Patents
Literature
181results about "Wind motor commissioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
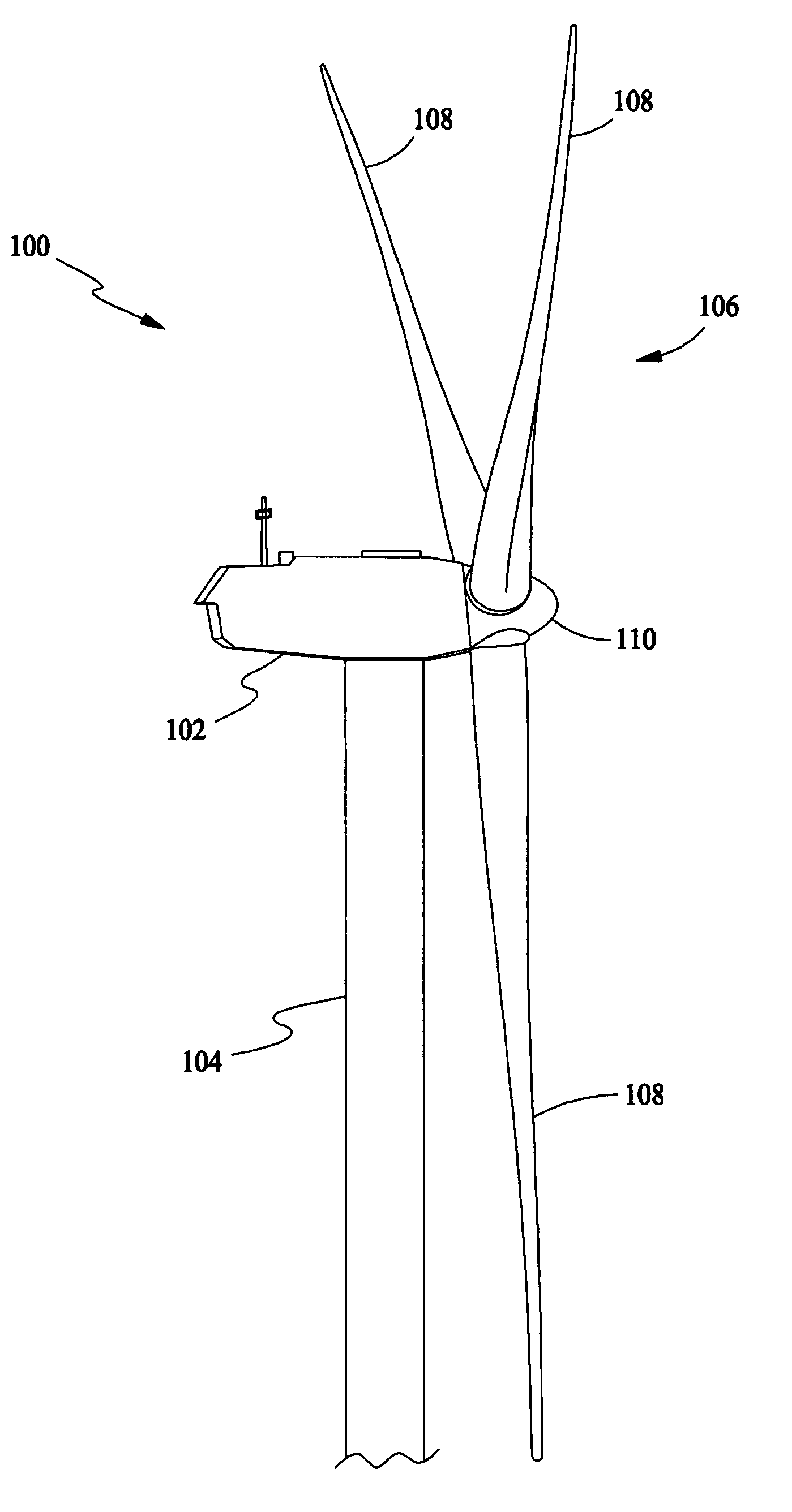
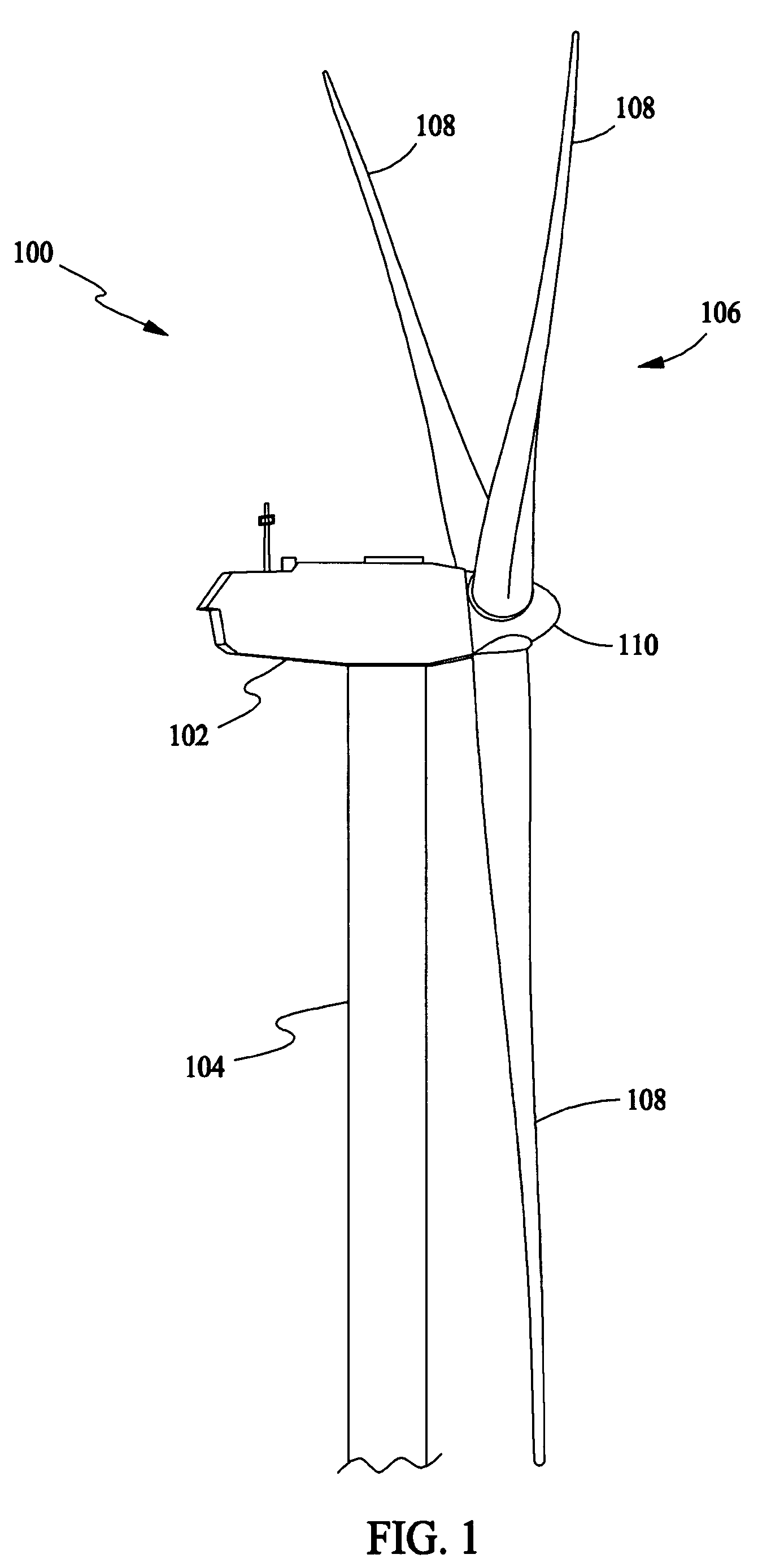
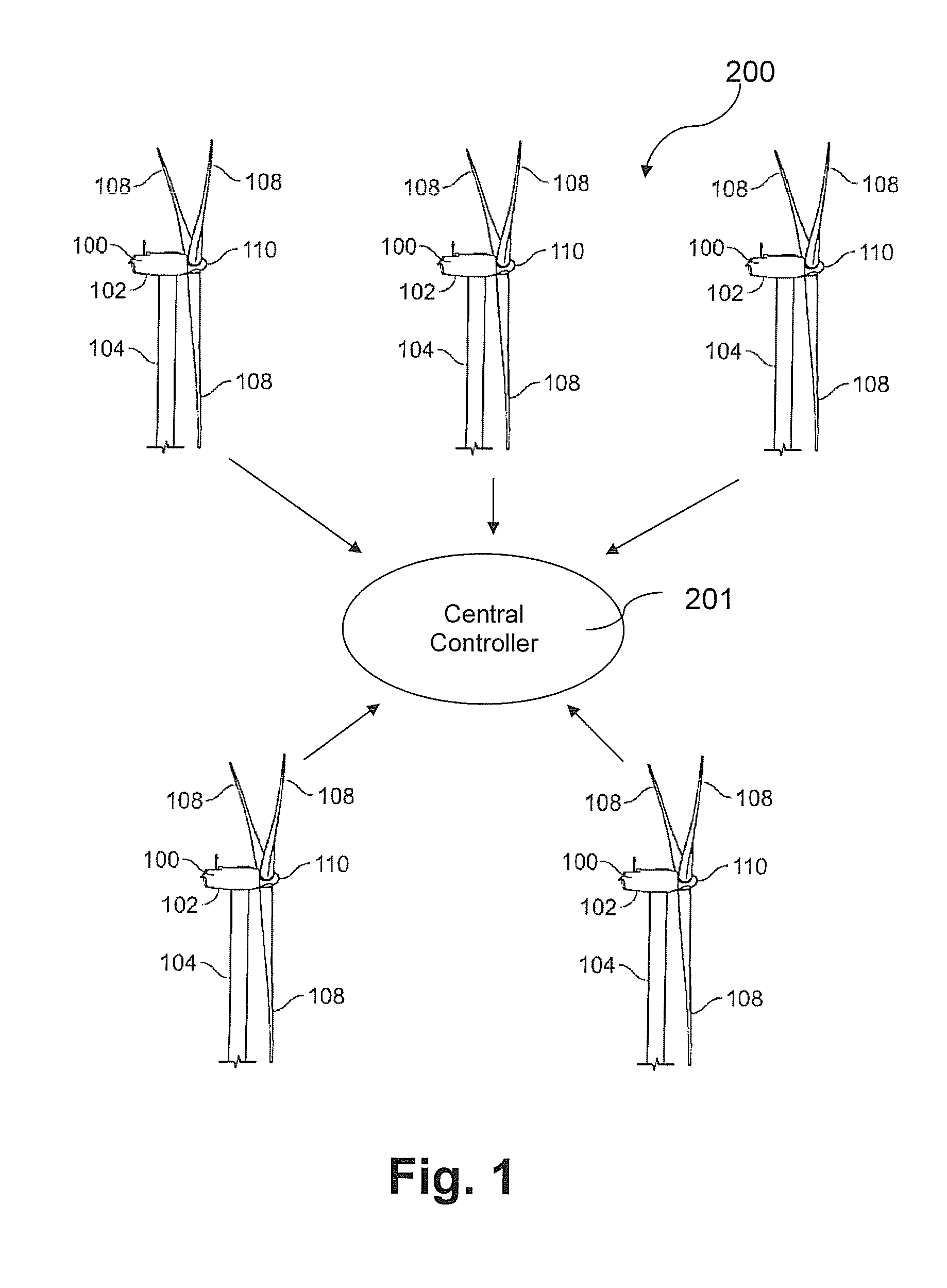
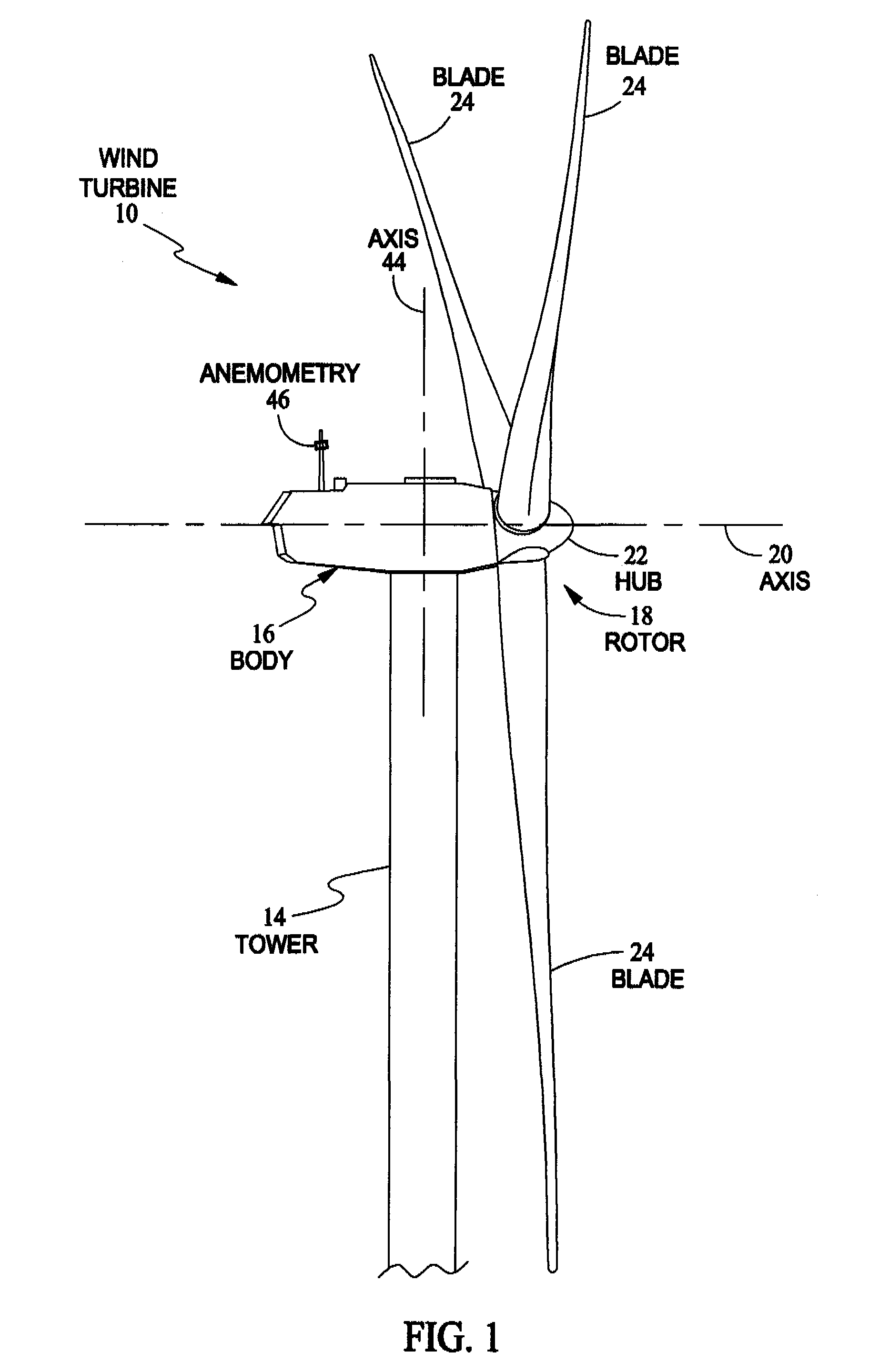
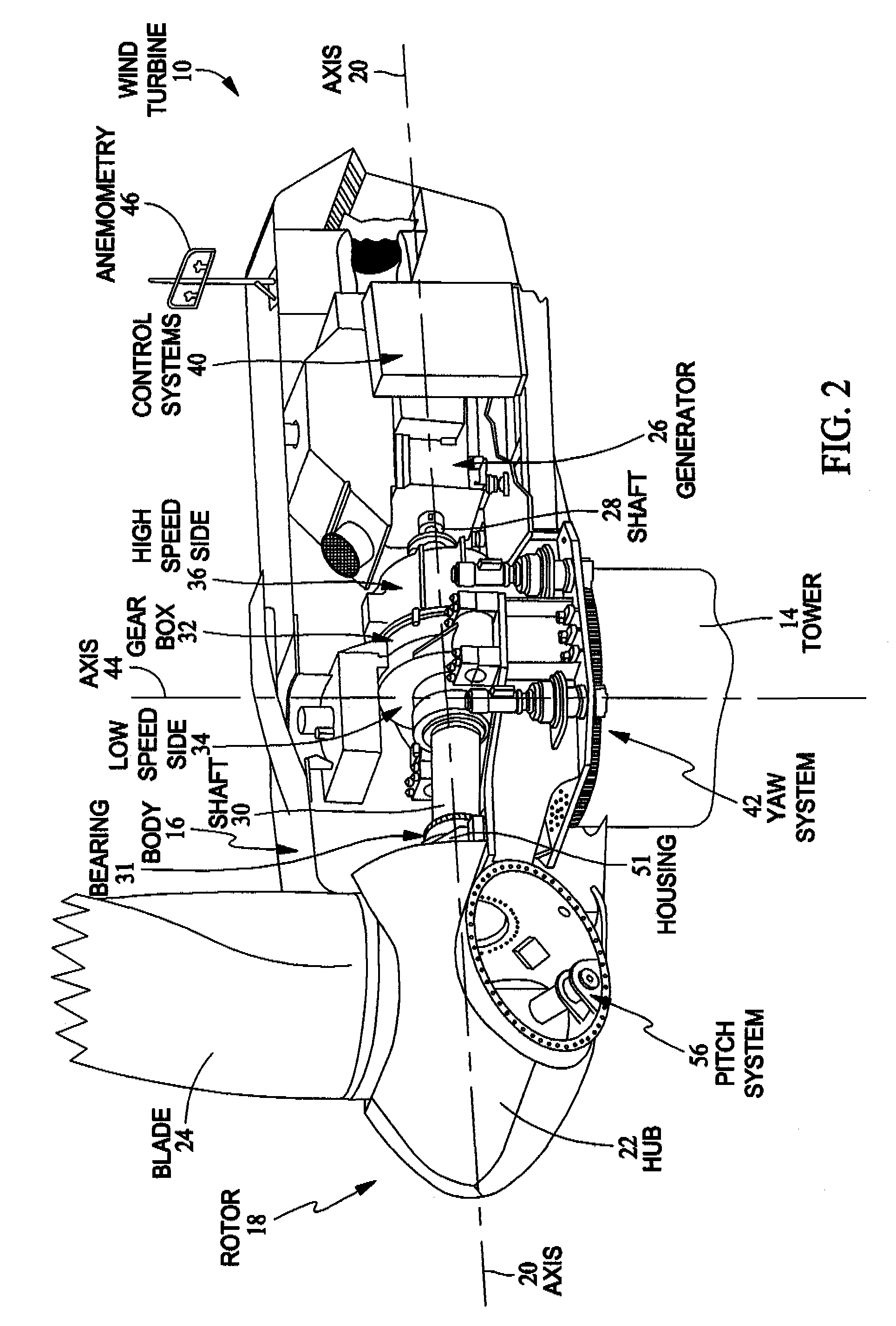
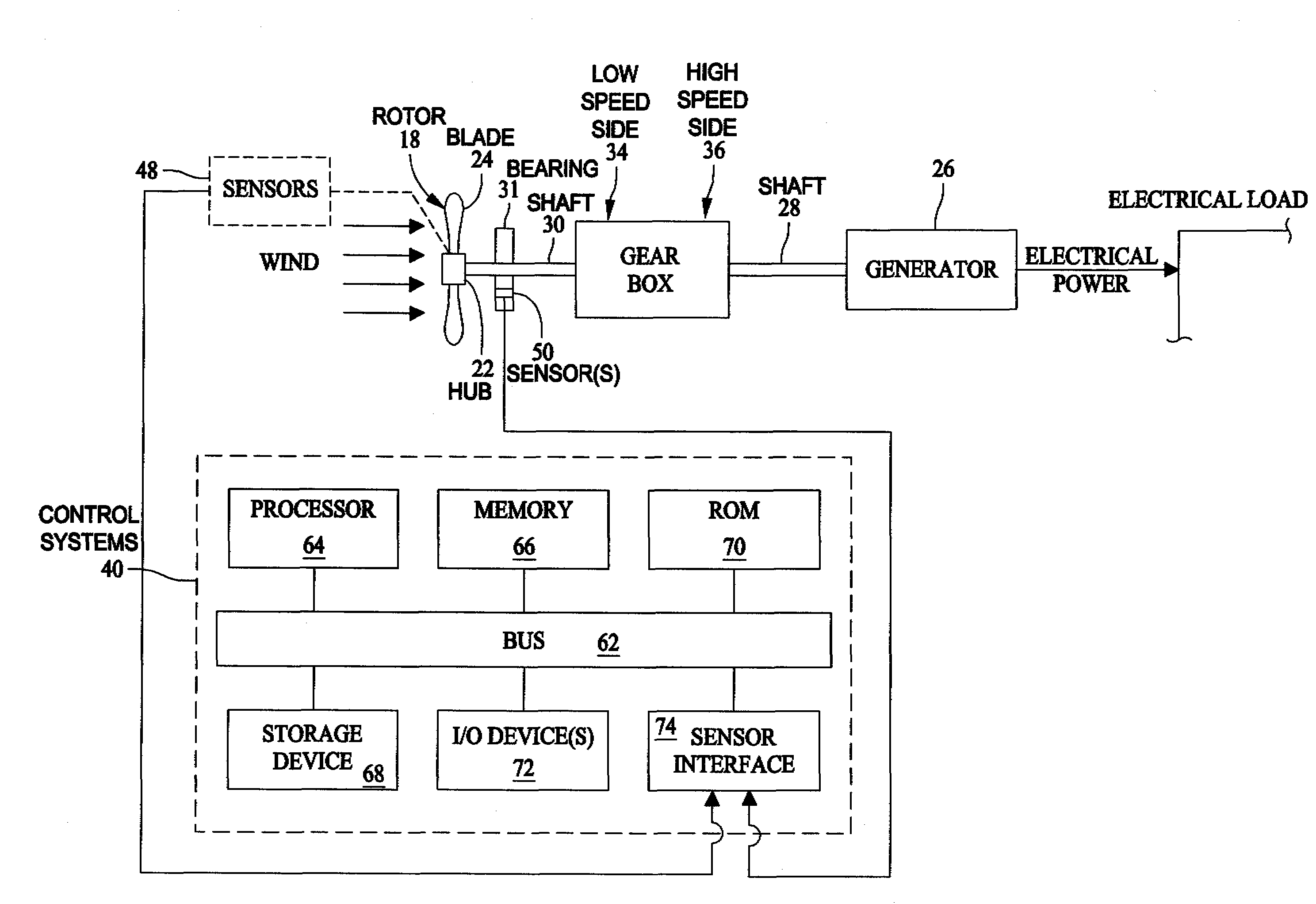
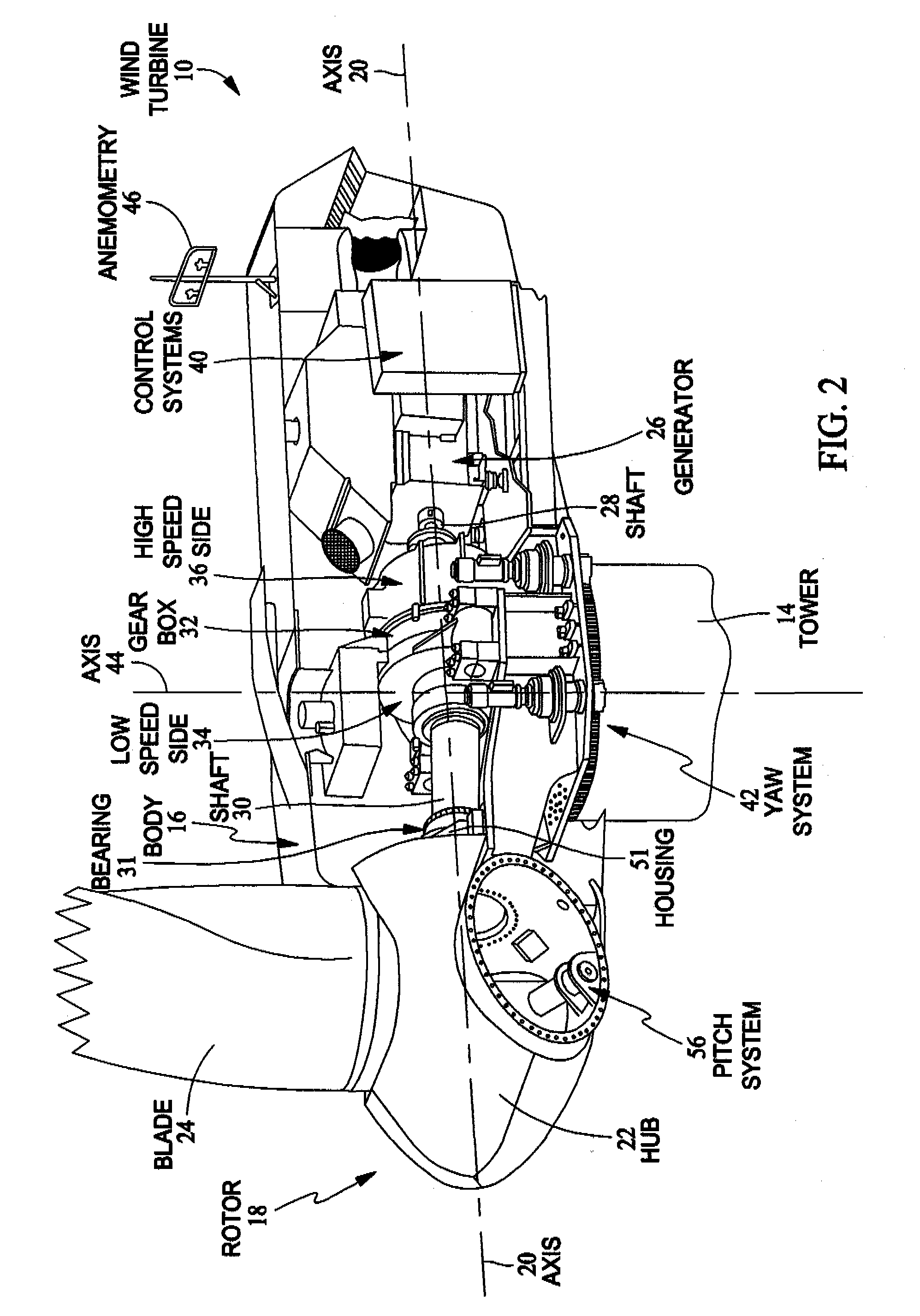
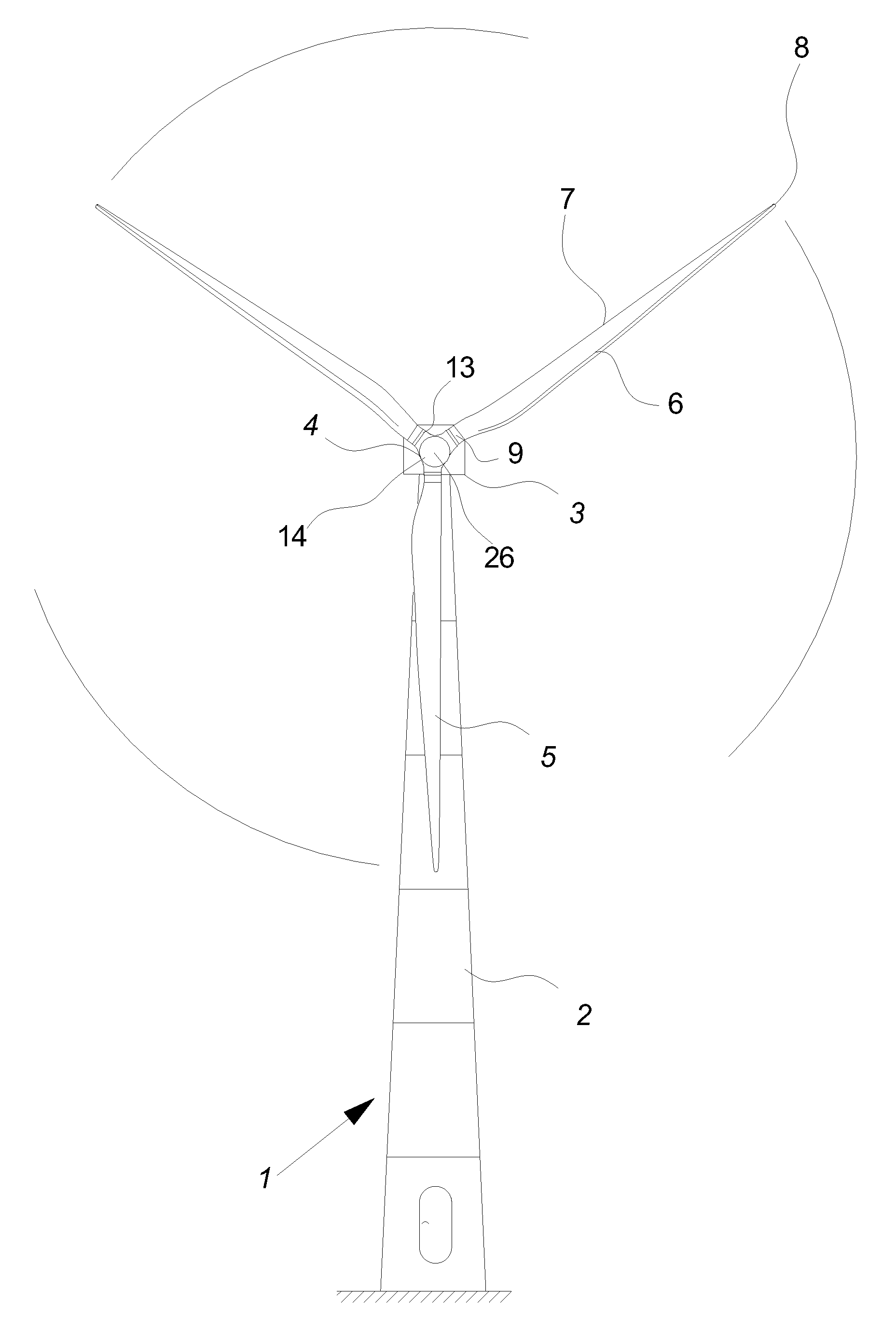
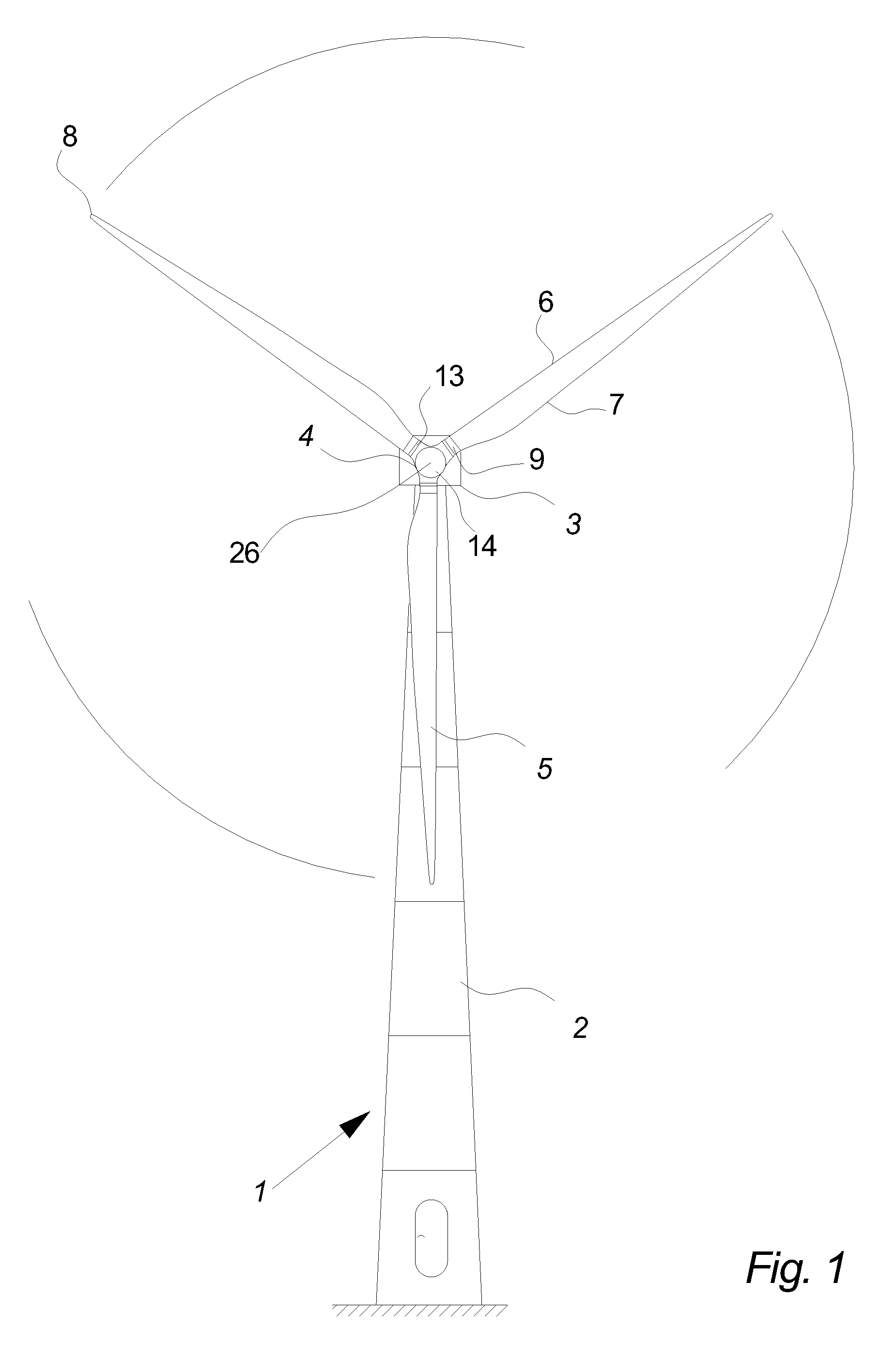
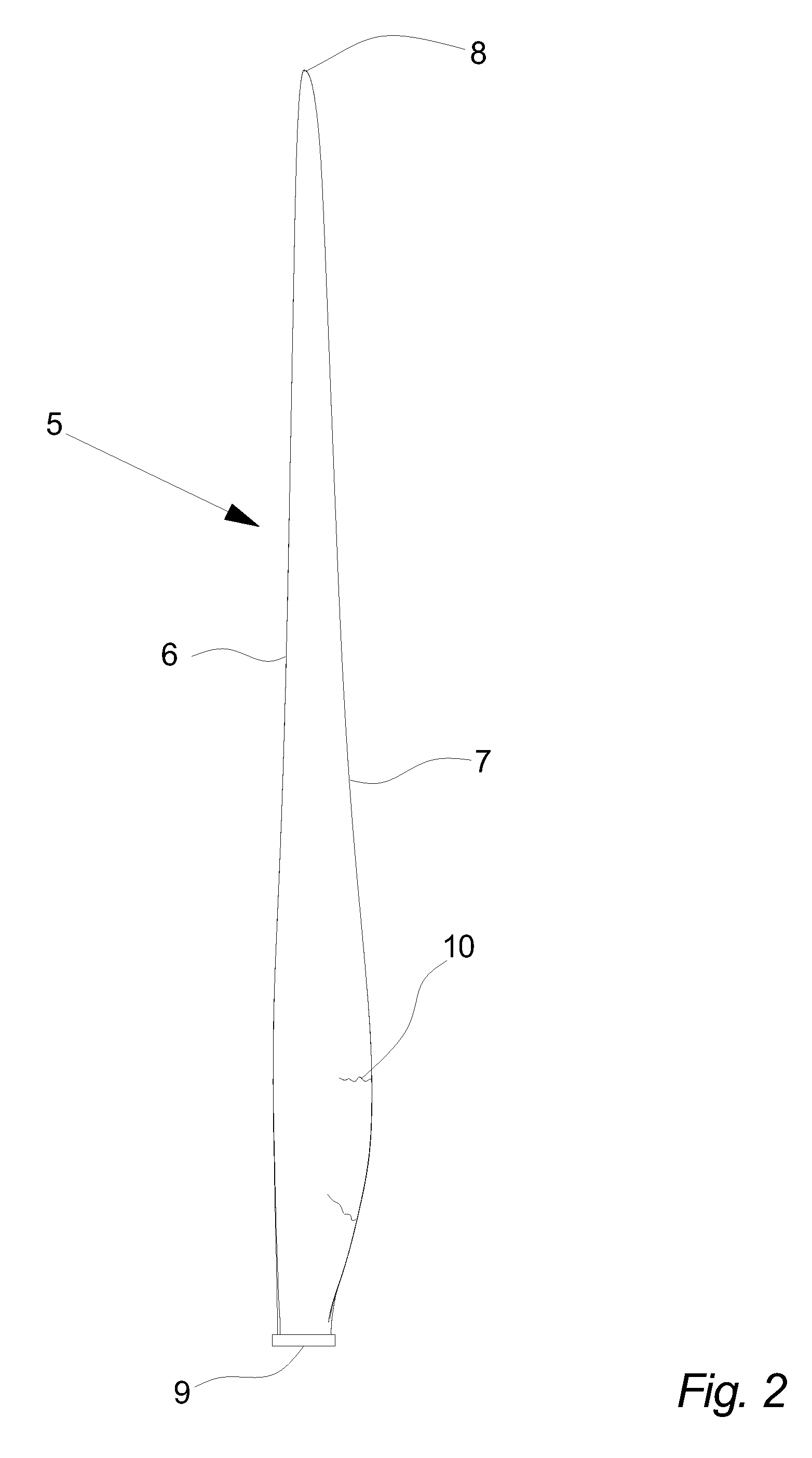
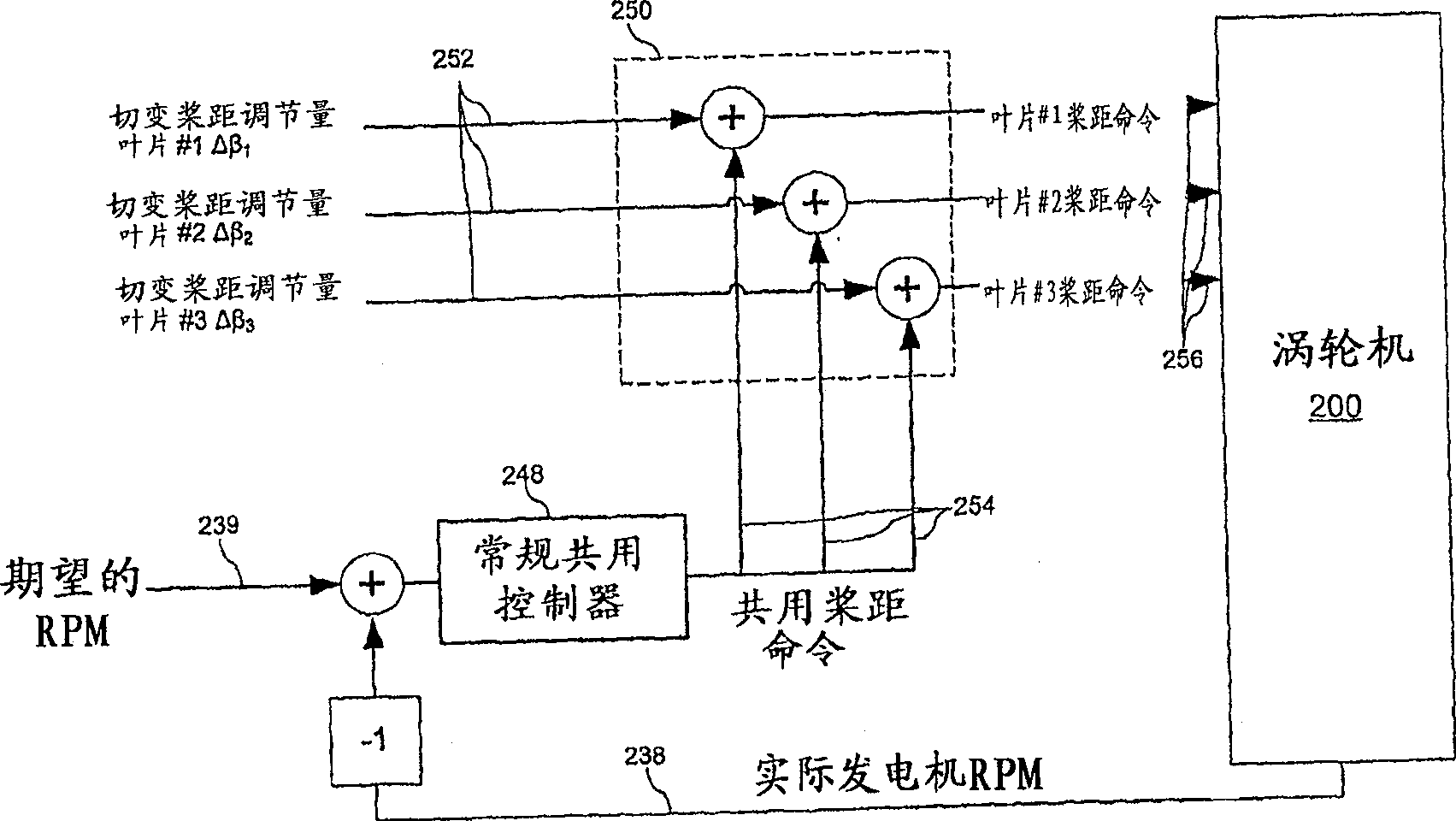
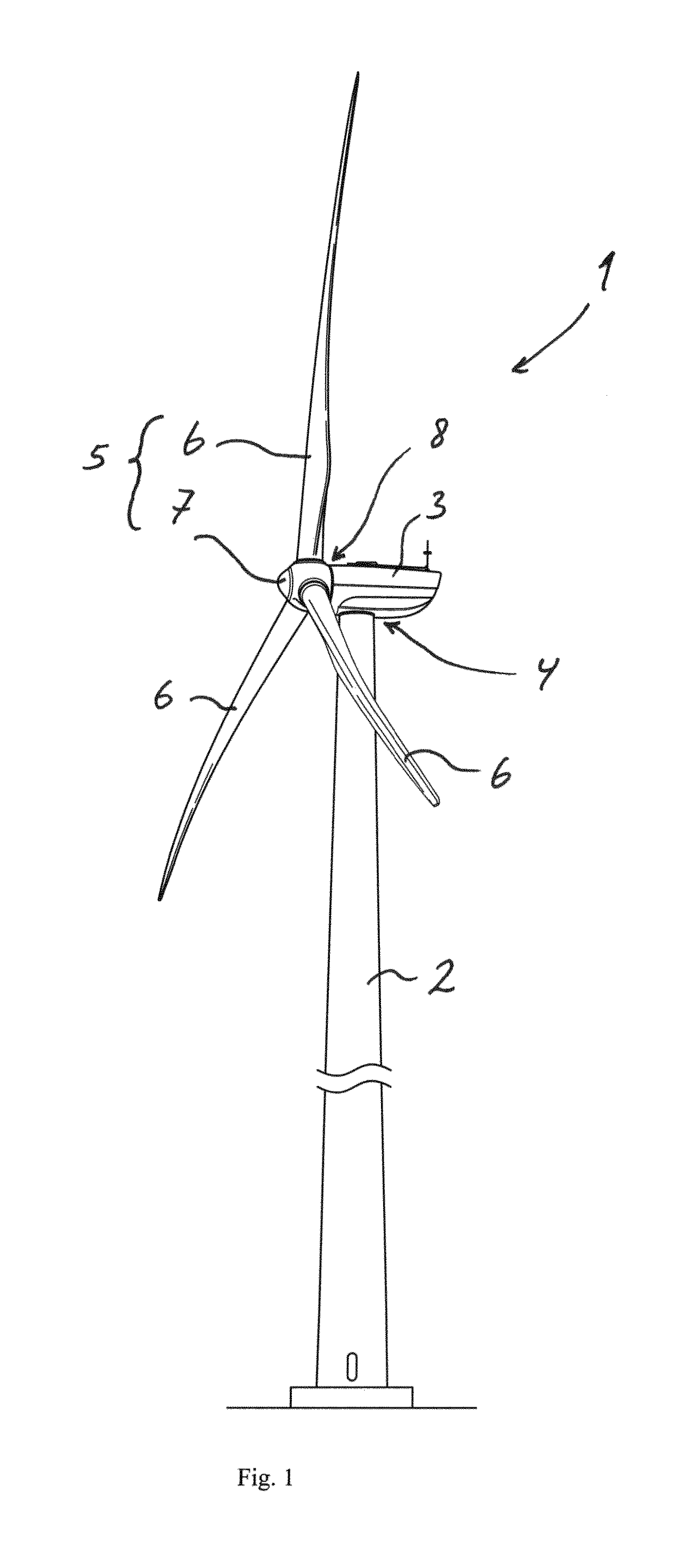
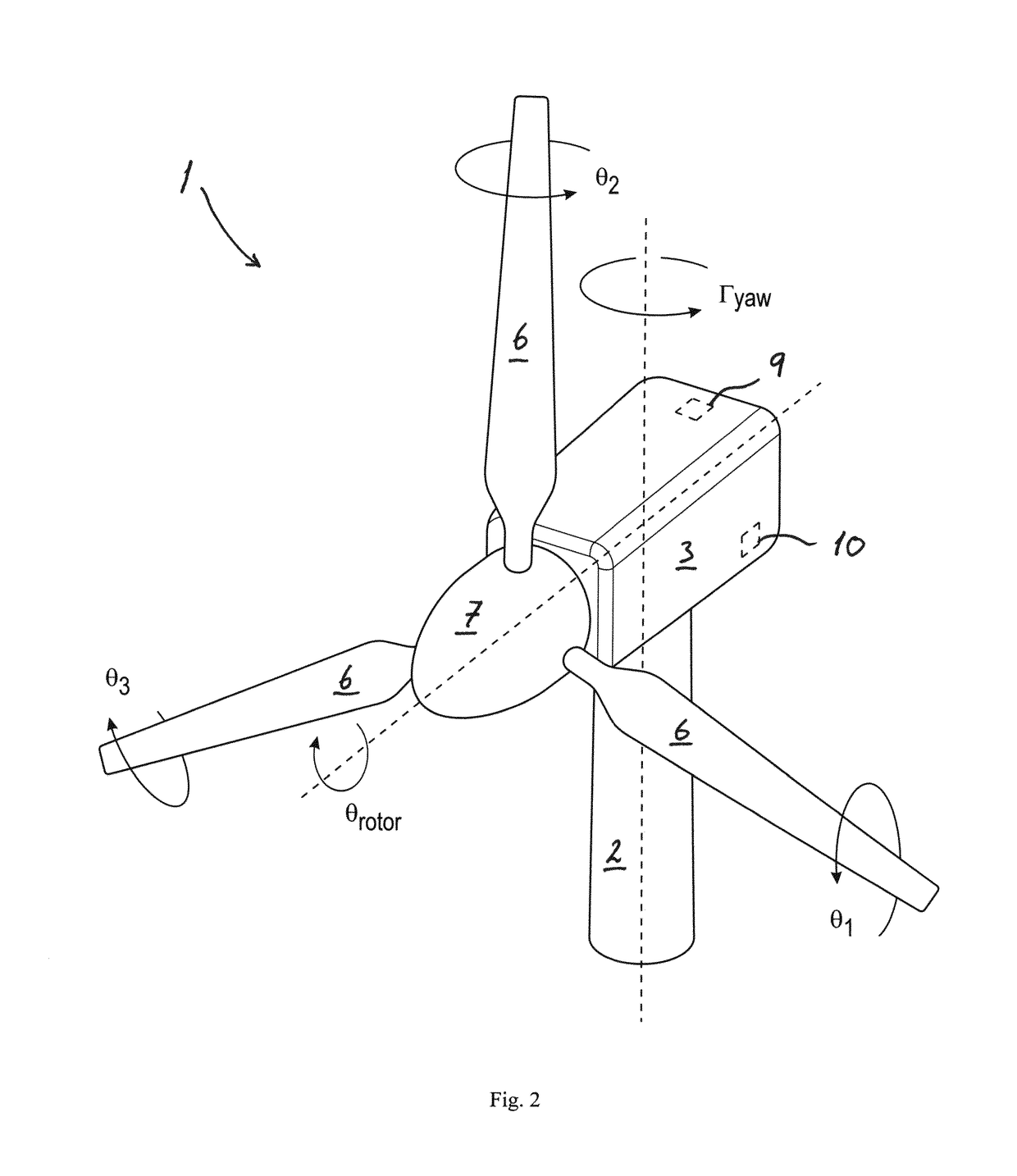
Methods and apparatus for reduction of asymmetric rotor loads in wind turbines
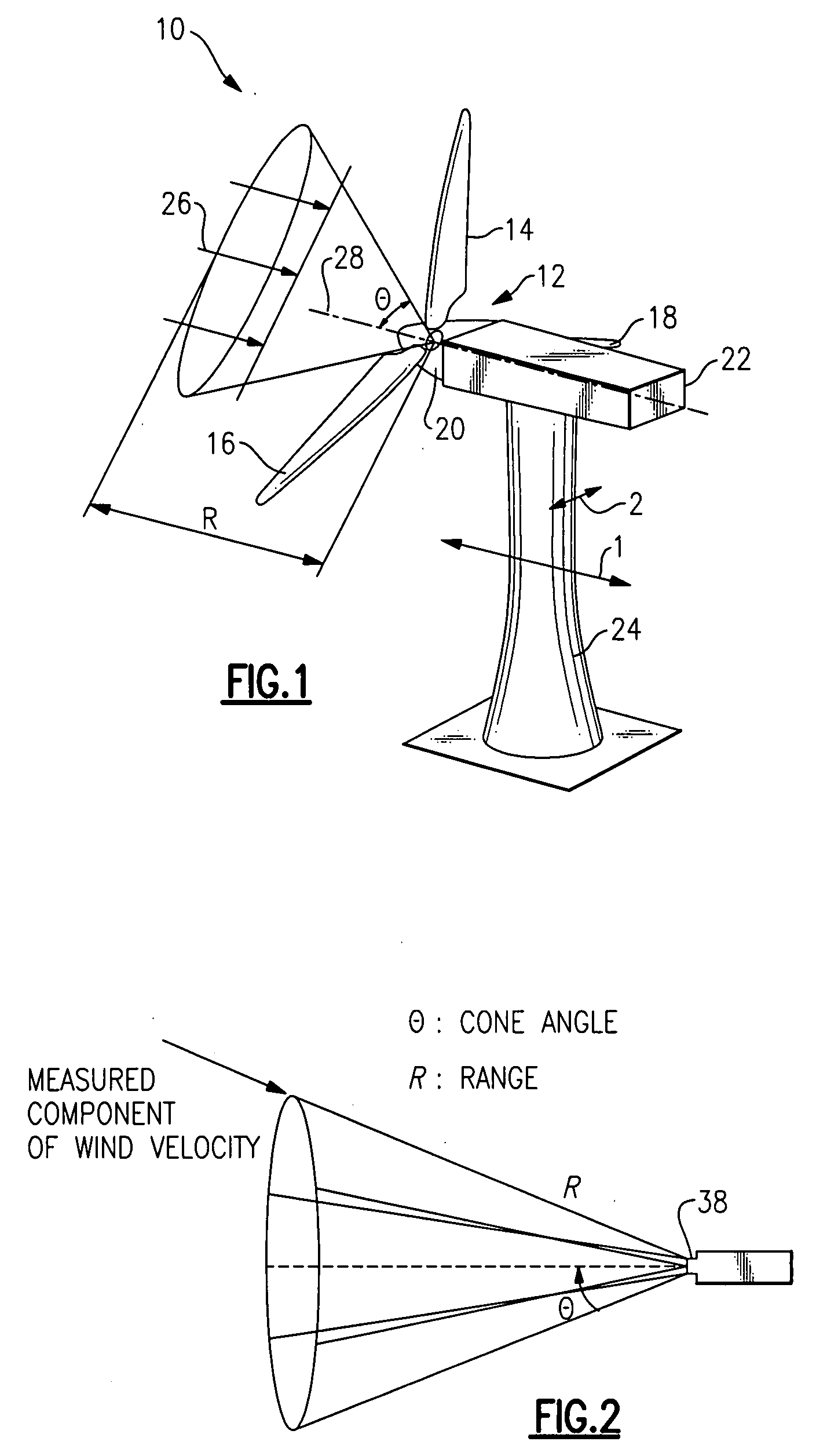
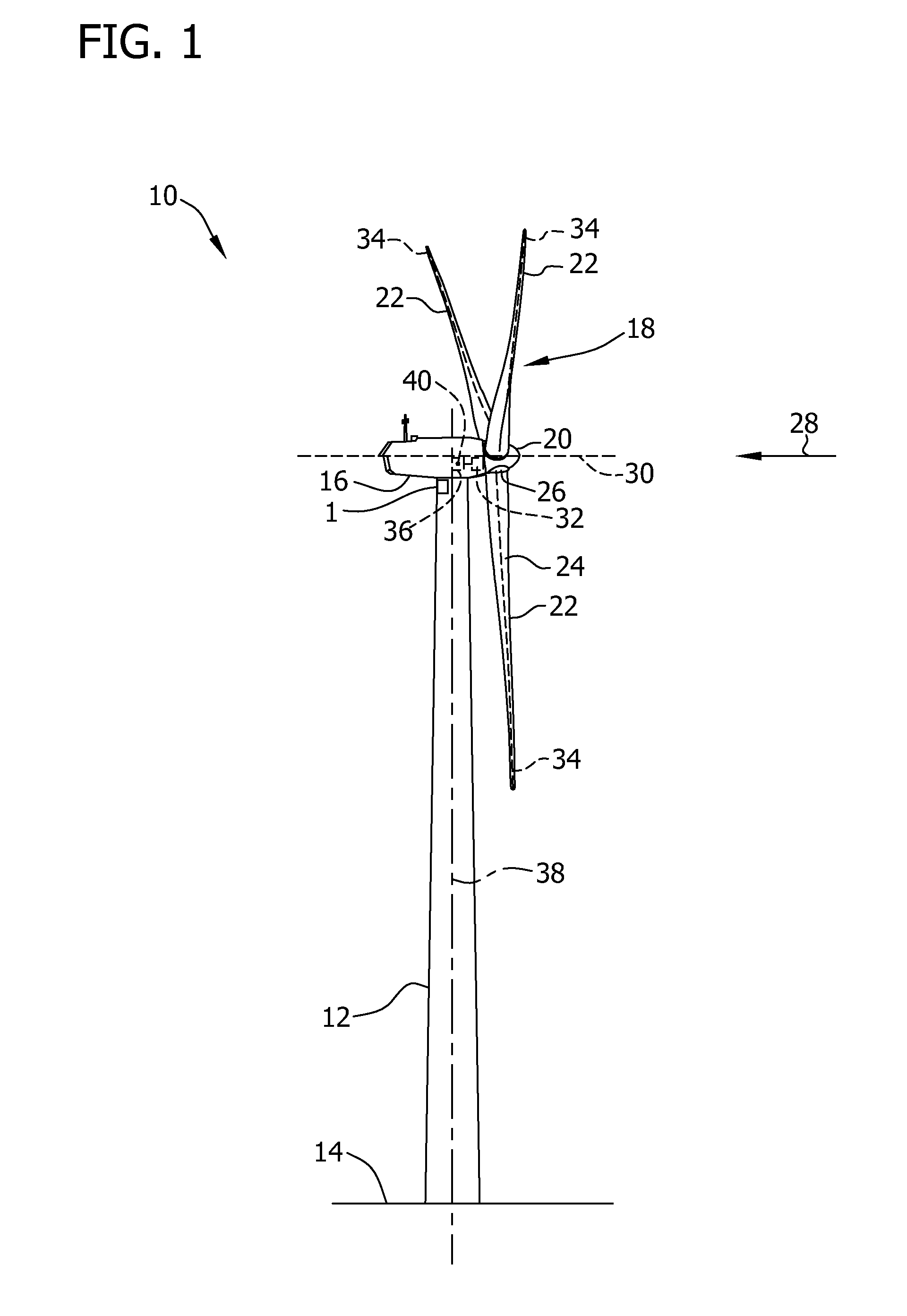
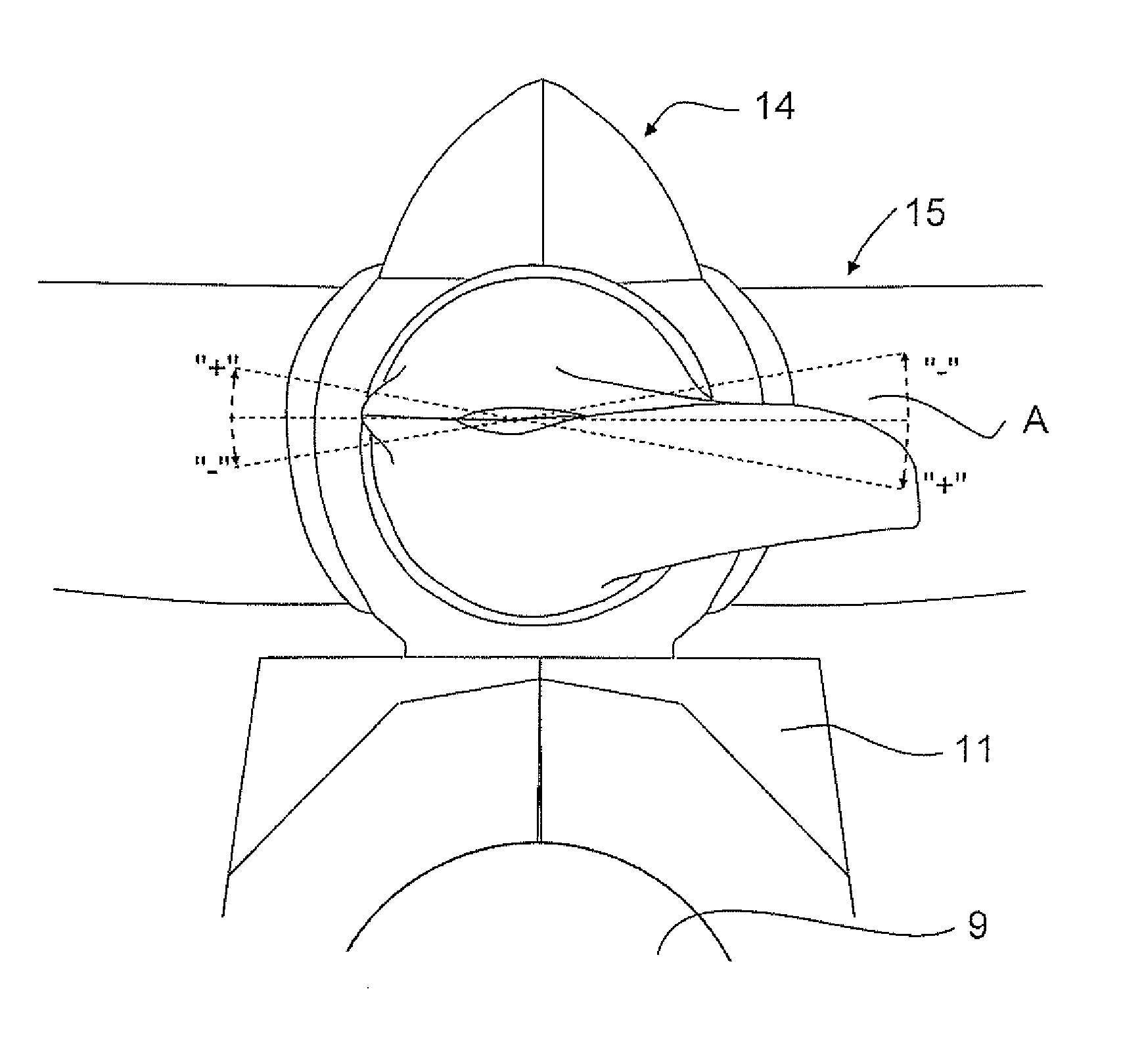
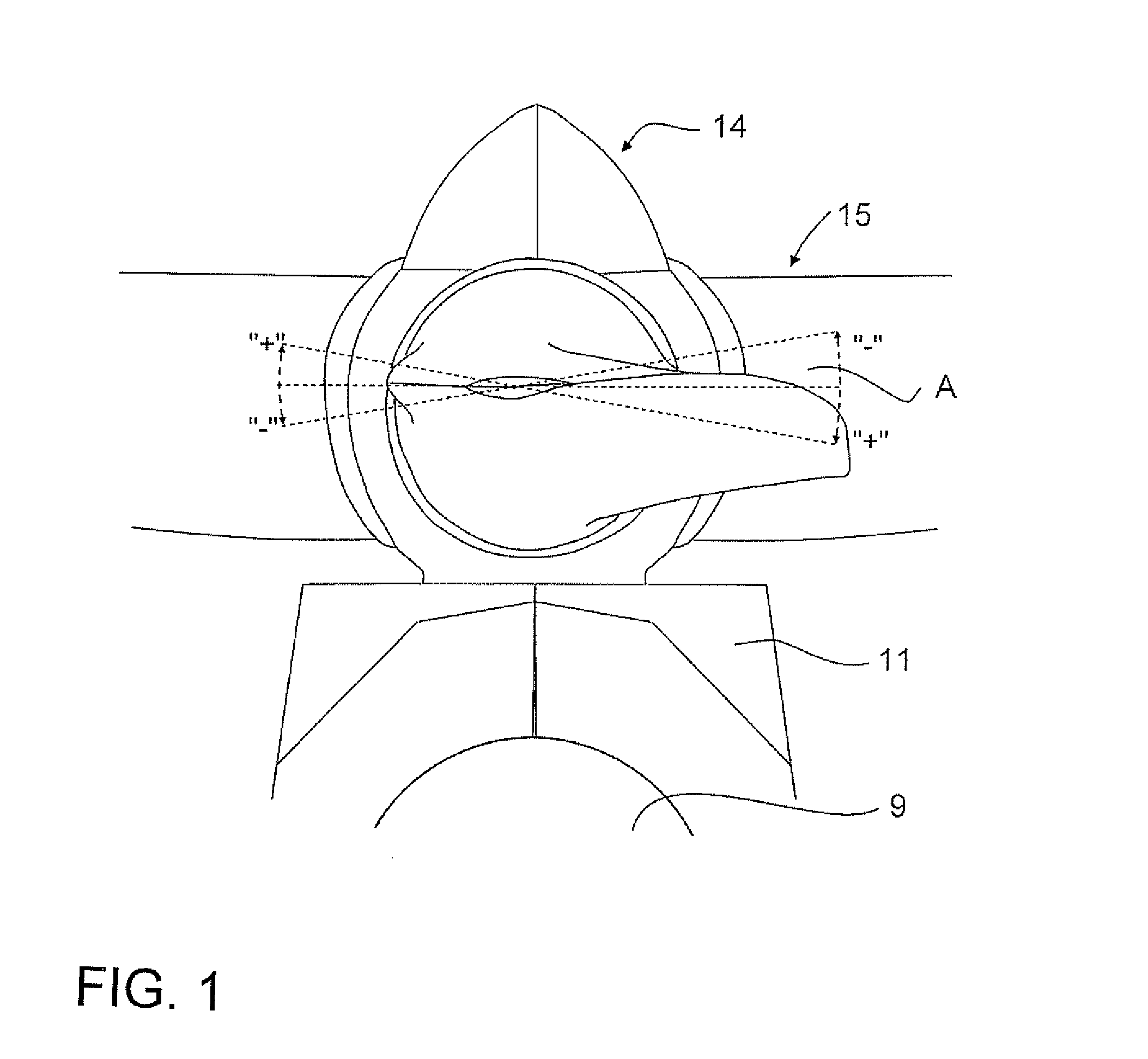
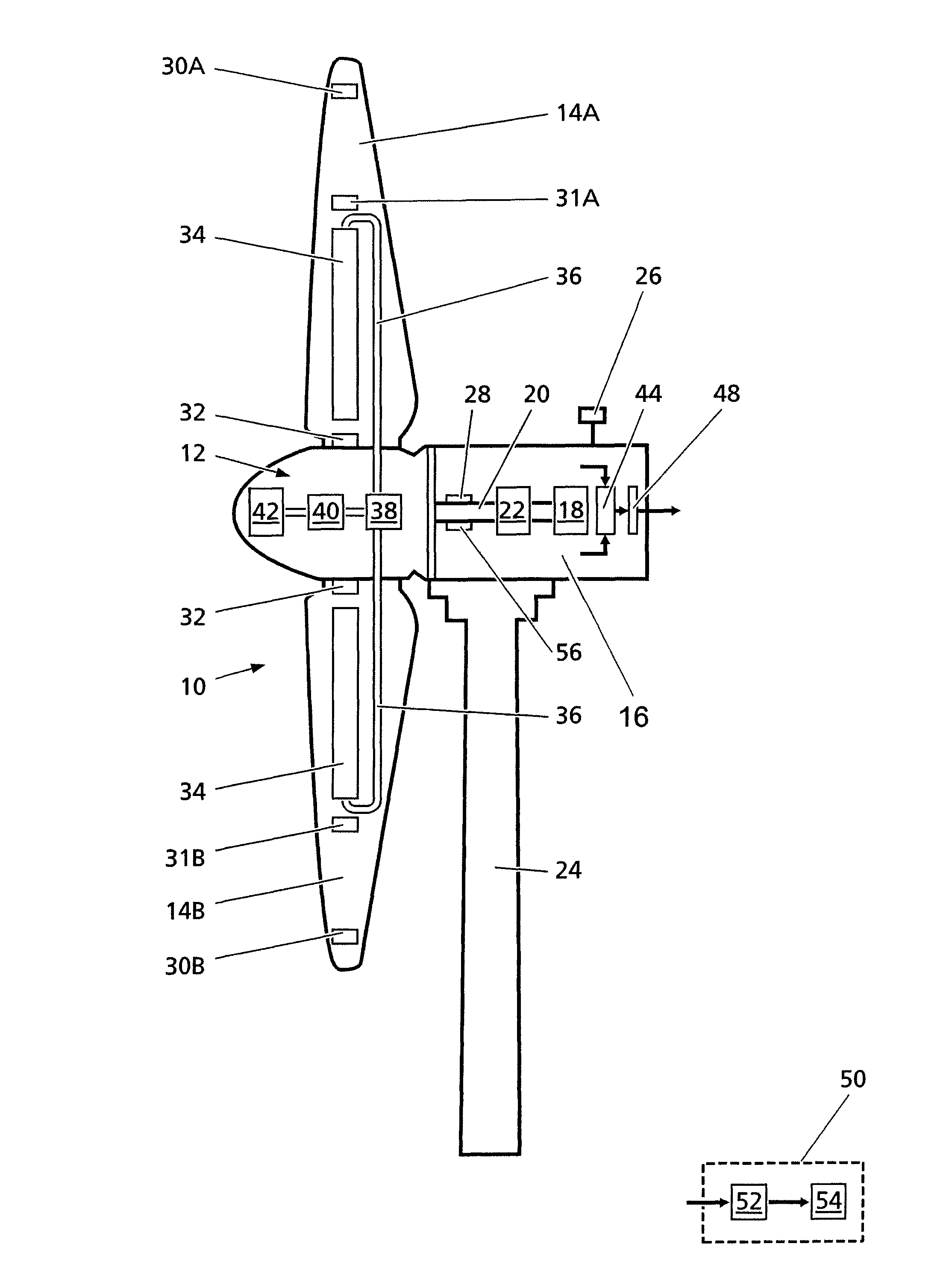
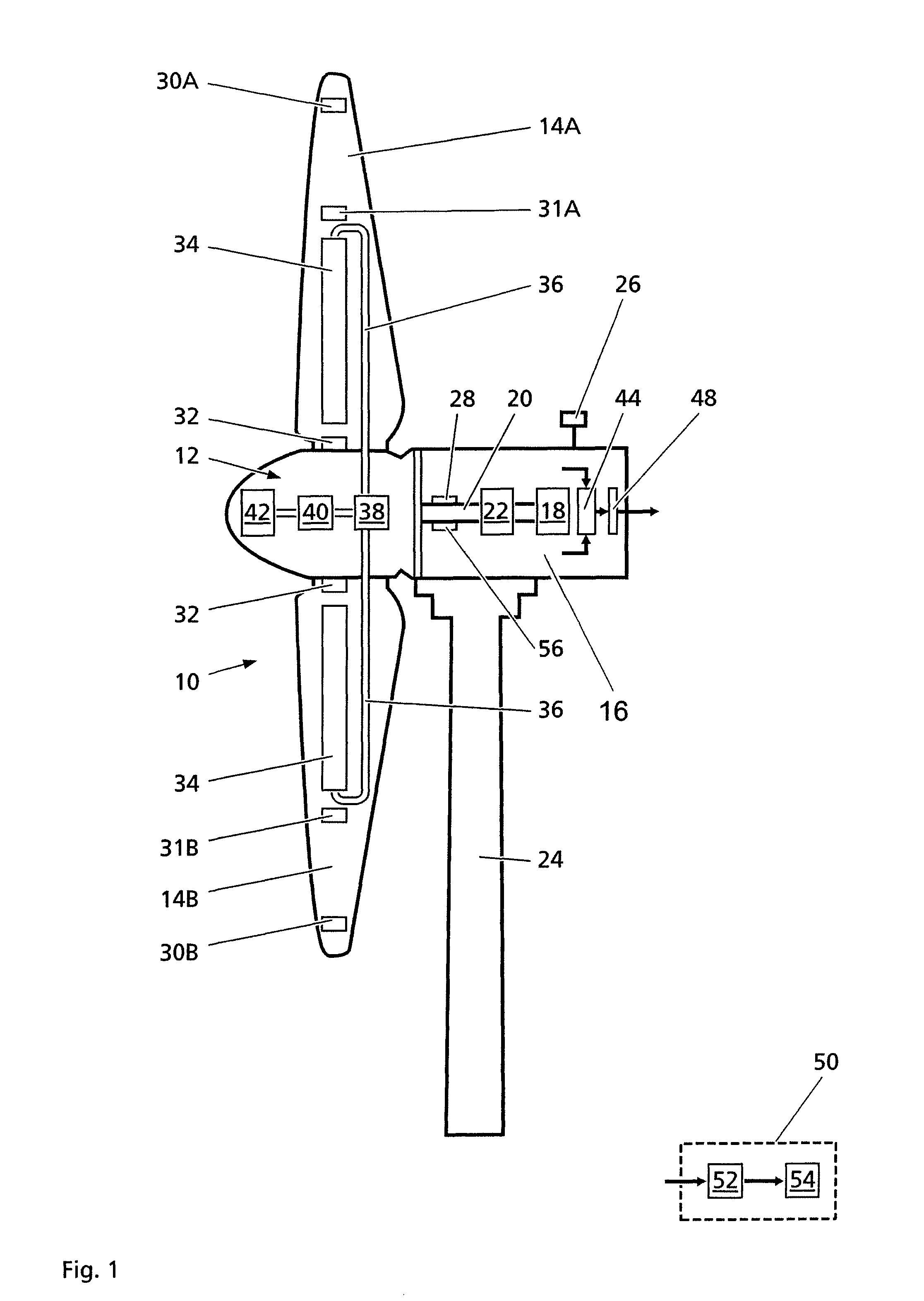
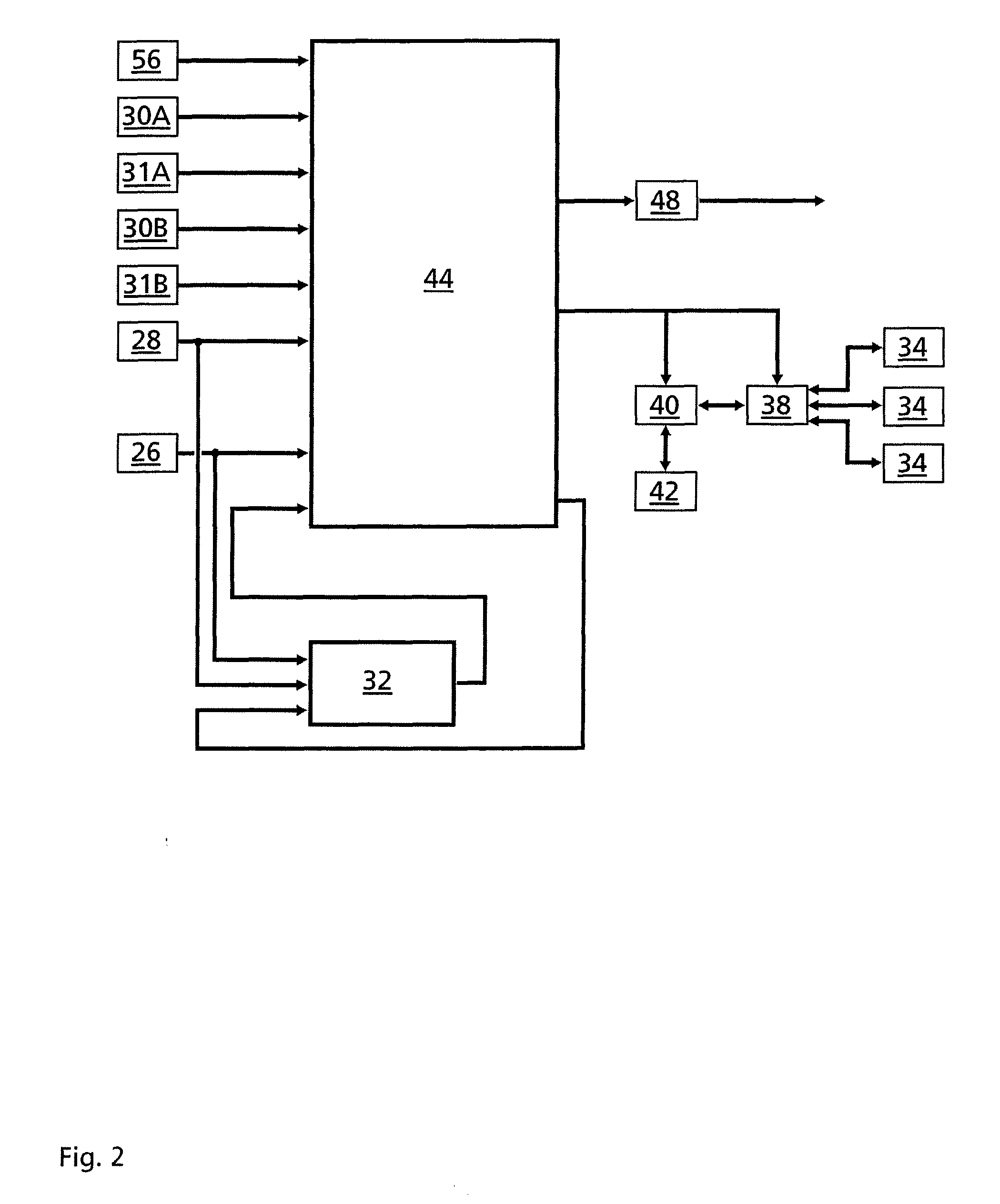
A method for reducing load and providing yaw alignment in a wind turbine includes measuring displacements or moments resulting from asymmetric loads on the wind turbine. These measured displacements or moments are used to determine a pitch for each rotor blade to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading and a favorable yaw orientation to reduce pitch activity. Yaw alignment of the wind turbine is adjusted in accordance with the favorable yaw orientation and the pitch of each rotor blade is adjusted in accordance with the determined pitch to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
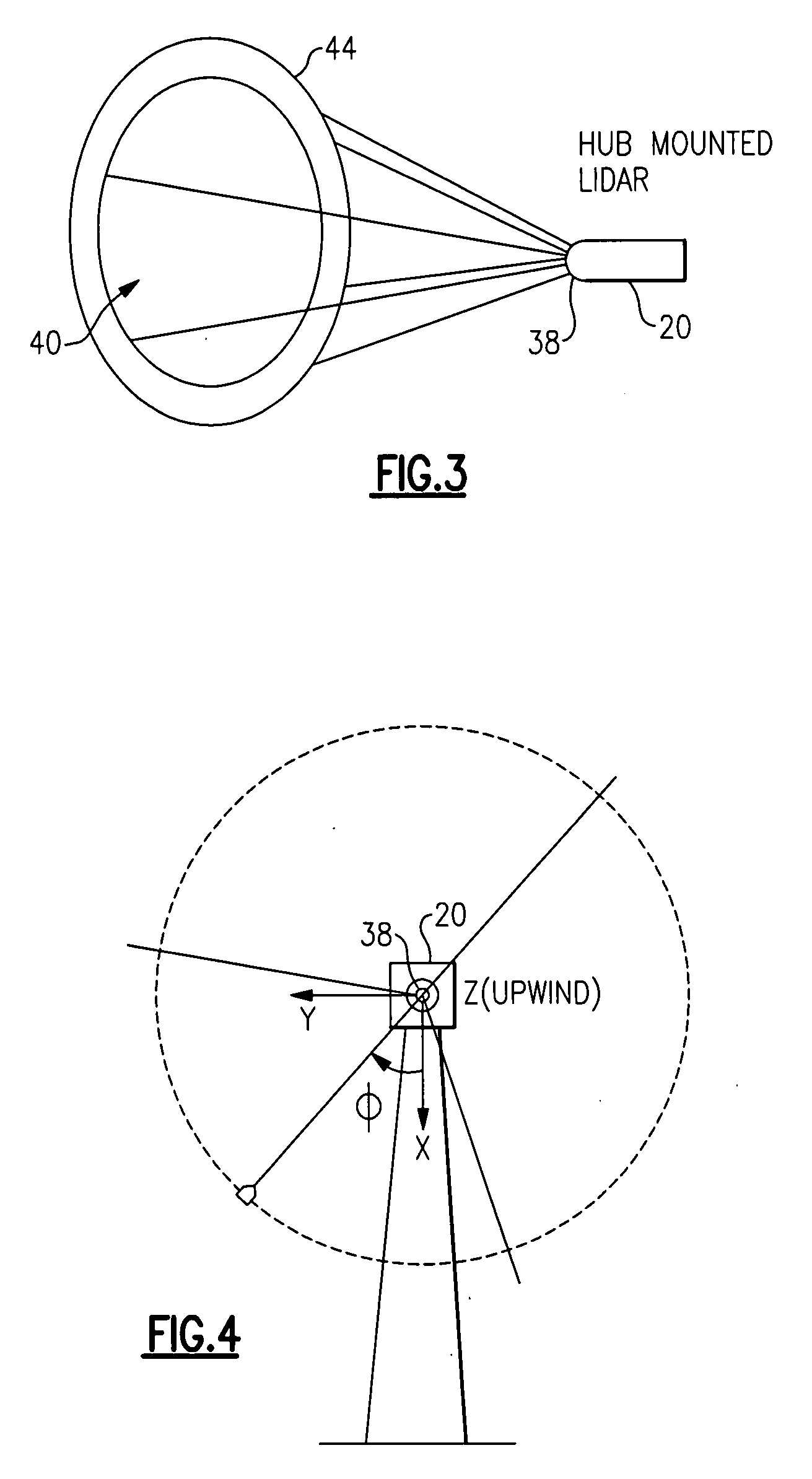
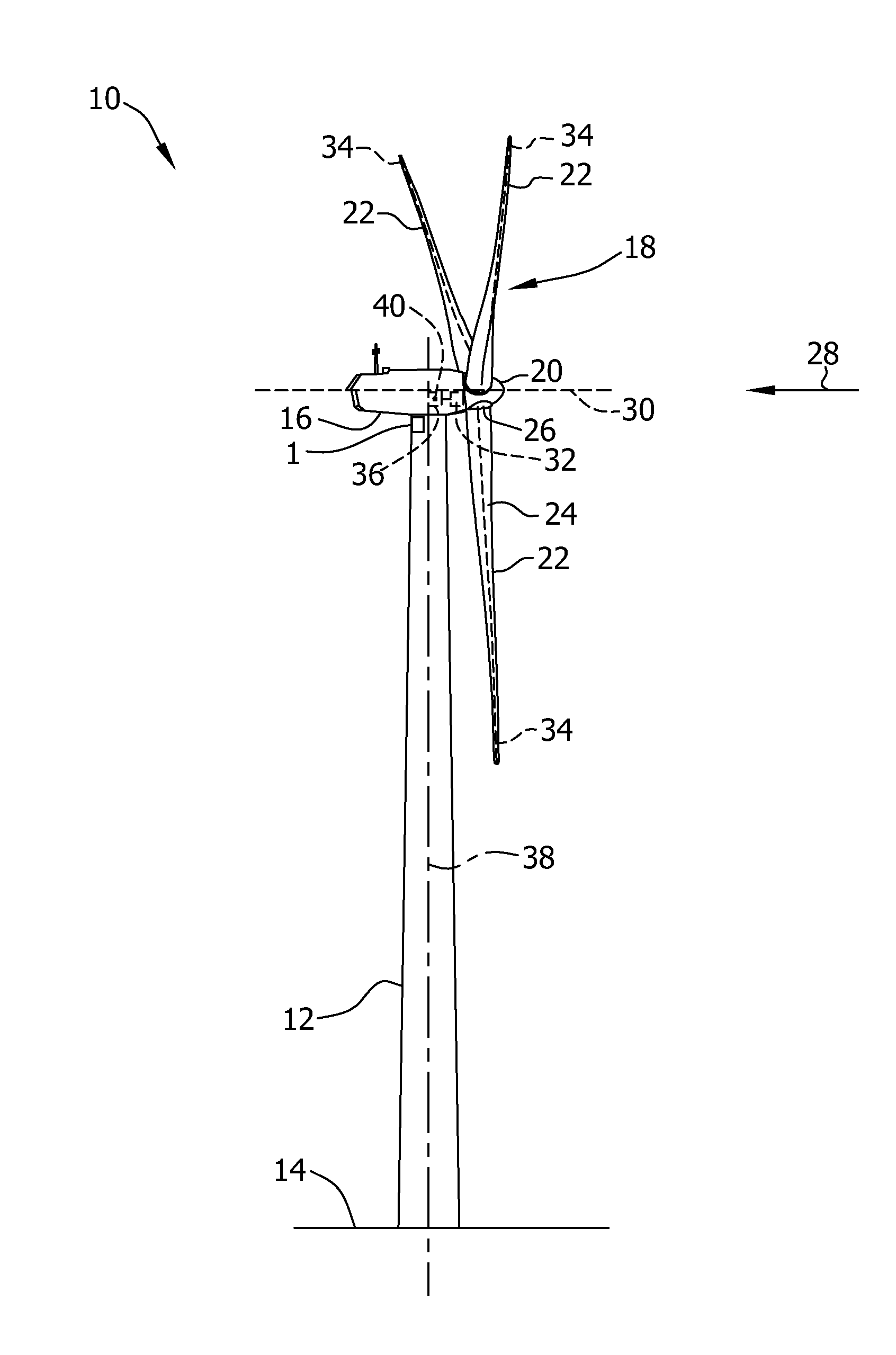
System and method for loads reduction in a horizontal-axis wind turbine using upwind information
A system and method provide a proactive mechanism to control pitching of the blades of a wind turbine to compensate for rotor imbalance during normal operation by pitching the blades individually or asymmetrically, based on turbulent wind gust measurements in front of the rotor, determined before it reaches the rotor blades.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for reduction of asymmetric rotor loads in wind turbines
