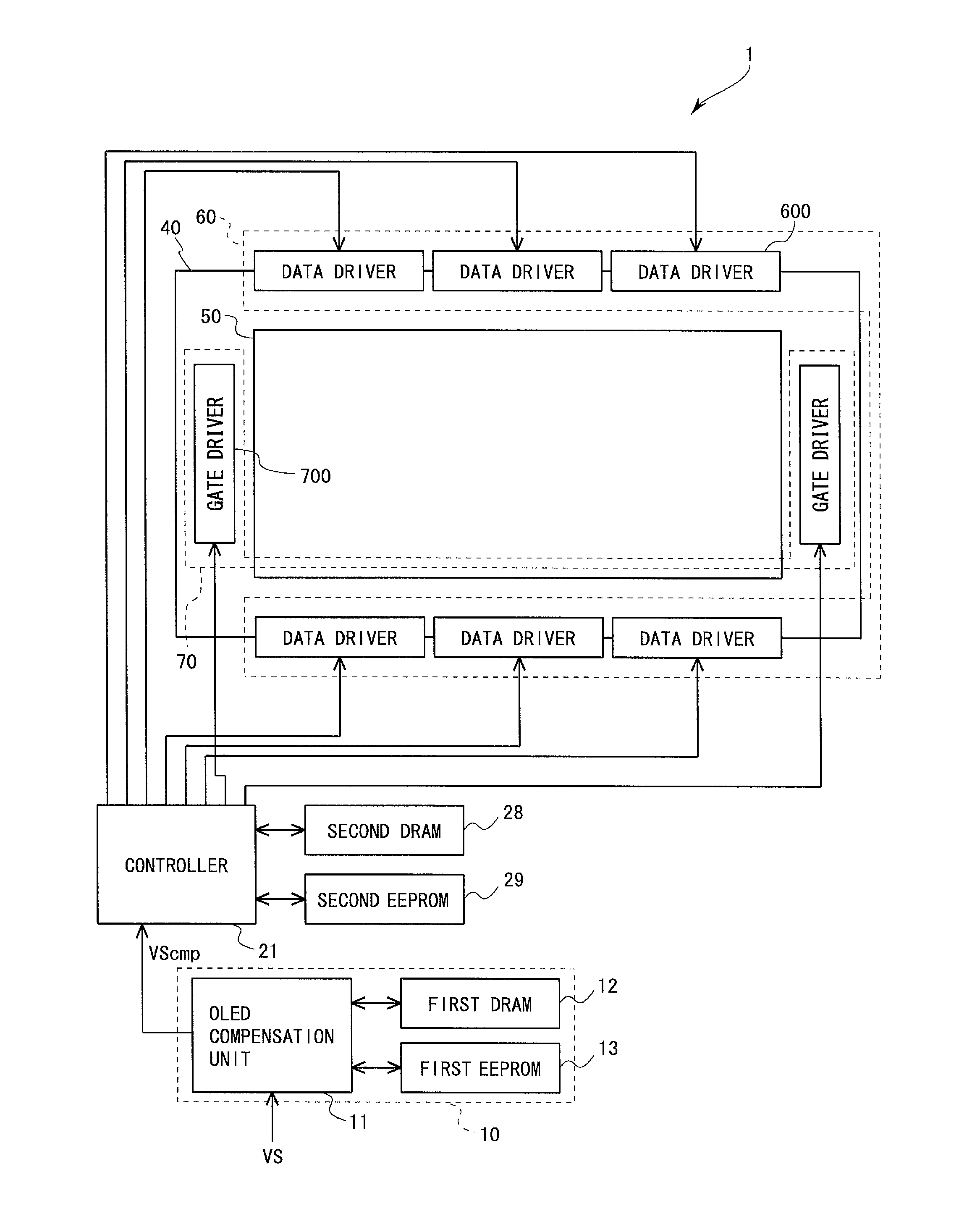
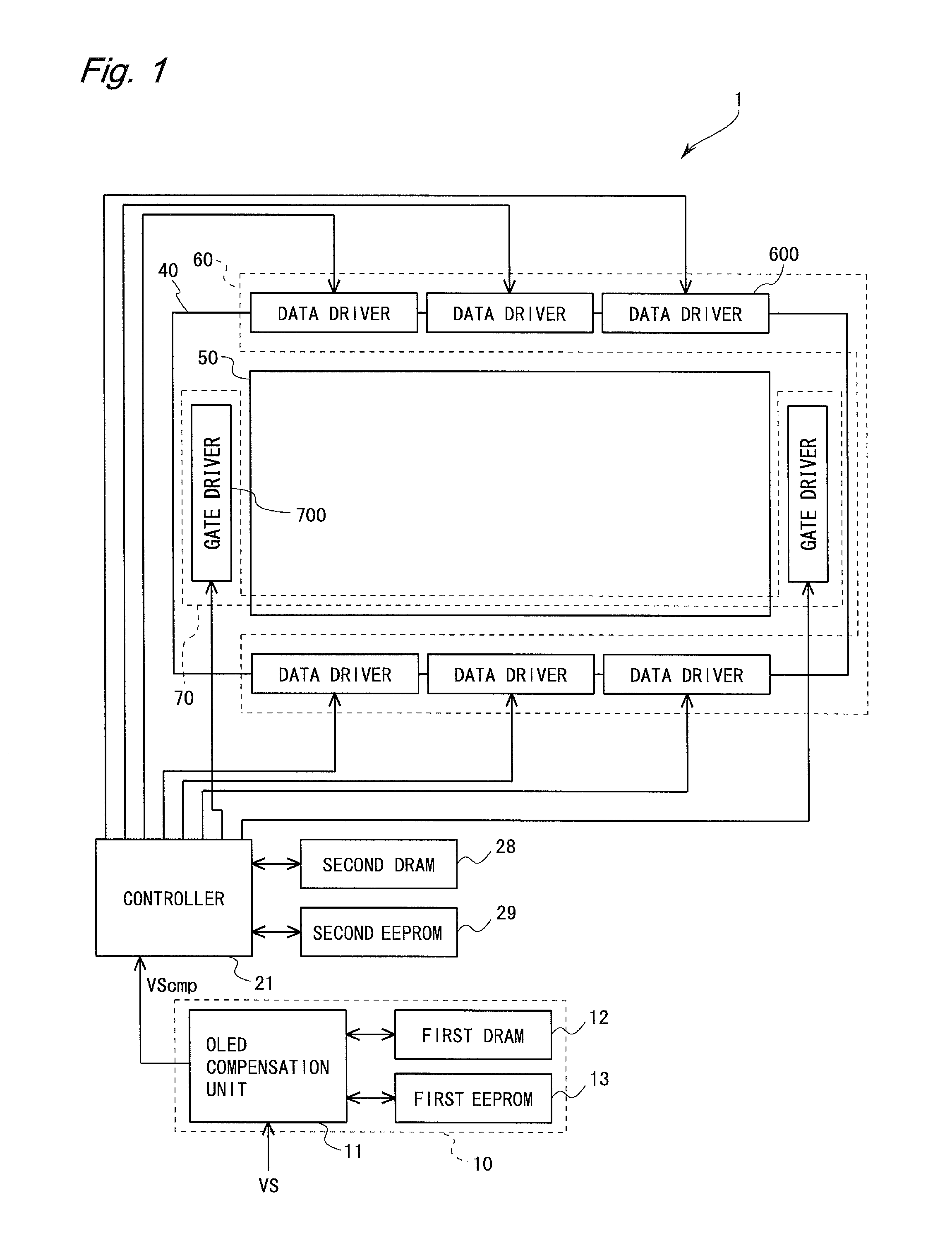
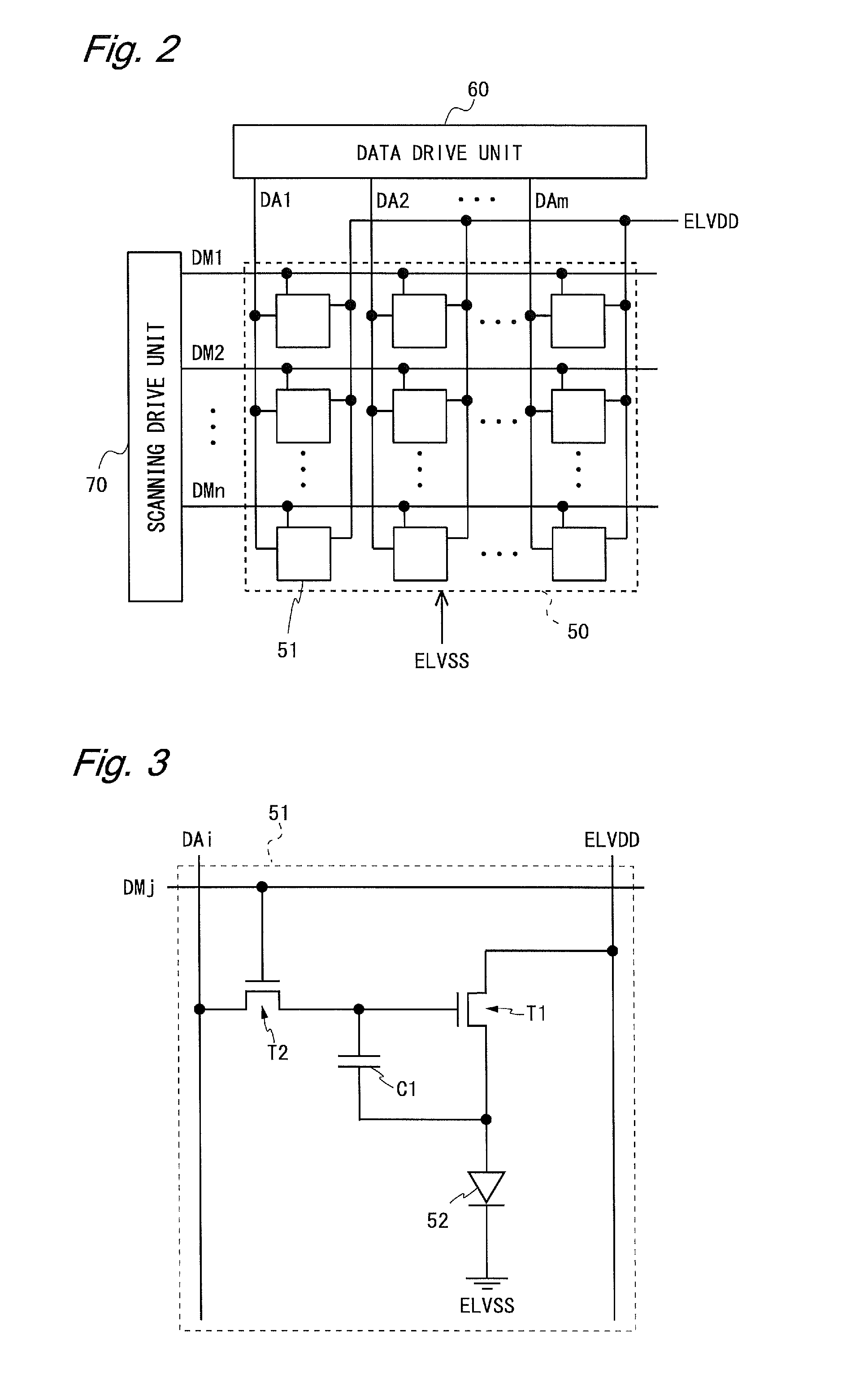
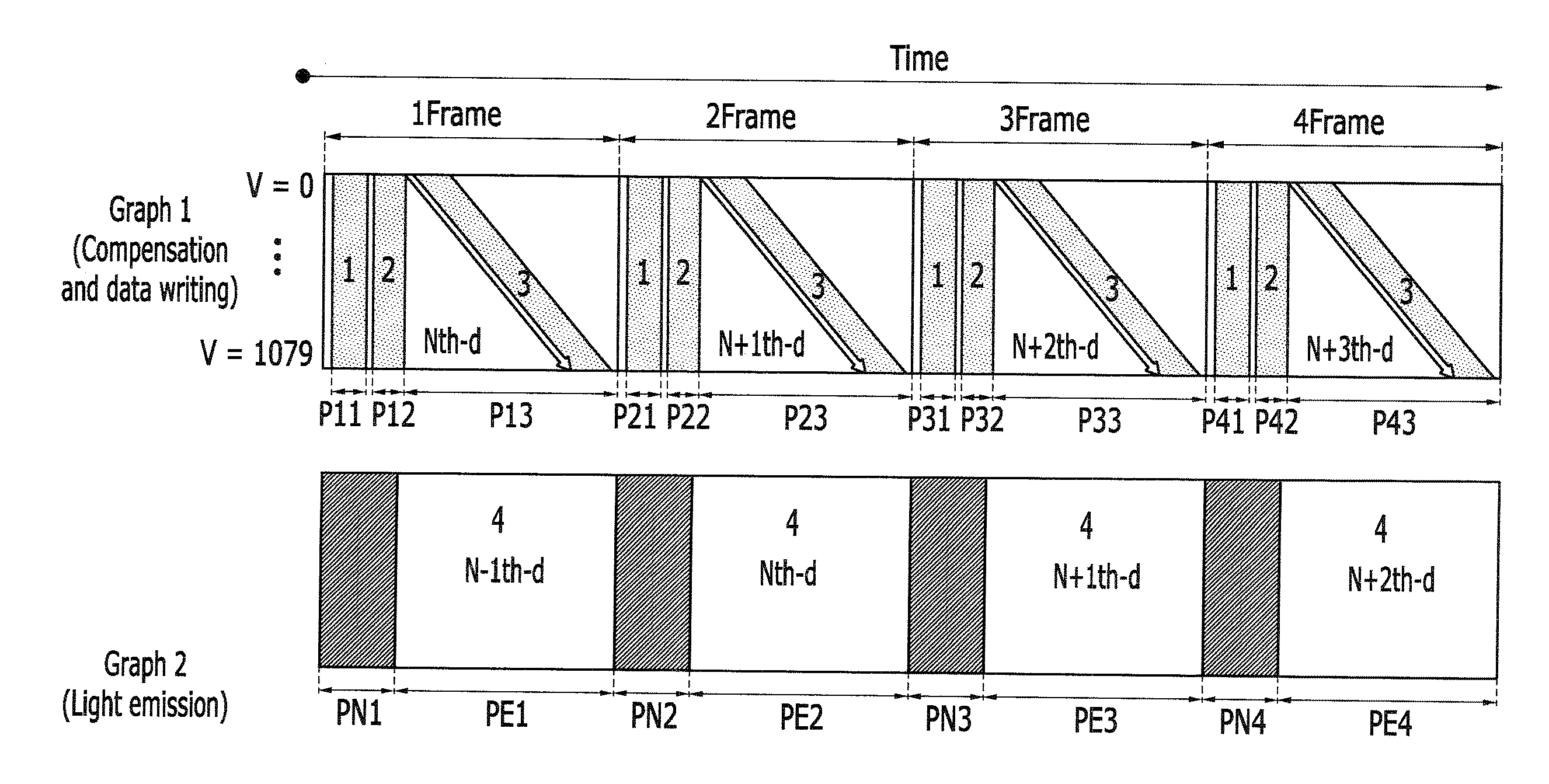
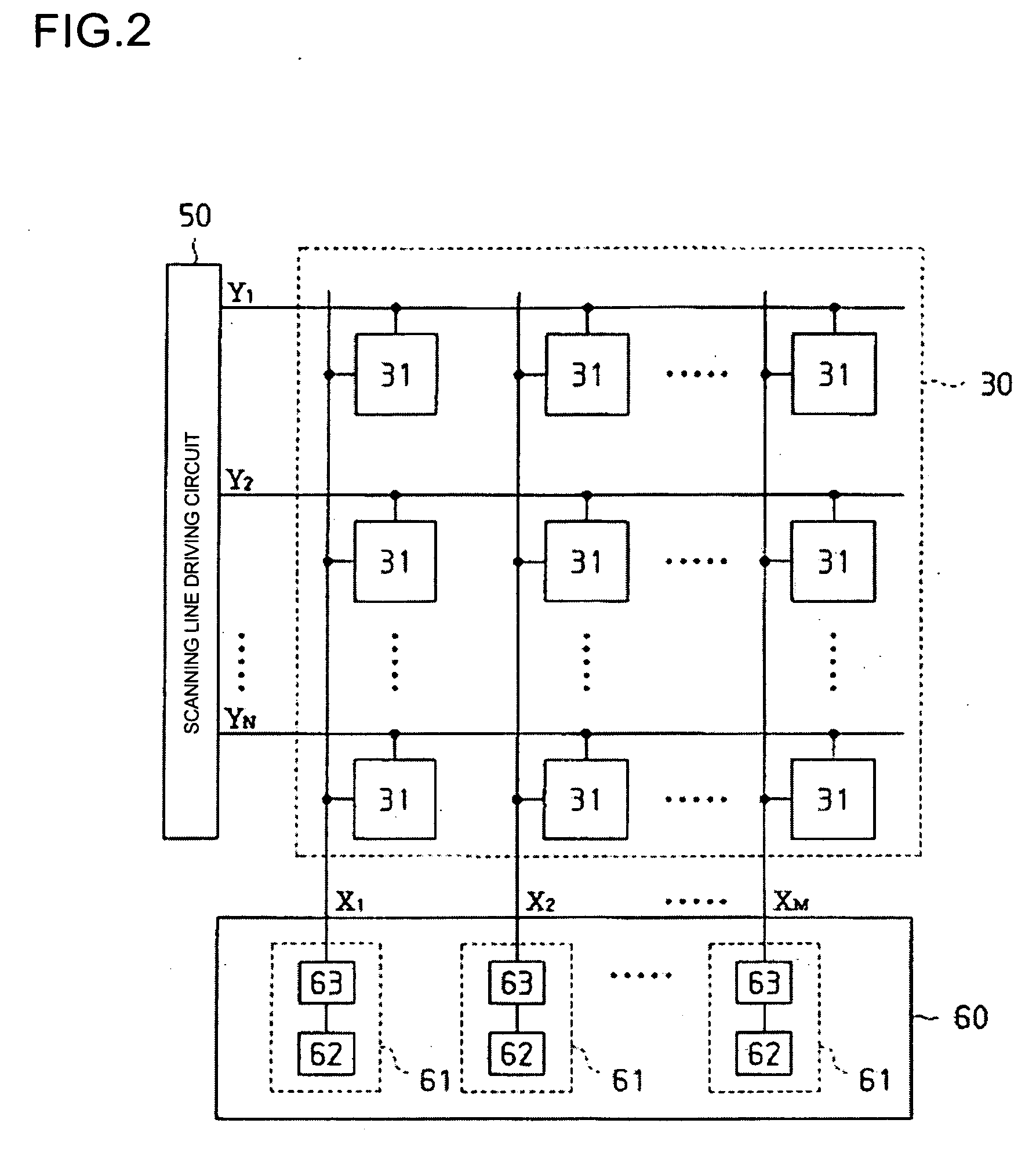
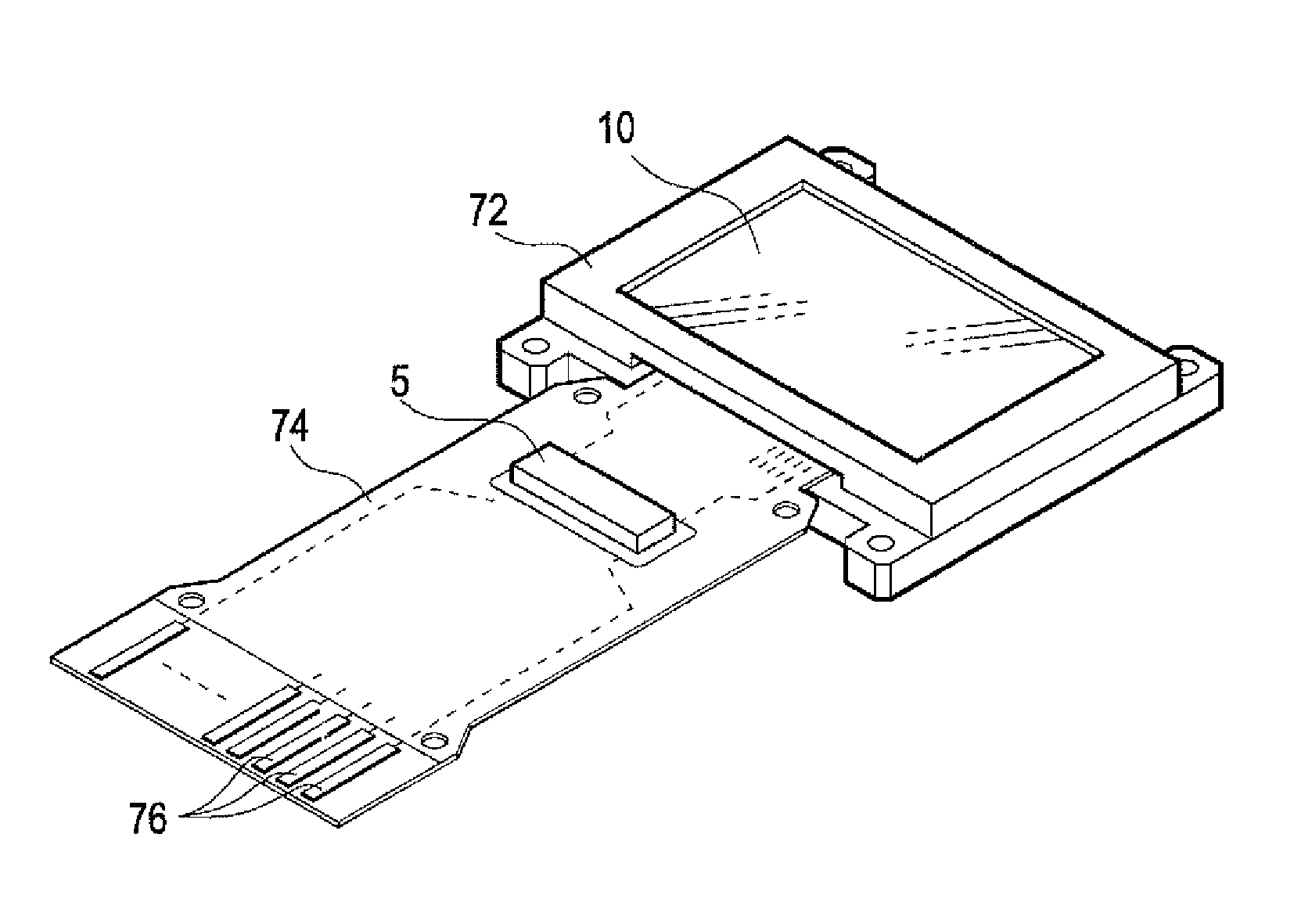
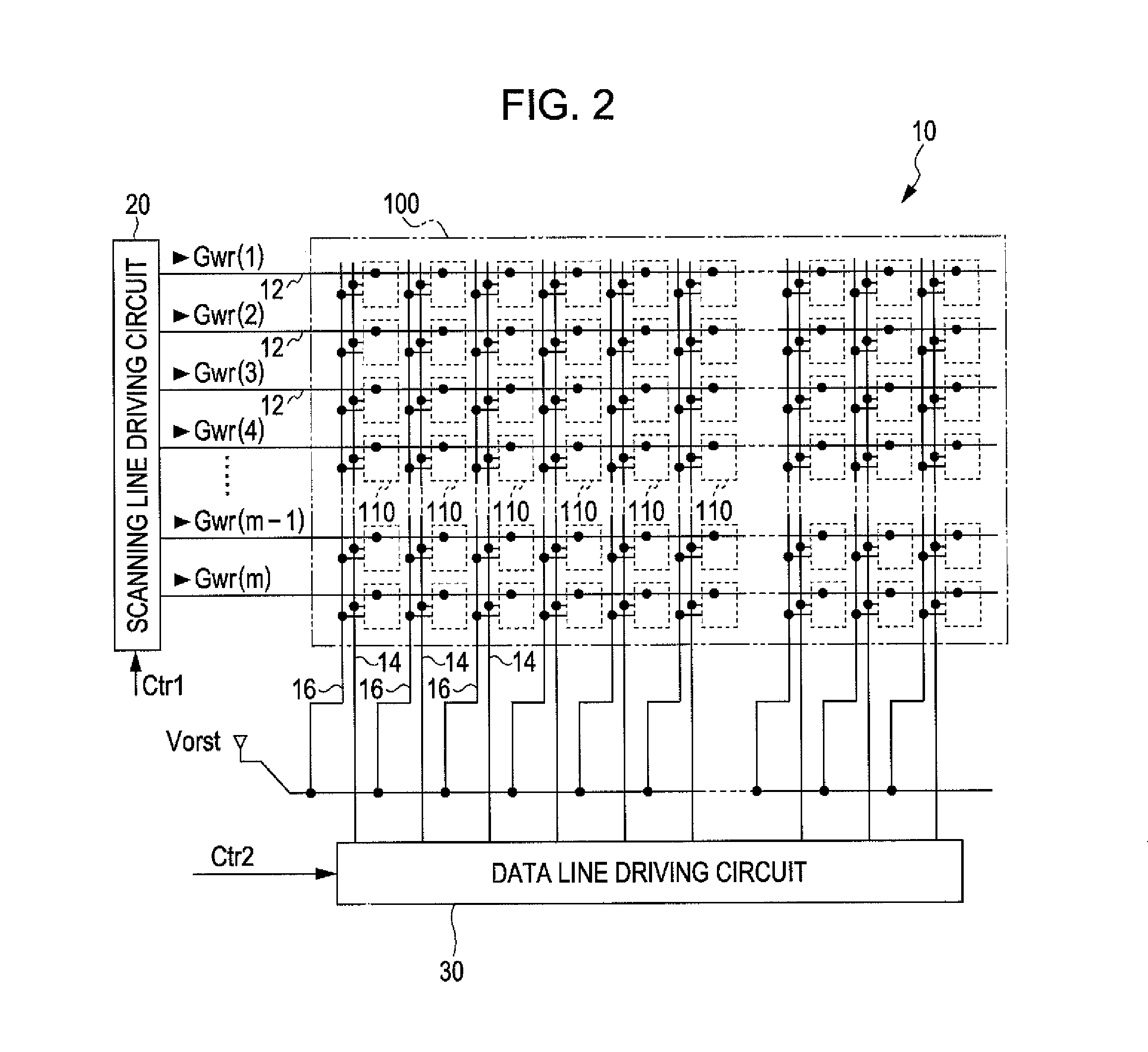
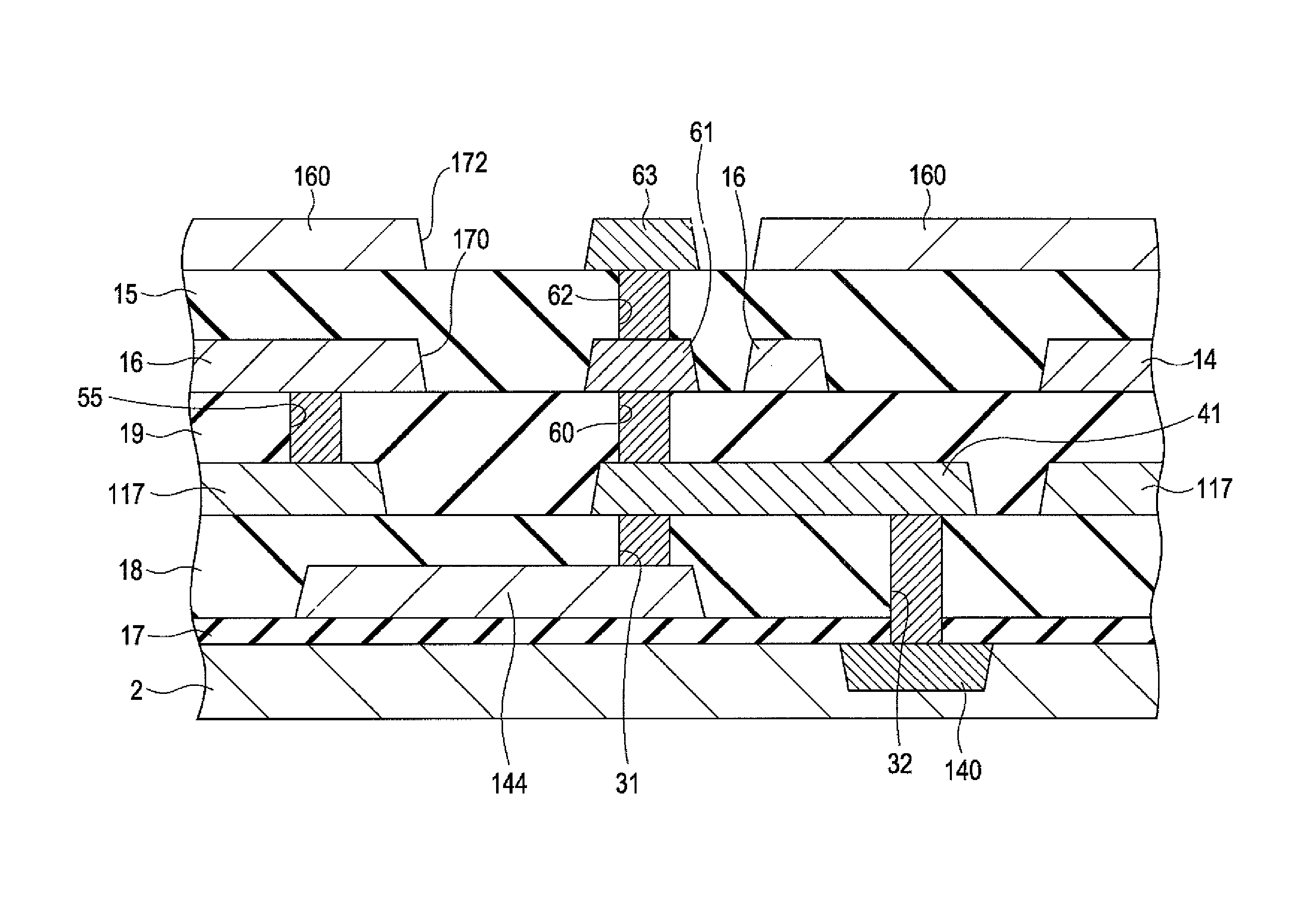
Method of driving display panel, luminance correction device for display panel, and driving device for display panel
InactiveUS7227519B1Relieve pressureExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceComputer science
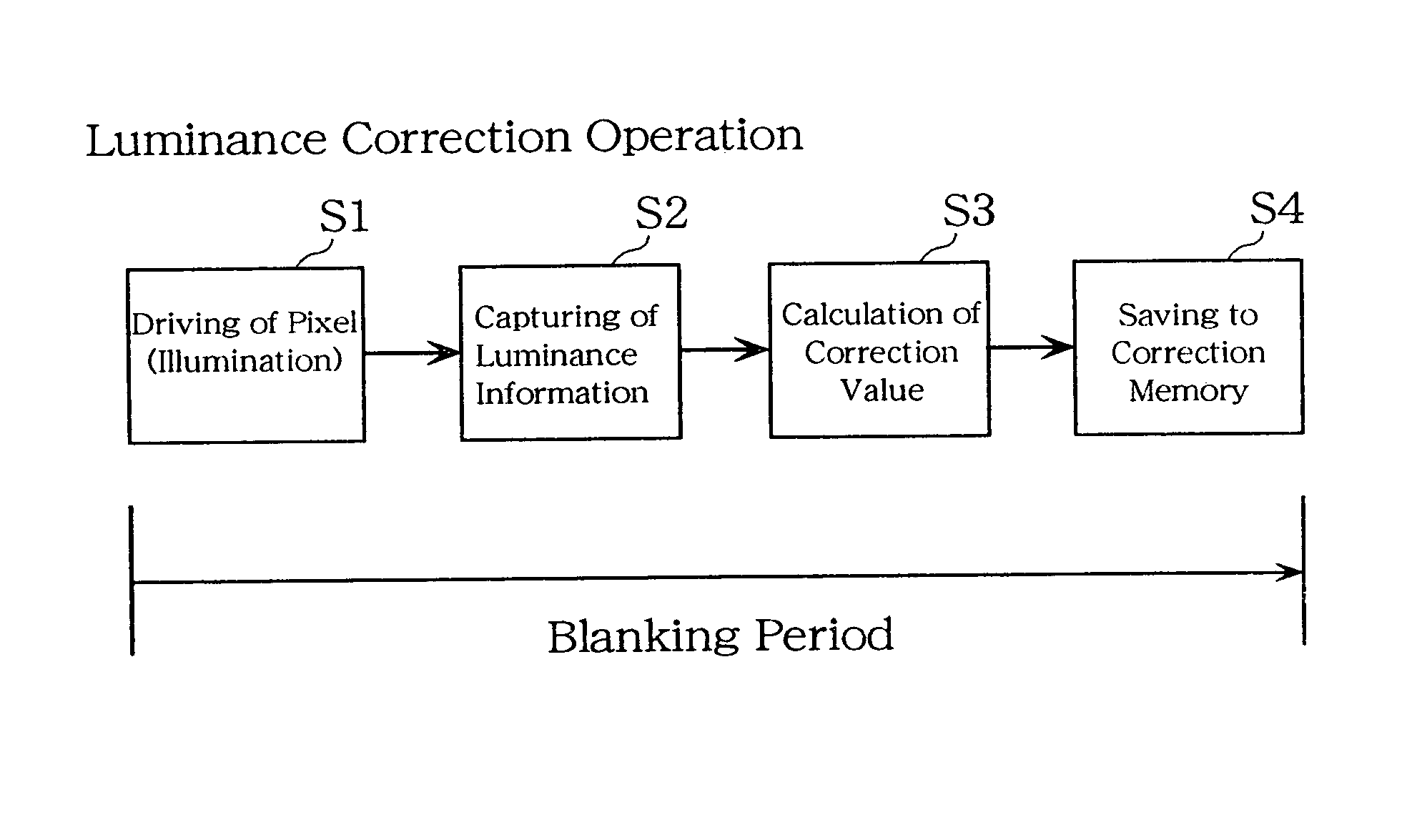
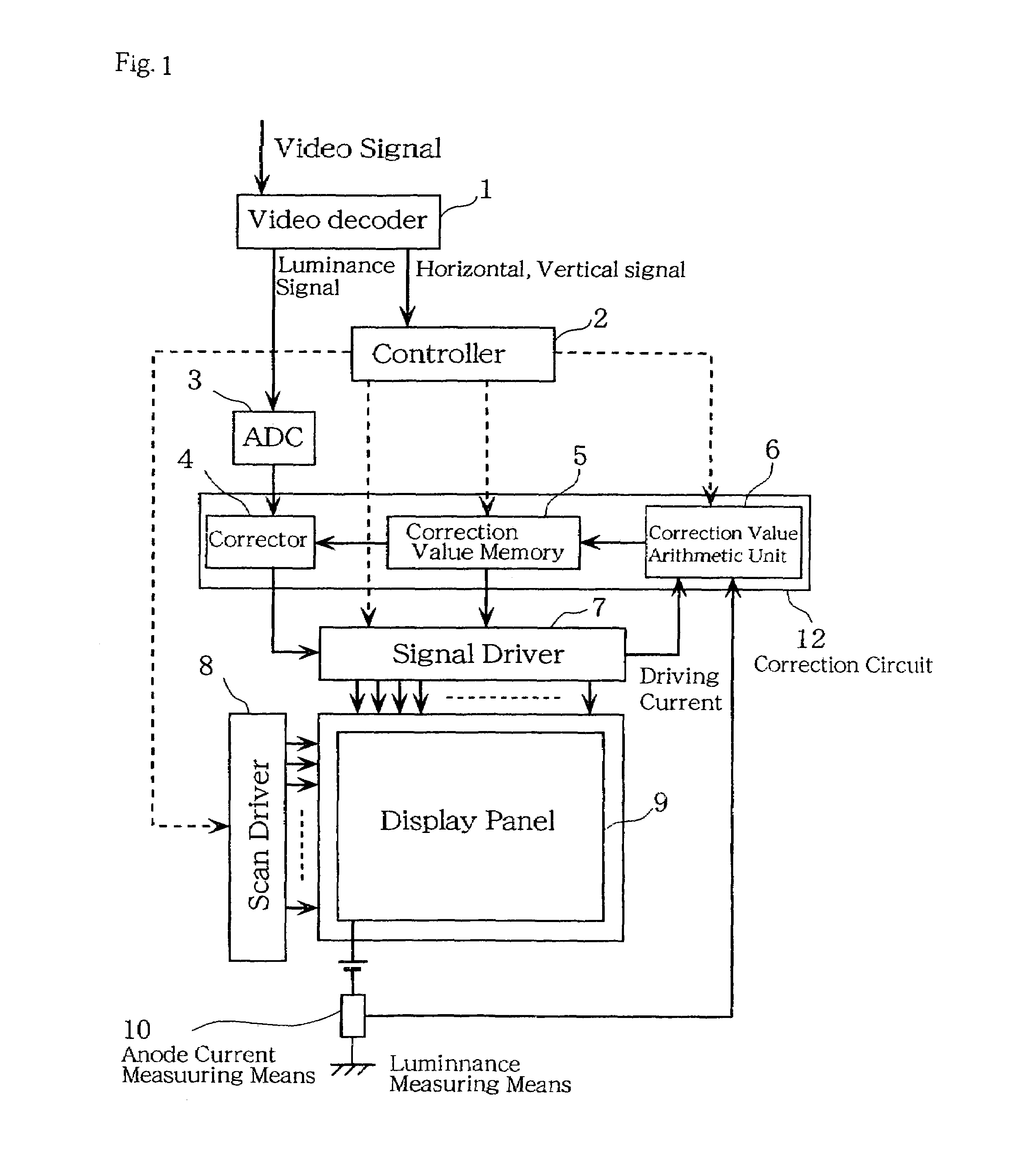
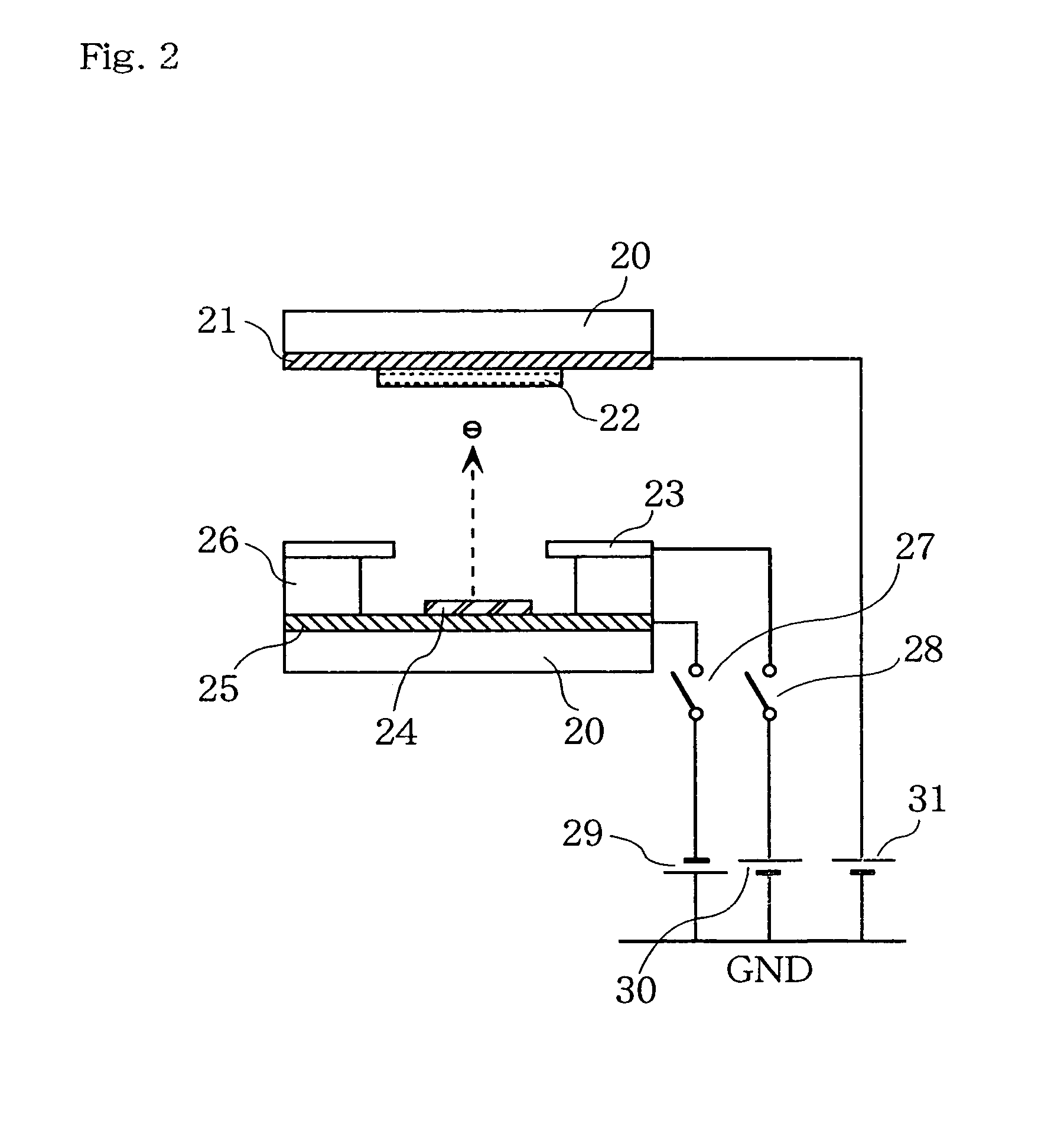
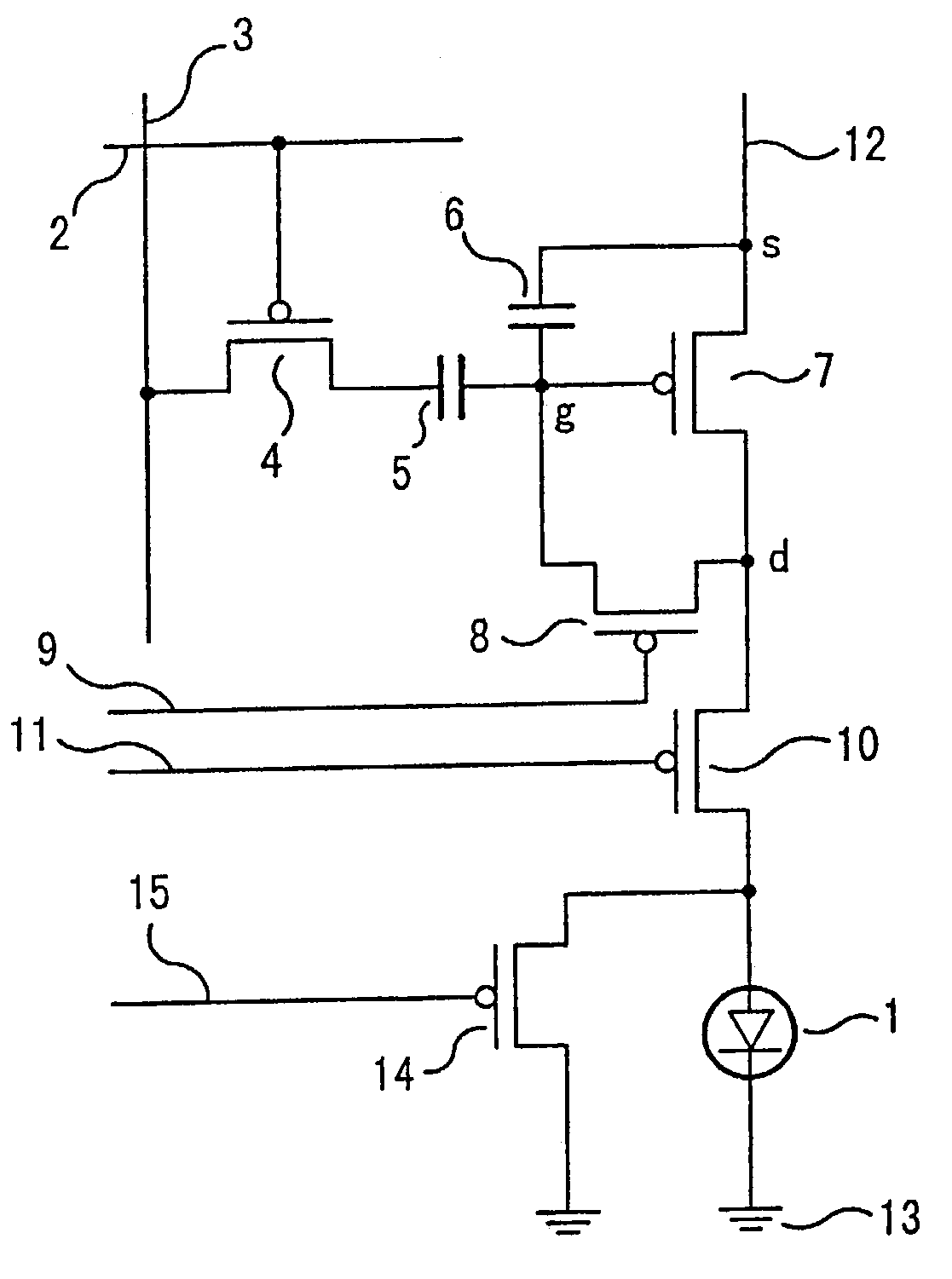
In conventional methods of correction luminance in displays, it has been necessary to interrupt video display during use in order to carry out correction. This is a problem in that interruptions are not good for workability from the perspective of the user of the image display device. In consideration of this, the present invention realizes a display without non-uniformity in illumination with respect to both initial characteristics and change over time by measuring anode current of an FED and creating a luminance correction memory. In addition, by illuminating arbitrary pixels during video idle periods, capturing the luminance information from the pixels, and renewing a correction memory based on this luminance information, correction for change over time is possible without interrupting video display. Thus, a display device that can maintain high quality images is provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Spontaneous light emitting display device
InactiveUS7154454B2Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesActive matrixDisplay device
In a driving circuit of a spontaneous light emitting display device driven as an active matrix, a noise current is prevented from flowing in a light emitting element when compensating for a threshold voltage of a transistor for controlling current flowing to the emitting element, enhancing precision in luminance. A switching element for short-circuiting electrodes of the spontaneous light emitting element for a period in which the noise current flows in the light emitting element bypasses the noise current.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20020125831A1Eliminate wasteEffective displayDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDriving currentLight emitting device
A light emitting device is provided, in which a change of luminance of an OLED is suppressed and a desired color display can be stably performed even if an organic light emitting layer is somewhat deteriorated or an environmental temperature is varied. Separately from a pixel portion for displaying an image, a pixel portion for measuring a driving current of the OLED is provided in the light emitting device. The driving current is measured in the pixel portion for measuring the driving current of the OLED, and a value of the voltage supplied to the above two pixel portions from a variable power supply is corrected such that the measured driving current has a reference value. With the above-described structure, a reduction of the luminance accompanied with the deterioration of the organic light emitting layer can be suppressed. As a result, a clear image can be displayed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Luminance correction system and method for correcting luminance of display panel
