Patents
Literature
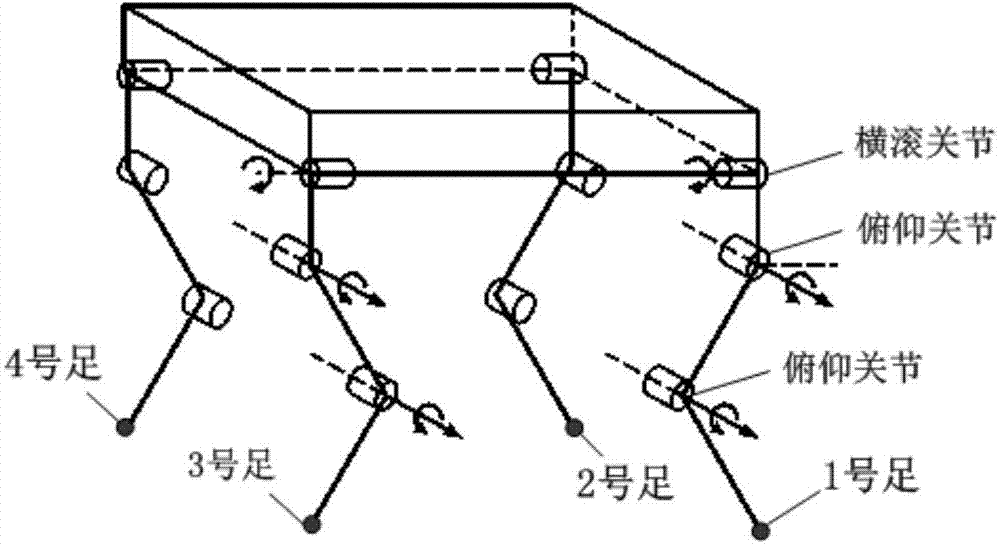
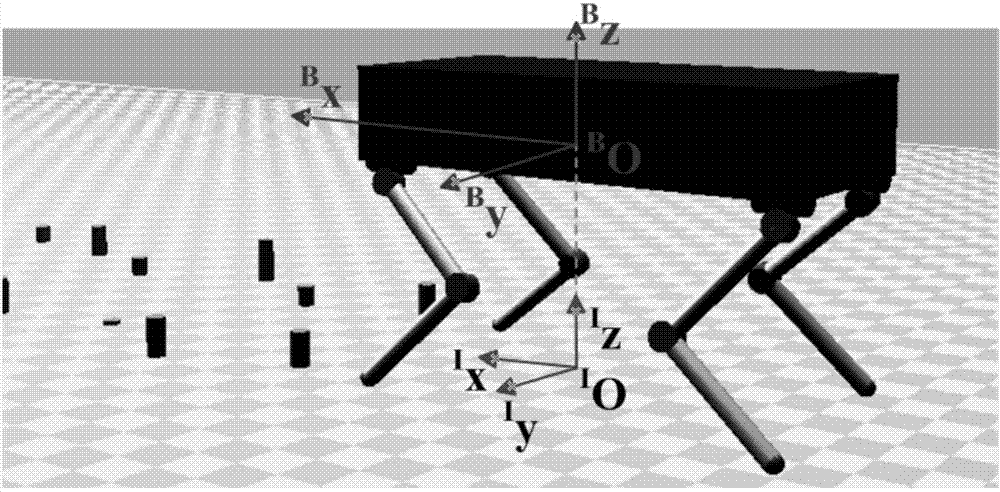
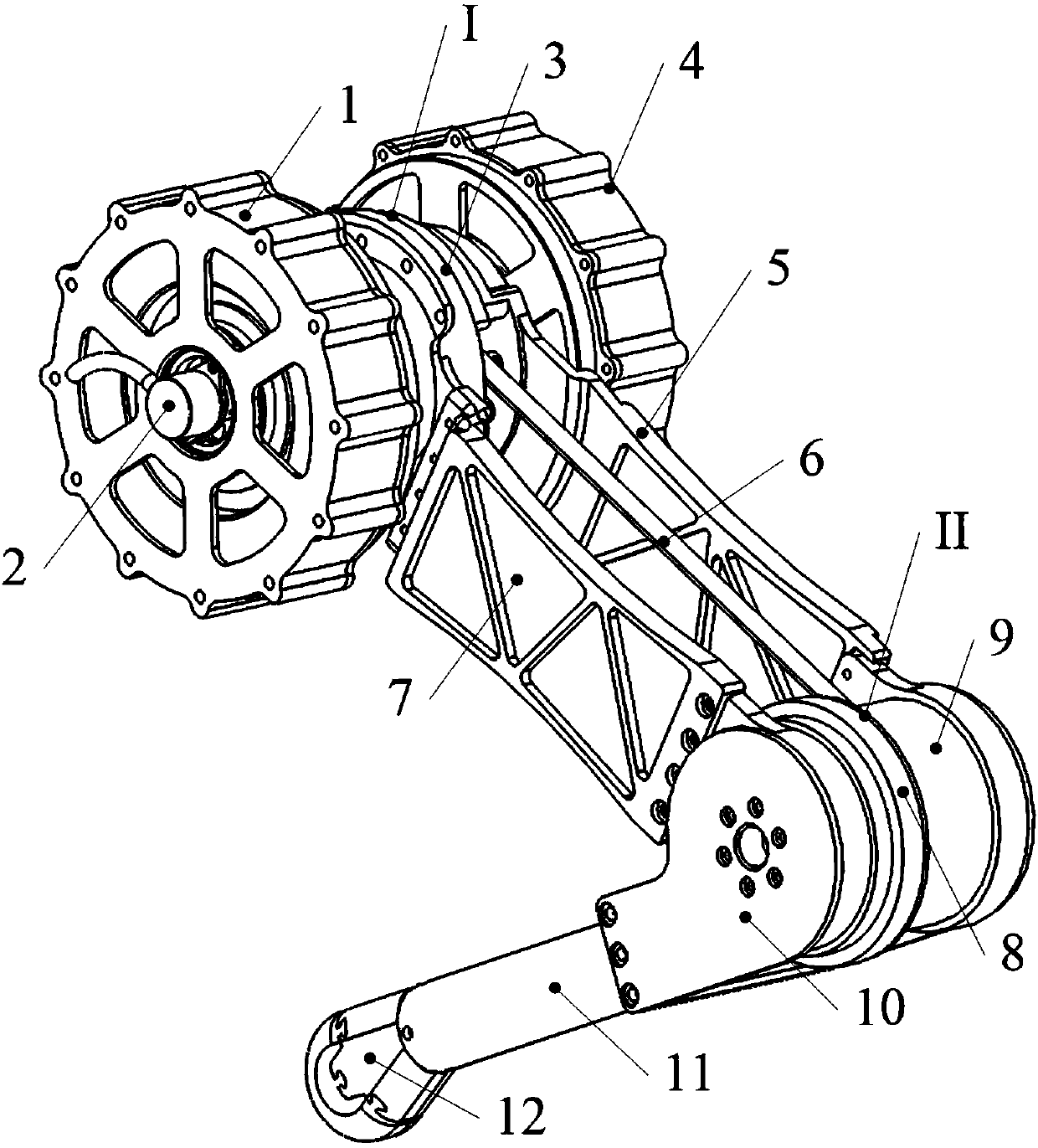
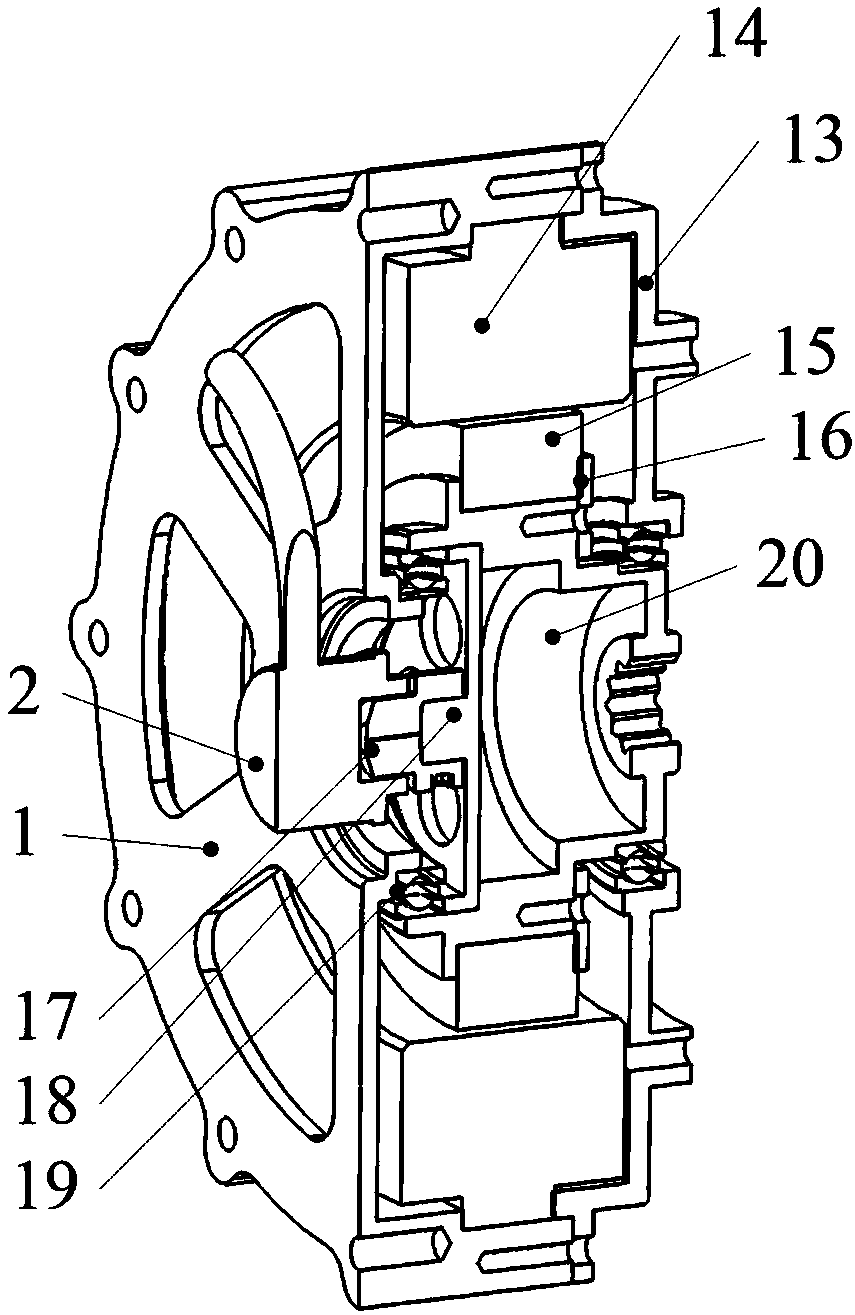
605 results about "Quadrupedal robot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
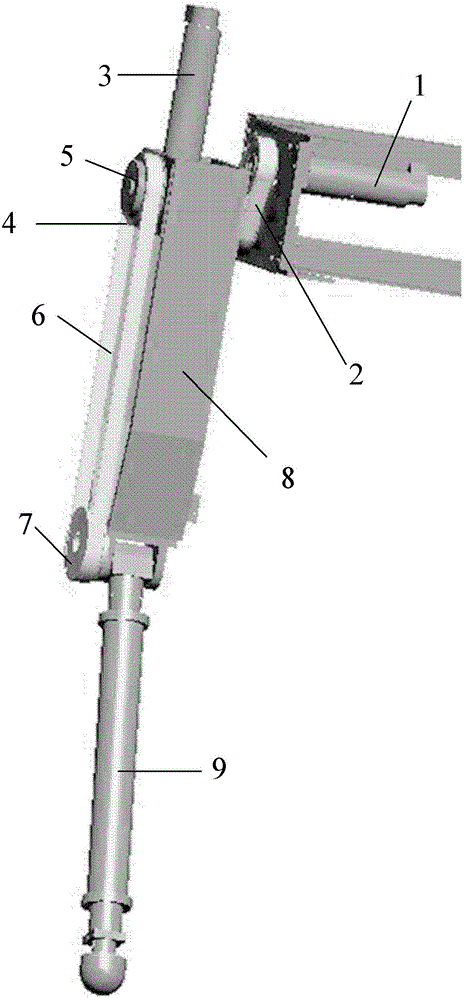
Hydraulically-driven four-foot robot
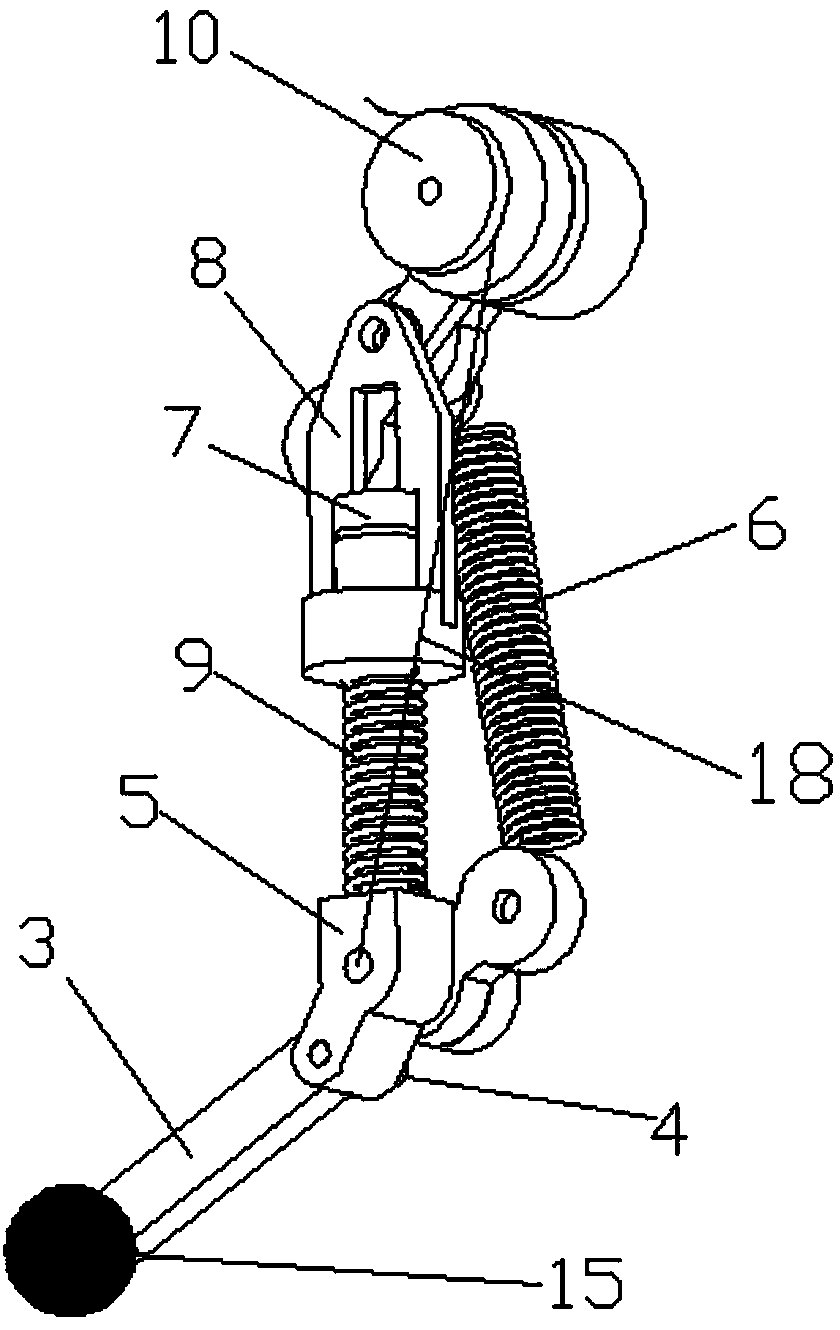
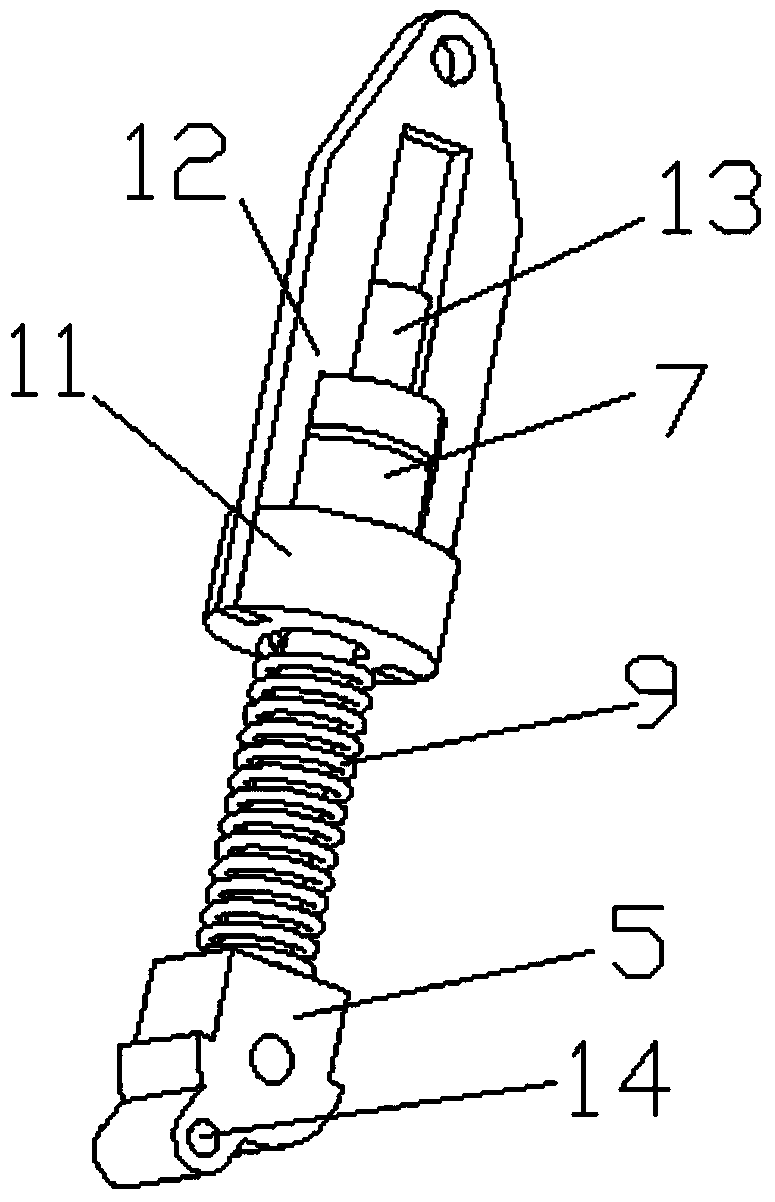
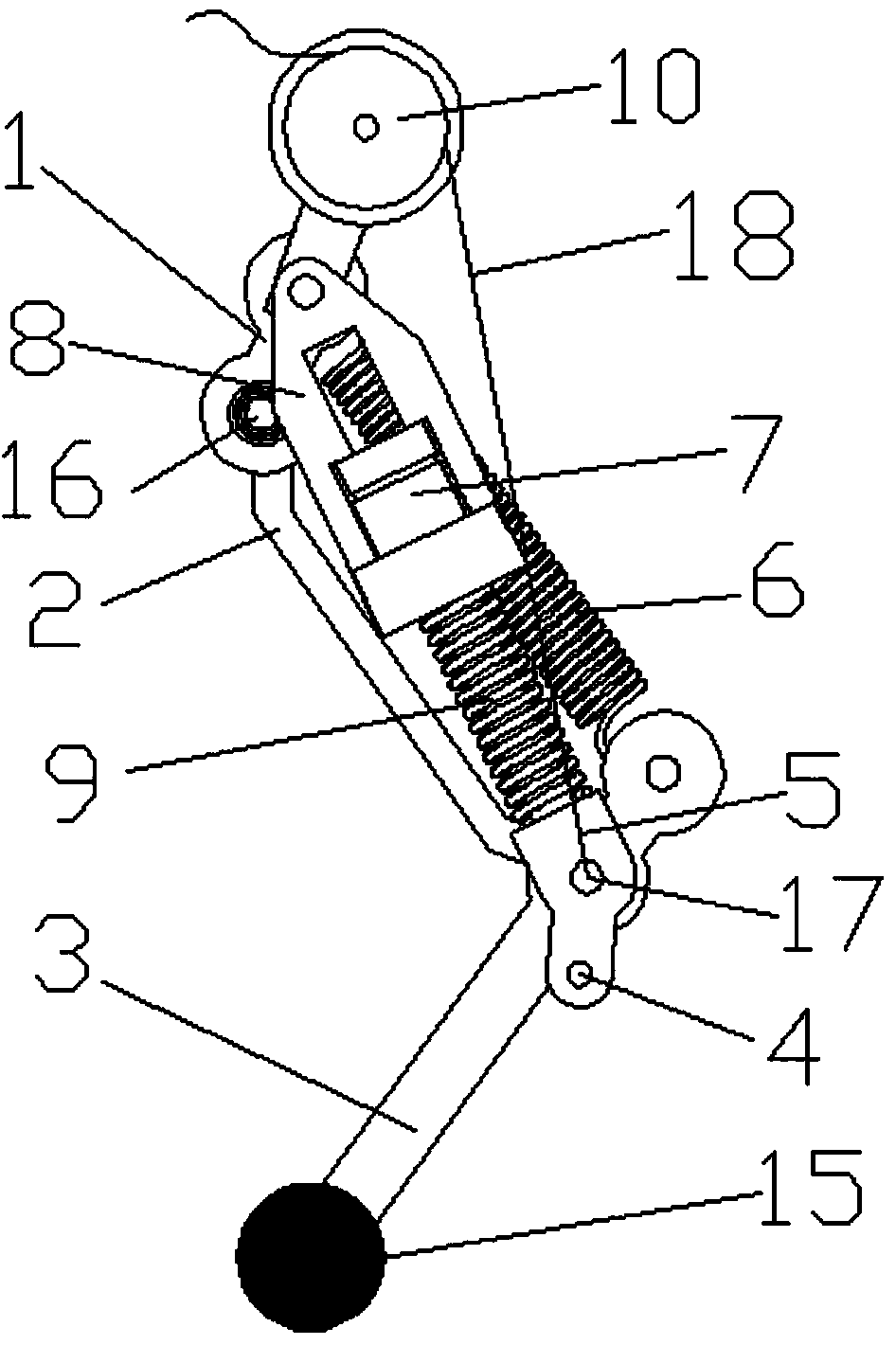
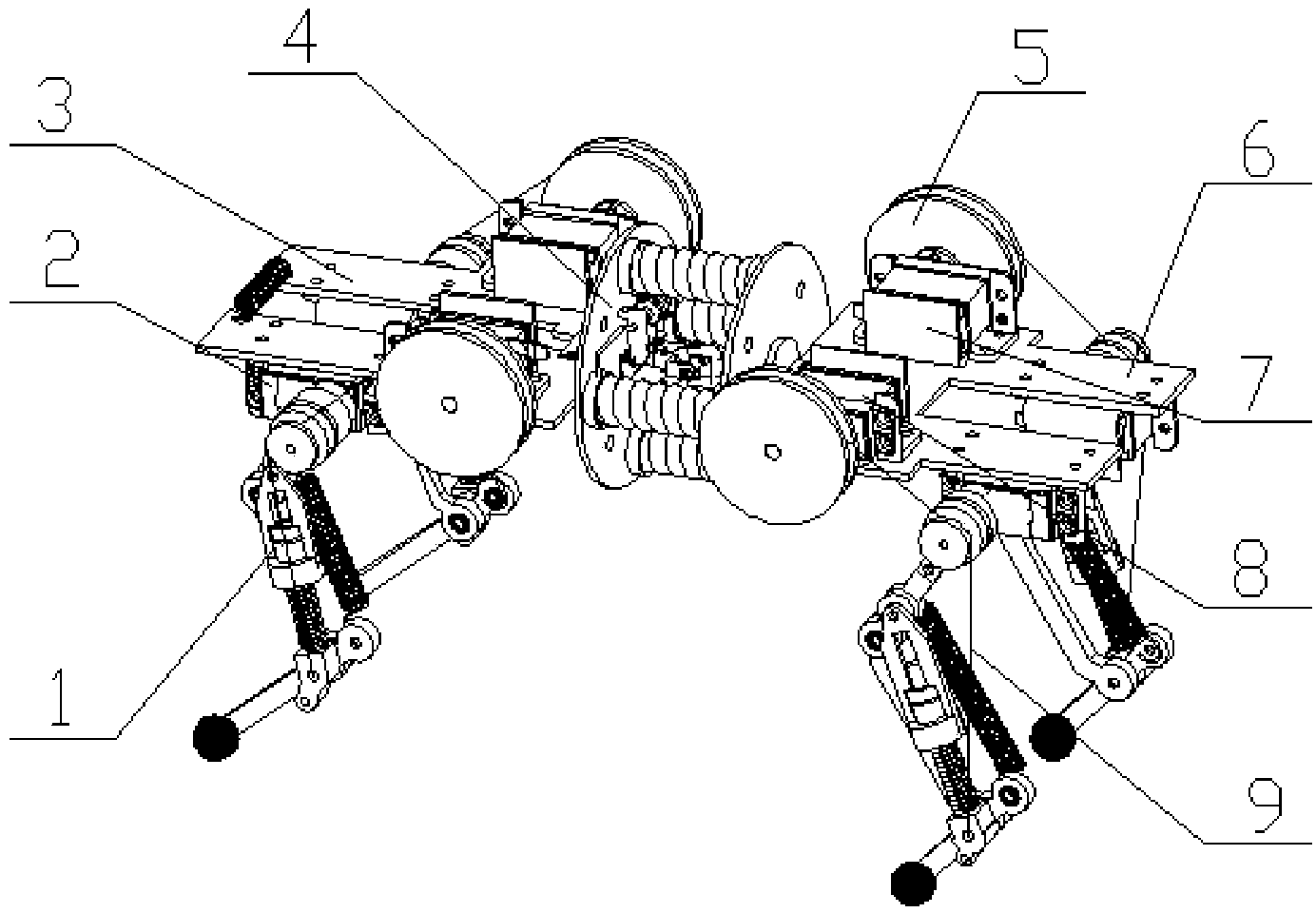
InactiveCN102001371AStable motion outputMeet the performance requirements of joint special movementVehiclesHydraulic cylinderControl engineering
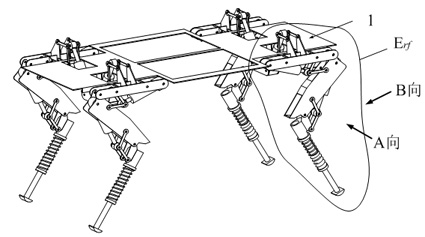
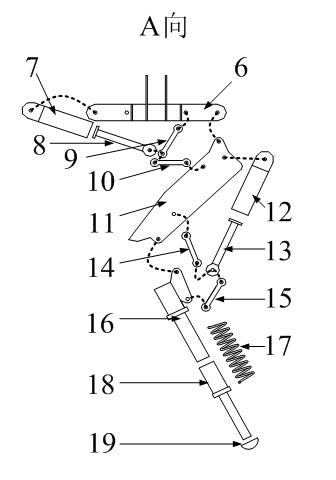
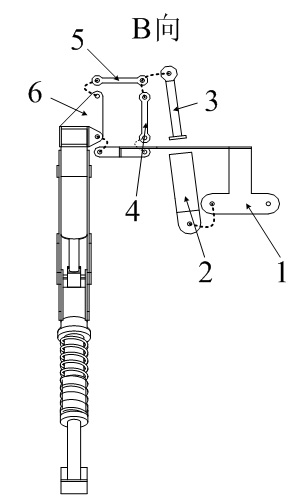
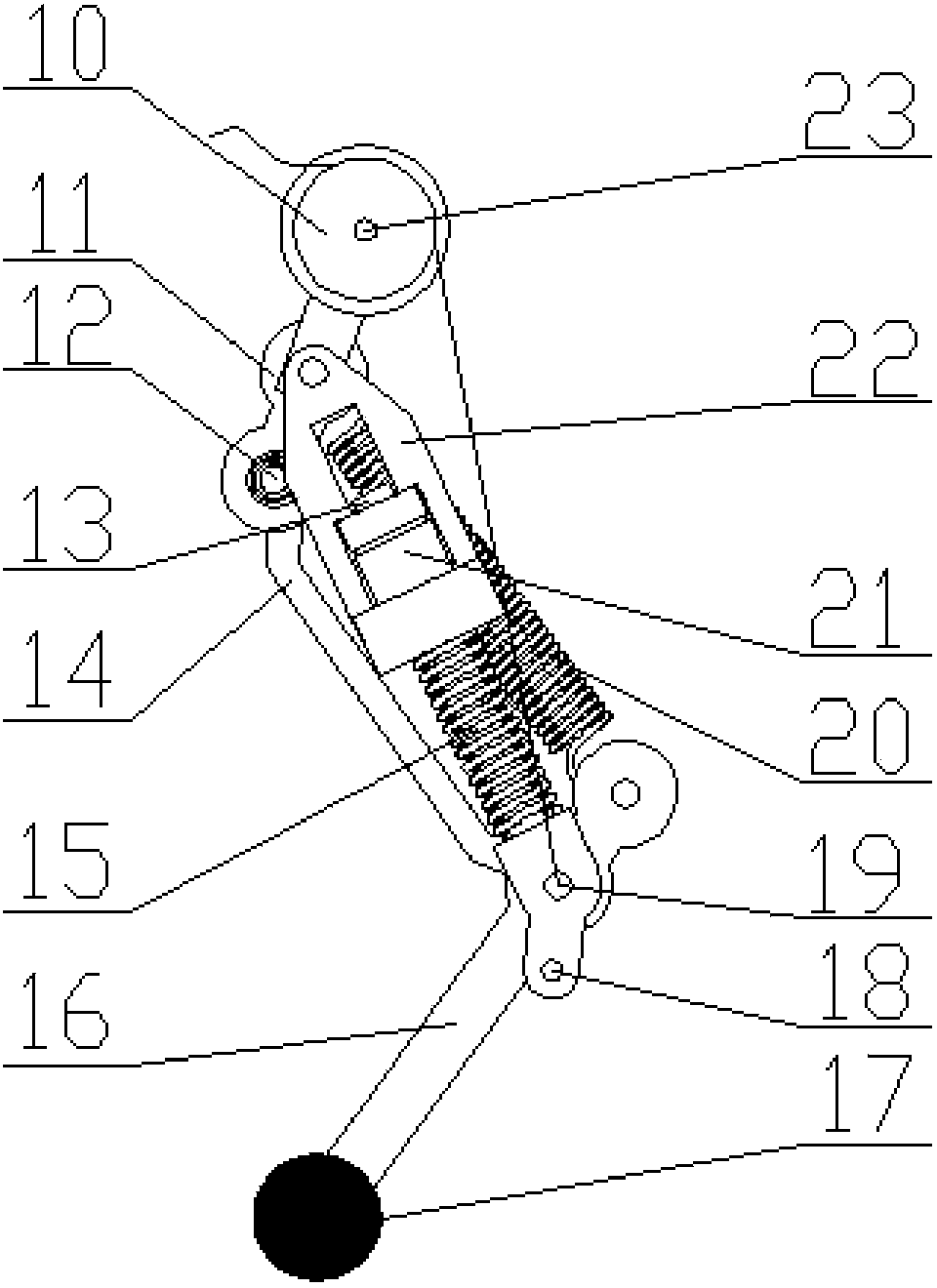
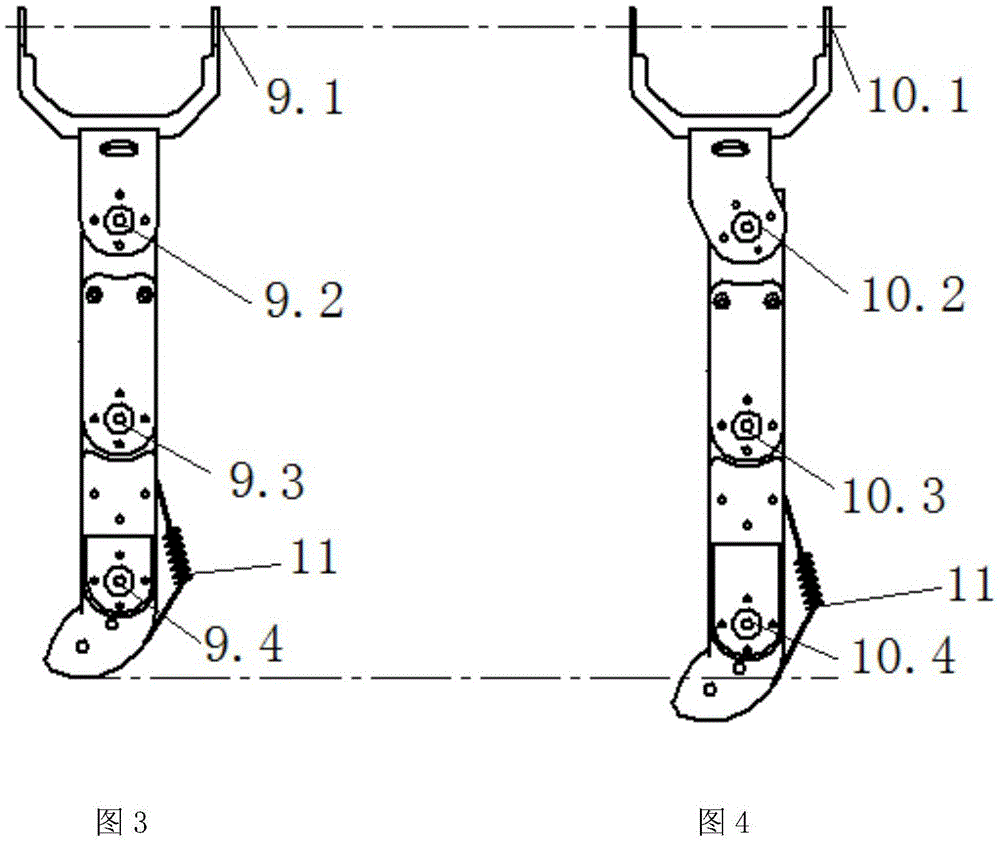
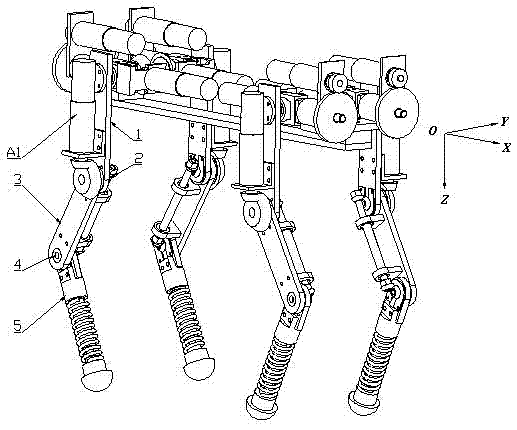
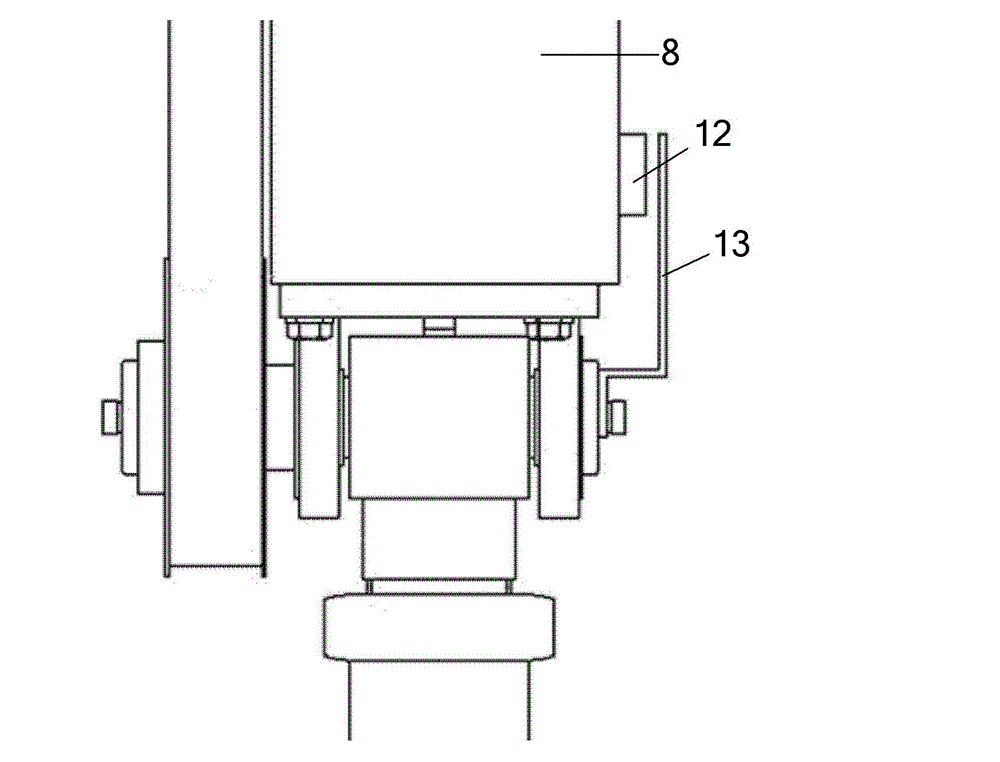
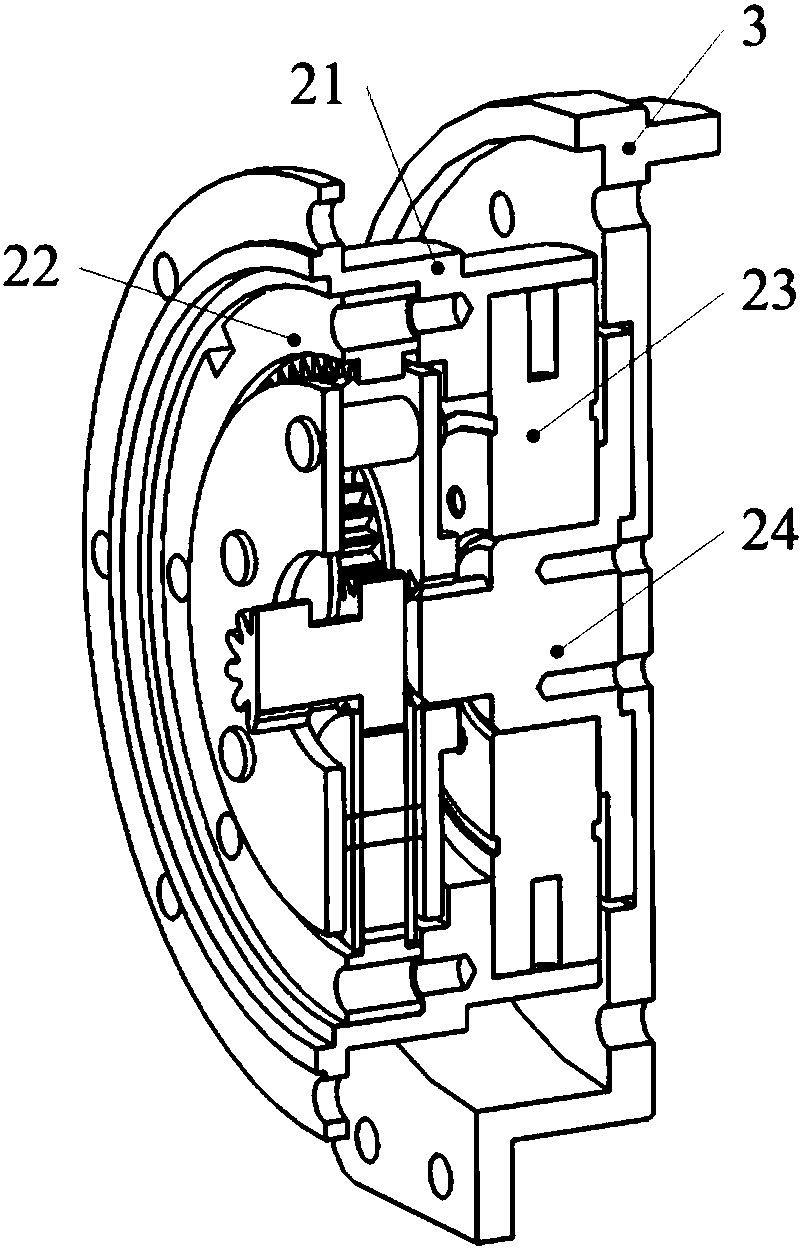
The invention relates to a hydraulically-driven four-foot robot which belongs to the field of robots. The robot comprises a machine body (1) and four legs arranged on the machine body, wherein each leg consists of a first hydraulic cylinder body (2), a first hydraulic cylinder telescopic rod (3), a first parallelogrammic I connecting rod (4), a first parallelogrammic II connecting rod (5), a pelvic part (6), a second hydraulic cylinder body (7), a second hydraulic cylinder telescopic rod (8), a second parallelogrammic I connecting