Patents
Literature
273 results about "Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
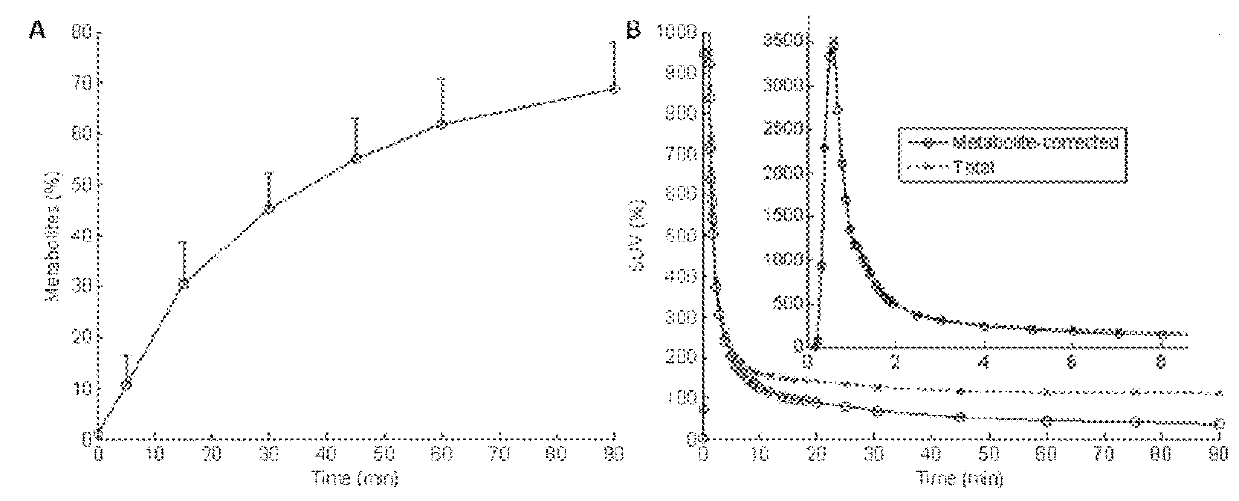
Acetylcholinesterase enzyme is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) is the inhibitor that inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme from breaking down acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors.
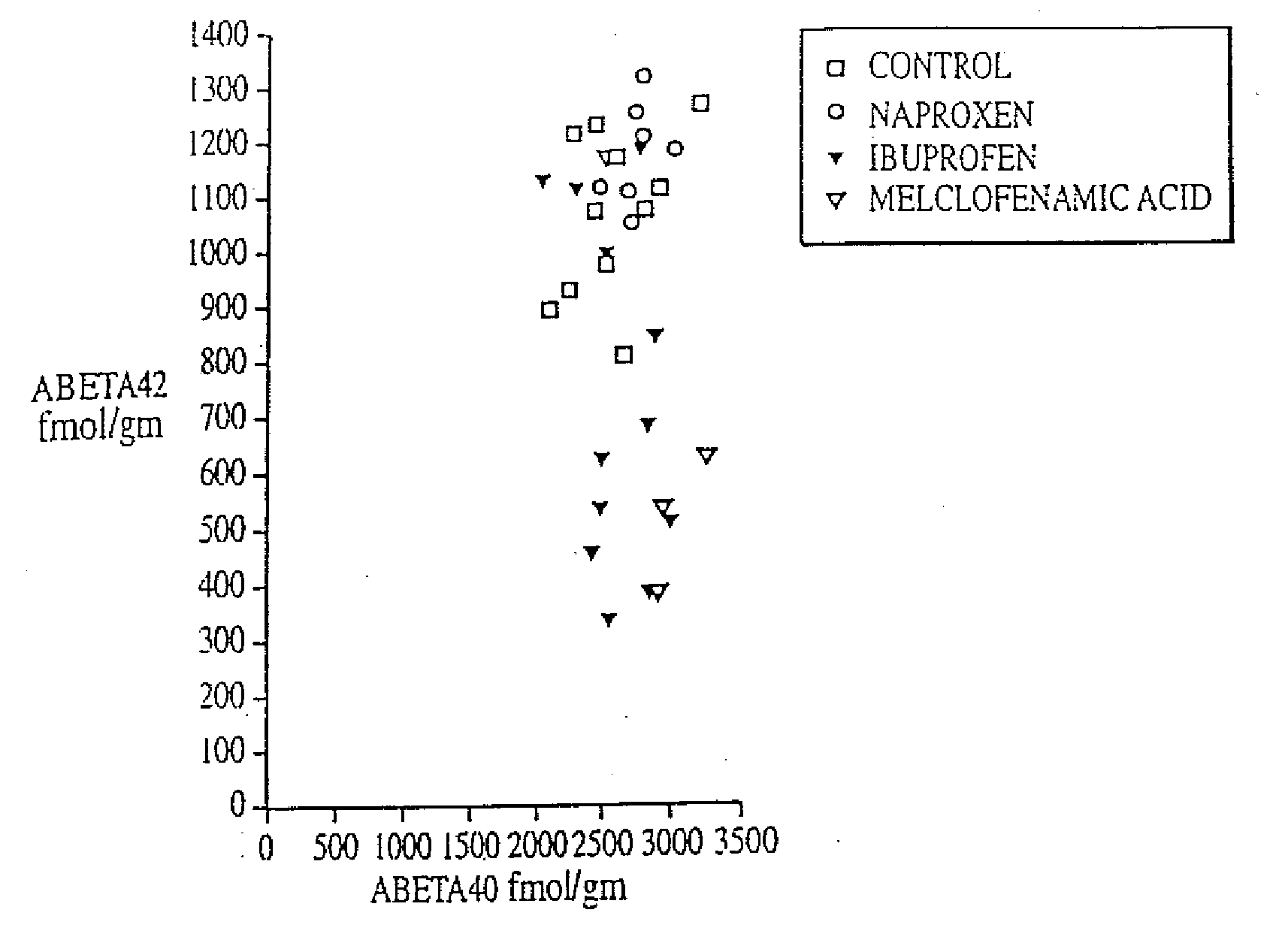
Abeta 42 lowering agents
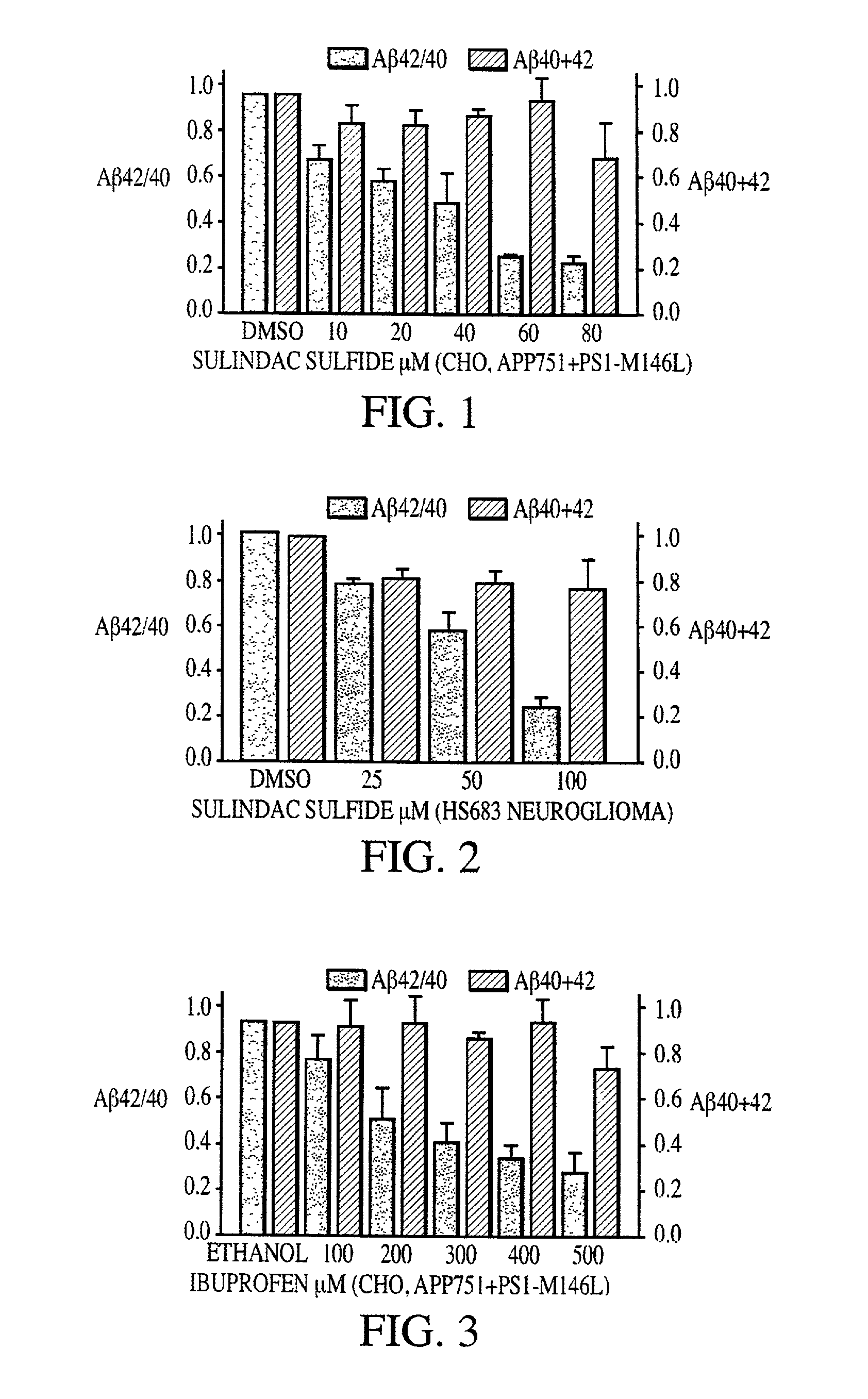
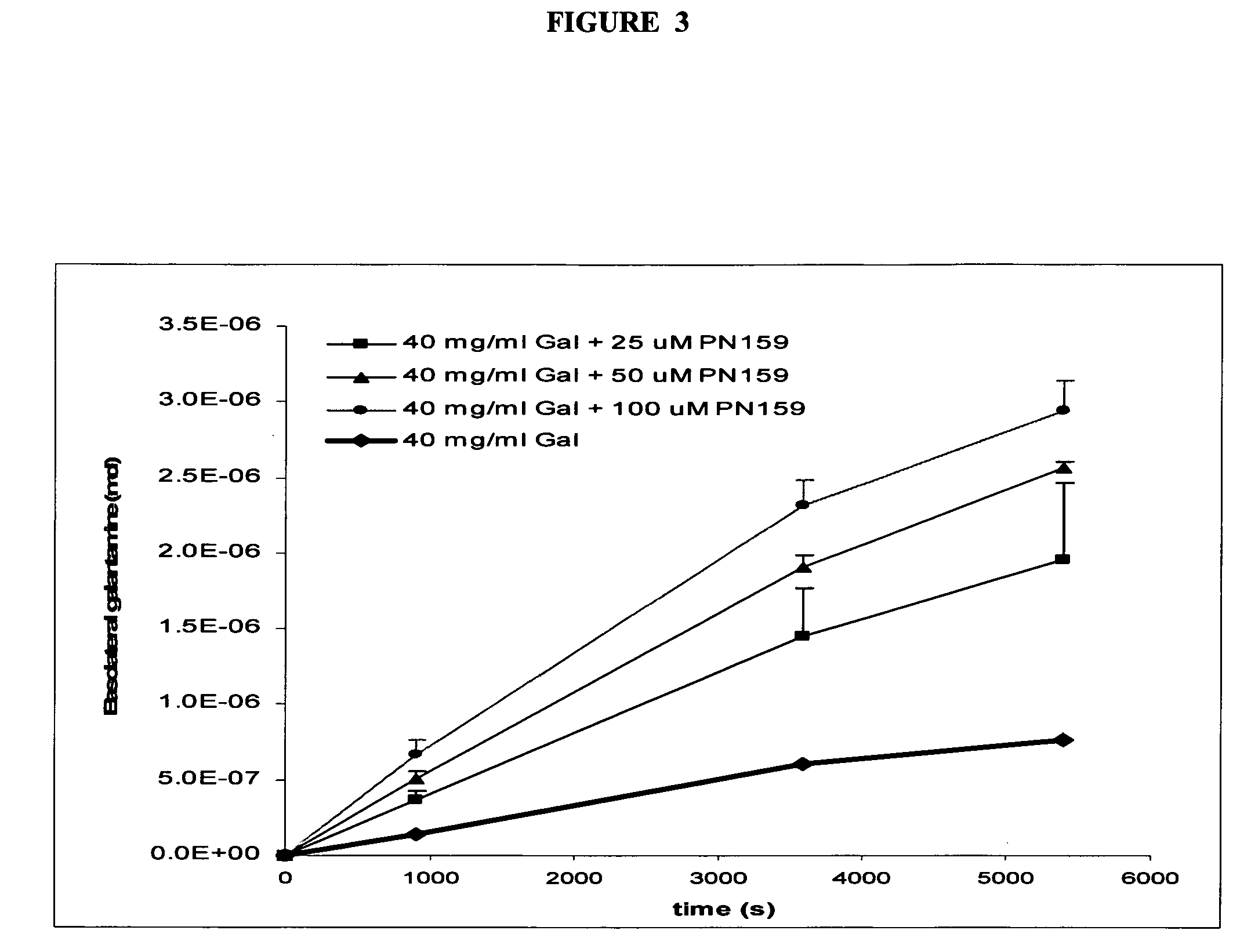
InactiveUS20020128319A1Prevent and delay and reverse progressionLower Level RequirementsCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningRegimenCholinesterase inhibition
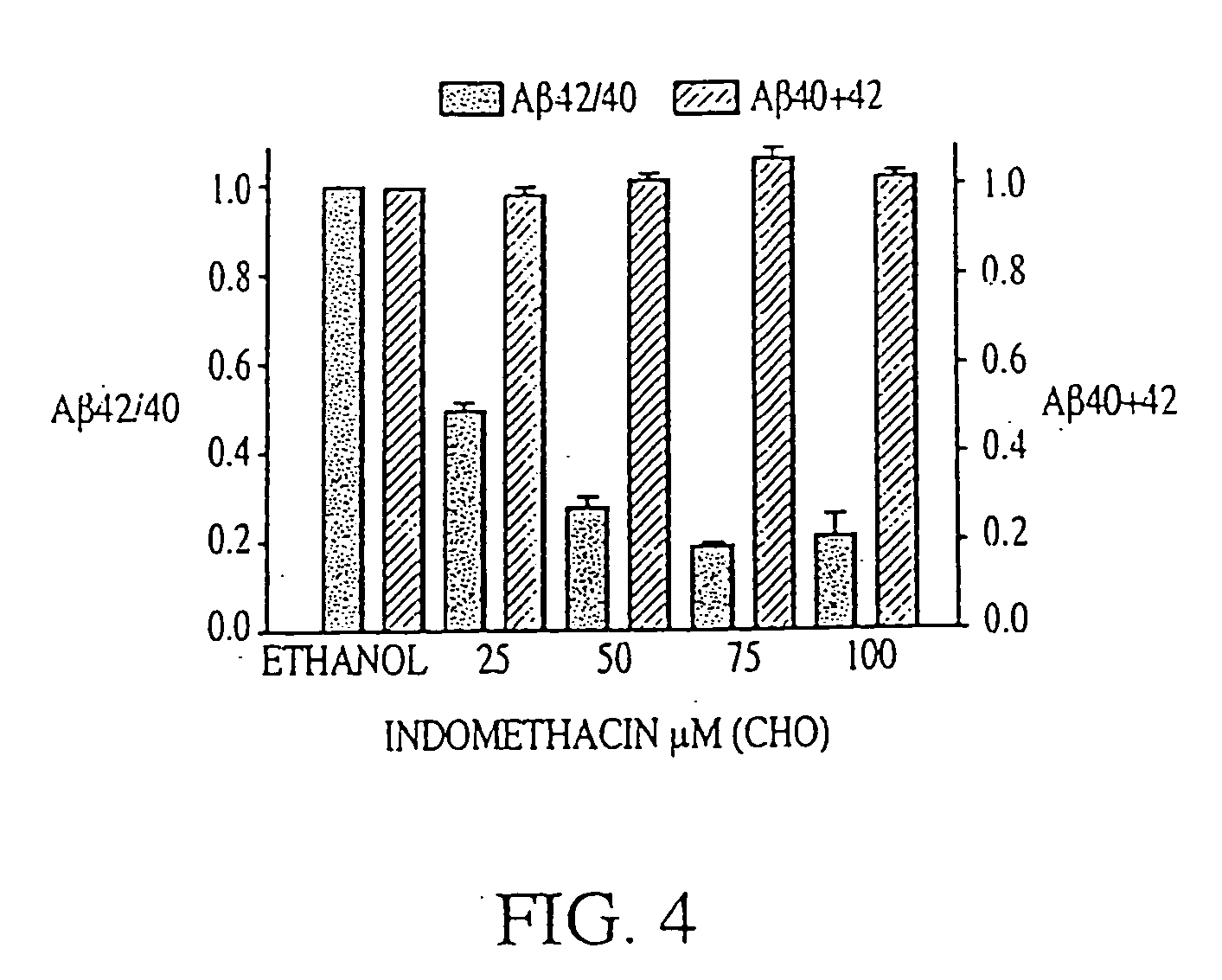
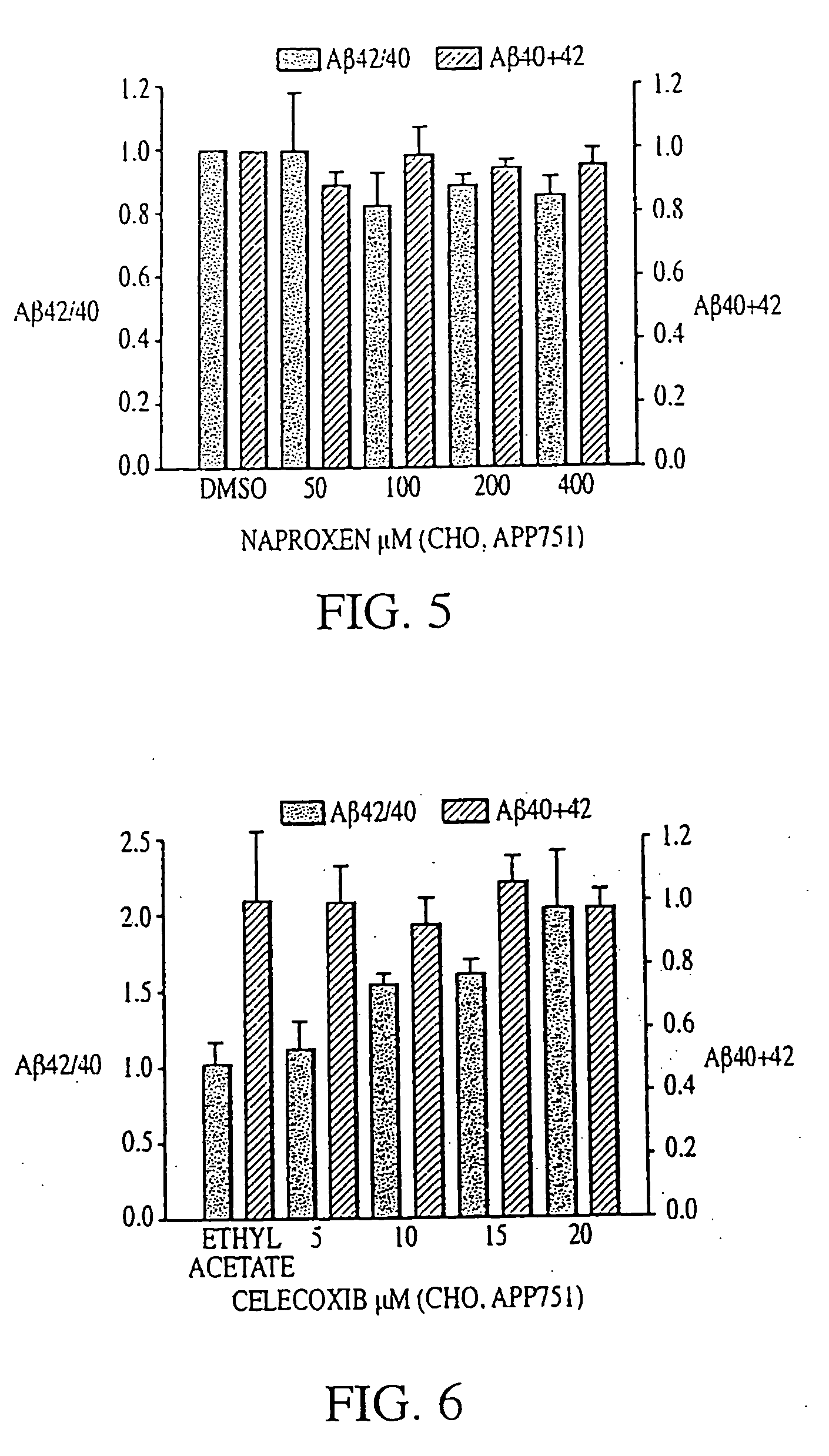
The invention provides a method of preventing, delaying, or reversing the progression of Alzheimer's disease by administering an A.beta..sub.42 lowering agent to a mammal under conditions in which levels of A.beta..sub.42 are selectively reduced, levels of A.beta..sub.38 are increased, and levels of A.beta..sub.40 are unchanged. The invention provides methods and materials for developing and identifying A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents. In addition, the invention provides methods for identifying agents that increase the risk of developing, or hasten progression of, Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides compositions of A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents and antioxidants, A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents and non-selective secretase inhibitors, as well as A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. The invention also provides kits containing A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and / or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as well as instructions related to dose regimens for A.beta..sub.42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
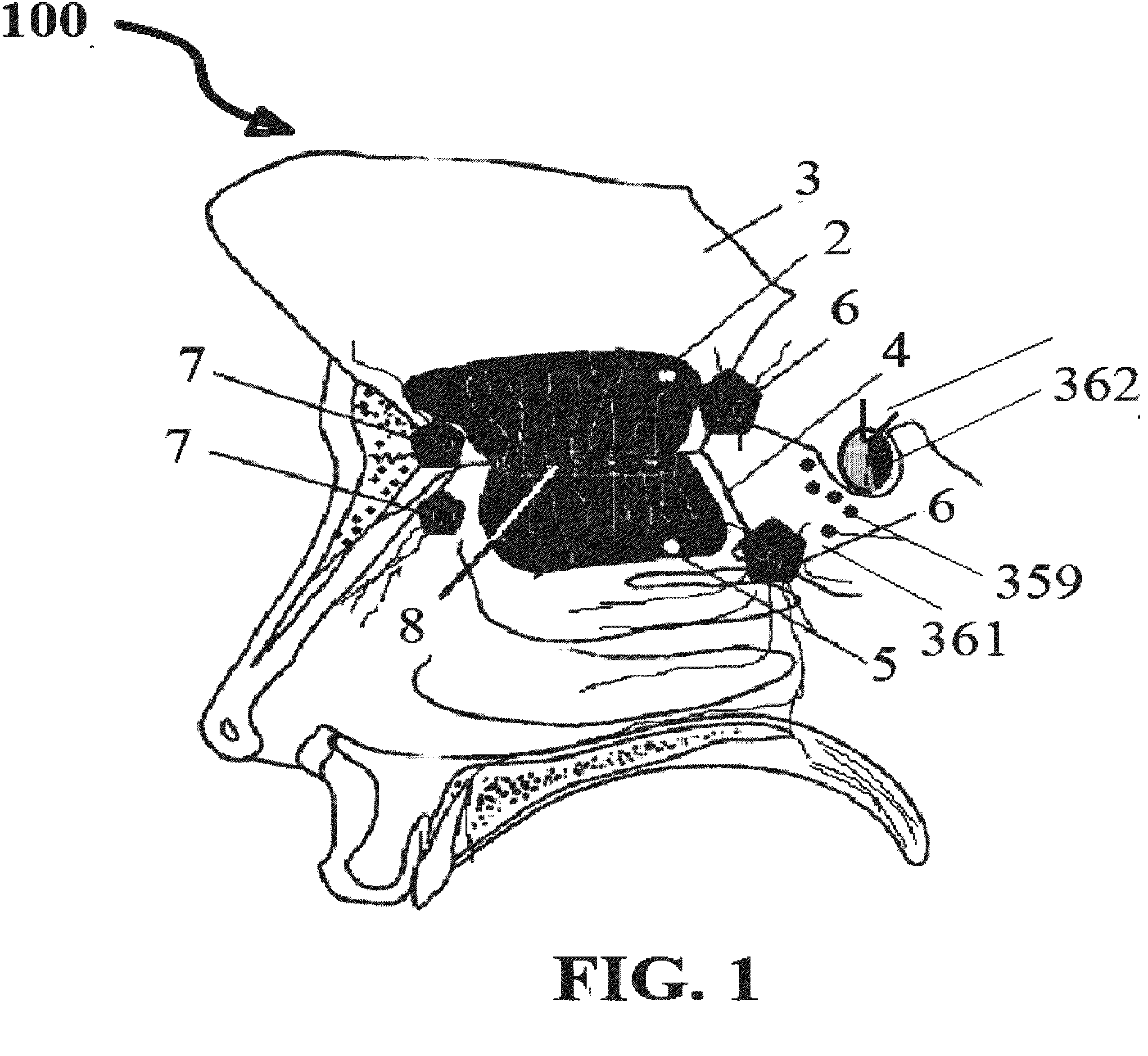
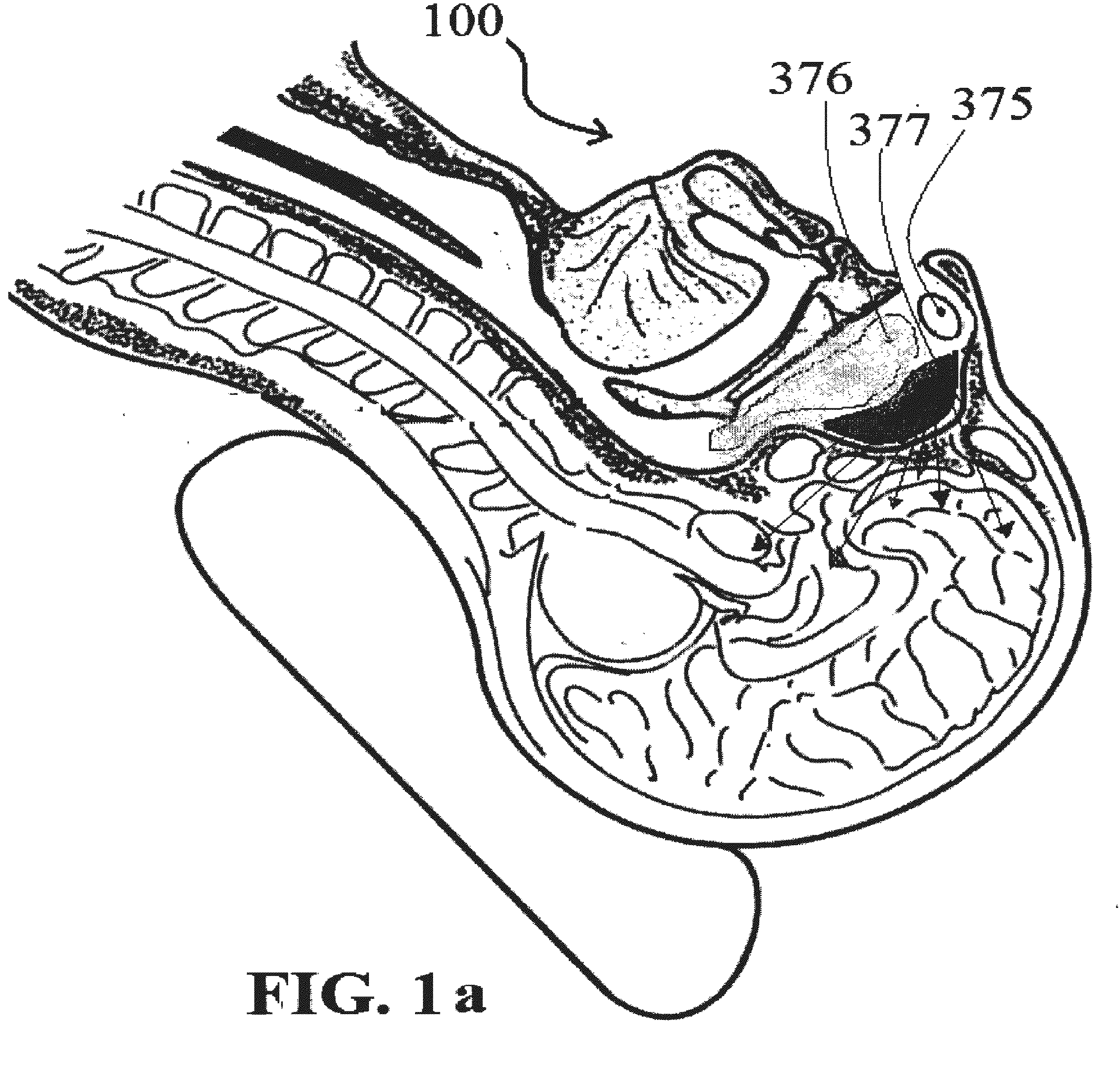
Alzheimer's disease treatment with multiple therapeutic agents delivered to the olfactory region through a special delivery catheter and iontophoresis
InactiveUS20120323214A1Reduce and preventAvoid destructionNervous disorderHead electrodesApoptosisExcitotoxicity
