Cooperative processing and recycling method for material containing iron and/or zinc, lead, copper and tin, and the like and molten steel slag
A technology of copper-tin, zinc-lead, which is applied in the field of co-processing and recycling of iron-containing or zinc-lead-copper-tin materials and molten steel slag, which can solve the problems of affecting the iron reduction speed, time-consuming and labor-intensive, and difficult to master
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
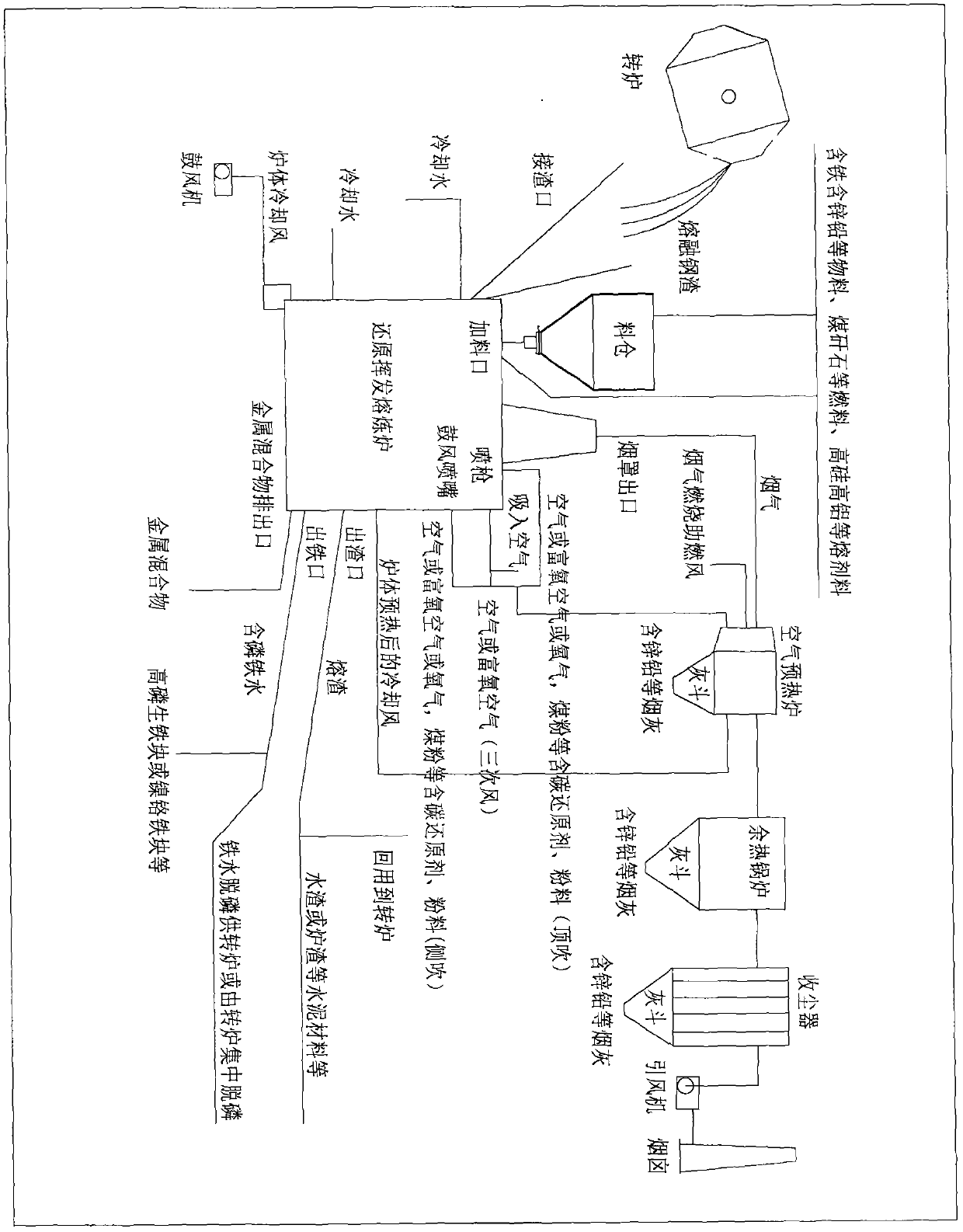
[0033] Embodiment 1: Prepare dried blast furnace gas ash, zinc-lead water slag powder, zinc-lead dust-removing ash, steelmaking sludge and dust-removing ash in the upper feeding bin of reduction volatilization smelting furnace device in the converter production area Compound pellets containing carbon, iron, zinc and lead, etc. made of carbon, the molar excess coefficient of reducing agent carbon is 1.1, and the block size is about 40mm. Lead slag blocks, coal gangue fuel, high-silicon iron ore, Silica, fluorite flux.
