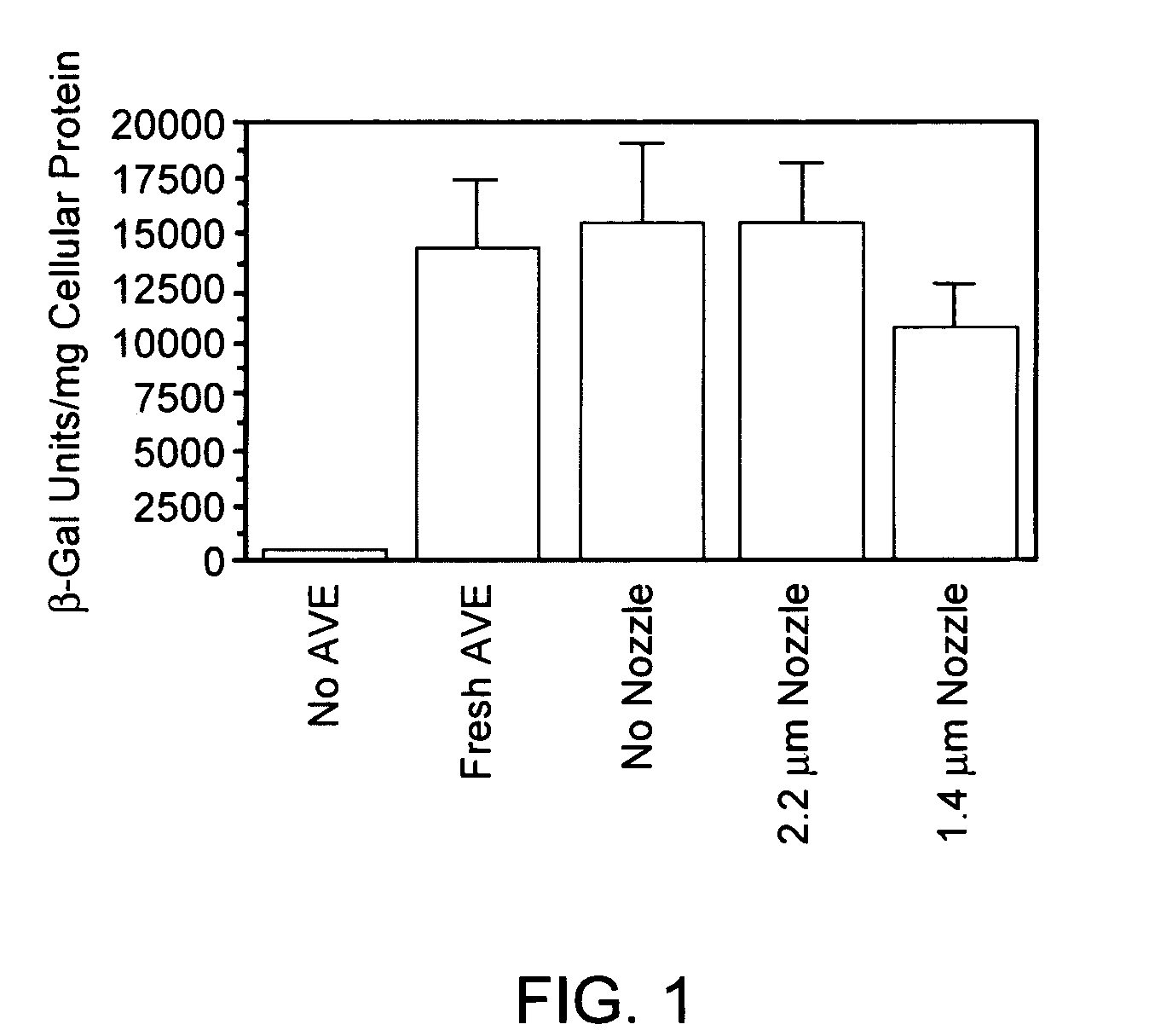
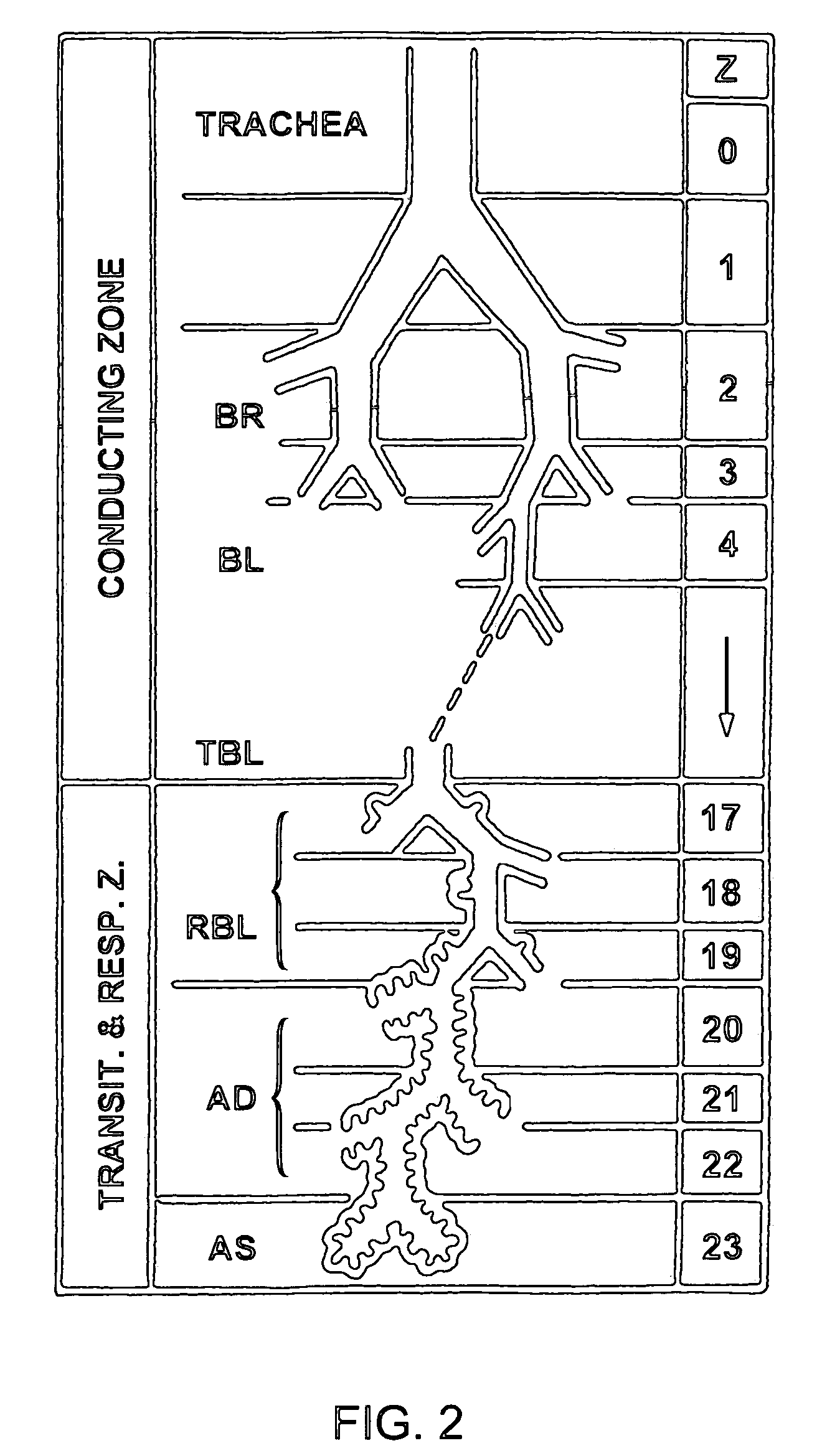
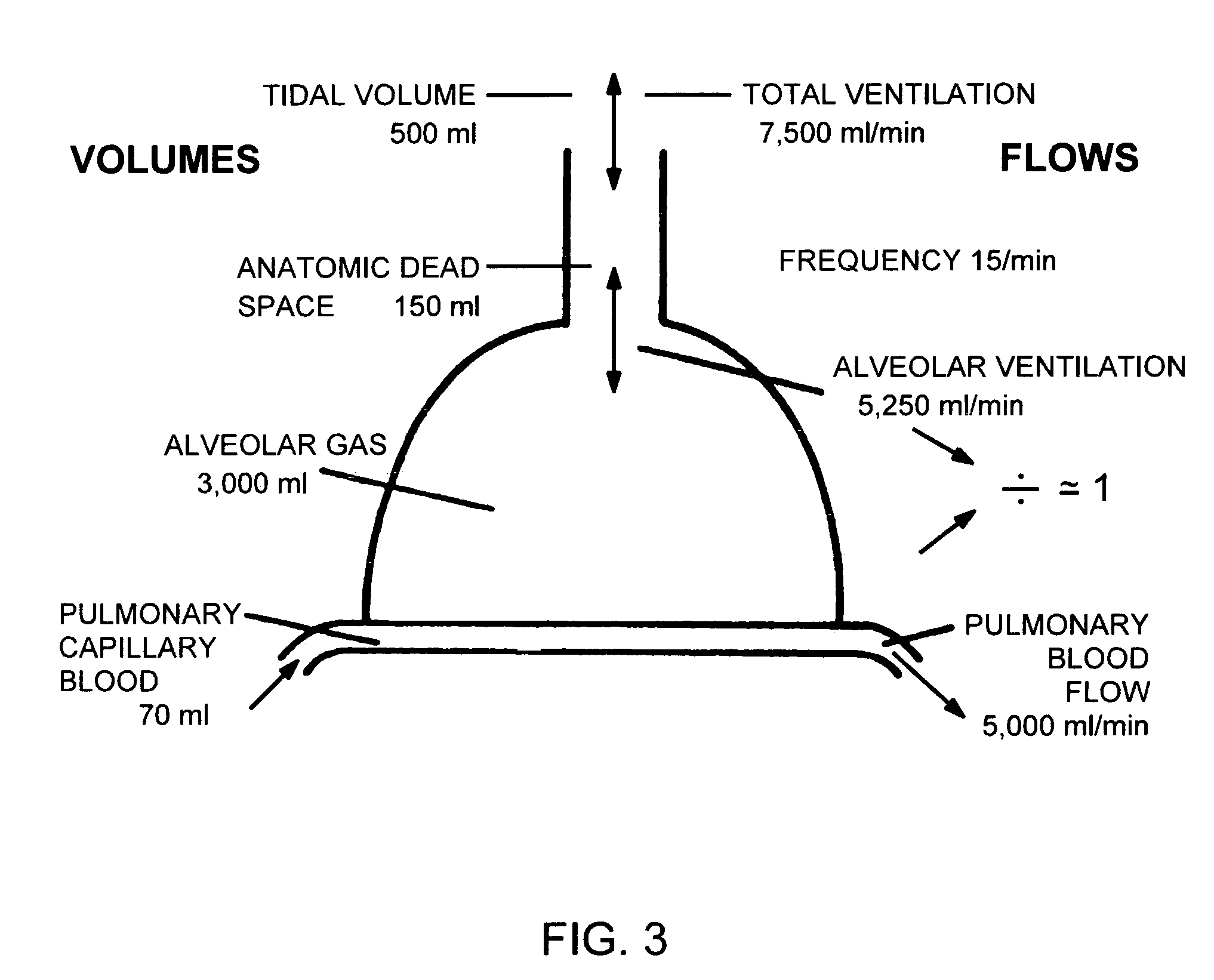
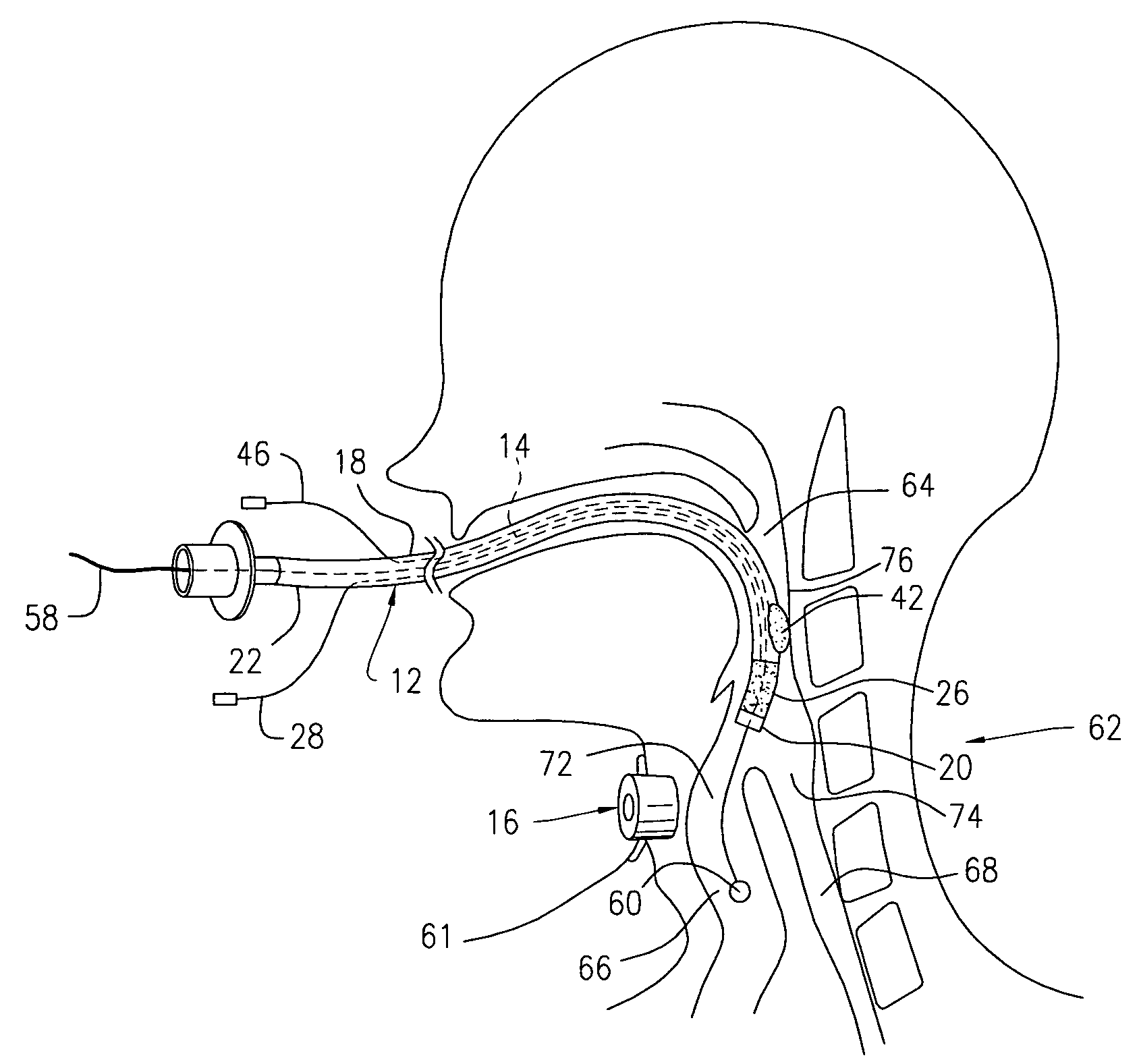
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Oropharyngeal structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
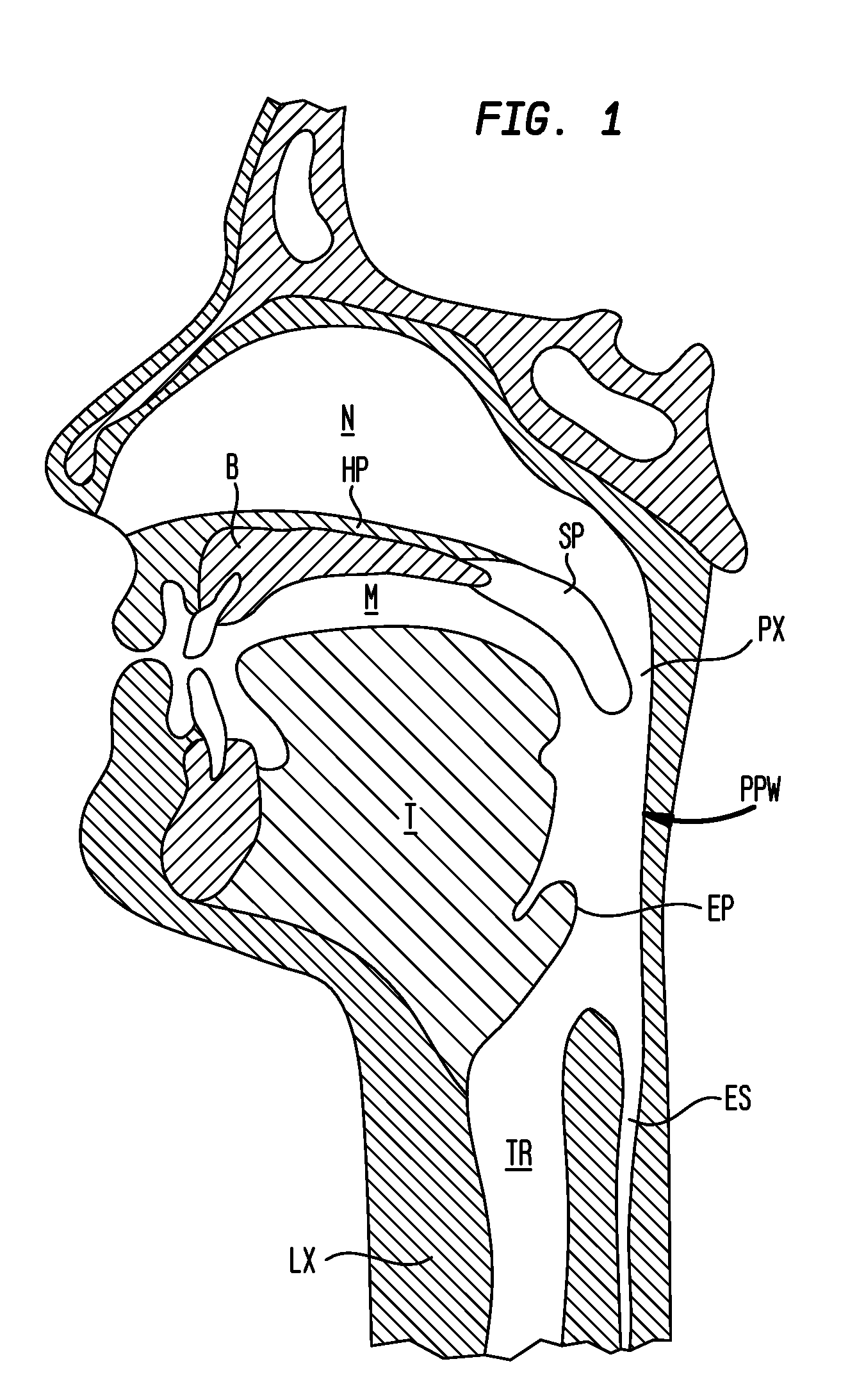
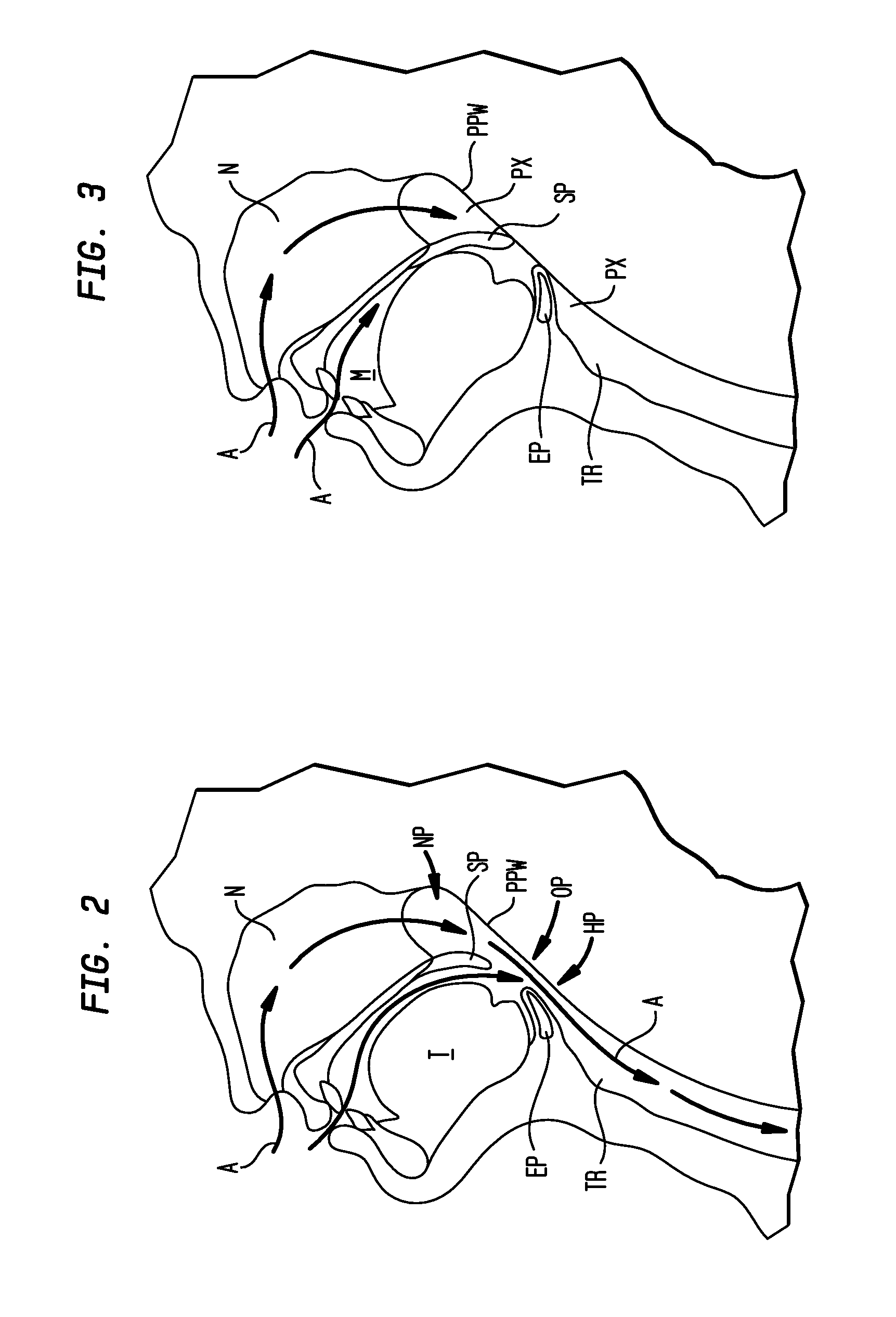
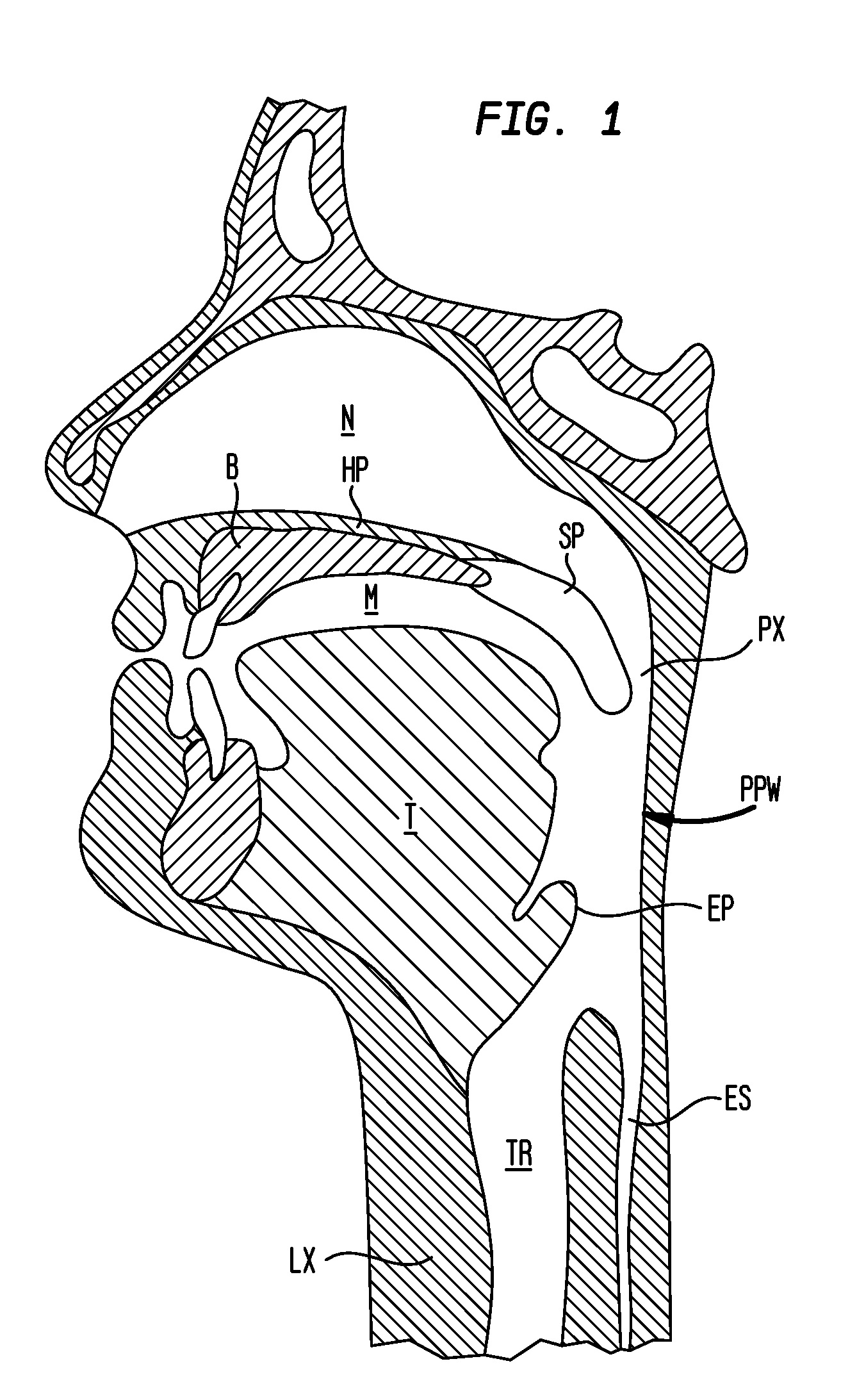
The adenoids, also known as the pharyngeal tonsils, are lymphoid tissue structures located in the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is an annular arrangement of lymphoid tissue in both the nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Electrosurgical system and method
InactiveUS7001380B2Lower impedanceMinimizing char formationCannulasDiagnosticsBenign conditionEnlarged tonsils
A method is disclosed for treating benign conditions, such as enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids located in a patient's throat or nasopharynx, or soft tissue lesions located in a patient's oropharynx or larynx. According to the method, a space containing the patient's nasopharynx, oropharynx or pharynx and larynx is isolated from the patient's trachea and lungs using an inflatable cuff tracheostomy tube or nasotracheal tube inserted in the patient's trachea. The cuff is inflated to occlude the trachea. The patient is placed in a supine position, whereupon at least a portion of the space containing the nasopharynx and / or oropharynx and larynx is filled with saline. An endoscope is then inserted into the space to view the operative site in which the tonsils or tissue lesion are to be treated. An electrosurgical instrument having an active tissue treatment electrode and a return electrode connected to an electrosurgical generator is then inserted into the space, either along side the endoscope or through the endoscope's working channel. The generator is then operated to apply a radio frequency voltage between the active and return electrodes of the electrosurgical instrument, whereby a conduction path is formed between the active and return electrodes, at least partially through the saline, whereupon the active electrode is manipulated to debulk or otherwise treat the soft tissue lesion or enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
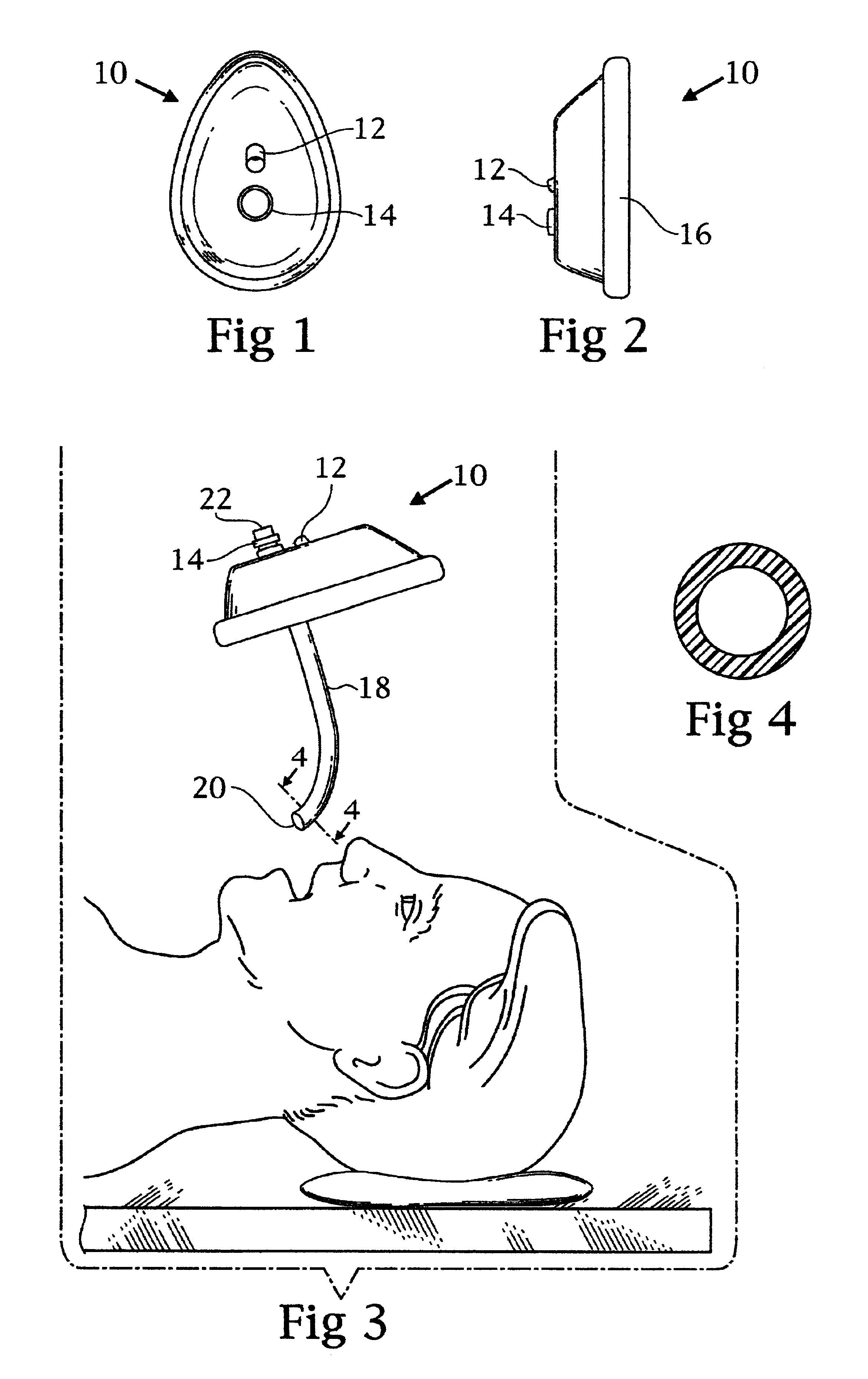
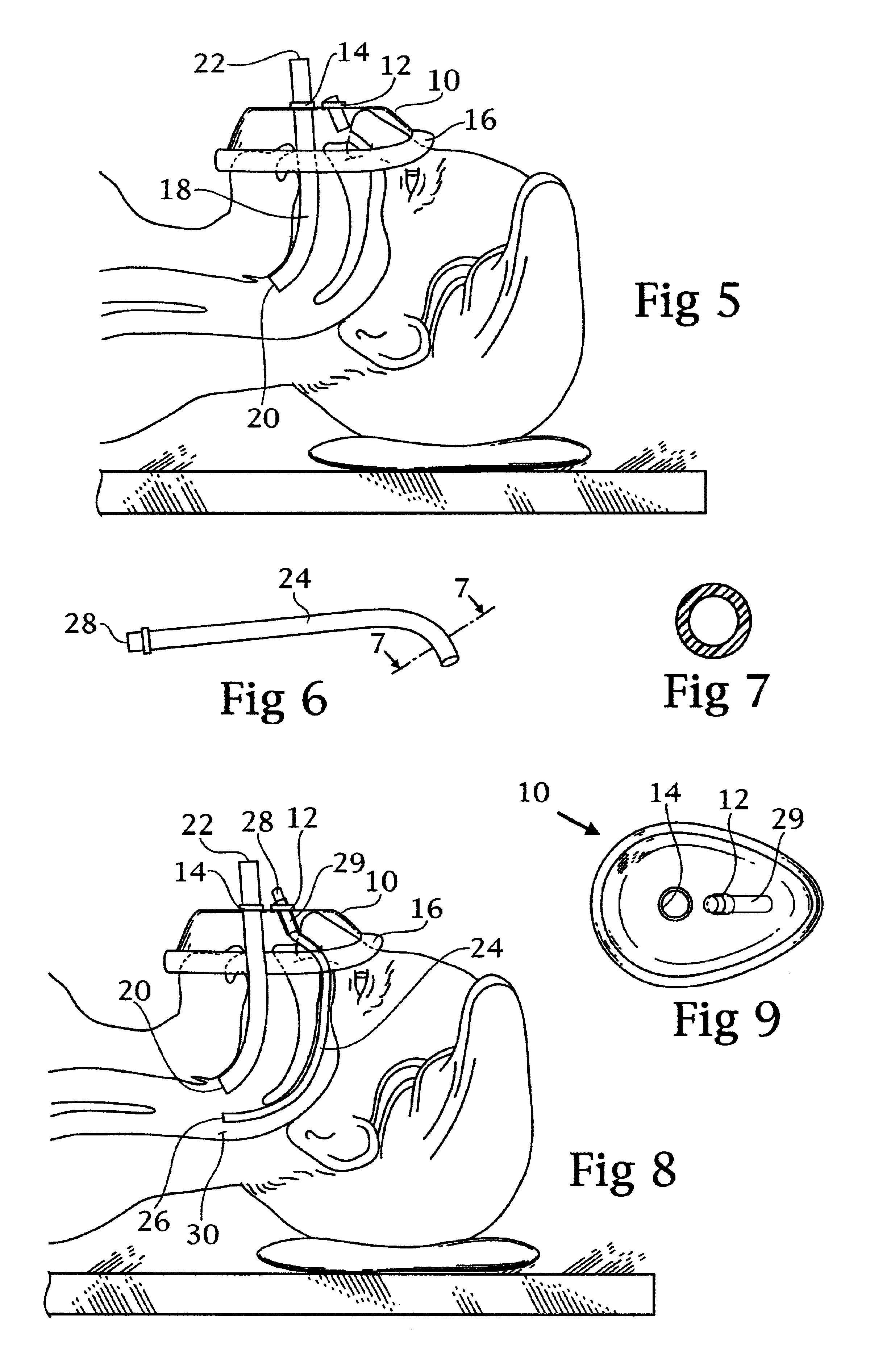
Double barrel ventilation mask for a patient
InactiveUS6860270B2Improve ventilationIncrease oxygenationRespiratory masksBreathing masksNasal passageNasal cavity
A face mask for ventilation of a patient. A face piece is disposed on the patient's face. An oral tube and a nasal tube are disposed through corresponding ports in the face piece. The oral tube extends through the mouth of the patient and the nasal tube extends through the nasal passage of the patient. The ends of the oral tube and the nasal tube are received in the posterior oropharynx of the patient. An adapter is connected to the ends of the oral tube and the nasal tube exteriorly of the face piece. Oxygen is introduced into an inlet port of the adapter wherein the oxygen enters the oral tube and the nasal tube concomitantly and ventilates the patient.