rod (9), a second parallelogrammic II connecting rod (10), thighs (11), a third hydraulic cylinder body (12), a third hydraulic cylinder telescopic rod (13), a third parallelogrammic I connecting rod (14), a third parallelogrammic II connecting rod (15), a crus (16), a spring (17), telescopic feet (18) and a soles (19). A telescopic four-connecting-rod joint transmission mechanism based on a parallelogram is adopted by the joint design of the hydraulically-driven four-foot robot, the joint control is simplified, and the moving performance of the foot type robot joints is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot with variable leg shape structures
InactiveCN103318289ASolve the lack of spaceImprove terrain adaptabilityVehiclesDynamic balanceKnee Joint
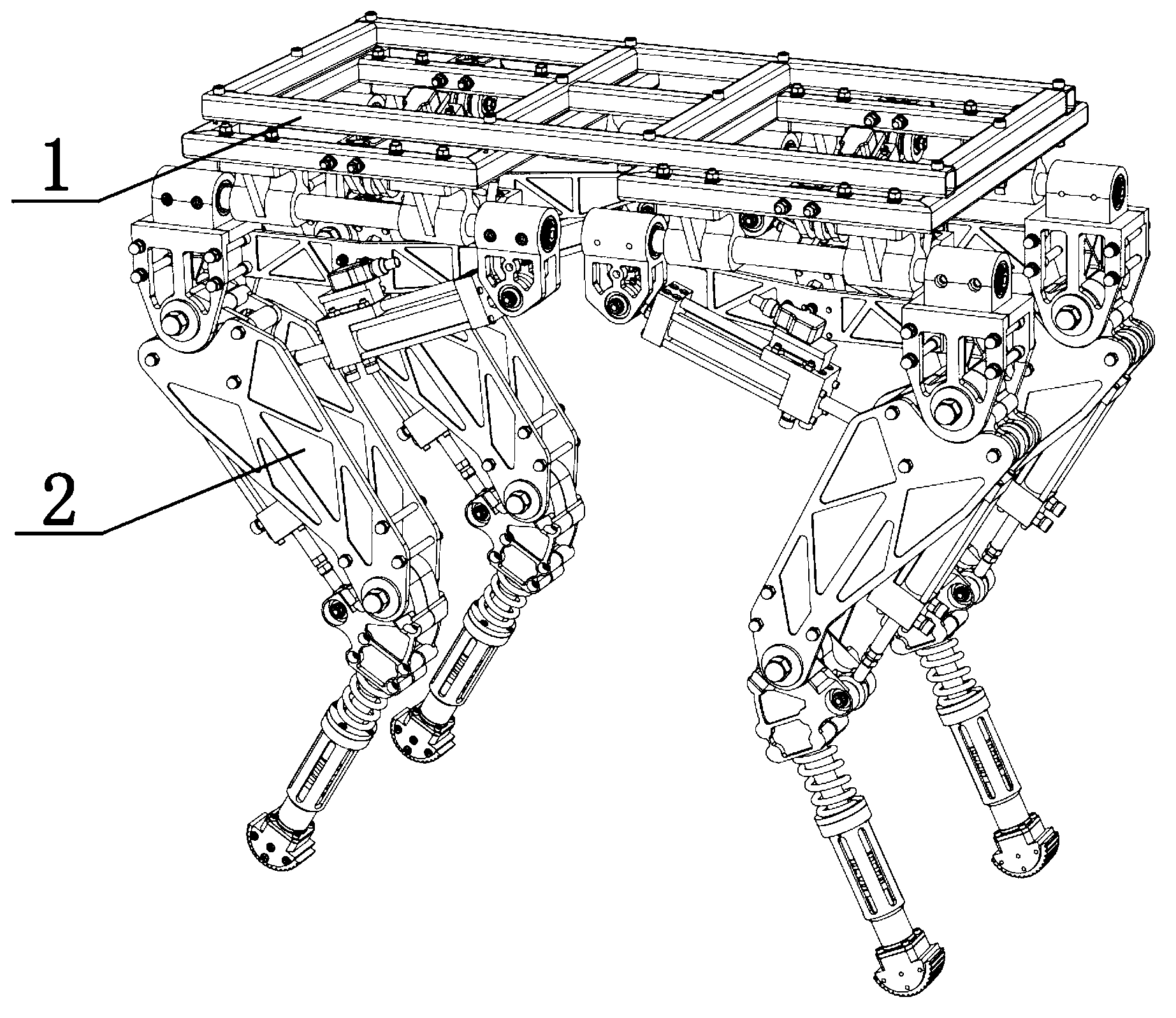
The invention discloses a hydraulic-drive four-leg robot. The modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot has the advantages that the hydraulic-drive four-leg robot is good in dynamic balance and high in topographical adaptability, loading capacity and cost performance, and is in a modular and bionic structural design, four leg shapes can be switched over by means of quickly assembling and disassembling subassemblies, the modular hydraulic-drive four-leg robot is multipurpose, and merits and shortcomings of various leg shapes are verified by experiments at a physical prototype stage; each single leg is provided with two leg sections, has three degrees of freedom and comprises a hip joint