Patents
Literature
69 results about "Bi ventricular" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
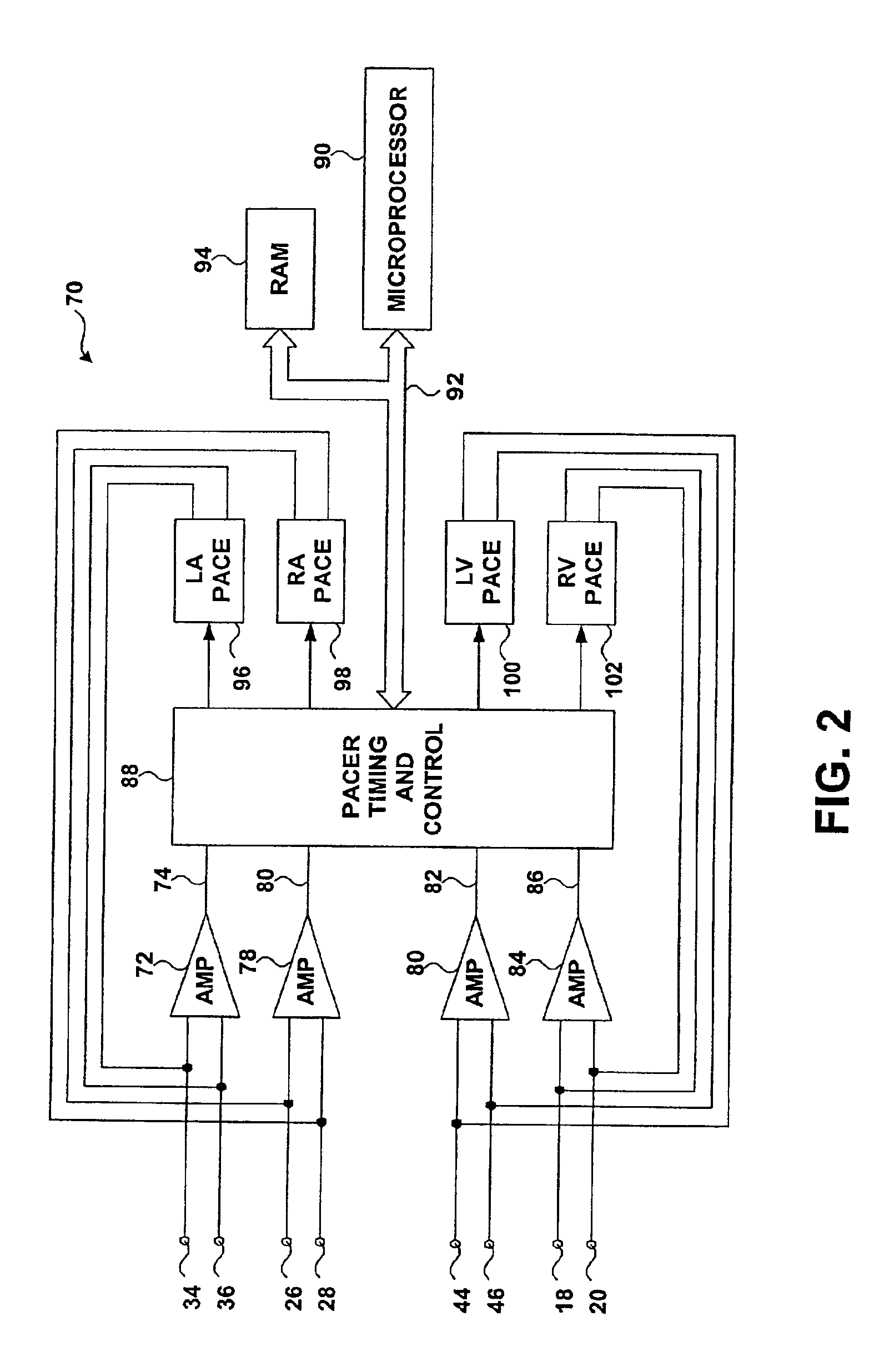
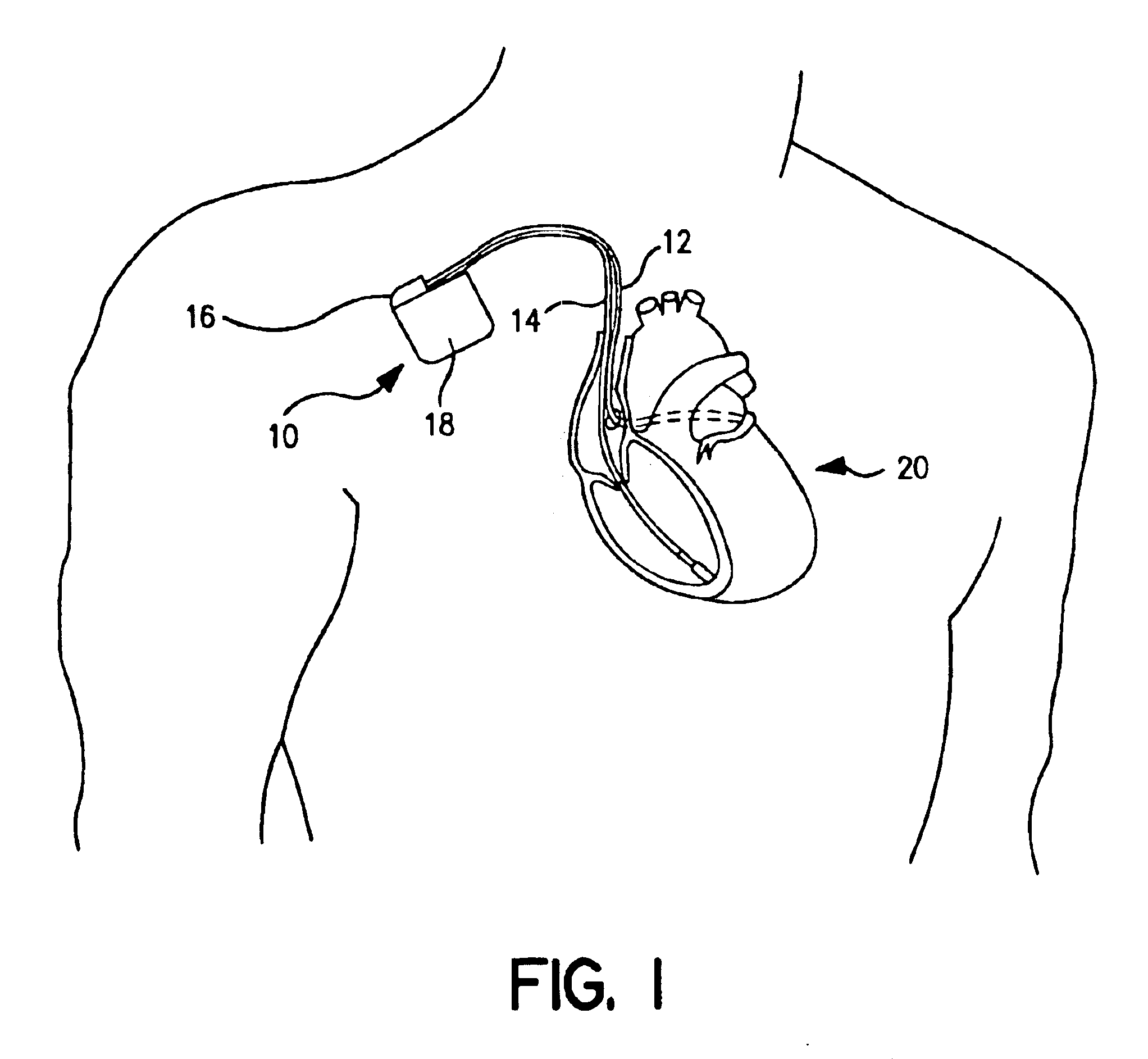
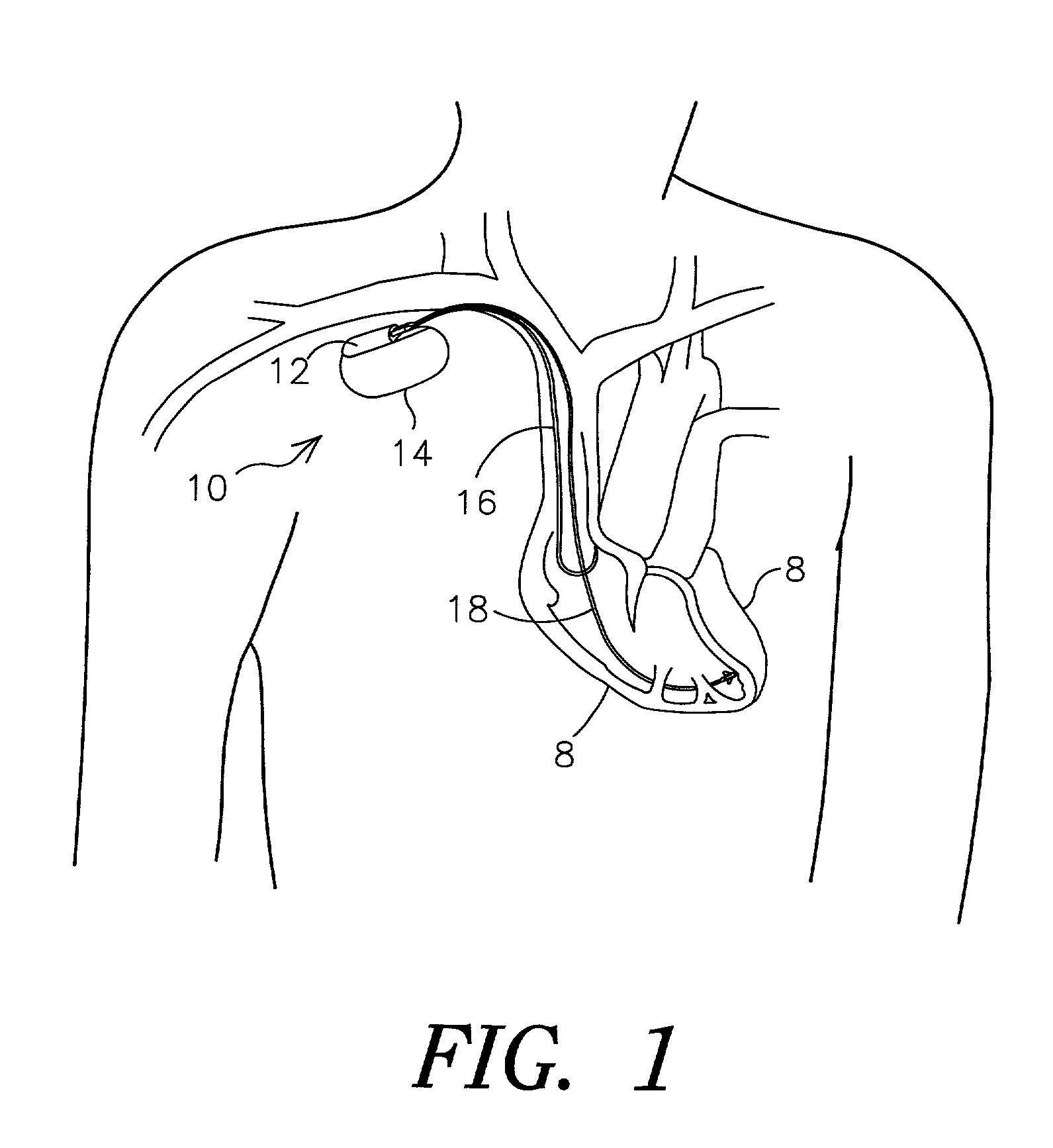
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
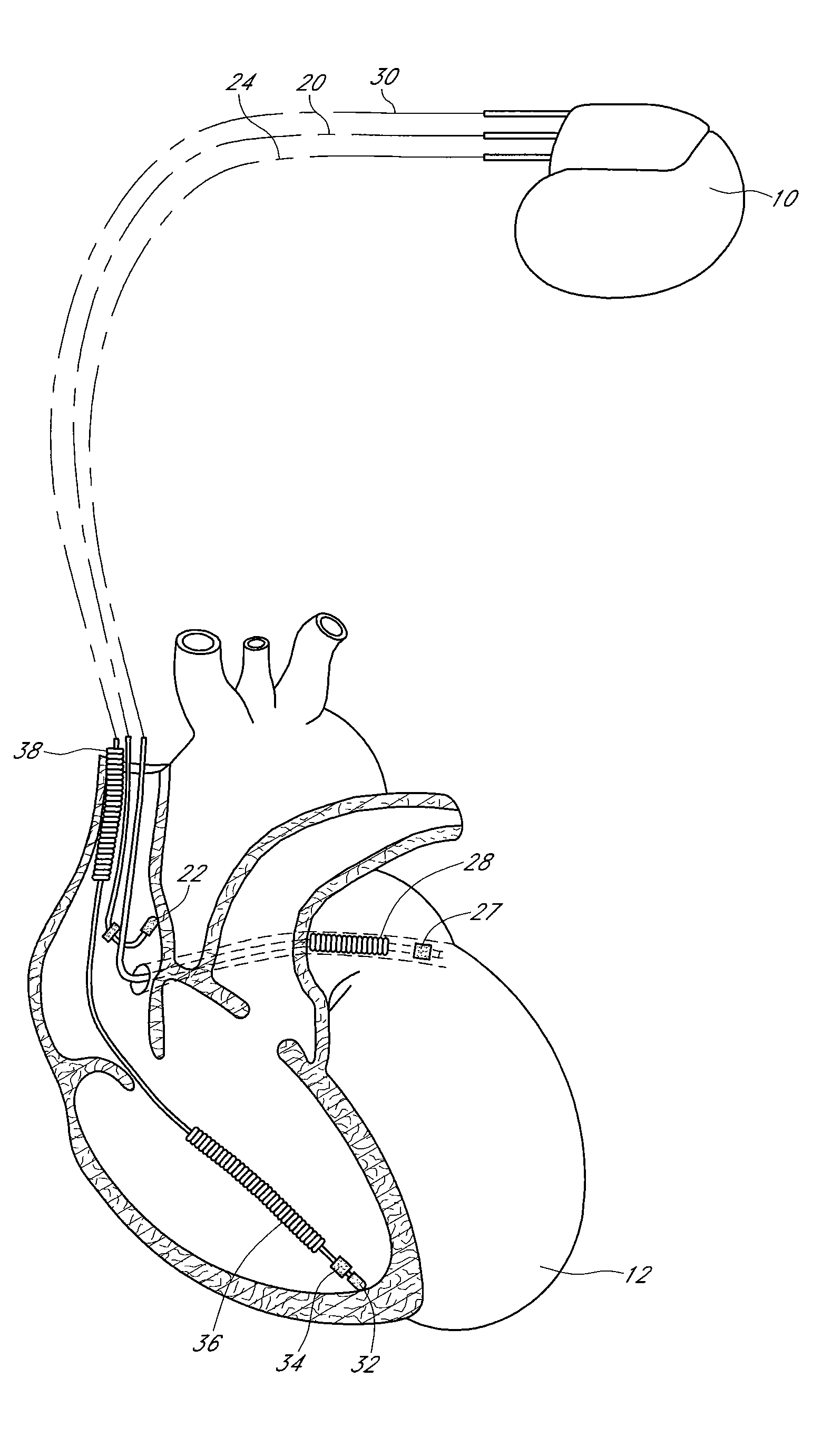
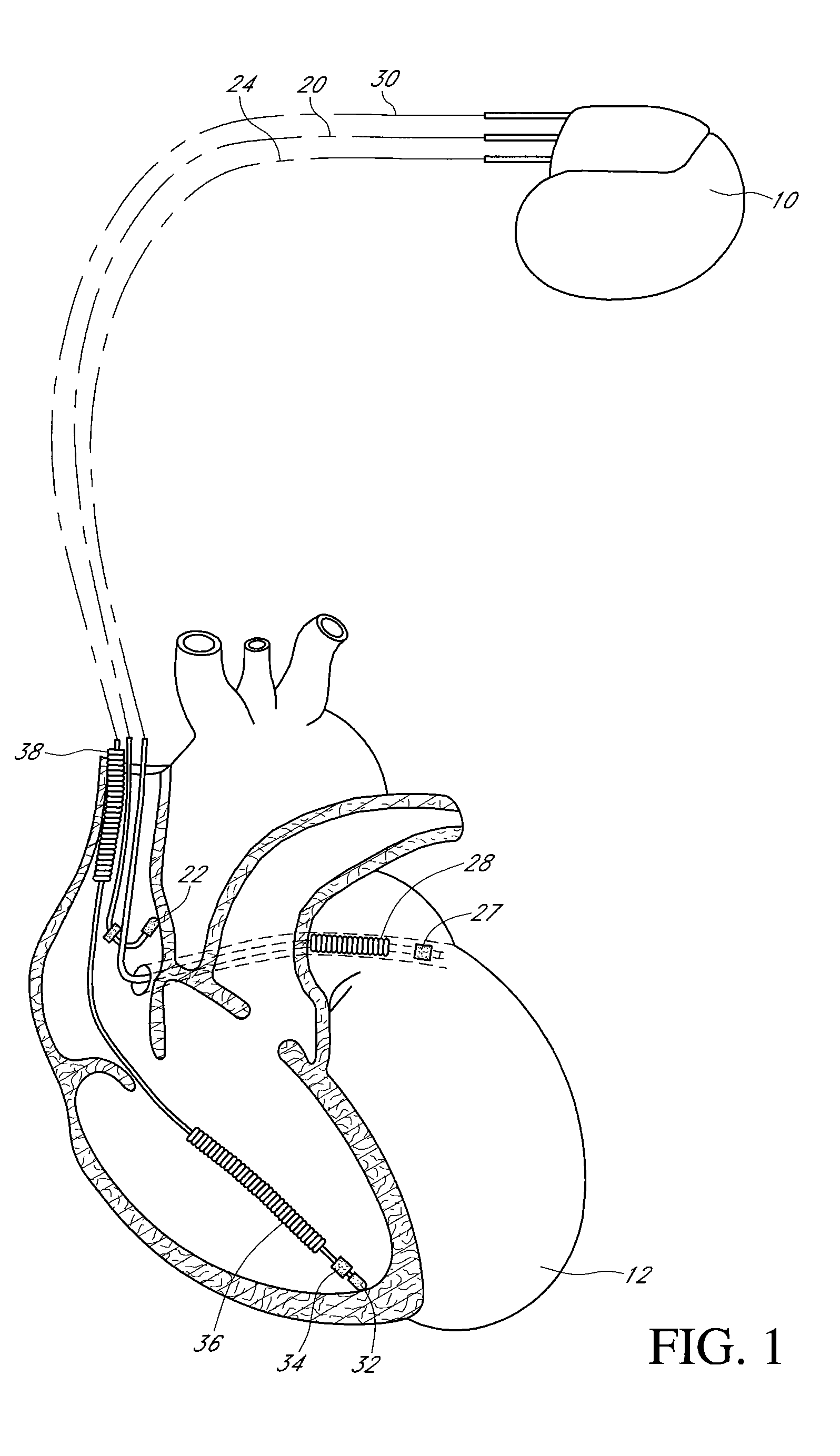
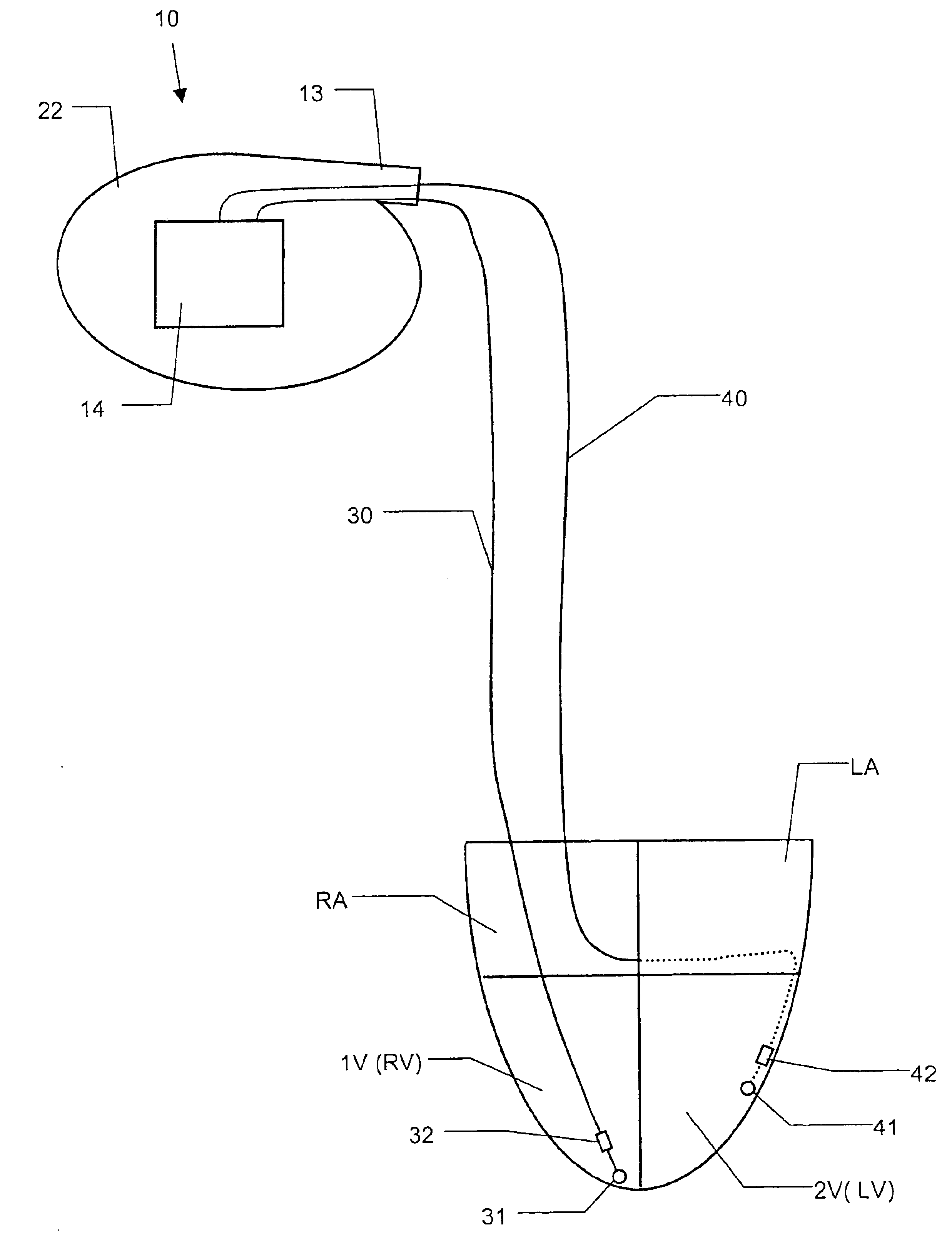
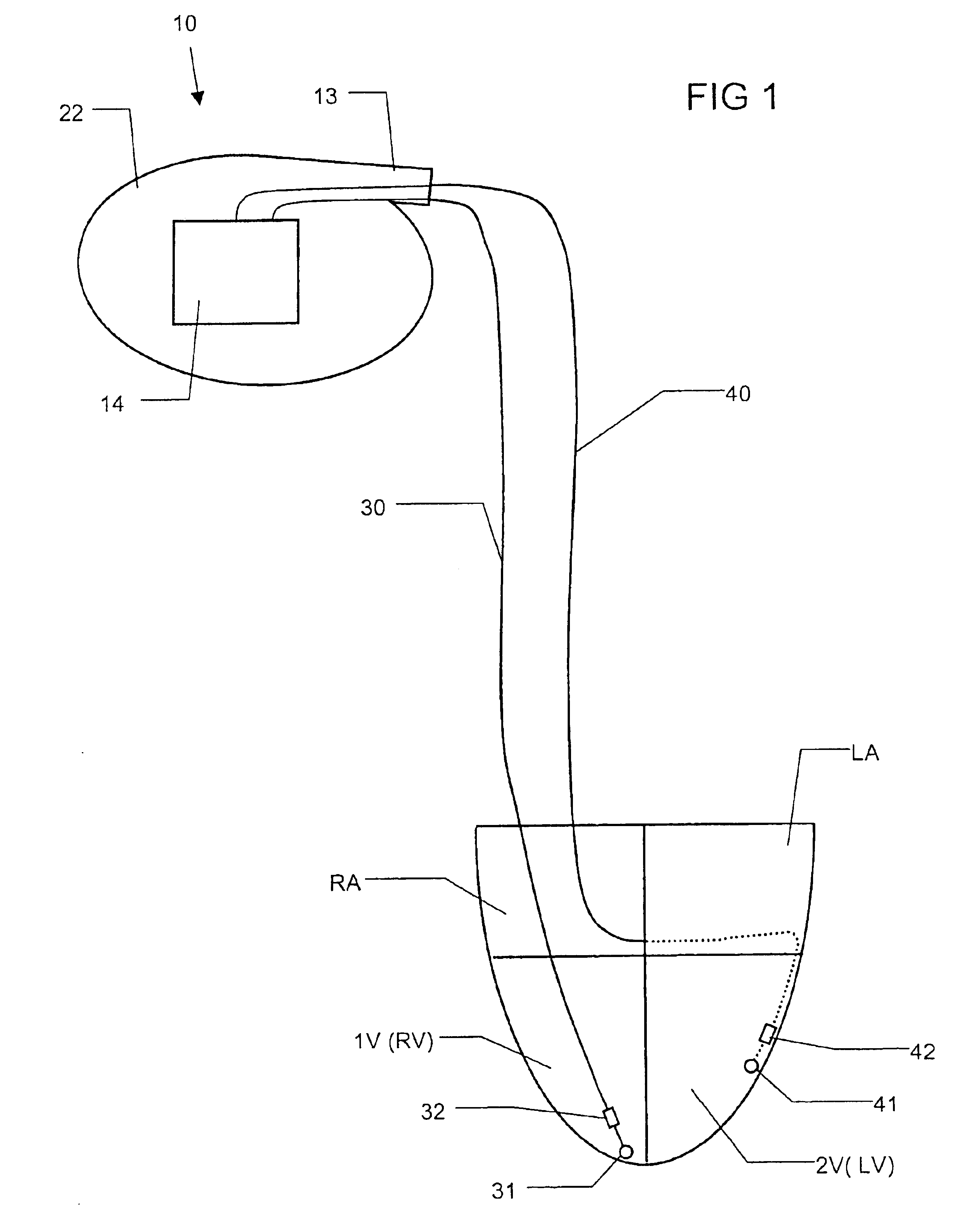
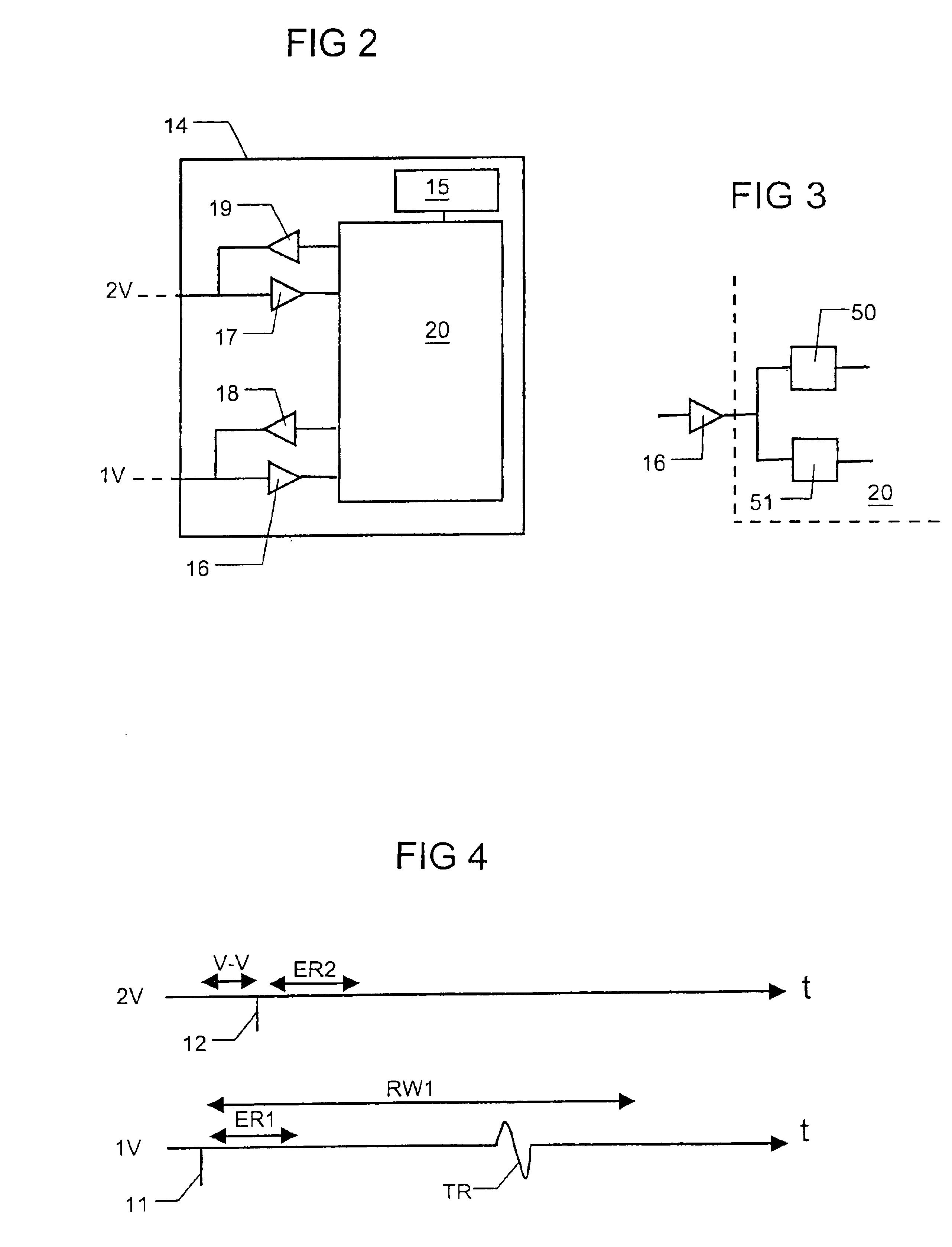
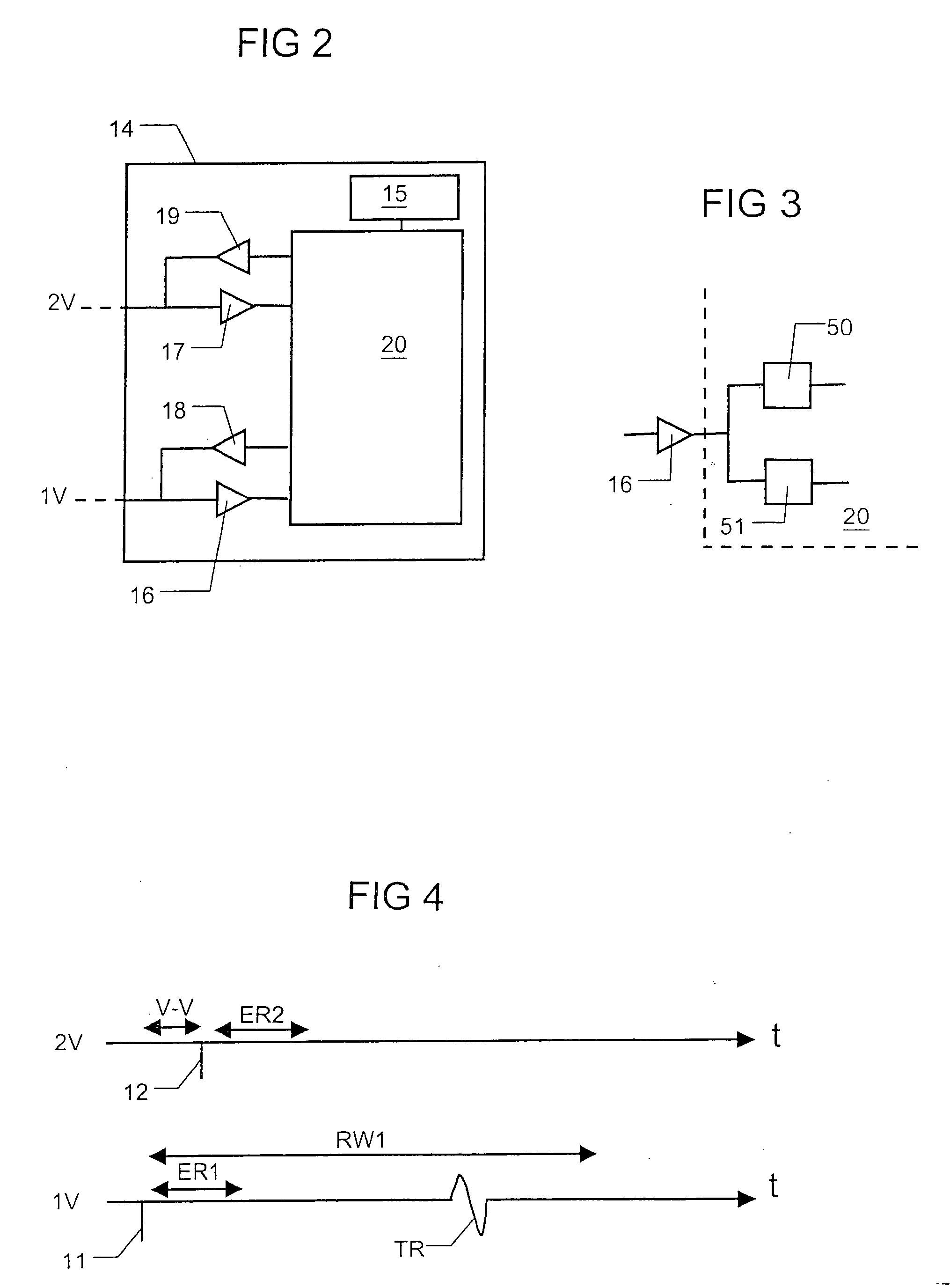
InactiveUS6738667B2Increase contractilityEasy to relaxCatheterHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleHeart chamber
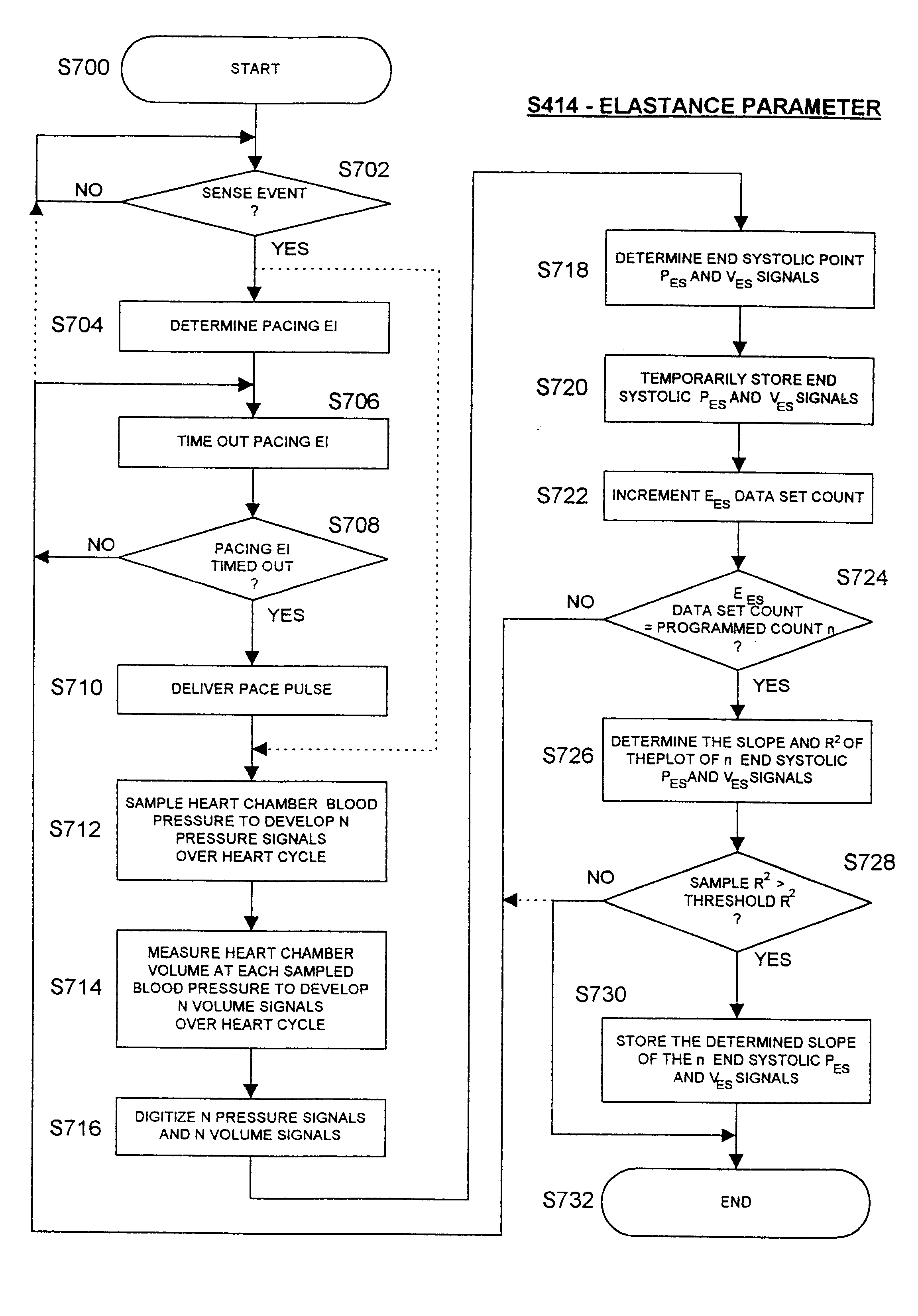
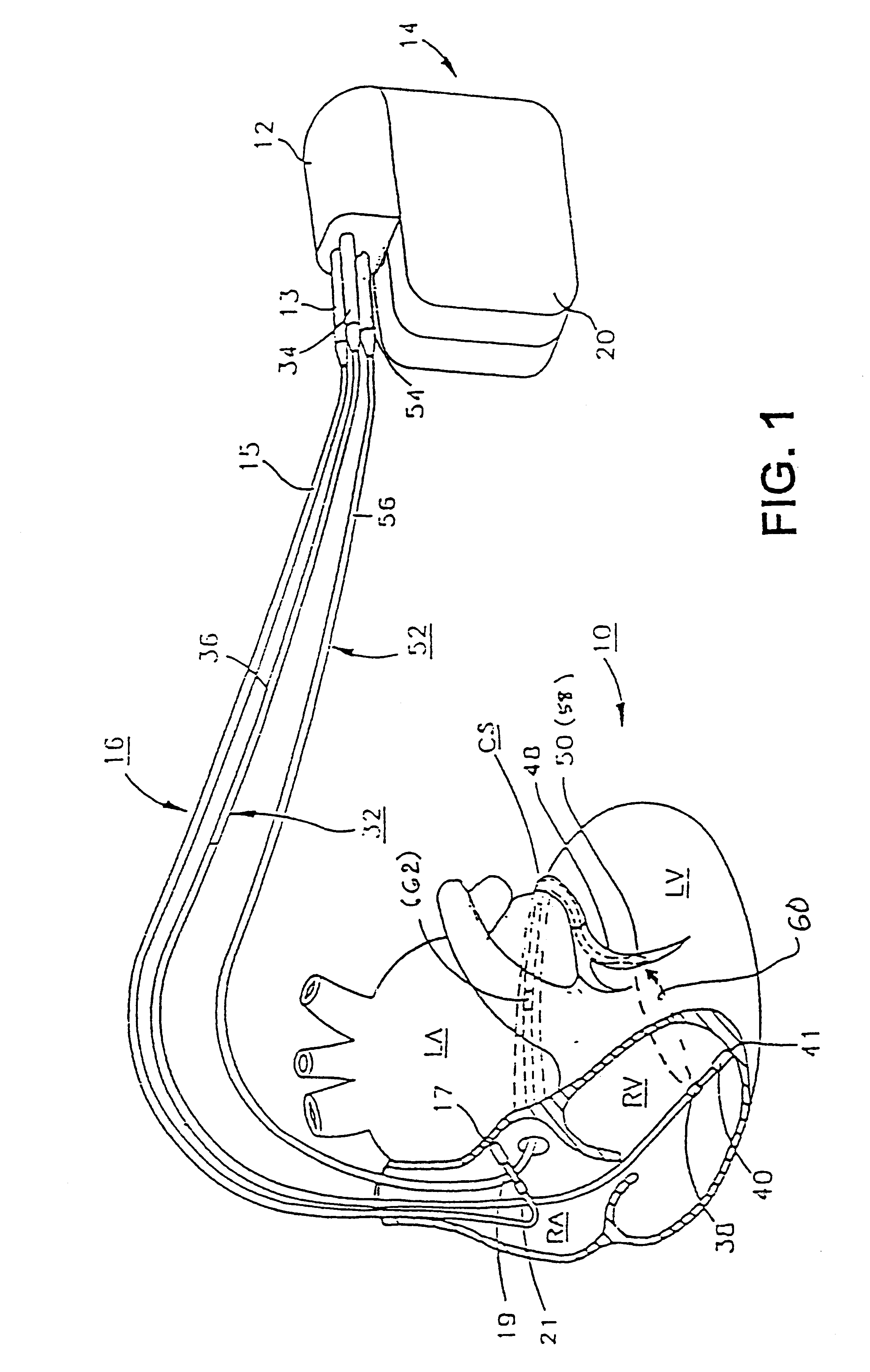
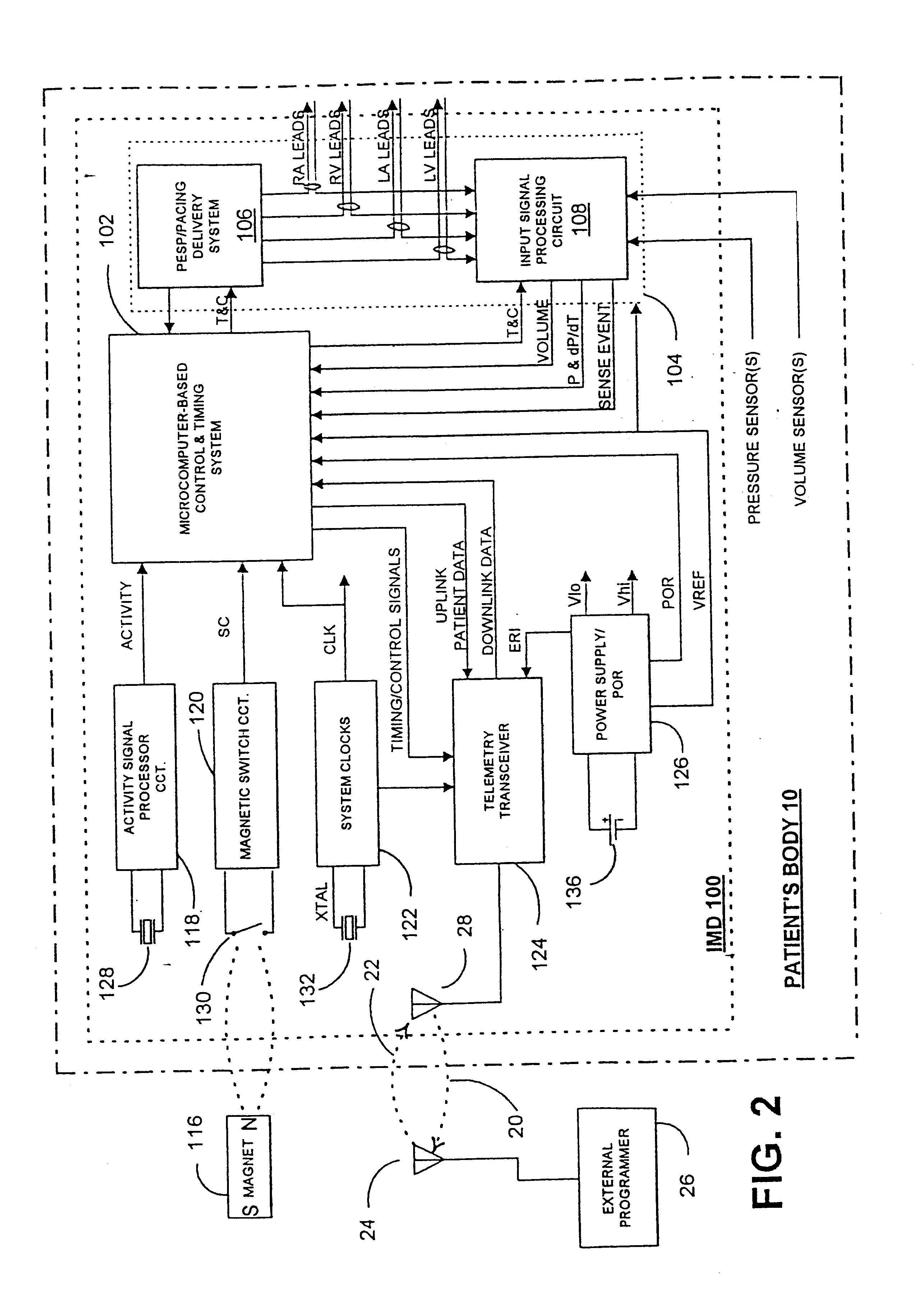
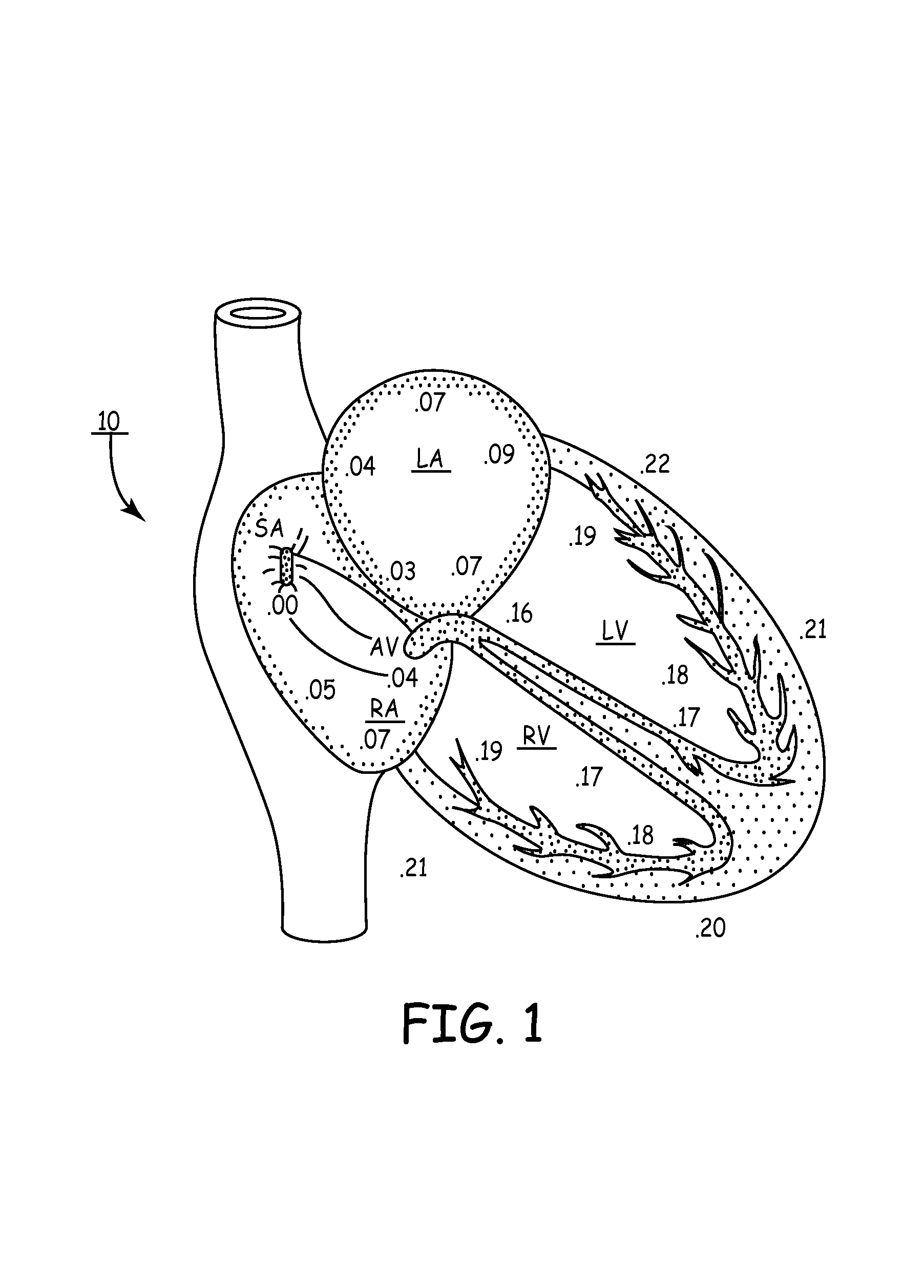
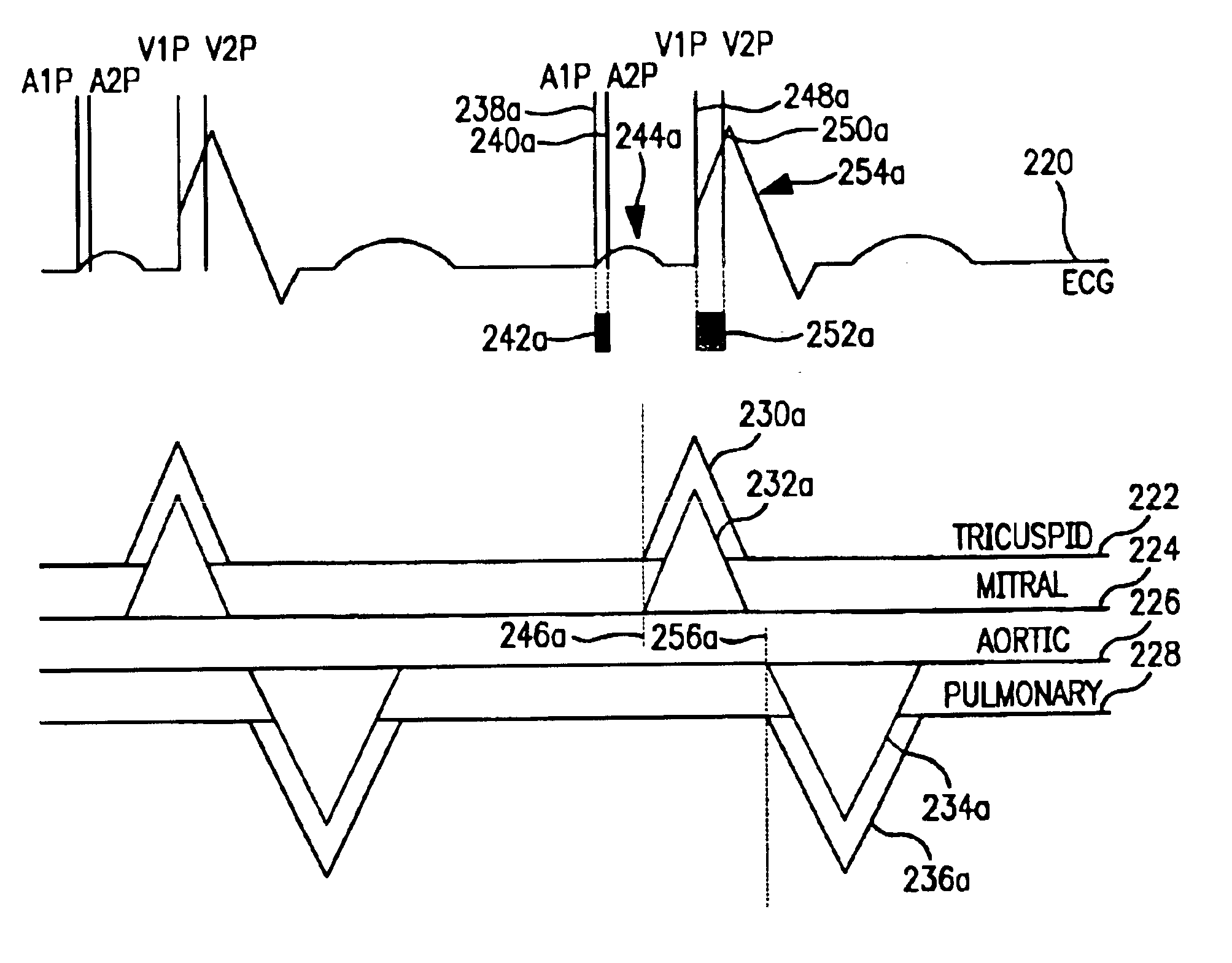
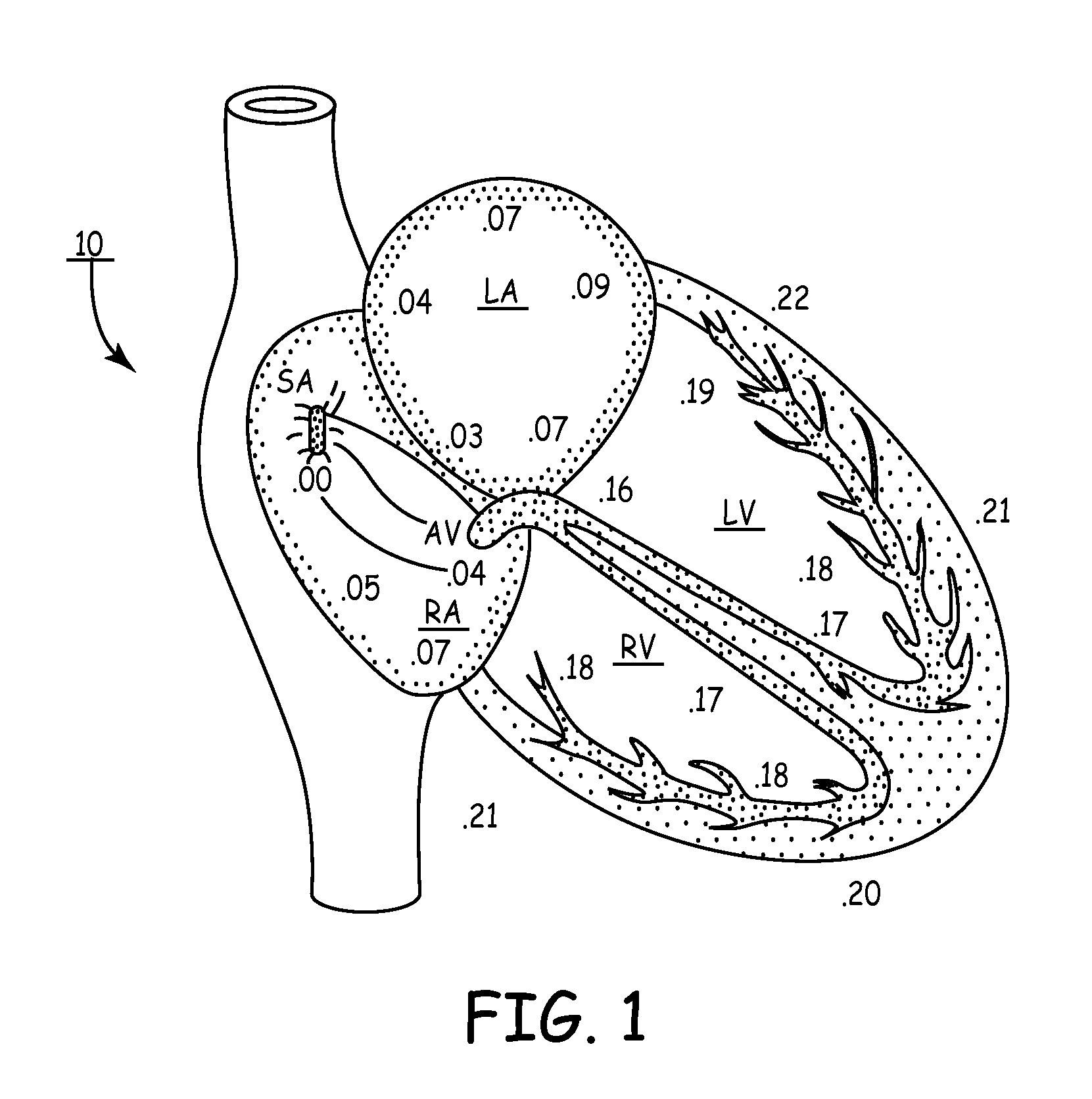
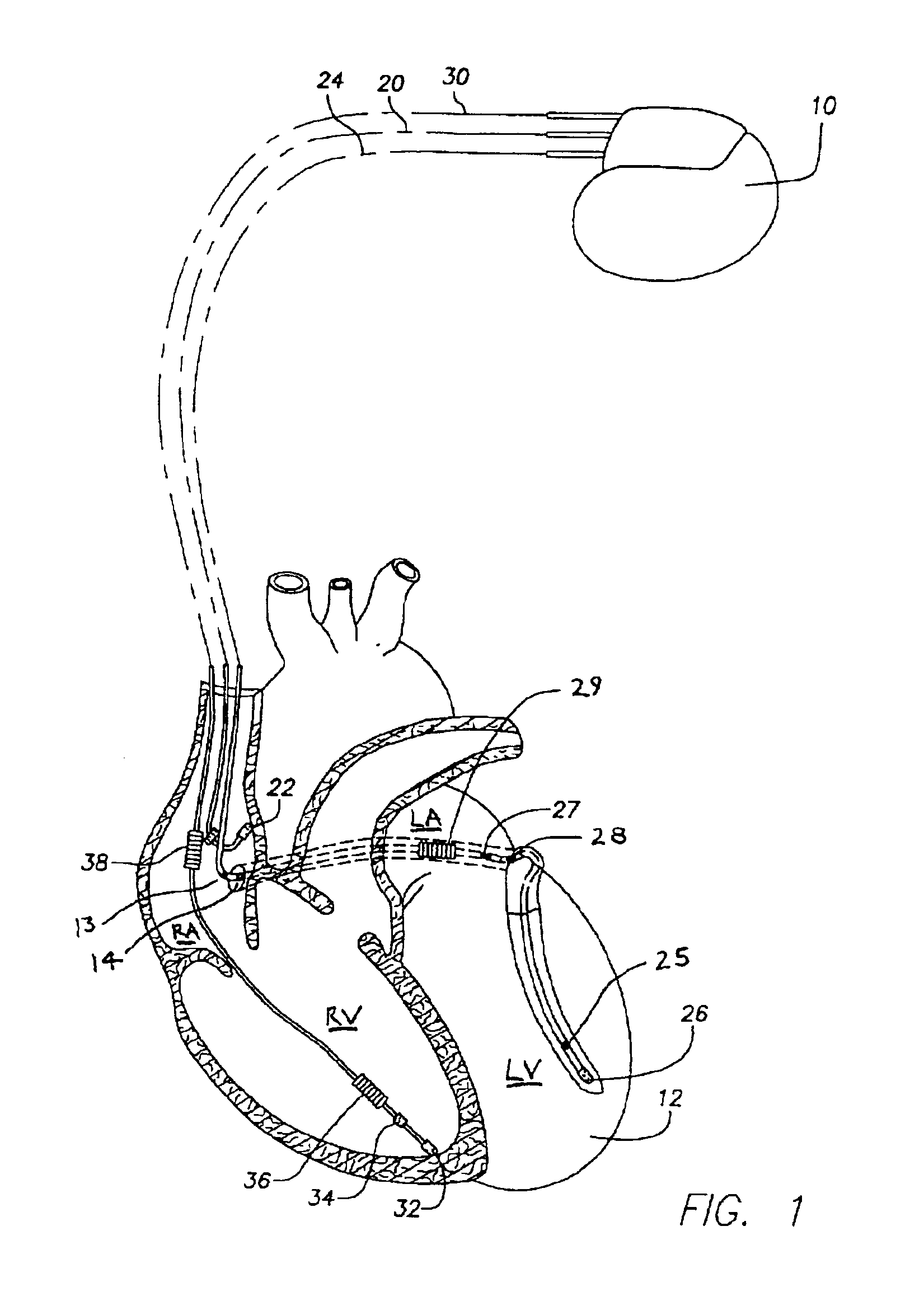
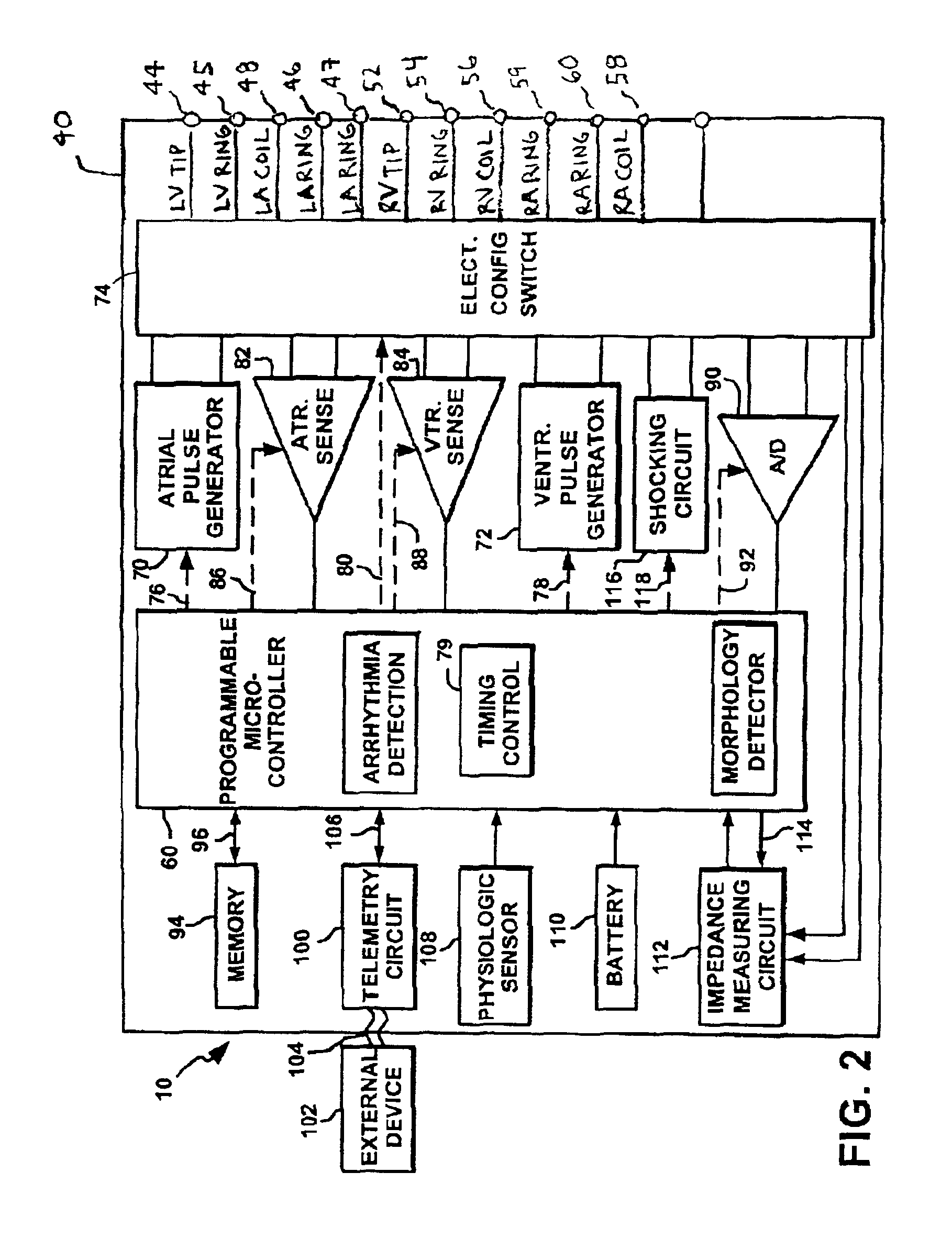
An implantable stimulator and monitor measures a group of heart failure parameters indicative of the state of heart failure employing EGM signals, measures of blood pressure including absolute pressure P, developed pressure (DP=systolic P-diastolic P), and / or dP / dt, and measures of heart chamber volume (V) over one or more cardiac cycles. These parameters include: (1) relaxation or