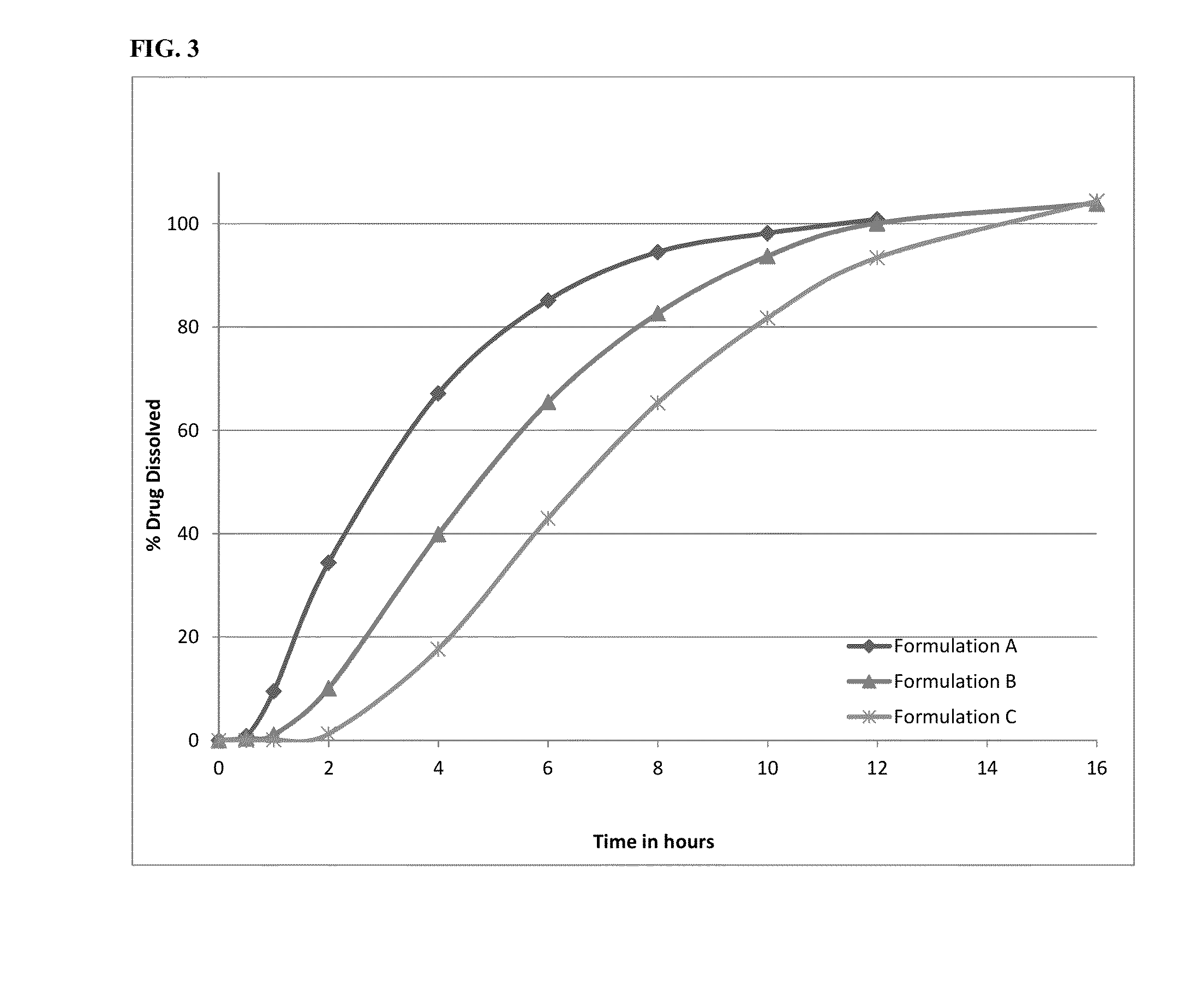
Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Improve gait" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
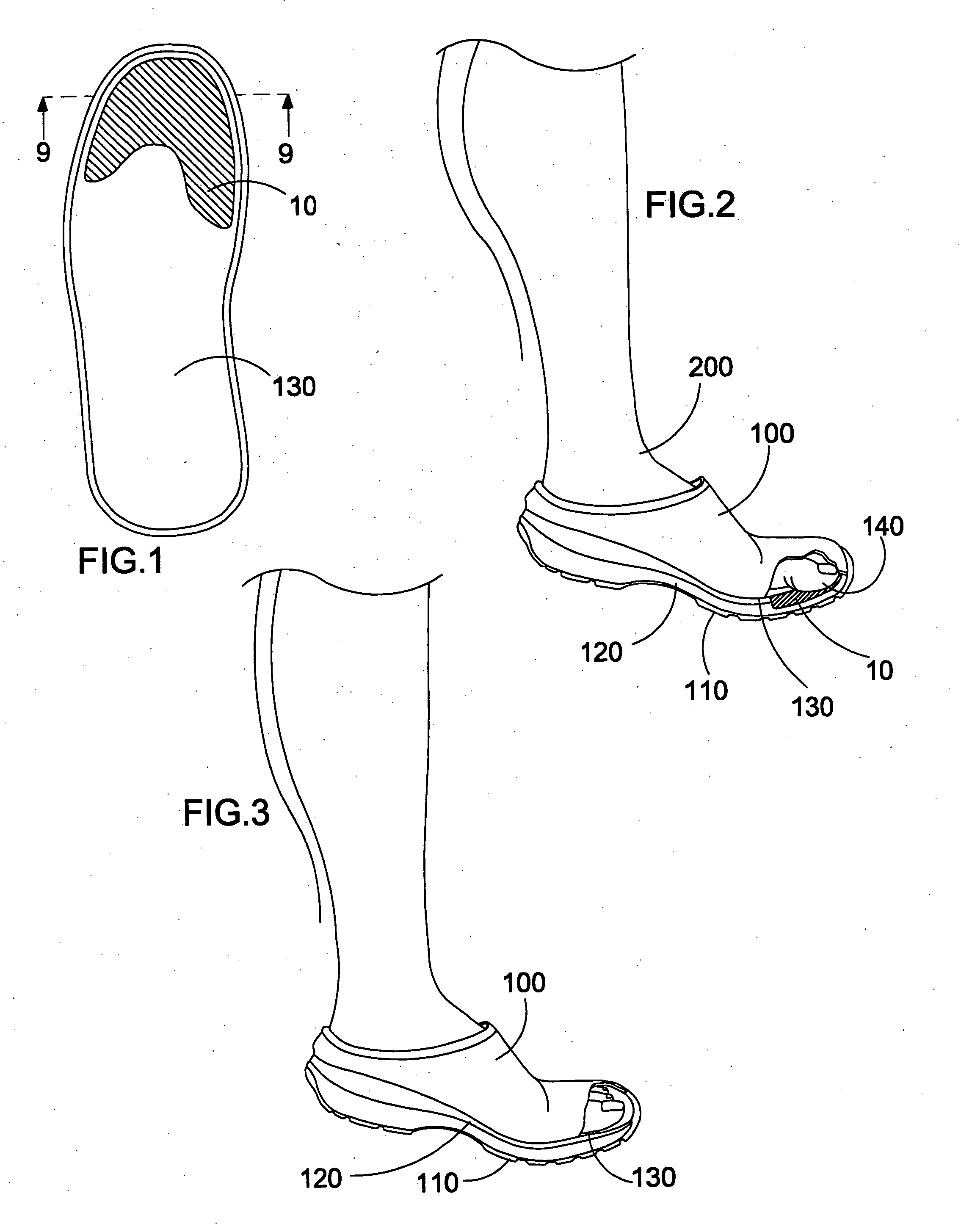
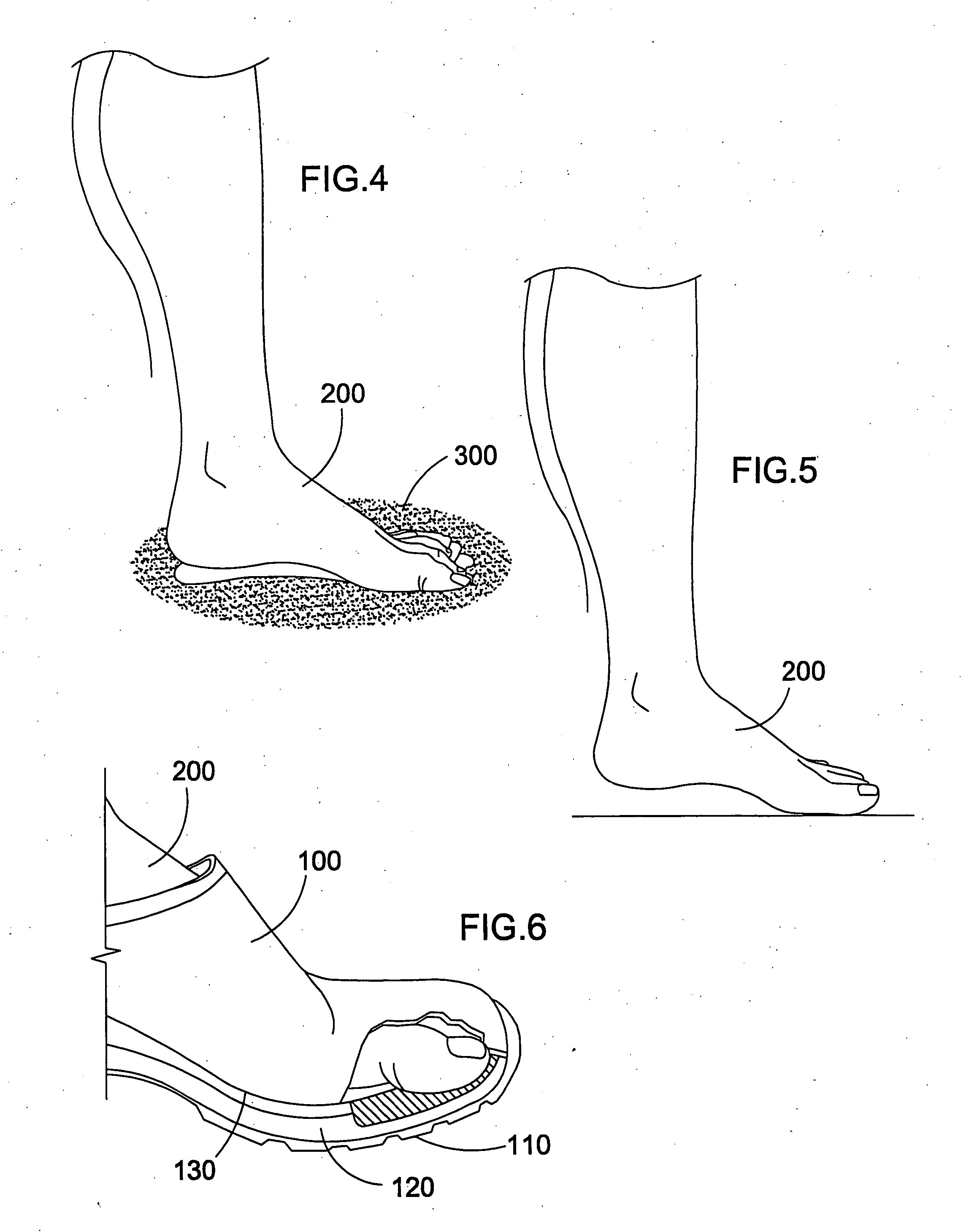
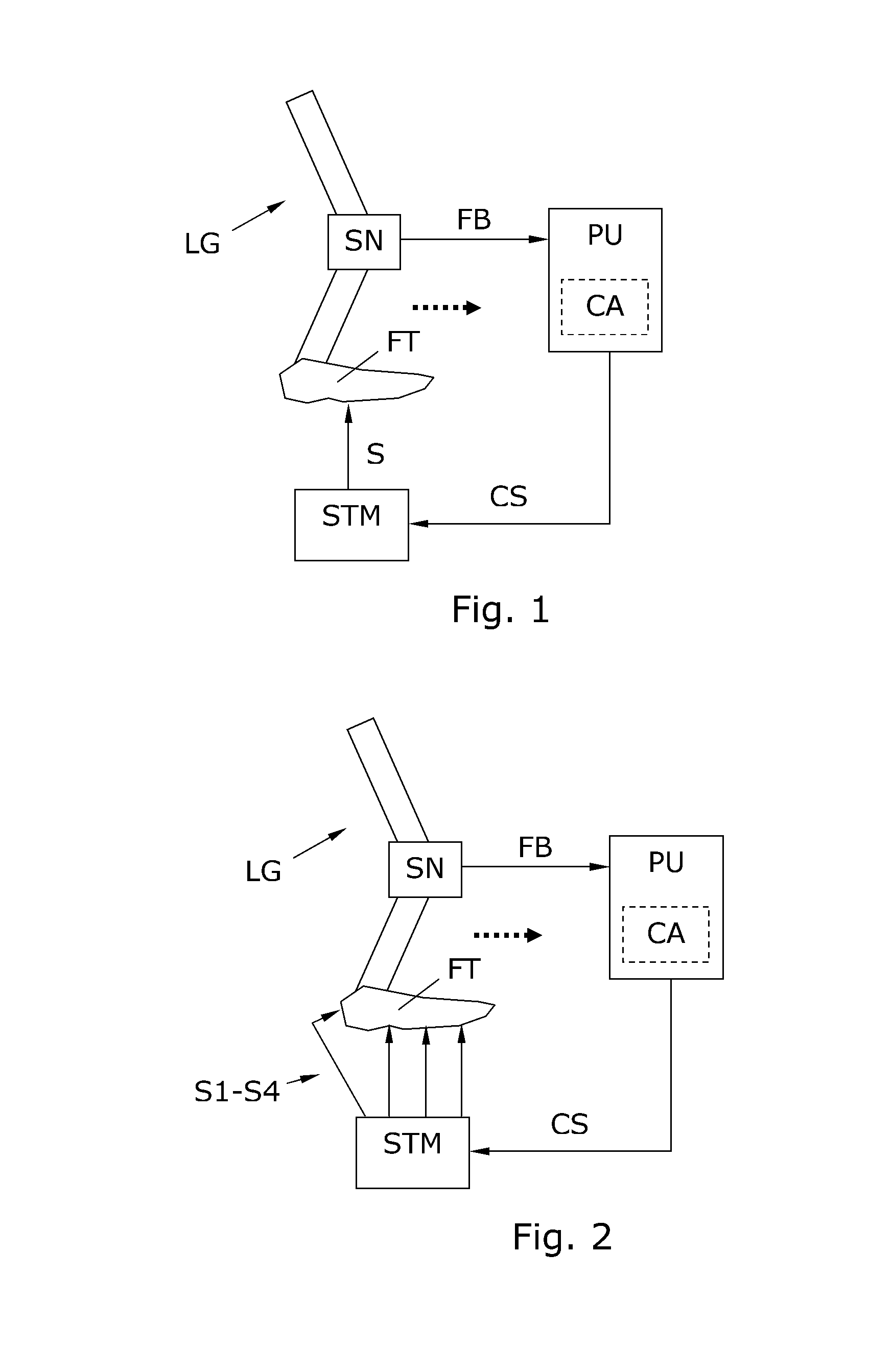
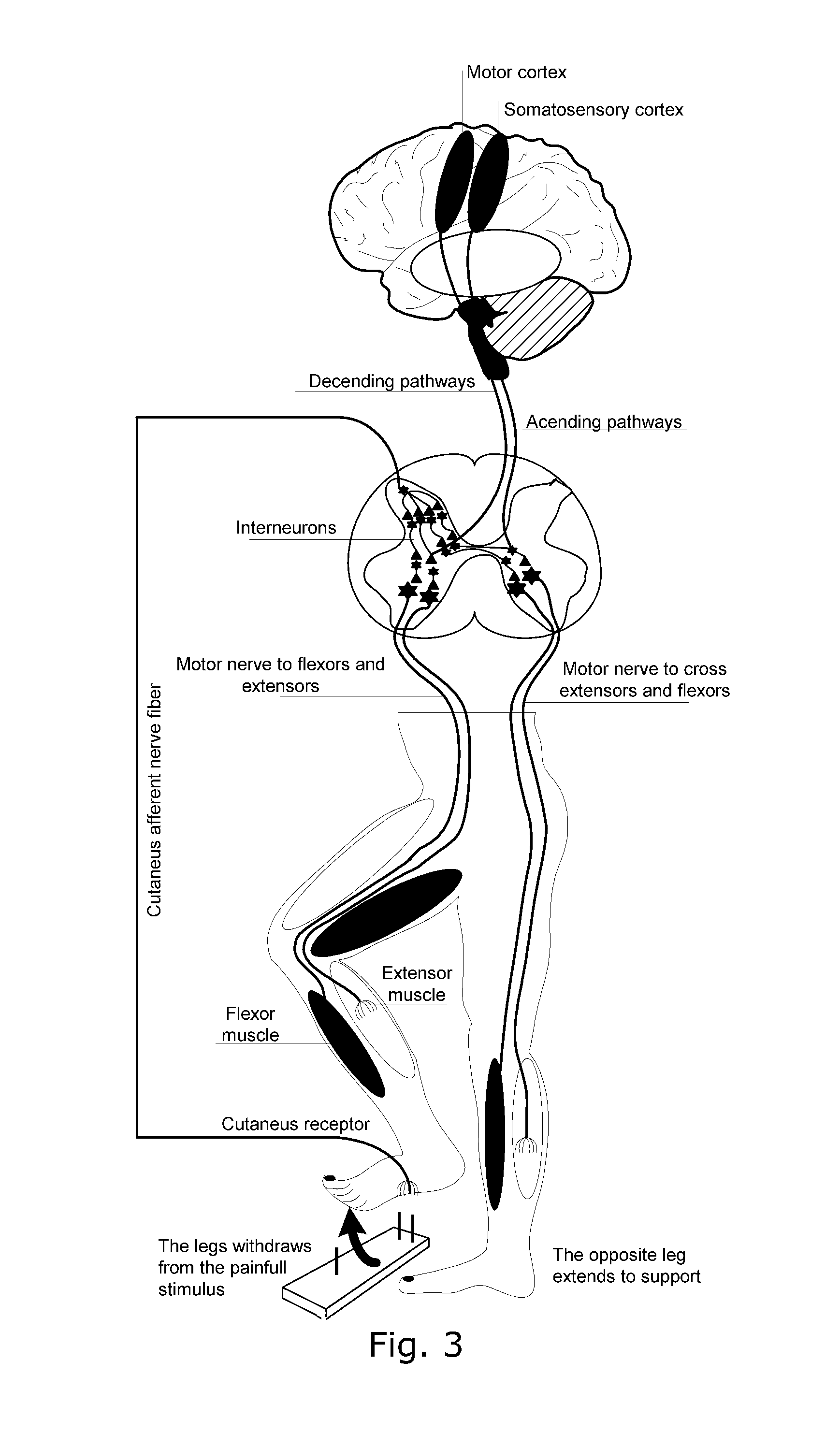
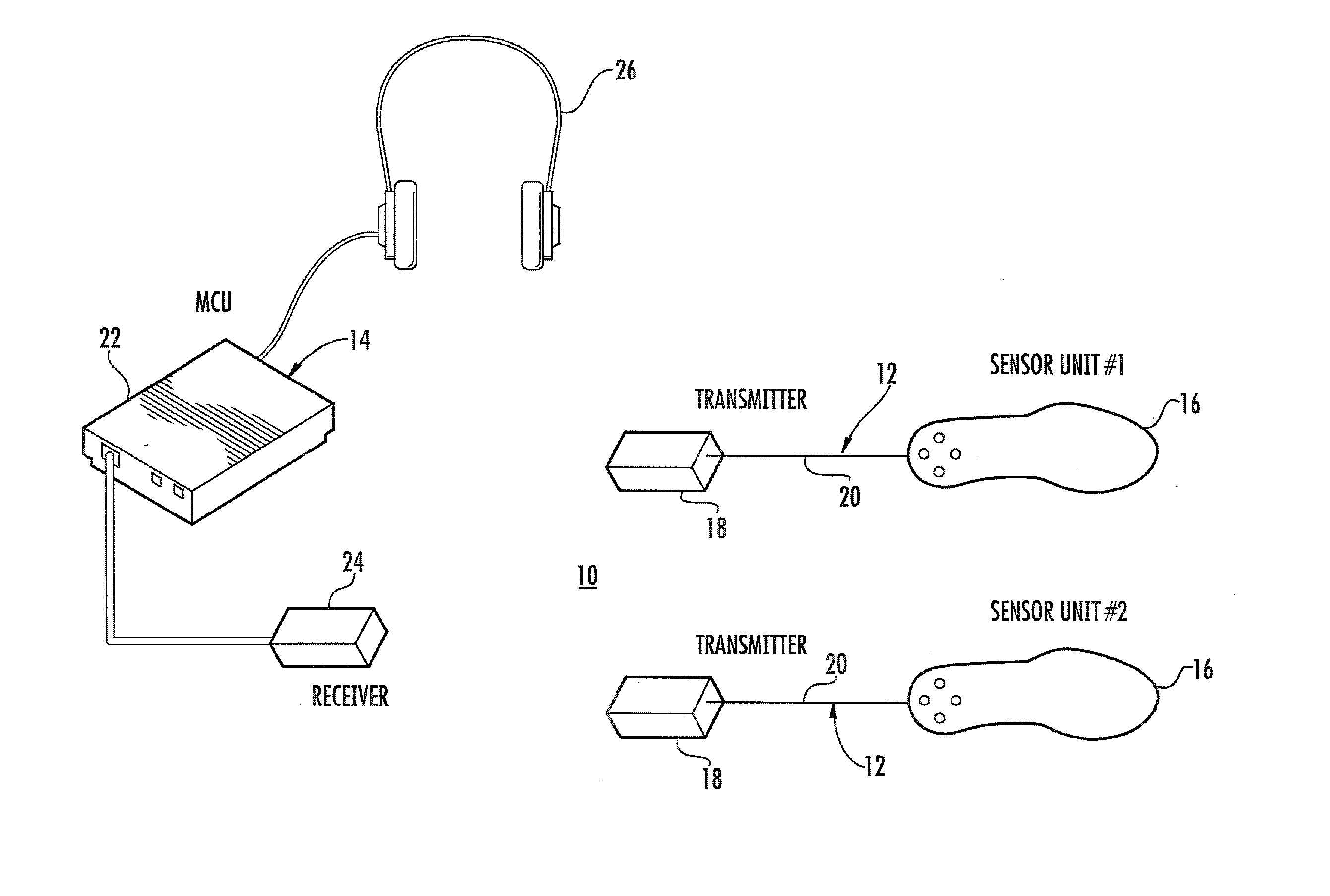
Method and device for reflex-based functional gait training
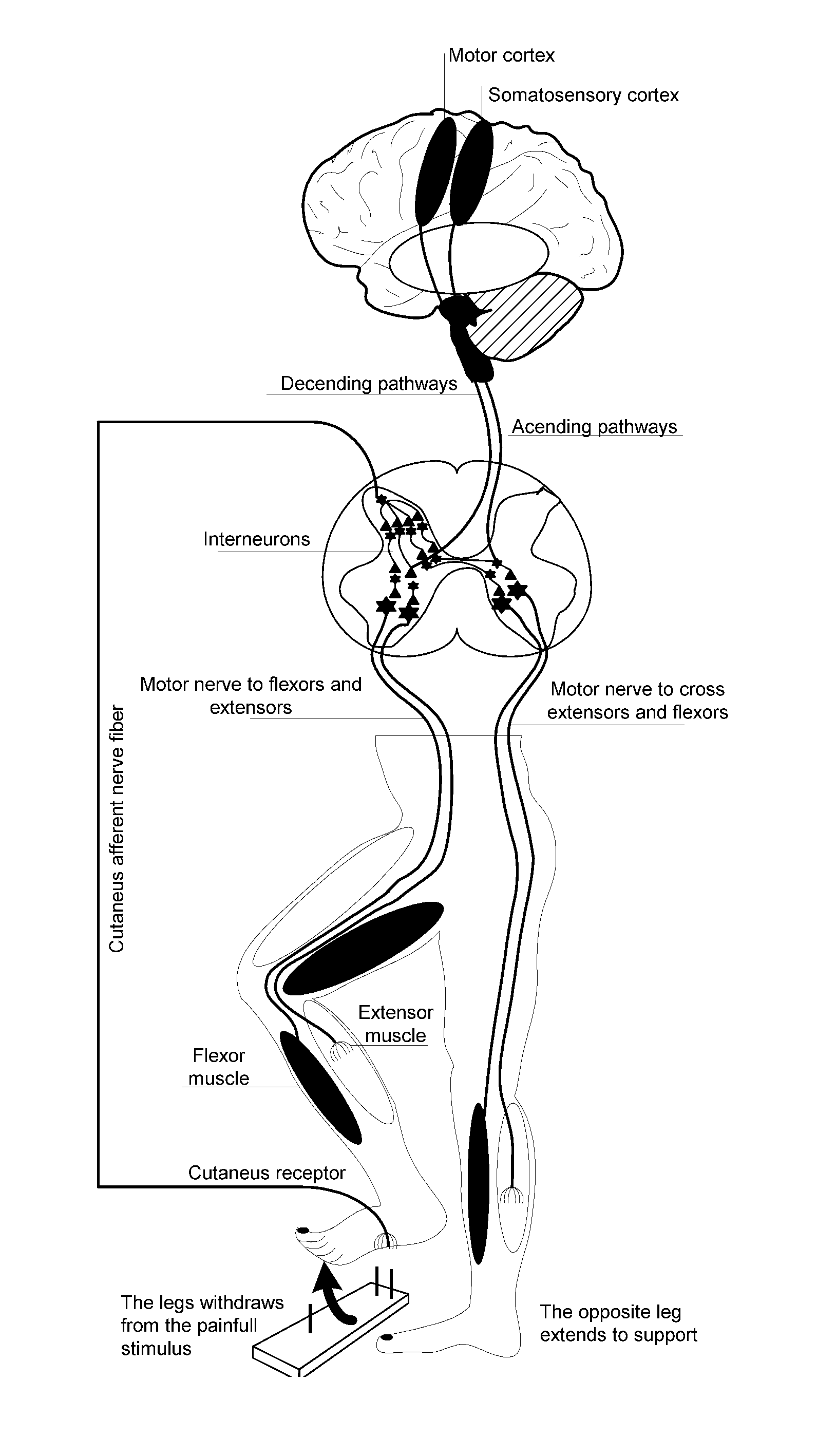
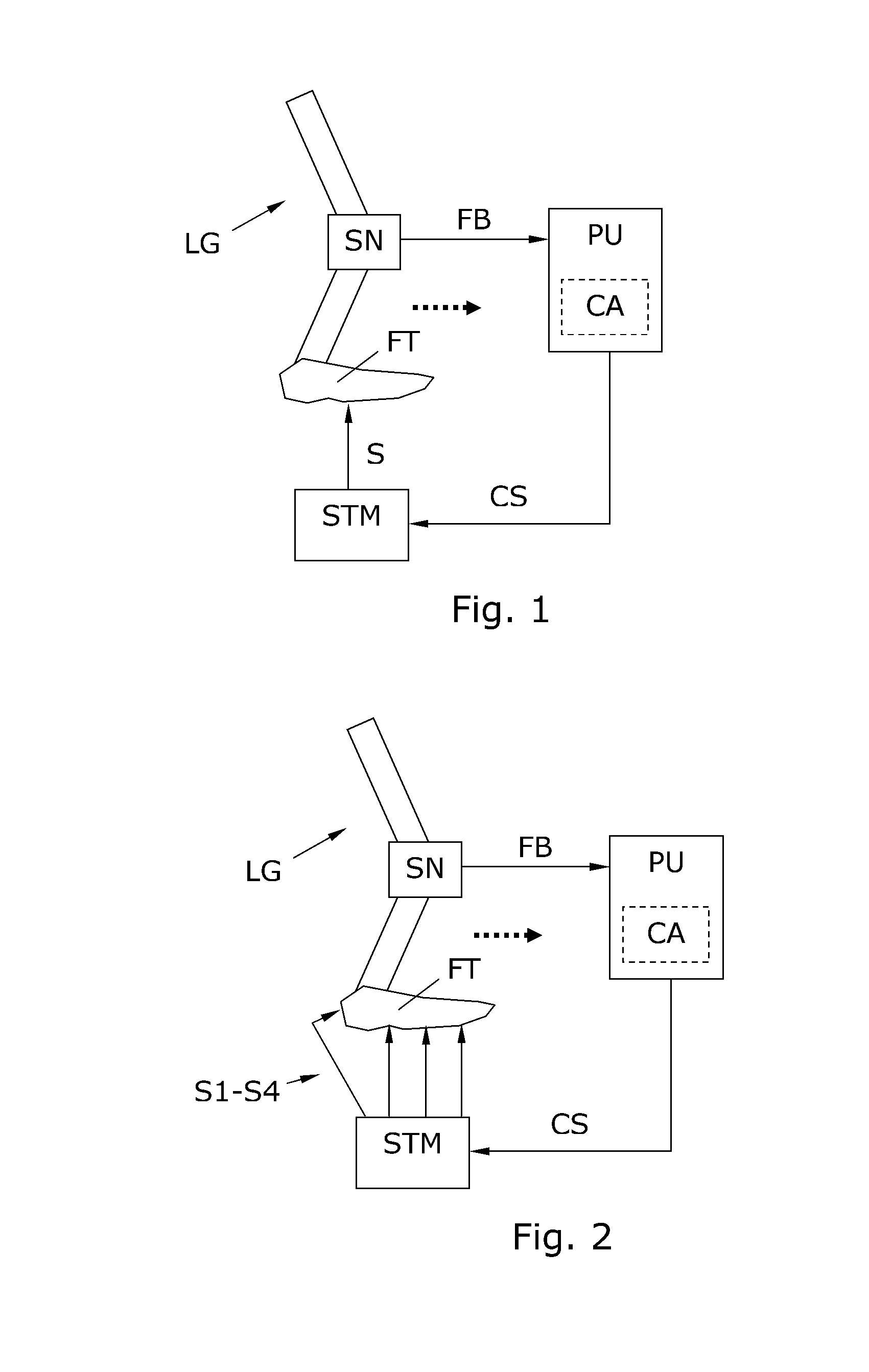
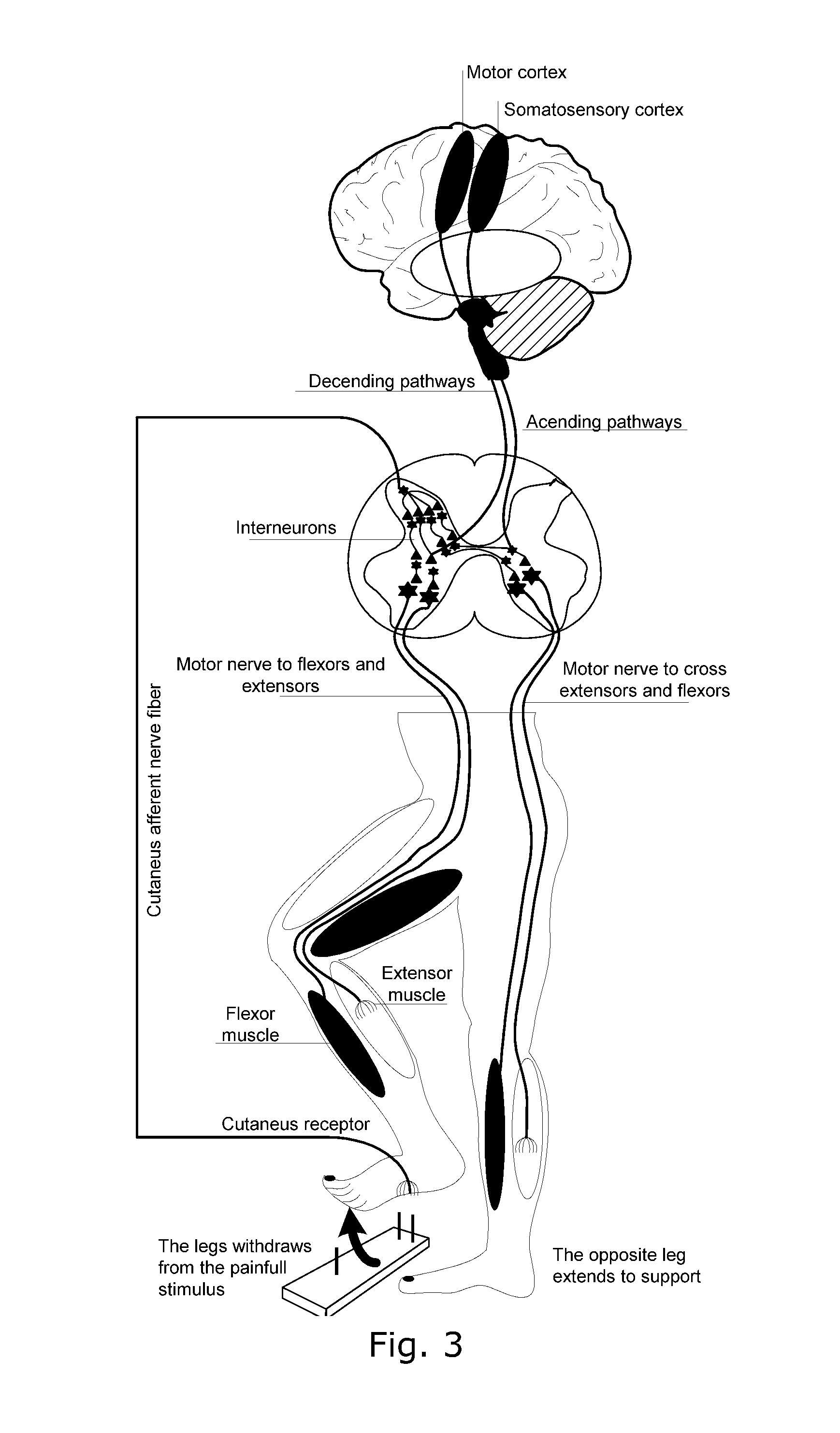
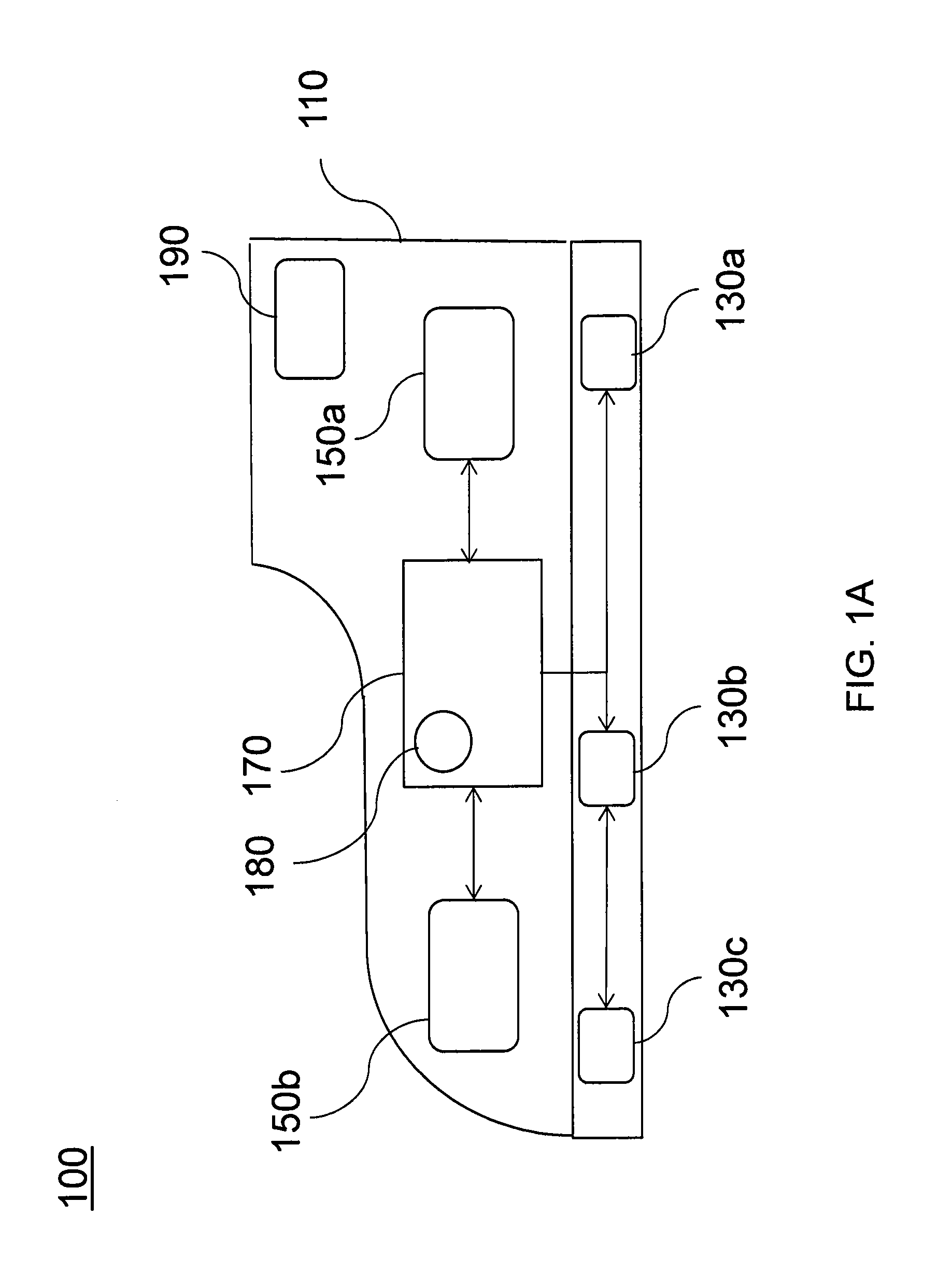
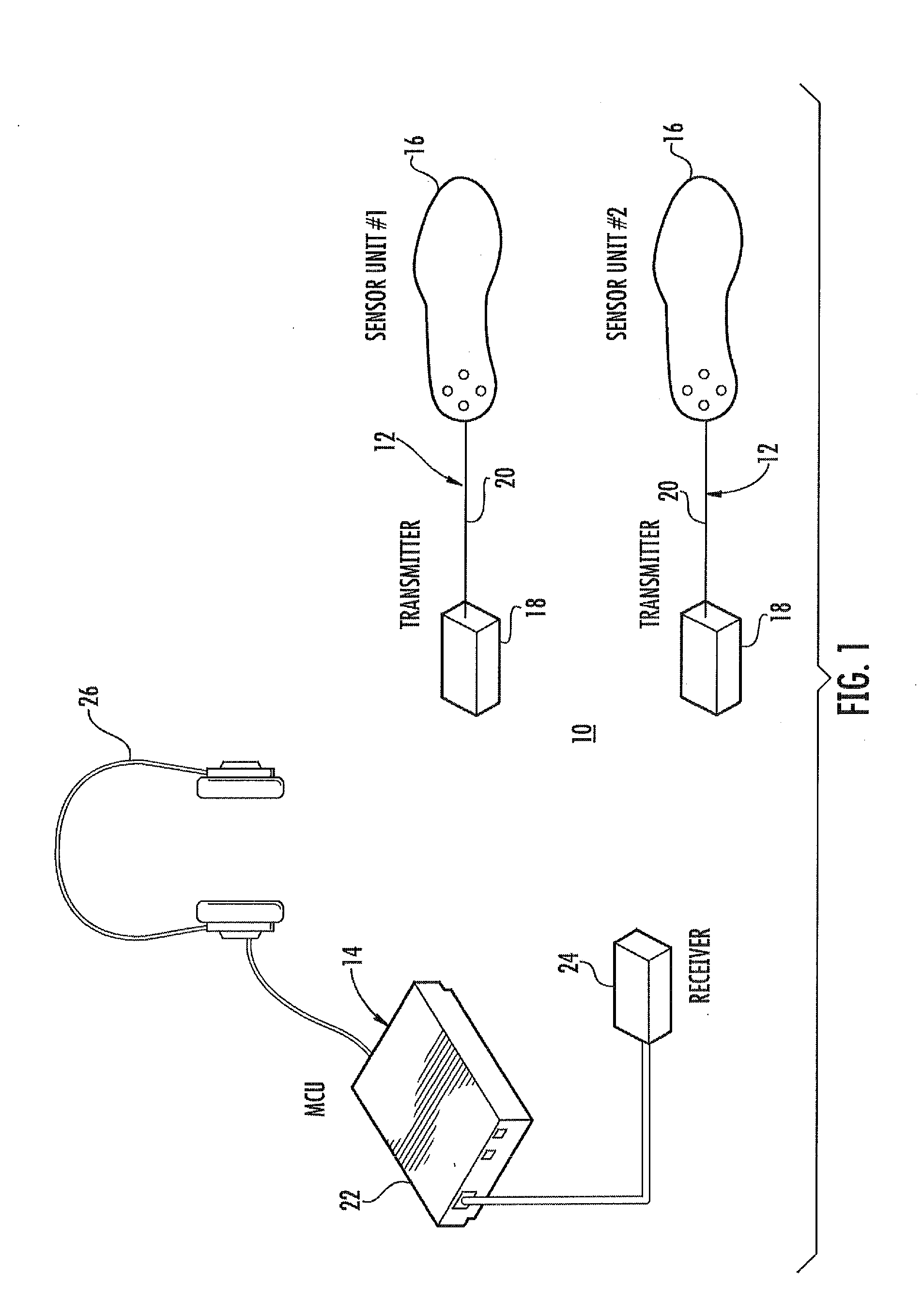
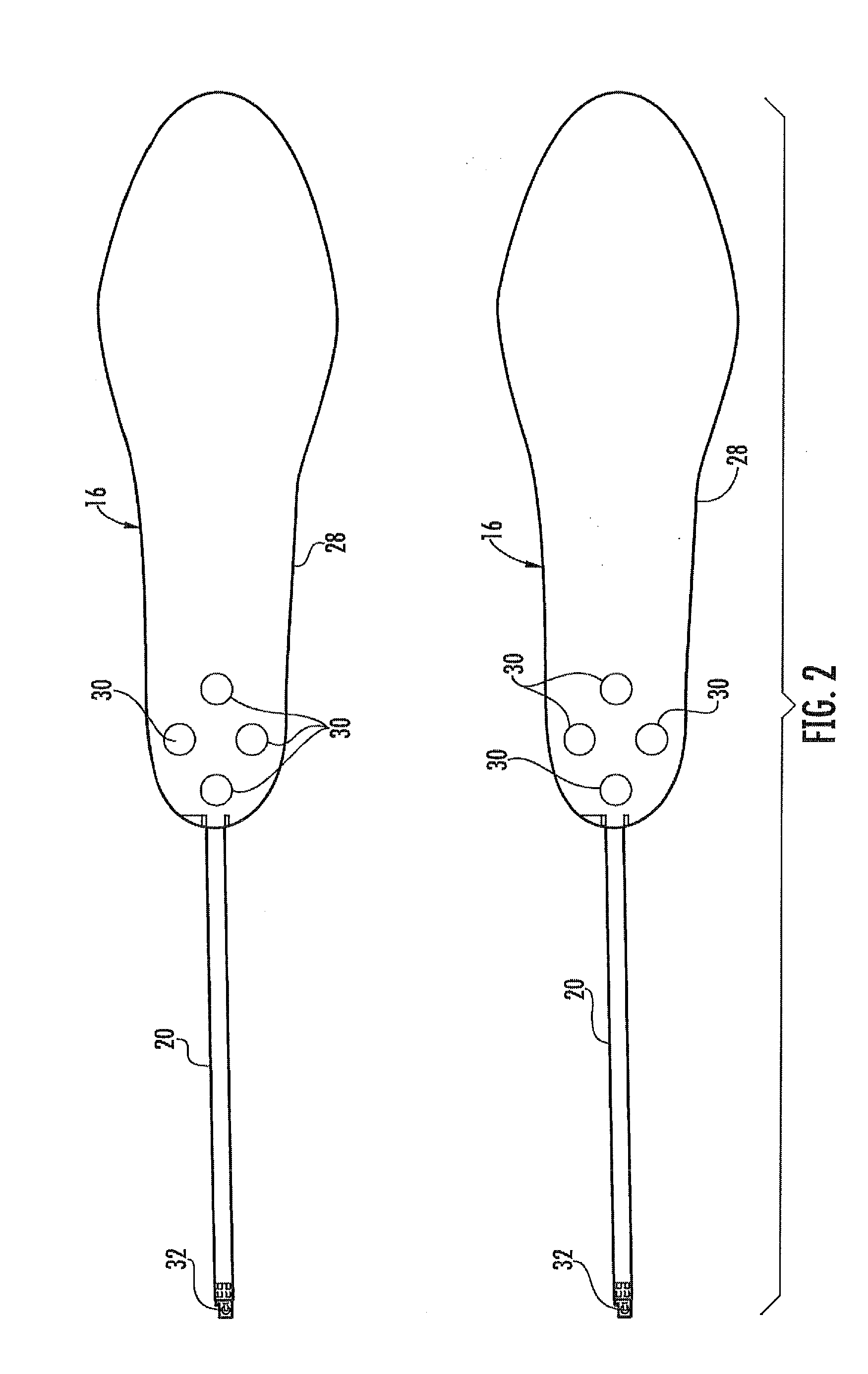
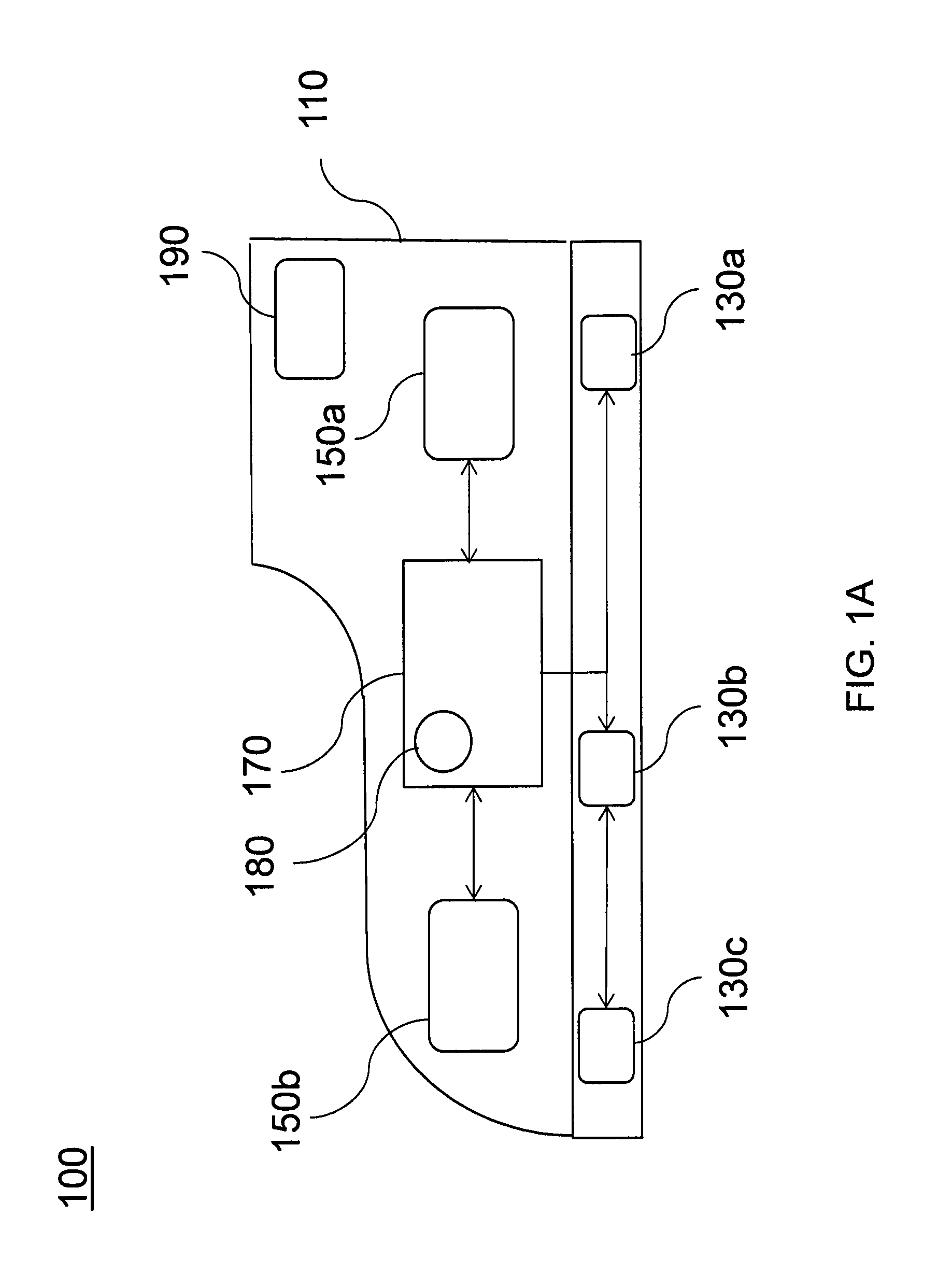
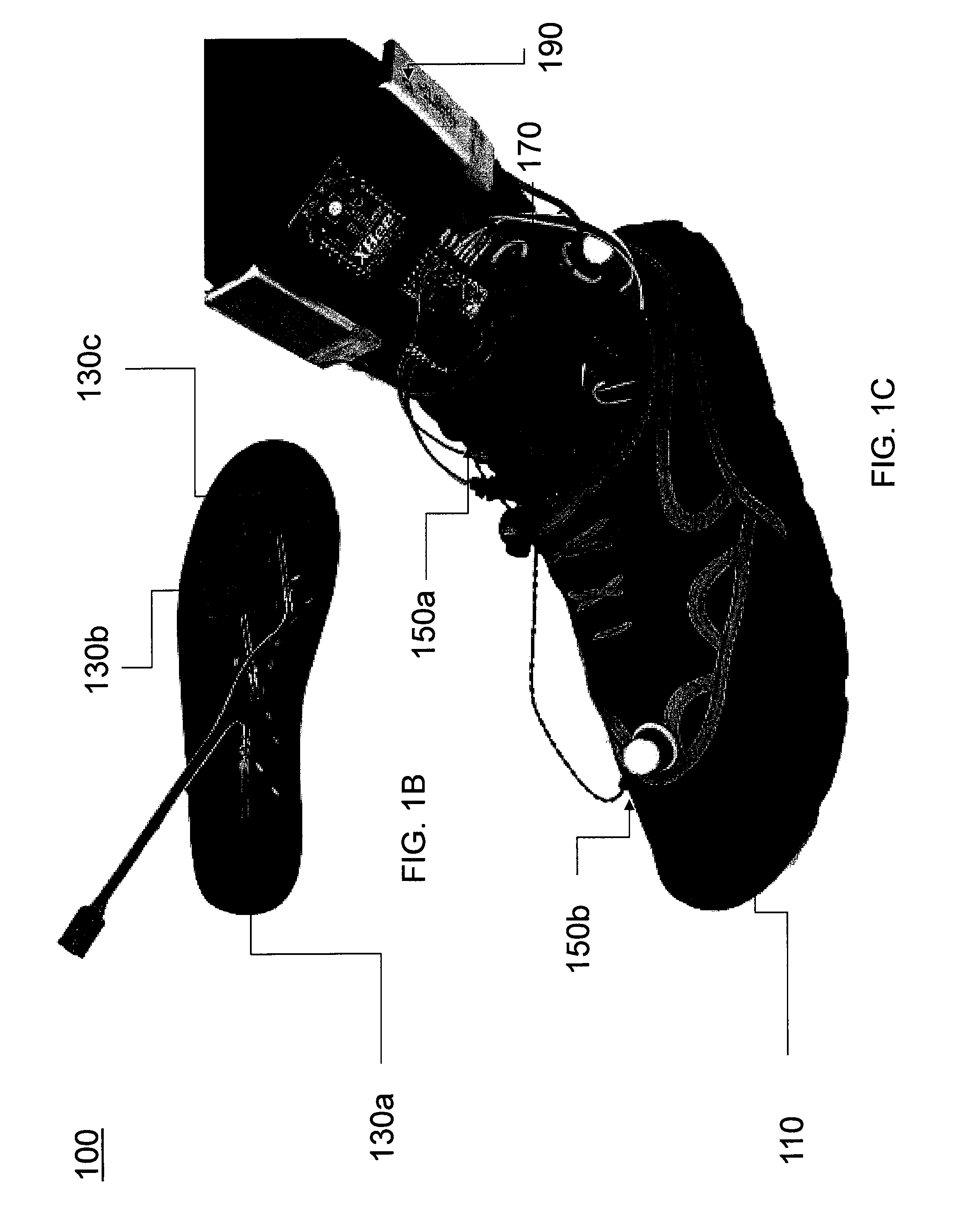
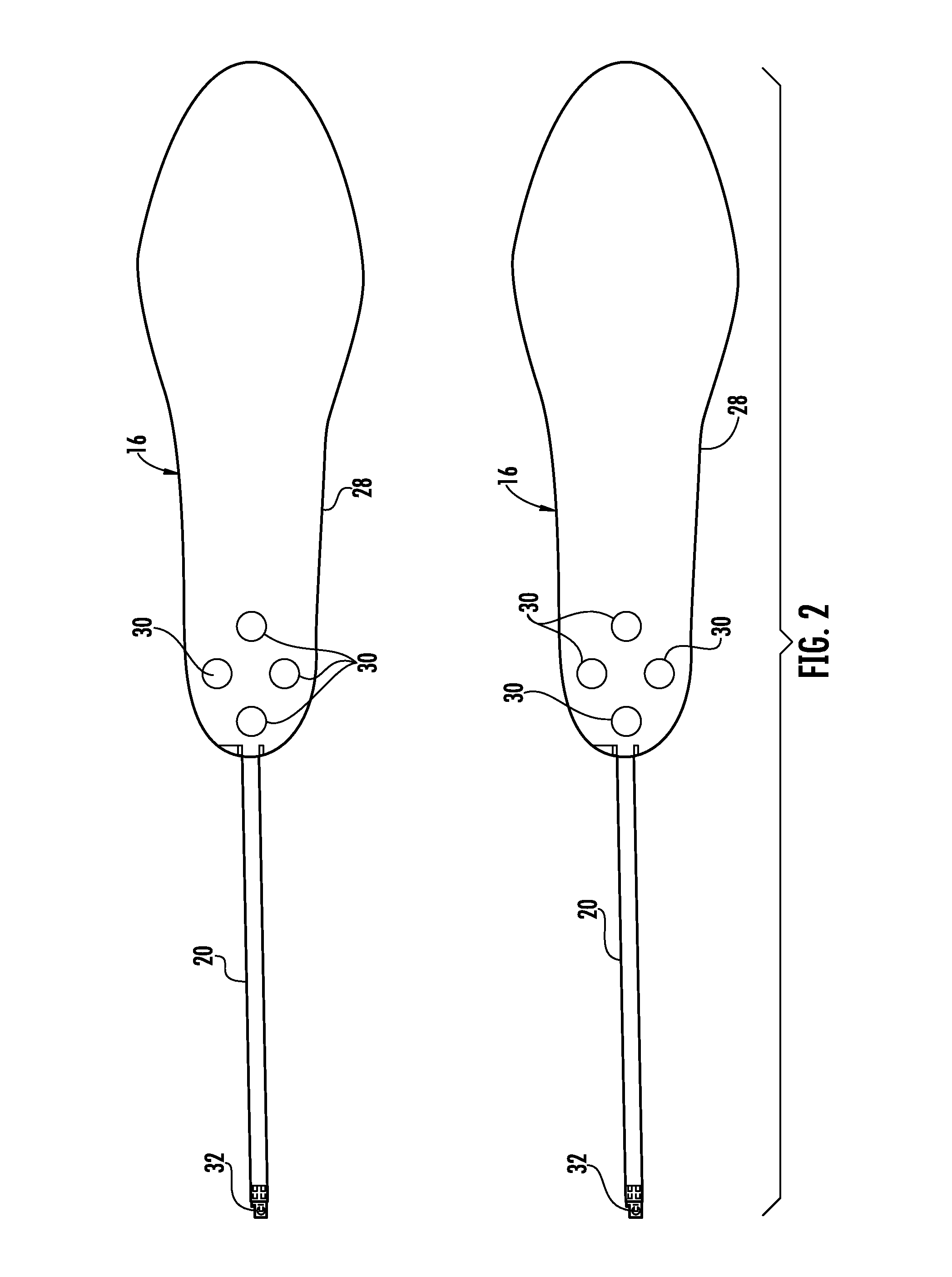
A device and method for gait training, such as for rehabilitation of a person after a stroke is provided. In some embodiments, the device comprises a stimulator, preferably electric stimulator, for provoking a spinal cord withdrawal reflex in the person by stimulation on the person's foot in response to a control signal. Hereby, the person's leg will move and initiate a gait swing. A sensor is placed to sense movement of the leg and provide a feedback signal accordingly. A processor unit with a processor runs a control algorithm which calculates the control signal in response to the feedback signal. Thus, the method is based on a closed-loop design, and the control signal is preferably calculated for each walking step, and it is preferably based on the feedback signal obtained from the preceding walking step. Hereby reflex habituation can be accounted for. Preferably, the stimulator has a plurality of stimulator channels with electrodes placed on different sites distributed on the sole of the foot and on the heel. The feedback signal may be based on accelerometer(s), and / or gyroscope(s), and / or goinometer(s) positioned on the leg and / or foot, e.g. partly or fully integrated in an in-sole for a shoe etc.
Owner:NORDIC NEUROSTIM APS
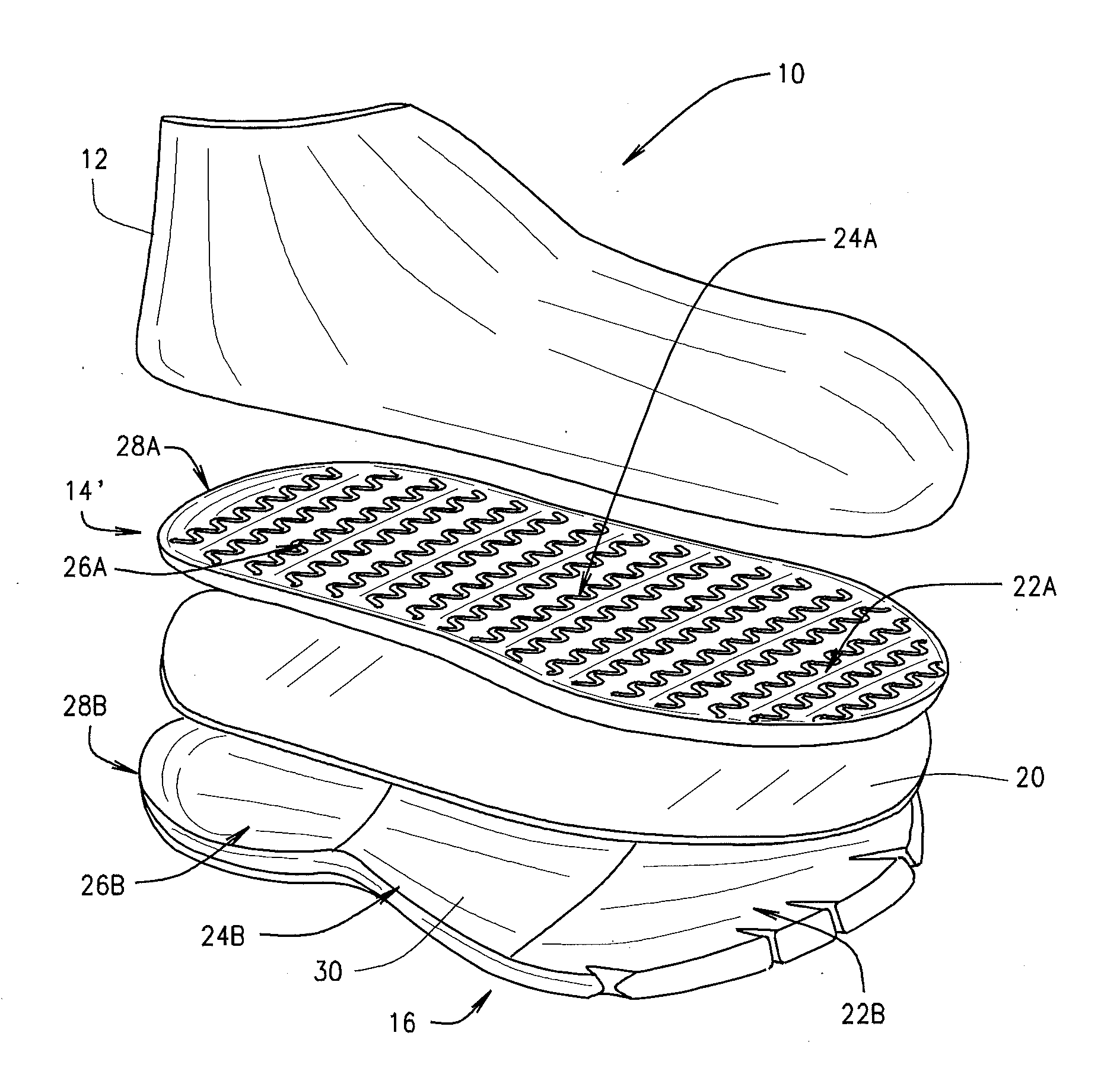
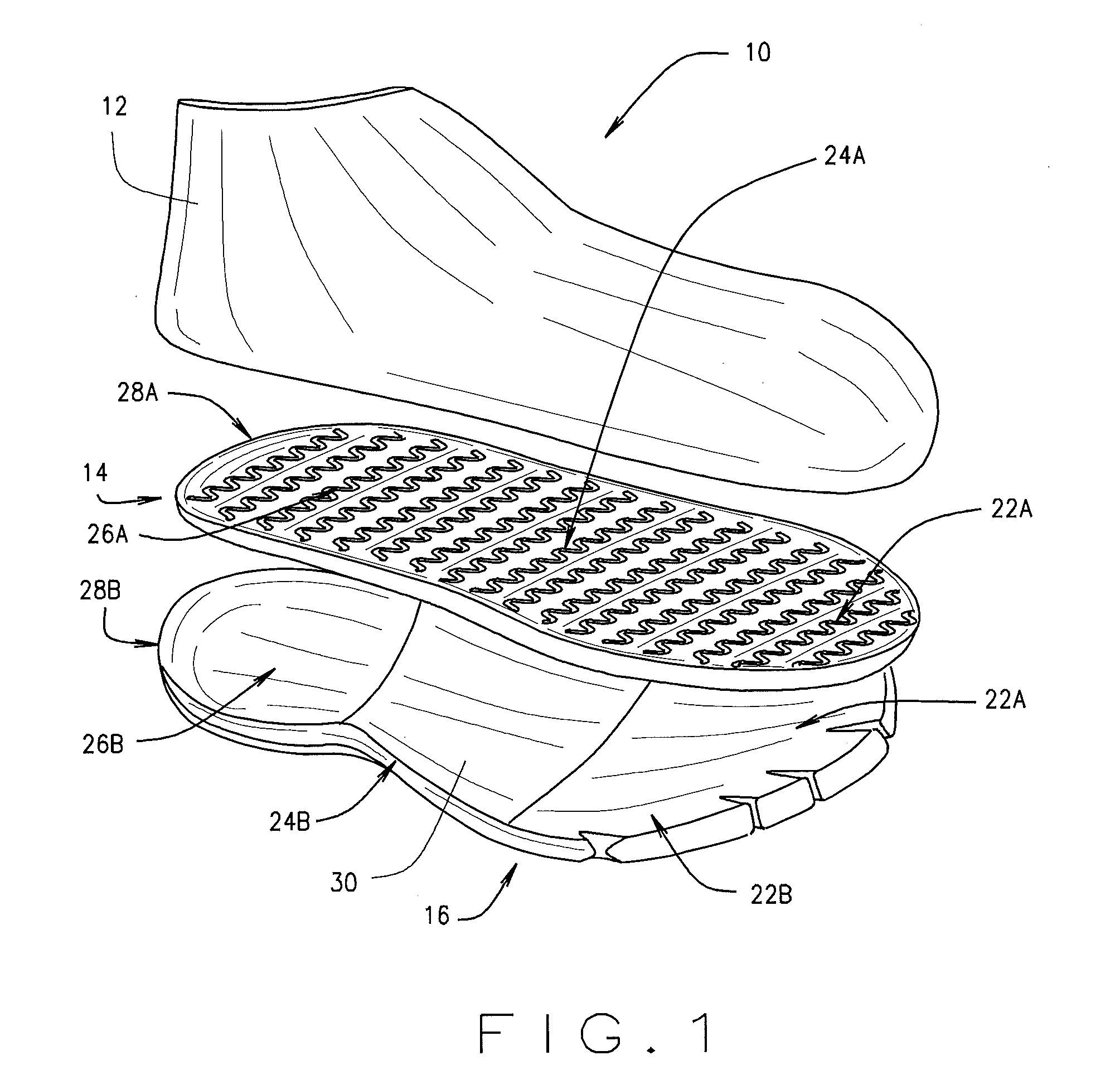
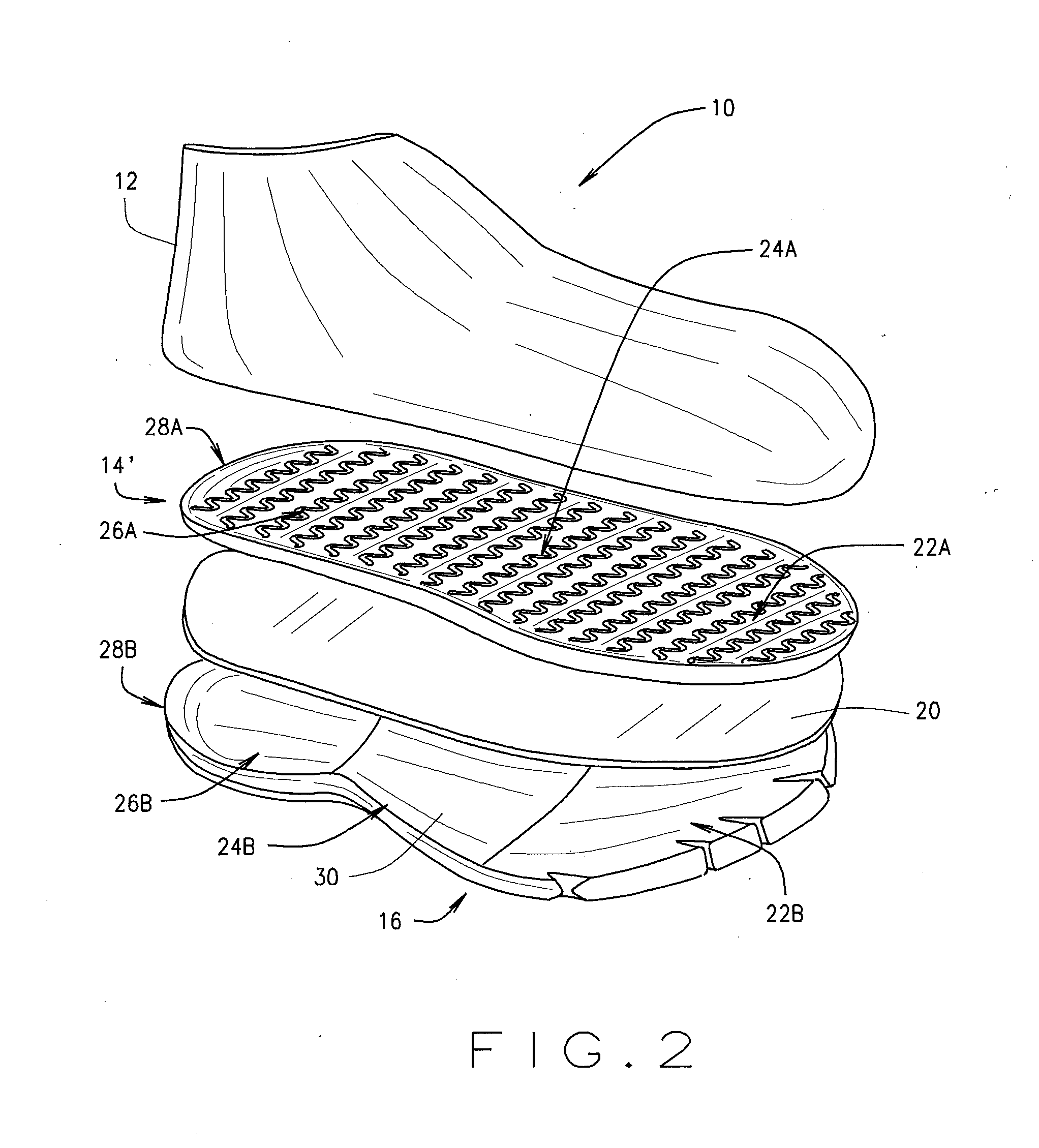
Shoe sole to improve walking, sensory response of the toes, and help develop leg muscles
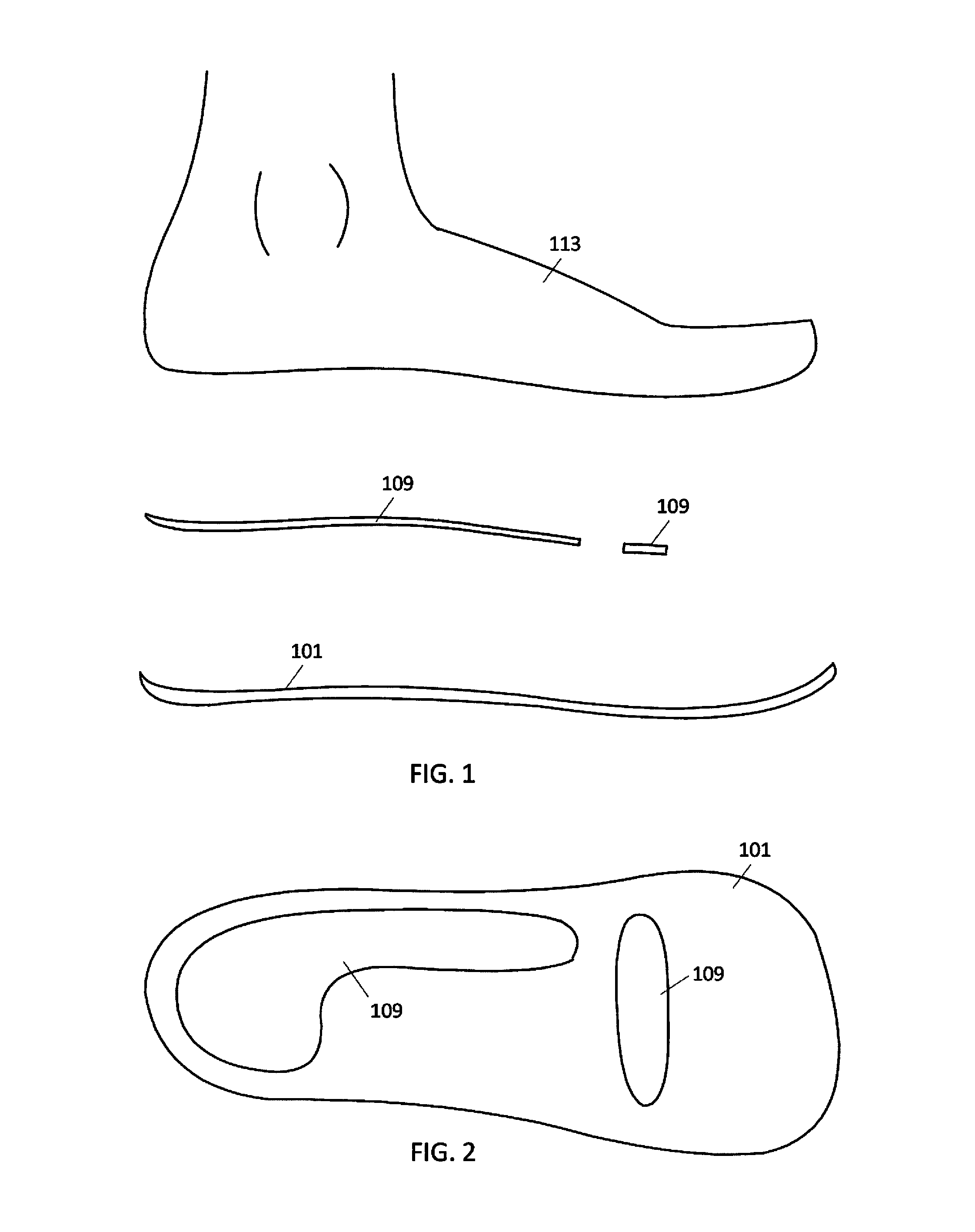
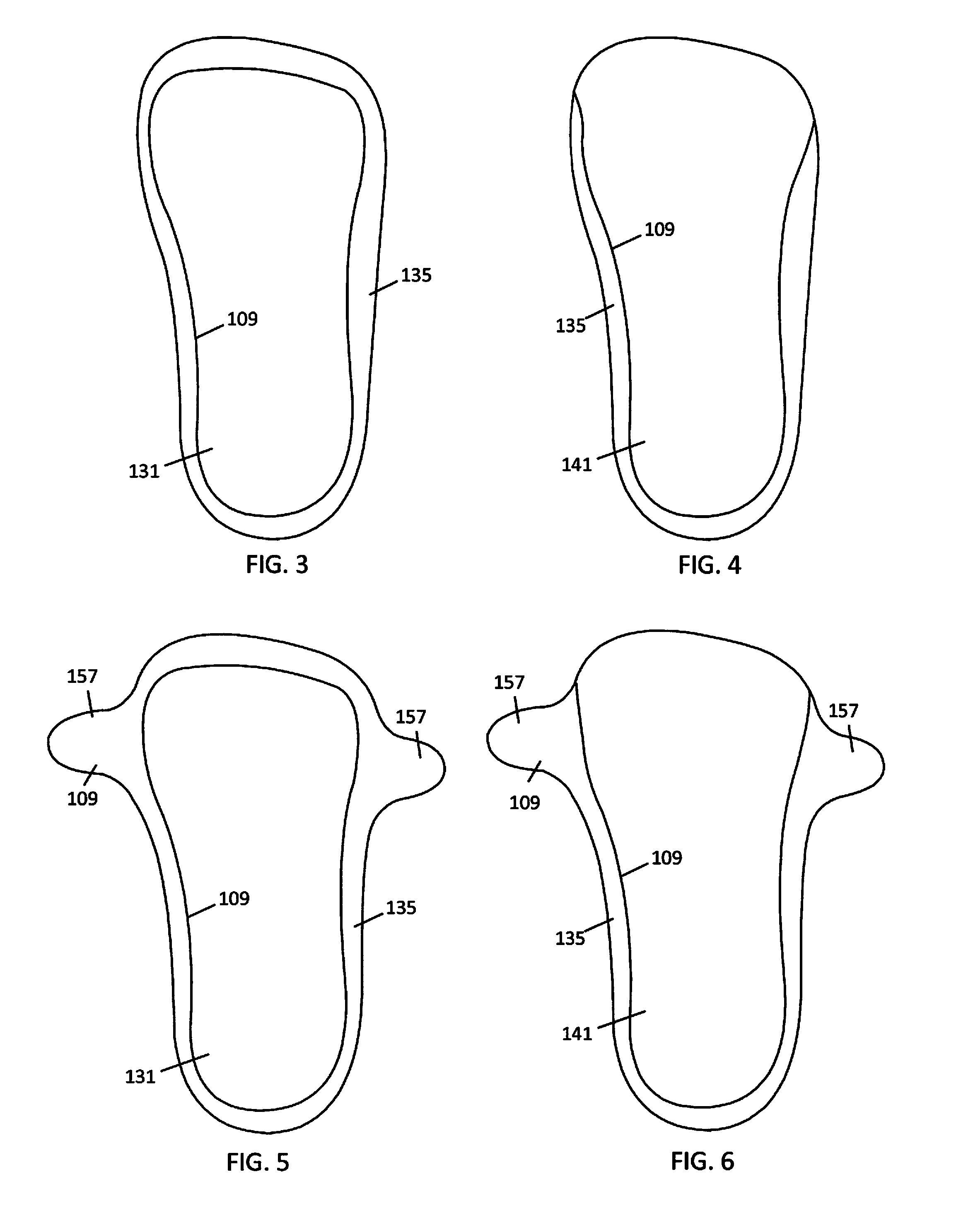
