Patents
Literature
33 results about "Ciliary sulcus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
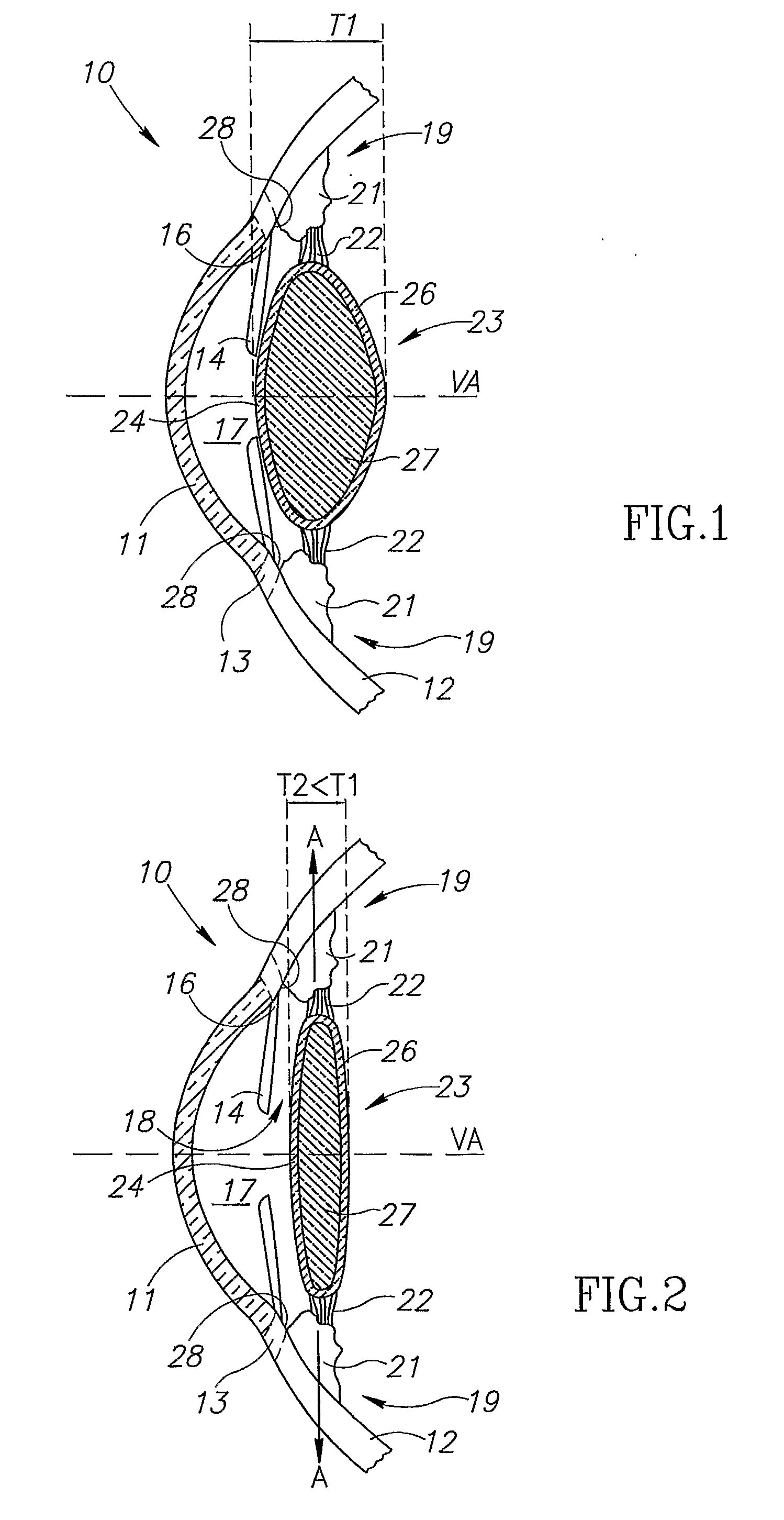
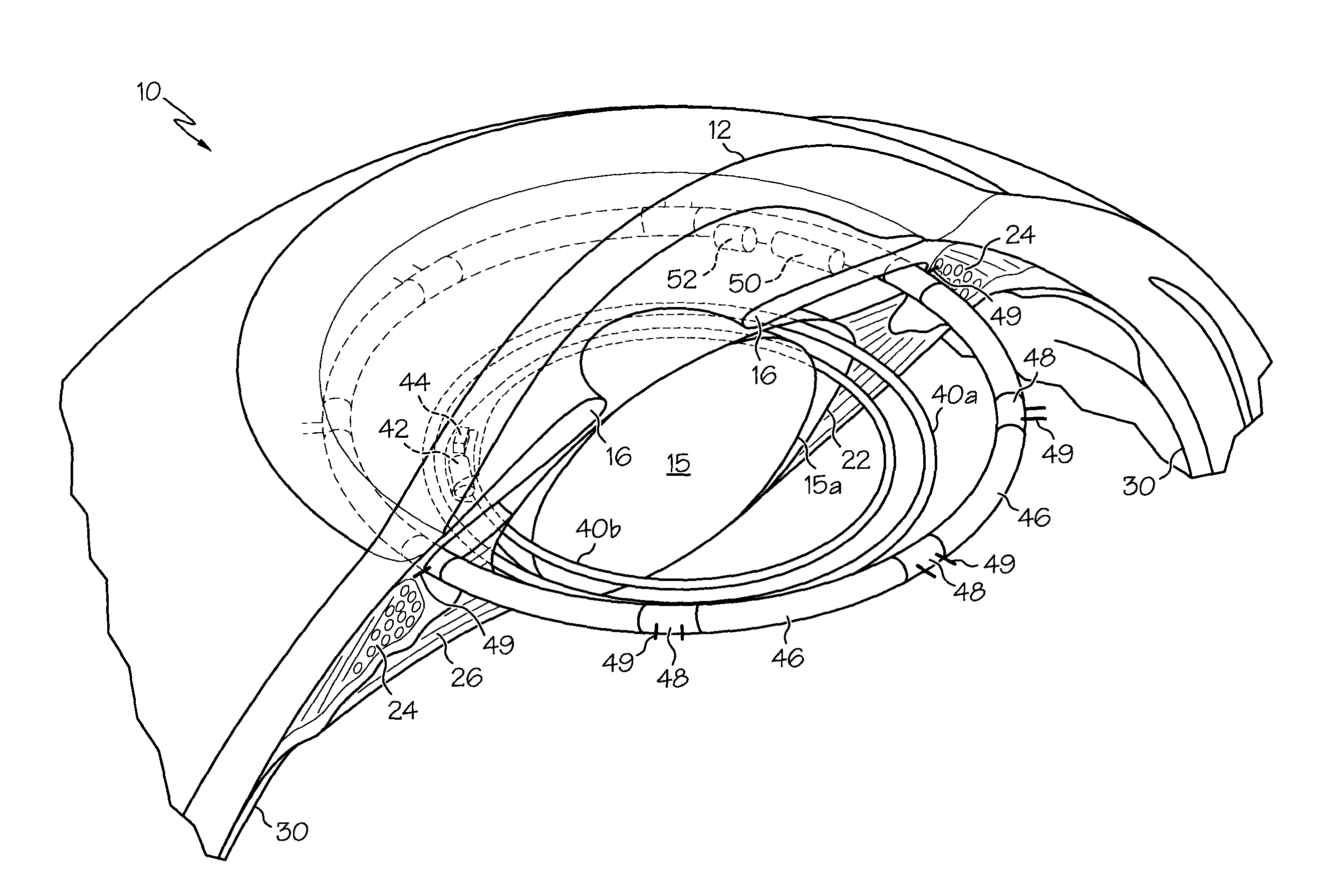
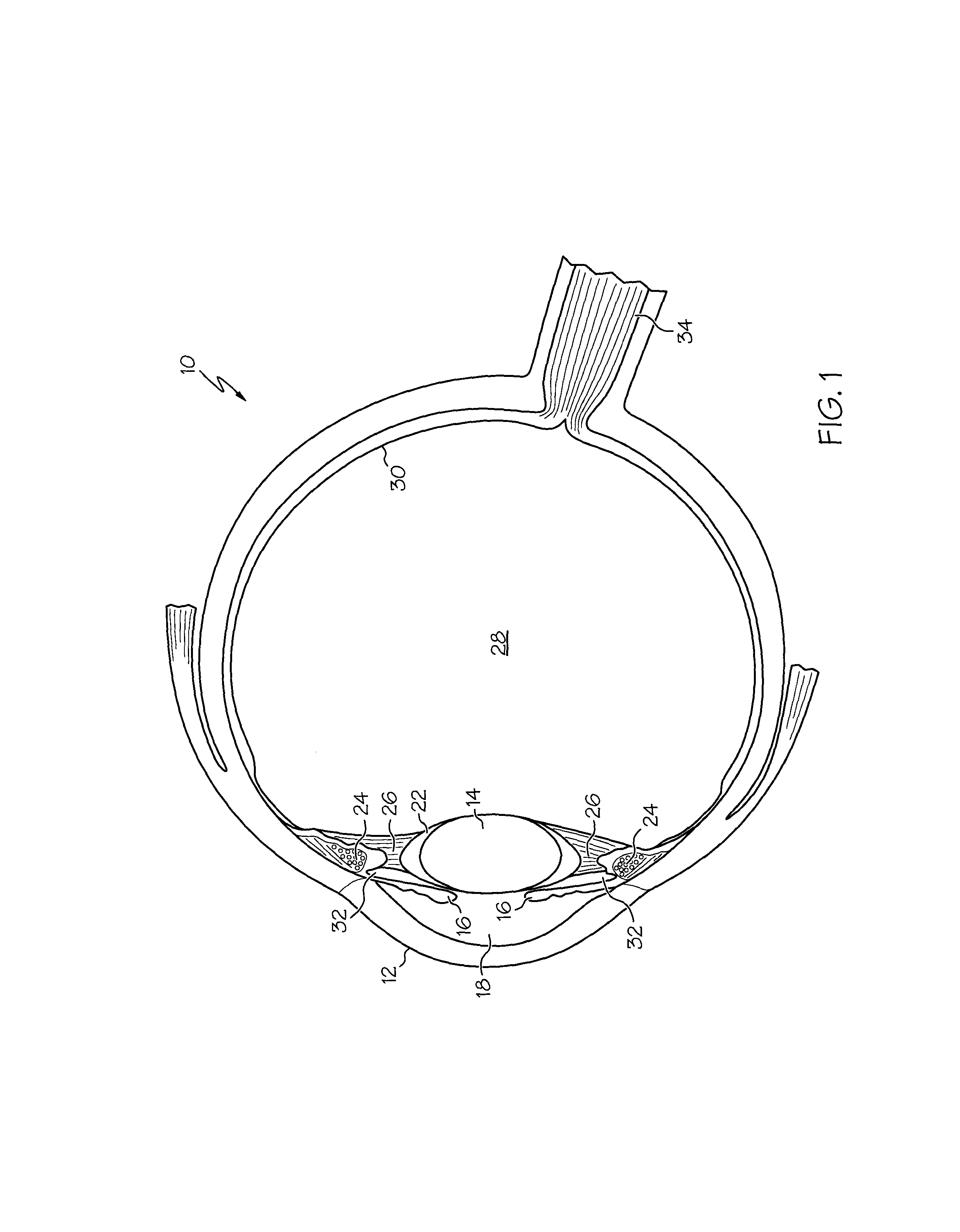
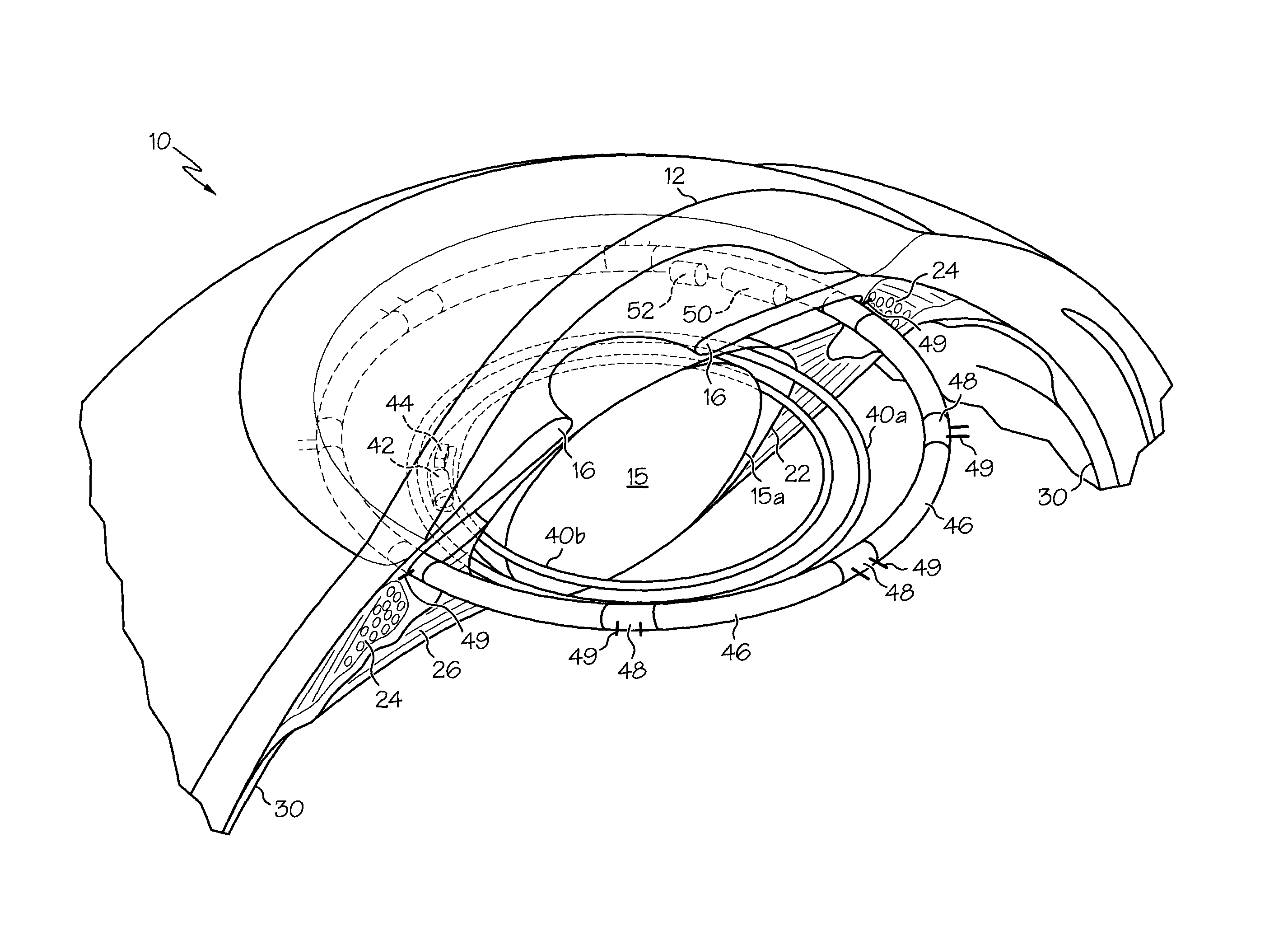
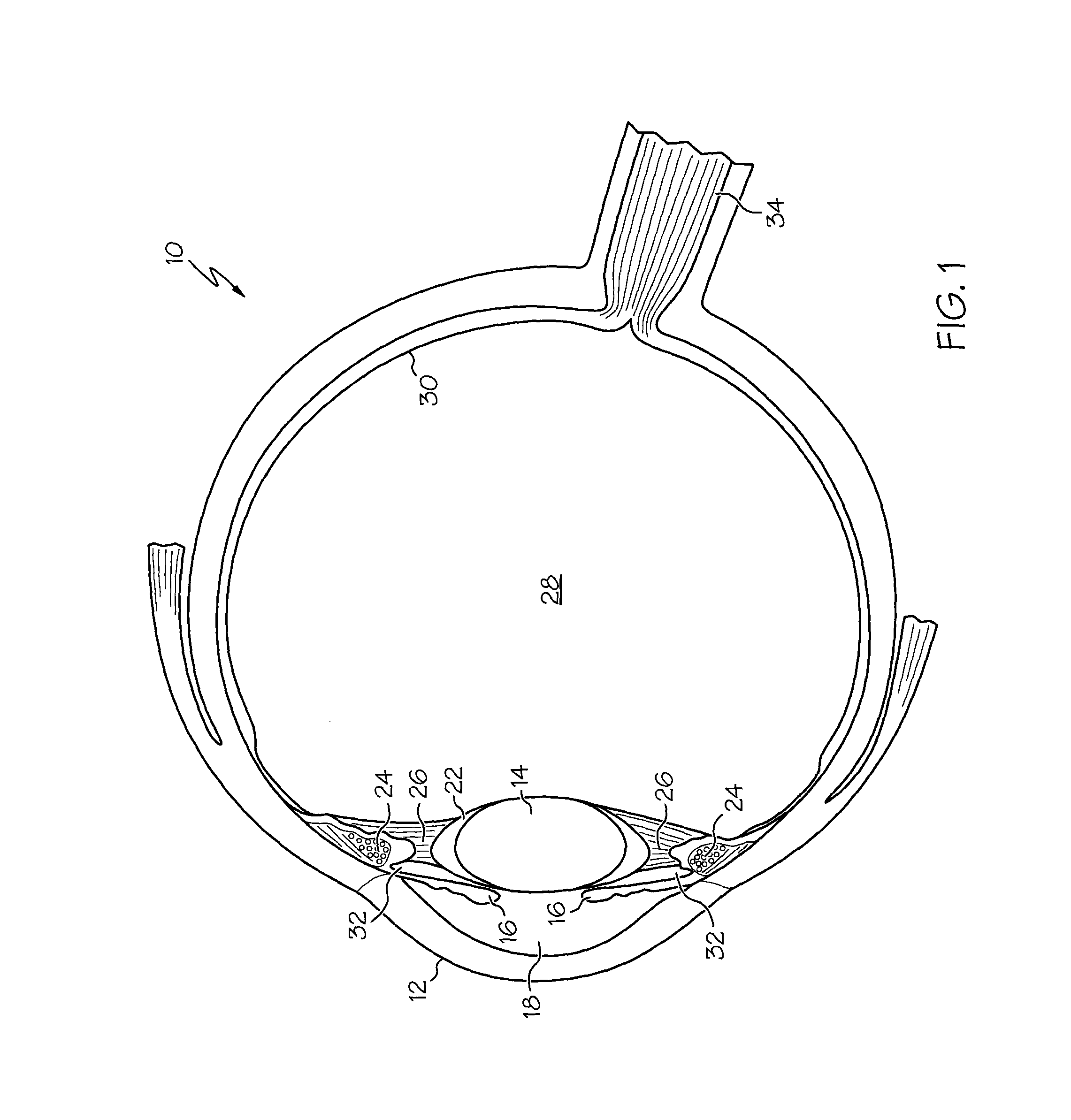
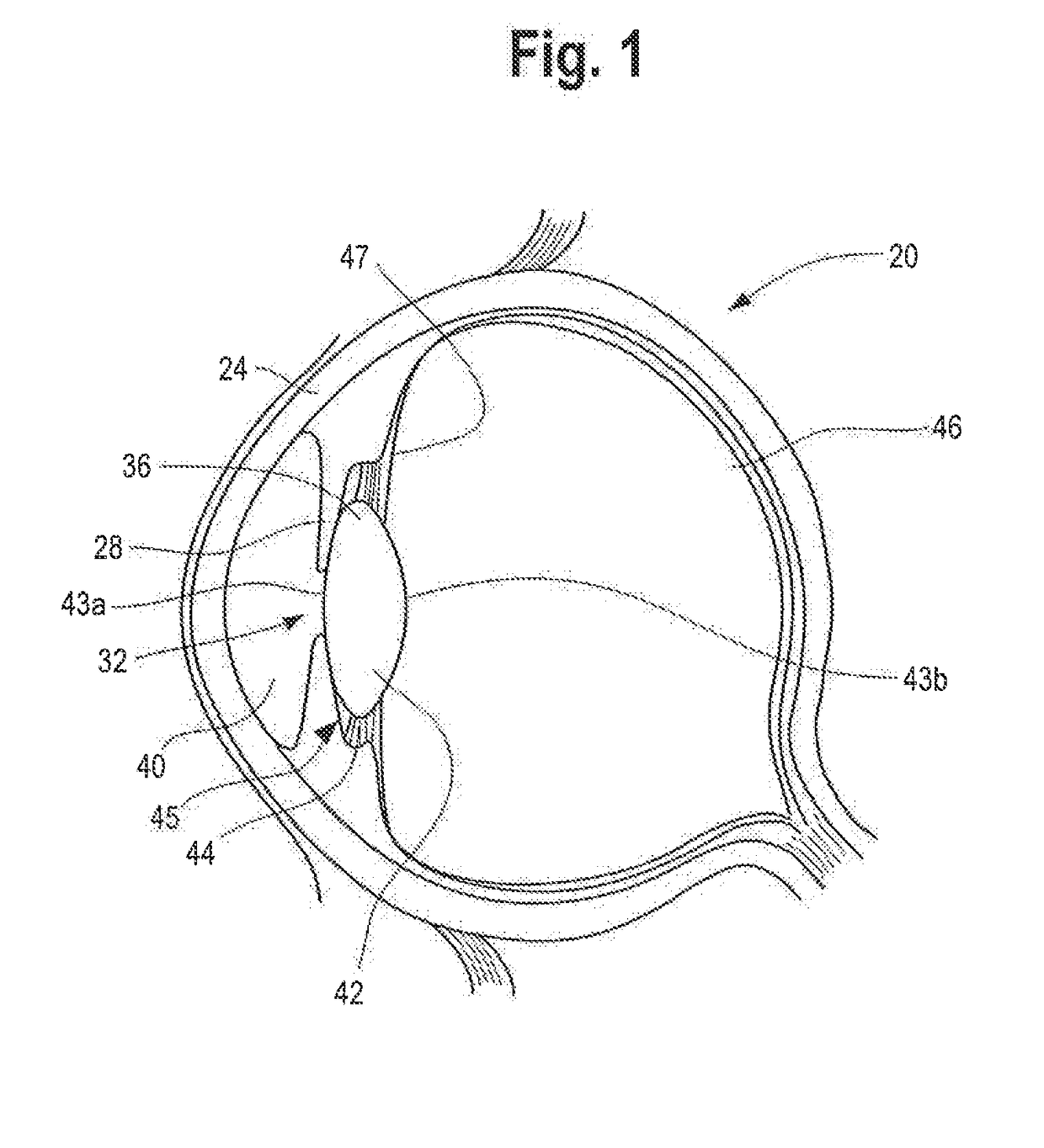
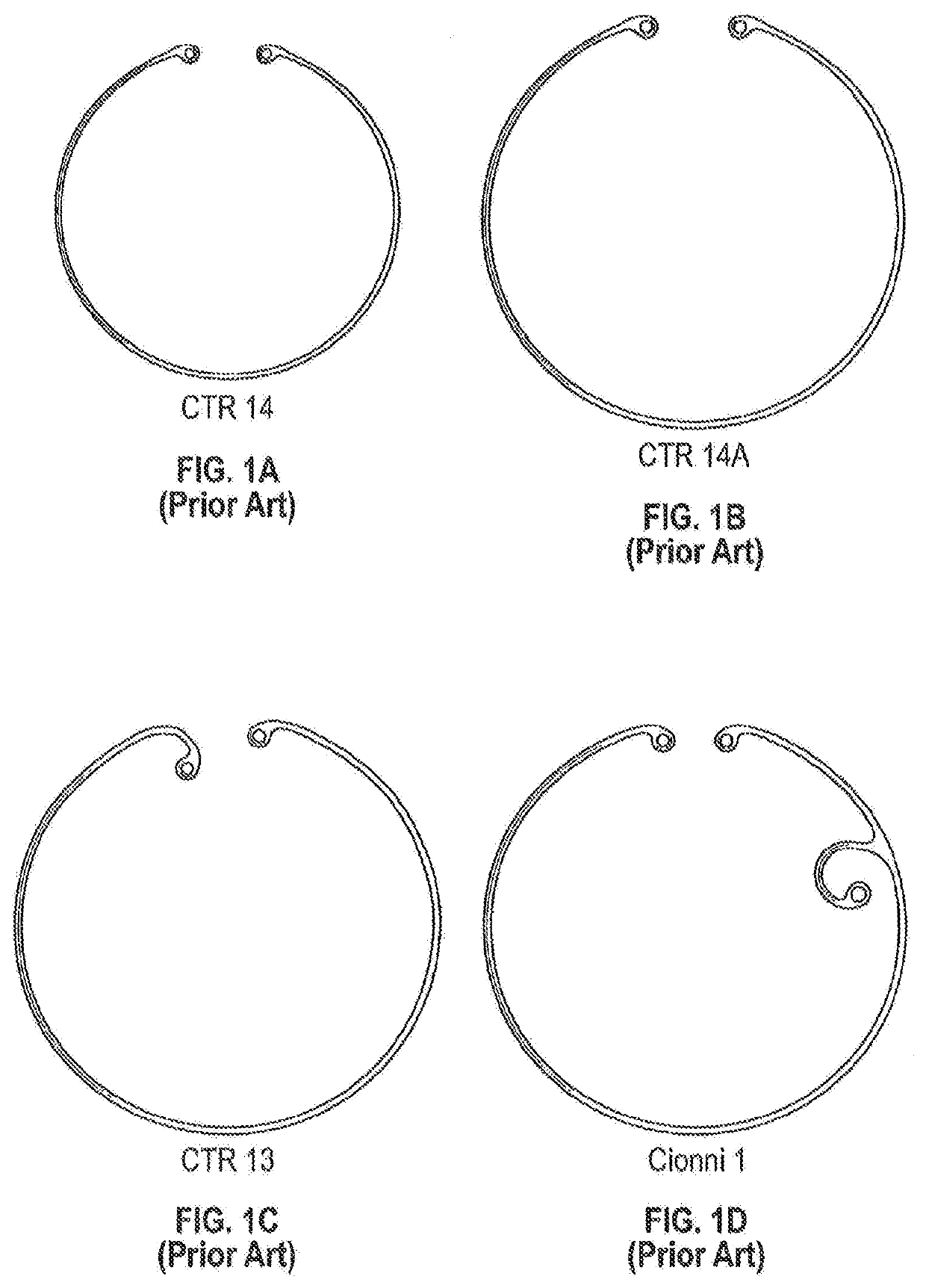
Ciliary sulcus fixation is the best second alternative site for fixation of the IOL in the presence of available capsular support. 3, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13 Several case series have been reported, indicating that a lens placed in the ciliary sulcus is reasonably safe and effective over the short term.