contraction time constant tau (.tau.); (2) mechanical restitution (MR), i.e., the mechanical response of a heart chamber to premature stimuli applied to the heart chamber; (3) recirculation fraction (RF), i.e., the rate of decay of PESP effects over a series of heart cycles; and (4) end systolic elastance (E.sub.ES), i.e., the ratios of end systolic blood pressure P to volume V. These heart failure parameters are determined periodically regardless of patient posture and activity level. The physician can determine whether a particular therapy is appropriate, prescribe the therapy for a period of time while again accumulating the stored patient data for a later review and assessment to determine whether the applied therapy is beneficial or not, thereby enabling periodic changes in therapy, if appropriate. Drug therapies and electrical stimulation therapies, including PESP stimulation, and pacing therapies including single chamber, dual chamber and multi-chamber (bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular) pacing can be delivered. In patient's prone to malignant tachyarrhythmias, the assessment of heart failure state can be taken into account in setting parameters of detection or classification of tachyarrhythmias and the therapies that are delivered.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
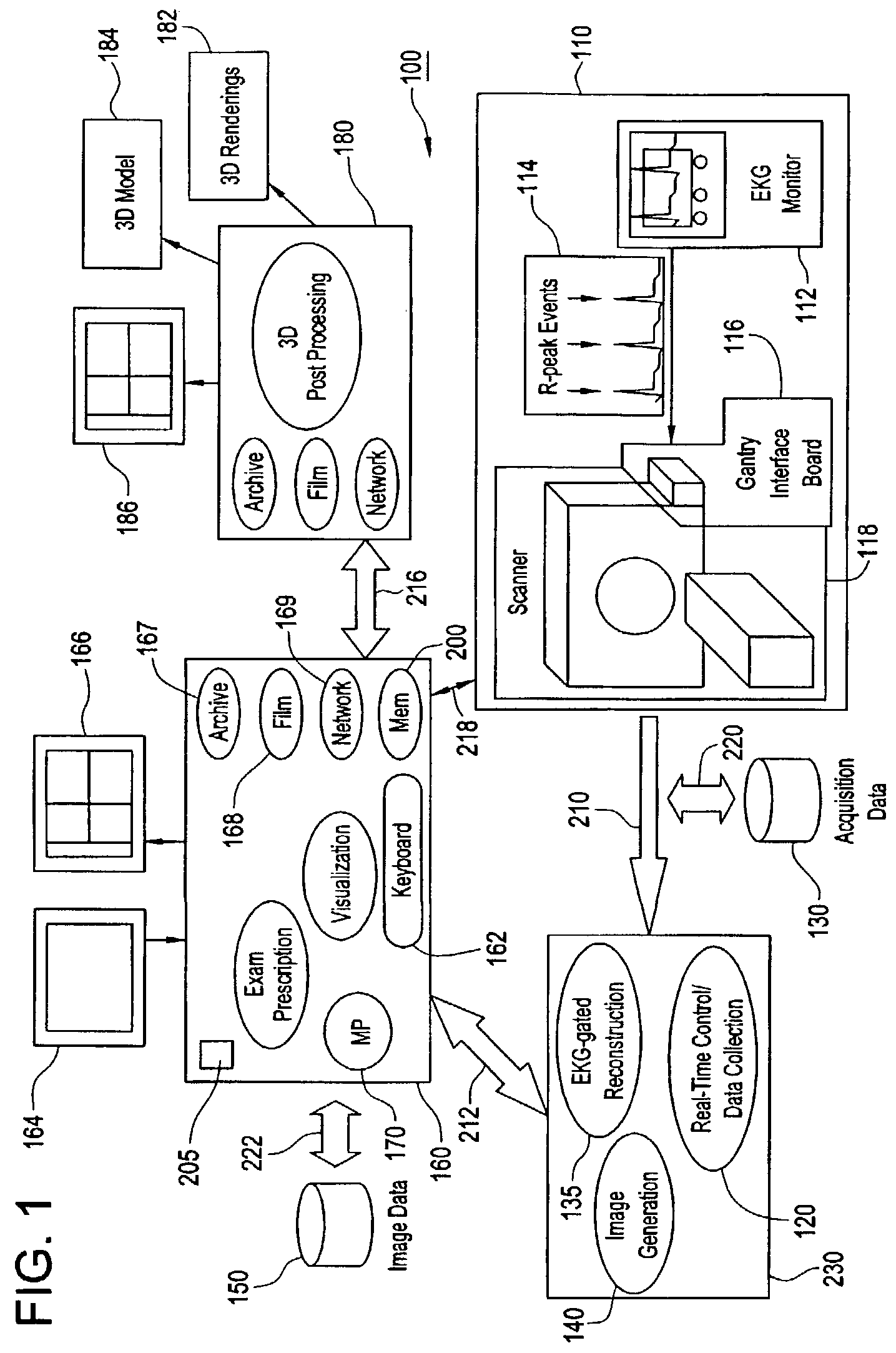