An improvement in the design of a shoe wherein a flexible material is placed inside the shoe sole at the level over the insole and below the toes of the foot and either above or also in line with the midsole, so that the wearer's toes rest along the flexible material when the wearer's foot is inserted into the shoe. The flexible material also extends to the area at the base of the big toe and behind the ball of the foot behind the big toe under the 1st metatarso-phalange joint base of the big toe. In a variation of the present invention, the flexible material only extends under the toes and does not extend behind the big toe. Therefore, in addition to all five toes resting on the flexible material, the ball of the foot area at the base of the big toe also rests on the flexible material. By filling the frontal section of the shoe sole with the flexible material, the flexible material permits the toes to curl downward when walking. The flexible material can be any type of-gel, deformable liquid or gel containing pack, polyurethane gel, silicone, soft rubber, foam, memory soft material, neoprene, polyvinyl, polyethylene, polyurethane and any type of natural or synthetic soft flexible material to simulate walking on sand.
Owner:KHANTZIS CARLOS A
Method and device for reflex-based functional gait training
ActiveUS8452410B2Increase opportunitiesImprove the quality of lifeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationAccelerometerGyroscope
A device and method for gait training, such as for rehabilitation of a person after a stroke is provided. In some embodiments, the device comprises a stimulator, preferably electric stimulator, for provoking a spinal cord withdrawal reflex in the person by stimulation on the person's foot in response to a control signal. Hereby, the person's leg will move and initiate a gait swing. A sensor is placed to sense movement of the leg and provide a feedback signal accordingly. A processor unit with a processor runs a control algorithm which calculates the control signal in response to the feedback signal. Thus, the method is based on a closed-loop design, and the control signal is preferably calculated for each walking step, and it is preferably based on the feedback signal obtained from the preceding walking step. Hereby reflex habituation can be accounted for. Preferably, the stimulator has a plurality of stimulator channels with electrodes placed on different sites distributed on the sole of the foot and on the heel. The feedback signal may be based on accelerometer(s), and / or gyroscope(s), and / or goinometer(s) positioned on the leg and / or foot, e.g. partly or fully integrated in an in-sole for a shoe etc.
