Patents
Literature
54 results about "Latching switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A latching switch is a switch that maintains its state after being activated. A push-to-make, push-to-break switch would therefore be a latching switch – each time you actuate it, whichever state the switch is left in will persist until the switch is actuated again.
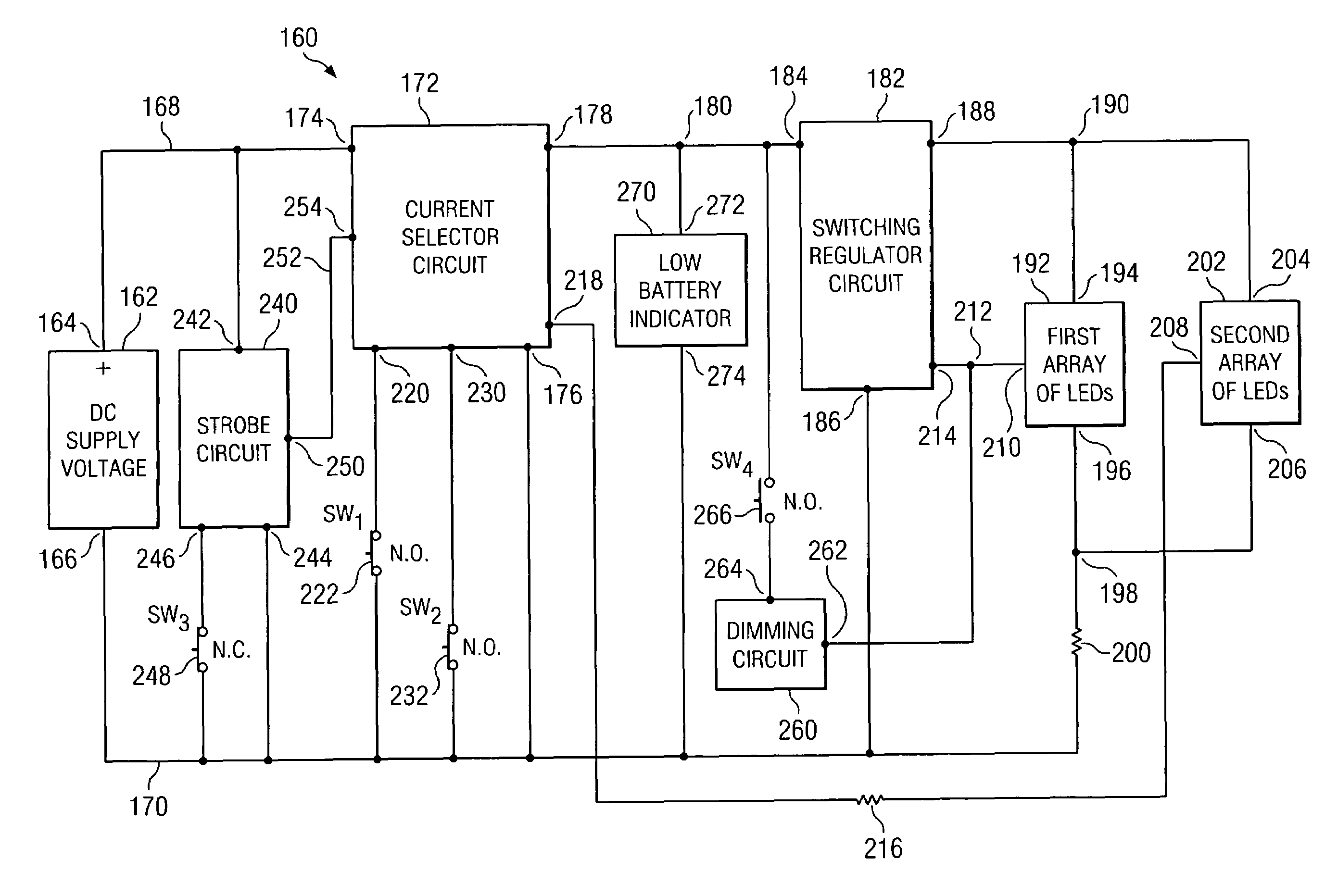
Circuit for illuminating multiple light emitting devices
ActiveUS7402961B2Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesCurrent loadDriver circuit
A single drive circuit is configured to drive disparate current loads of first and second combinations of compact light emitting devices with respective regulated constant currents. Standard push ON, push OFF latching switches provide independent control of the two lighting loads wherein each switch operates in three states including momentary ON, continuous ON, and OFF. The circuit is readily adapted to providing continuous or pulsed drive to the lighting arrays. Circuits for dimming control, strobe control, and a low battery indicator are also described.
Owner:BAYCO PRODS
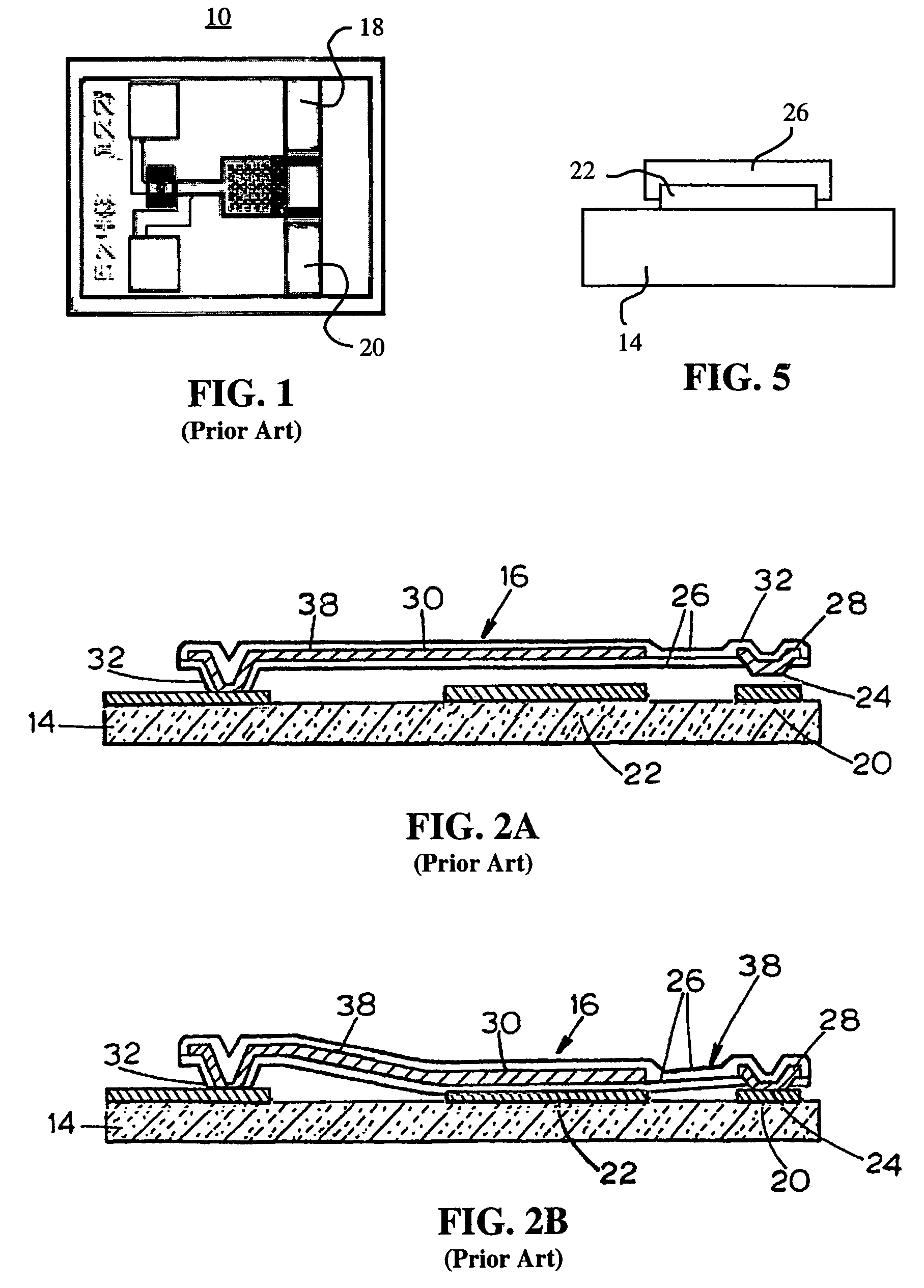
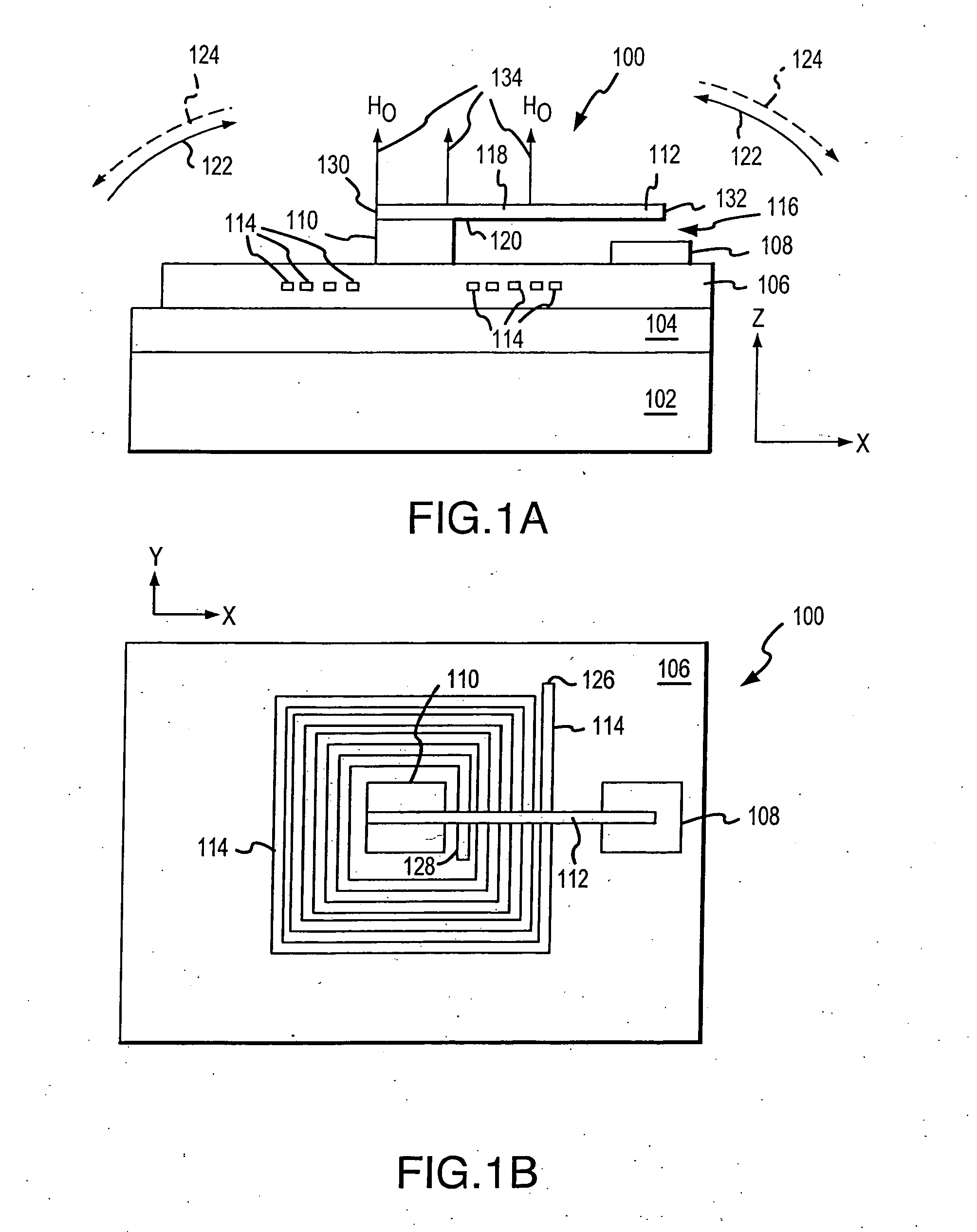
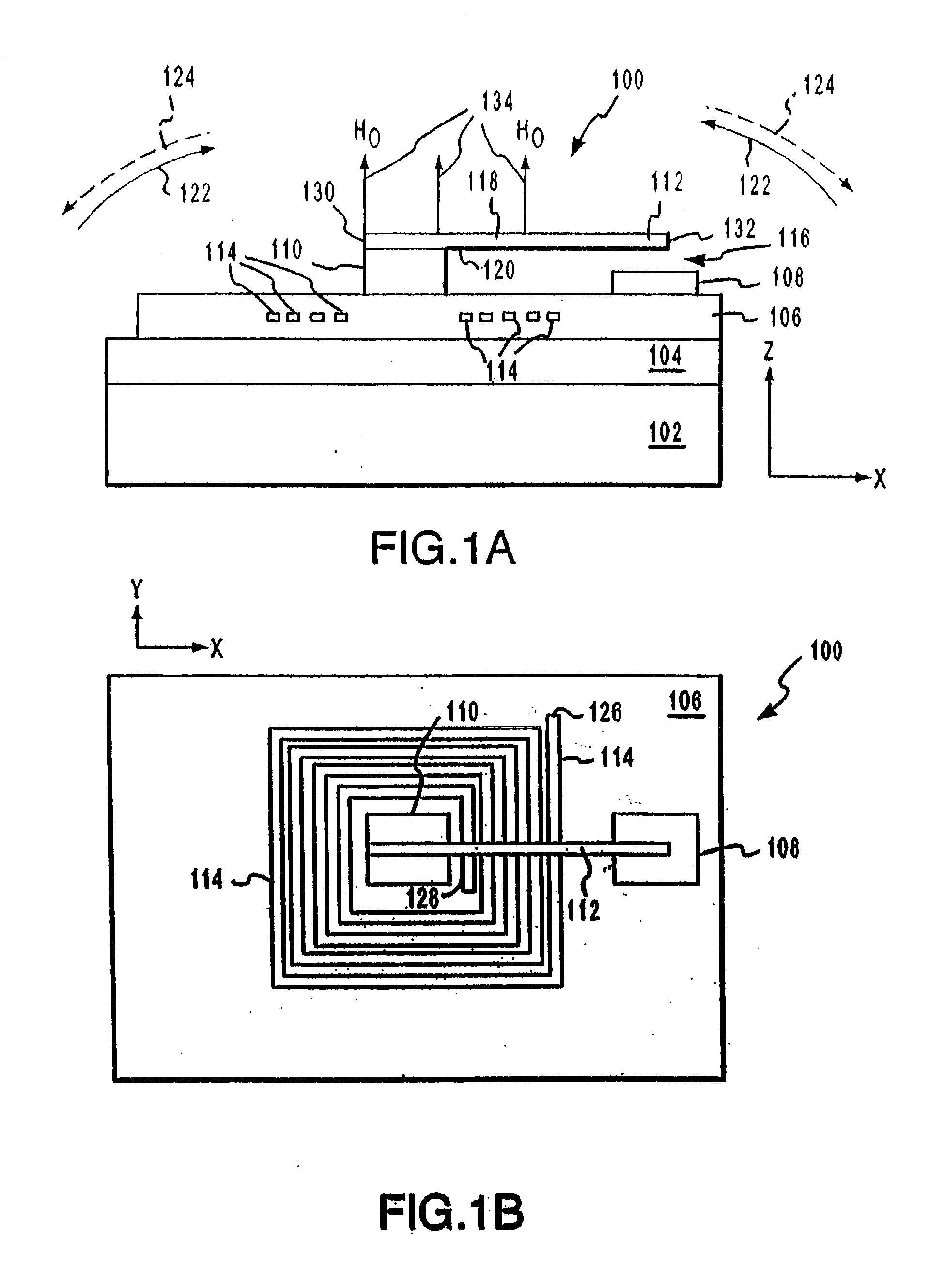
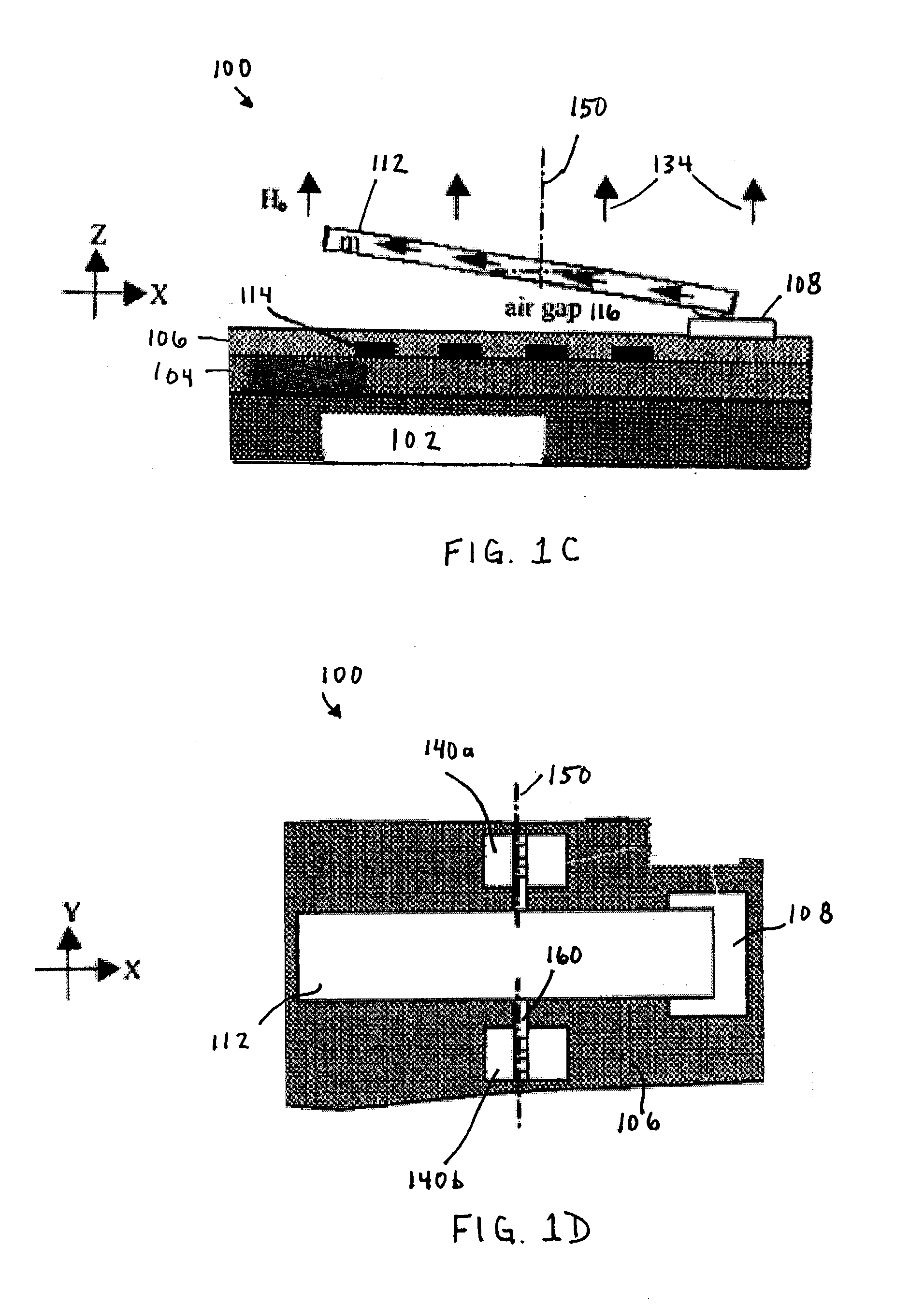
Micromagnetic latching switch packaging
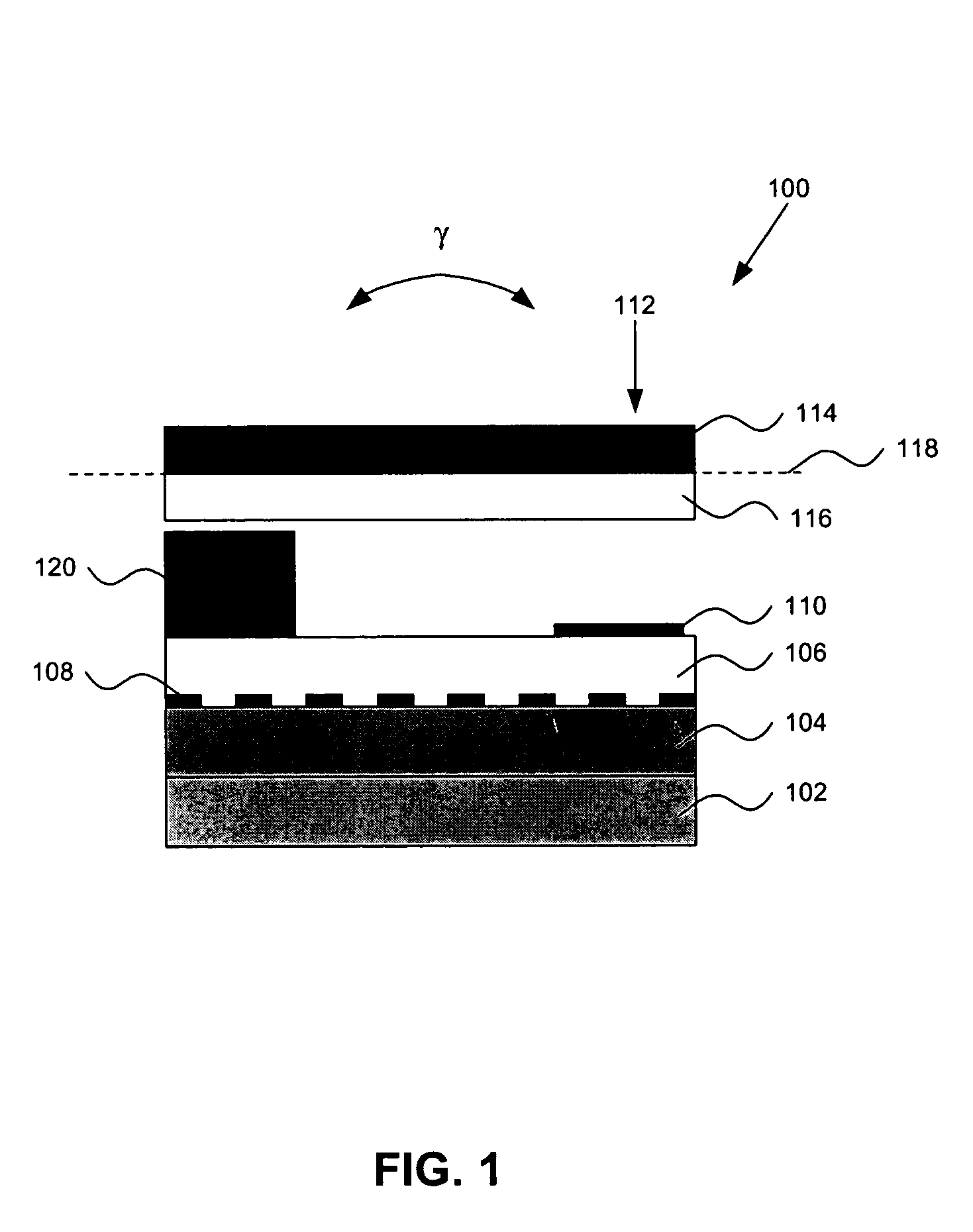
InactiveUS6894592B2Easy to manufactureImprove performanceElectromagnetic relay detailsElectrostrictive/piezoelectric relaysContact padLatching switch
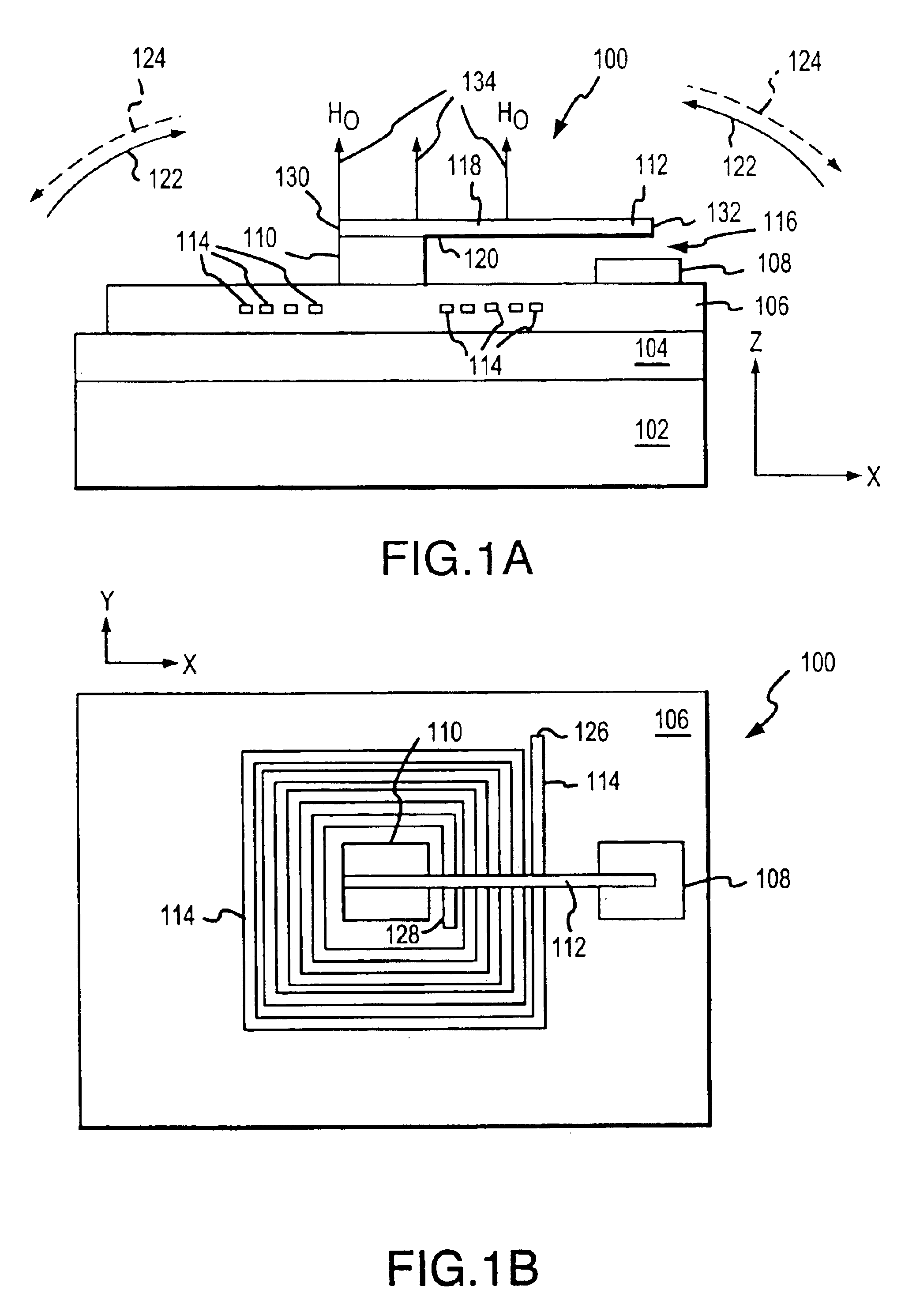
Packages for a micromachined magnetic latching switch, and methods for assembling the packages are described. In one aspect, a substrate is defined by opposing first and second surfaces. A micromagnetic switch integrated circuit (IC) chip is mounted to the first surface. A contact pad on the chip is coupled to a trace on the first surface. A permanent magnet is positioned closely adjacent to the chip. A cap is attached to the first surface. An inner surface of the cap forms an enclosure to enclose the chip on the first surface. The chip can be alternatively mounted to the inner surface of the cap. The chip can be oriented in a standard or flip-chip fashion. In another aspect, a moveable micro-machined cantilever is supported by a surface of a substrate. A cap is attached to the surface. An inner surface of the cap forms an enclosure that encloses the cantilever on the surface of the substrate. A permanent magnet is positioned closely adjacent to the cantilever. An electromagnet is attached to the inner surface or an outer surface of the cap.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Circuit for illuminating multiple light emitting devices
ActiveUS20070159008A1Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsPoint-like light sourceDriver circuitCurrent load
A single drive circuit is configured to drive disparate current loads of first and second combinations of compact light emitting devices with respective regulated constant currents. Standard push ON, push OFF latching switches provide independent control of the two lighting loads wherein each switch operates in three states including momentary ON, continuous ON, and OFF. The circuit is readily adapted to providing continuous or pulsed drive to the lighting arrays. Circuits for dimming control, strobe control, and a low battery indicator are also described.