Owner:SNIADACH JOSEPH A
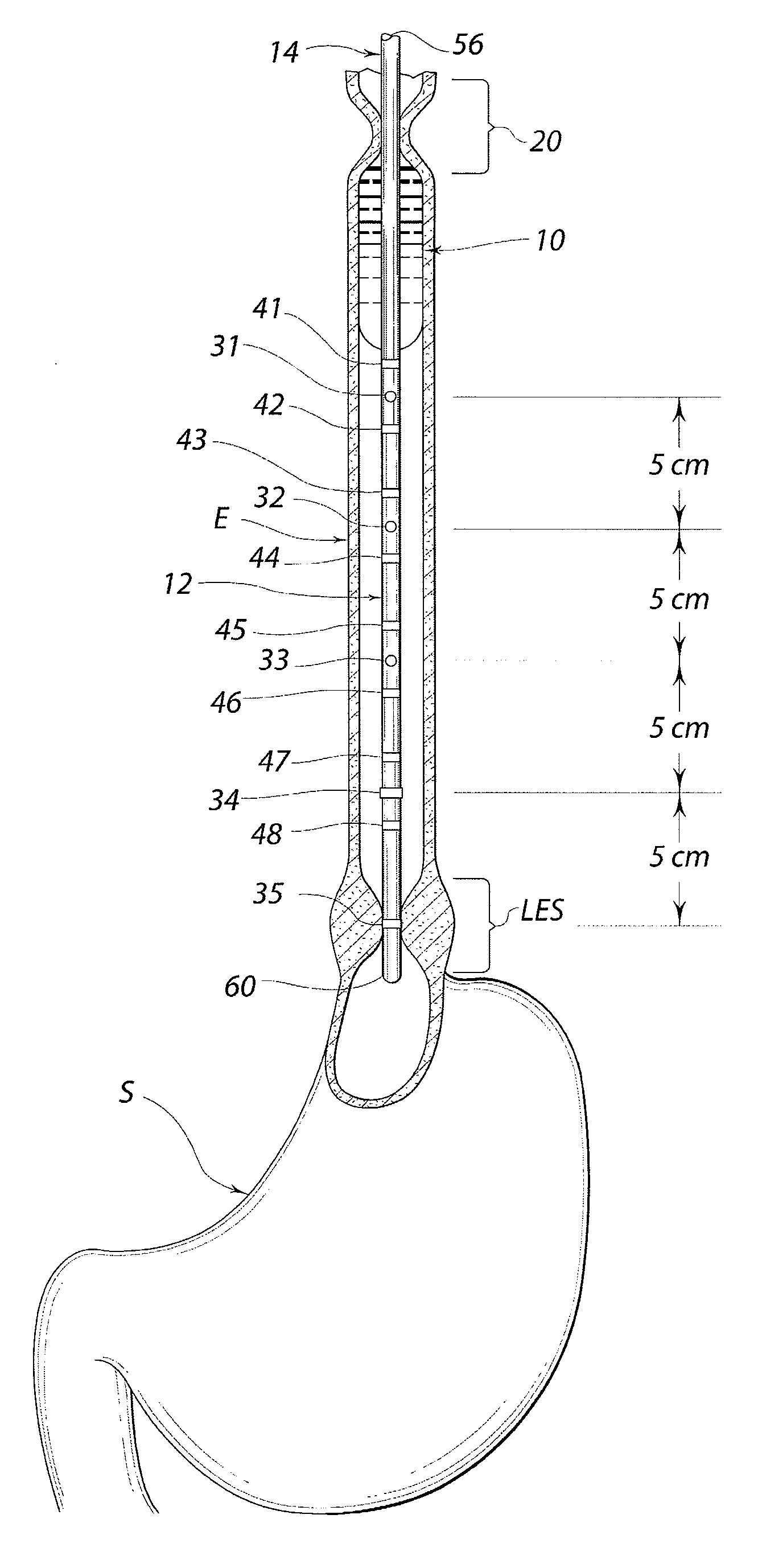
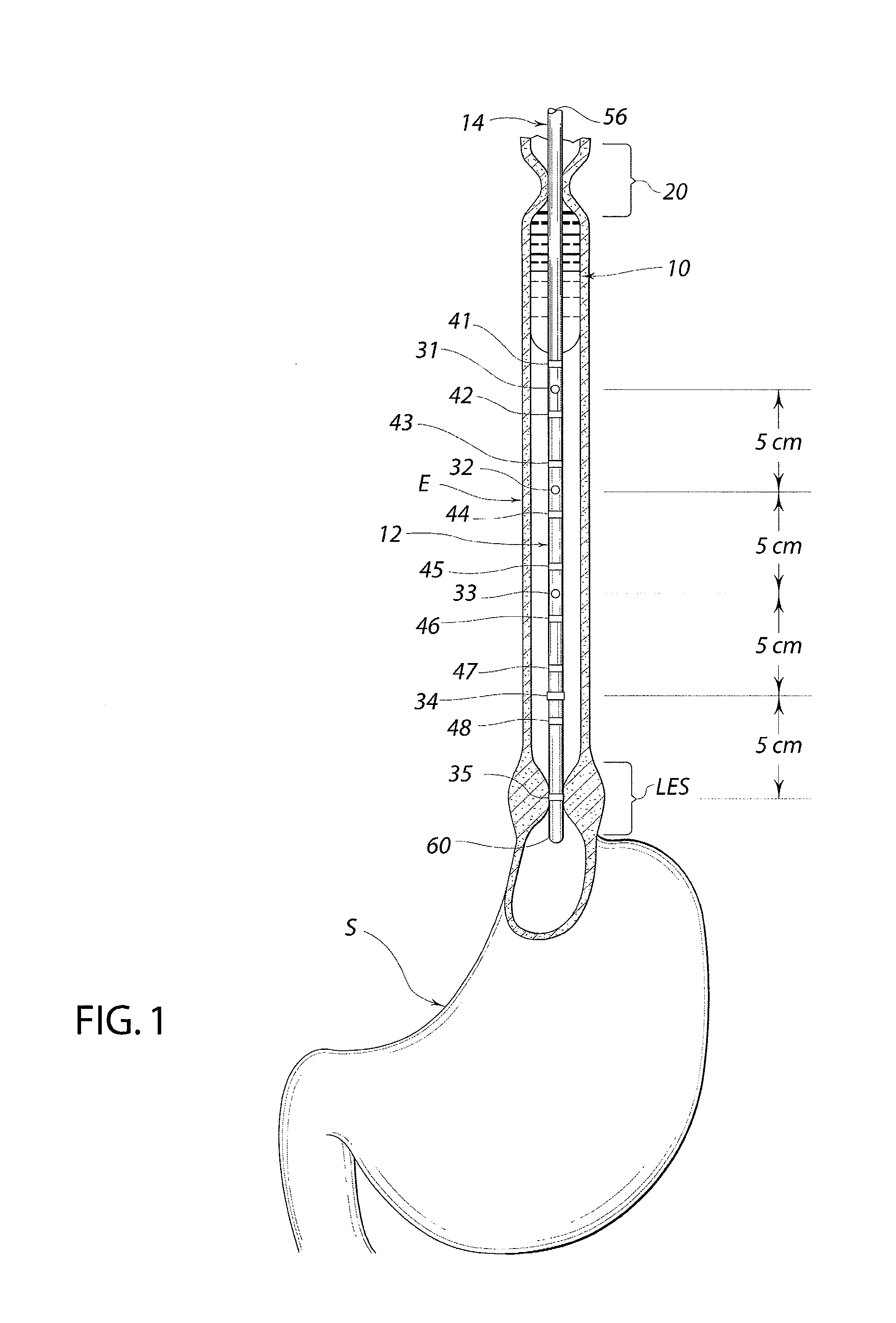
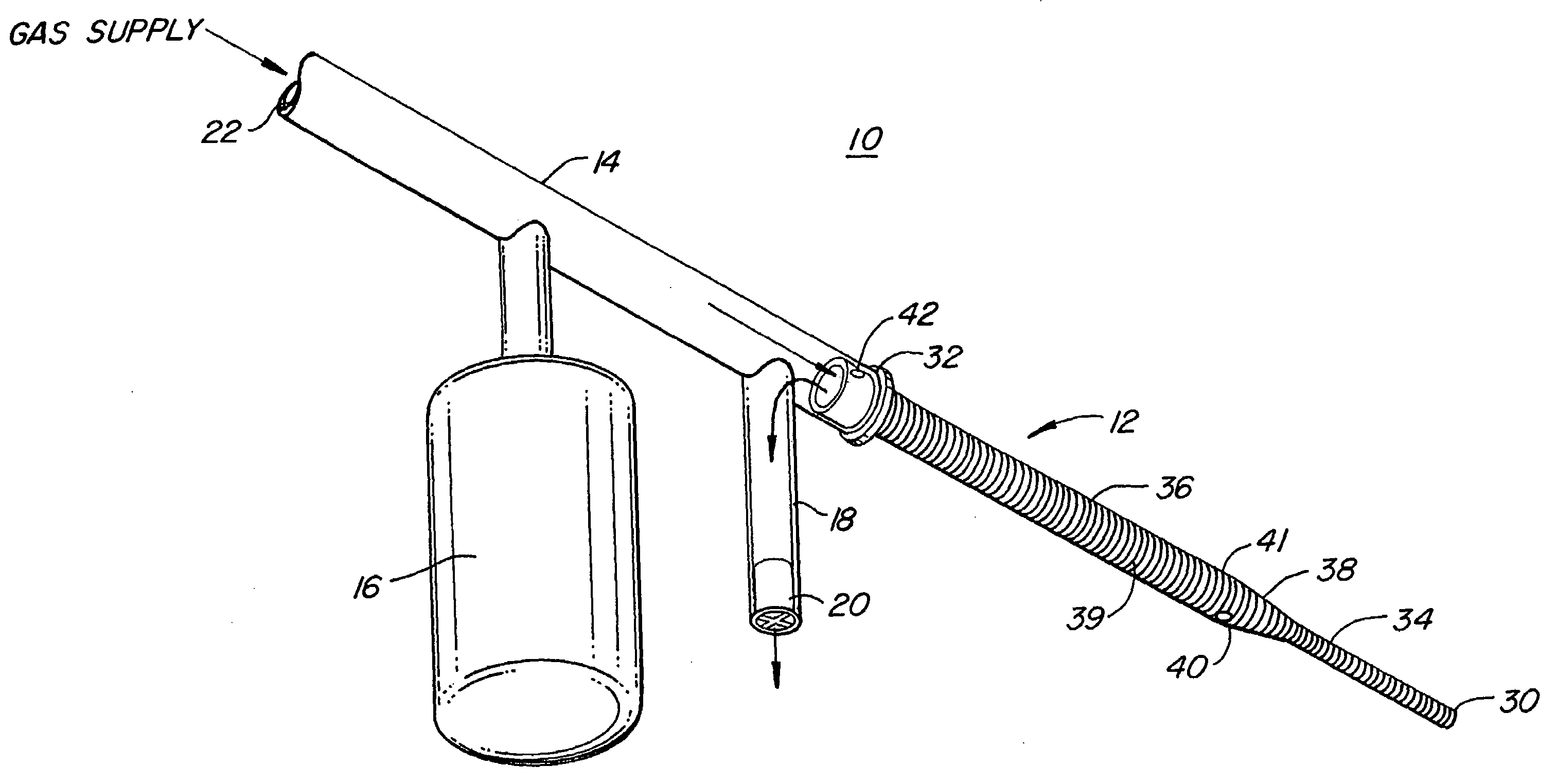
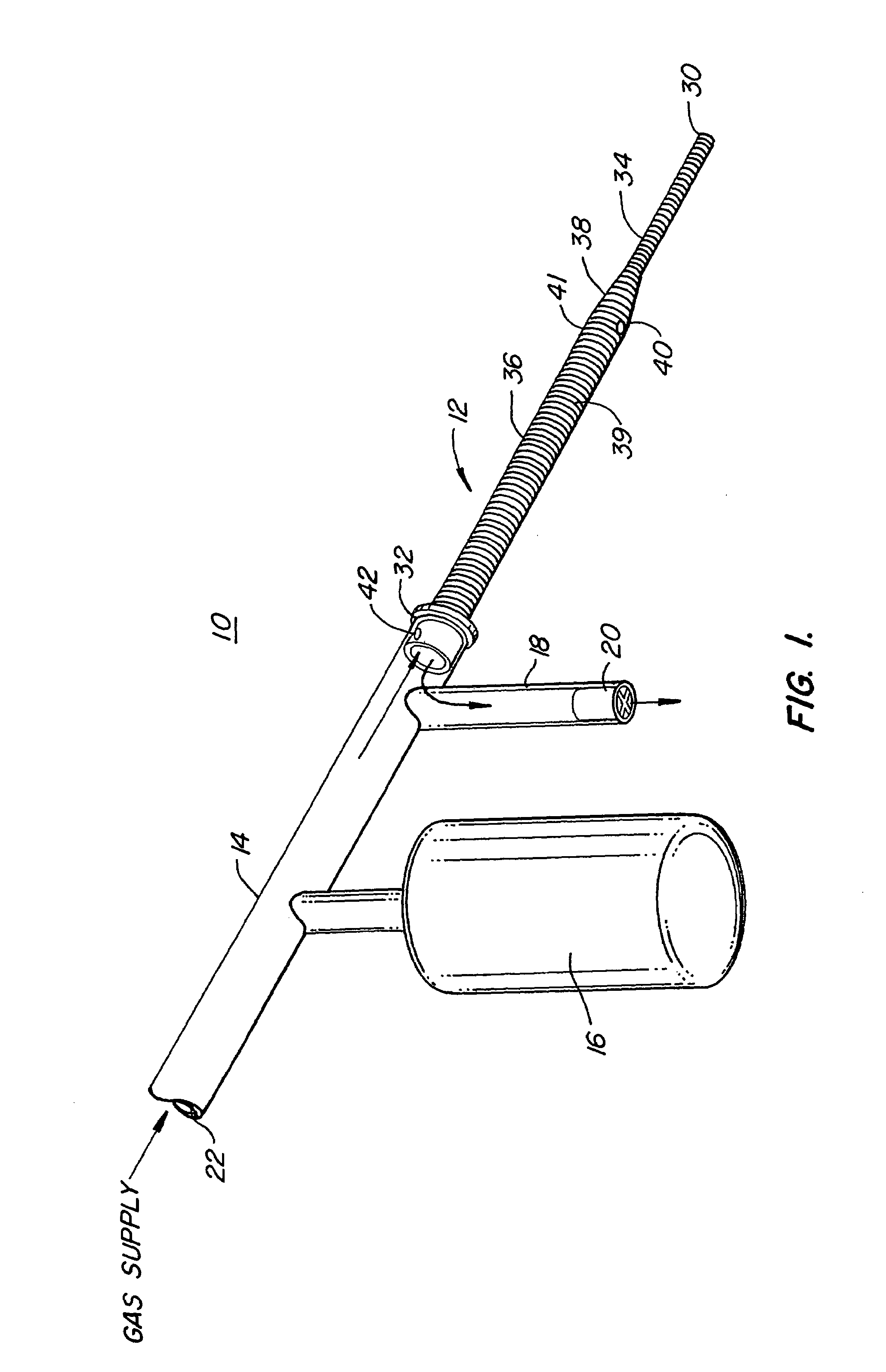
Standardized swallow challenge medium and method of use for esophageal function testing
ActiveUS7236820B2Long enough shelf lifeMeaningful resultDispersion deliverySurgeryMedicineEsophageal function
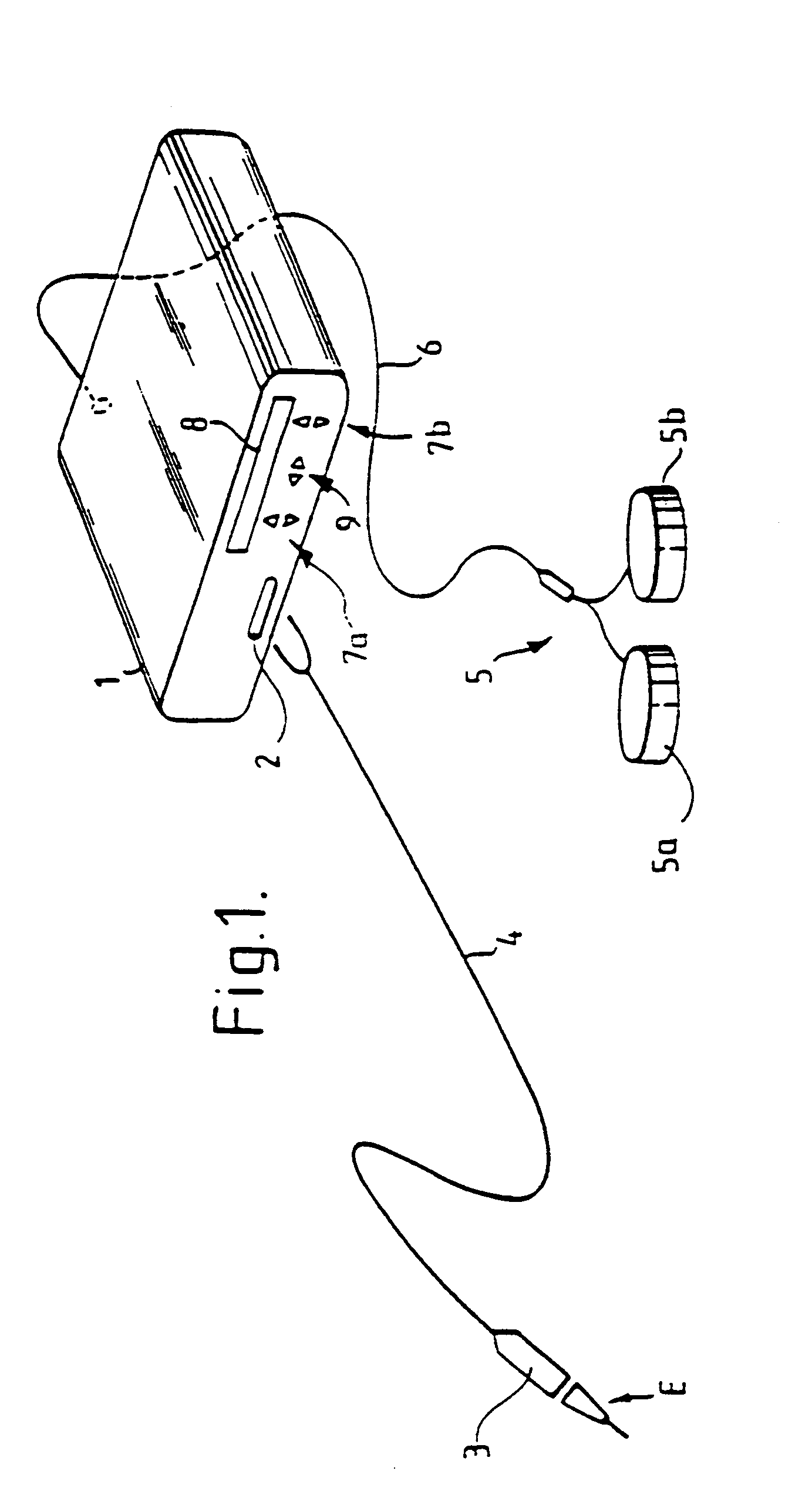
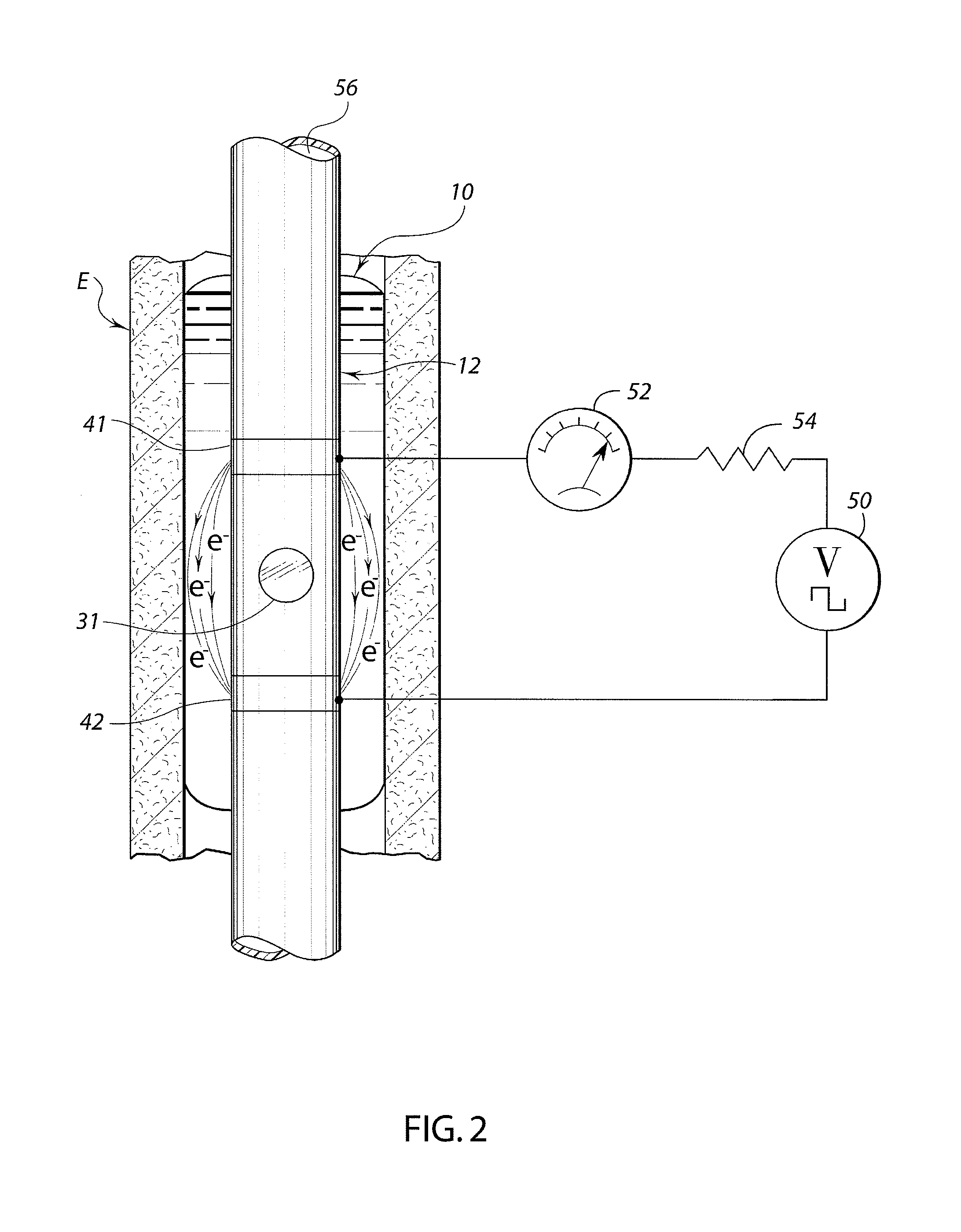
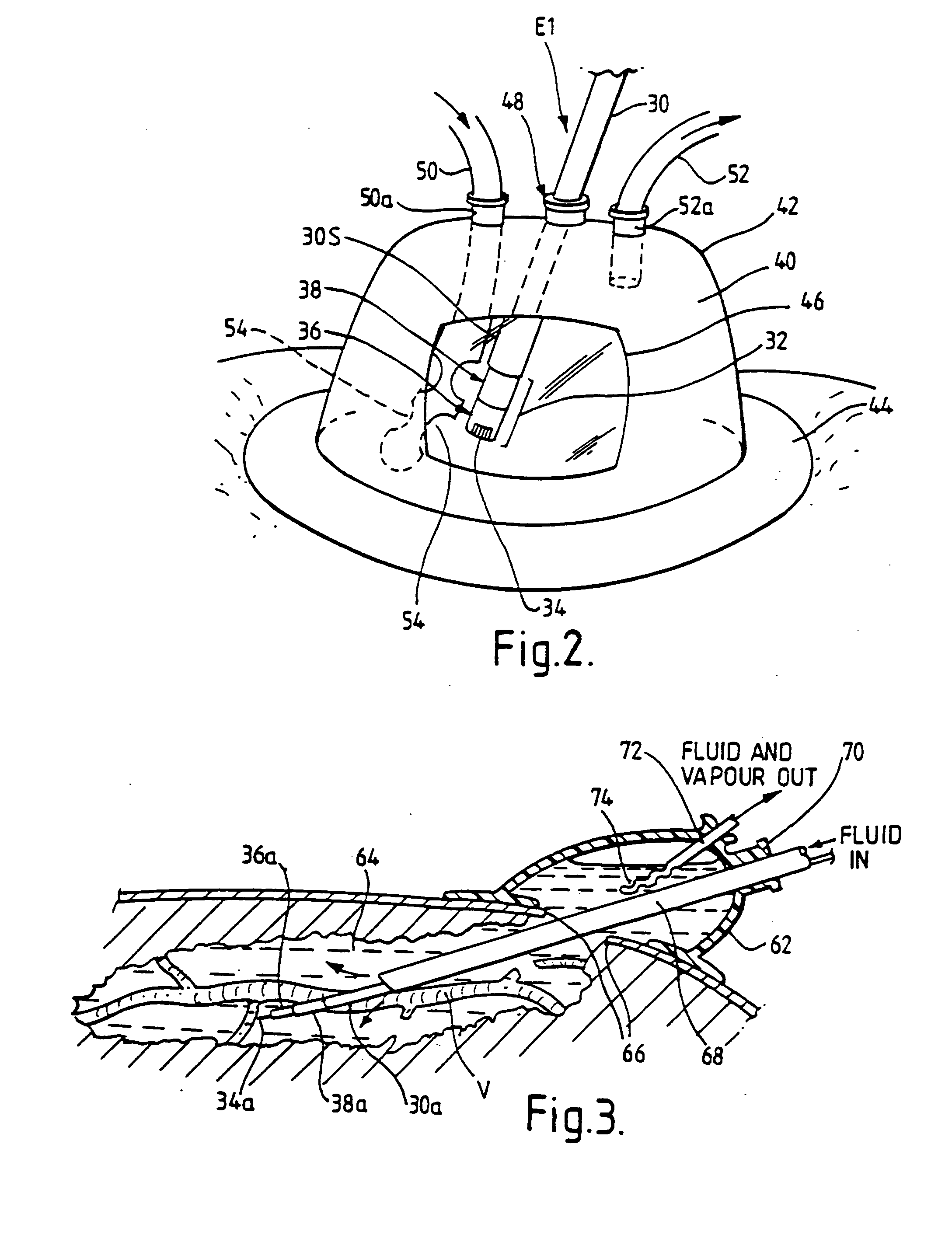
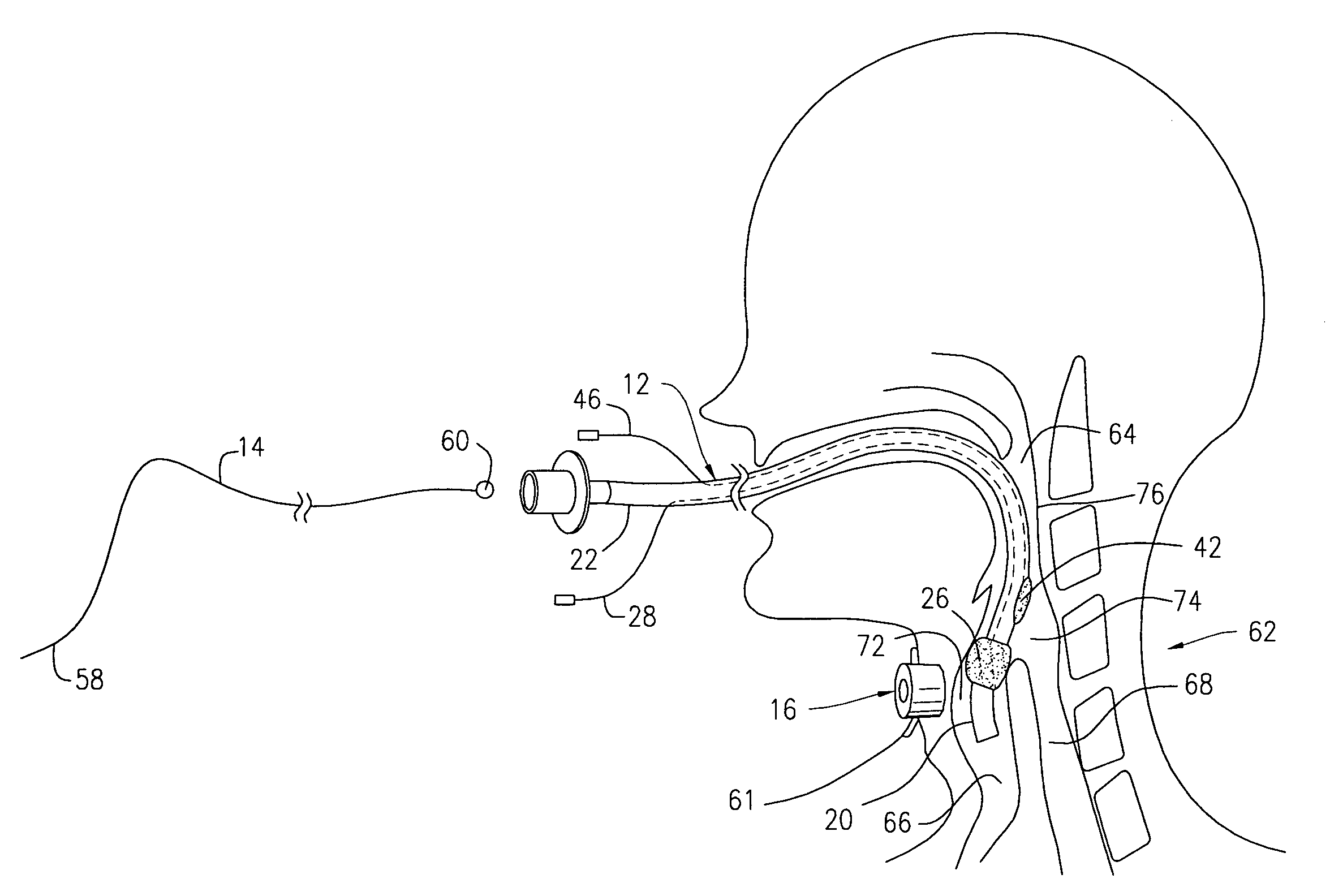
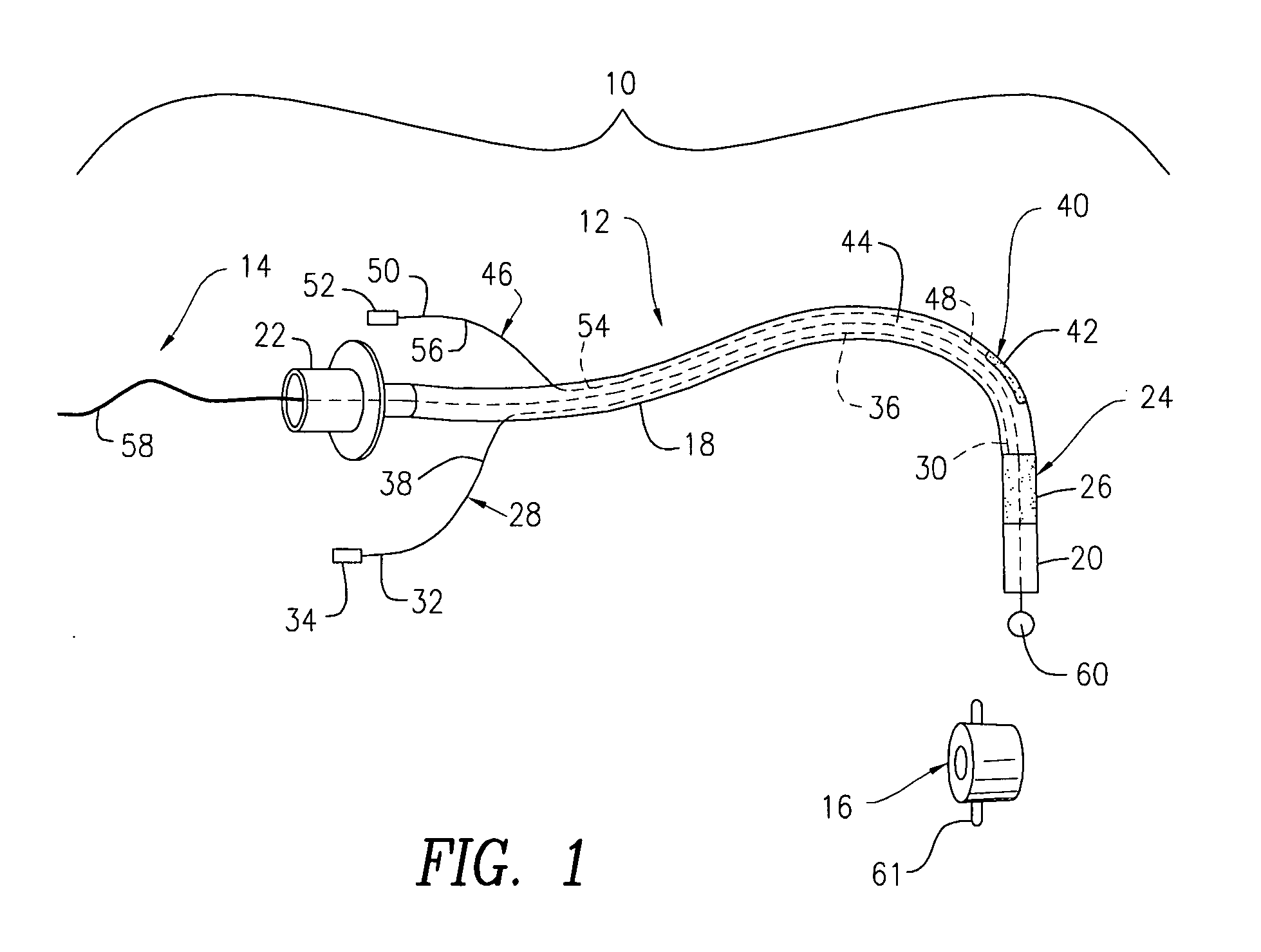
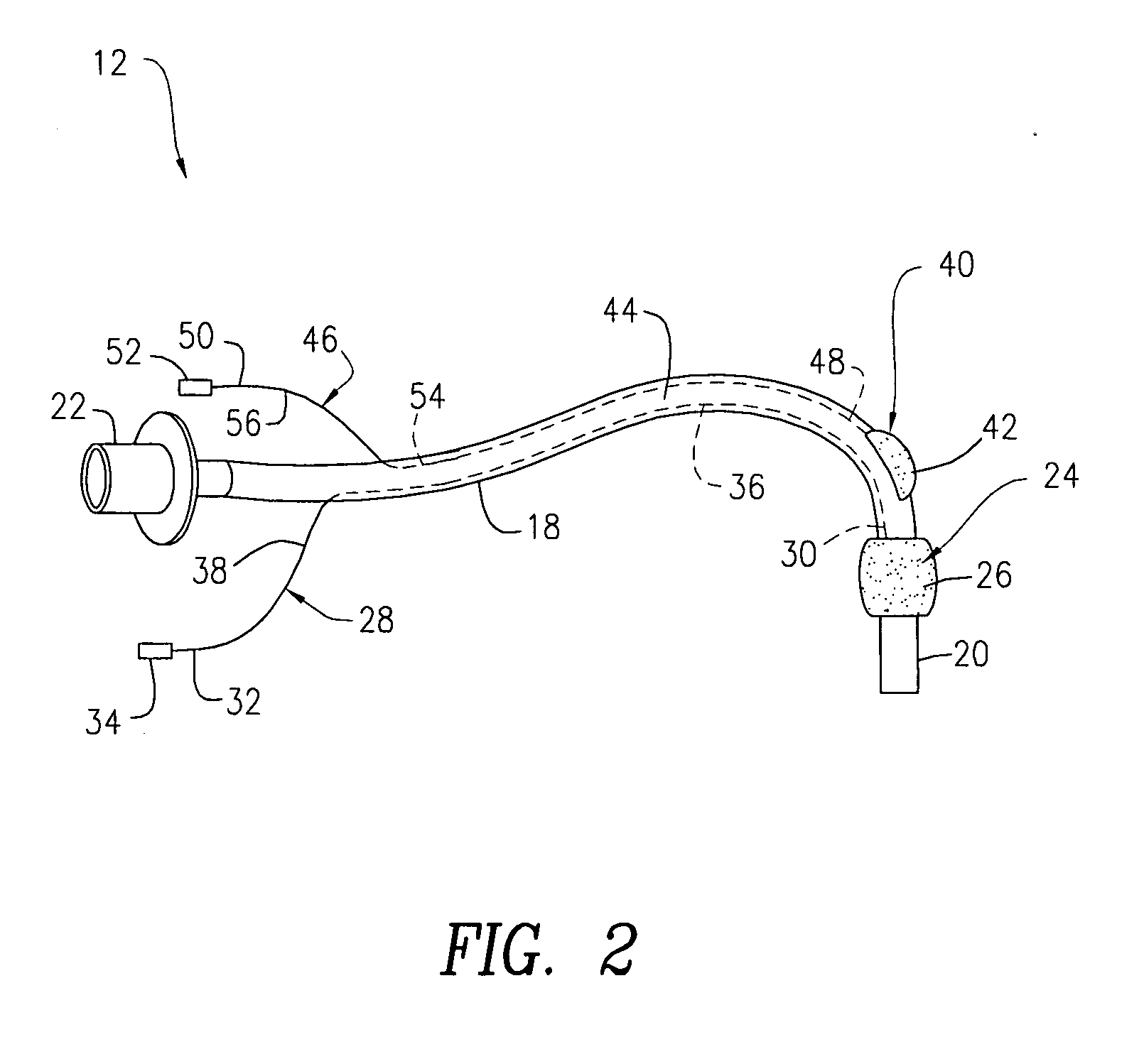
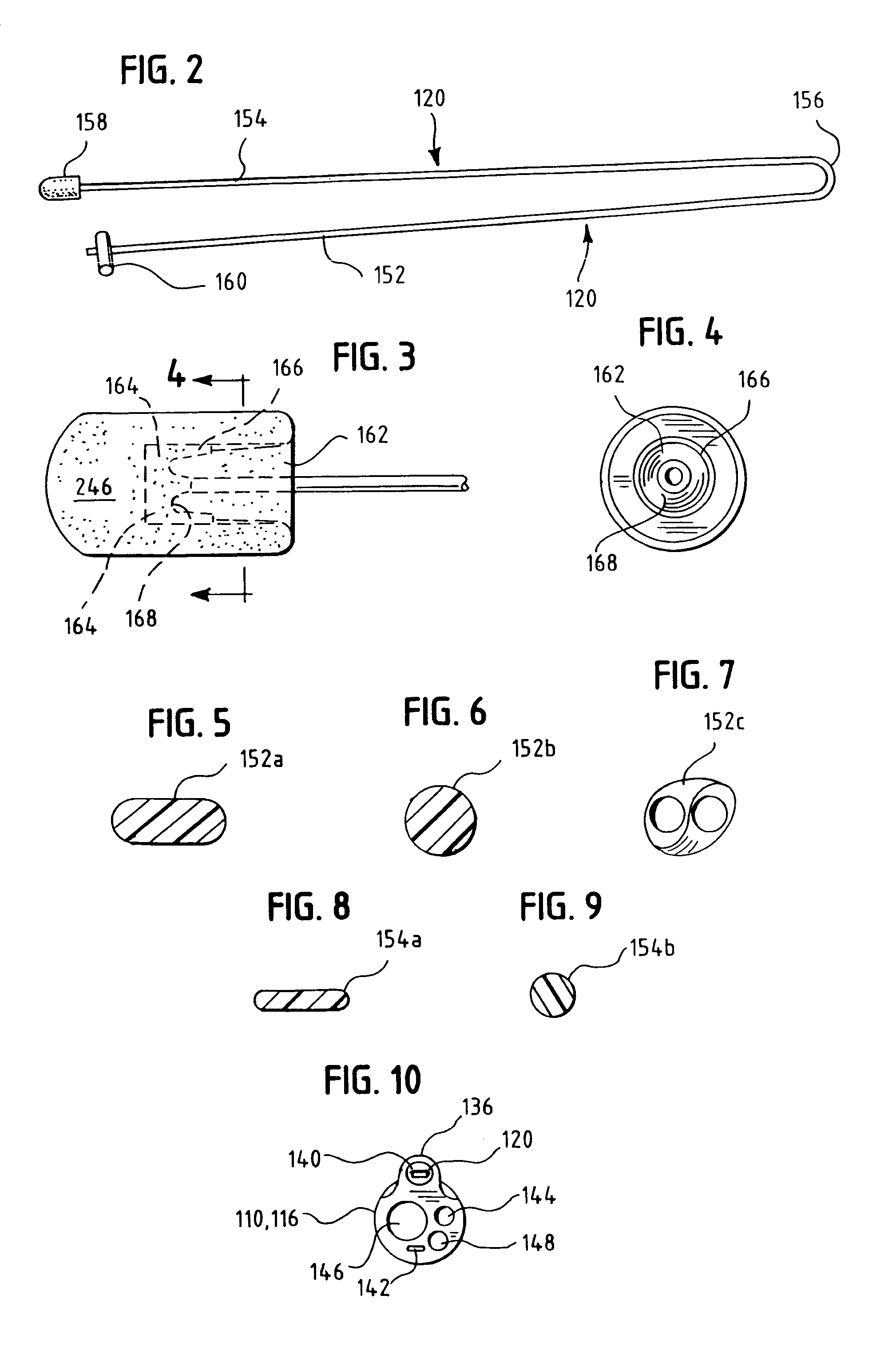
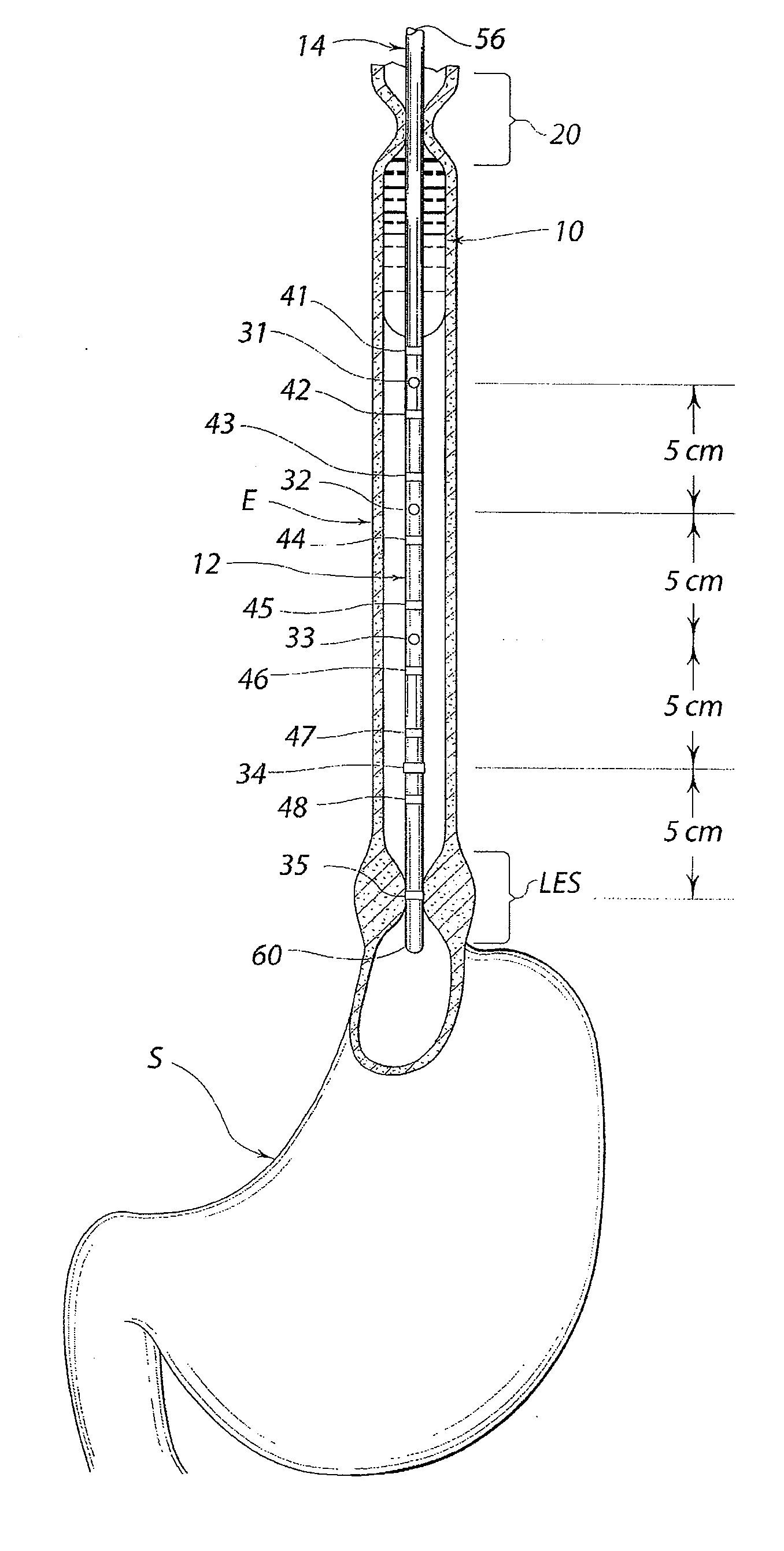
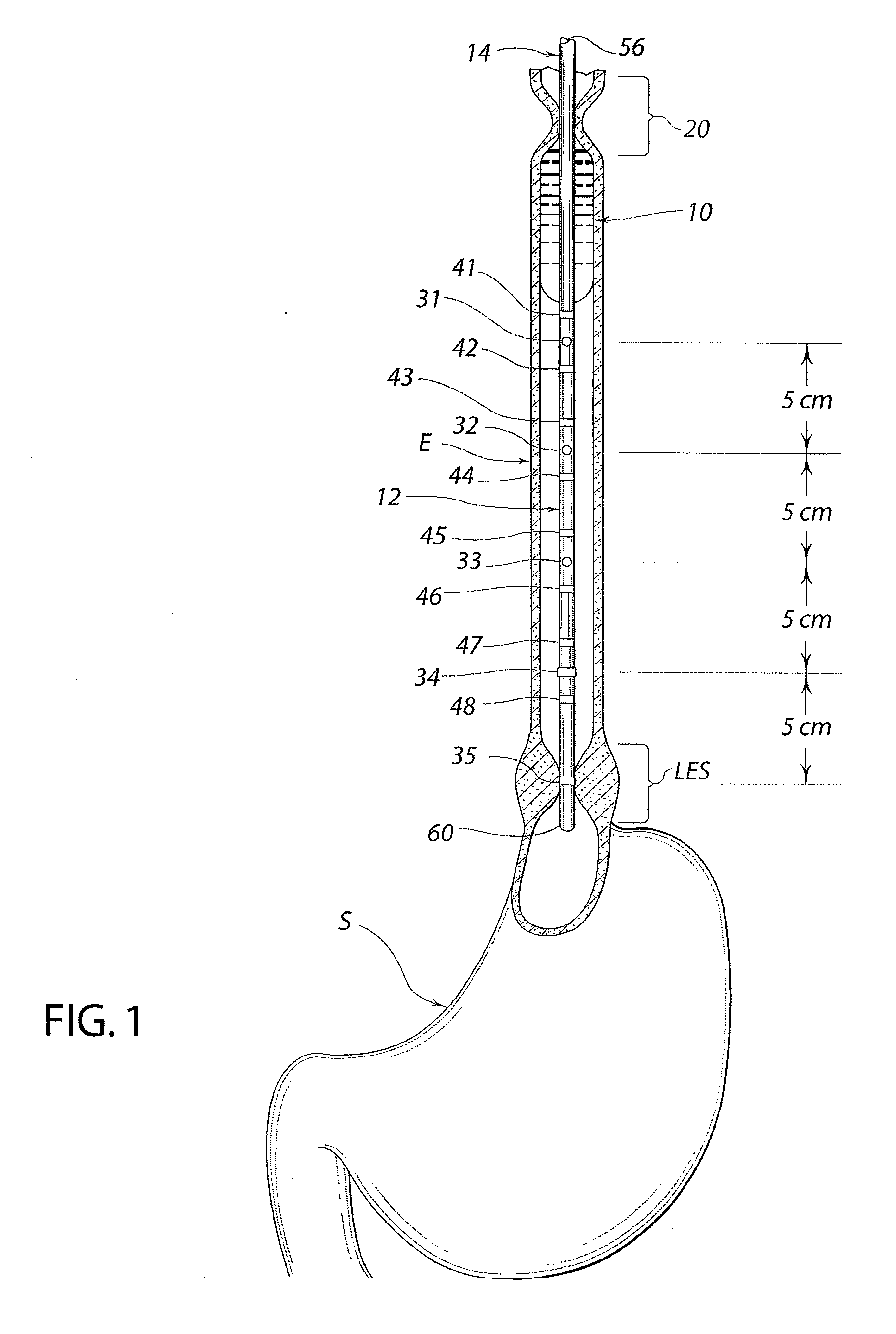
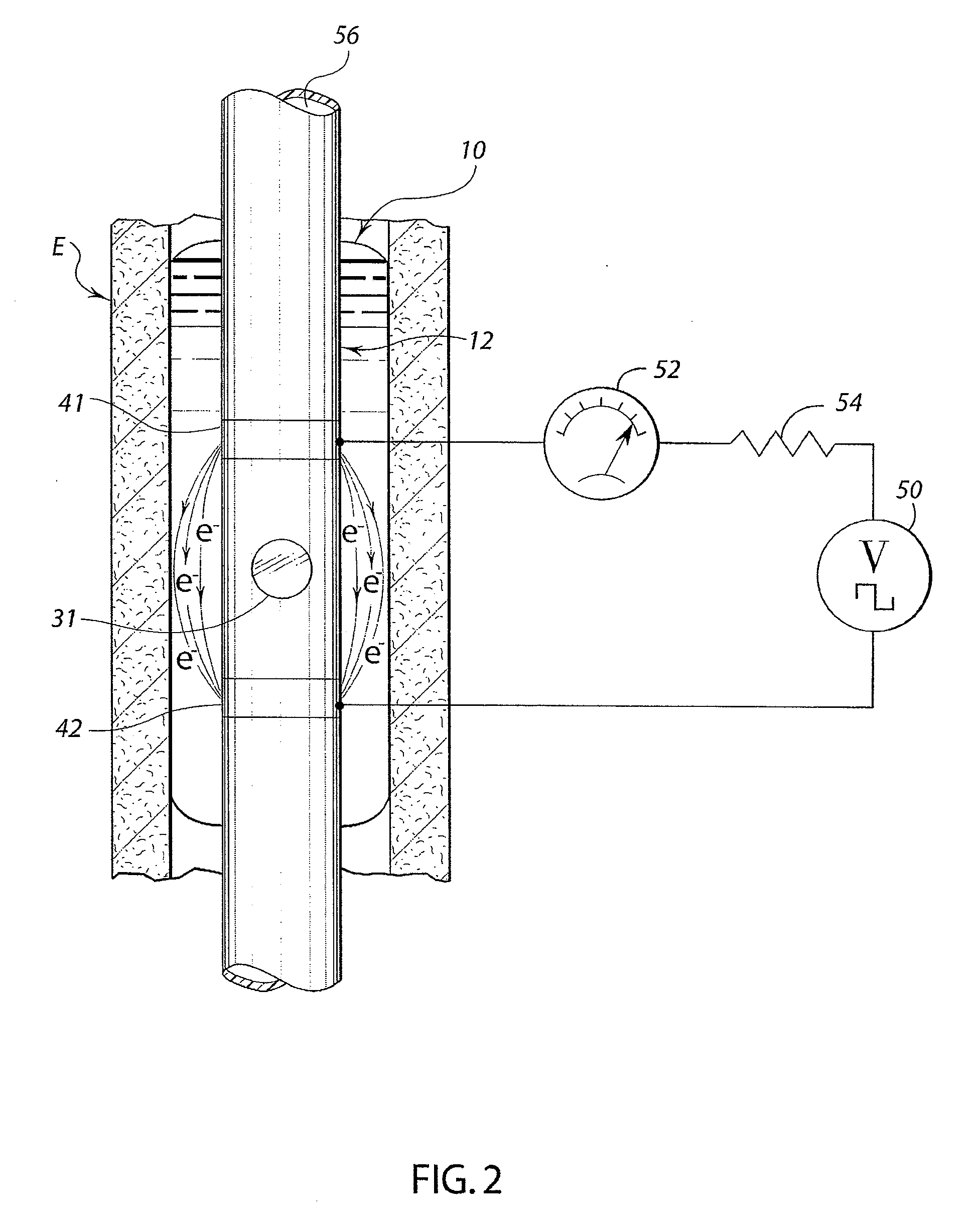
A swallow challenge medium (10) is thixotropic for easy swallowing and to provide enough viscosity for effective challenge to peristalsis (20) and has high ionic density for effective impedance measurements by contact with electrodes (41–48) positioned in a person's esophagus (E) or oropharynx during swallow testing. The medium (10) also has a high surface tension so as not to adhere to or coat the electrodes (41–48) or probe (12) surfaces. These physical characteristics are stabilized and consistent enough to provide standard for esophageal and / or oropharyngeal function testing and diagnostics.
Owner:DIVERSATEK HEALTHCARE INC
Endotracheal tube with suction attachment
InactiveUS20080011304A1Reducing medical complicationInhibition of secretionTracheal tubesEndotracheal tubeCuff
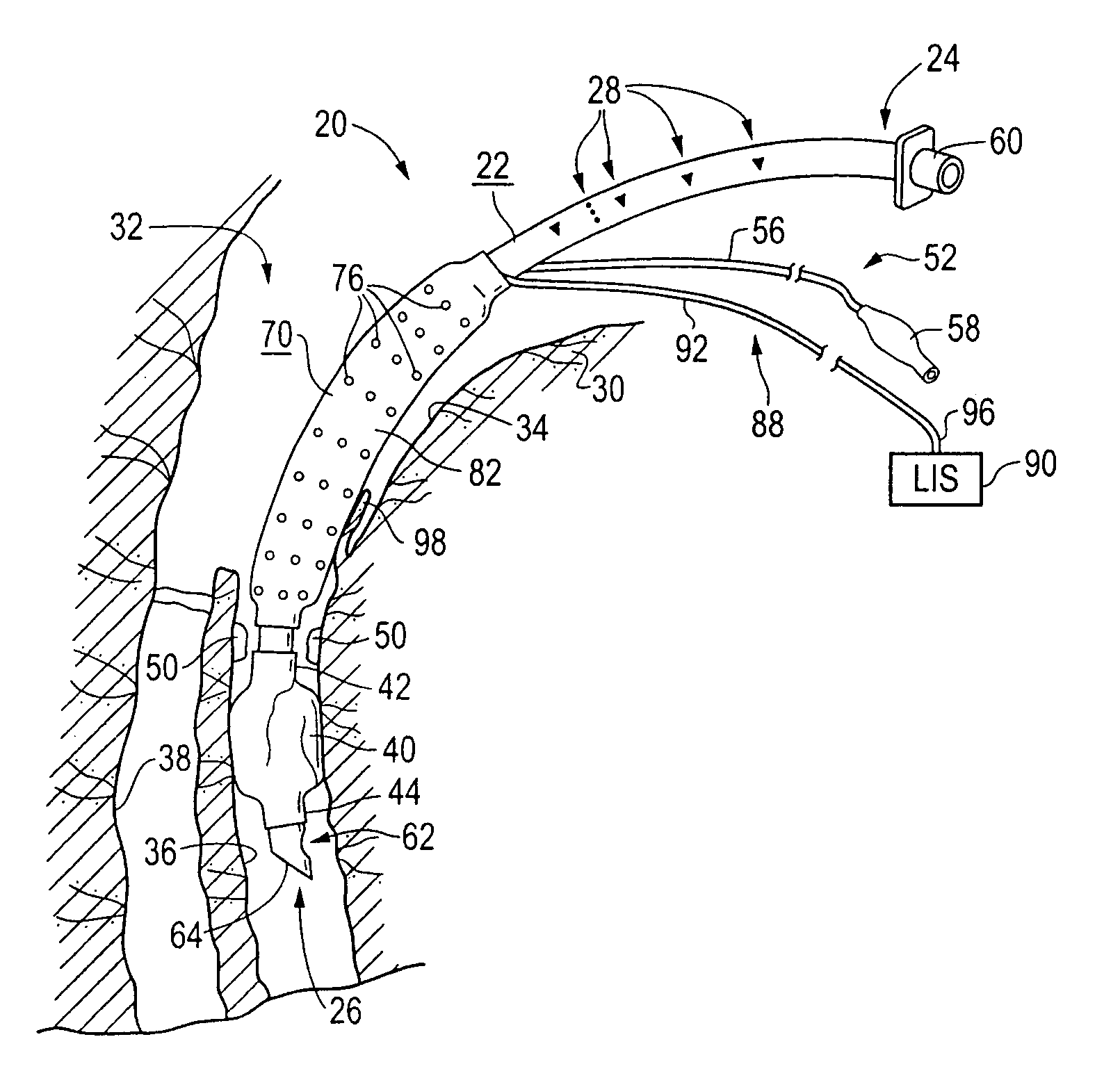
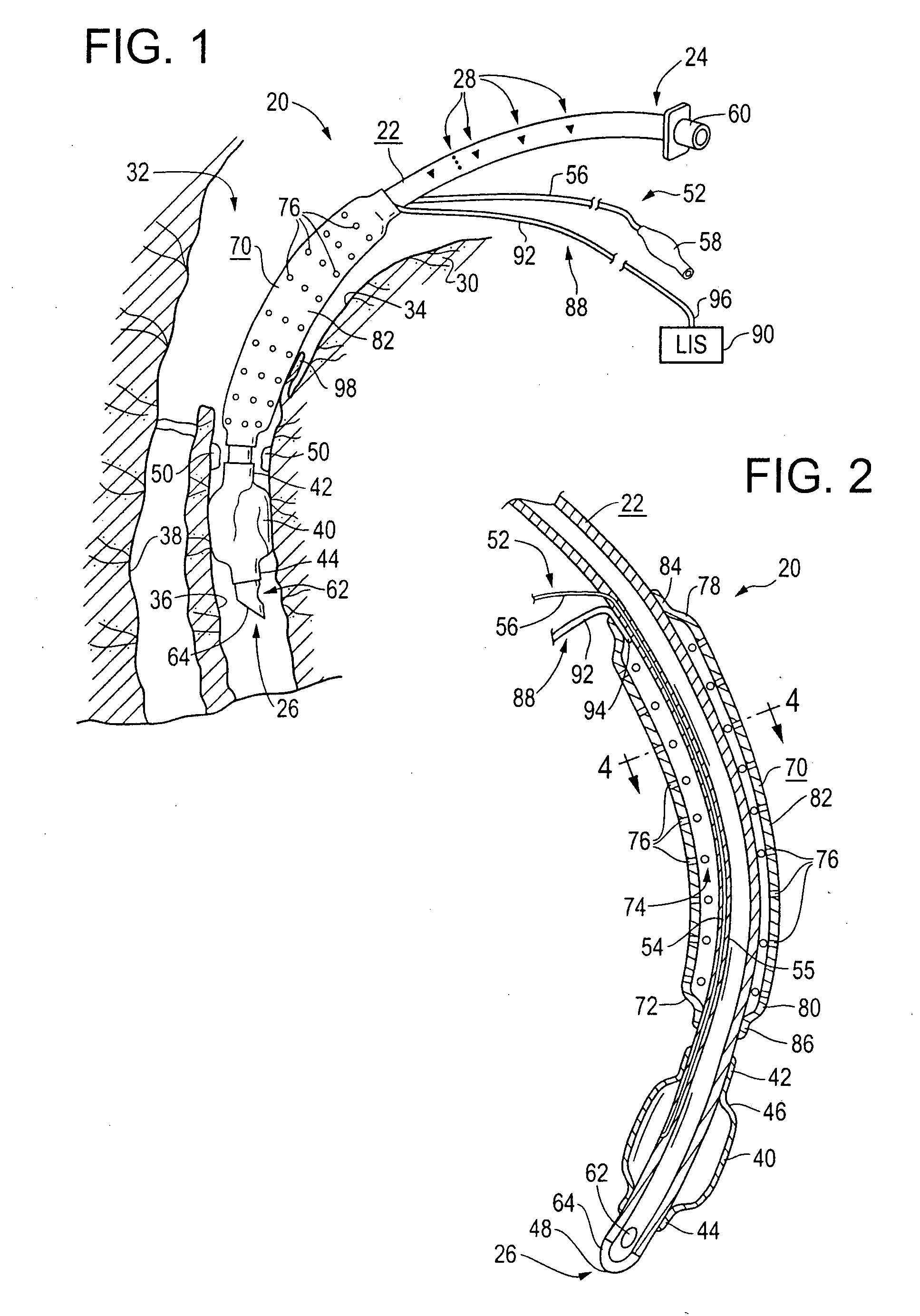
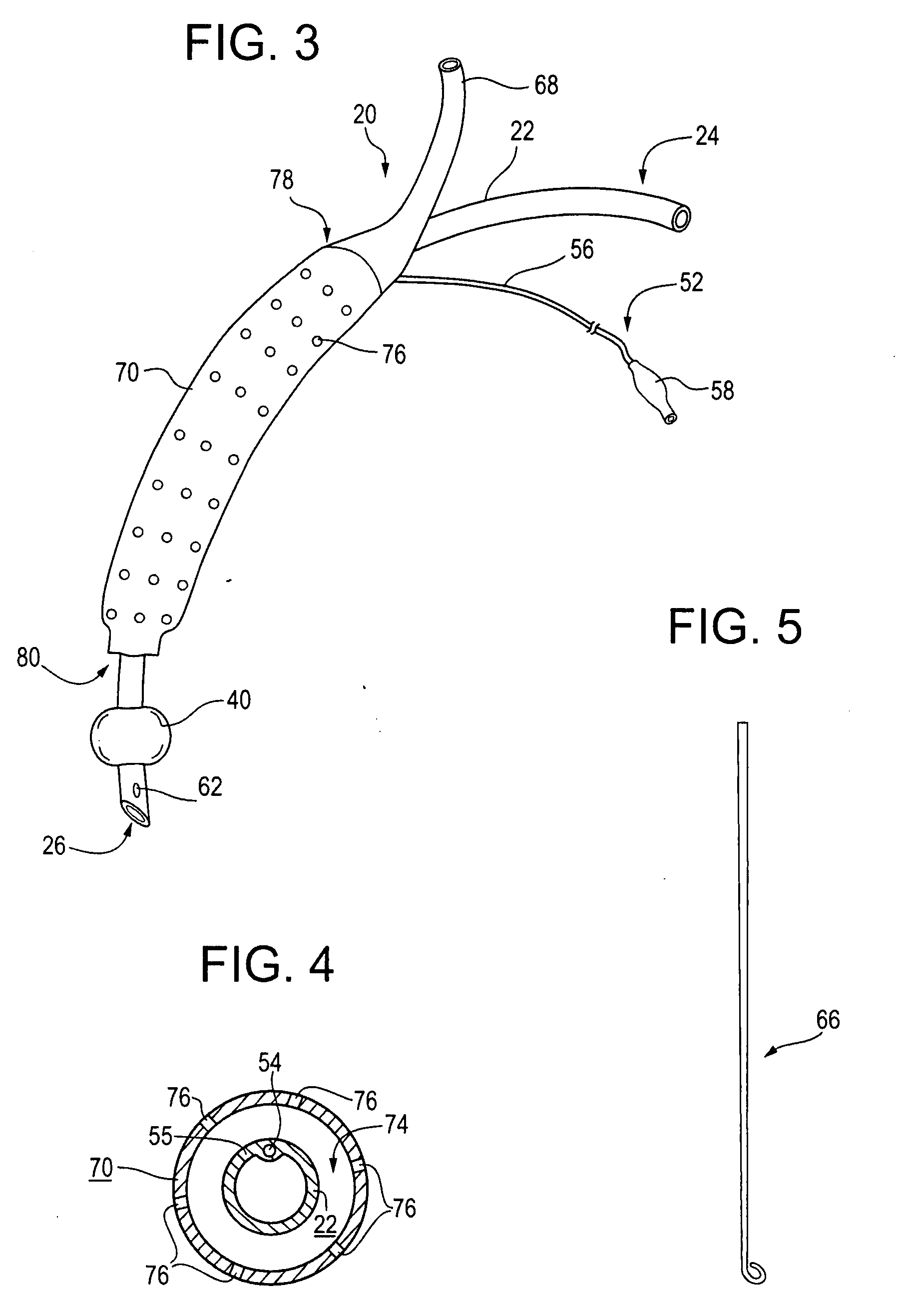
An improved endotracheal tube having a suction sleeve circumferentially thereabout with a plurality of suction holes or ports therein. The suction sleeve is spaced a distance above an inflatable balloon or cuff so that the vocal cords of a patient may rest between the sleeve and the cuff, and the suction sleeve, sealed at its top and bottom to the endotracheal tube, has a plurality of circumferentially and longitudinally-spaced suction holes therethrough for suctioning the pools of secretion that form in the hypopharynx and lower oropharynx of an intubated patient. Tubing is also provided for connecting a suction chamber between the suction sleeve and the main lumen of the endotracheal tube to a well-known low intermittent suction (“LIS”) device.
Owner:STEWART FERMIN V G
Integrated oral appliance for sleep-disordered breathing
ActiveUS20090241969A1Prevent airway closureMovement is lowTeeth fillingSnoring preventionLower dentitionNasal cavity
A custom, sized and fitted, integrated oral appliance is provided to treat breathing obstruction and restriction in the upper airway during sleep. Several novel features are integrated in a single device, which includes mandible repositioning to open the airway, and tongue restraint to prevent airway blockage. This device is comprised of a built-in air conduit to bypass nasal restriction and airway occlusion. In operation, the appliance is positioned in the oral cavity to firmly grip the upper and lower dentition using customized unshaped trays. Appliance positioning advances the mandible to an adjustable predetermined position and simultaneously restrains the tongue using flexible bristles attached to a spring-loaded, tongue-restraint-ac (TRAC) component. A hollow air conduit, built into the TRAC, spans the area between the users' lips and soft palate. It facilitates the flow of self-heated, moisturized air directly to (and from) the oropharynx to bypass airway obstructions and / or nasal restrictions.
Owner:DREAMSCAPE MEDICAL
Methods and devices for forming an auxiliary airway for treating obstructive sleep apnea
InactiveUS20100024830A1Problem in their useHigh acceptanceStentsTracheaeBiomedical engineeringSleep apnea
An auxiliary airway for treating obstructive sleep apnea is formed by implanting an elongated conduit beneath a pharyngeal wall of a pharynx. The elongated conduit has a proximal end in communication with a first region of the pharynx, a distal end in communication with a second region of the pharynx, and a section extending beneath the pharyngeal wall for bypassing an oropharynx region of the pharynx. The system includes a first opening in the pharyngeal wall in communication with a first opening in the elongated conduit, and a second opening in the pharyngeal wall in communication with a second opening in the elongated conduit. The system has a first anastomotic connector for coupling the first opening in the pharyngeal wall with the first opening in the conduit, and a second anastomotic connector for coupling the second opening in the pharyngeal wall with the second opening in the conduit.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Electrosurgical system and method
