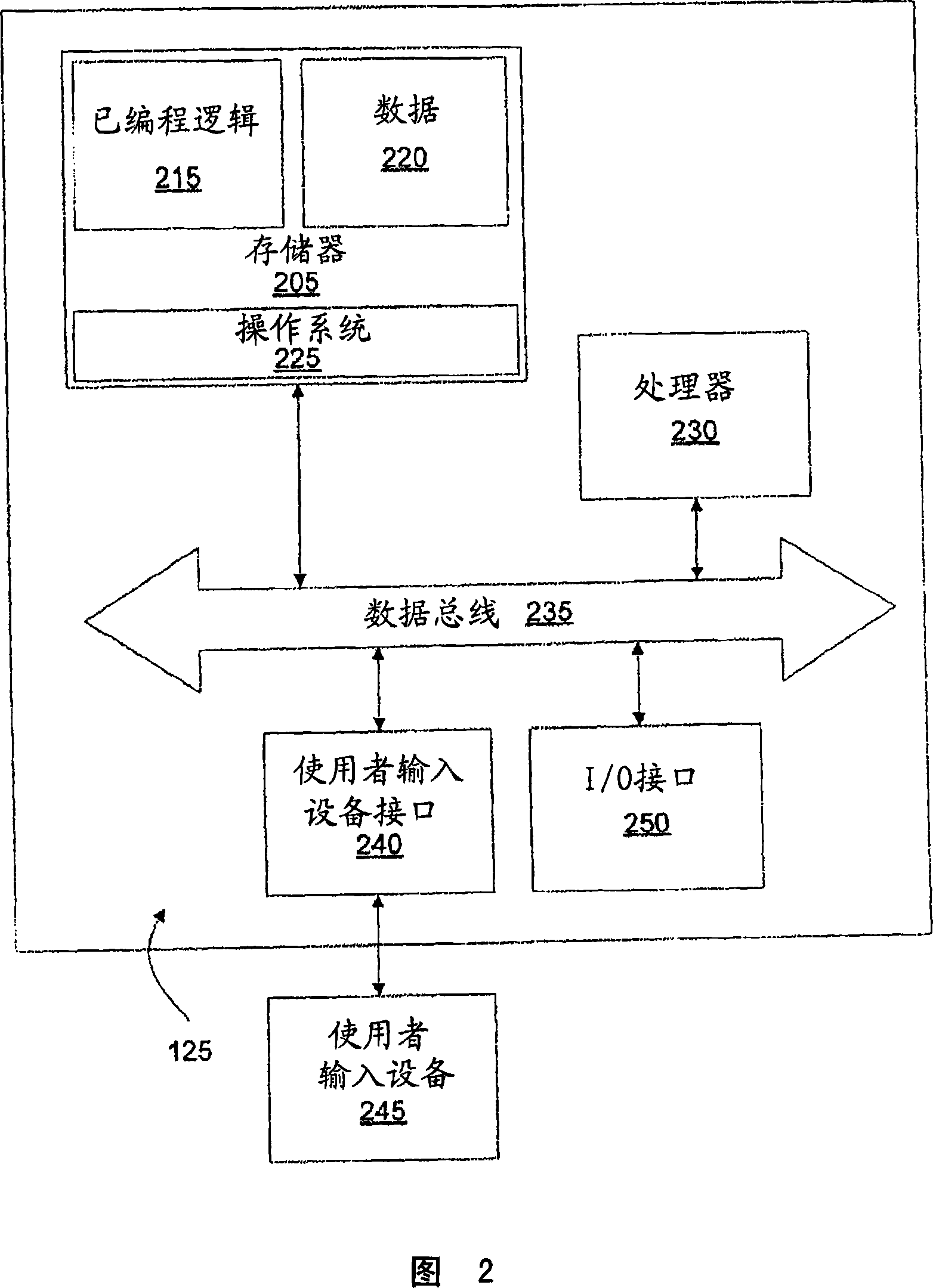
Patents
Literature
64results about "Engine life prolonging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
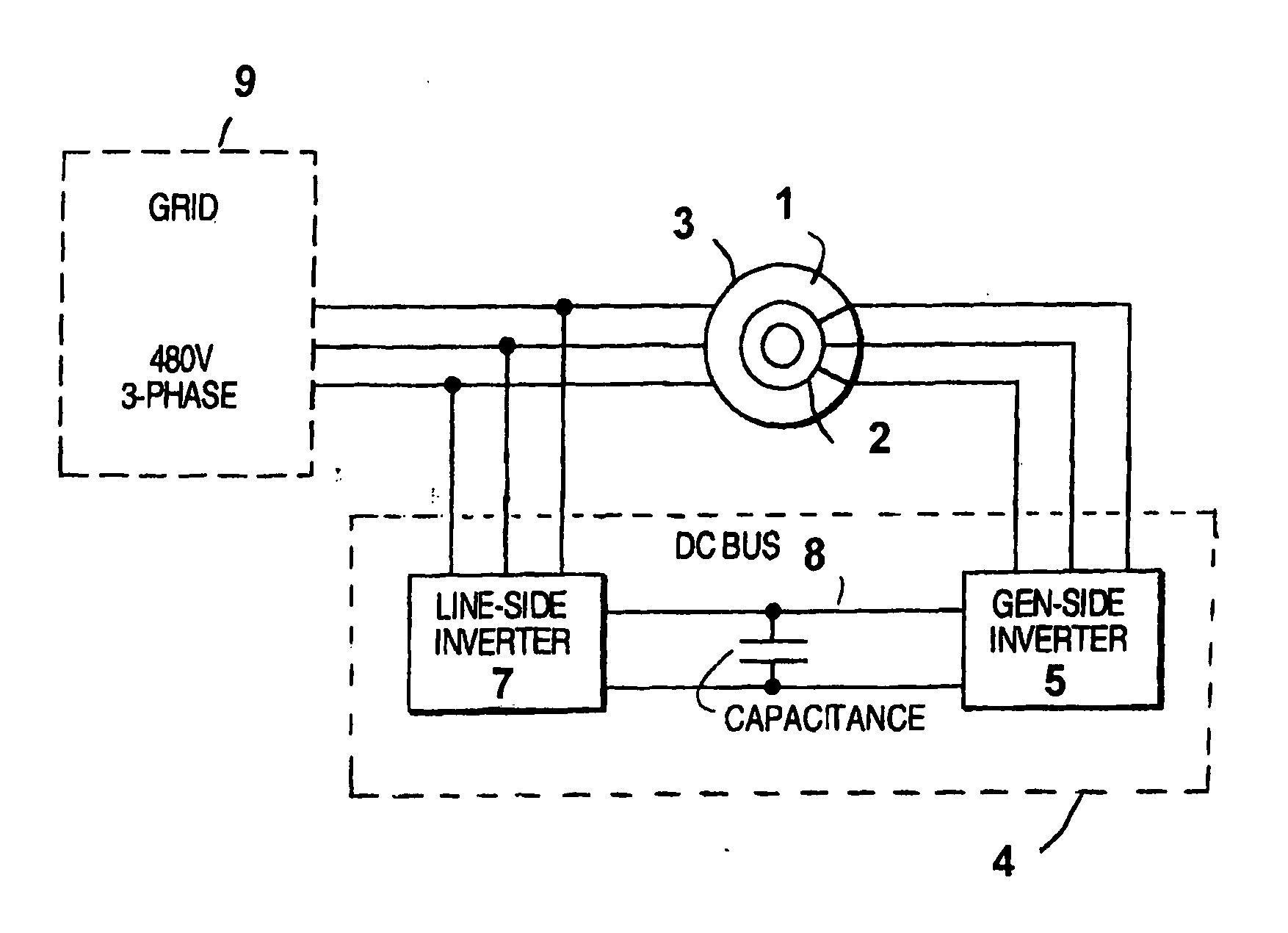
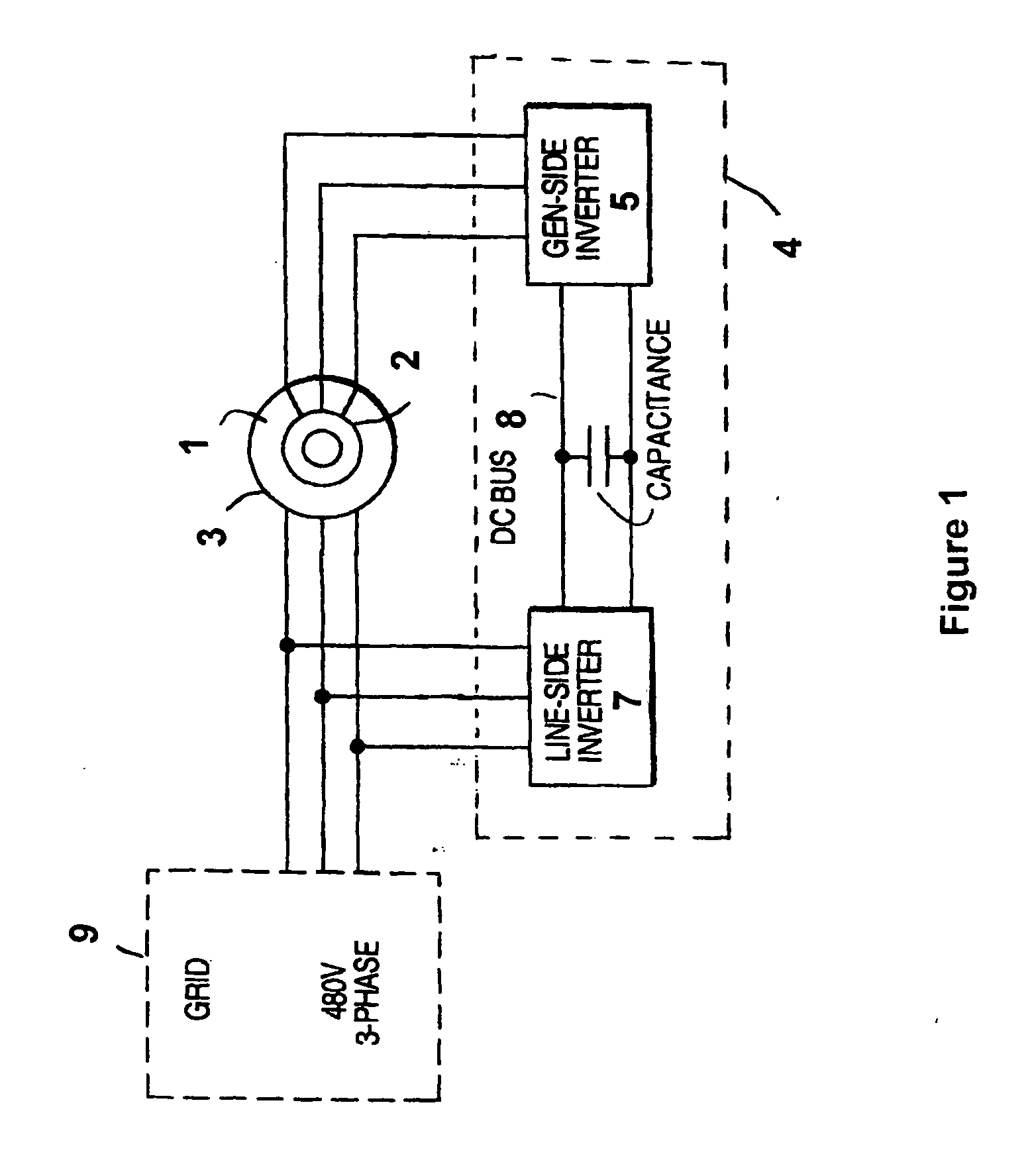
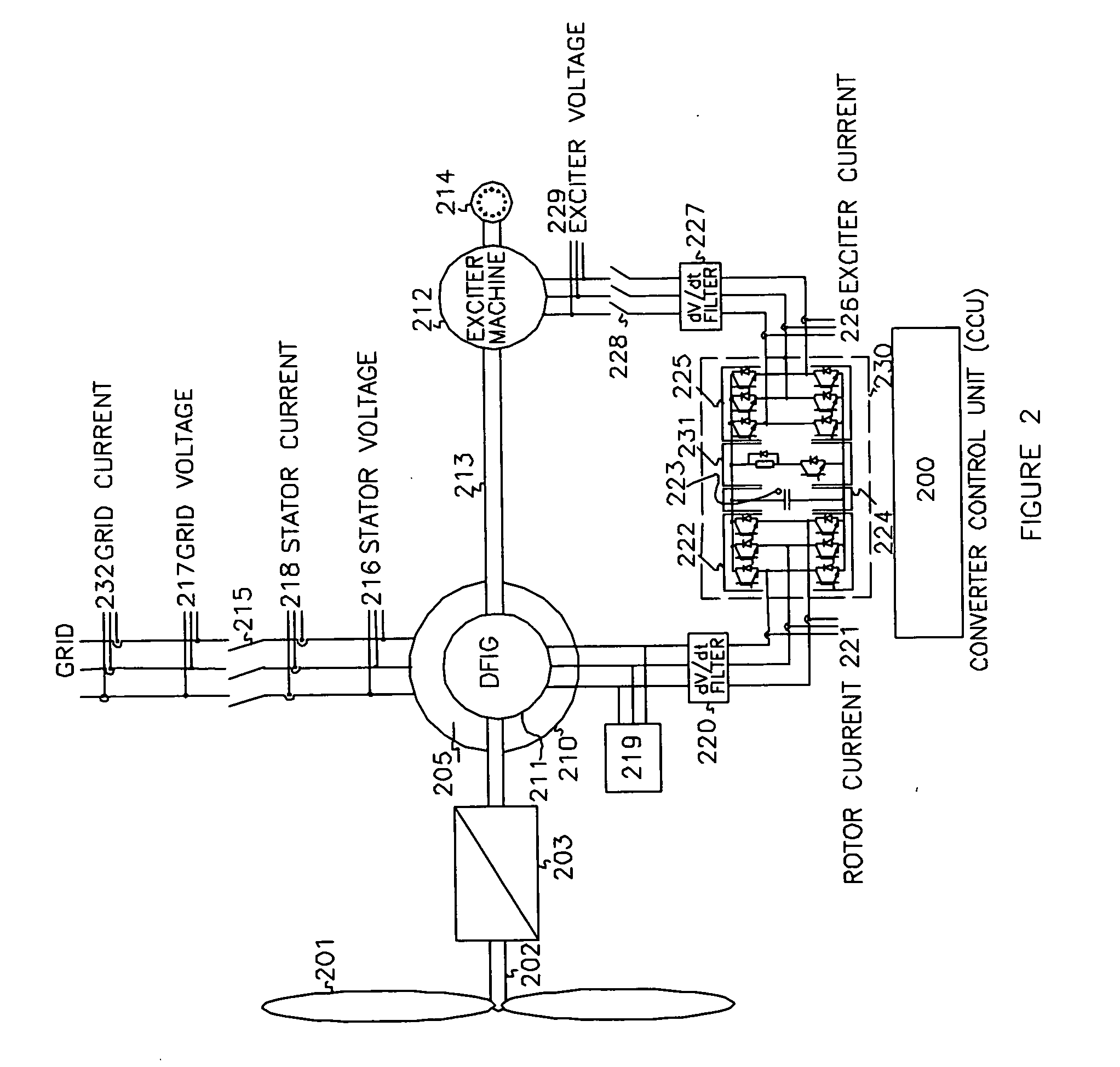
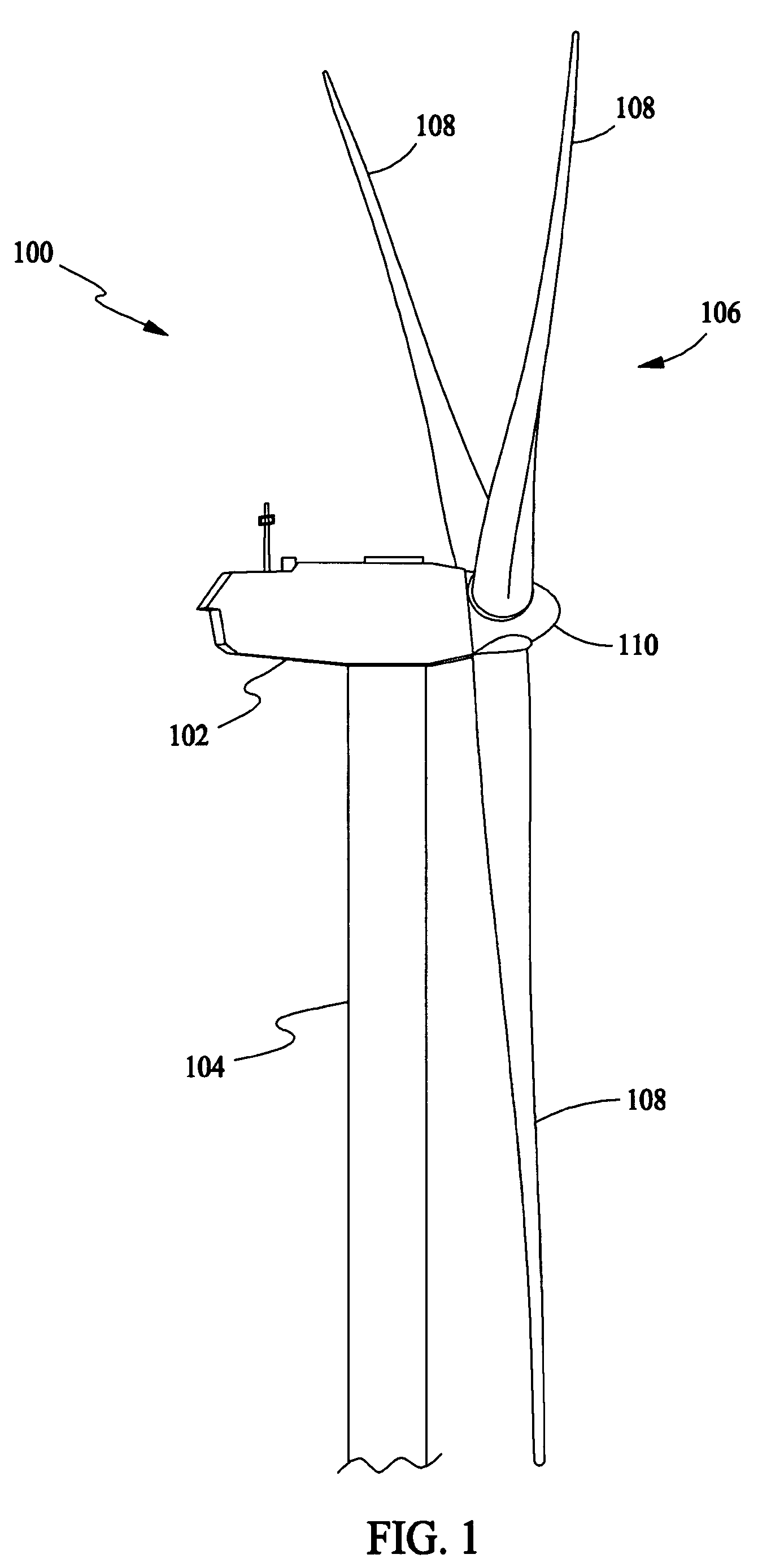
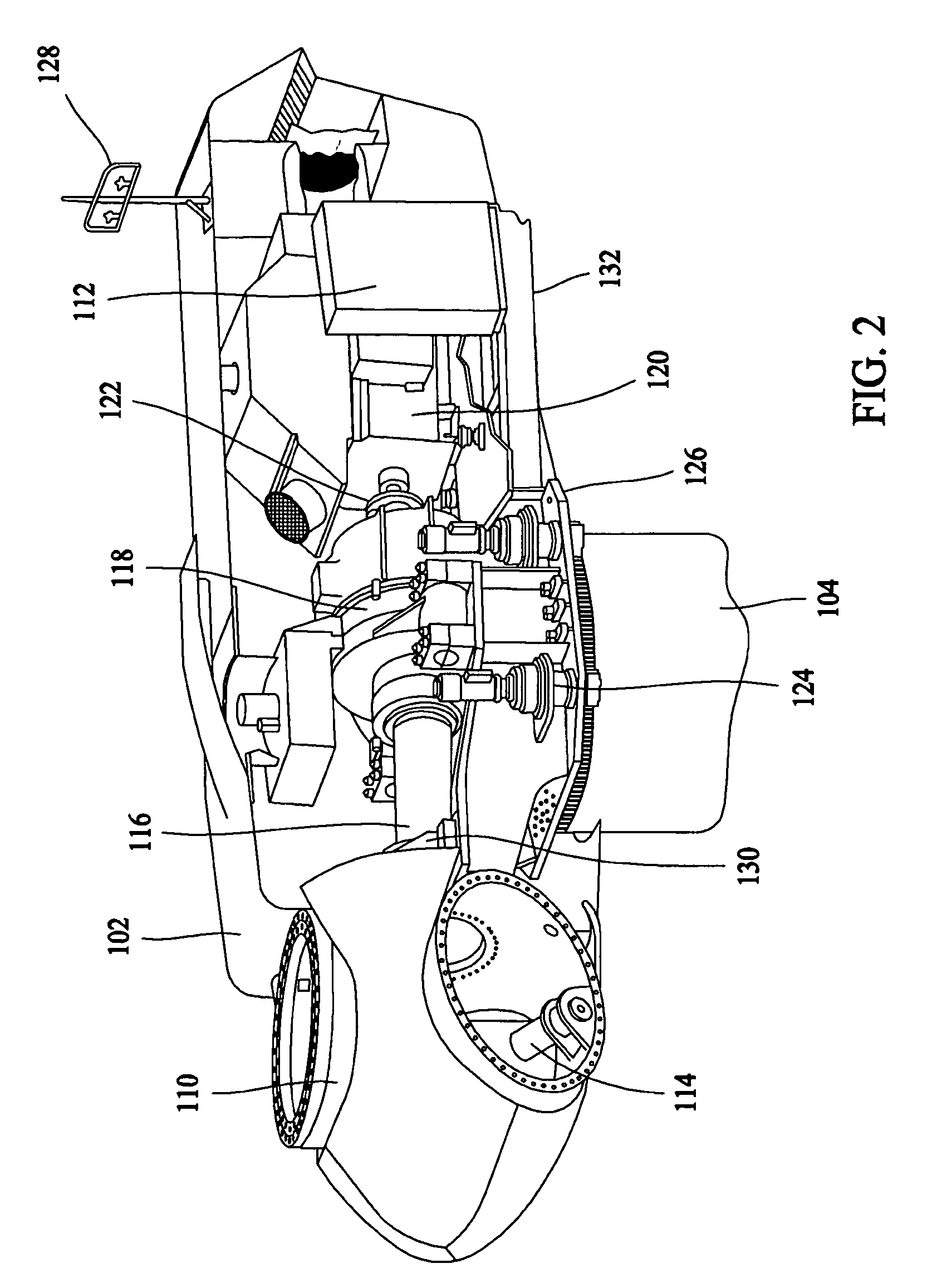
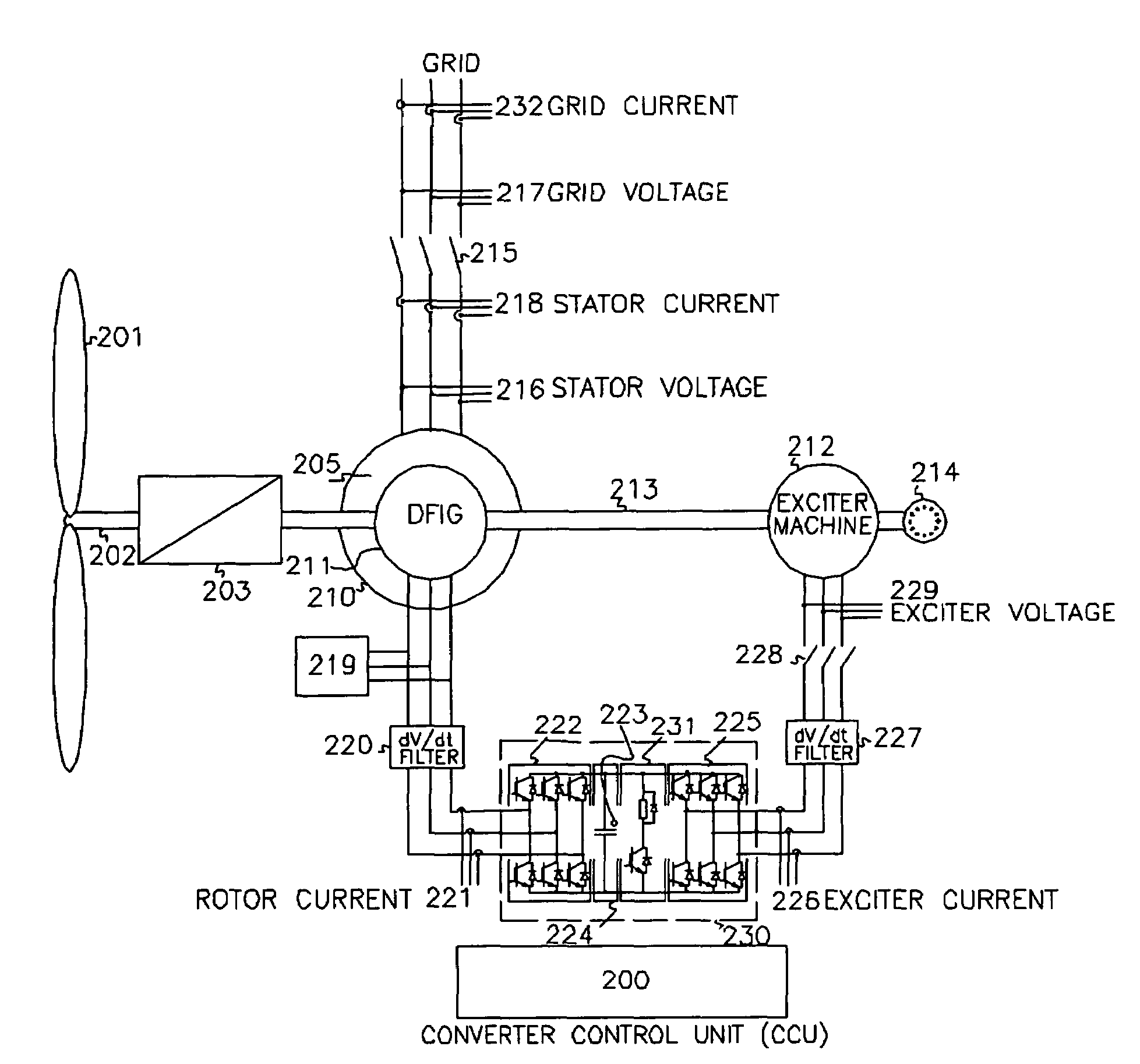
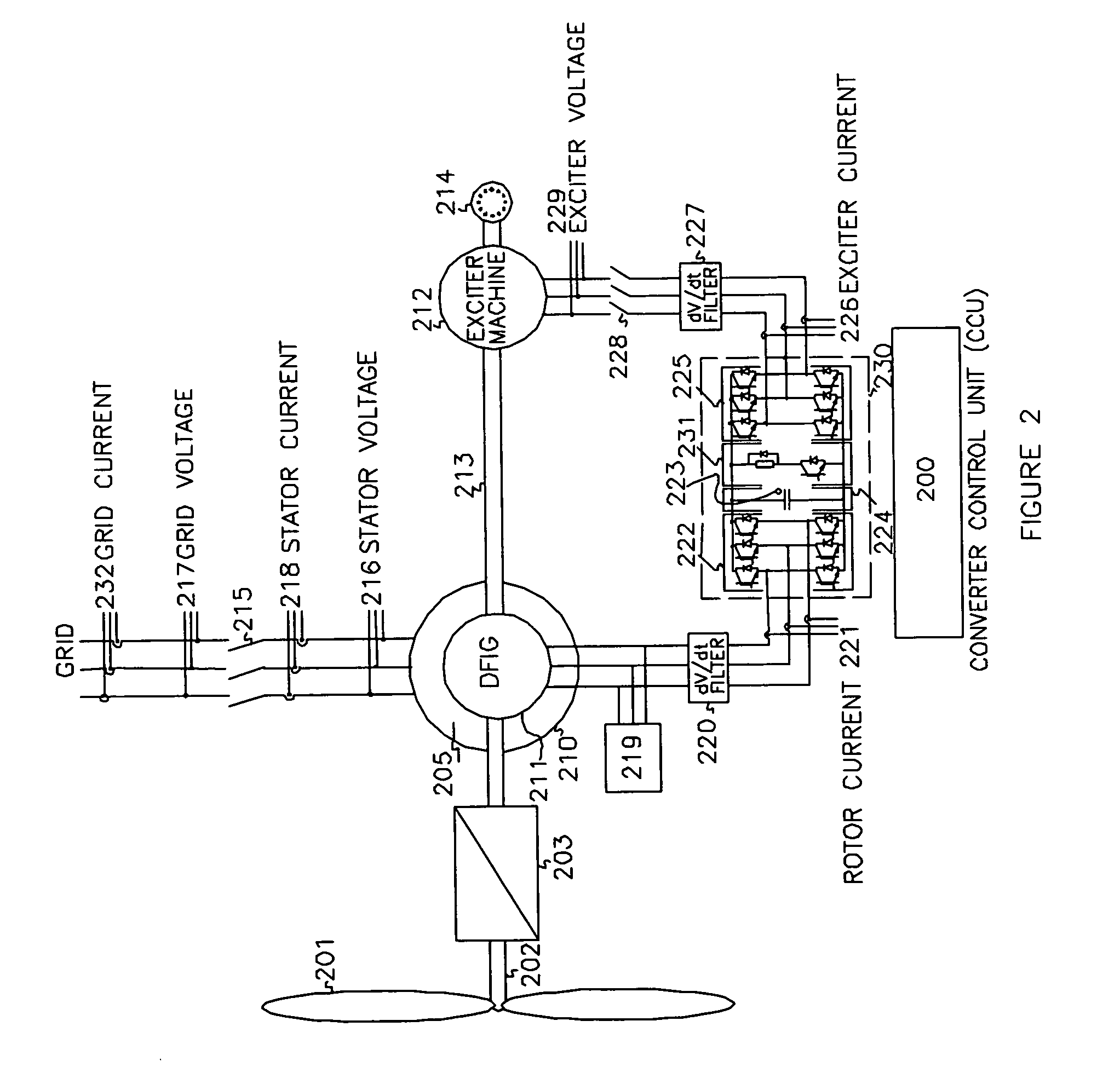
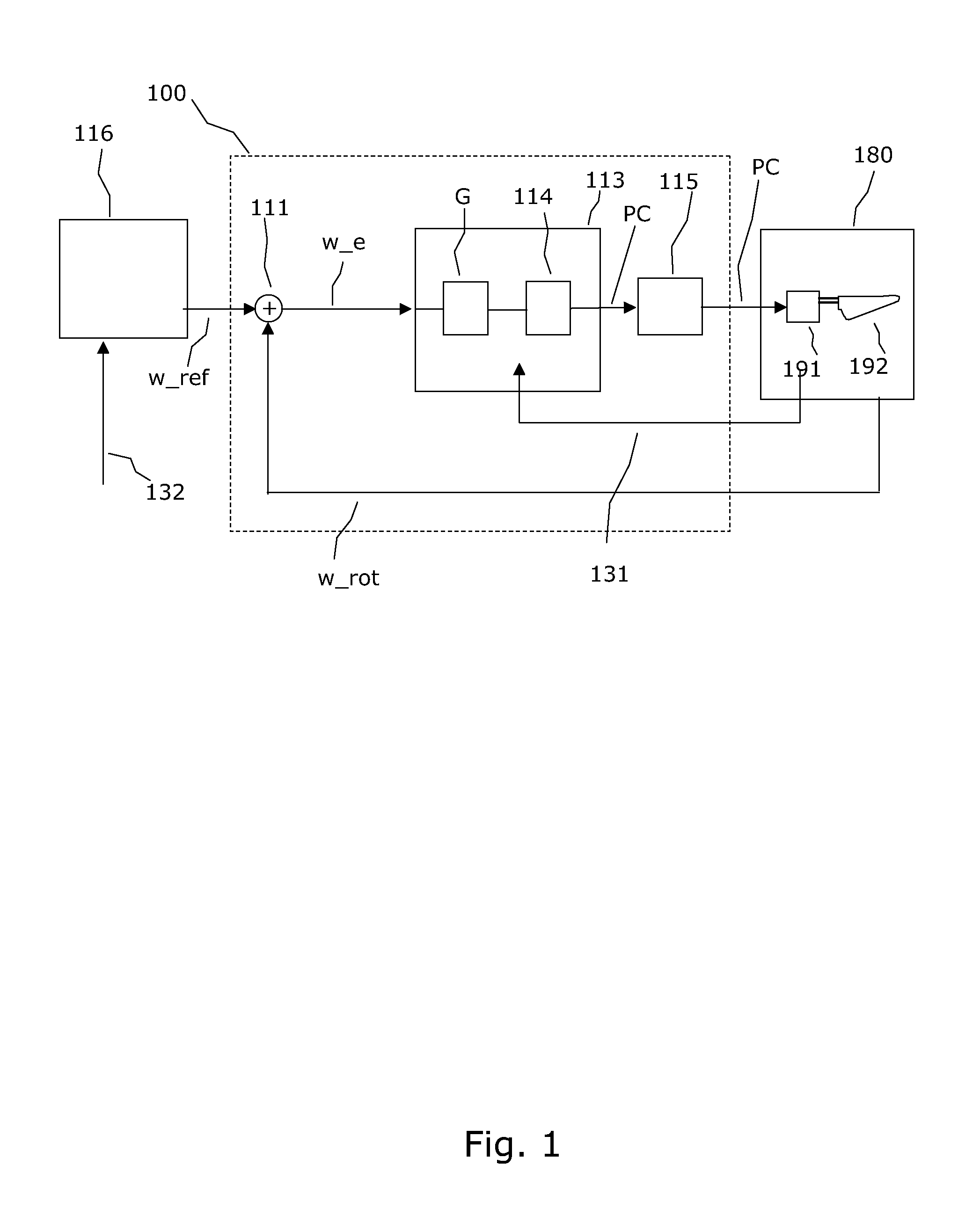
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS20070216164A1Avoiding undesired harmonic distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityHarmonic
A variable speed wind turbine having a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG), includes an exciter machine mechanically coupled to the DFIG and a power converter placed between a rotor of the DFIG and the exciter machine. Thus, the power converter is not directly connected to the grid avoiding the introduction of undesired harmonic distortion and achieving a better power quality fed into the utility grid. Moreover, the variable speed wind turbine includes a power control and a pitch regulation.
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
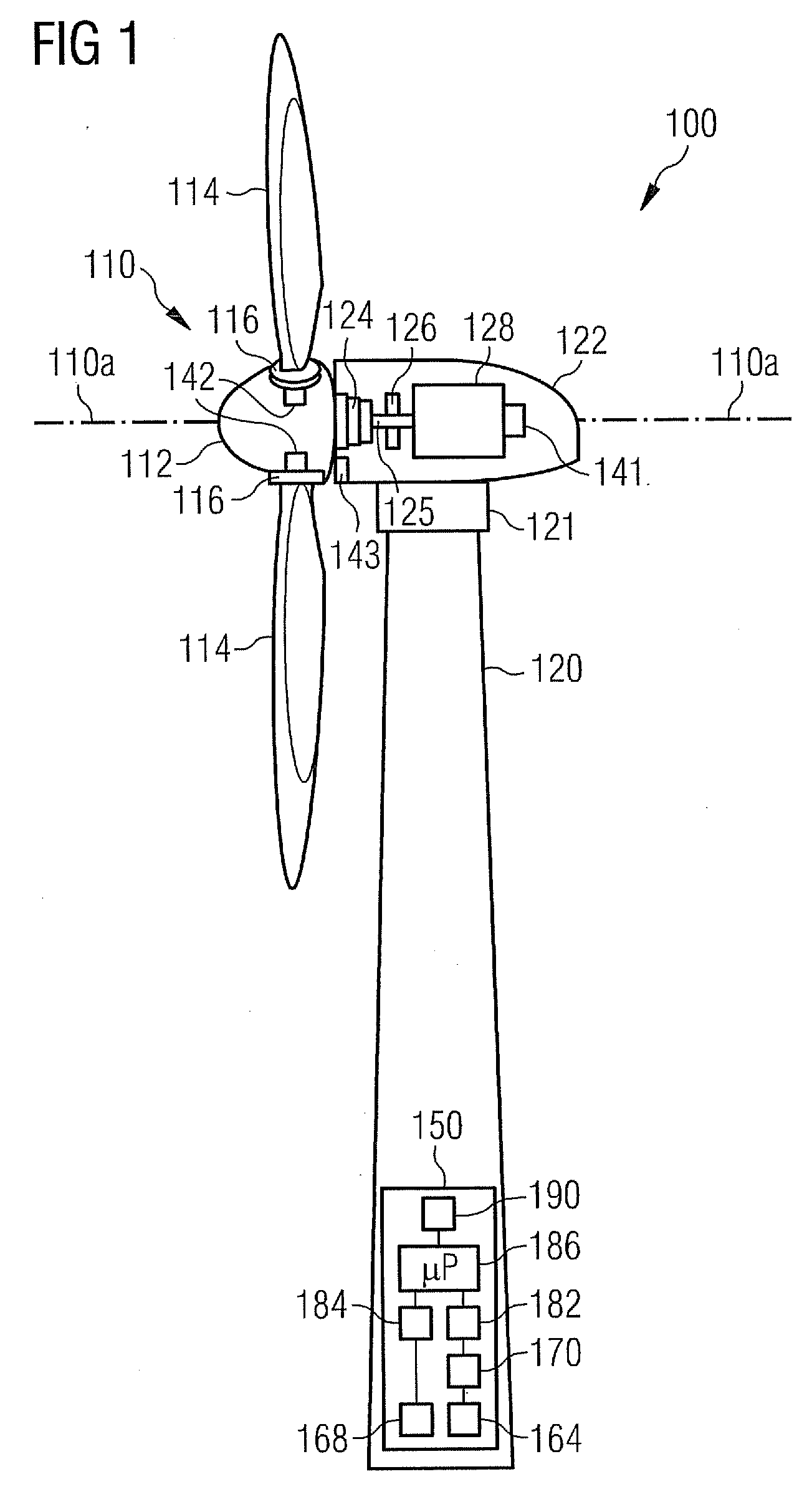
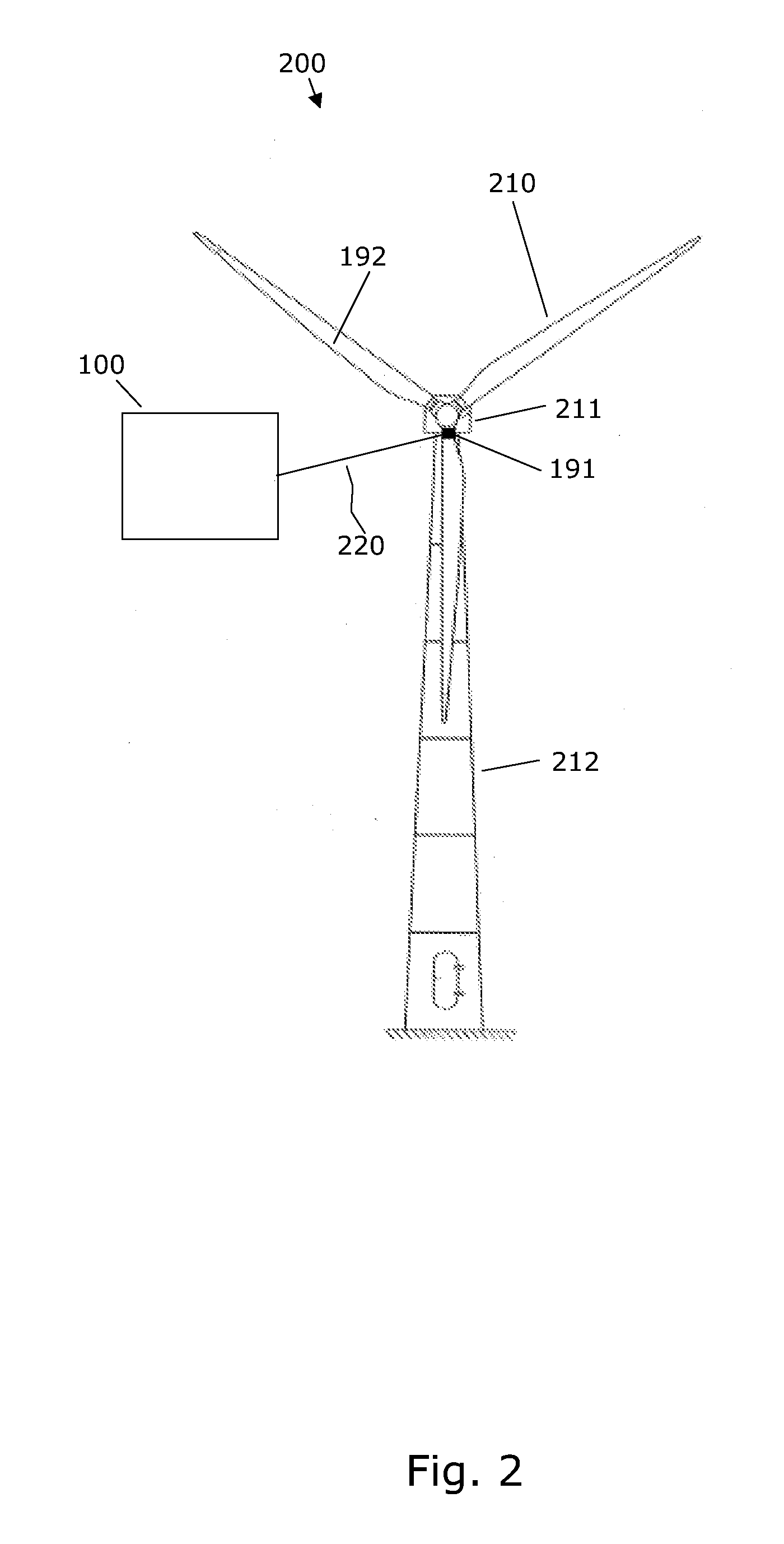
Methods and apparatus for reduction of asymmetric rotor loads in wind turbines
A method for reducing load and providing yaw alignment in a wind turbine includes measuring displacements or moments resulting from asymmetric loads on the wind turbine. These measured displacements or moments are used to determine a pitch for each rotor blade to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading and a favorable yaw orientation to reduce pitch activity. Yaw alignment of the wind turbine is adjusted in accordance with the favorable yaw orientation and the pitch of each rotor blade is adjusted in accordance with the determined pitch to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
Variable speed wind turbine having an exciter machine and a power converter not connected to the grid
ActiveUS7425771B2Avoid distortionImprove power qualityGenerator control circuitsVector control systemsPower qualityPower grid
Owner:INGETEAM POWER TECH
Methods and apparatus for reduction of asymmetric rotor loads in wind turbines
A method for reducing load and providing yaw alignment in a wind turbine includes measuring displacements or moments resulting from asymmetric loads on the wind turbine. These measured displacements or moments are used to determine a pitch for each rotor blade to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading and a favorable yaw orientation to reduce pitch activity. Yaw alignment of the wind turbine is adjusted in accordance with the favorable yaw orientation and the pitch of each rotor blade is adjusted in accordance with the determined pitch to reduce or counter asymmetric rotor loading.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and a system for controlling operation of a wind turbine