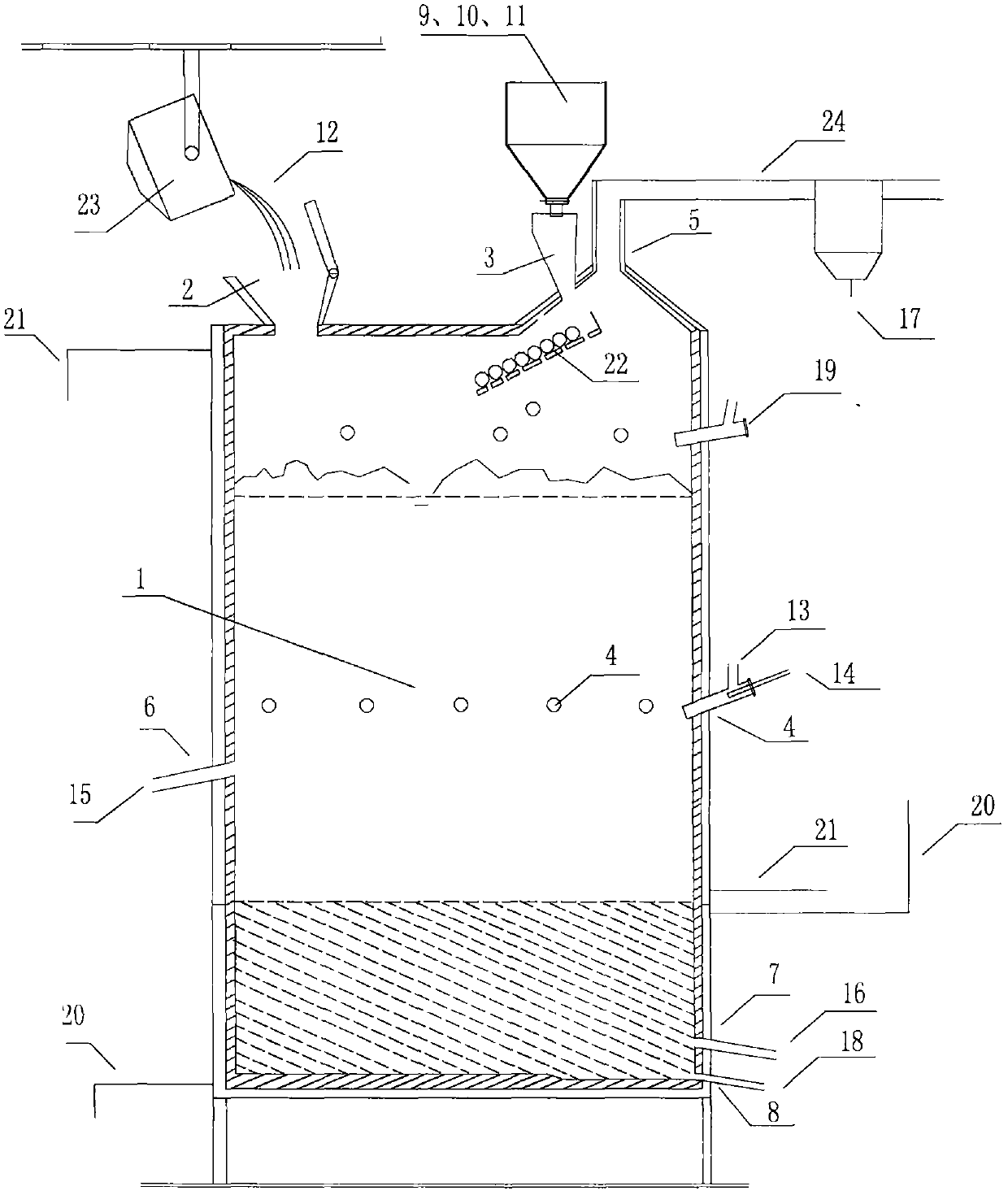
[0034] Step 1: First feed (initial feed, there is no sequence requirement for adding carbon-containing pellets and other bulk materials and adding molten steel slag) to start production (see attached figure 2 ), the carbon-containing pellets, high-silicon iron ore 9, coal gangue fuel 10 and silica flux material 11 are passed through the feeding port 3, and the molten steel slag 12 discharged from the converter and poured into the slag tank 23 for transfer is pas...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: In the upper feeding silo of the reducing volatilization smelting furnace device in the converter production area, the dried carbon-containing blast furnace gas ash, coal gangue powder, steelmaking sludge, waste incineration fly ash, copper slag, and sulfuric acid combustion are prepared. slag, cyanidation gold extraction slag, etc. compound pellets containing carbon, iron, zinc, lead, copper, gold and silver, etc., the molar excess coefficient of reducing agent carbon element is 1.3, the block size is about 40mm, and high-silicon iron ore is prepared Stone, coal gangue, silica flux. First add materials to start production (see attached figure 2 ), add a certain amount of carbon-containing pellets, high-silicon iron ore, coal gangue, and silica from the feeding port 3, then when the converter slag is discharged, the molten steel slag 12 is added to reduce the In the volatile smelting furnace 1, at the same time, oxygen-enriched air 13 is blown into the re...
