Method for preparing water-soluble astaxanthin and astaxanthin aqueous solution prepared by method
An astaxanthin, water-soluble technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, solvent extraction, etc., can solve the problems of complex operation process, poor selectivity, and increased production cost of enzyme preparations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
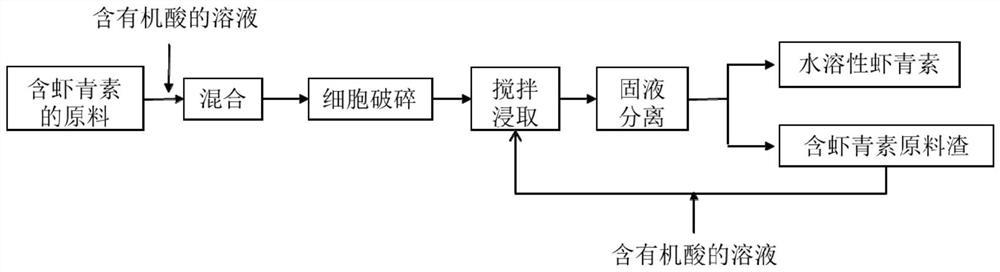
[0068] The schematic flow chart of the method for preparing water-soluble astaxanthin provided by the invention is as follows figure 1 As shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0069] (1) mixing the astaxanthin-containing raw material with a solution containing an organic acid, performing cell disruption, and obtaining a leaching solution;
[0070] (2) The leaching liquid described in step (1) is stirred and leached, and after solid-liquid separation, water-soluble astaxanthin is obtained;
[0071] (3) Mix the astaxanthin-containing raw material slag obtained from solid-liquid separation in step (2) with the solution containing organic acid to obtain a leaching solution, which is recycled to step (2) for at least one re-leaching.
[0072] 1. Embodiment
Embodiment 1
[0074] The present embodiment provides a method for preparing water-soluble astaxanthin, the method comprising the following steps:
[0075] (1) Take out Haematococcus pluvialis (wet algae) from the -20°C refrigerator and thaw, weigh 1g of Haematococcus pluvialis algae mud, add citric acid / sodium citrate with a concentration of 0.1mol / L and a pH of 6.0 20mL of buffer solution, then fully mixed, crushed the Haematococcus pluvialis mixture with an ultrasonic breaker for 30min to obtain the leaching solution;
[0076] (2) Transfer the leaching solution described in step (1) into a 50mL brown finger bottle, place it on a magnetic stirrer, and leaching for 24 hours at 25°C under airtight stirring in the dark;
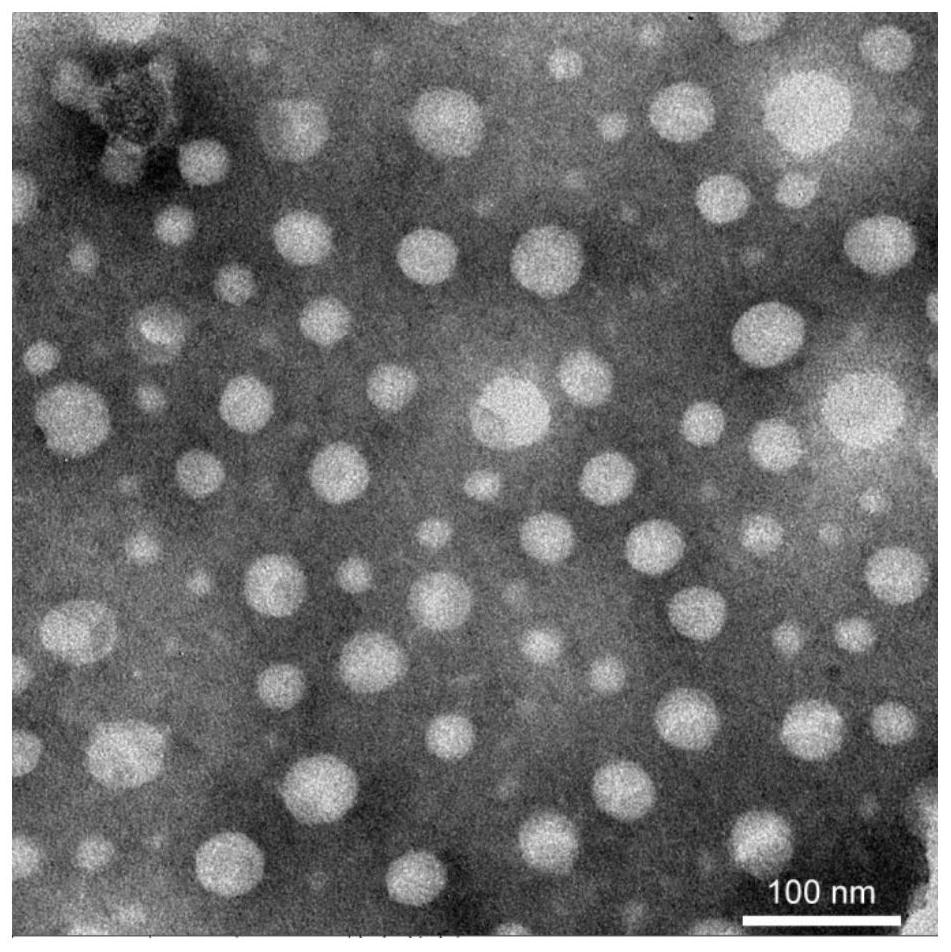
[0077] (3) Transfer the mixed solution after leaching in step (2) to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4°C and 8000rpm for 30min with a centrifuge, and filter the supernatant with a disposable filter with a pore size of 3 μm after centrifugation. A uniform and stable water-s...
Embodiment 2
[0081] This embodiment provides a method for preparing water-soluble astaxanthin. In addition to replacing the "citric acid / sodium citrate buffer with a pH of 6.0" in step (1) with "citric acid / sodium citrate with a pH of 3.0 Except sodium citrate buffer solution ", all the other are identical with embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com