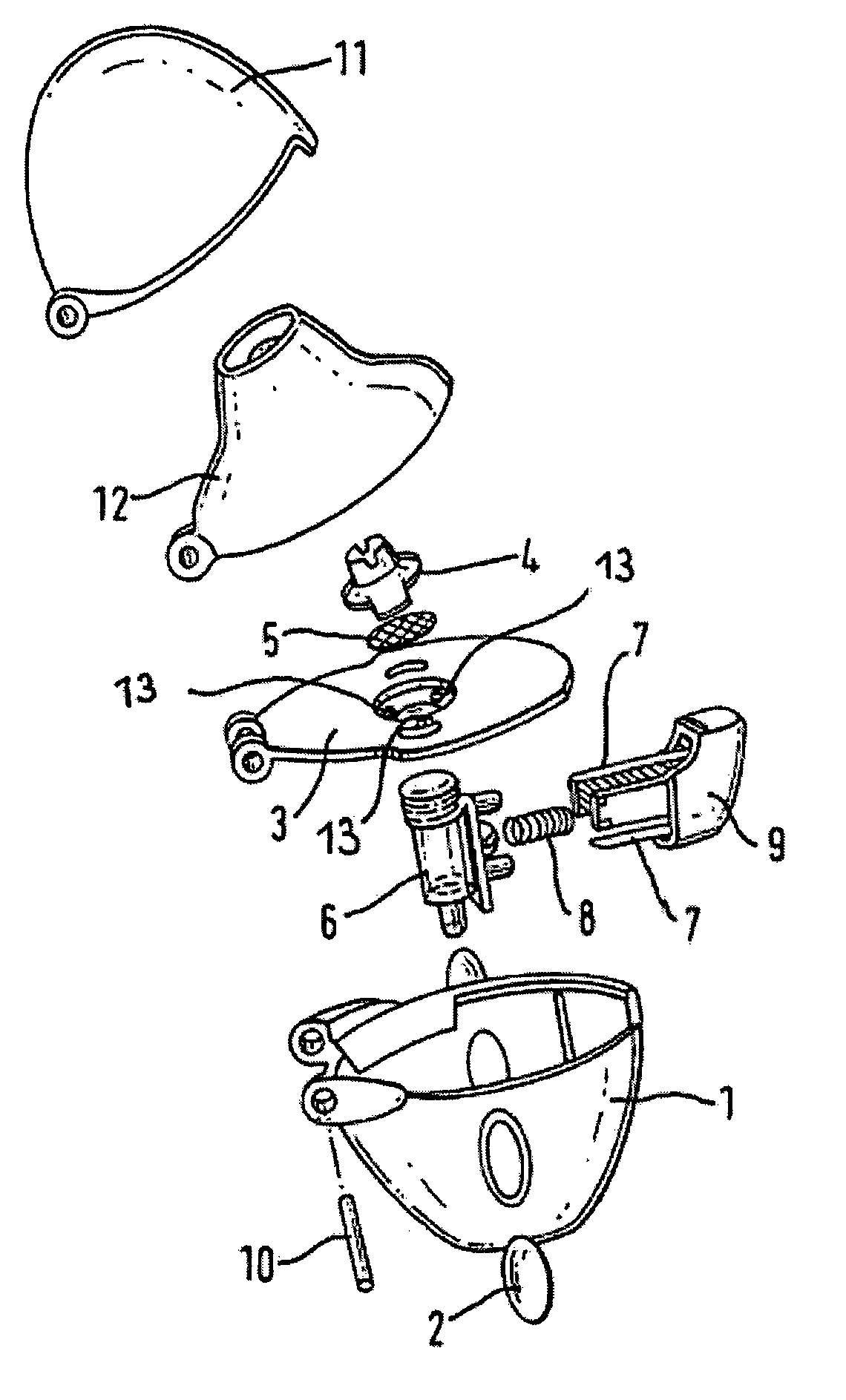
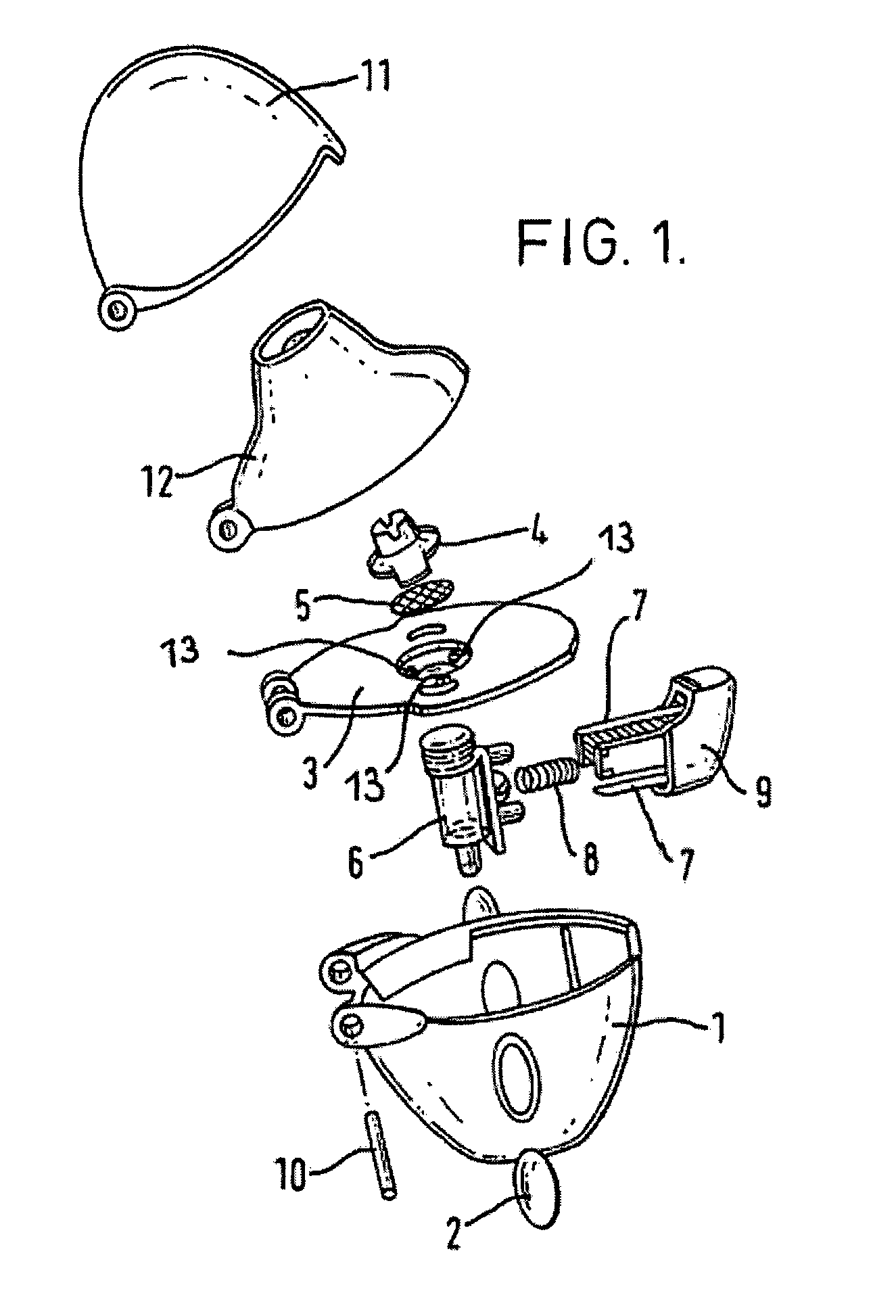
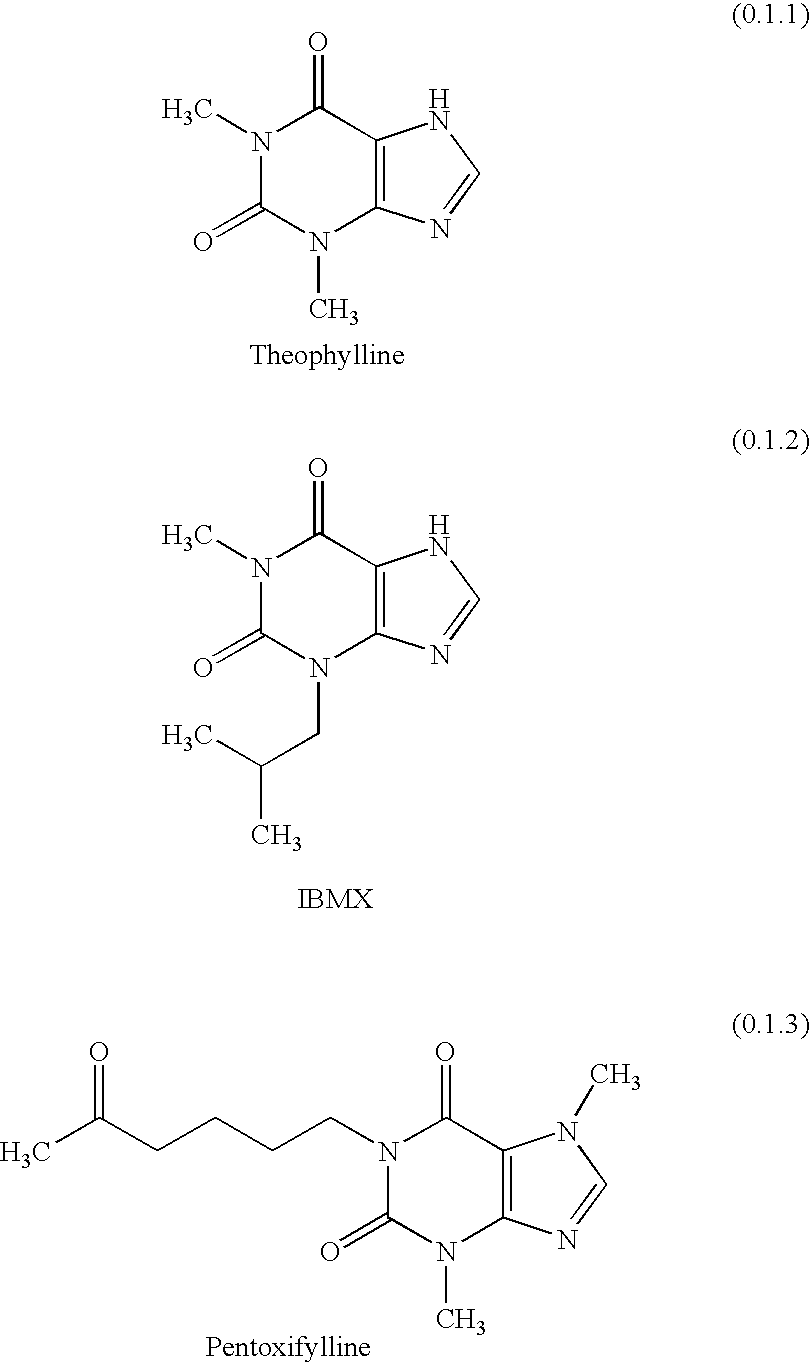
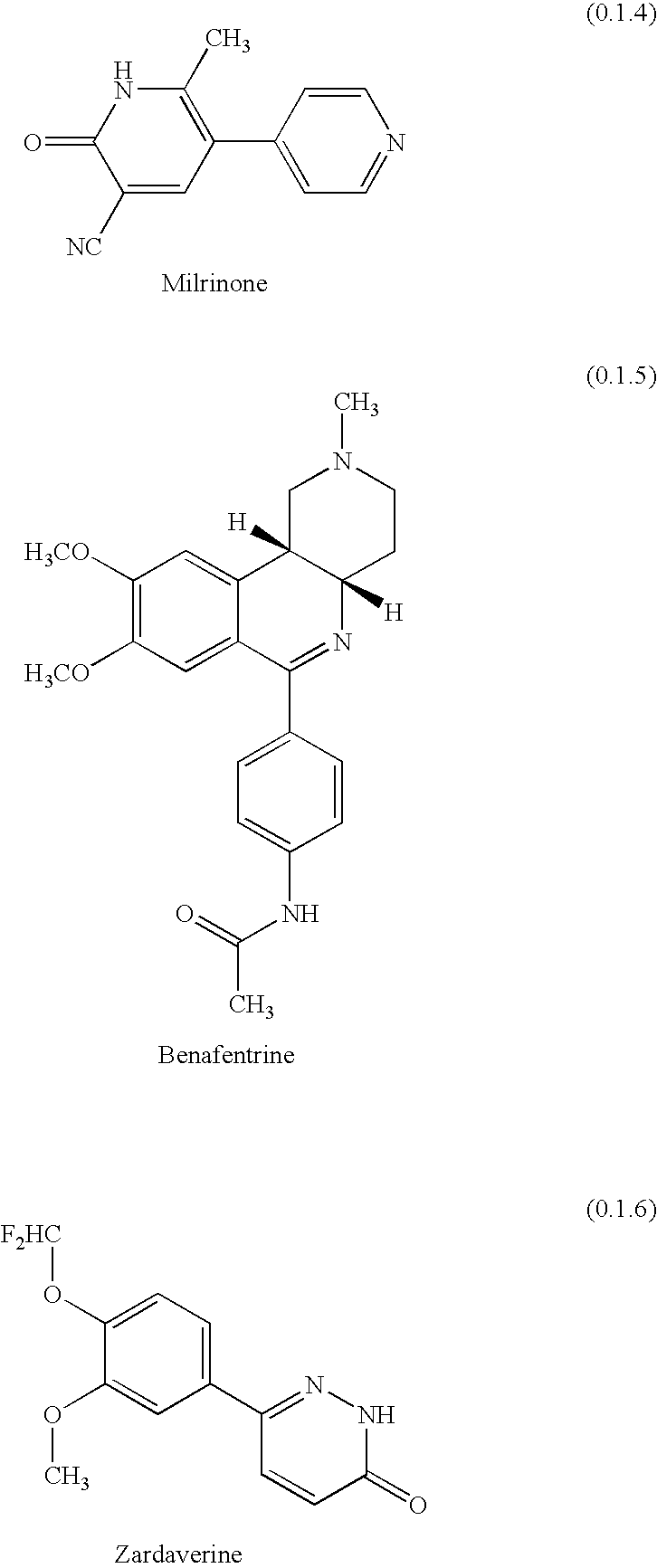
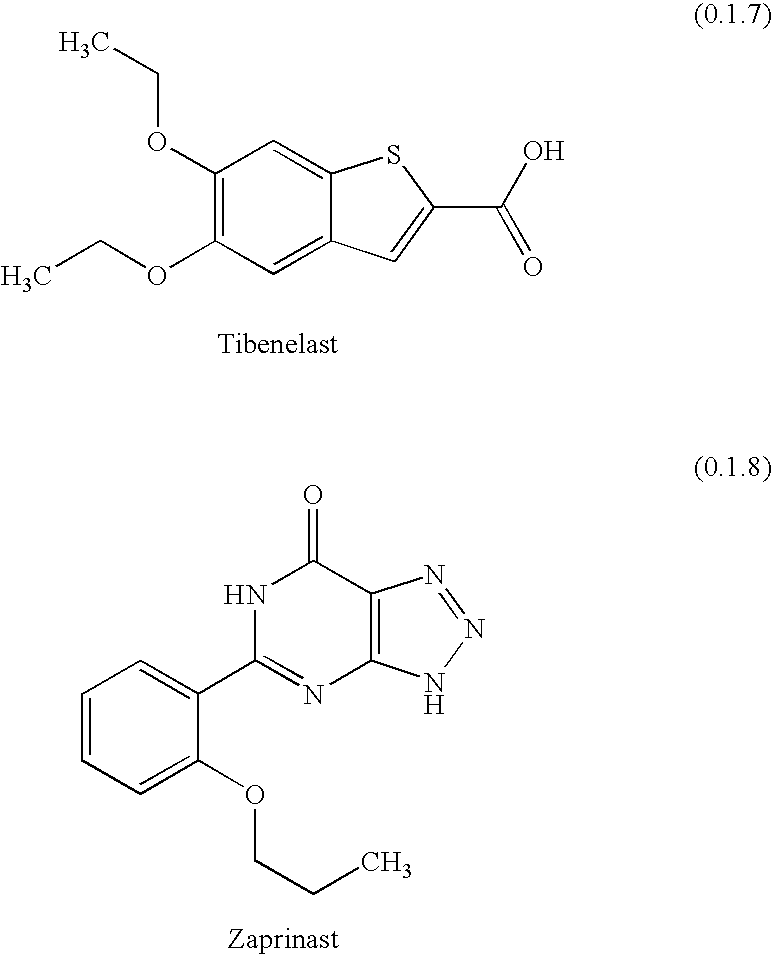
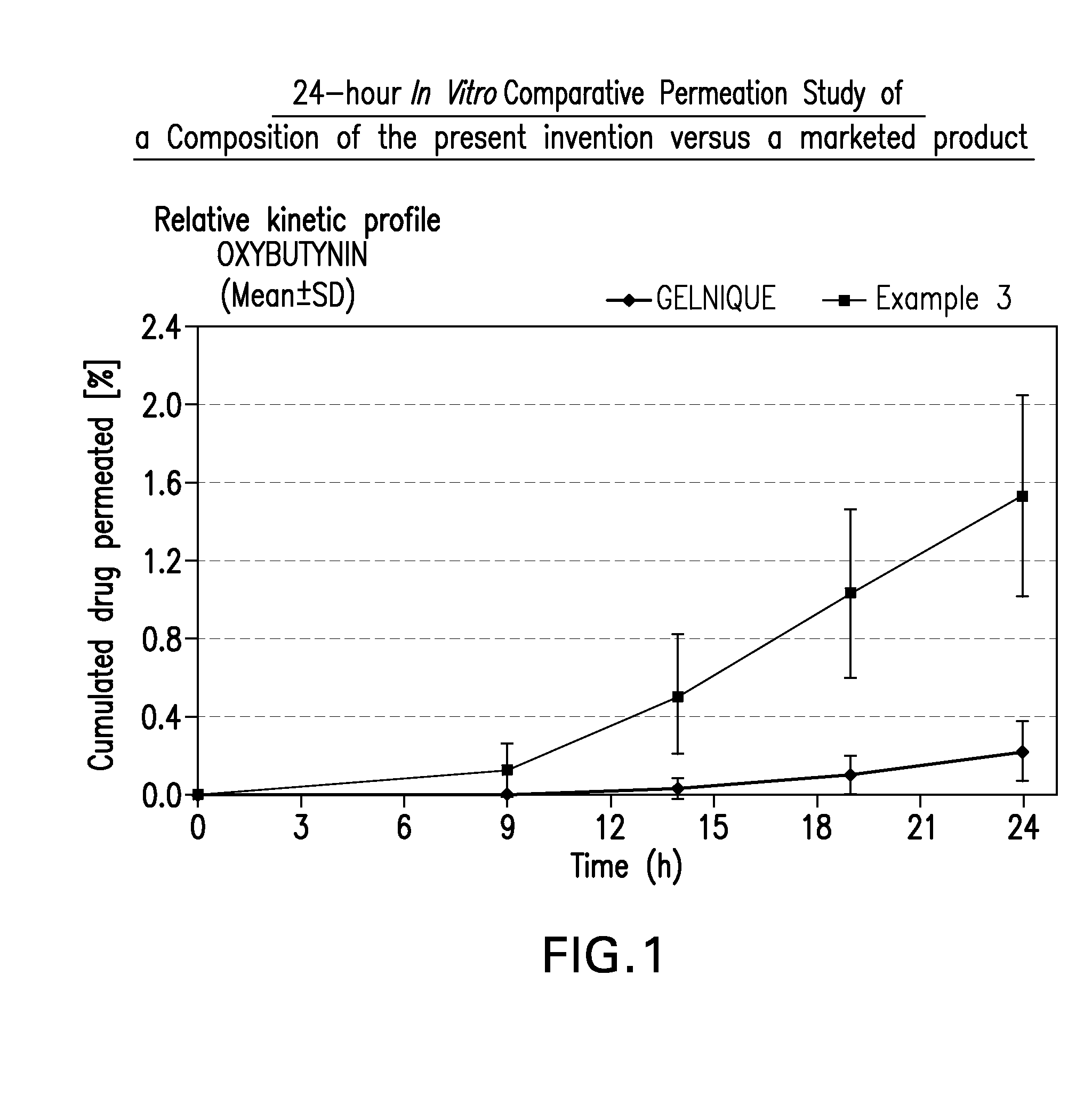
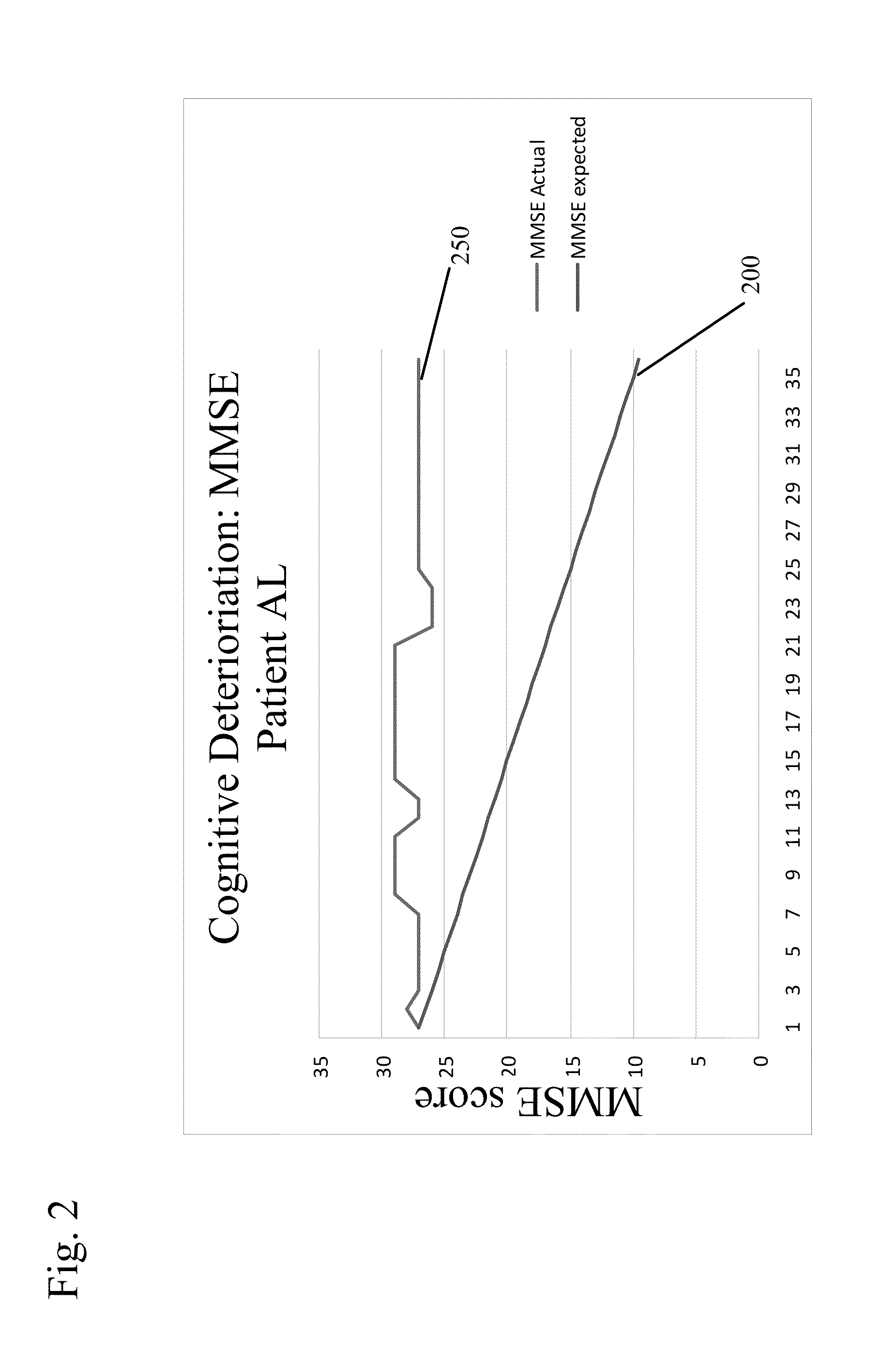
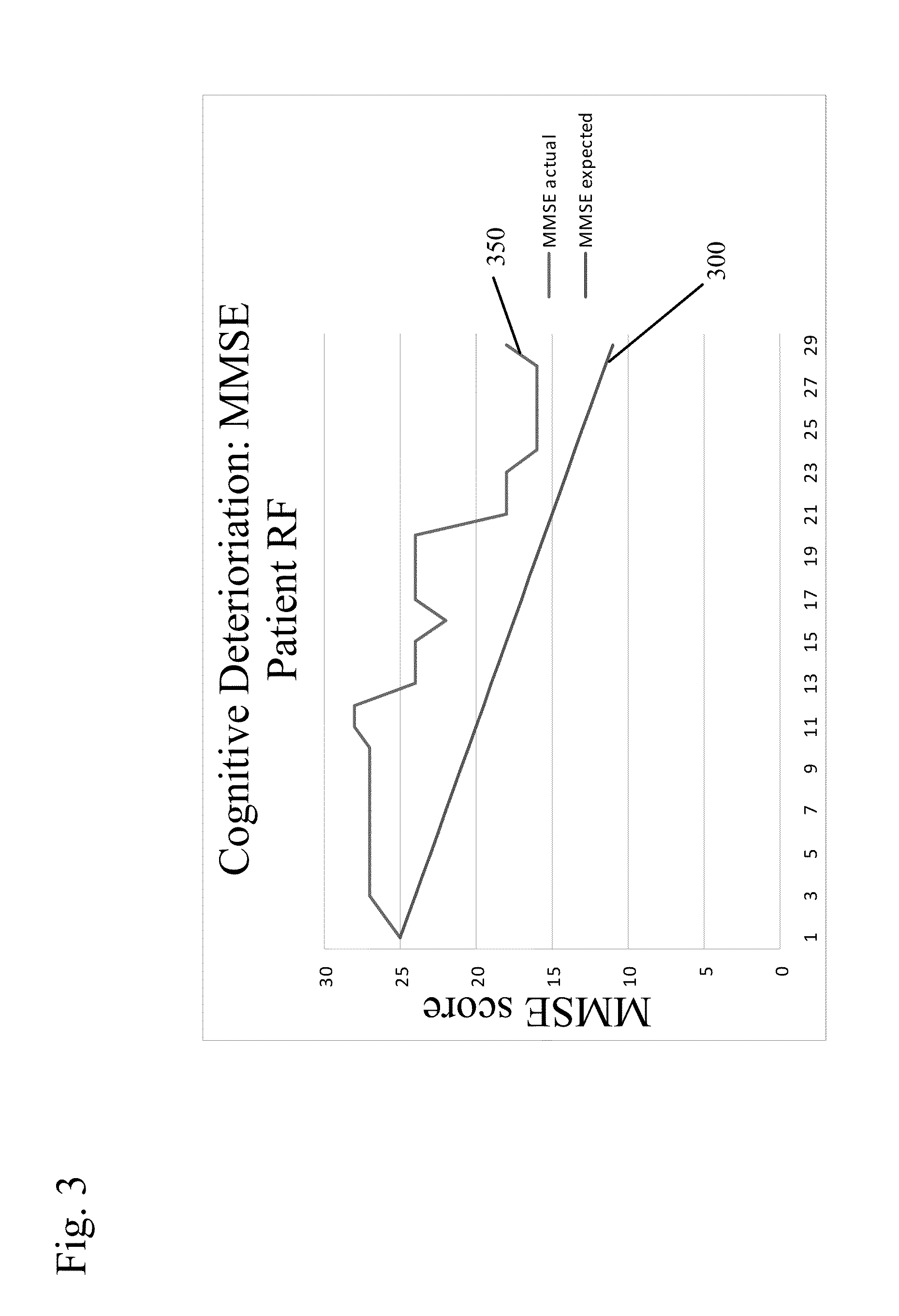
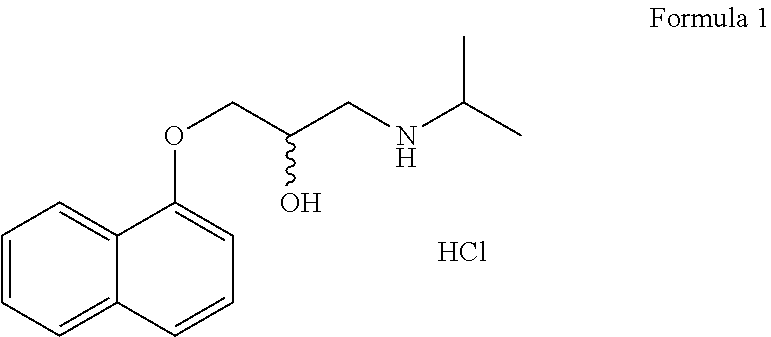
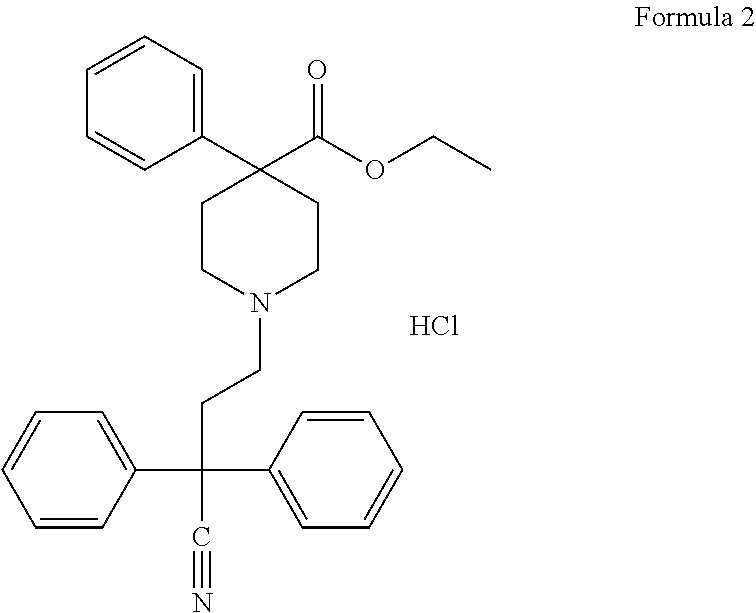
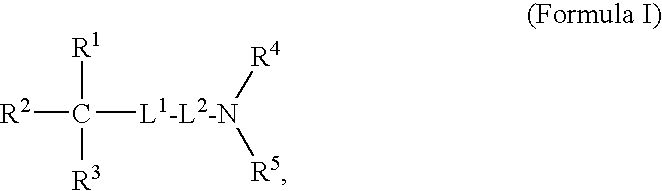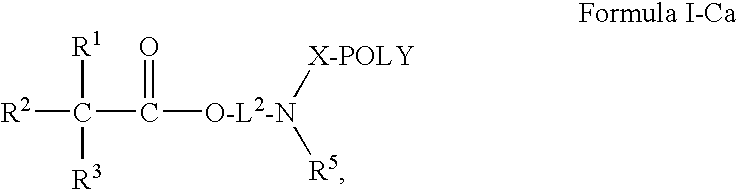Patents
Literature
54 results about "Anti cholinergic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anticholinergics are medications that are administered to lessen the nervous system's stimulation of smooth muscle tissue. An anticholinergic works by inhibiting the action of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter responsible for signaling nerve activity.