ActiveUS20170249890A1Improve accuracyEliminate variationStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceLightness
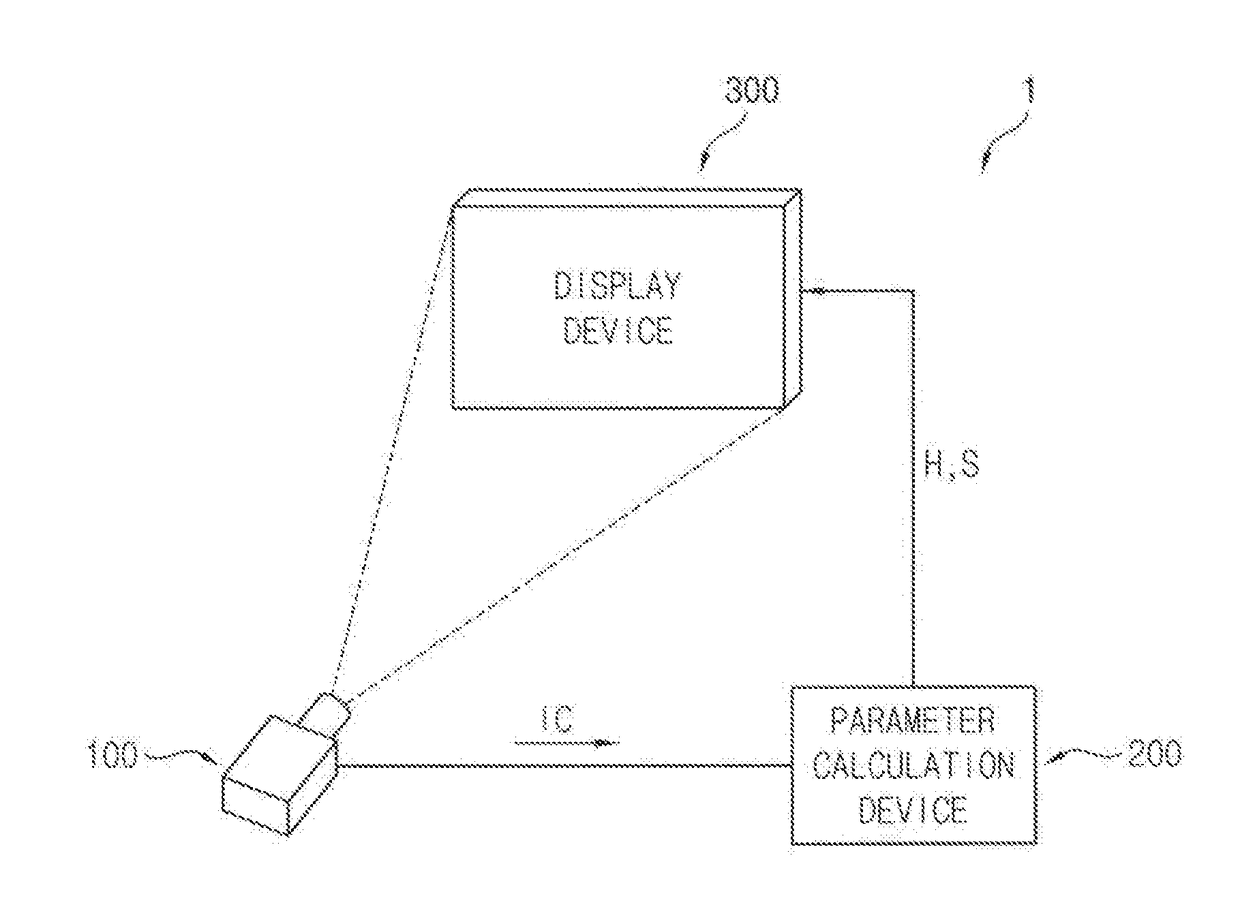
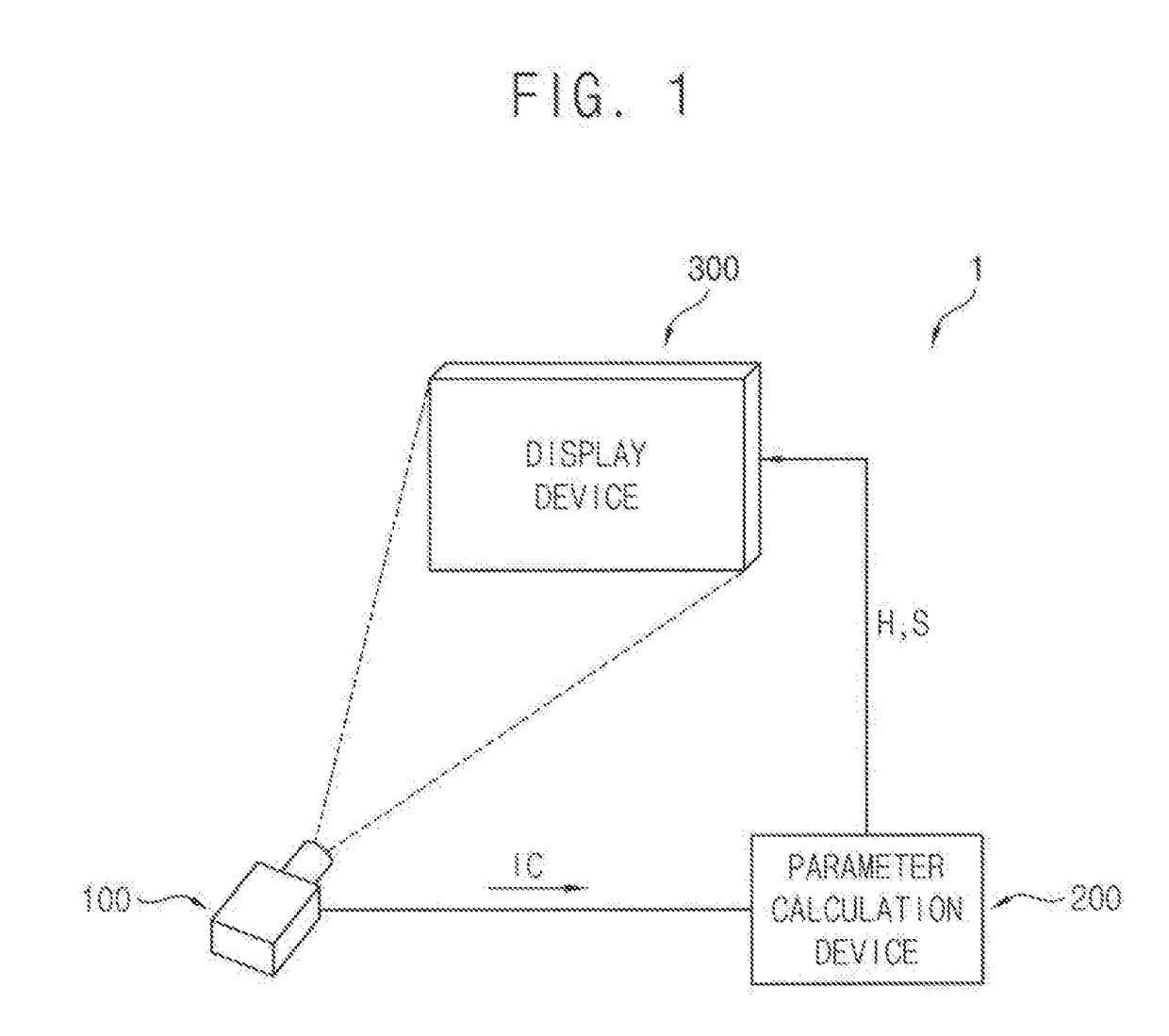
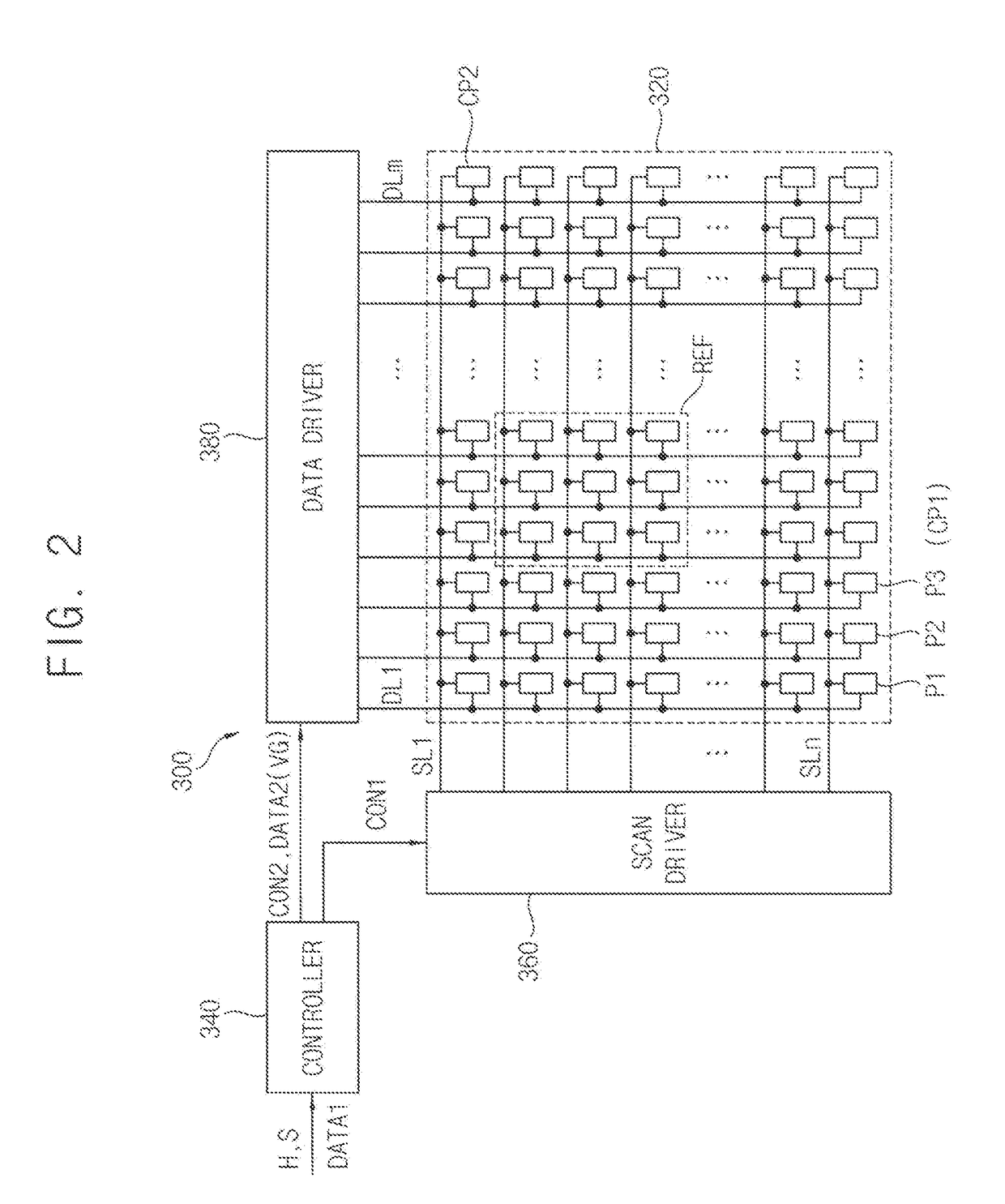
A luminance correction system includes an image pickup device configured to pick up a test image and generate pickup data, a parameter calculation device configured to calculate a first target luminance that is a maximum luminance of a reference area in a display panel and a detected maximum luminance that is a luminance of a correction target sub-pixel based on the pickup data with respect to a maximum grayscale, determine a second target luminance by correcting the first target luminance, and calculate correction parameters, and a display device including the display panel, the display device configured to compensate the input grayscale of the correction target sub-pixel to a target grayscale based on the correction parameters and generate a data voltage by adjusting upward a gamma voltage corresponding to the target grayscale.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Data processing device for display device, display device equipped with same and data processing method for display device
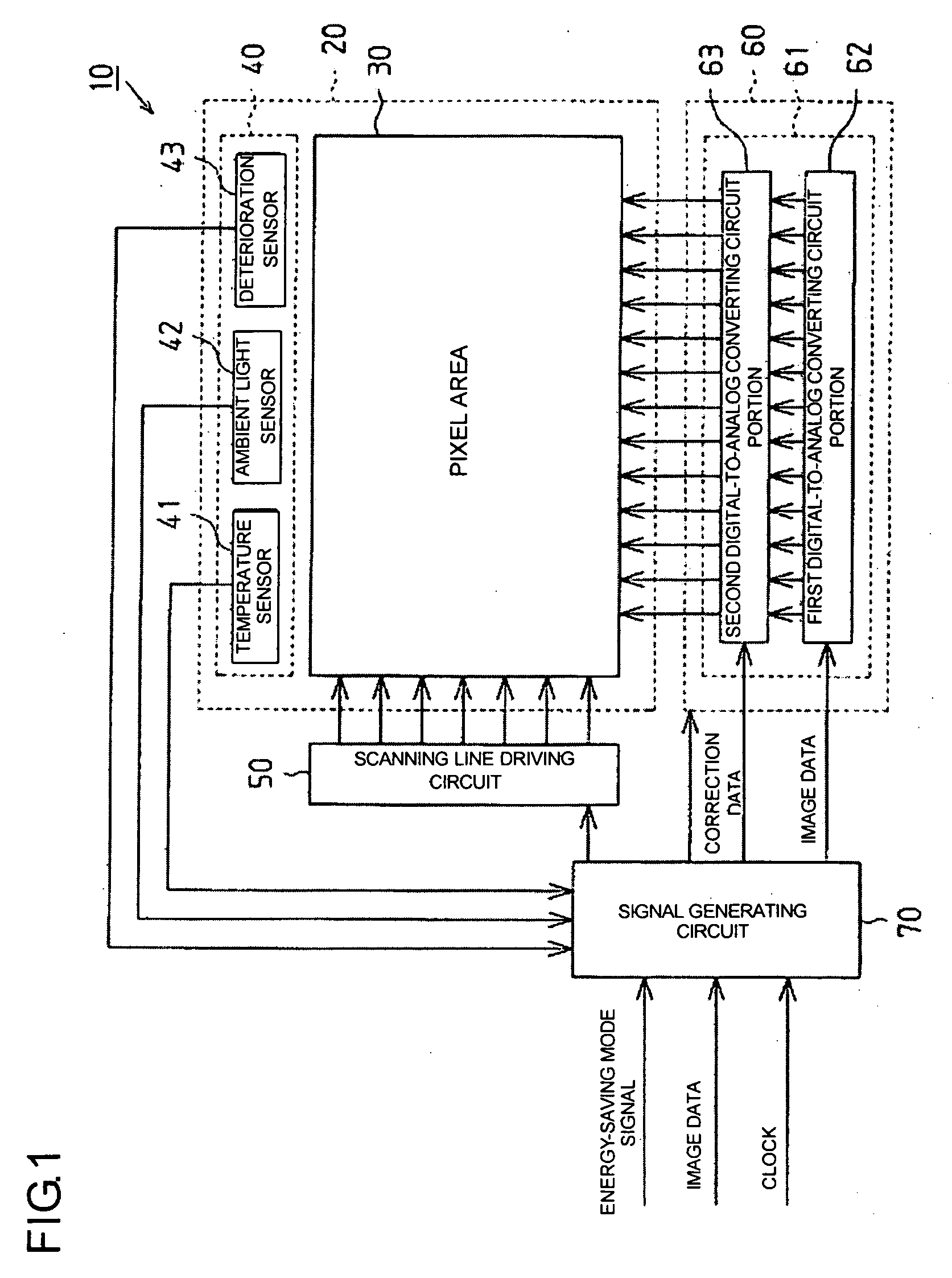
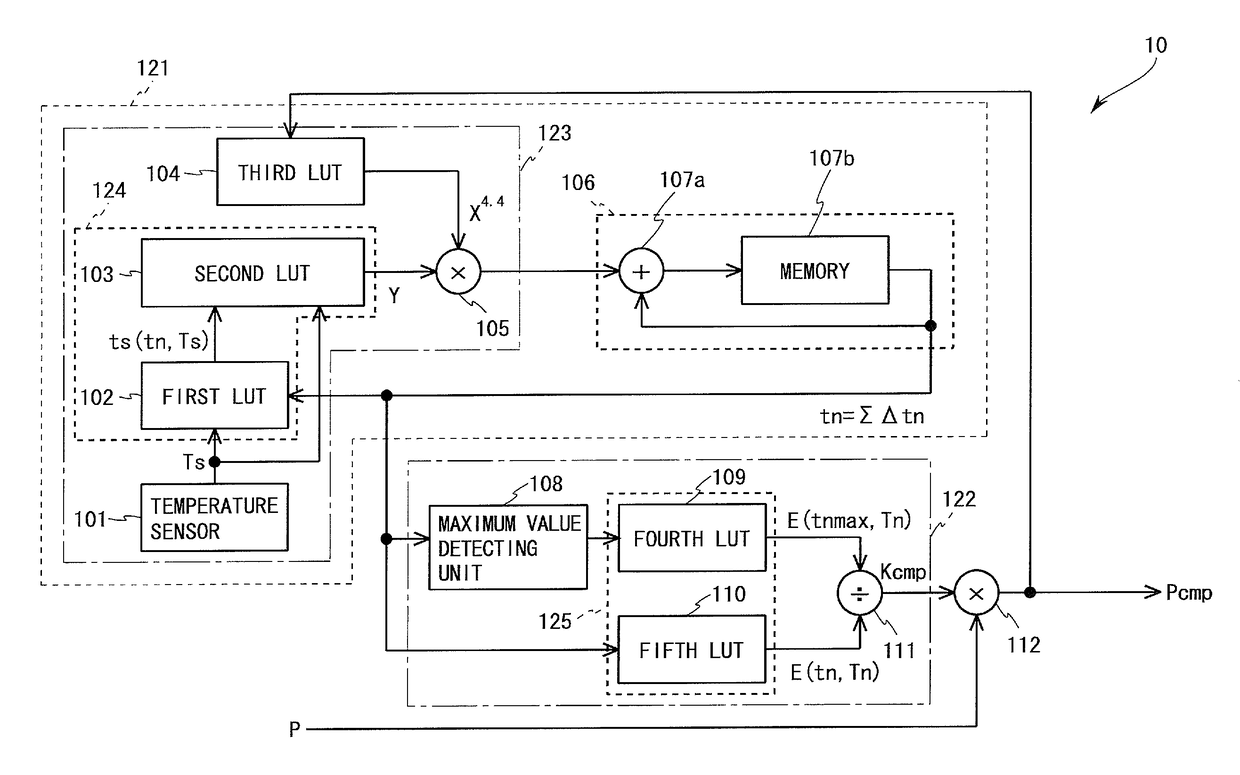
ActiveUS20150279324A1Suppressing time degradationIncrease in number can be suppressedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTemperature UnitDisplay device
A unit equivalent value acquiring unit acquires a normal-temperature unit equivalent use time Δtn by using a temperature sensor, first to third LUTs, and a first multiplying unit. An integration unit acquires an equivalent cumulative use time to by integrating the normal-temperature unit equivalent use time Δtn. A maximum value detecting unit detects a maximum equivalent cumulative use time tnmax. A dividing unit acquires a correction coefficient Kcmp by dividing total degradation E(tnmax,Tn) acquired by a fourth LUT by total degradation E(tn,Tn) acquired by a fifth LUT. Accordingly, there is provided a data processing device for a display device capable of preventing burn-in while suppressing time degradation of an electro-optical element and increase in the number of wires.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device and driving method of the same
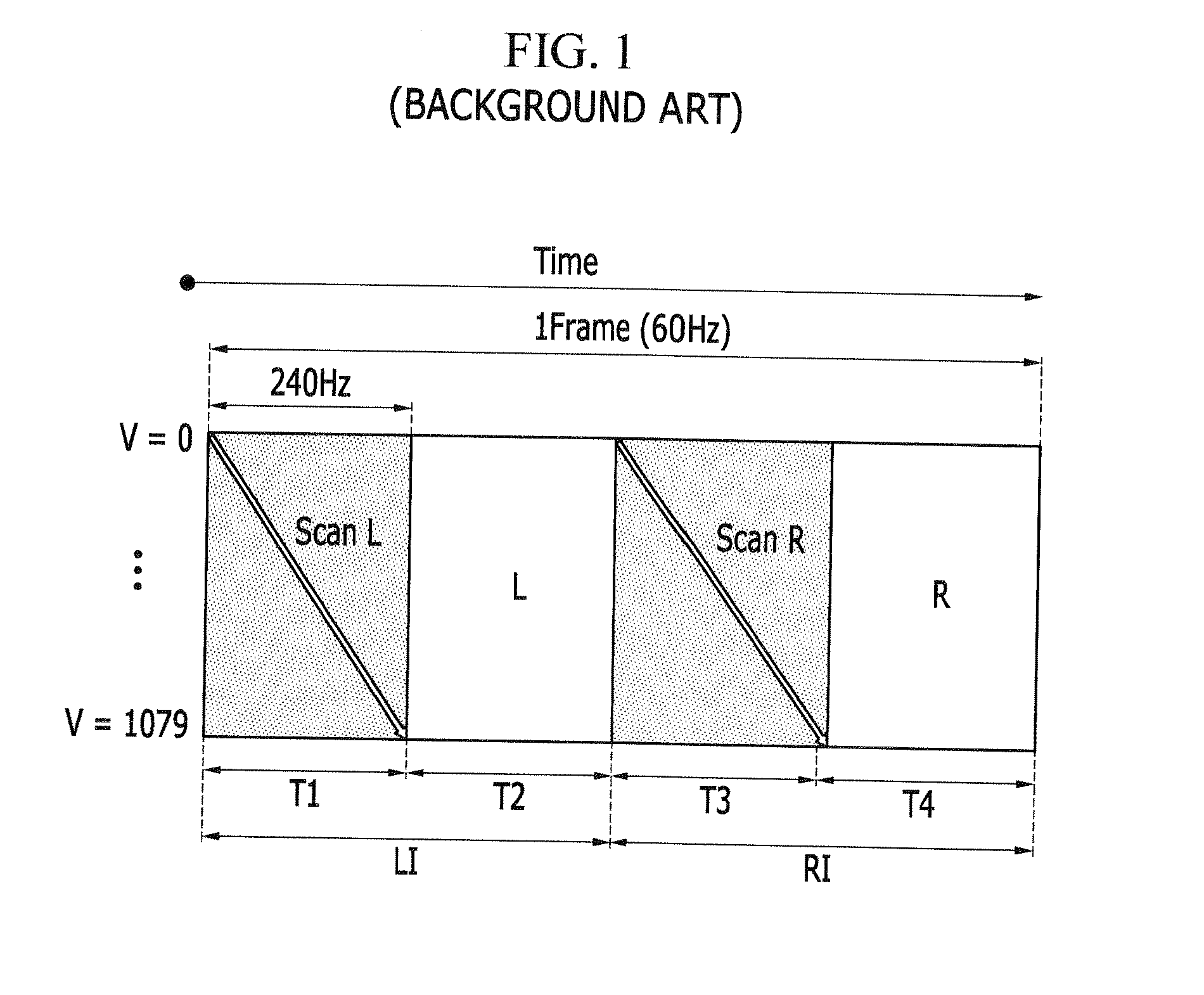
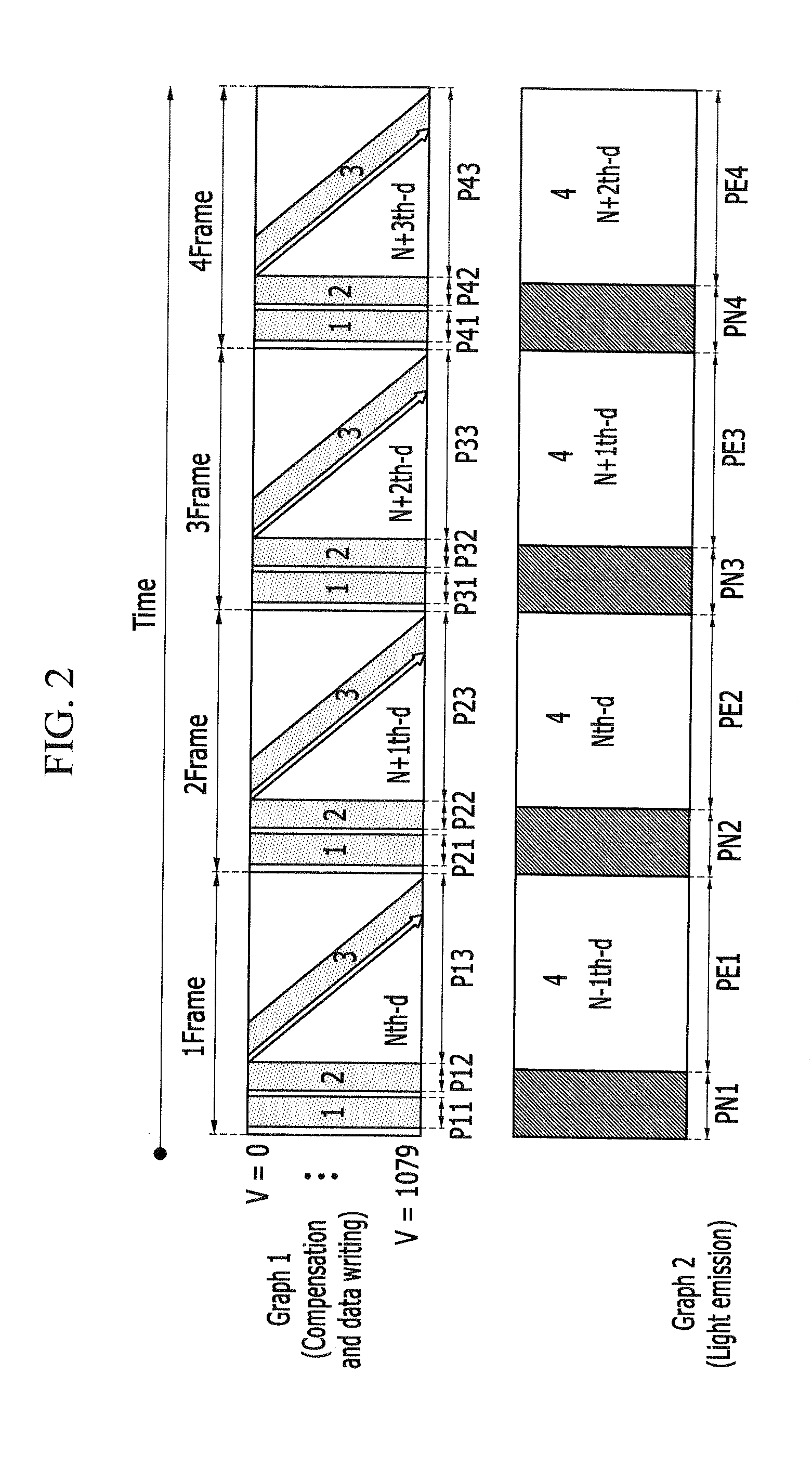
ActiveUS20140139505A1UniformityAccurate luminance expressionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsDriving currentPower flow
