Patents
Literature
31 results about "Safety critical application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
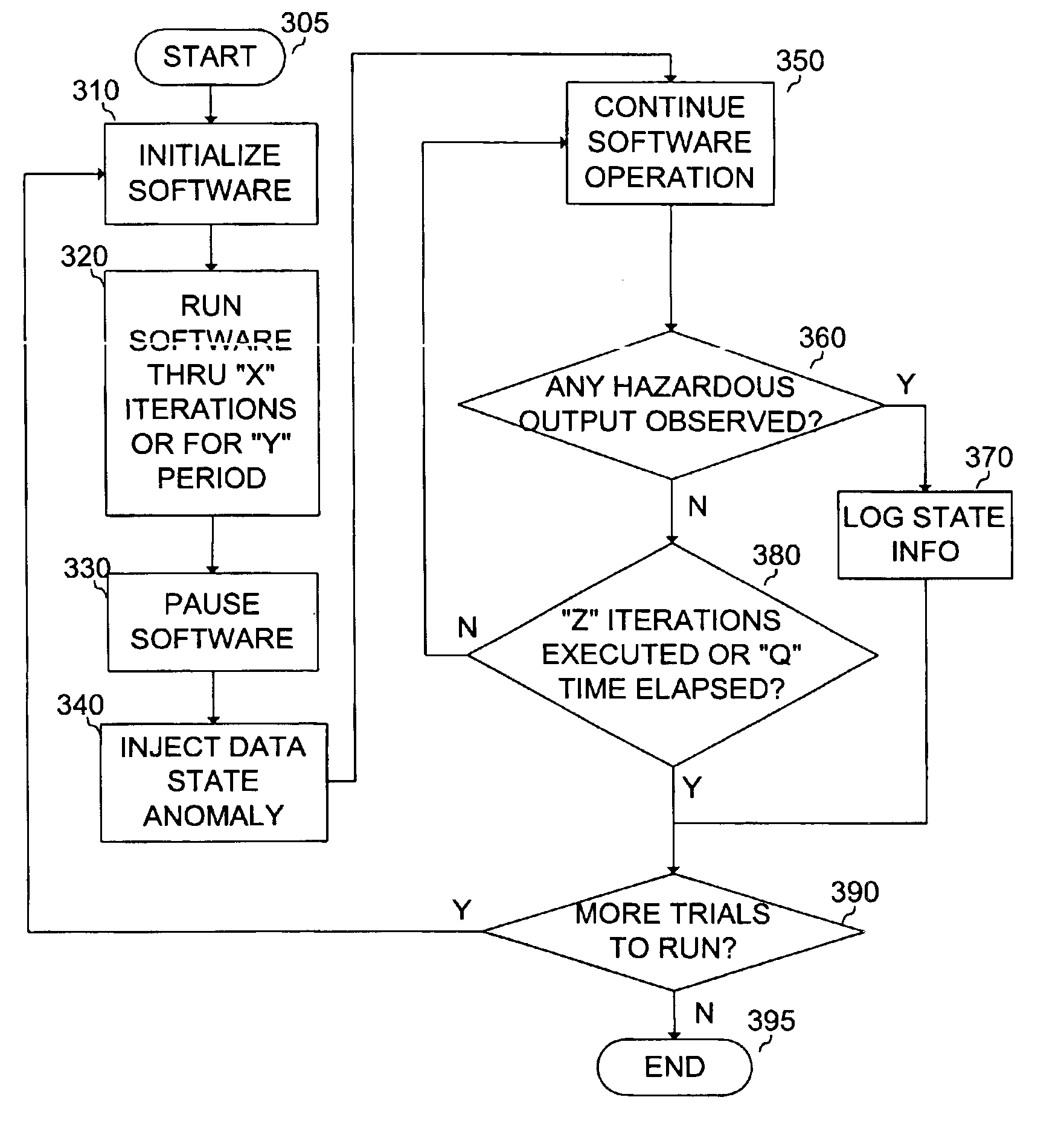
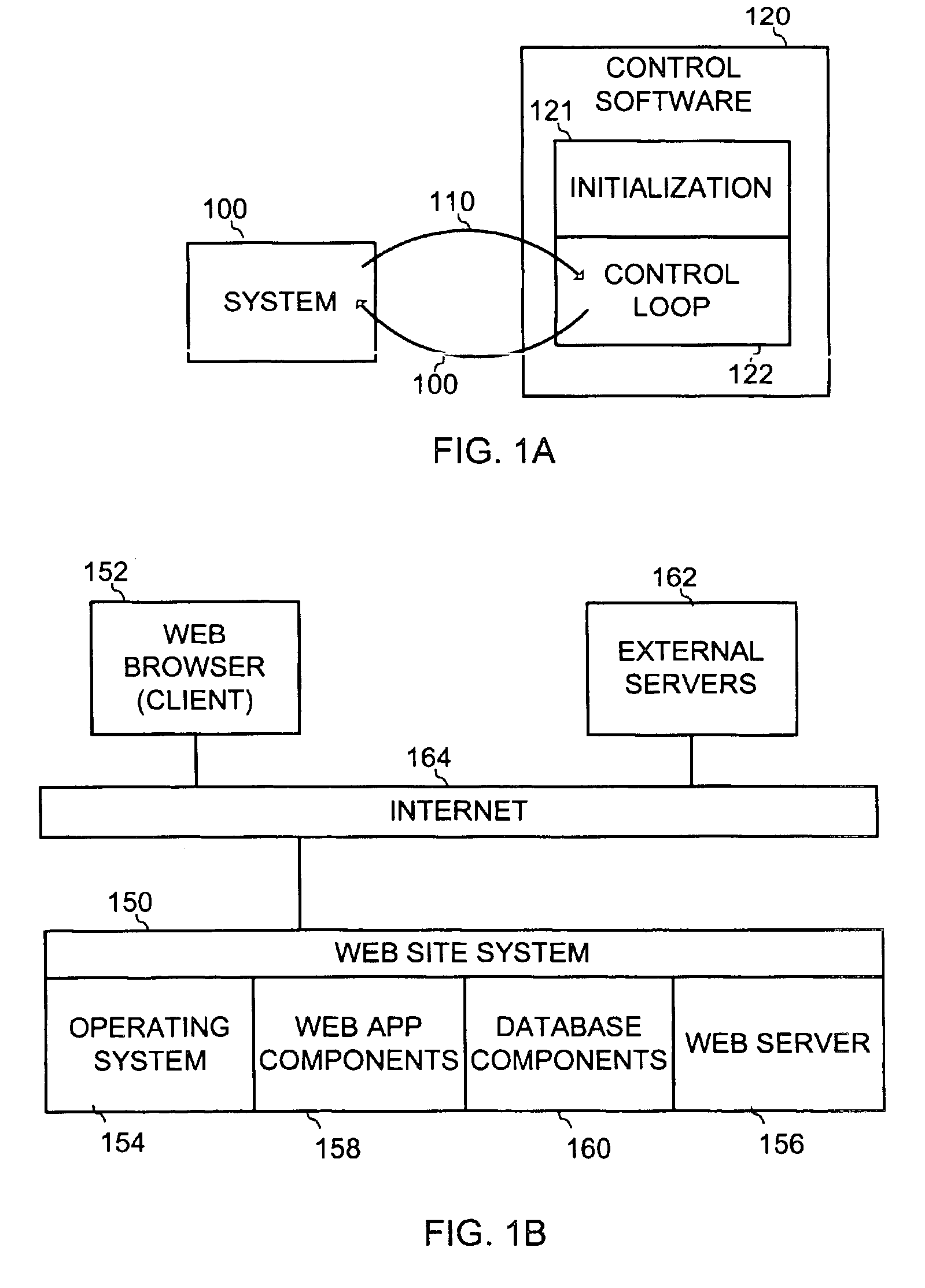
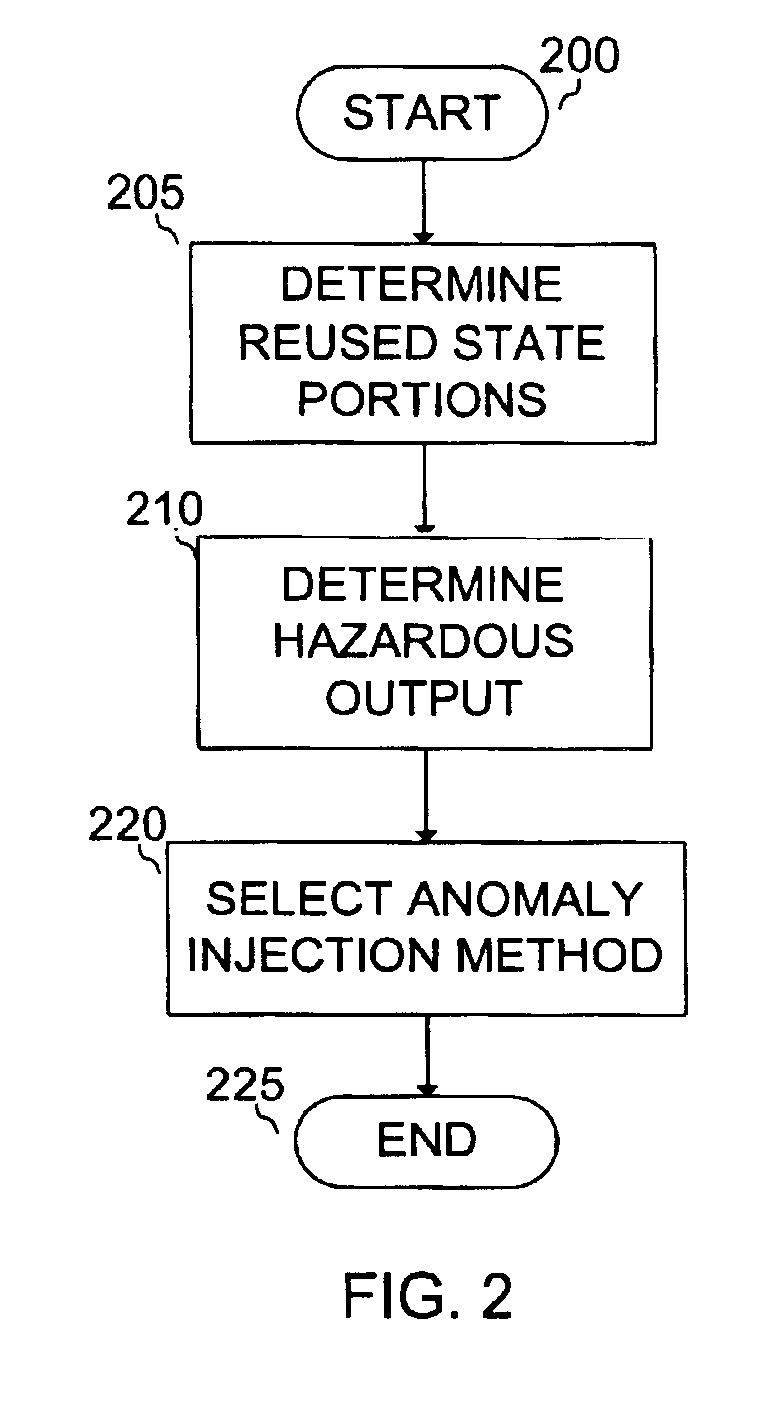
Method for reducing catastrophic failures in continuously operating software systems
InactiveUS7024592B1Accurate operationError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware systemProgram planning
A method for assessing how long continuously operating software systems can be expected to remain executing in a safe and / or reliable manner before anomalous conditions will ultimately lead to failure. For safety-critical applications the method can provide a safe upper bound on the time between rebooting. Also disclosed is an empirical technique for determining which portions of the state, if corrupted create the greatest risks to safe and / or reliable continual execution of the software. Armed with this information, developers, testers, and certifiers can create justifiable plans for the frequency with which the software should be rebooted. Further, they can customize and embed internal self-tests into those portions of the state found to have the greatest risks to safe and / or reliable, continual execution of the software. These self-tests can also warn when failures are likely to occur well in advance of the failures, so that the software may be safely rejuvenated to avert undesired or catastrophic conclusions.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
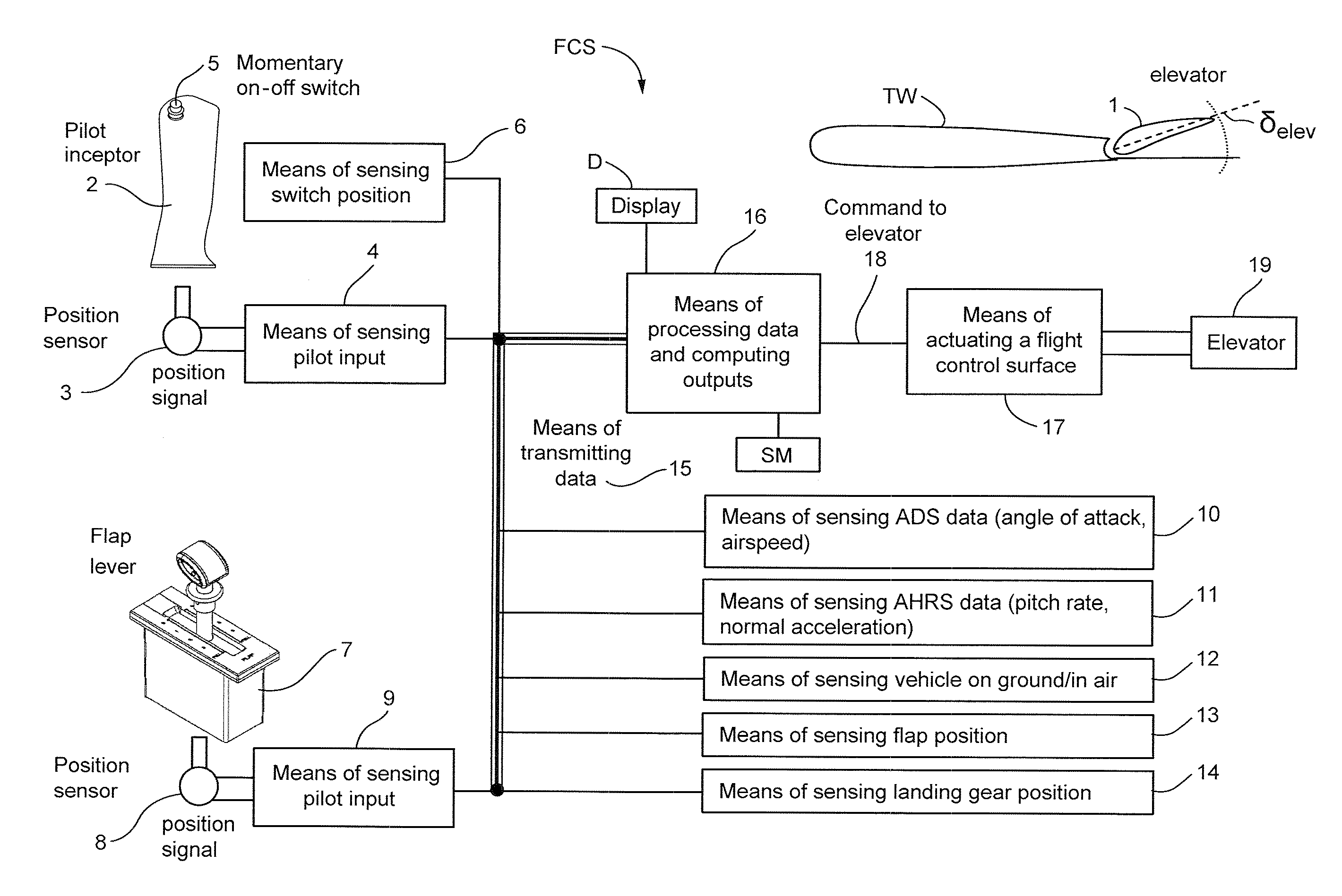
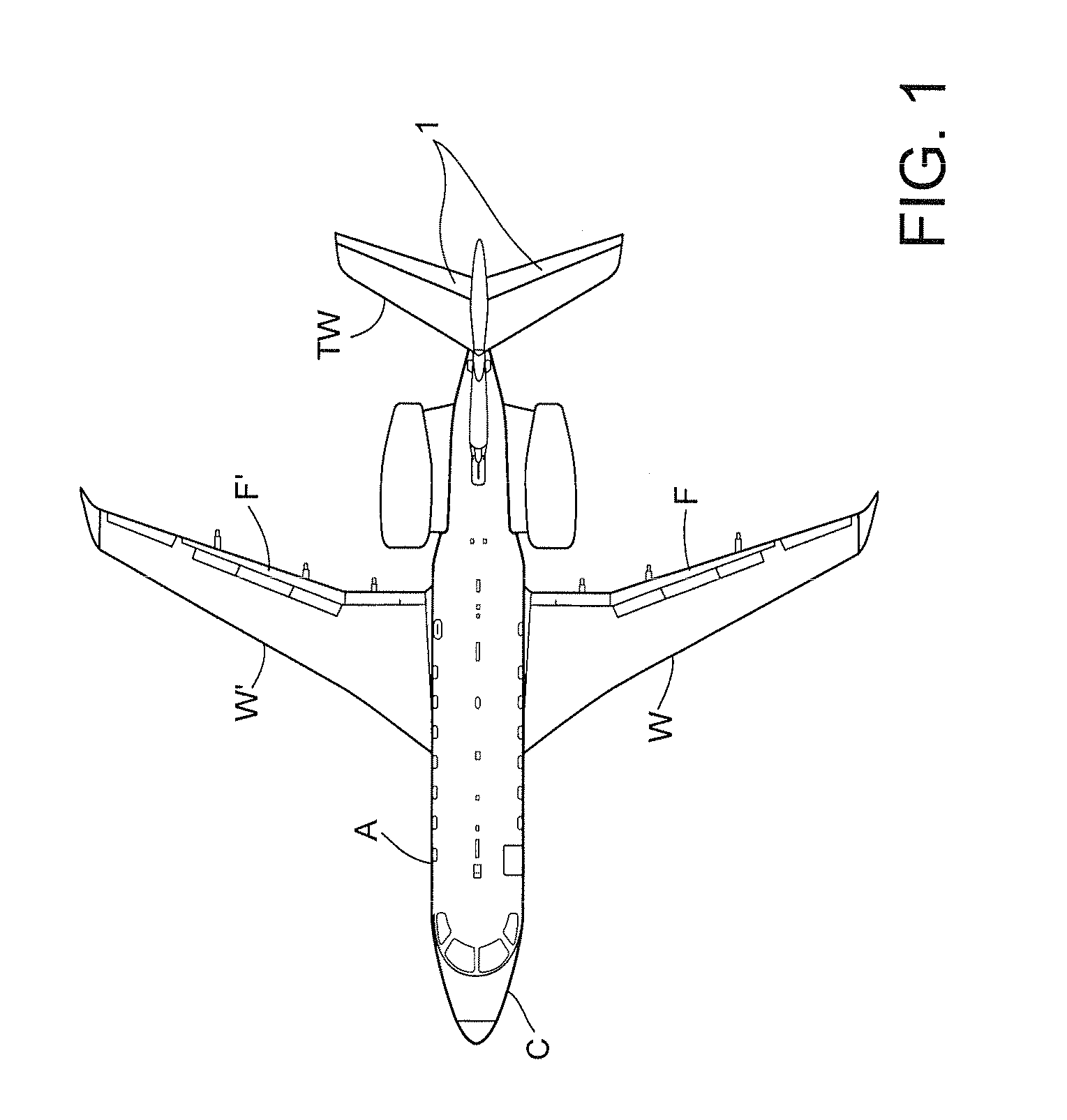
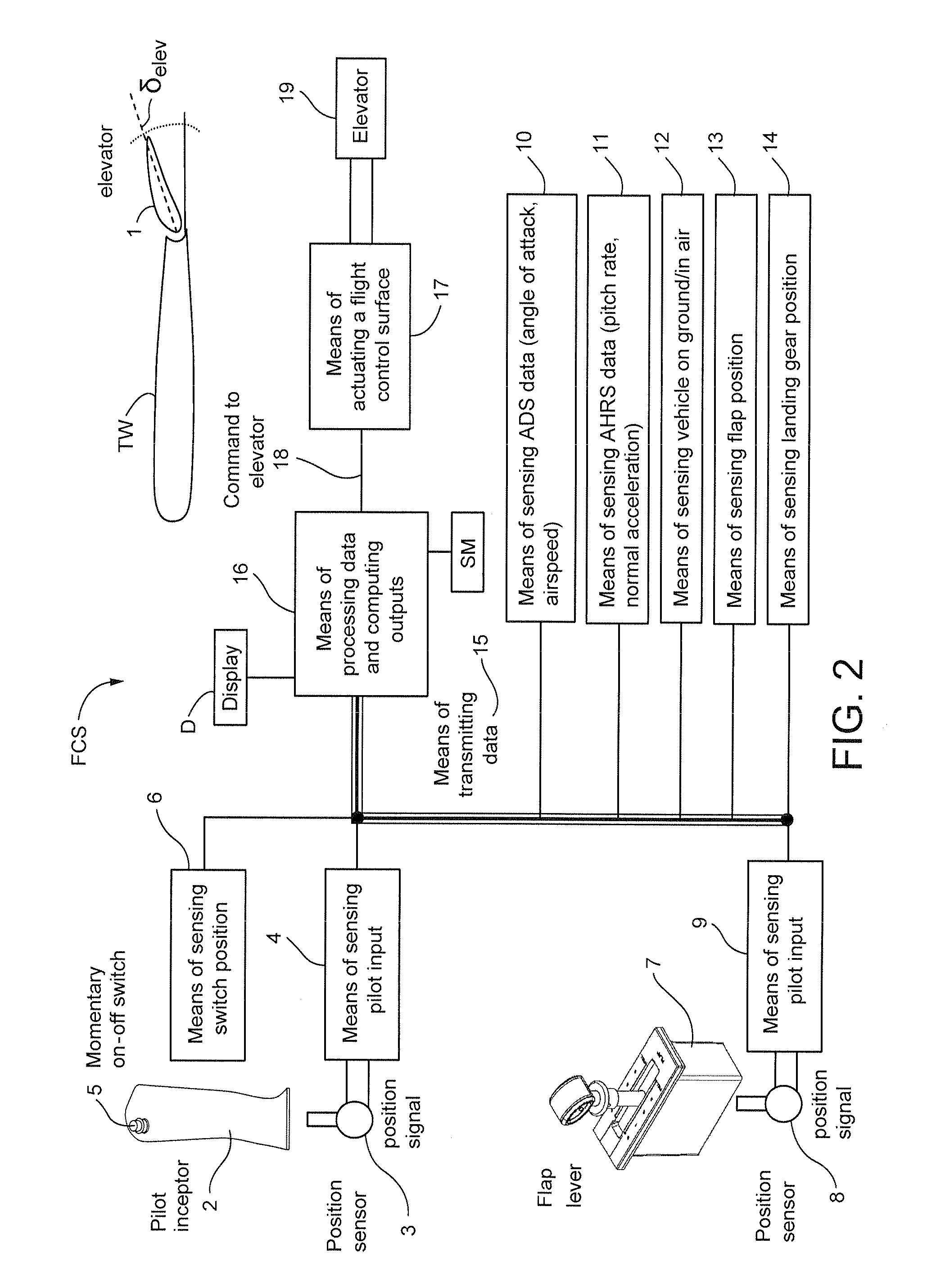
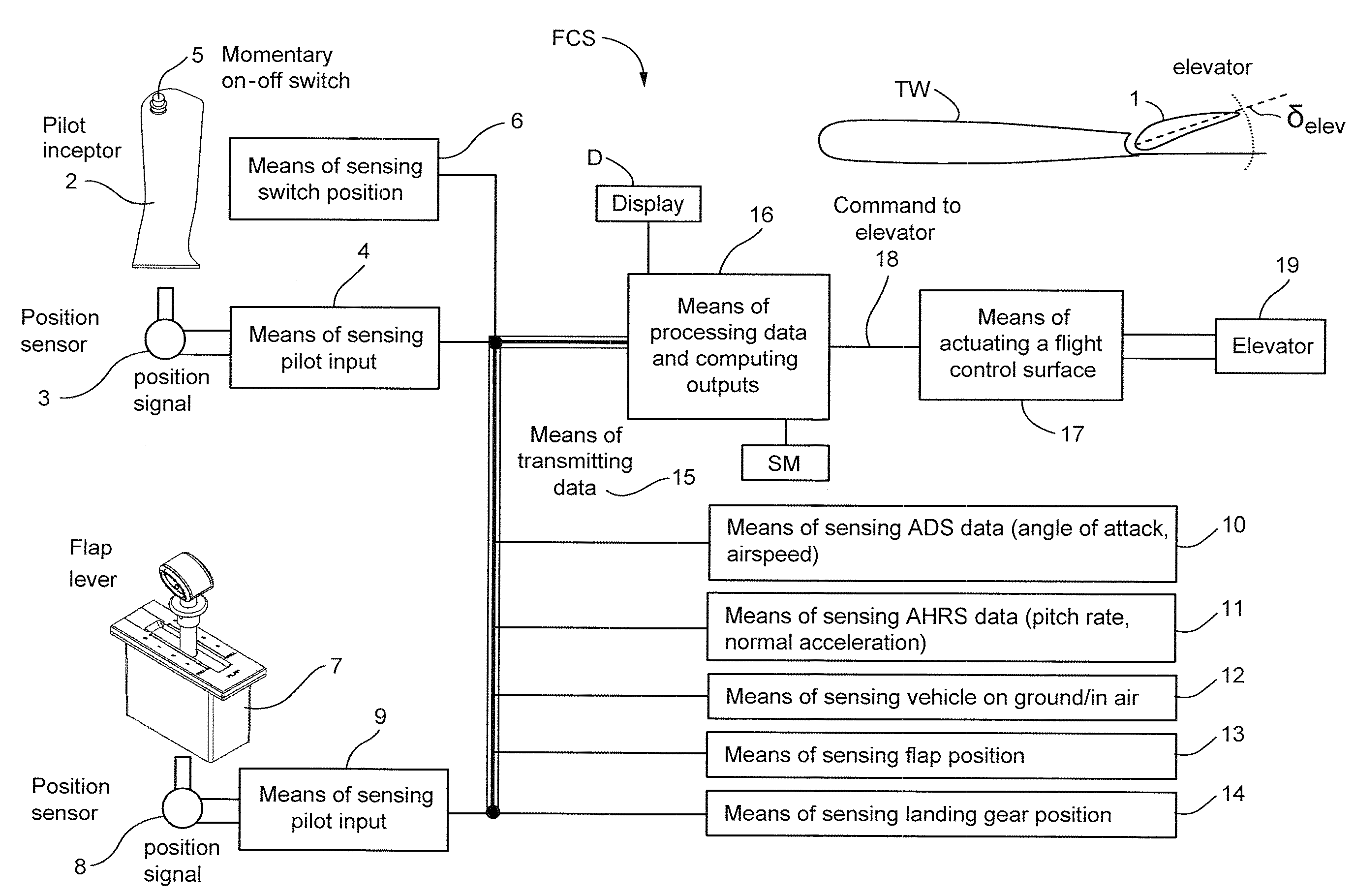
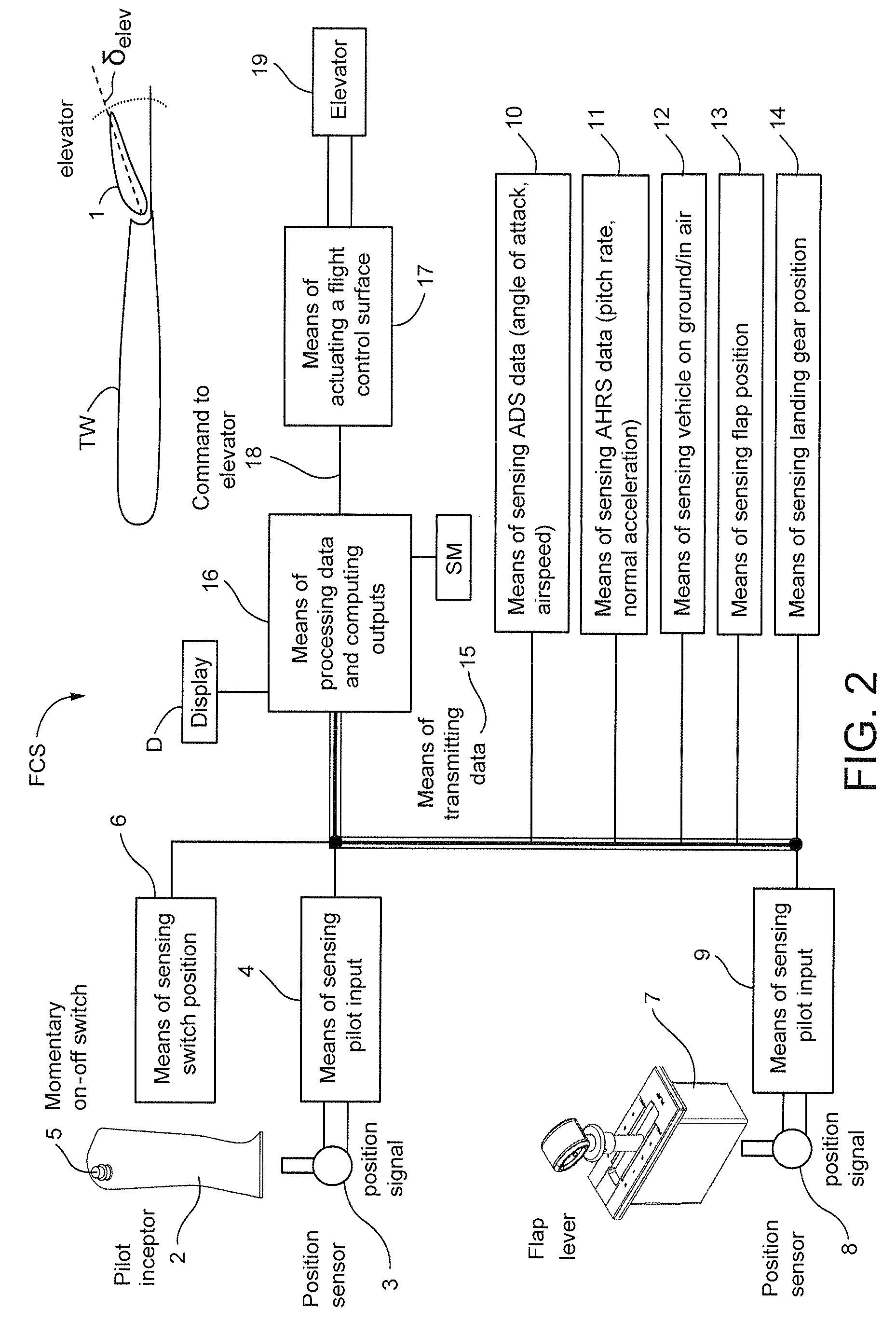
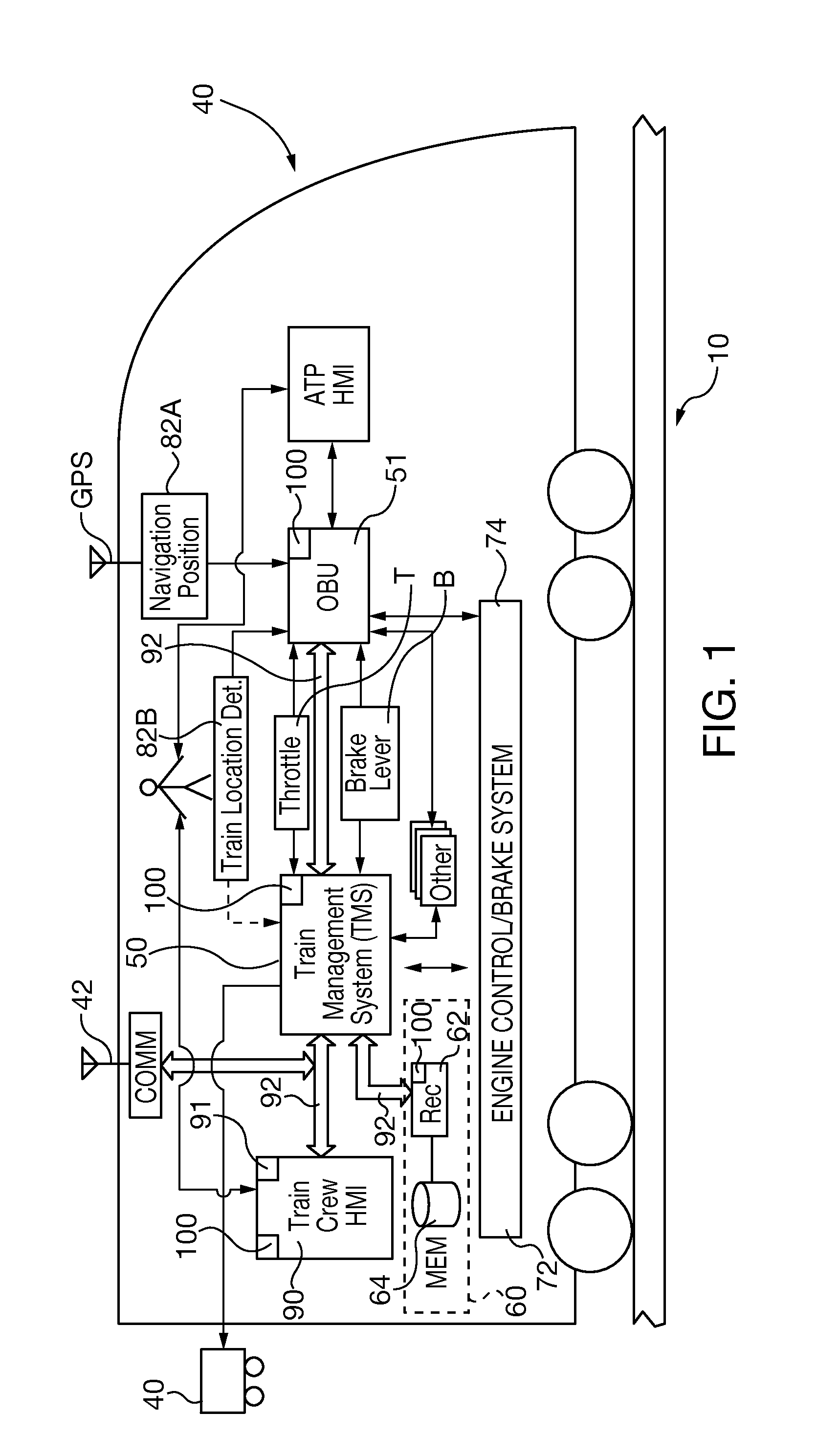
Flight Control System Mode And Method Providing Aircraft Speed Control Through The Usage Of Momentary On-Off Control
ActiveUS20130138274A1Economic securityEasy to operateAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAirplaneSafety critical application
A longitudinal control law is designed to optimize the flying qualities when aircraft is set to approach configuration, i.e. when the flap lever is set to the landing position and landing gears are locked down. Under such circumstances, the effort of trimming the aircraft speed can be extremely reduced by the usage of a momentary on-off switch or other control in the sidestick, instead of or in addition to a conventional trim up-down switch, making easier the task of airspeed selection by the pilot. This control law provides excellent handling qualities during approach and landing, with the benefit of not needing or using radio altimeter information in safety-critical applications.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
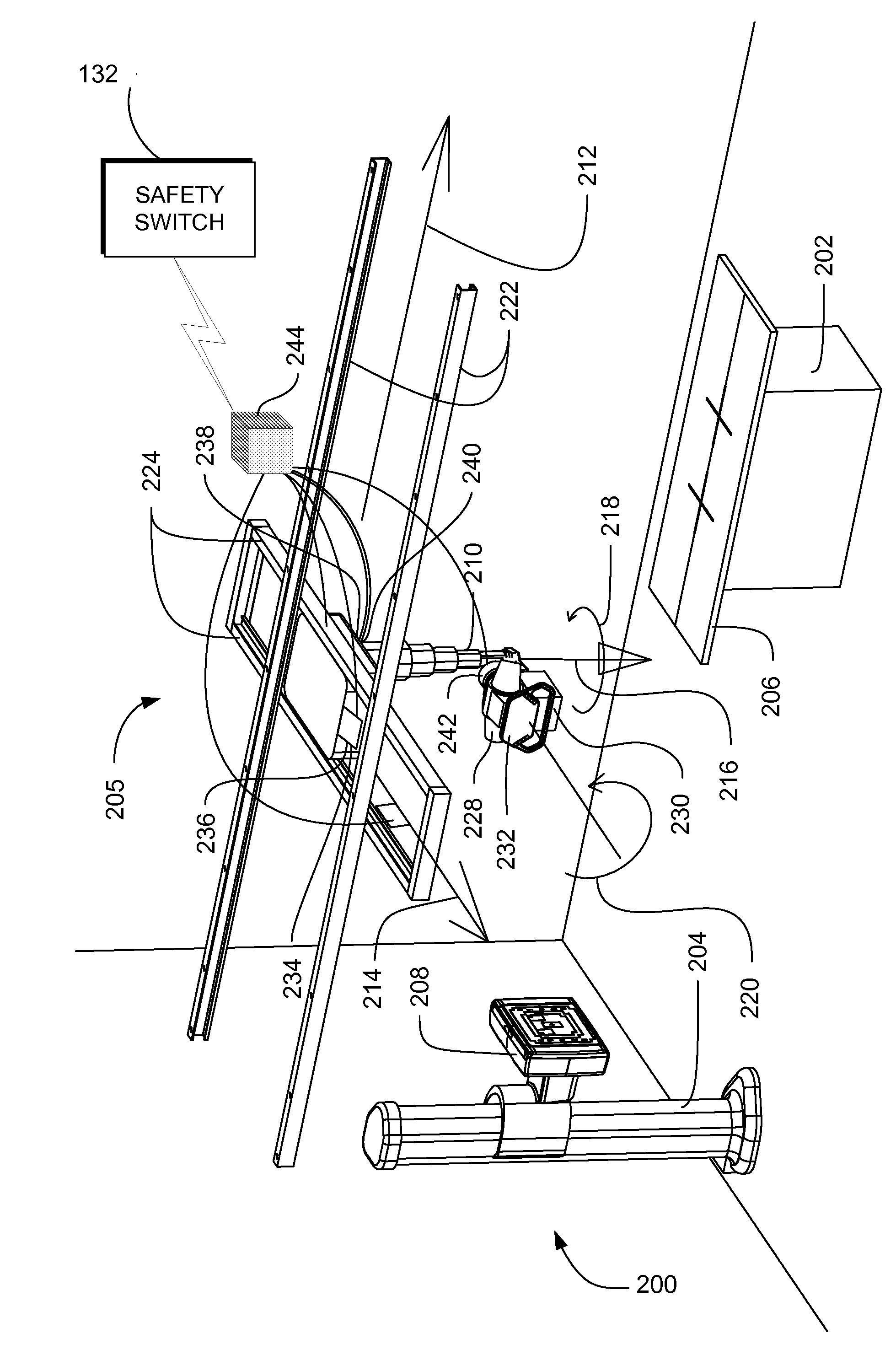
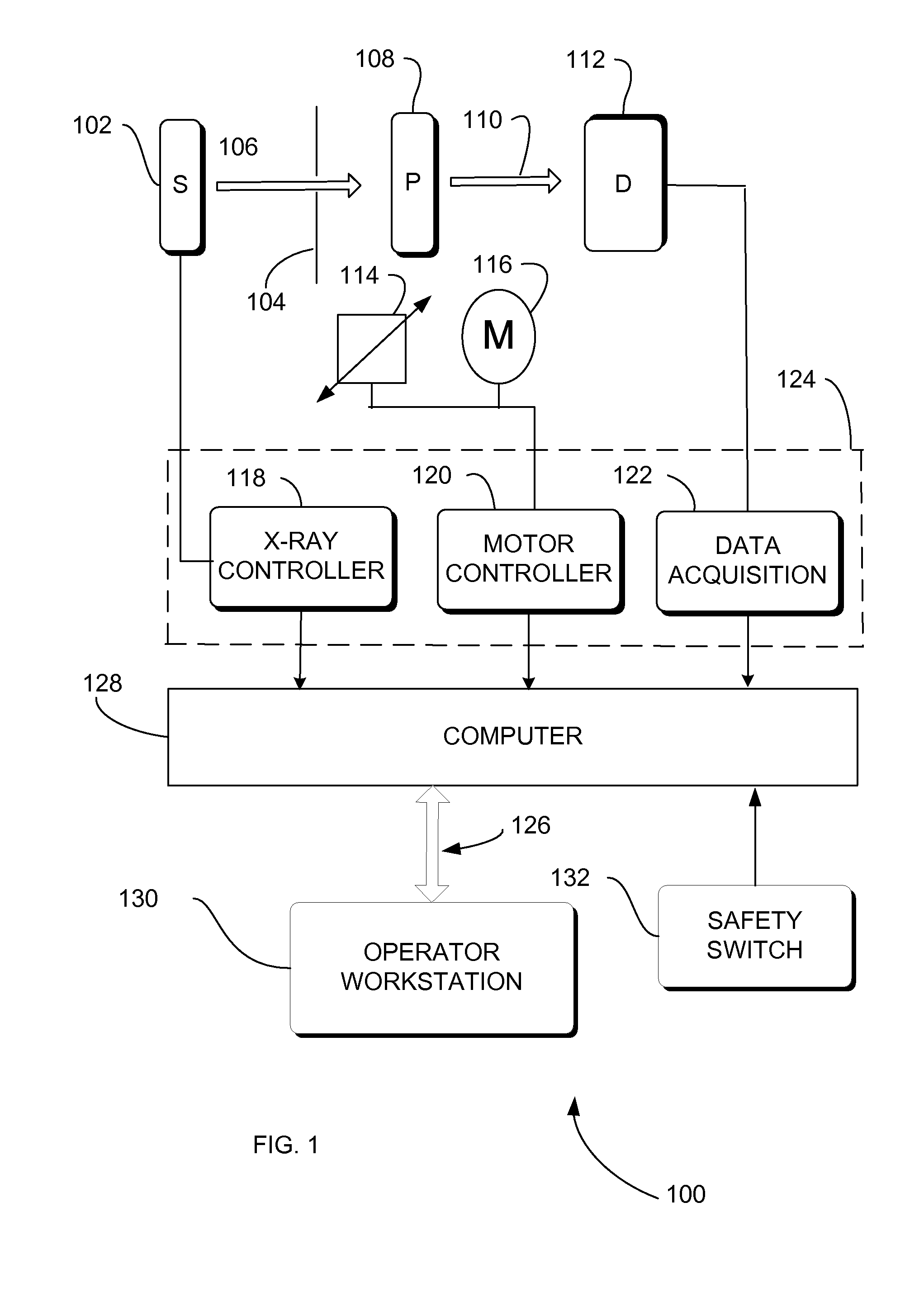
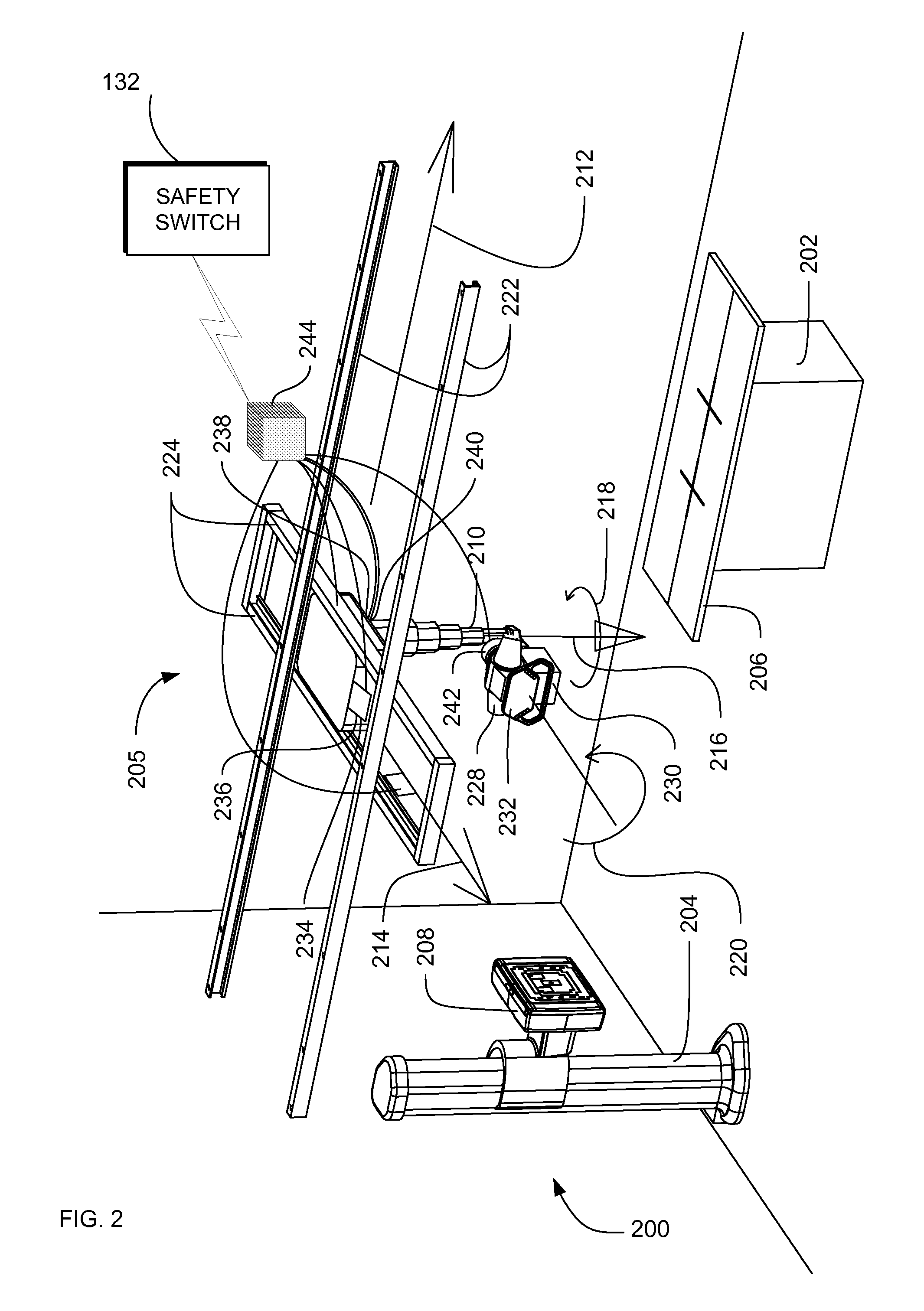
Redundant switch mechanism for safety-critical applications in medical systems