Owner:BAYCO PRODS
Automatic battery disconnect system
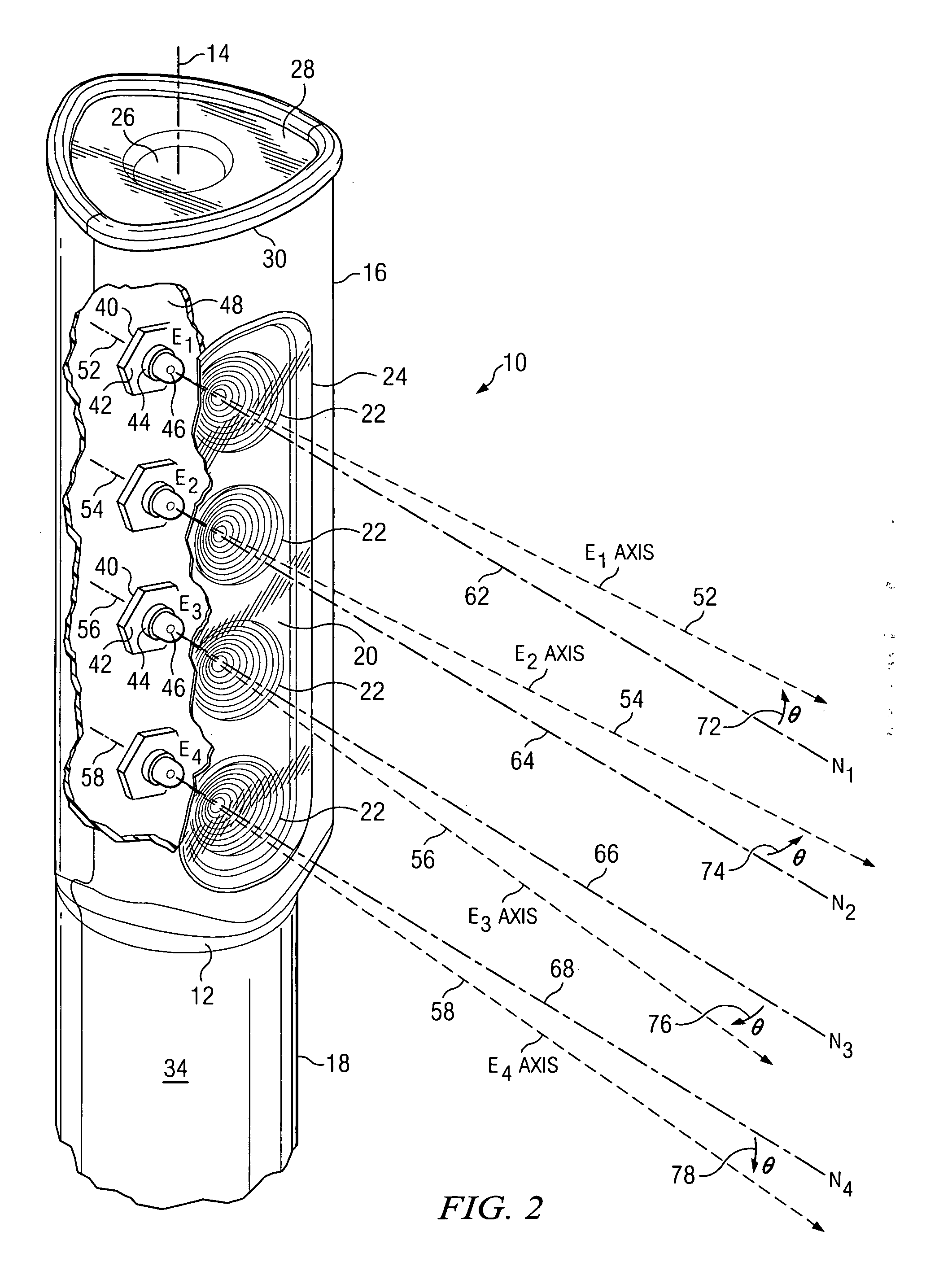
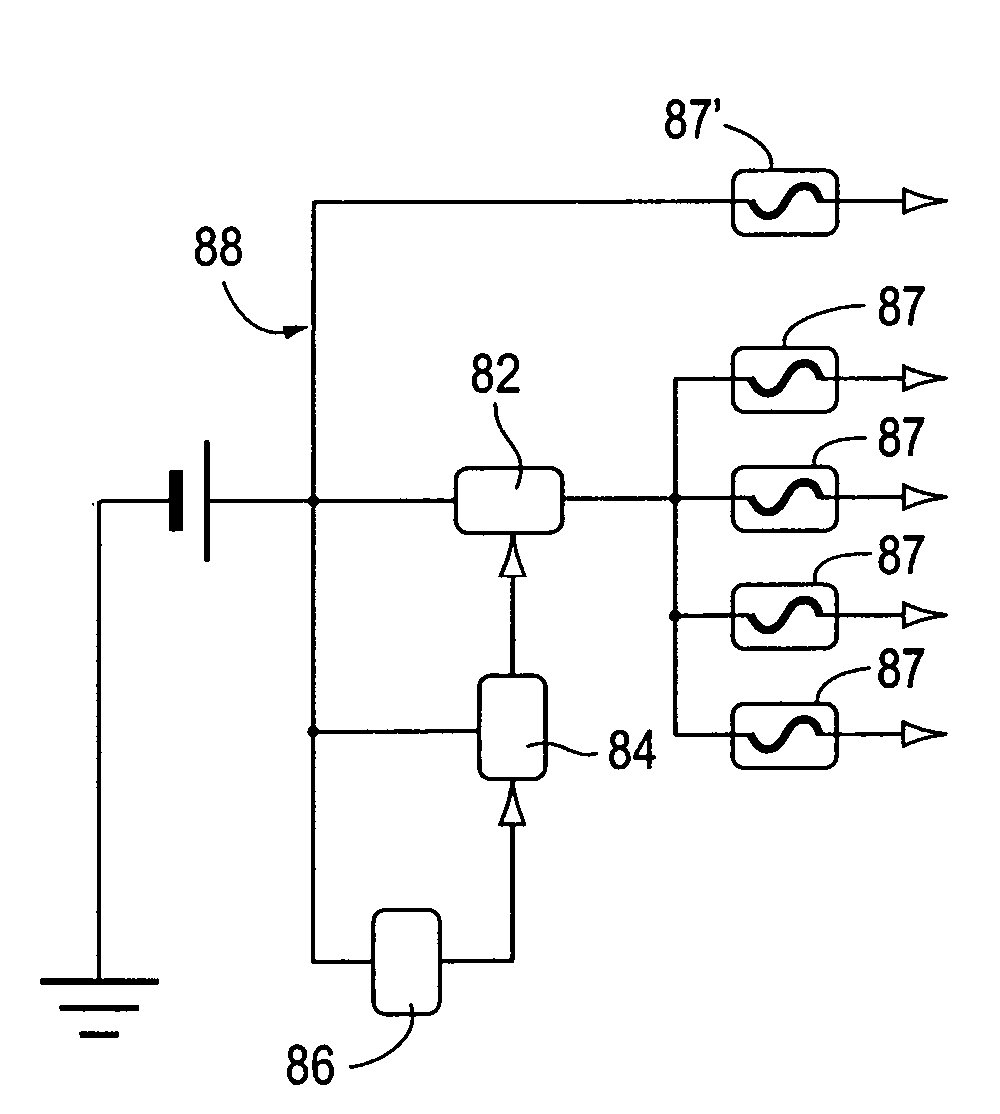
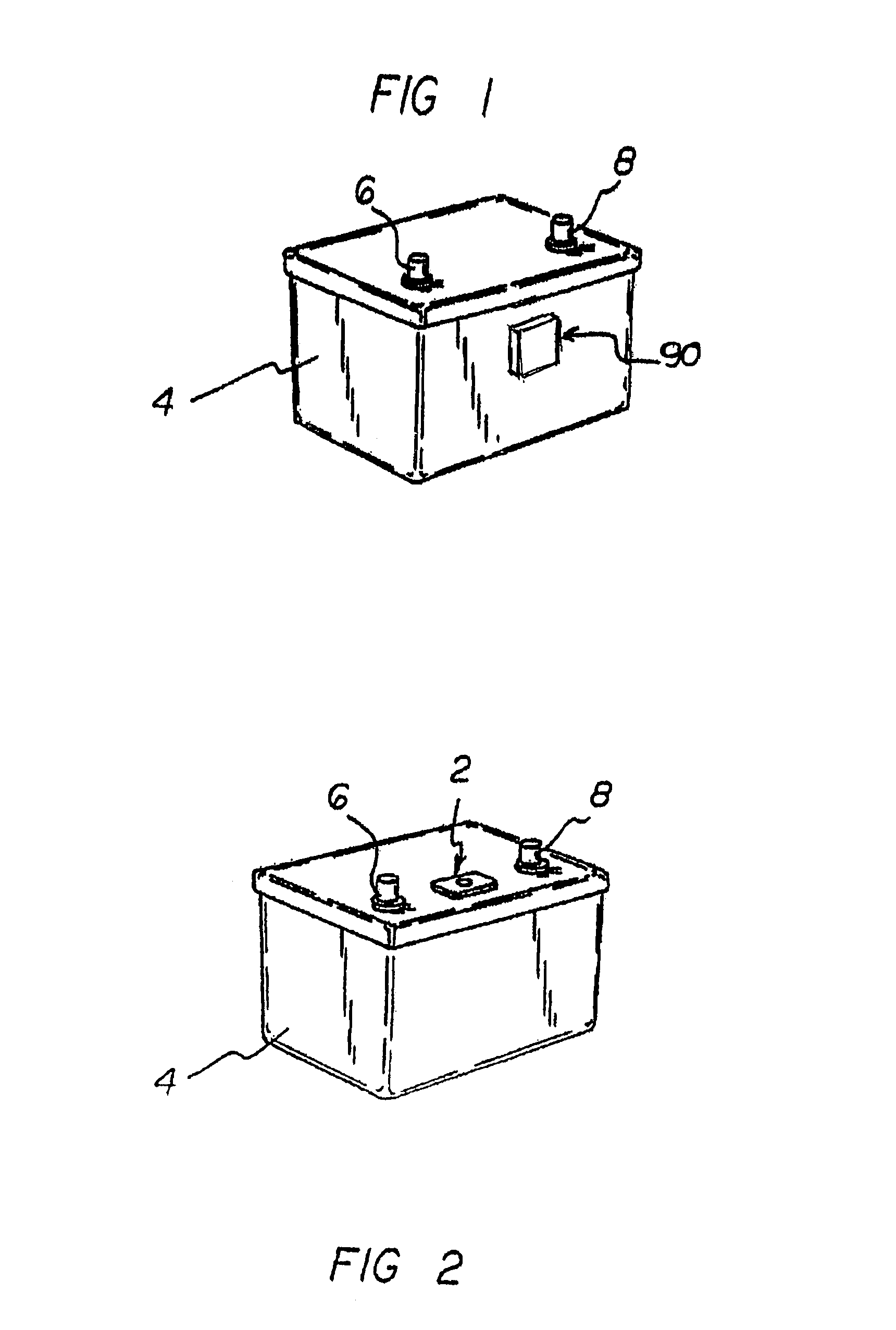
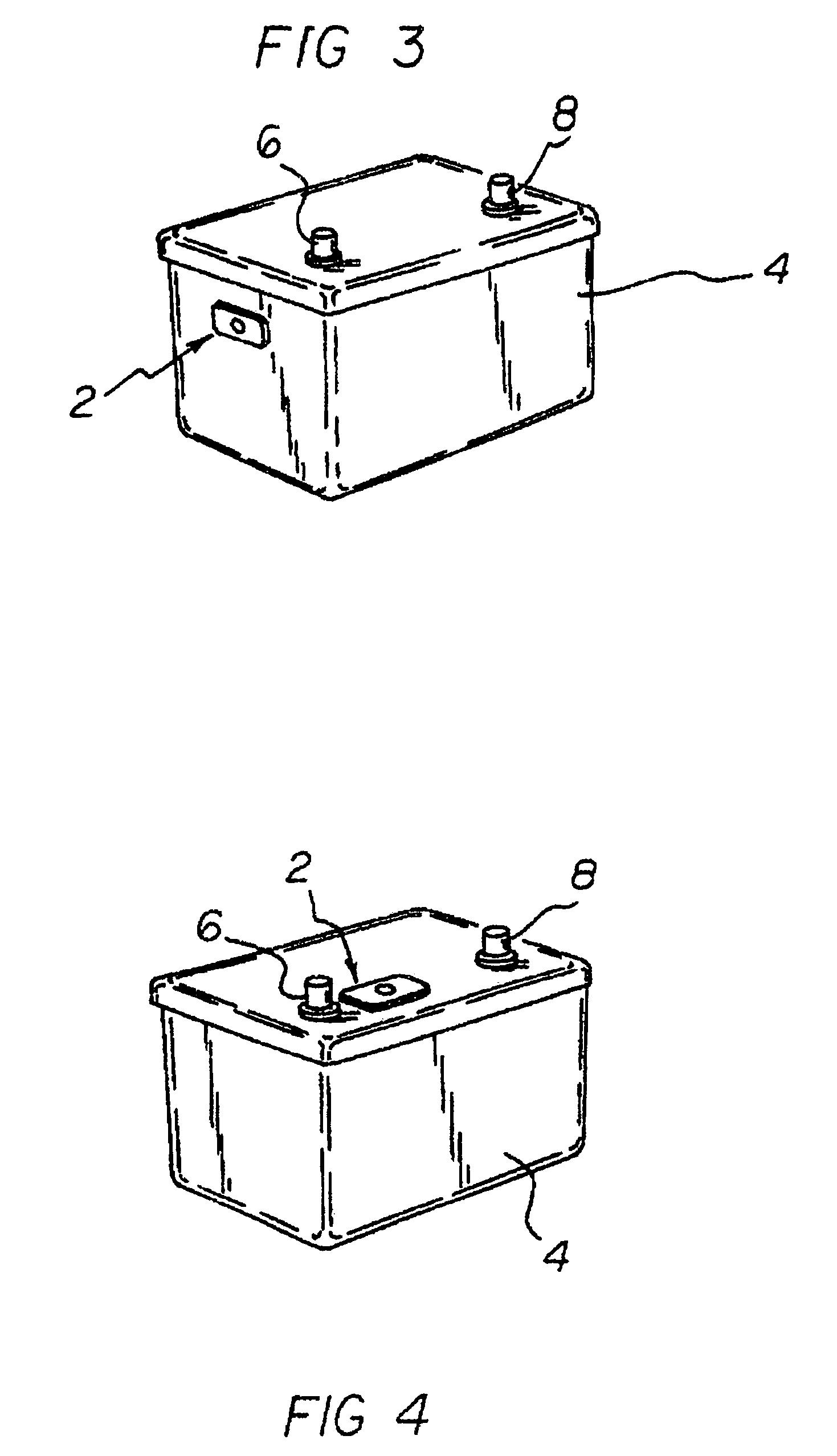
A safety battery disconnect system for disconnecting a vehicle battery from the electrical system of the vehicle when an impact exceeding a predetermined magnitude is detected while maintaining electrical power input from the battery to selected portions of the vehicle electrical system. The system includes a shock sensor connected to a latching switch interposed between the battery and the vehicle fused electrical input system and is preferably a unitary unit mounted on or in close proximity to the battery.
