Patents
Literature
368 results about "Mobile radiocommunication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
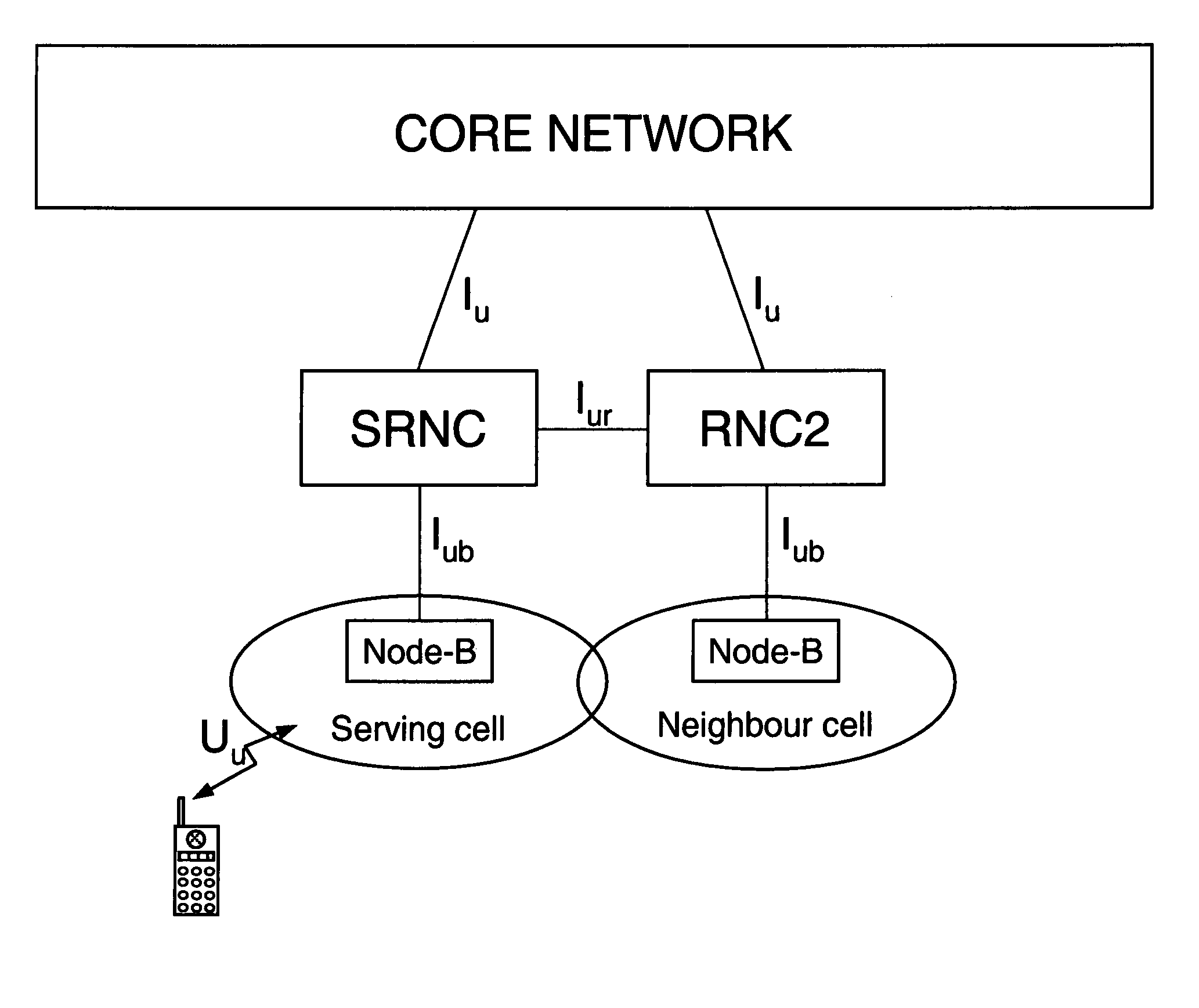
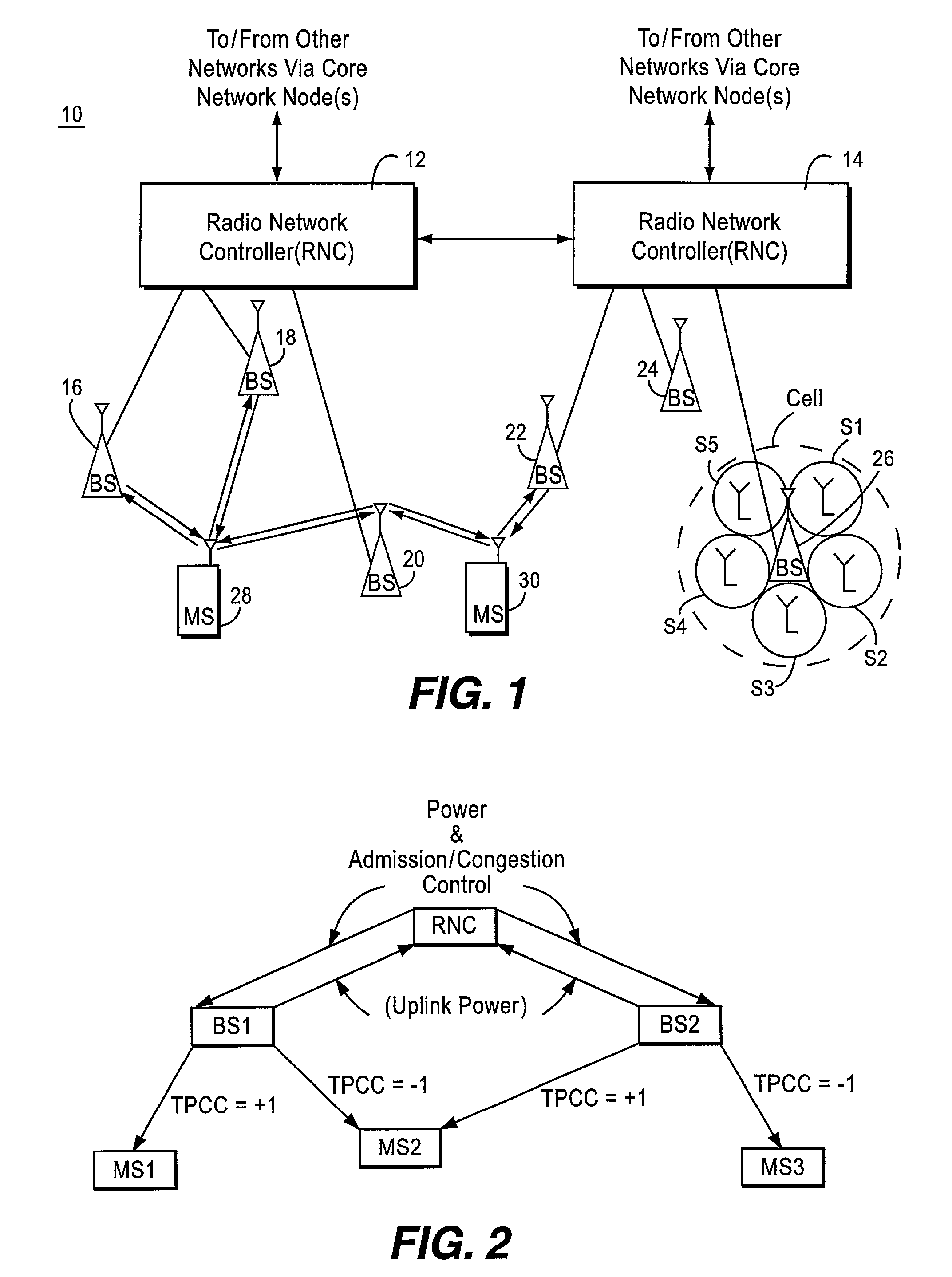
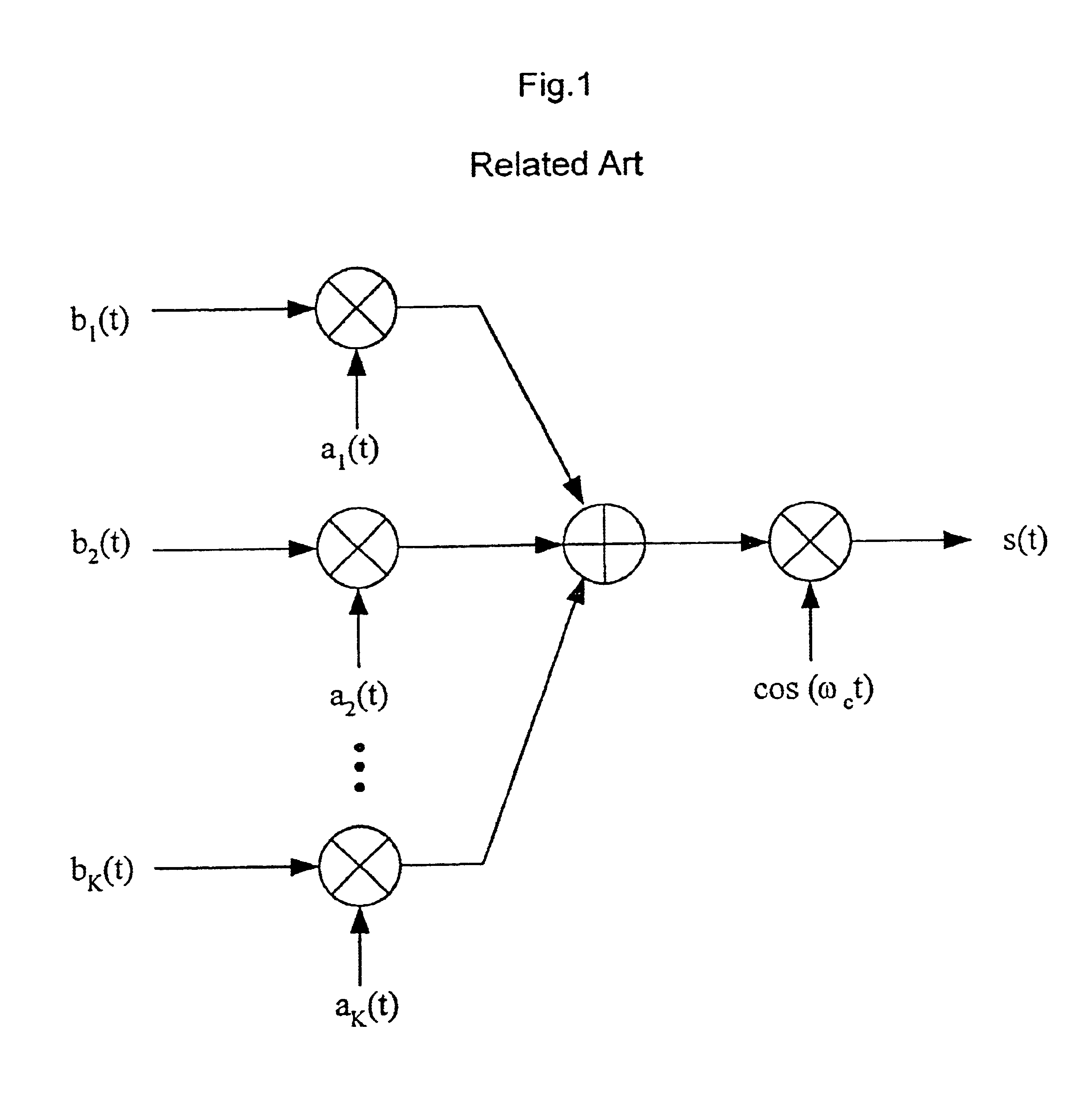
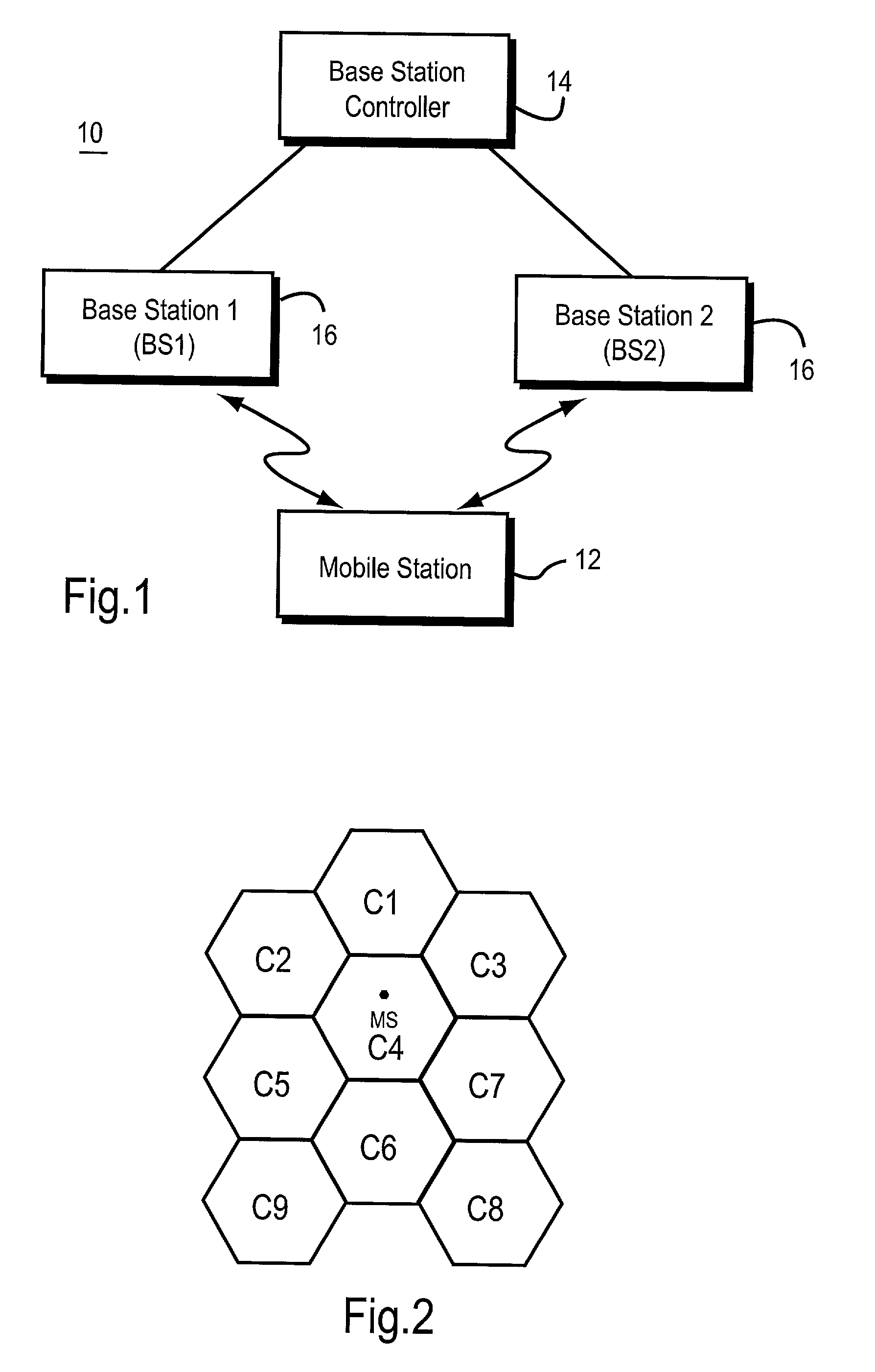
Common radio resource management method in a multi-RAT cellular telephone network
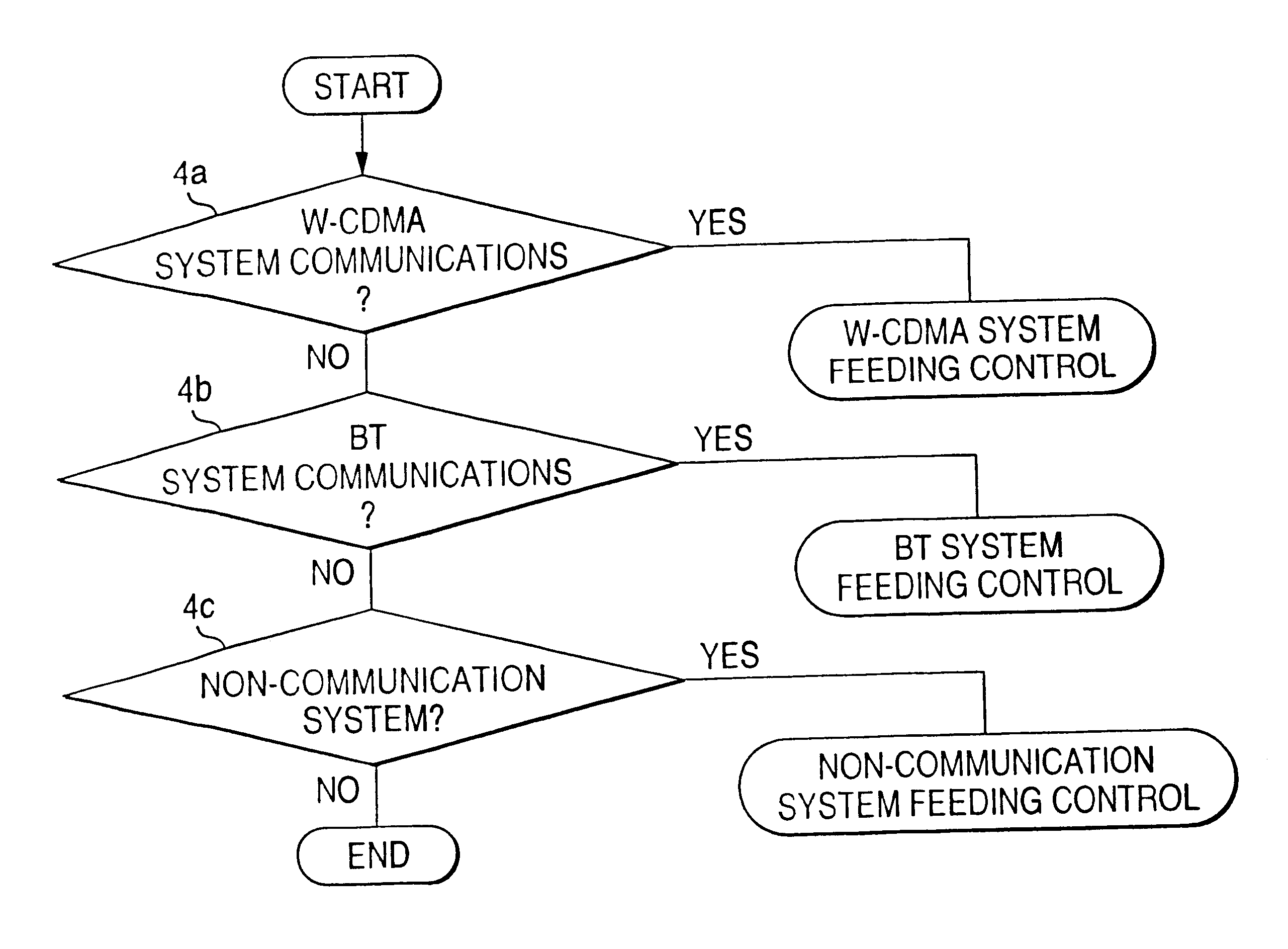
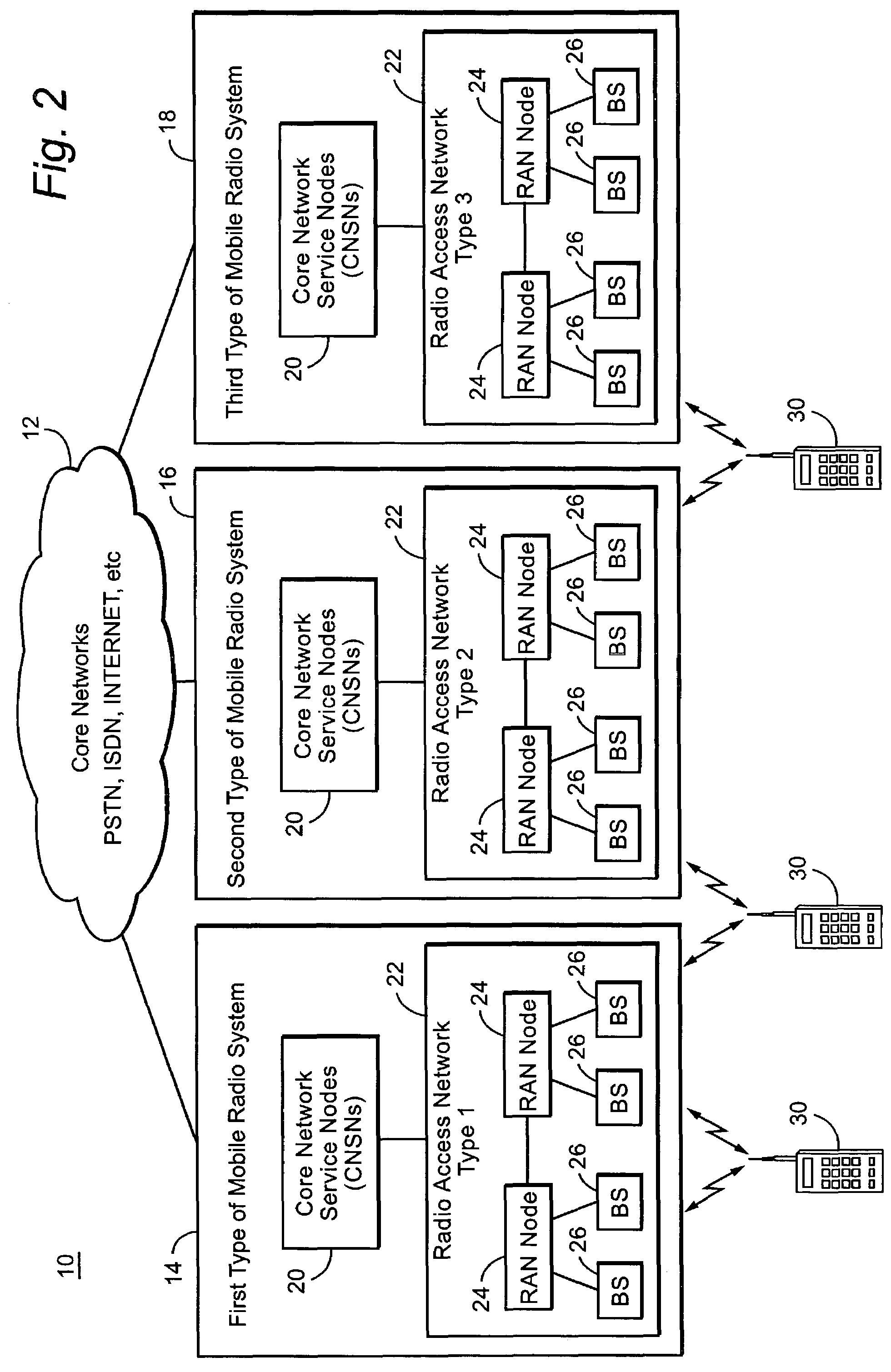
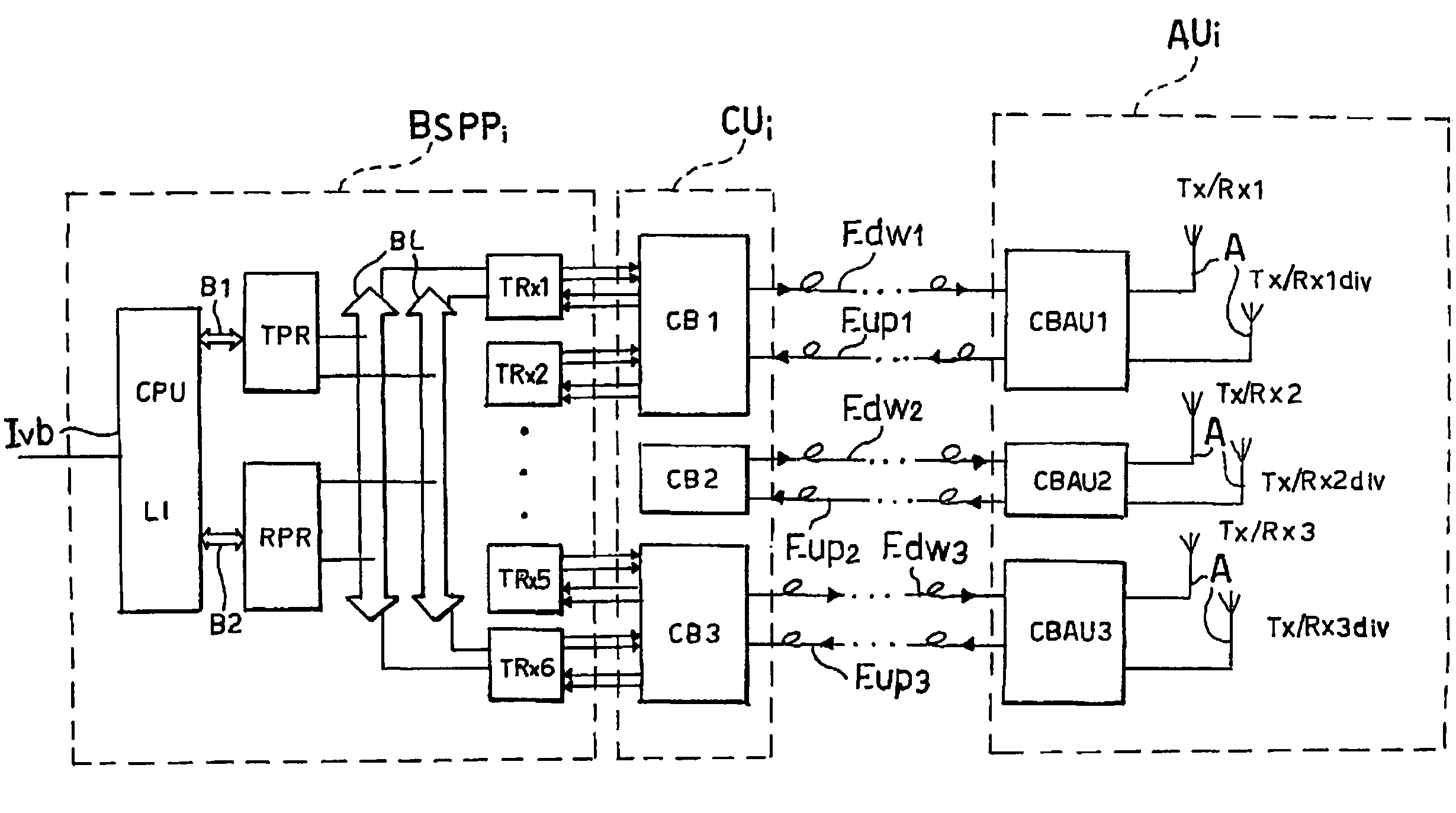
ActiveUS20050026616A1Avoid complex processAvoid problemsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular telephoneHandover
A Common radio resource management method is performed in a mobile radio communication network employing different radio access technologies that overlap over a geographic area subdivided into cells belonging to the domains of respective controllers which are connected to each other in overlapping or adjacent domains and to a core network by means of relevant interfaces. The controllers calculate new traffic-related Information Elements to be exchanged over the existing interfaces to the aim of planning handovers and / or cell reselections towards adjacent cells either of the same or different RAT. Cell capabilities and mobile terminal capabilitiess being also specified by respective IEs. Diversely from the conventional traffic-related IEs based on Cell Load parameters or Free Capacity, the new IEs include indications of the “availability” of bearer services in the cell in terms of maximum bitrate, either guaranteed or not guaranteed, that can currently be allowed to each bearer service.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
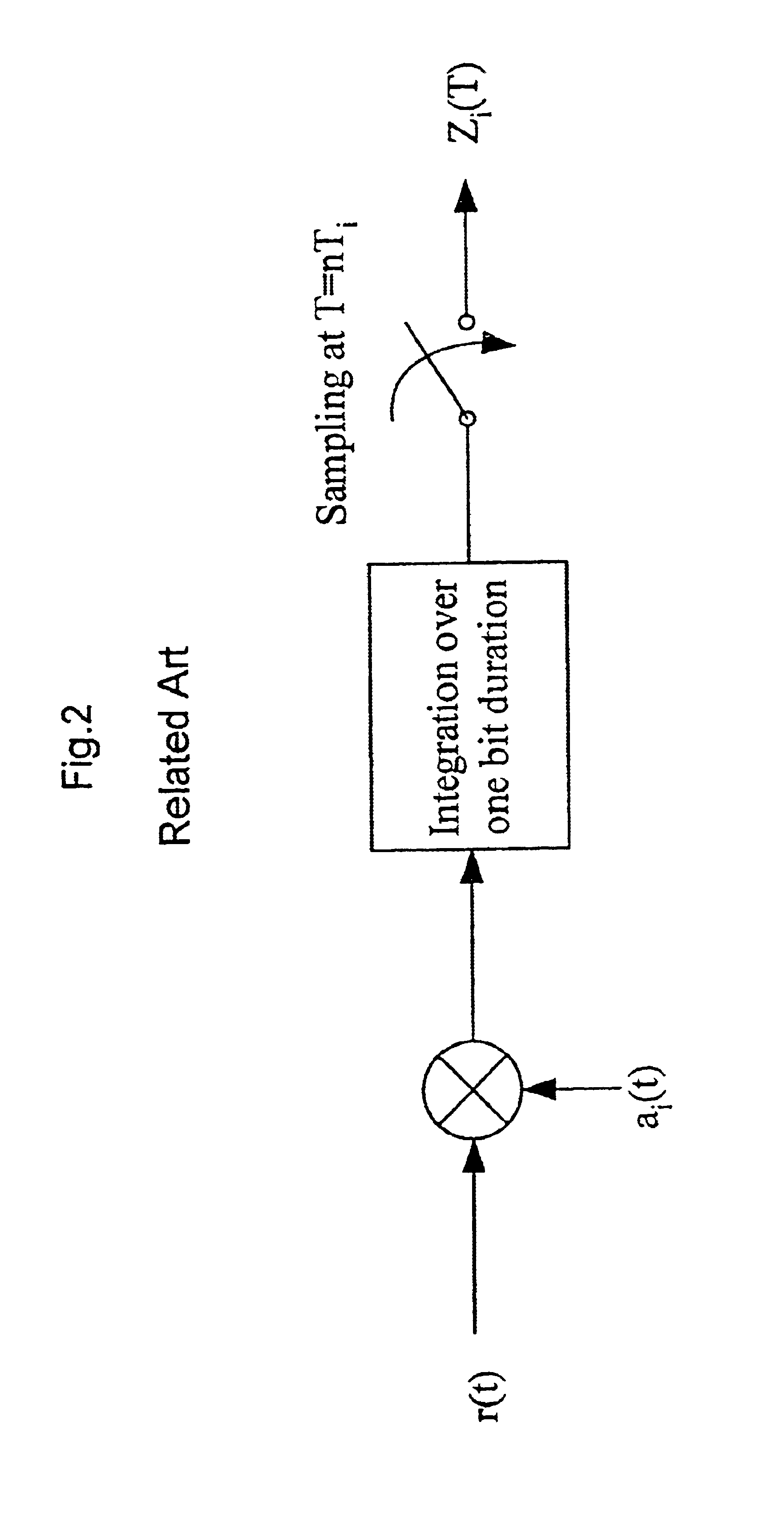
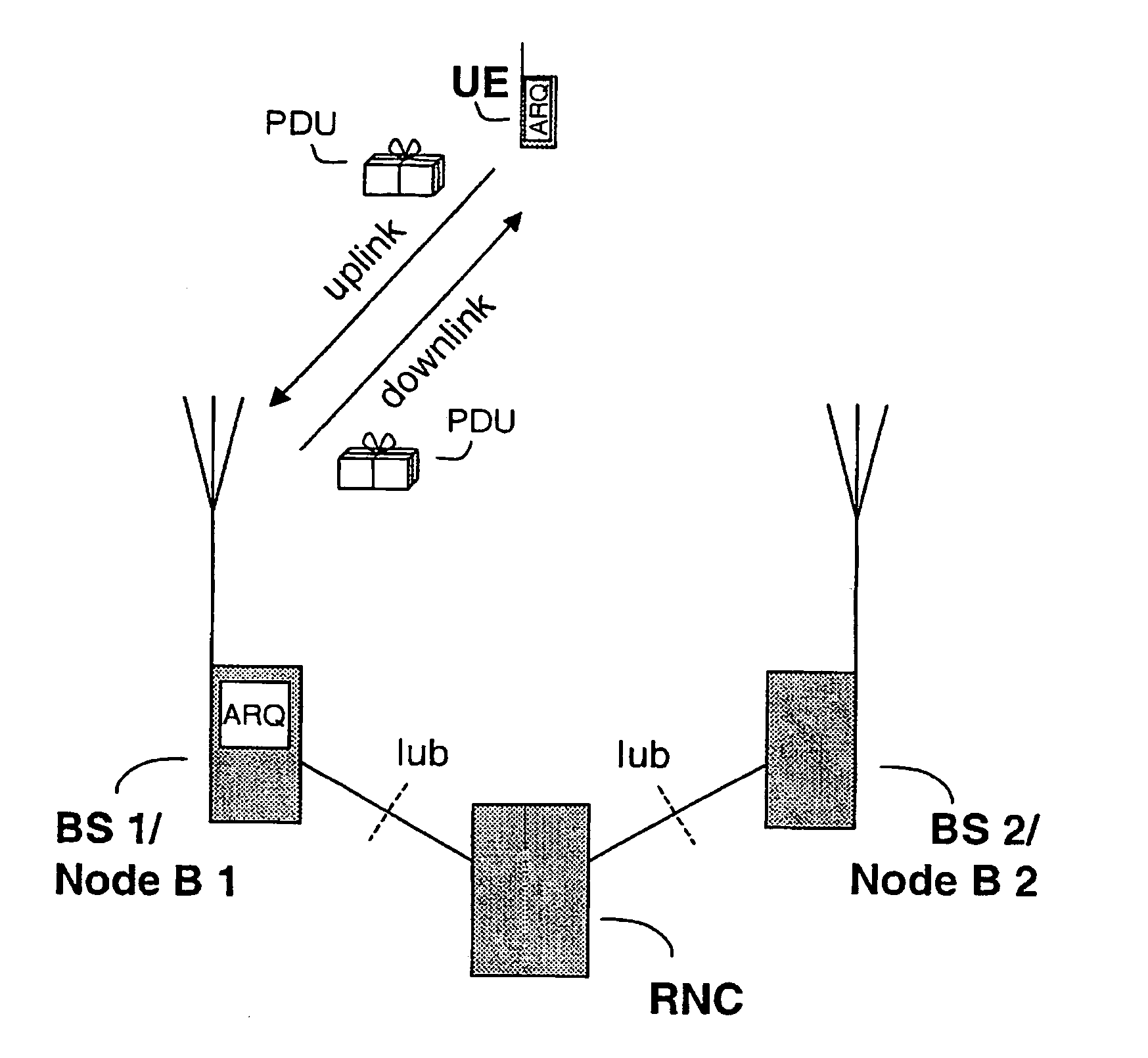
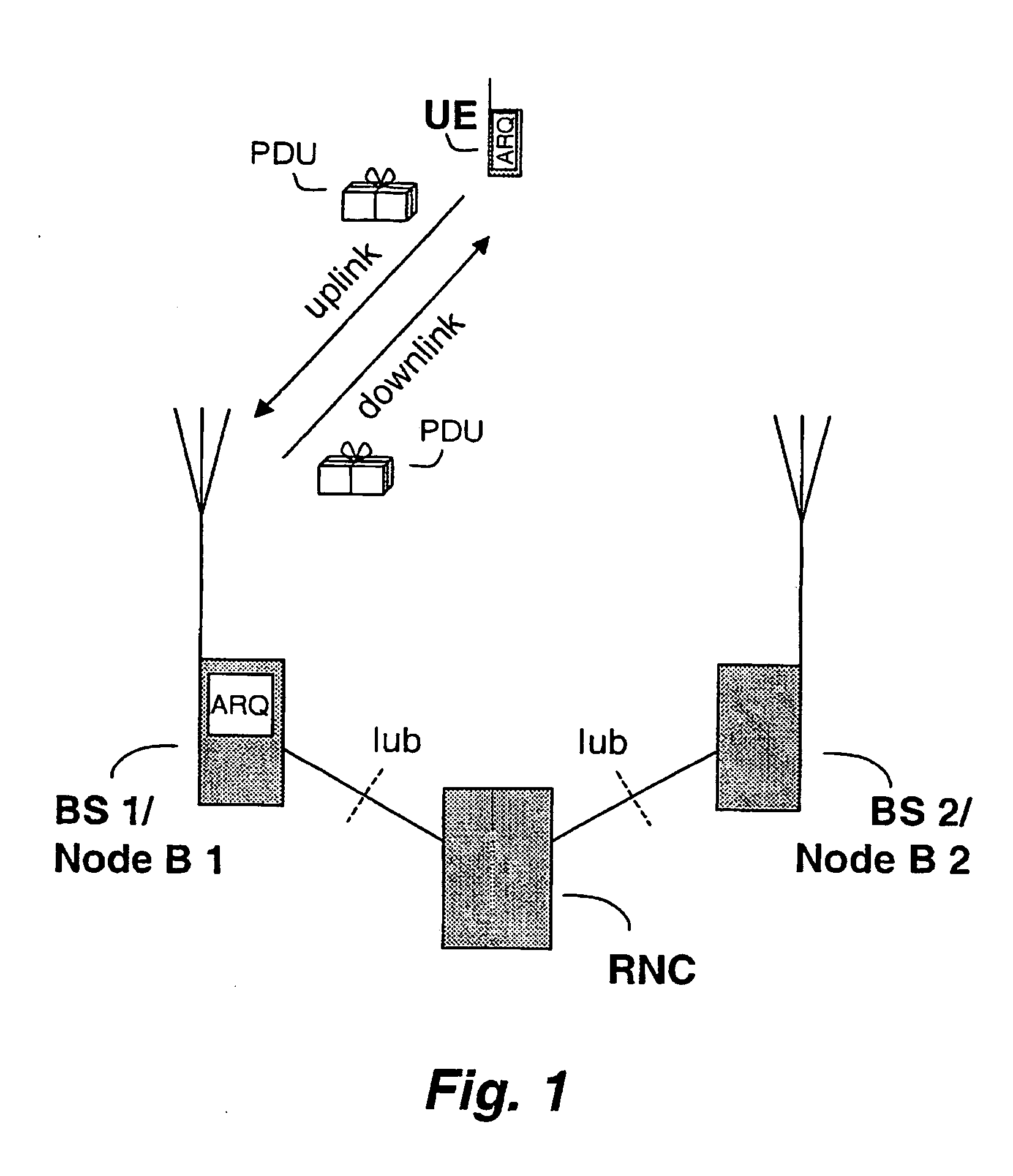
Method and system of retransmission
InactiveUS20040147236A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityRadio communicationsMobile radiocommunication
The present invention relates to gen-eration and transmis-sion of status reports utilizing available HARQ infor-ma-tion. The invention is well suited for a cellu-lar mo-bile radio communications sys-tem, particularly a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for displaying greetings in a mobile radio communications system