InactiveUS20050090819A1Lower impedanceChar formation undesirableCannulasDiagnosticsBenign conditionNose
A method is disclosed for treating benign conditions, such as enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids located in a patient's throat or nasopharynx, or soft tissue lesions located in a patient's oropharynx or larynx. According to the method, a space containing the patient's nasopharynx, oropharynx or pharynx and larynx is isolated from the patient's trachea and lungs using an inflatable cuff tracheostomy tube or nasotracheal tube inserted in the patient's trachea. The cuff is inflated to occlude the trachea. The patient is placed in a supine position, whereupon at least a portion of the space containing the nasopharynx and / or oropharynx and larynx is filled with saline. An endoscope is then inserted into the space to view the operative site in which the tonsils or tissue lesion are to be treated. An electrosurgical instrument having an active tissue treatment electrode and a return electrode connected to an electrosurgical generator is then inserted into the space, either along side the endoscope or through the endoscope's working channel. The generator is then operated to apply a radio frequency voltage between the active and return electrodes of the electrosurgical instrument, whereby a conduction path is formed between the active and return electrodes, at least partially through the saline, whereupon the active electrode is manipulated to debulk or otherwise treat the soft tissue lesion or enlarged tonsils and / or adenoids.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
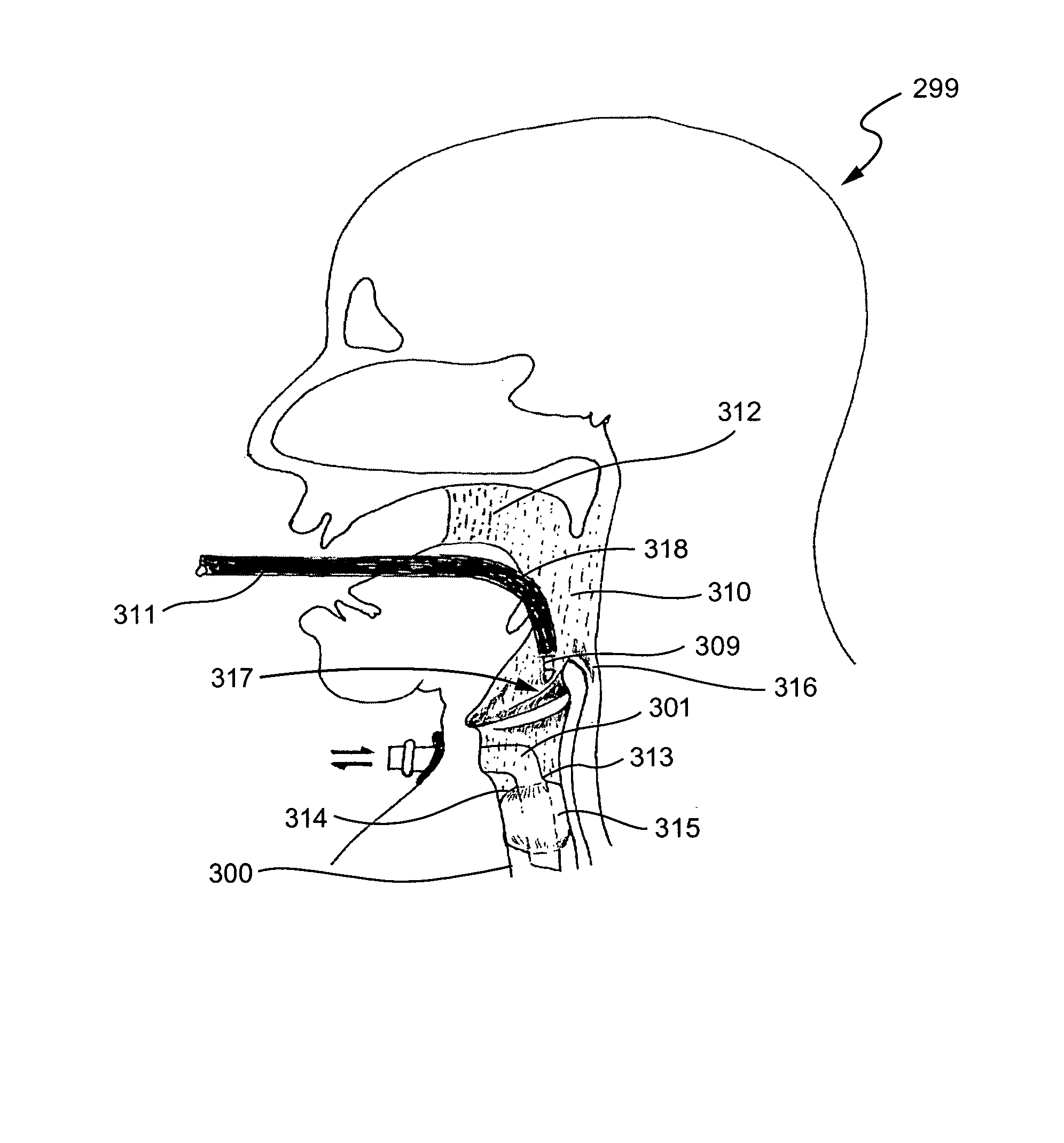
System and method for transcutaneous monitoring of endotracheal tube placement
The present invention relates to a tracheal intubation device and method for placing an endotracheal tube within a patient's trachea. More particularly, the endotracheal tube includes primary and secondary cuffs, in the form of inflatable balloons. A stillette is positioned within the endotracheal tube. The tracheal intubation device includes a guiding mechanism for guiding the stillette and the endotracheal tube within a patent's body. The guiding mechanism is positioned external to a patient and sized and shaped so as to transmit a signal and to receive a signal indicating the location of the stillette in a patient's body. After the endotracheal tube is positioned in the oropharynx, inflating the secondary cuff urges the endotracheal tube toward the trachea of a patient.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method and System for Tissue Fastening
InactiveUS20080215090A1Shorten the timeAddress bad outcomesSuture equipmentsStapling toolsUvulopalatopharyngoplastyReady to use
Fastening devices are provided that are designed to effectively close tissue as well as instruments for applying the inventive fastening devices. The devices are useful for closing tissue such as mucosa in the oral cavity, oropharynx, hypopharynx, laryngeal surfaces, oronasopharynx, or other mucosal tissues. In particular, uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), uvulopalatal flap (UPF) technique, and tonsillectomy can be assisted using the inventive system. Embodiments also provide methods of using the fastening devices and / or instruments, and kits including the fastening devices.
Owner:MIMOSA MEDICAL
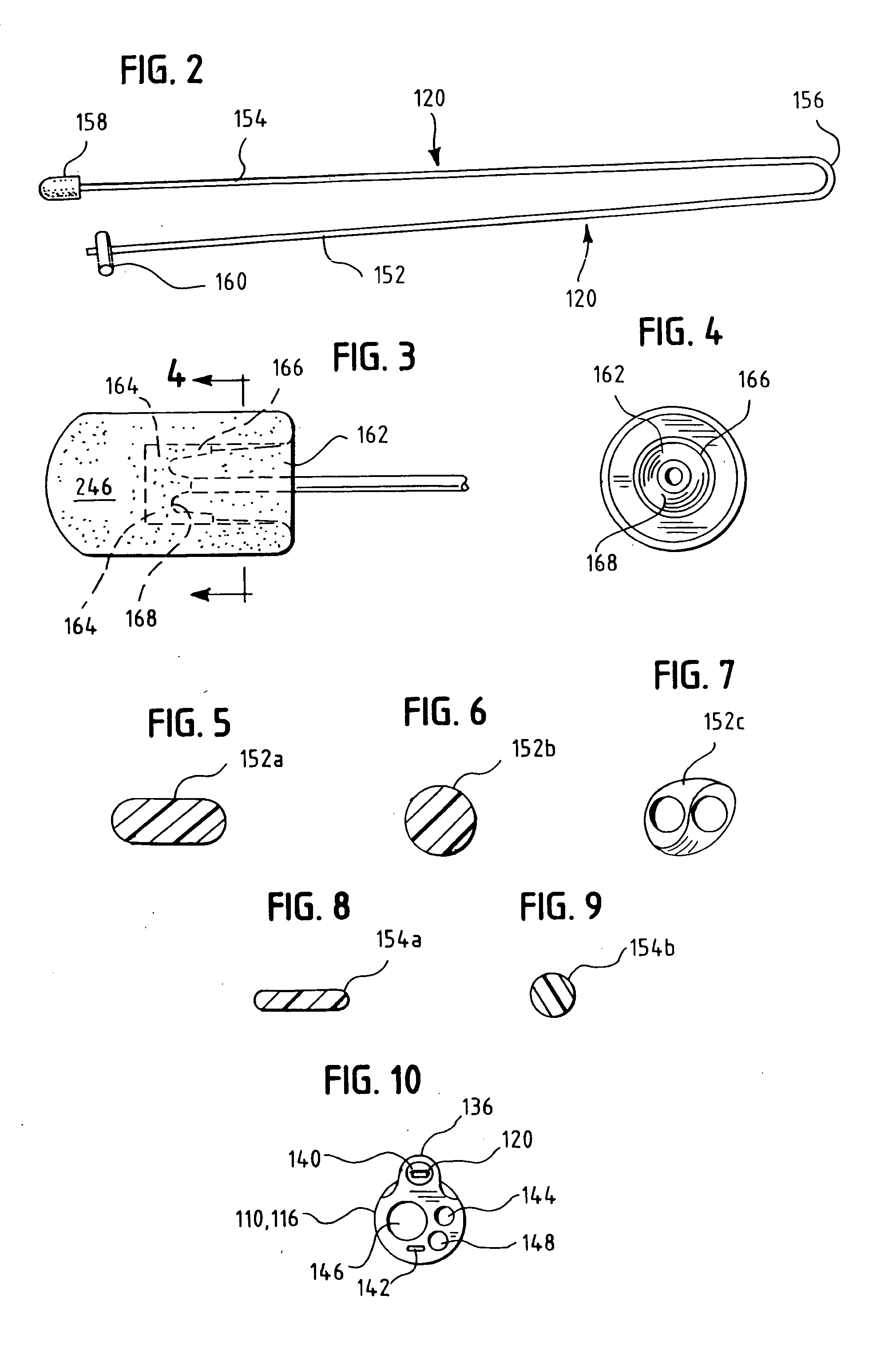
Insertion System and Methods for Nasogastric Tubes
ActiveUS20080004598A1Reduce disadvantagesEasy to controlDiagnosticsInfusion syringesNasal passageNasal passages
A nasogastric tube insertion system comprises a nasogastric tube, a guide element, and an inserter element. The inserter element has a slim, elongate main body, a handle attached to the body, and an anatomically curved insertion section. The guide element comprises a swallowable weight attached to a cord, string, monofilament line, tube, or other similar line. The swallowable weight may be ablative in the presence of stomach fluids or may be deflated to allow the guide element to be removed while the nasogastric tube remains in place. The inserter element is inserted through the patient's nasal passages and optionally into the oropharynx. The weight is released and the patient swallows it into the stomach. The guide element is threaded through the guide element retaining structure, and the nasogastric tube is safely inserted along the guide element into the patient's stomach. Chemical property indicators sensitive to fluids found in the stomach may be provided in the nasogastric tube or the guide element to verify correct placement of the nasogastric tube in the stomach.