Owner:ZDZIECH PETER M +1
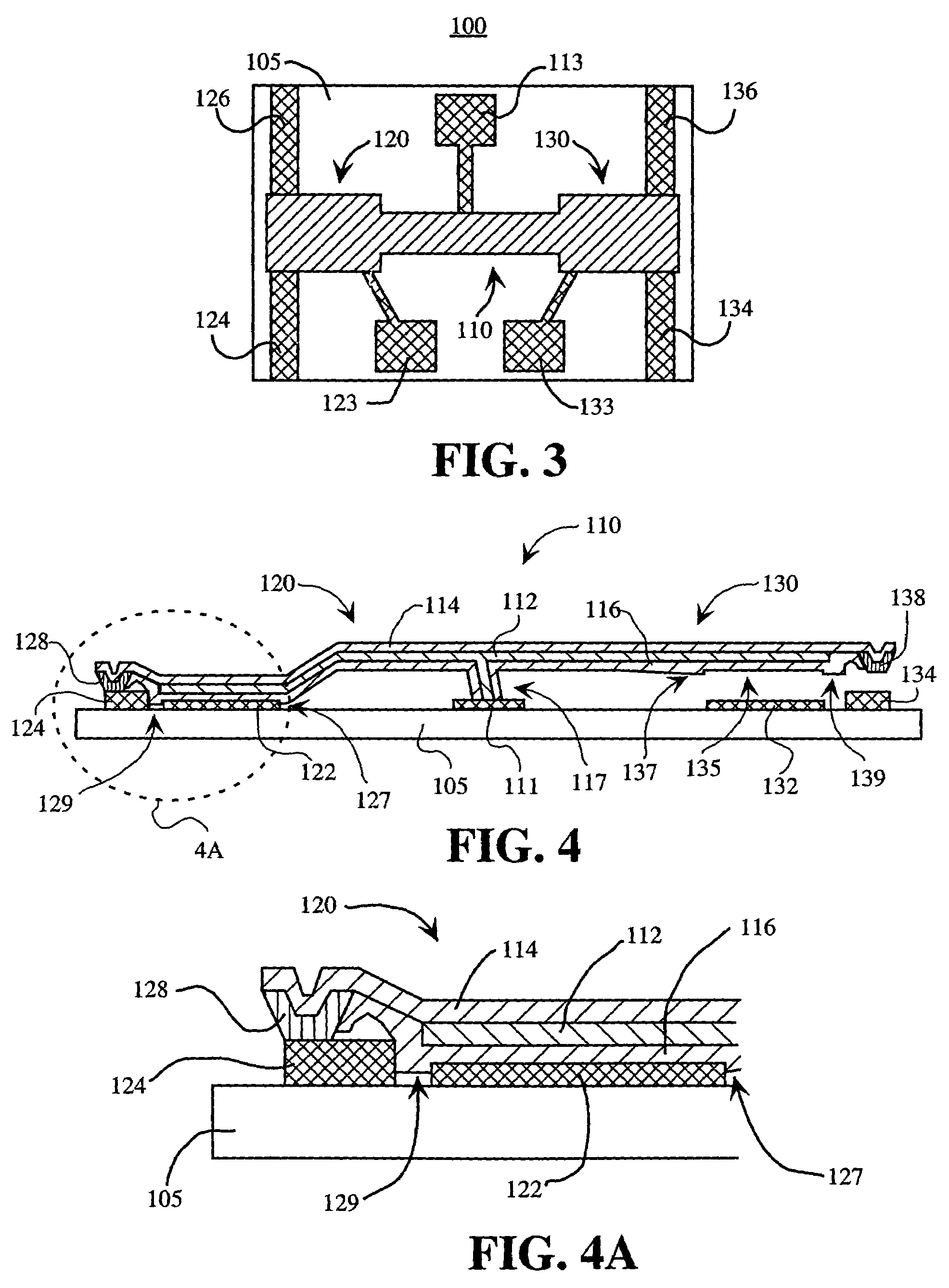
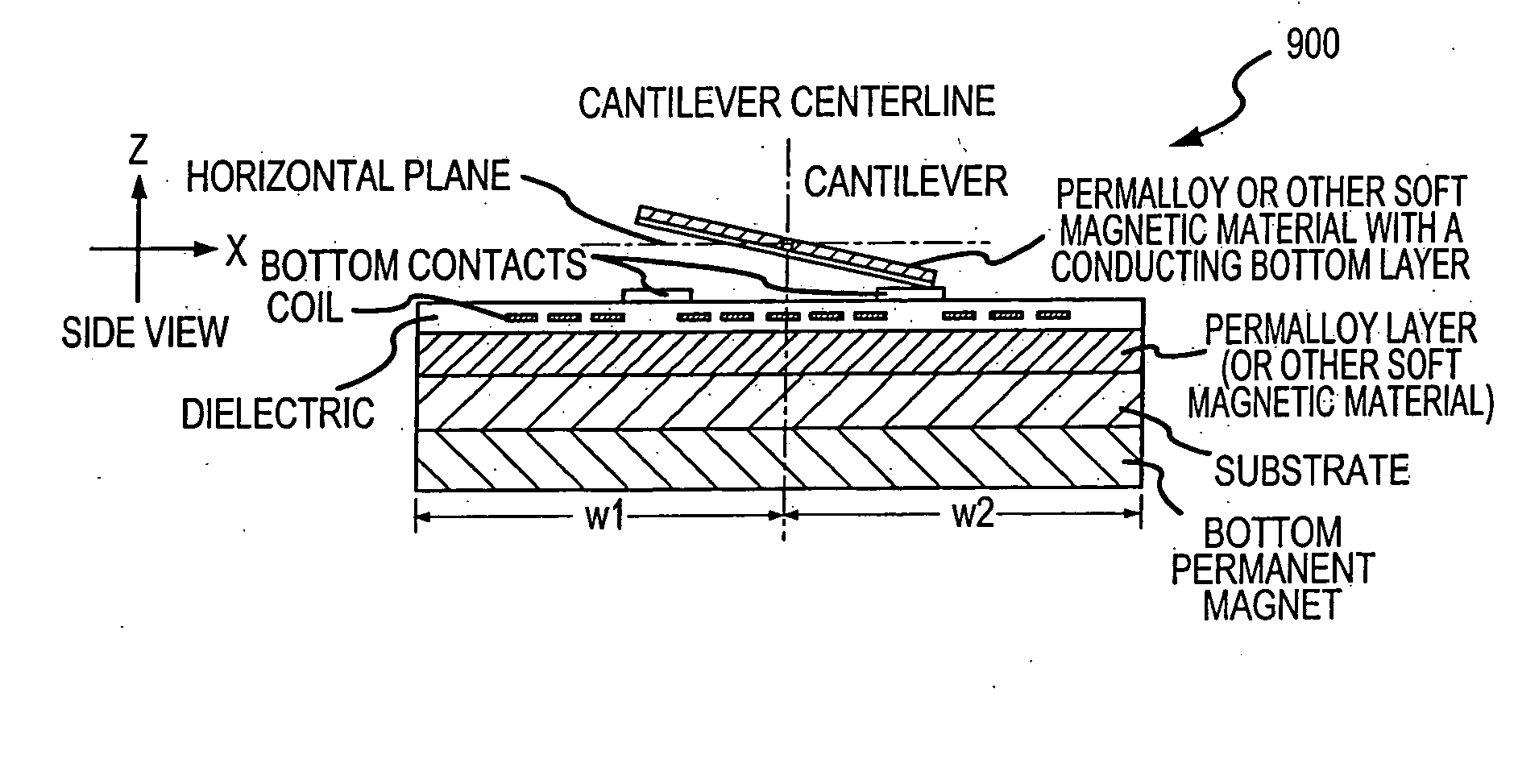
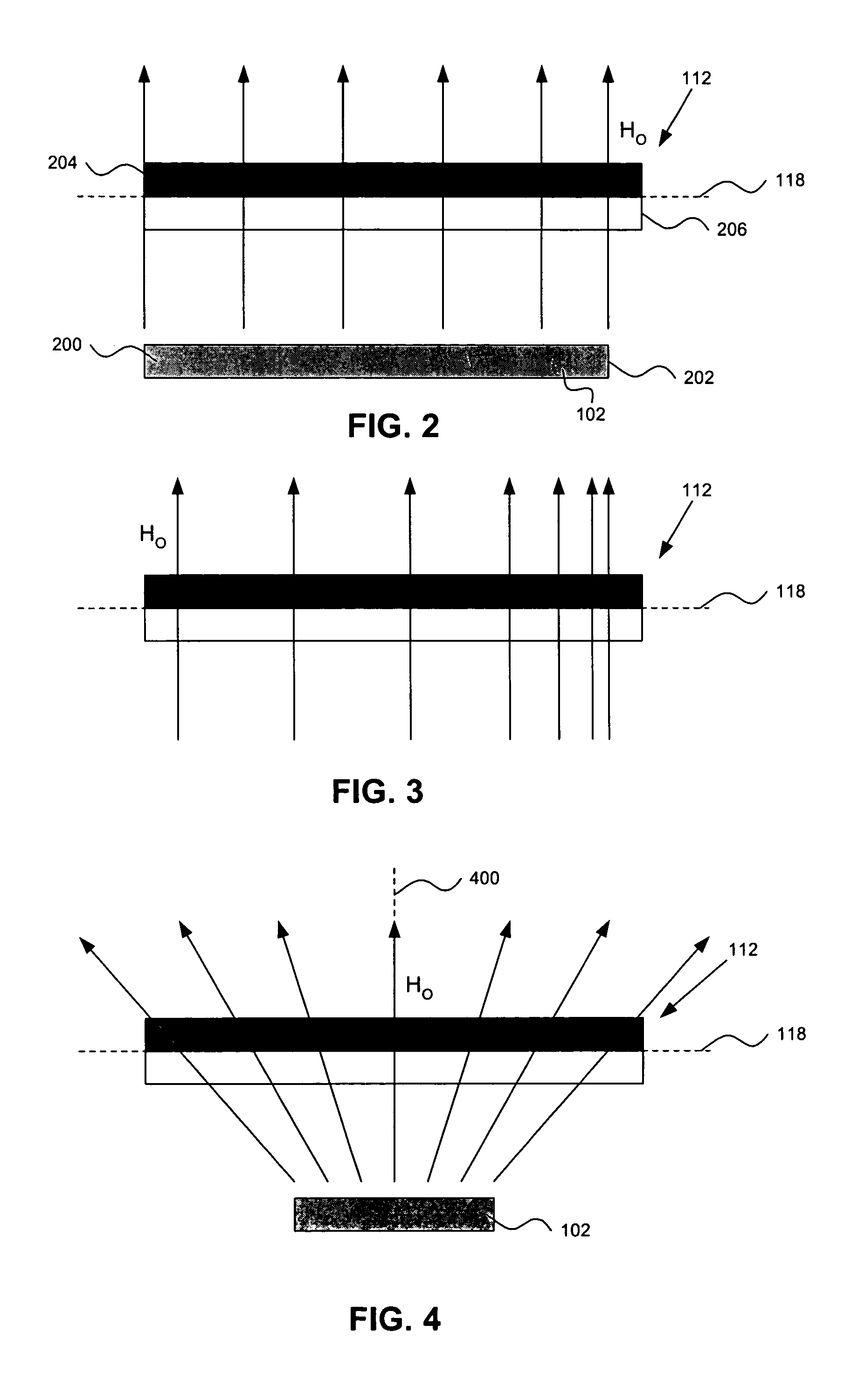
Micro-magnetic latching switches with a three-dimensional solenoid coil
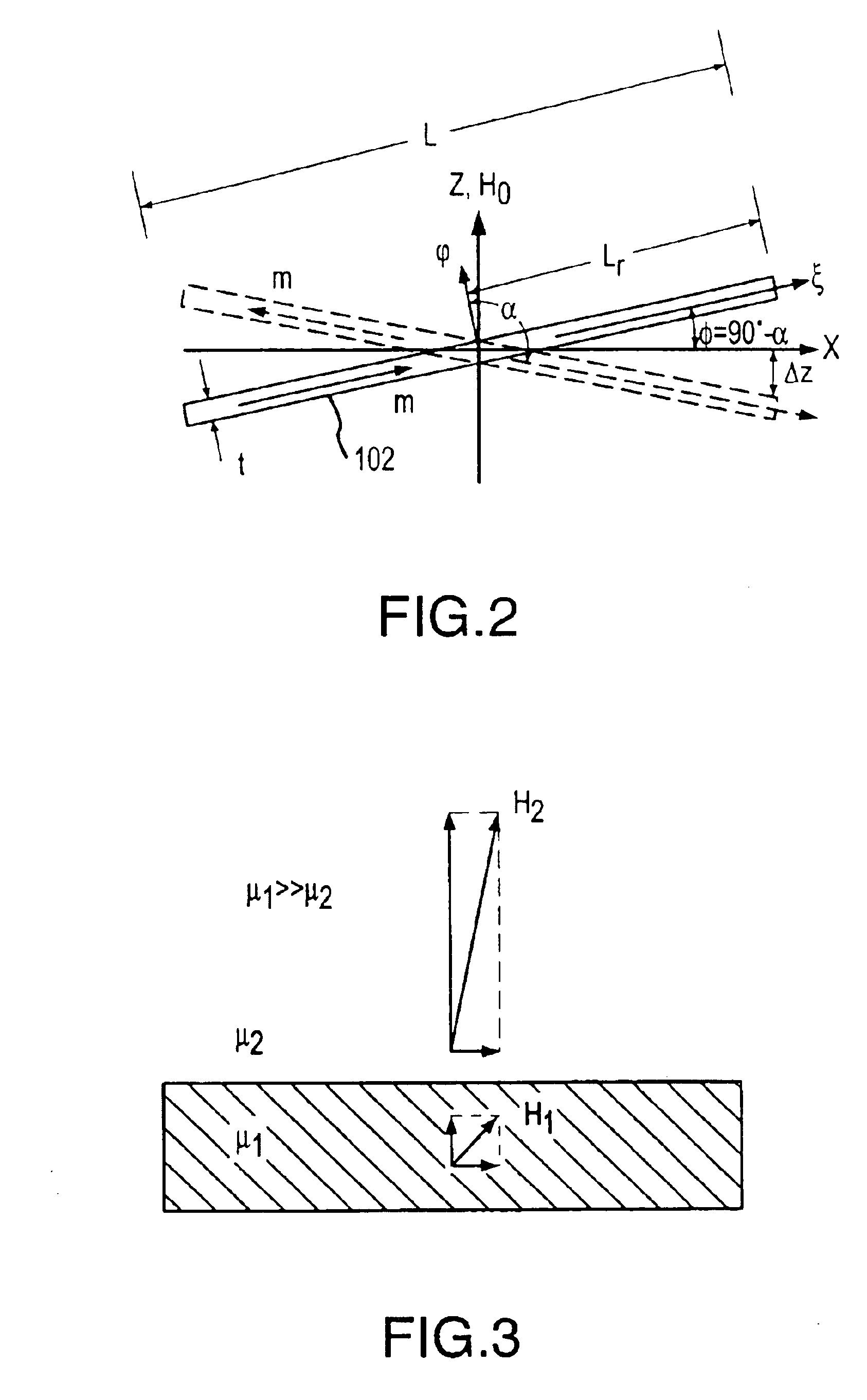
A micro-machined magnetic latching switch is described. A moveable micro-machined cantilever has a magnetic material and a longitudinal axis. The cantilever has a conducting layer. A permanent magnet produces a first magnetic field, which induces a magnetization in the magnetic material. The magnetization is characterized by a magnetization vector pointing in a direction along the longitudinal axis of the cantilever. The first magnetic field is approximately perpendicular to longitudinal axis. A three-dimensional solenoid coil produces a second magnetic field to switch the cantilever between a first stable state and a second stable state. The temporary current is input to the three-dimensional solenoid coil, producing the second magnetic field such that a component of the second magnetic field parallel to the longitudinal axis changes direction of the magnetization vector. The cantilever is thereby caused to switch between the first stable state and the second stable state.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Metal contact RF MEMS single pole double throw latching switch
Apparatus for a micro-electro-mechanical switch that provides single pole, double throw switching action. The switch has two input lines and two output lines. The switch has a seesaw cantilever arm with contacts at each end that electrically connect the input lines with the output lines. The cantilever arm is latched into position by frictional forces between structures on the cantilever arm and structures on the substrate in which the cantilever arm is disposed. The state of the switch is changed by applying an electrostatic force at one end of the cantilever arm to overcome the mechanical force holding the other end of the cantilever arm in place.
Owner:HRL LAB
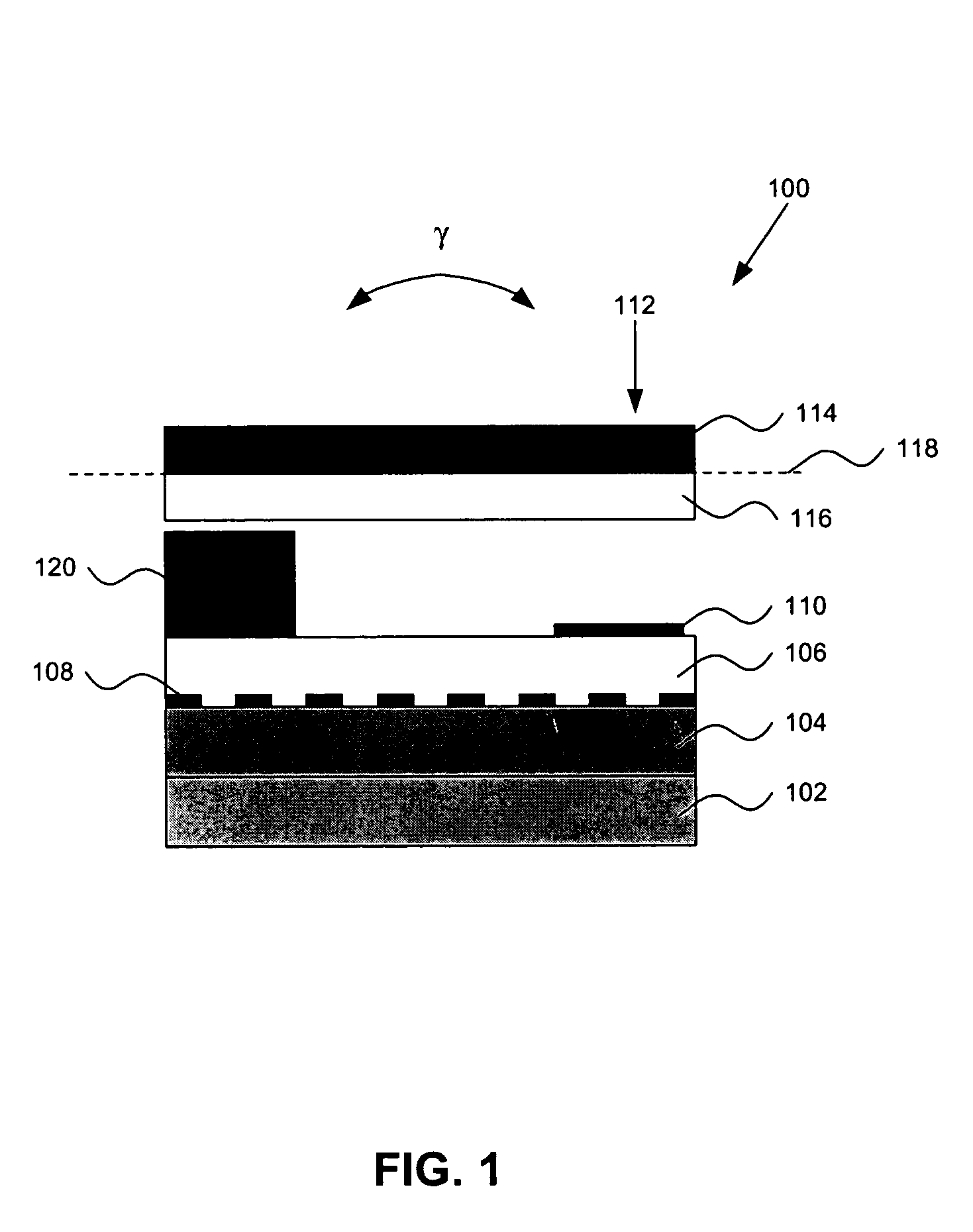
Micro-magnetic latching switch with relaxed permanent magnet alignment requirements
InactiveUS7023304B2Easy to manufactureImprove performancePermanent magnetsRelay detailsStable stateLatching switch
A micro magnetic latching device. The device comprises a substrate having a moveable element supported thereon. The moveable element (cantilever) has a long axis and a magnetic material. The device also has first and second magnets that produce a first magnetic field, which induces a magnetization in the magnetic material. The magnetization is characterized by a magnetization vector pointing in a direction along the long axis of the moveable element, wherein the first magnetic field is approximately perpendicular to a major central portion of the long axis. The device also has a coil that produces a second magnetic field to switch the movable element between two stable states, wherein only temporary application of the second magnetic field is required to change direction of the magnetization vector thereby causing the movable element to switch between the two stable states.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
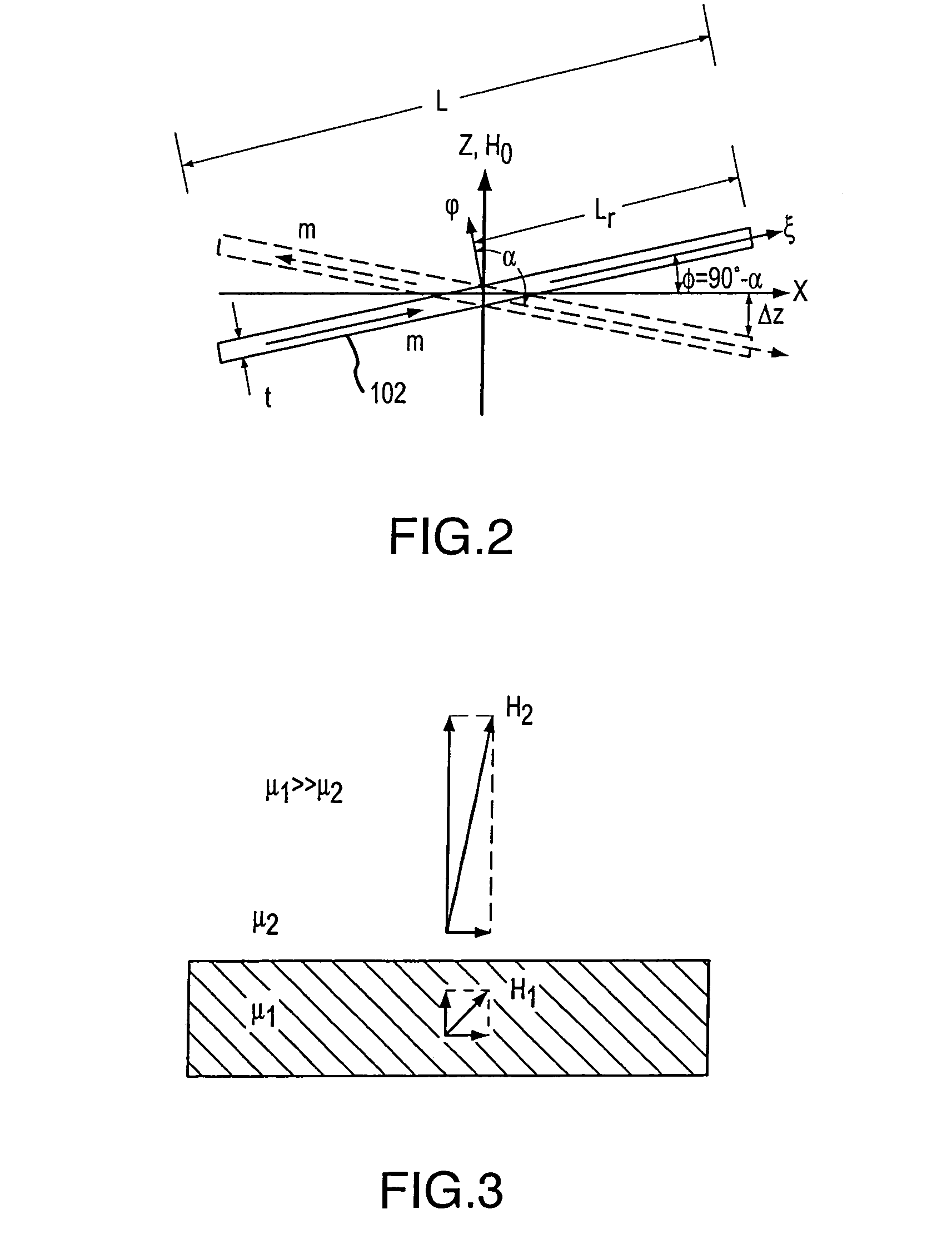
Exercise machine having full weight or half weight selection mechanism
InactiveUS7211030B1Cost-effective mannerTherapy exerciseMuscle exercising devicesLatching switchEngineering
A exercise machine has a pulley for user's flexibility to choose between training at the selected weight plates' full weight, or at the half weight when the pulley is engaged. A latching switch is used for easy selection of going between the full weight and half weight mode. A counter weight block is attached to an end of the cable, to keep the tension of the cable when the exercise machine is used in the full weight mode.