InactiveUS6088598ASpecial service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemAir interface
There is disclosed a method and apparatus for displaying greetings to mobile terminals identifying services associated with location based services. The system identifies a plurality of service zones in the system, and also transmits predefined services to mobile terminals when located in the service zones. The system transmits from each base station local zone profile information to each of the mobile terminals located in those service zones. Each mobile terminal has stored therein subscriber zone profile information for which that mobile terminal can receive location based services. The mobile terminal also stores an associated greeting for each zone of subscriber zone profile information. The mobile terminal compares transmitted local zone information with the list of stored subscriber zone profile information, and when a match is found, the mobile terminal displays the greeting associated with the subscriber zone profile information. By storing the associated greeting in the mobile terminal, the otherwise signaling of greeting information over the air interface is avoided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
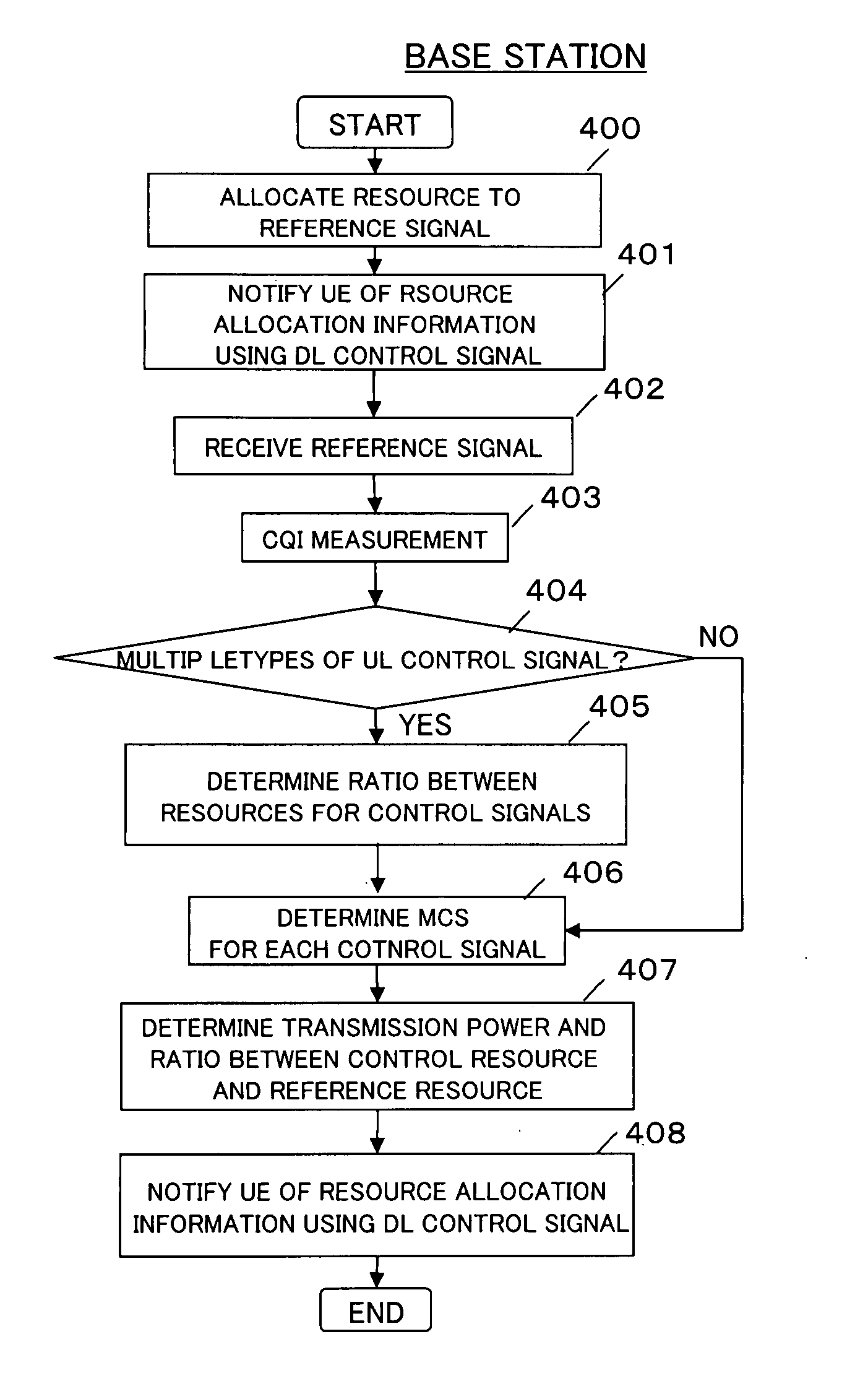
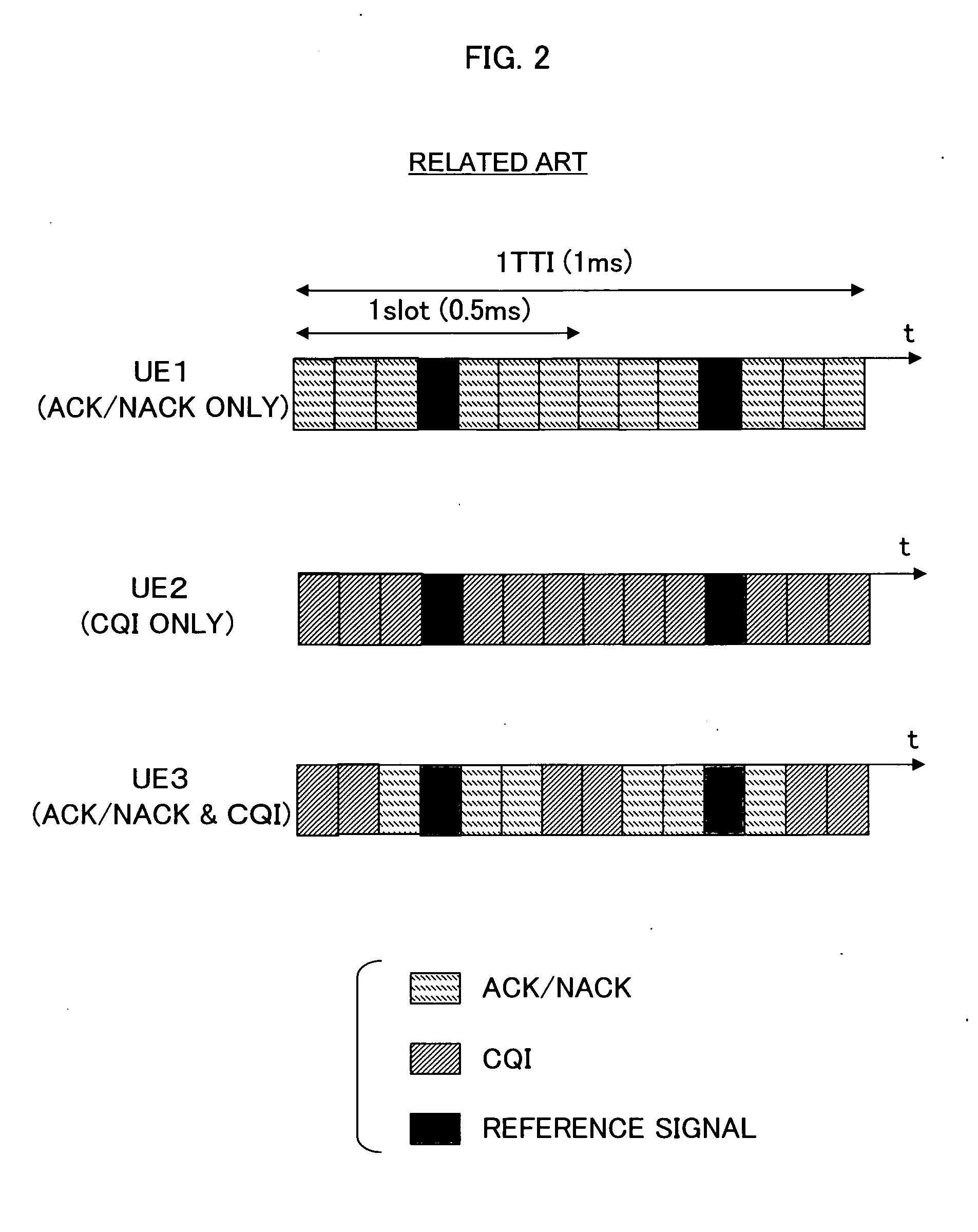
Resource allocation control method and device in mobile radio communications system
InactiveUS20080225788A1Effective distributionTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCommunications systemControl signal
For radio communications between a base station and a mobile station, resource allocation within a resource block including control resources used for control signals (CQI, ACK / NACK) and reference resources used for a reference signal is performed. The base station measures the quality of a channel between the mobile station and the base station itself. Based on the measured channel quality, the base station sets a ratio between resources for the control signals CQI and ACK / NACK in the control resources, and notifies the mobile station of the set resource ratio.