Anticholinergic powder formulations for inhalation
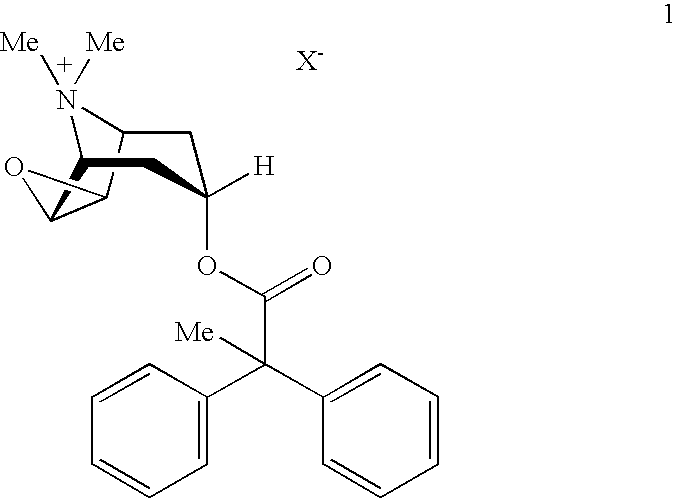
An inhalable powder comprising:(a) an active substance consisting essentially of a compound of formula 1 wherein X− is a pharmaceutically acceptable anion; and(b) a physiologically acceptable excipient having an average particle size of 10 μm to 50 μm,processes for preparing the inhalable powder, and methods of administration for the treatment of respiratory complaints, particularly for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
New uses for quaternary ammonium anticholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in patients being treated for cognitive impairment or acute delirium
ActiveUS20080114014A1Maximizing beneficial effectMaximize the effectBiocideNervous disorderSolubilityFecal incontinence
A method for treating the adverse effects of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of cognitive disorders such as acute delirium and cognitive impairment in elderly human patients. The administration of a clinically effective amount of a quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonist having very low lipid solubility substantially eliminates the adverse effects of urinary and / or fecal incontinence, nausea, bradycardia, bronchorrhea or brochospasm caused by the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors, without affecting the beneficial activity of the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors. This permits the administration of the optimum effective dosing of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to provide maximum benefit to the patient with the added benefit of reducing or eliminating the unwanted side effects of fecal and urinary incontinence. Further, the combination of rivastigmine and glycopyrrolate has been effective in significantly improving cognitive function in patients suffering from acute dementia or cognitive impairment.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
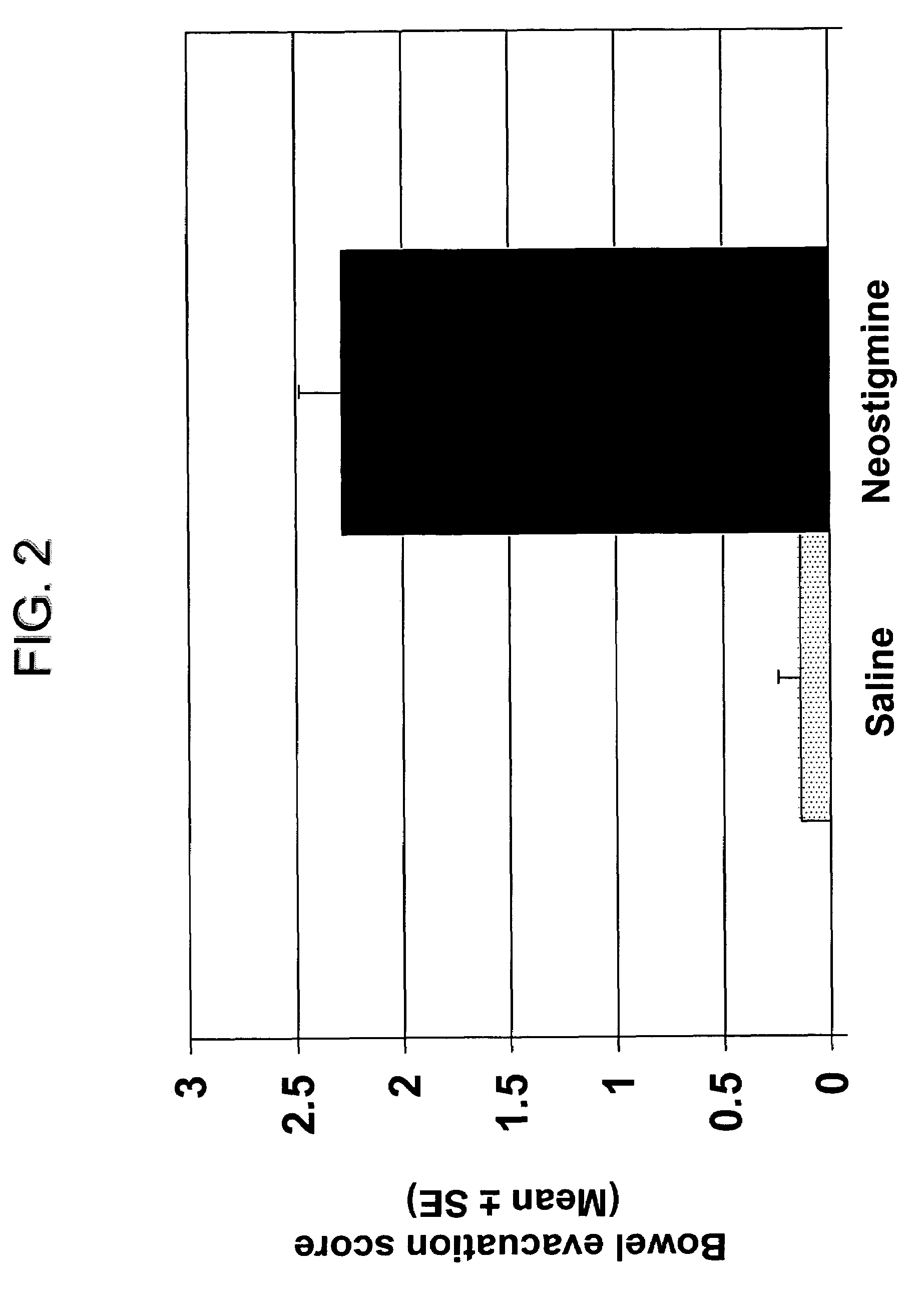
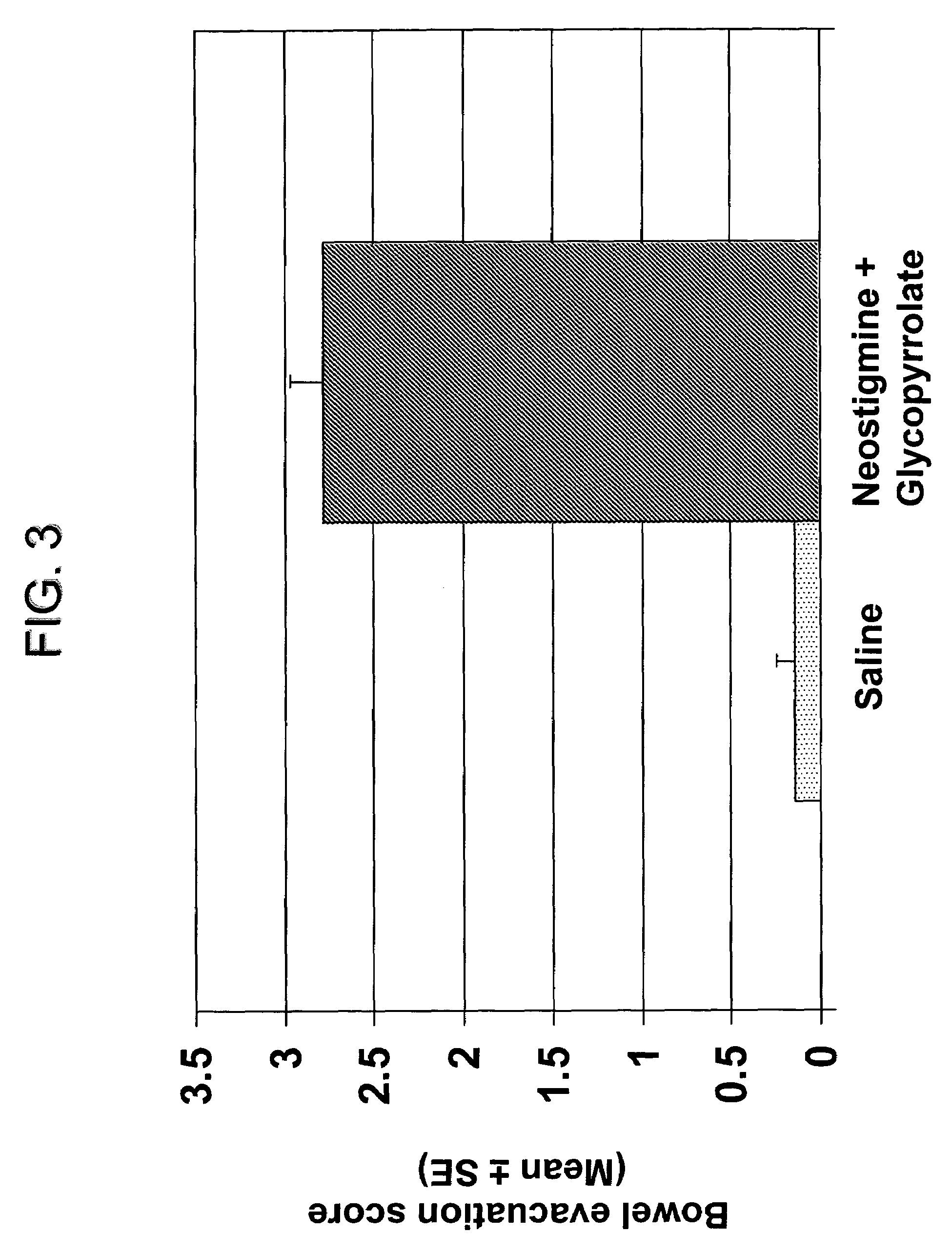
Compositions and methods for bowel care in individuals with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction
ActiveUS7635709B2Shorten the construction periodDifficult to administerBiocideAmine active ingredientsBowel careSide effect
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for on-going bowel care for persons with chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. The compositions and methods can be administered in a non-clinical setting. The compositions comprise acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for stimulating motility of the bowel in combination with anti-cholinergic agents to counteract the potentially dangerous cardiac side effects of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In some examples, the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, neostigmine, and the anti-cholinergic agent, glycopyrrolate, are combined in a pharmaceutical composition. Certain examples also provide the frequency and duration of administration of the disclosed drug combinations.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