ActiveUS20100332272A1Reduce in quantityTotal downtime of the wind turbine is reducedLevel controlWind motor controlTurbineWind force
A method and a system for controlling operation of a wind turbine are provided. The method includes determining at least one failure mode relating to one or more components of the wind turbine, estimating a remaining lifetime of the component under current operating conditions, determining one or more control schemes to control the operation of the wind turbine in order to adjust the remaining lifetime of the component to a desired remaining lifetime of the component, determining a power production yield for the determined one or more control schemes and selecting a determined control scheme for controlling the operation of the wind turbine that maximizes the power production yield.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
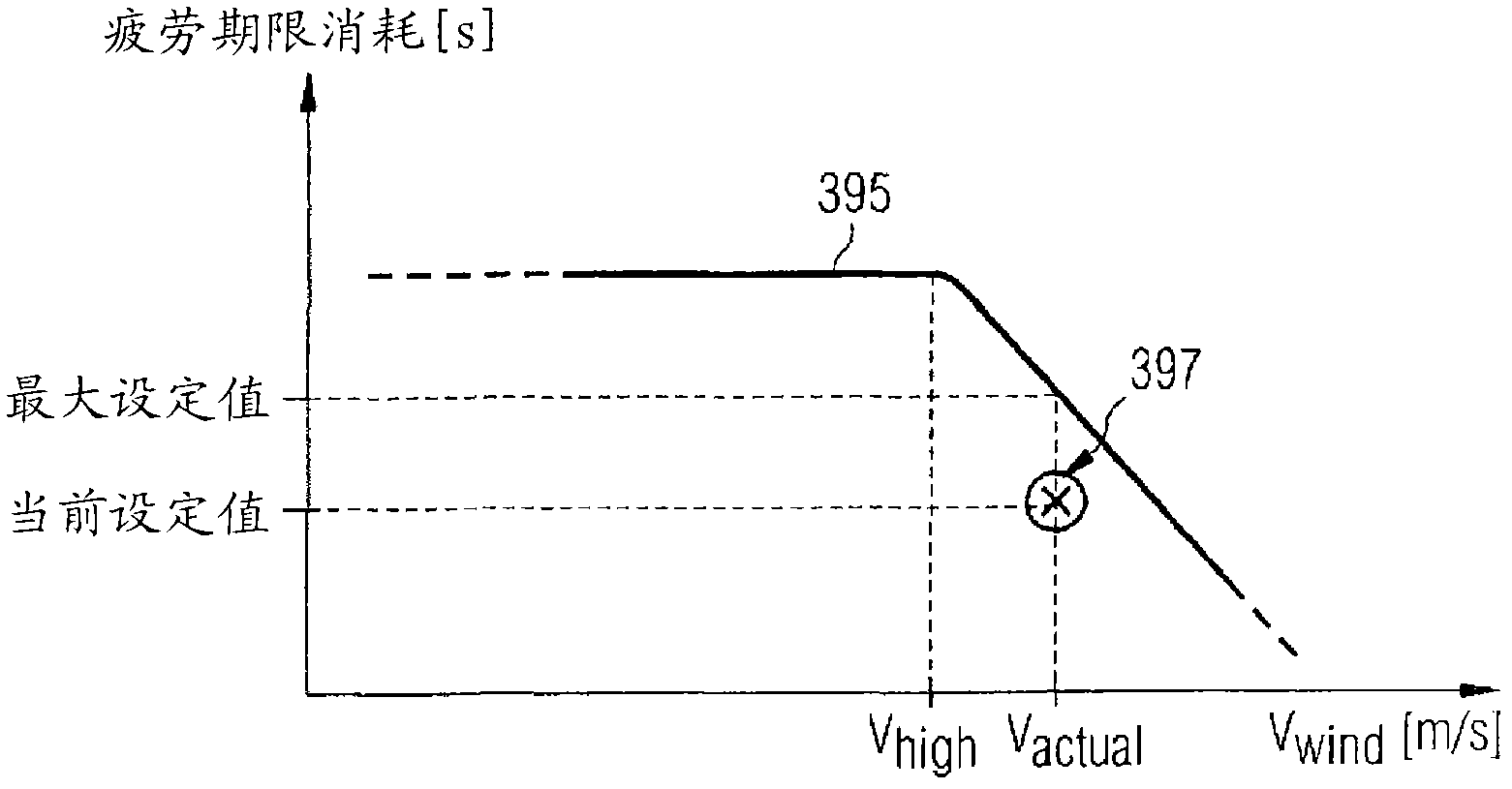
Wind speed dependent adaptation of a set point for a fatigue life of a structural component of a wind turbine
InactiveUS20110123331A1Efficient and flexible control procedureEfficient and flexiblePropellersPump componentsCurrent velocityControl system
A method for controlling an operation of a wind turbine with at least one structural component is provided. A fatigue life time consumption of the structural component is scheduled. A current velocity of a wind which is driving the wind turbine is determined. A current set point value for the fatigue life time consumption of the structural component based on the scheduled fatigue life time consumption of the structural component is specified and a maximum set point value for the fatigue life time consumption of the structural component based on the determined current wind velocity is specified. The wind turbine is operated depending on the specified current set point value and / or on the specified maximum set point value such that a mechanical load acting on the structural component is controlled. A machine load control system and a wind turbine are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
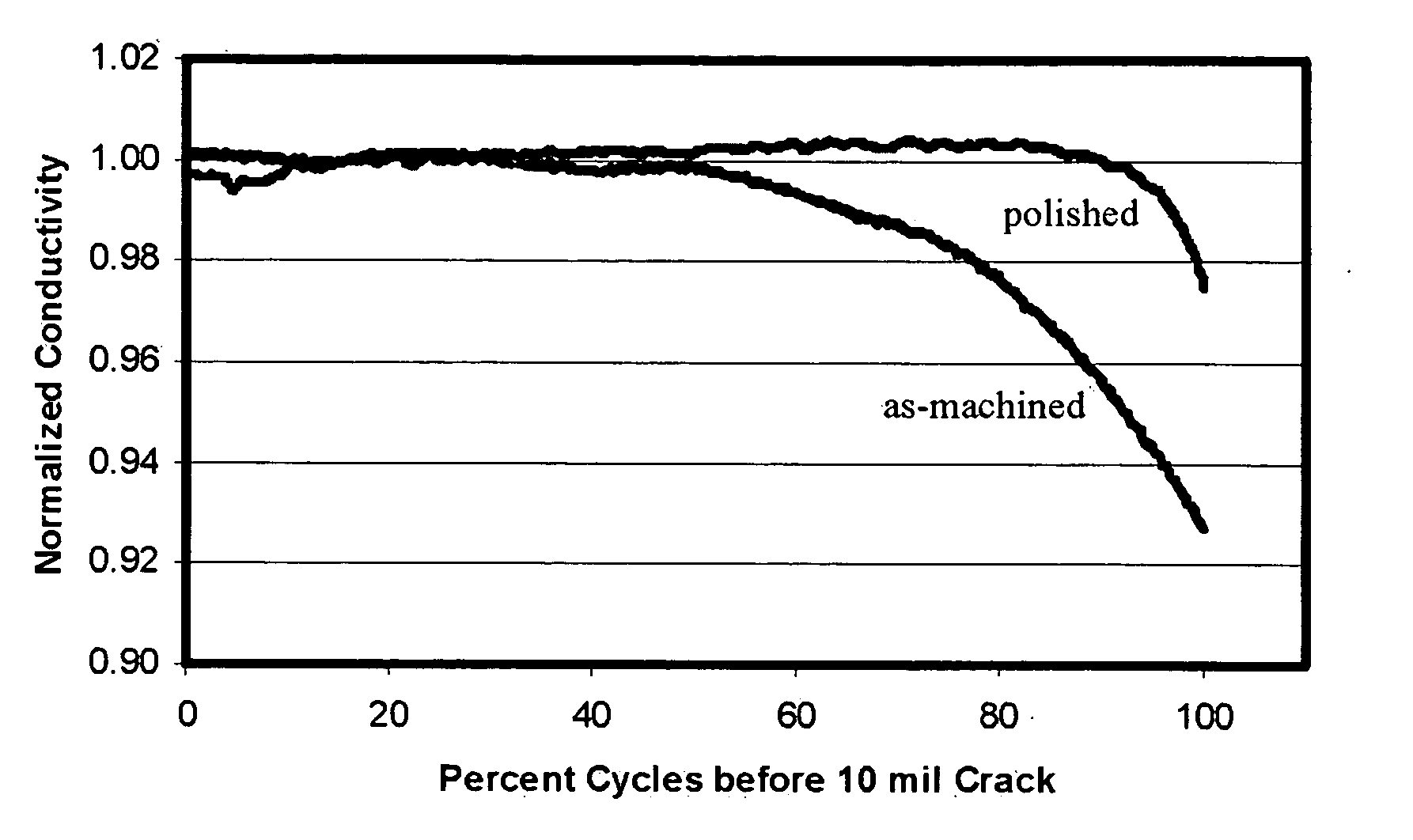
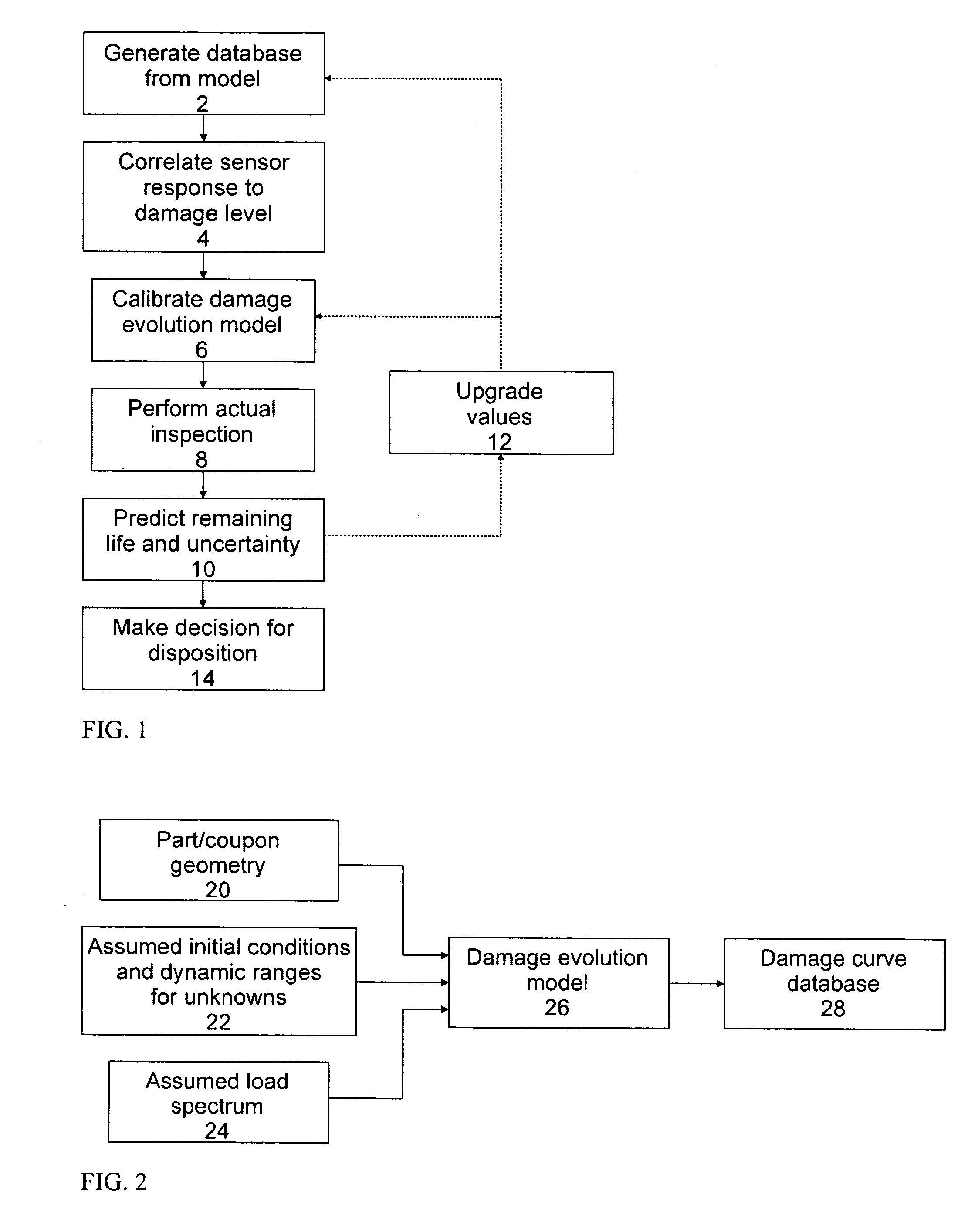
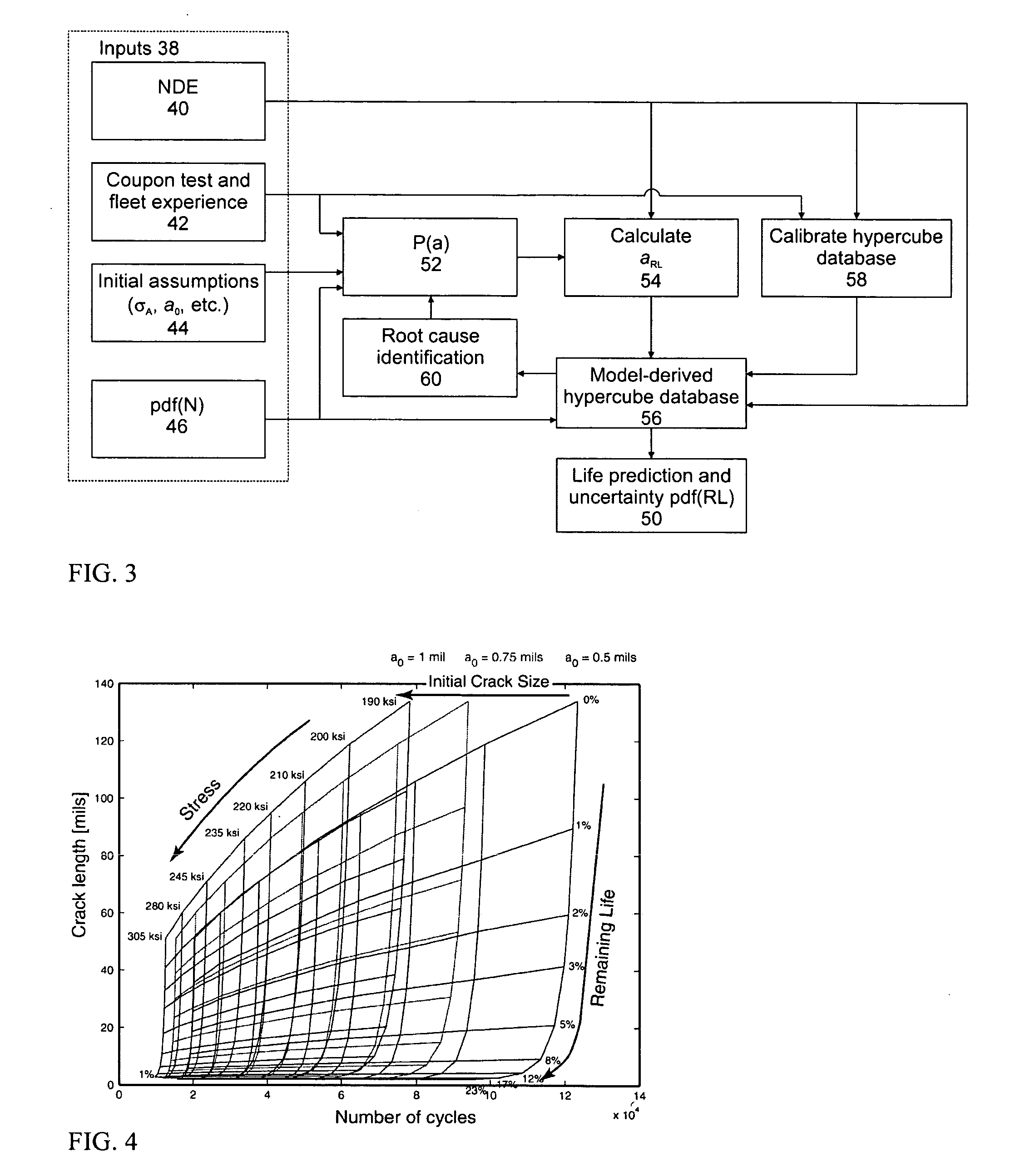
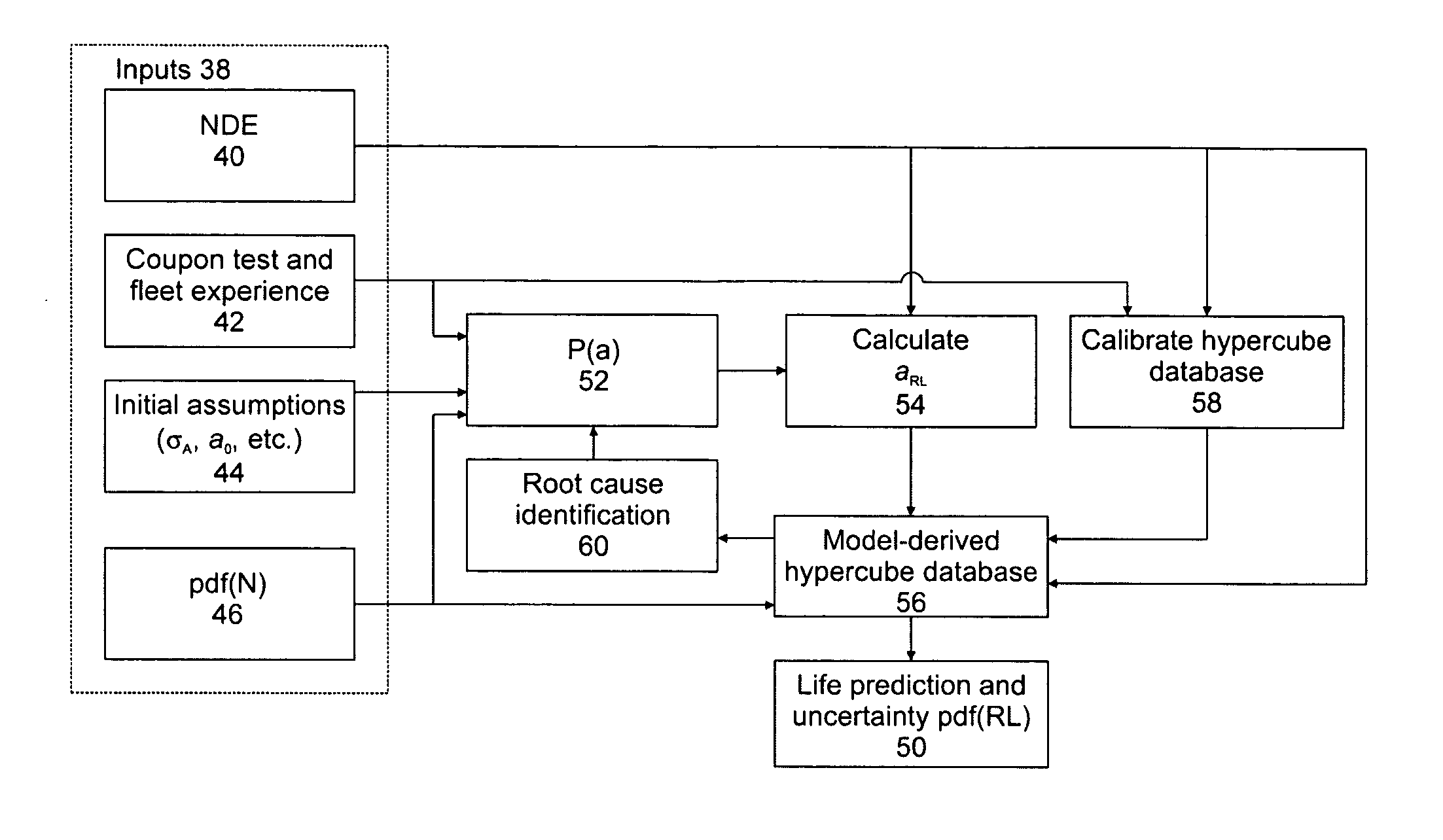
Remaining life prediction for individual components from sparse data
ActiveUS20070239407A1Effective calculationActive/predictive/anticipative controlElectric/magnetic roughness/irregularity measurementsRoot causeDecision taking
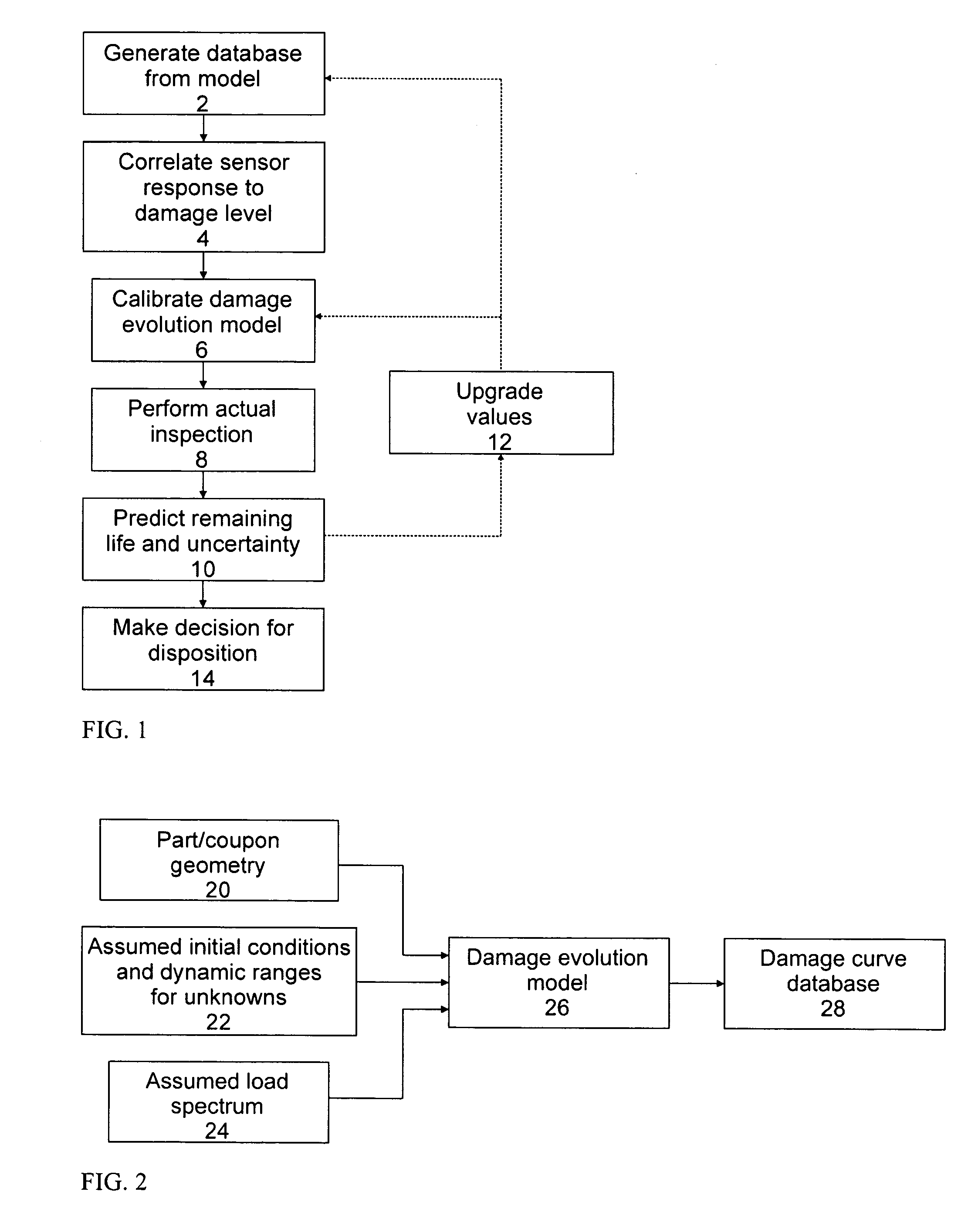