and thigh assembly, a knee joint and shank assembly and a side sway assembly; a side sway and connecting block combining form is adopted for each thigh portion according to a bionic principle, so that sufficient rigidity and strength are guaranteed, the hydraulic-drive four-leg robot can bear a load stably while the weight of the robot is reduced to the greatest extent, and sufficient activity space for hydraulic cylinders is guaranteed; shank portions comprise foot-end rubber pads and passive retractable bidirectional spring shock absorption mechanisms, and instant impact force generated when the robot is in contact with the ground can be effectively buffered and absorbed under multiple shock absorption actions; problems of limited service lives of components and vulnerability of electronic elements such as foot-end force sensors due to the fact that impact force disappears and springs are rebounded quickly when an existing robot leaves the ground can be solved by the aid of the bidirectional spring mechanisms.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
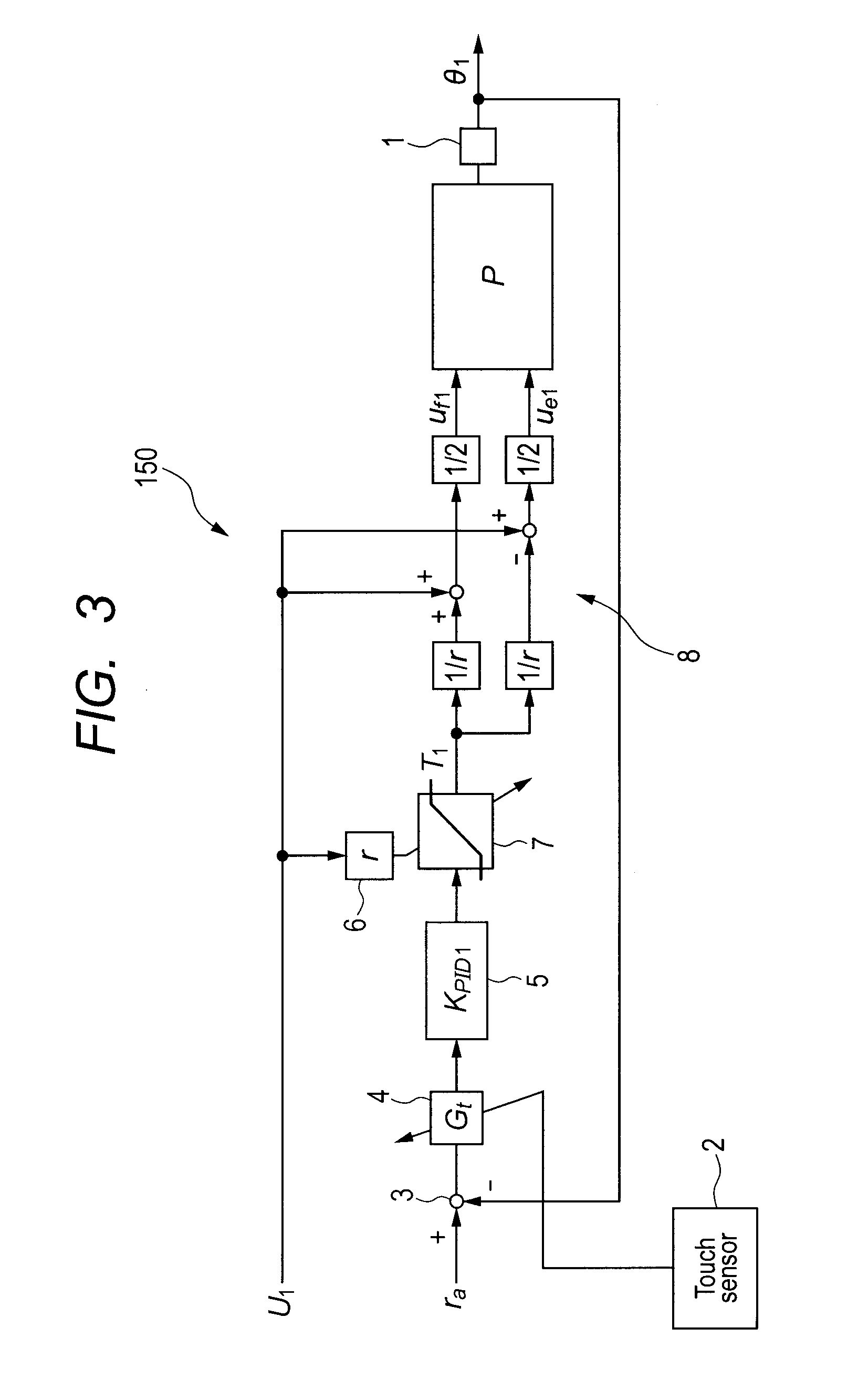
Robot system controlling method, robot system, and control apparatus for quadrupedal robot
InactiveUS20120072026A1Eliminate needEasy to adjustProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsQuadrupedal robot
An object of the present invention is to provide a robot system controlling method and robot system which perform link angle control and joint stiffness control through feedback control.
