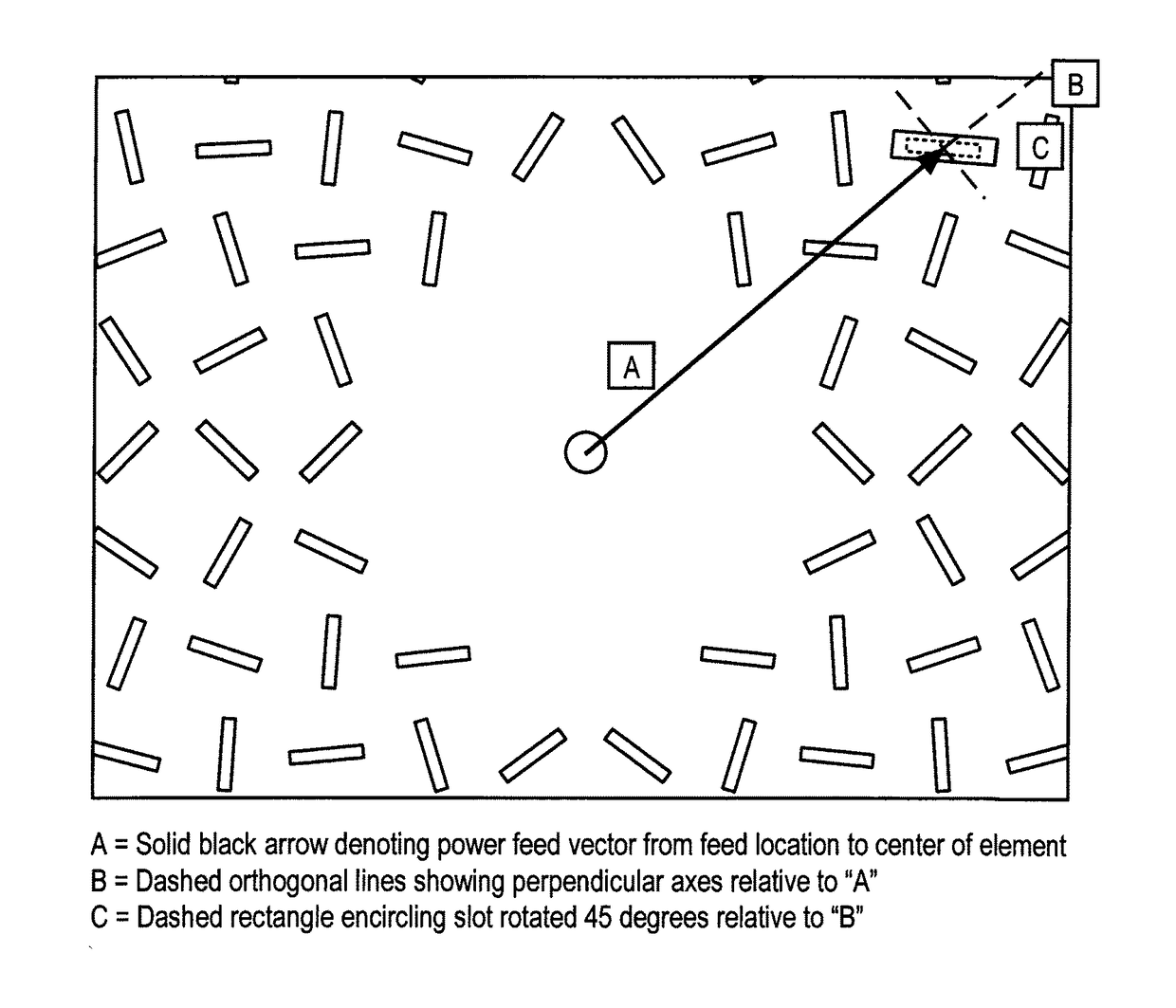
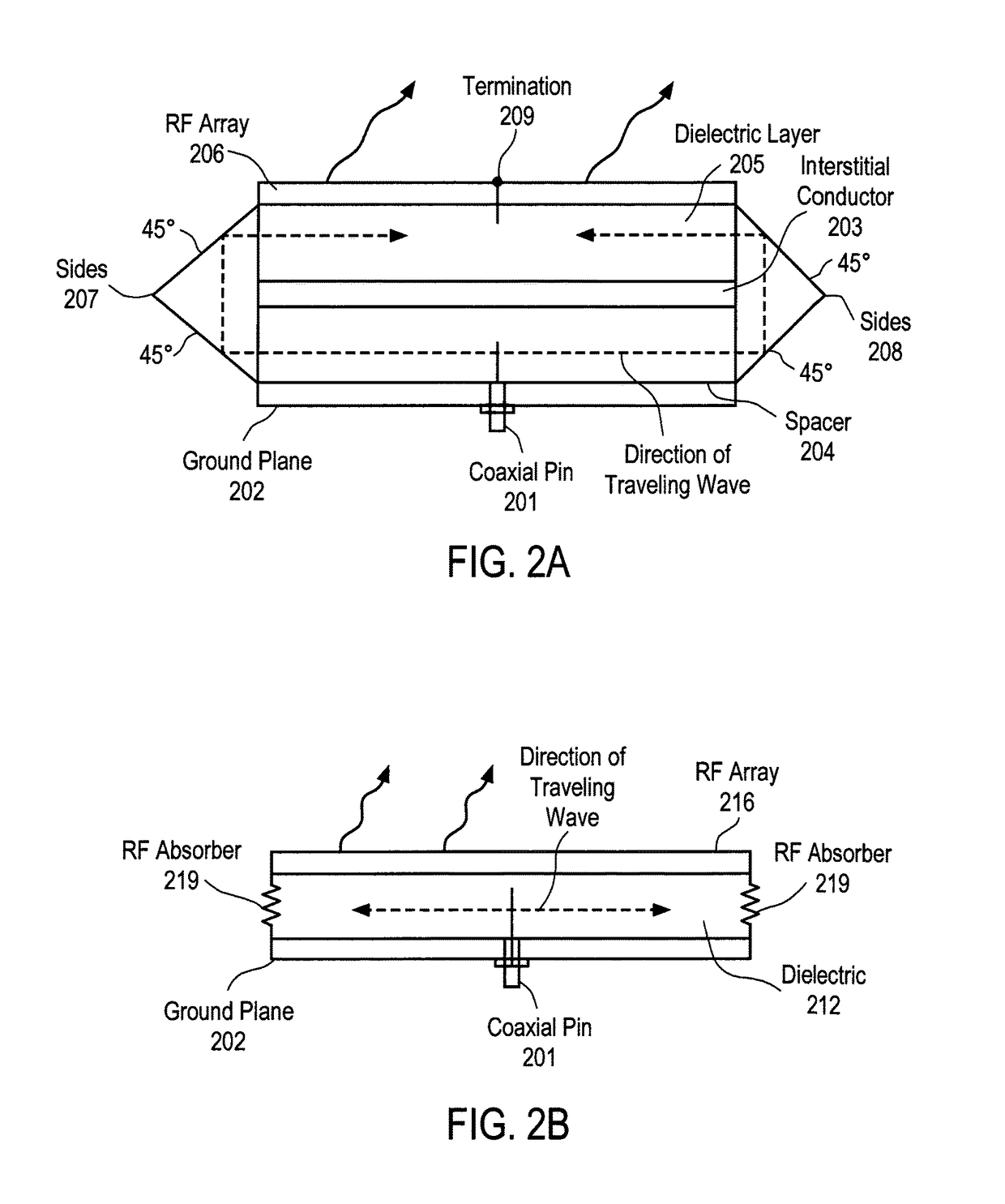
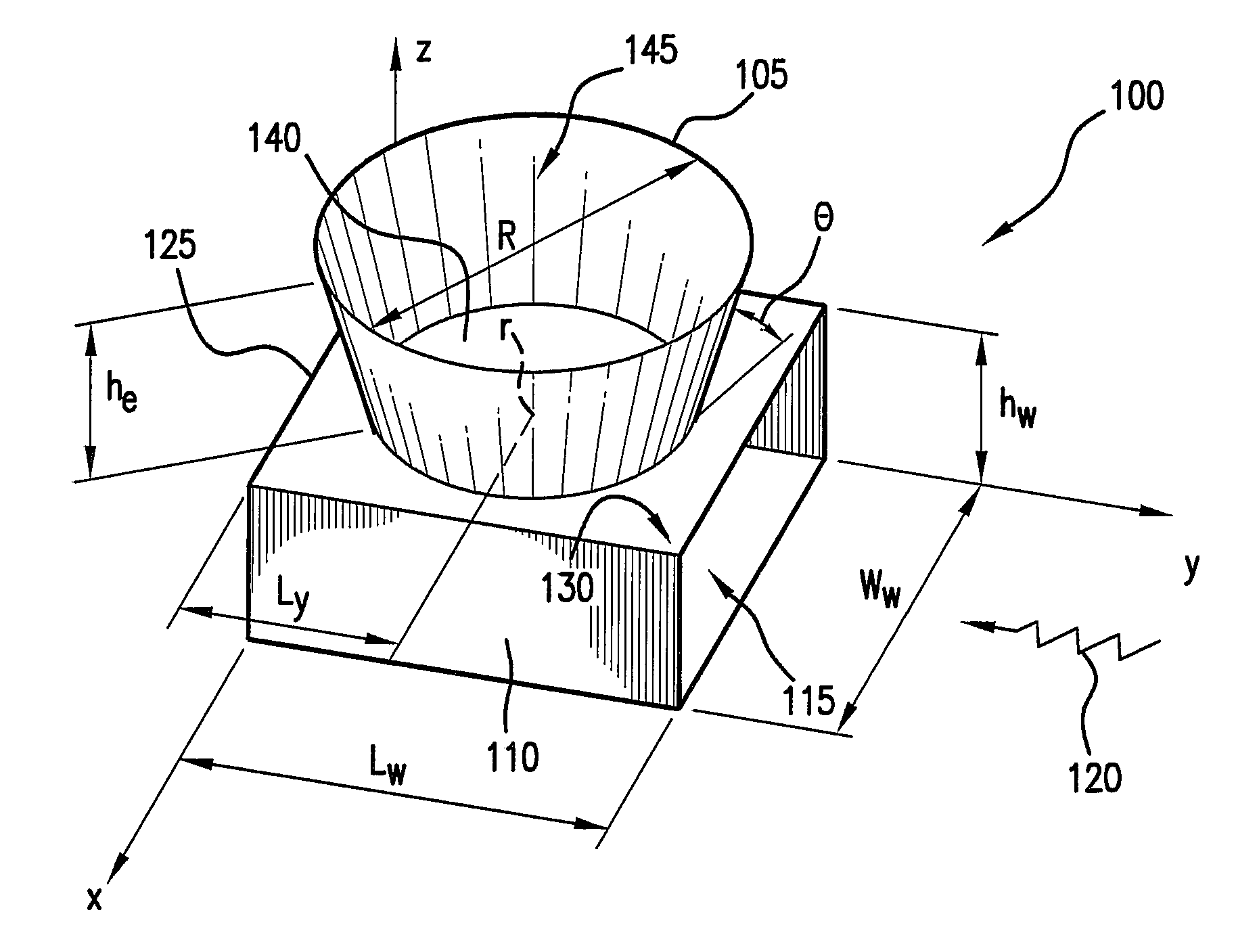
Patents
Literature
162results about "Radial guide fed arrays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dynamic polarization and coupling control from a steerable cylindrically fed holographic antenna
ActiveUS20150236412A1Improve performanceNon-resonant long antennasParallel-plate/lens fed arraysAntenna feedPhysics
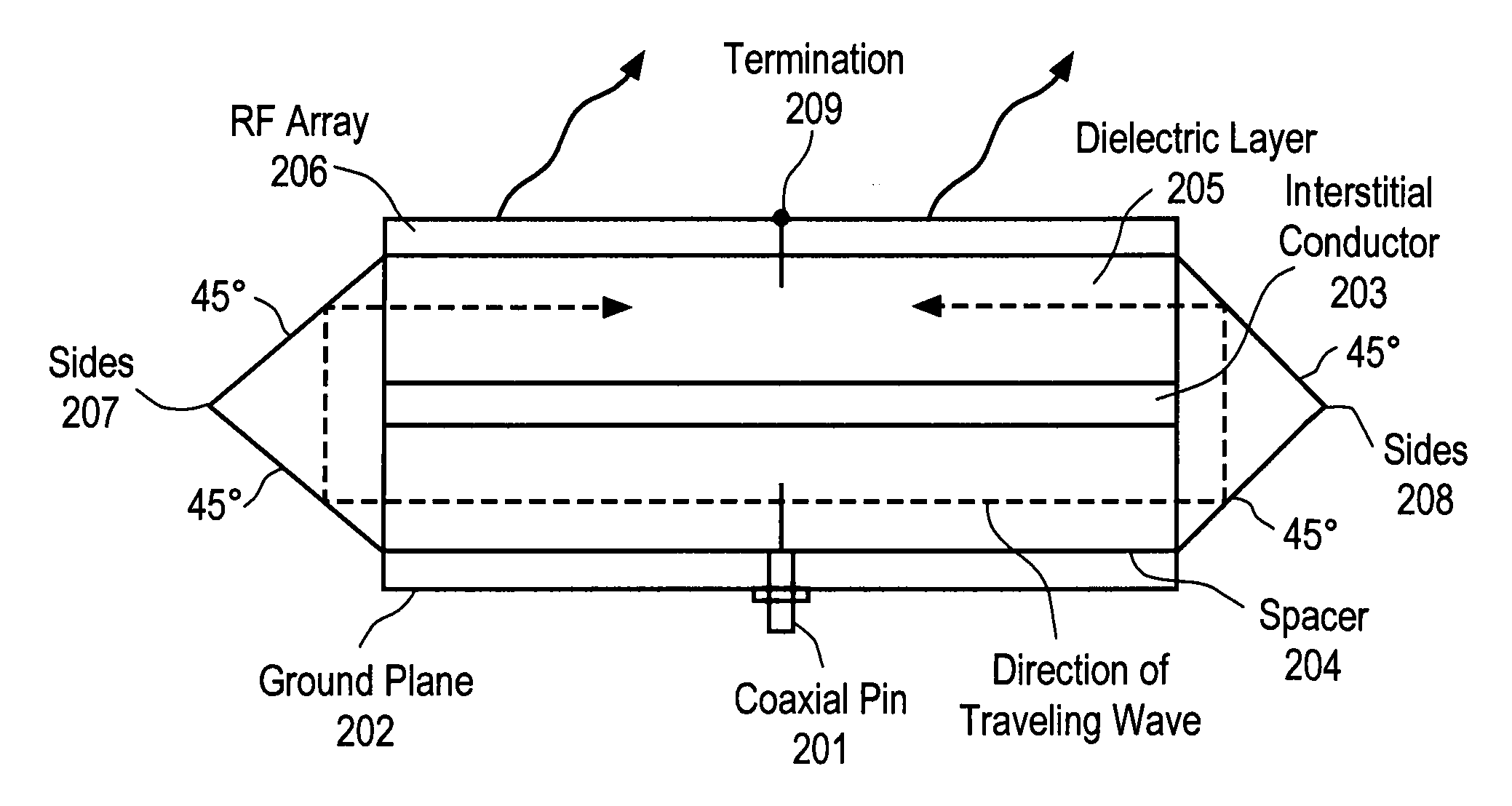
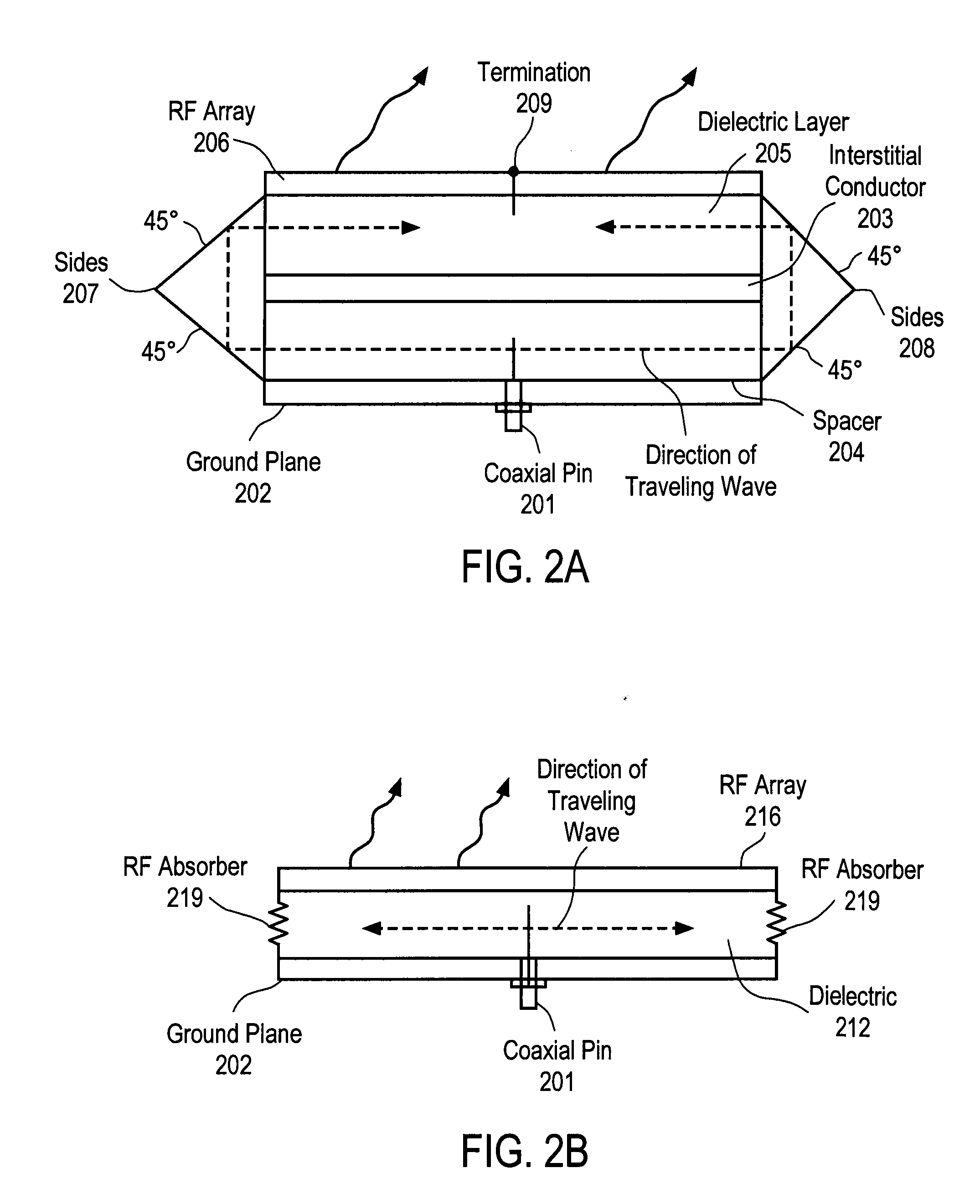
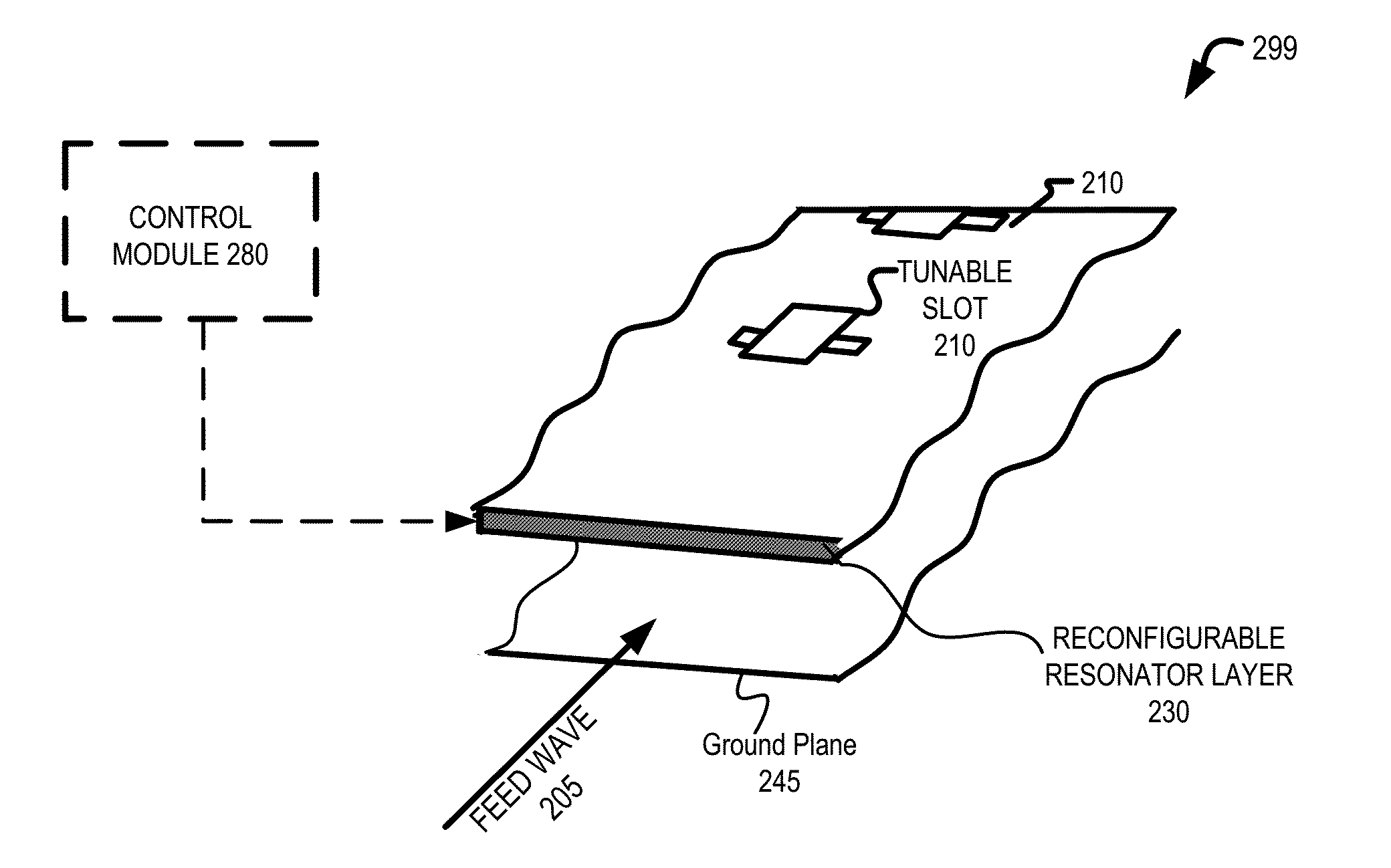
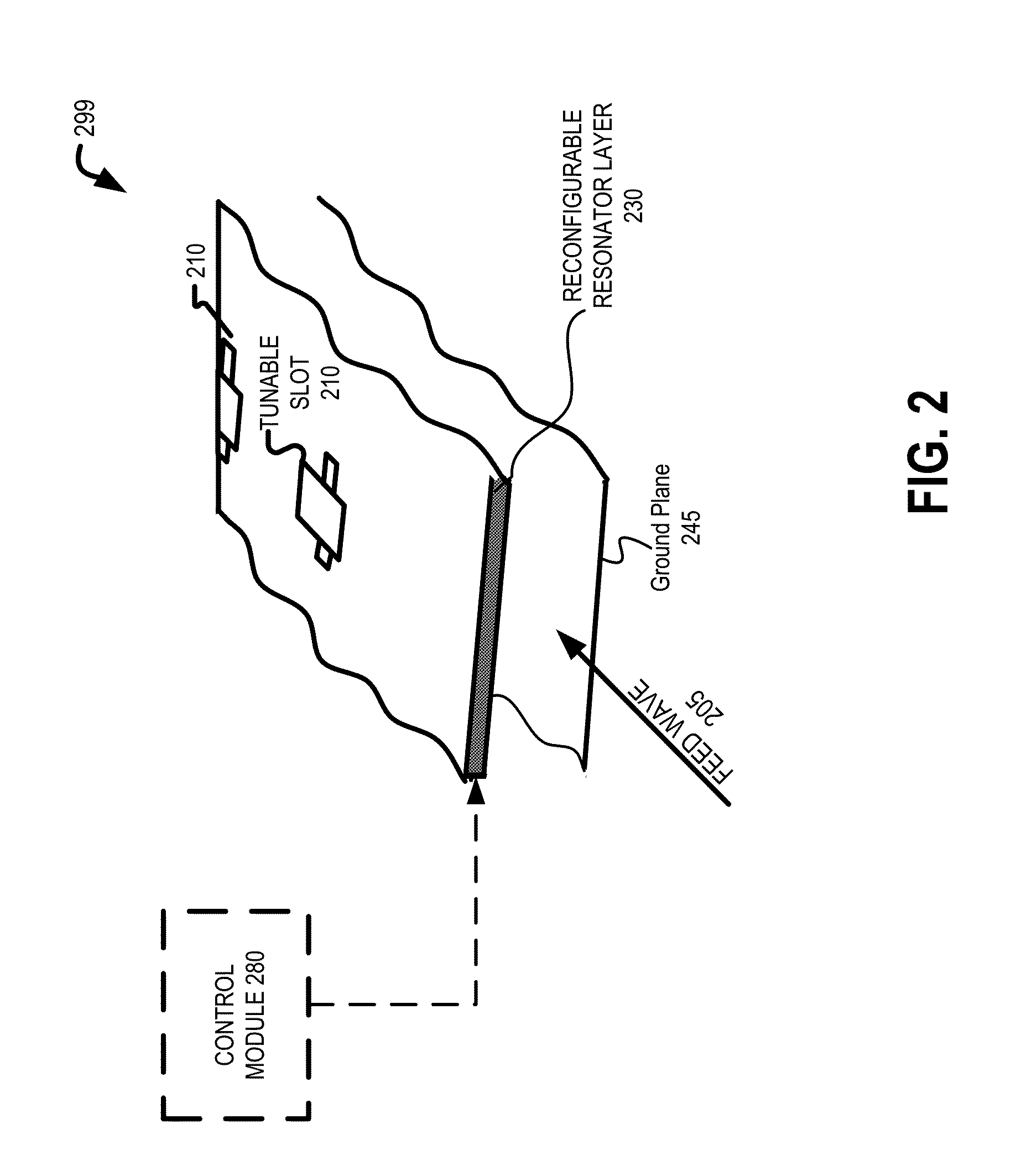
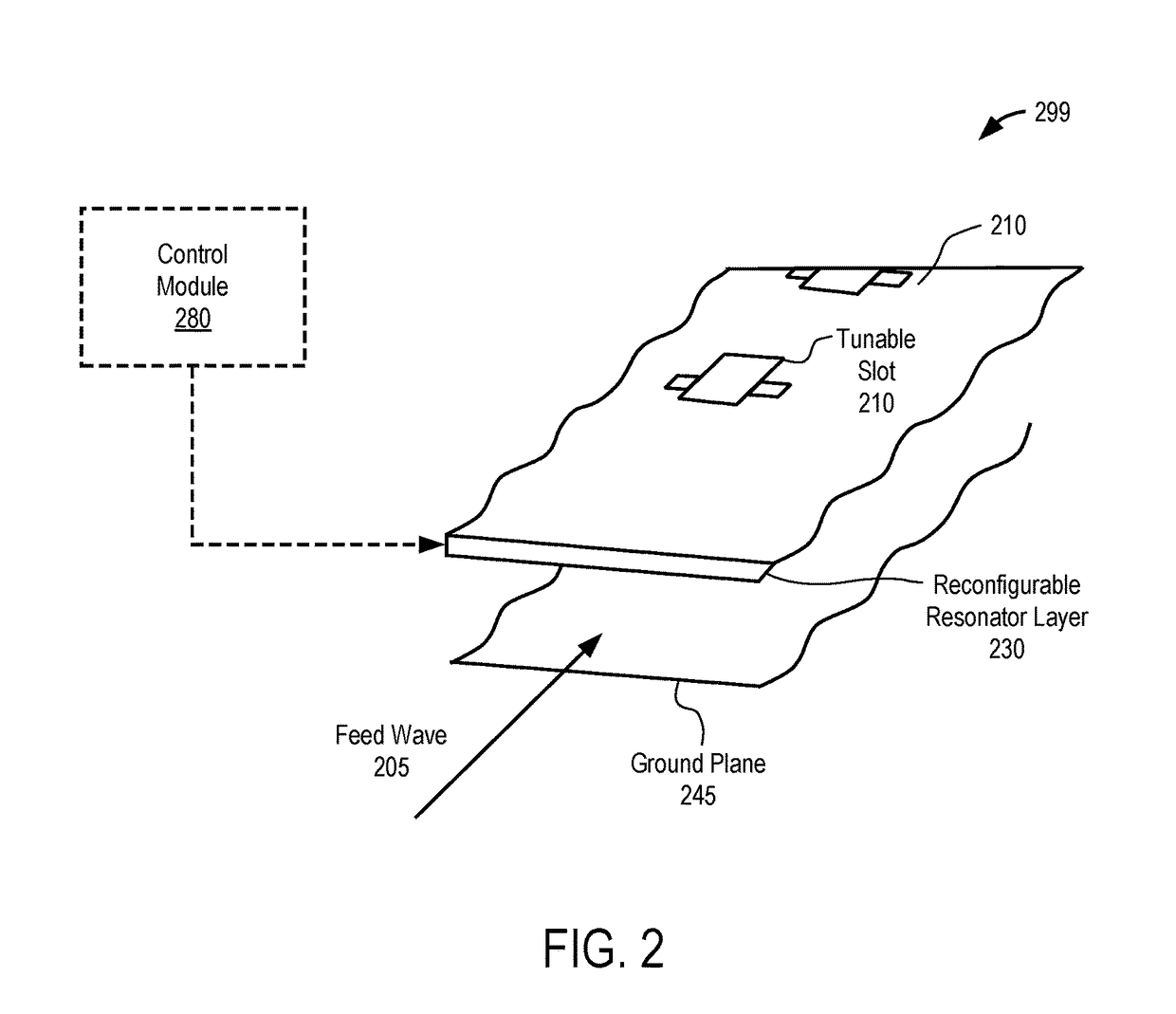
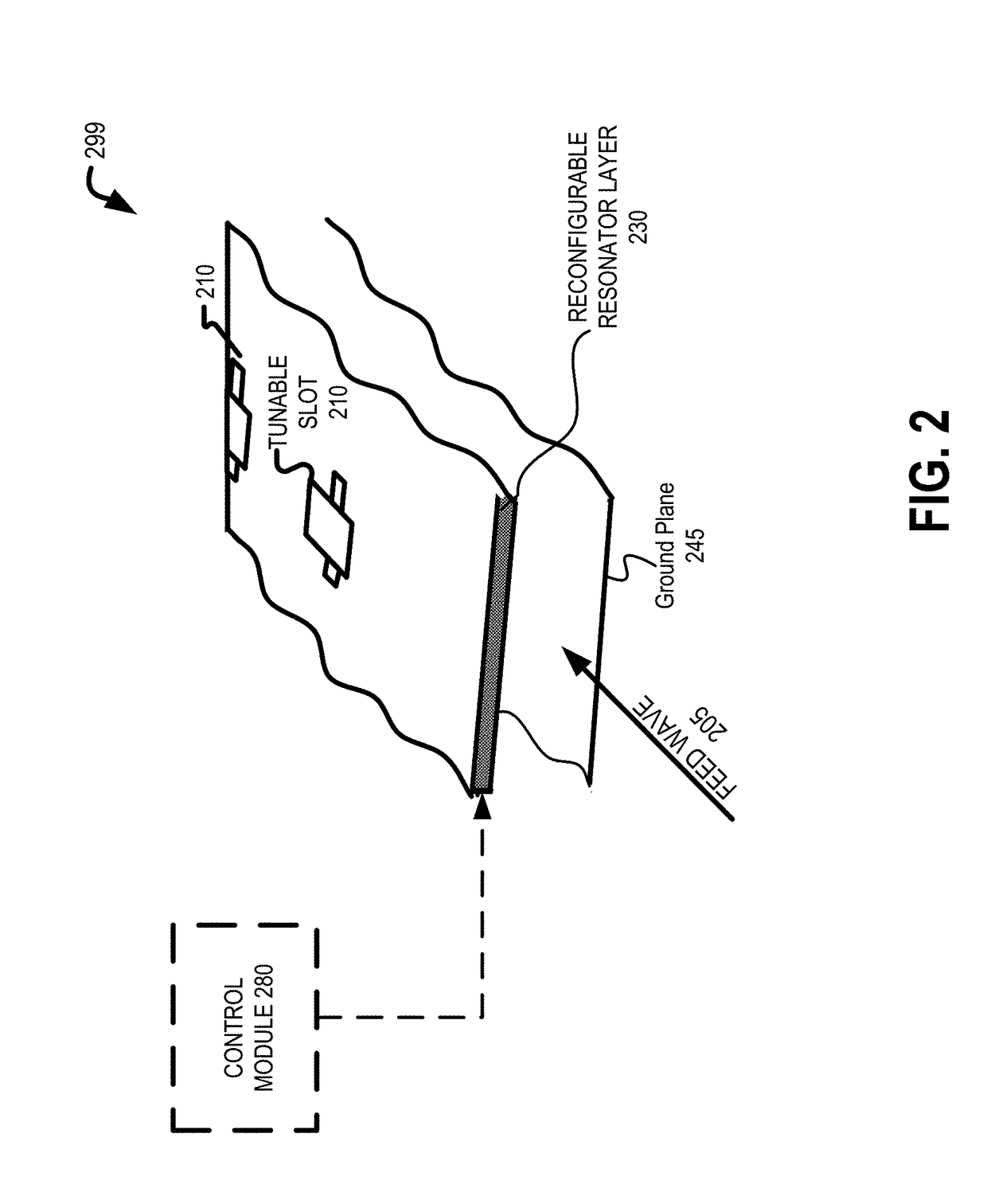
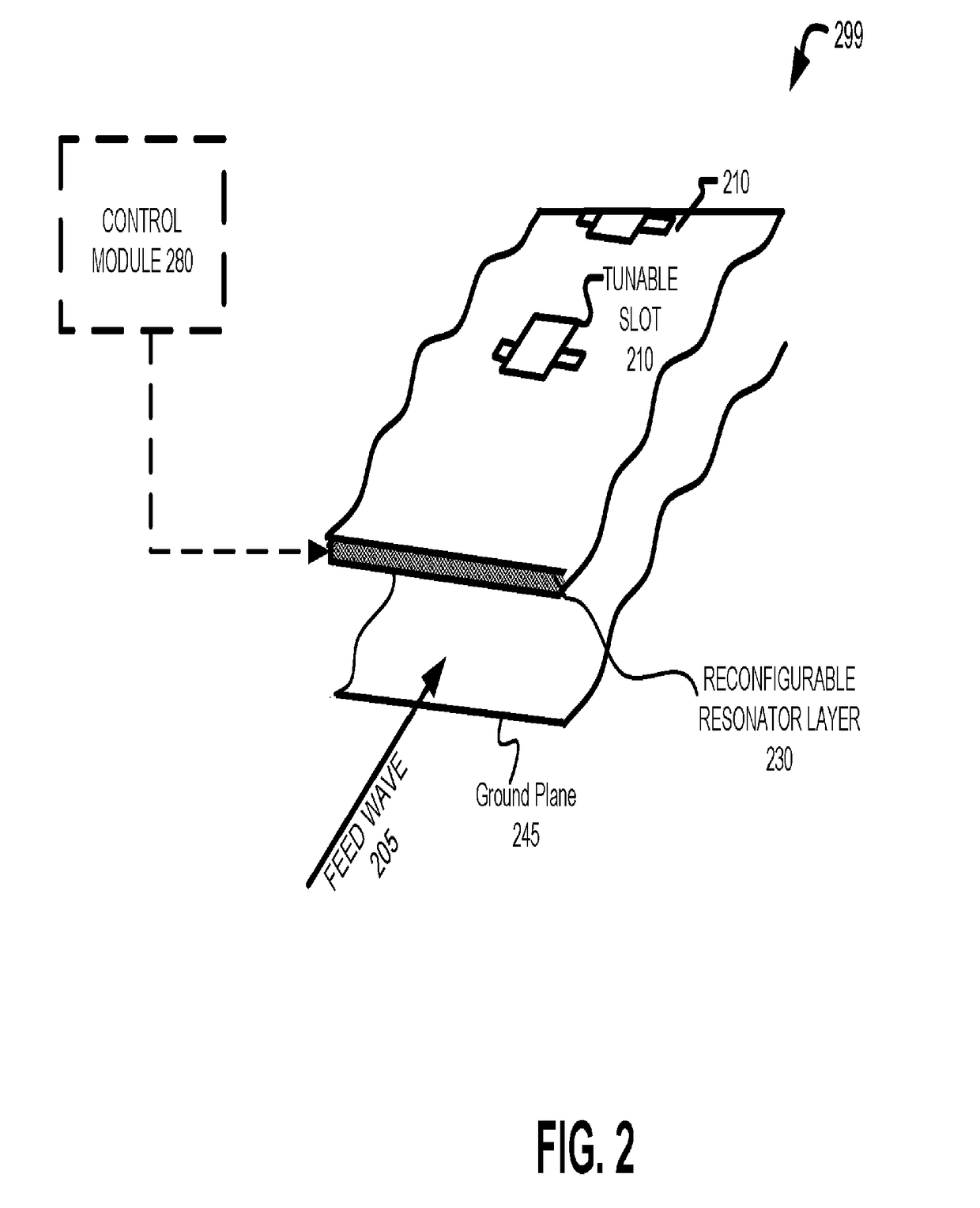
An apparatus is disclosed herein for a cylindrically fed antenna and method for using the same. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave and a tunable slotted array coupled to the antenna feed.