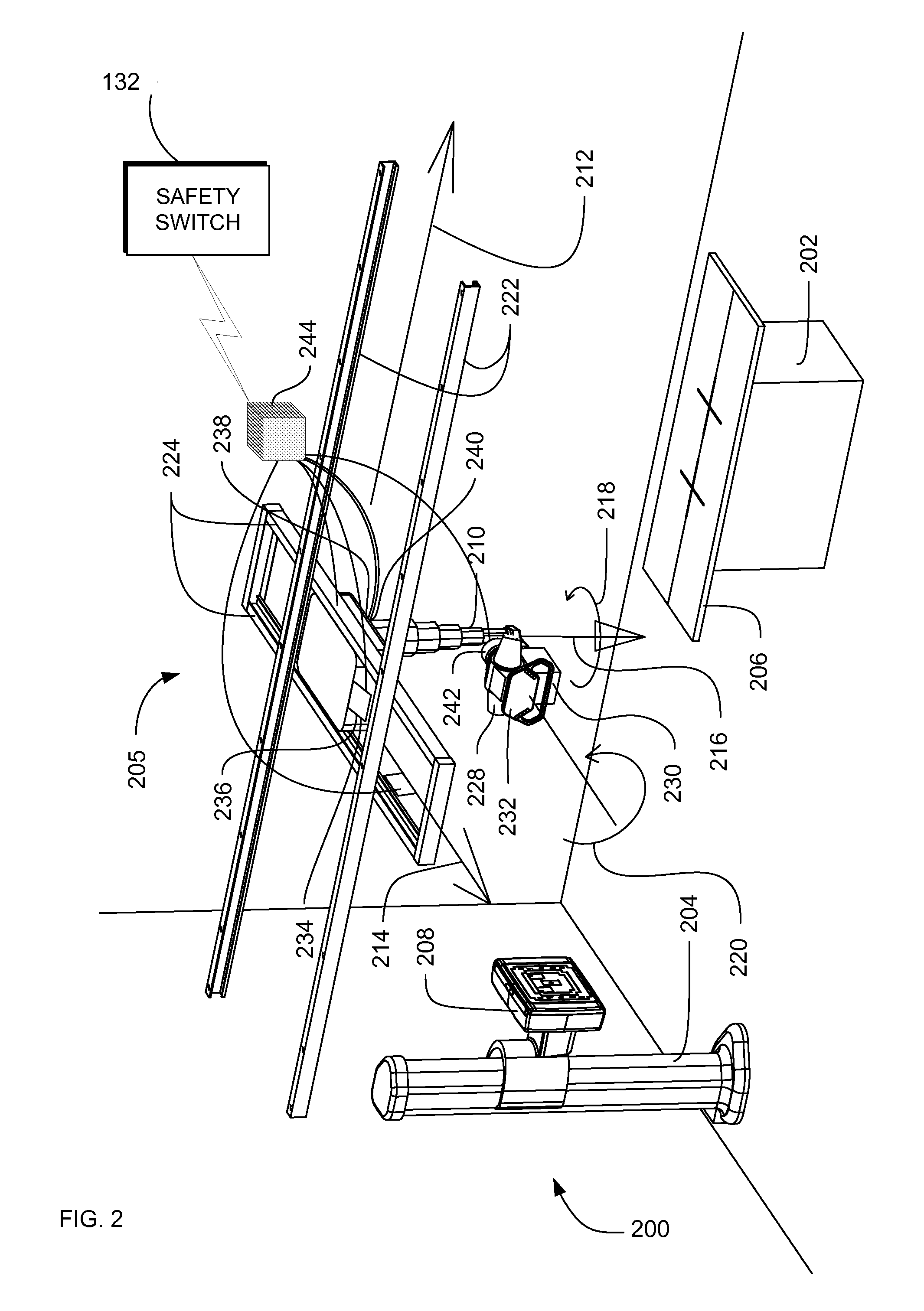
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a safety switch arrangement is assembled to prevent false activation of a subsystem in a medical system. In some embodiments, the safety switching arrangement comprises at least a first and a second type of switching element. In some embodiments, the first and the second type of switch each have an output that is processed by a processor, controller, or logic unit to produce an output signal for activating or deactivating a subsystem in the medical system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
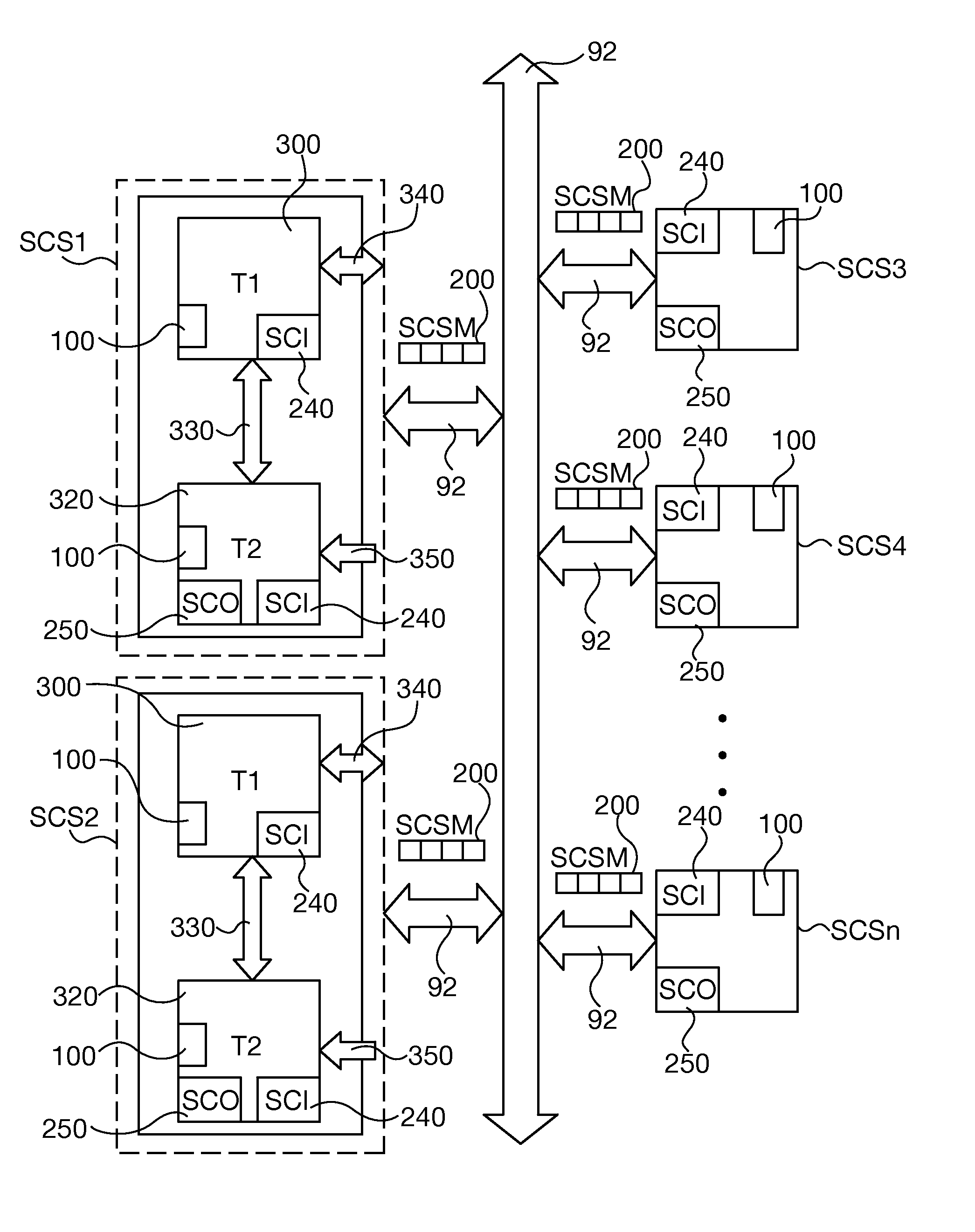
Railway safety critical systems with task redundancy and asymmetric communications capability
ActiveUS20140229040A1Reduce safety critical system control system procurement costIncrease the number ofAutomatic systemsDigital data processing detailsTechnical standardPersonal computer
A railway safety critical application system substitutes commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware and / or software for railway-domain specific product components, yet is validated to conform to railway safety critical system failure-free standards. The safety critical system uses a pair of tasks executed on a controller of a COTS personal computer or within a virtual environment with asymmetric communications capability. Both tasks receive and verify safety critical systems input message data and security code integrity and separately generate output data responsive to the input message. The first task has sole capability to send complete safety critical system output messages, but only the second task has the capability of generating the output security code. A failure of any of systems hardware, software or processing capability results failure to transmit a safety critical system output message or an output message that cannot be verified by other safety critical systems.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
Flight control system mode and method providing aircraft speed control through the usage of momentary on-off control
ActiveUS8606437B2Stable speedReduce effortAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsFlight vehicleSafety critical application
A longitudinal control law is designed to optimize the flying qualities when aircraft is set to approach configuration, i.e. when the flap lever is set to the landing position and landing gears are locked down. Under such circumstances, the effort of trimming the aircraft speed can be extremely reduced by the usage of a momentary on-off switch or other control in the sidestick, instead of or in addition to a conventional trim up-down switch, making easier the task of airspeed selection by the pilot. This control law provides excellent handling qualities during approach and landing, with the benefit of not needing or using radio altimeter information in safety-critical applications.