Owner:CRITICAL DEVICE CORP
Endotracheal tube using leak hole to lower dead space
InactiveUS7107991B2Efficient removalReduce dead spaceTracheal tubesBreathing masksLarynxEndotracheal tube
A tracheal tube ventilation apparatus to more effectively remove expired gases. In one preferred embodiment, one or more leak holes are created in the side walls of an endotracheal tube so that expired gases can leak out of the endotracheal tube above the larynx, such as into the back of the mouth (i.e., oropharynx). Each leak hole might advantageously have a diameter between 0.5 and 4.0 mm. In another preferred embodiment, a tube is attached to a proportionately larger leak hole (e.g., up to 8.0 mm) so that the expired gases can be directed away from the leak hole to a specific location, such as directed out of the mouth. In the case of mechanically controlled ventilation, a positive end expiratory pressure can be applied to this tube to mechanically assist with the process of exhaling. In each of these embodiments, it is preferred, but not required, that the endotracheal tube be an ultra-thin walled, two stage tube so as to further assist in the reduction of resistance to the flow of oxygen / air.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF
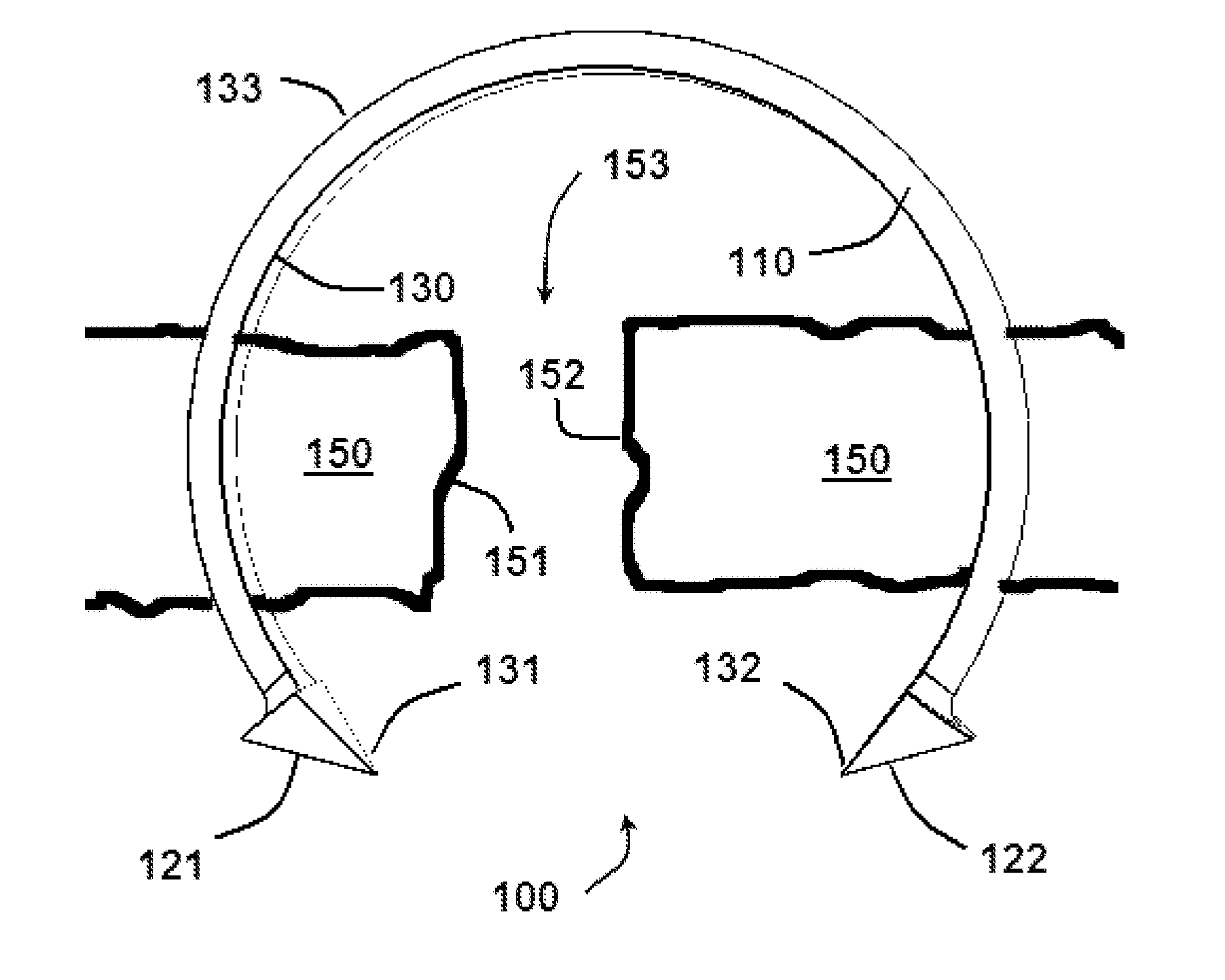
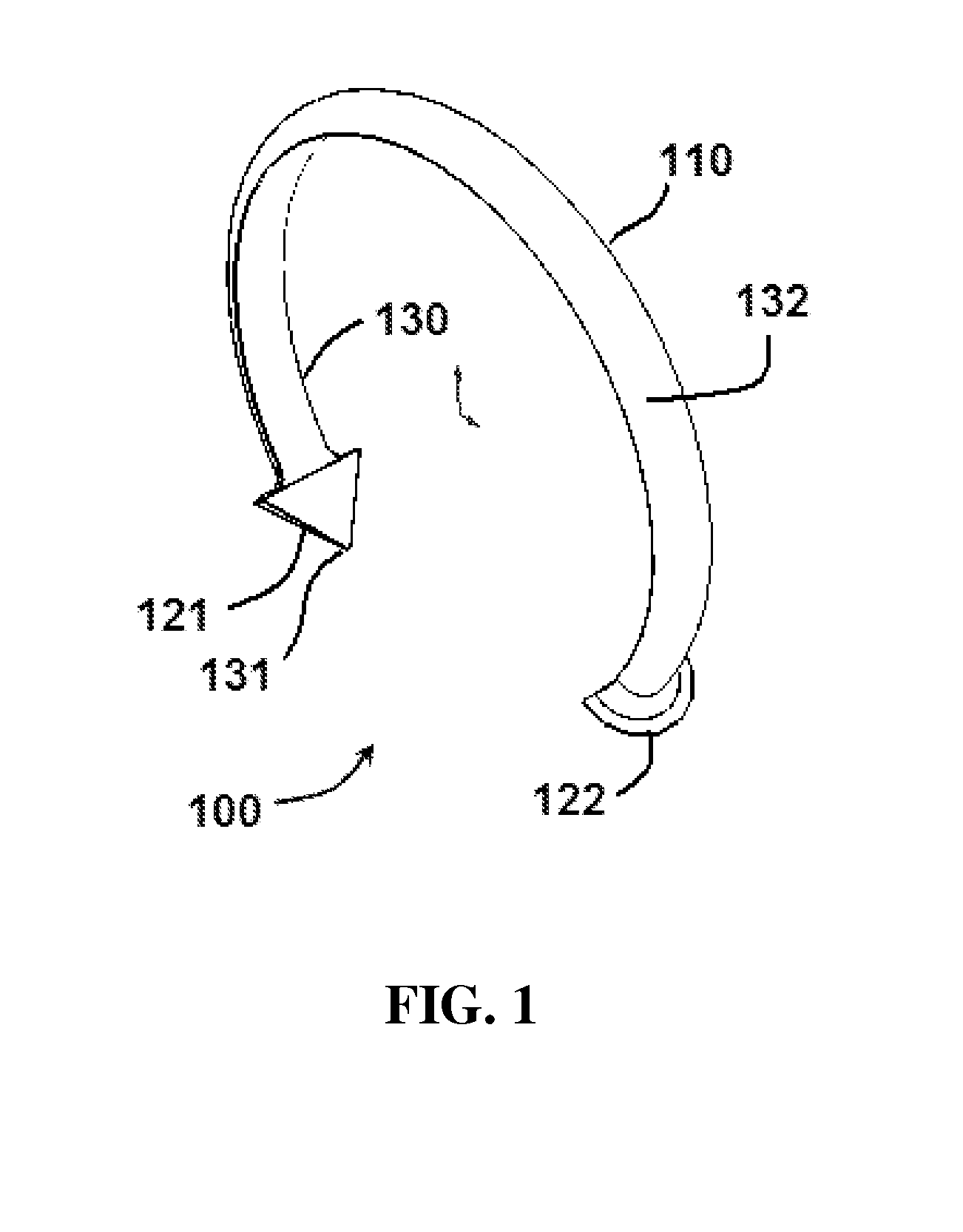
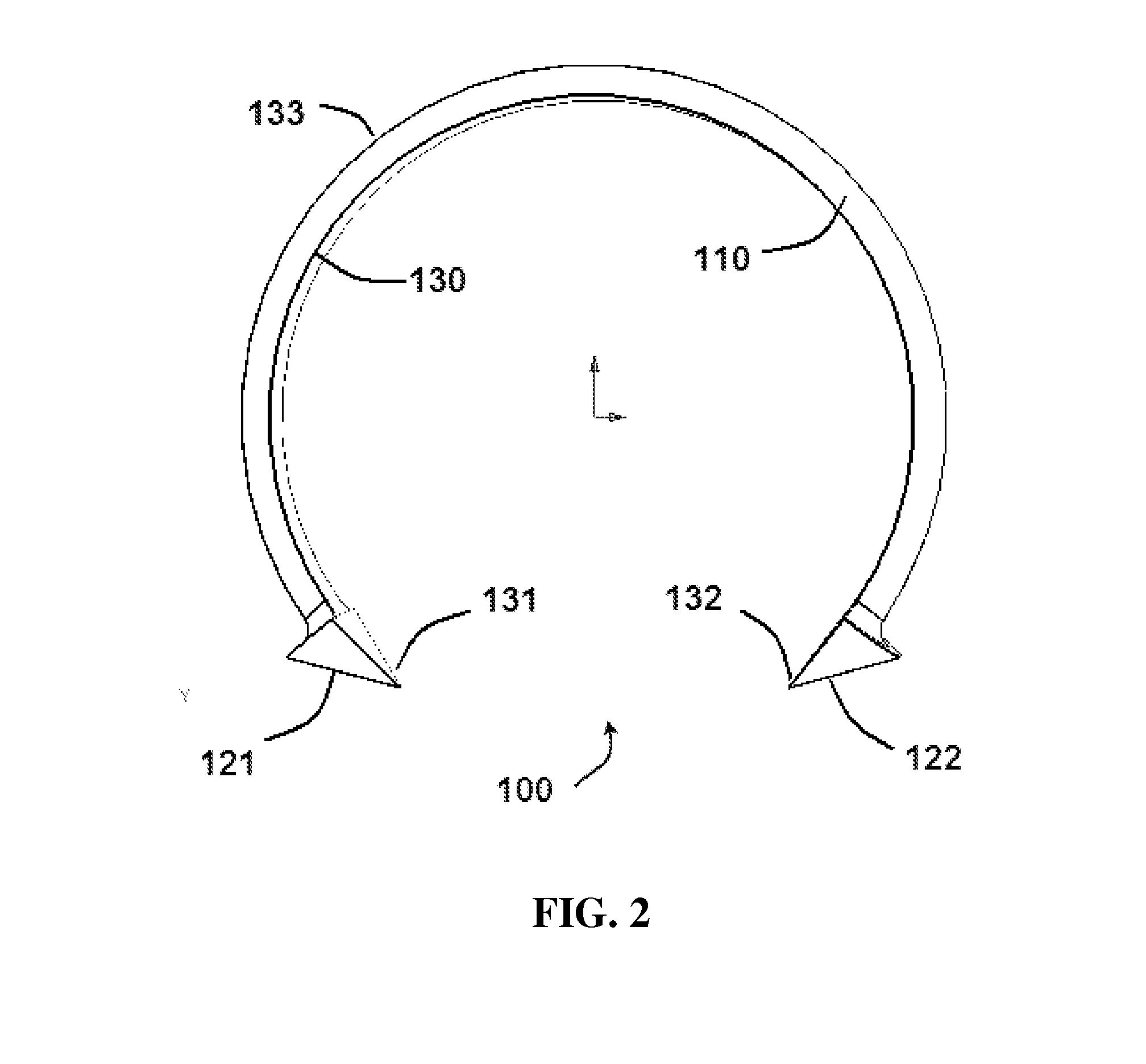
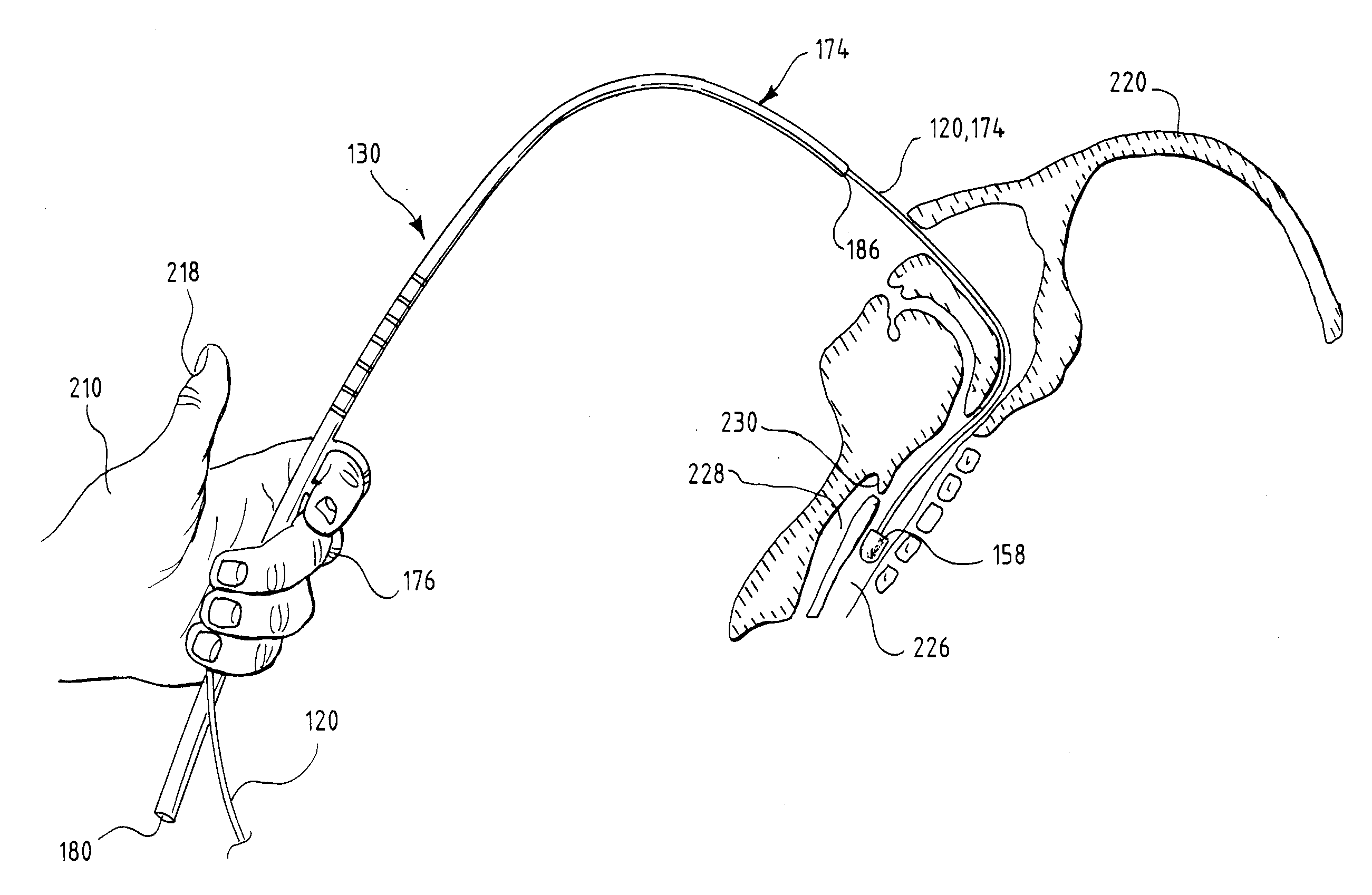
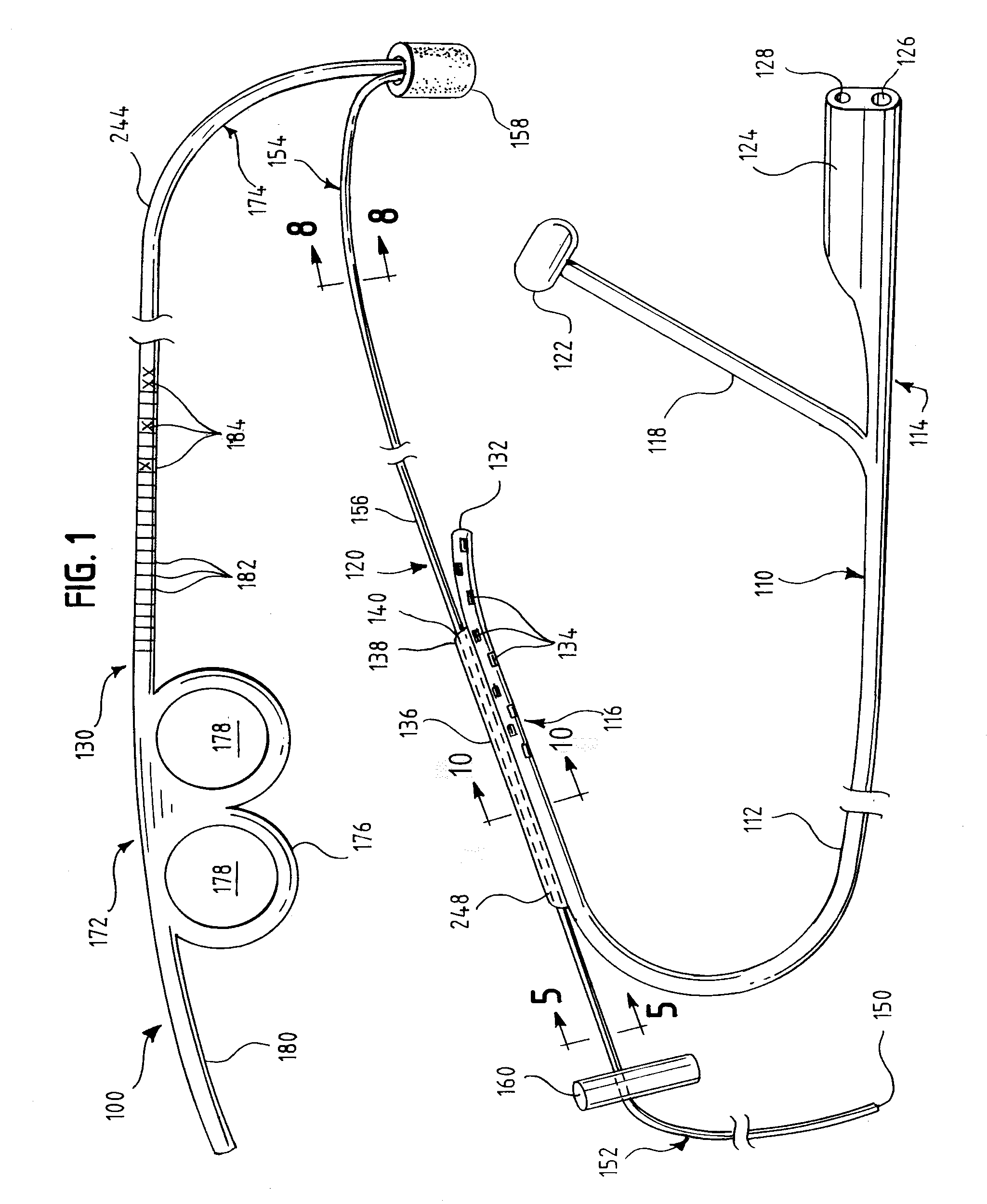
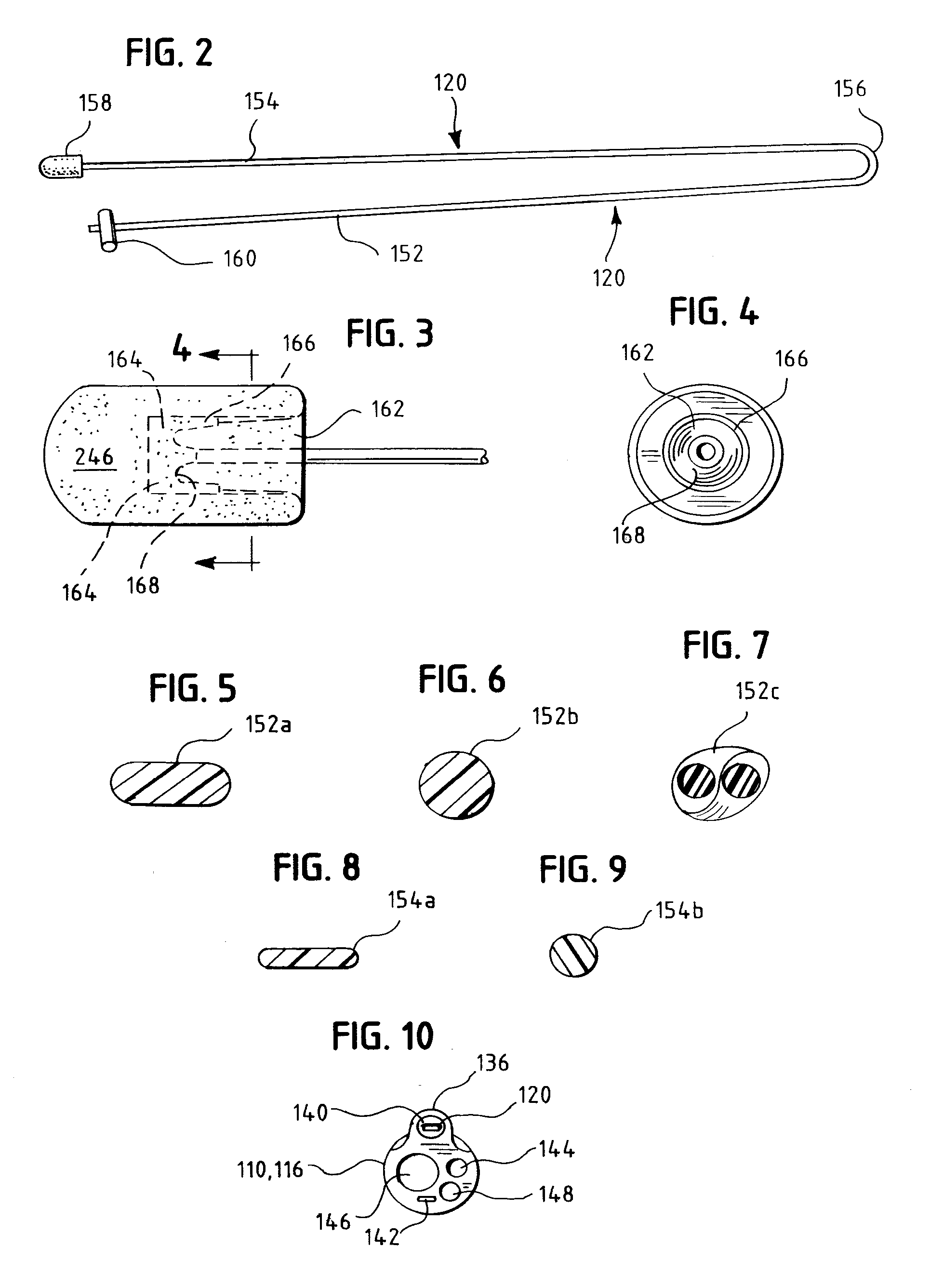
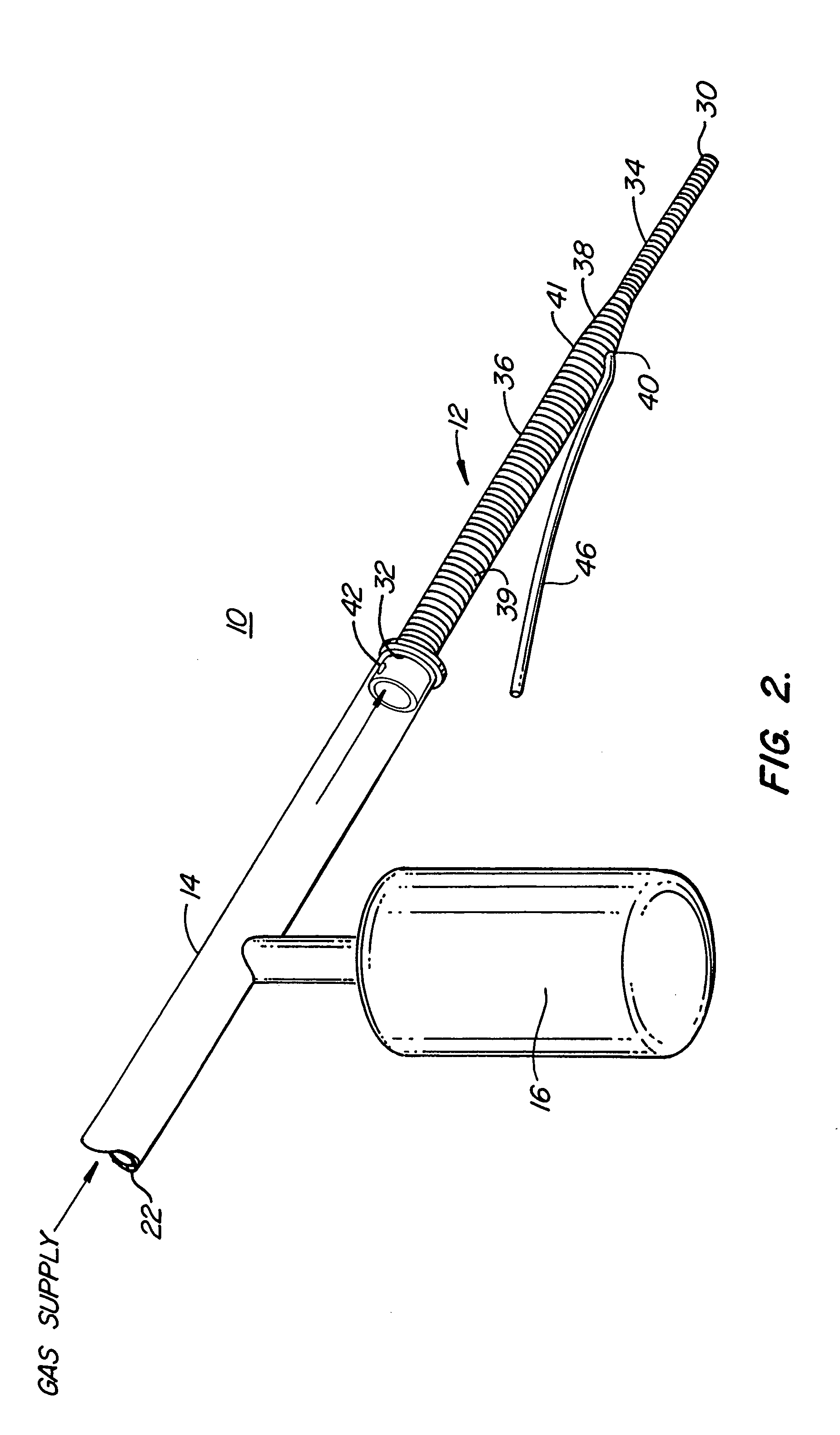
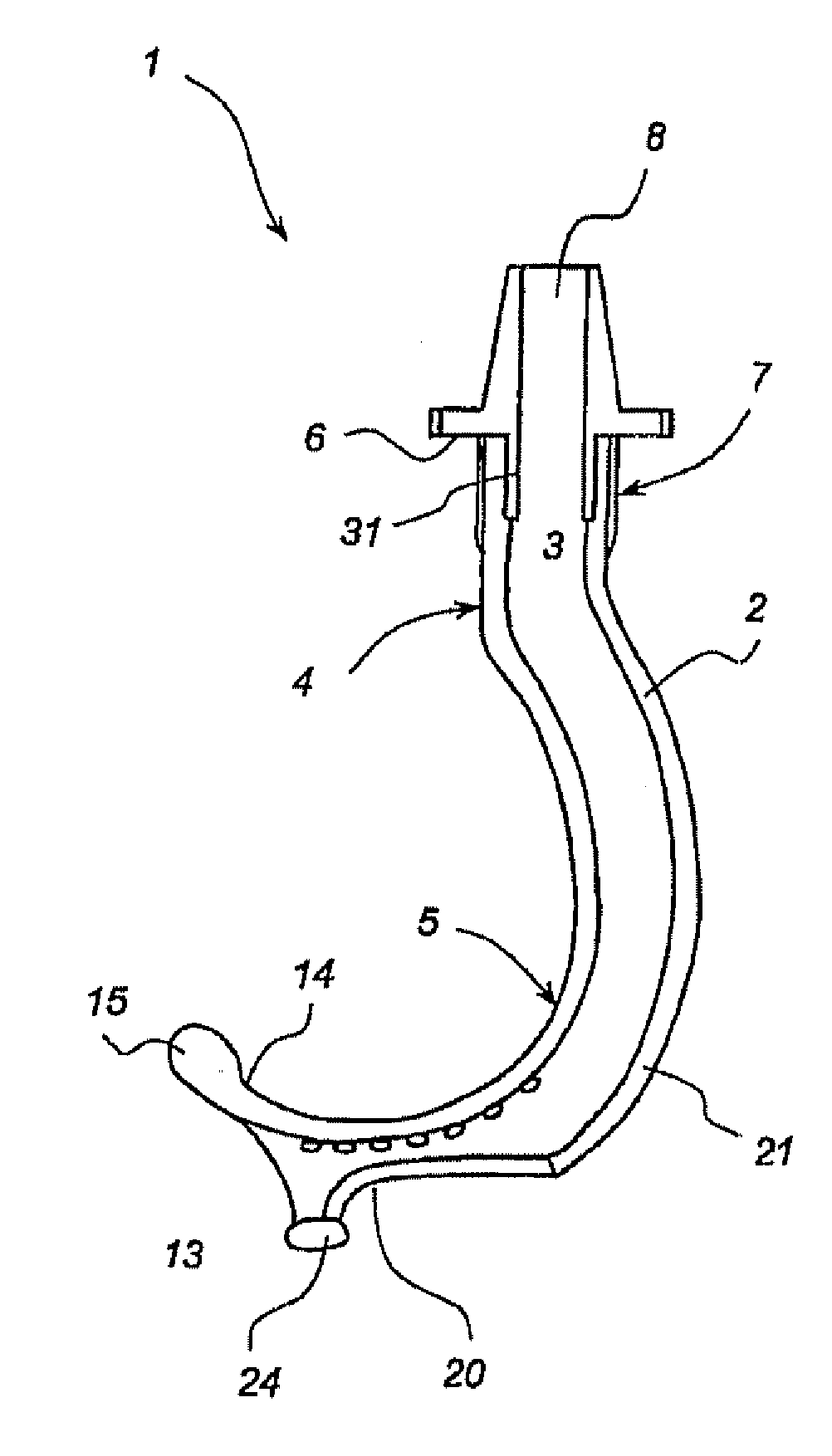
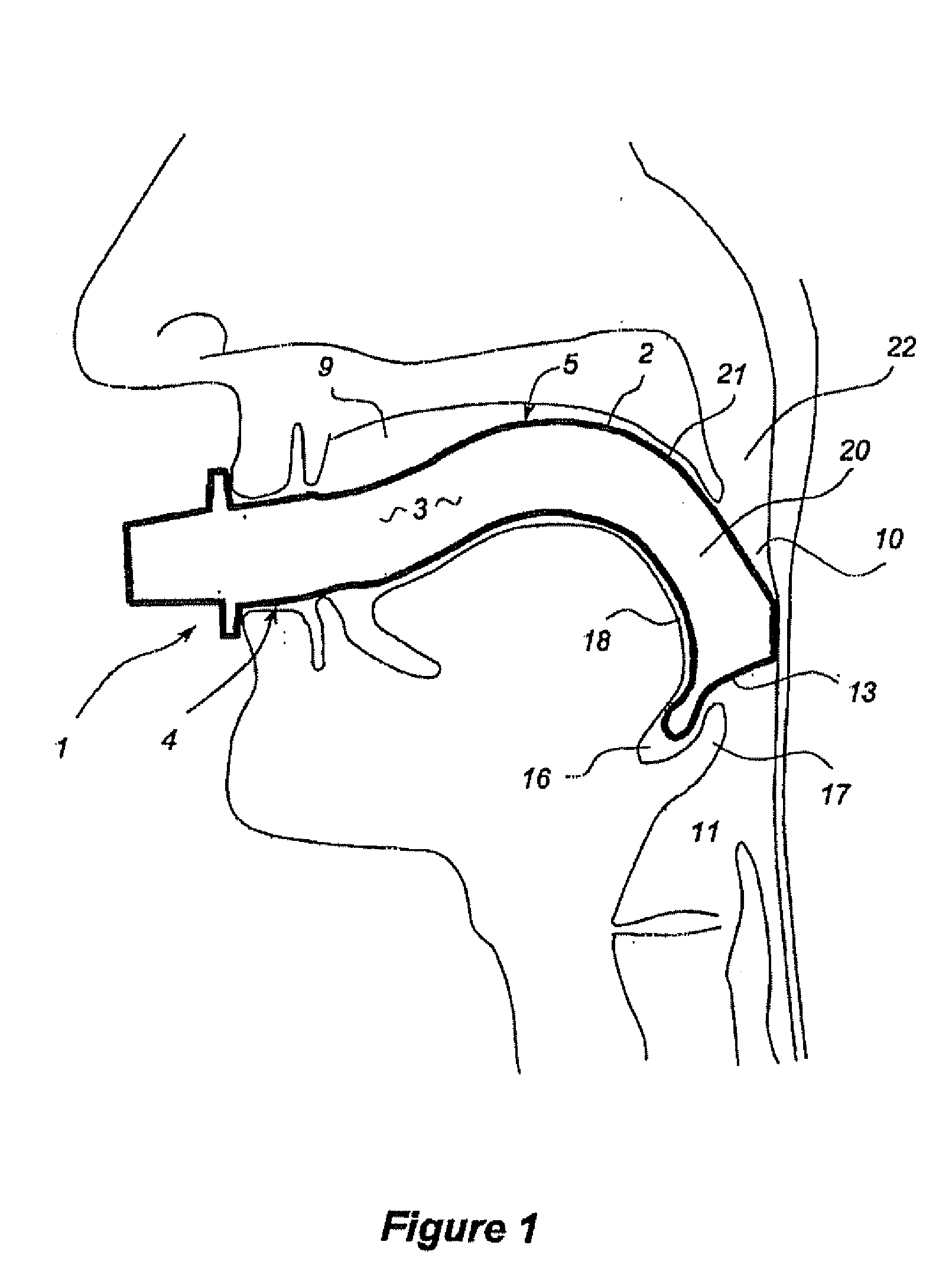
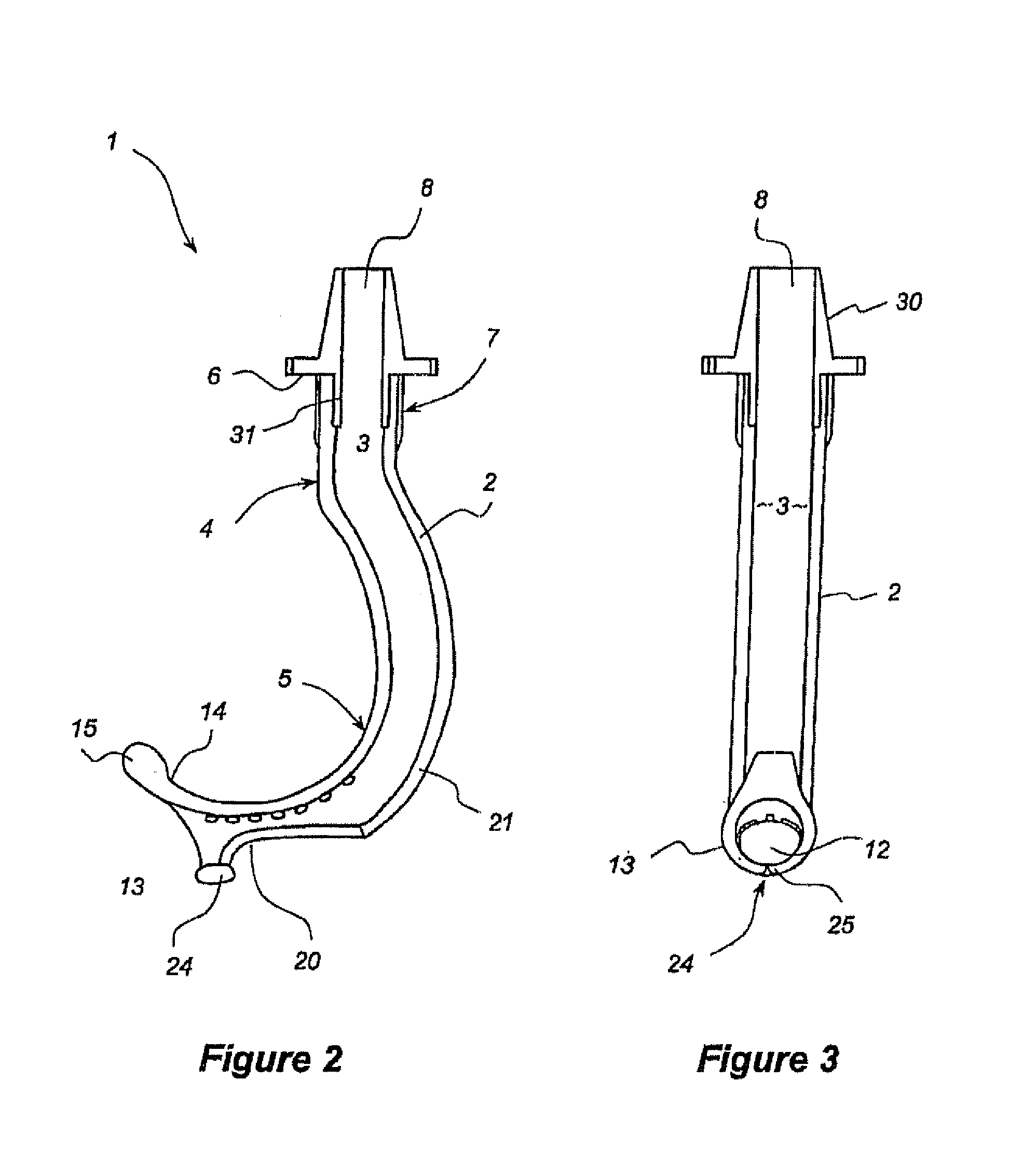
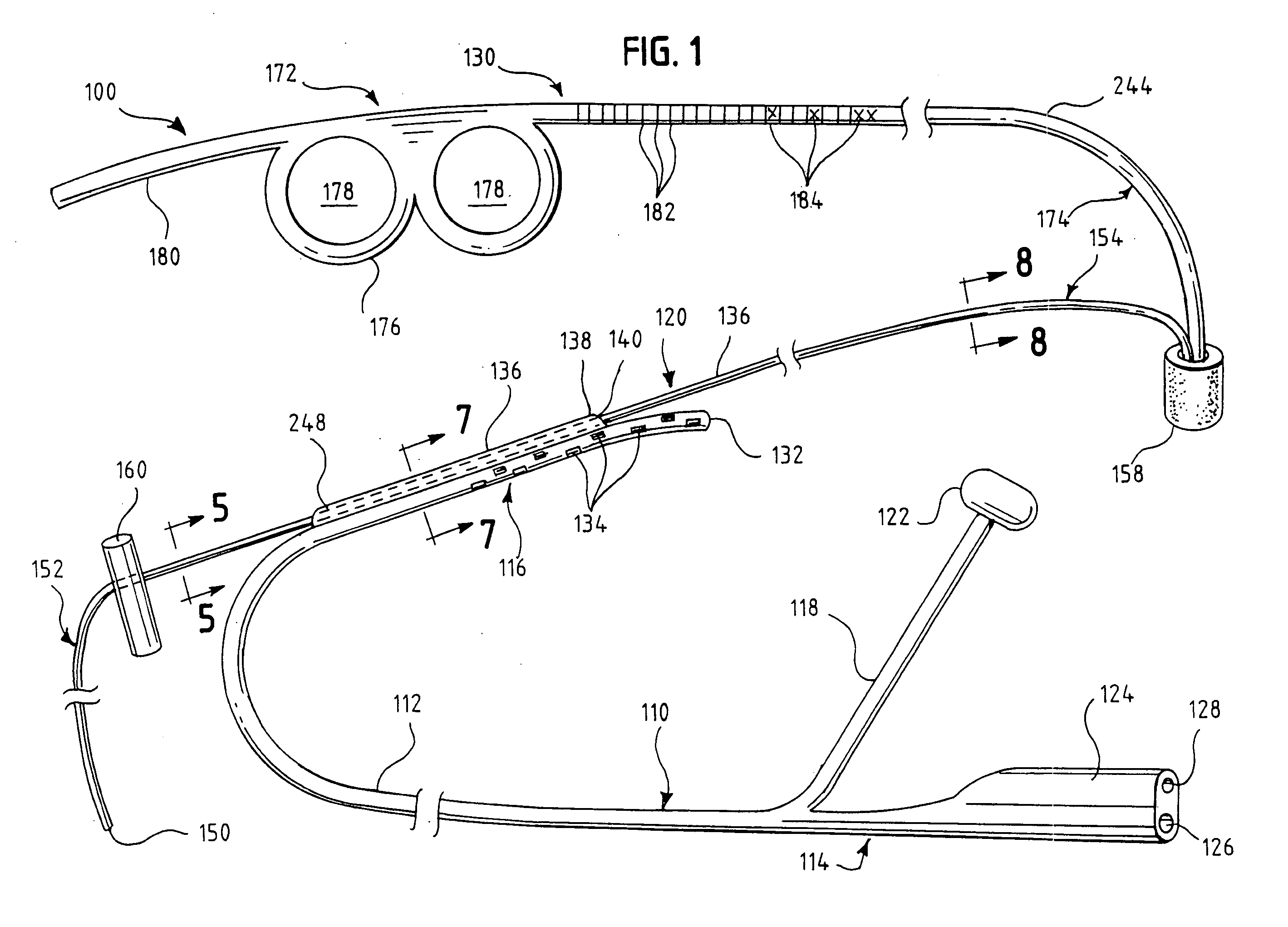
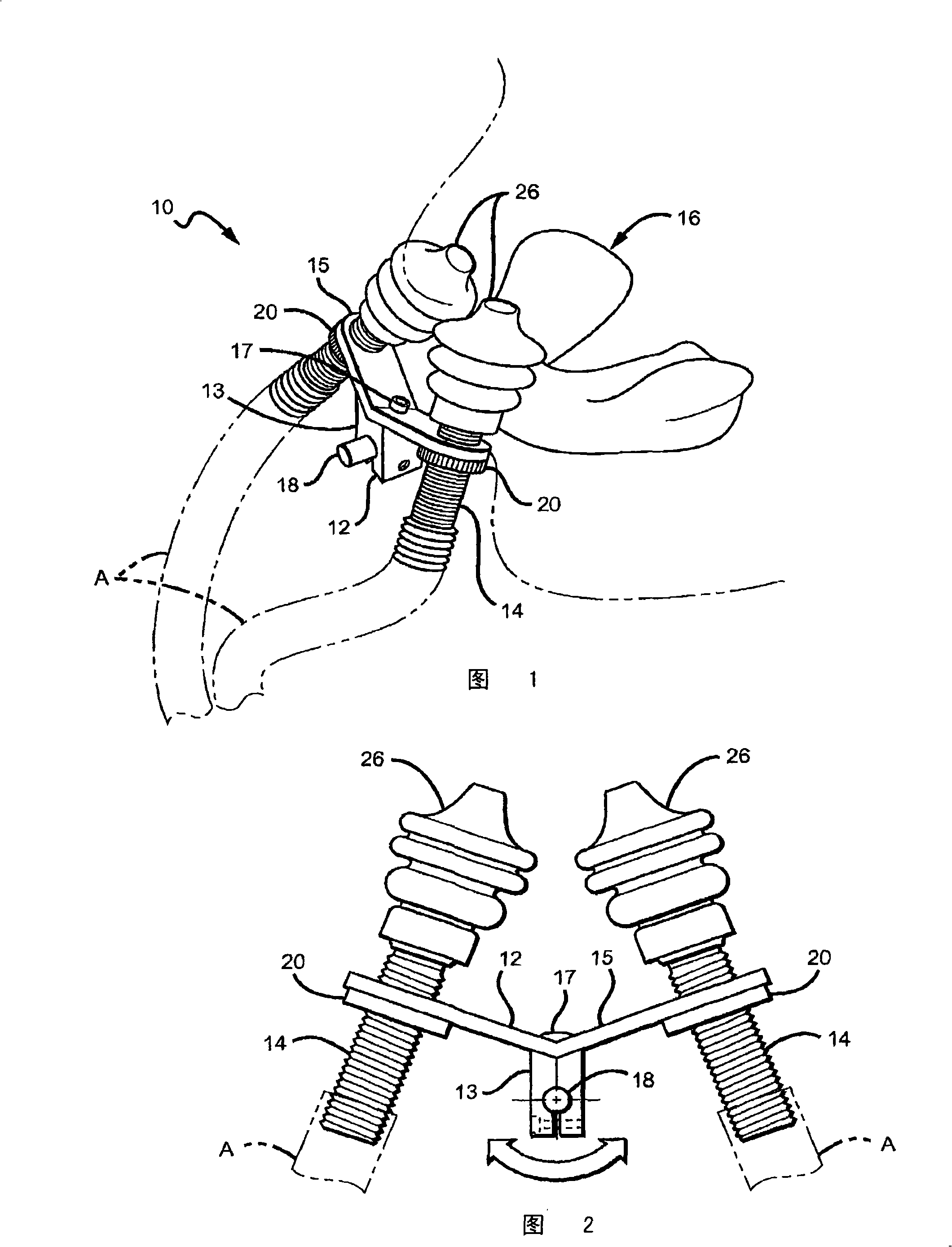
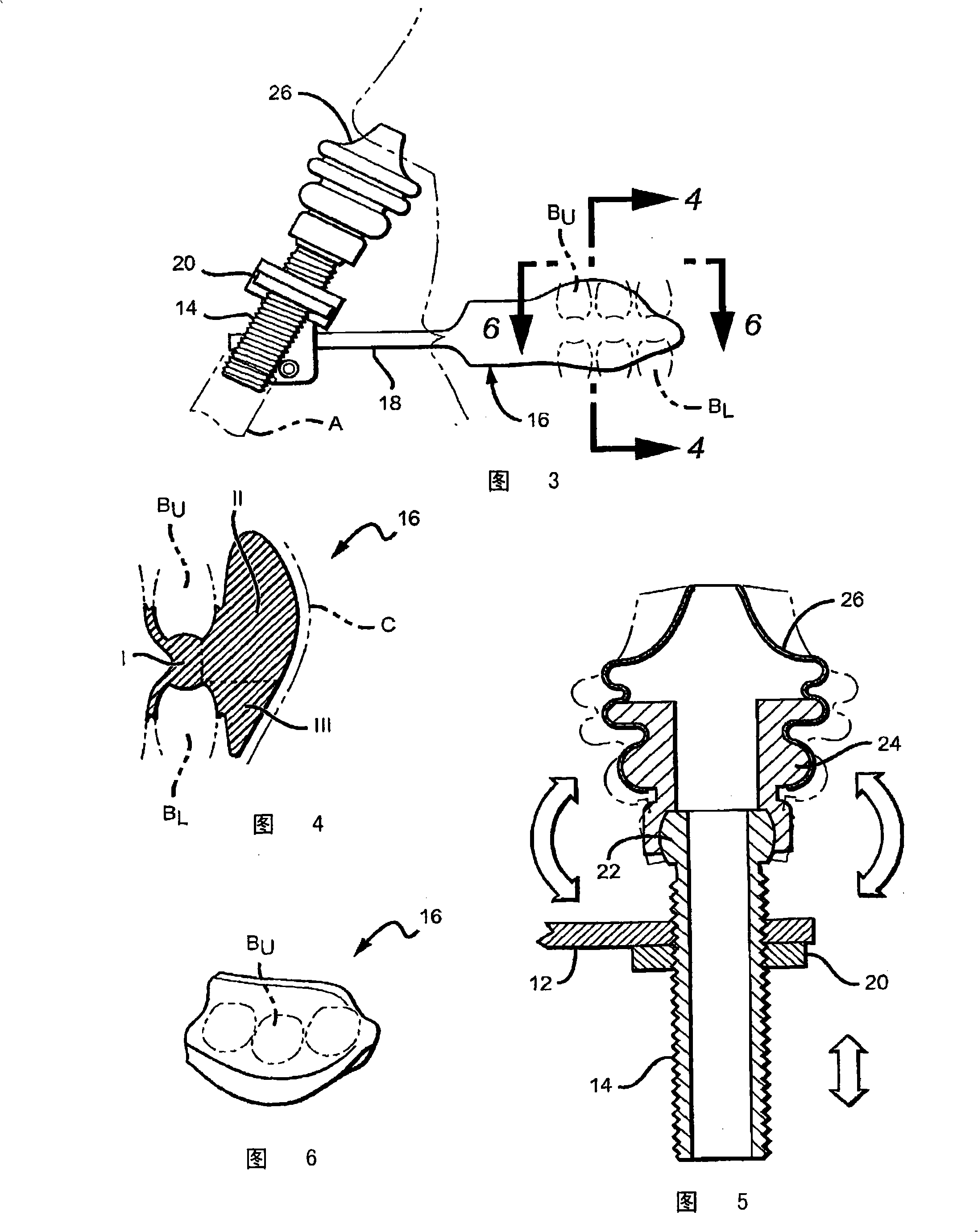
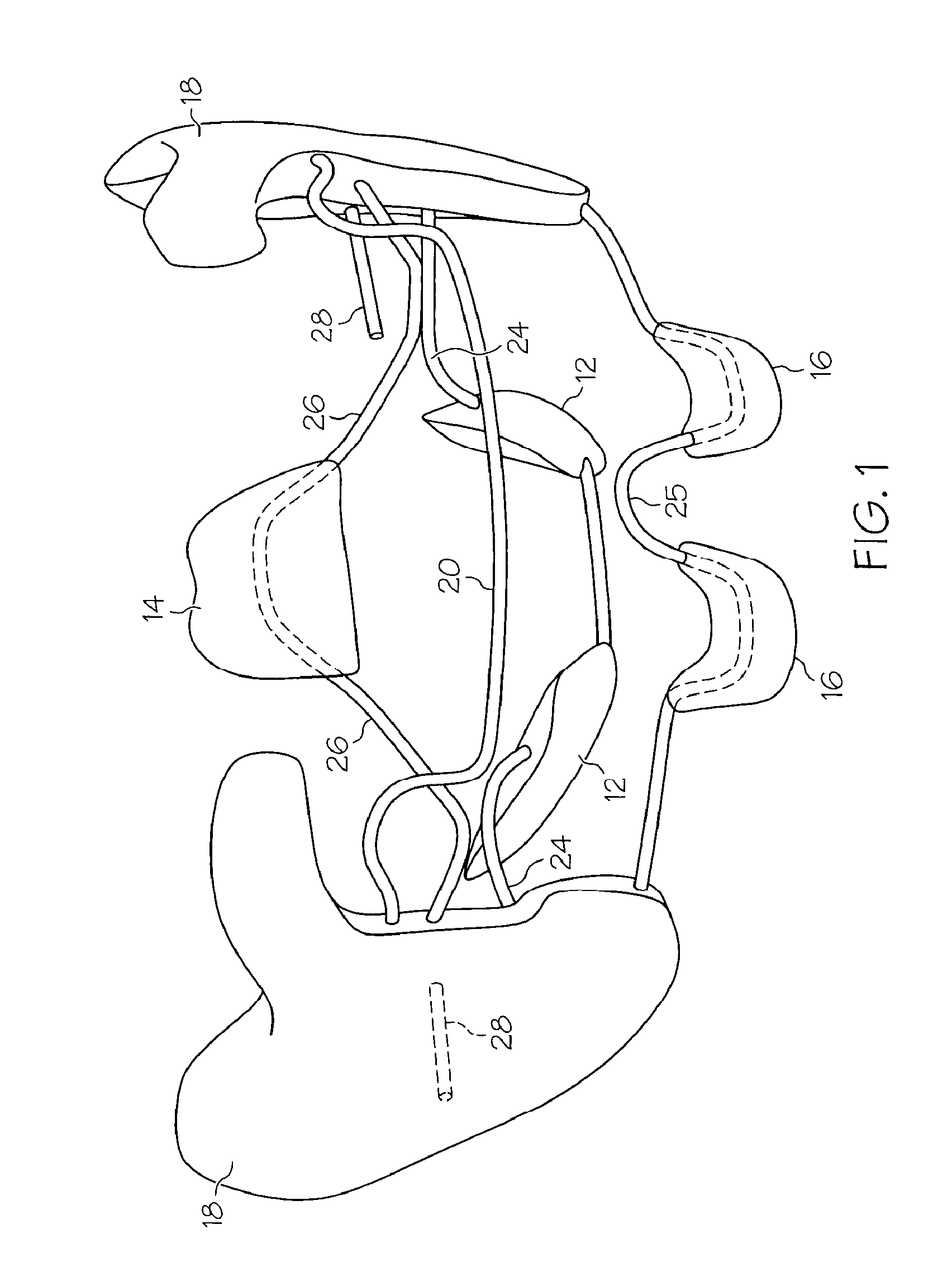
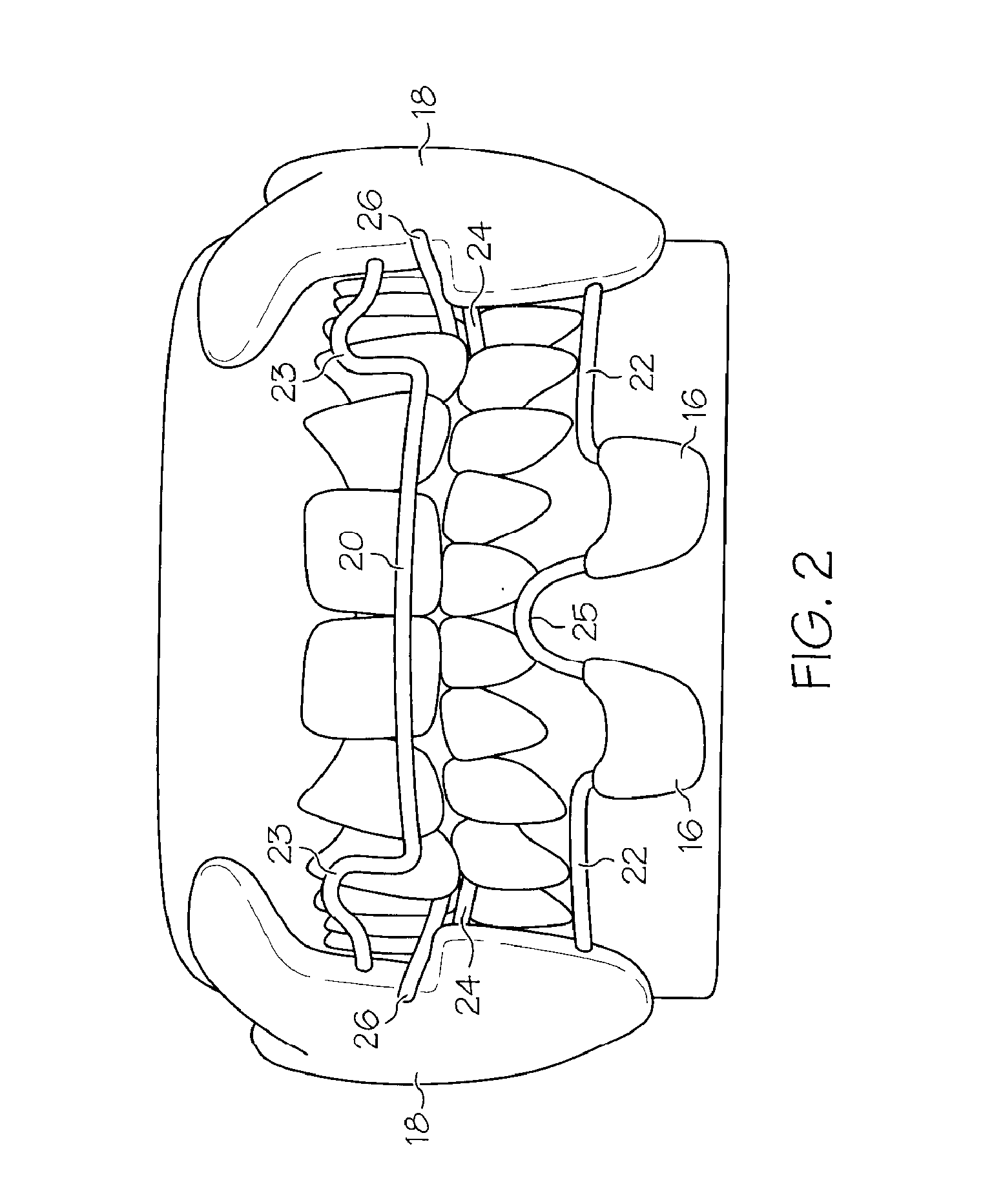