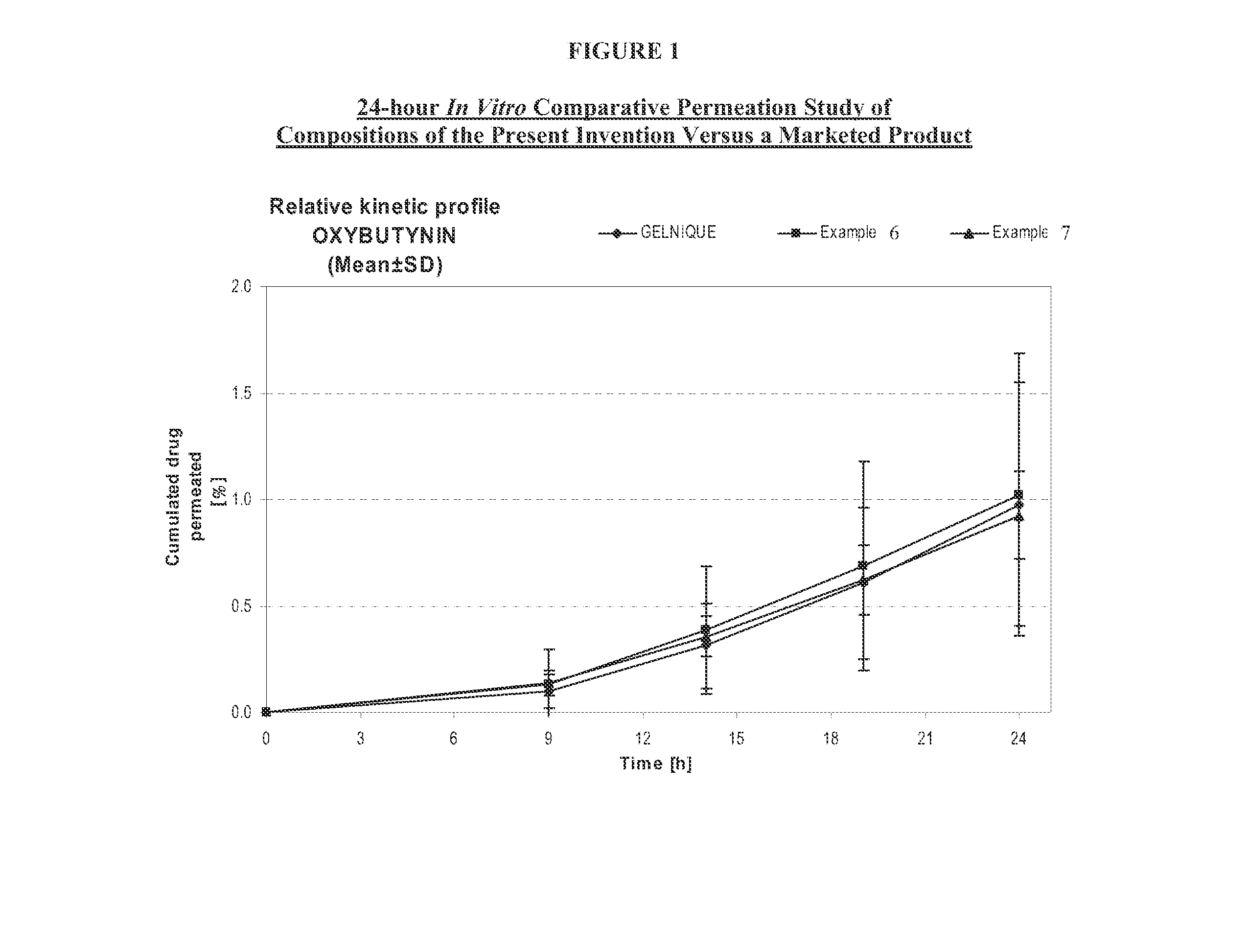
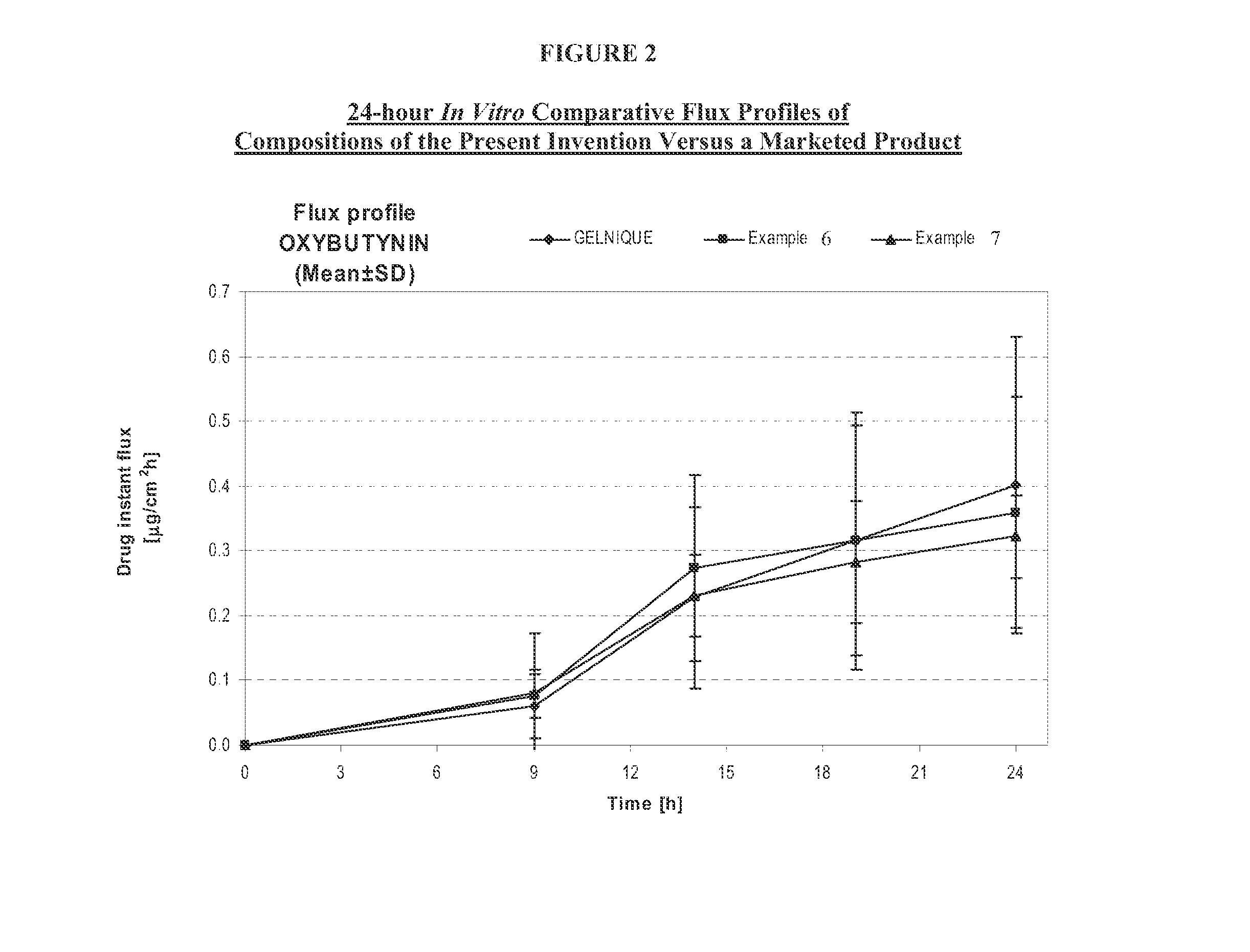
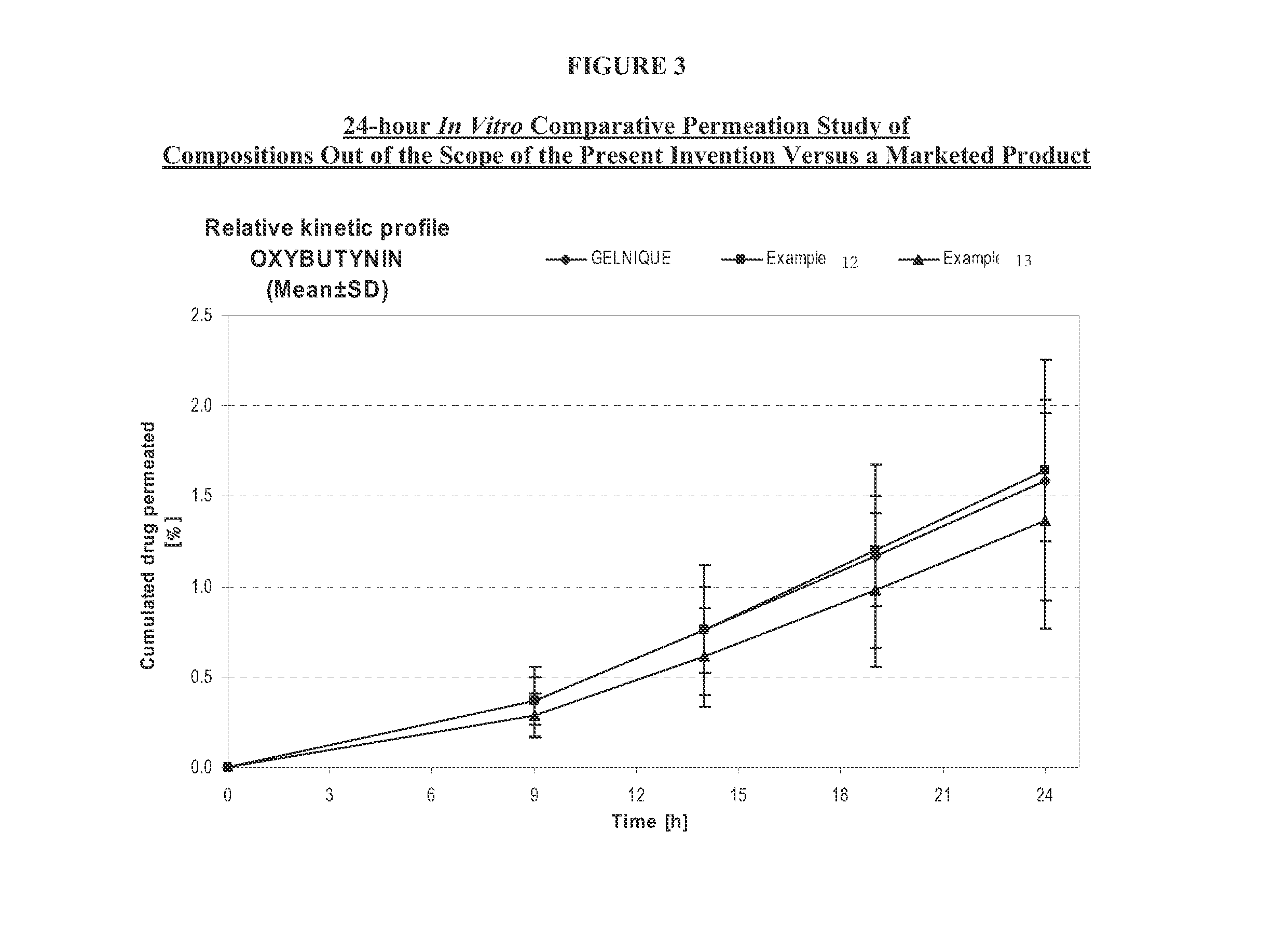
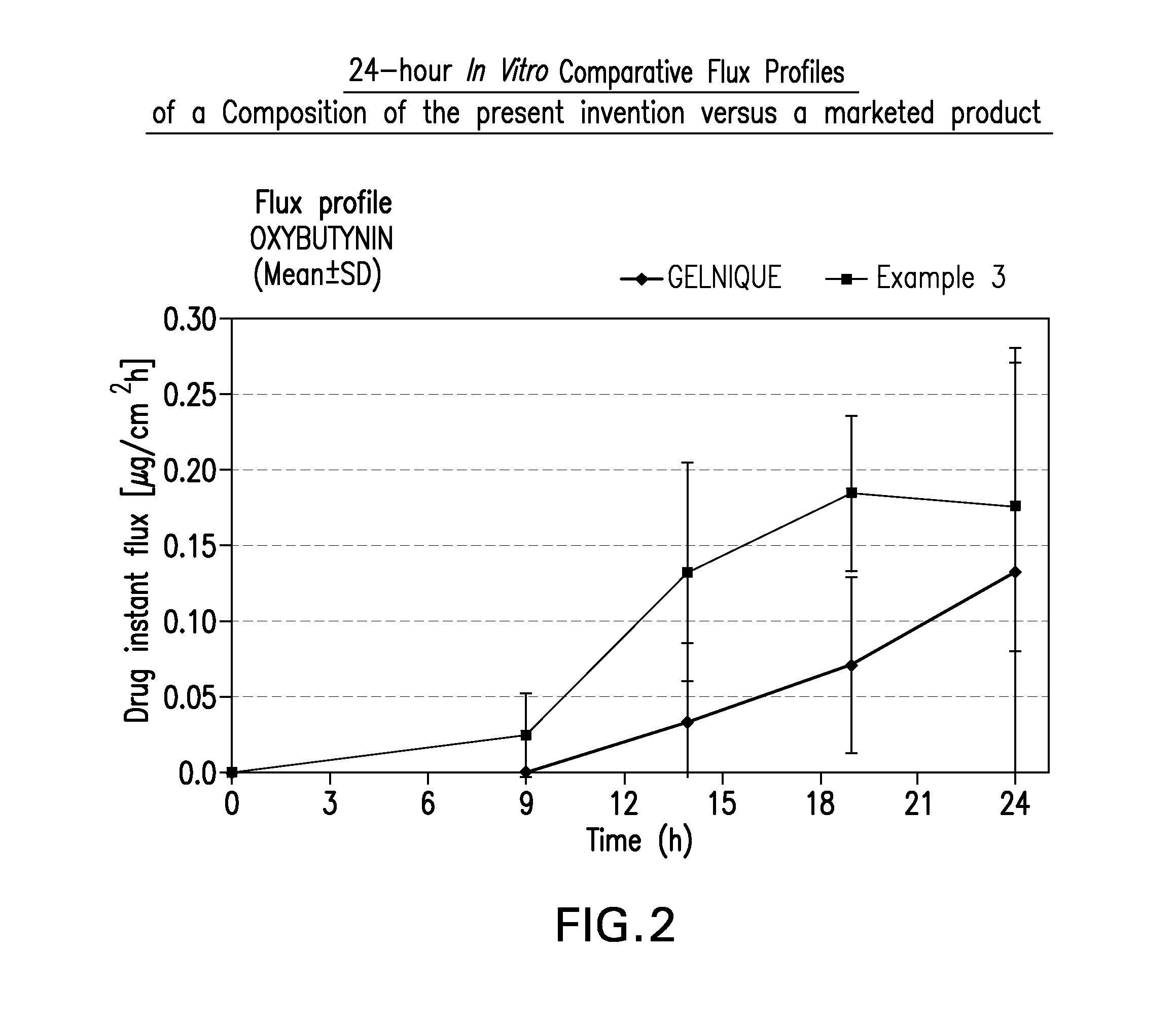
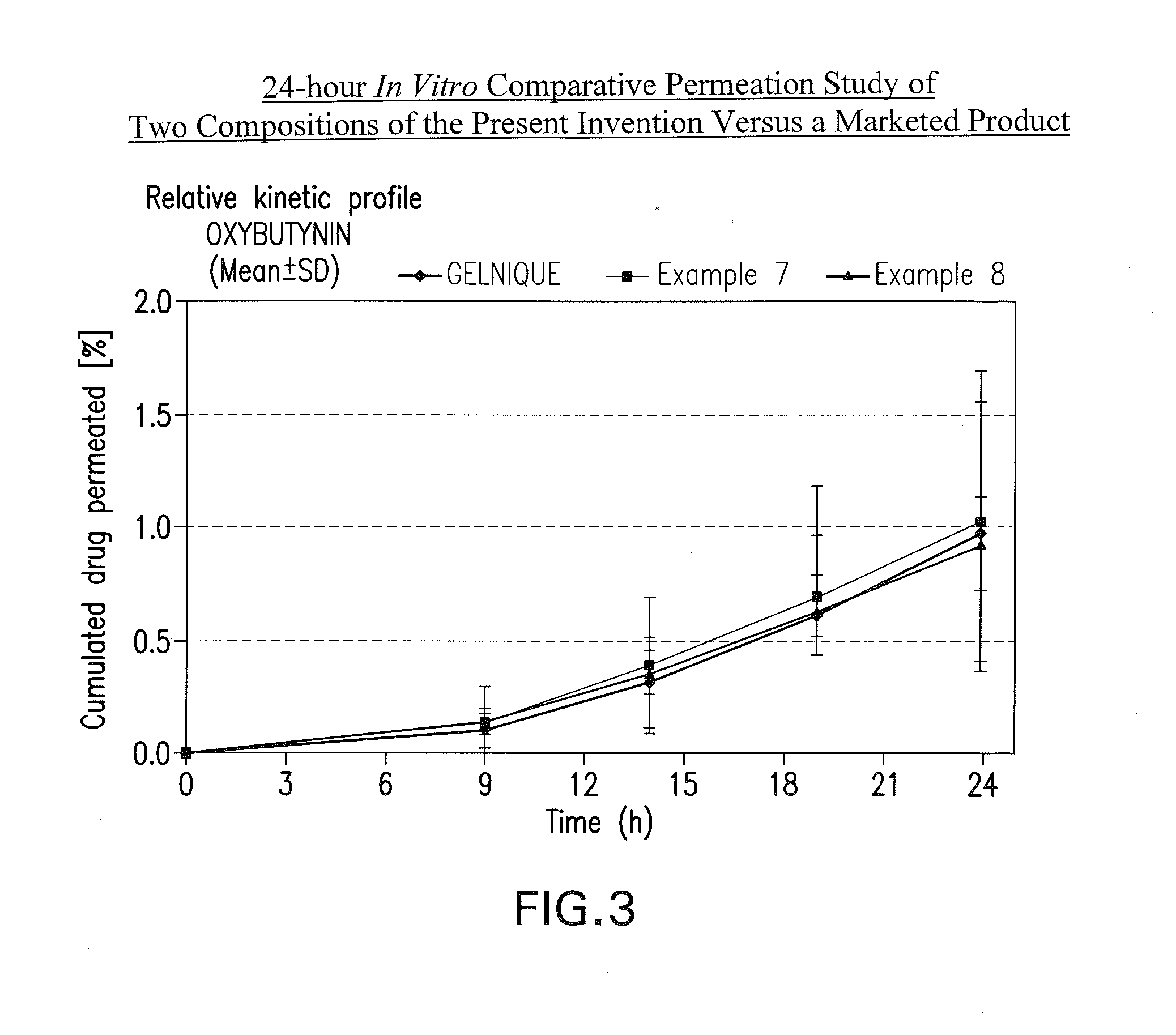
Transdermal compositions for Anti-cholinergic agents
InactiveUS20140037713A1Reduce morbidityAvoids undesirable odor and irritation effectsCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsOxybutyninSide effect
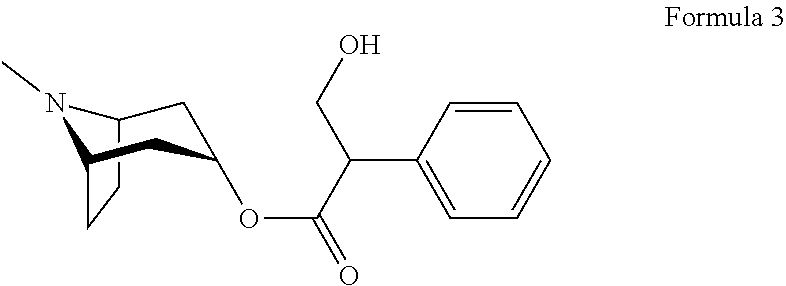
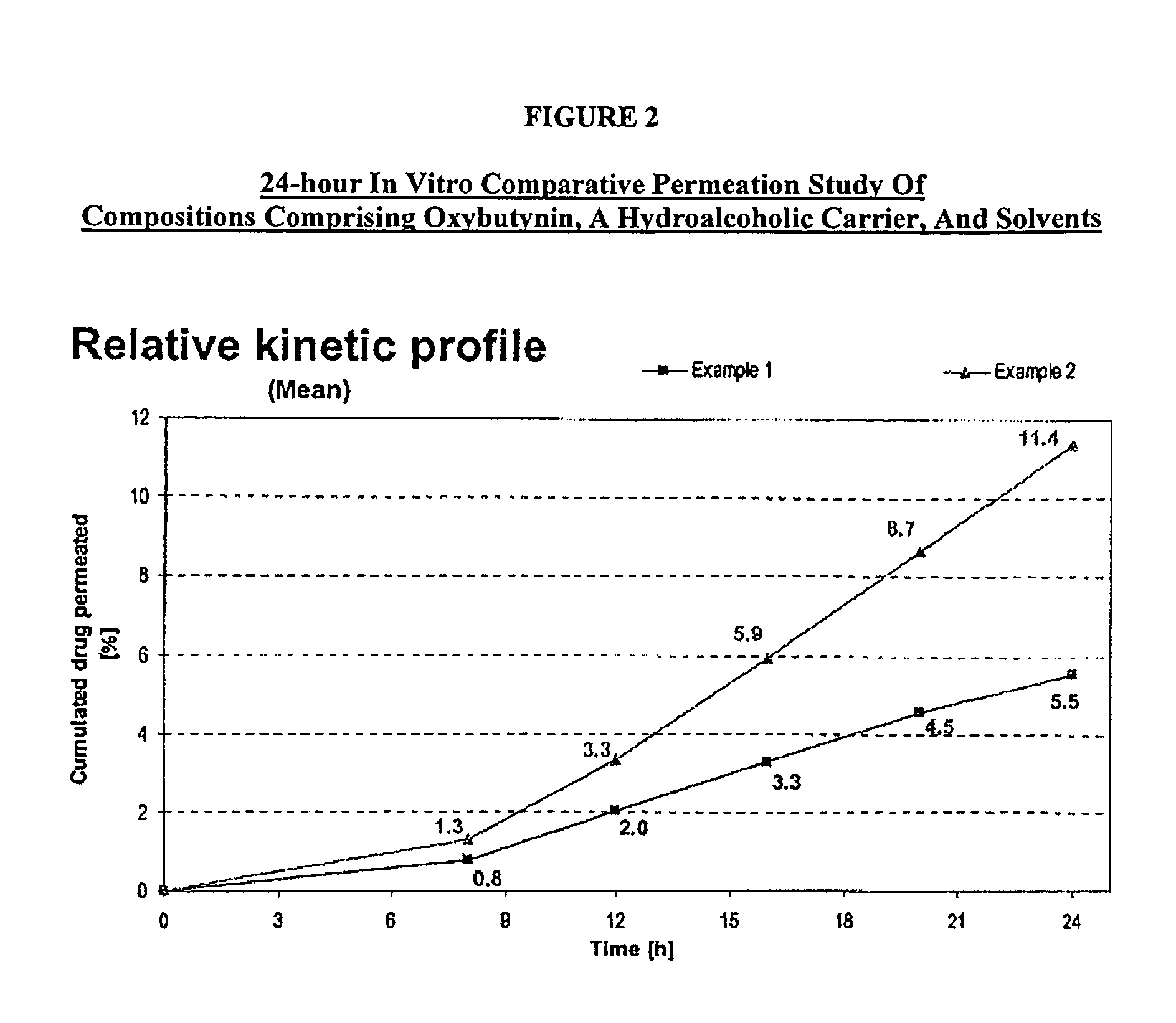
The present invention relates generally to compositions or formulations for transdermal or transmucosal administration of anti-cholinergic agents such as oxybutynin. The invention utilizes a novel delivery vehicle and is a substantially malodorous-free and irritation free transdermal formulation which is substantially live of long chain fatty alcohols, long-chain fatty acids, and long-chain fatty esters. A method is disclosed for treating a subject for hyperhidrosis with these formulations while reducing the incidences of peak concentrations of drug and undesirable side effects associated with oral anti-cholinergics.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
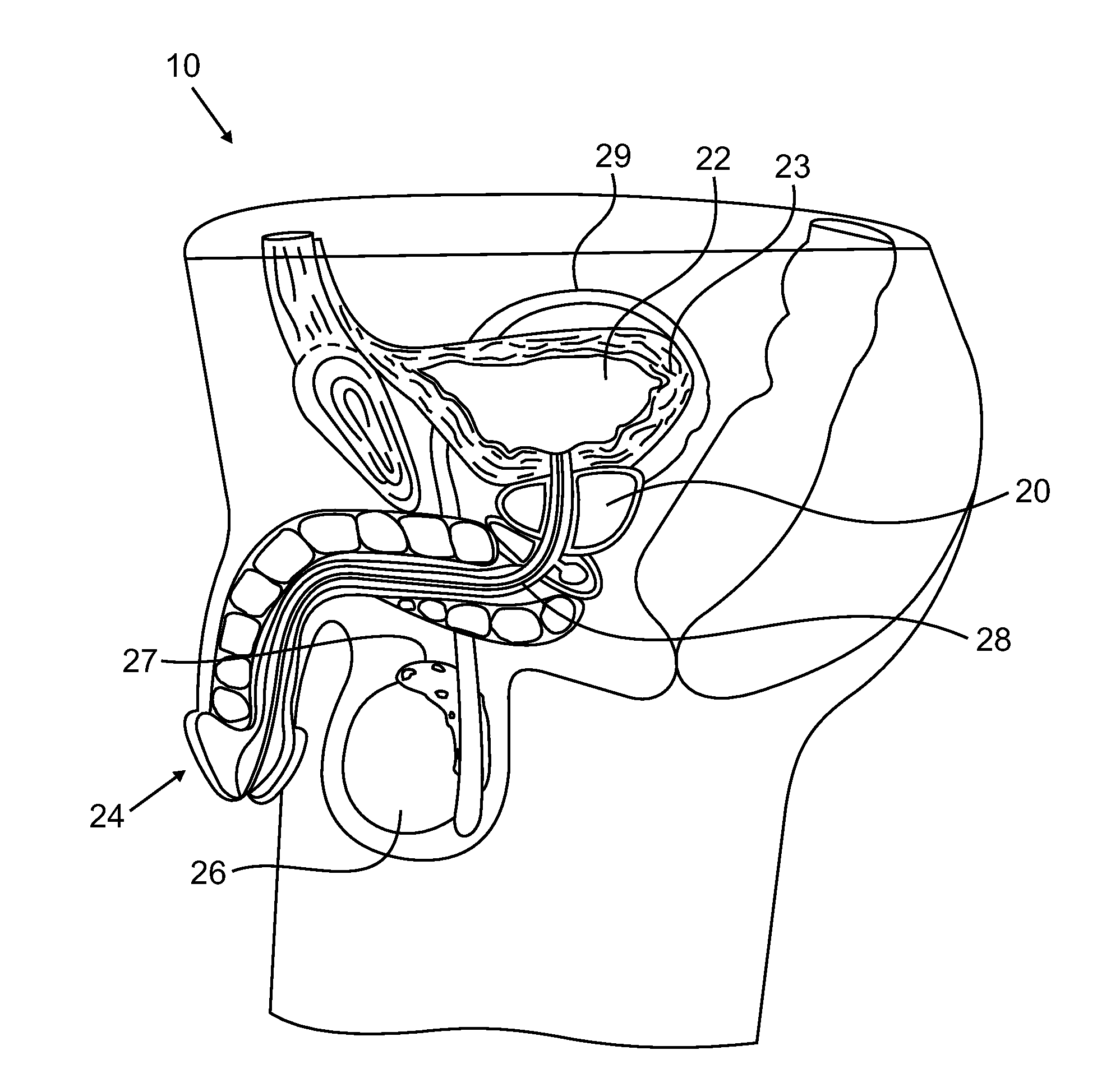
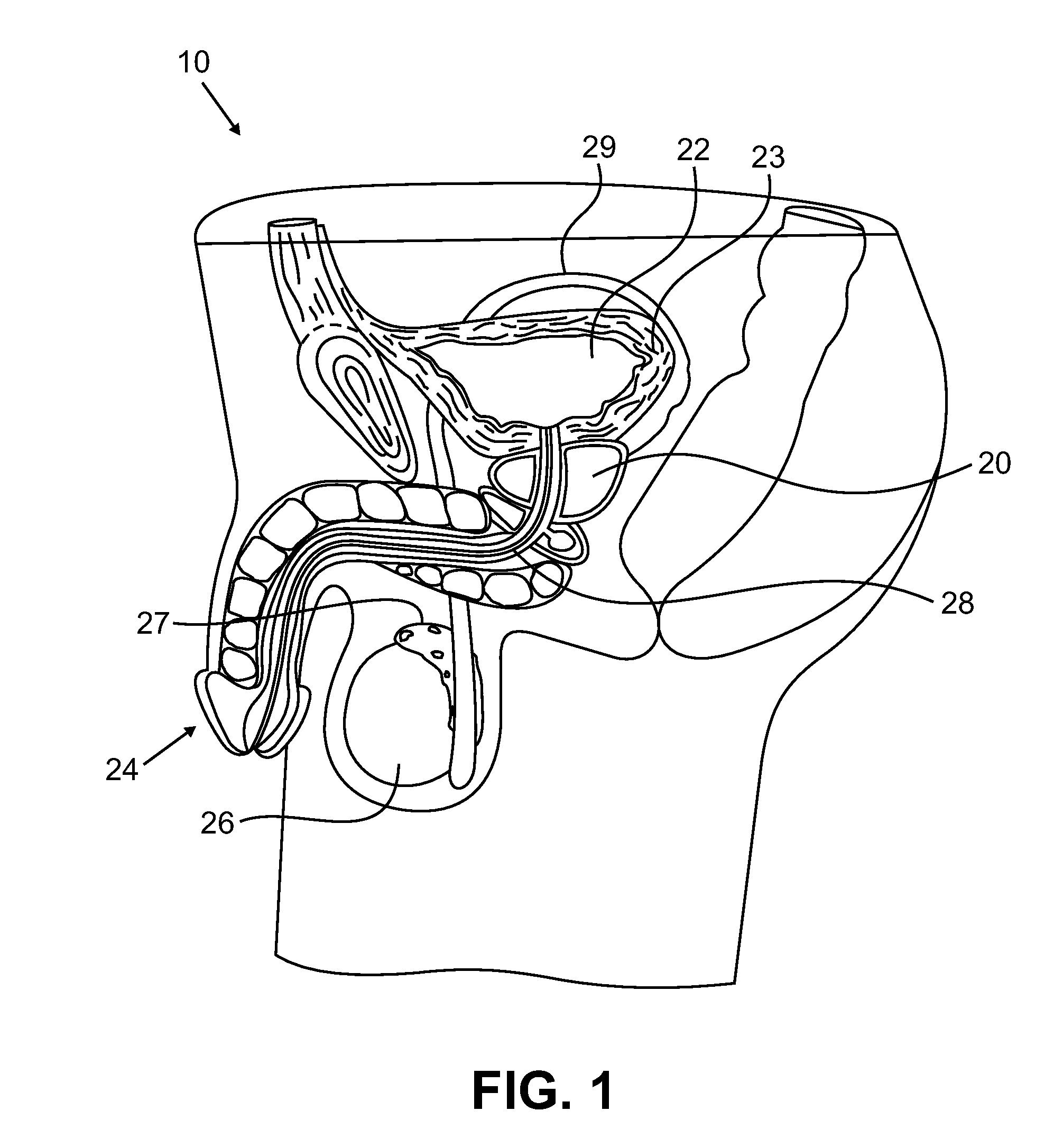
Urological medical devices for release of prostatically beneficial therapeutic agents
InactiveUS20080233167A1High quantity of drugAvoid the needAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiseaseGynecology
According to an aspect of the invention, urological medical devices are provided, which comprise a prostatically beneficial agent selected from alpha-adrenergic blockers, antispasmodic agents, anticholinergic / antimuscarinic agents, calcium channel blockers, anti-inflammatory agents, hormone-affecting agents, anti-cancer agents, and combinations thereof, among others. The urological medical devices are adapted for implantation or insertion into a subject's urinary tract, whereupon at least a portion of the prostatically beneficial agent is released into the subject's prostatic urethra. The release profile of the prostatically beneficial agent is effective to treat a prostatic disorder, for example, benign prostate hypertrophy, prostate cancer or prostatitis, among others. Other aspects of the invention are directed to treating prostatic disorders.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Combination of a PDE4 inhibitor and tiotropium or derivative thereof for treating obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases
InactiveUS20050107420A1Easy to controlInhibition is effectiveBiocideAnimal repellantsTiotropium bromidePDE4 Inhibitors