Owner:CAO GUOFANG
Automatic battery disconnect system
Owner:ZDZIECH PETER M +1
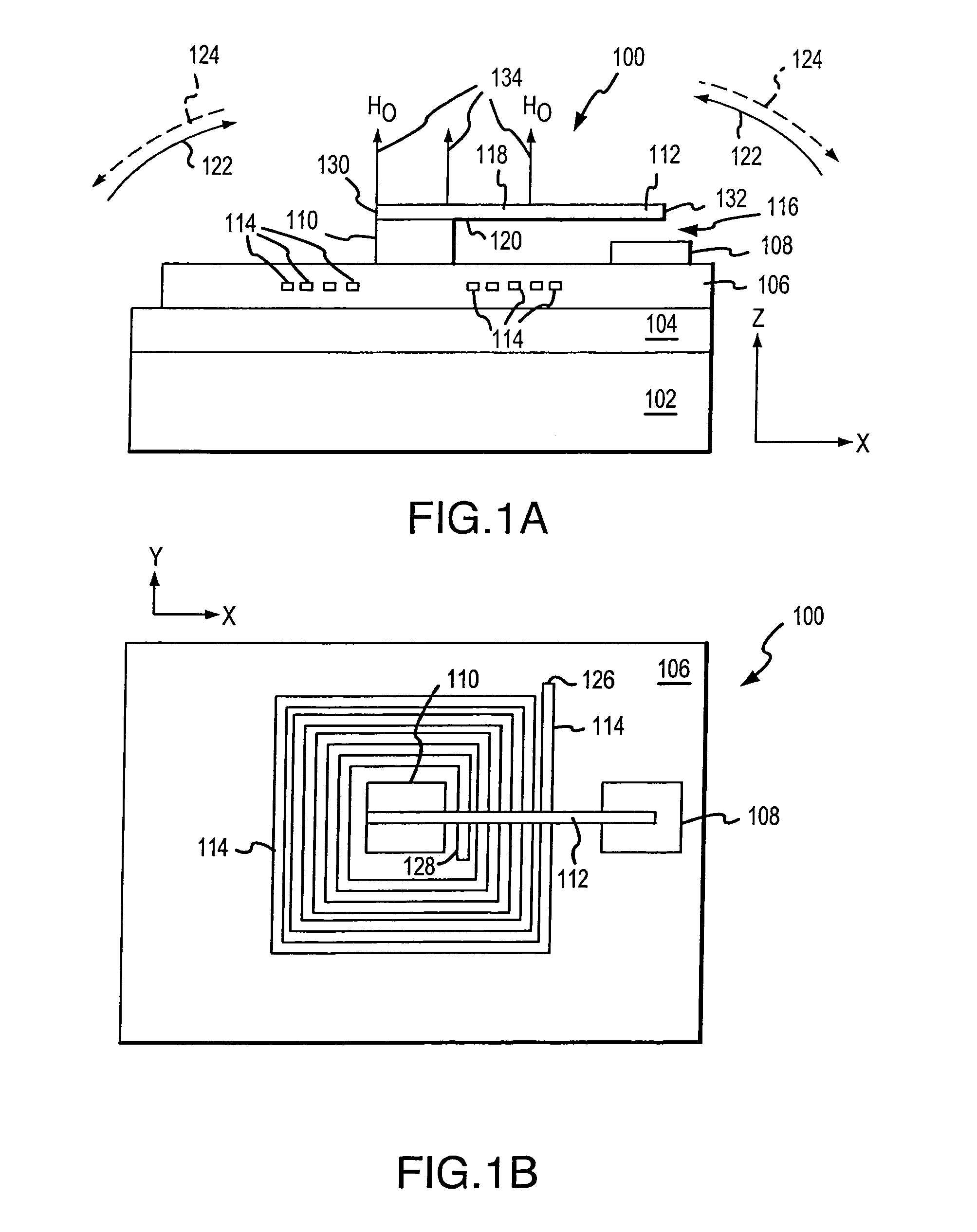
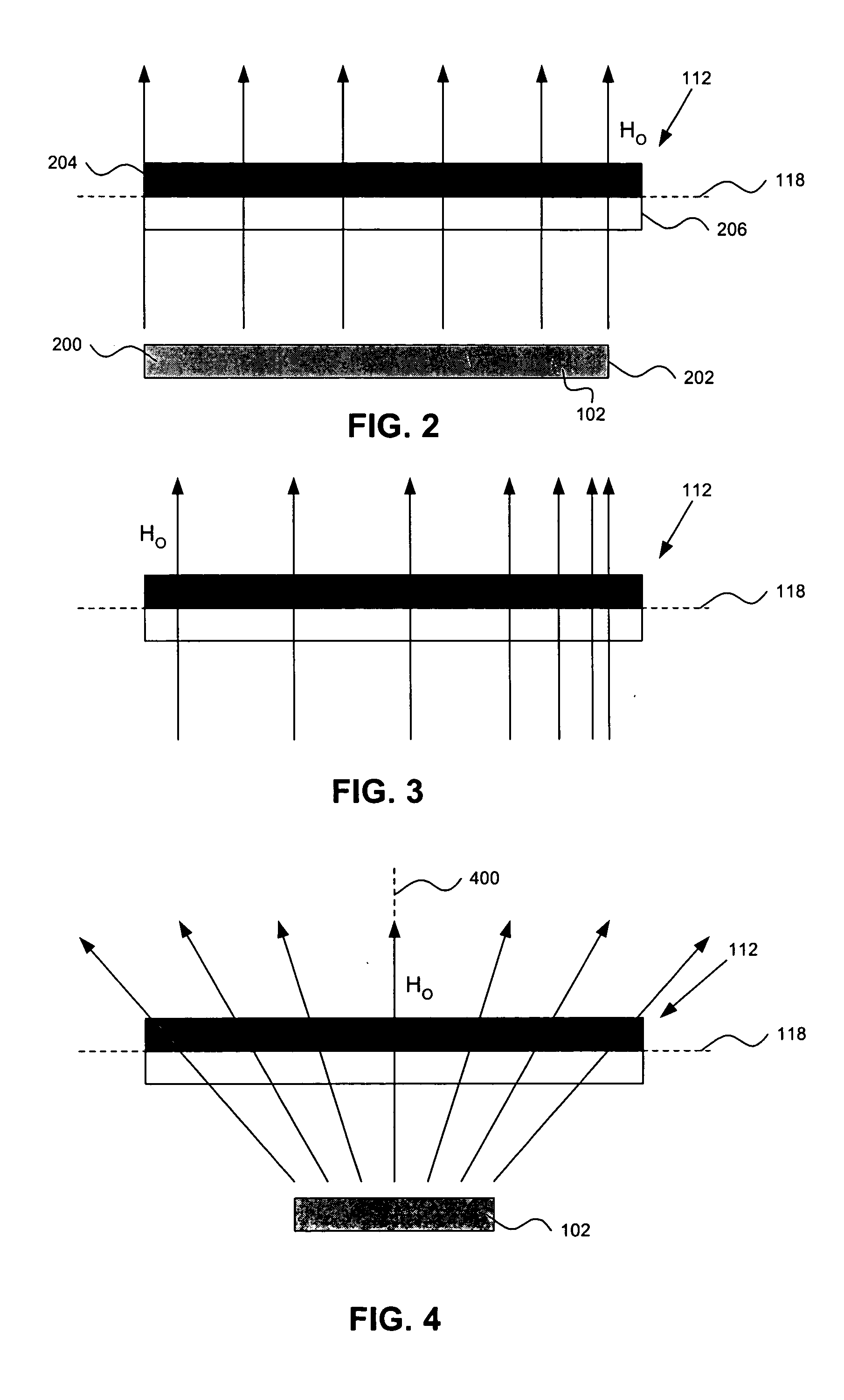
Micro magnetic non-latching switches and methods of making same
InactiveUS20050083156A1Improve performanceEasy to manufactureElectromagnetic relay detailsPolarised relaysRotational axisElectrical conductor
A micro magnetic switch includes a reference plane and a magnet located proximate to a supporting structure. The magnet produces a first magnetic field with uniformly spaced field lines approximately orthogonal to the reference plane, symmetrically spaced about a central axis, or non-uniformly spaced fields approximately orthogonal to the reference plane. The switch also includes a cantilever supported by the support structure. The cantilever has an axis of rotation lying in the reference plane and has magnetic material that makes the cantilever sensitive to the first magnetic field, such that the cantilever is configured to rotate about the axis of rotation between first and second states. The switch further includes a conductor located proximate to the supporting structure and the cantilever. The conductor is configured to conduct a current. The current produces a second magnetic field having a component approximately parallel to the reference plane and approximately perpendicular to the rotational axis of the cantilever, which causes the cantilever to switch between the first and second states. The switch still further includes a stopping device located proximate to the supporting structure. The stopping device is operable to stop the cantilever from rotating about the axis of symmetry beyond a point at which a longitudinal axis of the cantilever is approximately parallel to a longitudinal axis of the magnet.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Micro-magnetic latching switch with relaxed permanent magnet alignment requirements
InactiveUS20050007218A1Easy to manufactureImprove performancePermanent magnetsRelay detailsStable stateLatching switch
A micro magnetic latching device. The device comprises a substrate having a moveable element supported thereon. The moveable element (cantilever) has a long axis and a magnetic material. The device also has first and second magnets that produce a first magnetic field, which induces a magnetization in the magnetic material. The magnetization is characterized by a magnetization vector pointing in a direction along the long axis of the moveable element, wherein the first magnetic field is approximately perpendicular to a major central portion of the long axis. The device also has a coil that produces a second magnetic field to switch the movable element between two stable states, wherein only temporary application of the second magnetic field is required to change direction of the magnetization vector thereby causing the movable element to switch between the two stable states.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
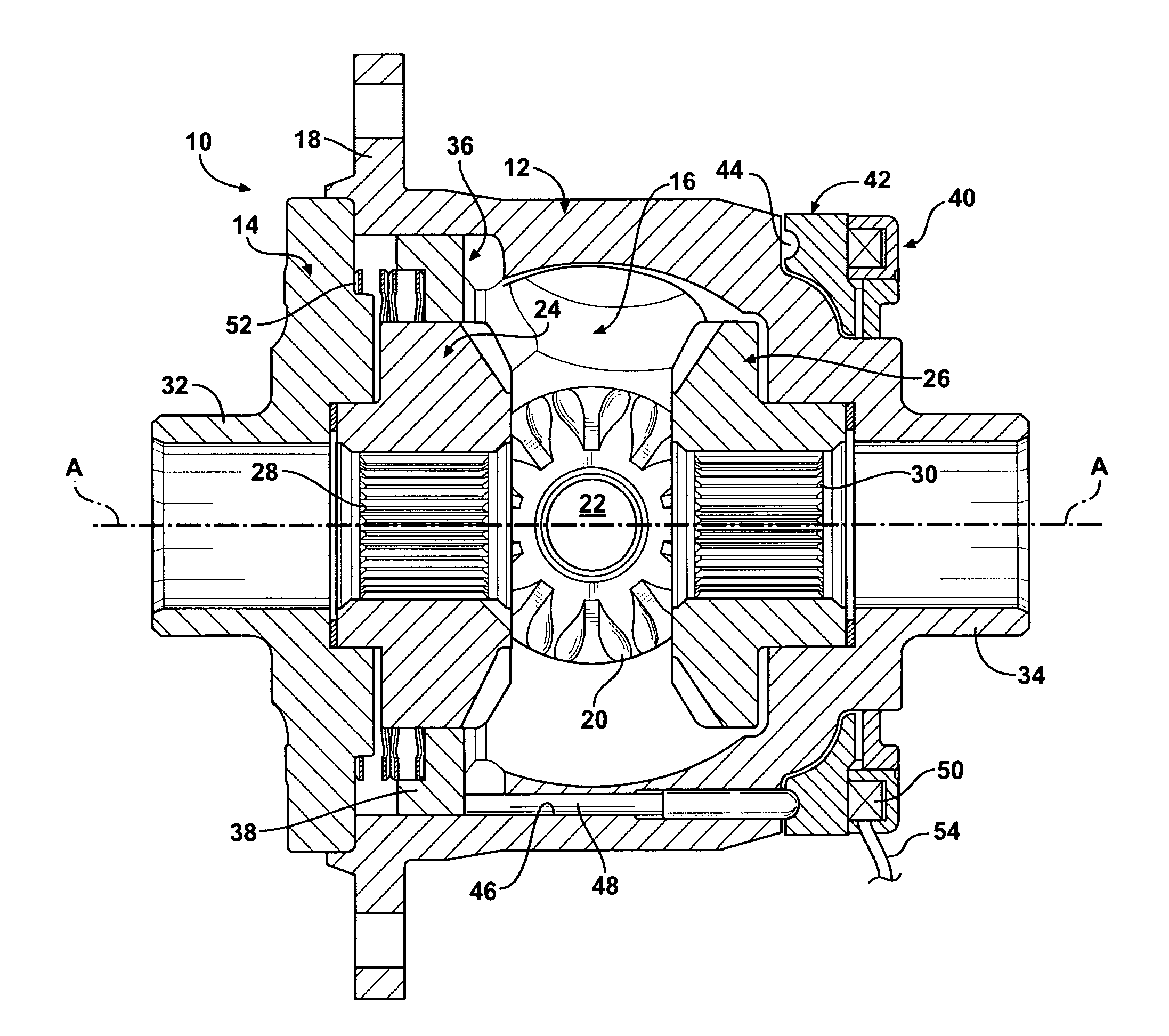
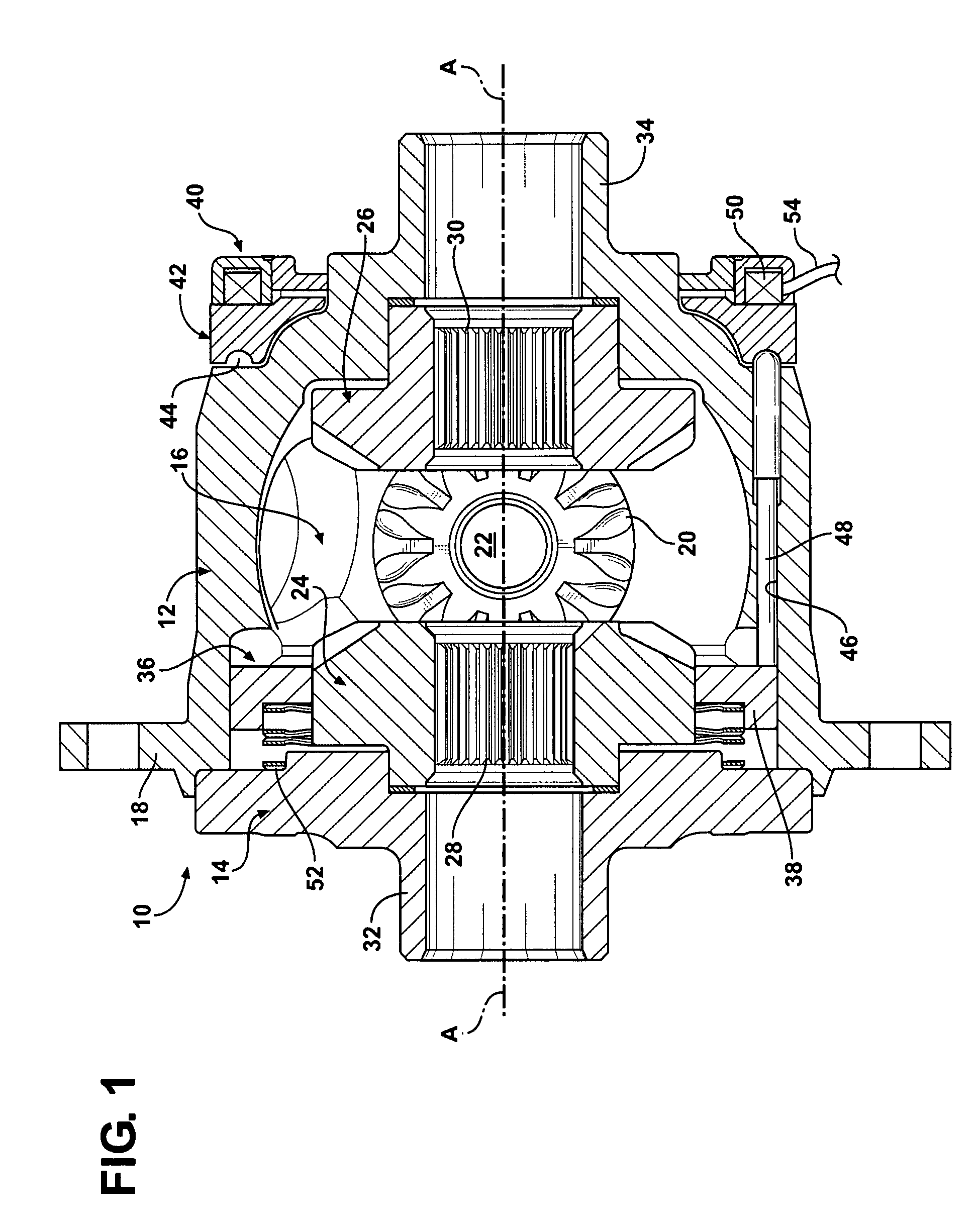
Electronically controlled locking differential having under-dash control system
InactiveUS20100298083A1Easy to controlImprove securityDigital data processing detailsDifferential gearingsDashboardElectricity
An electronically controlled locking differential includes an electromagnetic coil and a control system adapted to control operation of the differential. The control system has a module adapted to be mounted under a dashboard of a vehicle and a circuit electrically interfacing with the module. The circuit has a latching switch that is electrically connected to first and / or second sources of power and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. A latching component is electrically connected to the latching switch and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. The circuit is disabled when power to the control system is turned off and in “standby” mode when power to the control system is turned on. Upon the latching switch being activated, current flows through the circuit to activate the latching component, and the differential is actuated.
Owner:EATON CORP
Electronically controlled locking differential having under-dash control system
InactiveUS8109358B2Easy to controlImprove securityDigital data processing detailsDifferential gearingsElectricityDashboard
An electronically controlled locking differential includes an electromagnetic coil and a control system adapted to control operation of the differential. The control system has a module adapted to be mounted under a dashboard of a vehicle and a circuit electrically interfacing with the module. The circuit has a latching switch that is electrically connected to first and / or second sources of power and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. A latching component is electrically connected to the latching switch and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. The circuit is disabled when power to the control system is turned off and in “standby” mode when power to the control system is turned on. Upon the latching switch being activated, current flows through the circuit to activate the latching component, and the differential is actuated.