Embodiment 3
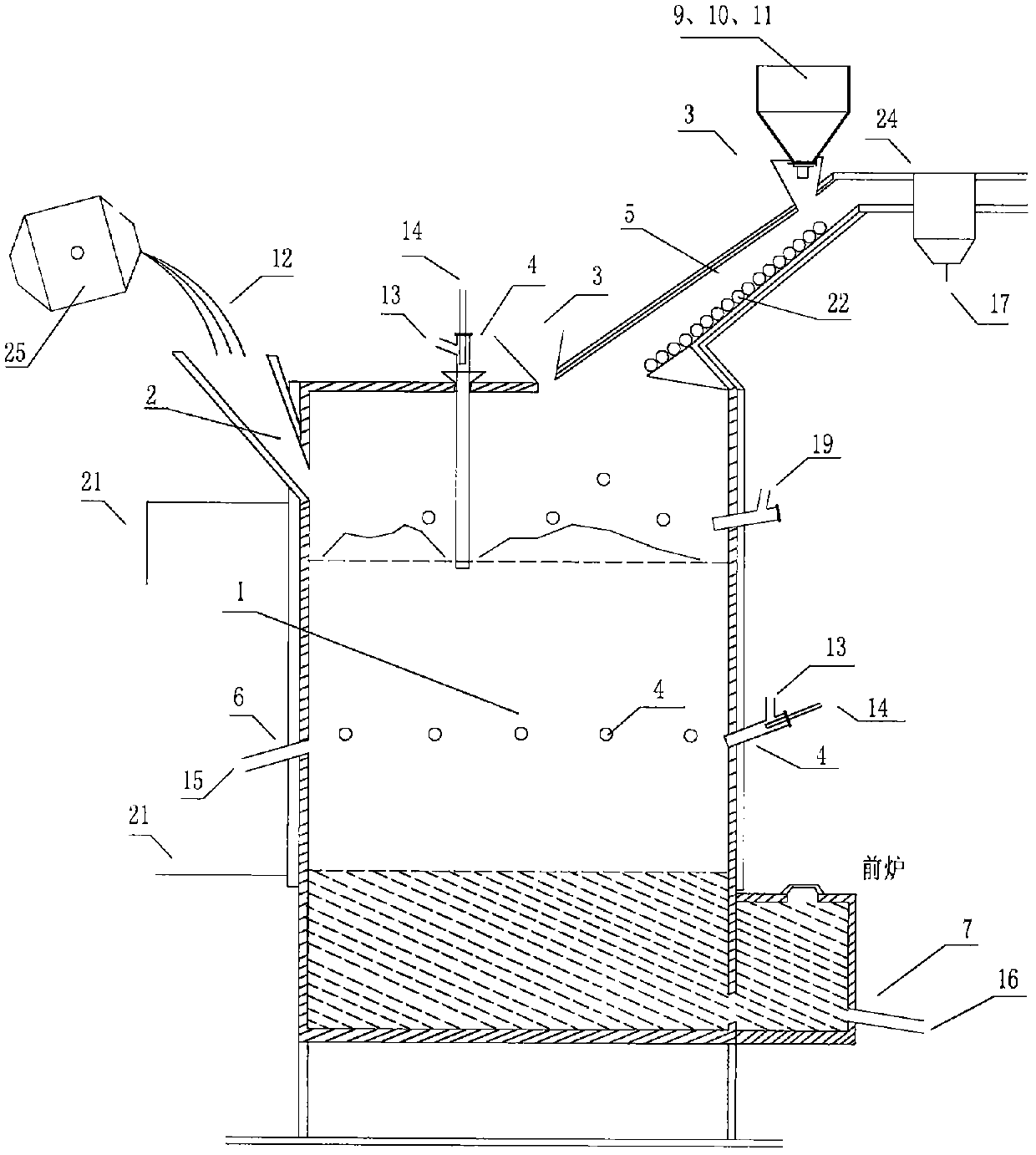
[0037] Embodiment 3: Prepare dried coal gangue powder, fly ash, steelmaking sludge, sintering and ironmaking dust, iron oxide scale, iron mud, etc. The produced carbon-containing and iron-containing pellets have a molar excess coefficient of reducing agent carbon of 1.2 and a block size of about 50 mm. Coal gangue fuel, high-silicon iron ore, and fluorite flux are prepared.
[0038] Step 1: first add materials to start production (see attached image 3 ), the carbon-containing pellets, high-silicon iron ore 9, and coal gangue fuel 10 are passed through the feeding port 3, and the high-temperature molten steel slag 12 discharged from the converter 25 is directly passed through the slag-connecting port 2 (long slag-connecting conduit), respectively adding reduction volatilization In the smelting furnace 1, at the same time, oxygen gas 13 is blasted into the reduction and volatilization smelting furnace 1 through the air blast nozzle 4, and coal powder 14 is sprayed together to p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com