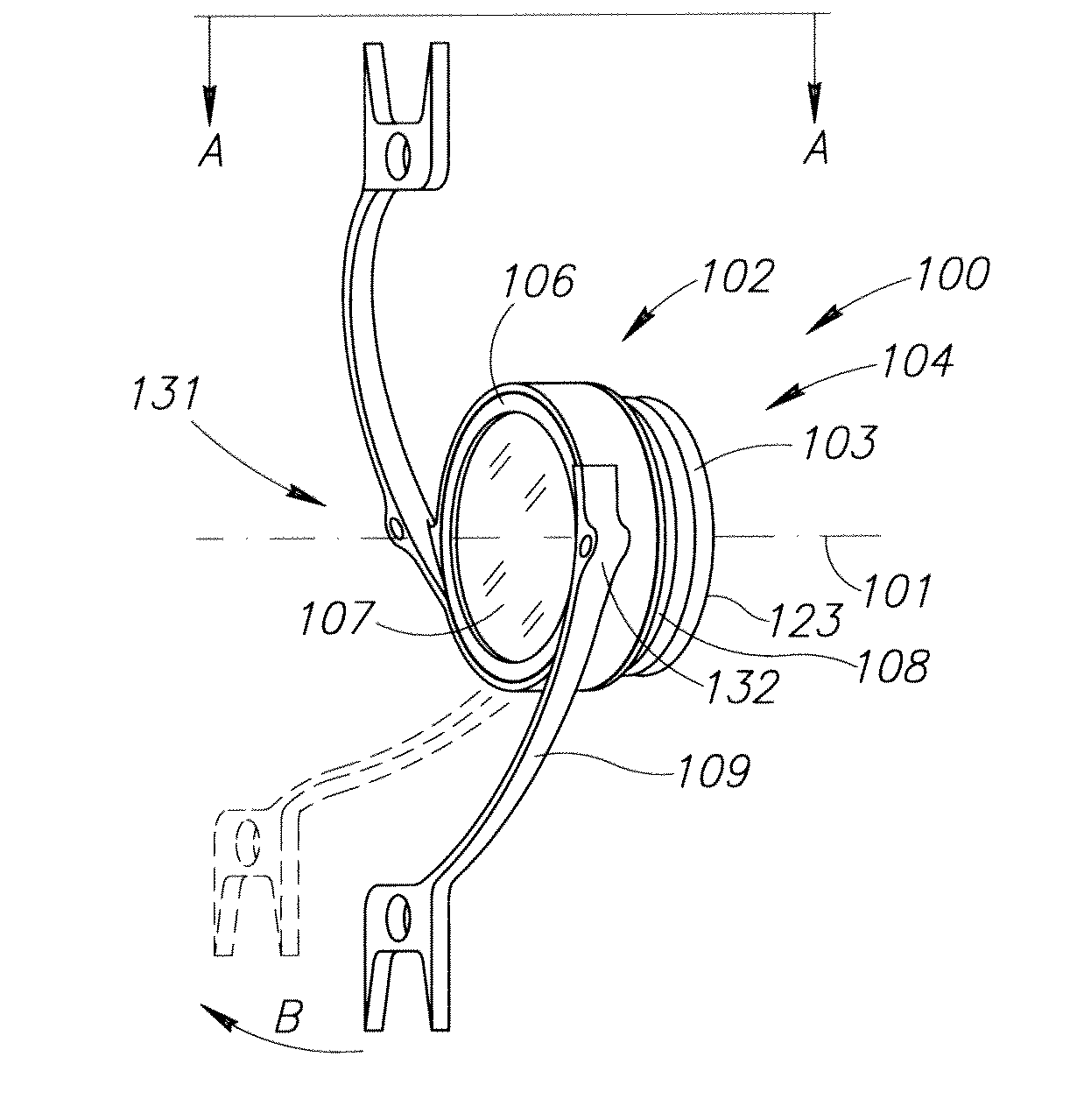
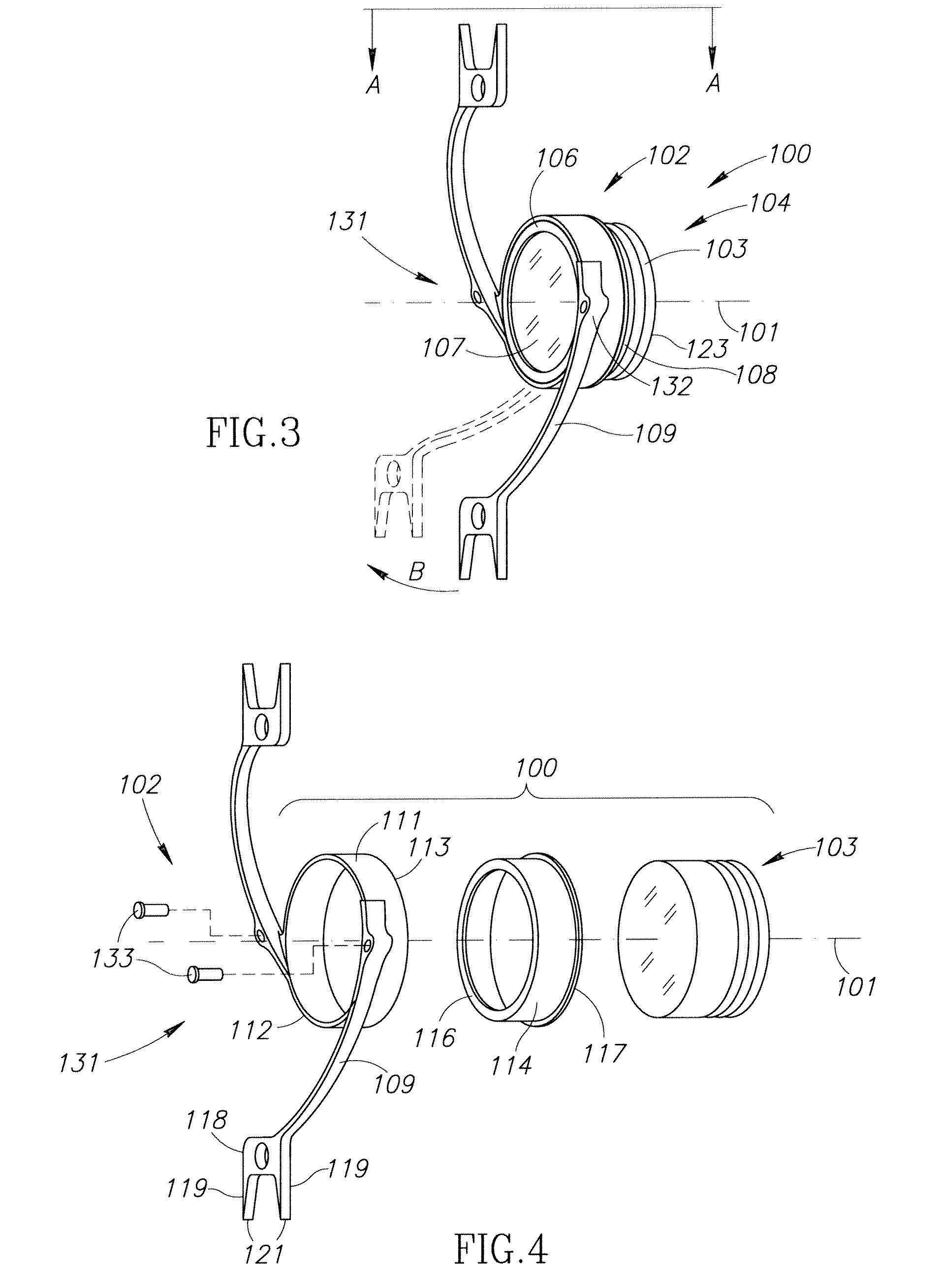
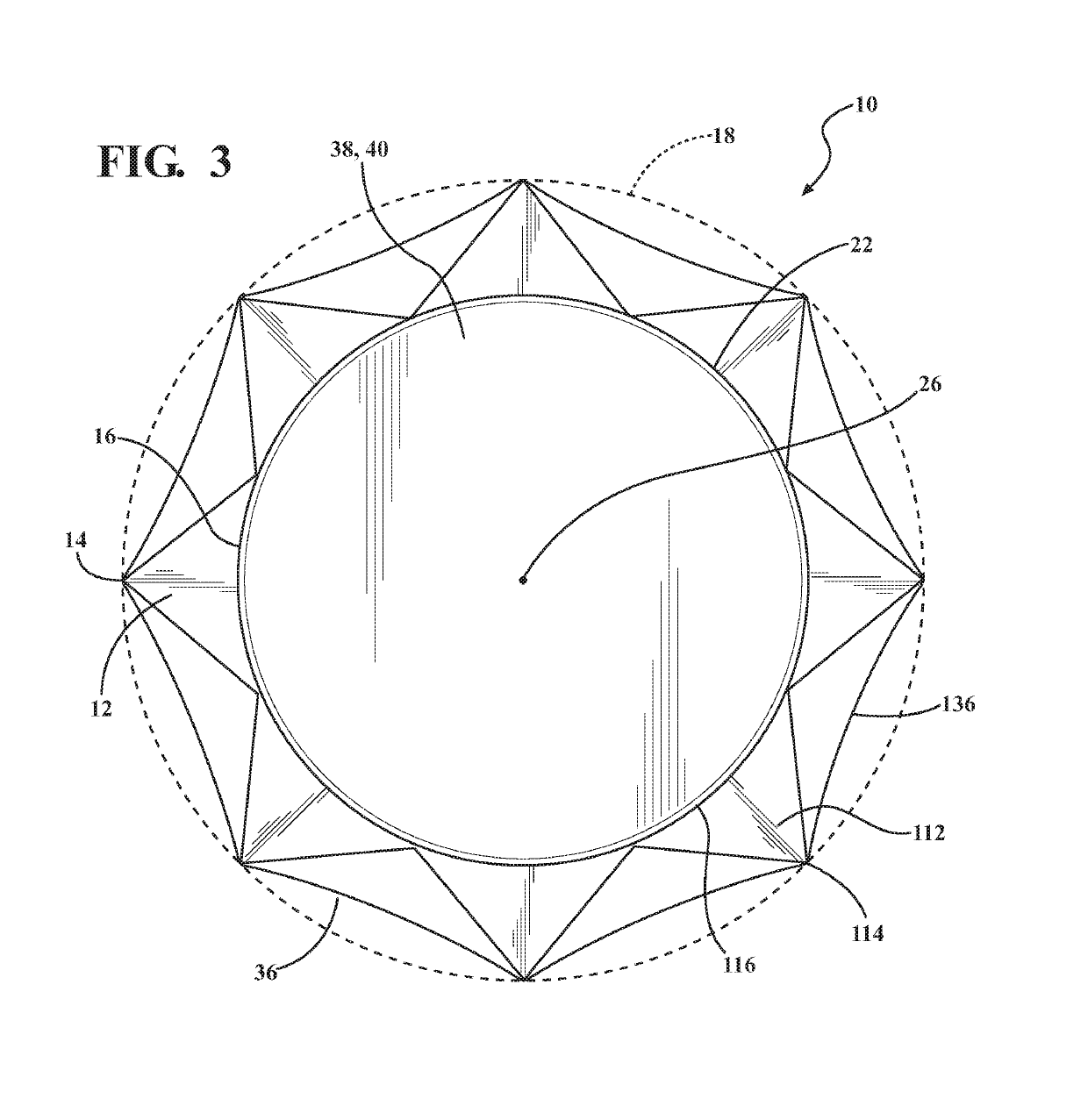
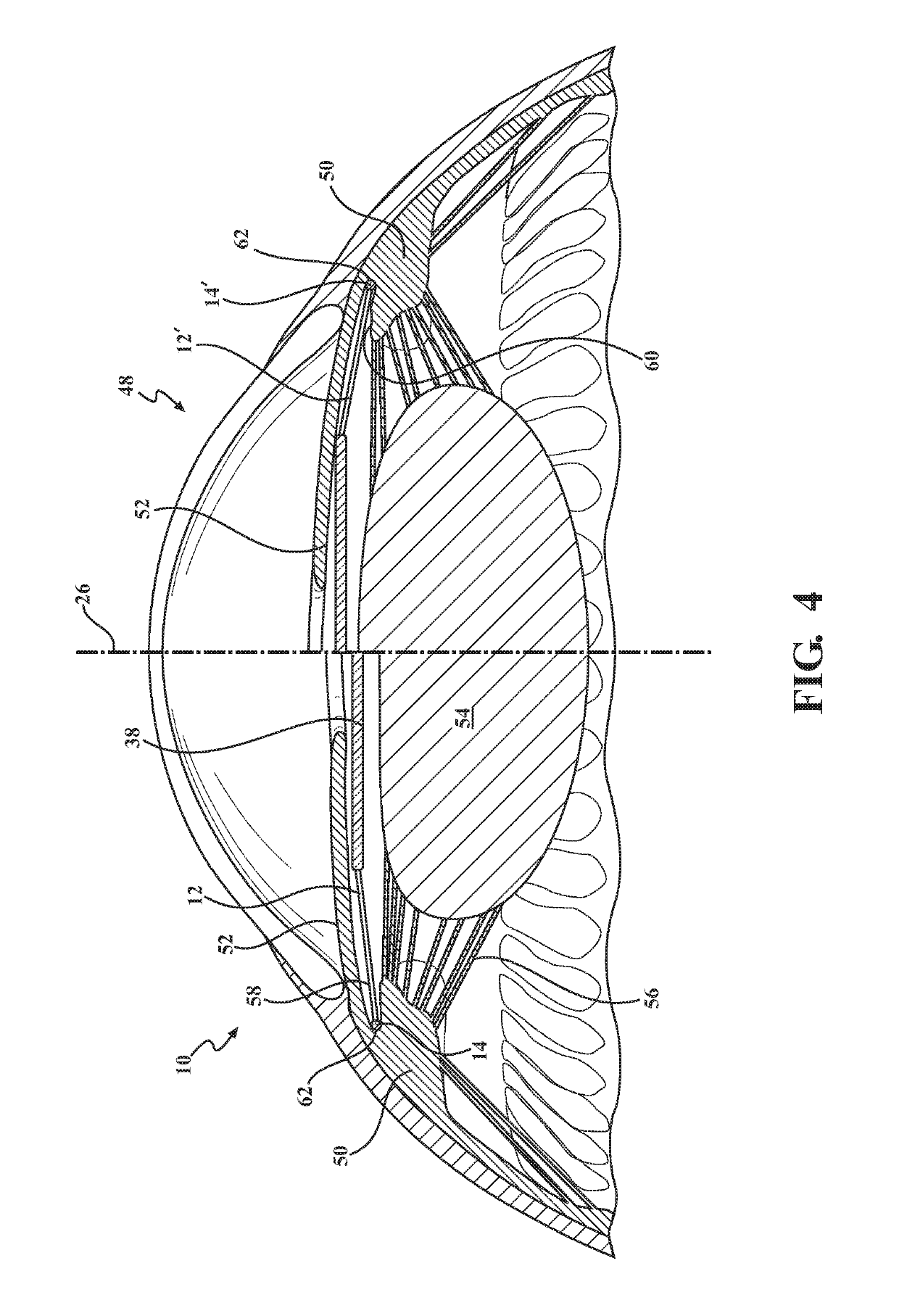
Accommodating Intraocular Lens Assemblies and Accommodation Measurement Implant
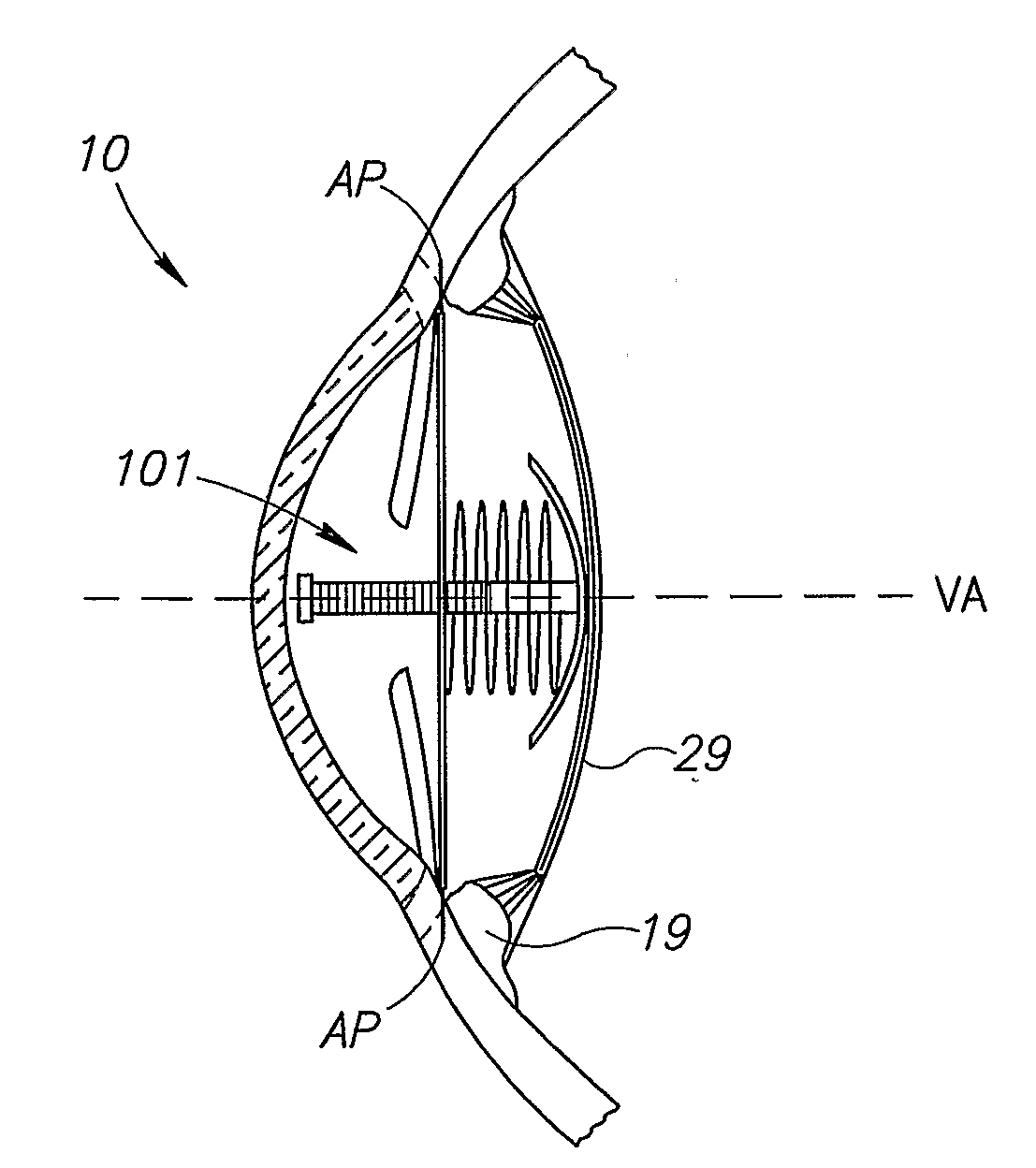
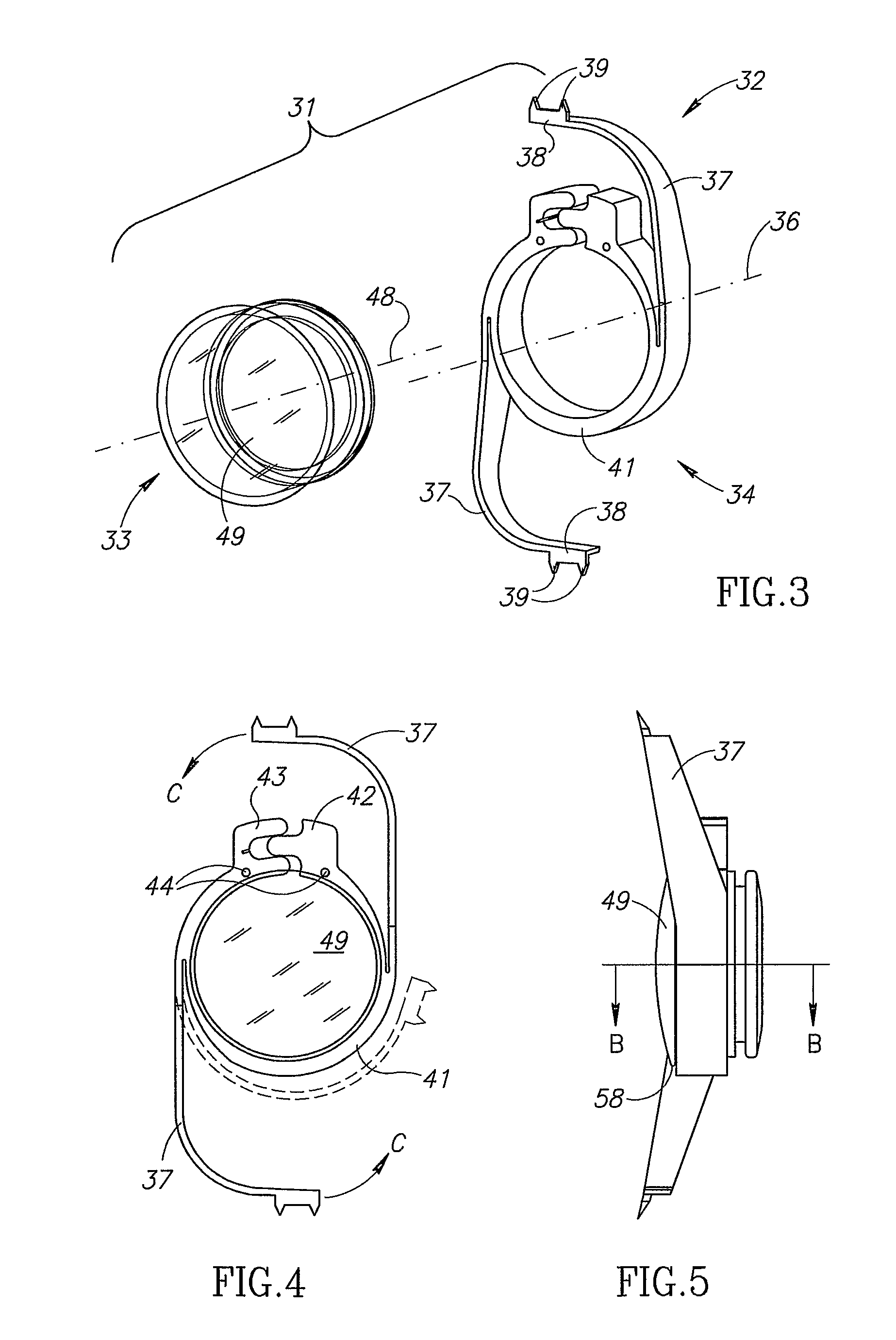
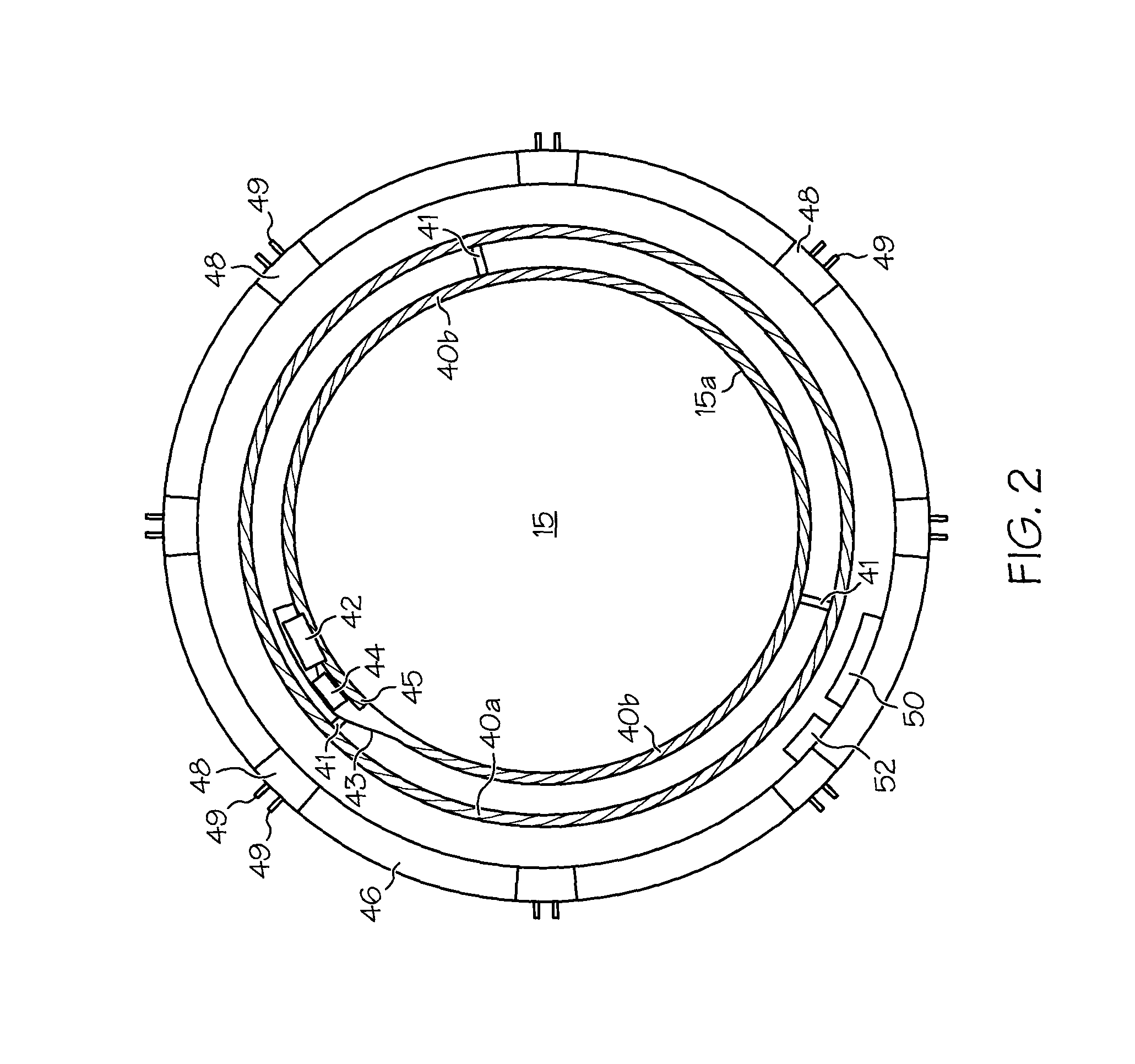
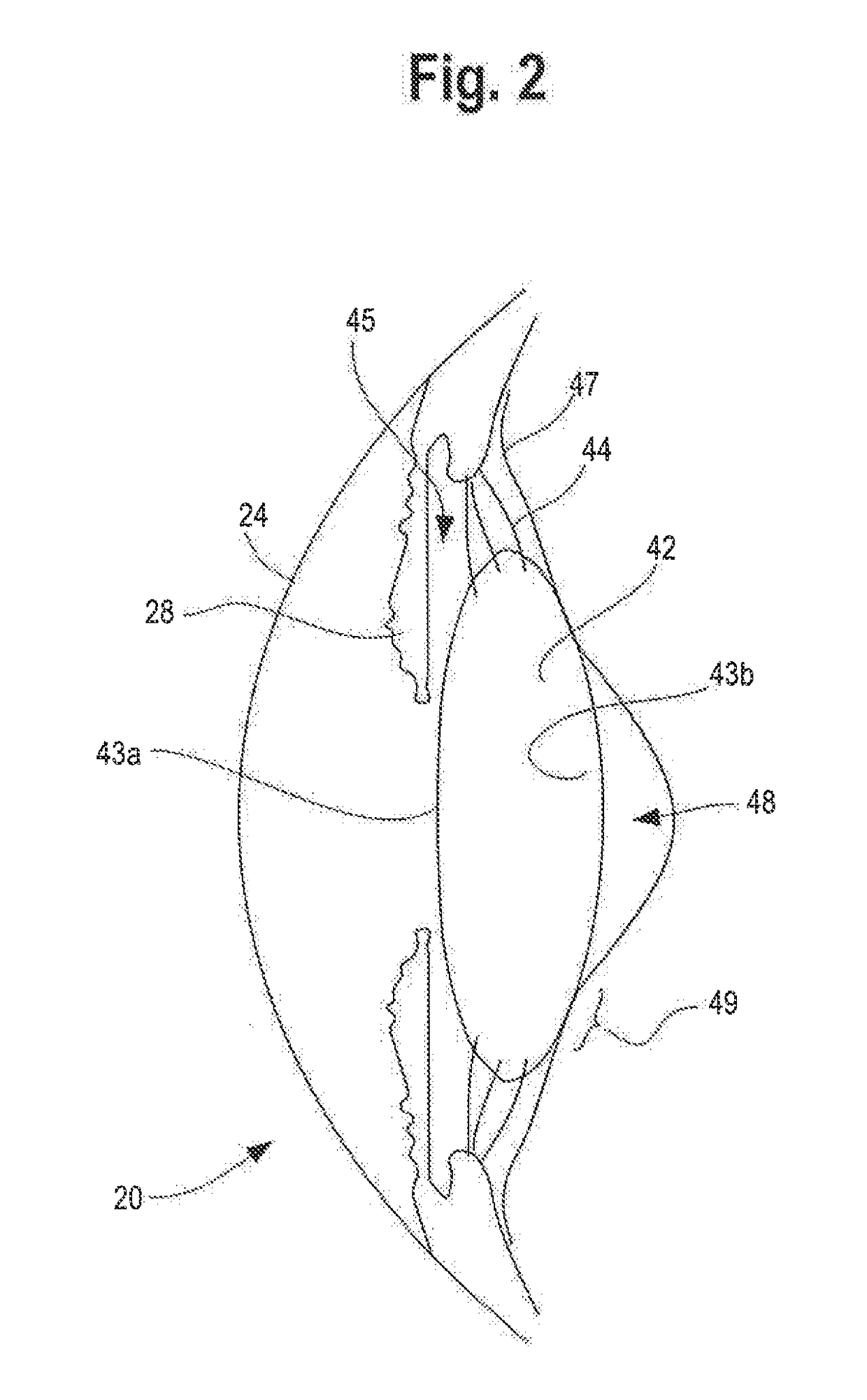
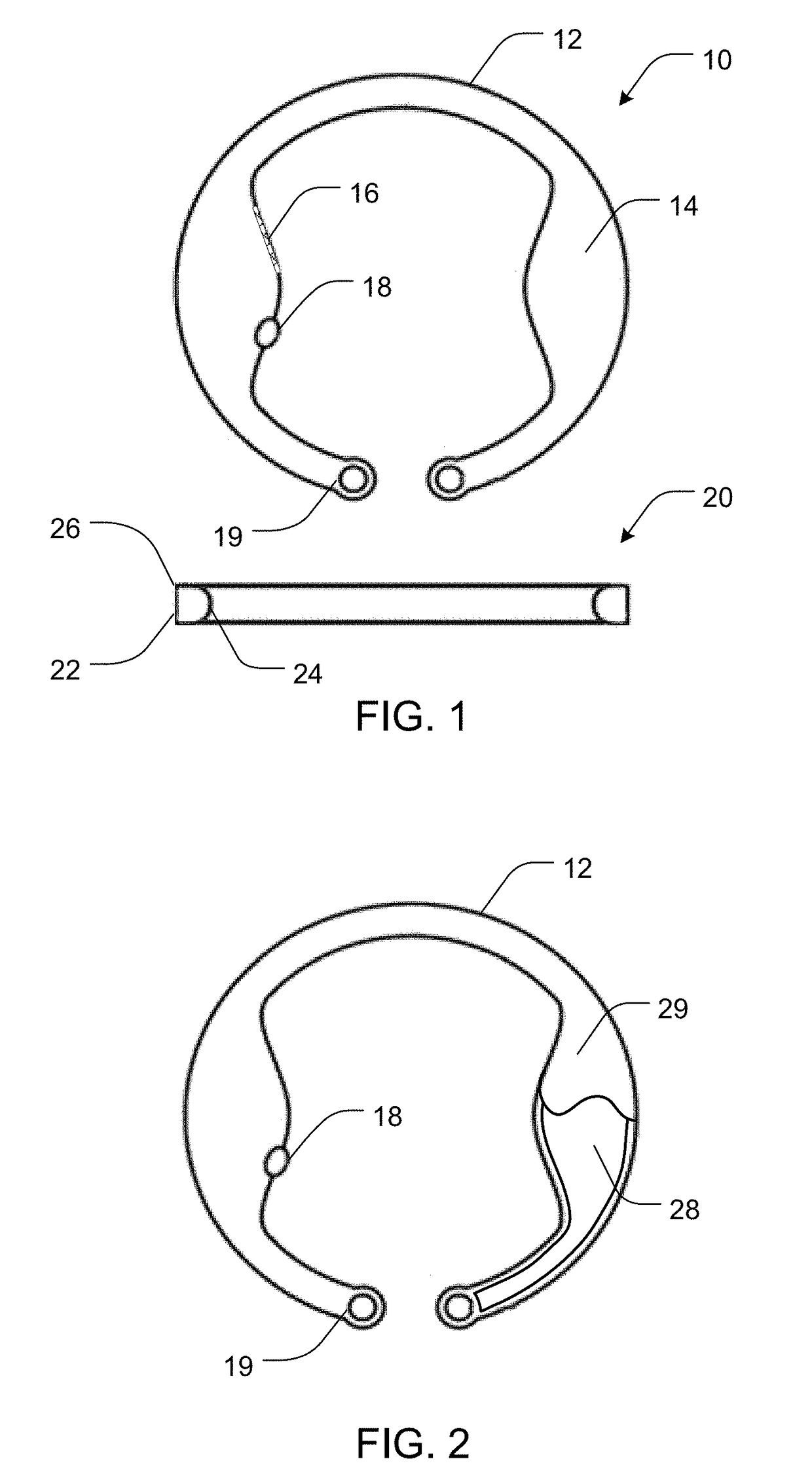
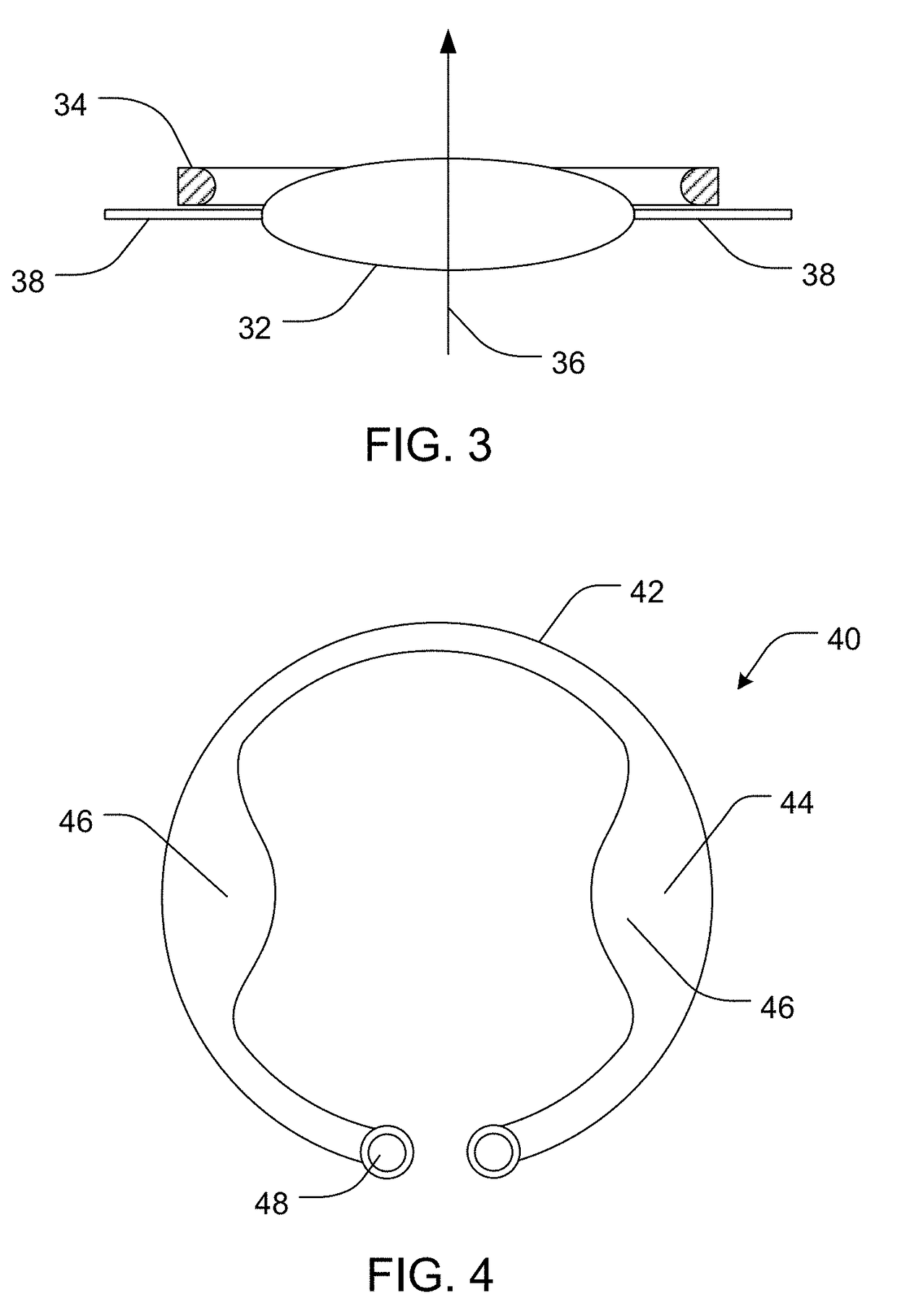
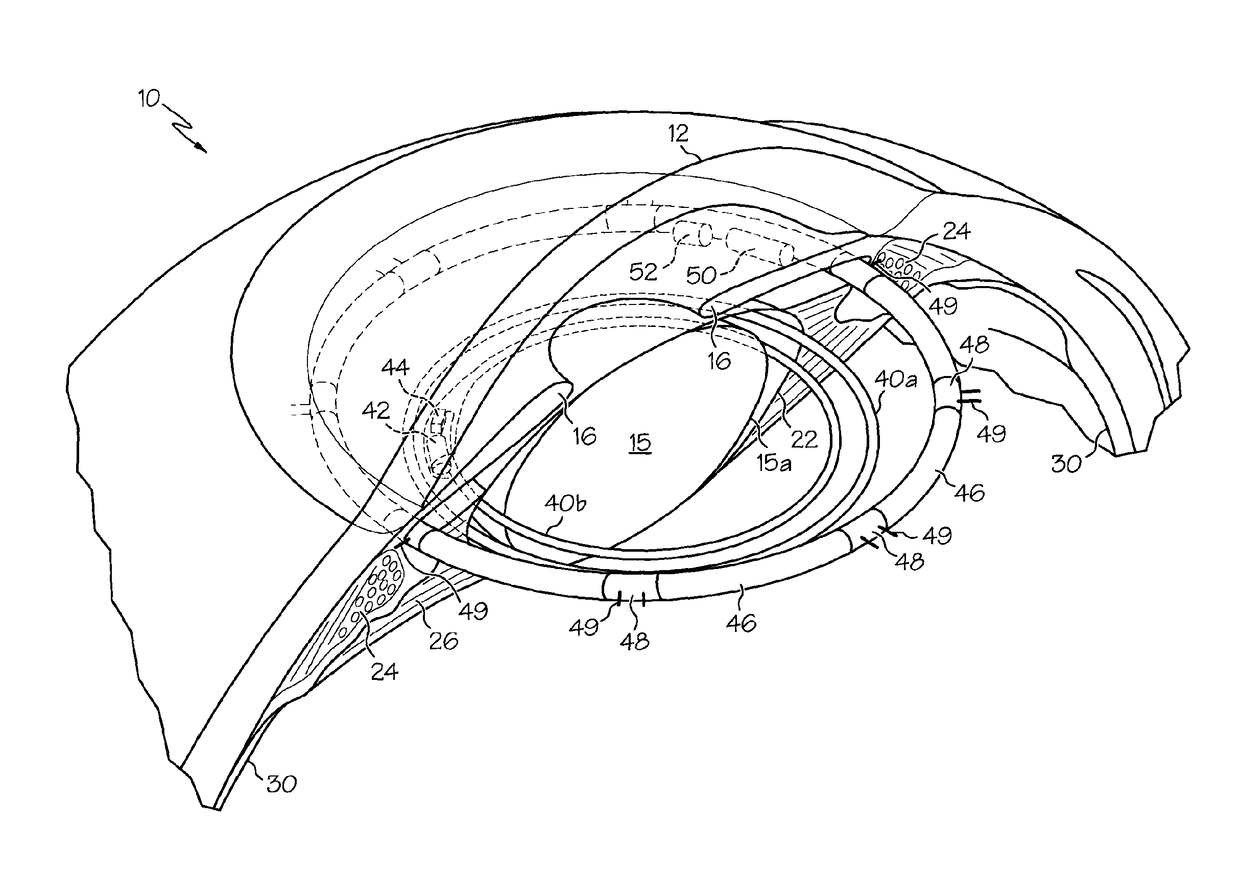
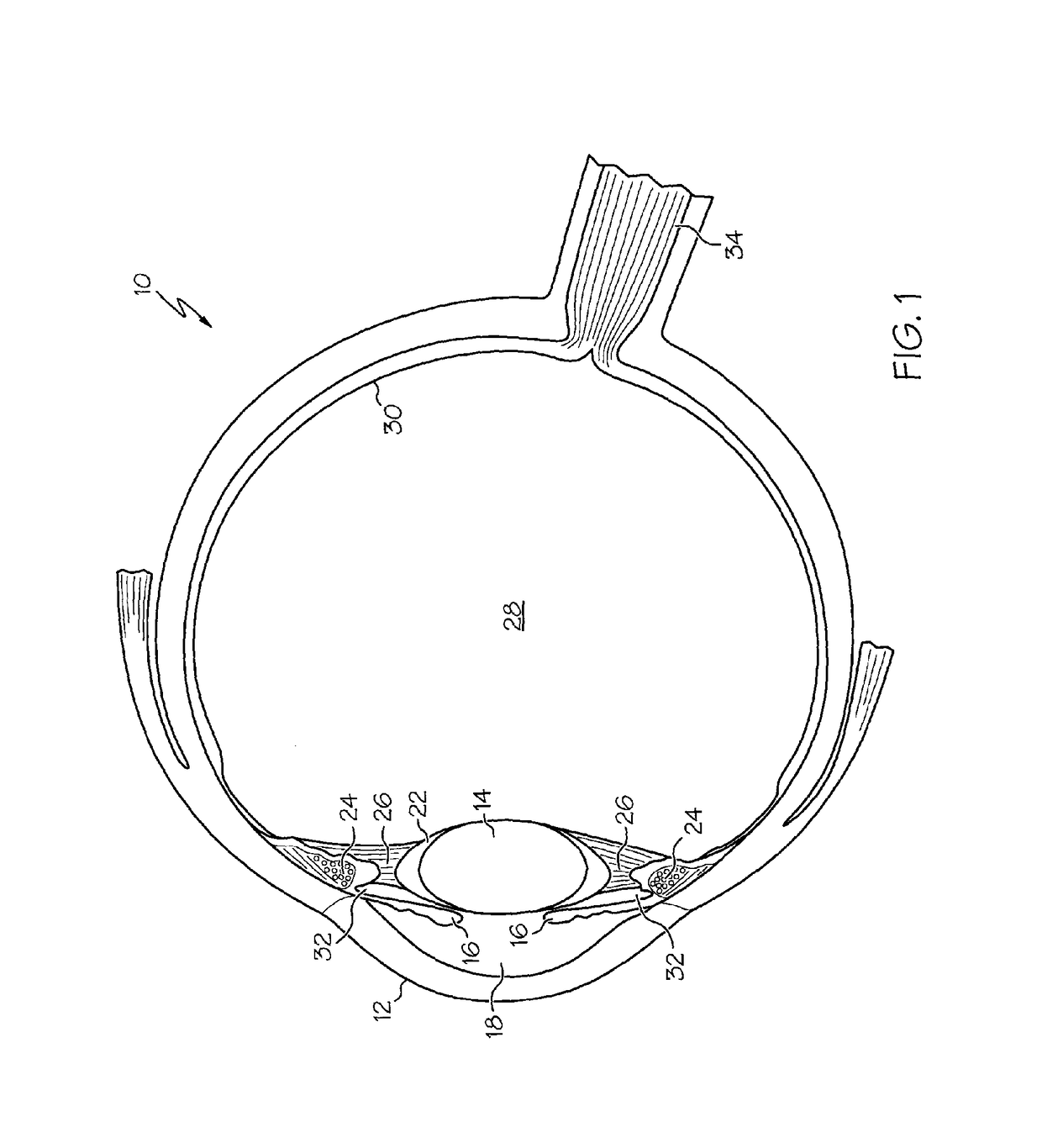
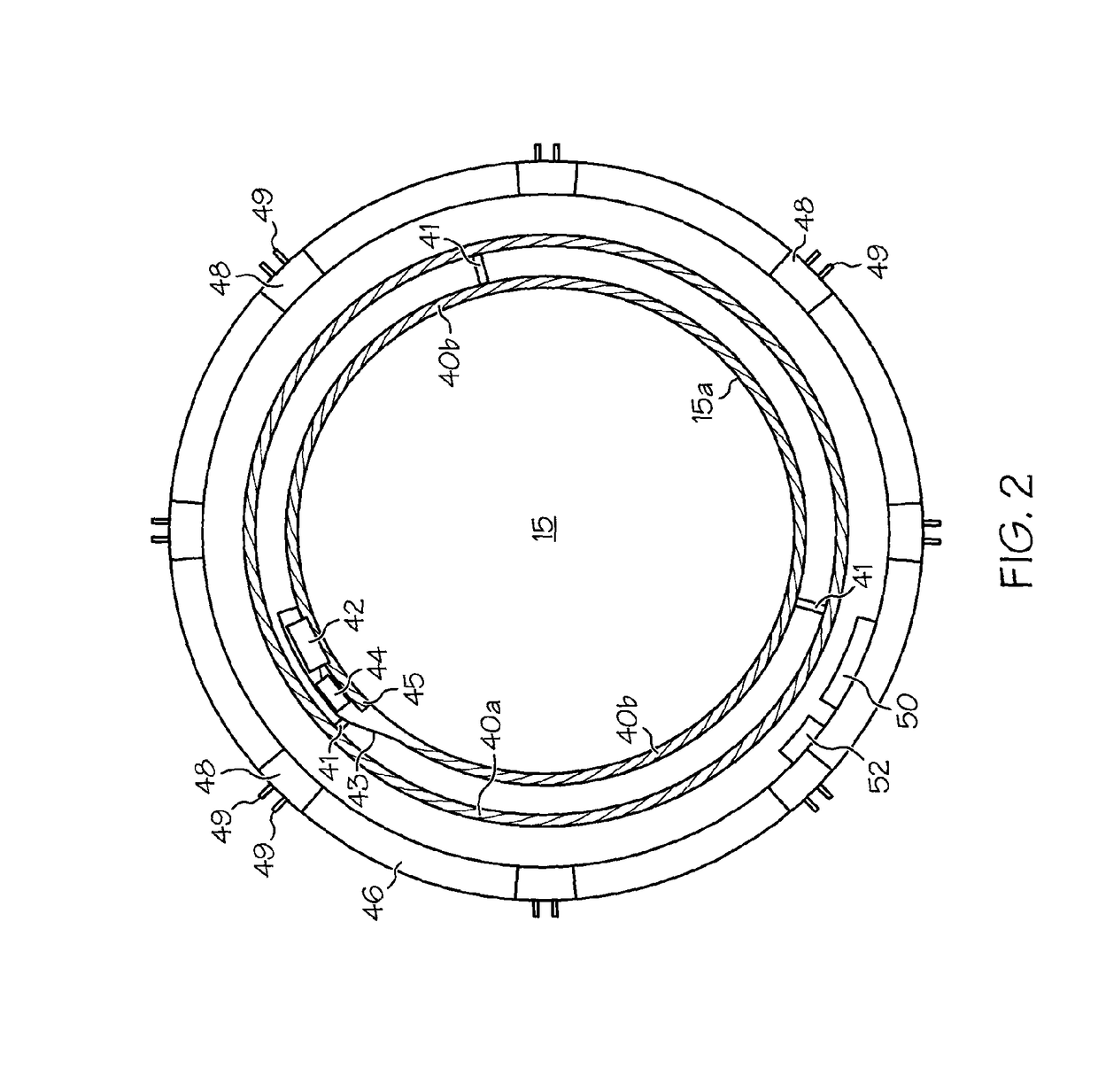
The present invention pertains to accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) assemblies including a haptics system for self-anchoring implantation in a human eye's annular ciliary sulcus for retaining an AIOL at a desired position along the human eye's visual axis, and an accommodation measurement implant (AMI) for determining accommodation and accommodation forces in an experimental set-up including an animal's eye.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Discrete pre-assembled monolithic aiol assemblages and aiol assemblies including same
InactiveUS20130116781A1Highly convenient in situ assemblySimplifying clinical procedureIntraocular lensSelf anchoringCiliary sulcus
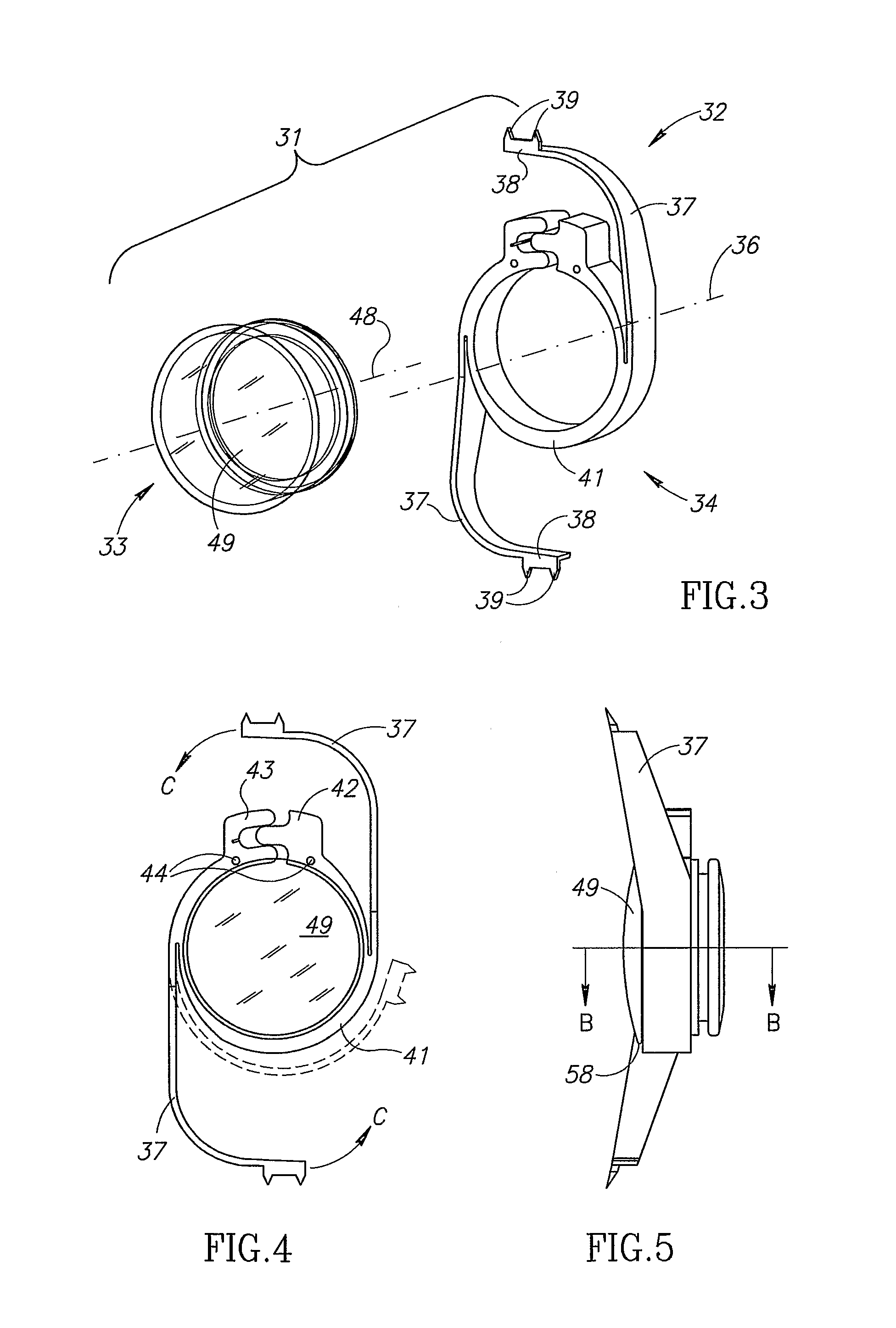
Accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) assemblies including a discrete pre-assembled monolithic AIOL assemblage and a discrete haptics system having a haptics ring and at least two elongated C-shaped haptics for self-anchoring in a human scleral wall at the ciliary sulcus. The AIOL assemblages include an AIOL capsule and an integrally formed base member. The AIOL assemblages also include an annular haptics support surround posterior to an anterior structure on implantation in a human eye of a supine human. AIOL assemblies are assembled in situ by mounting a haptics system onto a previously implanted AIOL assemblage. The haptics system bears against the annular haptics support surround. The anterior structure is freely telescopically received in the haptics ring.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Unitary accommodating intraocular lenses (AIOLs) and discrete base members for use therewith
InactiveUS8273123B2Drag minimizationImprove acuityIntraocular lensIntraocular pressureAxial compression
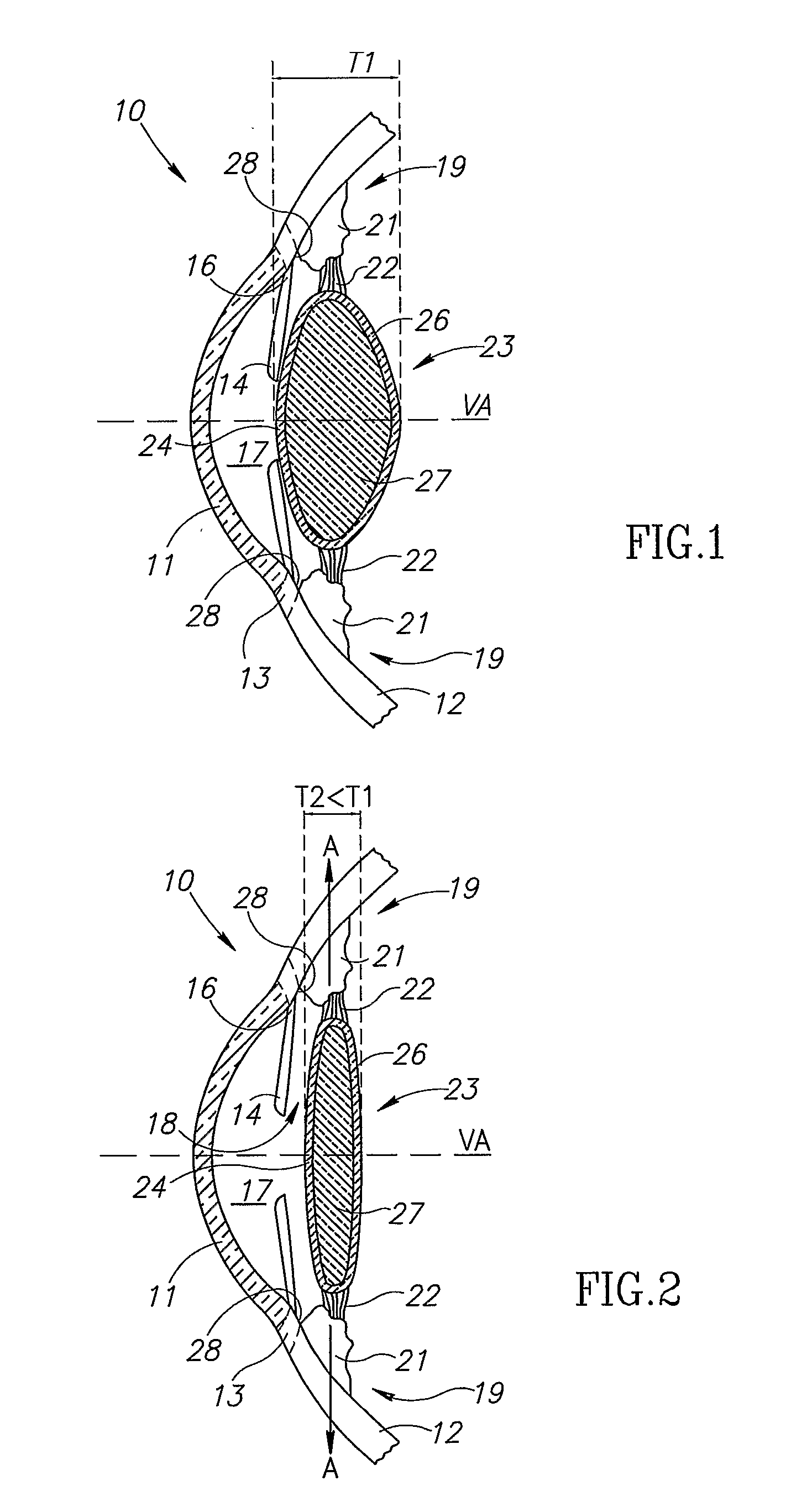