Owner:NEC CORP
Mobile radio communication system with macro and micro cell handoff based on mobile determined crossing rates and fading rates
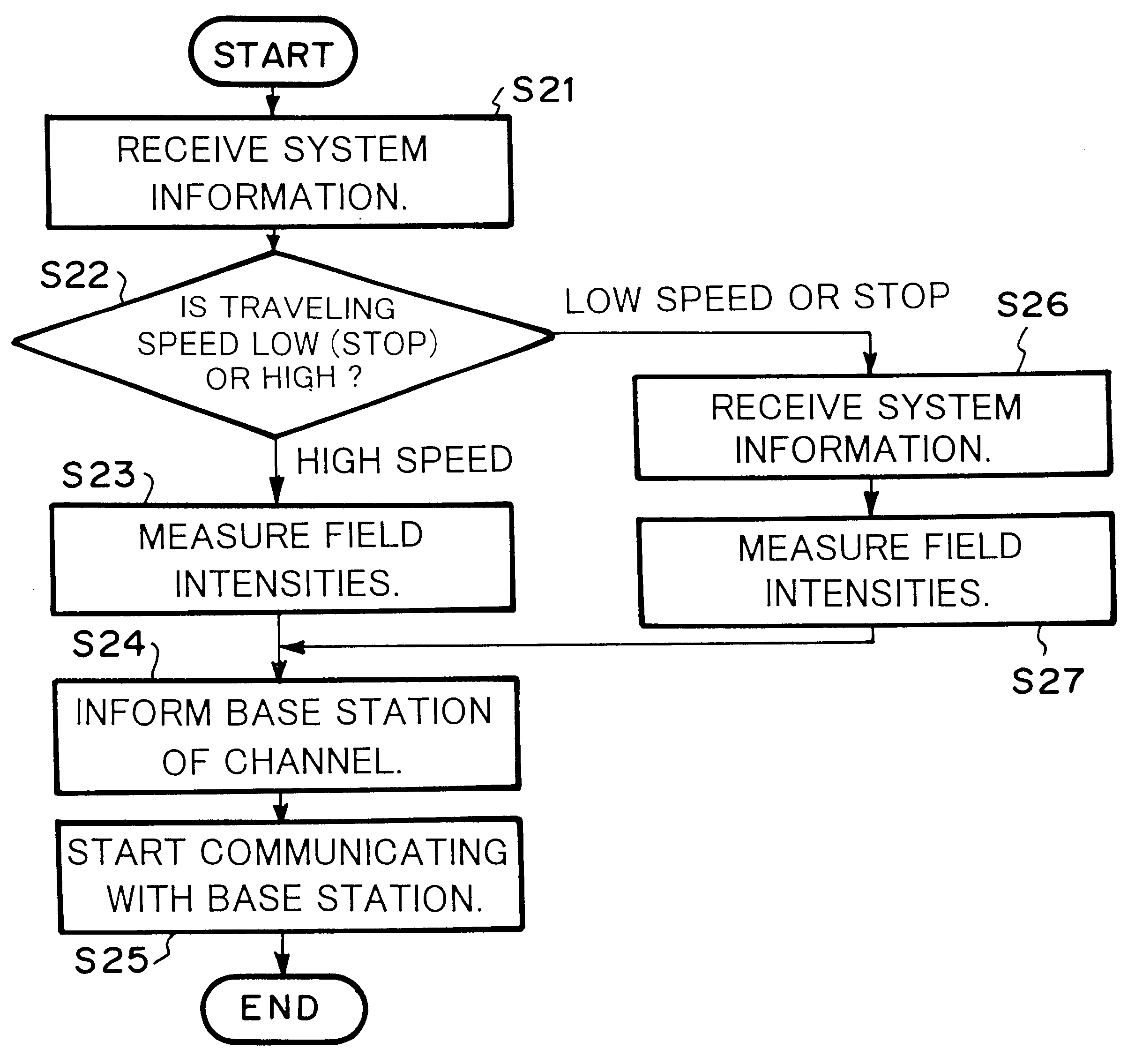
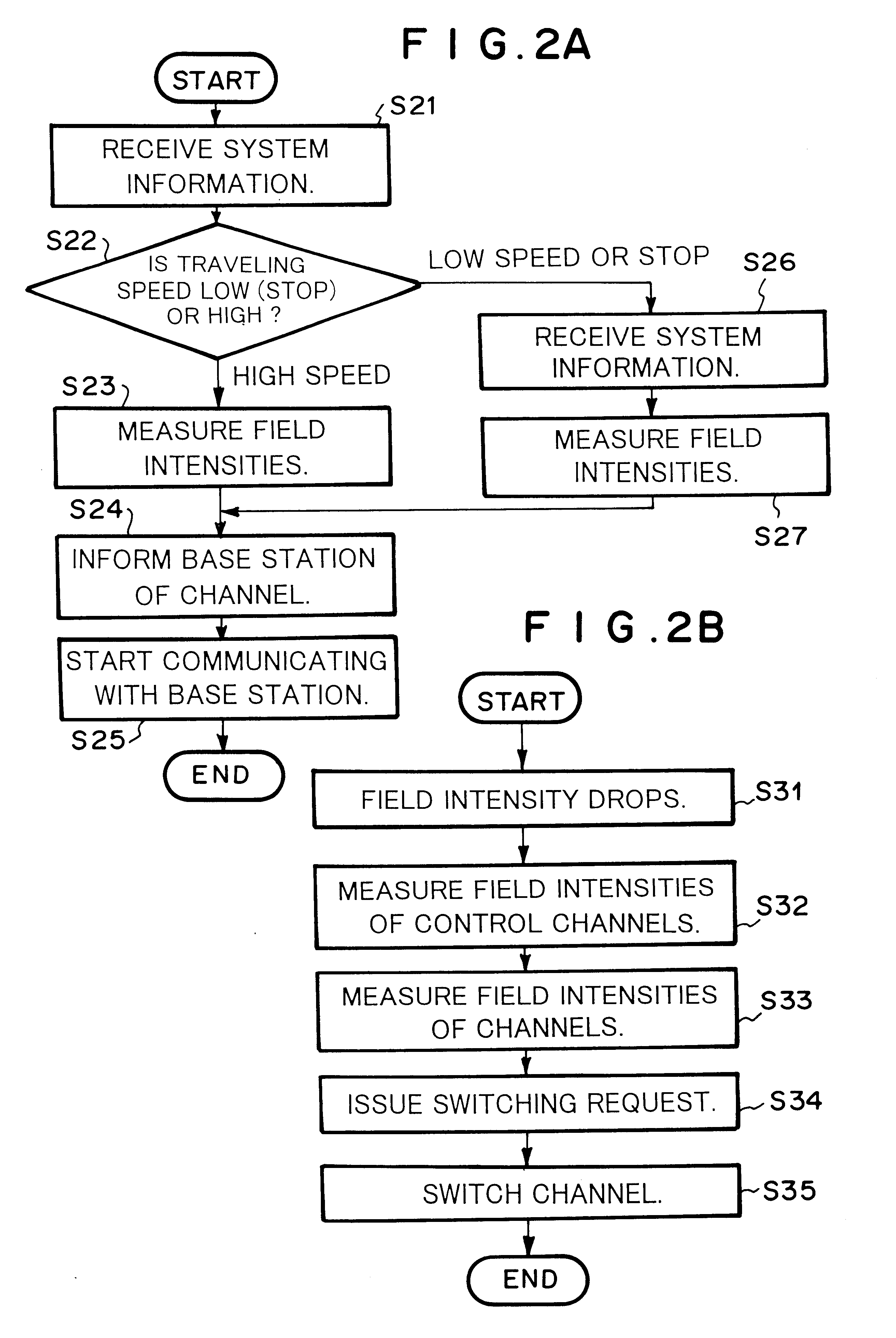
A radio base station broadcasts system information through a control channel. Each mobile station receives system information (at step S21) and determines the moving speed thereof (at step S22). When the mobile station is moving at high speed, the mobile station measures the field intensities of available channels on which the mobile station can communicate with a macro cell radio base station (at step S23 or S27). When the mobile station is moving at low speed, the mobile station measures the field intensities of available channels on which the mobile station can communicate with a micro cell radio base station (at step S27 or S23). However, when the radio base station to which the mobile station is moving is different from the radio base station from which the mobile station has received the control channel at first, the mobile station receives new system information from the relevant base station at step S26. The mobile station selects a channel corresponding to the measured result and starts communicating with the new radio base station (at steps S24 and S25).
Owner:NEC CORP
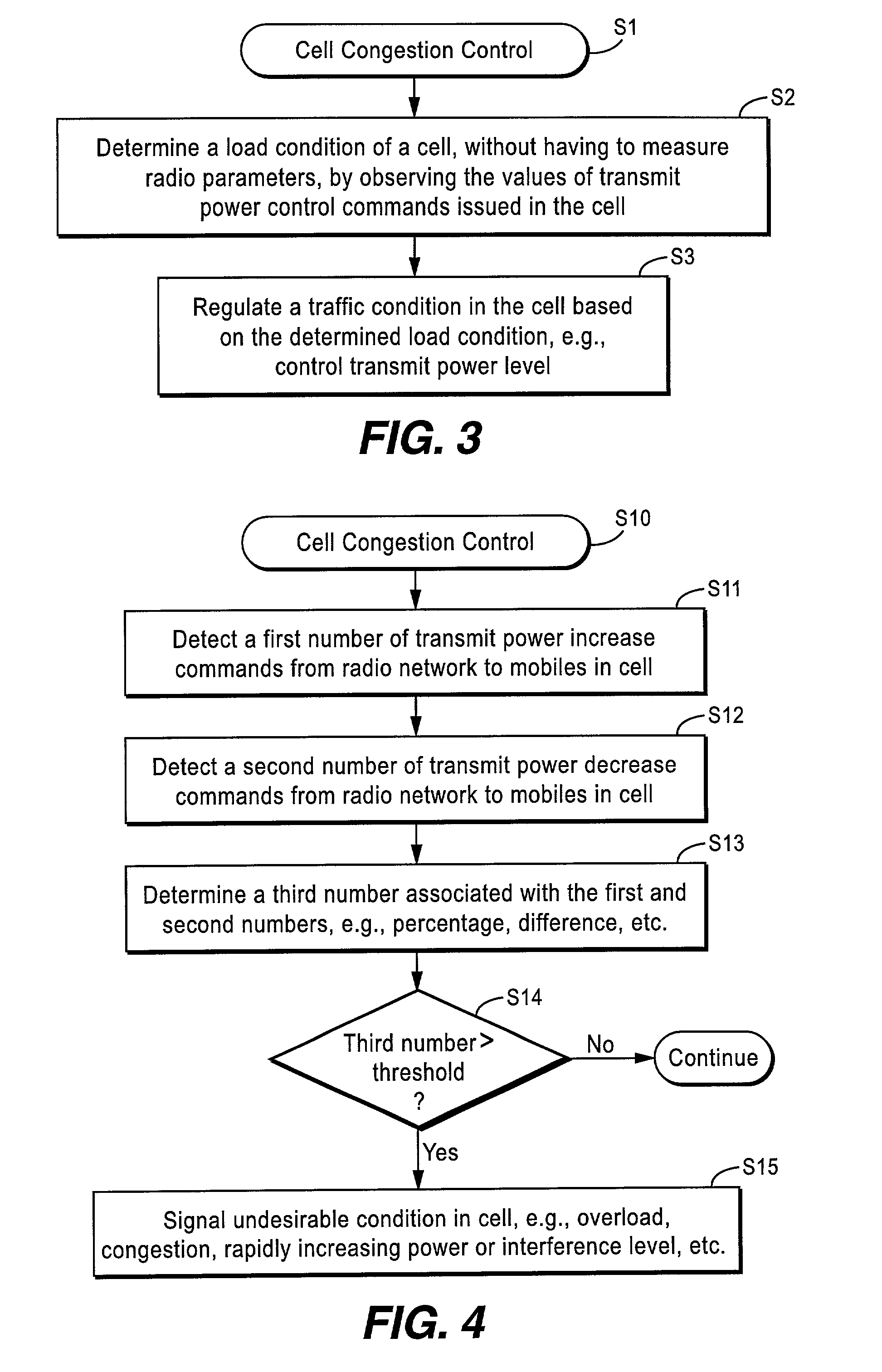
Congestion control in a CDMA-based mobile radio communications system
InactiveUS7016686B2Consumes less energyLight weightPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemTransmitted power
A load condition of a cell is determined without having to measure one or more radio parameters pertaining to the cell load, e.g., interference level. Based upon that determined load condition, a traffic condition of the cell may then be regulated, e.g., admission and / or congestion control, transmit power control, etc. The load condition is determined simply and accurately by observing the value (absolute or weighted) of transmit power control commands issued in the cell over a particular time period. To identify potential “false alarms” of increased cell loads, a radio parameter associated with another frequency band in another cellular system that impacts the load condition of the cell in the current cellular system is measured. A traffic condition in that cell is regulated based upon the determined load condition in the cell taking into account the measured radio parameter.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system of retransmission
InactiveUS7197317B2Easy loadingEliminate and reduce transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemMobile radio
The present invention relates to generation and transmission of status reports utilizing available HARQ information. The invention is well suited for a cellular mobile radio communications system, particularly a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Common radio resource management method in a multi-RAT cellular telephone network
ActiveUS7224977B2Avoid problemsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCellular telephoneHandover
A Common radio resource management method is performed in a mobile radio communication network employing different radio access technologies that overlap over a geographic area subdivided into cells belonging to the domains of respective controllers which are connected to each other in overlapping or adjacent domains and to a core network by means of relevant interfaces. The controllers calculate new traffic-related Information Elements to be exchanged over the existing interfaces to the aim of planning handovers and / or cell reselections towards adjacent cells either of the same or different RAT. Cell capabilities and mobile terminal capabilitiess being also specified by respective IEs. Diversely from the conventional traffic-related IEs based on Cell Load parameters or Free Capacity, the new IEs include indications of the “availability” of bearer services in the cell in terms of maximum bitrate, either guaranteed or not guaranteed, that can currently be allowed to each bearer service.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
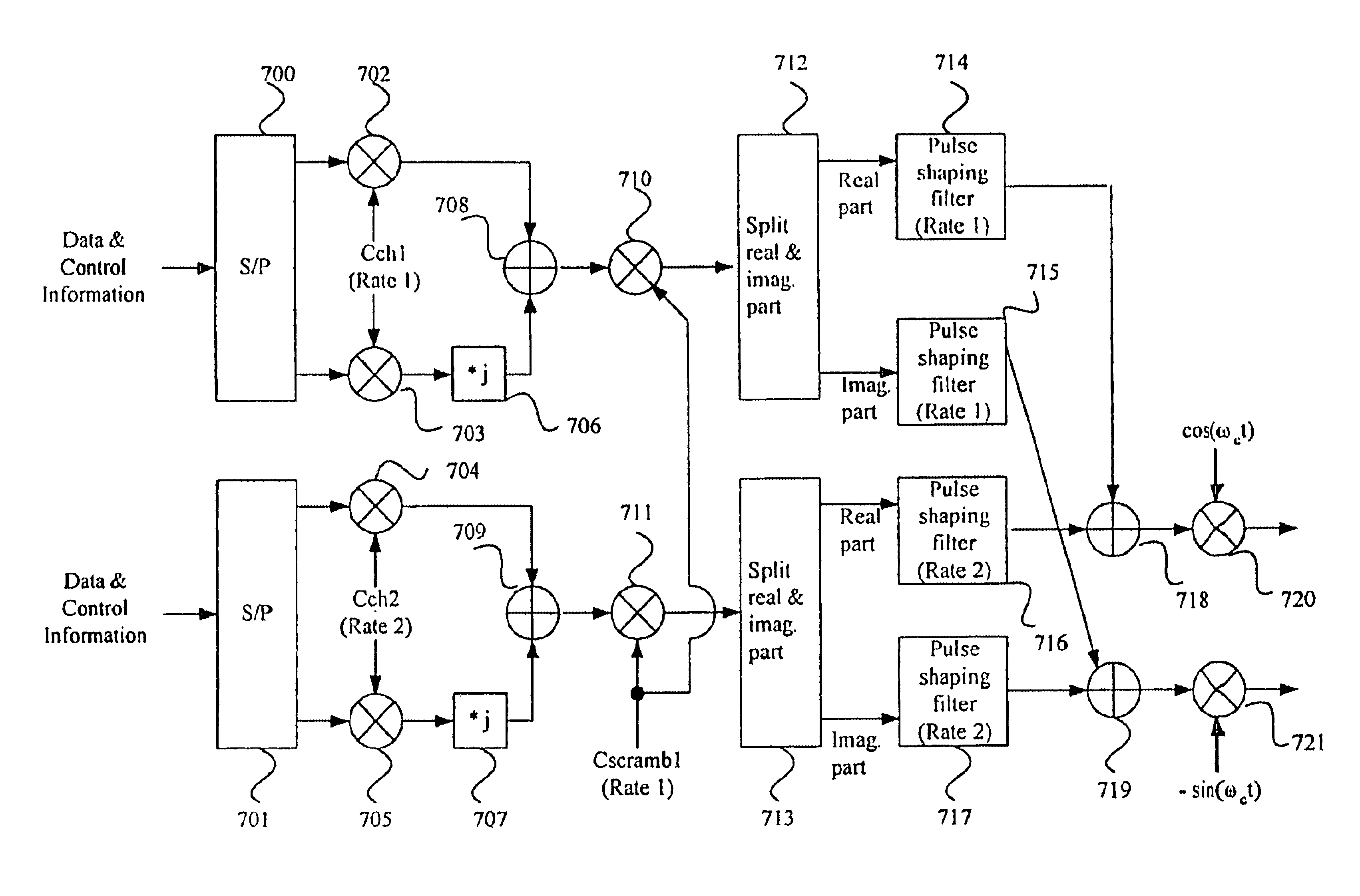
Scrambling codes and channelization codes for multiple chip rate signals in CDMA cellular mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6885691B1Minimizing interference signalInterference minimizationMultiplex code allocationOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemMobile radio
A system and method for allocating channelization code and scrambling code in multiple code rates is disclosed. In the present invention, many user signals that have various chip rates in overlaid frequency band can be transmitted with minimum interference between users, by allocating orthogonal spreading code in which the sum of bits for a period that is determined by the ratio of chip rates is canceled respectively, as channelization codes.
Owner:LG INFORMATION & COMM LTD
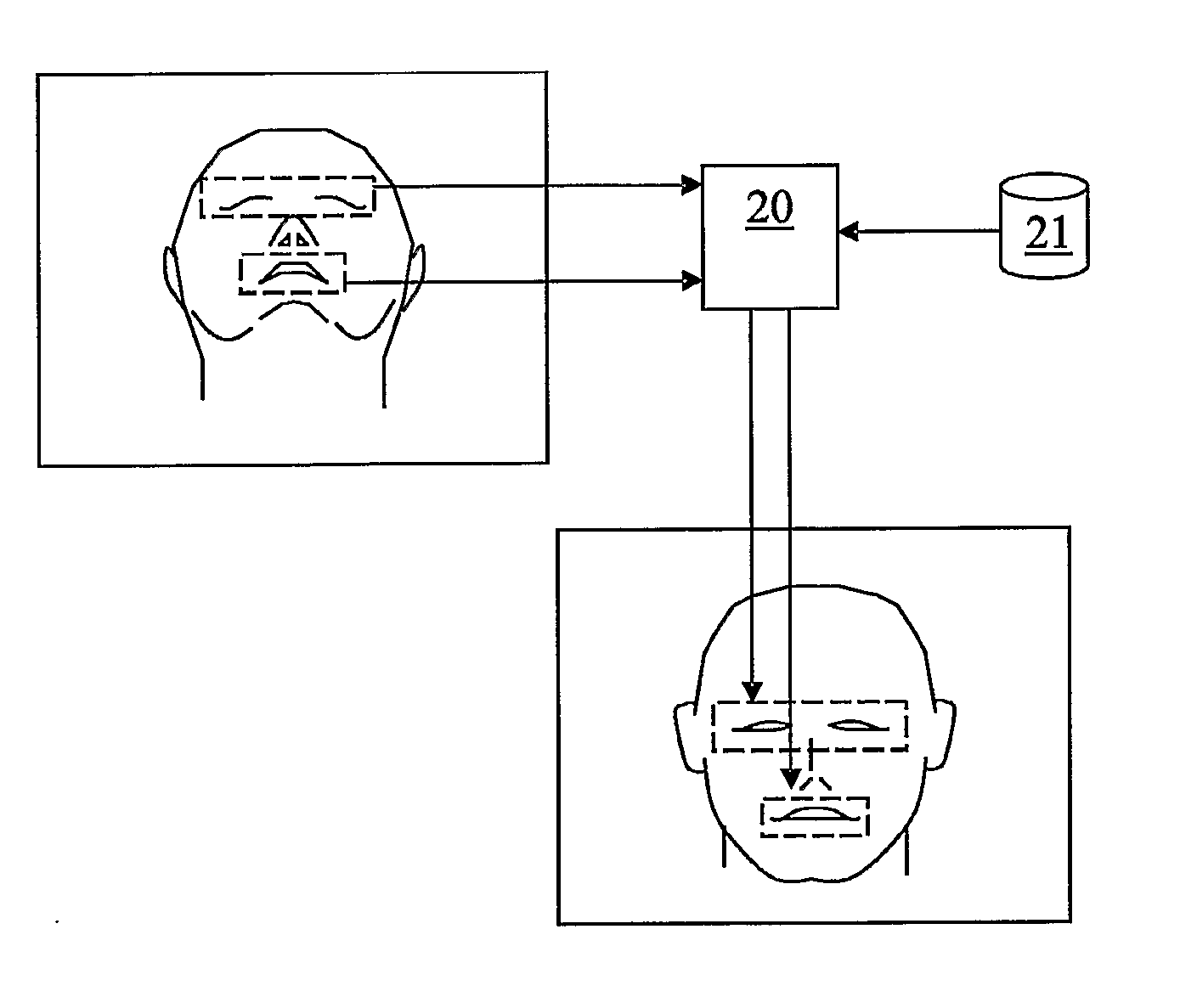
Face Image Correction
Methods for adjusting a picture of an object captured by a camera in a mobile radio communication terminal include defining a first camera angle relative to the object and capturing an image of the object by means of the camera from a second camera angle relative to the object. The second camera angle is offset from the first camera angle. The methods further include storing image data relating to the captured image, and generating an angularly adjusted image of the object in response to the image data and an angular relation between the first camera angle and the second camera angle. Corresponding mobile radio communication terminals are also disclosed. The terminals include an image processing system configured to process an image of an object captured by a camera from a second camera angle by generating an angularly adjusted image of the object in response to image data for the image, and in response to an angular relation between the second camera angle and a first camera angle.