Owner:EMBRAER SA
Railway safety critical systems with task redundancy and asymmetric communications capability
ActiveUS9233698B2Simplify railway safety critical systems overall designReduce procurement costsAutomatic systemsPoint-signal interlocking arrangmentsTechnical standardPersonal computer
A railway safety critical application system substitutes commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware and / or software for railway-domain specific product components, yet is validated to conform to railway safety critical system failure-free standards. The safety critical system uses a pair of tasks executed on a controller of a COTS personal computer or within a virtual environment with asymmetric communications capability. Both tasks receive and verify safety critical systems input message data and security code integrity and separately generate output data responsive to the input message. The first task has sole capability to send complete safety critical system output messages, but only the second task has the capability of generating the output security code. A failure of any of systems hardware, software or processing capability results failure to transmit a safety critical system output message or an output message that cannot be verified by other safety critical systems.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
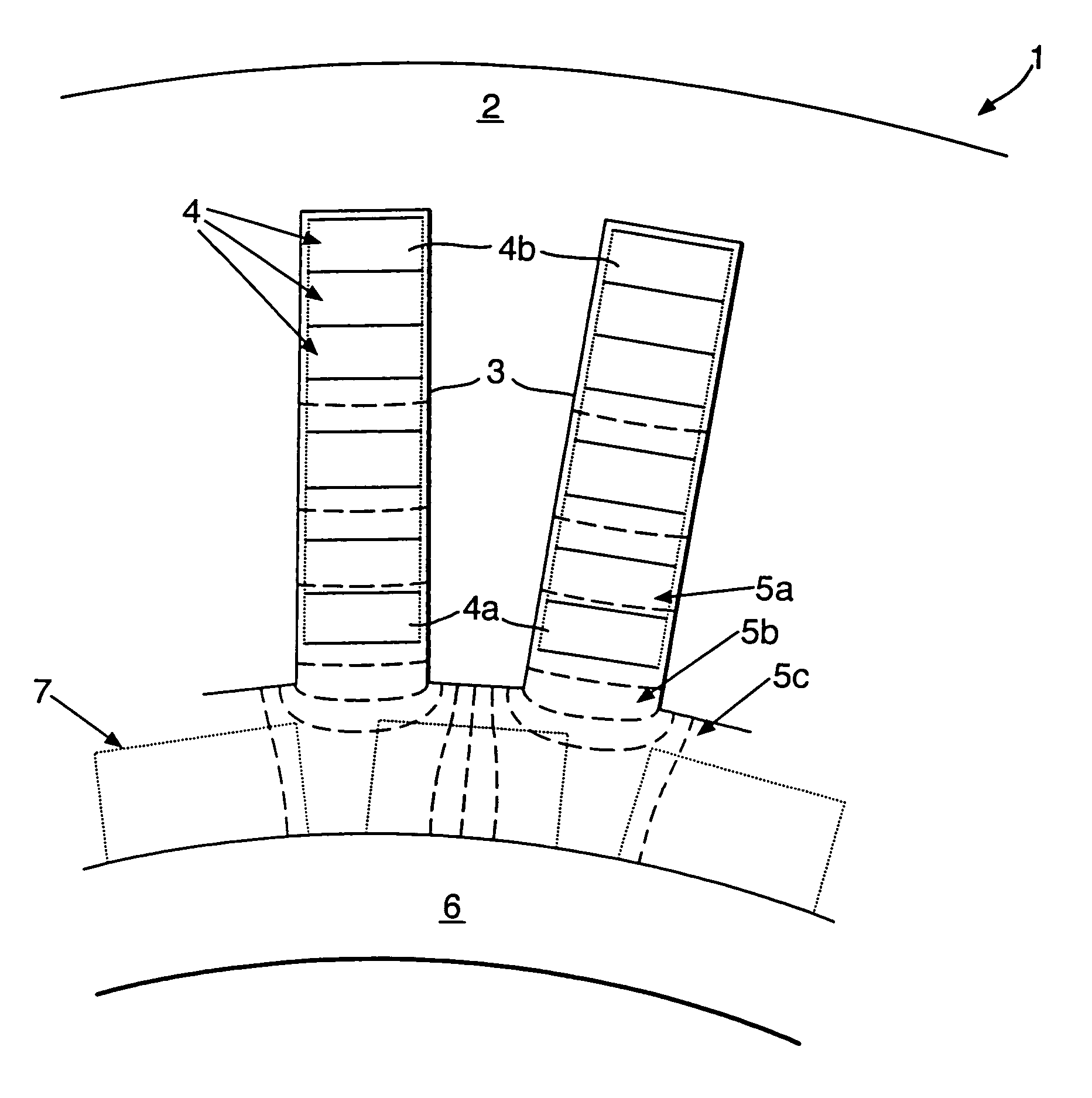
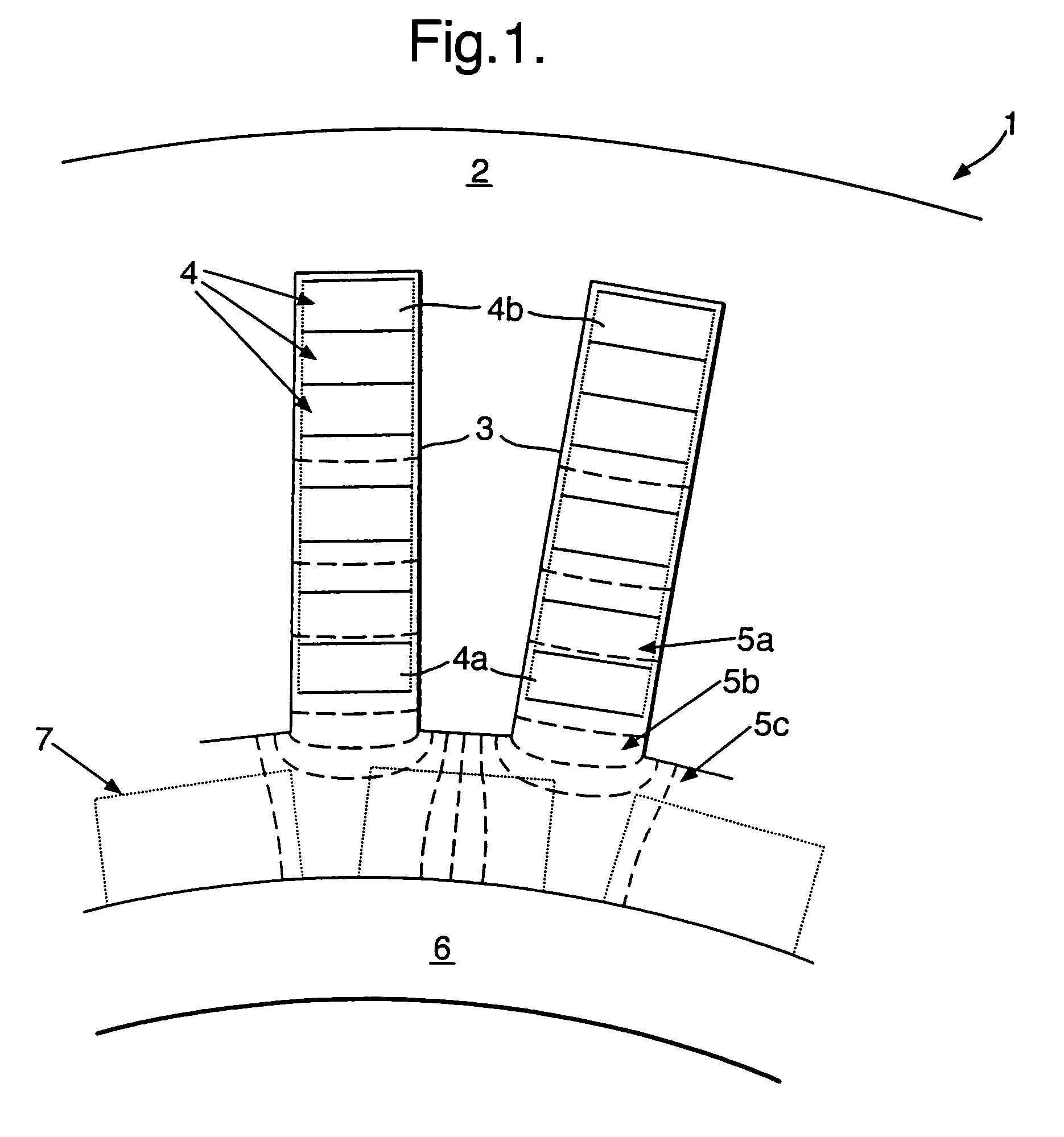
Motor coil-shorting detecting unit
InactiveUS7372676B2Effective protectionMore flowElectric motor controlEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionElectricityElectric machine
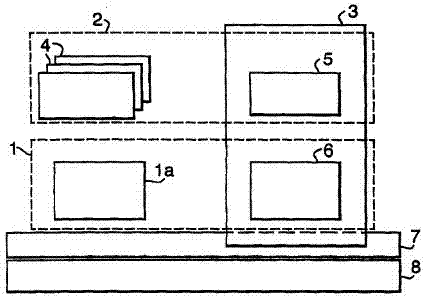
In order to be acceptable for safety critical applications, it is necessary for an electrical machine to allow continued operation despite an electrical short circuit in one of the operational phases of that electrical machine. It will be appreciated that an electrical short circuit creates excessive electrical current through the short circuit with significant heating and other detrimental effects. However, the electrical machine can operate with one operational phase disabled. In such circumstances, the present invention incorporates means for determining an electrical short circuit has occurred and then injects an electrical current approximately equal to or greater than the rated electrical current. In such circumstances, the operational phase or coil 4, 24, 34 is effectively protected despite the electrical short circuit and hence the electrical machine can continue to operate.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Computer interlocking software development and realization system based on formalized model development