This invention describes the administration of multiple therapeutic agents with insulin in conjunction with bexarotene, ketamine, monoclonal antibodies Etanercept, IGF-1, and acetylcholine esterase inhibitors physostigmine, for treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Insulin, improves memory; also augments and amplifies the effects of the adjuvant therapeutic agents (paracrine and intracrine effects) and consequently reduces the β amyloid, its soluble precursors, prevents damage to the neuronal skeletal network (taupathy), and blocks glutamate excitotoxicity, reduces brain inflammation, prevents apoptosis, and increases the acetylcholine levels in the neurons and synapses; by using a combination of insulin, bexarotene, ketamine, Etanercept, IGF-1, and physostigmine therapeutic agents. The results are achieved by using the specially designed Iontophoresis incorporated olfactory mucosal delivery (ORE) catheter device located at the olfactory nerves, sphenoid sinus, and adjacent structures described here, to transport the large molecules of therapeutic agents to treat AD delivered to the CNS bypassing BBB from ORE.
Owner:WEDGE THERAPEUTICS
Compositions and methods using acetylcholinesterase (ACE) inhibitors to treat central nervous system (CNS) disorders in mammals
InactiveUS20060003989A1Reduce deliveryImprove solubilityBiocideNervous disorderSolubilitySide effect
Methods and compositions of the invention employ acetylcholinesterase (ACE) inhibitors to prevent and treat diseases and other disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), including Alzheimer's disease. ACE inhibitors are administered for targeted delivery to the CNS, for example by intranasal delivery. The methods and compositions of the present invention yield therapeutic concentrations of ACE inhibitors in a CNS tissue or compartment without the attendant disadvantages, risks and side effects of oral or injection delivery. Exemplary ACE inhibitors for use within the invention include galantamine and various salts and derivatives of galantamine. Carboxylate salts of galantamine (e.g., galantamine gluconate, galantamine lactate, galantamine citrate and galantamine glucarate) described herein exhibit a significant increase in solubility compared to other forms of galantamine, such as galantamine hydrobromide.
Owner:NASTECH PHARMA
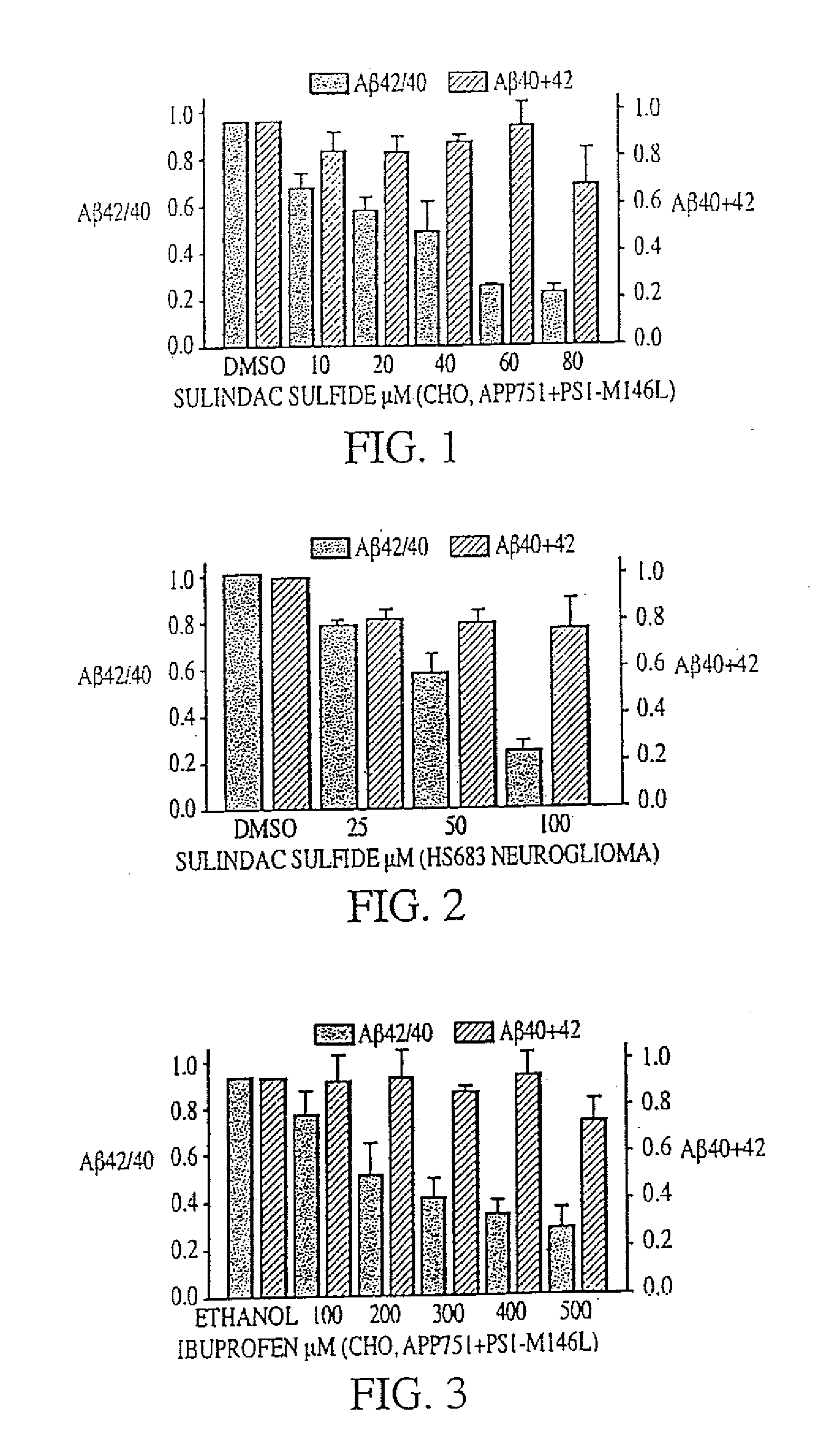