Owner:SONY CORP
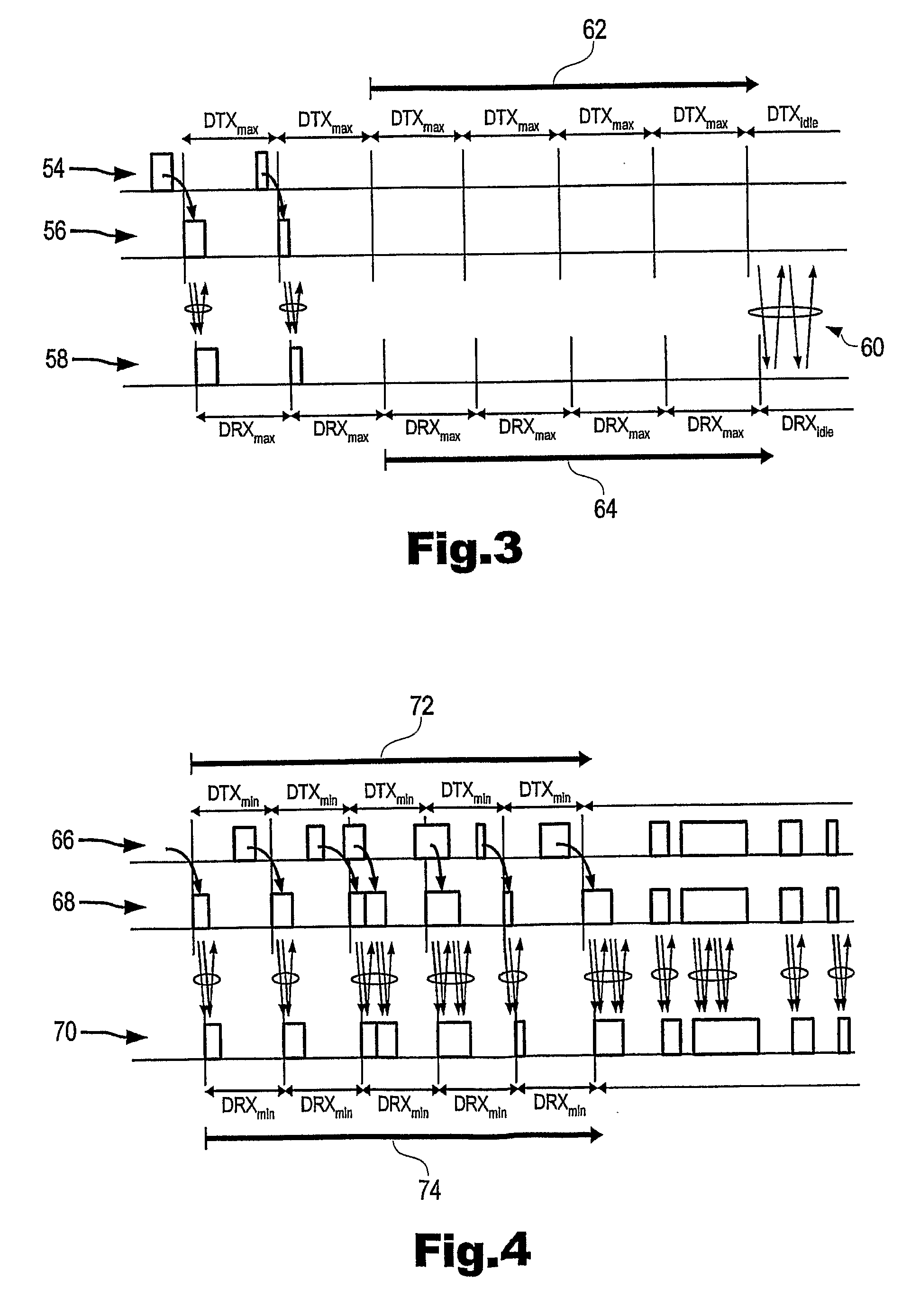
Discontinuous reception/transmission for mobile communication system
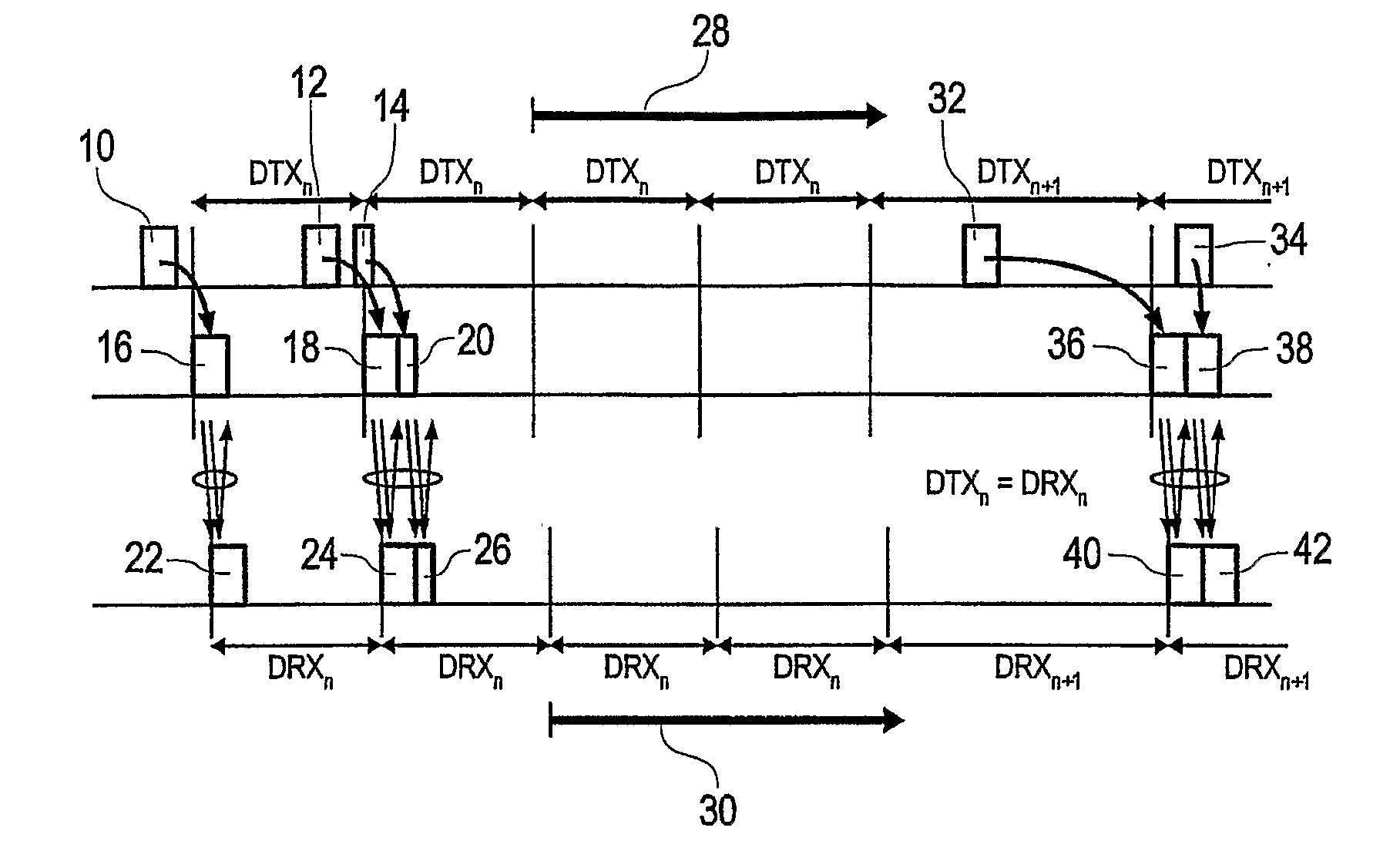
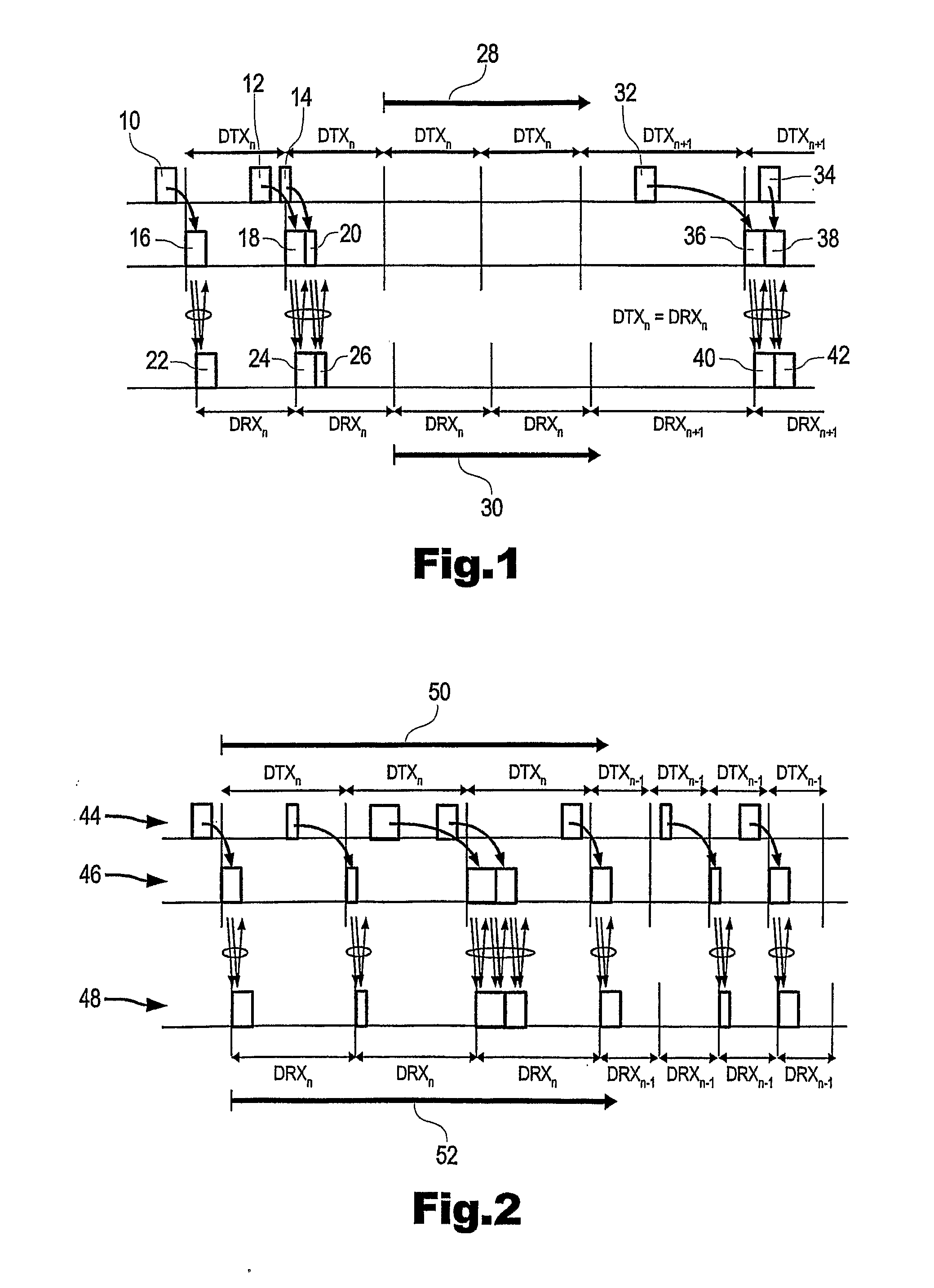
ActiveUS20100144299A1Good power saving performanceReduced packet latencyPower managementResonant long antennasMobile communication systemsMobile radio
The present invention provides for a method of controlling discontinuous reception cycles in a mobile radio communications device, and discontinuous transmission cycles in a mobile radio communication network device, and comprising the steps of monitoring the number of consecutive discontinuous reception and transmission periods within which no data is received, monitoring the number of consecutive discontinuous reception and transmission periods within which data is received, and varying the said discontinuous reception cycle responsive to the result of said monitoring.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
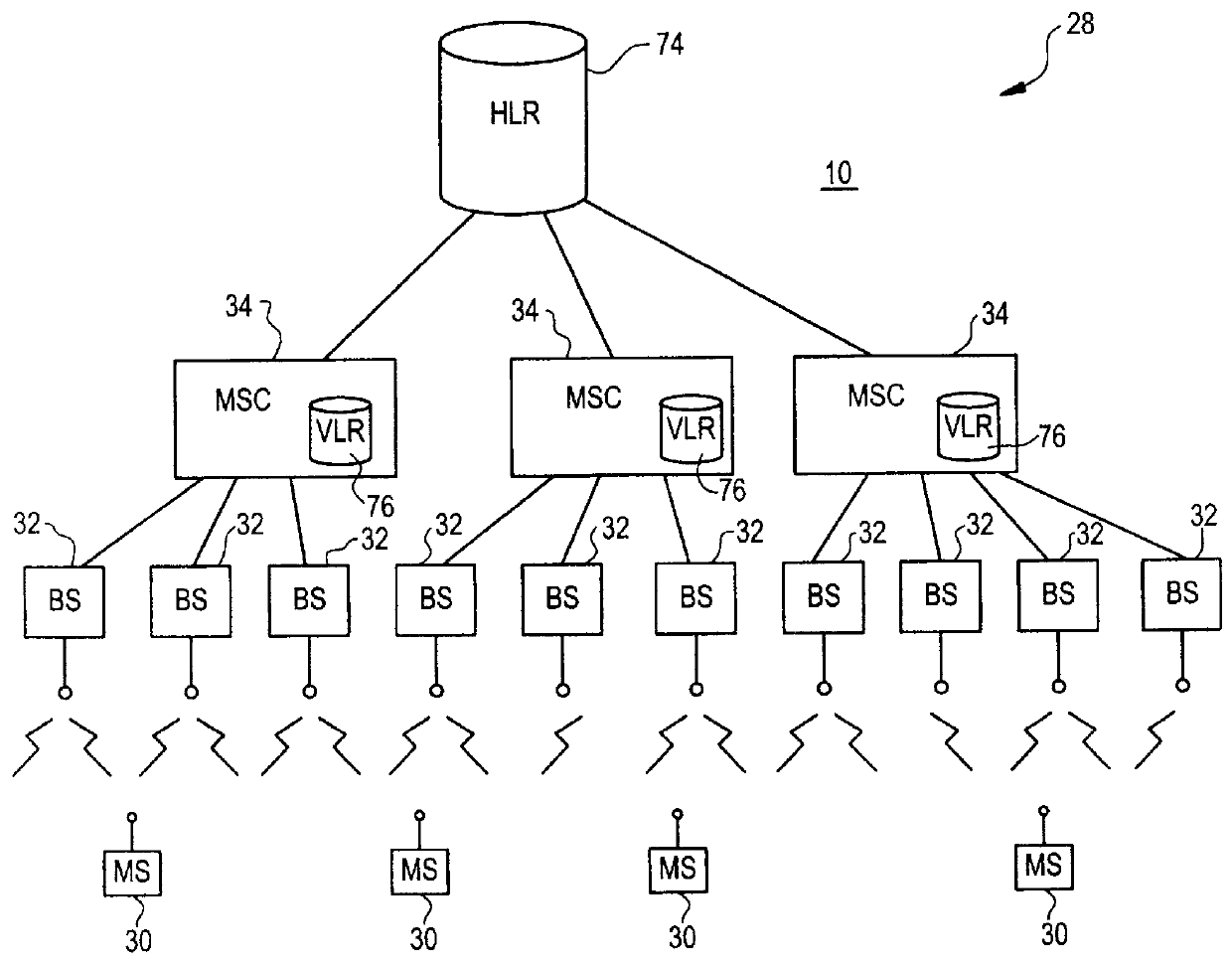
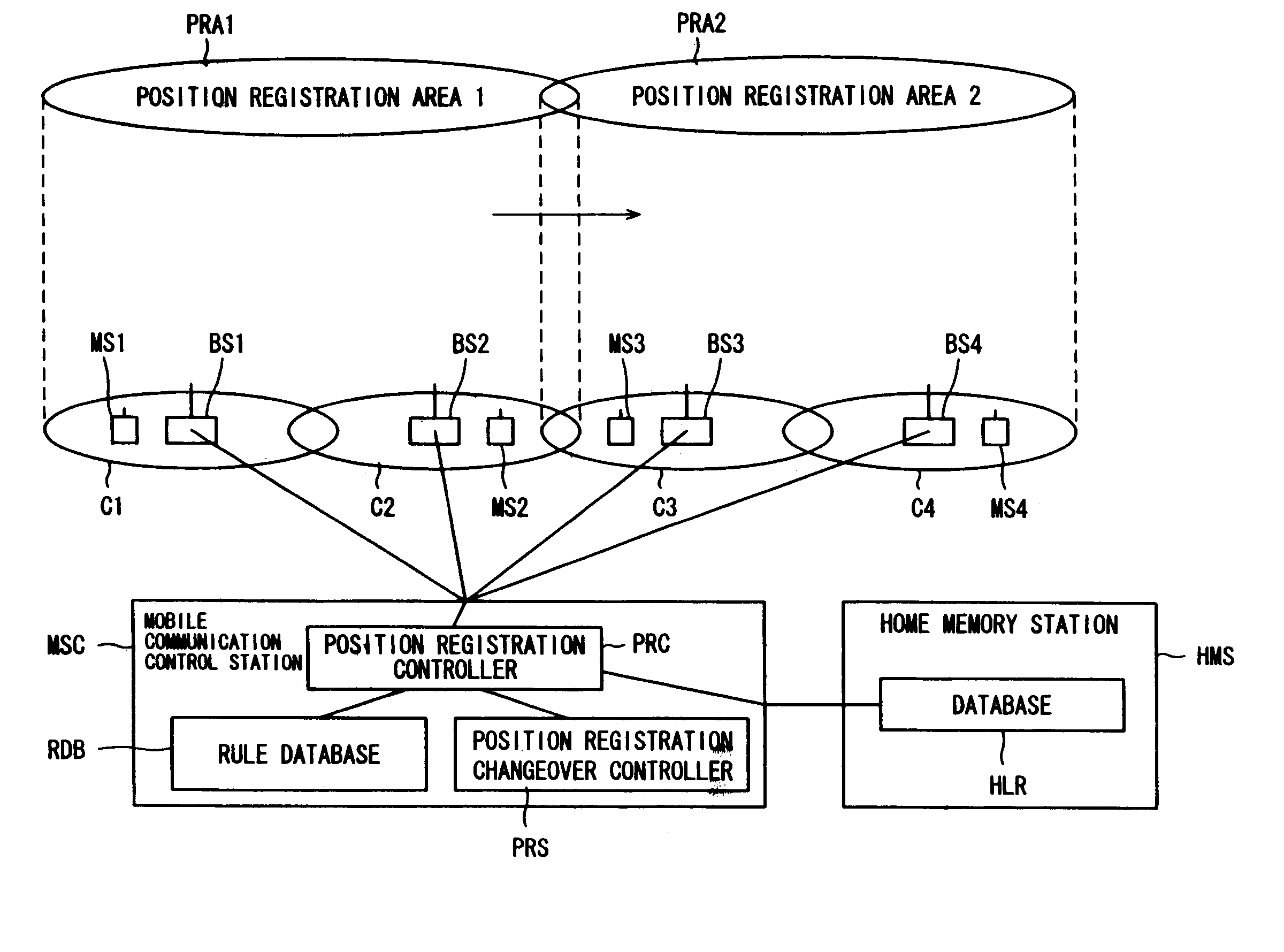
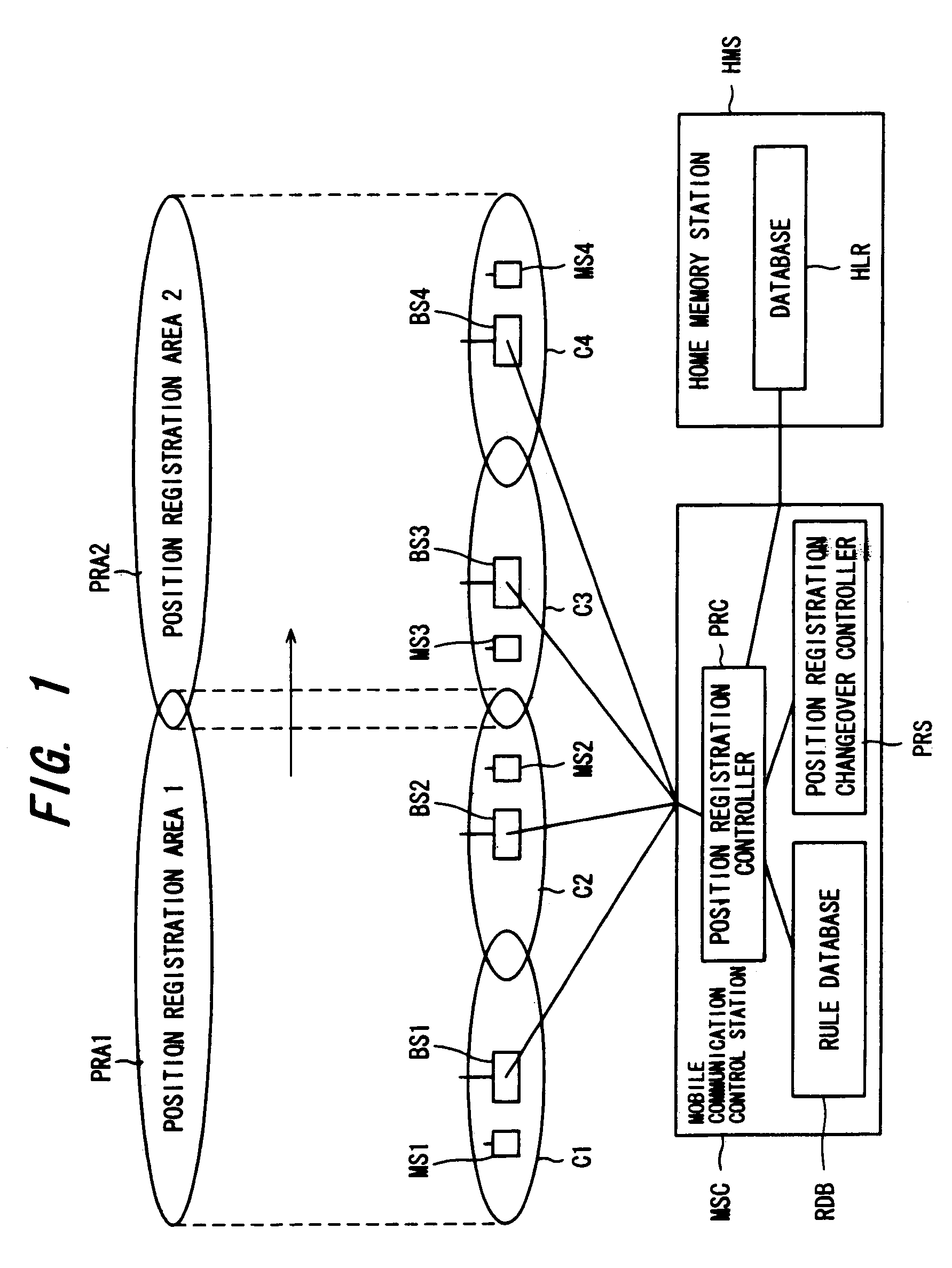
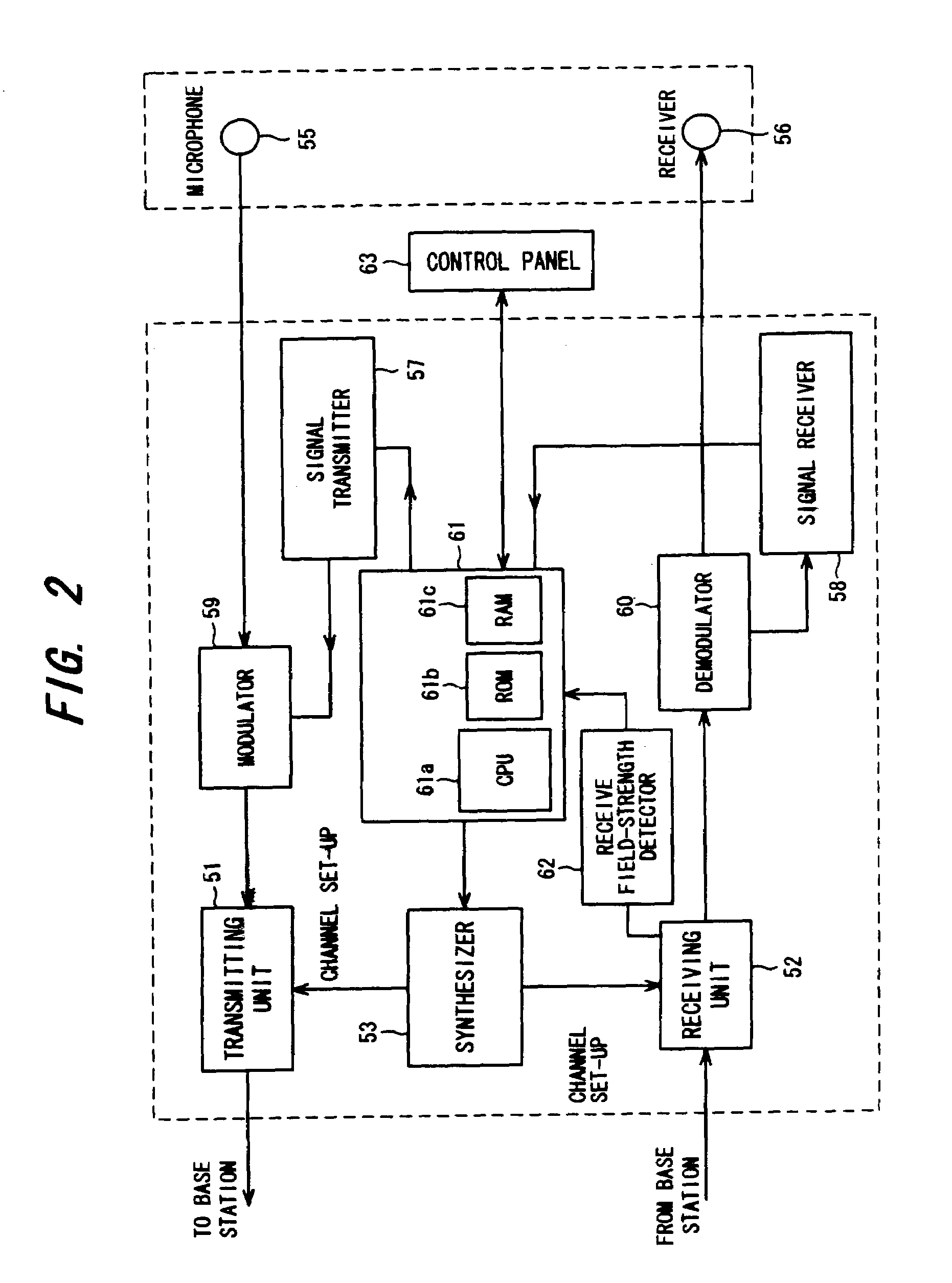
Mobile radio communication system and method of registering position therein
InactiveUS7142858B2Reduce the amount of controlReduce the amount requiredRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemMobile station
Disclosed is a mobile radio communication system in which a position registration area number is reported from a base station to a mobile station within a radio zone, position information indicating a position registration area in which a mobile station resides is registered in storage means based upon position registration information that has been transmitted from the mobile station, and when there is an incoming call to a mobile station, a paging call is placed from a plurality of base stations within the position registration area, in which the base station resides, based upon position information that has been read out of the memory means. Updating of the position registration area of a mobile station can be performed automatically on the network side without the mobile station transmitting position registration information to the network side. To achieve this, a rule for predicting the manner in which a mobile station will change a position registration area by moving is registered beforehand on the network side. Whether a state in which the rule is applicable has been attained is checked for every mobile station. If such a state is attained, the position registration area of the mobile station is updated based upon the rule.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method of parameterizing the display on mobile radio communications equipment co-operating with a subscriber identity module
InactiveUS6341228B1Great freedomCordless telephonesDevices with card reading facilityDisplay deviceMobile radio
A method of parameterizing the display on display means associated with a piece of radiocommunications mobile equipment co-operating with a subscriber identity module, the method having the following steps in order:said subscriber identity module sends a set of commands to said mobile equipment, said commands enabling the display on said display means to be parameterized; andsaid commands are executed by said mobile equipment on said display means.