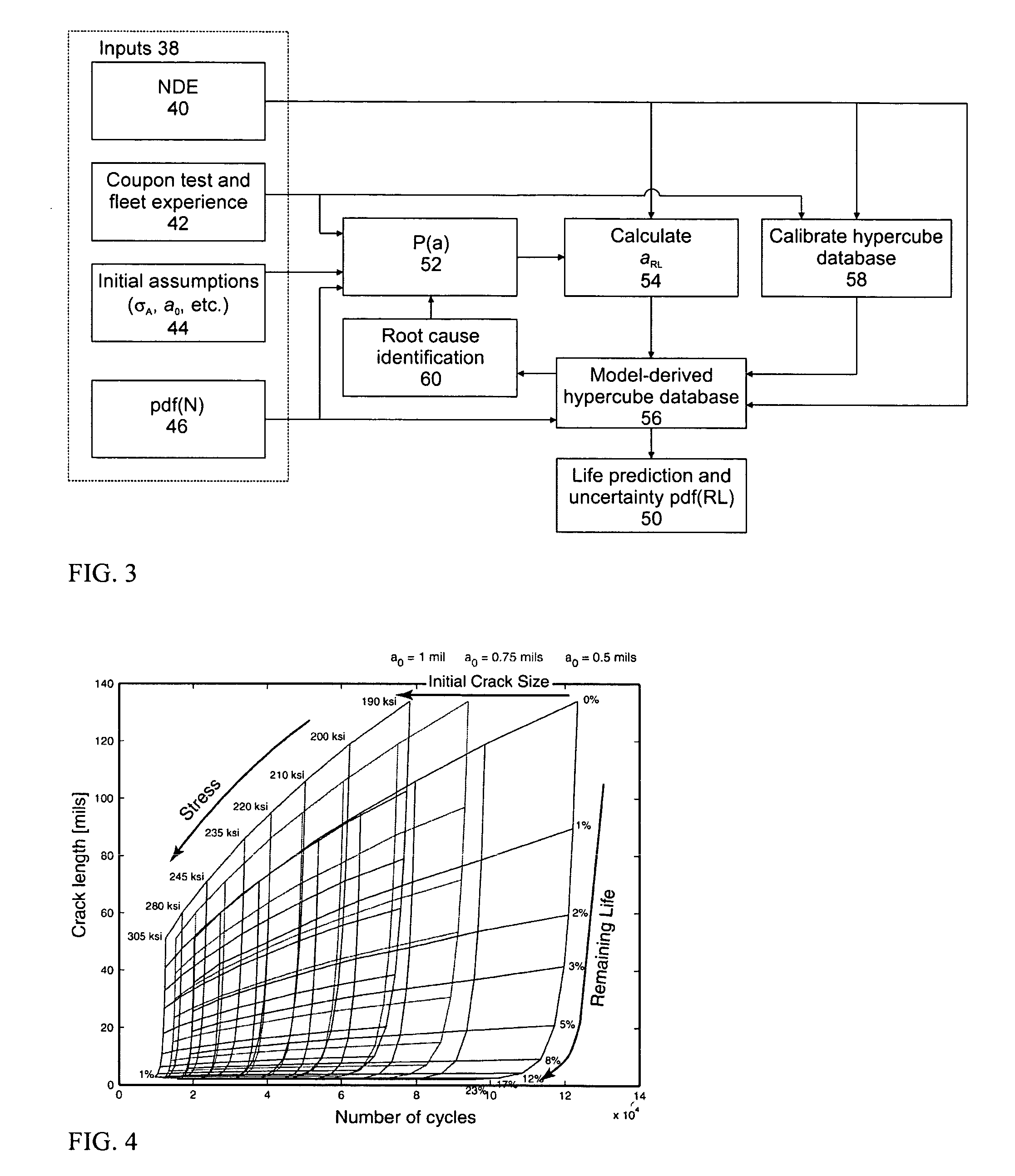
Predicting the remaining life of individual aircraft, fleets of aircraft, aircraft components and subpopulations of these components. This is accomplished through the use of precomputed databases of response that are generated from a model for the nonlinear system behavior prior to the time that decisions need to be made concerning the disposition of the system. The database is calibrated with a few data points, to account for unmodeled system variables, and then used with an input variable to predict future system behavior. These methods also permit identification of the root causes for observed system behavior. The use of the response databases also permits rapid estimations of uncertainty estimates for the system behavior, such as remaining life estimates, particularly, when subsets of an input variable distribution are passed through the database and scaled appropriately to construct the output distribution. A specific example is the prediction of remaining life for an aircraft component where the model calculates damage evolution, input variables are a crack size and the number of cycles, and the predicted parameters are the actual stress on the component and the remaining life.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
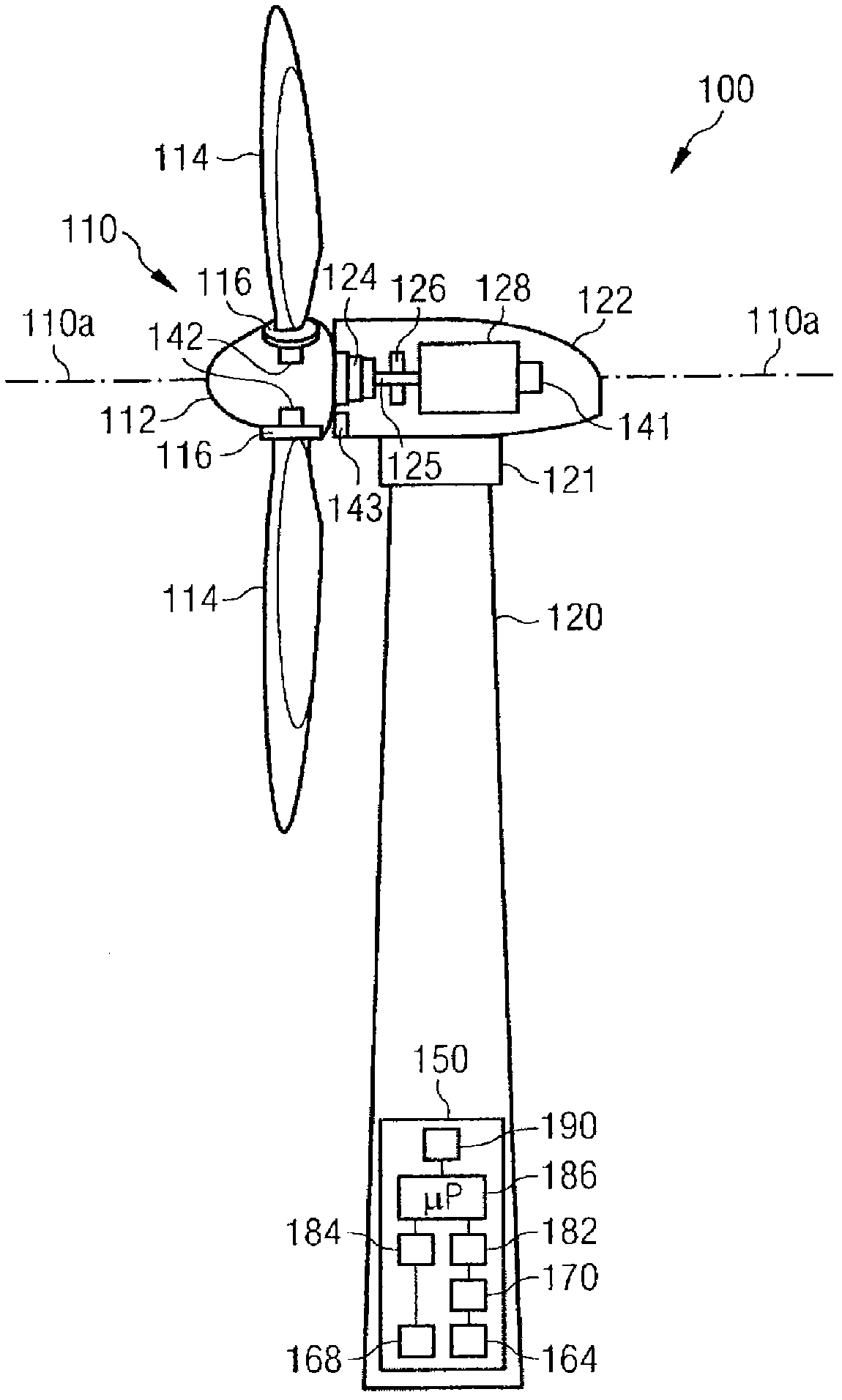
Method of operating a wind turbine
InactiveCN1900513AReduce power outputShorten speedOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlTurbineElectric generator
In a wind turbine and in a method of operating a wind turbine, the rotor speed and / or the power of the generator is reduced in response to a variable exceeding a predetermined value. Said variables belong to the group of variables consisting of wind direction and wind turbulence sensed by external sensors relative to the horizontal direction of the turbine main shaft and by one or Any other variable sensed by multiple sensors.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Pitch control of a wind turbine
A wind turbine control system suitable for minimising actuation of pitch actuators is disclosed. The control system uses an error gain schedule in full load control for reducing pitch actuation when the difference between the rotor speed and the reference rotor speed is not critical for the load of wind turbine components. The error gain schedule may be a nonlinear function which reduces the gain for low rotor speed errors. The use of the error gain schedule may reduce wear of the pitch actuators and may improve reduction of structural oscillations since focus removed from tracking the rotor speed reference when the speed error is low.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Wind speed dependent adaptation of a set point for a fatigue life of a structural component of a wind turbine