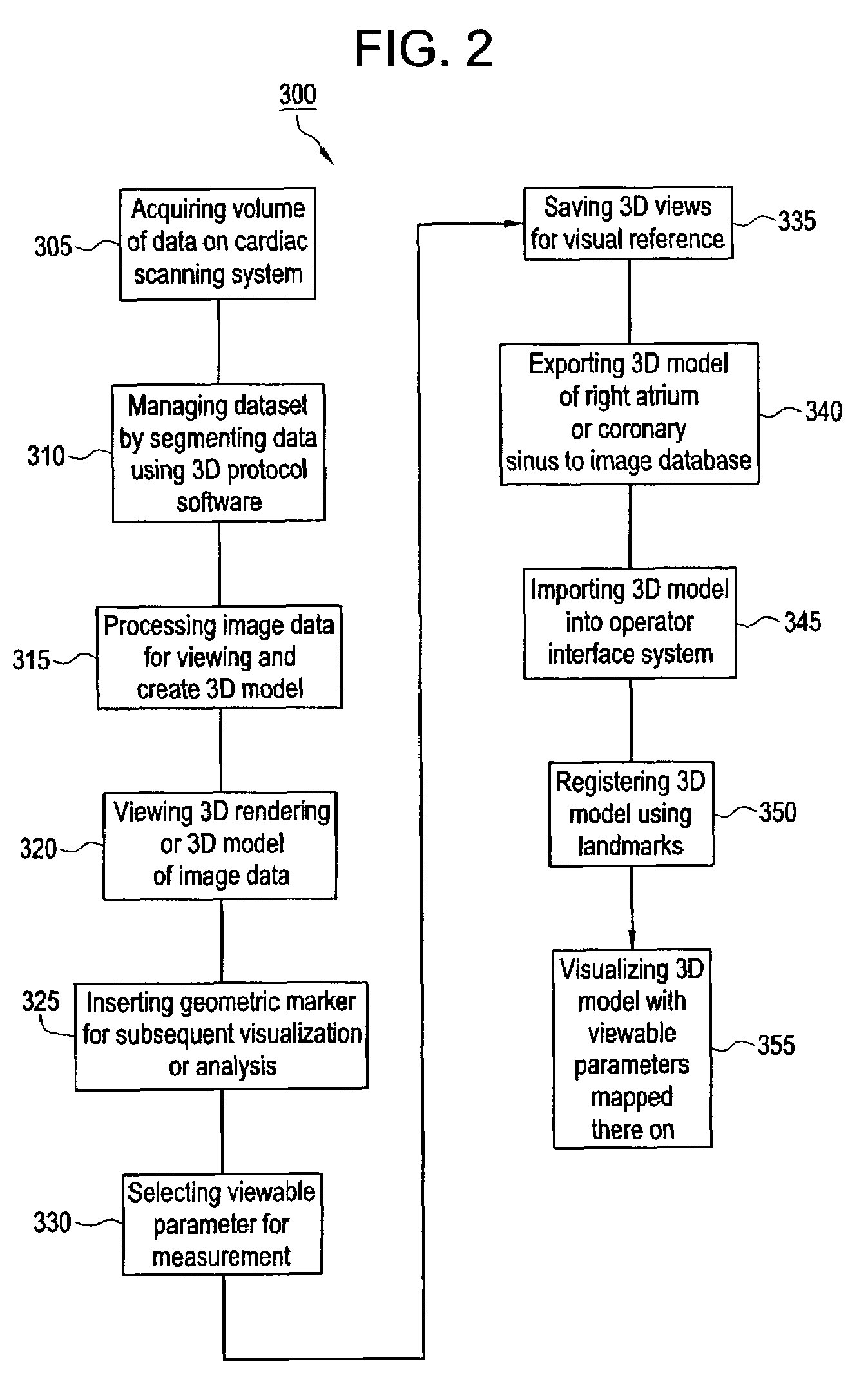
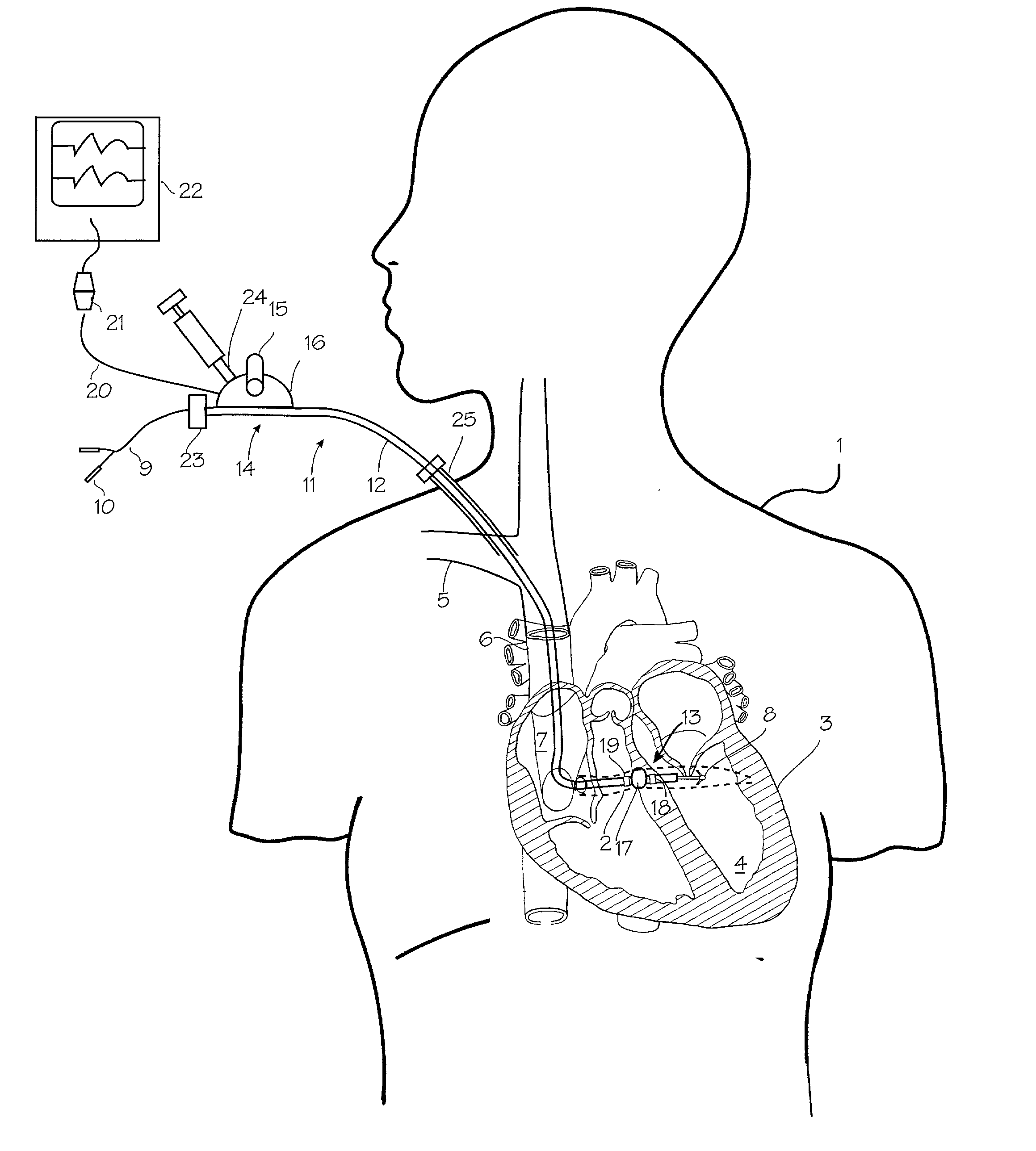
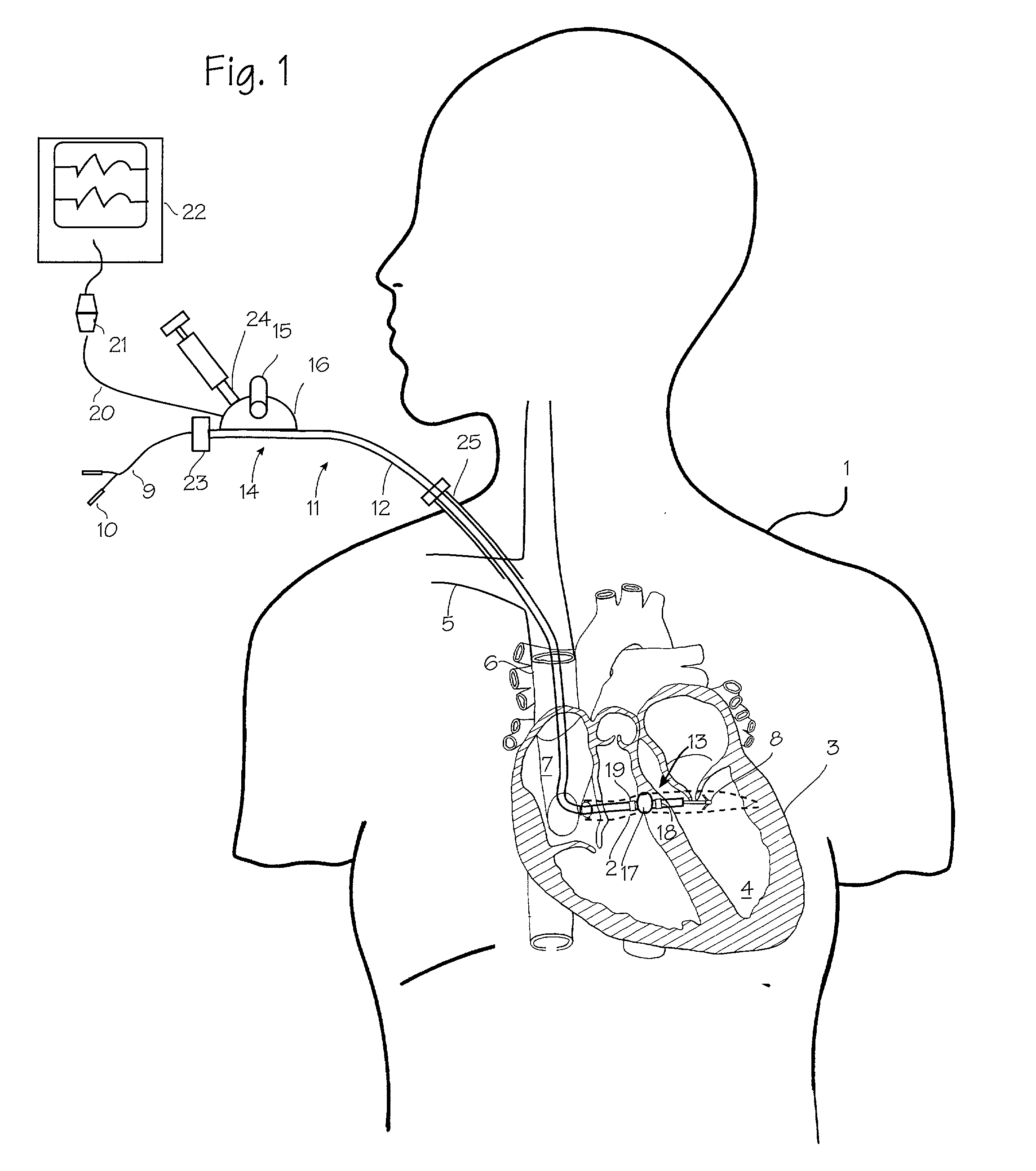
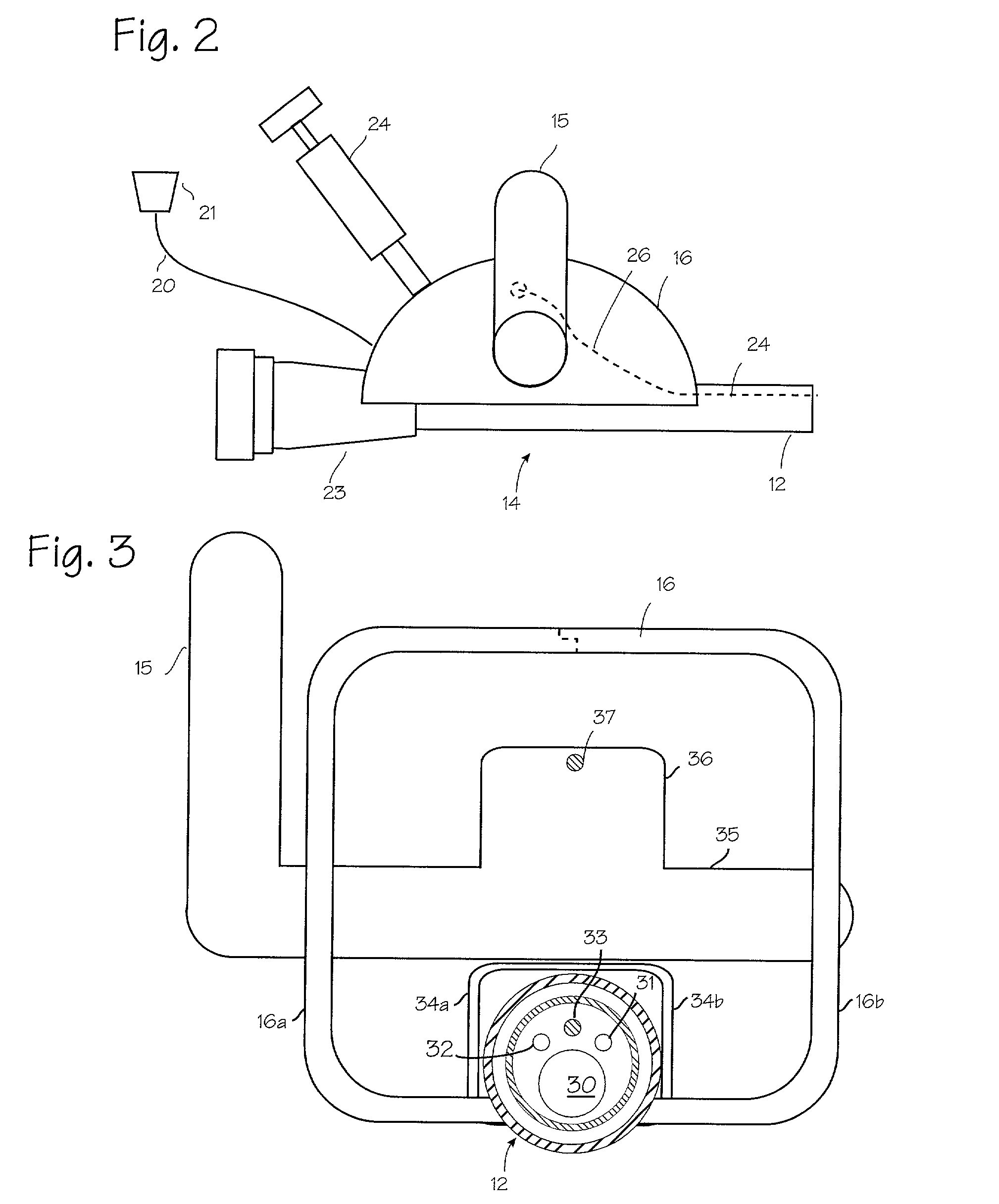
Method and apparatus for medical intervention procedure planning
InactiveUS7346381B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperator interfaceData acquisition
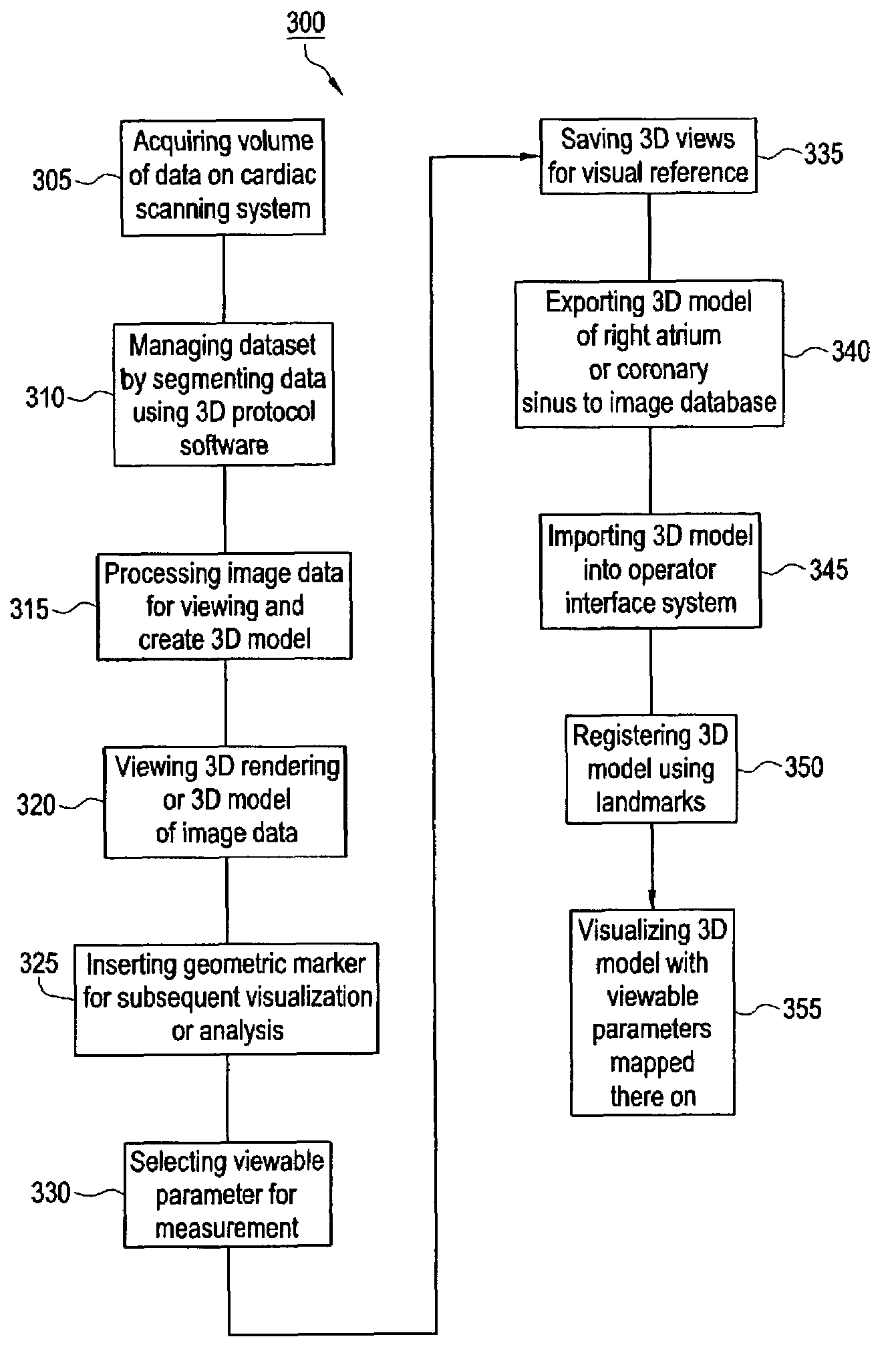
An imaging system for use in medical intervention procedure planning includes a medical scanner system for generating a volume of cardiac image data, a data acquisition system for acquiring the volume of cardiac image data, an image generation system for generating a viewable image from the volume of cardiac image data, a database for storing information from the data acquisition and image generation systems, an operator interface system for managing the medical scanner system, the data acquisition system, the image generation system, and the database, and a post-processing system for analyzing the volume of cardiac image data, displaying the viewable image and being responsive to the operator interface system. The operator interface system includes instructions for using the volume of cardiac image data and the viewable image for bi-ventricular pacing planning, atrial fibrillation procedure planning, or atrial flutter procedure planning.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