Owner:NORDIC NEUROSTIM APS
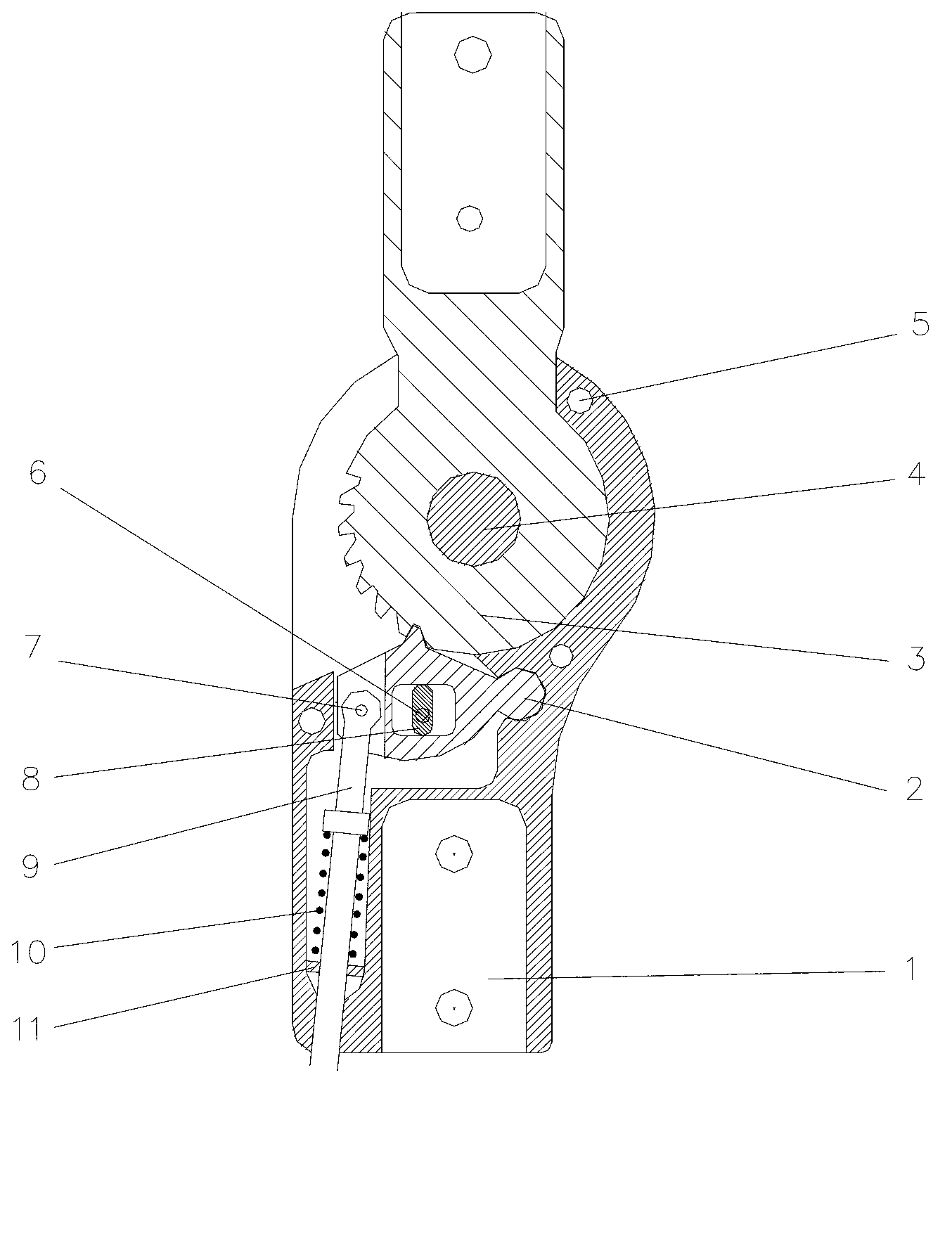
Knee-joint hinge of standing period control orthosis
InactiveCN103006362AImprove gaitIncrease active participationWalking aidsKnee orthosisOrthotic device
The invention belongs to the field of medical appliances, and relates to a novel knee-joint hinge of a standing period control orthosis for rehabilitation, in particular to the knee-joint hinge of the orthosis, which can be used for walking function training and walking function compensation of patients with lower limb paralysis such as spinal cord injury, infantile paralysis and the like, and can keep a certain physiological gait.
Owner:李建军 +3
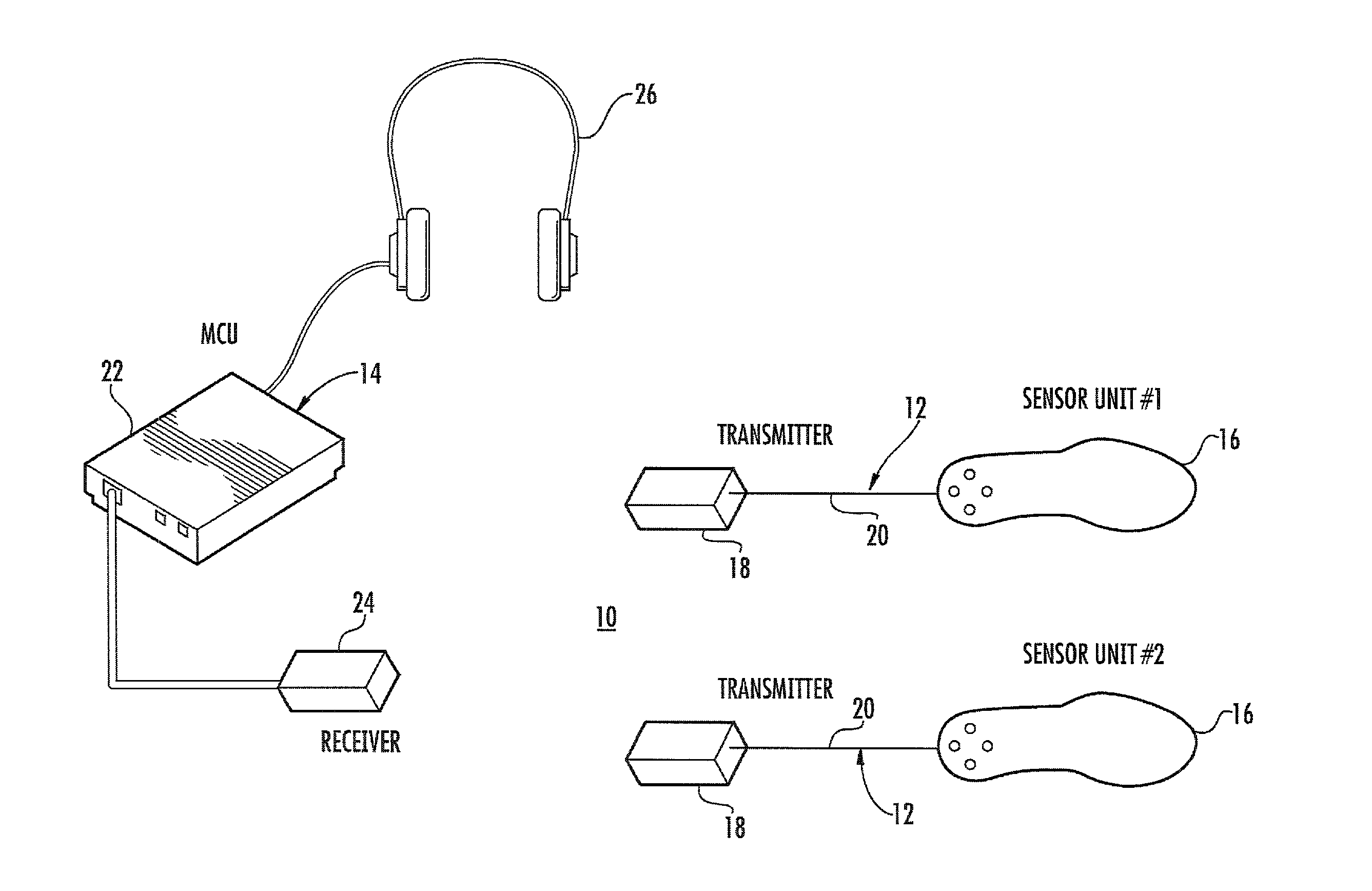
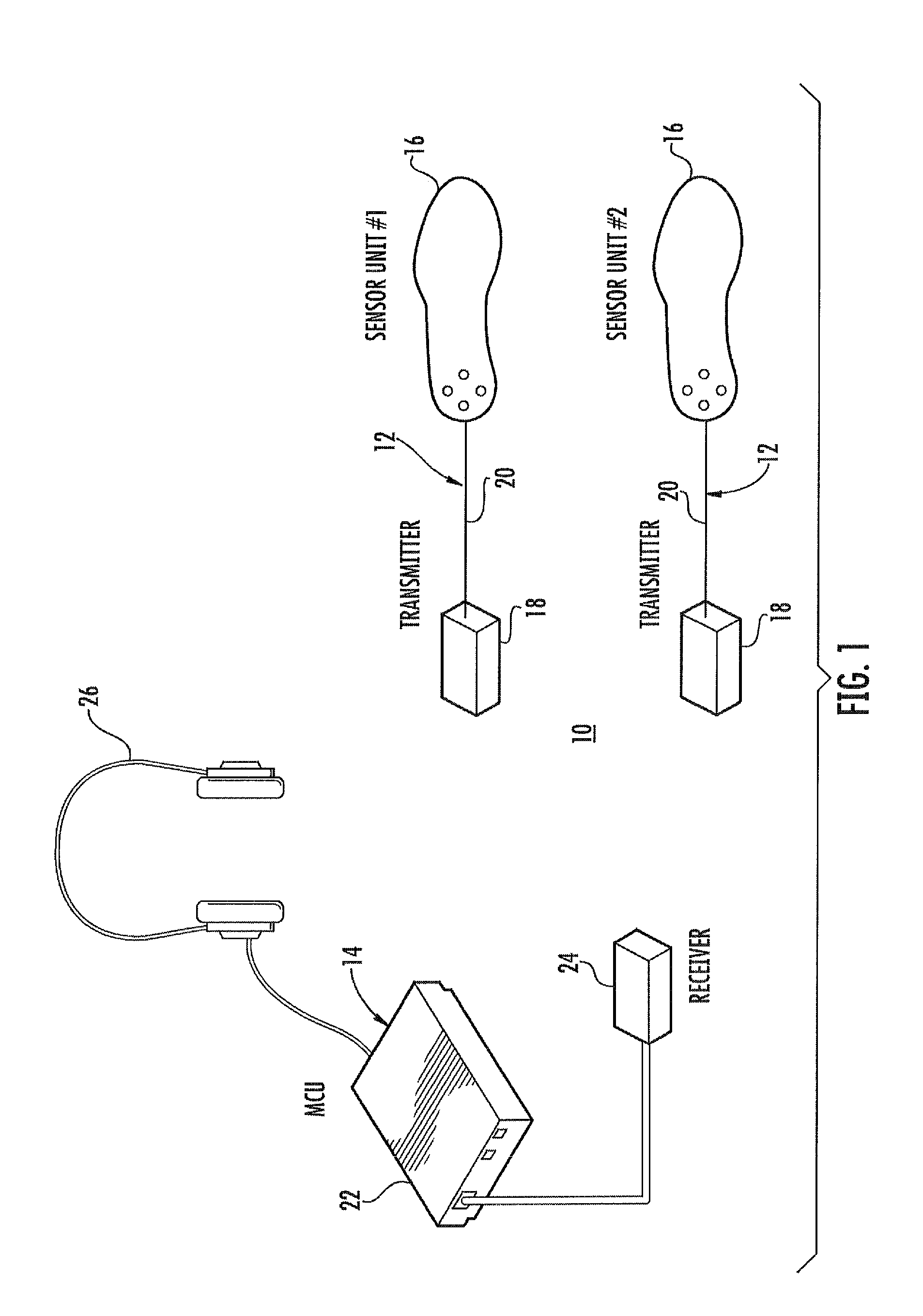
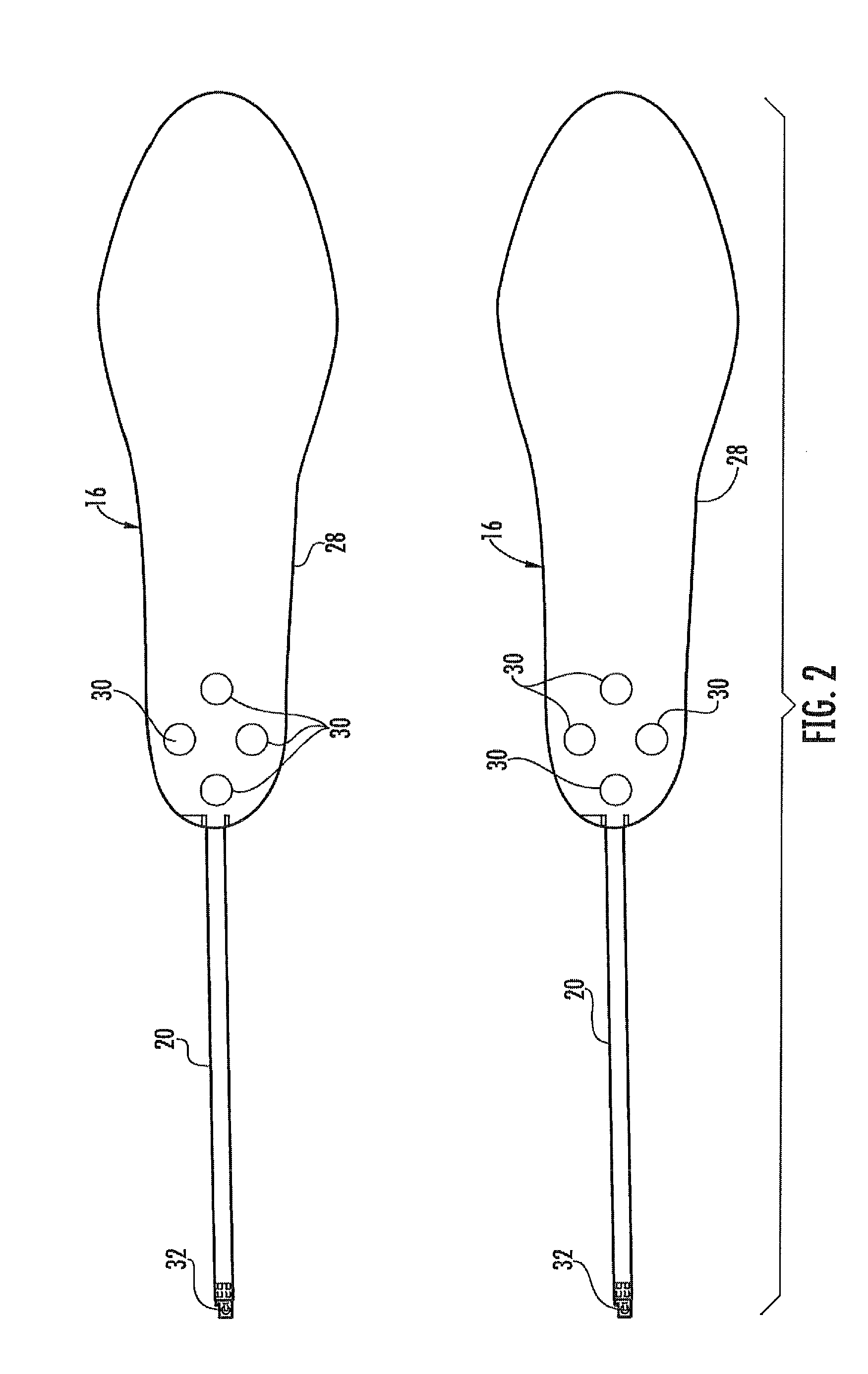
Vibratory feedback systems and methods
ActiveUS20120154153A1Improve gaitDiagnostics using vibrationsTactile signalling systemsEngineeringActuator
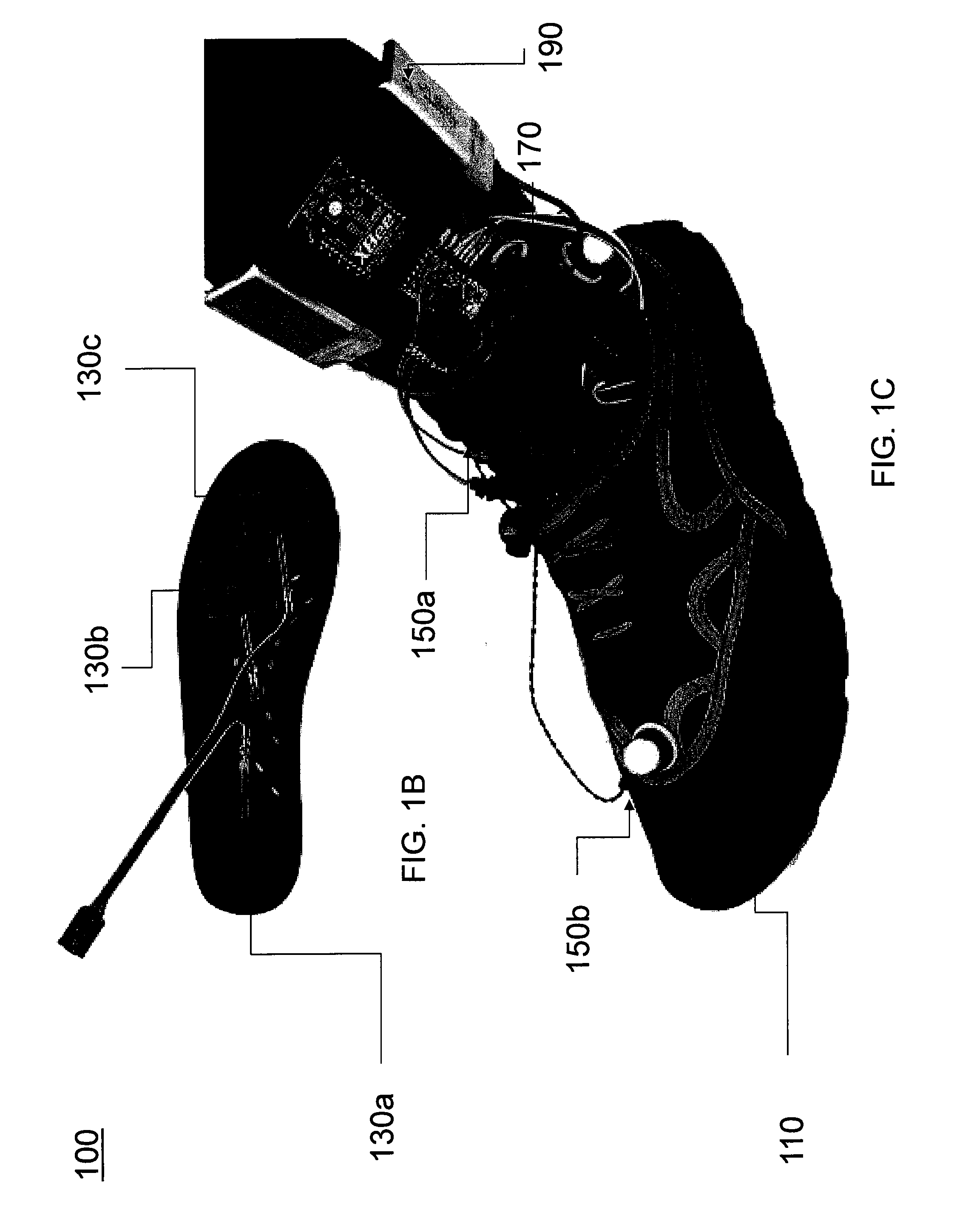
Vibratory feedback systems and methods are disclosed. A vibratory feedback system includes a shoe adapted to be secured to a user's foot, a plurality of force sensors and vibration actuators mounted on the shoe, and a microprocessor affixed to the shoe. The force sensors are configured to sense forces exerted by the user's foot. The vibration actuators are configured to provide vibrations to the user's foot. The microprocessor is coupled to receive data from the plurality of force sensors, and is programmed to actuate the plurality of vibration actuators to provide a first characteristic vibration to the user's foot based on the sensed forces. A method of improving the gait of a user includes enabling the user to ambulate with the vibratory feedback system secured to the user's foot, and providing a first characteristic vibration to the user's foot based on the sensed forces using the vibratory feedback system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
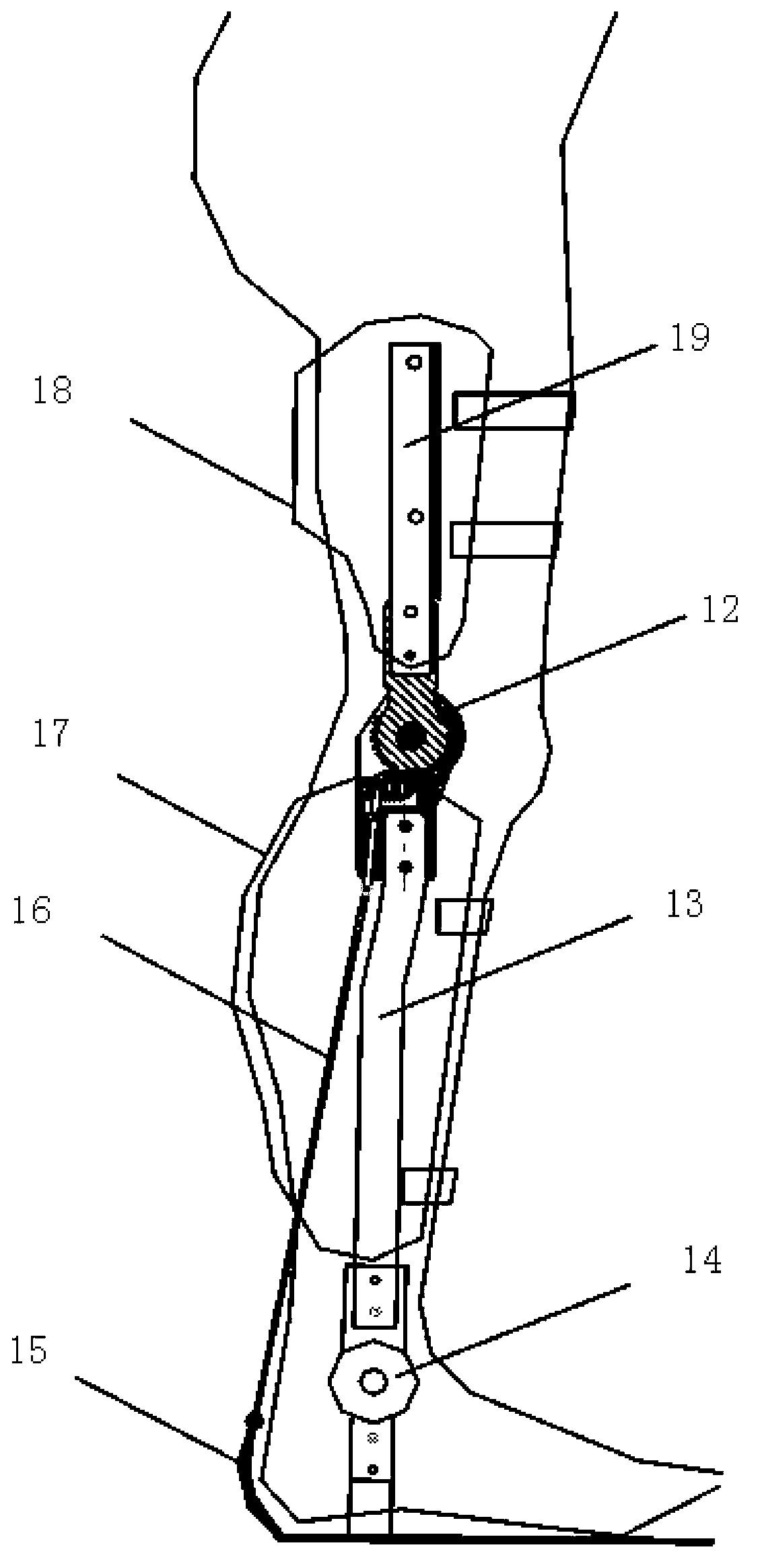
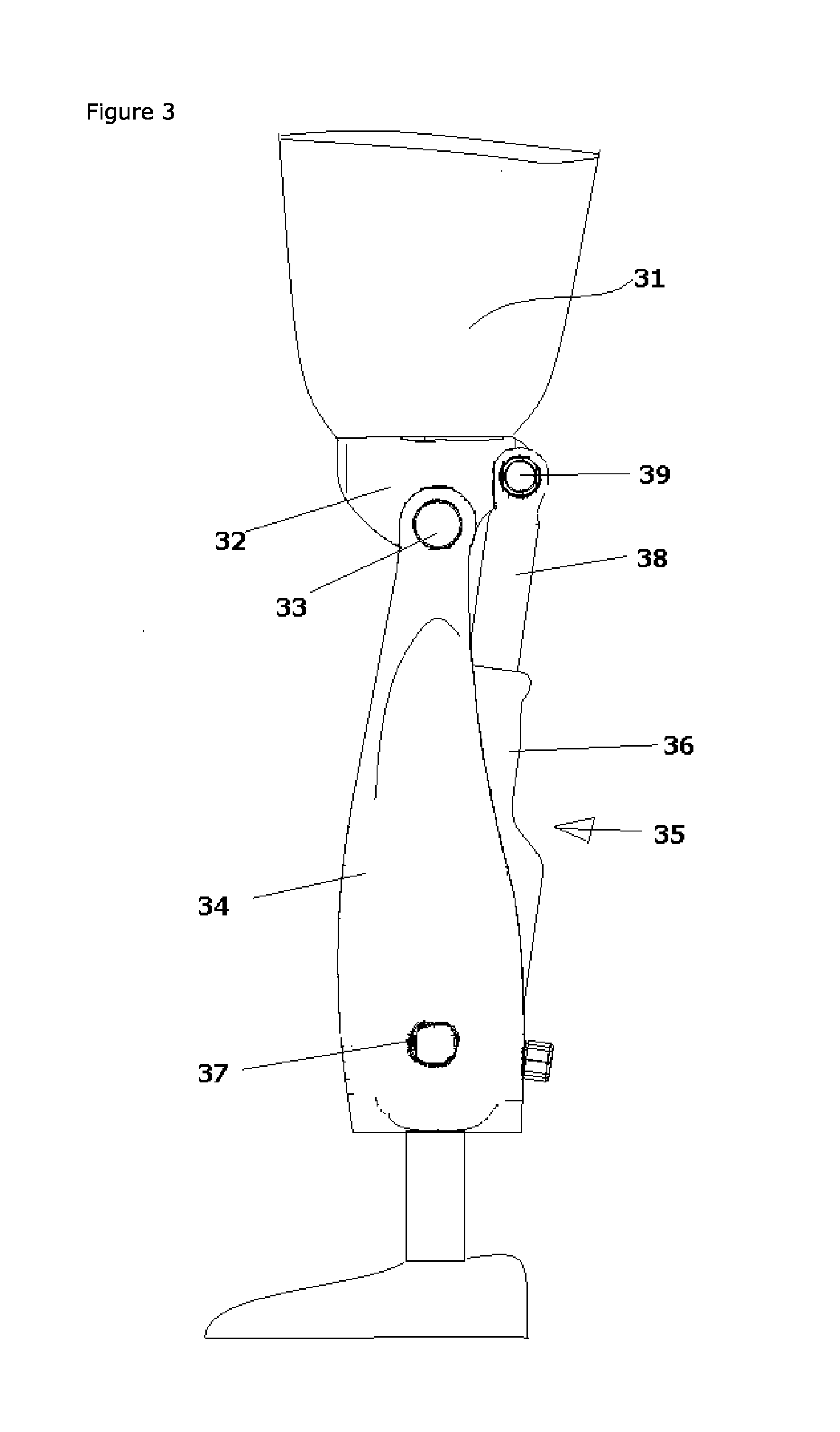
Hydrualic prosthetic joint
ActiveUS20160235558A1Keep openMemory is also lostSpringsArtificial legsDifferential pressureHuman motion
Owner:BOENDER JACOB QUINTUS LAURENCE ANTHONY +1
Gait symmetry measurement and improvement
