Method for removing organic pollutants in water by using hydroxyl free radicals generated by organic membrane
A technology based on organic pollutants and free radicals, applied in the field of photochemical technology and sewage treatment, can solve problems such as difficulty in popularization and application, high cost of ray method, poor continuous operability, etc. Effect of Water Treatment Costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
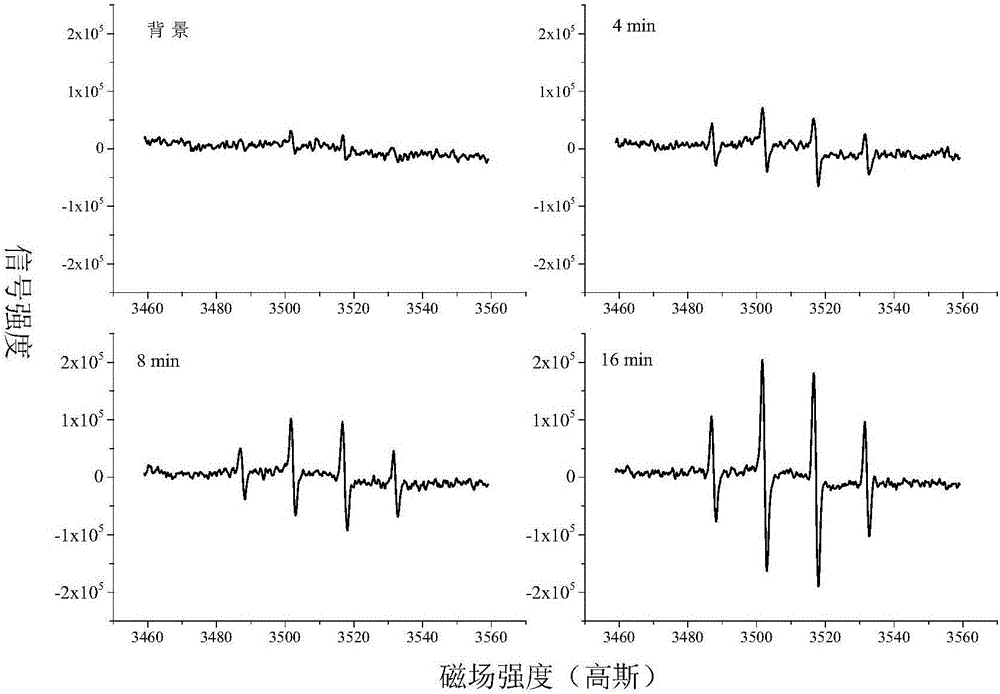
[0044] In this example, the ESR qualitative analysis of the photocatalytic generation of hydroxyl radicals on the surface of the nitrocellulose membrane was carried out.
[0045] Cut the nitrocellulose membrane into strips with a length of 2 cm and a width of 0.1 cm, insert them into a quartz sample tube, and inhale 100 mM picoline N-oxide (dimethyl pyridine N-oxide, DMPO for short), and carry out in-situ electron autosynthesis. Detection by spin resonance spectroscopy. In the case of 180W solar light, the generation of hydroxyl radicals is monitored in real time. The result is as figure 1 As shown, when there is no light, the background signal is basically a flat line. When the light is 4min, 8min and 16min, the characteristic signal of hydroxyl radical and DMPO adduct can be observed, and 4 peaks appear, and the peak height ratio is 1:2. :2:1, hyperfine splitting constant a H =a N =14.9 Gauss, the peak height increases linearly as the illumination time increases, confir...
Embodiment 2
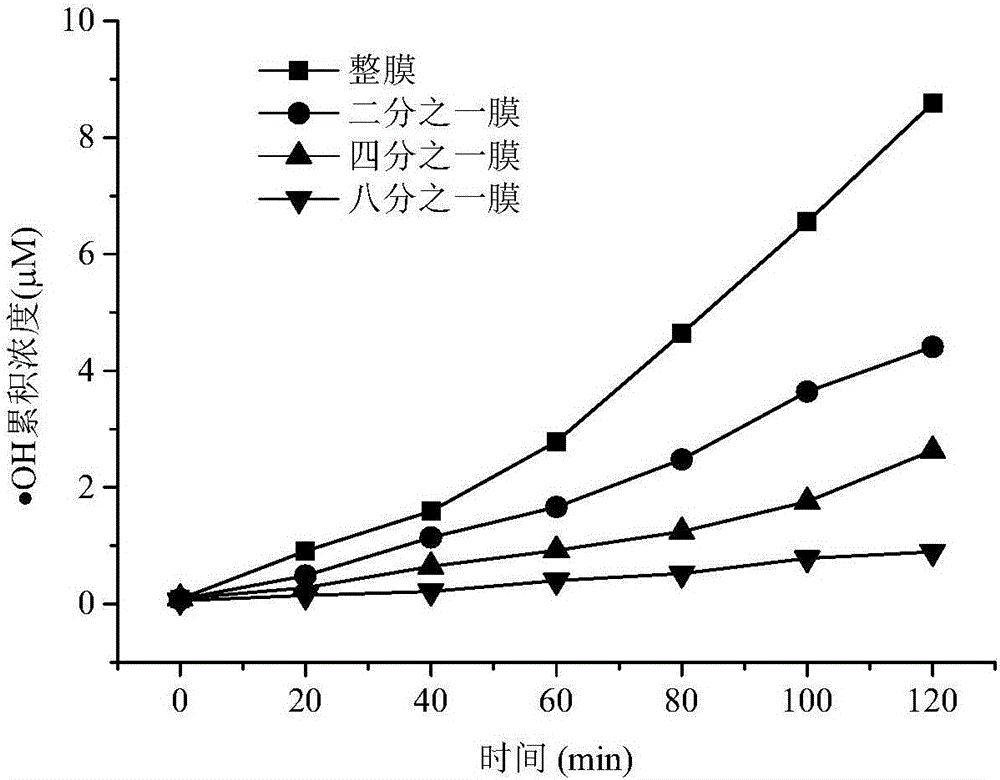
[0047] Embodiment 2 (generation situation of hydroxyl radicals under different membrane areas)