InactiveCN107808020AReadableMeet development requirementsSoftware testing/debuggingDesign optimisation/simulationSoftware development processOperational system
The invention relates to a computer interlocking software development and realization system based on formalized model development. The system includes: an interlocking software logic module, which isused for realizing interlocking logic processing functions of the system, wherein modeling and designing of the interlocking logic functions are carried out by adopting an SCADE (safety-critical application development environment) tool; an interlocking software application interface module, which provides information transmission channels of logical operations and external interfaces, and is used for realizing parsing and packaging of various types of communication message data of the external interfaces, and completing information exchange with the interlocking software logic module at thesame time; and a testing module, which is used for carrying out simulation testing and safety verification on model logic designs. Compared with the prior art, a model of the invention has the advantages such as the advantages that C-language code which is suitable for use in an embedded operating system can be verified or automatically generated, and the generated code meets a series of safety features.
Owner:CASCO SIGNAL
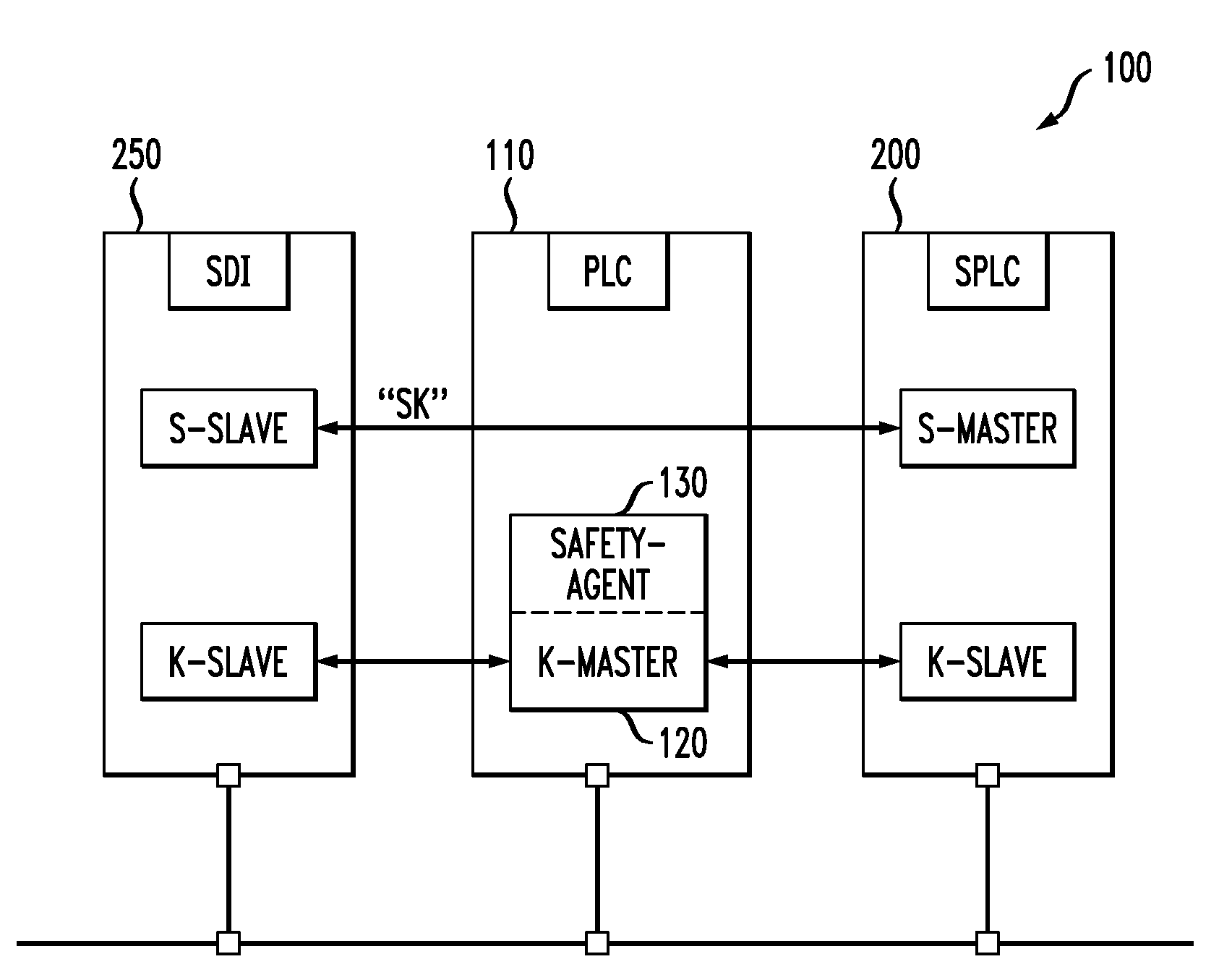
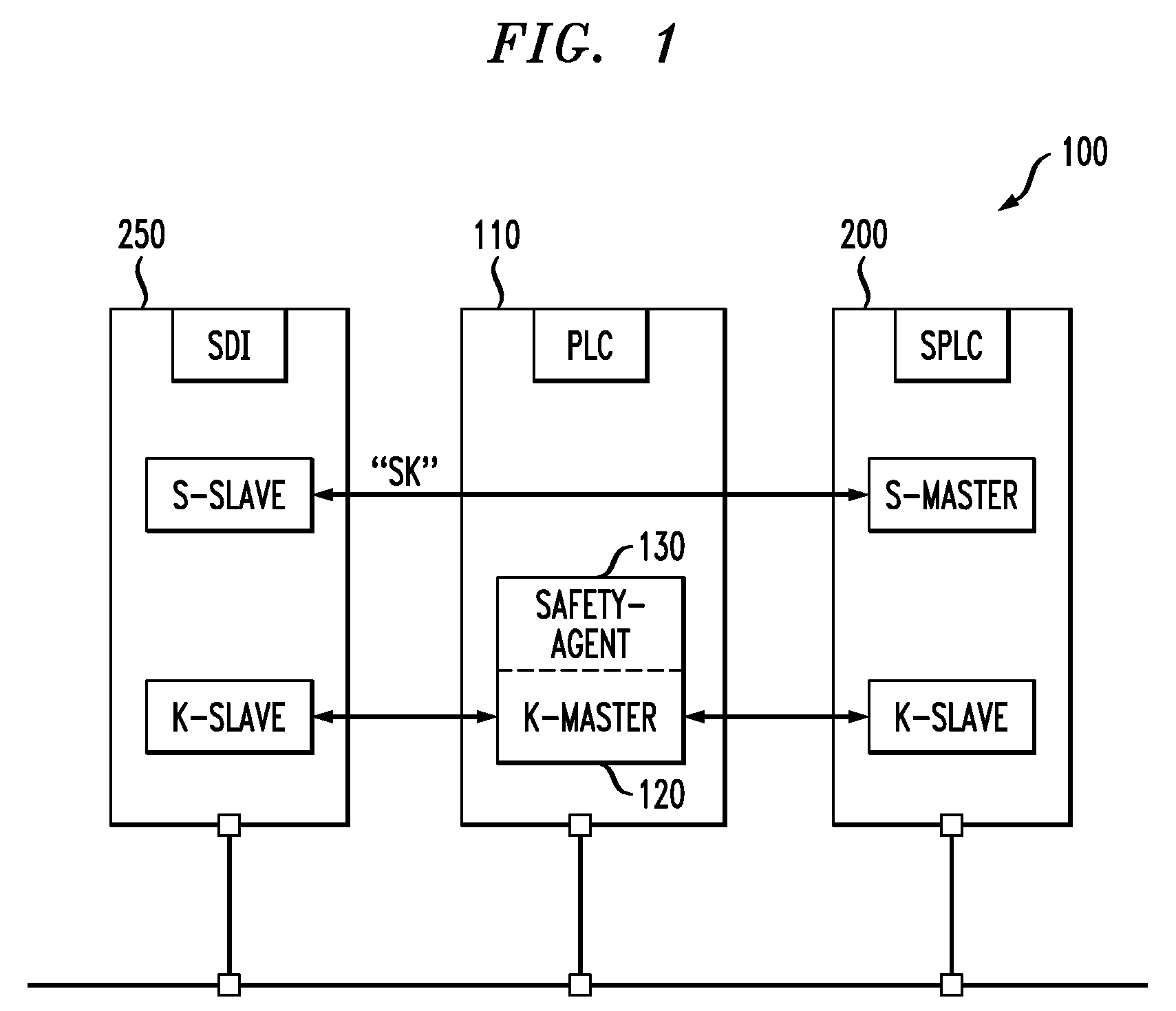
System for operating at least one non-safety-critical and at least one safety-critical process
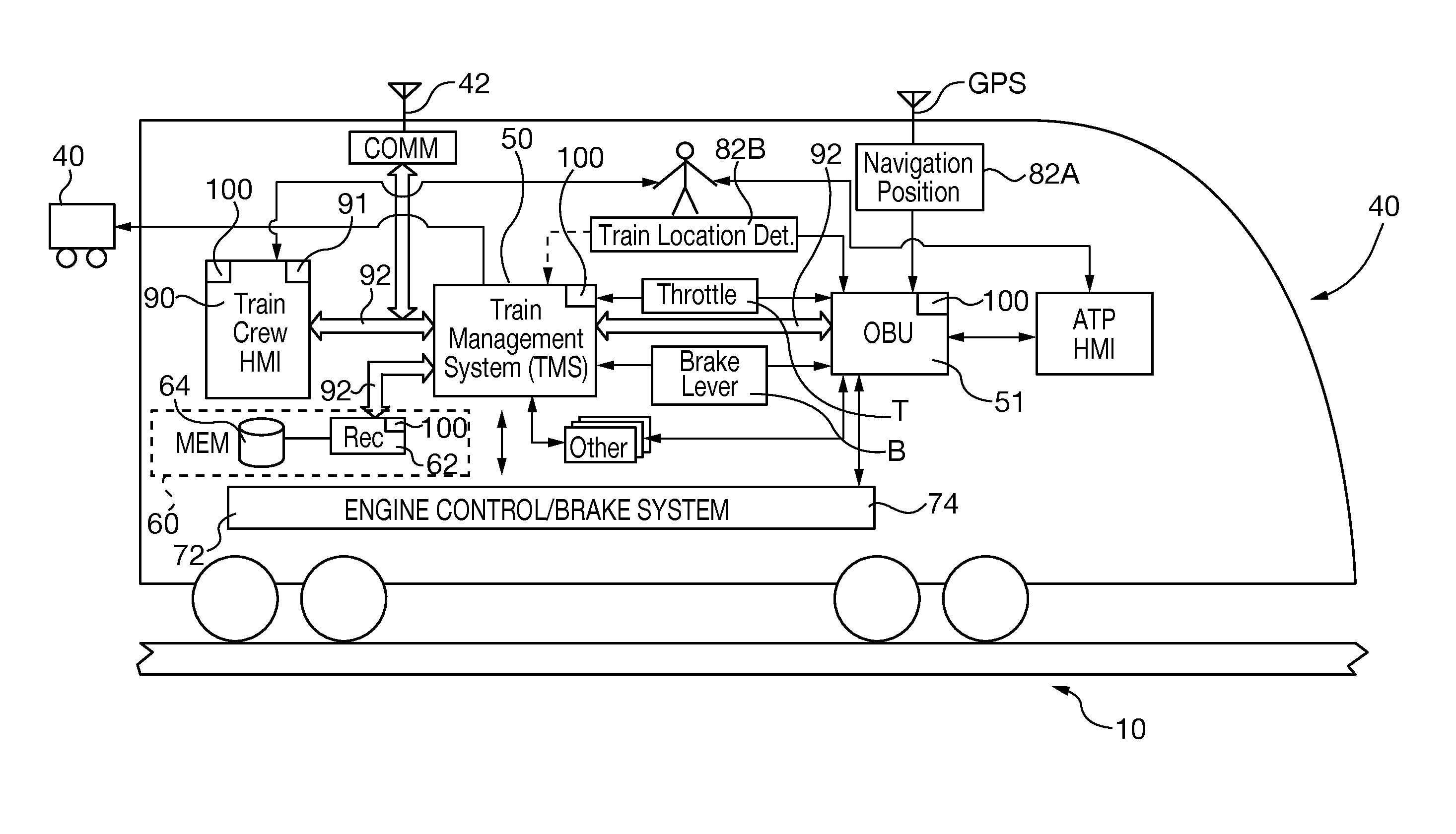
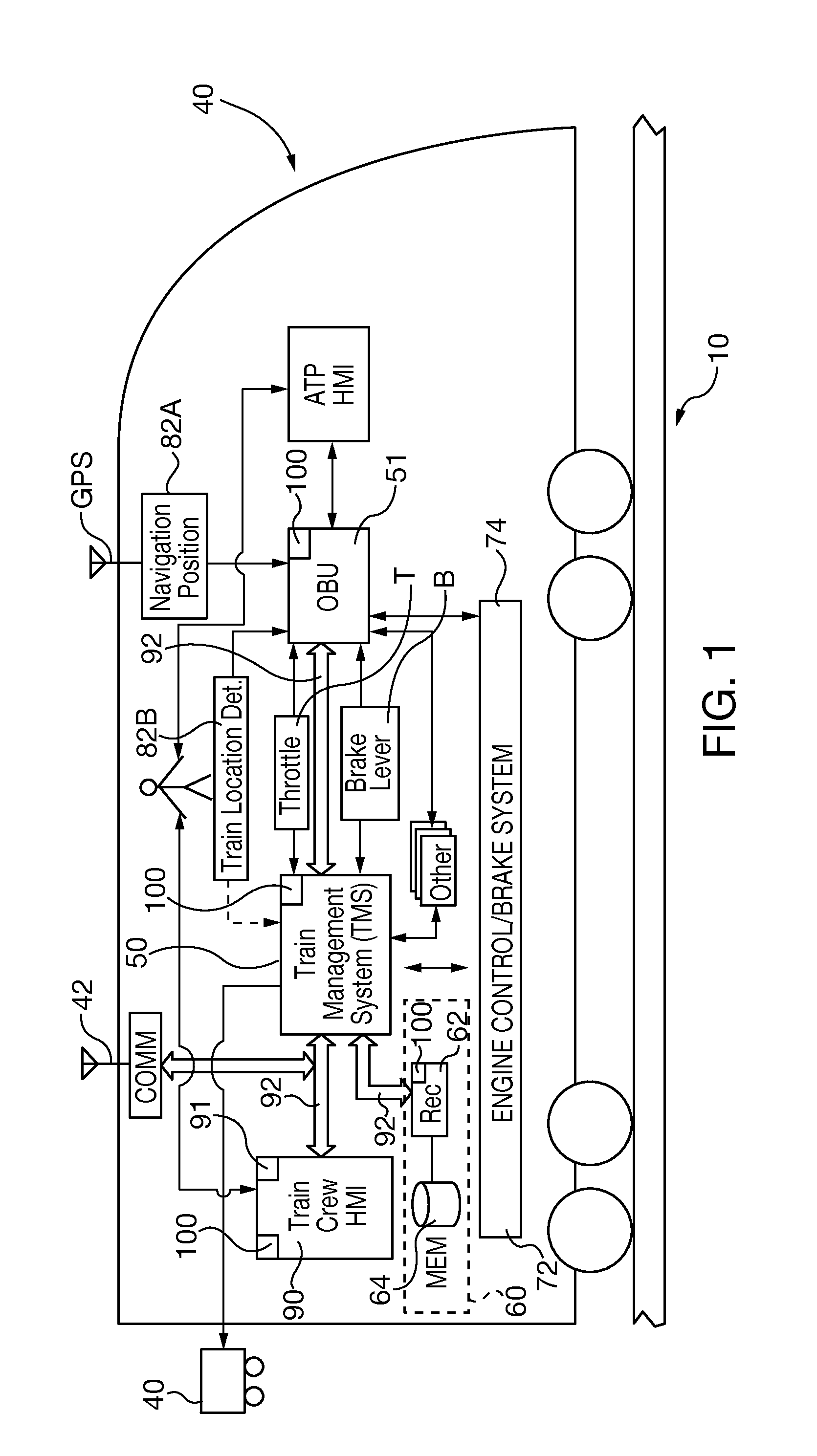
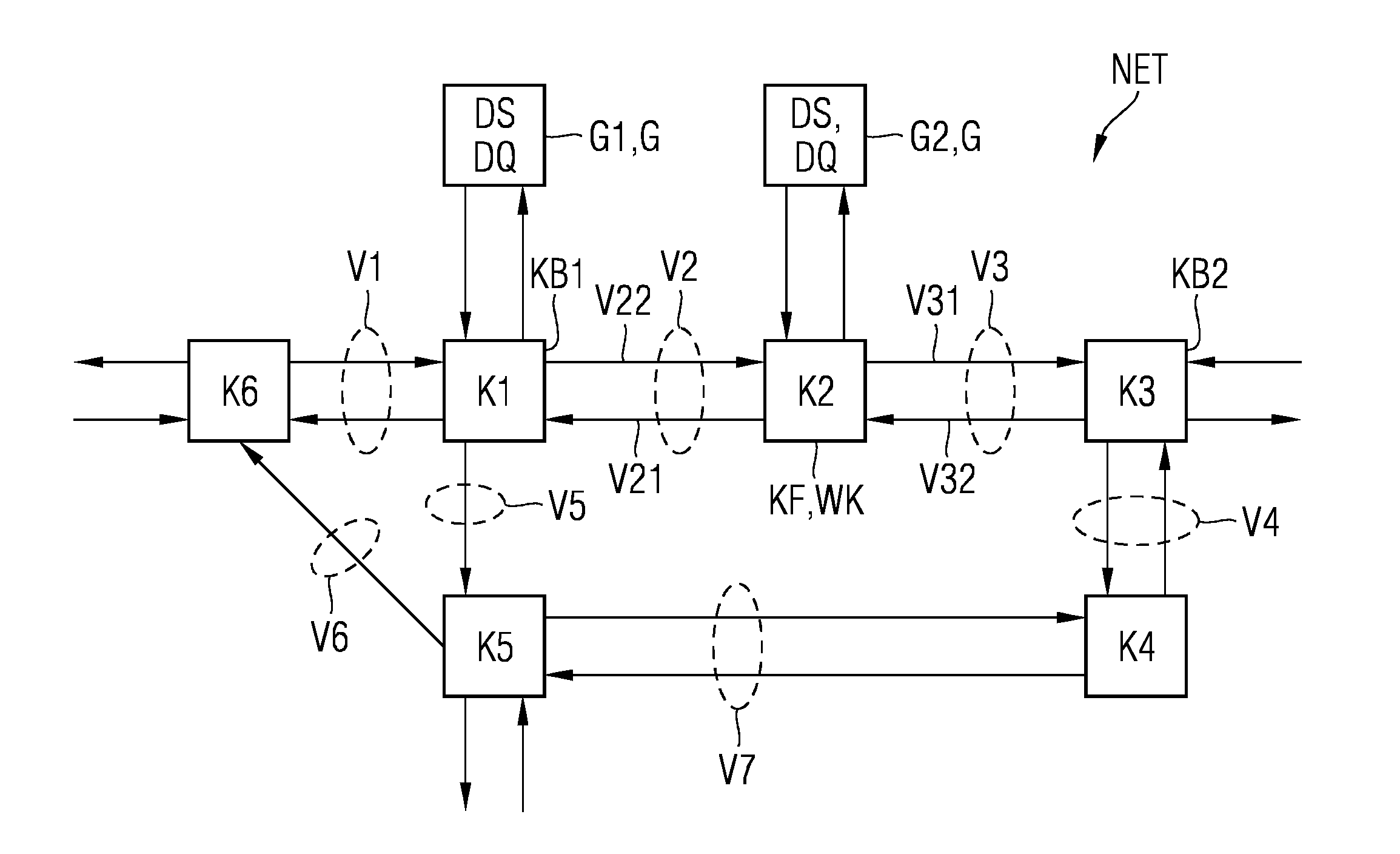
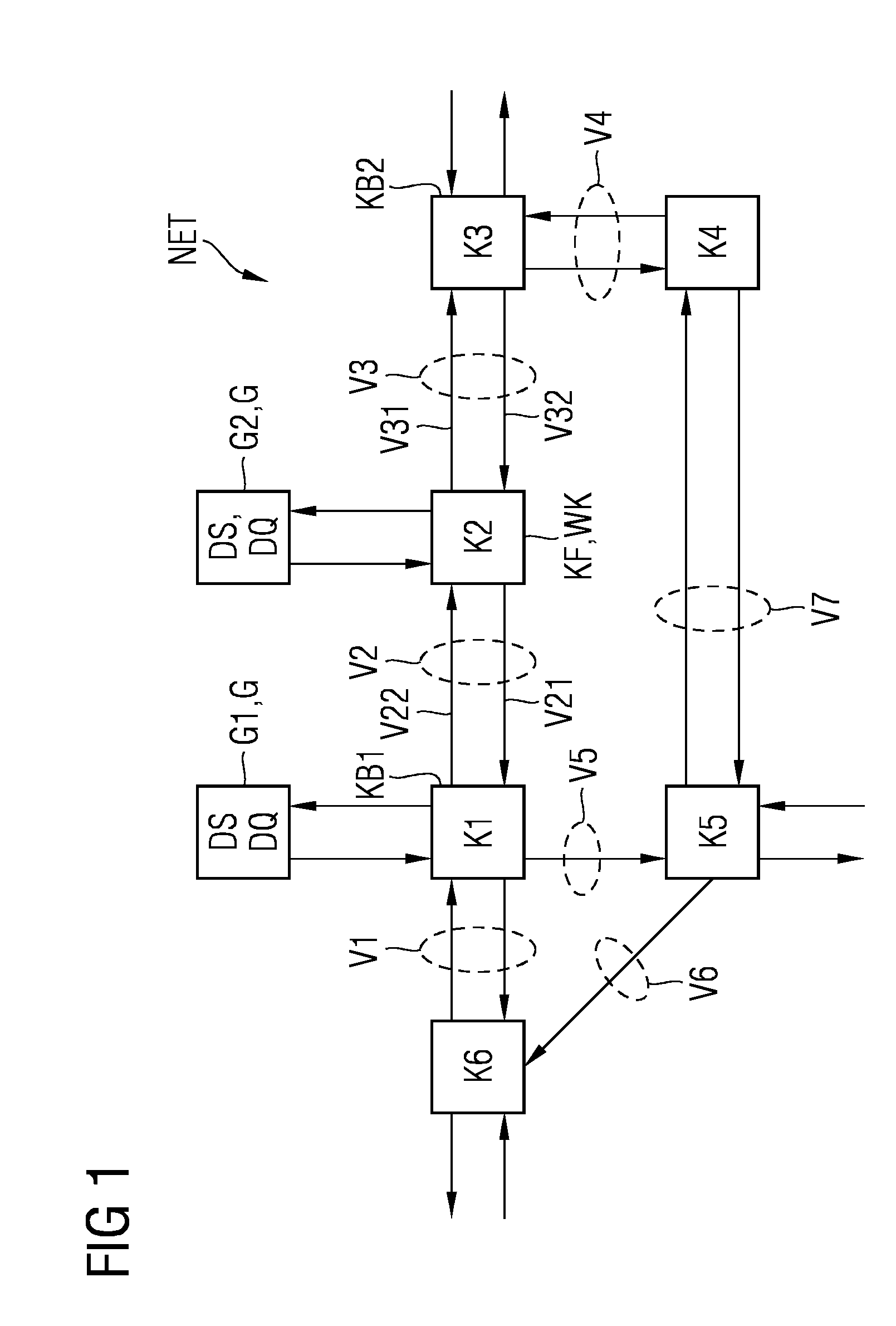
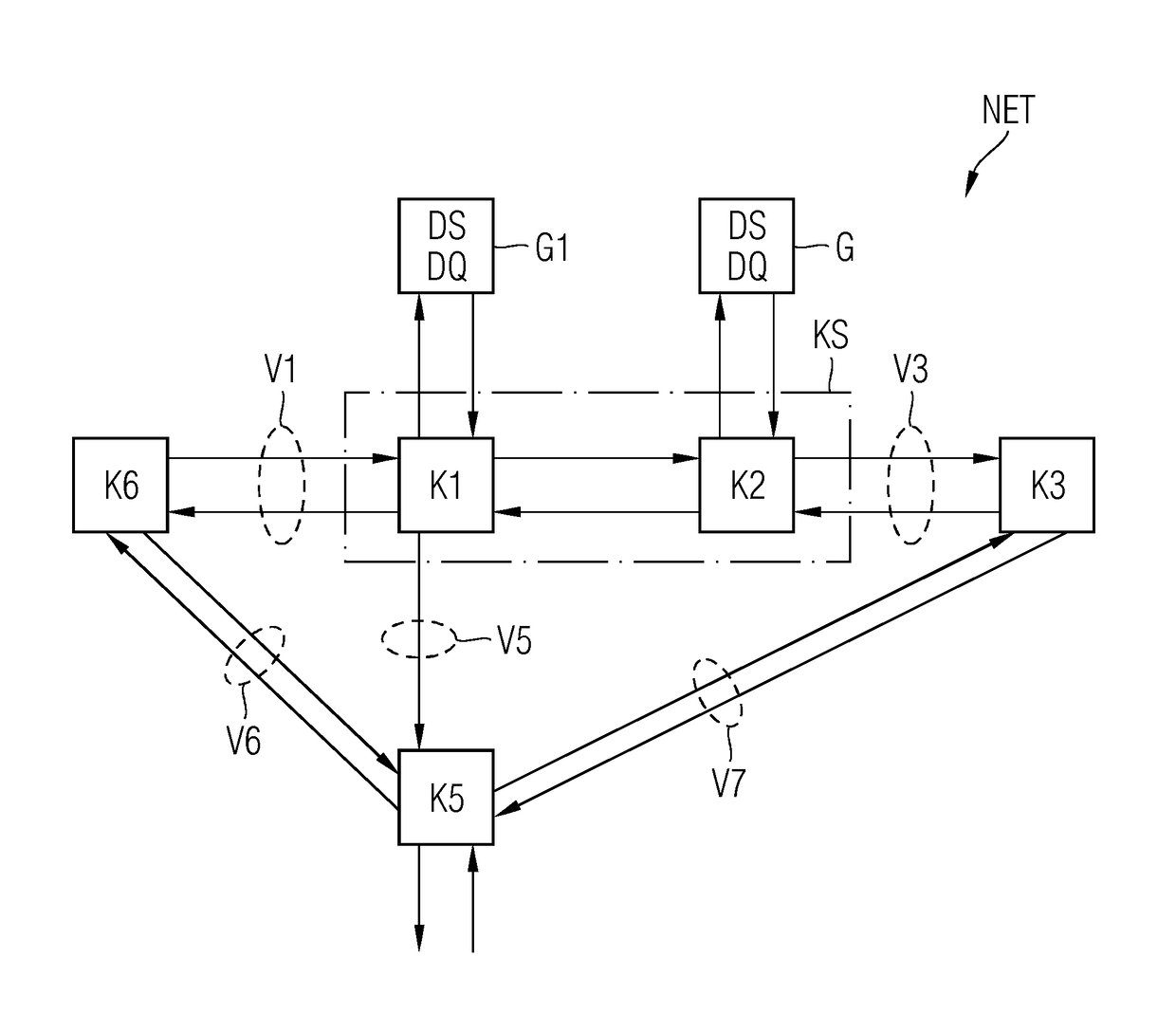
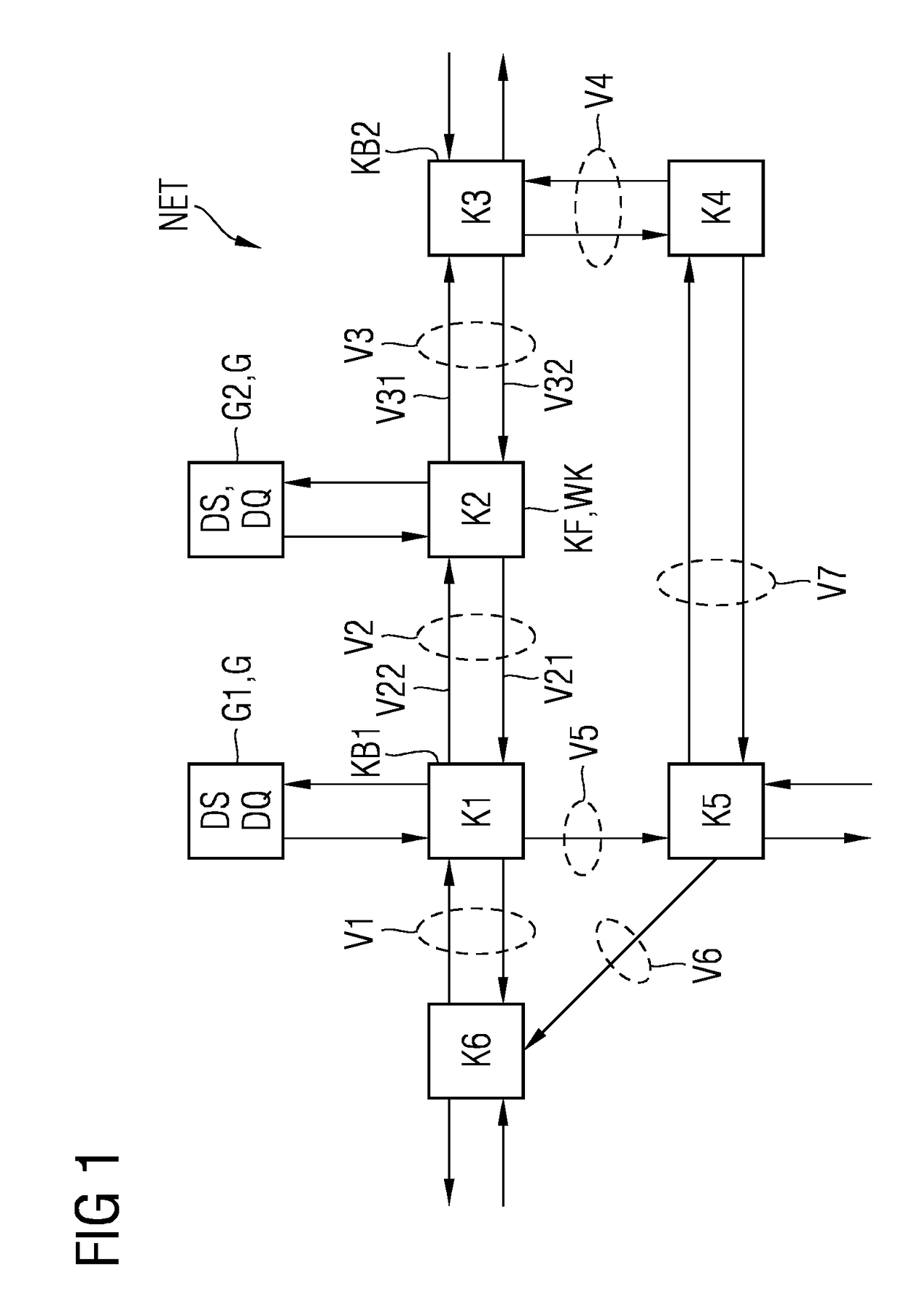
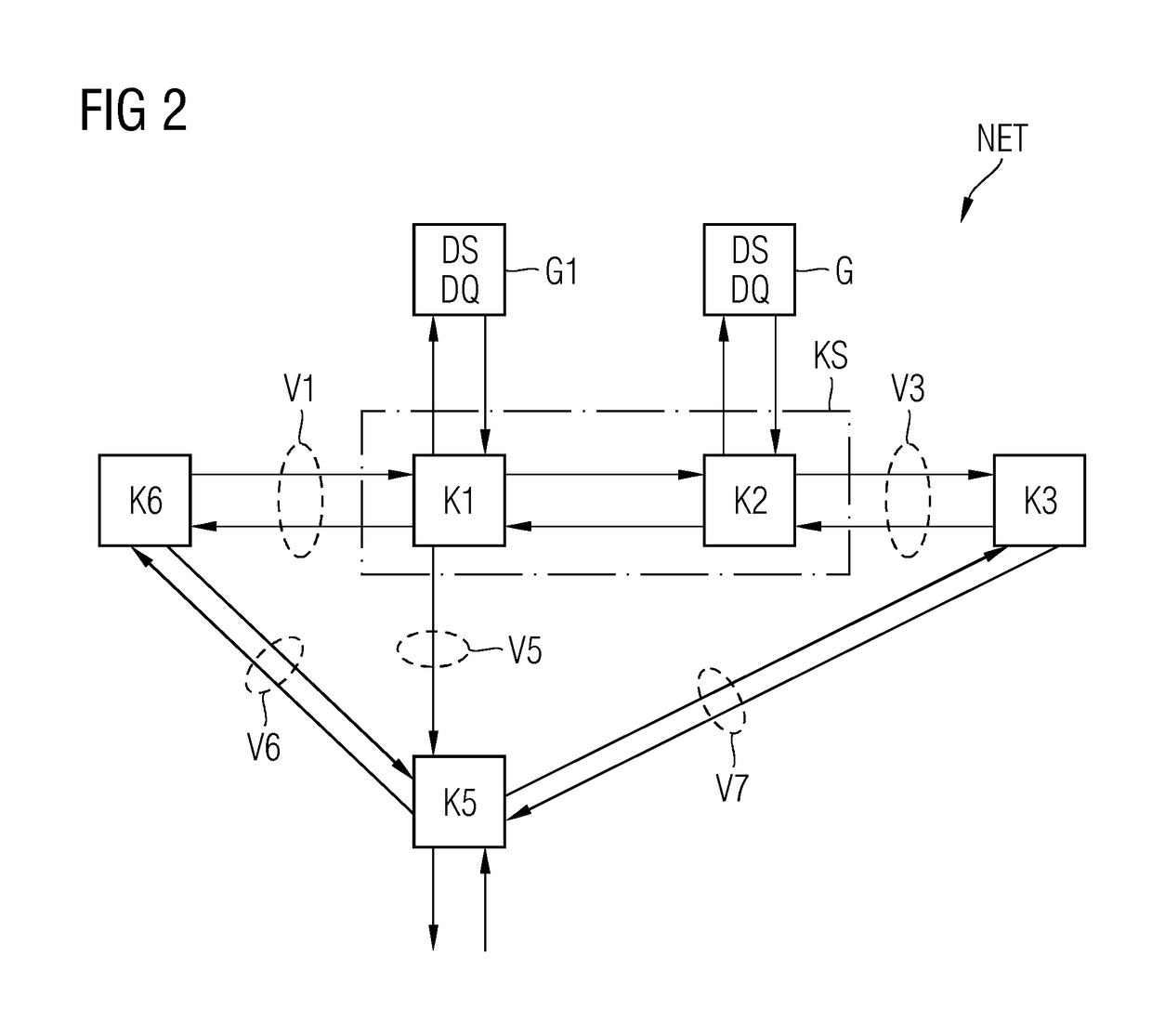
For the operation of at least one non-safety-critical application process and at least one safety-critical application process, the invention proposes a data processing and transmission system with a data transmission network, at least one non-safety-related network element linked to the non-safety-critical application process and connected to the network, and with at least one safety-related network element linked to the safety-critical application process, as well as with at least one master unit connected to the network, and a server unit connected to the network separately from the master unit, wherein the safety-related server unit controls the at least one safety-critical application process, specifically by processing safety-relevant data necessary for controlling the safety-critical application process and by organizing the transmission of the safety-relevant data over the network by means of at least one of the network elements and / or the master unit.