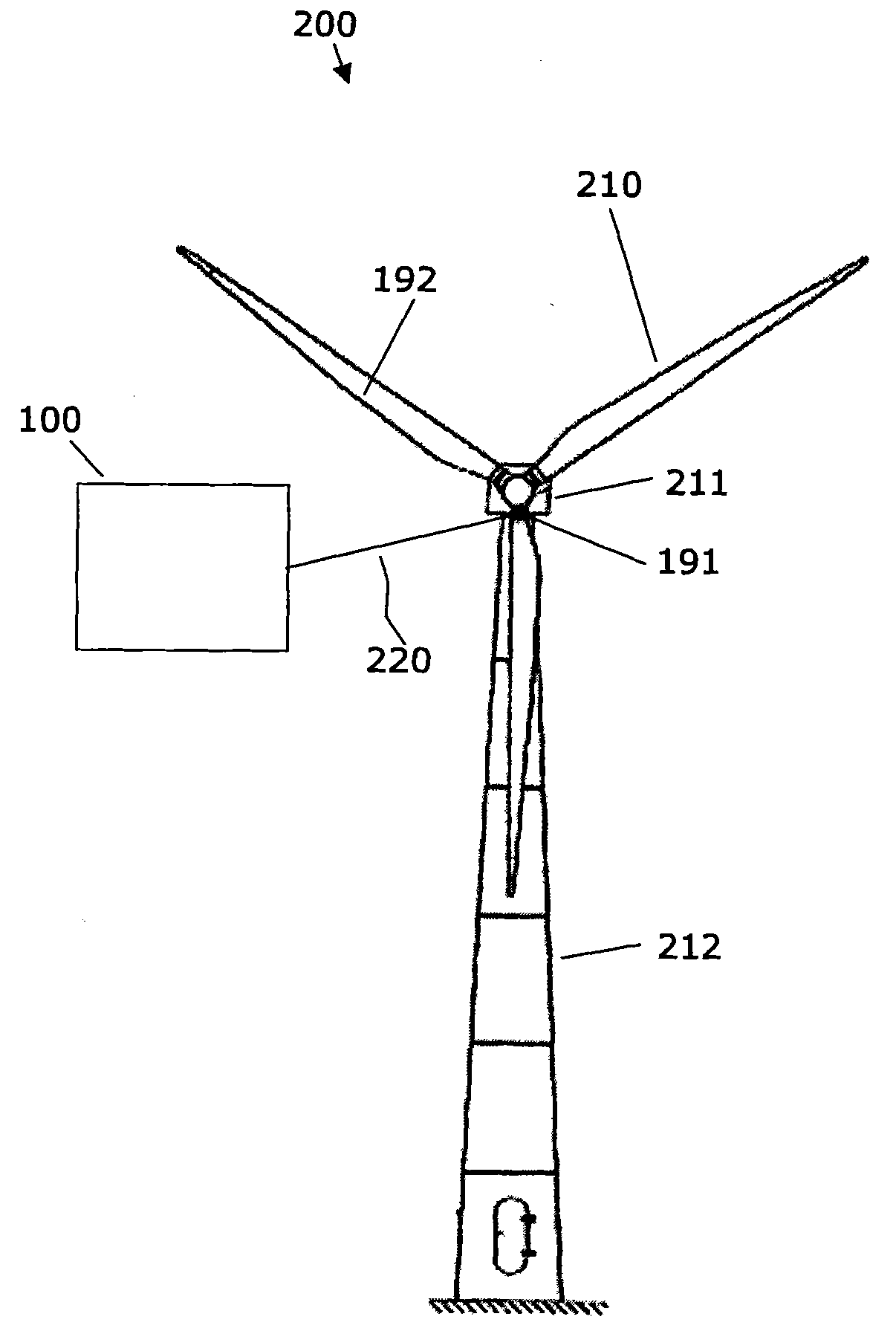
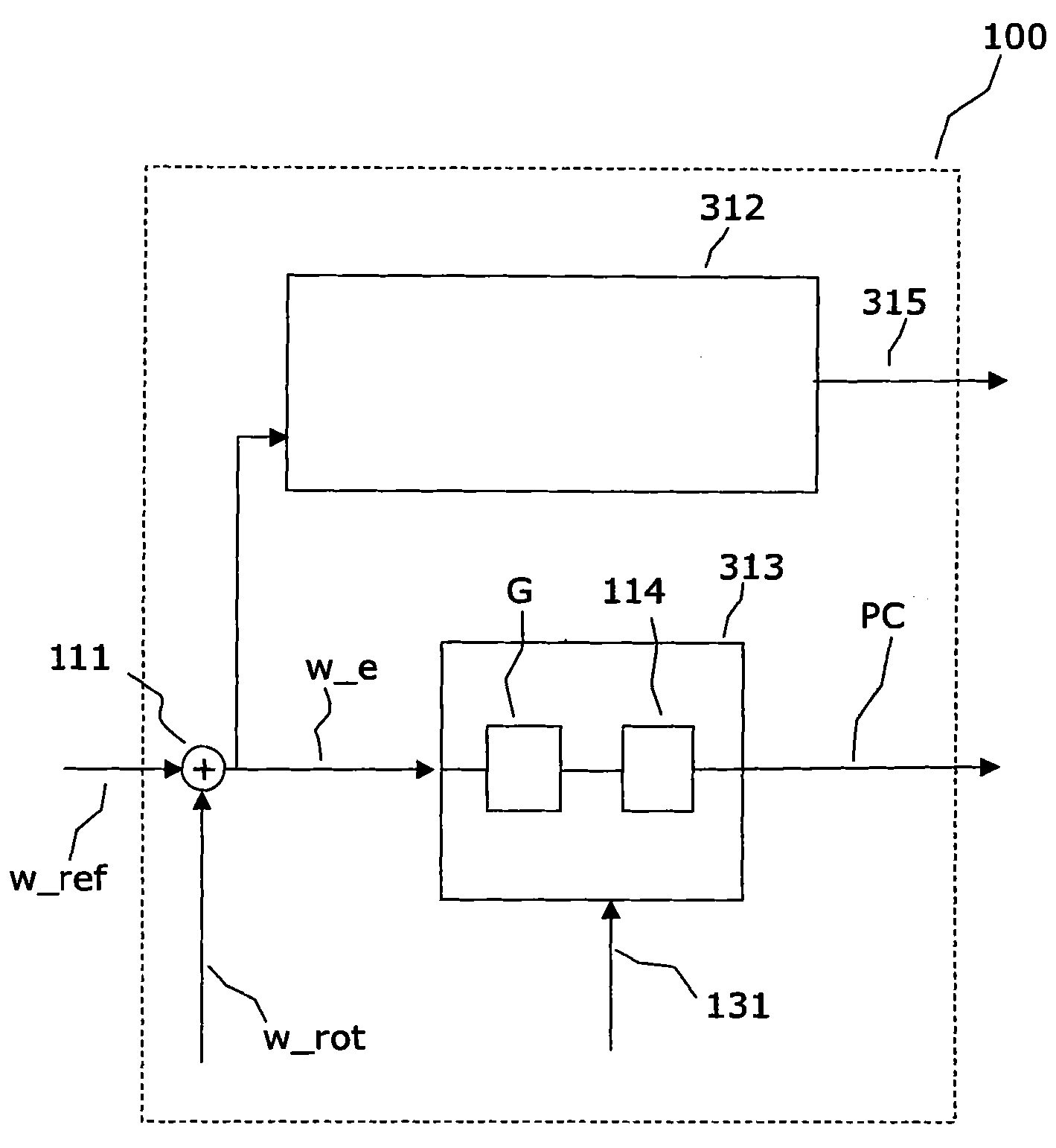
The invention relates to a wind speed dependent adaptation of a set point for a fatigue life of a structural component of a wind turbine. It is described a method for controlling the operation of a wind turbine (100) comprising at least one structural component. The described method comprises (a) scheduling a fatigue life time consumption of the structural component (114, 120, 122), (b) determining the current velocity of a wind which is driving the wind turbine, (c) specifying a current set point value for the fatigue life time consumption of the structural component based on the scheduled fatigue life time consumption of the structural component, (d) specifying a maximum set point value for the fatigue life time consumption of the structural component based on the determined current wind velocity, and (e) operating the wind turbine (100) depending on the specified current set point value and / or on the specified maximum set point value such that a mechanical load acting on the structural component is controlled. It is further described a machine load control system, a wind turbine and a computer program, which are adapted for carrying out and / or for controlling the described wind turbine operation control method.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
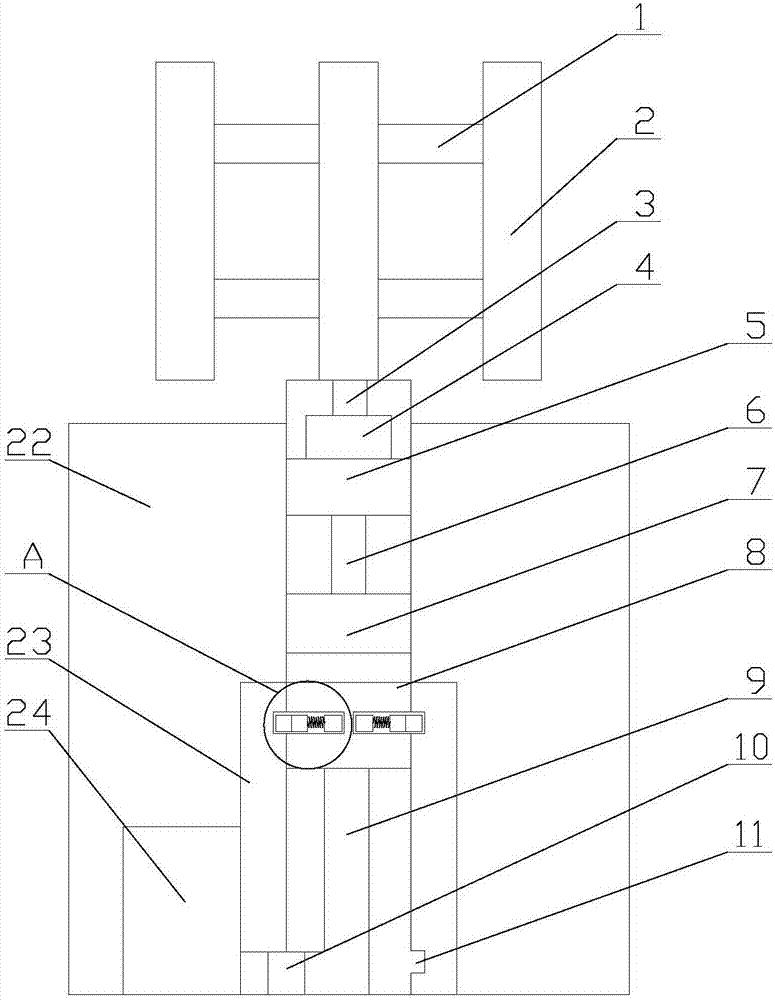
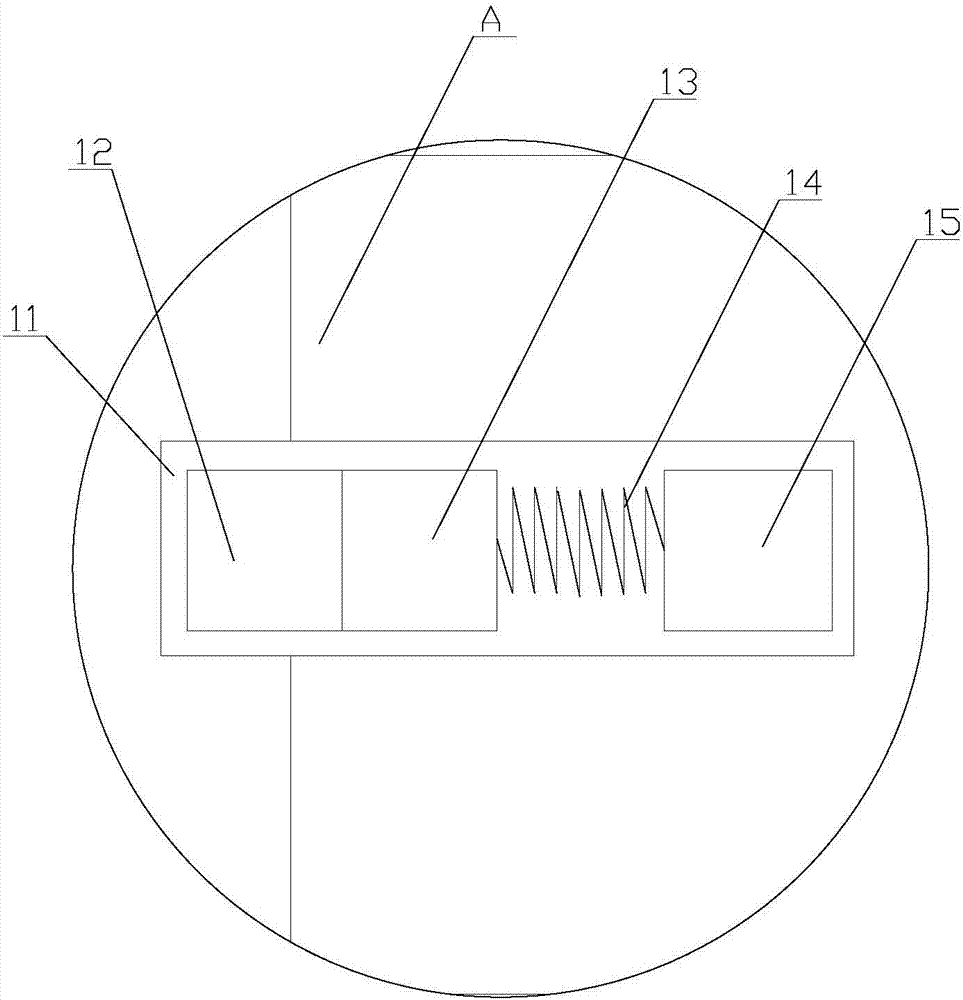
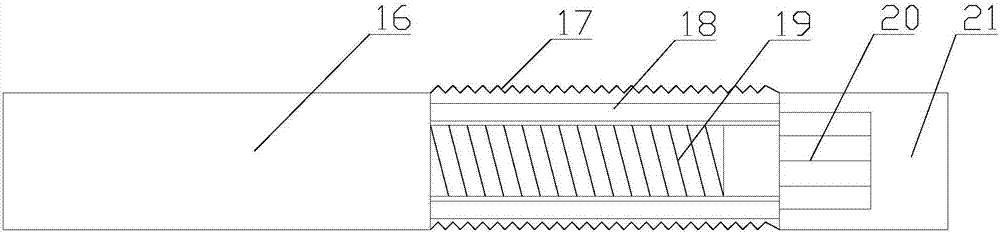
Bearing unit for a long rotor blade of a wind power installation, wind power installation comprising one such rotor blade bearing arrangement, and method for operating one such wind power installation
InactiveCN101194103APrevent or prevent damageAvoid wear and tearRoller bearingsWind motor controlRotational axisWind power
The invention relates to a bearing unit for a long rotor blade, especially a wind power installation, said bearing unit comprising two annular elements that can be rotated in relation to each other and are directly or indirectly connected to the rotor blade hub and to the rotor blade, and at least two running tracks that can be axially staggered in relation to each other and comprise peripheral rolling bodies with an approximately cylindrical shape, i.e. each comprising a lateral surface that is rotationally symmetrical to a rotational axis in a very precise manner. The aim of the invention is to be able to fully absorb the tipping moment caused by the wind pressure on the rotor blade and on the bearing unit, and optionally to absorb other forces and other moments. To this end, two running tracks are arranged between the two connection elements, are axially staggered in relation to each other, and comprise rolling bodies with an