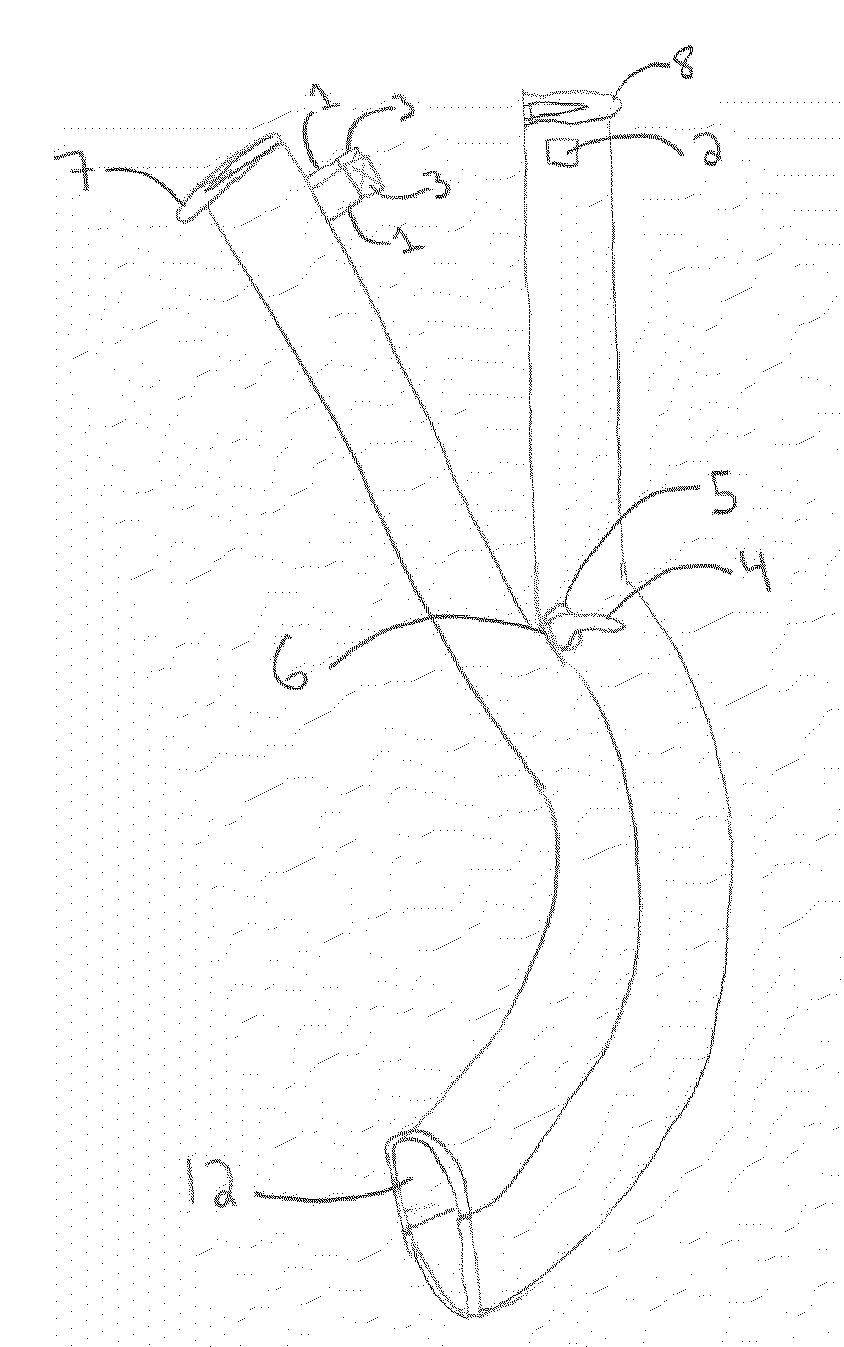
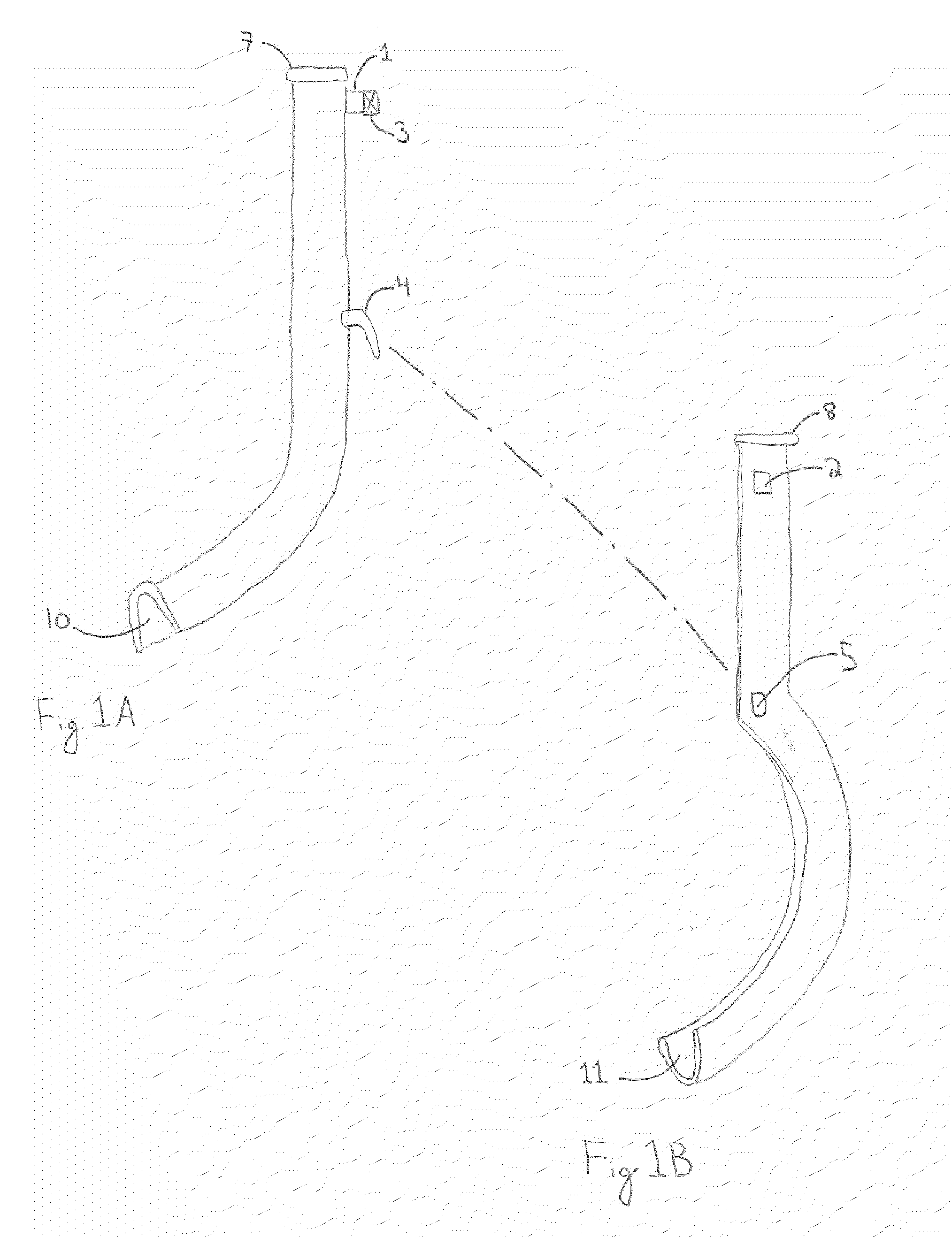
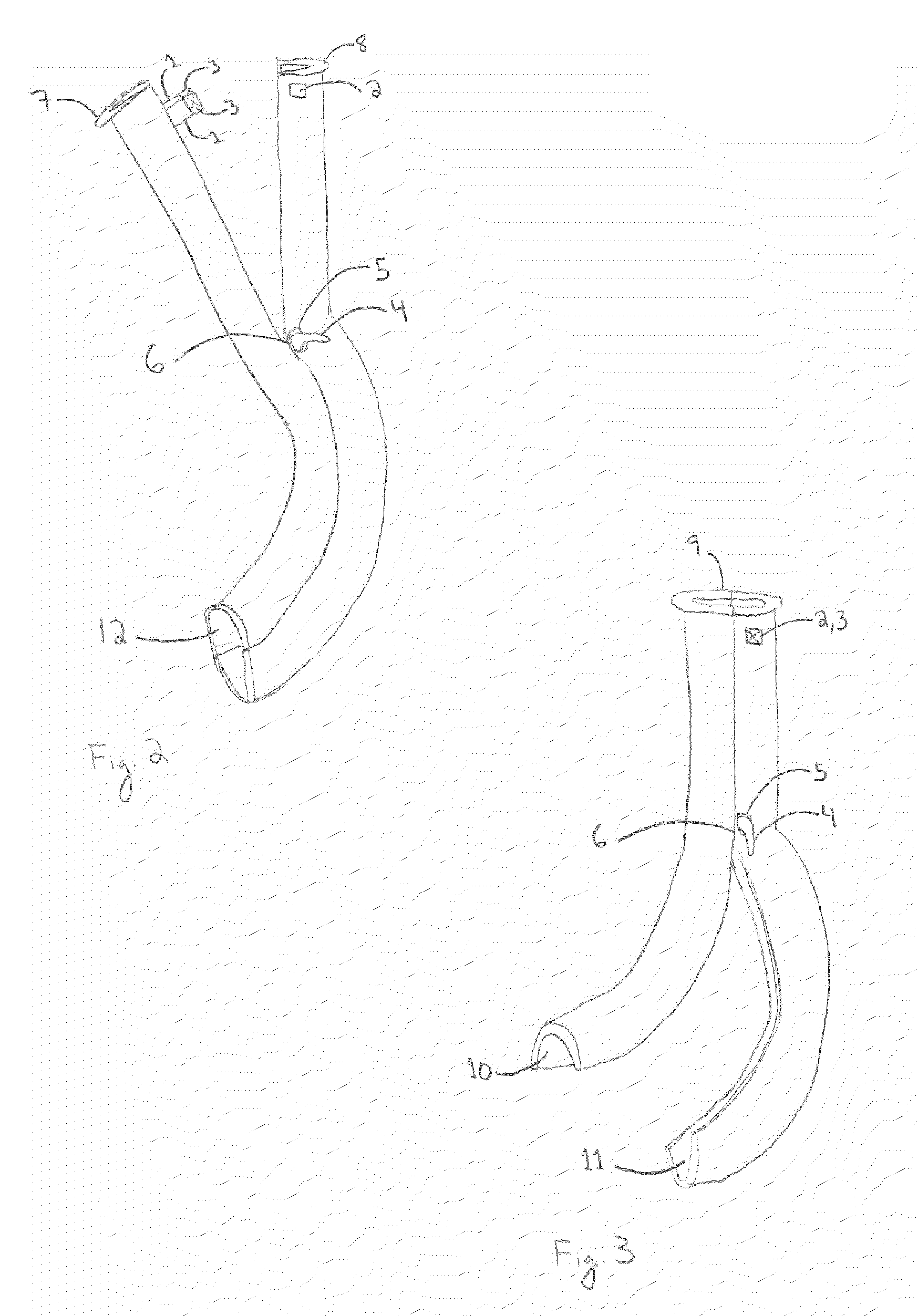
Oropharyngeal Airway Device
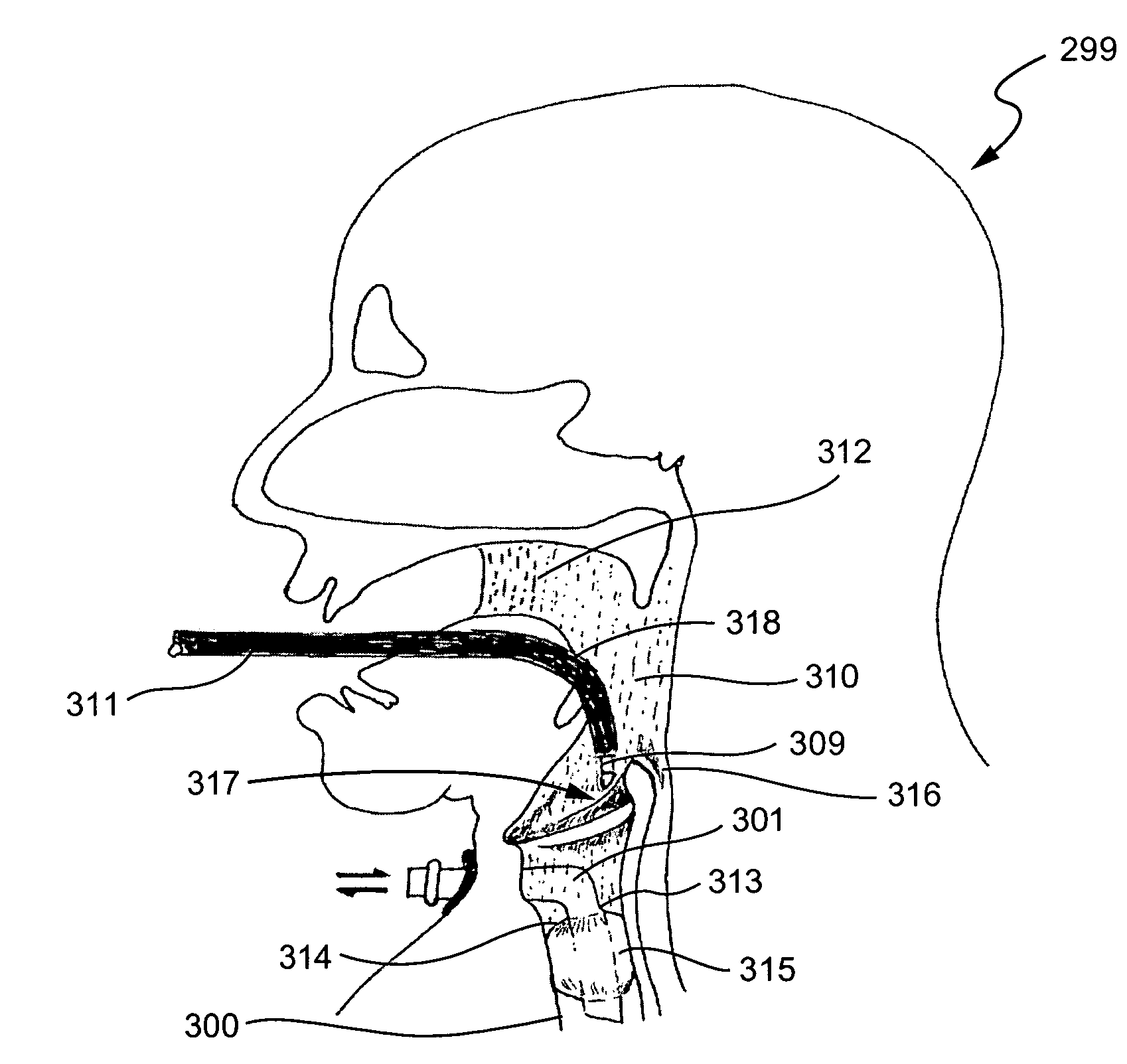
InactiveUS20080230054A1Easy to identifyExaggerate the locating formationTracheal tubesBronchoscopesGlottisOropharyngeal airway device
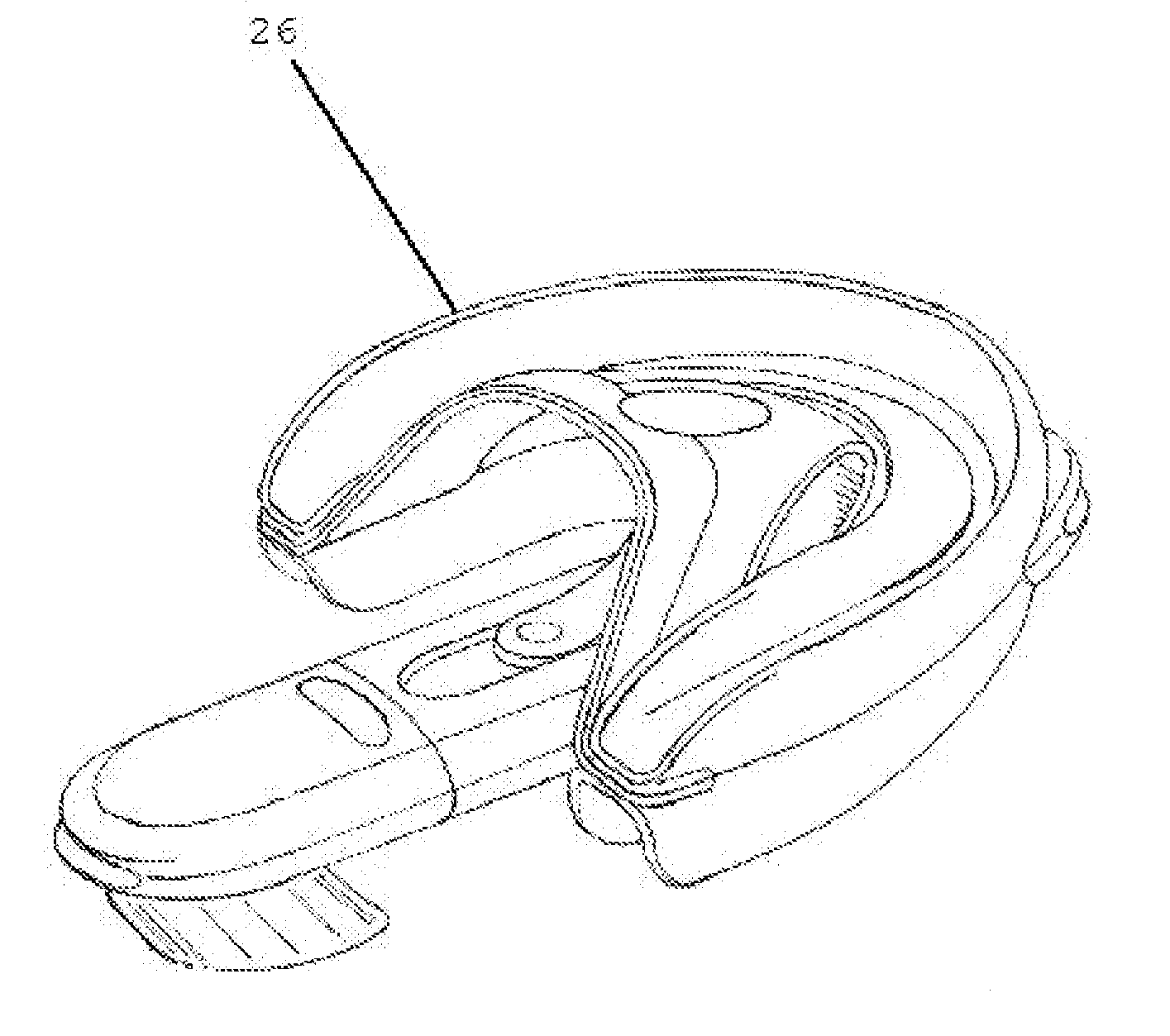
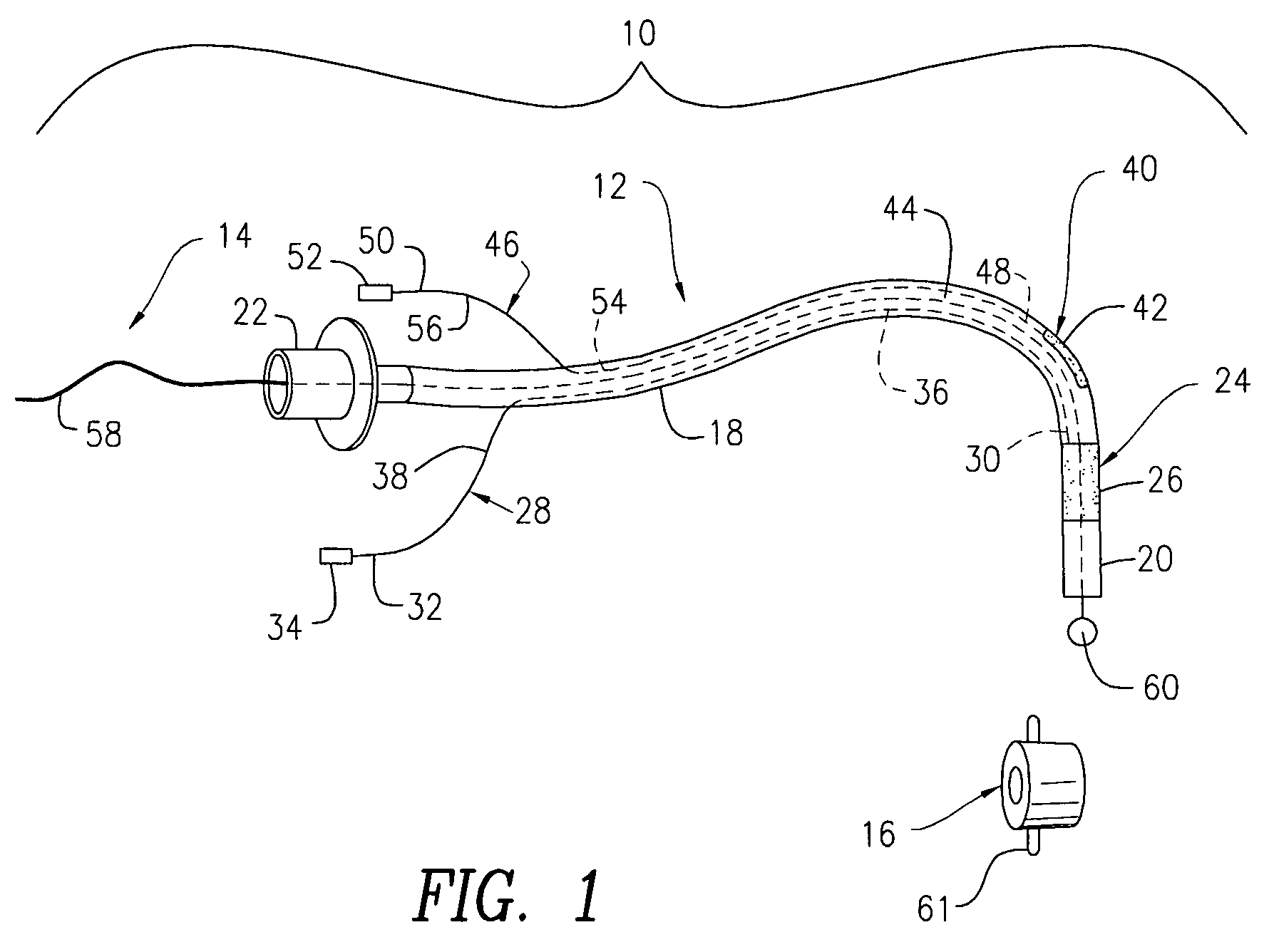
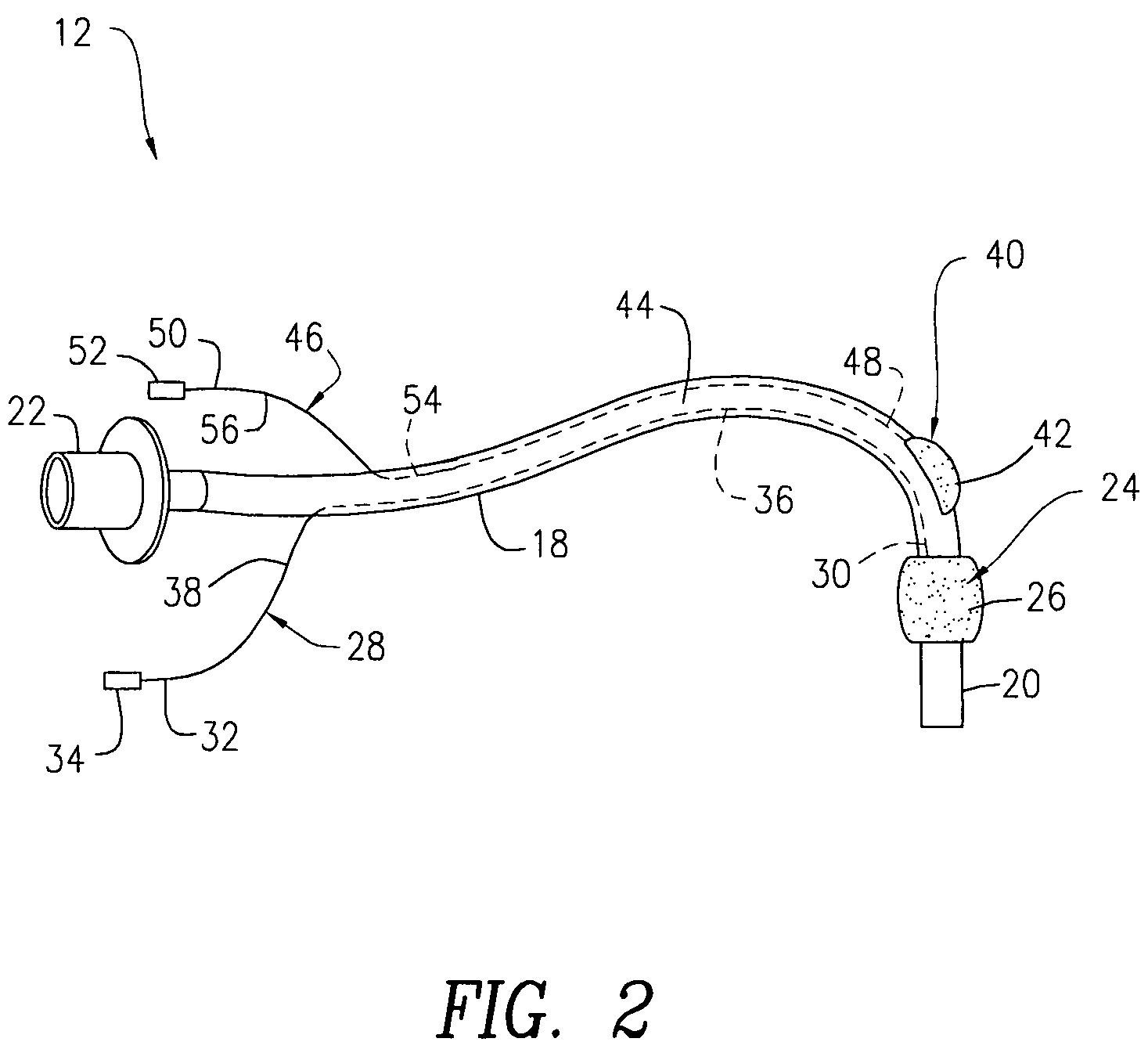
An oropharyngeal airway device (1) which includes a unitary tube (2) and a locating flange (6). The locating flange (6) forms, in combination with a first portion (4) of the tube (2), at least part of a mouthpiece (7) defining an inlet (8) to a passage (3). The flange (6) is adapted to locate adjacent an outer surface of the patient's mouth and the first portion (4) of the tube (2) extends into the mouth cavity. The tube (2) has a second portion (5), extending from said first portion (4), which has a distal end defining an outlet (12) to the tube (2) and which is adapted to extend to a location closely adjacent the base of the tongue. In use, the tube (2) is generally hook shaped with first portion (4) being substantially straight and the second portion (5) being of an arcuate form, extending obliquely from the first portion (4) and configured to follow the pharyngeal arc defined by the passage from the rear of the patient's mouth cavity through the oropharynx to a location adjacent the glottis. Alternatively or additionally to the tube shape described above, the outlet (12) at the distal end of the tube (2) can be defined by a first opening (13) that is configured to align with the opening to the larynx. Alternatively or additionally to the tube shape or the first opening described above, the device (1) can include internal markings (26) for guiding an endoscope therethrough.