Unitary accommodating intraocular lenses (AIOLs) including a haptics system for self-anchoring in a human eye's ciliary sulcus and a resiliently elastically compressible shape memory optical element having a continuously variable Diopter strength between a first Diopter strength in a non-compressed state and a second Diopter strength different than its first Diopter strength in a compressed state. The unitary AIOLS include an optical element with an exposed trailing surface and are intended to be used with a discrete base member for applying an axial compression force against the exposed trailing surface from a posterior direction. Some unitary AIOLs are intended to be used with either a purpose designed base member or a previously implanted standard in-the-bag IOL. Other unitary AIOLs are intended to be solely used with a purpose designed base member.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Accommodating intraocular lens
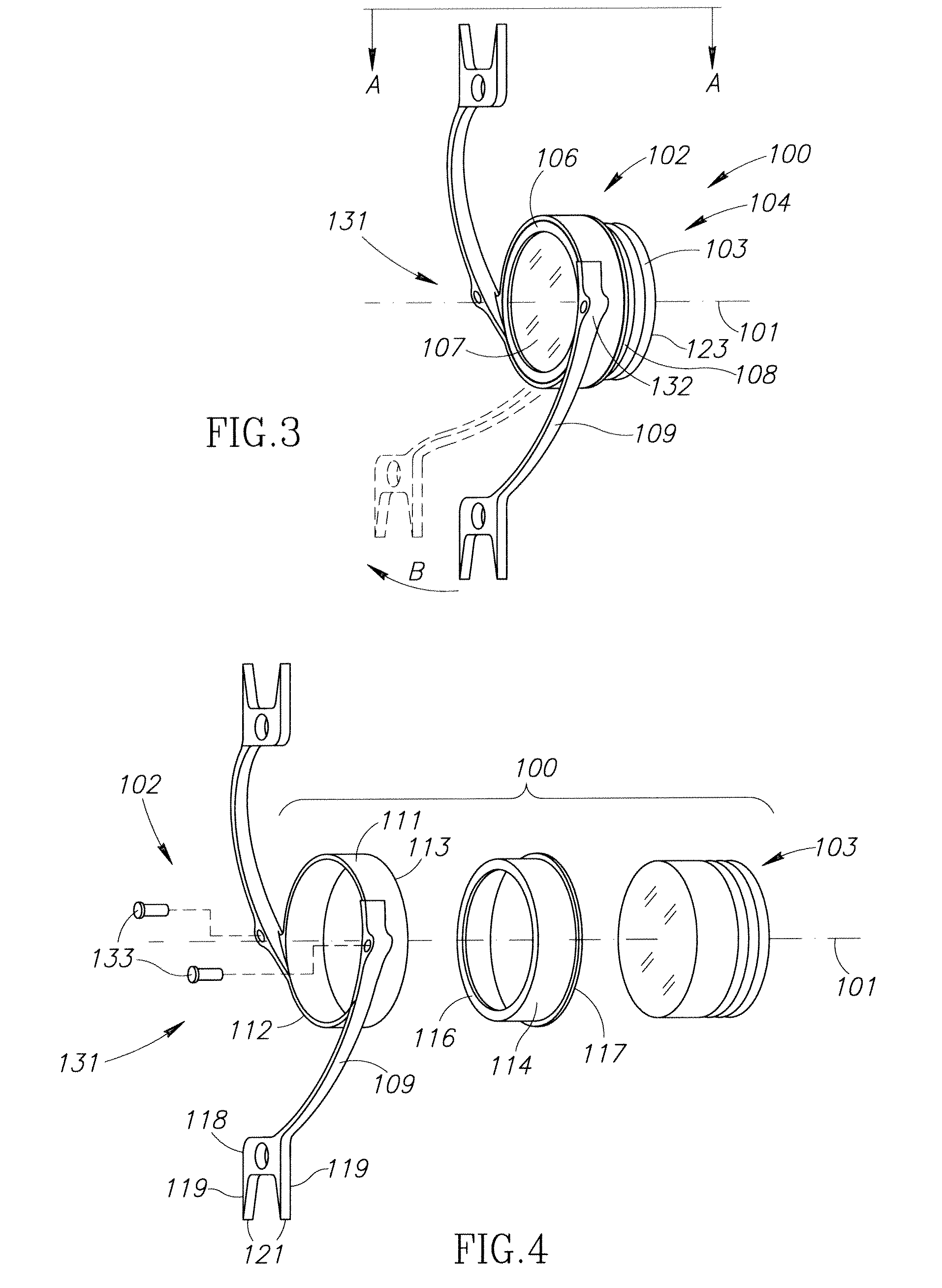
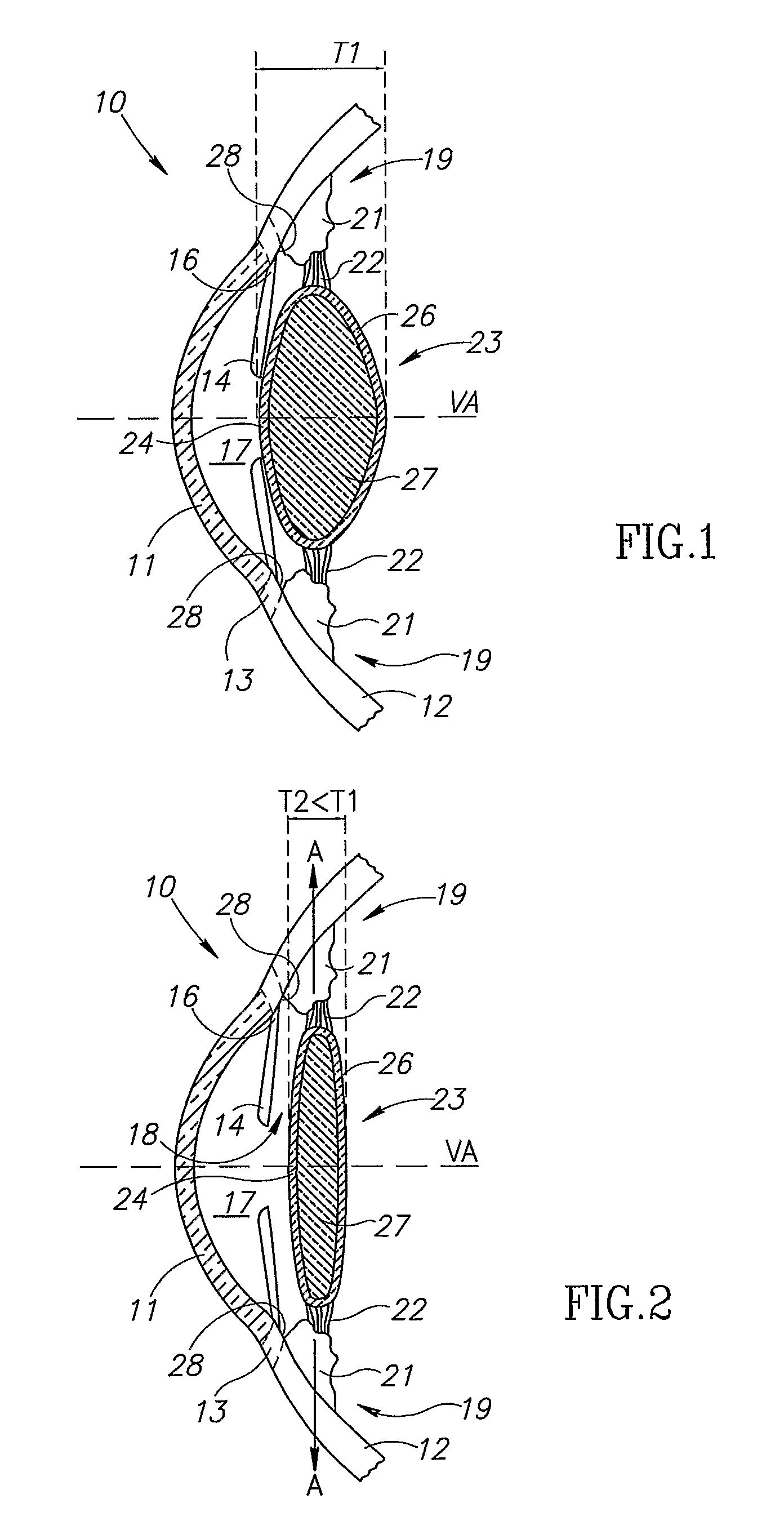
An intra ocular lens arrangement having positive and negative lens elements which move during the eye's accommodation response in order to improve the image on the retina of objects viewed by the eye over a wide range of distances. The positive and negative lens elements either can be linked mechanically to constrain their relative movements or not linked. The lenses are positioned by an operating surgeon following cataract extraction in either the eye's ciliary sulcus or lens capsule. Alternatively, one of the lenses may be inserted into an eye that already has a lens implanted therein to further improve a person's vision. An improved intra ocular lens has is an optic lens having at least two pairs of haptics that controls the movement of the optic lens along the optical axis of the eye in response to the movement of the ciliary muscle of the eye acting on the haptics during the accommodation response, one pair of haptics having one end hinged to the lower half of the optic lens and the second end connected to an upper portion of the ciliary muscle, and a second pair of haptics hinged to an upper half of the optic lens and to a lower potion of the ciliary muscle.
Owner:MAGNANTE PETER +3
Unitary Accommodating Intraocular Lenses (AIOLs) and Discrete Base Members For Use Therewith
InactiveUS20100121444A1Drag minimizationImprove acuityIntraocular lensIntraocular pressureAxial compression
Unitary accommodating intraocular lenses (AIOLs) including a haptics system for self-anchoring in a human eye's ciliary sulcus and a resiliently elastically compressible shape memory optical element having a continuously variable Diopter strength between a first Diopter strength in a non-compressed state and a second Diopter strength different than its first Diopter strength in a compressed state. The