The present invention relates to a combination of therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases comprising (I) a PDEIV inhibitor that is therapeutically effective in the treatment of said diseases when administered by inhalation; together with (II) an anti-cholinergic agent comprising a member selected from the group consisting of tiotropium and derivatives thereof that is therapeutically effective in the treatment of said diseases when administered by inhalation; as well as to a method of treating said obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases comprising administering to said mammal by inhalation a therapeutically effective amount of said combination of therapeutic agents; and a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier together with said combination of therapeutic agents; and a package containing a pharmaceutical composition for insertion into a device capable of simultaneous or sequential delivery of said pharmaceutical composition in the form of an aerosol or dry powder dispersion to said mammal, where said device is a metered dose inhaler or a dry powder inhaler. It is preferred that said anti-cholinergic agent component be tiotropium bromide.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Transdermal compositions for anticholinergic agents
InactiveUS20100216880A1Avoiding undesirable peak in drug concentrationReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsBiocideOxybutyninLong chain fatty acid
The present invention relates generally to compositions or formulations for transdermal or transmucosal administration of anticholinergic agents such as oxybutynin. The invention utilizes a novel delivery vehicle and is a substantially malodorous-free and irritation free transdermal formulation which is substantially free of long chain fatty alcohols, long-chain fatty acids, and long-chain fatty esters. A method is disclosed for treating a subject for urinary incontinence with these formulations while reducing the incidences of peak concentrations of drug and undesirable side effects associated with oral anticholinergics.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
Use of autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters inhibition and atrial parasympathetic fibers ablation for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to preserve drug effects
InactiveUSRE42961E1Increased occurrence of initiation of atrial flutterShorten the construction periodDiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsNervous systemRight atrium
Atrial arrhythmias, a major contributor to cardiovascular morbidity, are believed to be influenced by autonomic nervous system tone. The main purpose of this invention was to highlight new findings that have emerged in the study of effects of autonomic nervous system tone on atrial arrhythmias, and its interaction with class III antiarrhythmic drug effects. This invention evaluates the significance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation by determining the effects of autonomic nervous system using a vagal and stellar ganglions stimulation, and by using autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters infusion (norepinephrine, acetylcholine). This invention evaluates the autonomic nervous system effects on the atrial effective refractory period