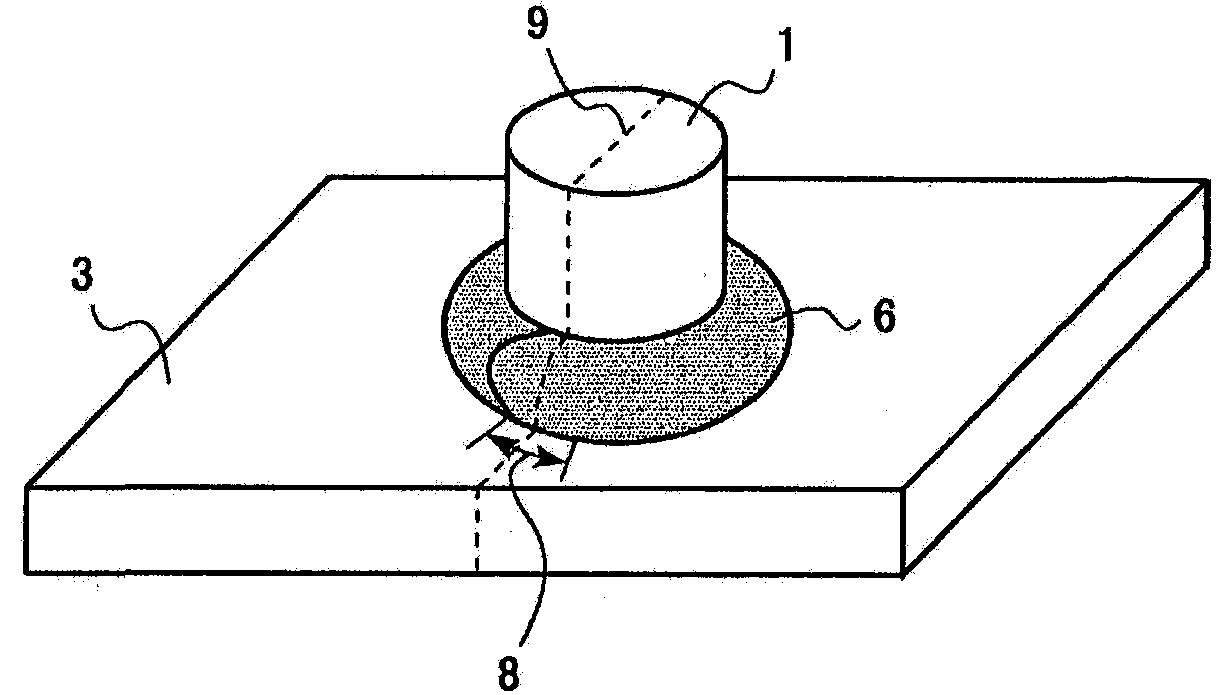
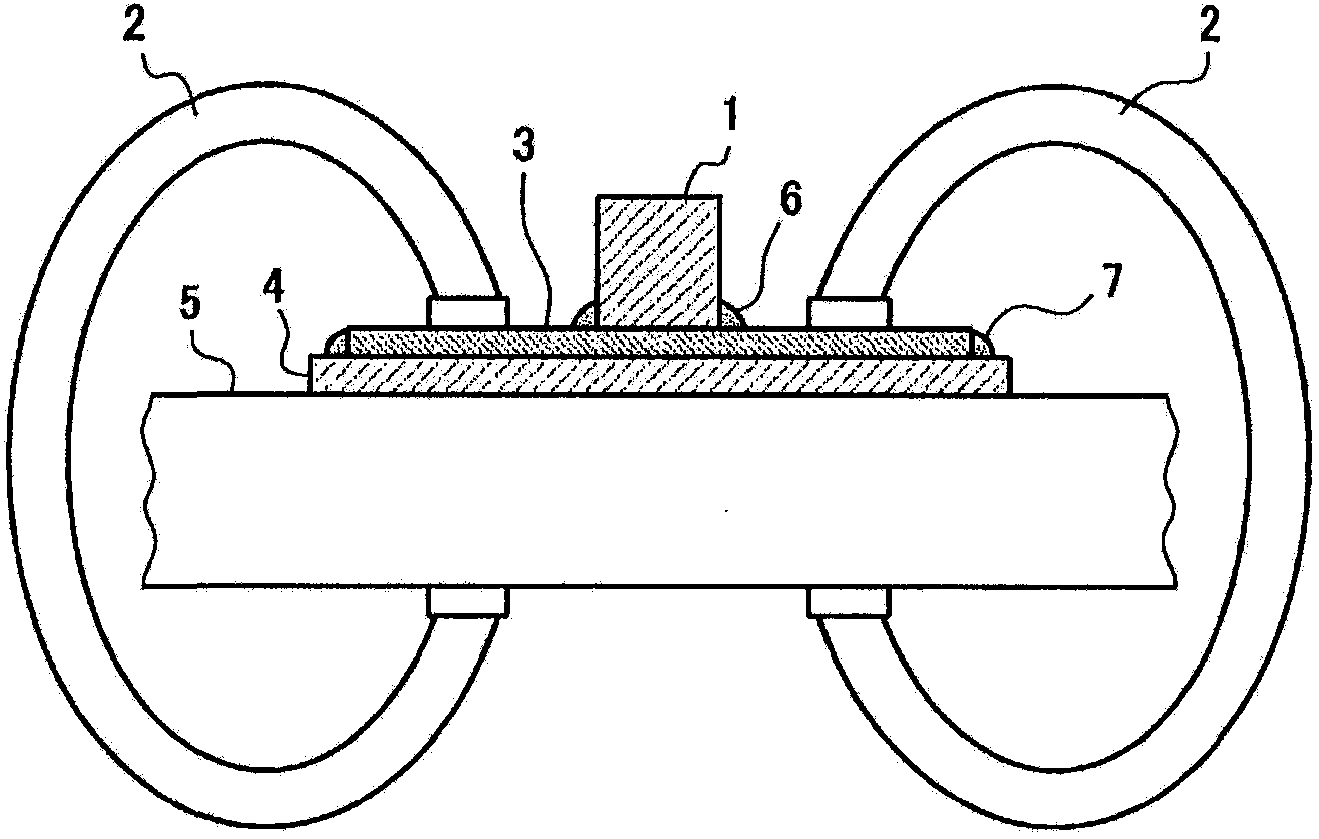
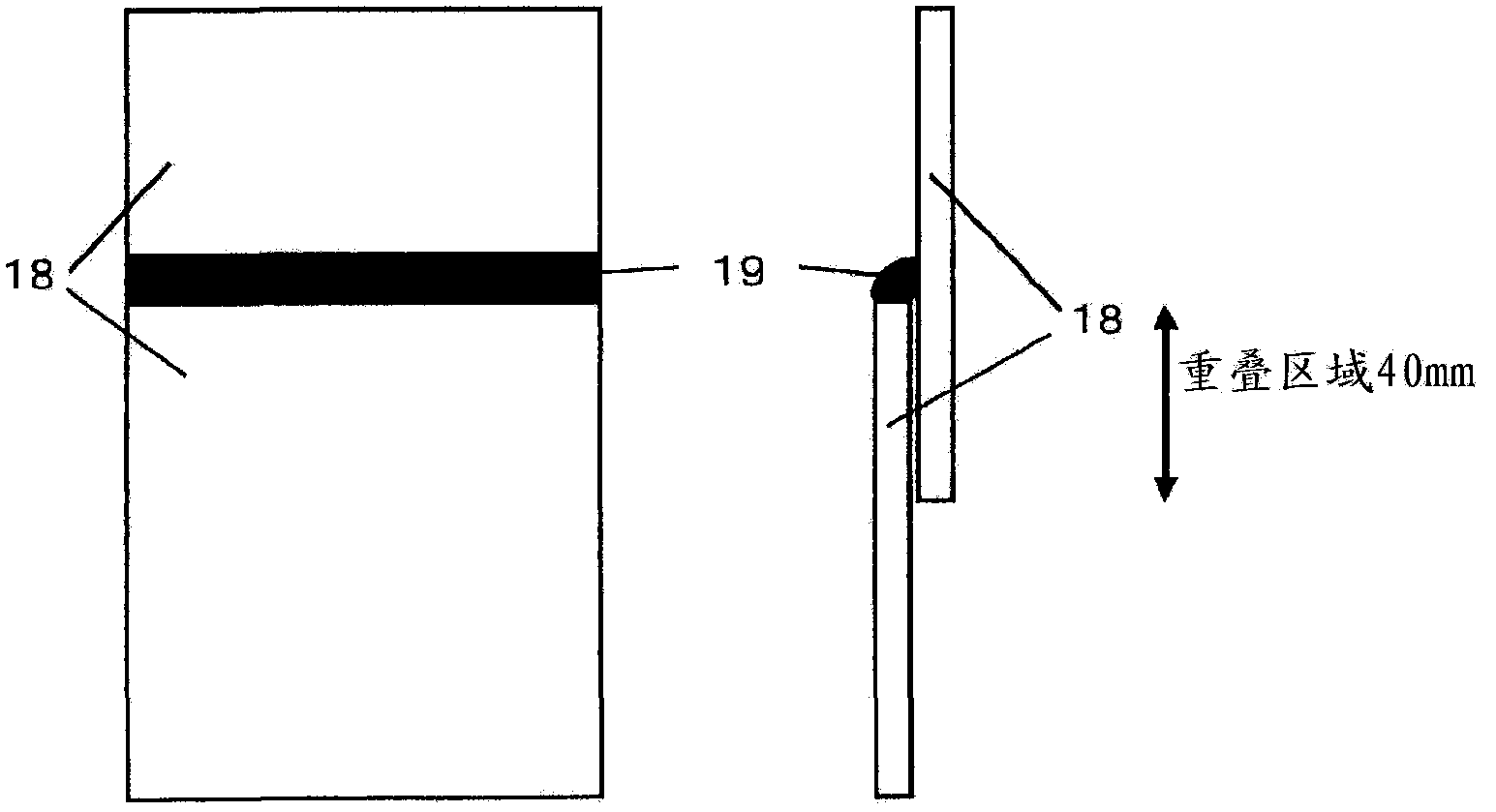
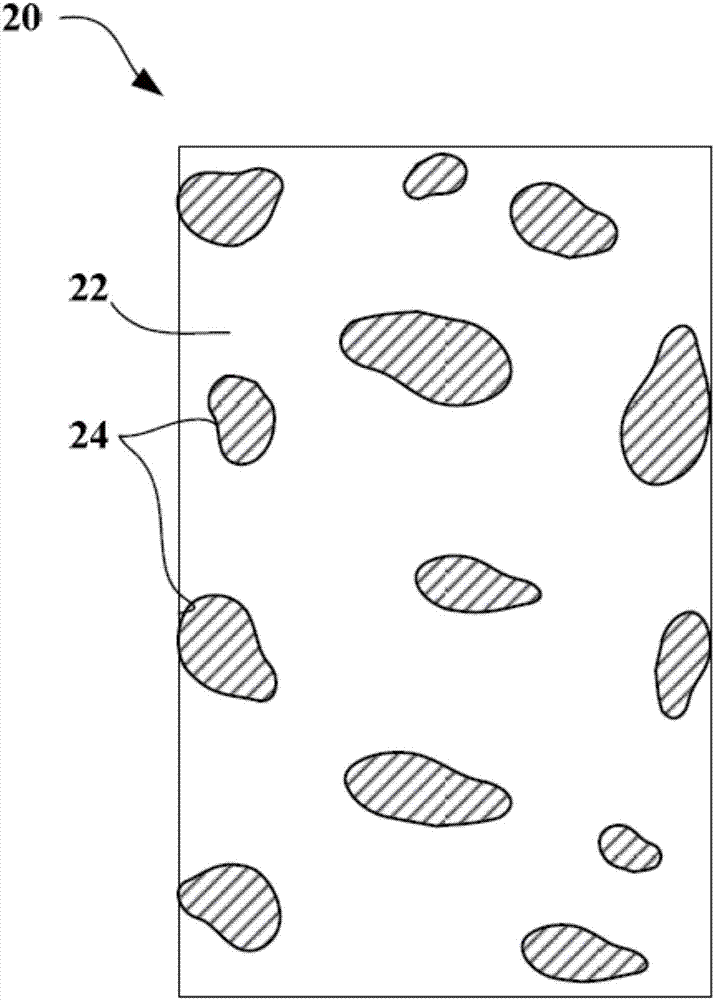
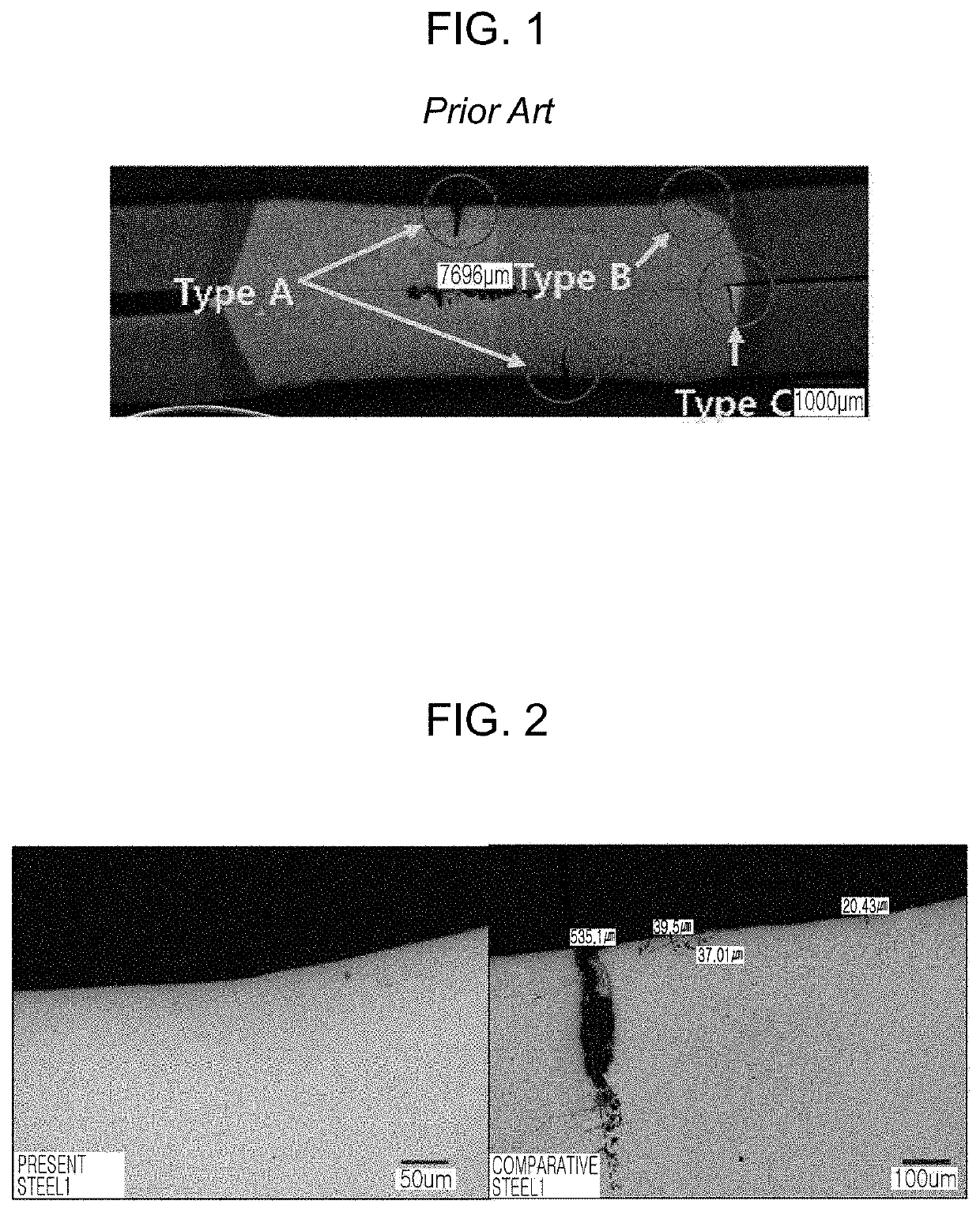
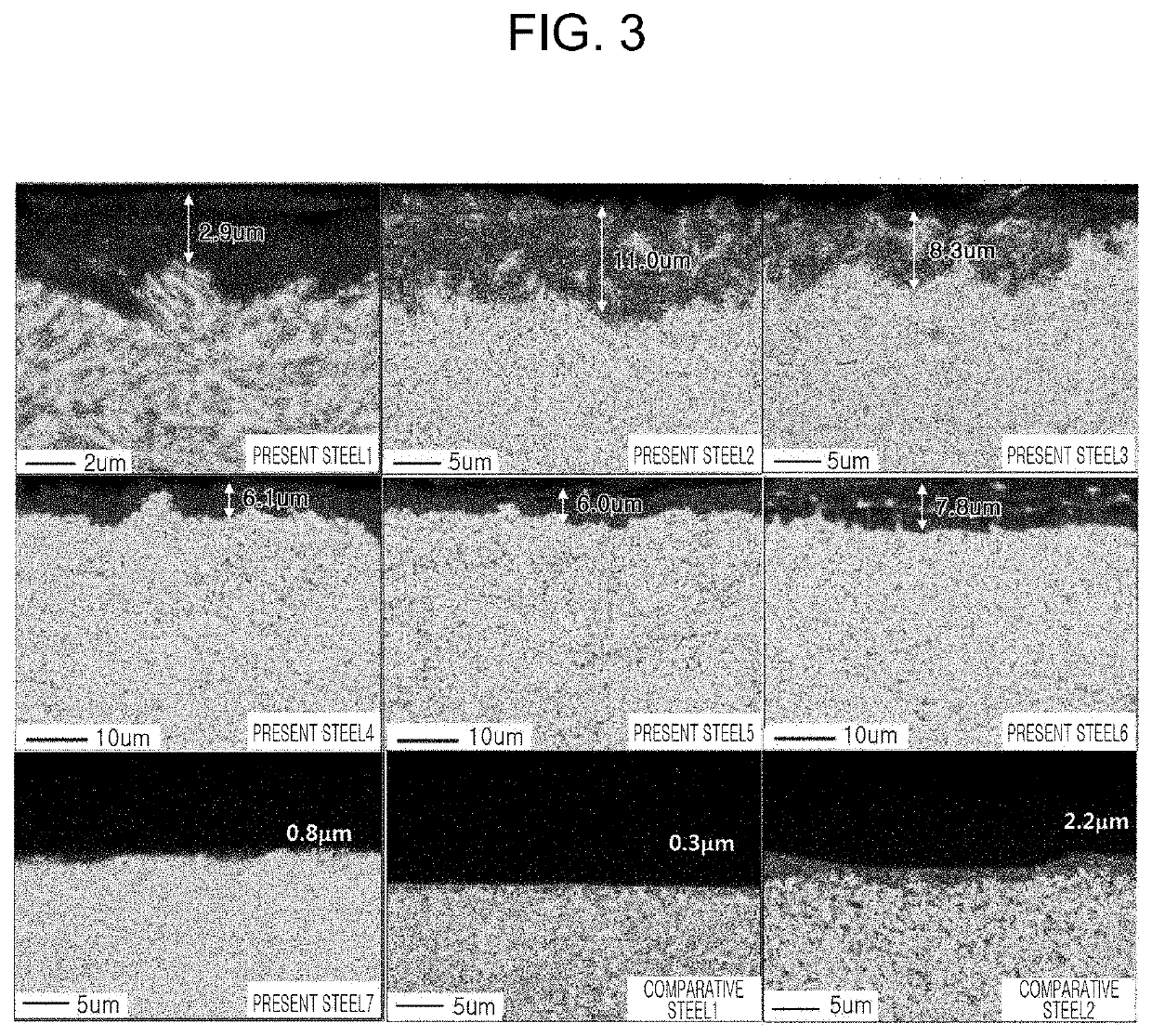
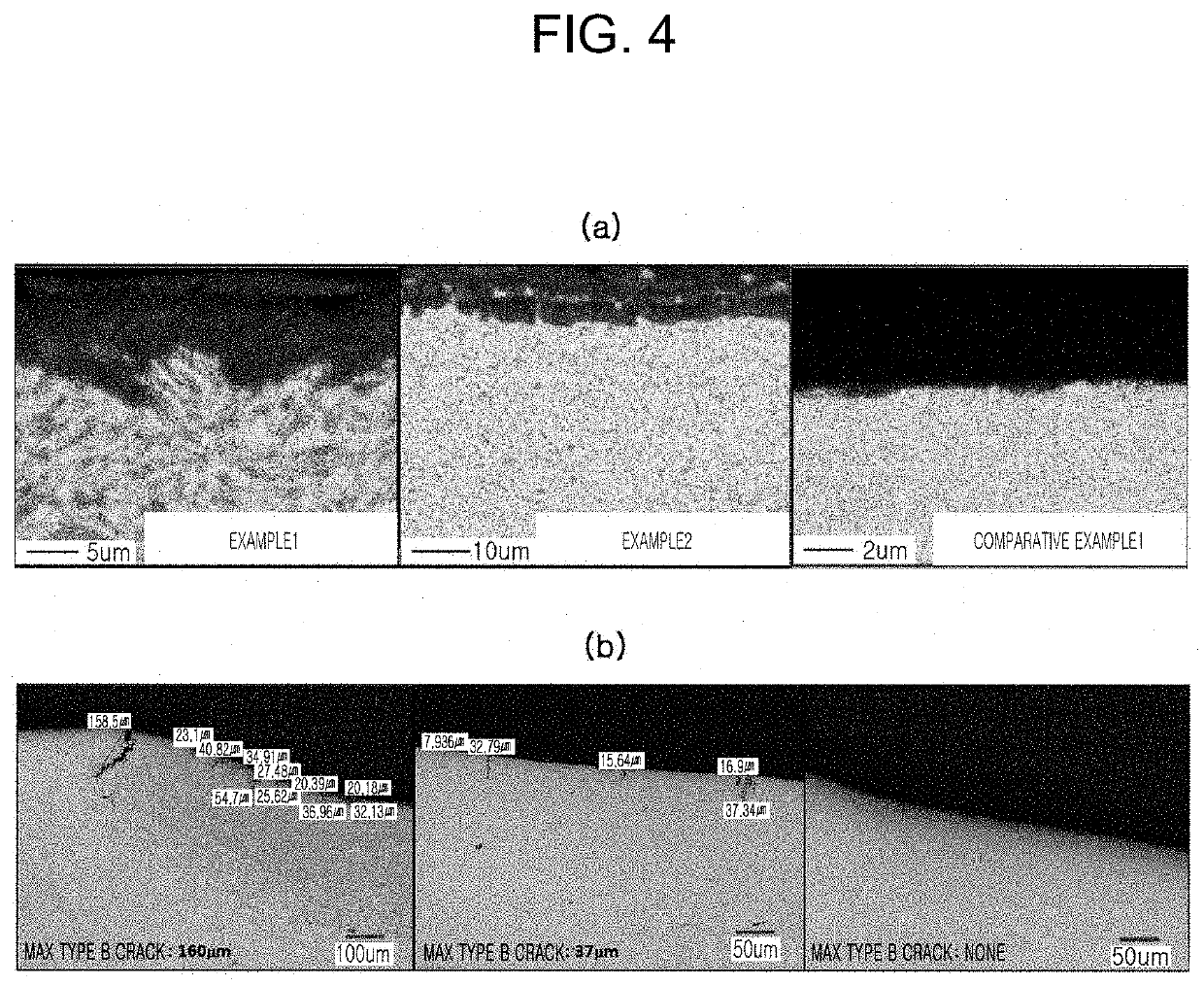
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Liquid metal embrittlement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
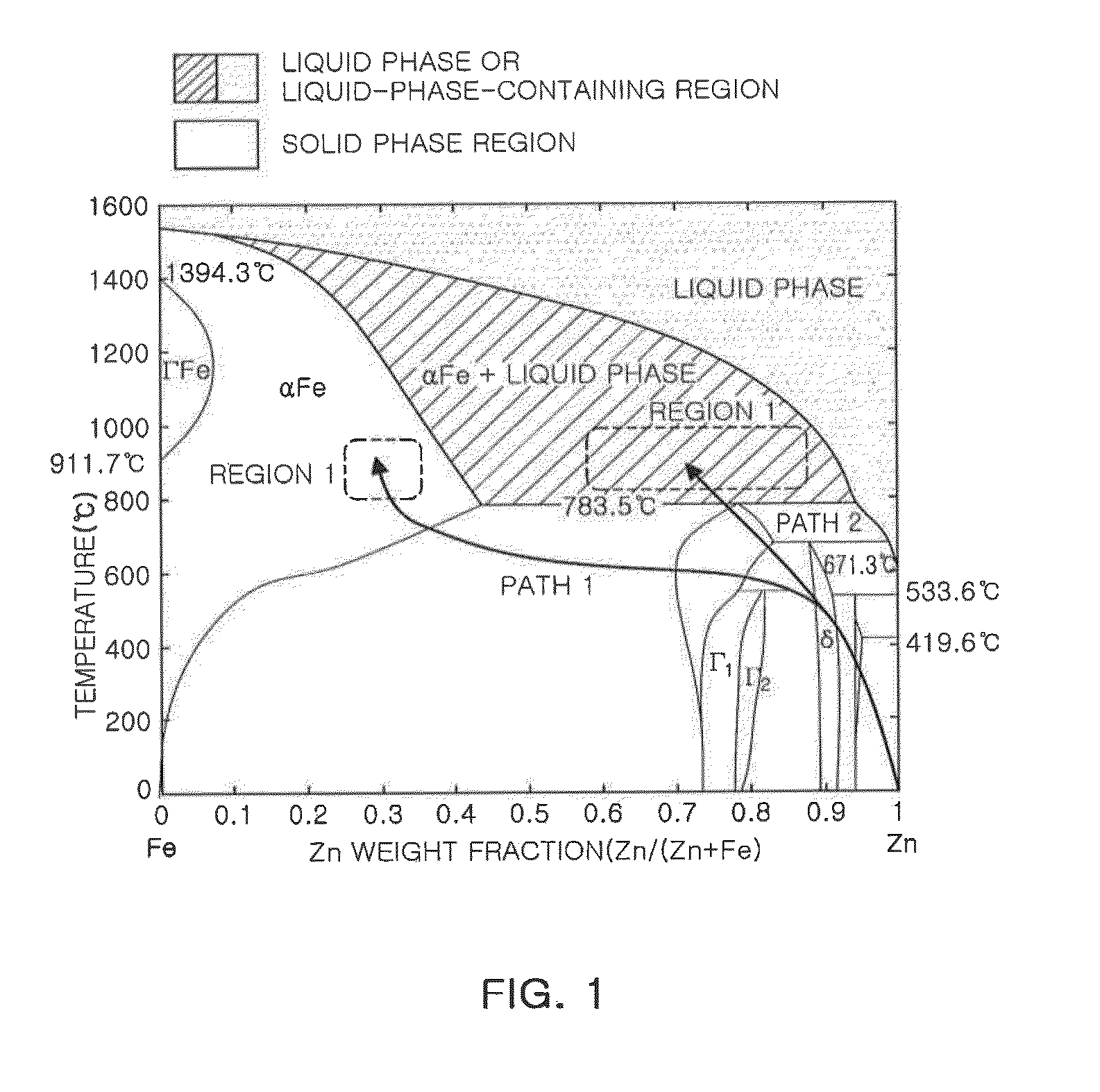
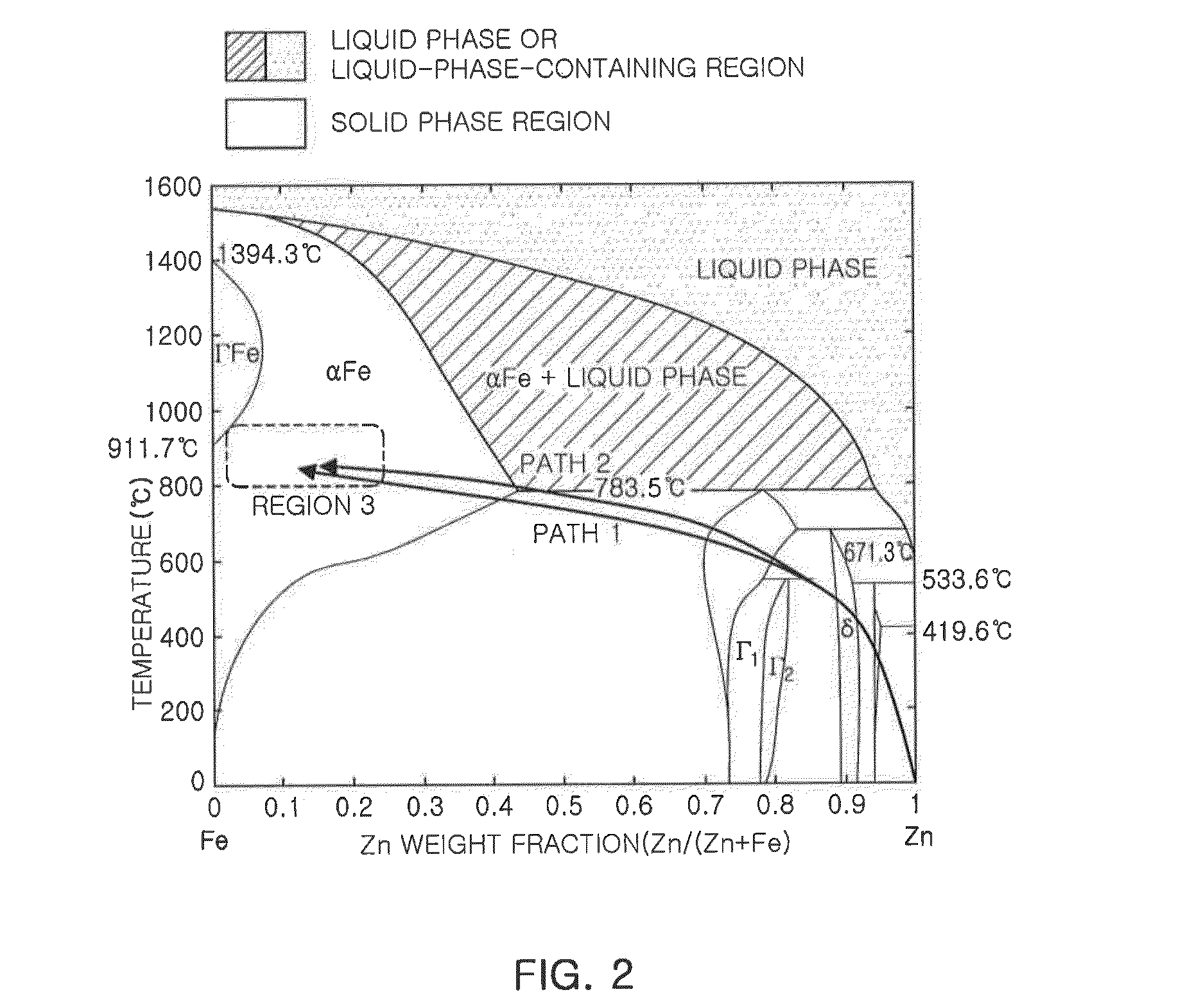
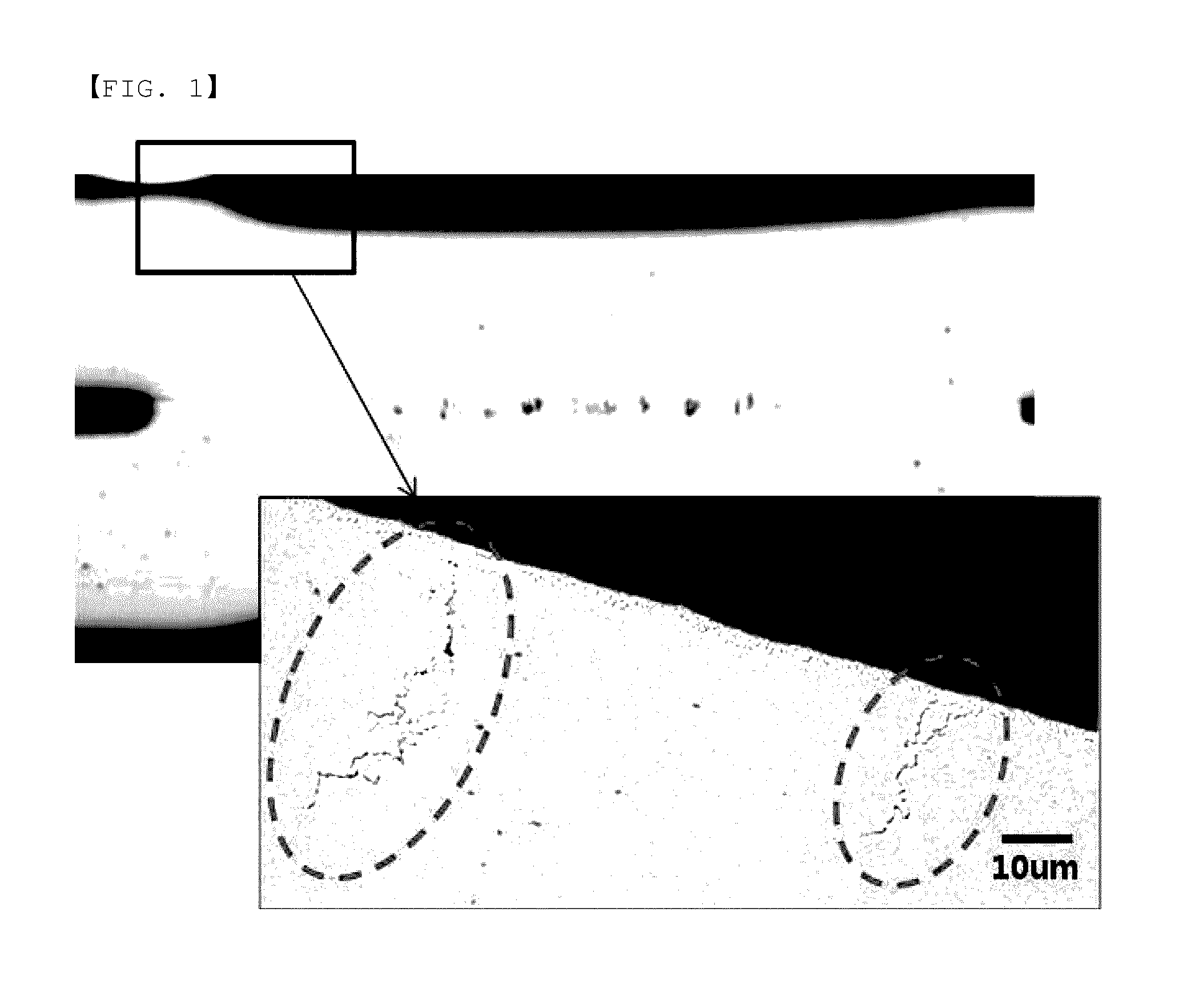
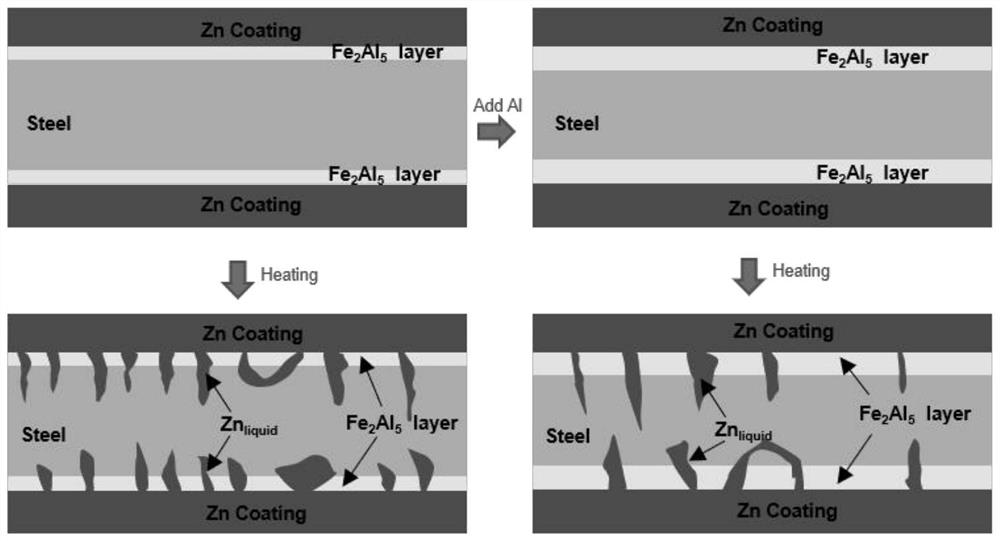