A display device and a driving method thereof. The display device includes a plurality of pixels, each receiving a predetermined on-bias voltage transferred through a data line during one frame, receiving a first image data signal corresponding to the corresponding frame through the data line and storing the same, and emitting light according to a driving current that corresponds to a second image data signal that corresponds to the previous frame of the corresponding frame, and a first period for storing the first image data signal and a second period for light emission according to a driving current corresponding to the second image data signal overlap each other in one frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
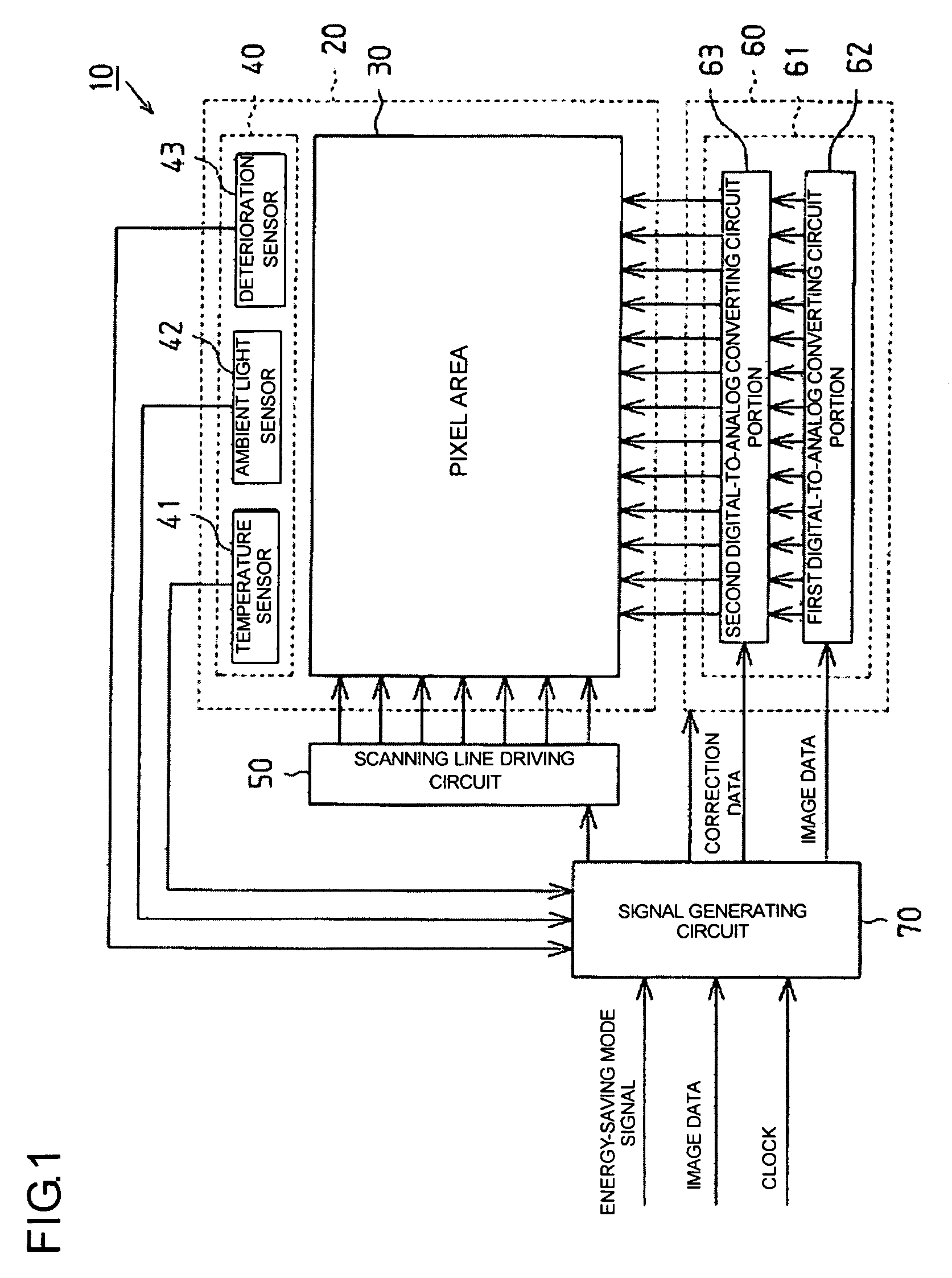
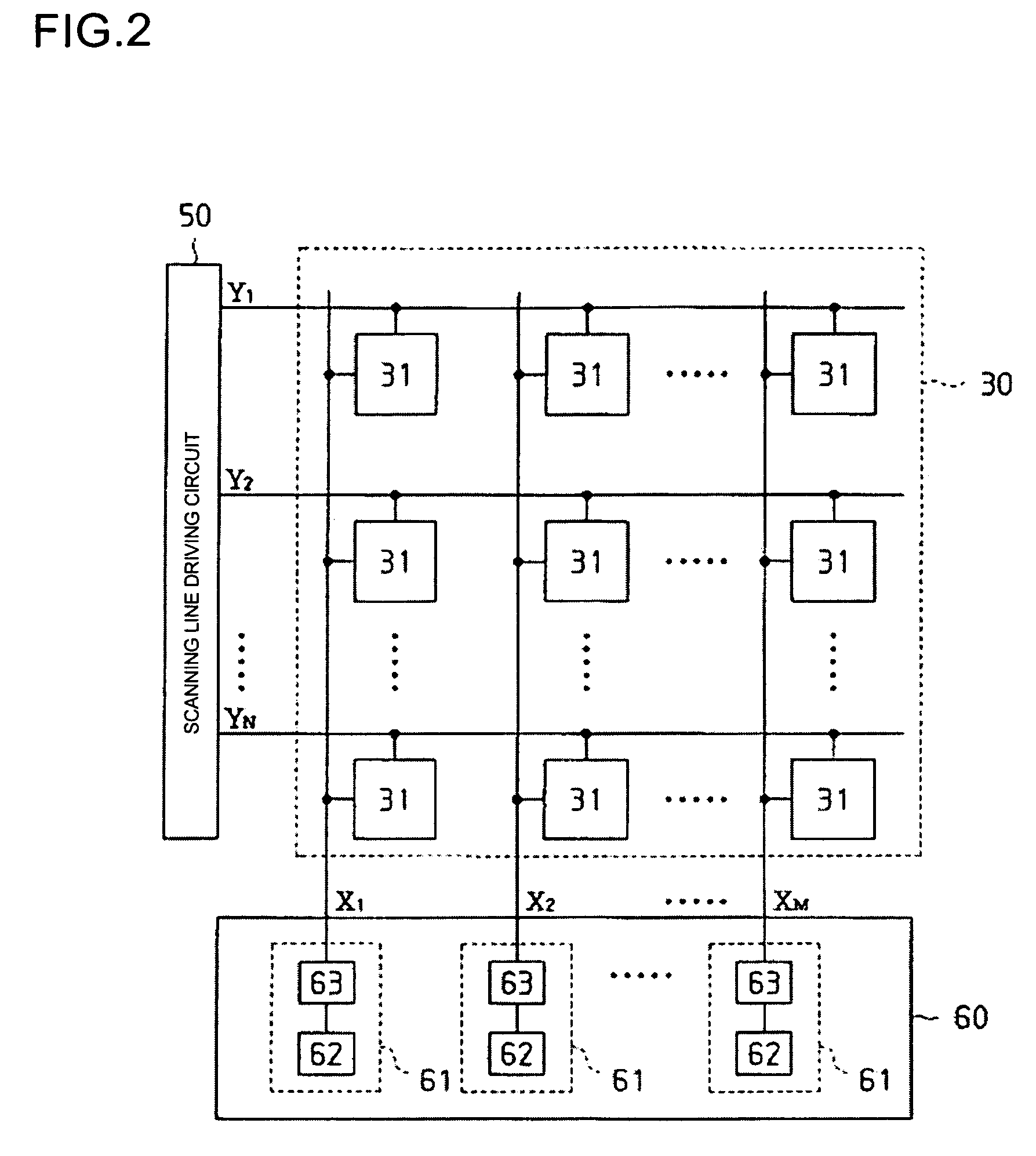
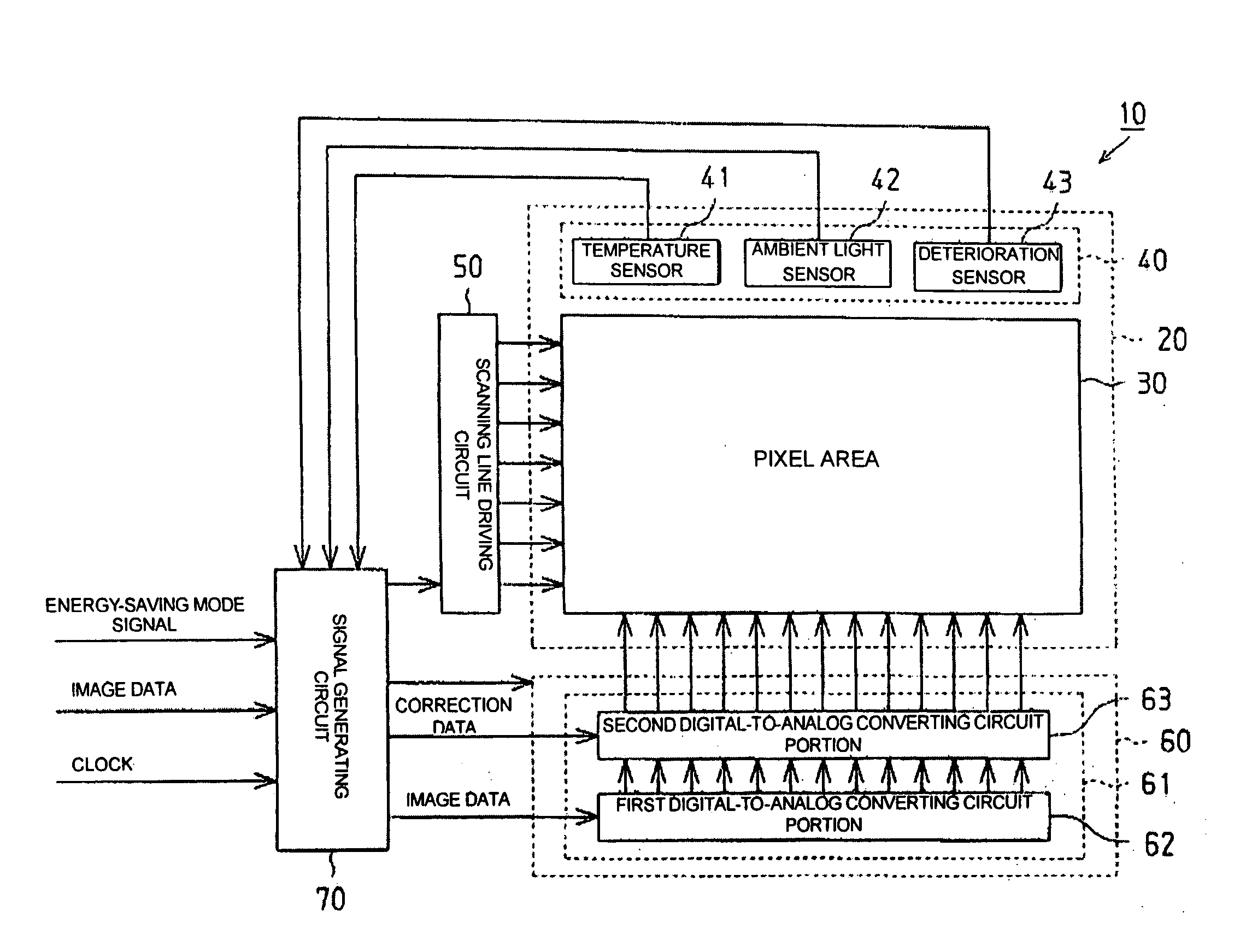
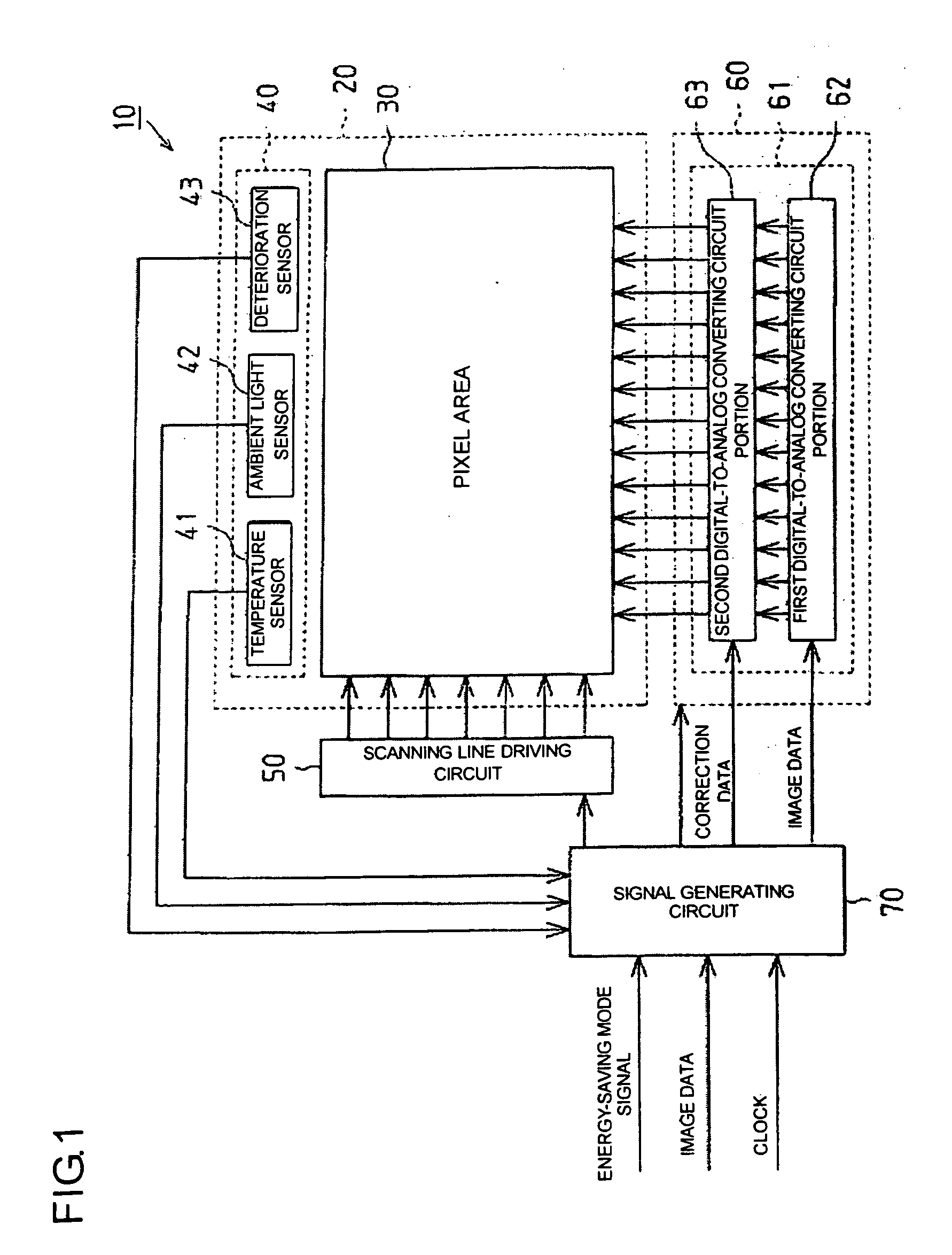
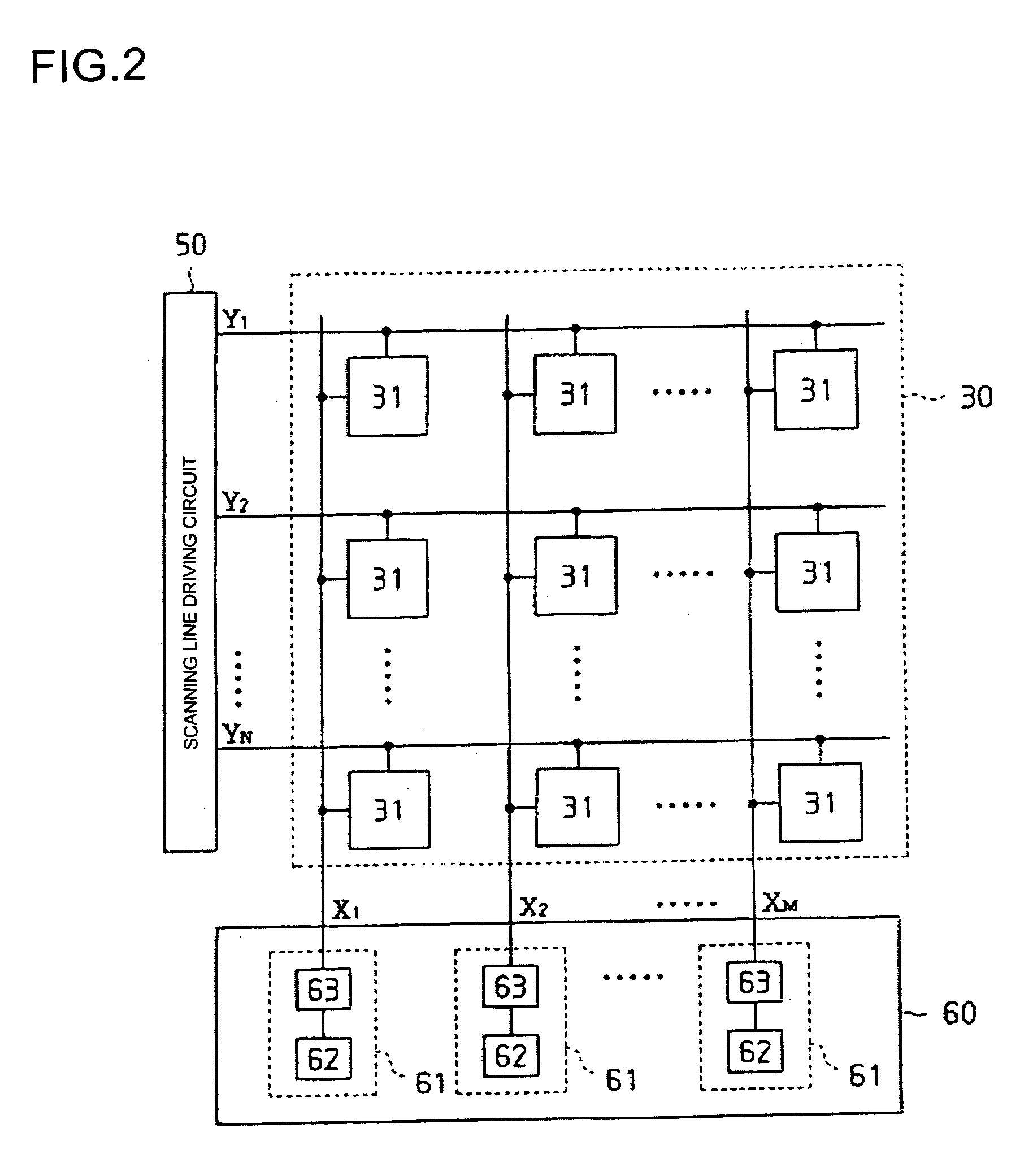
Digital-to-analog converting circuit, electrooptical device, and electronic apparatus
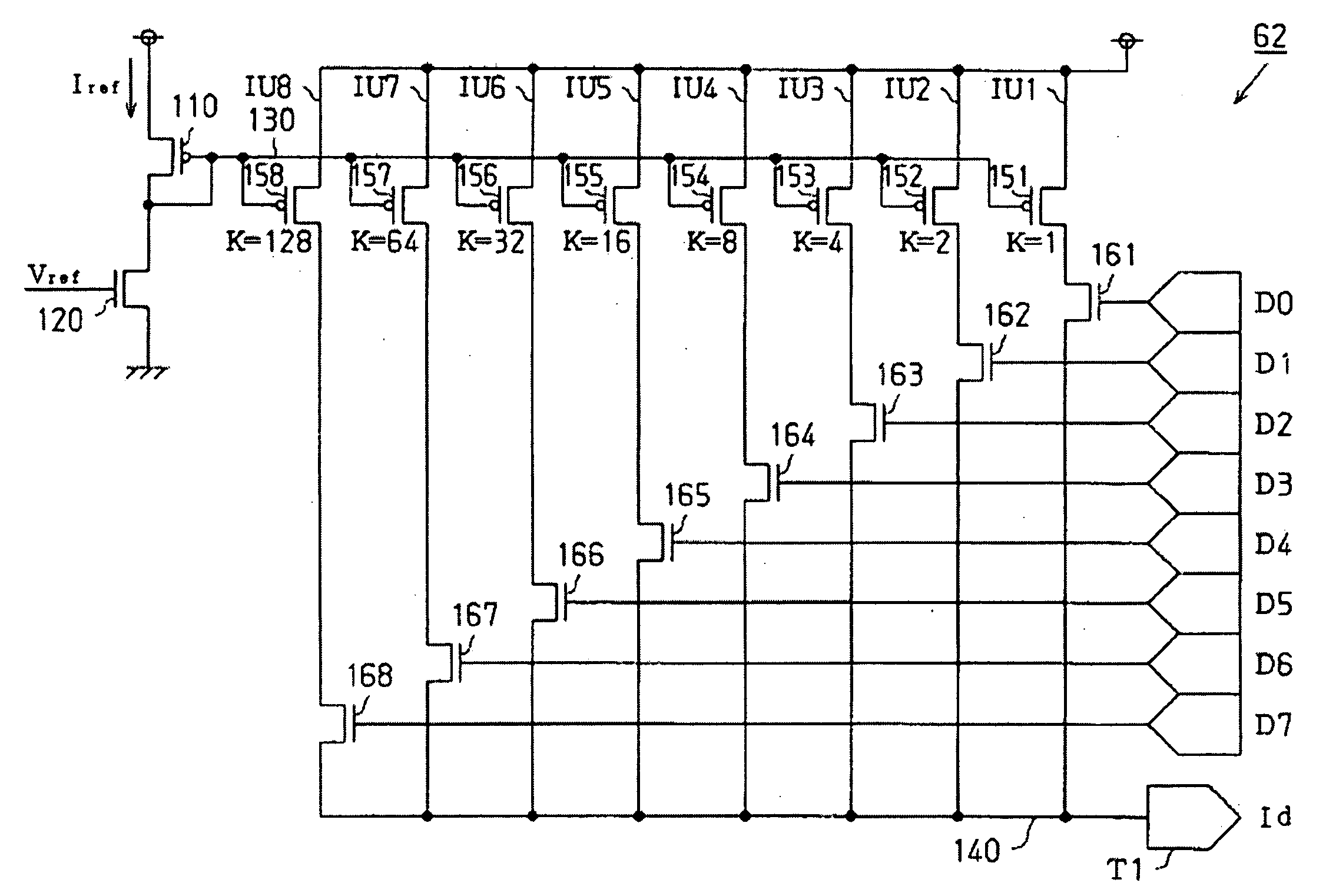
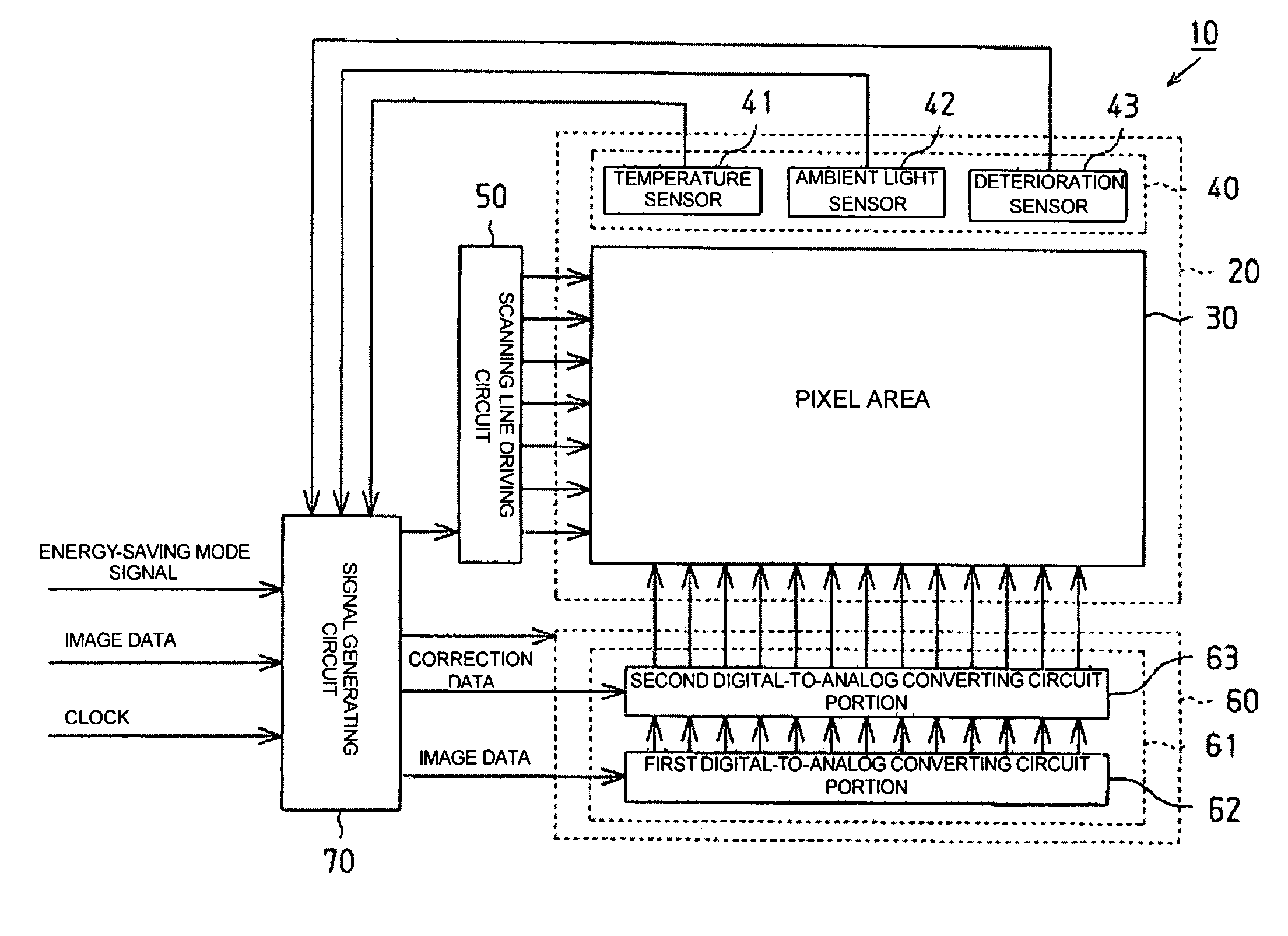
InactiveUS20050030214A1Accurate color reproductionLuminance can be correctedElectric signal transmission systemsStatic indicating devicesDigital dataImaging data
Aspects of the invention can provide a digital-to-analog converting circuit capable of, after converting digital data into an analog current, correcting the current value based on digital current correction data without any complex processing. The exemplary digital-to-analog converting circuit can include a first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion and a second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion. First digital data (image data) can input to the first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion, and second digital data (current correction data) can input to the second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion. After the first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion converts the image data into a first analog current, the second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion can correct the first analog current based on the current correction data, and outputs the corrected current as a second analog current.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
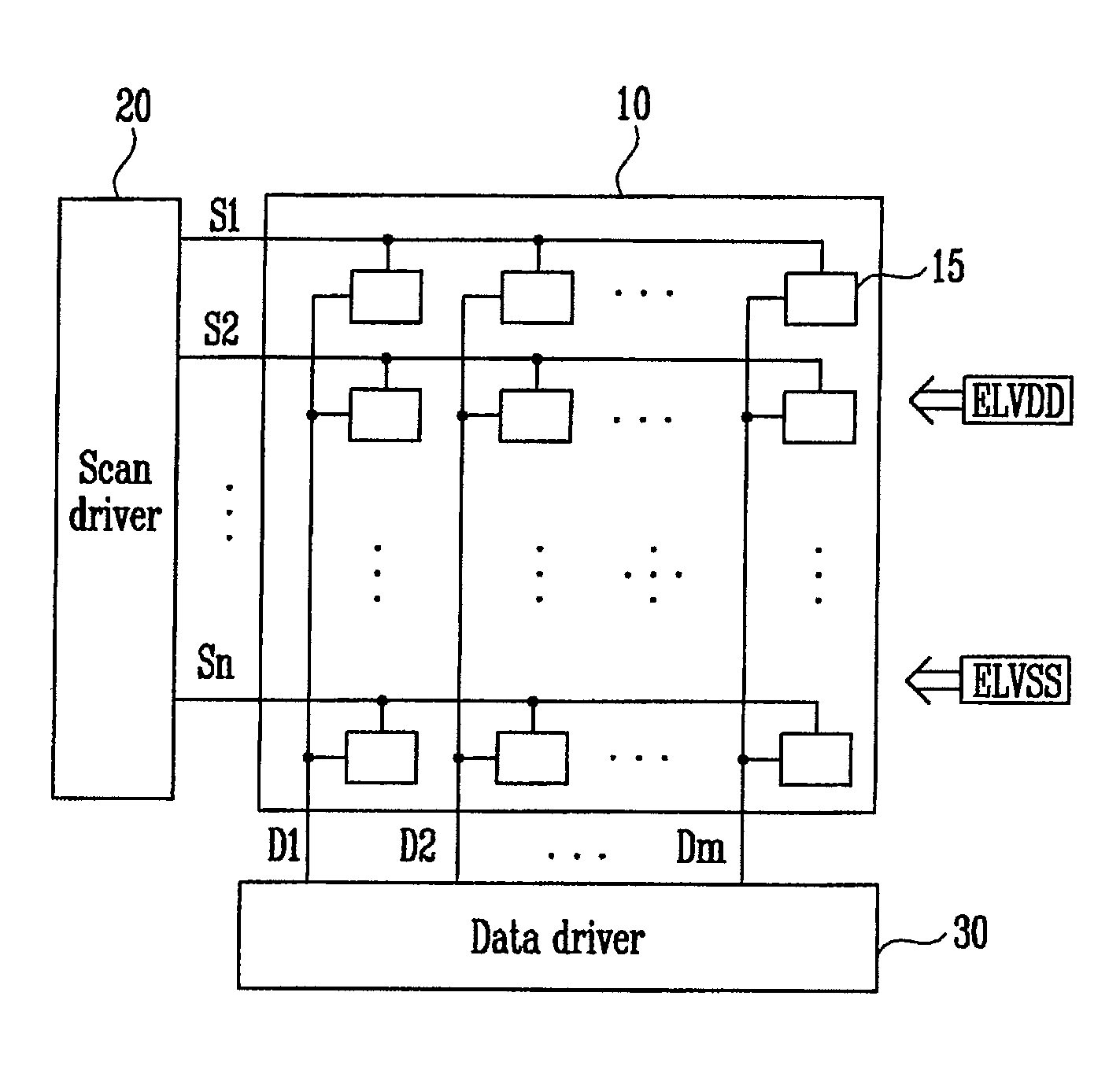
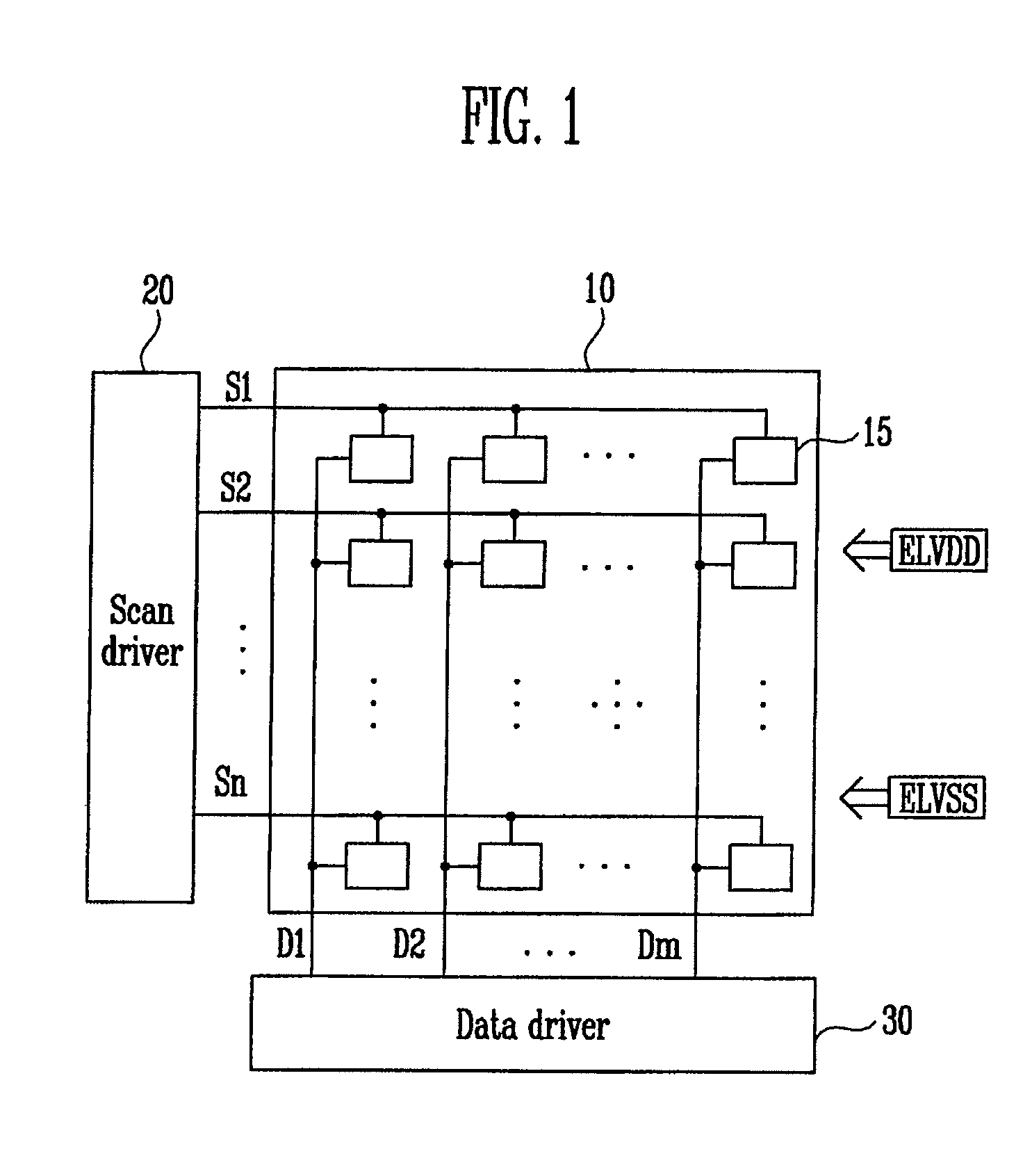
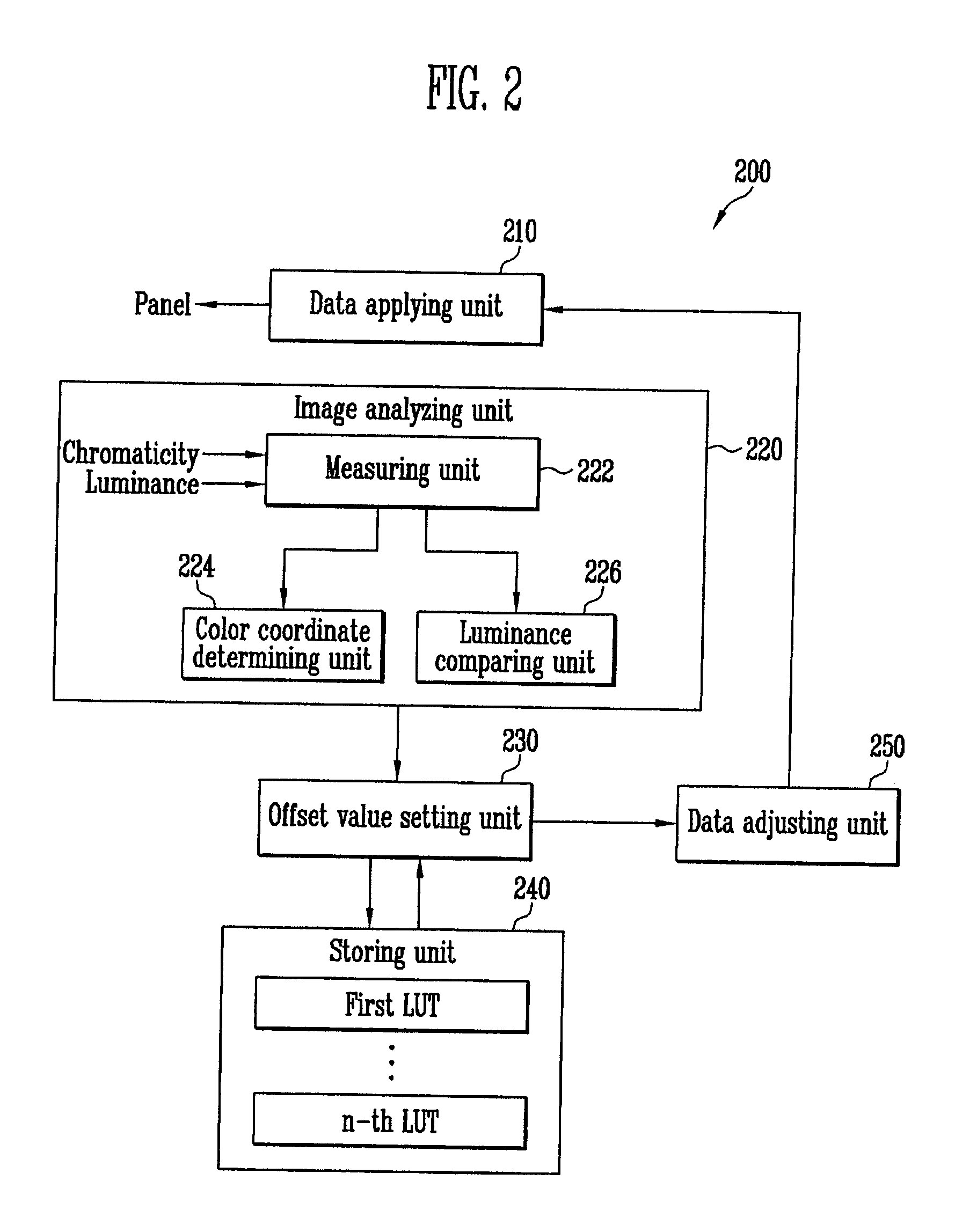
Luminance correction system and luminance correction method using the same
InactiveUS20110109661A1True colorCorrect luminanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingValue setDisplay device
A luminance correction system comprises: a data applying unit coupled to a panel of the flat panel display, and configured to apply data including center gamma value information according to a selected luminance mode to the panel; an image analyzing unit configured to analyze an image displayed on the panel according to the data and output at least one analyzed result; an offset value setting unit coupled to the image analyzing unit, and configured to generate a reference offset value corresponding to a center