duration and dispersion, atrial conduction velocity, atrial wavelength duration, excitable gap duration during a stable circuit (such atrial flutter circuit around an anatomical obstacle), and on the susceptibility of occurrence (initiation, maintenance and termination) of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias in canine. This invention also evaluates whether autonomic nervous system activation effects via a local neurotransimitters infusion into the right atria can alter those of class III antiarrhythmic drug, sotalol, during a sustained right atrial flutter. This invention represents an emergent need to set-up and develop a new class of anti-cholinergic drug therapy for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to combine this new anti-cholinergic class to antiarrhythmic drugs. Furthermore, this invention also highlights the importance of a local application of parasympathetic neurotransmitters / blockers and a catheter ablation of the area of right atrium with the highest density of parasympathetic fibers innervation. This may significantly reduce the occurrence of atrial arrhythmias and may preserve the antiarrhythmic effects of any drugs used for the treatment of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Combined Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor and Quaternary Ammonium Antimuscarinic Therapy to Alter Progression of Cognitive Diseases
ActiveUS20130172398A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectBiocideAmine active ingredientsDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
Use and composition for treating dementia
ActiveUS8404701B2Maximize the effectSymptoms improvedBiocideNervous disorderMaximum tolerated doseAnti cholinergic
Owner:CHASE PHARMA CORP
Crystalline anti-cholinergic tiotropium crystal
ActiveCN1634921ANo significant difference in formulation qualityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnticholinergic agentsTiotropium bromide
The invention relates to crystal unhydrous (1R,2R,4S,5S,7S)-7-[2-hydroxy-2,2-bis(2-thienyl) acetoxy]-9,9-dimethyl-3-oxa-9-azo cation tricyclo octane [3.3.1.02.4] nonane bromide, clinic use of tiotropium bromide anhydrous crystal as anti-cholinergic medicines, and preparation process of tiotropium bromide anhydrous crystal.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Combined acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and quaternary ammonium antimuscarinic therapy to alter progression of cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20150031897A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectOrganic chemistryEster active ingredientsDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
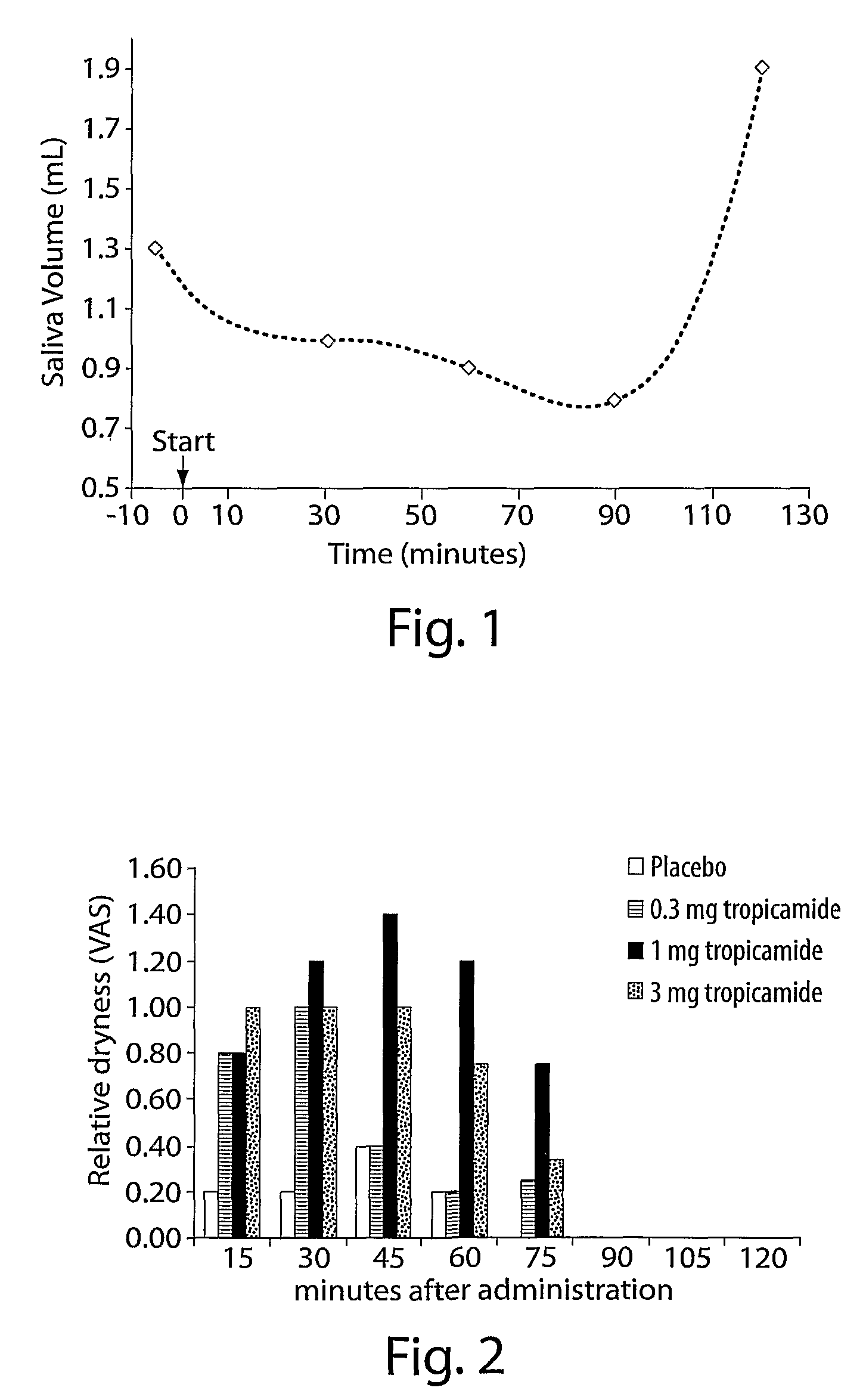
Methods And Compositions For Decreasing Saliva Production
ActiveUS20080102102A1Decrease saliva productionControl halitosisBiocideDigestive systemSialorrheaAnti cholinergic
The invention provides methods and compositions comprising an anti-cholinergic agent for decreasing saliva production and treating sialorrhea.