Owner:KYMETA
Combined antenna apertures allowing simultaneous multiple antenna functionality
ActiveUS20160233588A1Data augmentationHigh densitySimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna elementAntenna aperture
An antenna apparatus and method for use of the same are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises a single physical antenna aperture having at least two spatially interleaved antenna arrays of antenna elements, the antenna arrays being operable independently and simultaneously at distinct frequency bands.
Owner:KYMETA
Integrated waveguide antenna and array
ActiveUS20070273599A1Improve conversion efficiencySimple and inexpensive to manufactureLinear waveguide fed arraysLeaky-waveguide antennasBeam steeringWaveguide
An antenna is provided. The antenna may include at least one open-ended structure extending from a surface of a waveguide. The open-ended structure may have a cross section of many different shapes. The walls of the structure may be movable. The antenna structure may be rotated. The antenna may incorporate a number of different wave feeds. The antenna may provide two-dimensional beam steering.
Owner:ORR PARTNERS I
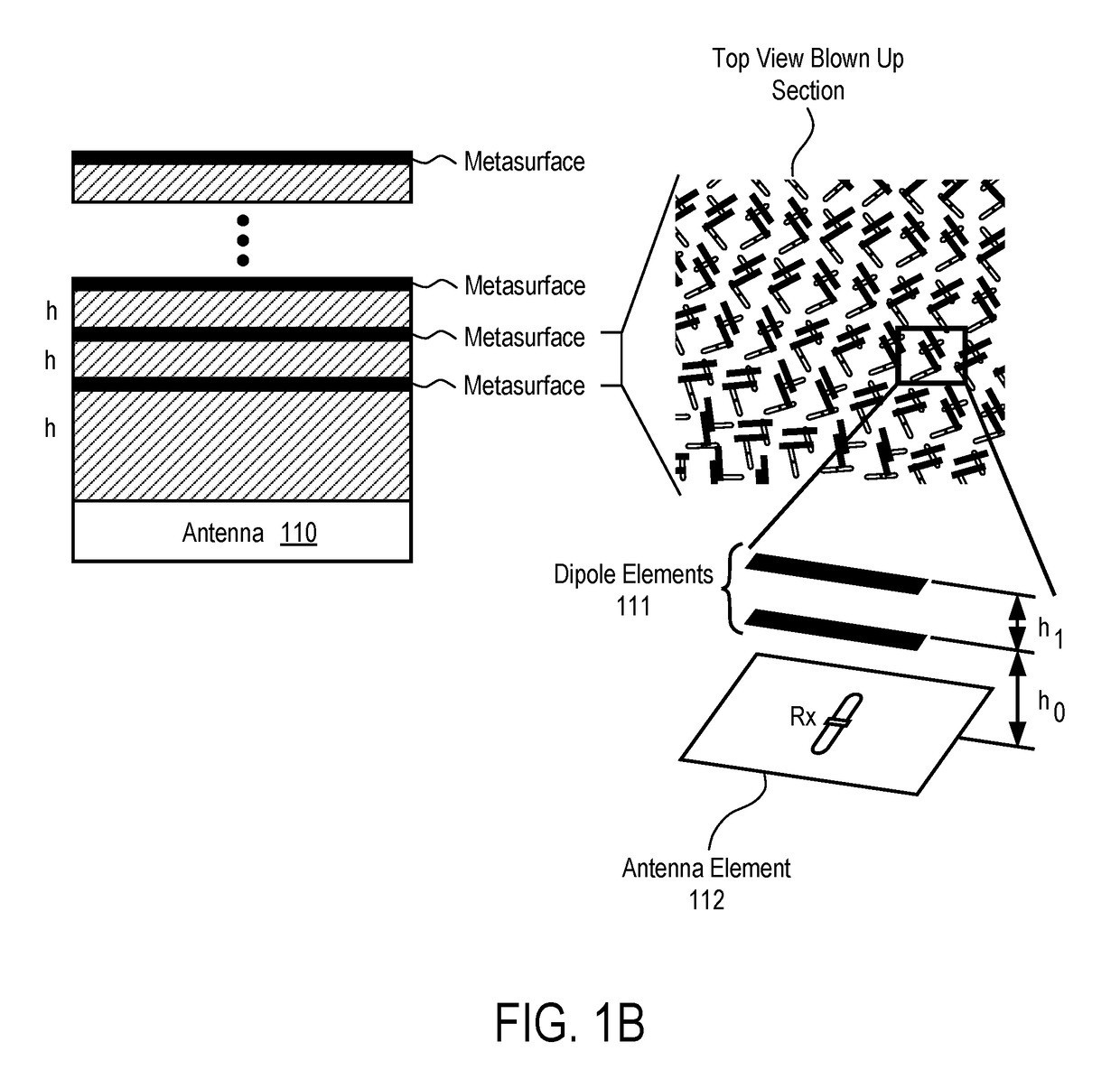
Impedance matching for an aperture antenna
ActiveUS20180076521A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsImpedance matchingAntenna element
A method and apparatus for impedance matching for an antenna aperture are described. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna aperture having at least one array of antenna elements operable to radiate radio frequency (RF) energy and an integrated composite stack structure coupled to the antenna aperture. The integrated composite stack structure includes a wide angle impedance matching network to provide impedance matching between the antenna aperture and free space and also puts dipole loading on antenna elements.
Owner:KYMETA
Dynamic polarization and coupling control from a steerable, multi-layered cylindrically fed holographic antenna
ActiveUS20150236415A1Improve performanceParallel-plate/lens fed arraysIndividually energised antenna arraysLight beamRadio frequency
An apparatus is disclosed herein for a cylindrically fed antenna and method for using the same. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises: an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave; a first layer coupled to the antenna feed and into which the feed wave propagates outwardly and concentrically from the feed; a second layer coupled to the first layer to cause the feed wave to be reflected at edges of the antenna and propagate inwardly through the second layer from the edges of the antenna; and a radio-frequency (RF) array coupled to the second layer, wherein the feed wave interacts with the RF array to generate a beam.
Owner:KYMETA
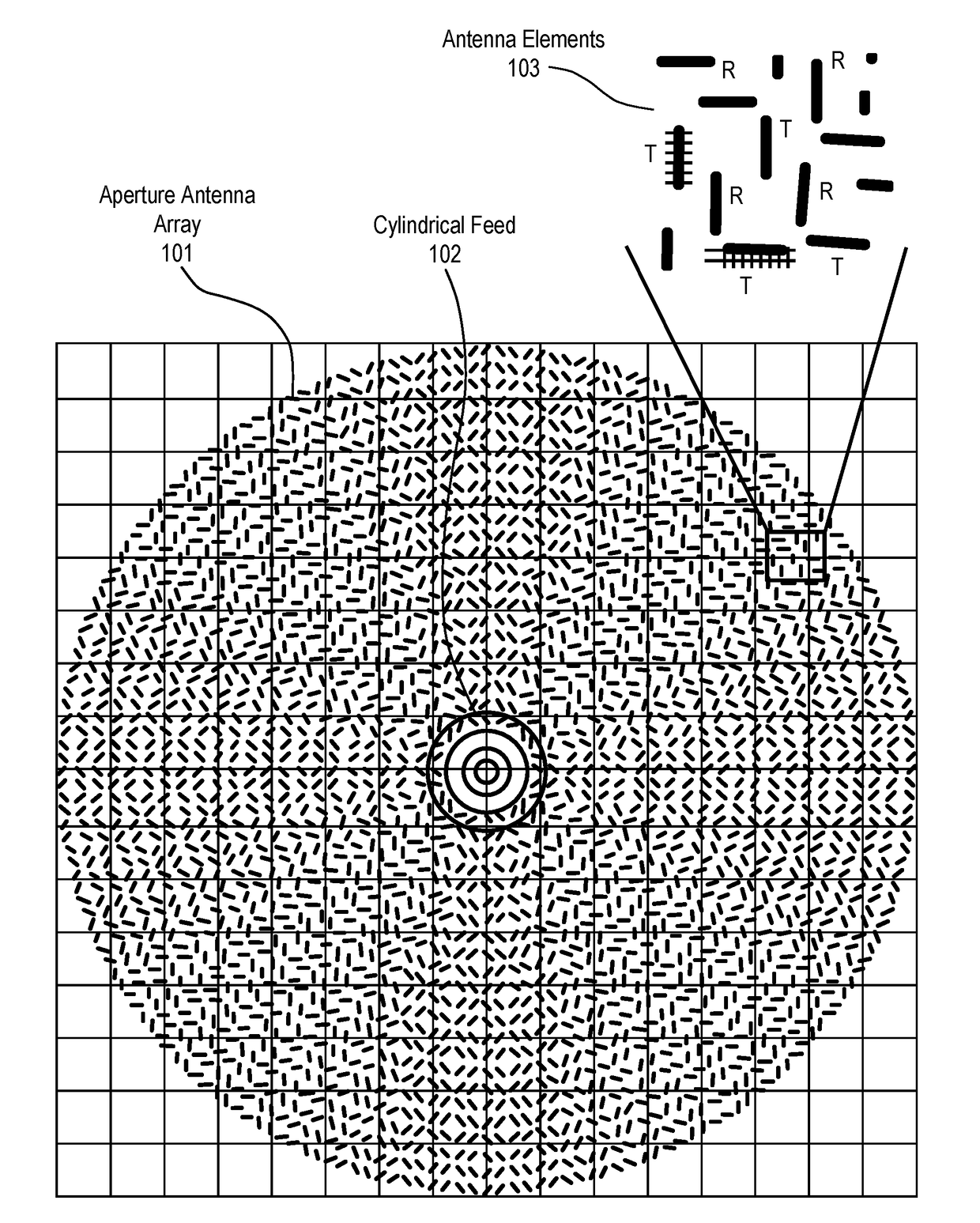
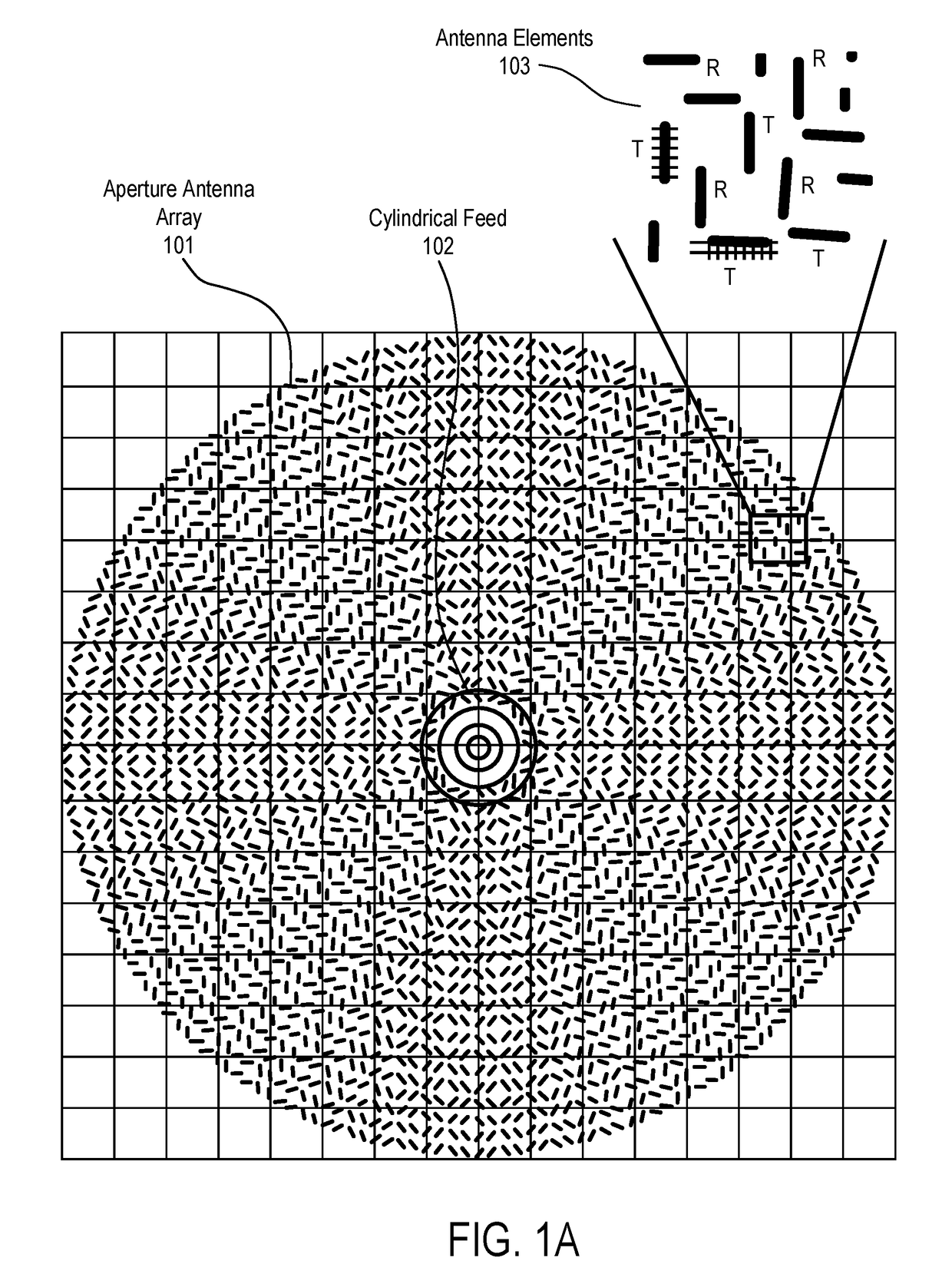
Aperture segmentation of a cylindrical feed antenna
ActiveUS20160261043A1Parallel-plate/lens fed arraysAntenna arrays manufactureAntenna elementAntenna feed
A method and apparatus for aperture segmentation are disclosed. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave and a physical antenna aperture coupled to the antenna feed and comprising a plurality of segments having antenna elements that form a plurality of closed concentric rings of antenna elements when combined, where the plurality of concentric rings are concentric with respect to the antenna feed.