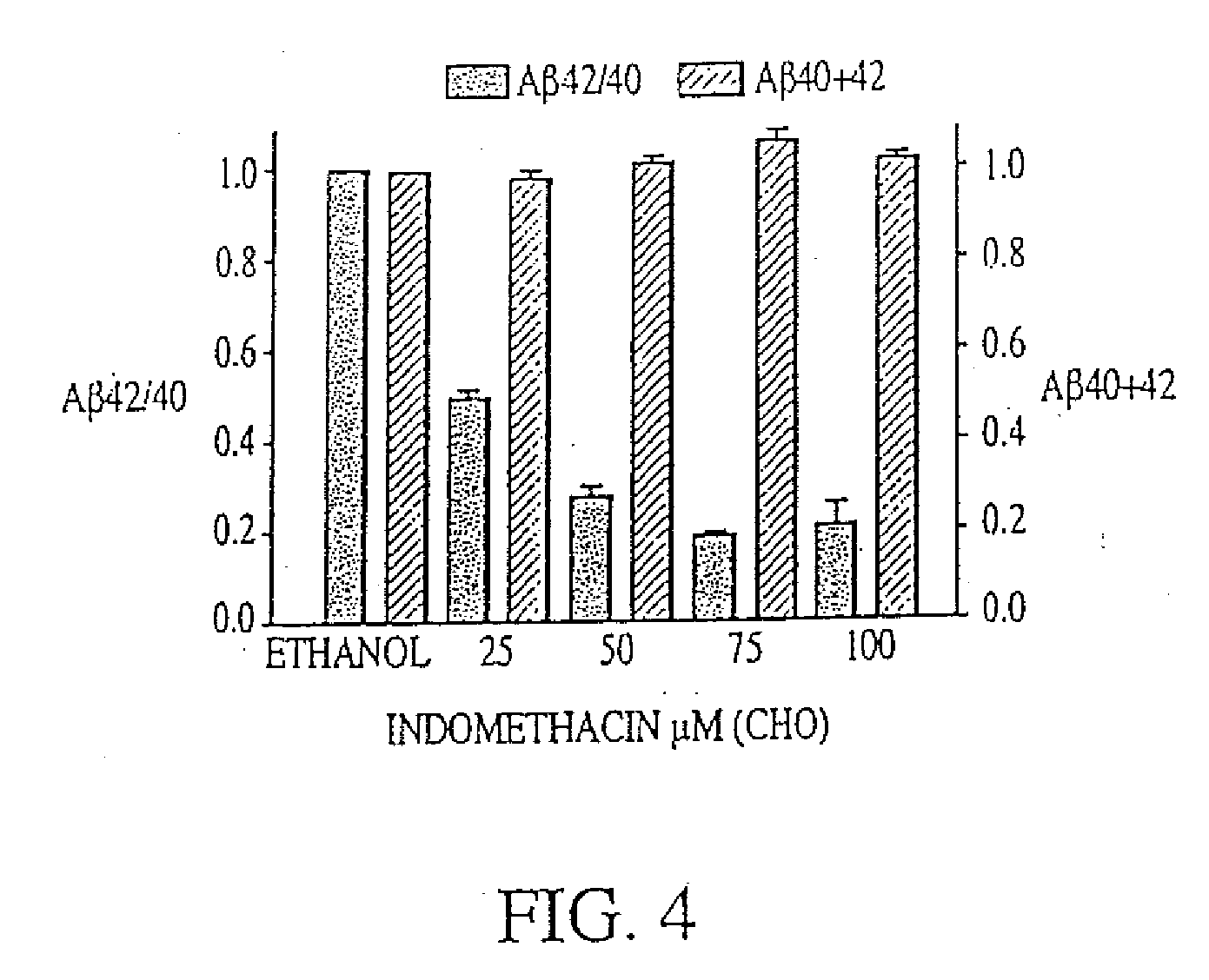
Combination therapy using 1-aminocyclohexane derivatives and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
InactiveUS20100227852A1Avoid damageReduce riskBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionRivastigmine
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Combination therapy using 1-aminocyclohexane derivatives and acetylcholinesterase and inhibitors
InactiveUS20090124659A1Avoid damageReduce riskBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionDepressant
The invention relates to a novel drug combination therapy useful in the treatment of dementia comprising administering an 1-aminocyclohexane derivative such as memantine or neramexane and an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) such as galantamine, tacrine, donepezil, or rivastigmine.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
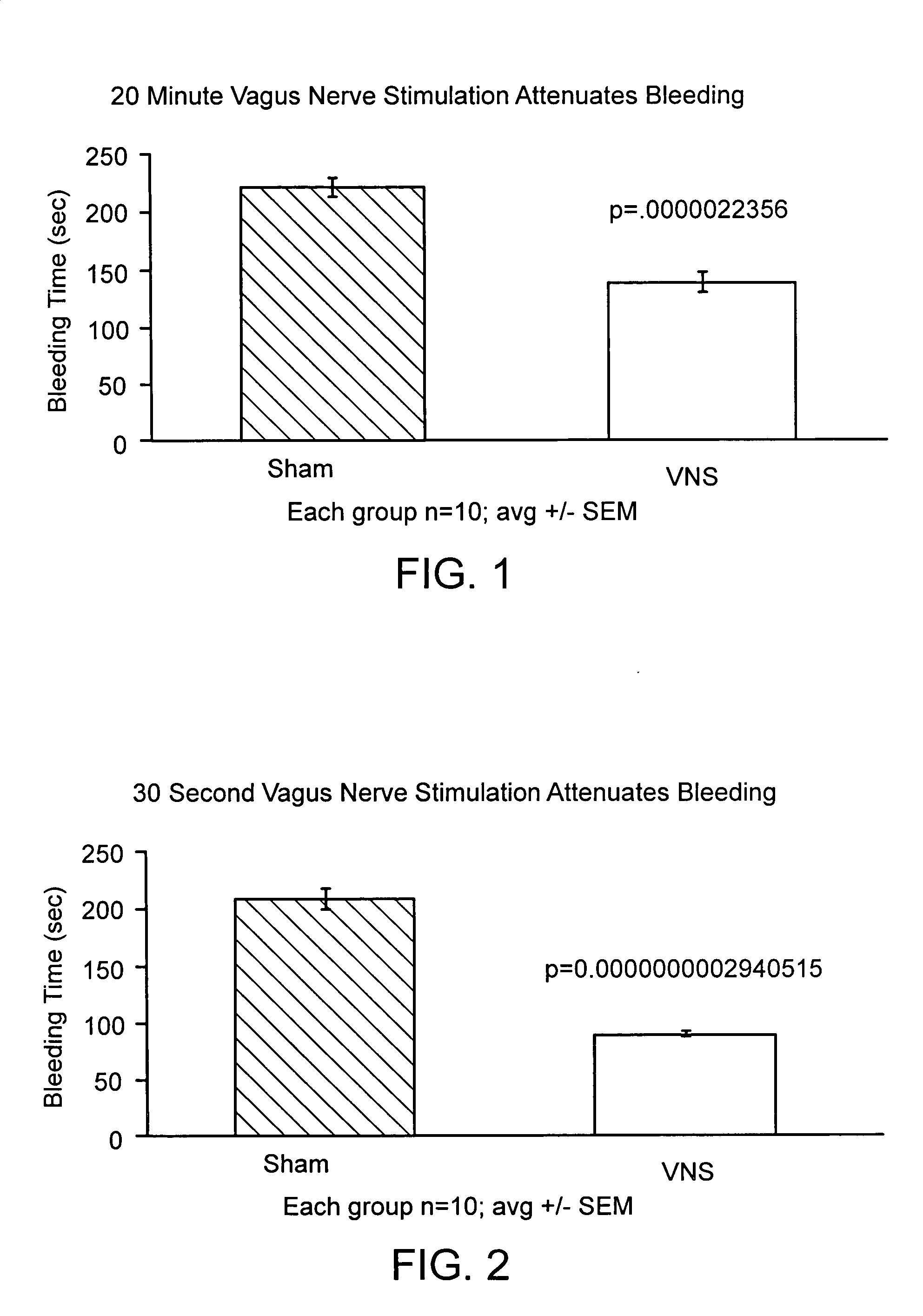
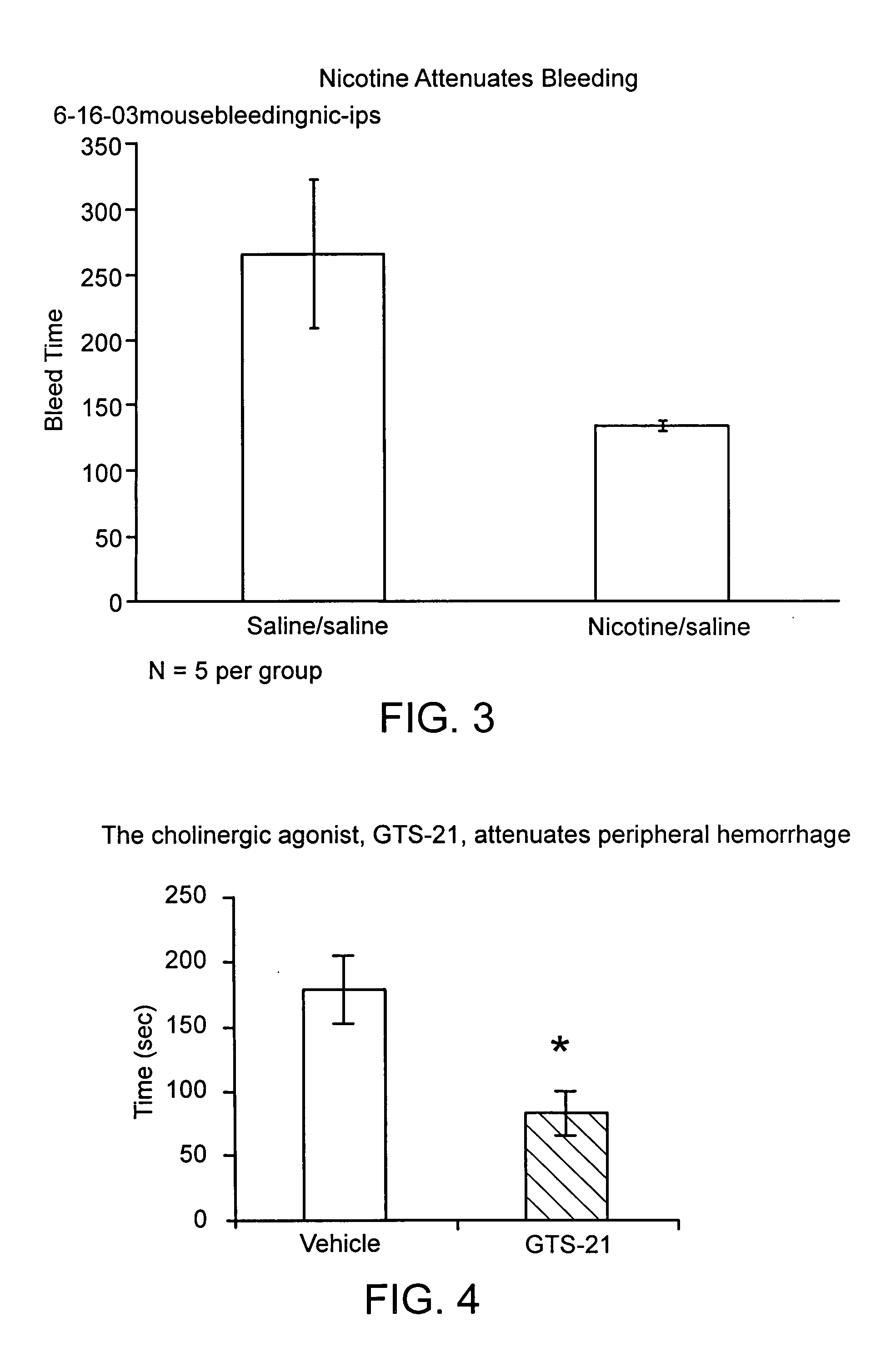
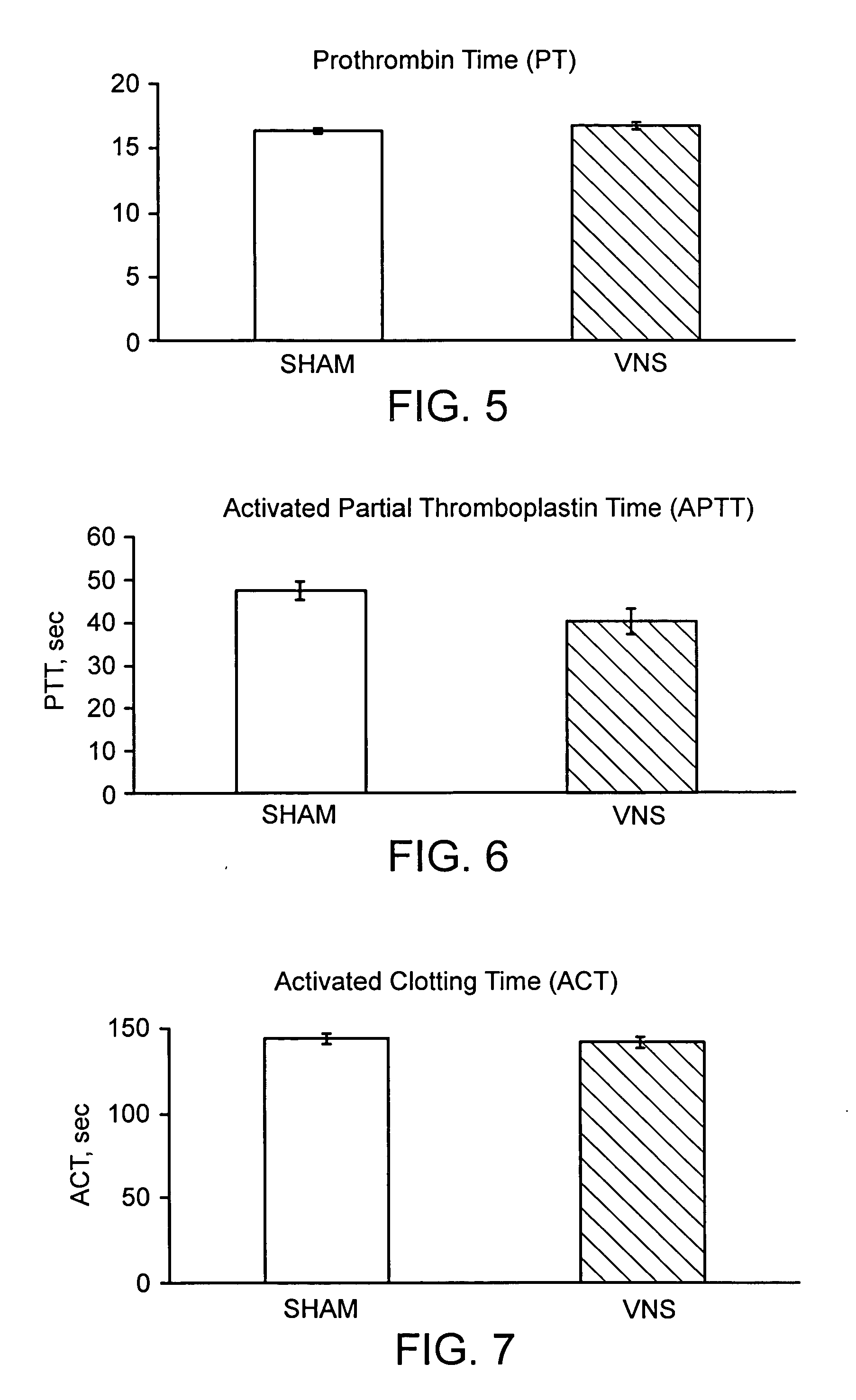
Neural tourniquet
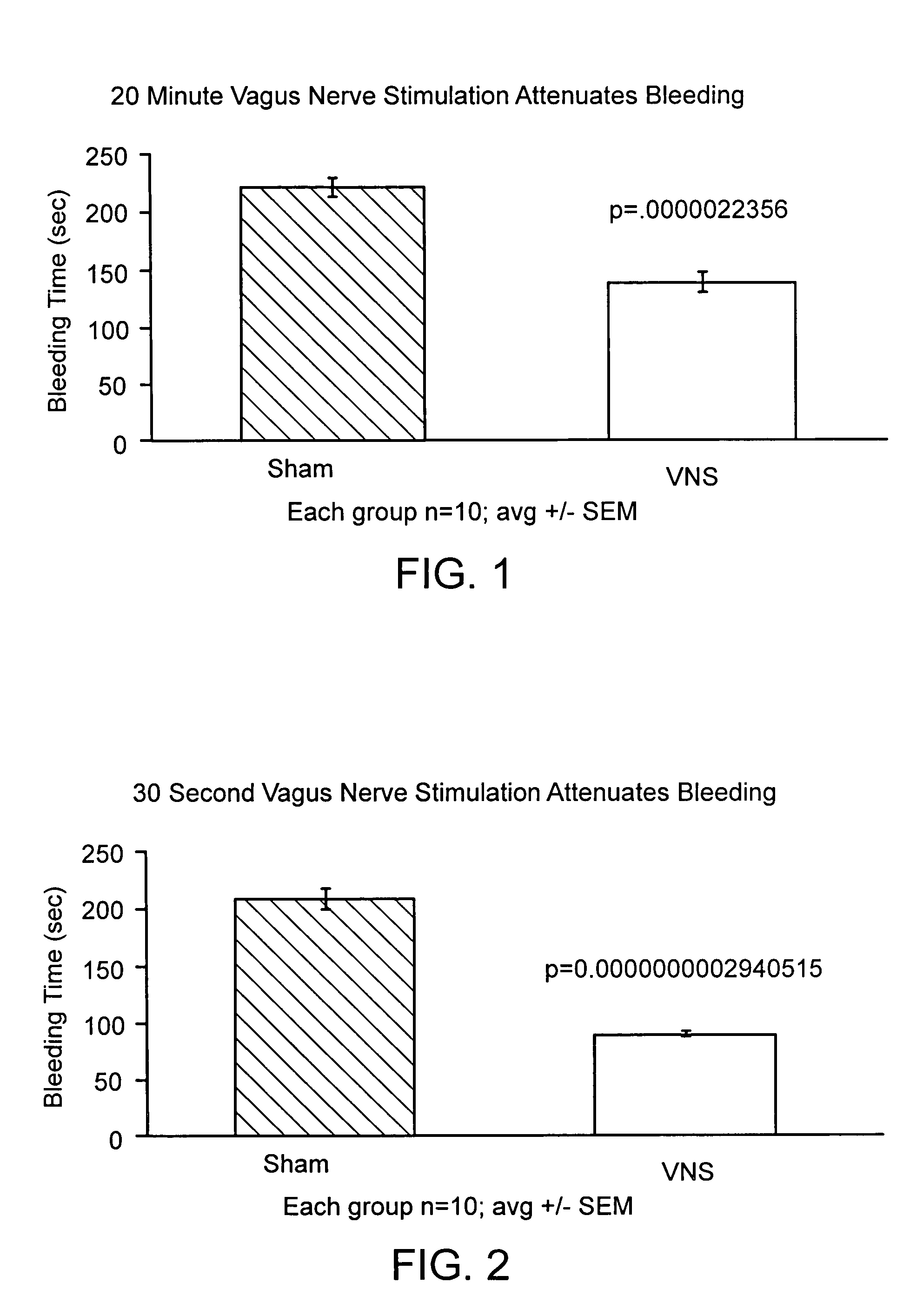
ActiveUS8729129B2BiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionCholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
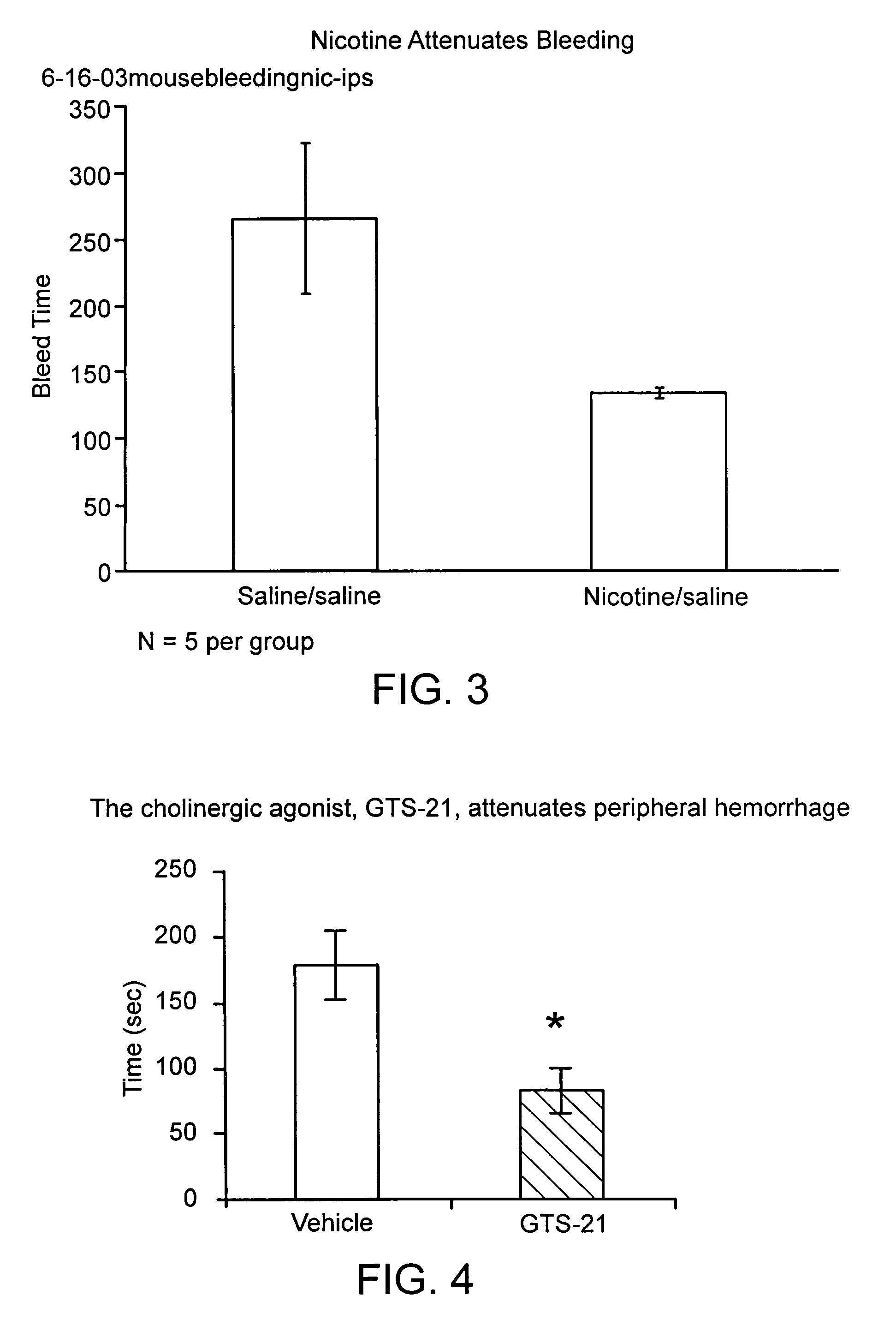
Disclosed is a method of reducing bleed time in a subject by activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in said subject. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can be activated by direct or indirect stimulation of the vagus nerve. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can also be activated by administering an effective amount of cholinergic agonist or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to the subject.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
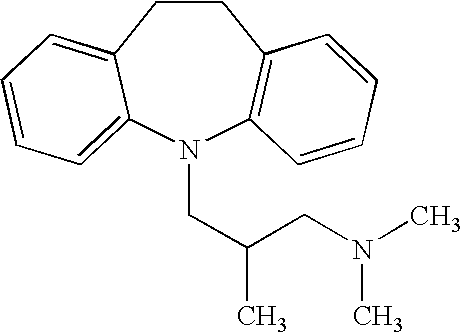
New uses for quaternary ammonium anticholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in patients being treated for cognitive impairment or acute delirium
ActiveUS20080114014A1Maximizing beneficial effectMaximize the effectBiocideNervous disorderSolubilityFecal incontinence