A gait-enhancing system and method of enhancing gait includes generating a reference signal having substantially equal durations between occurrences and providing the reference signal to a user. Contact between the feet of the user with a surface is received and occurrence of a trigger signal is generated in response to the contact. An occurrence of the trigger signal is compared with an occurrence of a reference signal, and a guidance signal is produced as a function of the amount of time that the trigger signal led or lagged the reference signal. The guidance signal is provided to the user in order to promote symmetry in stride between one foot and the other foot of the user, enhancing the user's gait.
Owner:INTERACTIVE METRONOME
Device and methods fo treating neurological disorders
ActiveUS20150119767A1Improving/restoring control functionImproving/restoring neurological neurological functionSolesGymnastic exercisingPsychiatryNeurological disorder
Owner:APOS MEDICAL ASSETS LTD
Adhesive footwear and devices
Footwear used for high performance activities such as running can be adhesively attached to the plantar surface of feet rather than uppers or straps. The upper surface of the protective layer of the footwear can have adhesive regions that secure the foot to the footwear and other regions that are not adhesively coupled to the foot. The adhesive regions can be under the heel, along the lateral side of the foot, under the first through fifth metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints and around the perimeter of the foot above the plantar surface.
Owner:TRAUNER KENNETH B
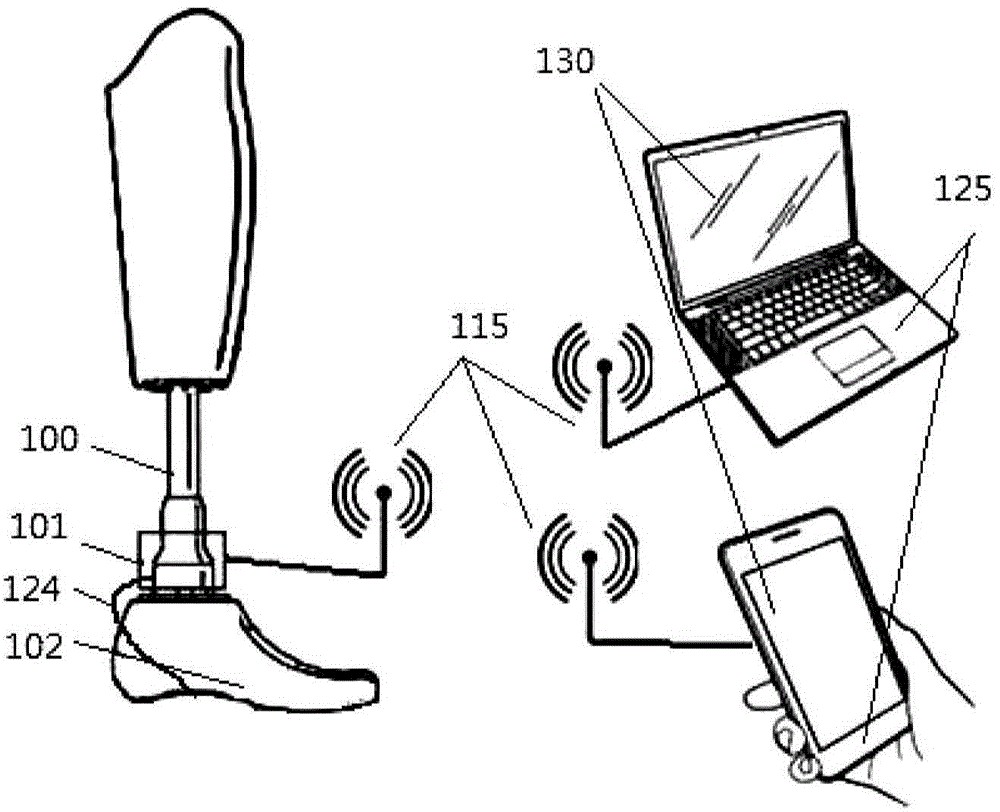
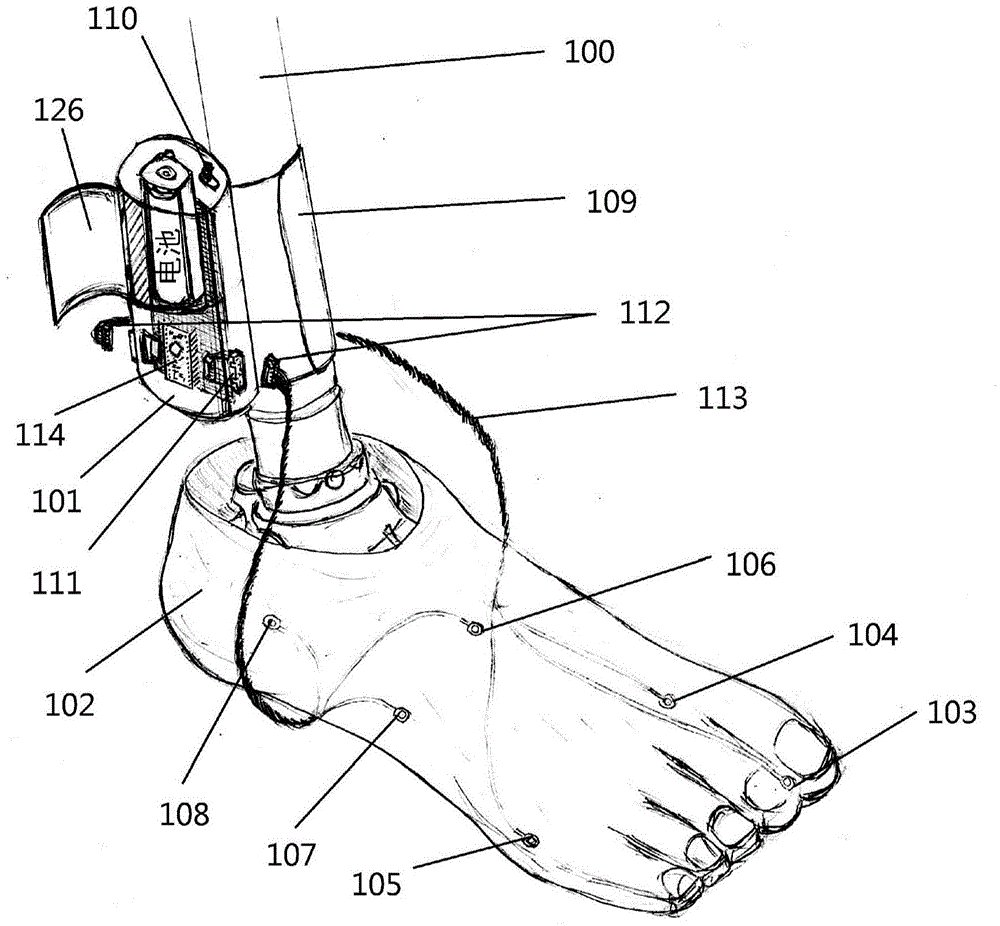
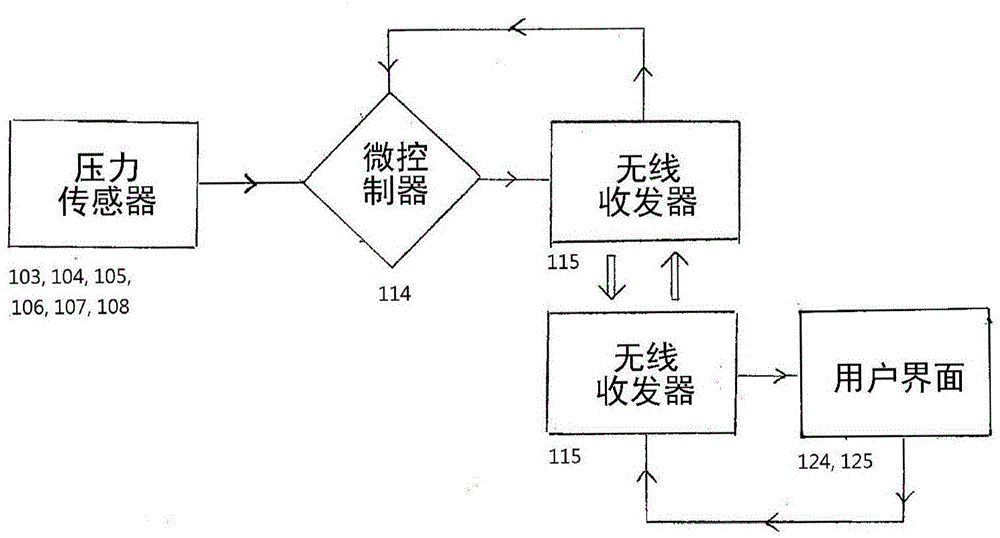
Lower-limb prosthesis alignment and gait analysis auxiliary system adopting foot pressure sensing technology
The invention provides an auxiliary system which is capable of assisting a limb prosthesis orthopedic doctor to assemble lower-limb prosthesis and helping an amputee to improve gait on the basis of a foot pressure signal of the amputee. The auxiliary system comprises a main circuit box, a sole pressure sensor assembly and an interface program, and the interface program is applied to a user interface. According to the auxiliary system, the main circuit box and the sole pressure sensor assembly are used together and are transmitted to the user interface in a wireless