Owner:PHOENIX CONTACT GMBH & CO KG
Redundant switch mechanism for safety-critical applications in medical systems
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which a safety switch arrangement is assembled to prevent false activation of a subsystem in a medical system. In some embodiments, the safety switching arrangement comprises at least a first and a second type of switching element. In some embodiments, the first and the second type of switch each have an output that is processed by a processor, controller, or logic unit to produce an output signal for activating or deactivating a subsystem in the medical system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
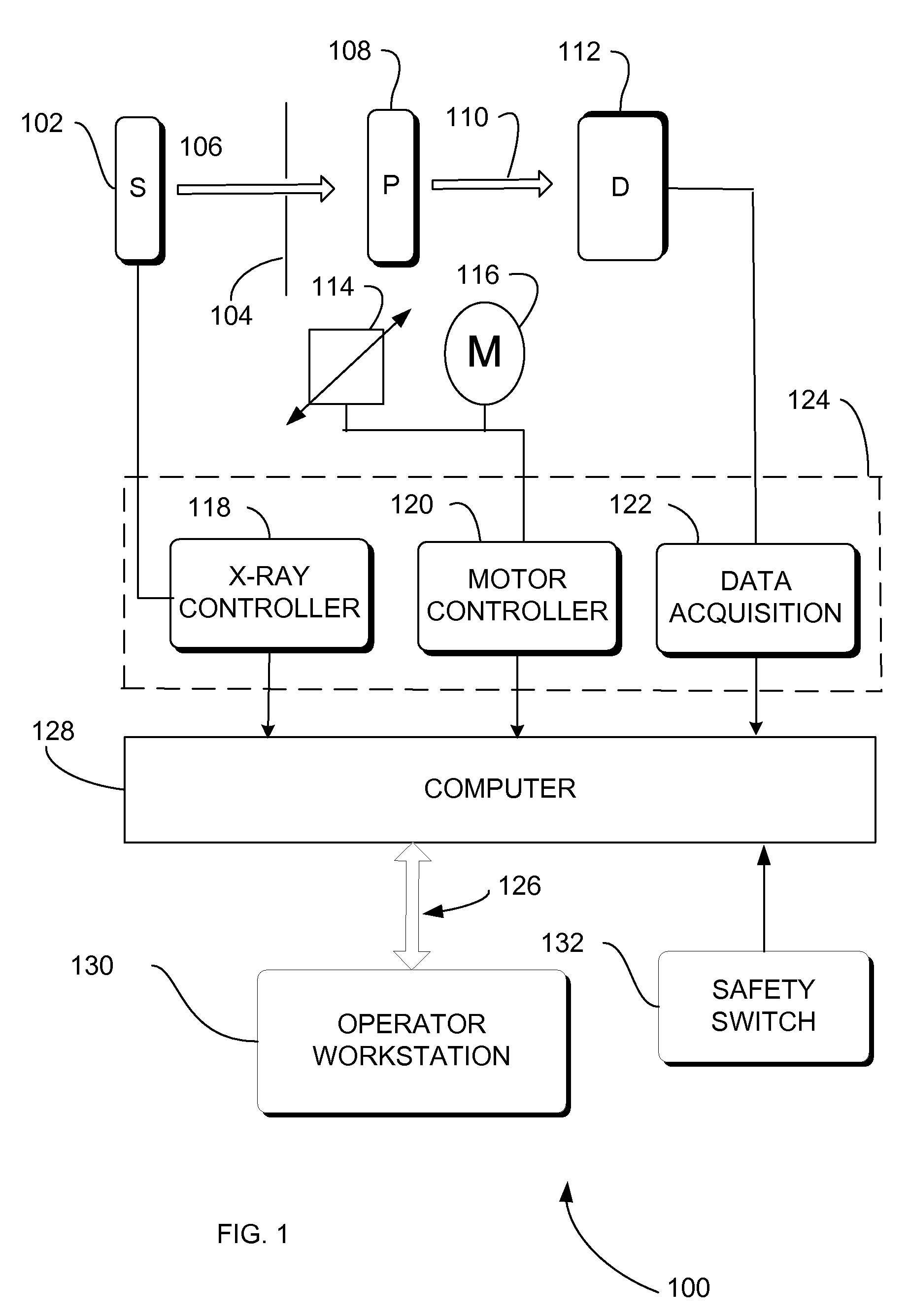
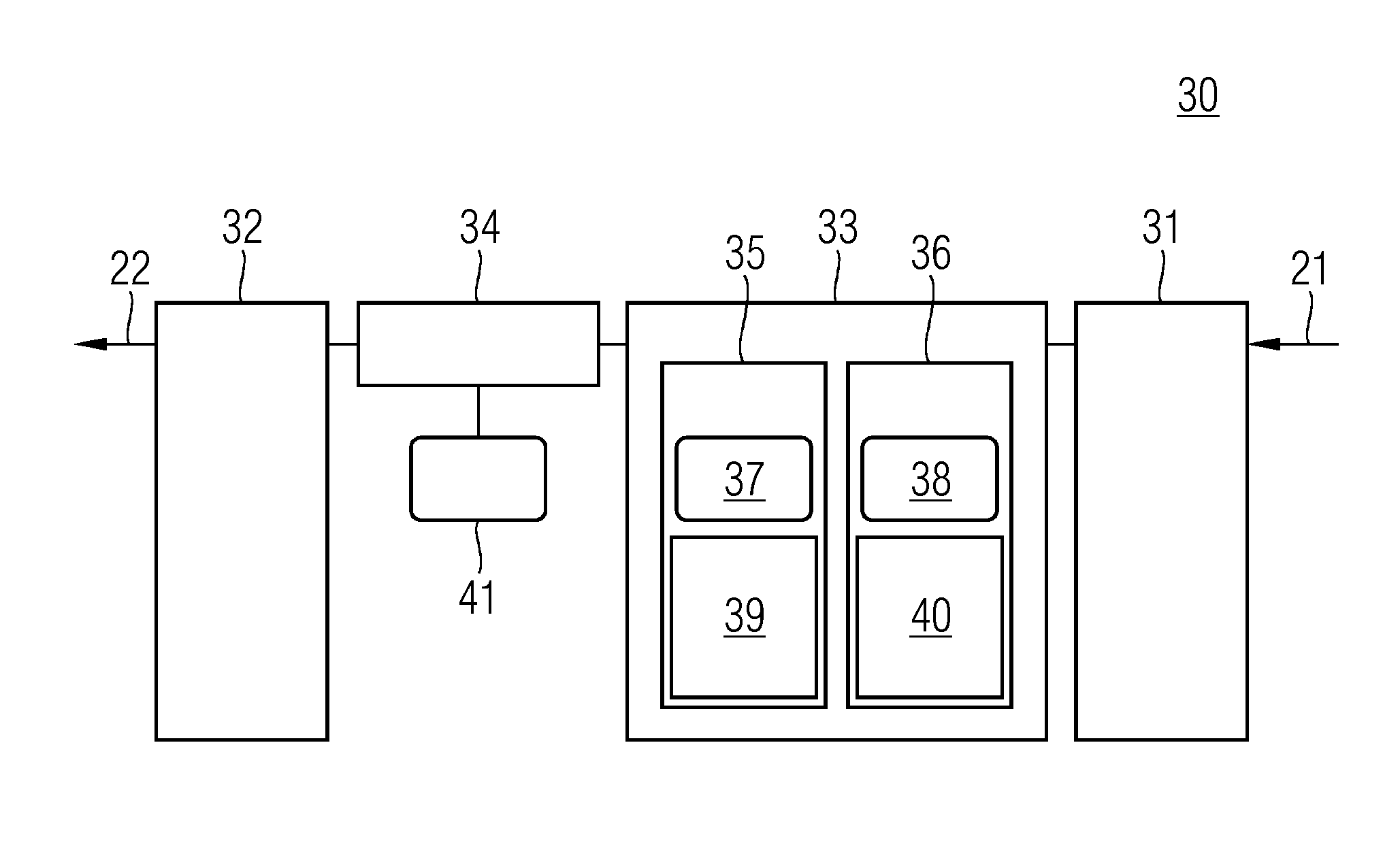
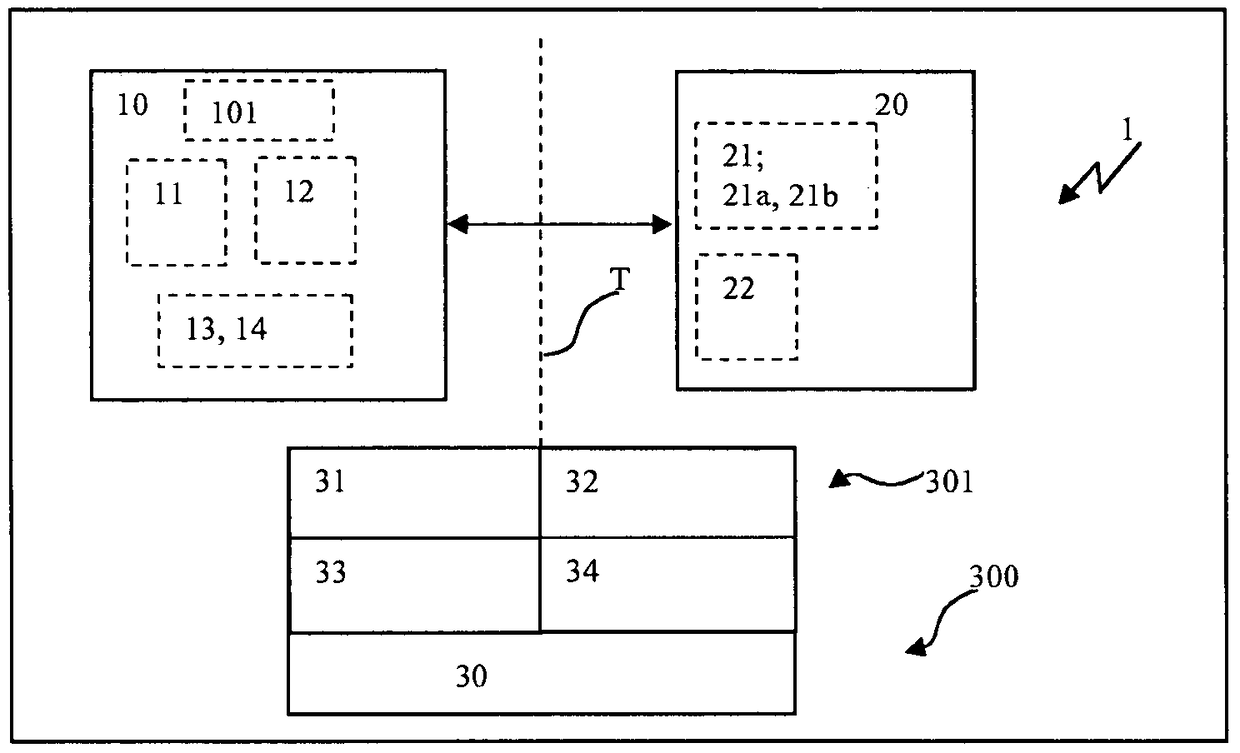
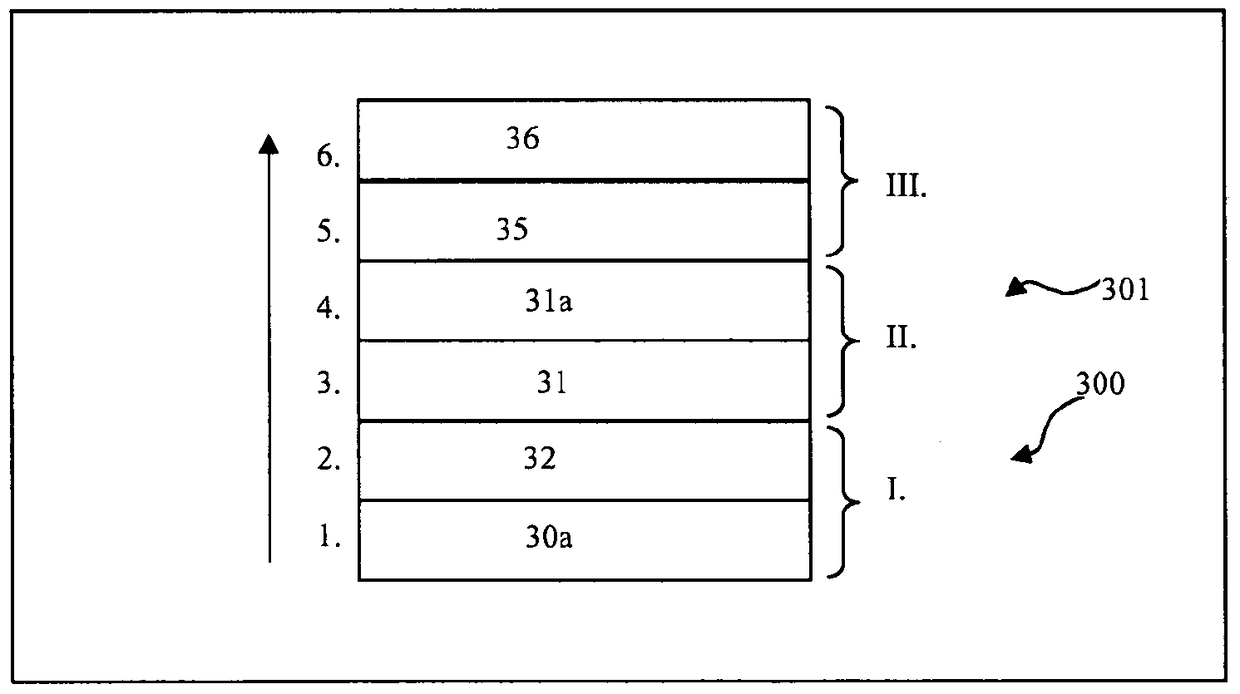
Apparatus and method for transmitting data
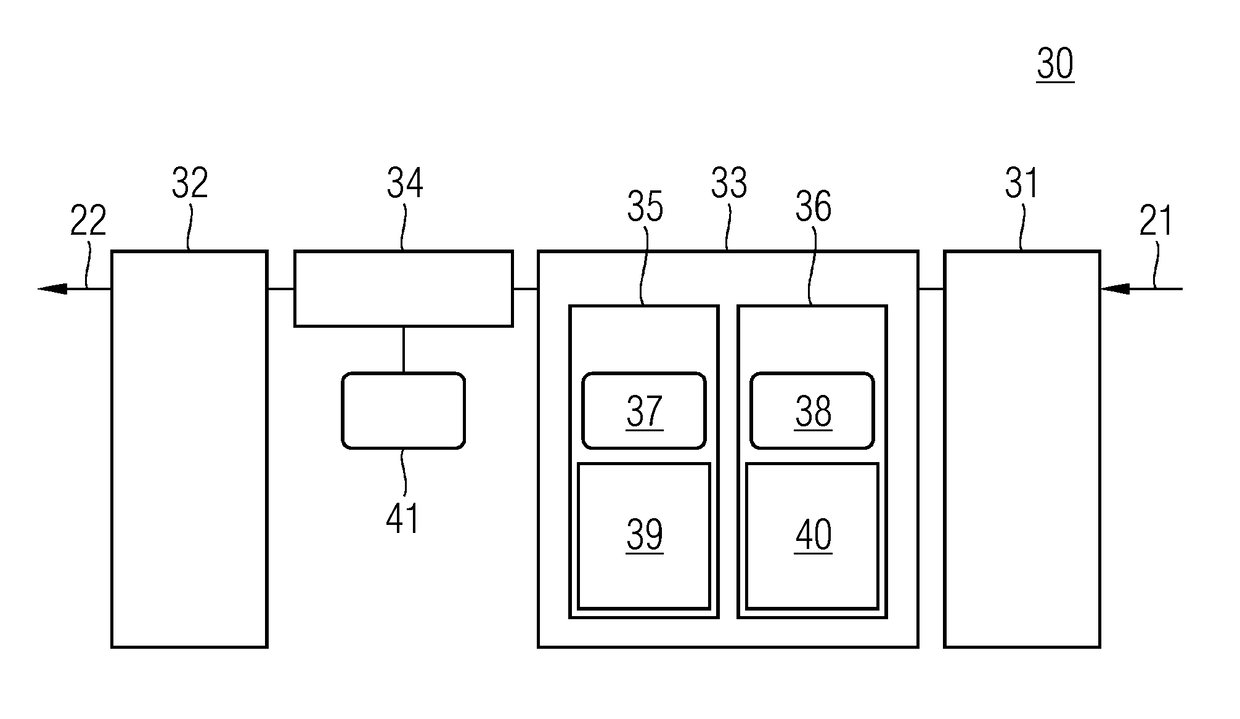
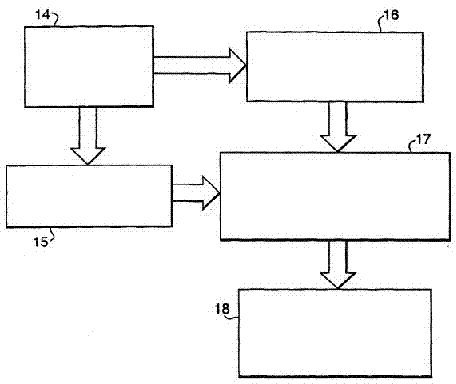
A method and an apparatus for transmitting data from a transmitter in a first communication network (21) to a receiver in a second, safety-critical application network (22) comprises an input buffer unit (31), an output buffer unit (32), a waiting unit (33) and a testing unit (34). The input buffer unit (31) provides the data that are to be transmitted. The waiting unit (33) detects an input time for the data that are to be transmitted, ascertains a dwell time for the data and stores the data that are to be transmitted and / or a check value for the data that are to be transmitted. The testing unit (34) is designed to test the data that are to be transmitted, following expiry of the dwell time, using a test pattern (41) that is up-to-date following expiry of the dwell time. The output buffer unit (32) is designed to provide the data for the receiver if the data have been deemed uncritical during the check. The test pattern preferably relates to a virus pattern.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method of Operating an Operator Control and Monitoring Device for Safety-Critical Applications
InactiveUS20130033443A1Improve securityProgramme controlSafety arrangmentsDisplay deviceControl zone
Owner:SIEMENS AG
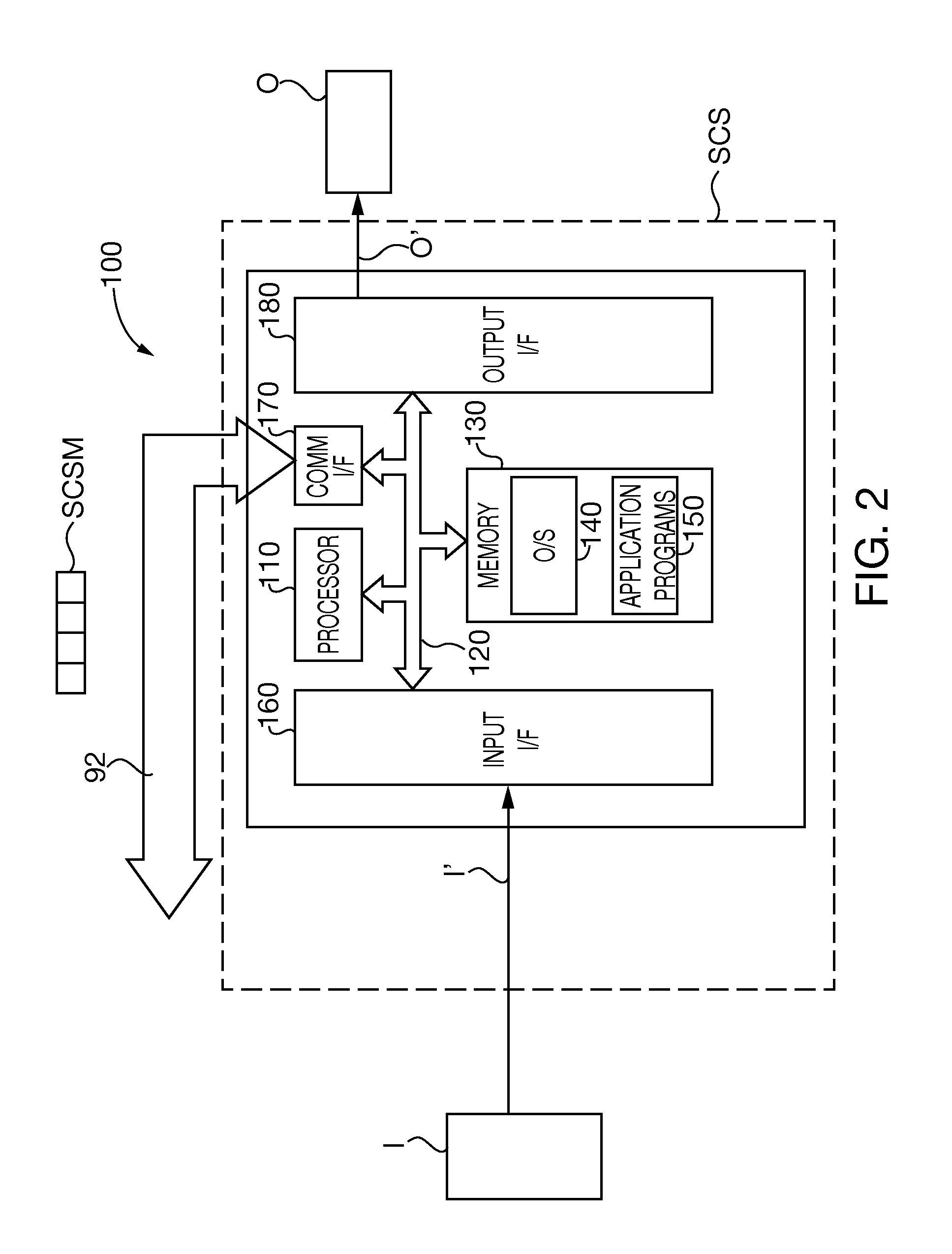
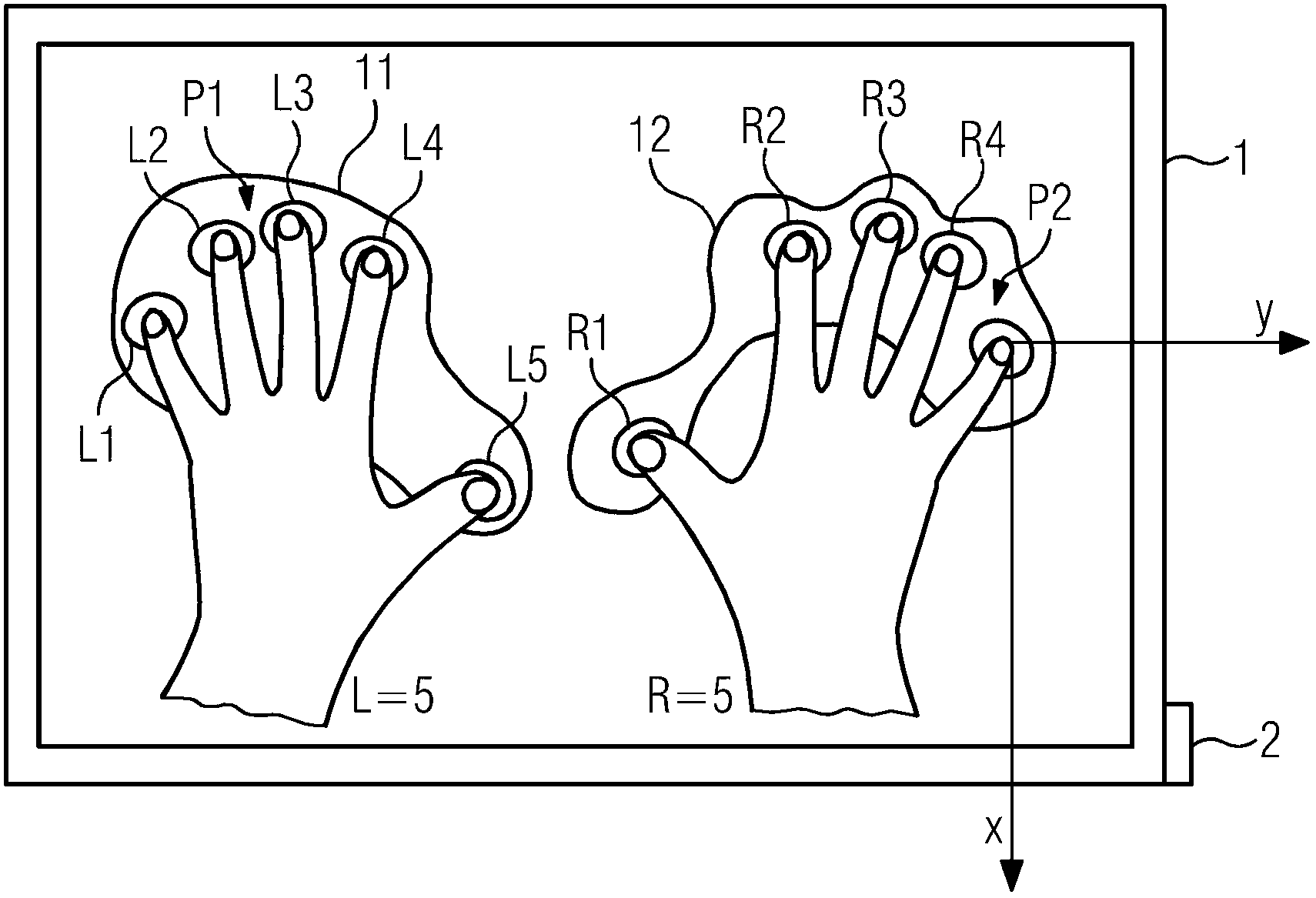
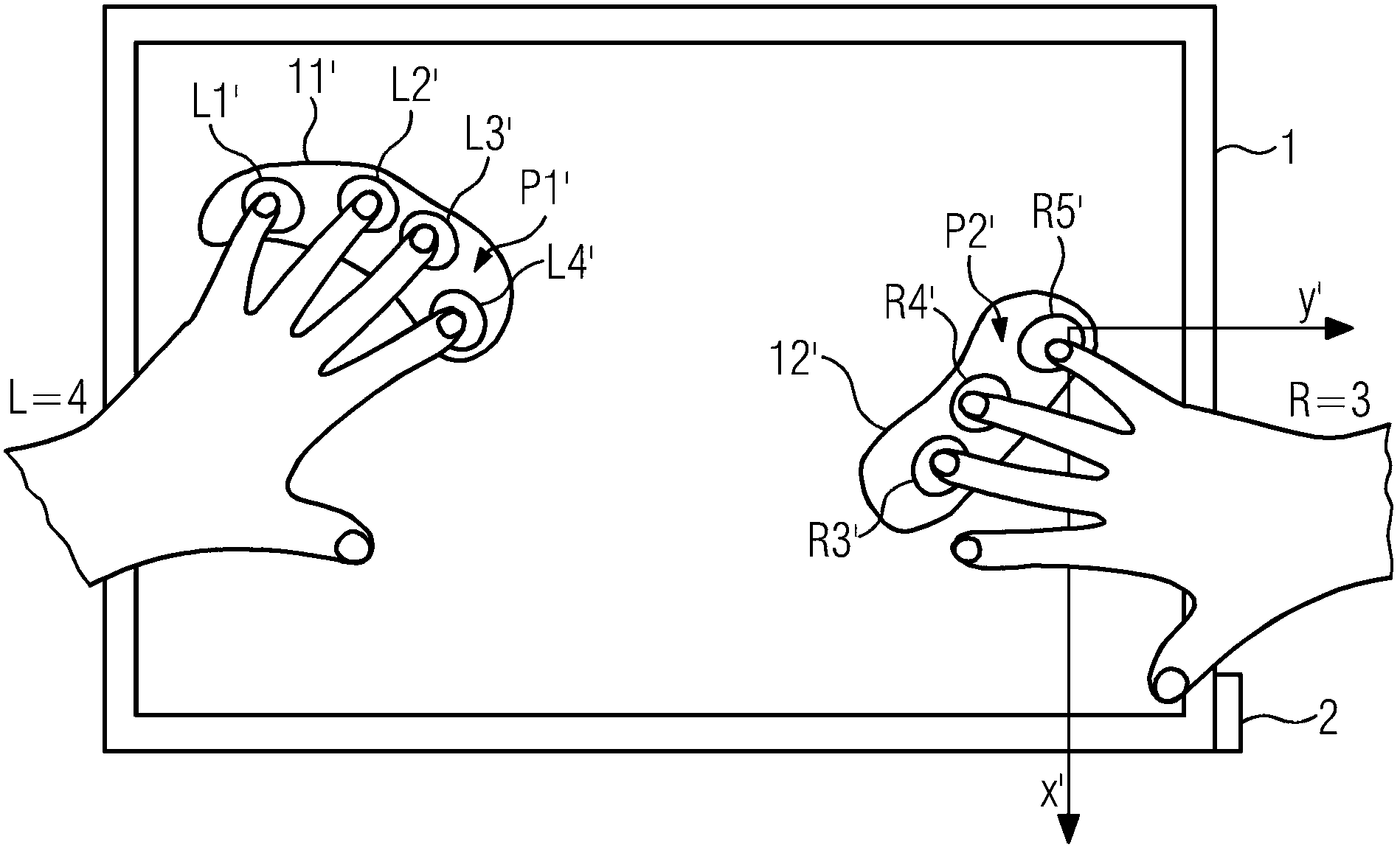
Integrated programmable device for safety critical applications
ActiveUS20060109841A1Easy to integrateImprove securityProgramme controlMultiplex system selection arrangementsEngineeringControl circuit
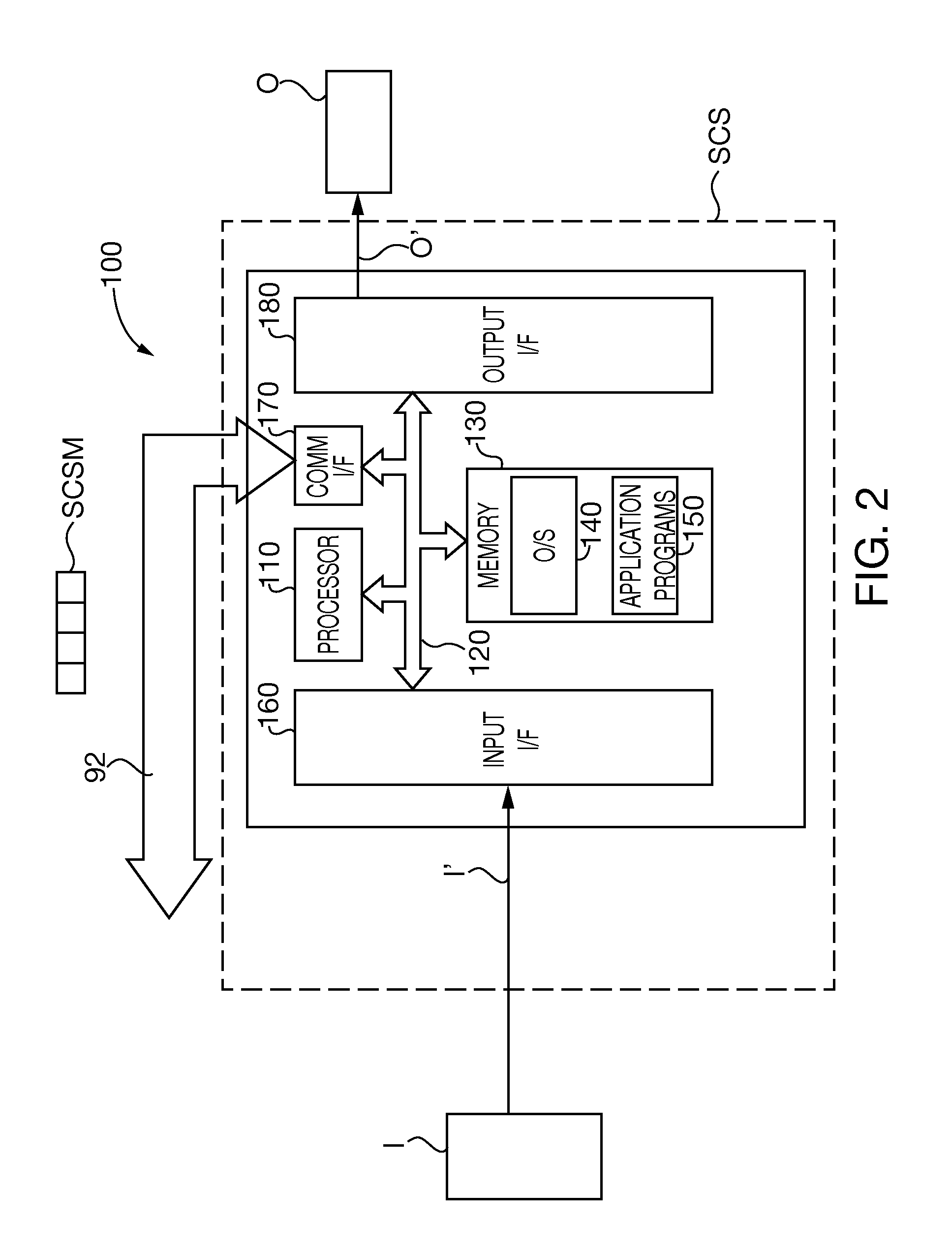
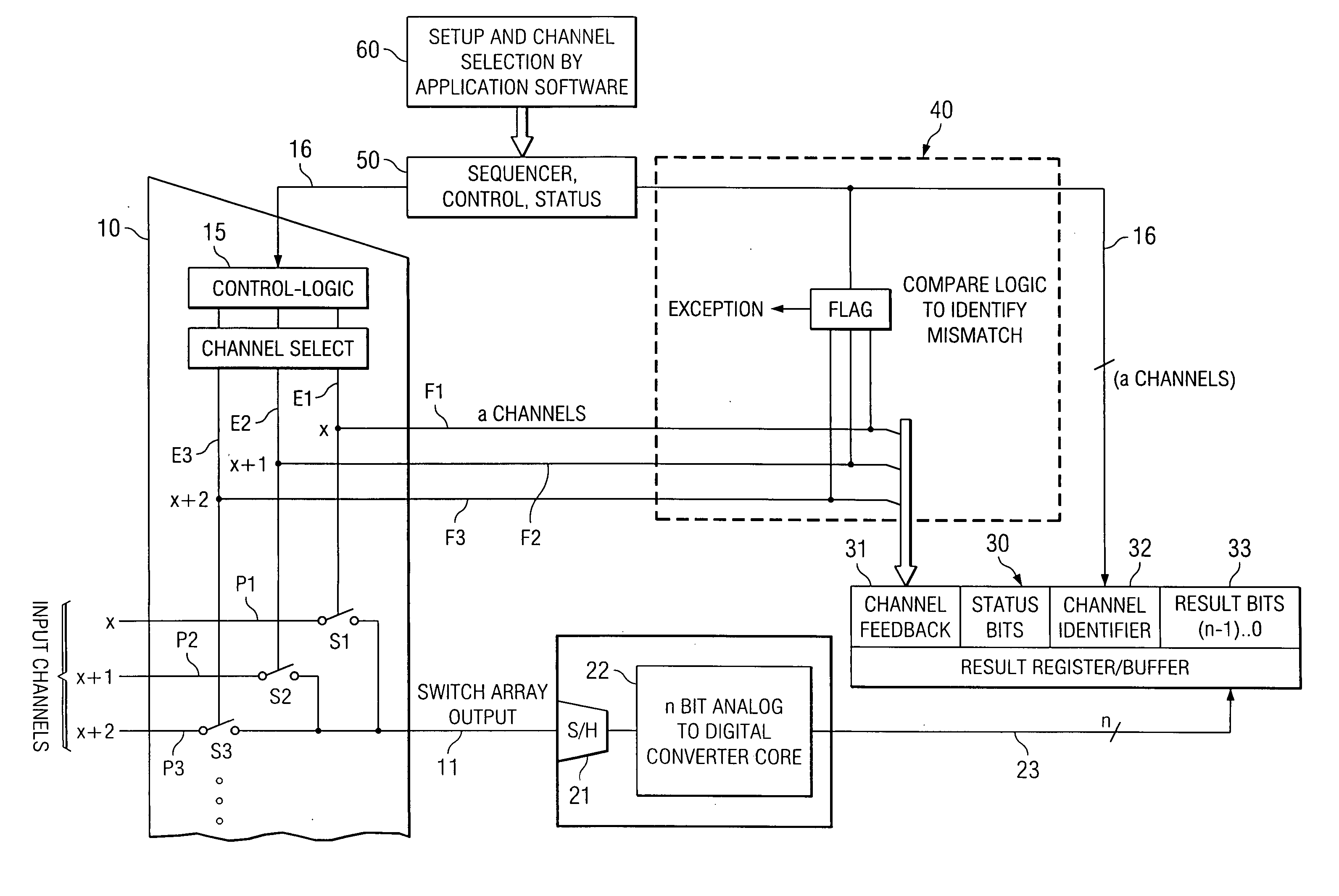
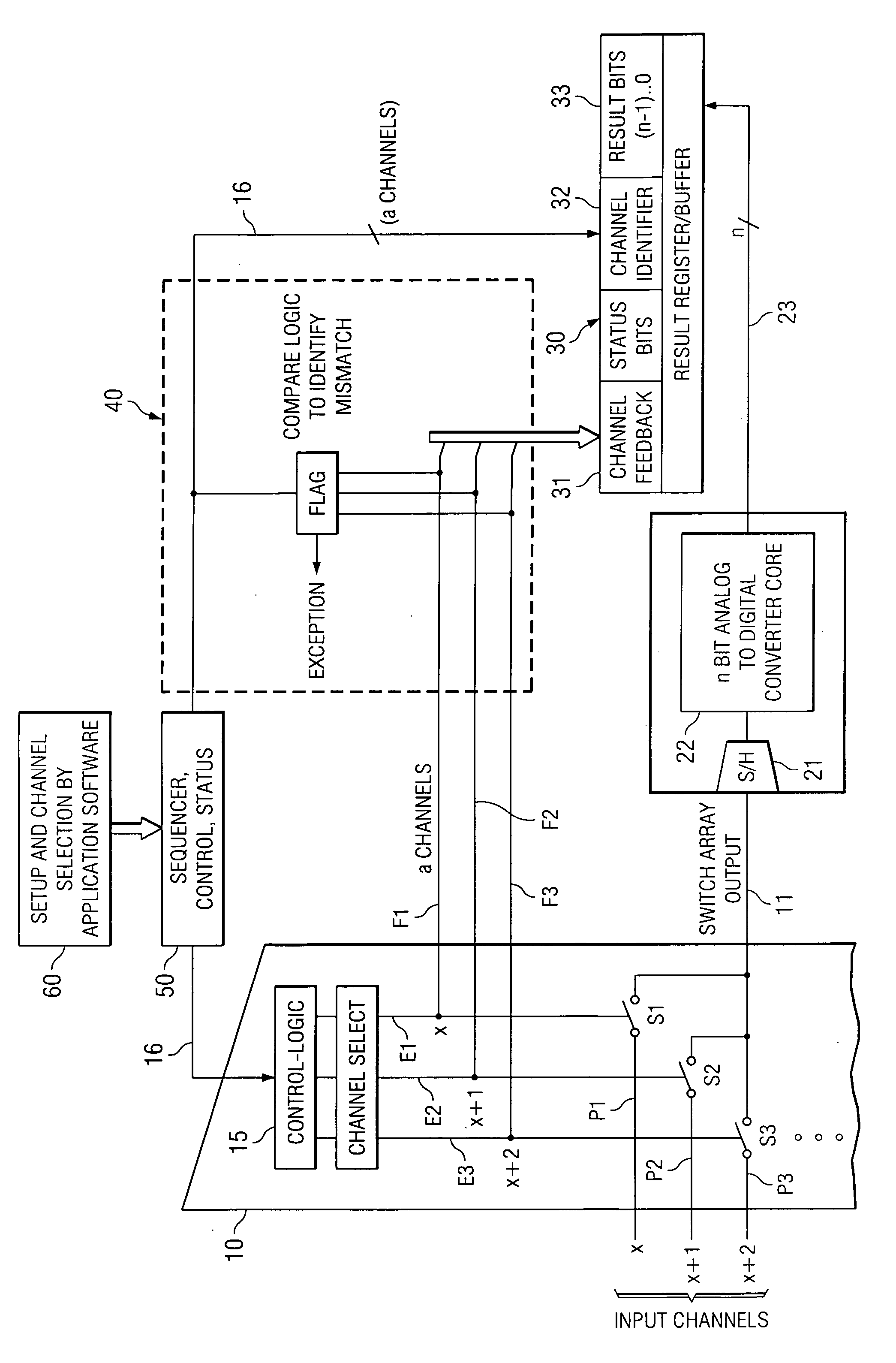
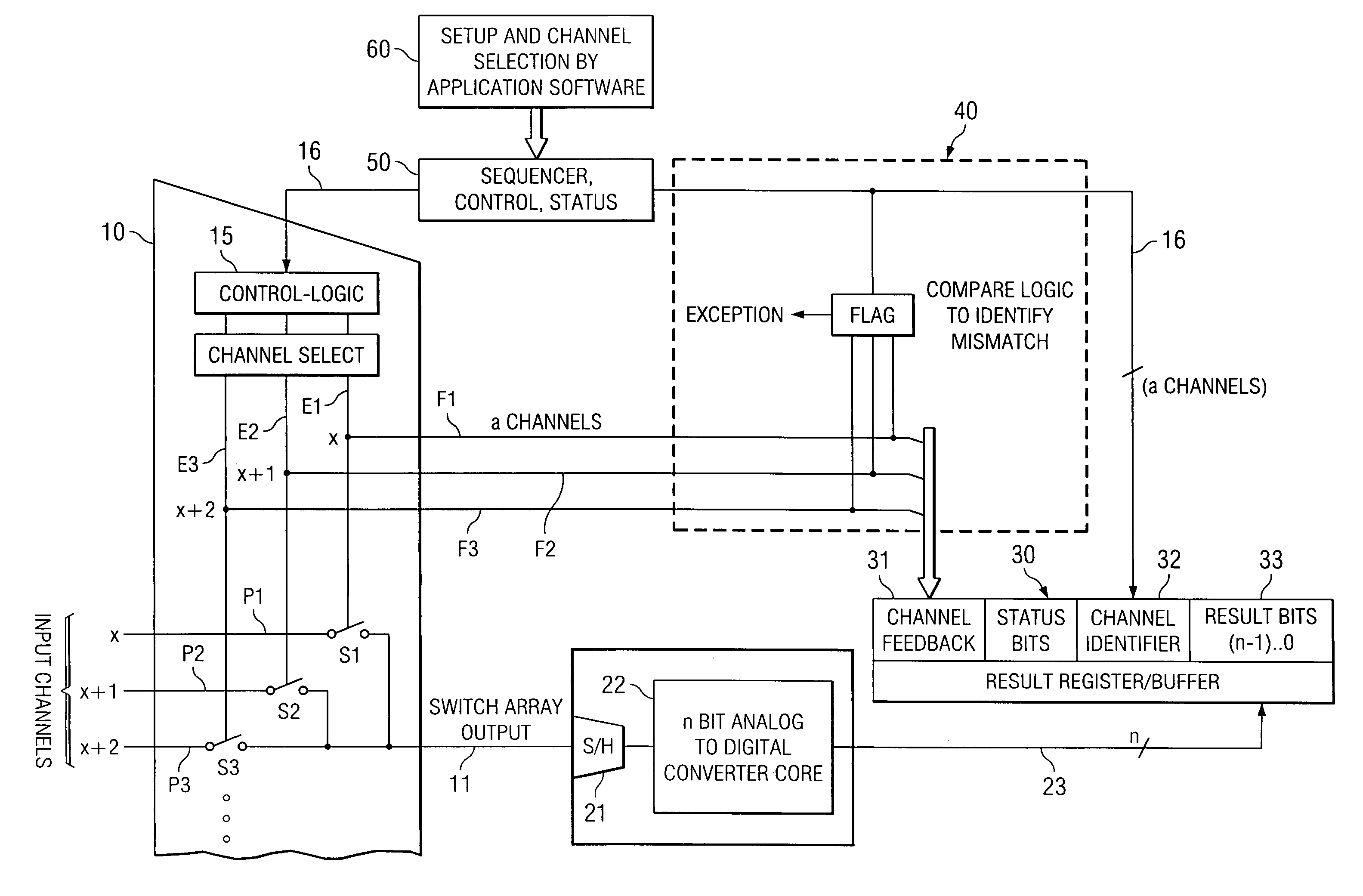
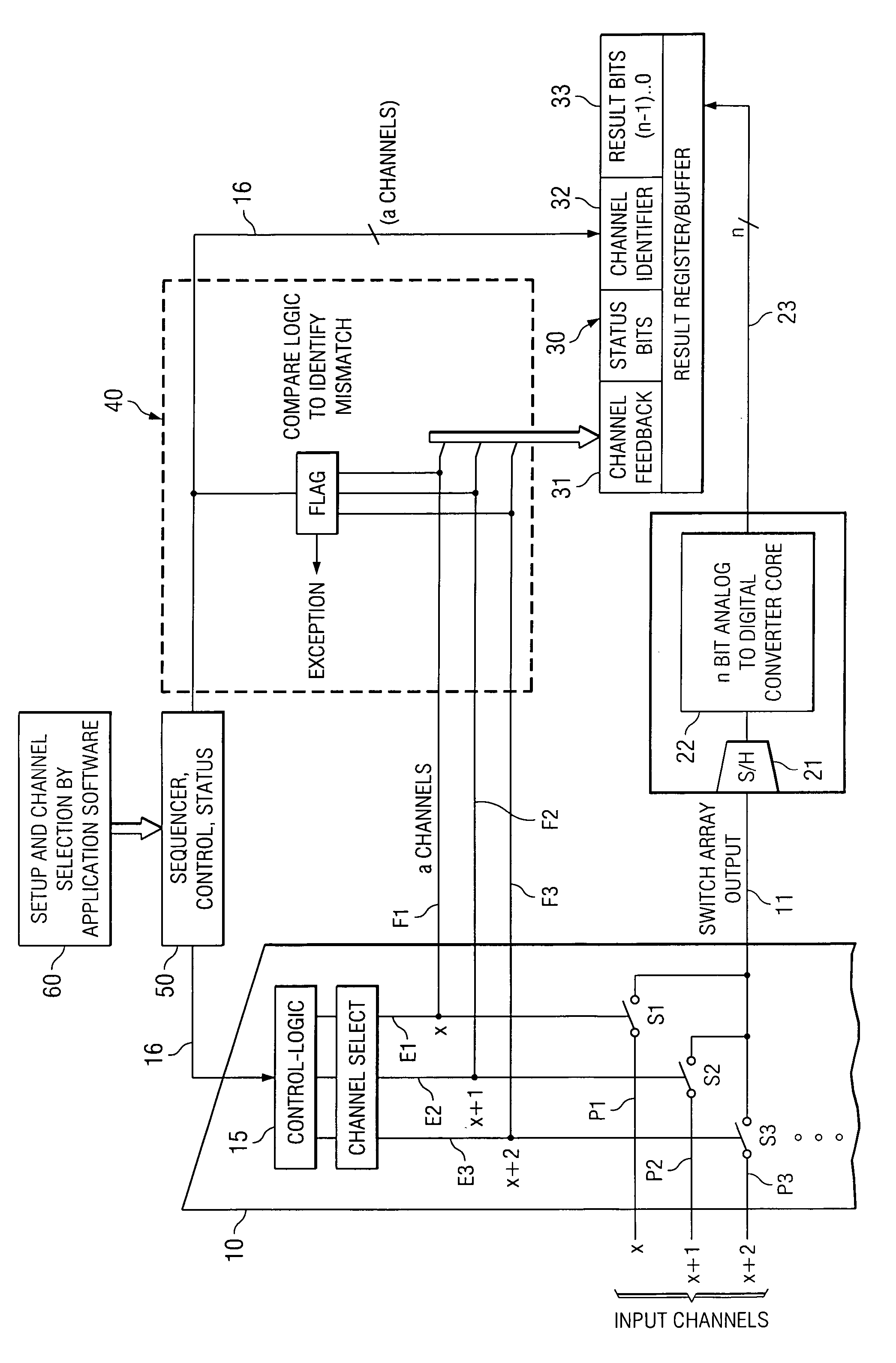