unitary AIOLS include an optical element with an exposed trailing surface and are intended to be used with a discrete base member for applying an axial compression force against the exposed trailing surface from a posterior direction. Some unitary AIOLs are intended to be used with either a purpose designed base member or a previously implanted standard in-the-bag IOL. Other unitary AIOLs are intended to be solely used with a purpose designed base member.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Accommodating intra-ocular lens system
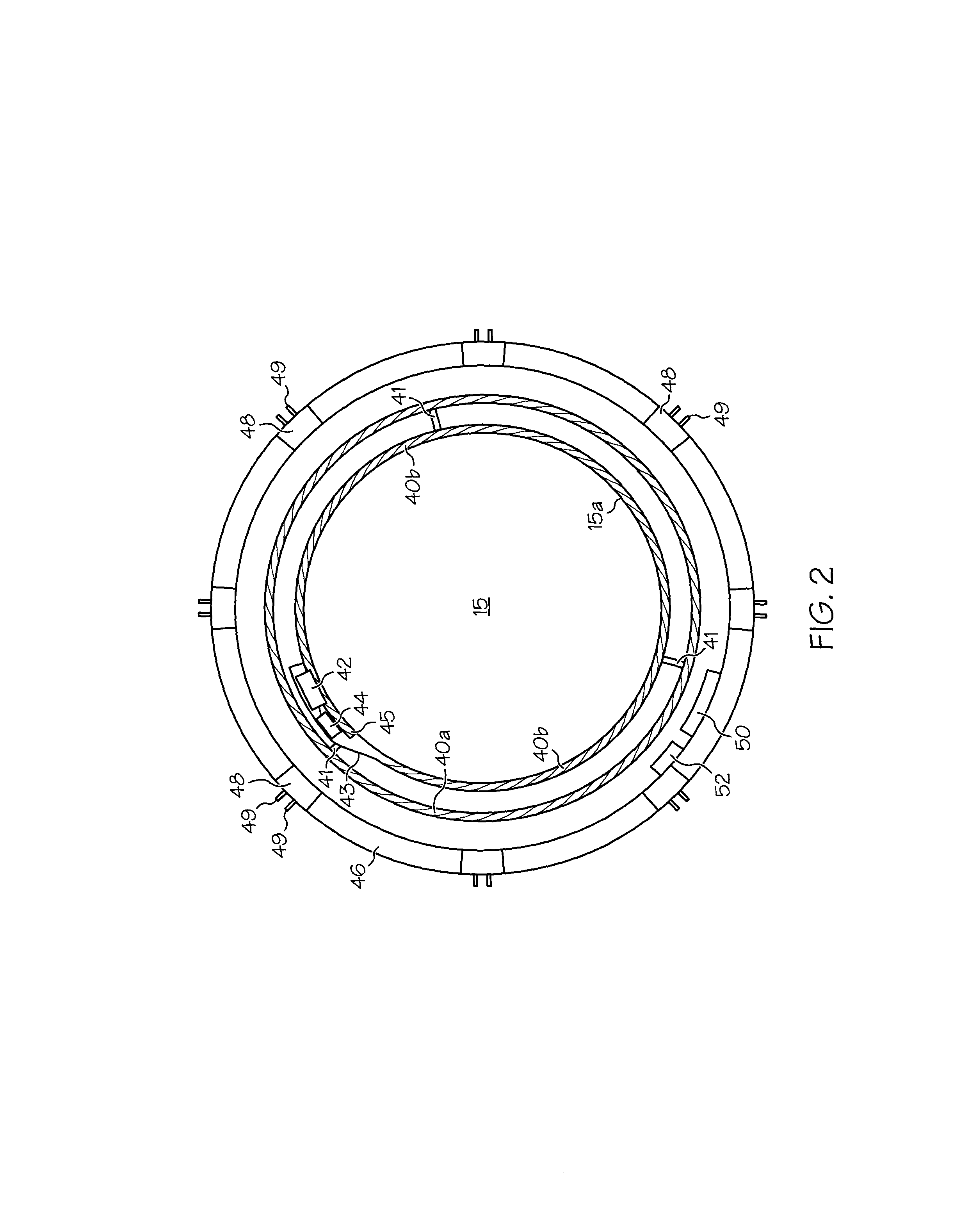
An implantable, compressible, accommodating intra-ocular lens (IOL) coupled to at least one sensor which detects a signal created by the ciliary muscle. A ciliary sulcus ring can house the at least one sensor, and the sensor can include miniaturized electrodes (ciliary muscle probes) for implanting into the ciliary muscle of the subject. A potentiometer / microcomputer can modulate the ciliary muscle signal detected by the sensor(s) into an electrical signal, and a transmitter sends this electrical signal to a micromotor, which causes compression of the IOL via an annular support ring system, causing a change in the IOL shape. The IOL can be part of an IOL complex including a compressible, accommodating IOL, an external lens membrane, and an annular support ring system. The annular support ring system provides a foundation for the micromotor to compress the IOL.
Owner:VISTA OCULAR
Accommodating intraocular lens assemblies and accommodation measurement implant
The present invention pertains to accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) assemblies including a haptics system for self-anchoring implantation in a human eye's annular ciliary sulcus for retaining an AIOL at a desired position along the human eye's visual axis, and an accommodation measurement implant (AMI) for determining accommodation and accommodation forces in an experimental set-up including an animal's eye.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
Intraocular lens insertion device
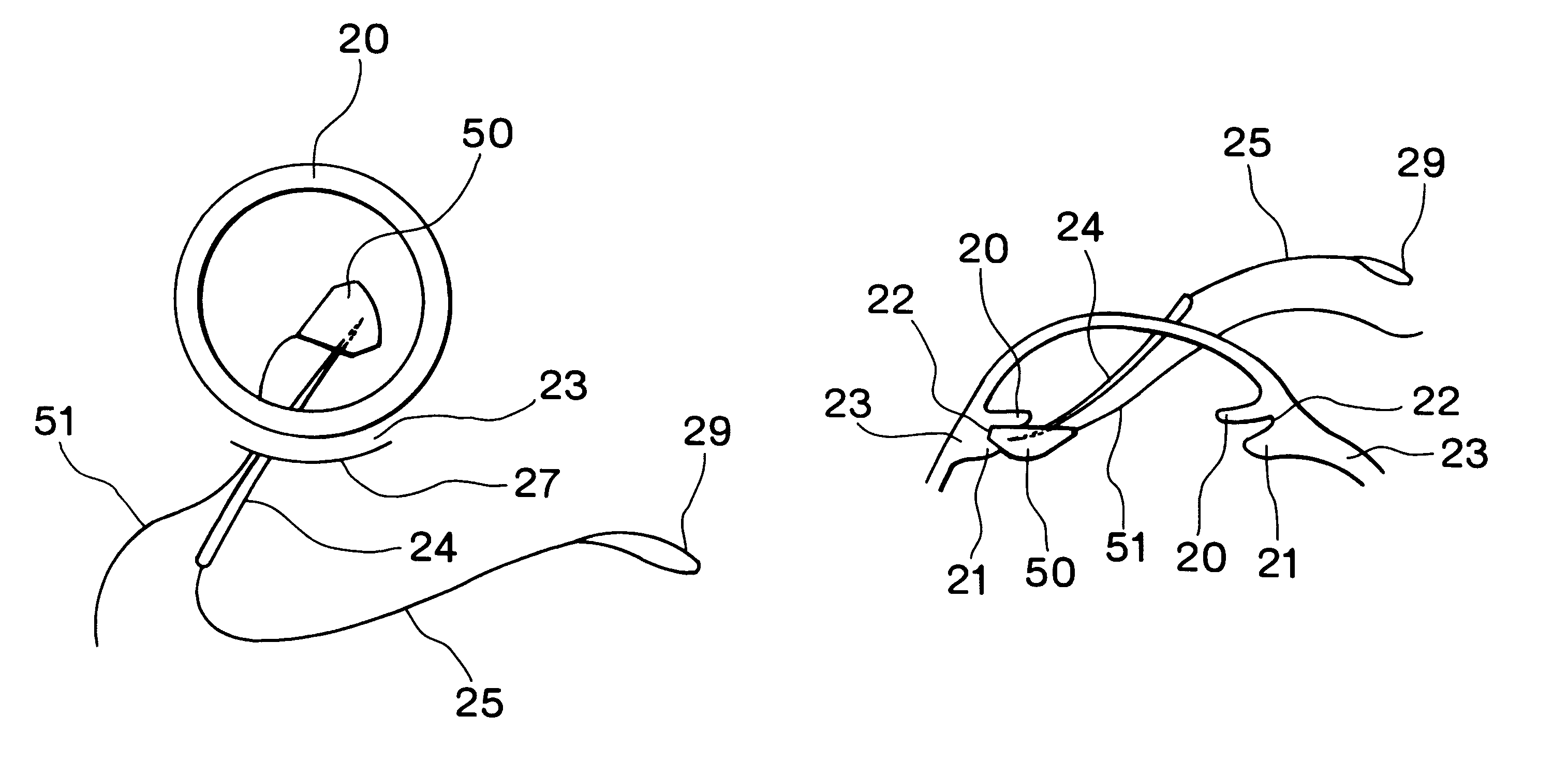
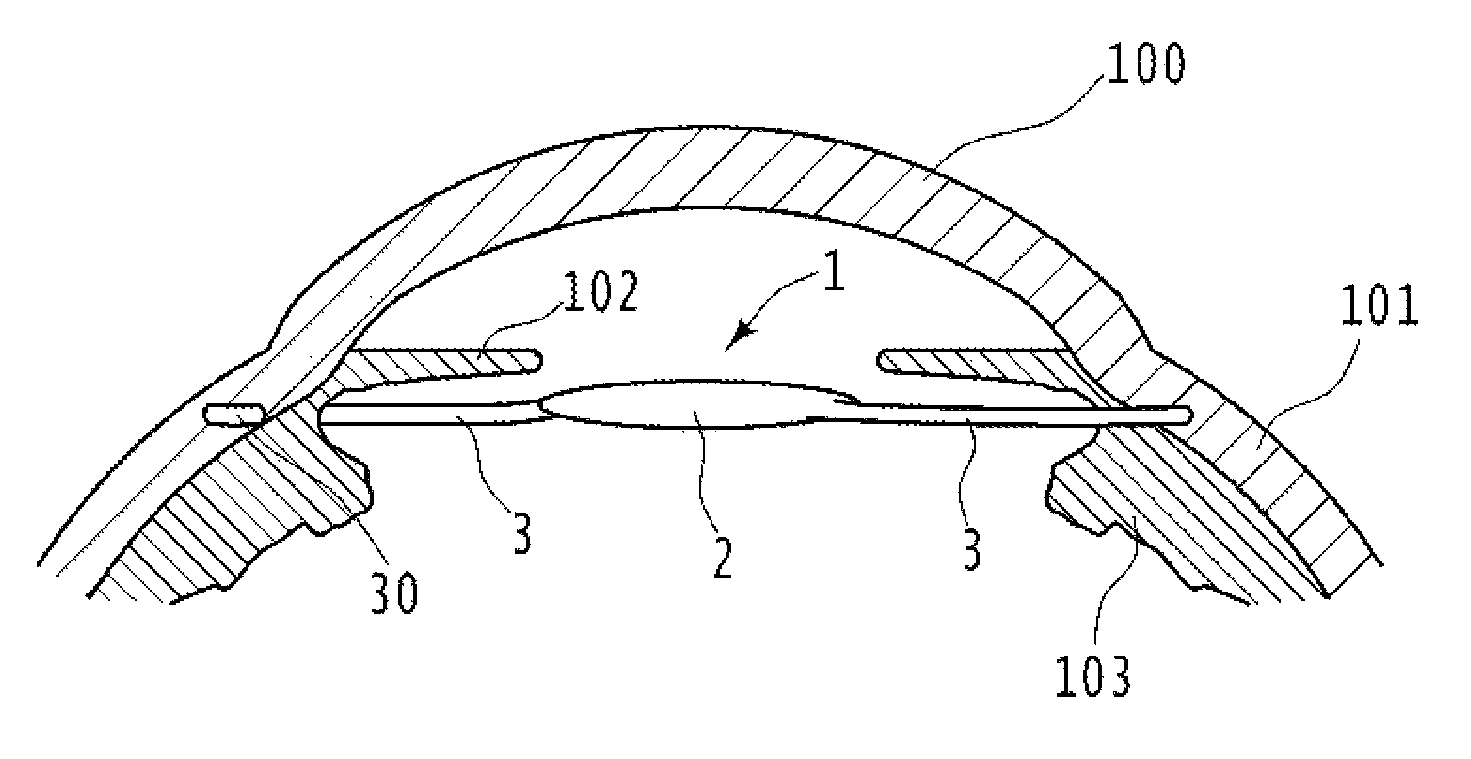
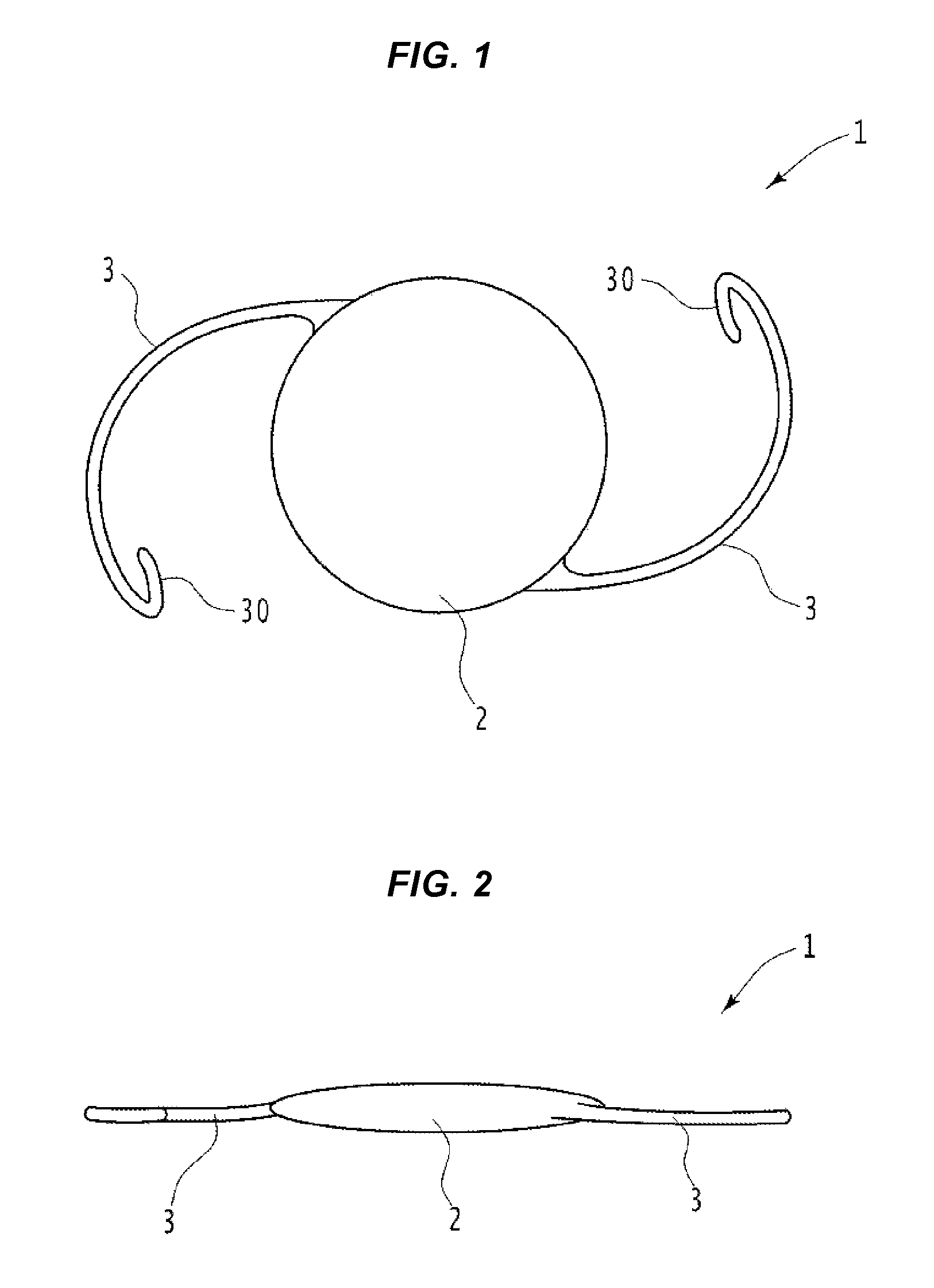
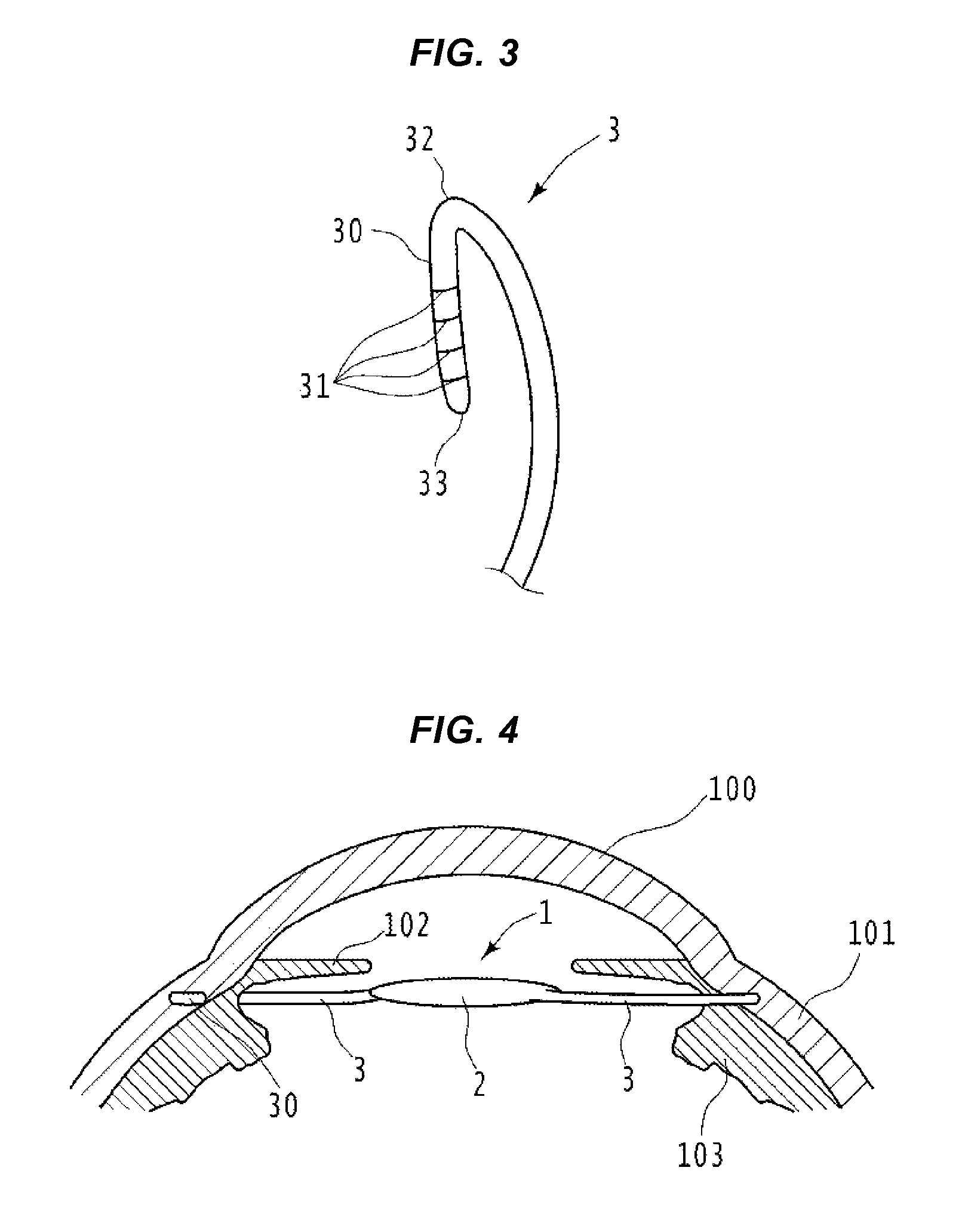
An intraocular lens insertion device comprises a pad formed by an elastic element harmless to a living body, a drawing thread mounted on a rear portion of the pad, and an insert portion formed at a front portion of the pad. The insert portion has a shape suitable to fit into a ciliary sulcus of an aphakic eye. The pad has a thickness capable of covering a tip end of a surgical needle.