A method for treating the adverse effects of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of cognitive disorders such as acute delirium and cognitive impairment in elderly human patients. The administration of a clinically effective amount of a quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonist having very low lipid solubility substantially eliminates the adverse effects of urinary and / or fecal incontinence, nausea, bradycardia, bronchorrhea or brochospasm caused by the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors, without affecting the beneficial activity of the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors. This permits the administration of the optimum effective dosing of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to provide maximum benefit to the patient with the added benefit of reducing or eliminating the unwanted side effects of fecal and urinary incontinence. Further, the combination of rivastigmine and glycopyrrolate has been effective in significantly improving cognitive function in patients suffering from acute dementia or cognitive impairment.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
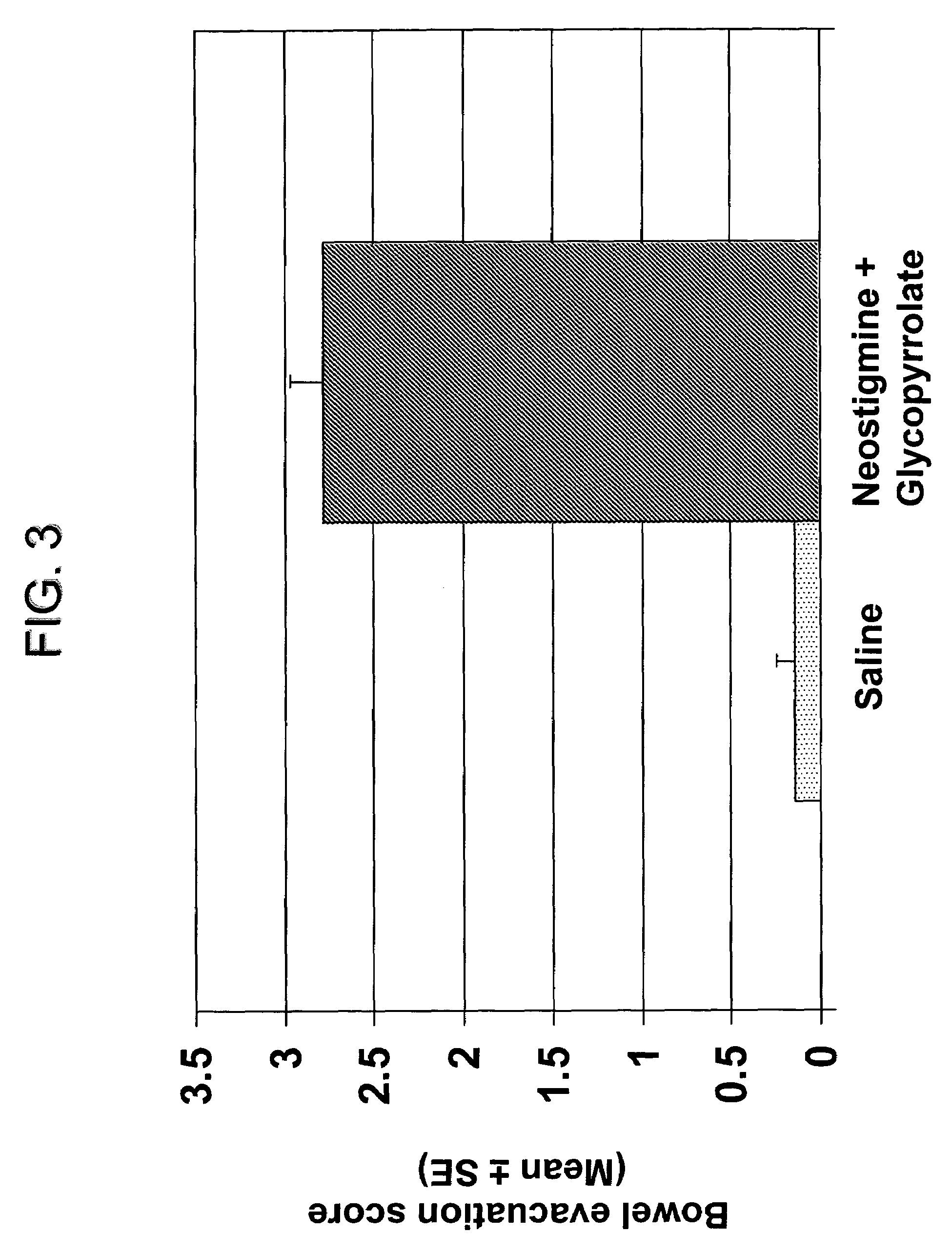
Compositions and methods for bowel care in individuals with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction
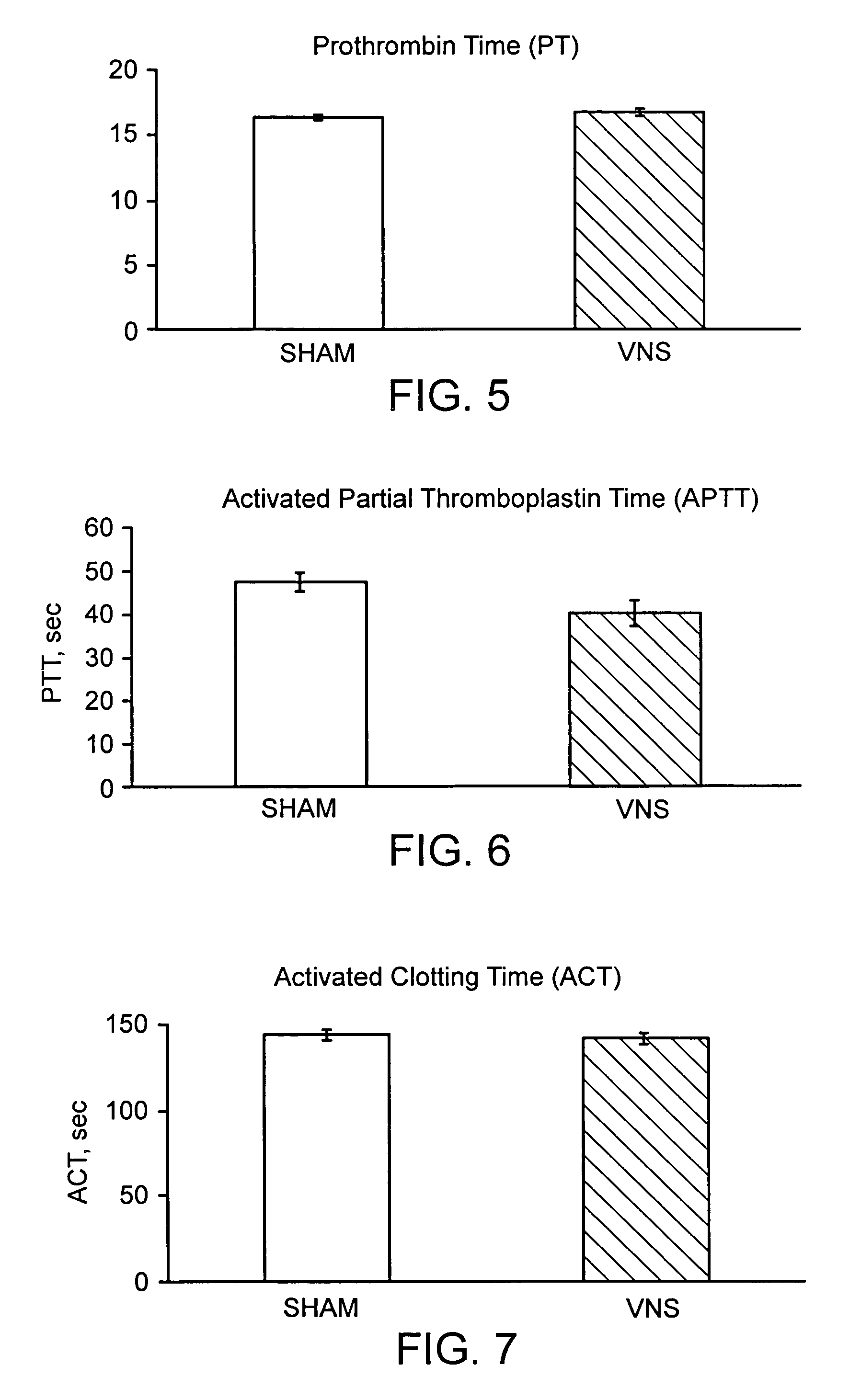
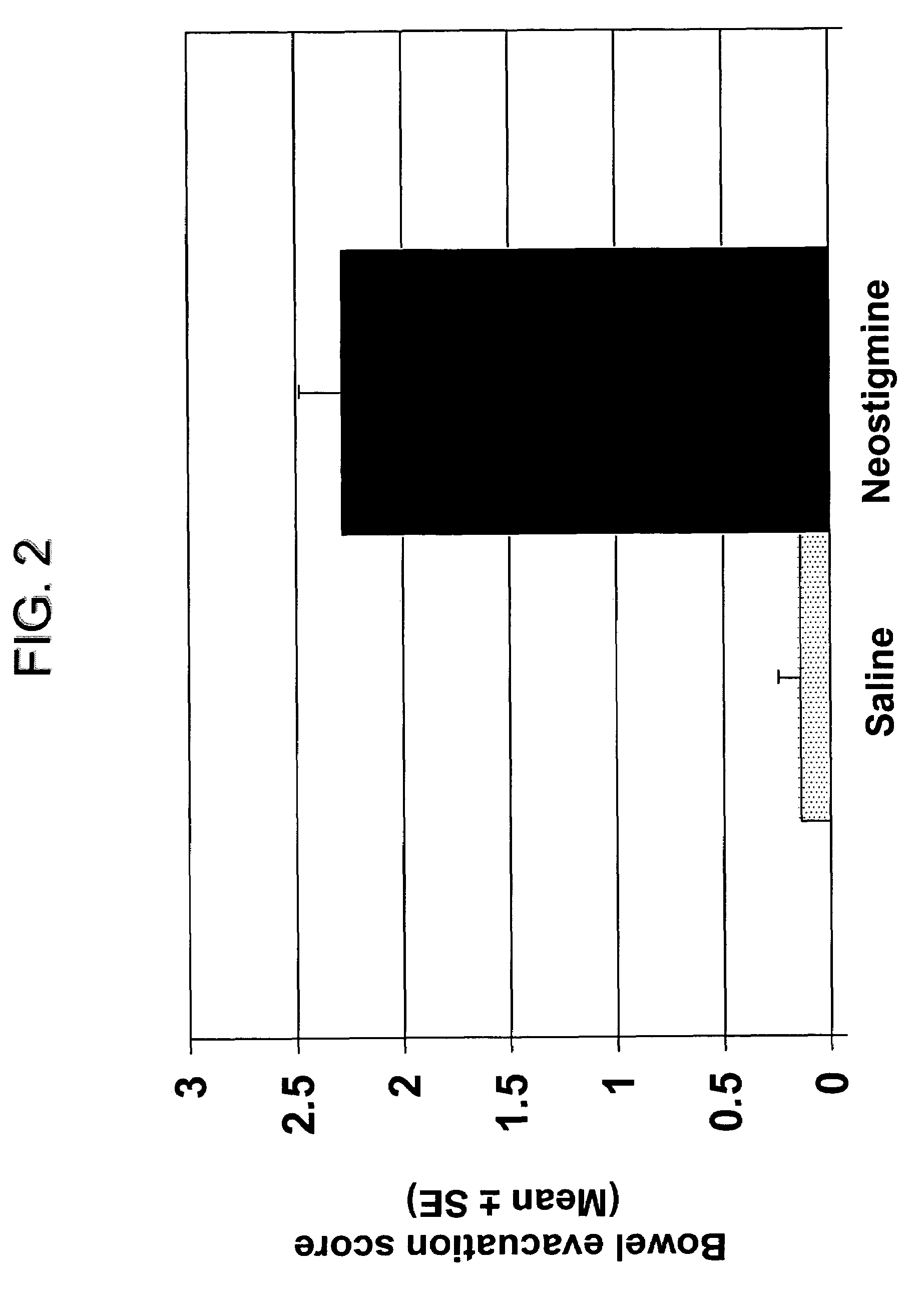
ActiveUS7635709B2Shorten the construction periodDifficult to administerBiocideAmine active ingredientsBowel careSide effect
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for on-going bowel care for persons with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. The compositions and methods can be administered in a non-clinical setting. The compositions comprise acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for stimulating motility of the bowel in combination with anti-cholinergic agents to counteract the potentially dangerous cardiac side effects of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In some examples, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, neostigmine, and the anti-cholinergic agent, glycopyrrolate, are combined in a pharmaceutical composition. Certain examples also provide the frequency and duration of administration of the disclosed drug combinations.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Neural tourniquet
ActiveUS20050282906A1BiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionCholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
