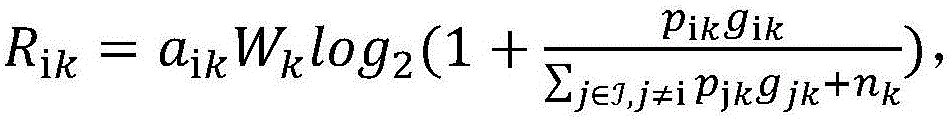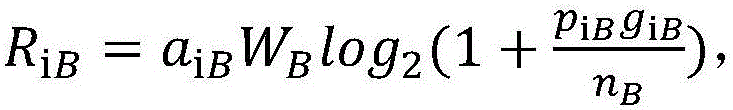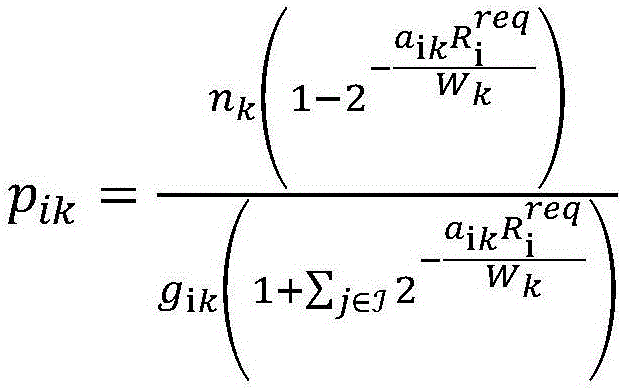Patents
Literature
35 results about "Cellular traffic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This article discusses the mobile cellular network aspect of teletraffic measurements. Mobile radio networks have traffic issues that do not arise in connection with the fixed line PSTN. Important aspects of cellular traffic include: quality of service targets, traffic capacity and cell size, spectral efficiency and sectorization, traffic capacity versus coverage, and channel holding time analysis.
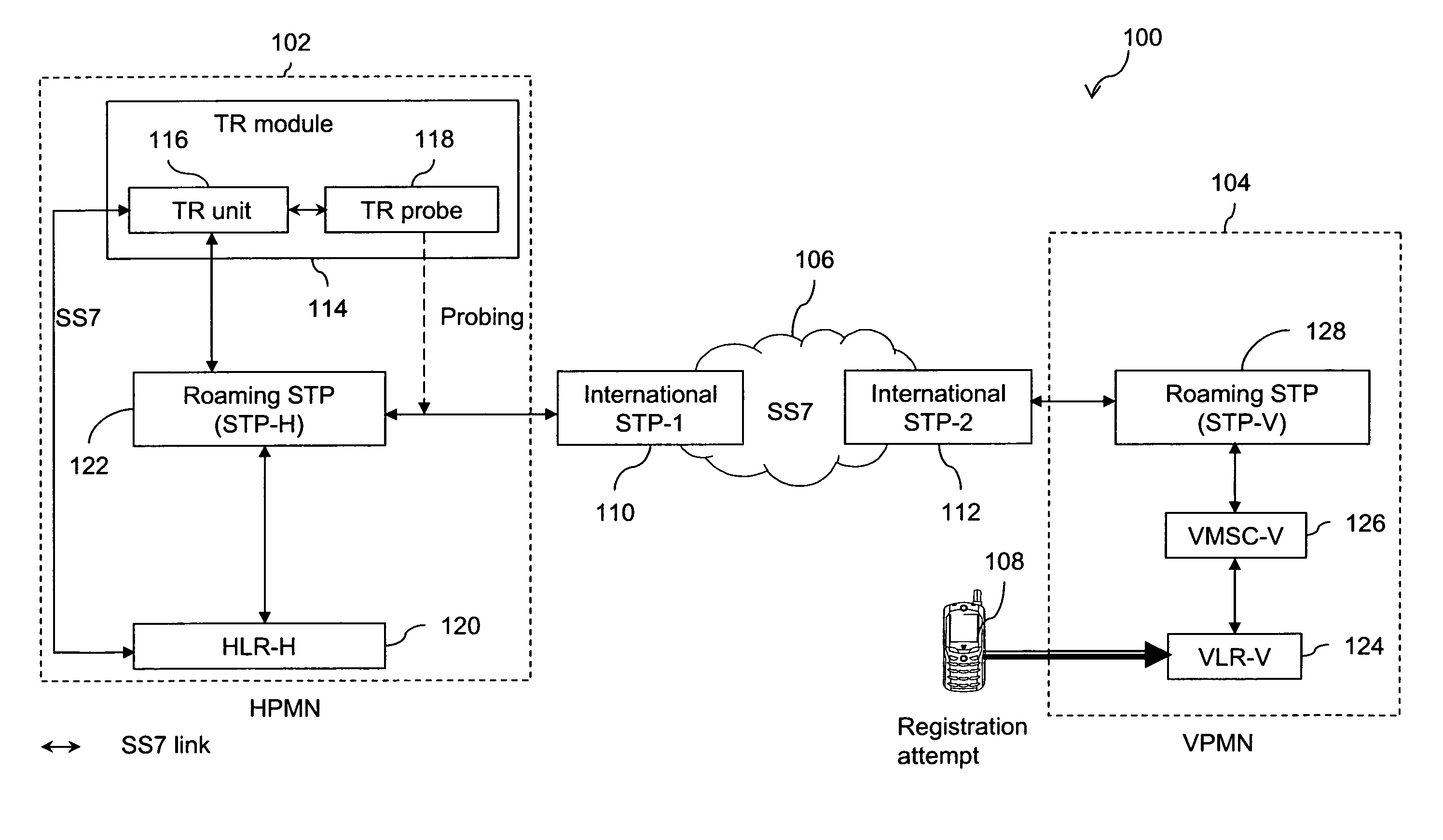
Method and system for providing GSMA IR. 73 SoR compliant cellular traffic redirection
InactiveUS20080020756A1Connection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDatabaseCellular traffic
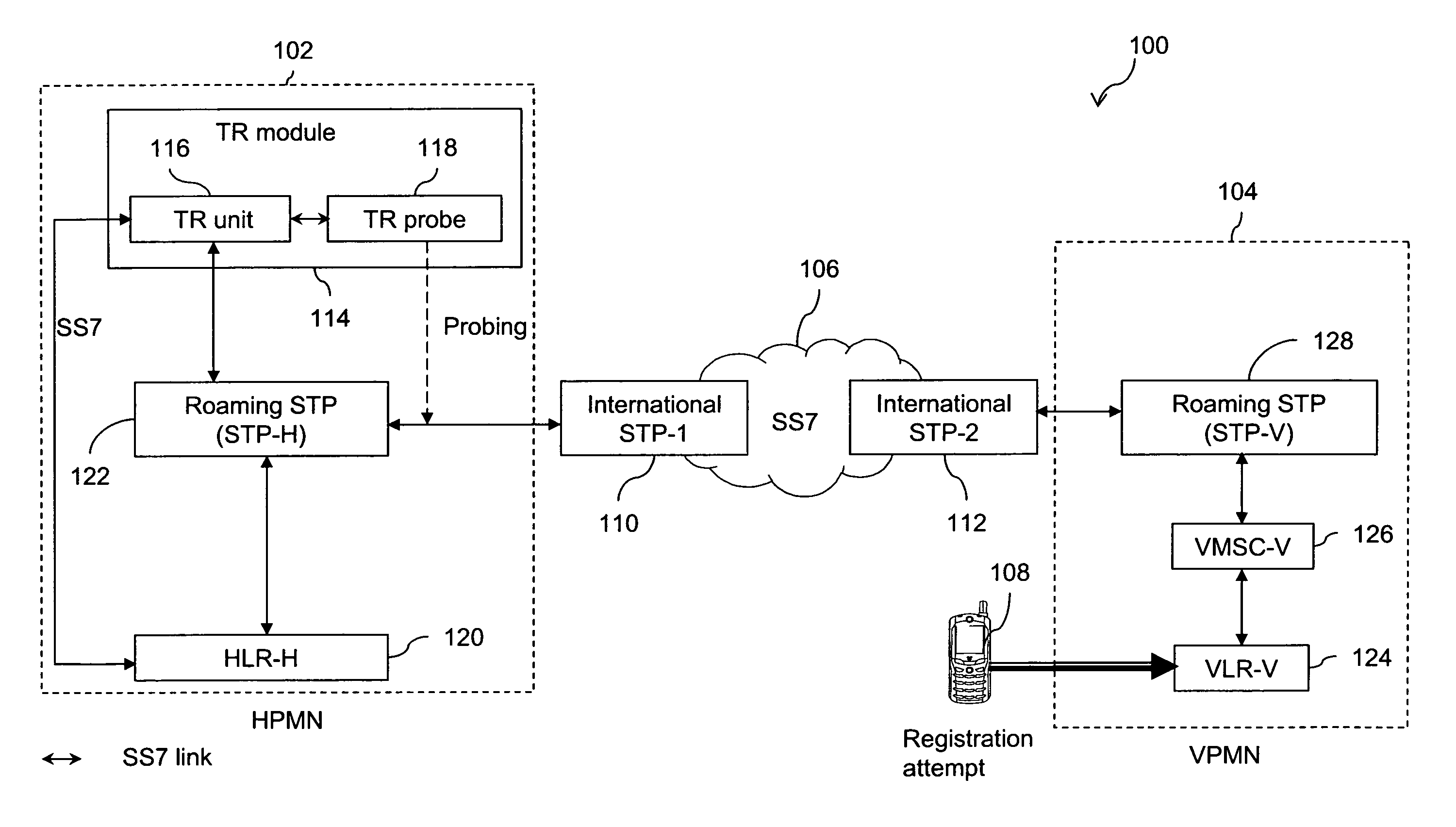
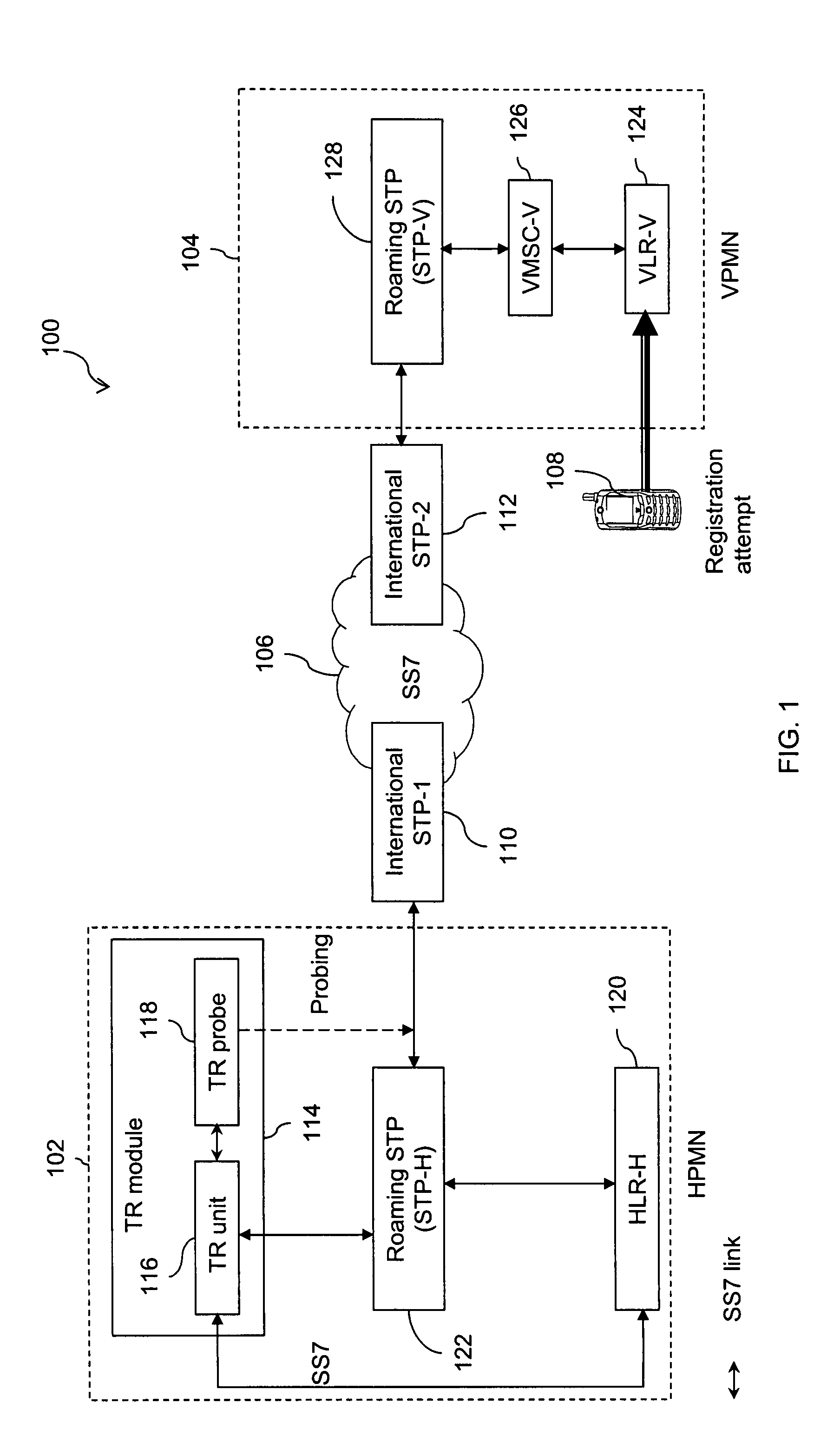
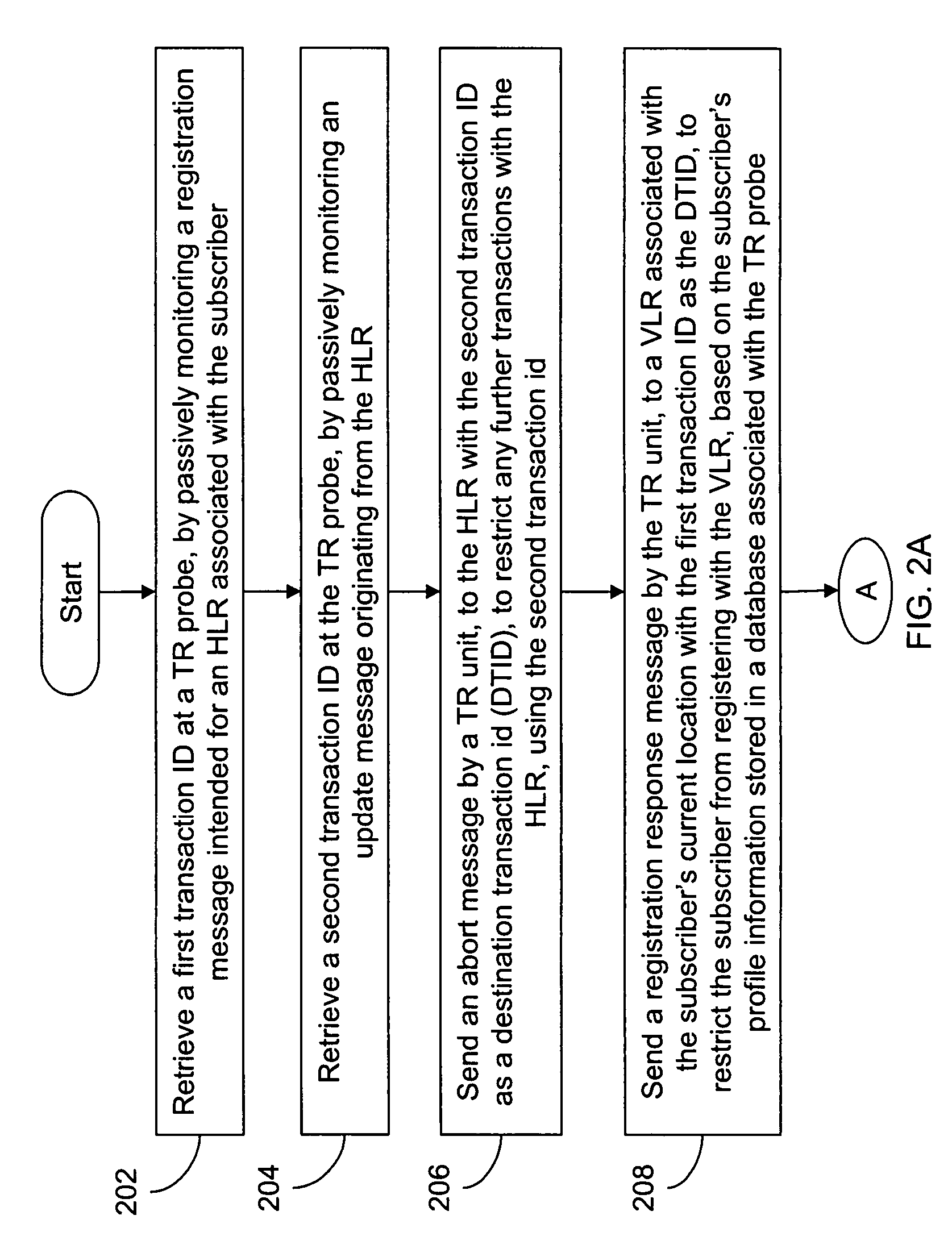
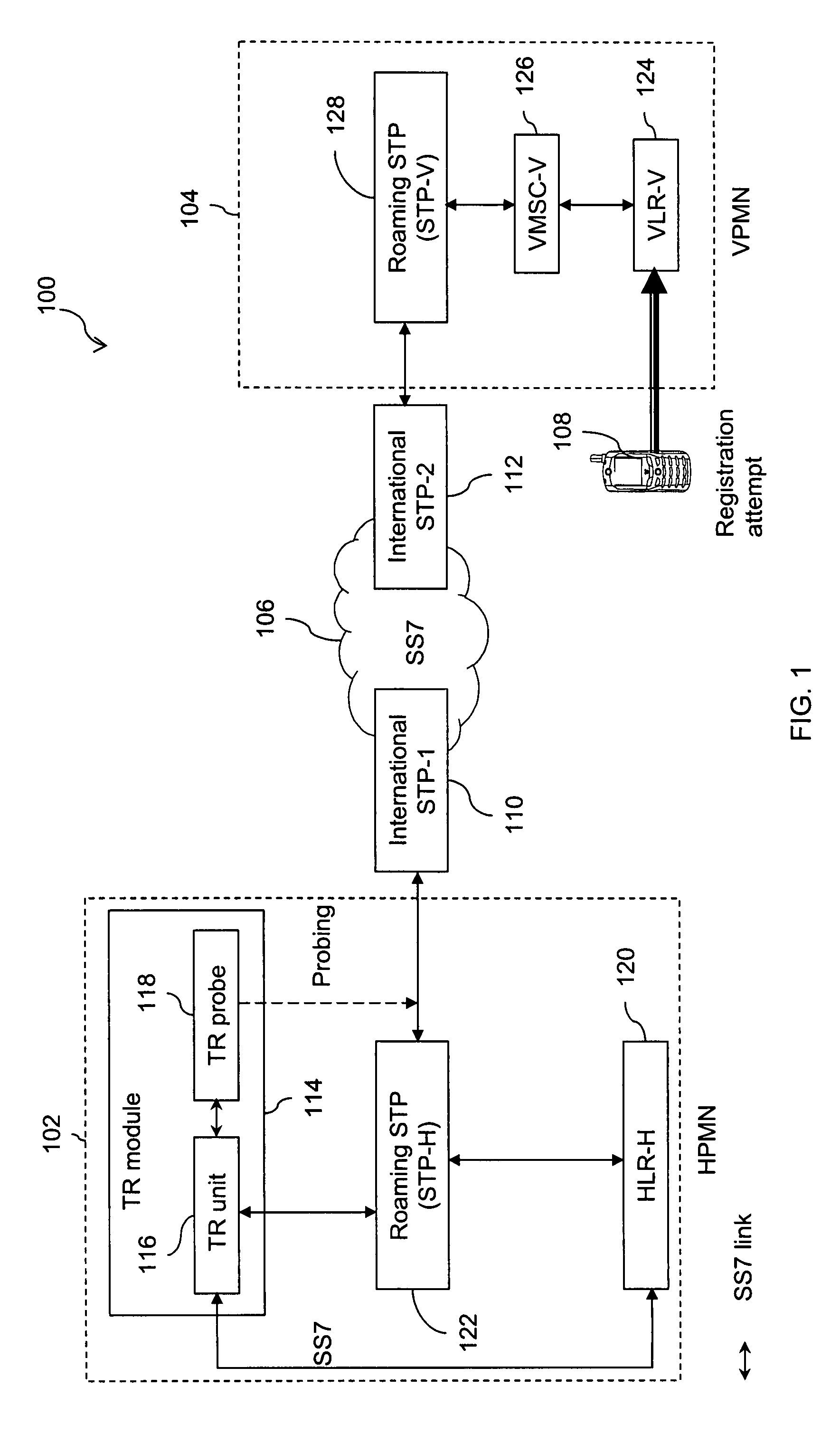
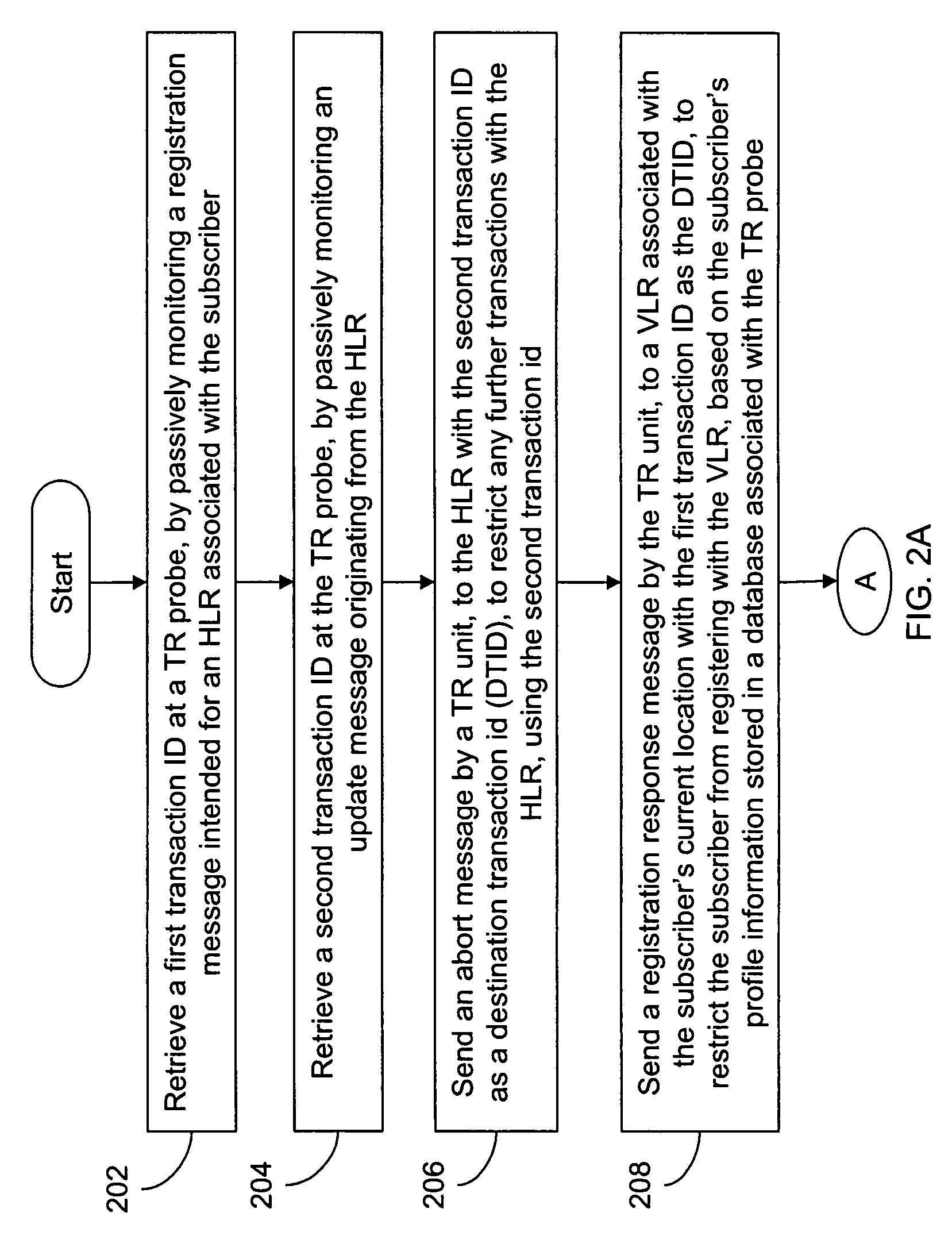
The present invention provides a passive monitoring method of redirecting roaming traffic associated with a subscriber. The method includes retrieving a first transaction ID at a TR probe, by passively monitoring a registration message intended for a home location information database. The method further includes retrieving a second transaction ID at the TR probe, by passively monitoring an update message originating from the home location information database. Further, the method includes sending an abort message by a TR unit, to the home location information database with the second transaction ID as a Destination Transaction ID (DTID) to restrict any further transactions with the home location information database using the second transaction ID. Finally, the method includes sending a registration response message by the TR unit, to a visited location information database with the first transaction ID as the DTID to restrict the subscriber from registering with the visited location information database, based on the subscriber's profile information stored in a database associated with the TR probe.