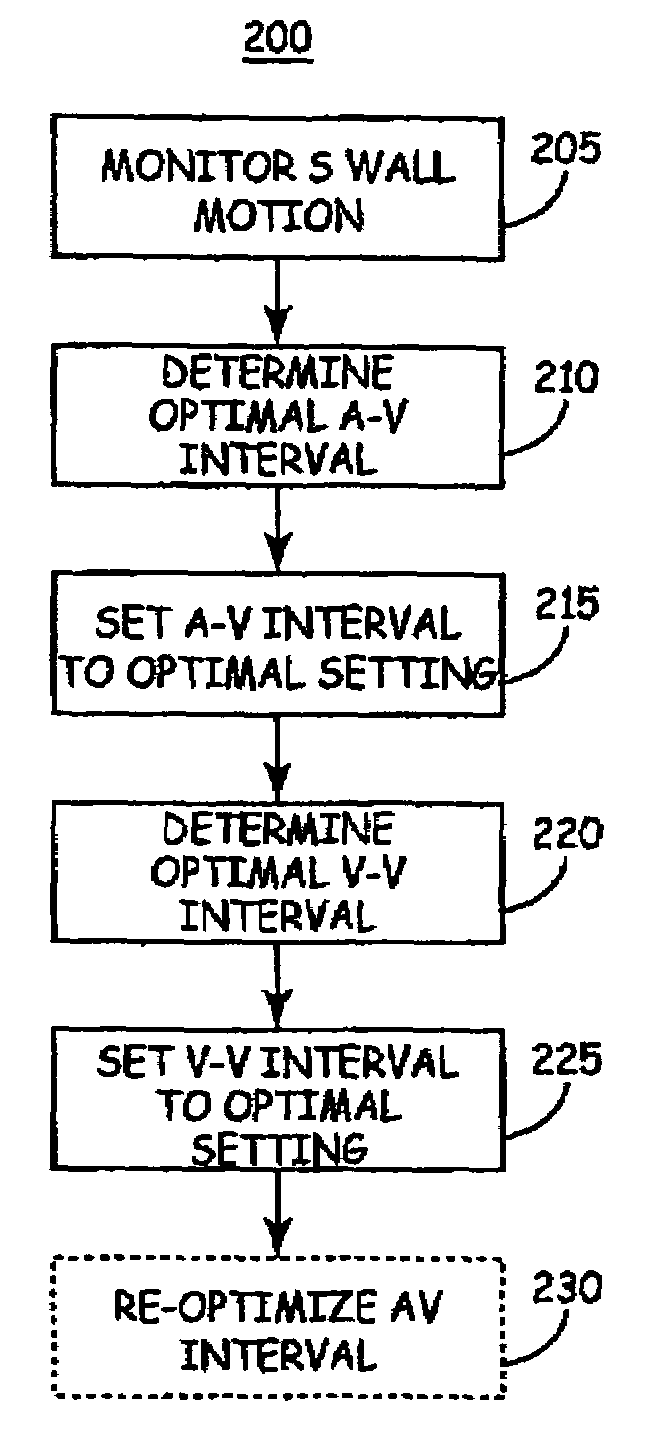
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
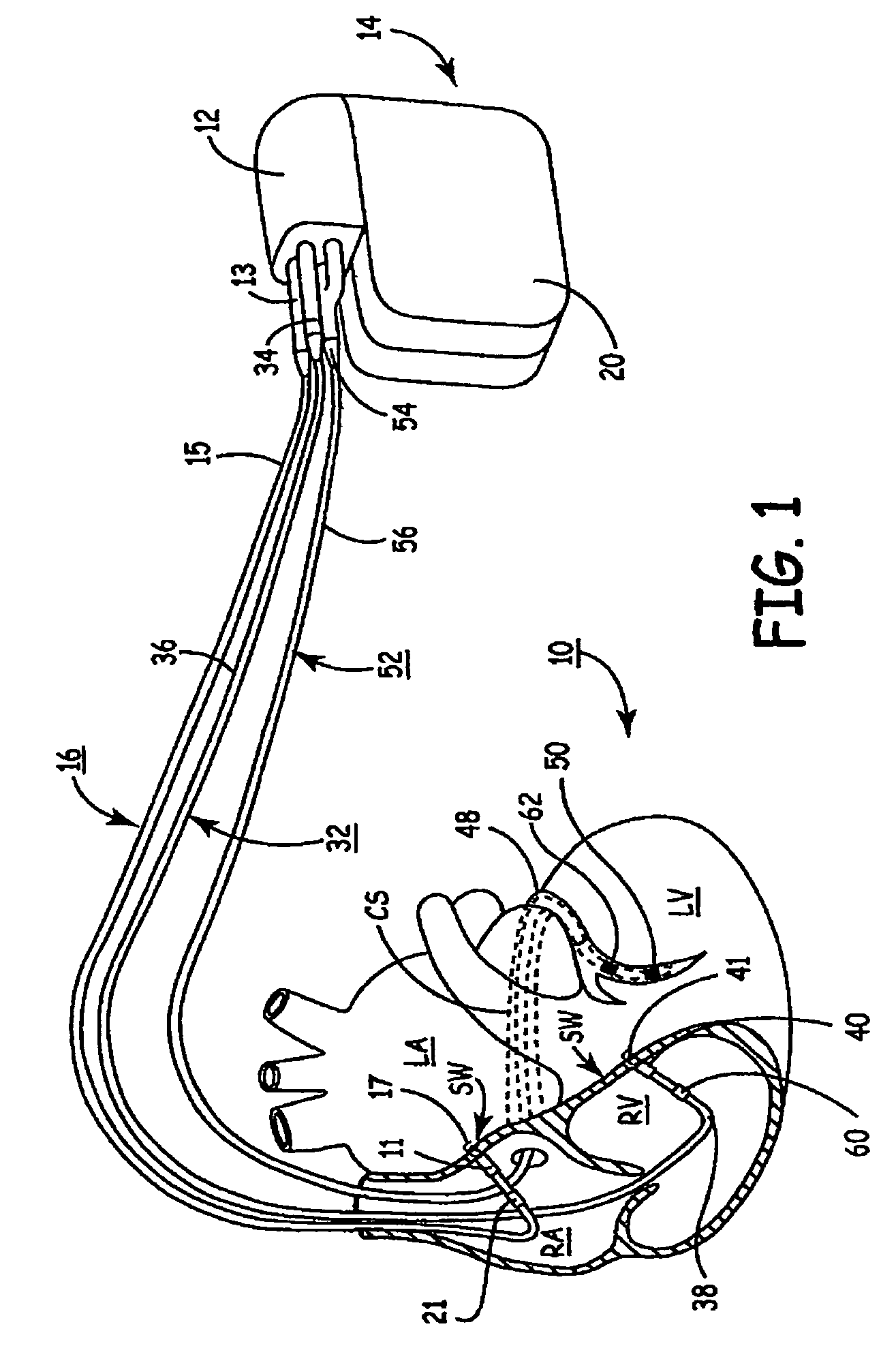
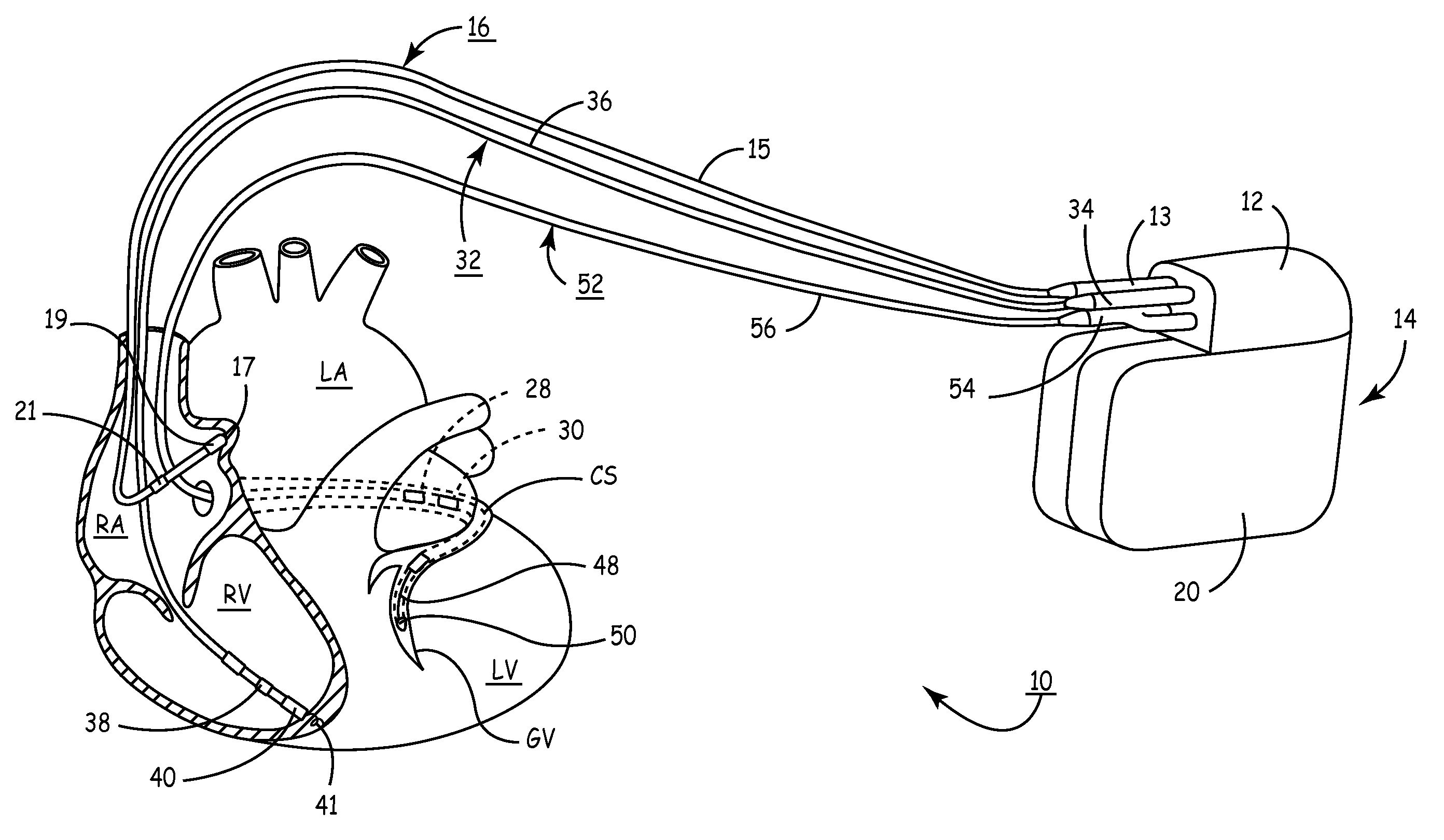
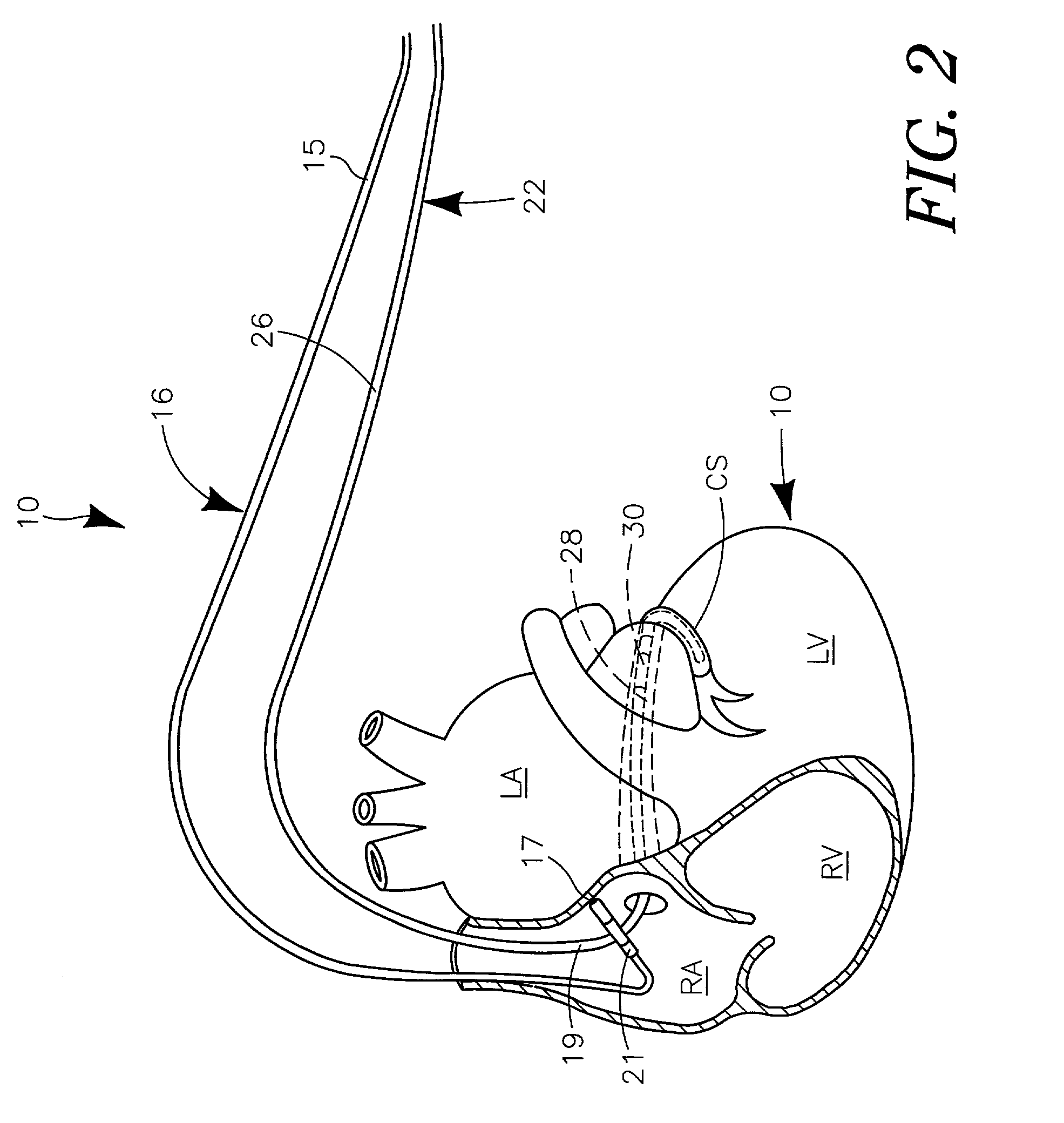
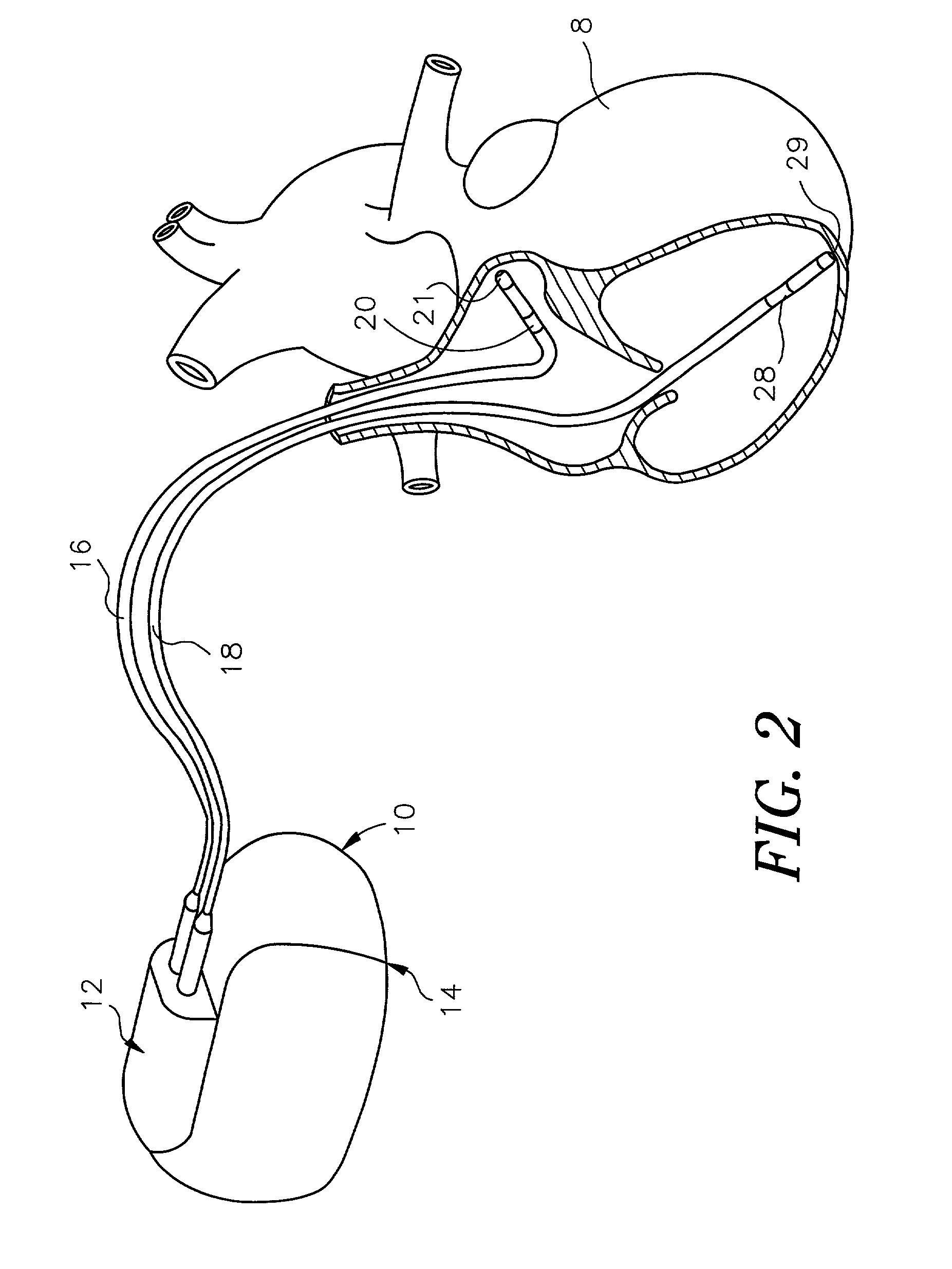
System and method for bi-ventricular fusion pacing
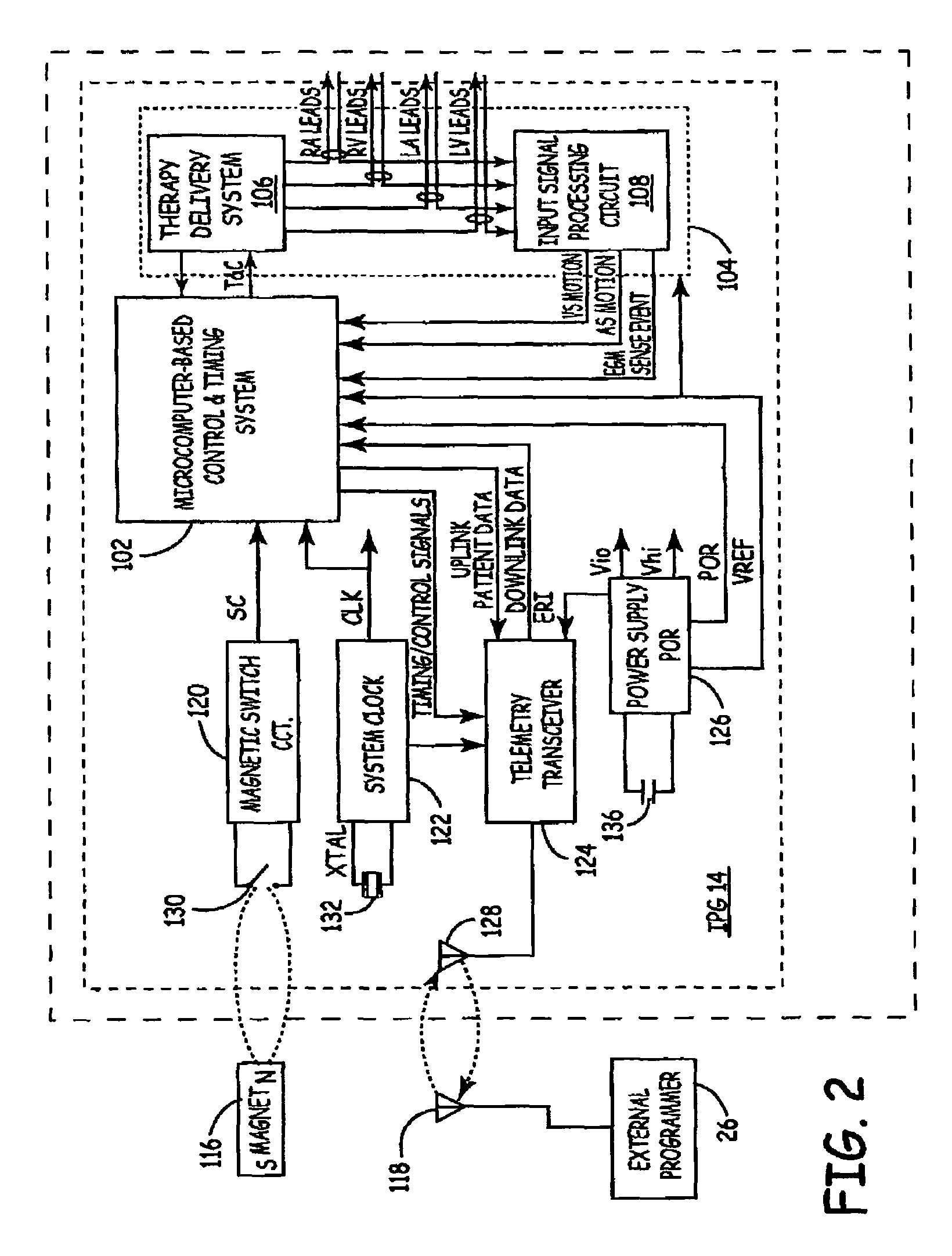
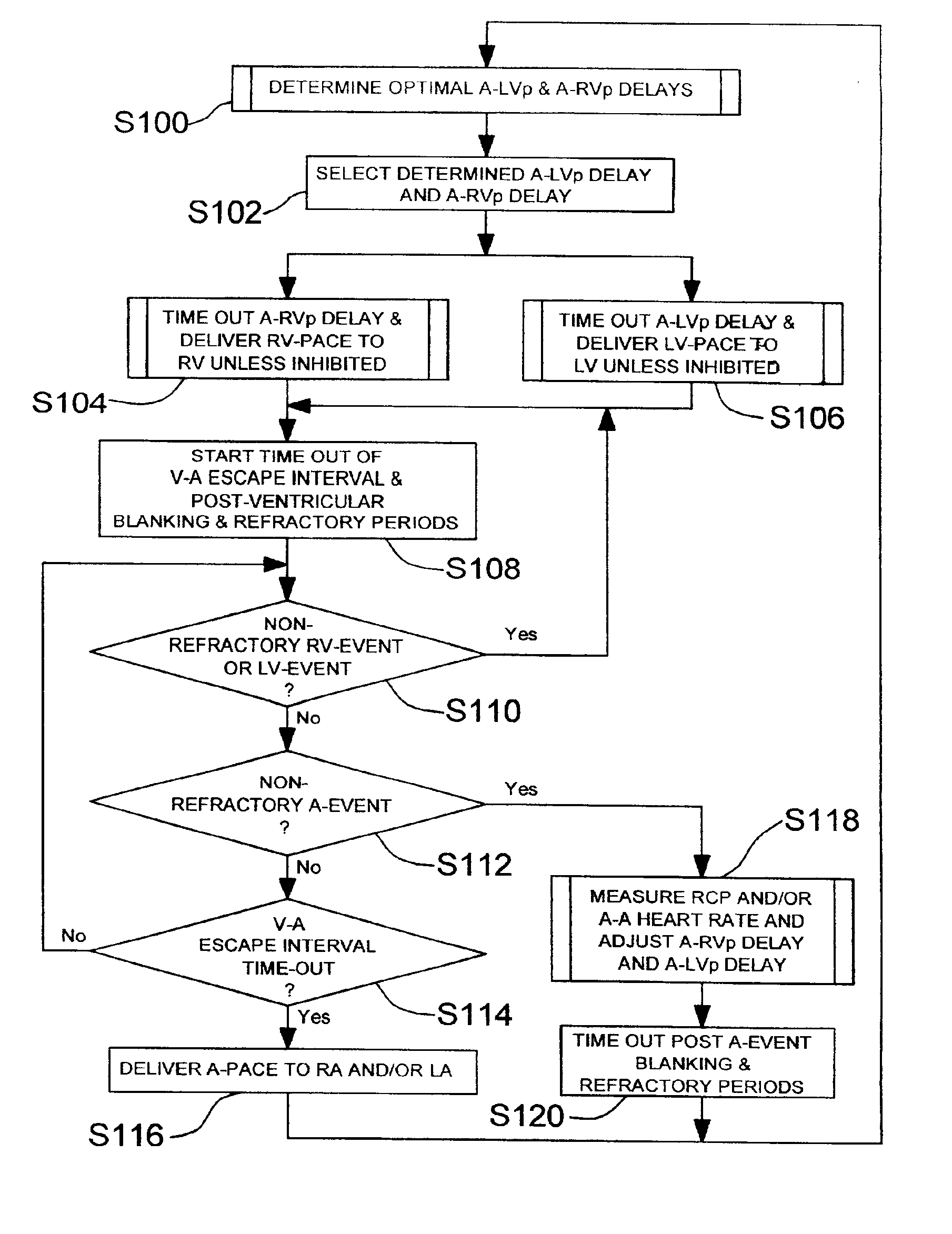
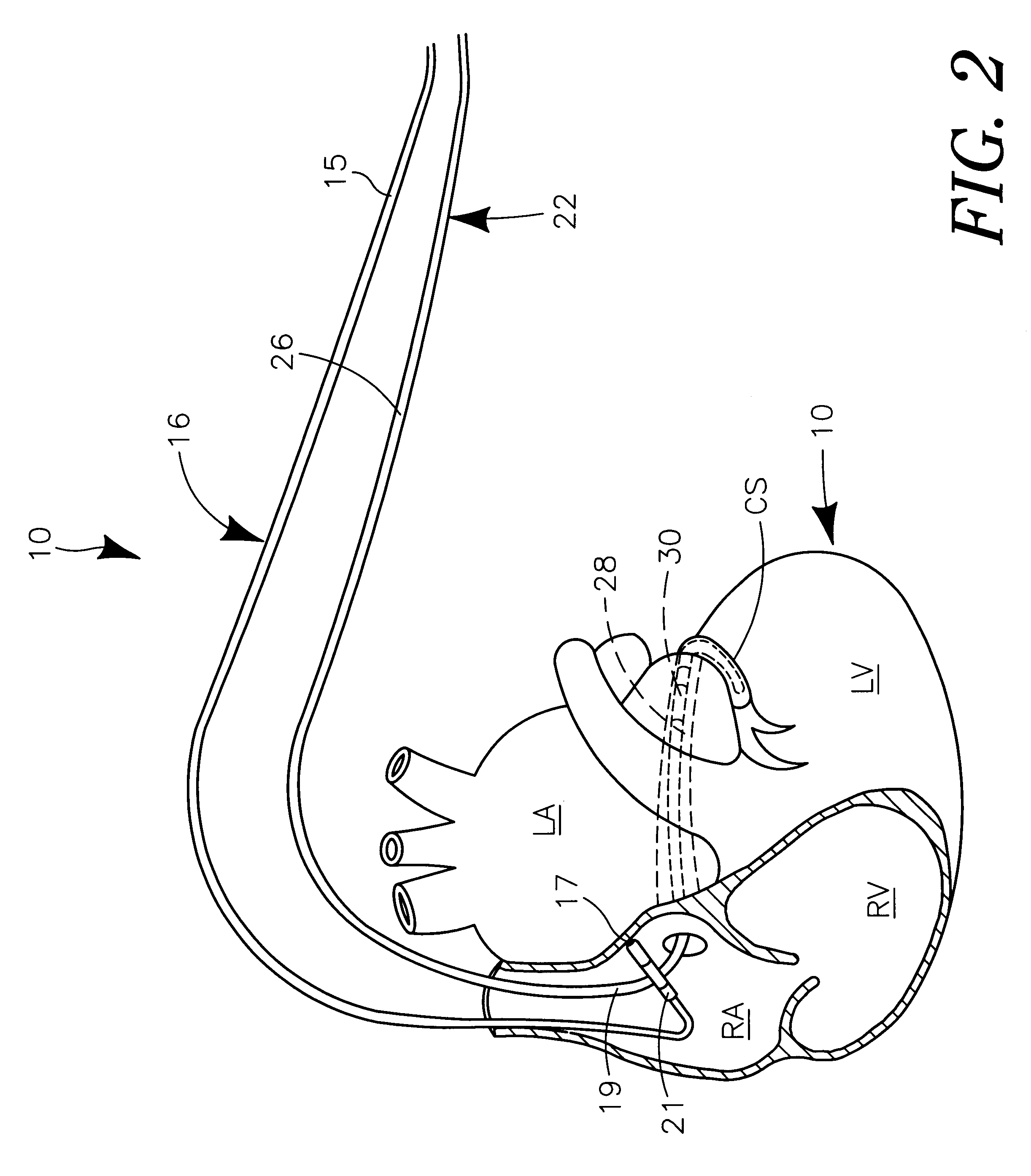
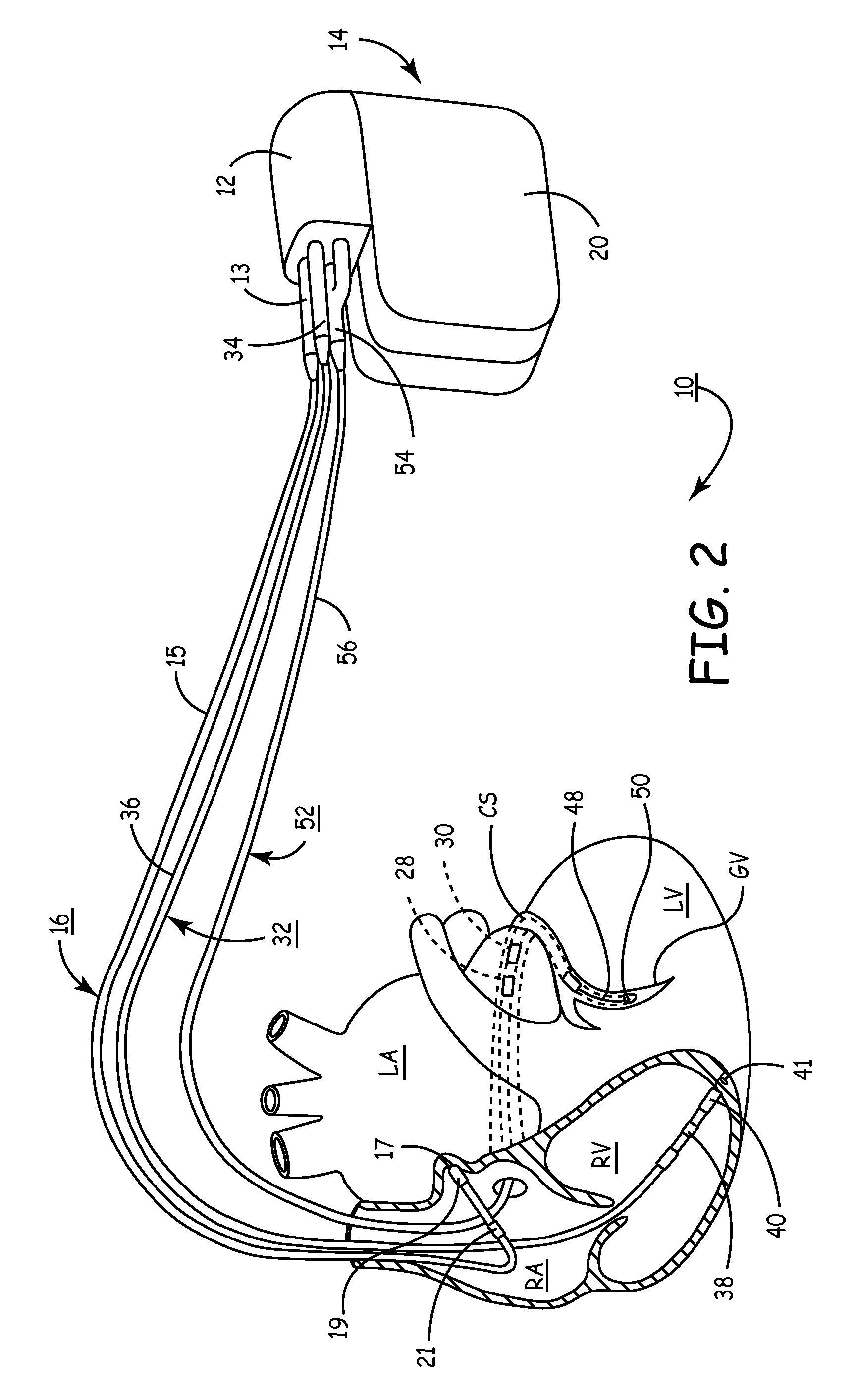
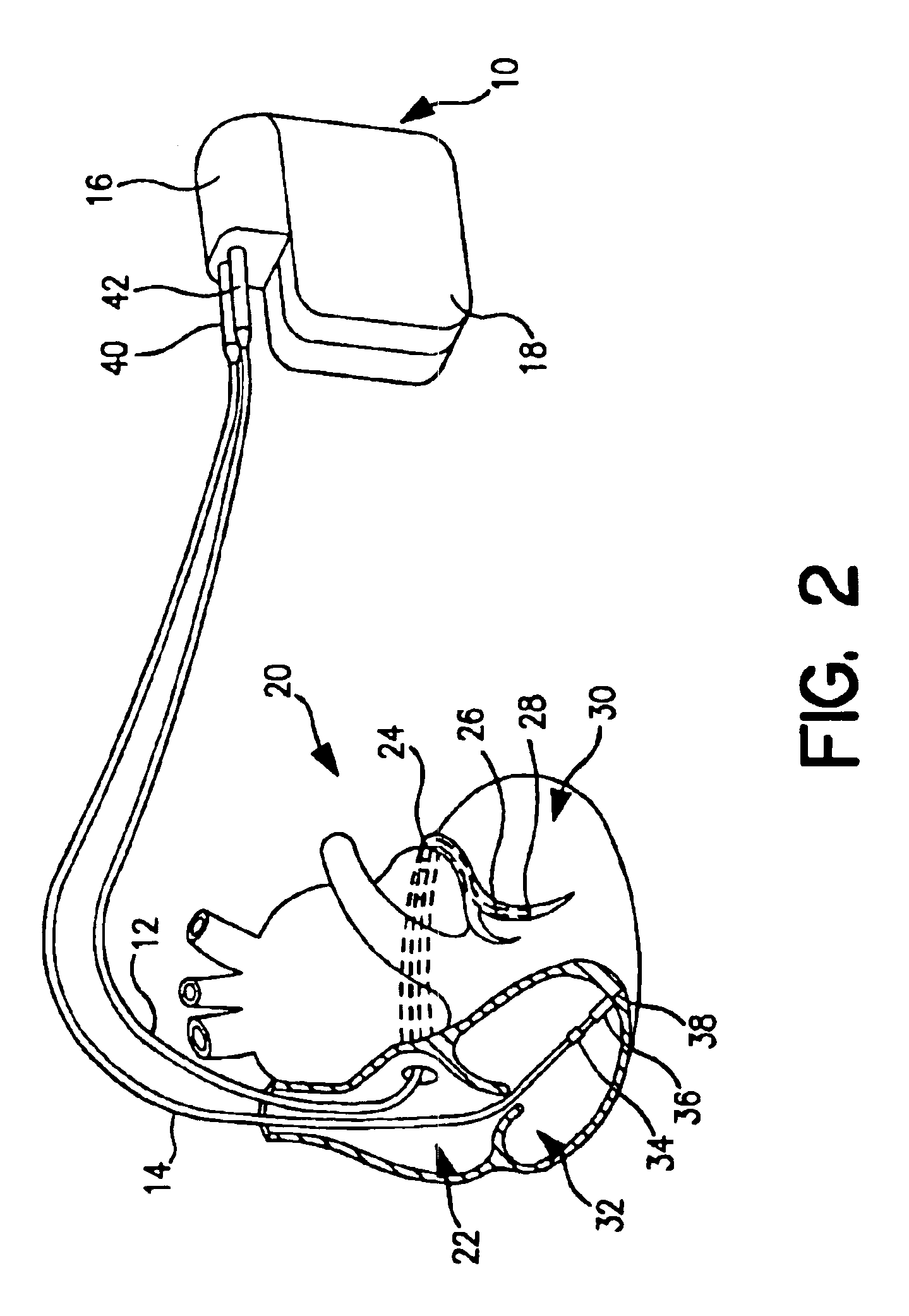
Bi-ventricular cardiac pacing systems and systems for improving cardiac function for heart failure patients that pace and sense in right and left ventricles of the heart and particularly pace in one of the right and left ventricles after an AV delay timed from a preceding atrial event and after a spontaneous depolarization in the other of the right and left ventricles to achieve fusion pacing. An A-RVp delay and an A-LVp delay are each determined from an intrinsic sensed A-RVs delay and an intrinsic A-LVs delay. If the derived A-LVp delay becomes substantially equal to or shorter than the intrinsic A-RVs delay, then the A-RVp delay is decremented to be shorter than the A-LVp delay. Bi-ventricular pacing of the RV and LV is then established closely timed to the intrinsic RV and LV depolarizations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