Disclosed is a method of reducing bleed time in a subject by activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in said subject. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can be activated by direct or indirect stimulation of the vagus nerve. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can also be activated by administering an effective amount of cholinergic agonist or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to the subject.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
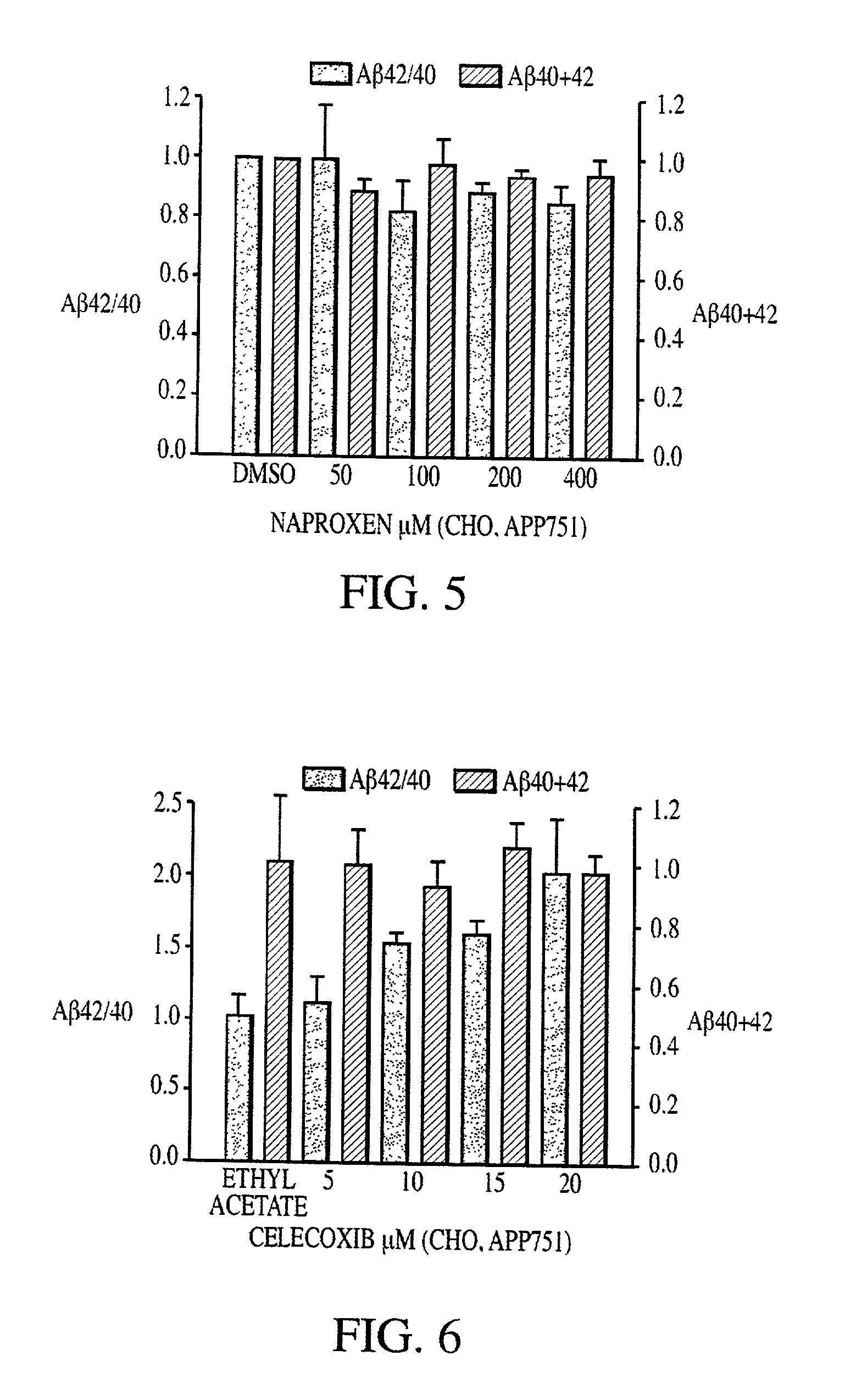
Method of reducing abeta42 and treating diseases
InactiveUS20080021085A1Increased risk of developingIncreased riskBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionRegimen
The invention provides a method of preventing, delaying, or reversing the progression of Alzheimer's disease by administering an Aβ42 lowering agent to a mammal under conditions in which levels of Aβ42 are selectively reduced, levels of Aβ38 are increased, and levels of Aβ40 are unchanged. The invention provides methods and materials for developing and identifying Aβ42 lowering agents. In addition, the invention provides methods for identifying agents that increase the risk of developing, or hasten progression of, Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides compositions of Aβ42 lowering agents and antioxidants, Aβ42 lowering agents and non-selective secretase inhibitors, as well as Aβ42 lowering agents and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. The invention also provides kits containing Aβ42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and / or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as well as instructions related to dose regimens for Aβ42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
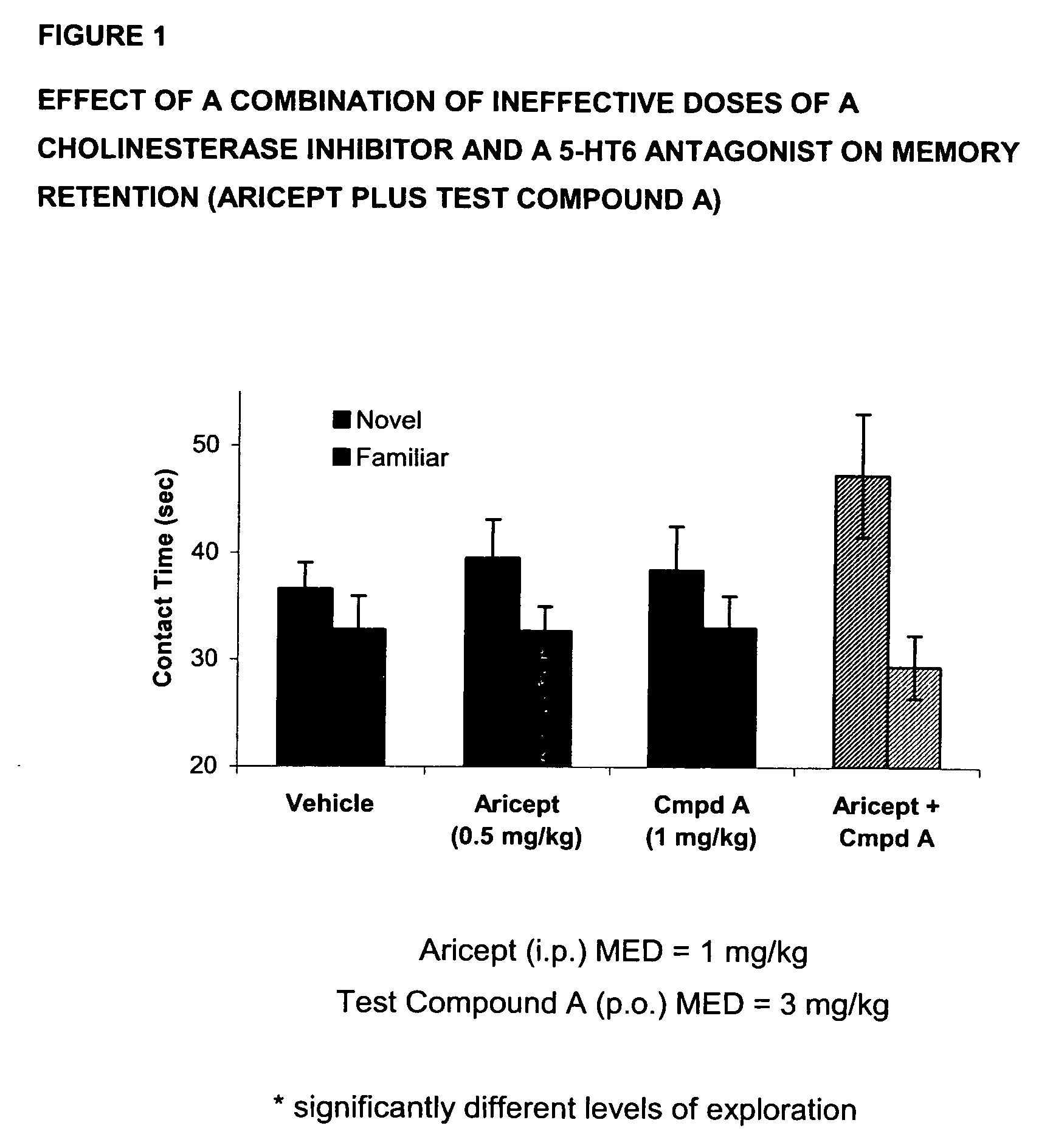
Method for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction
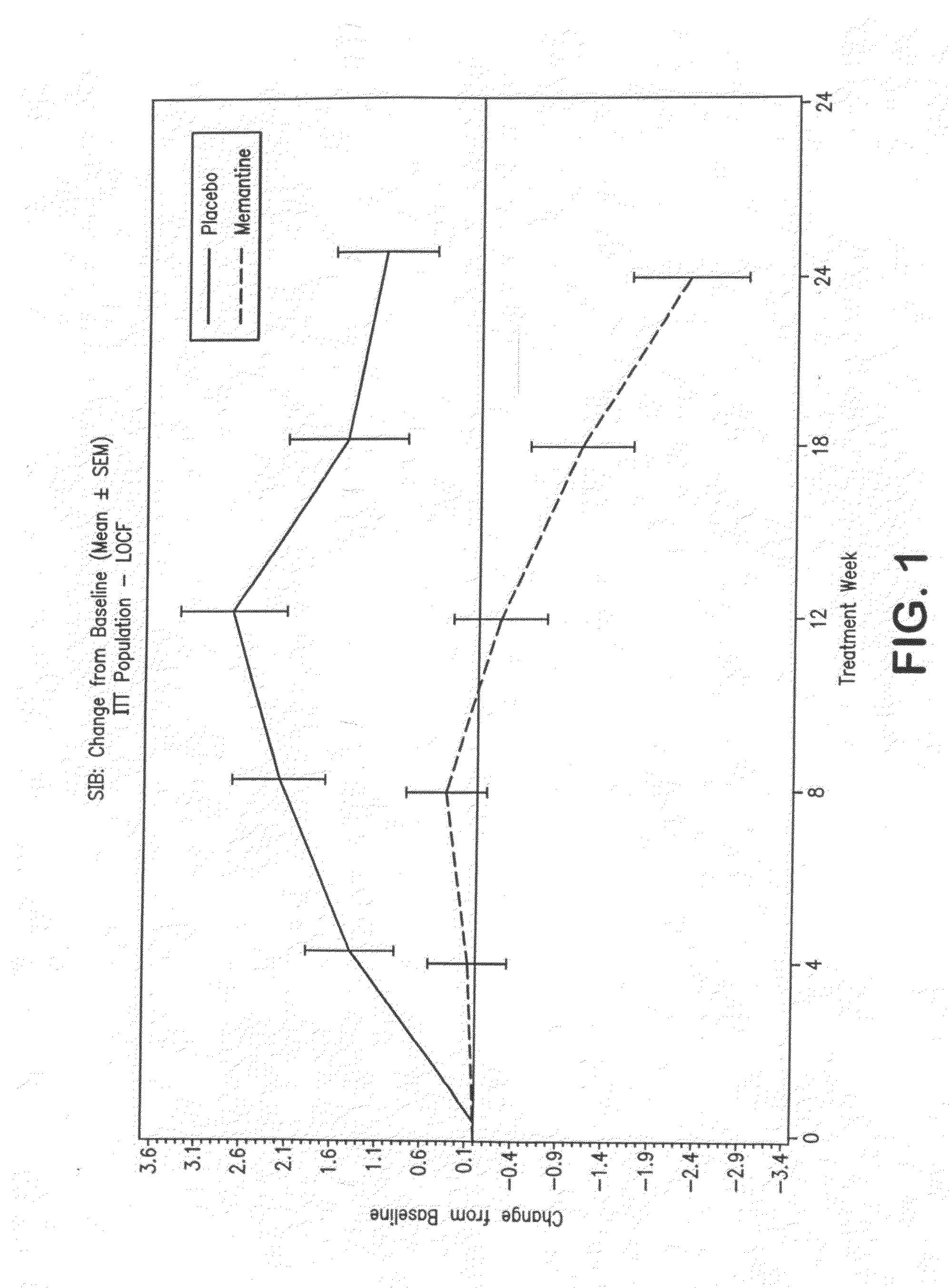
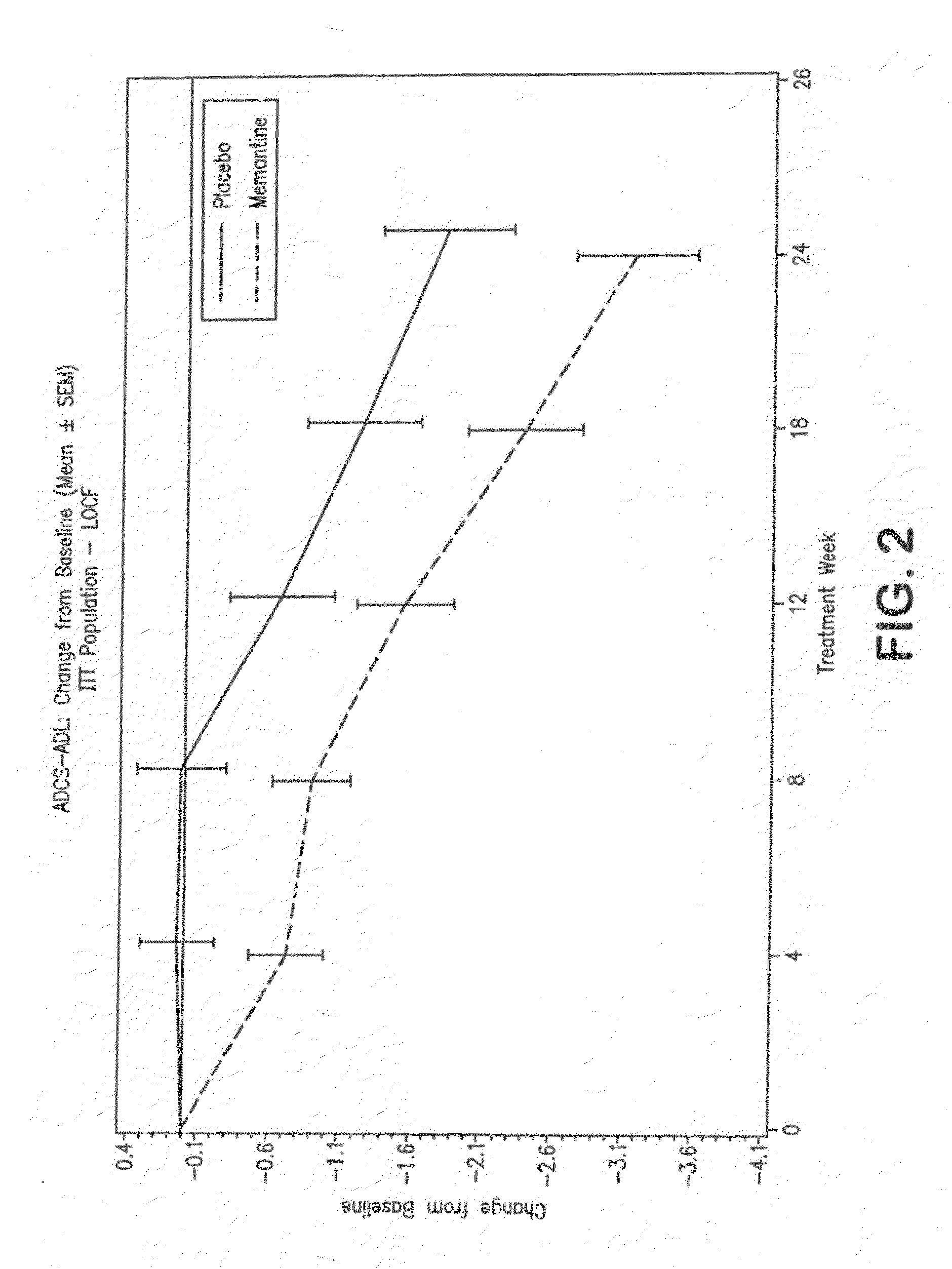
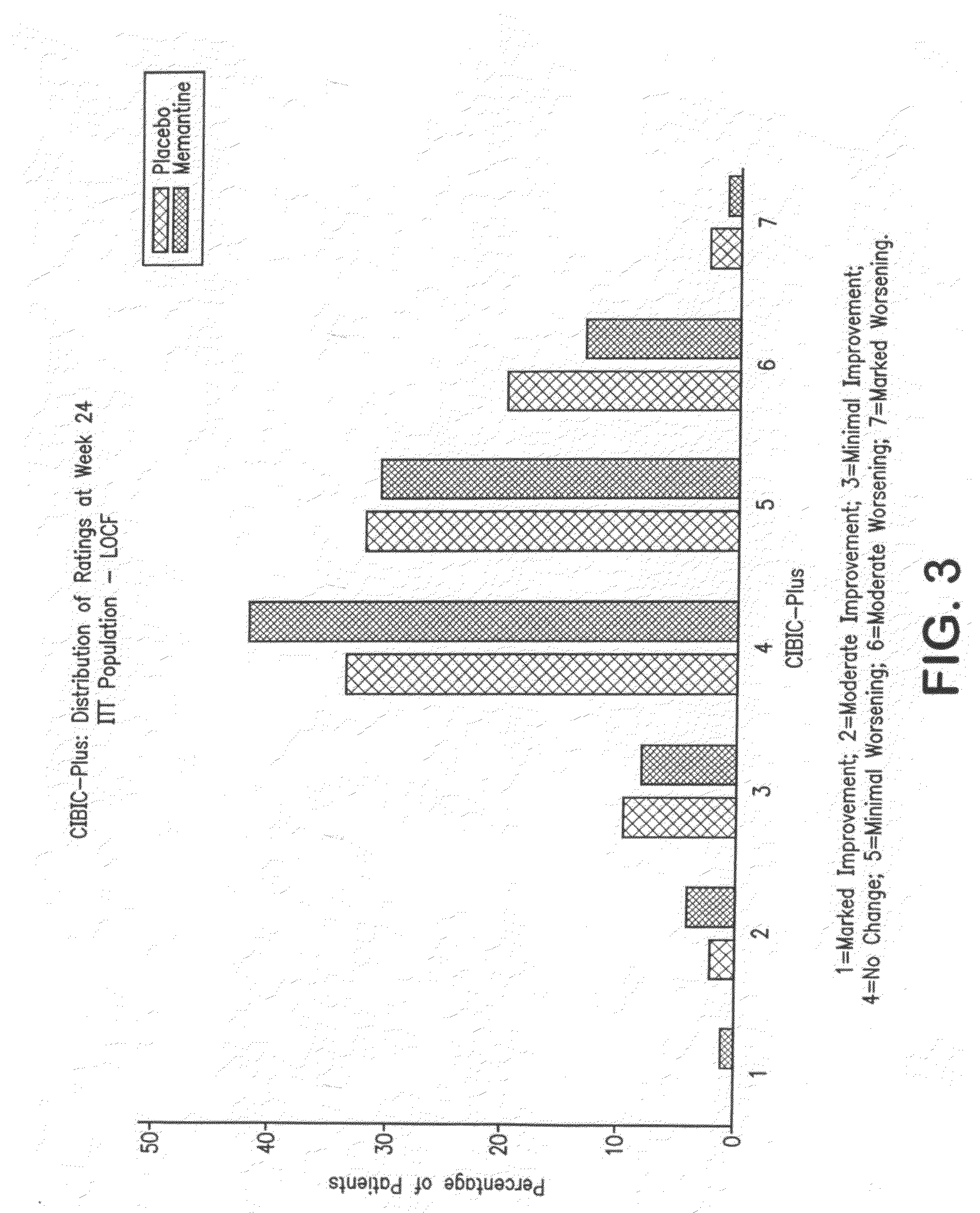
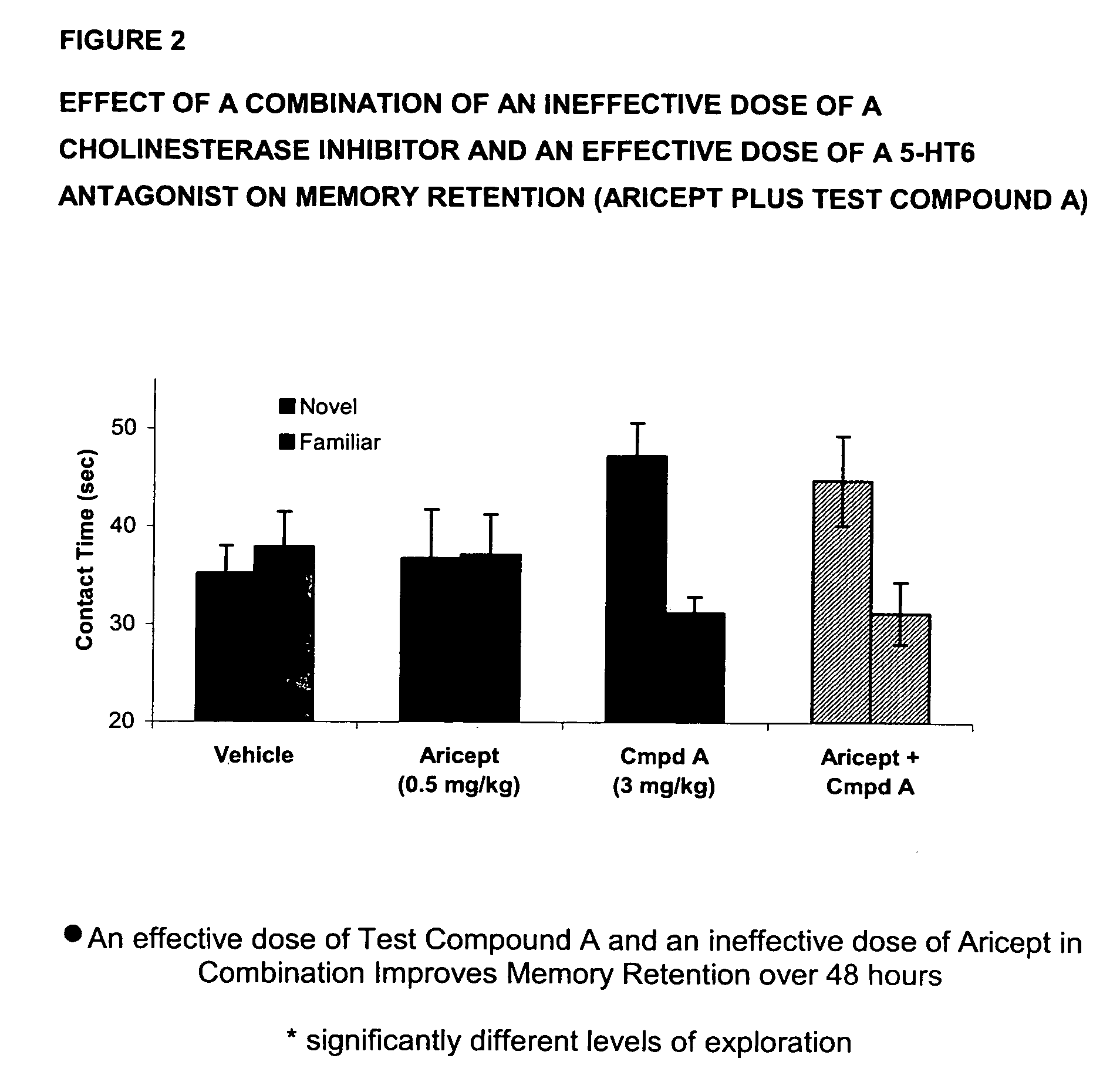
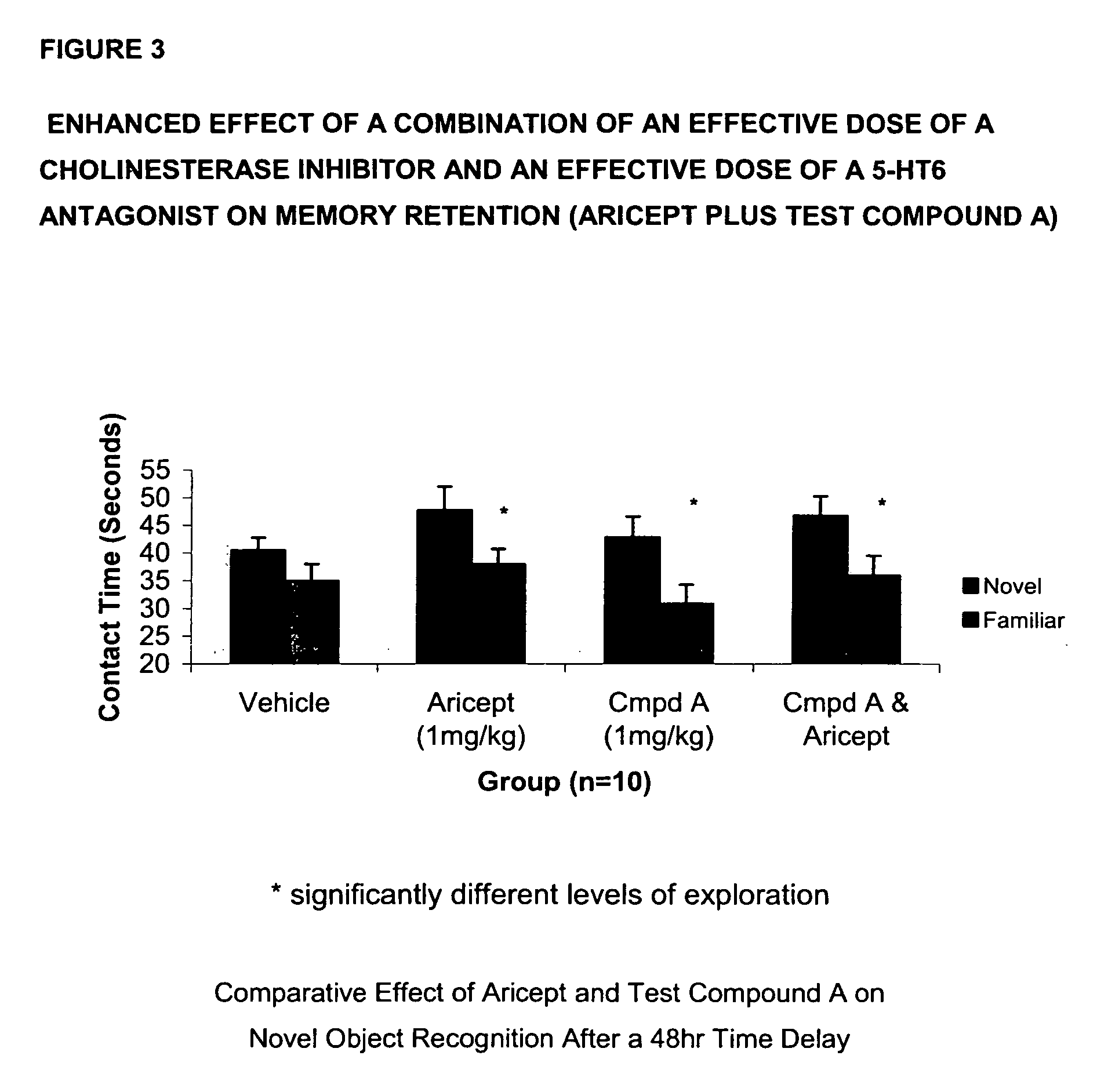
The present invention provides a method for the treatment of a cognitive disorder such as Alzheimer's disease in a patient in need thereof which comprises providing to said patient a therapeutically effective amount of a combination of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and a 5-hydroxytryptamine-6 antagonist.