Owner:MOBILEUM INC
Private wireless network
InactiveUS20050020240A1Interconnection arrangementsEmergency connection handlingPhysical spaceWireless mesh network
A system is provided to redirect a mobile station in range of a privately owned physical space / proximity onto a “reconstituted” private wireless network. The reconstituted private wireless network is contained and procured for the purpose of controlling incoming and out going cellular traffic to those mobile stations. Thus, a “quiet zone” is created whose size is defined by the coverage or radio frequency footprint of the privately wireless network within the physical space.
Owner:AEM GRP
Methods and system for dynamically switching off/on of base stations
ActiveUS20150382290A1Overcomes drawbackPower managementTransmission systemsCommunication interfaceNetwork conditions
Disclosed are methods and system for dynamically switching at least a base station in ON / OFF mode in a cellular network. The method comprises: determining traffic load information of BSs; exchanging the traffic load information between BSs; determining at least a preferred BS for one of a switched OFF mode and a switched ON mode. The system comprises: at least a coverage BS with a master controller; at least a capacity BS with a slave controller adapted to be in one of the switched ON mode and the switched OFF mode depending on network conditions and to satisfy cellular traffic loads, and at least a communication interface adapted to provide interface between at least the coverage BS and the capacity BS.
Owner:QATAR UNIV QSTP B
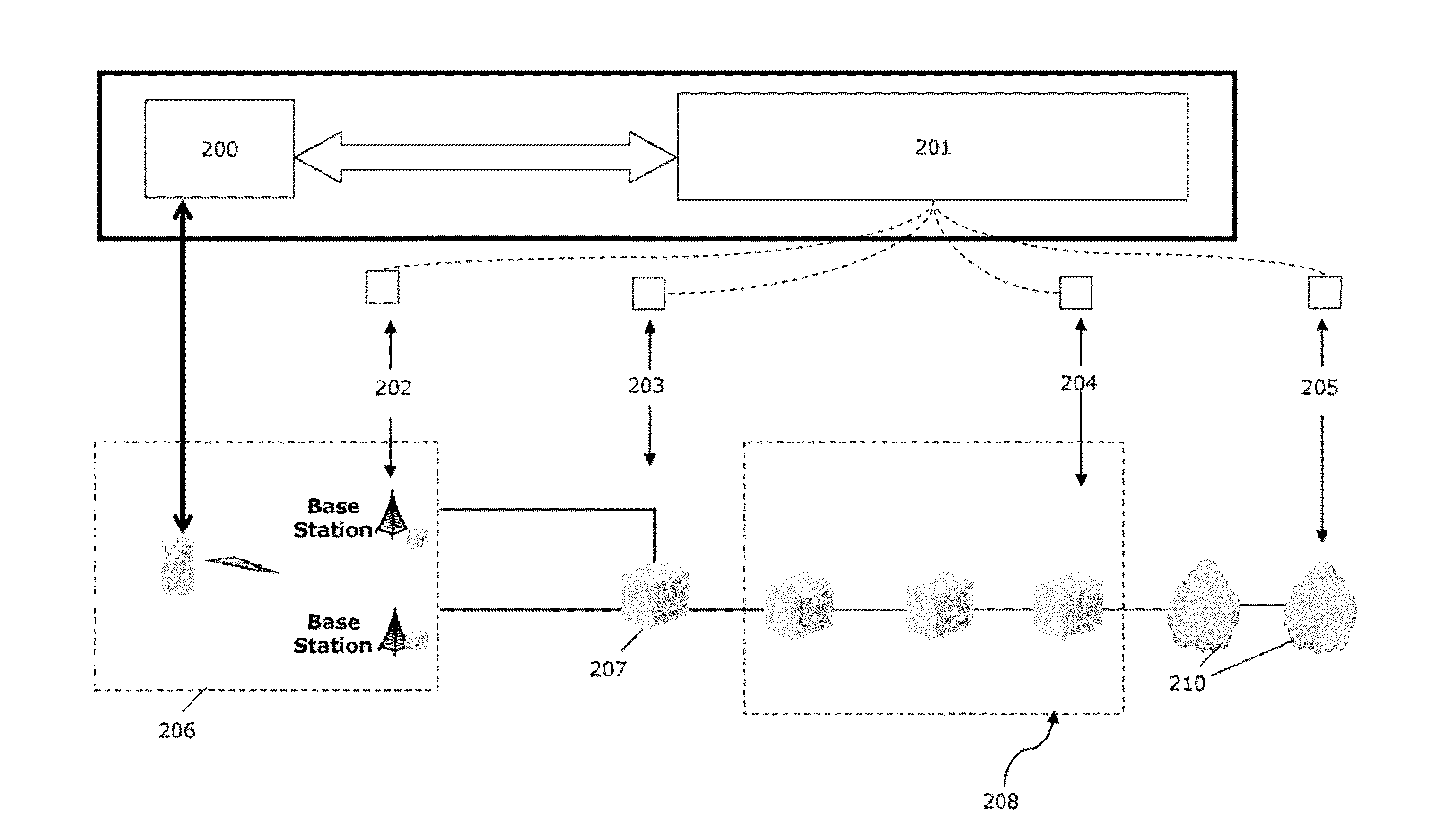
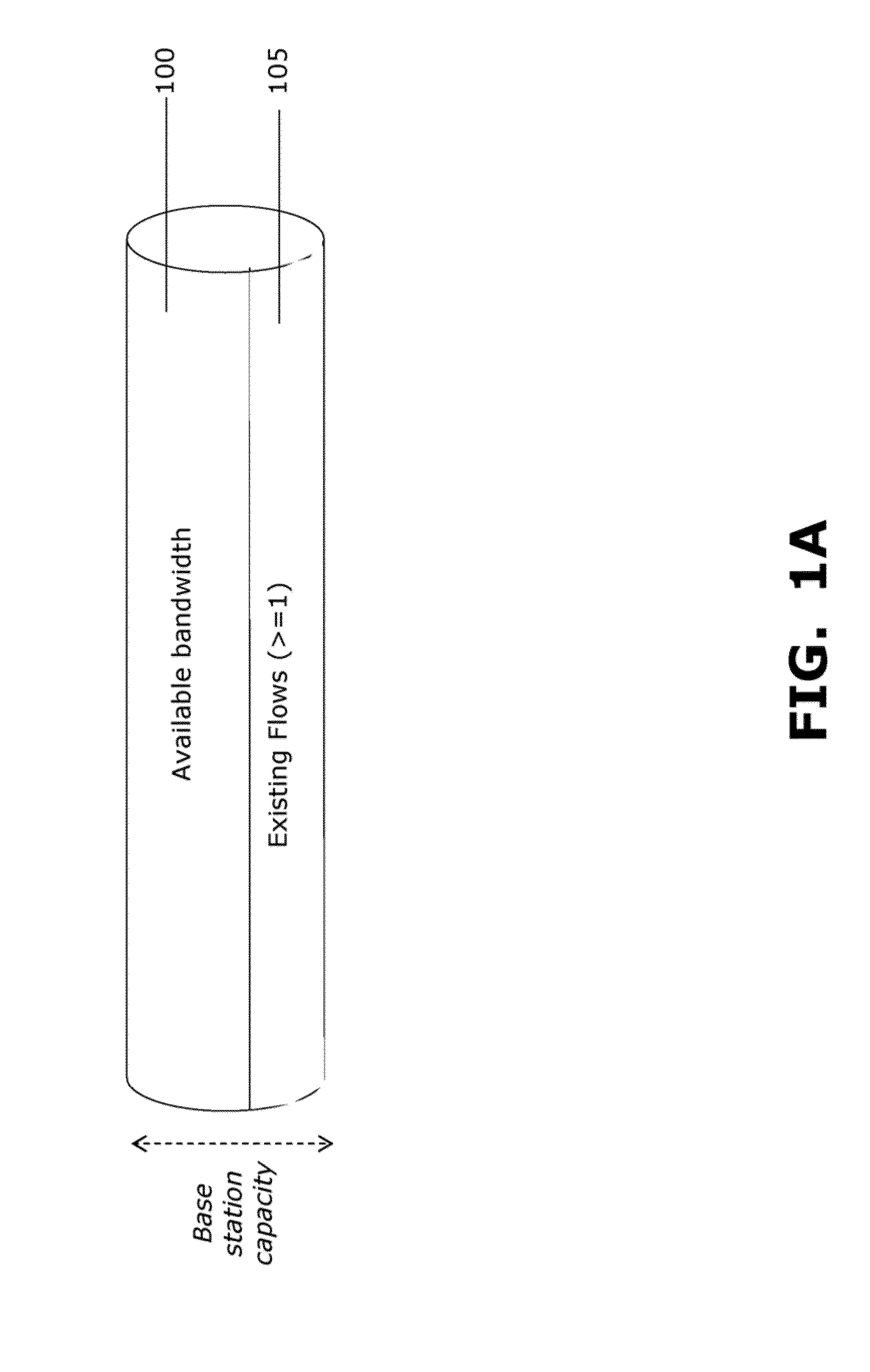
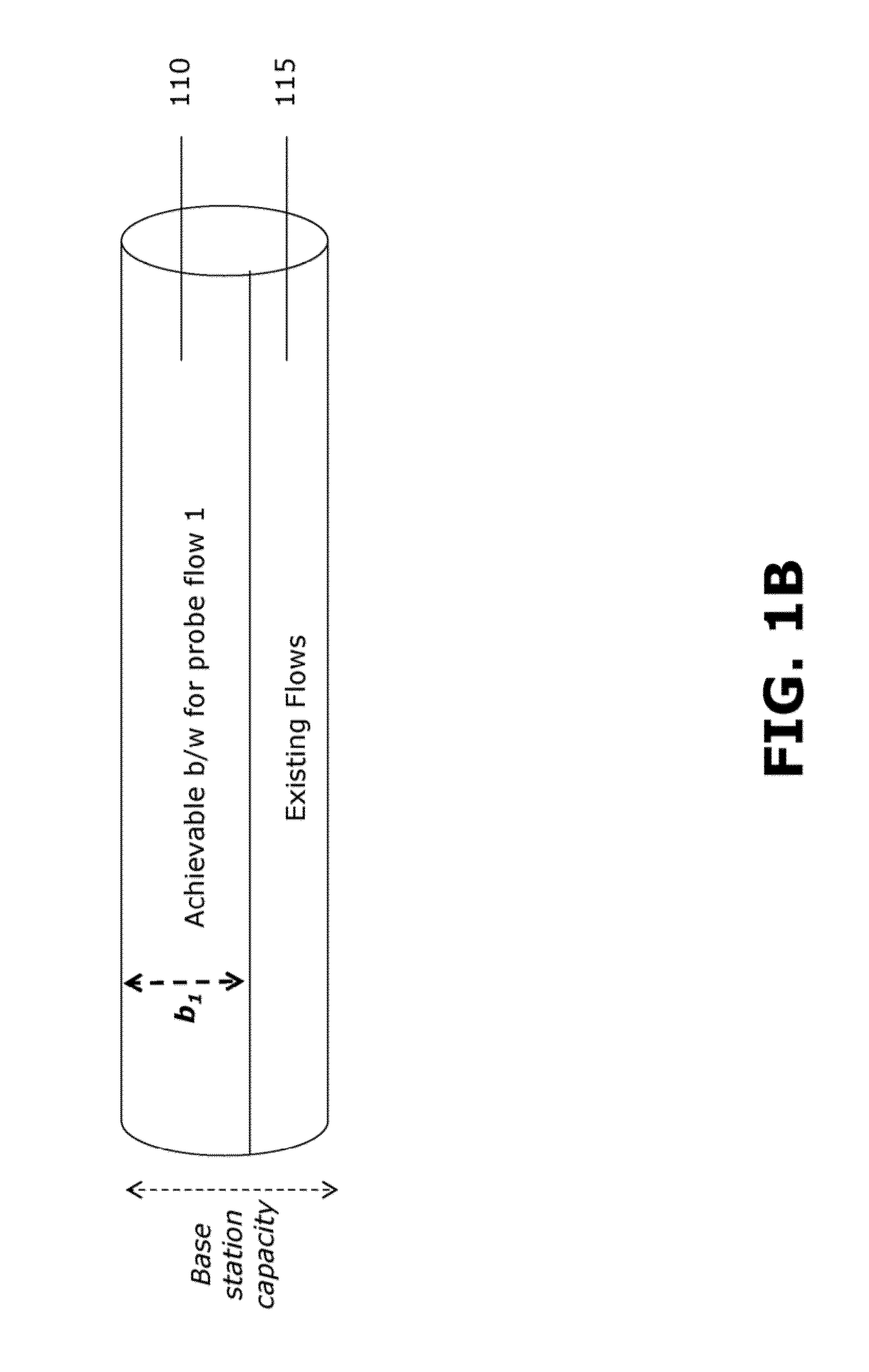
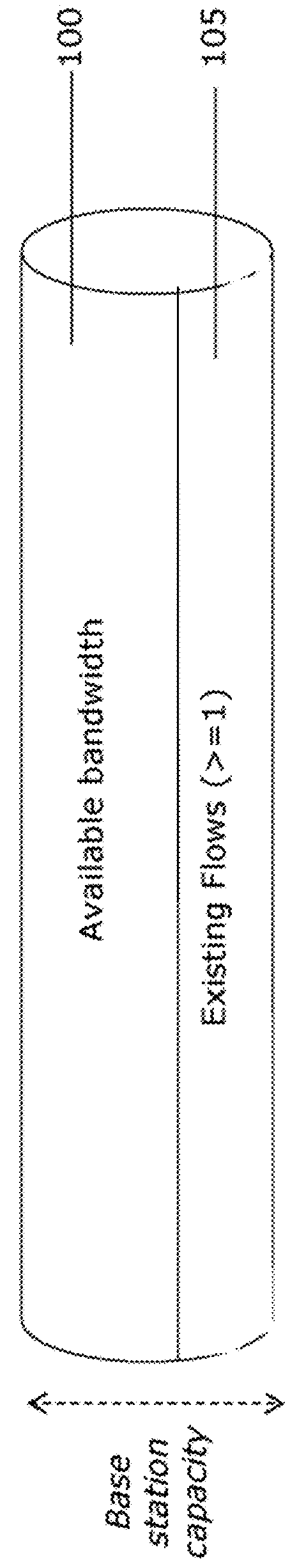
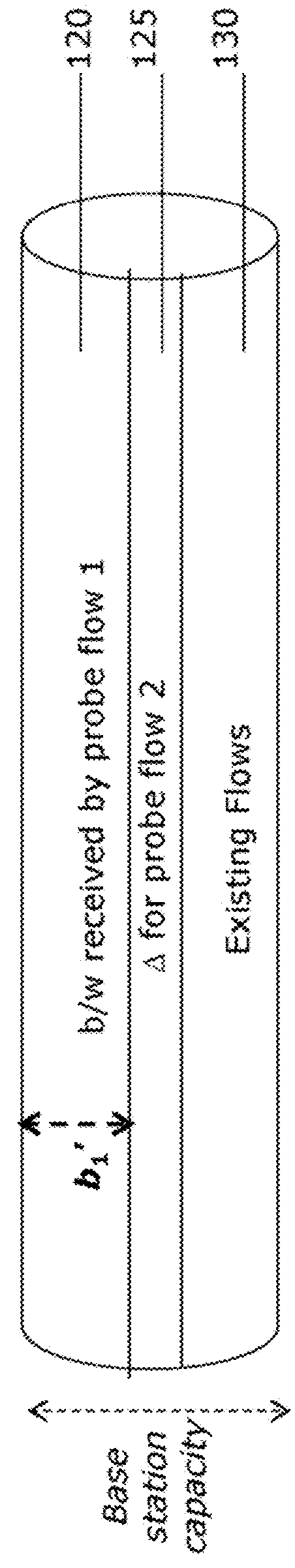
Estimating available bandwith in cellular networks
Systems and methods for estimating bandwidth. A first probe flow is sent into cellular traffic, and a first bandwidth quantity achieved by the first probe flow is measured. A second probe flow is sent into the cellular traffic, and a second bandwidth quantity achieved by the first probe flow while the second probe flow is in the cellular traffic is measured. The first bandwidth quantity and the second bandwidth quantity are compared, and at least one result from the comparing is determined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for providing GSMA IR. 73 SoR compliant cellular traffic redirection
The present invention provides a passive monitoring method of redirecting roaming traffic associated with a subscriber. The method includes retrieving a first transaction ID at a TR probe, by passively monitoring a registration message intended for a home location information database. The method further includes retrieving a second transaction ID at the TR probe, by passively monitoring an update message originating from the home location information database. Further, the method includes sending an abort message by a TR unit, to the home location information database with the second transaction ID as a Destination Transaction ID (DTID) to restrict any further transactions with the home location information database using the second transaction ID. Finally, the method includes sending a registration response message by the TR unit, to a visited location information database with the first transaction ID as the DTID to restrict the subscriber from registering with the visited location information database, based on the subscriber's profile information stored in a database associated with the TR probe.
Owner:MOBILEUM INC
Communication network route determination
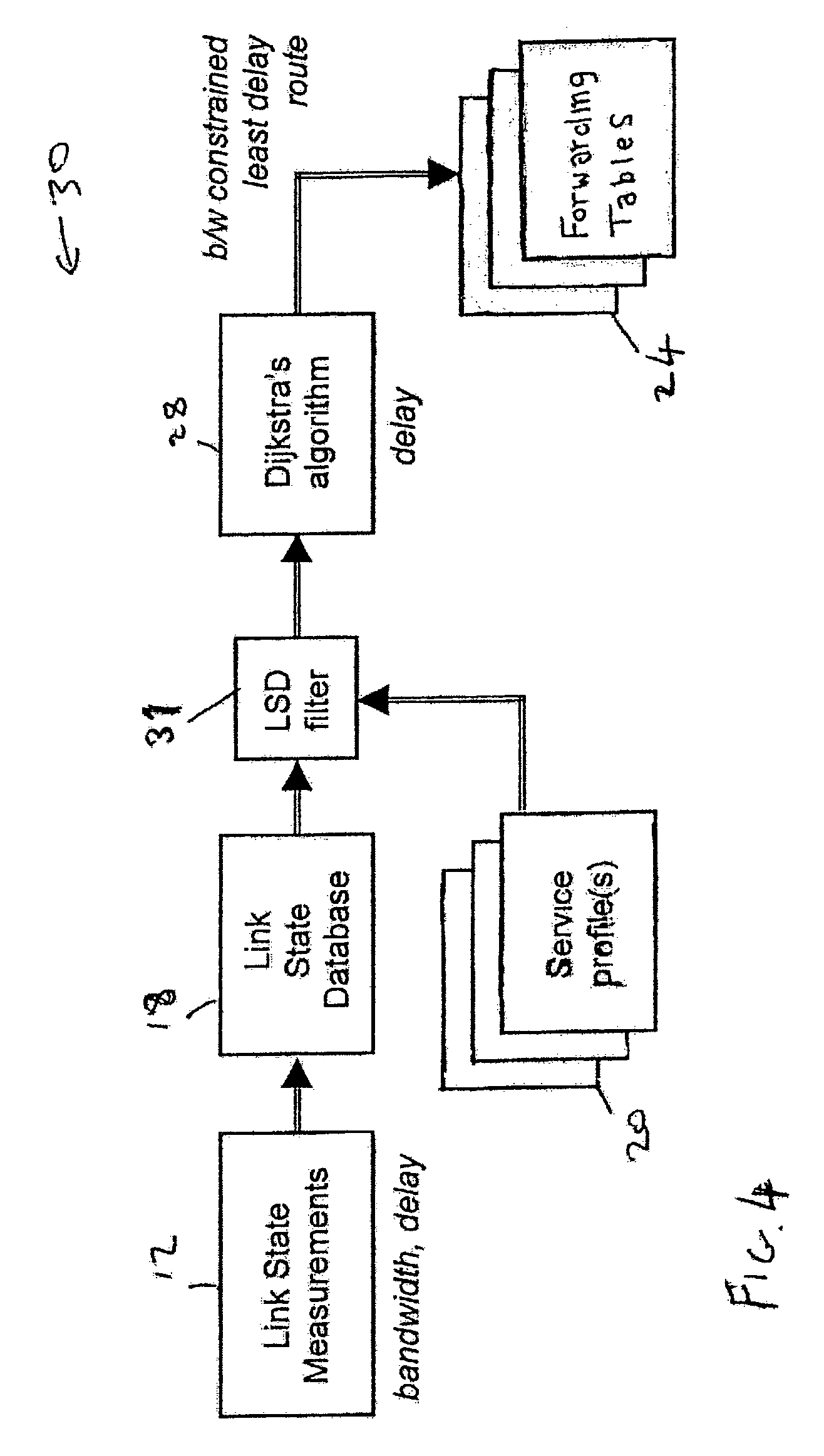
InactiveUS7561526B2Reduce decreaseEfficiently determinedError preventionTransmission systemsCurrent pointRouting algorithm
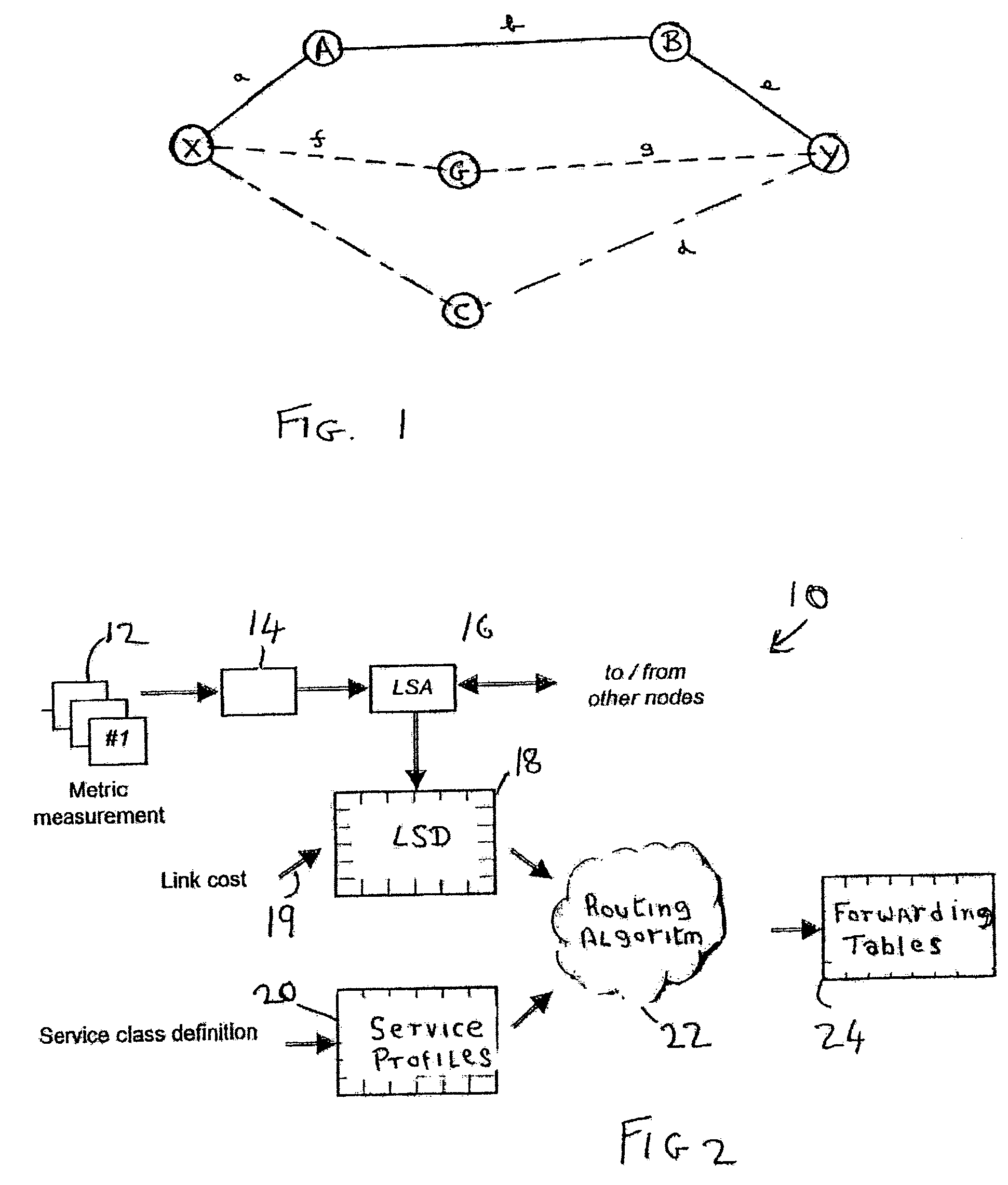
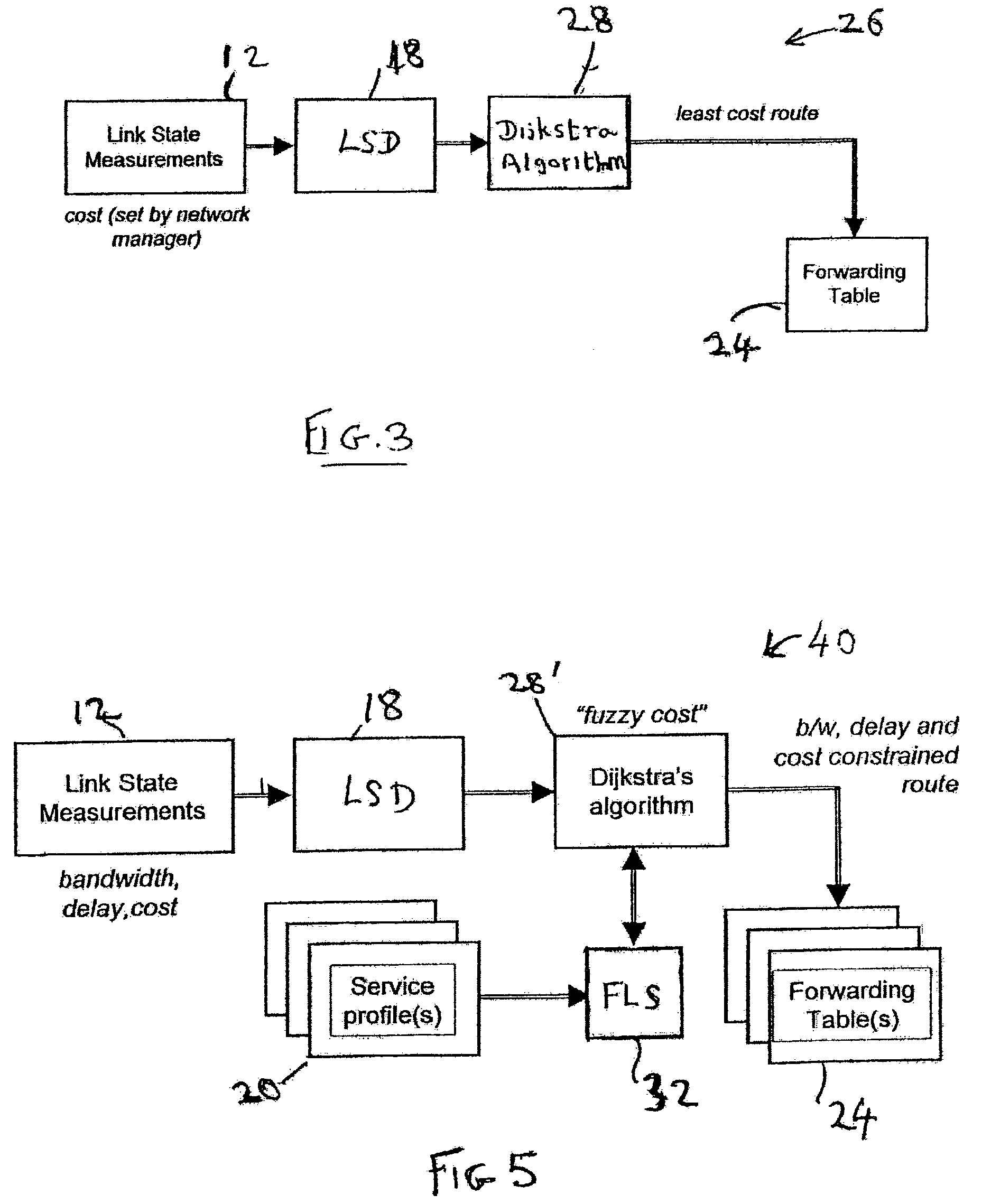