A method for reducing load and providing yaw alignment in a wind turbine includes measuring displacements or moments resulting from asymmetric loads on the wind turbine. These measured displacements or moments are used to determine a pitch for each rotor blade to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading and a favorable yaw orientation to reduce pitch activity. Yaw alignment of the wind turbine is adjusted in accordance with the favorable yaw orientation and the pitch of each rotor blade is adjusted in accordance with the determined pitch to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
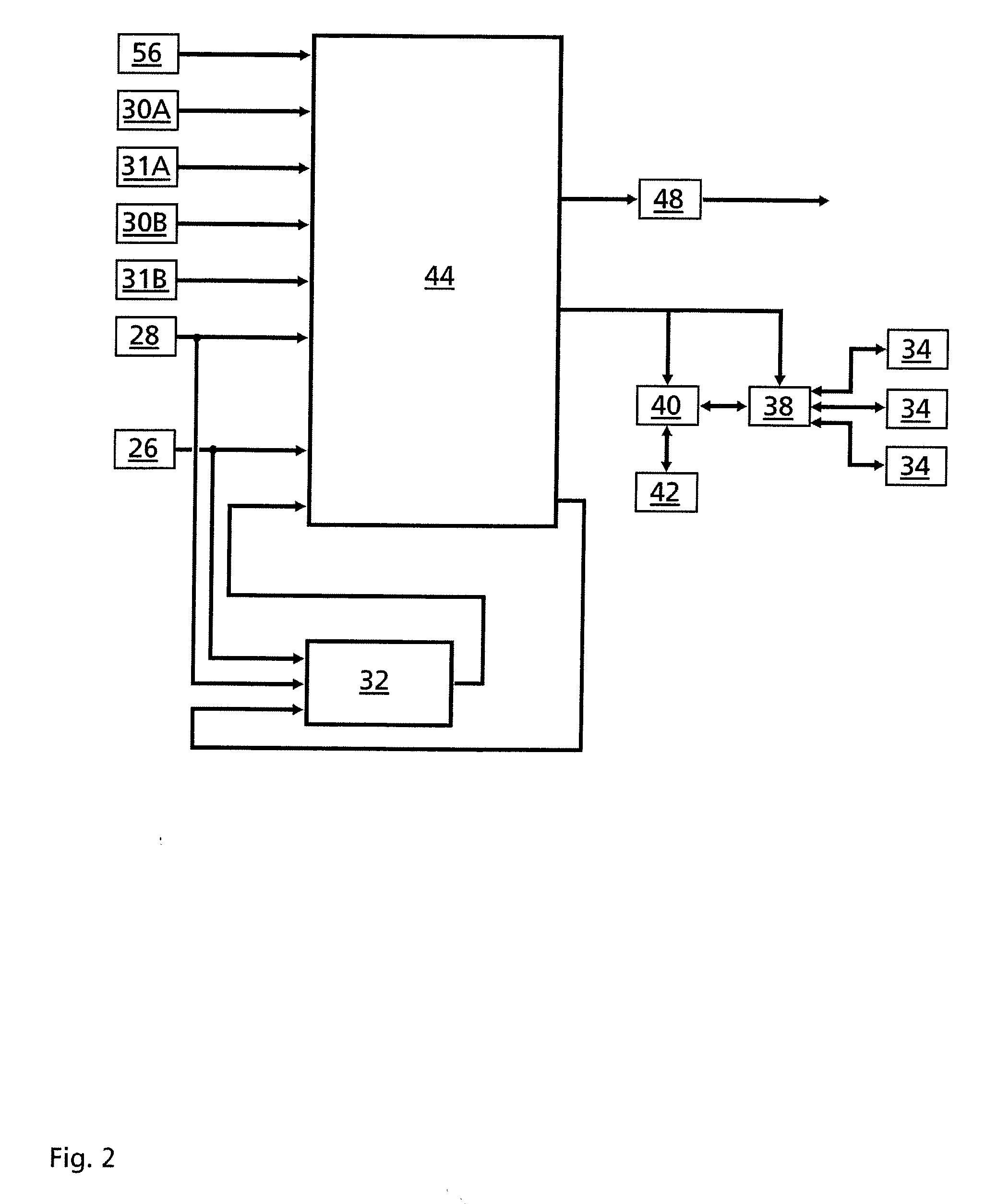
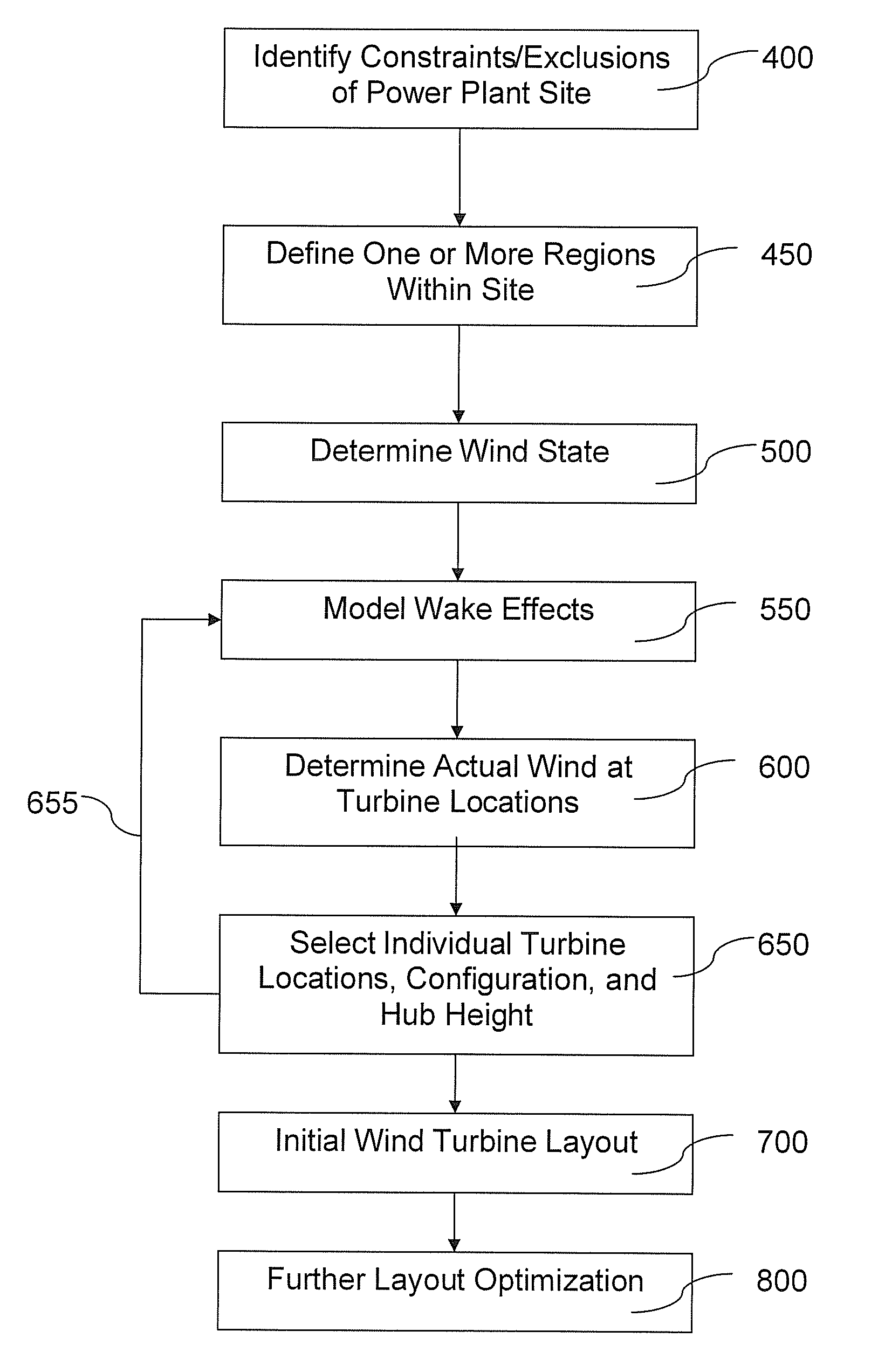
Method for enhancement of a wind plant layout with multiple wind turbines
ActiveUS20100138201A1High power outputMinimizes wake lossWind motor controlEngine fuctionsPower stationTurbine
The layout and configuration of wind turbines in a wind power plant includes identifying constraints of a power plant site and defining at least one region in the site for placement of a plurality of wind turbines. The wind state at the region in the site is determined. An actual wind condition at the various possible wind turbine locations within the site is determined by modeling the wind state with wake effects at the respective wind turbine locations, the wake effects resulting from cumulative placement of other wind turbines at various locations in the region. Individual wind turbine configuration and location within the region is then selected as a function of the actual wind conditions that each of the individual wind turbine locations to optimize power output of the individual wind turbines. The selection of turbine configuration includes selection of a turbine hub height that minimizes wake loss of the individual wind turbines as a function of the actual wind conditions predicted for the turbine location.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for loads reduction in a horizontal-axis wind turbine using upwind information
