Process and gas-film air tower for treating hydrazine contained sewage generated in production of azodimethylamide
A technology for azodicarbonamide and wastewater treatment, which is applied in water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, separation methods, etc., can solve the problems of sodium carbonate consumption, low treatment cost, and no effect. Achieve full gas-liquid contact, low processing cost, and reduce pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
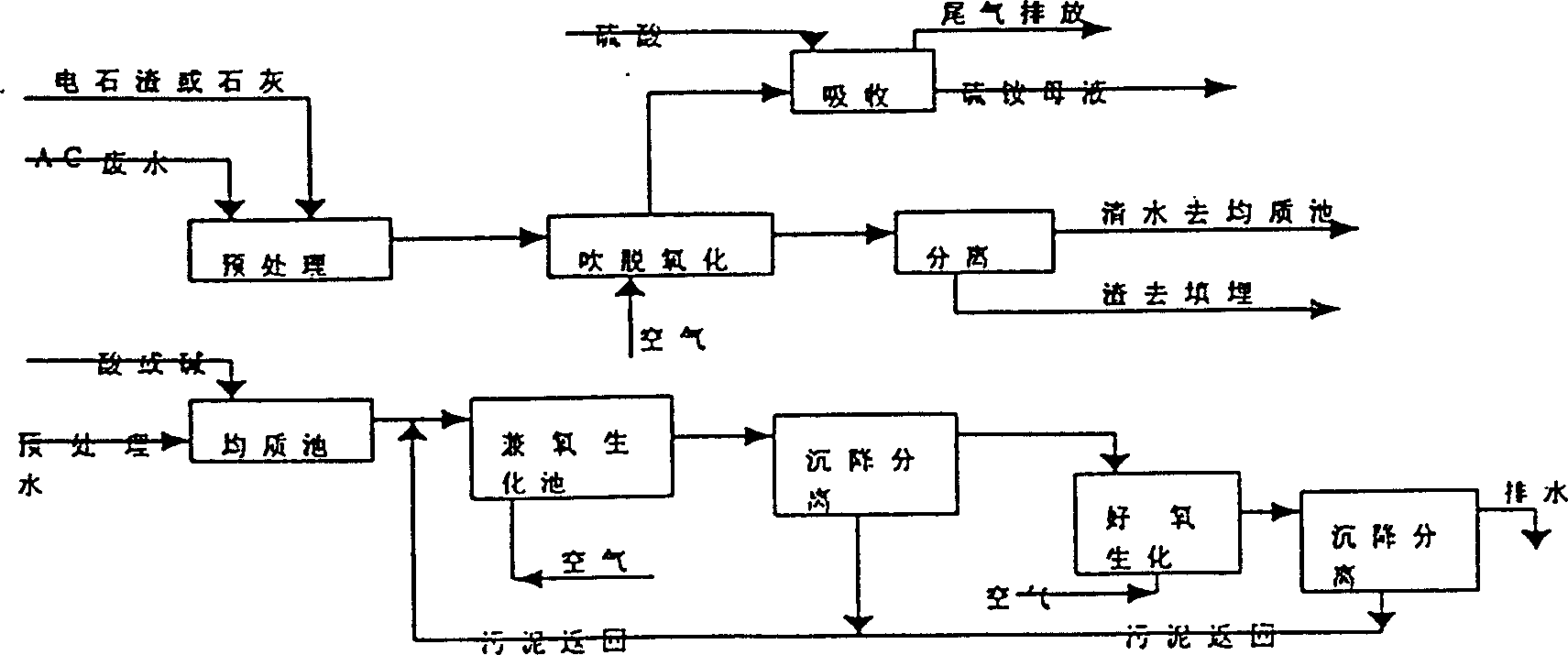
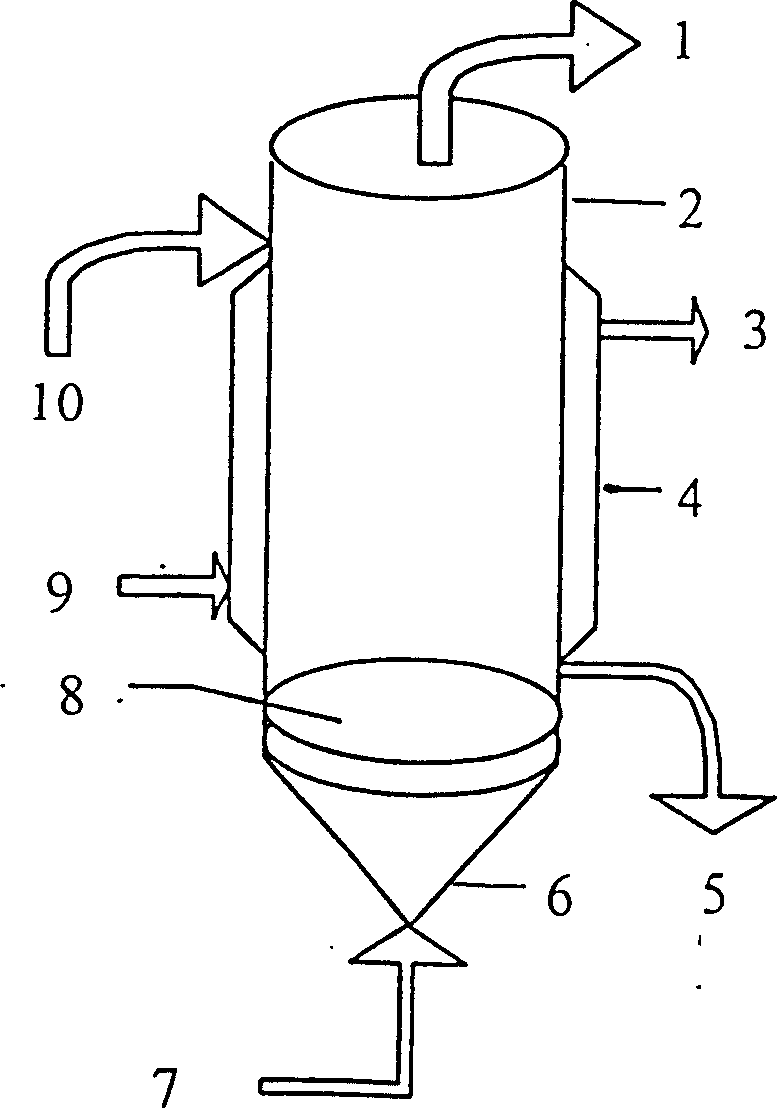
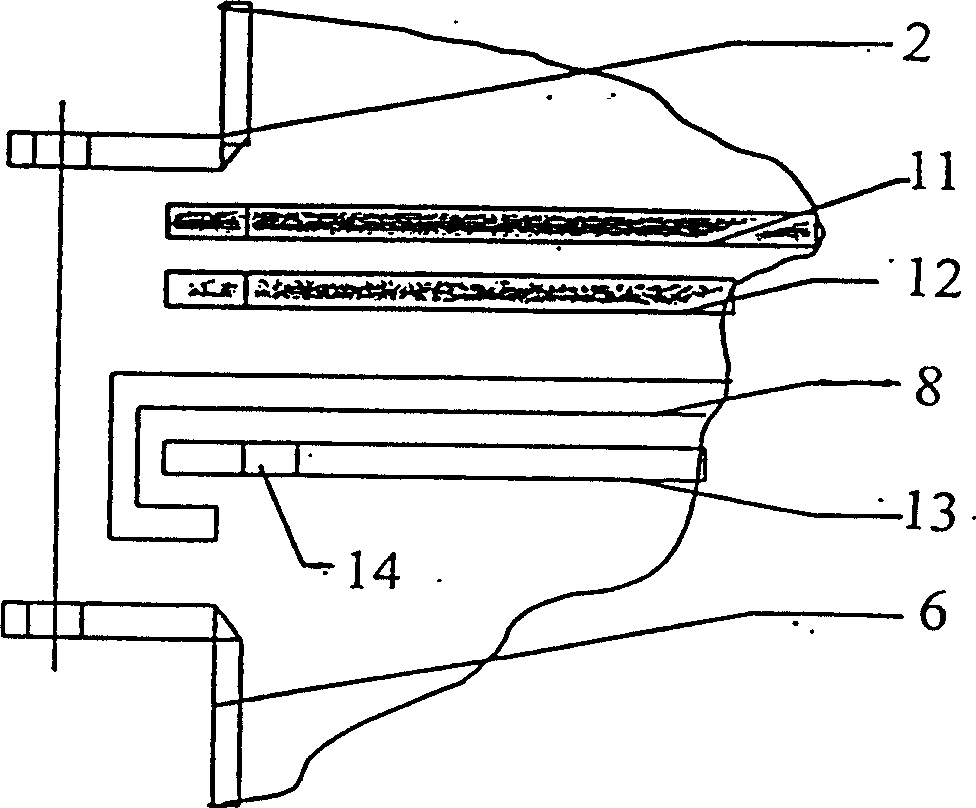
[0041] The treatment method of hydrazine-containing wastewater produced by the production of azodicarbonamide: the hydrazine-containing wastewater of azodicarbonamide is sent to the preprocessor through the sedimentation supernatant, and the calcium carbide slag is added, and the pH is adjusted to 10. The slurry is sent to the air film stripping Oxidation tower, under the conditions of temperature 50°C, gas-liquid ratio 300, pressure 0.01MPa, residence time 0.5 hours, carry out deoxidation, blow off the tail gas at the top of the tower, go through defoaming, cyclone separation, heat exchanger and then enter the absorption tower, use 50% of sulfuric acid is absorbed, non-condensable tail gas is discharged, the oxidizing liquid is discharged from the stripping tower into the filter press for pressure filtration, the filtrate enters the biochemical homogeneous pool, and the pretreated effluent is adjusted to pH6 with acid or alkali in the biochemical homogeneous pool, and Mix it w...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The treatment method for the hydrazine-containing wastewater produced by the production of azodicarbonamide is as follows: the hydrazine-containing wastewater of azodicarbonamide is sent to the preprocessor through the precipitation supernatant, and lime is added to adjust the pH to 14. The tower, under the conditions of temperature 98°C, gas-liquid ratio 900, pressure 0.2MPa, and residence time of 3 hours, blows off oxidation, and the tail gas blown off at the top of the tower enters the absorption tower after defoaming, cyclone separation, and heat exchanger, and uses 80 % sulfuric acid is absorbed, non-condensable tail gas is discharged, the oxidizing liquid is discharged from the stripping tower into the filter press for pressure filtration, the filtrate enters the biochemical homogeneous pool, and the pretreated effluent is adjusted to pH9 with acid or alkali in the biochemical homogeneous pool, and mixed with Mix other industrial biochemical wastewater or urban sew...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com