Owner:EATON CORP
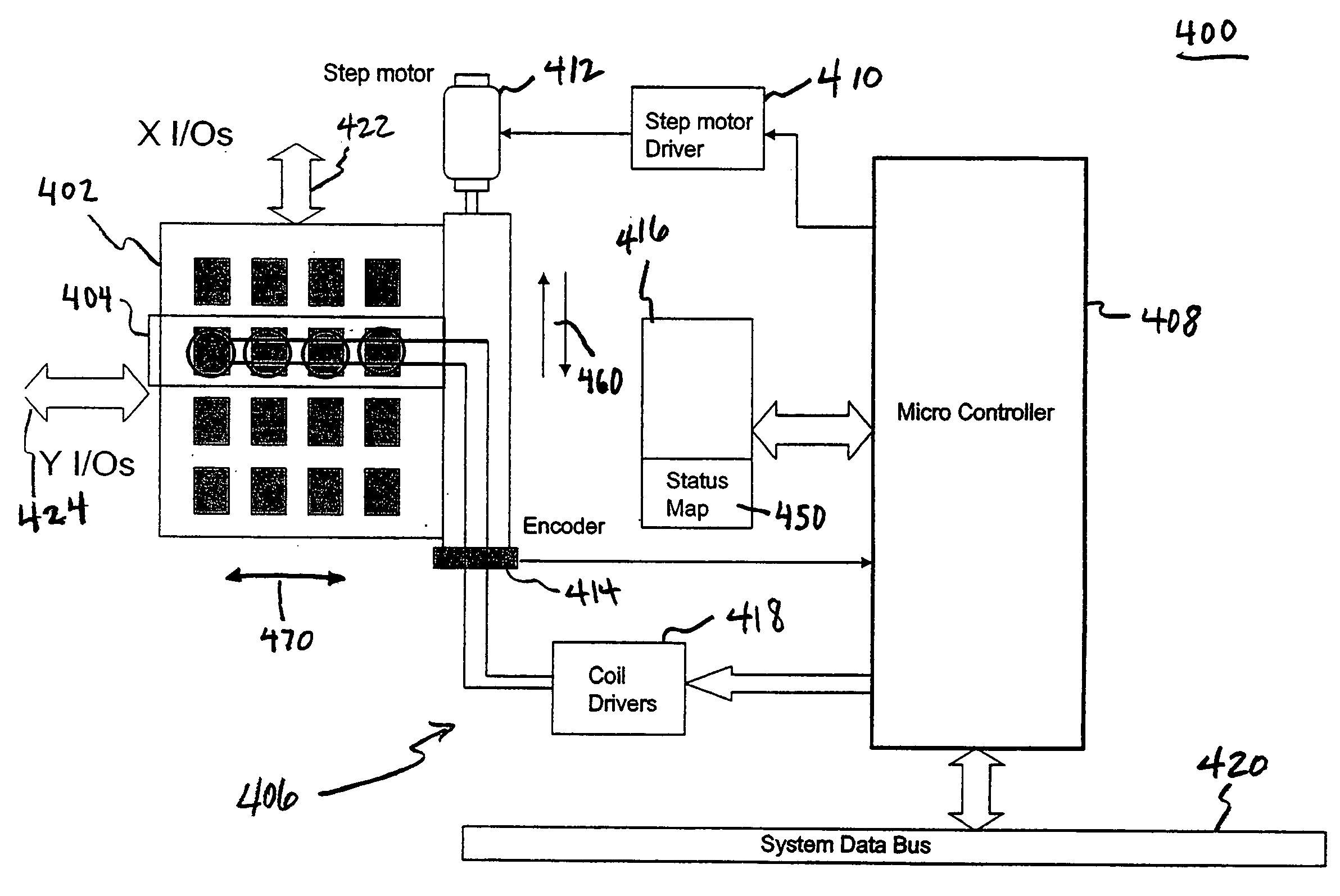
Latching micro-magnetic switch array
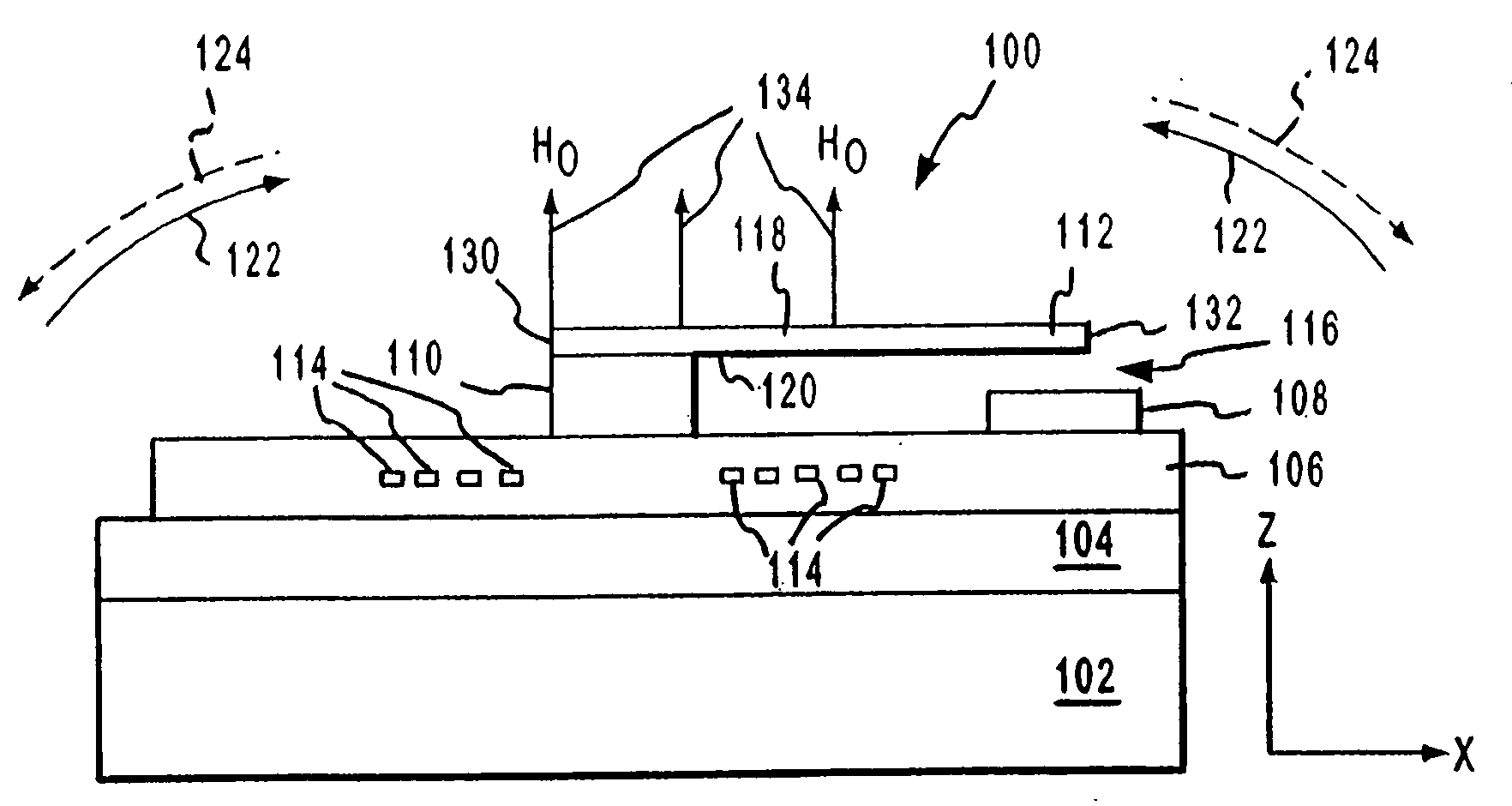
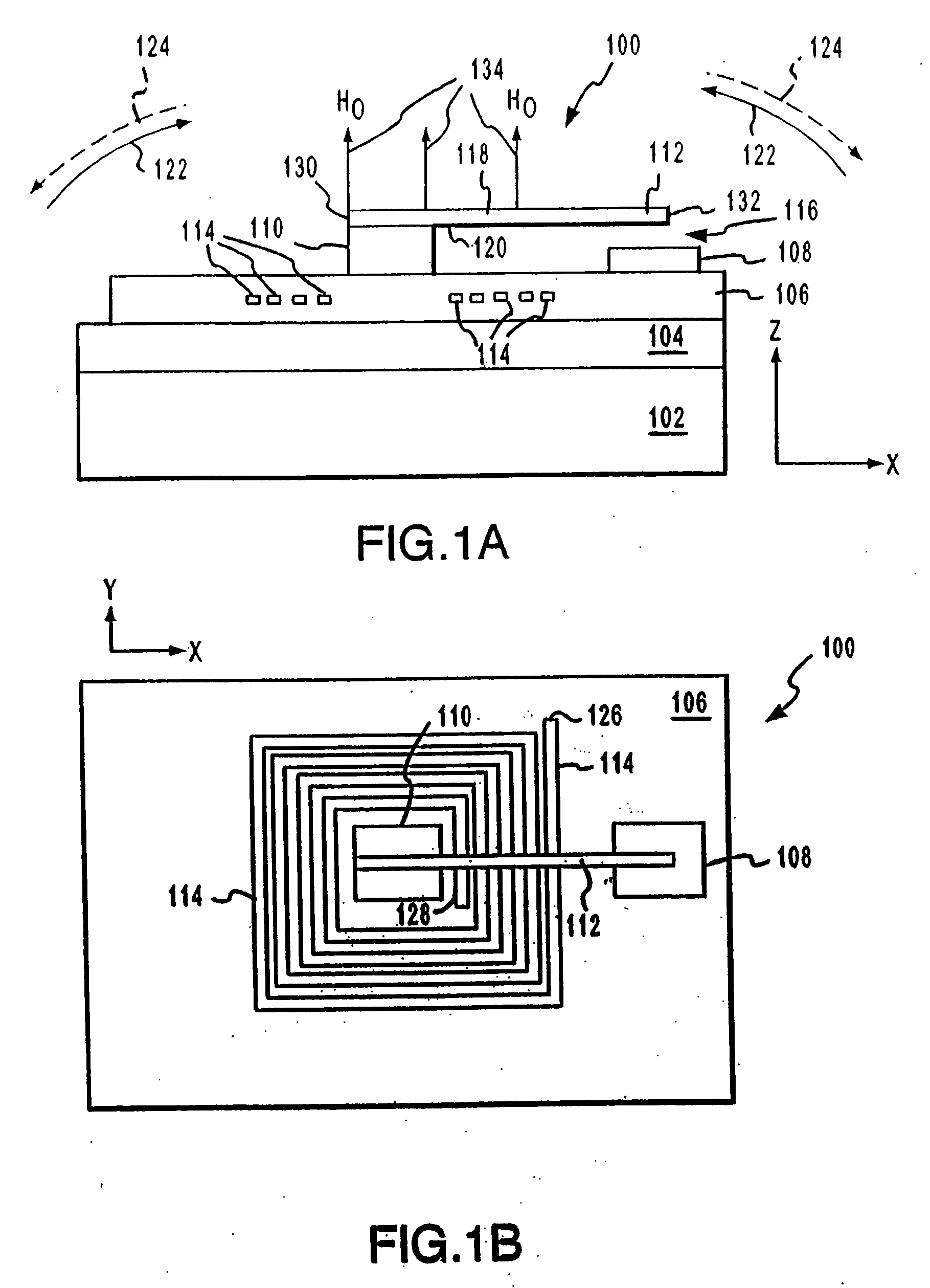
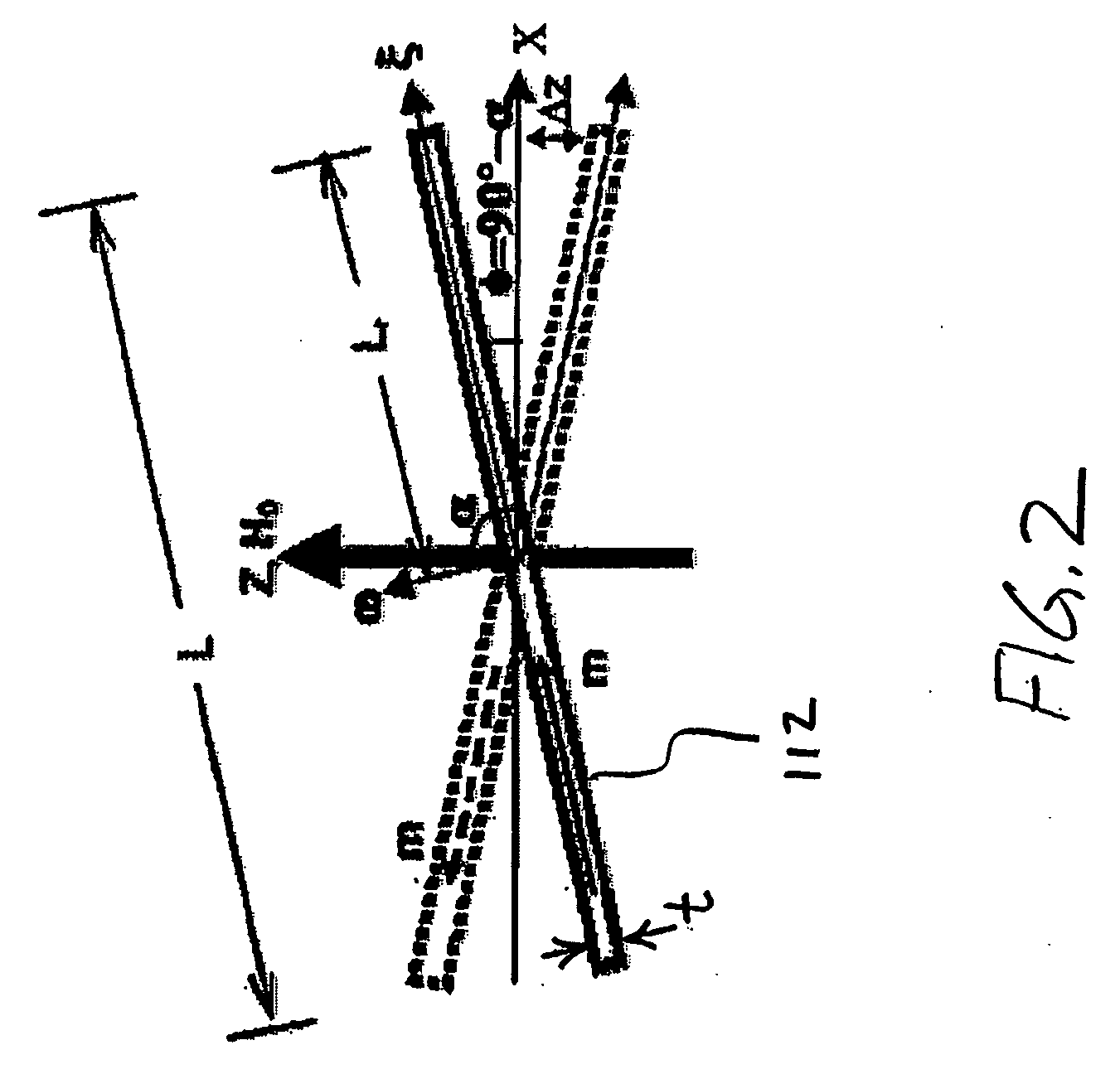
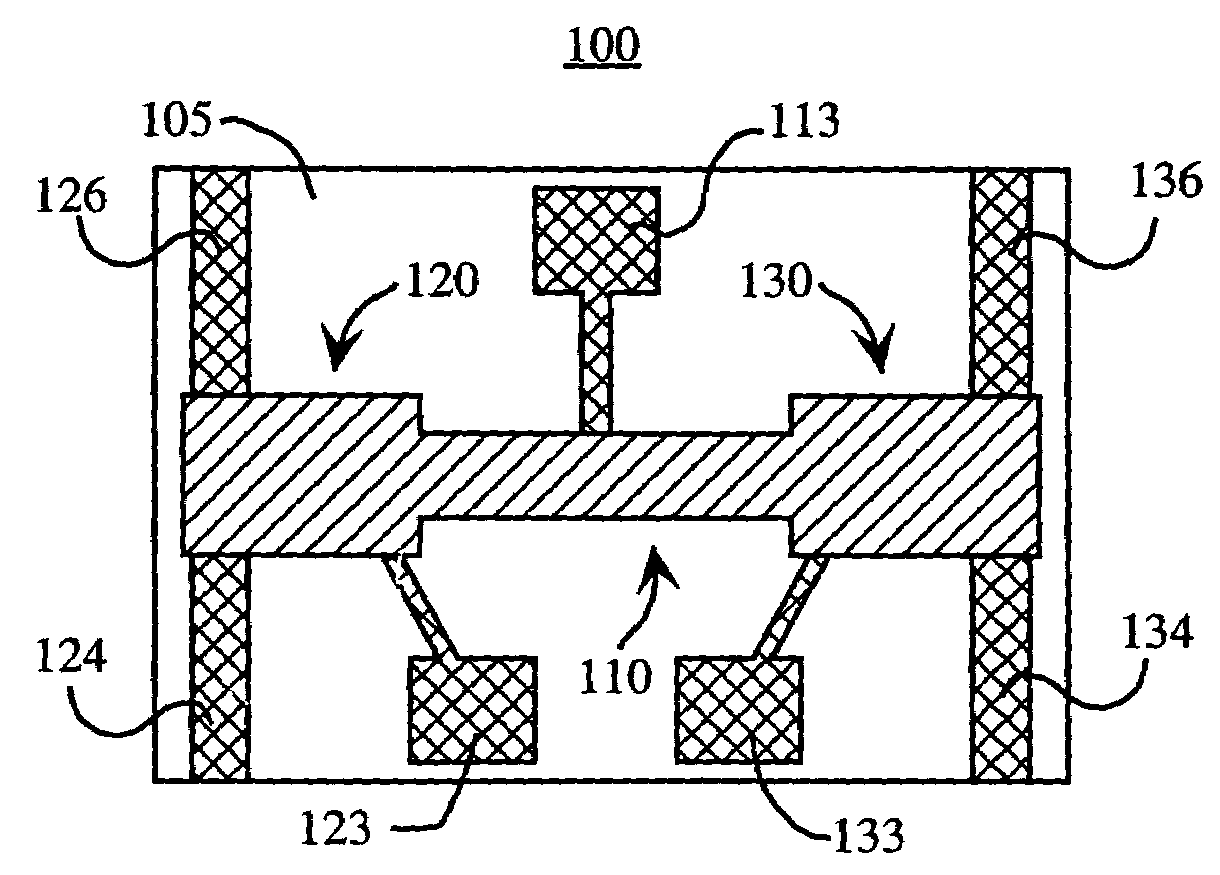
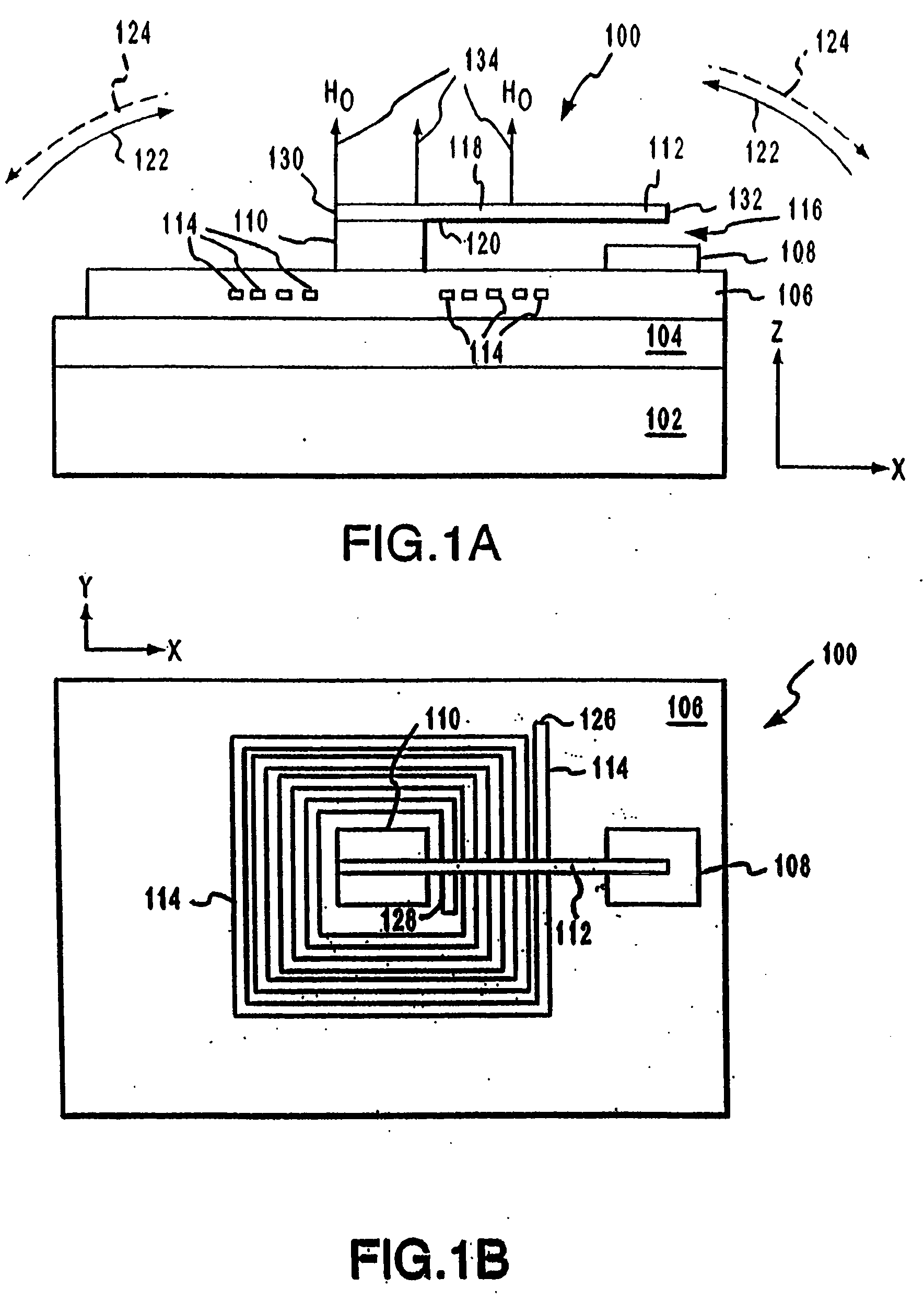
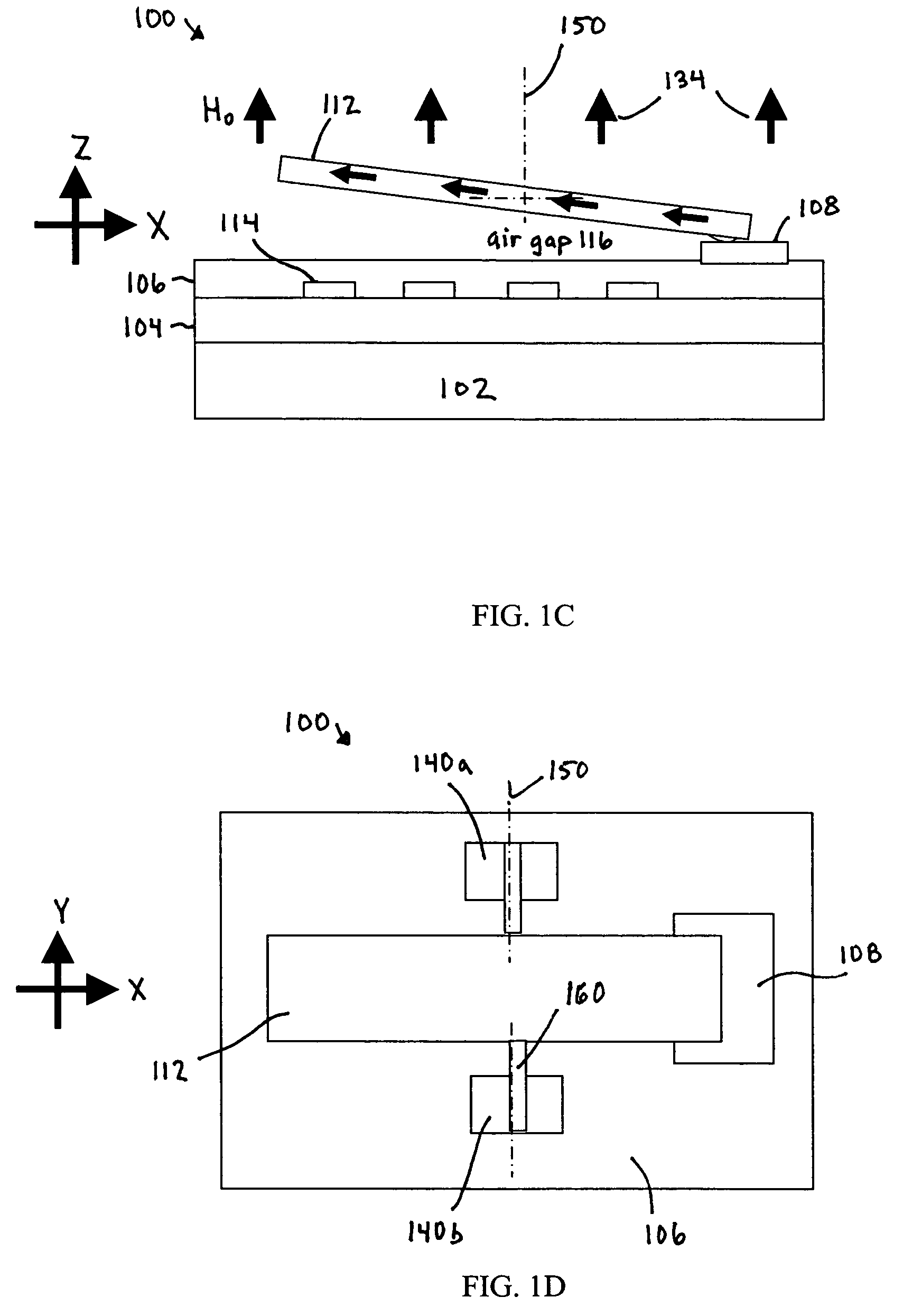
Systems and methods for actuating micro-magnetic latching switches in an array of micro-magnetic latching switches are described. The array of switches is defined by Y rows aligned with a first axis and X columns aligned with a second axis. Each switch in the array of switches is capable of being actuated by a coil. In an aspect, a row of coils is moved along the second axis to be positioned adjacent to a selected one of the Y rows of switches. A sufficient driving current is proved to a selected coil in the row of coils to actuate a selected switch in the selected one of the Y rows of switches. In another aspect, a plurality of first axis drive signals and a plurality of second axis drive signals are generated. These signals drive an array of coils, wherein each coil in the array of coils is positioned adjacent to a corresponding switch in the array of switches. Each first axis drive signal is coupled to coils in a corresponding column of coils in the array of coils. Each second axis drive signal is coupled to coils in a corresponding row of coils in the array of coils. In another aspect, a three-dimensional array of switches is actuated by drive signals that drive a three-dimensional array of coils.