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
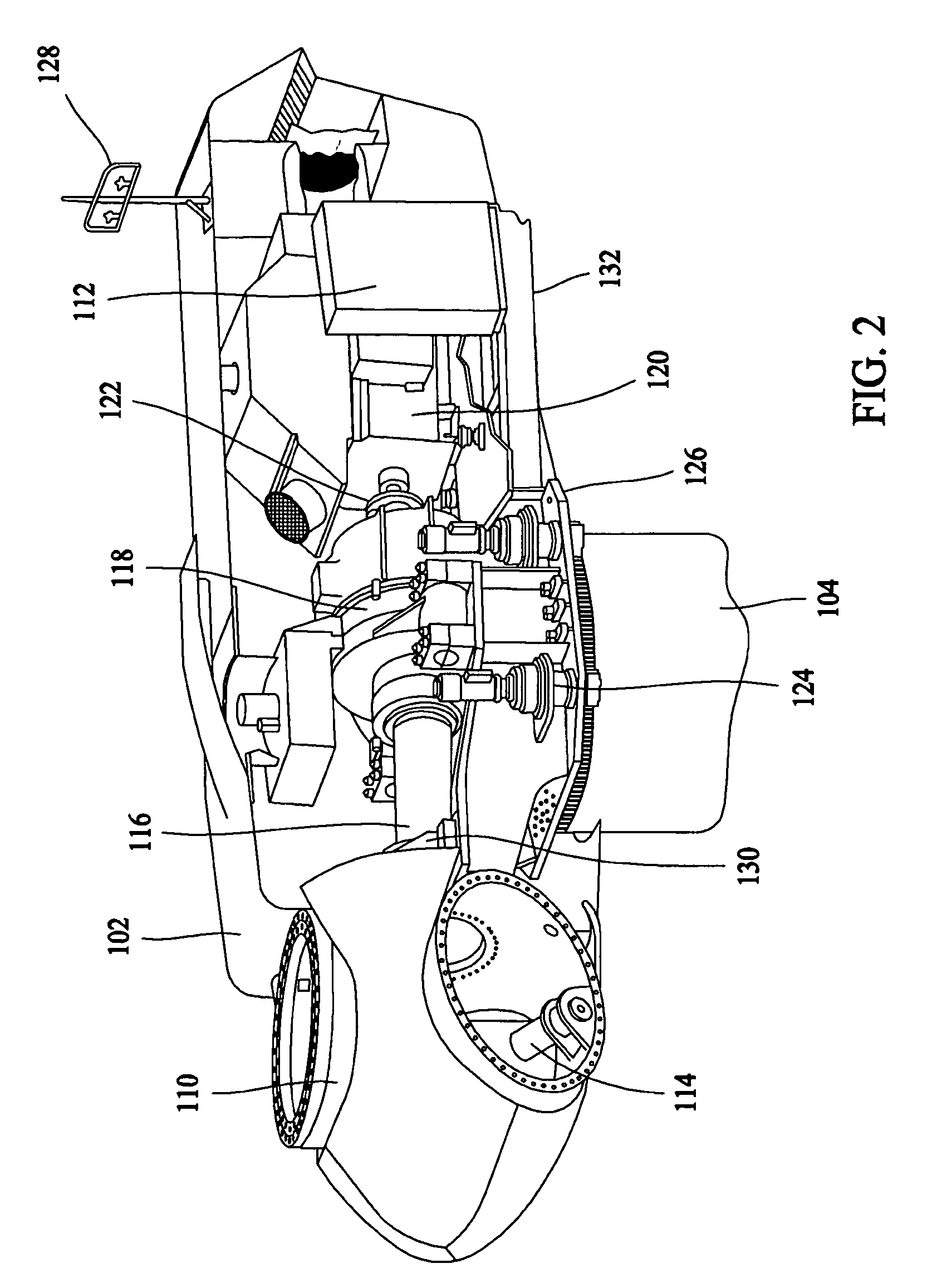
Methods and apparatus for balancing a rotor
ActiveUS7437264B2Facilitates reducing the at least one bending momentWind motor controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementMechanical engineeringBlade pitch
A method for balancing a rotor of a rotary machine, wherein the rotor includes at least two rotor blades and a rotor shaft, includes receiving at least one measurement of either a load, an acceleration, or a displacement that pertains to at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft, determining at least one value of the at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft based, at least in part, on the received at least one measurement, and determining a pitch offset angle value of at least one rotor blade that facilitates reducing the at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
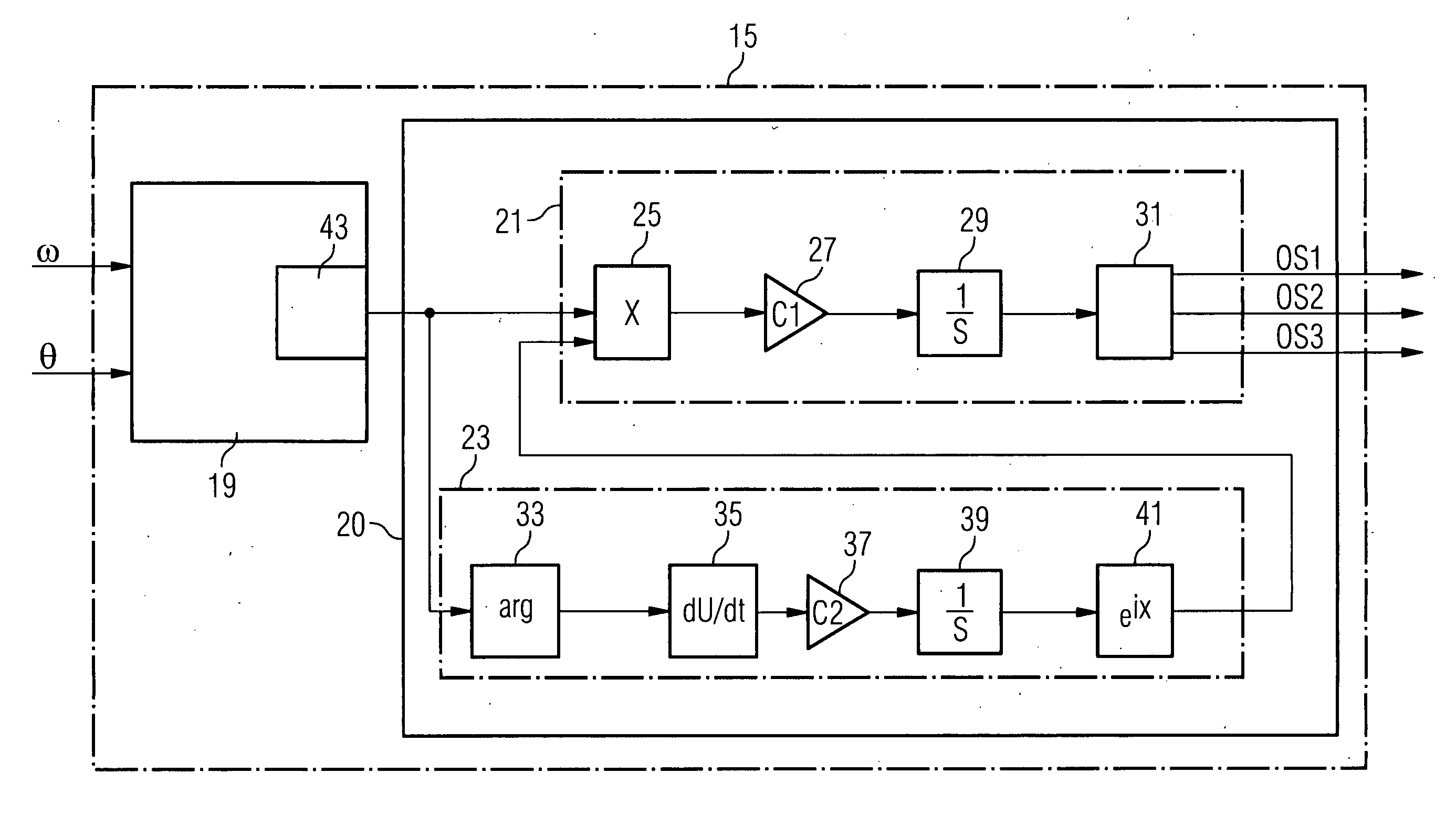
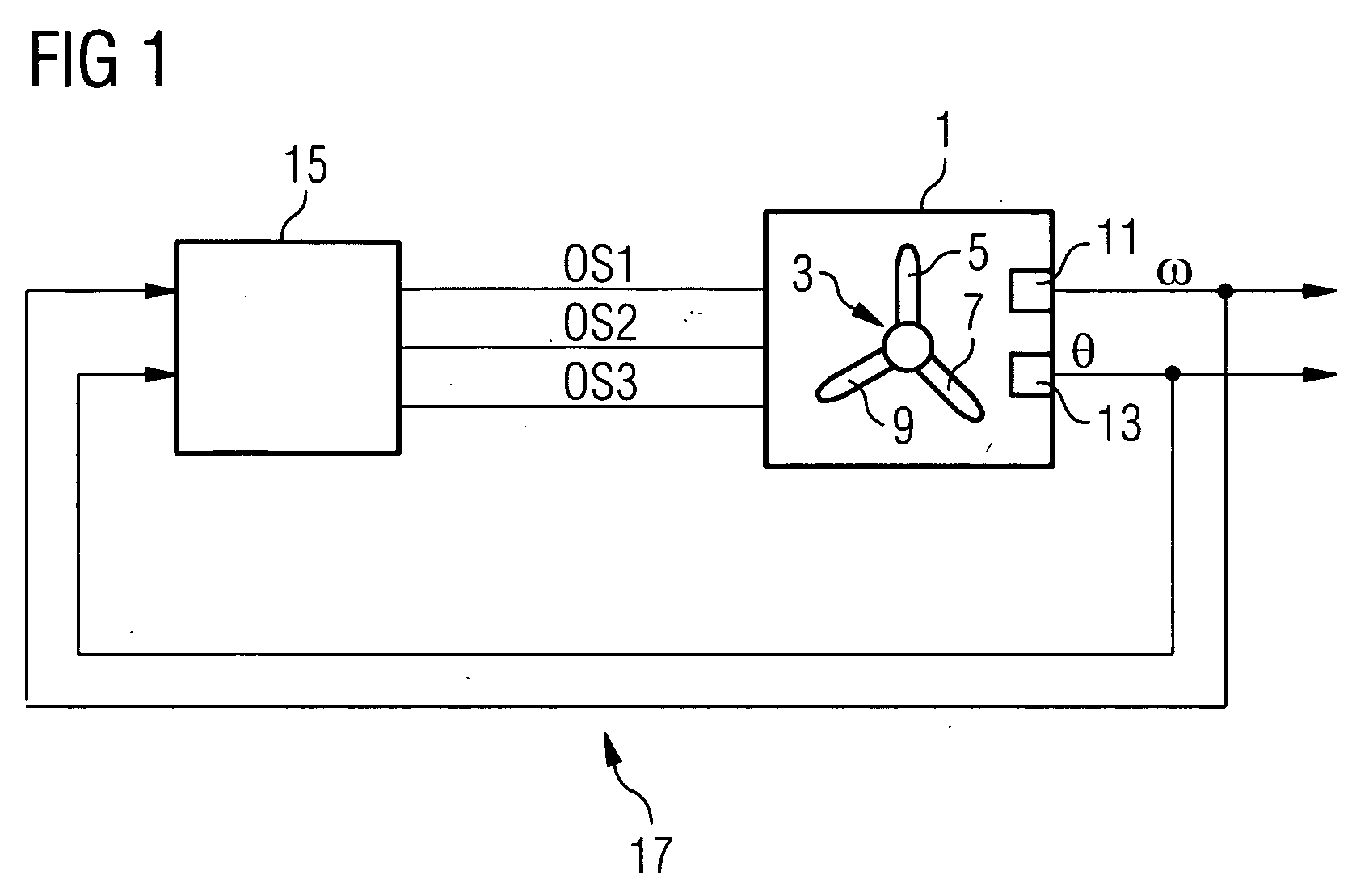
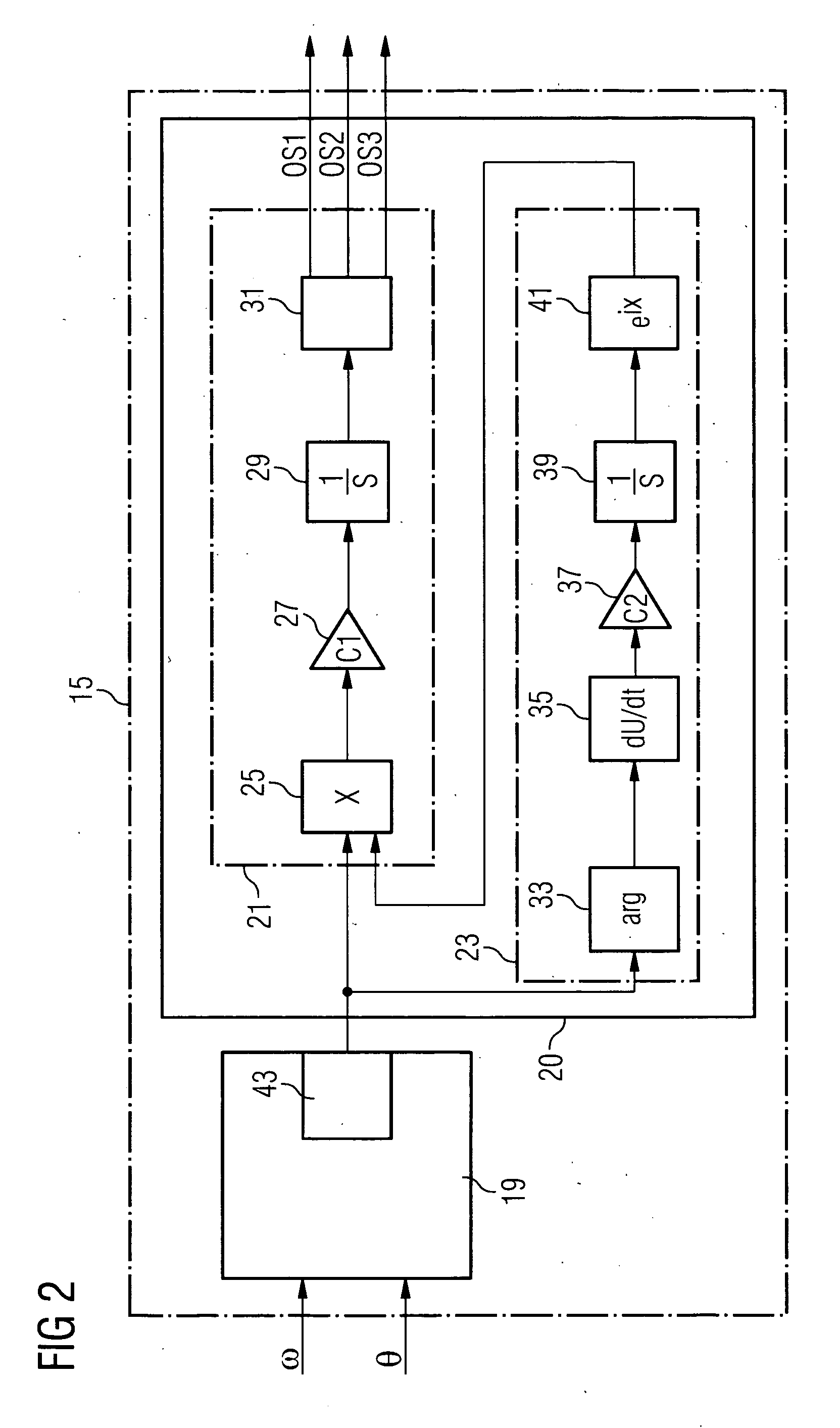
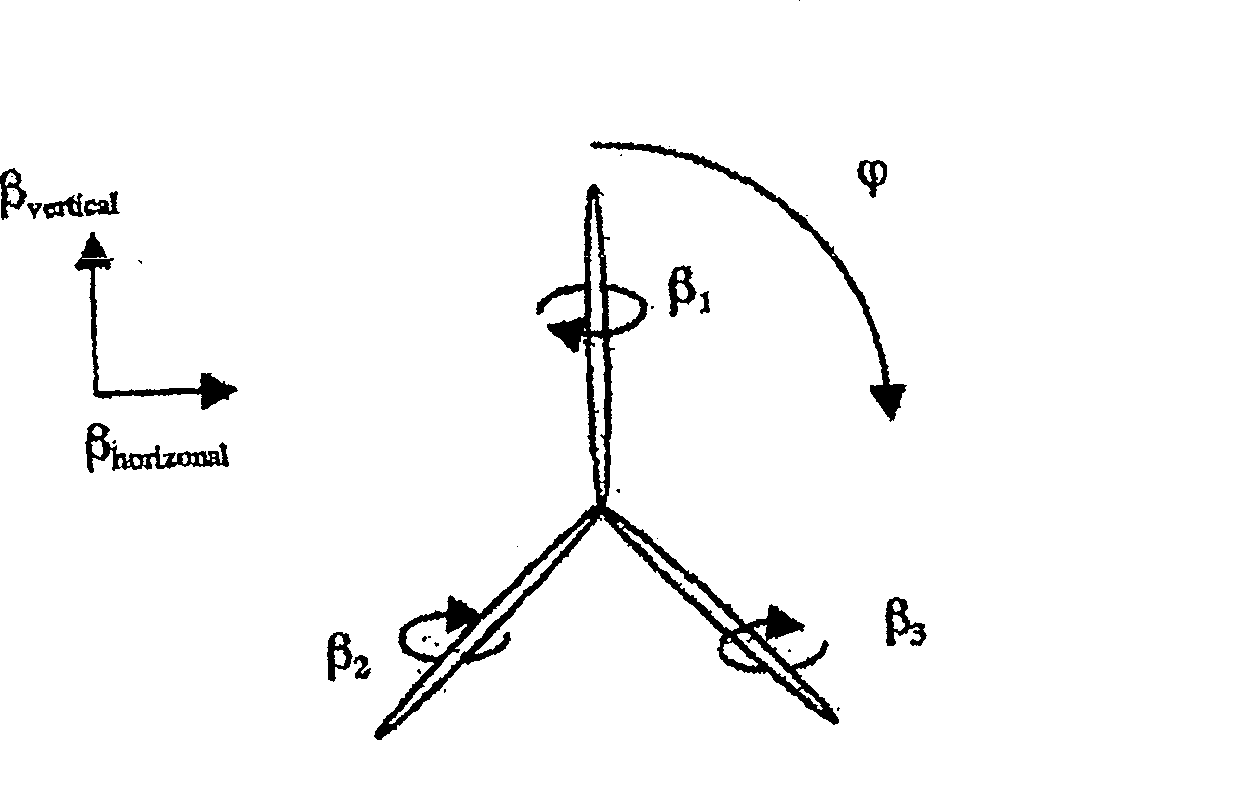
Method of reducing a structural unbalance in a wind turbine rotor and device for performing the method
Disclosed is a method of reducing a structural unbalance in a wind turbine rotor with pitch control and a control device for performing the method are provided. The method comprises the steps of: detecting a magnitude of the structural unbalance and its phase in relation the rotor's azimuth (θ) on the basis of a measurement of the rotor's azimuth (θ) and a measurement of the rotor speed or the generator speed (ω), establishing individual pitch angle offsets for each blade of the rotor on the basis of the magnitude and the phase, and adding the individual pitch angle offsets to the respective pitch angles of the blades of the rotor.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Methods and apparatus for balancing a rotor