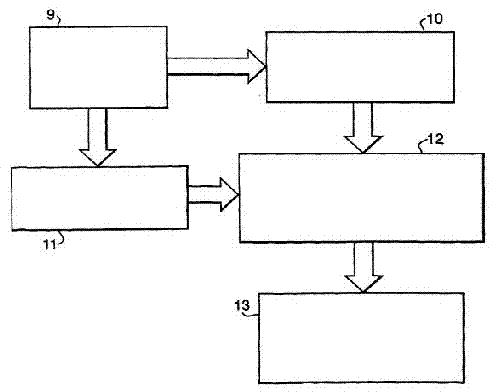
An integrated programmable device has a plurality of signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) connected to respective ones of a plurality of switching elements (S1, S2, S3). Each switching element (S1, S2, S3) has an associated enable line (E1, E2, E3). A control circuit (15) activates one or more selected signal inputs (P1-P3) in accordance with a channel select signal (16) via these enable lines (E1, E2, E3). Feedback lines (F1, F2, F3) are connected to corresponding enable lines (E1, E2, E3) to a channel feedback indicative of which signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) is enabled. This allows determination whether the enabled signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) correspond to the channel select signal (16) and initiates an exception handling in case of a mismatch. The comparison can be performed by a compare logic circuit (40) or the channel feedback can be stored in a memory (30) accessible by a software program (60), which performs the comparison.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Field device for determining or monitoring a physical or chemical process variable
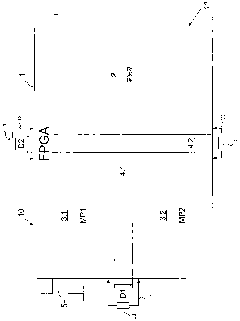
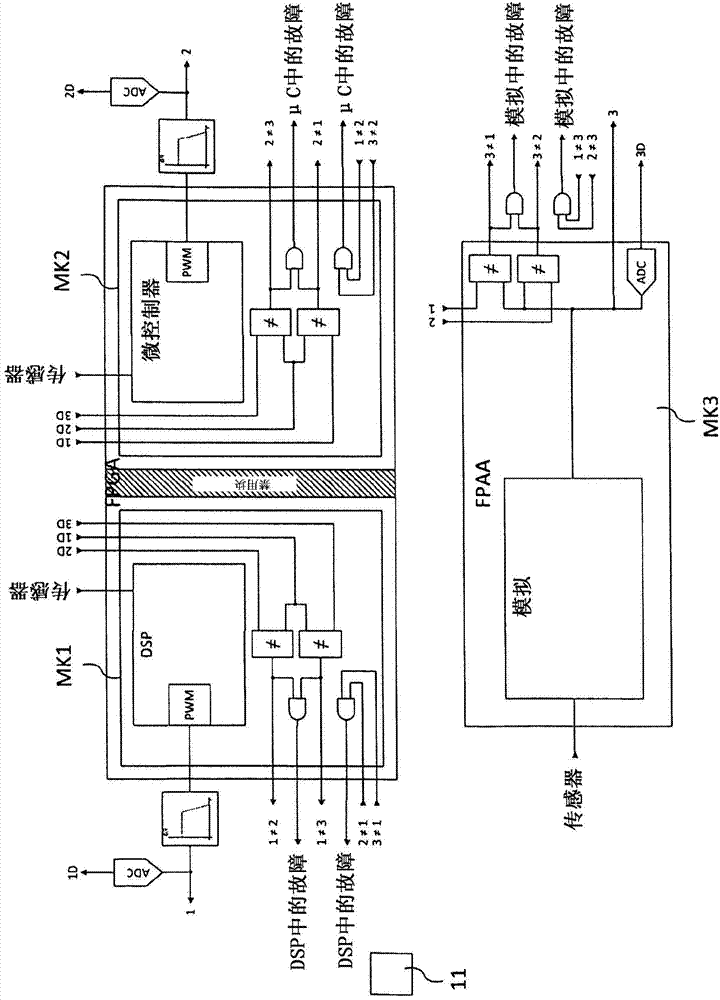
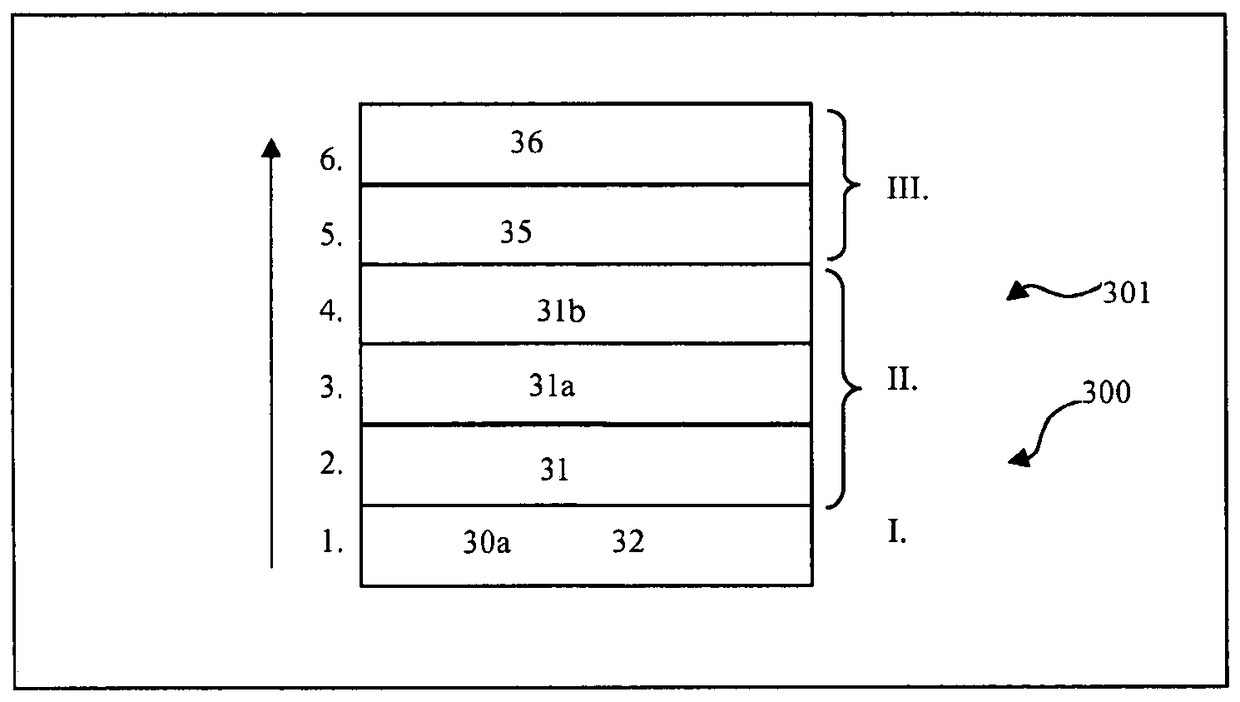
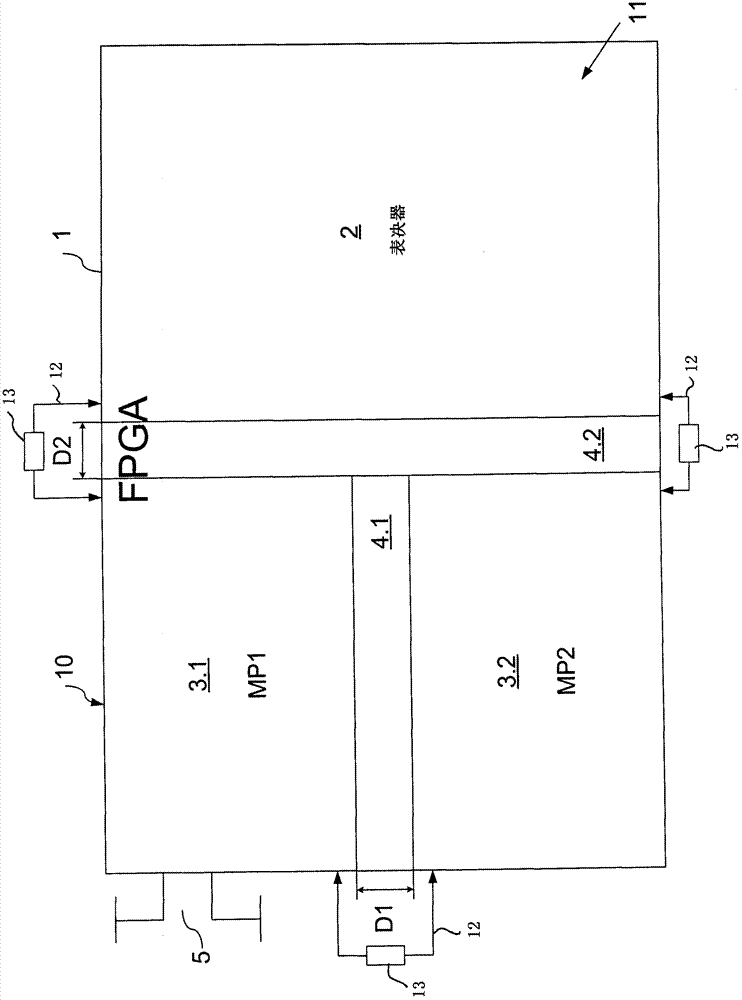
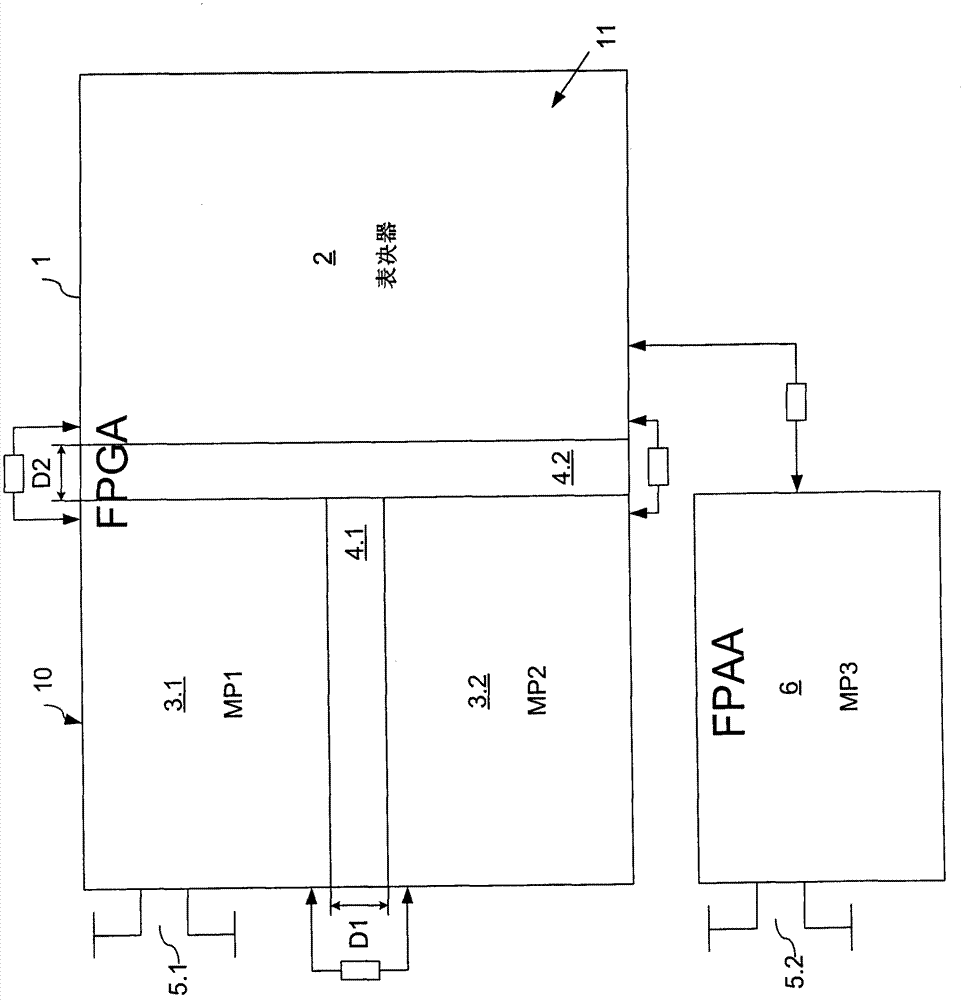
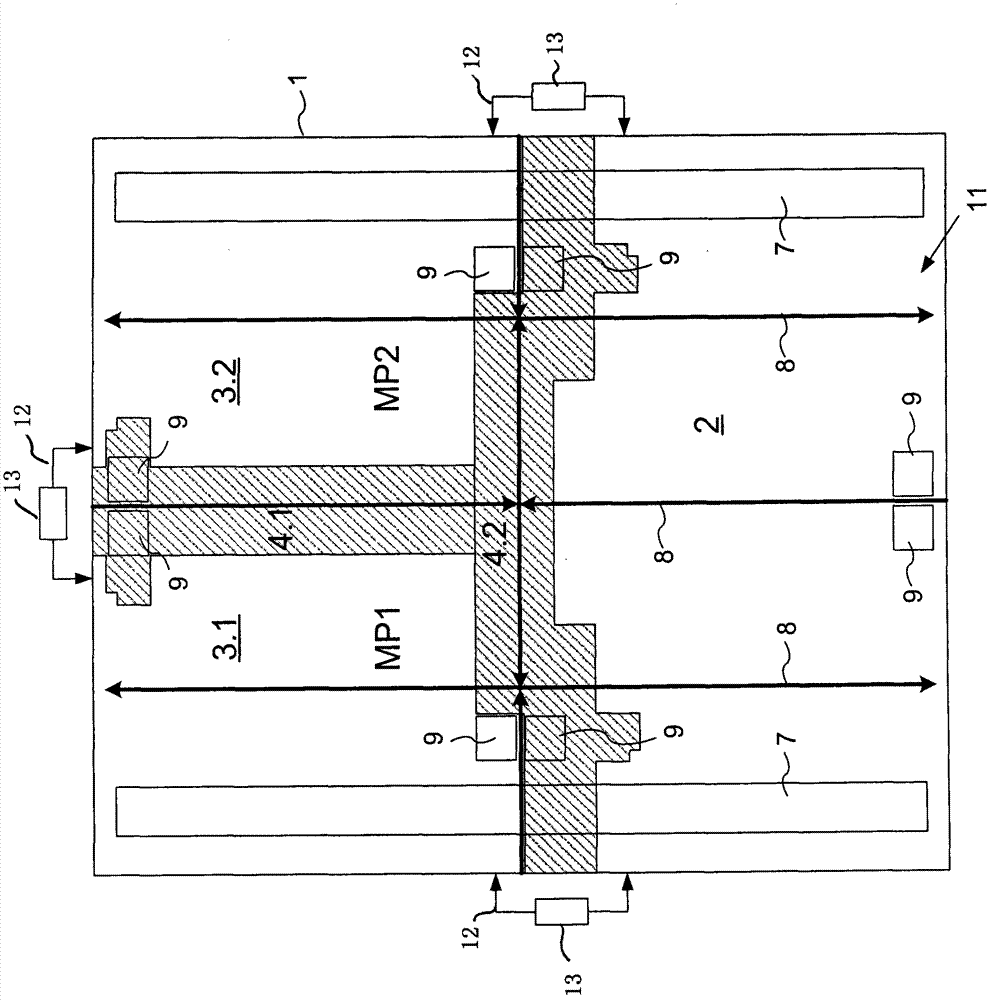
Field device for determining or monitoring a physical or chemical process variable, wherein the field device is composed of a sensor, which works according to a defined measuring principle, and a control / evaluation unit, which, as a function of a safety standard required for the particular safety-critical application, conditions and evaluates, along at least two equivalent measuring paths, measurement data delivered by the sensor. The control / evaluation unit is implemented on an FPGA, on which are provided at least a first section and a second section, wherein, in each section, a digital measuring path, which is composed of a plurality of software-based and / or hardware-based function modules, is dynamically reconfigurable. The sections are isolated from one another by permanently configured spacer regions, wherein the spacer regions are embodied in such a way, that a temperature and / or a voltage change in one of the sections has no influence on the other section or other sections, and, in the case of malfunction, no connection occurs between the sections.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
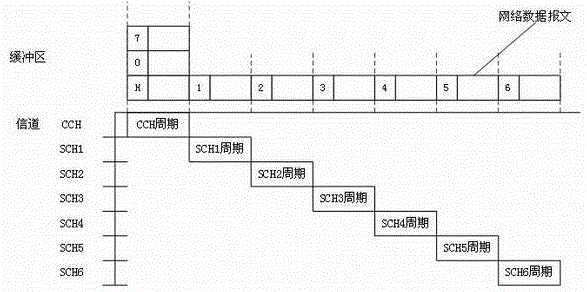
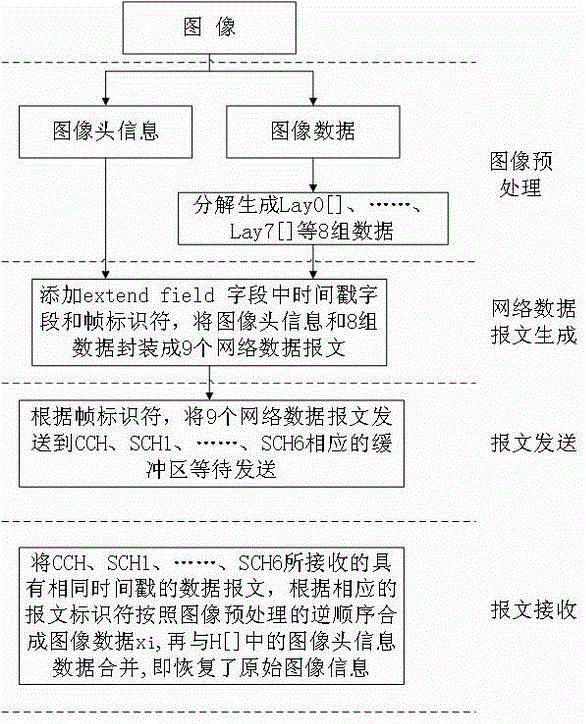
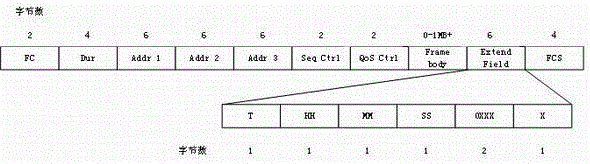
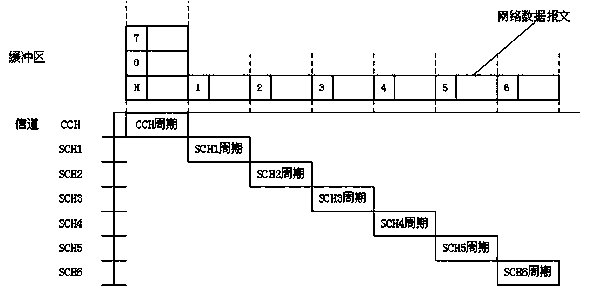