Owner:KYMETA
Portable electronic device with an antenna array and method for operating same
Apparatus includes a device housing, a device face, a printed circuit board (PCB), and an antenna array. The device housing has a shape characterized by an axis, a planar housing surface that is perpendicular to the axis, and a housing sidewall that is parallel to the axis. The housing sidewall is positioned along a periphery of a planar housing surface. The device face is positioned at an opposite end of the device housing from the planar housing surface. The PCB is positioned between and parallel to the planar housing surface and the device face. The antenna array has multiple antenna elements at least some of which are electrically coupled to the PCB. The antenna array is configured to concentrate radiation of radio waves laterally through a radiation plane that is parallel to the sidewall of the housing and that is perpendicular to the device face and the planar housing surface.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Integrated waveguide cavity antenna and reflector RF feed
InactiveUS20080117113A1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesParallel-plate/lens fed arraysIntegrated antennaRadiating element
An integrated antenna and reflector feed is provided which is structured as a waveguide cavity antenna or array having a curved reflector coupled to a sidewall of the waveguide cavity. A radiation source is situated facing the curved reflector and one or more radiating elements are provided on a top surface of the waveguide cavity. Several curved reflector feeds may be used, operating in the same or different frequencies.
Owner:ORR PARTNERS I
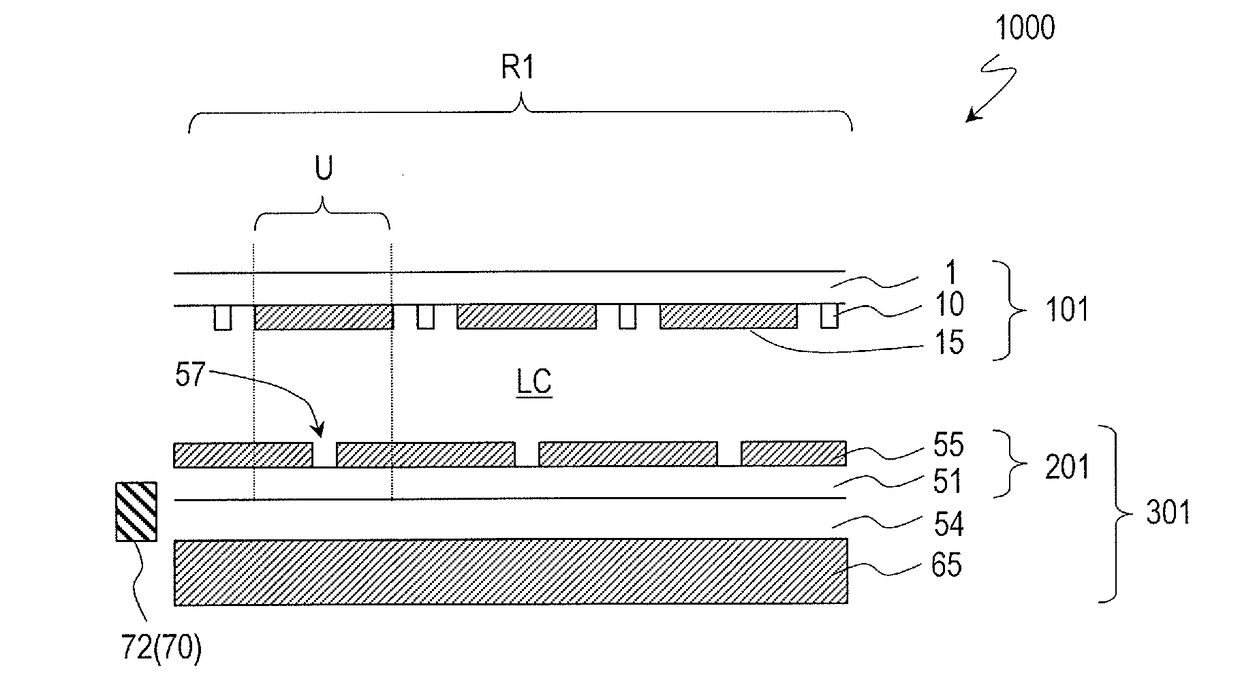
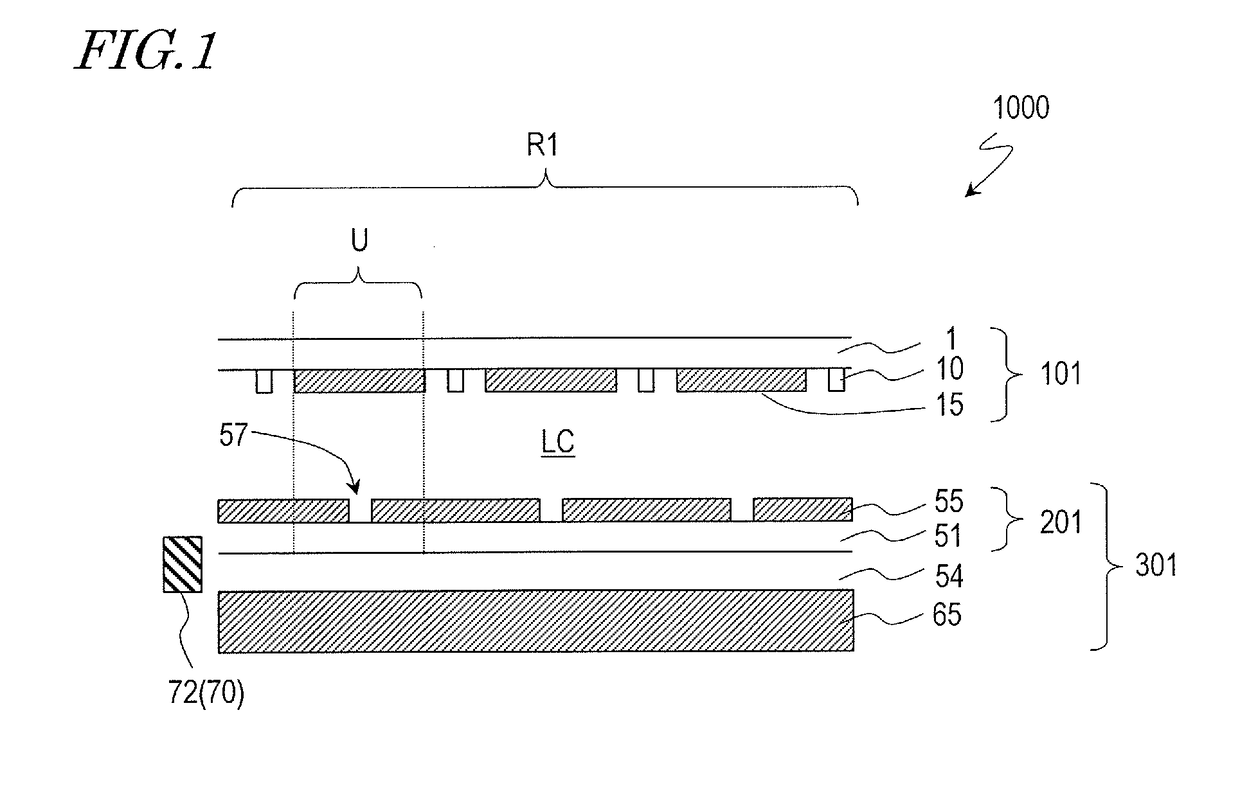
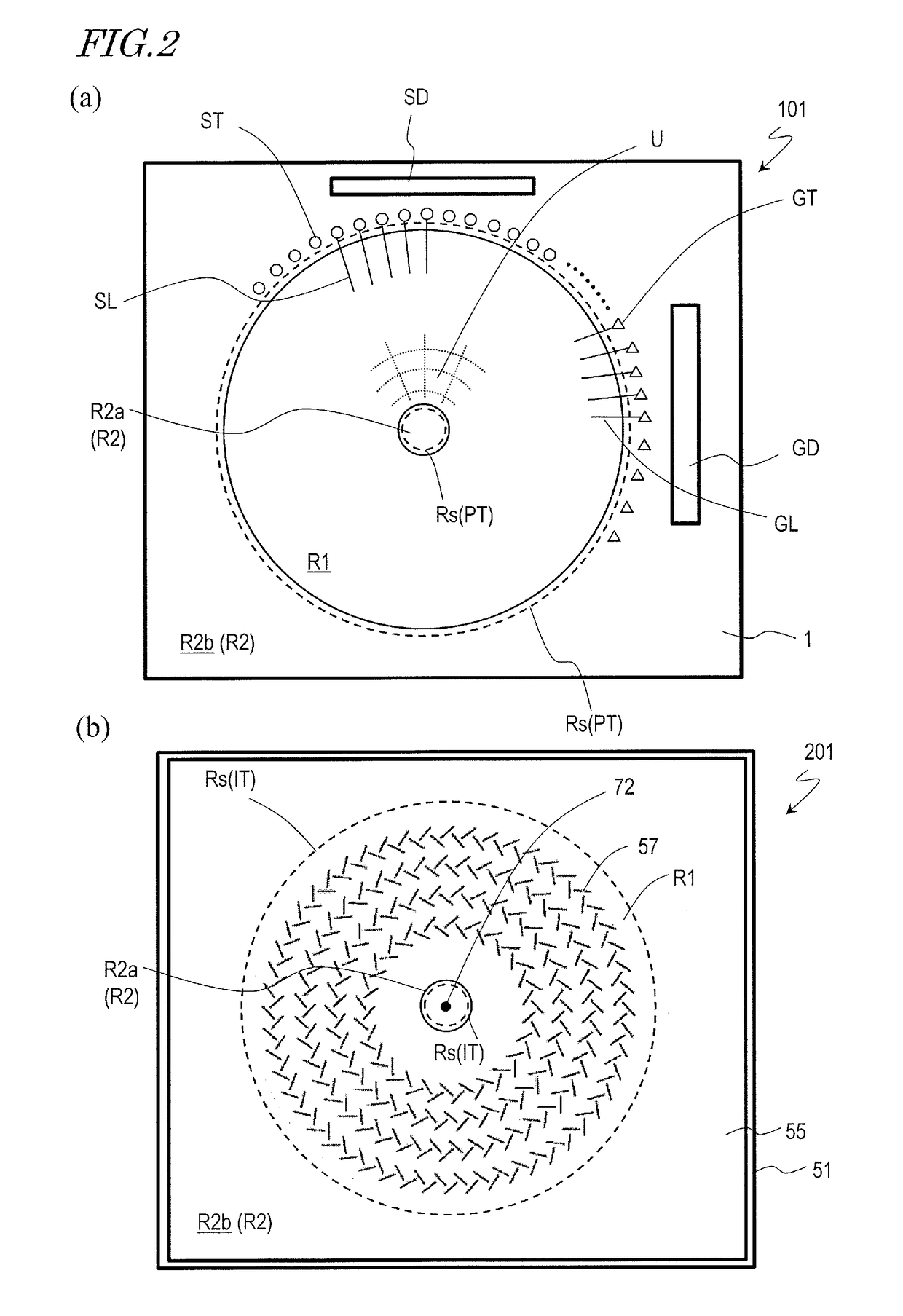
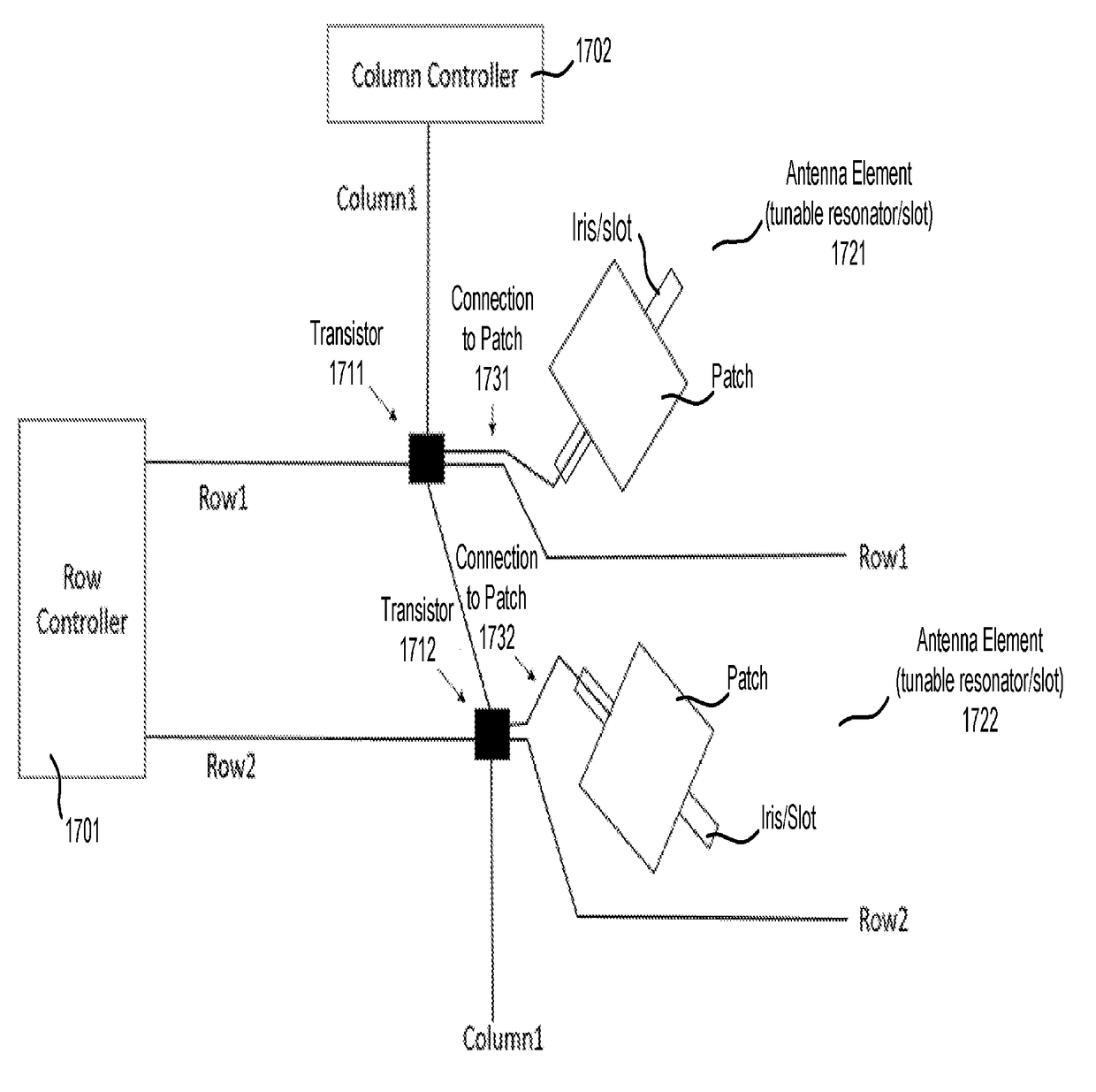
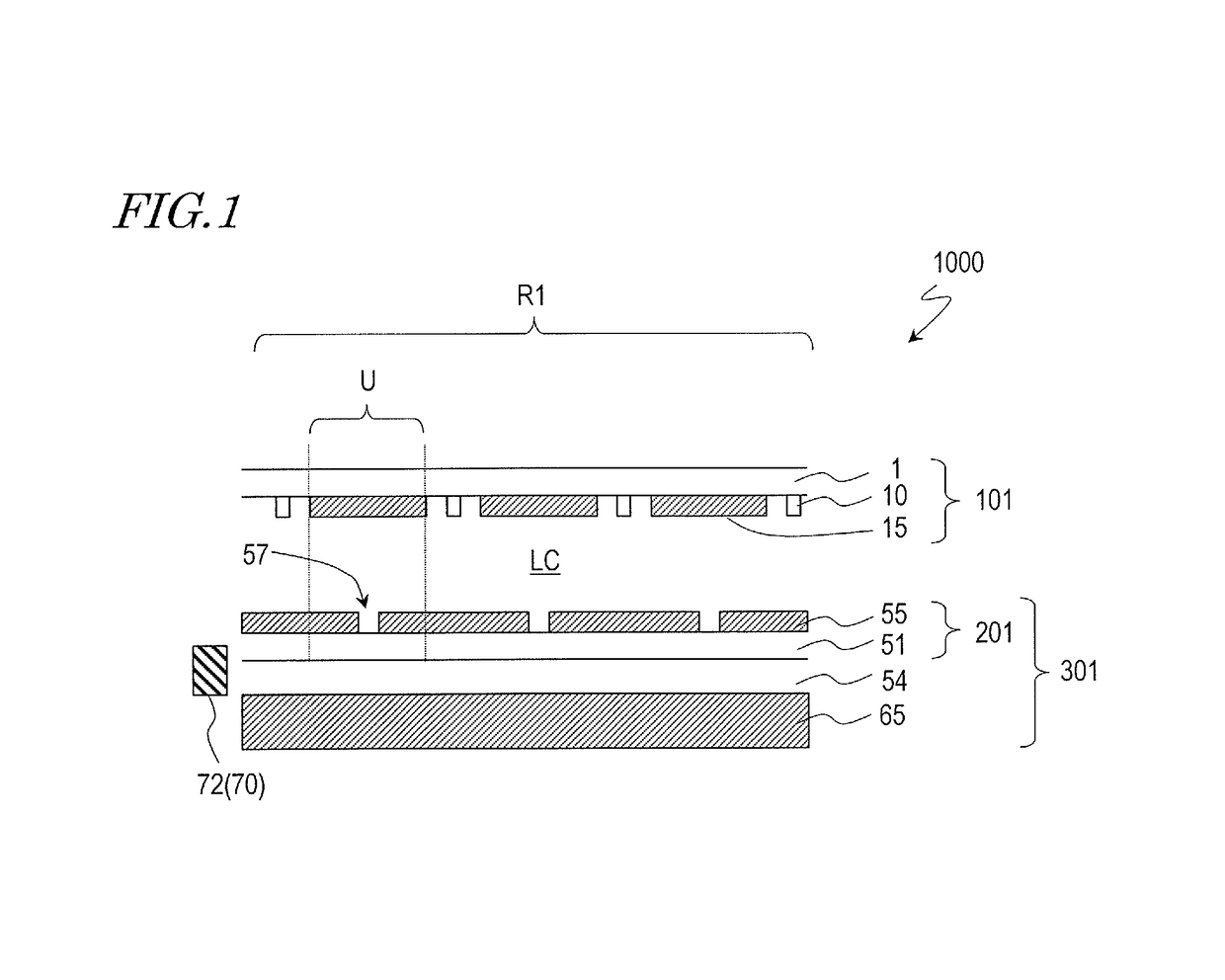
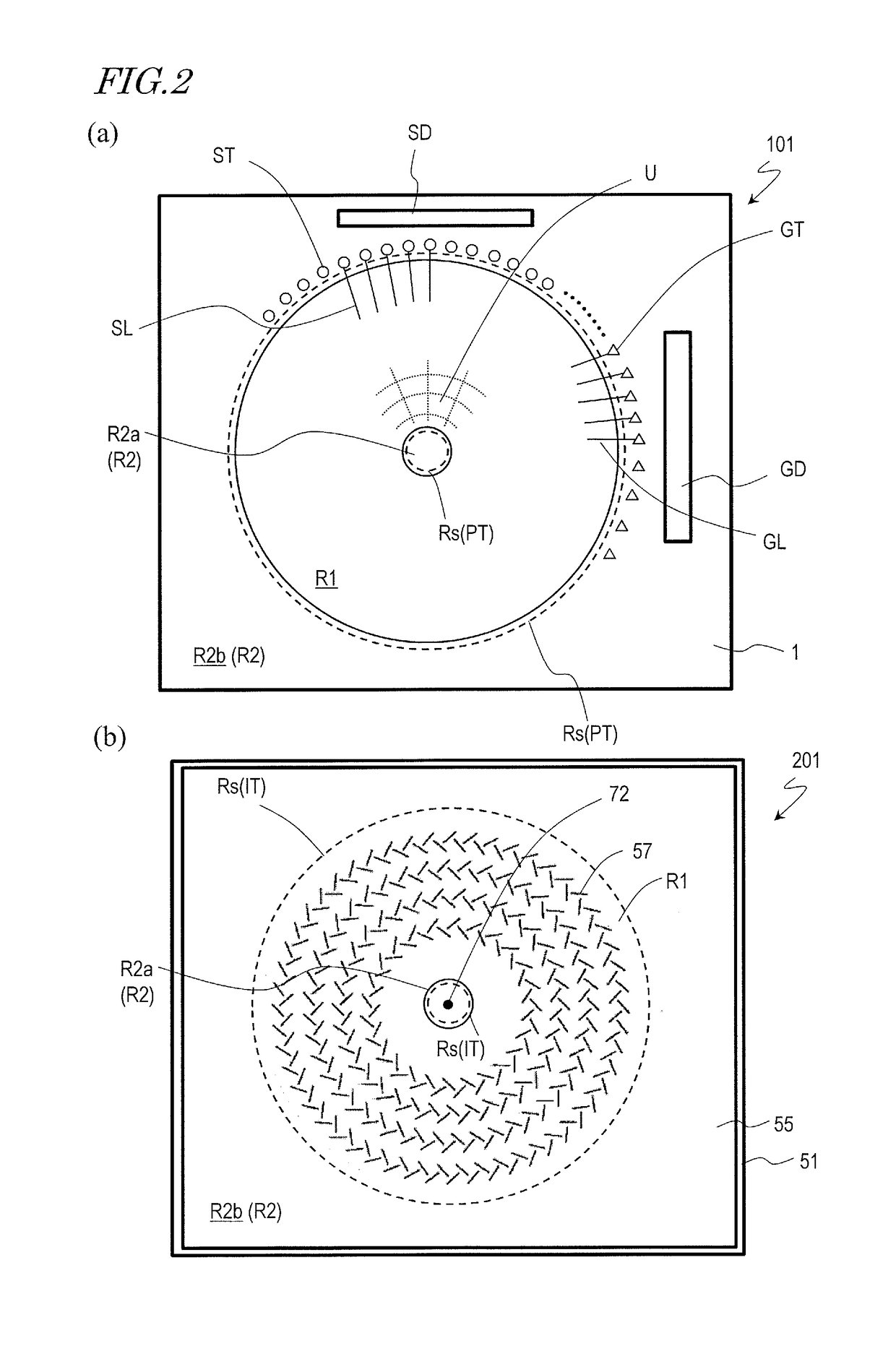
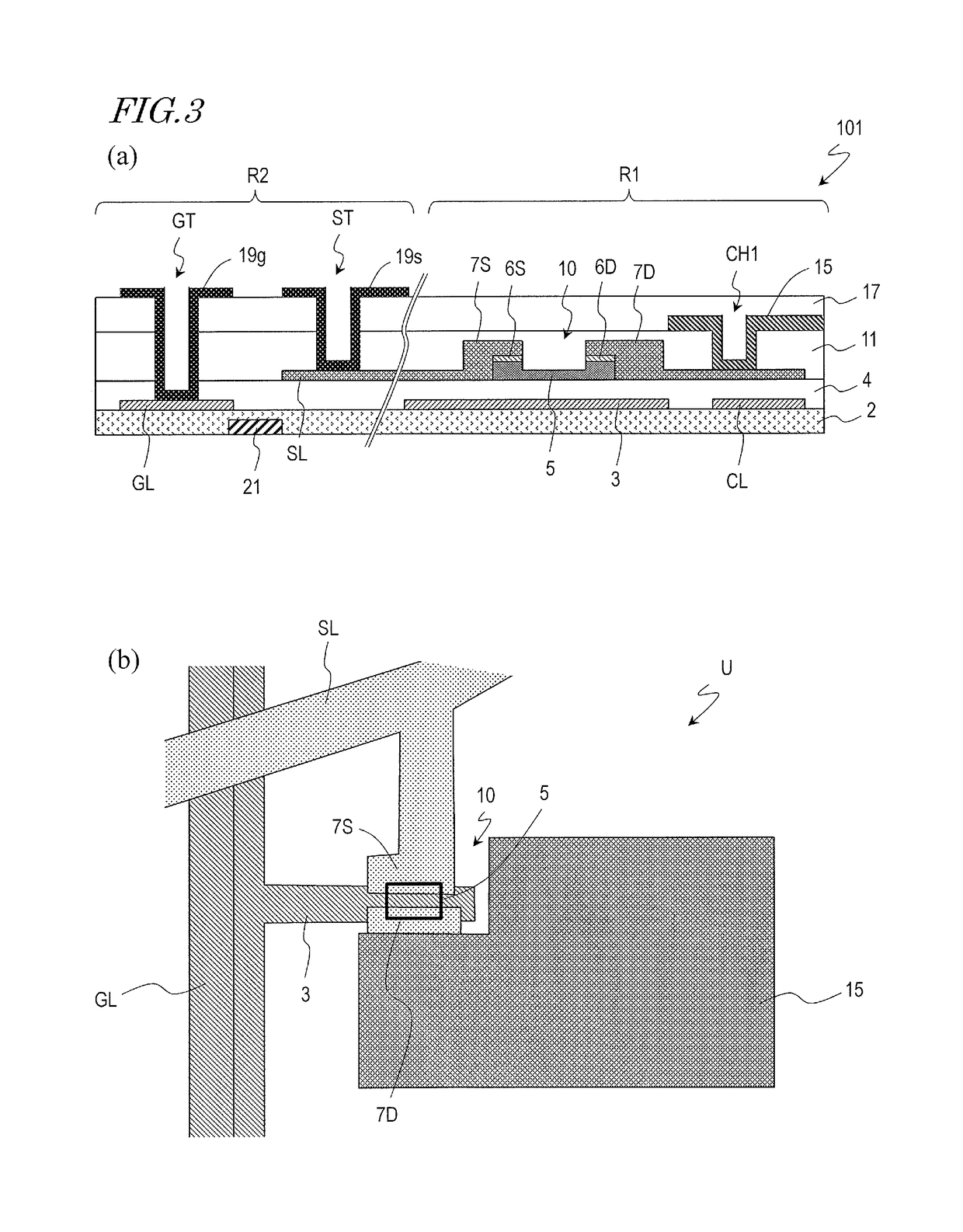
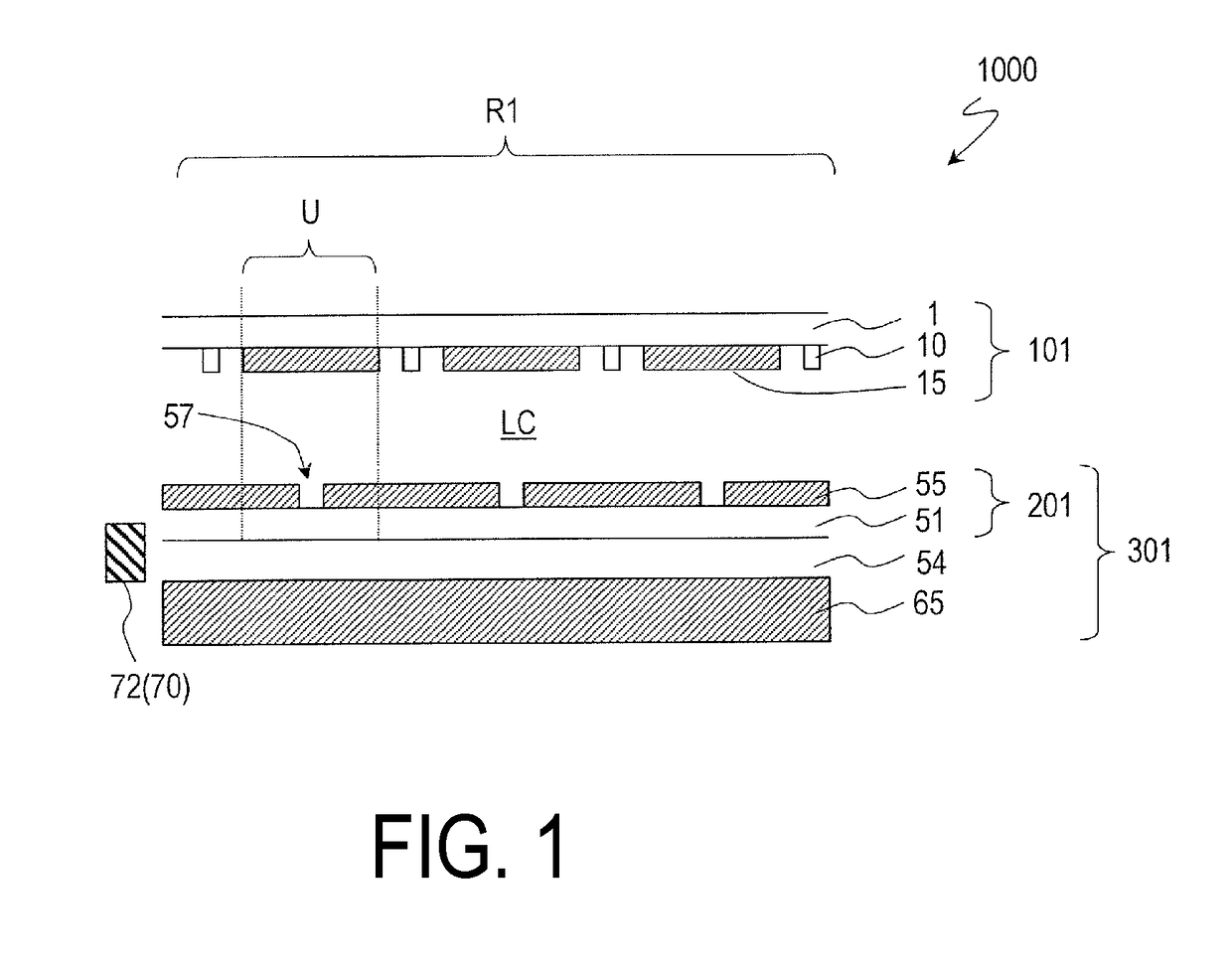
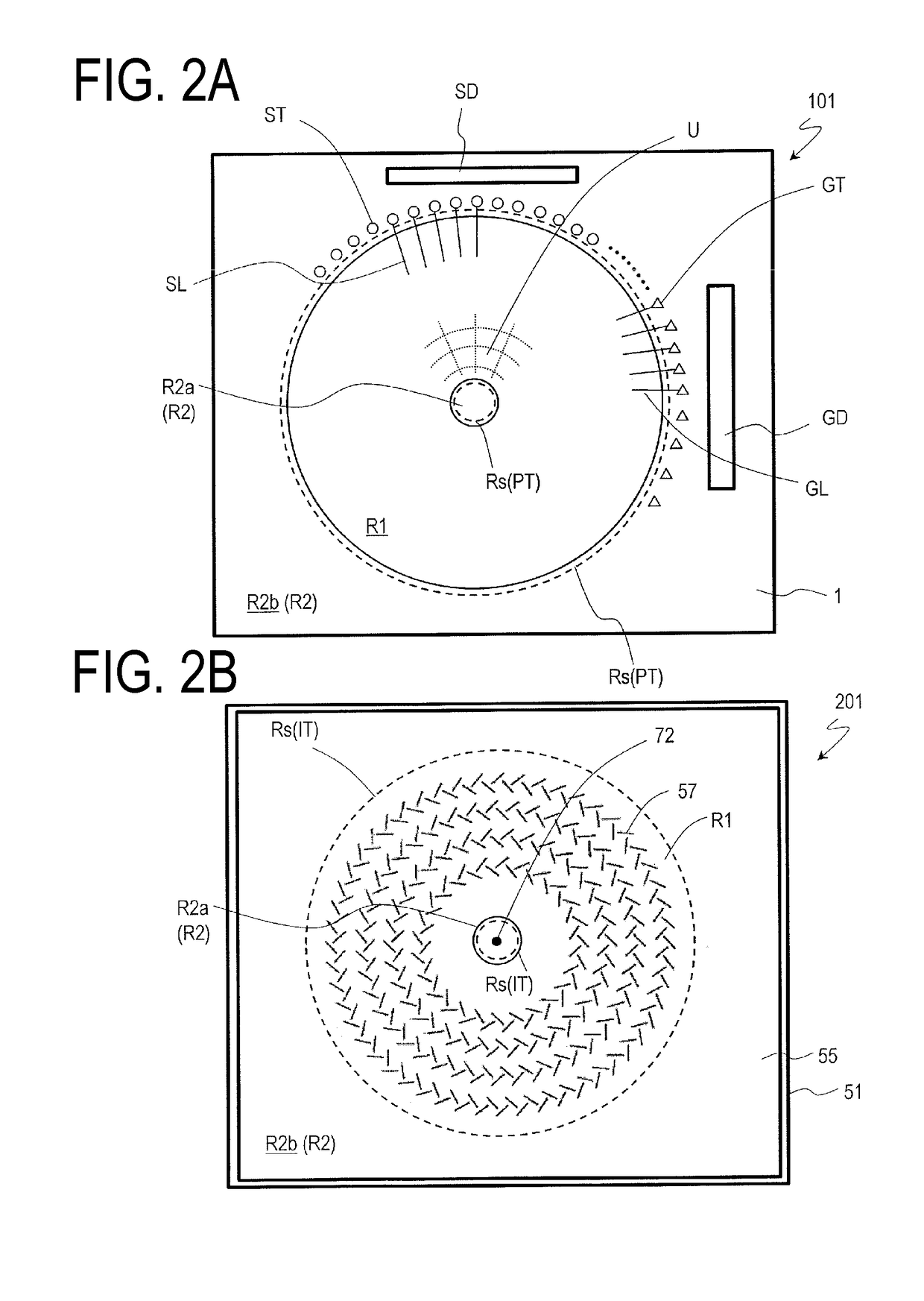
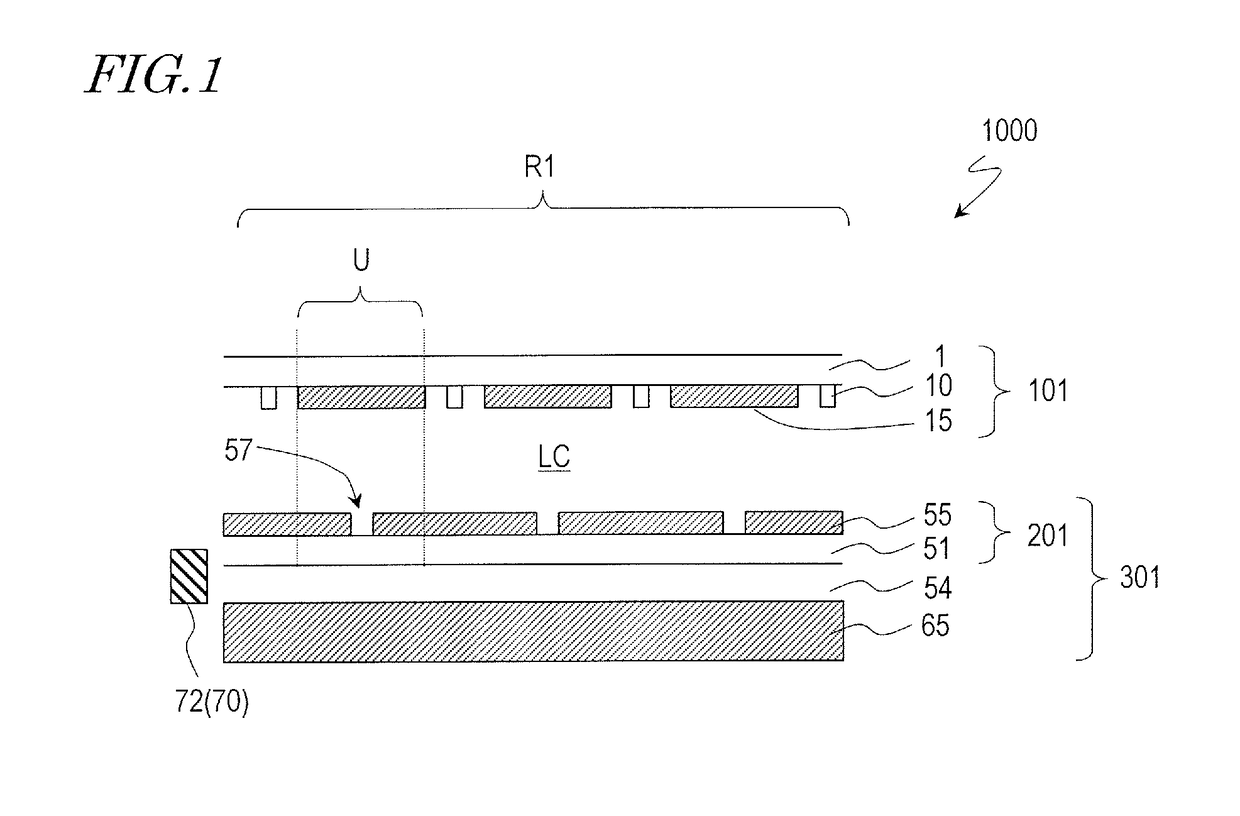
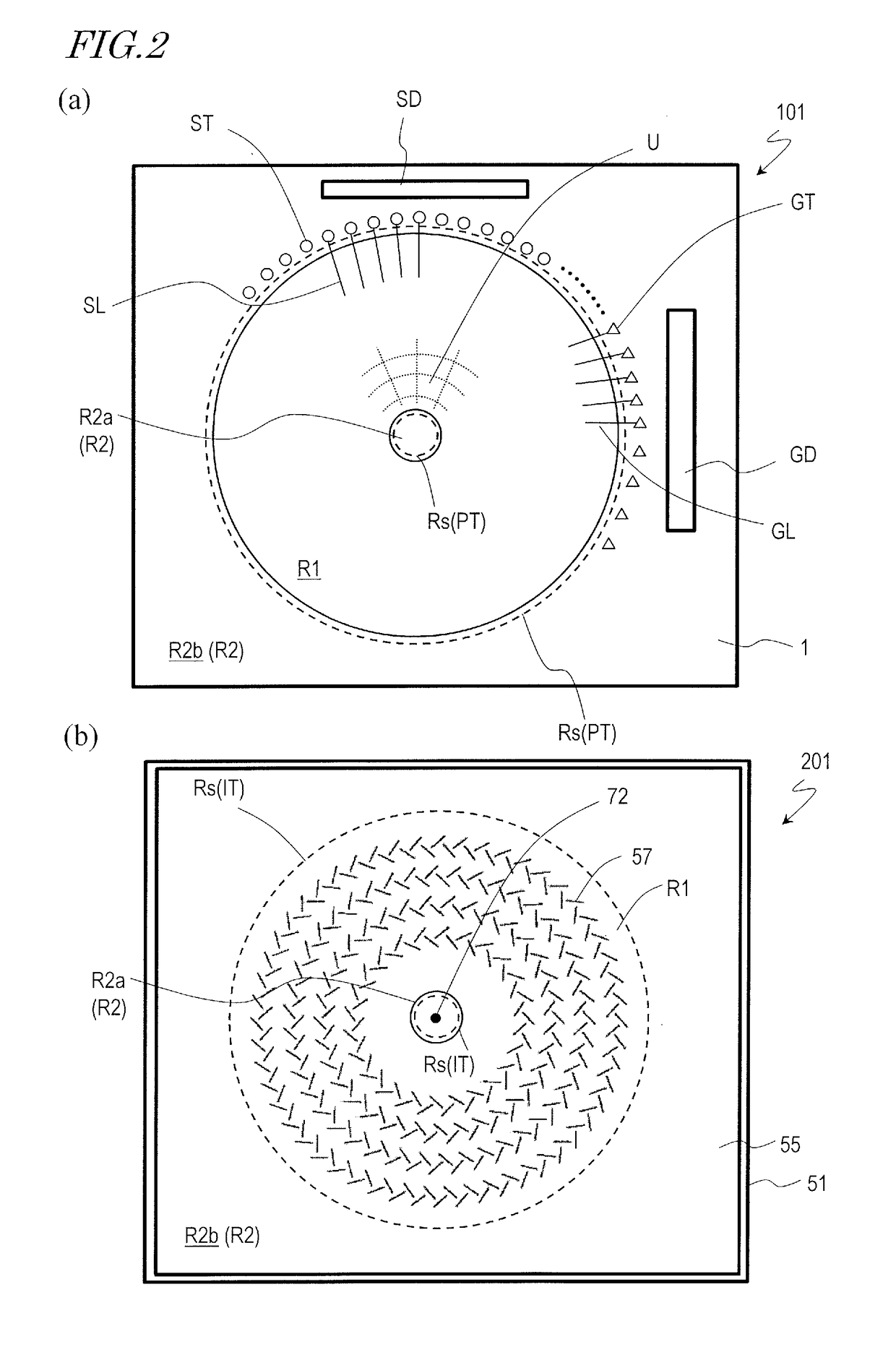
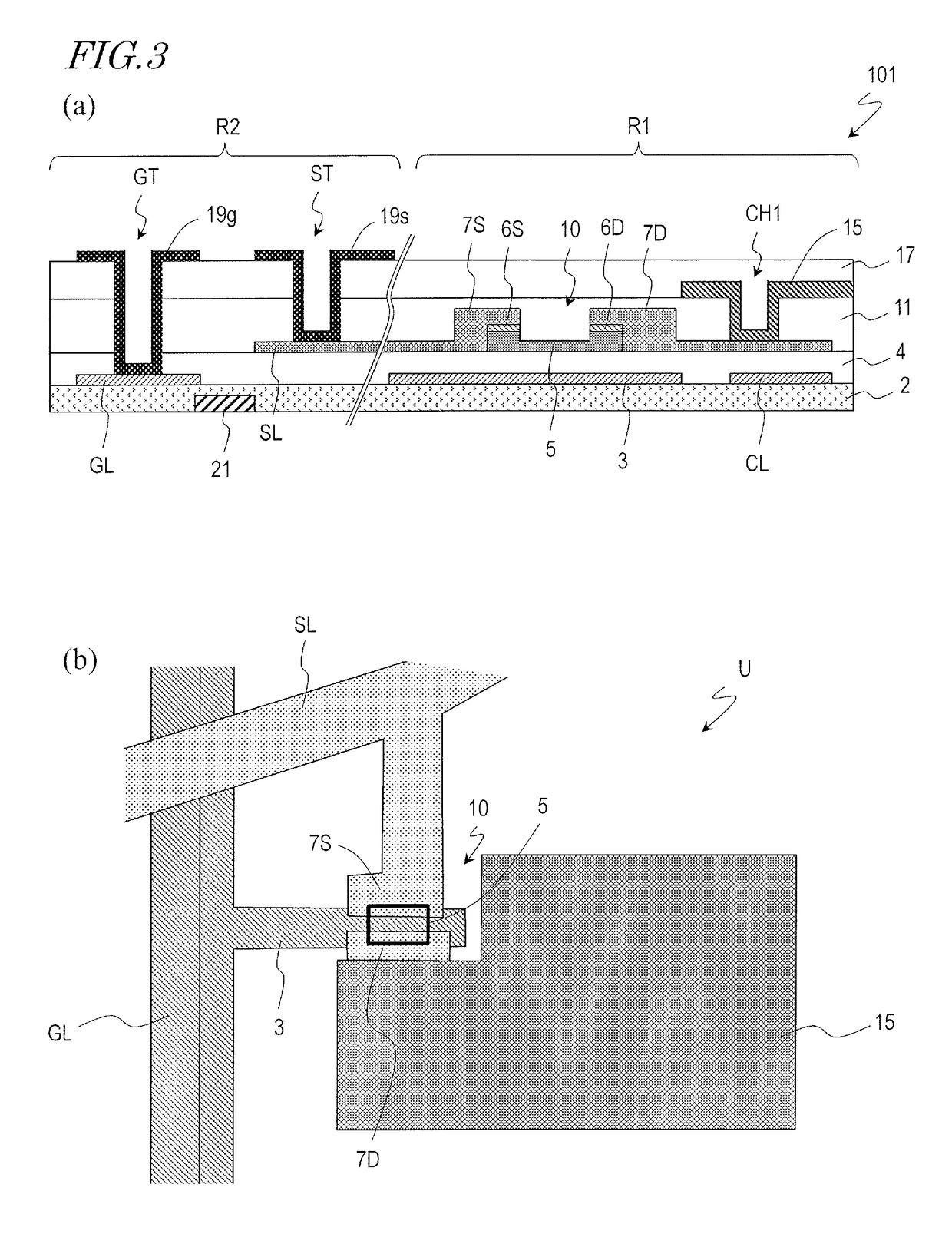
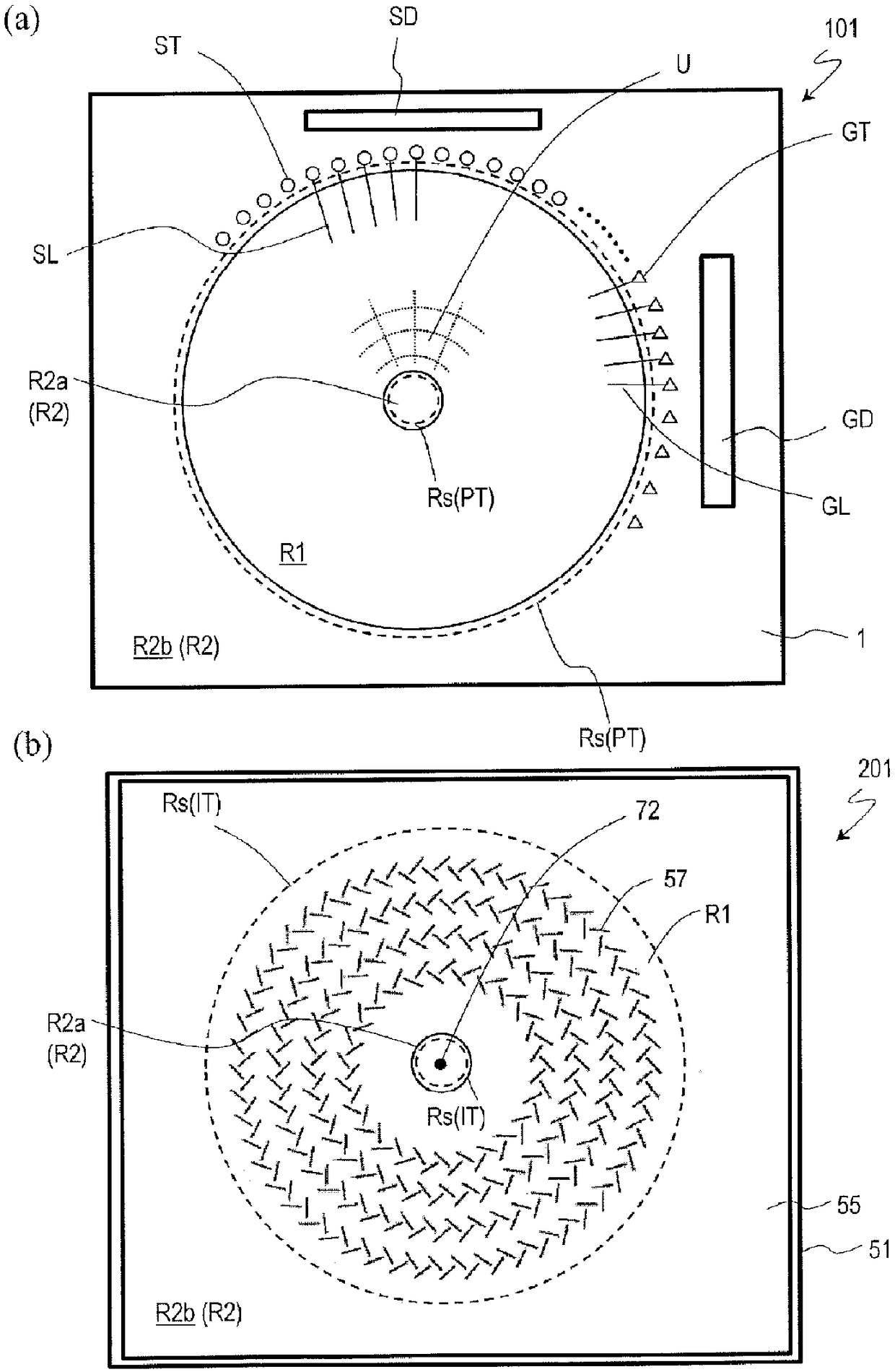
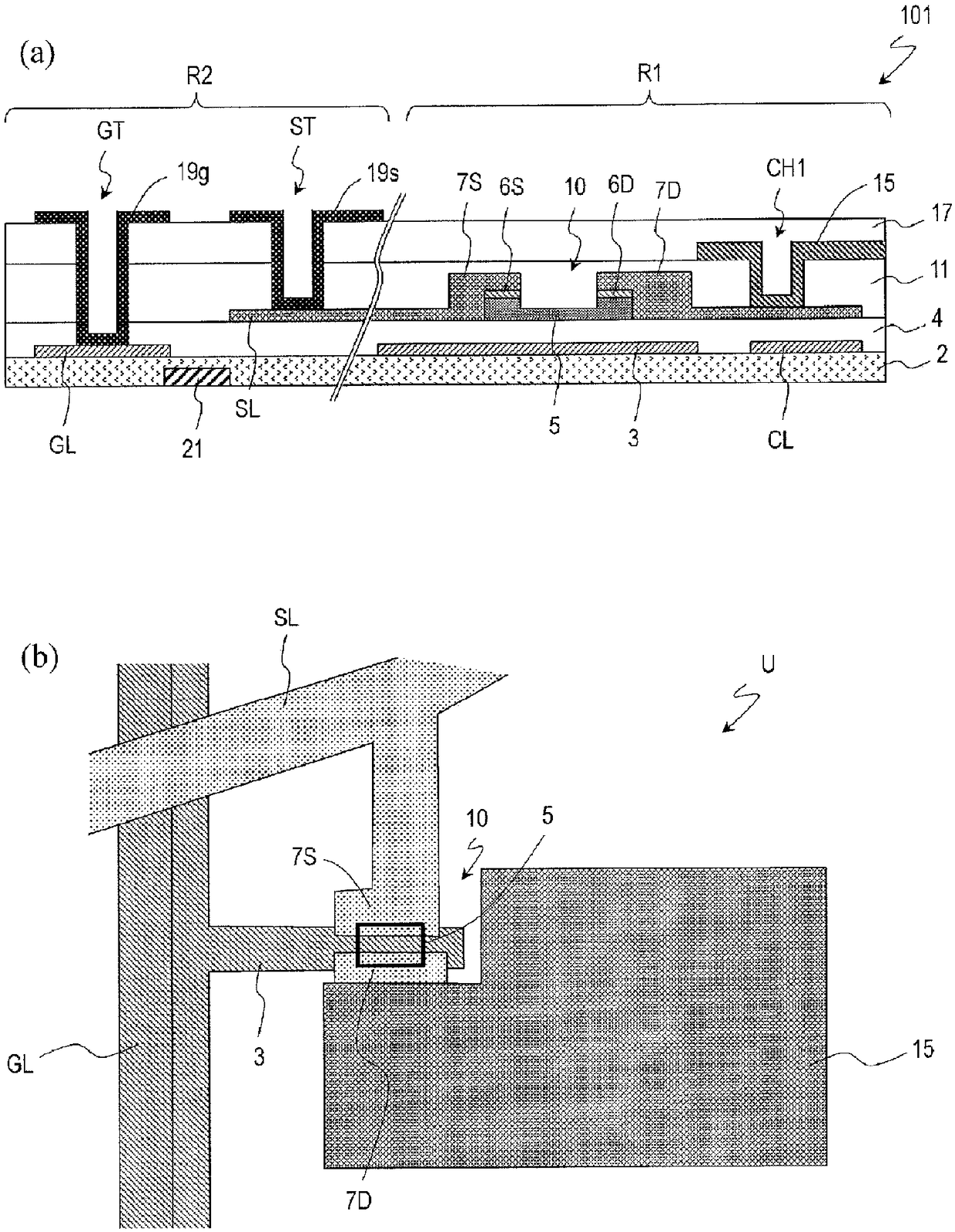
TFT substrate, scanning antenna using same, and method for manufacturing TFT substrate
A TFT substrate (101) including a plurality of antenna element regions (U) arranged on a dielectric substrate (1), the TFT substrate including a transmitting / receiving region including a plurality of antenna element regions, and a non-transmitting / receiving region located outside of the transmitting / receiving region, each of the plurality of antenna element regions (U) including: a thin film transistor (10); a first insulating layer (11) covering the thin film transistor and having a first opening (CH1) which exposes a drain electrode (7D) of the thin film transistor (10); and a patch electrode (15) formed on the first insulating layer (11) and in the first opening (CH1), and electrically connected to the drain electrode (7D) of the thin film transistor, wherein the patch electrode (15) includes a metal layer, and a thickness of the metal layer is greater than a thickness of a source electrode (7S) and the drain electrode (7D) of the thin film transistor.