ActiveUS20070294049A1Promote lowerFacilitates reducing the at least one bending momentWind motor controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method for balancing a rotor of a rotary machine, wherein the rotor includes at least two rotor blades and a rotor shaft, includes receiving at least one measurement of either a load, an acceleration, or a displacement that pertains to at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft, determining at least one value of the at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft based, at least in part, on the received at least one measurement, and determining a pitch offset angle value of at least one rotor blade that facilitates reducing the at least one bending moment acting on the rotor shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method For Damping Edgewise Oscillations In One Or More Blades Of A Wind Turbine, An Active Stall Controlled Wind Turbine And Use Hereof
A method for damping edgewise oscillations in one or more blades of a wind turbine includes the steps of detecting if one or more of the blades oscillates edgewise during operation of the wind turbine, and substantially cyclically generating a pitch angle difference between at least two of the blades. Further provided is an active stall controlled wind turbine and use hereof.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
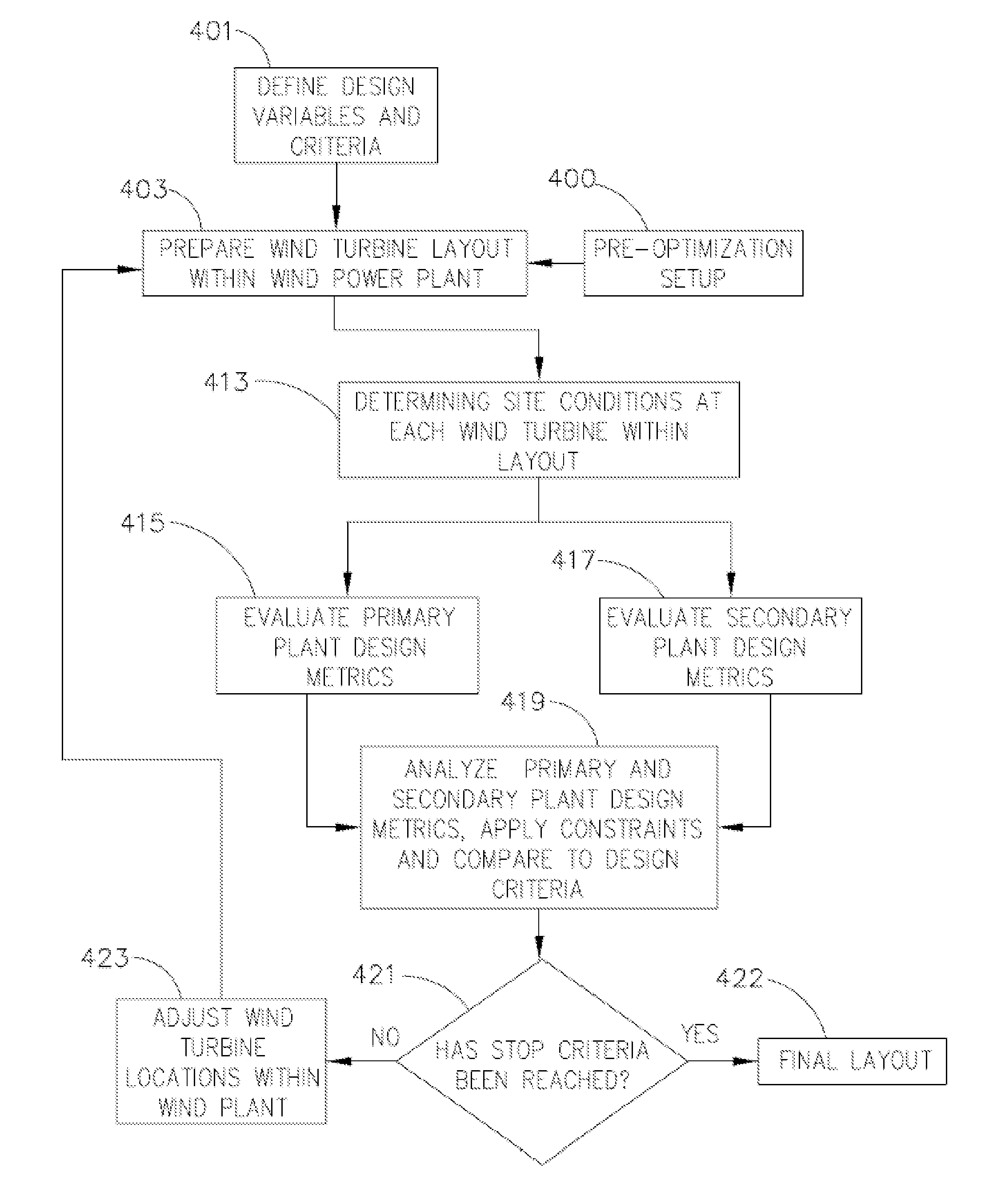
Method for wind turbine placement in a wind power plant
ActiveUS8050899B2Computationally efficient, accurate and robust platformLevel controlGas turbine plantsPower stationDesign standard
A method for determining wind turbine location within a wind power plant based on at least one design criteria. A wind turbine layout including at least one wind turbine location is prepared and site conditions at each wind turbine location are determined. One or more plant design metrics are evaluated in response to the site conditions. The plant design metrics are analyzed in response to the site conditions. The method further includes applying constraints to the wind turbine layout and comparing the plant design metrics to the design criteria and constraints. Thereafter, the wind turbine locations are selectively adjusted within the layout in response to the comparing step until a stop criteria is reached.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for validating wind farm performance improvements