mode. The auxiliary system mainly operates on the basis of the principles of computing and displaying standing and swinging times of the amputee during walking as well as a reference pressure center path during walking and standing, and comparing with corresponding standard data, so as to suggest the orthopedic doctor in the adjustment of the lower-limb prosthesis alignment and the gait of the amputee. The auxiliary system disclosed by the invention is helpful for the limb prosthesis orthopedic doctor in the adjustment of the lower-limb prosthesis alignment, the assessment of the gait of the amputee after alignment and in the gait training of the amputee.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
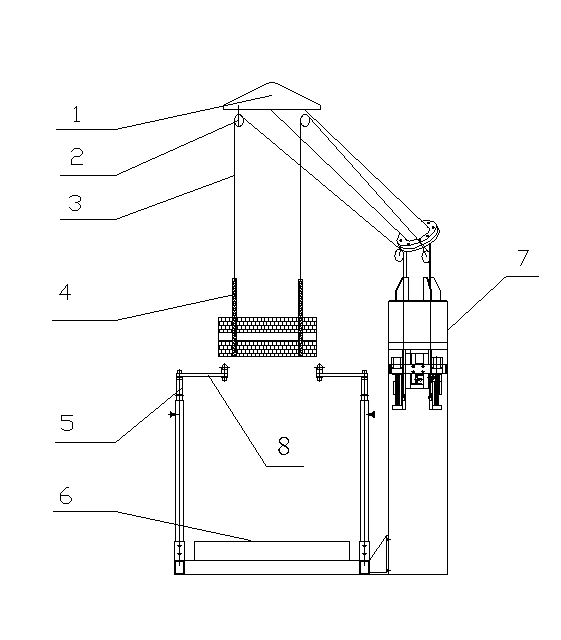
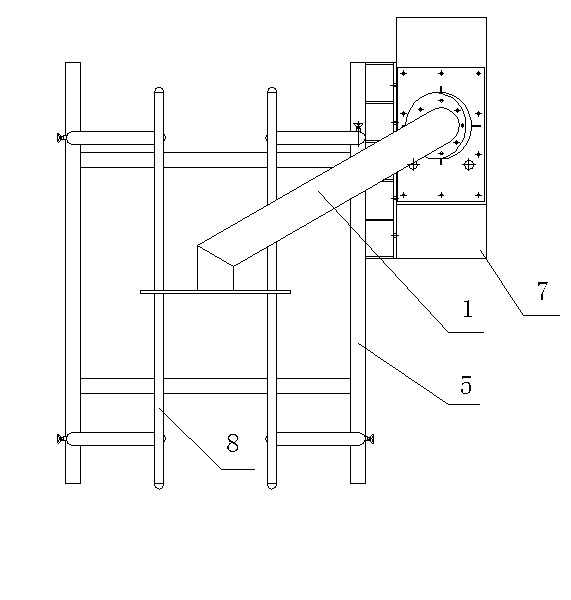
Balanced weight-losing suspension training device for double shoulders
ActiveCN103055470AImprove gaitImprove walking abilityMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesEngineeringTraining effect
The invention discloses a balanced weight-losing suspension training device for double shoulders. The balanced weight-losing suspension training device comprises a weight-losing box, weight-losing suspension vests, a pulley inhaul cable system and a medical treadmill, wherein a weight-losing training frame is fixed on the top of the weight-losing box; handrail frames are arranged on the two sides of the medical treadmill; handrails are arranged on the handrail frames; the weight-losing box comprises a box body; a lifting motor is arranged in the box body and is connected with a lifting lead screw rod; a balance weight seat is arranged on the upper part of the lifting lead screw rod; two lead screw balance weight rods loaded with slider balance weight blocks are arranged on the balance weight seat and are connected with an adjusting motor; a pulley suspension system comprises two inhaul cables and a plurality of pulleys connected to the weight-losing training frame; one ends of the two inhaul cables are respectively fixed on the two lead screw balance weight rods; and the inhaul cables are suspended above the medical treadmill by a guiding delay weight-losing training frame of the pulleys, and the weight-losing suspension vests are fixed at the ends of the inhauls. The balanced weight-losing suspension training device is reasonable in design, convenient to use and adjust, and good in training effect.