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
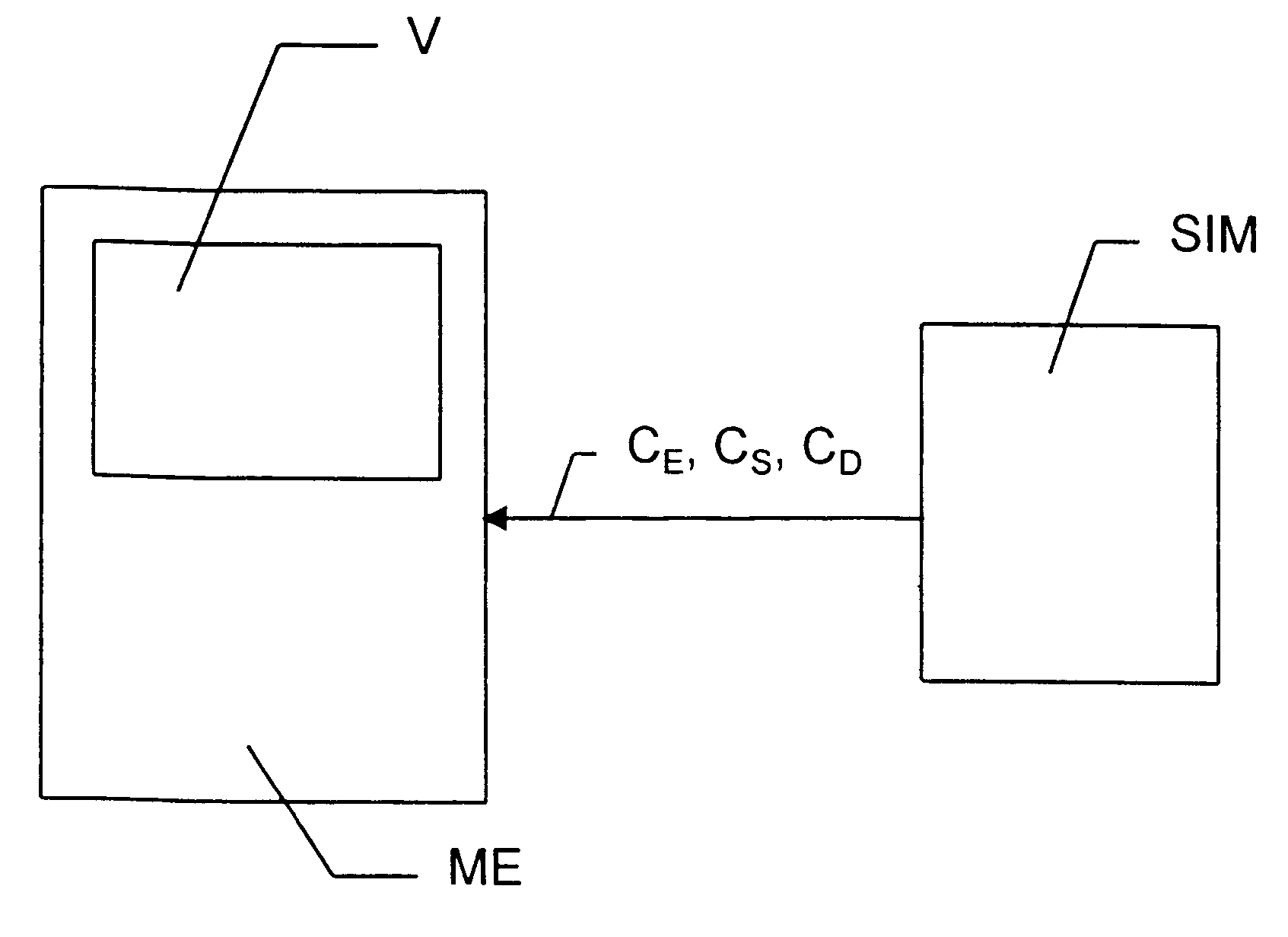
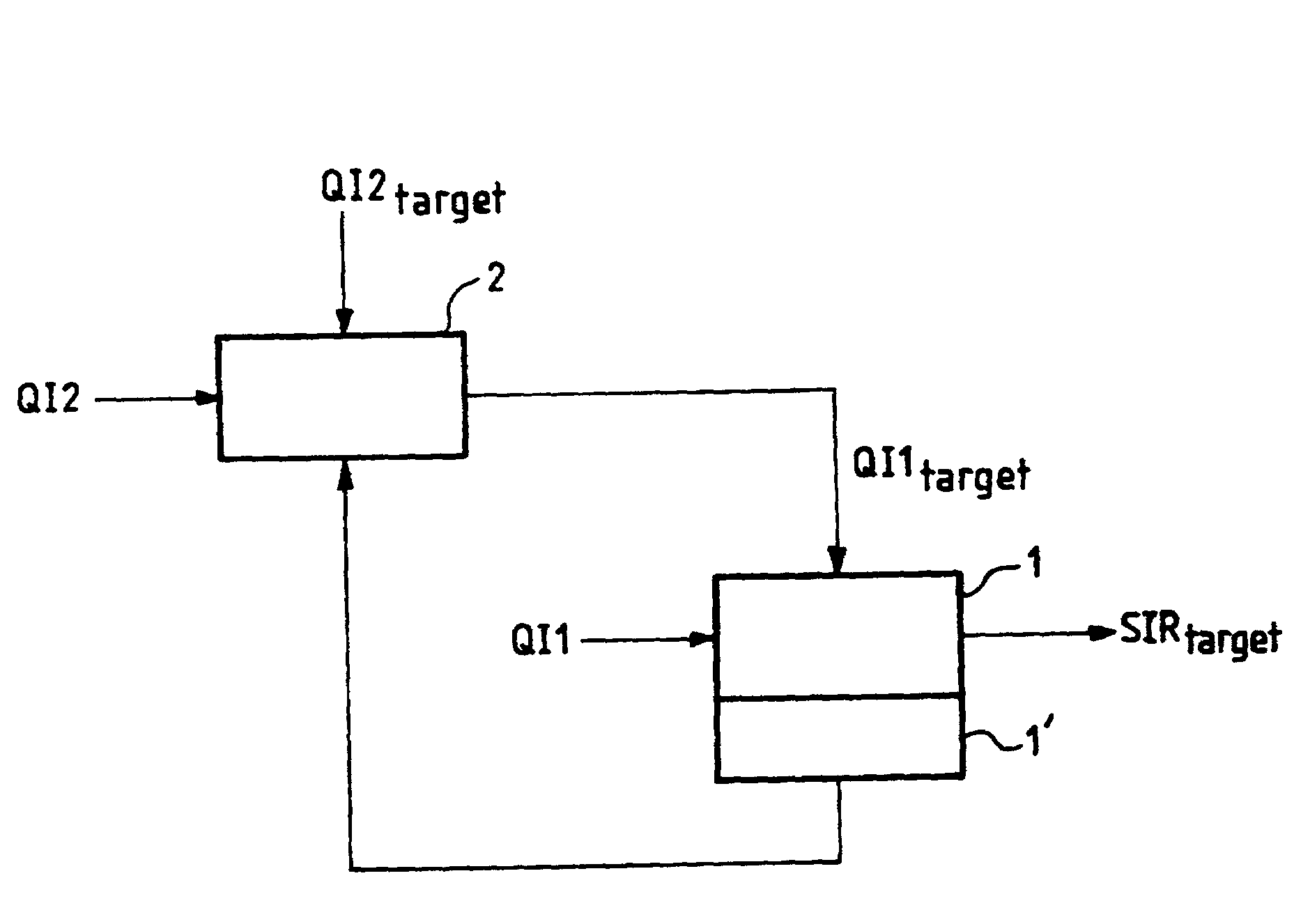
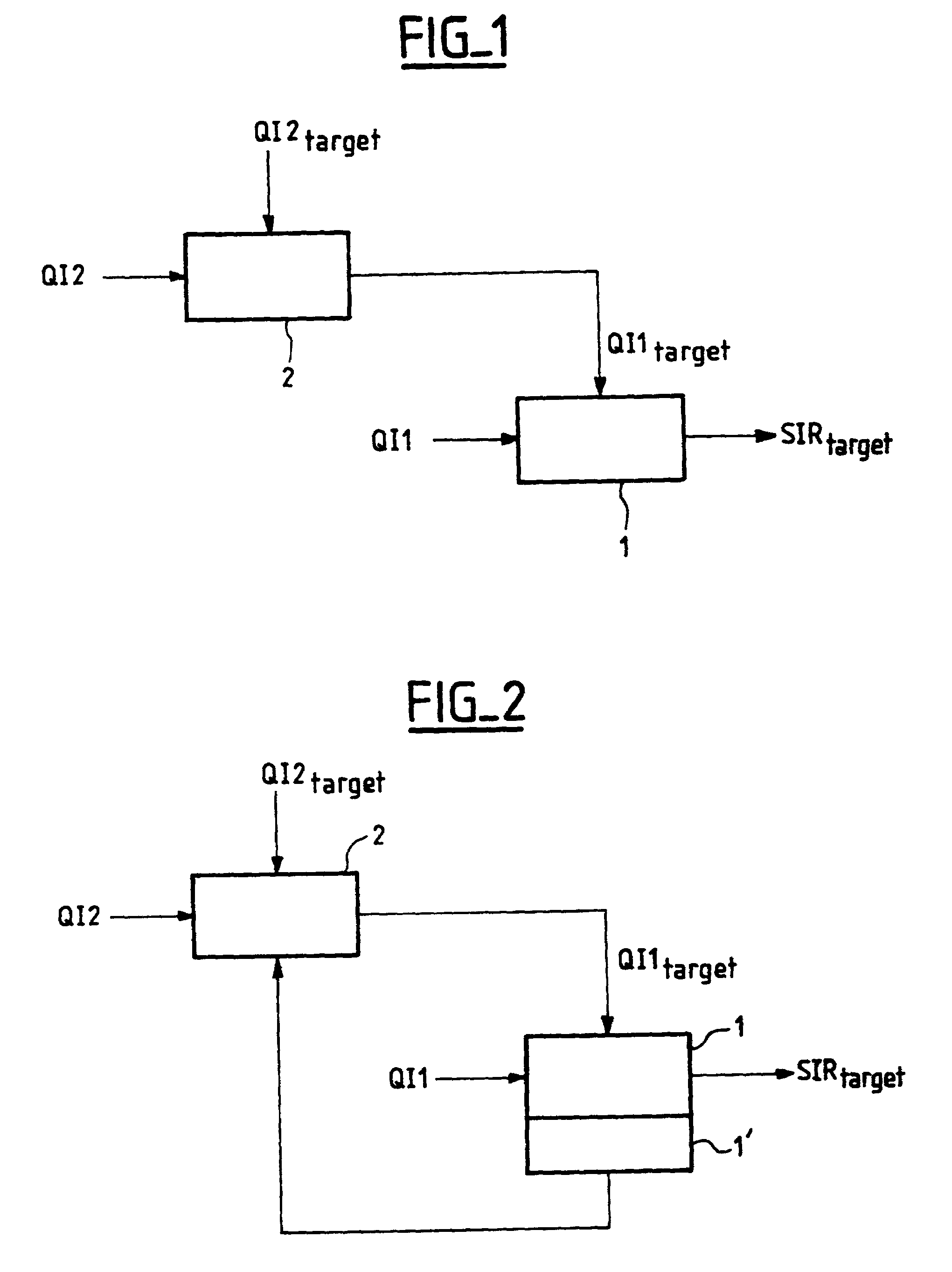
Method of adjusting the target value of an inner power control loop in a mobile radiocommunications system
InactiveUS20020187802A1Improve performanceAvoid disadvantagesPower managementTransmission control/equalisingInner loopEngineering
In one aspect, the present invention provides a method of adjusting the target value of an inner power control loop in a mobile radiocommunications system, in which method: said inner loop target value is adjusted by a control loop referred to as a "first outer loop" operating on the basis of a quality indicator referred to as a "first quality indicator" and of a target value for said first quality indicator referred to as a "first outer loop target value"; said first outer loop target value is adjusted by a control loop referred to as a "second outer loop" operating on the basis of a quality indicator referred to as a "second quality indicator" and of a target value for said second quality indicator referred to as a "second outer loop target value"; and said second quality indicator gives an error rate and said first outer loop target value is adjusted each time an error is detected.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Frame synchronization system between base stations of mobile radio communication system and base station device employing this system
InactiveUS6480483B2Little influenceShorten the timeSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexBase station identity codeCommunications system
The disclosure concerns an inter-base station frame synchronization system for use in a mobile communication system having at least one master base station and a plurality of slave base stations. The master base station is arranged to transmit a control channel signal to the slave base stations located around the master base station in synchronization with a reference frame timing. The slave base stations set a control channel signal observation period. The slave base stations are arranged to generate frame timing based on timings of a received control channel signal from the master base station or other slave base stations when the received control channel signal is received during the control channel signal observation period.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
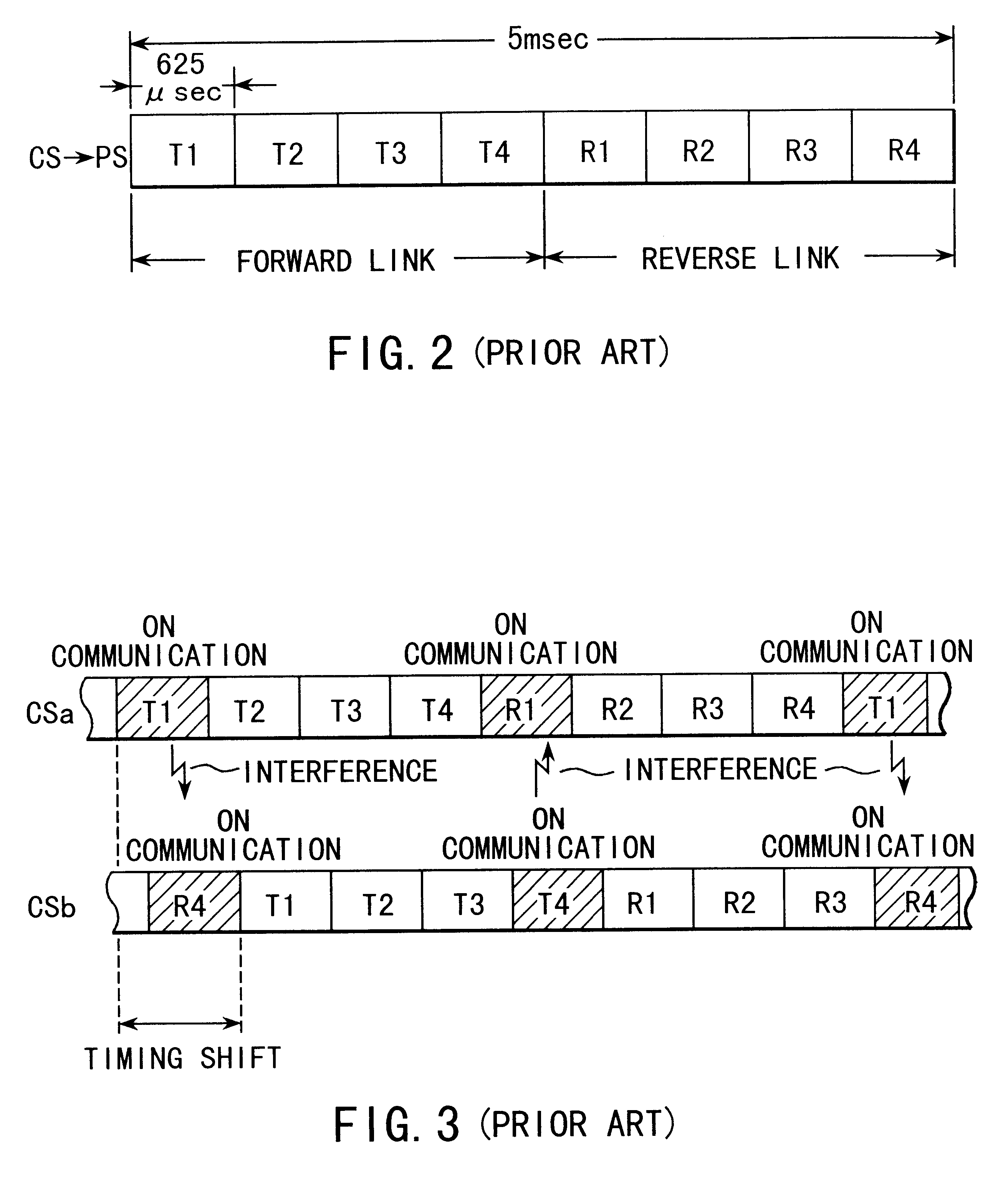
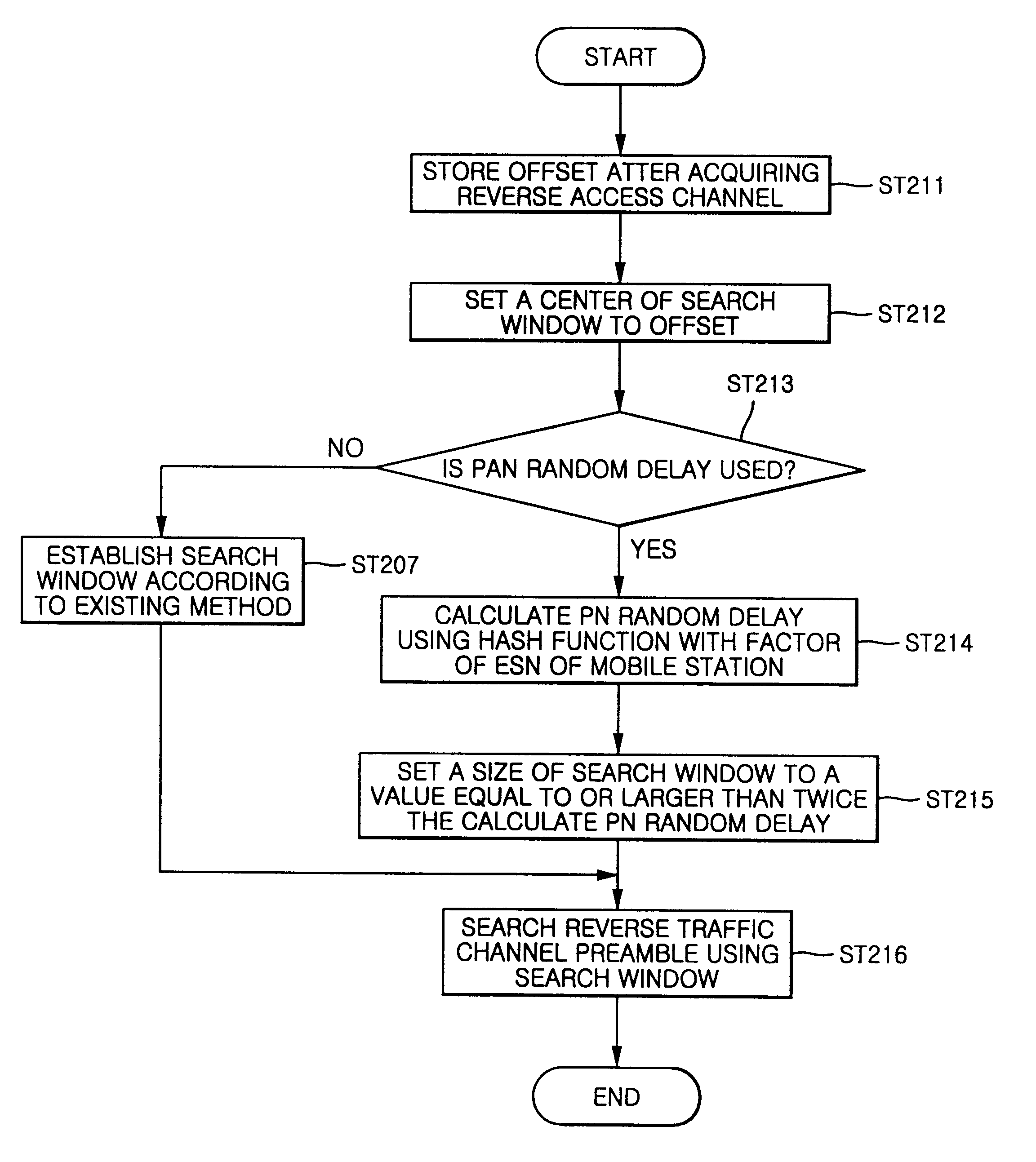
Method of searching reverse traffic channels in a CDMA mobile radio communication system
A method of searching reverse traffic channels in a code division multiple access (CDMA) mobile radio communication system for allowing for acquisition of reverse traffic channels without increase or decrease of size of a search window for traffic channels, the method comprising the steps of: storing an offset by a propagation delay after acquiring a reverse access channel; determining whether or not a pseudonoise (PN) random delay is employed for the reverse access channel and, when the PN random delay is used, calculating the PN random delay using a hash function with a factor of an electronic serial number (ESN) transmitted from a mobile station; computing the stored offset and the PN random delay and setting a new offset to a result of the computing; setting a center of a search window for searching the reverse traffic channel to the new offset and establishing the search window; and searching a reverse traffic channel preamble with the established search window.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC SONIC
Method for transmitting control frames and user data frames in mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6581176B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexCommunications systemStation
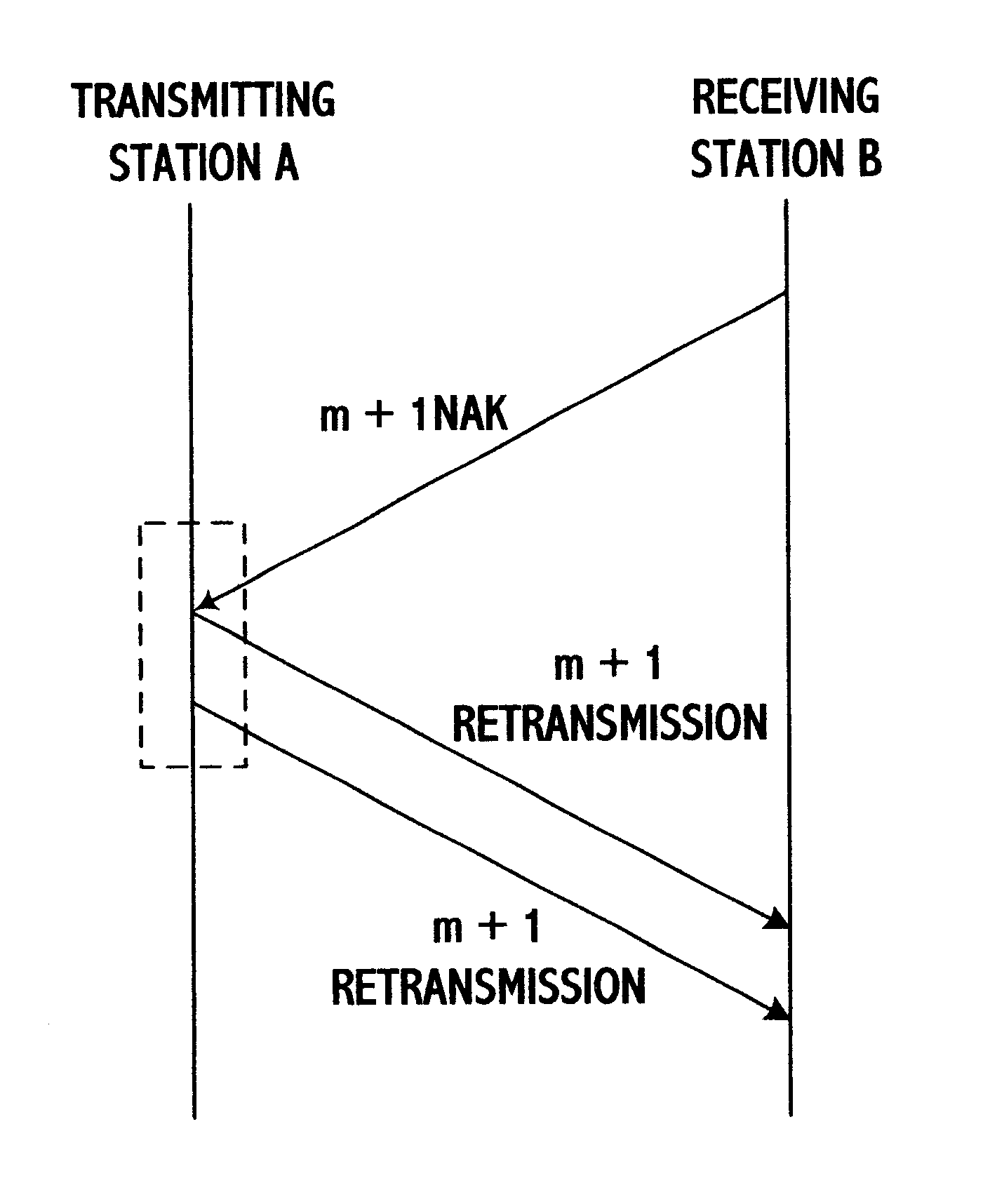
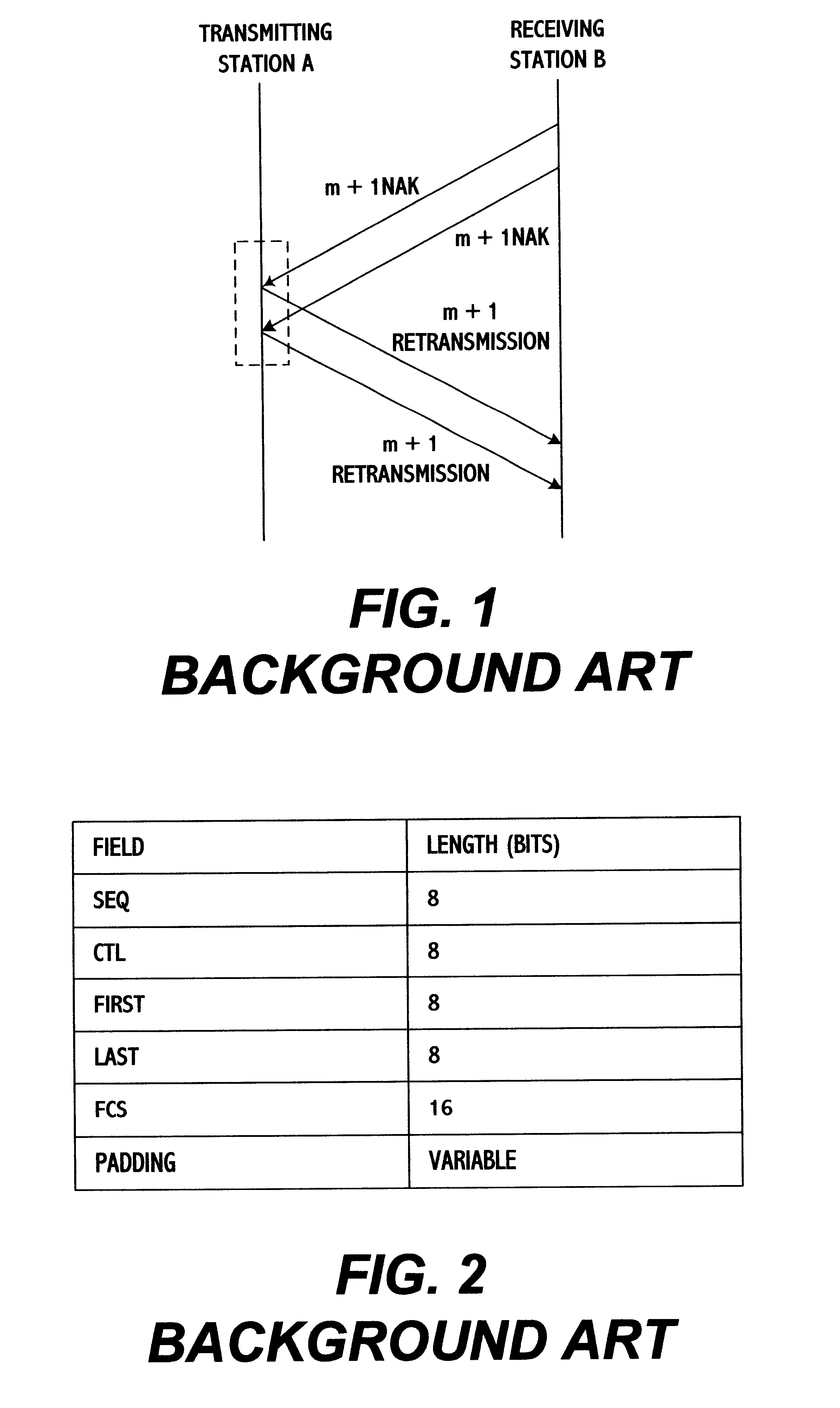
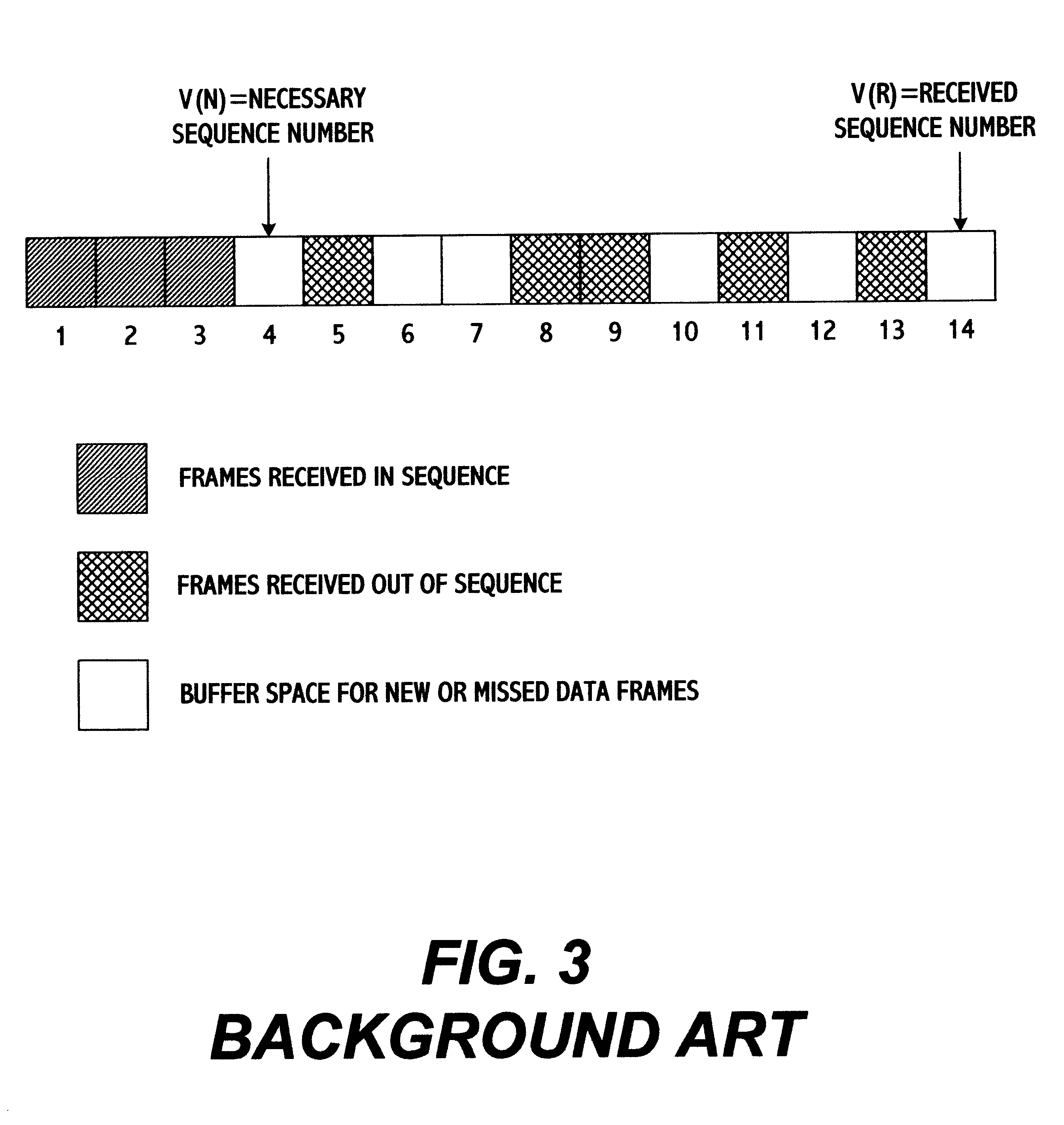
In a method for transmitting radio link protocol frames in a mobile radio communication system, if an error occurs on a radio section when user data frames of a radio link protocol (RLP) having respective different series numbers are transferred from a transmitting station to a receiving station, at least one missed user data frame is caused at the receiving station. At this time, the receiving station transmits, repeatedly by first times, a negative acknowledgement (NAK) control frame of the RLP for at least one missed user data frame, to the transmitting station. The transmitting station sends, by second times different from the first times, at least one missed user data frame in response to the received NAK control frame, to the receiving station. Particularly, series numbers of respective missed user data frames are sent through one NAK control frame to the transmitting station, at equal time when a timer for an NAK is expired, to accordingly result in reducing the number of the total NAK control frames and increasing a throughput per unit time.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