The present disclosure is directed to systems and methods for validating wind farm performance improvements so as to optimize wind farm performance. In one embodiment, the method includes operating, via a controller, the wind farm in a first operating mode. Another step includes collecting a first set of operating data, via a processor, during the first operating mode. A further step includes operating, via the controller, the wind farm in a second operating mode. The method also includes collecting a second set of operating data, via the processor, during the second operating mode. Next, the method includes normalizing the first and second sets of operating data based on wind speed distributions. As such, another step includes comparing, via the processor, the normalized first and second sets of operating data so as to validate one or more wind farm performance measurements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
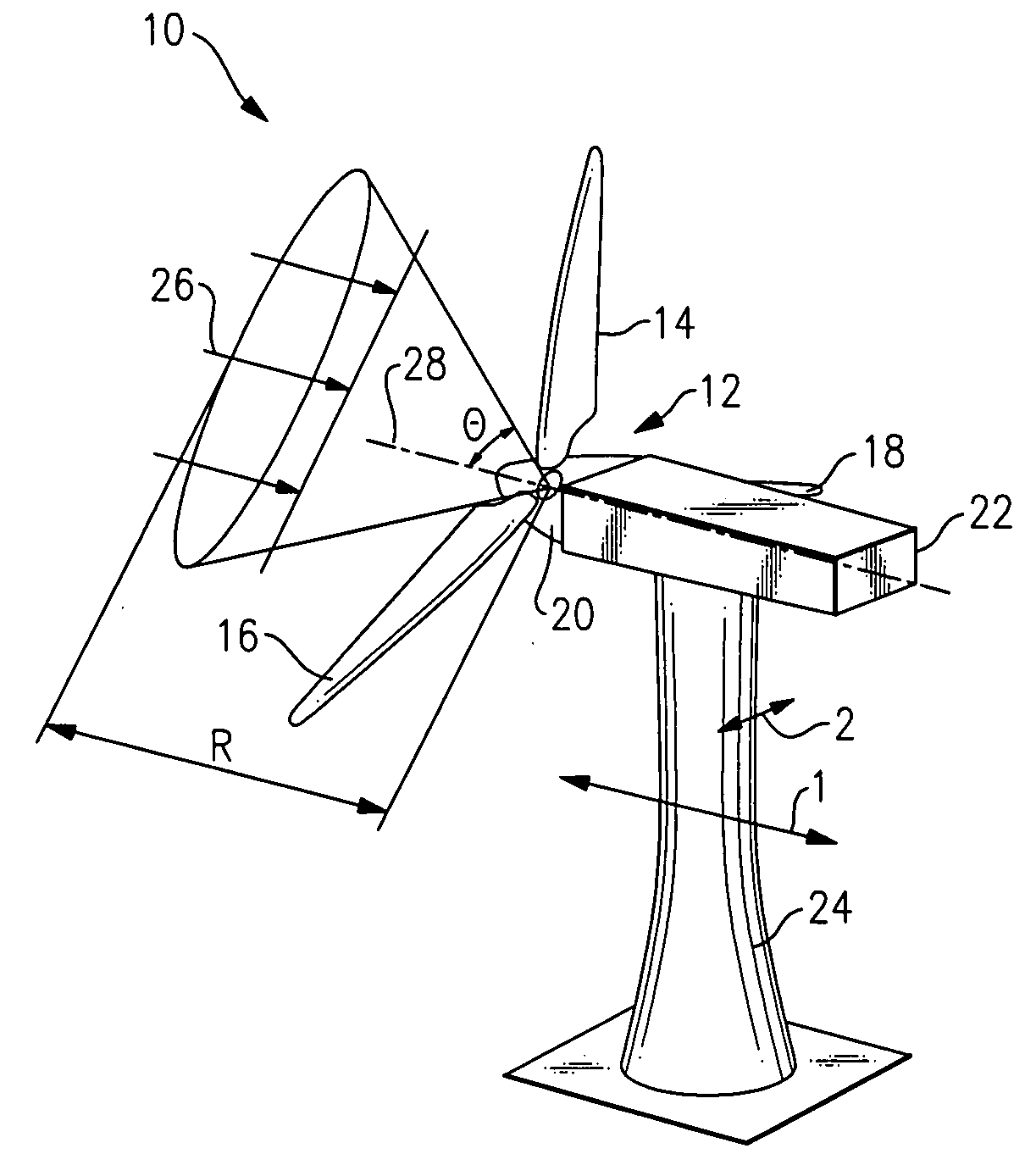
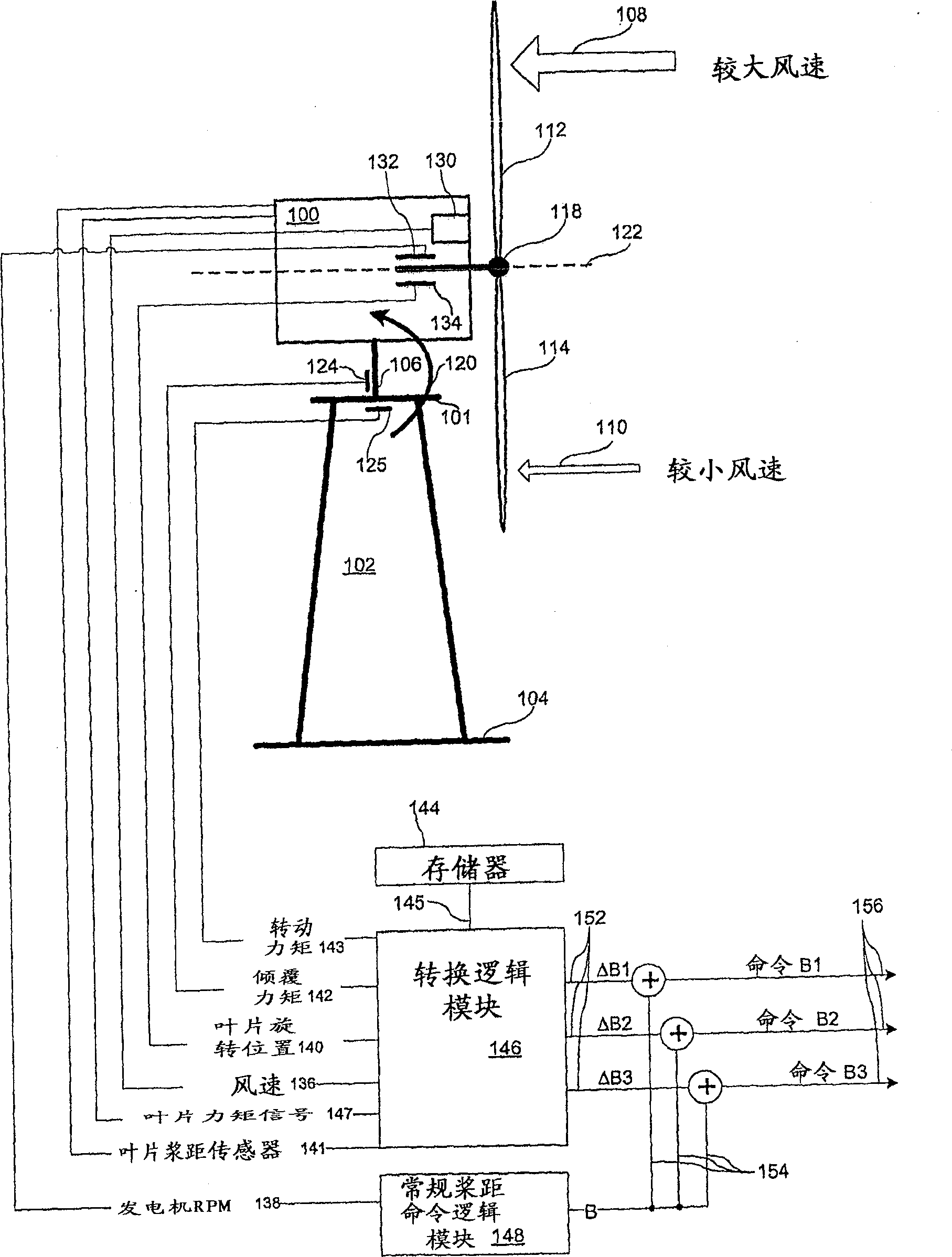
Wind turbine with blade pitch control to compensate for wind shear and wind misalignment
InactiveCN101523048ASmooth returnOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlWind shearBlade pitch
A wind turbine rotor load control. The pitch of the blades is controlled in a conventional manner by a command component, a rotor blade pitch command signal. A storage contains stored values of a set of moments for various wind speeds. A moment sensor provides a moment signal output. An instantaneous wind speed indicator provides an instantaneous wind speed value output. A conversion logic connected to the moment signal and to the instantaneous wind speed value, provides a calculated pitch modulation command. Combining logic connected to the calculated blade pitch modulation command and to the collective pitch command, provides a combined blade pitch command, which includes compensation for instantaneous moment deviations of the wind turbine.