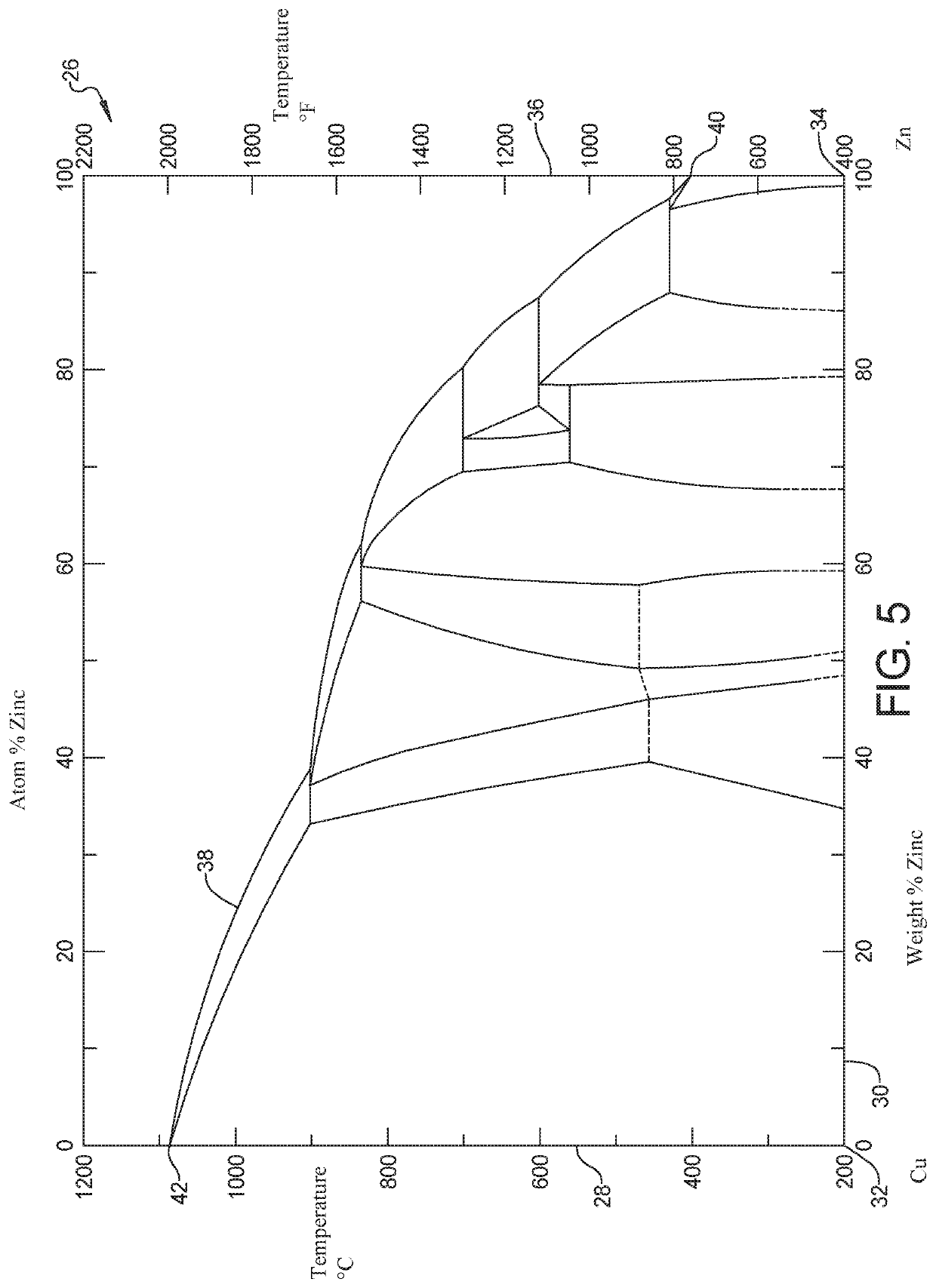
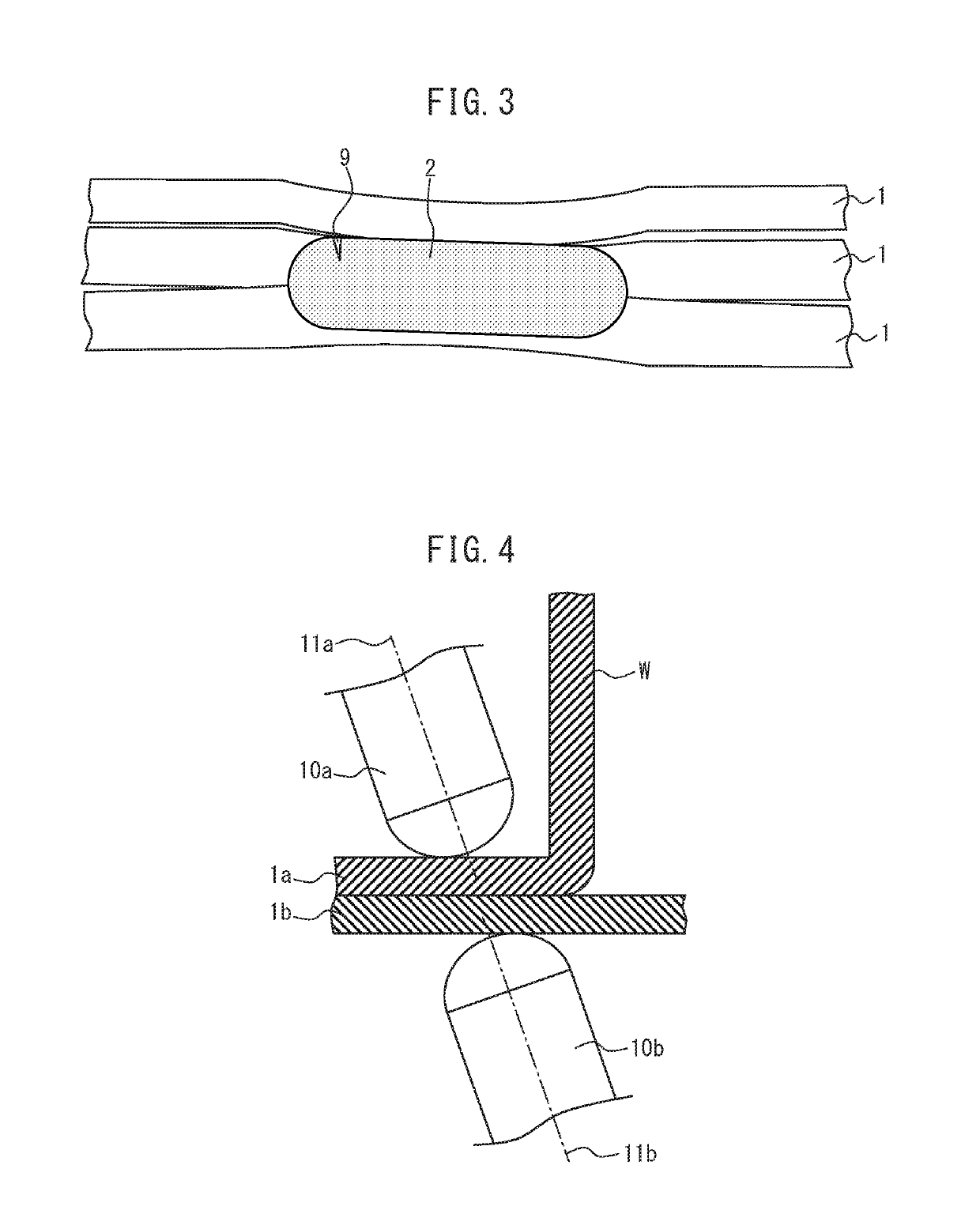
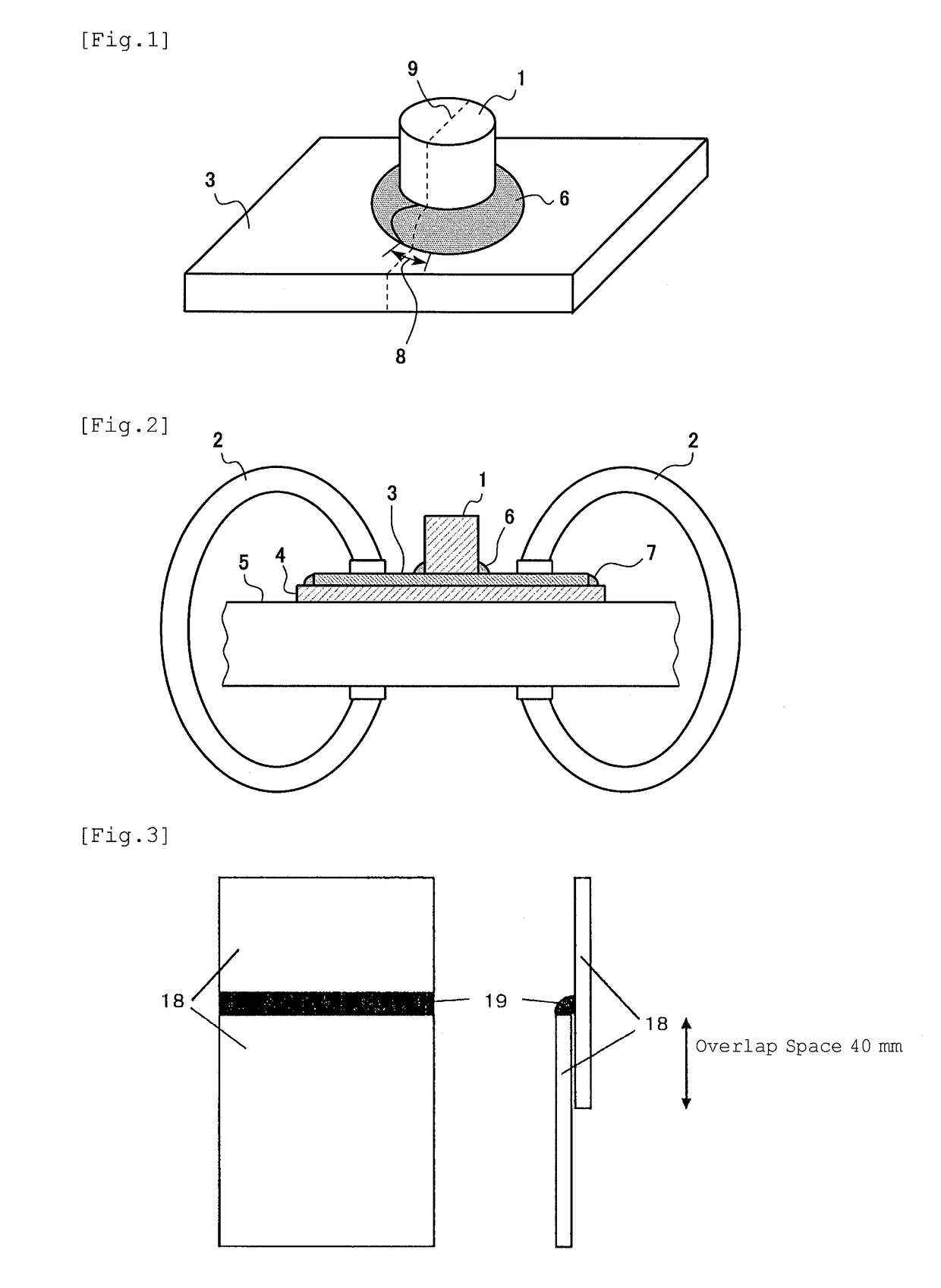
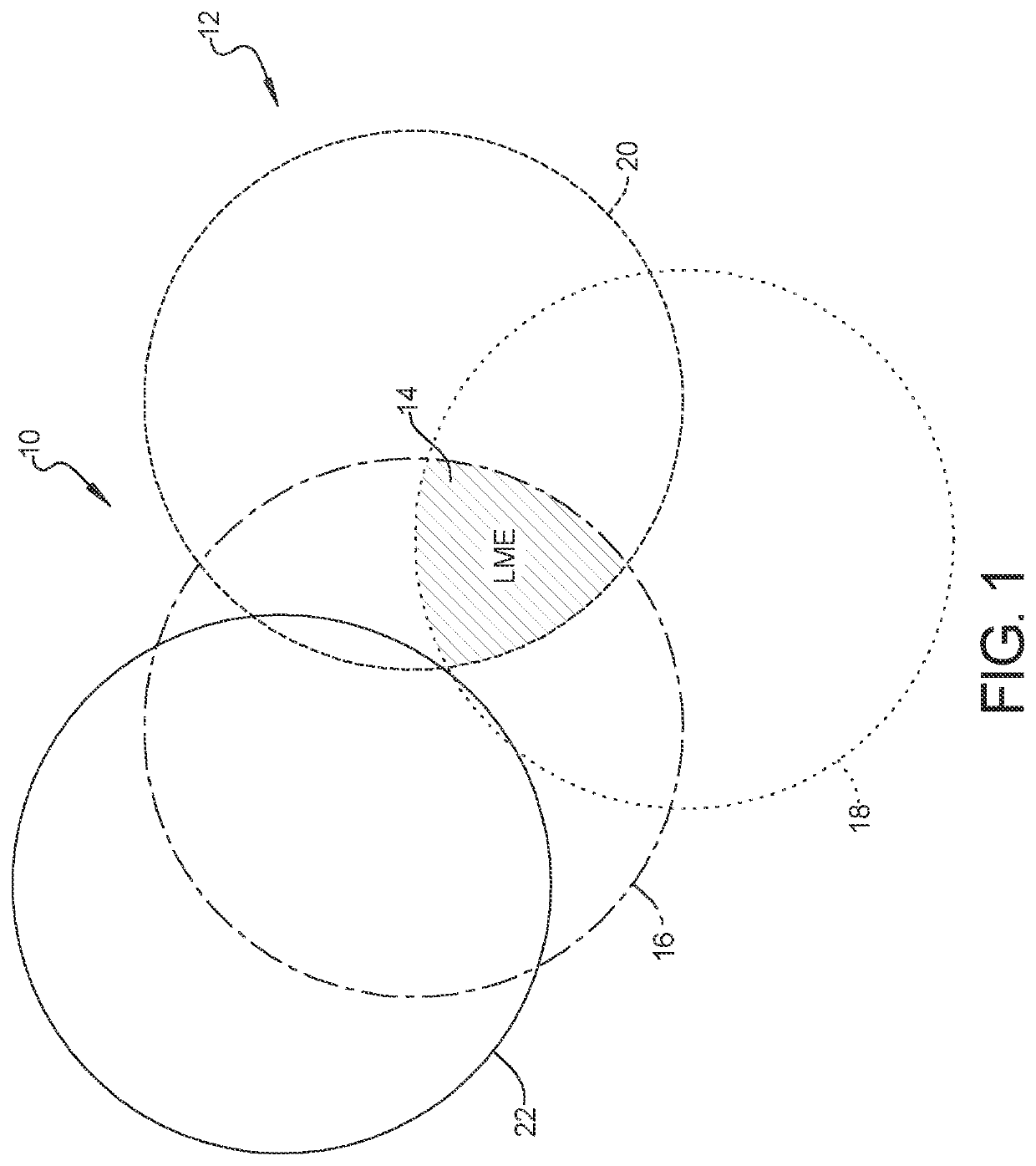
Liquid metal embrittlement, also known as liquid metal induced embrittlement, is a phenomenon of practical importance, where certain ductile metals experience drastic loss in tensile ductility or undergo brittle fracture when exposed to specific liquid metals. Generally, a tensile stress, either externally applied or internally present, is needed to induce embrittlement. Exceptions to this rule have been observed, as in the case of aluminium in the presence of liquid gallium. This phenomenon has been studied since the beginning of the 20th century. Many of its phenomenological characteristics are known and several mechanisms have been proposed to explain it. The practical significance of liquid metal embrittlement is revealed by the observation that several steels experience ductility losses and cracking during hot-dip galvanizing or during subsequent fabrication. Cracking can occur catastrophically and very high crack growth rates have been measured.