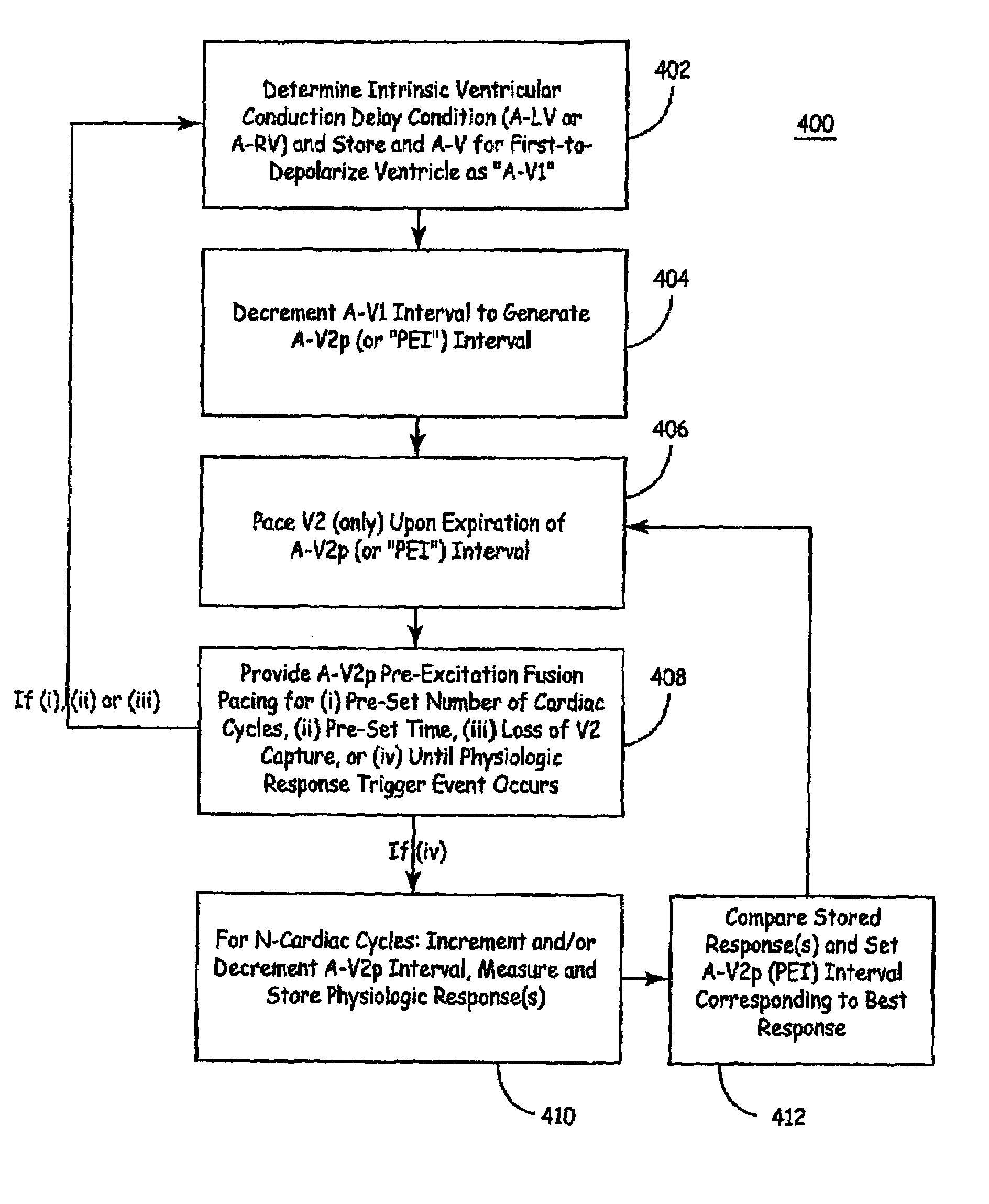
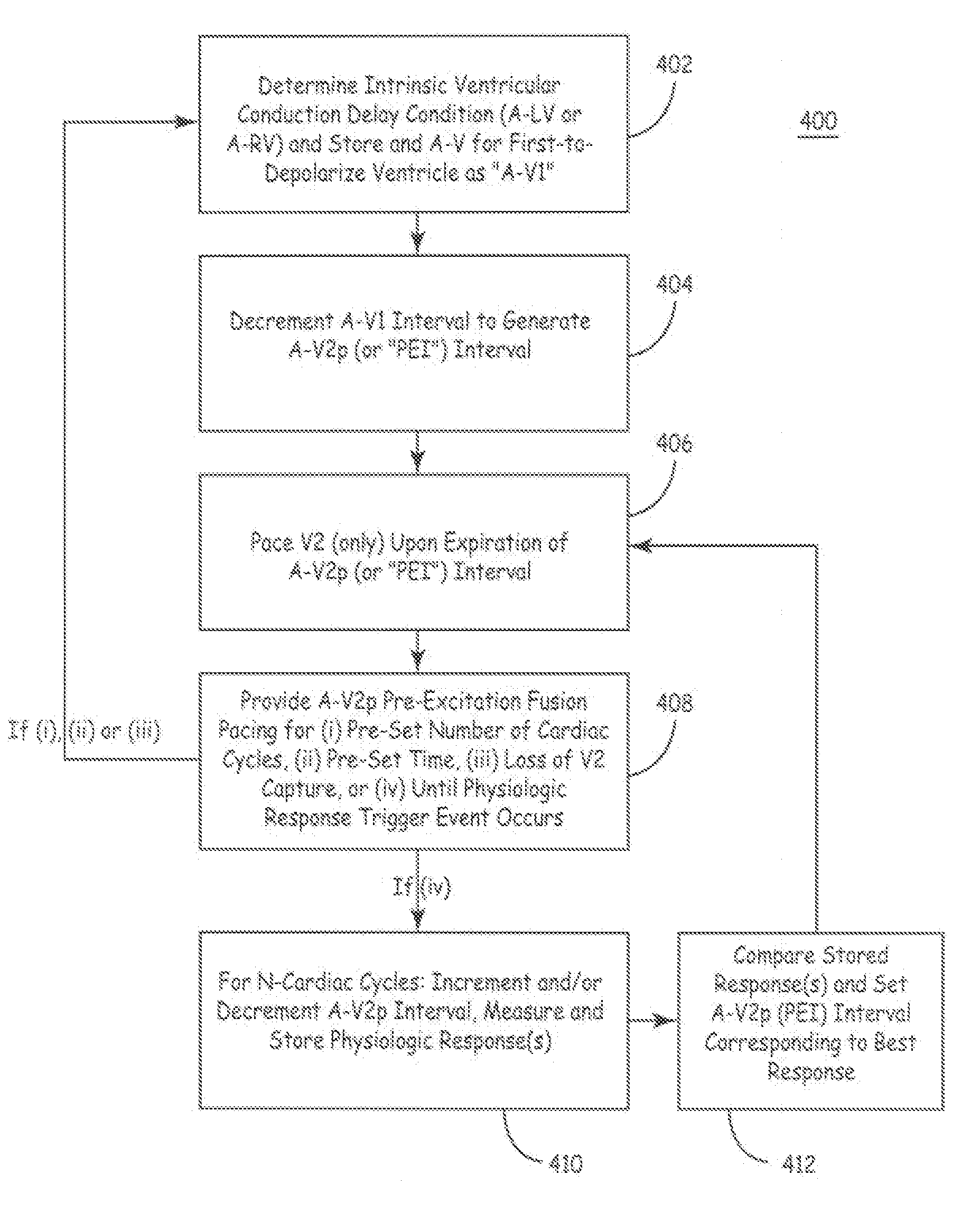
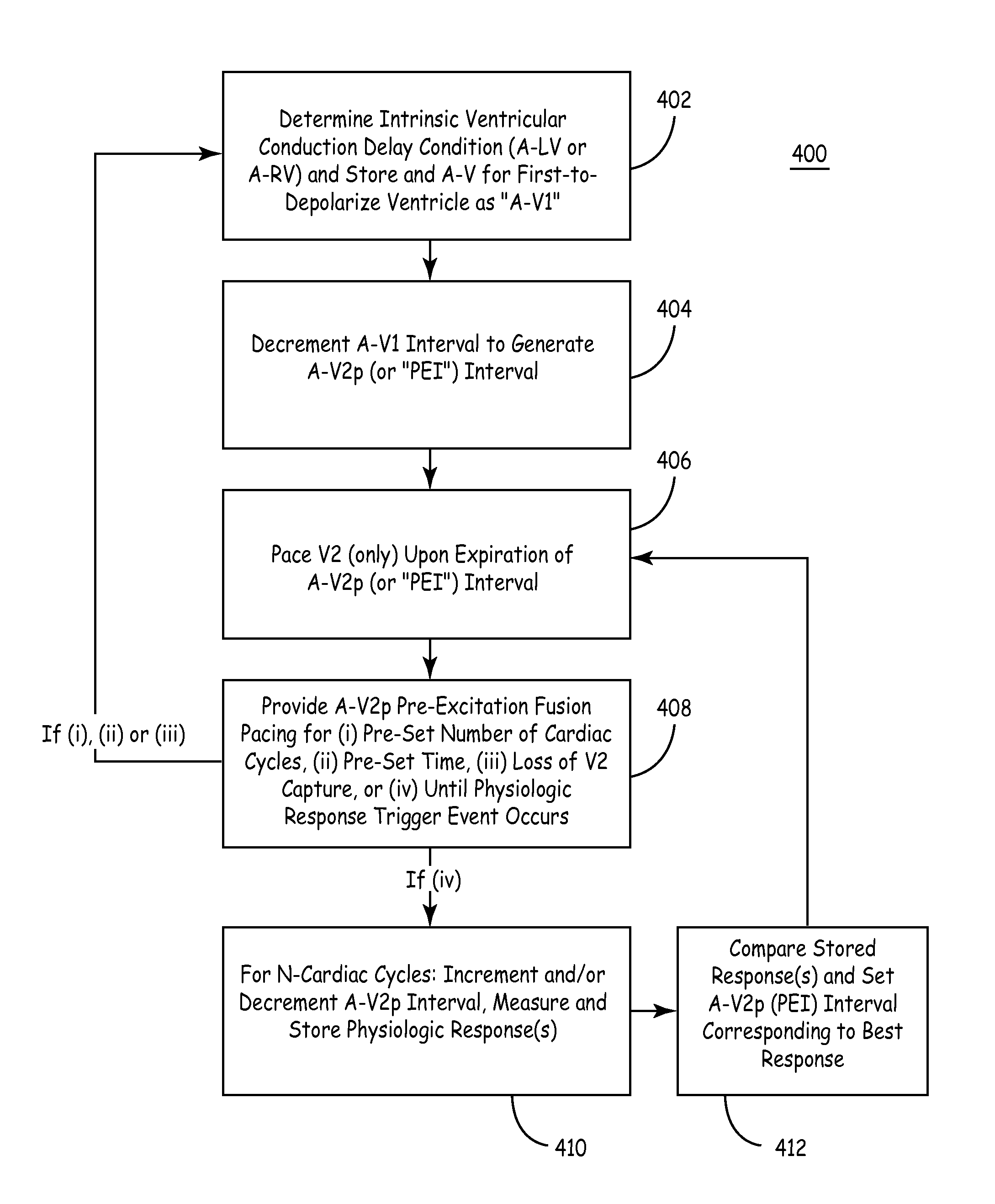
Apparatus and methods of energy efficient, atrial-based Bi-ventricular fusion-pacing
The bi-ventricular implantable pulse generator described and depicted herein enables hemodynamic efficiencies for patients suffering from intraventricular conduction delays or conduction blockage. The pulse generator effectively overcomes such conduction delay or block (e.g., left bundle branch block, “LBBB,” or right bundle branch block, “RBBB”) by delivering a novel form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Specifically, a single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is triggered from an atrial event (e.g., intrinsic or evoked depolarization). The triggering event may emanate from the right atrium (RA) or the left atrium (LA). A single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is delivered prior to the intrinsic depolarization of the other ventricle and thus promotes intraventricular electromechanical synchrony during CRT delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
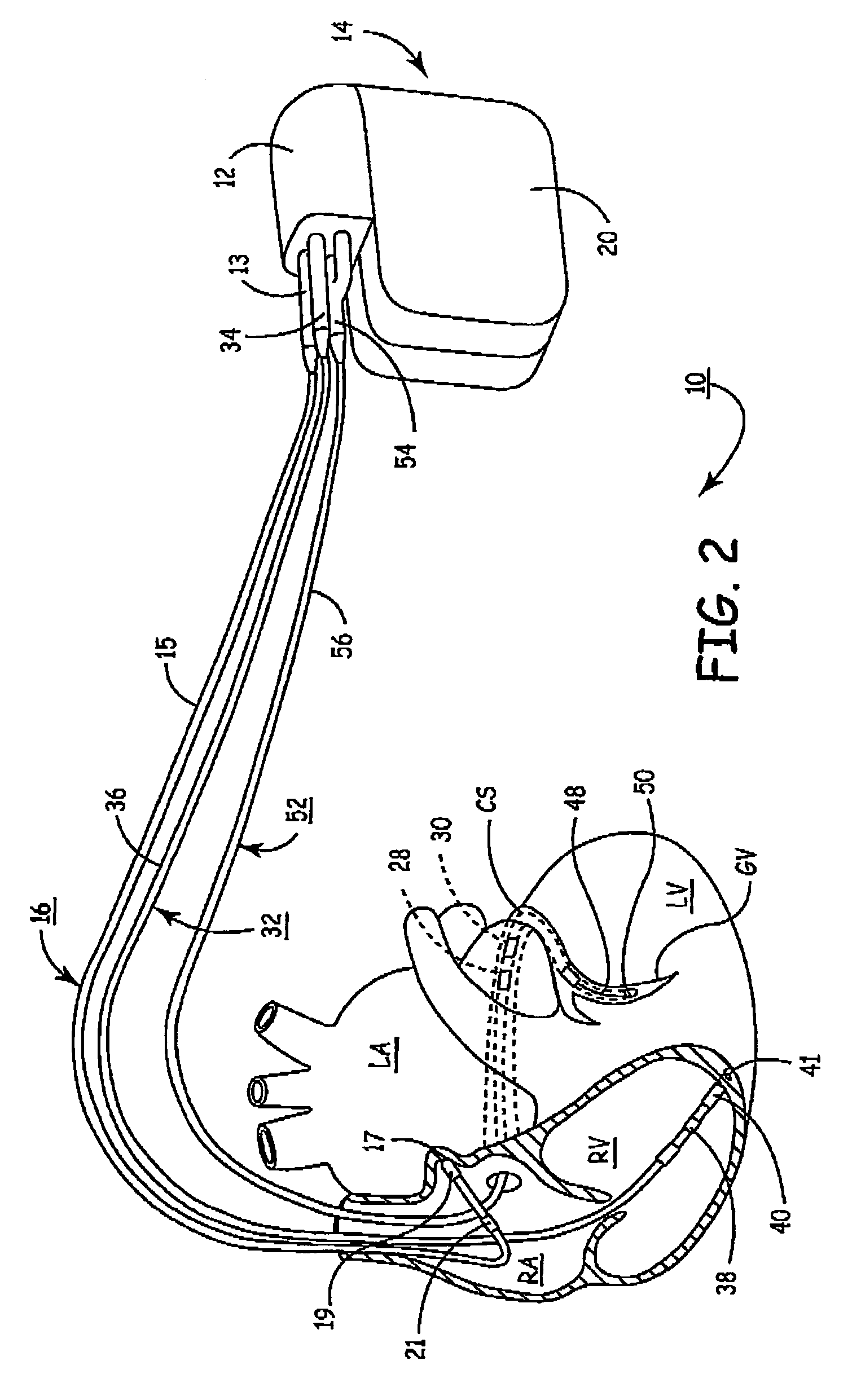
Bi-atrial and/or bi-ventricular patient safety cable and methods regarding same
InactiveUS6466824B1Transvascular endocardial electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsElectrical conductorY connector