Owner:SHARP KK
Distributed direct drive arrangement for driving cells
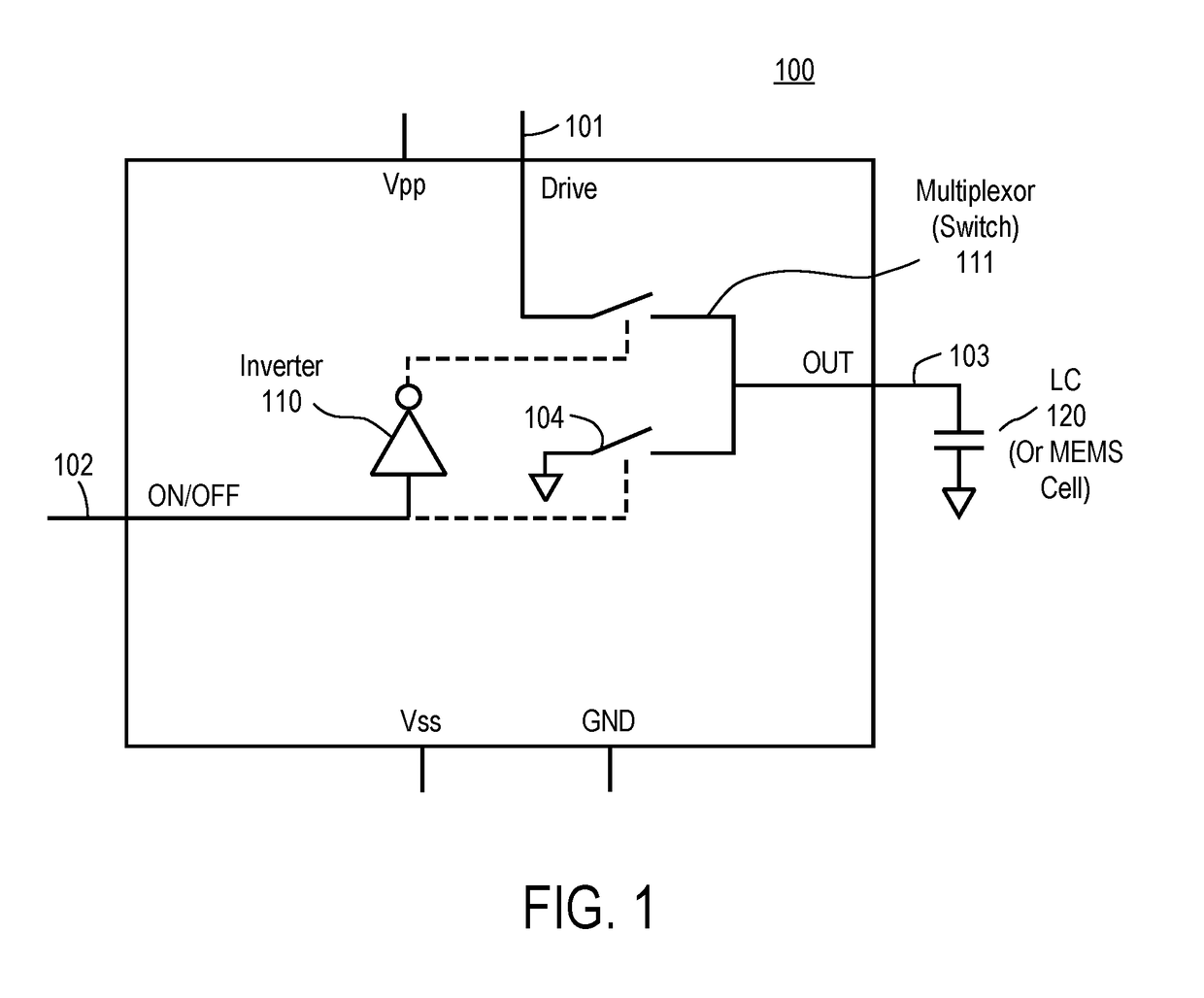
ActiveUS20170170572A1Radiating elements structural formsParallel-plate/lens fed arraysDriver circuitEngineering
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for a direct drive mechanism for driving cells (e.g., liquid crystal (LC) cells, RF MEMS cells, etc.). In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna element array having a plurality of antenna elements with each antenna element having one or more cells (e.g., liquid crystal (LC) cell, RF MEMS cell, etc.); drive circuitry coupled to cells in the antenna element array to provide a voltage to each of the cells; and memory to store a data value for each cell to determine whether the cell is on or off.
Owner:KYMETA
Slotted waveguide antenna for near-field focalization of electromagnetic radiation
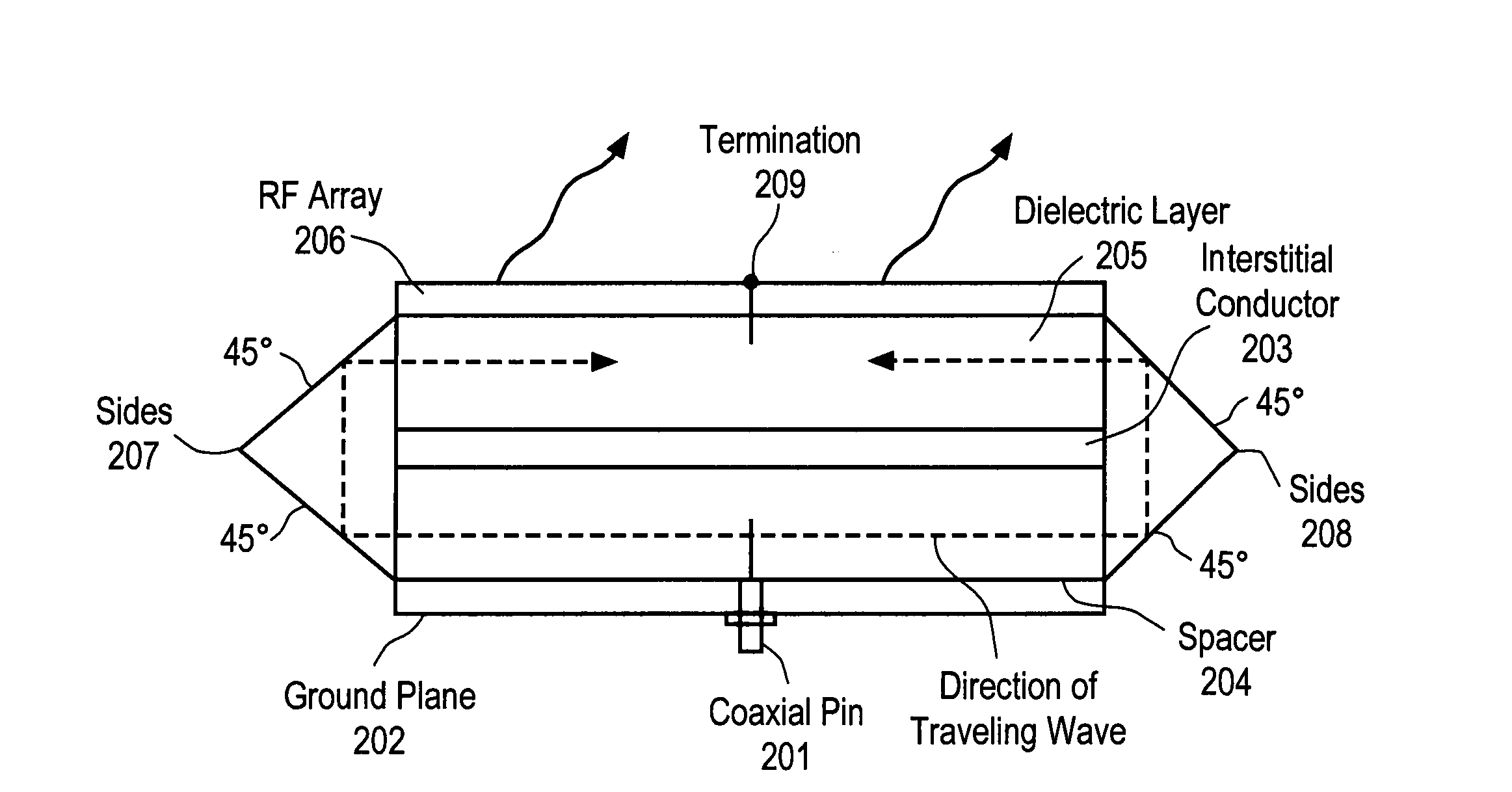
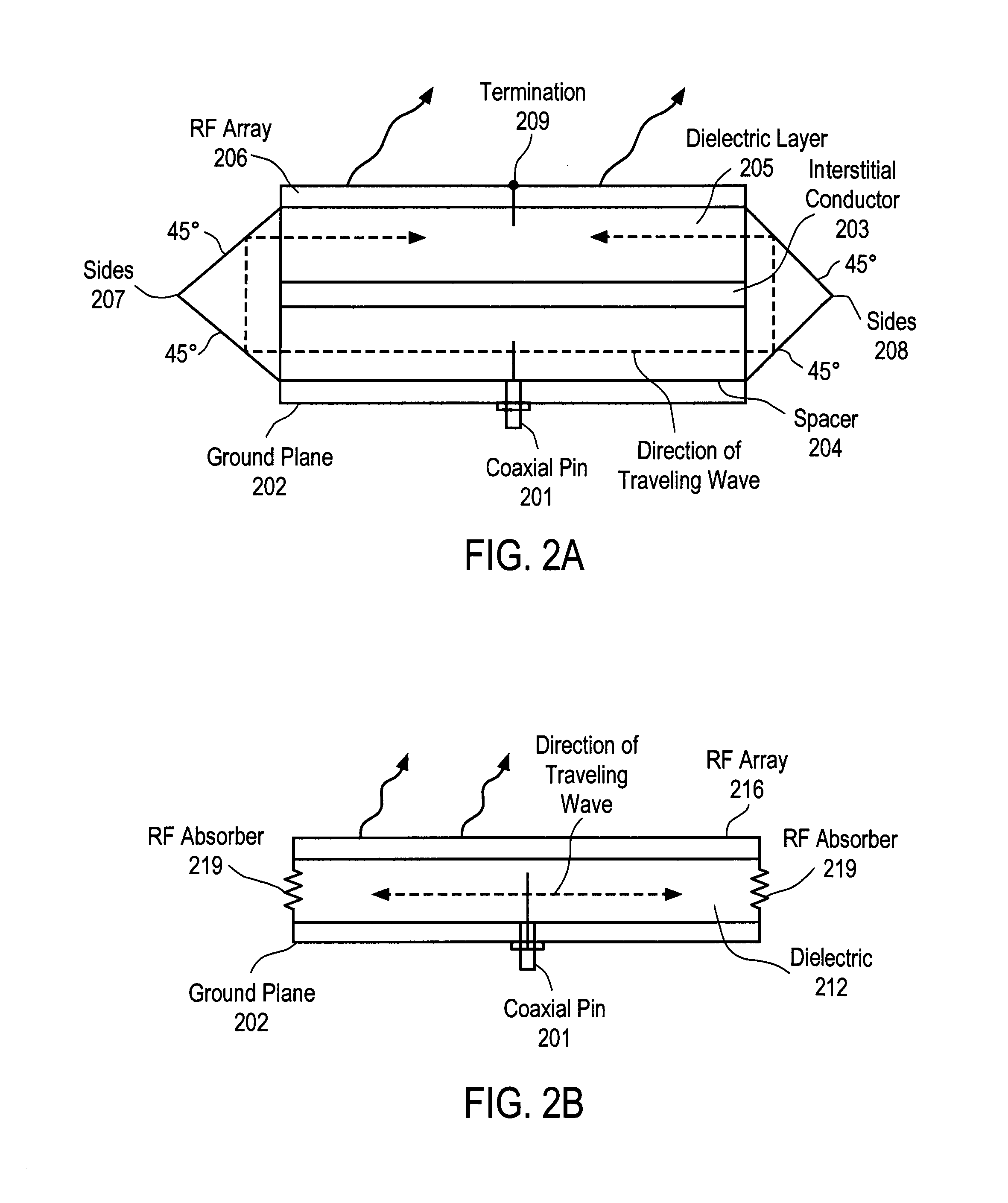
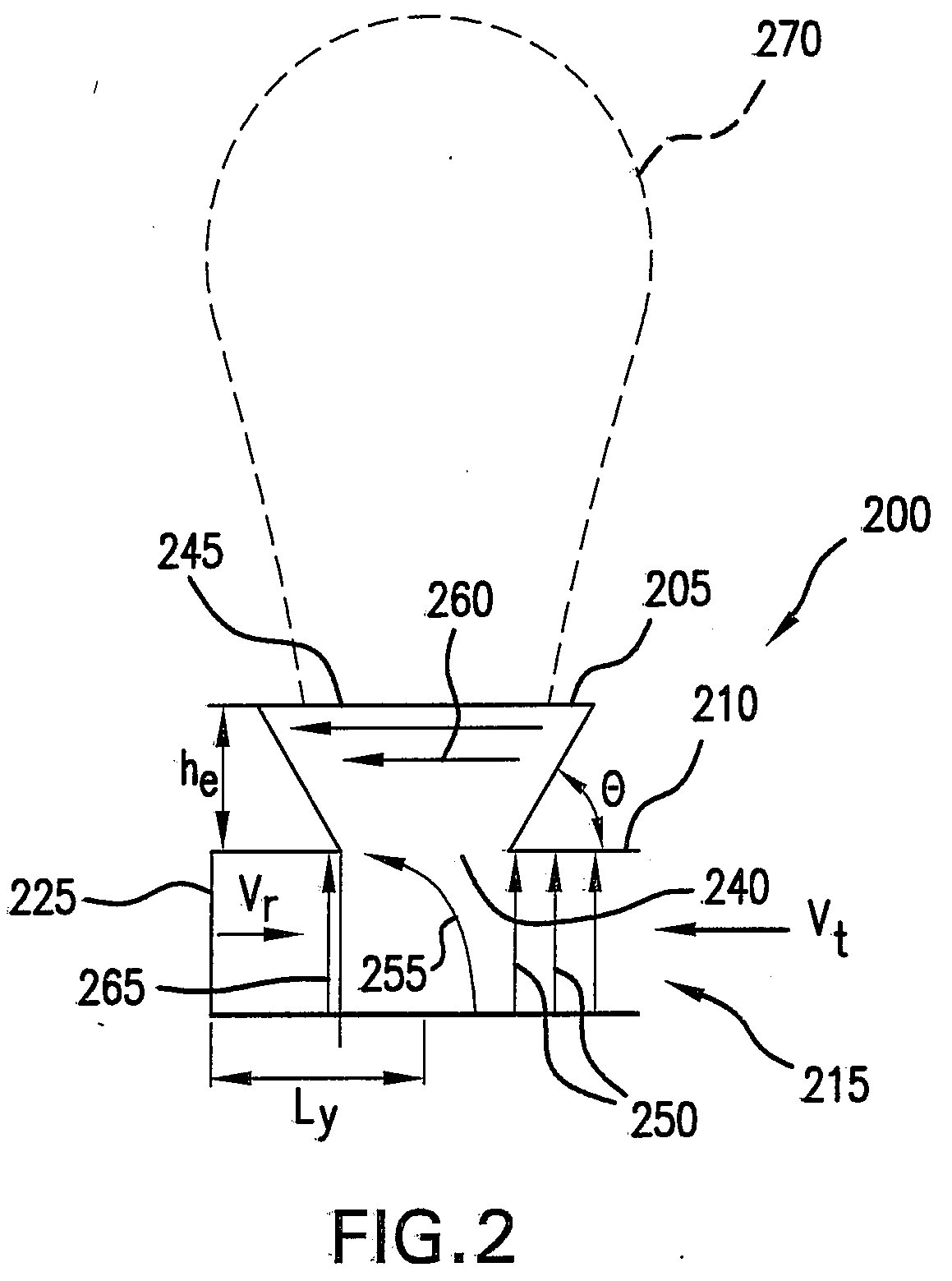
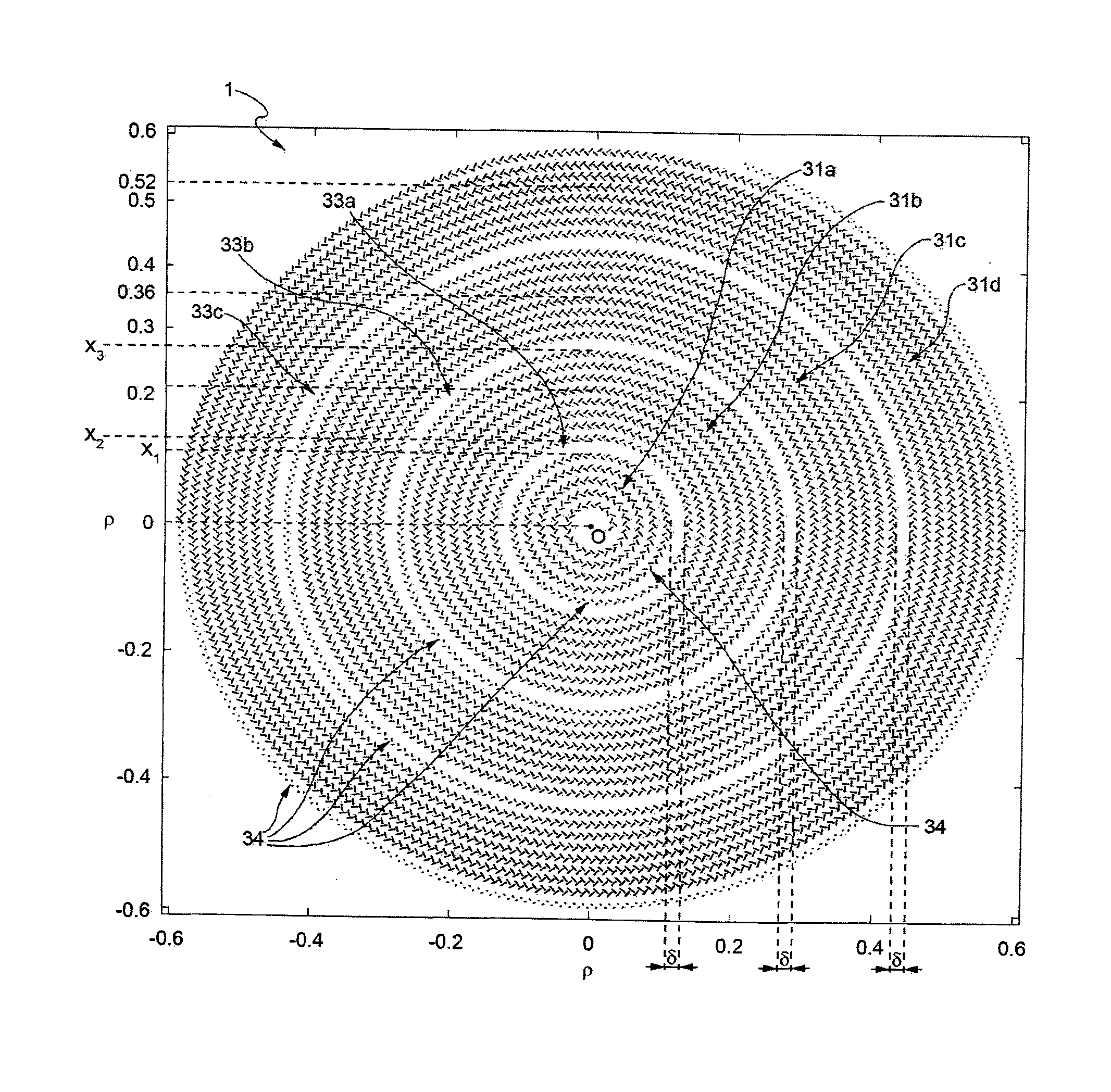
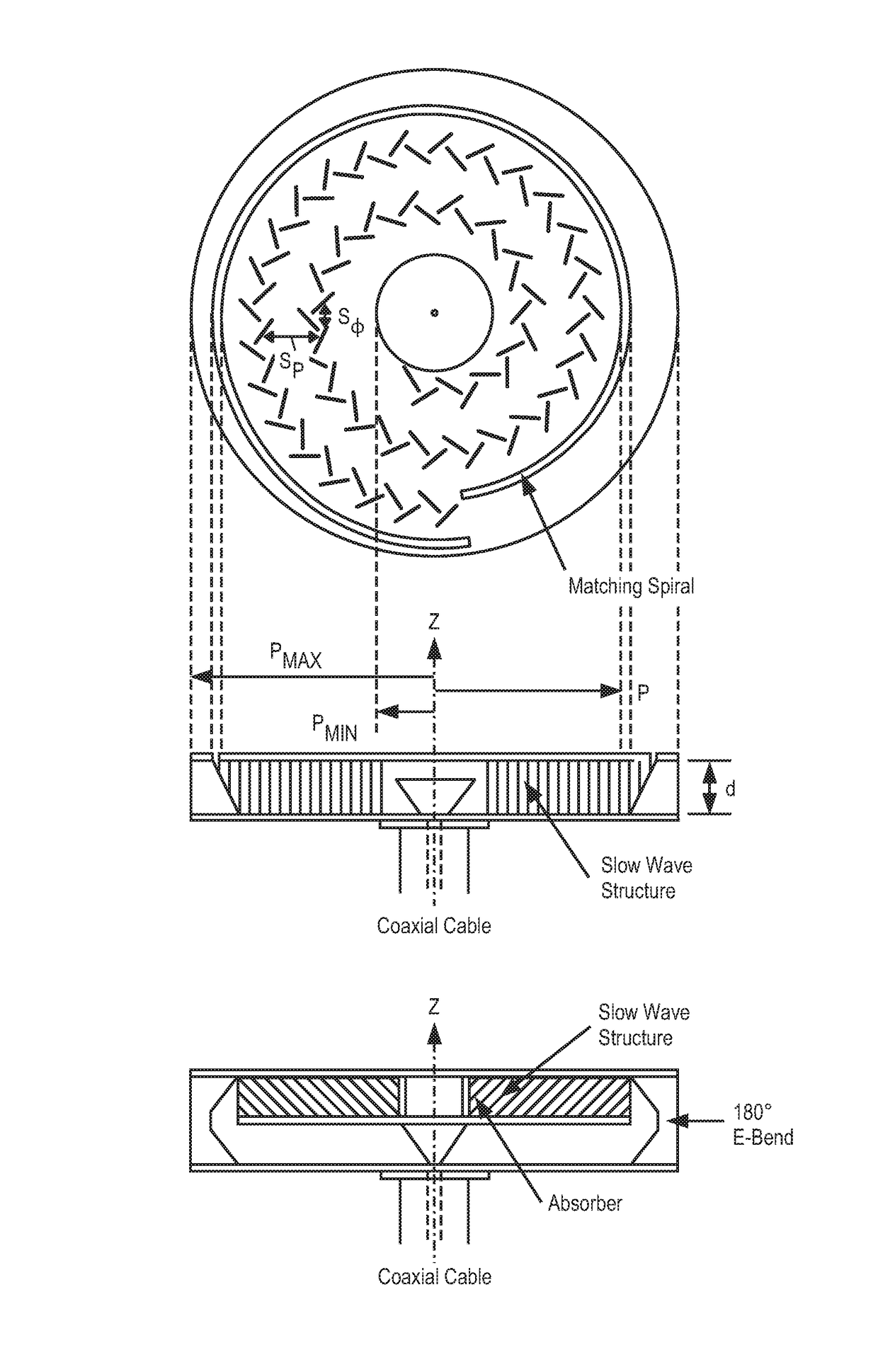
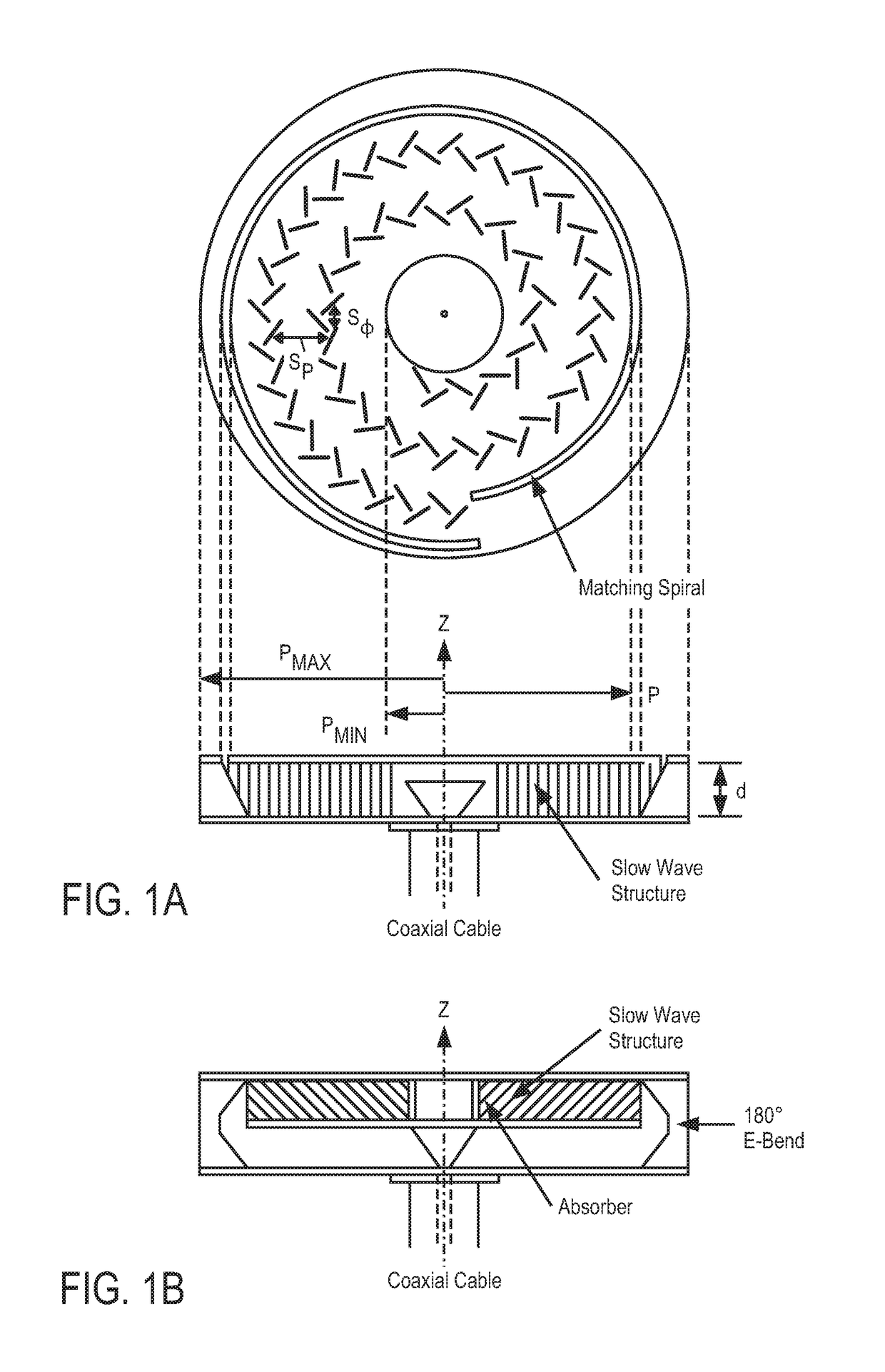
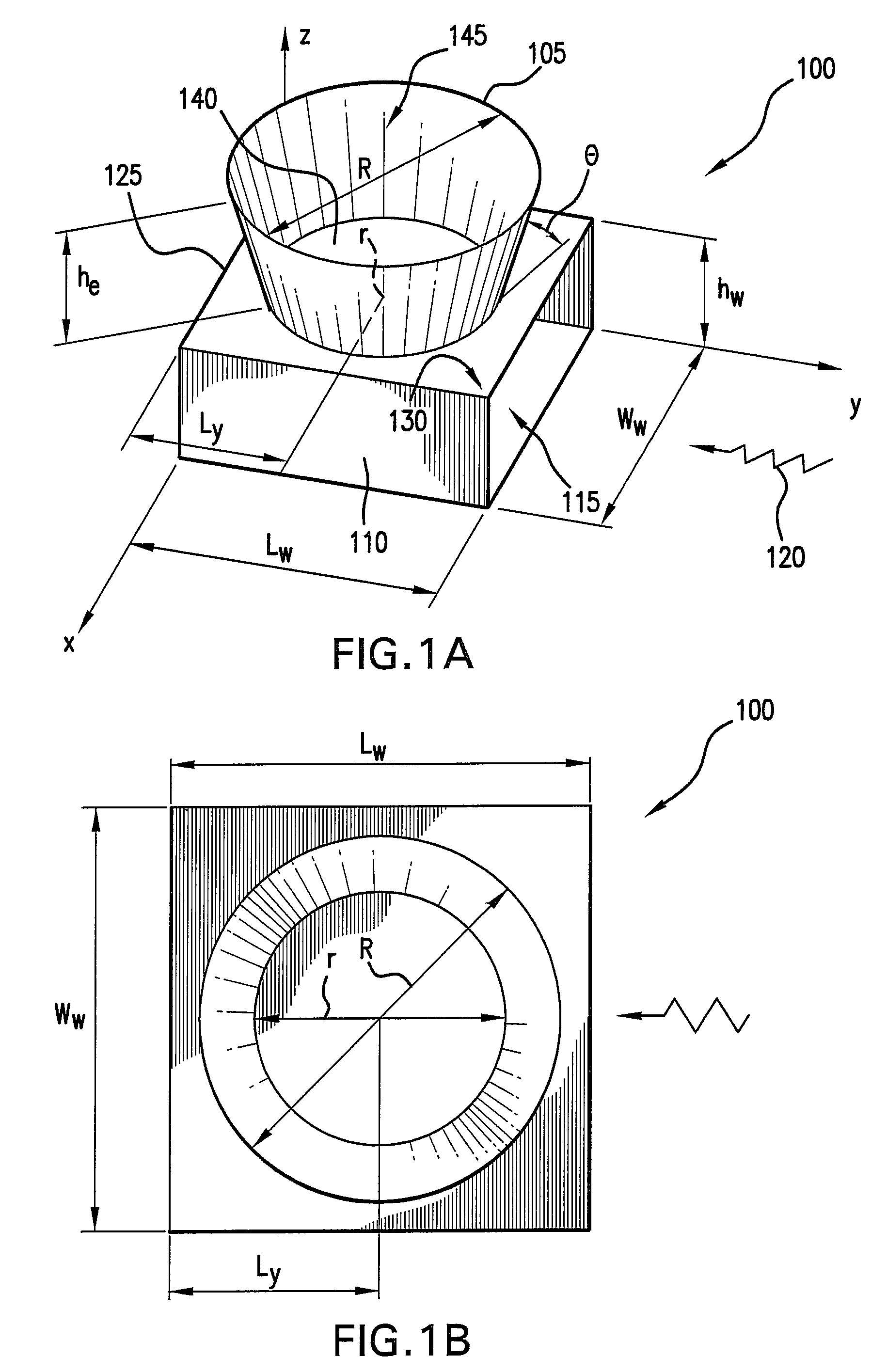
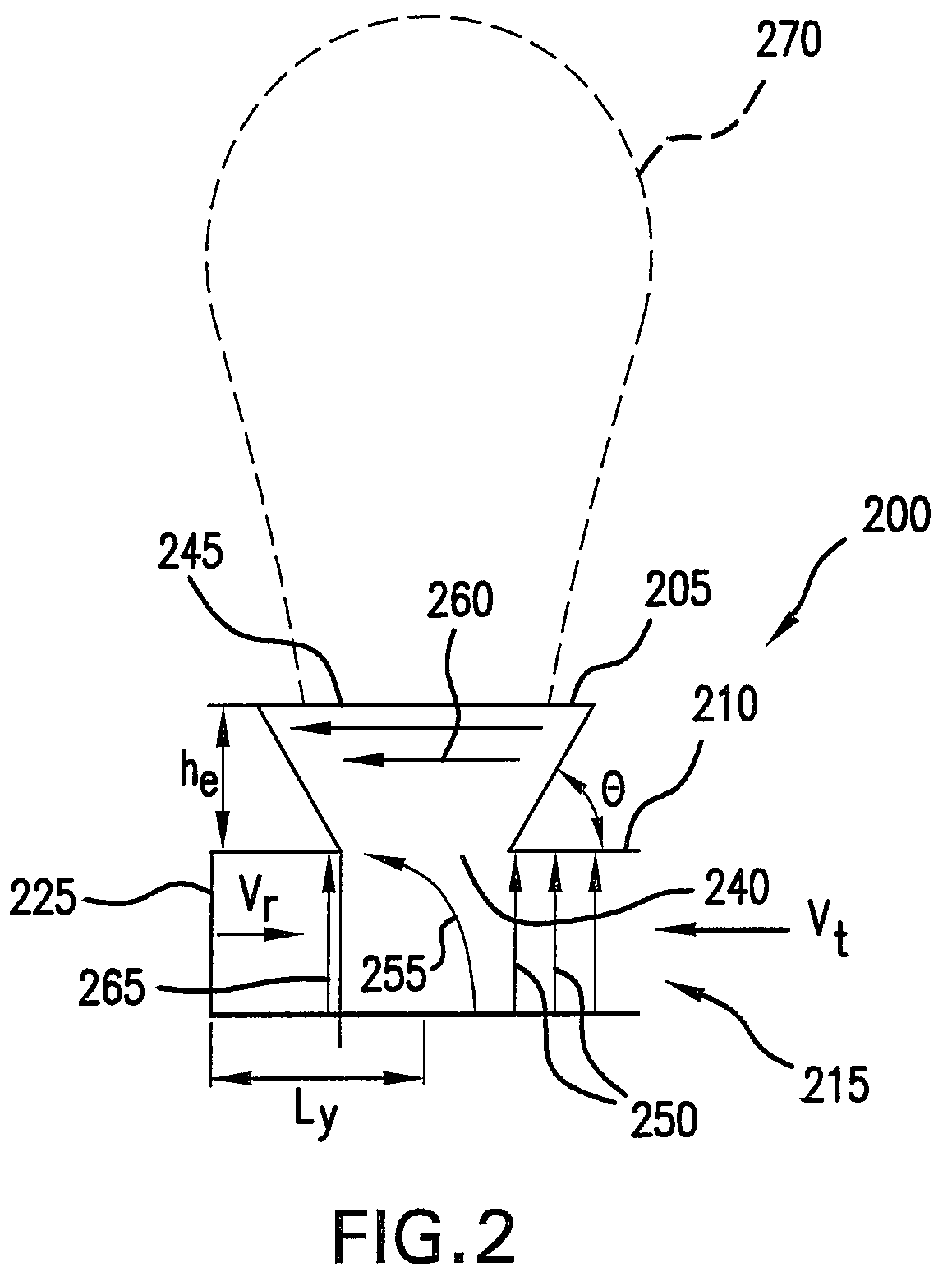
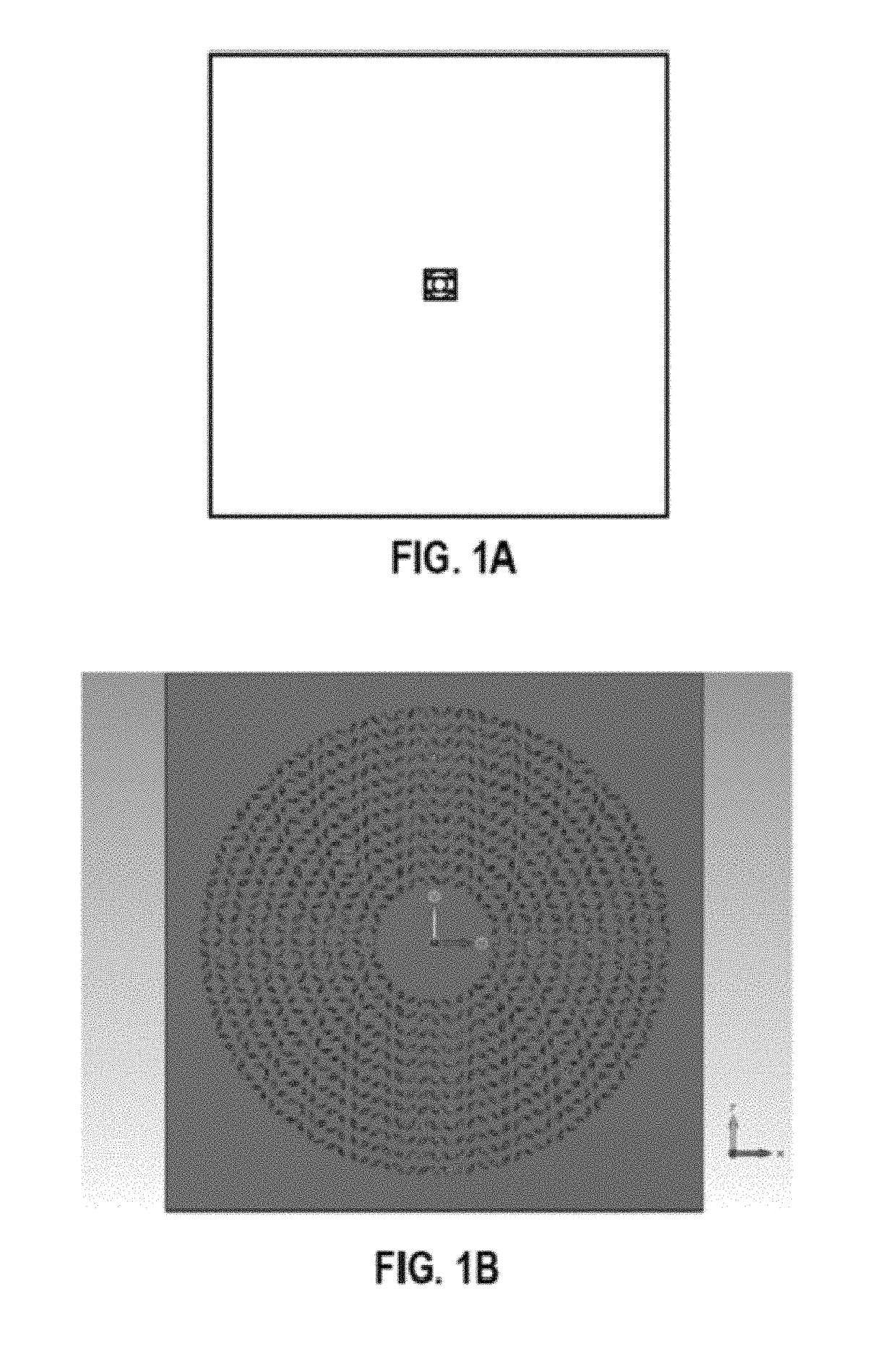
ActiveUS20140354498A1Overcomes drawbackSlot antennasRadial guide fed arraysSlotted waveguideRadial waveguide
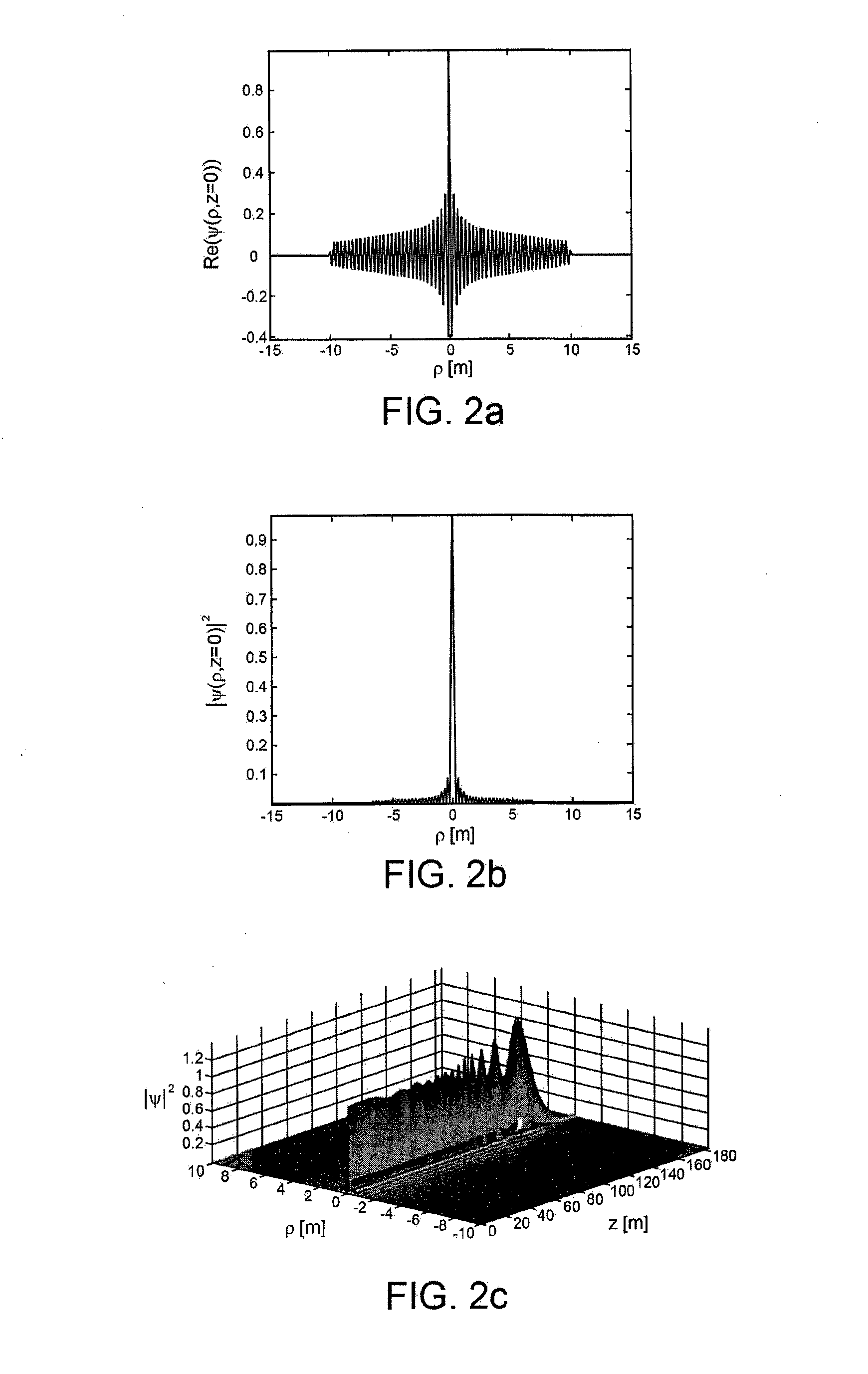
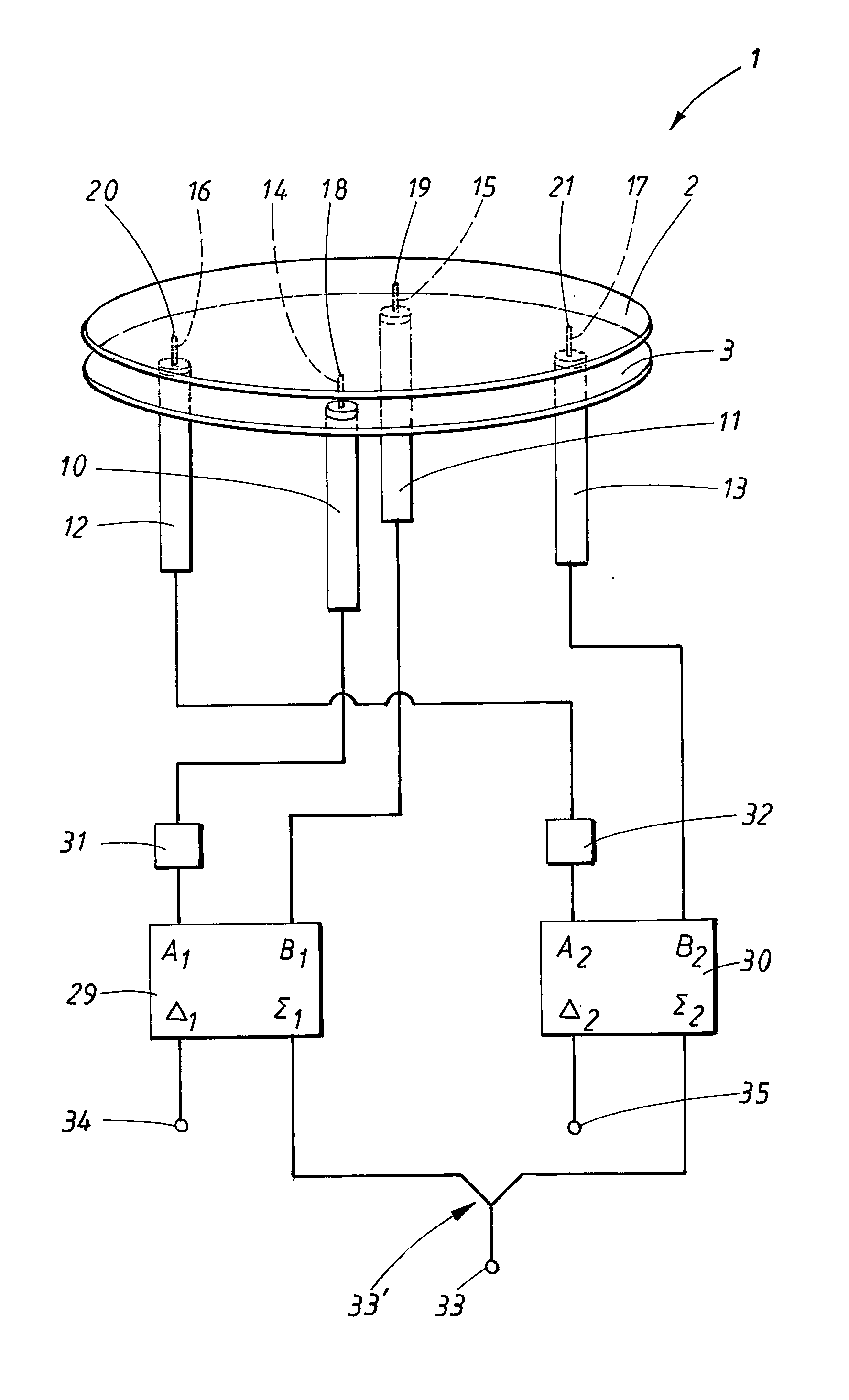
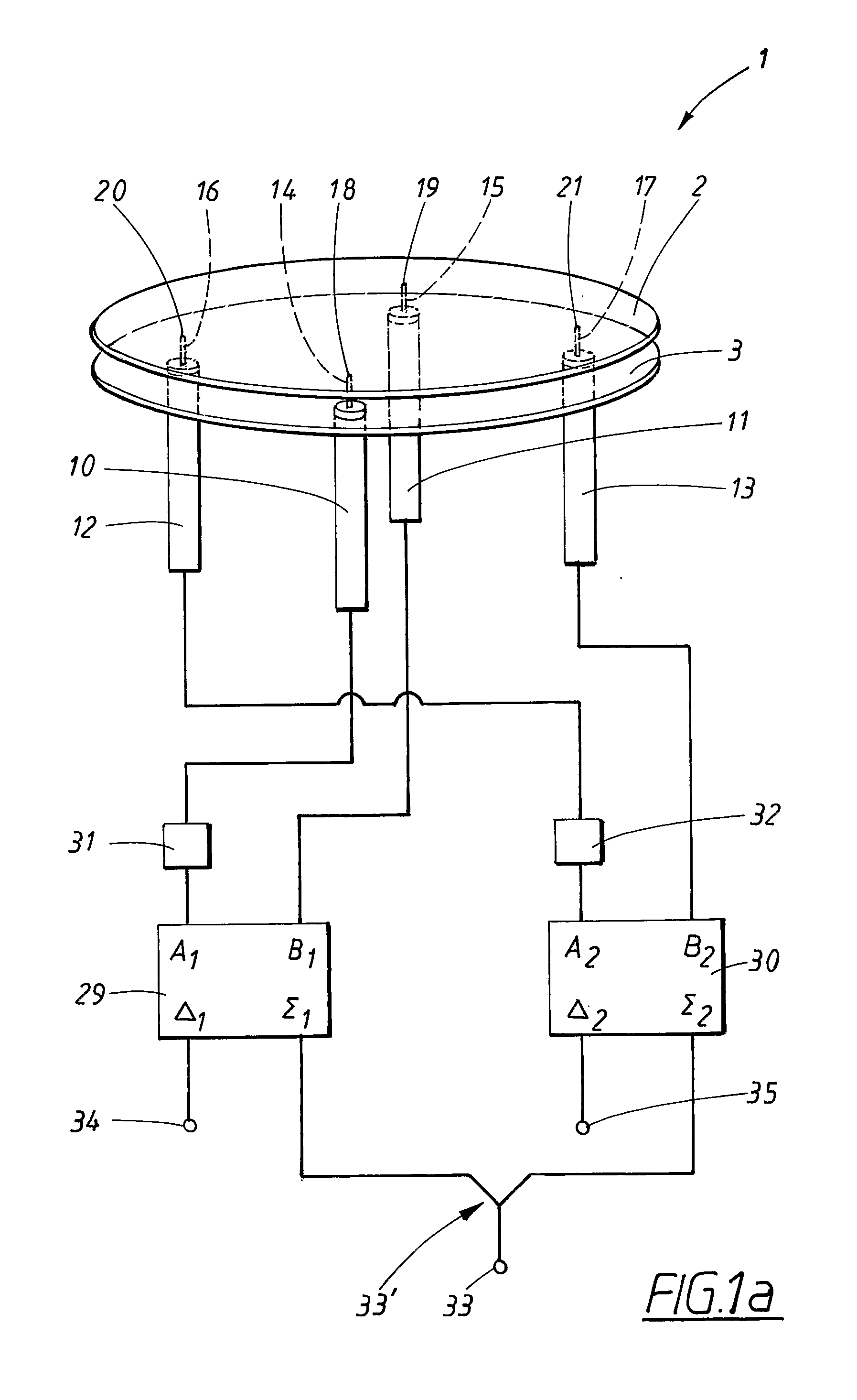
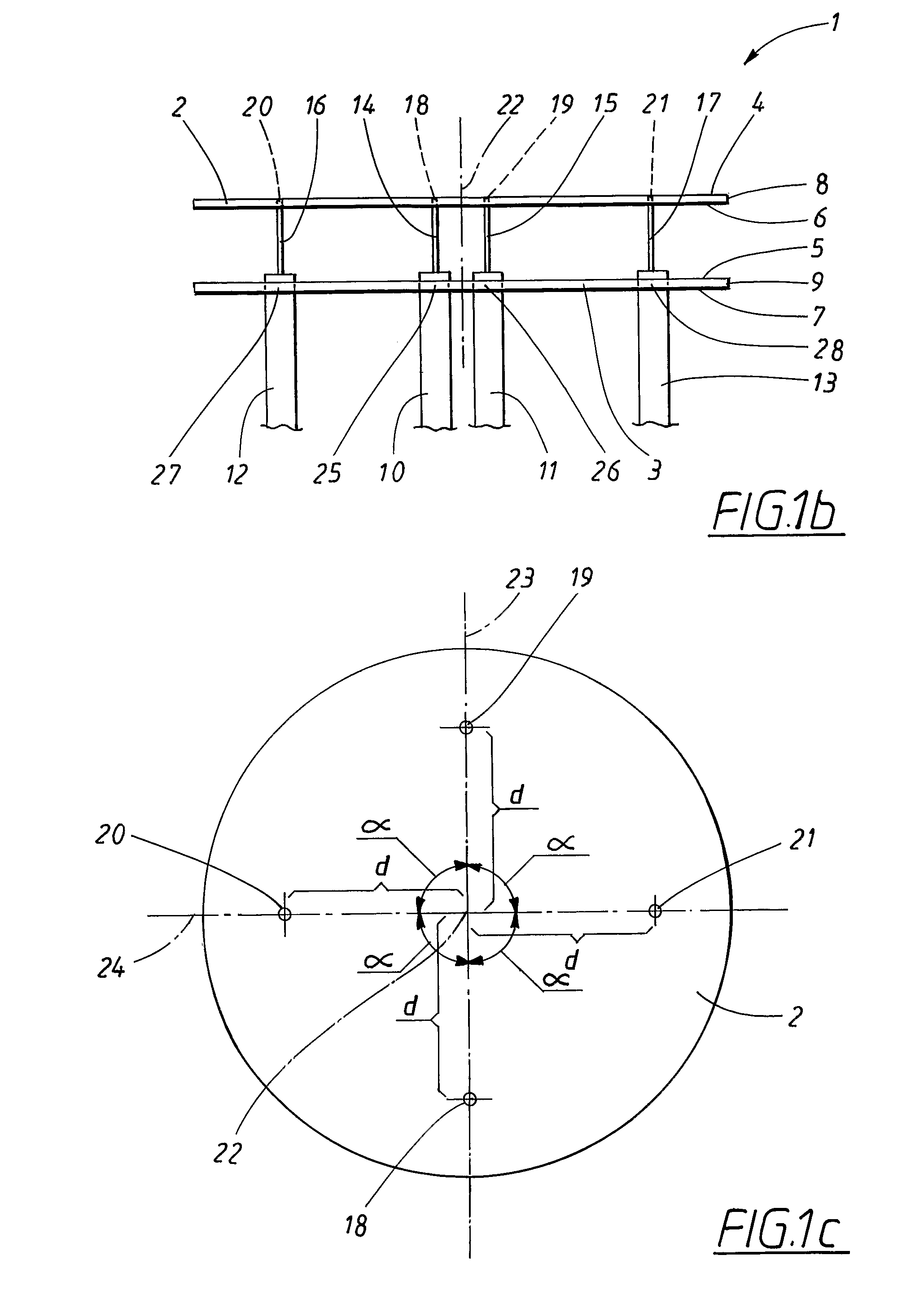
A radial slot antenna (1; 60) comprising a radial waveguide, which includes an upper plate (5), having a centroid (O) and an edge region (14) and provided with a plurality of radiating apertures (4), formed as slots in the upper plate (5), which develop according to an ideal annular pattern (16) around the centroid (O). The radiating apertures (4) are arranged in such a way as to form at least one first radiating region (31a) and one second radiating region (31b), which are distinct and radially separated by a dwell region (33a) without radiating apertures and