A communications network comprises a plurality of linked nodes between a source and a destination. At each node the state of the network and its links are measured and stored with advertisements from other links. The node also performs a routing algorithm to define the instantaneously best path to the destination for the current network state. The routing algorithm responds to a plurality of metrics, including costs of links, and may use fuzzy logic which derives a fuzzy cost for candidate paths to derive a least fuzzy cost path to be followed. Traffic is shared between a path which is determined to be the best, at the current point in time, and a path which has previously been determined as the best path. The network can be a network which carries mobile cellular traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
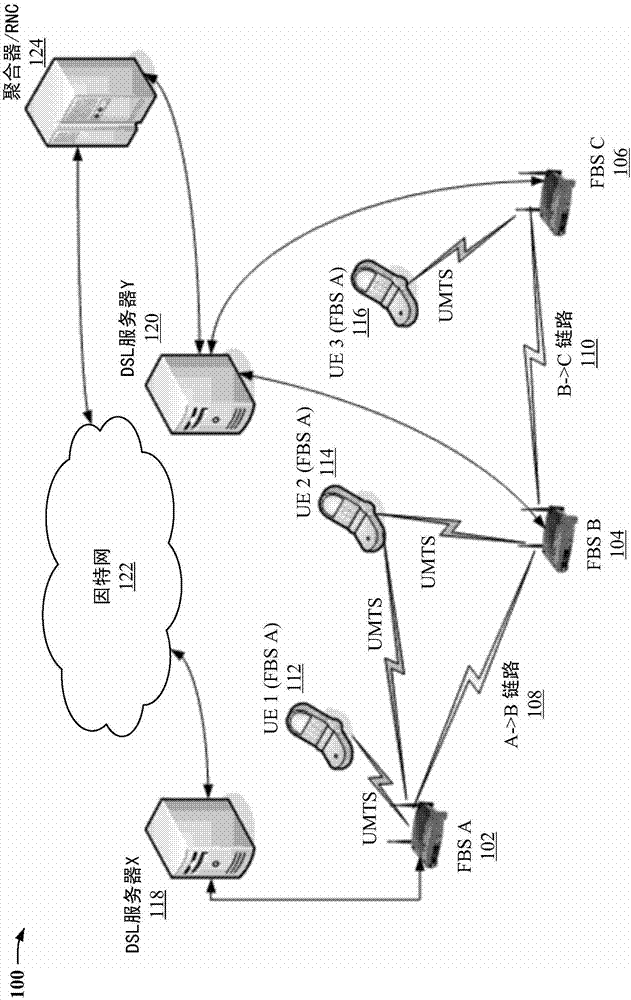
Backhaul network for femto base stations
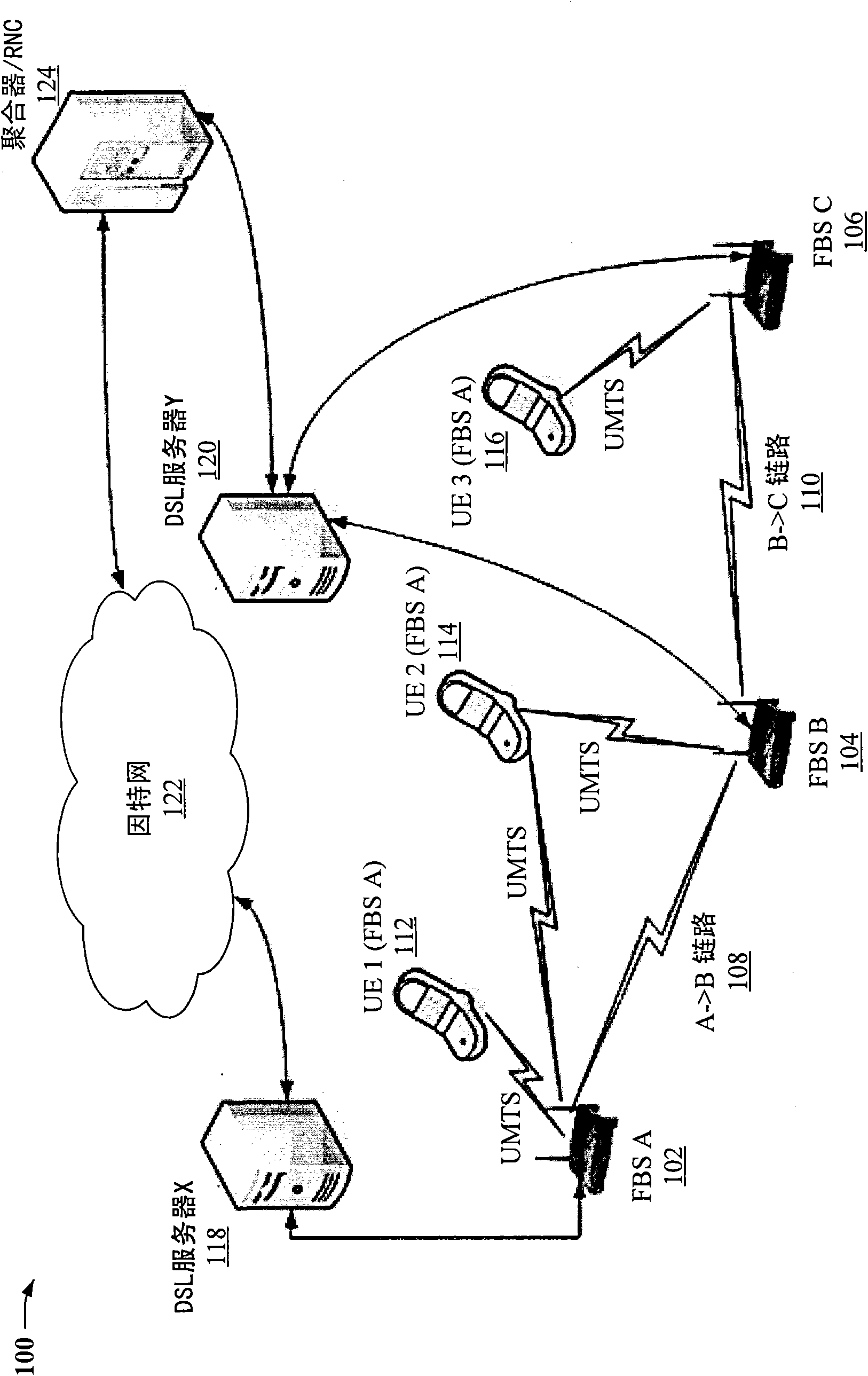
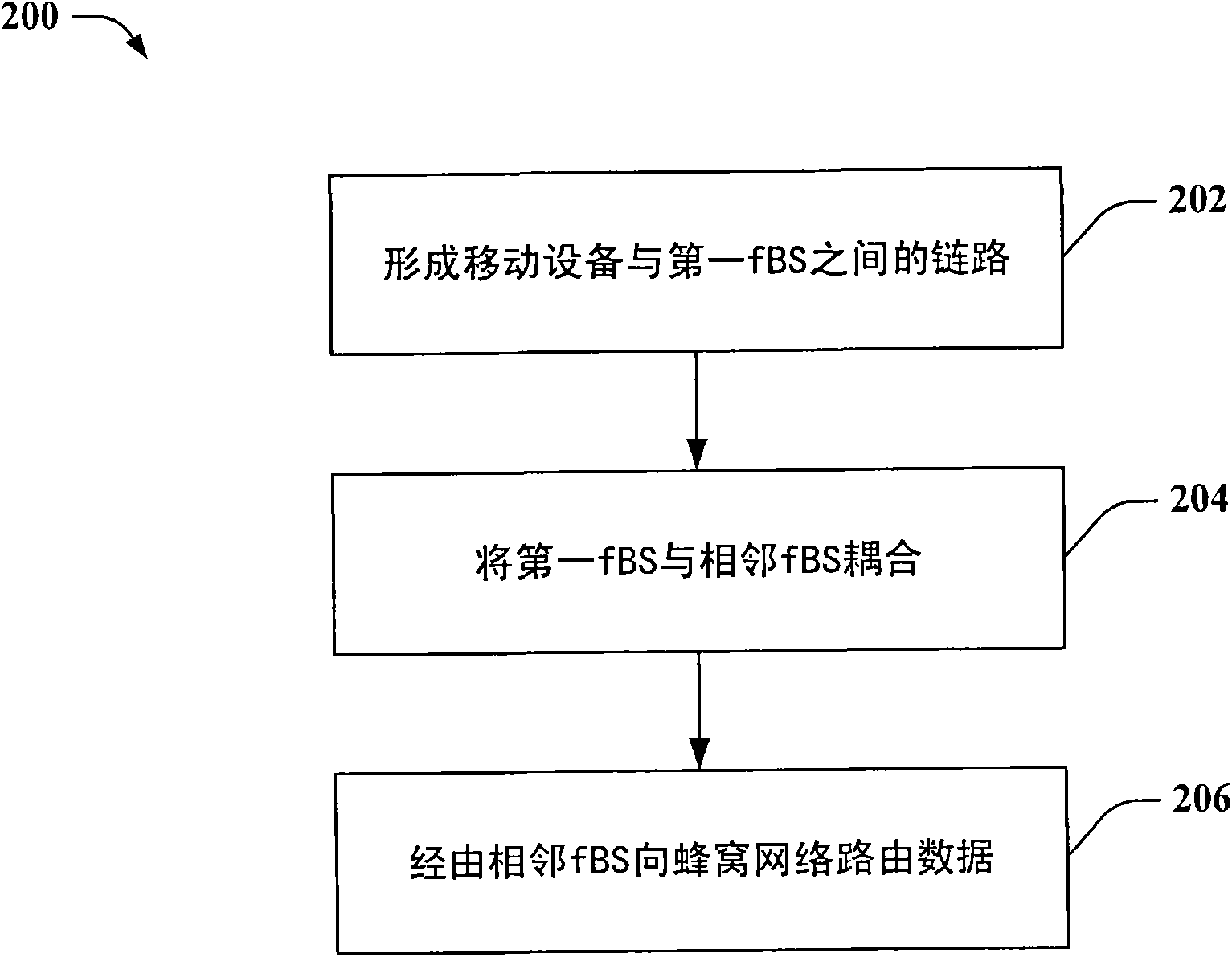
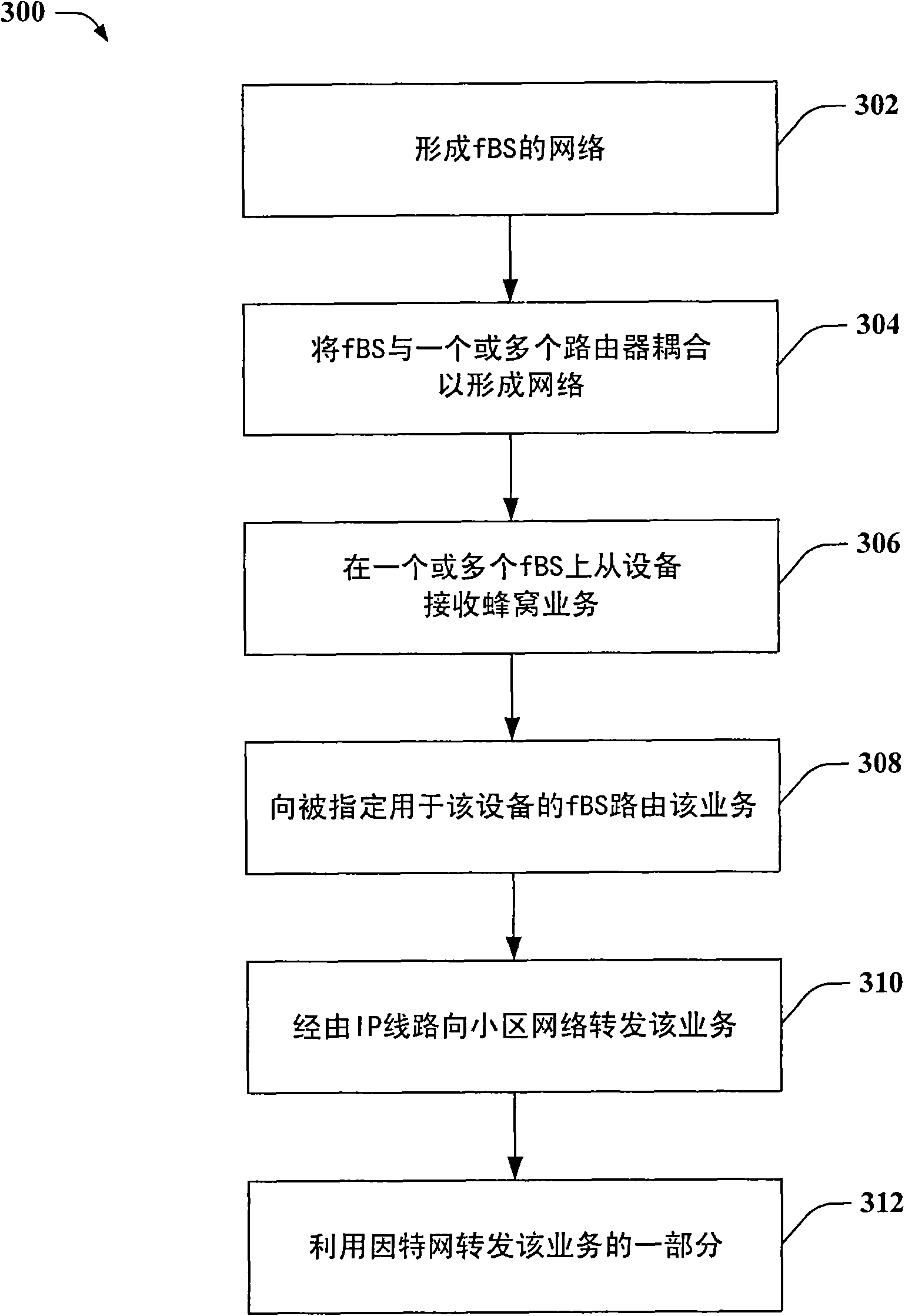
InactiveCN101658059APower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile deviceFemto base stations
Providing an inter-femto Base Station (fBS) network to facilitate low interference, low power cellular access utilizing two or more fBSs is provided herein. For example, a group of fBSs can be inter-connected by a wired and / or wireless communication network. Multiple fBSs then can link with a mobile device and coordinate cellular traffic amongst the fBS network to facilitate hand-off related communication. Additionally, cellular traffic can be forwarded from one or more fBSs to an appropriate fBS designated to carry cellular traffic for each mobile device. Furthermore, by inter-connecting multiple fBSs, multi-base station cellular-type hand-off can be supported by the fBS network, while preserving predetermined cellular interface constraints associated with such mobile devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wireless cellular network flow prediction method based on deep transfer learning and cross-domain data fusion
ActiveCN112291807AImprove forecast accuracyReduce training dataCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setInternet traffic
The invention discloses a wireless cellular network flow prediction method based on deep transfer learning and cross-domain data fusion, and belongs to the technical field of intelligent communication. Similarity among three services of short messages, telephones and the Internet and the similarity among different regions are analyzed, a plurality of cross-domain data sets is fused, and a space-time cross-domain neural network model is adopted to predict the wireless cellular traffic; a cross-service and region fusion transfer learning strategy based on a space-time cross-domain neural networkmodel (STC-N) is provided, and the prediction precision of a target domain is improved according to data characteristics of a source domain. The method can verify that the more comprehensive the considered data set is, the higher the prediction precision of the model is; in addition, the proposed transfer learning strategy can reduce the training data, calculation capability and generalization capability required for constructing the deep learning model.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
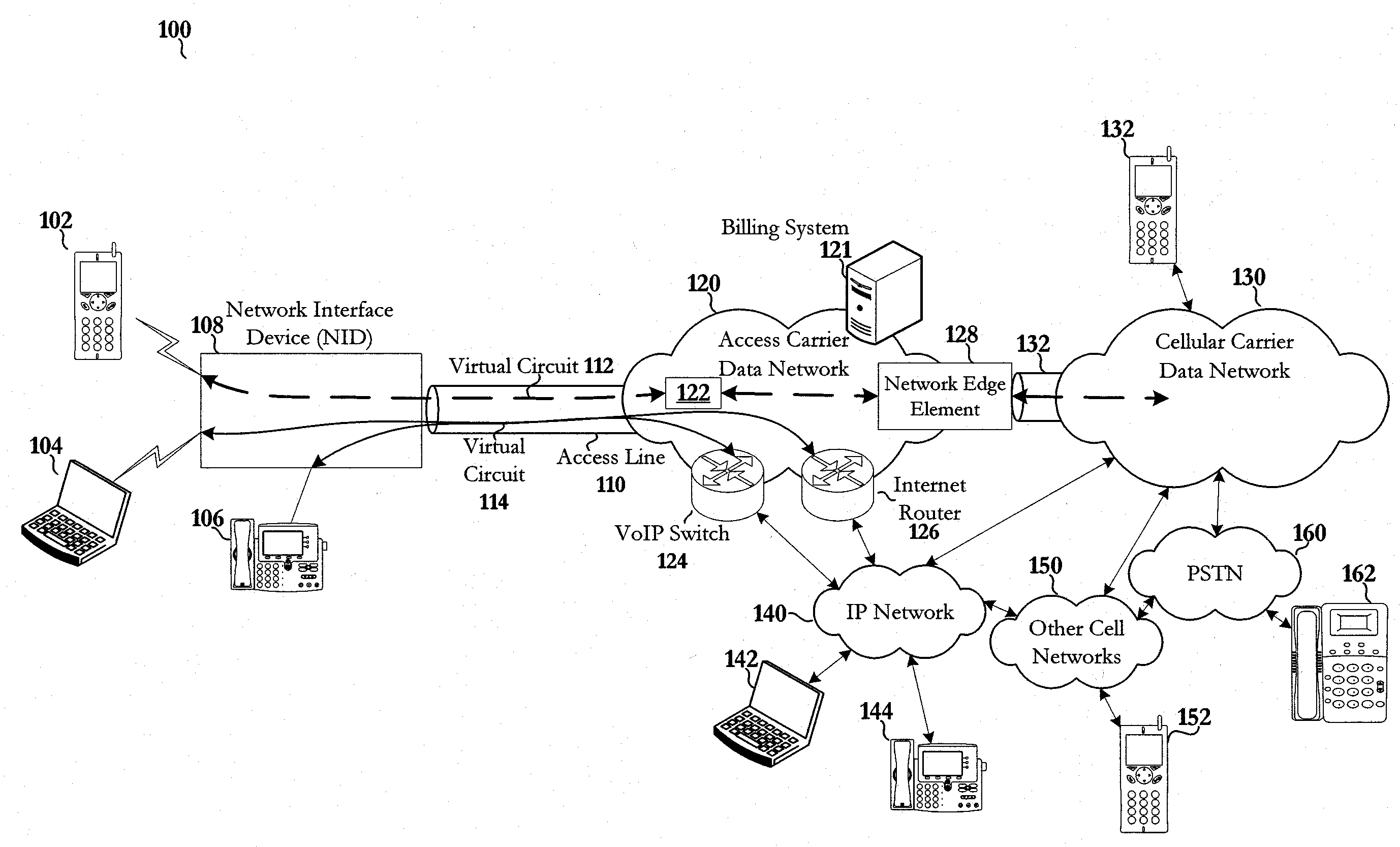
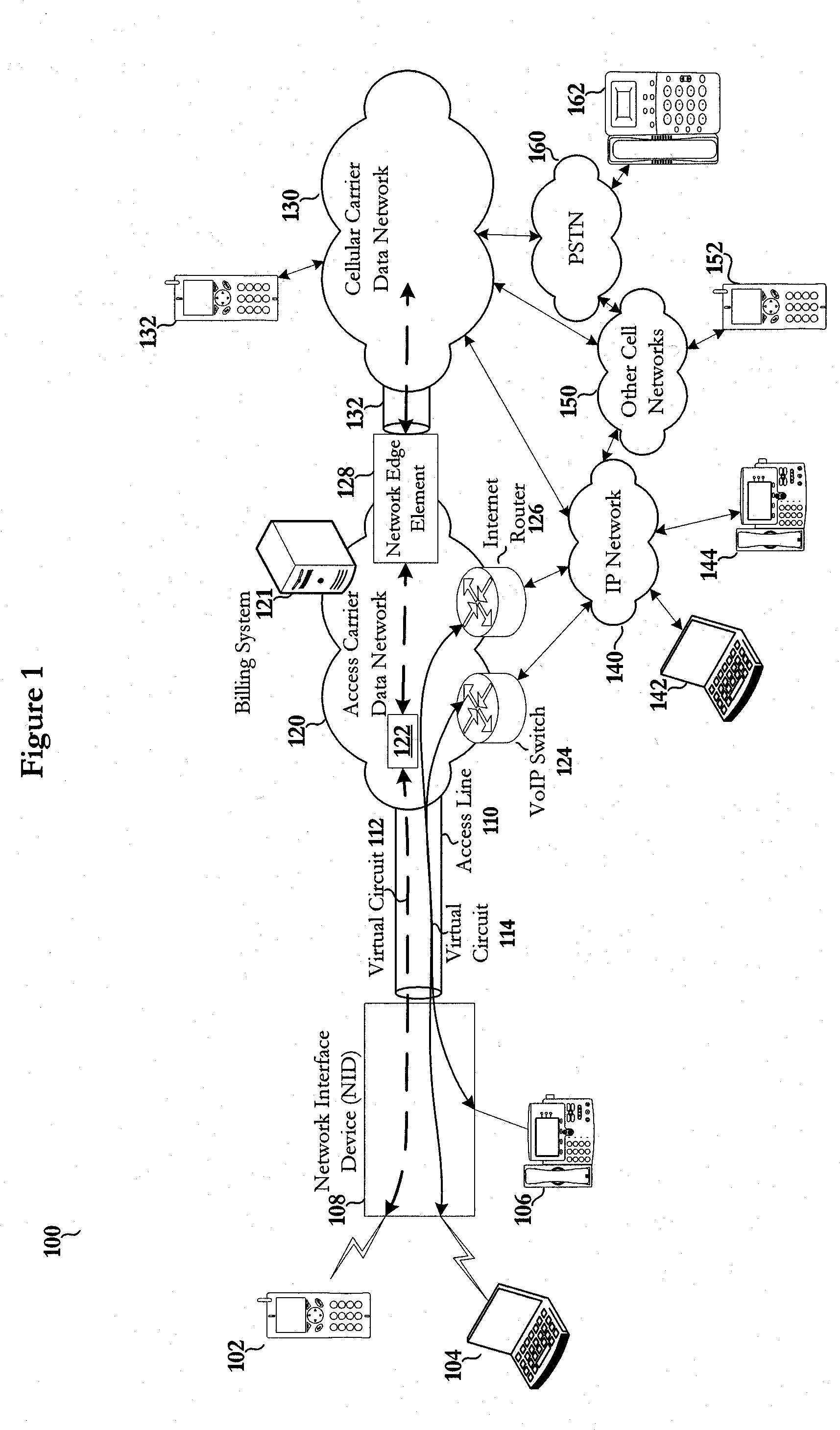
System and method for providing end to end quality of service for cellular voice traffic over a data network
ActiveUS20100260100A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesNetwork-to-network interfaceService provision
Embodiments of the disclosed invention include a system and method for providing end to end quality of service for cellular voice traffic over a data network. For example, in one embodiment, the method includes tagging outgoing cellular traffic at a network interface device with a prioritization marking to produce prioritized data and transmitting the prioritized data directly to an access carrier network associated with providing an access line to the cellular network interface device. The method maintains, at the access carrier network, the prioritization marking of the outgoing cellular traffic for routing the outgoing cellular traffic through the access carrier network. The method hands off the prioritized data directly to a cellular service provider network associated with the cellular device via a directly connected network to network interface.