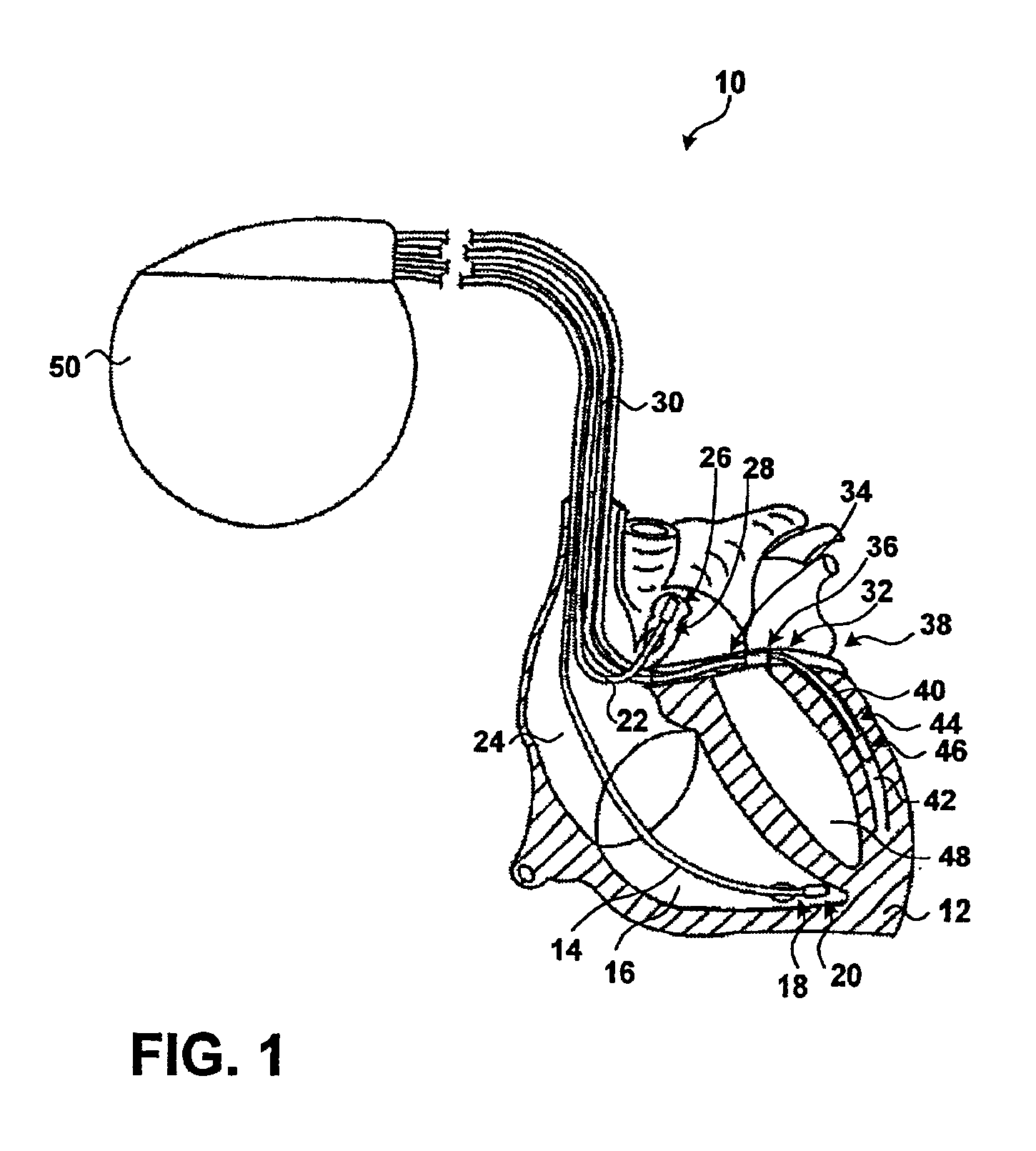
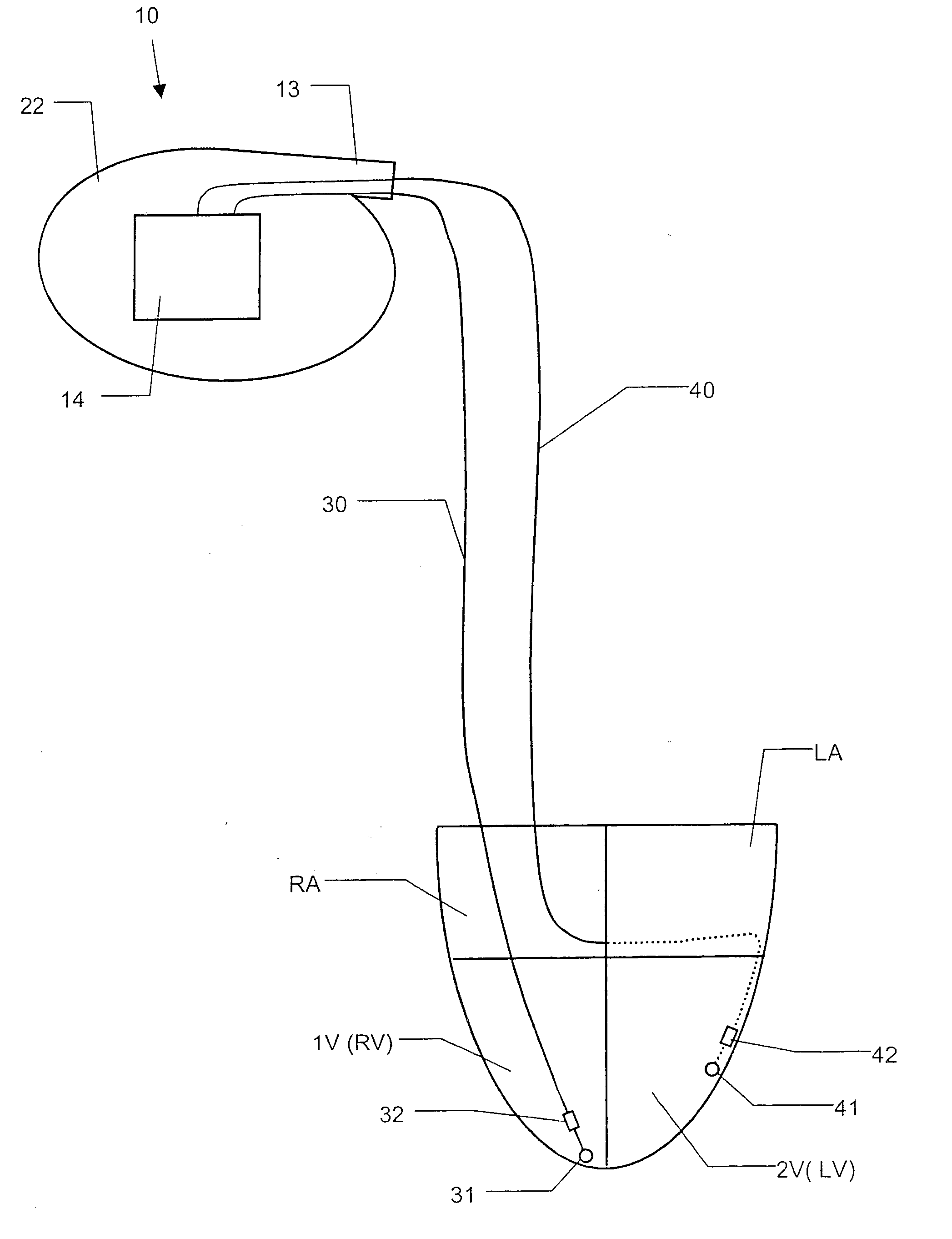
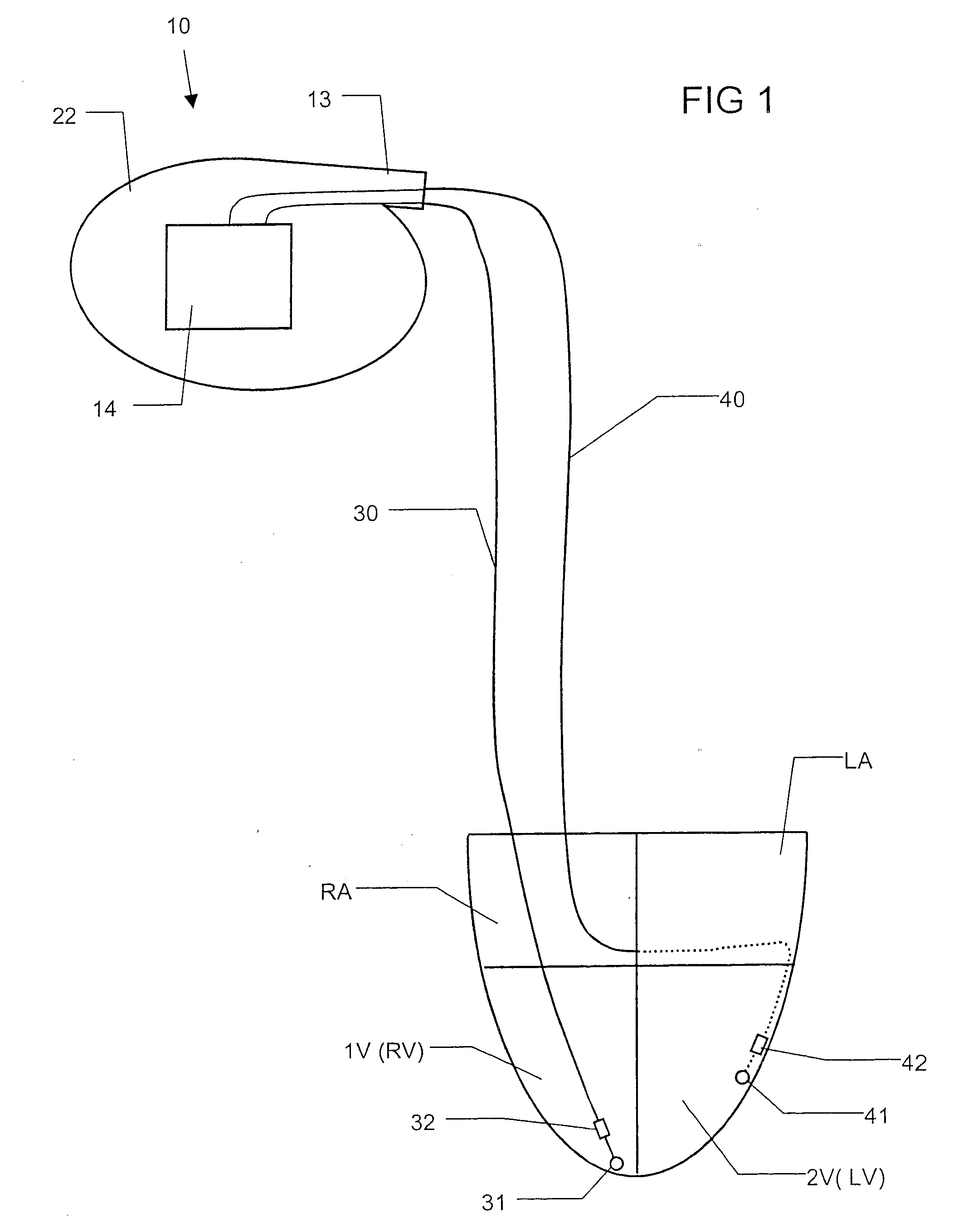
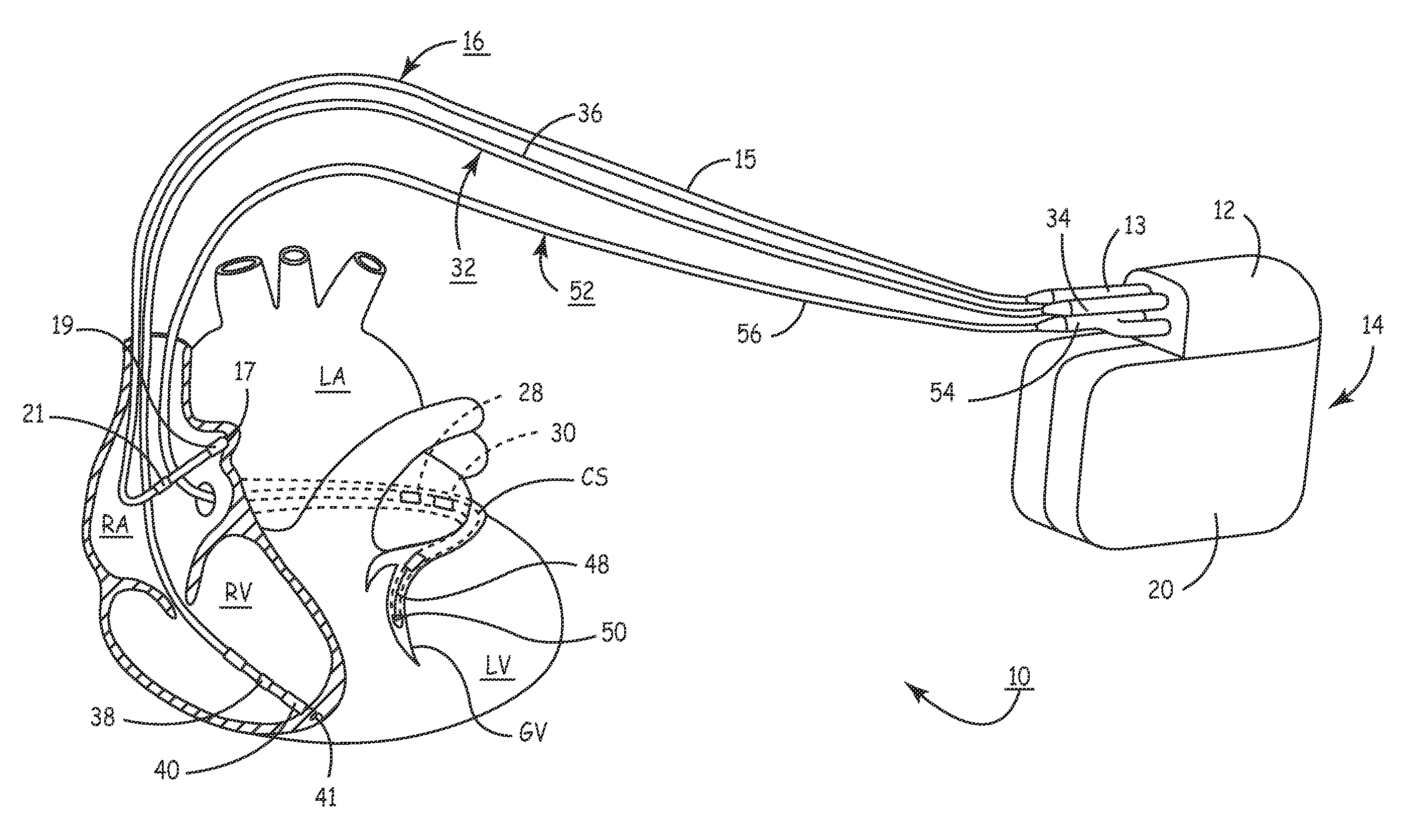
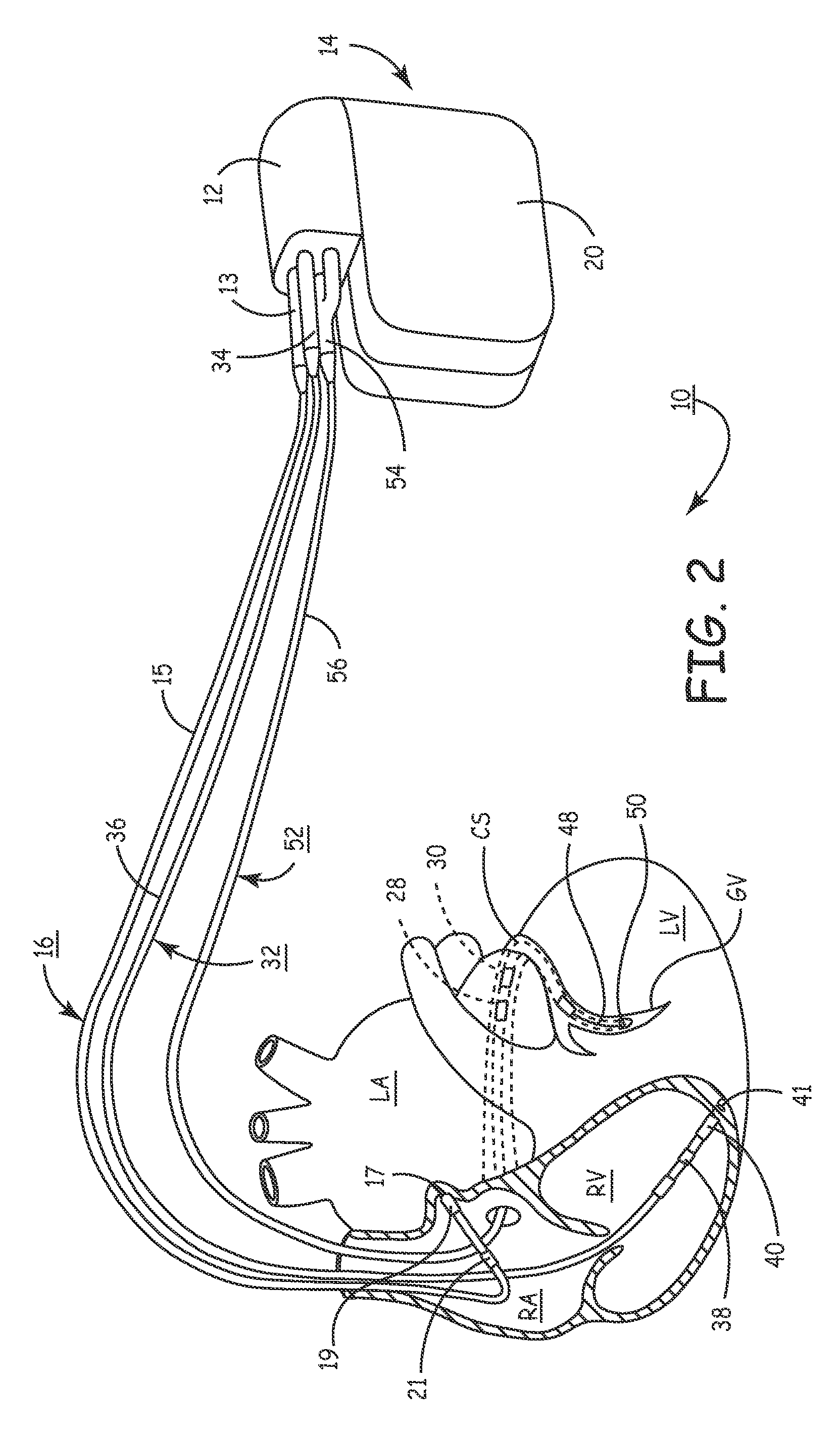
A bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular patient safety cable includes a multi-conductor insulated external cable having a Y-connector portion, an external lead connector assembly, and two or more lead adaptors. The patient safety cable is used to electrically connect one or more implantable leads "in parallel" to an external medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
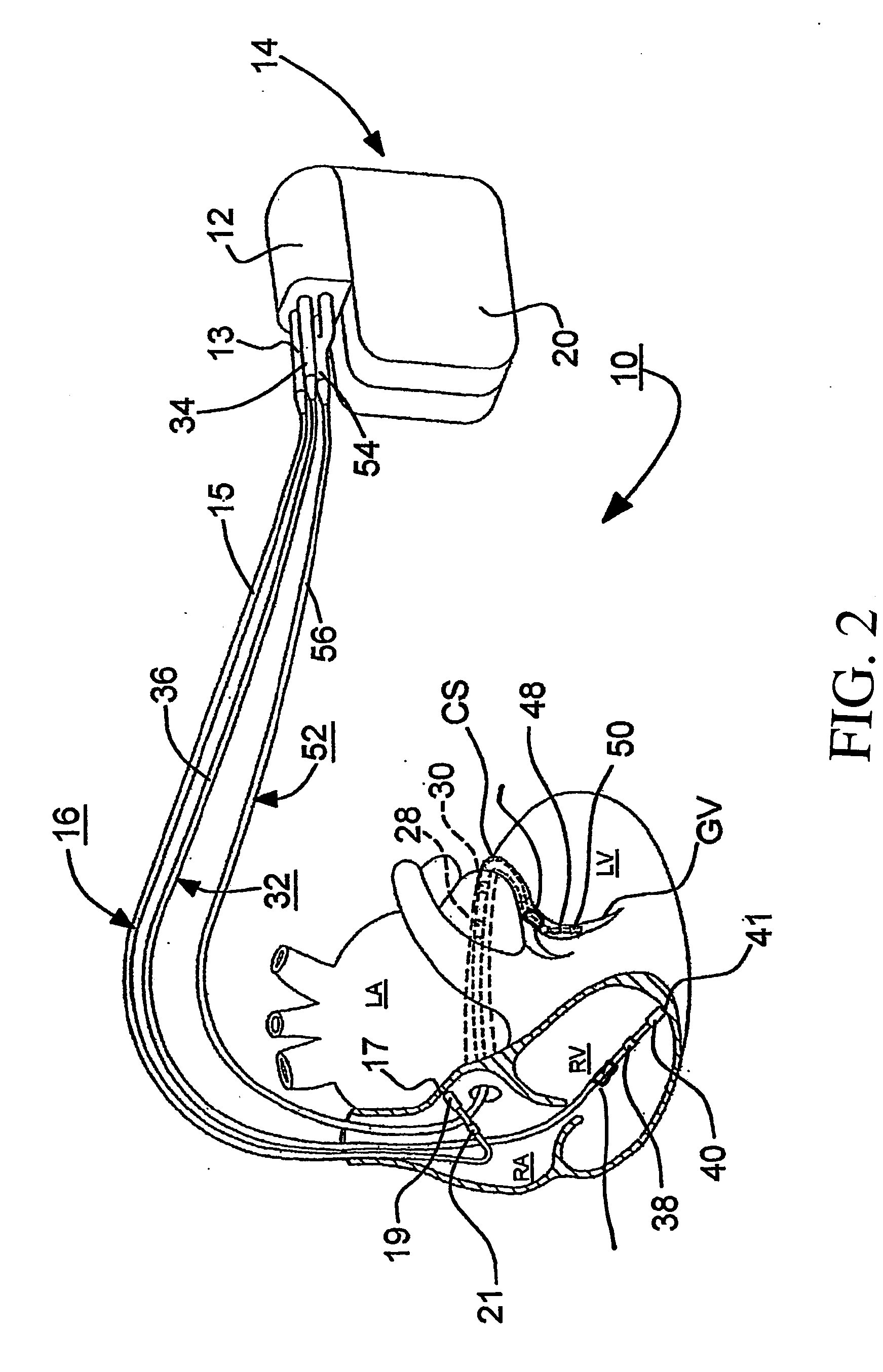
Bi-ventricular ventricular capture management in cardiac resyncronization therapy delivery devices
InactiveUS20060155338A1Great likelihoodSignificant comprehensive benefitsHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular conductionCardiac conduction
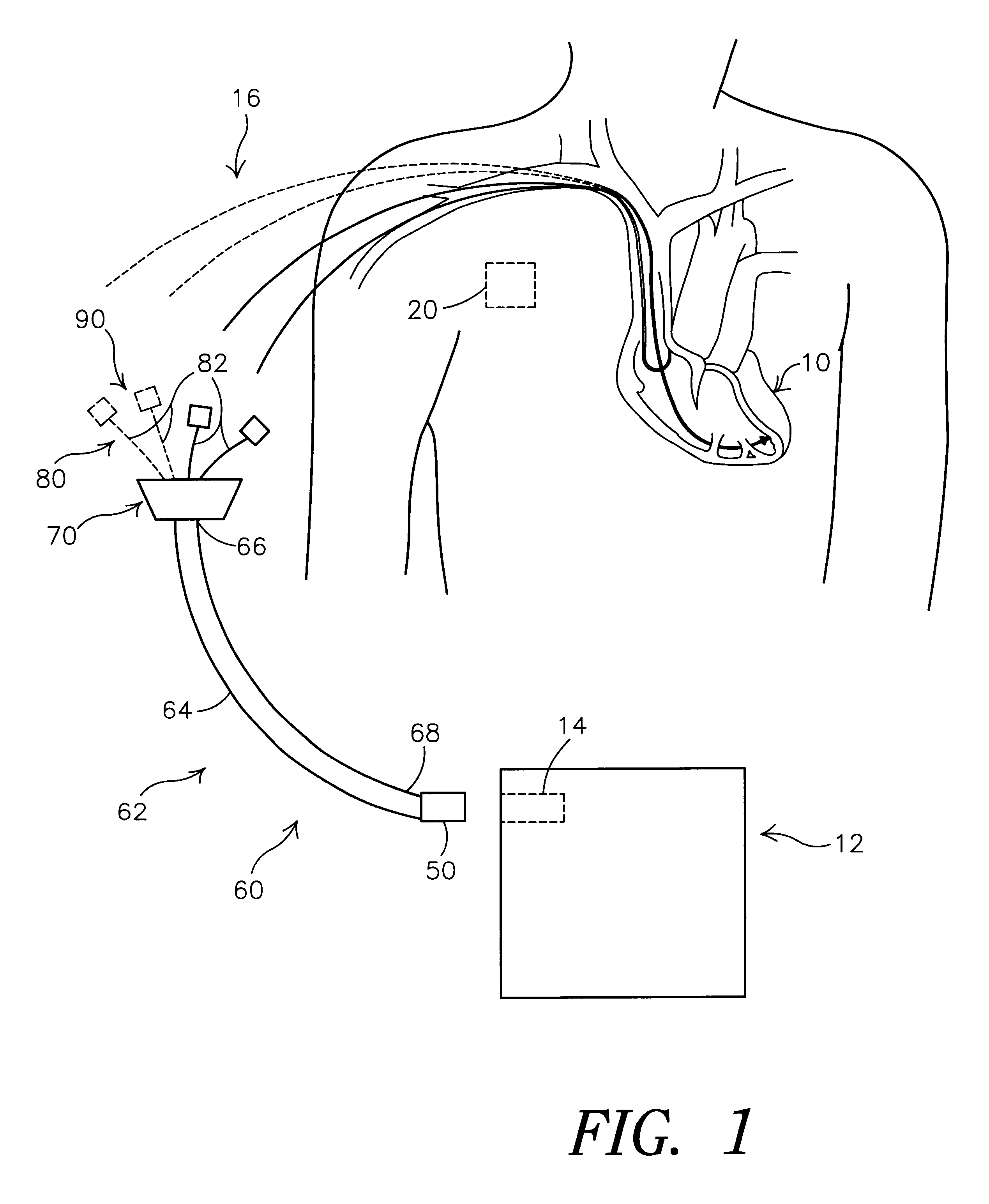
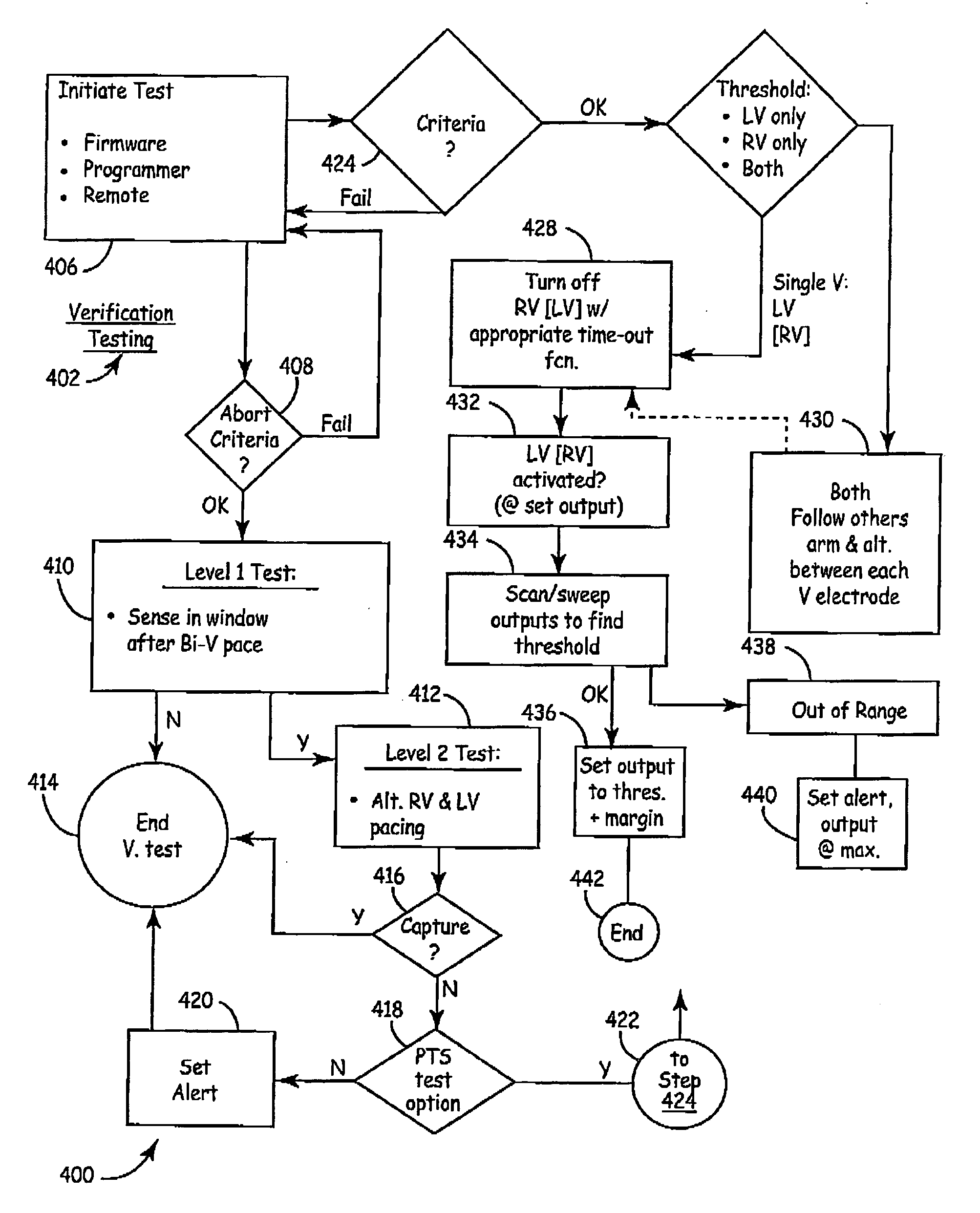
The present invention provides a technique for verifying pacing capture of a ventricular chamber, particularly to ensure desired delivery of a ventricular pacing regime (e.g., “CRT”). The invention also provides ventricular capture management by delivering a single ventricular pacing stimulus and checking inter-ventricular conduction during a temporal window to determine