wherein, in the first and second radiating regions (31a, 31b), radially adjacent radiating apertures (4) are separated from one another by a respective mutual radial distance, the dwell region (33a) having a radial width (δ) greater than the mutual radial distances of the radiating apertures (4) in the first and second radiating regions (31a, 31b). The slot antenna further comprises a signal feeder (10) operable for supplying am electromagnetic field (Ψ0, Ψ1) so as to assume, in the first and second radiating regions, opposite phases, in such a way that the electromagnetic field emitted by the slot antenna can be expressed via Bessel functions.
Owner:SELEX ES
Aperture segmentation of a cylindrical feed antenna
A method and apparatus for aperture segmentation are disclosed. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave and a physical antenna aperture coupled to the antenna feed and comprising a plurality of segments having antenna elements that form a plurality of closed concentric rings of antenna elements when combined, where the plurality of concentric rings are concentric with respect to the antenna feed.
Owner:KYMETA
Dynamic polarization and coupling control for a steerable cylindrically fed holographic antenna
ActiveCN105960735AGood beam performanceRadiating elements structural formsParallel-plate/lens fed arraysAntenna feedPhysics
An apparatus is disclosed herein for a cylindrically fed antenna and method for using the same. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave and a tunable slotted array coupled to the antenna feed.
Owner:KYMETA
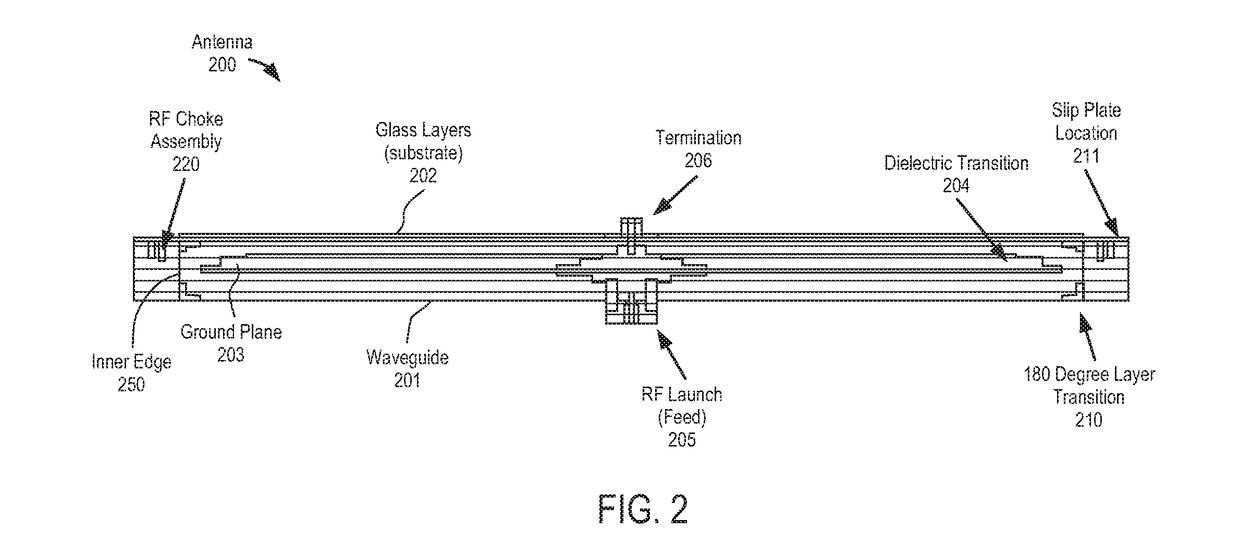
Broadband RF radial waveguide feed with integrated glass transition
An antenna and method for using the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, an antenna comprises a radial waveguide; an aperture operable to radiate radio frequency (RF) signals in response to an RF feed wave fed by the radial waveguide; and a radio frequency (RF) choke operable to block RF energy from exiting through a gap between outer portions of the waveguide and the aperture.