Owner:JIANGSU SUYUN MEDICAL MATERIALS
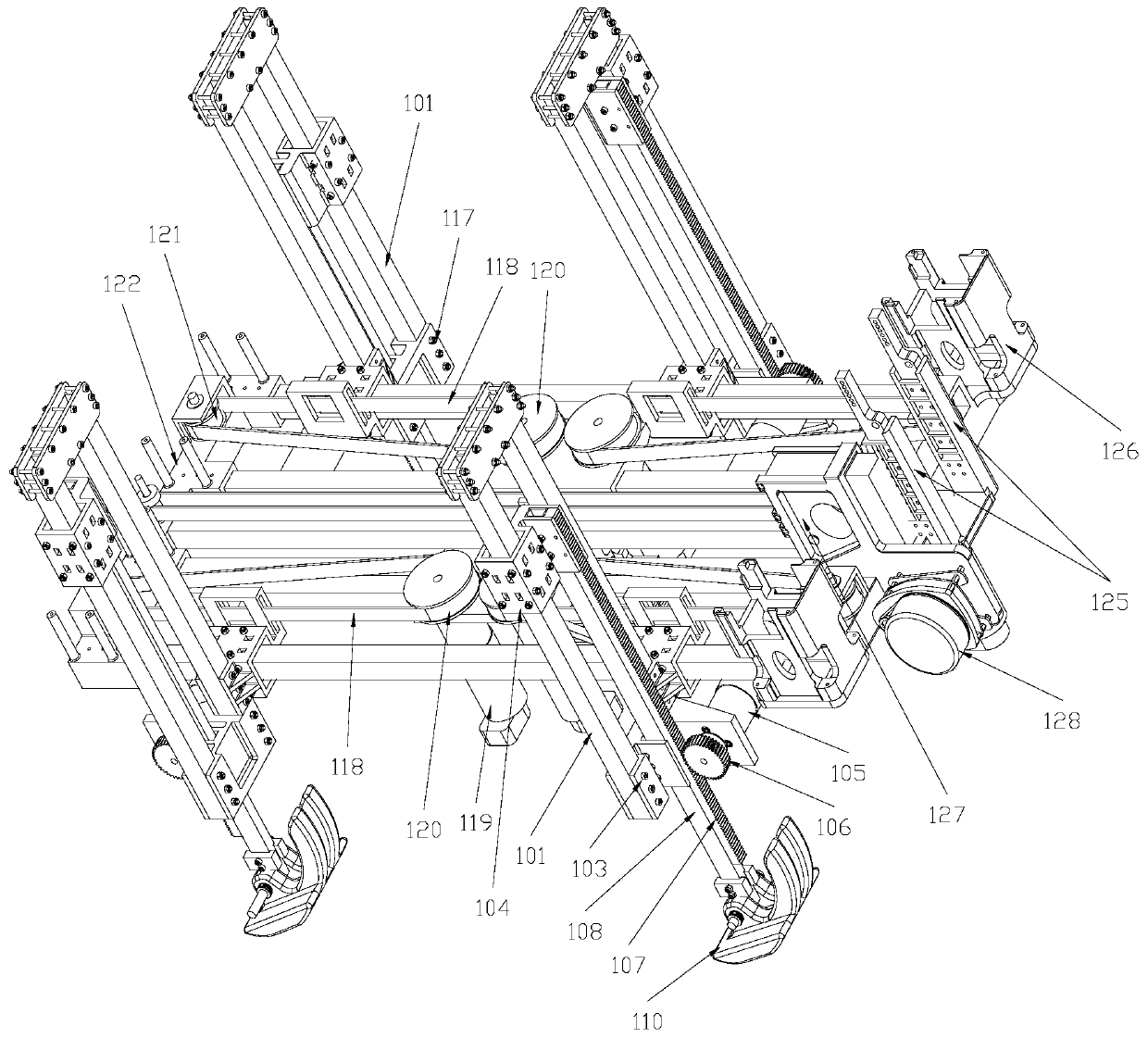
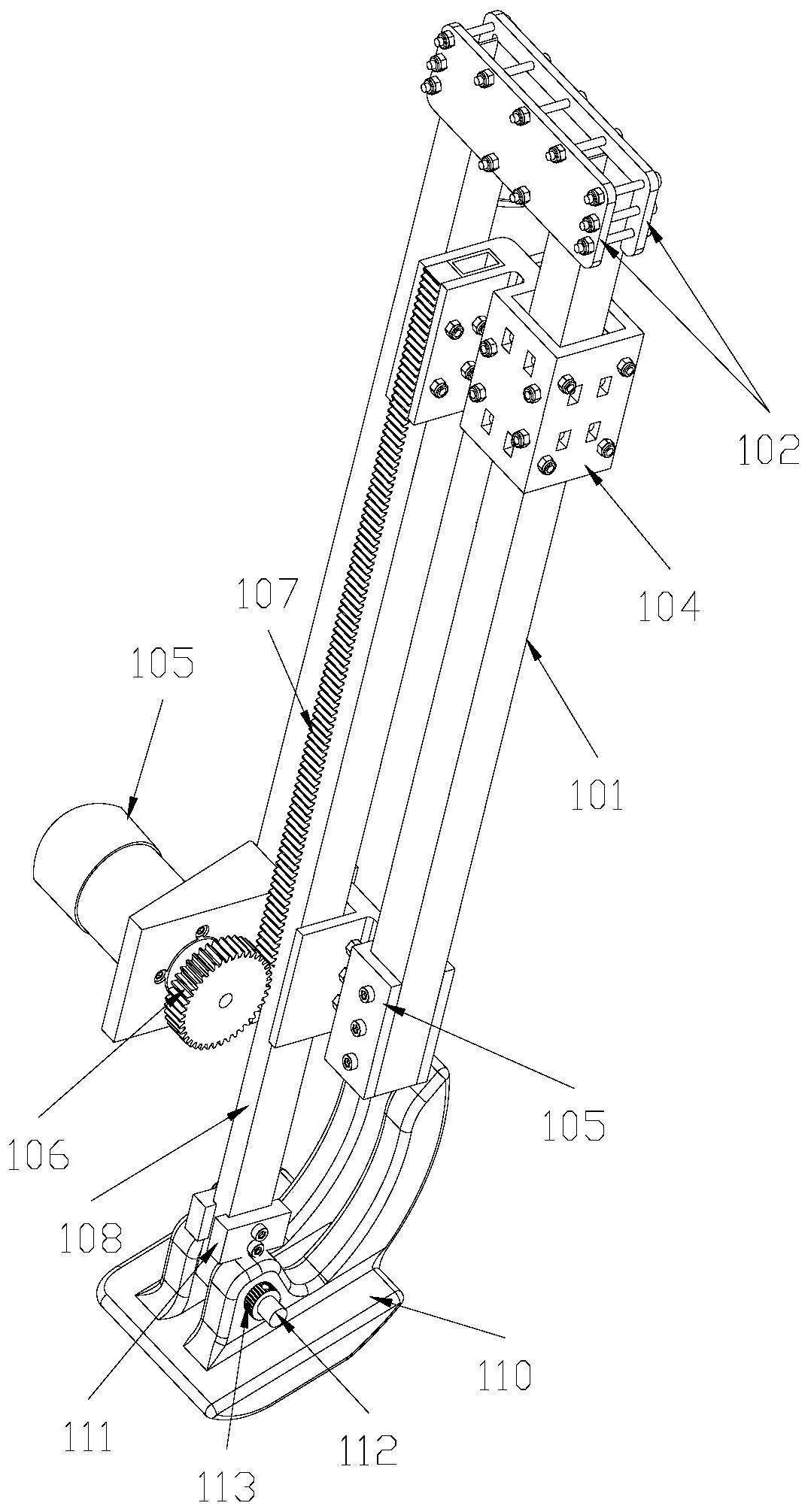
Quadruped robot capable of achieving gait control through front-rear traction and up-down rolling
The invention provides a quadruped robot capable of achieving gait control through front-rear traction and up-down rolling, and belongs to the field of robots. The quadruped robot includes a body frame, a shank support tube, a leg support frame, a longitudinal driving unit, a longitudinal moving sliding block, a foot structure, a transverse driving unit and a transverse moving sliding block, and the foot structure is connected with a rotating shaft of the lower end of the shank support tube, the longitudinal moving sliding block is slidably connected with the leg support frame, and the longitudinal moving sliding block is fixedly connected with the shank support tube and the longitudinal driving unit to make the longitudinal driving unit drives the shank support tube move up and down alongthe leg support frame; and the sliding block end of the transverse moving sliding block is slidably connected with an outside crossbar of the body frame, and the transverse moving sliding block is fixedly connected with the leg support frame and the transverse drive unit to make the transverse driving unit drive the leg support frame to move transversely along the outside crossbar of the body frame. The quadruped robot has the advantages of simple gait, low cost, simple structure, and high feasibility and generalizability.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Gait symmetry measurement and improvement
A gait-enhancing system and method of enhancing gait includes generating a reference signal having substantially equal durations between occurrences and providing the reference signal to a user. Contact between the feet of the user with a surface is received and occurrence of a trigger signal is generated in response to the contact. An occurrence of the trigger signal is compared with an occurrence of a reference signal, and a guidance signal is produced as a function of the amount of time that the trigger signal led or lagged the reference signal. The guidance signal is provided to the user in order to promote symmetry in stride between one foot and the other foot of the user, enhancing the user's gait.
Owner:INTERACTIVE METRONOME
Footwear promoting natural motion
InactiveUS20120304489A1Torsional stiffness is still limitedMinimizing restrictionSolesUpperGround contactEngineering
A shoe is designed to enable unhindered natural foot motion between the foot and the ground. The shoe is constructed with a cupped heel, a contoured arch, a radiused forepart and neutral heel / forefoot position to create a foot bed that anatomically cradles a wearer's foot. A soft, flexible strobel stitched insole is added, which utilizes encapsulated high resiliency foam. The outsole is sculpted to have rounded natural edges and an anatomically correct flex location toward the forefoot of the shoe where softer, more flexible materials are used. The outsole is further designed with harder, protective materials strategically placed in high ground-contact areas to deliver protection and support. An optional midfoot support element may be positioned between the insole and outsole to control torsional stiffness. Upper materials are selected to minimize restriction of movement and promote breathability.
Owner:BROWN SHOE
Footwear with integrated energy wave sockliner
InactiveUS20130318817A1Minimizing restrictionTorsional stiffness is still limitedSolesUpperEngineeringMechanical engineering
A shoe assembly is designed to enable unhindered natural foot motion between the foot and the ground. The shoe assembly includes an integrated anatomically shaped sockliner and outsole. The sockliner includes a top face and a bottom face, each having a generally planar surface, extending along a base plane. On the top face of the sockliner, a plurality of grooves extend across the base plane in a generally undulating pattern for engagement with the sole of the foot. The bottom face of the sockliner may include a plurality of alternating ridges and / or valleys extending from the inside to the outside of the foot in a generally undulating pattern for engagement with the outsole. A strobel insole of encapsulated high resiliency foam may be positioned between the sockliner and the outsole. An optional midfoot support element may be positioned between the insole and outsole to control tortional stiffness.
Owner:BROWN SHOE
Vibratory feedback systems and methods
Vibratory feedback systems and methods are disclosed. A vibratory feedback system includes a shoe adapted to be secured to a user's foot, a plurality of force sensors and vibration actuators mounted on the shoe, and a microprocessor affixed to the shoe. The force sensors are configured to sense forces exerted by the user's foot. The vibration actuators are configured to provide vibrations to the user's foot. The microprocessor is coupled to receive data from the plurality of force sensors, and is programmed to actuate the plurality of vibration actuators to provide a first characteristic vibration to the user's foot based on the sensed forces. A method of improving the gait of a user includes enabling the user to ambulate with the vibratory feedback system secured to the user's foot, and providing a first characteristic vibration to the user's foot based on the sensed forces using the vibratory feedback system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Methods of administering amantadine compositions
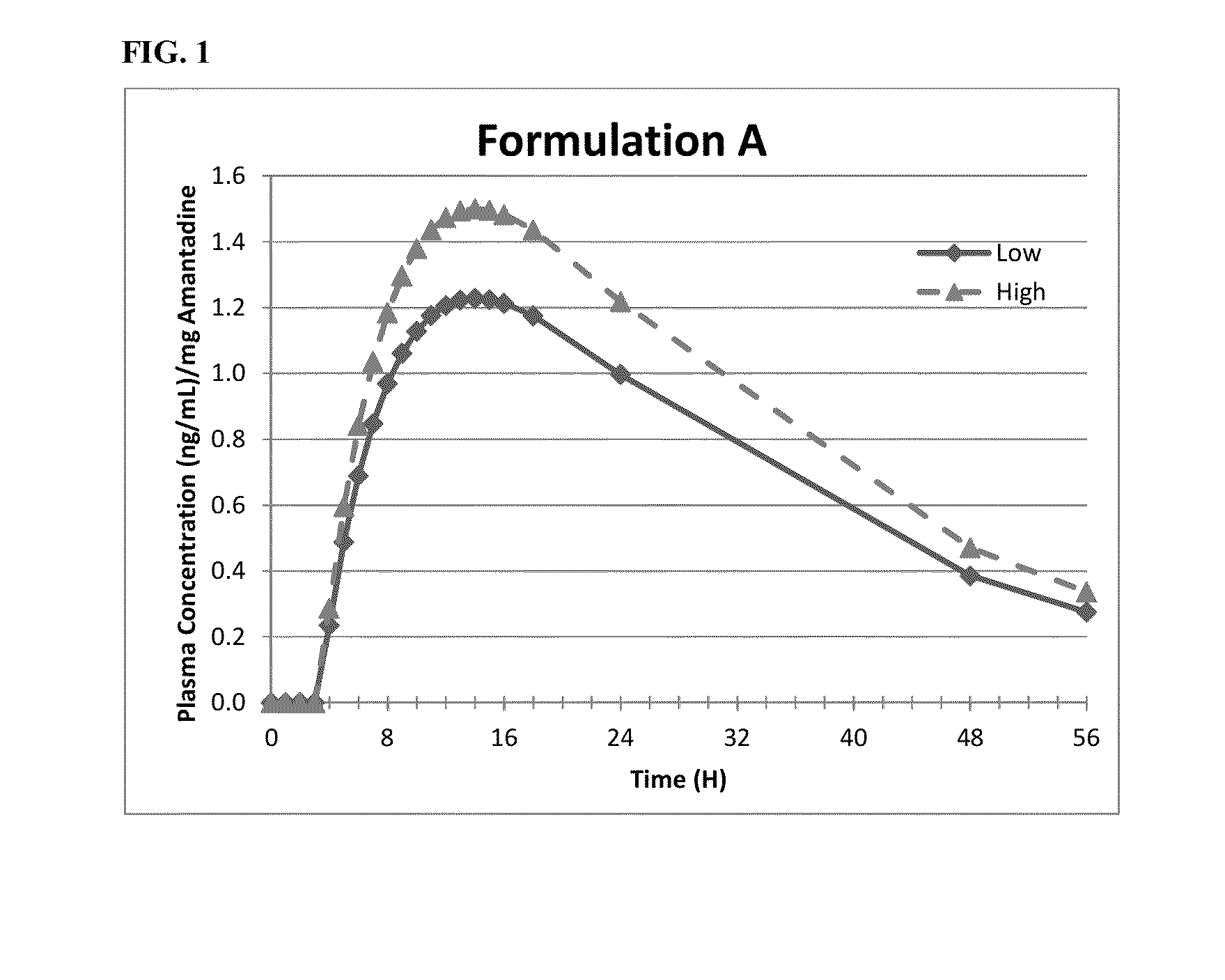
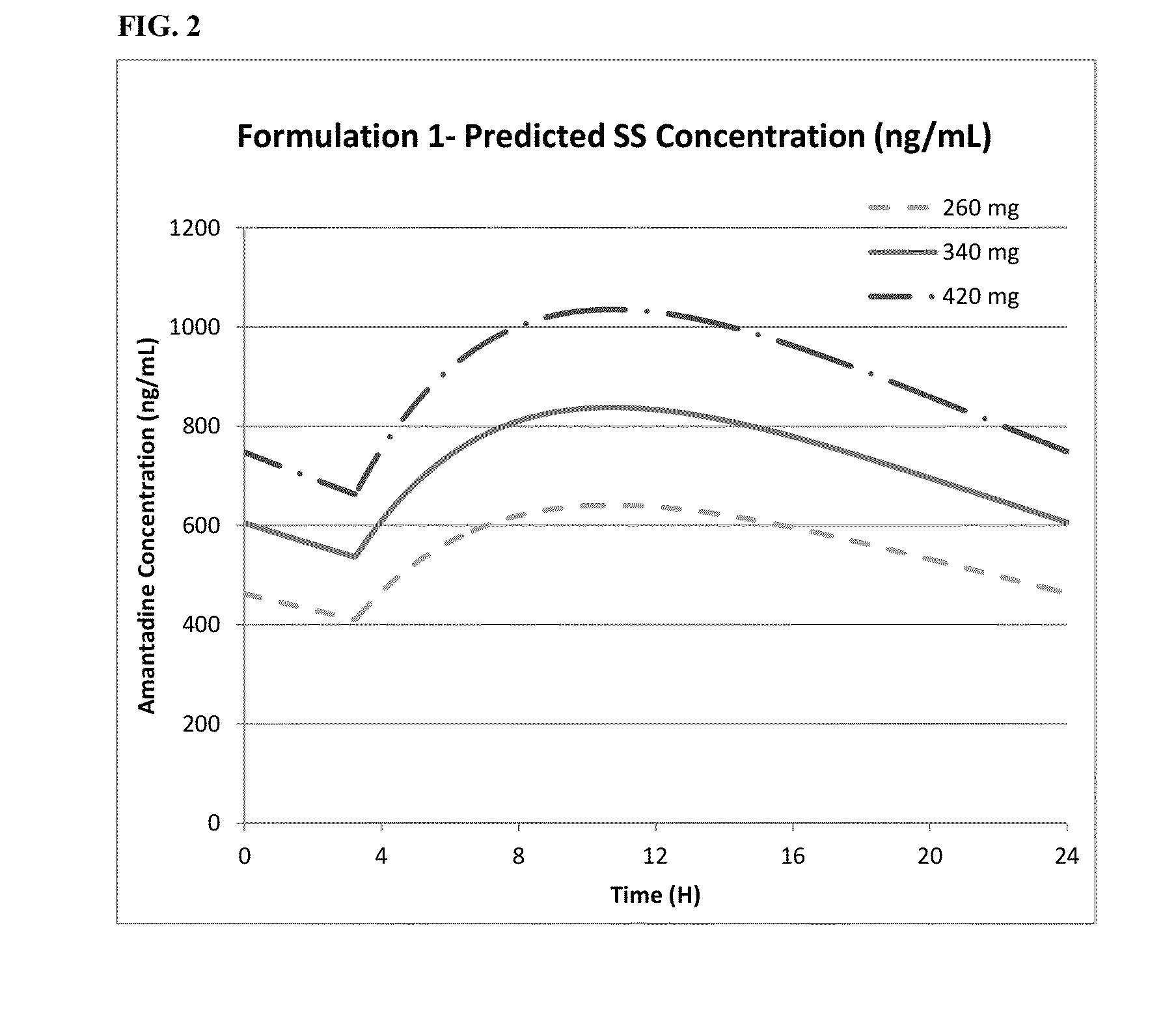
InactiveUS20160228388A1Easy to manageEliminate side effectsMuscular disorderNeuromuscular disorderAmantadineMovement disorders
Methods of administration of amantadine to improve movement disorders are described, as well as compositions suitable therefor.