Owner:CANON KK
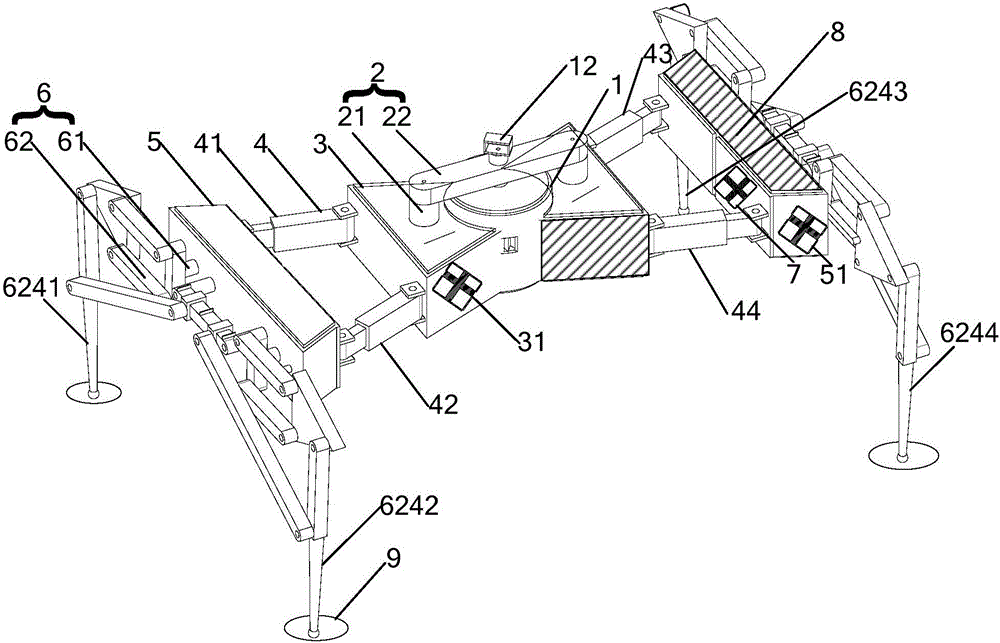
Biomimetic quadruped robot provided with head and tail balance adjustment devices
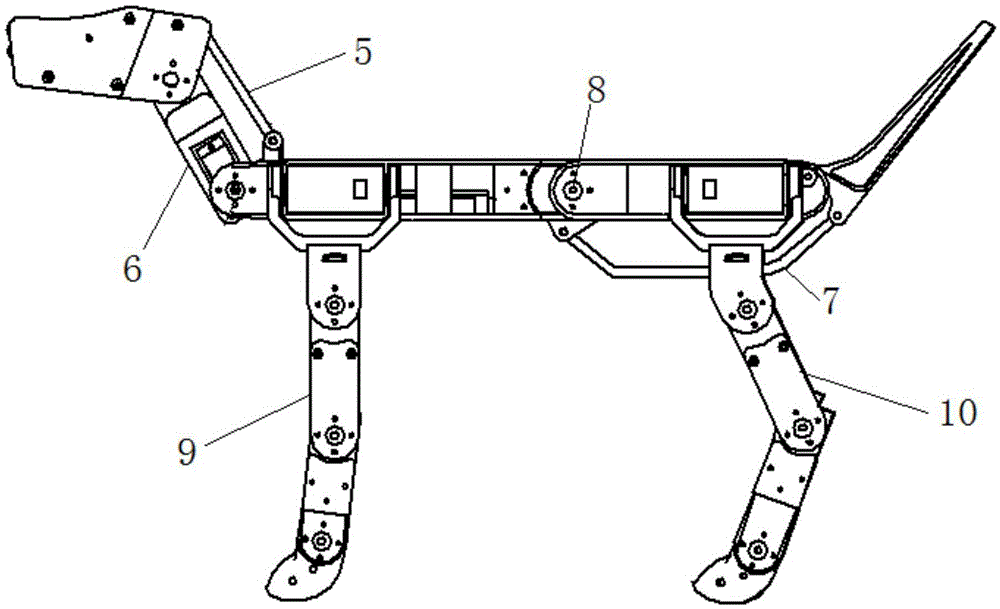
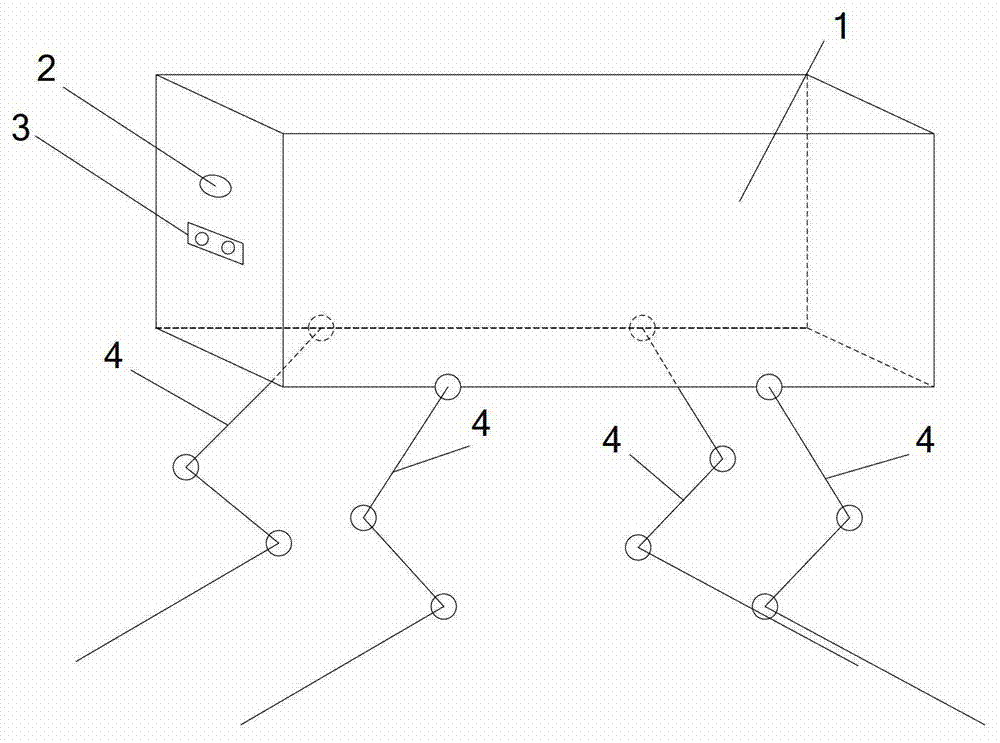
The invention relates to a biomimetic quadruped robot provided with head and tail balance adjustment devices. The biomimetic quadruped robot comprises a trunk, a head balance adjustment device, a tail balance adjustment device and four robot legs, wherein the four robot legs are distributed under the robot trunk, and the head balance adjustment device and the tail balance adjustment device are located on a trunk front portion cross beam and a trunk back portion cross beam. The biomimetic quadruped robot uses a digital steering engine as a driver, and the steering engine can achieve speed and position control and feed back speed, positions, force moment and other information and facilitates on-line observation of a motion state of the robot. Each leg is provided with three driving freedom degrees and one driven extension freedom degree, three-dimensional space motion can be achieved, and the robot can have strong adaptive capacity to complex environments and obstacle crossing ability. The centre-of-gravity position of the robot can be timely adjusted when the robot with the head and tail balance adjustment devices walks in a static state, and the stability of the robot is improved. When the robot is in a unstable state, namely turns over, and reverse rotation force moment is produced by rapidly rotating the head and the tail to prevent the robot from turning over and being restored to be in a balanced state. The biomimetic quadruped robot provided with the head and tail balance adjustment devices is suitable for the multiple fields of military affairs civil cargo transportation, anti-terrorist devices, filed probing, planetary exploration and the like under complex terrain environments.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
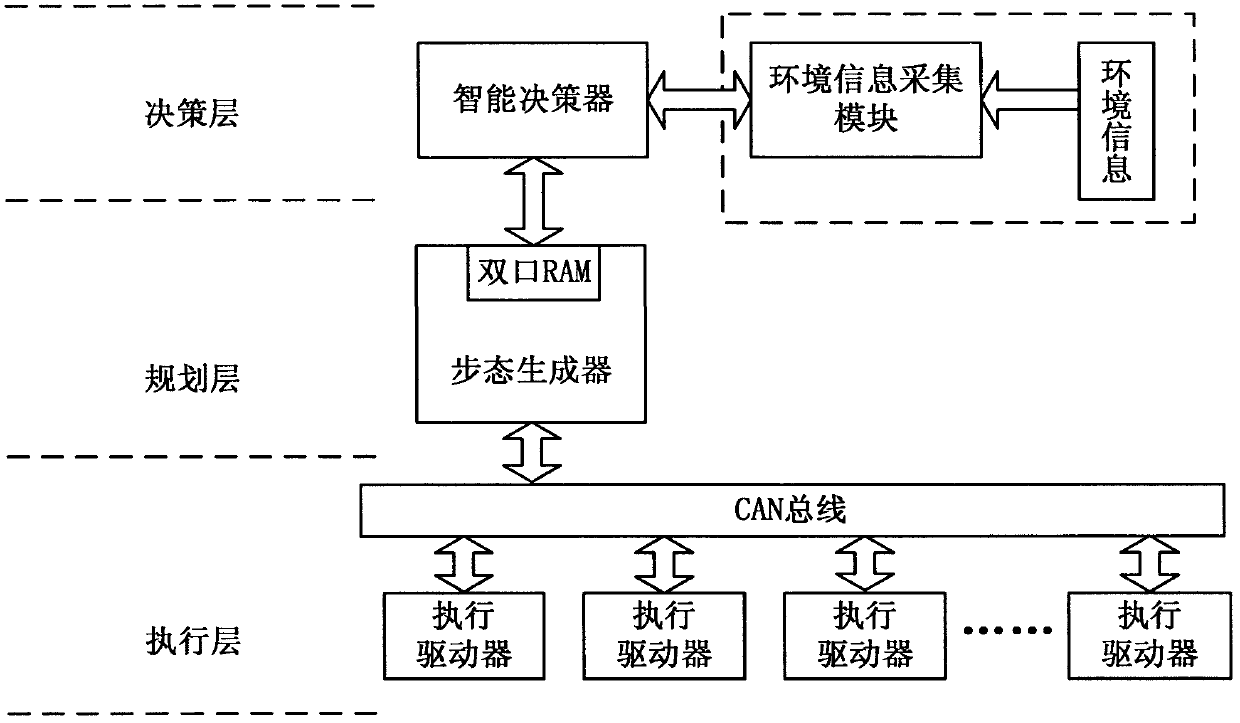
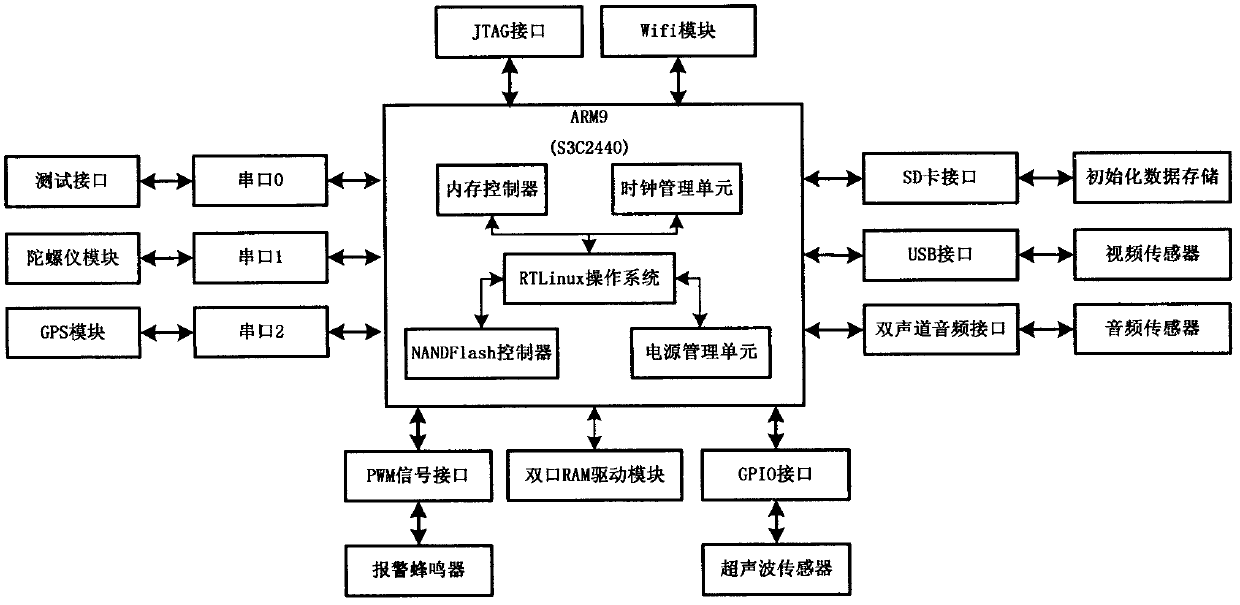
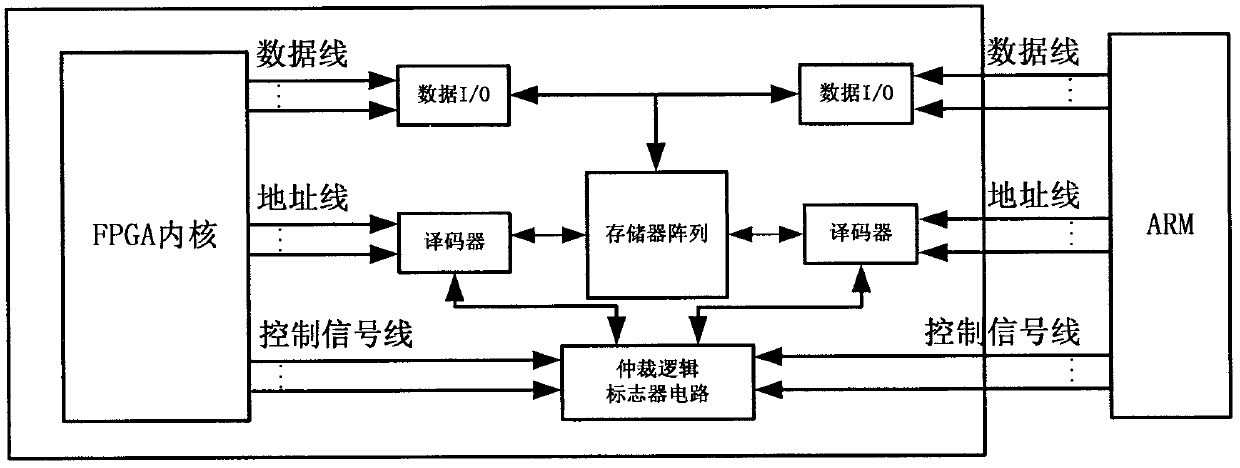
Combined type bionic quadruped robot controller
InactiveCN102637036AIntegrity guaranteedImprove adaptabilityPosition/course control in two dimensionsOperational systemNervous system
The invention relates to a combined type bionic quadruped robot controller, which is in a structure similar to a vertebrate nervous system, wherein the controller is divided into a decision layer, a planning layer and an execution layer which respectively correspond to a higher nervous center, a lower nervous center and a motor nerve of an animal. The decision layer for realizing that the robot senses the working environment and generates corresponding motion decision instructions consists of an ARM9 (advanced RISC (reduced instruction-set computer) machine 9) and an environmental information acquisition system, and a real-time operating system is embedded in the ARM9. The core of the planning layer is a walking pattern generator, and is used for planning and solving the motion parameters of each joint according to the decision instructions from the upper layer. The execution layer for controlling the current, the position and the speed of a driving motor in three closed loops consists of a motor controller using a digital signal processor as the core. Data can be effectively transmitted among the three layers in real time through a dual-port RAM (random-access memory) and a CAN (controller area network) bus network. The combined type bionic quadruped robot controller disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high reliability, high flexibility, extension easiness and maintenance easiness, and has a broad application prospect in the technical field of bionic legged robots.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Air-ground amphibious spherical metamorphic robot based on metamorphic principle
InactiveCN104260605AGuaranteed stabilitySmall geometryConvertible vehiclesComputer moduleMetamorphic robots
The invention discloses an air-ground amphibious spherical metamorphic robot based on a metamorphic principle. The robot mainly comprises a flying module and a traveling module. The flying module comprises a symmetrical four-connecting bar mechanism driven by a worm and worm wheel motor, and the four-connecting bar mechanism realizes to automatically fold a stand to adapt to different requirements for the robot structure under a spherical un-deformed state, a terrestrial state and an aerial state. The traveling module uses a 8-freedom four-foot robot, the shanks are driven to move through the four-connecting bar mechanism, and arc plates fitting with the shanks partially fit with the lower semi-spherical shell under the un-deformed state so as to form the spherical shape. When preparing to fly, the upper semi-spherical shell gives place to support arms for folding the stand through moving upwardly. After the support arms stretch to the right positions, the upper semi-spherical shell moves downward to restore. A crank block mechanism is used for driving the upper semi-spherical shell. The air-ground amphibious spherical metamorphic robot based on the metamorphic principle is featured with small volume, reasonable structure, simple and beautiful shape, outstanding movement performance, easiness and high efficiency in control, strong anti-interference ability and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Quadruped robot motion planning method oriented to unknown rough terrain
ActiveCN107065867AAchieve adaptiveAchieving Continuous Adaptive WalkingPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesTerrainRobot motion planning
The invention discloses a quadruped robot motion planning method oriented to an unknown rough terrain. A quadruped robot uses a crawling gait in a rough terrain. In a single-legged swing phase, a swinging leg swings along a planned foot trajectory and the center of gravity of the robot moves forwards along the planned path by means of the motion of supporting legs. In a four-foot stance phase, the center of gravity of the robot laterally moves while moving forwards along the planned path. The quadruped robot motion planning method achieves robot online trajectory planning based on COG and ZMP dual-stability criteria, takes full account of the possibility of advanced landing and lagged landing of the swinging leg for the unknown terrain, and estimates the parameter of the unknown terrain by the landing planning and the sensing strategy of the swinging leg. Thus, the robot adaptively adapts to the height and the slope of the unknown terrain, and achieves continuous adaptive walking for the unknown rough terrain according to a motion planning result.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Quadruped robot leg with elastic four-rod mechanism
The invention provides a quadruped robot leg with an elastic four-rod mechanism. The quadruped robot leg comprises a thigh, a shank, a foot, a tension spring and a reeling wheel, wherein one end of the thigh is connected with an output shaft of a power source to form a hip joint; the reeling wheel and the end of the thigh are connected by a transmission pair and the axis of the reeling wheel is coaxial to the output shaft of the power source; the other end of the thigh is connected with one end of the shank by a transmission pair to form a knee joint, and the other end of the shank is connected with a quarter part of the foot by a transmission pair to form an ankle joint; one end of the tension spring is connected with the middle part of the thigh by a transmission pair and the other end of tension spring is connected with the end of one foot by a transmission pair; one end of a steel wire rope is fixedly arranged on the ankle joint and the steel wire ripe spans across the reeling wheel to be connected with the power source. According to the quadruped robot leg, a driven degree of freedom is adopted and the loss of energy is reduced; the driven degree of freedom is realized by a four-connection-rod mechanism; a spring is arranged on one side of the four-connection-rod mechanism so that the four-connection-rod mechanism can be freely retracted in a certain range and the free movement of the foot of the leg is realized.
Owner:哈尔滨斑之斓海洋科技有限公司
Bionic four-foot robot provided with spinal joint and elastic legs
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot with environment sensing ability and control method
ActiveCN105599821AWide time rangeSolve the problem of inconsistent detection distanceProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersVehiclesElectricityComputer module
The invention discloses an electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot with the environment sensing ability and a control method. A head is hinged to a front body through a neck and a head connecting rod, the head is linked with the neck, and the front body is hinged to a back body; a tail is arranged at the back part of the back body, and is also hinged to the front body through a tail connecting rod; front legs are respectively arranged on the two sides of the front body; back legs are respectively arranged on the two sides of the back body; the length of the back legs are larger than that of the front legs; the widest part of the front body is wider than the widest part of the back body; the electric driven biomimetic four-leg robot further comprises an environment sensing sensor group and a camera; the environment sensing sensor group and the camera are connected with a central processing unit; the output end of the central processing unit is connected with an electric driven execution system; a power management module supplies power for the environment sensing sensor group, the central processing unit and the electric driven execution system. Through the adoption of the electric driven control mode, the biomimetic four-leg robot can realize dynamic sensing, autonomous navigation and real-time following on environment, and can adapt to biomimetic gait motion planning with topographical changes and random disturbance.