Owner:CENTURYLINK INTPROP
Network flow prediction method based on attention multi-component space-time cross-domain neural network model
ActiveCN112532439AEfficient fusionHigh precisionNeural architecturesData switching networksTraffic predictionTimestamp
The invention discloses a network traffic prediction method based on an attention multi-component space-time cross-domain neural network model, belongs to the technical field of intelligent communication, and solves the problem of prediction of wireless cellular network traffic. The method comprises the following steps: dividing wireless cellular flow data into neighbor data, daily period data andweek period data according to periodic characteristics; modeling the neighbor data, the daily period data and the week period data through a conv-LSTM structure or a conv-GRU structure; distributingdifferent weights to the three kinds of feature data in a self-adaptive mode through an action layer, improving the feature extraction capacity of the three kinds of feature data, and restraining feature information interfering with the prediction moment; and finally, in combination with timestamp feature embedding and multi-cross-domain data fusion, jointly assisting the model to perform trafficprediction. The model can effectively utilize the periodic characteristics of the wireless cellular traffic data, saves the model training time, greatly reduces the workload, and further improves theprediction performance of the network traffic.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
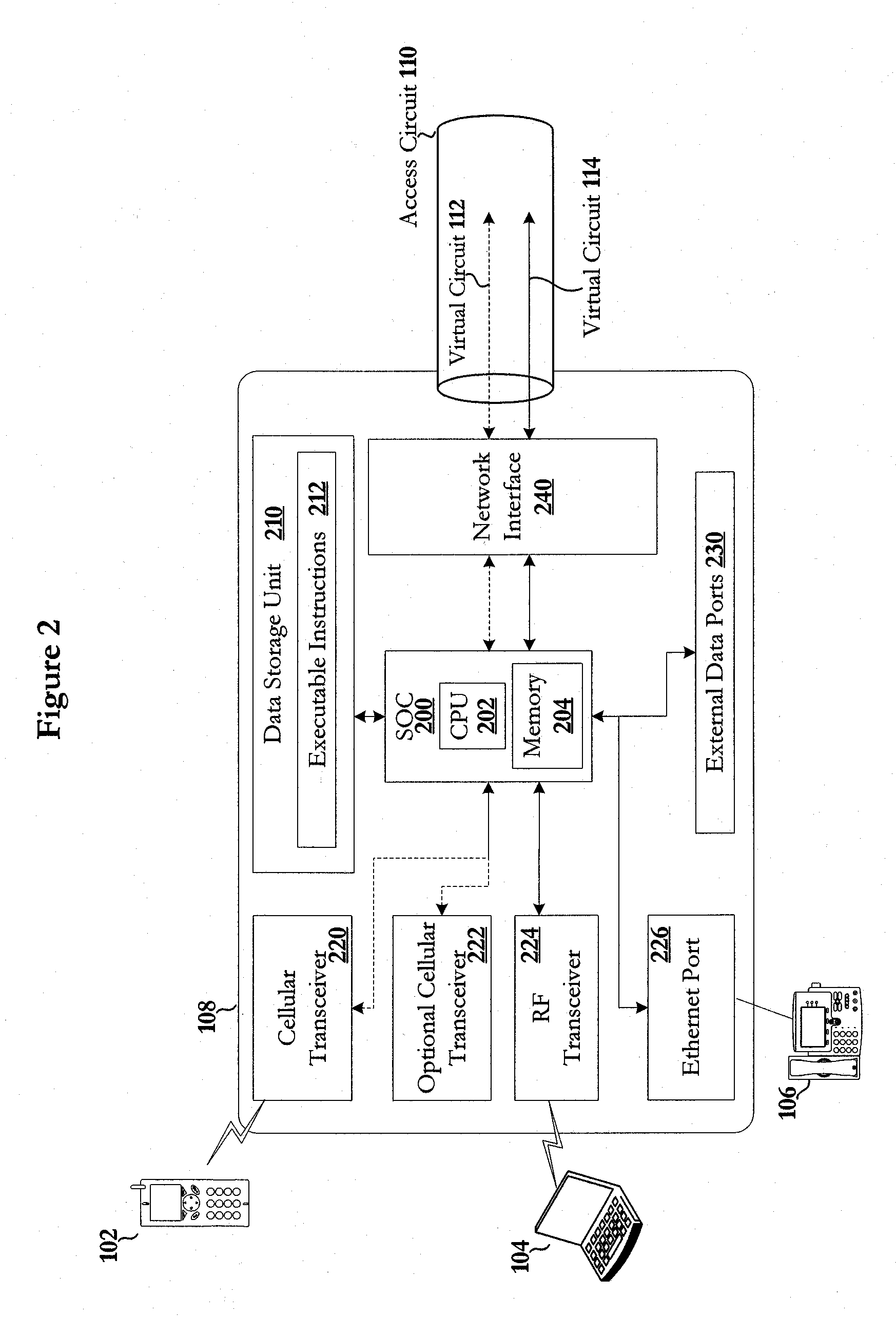
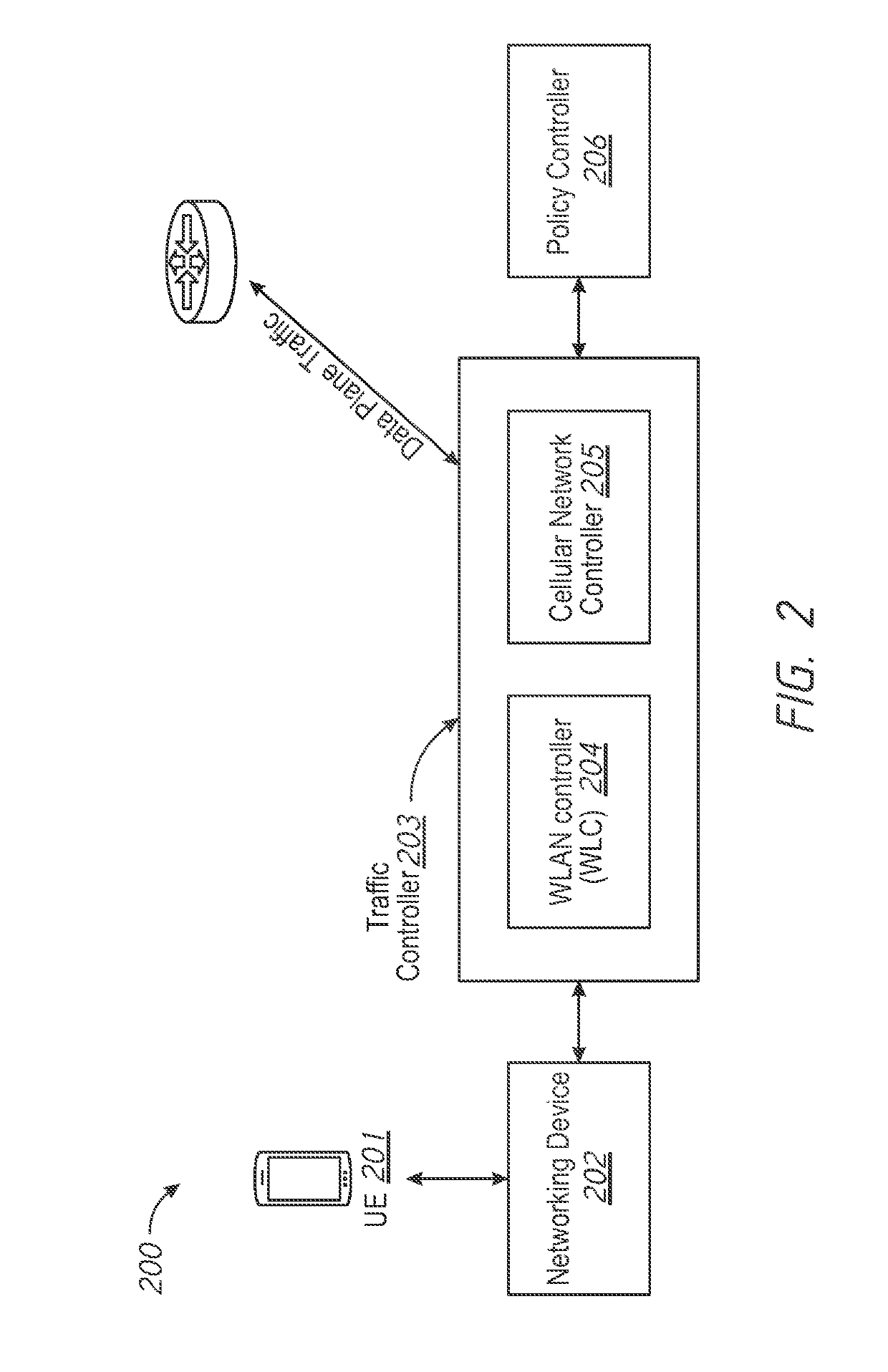
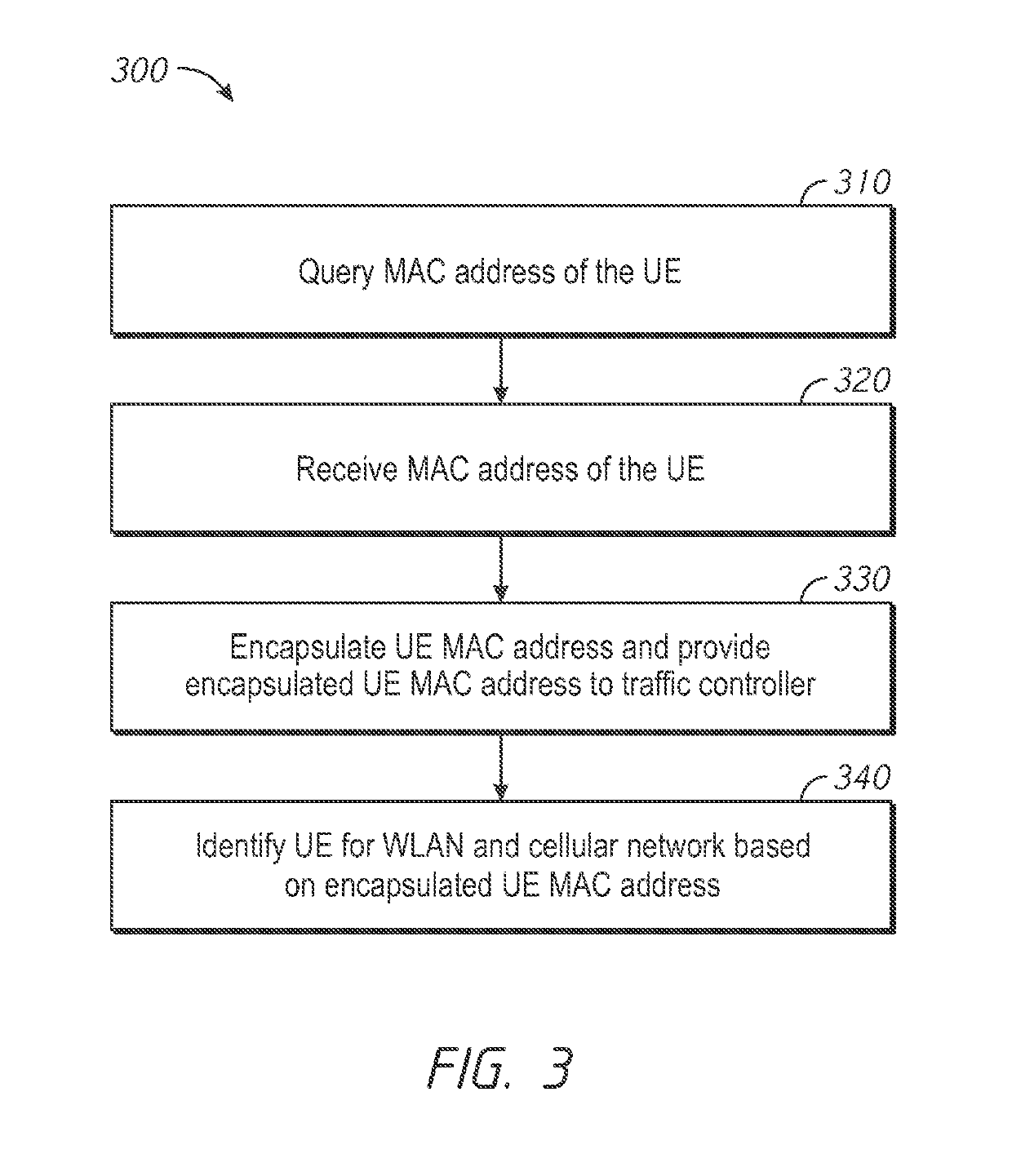
Enhancing Visibility in a Heterogeneous Network
ActiveUS20190124541A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesVisibilityHeterogeneous network
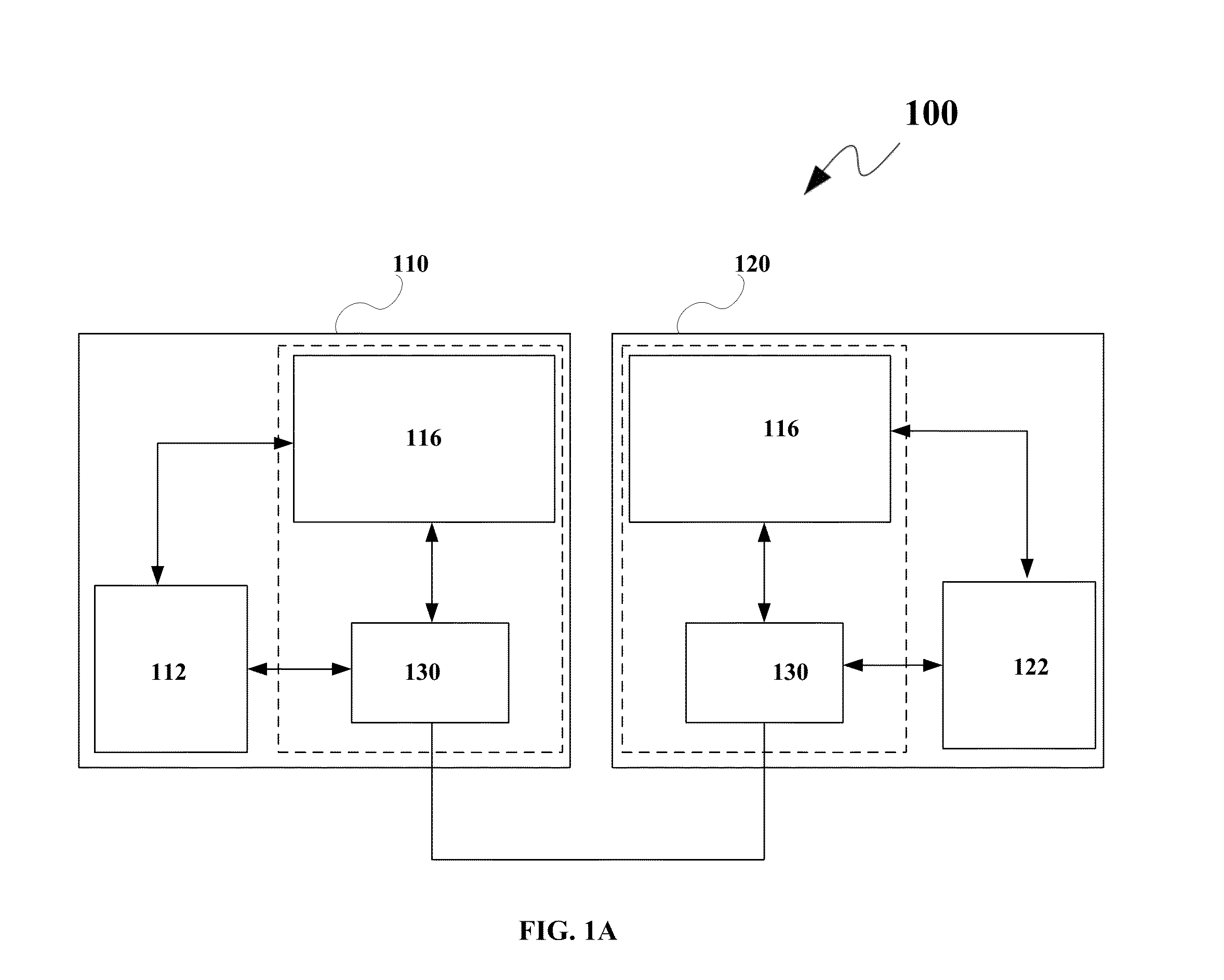
A method for providing enhanced visibility in heterogeneous network. The method comprises receiving, at a networking device housing a cellular base station and a WLAN access point, cellular network traffic from an electronic device. The method further comprises receiving, at the networking device, WLAN traffic from the electronic device and encapsulating, at the networking device, the cellular network traffic and the WLAN traffic using a common protocol. The method further comprises transmitting the encapsulated cellular traffic and the encapsulated WLAN traffic to a controller.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and system for dynamically switching off/on of base stations
ActiveUS9485725B2Overcomes drawbackPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunication interfaceNetwork conditions
Disclosed are methods and system for dynamically switching at least a base station in ON / OFF mode in a cellular network. The method comprises: determining traffic load information of BSs; exchanging the traffic load information between BSs; determining at least a preferred BS for one of a switched OFF mode and a switched ON mode. The system comprises: at least a coverage BS with a master controller; at least a capacity BS with a slave controller adapted to be in one of the switched ON mode and the switched OFF mode depending on network conditions and to satisfy cellular traffic loads, and at least a communication interface adapted to provide interface between at least the coverage BS and the capacity BS.