gamma value for a reference luminance and the at least one analyzed result, and to generate an additional offset value corresponding to the second luminance mode and the at least one analyzed result when a second luminance mode is selected; and a data adjusting unit coupled to the offset value setting unit, and configured to adjust the data according to the reference offset value and supply the adjusted data to the data applying unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20130306996A1Reduce degradationReduces invasion of noiseStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectric equipment
An electro-optical device includes a scanning line and a data line intersecting each other, a pixel circuit provided at a position corresponding to an intersection of the scanning line and the data line, and a power supply wiring line that supplies a given potential. The pixel circuit includes a light emitting element and a driving transistor configured to control a current flowing through the light emitting element. A gate electrode of the driving transistor is electrically connected via a first relay electrode to a given node. The first relay electrode is formed in the same layer as the power supply wiring line and the data line. The first relay electrode is surrounded on at least three sides by the power supply line.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Display Device And Display Control Method
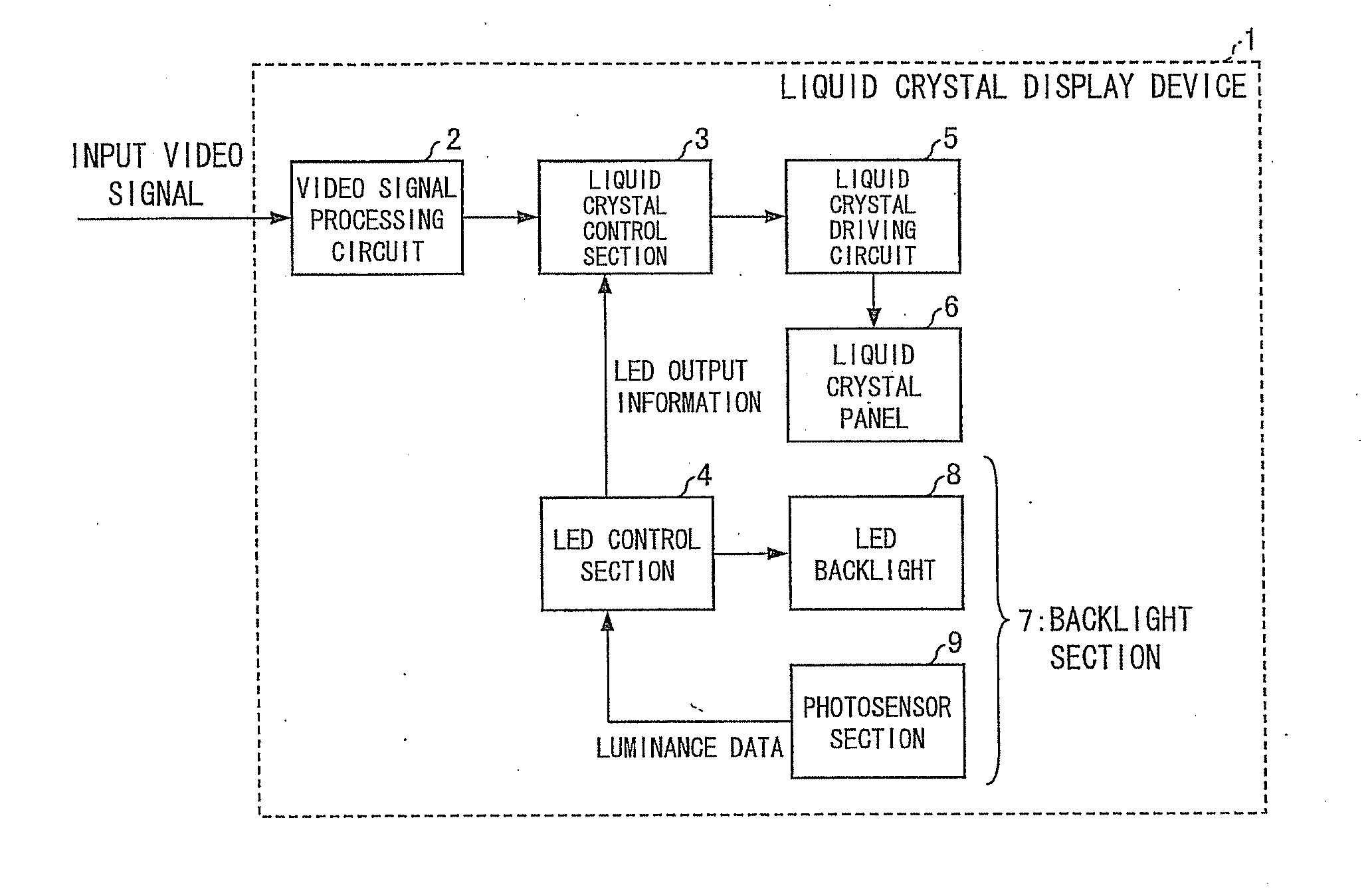
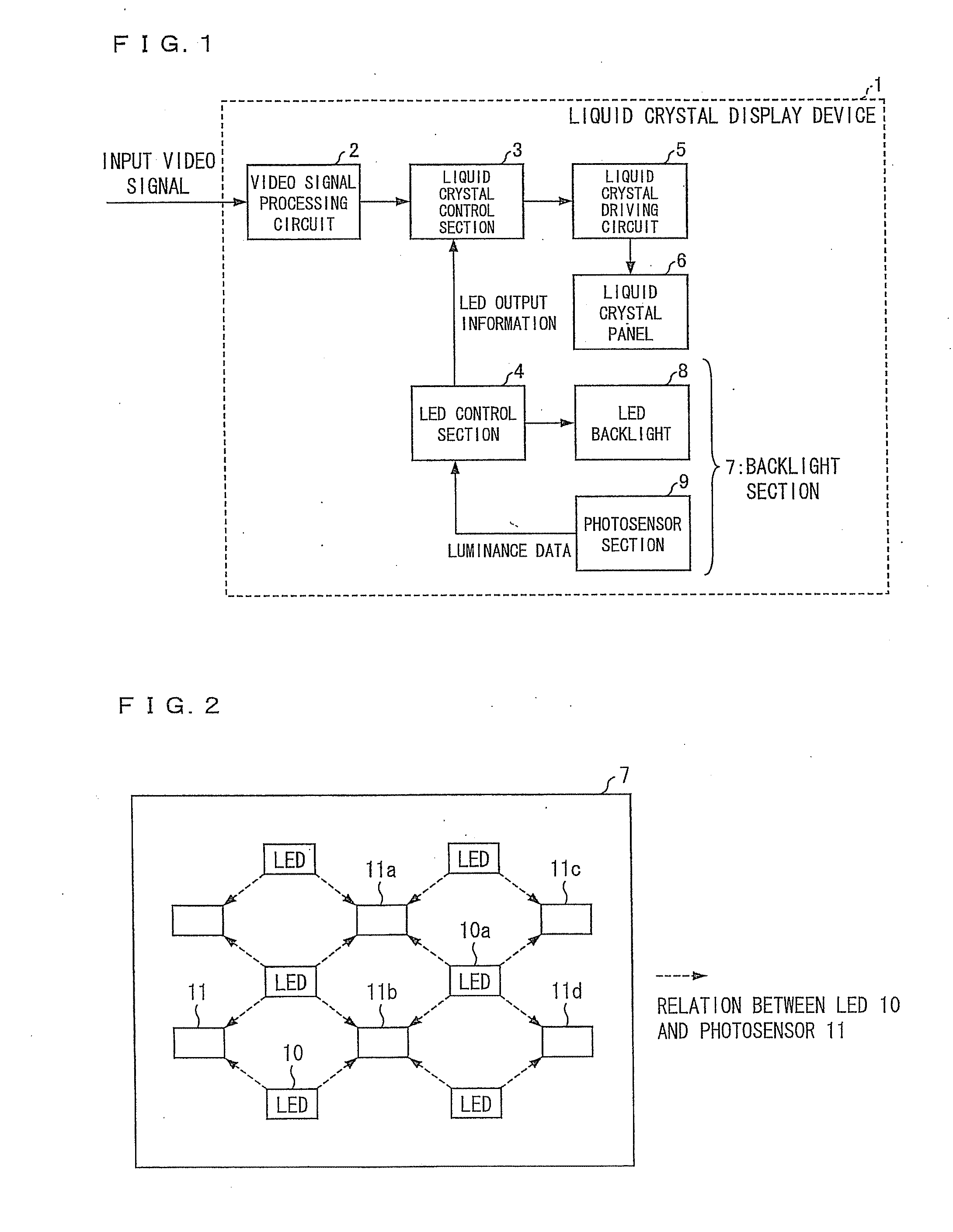
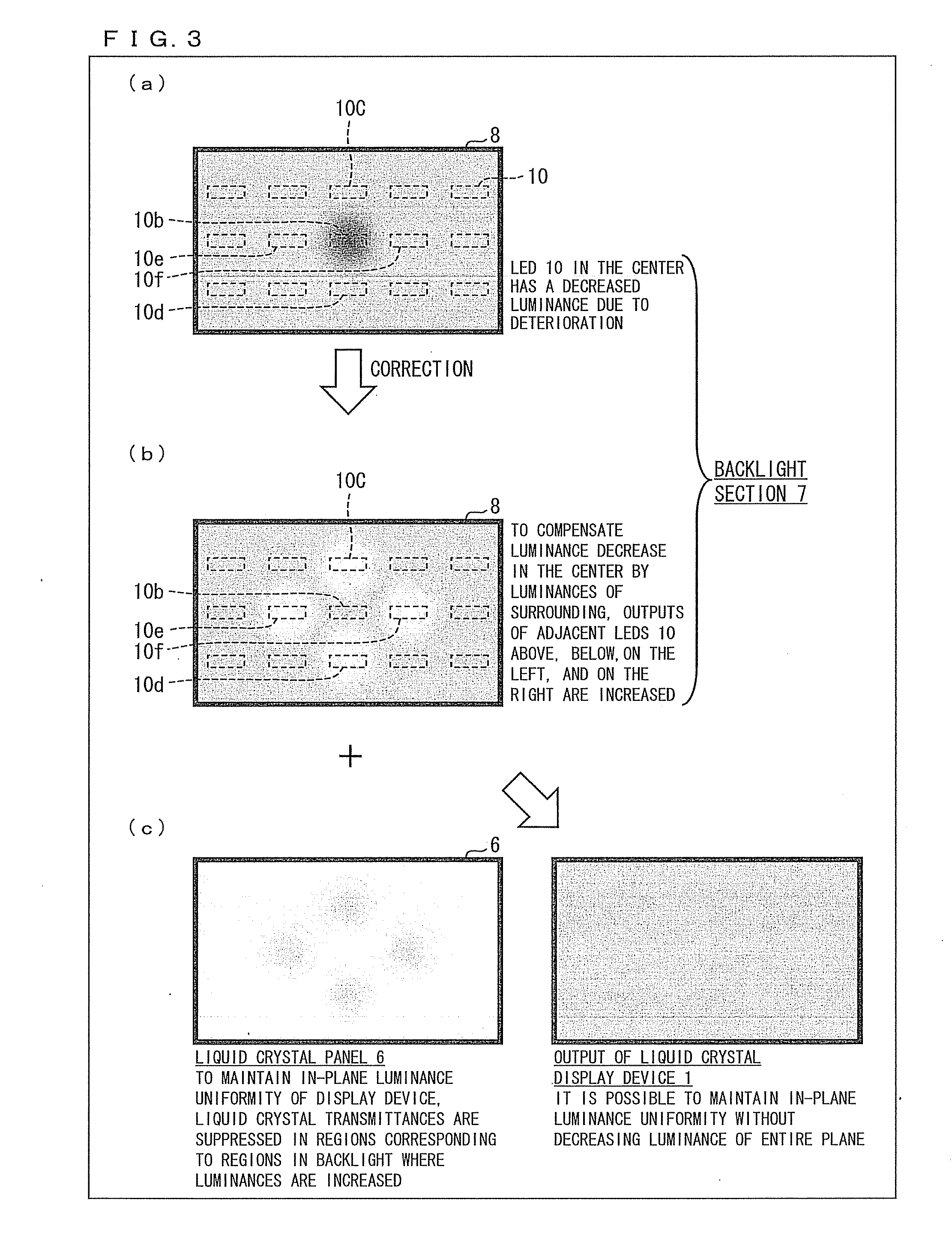
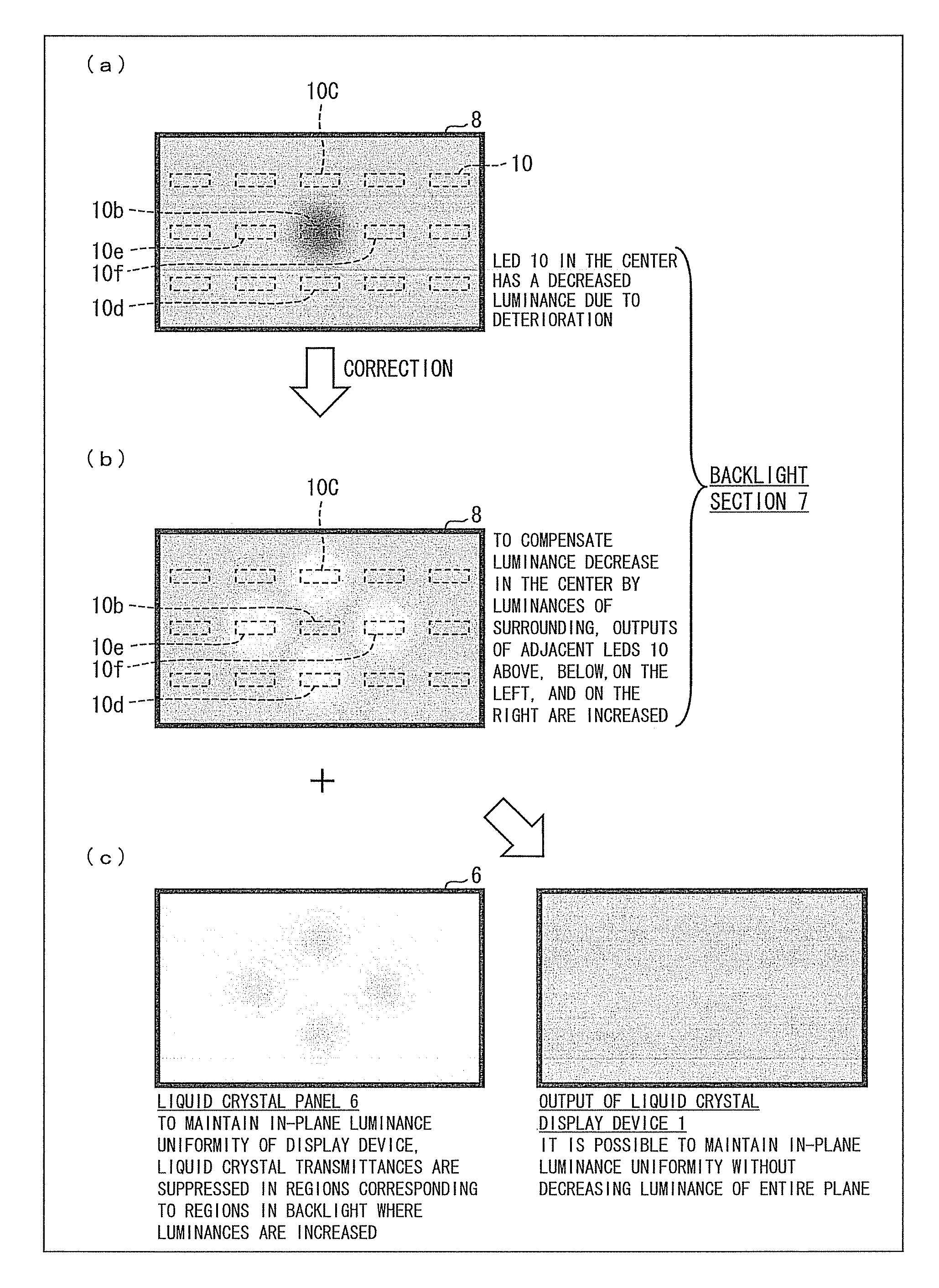
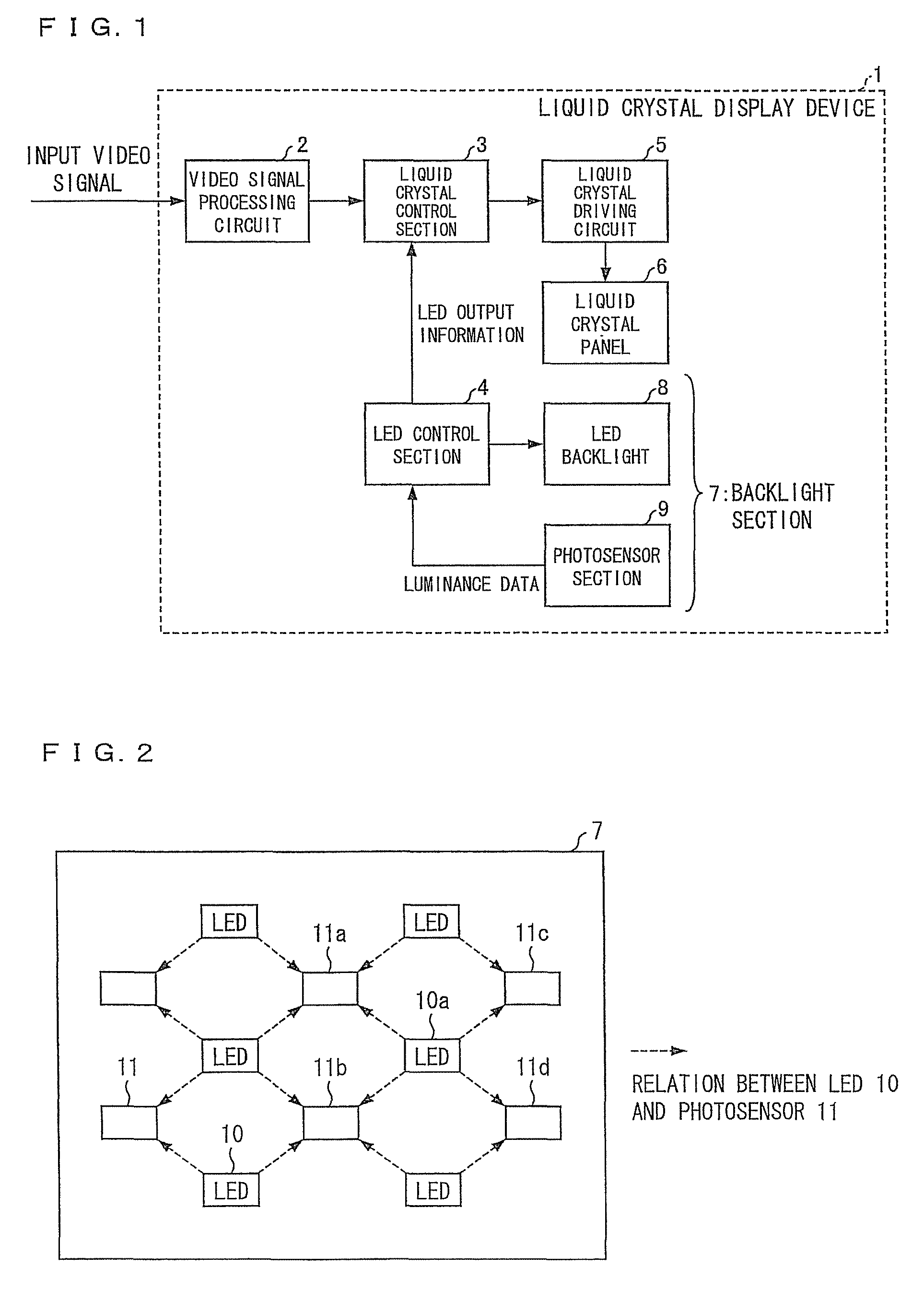
ActiveUS20120075274A1Correct luminance non-uniformityDecrease in luminanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A display device includes: an LED control section (4) for carrying out control in which (i) an output luminance of an LED (10) whose measured luminance is deviated from a reference luminance or (ii) output luminances of peripheral LEDs (10) which are provided around the LED (10) is or are corrected, respectively, by using control information of the plurality of LEDs, which control information contains (a) information on measured luminances of the plurality of LEDs, the information being obtained by the plurality of photosensors (11) and (b) positional information of the plurality of LEDs, the positional information being obtained by the plurality of photosensors (11), and a liquid crystal display control section (3) for controlling, based on (i) video signals which have been subjected to the video signal process and are supplied from a video signal processing section (2) and (ii) the control information supplied from the LED control section (4), (a) levels of video signals to be supplied to pixels corresponding to the LED (10), whose output luminance is corrected or (b) levels of video signals to be supplied to pixels corresponding to the peripheral LEDs, whose output luminances are corrected, the reference luminance being a luminance which is originally expected to be outputted from each of the plurality of LEDs.