Owner:SHANDONG YOUBAOTE INTELLIGENT ROBOTICS CO LTD
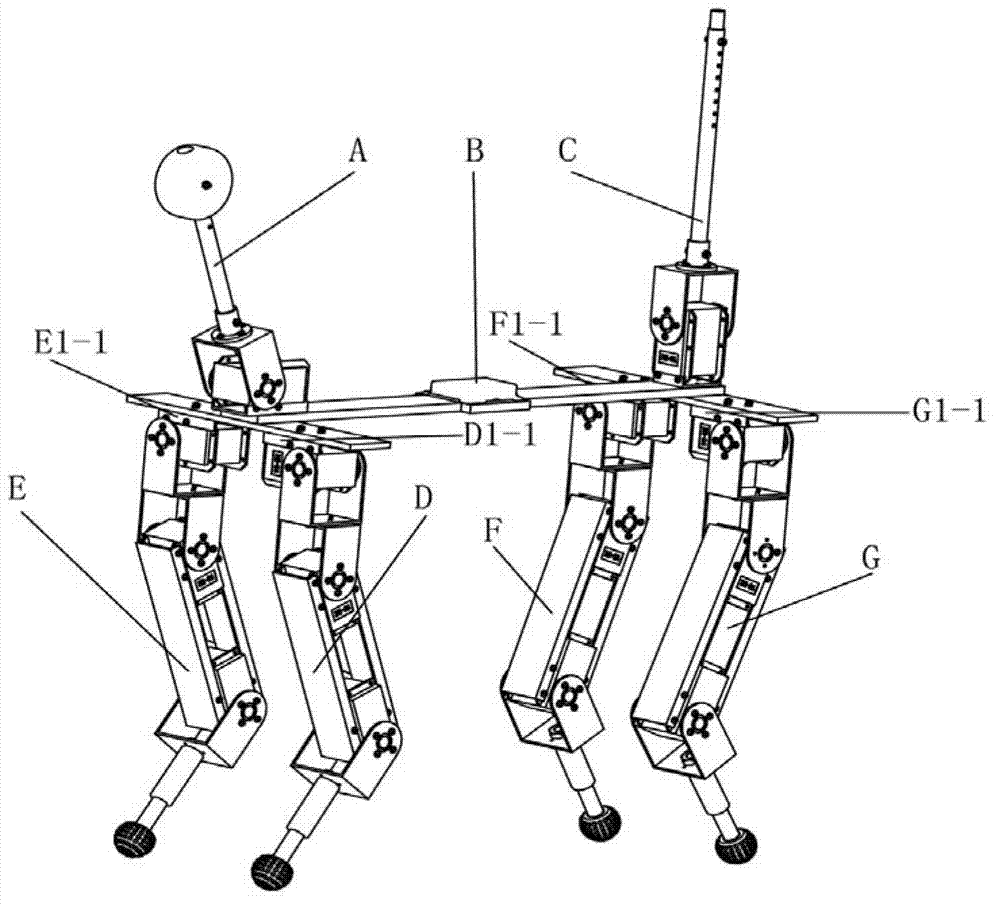
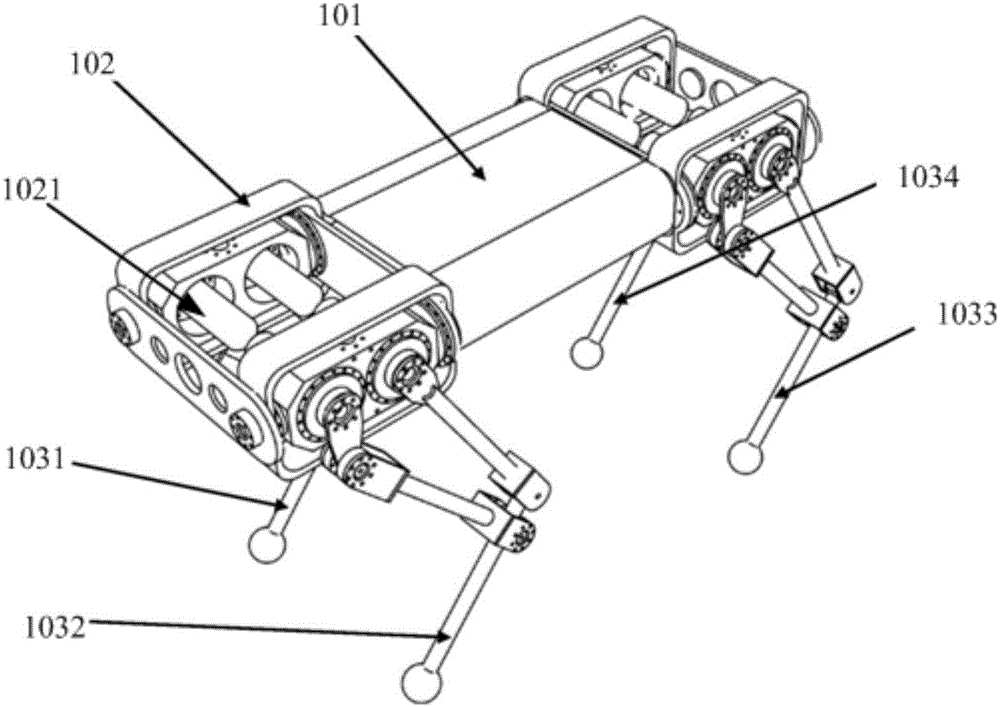
Quadruped robot
The invention provides a quadruped robot, comprising a cylindrical machine body; two twisting machine bodies symmetrically connected to the side face of the cylindrical machine body, wherein a joining face of the twisting machine bodies is matched with the shape of the side face of the cylindrical machine body; a telescopic arm connected to both ends of one face of every twisting machine body back to the cylindrical machine body, wherein the telescopic arm is connected with first driving motors of the twisting machine body; a leg base connected to one end back to the twisting machine body in a tensioning manner, and the leg base is fixedly provided with a second driving motor; a leg movement mechanism connected to two ends of one face of the leg base back to the cylindrical machine body; the leg movement mechanism comprises a leg driving gear and a leg movement body; the leg driving gear is electrically connected with the second driving motor and the rotating shaft thereof is the same as the length direction of the telescopic arm, the driving shaft of the leg driving gear is vertically connected with the leg movement body. The quadruped robot can adapt to the environment with complex geological characteristics.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Quadruped robot path planning method and system based on improved A* algorithm
InactiveCN108646765ARealize virtual inflationSolve the blockagePosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationRobot path planning
The invention discloses a quadruped robot path planning method and system based on an improved A* algorithm. The method comprises the steps of constructing an environment raster map,and representing aquadruped robot and a target position through raster coordinates; on the basis of the smallest distance between the edge of a robot body and the center of the quadruped robot,performing initial expansion on the raster where a barrier is located,and enabling the barrier and the raster obtained after initial expansion to jointly form the minimum impassable region; according to the the safe distanceneeded by actual operation of the quadruped robot,determining the outward expansion raster layer number on the basis of the minimum impassable region,and adopting the raster obtained after outward expansion inside the region as a barrier virtual expansion raster; utilizing the improved A* algorithm for determining a passing price value from the initial raster and the target raster,and determiningthe corresponding path obtained when the passing price value from the initial raster point to the target raster point is minimum is determined as the optimal path. The problem that a narrow channel is blocked can be avoided while the quadruped robot is driven to move away from the barrier.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
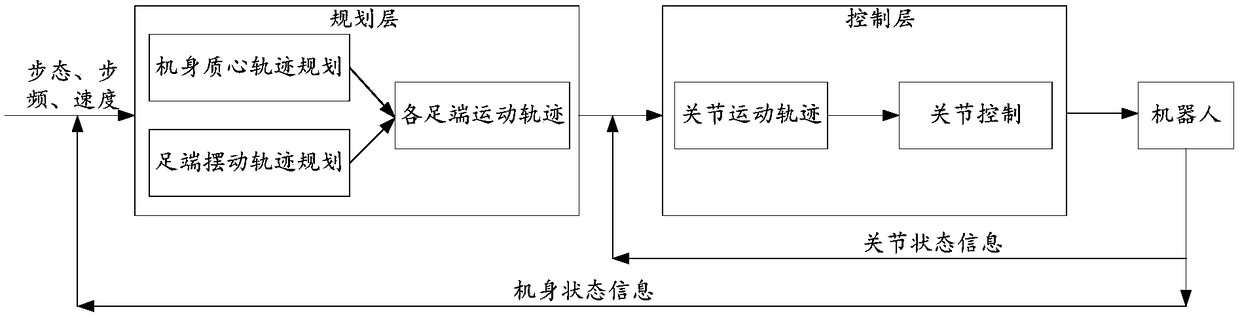
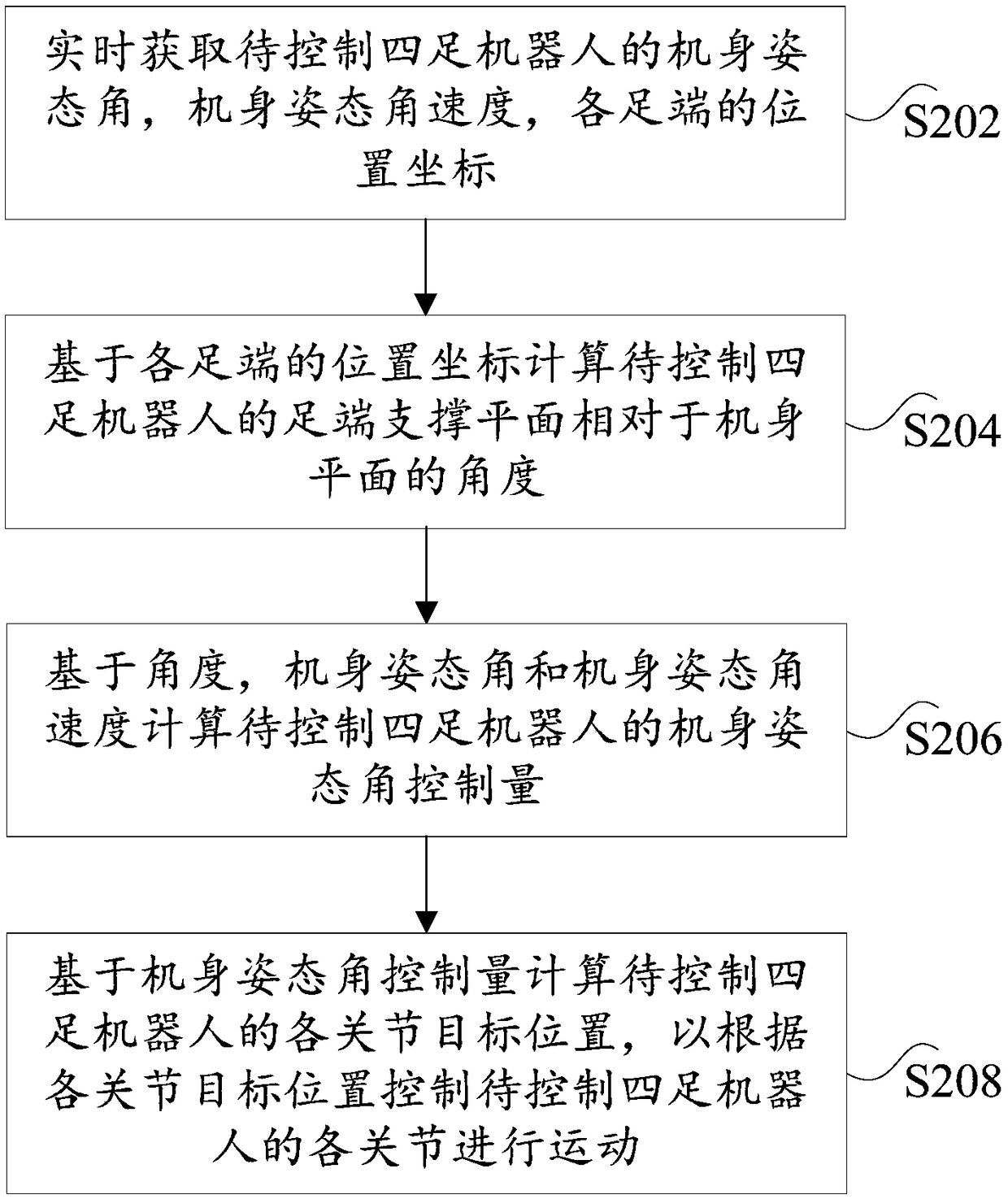
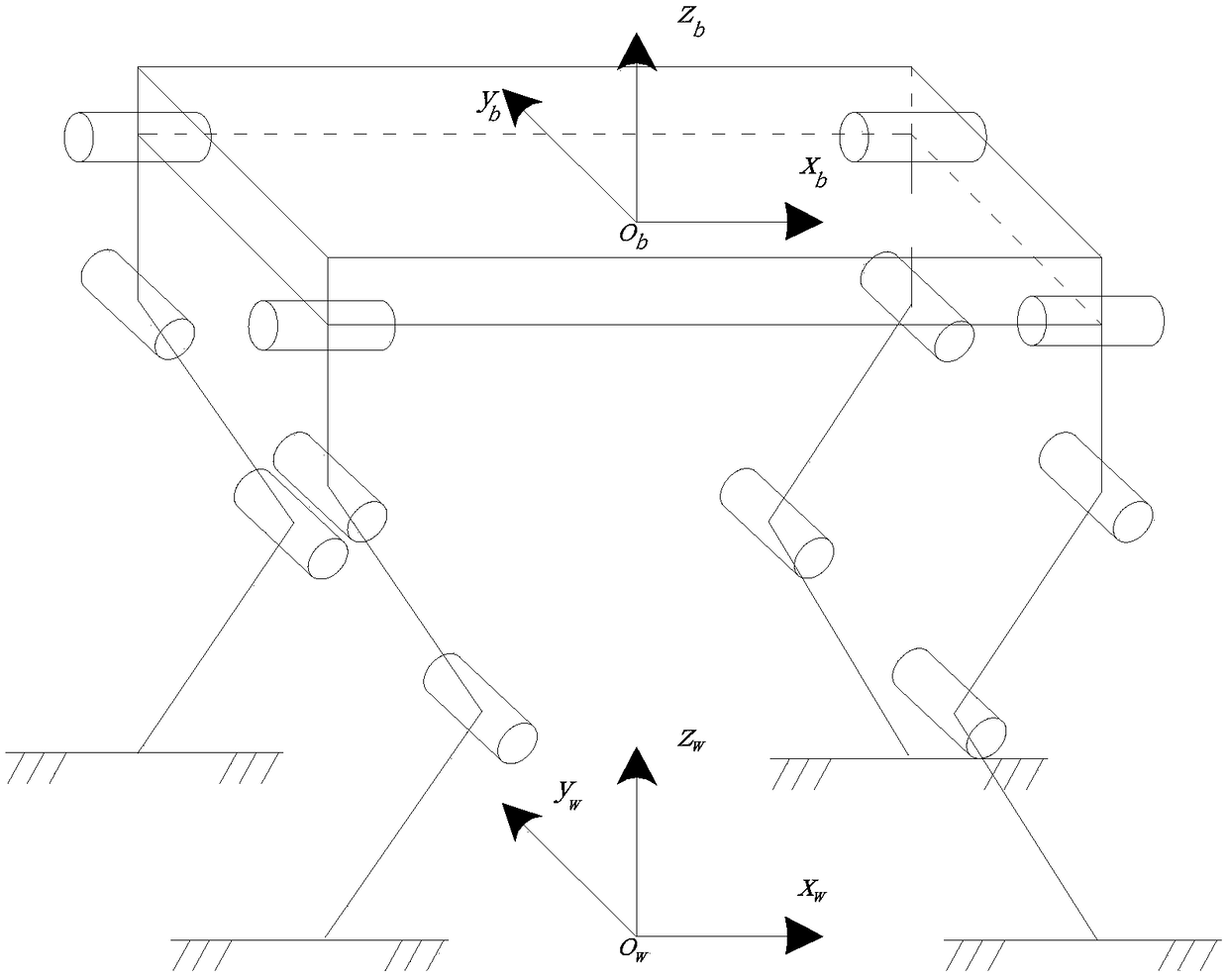
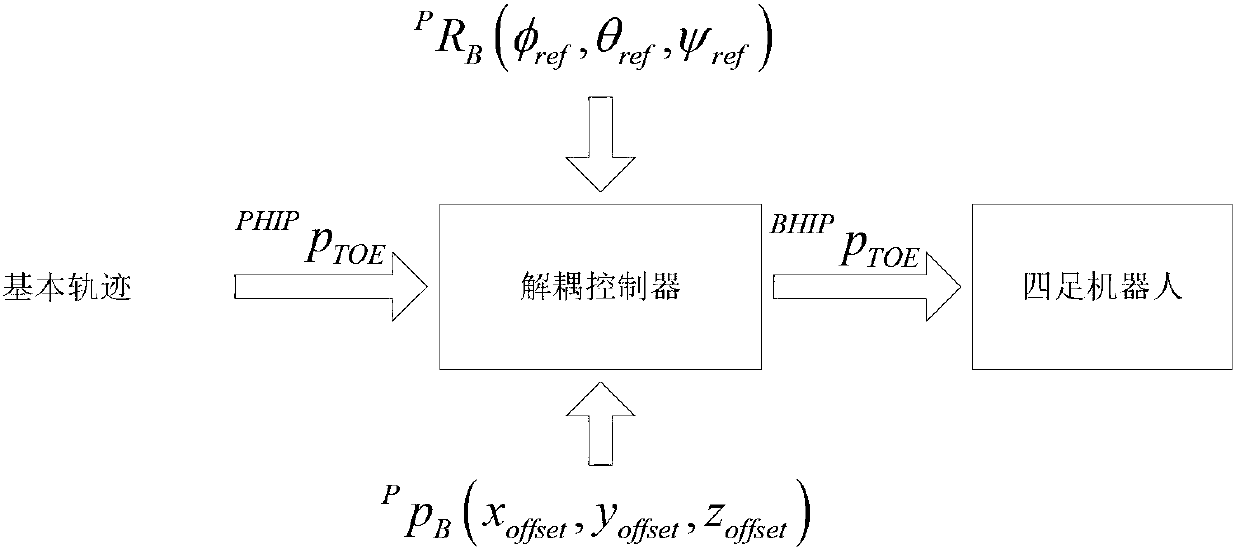
Quadruped robot body posture control method and quadruped robot body posture control device
ActiveCN109093626AImprove motion stabilityImprove terrain adaptabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorTerrainBody posture
The invention provides a quadruped robot body posture control method and a quadruped robot body posture control device. The method includes acquiring robot body posture angle, a robot body posture angular speed and position coordinates of all leg ends of a to-be-controlled quadruped robot in real time; computing an angle of a leg end supporting plane of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot relative to a robot body plane on the basis of the leg end position coordinates; computing a robot body posture angle control quantity of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot on the basis of the angle, the robot body posture angle and the robot body posture angular speed; computing all joint target positions of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot on the basis of the robot body posture angle control quantity, and controlling all joints of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot to move according to all the joint target positions. The quadruped robot body posture control method has the advantages that the method can achieve real-time robot body posture control of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot, and the movement stability and the terrain adaptability of the to-be-controlled quadruped robot are enhanced, so that the technical problem that the movement stability of the quadruped robot is affected severely by the poor real-time performance of an existing posture adjustment mode is relieved.