Owner:SUGIURA TAKESHI
Accommodating intra-ocular lens system
An implantable, compressible, accommodating intra-ocular lens (IOL) coupled to at least one sensor which detects a signal created by the ciliary muscle. A ciliary sulcus ring can house the at least one sensor, and the sensor can include miniaturized electrodes (ciliary muscle probes) for implanting into the ciliary muscle of the subject. A potentiometer / microcomputer can modulate the ciliary muscle signal detected by the sensor(s) into an electrical signal, and a transmitter sends this electrical signal to a micromotor, which causes compression of the IOL via an annular support ring system, causing a change in the IOL shape. The IOL can be part of an IOL complex including a compressible, accommodating IOL, an external lens membrane, and an annular support ring system. The annular support ring system provides a foundation for the micromotor to compress the IOL.
Owner:VISTA OCULAR
Accommodating intraocular lens assembly
A method of positioning an accommodating intraocular lens assembly in an eye can include implanting an accommodating intraocular lens assembly having a positive power lens in the eye. The accommodating intraocular lens assembly can also include a plurality of stanchions extending between base ends and distal ends. The base ends can be disposed in spaced relation to one another about a first arcuate periphery positioned in a ciliary sulcus of the eye. The distal ends can be disposed about a second arcuate periphery extending in a second plane positioned forward and outside of a capsular bag of the eye. The positive-power lens can be connected with the plurality of distal ends whereby a center of the positive power lens is moved along the central optic axis in response to contraction of the first arcuate periphery by contraction of the ciliary sulcus.
Owner:DUDEE JITANDER +1
Small aperture (pinhole) intraocular implant to increase depth of focus
InactiveUS20140379078A1Increase depth of focusMinimize impactIntraocular lensLighting spectrumLens implant
Small aperture (pinhole) intraocular implant to increase depth of focus comprising a diaphragm juxtaposed to the front surface of a lens implanted previously, having its anterior surface convex and its posterior surface concave. The diaphragm is held in position by inserting engaging means in the ciliary sulcus.It is proposed that said diaphragm is opaque to a visible light spectrum and transparent to light in the infrared range and is equipped with passage means of visible light in its central region, such as a through hole whose diameter is between 1 mm and 2.5 mm.The constriction of the incident light rays increases the depth of focus, featuring a pinhole effect. The engagement means may be provided by two handles shaped with curved proximal ends joined to the peripheral edge of said diaphragm and having substantially circular section with a diameter between 80 μm and 800 μm or two handles of the same material as the diaphragm and constituting an extension of this edge, or even one elongated platform whose center is located in the small-diameter circular opening.
Owner:TRINDADE CLAUDIO
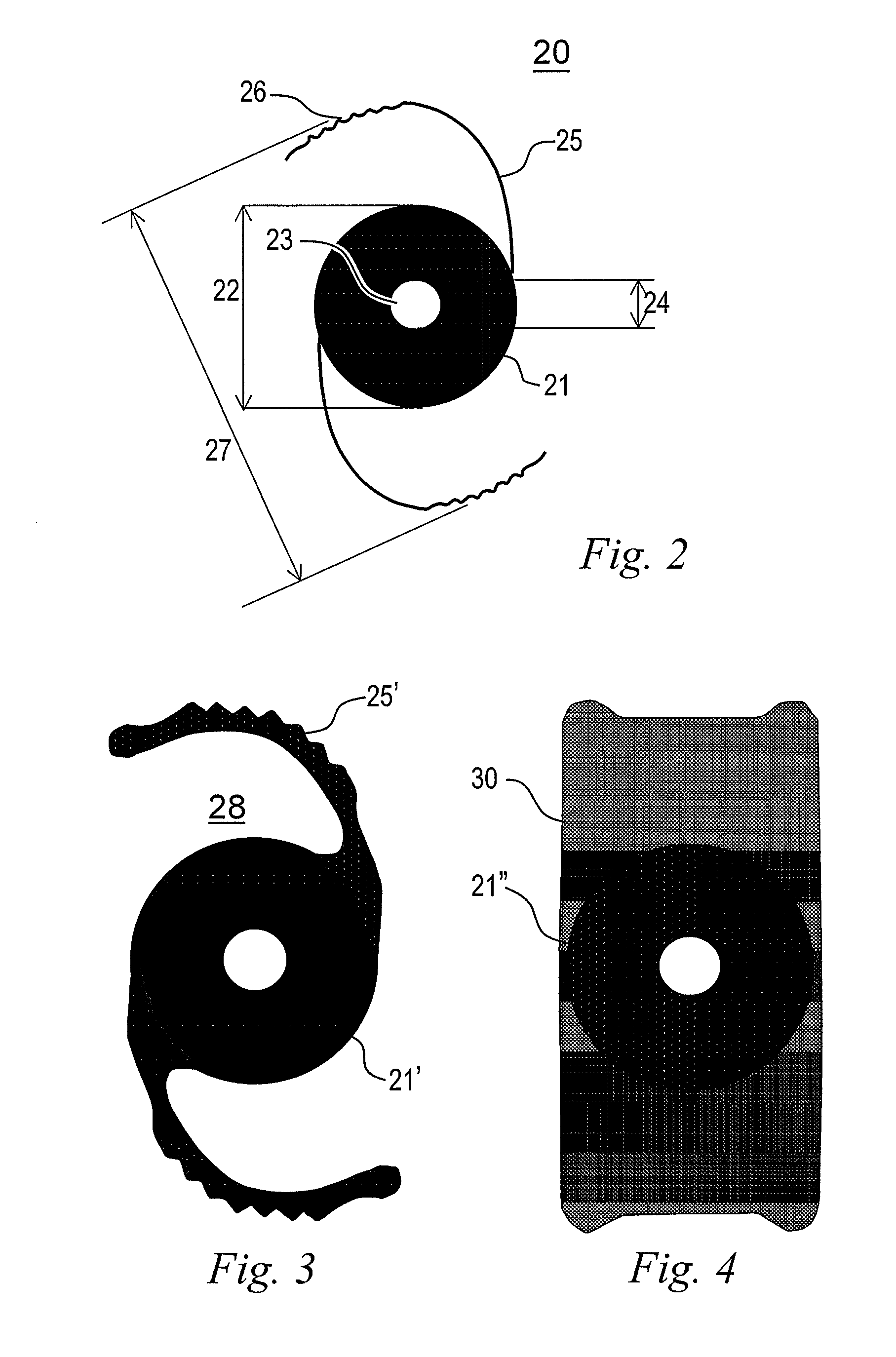
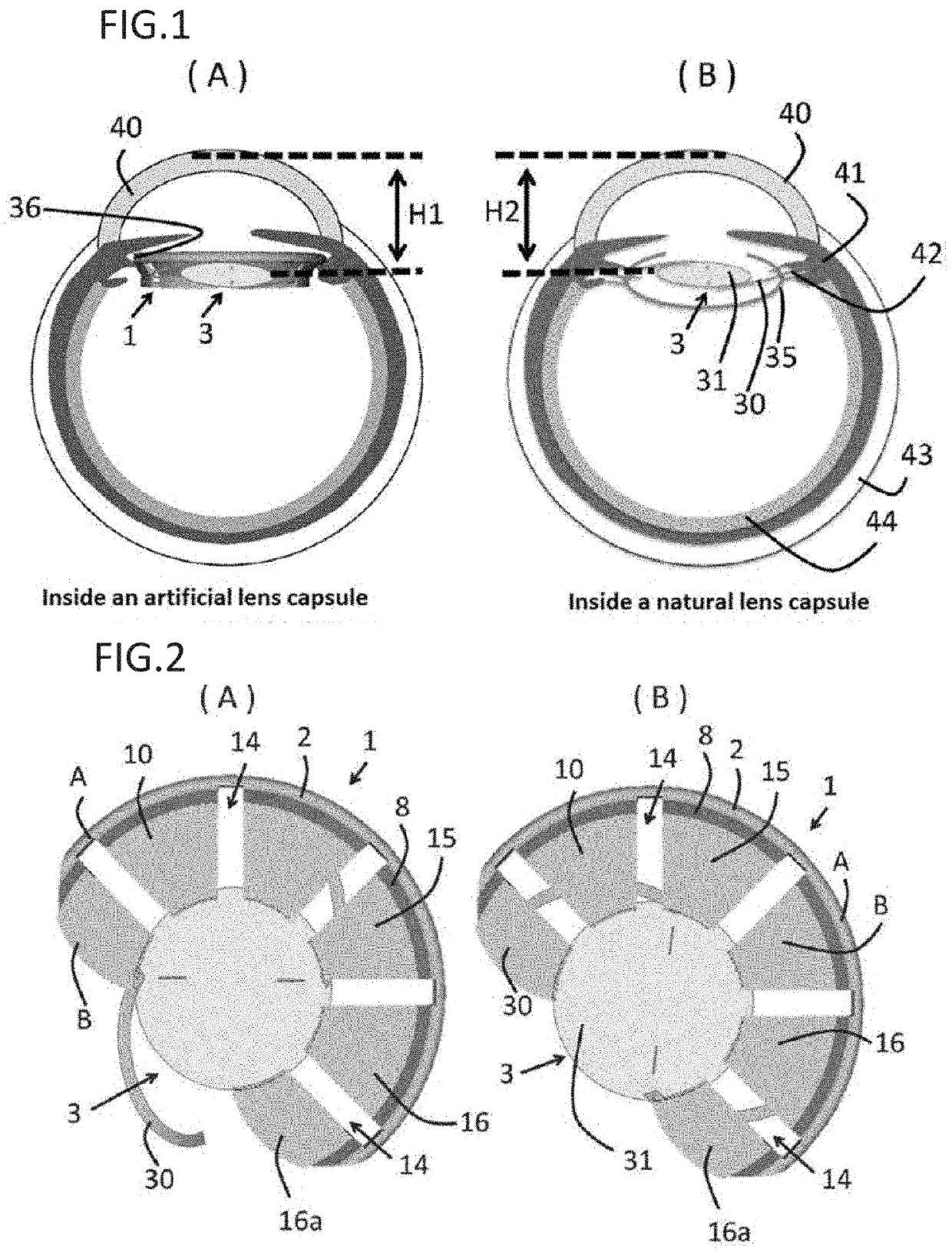
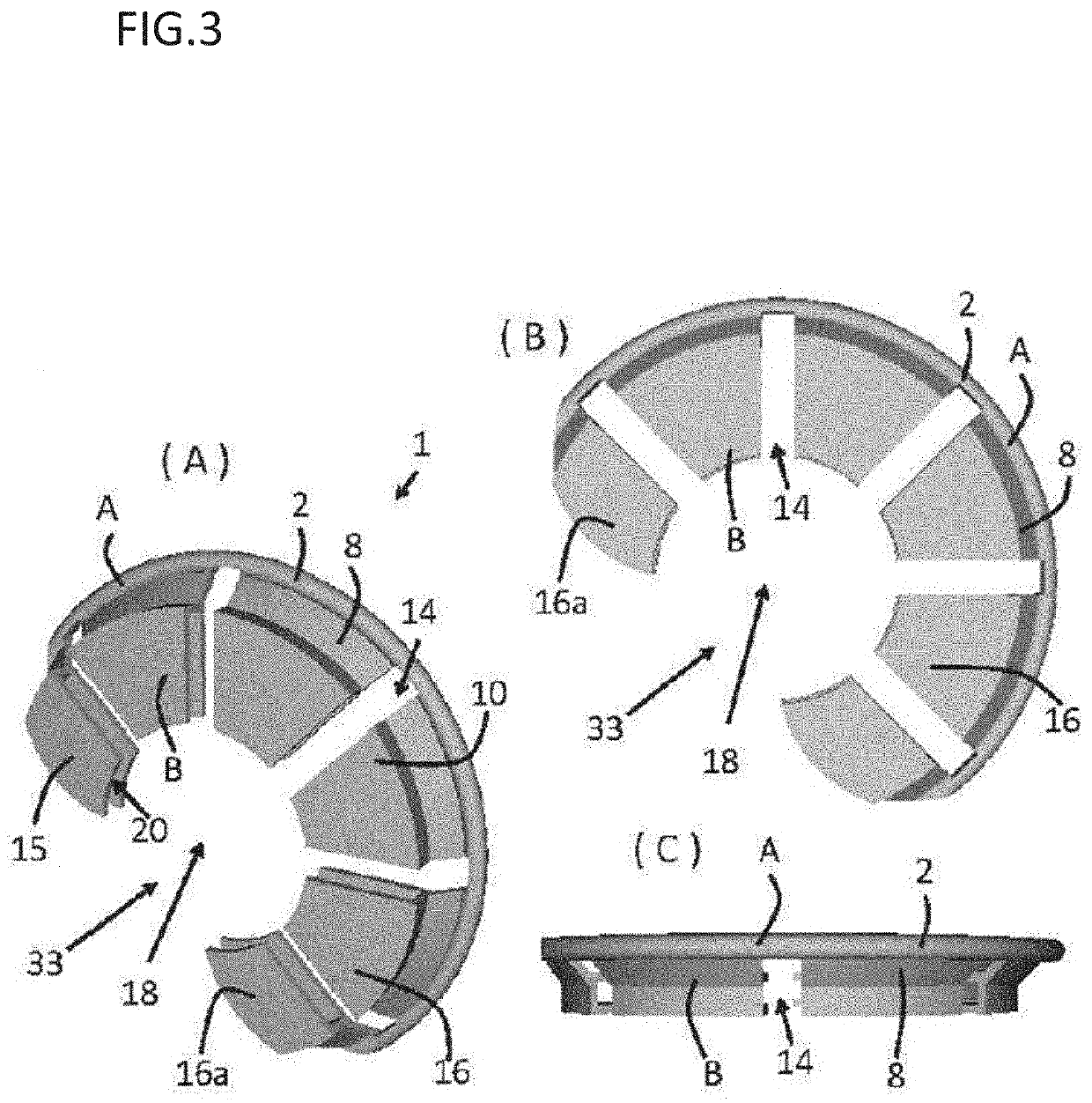
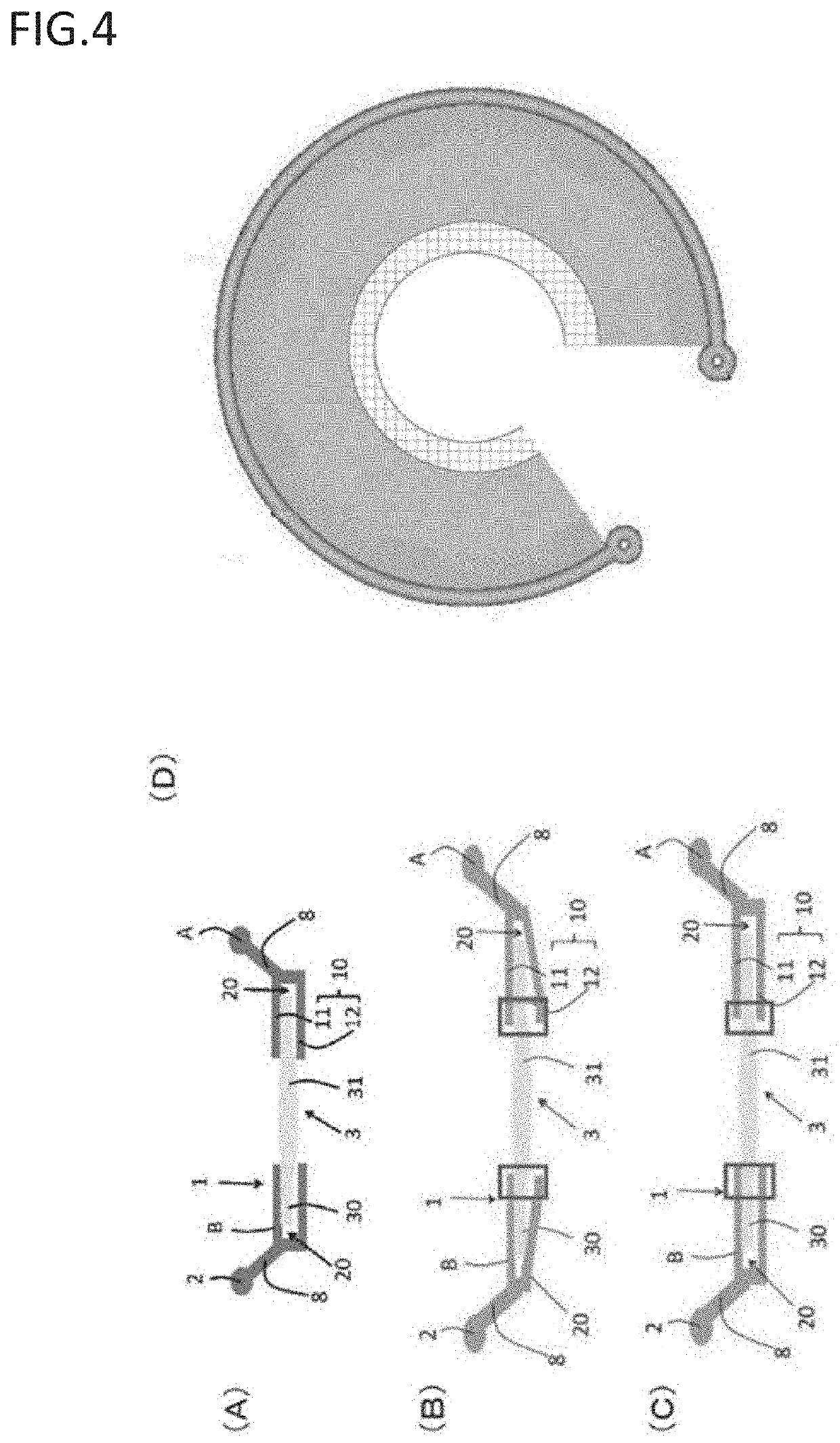
Artificial lens capsule
PendingUS20200000575A1Good deformabilityReduce manufacturing costIntraocular lensOptometryIntraocular lenses
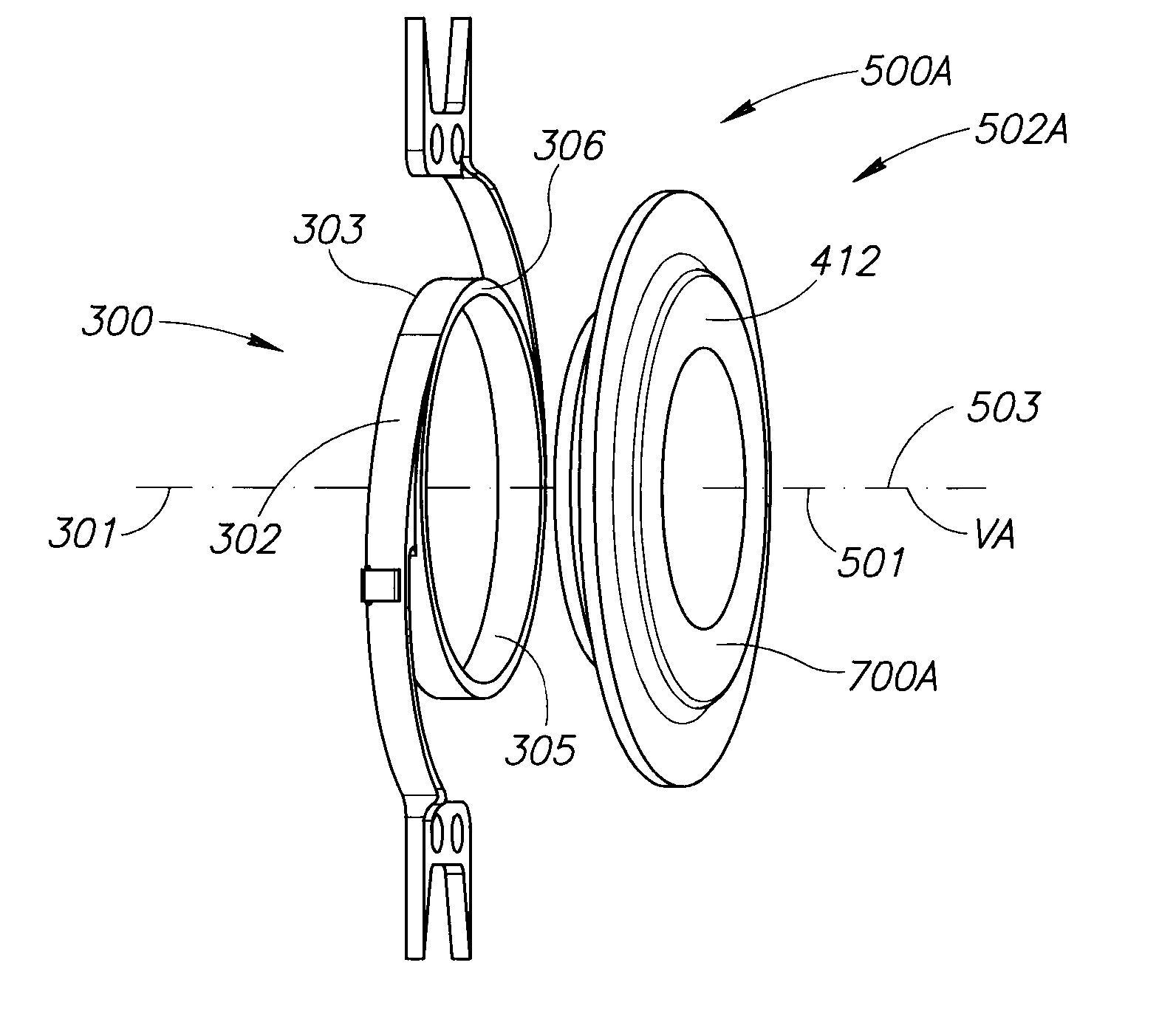
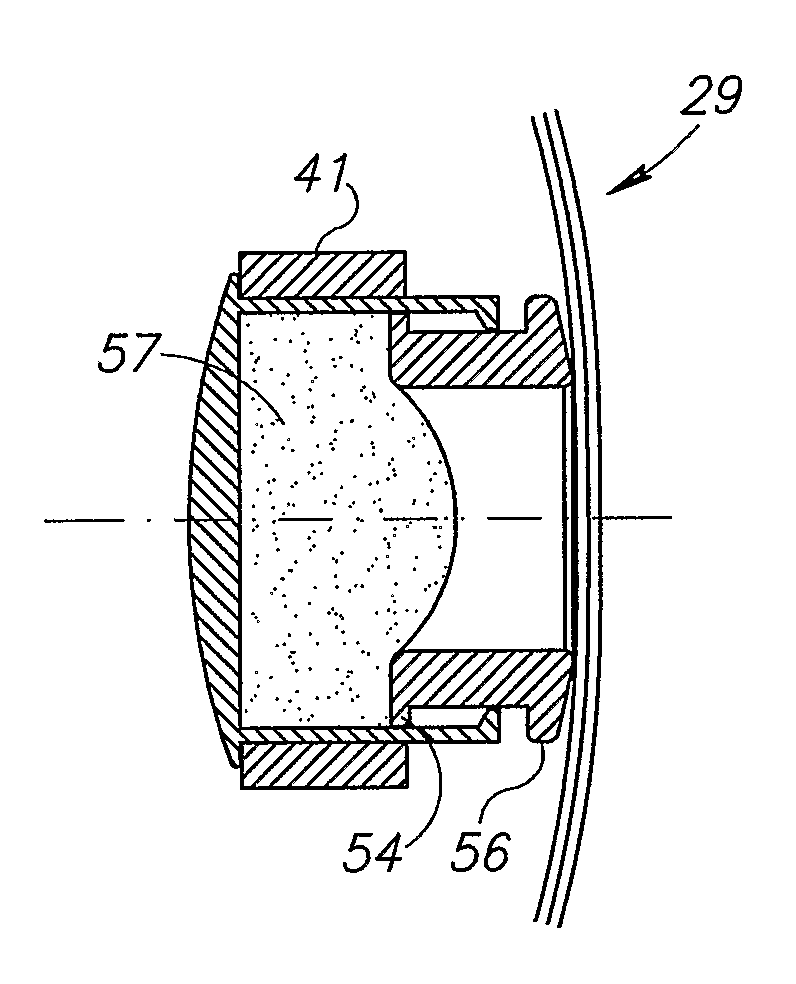
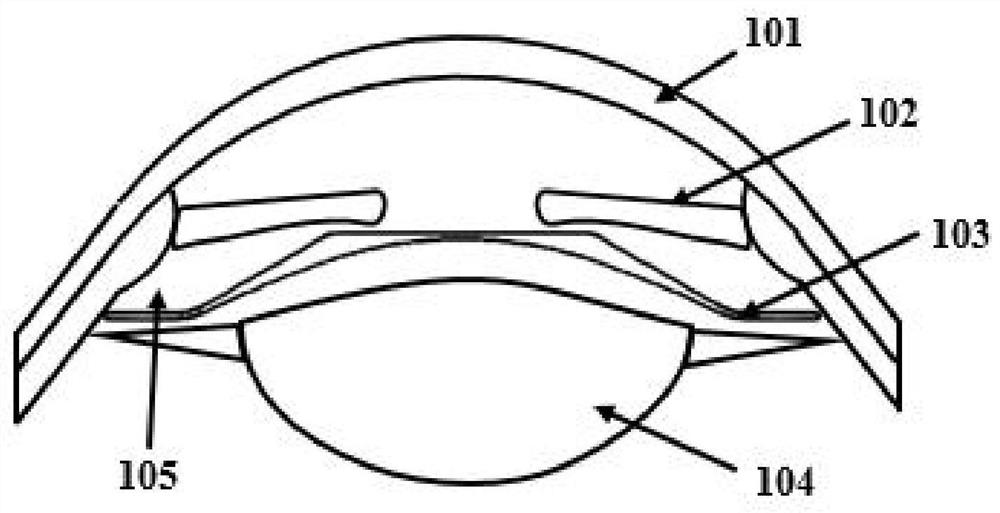
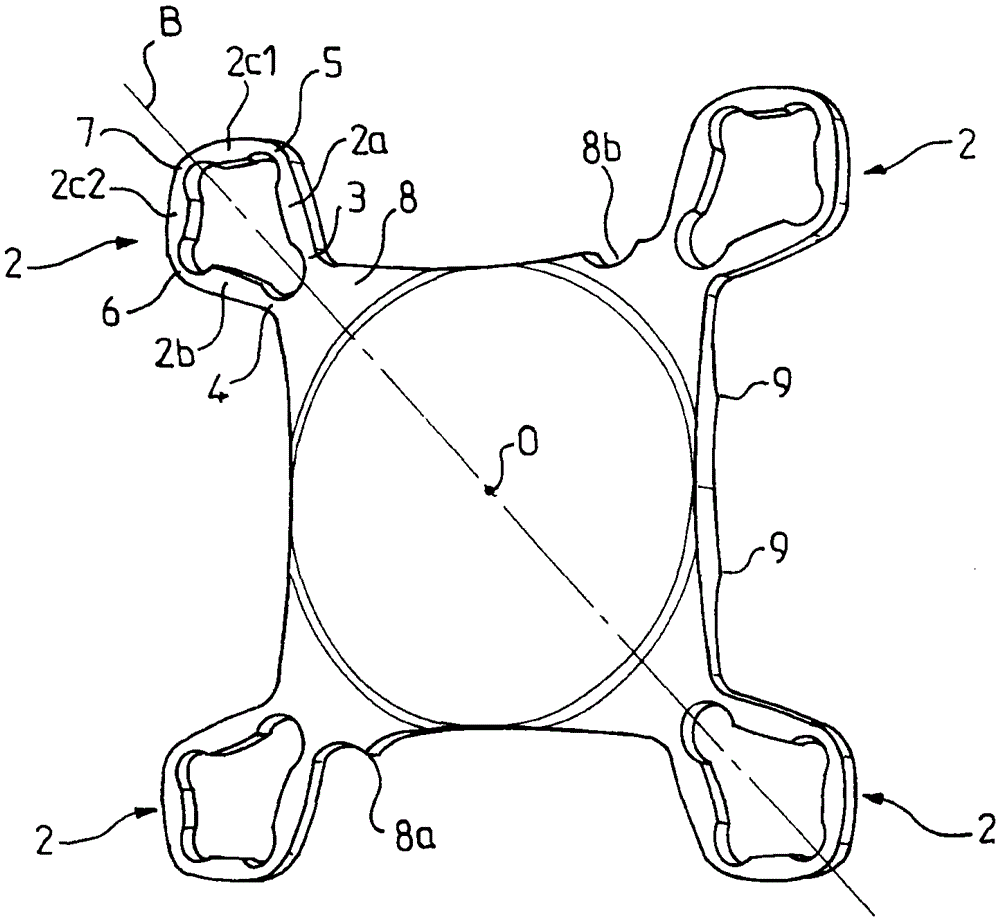
Provided is an intraocular lens affixing device which makes it possible to affix an intraocular lens of any kind with respect to the inside of an eye with a ruptured or deleted lens capsule. The intraocular lens affixing device is provided with a device support portion (A) and an intraocular lens housing portion (B) connected to the device support portion (A). The device support portion (A) includes a frame 2 having a shape matching a ciliary sulcus 36. Also provided is an affixing kit for inserting an intraocular lens, the kit being provided with a) an intraocular lens affixing device; and b) an injector for injecting the affixing device.