Owner:ADAMAS PHARMA LLC
Device and methods of treating neurological disorders
ActiveUS9693927B2Improving/restoring controlImproving/restoring functionSolesGymnastic exercisingDiseasePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:APOS MEDICAL ASSETS LTD
Apparatus comprising a support system for a user and its operation in a gravity-assist mode
InactiveUS20210283001A1Skilled locomotionPromote recoverySpinal electrodesProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSpinal cord lesion
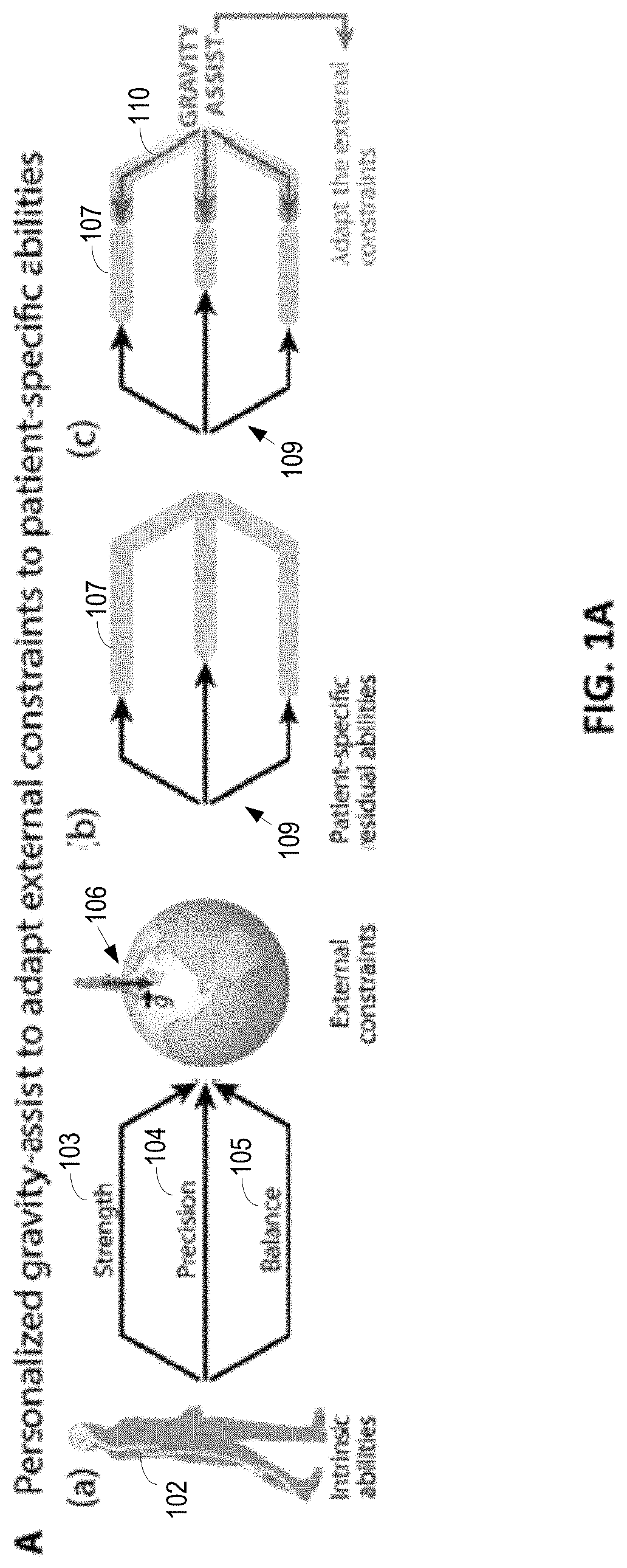
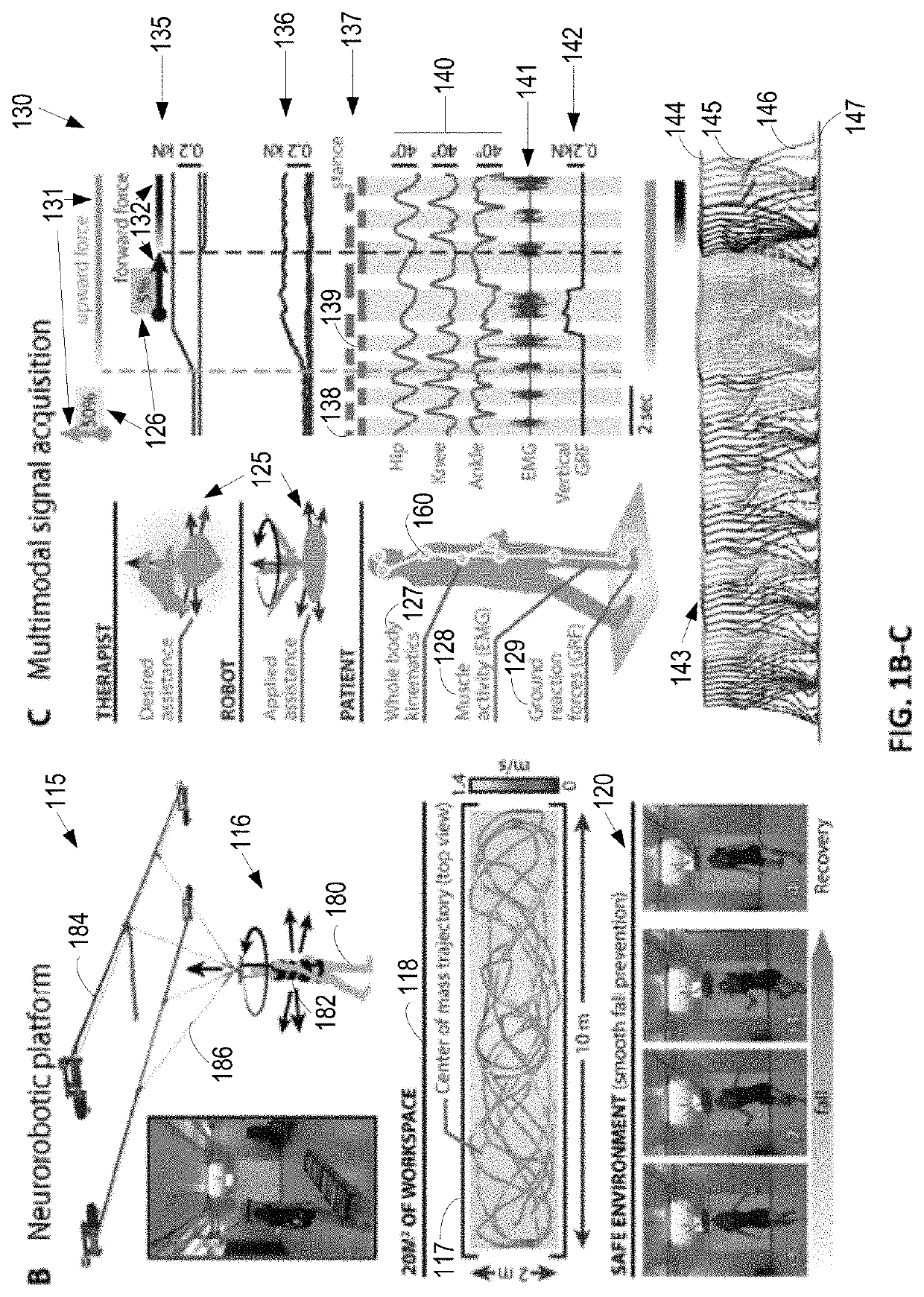
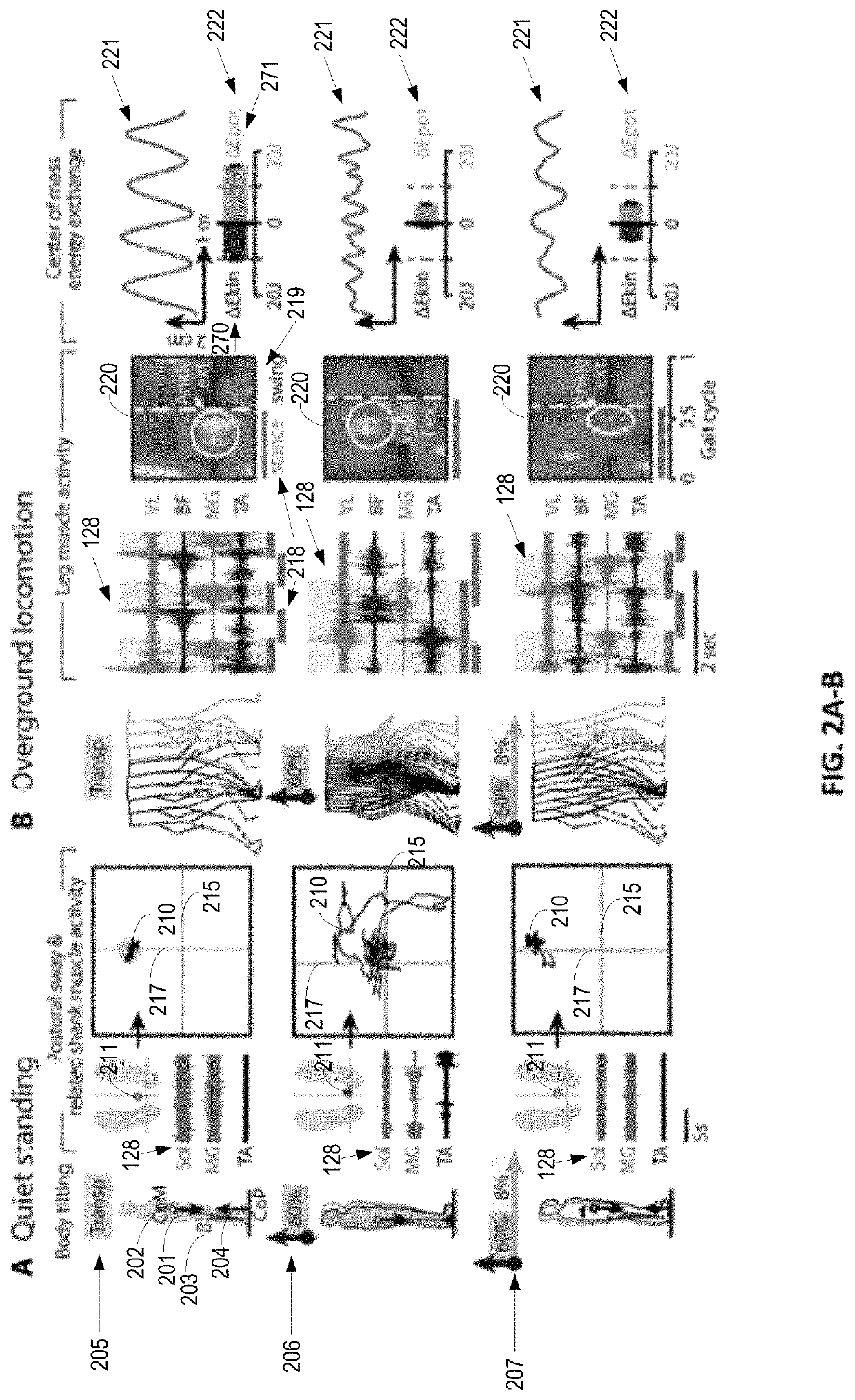
The present application relates to devices and systems for rehabilitation of the locomotor system, for example limbs. In particular, the present application discloses an apparatus, more in particular a robotic platform capable of optimizing gravity-dependent trunk movements, enabling overground locomotion in non-ambulatory individuals with spinal cord injury and stroke, while promoting durable motor improvement when delivered during gait rehabilitation facilitated by electrical spinal cord stimulation.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Orthopedic shoe appliance
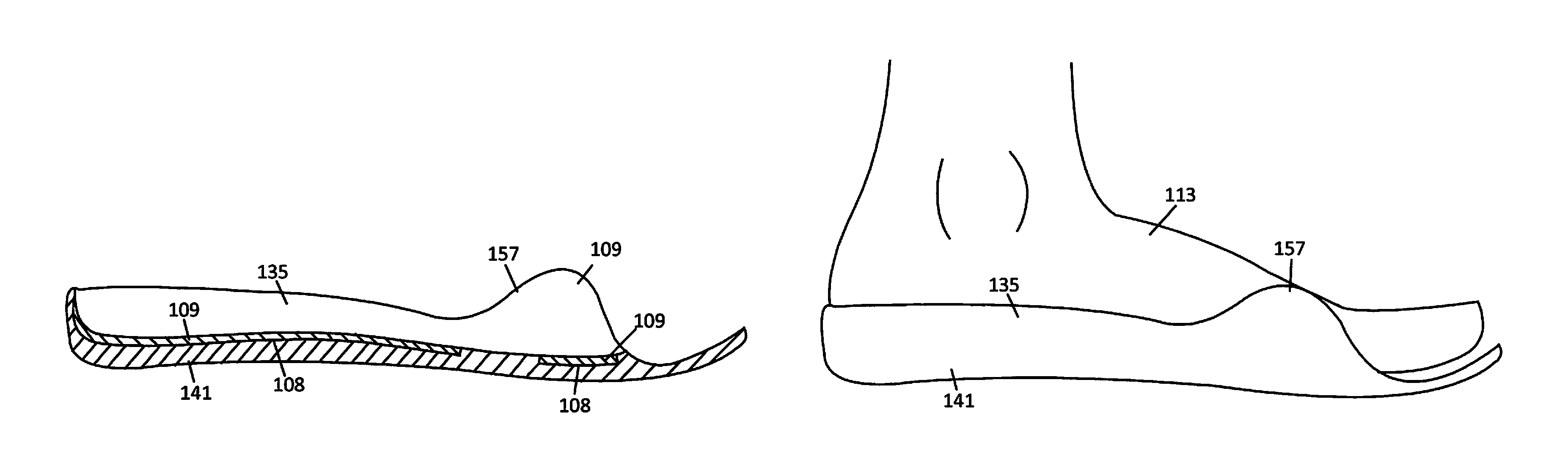
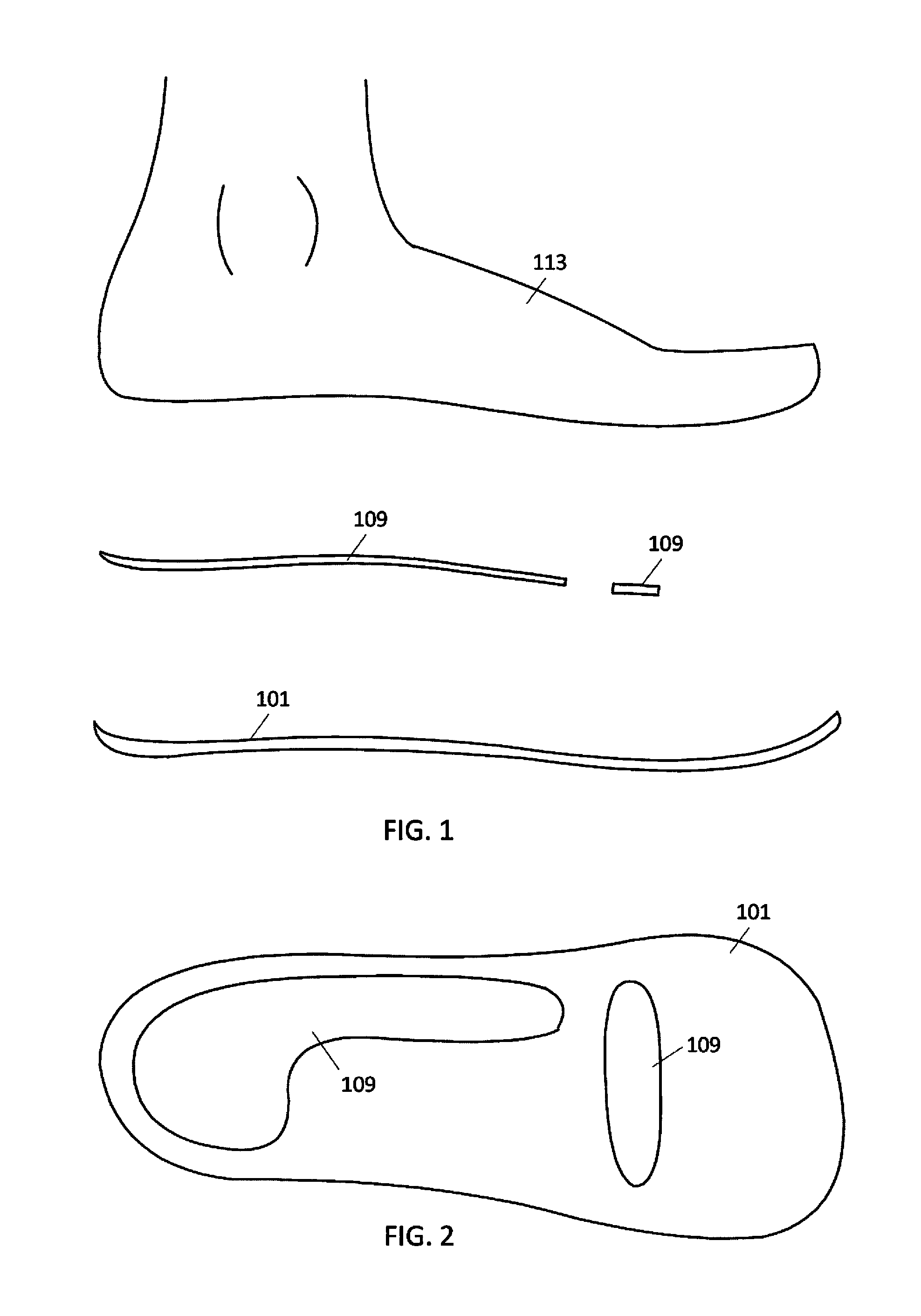
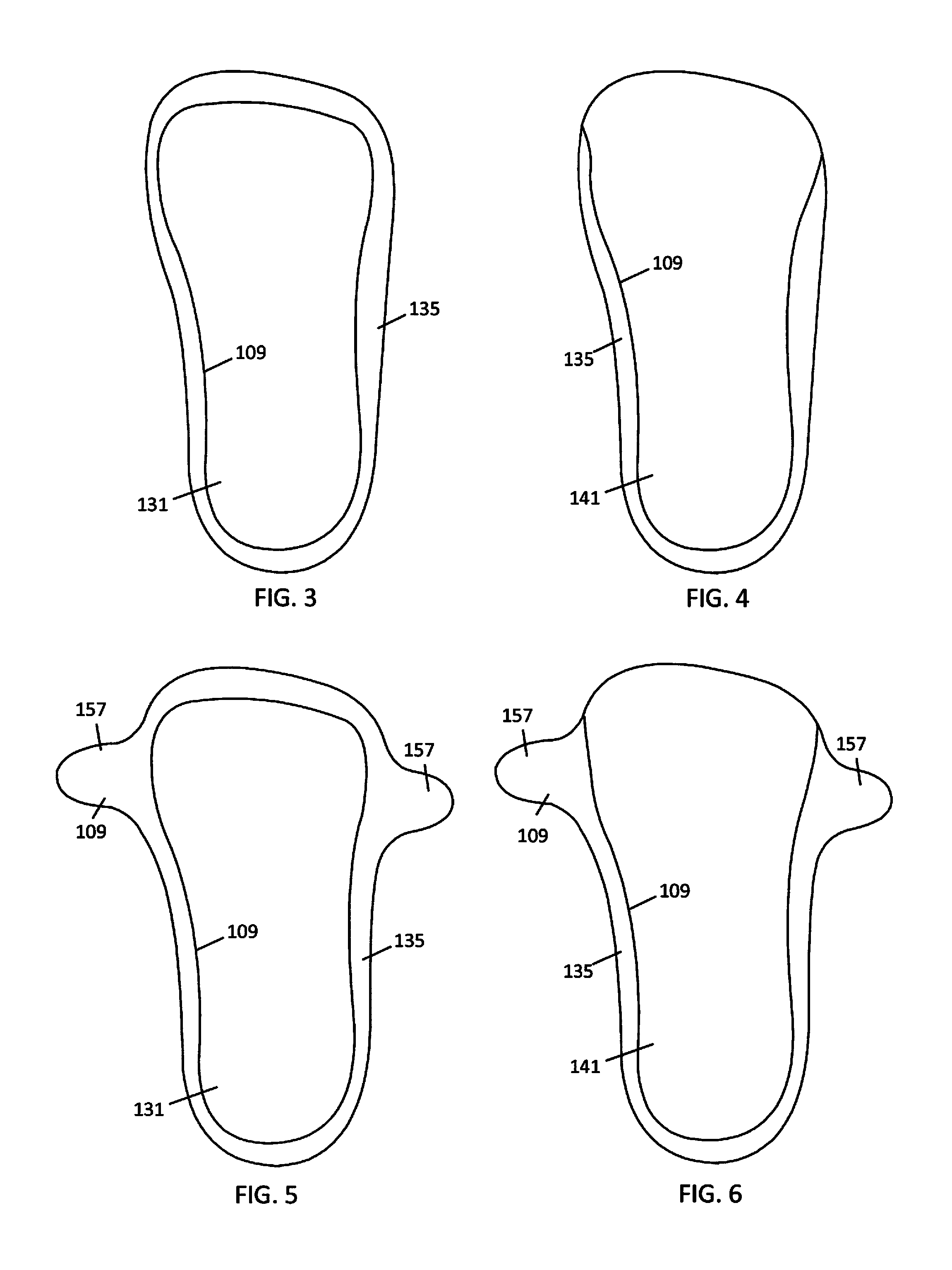
An orthopedic shoe appliance includes a pad for providing support for midfoot arches, the second metatarsal, and the third metatarsal of a foot, wherein the pad does not provide substantial support under a heel of the foot or under the first metatarsal, the fourth metatarsal, and the fifth metatarsal. A method for manufacturing an orthopedic appliance includes obtaining a pad; and shaping the pad to provide support for midfoot arches, the second metatarsal, and the third metatarsal of a foot, but not provide substantial support under a heel of the foot or under the first metatarsal, the fourth metatarsal, and the fifth metatarsal.