Owner:NEUROHEALING PHARMA INC
Combined Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor and Quaternary Ammonium Antimuscarinic Therapy to Alter Progression of Cognitive Diseases
ActiveUS20130172379A1Prevents or substantially ameliorates the undesired side effects of acetyl-cholinesteraseMaximize the effectBiocideOrganic chemistryDementia with Lewy bodiesPsychiatry
A method administers quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in combination with acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to treat either cognitive impairment or acute delirium. This therapy results in a modification of a cognitive disorder or disease, namely a slow down in the disease progression. In one preferred embodiment, the disease is dementia with Lewy Bodies. New formulations for quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists are also disclosed.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
Compositions and Methods for Treating Social Anxiety
InactiveUS20110218215A1Preventing social phobiaStop formationBiocideNervous disorderAtropine sulfateMedicine
The disclosure provides a pharmaceutical composition for treating social anxiety, performance anxiety, and social phobia comprising a therapeutic amount for die treatment of a patient of a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist, an anti-diarrheal compound, and an optional anticholinergic compound. The β-adrenergic receptor antagonist may be the lipophilic β-blocker propranolol HCl, the anti-diarrheal compound may be the opioid diphenoxylate HCl, and the optional anticholinergic compound may be atropine sulfate. The composition for treating performance anxiety and social phobia can further include a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. A method of preventing or treating social anxiety, performance anxiety, and social phobia in a patient is also provided, comprising administering a composition of the disclosure to a patient in need of such treatment. The composition administered in the present method comprises a therapeutic amount of a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist, an anti-diarrheal compound, and an optional anticholinergic compound.
Owner:HOLLY BENJAMIN D
Method and composition for treating alzheimer-type dementia
InactiveUS20110201597A1Extended durationFunction increaseBiocideNervous disorderNK1 receptor antagonistMaximum tolerated dose
There is described a method for increasing the maximal tolerated dose and thus the efficacy of an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) in a patient suffering from an Alzheimer type dementia by decreasing concomitant adverse effects by administration of said AChEI in combination with a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent, whereby an enhanced acetylcholinesterase inhibition in the CNS of said patient is achieved and alleviation of the symptoms of Alzheimer type dementia in said patient is thereby improved to a greater extent. The use of a non-anticholinergic antiemetic agent for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of Alzheimer type dementia in combination with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI) and pharmaceutical compositions comprising (a) a 5HT3 receptor antagonist, a dopamine antagonist, a H1-receptor antagonist, a cannabinoid agonist, aprepitant or casopitant as an antiemetic agent and (b) an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor are also described.
Owner:CHASE PHARMA CORP
Medicine for treating post stroke depression and application thereof
InactiveCN104208583ALow priceEasy to acceptOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSalvia miltiorrhizaCannabis
The invention relates to a medicine for treating post stroke depression and an application thereof. The medicine is prepared from the following medicinal raw materials in parts by weight: 25-35 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, 25-35 parts of rhizoma acori graminei, 10-20 parts of ligusticum wallichii, 10-20 parts of radix paeoniae alba, 10-20 parts of polygala tenuifolia, 5-15 parts of safflower carthamus, 5-15 parts of peach kernel, 7-17 parts of prepared rhizoma cyperi, 5-15 parts of radix bupleuri, 5-15 parts of fructus aurantii, 5-15 parts of radix curcumae, 4-8 parts of pericarpium citri reticulatae viride, 10-20 parts of endothelium corneum gigeriae galli, 25-35 parts of fructus cannabis, 25-35 parts of spina date seed and 25-35 parts of tuber fleeceflower stem. The invention further relates to a composition containing the medicine and fluoxetine hydrochloride. The medicine combined with antidepressant is capable of accelerating the drug effect taking speed, the dose can be controlled, the course of treatment can be shortened, the 'contradictory phenomena' and 'anticholinergic side effect' can be reduced, the effect of the medicine by combining comprehensive rehabilitation therapy is relatively remarkable in the treatment process, and the medicine is capable of gradually replacing the antidepressant in the later period of treatment.
Owner:上海市闸北区中医医院
Permeation enhancing compositions for anticholinergic agents
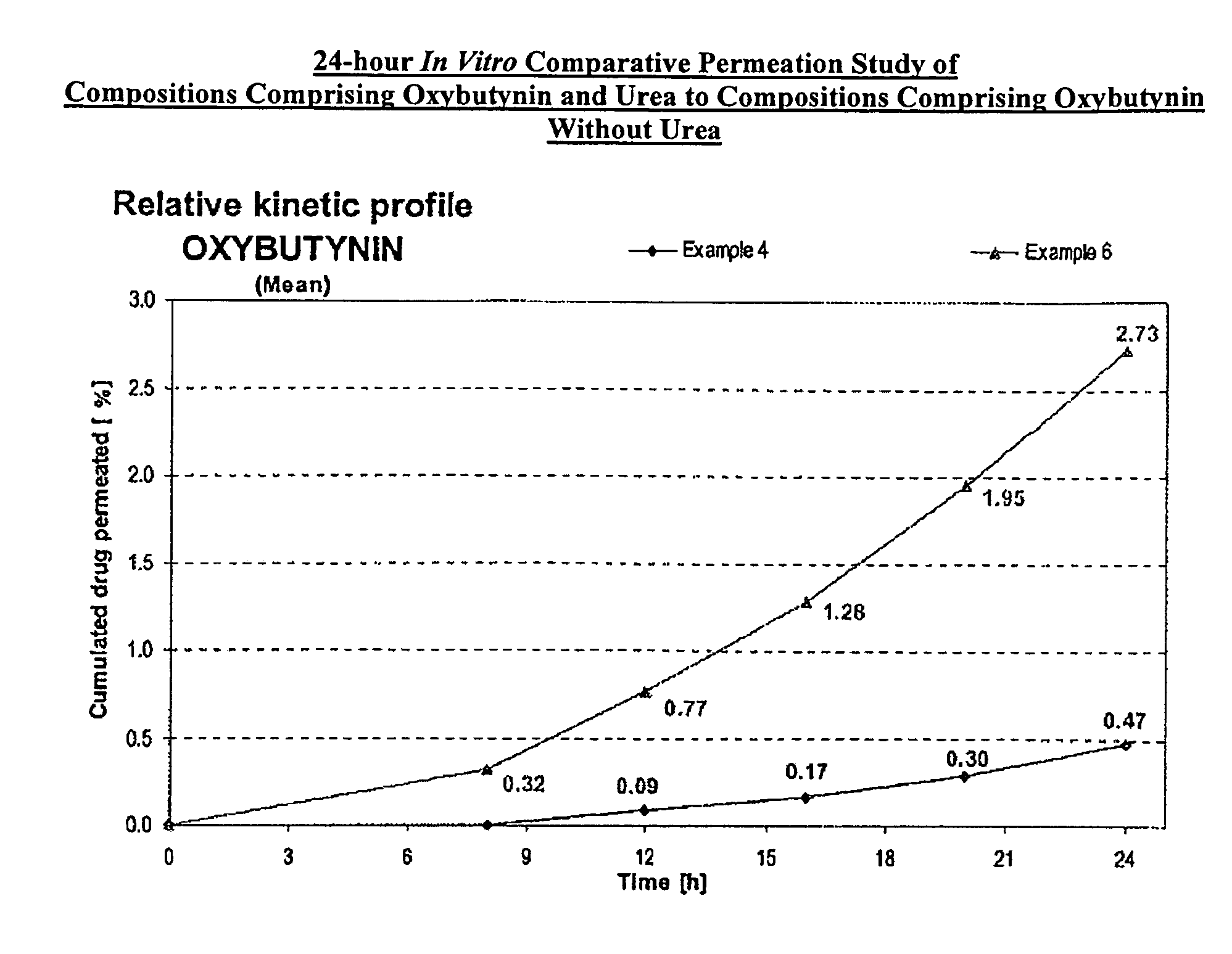
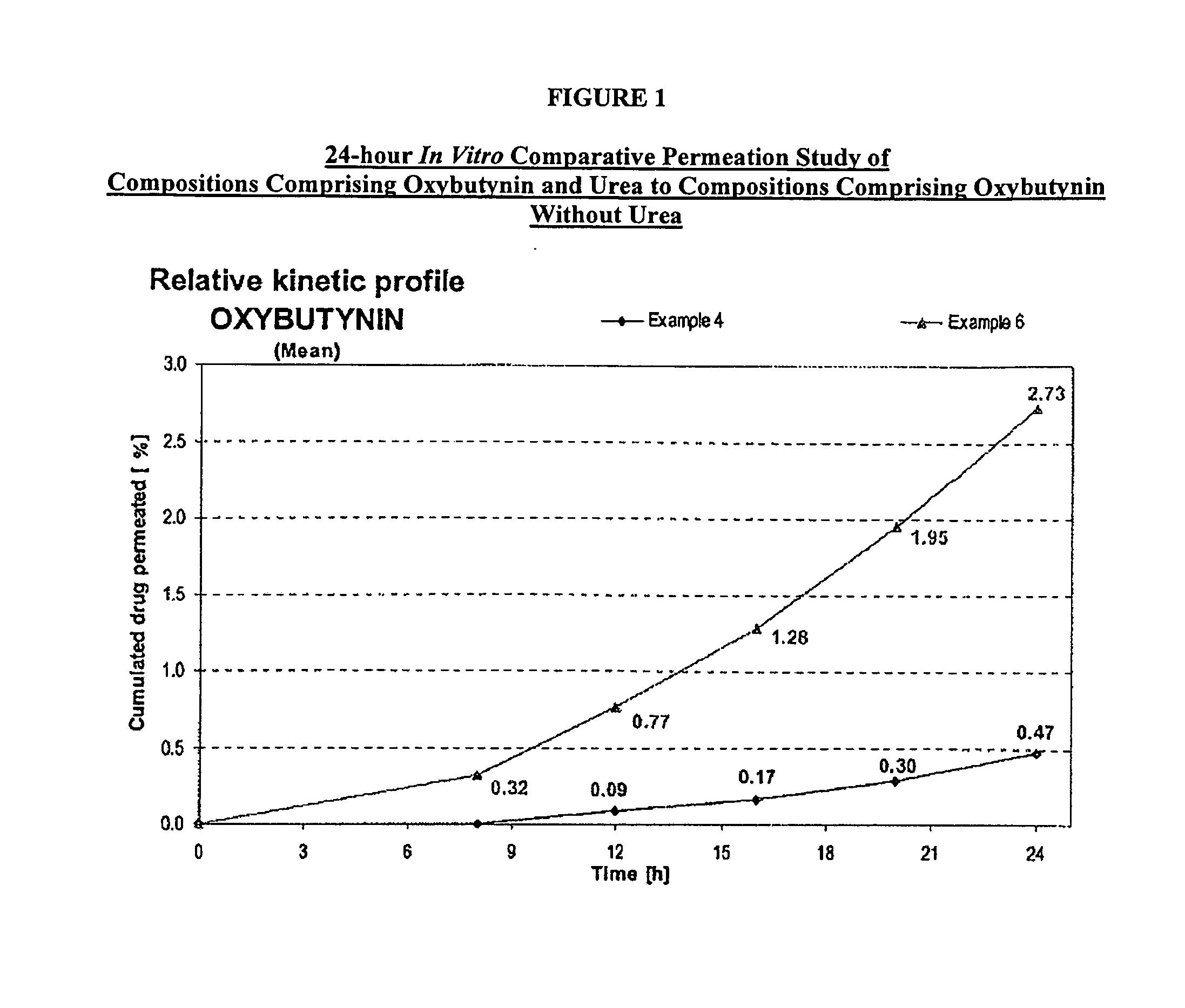
InactiveUS20080260842A1Avoiding undesirable peak in drug concentrationReduce morbidityBiocideAerosol deliveryOxybutyninAnticholinergic agents
A transdermal or topical skin-friendly composition including anticholinergic agents, such as oxybutynin, a urea-containing compound and a carrier system. A method is disclosed for treating a subject for urinary incontinence while reducing the incidences of peak concentrations of drug and undesirable side effects associated with oral anticholinergics.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA IPL
Combination of adrenergic agonist and tricyclo-alkylamine for relieving chronic pain without adverse side effects
This invention discloses that a combination of two drugs, from two different and previously unrelated categories, provides effective and long-lasting relief from neuropathic pain. Both drugs can be taken orally, in a convenient, painless, non-invasive manner that does not require injections. One drug in this combination is an alpha2 adrenergic agonist, exemplified by clonidine. The other drug in the pain-relieving combination has a tri-cyclo-alkyl-amine (TCAA) structure. At least some TCAA drugs have antagonist (receptor-blocking) activity at two entirely different classes of neuronal receptors: the muscarinic subclass of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors, and the NMDA subclass of glutamate receptors. Such drugs include ethopropazine, normally used as an anti-cholinergic drug, and desipramine, normally used as an anti-depressant. Tests by the Applicants have shown that at least some TCAA drugs can relieve neuropathic pain to a limited extent, but at the doses required to relieve pain, they cause adverse side effects, and any pain relief is relatively brief and short-lived. However, when a TCAA drug such as ethopropazine is administered together with an alpha2 adrenergic agonist such as clonidine, these drugs mutually potentiate one another's neuropathic pain-relieving action, and provide potent and sustained neuropathic pain relief, even when each agent is administered at a low dosage that is below its threshold for causing adverse side effects. Accordingly, this drug combination can provide safe and effective relief of neuropathic pain and possibly other types of chronic and / or intractable pain, at dosages which are so low that they do not pose serious risks of adverse side effects.
Owner:OLNEY JOHN W +2
Combination of an adenosine A2A-receptor agonist and tiotropium or a derivative thereof for treating obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases
InactiveUS20050250730A1Easy to controlInhibition is effectiveBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseAnticholinergic agents
A combination of therapeutic agents useful in the treatment of obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases comprising (i) an adenosine A2A receptor agonist; and (ii) an anti-cholinergic agent, preferably comprising a member selected from the group consisting of tiotropium and derivatives thereof; the combination being therapeutically effective in the treatment of the diseases when administered by inhalation; as well as to a method of treating the obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases comprising administering separately, simultaneously or sequentially to the mammal by inhalation a therapeutically effective amount of the combination of therapeutic agents; as well as to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier together with the combination of therapeutic agents; as well as to a product containing the compounds of the combination for separate, simultaneous or sequential administration by inhalation to a mammal for the treatment of obstructive airways and other inflammatory diseases. It is preferred that the anti-cholinergic agent component be tiotropium bromide.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20060110449A1Reduce adverse effectsImproved degradation profileBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseAnticholinergic Drugs
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Modified anticholinergic neurotoxins as modulators of the autoimmune reaction
ActiveUS8034777B2Long maintenance periodPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAutoimmune ReactionsAlpha-neurotoxin
The invention comprises a composition of matter and method of its use for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in humans. The composition is a modified anticholinergic alpha-neurotoxin. Alpha-neurotoxin solution, such as cobratoxin, is filter sterilized to remove bacteria. It is modified using H2O2. Any suitable preservative for parenteral administration can be employed such as methyl paraben, benzalkonium chloride or metacreosol. It is preferred that the composition is administered every other day or daily. The composition may be administered orally, subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. Parenterally, either subcutaneous or intramuscular injection is preferred.