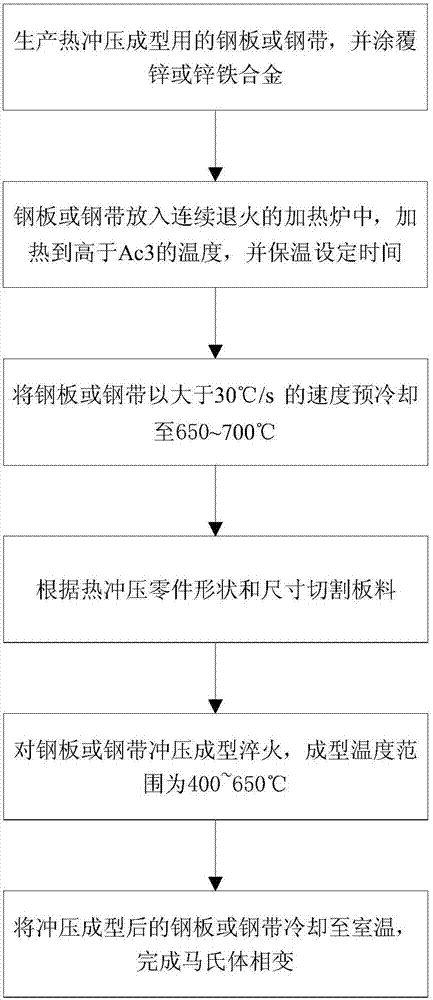
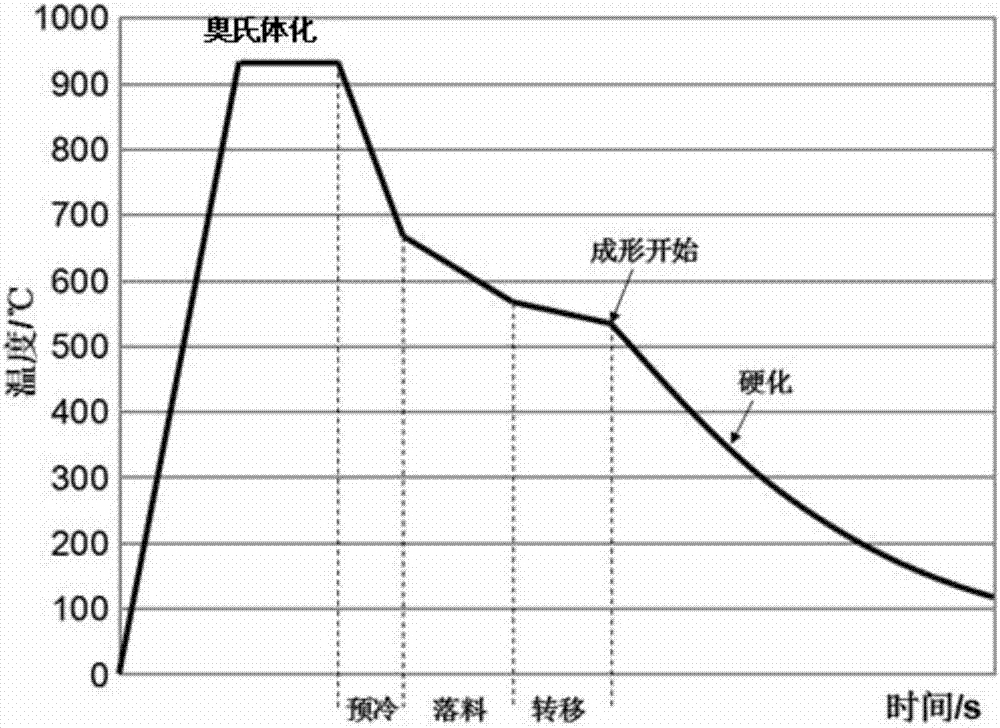
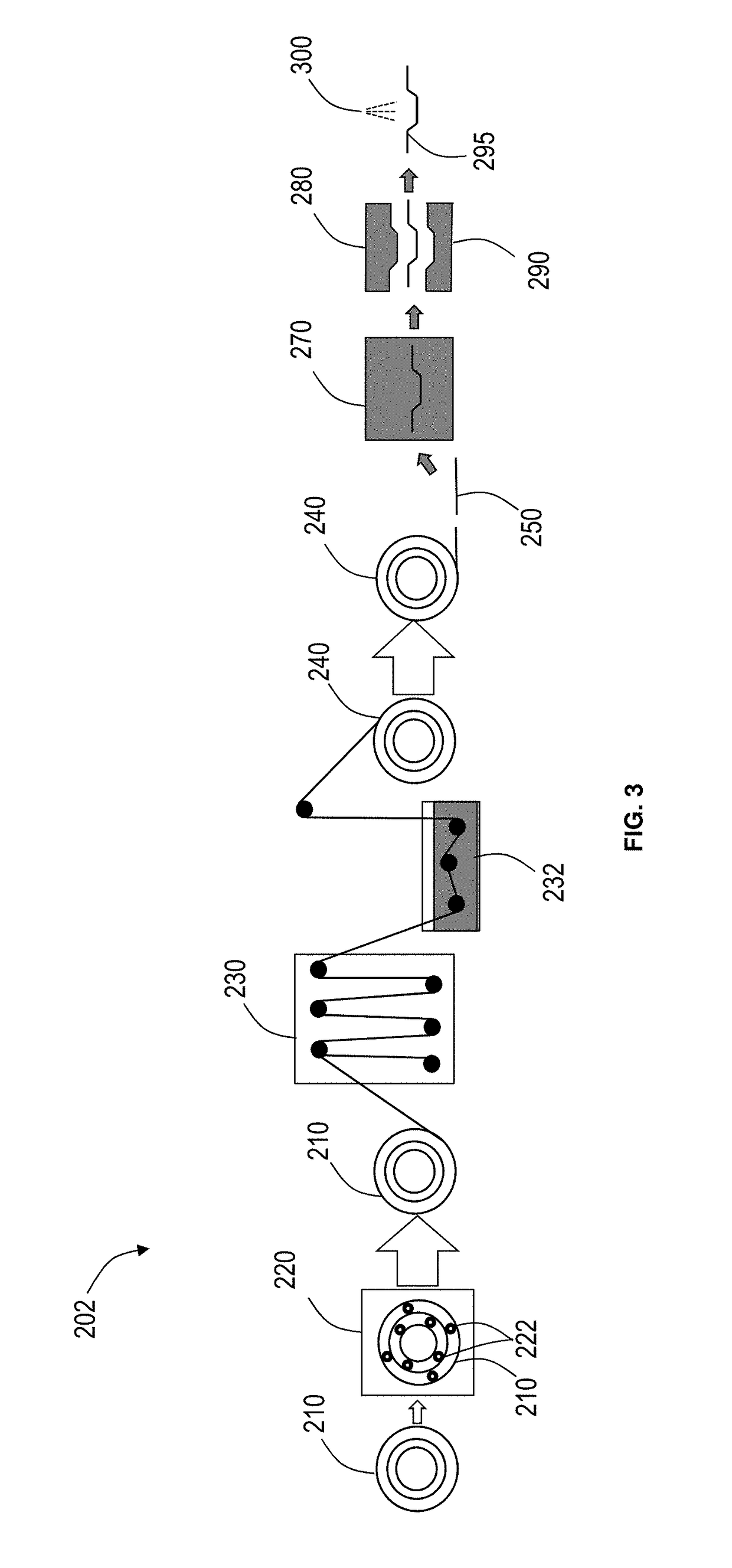
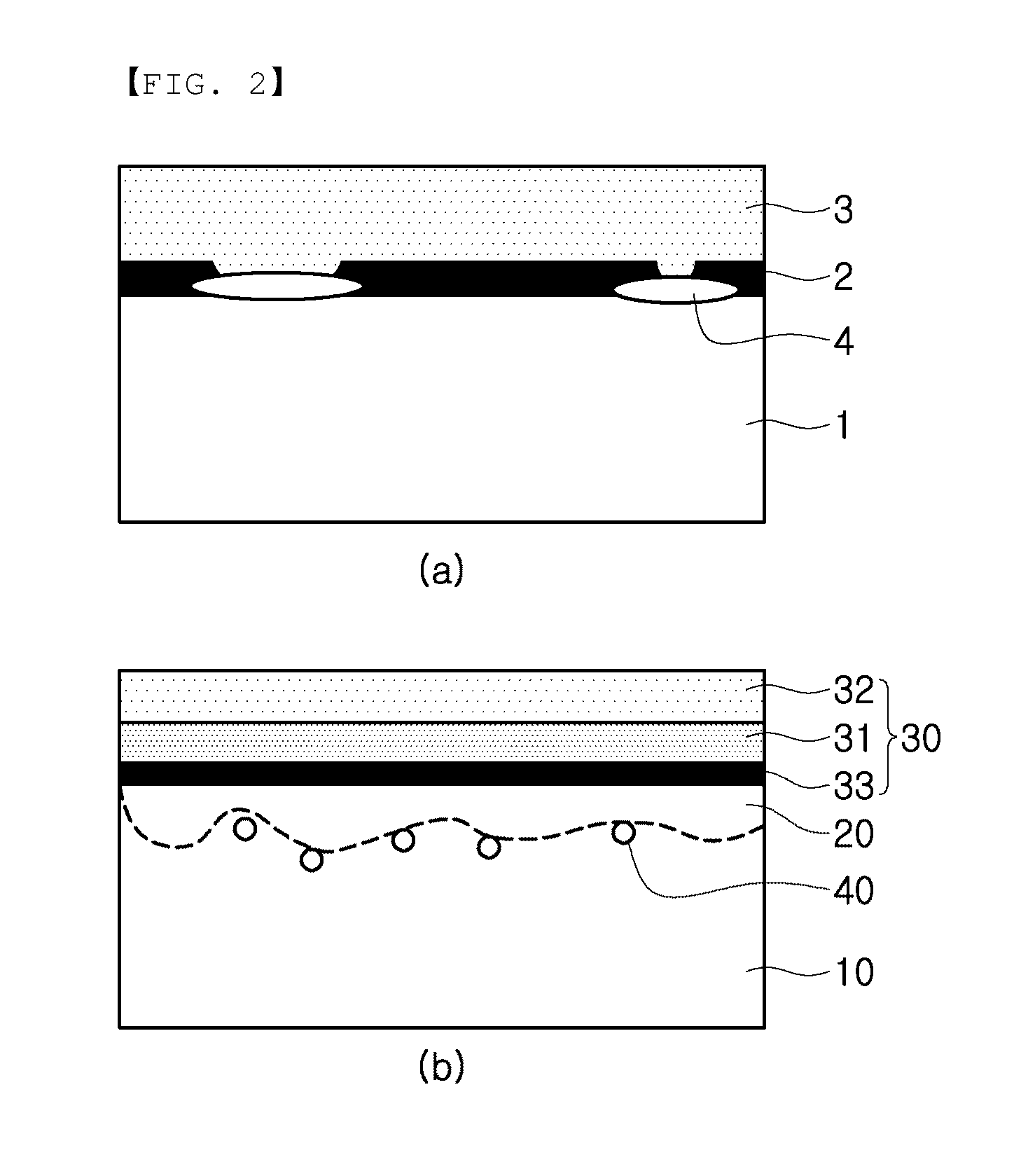
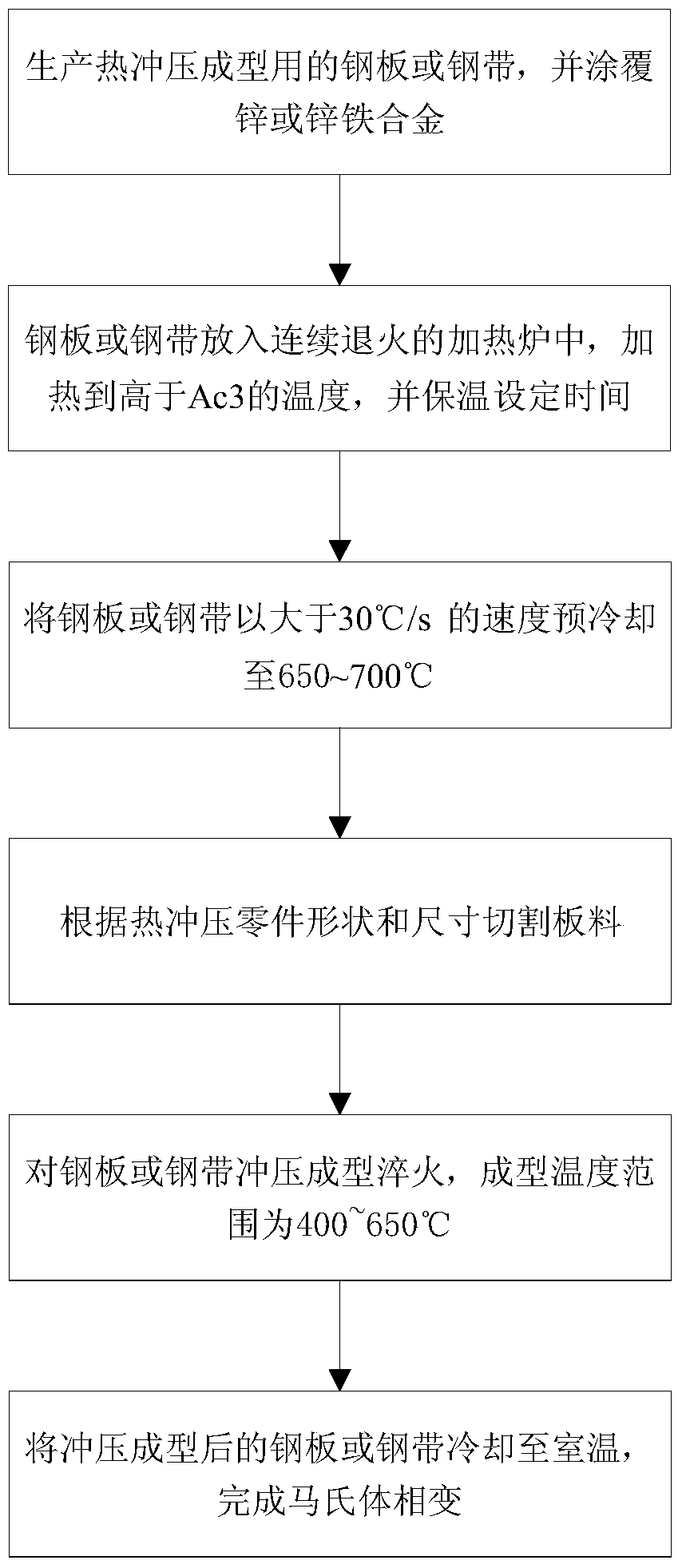
Hot-stamping forming method for zinc plating steel plate or steel strip
ActiveCN107127238ALow heating temperatureShort holding timeShaping toolsHot-dipping/immersion processesHot stampingSheet steel
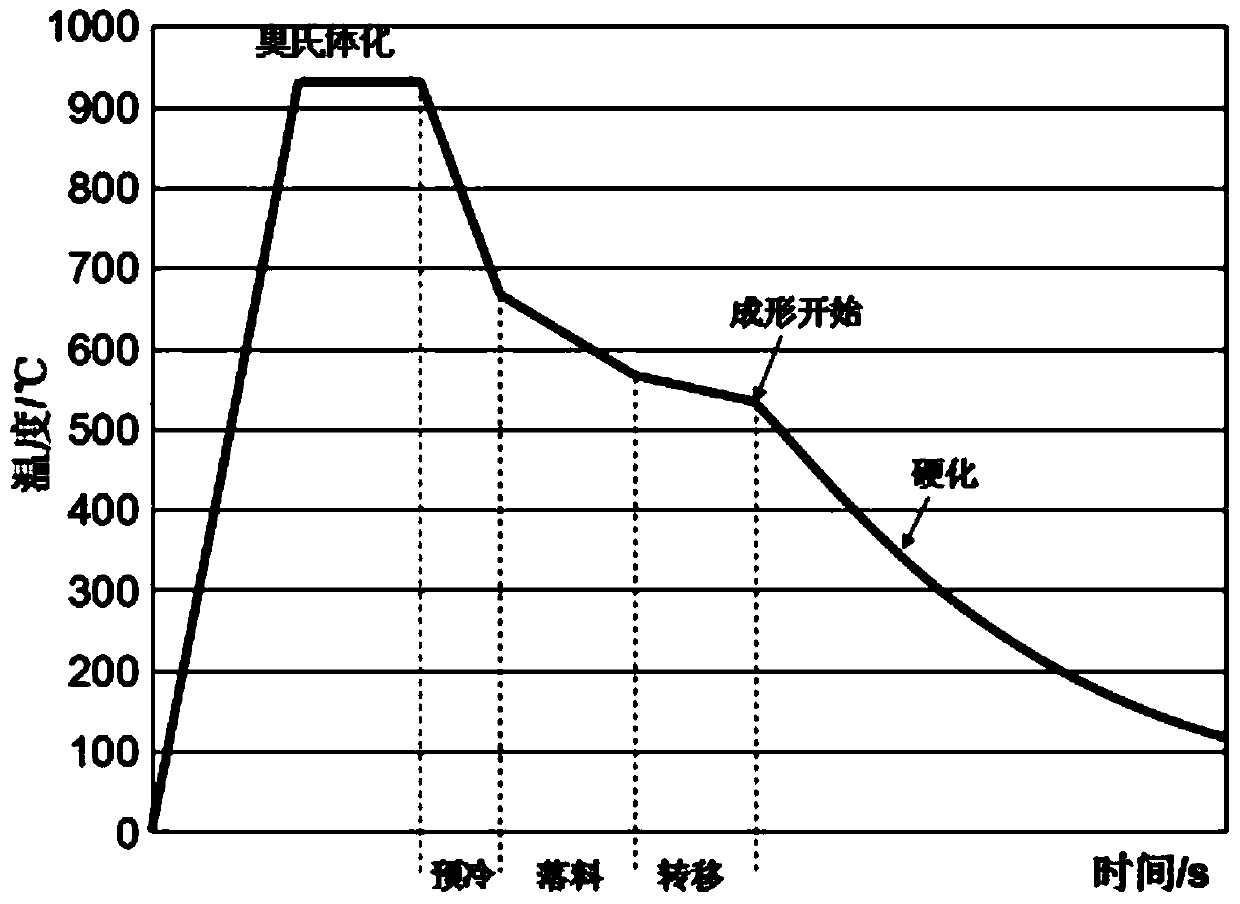
The invention relates to a hot-stamping forming method for a zinc plating steel plate or a steel strip. According to the hot-stamping forming method, the steel plate or the steel strip is conveyed into a vertical heating annealing furnace, the temperature is kept for a certain time, the steel plate is completely austenitized, a pre-cooling device is used when the steel plate leaves the annealing furnace, the steel plate is cooled to 650-700 DEG C at the cooling rate higher than 30 DEG C / s, then blanking is performed according to the part shape and size, then the steel plate is quickly transferred into a mold for hot-stamping forming, the steel plate is hardened at the speed higher than 30 DEG C / s, and the hot-stamping forming temperature is kept between 400 DEG C and 650 DEG C. Base plate cracks caused by partial stress and liquid metal embrittlement (LME) can be avoided, and the method is used for solving the problem that the base plate cracks cannot be avoided for existing zinc-based hot-stamping formed steel.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Mitigating liquid metal embrittlement in zinc-coated press hardened steels
InactiveUS20180237877A1High strengthSolve the lack of ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSurface layerMicrometer
Methods of reducing liquid metal embrittlement (LME) in zinc-coated high-strength steel alloys are provided. In one variation, the method includes decarburizing an exposed surface of a high-strength steel alloy to form a decarburized surface layer. The decarburized surface layer has a thickness of less than or equal to about 50 micrometers. The decarburized surface layer may have greater than or equal to about 80 volume % ferrite. The method also includes applying a zinc-based coating to the decarburized surface layer. A blank is formed from the high-strength steel alloy. The method also includes heating and press hardening the blank to form a press-hardened component having an ultimate tensile strength of greater than or equal to about 1,100 MPa that is substantially free of liquid metal embrittlement.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Weld Joint Formed with Stainless Steel-Based Weld Metal for Welding a Zinc-Based Alloy Coated Steel Sheet
ActiveUS20090158889A1Improve corrosion resistanceIncreased durabilityElectric discharge heatingWelding/cutting media/materialsCrack resistanceAlloy coating
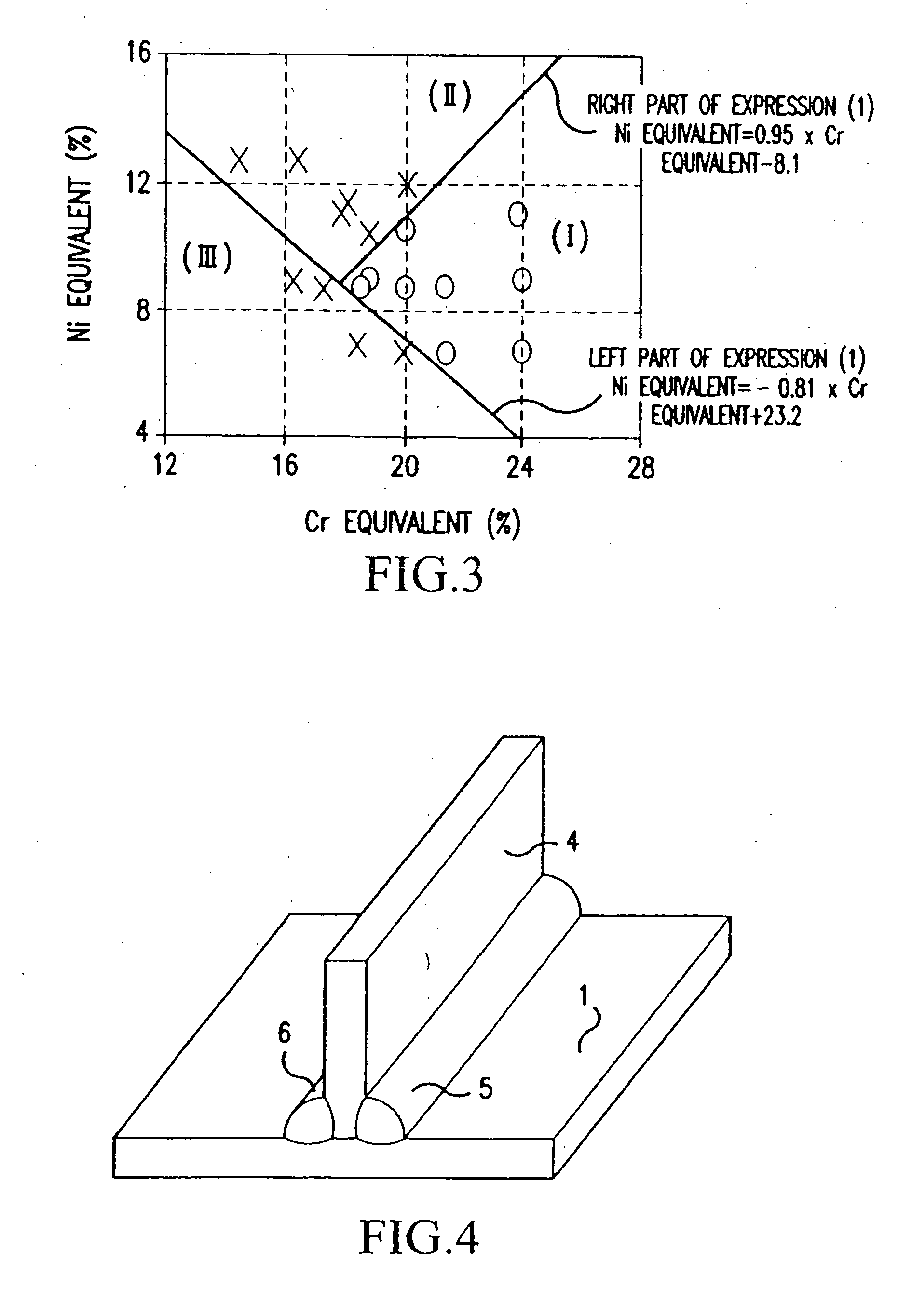
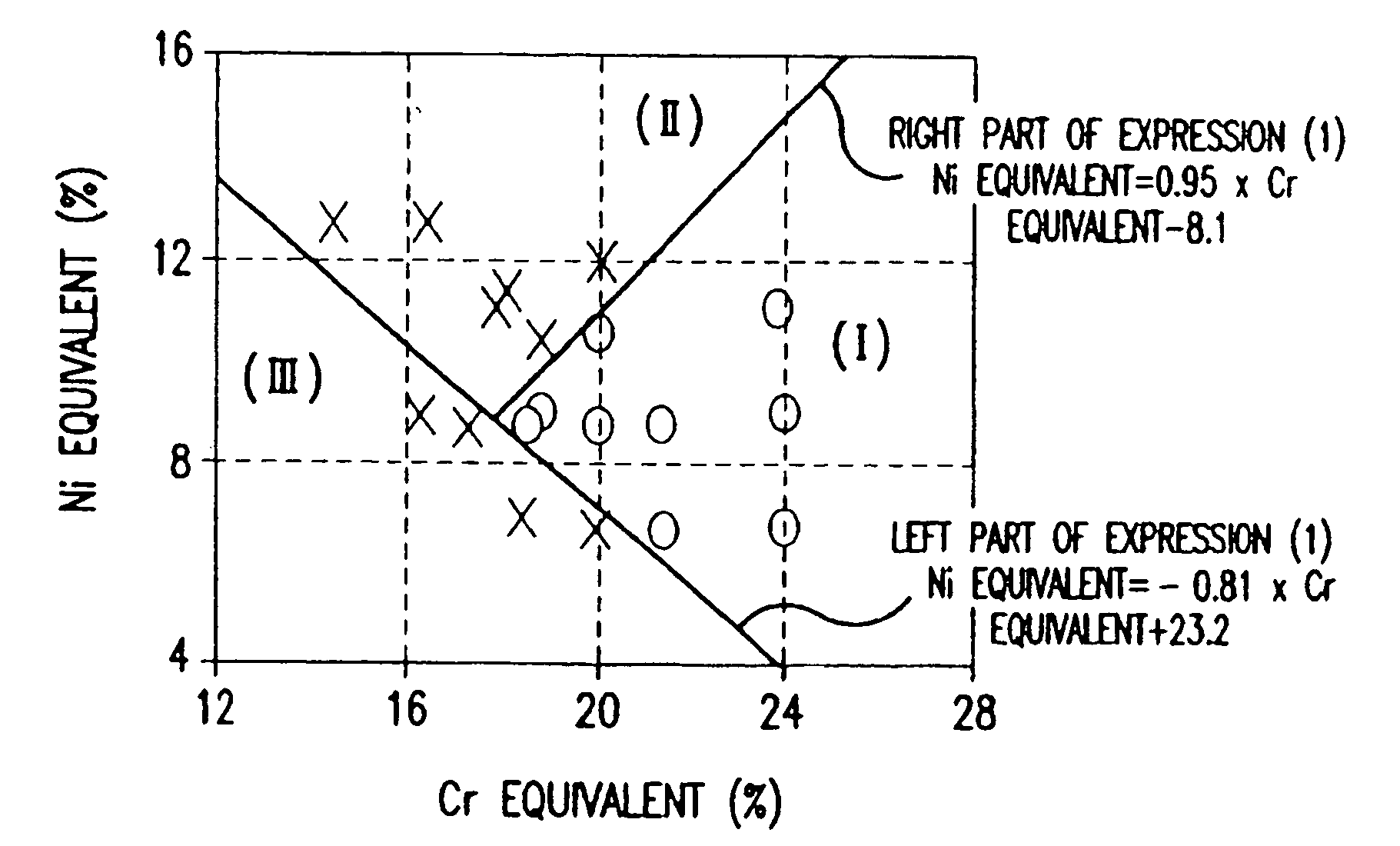
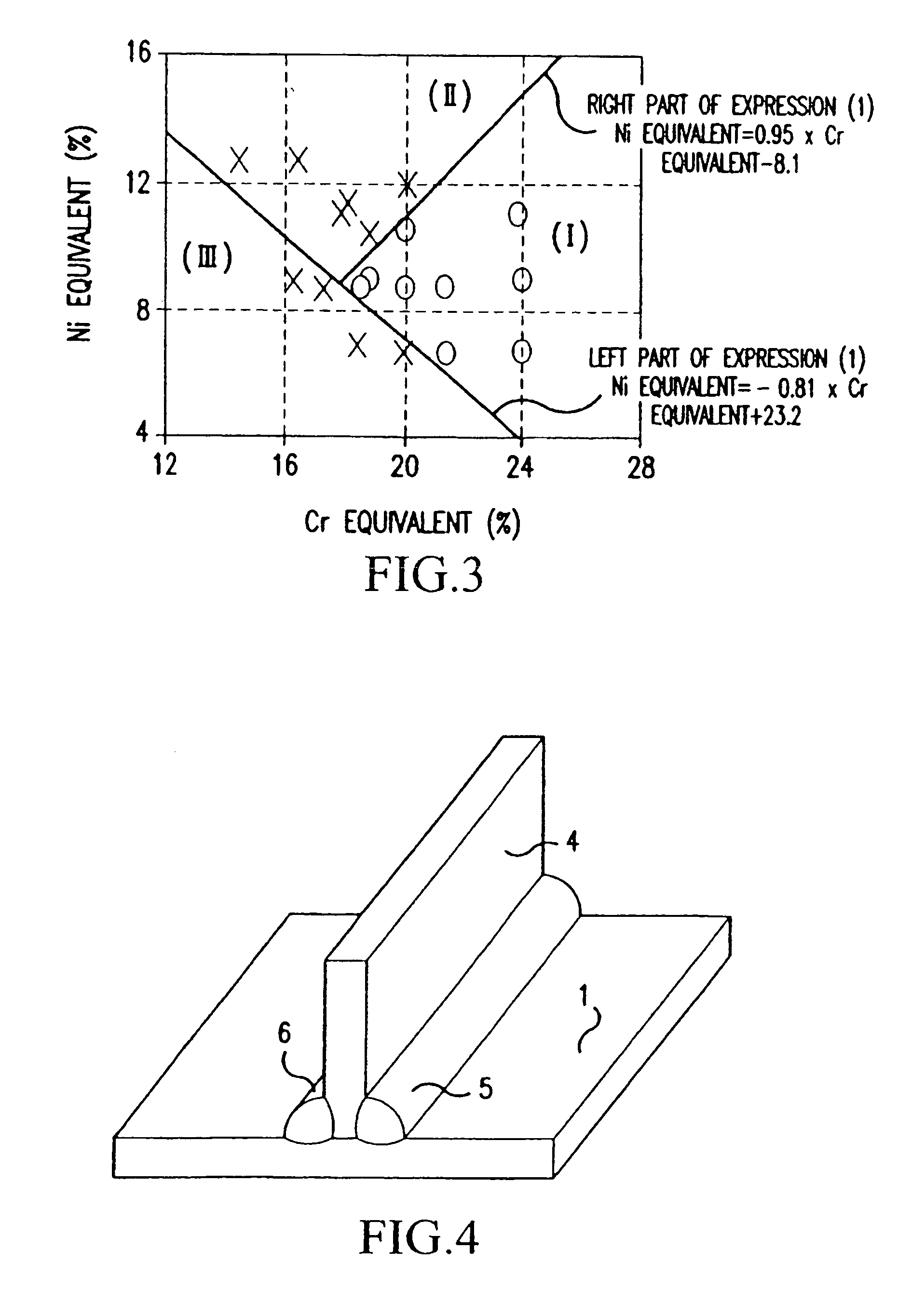
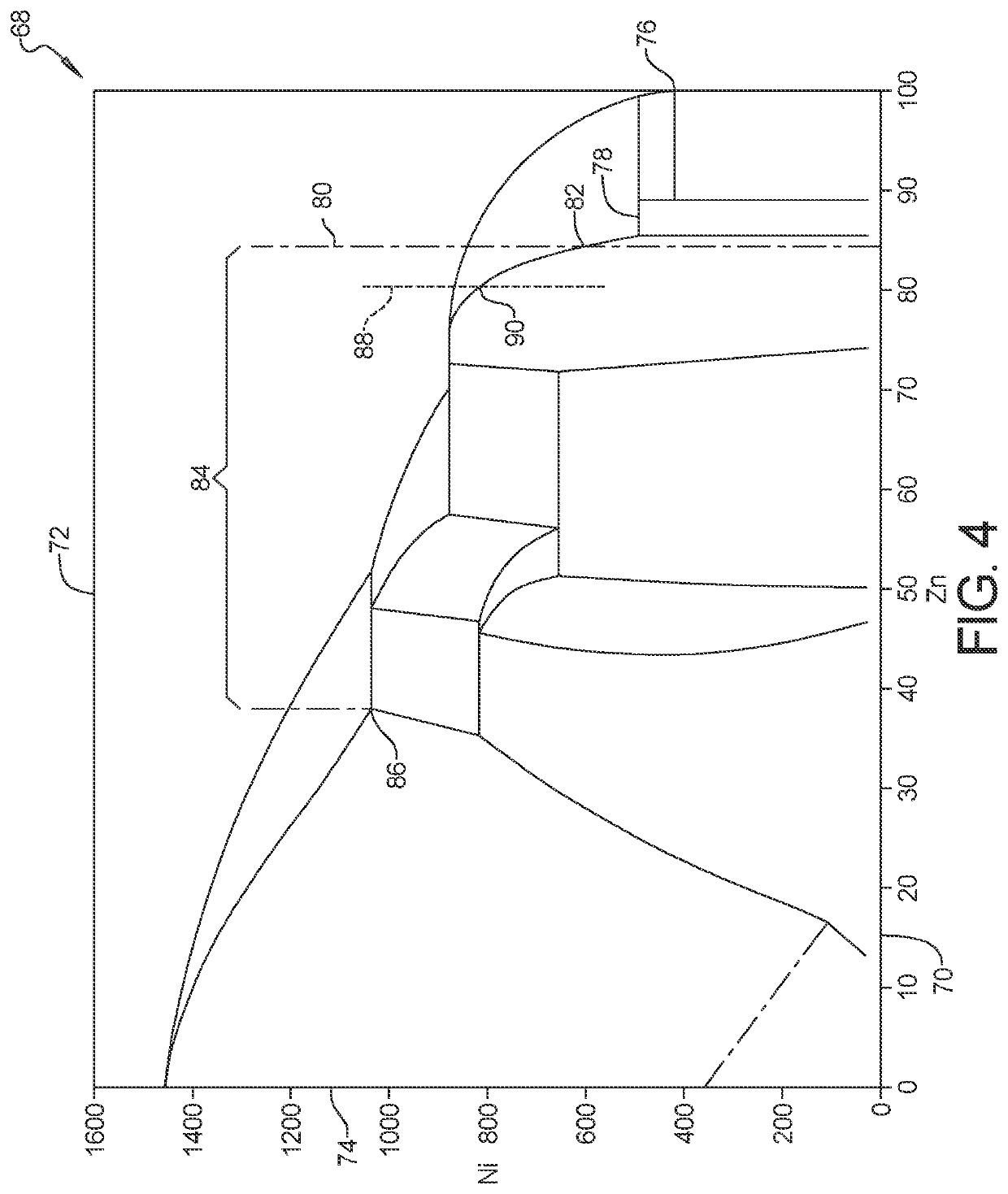
Disclosed are a weld joint and a stainless steel-based weld metal composition for the weld joint. The composition and weld joint made therefrom are suitable for welding a zinc-based alloy coated steel sheet. The weld is excellent in corrosion resistance and liquid-metal embrittlement crack resistance. This is accomplished by inhibiting liquid-metal embrittlement cracks of the stainless-steel-based weld metal when the zinc-based alloy coating steel sheet is welded using the stainless-steel-based weld metal. The weld joint comprises a welded portion of weld metal made of stainless-steel-based components, the weld metal containing in mass percent (%): C: 0.01-0.1; Si: 0.1-1; Mn: 0.5-2.5; Ni: 5-11; and Cr: 17-25, and the balance being iron and residual impurities, wherein the following expression are met: −0.81×Cr equivalent+23.2≦Ni equivalent≦0.95×Cr equivalent−8.1 . . . (1); Ni equivalent=Ni+30×C+0.5×Mn+30×N . . . (2); Cr equivalent=Cr+Mo+1.5×Si . . . (3).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Zn-Al-Mg BASED ALLOY HOT-DIP PLATED STEEL SHEET, AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE SAME