Owner:QATAR UNIV QSTP B
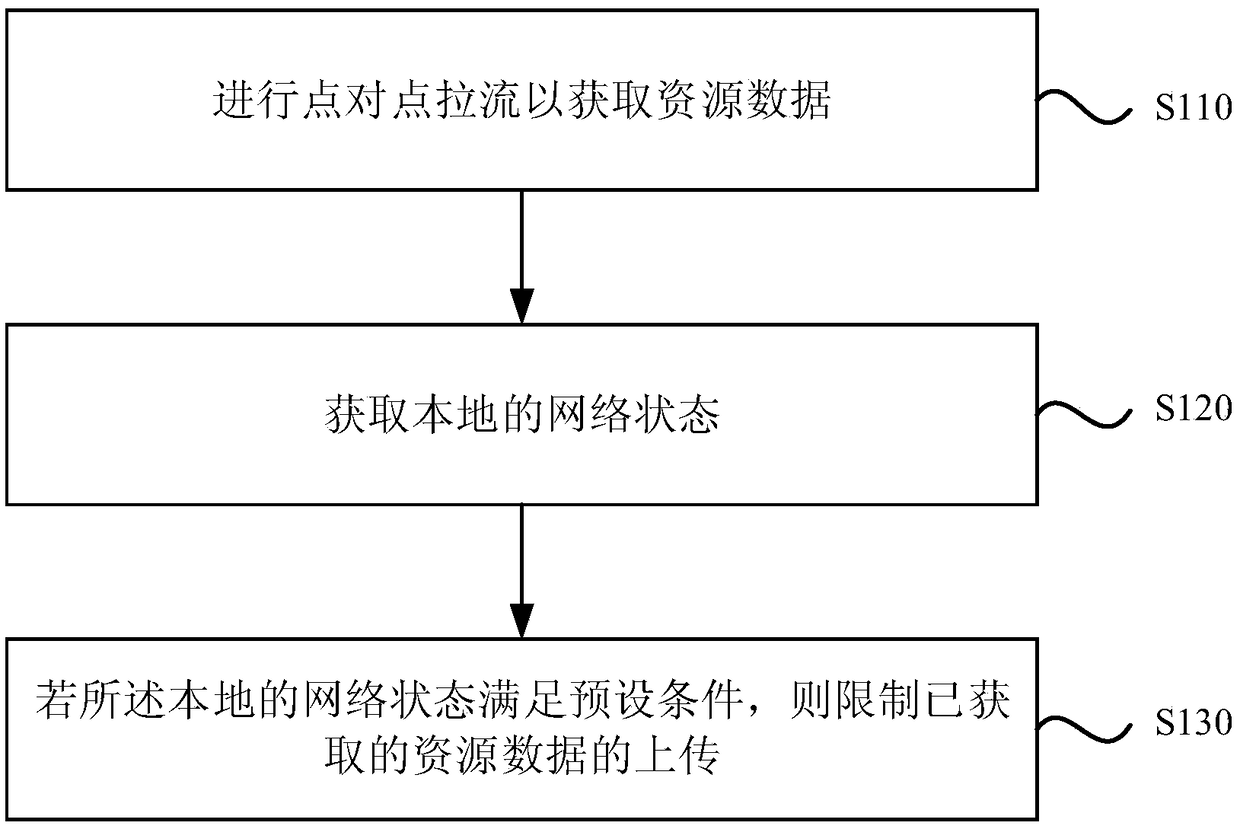
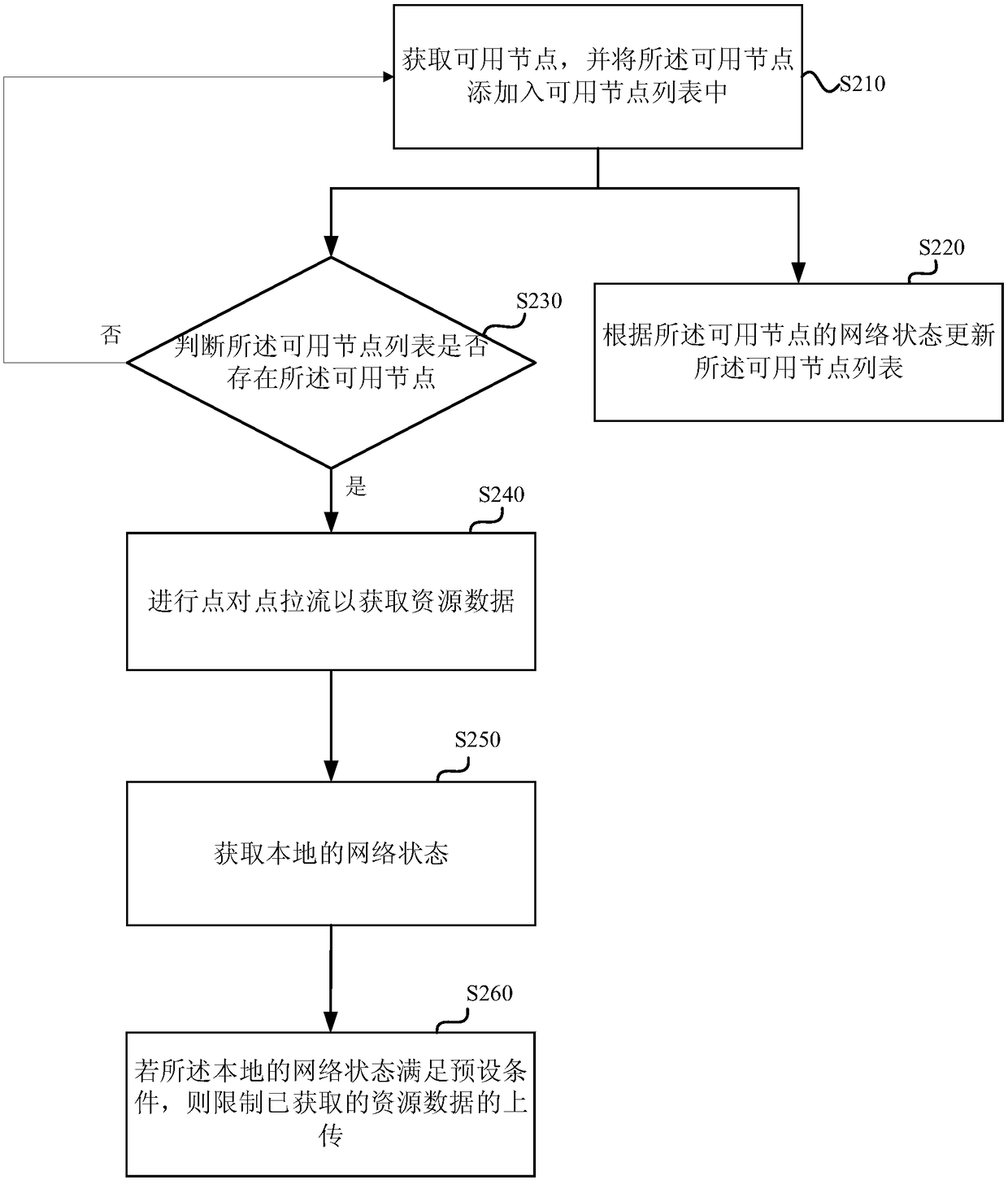
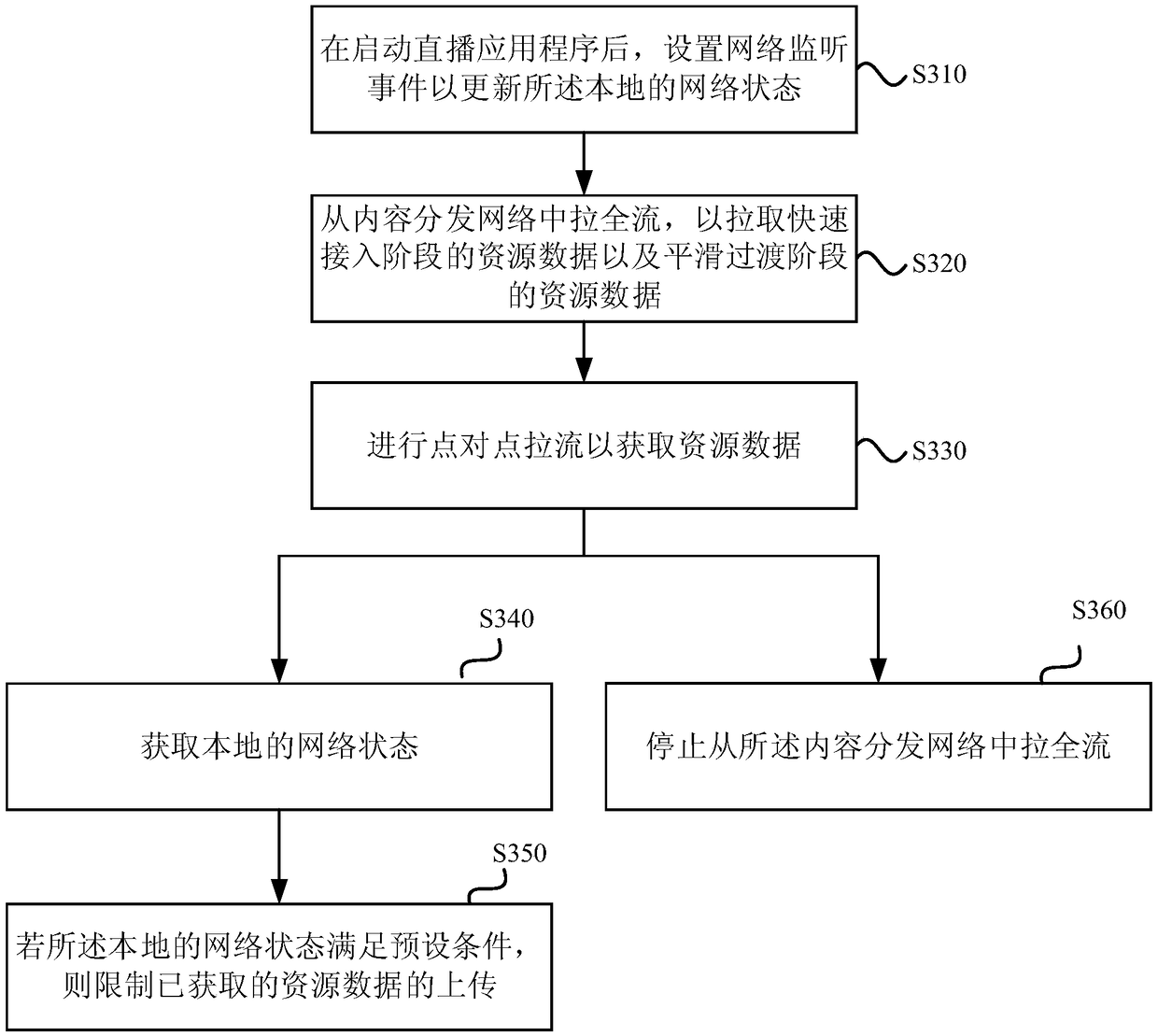
Cellular network traffic-pulling method, device and apparatus, and storage medium
InactiveCN109379765ASolve the problem of fee flowImprove fluencyNetwork traffic/resource managementSelective content distributionTraffic capacityCellular data
Embodiments of the invention disclose a cellular network traffic-pulling method, device and apparatus, and a storage medium. The method includes steps: obtaining resource data through point-to-point traffic pulling; obtaining a local network state; and restricting uploading of the obtained resource data if the local network state satisfies a preset condition, wherein the preset condition refers tothat the network state is a cellular data network and the traffic is limited. The problem of traffic consumption brought by point-to-point traffic pulling for cellular data users is solved, the cellular network users are allowed to participate in the point-to-point network to improve the playing smoothness of live-broadcasting videos, and the traffic and the cost are reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUYA TECH CO LTD
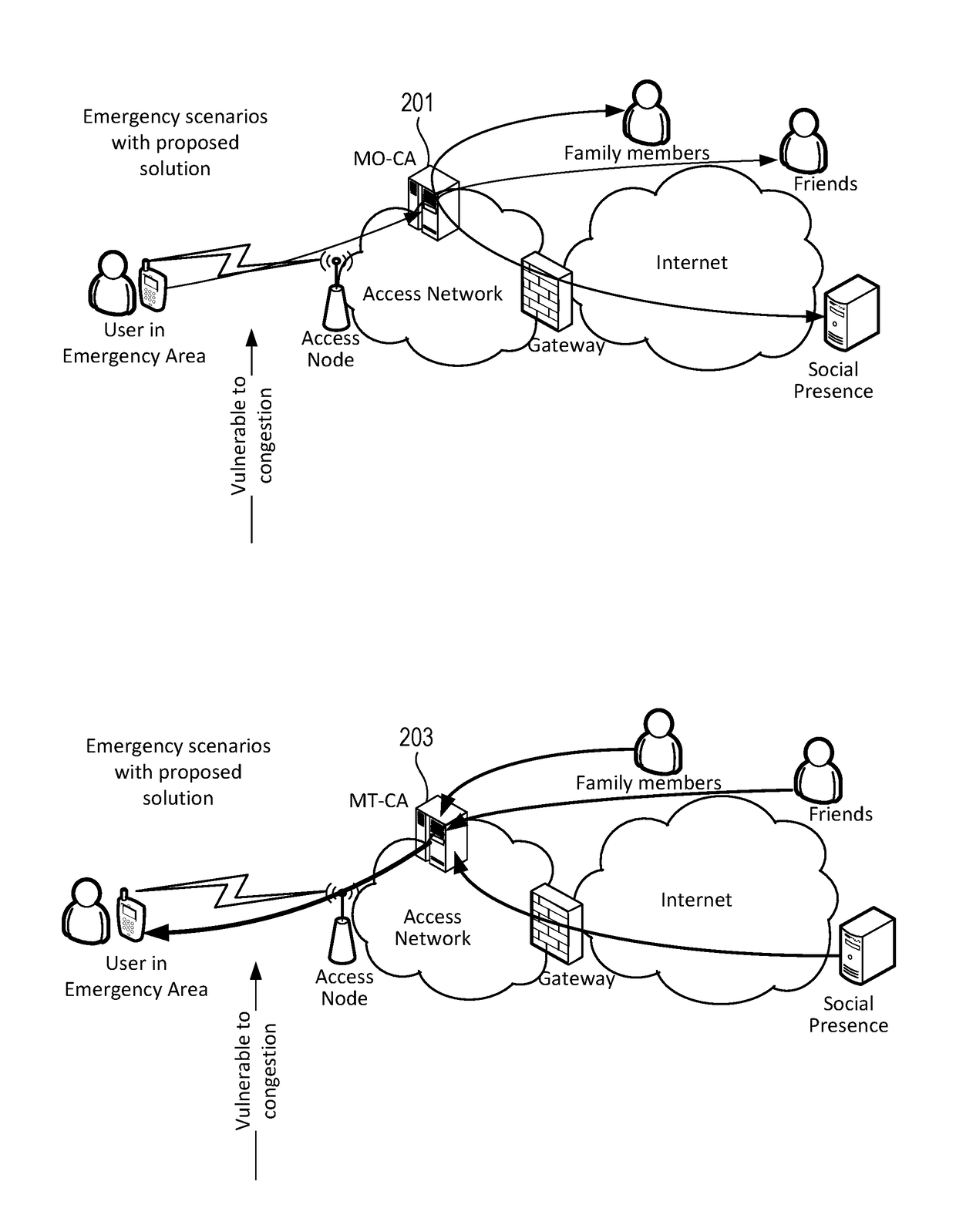
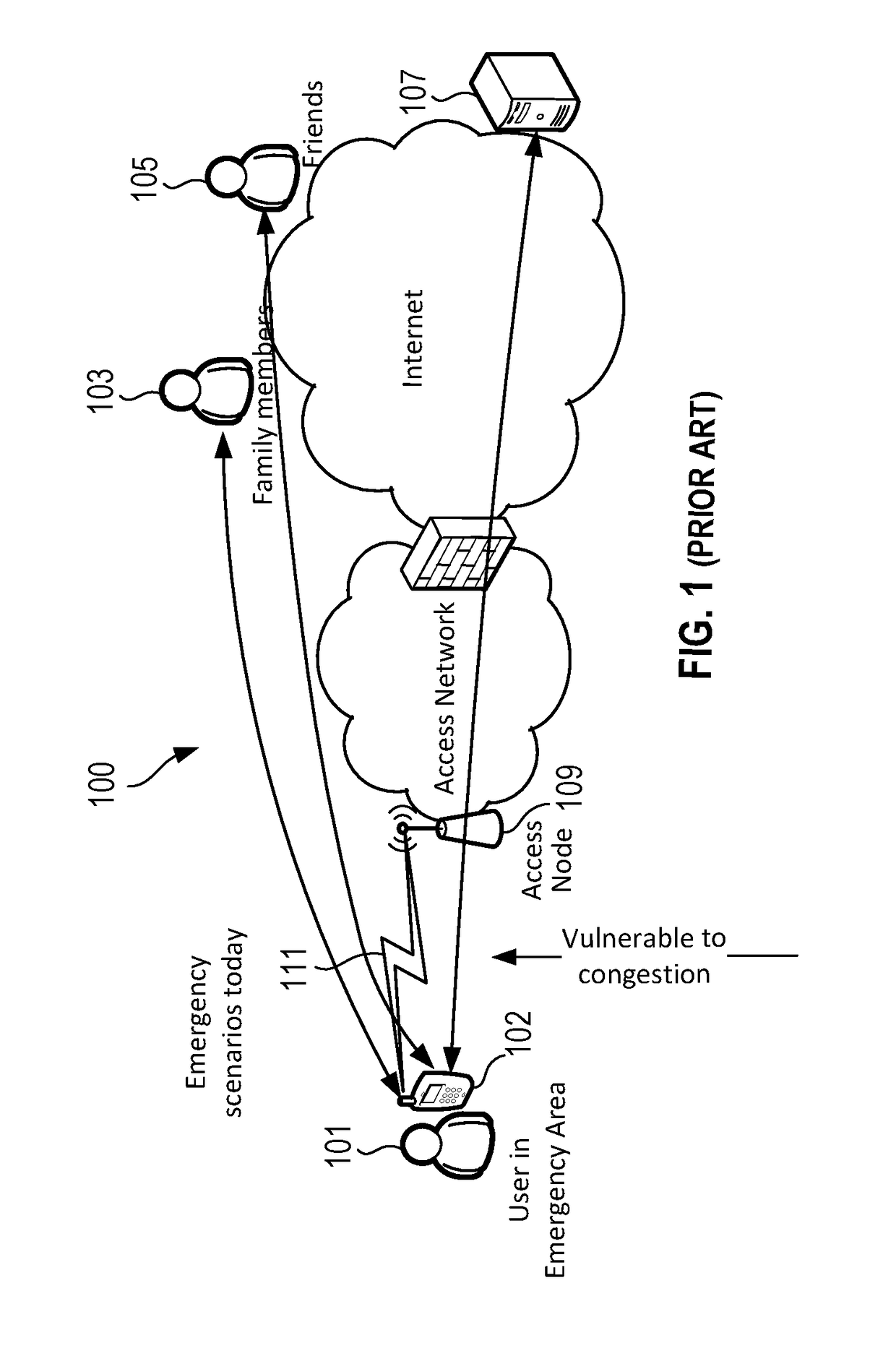
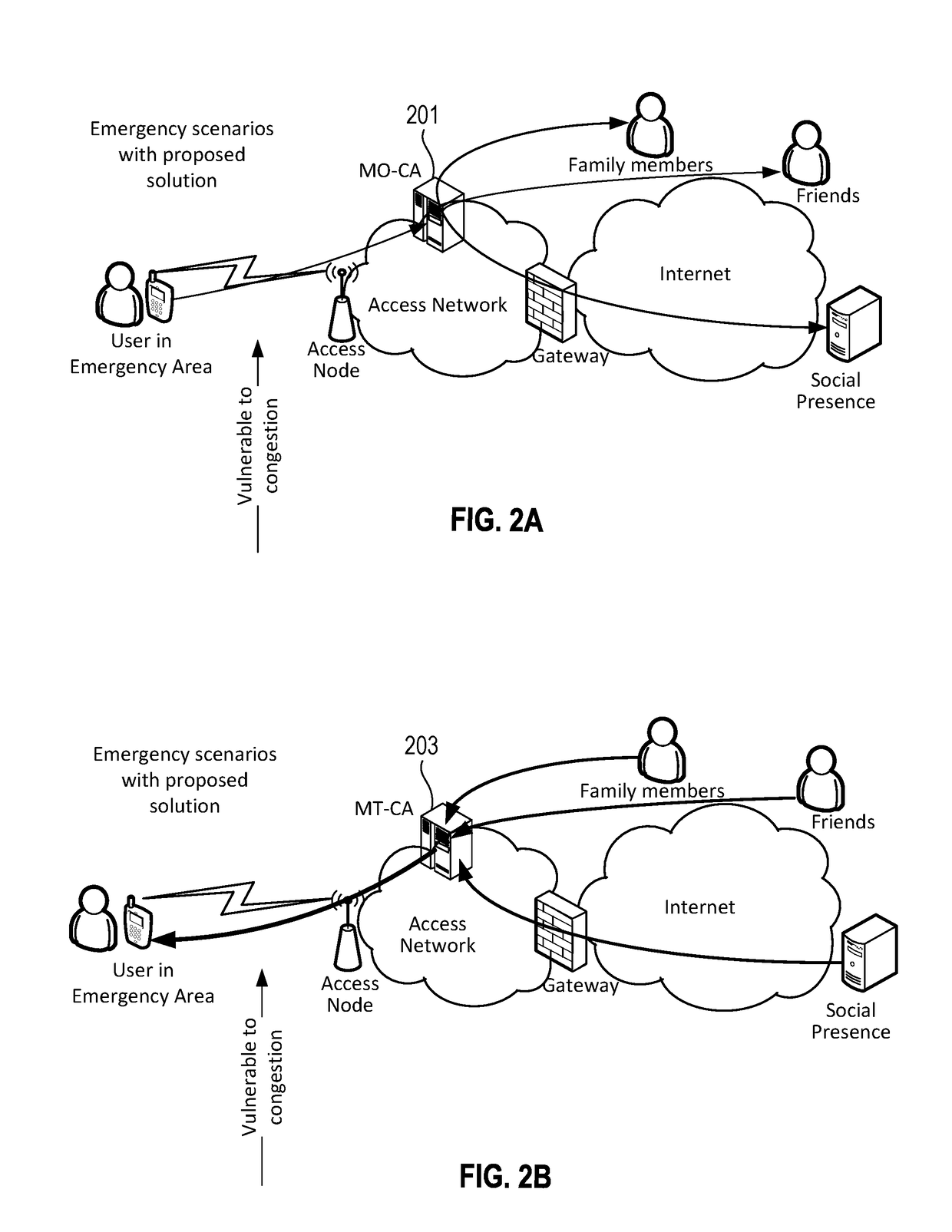
Emergency Mode Mobile Call Agent
InactiveUS20170180540A1Connection managementBroadcast service distributionTelecommunicationsRadio access network
An emergency mobile call agent includes a mobile originating call agent and a mobile terminating call agent. The mobile originating call agent responds to receiving an emergency notification and the emergency being above an emergency threshold condition, by notifying a contact list associated with a user that the user is impacted by the emergency. The mobile originating call agent may notify the contact list if the emergency is at or above a threshold emergency level set by the user. The mobile terminating call agent controls cellular traffic by evaluating one or more aspects of radio access network (RAN) loading and diverting incoming traffic to a user impacted by the emergency to another form of communication if RAN loading is too high for the traffic.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Dynamic sorting-based device and base station connection method in cellular flow unloading network
ActiveCN105764121AEasy accessImprove efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransmitted powerComputer science
The invention discloses a dynamic sorting-based device and base station connection method in a cellular flow unloading network. The method comprises the following steps: (1) multiple APs are deployed near a user for providing service for the user, the user can select to be accessed to an AP or a BS, and a benefit function is given to evaluate current benefits of the user; (2) through calculation, after a problem is layered, once the user access mode is found to be determined, the transmitting power of the user is determined accordingly, the benefit function is only related to the user access condition, and thus, the optimal user access only needs to be found for determining the optical system benefits; and (3) according to restrictive conditions C1 and C2 and in combination with a target function given in the second step, the user access mode is selected to maximize the benefits of the overall system. Superior user access can be quickly and effectively found, the power distribution of the user is determined at the same time, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Reducing cost of cellular backhaul
InactiveCN1998254ALow costNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsThe InternetCellular traffic
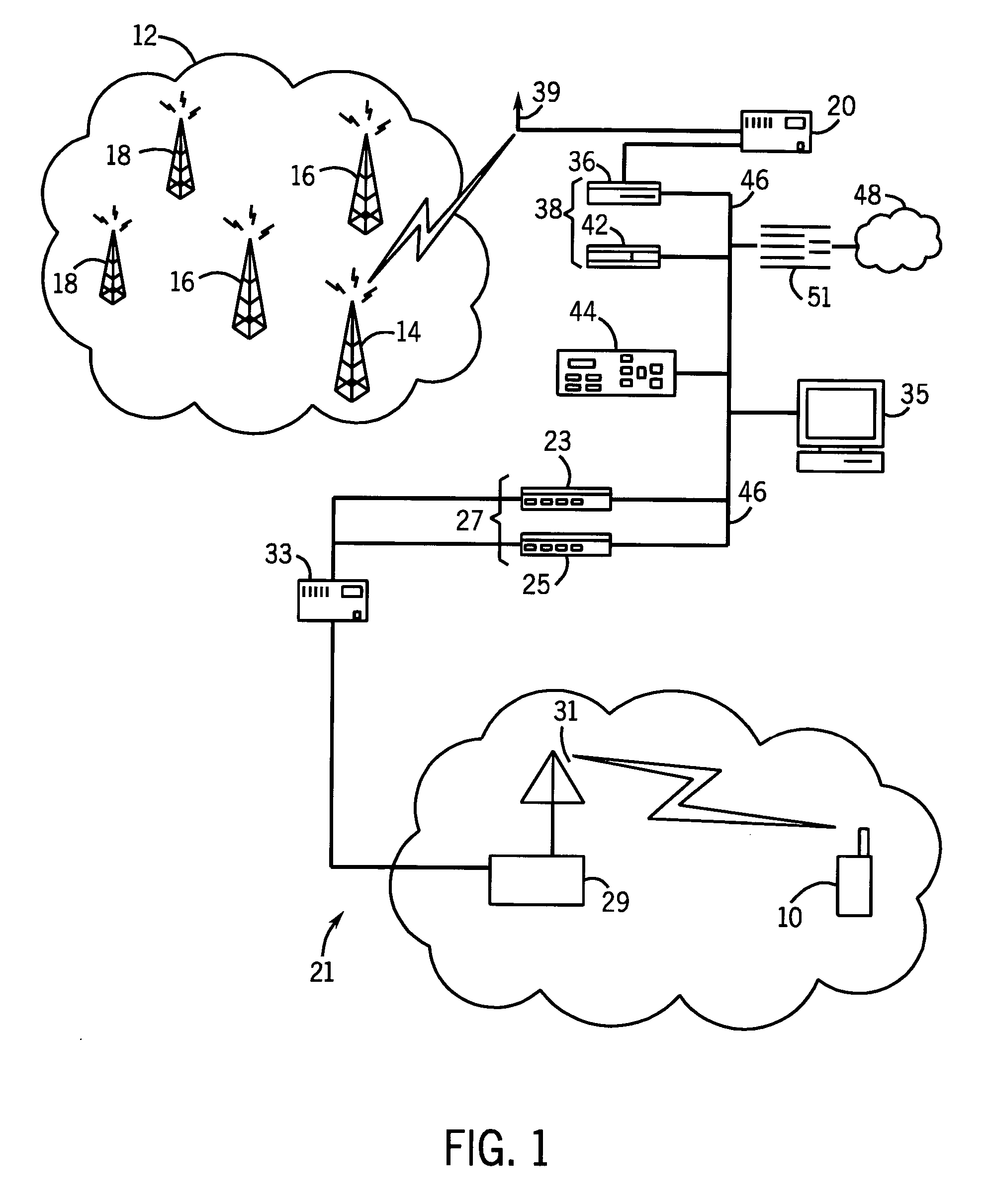
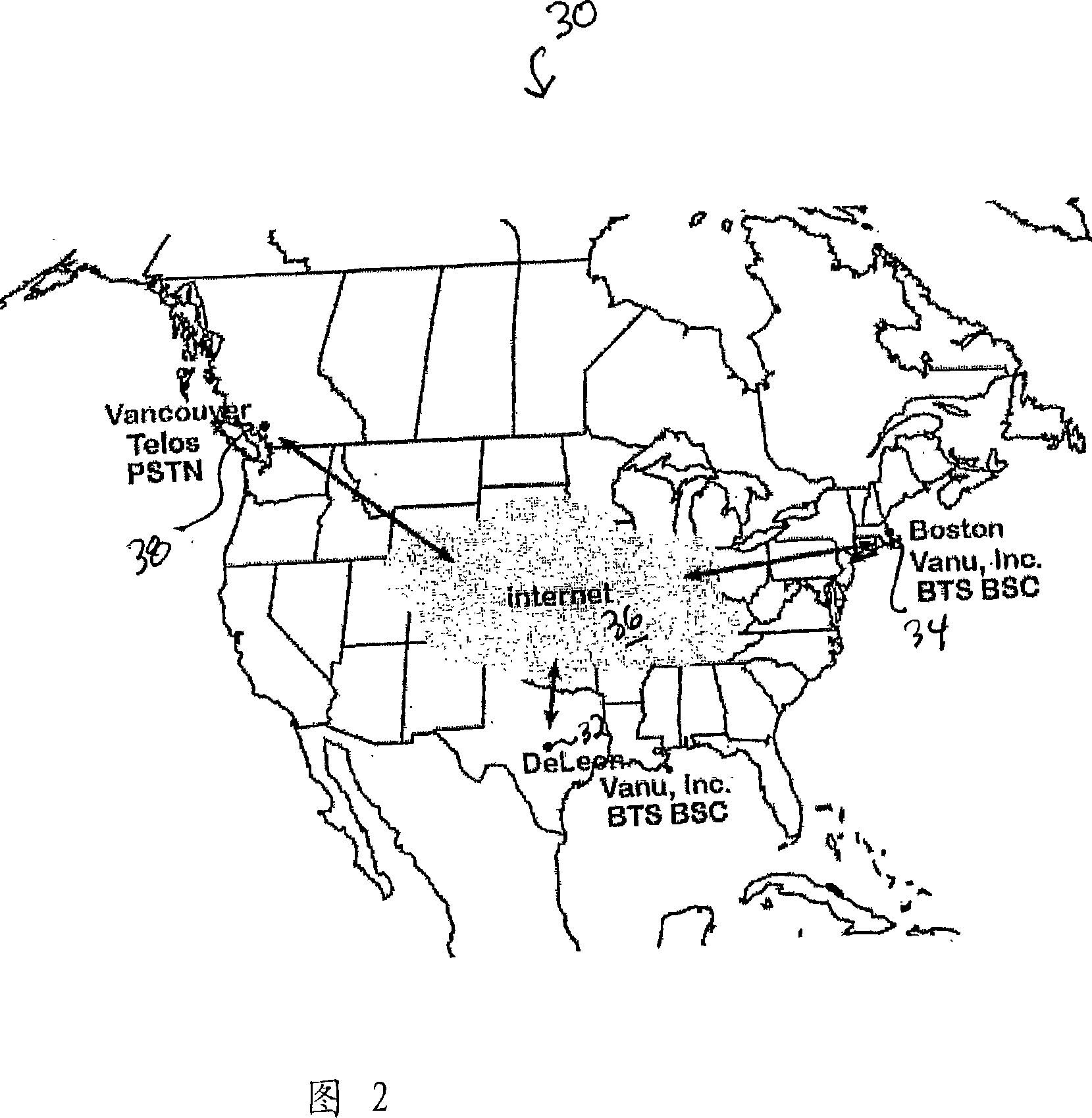
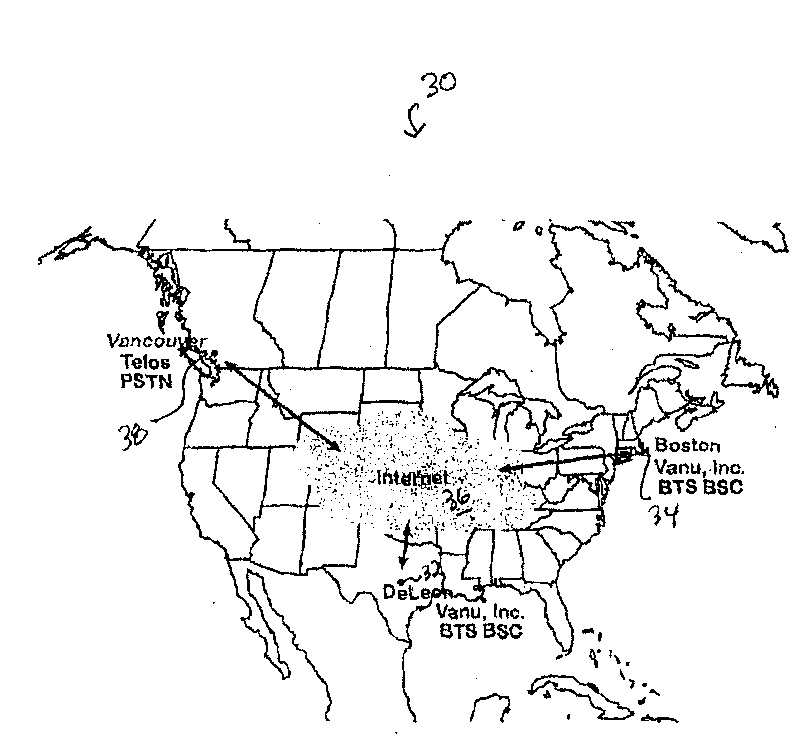
Methods and systems for reducing the cost of cellular backhaul are disclosed. The methods and systems include using the public Internet (138) to backhaul cellular traffic given the wide availability and relatively low cost of Internet connections compared with dedicated T1 lines. Re-distribution of switching functionality between a base station (136) and a base station controller (140) is achieved by moving some of the switching functionality from the base station controller to the base station.