Owner:WESTERN SYDNEY LOCAL HEALTH DISTRICT
Insertion system and methods for nasogastric tubes
ActiveUS7699818B2Reduce disadvantagesEasy to controlDiagnosticsInfusion syringesNasal passageNasal cavity
A nasogastric tube insertion system comprises a nasogastric tube, a guide element, and an inserter element. The inserter element has a slim, elongate main body, a handle attached to the body, and an anatomically curved insertion section. The guide element comprises a swallowable weight attached to a cord, string, monofilament line, tube, or other similar line. The swallowable weight may be ablative in the presence of stomach fluids or may be deflated to allow the guide element to be removed while the nasogastric tube remains in place. The inserter element is inserted through the patient's nasal passages and optionally into the oropharynx. The weight is released and the patient swallows it into the stomach. The guide element is threaded through the guide element retaining structure, and the nasogastric tube is safely inserted along the guide element into the patient's stomach. Chemical property indicators sensitive to fluids found in the stomach may be provided in the nasogastric tube or the guide element to verify correct placement of the nasogastric tube in the stomach.
Owner:CRITICAL DEVICE CORP
Nasogastric tube insertion system and method
ActiveUS20060189947A1Reduce disadvantagesReadily grasped and controlledInfusion syringesSurgical needlesNasal passageNasal passages
A nasogastric tube insertion system comprises a nasogastric tube, a guide element, and an inserter element. The inserter element has a slim, elongate main body, a handle attached to the body, and an anatomically curved insertion section. The guide element comprises a swallowable weight attached to a cord, string, monofilament line, or other similar line. The nasogastric tube comprises a tube having one or more interior bores or lumina and a guide element capture structure. In use, the swallowable weight is placed onto the end of the inserter element. The inserter element is inserted through the patient's nasal passages and optionally into the oropharynx. The weight is released and the patient swallows it into the stomach. The guide element is threaded through the guide element retaining structure, and the nasogastric tube is safely inserted along the guide element into the patient's stomach. The tube and guide element are removed together when no longer needed.
Owner:CRITICAL DEVICE CORP
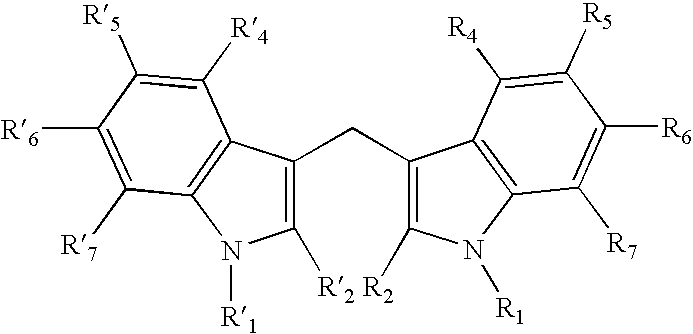
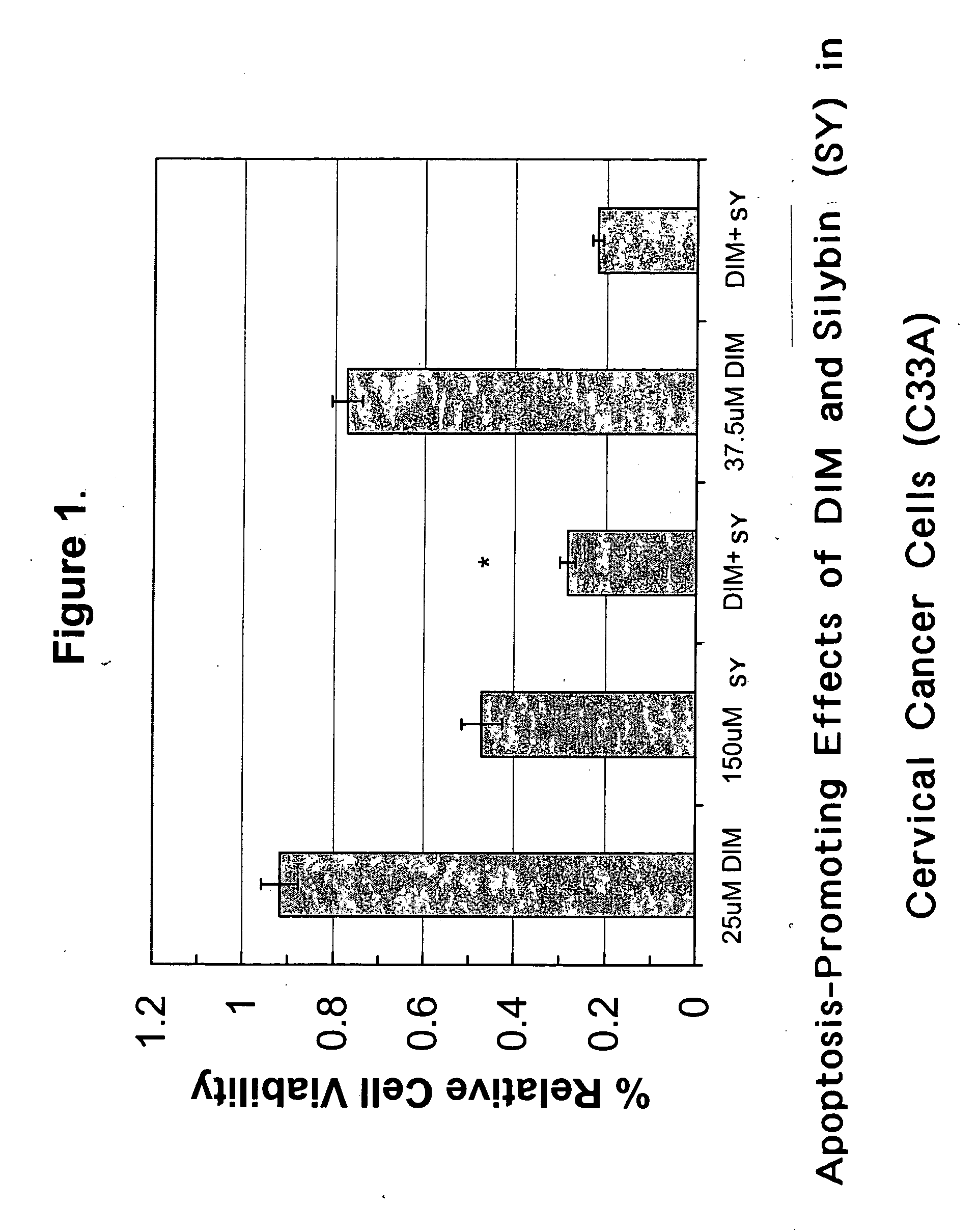
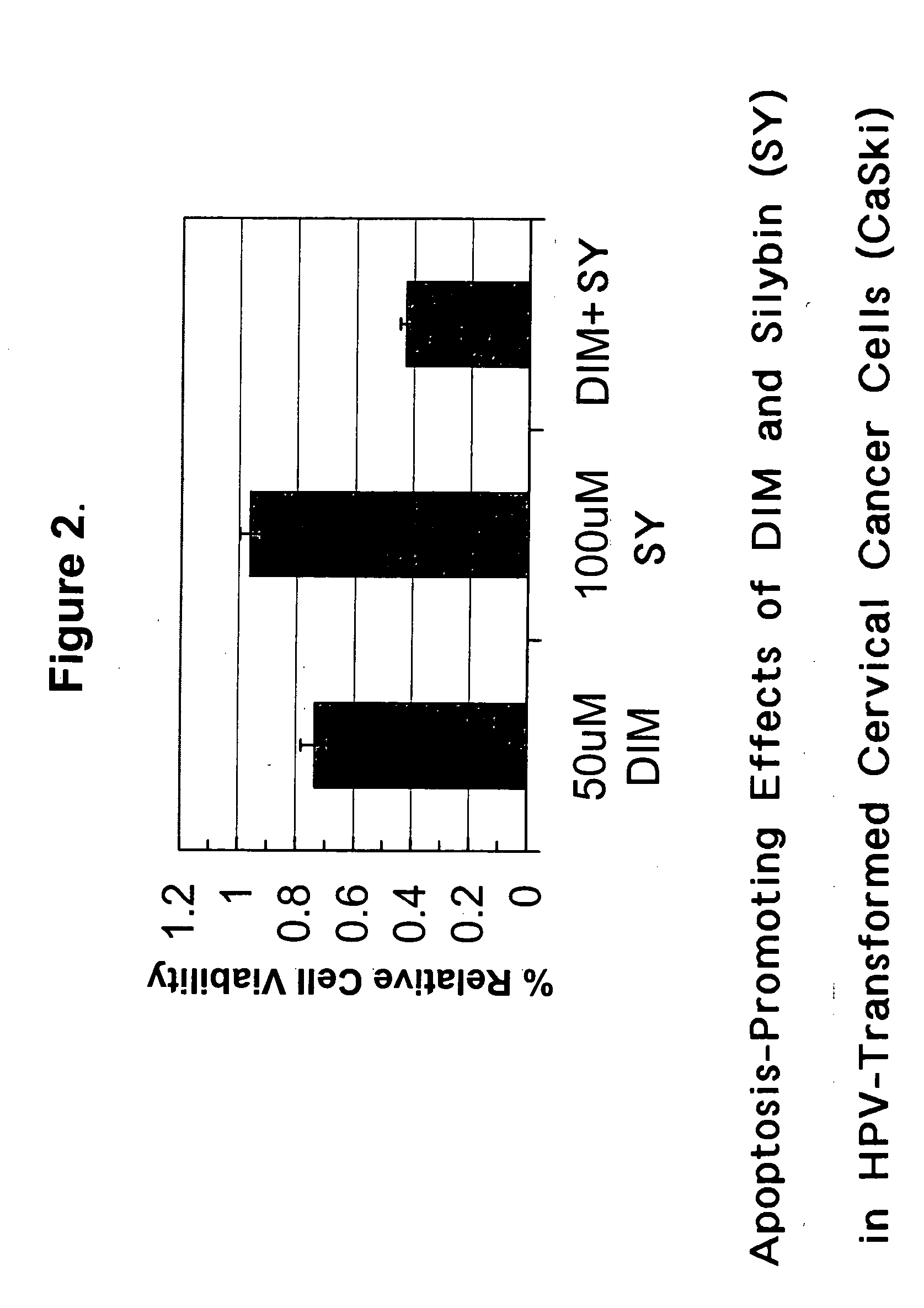
Combined use of cruciferous indoles and chelators for the treatment of papillomavirus-related conditions
Synergistic compositions and methods are disclosed for using cruciferous indoles with iron / zinc chelators in the treatment of papillomavirus-related conditions. These synergistic compositions of diindolylymethane (DIM), related trimeric derivatives, and related indole derivatives include combinations with deferoxamine, deferiprone, bipyridyl, Desferri-exochelin, picolinic acid, 3-hydroxypicolinic acid, and sodium butyrate as iron / zinc chelators. The methods described comprise more effective therapies for common cutaneous warts (verrucae) and related dysplasias of the oropharynx, genitalia, and uterine cervix.
Owner:BIORESPONSE
Insertion system and methods for nasogastric tubes including feeding tubes
ActiveUS7740620B2Reduce disadvantagesReadily grasped and controlledInfusion syringesSurgical needlesNasal passageNasal passages
A nasogastric tube insertion system comprises a nasogastric tube, a guide element, and an inserter element. The inserter element has a slim, elongate main body, a handle attached to the body, and an anatomically curved insertion section. The guide element comprises a swallowable weight attached to a cord, string, monofilament line, or other similar line. The nasogastric tube may be a nasogastric feeding tube and comprises a tube having one or more interior bores or lumina and a guide element capture structure. In use, the swallowable weight is placed onto the end of the inserter element. The inserter element is inserted through the patient's nasal passages and optionally into the oropharynx. The weight is released and the patient swallows it into the stomach. The guide element is threaded through the guide element retaining structure, and the nasogastric tube is safely inserted along the guide element into the patient's stomach. The tube and guide element are removed together when no longer needed.
Owner:CRITICAL DEVICE CORP
Method and device for treating sleep apnea
An improved treatment of obstructive sleep apnea is disclosed. A method and various device combinations are presented. The device combinations describe optimal adjustments to properly position a nasal pillow in each of a patient's nares. A novel swivel joint is described to which a nasal pillow is slip-fit over. The swivel joint prevents loss of a proper seal between the nasal pillow and nare which may otherwise occur as a result of head movement. Also presented is an improved obturator mouthpiece design which substantially eliminates air flow through the oral cavity resulting from leakage in the oropharynx.
Owner:JOHN C JEPPESEN DMD
Intraoral apparatus for treating upper airway disorders
ActiveUS20110232651A1Reduce resistanceChange configurationSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiseasePartial obstruction
A removable intraoral apparatus for improving airway patency is described. Wearing the apparatus alters the position, configuration and freedom of movement of the tongue, the muscles of mastication, as well as the pharyngeal and facial muscles. The apparatus is useful for correcting snoring and / or obstructive sleep apnea due to intermittent closures or partial obstructions occurring in the oropharynx during sleep. The apparatus of the invention can improve various types of airway disorders and improve oral functions by changing the position, configuration and freedom of movement of selected portions of the tongue and mouth, reducing the resistance to air flow in the mouth and pharynx, re-orienting and reprogramming the muscles of the mouth and tongue, and maintaining a proper oral systemic balance.
Owner:TNT LABS
Diindolylmethane for the treatment of HPV infection
New methods and compositions are disclosed that comprise the phytochemical Diindolylmethane, alone or in combination with immune potentiating steroids. These methods and compositions are utilized to treat subjects suffering from common cutaneous warts (verrucae) and Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) related conditions of the oropharynx, larynx, genitalia, and uterine cervix.
Owner:BIORESPONSE
Methods and devices for forming an auxiliary airway for treating obstructive sleep apnea
An auxiliary airway for treating obstructive sleep apnea is formed by implanting an elongated conduit beneath a pharyngeal wall of a pharynx. The elongated conduit has a proximal end in communication with a first region of the pharynx, a distal end in communication with a second region of the pharynx, and a section extending beneath the pharyngeal wall for bypassing an oropharynx region of the pharynx. The system includes a first opening in the pharyngeal wall in communication with a first opening in the elongated conduit, and a second opening in the pharyngeal wall in communication with a second opening in the elongated conduit. The system has a first anastomotic connector for coupling the first opening in the pharyngeal wall with the first opening in the conduit, and a second anastomotic connector for coupling the second opening in the pharyngeal wall with the second opening in the conduit.
Owner:ETHICON INC
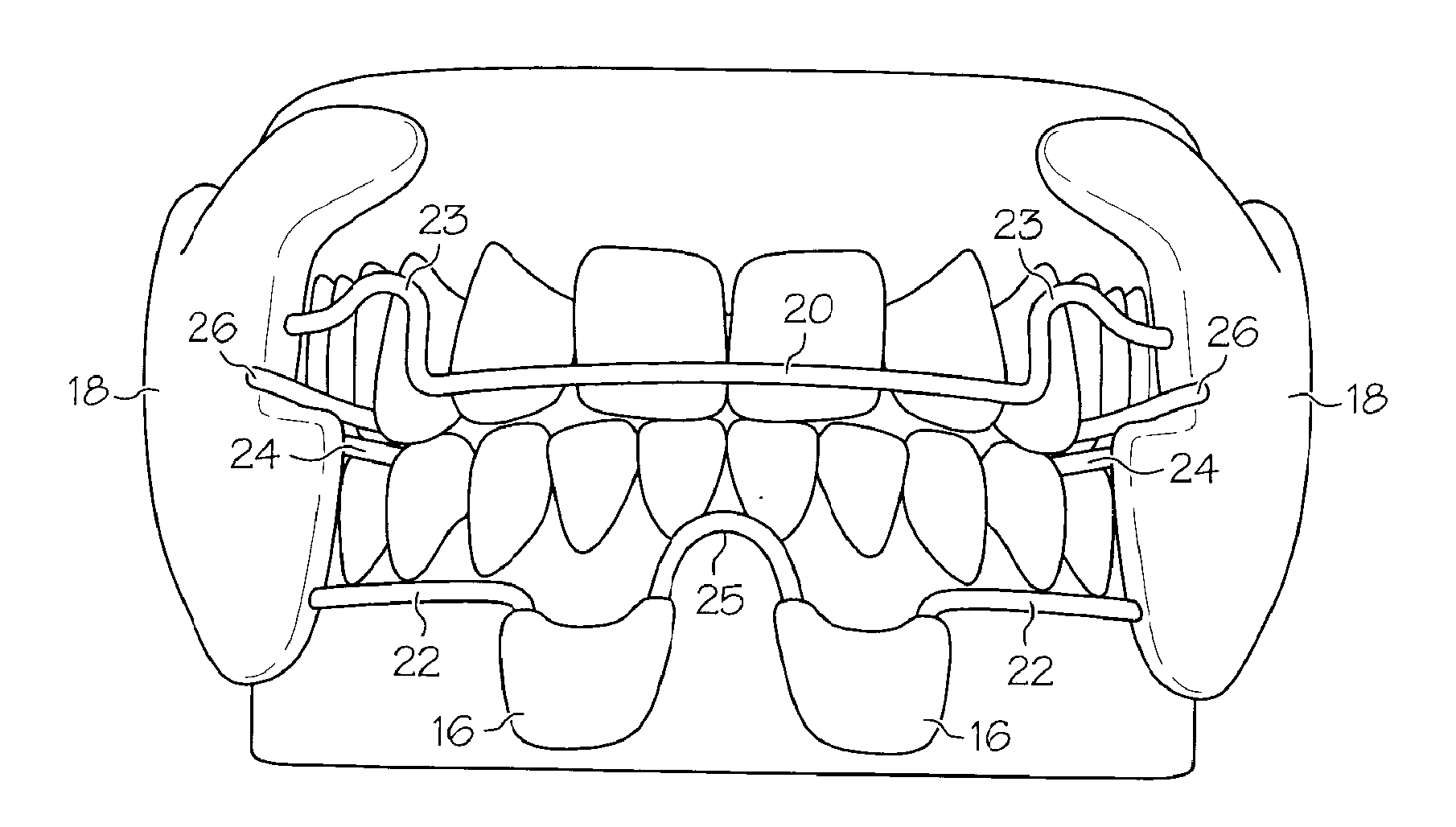
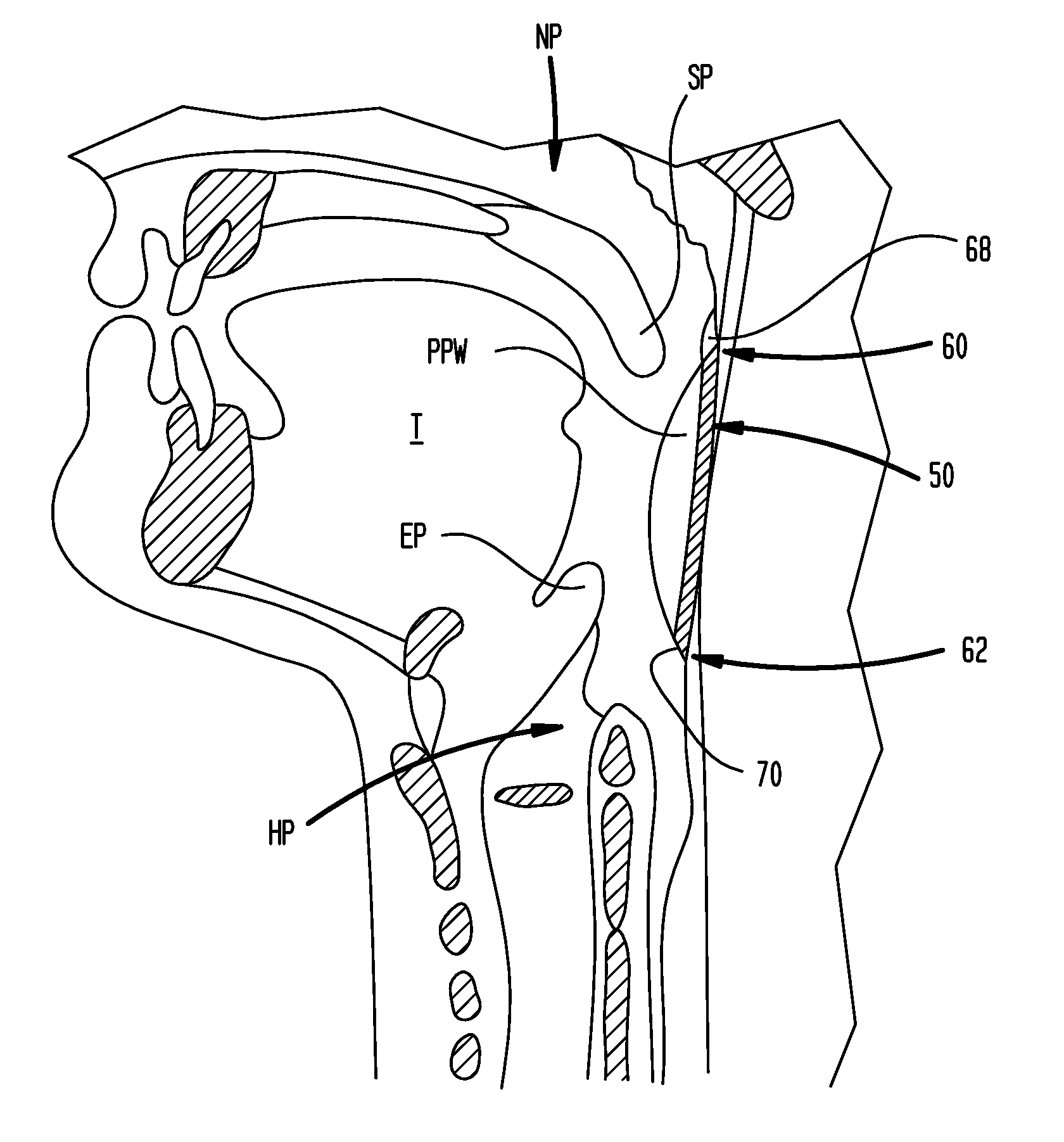
Oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airway having a breathing indicator
InactiveUS20120048278A1Reduce obstaclesTracheal tubesMedical devicesNasopharyngeal airwayOropharyngeal airway
An oropharyngeal airway configured for placement within a mouth of a patient to create a passageway between a mouth of a patient and the posterior pharyngeal wall that includes a passageway body, a flange assembly and a reactive material. The flange assembly is positioned at the end of the body and includes spaced apart upper and lower flange portions, which define a passageway therebetween which is in communication with the opening of the passageway body. The reactive material cooperates with the flange assembly and the passageway defined by the spaced apart flange portions. The reactive material provides qualitative visual indication as to whether the patient is effectively ventilating. A nasopharyngeal airway is likewise disclosed, as is a flange assembly which can be coupled to existing airways.
Owner:YASICK ANTHONY JOHN
Methods of delivering aerosolized polynucleotides to the respiratory tract
Methods and devices for delivering aerosolized formulations containing polynucleotides to specified regions within a subject's respiratory tract are disclosed. The methods find use in the delivery of ribozymes, antisense polynucleotides, and DNA and RNA expression vectors into airway epithelial cells, alveoli, pulmonary macrophages and other cells in the respiratory tract (including the oropharynx, nose, nasopharynx). These methods may be used for optimization of transfection efficiency and expression in vivo, and for in vivo expression, for example for generating an immune response, or inducing immunological tolerance.
Owner:ARADIGM
System and method for transcutaneous monitoring of endotracheal tube placement
The present invention relates to a tracheal intubation device and method for placing an endotracheal tube within a patient's trachea. More particularly, the endotracheal tube includes primary and secondary cuffs, in the form of inflatable balloons. A stillette is positioned within the endotracheal tube. The tracheal intubation device includes a guiding mechanism for guiding the stillette and the endotracheal tube within a patent's body. The guiding mechanism is positioned external to a patient and sized and shaped so as to transmit a signal and to receive a signal indicating the location of the stillette in a patient's body. After the endotracheal tube is positioned in the oropharynx, inflating the secondary cuff urges the endotracheal tube toward the trachea of a patient.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Nasogastric tube insertion system and method
ActiveUS7695459B2Reduce disadvantagesReadily grasped and controlledInfusion syringesSurgical needlesNasal passageNasal passages
A nasogastric tube insertion system comprises a nasogastric tube, a guide element, and an inserter element. The inserter element has a slim, elongate main body, a handle attached to the body, and an anatomically curved insertion section. The guide element comprises a swallowable weight attached to a cord, string, monofilament line, or other similar line. The nasogastric tube comprises a tube having one or more interior bores or lumina and a guide element capture structure. In use, the swallowable weight is placed onto the end of the inserter element. The inserter element is inserted through the patient's nasal passages and optionally into the oropharynx. The weight is released and the patient swallows it into the stomach. The guide element is threaded through the guide element retaining structure, and the nasogastric tube is safely inserted along the guide element into the patient's stomach. The tube and guide element are removed together when no longer needed.