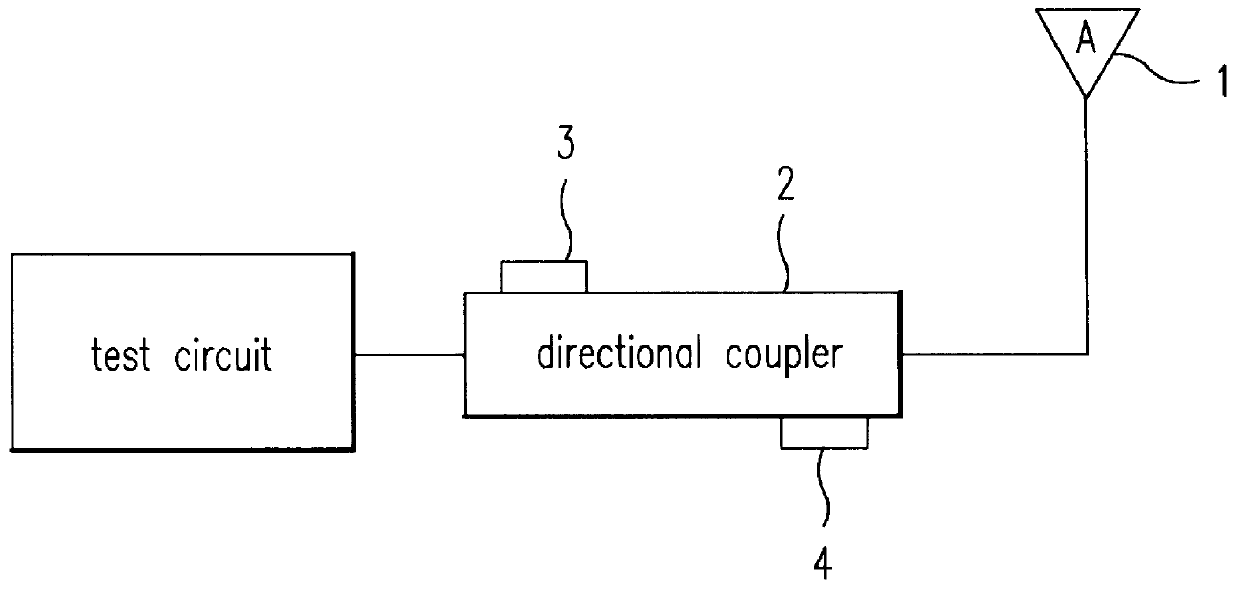
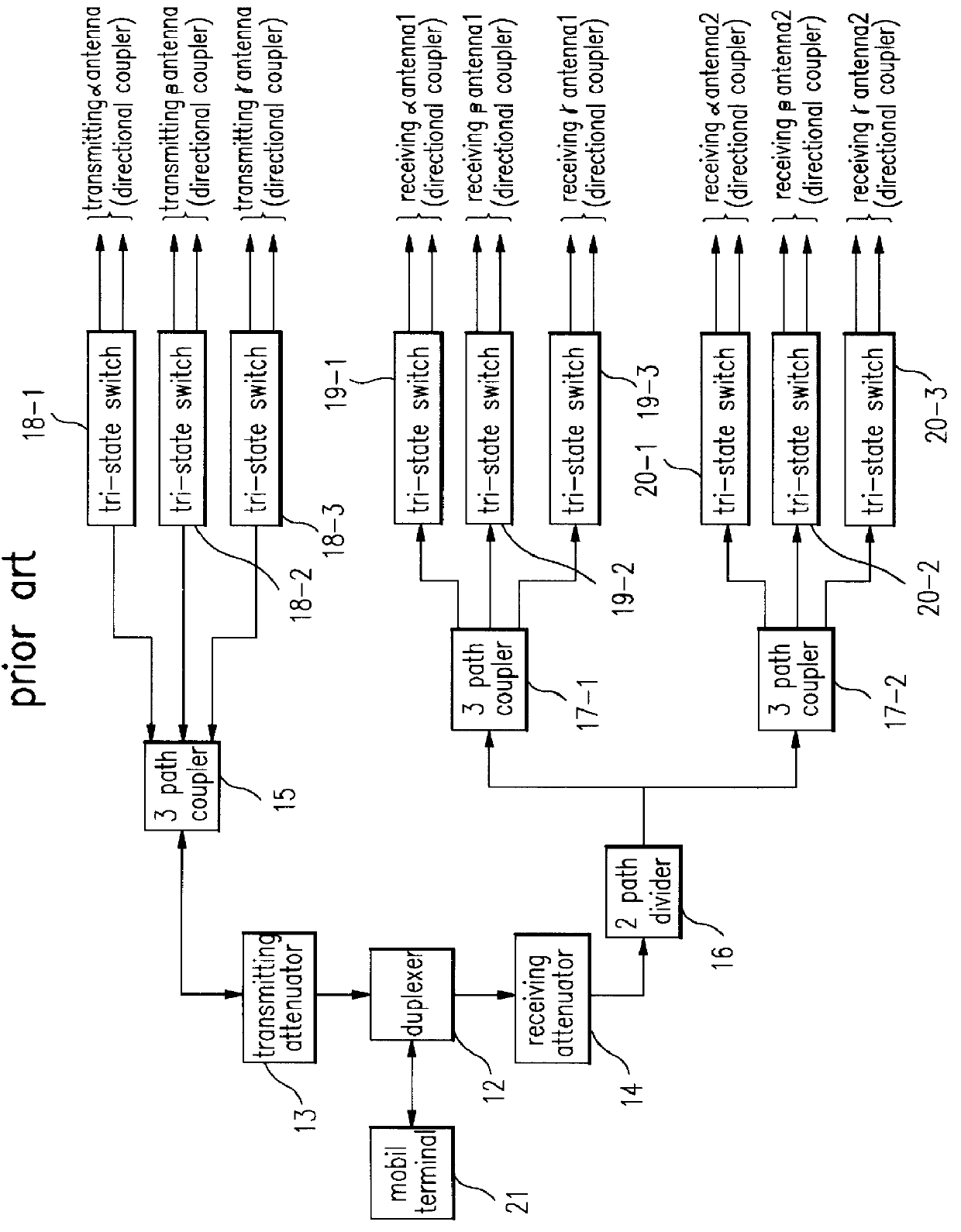
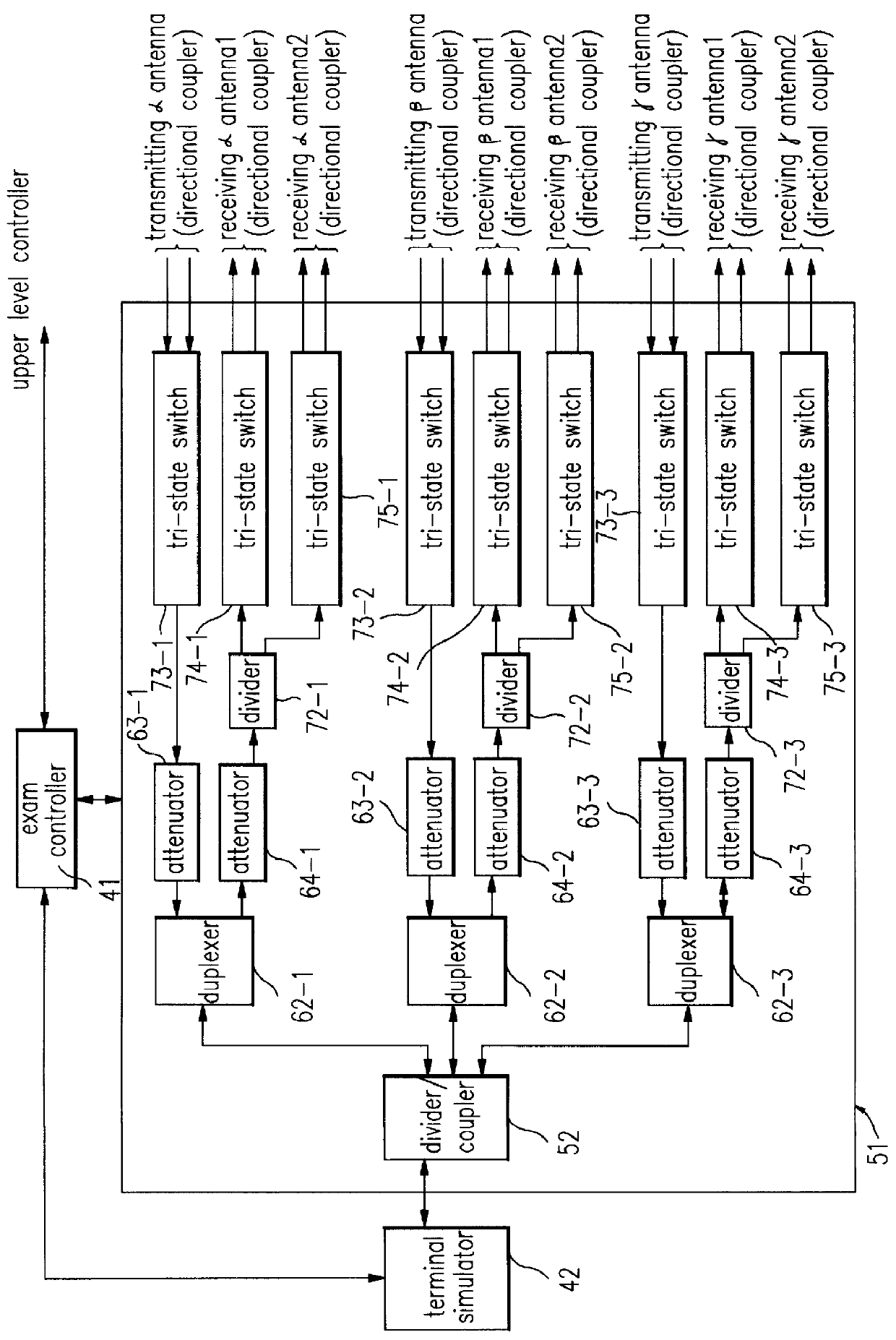
Test circuit of base station for mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6128474AReceivers monitoringTransmission systemsCommunications systemRadio frequency signal
A test circuit of a base station for use of a mobile radio communication system includes a terminal simulator for analyzing radio frequency signals provided from the base station and outputting the analyzed signals to an exam controller; a radio frequency signal path adjuster connected to the terminal simulator, for adjusting a combination and division of radio frequency signals, and a selection of a test path and a level of signals; and the exam controller connected with the radio frequency signal path adjuster, the terminal simulator and an upper level controller, the exam controller being for operating according to a test instruction of the upper level controller or controlling the radio frequency signal path adjuster and the terminal simulator to thereby execute a test and inform the upper level controller of the test result; whereby enabling the test circuit to be performed in a mutual test between sectors of the base station and an unmanned automation test.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Method and system of channel adaptation
InactiveUS20060098688A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemEngineering
The present invention relates to transmissions and retransmissions in a communications system. It reveals a method and system for backward compatible detection of an introduced channel sub-frame structure particularly well suited for data transmissions. The invention is well suited for a cellular mobile radio communications system, particularly a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System, UMTS.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Control device for controlling power level between frequency assignment in radio frequency receiving device of mobile radio communication base station system in CDMA system
Disclosed is a control device for controlling power level between frequency assignment in an RF receiving device of a mobile radio communication base station system in a CDMA system capable of lowering the power level of the frequency assignment signal having a relatively high power difference, after the detection of the power level by the frequency assignment, to thereby minimize the power level difference between the frequency assignment and then, executing an AGC for three frequency assignment, whereby the performance deterioration of the whole channels, which is caused due to the disappearance of the frequency assignment signal having a relatively low power difference by the frequency assignment having the high power difference, can be prevented.
Owner:USRCOM KOREA
Mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS6370377B1Reduce tracking timeActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentOmnidirectional antennaCommunications system
A mobile radio communication system which does not need an omnidirectional channel for both a base station and a mobile station to track each other and uses only a narrow beam channel and can reduce a tracking time than before for an adjacent base station and a mobile station to search each other while a visiting area base station and the mobile station are communicating in the overlapped area. The base station and the mobile station comprise a unit for transmitting and receiving in forward or reverse channel, in different frequency, in different tracking channel using a narrow beam. Both the mobile station and the visiting area base station search the location each other, and after searched, they assign the frequency and the beam used in the tracking channel. At the same time, by comprising a searching slot in an information channel to search an adjacent base station while communicating with the visiting area base station, a tracking of other adjacent base station can be performed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Radio Mobile Unit Location System
InactiveUS20080287116A1Improve accuracyLow costPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork variableMobile radio
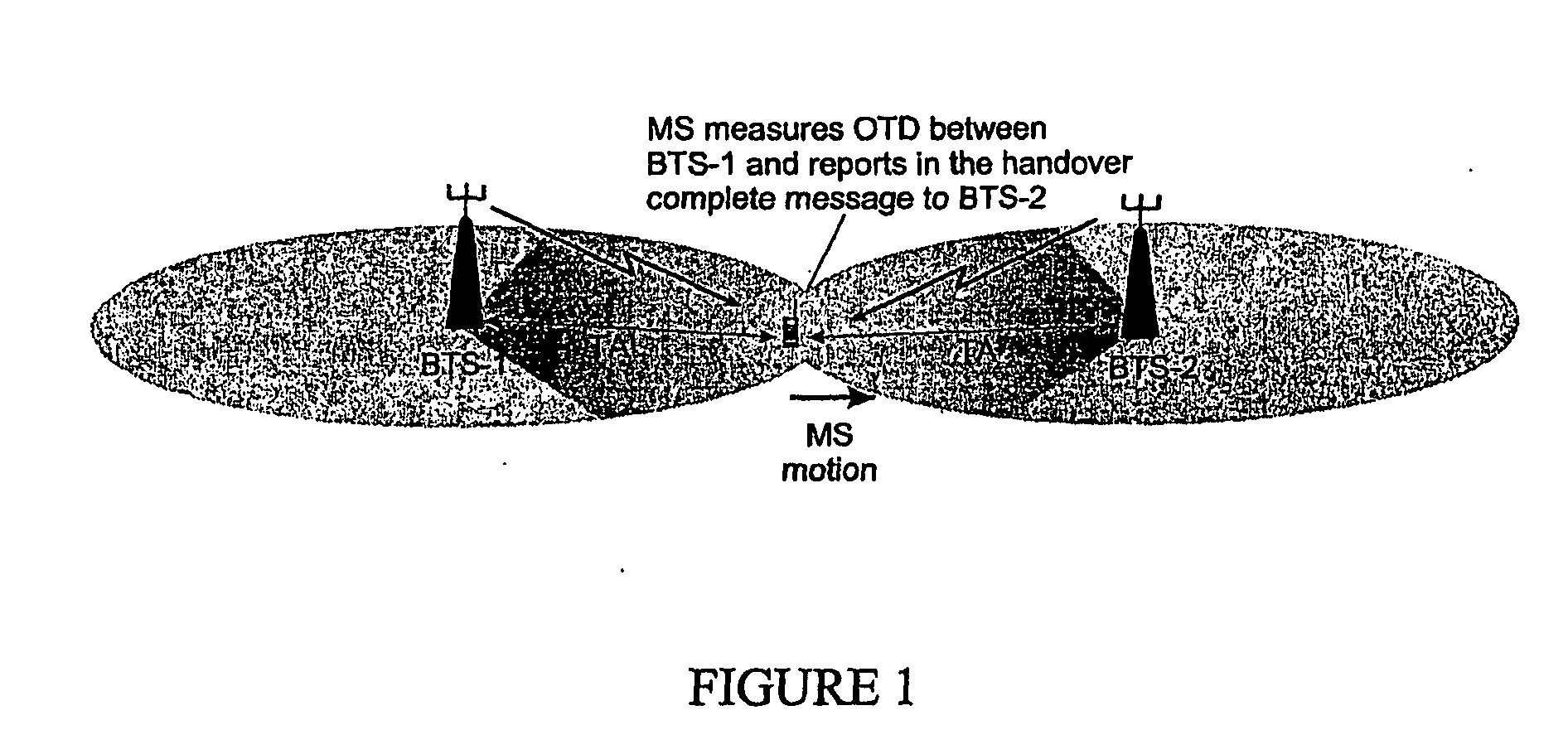
Disclosed is a method for locating a mobile radio unit within a mobile radio communications network. The method provides for the calculation of network variables such as a Real Time Difference (RTD) between network elements, from measurements already available to the network from, for example, handovers between network elements. The method provides for the location of radio mobile units without having to synchronise network elements such as BTSs or LMUs.