Owner:SIASUN CO LTD
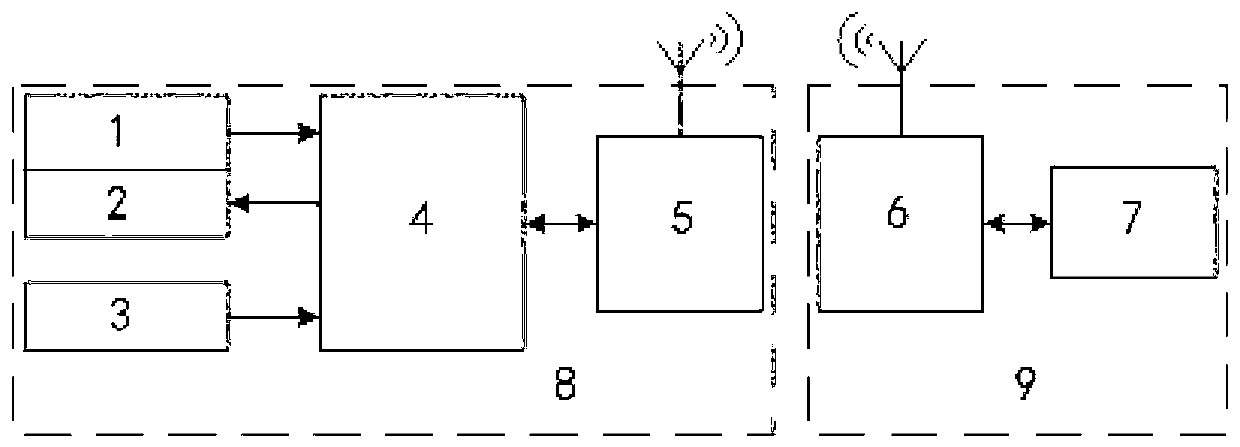
Quadruped robot remote control system and remote control method thereof
ActiveCN103345285ASimple and friendly interfaceChange movement speedTotal factory controlSimultaneous control of multiple variablesLiquid-crystal displayRemote control
The invention discloses a quadruped robot remote control system and a remote control method thereof. The remote control system comprises a controller I. The controller I receives and processes a touch screen and rocker signals and is communicated with a controller II of a quadruped robot through a wireless communication module I and a wireless communication module II of the quadruped robot, and the controller I also receives feedback information of the controller II and displays the feedback information of the controller II through a liquid crystal display screen. By means of the quadruped robot of the remote control system, the remote control method is simple and visualized, the remote control system is especially suitable for flexible control and state monitoring for the quadruped robot, can be interact with a user, then sends control commands and parameters, and setting and sending the commands and parameters to the quadruped robot, and finally displays the state fed back by the quadruped robot, and monitoring for the quadruped robot is achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot
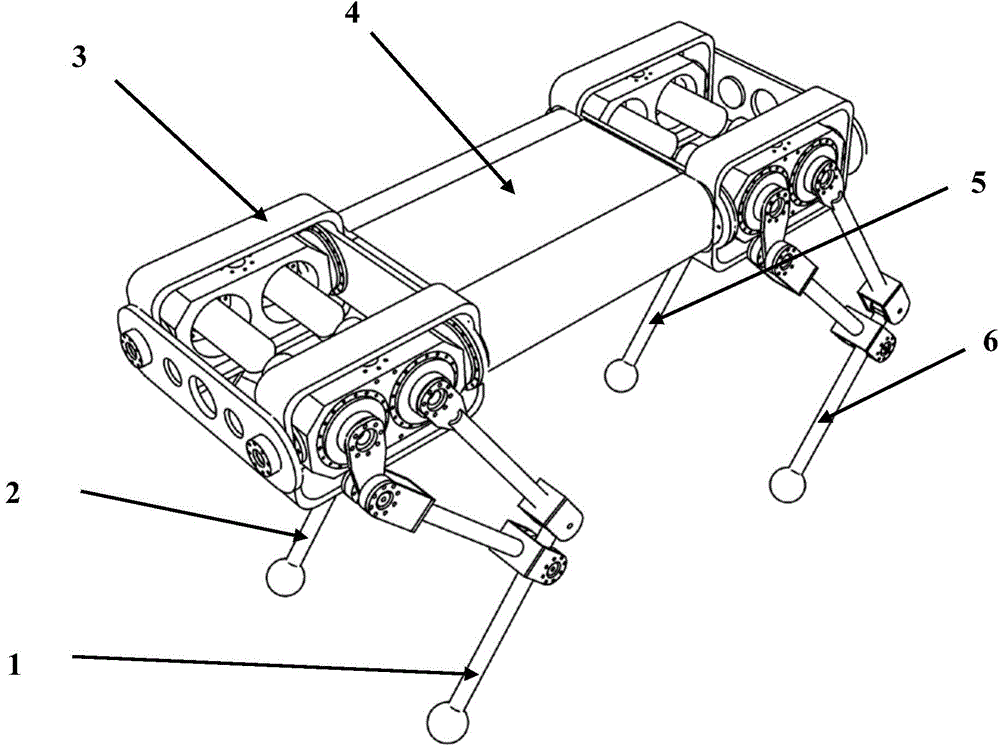
The invention relates to an electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot. The electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot is a twelve-degree-of-freedom pure electrically-driven small mammalian bionic four-leg robot. The robot is of a four-leg robot mechanism structure designed based on the bionic structure and the motion feature of a four-leg mammal. The electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot comprises a mechanical system and a power and motion control system. The simplified mechanical structure and a highly-integrated small real-time motion control system are adopted in the electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot. Each leg of the robot is provided with three low damping moment control joints directly driven by a permanent-magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), each leg is provided with a spring energy storage mechanism, and therefore the four-leg robot has the higher energy using efficiency. Multiple motion gaits such as creeping, walking, trotting and running can be achieved through the electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot, and the electrically-driven small bionic four-leg robot has the advantages of being simple in mechanical structure, ultra-low in noise, and low in cost, achieving dynamic self-balancing and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
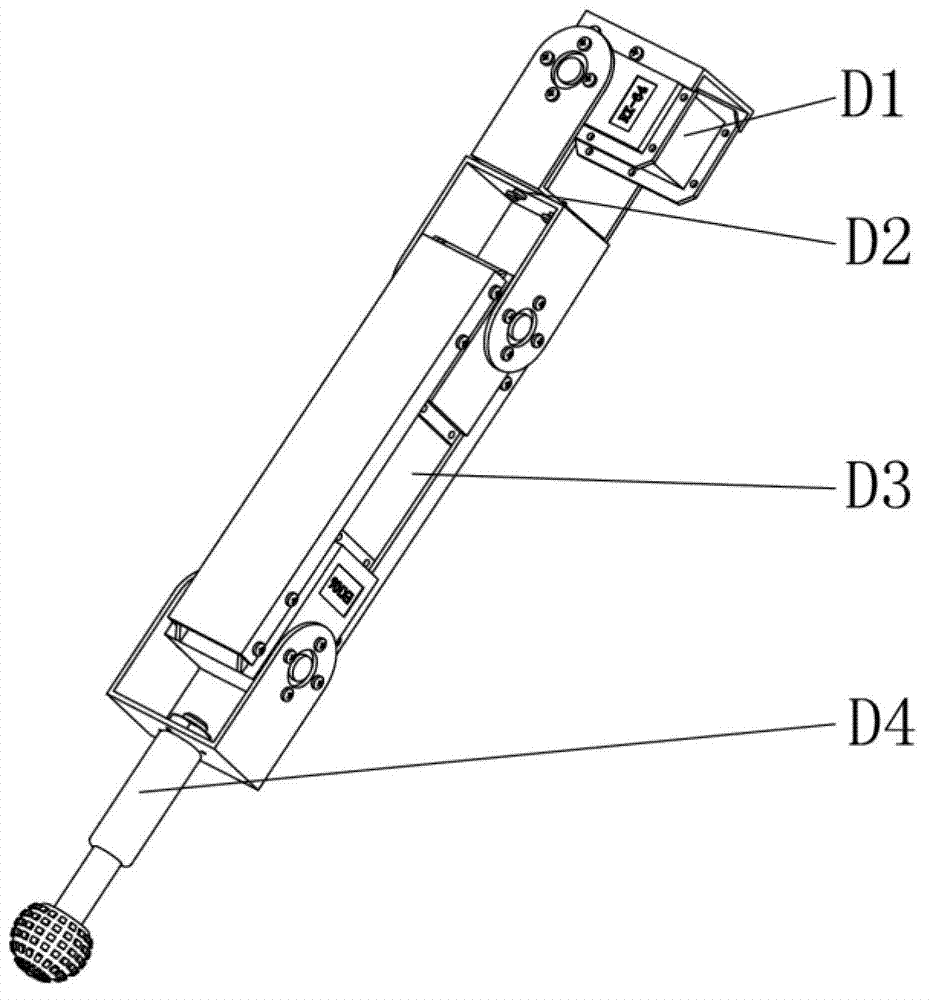
Leg mechanism for four-legged robots
The invention relates to a leg mechanism for four-legged robots, the leg mechanism comprises a drive motor, a femur mechanism, a knee-joint hinge, a tibia mechanism, a naked joint hinge and a metatarsus mechanism, wherein the femur mechanism is hinged with the tibia mechanism by the knee-joint hinge; the drive motor is fixed on the femur mechanism, and an output shaft of the drive motor drives the tibia mechanism to rotate by a bevel gear transmission mechanism in the knee-joint hinge; the tibia mechanism is hinged with the metatarsus mechanism by the naked joint hinge; and the drive motor drives the metatarsus mechanism to rotate by the bevel gear transmission mechanism in the knee-joint hinge and a bevel gear transmission mechanism in the naked joint hinge. In the invention, the number of joints of a leg structure is increased under the condition of not increasing the degree of freedom, so that the leg movement of the robot is more flexible, and the leg mechanism has the advantage of better movement performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Bionic quadruped robot with energy storage effect
InactiveCN104149871AWalk fastLarge front and rear stridesAuxillary drivesVehiclesEngineeringEnergy storage
The invention belongs to the field of bionic robots and relates to a bionic quadruped robot with energy storage effect. The rigid spine of the existing bionic quadruped robot is modified. The bionic quadruped robot comprises a front trunk, a rear trunk, a spine, a left front leg unit, a right front leg unit, a left rear leg unit and a right rear leg unit. The front trunk and the rear trunk are connected with front and rear ends of the spine, respectively. The spine can drive the front trunk to rotate relative to the rear trunk. The left front leg unit, the right front leg unit, the left rear leg unit and the right rear left leg unit have same structures and are connected to left and right sides of the front and rear trunks, respectively. The spine is added between the front and rear trunks; the whole shape is more approximate to a true quadruped animal; when the robot walks, the front and rear trunks allow a larger step through the spine pitching up or down, and the robot can walk faster; less energy is lost when the robot touches the ground, motion stability is improved, and utilization rate of energy is increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
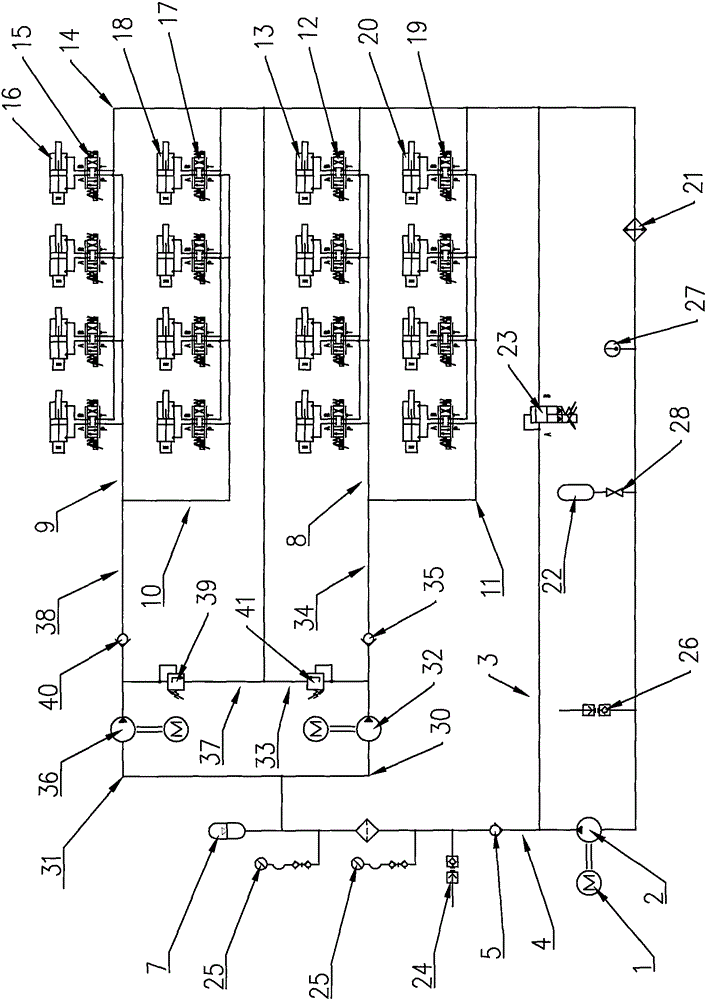
Electric servo hydraulic power source drive system of four-foot robot
ActiveCN105156382APlay a role in maintaining pressureEasy to check for faultsProgramme-controlled manipulatorServomotor componentsHydraulic pumpHigh pressure
An electric servo hydraulic power source drive system of a four-foot robot comprises a quantitative gear pump. The oil outlet of the quantitative gear pump is connected with the inlet of a high-pressure oil pipe. The outlet of the high-pressure oil pipe is connected with the inlet of a left oil supply pipe and the inlet of a right oil supply pipe. The left oil supply pipe is connected with a left hydraulic pump in series. The outlet of the left oil supply pipe is connected with the inlet of a left overflow pipe and the inlet of a left supercharging oil pipe. The middle of the left overflow pipe is connected with a left overflow valve in series. The outlet of the left supercharging oil pipe is connected with the oil inlet of a left front leg oil supply pipe and the oil inlet of a right rear leg oil supply pipe. The right oil supply pipe is connected with a right hydraulic pump in series, and the outlet of the right oil supply pipe is connected with the inlet of a right overflow pipe and the inlet of a right supercharging oil pipe. The middle of the right overflow pipe is connected with a right overflow valve in series. The outlet of the right supercharging oil pipe is connected with the oil inlet of a right front leg oil supply pipe and the oil inlet of a left rear leg oil supply pipe. According to the purpose, the electric servo hydraulic power source drive system of the four-foot robot is light, large in effective volume, constant in oil supplementing pressure, long in driving mileage, low in noise, long in service life, and stable and reliable in performance.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
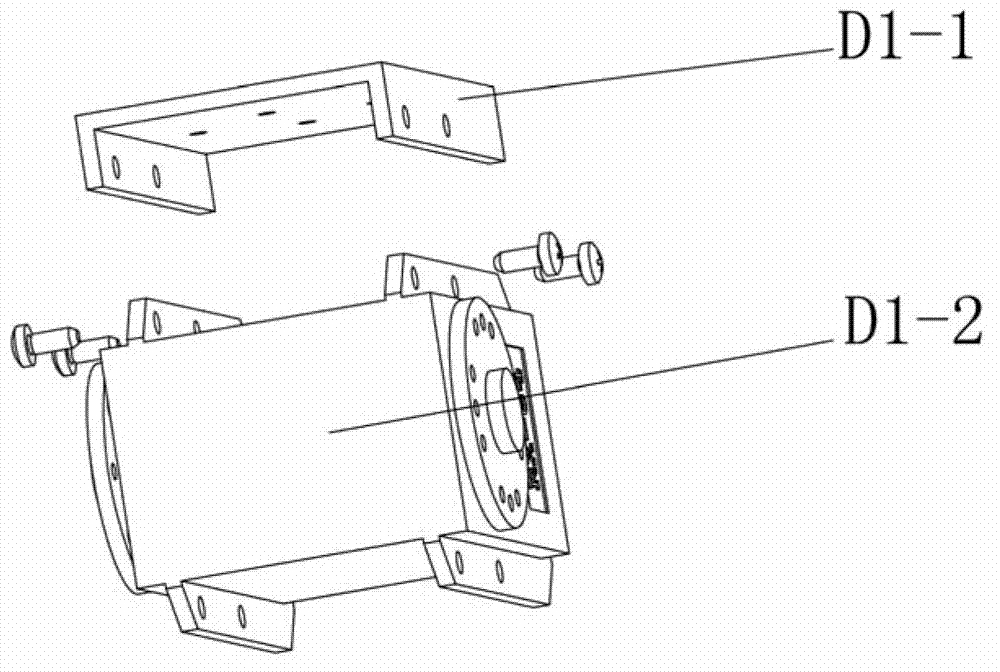
Leg-foot mechanism with low rotational inertia configuration for four-footed robot
The invention discloses a leg-foot mechanism with low rotational inertia configuration for a robot. The leg-foot mechanism comprises hip joints, thighs, knee joints and shanks and also comprises a hip joint motor fixedly connected with a robot body, the hip joint motor comprises a power output shaft vertical to the axial direction of one of the thighs, and the power output shaft drives a pivotal part of the hip joint by virtue of a hip joint synchronous belt, thus the thighs are driven to rotate relative to the body; besides, the leg-foot mechanism also comprises knee joint motors which are arranged at the upper parts of the thighs, each knee joint motor comprises the power output shaft parallel to the axial direction of one of the thighs, a first belt wheel is connected with the power output shafts of the knee joint motors by virtue of a worm gear, so that the first belt wheel rotates for 90 degrees for conversion, and the first belt wheel drives a second belt wheel to rotate by virtue of a knee joint synchronous belt, thus the shanks are driven to rotate relative to the fixing parts of the knee joints. According to the leg-foot mechanism disclosed by the invention, rotational inertia of the hip joints is reduced, the maximum power utilization of the hip joint motor can be realized, and the robot can walk more smoothly.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quadruped robot motion planning method for facing complex terrain
InactiveCN103085070ASafe and smooth autonomous movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorTerrainRobot motion planning
The invention provides a quadruped robot motion planning method for facing complex terrain. According to moving object of a quadruped robot, and local environment information and terrain information which are detected by a sensor, movement direction at the current moment of the quadruped robot is confirmed and generate local moving object of the quadruped robot in Cartesian space. According to the local moving object of the quadruped robot in the Cartesian space and the terrain information detected by the sensor, a motion path sequence is generated in quadruped robot configuration space through a rapid random tree algorithm, and the quadruped robot moves according to the motion path sequence until reaches the local moving object. Above steps are repeated until the quadruped robot reaches a set target. Due to the fact that a body motion planning in the Cartesian space and each joint configuration planning in the configuration space are combined, and a motion path sequence of each joint of the quadruped robot is generated according to present environment of the quadruped robot, safe and stable voluntary movement of the quadruped robot in the complex terrain is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for generating free gaits for four-footed bionic robot
ActiveCN104267720ASufficient marginImprove terrain adaptabilityVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlTerrainFoot supports
The invention relates to a method for generating free gaits for a four-footed bionic robot. All of the free gaits of the four-footed robot are programmed according to moving periods, and each moving period comprises a four-footed supporting stage and a stepping stage; at the four-footed supporting stages, four feet of the robot are all positioned at supporting phases, the center of gravity of the robot moves in the advancing direction and the side directions of the advancing direction, in the advancing direction, the robot moves the largest advancing distance allowed by a current state, and in the side directions, the moving distance of the robot is determined taking account of the stability and the energy consumption of the robot at the same time; at the stepping stages, one foot of the robot is positioned at a swinging phase, and the other three feet of the robot are positioned at the supporting phases; when the swing foot of the robot for a certain moving period comes in contact with the ground, the movement of the robot for the next moving period is programmed. Through the adoption of the method, the adaptability of the four-footed robot to terrain is effectively improved, the stability of the robot can be improved, the continuity of the movement of the robot is ensured, the energy consumption is reduced, and the mean movement speed is accelerated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
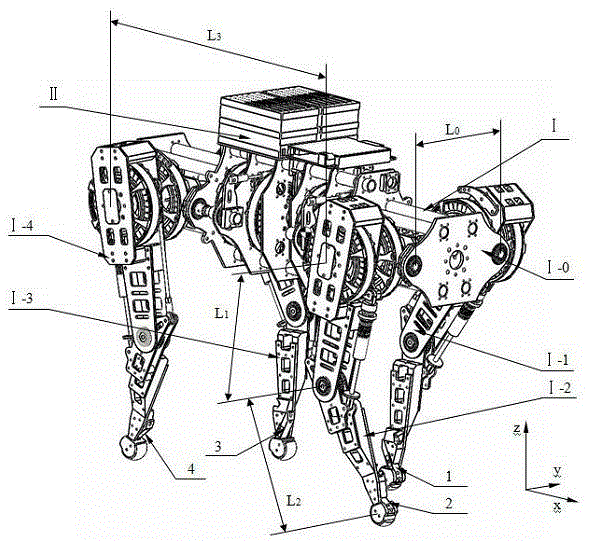
Single leg structure of electric quadruped robot
PendingCN107651041ALight in massSmall moment of inertiaVehiclesThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to a single leg structure of an electric quadruped robot. The single leg structure comprises a hip joint, a knee joint, a thigh connecting rod, a shank connecting rod and a foot,the hip joint comprises a first hip joint body and a second hip joint body, the second hip joint body is connected with the power output end of the first hip joint body, the knee joint is connected with the power output end of the first hip joint body through the thigh connecting rod, the knee joint is in rigid connection with the second hip joint body, the power output end of the second hip joint body is connected with power input end of the knee joint through the transmission mechanism, the shank is fixedly connected to the power output end of the knee joint, and the foot is connected to the shank. According to the structure, the low quality and low rotating inertia of the thigh and the shank is guaranteed, the good motion performance is achieved, the structure is simple and compact, itis guaranteed that the knee joint and the hip joint of the single leg have the good reverse drive characteristic, and the single leg structure can be used for assembling the electric quadruped robotwhich is capable of bouncing and high in load deadweight ratio.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
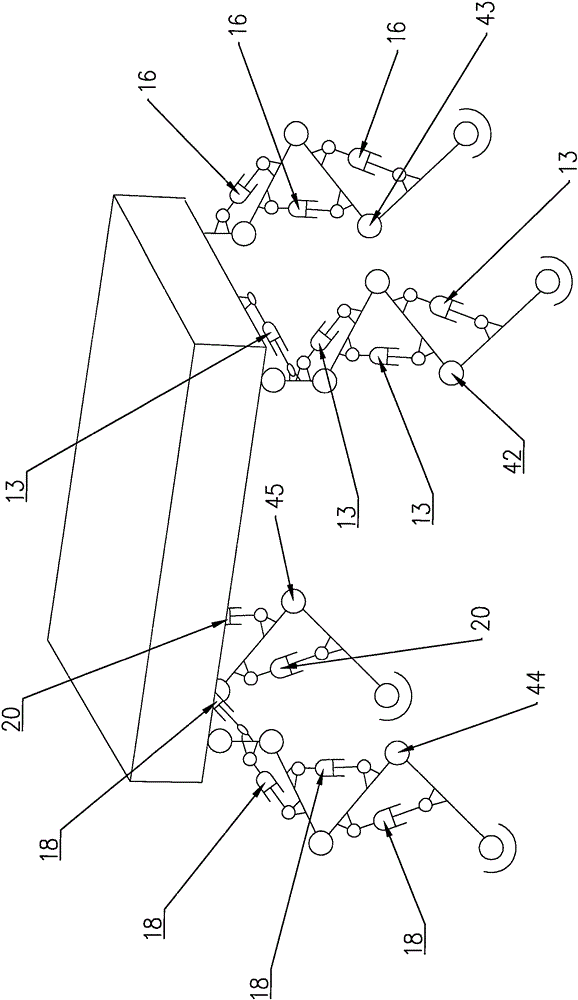
Hydraulic driving four-footed robot with space hybrid leg structure
The invention provides a hydraulic driving four-footed robot with a space hybrid leg structure. The hydraulic drive space four-footed robot is composed of a rack and space hybrid legs which are symmetrical in structure; each hybrid leg comprises three hydraulic driving oil cylinders, a leg rack, a swing rod, a connection rod, thighs, shanks and feet; each hybrid leg is provided with three drivingdegrees of freedom; the hydraulic driving oil cylinder A drives the whole leg to carry out side swing movement; and the hydraulic driving oil cylinder B and the hydraulic driving oil cylinder C are capable of cooperatively driving the feet to carry out plane parallel movement output in the plane of a leg mechanism. The feet are connected through buffering so that vibration absorption, energy storage and reutilization can be finished in a striding period. Four legs are symmetrically distributed or equidirectionally distributed so that an omnibearing movement of the robot can be realized through a certain tread. The hydraulic driving four-footed robot with the space hybrid leg structure provided by the invention is simple in structure, easy to control and high in kinematic accuracy, has a high-speed response capability and a high bearing capability, and is applicable to high-speed and high-load transportation work and dangerous environment work under complicated non-structure topographic conditions in the wild.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Four-footed robot
The invention discloses a four-footed robot, which is characterized by mainly comprising a rack, a dust shield and four mechanical legs with identical structures; the rack is internally provided with twelve servo motors, which comprise four lifting motors, four propelling motors and four swinging motors and are used for driving the four mechanical legs, and every three motors control one mechanical leg to realize rising, lowering, advancing, retreating and side swinging movements of the mechanical leg; the rack comprises connecting plates, a square mounting plate and a rod; the connecting plates are located on two sides of the square mounting plate and are used for fixing the square mounting plate, and all the components are mutually fixedly connected by screws; the dust shield and the rack are mutually fixedly connected by screws; each leg part structure mainly comprises one swinging motor, one lifting motor, one propelling motor, a support plate, a lifting rod, a tail end rod, a long propelling rod, a short propelling rod, a No. 1 short shaft, a No. 2 short shaft and a support shaft; all mechanisms of each leg part are divided into a lifting system, a propelling system and a swinging system according to the functions in the moving process.