Owner:KYMETA
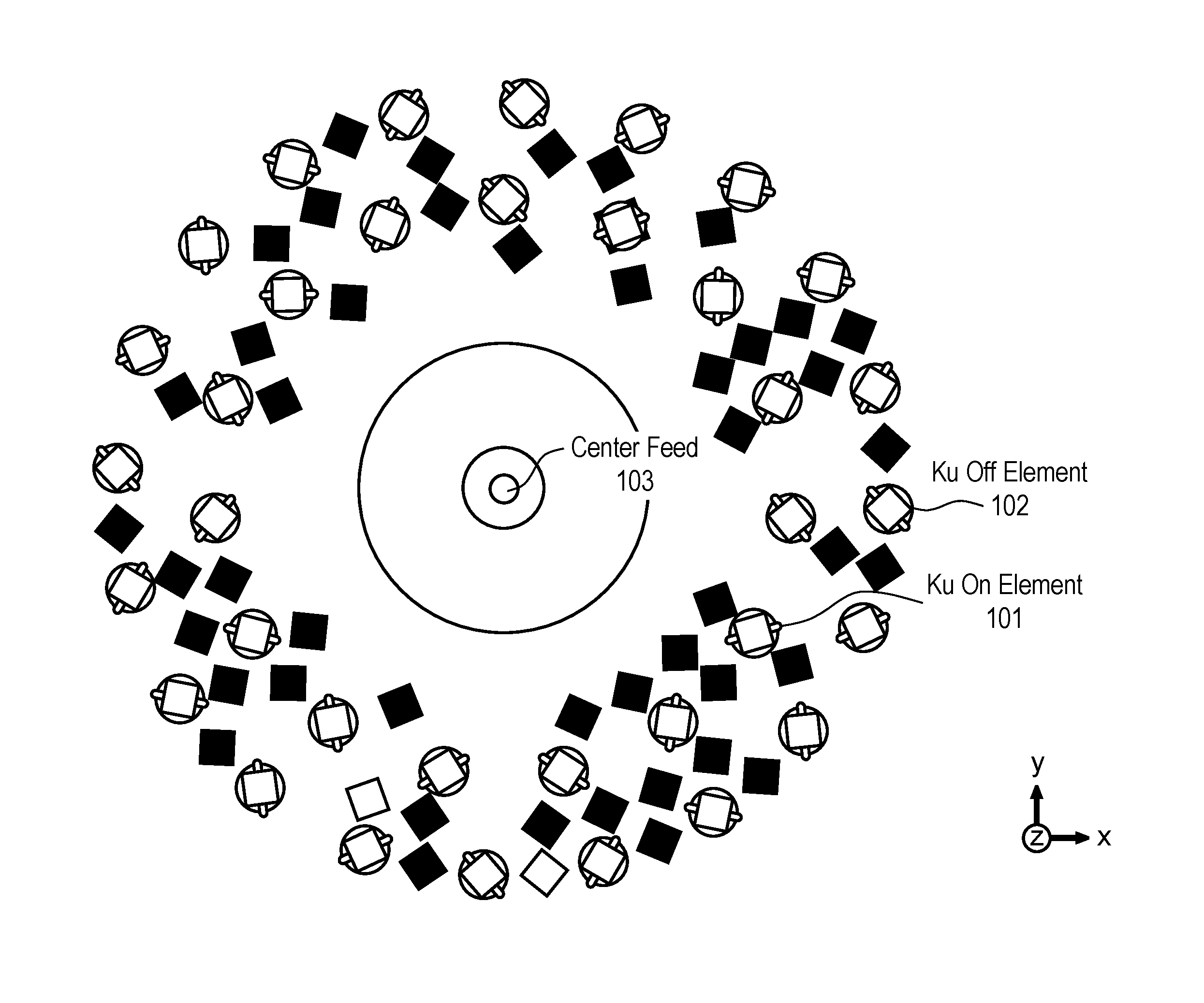
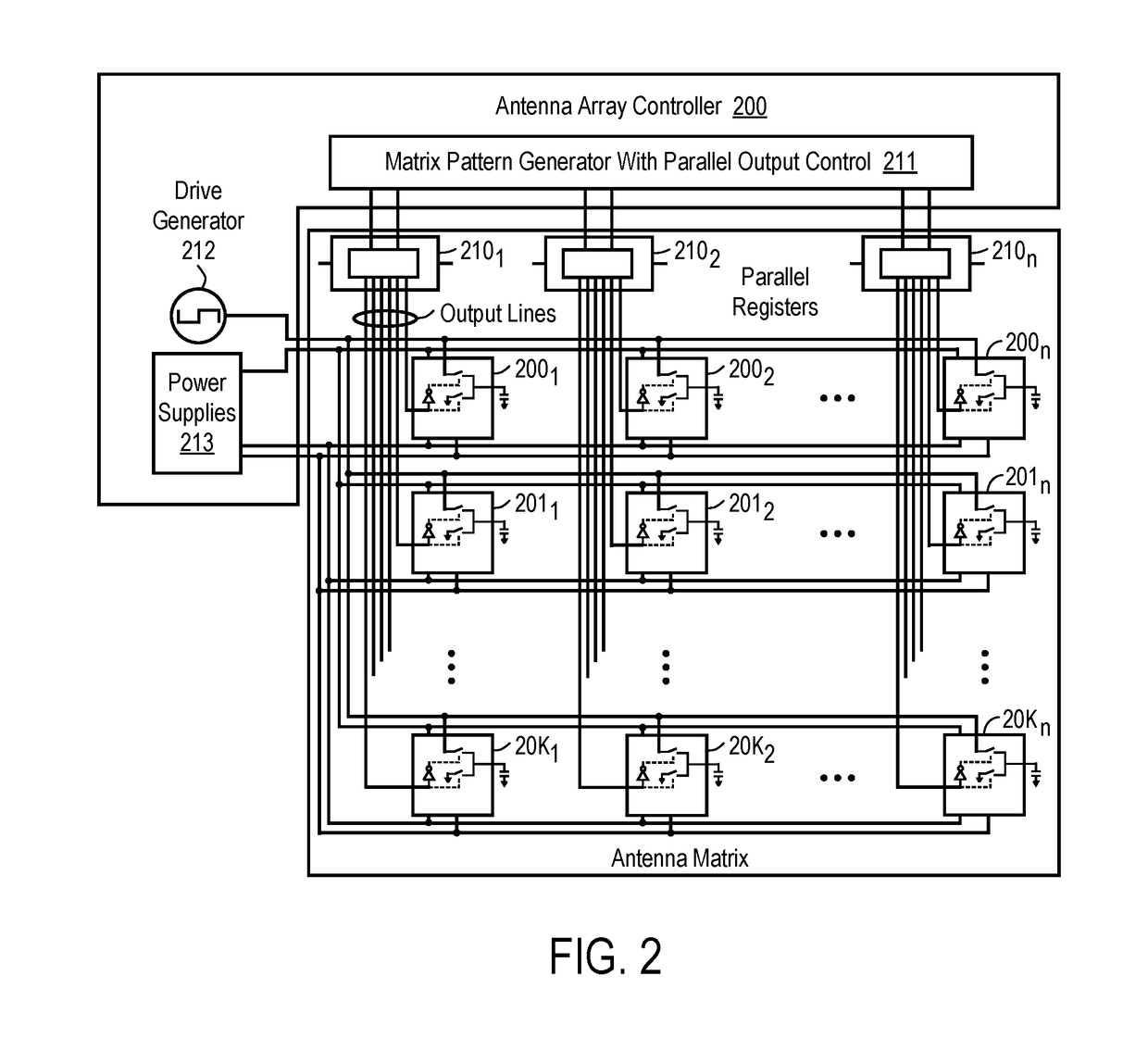
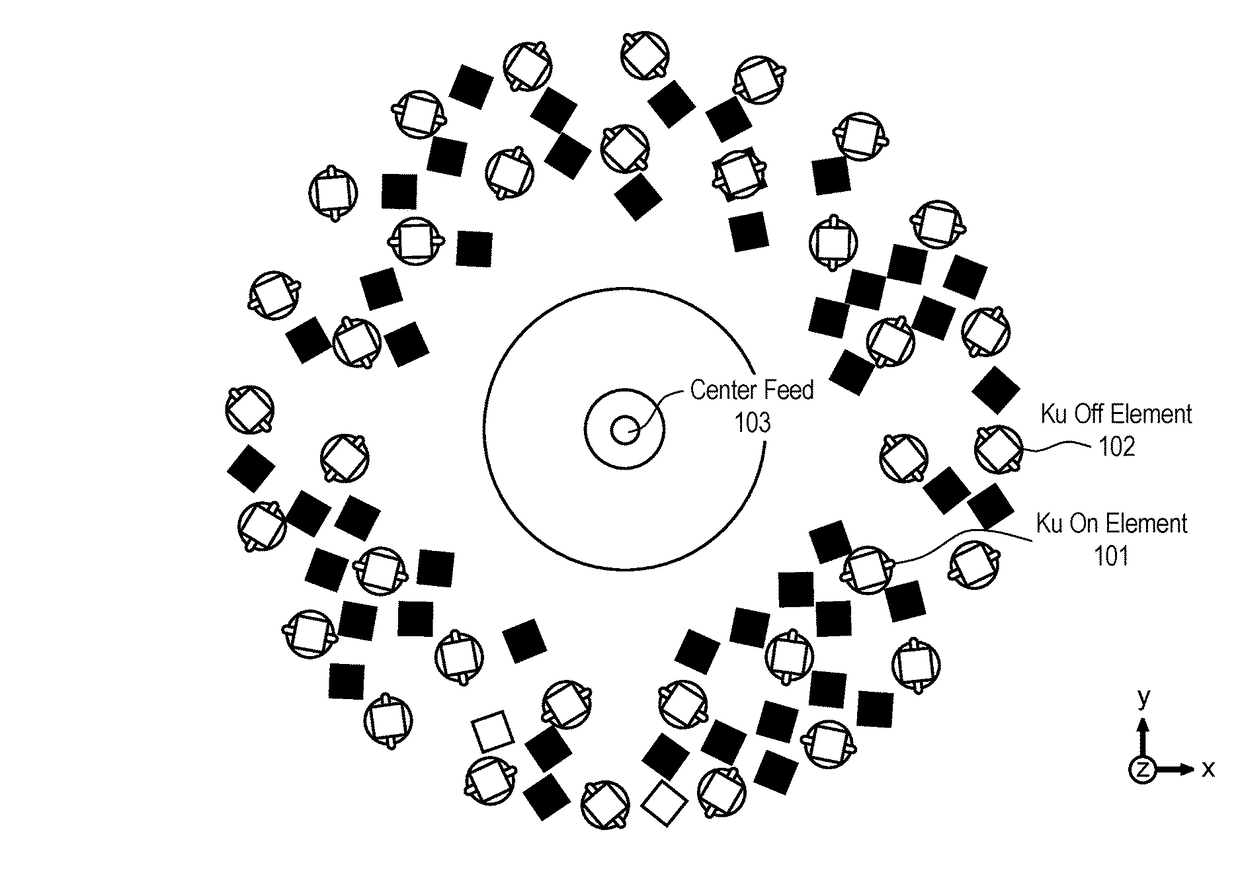
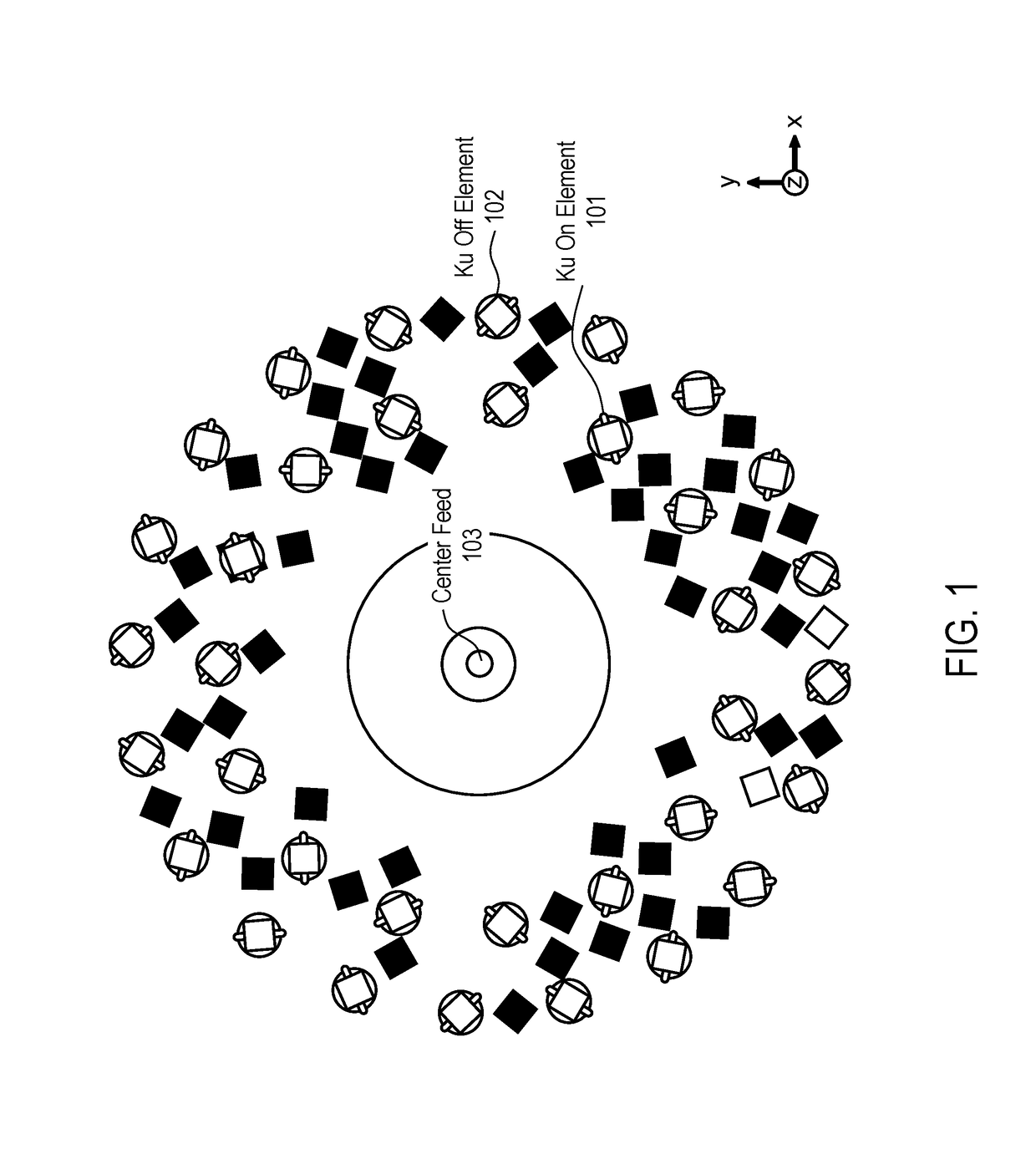
Antenna element placement for a cylindrical feed antenna
ActiveUS9905921B2Antenna arrays manufactureIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna elementAntenna feed
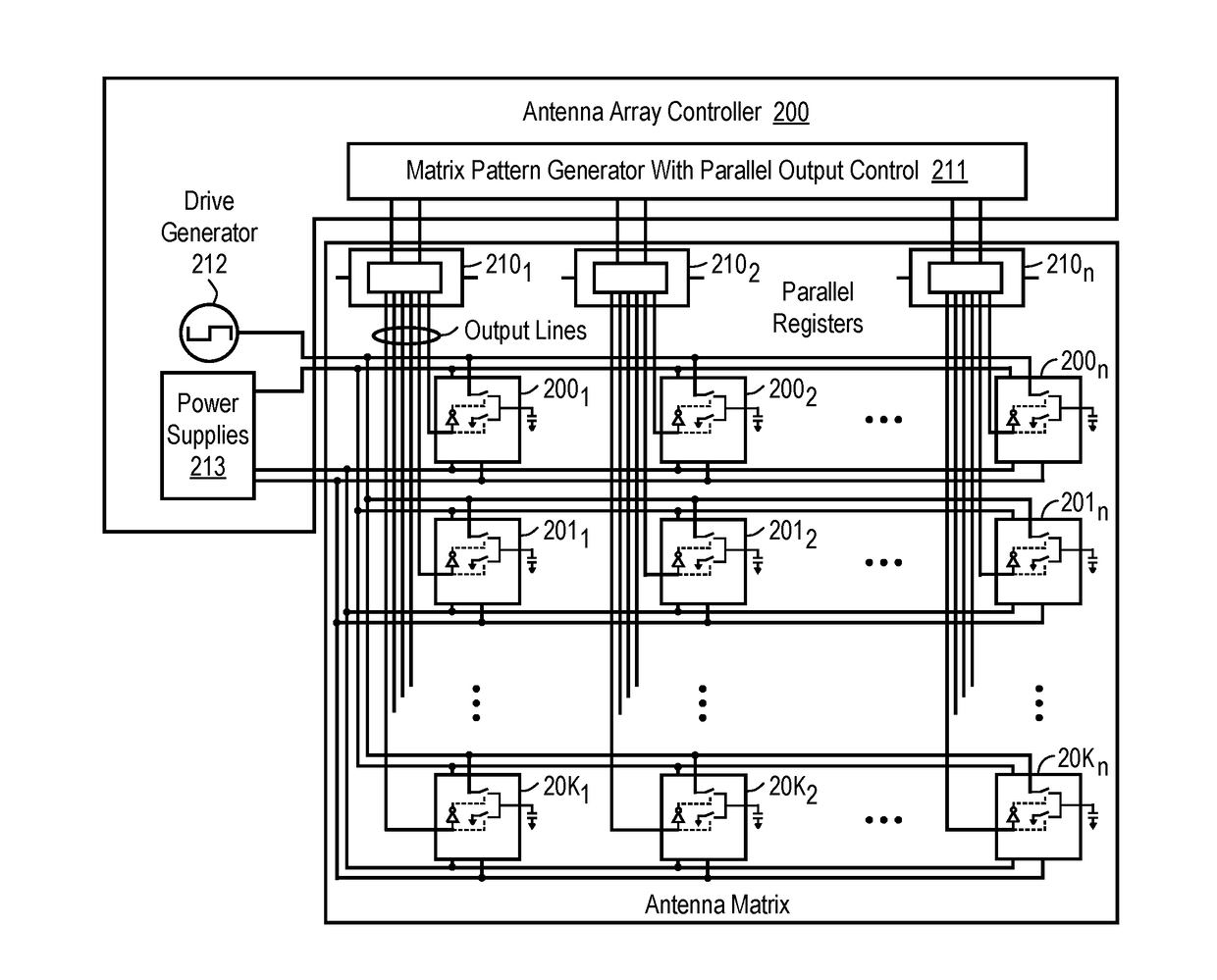
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for antenna element placement are disclosed. In one embodiment, an antenna comprises an antenna feed to input a cylindrical feed wave; a single physical antenna aperture having at least one antenna array of antenna elements, where the antenna elements are located on a plurality of concentric rings concentrically located relative to an antenna feed, wherein rings of the plurality of concentric rings are separated by a ring-to-ring distance, wherein a first distance between elements along rings of the plurality of concentric rings is a function of a second distance between rings of the plurality of concentric rings; and a controller to control each antenna element of the array separately using matrix drive circuitry, where each of the antenna elements is uniquely addressed by the matrix drive circuitry.
Owner:KYMETA
Dynamic polarization and coupling control from a steerable cylindrically fed holographic antenna
ActiveUS9887456B2Improve performanceNon-resonant long antennasParallel-plate/lens fed arraysSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:KYMETA
Integrated waveguide antenna and array
ActiveUS7466281B2Improve conversion efficiencyReduce manufacturing costLinear waveguide fed arraysRadial guide fed arraysBeam steeringWaveguide
An antenna is provided. The antenna may include at least one open-ended structure extending from a surface of a waveguide. The open-ended structure may have a cross section of many different shapes. The walls of the structure may be movable. The antenna structure may be rotated. The antenna may incorporate a number of different wave feeds. The antenna may provide two-dimensional beam steering.
Owner:ORR PARTNERS I
Triple Polarized Patch Antenna
ActiveUS20080100530A1Easy to manufactureAvoid taking up spaceSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An antenna arrangement for a Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) radio system, the antenna arrangement transmitting and receiving in three essentially uncorrelated polarizations. The arrangement includes first and second patches, and four feeding points for feeding the first patch. In one mode of operation, the feeding points are fed in phase with each other, resulting in a first constant E-field in a slot between the edges of the patches. In a second operating mode, the first and second feeding points are fed 180 degrees out of phase with each other, resulting in a second E-field in the slot having a first sinusoidal variation. In a third operating mode, the third and fourth feeding points are fed 180 degrees out of phase with each other, resulting in a third E-field in the slot having a second sinusoidal variation uncorrelated with the first sinusoidal variation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
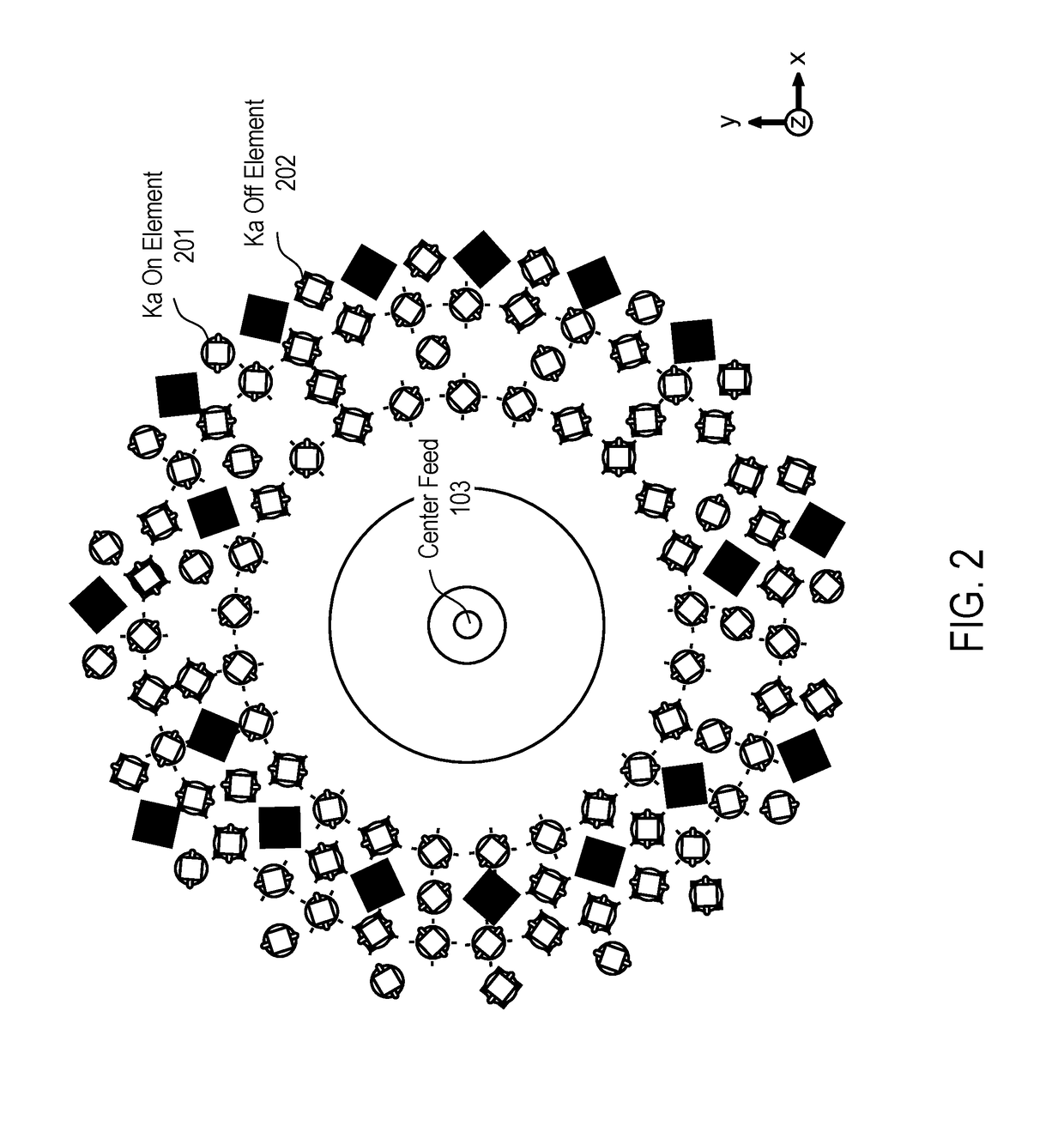
Combined antenna apertures allowing simultaneous multiple antenna functionality
ActiveUS9893435B2Data augmentationHigh densitySimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna elementAntenna aperture
An antenna apparatus and method for use of the same are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises a single physical antenna aperture having at least two spatially interleaved antenna arrays of antenna elements, the antenna arrays being operable independently and simultaneously at distinct frequency bands.
Owner:KYMETA
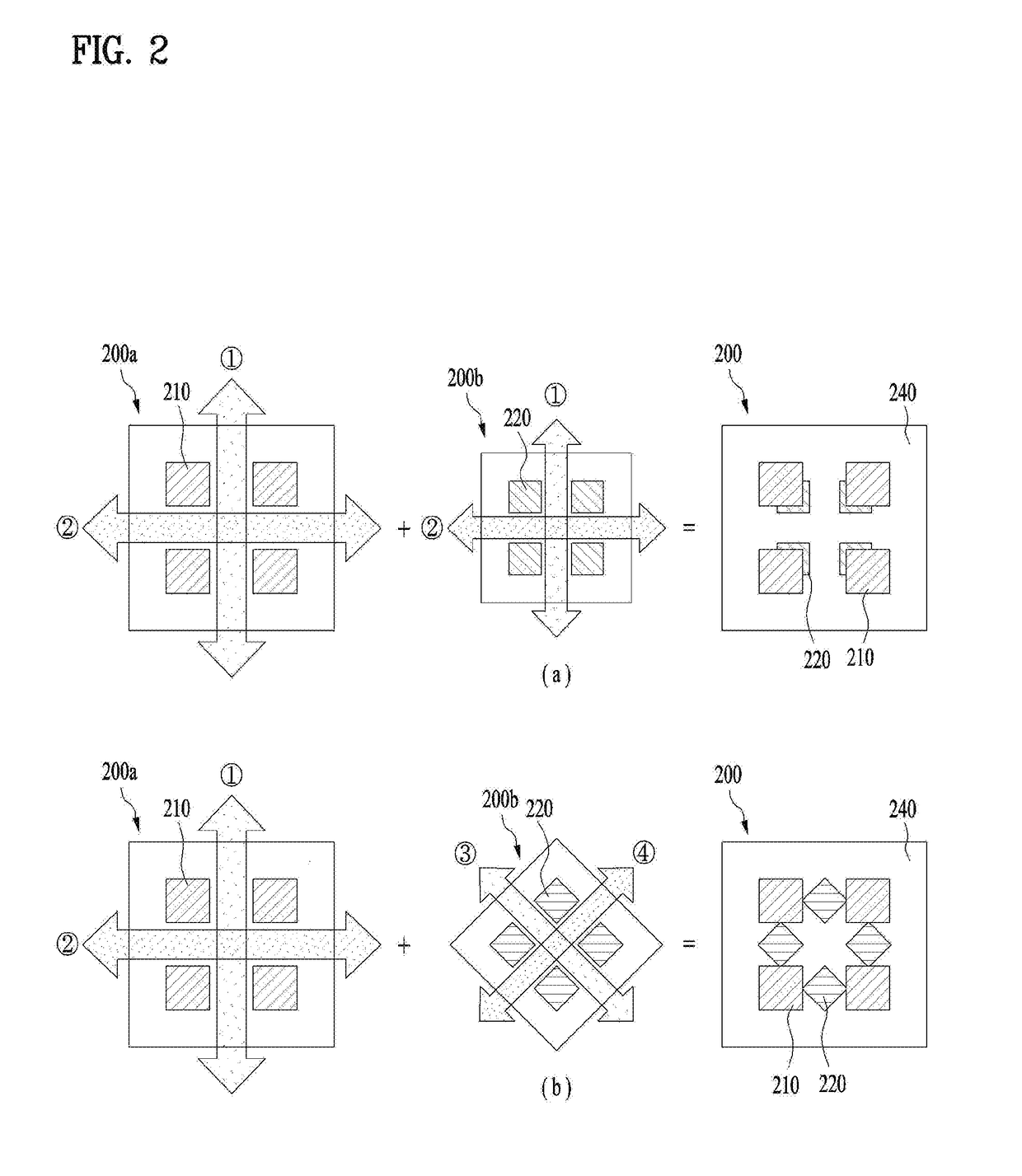
Array antenna and mobile terminal
InactiveUS20190036231A1Reduce distractionsSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsPhysicsRadiation
An array antenna includes a substrate, first radiation elements disposed at the substrate at equal intervals, second radiation elements disposed at the substrate at equal intervals, the second radiation elements being located between the first radiation elements, a first power supply unit located at the end of each first radiation element in a first direction for supplying power to the first radiation element, a second power supply unit located at the end of each first radiation element in a second direction, which is perpendicular to the first direction, for supplying power to the first radiation element, a third power supply unit located at the end of each second radiation element in a third direction for supplying power to the second radiation element, and a fourth power supply unit located at the end of each second radiation element in a fourth direction, which is perpendicular to the third direction.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method to assemble aperture segments of a cylindrical feed antenna
ActiveUS20170331186A1Antenna arrays manufactureIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna apertureElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of assembling an antenna aperture from a plurality of antenna aperture segments is described. The method may include placing a first aperture segment relative to a second aperture segment to partially form the antenna aperture. Furthermore, an overlap of the first aperture segment overlaps a complementary underlap of the second aperture segment at a seam. The method may also include joining the overlap of the first aperture segment to the underlap of the second aperture segment to partially form the antenna aperture.