approximately cylindrical shape, said rolling bodies being oriented in such a way that the rotational axes thereof intersect the longitudinal axis of the rotor blade in question at an angle of between 30° and 90°. The invention also rates to a wind power installation provided with one such rotor blade bearing arrangement, and to a method for operating one such wind power installation. The at least one rotor blade in question is continuously rotted about the longitudinal axis thereof during the option of the wind power installation.
Owner:IMO HOLDING GMBH
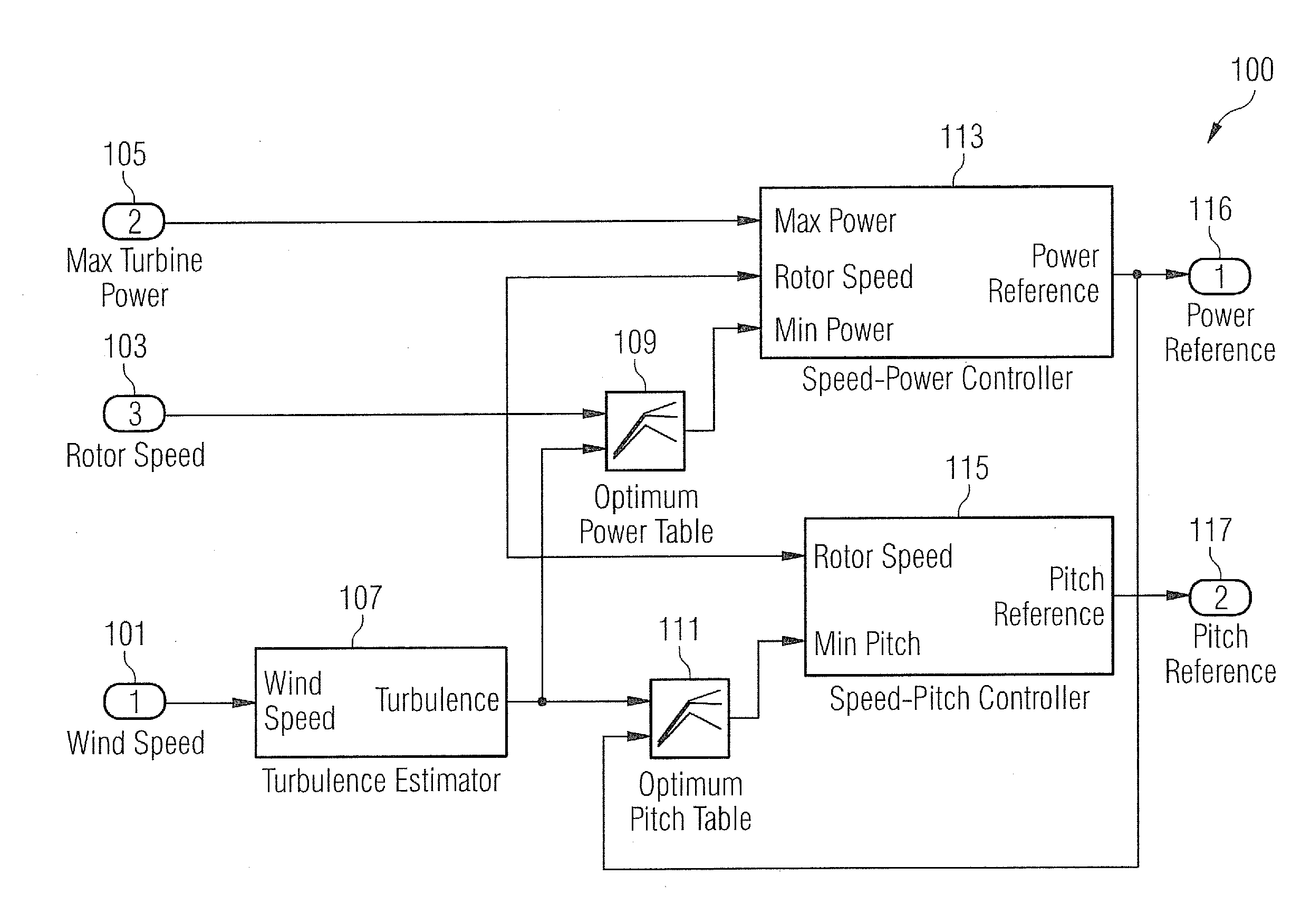
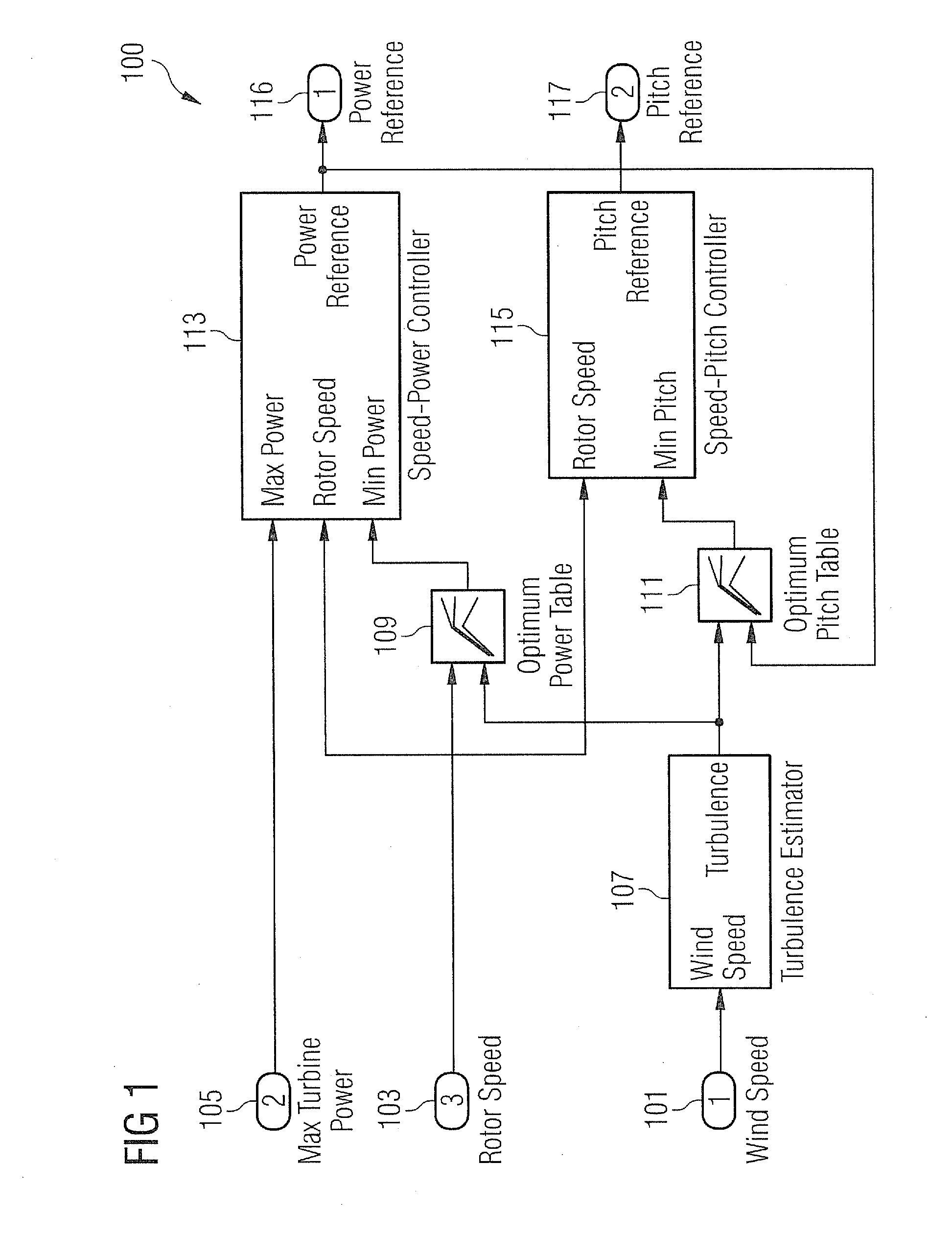
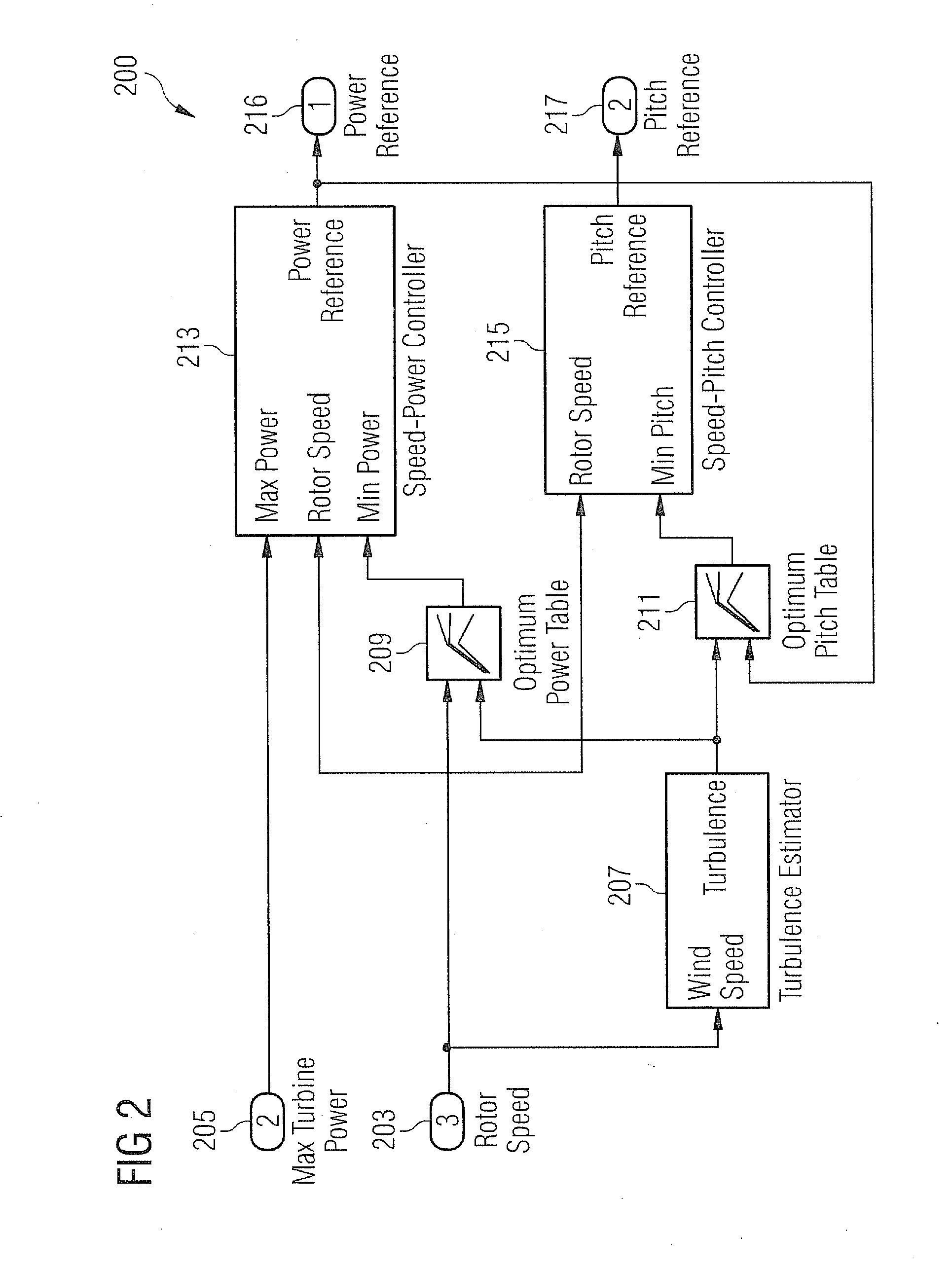
Methods and systems for generating wind turbine control schedules
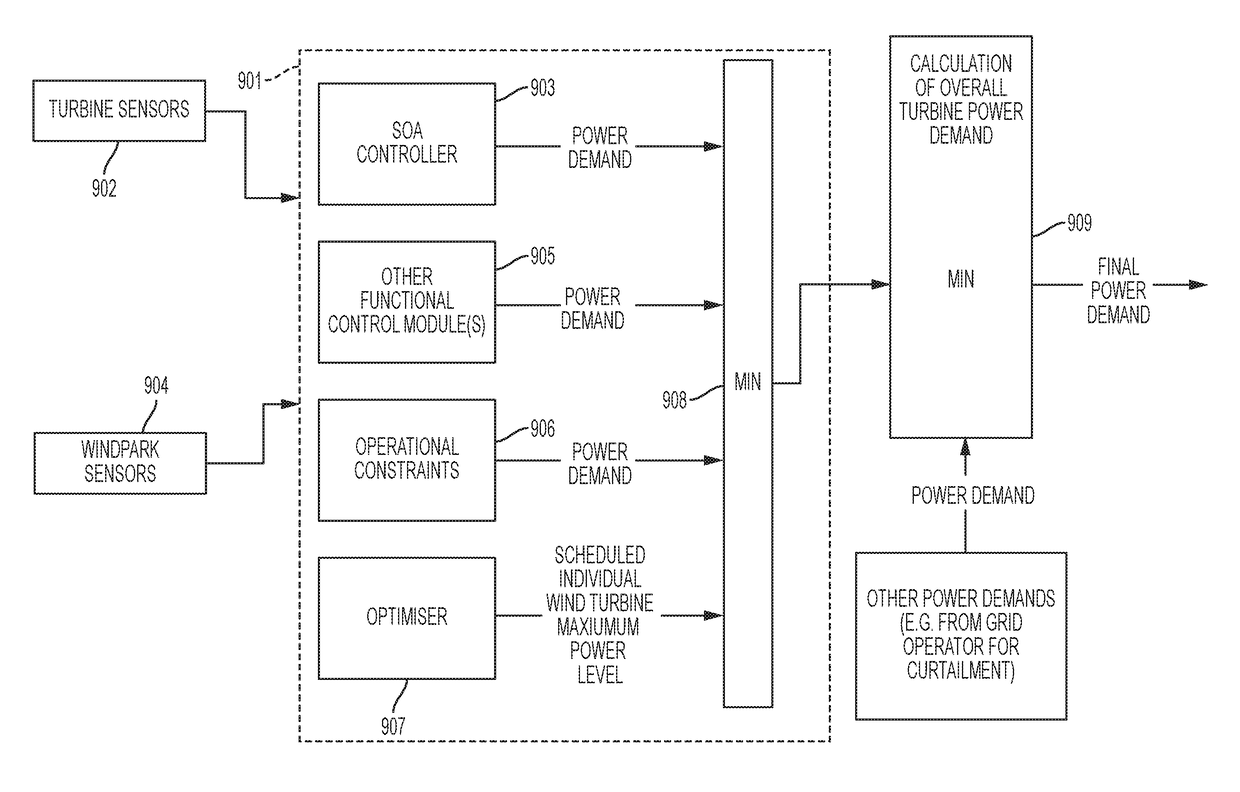
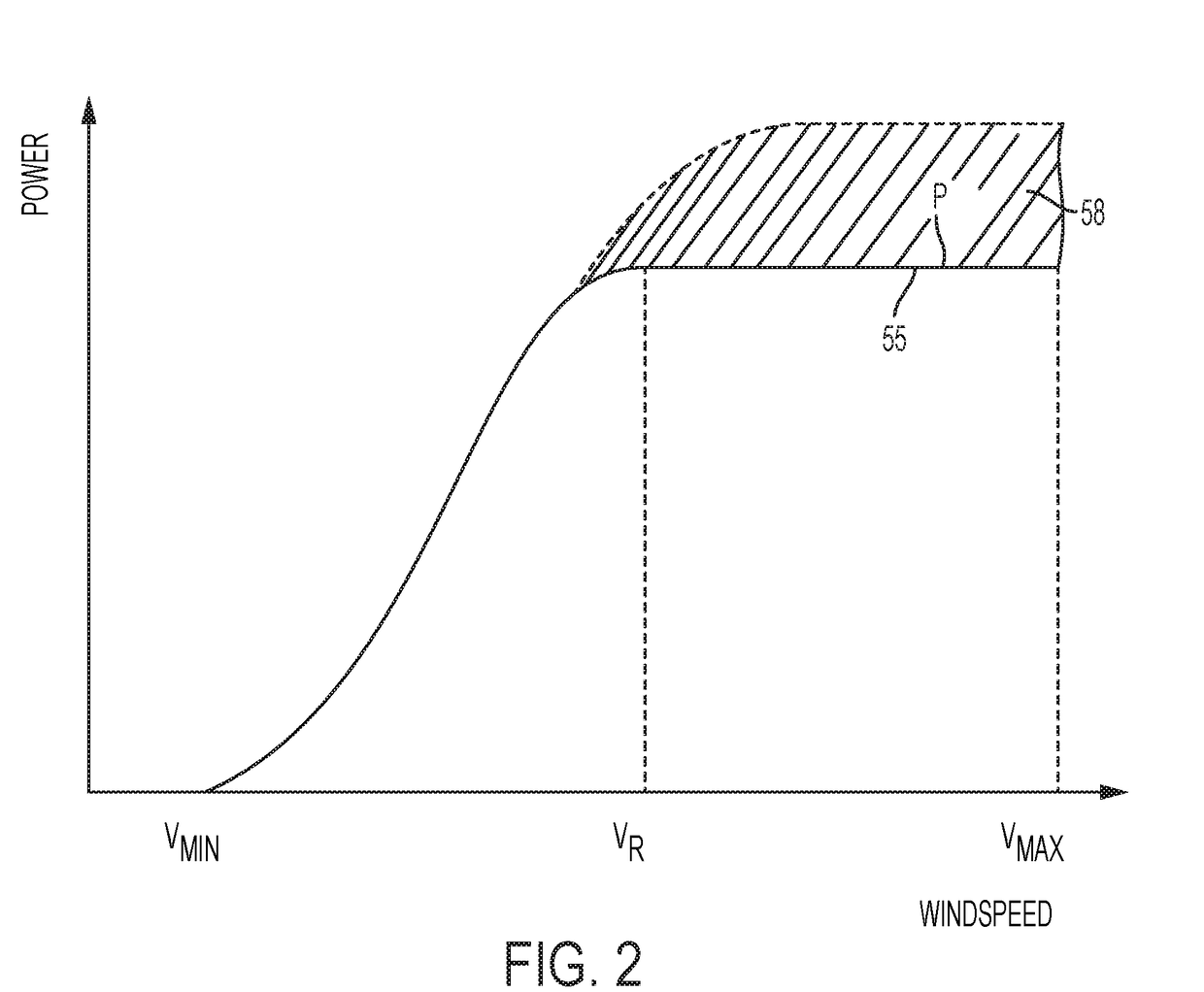
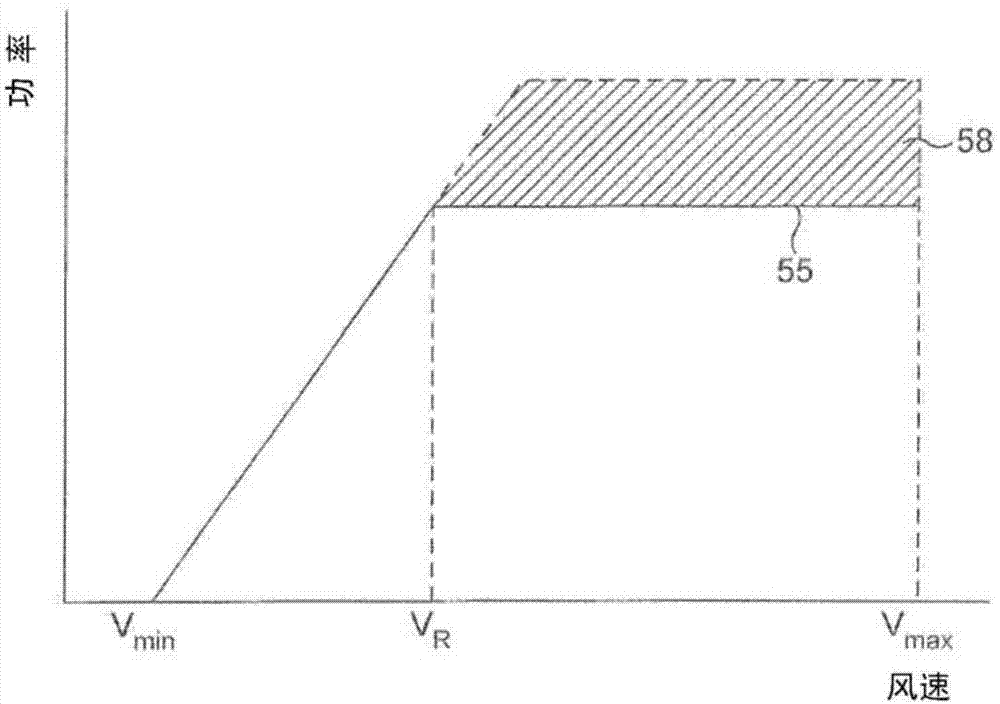
A method of generating a control schedule for a wind turbine is provided, the control schedule indicating how the turbine maximum power level varies over time, the method comprising: receiving input indicative of a target minimum wind turbine lifetime; determining a value indicative of the current remaining fatigue lifetime of the wind turbine or one or more turbine components, based on measured wind turbine site and / or operating data; and varying a parameter of an initial predefined control schedule that specifies how the turbine maximum power level varies over time. The parameter is varied by: (i) adjusting the parameter of the initial predefined control schedule; (ii) estimating the future fatigue lifetime consumed by the wind turbine or the one or more turbine components, over the duration of the varied control schedule, based upon the varied control schedule; and (iii) repeating steps (i) and (ii) until the estimated future fatigue lifetime consumed by the wind turbine or each of the one or more turbine components is sufficient to allow the target minimum wind turbine life to be reached.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
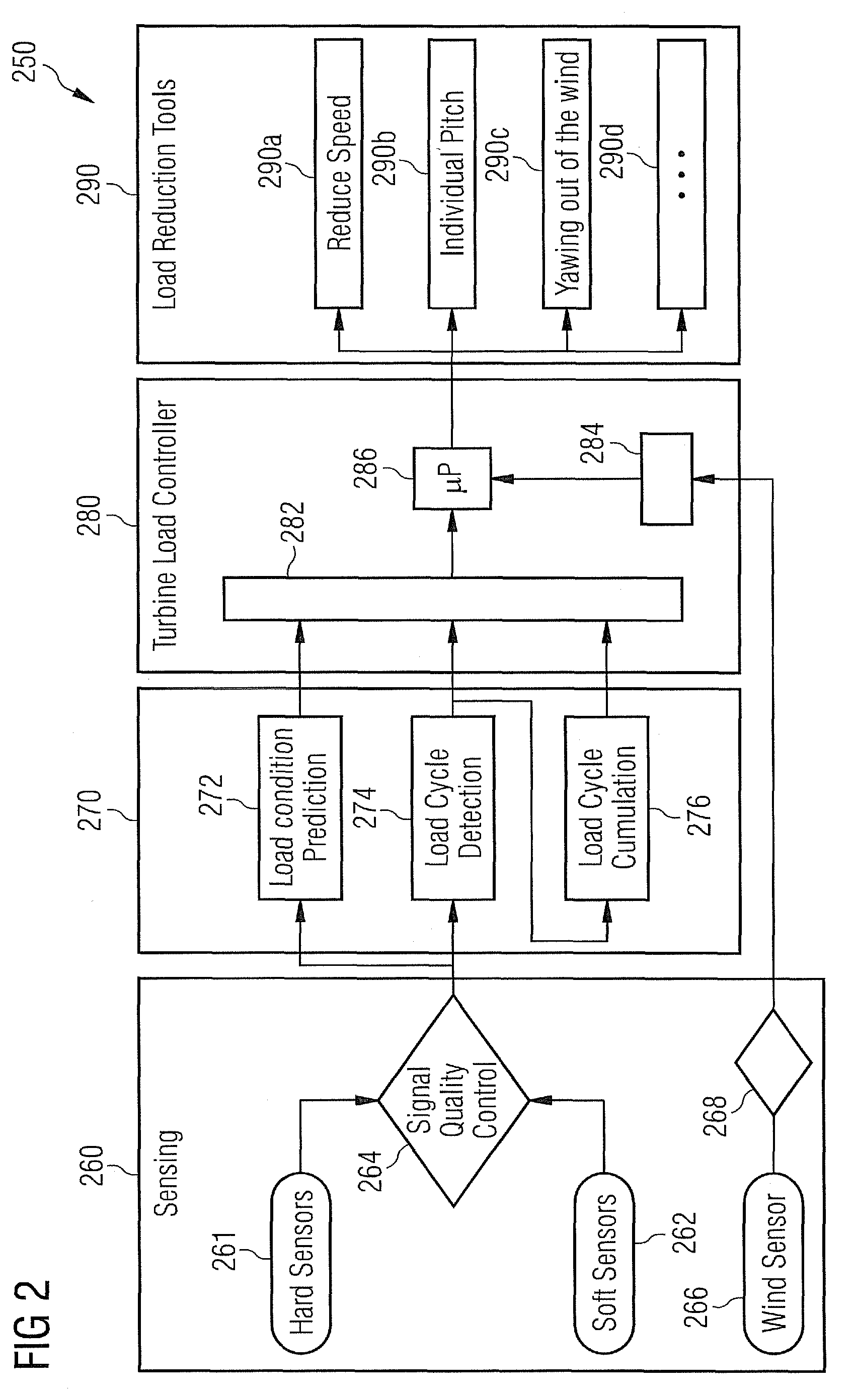
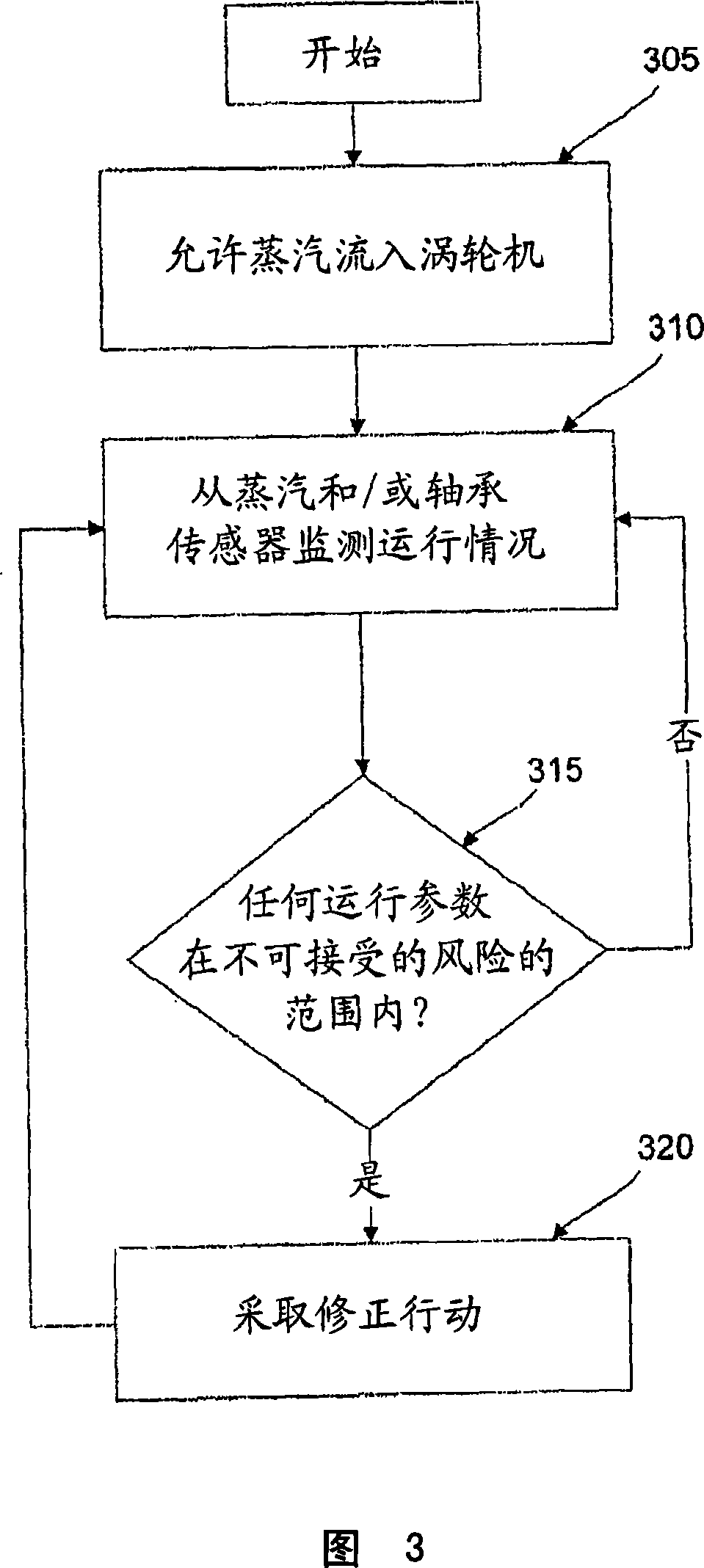
Systems and methods for detecting undesirable operation of a turbine
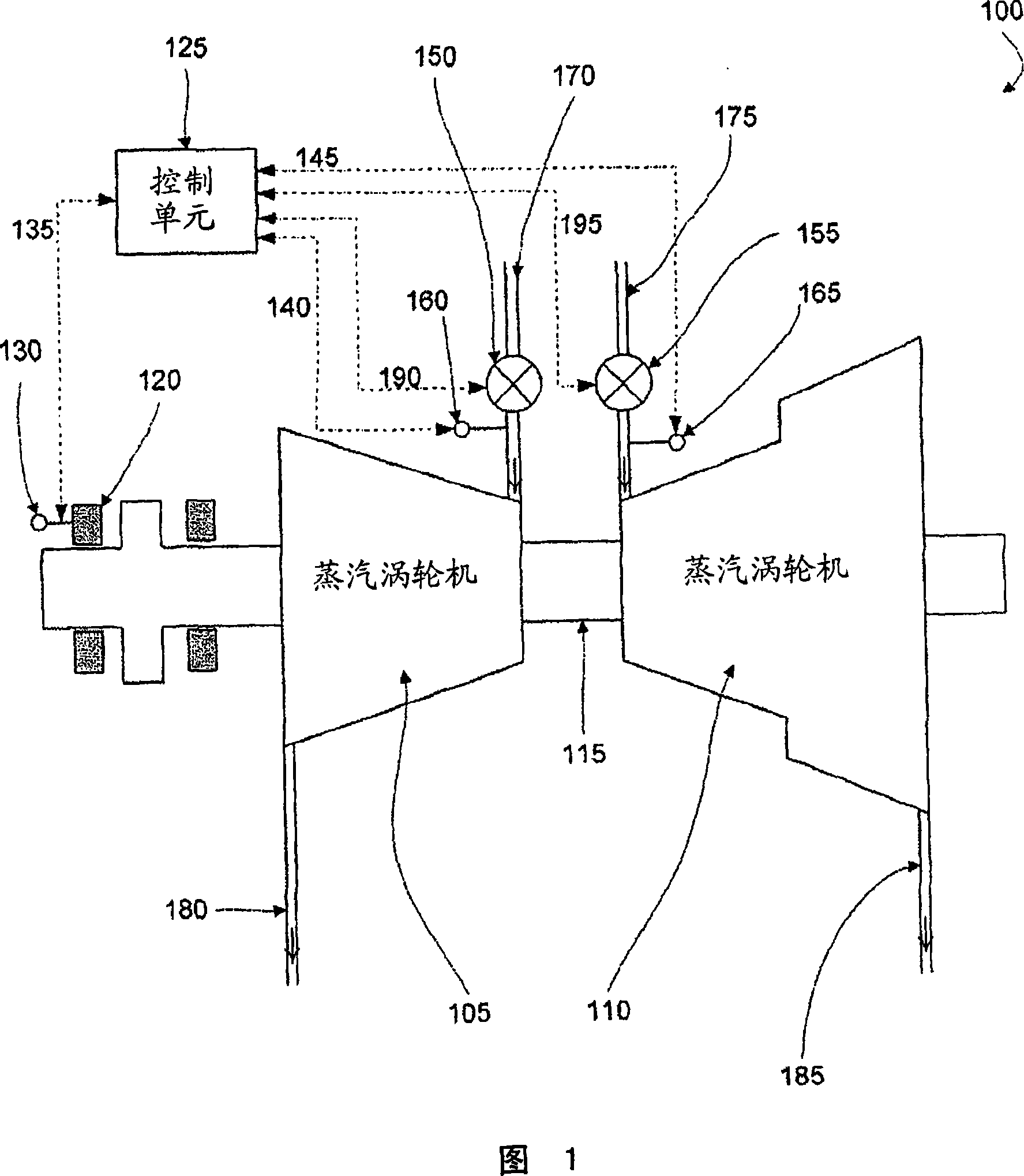
Systems and methods of detecting and correcting the undesirable operation of a turbine by monitoring one or more sensor devices, where each sensor device monitors one or more operating parameter values associated with various turbine components. If any of the sensor devices detects that a particular operating parameter associated with one or more turbine components is operating in a range of unacceptable risk, then corrective action is taken which may include opening and or closing one or more of the steam values associated with an inlet pipe until that particular operating parameter of the turbine is no longer operating in a range of unacceptable risk.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control of wind turbines