Owner:CRITICAL DEVICE CORP
Method of esophageal function testing with a standardized thixotropic swallow challenge medium
ActiveUS20070225613A1Long enough shelf lifeMeaningful resultDispersion deliverySurgeryMedicineEsophageal function
Owner:DIVERSATEK HEALTHCARE INC
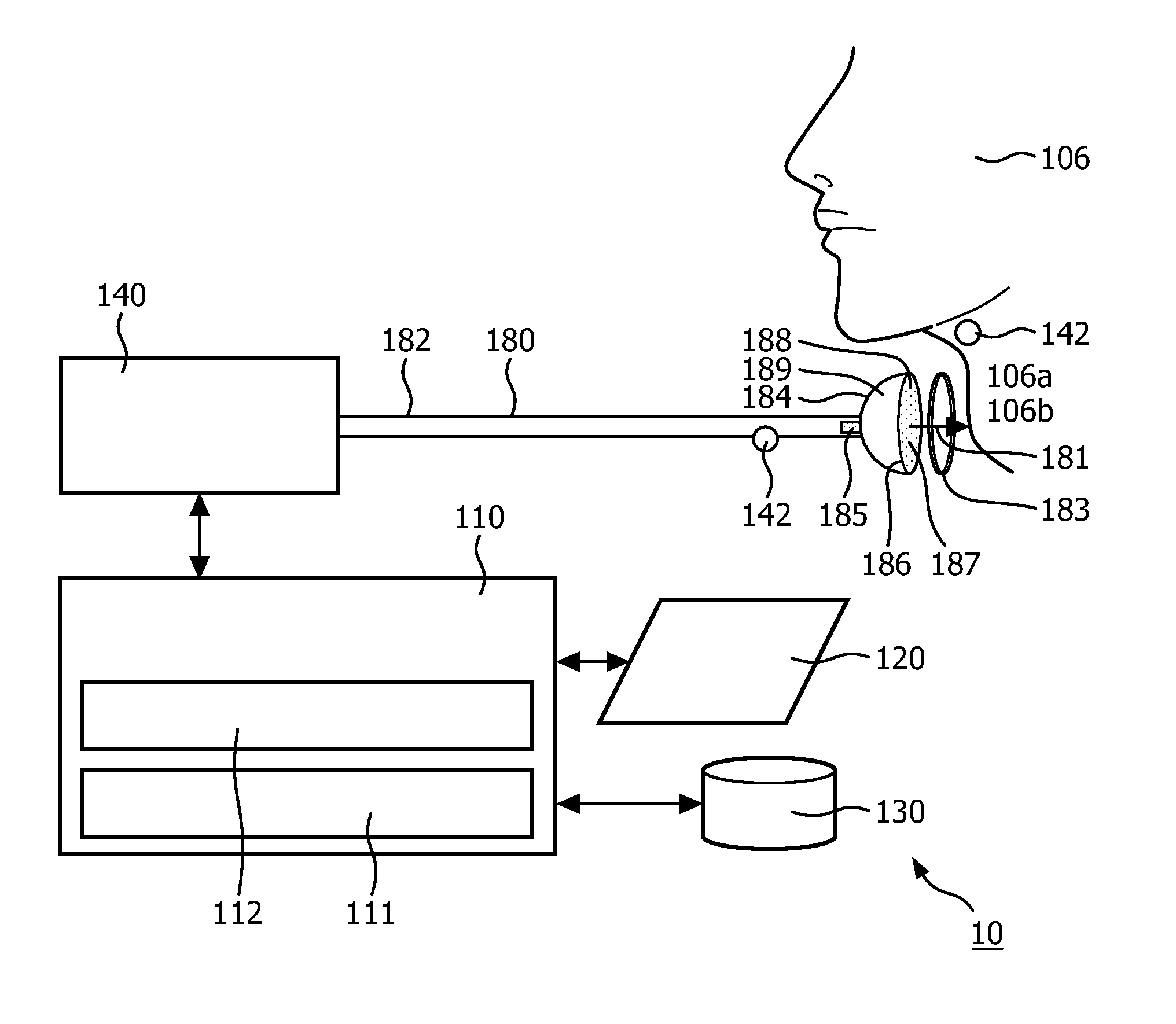
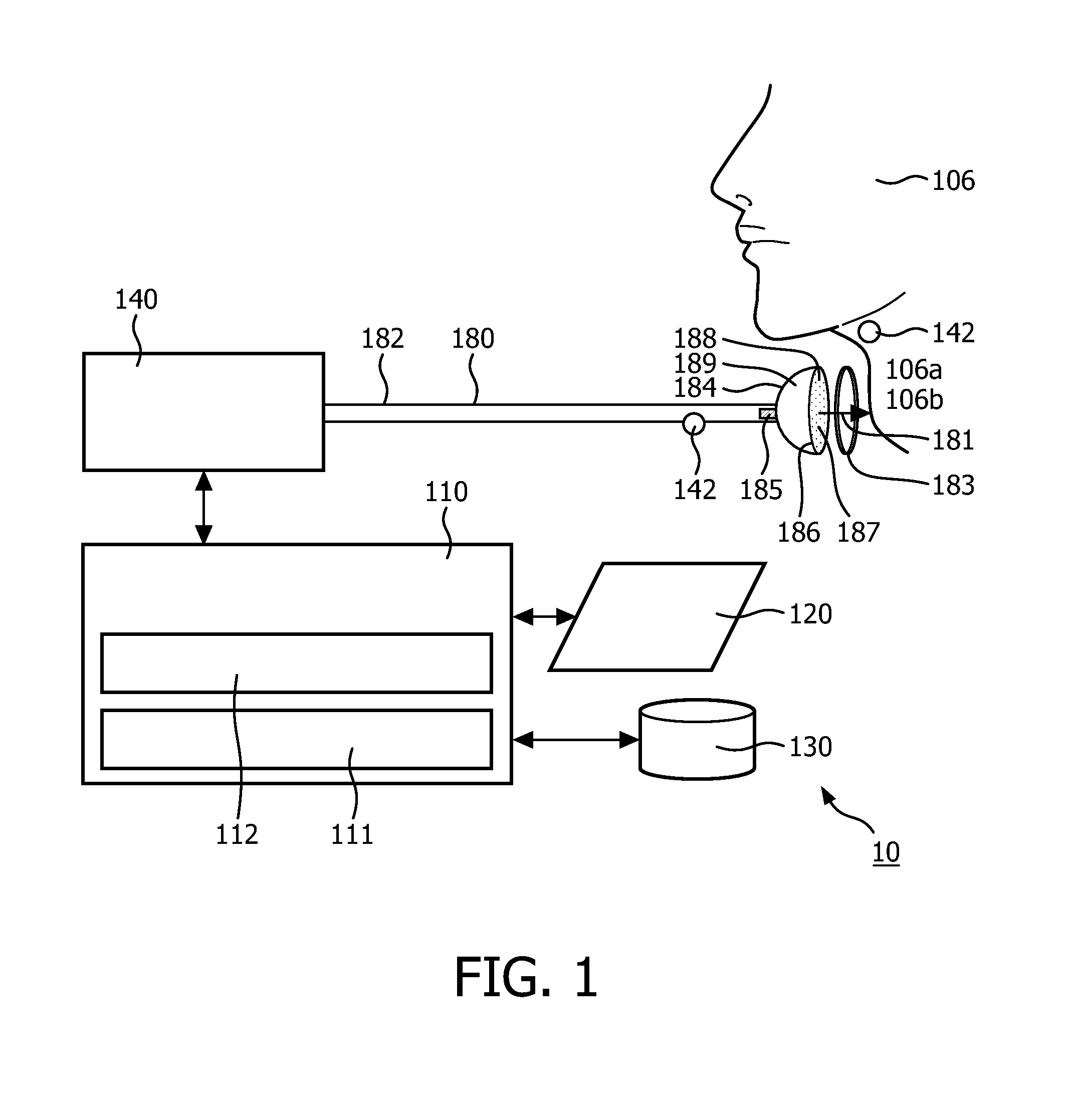
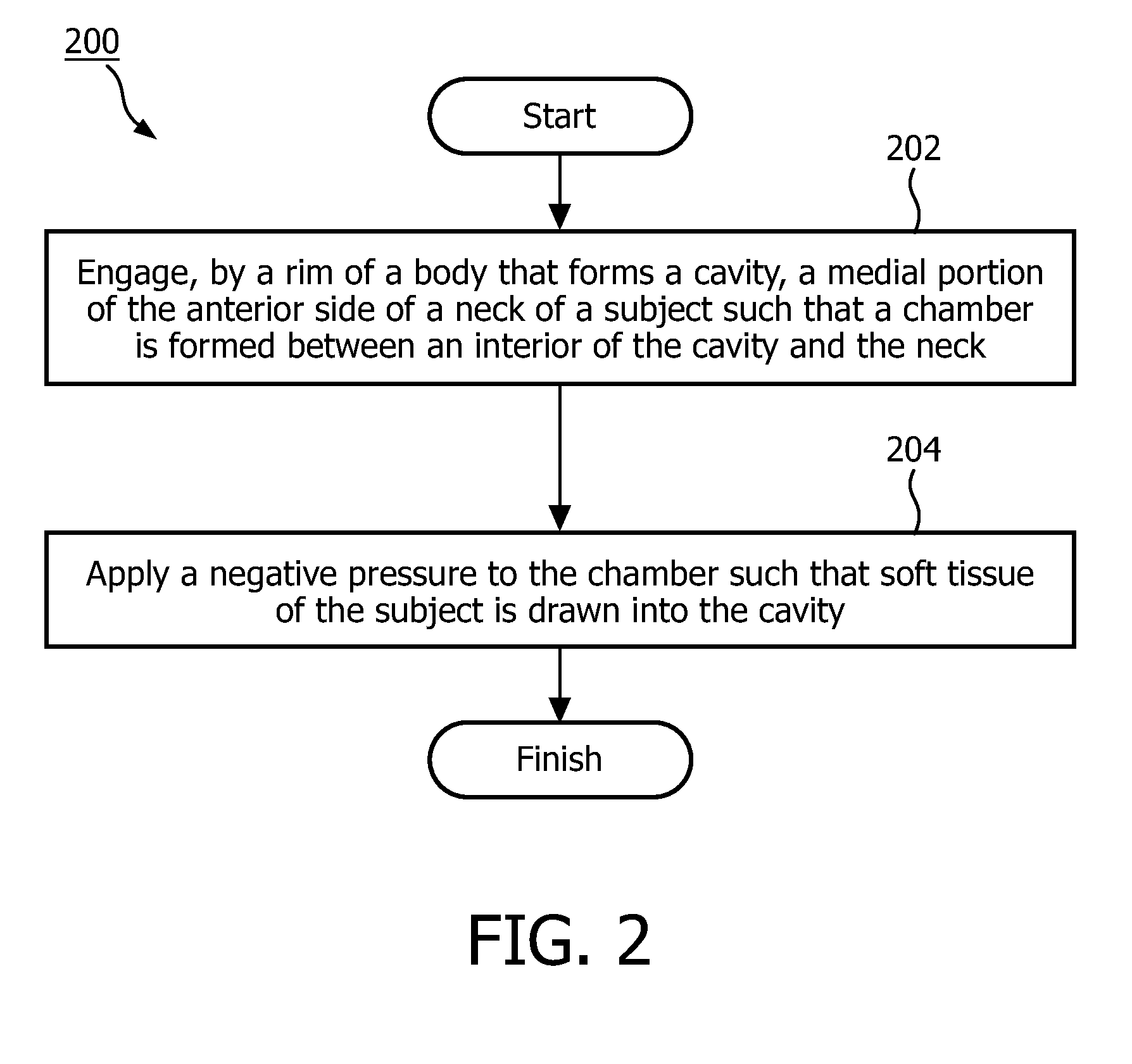
Negative pressure on neck to treat obstructive sleep apnea
InactiveUS20150126912A1Reduce temporary airway obstructionReduce obstructionSnoring preventionSuction-kneading massageAtmospheric pressureBronchial obstruction
Systems and methods to treat obstructive sleep apnea draw soft tissue of the front of the neck of the subject, in particular at or near the oropharynx, into a cavity by applying negative pressure. The opening of the cavity is formed by a rim of a body that is configured to be engaged, externally, with a medial portion of the anterior side of the neck such that engagement between the rim and the neck forms a chamber that can be sealed from atmospheric pressure. Movement of the soft tissue may thus reduce temporary airway obstruction.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Articulated Oral Airway
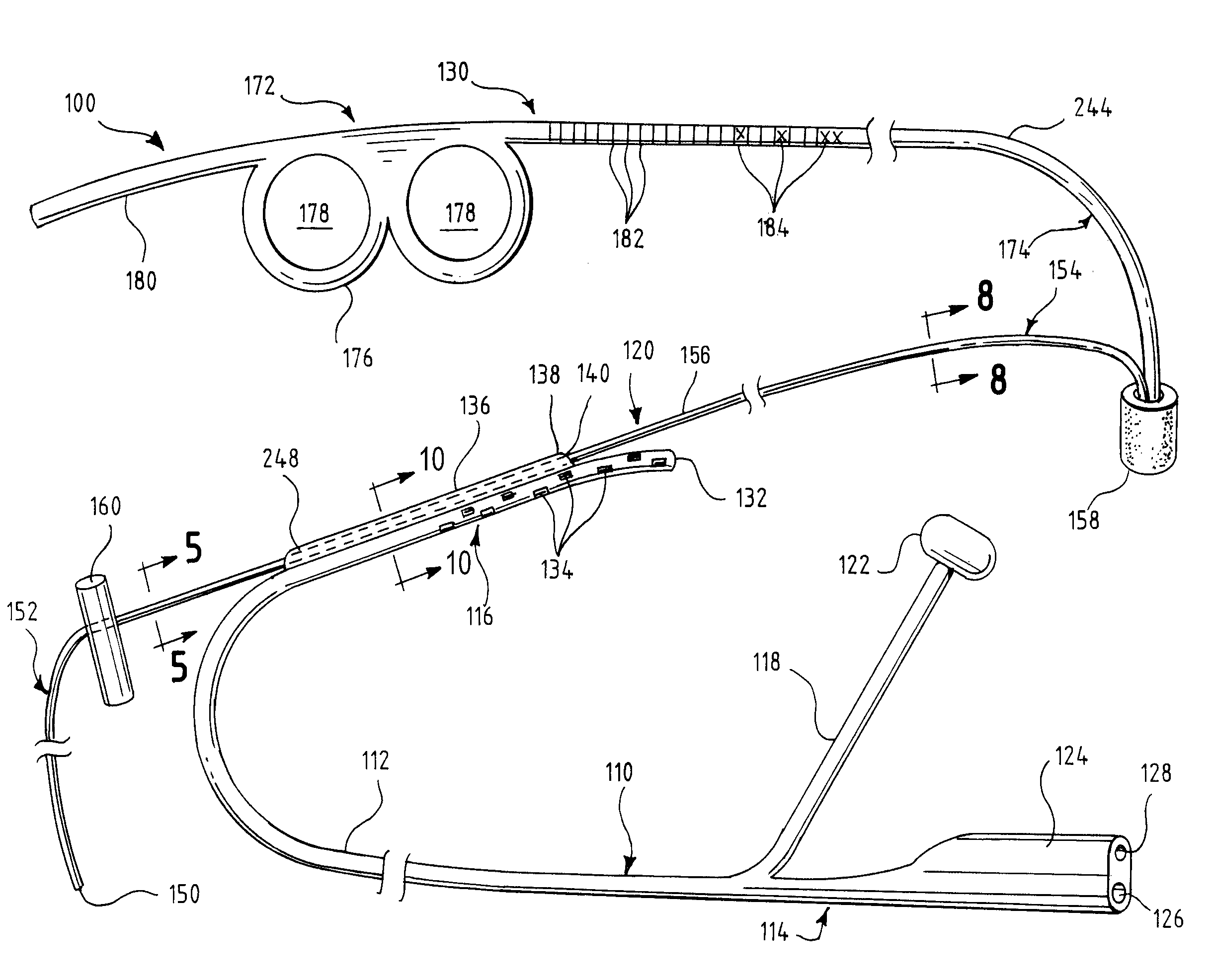
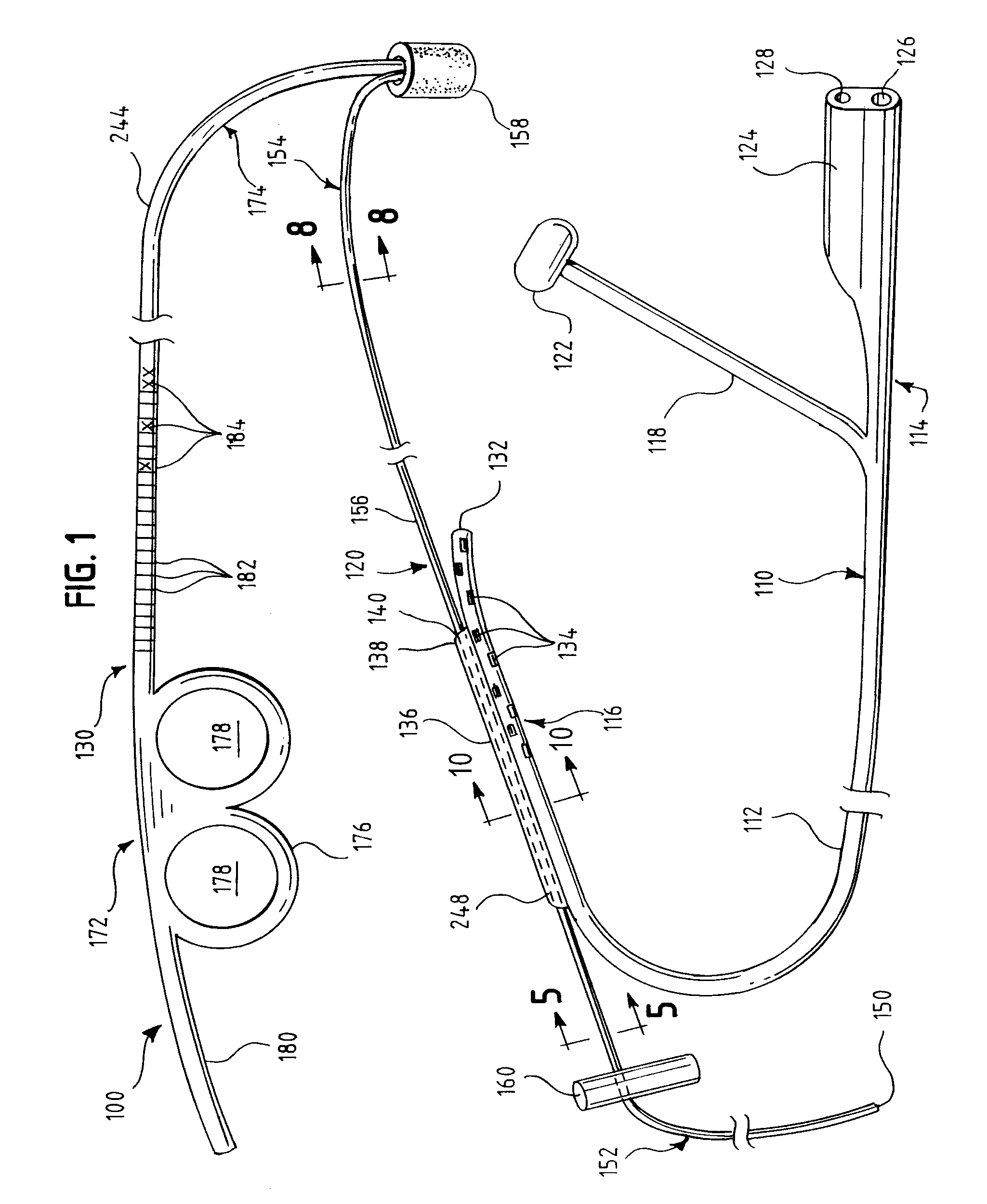
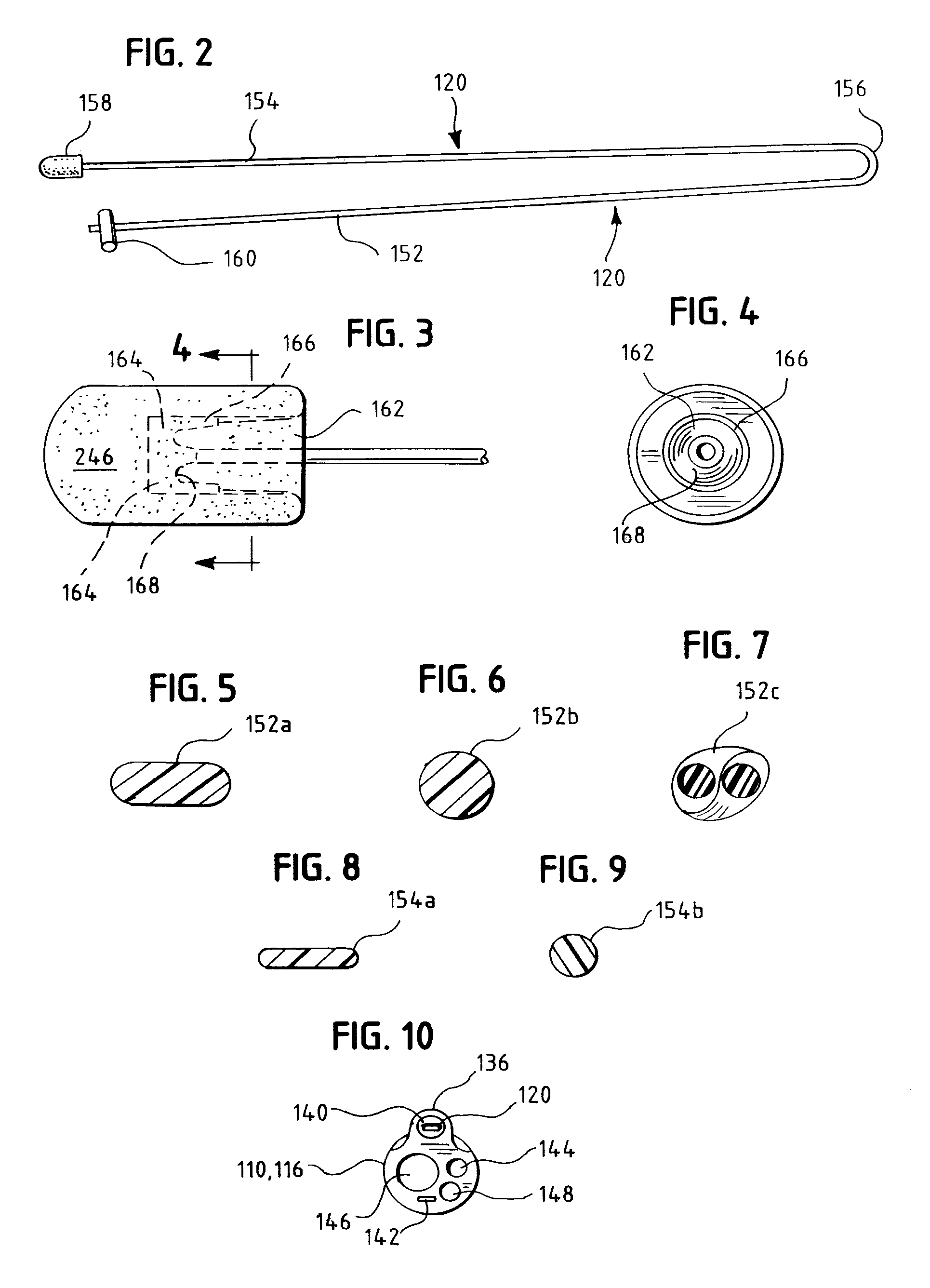
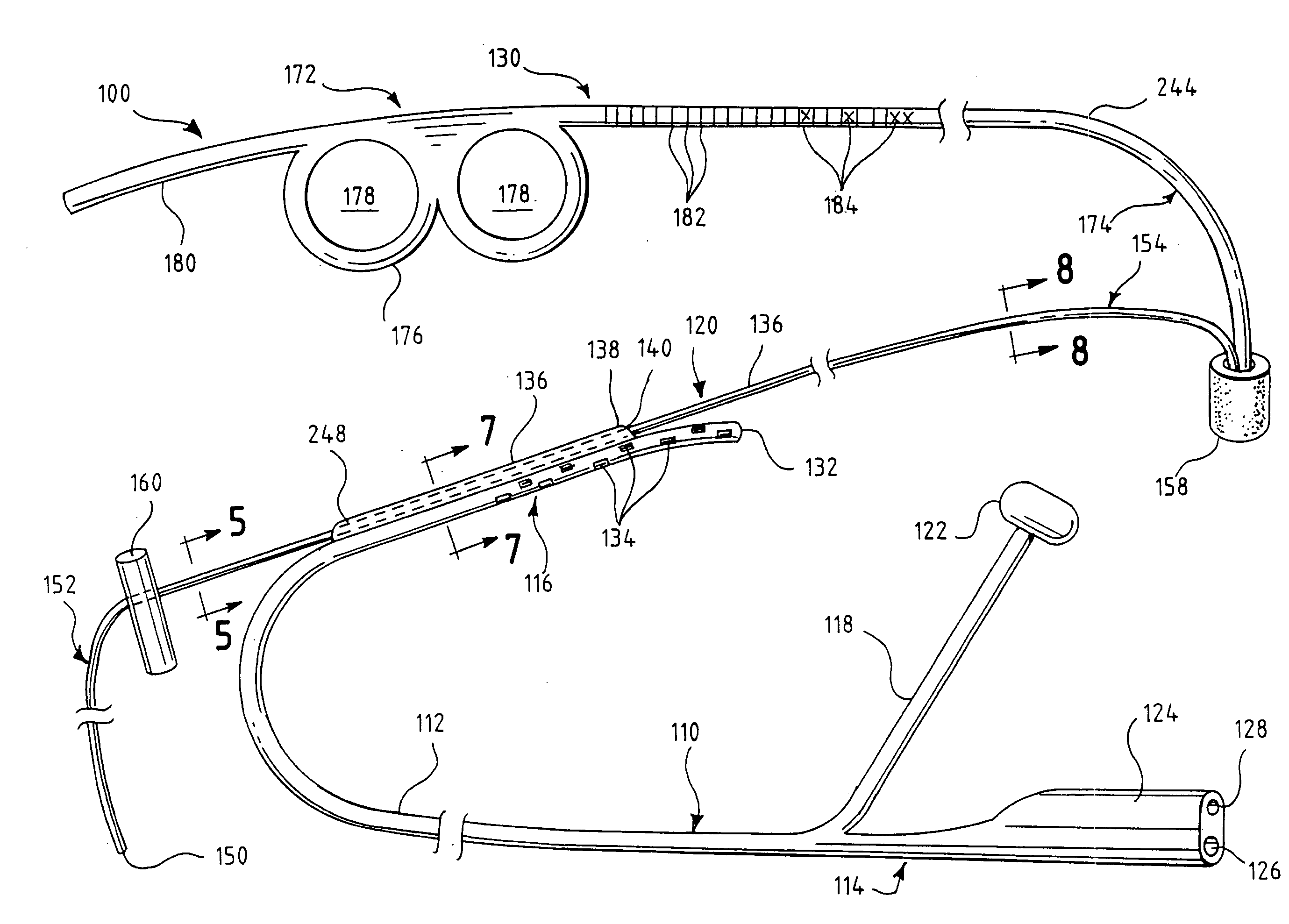
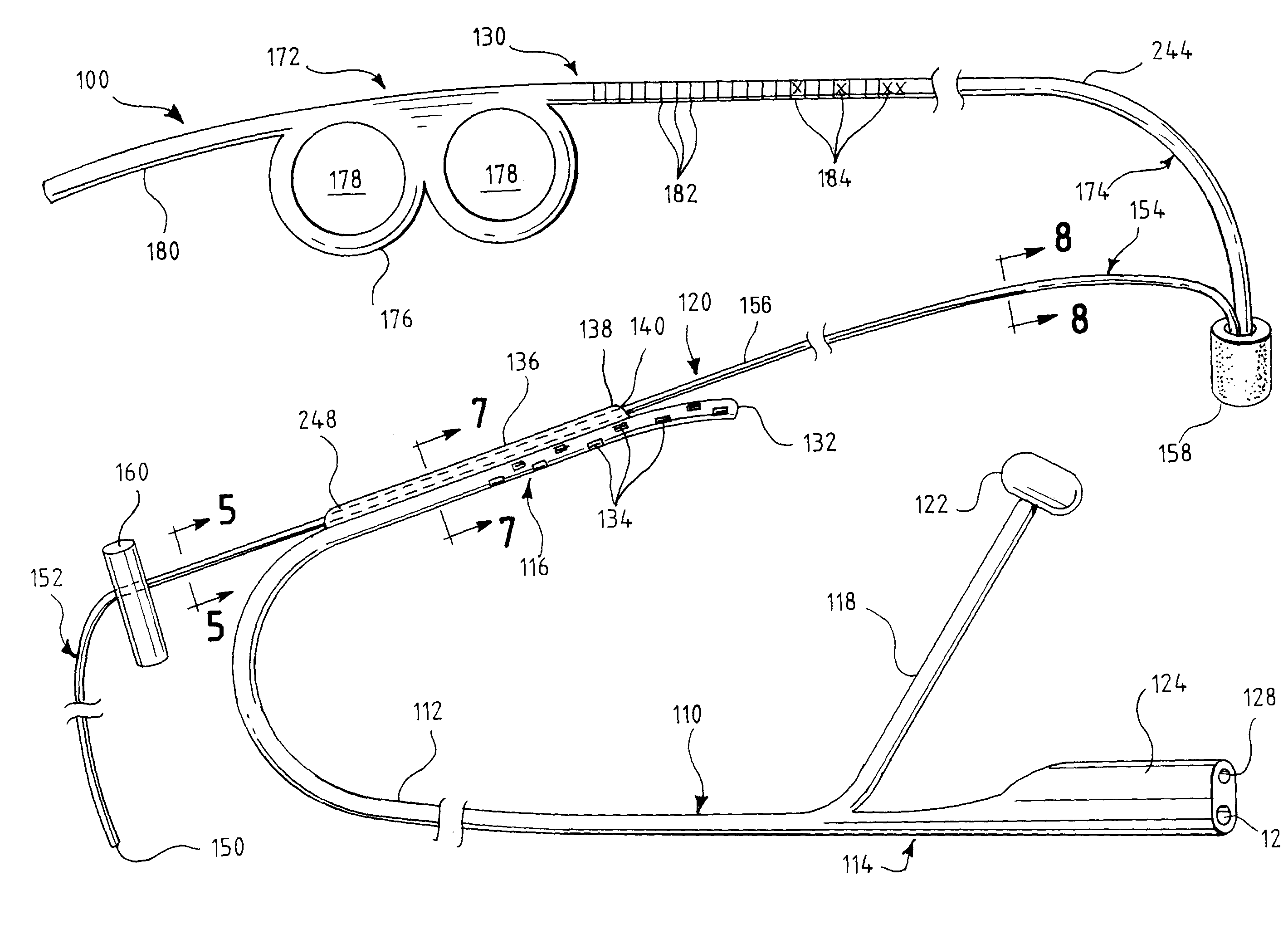
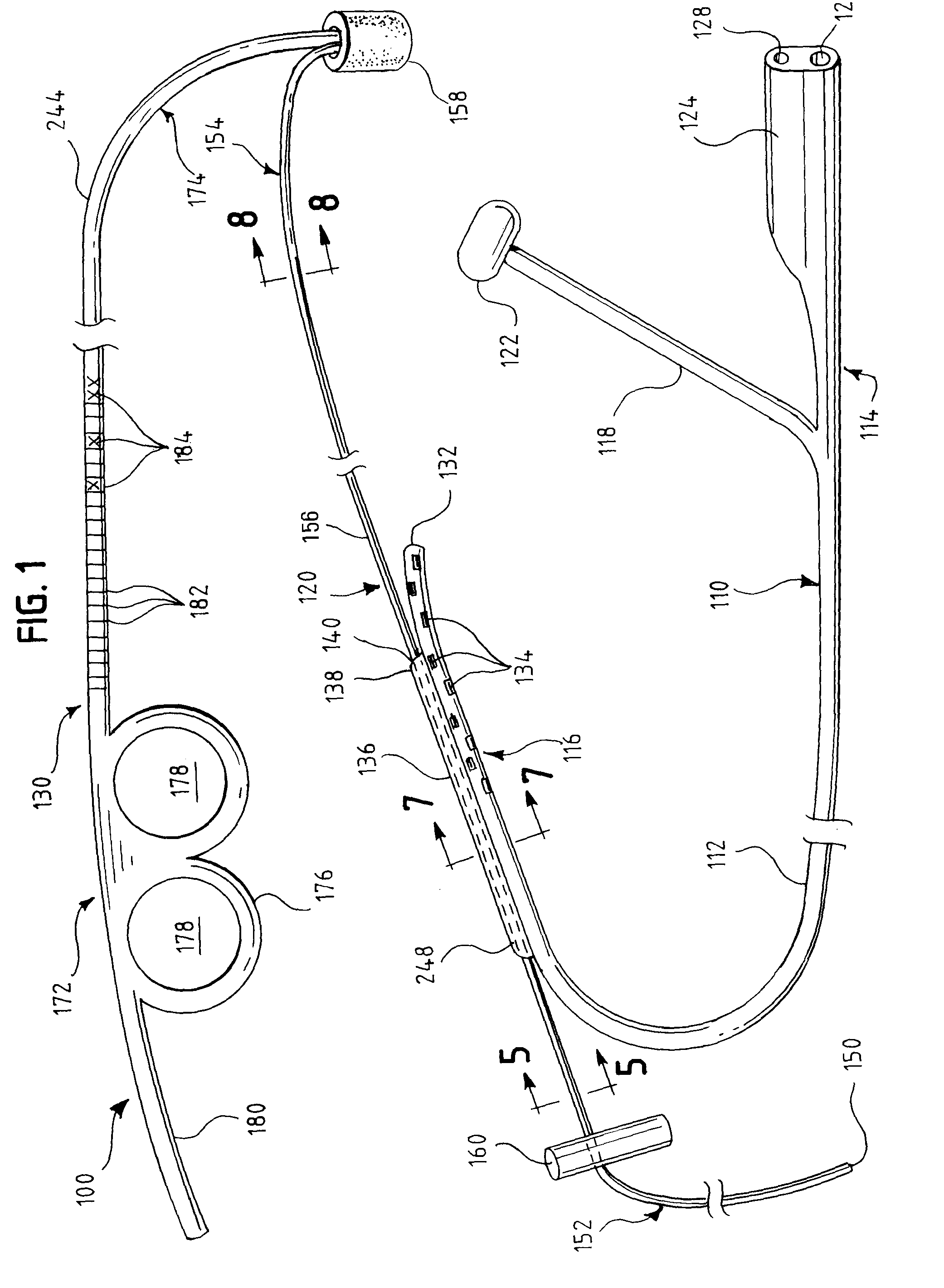
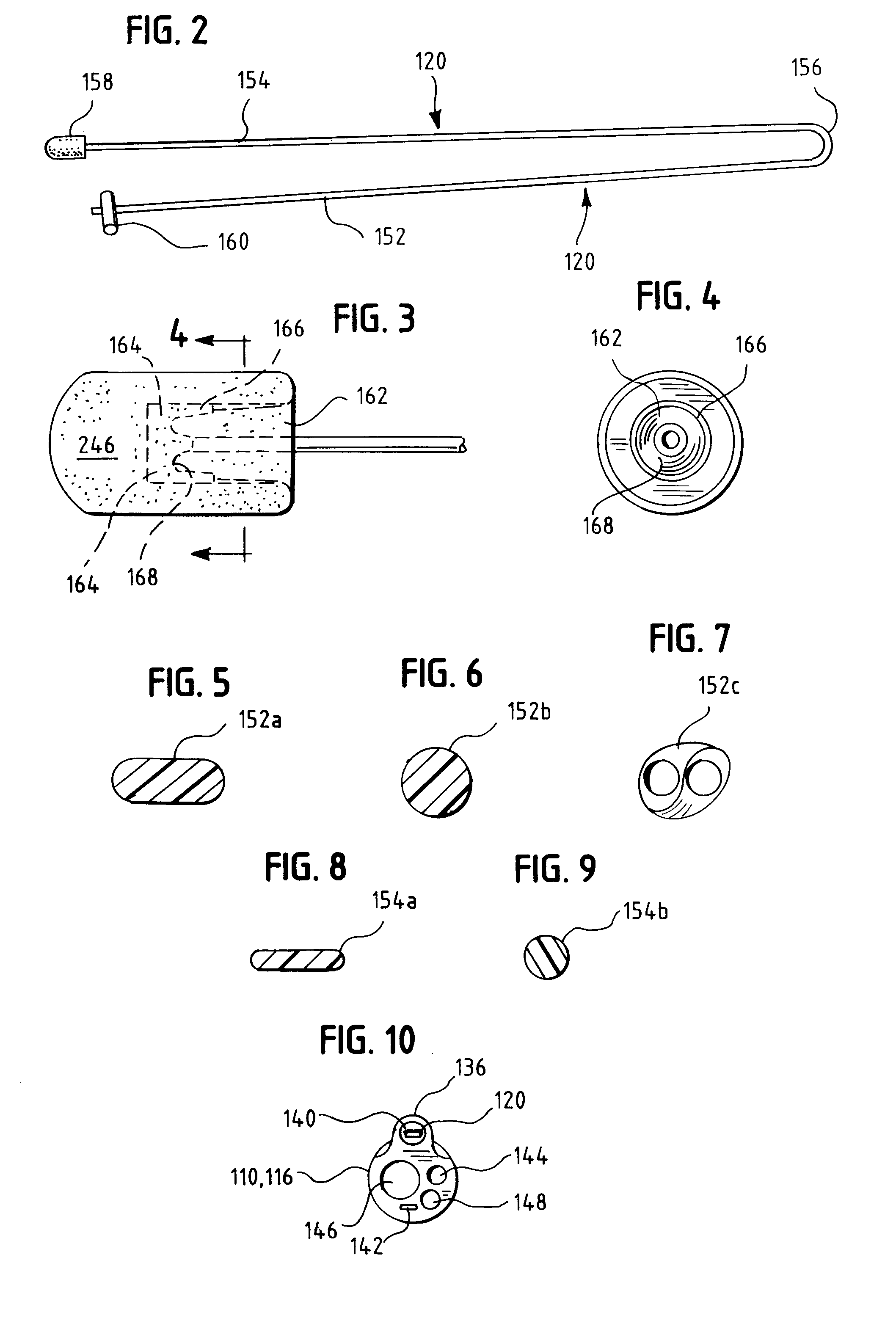
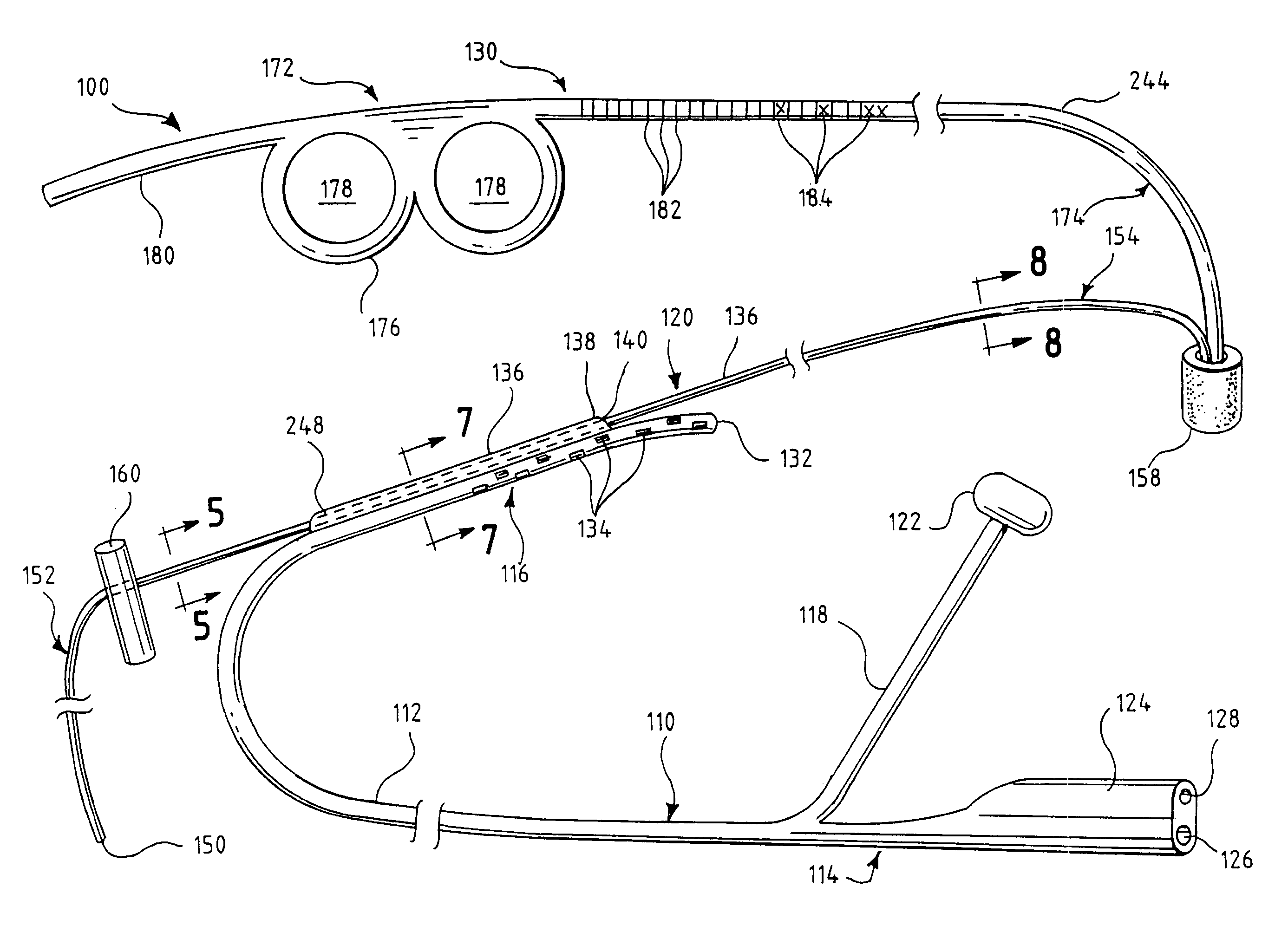
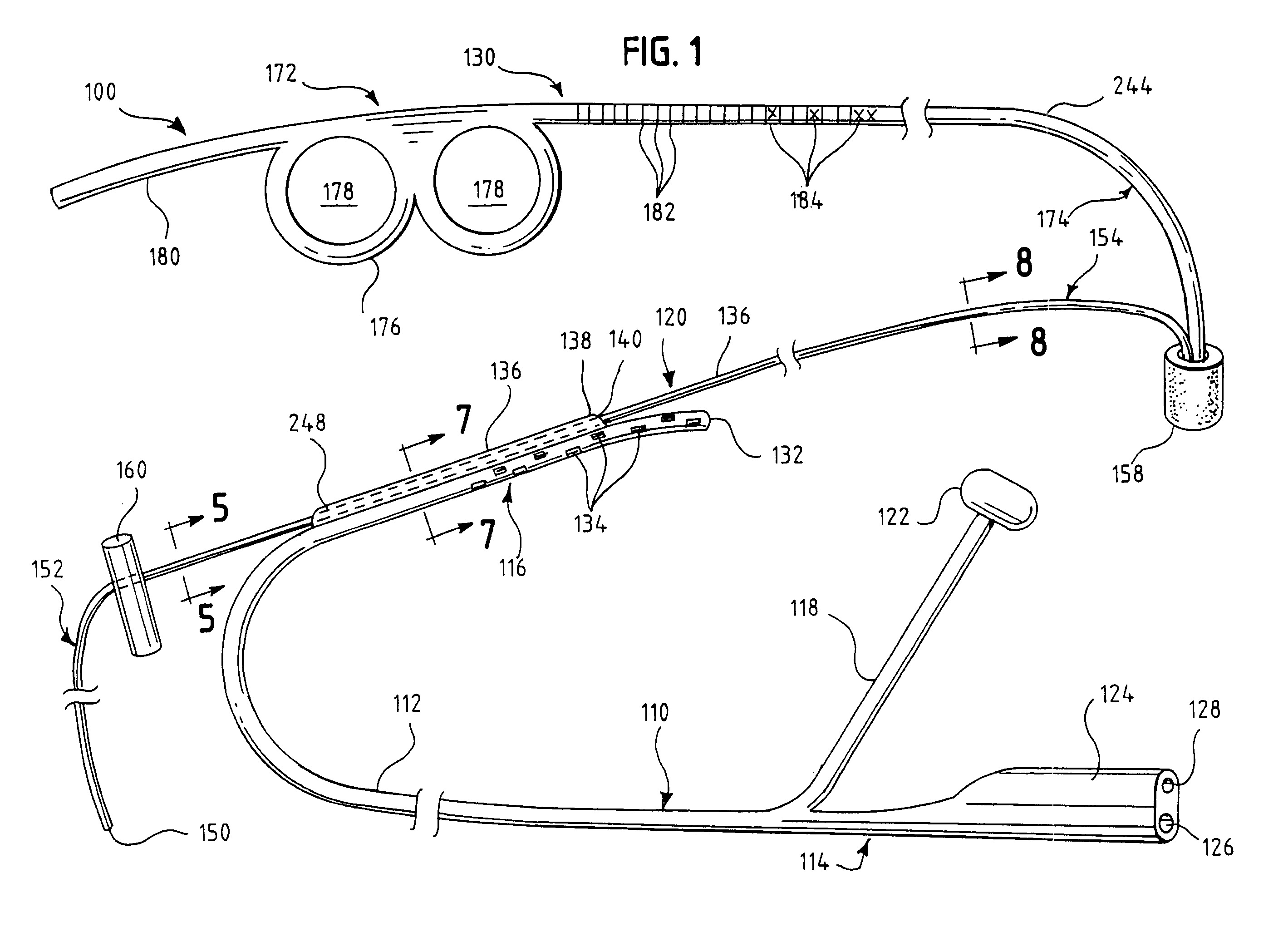
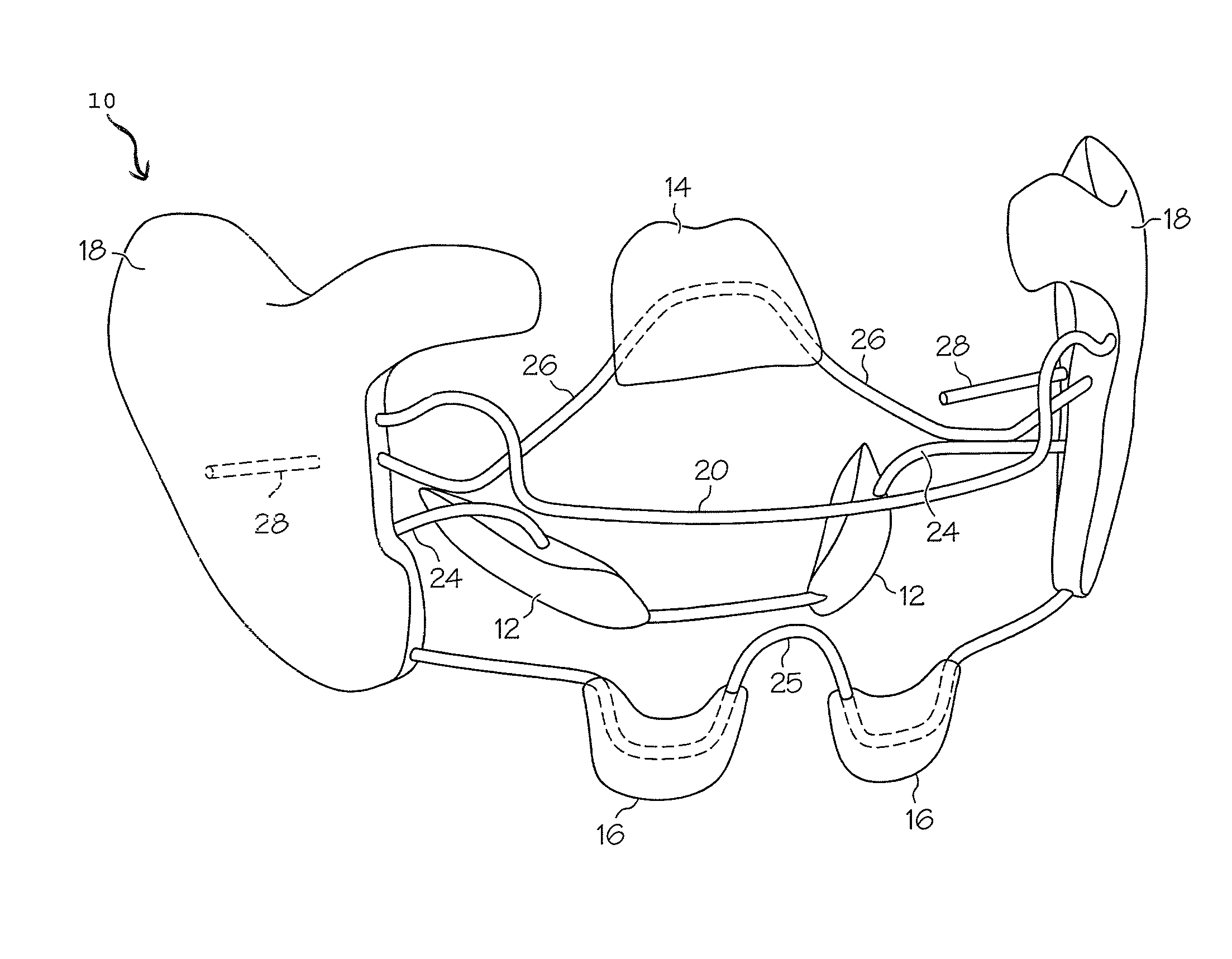
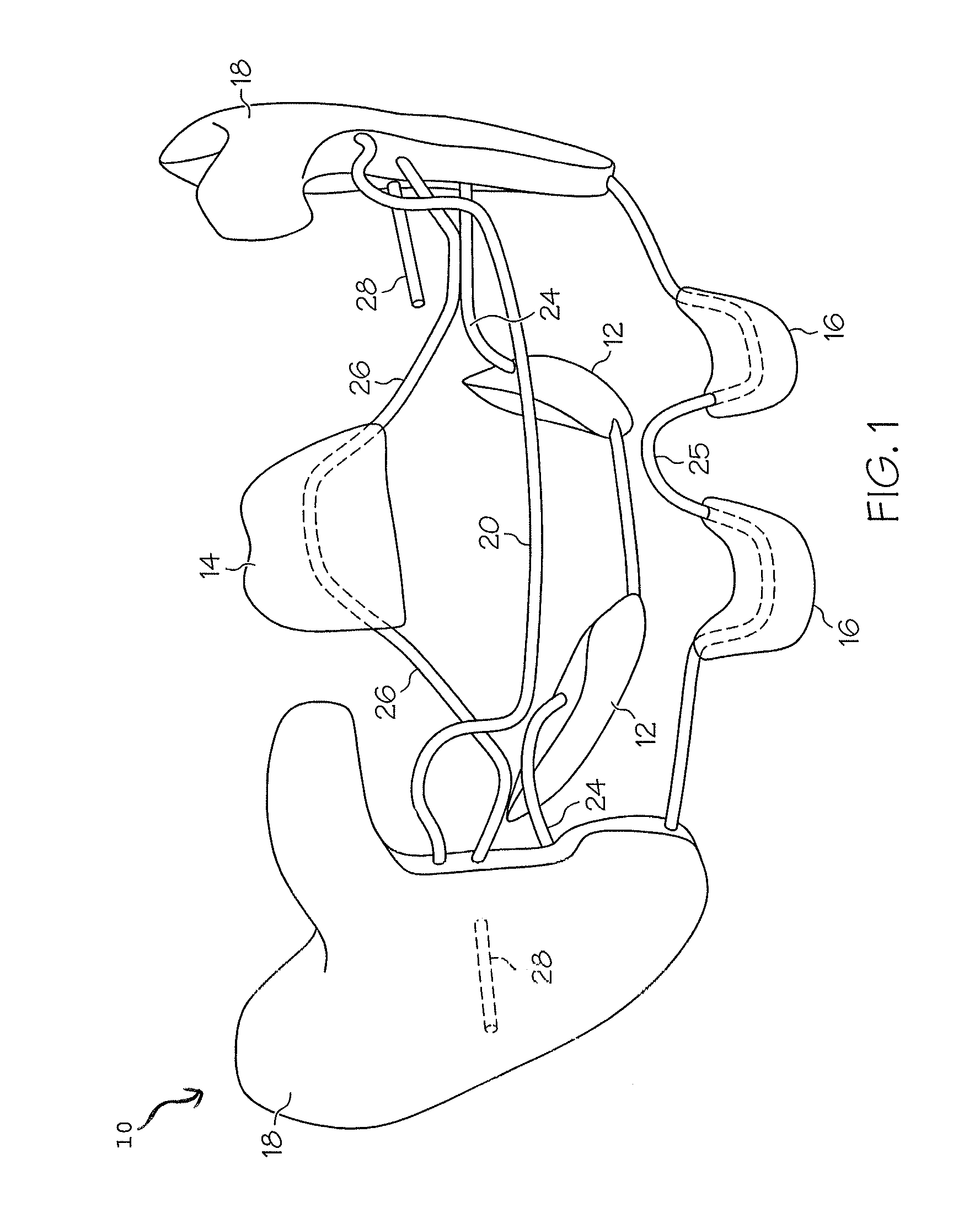
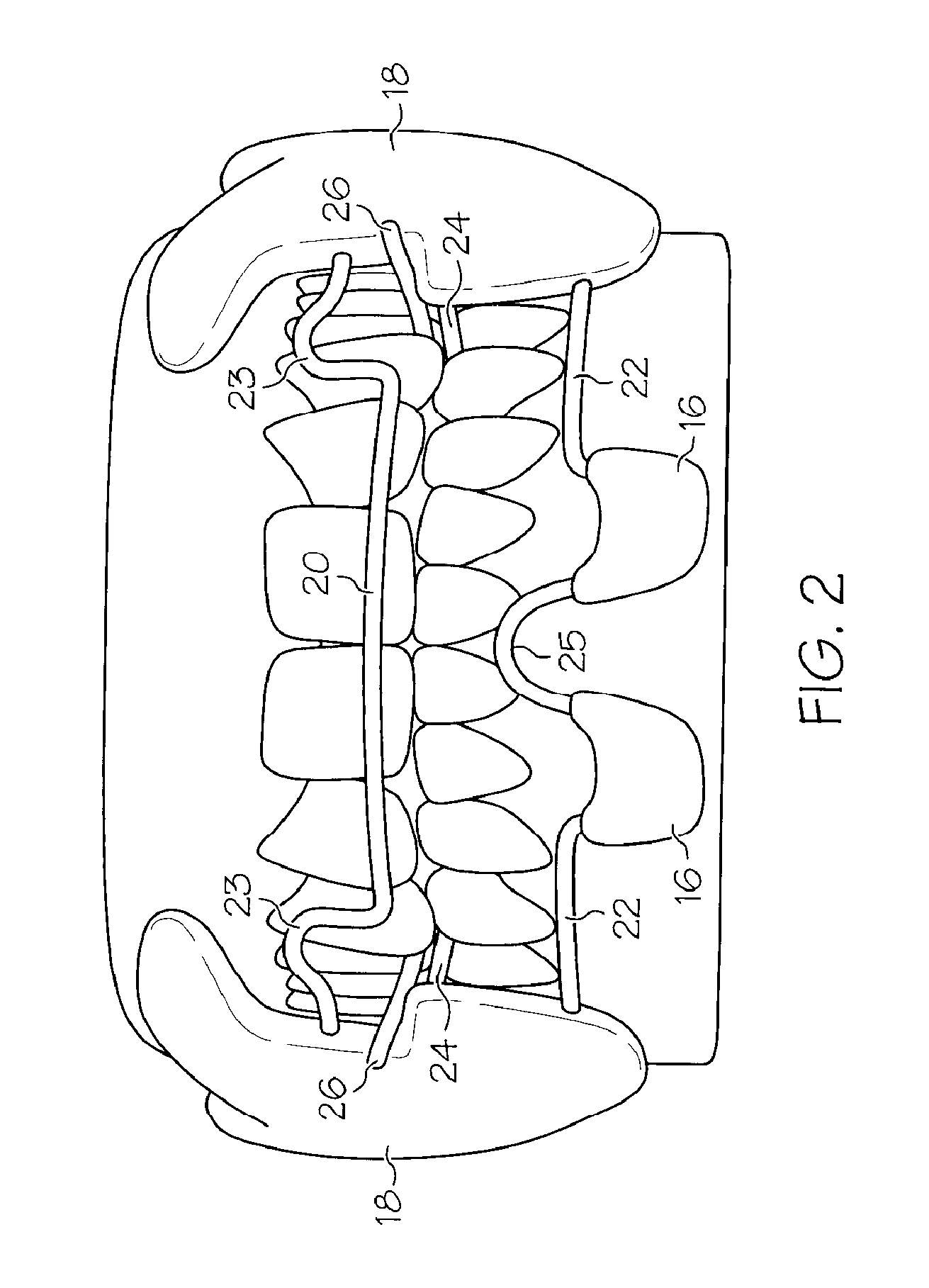
One embodiment of an oral airway comprised of two articulating parts which displace the tongue anteriorly and stent open the oropharynx. This device reversibly locks in a conformation which allows it to be used as a conduit for a fiberoptic scope or other airway device. An adjunct to airway management which can be used when mask ventilation or endotracheal intubation is indicated and can be removed easily after intubation without manipulation of the endotracheal tube. Other embodiments are described as shown.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
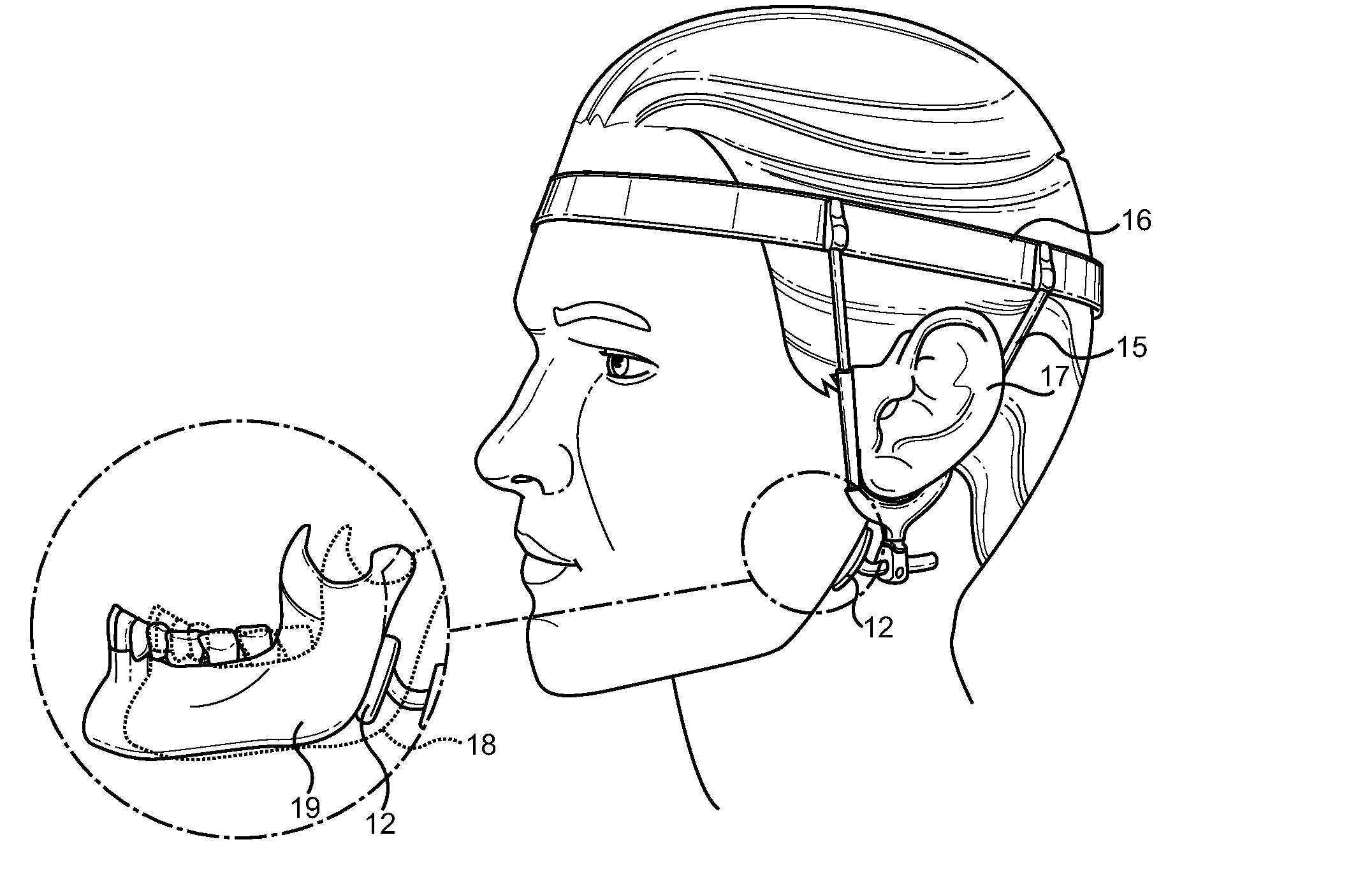
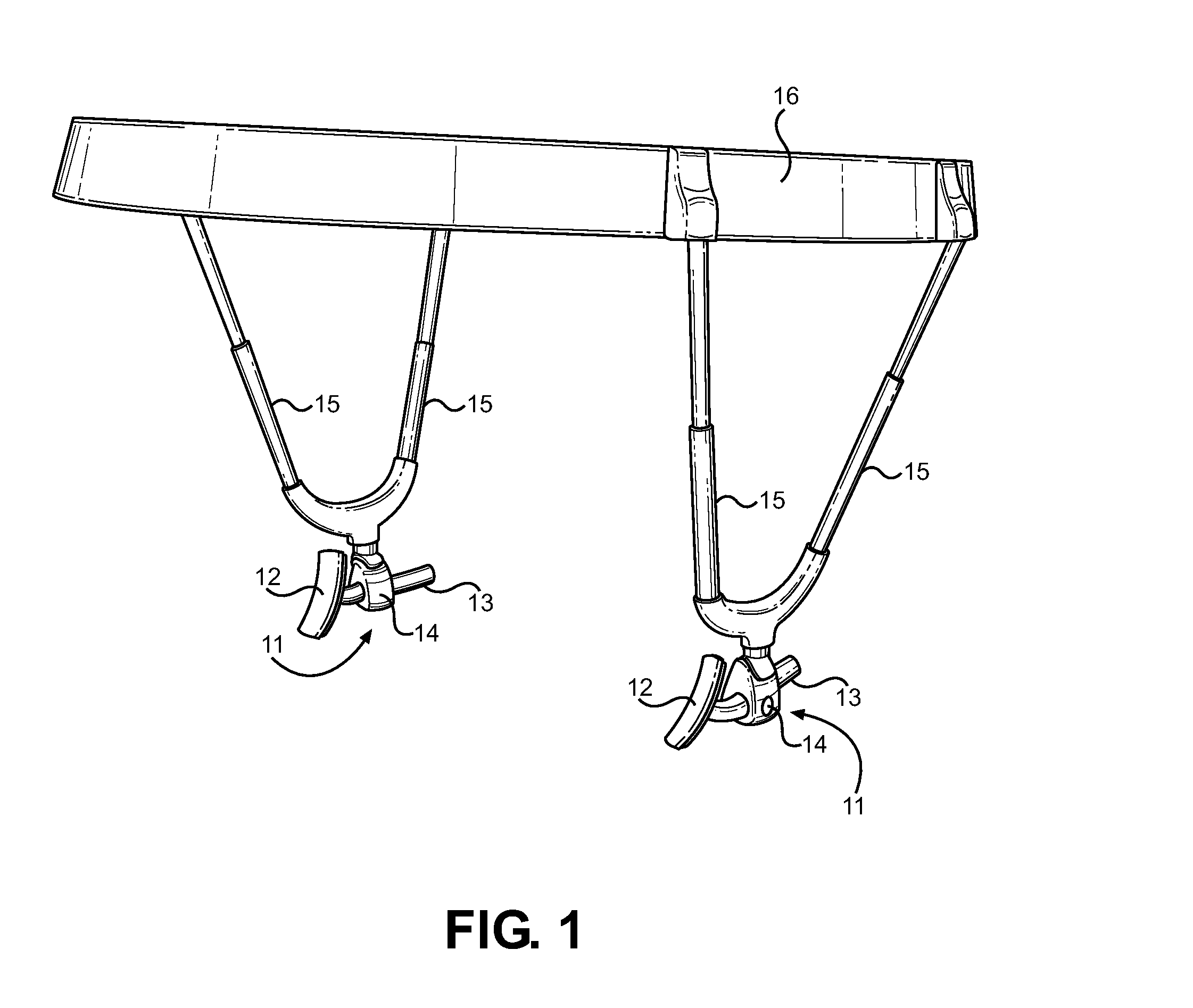
Jaw Thrust Appliance