Owner:MAGFUSION
Electronically controlled locking differential having logic-control wire harness
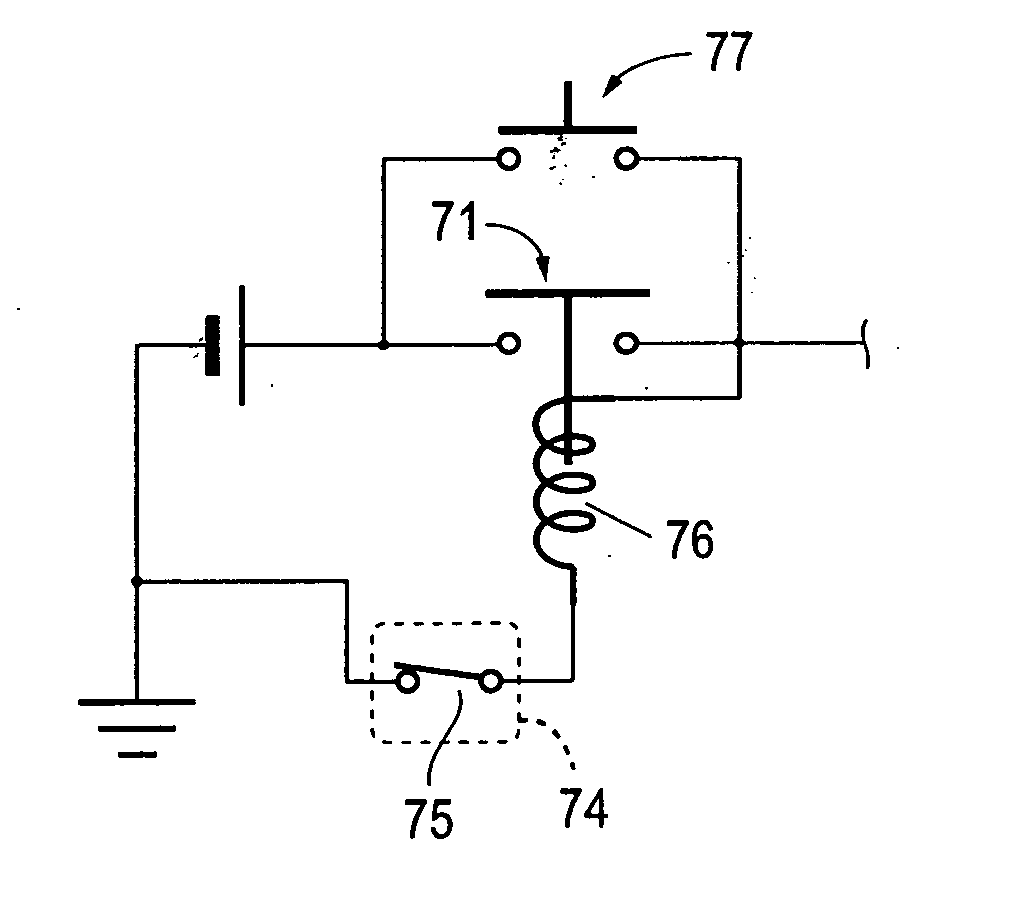
ActiveUS8100805B2Solution to short lifeActuation can be preventedBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsDifferential gearingsElectricityLatching switch
An electronically controlled locking differential includes an electromagnetic coil and a wire harness adapted to logically control operation of the differential and having a circuit. The circuit has a latching switch that is electrically connected to a first source of power and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. A double-pole, double-throw control relay is electrically connected to the latching switch and includes a first switch, a second switch, and a coil. The second switch is adapted to “jump” the latching switch. The circuit is disabled when power to the harness is turned off and in “standby” mode when power to the harness is turned on. Upon the latching switch being activated, current flows from a starting point of the circuit through the circuit to activate the relay, the first switch closes to energize the differential, the second switch closes such that the current “jumps” the latching switch, and the differential is actuated.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Metal contact RF MEMS single pole double throw latching switch
InactiveUS7629194B1Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLatching switchCantilever
Apparatus for a micro-electro-mechanical switch that provides single pole, double throw switching action. The switch has two input lines and two output lines. The switch has a seesaw cantilever arm with contacts at each end that electrically connect the input lines with the output lines. The cantilever arm is latched into position by frictional forces between structures on the cantilever arm and structures on the substrate in which the cantilever arm is disposed. The state of the switch is changed by applying an electrostatic force at one end of the cantilever arm to overcome the mechanical force holding the other end of the cantilever arm in place.
Owner:HRL LAB
Alternating-current zero-crossing action non-arc switch and working method thereof
ActiveCN113823526ASolve protection problemsArc eliminationMagnetic movement switchesLatching switchEngineering
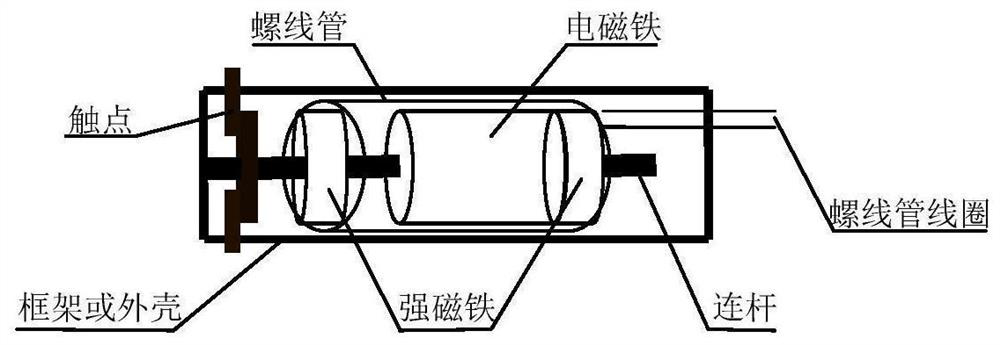
The invention relates to an alternating-current zero-crossing action non-arc switch and a working method thereof. The alternating-current zero-crossing action non-arc switch comprises two neodymium-iron-boron strong magnets, an electromagnet, a solenoid and a main contact, wherein the two neodymium-iron-boron strong magnets comprise a first neodymium-iron-boron strong magnet and a second neodymium-iron-boron strong magnet; the two neodymium-iron-boron strong magnets and the electromagnet are arranged in the solenoid, the electromagnet is located between the two neodymium-iron-boron strong magnets, the two neodymium-iron-boron strong magnets with opposite polarities are used as pistons and driven by the electromagnet, and a push-pull piston type high-speed magnetic latching switch driven by the electromagnet is formed. The electromagnet is driven by the current of the solenoid, on and off of the switch are controlled by changing the current direction of the solenoid, a basis is provided for calculation of zero-crossing action, in order to achieve accurate zero-crossing action, the switch is further provided with a voltage zero-crossing detector and a current zero-crossing detector, and calculation data are provided for zero-crossing driving, so that the switch is connected during voltage zero-crossing and disconnected during current zero-crossing, thereby realizing alternating-current arc-free operation.
Owner:杨帆
Electronically controlled locking differential having logic-control wire harness
ActiveUS20100298082A1Solution to short lifeActuation can be preventedBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsDifferential gearingsElectricityLatching switch
An electronically controlled locking differential includes an electromagnetic coil and a wire harness adapted to logically control operation of the differential and having a circuit. The circuit has a latching switch that is electrically connected to a first source of power and adapted to provide latching power of the differential. A double-pole, double-throw control relay is electrically connected to the latching switch and includes a first switch, a second switch, and a coil. The second switch is adapted to “jump” the latching switch. The circuit is disabled when power to the harness is turned off and in “standby” mode when power to the harness is turned on. Upon the latching switch being activated, current flows from a starting point of the circuit through the circuit to activate the relay, the first switch closes to energize the differential, the second switch closes such that the current “jumps” the latching switch, and the differential is actuated.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
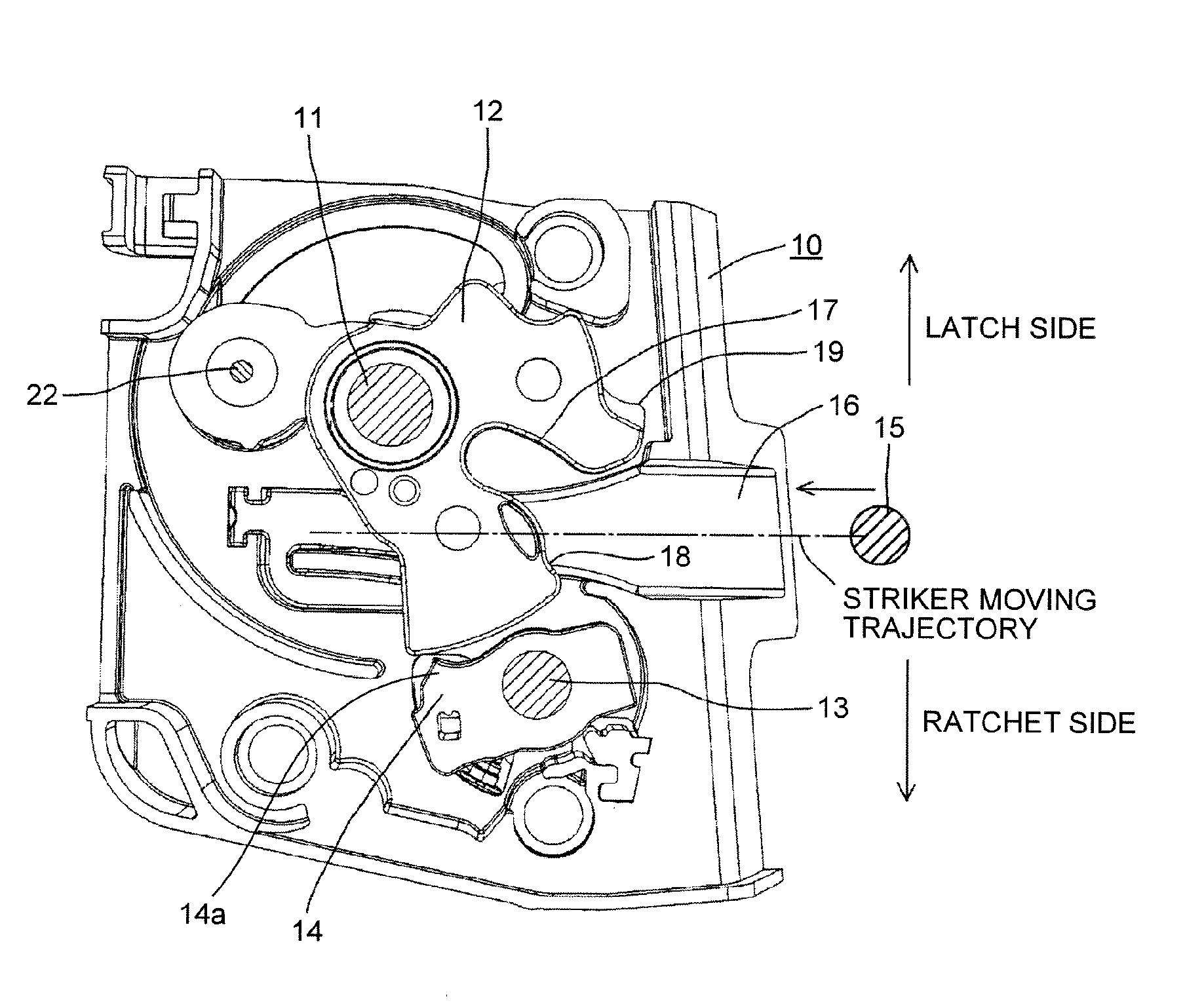
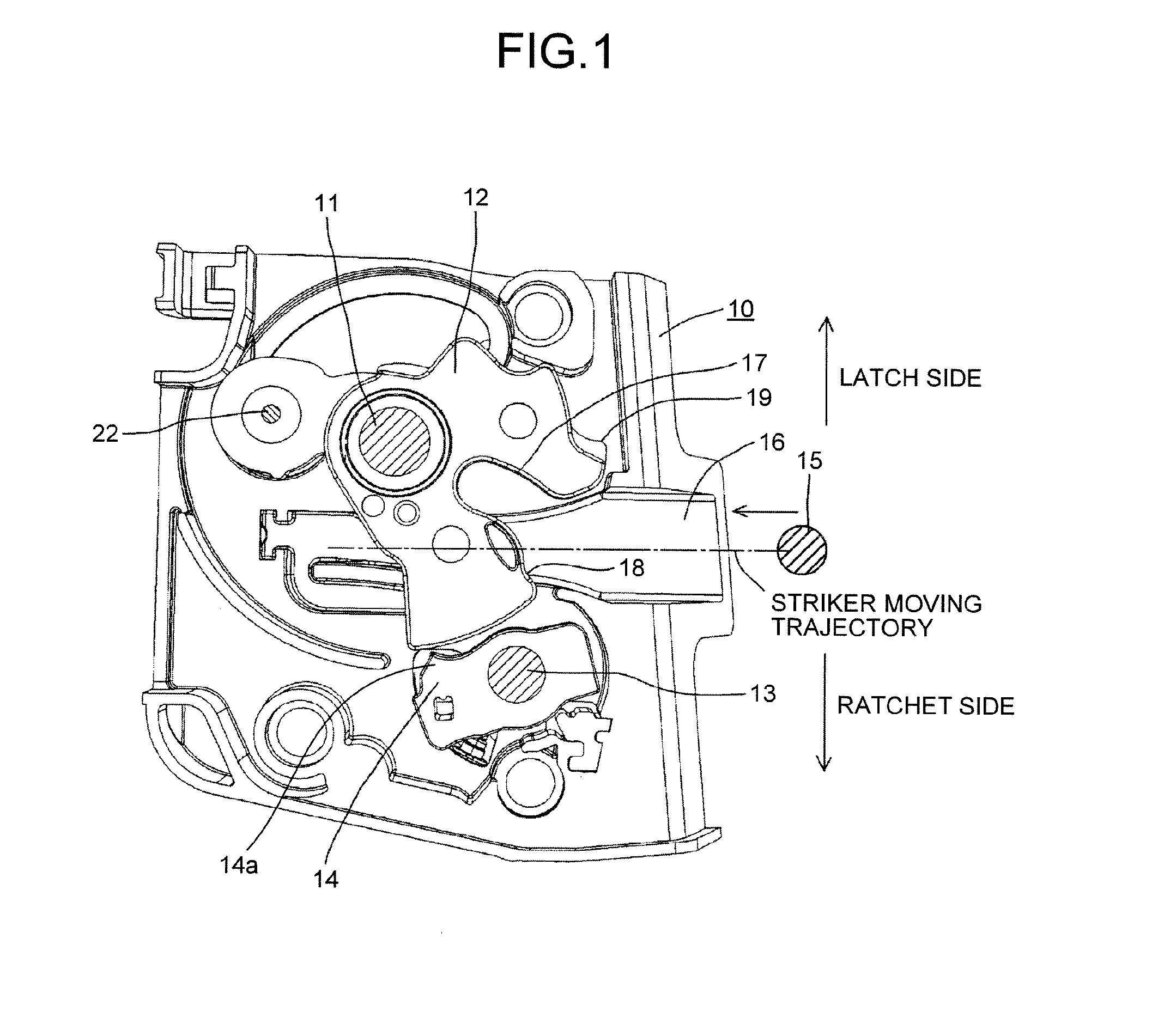
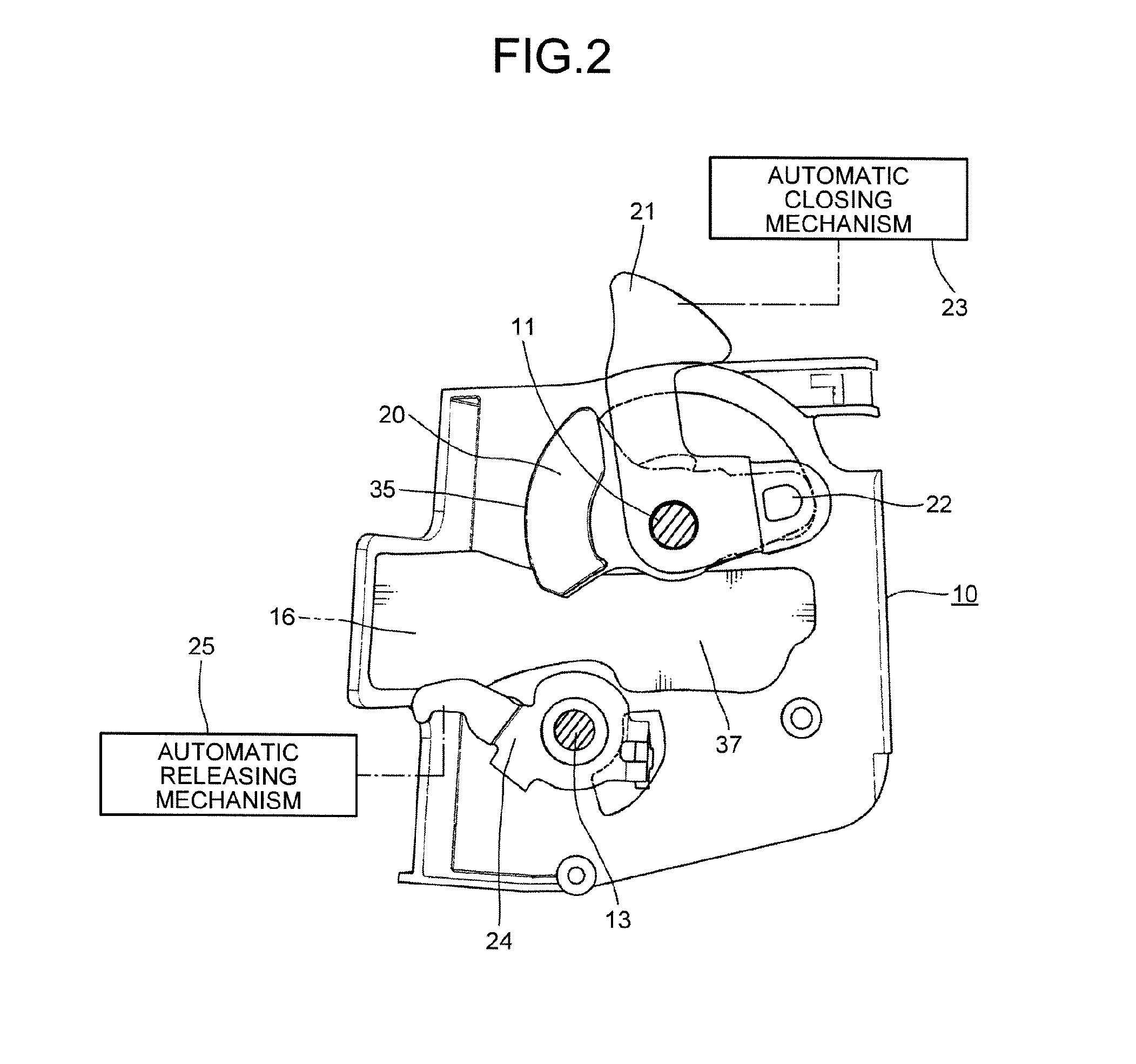
Switch assembly of vehicle door latch device
ActiveUS20160060914A1Prevent reversalConstruction fastening devicesElectrical locking circuitsLatching switchEngineering
A switch assembly of a vehicle door latch device, the switch assembly includes: a latch switch detecting a position of a latch, the latch being pivotally supported by a latch shaft to be engaged with a striker; a ratchet switch that detecting a position of a ratchet, the ratchet being pivotally supported by a ratchet shaft to be engaged with the latch and prevented reverse rotation of the latch; and a one common switch case that the latch switch and the ratchet switch are installed in the one common switch case. The latch shaft and the ratchet shaft are arranged to be isolated across a striker moving trajectory of the striker. The one common switch case is arranged on a latch body on one side of a striker moving trajectory.