Owner:SHAANXI JIULI ROBOT MFG +1
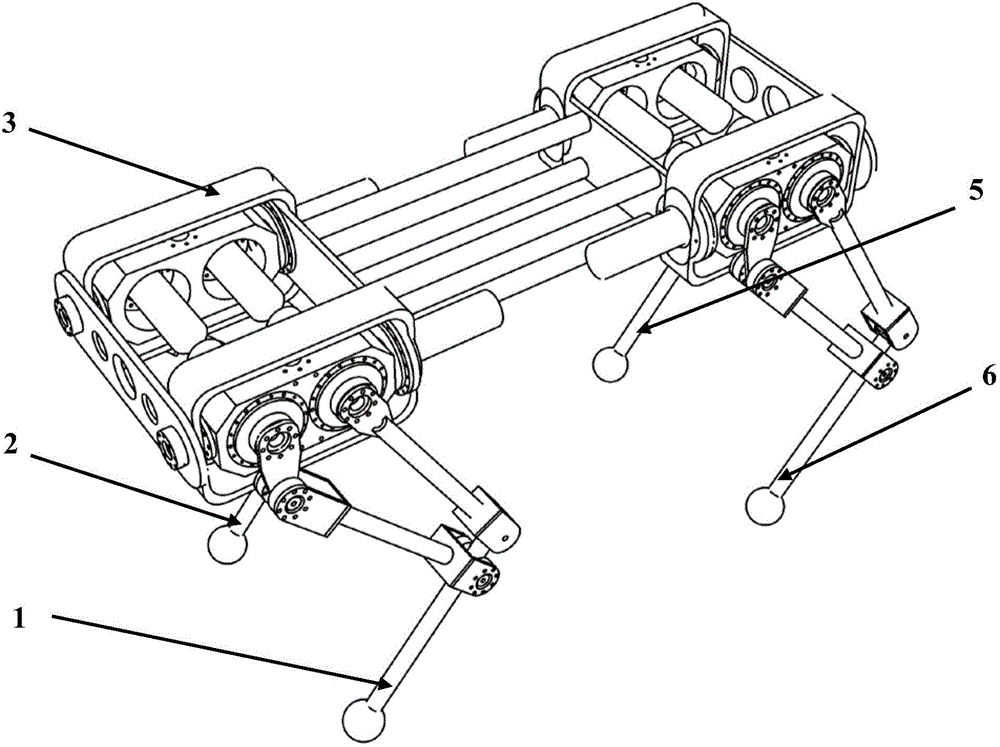
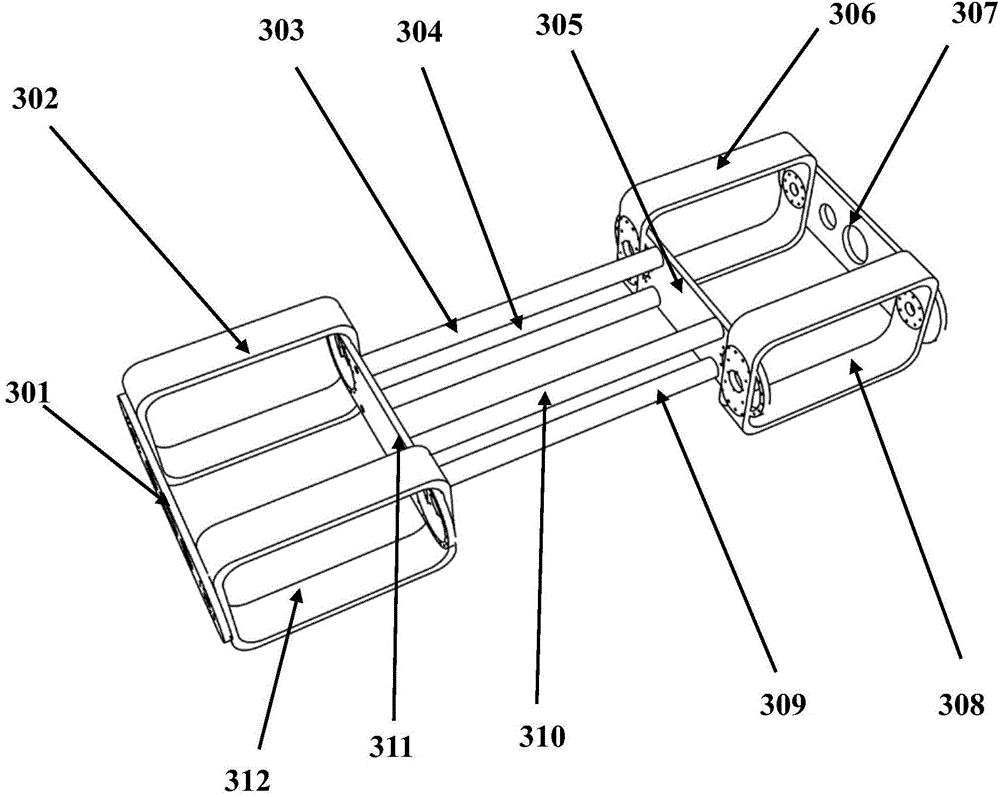
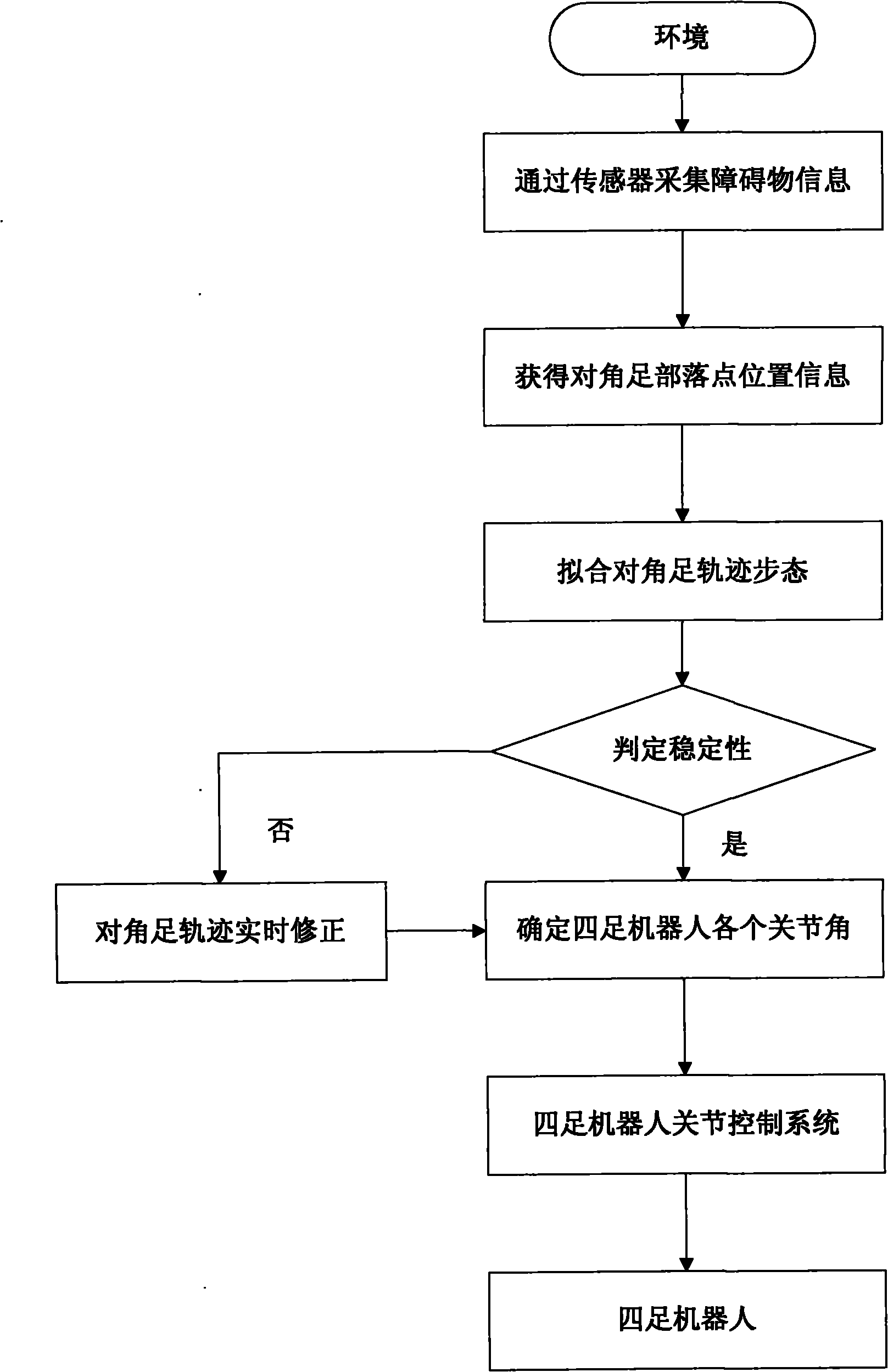
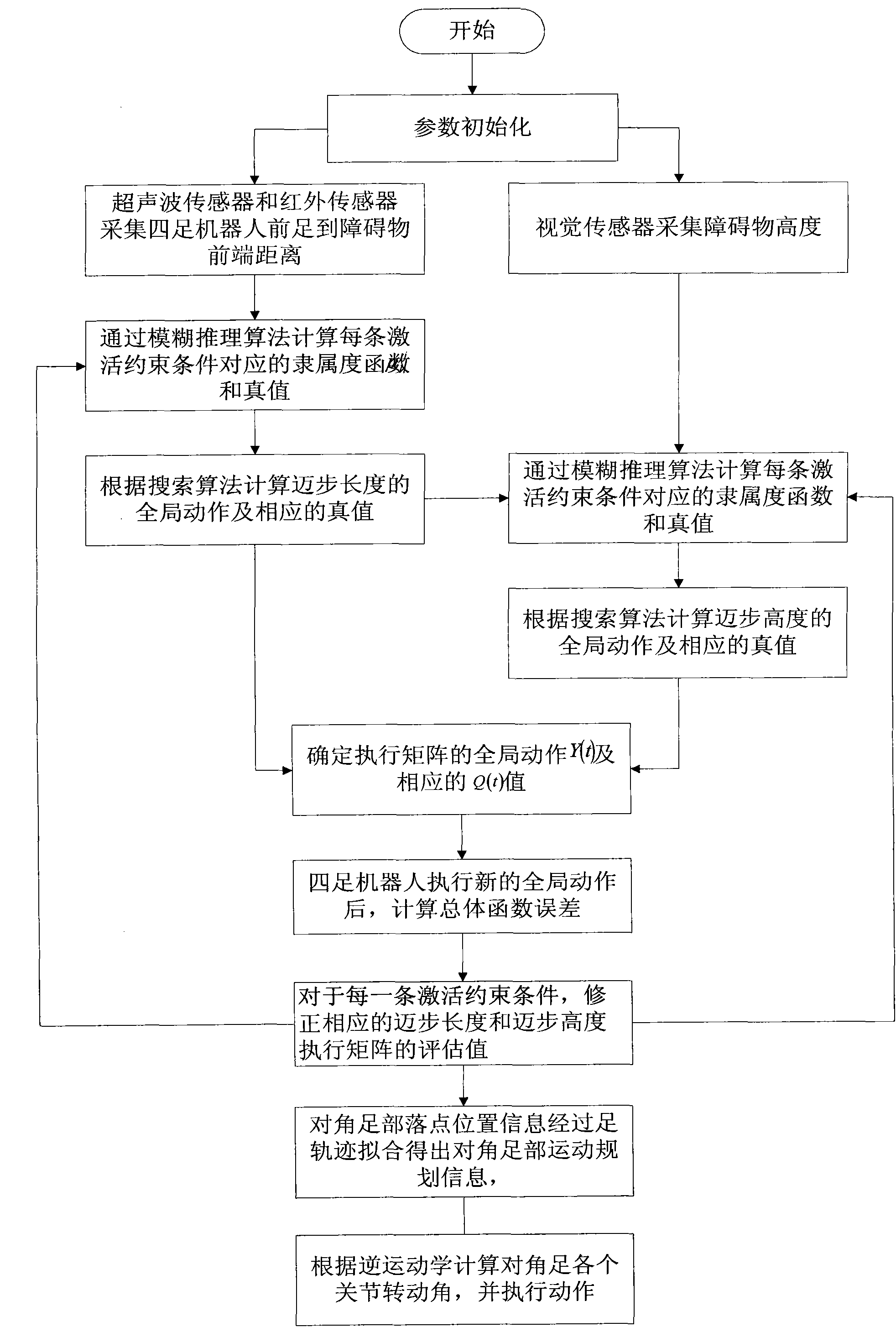
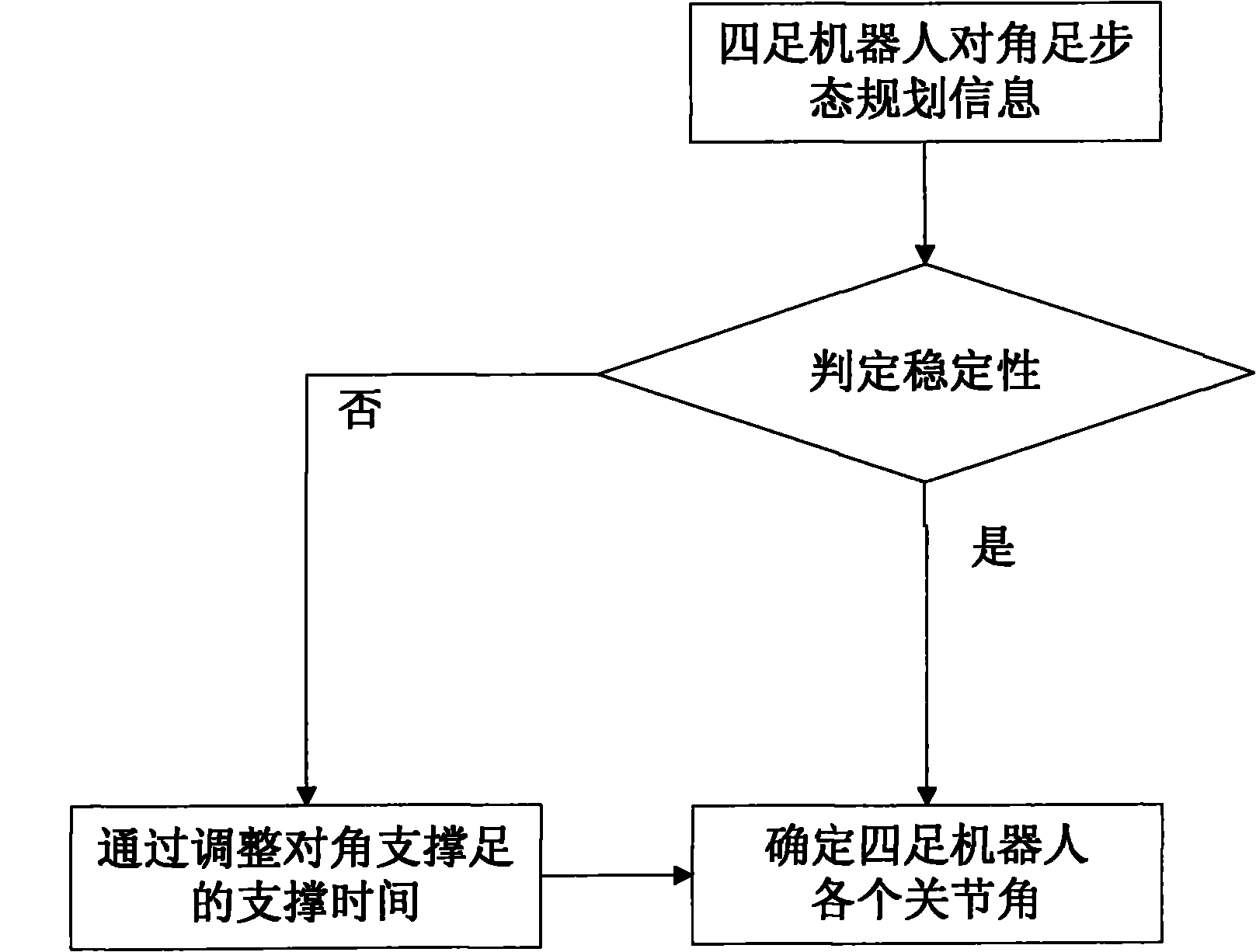
Self-adaptive control method for diagonal gait of four-footed robot
InactiveCN102156484AImprove execution efficiencyClear division of laborControl without using feedbackTerrainEngineering
The invention discloses a self-adaptive control method for diagonal gait of a four-footed robot, which is used for self-adaptively controlling the walking of the four-footed robot in the nonstructural terrain with the diagonal gait. The self-adaptive control method bases on a fuzzy reasoning learning method and a foot trajectory real-time correction method and takes the diagonal gait as the motion mode so as to comprehensively control a robot body to adapt for the nonstructural environment. The gait planning is carried out on the environmental information collected by the sensor through the fuzzy reasoning learning method; the stability judgment is carried out on the gait planning information; if the planned four-footed robot has stable diagonal gait, the joint corner information is sent to a control system; if not, the supporting time of the diagonal feet is corrected by the foot trajectory real-time correction method so that the four-footed robot has better stability when walking under the changed gait in the nonstructural terrain. The self-adaptive control method is used for correcting foot trajectory planning and walking stability under changed gait when the four-footed robot walks diagonally in a dynamic way, thus realizing the self-perception, self-correction and self-adjustment of the four-footed robot.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Walking mechanism of cam driving control type quadruped robot
InactiveCN101791994AOvercoming structural complexityOvercoming structural precisionVehiclesEngineeringCam
The invention discloses a walking mechanism of a cam driving control type quadruped robot, which comprises a front leg component and a rear leg component with the same structure, a front leg fixing support frame and a rear leg fixing support frame which are respectively positioned above the front leg component and the rear leg component and are used for fixing and supporting the front leg component and the rear leg component, a front leg three-cam driving control component and a rear leg three-cam driving control component respectively positioned above the front leg fixing support frame and rear leg fixing support frame and matched with the front leg component and the rear leg component, a front and rear leg universal connection component positioned between the front leg fixing support frame and the rear leg fixing support frame and used for connecting the front leg component and the rear leg component, and a DC servo drive motor fixedly arranged above the rear leg fixing support frame and matched with the front and rear leg universal connection component, wherein the front leg fixing support frame and the rear leg fixing support frame are symmetrically arranged at both ends of the front and rear leg universal connection component. The walking mechanism of the cam driving control type quadruped robot has the advantages of simple structure, high control precision, low cost and light weight.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
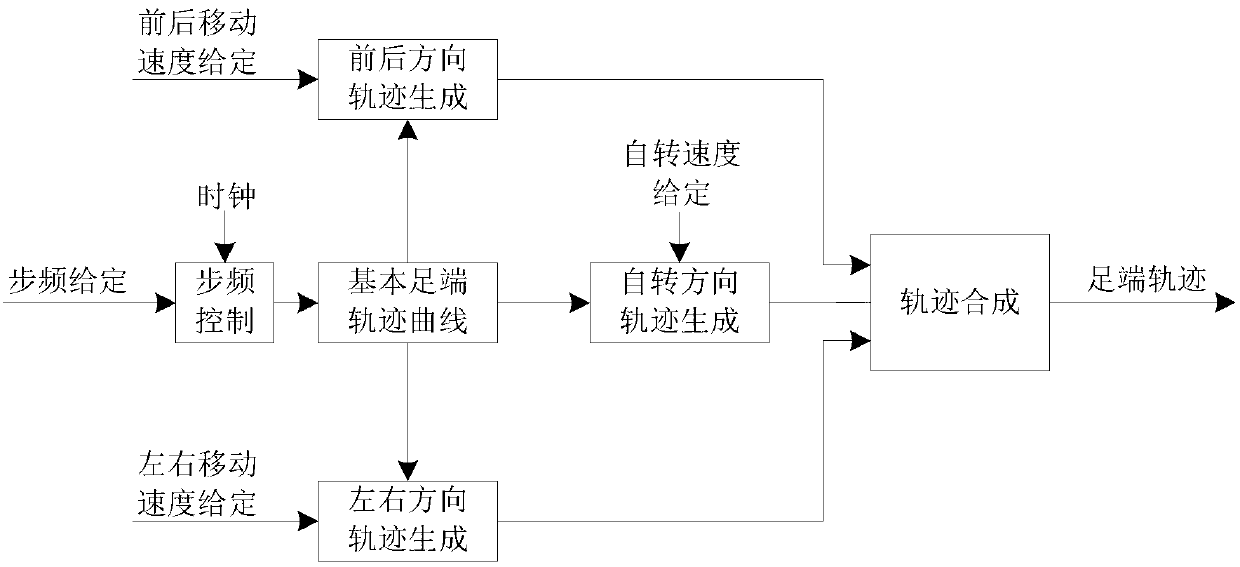
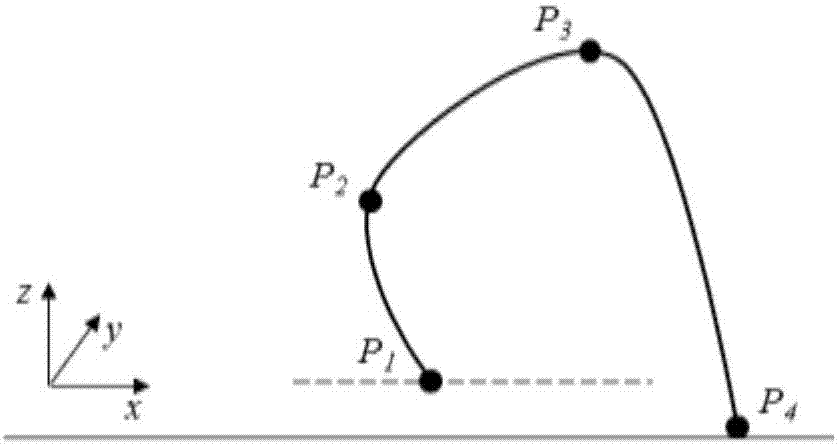
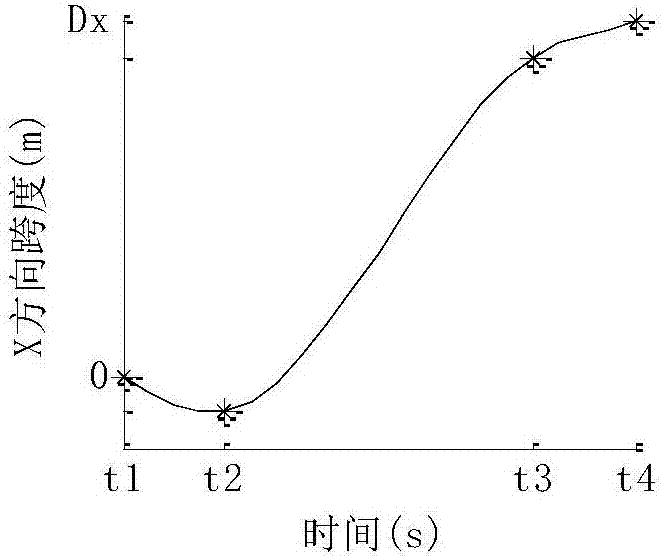
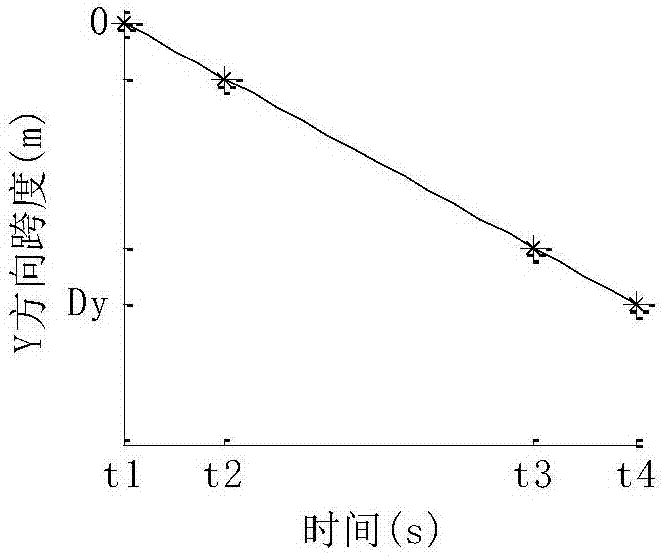
Method for planning quadruped robot foot end swinging track
PendingCN107065907ARealize the obstacle avoidance functionRealize the function of overcoming obstaclesAttitude controlState parameterEngineering
The invention relates to a method for planning the quadruped robot foot end swinging track. The method includes designing the curve end point state parameter in the foot end swinging process according to the swinging span and the swinging phase duration of the foot ends; and fitting the foot end swinging track. The method for planning the foot end swinging track achieves the barrier avoidance function when the leg lifting sage has the backward and upward motion trend; can better realize the barrier avoidance function when the walking direction has the backward and upward motion trend; and moreover, the foot end swinging track parameter can be adjusted in real time to be flexibly adapted to the landform, so that the passing capability of the quadruped robot on the complex rough landform is improved.