[0048] In a 100mL beaker, add 50mL of 10mM benzene solution, put the whole, one-half, one-fourth and one-eighth nitrocellulose membranes with a diameter of 47mm (φ47mm), and make the membrane The film is still at the bottom of the beaker and placed under a 180W sun lamp to irradiate. The hydroxyl radical formed by the nitrocellulose membrane reacts with benzene to generate phenol. Samples were taken every 20 minutes, and the change of phenol concentration in the solution was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography, reflecting the generation of hydroxyl radicals. The result is as figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that the amount of hydroxyl radicals produced is basically linear with the increase in the area of the nitrocellulose membrane, indicating that the nitrocellulose membrane can generate hydroxyl radicals quantitatively and stably. In order to clarify the caus...
Embodiment 3
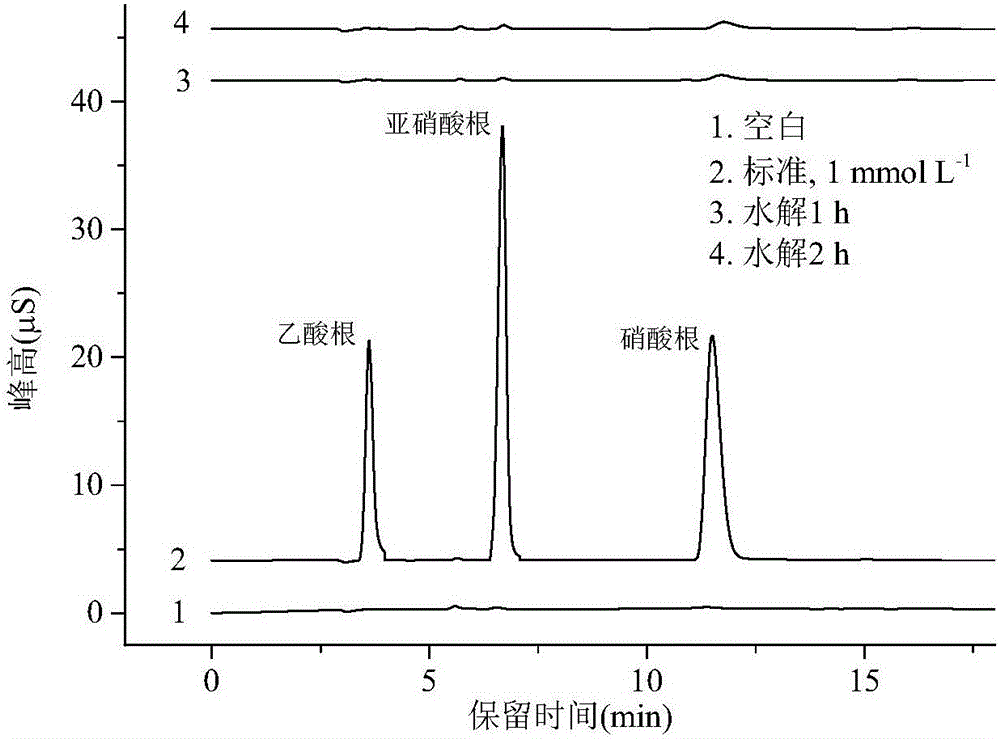
[0049] Embodiment 3 (solution phase nitrate radical and nitrite radical illumination produce the elimination of hydroxyl radical)
[0050] In terms of chemical structure, nitrocellulose membrane is a nitrate ester of cellulose, which may undergo hydrolysis to produce nitrate or nitrite. At present, it cannot be ruled out that the latter two can also produce hydroxyl radicals under light. In order to rule out the above possibility, the hydrolysis experiment of nitrocellulose membrane was carried out. Put a φ47mm nitrocellulose membrane in pure water, hydrolyze it at 35°C, use ion chromatography to measure the nitrate and nitrite produced by hydrolysis, and compare it with the blank and standard, the results are as follows image 3 shown. It can be seen that the nitrocellulose membrane can only be slightly hydrolyzed in water; compared with the standard, after 2 hours of hydrolysis, only 0.8 μM nitrite and 2.3 μM nitrate were produced in the solution. Under the same conditions...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com