ActiveUS20130337287A1Improve workabilityImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesCrack resistanceChemical composition
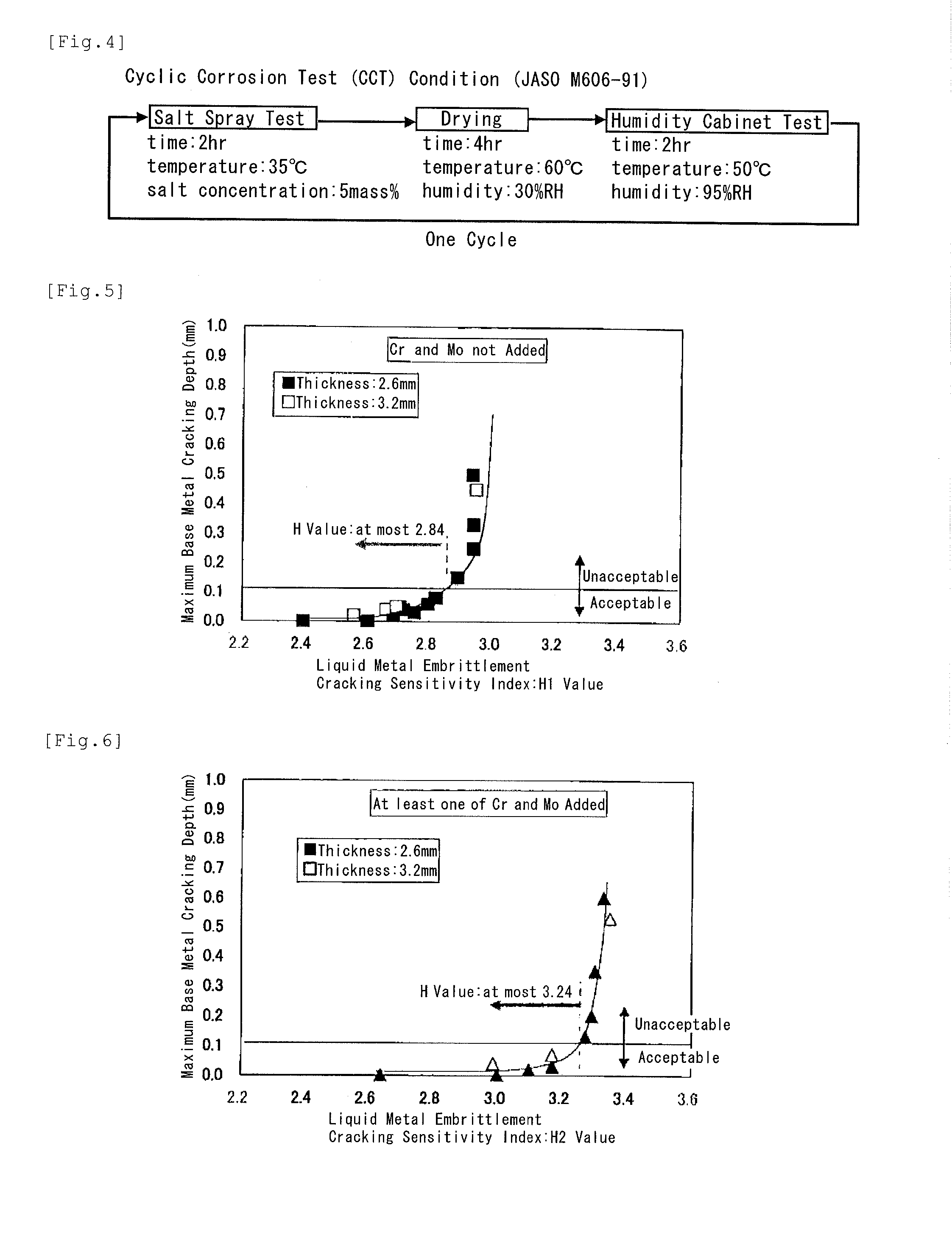
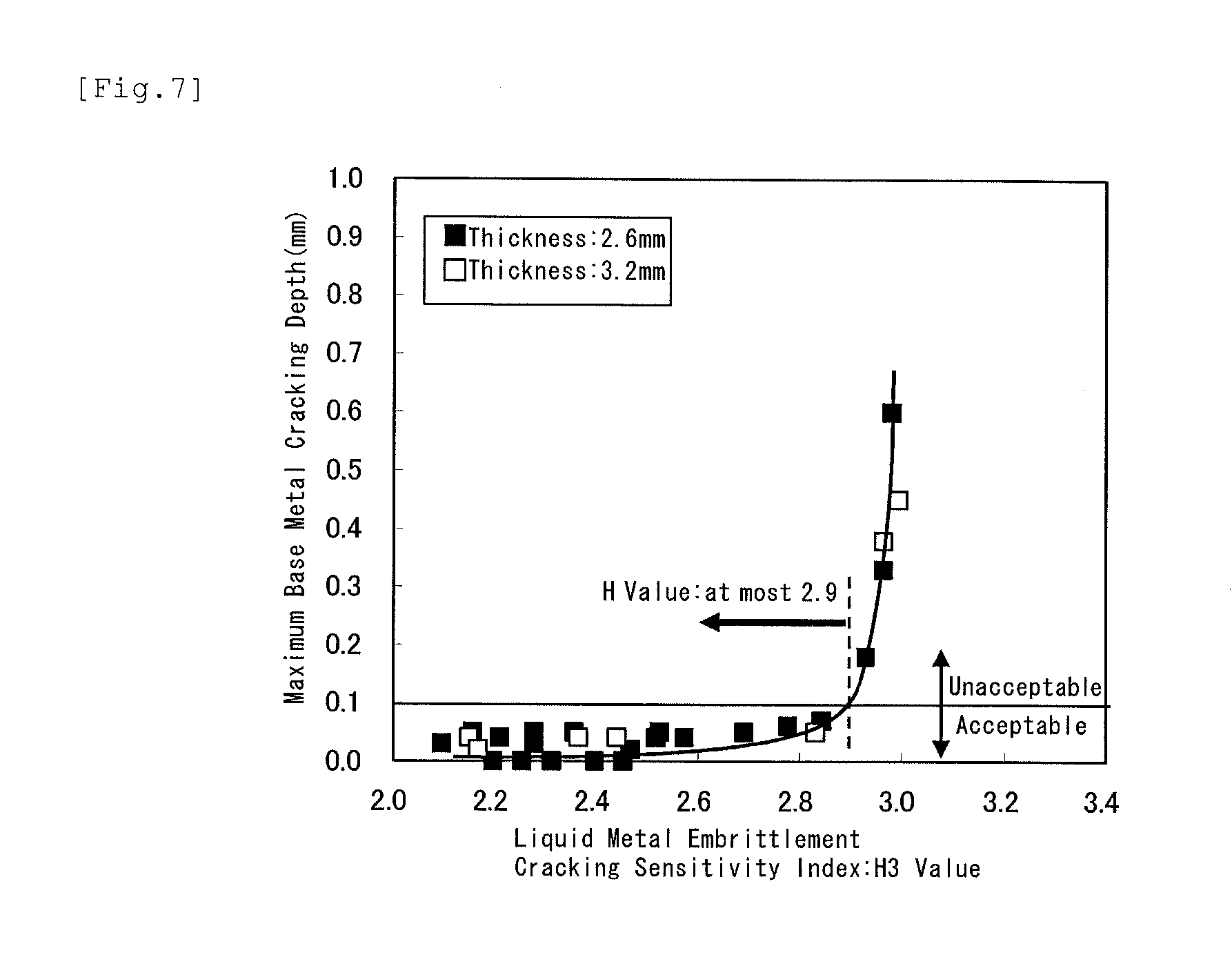
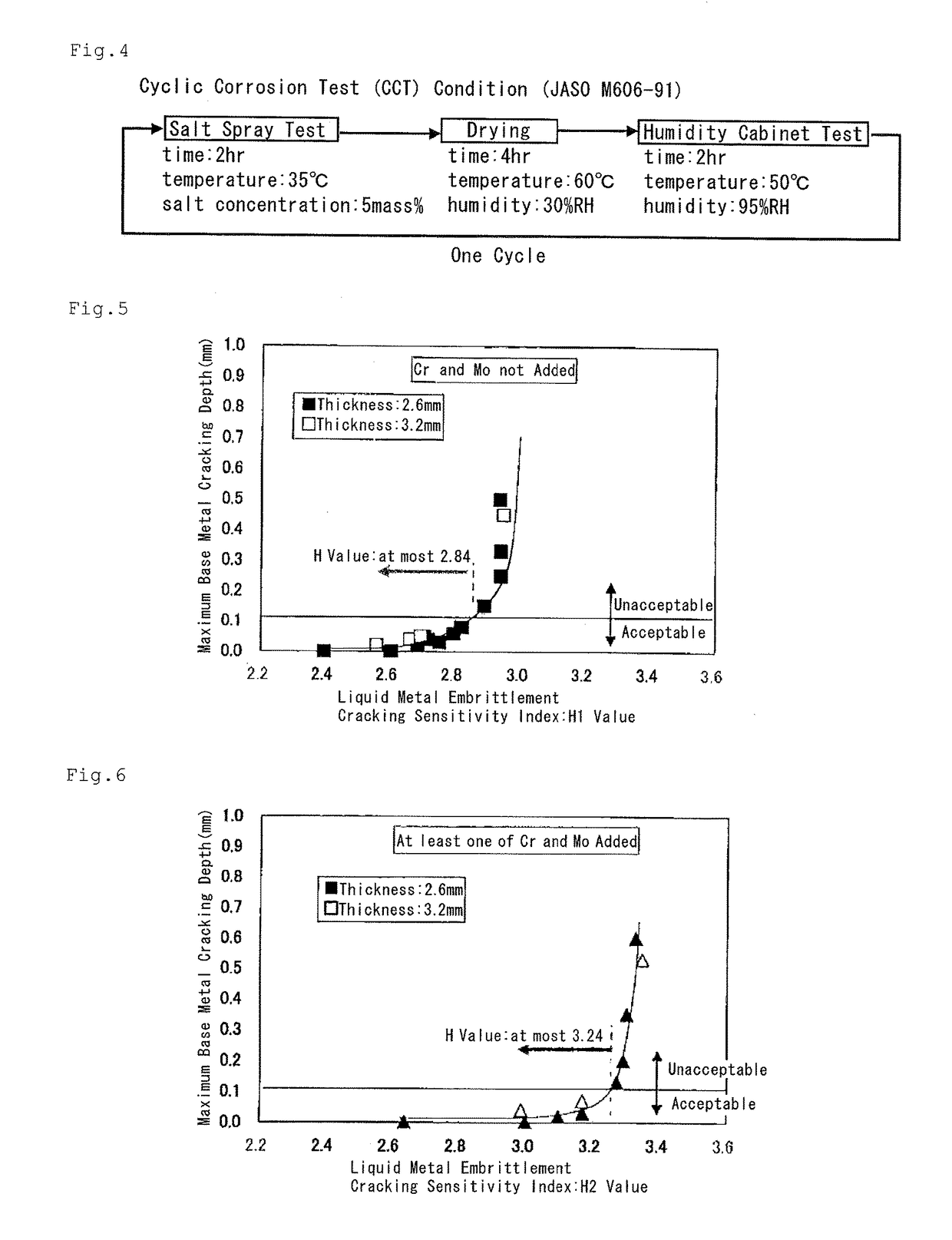
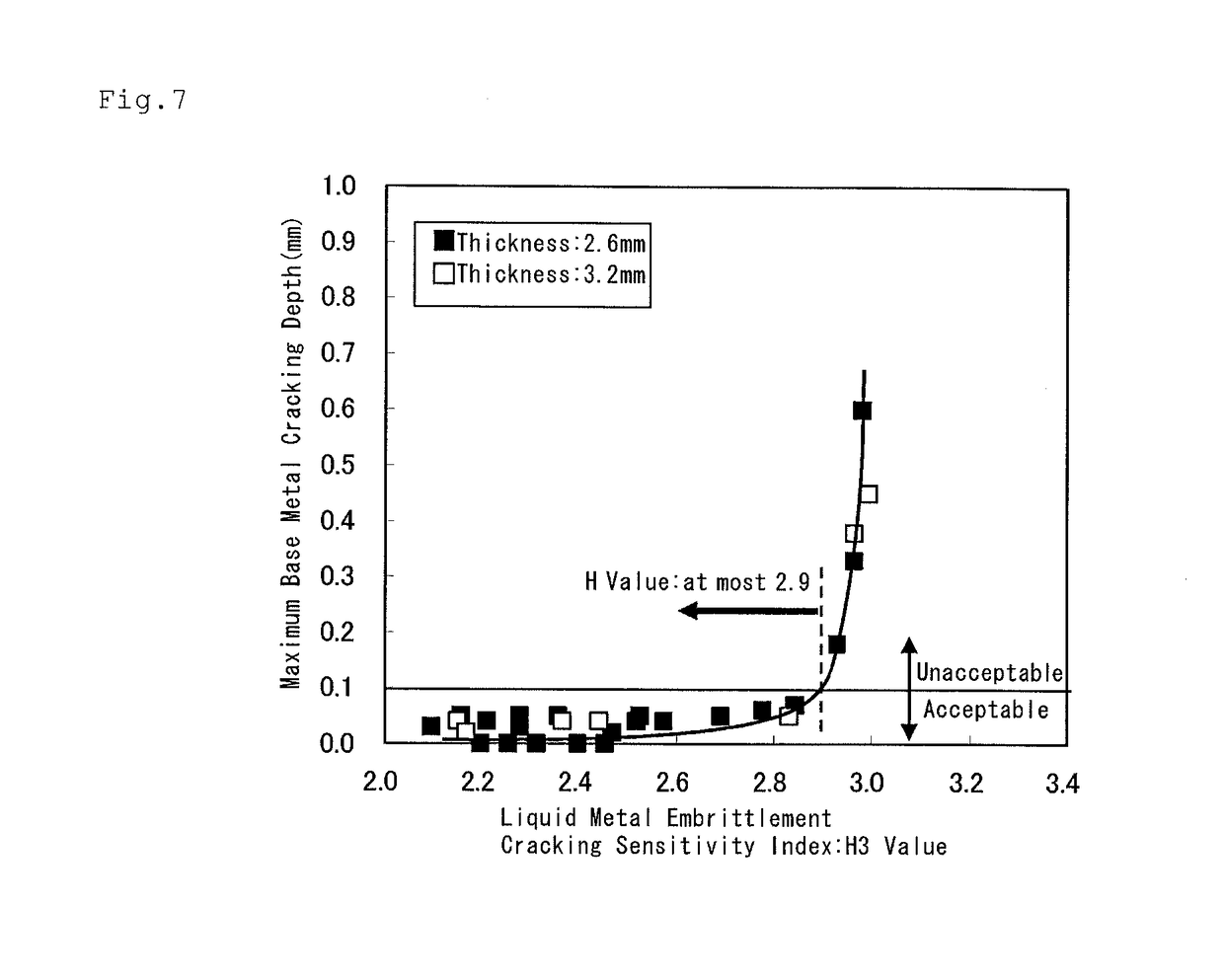
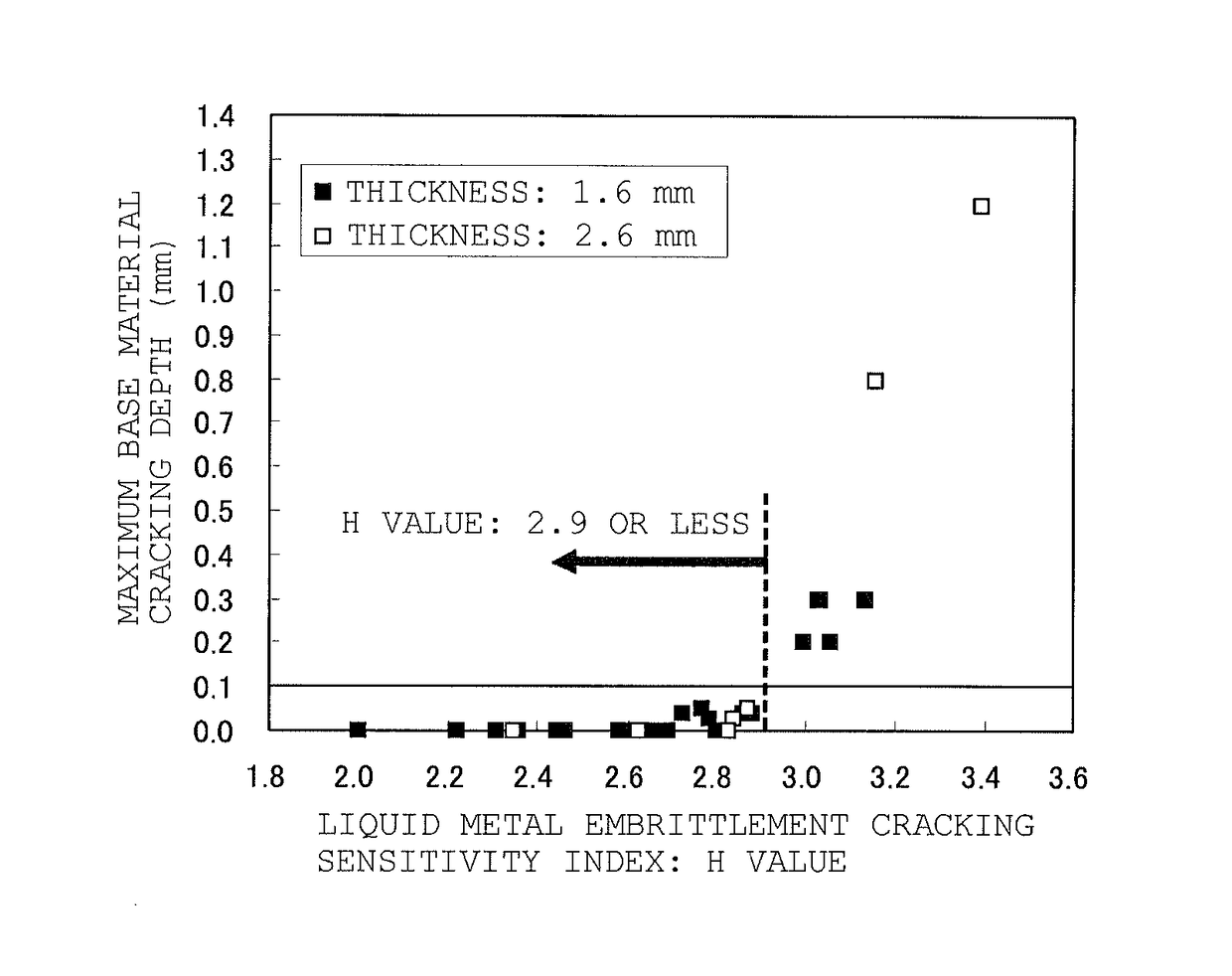
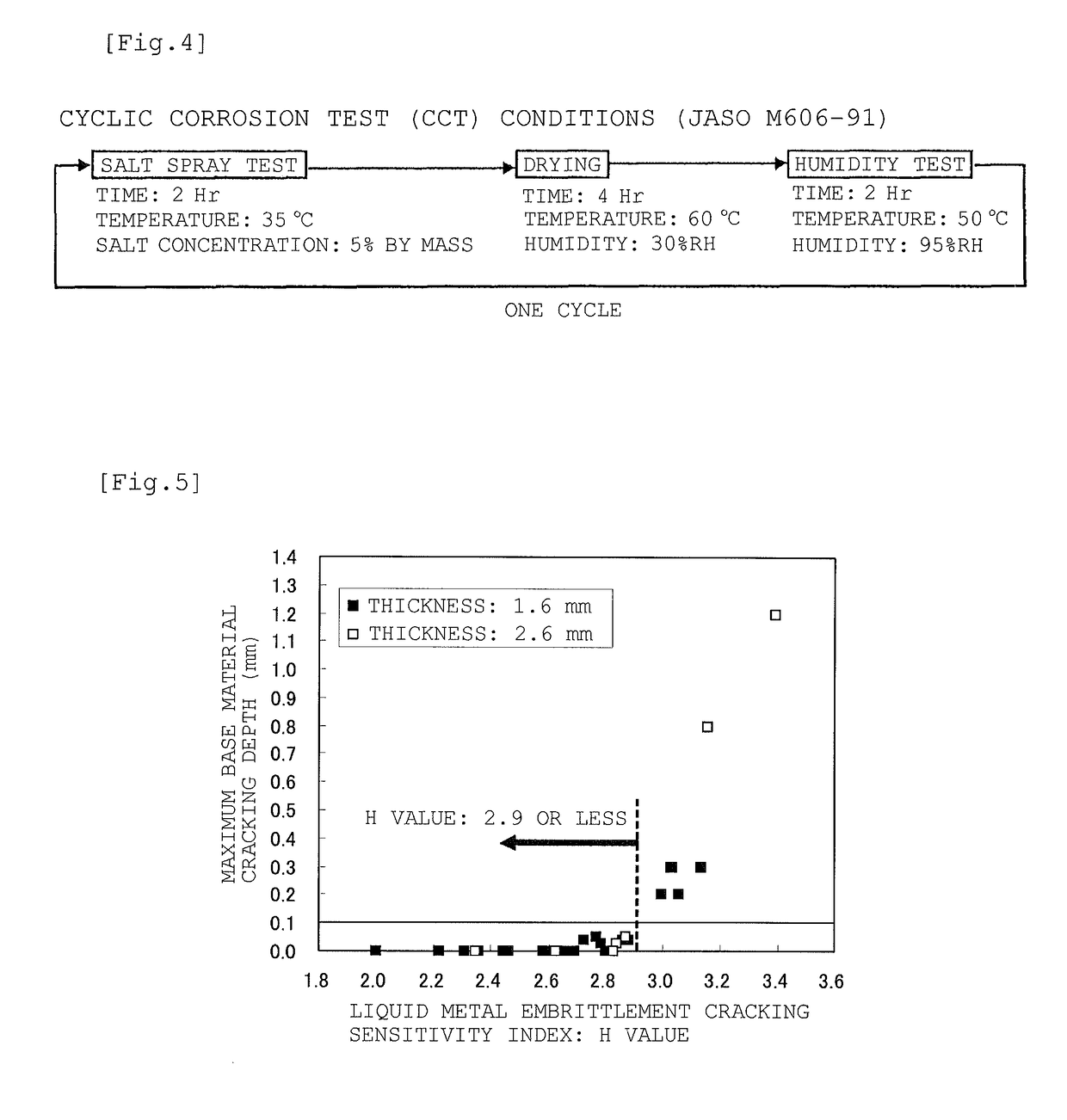
[Problem] To provide a steel sheet hot-dip-plated with a Zn—Al—Mg-based alloy coating, which is remarkably improved in point of all the burring workability, the liquid metal embrittlement cracking resistance and the corrosion resistance in the welded part thereof, as a steel material favorable for arc-welded structural members.[Means for Resolution] A plated steel sheet having a Zn—Al—Mg-based alloy coating layer formed by hot-dipping on the surface of a base steel sheet for welded structural members, wherein the base steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and has a metallographic structure of such that Ti-containing precipitates having a mean particle diameter of at most 20 nm are dispersed in the matrix formed of a ferrite phase therein, and wherein the liquid metal embrittlement cracking sensitivity index H3 value of the base steel sheet represented by the following formula (3) and indicating the relationship between the contents of the steel components and the thickness t (mm) of the steel sheet is at most 2.90:H3 Value=C / 0.2+Si / 5.0+Mn / 1.3+Cr / 1.0+Mo / 1.2+0.4t−0.7(Cr+Mo)1 / 2 (3)
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
Galvanized high-strength steel resistance spot welding method with good joint performance
ActiveCN108015401AImprove plasticityImprove the fracture modeWelding electric suppliesElectrical resistance and conductanceCrazing
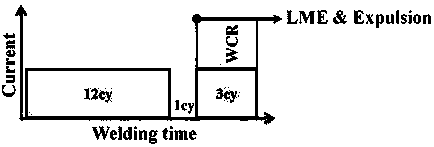
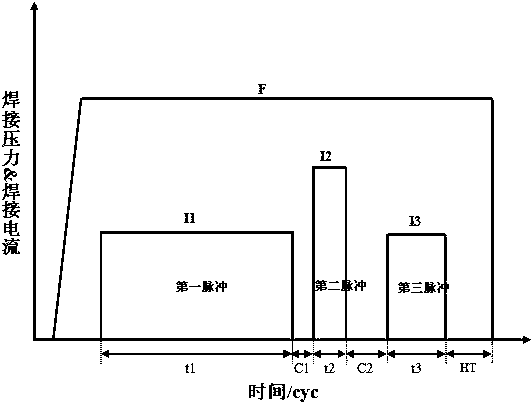
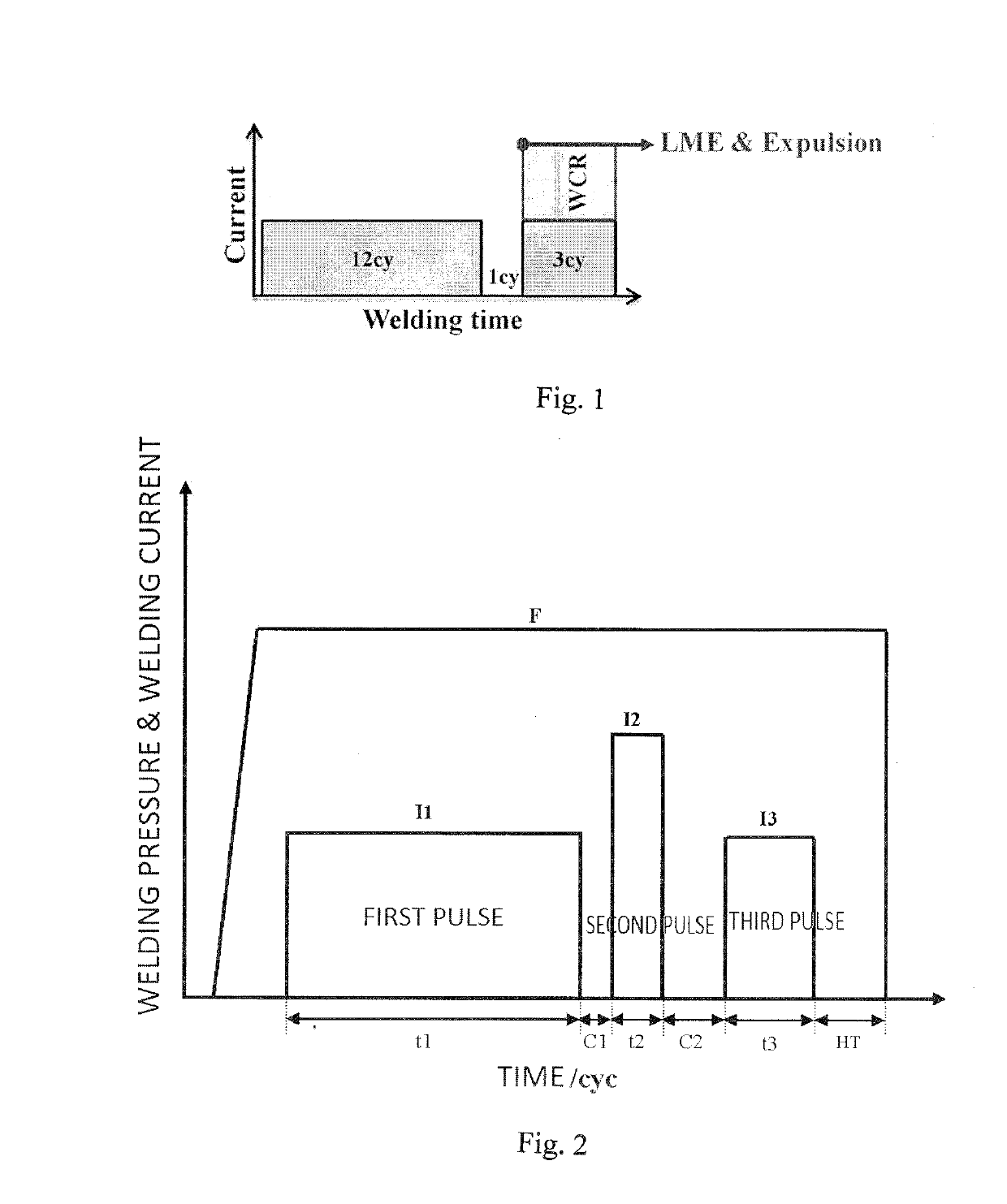
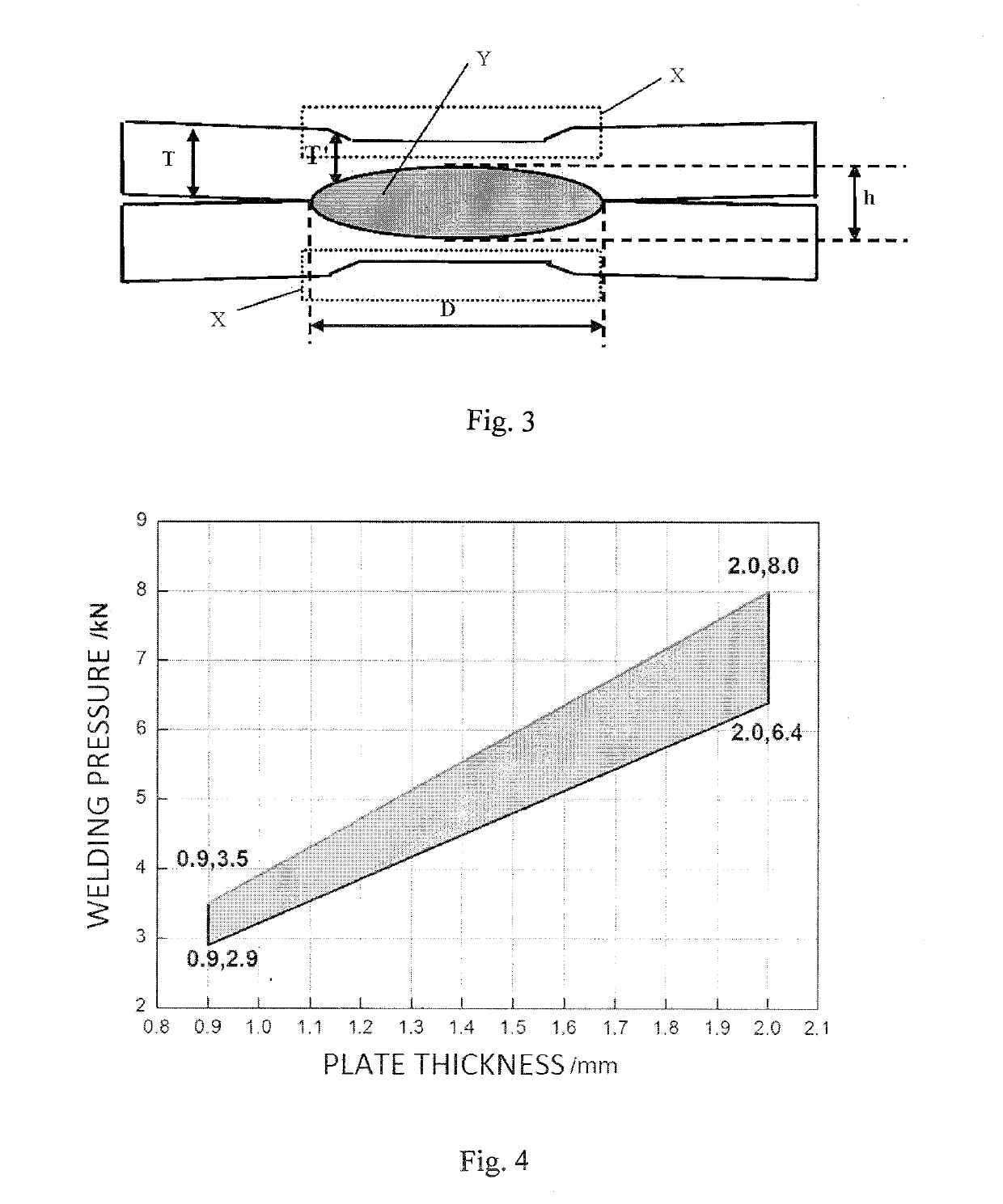
The invention relates to a resistance spot welding method of a galvanized steel plate with tensile strength larger than or equal to 590 Mpa. According to the galvanized high-strength steel resistancespot welding method with the good joint performance, three welding pulses are used in a spot welding period; the first welding pulse and the second welding pulse are used for generating a nugget and restraining the generation of the liquid metal embrittlement (LME) crack, wherein the first welding pulse generates the nugget with the diameter of 3.75 T<1 / 2>-4.25 T<1 / 2>, and the T in the formula isthe plate thickness; the second welding pulse makes the nugget grow slowly; the third welding pulse is a slow-cooling pulse and is used for improving the plasticity of the welding spot. According to the first welding pulse, by setting the time t1 of the first welding pulse and carrying out a test, the welding current I1 of the first welding pulse is obtained, wherein the welding current I1 of thefirst welding pulse is the welding current corresponding to when the nugget with the diameter of 3.75 T<1 / 2>-4.25 T<1 / 2> is generated; and the welding current I2 and the time t2 of the second weldingpulse and the welding current I3 and the time t3 of the third welding pulse are obtained by calculating the welding current I1 and the time t1 of the first welding pulse.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Plated steel sheet having plated layer with excellent stability for hot press molding
ActiveUS20140120366A1Uniform alloyingAvoid damageHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingSheet steelZinc
The present invention relates to a plated steel sheet having a plated layer with excellent stability for hot press molding, and more specifically, to a plated steel sheet having a plated layer with excellent stability for hot press molding in which a LME (Liquid Metal Embrittlement) phenomenon caused by a zinc enrichment region included in the plated layer is suppressed during hot press molding.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Hot dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent resistance to cracking due to liquid metal embrittlement
InactiveUS20160319415A1Avoid layeringOccurrence of cracking caused by liquid metal embrittlement may be suppressedHot-dipping/immersion processesSuperimposed coating processSheet steelIn vehicle