if the stimulus captured. If a loss-of-capture (LOC) signal results from the capture management testing, then the applied pacing pulses are modified and the conduction test repeated. If LOC, an alert message can issue. Other aspects include: use of a trend of A-RV / LV and LV-RV timing intervals to monitor changes in the patient's heart conduction properties; bi-ventricular verification test and search—while still pacing BiV by detecting latent sense; single-V pacing threshold search, use of timing of sense in other V chamber to establish capture and LOC windows; (iv) use of a premature V pace rather than short AV interval if VV cannot be discriminated from AV; (v) option to run a threshold search only if the Bi-ventricular verification test fails.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
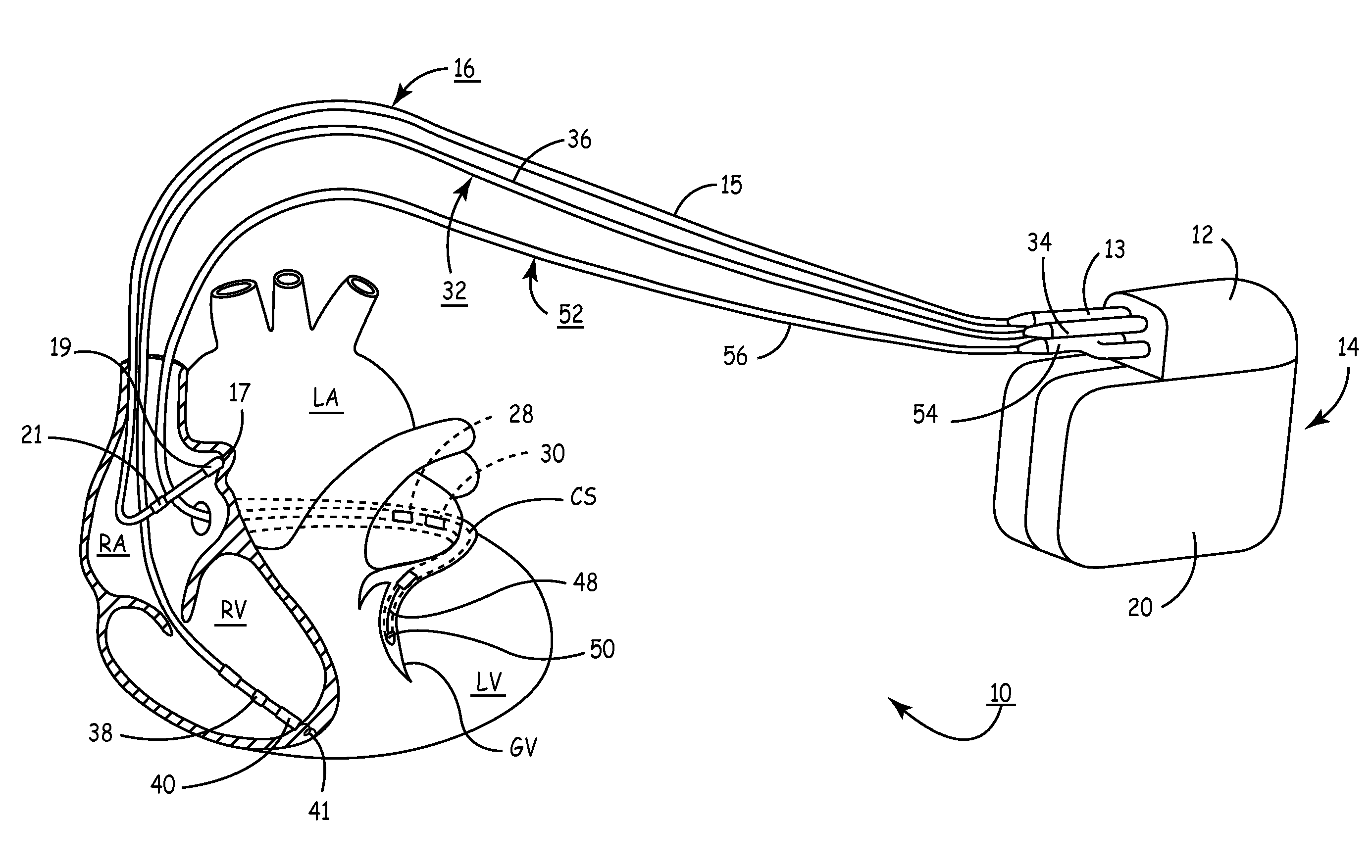
Catheter systems and methods for placing bi-ventricular pacing leads
ActiveUS20030229386A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesImplanted pacemakerCardiac pacemaker electrode
A catheter system suitable for implanting pacemaker leads. A guide catheter is provided with steering capability, and the necessary steering components are modified to permit the catheter to be sliced during withdrawal, so that the proximal forced applied to the pacemaker lead is minimized and the lead is less likely to be dislodged.