Owner:SEEKER WIRELESS PTY LTD
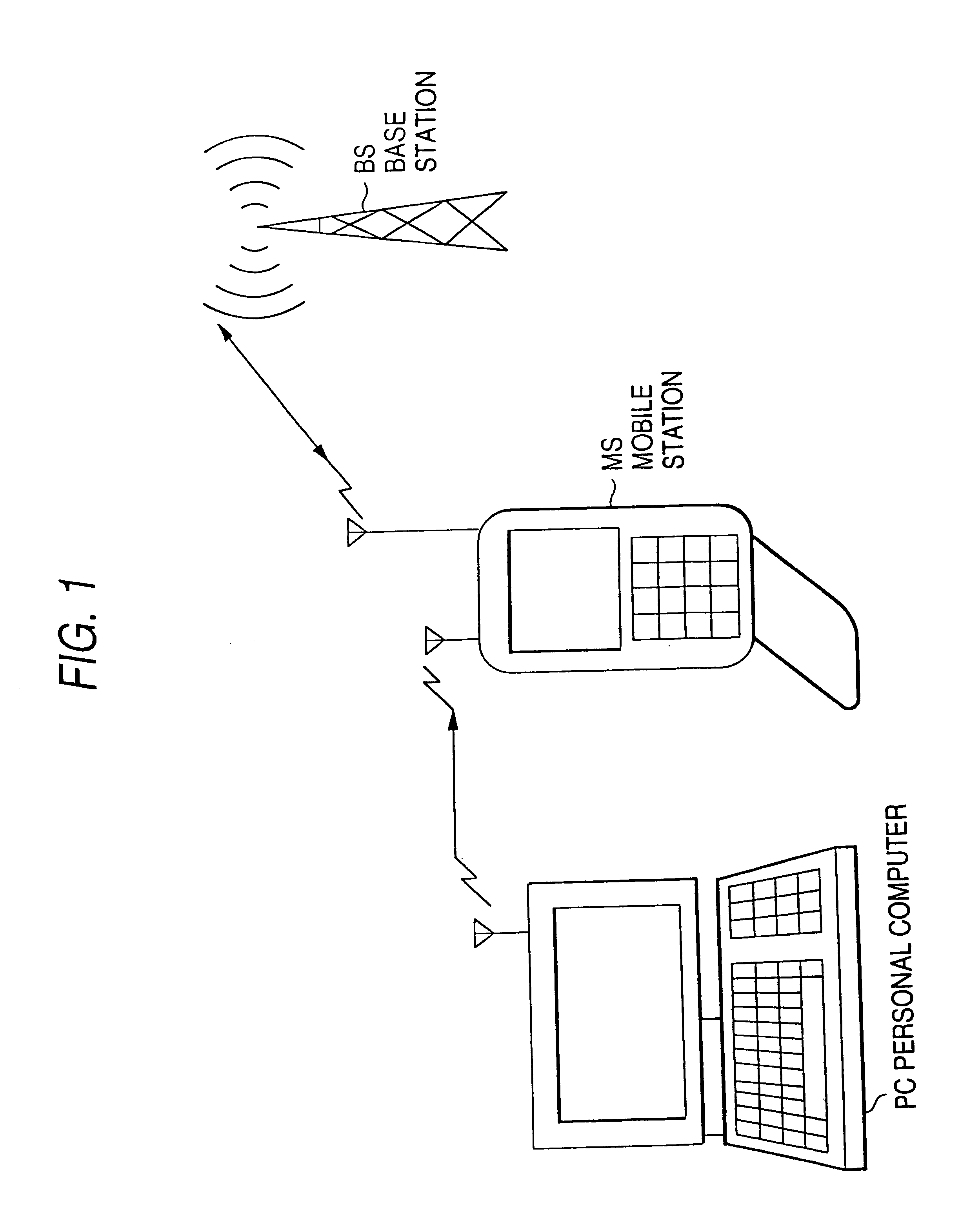
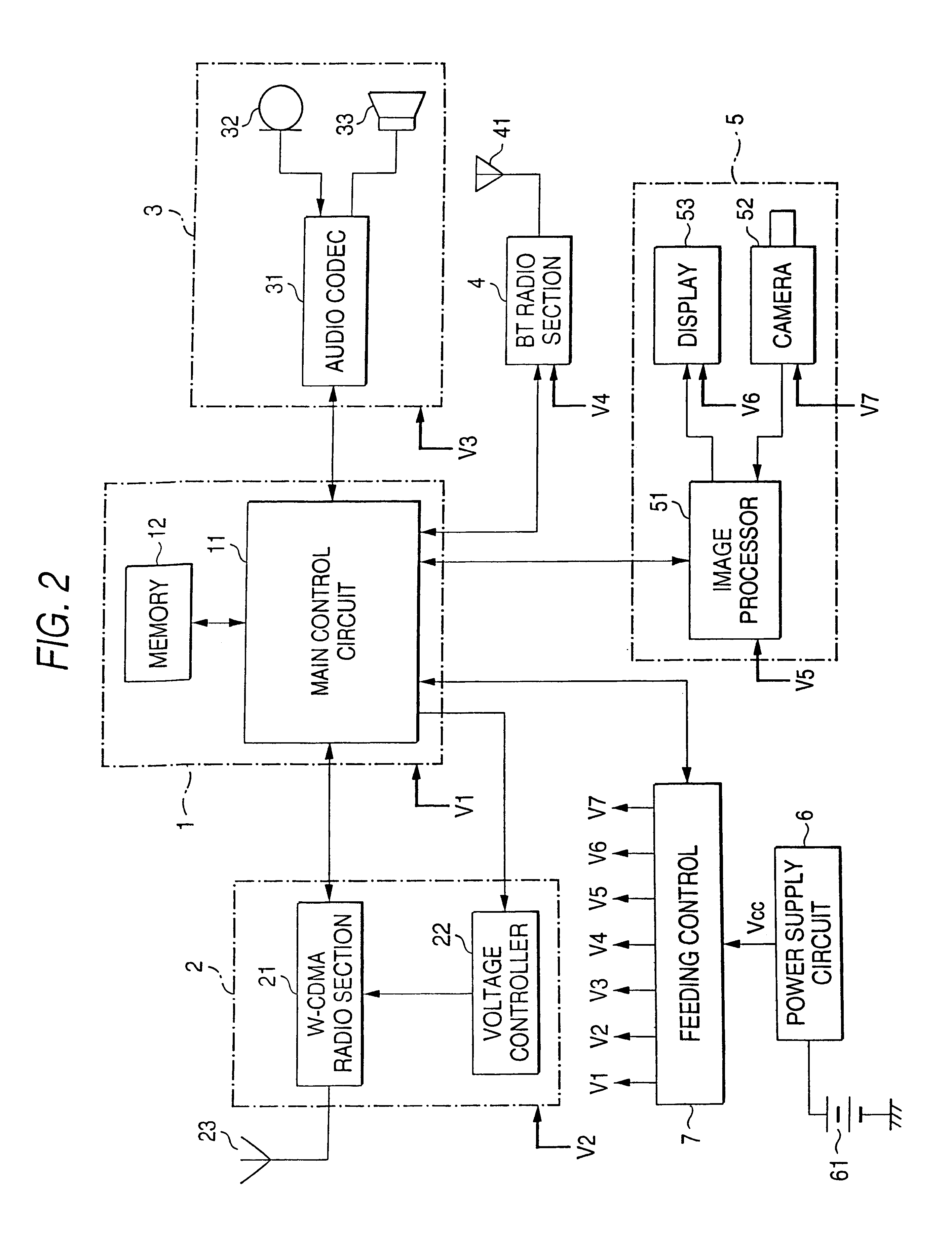
Mobile radio communication terminal
InactiveUS6993357B1Improve power supply capacityDownsizesPower managementTime-division multiplexOperation modeEngineering
In a mobile radio communication terminal includes a feeding controller 7 with a feeding control table. In the feeding control table 7 is stored the on / off state of the power to each circuit in correspondence with all operation modes for the apparatus. In case an operation mode is reported from the main control circuit 11 prior to the operation, output Vcc of the power supply circuit 6 is fed to the minimum circuits necessary for execution of the operation mode according to the operation mode and information stored in the feeding control table 7, and power to the remaining circuits is shut off or reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU TOSHIBA MOBILE COMM LTD
Method for operating terminals of a mobile radio communication system
InactiveUS20060040661A1Method implementationSimple and effective of handlingAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesCommunications systemWireless lan
A system and method is disclosed for operating terminals of a mobile radio communication system operating preferably under an UMTS standard in at least one wireless local area network (WLAN). At least one piece of access data can be stored on the terminal, with the access data being encoded in such a way that the access data comprises at least one first piece of identifying data for the mobile radio communication system and at least one second piece of identifying data for the local area network.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
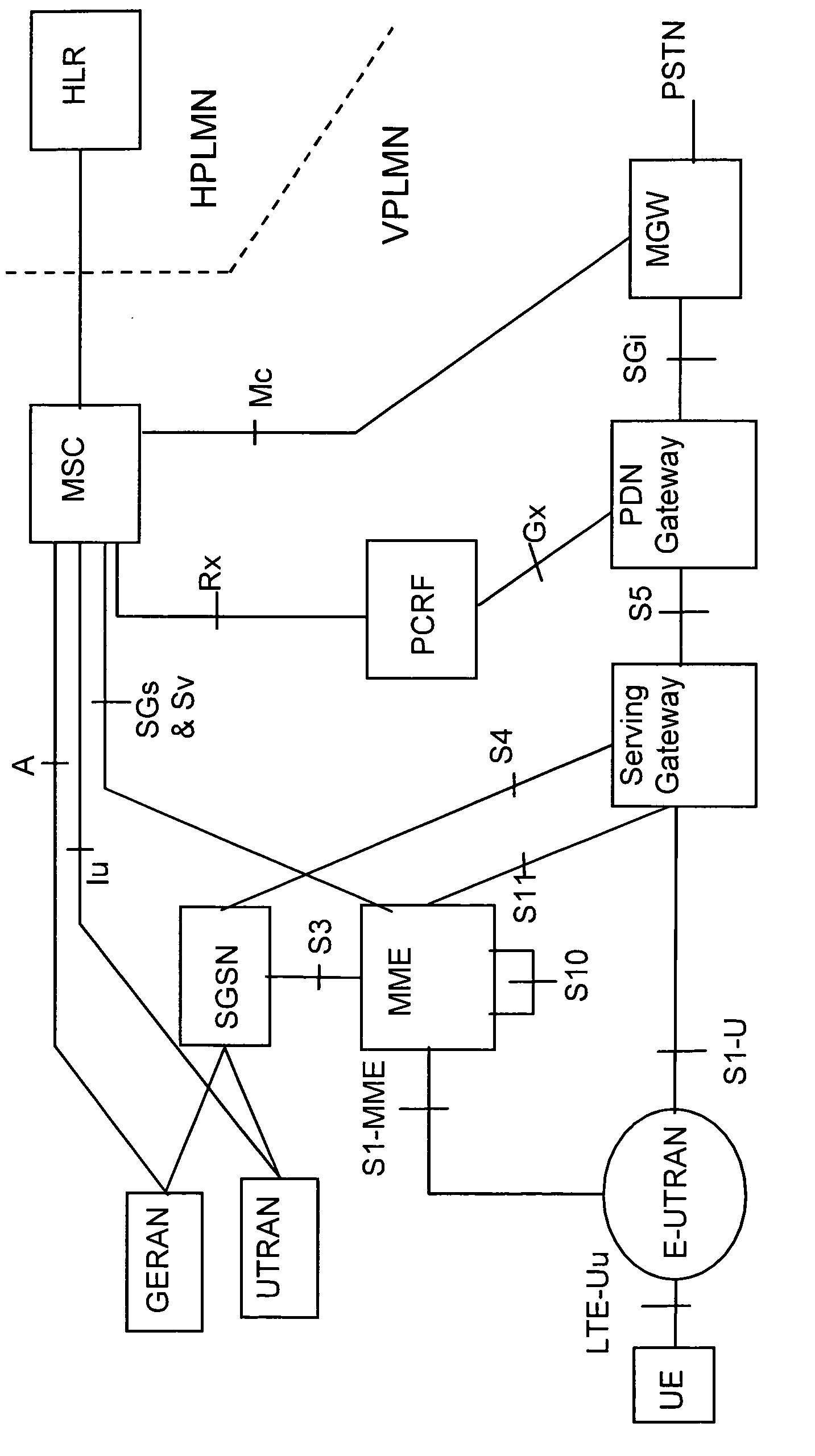
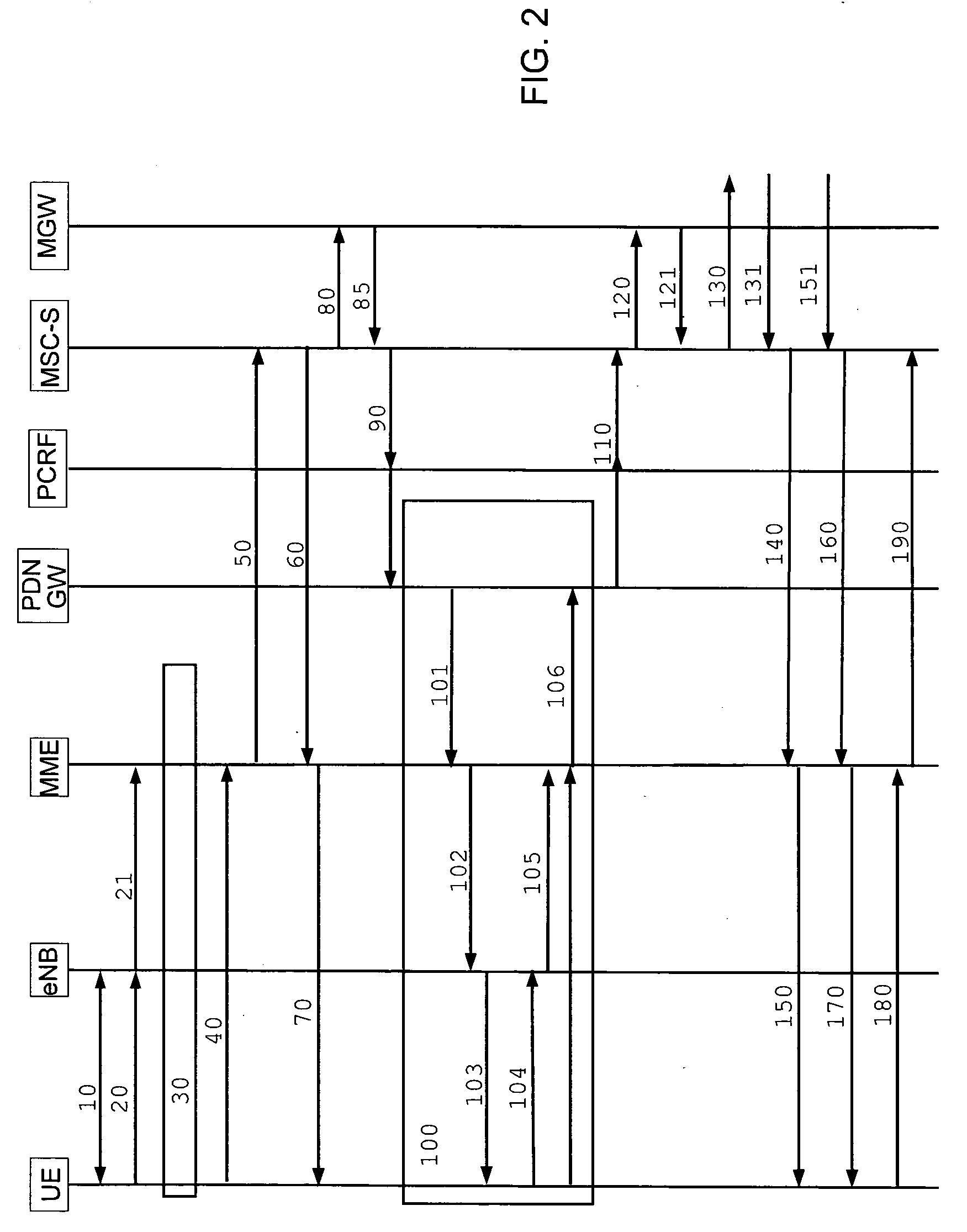
Circuit-switched services over LTE
ActiveUS20110069618A1Short set-up timeMinimal modificationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSystem Architecture EvolutionCommunications system
A mobile radio communication system and method of initiating a circuit-switched service at a mobile station over a System Architecture Evolution (SAE) core network using packet-switched communications between the mobile station and the SAE core network is provided. The method includes communicating service handling information between a Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) and the mobile station through a Mobility Management Entity (MME) of the SAE core network; sending instructions from the MSC for setting up the circuit-switched service through a Media Gateway, coupled to at least one network external to the SAE core network; providing packet-switched addressing information for the Media Gateway to the mobile station; and initiating the circuit-switched service at the mobile station over the SAE core network and through the Media Gateway.