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent resistance to cracking caused by liquid metal embrittlement is provided. The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent resistance to cracking caused by liquid metal embrittlement includes a base steel sheet having a microstructure in which an austenite fraction is 90 area % or more; and a hot-dip galvanizing layer formed on the base steel sheet, wherein the hot-dip galvanizing layer includes an Fe—Zn alloy layer; and a Zn layer formed on the Fe—Zn alloy layer, and the Fe—Zn alloy layer has a thickness of [(3.4×t) / 6]μm or more, where t is a thickness of the hot-dip galvanizing layer. In addition, provided is the hot-dip galvanized steel sheet in which plating layer delamination easily occurring in vehicle welding and molding conditions according to the related art, is prevented, and cracking caused by liquid metal embrittlement is suppressed.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Controlling Liquid Metal Embrittlement In Galvanized Press-Hardened Components
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Steel sheet hot-dip-coated with Zn-Al-Mg-based system, and process of manufacturing same
ActiveCN103415641AWill not be brittle and crackedWill not cause brittle crackingHot-dipping/immersion processesVehicle componentsCrack resistanceSheet steel
[Problem] To provide a steel sheet hot-dip-plated with a Zn-Al-Mg-based alloy coating, which is remarkably improved in point of all the burring workability, the liquid metal embrittlement cracking resistance and the corrosion resistance in the welded part thereof, as a steel material favorable for arc-welded structural members. [Means for Resolution] A plated steel sheet having a Zn-Al-Mg-based alloy coating layer formed by hot-dipping on the surface of a base steel sheet for welded structural members, wherein the base steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and has a metallographic structure of such that Ti-containing precipitates having a mean particle diameter of at most 20 nm are dispersed in the matrix formed of a ferrite phase therein, and wherein the liquid metal embrittlement cracking sensitivity index H3 value of the base steel sheet represented by the following formula (3) and indicating the relationship between the contents of the steel components and the thickness t (mm) of the steel sheet is at most 2.90: H3 Value=C / 0.2+Si / 5.0+Mn / 1.3+Cr / 1.0+Mo / 1.2+0.4t-0.7(Cr+Mo)1 / 2(3)
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
Zinc-coated hot formed high strength steel part with through-thickness gradient microstructure
Methods of strengthening surface regions of high-strength transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) steel are provided. The method may comprise shot peening at least one region of an exposed surface of a hot-formed press-hardened component comprising a high-strength steel. Prior to shot peening, the component has a microstructure comprising >=about 5% by volume retained austenite in a matrix of martensite. The shot peening is conducted at a temperature of <about 150DEG. and forms at least one hardened surface region comprising <=about 2% by volume austenite. The TRIP steel may be zinc-coated and having a surface coating comprising zinc and substantially free of liquid metal embrittlement (LME). Zinc-coated hot-formed press-hardened components, including automotive components, formed from such methods are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Aluminum-rich series zinc-based plating layer material capable of reducing brittleness caused by liquid metal in hot forming process and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113862518AOxidation is notControl brittle fractureHot-dipping/immersion processesAlloyLiquid metal