Owner:KYMETA
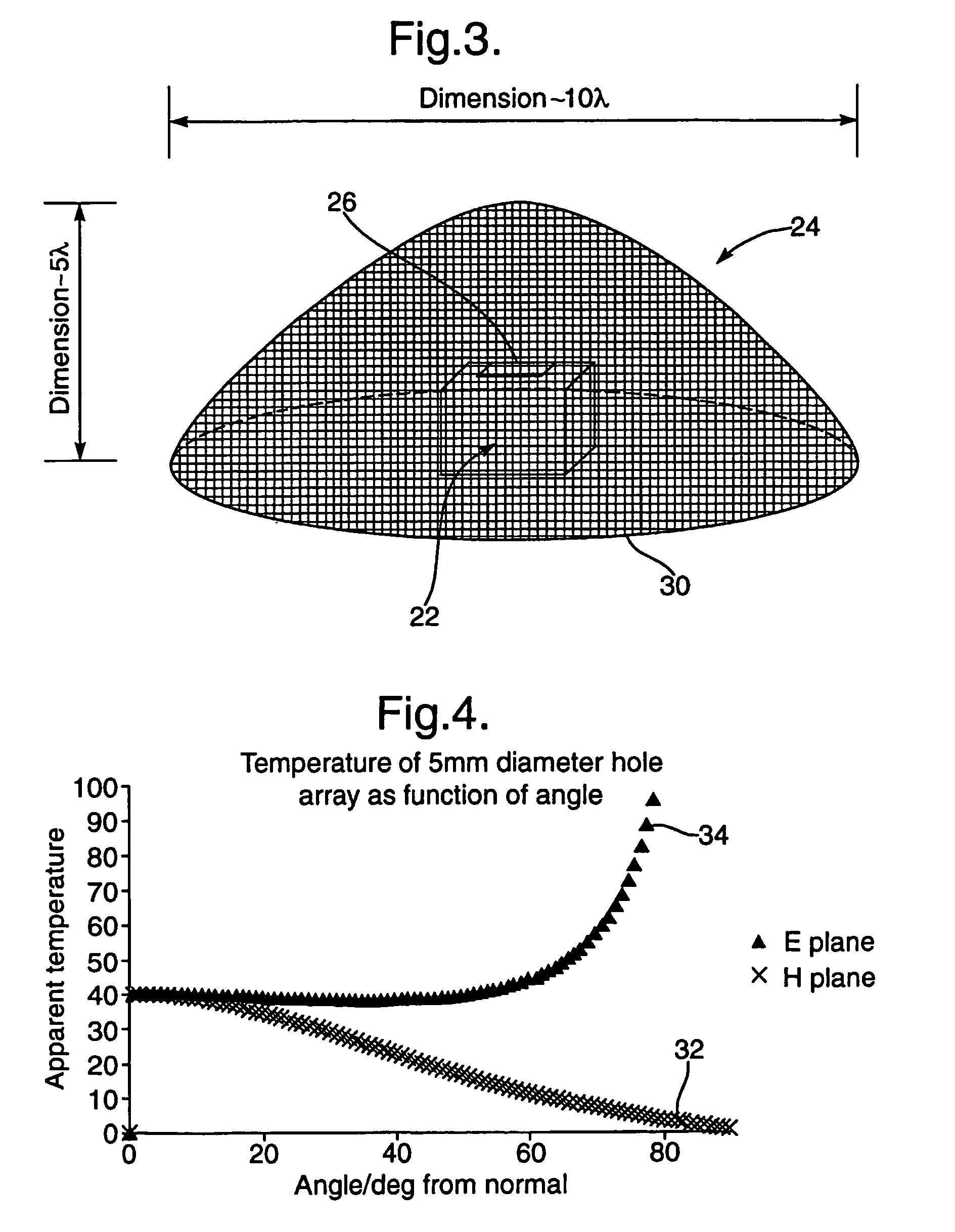
Millimetre-wave illumination source
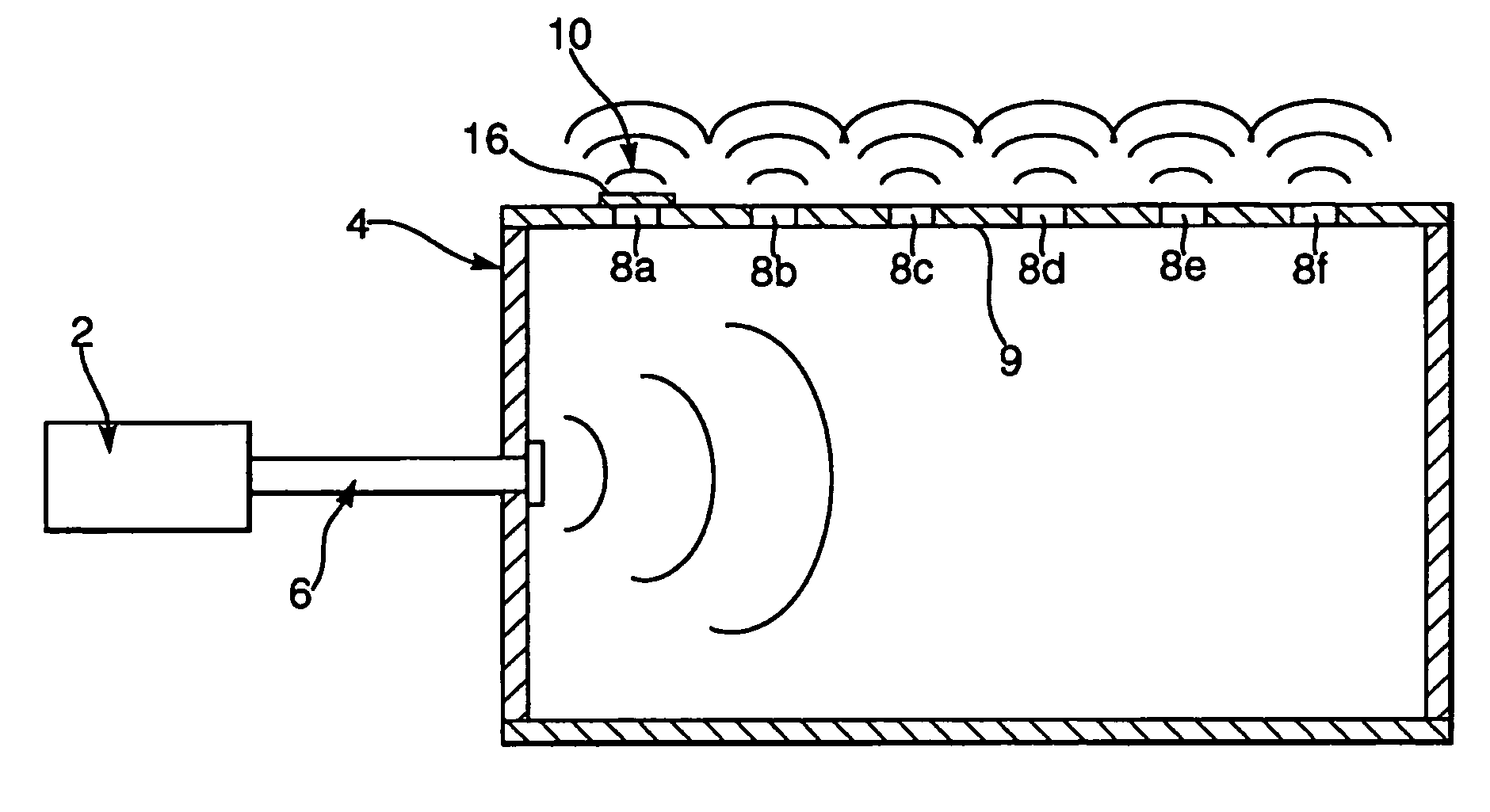
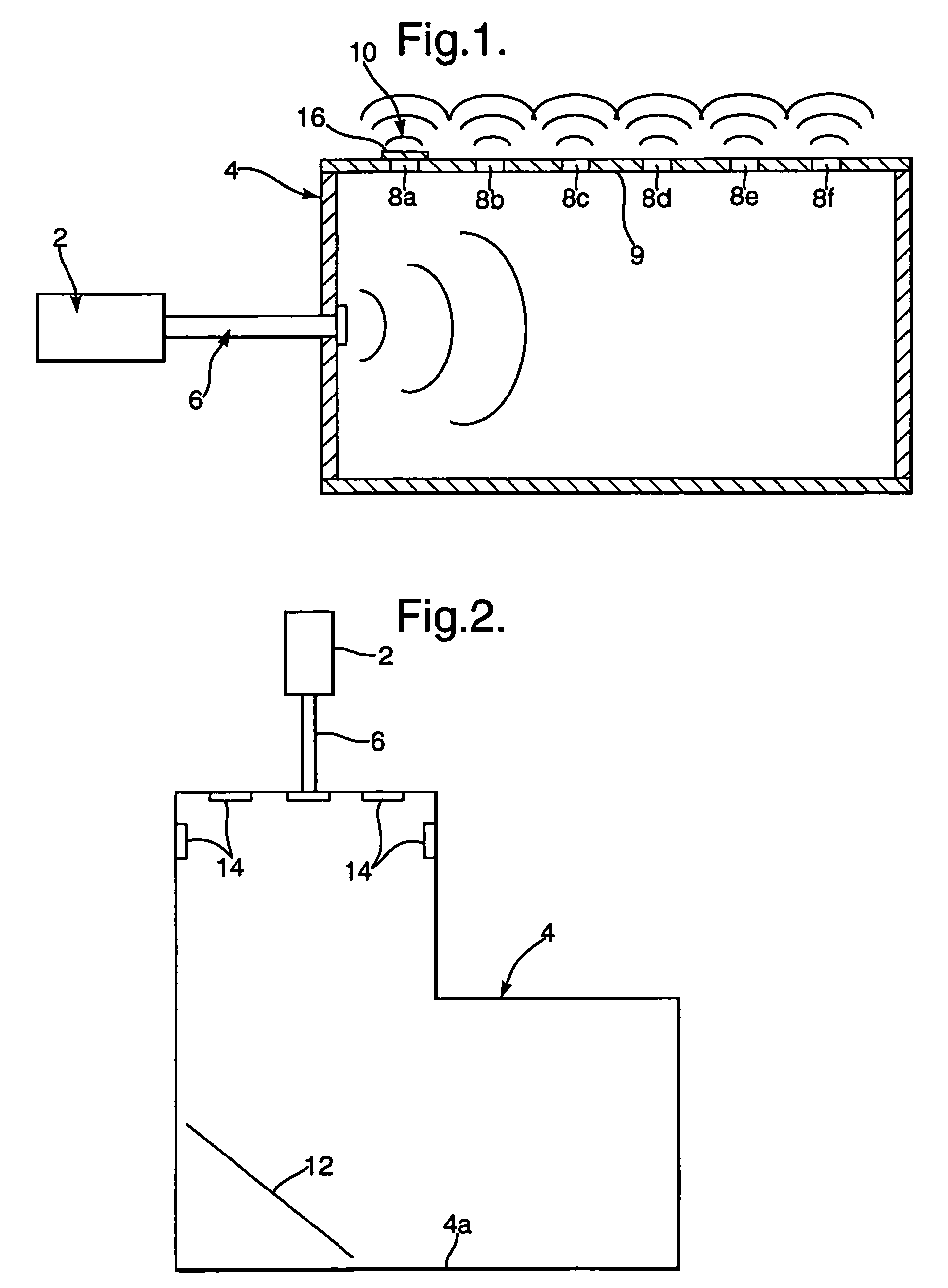
InactiveUS7358890B2Less powerConvenient lightingGeological detection using milimetre wavesIndividually energised antenna arraysPath lengthMillimetre wave
An illumination source of predominantly non-directional and incoherent millimeter-wave radiation for illuminating an area for passive millimeter-wave imaging comprises a container with at least a partly reflective internal surface and a plurality of exit apertures and a primary source of millimeter-wave radiation for emitting millimeter-wave radiation into the container. The primary source and the container are arranged so that a proportion of the millimeter-wave radiation emitted by the source undergoes reflection within the container before being emitted through the apertures, such that the different paths lengths are at least equal to the coherence length of the radiation. This is facilitated if the bandwidth of the radiation is preferably at least 1 GHz. The container may be a box in which a waveguide is used to couple radiation from the primary source into the box. Alternatively, the container may be formed from a mesh and the plurality of holes is provided by the holes in the mesh.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
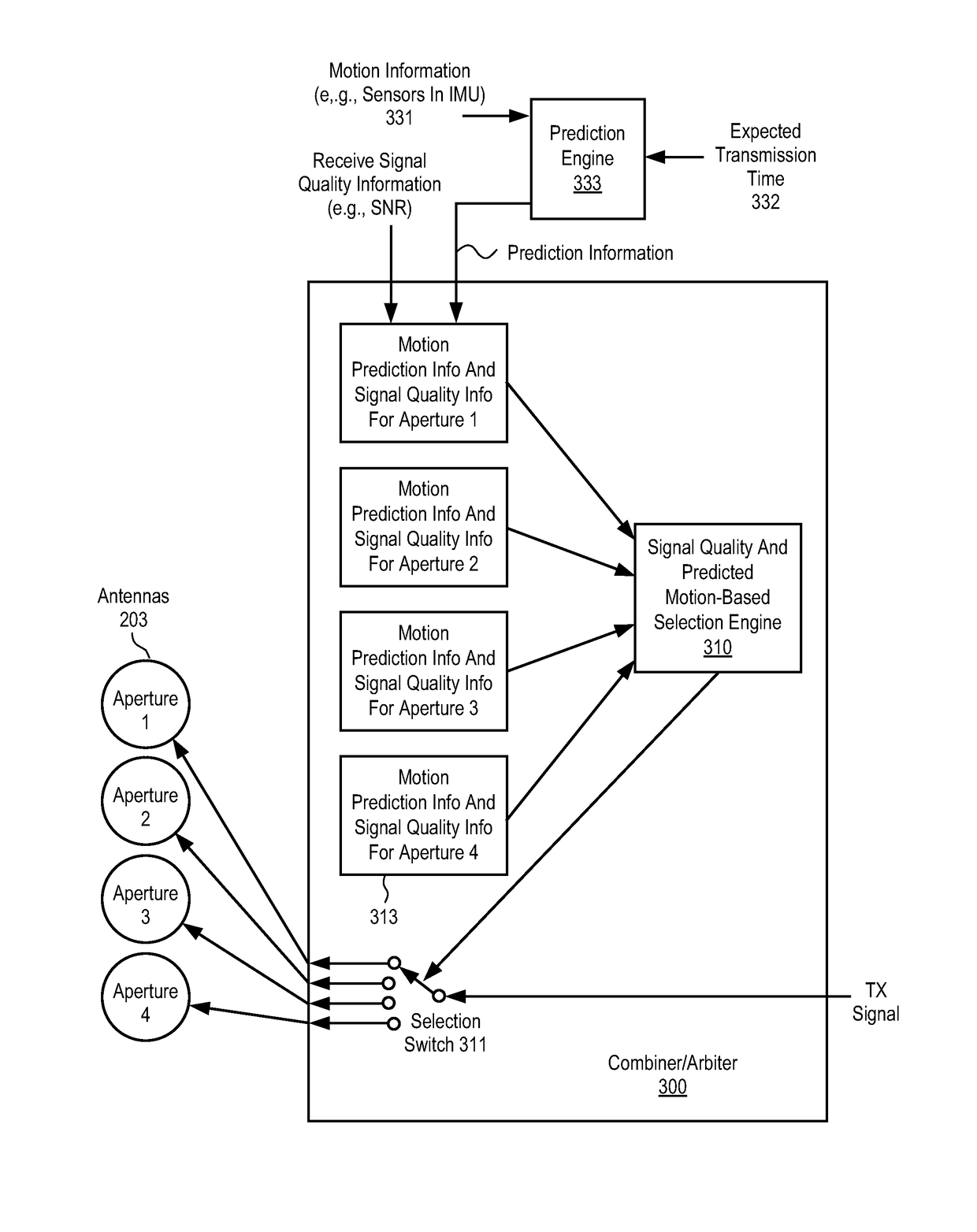
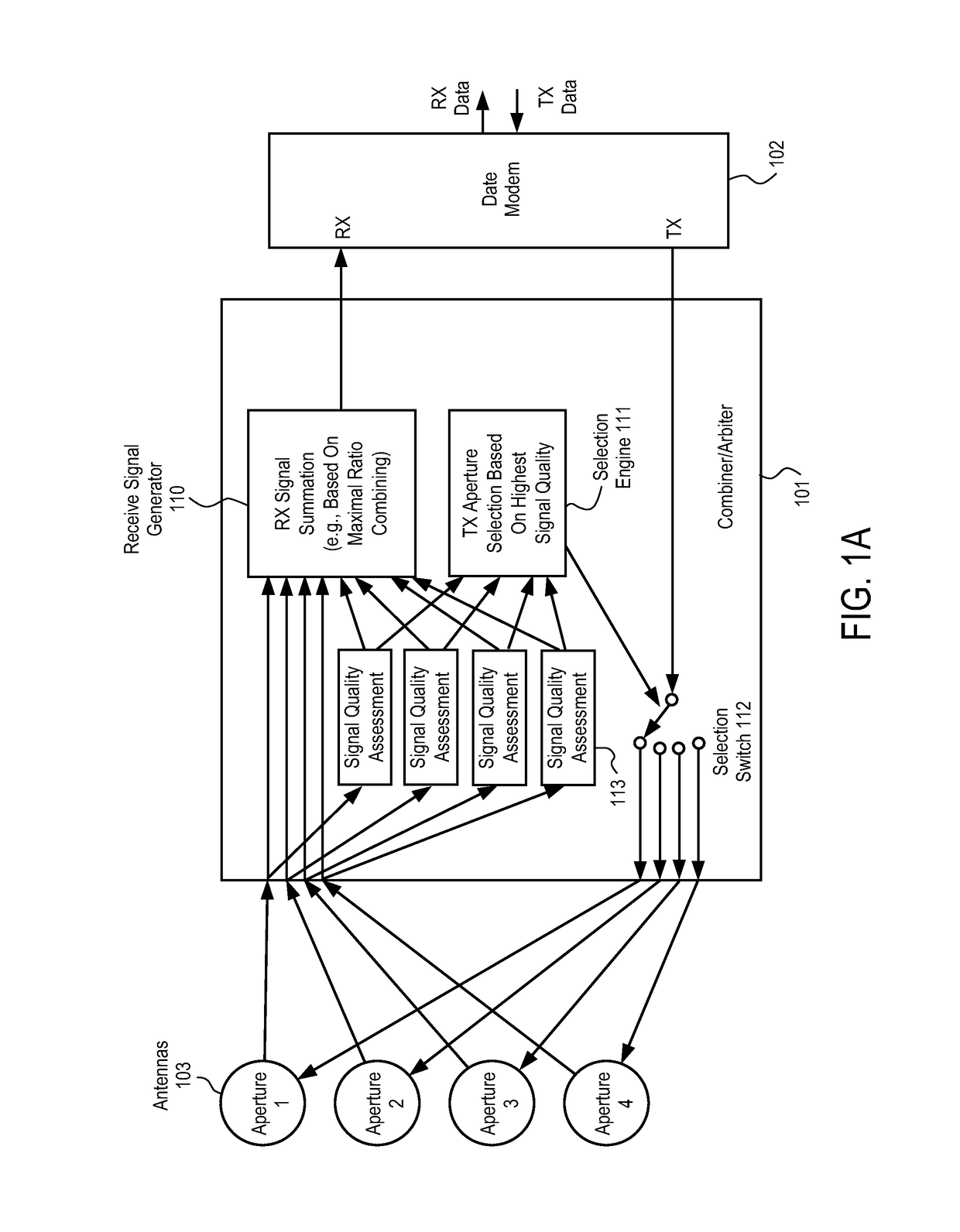
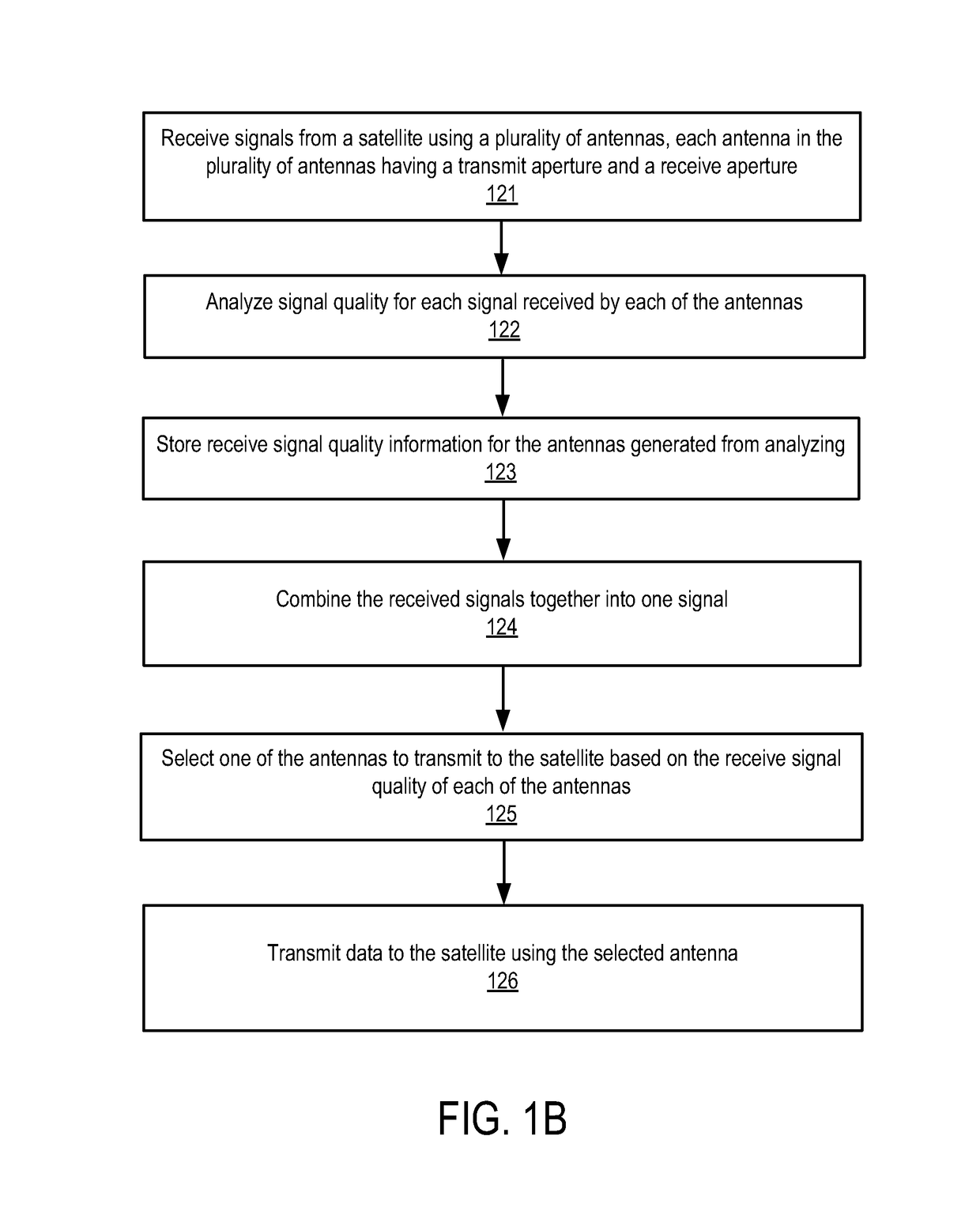
Antenna combiner
ActiveUS10128931B2Spatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsSignal qualitySignal analyzer
An antenna combiner with transmission arbitration and method for using the same are described. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a plurality of antennas to receive signals from a satellite, each antenna in the plurality of antennas having a transmit aperture and a receive aperture, and wherein the receive aperture is operable to receive one of the signals from the satellite; a plurality of signal analyzers coupled to the plurality of antennas, each signal analyzer operable to determine signal quality of a distinct one antenna of the plurality of antennas; an arbiter coupled to the plurality of signal analyzers and operable to select one antenna of the plurality of antennas to transmit to the satellite based on results of determining the signal quality; and a first selector coupled to the arbiter and the plurality of antennas to cause data to be sent to the one antenna selected for transmission to the satellite.
Owner:KYMETA
TFT substrate, scanning antenna using same, and method for manufacturing TFT substrate
Owner:SHARP KK
Scanning antenna and method for driving same
A scanning antenna is a scanning antenna in which antenna units U are arranged, and includes a TFT substrate including a first dielectric substrate, TFTs, a plurality of gate bus lines, source bus lines, and patch electrodes; a slot substrate including a second dielectric substrate, and a slot electrode formed on a first main surface of the second dielectric substrate; a liquid crystal layer LC provided between the TFT substrate and the slot substrate; and a reflective conductive plate provided opposing a second main surface of the second dielectric substrate opposite to the first main surface via a dielectric layer. The slot electrode includes slots arranged in correspondence with the plurality of patch electrodes, and each of the patch electrodes is connected to a drain of a corresponding TFT and is supplied with a data signal from a corresponding source bus line while selected by a scanning signal supplied from the gate bus line of the corresponding TFT. The frequency at which the polarity of the voltage applied to each of the plurality of patch electrodes is inverted is greater than or equal to 300 Hz.
Owner:SHARP KK
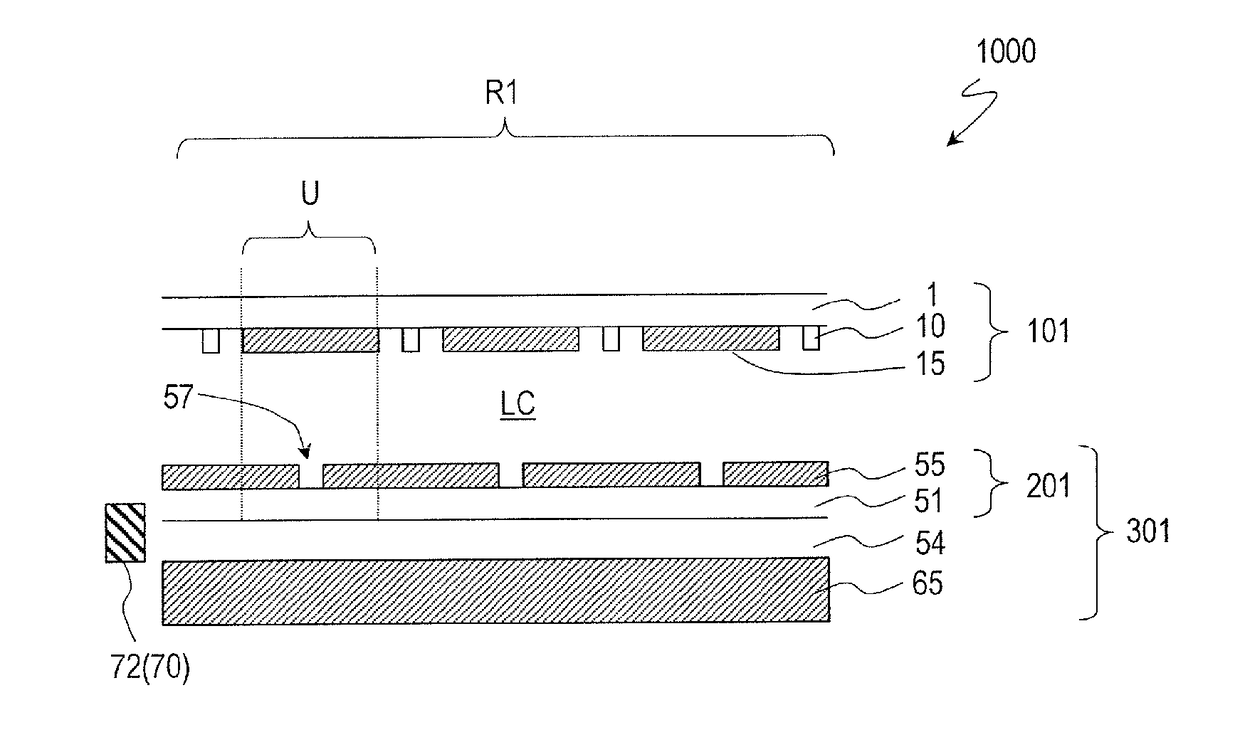
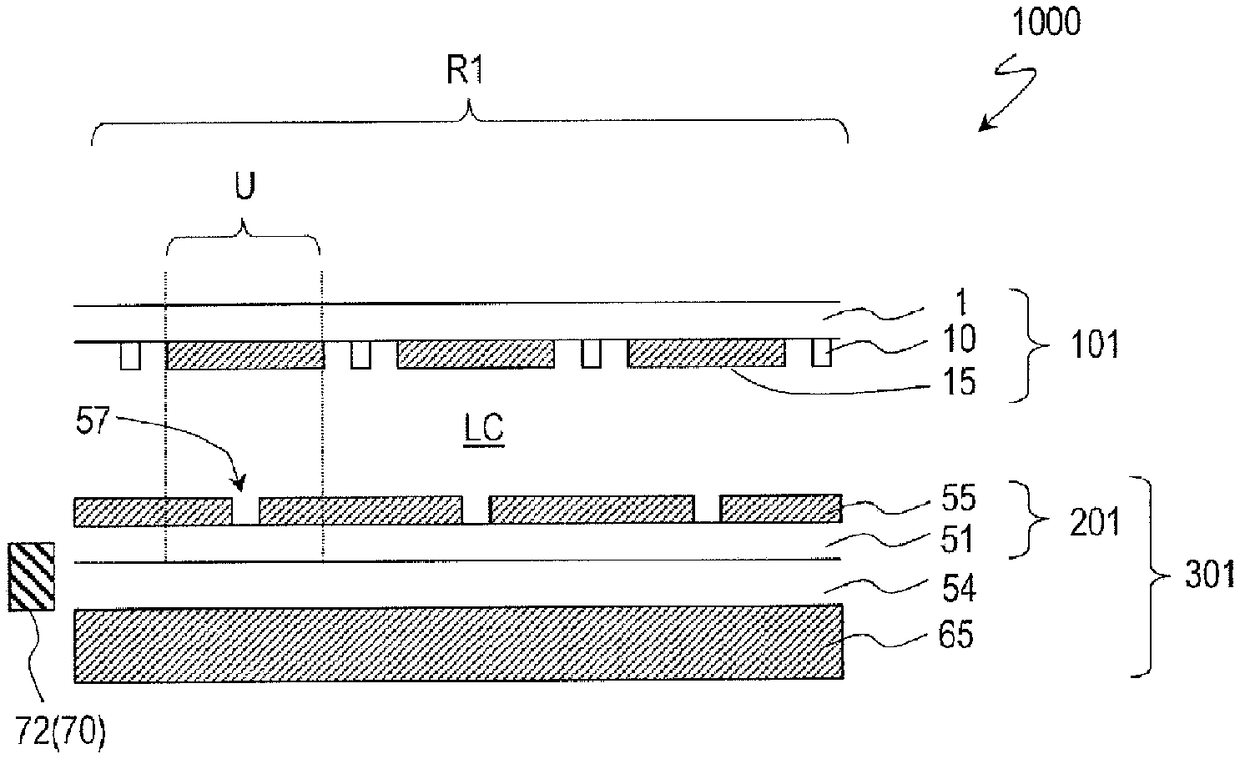
Scanning antenna comprising a liquid crystal layer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS10153550B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid-crystal displayPatch electrode
A scanned antenna (1000) is a scanned antenna including antenna elements (U) arranged together, the scanned antenna comprising: a TFT substrate including a first dielectric substrate (1), TFTs, gate bus lines, source bus lines, and patch electrodes (15); a slot substrate (201) including a second dielectric substrate (51), and a slot electrode (55) formed on a first primary surface of the second dielectric substrate; a liquid crystal layer (LC) provided between the TFT substrate and the slot substrate; and a reflective conductive plate (65) arranged so as to oppose a second primary surface of the second dielectric substrate (51) with a dielectric layer (54) interposed therebetween, the second primary surface being on an opposite side from the first primary surface. The TFT substrate (TFT substrate portion (101Cb)) includes a terminal region (TR) outside of the seal portion (73), and the gate bus lines or the source bus lines are connected to gate terminal portions or source terminal portions formed in the terminal region via a transparent conductive layer (14b) provided between the seal portion (73) and the TFT substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
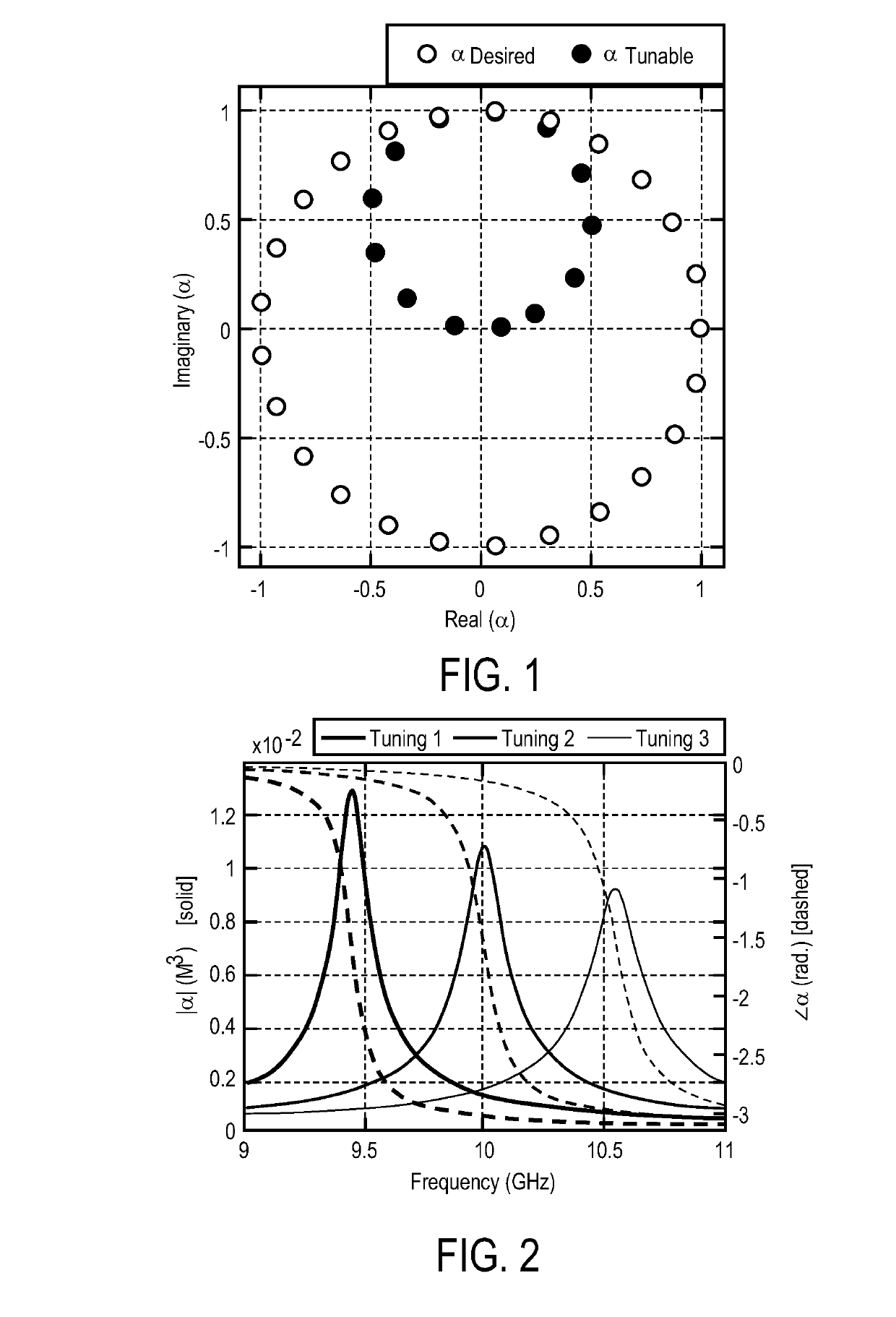
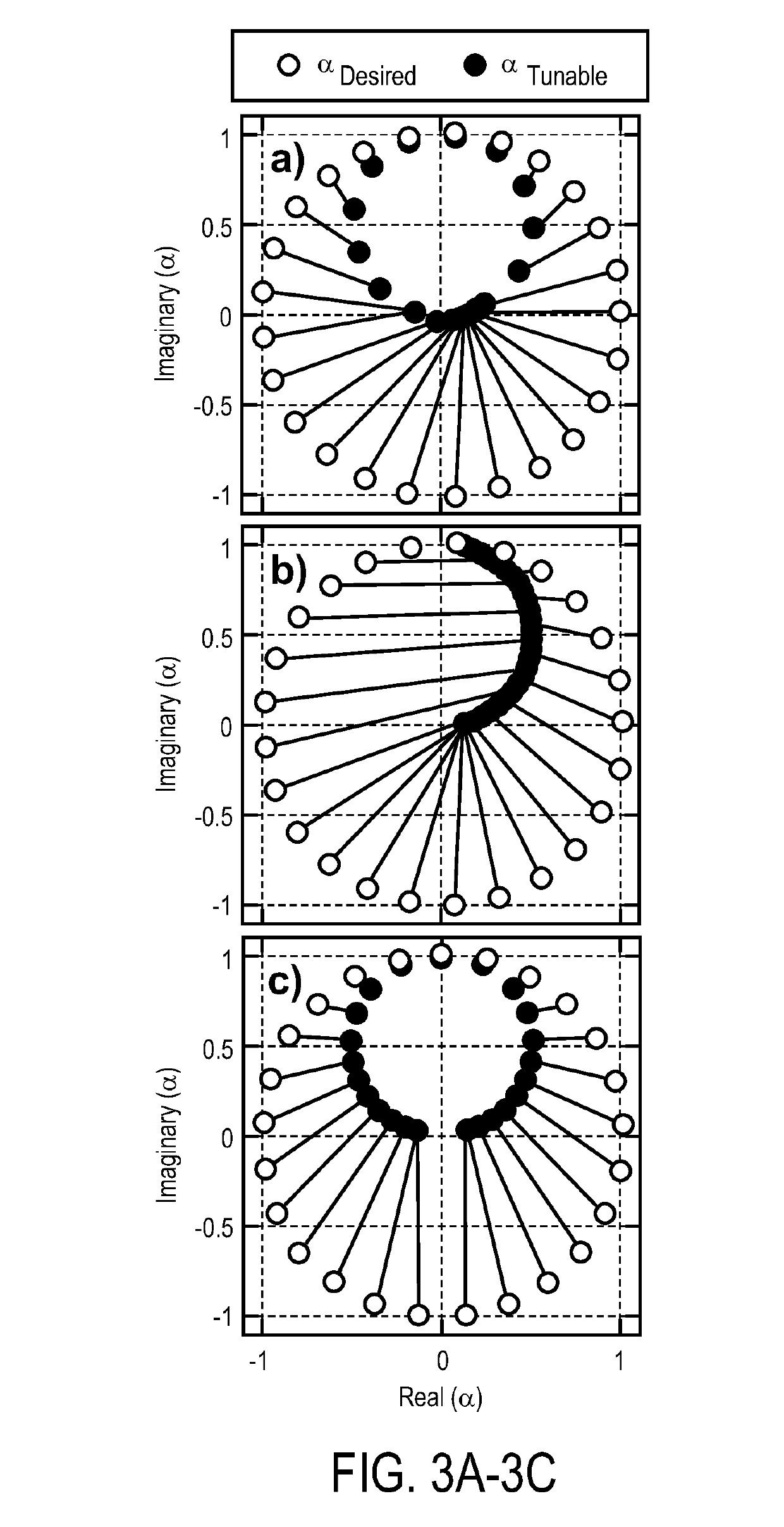
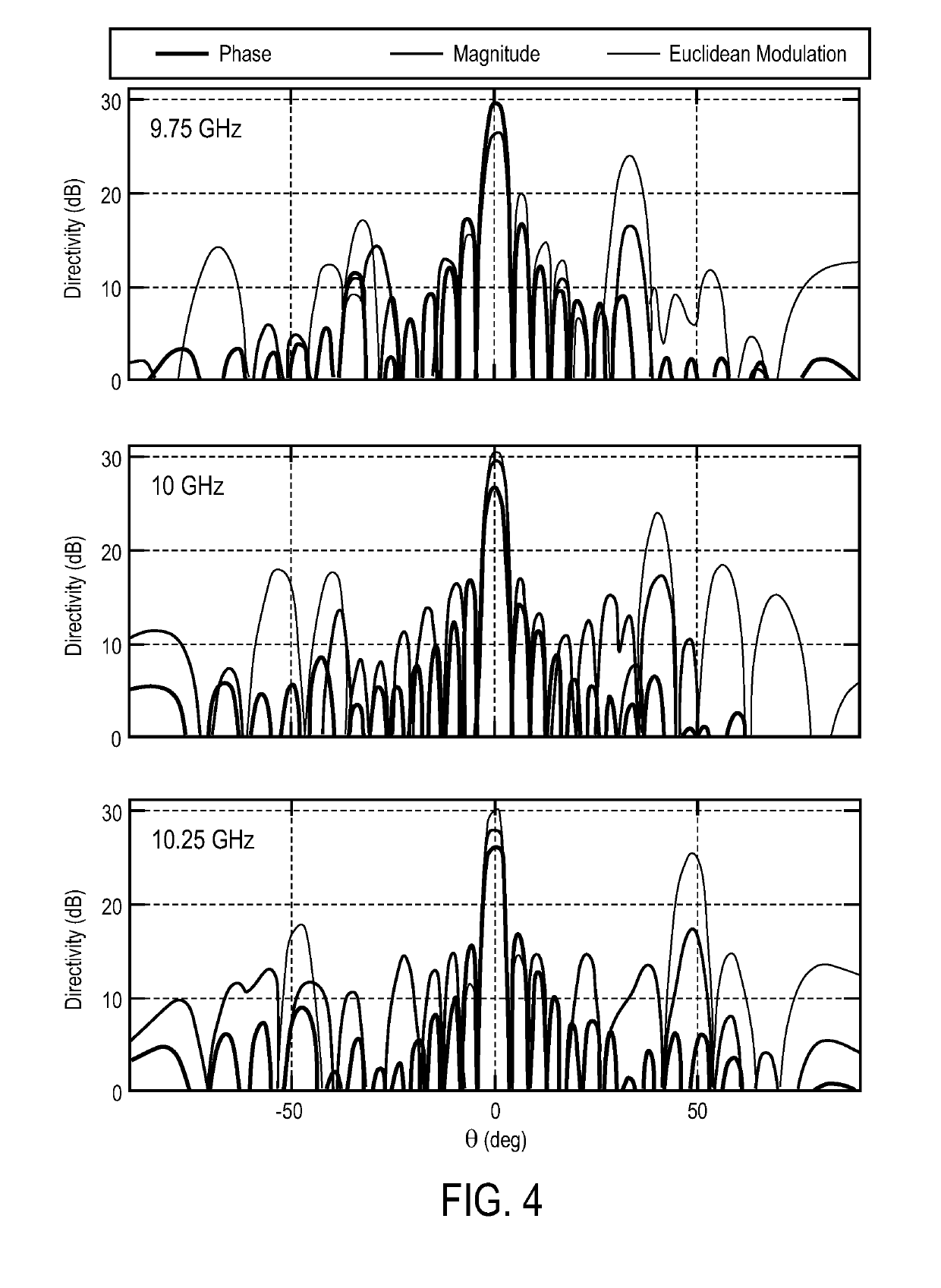
Restricted euclidean modulation
ActiveUS20190238375A1Polarisation/directional diversityRadiating elements structural formsAntenna elementRadio frequency
A method and apparatus for using Euclidean modulation in an antenna are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for controlling an antenna comprises mapping a desired modulation to achievable modulation states, mapping modulation values associated with the achievable modulation states to one or more control parameters, and controlling radio frequency (RF) radiating antenna elements using the one or more control parameters to perform beam forming.