Owner:WYETH LLC
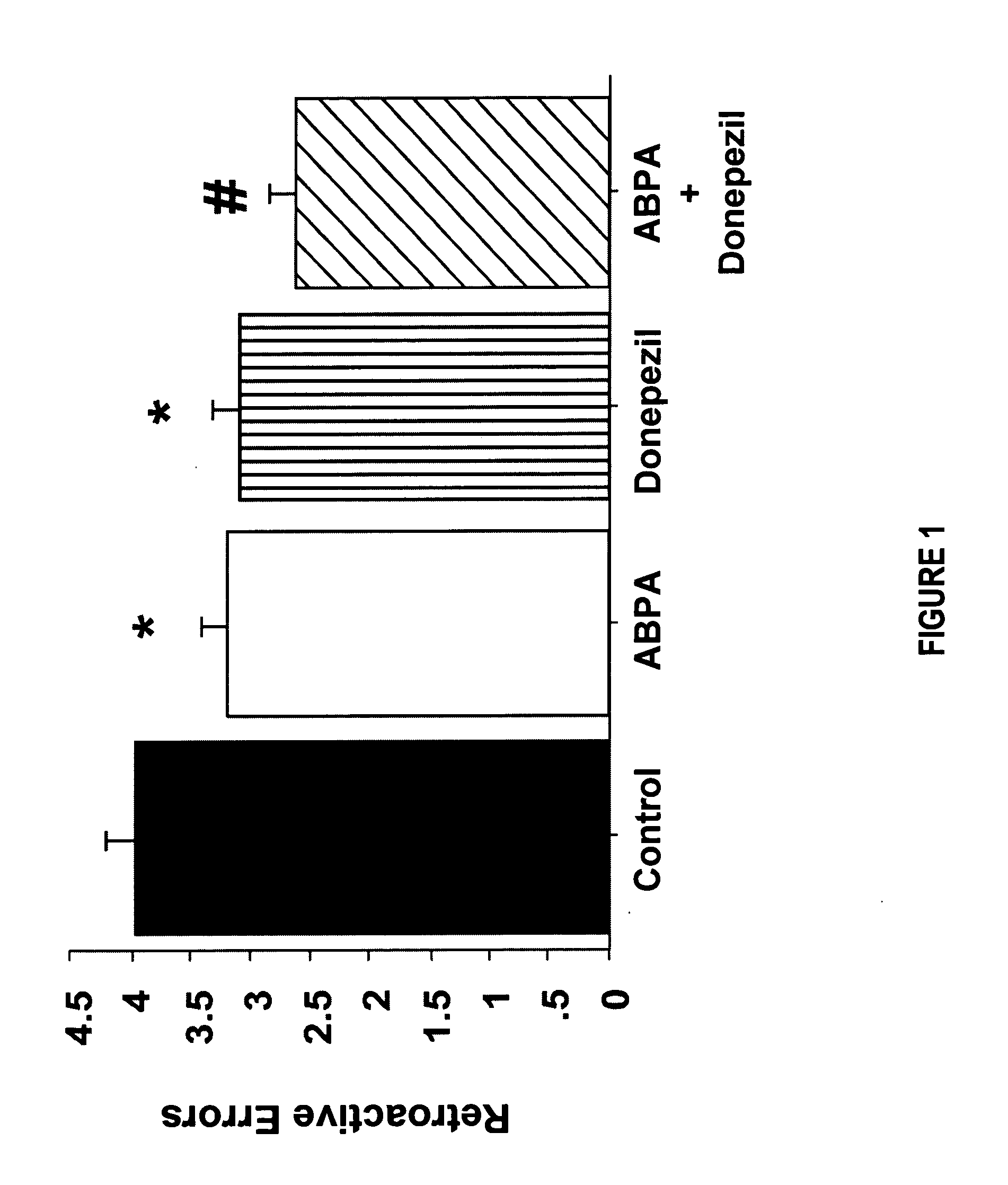
Combined Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor and Quaternary Ammonium Antimuscarinic Therapy to Alter Progression of Cognitive Diseases
ActiveUS20130172398A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectBiocideAmine active ingredientsDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
Methods of treating alzheimer's disease and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
ActiveUS20140073681A1Good effectImprove and augment effectBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionBenzylamine
The present invention describes methods of treating dementia comprising administering an effective daily dose of N-(2-(6-fluoro-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl-(2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropoxy)benzylamine to improve or augment the effect of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Use and composition for treating dementia
ActiveUS8404701B2Maximize the effectSymptoms improvedBiocideNervous disorderMaximum tolerated doseAnti cholinergic
Owner:CHASE PHARMA CORP
Methods of treating alzheimer's disease and pharmaceutical compositions thereof
ActiveUS9375418B2Nervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCholinesterase inhibitionBenzylamine
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
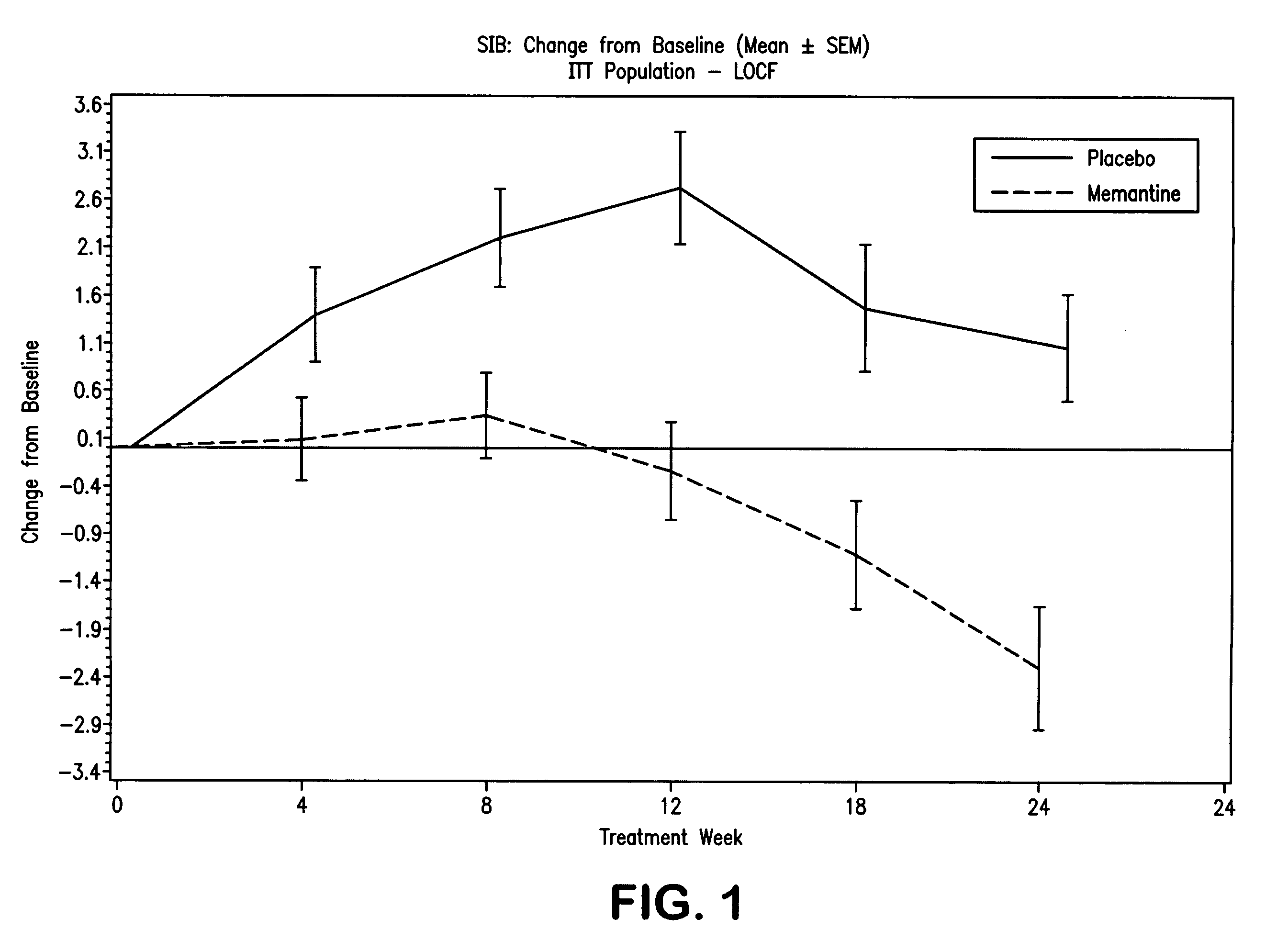
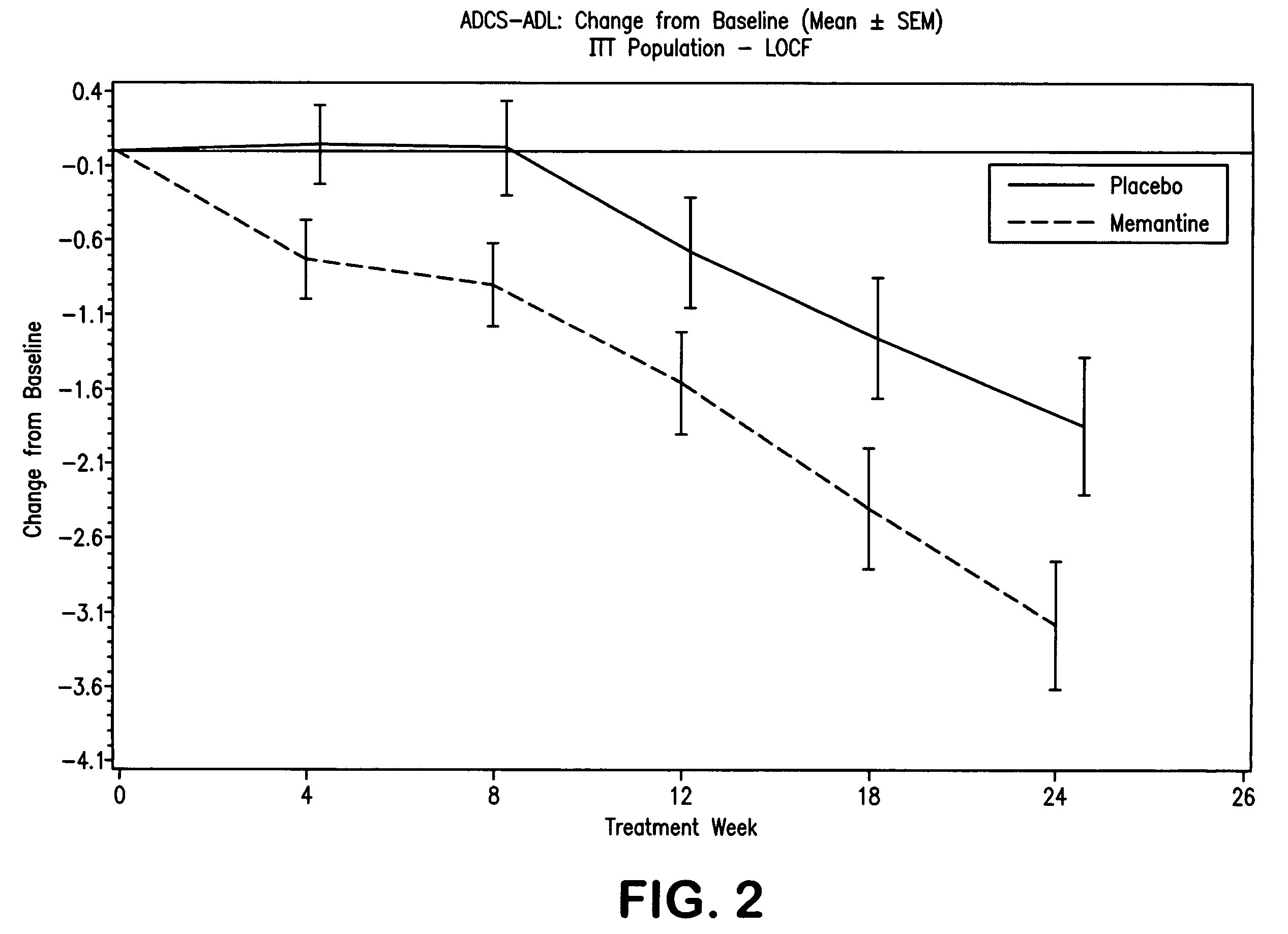
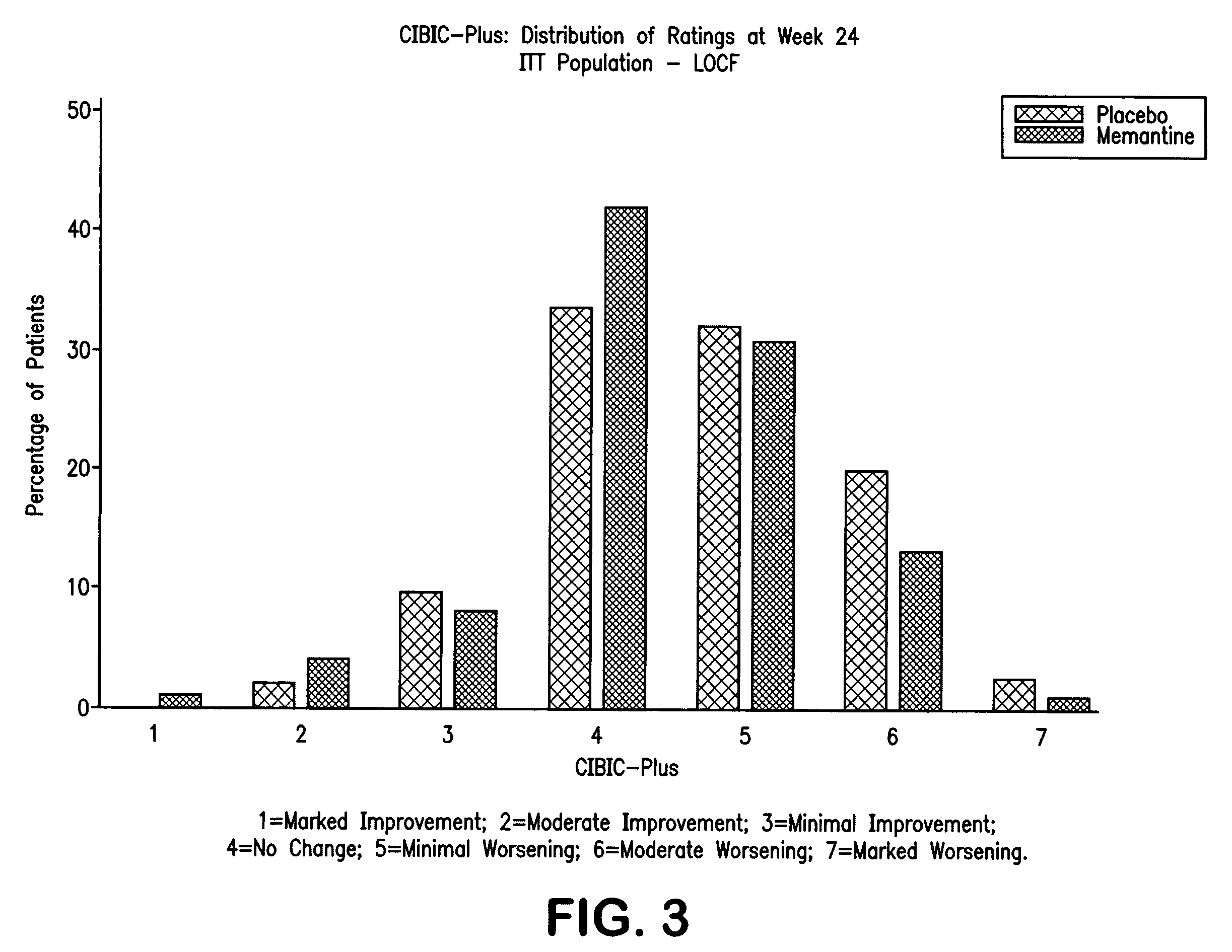
1-Aminocyclohexane derivatives for the treatment of agitation and other behavioral disorders, especially those associated with alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20050203191A1Minimal toxicityGood effectBiocideNervous disorderAcetylcholinesterase inhibitorCentral nervous system
The present invention relates to the treatment of behavioral disorders, especially agitation, associated with a central nervous system (CNS) disorder, especially Alzheimer's disease (AD), cerebrovascular disease (VaD), or Down's Syndrome, in a mammal, comprising administering to said mammal an 1-aminocyclohexane, alone or in combination with a acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In one embodiment, the 1-aminocyclohexane is memantine.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
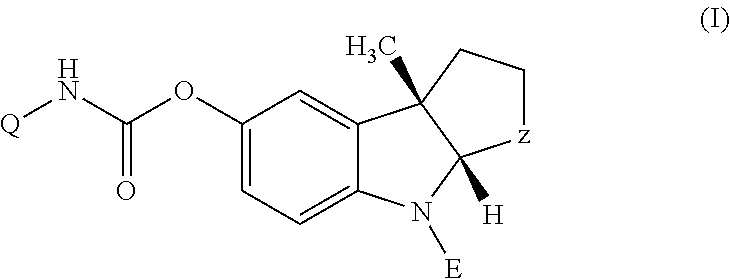
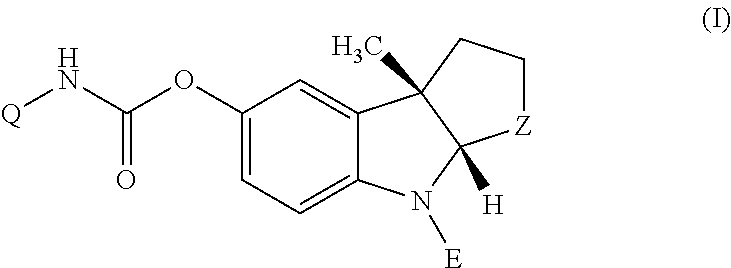
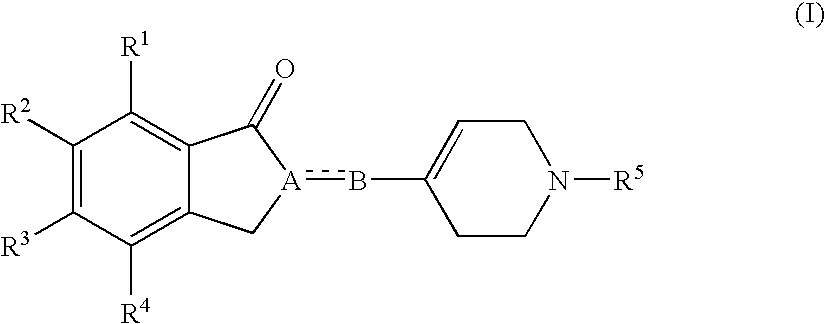
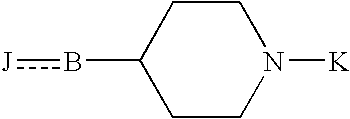
(1-Indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compounds
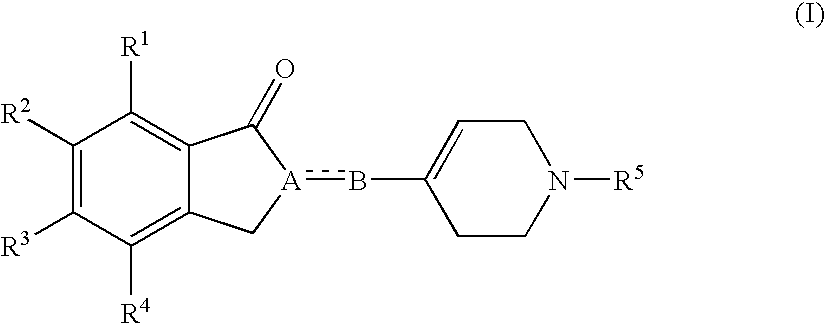
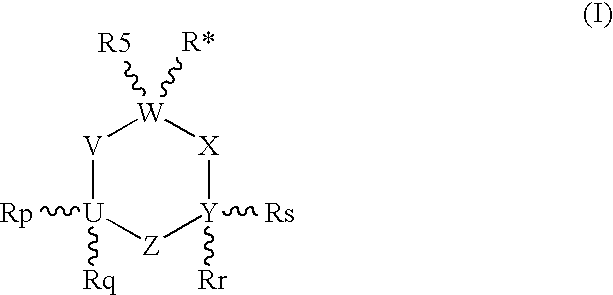
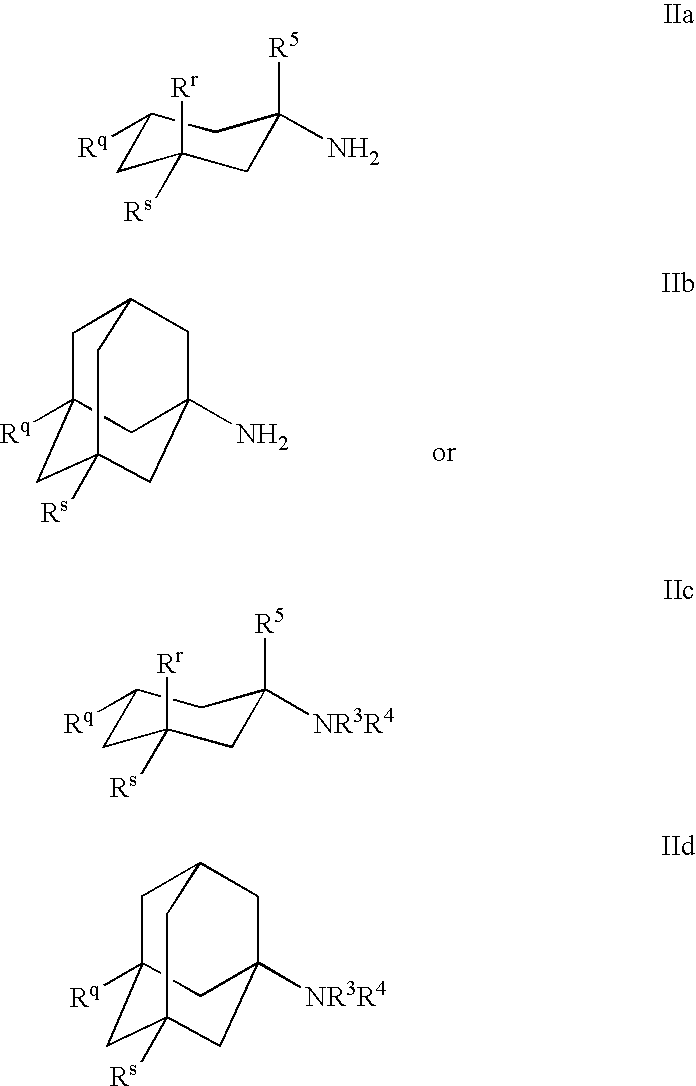
The present invention provides an excellent sigma receptor binding agent and / or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor containing an (1-indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compound. More specifically, it provides an (1-indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compound represented by the following formula, a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof or a hydrate thereof: In the formula (I), R1, R2, R3 and R4 are the same as or different from each other.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
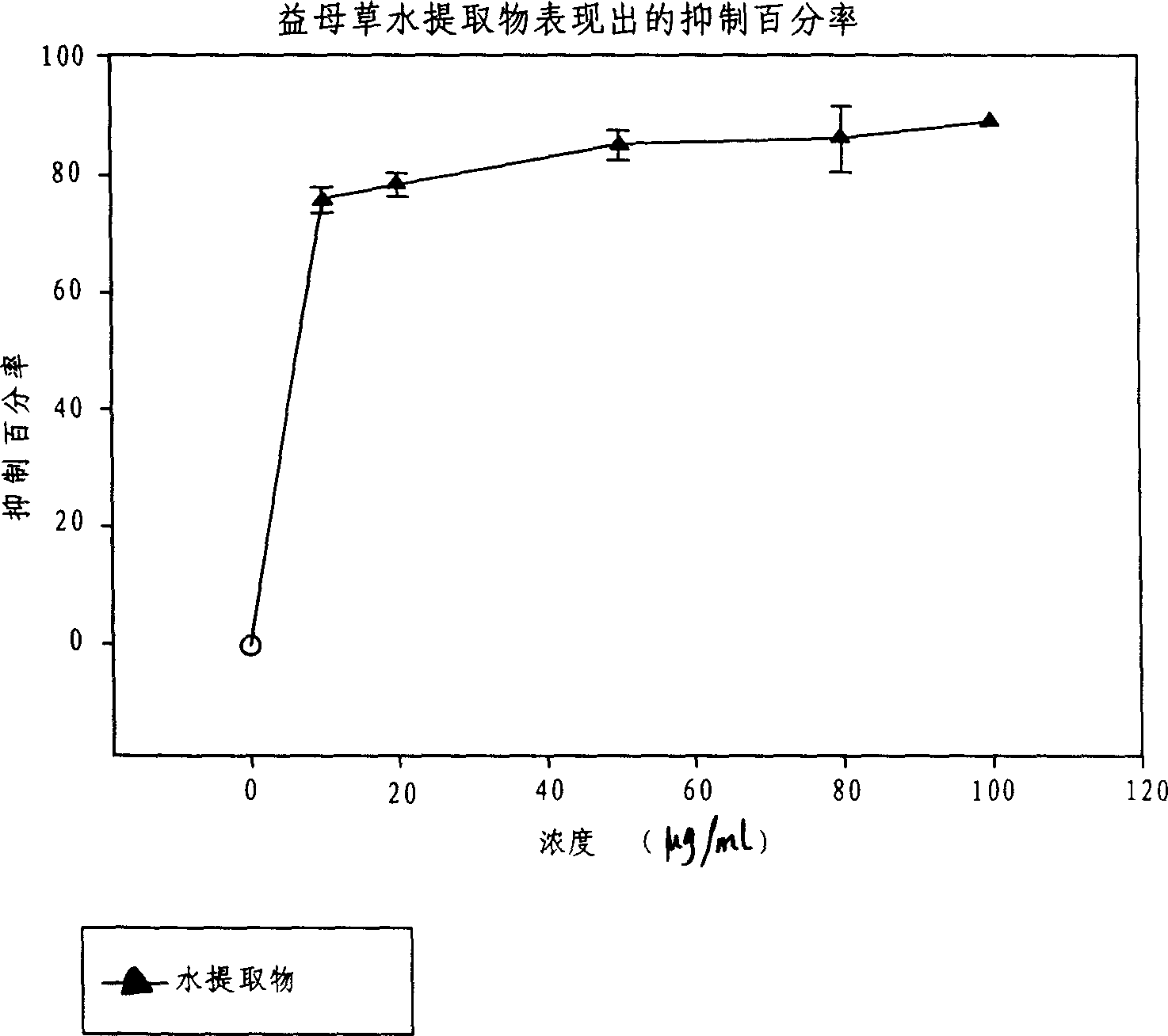
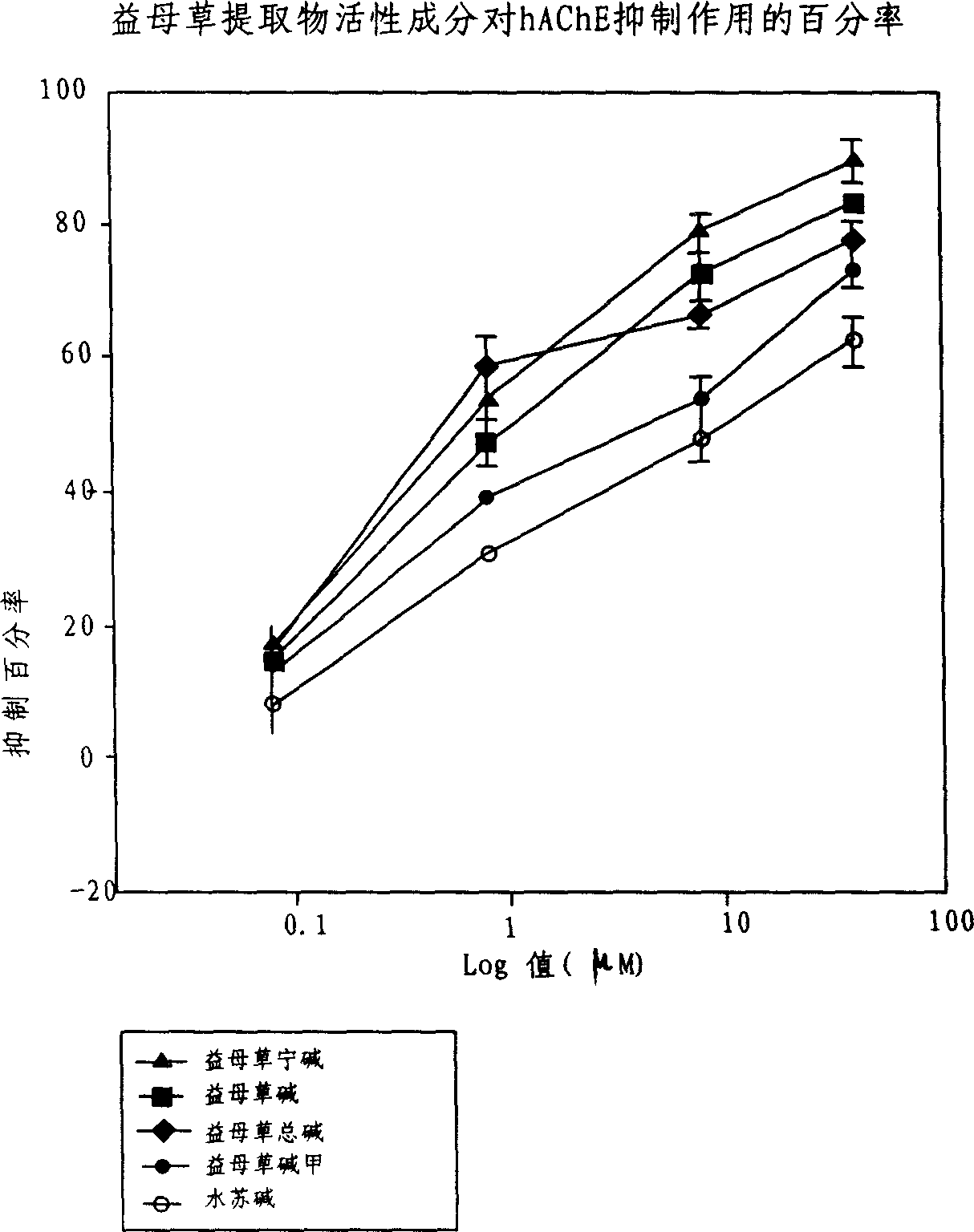
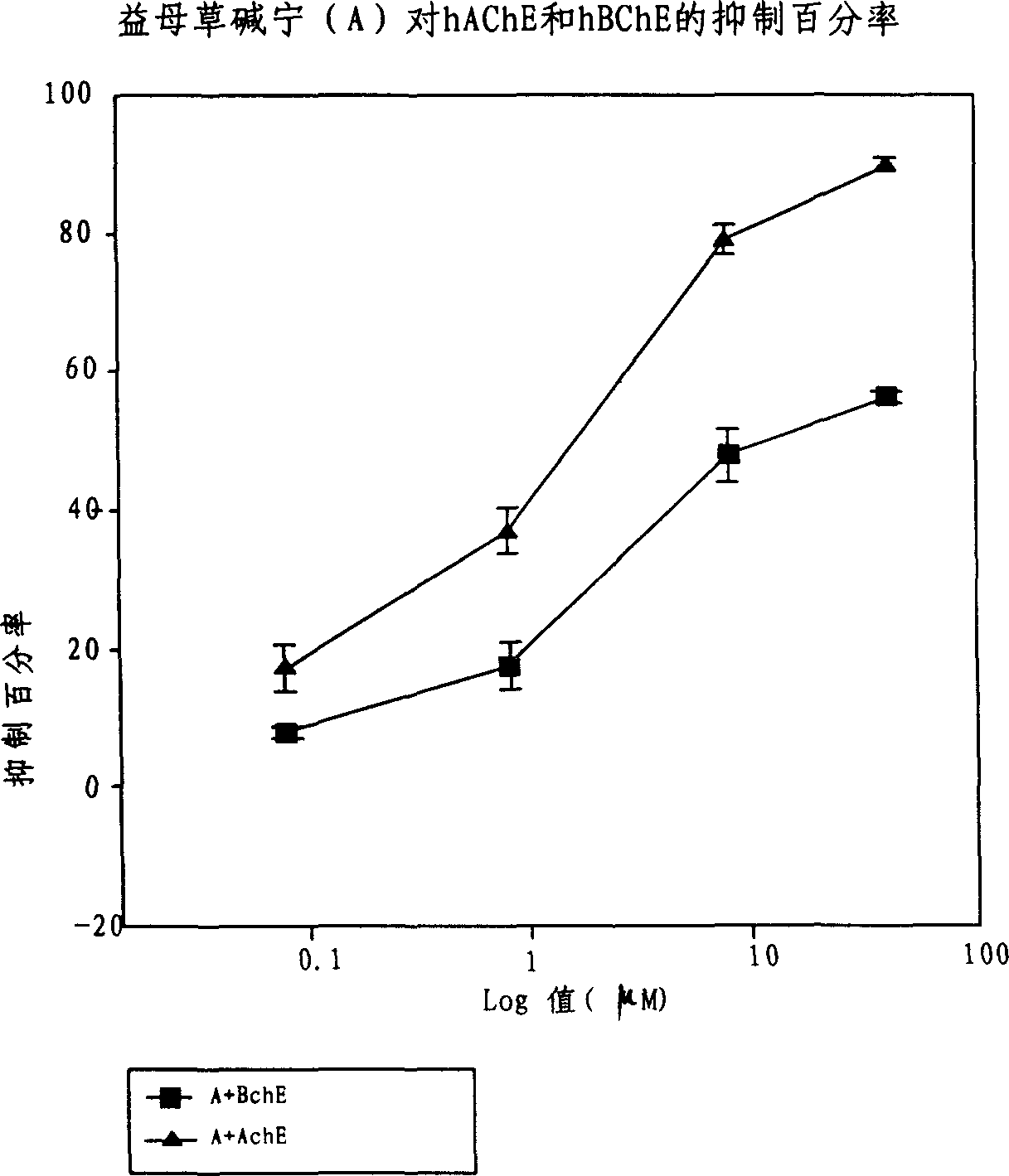
Application of acetylcholine esterase inhibitor medication of Yidancao extractive as cholinomimetic
InactiveCN1915292AEnhance pharmacological effectsRich sourcesNervous disorderDigestive systemDiseaseDepressant
An application of the motherwort's extract including leonurinine, leonurine, general leonurine, leonurine A, cadabine in preparing the medicines as acetylcholinesterase depressant for treating and preventing more than 20 diseases including senile dementia, Parkinson's disease, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, etc is disclosed.
Owner:郝书平
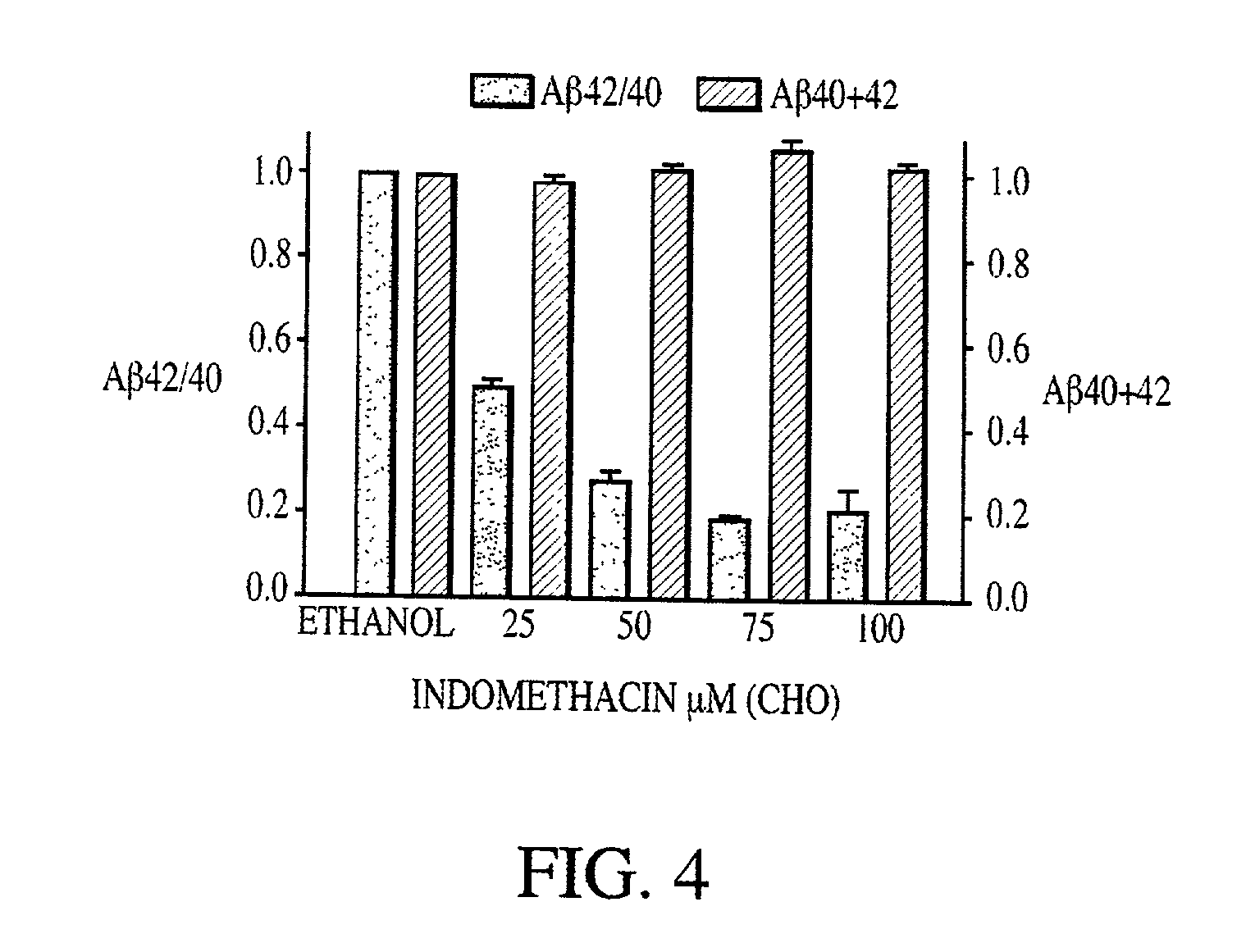
Method of reducing Abeta42 and treating diseases
InactiveUS20060004086A1Increased riskSpeed up progressBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRegimenCholinesterase inhibition
The invention provides a method of preventing, delaying, or reversing the progression of Alzheimer's disease by administering an Aβ42 lowering agent to a mammal under conditions in which levels of Aβ42 are selectively reduced, levels of Aβ38 are increased, and levels of Aβ40 are unchanged. The invention provides methods and materials for developing and identifying Aβ42 lowering agents. In addition, the invention provides methods for identifying agents that increase the risk of developing, or hasten progression of, Alzheimer's disease. The invention also provides compositions of Aβ42 lowering agents and antioxidants, Aβ42 lowering agents and non-selective secretase inhibitors, as well as Aβ42 lowering agents and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. The invention also provides kits containing Aβ42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and / or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as well as instructions related to dose regimens for Aβ42 lowering agents, antioxidants, non-selective secretase inhibitors, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