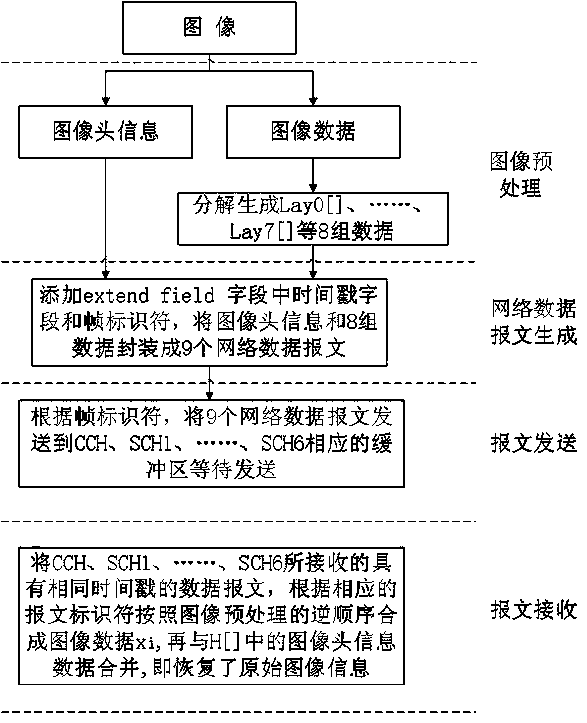
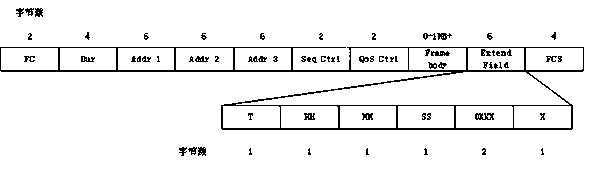
Multi-channel concurrent image transmission method based on IEEE802.11p protocol
ActiveCN105142180AReduce the burden onEnsure real-time application requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementTelevision systemsQuality of serviceNetwork communication
The invention relates to a multi-channel concurrent image transmission method based on an IEEE802.11p protocol, belonging to the technical field of real-time transmission of image information. The multi-channel concurrent image transmission method comprises the following steps: decomposing image data in each frame to be transmitted into 9 sets of data at first, packaging the 9 sets of data to form 9 network communication messages, and sequentially transmitting the 9 network communication messages according to one original CCH (Control Channel) and six original SCHs (Synchronous Channels) of the IEEE802.11p protocol in a period polling mode. Therefore, the original single-channel transmission of the image information is converted into CCH and SCH multi-channel cooperative concurrent transmission, so that burden is greatly reduced; simultaneously, real-time application requirements of the image information are also ensured; compared with the single-channel transmission, the transmission speed of the multi-channel concurrent transmission method is increased by 3 times; the vulnerability that system messages or other communication messages facing to safety-critical applications are congested while being transmitted by directly utilizing the CCH is avoided; and the service quality of other real-time applications facing to the safety-critical applications is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and method for transmitting data
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Field device for determining or monitoring process variable in automation technology
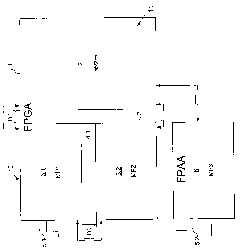
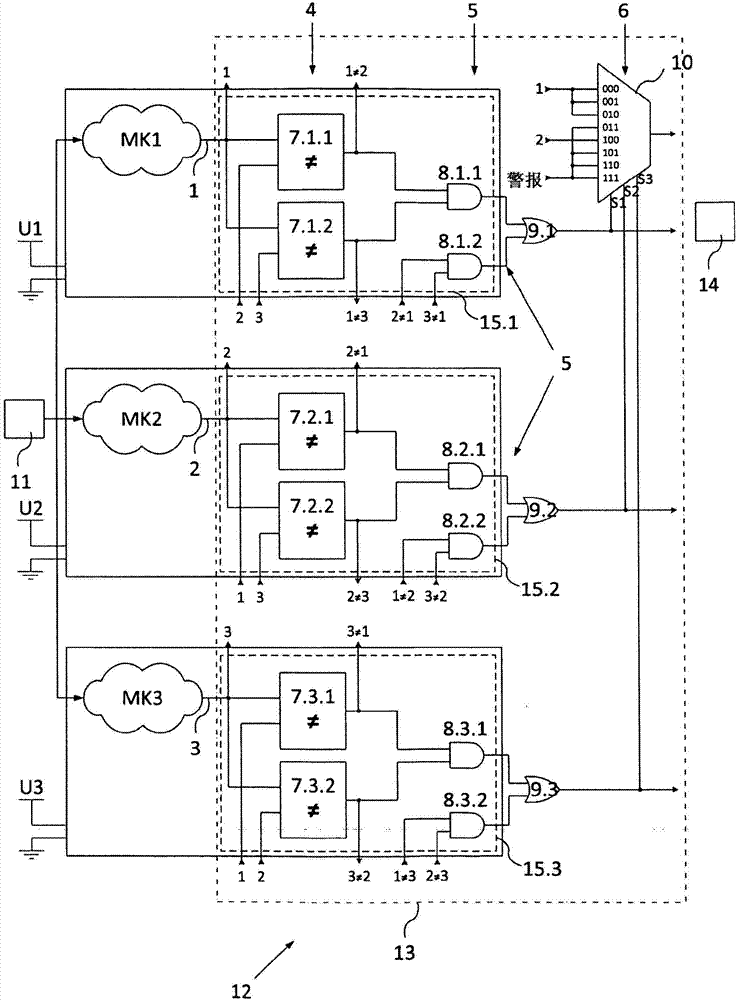
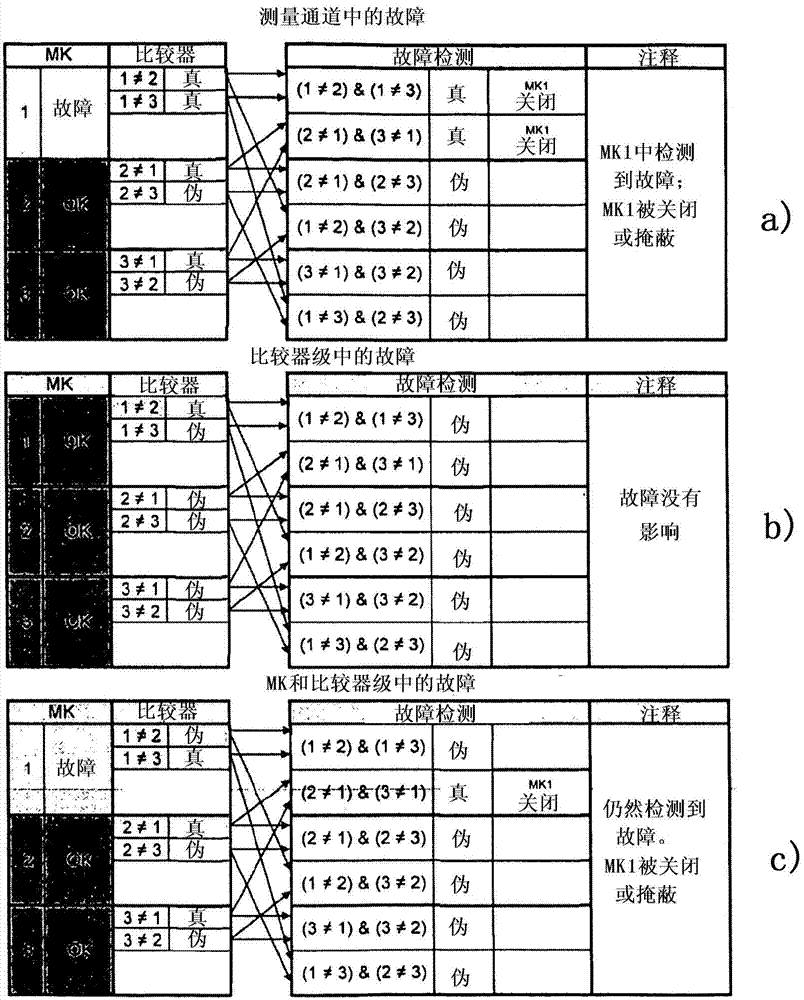
The invention relates to a field device for determining or monitoring a process variable in automation technology, wherein the field device satisfies a safety standard that is required in a predetermined safety-critical application, with a sensor (11) operating according to a defined measuring principle and with a control / evaluation unit (12) that processes and evaluates measurement data supplied by the sensor (11) along at least three measuring channels (MK) designed to be redundant and / or diverse, and wherein a voter (13) which consists of a plurality of components that are at least in part designed so as to be doubly redundant, is associated with the control / evaluation unit (12).