ActiveUS20120186591A1Prevent asphyxiationAvoid aspirationTeeth fillingGymnastic exercisingMedicineJaw-thrust maneuver
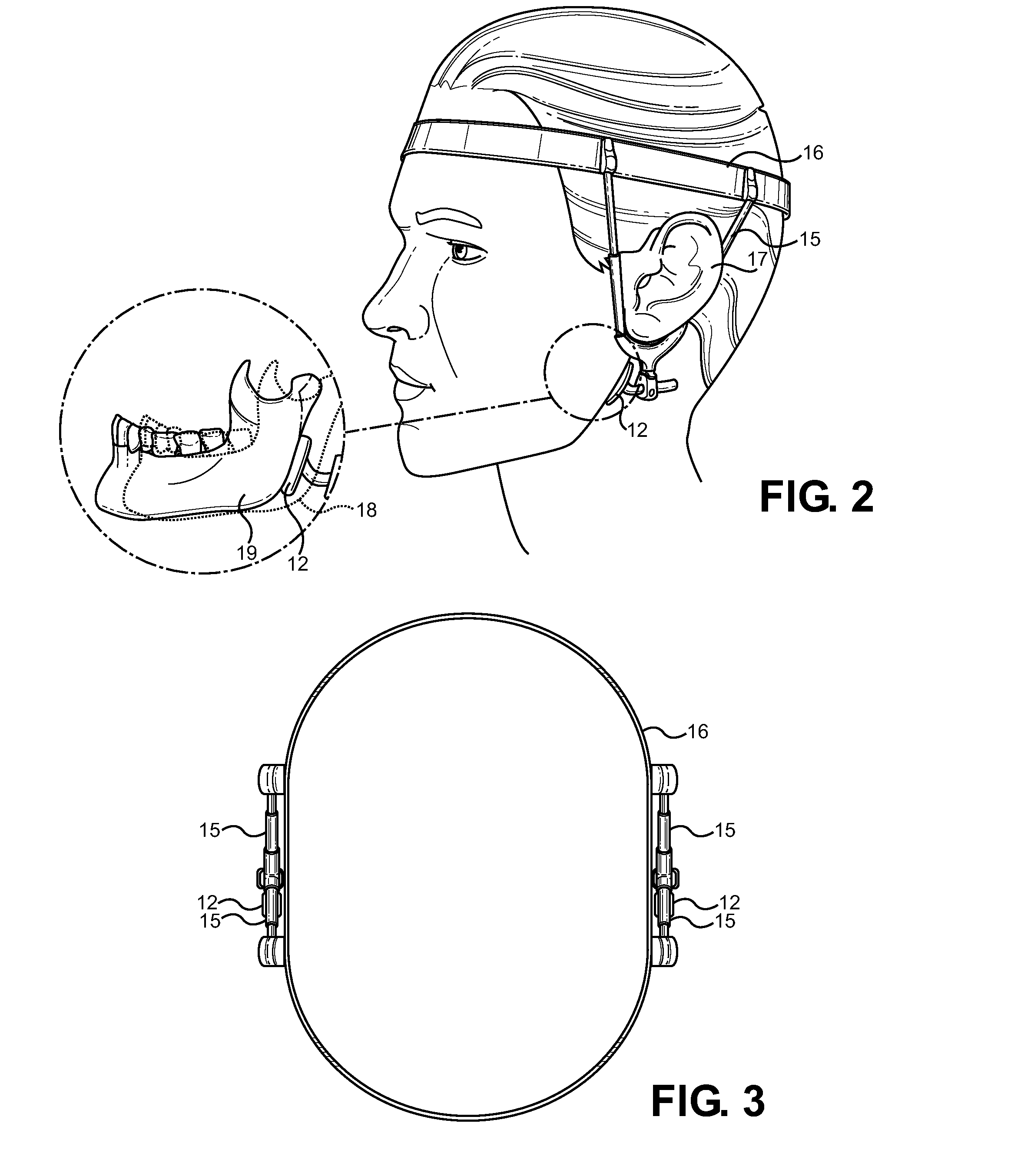
An extra-oral medical device is disclosed for treating respiratory conditions and maintaining an open airway. The device comprises a pair of jaw thrusters that affix to a headgear appliance encircling or otherwise attaching around a user's head. The thrusters include a pair of pads that attach to the headgear via two adjustable ear surrounds and place a forward load against the angle of a user's mandible. The forward load forces the mandible and the tongue forward, displacing the tongue from the posterior oropharynx and performing a jaw thrust maneuver for airway management. The device is adapted for medical and personal use, wherein the headgear can be worn while sleeping to treat sleep apnea, excessive snoring and other respiratory disorders, or alternatively may be used by medical professionals to maintain an open airway during a procedure or medical emergency.
Owner:SETHI MANU +1
Intraoral apparatus for treating upper airway disorders
ActiveUS8371309B2Reduce resistanceChange configurationSnoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDiseasePartial obstruction
Owner:TNT LABS
Esophageal intubation and airway management system and method
InactiveUS20080105263A1Avoid aspirationPrevents a strong gag reflexTracheal tubesBronchoscopesReflexTherapeutic Devices
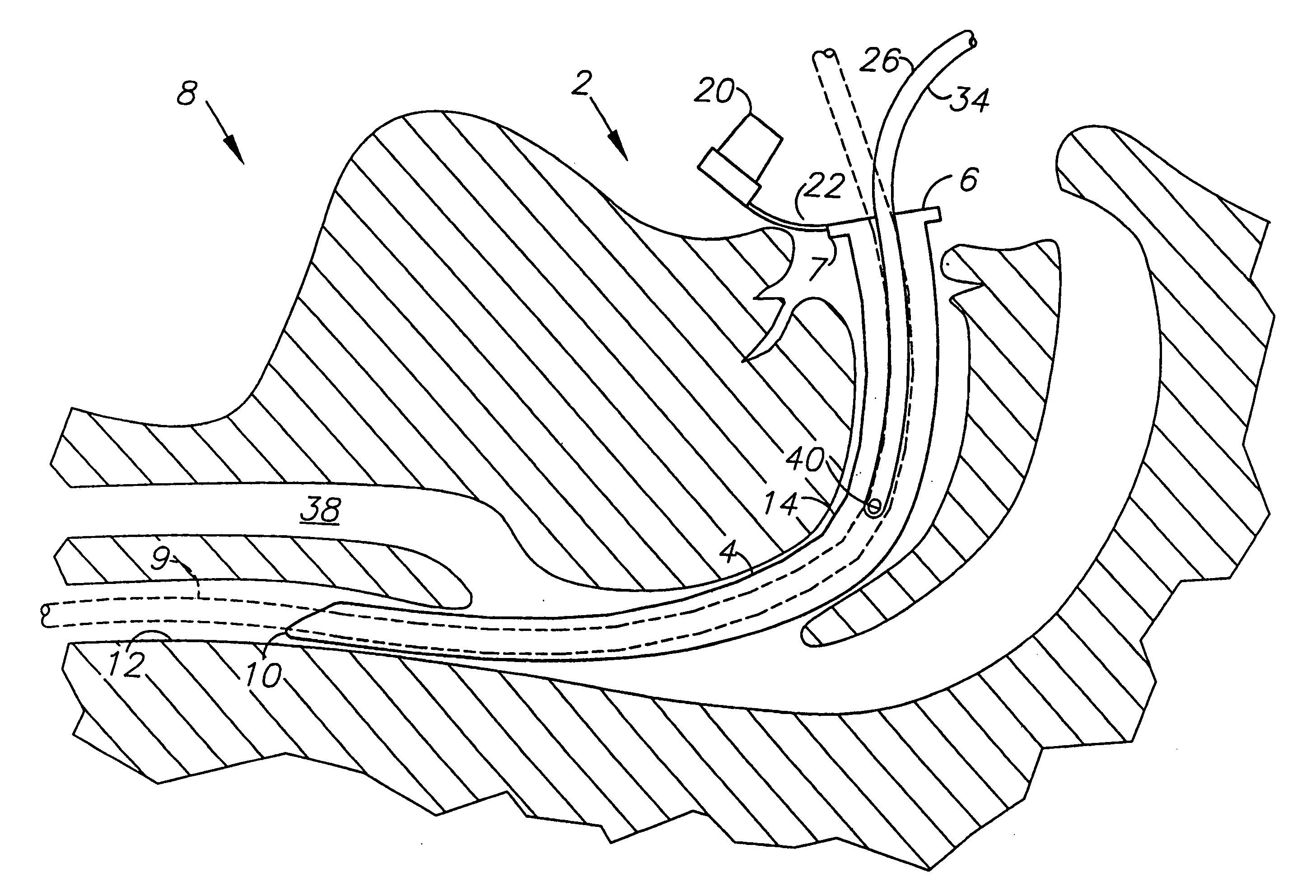
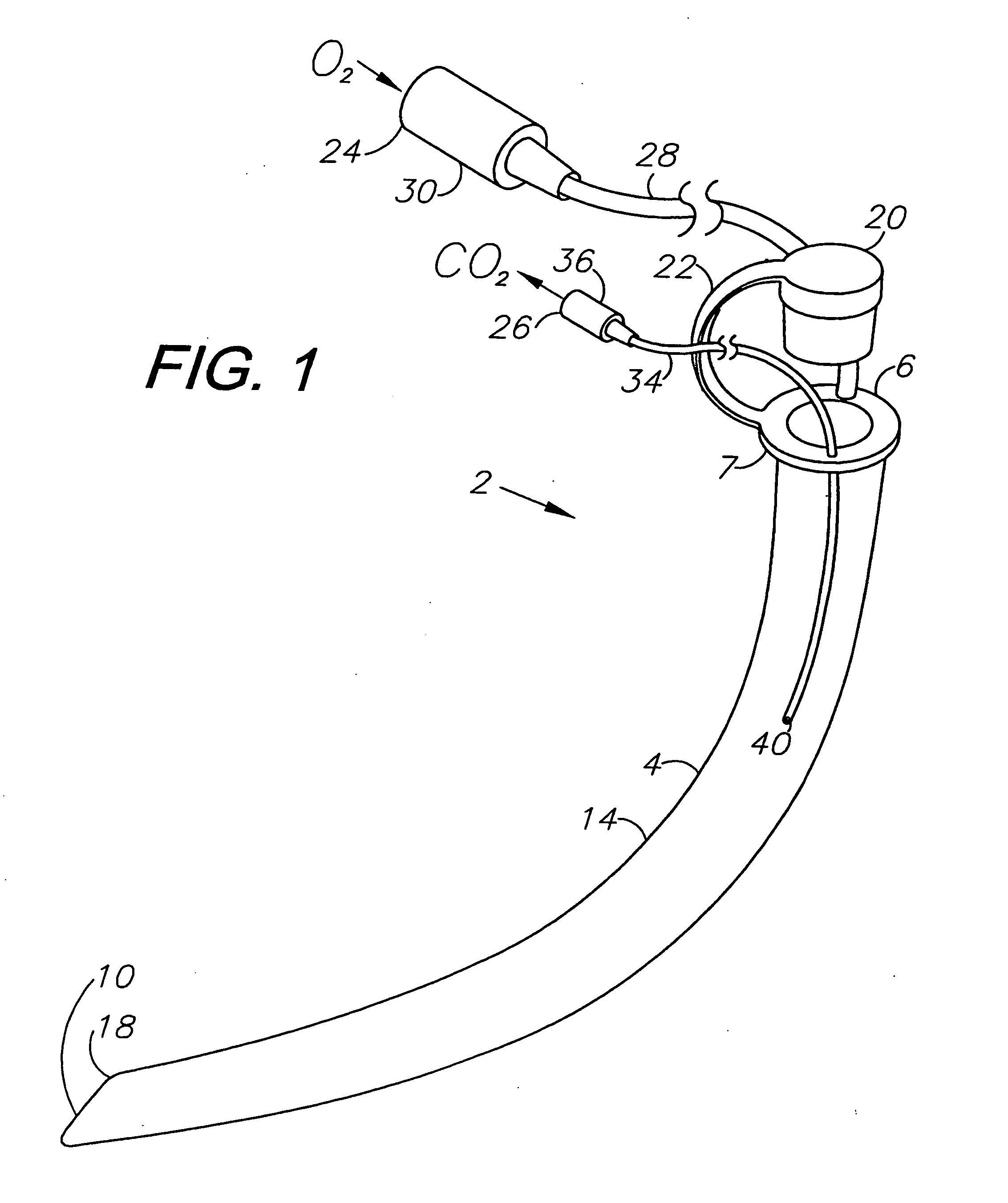
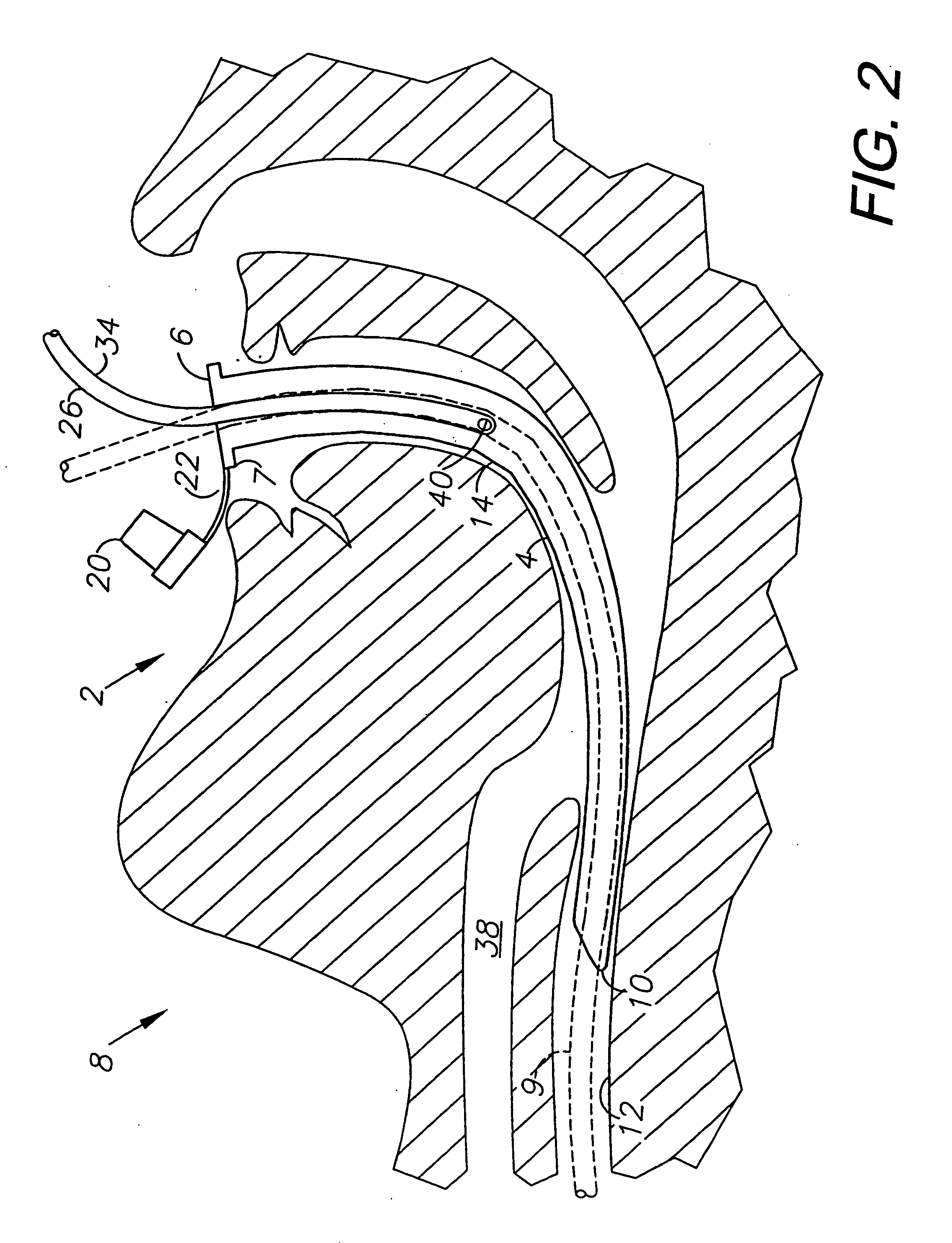
An esophageal intubation system includes a main tube with a tapered body, proximal and distal ends and a bore extending between and open at the ends. The main tube is inserted into the oropharynx and its distal end extends into the upper esophagus in order to provide a conduit for esophagoscopes, gastroscopes and related diagnostic and treatment equipment. A first auxiliary tube assembly delivers O2 close to the larynx. A second ancillary tube assembly samples CO2 from the larynx region. An esophageal intubation method includes the steps of moderately sedating a patient, placing a main esophageal tube in the oropharynx and partway into the upper esophagus, passing an esophagoscope or a gastroscope through the main tube and into the esophagus or stomach while minimizing the gag reflex, delivering O2 and sampling CO2 from the pharynx region.
Owner:JADHAV KISHOR B
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com