The invention discloses an aluminum-rich series zinc-based plating layer material capable of reducing brittleness caused by liquid metal in a hot forming process and a preparation method thereof. A Zn-Al-Mg alloy plating layer is prepared by mainly adjusting the content of Al and Mg in a plating solution and controlling the content proportion of the Al to the Mg, and the Zn-Al-Mg alloy plating layer comprises the following components including, by mass, 0.2%-5% of Al, less than or equal to 2.5% of Mg, 0-2% of Si, 0-1% of Ti, 0-3% of RE and the balance Zn and some inevitable impurities, wherein the RE is at least one element of La and Ce. According to the method, plating layer materials with different element contents are prepared for a 22MnB5 steel plate; and through a plating layer preparation-hot dipping experiment, austenitizing treatment, plating layer and steel plate structure observation and steel plate hot tensile experiment detection, the material has the performance of inhibiting liquid metal embrittlement and high corrosion resistance, the problem of embrittlement caused by the liquid metal in the hot stamping forming process of the high-strength steel plate plated with the aluminum-rich zinc-based plating layer is solved, the corrosion resistance of the plating layer is achieved, and the oxidation problem of the plating solution in the hot dipping process is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
METHOD FOR PRODUCING ARC-WELDED Zn-Al-Mg ALLOY COATED STEEL PLATE STRUCTURAL MEMBER
InactiveUS20150231726A1Excellent liquid metal embrittlement cracking resistanceIncrease costHot-dipping/immersion processesArc welding apparatusSheet steelCrack resistance
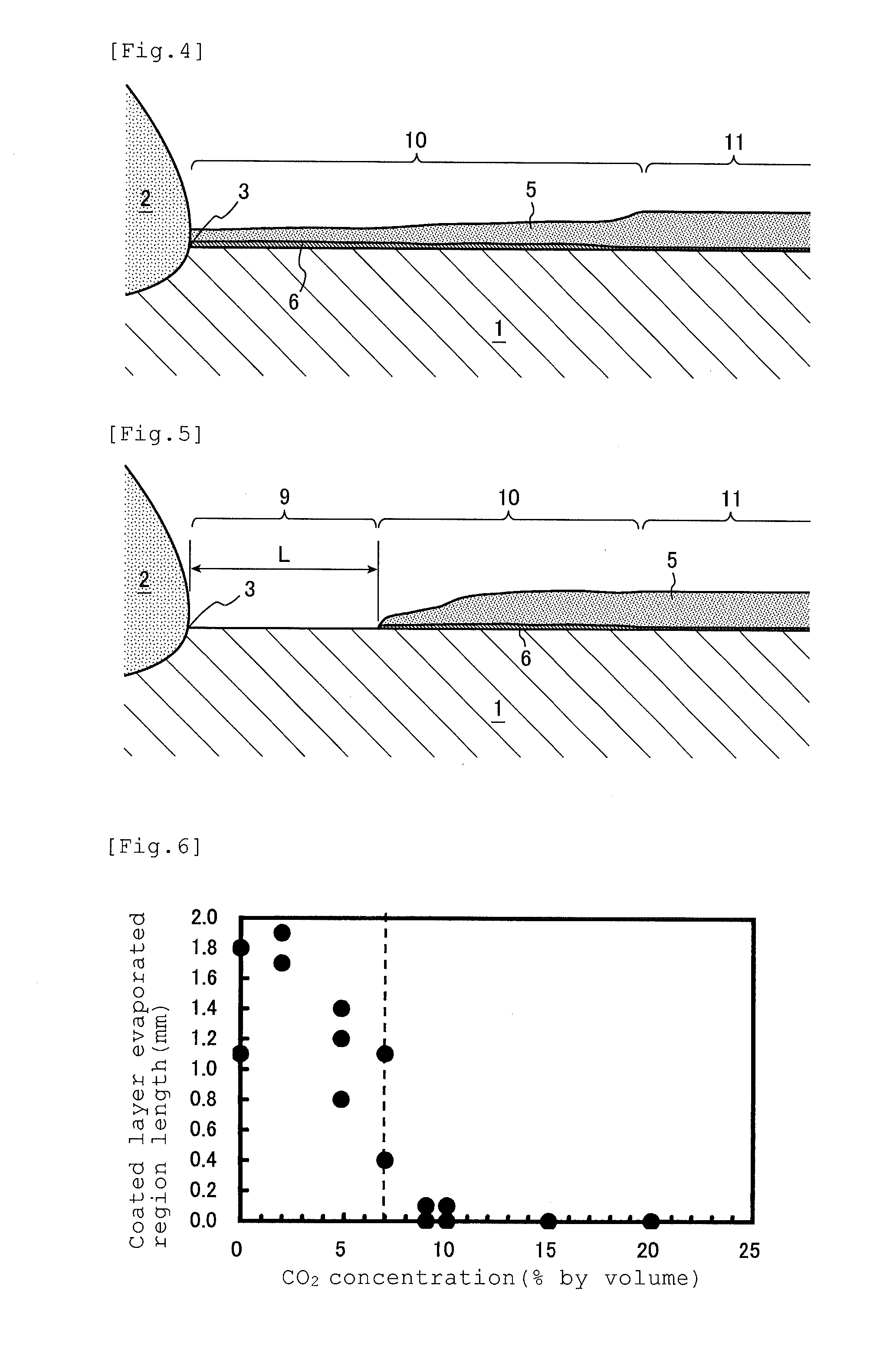
A method for producing an arc-welded Zn—Al—Mg alloy coated steel plate structural member excellent in liquid metal embrittlement cracking resistance is provided. The method contains a step of joining steel members by gas-shielded arc-welding to produce a welded structural member, at least one of the steel members to be used is a hot dip Zn—Al—Mg alloy coated steel plate member, and the shield gas contains an Ar gas, a He gas or an Ar—He mixed gas as a base gas with a CO2 concentration controlled in a range of from 0 to 7% by volume.
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
Weld joint formed with stainless steel-based weld metal for welding a zinc-based alloy coated steel sheet
ActiveUS7767314B2Improve corrosion resistanceIncreased durabilityElectric discharge heatingWelding/cutting media/materialsCrack resistanceSheet steel
Disclosed are a weld joint and a stainless steel-based weld metal composition for the weld joint. The composition and weld joint made therefrom are suitable for welding a zinc-based alloy coated steel sheet. The weld is excellent in corrosion resistance and liquid-metal embrittlement crack resistance. This is accomplished by inhibiting liquid-metal embrittlement cracks of the stainless-steel-based weld metal when the zinc-based alloy coating steel sheet is welded using the stainless-steel-based weld metal. The weld joint comprises a welded portion of weld metal made of stainless-steel-based components, the weld metal containing in mass percent (%): C: 0.01-0.1; Si: 0.1-1; Mn: 0.5-2.5; Ni: 5-11; and Cr: 17-25, and the balance being iron and residual impurities, wherein the following expression are met: −0.81×Cr equivalent+23.2≦Ni equivalent≦0.95×Cr equivalent−8.1 . . . (1); Ni equivalent=Ni+30×C+0.5×Mn+30×N . . . (2); Cr equivalent=Cr+Mo+1.5×Si . . . (3).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-dip zinc alloy coated steel sheet excellent in coating adhesion, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20160024632A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove the immunityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelZinc alloys
[Problem] To produce a hot-dip Zn—Al—Mg alloy coated steel sheet that is excellent in coating adhesion, by using, as a base sheet for coating, a steel sheet that is imparted with resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracking by adding B.[Solution] A hot-dip zinc alloy coated steel sheet excellent in coating adhesion containing at least one of a Si simple oxide, a Mn simple oxide, a Cr simple oxide, a Si—Mn composite oxide, a Si—Cr composite oxide, a Mn—Cr composite oxide, and a Si—Mn—Cr composite oxide in a portion within 10 μm from an interface between a steel sheet as a base sheet for coating, and a hot-dip galvanized layer formed on a surface thereof.