Owner:SHARP KK
Electric current driving type display device
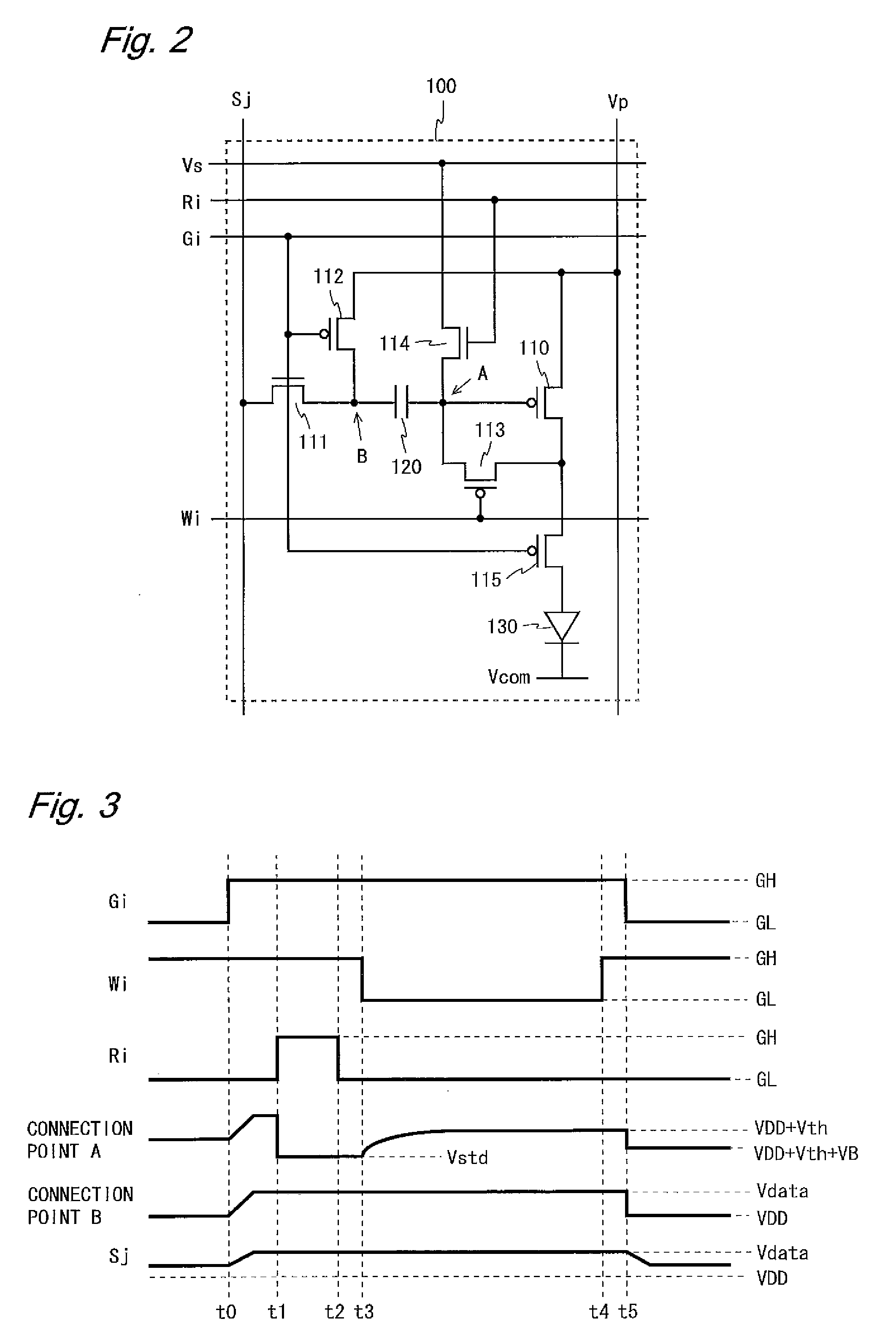
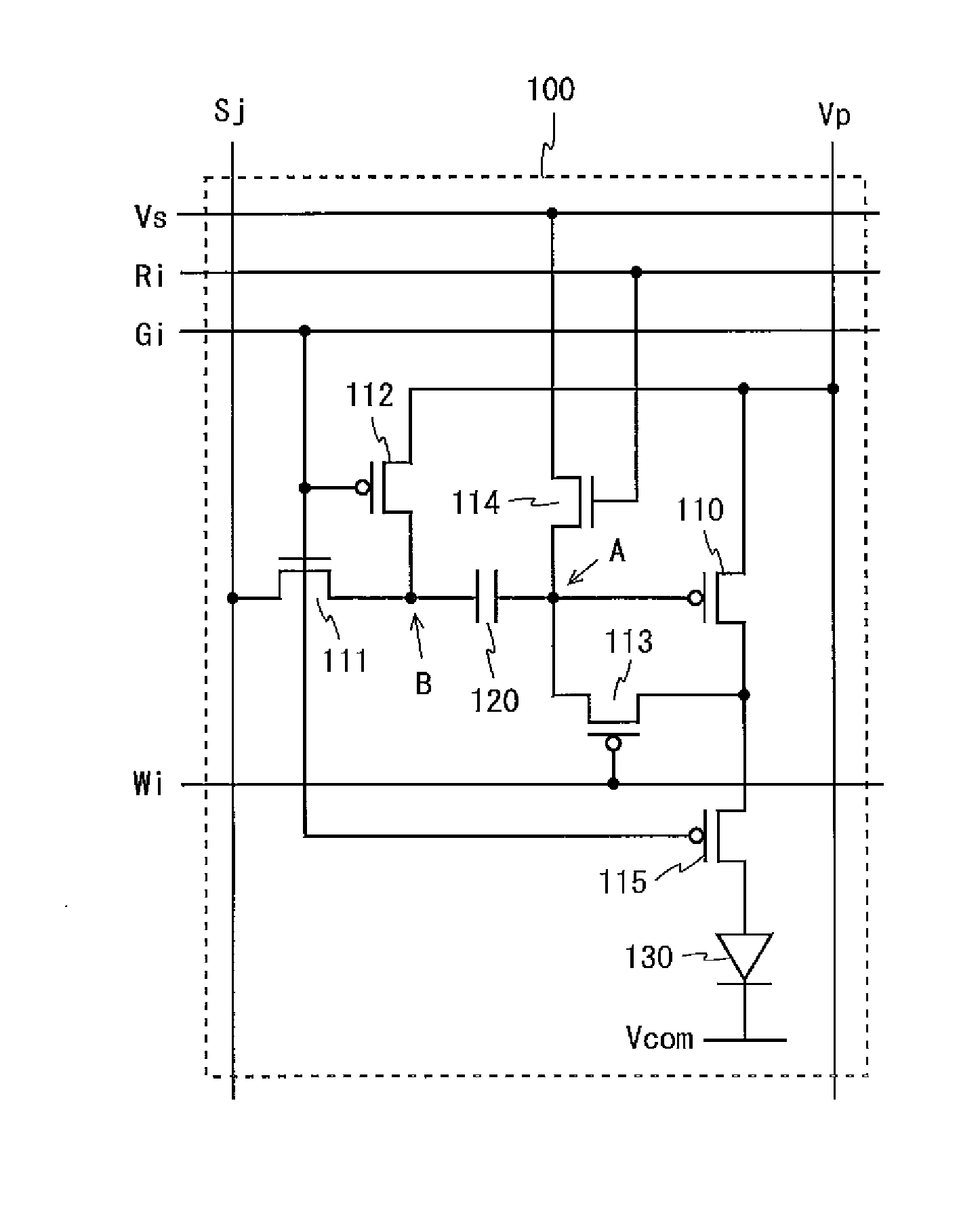
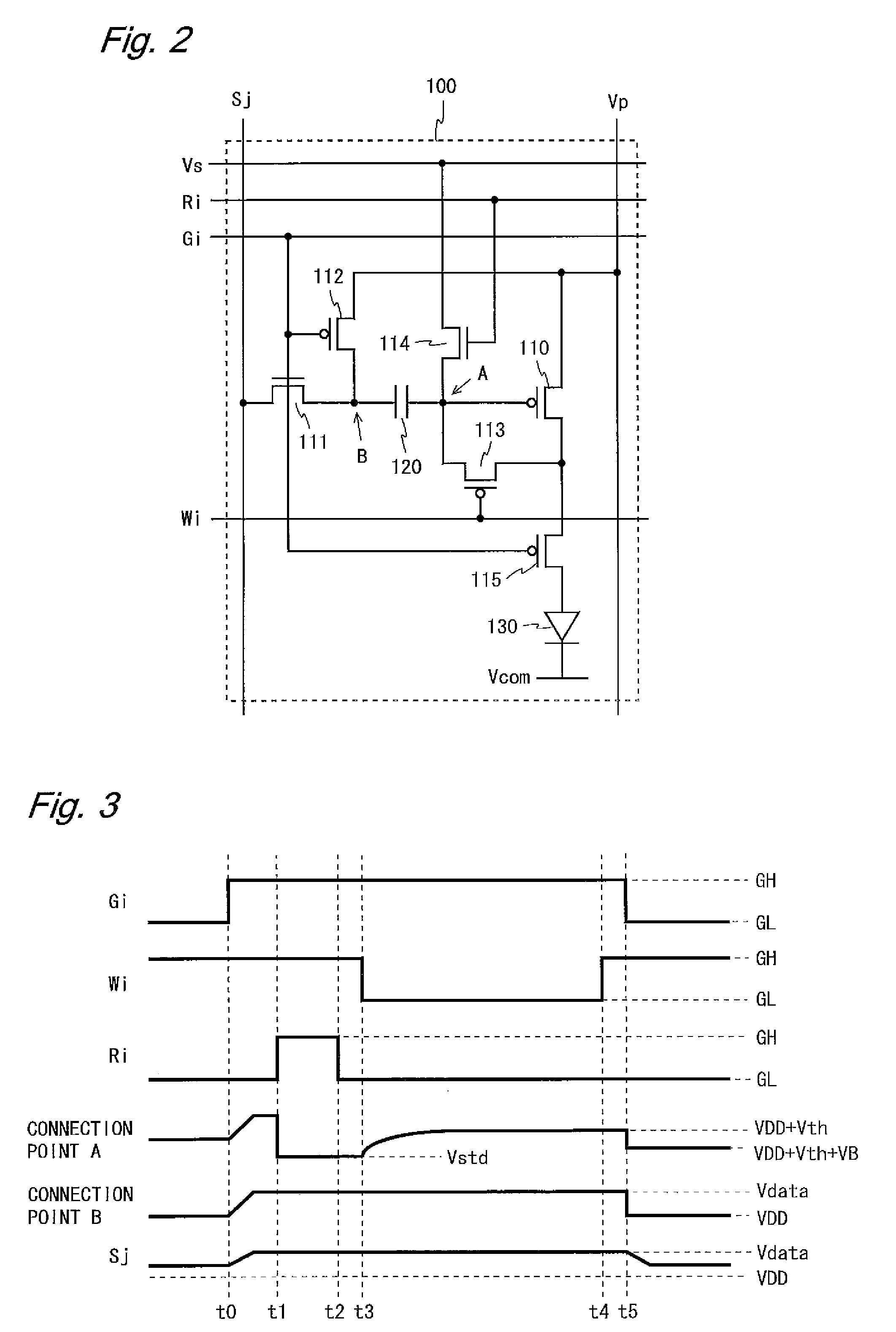
ActiveUS20090040150A1Enhance display qualityNumber be smallStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDriven elementEngineering
In a pixel circuit 100, a driving TFT 110, a switching TFT 115, and an organic EL element 130 are provided between a power supply wiring line Vp and a common cathode Vcom and a capacitor 120 and a switching TFT 111 are provided between a gate terminal of the driving TFT 110 and a data line Sj. A switching TFT 112 is provided between a connection point B between the capacitor 120 and the switching TFT 111 and the power supply wiring line Vp, a switching TFT 113 is provided between the gate and drain terminals of the driving TFT 110, and a switching TFT 114 is provided between the gate terminal of the driving TFT 110 and a reference supply wiring line Vs. A potential that brings the driving TFT 110 into a conduction state is applied to the reference supply wiring line Vs. Thus, variations in the threshold voltage of a drive element can be properly compensated for and unwanted light emission from an electro-optical element can be prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device and driving method thereof
In order to keep the luminance of a light emitting element constant, the correction is performed by an external device such as a computer, in which case a display device is inevitably complicated and increased in size. Even when degradation characteristics of the light emitting element are previously stored in a computer, the degradation characteristics vary at random depending on hysteresis of the light emitting element; therefore, changes in luminance cannot be corrected. According to the invention, a display device includes a displaying light emitting element provided in a display portion and a plurality of monitoring light emitting elements having the similar characteristics as the displaying light emitting element. At least one of the monitoring light emitting elements is operated under a condition different from the displaying light emitting element, and the ratio of the total amount of charge flowing through the displaying light emitting element to that flowing through the monitoring light emitting element is controlled to satisfy a certain relation in view of luminance degradation. When the one monitoring light emitting element reaches a predetermined voltage or time, the connection is switched from the one monitoring light emitting element to another monitoring light emitting element that has been operated under the same condition as the displaying light emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
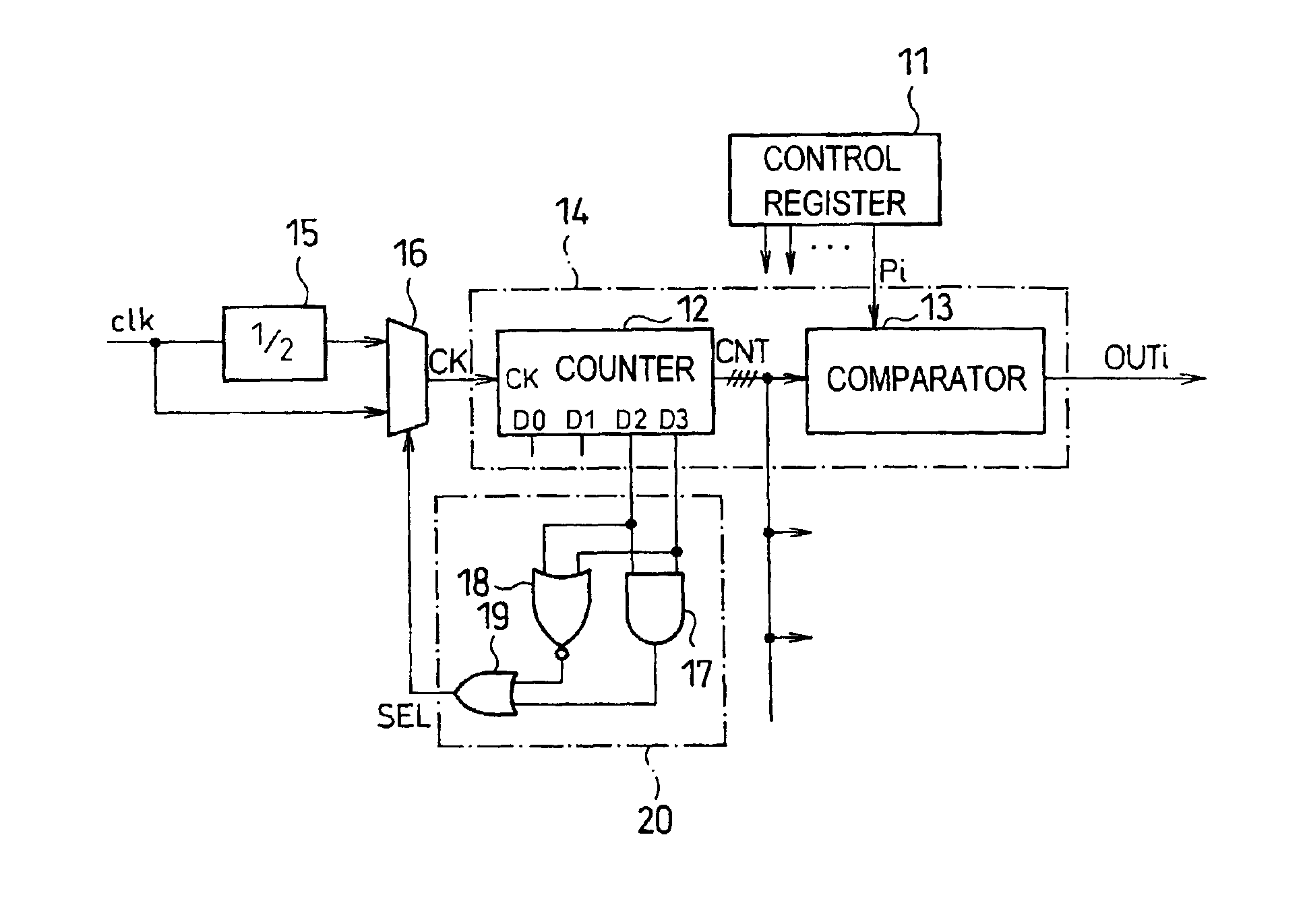
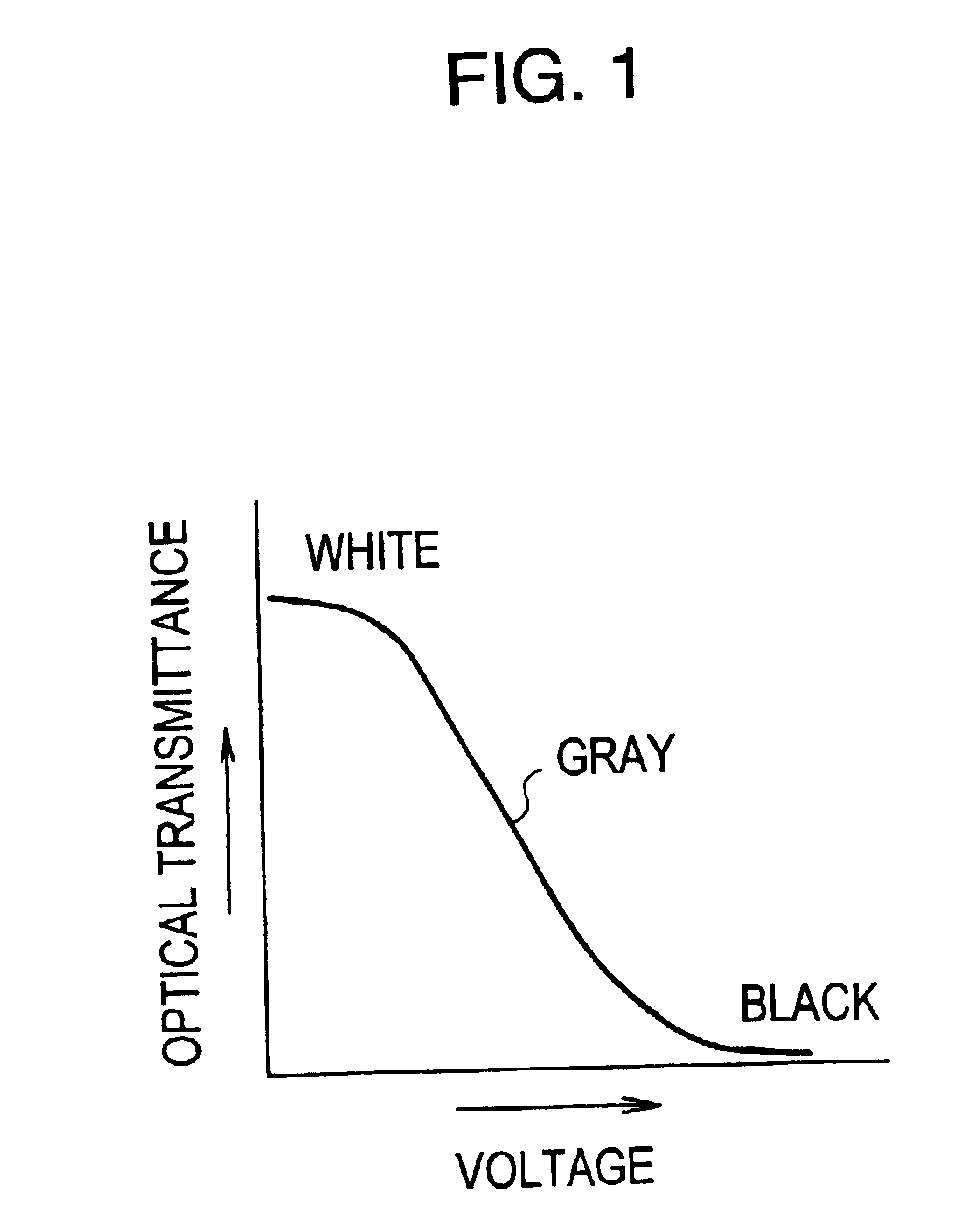
LCD driver
InactiveUS6956549B2Simple structureLuminance can be correctedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayClock rate