Owner:MITSUI KINZOKU ACT
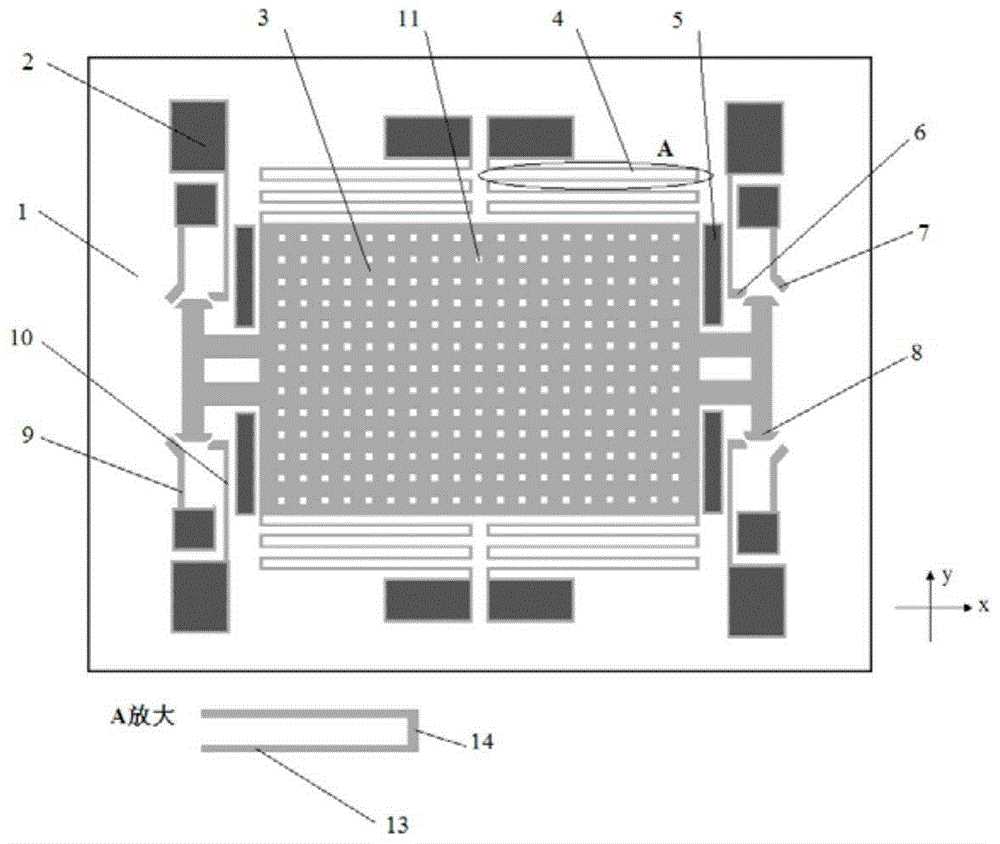
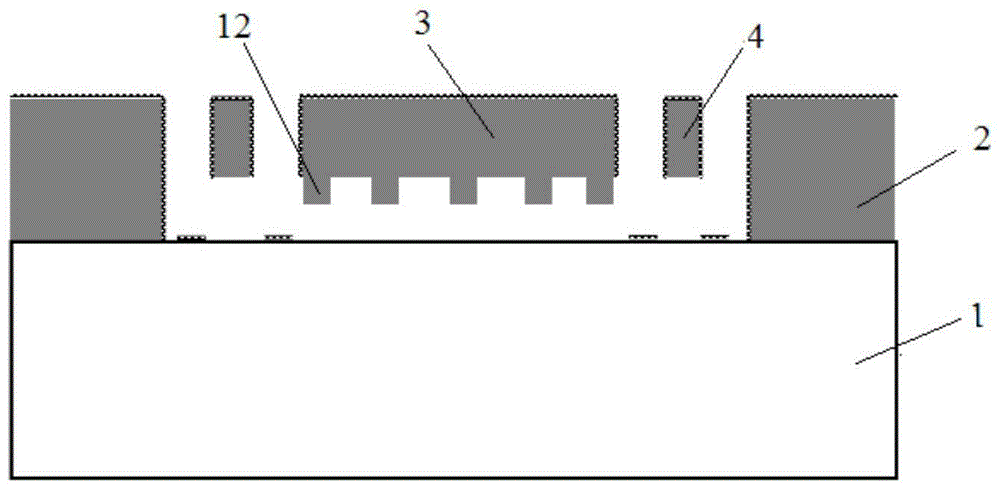
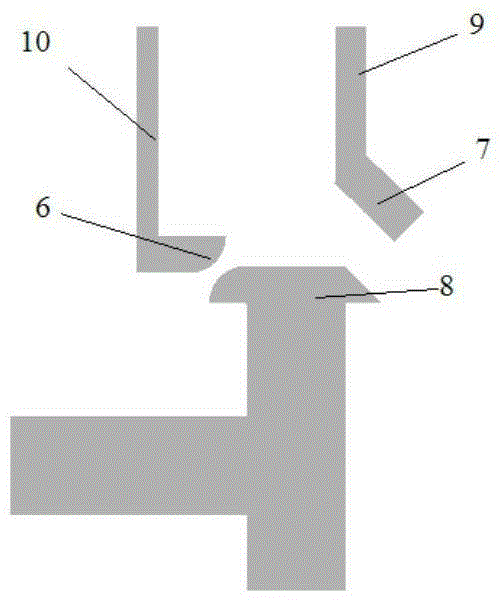
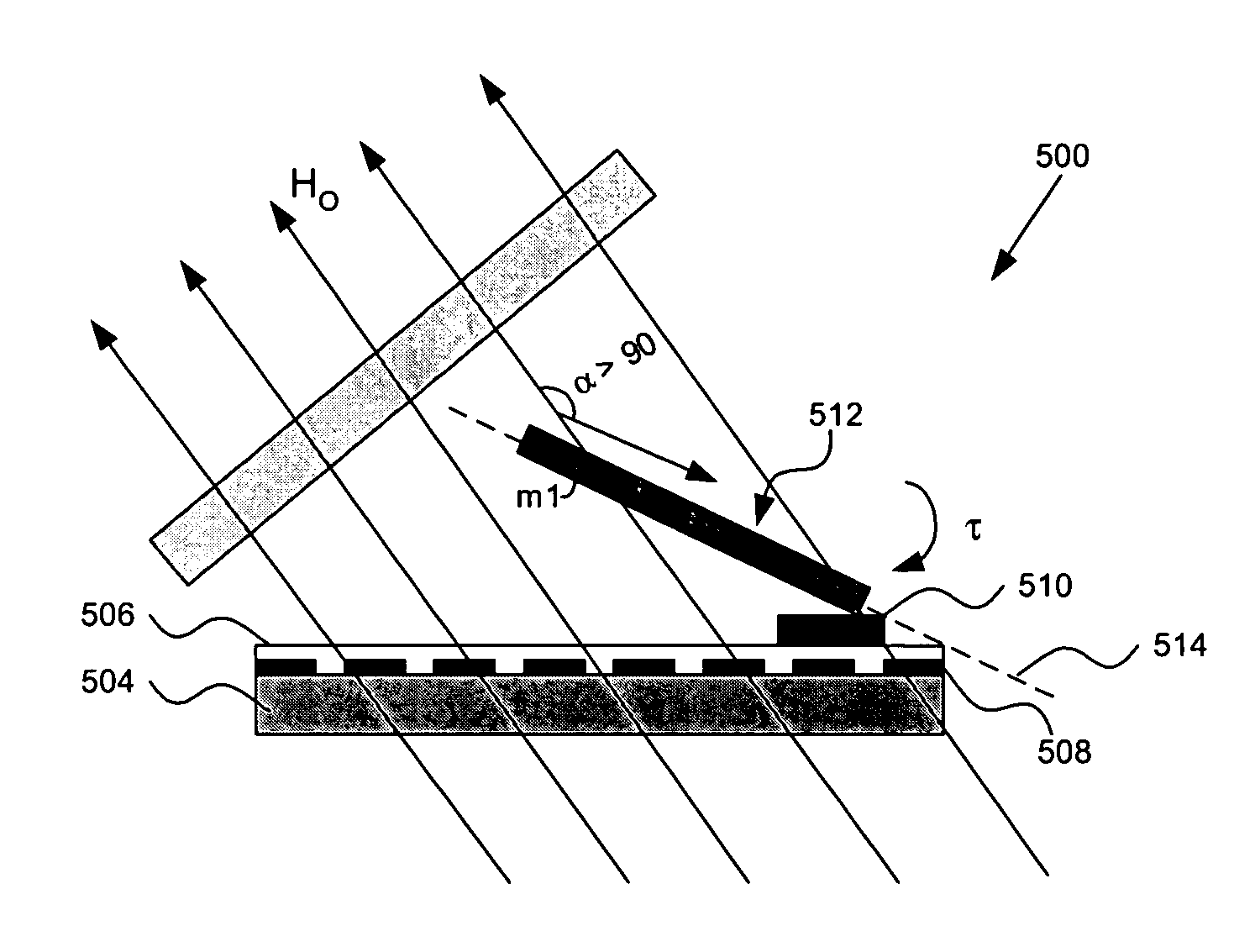
Low-g micromechanical acceleration latching switch
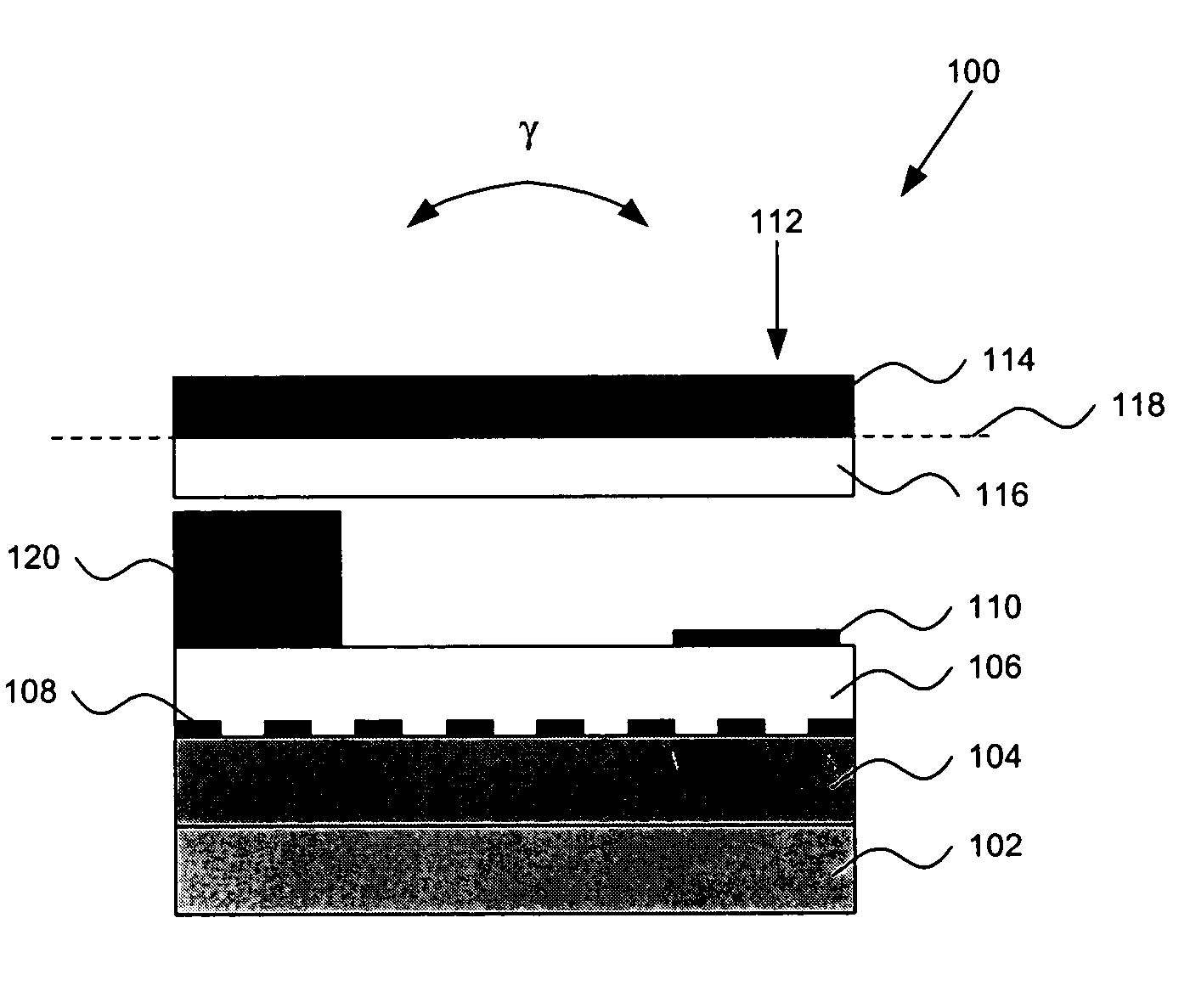
The invention discloses a low-g micromechanical acceleration latching switch. The low-g micromechanical acceleration latching switch comprises an insulation substrate, a detection mass block, a plurality of anchor points, a plurality of contacts, a plurality of contact support beams, a plurality of detection mass block support beams and a plurality of overload protection structures; and the anchor points, the contacts, the contact support beams, the detection mass block support beams and the overload protection structures are symmetrically distributed relative to the X axis and the Y axis of the insulation substrate. The movable contacts of the micromechanical switch adopt hemispherical and wedge-shaped composite structures and form line contacts with side contacts, and energy loss in the motion process is reduced; the movable contacts form face contacts with the induction contacts, contact resistance values are reduced, and contact reliability is improved; the detection mass block, the flexible beams, the contacts and the anchor points are distributed in a completely axisymmetric manner, and bidirectional latching in plus or minus Y directions can be achieved; the detection mass block support beams are symmetrically distributed on two sides of the detection mass block, the structural layout is reasonable, and low-g latching is easy to achieve; and, through adjustments of gaps between the detection mass block, the flexible beams and the contacts, a latching threshold can be convenient to adjust, and the threshold scope is wide.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Slam latch assembly, and its operation method, and latch lock assembly operated according to the method
ActiveCN100564784CPivot movement preventsLinear motion preventionWing handlesConstruction fastening devicesLatching switchPush-button
A latch with a pop-up button. When the button is extended, it provides a handle on the door for pulling. With the button raised or lowered, the door can be closed. With the button raised, the latch catch can be disengaged from a retainer mounted on the door frame by pulling the door open. With the button down, the latch catch remains in the extended position behind the keeper and cannot pull the door open. The latch also includes means for selectively retaining the button in the lowered position, and means for resisting rotational movement of the latch catch when the button is in the lowered position.
Owner:SOUTHCO
Electric leakage detection and protection circuit
InactiveCN102157916AImprove securityWith end-of-life detectionElectrical testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent limitingLatching switch
The invention discloses an electric leakage detection and protection circuit which is characterized by comprising an end-of-life detection switch, controlled by an electromagnetic latching mechanism, and a latching switch. An anode of a thyristor is connected with a live line of a power input end through the latching switch and a trip coil, and an iron core is embedded in the trip coil; a cathode of the thyristor is connected with a zero line of the power input end; the end-of-life detection switch and a current-limiting resistor are serially connected to form a simulated leakage current generating circuit for completing an end-of-life detection function; and one end of the simulated leakage current generating circuit is connected with the zero line of the power input end passing through an induction coil and a self-excitation coil, and the other end is connected with the live line of the power input end through the trip coil. When a reset button is tripped, the end-of-life detection switch is closed, and the latching switch is off; when the reset button is reset, the end-of-life detection switch is off, and the latching switch is on; and when the reset button is pressed, the latching switch is on, and the end-of-life detection switch is off.
Owner:黄华道
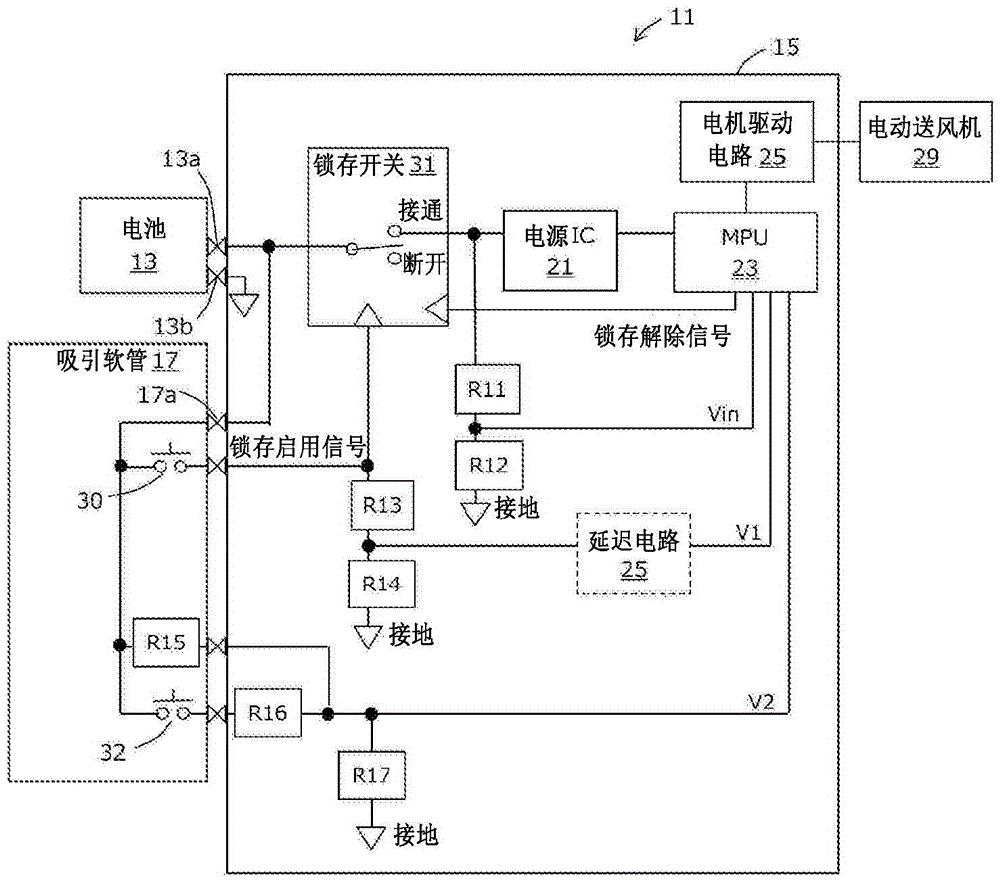
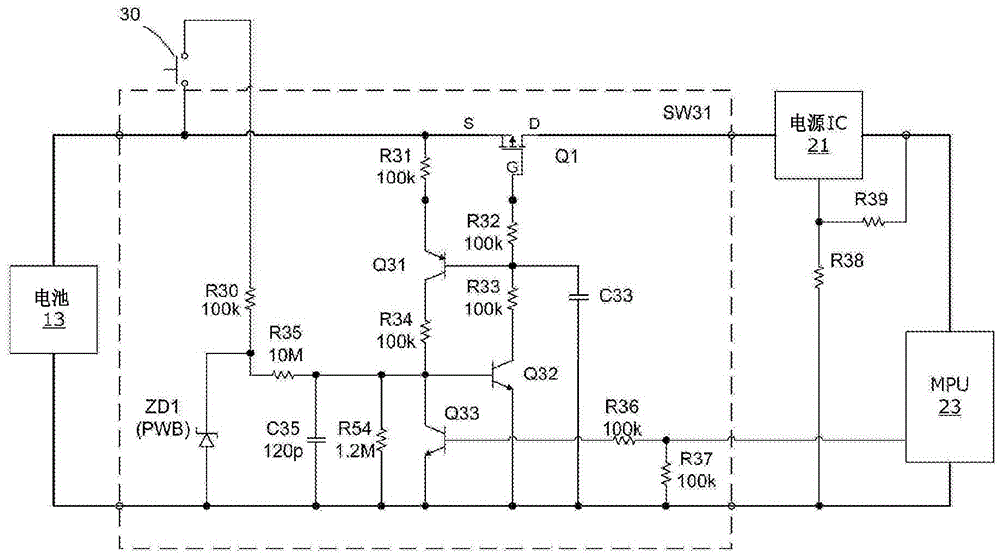
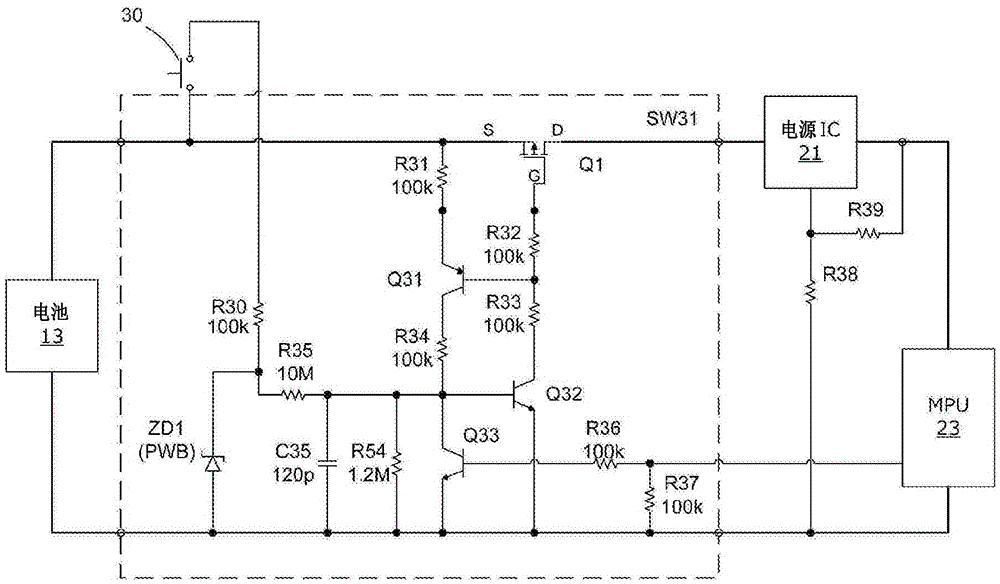
Battery-driven electronic device
ActiveCN105492995AAvoid misuseDc network circuit arrangementsElectric motor controlLatching switchElectrical battery
A battery-driven electronic device provided with the following: a battery that has battery terminals; a computer to which power is supplied from said battery; a self-holding latching switch that is connected between the battery and the computer and turns the supply of power to the computer on and off; a momentary switch that, when turned on, applies the voltage across the battery terminals to a trigger input for the latching switch, latching said latching switch to an on state; a battery-monitoring circuit whereby the battery-terminal voltage is converted to a battery-monitoring voltage that can be read by the computer; a switch-monitoring circuit whereby the battery-terminal voltage via the momentary switch is converted into a switch-monitoring voltage that can be read by the computer; and a latch-releasing circuit that turns the latching switch off in response to output from the computer. When power is supplied to the computer and the computer starts executing a process, the computer compares the switch-monitoring voltage to the battery-monitoring voltage, and if the difference between said voltages is above a range that is predetermined so as to correspond to the on state of the momentary switch, the computer activates the latch-releasing circuit.