ActiveCN103946540AOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlElectricity pricingElectricity price
A wind turbine power plant comprises a plurality of wind turbines, each having a rated output and under the control of a power plant controller. The power plant also has a rated output which may be over-rated in response to one or more of electricity pricing data, power plant age and operator demand. The power plant controller can send over-rating demand signals to individual turbines. The controllers at the turbines include a fatigue life usage estimator which estimates a measure of the fatigue life consumed by key components of the turbine. If this measure exceeds a target value for any component, over-rating is prevented at that turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method and system for adjusting a power parameter of a wind turbine
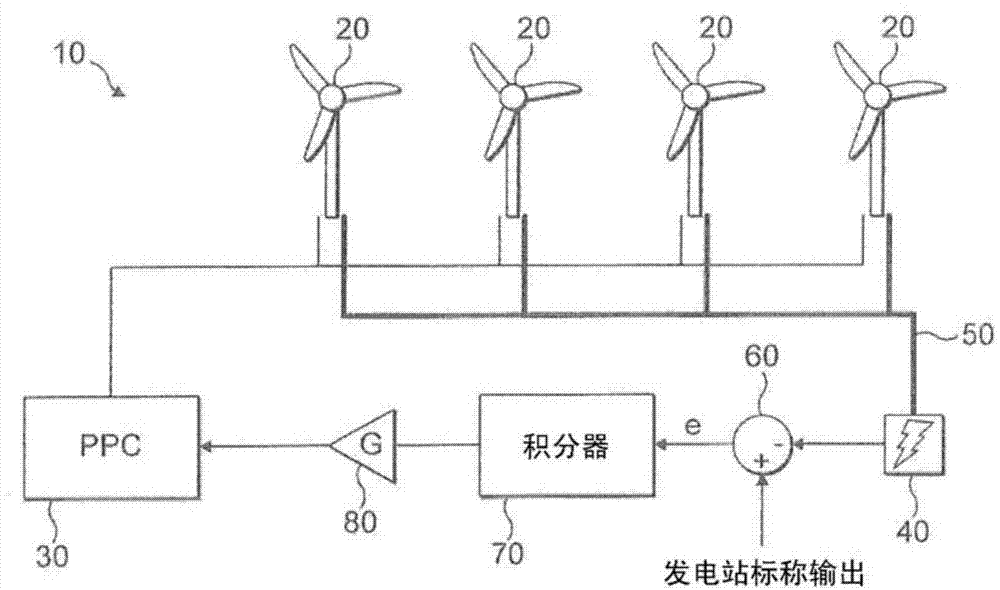
ActiveUS20120091713A1Reduce resistanceReduce loadWind motor controlEngine fuctionsPower parameterEngineering
A method for adjusting a power parameter of a wind turbine is disclosed. The method includes determining a load parameter indicative of a mechanical load of the wind turbine; estimating a turbulence of a wind speed based on the determined load parameter; and adjusting the power parameter relating to a power of the wind turbine based on the estimated turbulence. A system for adjusting a power parameter of a wind turbine is also described.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Method for controlling a wind power park and a wind power park controlled by such method
InactiveUS20130038060A1Cost of energyLow production costOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlElectricityGrid operator
A method for controlling a wind power park including the steps of: collecting information relating to meteorological conditions at the location of the wind power park, estimating for each of a plurality of the wind turbines the production costs per unit energy at different load levels of the respective wind turbine, collecting information from a utility grid operator relating to energy prices and possible requirements relating to the amount of power delivered from the wind power park to the utility grid, controlling the wind power park by deciding on a total amount of power to be delivered from the wind power park and distributing the decided power production between individual wind turbines, and repeating the above steps in order to obtain a dynamic control of the wind power park. Further, a wind power park being controlled by such method is disclosed.