Owner:CLUFFY LLC
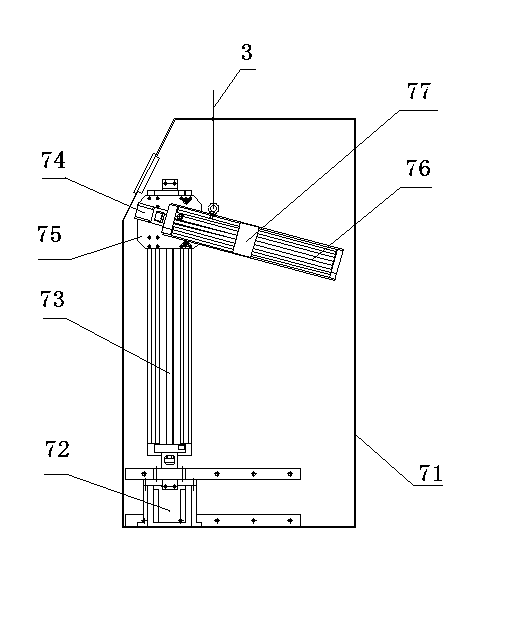
Shoulder Balance Weight Loss Suspension Training Device and Weight Loss Box
ActiveCN103830881BAchieving Adaptive BalanceNot easy to moveMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesElectric machineryEngineering
A double-shoulder balance weight reduction suspension training device comprises a weight reduction suspension vest, a weight reduction training frame, a pulley inhaul cable system, a left armrest device and a right armrest device. Two weight reduction boxes are fixed on the left standing column and the right standing column of the weight reduction training frame. A motor winch system is disposed in each weight reduction box. Stacked weight reduction blocks are disposed in each weight reduction box. A weight reduction block connecting rod and a guide rod are further disposed in each weight reduction box. The lower end of each guide rod is connected with the bottom of the corresponding weight reduction box. A suspension pulley is fixed at the upper end of each weight reduction block connecting rod. Inserting holes as many as the weight reduction blocks are formed in each weight reduction block connecting rod. A slot is formed in each weight reduction block. Bolts are disposed in the slots and the inserting holes. The weight reduction blocks are connected to the corresponding weight reduction block connecting rod through the bolts. The double-shoulder balance weight reduction suspension training device has the advantages that a paint is assisted to perform lower limb rehabilitation training in a standing state by the two independent weight reduction boxes, load adjustment can be performed according to different needs of two sides of the body of the patient, buffer effect of the suspension of the patient is provided by the weight reduction block connecting rods and the suspension pulleys, and comfortableness of the patient is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU SUYUN MEDICAL MATERIALS
Methods of treating parkinson's disease using halogenated volatile compounds
ActiveUS20100047187A1Improve gaitIncreasing dopamine turnoverBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides methods of using halogenated volatile compounds, e.g., halogenated ether, for treating a neurological disorder, e.g., Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Adhesive footwear and devices
Footwear used for high performance activities such as running can be adhesively attached to the plantar surface of feet rather than uppers or straps. The upper surface of the protective layer of the footwear can have adhesive regions that secure the foot to the footwear and other regions that are not adhesively coupled to the foot. The adhesive regions can be under the heel, along the lateral side of the foot, under the first through fifth metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints and around the perimeter of the foot above the plantar surface.
Owner:TRAUNER KENNETH B
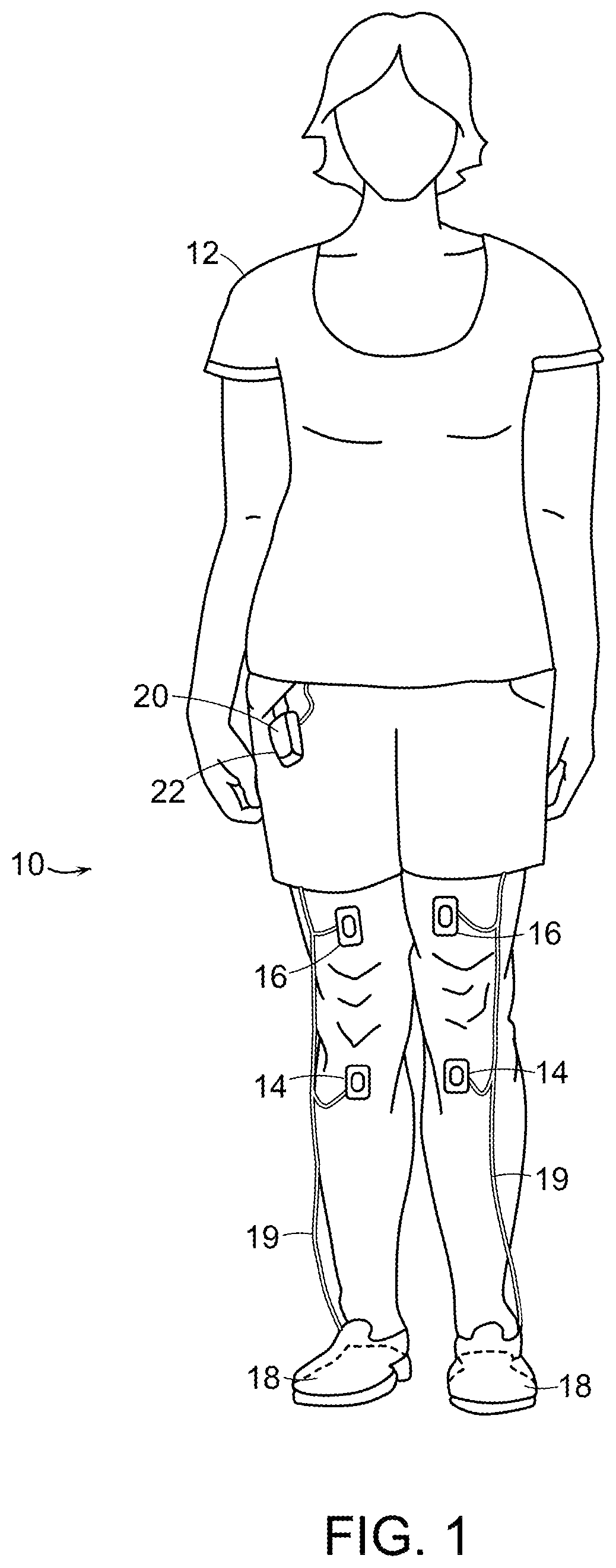
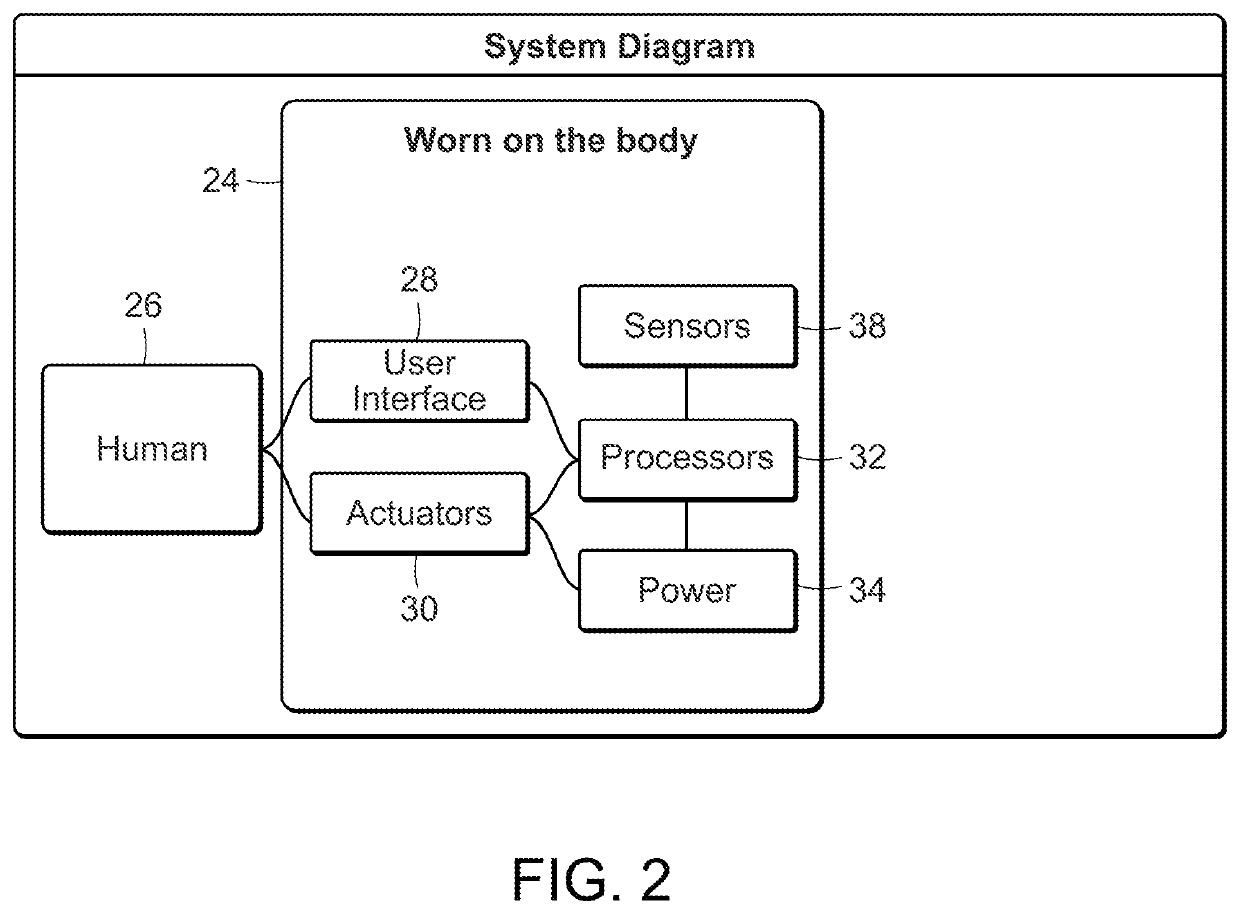
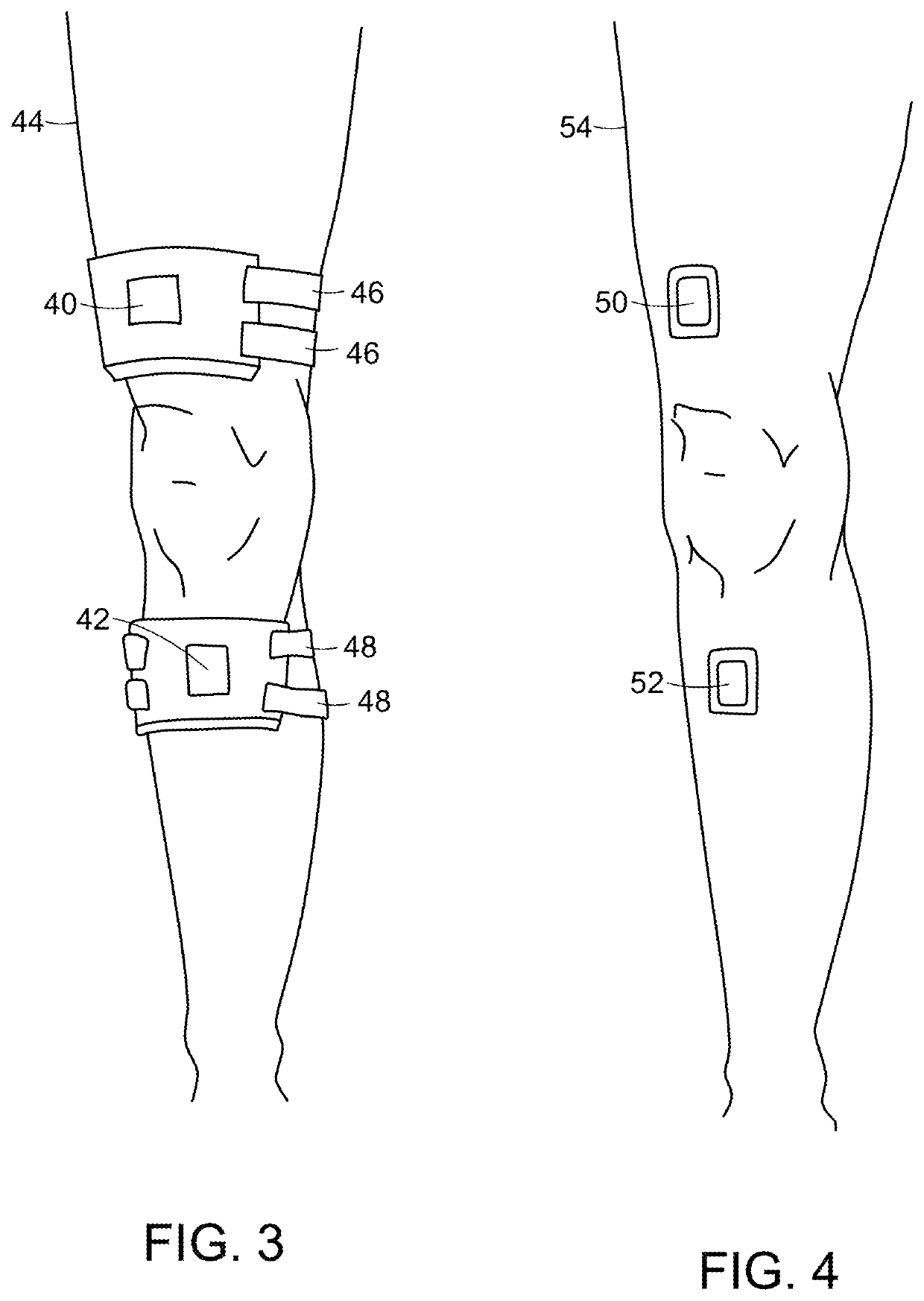
Feedback method and wearable device to monitor and modulate knee adduction moment
ActiveUS10993639B2Improve gaitElectrotherapyInertial sensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee Joint
Knee adduction moment of an untethered human during gait is modulated by determining at least one feature associated with instantaneous knee adduction moment of the untethered human during a gait cycle. Feedback to be transmitted to the human is, optionally, derived from the feature, such as by comparing the at least one feature to a value, such as a target value. The feature, or feedback derived from the feature, is transmitted to the human for response by the human, thereby modulating knee adduction moment of the untethered human during the gait.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
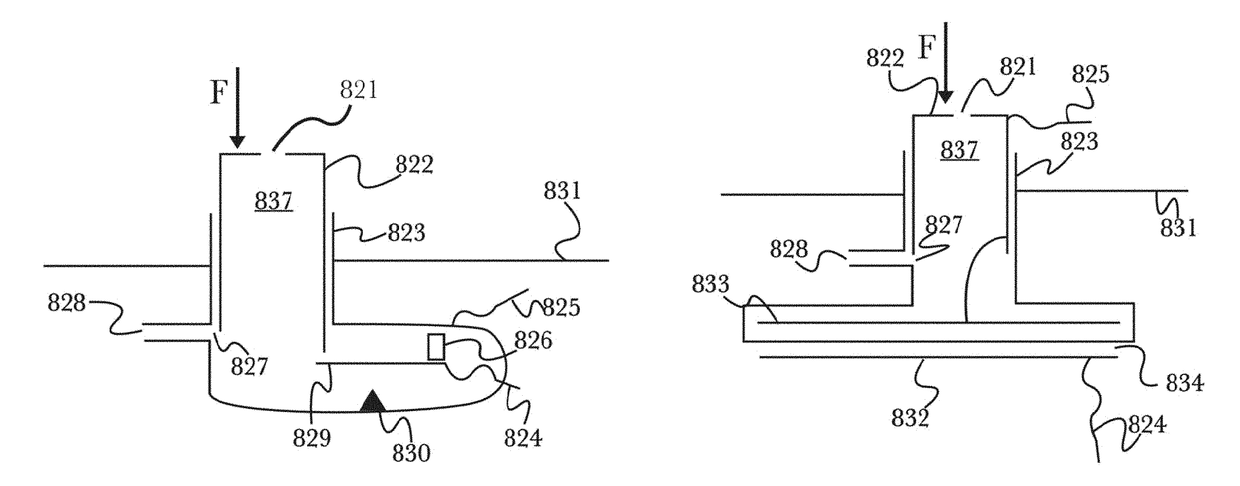
Hydraulic prosthetic joint
ActiveUS10085857B2Quick changeImprove the immunitySpringsArtificial legsDifferential pressureHydraulic fluid
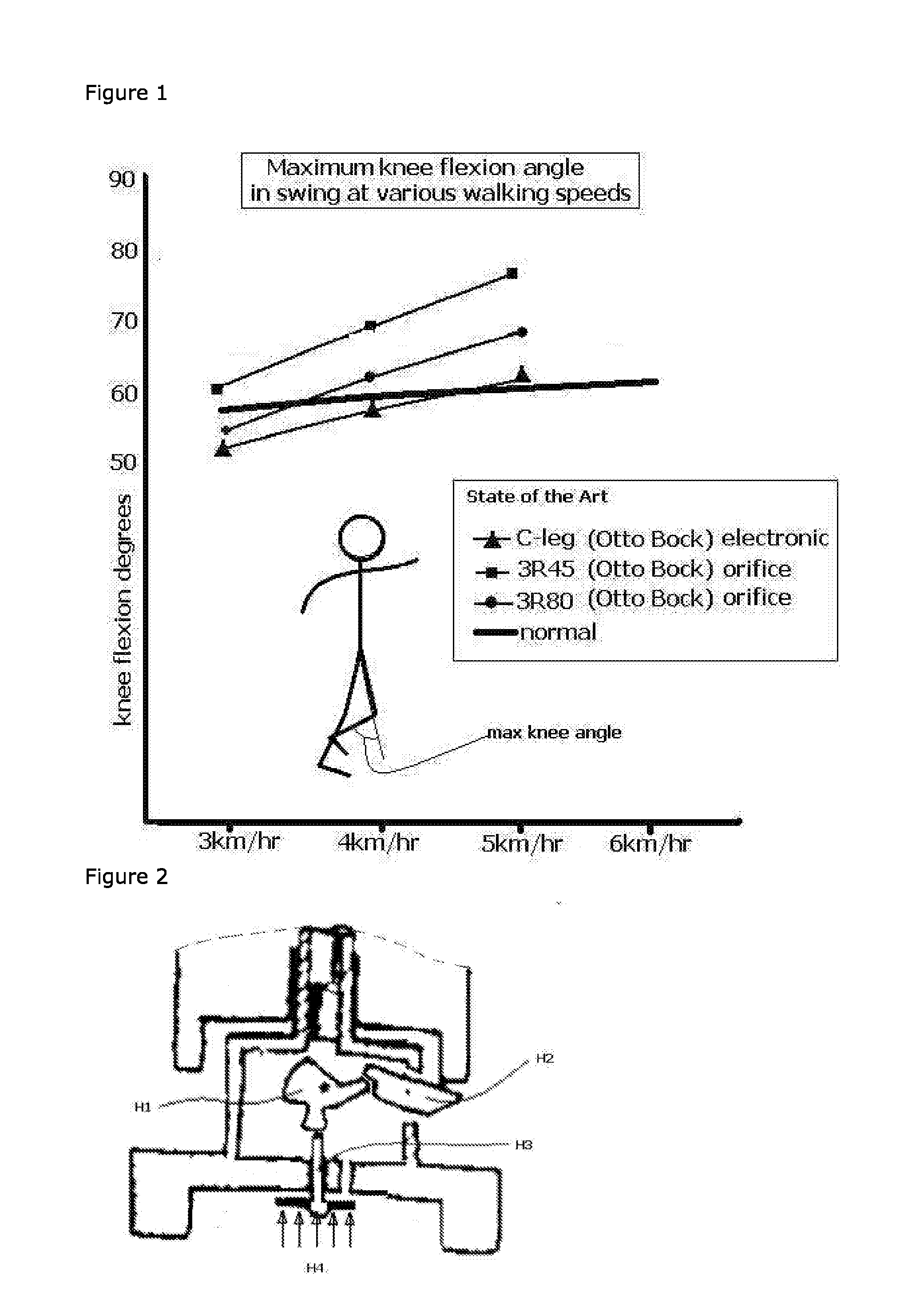
The present invention relates to artificial limbs generally and to joints for the same. In particular, the present invention provides hydraulic functional units, generally classified as damping devices as connected between artificial limbs whereby enabling movement of artificial joints to closely correspond with natural human movement. In accordance with the invention, there is provided hydraulic damper control elements for prostheses which utilize a pressure differential due fluid flow as a direct control input for a at least one hydraulic valve. The valve can comprise a moveable element which abuts a mounted element which reduces the size of an aperture as the force increases. Further, a moveable body acts upon the valve enabling increase or decrease of flow of hydraulic fluid through the valve, whereby enabling an increase in gait by way of reduction of resistance to flow or reducing or stopping flow by way of a stumble recovery mechanism.
Owner:BOENDER JACOB QUINTUS LAURENCE ANTHONY +1
Method of enhancing gait of a user
InactiveUS20150133825A1Easy to useProvide flexibilityPerson identificationSensorsGaitComputer science
A gait-enhancing system and method of enhancing gait includes generating a reference signal having substantially equal durations between occurrences and providing the reference signal to a user. Contact between the feet of the user with a surface is received and occurrence of a trigger signal is generated in response to the contact. An occurrence of the trigger signal is compared with an occurrence of a reference signal, and a guidance signal is produced as a function of the amount of time that the trigger signal led or lagged the reference signal. The guidance signal is provided to the user in order to promote symmetry in stride between one foot and the other foot of the user, enhancing the user's gait.
Owner:INTERACTIVE METRONOME
Comprehensive function rehabilitation training device for senile weak patients
InactiveCN113616994AIncrease muscle strengthIngenious structureMuscle exercising devicesMuscle strengthFoot supports
The invention relates to a comprehensive function rehabilitation training device for senile weak patients which comprises a main supporting frame. A rotatable seat frame is installed on the main supporting frame in a suspended mode, a seat is installed in the seat frame, upper limb comprehensive exercise devices are arranged on the upper portion and in front of the seat, and a lower limb comprehensive exercise device is arranged on the lower portion of the seat. The upper limb comprehensive exercise device comprises a grip strength exercise device and a double-arm lifting opening and closing exercise device, and the lower limb exercise device comprises a foot supporting plate, an elastic telescopic rod, an ankle limiting rod and a limiting rod support. According to the invention, the senile weak patient can comprehensively exercise four limbs, the blood circulation of the four limbs is promoted, the muscle strength of the limbs is enhanced, and the senile weak syndrome is comprehensively resisted. The grip strength exercise device can be used for exercising palm parts and enhancing far-end circulation. The double-arm lifting opening and closing exercise device can be used for exercising shoulder joints, improving the flexibility and coordination of active movement of a finger system, promoting movement of hand muscles and cervical vertebra, and enabling a patient to do foot-pad exercise and lower limb flexion and extension movement.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Artificial meromelia extremity and its making and installing process
The artificial meromelia extremity without joint has an end to be fitted with meromelia bone and an enlarged part at the other end to suspend artificial limb and bear boby's weight. It is made of one or several kinds of metal, ceramic, polymer, plastic and other materials through molding or machining. Its upper end as inserting part has outer size fitting the cavity of the meromelia bone to be connected and embossed surface with longitudinal grooves and its enlarged lower part has a boss to be contact with meromelia bone at joint with the inserted part. The artificial meromelia extremity can be connected closely with meromelia bone for facilitating the installation and use of artificial limb.
Owner:SHANGHAI KESHENG PROSTHESES
Arch Support Brace
InactiveUS20160206463A1Providing tensionRelieving arch painNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHeel strikeEngineering
The device is comprised of a generic cushioned shock absorbing type material orthotic support structure attached to the brace layer. The orthotic support structure comprises a raised midsole that tapers at the anterior end and transitions into a heel cushion which surrounds the bottom of the wearer's heel at the posterior end. The orthotic support structure continues to the heel, where it provides a cup to form to the shape of the heel.
Owner:WATSON JEFFREY J
Orthopedic shoe appliance
An orthopedic shoe appliance includes a pad for providing support for midfoot arches, the second metatarsal, and the third metatarsal of a foot, wherein the pad does not provide substantial support under a heel of the foot or under the first metatarsal, the fourth metatarsal, and the fifth metatarsal. A method for manufacturing an orthopedic appliance includes obtaining a pad; and shaping the pad to provide support for midfoot arches, the second metatarsal, and the third metatarsal of a foot, but not provide substantial support under a heel of the foot or under the first metatarsal, the fourth metatarsal, and the fifth metatarsal.
Owner:CLUFFY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com