Owner:VANU INC
Broadband cellular network device
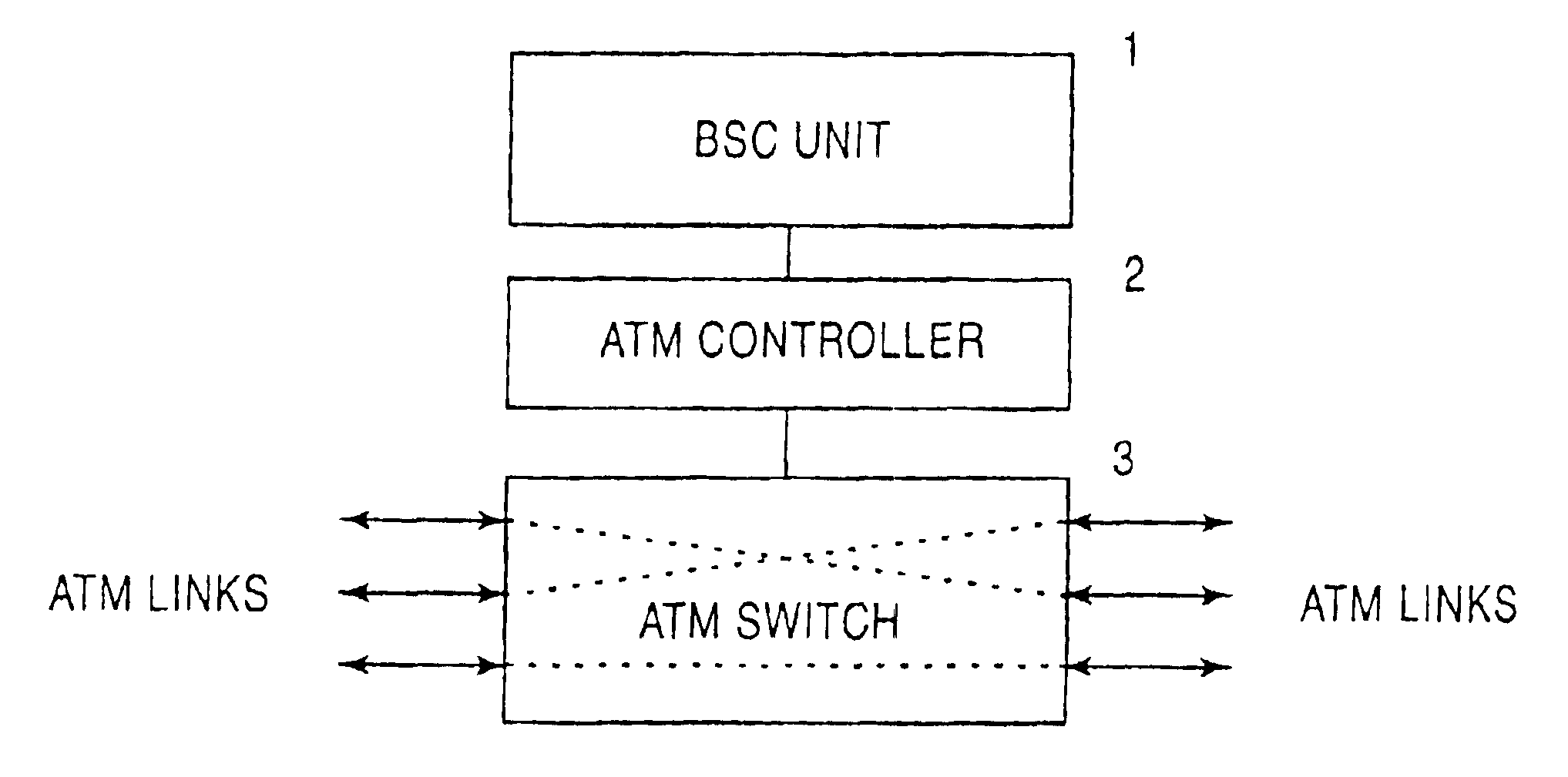
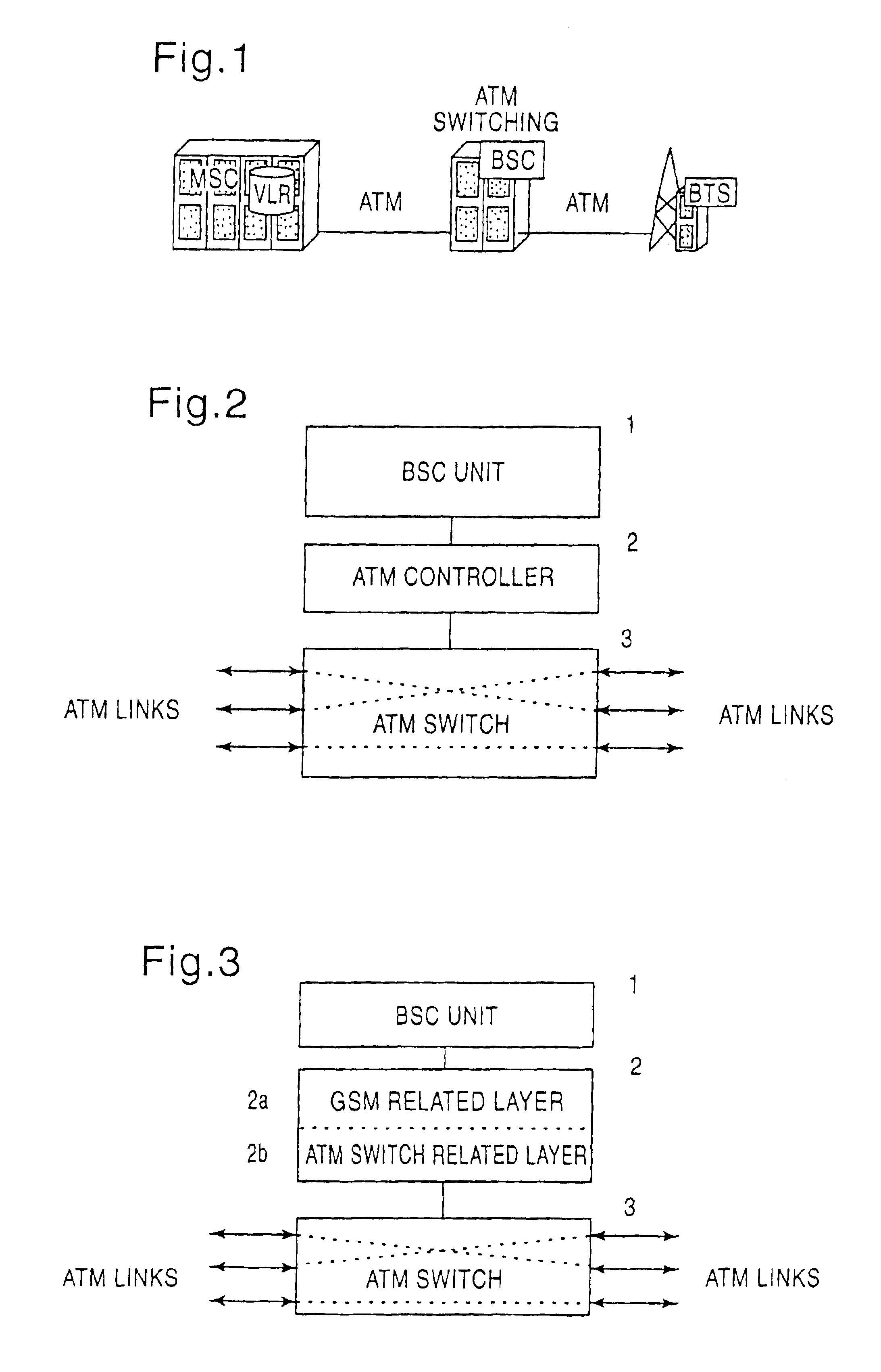
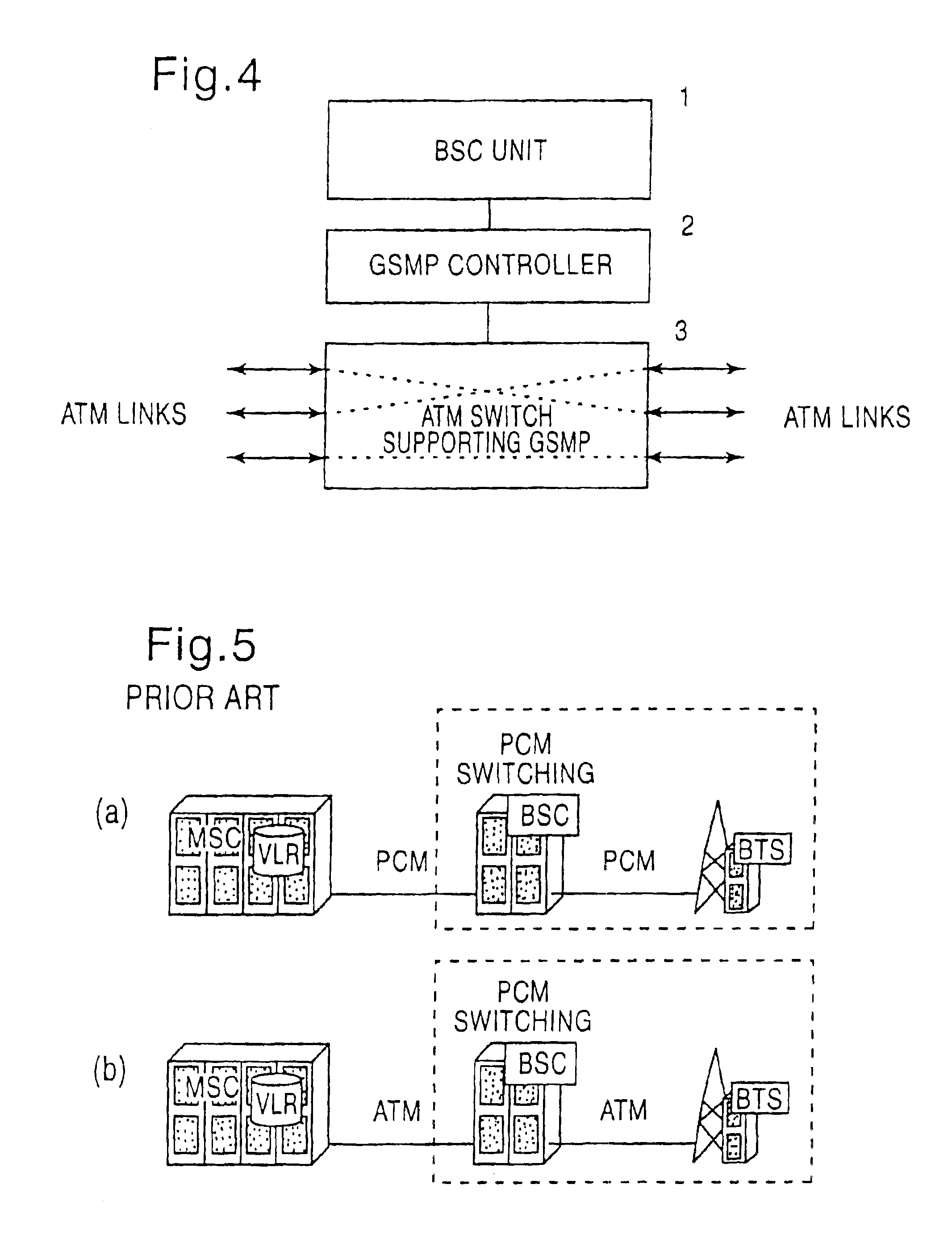
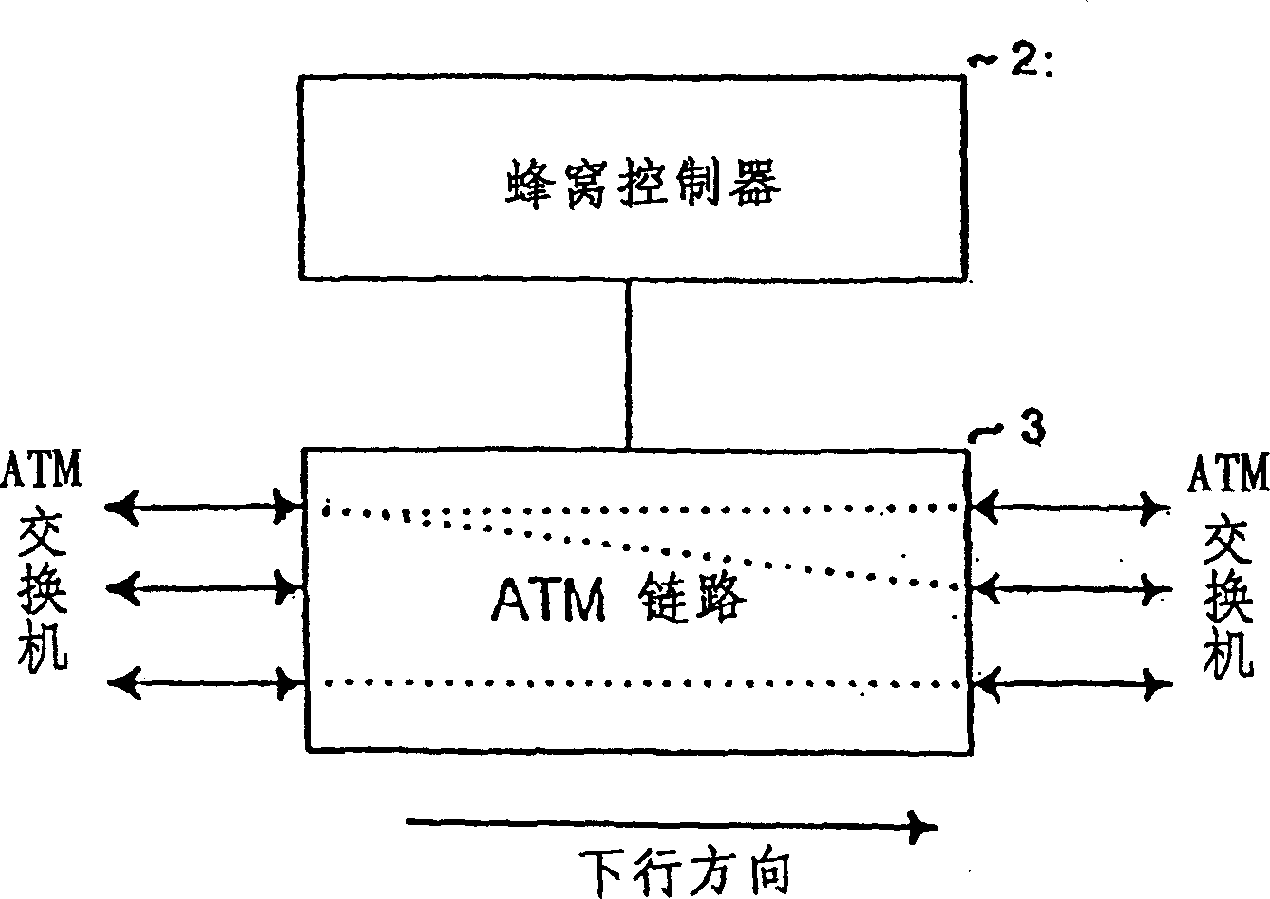
InactiveUS6859447B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAtm switchingTransfer mode
A broadband cellular network device comprises a base station controller unit (1), an asynchrouous transfer mode controller (2) adapted to control the distribution of cellular traffic consisting of asynchrouous transfer mode cells in trunking mobile communication networks based on ATM technology, and an asynchrouous transfer mode switching means (3) controlled by said asynchrouous transfer mode controller (2). The base station controller unit (1), the asynchrouous transfer mode controller (2) and the asynchrouous transfer mode switching means (3) form an ATM based base station controller (BSC) capable of performing ATM switching and adapted to replace PCM based base station controllers in base station subsystems (BSS) of asynchrouous transfer mode based cellular networks.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Backhaul network for femto base stations
InactiveCN107018516APower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementInterference (communication)Mobile device
Providing an inter-femto Base Station (fBS) network to facilitate low interference, low power cellular access utilizing two or more fBSs is provided herein. For example, a group of fBSs can be inter-connected by a wired and / or wireless communication network. Multiple fBSs then can link with a mobile device and coordinate cellular traffic amongst the fBS network to facilitate hand-off related communication. Additionally, cellular traffic can be forwarded from one or more fBSs to an appropriate fBS designated to carry cellular traffic for each mobile device. Furthermore, by inter-connecting multiple fBSs, multi-base station cellular-type hand-off can be supported by the fBS network, while preserving predetermined cellular interface constraints associated with such mobile devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
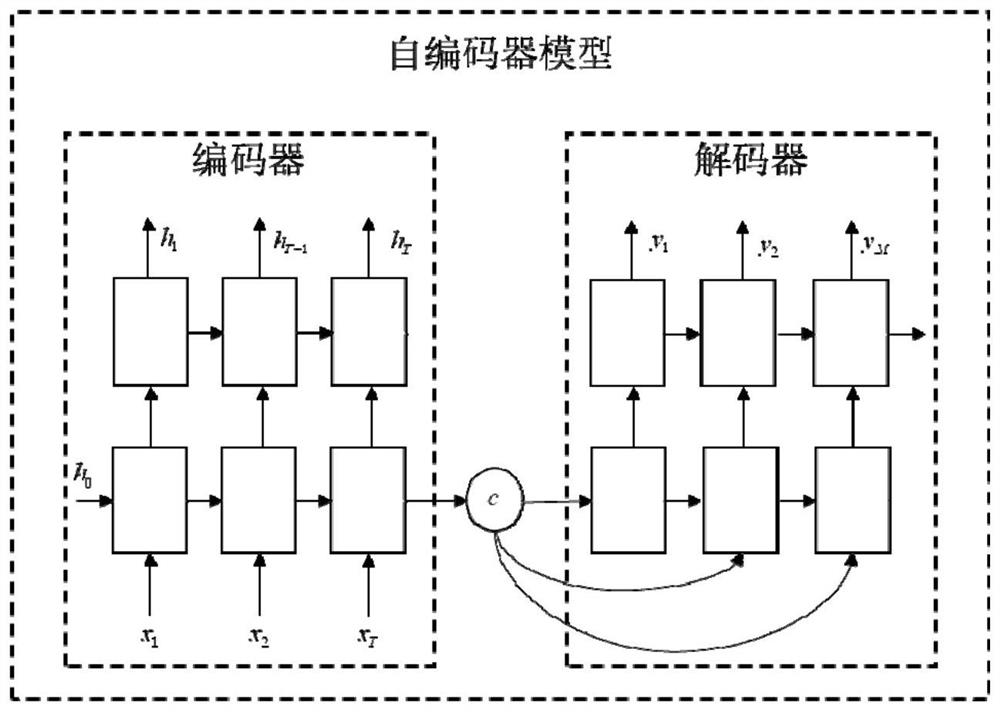
Mobile network traffic anomaly detection method and system based on feature dimension reduction
PendingCN113747441AImplement anomaly detection functionOptimize allocationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature DimensionInternet traffic
The invention discloses a mobile network traffic anomaly detection method and system based on feature dimensionality reduction, and the method comprises the steps: dividing a city region into M * N grid regions according to the distribution of city base stations, and aggregating the cellular traffic value of each grid region by using pandas to obtain a cellular traffic total value with an hour as a unit; dividing a detection time period into K time slots to form a time sequence vector, and taking the time sequence vector as an original cellular flow vector xj; extracting low-dimensional traffic features cj from the original cellular traffic vectors xj of all grid areas by using an LSTM auto-encoder; determining suspicious abnormal low-dimensional traffic features in the low-dimensional traffic features corresponding to all the grid regions; using the K-means clustering for carrying out anomaly confirmation on the suspicious and abnormal low-dimensional traffic features, completing mobile network traffic anomaly detection based on feature dimension reduction. The method and the system can realize anomaly detection of the mobile network traffic and have the advantages of being large in number of processing areas and short in data processing time.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
User access and power joint scheduling method based on packet switching in cellular traffic unloading network
ActiveCN105682211AImprove efficiencyExcellent user accessPower managementAssess restrictionSimulation basedAlgorithm convergence
The invention relates to a user access and power joint scheduling method based on packet switching in a cellular traffic unloading network. The user access and power joint scheduling method comprises the following steps that: (1), to enable more users to be accessed to an AP and enable the transmitting power of the users to be low as much as possible, a benefit function is given, such that whether a current network is good or bad can be judged; (2), because the benefit function is only related to the access conditions of the users, the optimal system benefit can be determined only in need of searching the optimal user access; and (3), the access selection of the users can become difficult along with increasing of the number of the users; a user packet switching method based on a simulated annealing algorithm is adopted; accesses of the users are continuously replaced; a solution for enabling a target function to become good is accepted; simultaneously, a poor solution is accepted at a certain probability; furthermore, the poor solution acceptation probability is continuously reduced; and finally, a near-optimal solution is obtained through algorithm convergence. According to the invention, the optimal user access can also be found rapidly and effectively while the efficiency of the system is increased; and simultaneously, the power distribution of the users is determined.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
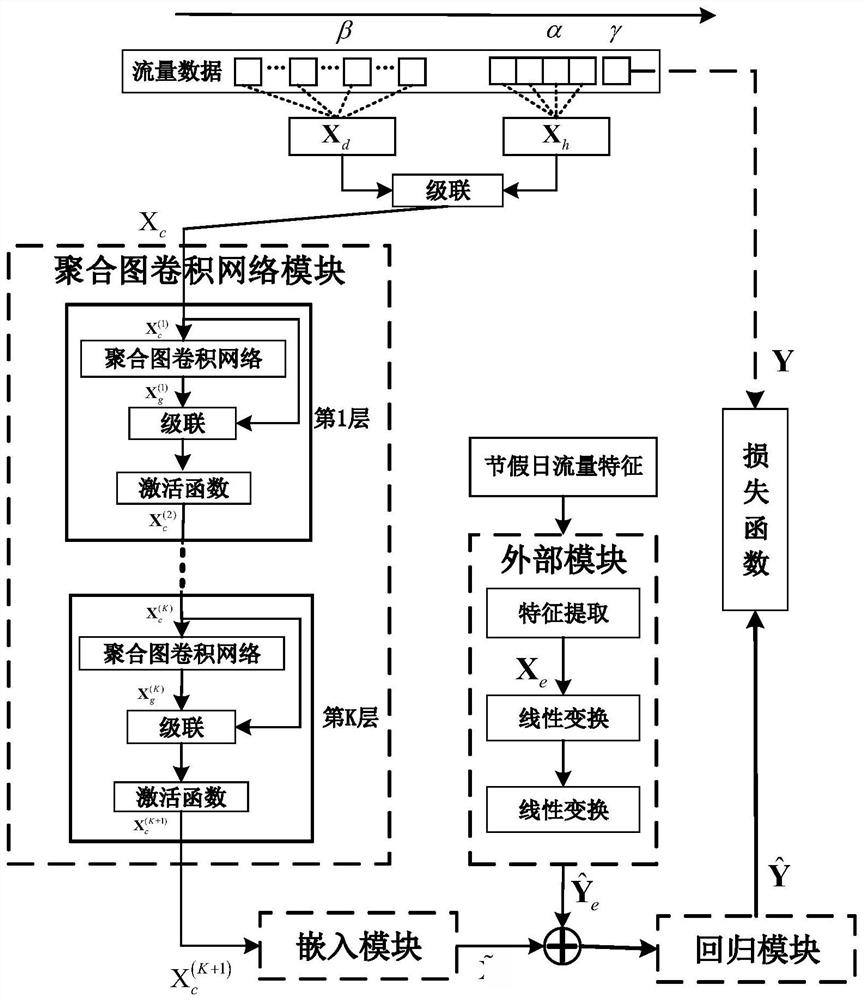
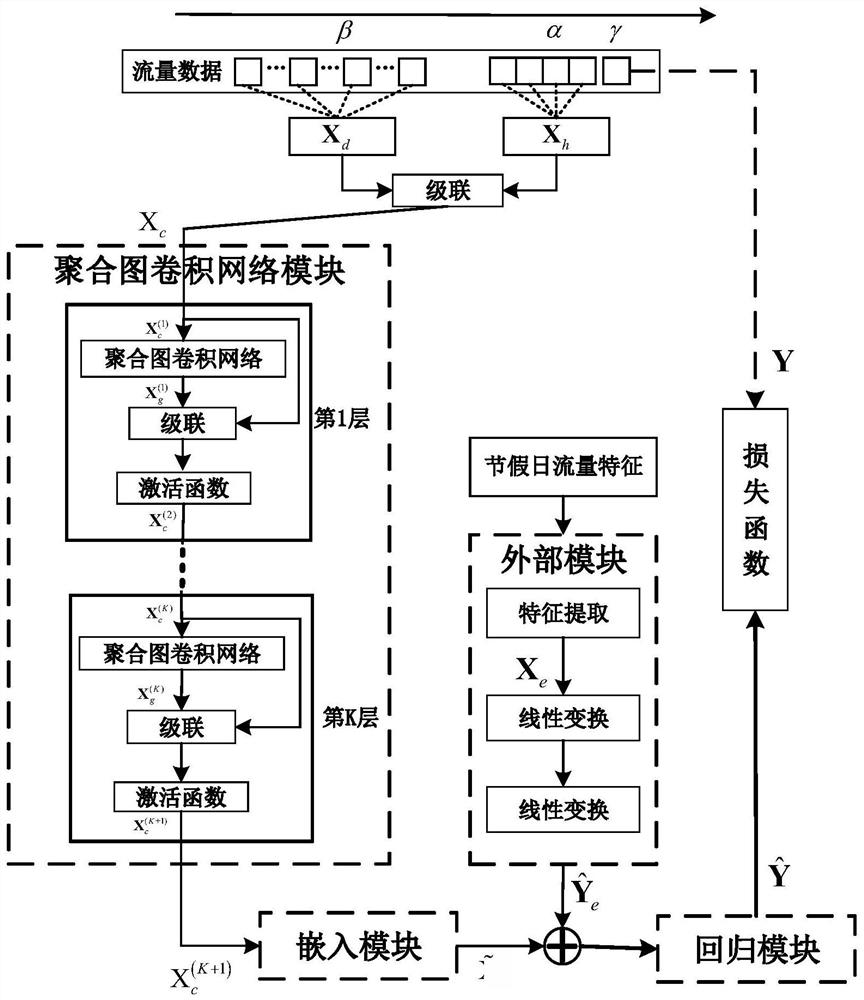
Mobile cellular traffic efficient prediction method based on space-time aggregation graph convolutional network
ActiveCN114158085ASmall loss functionForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmEngineering
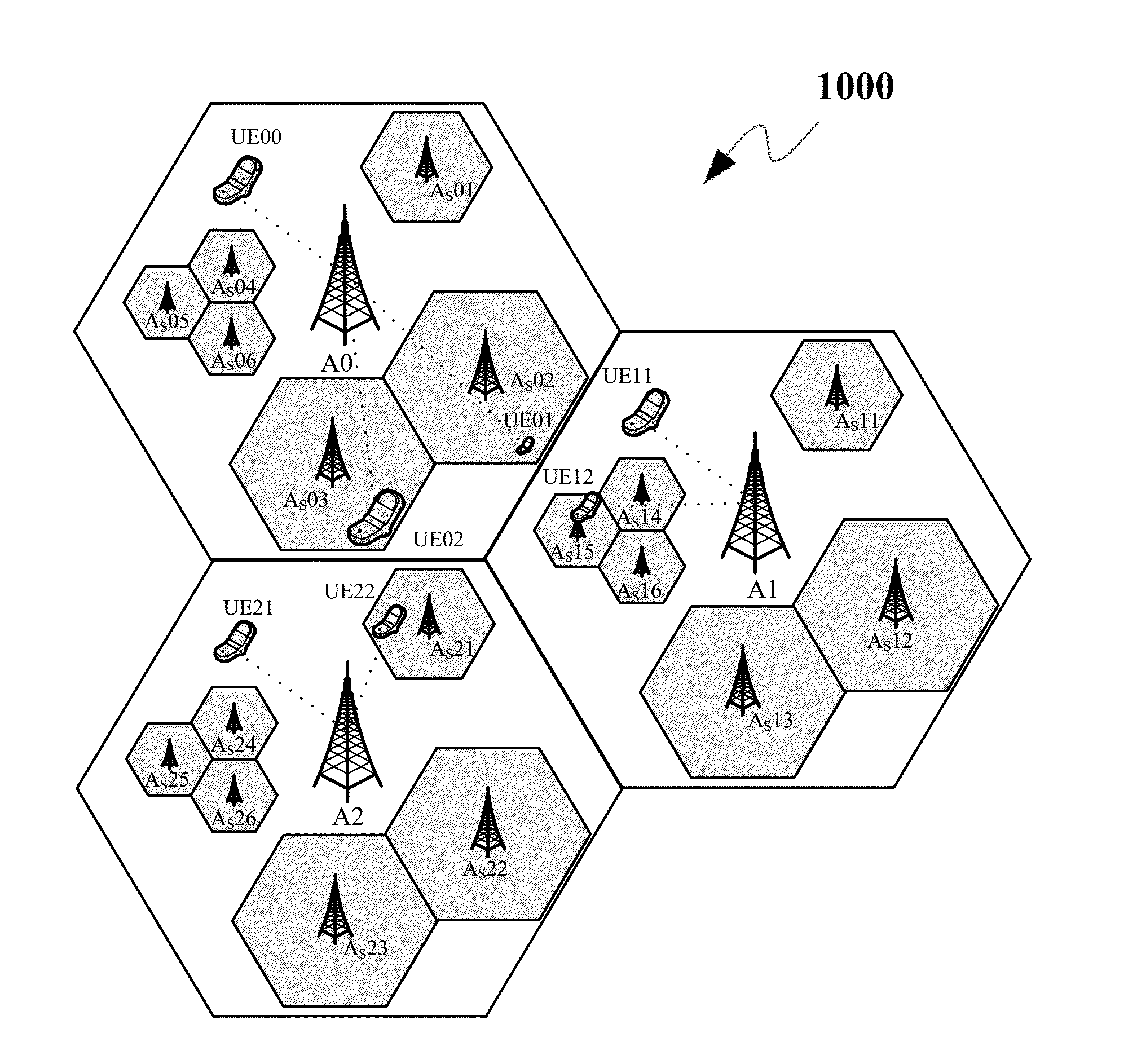
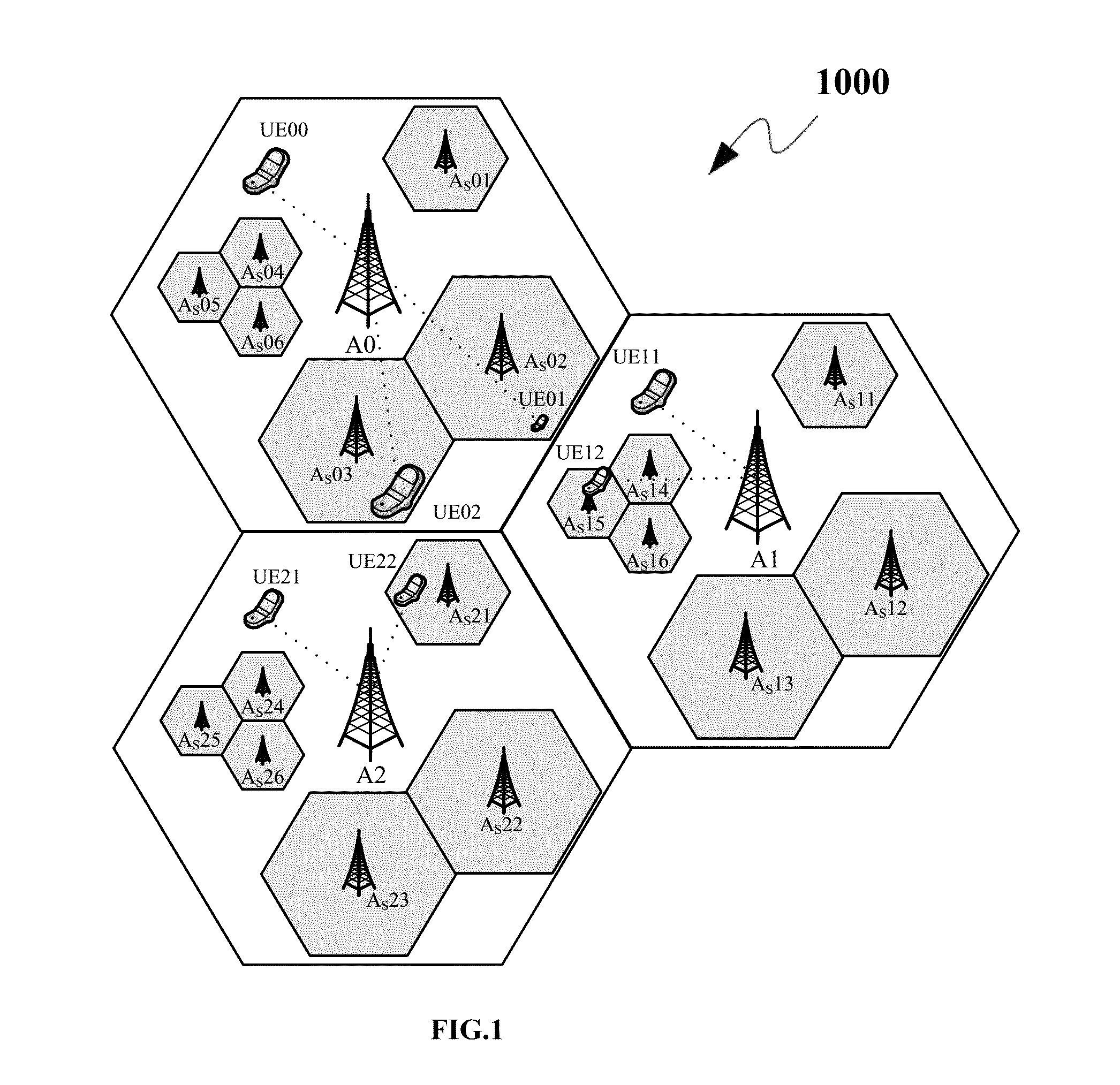
The invention discloses a mobile cellular traffic efficient prediction method based on a space-time aggregation graph convolutional network, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, dividing a prediction region into a plurality of sub-regions by the aggregation graph convolutional network, taking the sub-regions as nodes in the network, and performing modeling on a daily historical mode and a current mode per hour of mobile traffic, and capturing the complex space-time correlation of all nodes across different time. And then, the outputs of the K layers of aggregation graph convolutional network modules are connected through an embedded module. And then, fusing the prediction information with external features extracted by an external module by using a regression module to obtain a final mobile traffic prediction result, and updating model parameters to obtain a minimum loss function. According to the invention, the prediction performance of the mobile cellular traffic is effectively improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method, system and device for predicting cellular flow and medium