Owner:KYOTO PREFECTURAL PUBLIC UNIV CORP
Intraocular lens
Owner:CHUKYO MEDICAL
Posterior chamber type progressive multi-focus intraocular lens with lens eye
The invention discloses a posterior chamber type progressive multi-focus intraocular lens with a lens eye, wherein theintraocular lens is made of a soft transparent hydrophilic or hydrophobic acrylic material, comprises an optical area, a support part at the edge of the optical area and a support loop, and is implanted behind an iris and in front of a natural lens (ciliary sulcus). The intraocular lens optical area has a far vision area and a near vision area at the same time, the diopter can be stably transited from the far vision area to the near vision area in a progressive mode, one of the front surface and the rear surface of the intraocular lens optical area is generally a spherical surface or an aspheric surface, and the other surface is a progressive free-form surface. After the intraocular lens is implanted, the eyesight of myopia and presbyopia of the middle-aged and elderly people can be corrected at the same time, and the middle-aged and elderly people having requirements for mobile phones, reading and entertainment can take off glasses truly.
Owner:TIANJIN SHI JI KANG TAI BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
Intraocular lens and methods for implanting the same
An intraocular lens has central lens body with a first and second, opposite posterior and anterior surfaces, the posterior and anterior surfaces meeting in a rounded peripheral side surface. The lens further has at least a pair of haptics extending from the peripheral side surface of the central lens body, each of the haptics having an arcuate configuration so that a radially distal end of each haptic is engageable within the ciliary sulcus of the eye. The haptics engageable with the ciliary sulcus for stabilizing the central lens body at a location posterior, or rearward, of both the lens capsule anterior and posterior portions, such that the central lens body seals the anterior and posterior portions together proximal to a capsulotomy in each of the anterior and posterior portions.
Owner:ARBISSER LISA
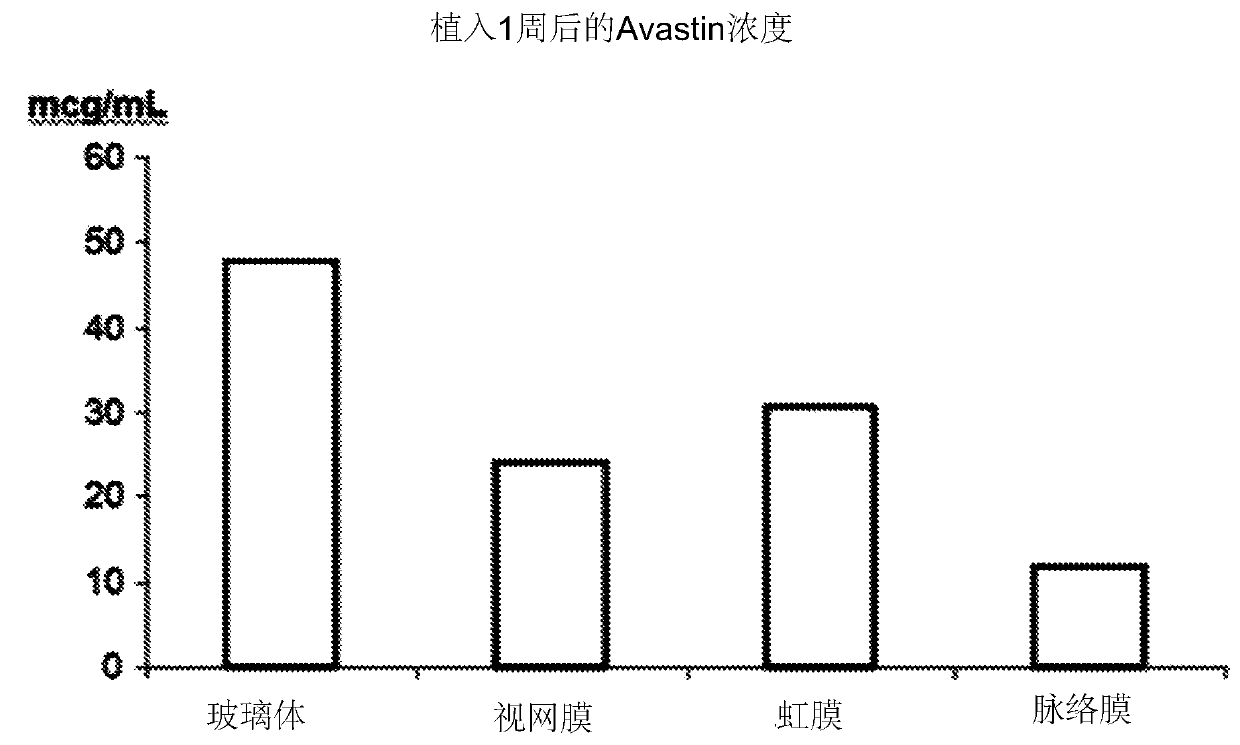
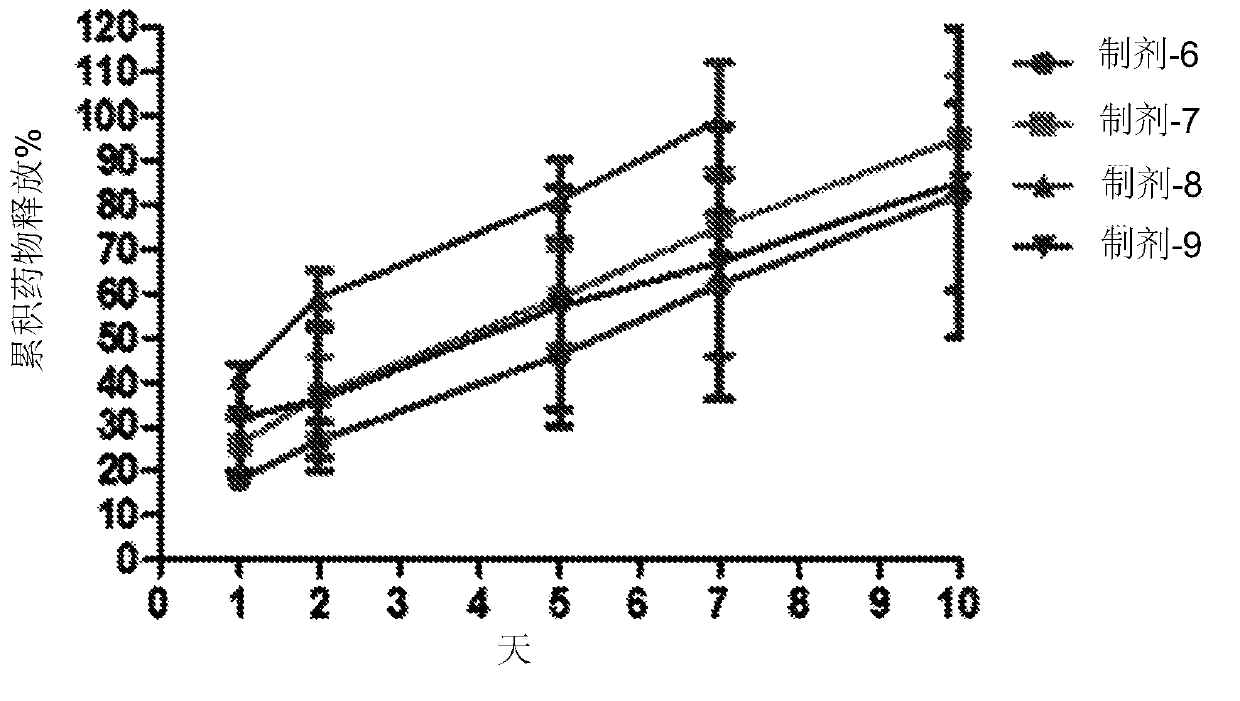
Ocular biodegradable drug implant and method of its use
A biodegradable drug implant includes a PLG matrix and a non-steroid anti inflammation drug, for example diclofenac sodium. The implant is inserted into the eye in the anterior chamber, for example in the ciliary sulcus, following eye surgery. A method for treating and or preventing inflammation of the eye following eye surgery includes placing the implant in the anterior portion of the eye.
Owner:LENSTEC BARBADOS
Intraocular drug delivery device and associated methods
Devices, systems, and methods for delivery of an active agent into the eye of a subject can include an intraocular active agent delivery device including an active agent dispersed within a biodegradable active agent matrix. The active agent includes dexamethasone and the delivery device is adapted to fit within a lens capsule or ciliary sulcus of an eye. The delivery device can be inserted into the lens capsule or ciliary sulcus of an eye during cataract surgery or for treatment of uveitis.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Accommodating intra-ocular lens system
An implantable, compressible, accommodating intra-ocular lens (IOL) coupled to at least one sensor which detects a signal created by the ciliary muscle. A ciliary sulcus ring can house the at least one sensor, and the sensor can include miniaturized electrodes (ciliary muscle probes) for implanting into the ciliary muscle of the subject. A potentiometer / microcomputer can modulate the ciliary muscle signal detected by the sensor(s) into an electrical signal, and a transmitter sends this electrical signal to a micromotor, which causes compression of the IOL via an annular support ring system, causing a change in the IOL shape. The IOL can be part of an IOL complex including a compressible, accommodating IOL, an external lens membrane, and an annular support ring system. The annular support ring system provides a foundation for the micromotor to compress the IOL.
Owner:VISTA OCULAR
An ultra-thin zero spherical aberration implantable lens for myopia
ActiveCN113040976BPromote circulationReduce generationIntraocular lensOptical surfaceReoperative surgery
The invention discloses an ultra-thin zero-spherical-aberration implantable myopia lens. The lens is made of transparent hydrophilic polymethacrylate material, and includes an optical zone of the lens and plate-shaped supporting haptics along the edge of the optical zone of the lens. , used for surgical implantation to correct the vision of myopia. The implantation position is located behind the iris and before the natural lens (ciliary sulcus). The optical zone of the lens of the present invention is composed of a plano-concave optical surface, has an ultra-thin axial thickness, and increases The gap between the lens and the natural lens is reduced, the risk of post-cataract is reduced, and at the same time, it is convenient for surgical implantation or removal; the optical zone of the lens of the present invention has zero spherical aberration distribution, and does not cause total spherical aberration of the human eye after implantation Changes, correcting vision while increasing the natural comfort of the patient's eyes after surgery.
Owner:TIANJIN SHI JI KANG TAI BIOMEDICAL ENG CO LTD
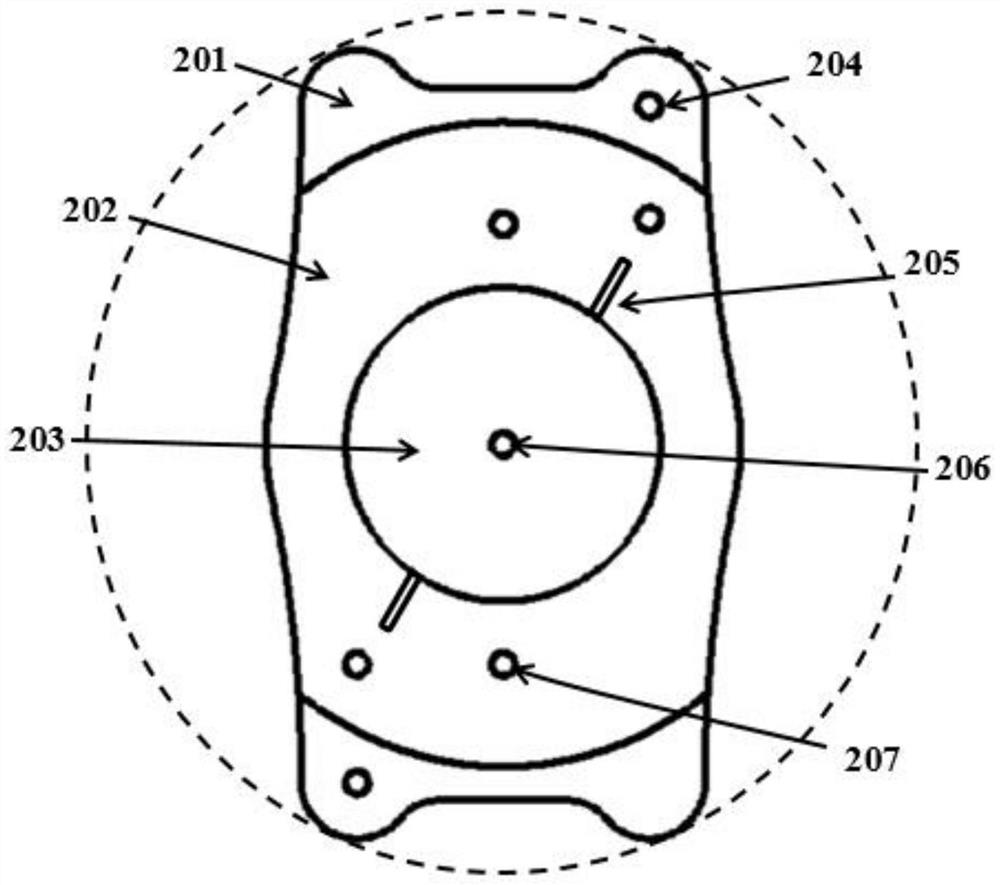
Ciliary sulcus positioner
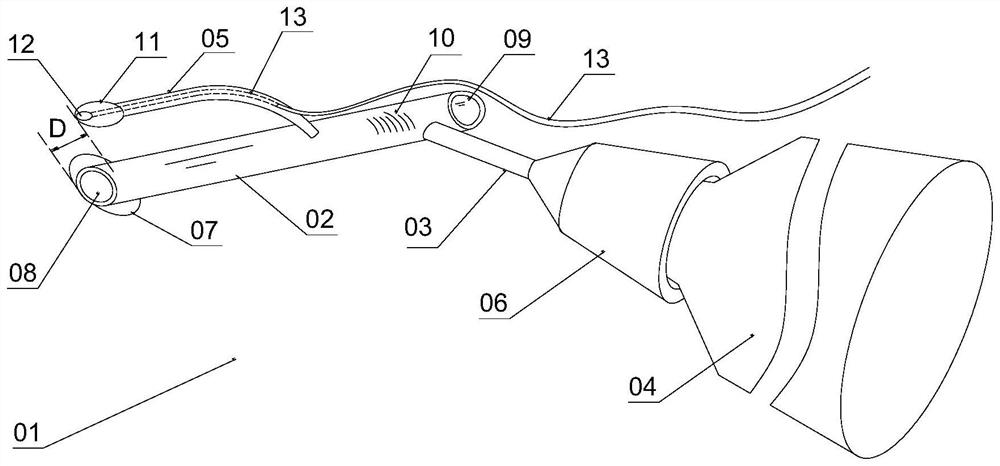
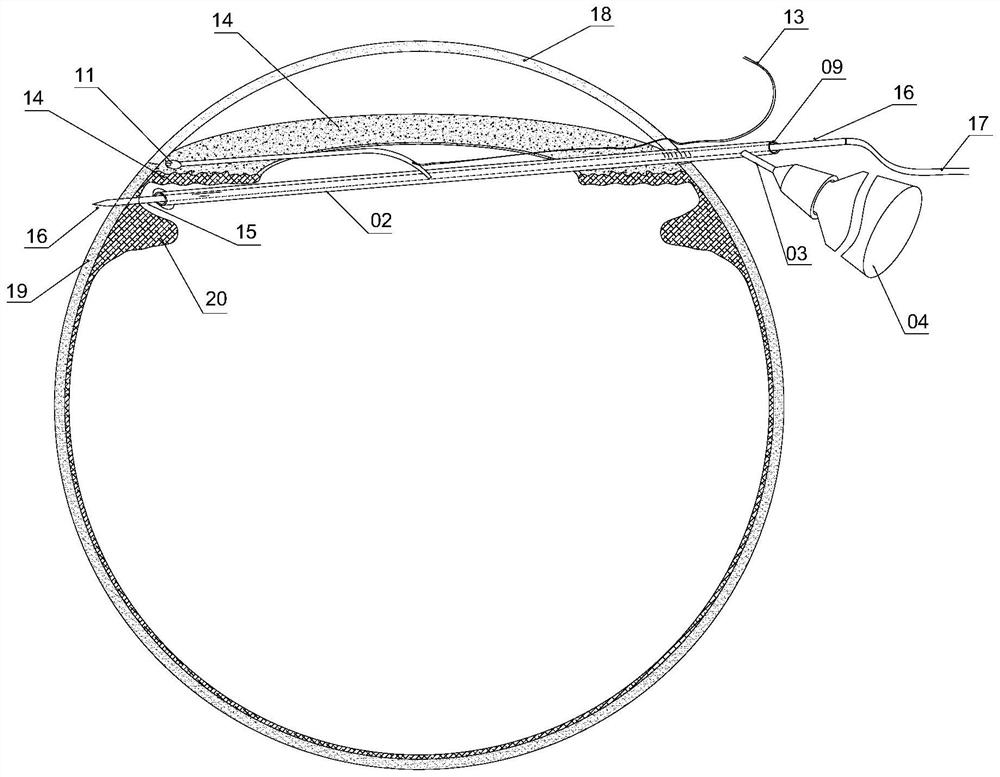
The ciliary sulcus positioner comprises a guide tube which is of a straight tube structure, and a puncture needle is arranged in the guide tube in a penetrating mode; the guide tube is provided with a front end serving as an insertion end and a rear end opposite to the front end; the front end is provided with a front end opening for the puncture needle to penetrate out, and the rear end is provided with a rear end opening for the puncture needle to penetrate in; scale marks are further arranged on the tube wall of the guide tube. The pointer is connected with the guide tube and moves together with the guide tube; the pointer is provided with an indicating end adjacent to the front end of the guide tube; the indicating end is provided with a light emitting part which can be controlled to emit light; the distance between the indicating end of the indicating pointer and the front end is 1-5 mm. The whole pointer and the guide tube extend forwards together, and the indicating end of the pointer and the front end of the guide tube are spaced to form a spacing opening for clamping an iris between the pointer and the guide tube.
Owner:王素常
Small incision implanted ciliary groove fixing artificial lens stent
InactiveCN113855383AImprove stabilityGood centering effectLaser surgeryIntraocular lensSurgical operationSurgical Manipulation
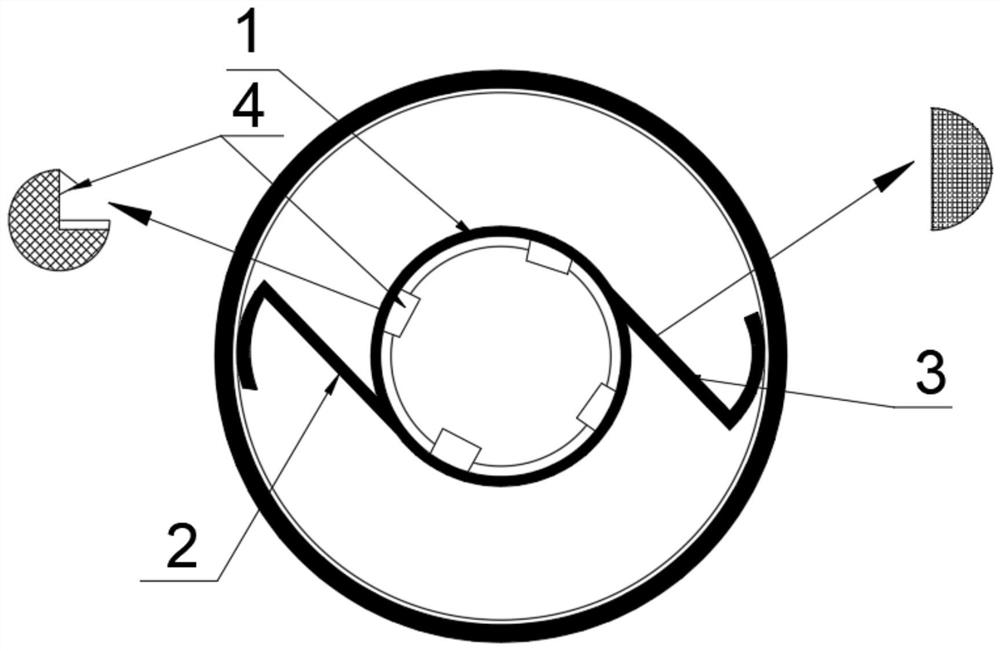
The invention discloses a small incision implanted ciliary groove fixing intraocular lens stent which comprises a stent ring, a first stent loop and a second stent loop are arranged on the outer side of the stent ring, the two ends of the first stent loop and the two ends of the second stent loop are each of a Z-shaped structure, and the outer side of the first stent loop and the outer side of the second stent loop are used for being placed on a ciliary groove. By the adoption of the structure, the surgical operation steps of implanting the intraocular lens after the cataract surgery of complex cases are simplified, damage to eyeballs is reduced, and the stability and neutrality of fixing the intraocular lens in ciliary sulcus after the surgery are improved; and moreover, the stent type design is adopted, different types of intraocular lenses with different functions can be replaced according to the vision requirements of patients in the short-term and long-term operation.