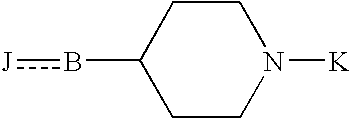
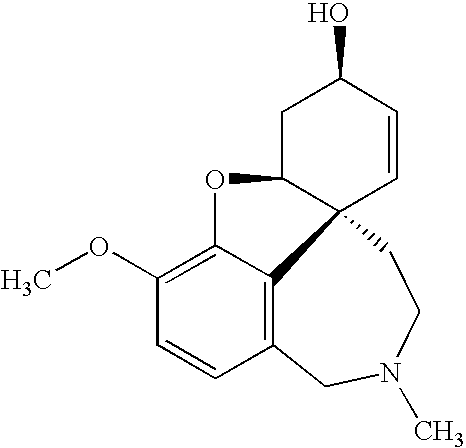
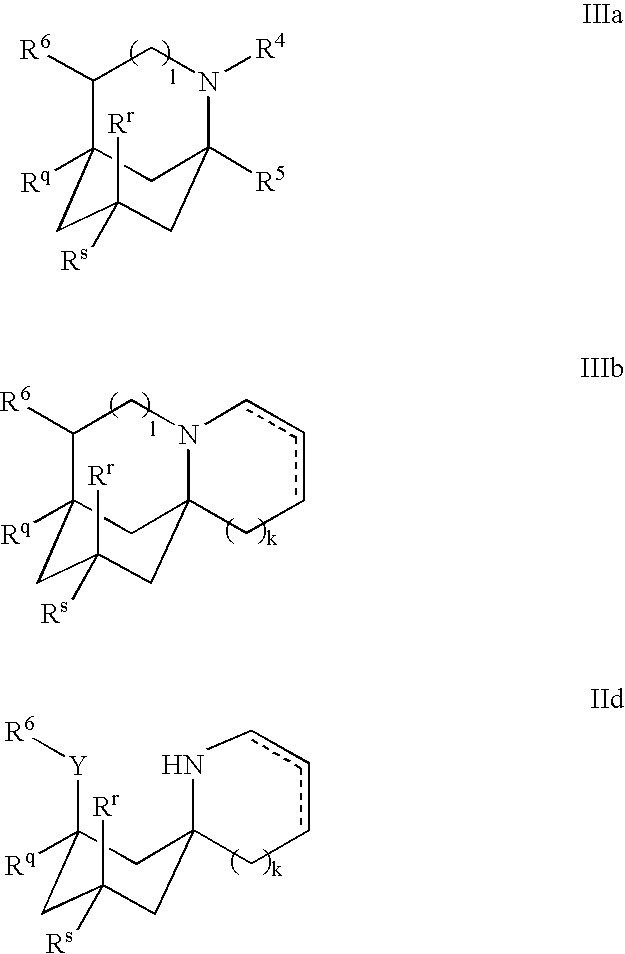
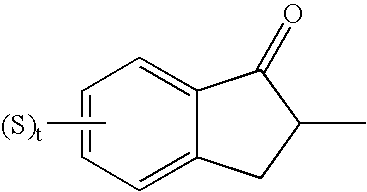
1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine
The present invention provides a novel compound useful as a medicament, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and an agent for preventing, treating and improving various kinds of senile dementia, Alzheimer-type senile dementia, cerebrovascular dementia or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, namely, 1-benzyl-4-[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanone)-2-yl]methylpiperidine represented by the following formula:or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a process for producing the same.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
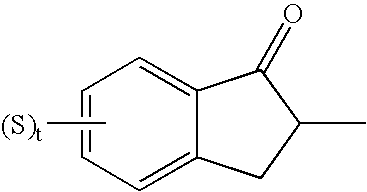
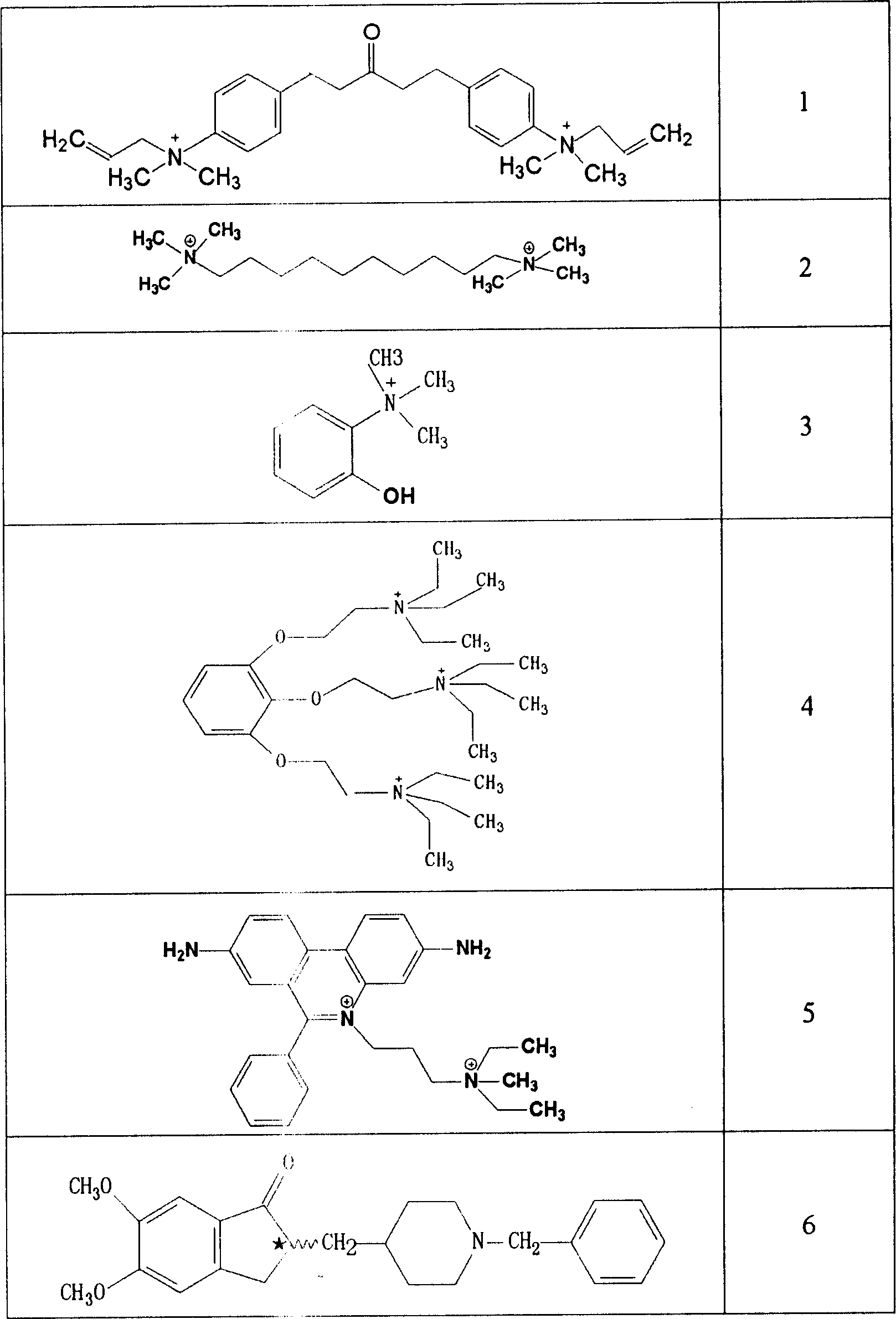
Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and relates to a thiazolo(3,2-b)-1,2,4-triazine derivative and applications thereof. The thiazolo(3,2-b)-1,2,4-triazine derivative includes stereoisomers and pharmaceutically applicable salts of the compound, and has a general structural formula as shown follow. The thiazolo(3,2-b)-1,2,4-triazine derivative and the salts added by pharmaceutically applicable acids of the compound can be used by combining with the existing medicaments or separately as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for enhancing the memory of patients suffering from dementia and alzheimer.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Combined acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and quaternary ammonium antimuscarinic therapy to alter progression of cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20150031897A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectOrganic chemistryEster active ingredientsDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
(1-Indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compounds
The present invention provides an excellent sigma receptor binding agent and / or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor containing an (1-indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compound. More specifically, it provides an (1-indanone)-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) compound represented by the following formula, a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof or a hydrate thereof:In the formula (I), R1, R2, R3 and R4 are the same as or different from each other.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
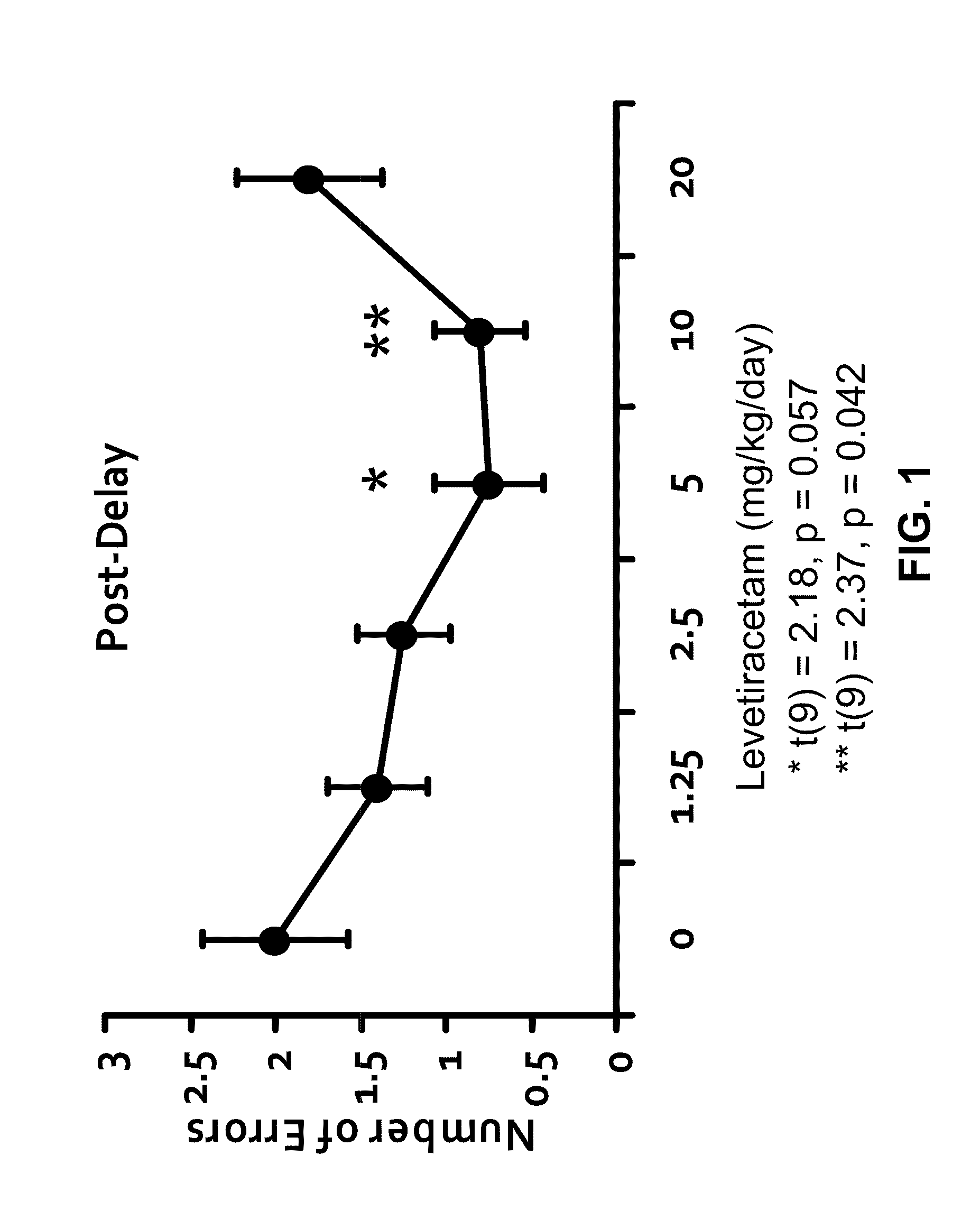
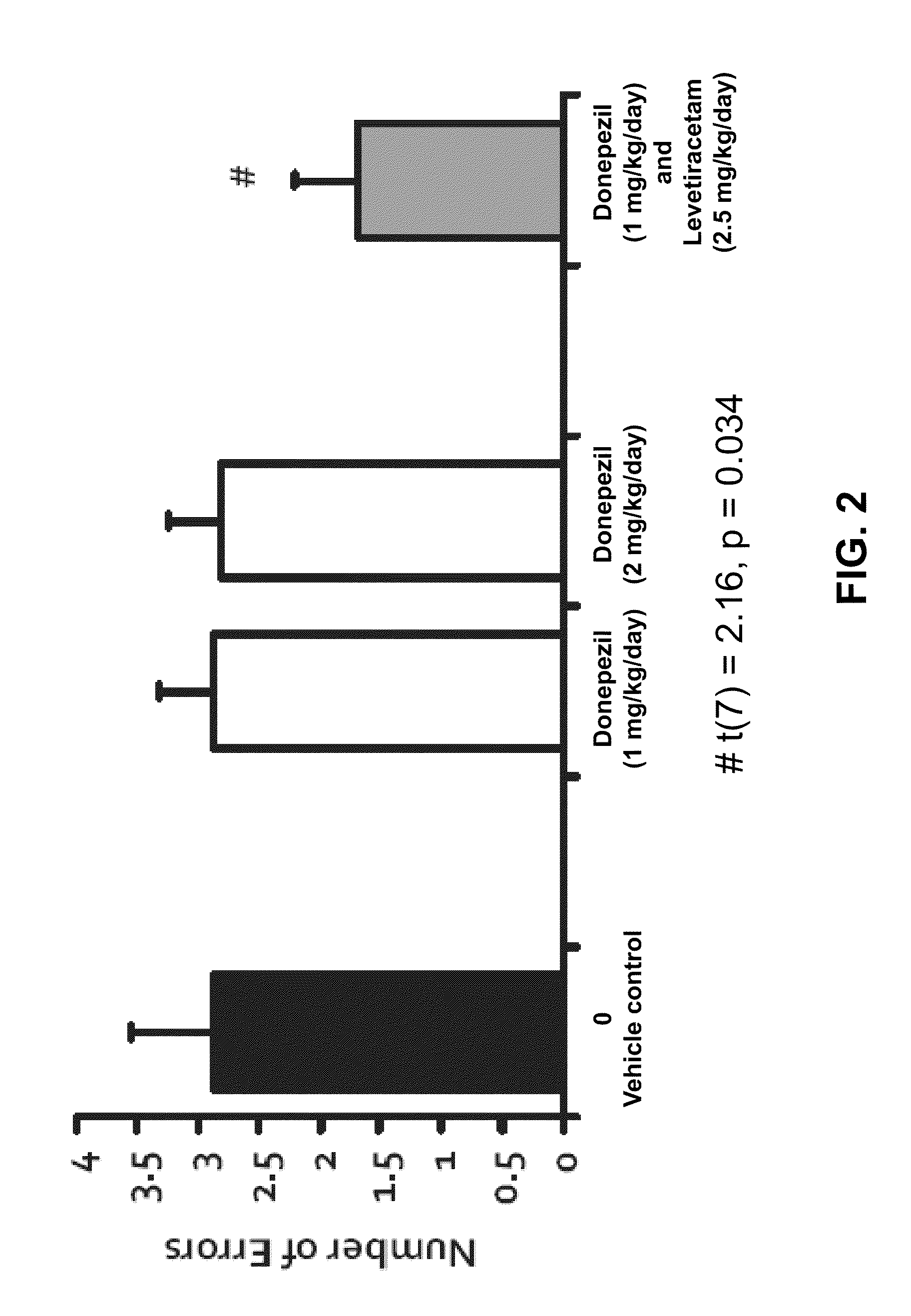
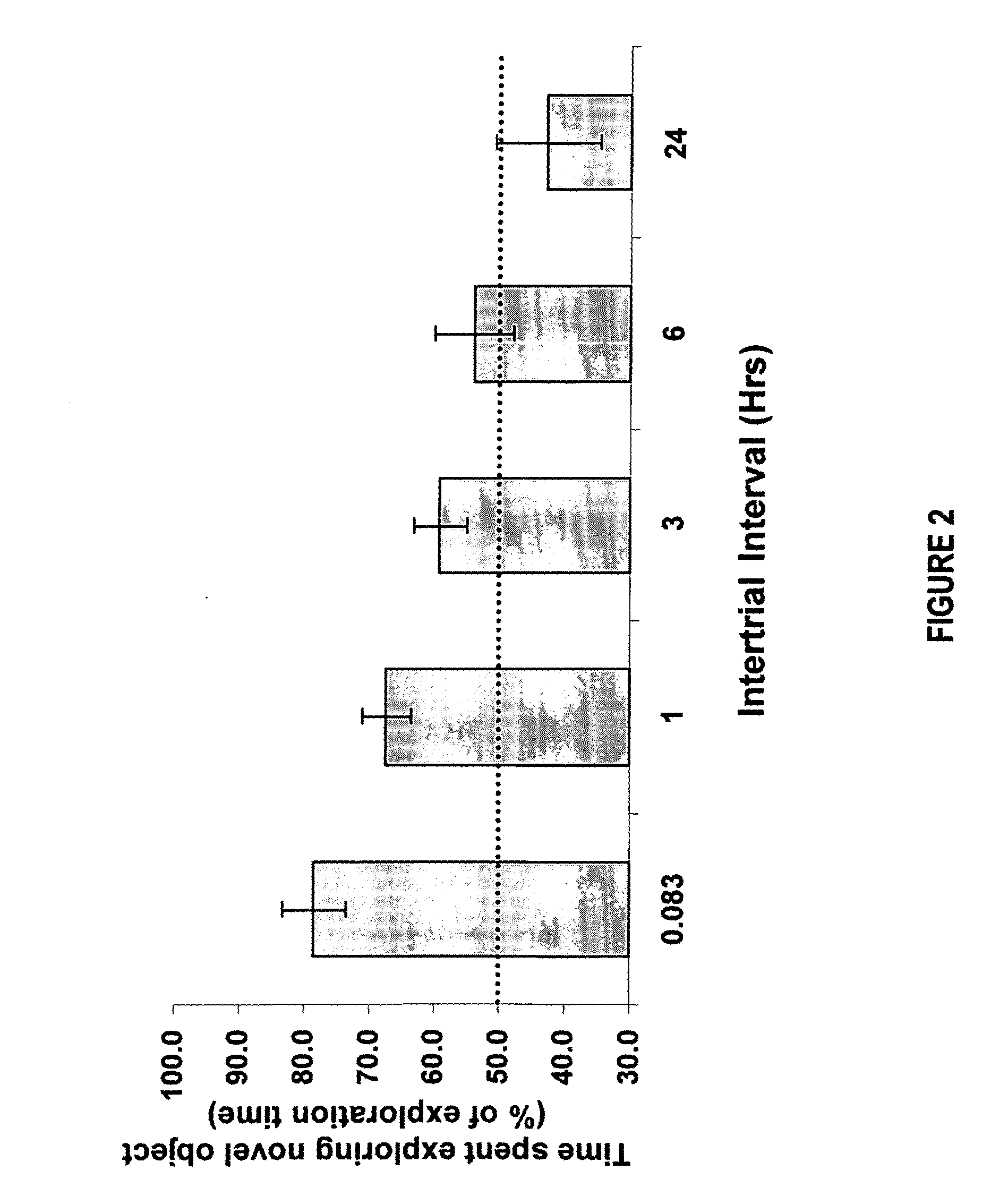
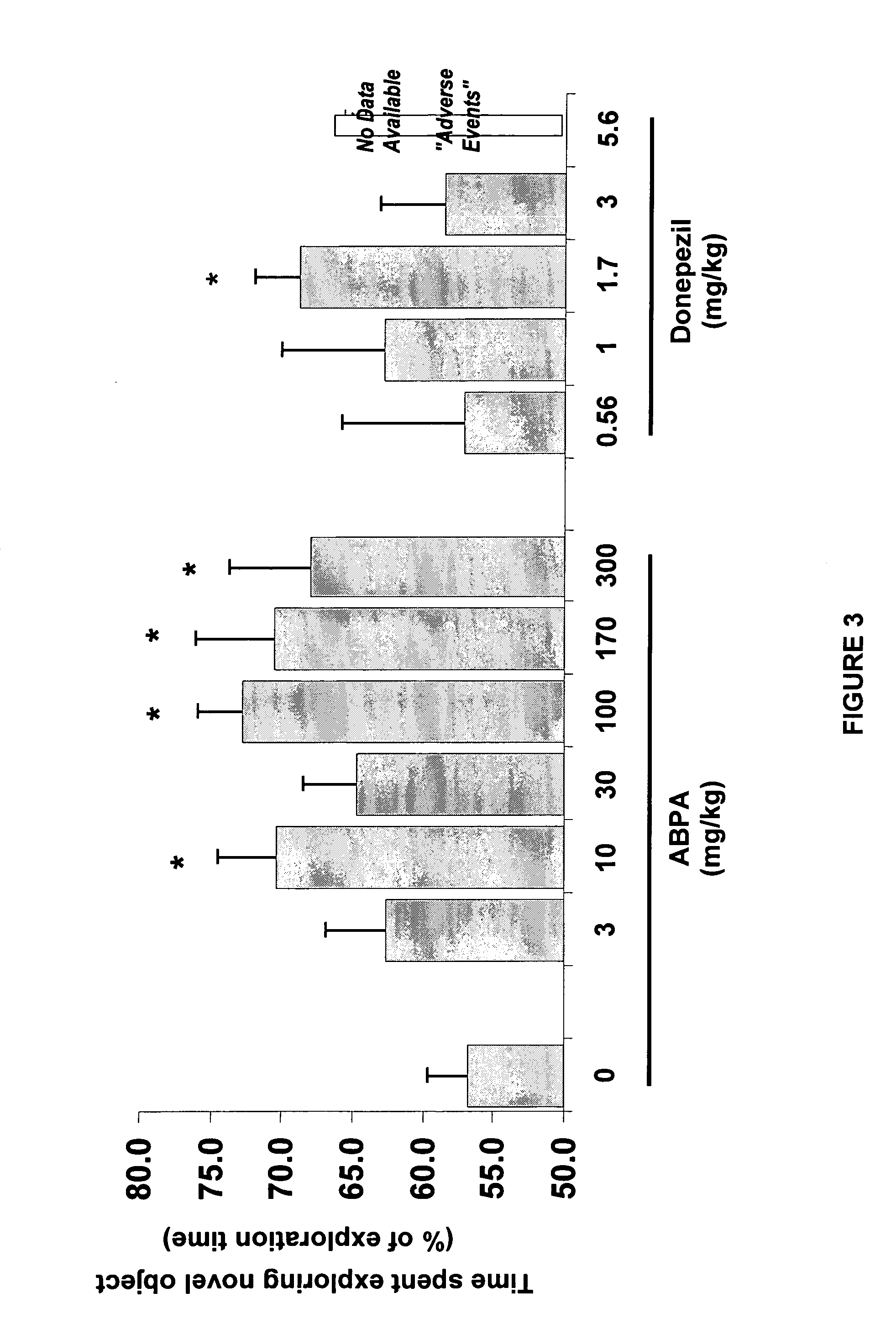
Methods and compositions for improving cognitive function
InactiveUS20110212928A1Prevent and slow progressionImprove cognitive functionBiocideNervous disorderMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Synaptic vesicle
The invention relates to methods and compositions for improving cognitive function by using a combination of a synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) inhibitor and an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, polymorphs thereof. In particular, it relates to the use of a combination of an SV2A inhibitor and an AChEI in treating a central nervous system disorder with cognitive impairment in a subject in need or at risk thereof, including, without limitation, subjects having or at risk for age-related cognitive impairment, Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), dementia, Alzheimer's Disease (AD), prodromal AD, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), schizophrenia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and cancer-therapy-related cognitive impairment.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Combined Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor and Quaternary Ammonium Antimuscarinic Therapy to Alter Progression of Cognitive Diseases
ActiveUS20130172379A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectBiocideOrganic chemistryDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
Method for improving cognitive function by co-administration of a GABAB receptor antagonist and an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
InactiveUS20050267077A1Improve cognitive functionBiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionCo administration
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improving cognitive function by administering a GABAB receptor antagonist and an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and composition for treating alzheimer-type dementia