Owner:RECEPTOPHARM
Process for preparing a dry powder formulation comprising an anticholinergic, a corticosteroid and a beta-adrenergic
Dry powder formulations for inhalation containing a combination of an anti-cholinergic, a long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist, and a corticosteroid are useful for the prevention and / or treatment of an inflammatory and / or obstructive airways disease.
Owner:CHIESI FARM SPA
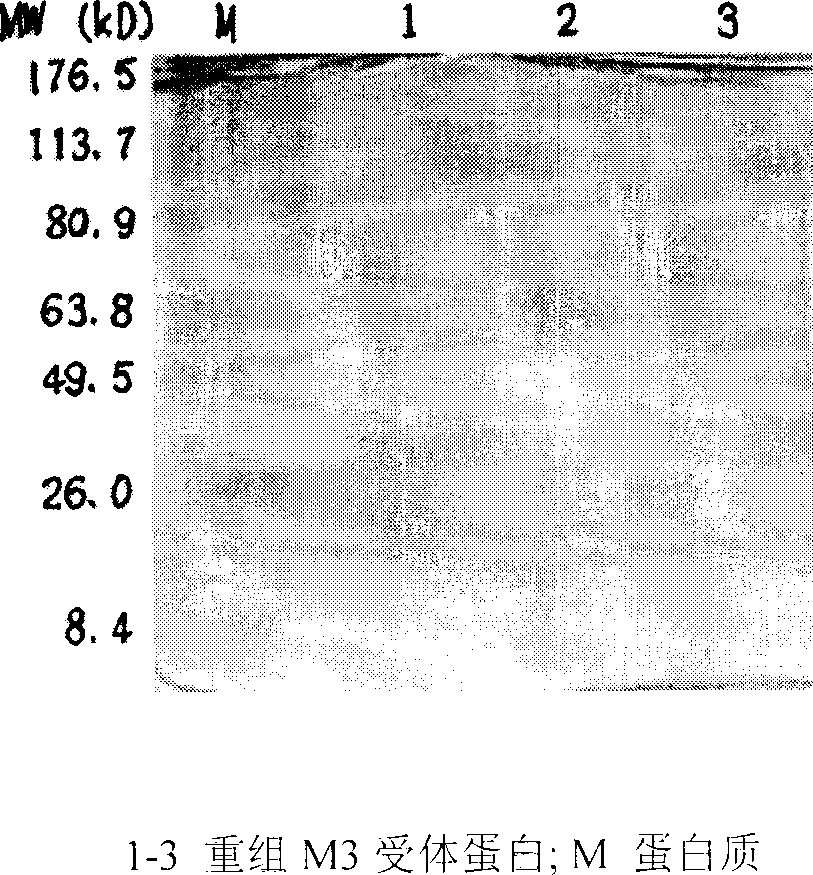
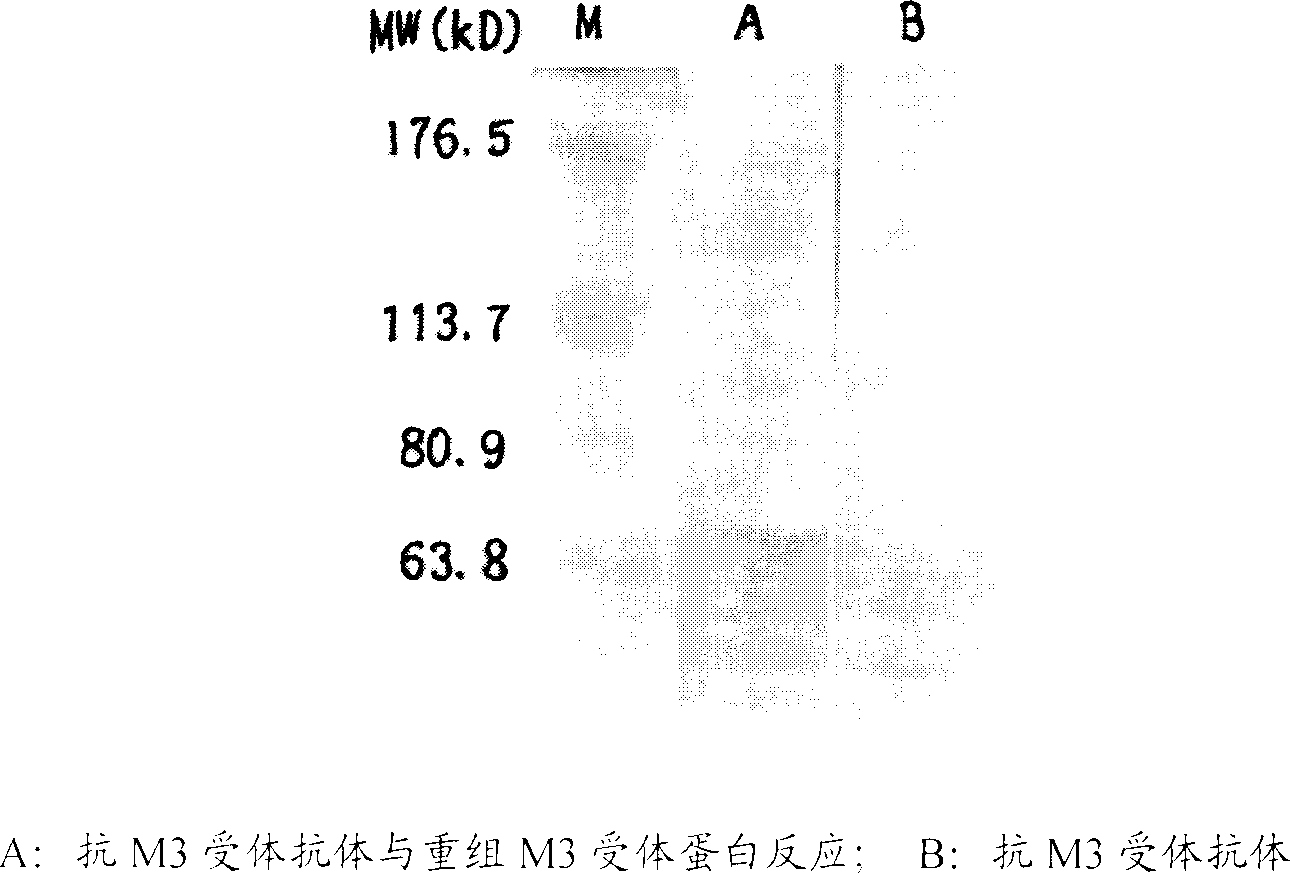
Use of anticholinergic M3-type receptor antibody determination for diagonsing sicca syndrome
InactiveCN1896101ACell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingTrue positive rateSicca syndrome
Determination of anticholinergic M3 receptor and antibody is used to diagnose sicca syndrome. It has excellent sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Uses for quaternary ammonium anticholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonists in patients being treated for cognitive impairment or acute delirium
A method for treating the adverse effects of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors used in the treatment of cognitive disorders such as acute delirium and cognitive impairment in elderly human patients. The administration of a clinically effective amount of a quaternary ammonium anti-cholinergic muscarinic receptor antagonist having very low lipid solubility substantially eliminates the adverse effects of urinary and / or fecal incontinence, nausea, bradycardia, bronchorrhea or brochospasm caused by the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors, without affecting the beneficial activity of the acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors. This permits the administration of the optimum effective dosing of acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors to provide maximum benefit to the patient with the added benefit of reducing or eliminating the unwanted side effects of fecal and urinary incontinence. Further, the combination of rivastigmine and glycopyrrolate has been effective in significantly improving cognitive function in patients suffering from acute dementia or cognitive impairment.
Owner:QAAM PHARMA LLC
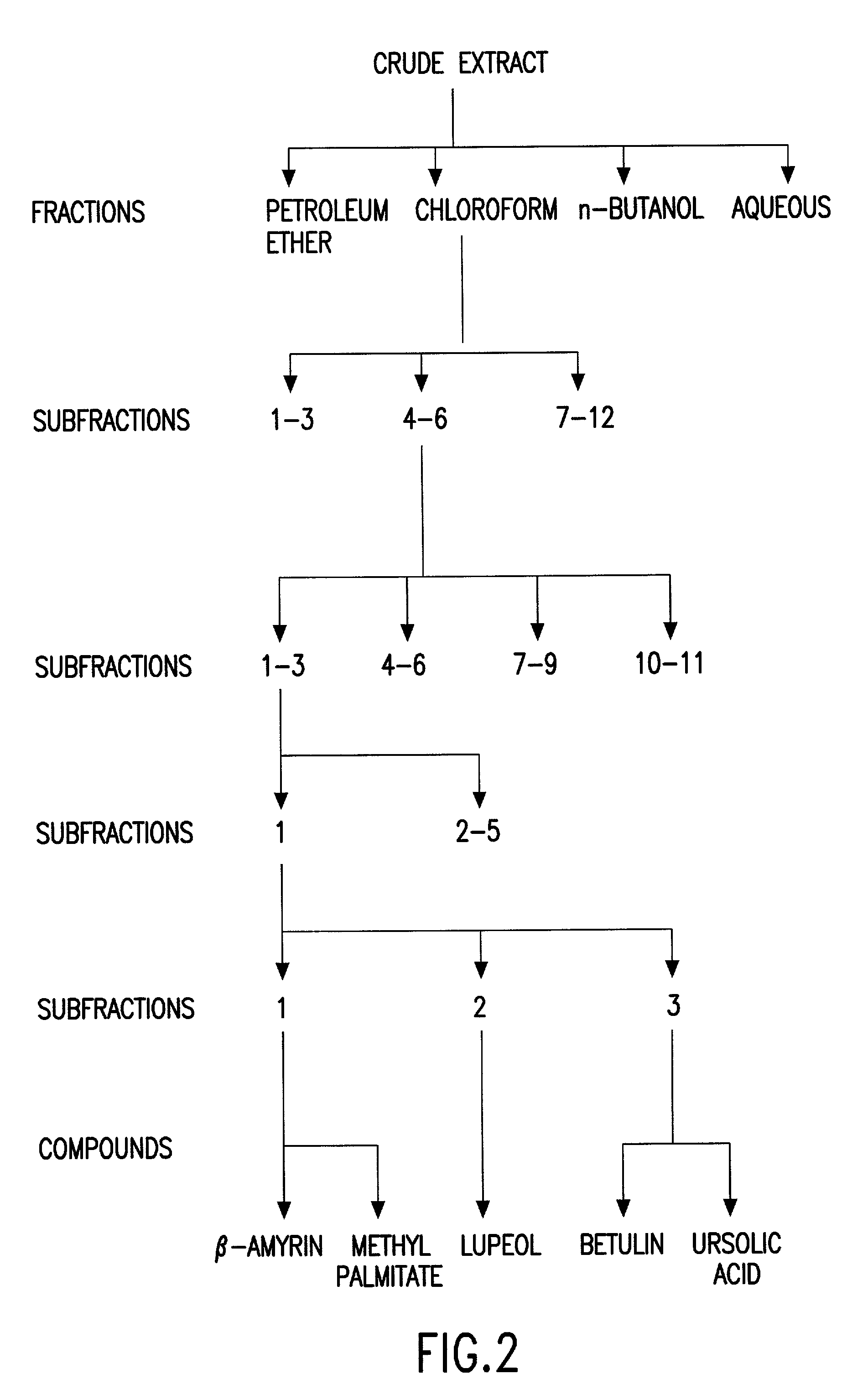
Biologically active chloroform fraction of an extract obtained from a mangroone plant Salvadora persica L
The invention discloses a process of extracting, fractionating and purifying bioactive molecules from an associated mangrove plant, methods of screening for pharmacological activities of crude extract, its fractions and purified compounds and use of the chloroform fraction of the crude extract as anti-spasmodic, anti-arrhythmic and anti-cholinergic agent.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
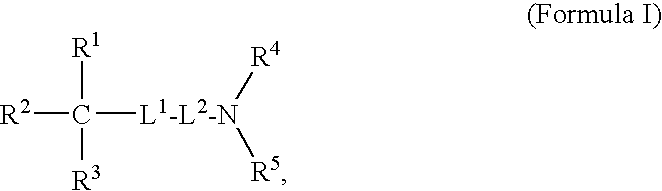
Oligomer-Anticholinergic Agent Conjugates
The invention provides anticholinergic agents that are chemically modified by covalent attachment of a water-soluble oligomer. A conjugate of the invention, when administered by any of a number of administration routes, exhibits characteristics that are different as compared to the characteristics of the anticholinergic agent not attached to the water-soluble oligomer.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Urological medical devices for release of prostatically beneficial therapeutic agents
According to an aspect of the invention, urological medical devices are provided, which comprise a prostatically beneficial agent selected from alpha-adrenergic blockers, antispasmodic agents, anticholinergic / antimuscarinic agents, calcium channel blockers, anti-inflammatory agents, hormone affecting agents, anti-cancer agents, and combinations thereof, among others. The urological medical devices are adapted for implantation or insertion into a subject's urinary tract, whereupon at least a portion of the prostatically beneficial agent is released into the subject's prostatic urethra. The release profile of the prostatically beneficial agent is effective to treat a prostatic disorder, for example, benign prostate hypertrophy, prostate cancer or prostatitis, among others. Other aspects of the invention are directed to treating prostatic disorders.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and compositions for decreasing saliva production
ActiveUS9198897B2Reduce productionDiminished swallowing reflexBiocideDigestive systemSialorrheaAnti cholinergic
The invention provides methods and compositions comprising an anti-cholinergic agent for decreasing saliva production and treating sialorrhea.
Owner:NEUROHEALING PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com