Owner:CHINA NORTH VEHICLE RES INST
Electric quadruped robot with variable mechanism configuration
The invention discloses an electric quadruped robot with variable mechanism configuration. The electric quadruped robot with the variable mechanism configuration comprises a trunk and four legs connected to the trunk; each leg comprises three transmission chains which are respectively a first transmission chain, a second transmission chain and a third transmission chain, the first transmission chain is connected with the trunk, the second transmission chain is connected with the first transmission chain, and the third transmission chain is connected with the second transmission chain. The first transmission chain drives a hip joint axis to rotate, the second transmission chain drives a thigh rod piece to rotate, and the third transmission chain drives a shank rod piece to move. The mechanism configuration of the electric quadruped robot can be transformed according to specific terrains, the electric quadruped robot has multiple motion modes of quadruped crawling, quadruped walking and partial crawling-partial walking, when the mechanism configuration of crawling is used, the electric quadruped robot is high in stability, and can better pass through rugged and complex terrains; when the mechanism configuration of walking is adopted, the electric quadruped robot is quick in action speed and high in efficiency and energy utilization rate; the electric quadruped robot with the variable mechanism configuration is driven by the motor, therefore, noises can be greatly reduced, and a mechanical main body is lighter and more flexible.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Four-foot robot working space track generating method based on certified program generator (CPG) mechanism
InactiveCN103092197AAchieve gait transitionAchieve steeringAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsWave shapeQuadrupedal robot
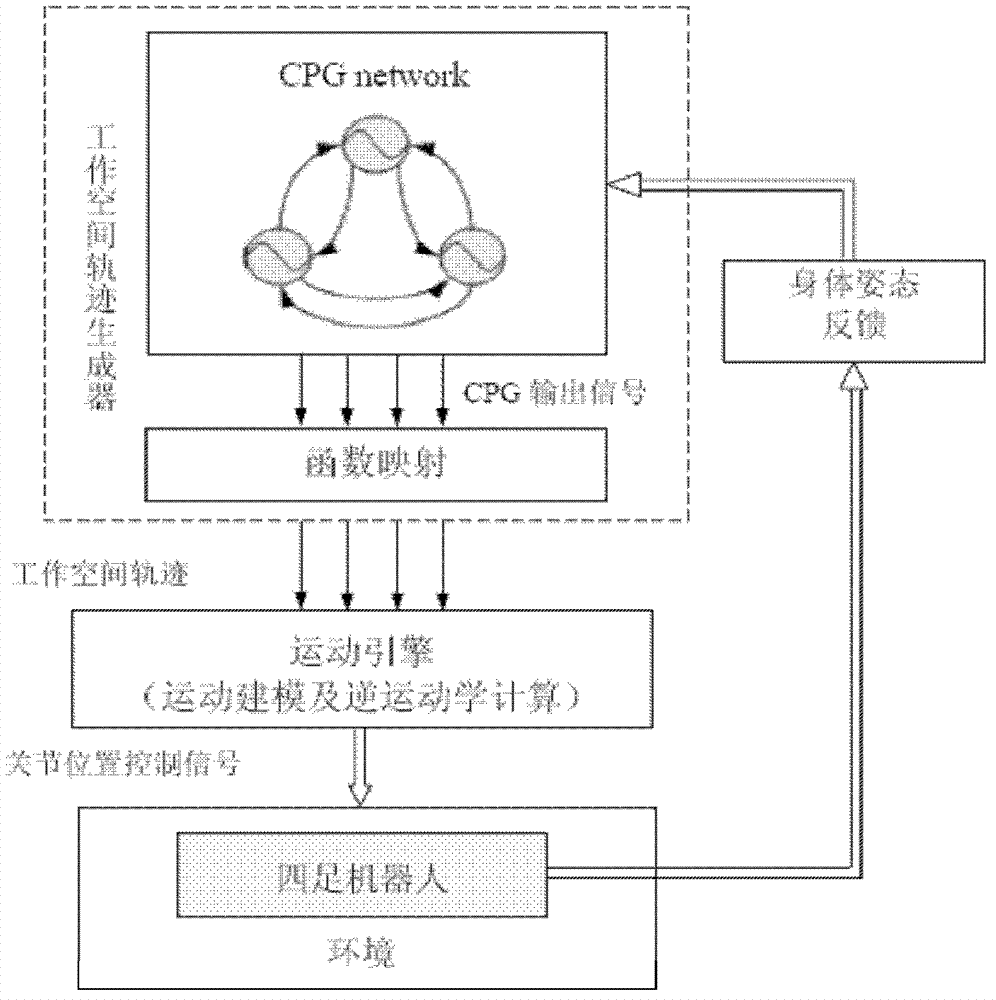
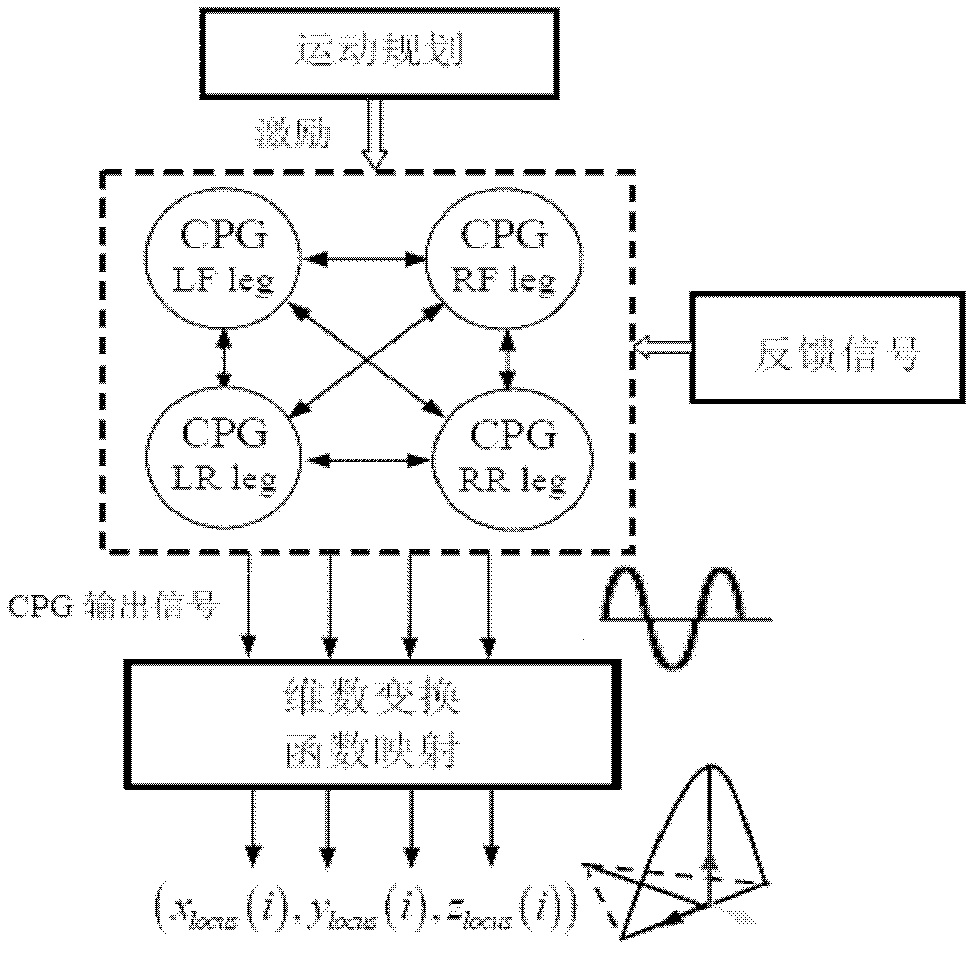
The invention relates to a four-foot robot working space track generating method based on the certified program generator (CPG) mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: four CPG units distributed at four foot ends of a robot being utilized to be mutually coupled to constitute a CPG network capable of generating periodical output wave-shaped signals; obtaining a working space track of the robot after conducting dimension expansion and functional transformation on the periodical output signals by utilization of a designed mapping function; benefiting from rich dynamic characteristics of the CPG network so that the on-line generated working space track can be modulated based on CPG parameters and has certain adaptability; and designing a motion engine system to map the working space track to a joint space of the robot so as to control freedom degree of all joints of the robot and realize control of walking with certain adaptability. According to the method, bionic mechanism simulation is conducted based on the tail end rail of the robot. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of improving environment adaptability and robustness of robot walking, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Leg-wheel type quadruped robot
The invention discloses a leg-wheel type quadruped robot which comprises a body, wherein a body support is arranged under the body, four three-degree-of-freedom leg-wheel movement branched chains are arranged on the body and can be changed into wheels and legs, and inter-transformation between legs and wheels of the robot can be achieved quickly. The three-degree-of-freedom leg-wheel movement branched chains can be changed into legs on uneven roads, and therefore, strong adaptive capacity and good passability are achieved. The three-degree-of-freedom leg-wheel movement branched chains can be changed into wheels on even roads, and therefore, high speed and good maneuverability are achieved. The leg-wheel type quadruped robot is simple in structure and low in cost and has good economical and applicable value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com