ActiveCN114039871AComplete modelingHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesCellular trafficConvolution
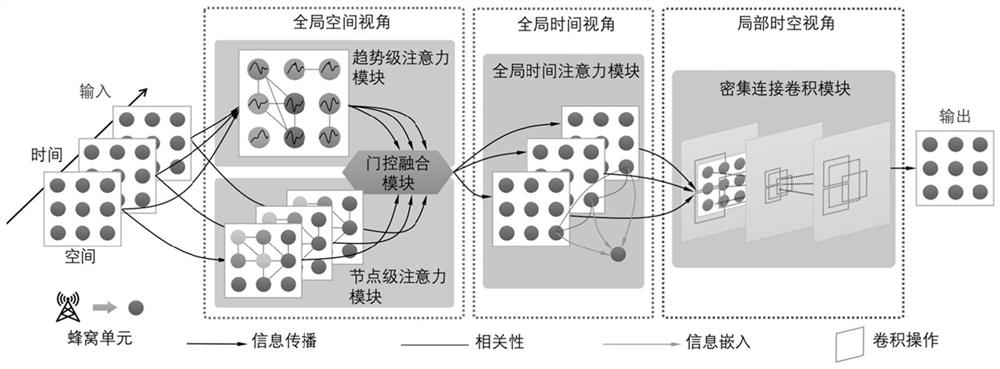
The invention discloses a method, a system and a device for predicting cellular flow and medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring cellular flow data; carrying out feature extraction on the cellular flow data from a global space view angle, a global time view angle and a local space-time view angle in sequence; predicting cellular flow according to the extracted features; wherein an attention mechanism is adopted to obtain node-level global spatial correlation and trend-level global spatial correlation of different cellular flow units, and the global spatial correlation of the two levels is fused; acquiring global correlation of data of the same cellular flow unit at different historical moments by adopting an attention mechanism; after global space-time correlation capture is completed by adopting convolution operation,capturing local space-time correlation continuesely. The method comprehensively captures the space-time correlation of the cellular flow from a global space view angle, a global time view angle and a local space-time view angle, realizes complete modeling of the space-time characteristics of the cellular flow, and can be widely applied to the technical field of communication.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Broadband cellular network device
InactiveCN1174644CImprove bandwidth efficiencyBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverBroadband
A broadband cellular network device comprises a cellular controller means adapted to control the distribution of cellular traffic consisting of asynchronous transfer mode cells in trunking mobile communication networks based on ATM technology, and an asynchronous transfer mode switching means controlled by said cellular controller means and adapted to multicast said cellular traffic to downlink base transceiver stations using multicast properties of the asynchronous transfer mode switching means.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
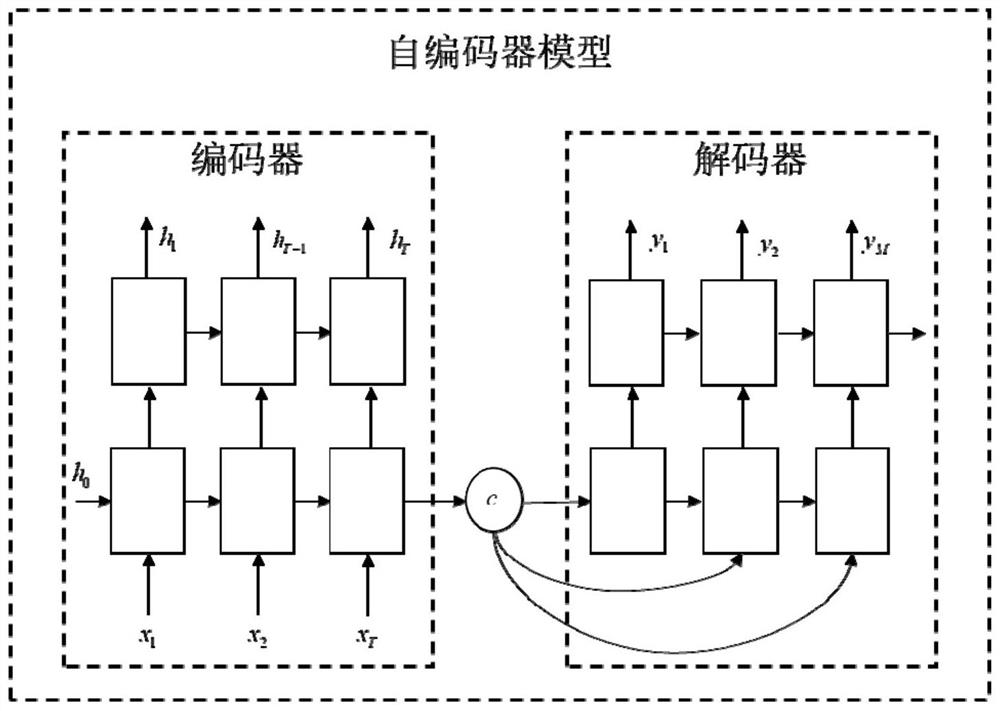
Multi-data-set joint prediction method based on attention mechanism
The invention discloses a multi-data-set joint prediction method based on an attention mechanism, and the method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out the anomaly detection of different types of activity data in a CDR data set through employing a mobile network anomaly detection method based on feature extraction, removing abnormal activity data, and then respectively putting each type of activity data into a recurrent neural network with the same structure; 2) inputting an output result of each recurrent neural network into an attention unit, and inputting an output result of the attention unit into the recurrent neural network for flow data prediction; and 3) taking the output of the recurrent neural network used for traffic data prediction as a prediction result of the cellular traffic. The method can accurately predict the traffic data at the future moment.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A Seed Node Selection Method for Offloading Cellular Traffic Through Opportunistic Mobile Networks
The seed node selection method of offloading cellular traffic through opportunistic mobile network, passing through the cellular network to some selected initial seeds in the mobile network, and then disseminating for free by using opportunistic communication, all nodes in the mobile network can access the cellular network ; Find the optimal number of initial seeds to maximize the overall content utility value, taking into account the cost of direct delivery over the cellular network and the freshness of the delivered content; define the content utility value gain, and calculate the delivery over the cellular network Optimal number of copies of content k ; Based on the seed selection method, to find the optimal number of initial seeds to maximize the overall content utility value of the nodes in the network. The method of the present invention considers the freshness of the content and the transmission cost from the cellular network to the initial seed. In order to solve the utility optimization problem, two seed selection methods are proposed to find the optimal number of initial seeds so that the overall content utility value of the nodes in the network maximize.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Estimating available bandwith in cellular networks
InactiveUS9231843B2Data switching networksWireless communicationDistributed computingCellular traffic
Systems and methods for estimating bandwidth. A first probe flow is sent into cellular traffic, and a first bandwidth quantity achieved by the first probe flow is measured. A second probe flow is sent into the cellular traffic, and a second bandwidth quantity achieved by the first probe flow while the second probe flow is in the cellular traffic is measured. The first bandwidth quantity and the second bandwidth quantity are compared, and at least one result from the comparing is determined.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Flow forecasting for mobile users in cellular networks
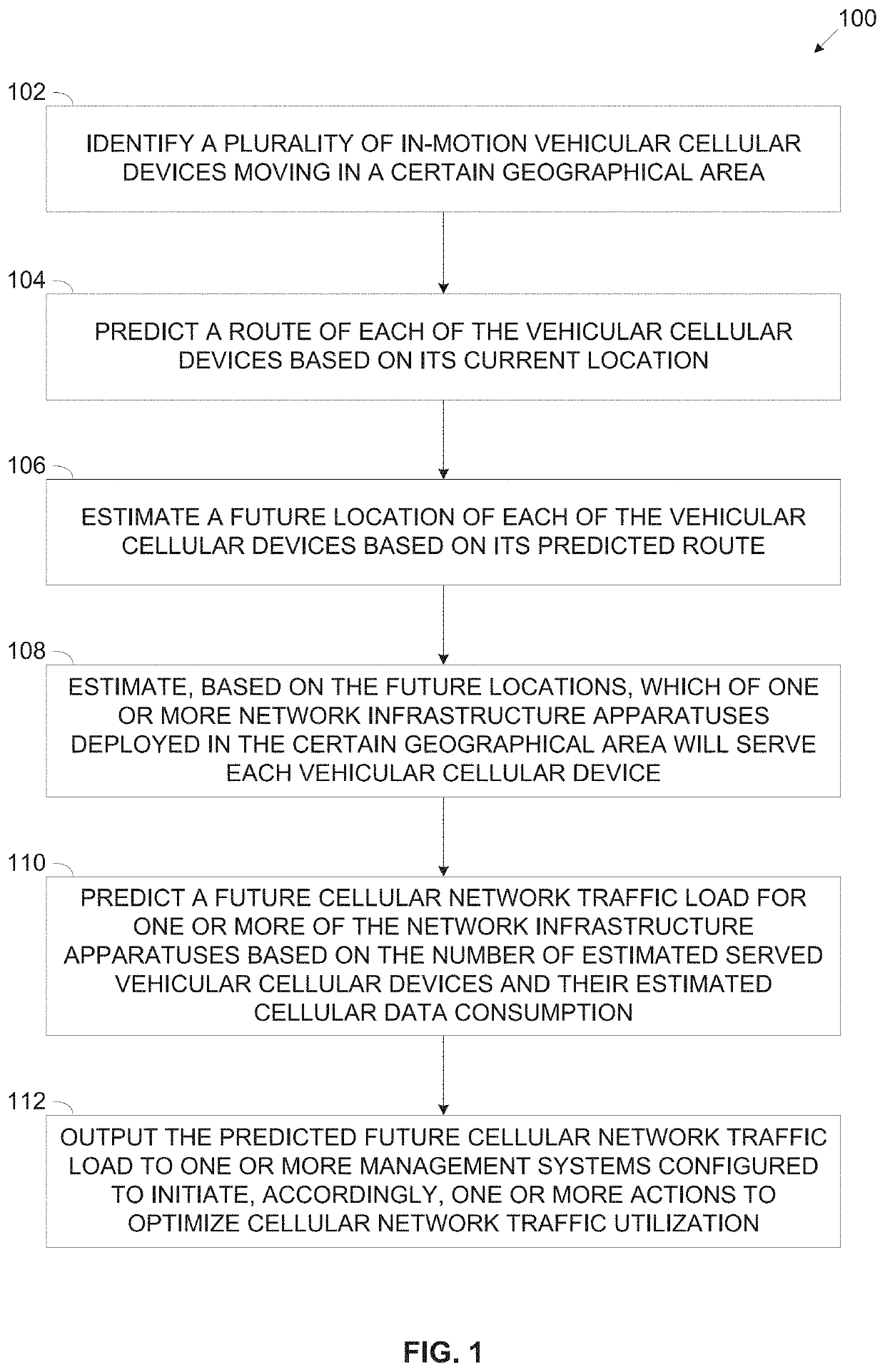
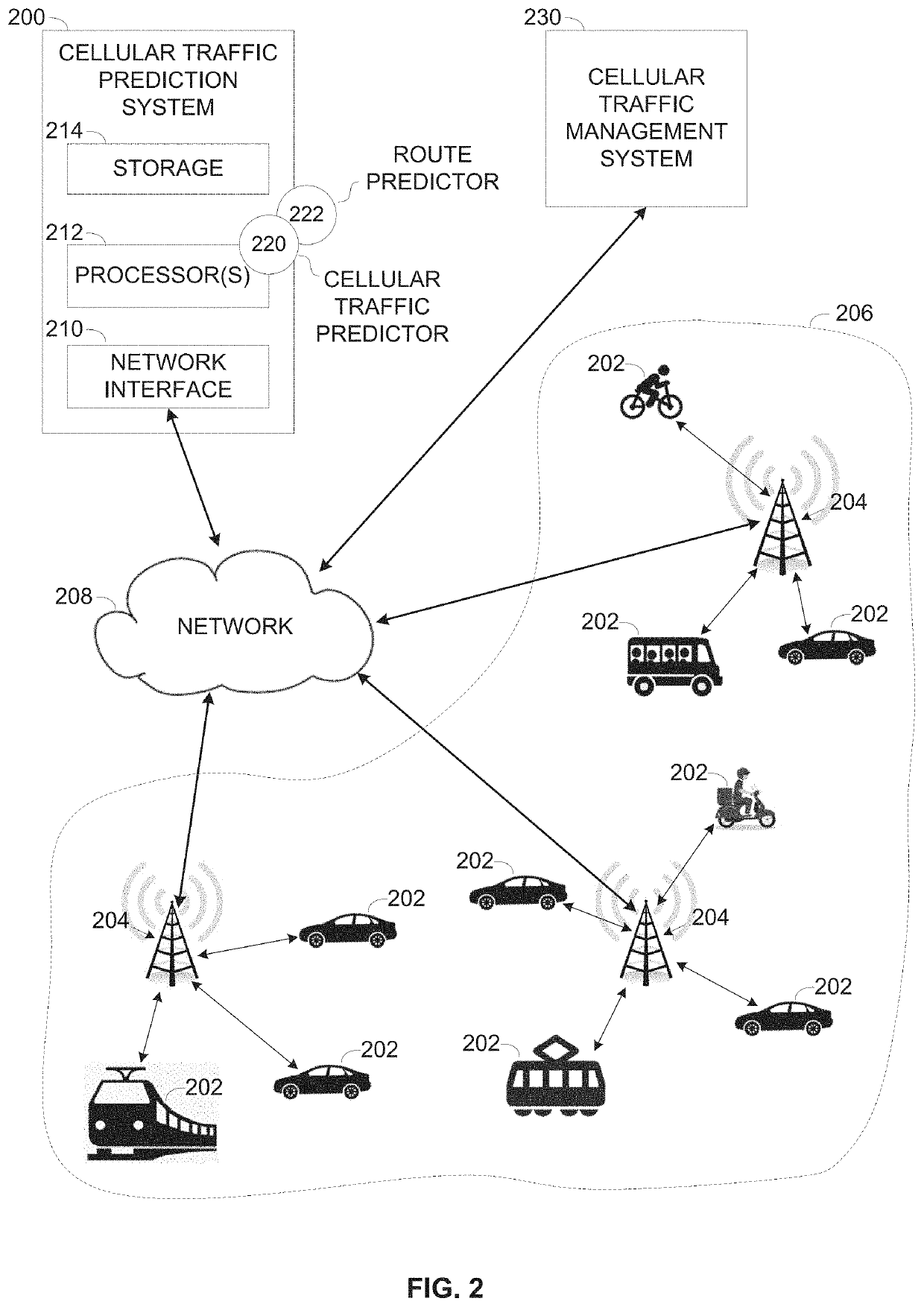
InactiveUS20220110021A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching networksTraffic predictionEngineering
Disclosed herein are methods, systems and computer program products for predicting a cellular traffic load in a certain geographical area deployed with a plurality of network infrastructure apparatuses by identifying in-motion vehicular cellular devices moving in the certain geographical area and using one or more trained Machine Learning (ML) Models to predict the future cellular traffic load for one or more of the plurality of network infrastructure apparatuses based on an estimated future location of the vehicular cellular devices and a predicted cellular data consumption of the vehicular cellular devices. The future cellular traffic load may be provided to one or more cellular traffic management systems which may take one or more actions in advance based on the predicted future cellular traffic load.