An LCD driver compares an image signal with a count of a counter repeatedly counting a clock. Based on the result of the comparison, the LCD driver outputs pulses each having a duty factor in accord with the image signal. When the count is not between first and second predetermined numbers, the frequency of the clock supplied to the counter is switched from a fundamental frequency to a low-frequency, thereby controlling the width of a drive voltage of a liquid crystal display cell and correcting the image signal in association with the S-shape characteristic of optical transmittance of the liquid crystal display cell. This LCD driver is advantageously simple in structure.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
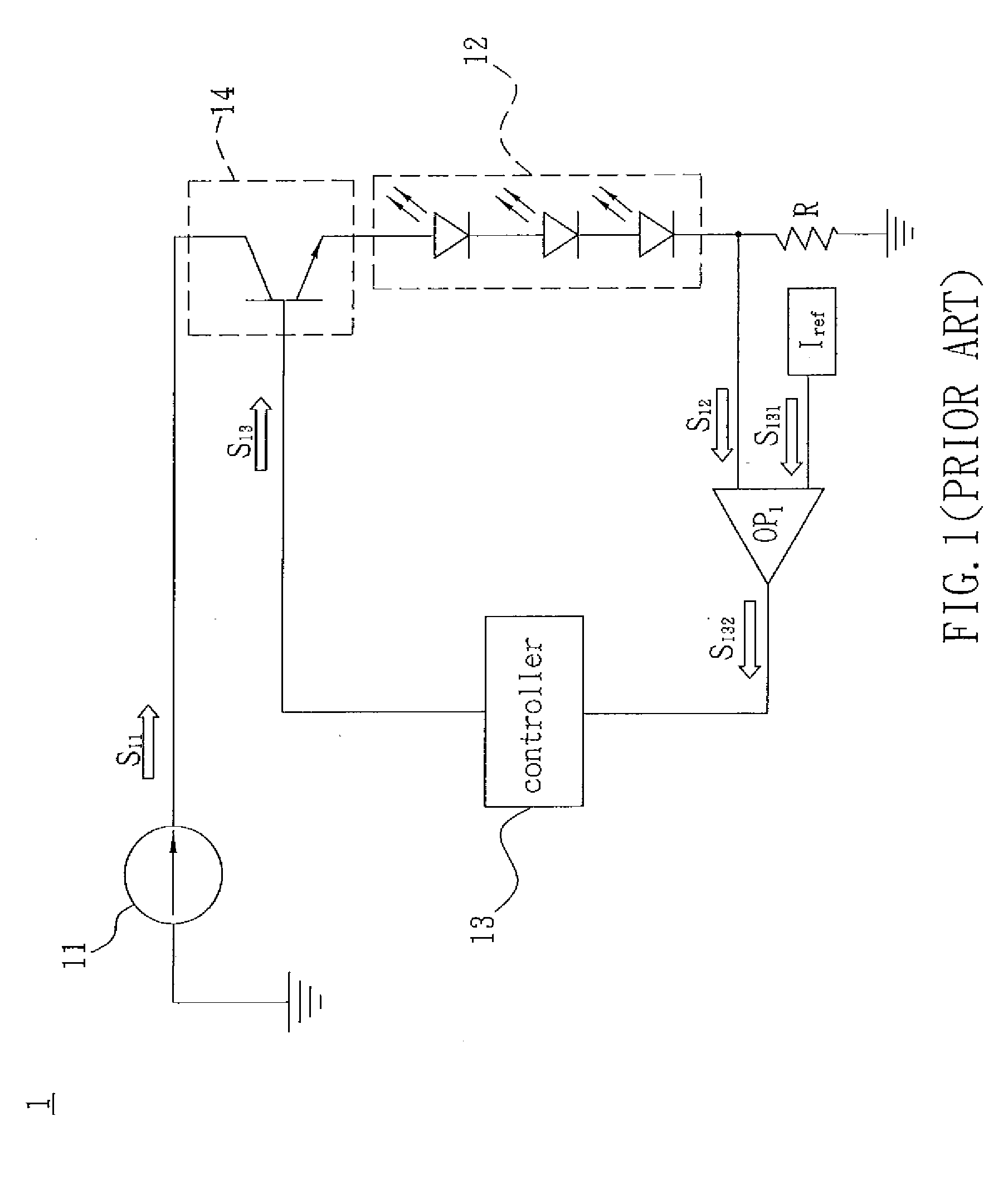
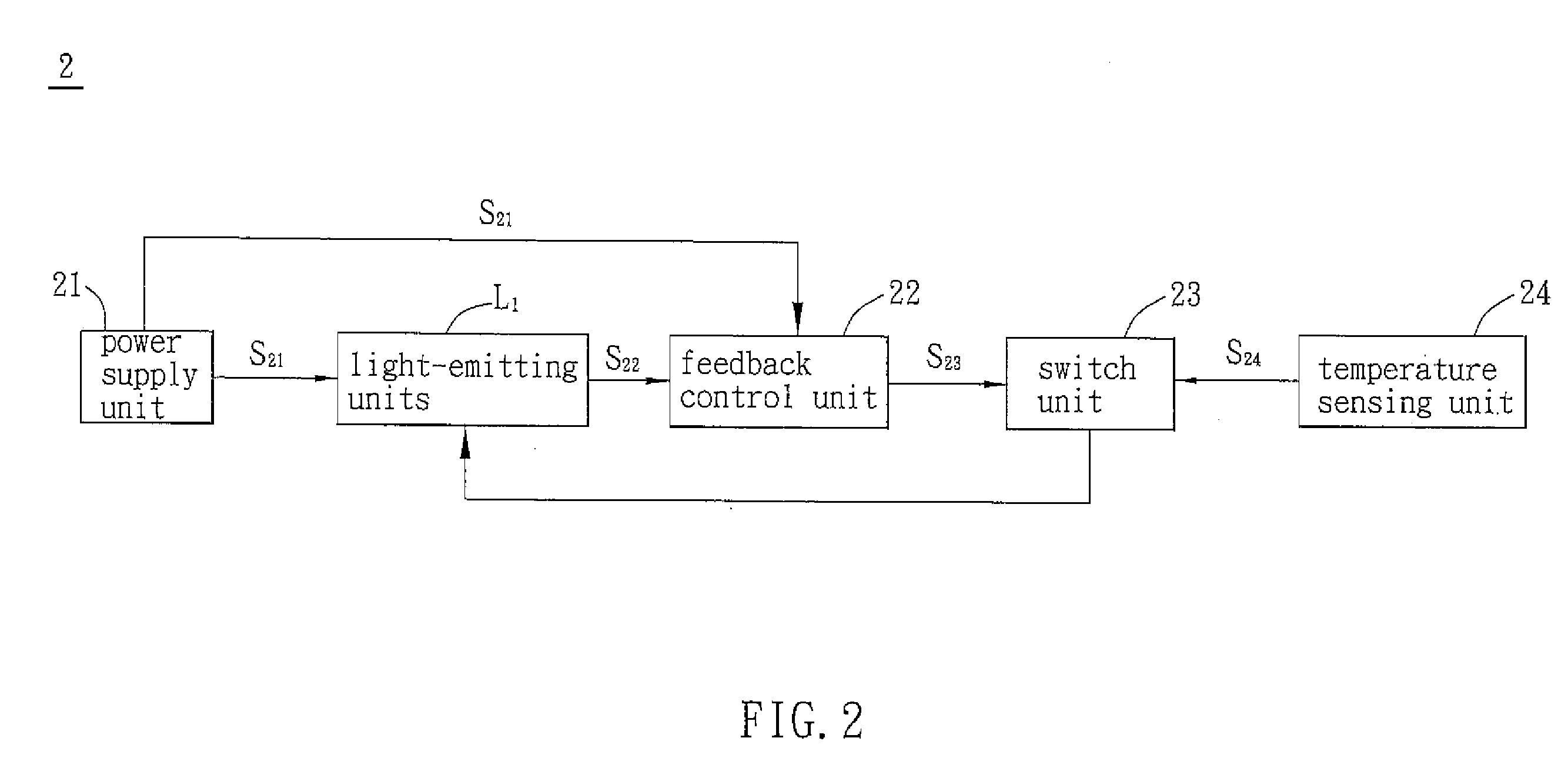
Liquid crystal display apparatus, backlight module and light source driving device thereof
InactiveUS20080231621A1Reduce power consumptionEasy to controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A light source driving device for driving a plurality of light-emitting units includes a power supply unit and a feedback control unit. The power supply unit is electrically connected to the light-emitting units and outputs a driving signal for driving the light-emitting units. The feedback control unit is electrically connected to the power supply unit and between any two light-emitting units, and retrieves a feedback signal from the light-emitting units to generate a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal for controlling the light-emitting units.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
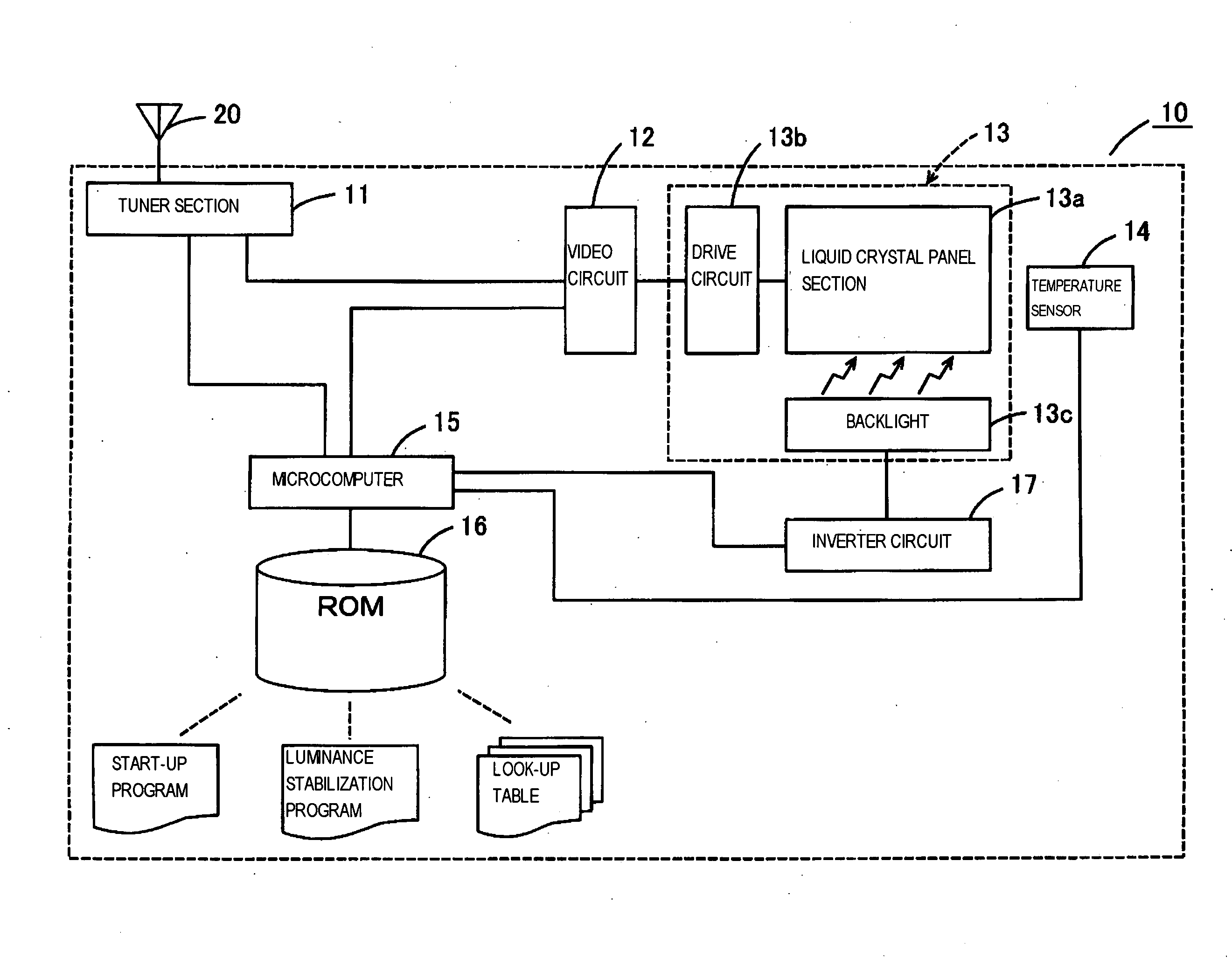
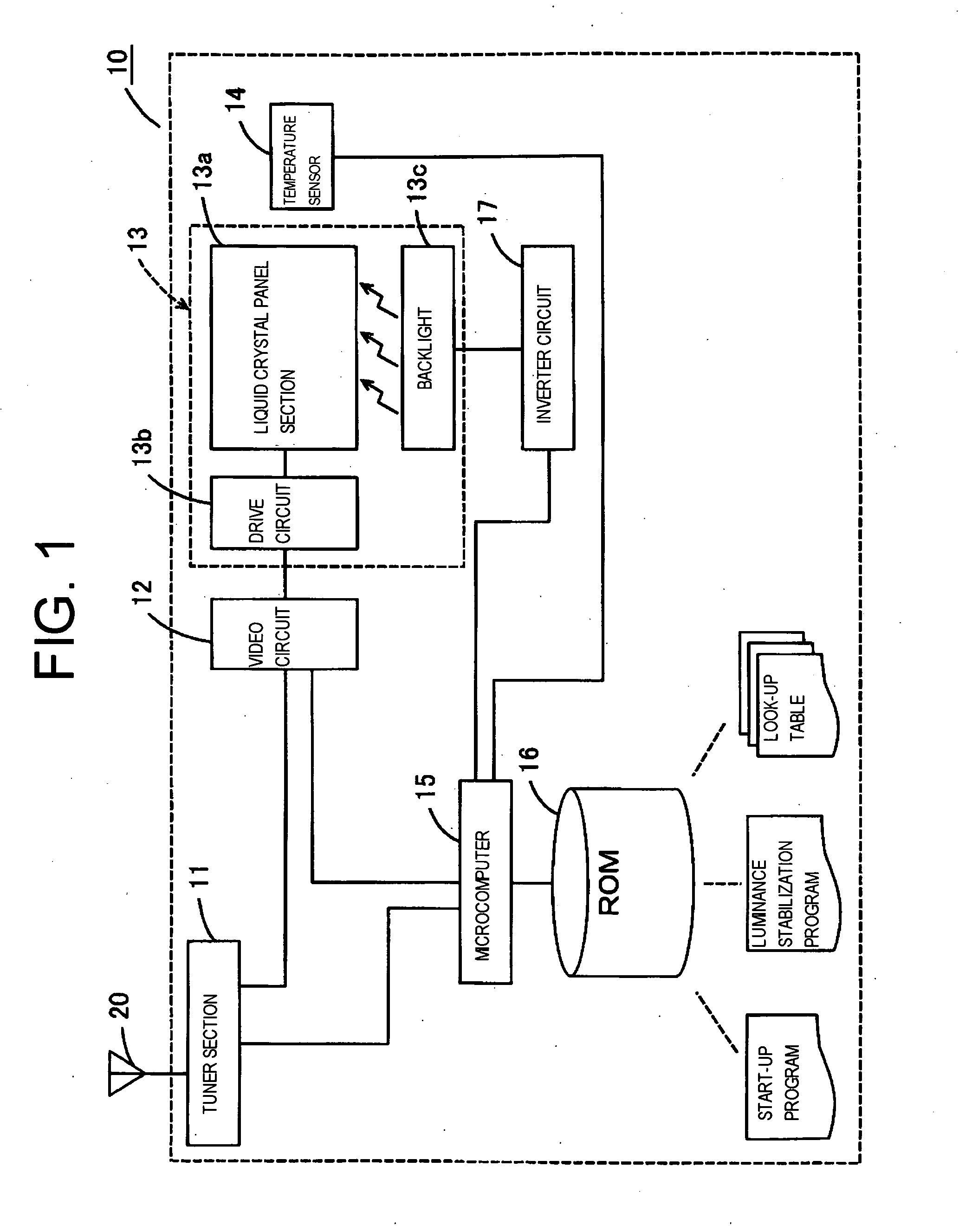
Liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal television
InactiveUS20090027327A1Simple configurationLuminance can be correctedStatic indicating devicesMicrocomputerLCD television
A liquid crystal display device capable of correcting variation in luminance in a drive beginning period of the liquid crystal display device with a simple configuration by a microcomputer 15 referring to a luminance stabilization program and a look-up table recorded on a ROM 16 and executing contrast adjustment of the video signal by the video circuit 12 based on the look-up table, and a liquid crystal television using the liquid crystal display device are provided.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
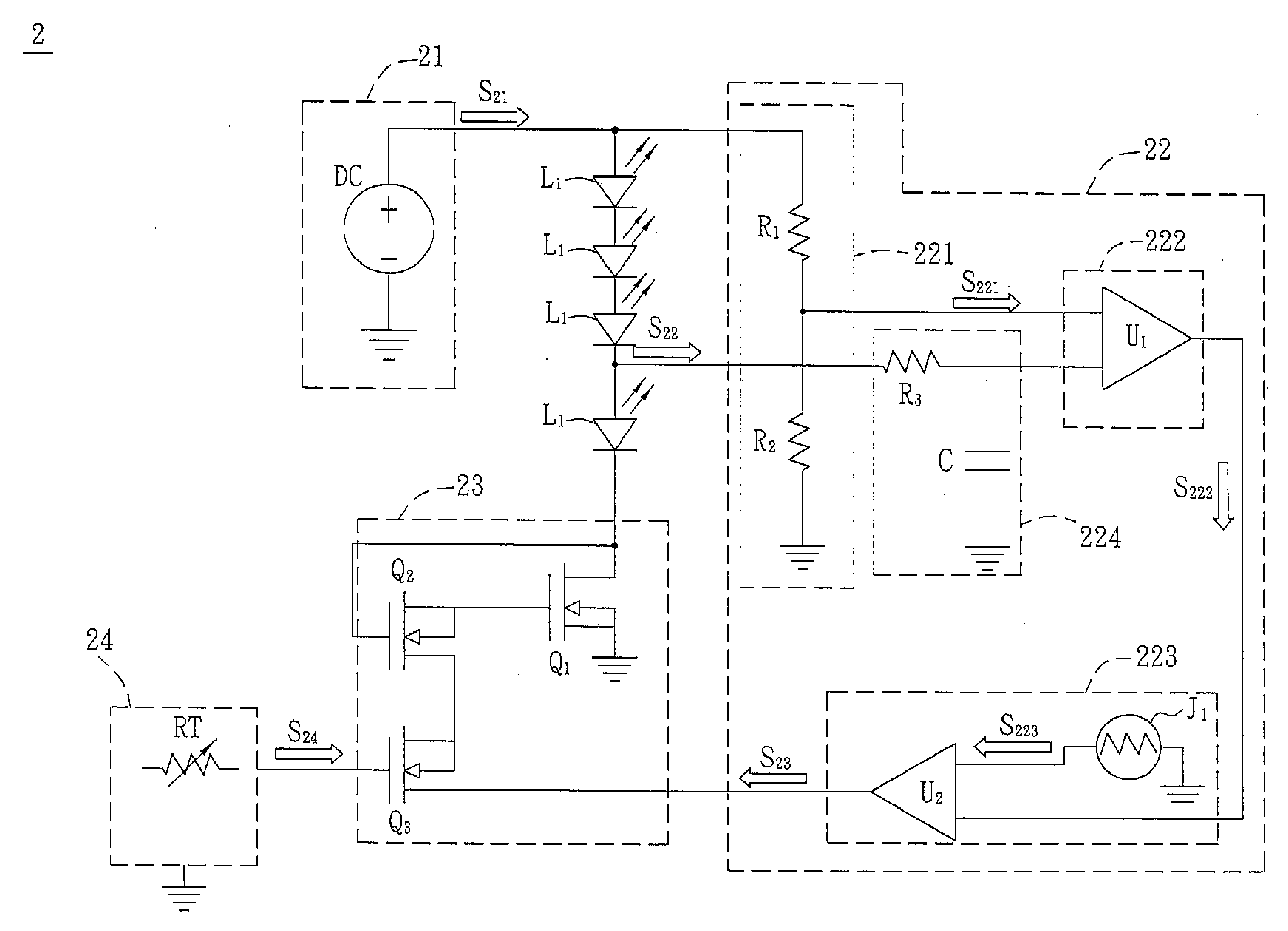
LED driver circuit capable of adjusting output current
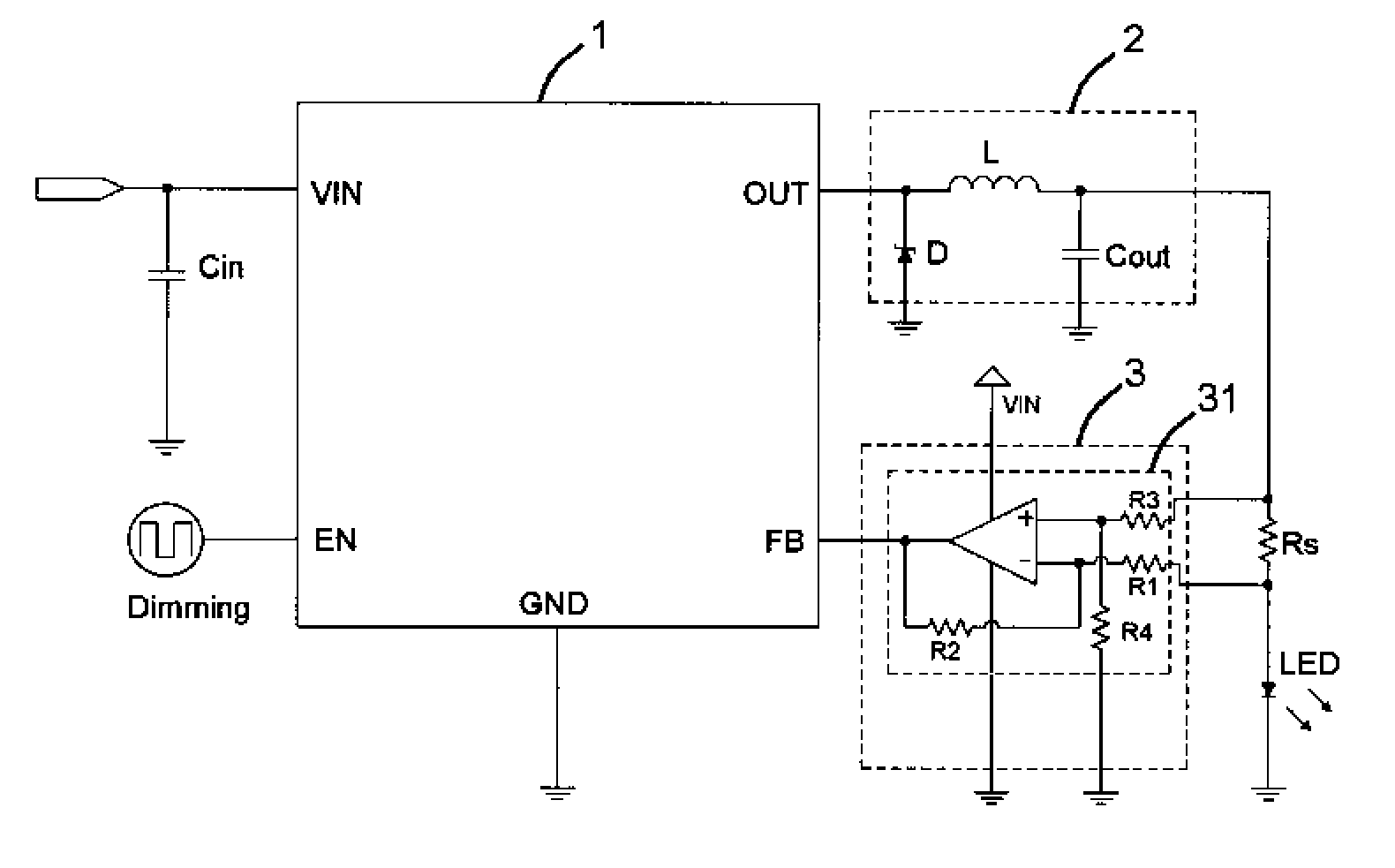
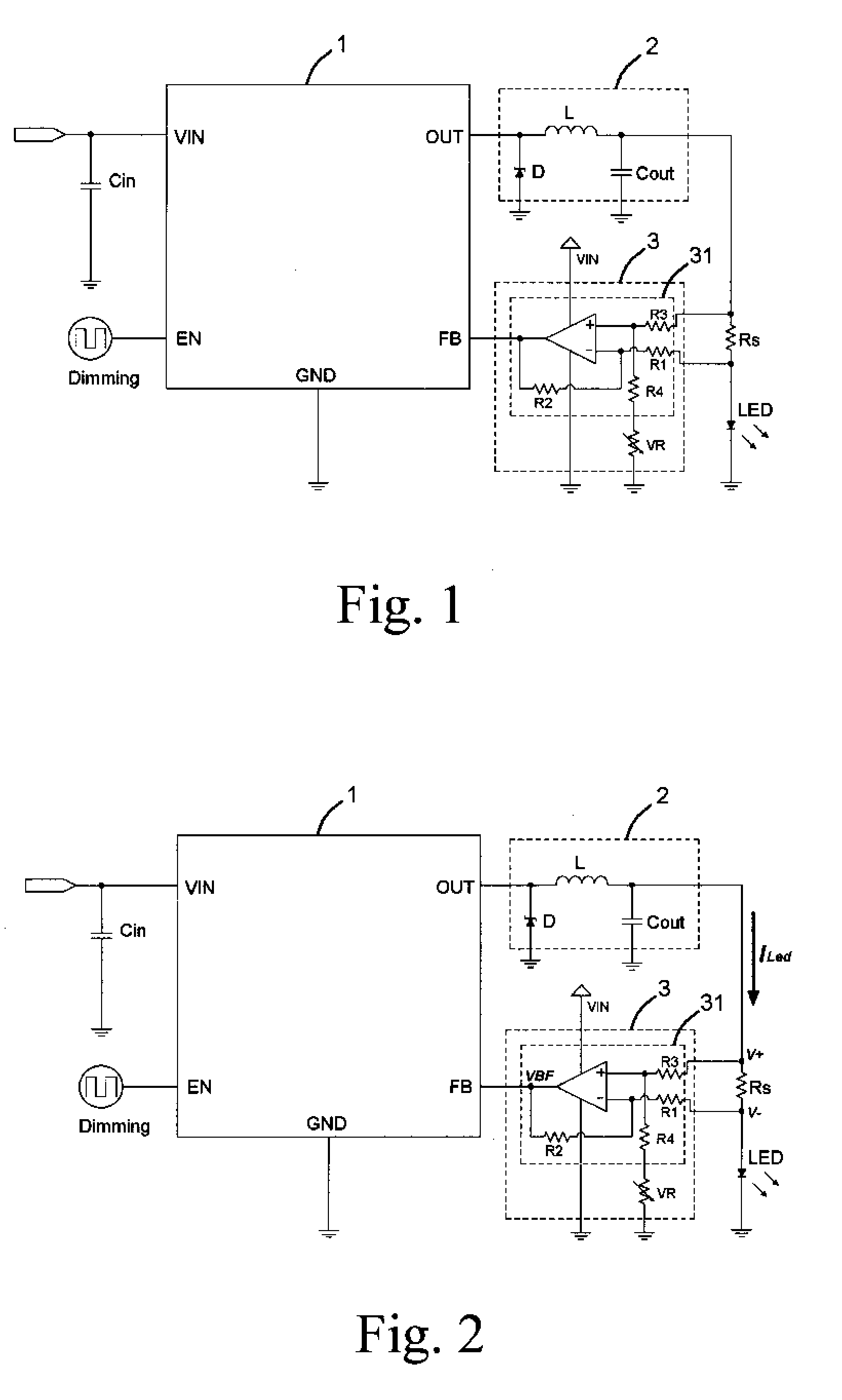
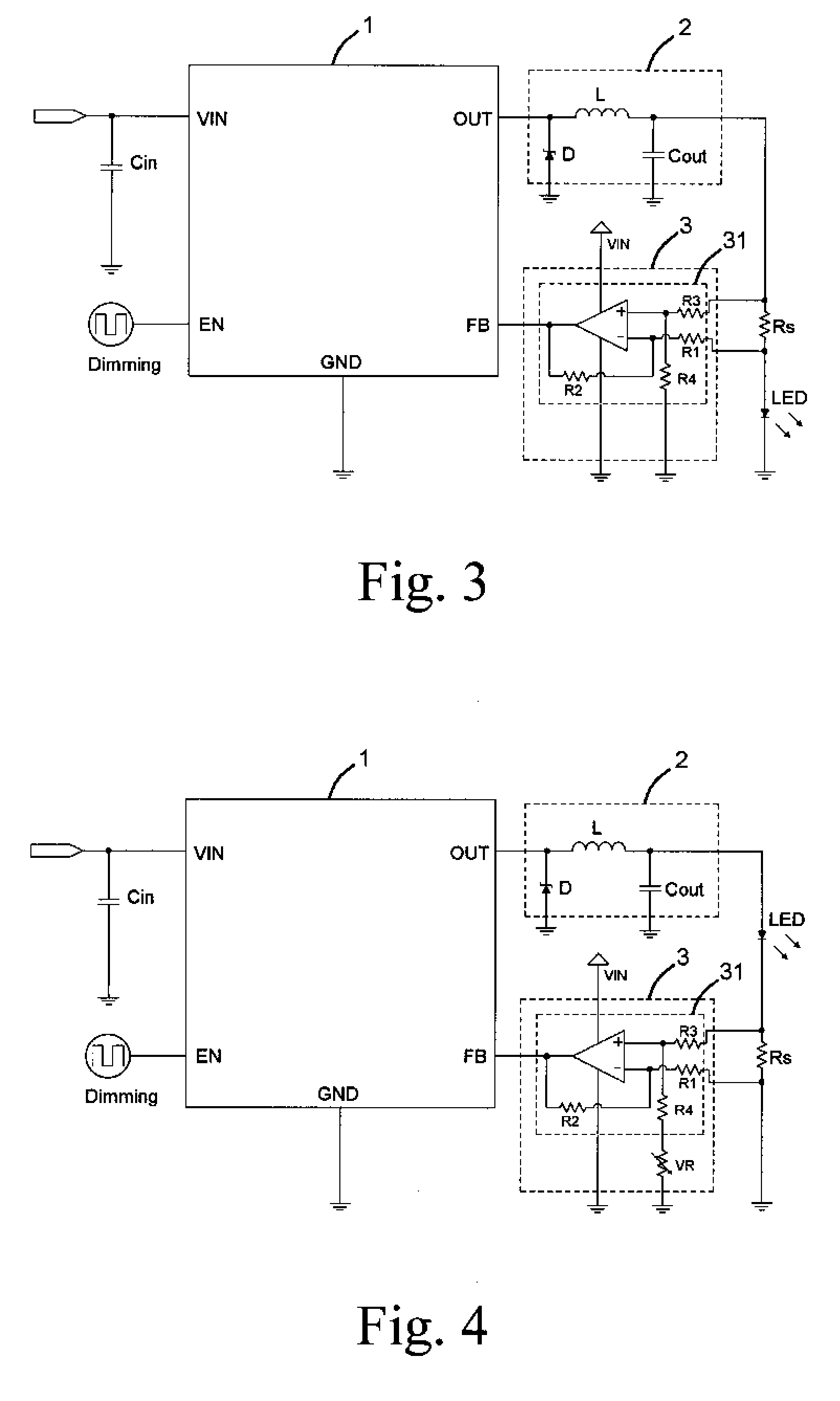
InactiveUS7714520B2Low costControl performanceElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementPower controllerVoltage regulation
An LED driver circuit includes a power controller, a voltage regulator, a detecting resistor, a light emitting device, and a voltage detecting circuit. The voltage detecting circuit has a first input end connected to a higher potential end of the detecting resistor, and a second input end thereof is connected to a lower potential end of the detecting resistor. The output end of the voltage detecting circuit is connected to a feedback end of the power controller so as to output a detected voltage signal to the power controller for adjusting the output voltage and supplying a stable and proper value of current to the light emitting device. The voltage detecting circuit is a differential amplifier capable of detecting the voltage difference between the detecting resistor and amplifying it as a feedback to the power controller. Therefore, the output current from the power controller is precisely controlled.