InactiveUS20110201597A1Extended durationFunction increaseBiocideNervous disorderNK1 receptor antagonistMaximum tolerated dose
There is described a method for increasing the maximal tolerated dose and thus the efficacy of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) in a patient suffering from an Alzheimer type dementia by decreasing concomitant adverse effects by administration of said AChEI in combination with a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent, whereby an enhanced acetylcholinesterase inhibition in the CNS of said patient is achieved and alleviation of the symptoms of Alzheimer type dementia in said patient is thereby improved to a greater extent. The use of a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of Alzheimer type dementia in combination with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) and pharmaceutical compositions comprising (a) a 5HT3 receptor antagonist, a dopamine antagonist, a H1-receptor antagonist, a cannabinoid agonist, aprepitant or casopitant as an antiemetic agent and (b) an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor are also described.
Owner:CHASE PHARMA CORP
Methods and compositions for treatment of nicotine dependence and dementias
InactiveUS20050277626A1Easy to useIncrease heightBiocideNervous disorderTricyclic antidepressantTricyclic anti-depressants
In accordance with the present invention, it has been unexpectedly found that the administration of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor in combination with a tricyclic antidepressant having anti-muscarinic properties provides a highly effective and well tolerated treatment for nicotine dependence and dementias, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD). In one aspect, it is effective in the treatment of nicotine dependence, as well as in the treatment and mitigation of nicotine withdrawal symptoms and in the effectuation of smoking cessation. In another aspect, it is effect in the treatment and mitigation of dementias such as Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:NEUROCURE
Anticholinergic neuroprotective composition and methods
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising propiverine, trospium or glycopyrrolate; and a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent. It is also related to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a high dose of solifenacin or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof; and a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent. Pharmaceutical compositions containing high dose of nsPAChA for use for increasing the AChEI blood concentrations and for combating neurodegeneration are also described. The invention also relates to a method for inducing neuroprotection and combating neurodegeneration in a patient suffering from Alzheimer type dementia as well as to a method for increasing the blood levels of an acetyl choline esterase inhibitor (AChEI) in a human subject treated with an AChEI dose.
Owner:CHASE PHARMA CORP
Use of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for preparing diabetes medicines
InactiveCN1709508AEffective treatmentImprove symptoms of hyperglycemiaPharmaceutical active ingredientsCholinesterase inhibitionCholinesterase
The present invention relates to an application of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for curing diabetes. The described inhibitor includes all the compounds which can inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity and have the action for curing diabetes. The invented experimental results show that these inhibitors have the actions of inhibiting beta-cell death and reducing blood sugar concentration of diabetic model mouse, and can effectively cure or improve diabetes symptom.
Owner:CELL STAR BIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine 1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0c3725d-7354-419e-ad7f-870a9e8cd4fd/US06277866-20010821-C00001.png)
![1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine 1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0c3725d-7354-419e-ad7f-870a9e8cd4fd/US06277866-20010821-C00002.png)
![1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine 1-benzyl-4[(5,6-dimethoxy-2-fluoro-1-indanon)-2-yl]methylpiperidine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e0c3725d-7354-419e-ad7f-870a9e8cd4fd/US06277866-20010821-C00003.png)
![Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/77452d3d-bf93-492b-b940-f43707ffc161/a200910010552c00021.PNG)
![Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/77452d3d-bf93-492b-b940-f43707ffc161/a200910010552c00022.PNG)
![Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof Thiazolo[3,2-b]-1,2,4-triazine derivative and use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/77452d3d-bf93-492b-b940-f43707ffc161/a200910010552c00031.PNG)