Owner:何爱平
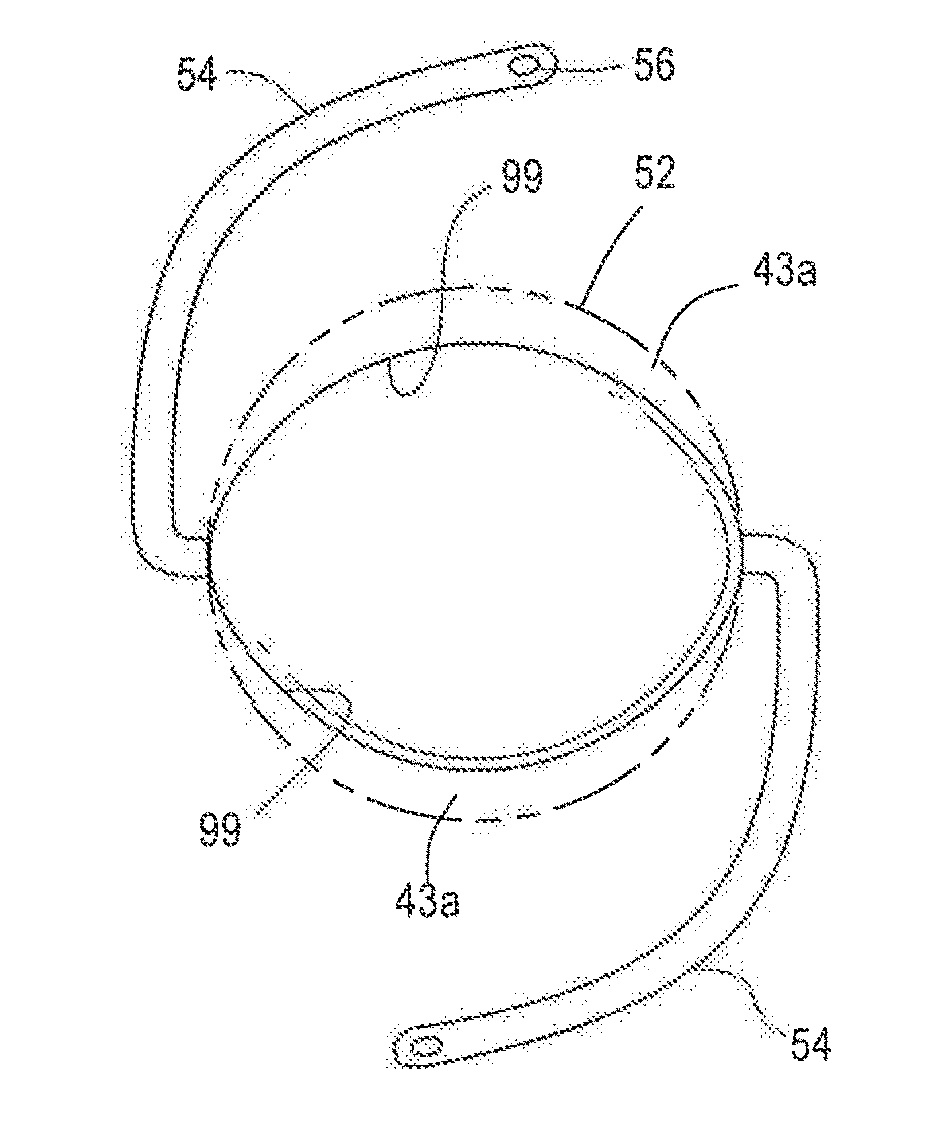
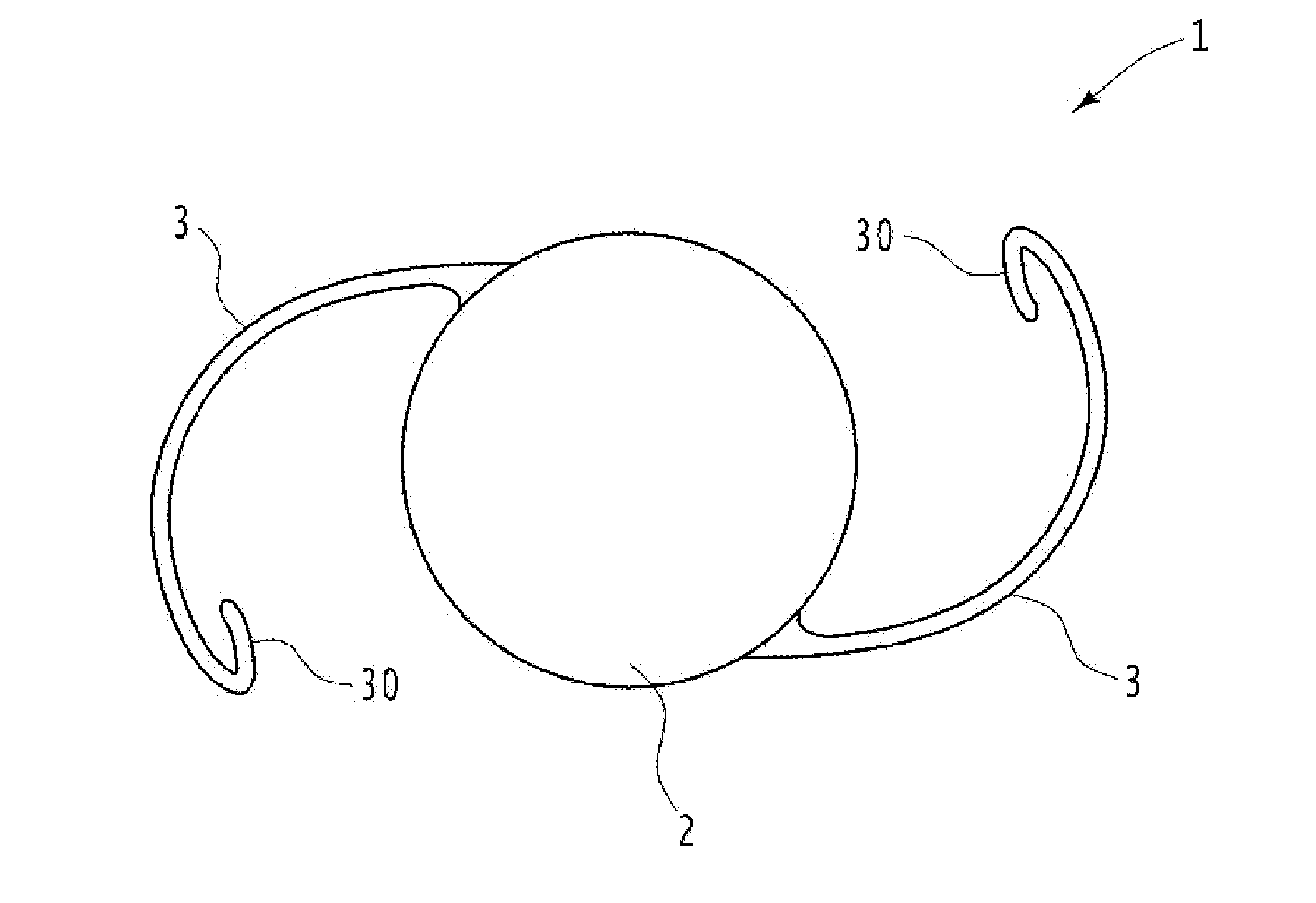
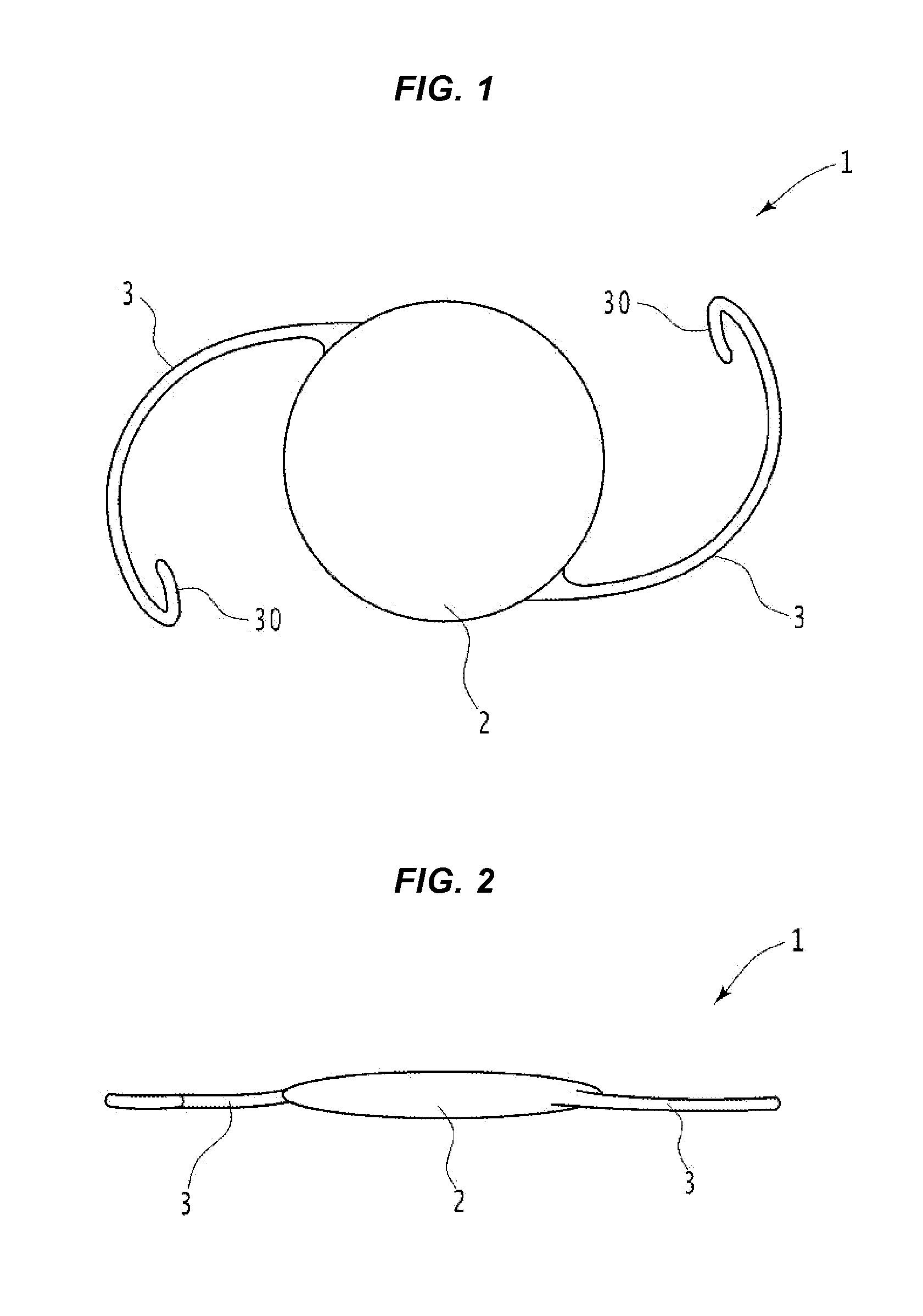
Posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens
PendingCN112566589AImprove axialImprove stabilityIntraocular lensPosterior chamber phakic intraocular lensOptometry
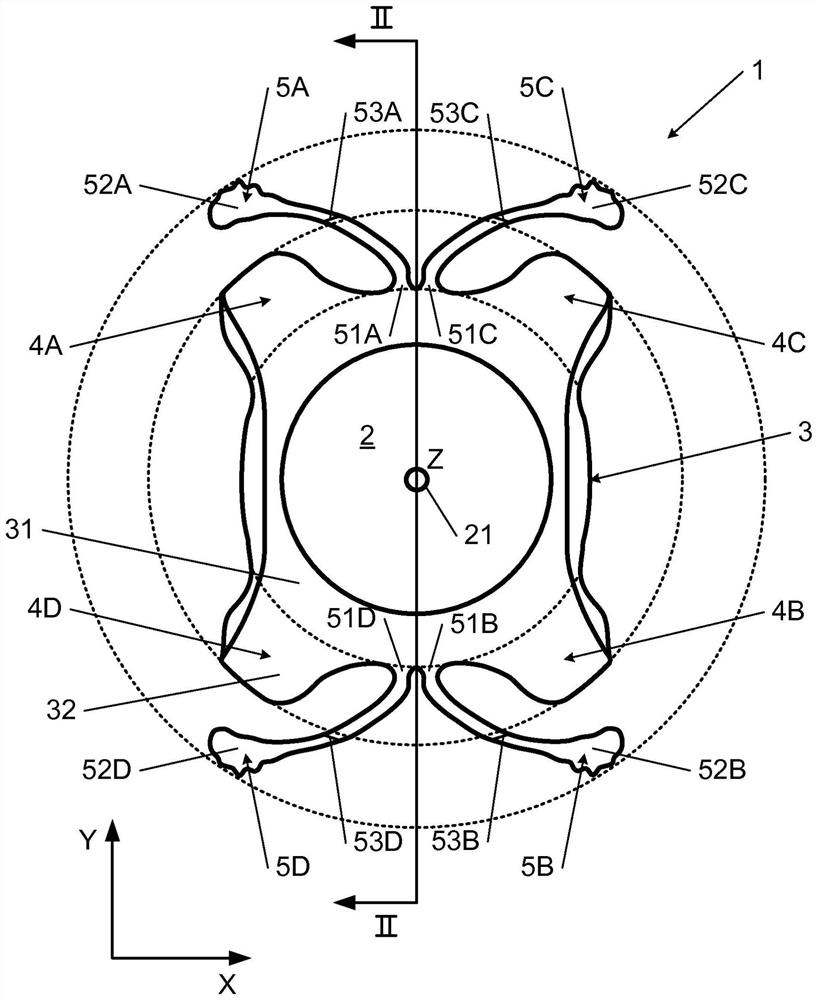
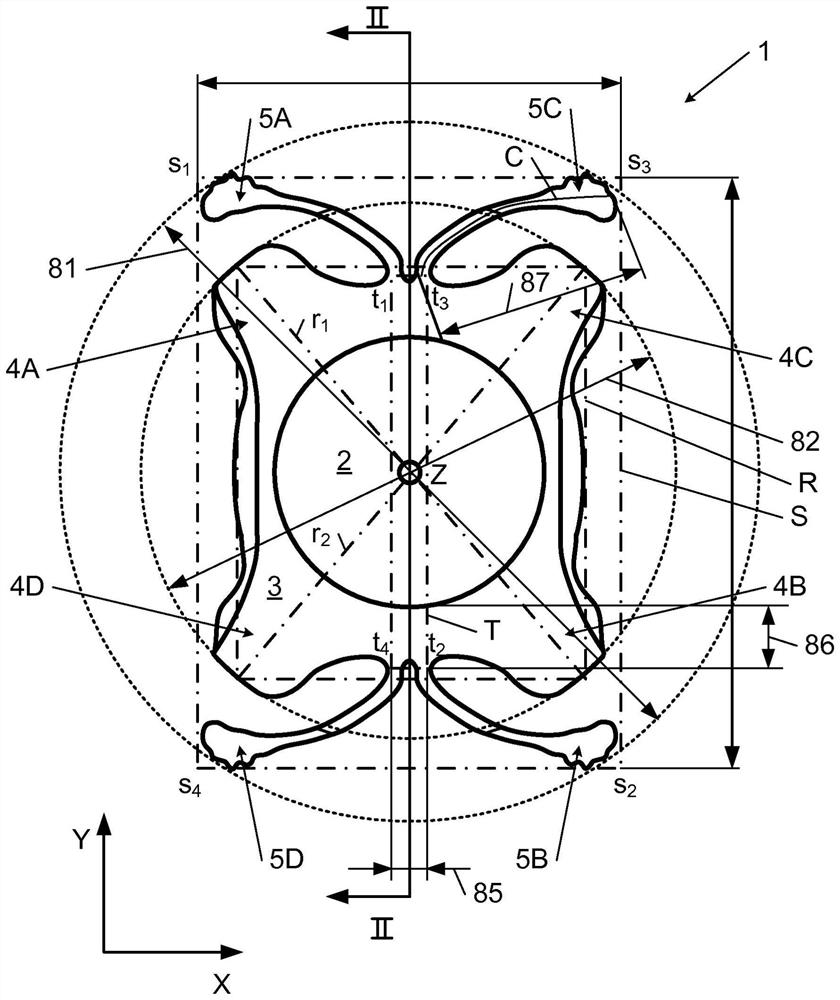
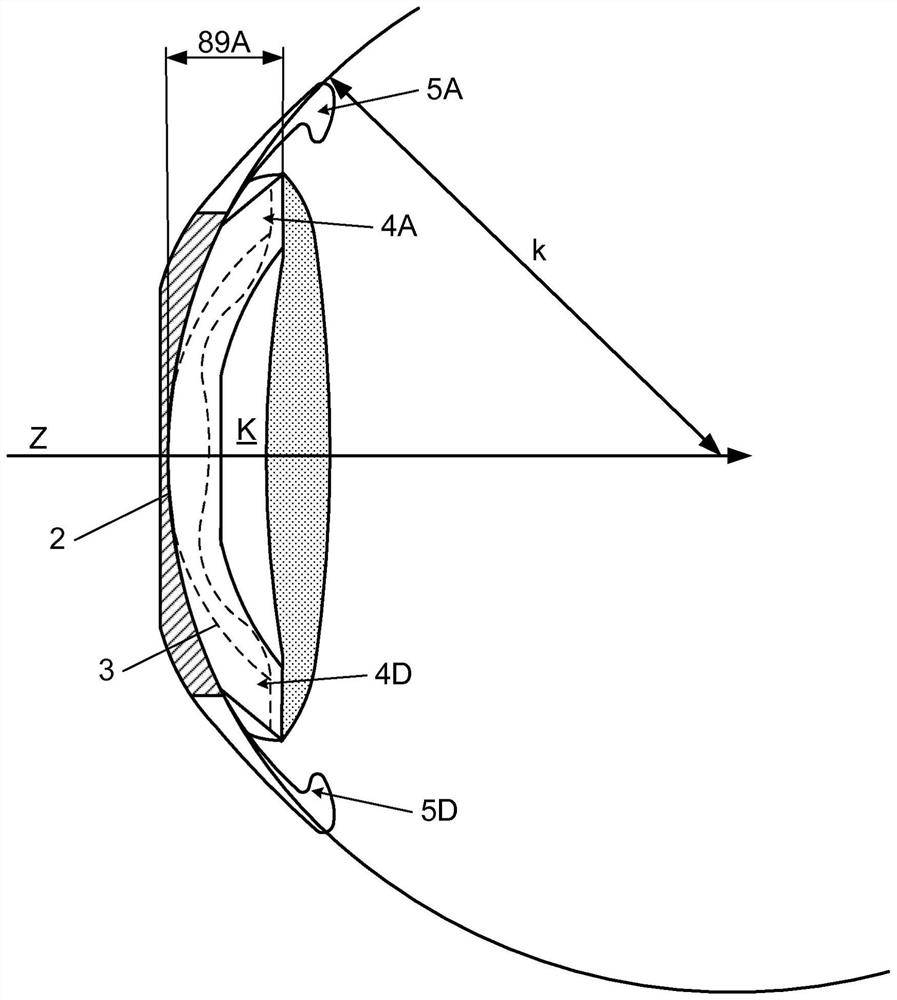
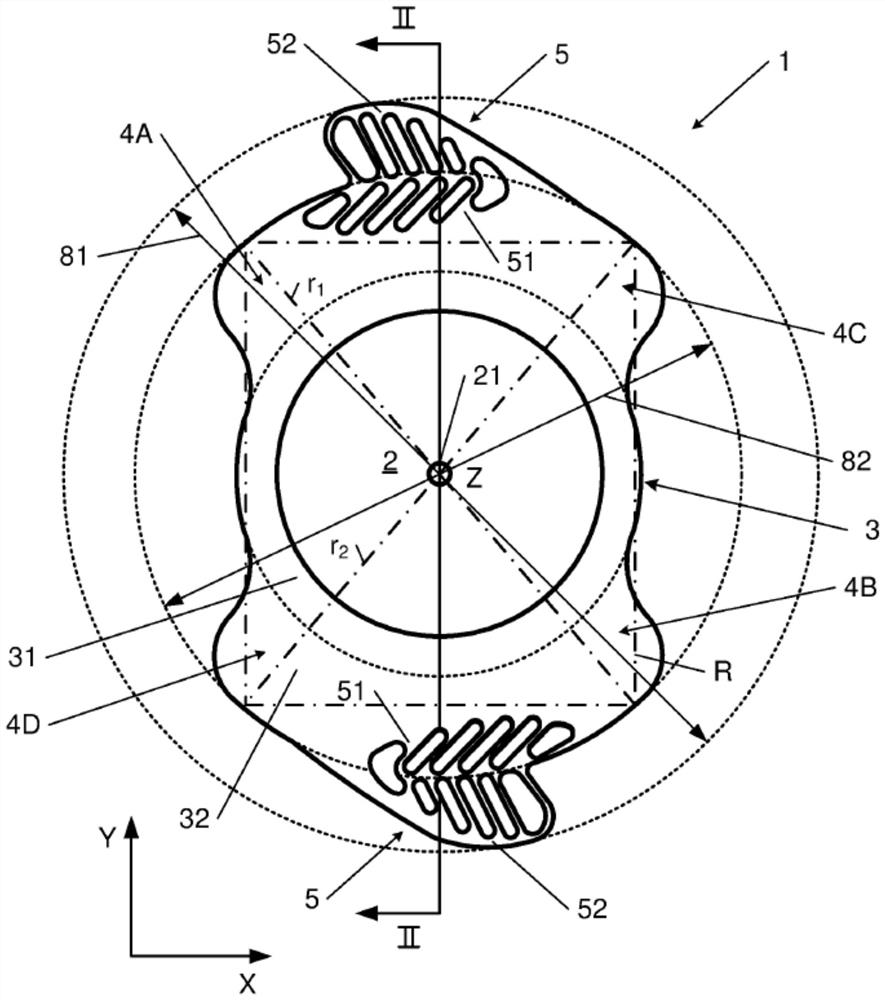
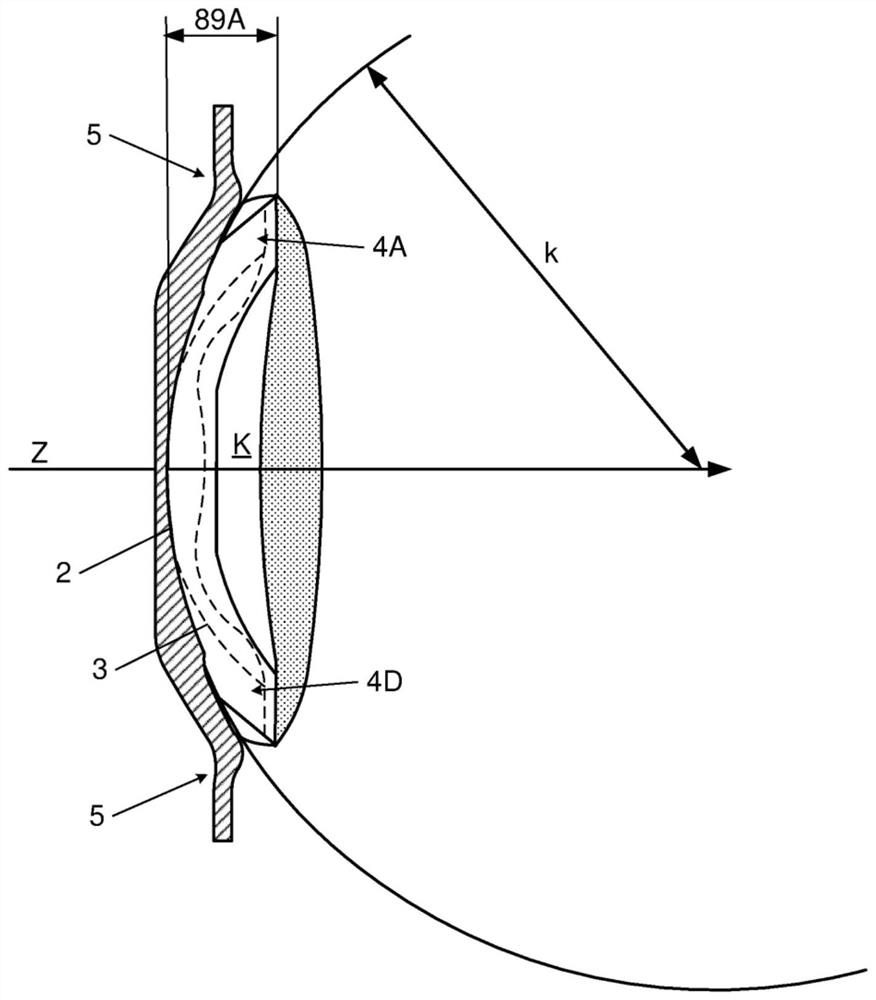
The invention relates to a posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens (1) comprising a central optical part (2), a peripheral haptic part (3) comprising a plurality of support elements (4A-D) arrangedto lie on a ciliary zonule of an eye, and a plurality of flexible elongated haptics (5A-D) arranged to hook into a ciliary sulcus of the eye.