Owner:KYMETA
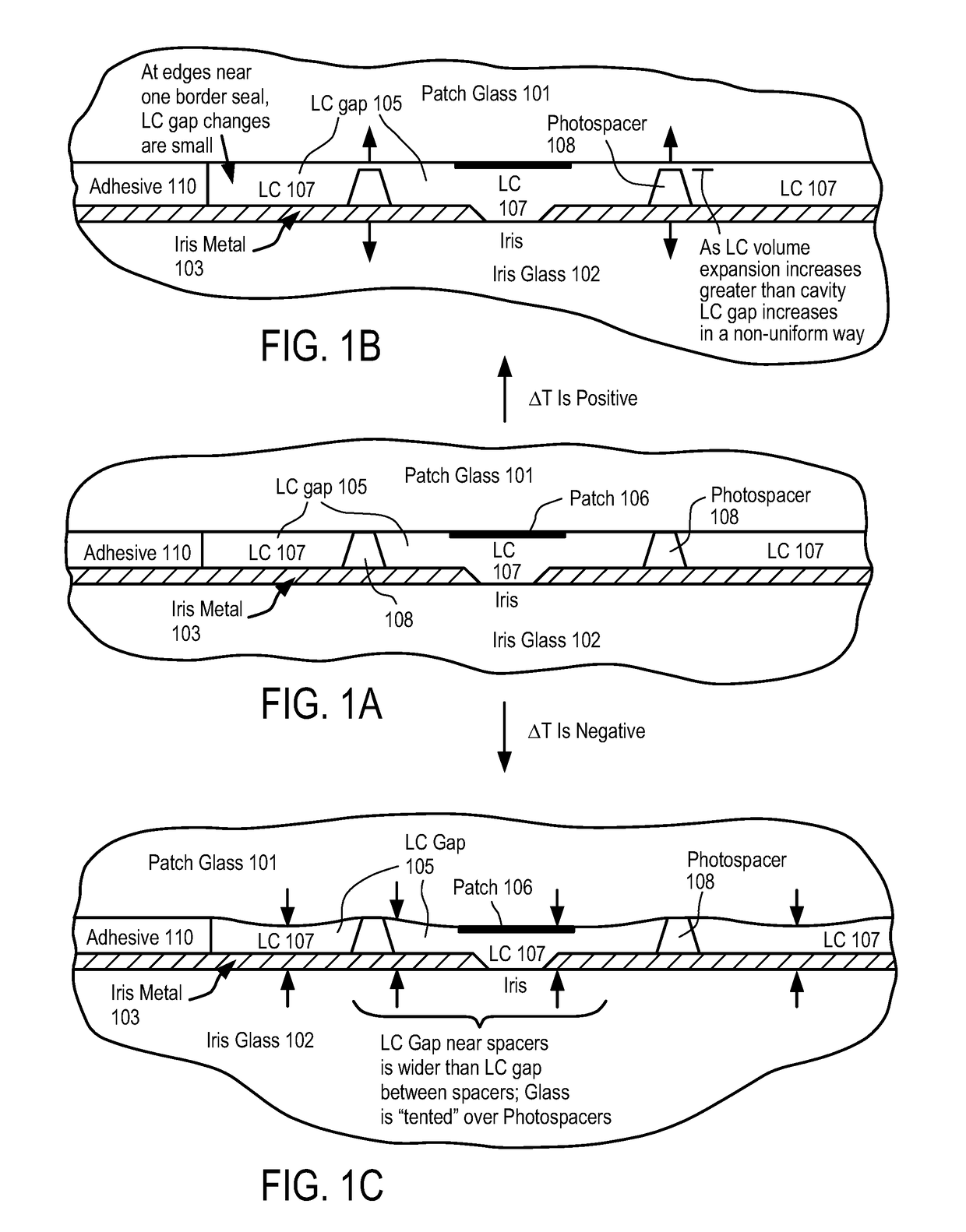
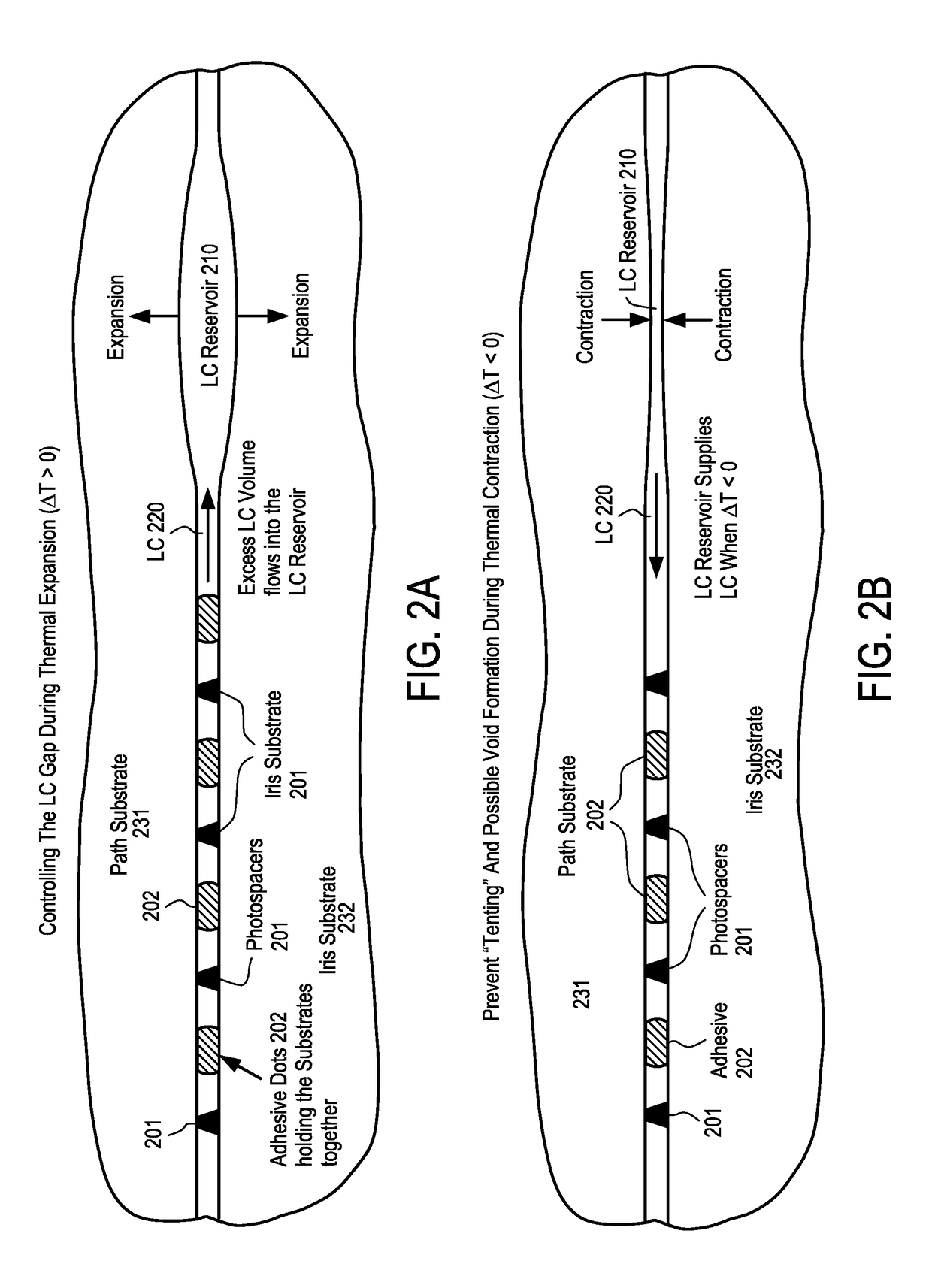
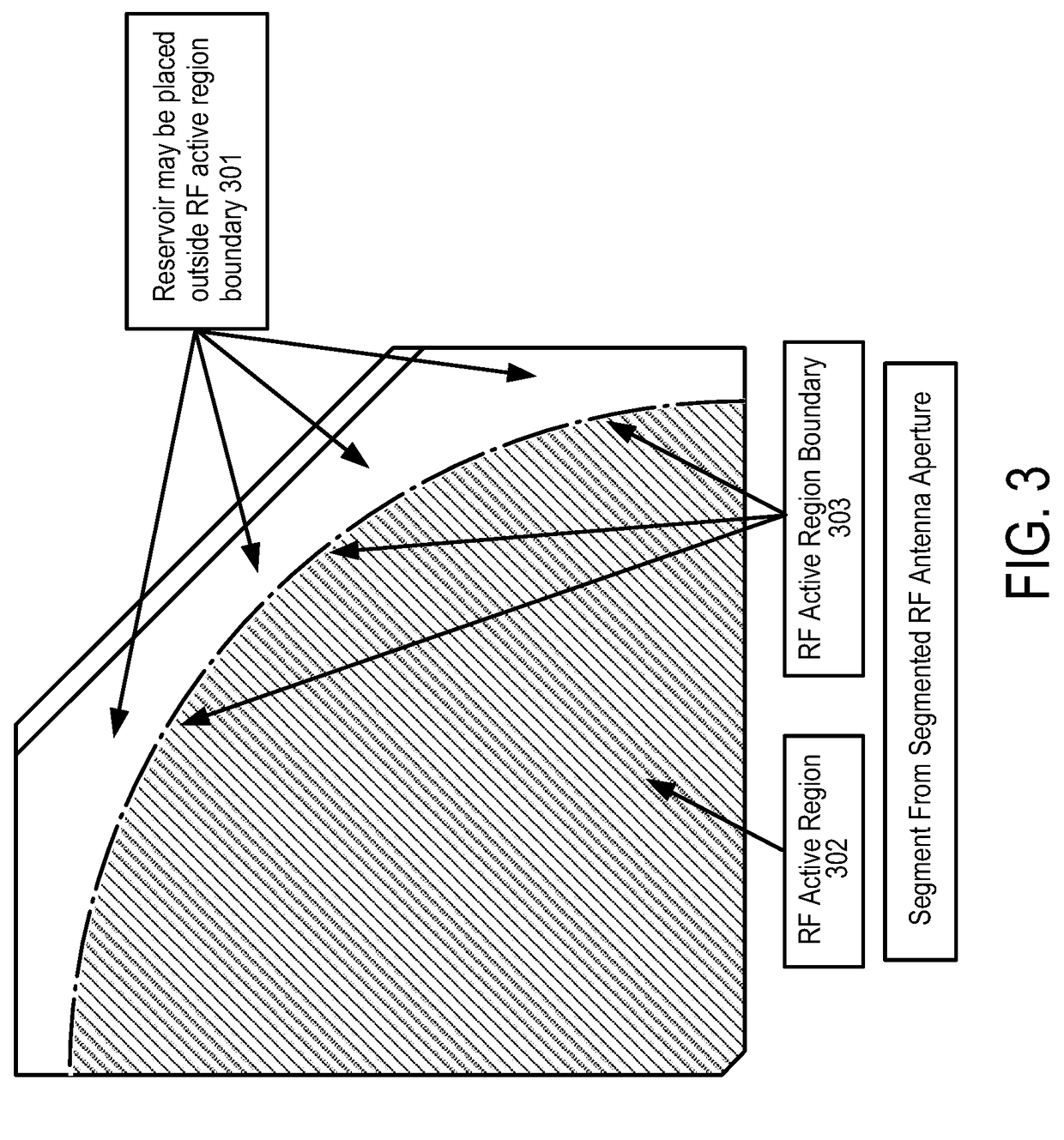
Lc reservoir
ActiveUS20180358690A1Static indicating devicesRadiating elements structural formsRadio frequencyAntenna element
An apparatus for exchanging liquid crystal (LC) between two areas of an antenna array and method for using the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, the antenna comprises an antenna element array having a plurality of radiating radio-frequency (RF) antenna elements formed using portions of first and second substrates with a liquid crystal (LC) therebetween, and a structure between the first and second substrates and outside the area of the RF antenna elements to collect LC from an area between the first and second substrates forming the RF antenna elements due to LC expansion.
Owner:KYMETA
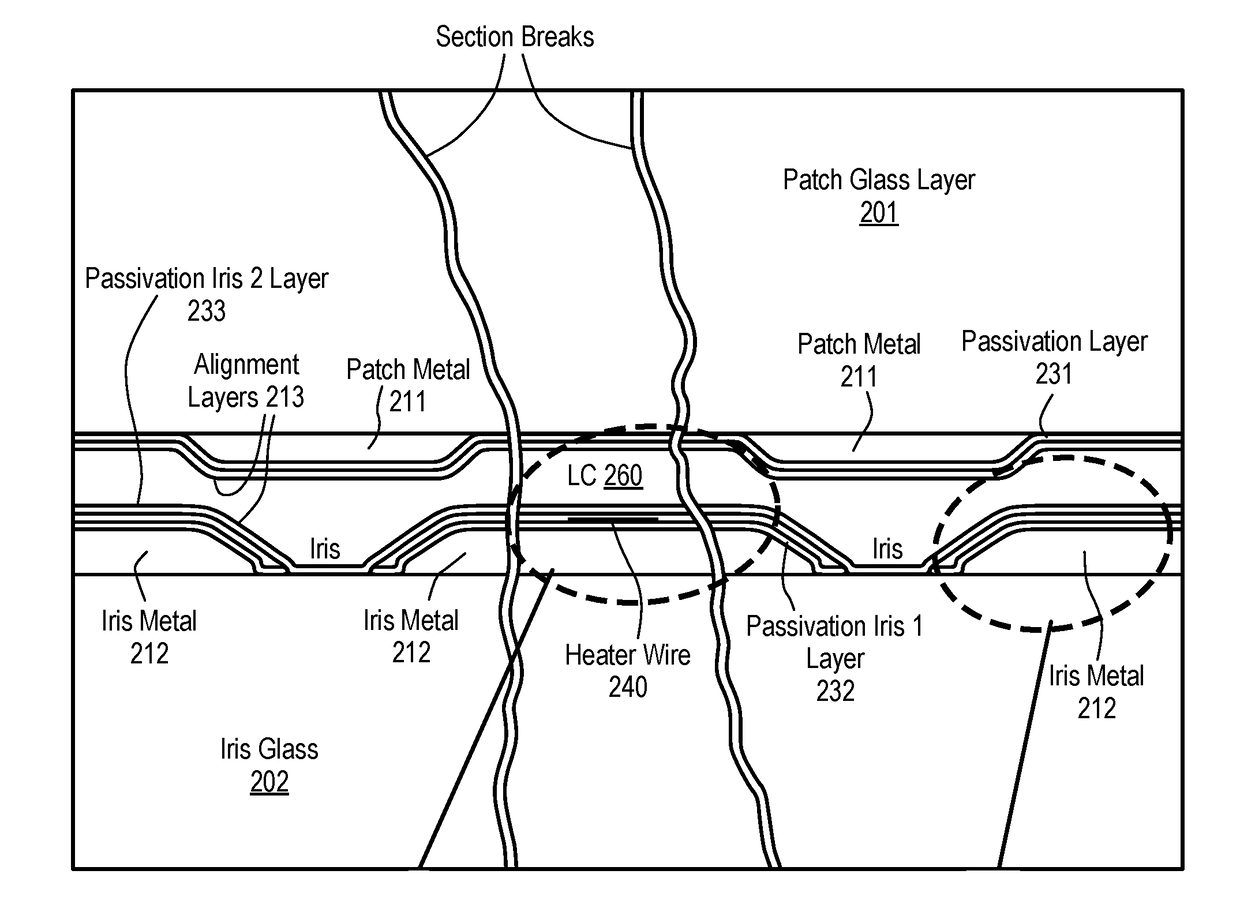
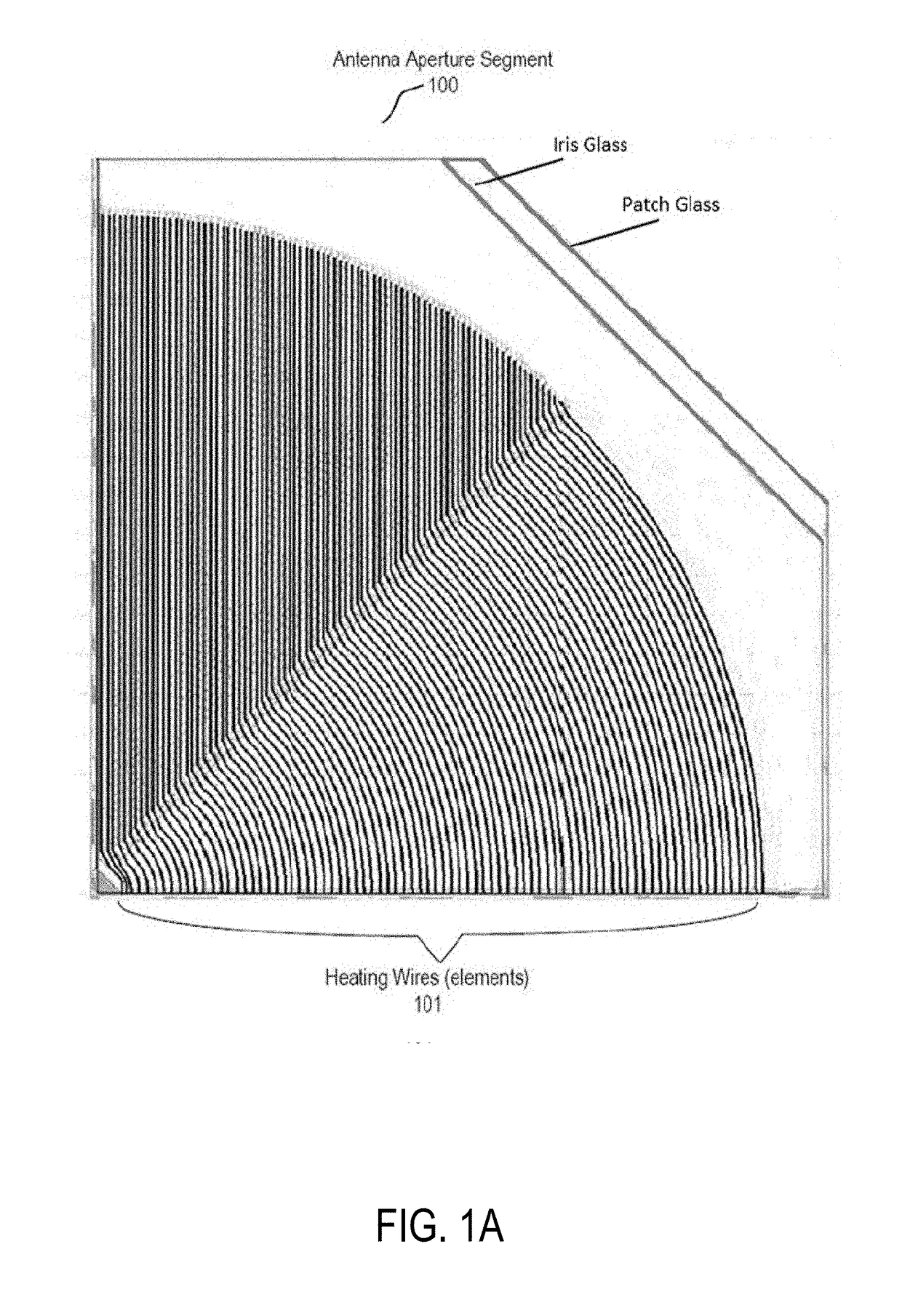
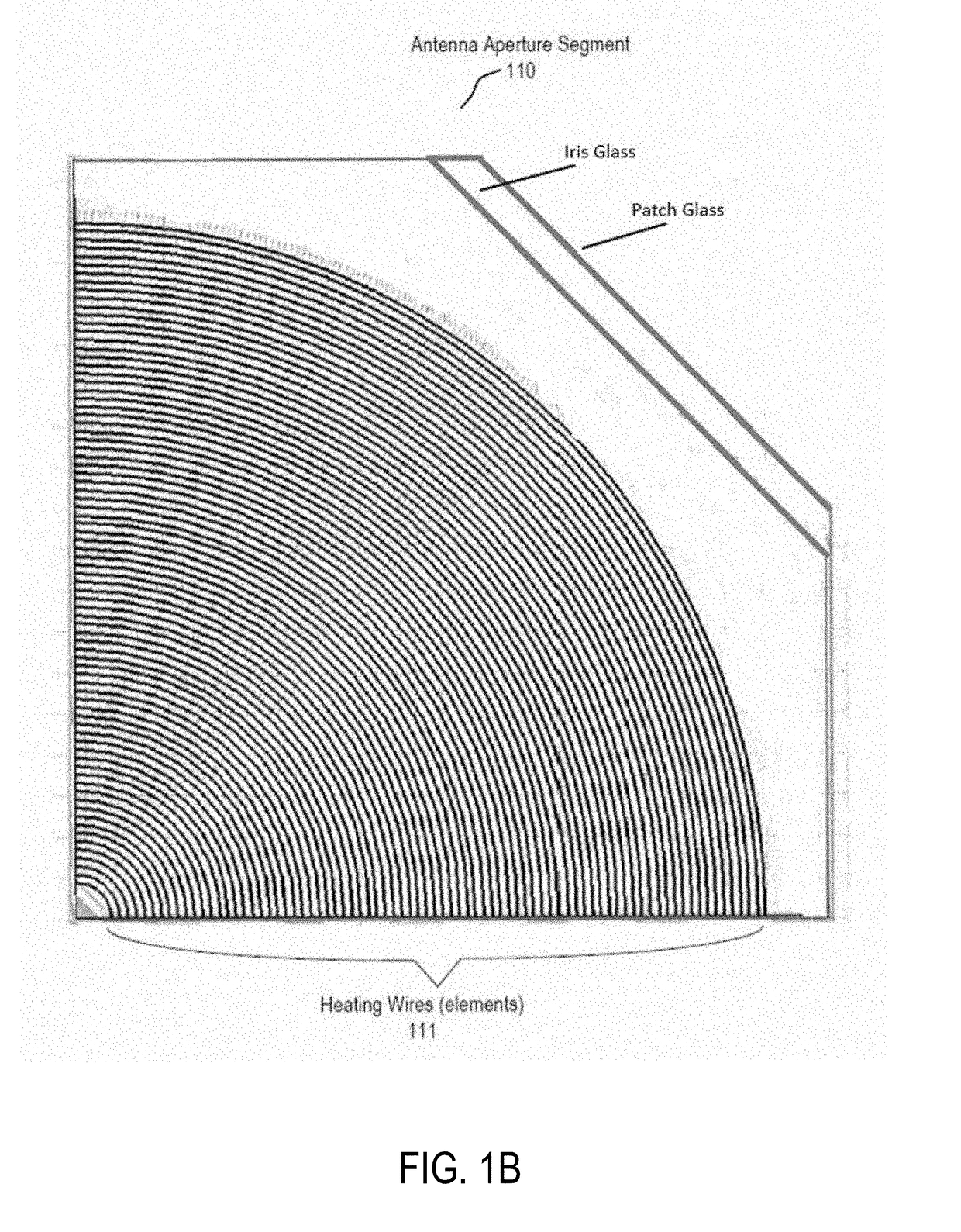
Internal heater for RF apertures
ActiveUS20180146511A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringRadio frequency
A heater for a radio frequency (RF) antenna and method for using the same are disclosed. In one embodiment, an antenna comprises a physical antenna aperture having an array of RF antenna elements; and a plurality of heating elements, each heating element being between pairs of RF elements of the array of RF elements.
Owner:KYMETA
Scanned antenna and method for manufacturing same
A scanned antenna (1000) is a scanned antenna in which antenna units U are arranged and which comprises: a first dielectric substrate (1); a TFT substrate (101) including TFTs, gate bus lines, sourcebus lines, and patch electrodes (15); a slot substrate (201) including a second dielectric substrate (51) and a slot electrode (55) formed on a first main surface of the second dielectric substrate; aliquid crystal layer LC provided between the TFT substrate and the slot substrate; and a reflective conductor plate (65) disposed so as to oppose , across a dielectric layer (54), a second main surface of the second dielectric substrate (51) on the opposite side from the first main surface. The slot electrode includes slots disposed corresponding to each of the patch electrodes, and the second dielectric substrate (51) and the slot electrode (55) have an adhesive layer (92) formed therebetween from a heat-curable or photo-curable adhesive material.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com