Owner:LIU DA YI
Electric current driving type display device
ActiveUS8325118B2Variation in threshold voltageLuminance can be correctedCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SHARP KK
Digital-to-analog converting circuit, electrooptical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7006026B2Easy to correctSimple circuit configurationElectric signal transmission systemsStatic indicating devicesDigital dataImaging data
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
LED display apparatus and video display apparatus
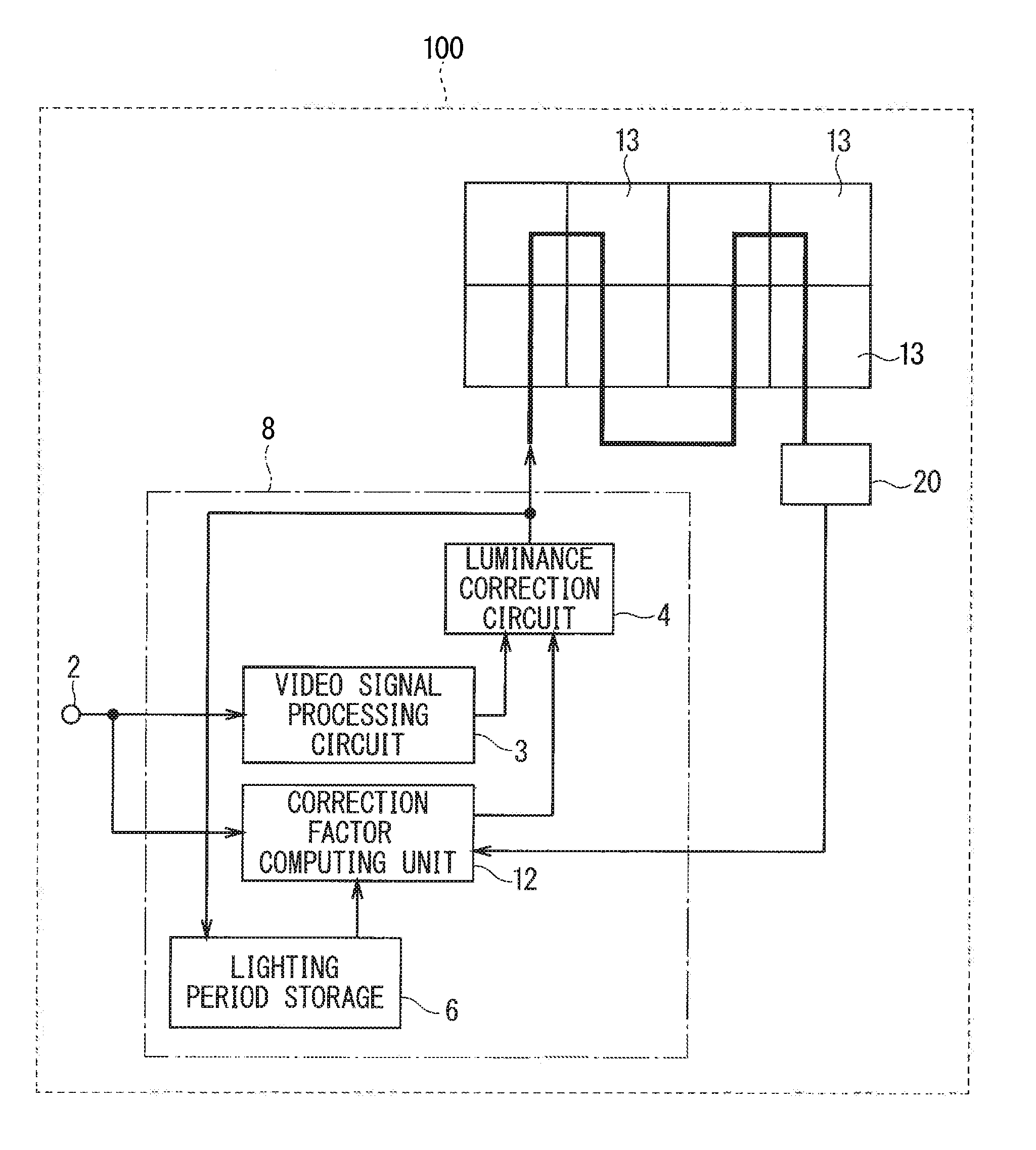
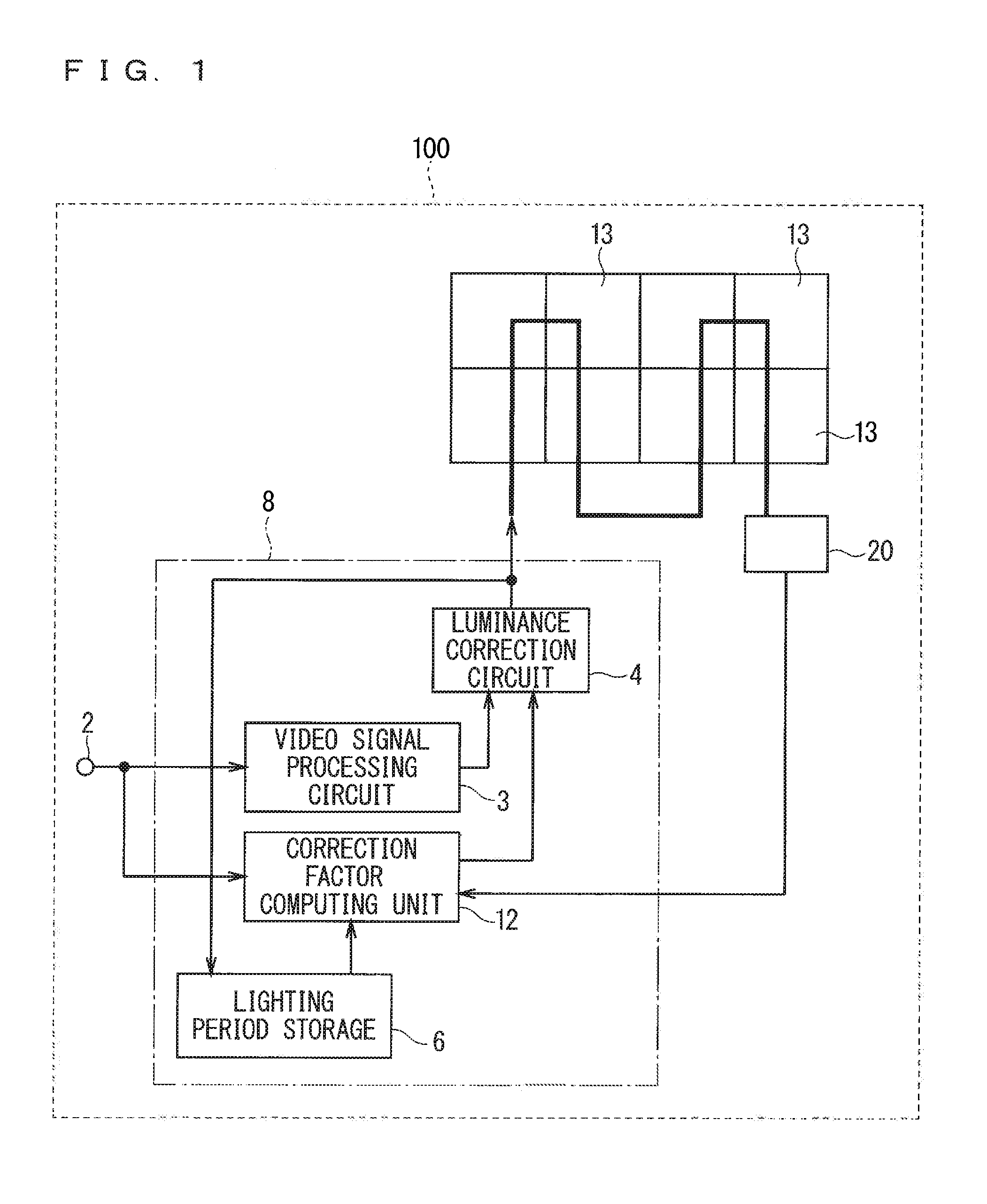
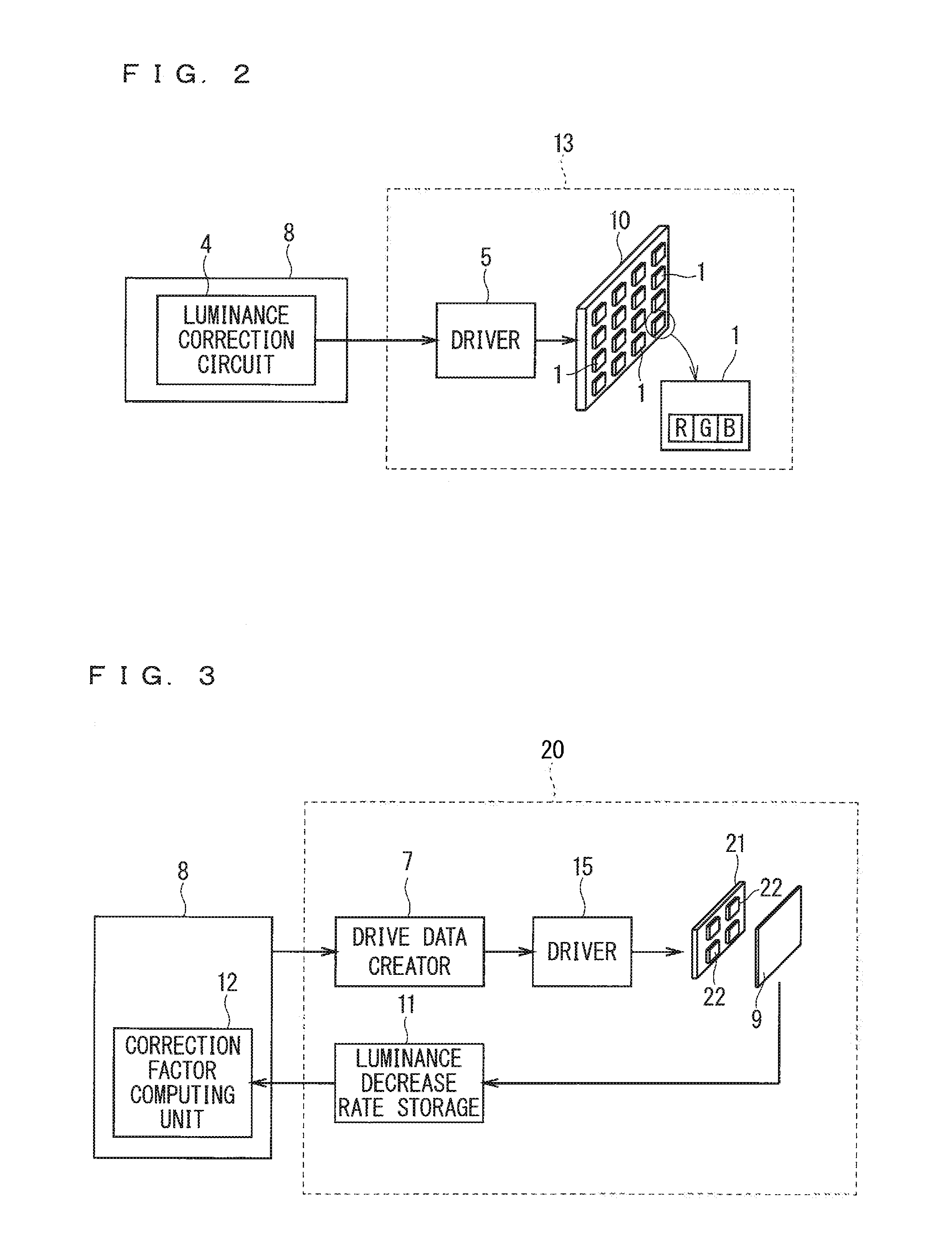
InactiveUS20160343349A1Poor viewabilityHigh precisionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLED displayComputer science
An LED display apparatus includes an LED aging unit, a correction factor computing unit, and a luminance correction circuit. The LED aging unit includes an LED aging display that includes at least one second LED, a luminance measurer that measures luminance decrease rates of the second LED per color correspondently to lighting periods of first LEDs, and a luminance decrease rate storage that stores the luminance decrease rates. The correction factor computing unit computes correction factors for correcting luminances of the first LEDs per color in accordance with cumulative lighting periods of the first LEDs of corresponding colors and the luminance decrease rates of corresponding colors. The luminance correction circuit corrects the luminance of the first LEDs per color in accordance with the correction factors.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Digital-to-analog converting circuit, electroopitcal device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20060017589A1Easy to correctSimple circuit configurationElectric signal transmission systemsSolid-state devicesDigital dataEngineering
Aspects of the invention can provide a digital-to-analog converting circuit capable of, after converting digital data into an analog current, correcting the current value based on digital current correction data without any complex processing. The exemplary digital-to-analog converting circuit can include a first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion and a second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion. First digital data (image data) can input to the first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion, and second digital data (current correction data) can input to the second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion. After the first digital-to-analog converting circuit portion converts the image data into a first analog current, the second digital-to-analog converting circuit portion can correct the first analog current based on the current correction data, and outputs the corrected current as a second analog current.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS9224908B2Reduce degradationReduces invasion of noiseStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectron
An electro-optical device includes a scanning line and a data line intersecting each other, a pixel circuit provided at a position corresponding to an intersection of the scanning line and the data line, and a power supply wiring line that supplies a given potential. The pixel circuit includes a light emitting element and a driving transistor configured to control a current flowing through the light emitting element. A gate electrode of the driving transistor is electrically connected via a first relay electrode to a given node. The first relay electrode is formed in the same layer as the power supply wiring line and the data line. The first relay electrode is surrounded on at least three sides by the power supply line.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
LED driver circuit capable of adjusting output current
InactiveUS20090309510A1Stable and proper valueReduce current noiseElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementPower controllerVoltage regulation
Owner:LIU DA YI
Video display apparatus for correcting luminance difference between display pixels
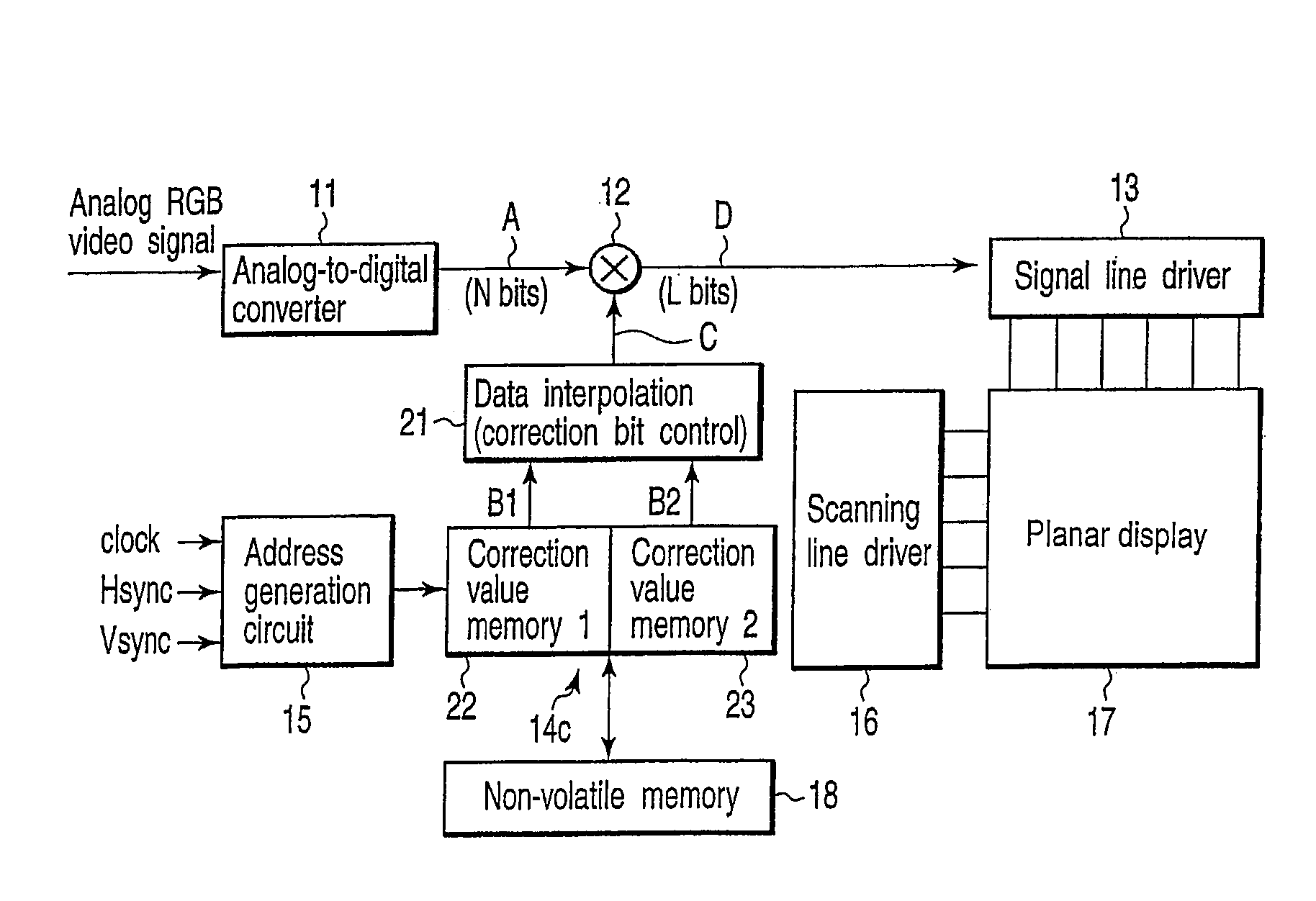
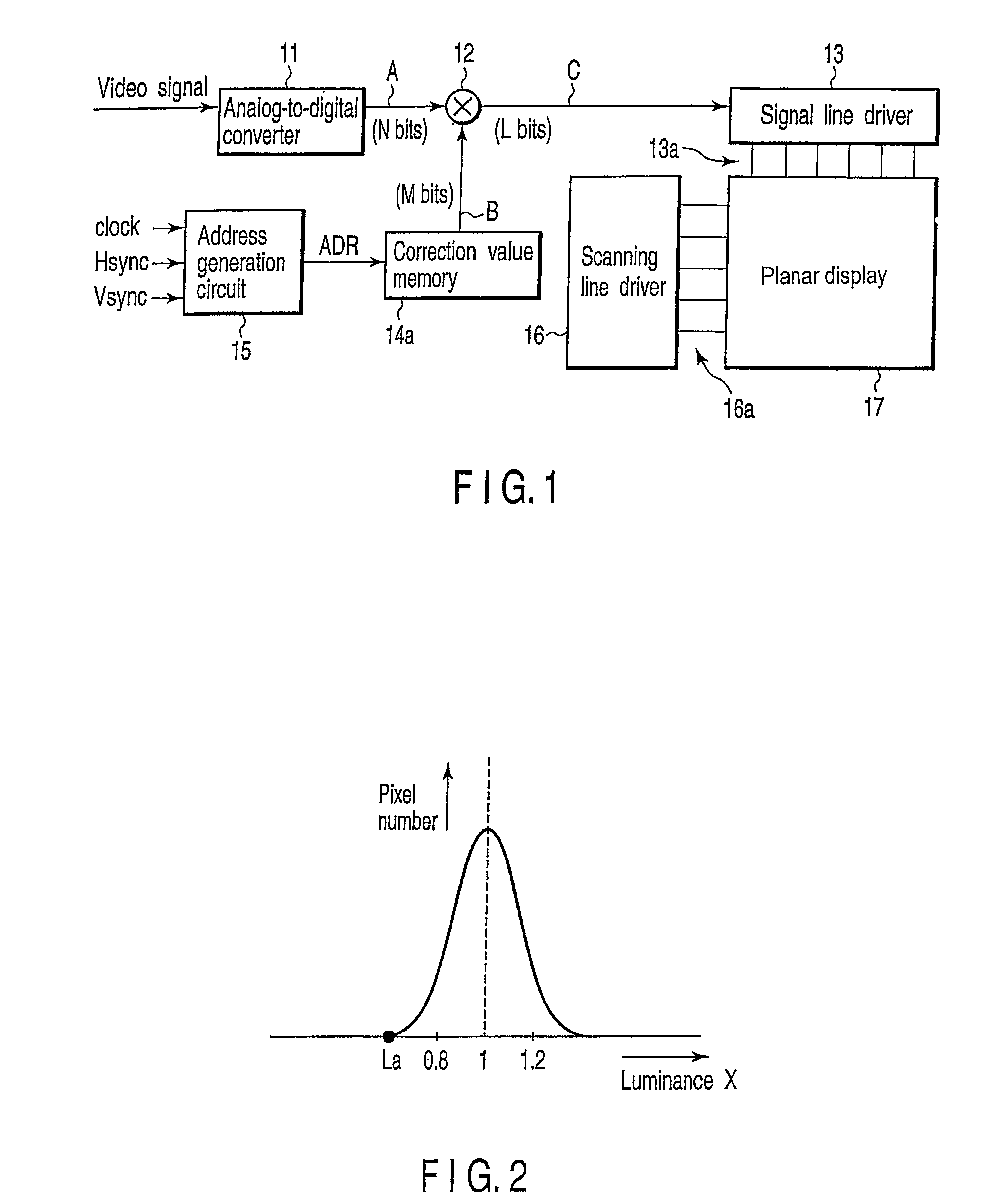
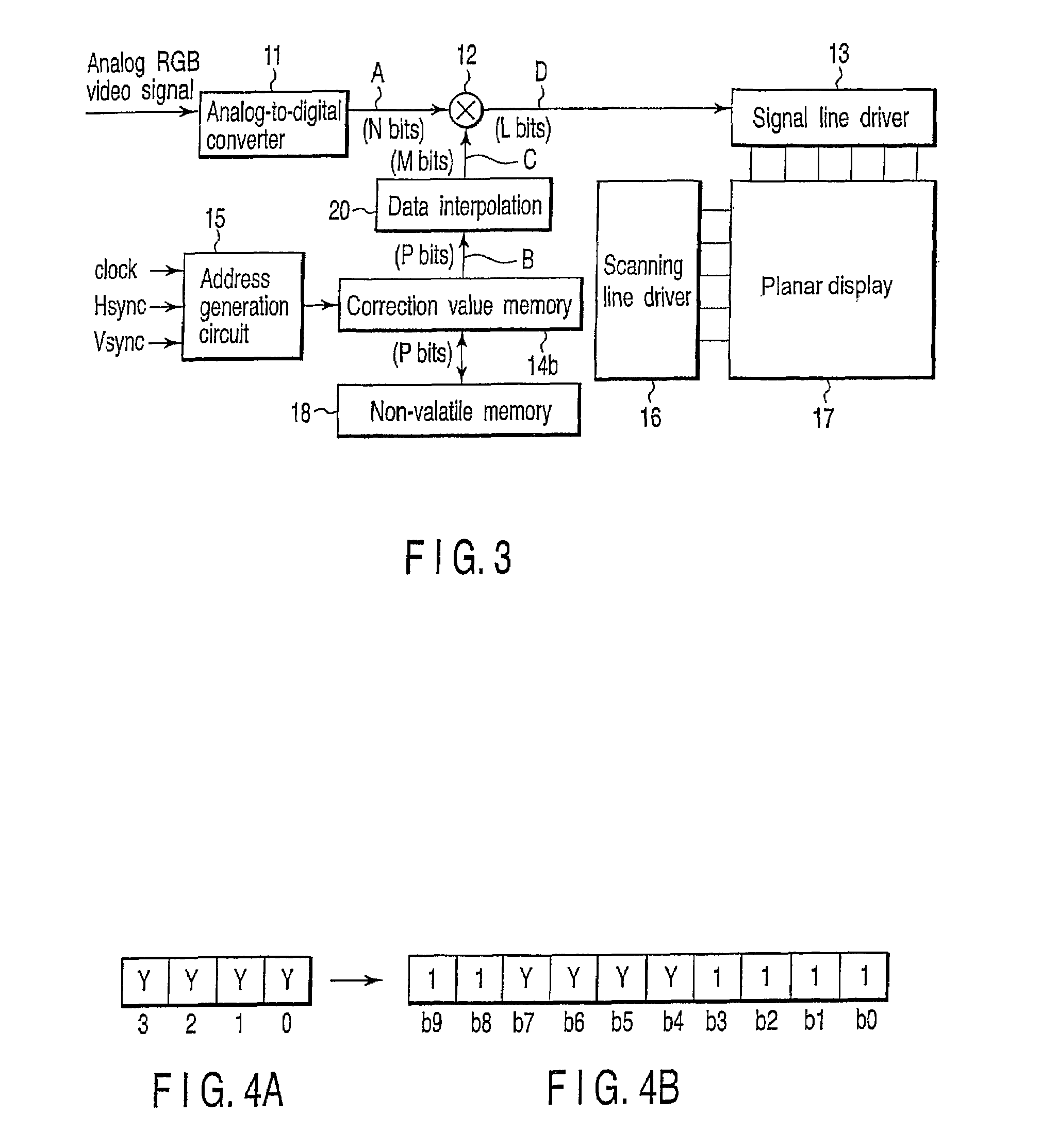
InactiveUS7345713B2Luminance of display is correctedDecrease in luminanceTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsDigital videoDisplay device
An analog-to-digital converter converts a video signal into a digital video signal consisting of N bits and outputs the converted signal. A correction value memory stores correction data consisting of M bits which is used to correct the difference in luminance between display pixels on a display. A multiplier multiplies the video signal consisting of N bits output from the analog-to-digital converter by the correction data consisting of M bits stored in the correction value memory, and outputs a video signal consisting of L bits with which the difference in luminance between display pixels on the display is corrected.
Owner:TOSHIBA VISUAL SOLUTIONS CORPORATION
Method and device for reducing image color noise
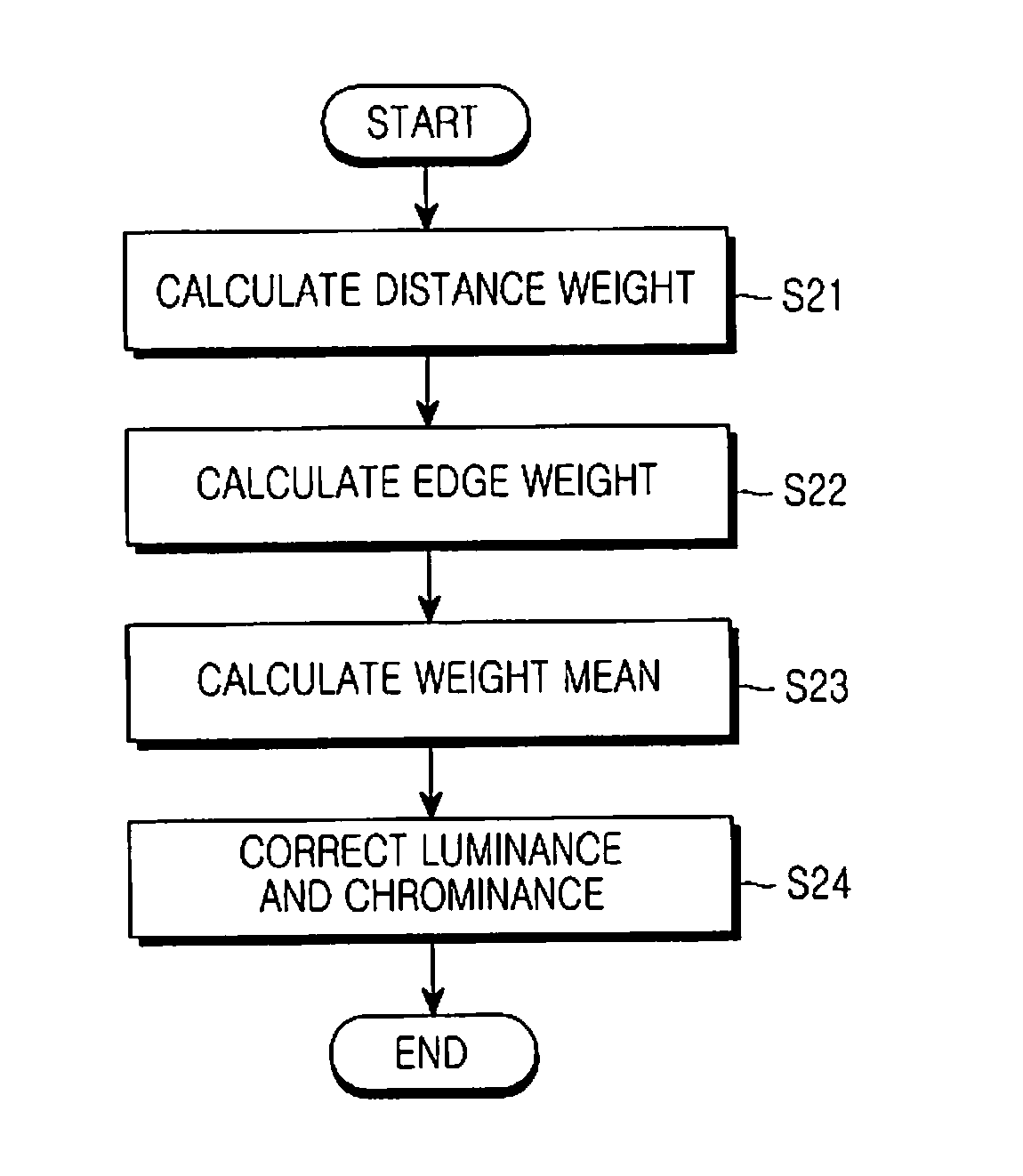
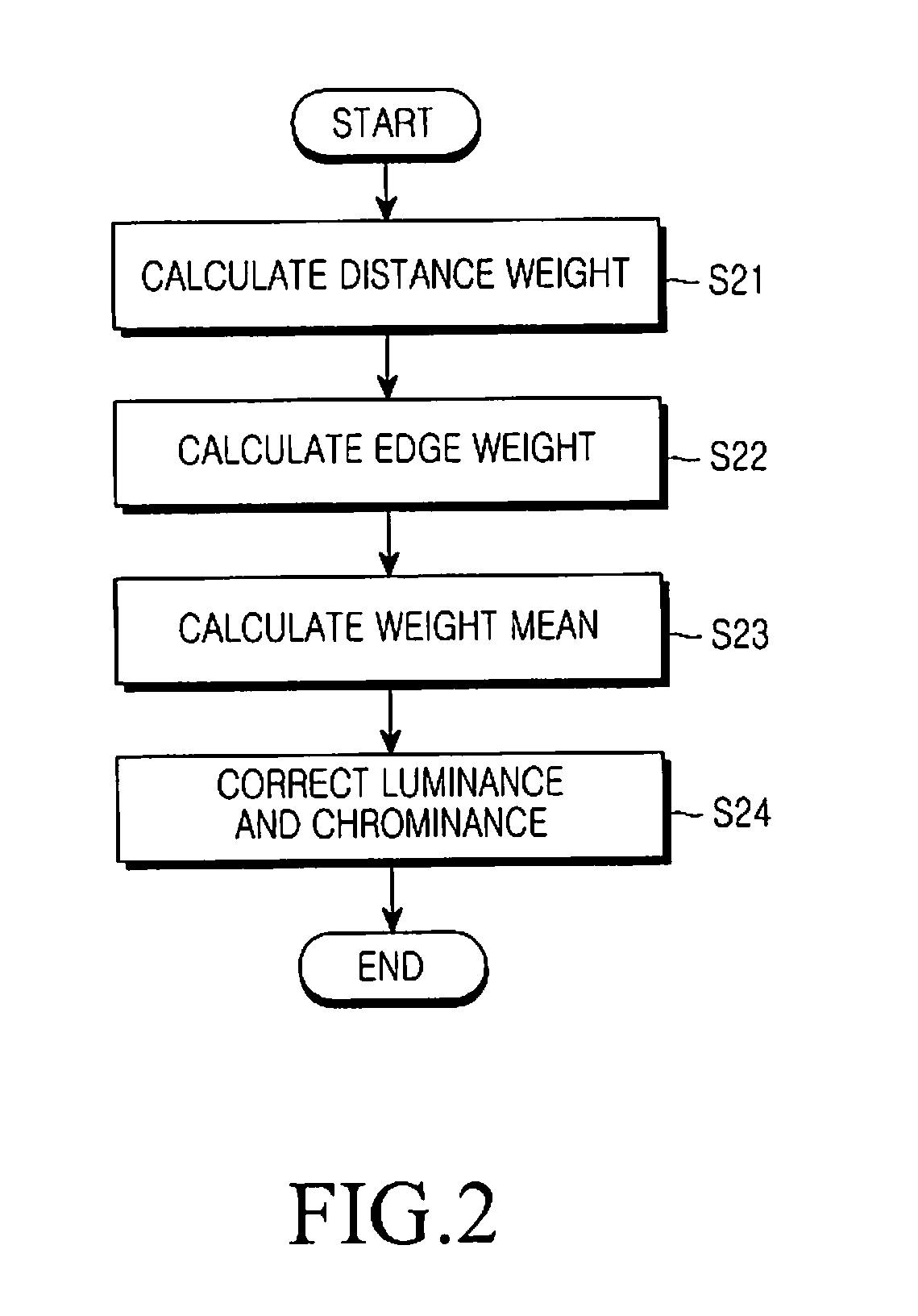
InactiveUS20110221937A1Reduce noiseHigh definitionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer scienceLightness
A device and method for reducing color noise of an image by using a distance weight depending on a distance from a central pixel for each pixel of an image and an edge weight depending on the difference in luminance and chrominance with the central pixel is provided, which can effectively reduce the color noise of the image by using the correlation between the luminance and the chrominance and edge characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data processing device for display device, display device equipped with same and data processing method for display device
ActiveUS9818373B2Suppressing time degradationIncrease in number can be suppressedCathode-ray tube indicatorsTemperature UnitDisplay device
A unit equivalent value acquiring unit acquires a normal-temperature unit equivalent use time Δtn by using a temperature sensor, first to third LUTs, and a first multiplying unit. An integration unit acquires an equivalent cumulative use time to by integrating the normal-temperature unit equivalent use time Δtn. A maximum value detecting unit detects a maximum equivalent cumulative use time tnmax. A dividing unit acquires a correction coefficient Kcmp by dividing total degradation E(tnmax,Tn) acquired by a fourth LUT by total degradation E(tn,Tn) acquired by a fifth LUT. Accordingly, there is provided a data processing device for a display device capable of preventing burn-in while suppressing time degradation of an electro-optical element and increase in the number of wires.