Owner:CONTINUAL LTD
Method and system for wireless voice and data transmission backhaul
InactiveCN1998254BNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesThe InternetData transmission
Methods and systems for reducing the cost of cellular backhaul are disclosed. The methods and systems include using the public Internet (138) to backhaul cellular traffic given the wide availability and relatively low cost of Internet connections compared with dedicated T1 lines. Re-distribution of switching functionality between a base station (136) and a base station controller (140) is achievedby moving some of the switching functionality from the base station controller to the base station.
Owner:VANU INC
A Data Selective Caching Method Based on Cooperative Caching
ActiveCN107623720BEfficient use ofMaximize uninstallNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionOriginal dataData selection
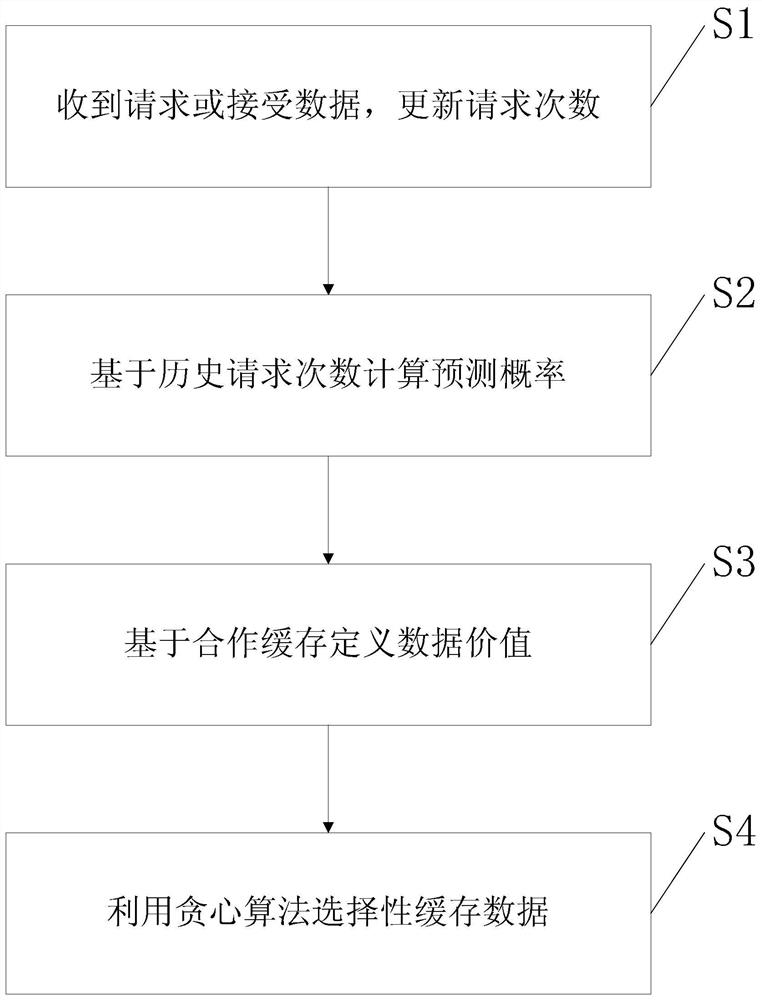
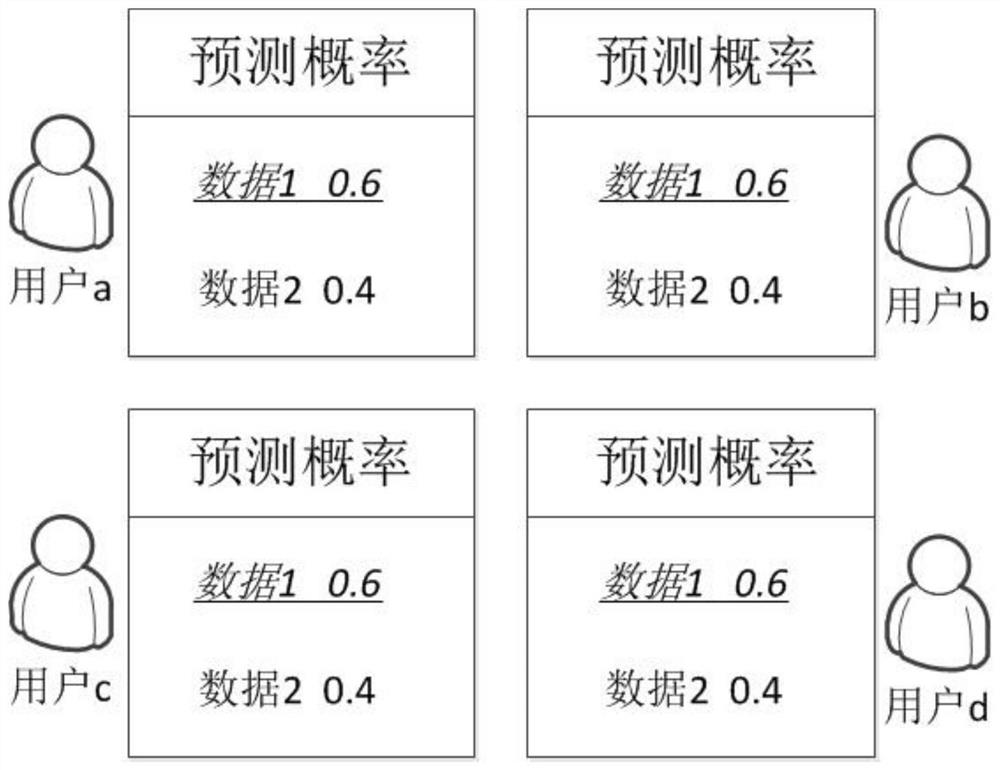
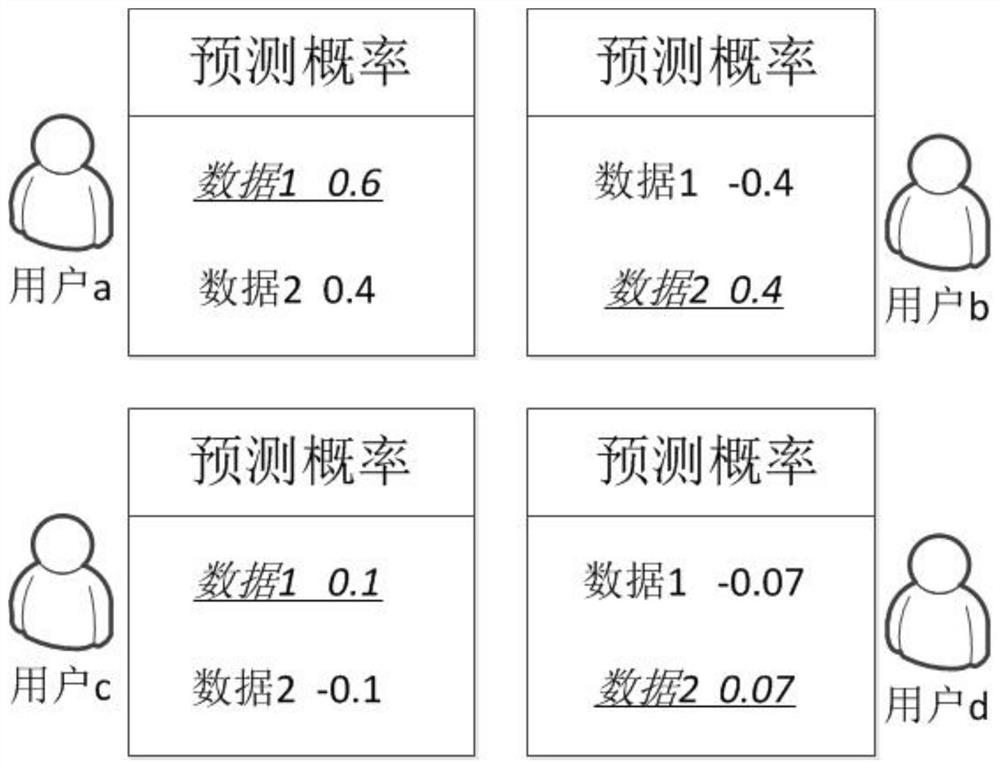
The present invention relates to a data selective caching method based on cooperative caching, which includes the following steps: Step S1, when the current user receives a request for each data from an adjacent user, or receives each data from an adjacent user or a base station, record and update The number of requests for each data; step S2, the current user predicts the probability that each data will be requested in the future according to the number of requests for each data, so as to obtain the predicted probability of each data; step S3, the current user asks and collects neighboring users before caching each data The memory cache situation of the user, combined with the size of each data and the prediction probability of each data, defines the value of each data; and step S4, if the current user's memory is not full, cache the received data, otherwise, according to the size of each data As well as the value of each data, a greedy algorithm is used to determine whether to cache the received data to replace the original data in the memory. The invention efficiently utilizes the limited memory capacity of the terminal, and realizes the maximum cellular traffic unloading.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
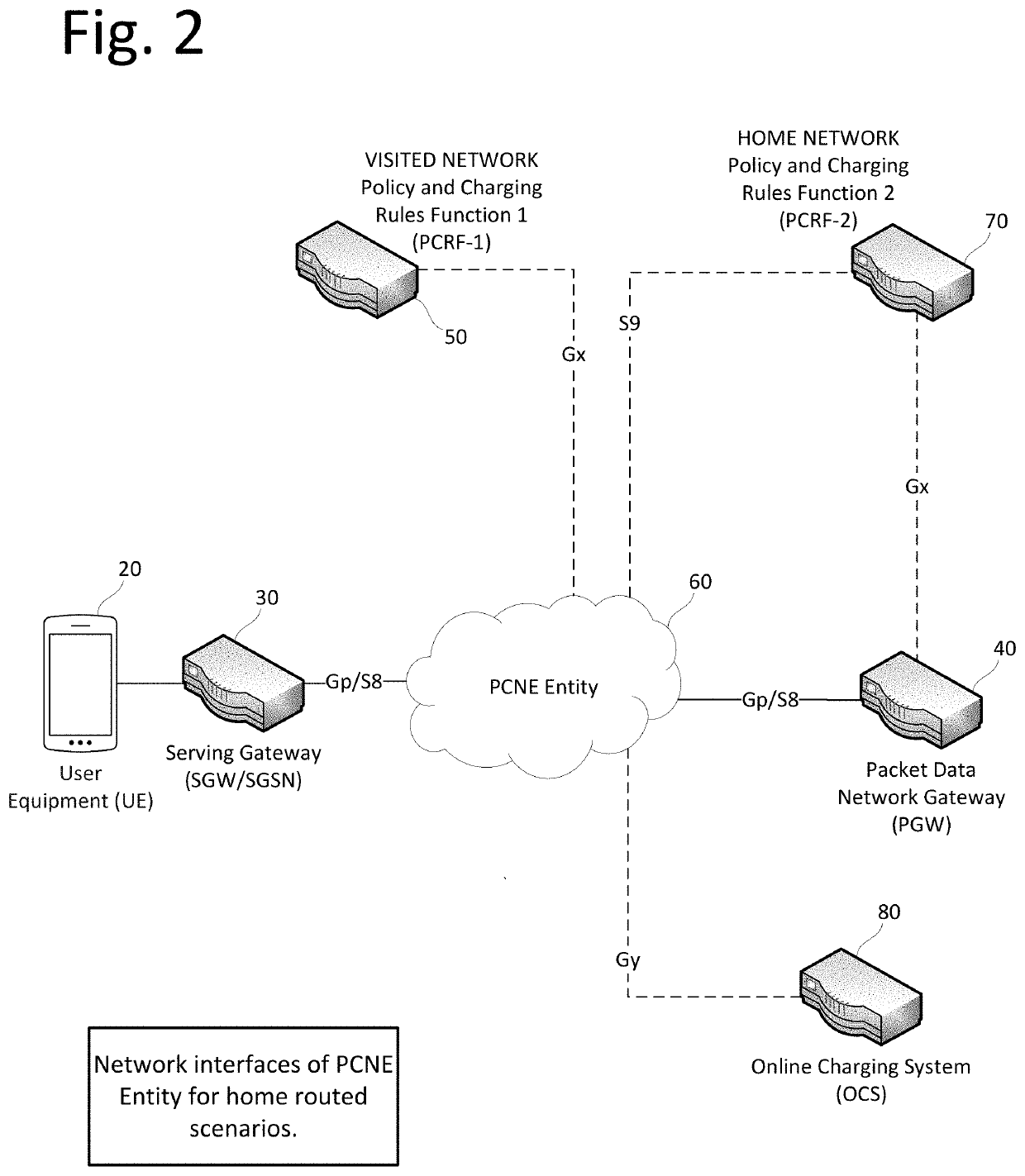
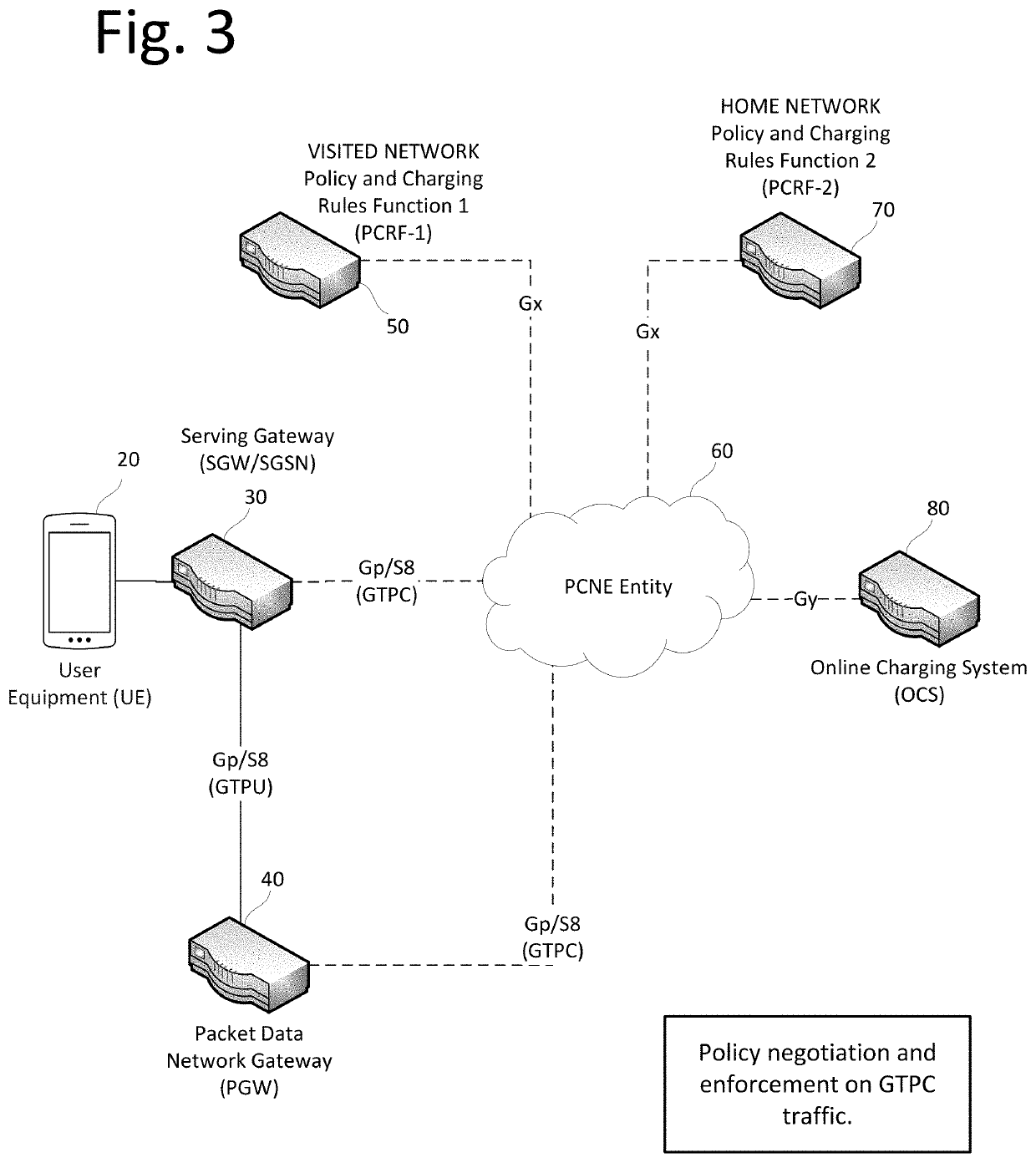
Roaming cellular traffic policy and charging negotiation and enforcement entity
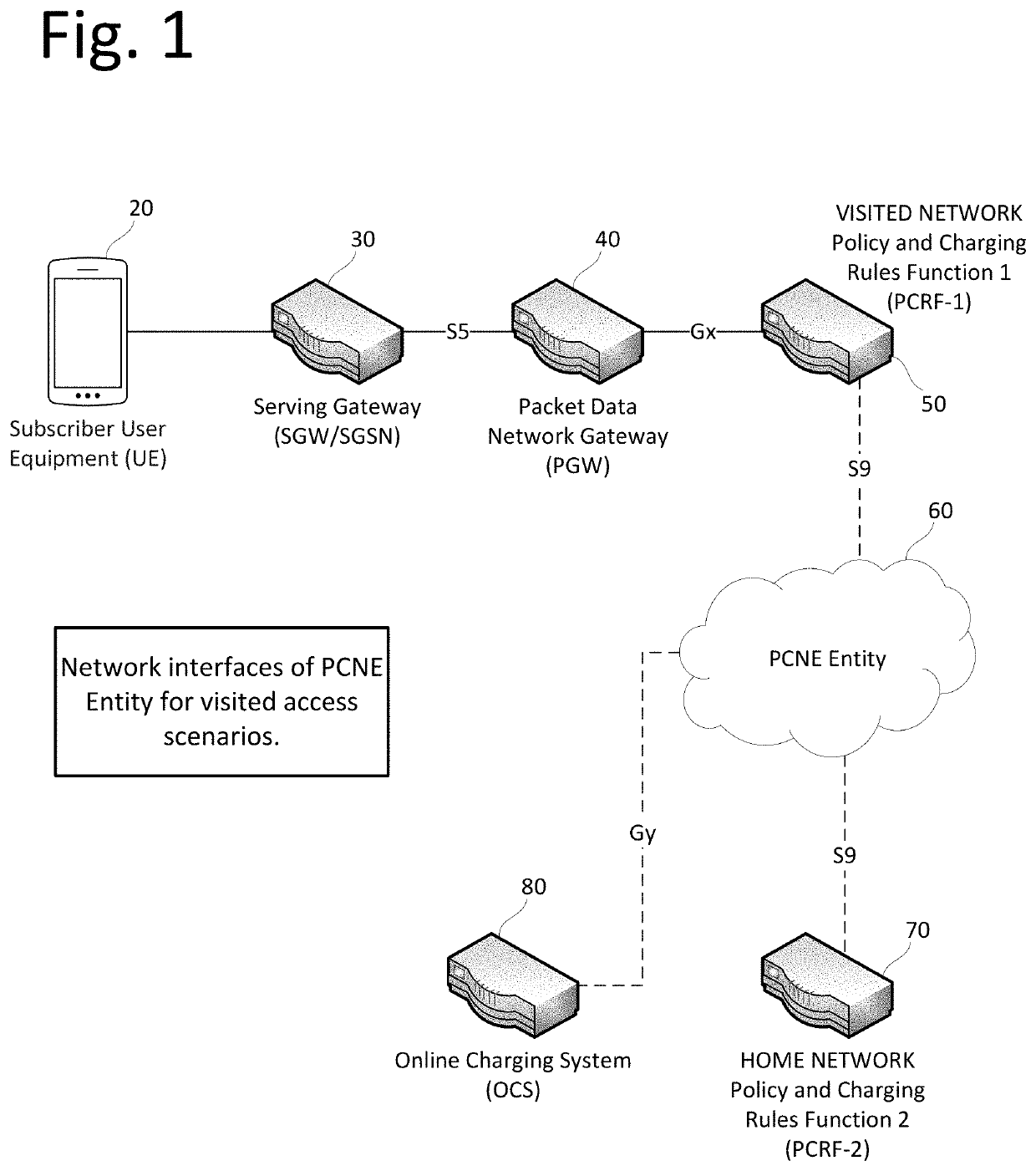
ActiveUS10645230B1Avoid overuseOptimize bandwidthAccounting/billing servicesNetwork topologiesVirtualizationCyber operations
A virtualized Policy, Charging, Negotiation and Enforcement Entity (PCNE) is disclosed for serving cellular traffic across multiple networks. The PCNE manages signaling and user payloads to apply policies compliant to concerned networks in real time. The PCNE provides policy control to a Home network even when its outbound subscriber traffic is locally offloaded at a Visited network or IP Packet Exchange (IPX) cloud. The PCNE protects the Visited network against capacity overuse by inbound subscriber traffic, thereby providing joint control to the Home and Visited network operators resulting in optimal use of bandwidth and resources along with consistent subscriber experience. The PCNE enables the Home network operator to implement domestic quota buckets and policies while its subscriber is roaming in the Visited network by applying differential policy and charging rules. Traffic can be offloaded to a preferred packet data gateway after enforcing the negotiated policies.
Owner:SYNIVERSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com