Owner:K B ELECTRONICS INC
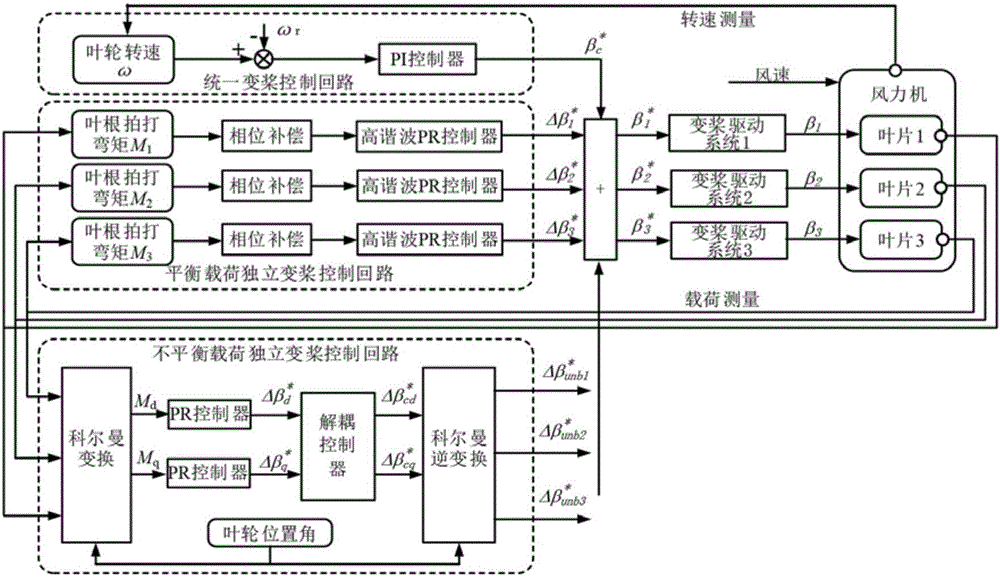
Individual pitch control method and device for inhibiting loading of wind generation set
ActiveCN106014857AImprove reliabilityExtended service lifeWind motor controlEngine fuctionsImpellerElectricity
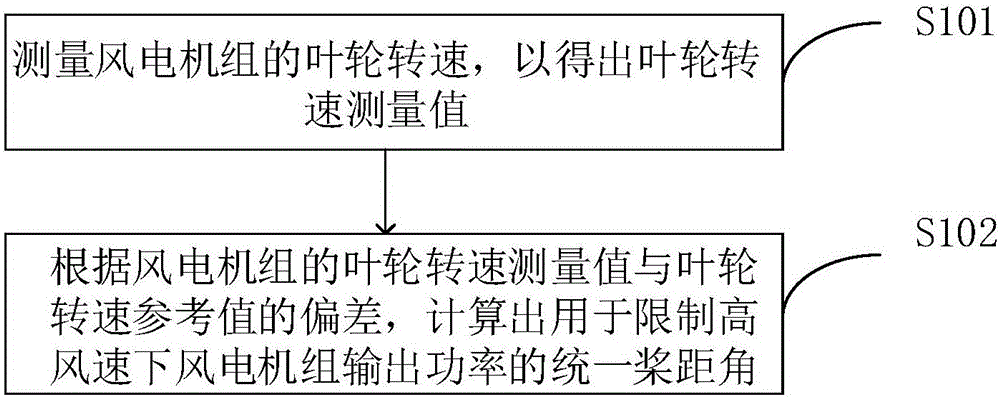
The invention discloses an individual pitch control method and device for inhibiting loading of a wind generation set. The method comprises the steps of generating a unified pitch angle used for limiting the output power of the wind generation set at the high wind speed according to rotating speeds of impellers; generating first deviation pitch angles used for inhibiting balanced loading of blades according to blade root loading measured values obtained after phase compensation; generating second deviation pitch angles used for inhibiting unbalanced loading of hubs according to the blade root loading measured values; and calculating a final pitch angle according to the unified pitch angle, the first deviation pitch angles and the second deviation pitch angles. According to the individual pitch control method and device for inhibiting loading of the wind generation set, the final pitch angle is calculated according to the unified pitch angle, the first deviation pitch angles and the second deviation pitch angles; meanwhile, balanced loading and unbalanced loading of the wind generation set are inhibited; and thus reliability of the wind generation set is improved, and the service life of the wind generation set is prolonged.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID JIBEI ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Method of controlling a wind turbine
InactiveCN101509468AElectrical variable reductionRotational speed controlOptimise machine performanceControl signalEngineering
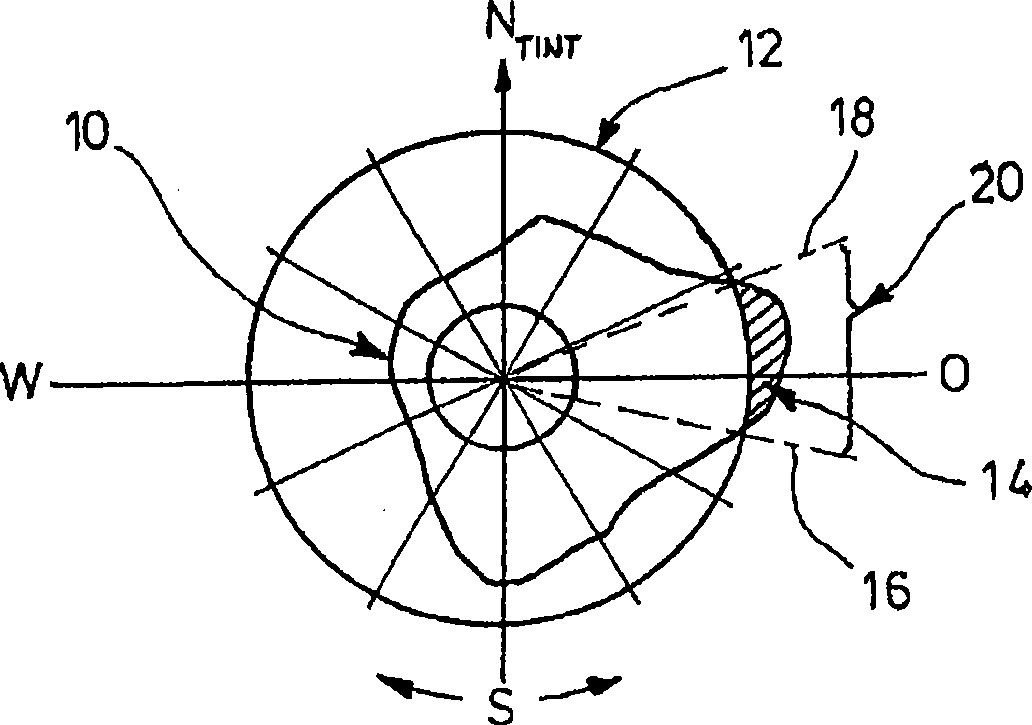
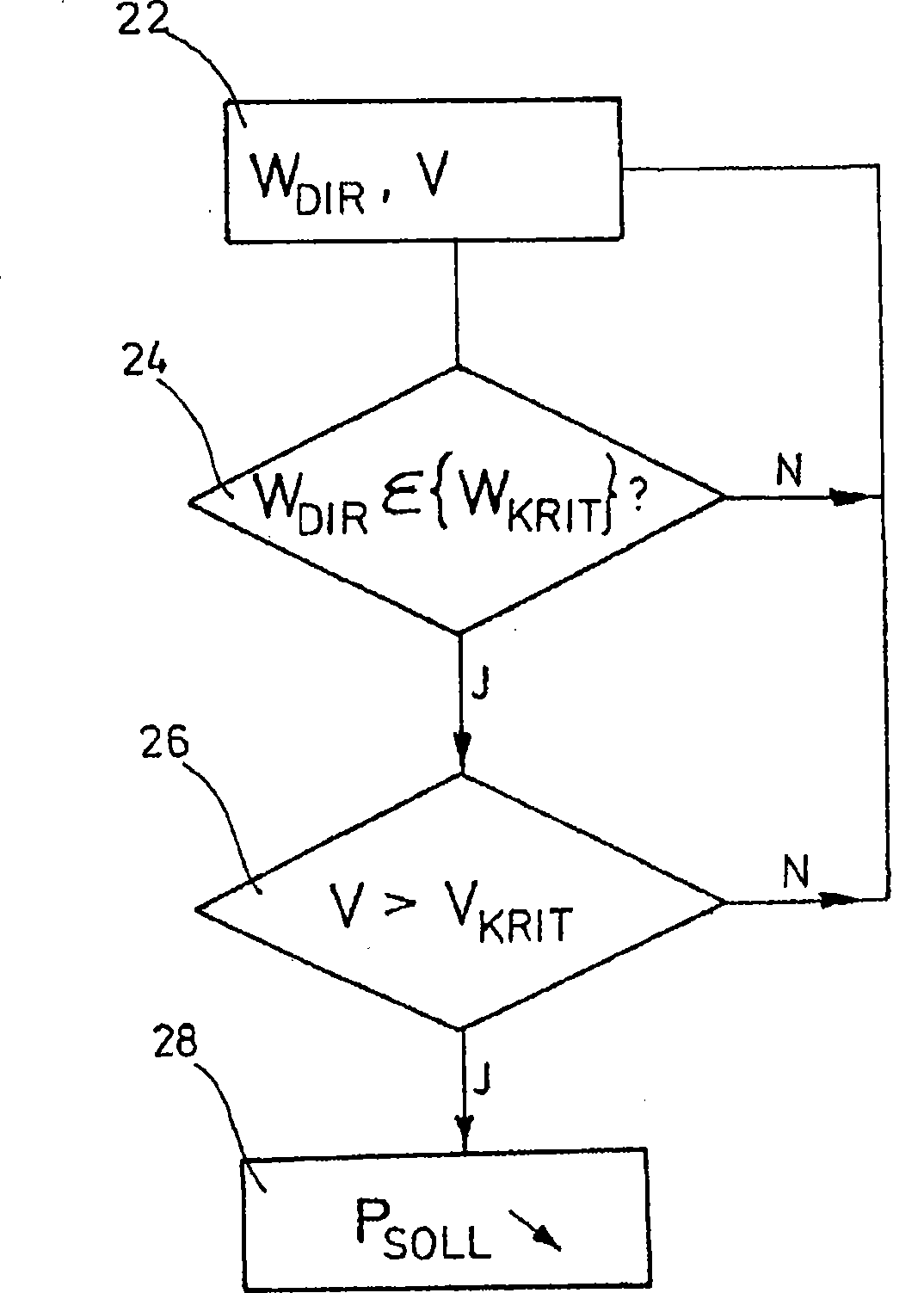
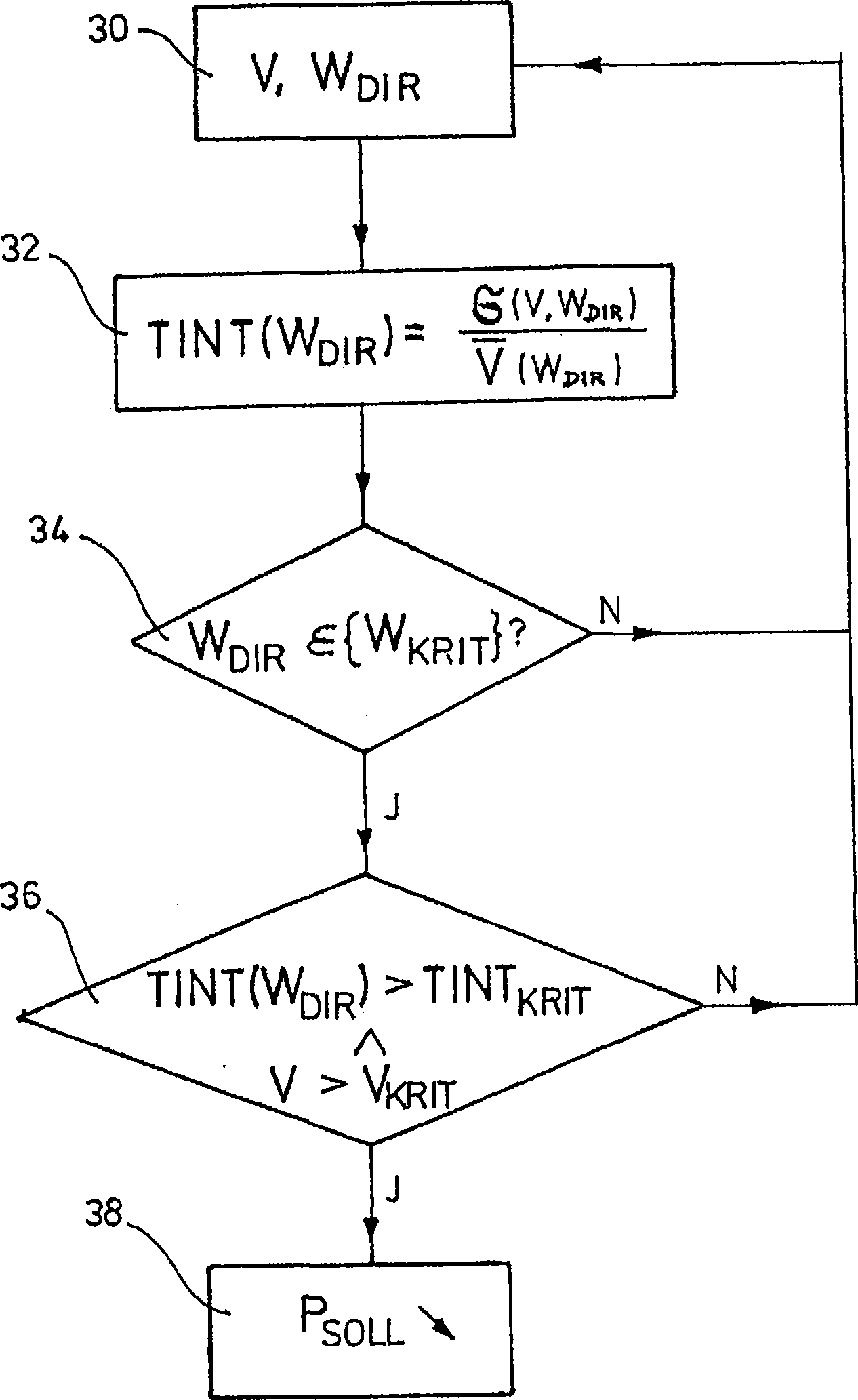
A method for the operation of a wind energy plant, with an operation management, which can preset a desired value for an electric variable of the wind energy plant to be generated; a wind measurement device, which can capture the wind direction and the wind velocity, and a control unit, on which the measured values for the wind velocity and the wind direction are present, and in which a maximum value for the turbulence intensity is filed, the following procedural steps proceed in the method: from a turbulence intensity depending on the wind direction, the control unit determines one or more sectors of critical wind directions, in which the turbulence intensity exceeds the maximum value for the turbulence intensity, the control unit generates a control signal for the operation management, in order to reduce the desired value of the electric variable to be generated when the measured wind direction is in a sector of the critical wind directions, and a determined characteristic value exceeds a predetermined maximum value for the characteristic value.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
Method and a system for controlling operation of a wind turbine
ActiveUS8577509B2Total downtime of the wind turbine is reducedAvoid difficult choicesLevel controlWind motor controlTurbineReliability engineering
A method and a system for controlling operation of a wind turbine are provided. The method includes determining at least one failure mode relating to one or more components of the wind turbine, estimating a remaining lifetime of the component under current operating conditions, determining one or more control schemes to control the operation of the wind turbine in order to adjust the remaining lifetime of the component to a desired remaining lifetime of the component, determining a power production yield for the determined one or more control schemes and selecting a determined control scheme for controlling the operation of the wind turbine that maximizes the power production yield.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Pitch control of a wind turbine
ActiveCN102317622AReduce wearActuation reductionWind motor controlActive/predictive/anticipative controlControl systemActuator
A wind turbine control system suitable for minimising actuation of pitch actuators is disclosed. The control system uses an error gain schedule in full load control for reducing pitch actuation when the difference between the rotor speed and the reference rotor speed is not critical for the load of wind turbine components. The error gain schedule may be a nonlinear function which reduces the gain for low rotor speed errors. The use of the error gain schedule may reduce wear of the pitch actuators and may improve reduction of structural oscillations since focus removed from tracking the rotor speed reference when the speed error is low.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Turbine blade fatigue life evaluating method
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Methods of operating a wind turbine
ActiveUS20190178231A1Improve usabilityEasy to operateWind motor controlWind motor combinationsTurbineWind speed
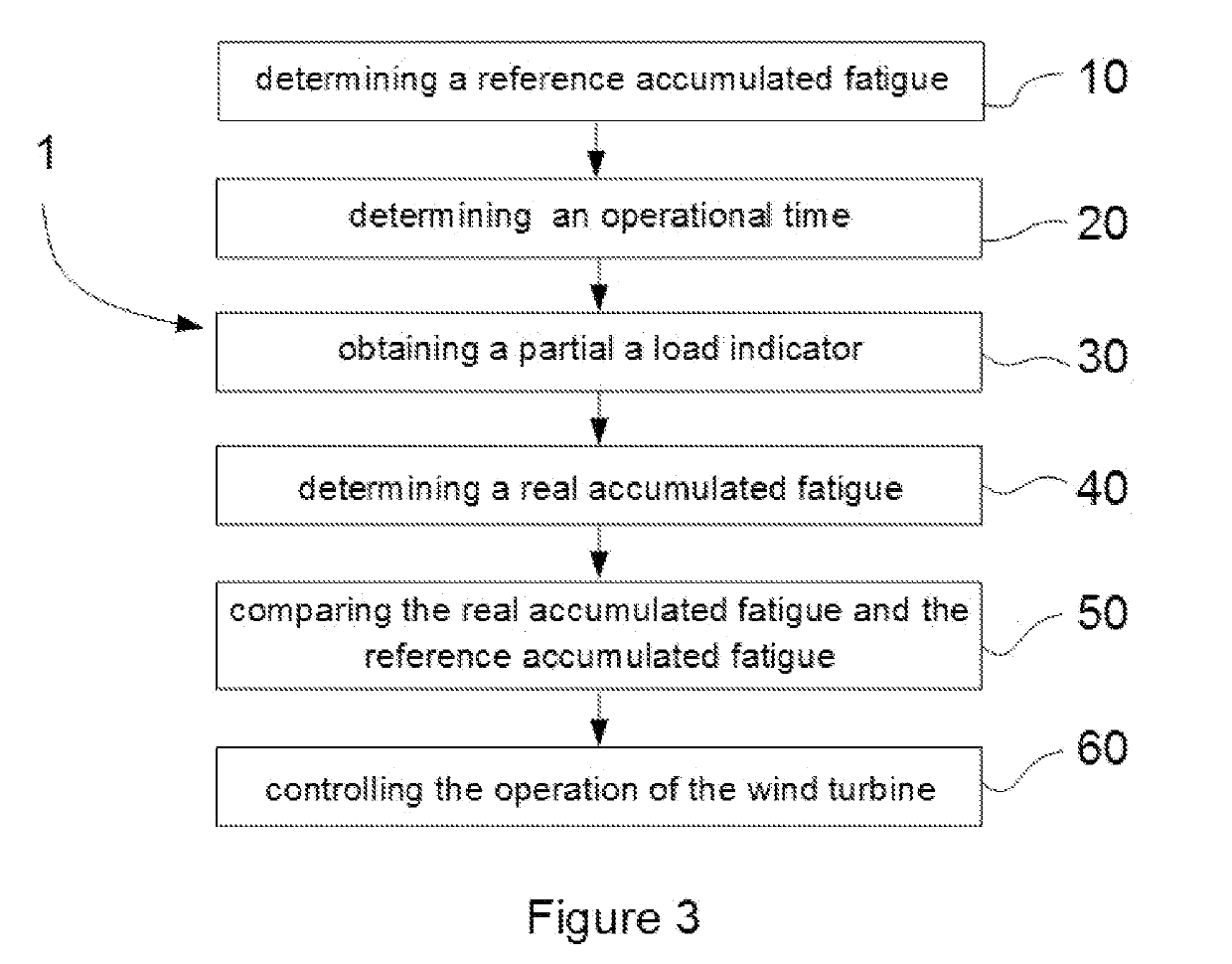
A method of operating a wind turbine and a method of determining fatigue in a wind turbine component are provided. The method of operating a wind turbine comprises determining a reference accumulated fatigue, determining an operational time, obtaining a partial load indicator, determining a real accumulated fatigue, comparing the real accumulated fatigue and the reference accumulated fatigue and controlling the operation of the wind turbine. The method of determining fatigue in a wind turbine component comprises determining an operational time, obtaining wind speed, obtaining turbulence intensity, determining a time for each combination of wind speed and turbulence intensity and determining a real accumulated fatigue. In a further aspect, this is also provided a wind turbine controller configured to perform any of the methods herein disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
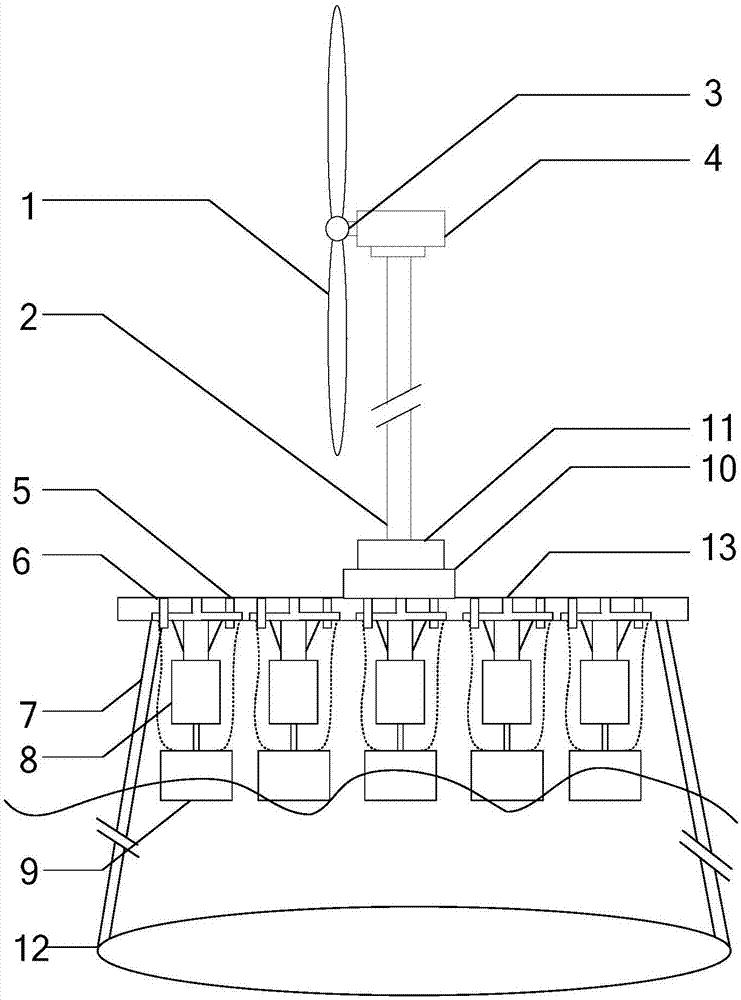
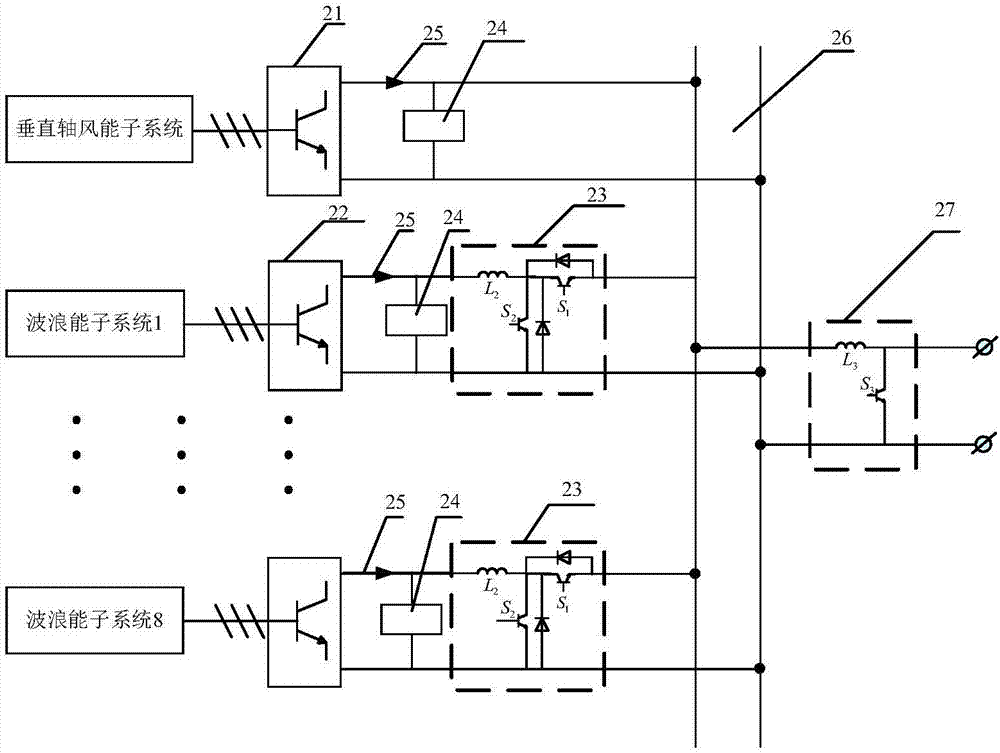
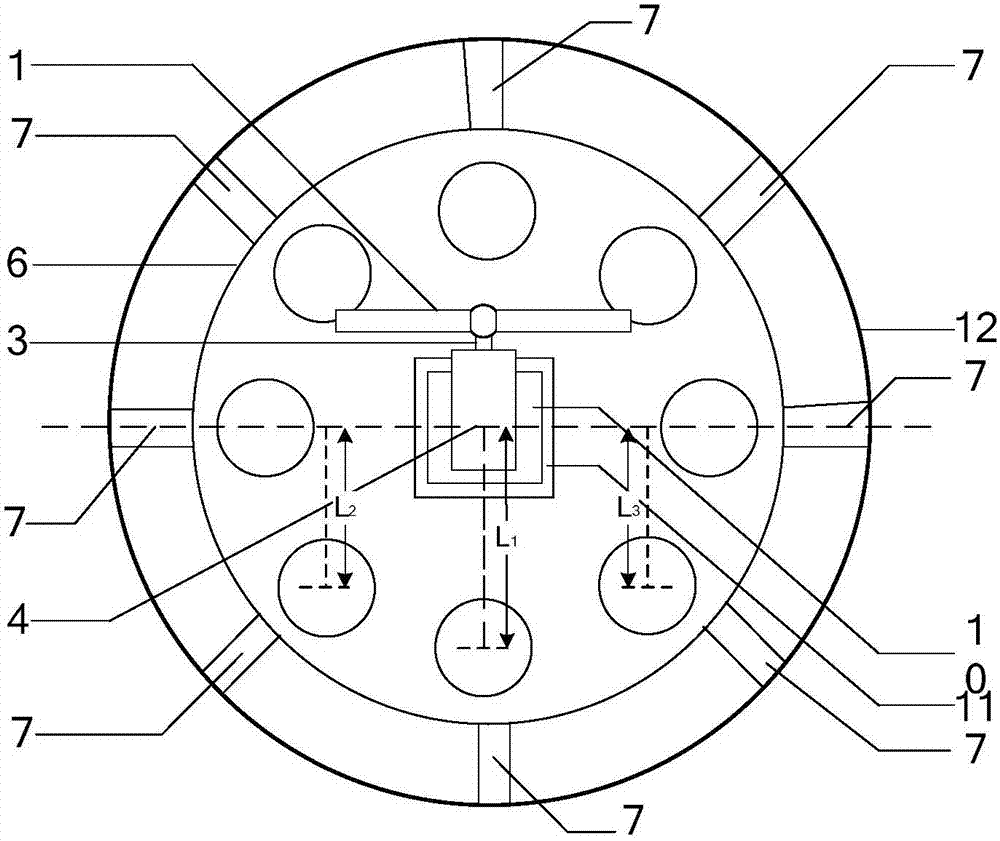
Flexible direct-current transmission wind and wave hybrid power generation system
PendingCN107882686ASmoothing volatilityCalming Intermittent ProblemsWind motor controlWind energy with water energyEngineeringWind power generation
The invention discloses a flexible direct-current transmission wind and wave hybrid power generation system. The flexible direct-current transmission wind and wave hybrid power generation system comprises a mouse cage type tower frame platform, a wind energy subsystem, a wave energy subsystem, a power regulation unit and a flexible direct-current power transmission station; wind power generation and wave energy power generation are combined, the characteristic that dynamic response of the wave energy subsystem is rapid is fully exerted, wind power generation fluctuation power restraining and tower frame platform inclination active regulation can be achieved, the mouse cage type tower frame platform supports the wind and wave hybrid power generation system, a rigid oval floating body passively regulates the inclination angle of a tower frame, the wave energy subsystem is inversely hung on a round platform, power generation and electric modes can be rapidly switched according to the station, and power grid scheduling power and tower frame inclination angle stability can be ensured; the power regulation unit achieves wind and wave maximum power capturing and power dual-way flowing; the flexible direct-current power transmission station finishes converging and feed of wind wave capturing power. Wind and power output power and tower frame inclination angle stability can be improved,the mounting and maintaining cost can be greatly reduced, and development of the wind and wave hybrid power generation system can be promoted.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Initialisation of wind turbine control functions
ActiveUS20180180024A1Increase powerReduce power outputWind motor controlComputer controlPower stationTurbine