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Detection of a faulty node in a network
Methods and apparatuses for increasing quality of service in a network having nodes if there is a faulty node which can result in data traffic being overloaded in at least one part of the network are provided. The disclosed embodiments of the invention can be used in the field of safety-critical applications, such as medial applications, monitoring devices, and in-vehicle communication systems.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Actuation of a technical system based on solutions of relaxed abduction
ActiveUS9449275B2Solve problemsMathematical modelsSimulator controlRepresentation languagePower station
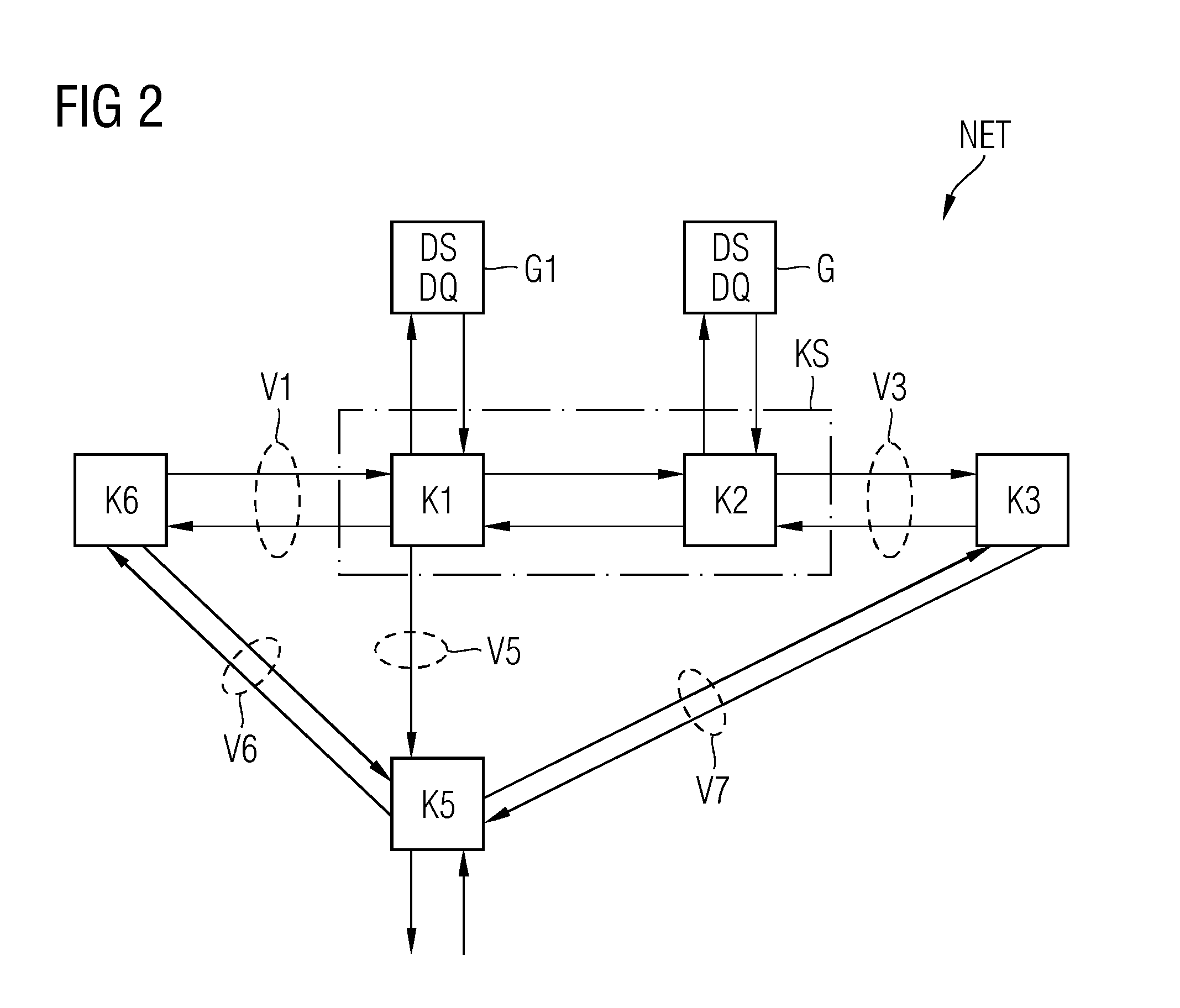
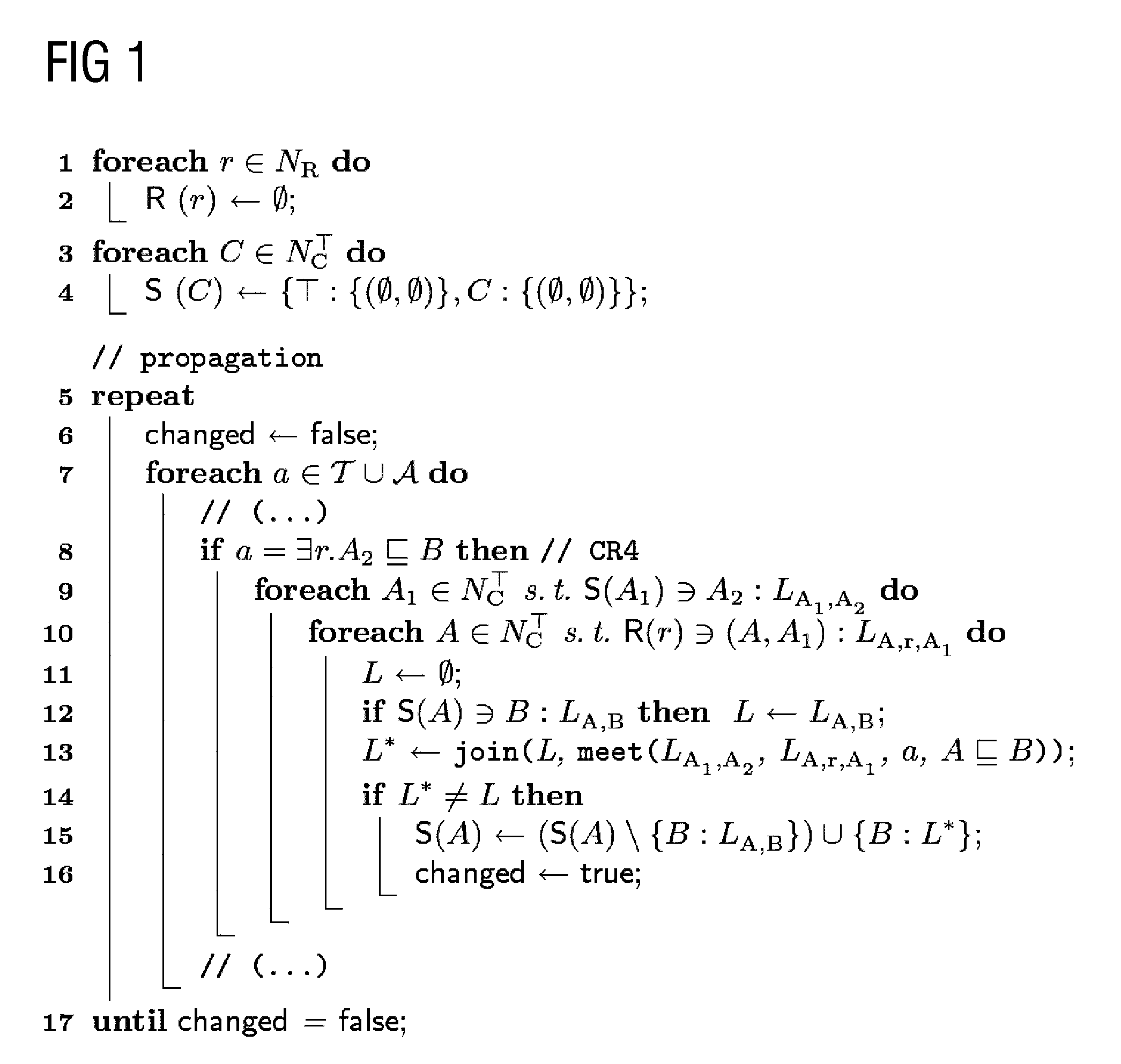
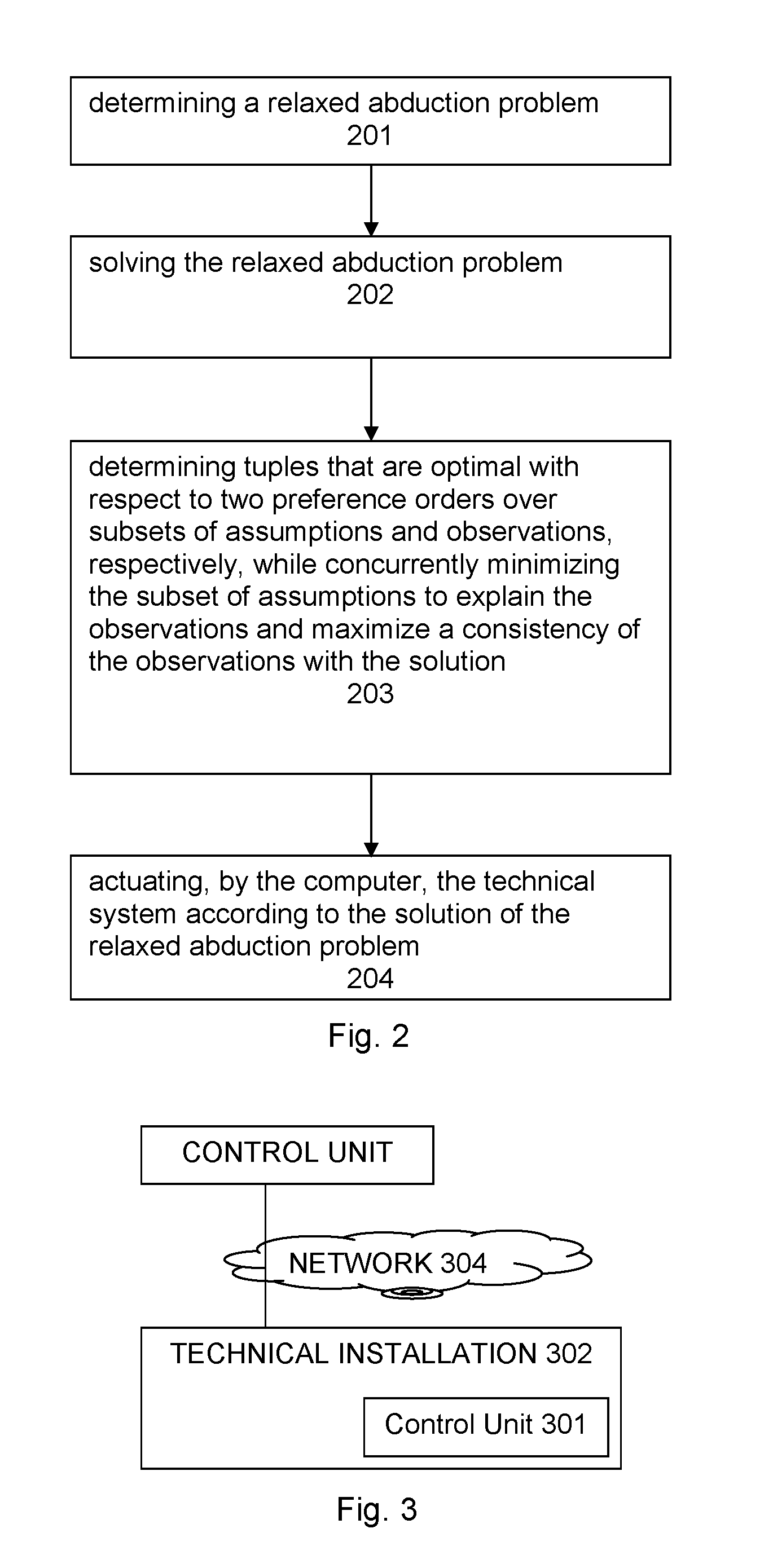
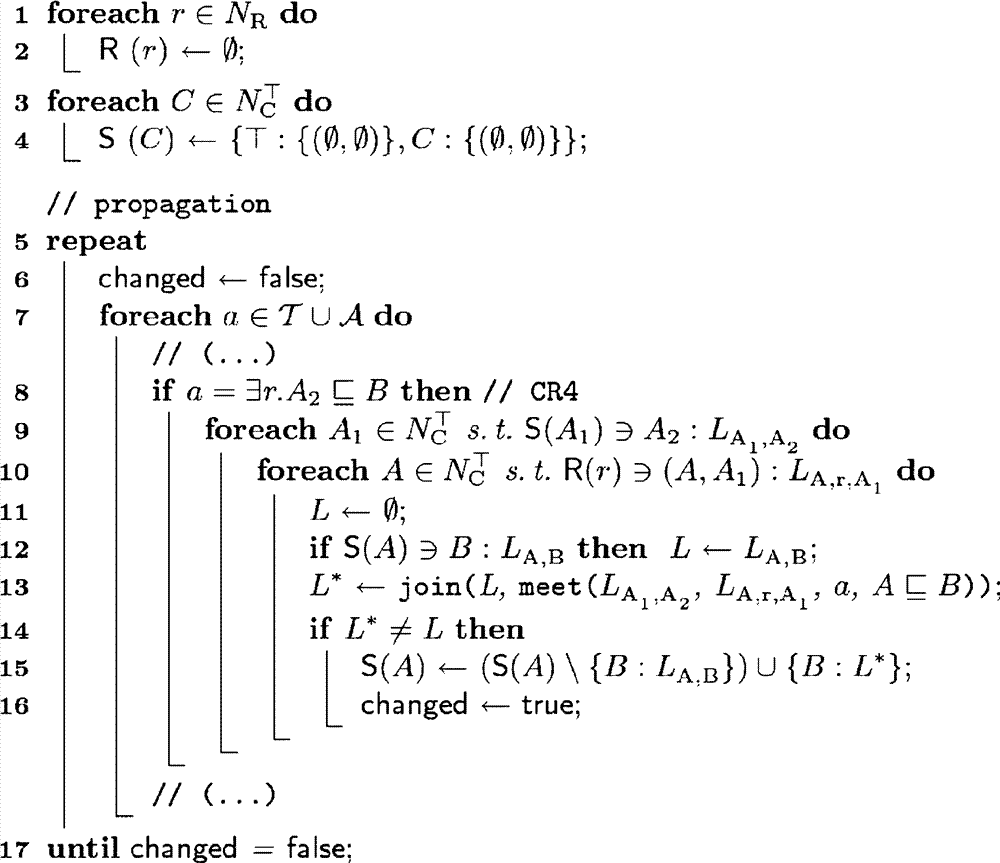
To enable efficient abduction even for observations that are faulty or inadequately modeled, a relaxed abduction problem is proposed in order to explain the largest possible part of the observations with as few assumptions as possible. On the basis of two preference orders over a subset of observations and a subset of assumptions, tuples can therefore be determined such that the theory, together with the subset of assumptions, explains the subset of observations. The formulation as a multi-criteria optimization problem eliminates the need to offset assumptions made and explained observations against one another. Due to the technical soundness of the approach, specific properties of the set of results (such as correctness, completeness etc.), can be checked, which is particularly advantageous in safety-critical applications. The complexity of the problem-solving process can be influenced and therefore flexibly adapted in terms of domain requirements through the selection of the underlying representation language and preference relations. The invention can be applied to any technical system, e.g. plants or power stations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Actuation of a technical system
ActiveCN103782245ASolving relaxed abductive inference problemsSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringAbductive reasoningGuideline
To enable efficient abduction even for observations that are faulty or inadequately modeled, a relaxed abduction problem is proposed in order to explain the largest possible part of the observations with as few assumptions as possible. On the basis of two preference orders over a subset of observations and a subset of assumptions, tuples can therefore be determined such that the theory, together with the subset of assumptions, explains the subset of observations. The formulation as a multi-criteria optimization problem eliminates the need to offset assumptions made and explained observations against one another. Due to the technical soundness of the approach, specific properties of the set of results (such as correctness, completeness etc.), can be checked, which is particularly advantageous in safety-critical applications. The complexity of the problem-solving process can be influenced and therefore flexibly adapted in terms of domain requirements through the selection of the underlying representation language and preference relations. The invention can be applied to any technical system, e.g. plants or power stations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Integrated programmable device for safety critical applications
ActiveUS7573830B2Easy to integrateImprove securityMultiplex system selection arrangementsProgramme controlControl circuitSafety critical application
An integrated programmable device has a plurality of signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) connected to respective ones of a plurality of switching elements (S1, S2, S3). Each switching element (S1, S2, S3) has an associated enable line (E1, E2, E3). A control circuit (15) activates one or more selected signal inputs (P1-P3) in accordance with a channel select signal (16) via these enable lines (E1, E2, E3). Feedback lines (F1, F2, F3) are connected to corresponding enable lines (E1, E2, E3) to a channel feedback indicative of which signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) is enabled. This allows determination whether the enabled signal inputs (P1, P2, P3) correspond to the channel select signal (16) and initiates an exception handling in case of a mismatch. The comparison can be performed by a compare logic circuit (40) or the channel feedback can be stored in a memory (30) accessible by a software program (60), which performs the comparison.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
A method of image multi-channel concurrent transmission based on ieee802.11p protocol
ActiveCN105142180BReduce the burden onEnsure real-time application requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementTelevision systemsQuality of serviceNetwork communication
The invention relates to a multi-channel concurrent image transmission method based on an IEEE802.11p protocol, belonging to the technical field of real-time transmission of image information. The multi-channel concurrent image transmission method comprises the following steps: decomposing image data in each frame to be transmitted into 9 sets of data at first, packaging the 9 sets of data to form 9 network communication messages, and sequentially transmitting the 9 network communication messages according to one original CCH (Control Channel) and six original SCHs (Synchronous Channels) of the IEEE802.11p protocol in a period polling mode. Therefore, the original single-channel transmission of the image information is converted into CCH and SCH multi-channel cooperative concurrent transmission, so that burden is greatly reduced; simultaneously, real-time application requirements of the image information are also ensured; compared with the single-channel transmission, the transmission speed of the multi-channel concurrent transmission method is increased by 3 times; the vulnerability that system messages or other communication messages facing to safety-critical applications are congested while being transmitted by directly utilizing the CCH is avoided; and the service quality of other real-time applications facing to the safety-critical applications is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Diverse redundancy approach for safety critical applications
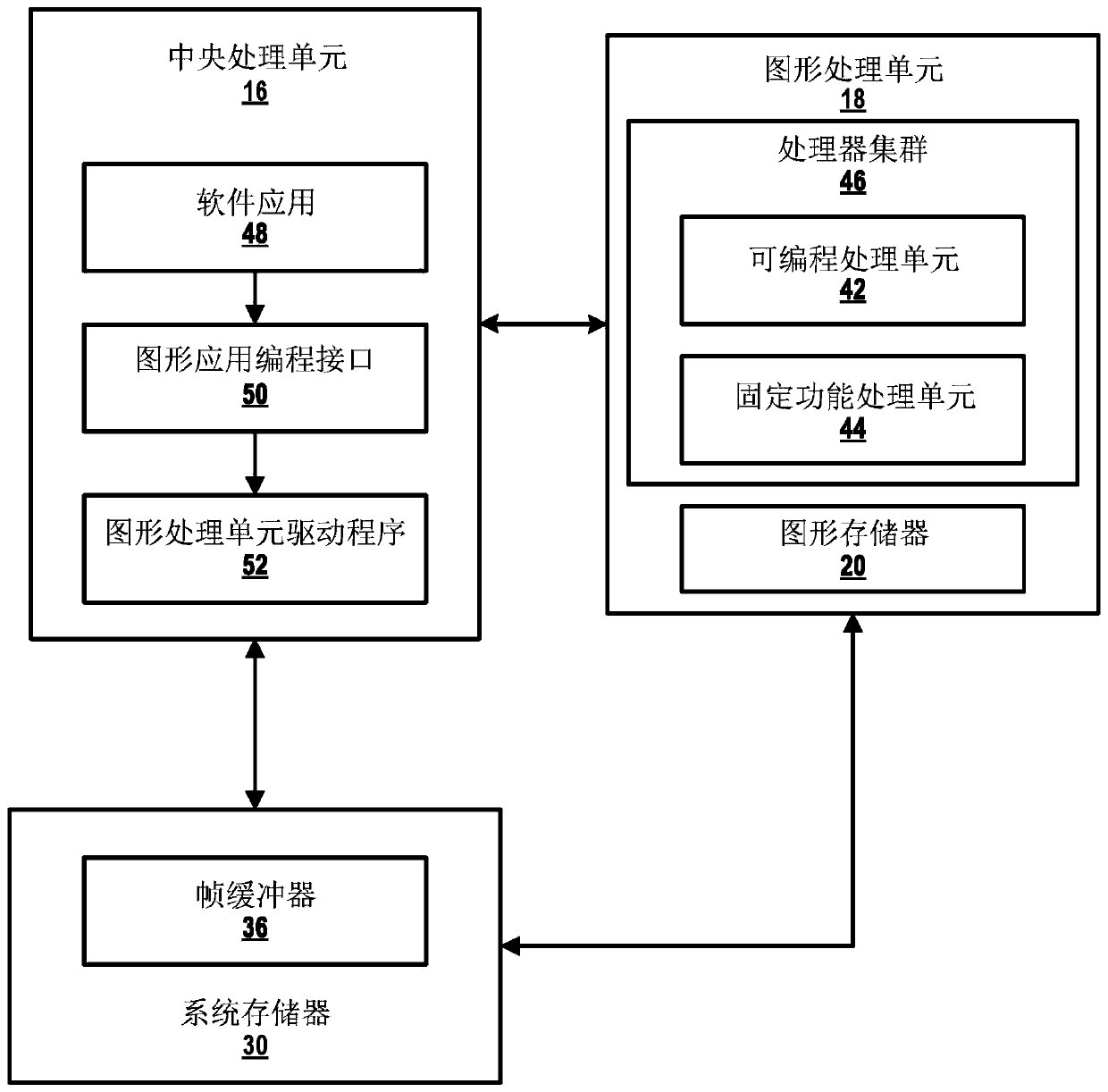
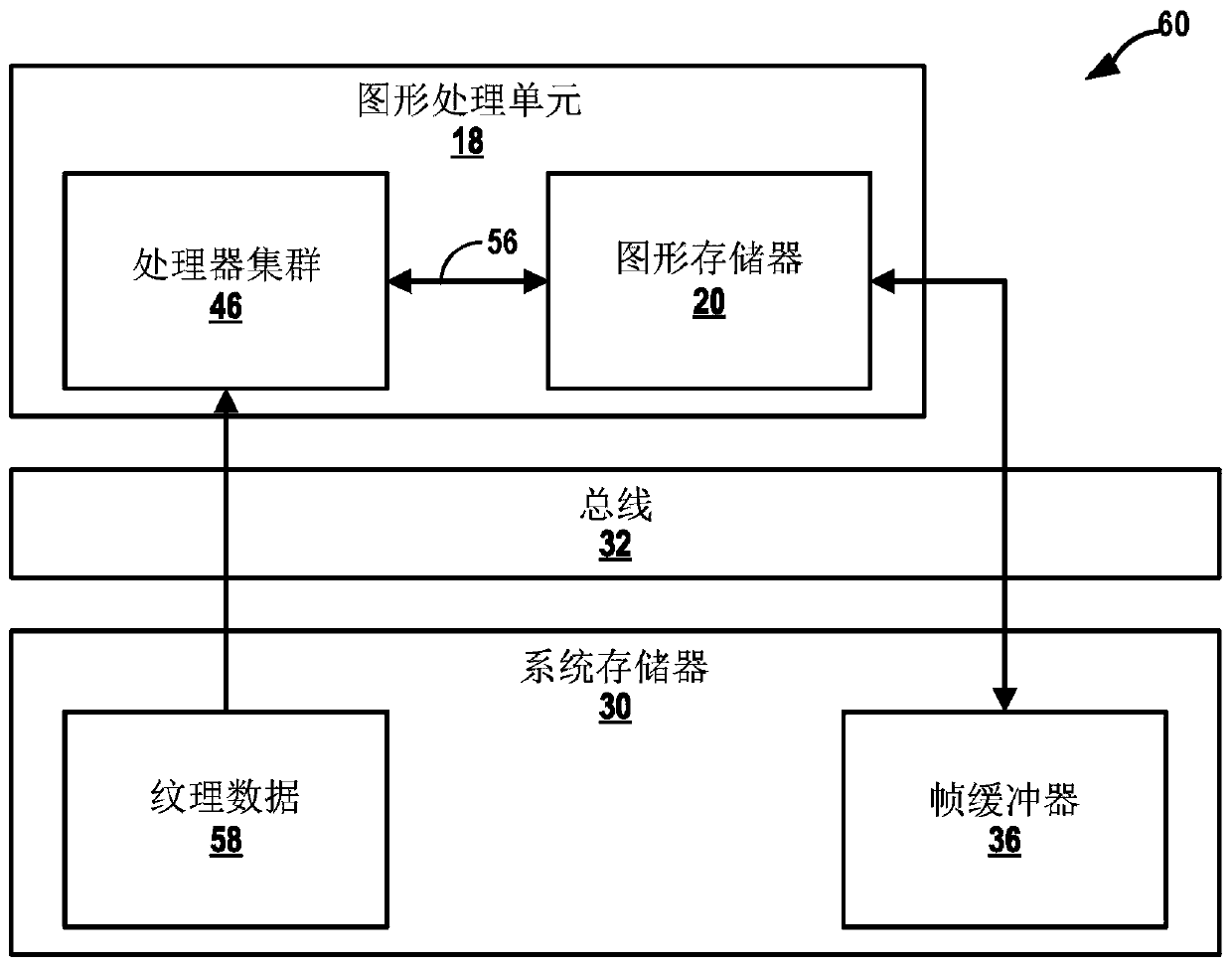
A graphics processing unit (GPU) of a GPU subsystem of a computing device operates in a first rendering mode to process graphics data to produce a first image. The GPU operates in a second rendering mode to process the graphics data to produce a second image. The computing device detects whether a fault has occurred in the GPU subsystem based at least in part on comparing the first image with thesecond image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Automatic development of software codes
InactiveCN102541553AReduce development costsReduce lifetime costsSpecific program execution arrangementsState modelSoftware engineering
Development of validated software codes is a troublesome but important process, in particular for the condition that takes security key application programs into consideration. The invention provides a method for generating validated software codes according to demand, which comprises the following steps: (1) using software to generate the demanded state model; (2) using the state model to develop the software code description of the state model and the mathematic description of the state model; and (3) comparing the software codes with the mathematic description so as to validate that the software code description is correct expression of the mathematic description.
Owner:SUZHOU MINGXING TECH
Detection of a faulty node in a network
Methods and apparatuses for increasing quality of service in a network having nodes if there is a faulty node which can result in data traffic being overloaded in at least one part of the network are provided. The disclosed embodiments of the invention can be used in the field of safety-critical applications, such as medial applications, monitoring devices, and in-vehicle communication systems.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method of Operating an Operator Control and Monitoring Device for Safety-Critical Applications
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Apparatus and methods for safety-critical applications
ActiveCN104508578BProgram initiation/switchingError detection/correctionComputer hardwareHardware architecture
Owner:盈德克勒电控有限公司
Field device for determining or monitoring a physical or chemical process variable
A field device for determining or monitoring a physical or chemical process variable, wherein the field device is composed of a sensor, which works according to a defined measuring principle, and a control / evaluation unit (10), which, as a function of a safety standard required for the particular safety-critical application, conditions and evaluates, along at least two equivalent measuring paths (MP1, MP2), measurement data delivered by the sensor. The control / evaluation unit is implemented on an FPGA (1), on which are provided at least a first section (3.1) and a second section (3.2), wherein, in each section (3.1, 3.2), a digital measuring path (MP1, MP2), which is composed of a plurality of software-based and / or hardware-based function modules, is dynamically reconfigurable. The sections are isolated from one another by permanently configured spacer regions (4.1, 4.2), wherein the spacer regions (4.1, 4.2) are embodied in such a way, that a temperature and / or a voltage change in one of the sections (MP1; MP2) has no influence on the other section (MP2; MP1) or other sections, and, in the case of malfunction, no connection occurs between the sections (MP1, MP2). The control / evaluation unit (10), as a function of the particular defined safety-critical application, partially dynamically reconfigures the function modules in the measuring paths (MP1, MP2) in such a manner, that the field device fulfills the required safety standard. Preferably a voter / microcontroller is used to compare measurement data in the measuring paths and is capable of reconfiguring the function modules and generating a warning of defective data.
Owner:EHNDRESS KHAUZER GMBKH KO KG
Method for transmitting data in a wireless radio network
InactiveCN101766039BLow failure rateProbability of failureNetwork topologiesNetwork planningRadio networksTime delays
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com