Owner:CLIPPER WINDPOWER INC
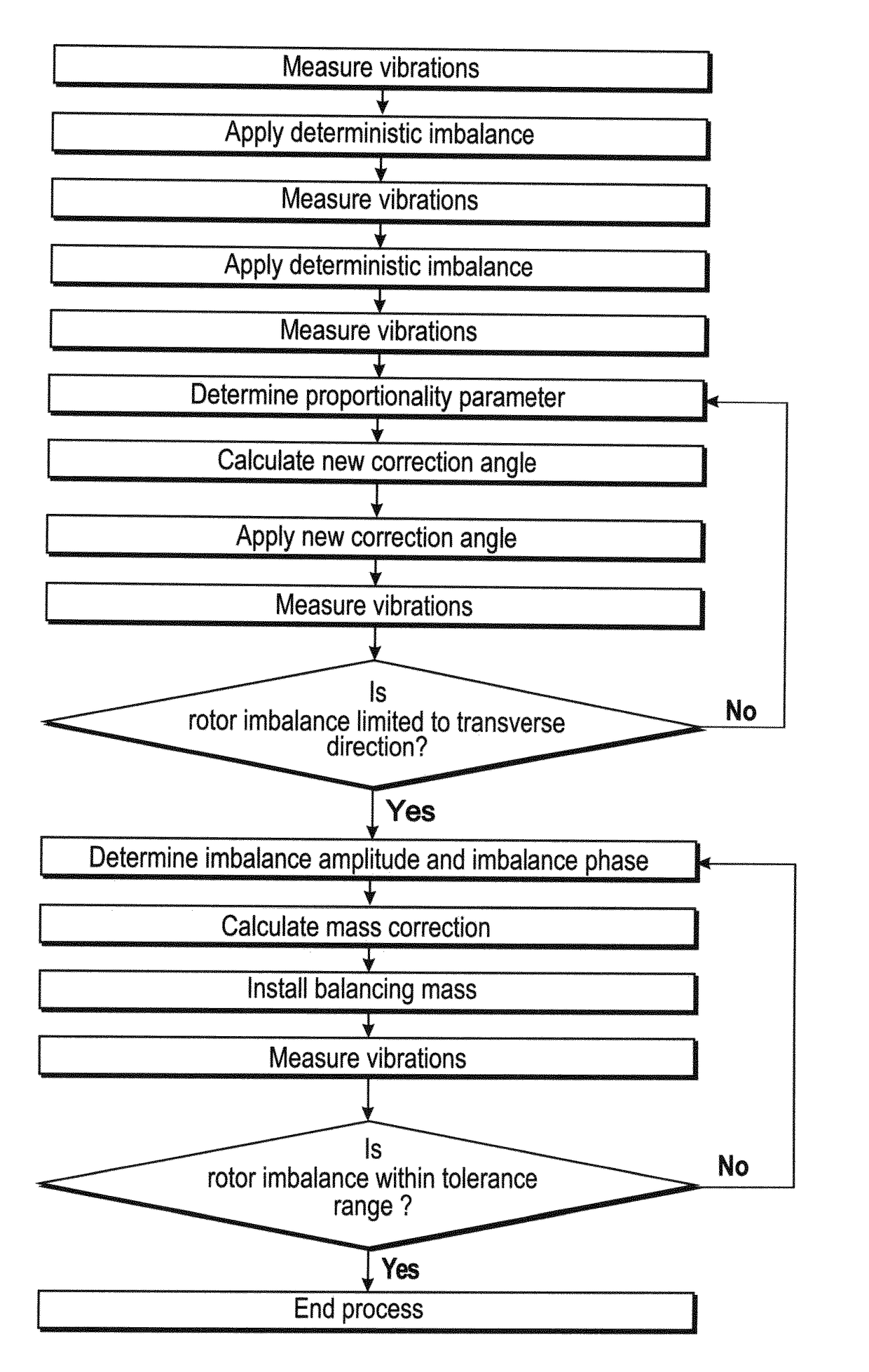
Method of Correcting Rotor Imbalance and Wind Turbine Thereof
ActiveUS20180142676A1Shorten the timeLow costWind motor controlMachines/enginesTurbine bladeEngineering
The present invention relates to a method of correcting rotor imbalance and a wind turbine thereof. The correction method comprises measuring the vibrations within at least one time window and determining an imbalance factor and an imbalance phase. The values of the parameters in the equation for calculating the correction action are then updated based on the imbalance factor and an imbalance phase. A correction angle for each of the wind turbine blades is calculated using these adjusted parameters. The correction angle is used to aerodynamically balance the rotor, and a model may be used to determine the initial values of the parameters. Another imbalance factor and imbalance phase is determined based on another set of measurements. This imbalance factor is then used to calculate a mass moment for correcting the mass imbalance in the wind turbine blades. The weight and location of a balancing mass is finally calculated based on this mass moment and installed in the respective wind turbine blades.
Owner:ENVISION ENERGY DENMARK
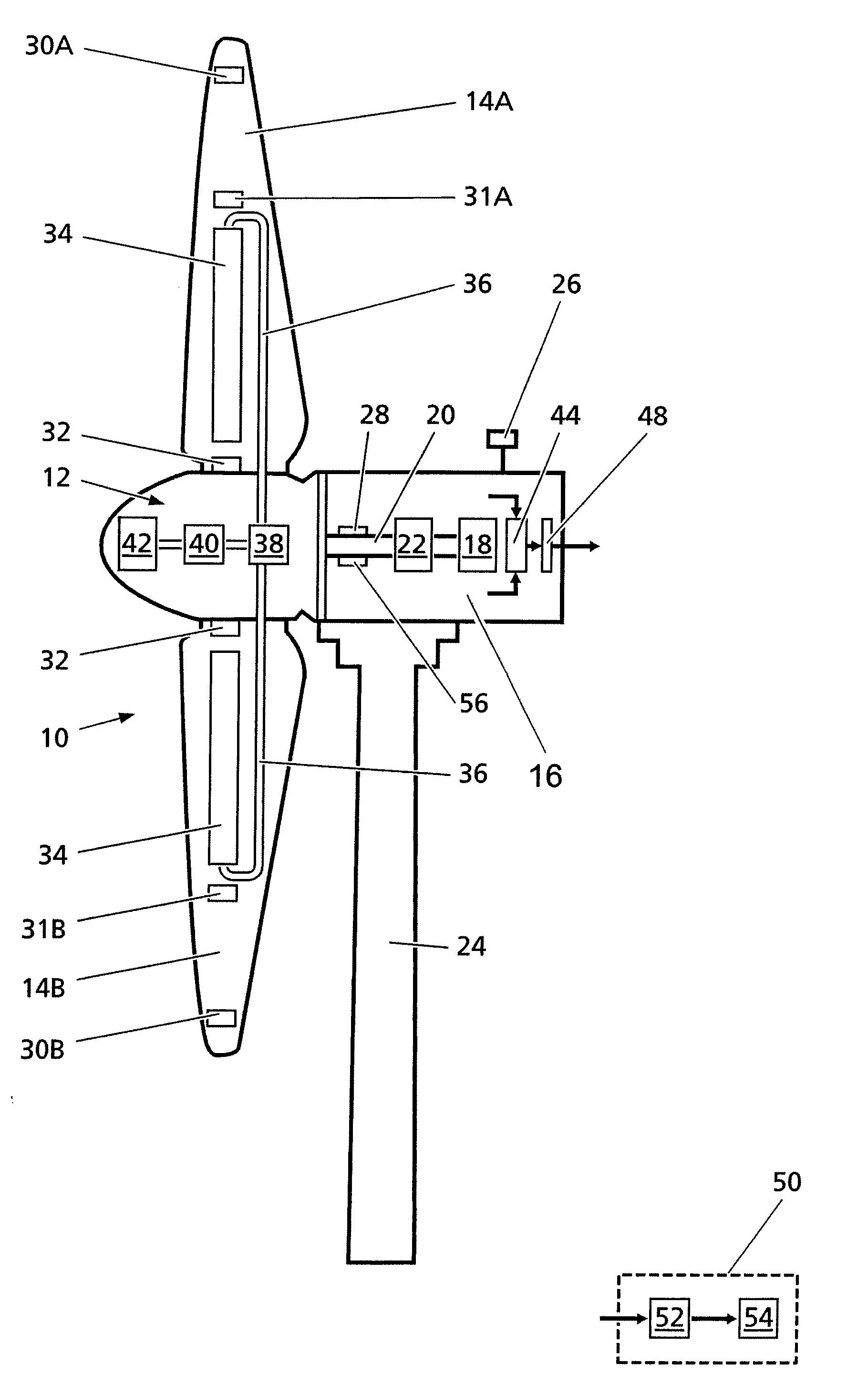
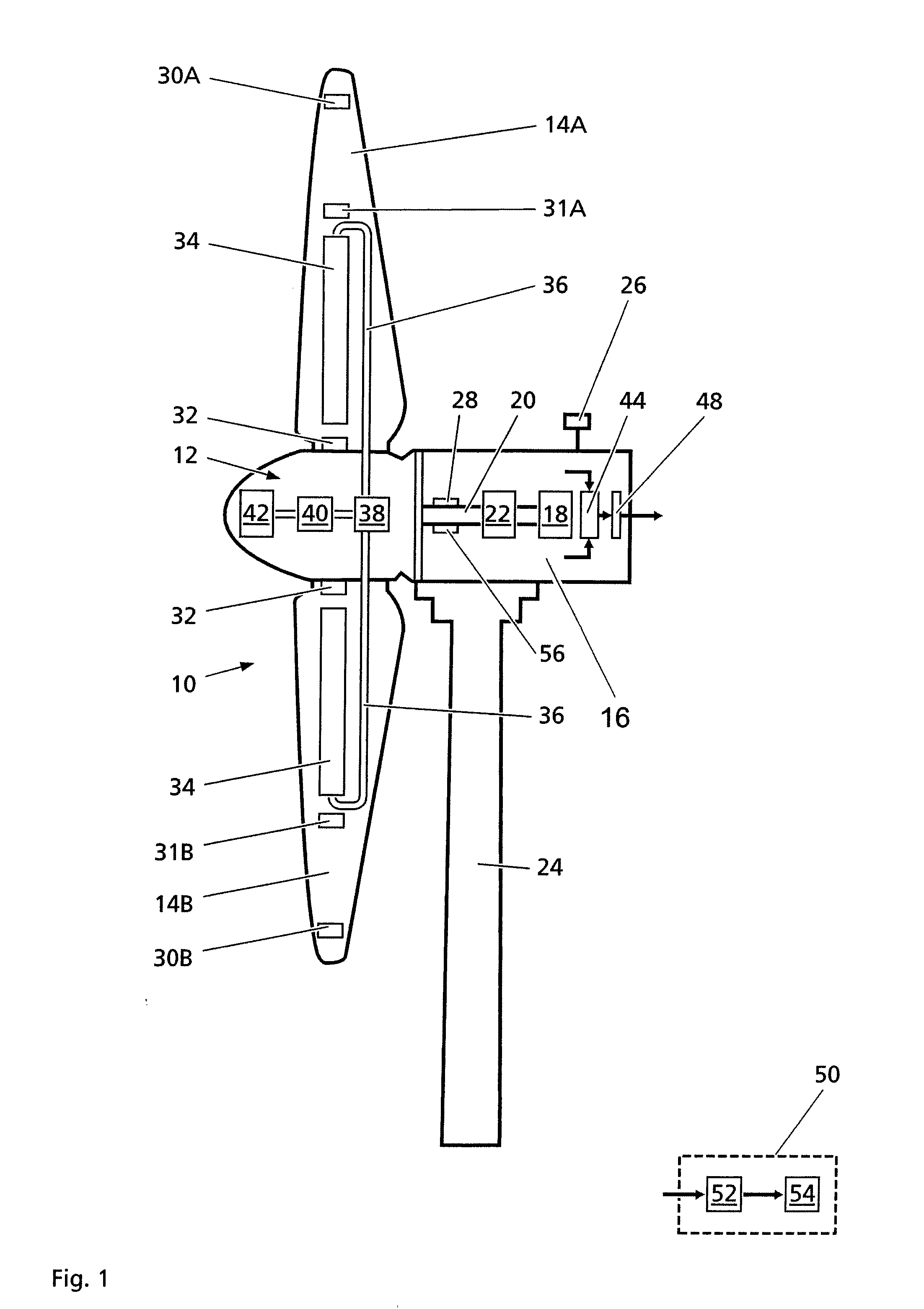
Wind turbine with monitoring sensors
ActiveUS20100209247A1Reliable assessmentAchieve accuracyPropellersWind motor controlLiquid tankTransfer mechanism
A vibration-resistant wind turbine and process for operation is provided. The wind turbine has a rotor with at least two blades, each of which includes an inclinometer arrangement with at least two axes, and an evaluating unit. The evaluating unit determines the bending and / or twisting of the blade relative to the longitudinal axis of the blade on the basis of signals from the inclinometer arrangement for each blade during operation. Each rotor blade further has at least one liquid tank which is capable of receiving or transferring liquid from or to a liquid reservoir via a transfer mechanism in response to the determined bending and / or twisting of the rotor blades to reduce vibration caused by imbalances, thereby extending the service life of the wind turbine.
Owner:PRUTECHNIK DIETER BUSCH AG
Method for enhancement of a wind plant layout with multiple wind turbines
ActiveUS7941304B2High power outputMinimizes wake lossWind motor controlEngine fuctionsPower stationEngineering
The layout and configuration of wind turbines in a wind power plant includes identifying constraints of a power plant site and defining at least one region in the site for placement of a plurality of wind turbines. The wind state at the region in the site is determined. An actual wind condition at the various possible wind turbine locations within the site is determined by modeling the wind state with wake effects at the respective wind turbine locations. Individual wind turbine configuration and location within the region is then selected as a function of the actual wind conditions each of the individual wind turbine locations to optimize power output of the individual wind turbines. The selection of turbine configuration includes selection of a turbine hub height that minimizes wake loss of the individual wind turbines as a function of the actual wind conditions predicted for the turbine location.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Balancing of Wind Turbine Parts
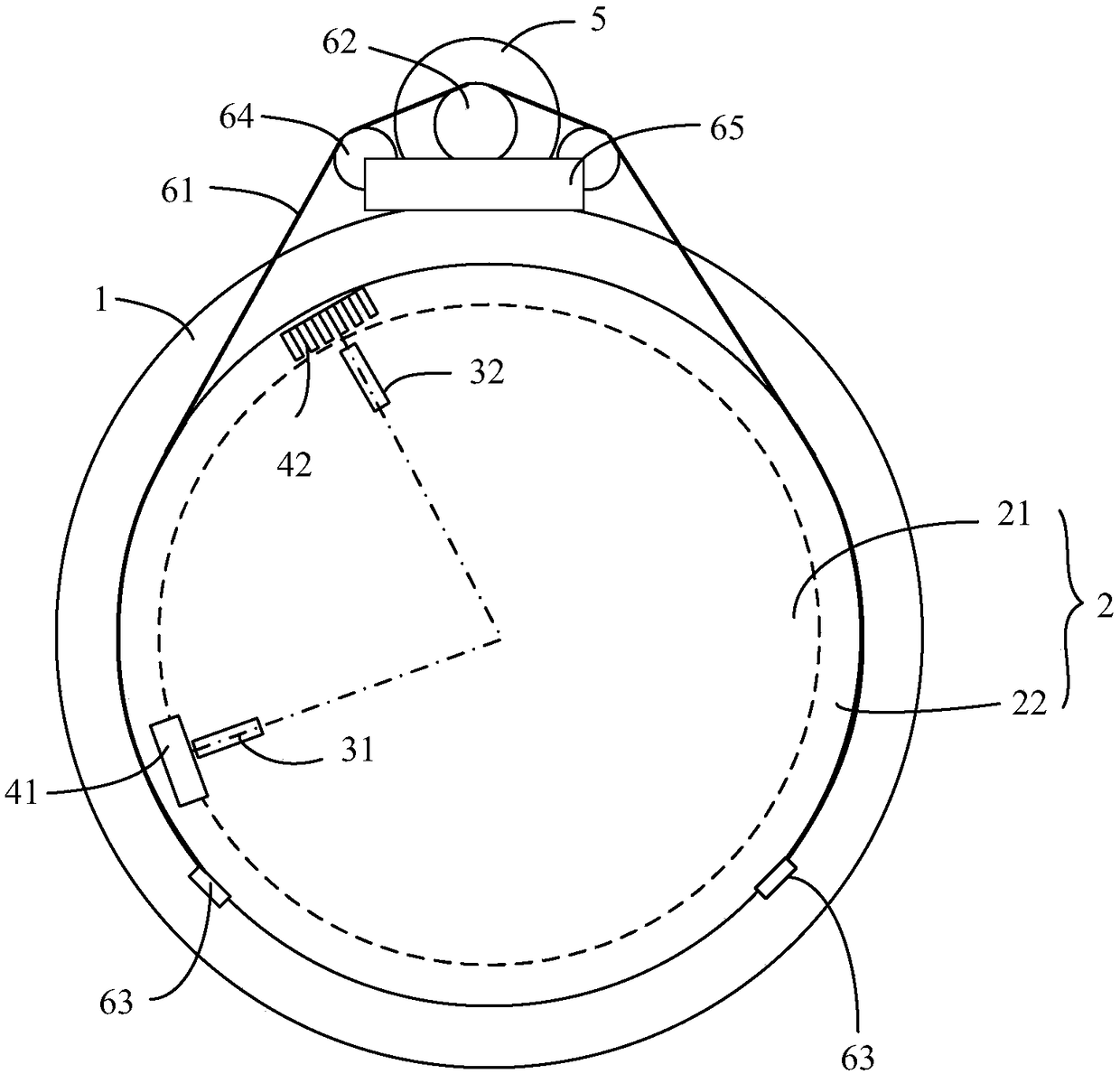
InactiveUS20120200699A1Eliminate vibrationError minimizationEngine fuctionsStatic/dynamic balance measurementNacelleAngular degrees
A wind of the type having a tower and a nacelle with a rotor rotatably connected to the nacelle for rotating about a rotor axis and having a plurality of equally spaced blades has the rotor balanced by firstly taking a measurement of torsional vibration and then by using photographic techniques to analyze dynamic imbalance caused by differences in the angle of attack of the blades. The torsional vibration is detected using two sensors at positions mirrored exactly in distance to the left and right of the rotor axis and detecting vibration in the axial direction. The angle of attack is measured by analyzing images of the tip of the blade where, during the analysis, distortion in angles at different locations in the image are corrected, in dependence upon a prior analysis of an image taken by the camera relative to a known image.