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
Method of resistance spot welding of galvanized high-strength steel with good joint performance
ActiveUS20190321907A1Improve plasticityImprove joint performanceWelding electric suppliesElectrical resistance and conductanceSheet steel
A resistance spot welding method of galvanized high-strength steel with good joint performance, wherein: three welding pulses are used within one spot welding schedule; a first welding pulse and a second welding pulse are used for generating a nugget and suppressing the generation of liquid metal embrittlement (LME) cracks, wherein the first welding pulse generates a nugget having a diameter of 3.75T½-4.25T½ in which T represents a plate thickness; the second welding pulse causes the nugget to grow slowly; and a third welding pulse which is a tempering pulse is used for improving plasticity of a welding spot. A time t1 of the first welding pulse is set and a welding current I1 of the first welding pulse is obtained through tests, and the welding current I1 of the first welding pulse is a welding current upon generating the nugget having the diameter of 3.75T½-4.25T½; and a welding current I2 and a time t2 of the second welding pulse, and a welding current I3 and a time t3 of the third welding pulse are calculated by the welding current I1 and the time t1 of the first welding pulse. By the resistance spot welding method of galvanized high-strength steel, the liquid metal embrittlement cracks during the spot welding of the high-strength steel galvanized plates can be effectively suppressed, meanwhile, the plasticity of the welding point is improved, and the probability of button pullout failure of the welding point during broken testing is increased. Therefore, the joint by spot welding of the high-strength steel galvanized plates with more reliable quality and more excellent performance is obtained, and a useful guidance can be provided for the welding production of the high-strength steel galvanized plates.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength plated steel plate for welded structural member, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20160032438A1Increased durabilityImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesMartensiteMaterials science
A high-strength plated steel plate for a welded structural member having a steel composition containing from 0.050 to 0.150% of C, from 0.001 to 1.00% of Si, from 1.00 to 2.50% of Mn, from 0.005 to 0.050% of P, from 0.001 to 0.020% of S, and from 0.005 to 0.100% of Al, having a steel base material having a metal structure containing a ferrite phase and a second phase containing mainly martensite having an average crystal grain diameter of 8 mm or less, and having a chemical composition and a thickness t (mm) of the steel base material regulated to obtain a value, C / 0.2+Si / 5.0+Mn / 1.3+Cr / 1.0+Mo / 1.2+0.4t−0.7(Cr+Mo)1 / 2, of 2.9 or less. The high-strength plated steel plate is excellent in corrosion resistance of the welded portion, resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracking, and bending workability.
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
Zinc-coated steel sheet with high resistance spot weldability
ActiveUS20200181729A1High strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesCrazingZinc alloys
Owner:ARCELORMITTAL INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO SL
Pretreatment of weld flanges to mitigate liquid metal embrittlement cracking in resistance welding of galvanized steels
InactiveUS20200016679A1Mitigate liquid metal embrittlement crackingReduce crackingHot-dipping/immersion processesMolten spray coatingAlloyLiquid metal
A method to mitigate liquid metal embrittlement cracking in resistance welding of galvanized steels includes modifying at least one face of a steel member to create a first workpiece by: applying a zinc containing material in a first layer to the at least one face of the steel member; and spraying a second layer of a copper containing material onto the first layer of the zinc containing material. The at least one face of the first workpiece is abutted to a second workpiece of a steel material. A resistance welding operation is performed to join the first workpiece to the second workpiece. A temperature of the resistance welding operation locally melts the zinc containing material and the copper containing material to create a brass alloy of the zinc containing material and the copper containing material.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
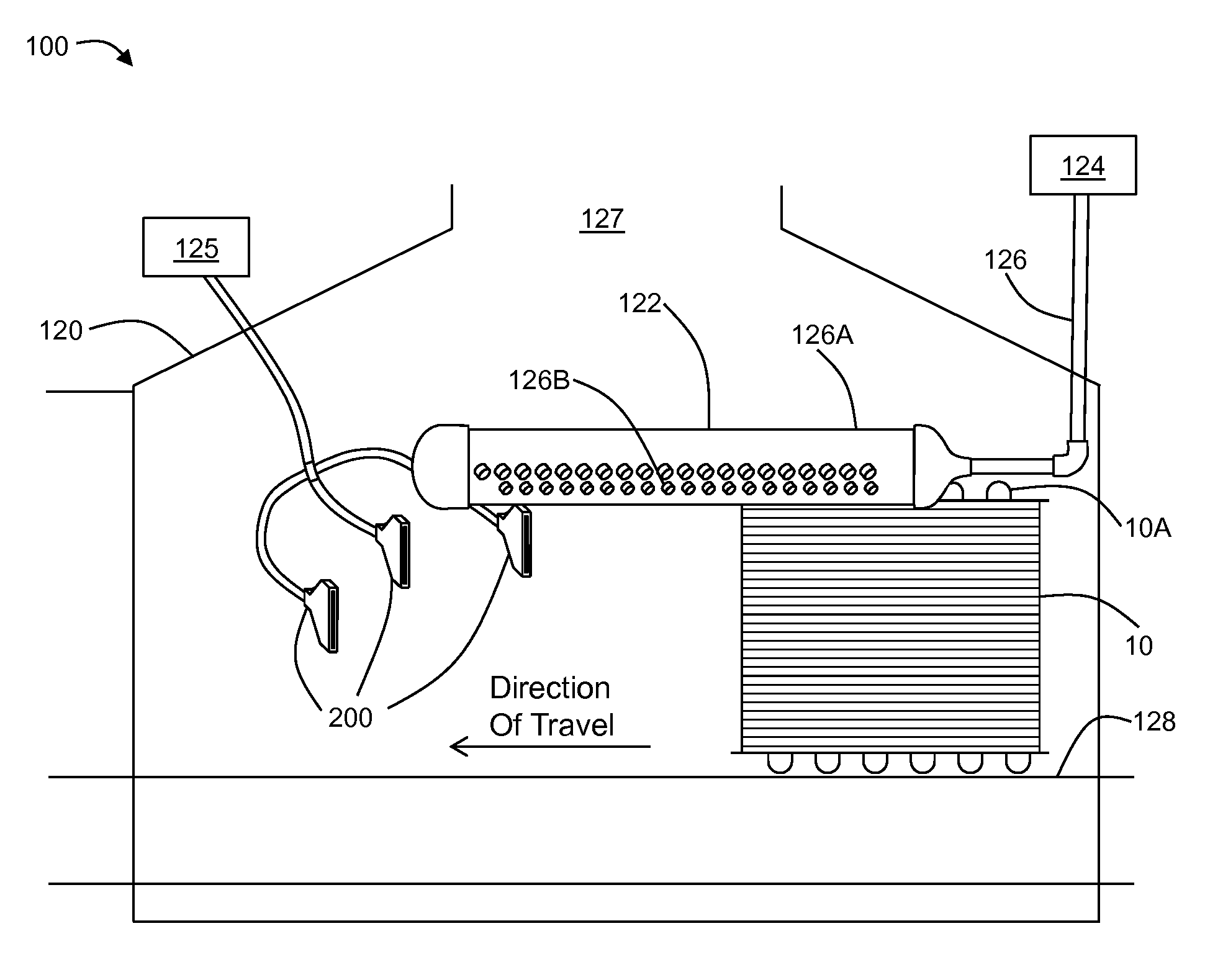
Cooling system to reduce liquid metal embrittlement in metal tube and pipe
InactiveUS20160271716A1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesStationary conduit assembliesMetalMaterials science
Owner:LUVATA ALLTOP ZHONGSHAN LTD
Steel sheet having excellent resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracks and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS11299793B2High strengthLower performance requirementsHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingMartensiteAustenite
Provided is a steel sheet having excellent resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracks and a method for manufacturing the same. The steel sheet includes, by weight %, 0.04% to 0.35% of C, 0.99% or less of Al+Si, 3.5% to 10% of Mn, 0.05% or less of P (excluding 0%), 0.02% or less of S (excluding 0%), and 0.02% or less of N (excluding 0%) with a remainder of Fe and other inevitable impurities, wherein the steel sheet comprises a microstructure comprising at least 10% of residual austenite, at least 60% of annealed martensite and 20% or less of alpha martensite and epsilon martensite, by volume fraction, and an average thickness of a Mn-depleted layer is at least 0.5 μm from a product surface.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A hot stamping forming method for zinc-based coated steel sheet or steel strip
ActiveCN107127238BLow heating temperatureShort holding timeHot-dipping/immersion processesShaping toolsHot stampingSheet steel
The invention relates to a hot-stamping forming method for a zinc plating steel plate or a steel strip. According to the hot-stamping forming method, the steel plate or the steel strip is conveyed into a vertical heating annealing furnace, the temperature is kept for a certain time, the steel plate is completely austenitized, a pre-cooling device is used when the steel plate leaves the annealing furnace, the steel plate is cooled to 650-700 DEG C at the cooling rate higher than 30 DEG C / s, then blanking is performed according to the part shape and size, then the steel plate is quickly transferred into a mold for hot-stamping forming, the steel plate is hardened at the speed higher than 30 DEG C / s, and the hot-stamping forming temperature is kept between 400 DEG C and 650 DEG C. Base plate cracks caused by partial stress and liquid metal embrittlement (LME) can be avoided, and the method is used for solving the problem that the base plate cracks cannot be avoided for existing zinc-based hot-stamping formed steel.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A Method for the Manufacturing of Liquid Metal Embrittlement Resistant Zinc Coated Steel Sheet
ActiveUS20200263284A1High LME resistance behaviorImproves LME resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesZincMetal
The present invention relates to a method for the manufacture of a coated steel sheet comprising the following successive steps: A. the coating of the steel sheet with a first coating consisting of nickel and having a thickness between 600 nm and 1400 nm, the steel sheet having the following composition in weight: 0.10<C<0.40%, 1.5<Mn<3.0%, 0.7<Si<3.0%, 0.05<Al<1.0%, 0.75<(Si+Al)<3.0%, and on a purely optional basis, one or more elements such as Nb≤0.5%, B≤0.010%, Cr≤1.0%, Mo≤0.50%, Ni≤1.0%, Ti≤0.5%, the remainder of the composition making up of iron and inevitable impurities resulting from the elaboration, B. the recrystallization annealing at a temperature between 820 to 1200° C., C. the coating with a second coating based on zinc not comprising nickel.
Owner:ARCELORMITTAL INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO SL
Steel sheet having excellent resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracks and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20200140971A1High strengthLow material performance requirementsHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingMartensiteAustenite
Provided is a steel sheet having excellent resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracks and a method for manufacturing the same. The steel sheet includes, by weight %: 0.04% to 0.35% of C, 0.99% or less of Al+Si, 3.5% to 10% of Mn, 0.05% or less of P(excluding 0%), 0.02% or less of S(excluding 0%), and 0.02% or less of N (excluding 0%) with a remainder of Fe and other inevitable impurities, wherein the steel sheet comprises a microstructure comprising at least 10% of residual austenite, at least 60% of annealed martensite and 20% or less of alpha martensite and epsilon martensite, by volume fraction, and an average thickness of a Mn-depleted layer is at least 0.5 μm from a product surface.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High temperature coatings to mitigate weld cracking in resistance welding
ActiveUS11441039B2Reducing base strengthReduce crackingCellsHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid metal embrittlementEmbrittlement
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Galvanized hot-formed steel components with custom features
Methods of selectively cooling and quenching surface regions of high-strength transformation induced plasticity (TRIP) steel are provided. The method may comprise selectively cooling at least one region of an exposed surface of a hot-formed press-hardened component comprising a high-strength steel. Prior to selective cooling, the component has a microstructure comprising ≥about 5% by volume retained austenite in a matrix of martensite. The selective cooling is conducted at a temperature of ≤about −40° C. and forms at least one quenched region comprising ≤about 2% by volume austenite. The TRIP steel may be zinc-coated and having a surface coating comprising zinc and substantially free of liquid metal embrittlement (LME). Zinc-coated hot-formed press-hardened components, including automotive components, formed from such methods are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Zn—Al—Mg based alloy hot-dip plated steel sheet, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS9592772B2Improve workabilityImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesVehicle componentsCrack resistanceChemical composition
[Problem] To provide a steel sheet hot-dip-plated with a Zn—Al—Mg-based alloy coating, which is remarkably improved in point of all the burring workability, the liquid metal embrittlement cracking resistance and the corrosion resistance in the welded part thereof, as a steel material favorable for arc-welded structural members.[Means for Resolution] A plated steel sheet having a Zn—Al—Mg-based alloy coating layer formed by hot-dipping on the surface of a base steel sheet for welded structural members, wherein the base steel sheet has a specific chemical composition and has a metallographic structure of such that Ti-containing precipitates having a mean particle diameter of at most 20 nm are dispersed in the matrix formed of a ferrite phase therein, and wherein the liquid metal embrittlement cracking sensitivity index H3 value of the base steel sheet represented by the following formula (3) and indicating the relationship between the contents of the steel components and the thickness t (mm) of the steel sheet is at most 2.90:H3 Value=C / 0.2+Si / 5.0+Mn / 1.3+Cr / 1.0+Mo / 1.2+0.4t−0.7(Cr+Mo)1 / 2 (3)
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
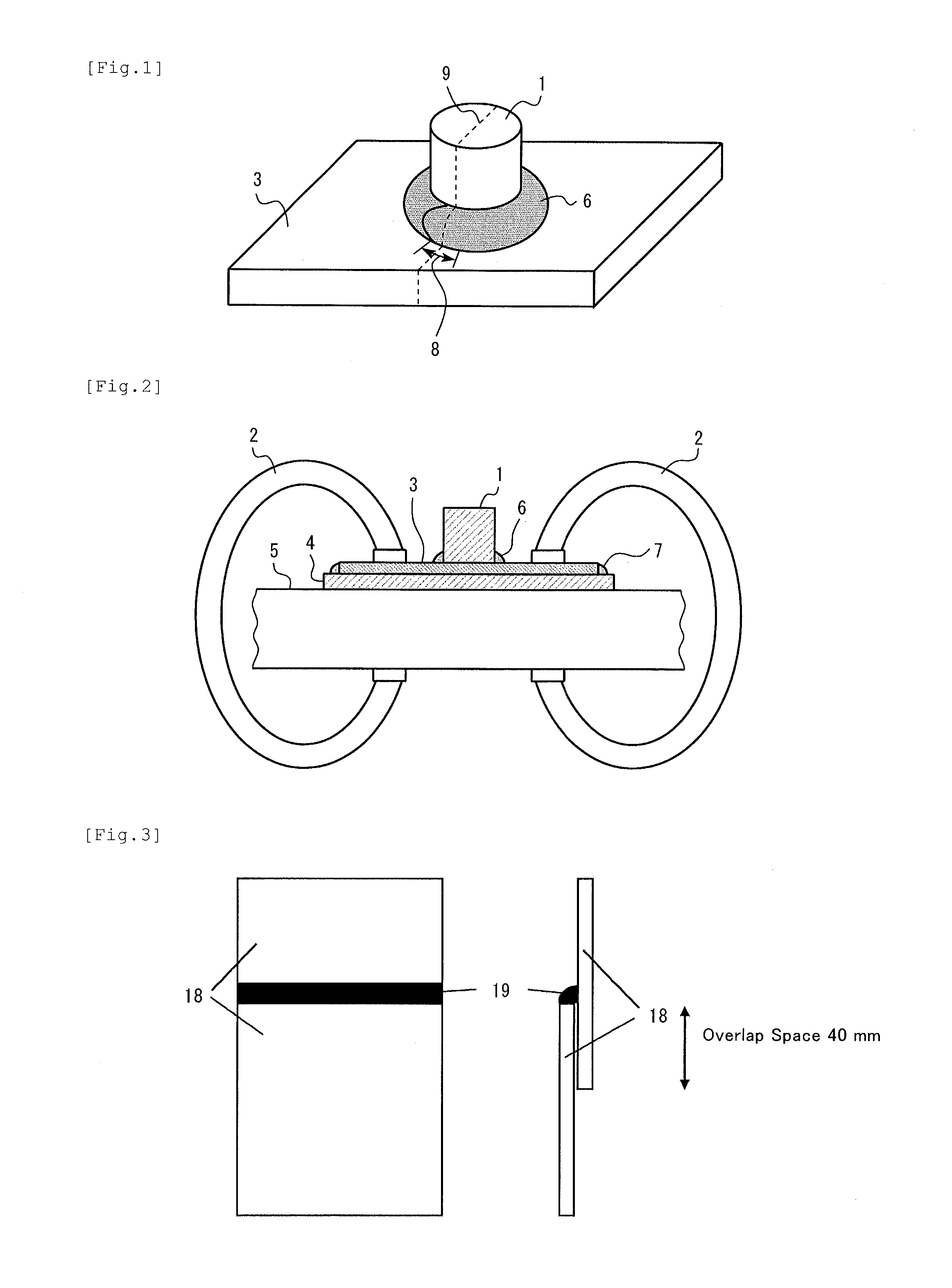
Method of spot welding
ActiveUS10350701B2Occurrence of liquid metal embrittlement cracking can be easily preventedVehicle componentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSheet steelSpot welding
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High-strength plated steel plate for welded structural member, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS10100395B2Increased durabilityImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelChemical composition
A high-strength plated steel plate for a welded structural member having a steel composition containing from 0.050 to 0.150% of C, from 0.001 to 1.00% of Si, from 1.00 to 2.50% of Mn, from 0.005 to 0.050% of P, from 0.001 to 0.020% of S, and from 0.005 to 0.100% of Al, having a steel base material having a metal structure containing a ferrite phase and a second phase containing mainly martensite having an average crystal grain diameter of 8 mm or less, and having a chemical composition and a thickness t (mm) of the steel base material regulated to obtain a value, C / 0.2+Si / 5.0+Mn / 1.3+Cr / 1.0+Mo / 1.2+0.4t−0.7(Cr+Mo)1 / 2, of 2.9 or less. The high-strength plated steel plate is excellent in corrosion resistance of the welded portion, resistance to liquid metal embrittlement cracking, and bending workability.
Owner:NISSHIN STEEL CO LTD
High temperature coatings to mitigate weld cracking in resistance welding
ActiveUS20220195207A1Mitigate liquid metal embrittlement (LME) crackingReduce generationHot-dipping/immersion processesCellsLiquid metal embrittlementEmbrittlement
A high temperature substrate coating to mitigate liquid metal embrittlement (LME) cracking in automobile vehicles includes a substrate. A coating is disposed on the substrate, the coating being one of a zinc-based material and an aluminum-based material, with the coating having a melting point of at least 500° C.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Multi-material component and methods of making thereof
A multi-material component joined by a high entropy alloy is provided, as well as methods of making a multi-material component by joining materials with high entropy alloys to reduce or eliminate liquid metal embrittlement (LME) cracks.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com