Owner:VODAFONE IP LICENSING
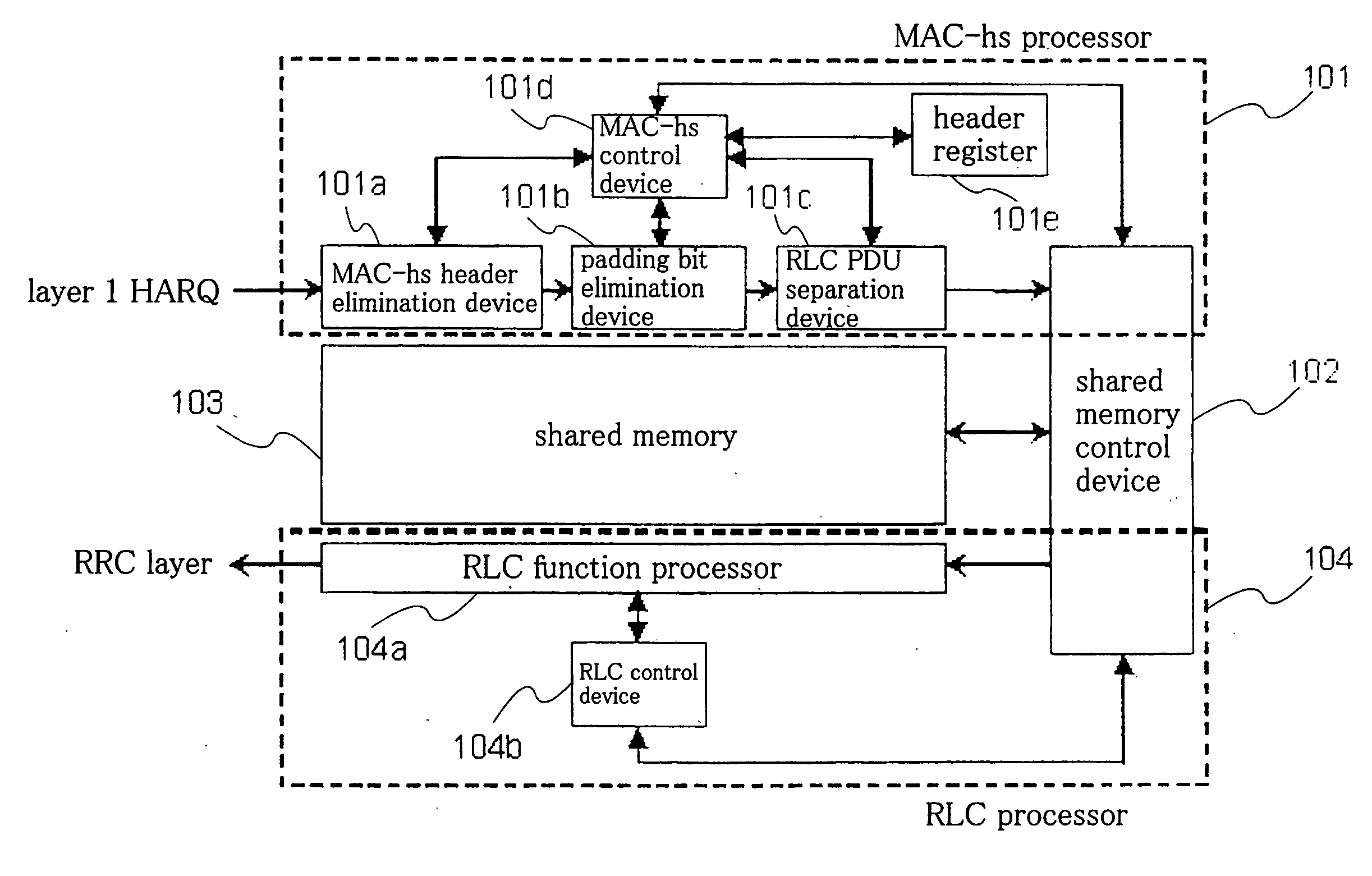
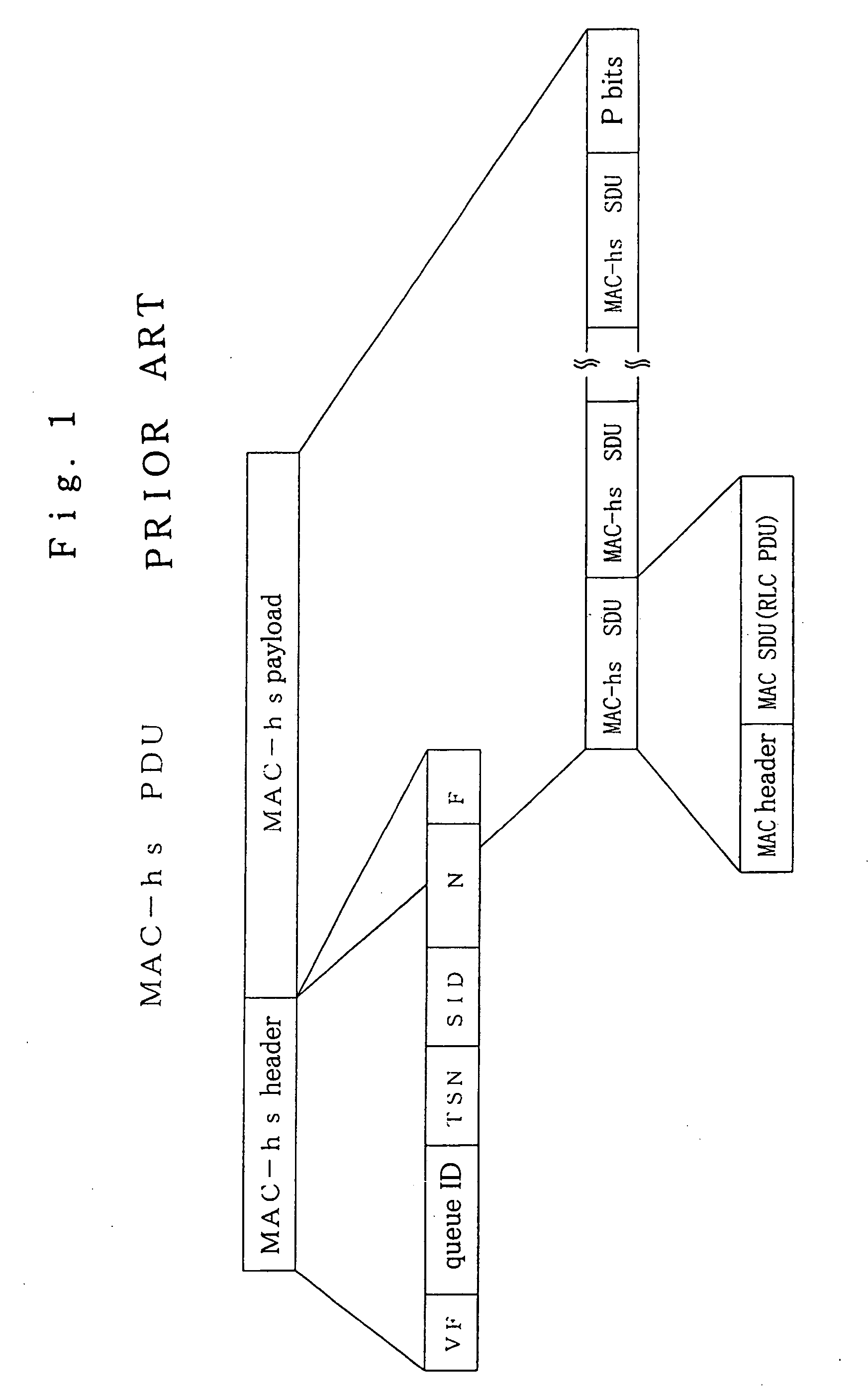
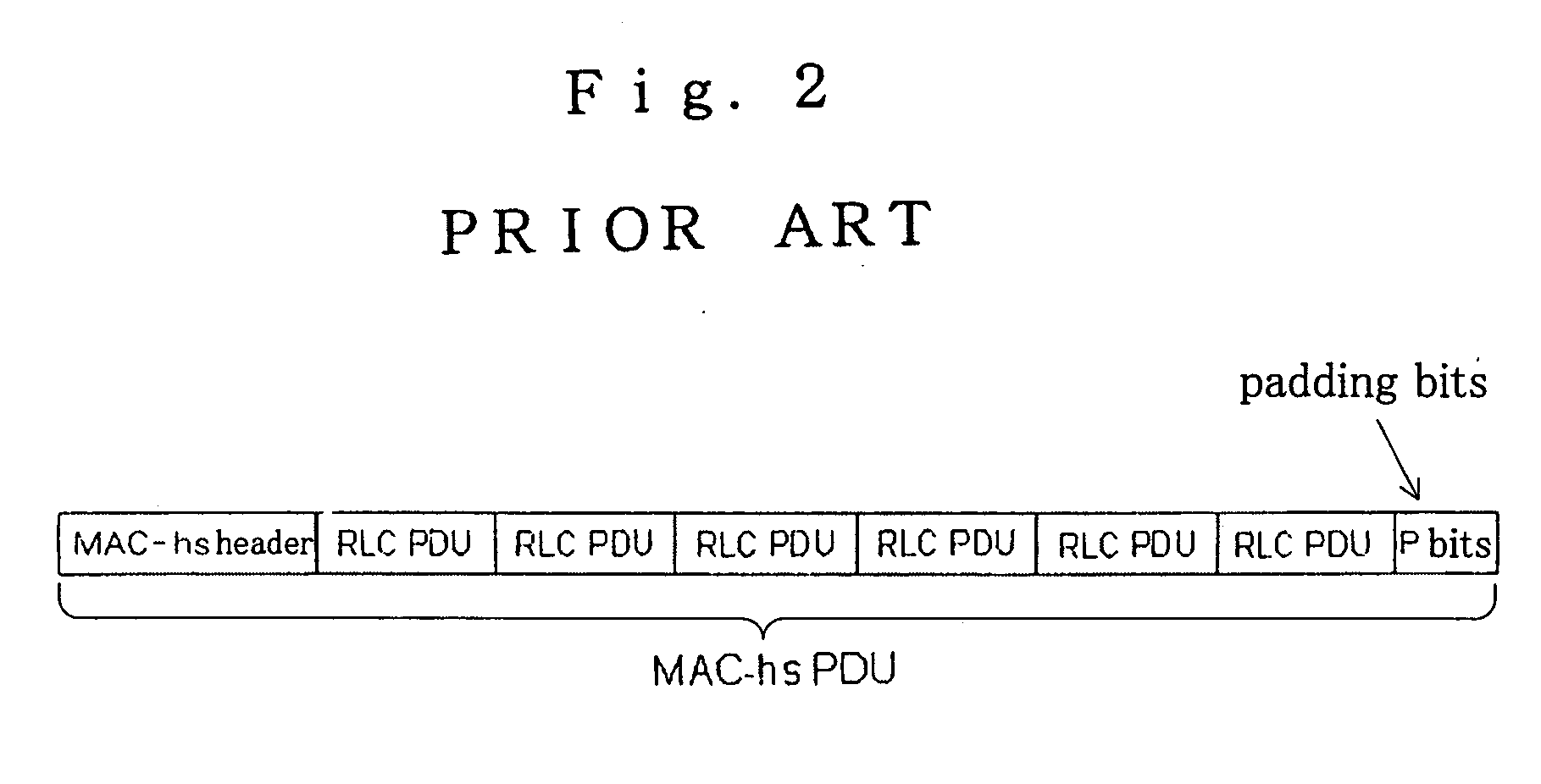
Mobile radio communication terminal device capable of realizing a MAC-HS buffer and RLC buffer in one physical memory and suppressing memory capacity
InactiveUS20060002416A1Increase capacityImprove throughputError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementMemory addressTerminal equipment
A mobile radio communication terminal device can suppress increase in memory capacity and realize a MAC-hs buffer and an RLC buffer as a single physical memory. A MAC-hs processor separates packet data of MAC-hs PDU units that are received as input into packet data of RLC PDU units and then supply these data together with sequence numbers to a shared memory control device. A shared memory is a single physical memory that functions as the MAC-hs buffer and the RLC buffer. The shared memory control device assigns memory addresses of the shared memory in RLC PDU units in advance, and writes packet data of RLC PDU units that are applied as input from the MAC-hs processor to the corresponding memory addresses of the shared memory.
Owner:NEC CORP
Mobile radio communication apparatus
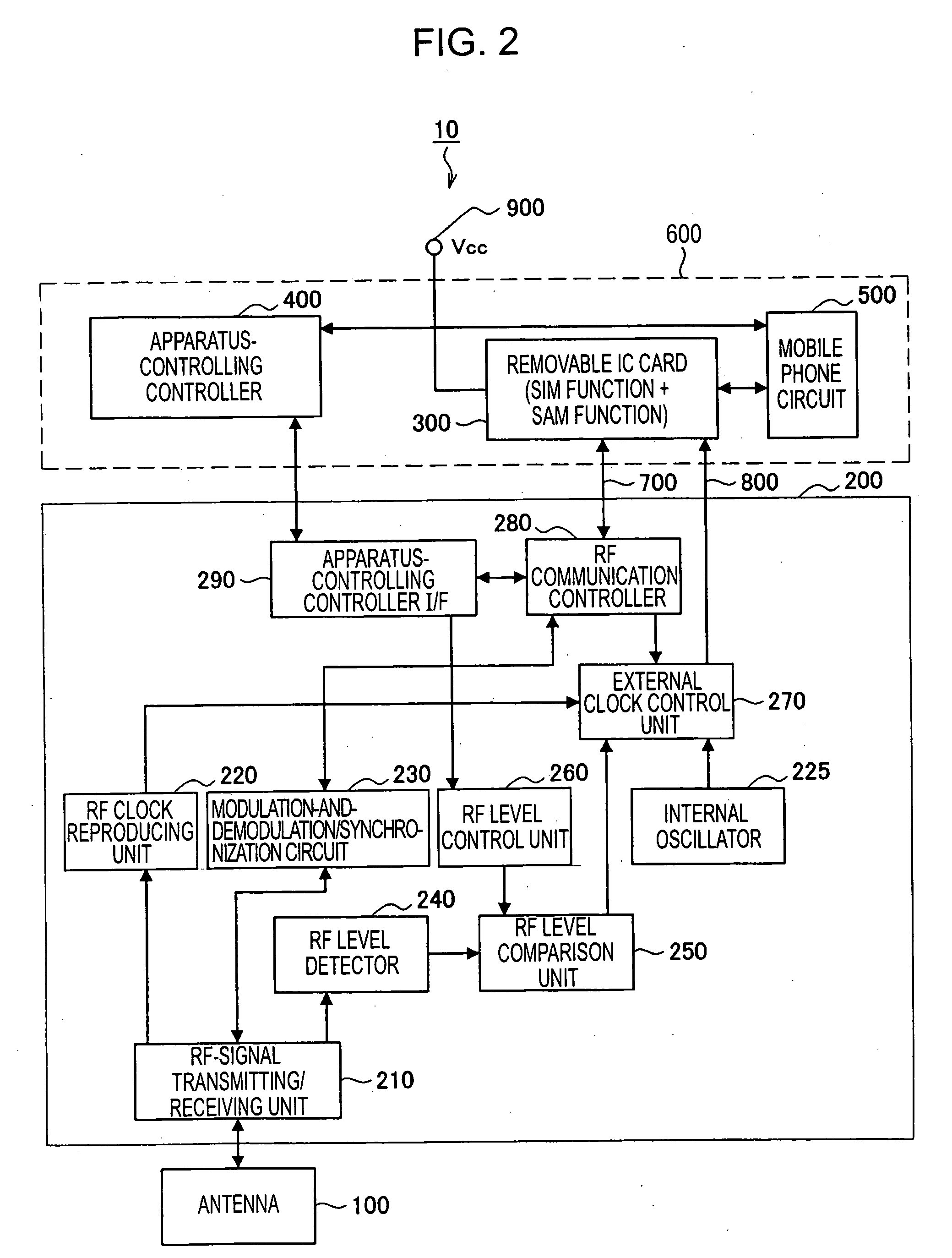
InactiveUS20070026893A1Maintain compatibilityCo-operative working arrangementsNear-field systems using receiversMobile radioComputer science
A mobile radio communication device can automatically initialize the mode of a SAM card (or the SAM function area of an IC card) after executing radio communication with an external radio communication apparatus. The mobile radio communication device transmits / receives data to / from an external radio communication apparatus located in an area that allows radio communication. In the mobile radio communication device, an IC card that receives power supply from a mobile radio communication device main-unit, that manages data transmitted / received to / from the external radio communication apparatus, and that manages a communication mode state of the mobile radio communication device is detachably connected to the mobile radio communication device main-unit. The mobile radio communication device further includes radio-signal strength determining means for determining whether or not a strength of radio signals received from the external radio communication apparatus is less than or equal to a preset threshold value, and IC-card-mode initializing means for resetting a mode of the IC card to an initial state when the radio-signal strength determining means determines that the strength of the radio signals is less than or equal to the threshold value.
Owner:SONY CORP
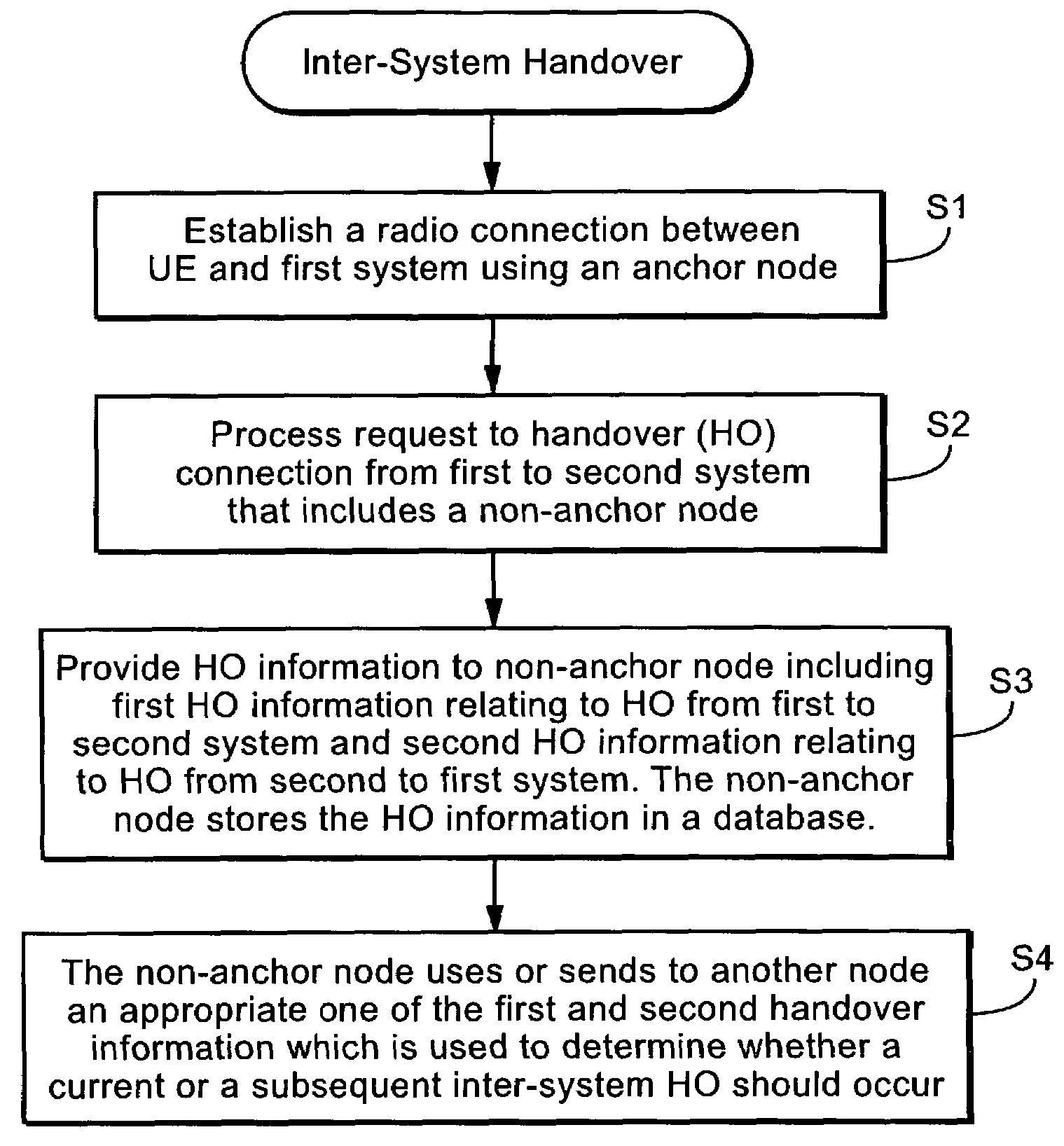
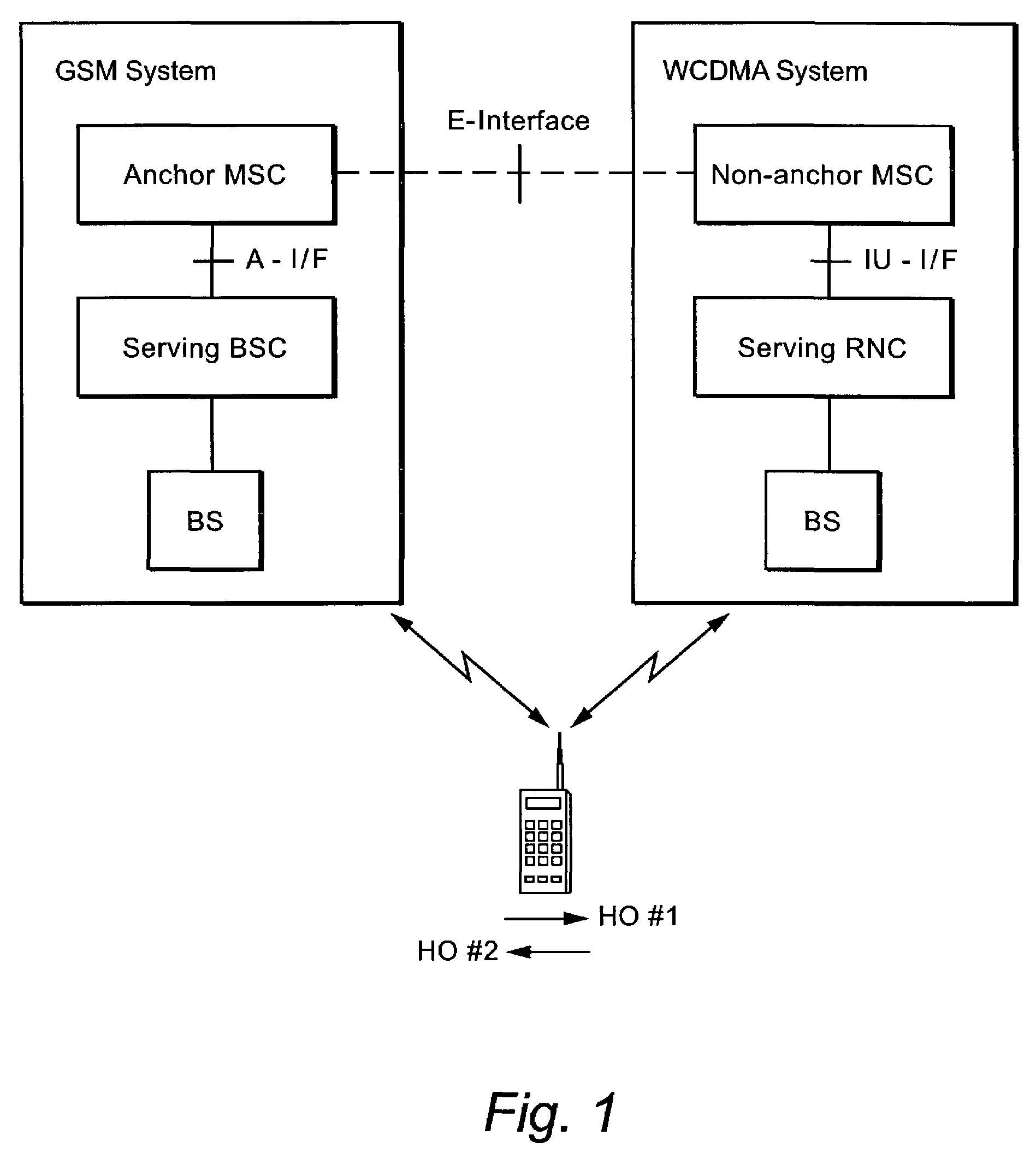
Service-based inter-system handover
InactiveUS7257403B2Facilitate operator controlComplicates such functionalityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyCommunications system
The present invention facilitates control over inter-system handover between different types of radio access technologies. Assuming a radio connection has been established between a first mobile radio communications system and a user equipment (UE) using an anchor node, a request is made for handover of the UE connection to a second mobile radio communications system that includes a non-anchor node. UE handover information is provided to the non-anchor node. The UE handover information includes first radio handover information relating to handover of the connection from the first mobile radio communication system to the second mobile radio communication system and second handover information relating to handover from the second mobile radio communications system to the first mobile radio communications system. The non-anchor node forwards to a node in the target network the UE handover information having the protocol format recognized by that node. As a result, the node can readily interpret the information element to determine if the UE subscription and / or type of call warrant or permit a subsequent inter-system handover.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Radio base station receiver having digital filtering and reduced sampling frequency
ActiveUS7565170B2Increase the number ofAllow useError preventionPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency spectrumDigital filter
A station for processing a first signal which can be generated by a mobile terminal and belongs to a plurality of signals for mobile radio communications networks. The stations include an input able to receive from an antenna the first signal associated with a first band and at least one adjacent signal of said plurality associated with a second band adjacent to that of the first signal; a processing stage for generating from the first digital signal at a first sampling frequency, this first digital signal including a useful spectral content of the first signal and an interfering spectral content associated with the adjacent signal; a digital filter for processing the first digital signal, attenuating the interfering spectral content, and for providing a filtered digital signal including at least part of the useful special content sampled at a second sampling frequency less than the first sampling frequency and an electro-optical converter for generating from the filtered digital signal electromagnetic radiation to be transmitted on a waveguide.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Method and apparatus for determining a location of a mobile radio
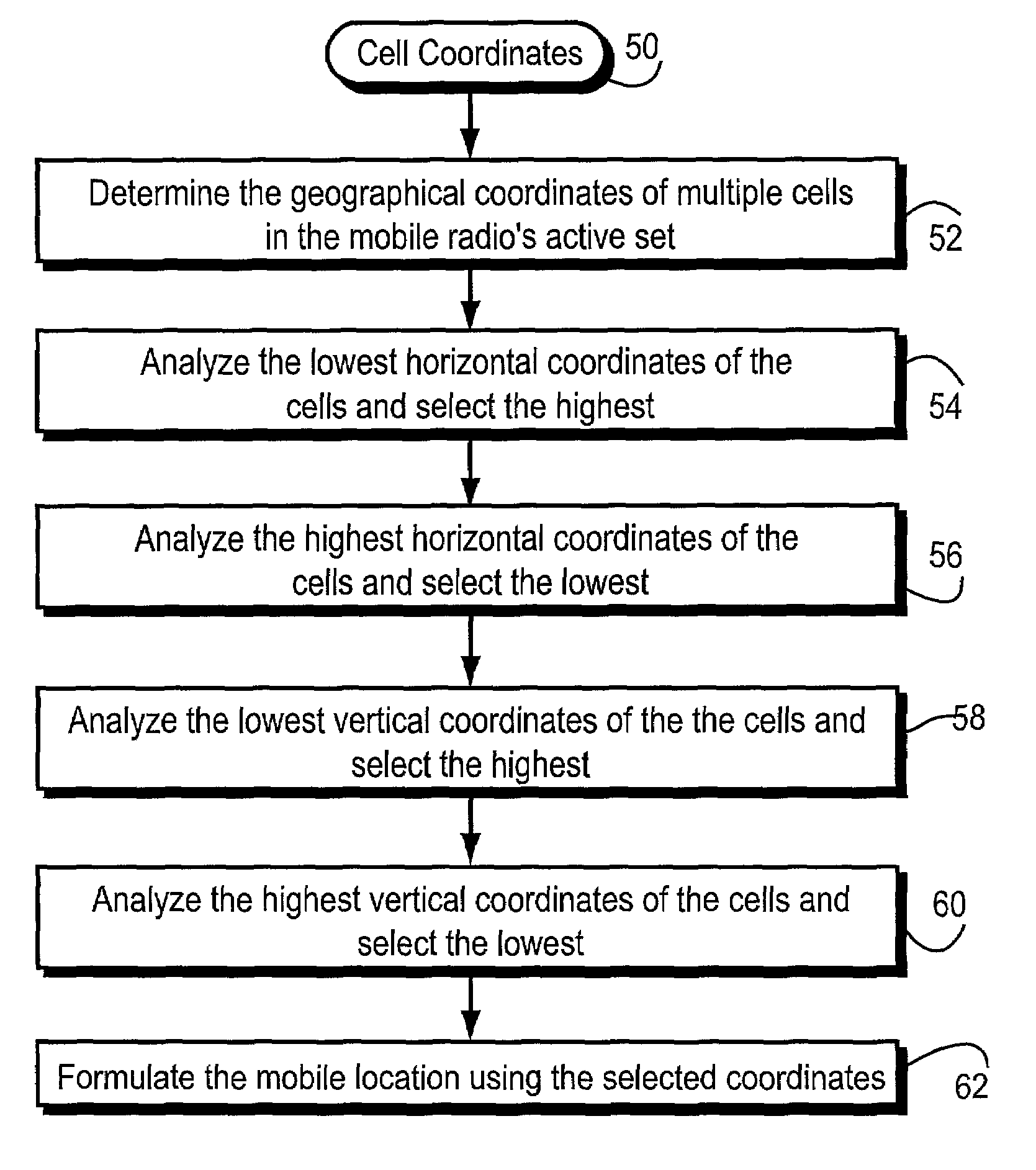
InactiveUS7027819B2Reliable and accurate to determineLarge area/cellDirection finders using radio wavesTelephonic communicationCurrent cellRadio networks
Cell coordinates available in the radio network is used to determine an area where the mobile radio is located and does not rely upon mobile radio measurements. Such cell coordinates for cells currently associated with the mobile radio are used by the radio network to determine a location of the mobile radio. Those current cells may include cells that are candidates for supporting a communication with the mobile radio, an active set of cells, cells that are currently supporting communication with the mobile radio, or some other set of cells geographically associated with the mobile radio.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com