Owner:BUNGE STEFFEN
Wind power plant having multiple construction sections
InactiveUS20110232071A1Reliable settingsConstruction of to reducedEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsPeaking power plantPower station
Owner:WOBBEN ALOYS
Wind turbine generator dynamic response analysis method based on multi-platform co-simulation
InactiveCN108694277ASimple structural designUncovering Coupled Operating CharacteristicsEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesElement modelMulti platform
The invention discloses a wind turbine generator dynamic response analysis method based on multi-platform co-simulation, and belongs to the technical field of wind turbine generators. Aiming at structural components of a wind turbine generator, 3D solid modeling is completed through a Creo platform, and a Creo model is imported into an ABAQUS finite element platform. According to the actual working conditions, the correct constraint relationship of each part of a finite element model of a whole unit in the ABAQUS is set, and simulation is conducted to obtain the intrinsic frequency and mode shape of an impeller assembly and the whole unit. Coupling response between the inside of the unit, that is, between an impeller and a tower, is discussed through response simulation, the natural vibration characteristics of key components and the whole unit are studied by using a finite element simulation method, the dynamic response characteristics of the wind turbine generator are obtained by using time-varying wind pressure distribution as the main excitation load, the wind turbine generator dynamic response analysis method based on multi-platform co-simulation has significances to improvingthe structure design of the unit and formulating effective diagnosis strategies.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Single piece electric assembly for connecting an off-shore wind turbine with an electric subsea cable, wind turbine, wind turbine cluster and method for mounting such an electric assembly to a wind turbine tower
ActiveUS20150108764A1Easy to installMore reliableSubstation/switching arrangement detailsEngine manufactureOcean bottomElectricity
An electric assembly for electrically connecting at least one wind turbine being located off-shore with an electric subsea cable being connected to an on-shore power grid is provided. The electric assembly has (a) a transformer for transforming a first voltage level being provided by the at least one wind turbine to a second voltage level of the subsea cable, and (b) an external equipment being electrically and mechanically connected to the transformer for controlling an operation of at least the transformer. The transformer and the electric equipment are formed by a preinstalled package, which can be mechanically handled as a single piece. Further, a wind turbine having such an electric assembly, a wind turbine cluster having such a wind turbine, and a method for mounting such an electric assembly to a tower of a wind turbine are provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
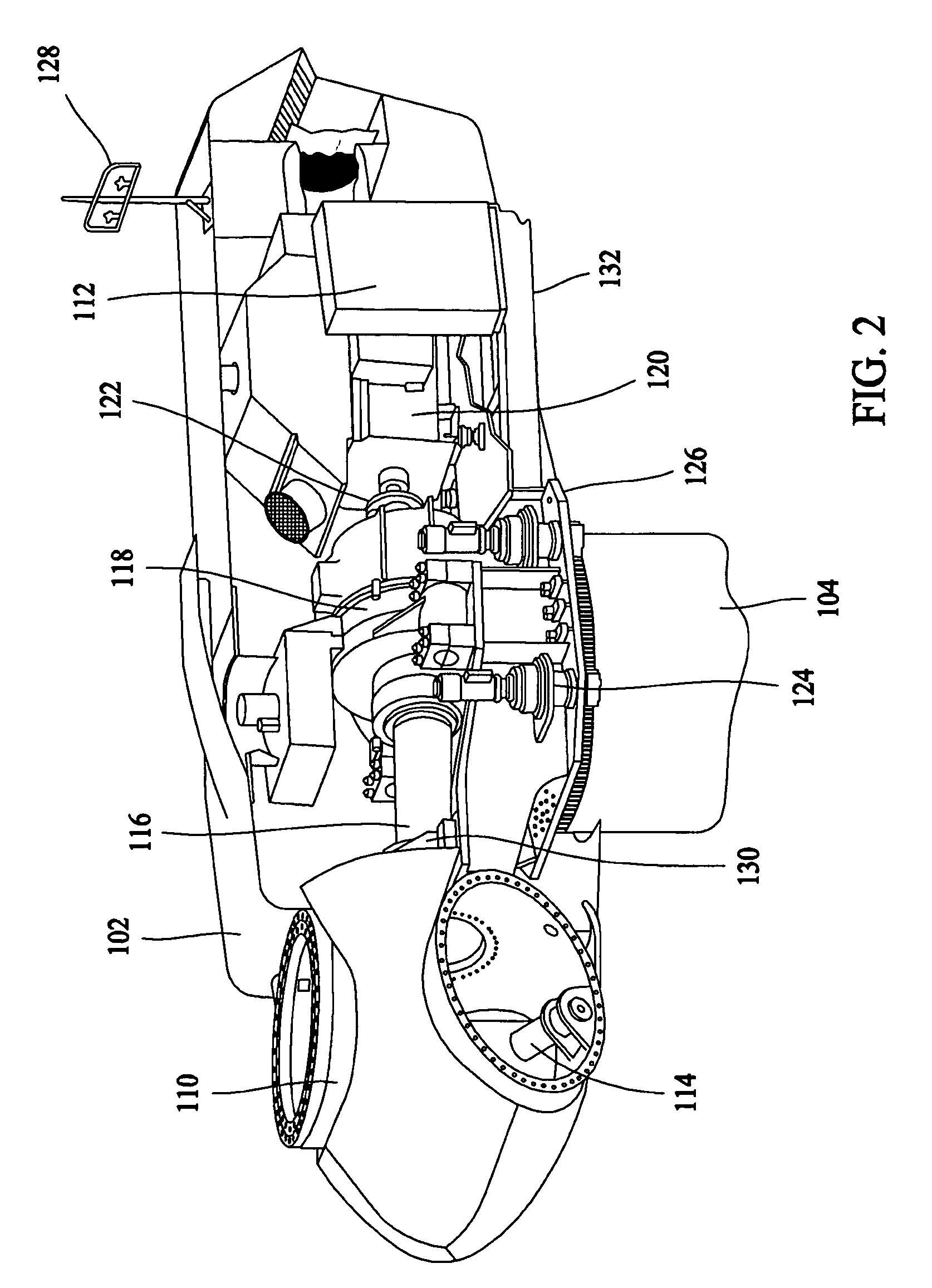
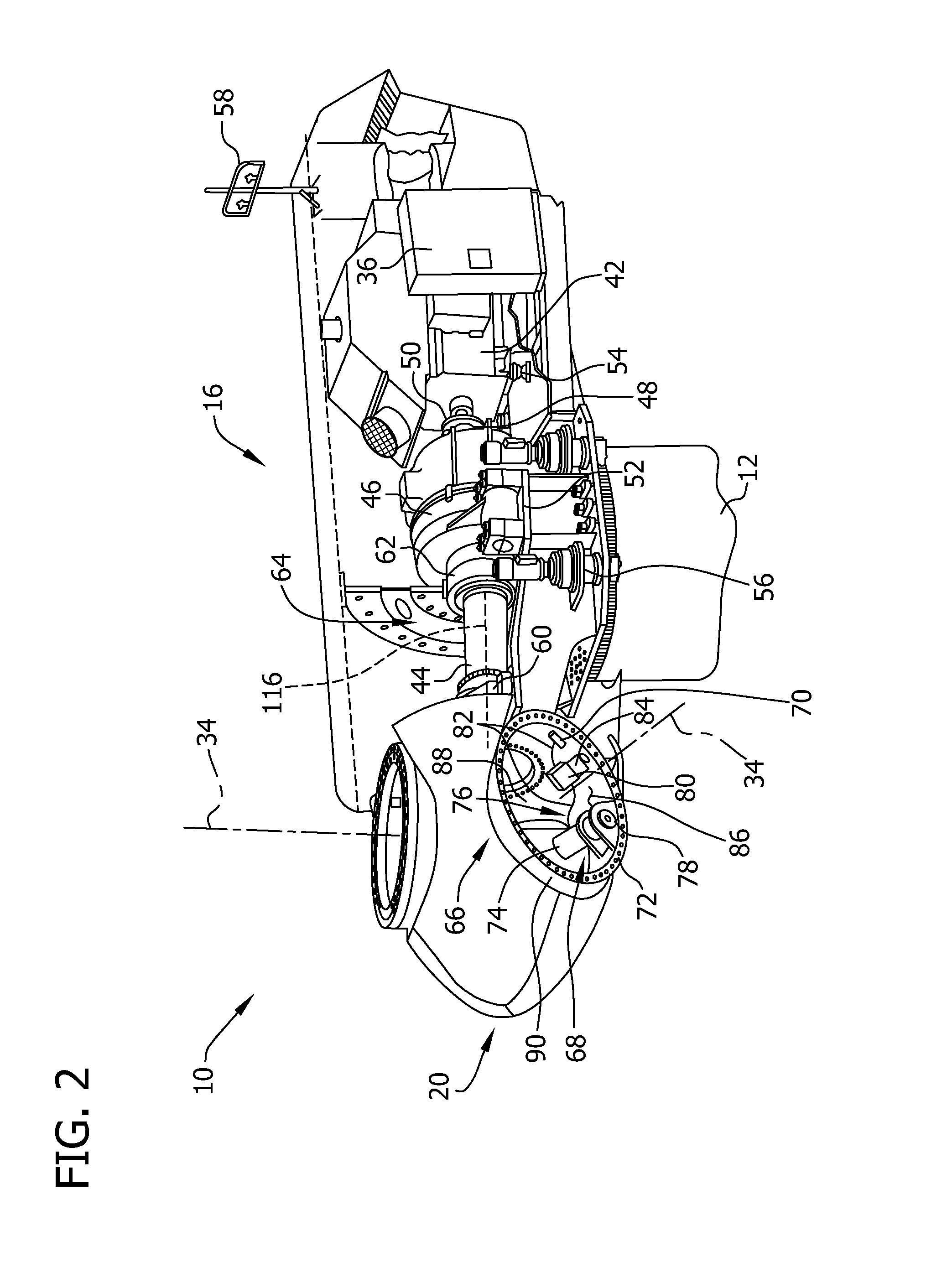
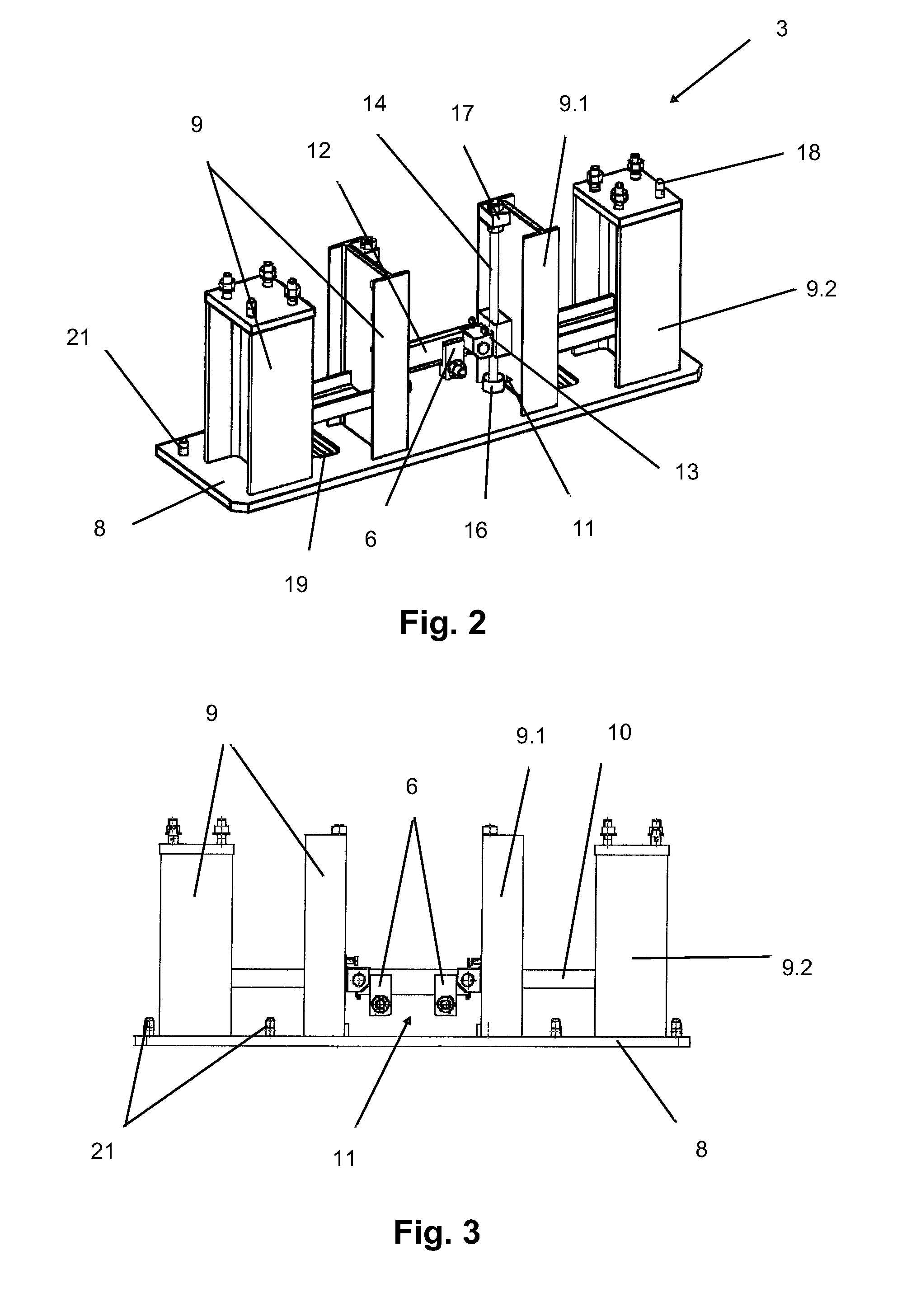
Method and apparatus for aligning a wind turbine generator
A method and apparatus for aligning an input shaft of a wind turbine generator with an output shaft of a wind turbine are disclosed. Preferably, the method includes placing a push plate of a wind turbine alignment tool into pressing contact with a selected support flange of a wind turbine generator identified by a misalignment measurement device. With the push plate positioned, an indexing means of the wind turbine alignment tool is advanced along an adjustment link member of the wind turbine alignment tool to impart an alignment force onto the selected support flange to align the input shaft of the wind turbine generator with the output shaft of the wind turbine. The method preferably concludes by rechecking the alignment of the input shaft of the wind turbine generator with the output shaft of the wind turbine.
Owner:DISCOVERY SOLAR ENERGY LLC
Tool for transporting towers
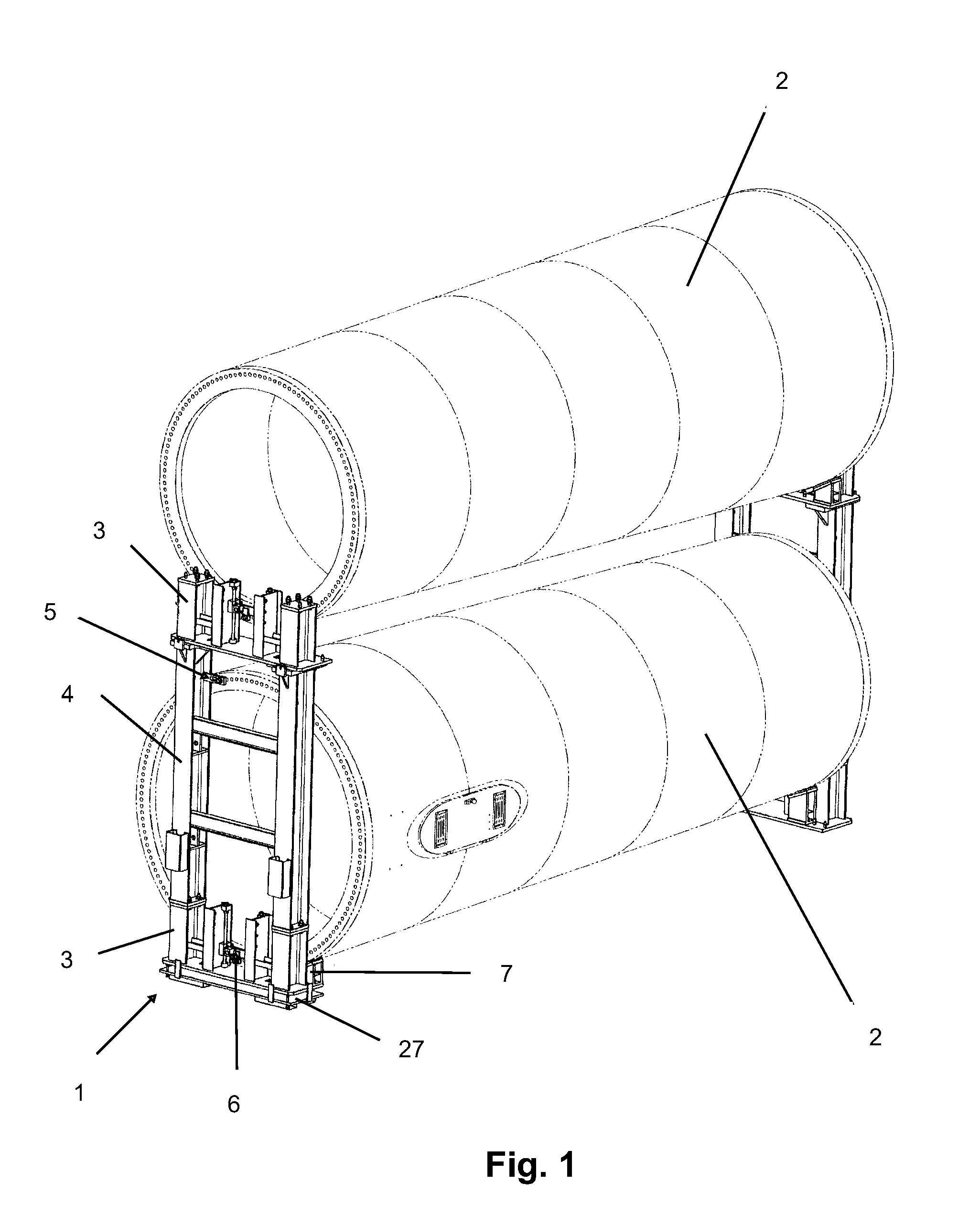
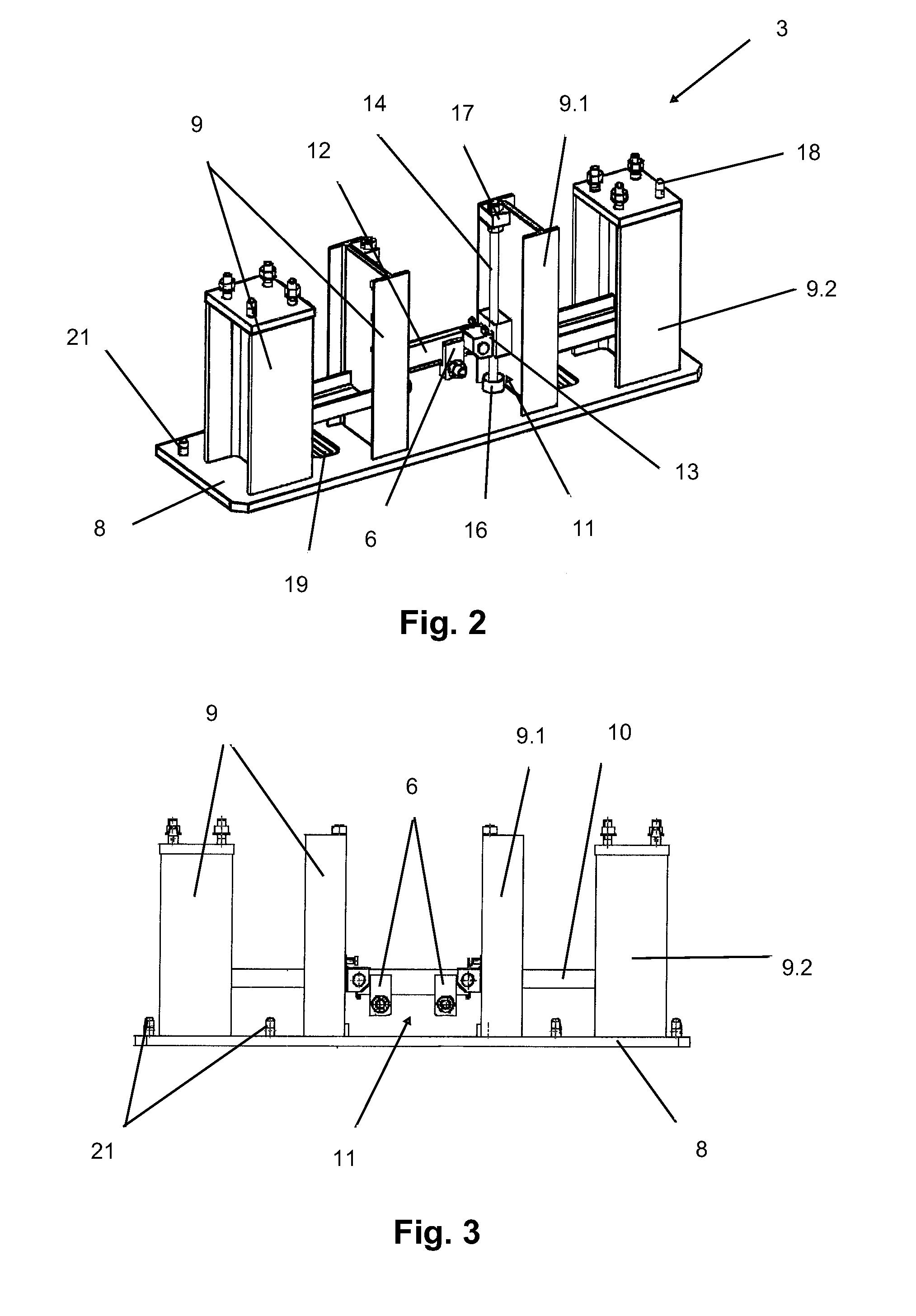
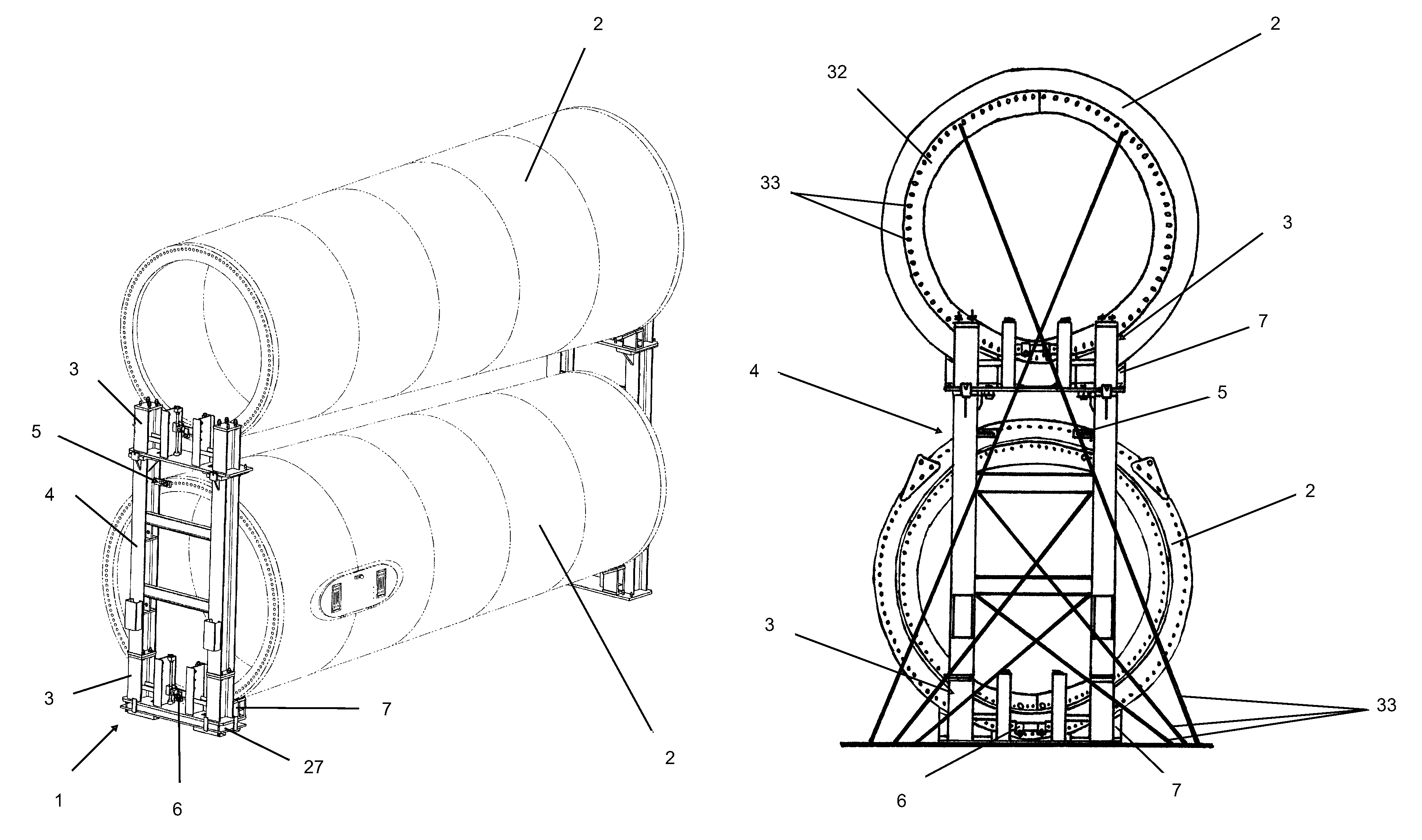
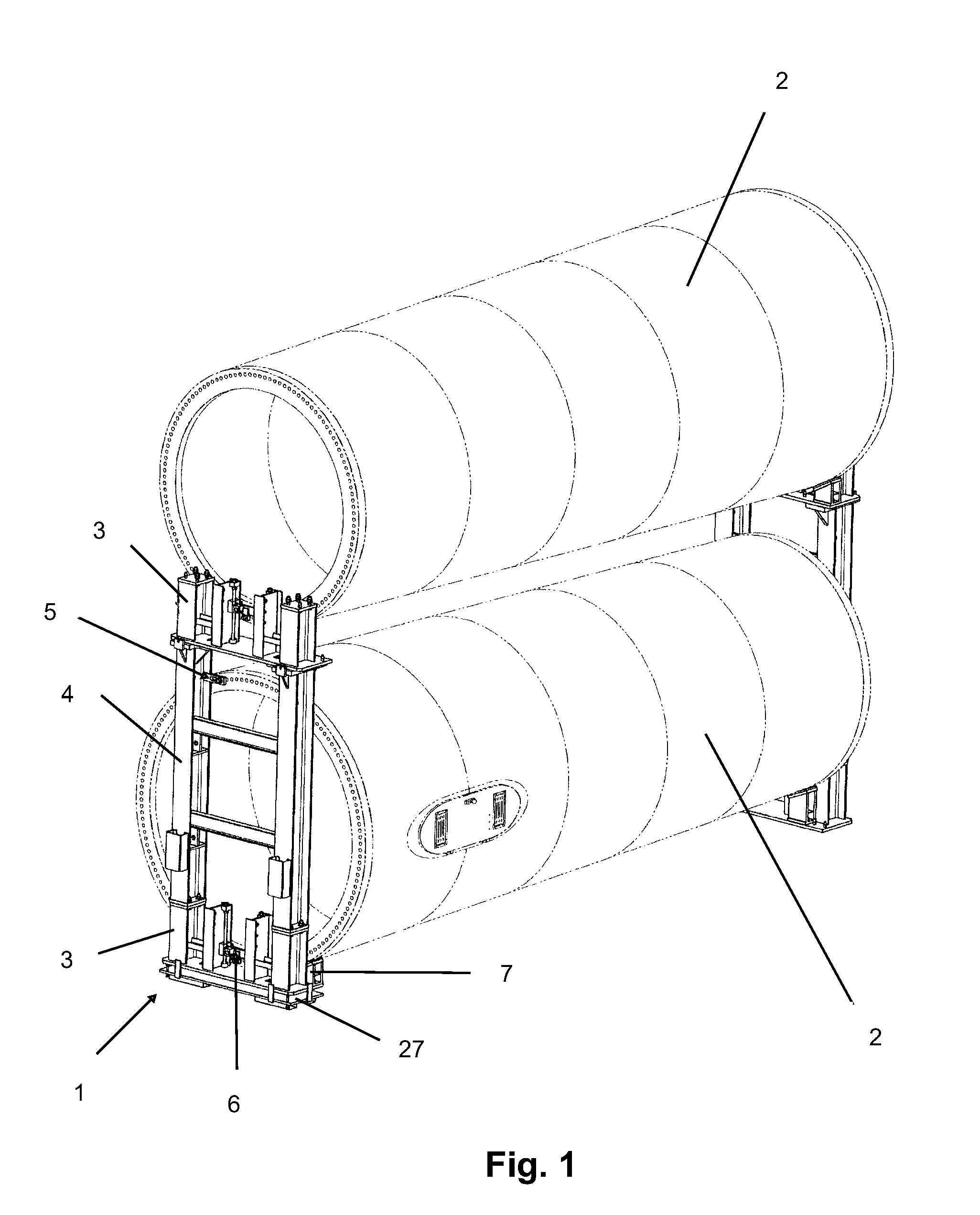
InactiveUS20110255934A1Transportation safetyWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsTowerTurbine
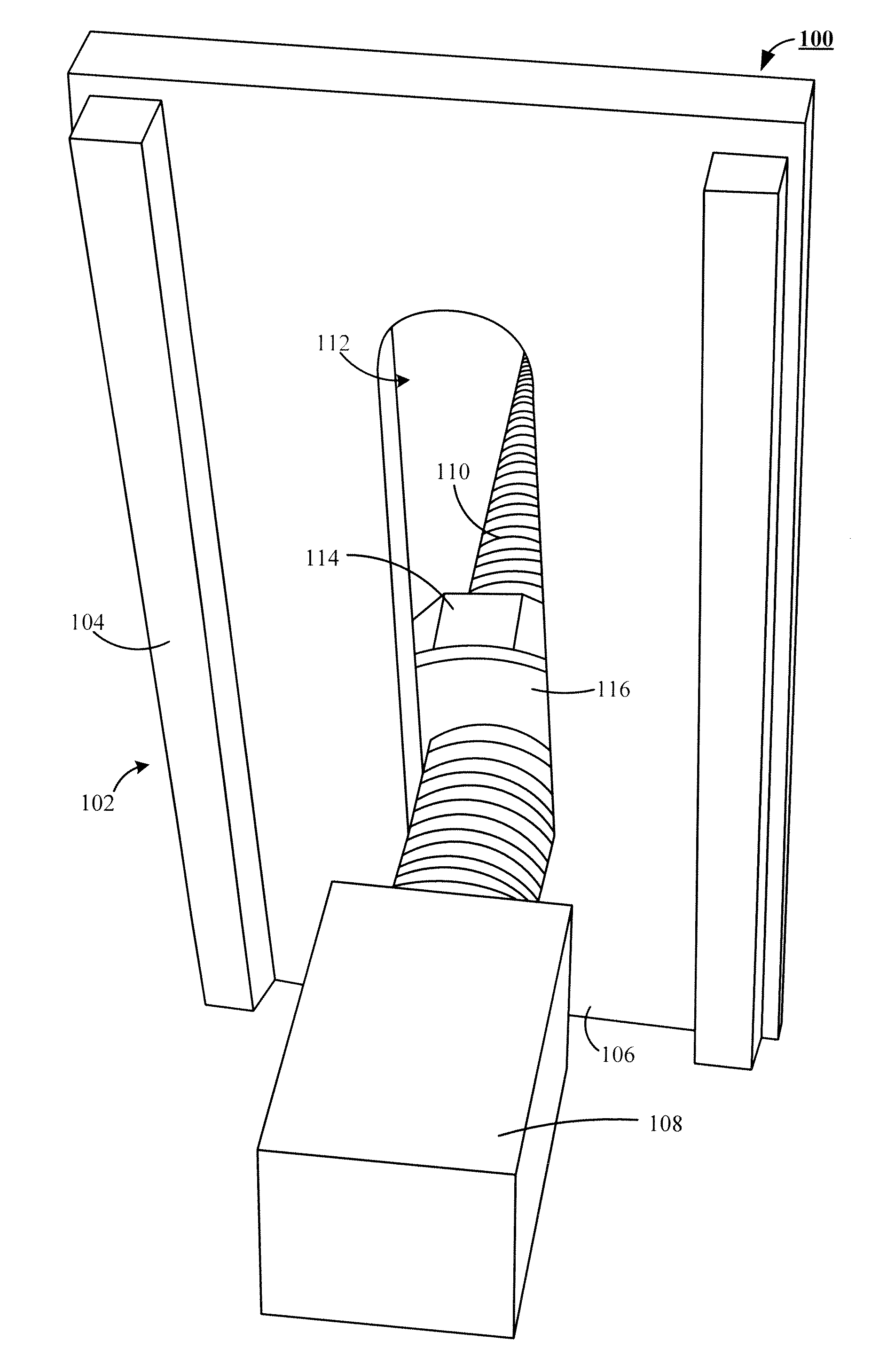
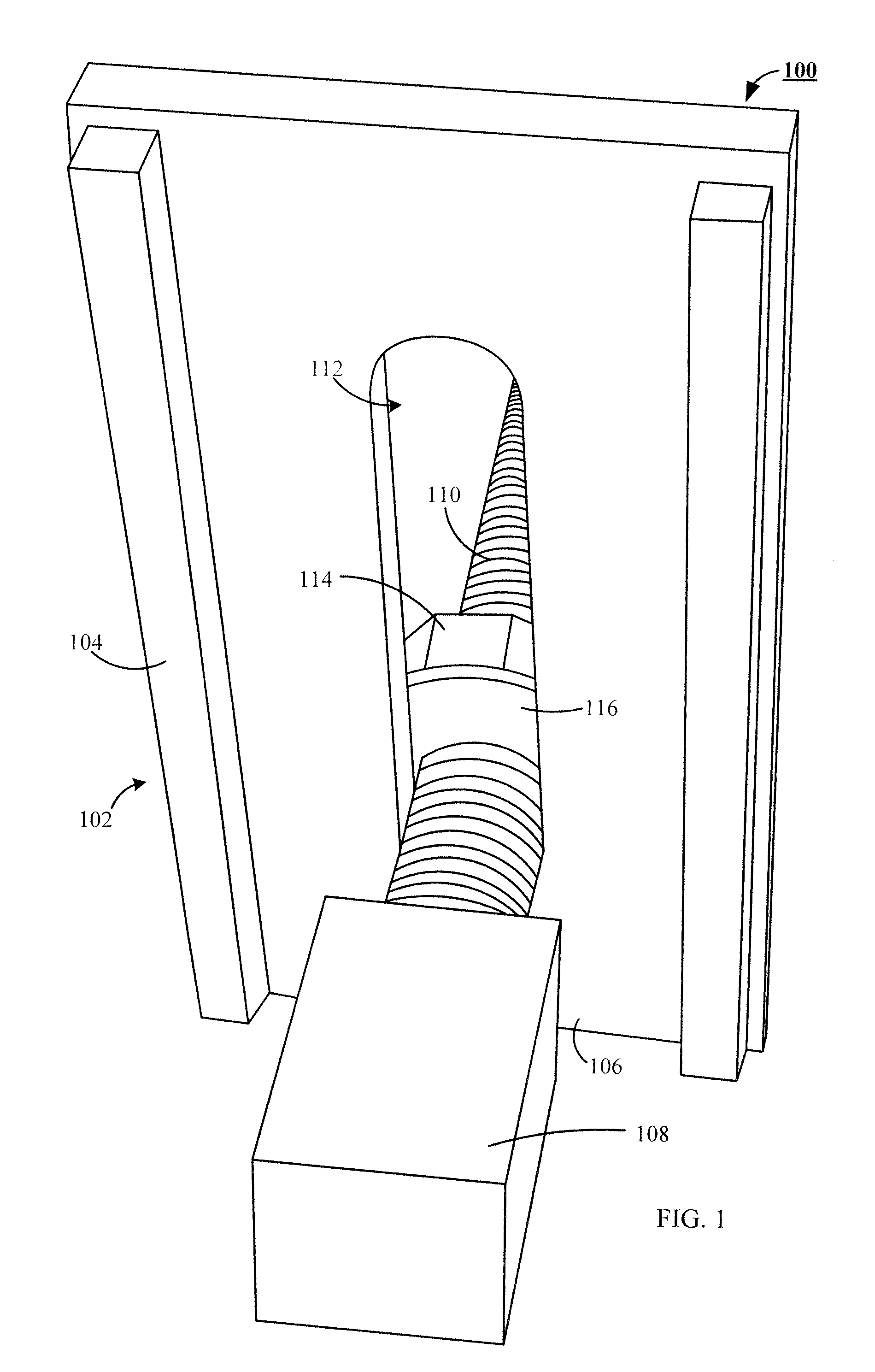
Tool for tower transport, of the type that are used for transporting large-sized parts, such as sections (2) of wind turbine tower, for application in any means of transport (railway, road and sea) that includes a series of modular parts made up by some modules (3 and 4), some clamps (5 and 6), some chocks (7), a balancing tool (27) and some fastening elements (20, 33) that combined allow anchoring any type of section (2) in any means of transport.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
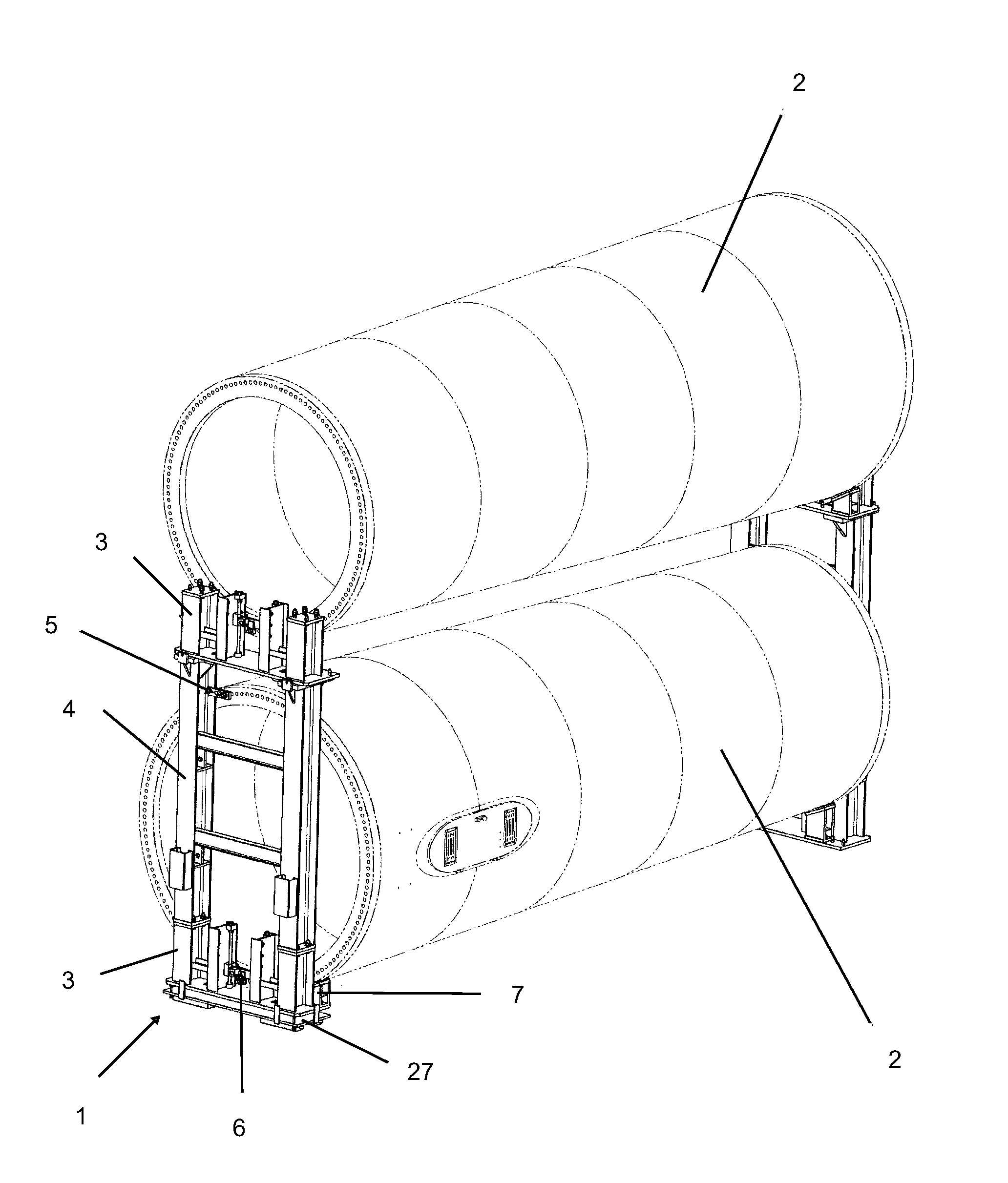
Transporting tool for tower sections of a wind turbine
A transporting tool for tower transporting sections of wind turbine tower by railway, road and sea transport vehicles that includes a lower module, with bottom clamps and an upper module, with upper clamps, chocks mounted to the tower module, and fastening elements that combined allow anchoring the tower section, for transport.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Mechanical device for suppressing resonant vibration of large-scale wind generating set