A method for controlling a wind turbine is provided. The wind turbine is a turbine of the type that is operated to perform a control function that controls the amount of power produced based upon measures of fatigue life consumption of one or more turbine components. The method comprises initialising the control function by: over-riding or bypassing (405) the control function for a predetermined period of time, such that power produced by the wind turbine is not altered based upon the determined measures of fatigue life consumption; during the predetermined period of time, operating (407) one or more fatigue lifetime usage estimation algorithms, to determine a measure of the fatigue life consumed by each of the one or more turbine components; and after the predetermined period of time has elapsed, activating (409) the control function and using, in the control function, at least one of the measures of fatigue life consumption determined during the predetermined period of time. A corresponding wind turbine controller and wind power plant controller are also provided.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Method for starting a wind turbine after a stoppage and wind turbine for carrying out this method
Disclosed is a method for starting a wind driven plant after operation stopping, wherein the wind driven plant is provided with a speed variator and an operation manager capable of controlling at least one operation variable B which is important for the speed variator of the wind device at an expected value BSoll, after the operation is stopped, the expected value BSoll is limited by a maximum value BMax preset according to measured temperature of the speed variator and / or speed variator lubricant.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
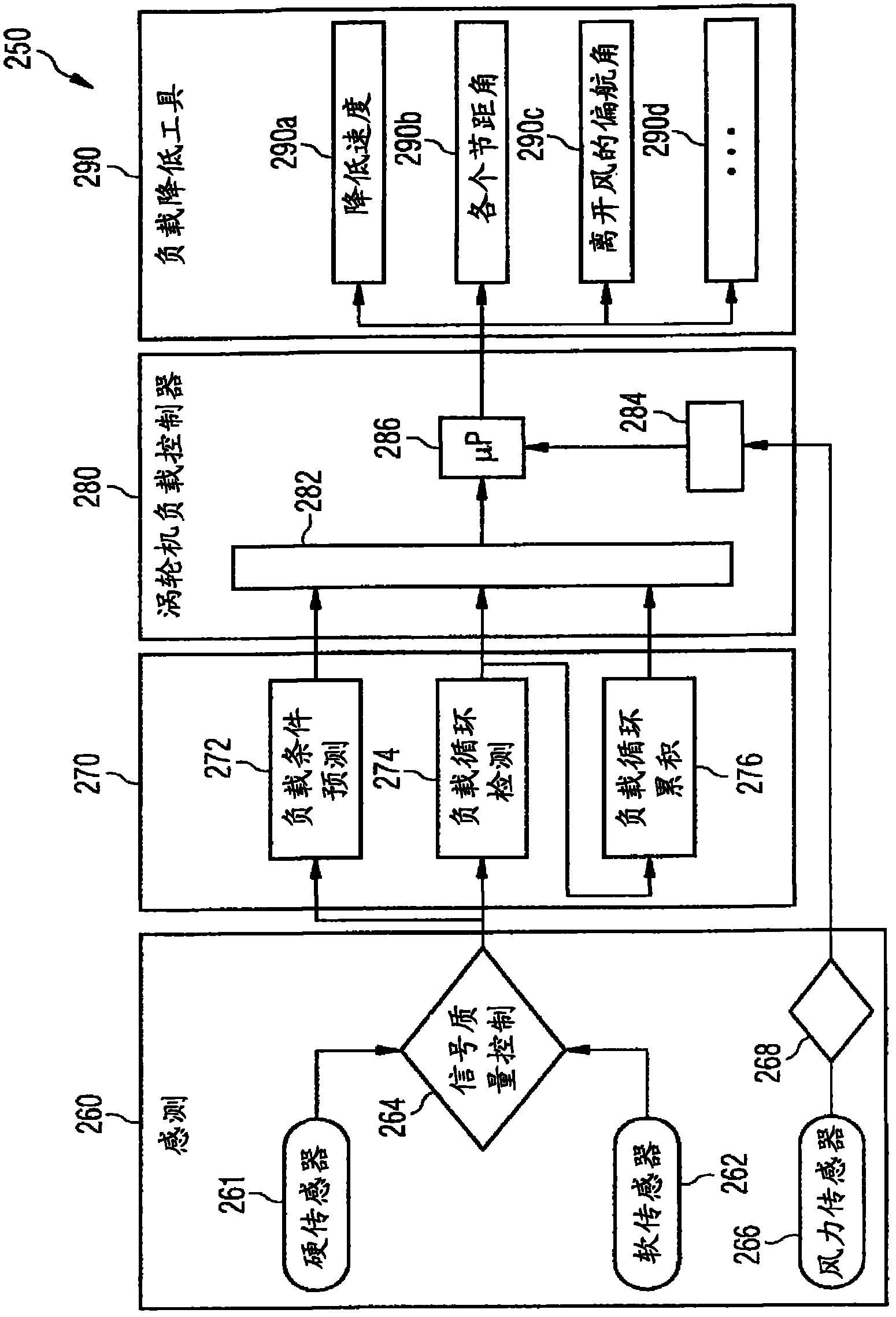
Load reducing system of wind generator set and working method of load reducing system
PendingCN106351792AReduce structural loadsOvercome limitationsWind motor controlMachines/enginesElectricityNetwork interface device
The invention discloses a load reducing system of a wind generator set and a working method of the load reducing system. The system comprises a machine readable storage device, display equipment, a display adapter, input equipment, sensors, a processor, a peripheral interface, a memory and network interface equipment, wherein the machine readable storage device, the display adapter, the input equipment, the sensors, the processor, the peripheral interface, the memory and the network interface equipment are in communication through a bus, the display equipment is in communication with the bus through the display adapter, and the network interface equipment is in communication with remote equipment through a network. The method includes the steps of inputting initial data, collecting parameters of all the sensors, selecting an operating mode and controlling a fan to enter the selected mode. According to the system and the method, various parameters in the operating process of the fan are collected, a variable pitch system, a yaw system, a braking system and the like are integrated, the structural load of the fan is effectively reduced, and the limitation of independent operation of the systems on reduction of the structural load is avoided.
Owner:DALIAN DESIGN INST CO LTD CHINA FIRST HEAVY IND +1
Method for starting up a wind energy plant after an operation stoppage and wind energy plant which can execute the method
InactiveUS7809477B2Obtainable lifetime of the drive train components can be prolongedEasy to wearPropellersLevel controlEngineeringWind power
A method for starting up a wind energy plant after an operation stoppage, wherein the wind energy plant has a gearbox in the drive train and an operation management which can control at least one operational variable significant for the strain of the gearbox B of the wind energy plant to a desired value BSoll, wherein after the operation stoppage, the desired value BSoll is limited by a maximum value BMax, which is preset depending on a measured temperature of a gearbox component and / or of a lubricant for the gearbox.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SE & CO KG
Control of wind turbines
ActiveUS9644609B2Without risk of damageShort lifeOptimise machine performanceWind motor controlElectricity pricingPower station
A wind turbine power plant comprises a plurality of wind turbines, each having a rated output and under the control of a power plant controller. The power plant also has a rated output which may be over-rated in response to one or more of electricity pricing data, power plant age and operator demand. The power plant controller can send over-rating demand signals to individual turbines. The controllers at the turbines include a fatigue life usage estimator which estimates a measure of the fatigue life consumed by key components of the turbine. If this measure exceeds a target value for any component, over-rating is prevented at that turbine.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Roof wind driven generator with windproof function
InactiveCN107084096AWith windproof functionWindproof function preventionRotational speed controlEngine manufactureWind drivenWind force
The invention relates to a roof wind driven generator with a windproof function. The roof wind driven generator comprises a supporting column, a fan blade mechanism, a gearbox, a low-speed rotating shaft, an electricity generation mechanism, a PLC, a waterproof bucket and a lifting mechanism. The fan blade mechanism comprises fan blades, a high-speed rotating shaft, an encoder and a telescopic assembly. The telescopic assembly comprises a fixing block, a motor, a lead screw and a walking rod. The lifting mechanism comprises a lifting block, a hydraulic box, a hydraulic groove and a pump body. According to the roof wind driven generator with the windproof function, the design structure is ingenious, practicability is high, and the encoder detects the rotating frequency of the high-speed rotating shaft when wind power is too high; when the rotating frequency is too large, the distance between every two adjacent fan blades is reduced through the PLC under the assistance of the telescopic mechanism, so that the sectional area for wind is reduced, the speed of the fan blades is reduced, and the problem that equipment is damaged due to the too large rotating frequency is avoided; and when the rotating frequency is still too large, at the moment, wind power is quite large, the fan blades are moved by the lifting mechanism into the windproof bucket, and the roof wind driven generator with the windproof function is prevented from being broken by high wind.
Owner:SHENZHEN NAISHIDI TECH DEV CO LTD
Remaining life prediction for individual components from sparse data
ActiveUS8768657B2Active/predictive/anticipative controlDigital computer detailsDecision takingRoot cause
Predicting the remaining life of individual aircraft, fleets of aircraft, aircraft components and subpopulations of these components. This is accomplished through the use of precomputed databases of response that are generated from a model for the nonlinear system behavior prior to the time that decisions need to be made concerning the disposition of the system. The database is calibrated with a few data points, to account for unmodeled system variables, and then used with an input variable to predict future system behavior. These methods also permit identification of the root causes for observed system behavior. The use of the response databases also permits rapid estimations of uncertainty estimates for the system behavior, such as remaining life estimates, particularly, when subsets of an input variable distribution are passed through the database and scaled appropriately to construct the output distribution. A specific example is the prediction of remaining life for an aircraft component where the model calculates damage evolution, input variables are a crack size and the number of cycles, and the predicted parameters are the actual stress on the component and the remaining life.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com