Owner:SHARP KK
Hidden dryer door switch
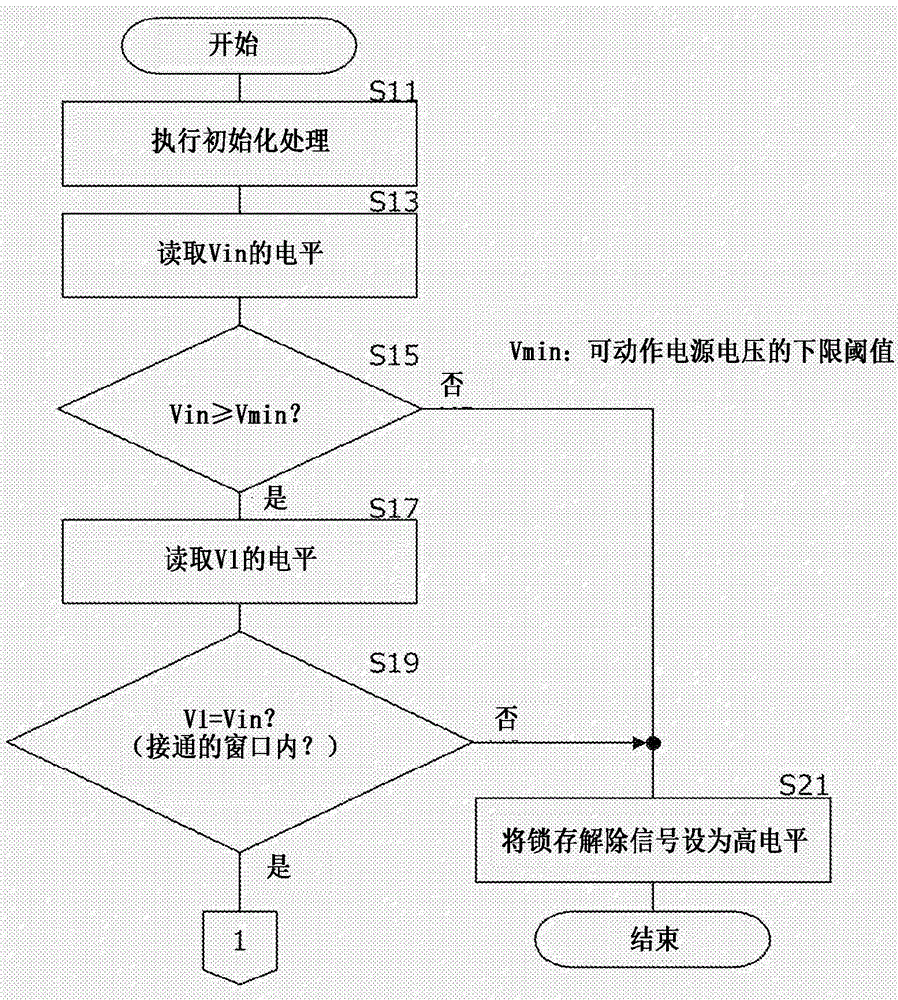
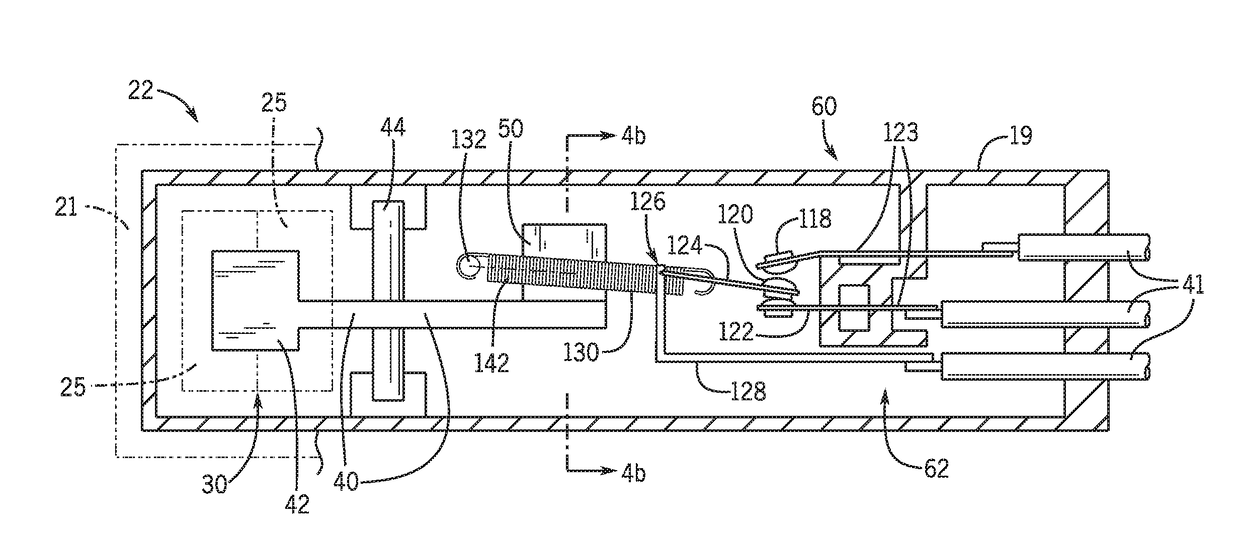
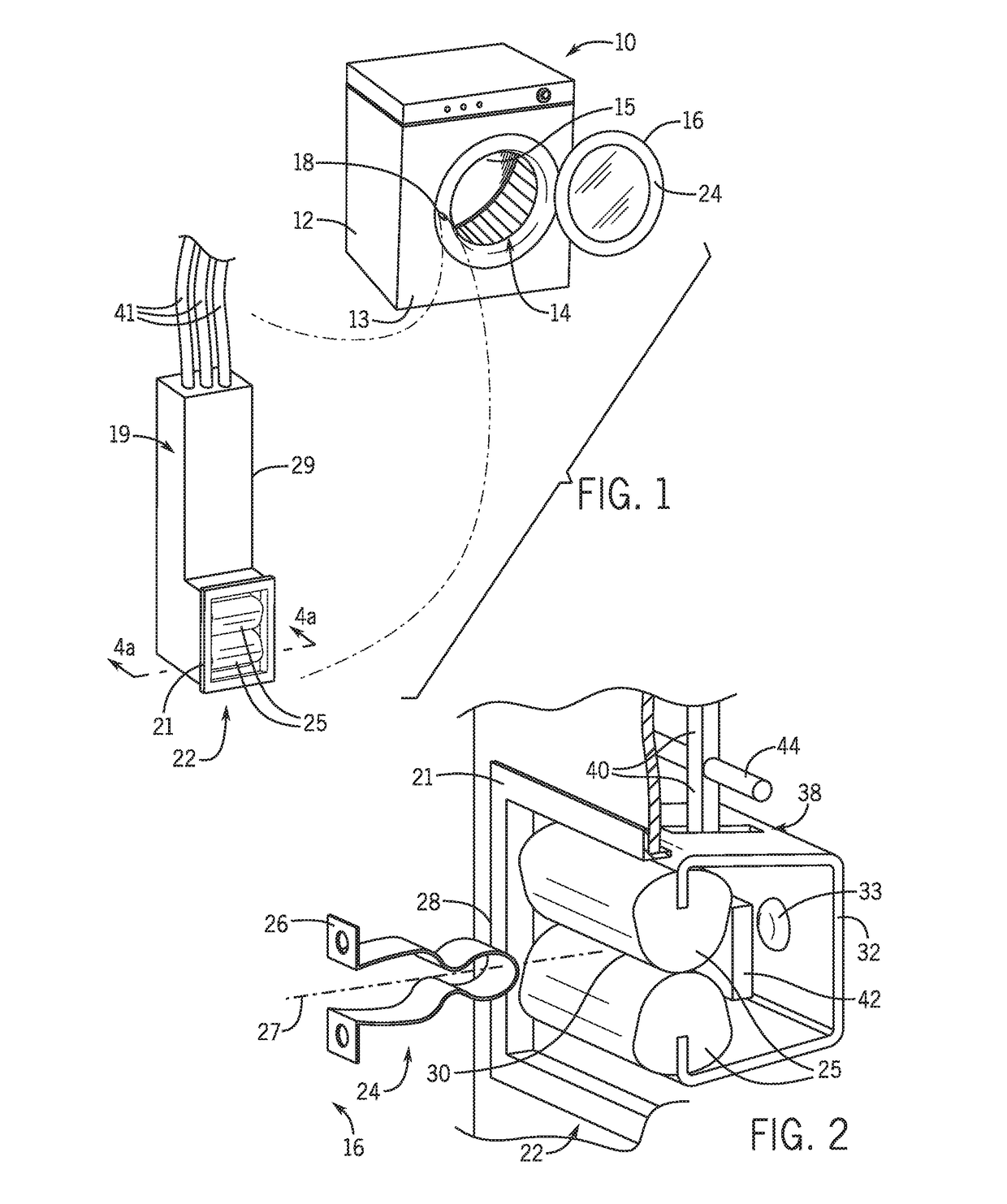
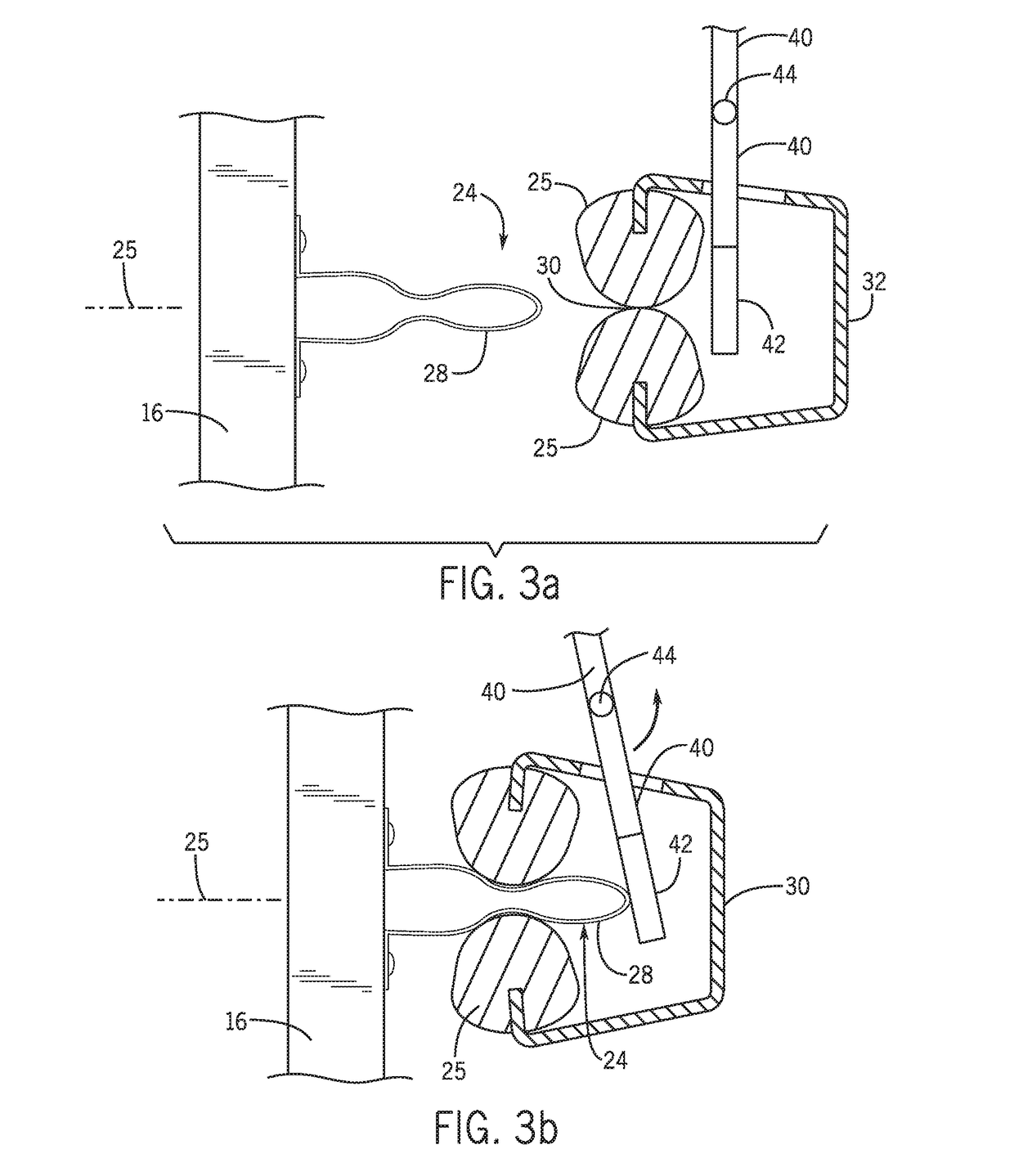
ActiveUS20170175321A1Eliminate pollutionContact operating partsOther washing machinesLatching switchEngineering
A latch switch assembly for an appliance or the like provides spring-loaded jaws to retain a latch strike when a door of the appliance is closed and a switch operator positioned behind spring-loaded jaws be activated by the latch strike when it is received.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Battery-driven electronic device
InactiveCN105531901AInstall probeBatteries circuit arrangementsCurrent conducting connectionsLatching switchElectrical battery
This battery-driven electronic device is provided with: a battery that is detachable from a main body; a computer that is disposed in the main body and operates using the power supply voltage from the battery; a self-supporting latching switch that is connected between the battery and the computer and turns the power supply voltage to the computer on and off; and a mounting detection circuit that turns the latching switch to an on state in response to the mounting of the battery.
Owner:SHARP KK
Micro magnetic non-latching switches and methods of making same
InactiveUS7183884B2Improve performanceEasy to manufactureElectromagnetic relay detailsPolarised relaysRotational axisAxis of symmetry
A micro magnetic switch includes a reference plane and a magnet located proximate to a supporting structure. The magnet produces a first magnetic field with uniformly spaced field lines approximately orthogonal to the reference plane, symmetrically spaced about a central axis, or non-uniformly spaced fields approximately orthogonal to the reference plane. The switch also includes a cantilever supported by the support structure. The cantilever has an axis of rotation lying in the reference plane and has magnetic material that makes the cantilever sensitive to the first magnetic field, such that the cantilever is configured to rotate about the axis of rotation between first and second states. The switch further includes a conductor located proximate to the supporting structure and the cantilever. The conductor is configured to conduct a current. The current produces a second magnetic field having a component approximately parallel to the reference plane and approximately perpendicular to the rotational axis of the cantilever, which causes the cantilever to switch between the first and second states. The switch still further includes a stopping device located proximate to the supporting structure. The stopping device is operable to stop the cantilever from rotating about the axis of symmetry beyond a point at which a longitudinal axis of the cantilever is approximately parallel to a longitudinal axis of the magnet.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Voltage regulation tap switch and usage method of voltage regulation tap switch
ActiveCN108333983AAvoid damageSolve the problem of being easily damaged by impactProgramme controlComputer controlOvervoltageLatching switch
The invention provides a voltage regulation tap switch and a usage method of the voltage regulation tap switch. According to the invention, in the voltage regulation tap switch, a thyristor is connected to a magnetic latching switch. By means of the voltage regulation tap switch provided with the thyristor, the problem that in the related art, an on-load tap switch is prone to being impacted and damaged is solved. The damage to the thyristor is avoided. Meanwhile, in the voltage regulation switching process, no inrush current is generated, and the operation overvoltage is avoided.
Owner:STATE GRID BEIJING ELECTRIC POWER +1
Automated mobile compressed hydrogen fuel source management for mobile power generation applications
ActiveUS20210218043A1Reactant parameters controlGas handling/storage effectsLatching switchFuel tank
A pressure-based latching switch includes a shuttle valve, a first valve and a second valve. The shuttle valve may switch a fuel through one of a first port and a second port in response to a greater pressure of the fuel at the ports. The first valve may switch a fuel to the first port while a second pressure of the fuel at the second port is less than a second threshold pressure. The second valve may switch the fuel to the second port while a first pressure of the fuel at the first port is less than a first threshold pressure. The pressure-based latching switch may change the fuel supplied to the fuel cell system automatically from a first fuel tank to a second fuel tank in response to the first pressure of the fuel falling below the first threshold pressure.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
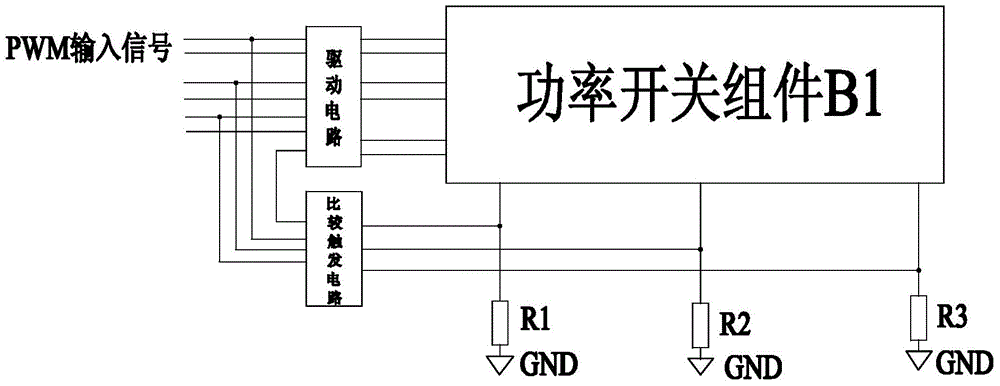
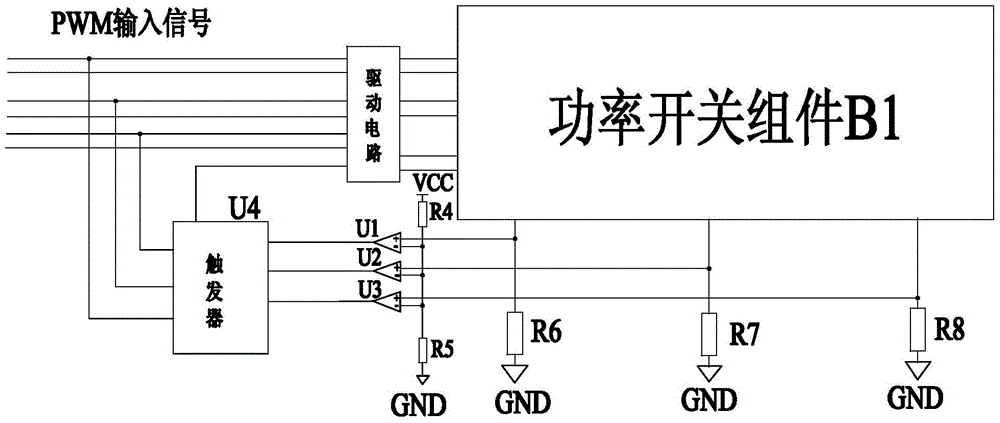
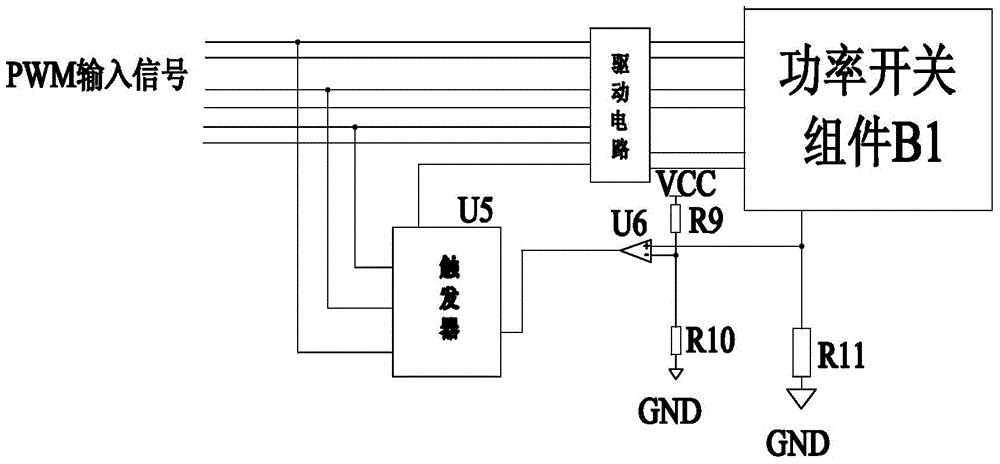
A single-cycle current control power module device
ActiveCN104037718BImprove reliabilitySafety protectionArrangements responsive to excess currentControl powerPower flow
Owner:WUXI NCE POWER
Latching micro-magnetic switch array
InactiveUS20060146470A1Improve performanceEasy to manufactureElectromagnetic relay detailsSelector switchesDriving currentLatching switch
Systems and methods for actuating micro-magnetic latching switches in an array of micro-magnetic latching switches are described. The array of switches is defined by Y rows aligned with a first axis and X columns aligned with a second axis. Each switch in the array of switches is capable of being actuated by a coil. In an aspect, a row of coils is moved along the second axis to be positioned adjacent to a selected one of the Y rows of switches. A sufficient driving current is proved to a selected coil in the row of coils to actuate a selected switch in the selected one of the Y rows of switches. In another aspect, a plurality of first axis drive signals and a plurality of second axis drive signals are generated. These signals drive an array of coils, wherein each coil in the array of coils is positioned adjacent to a corresponding switch in the array of switches. Each first axis drive signal is coupled to coils in a corresponding column of coils in the array of coils. Each second axis drive signal is coupled to coils in a corresponding row of coils in the array of coils. In another aspect, a three-dimensional array of switches is actuated by drive signals that drive a three-dimensional array of coils.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com