PendingCN107013418AAvoid destructionAvoid resonanceMachines/enginesWind motor monitoringEngineeringElectric generator
The invention relates to a device for suppressing the resonant vibration of a large-scale wind generating set, and particularly to a mechanical device used for suppressing the resonant vibration by changing the inherent frequency of a wind-driven generator by altering the mass distribution of the large-scale wind generating set. According to the mechanical device for suppressing the resonant vibration of the large-scale wind generating set, vibration data of the wind generating set can be collected in real time and a response is made accordingly in time; the rotating parts of blades do not need to be adjusted, and the wind energy utilization ratio is not reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Core material for balanced rotor blade
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Wind/tidal power generation bearing
InactiveUS20150192174A1Prevent leakageEasy to installRoller bearingsShaftsRolling-element bearingEngineering
The wind / tidal power generation bearing for supporting a main shaft of a wind power generator or a main shaft of a tidal power generator includes a rolling bearing including an inner ring, an outer ring and a plurality of rollers disposed between the inner ring and the outer ring. The plurality of rollers are arranged in a circumferential direction such that axes of alternate rollers or alternate sets of a plurality of rollers intersect each other, thereby reducing a bearing width as compared to a double row tapered roller bearing or the like of the conventional art. Therefore, in the wind power generator or the tidal power generator, a space in an axial direction can be saved as compared to the conventional art.
Owner:NTN CORP
Wind turbine with monitoring sensors
ActiveUS8672625B2Reliable assessmentAchieve accuracyPropellersWind motor controlTransfer mechanismTurbine
Owner:PRUTECHNIK DIETER BUSCH AG
Variable-propeller system and blade zero position calibrating method
InactiveCN108180109AZero position calibration achievedGuaranteed uptimeWind motor controlMachines/enginesPropellerEngineering
The invention relates to a variable-propeller system and a blade zero position calibrating method. The variable-propeller system comprises a variable-propeller bearing, a position detecting assembly and a trigger assembly, wherein the position detecting assembly comprises a first switch assembly for detecting whether a blade is at a first angle or not and a second switch assembly for detecting whether the blade is at a second angle or not; the trigger assembly comprises a first trigger part and a second trigger part which are arranged in the peripheral direction of a rotary ring in a spaced mode; when the trigger part and the second trigger part rotate along with the rotary ring, the first trigger part can trigger the first switch assembly and the second trigger part can trigger the secondswitch assembly; and when the first trigger part rotates to the trigger range of the first switch assembly, the second trigger part is positioned in the trigger range of the second switch assembly. The variable-propeller system can be used for checking the practical position of the blade and also can be used for calibrating the zero position of the blade, so that safe operation of a wind generating set is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
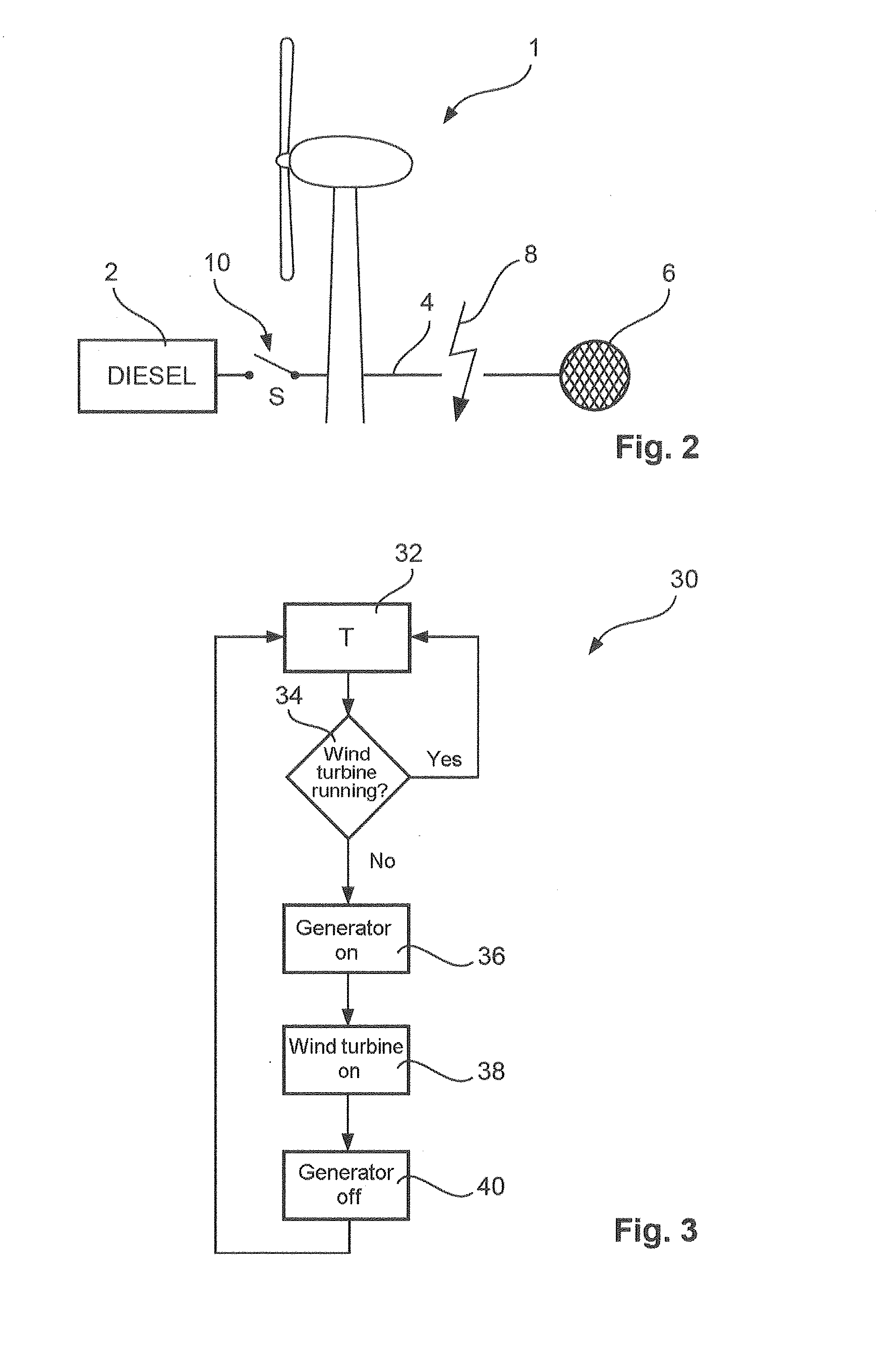
Method for the control of a wind turbine with no mains support available
ActiveUS20150042094A1Inhibit deteriorationPower generation is also lowWind motor controlEngine fuctionsElectricityTurbine
The invention relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine that comprises a generator, is provided to feed electrical power into an electricity supply grid but has not yet been connected to the electricity supply grid, comprising the steps: generating electrical power using the generator and supplying electrical elements of the wind turbine with the power generated, and to a wind turbine for generating electrical power from the wind and for feeding the electrical power generated into an electricity supply grid, wherein a method according to one of the preceding claims is carried out.
Owner:WOBBEN PROPERTIES GMBH
Single piece electric assembly for connecting an off-shore wind turbine with an electric subsea cable, wind turbine, wind turbine cluster and method for mounting such an electric assembly to a wind turbine tower
ActiveUS9377009B2Easy to installMore reliableSubstation/switching arrangement detailsEngine manufactureOcean bottomElectricity
An electric assembly for electrically connecting at least one wind turbine being located off-shore with an electric subsea cable being connected to an on-shore power grid is provided. The electric assembly has (a) a transformer for transforming a first voltage level being provided by the at least one wind turbine to a second voltage level of the subsea cable, and (b) an external equipment being electrically and mechanically connected to the transformer for controlling an operation of at least the transformer. The transformer and the electric equipment are formed by a preinstalled package, which can be mechanically handled as a single piece. Further, a wind turbine having such an electric assembly, a wind turbine cluster having such a wind turbine, and a method for mounting such an electric assembly to a tower of a wind turbine are provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com