Owner:SHARP KK
Flat panel display
InactiveUS7002302B2Luminance can be correctedExtend the life cycleTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesHigh resistanceDisplay device
The present invention discloses an organic light emitting diode capable of obtaining proper luminance and long life cycle by controlling an amount of current flowing through an organic electroluminescent device per unit pixel. The organic light emitting diode includes a luminescent device and first and second transistors for driving the luminescent device, wherein the first and second transistors have different resistance values. The first transistor is a driving transistor for driving the luminescent device. The second transistor is a switching transistor for switching on and off the driving transistor. The driving transistor may have a higher resistance value than the switching transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
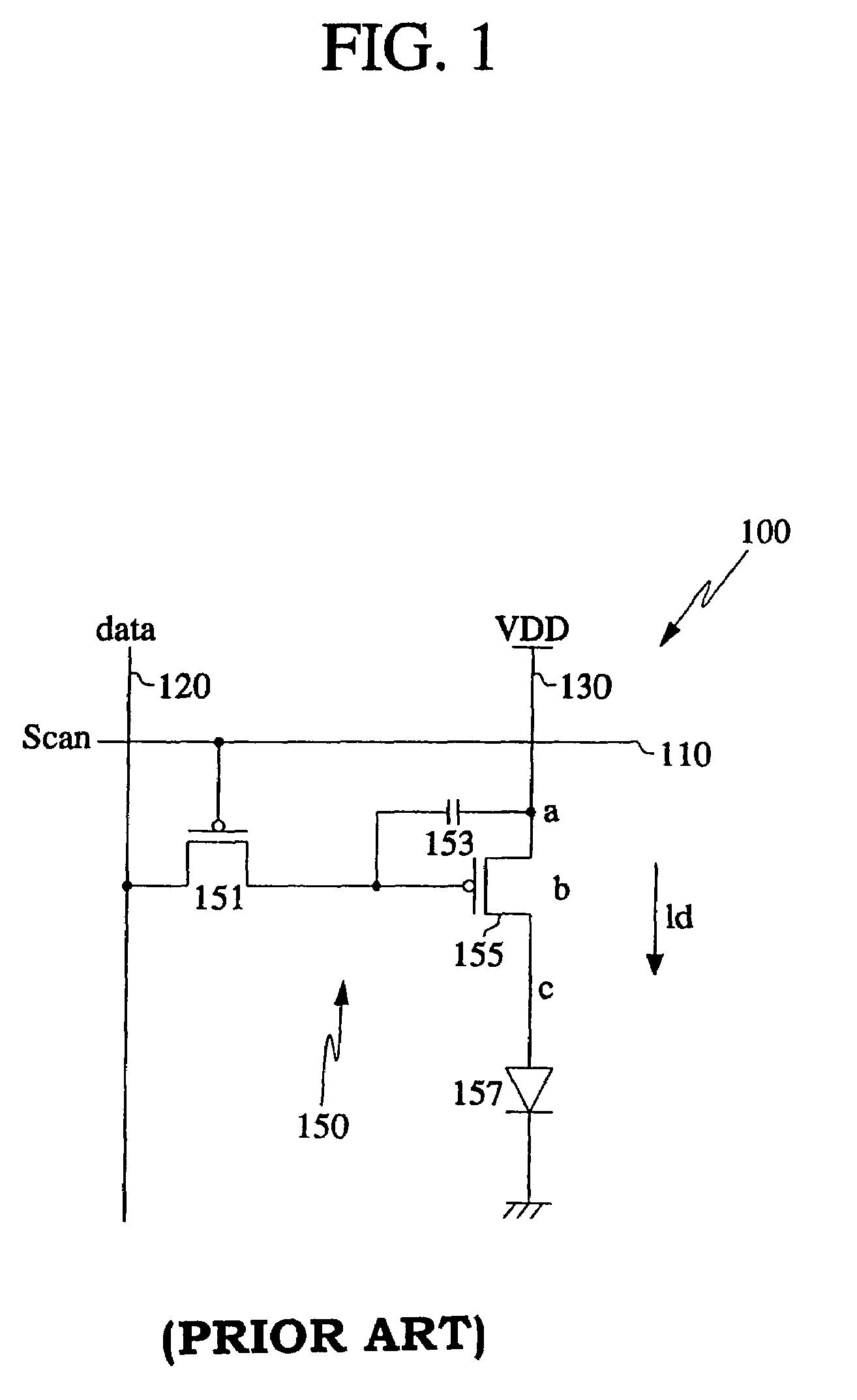
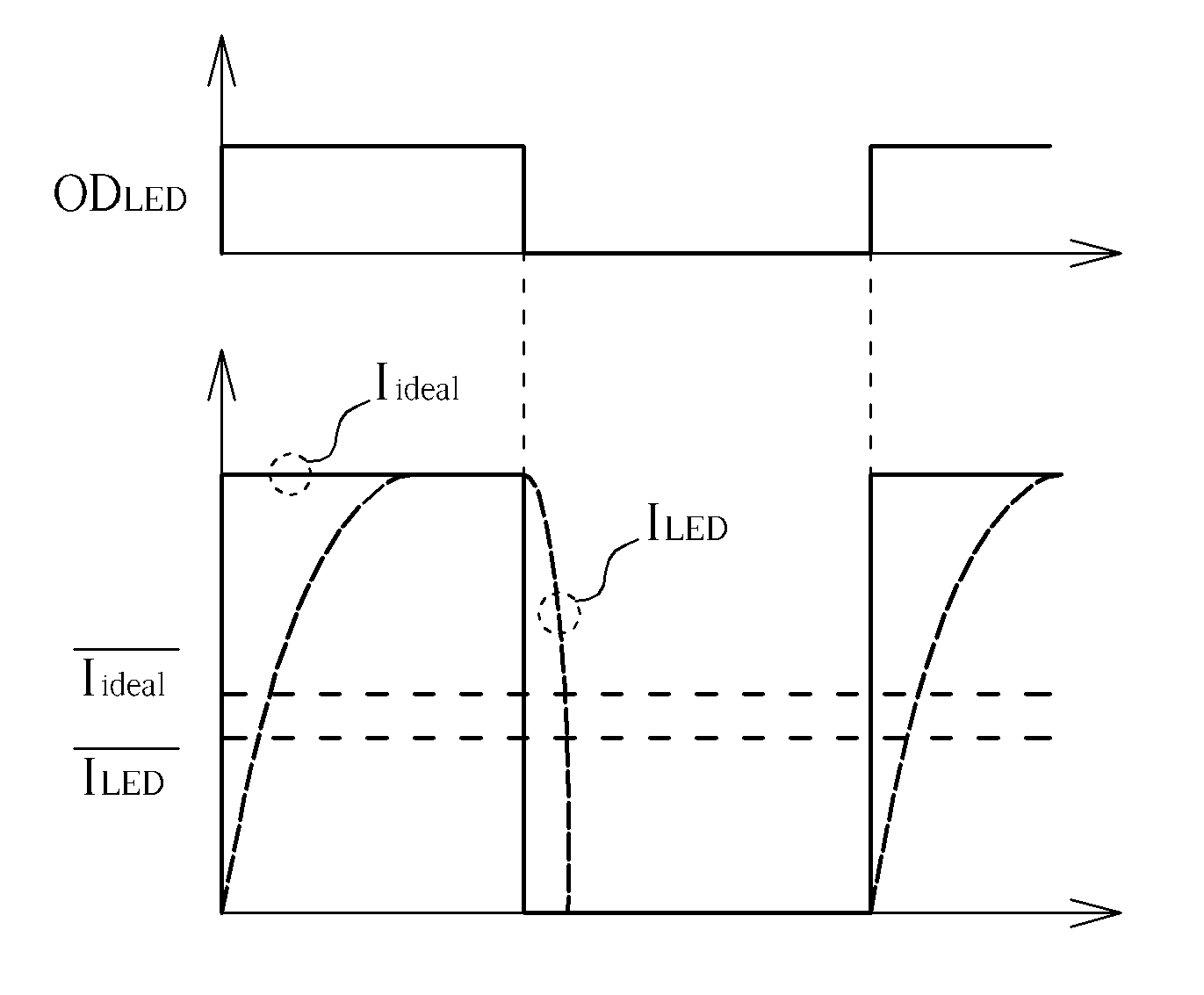
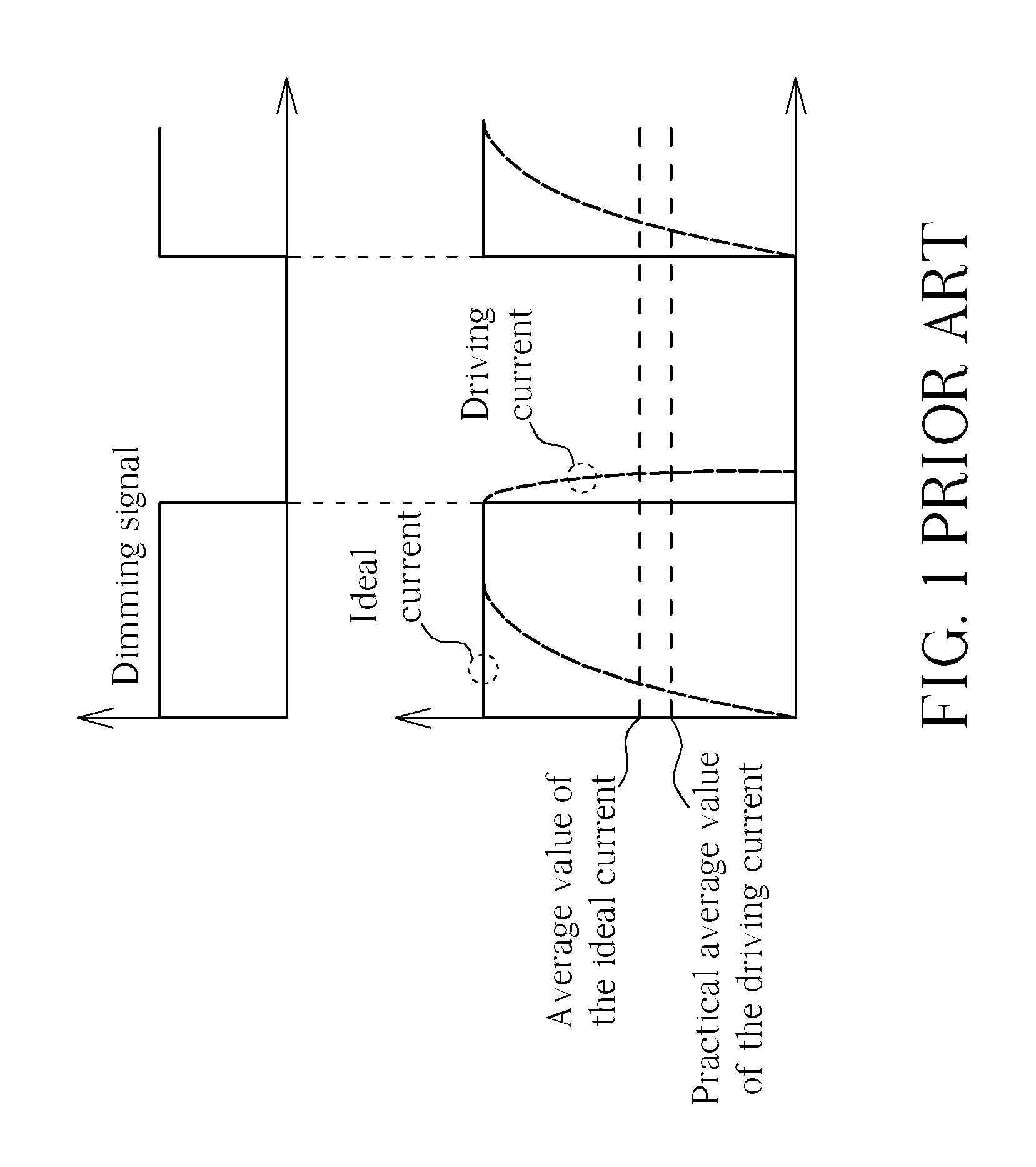
Method of dimming
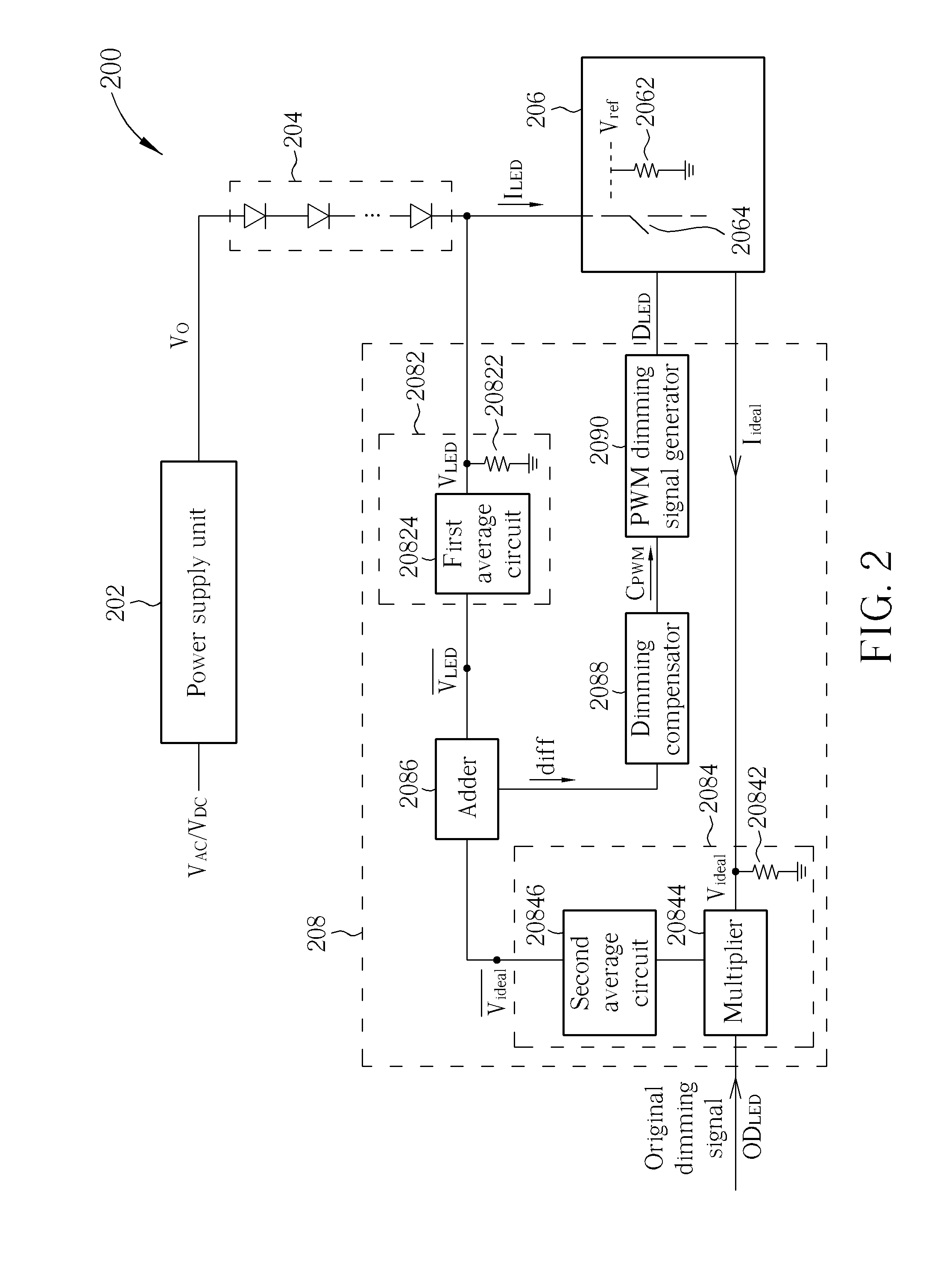
InactiveUS20120019155A1Luminance can be correctedImprove display qualityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentEngineering
A power supply unit provides a voltage, and a driving current to a series of light emitting diodes. A dimming unit adjusts a duty cycle of an original dimming signal to generate a dimming signal according to the driving current and an ideal current. A current sink coupled to the series of light emitting diodes adjusts a duty cycle of the driving current according to the dimming signal.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
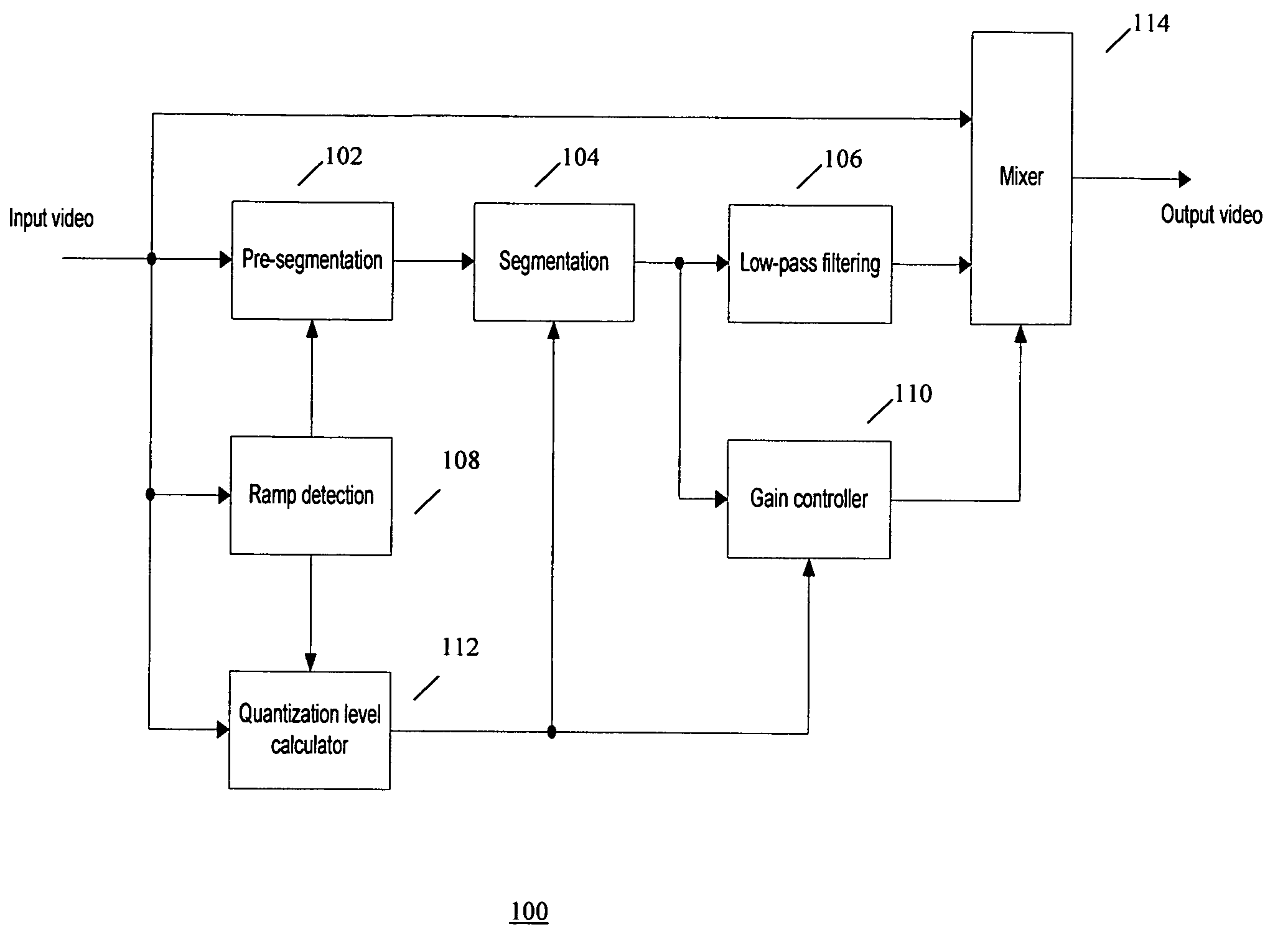
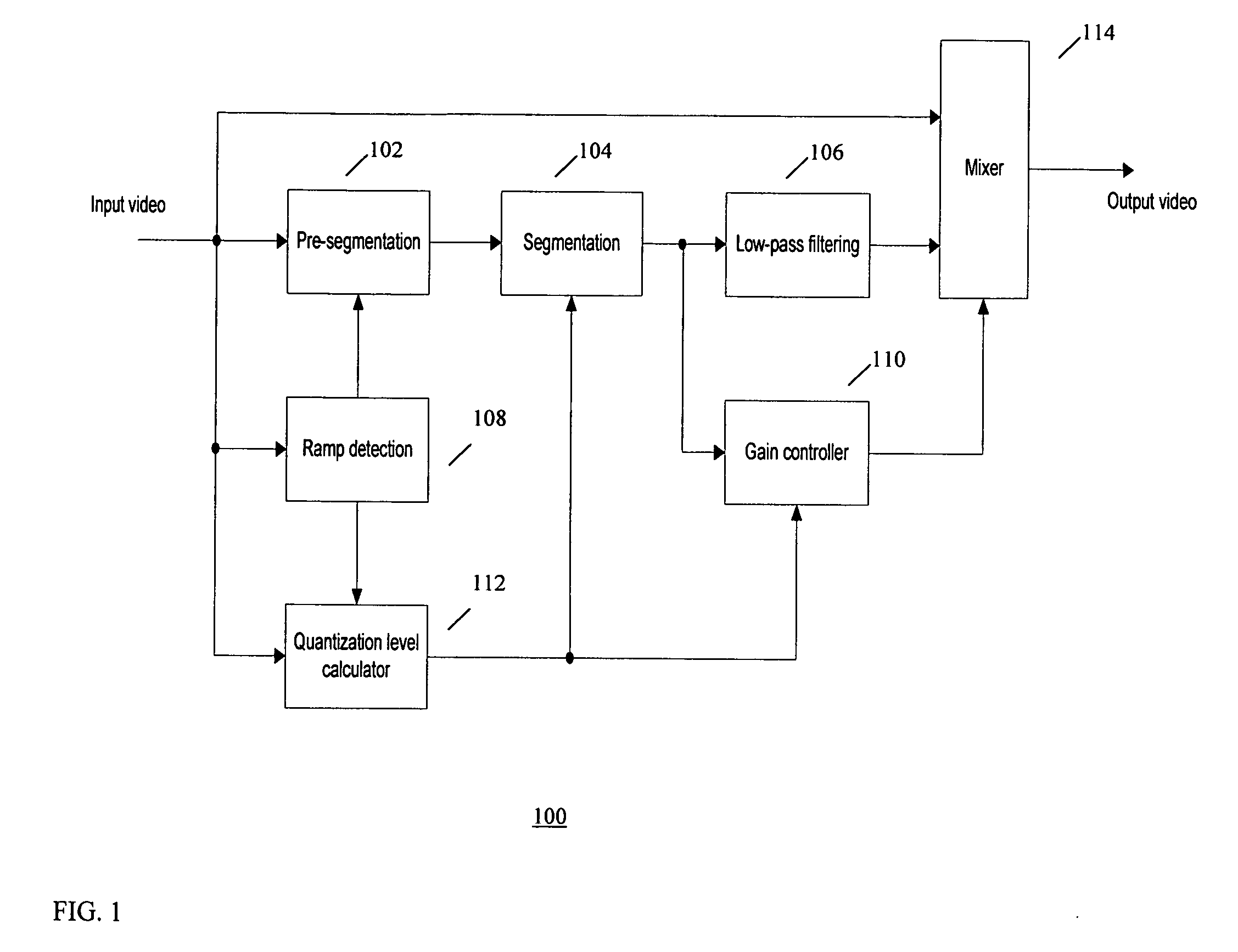
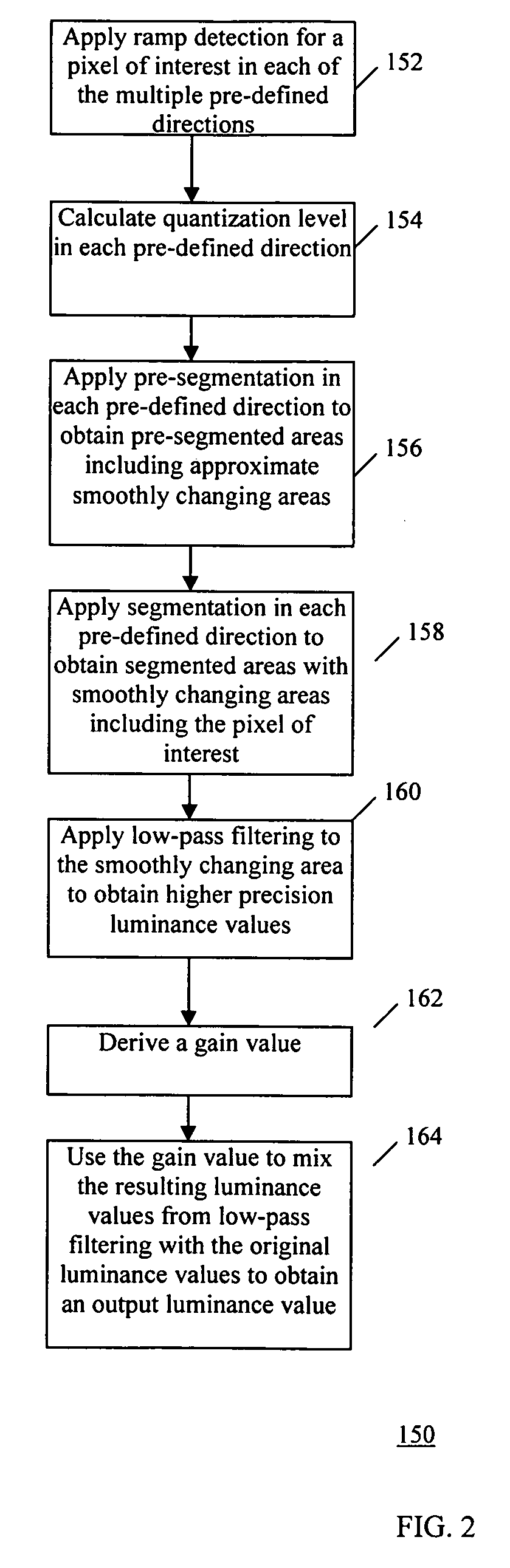
Method and system for adaptive quantization layer reduction in image processing applications
InactiveUS20080175474A1High precision luminanceReduced quantization artifactTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging processing
A method and a system for adaptively (dynamically) reducing quantization layer reduction for removing quantization artifacts in quantized video signals is provided. Adaptively reducing quantization layer reduction involves detecting if a selected pixel in a quantized image belongs to a ramp area in each of multiple pre-defined directions, dynamically selecting a quantization level for each of the pre-defined directions based on the corresponding detection results, and refining the pixel based on the selected quantization levels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display device and display control method
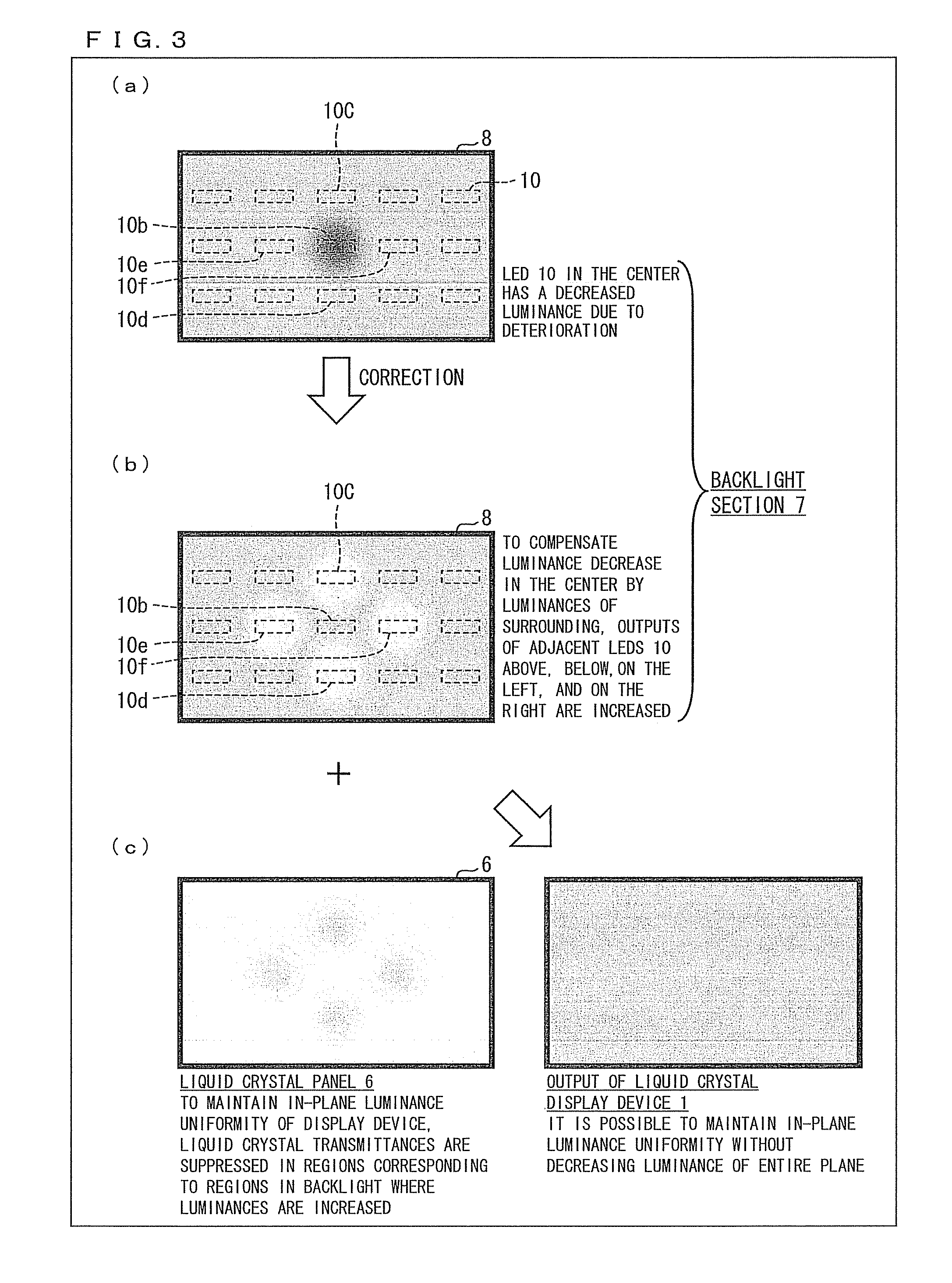
ActiveUS8791932B2Luminance can be correctedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A display device includes: an LED control section (4) for carrying out control in which (i) an output luminance of an LED (10) whose measured luminance is deviated from a reference luminance or (ii) output luminances of peripheral LEDs (10) which are provided around the LED (10) is or are corrected, respectively, by using control information of the plurality of LEDs, which control information contains (a) information on measured luminances of the plurality of LEDs, the information being obtained by the plurality of photosensors (11) and (b) positional information of the plurality of LEDs, the positional information being obtained by the plurality of photosensors (11), and a liquid crystal display control section (3) for controlling, based on (i) video signals which have been subjected to the video signal process and are supplied from a video signal processing section (2) and (ii) the control information supplied from the LED control section (4), (a) levels of video signals to be supplied to pixels corresponding to the LED (10), whose output luminance is corrected or (b) levels of video signals to be supplied to pixels corresponding to the peripheral LEDs, whose output luminances are corrected, the reference luminance being a luminance which is originally expected to be outputted from each of the plurality of LEDs.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device and driving method of the same
ActiveUS9117390B2Improve responseSimple displacementCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsDriving currentPower flow
A display device and a driving method thereof. The display device includes a plurality of pixels, each receiving a predetermined on-bias voltage transferred through a data line during one frame, receiving a first image data signal corresponding to the corresponding frame through the data line and storing the same, and emitting light according to a driving current that corresponds to a second image data signal that corresponds to the previous frame of the corresponding frame, and a first period for storing the first image data signal and a second period for light emission according to a driving current corresponding to the second image data signal overlap each other in one frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com