Owner:PHYSIOL
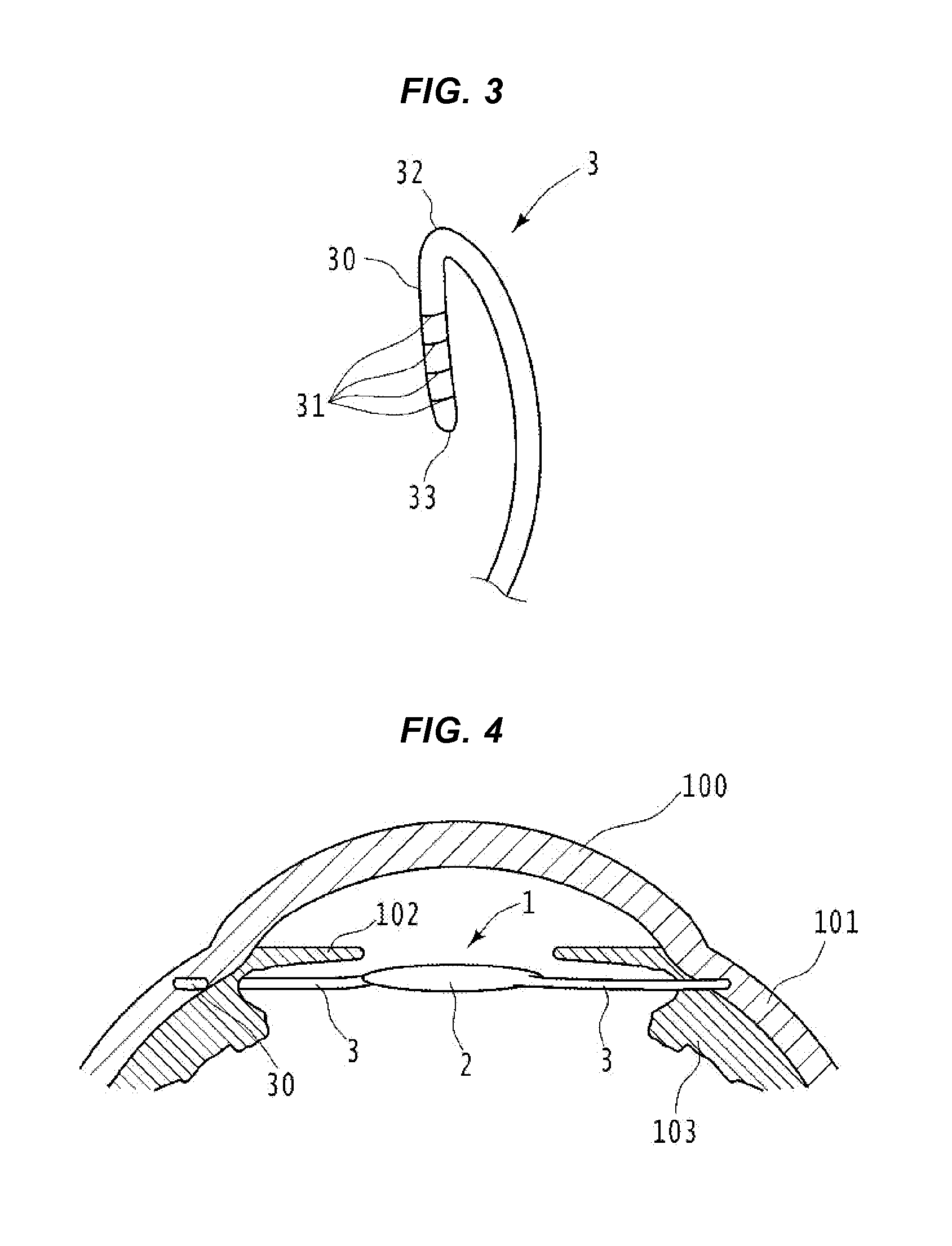
Improved haptic device for ciliary sulcus implants
Owner:QMP HLDG
Posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens
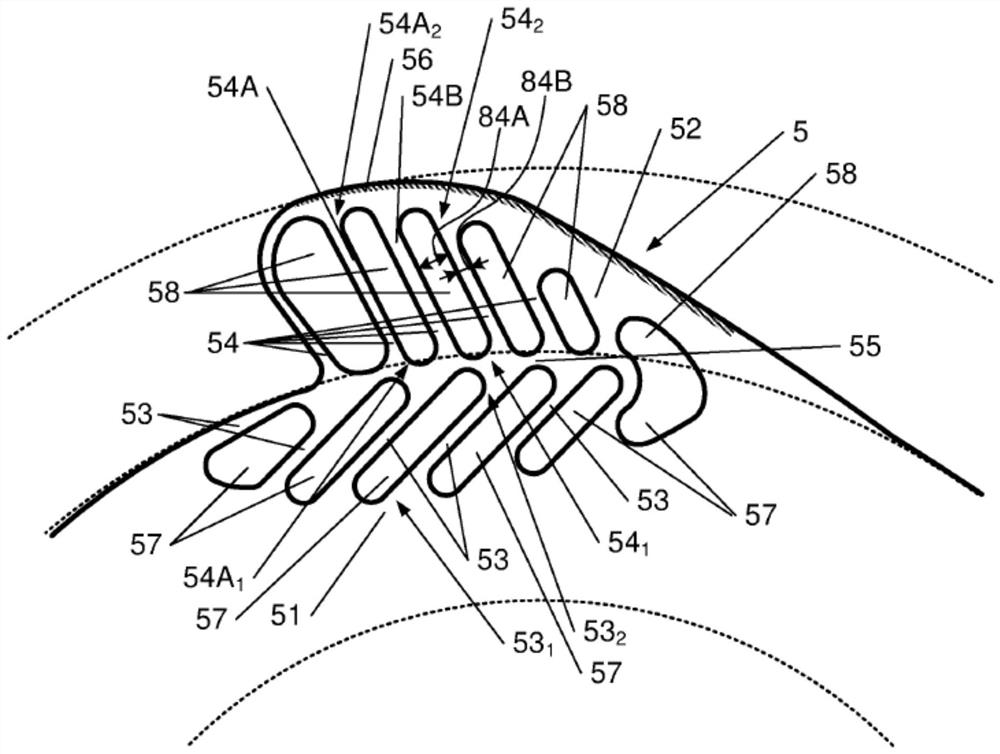
The present invention relates to a posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens (1) comprising a central optical part (2), a peripheral haptic part (3) comprising a plurality of support elements (4A-D) arranged to lie on a ciliary zonule of an eye, and at least one flexible haptic (5) comprising a reticulated distal region (52) arranged to lay into a ciliary sulcus of the eye.
Owner:PHYSIOL
Implantable intraocular drug delivery devices
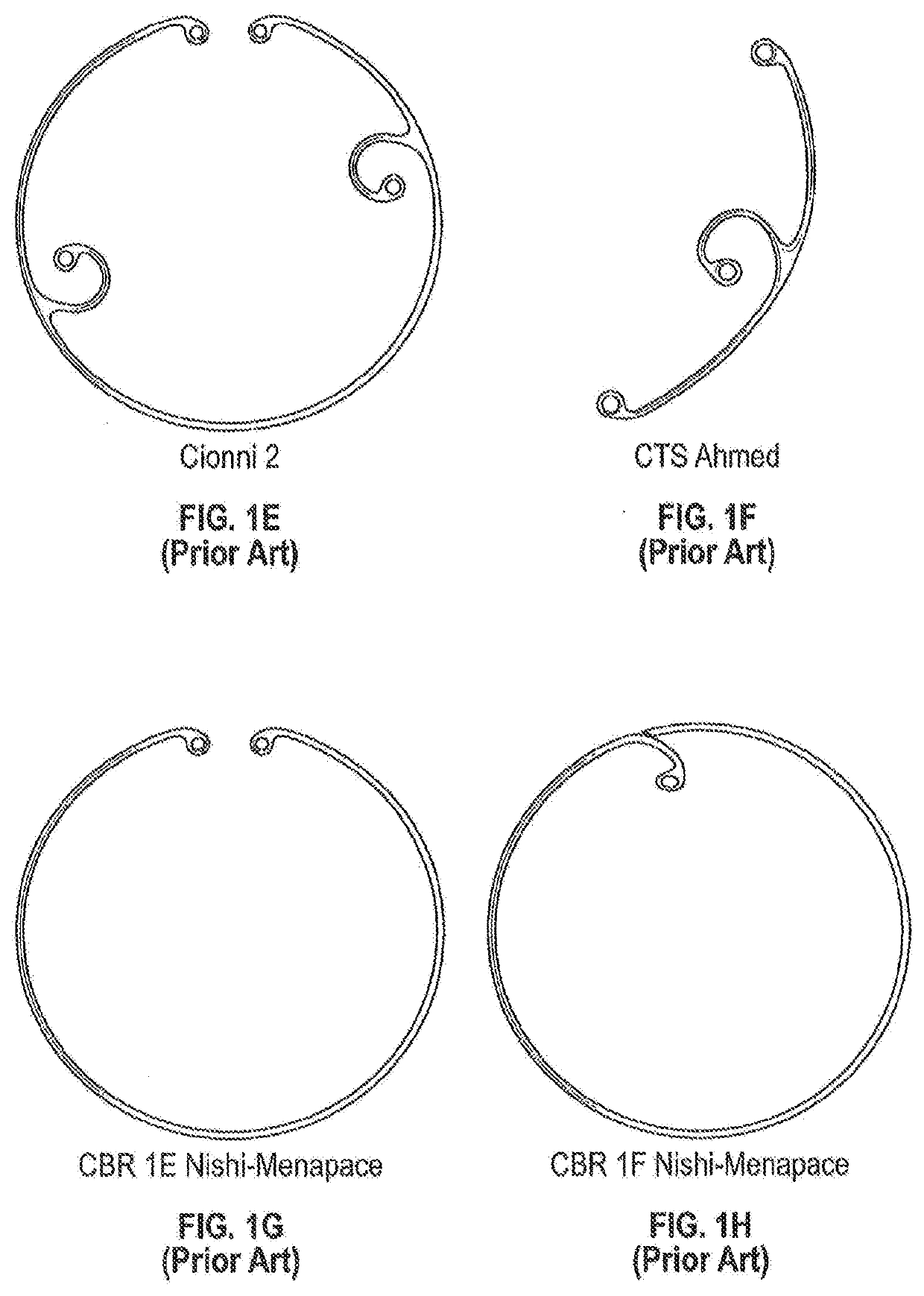
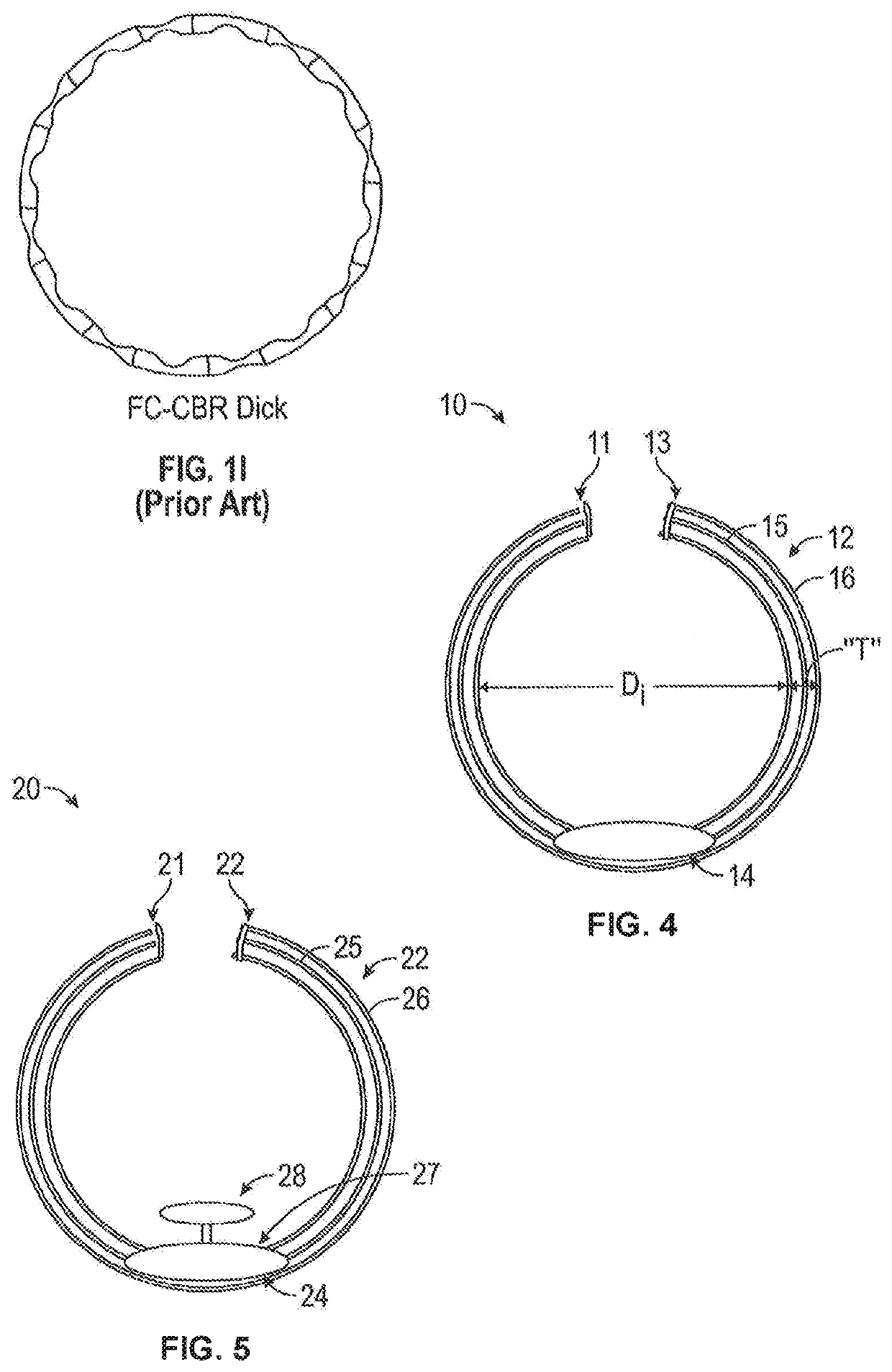
The present disclosure relates to the field of implantable intraocular drug delivery devices. In particular, the present disclosure relates to intraocular drug delivery devices integrated into a capsular tension ring (“CTR”) that is designed for implantation in the capsule or the ciliary sulcus during a cataract extraction and intraocular lens implantation procedure.
Owner:QURA INC
Accommodating intraocular lens assembly
A method of positioning an accommodating intraocular lens assembly in an eye can include implanting an accommodating intraocular lens assembly having a positive power lens in the eye. The accommodating intraocular lens assembly can also include a plurality of stanchions extending between base ends and distal ends. The base ends can be disposed in spaced relation to one another about a first arcuate periphery positioned in a ciliary sulcus of the eye. The distal ends can be disposed about a second arcuate periphery extending in a second plane positioned forward and outside of a capsular bag of the eye. The positive-power lens can be connected with the plurality of distal ends whereby a center of the positive power lens is moved along the central optic axis in response to contraction of the first arcuate periphery by contraction of the ciliary sulcus.
Owner:DUDEE JITANDER +1
Intraocular lens
Provided is an intraocular lens including a lens and a pair of right and left loop-shaped support portions, and a folding-back portion is provided in the front end of each support portion. A sclera tunnel is formed in the circumferential direction at a position of a depth corresponding to the half of the thickness of the sclera in two symmetrical positions with respect to the visual axis in a portion adjacent to a limbus of the sclera. The front end of the support portion is extracted from the ciliary sulcus and is inserted into the sclera tunnel, so that the intraocular lens is fixed into the eye. Furthermore, at that time, the folding-back portion is hooked to a certain portion inside the sclera tunnel, so that the support portion is strongly restrained inside the sclera tunnel. As a result, the intraocular lens is more reliably fixed.
Owner:CHUKYO MEDICAL
Method for designing intraocular lens for providing vision correction to patient due to loss of vision by AMD and positioning mechanism for intraocular lens
PendingCN110859686ATotal diopter increaseImprove reading visionIntraocular lensCapsular bagOptic system
The present invention provides a method for designing an intraocular lens for providing vision correction to a patient due to loss of vision by AMD, an eyeball optical model based on optical characteristics and aberration characteristics of a natural human eye comprises a cornea, a visual axis and an eccentric iris, wherein the front surface and the rear surface of the cornea are aspheric, the visual axis inclines relative to the symmetry axis of the eyes, the eccentric iris is eccentric to an entrance pupil, and a natural intraocular lens model with double aspheric surfaces is implanted intoa capsular bag of an eyeball; at least one aspheric intraocular lens is implanted into the eyeball; the intraocular lens is positioned between the iris and the capsular bag in the model eye and is positioned in the ciliary sulcus; the intraocular lens, the cornea and the natural intraocular lens model form a coaxial optical system; after the intraocular lens is tightly attached to the iris, the caliber of the intraocular lens is matched with the diameter of the iris in a reduced state.
Owner:易虹 +1
Intraocular drug delivery device and associated methods
Devices, systems, and methods for delivery of an active agent from the lens capsule to a posterior segment of the eye of a subject can include an intraocular active agent delivery device including anactive agent dispersed within a biodegradable active agent matrix. The active agent includes dexamethasone and the delivery device is adapted to fit within a lens capsule or ciliary sulcus of an eye.The delivery device can be inserted into the lens capsule or ciliary sulcus of an eye during cataract surgery or for treatment of uveitis.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
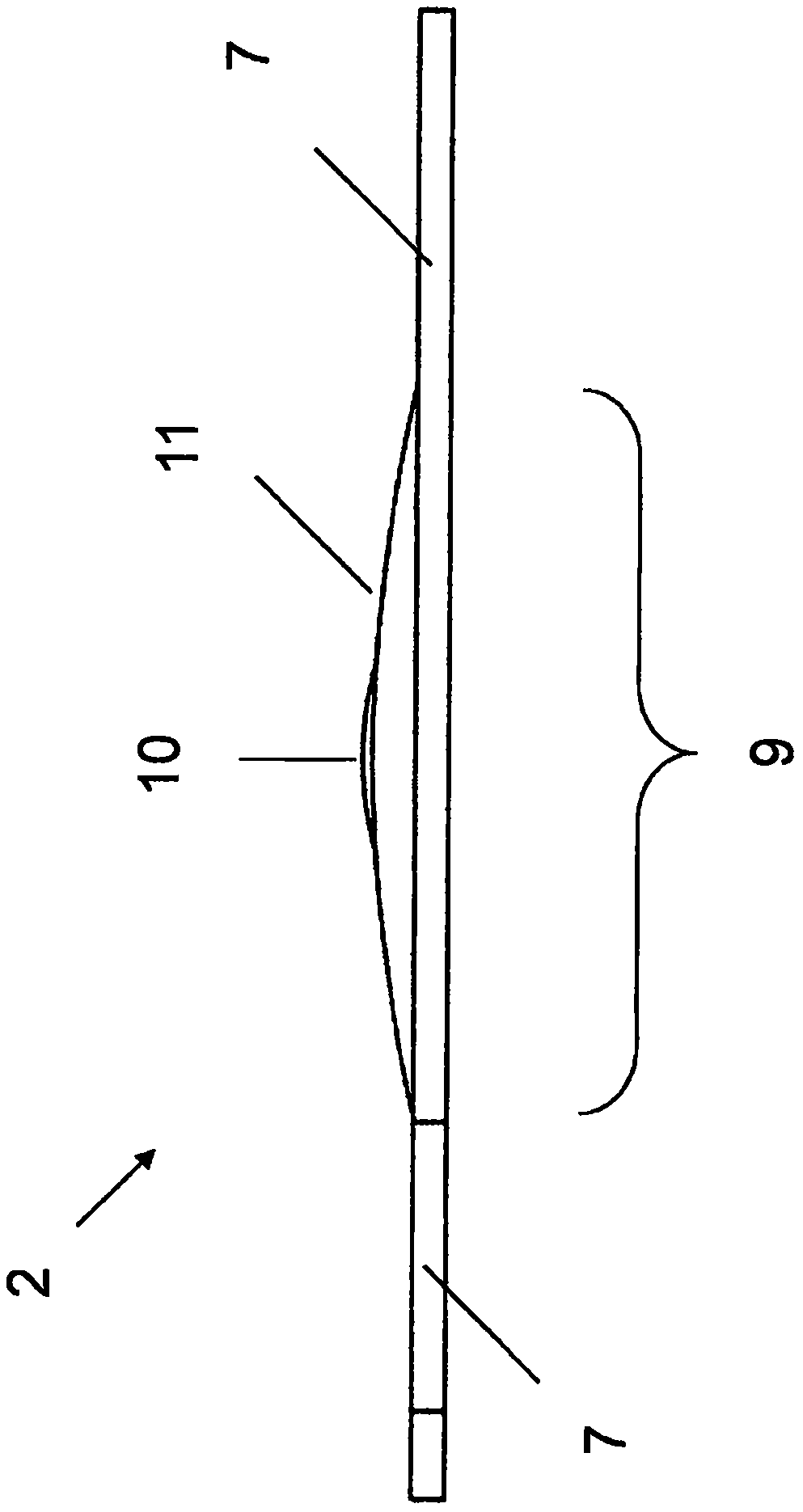
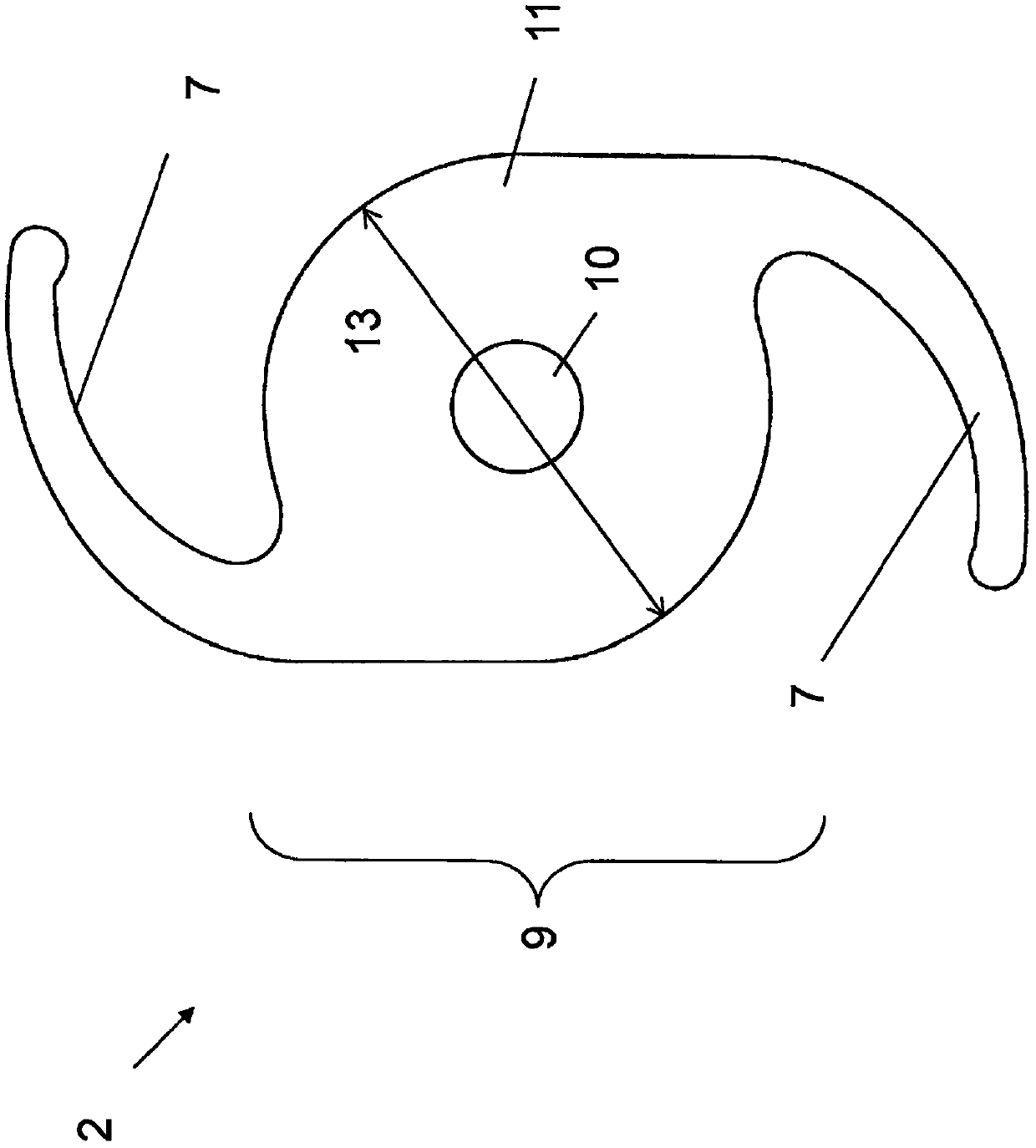
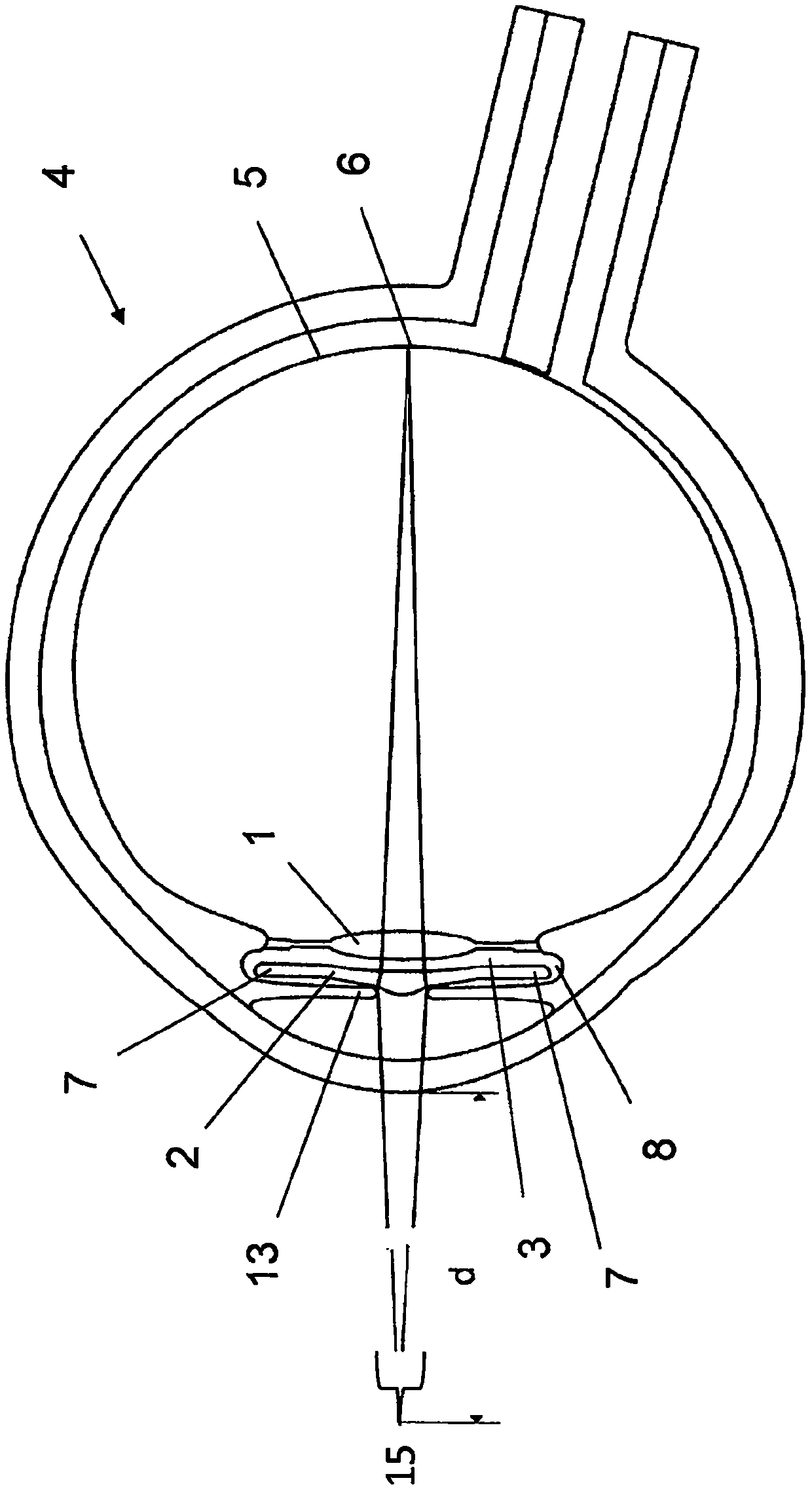
Two-stage intraocular lens with magnifying coaxial optic
A two-stage foldable intraocular lens IOL (2) is provided which is surgically implanted in a patient's pseudophakic eye in addition to at least one primary IOL (1) already implanted. The secondary IOL (2) is placed optically coaxially with the primary IOL (1), focusing the combined image onto the retina (5) of the patient's eye (4), which additionally magnifies the macula projecting onto the retina (5) (6) At least the middle portion of the image on one phase IOL. A secondary IOL (2) includes one or more haptics (7) for anchoring and stabilizing it within the ciliary sulcus (8) of the patient's eye (4), and an optically active portion (9) designed to The image is projected through a primary IOL (1) onto the retina (5). The optically active portion (9) of a secondary IOL (2) consists of a central optic (10) and a peripheral optic (11) extending around the central optic (10) forming two distinct but coaxial Positioning the lens. The central optic (10) is designed to form a positive lens that provides a minimum of 5D, up to a maximum of 25D of additional refraction to the refraction provided by the peripheral optic (11) of the secondary IOL (2).
Owner:INVESTMED KFT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com