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Identification of electro-mechanical dysynchrony with a non-cardiac resynchronization therapeutic device
ActiveUS20100121403A1Facilitate identifying dysynchronyEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsTherapeutic DevicesHeart chamber
An implantable cardiac therapy device and methods of using a device including an implantable stimulation pulse generator, one or more implantable leads defining sensing and stimulation circuits adapted to sense and deliver therapy in at least one right side heart chamber, and an implantable controller in communication with the stimulation pulse generator and the one or more patient leads so as to receive sensed signals indicative of a patient's physiologic activity and deliver indicated therapy. The controller is adapted to monitor at least one indicator of cardiac dysynchrony and to compare the at least one indicator to a determined dysynchrony threshold. The threshold is determined for indications that the patient be further evaluated for cardiac resynchronization therapy. The controller is further adapted to set an alert when the at least one indicator exceeds the threshold to indicate to a clinician that evaluation for bi-ventricular pacing might be indicated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Automatic LV/RV capture verification and diagnostics
ActiveUS7555336B2Significant comprehensive benefitsPrecise deliveryHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular conductionRat heart
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Adjustable cardiac resynchronization
InactiveUS6842642B2Decrease in paceSave battery powerHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityCardiac pacemaker electrode
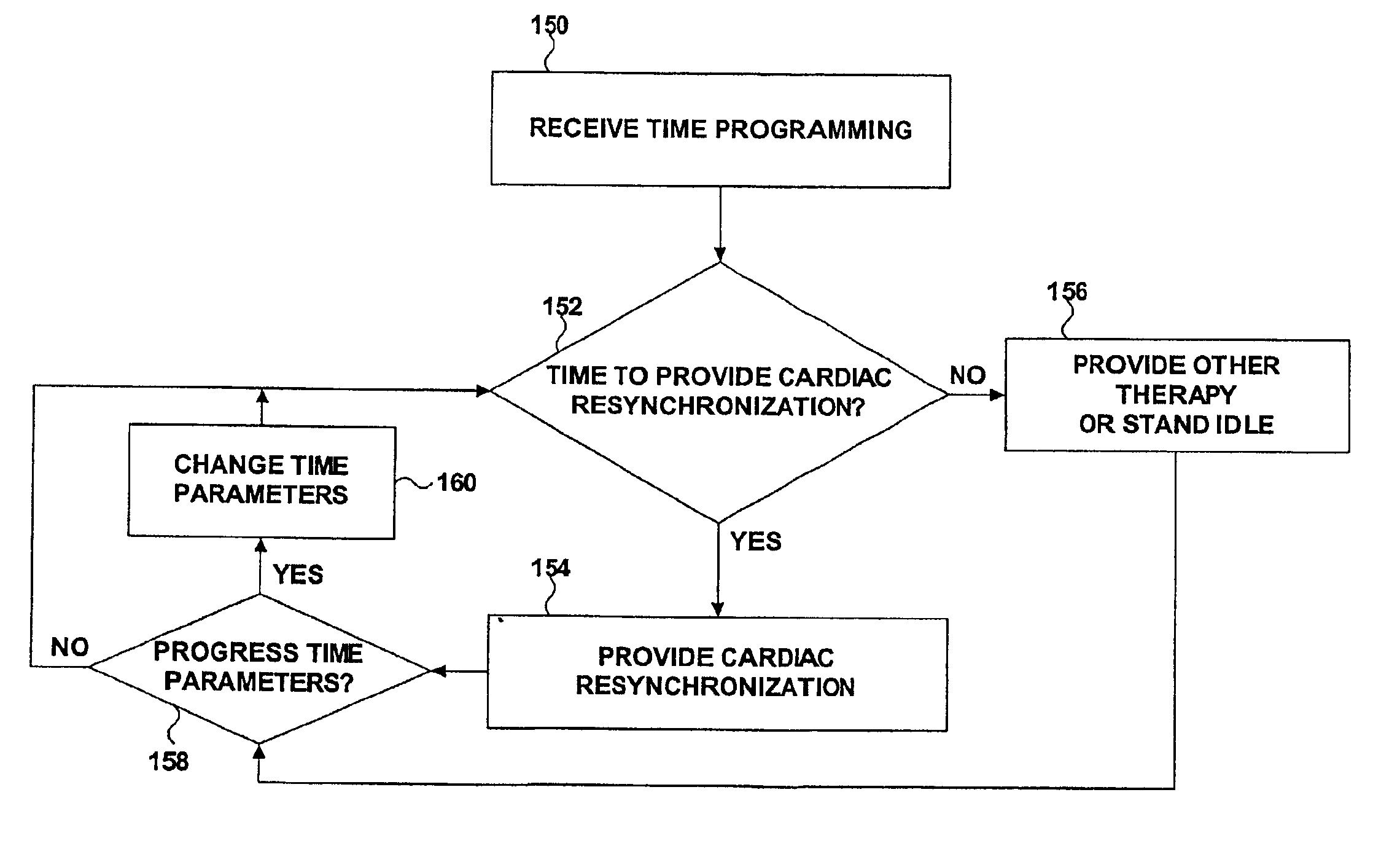
Techniques are presented for providing adjustable cardiac resynchronization with an implanted medical device such as a pacemaker. For example, cardiac resynchronization may be provided during some time periods but not during other time periods, or cardiac resynchronization may be provided in response to selected sensed events. Adjustable cardiac resynchronization is applicable to therapy such as bi-ventricular pacing, in which both ventricles of the heart are paced in response to sensed atrial events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for monitoring an organ of a patient
ActiveUS20100280397A1ElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyCongestive heart failure chfSkeletal muscle
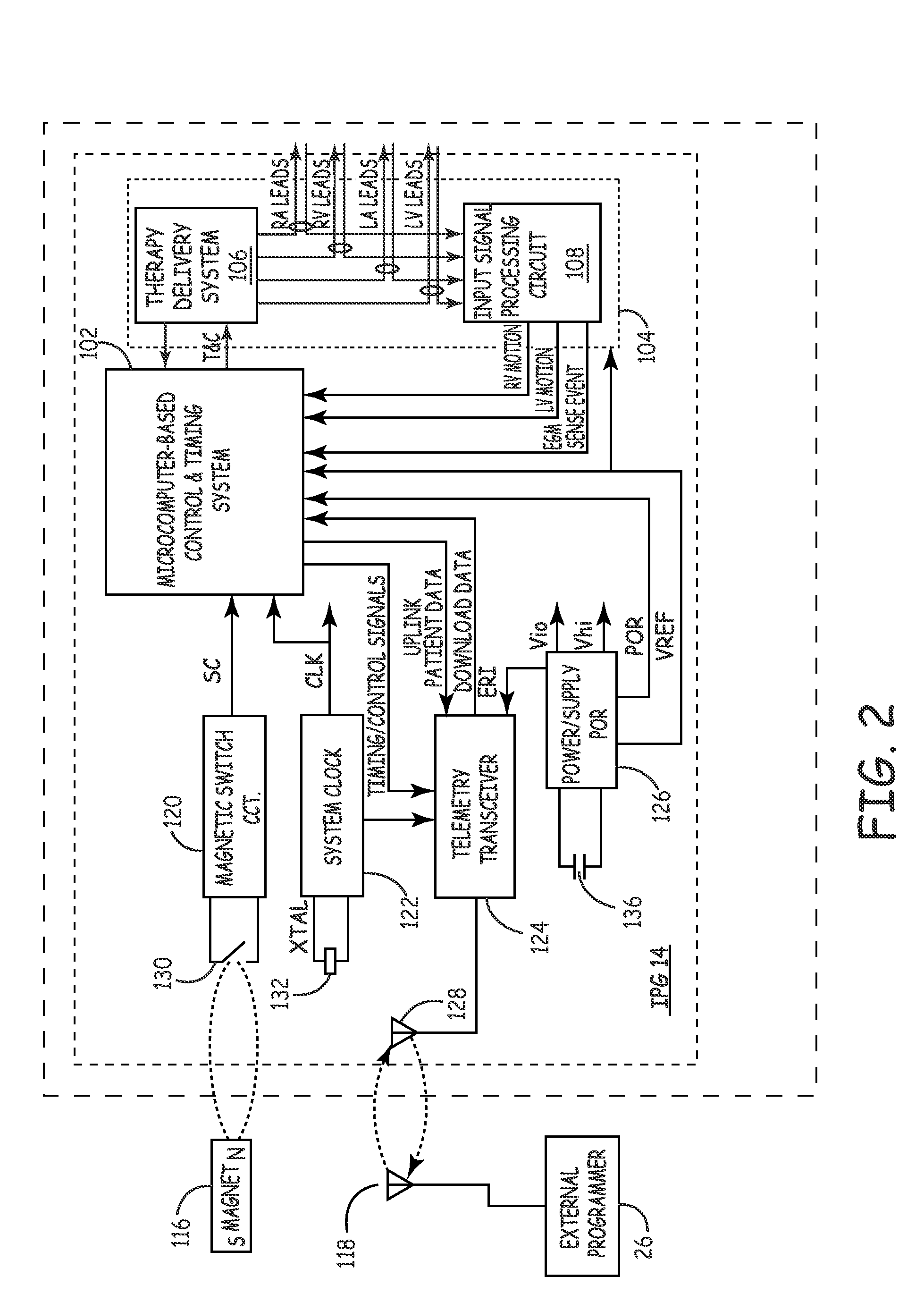
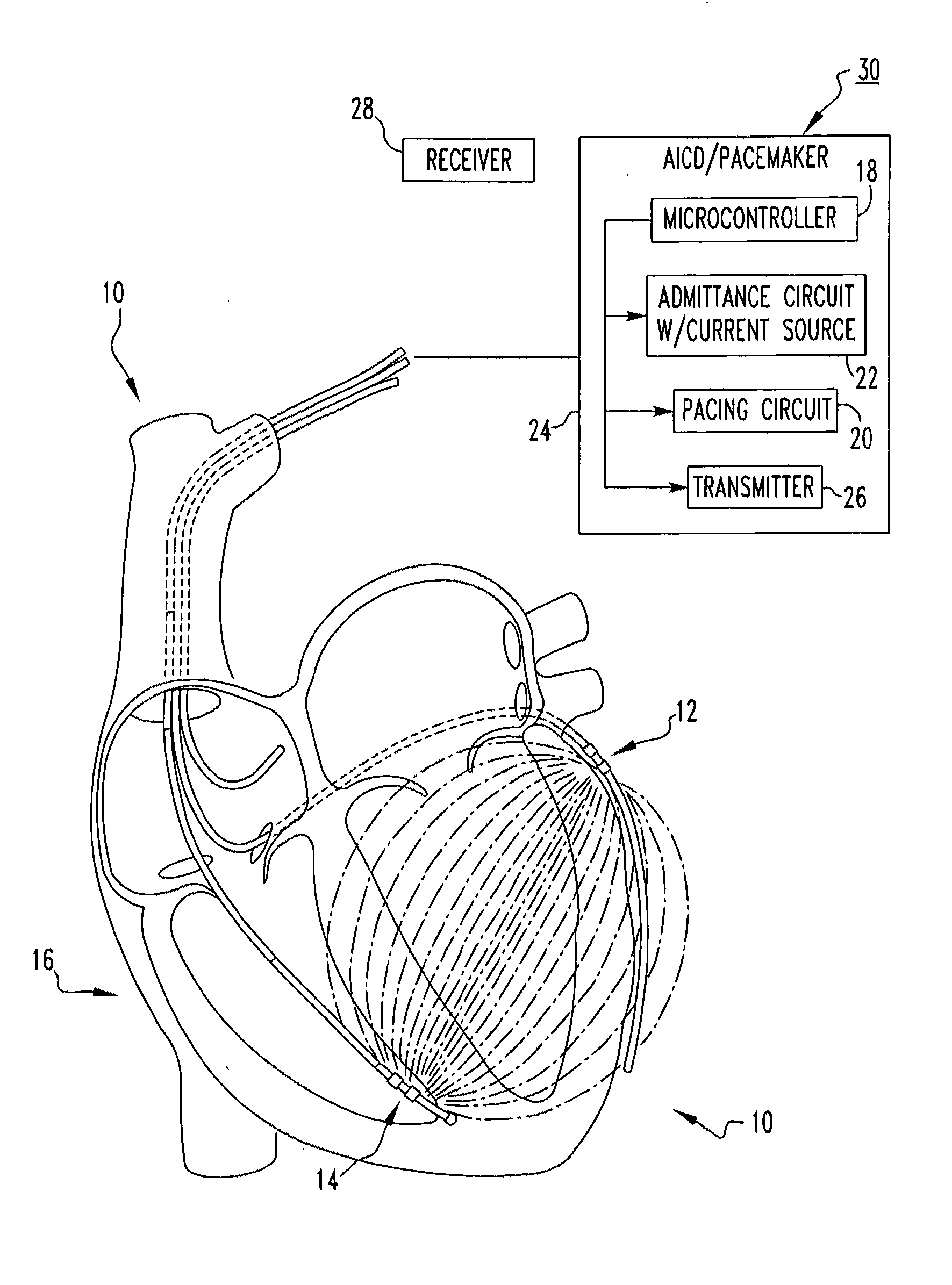
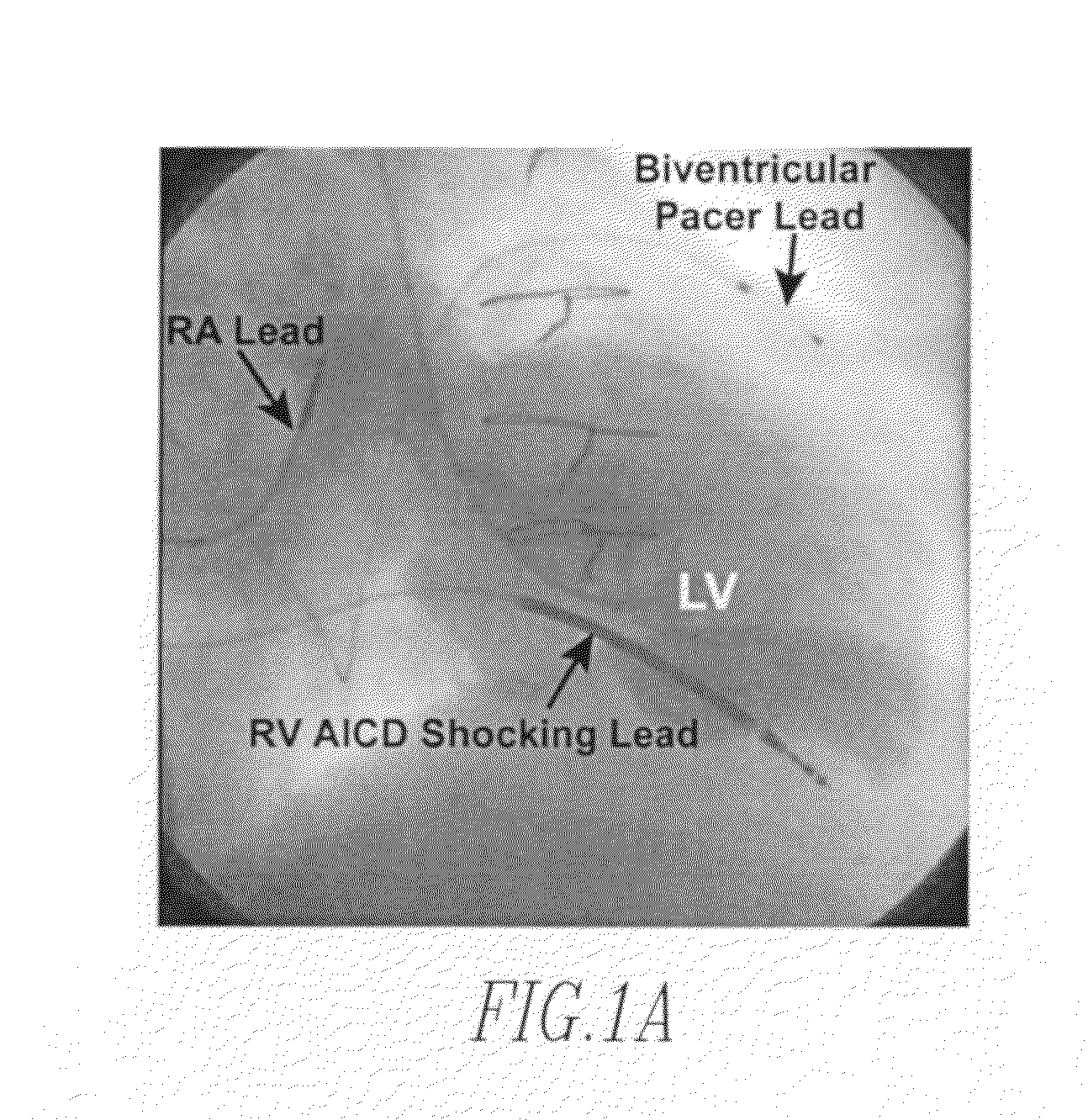
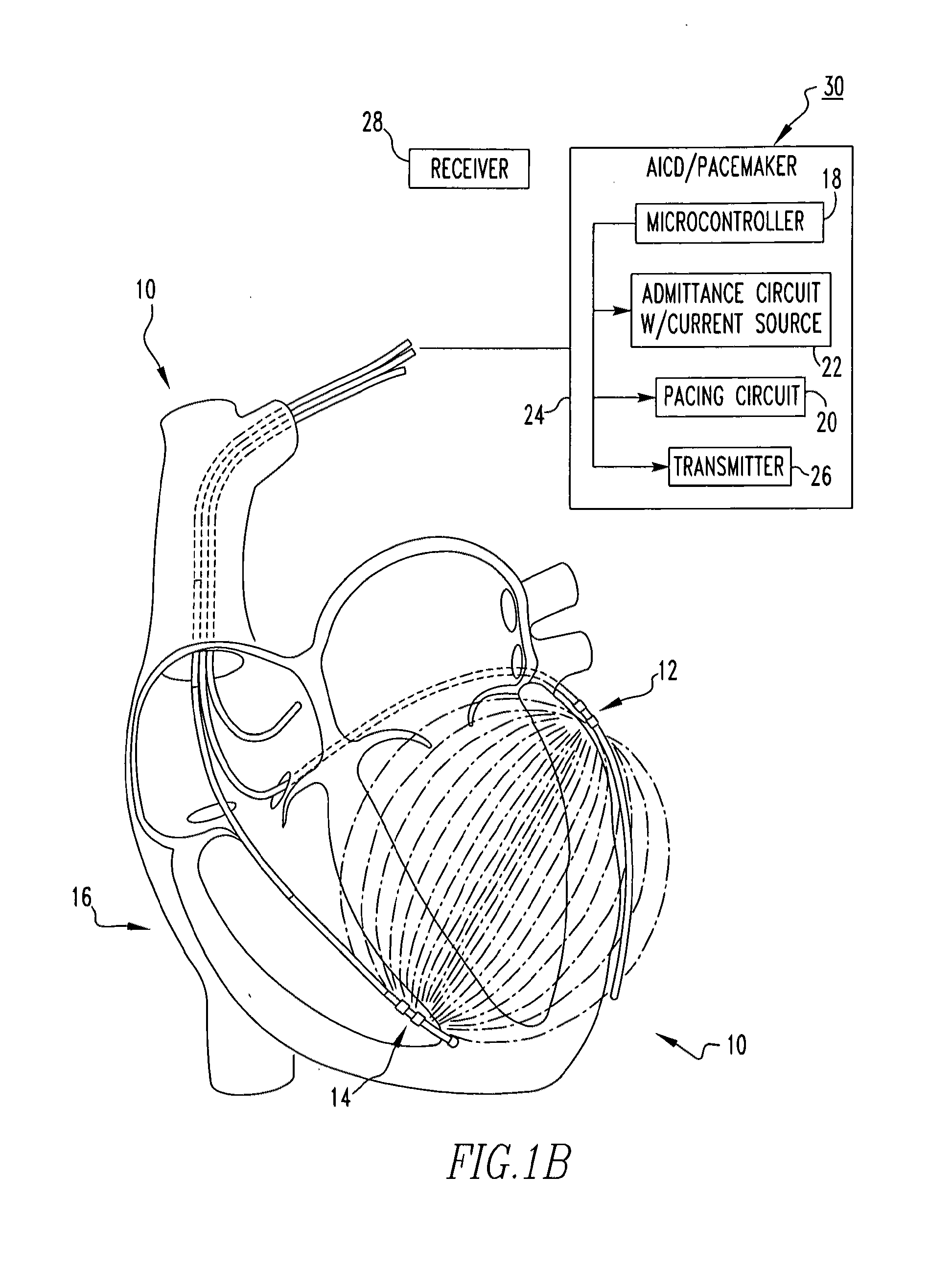
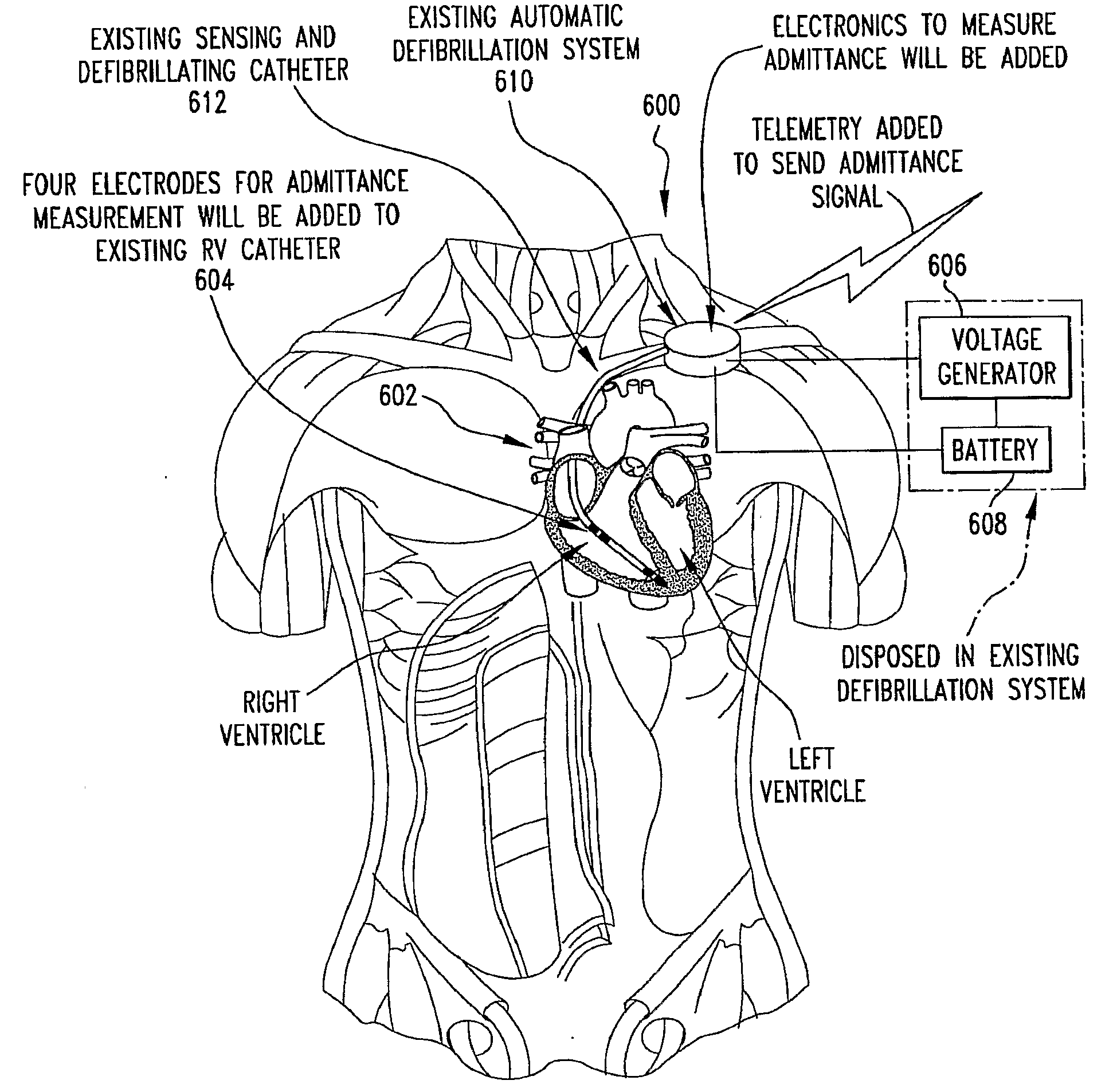
An apparatus for determining tissue versus fluid components of an organ include a detector that generates a detector signal based on electrical signals derived from tissue and fluid. The apparatus includes a signal processor in communication with the detector which subtracts in real time a tissue component from the detector signal and produces a fluid volume signal. A method for monitoring a patient's fluid volume of a patient's organ. An apparatus for monitoring a patient's organ. A method for monitoring a patient's organ. A method to piggyback an admittance system onto a AICD / Bi-ventricular Pacemaker for a heart of a patient, in particular a weakened heart having features consistent with congestive heart failure. An apparatus for monitoring an organ, such as a heart, lungs, brain, skeletal muscle, and bladder of a patient which includes a detector which detects the admittance of the organ. The apparatus includes a transmitter in communication with the detector which transmits a wireless signal indicative of the admittance of the organ. A method for monitoring an organ of a patient includes the steps of detecting with a detector the admittance of the organ. There is the step of transmitting with a transmitter in communication with the detector a wireless signal indicative of admittance of the organ.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
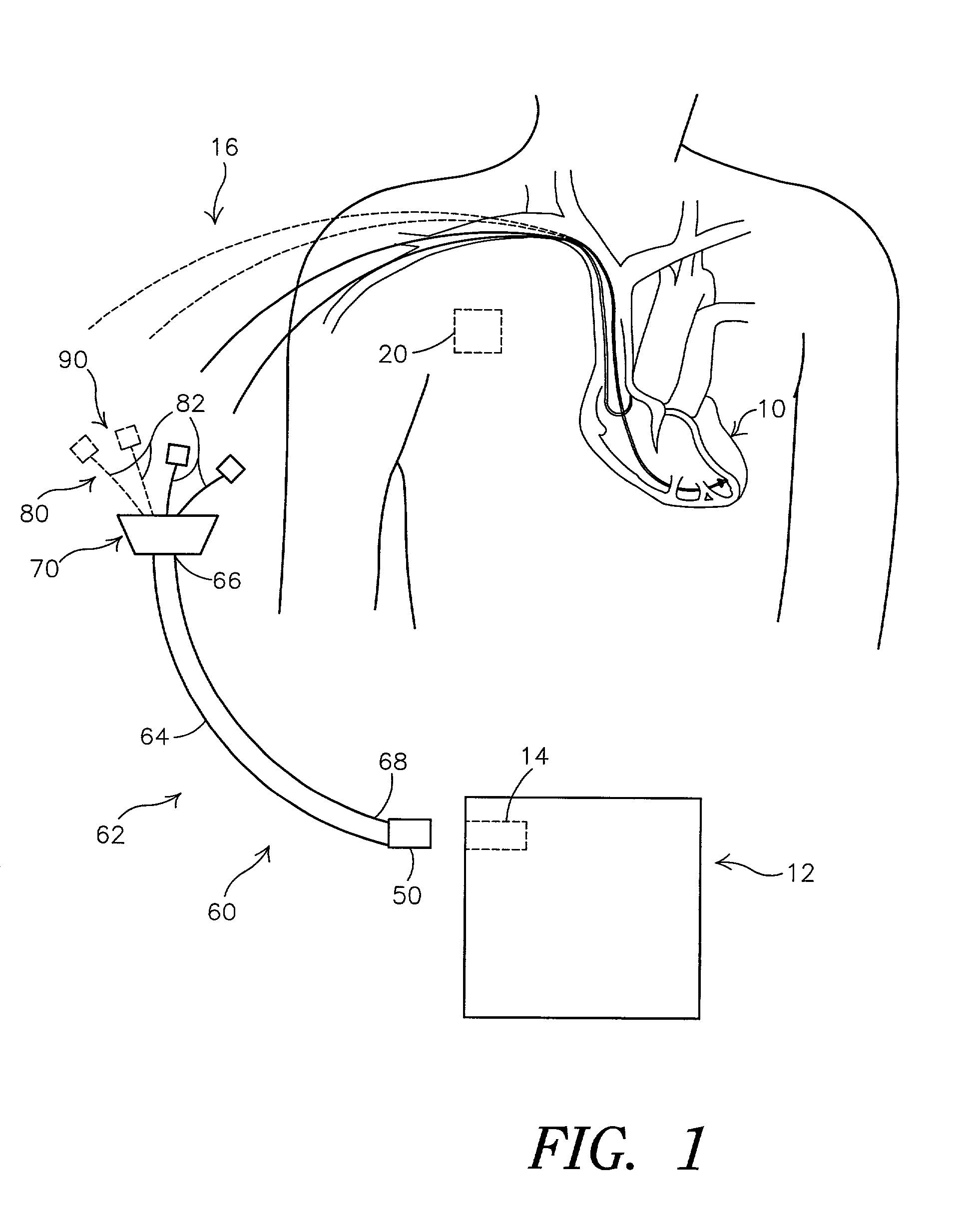
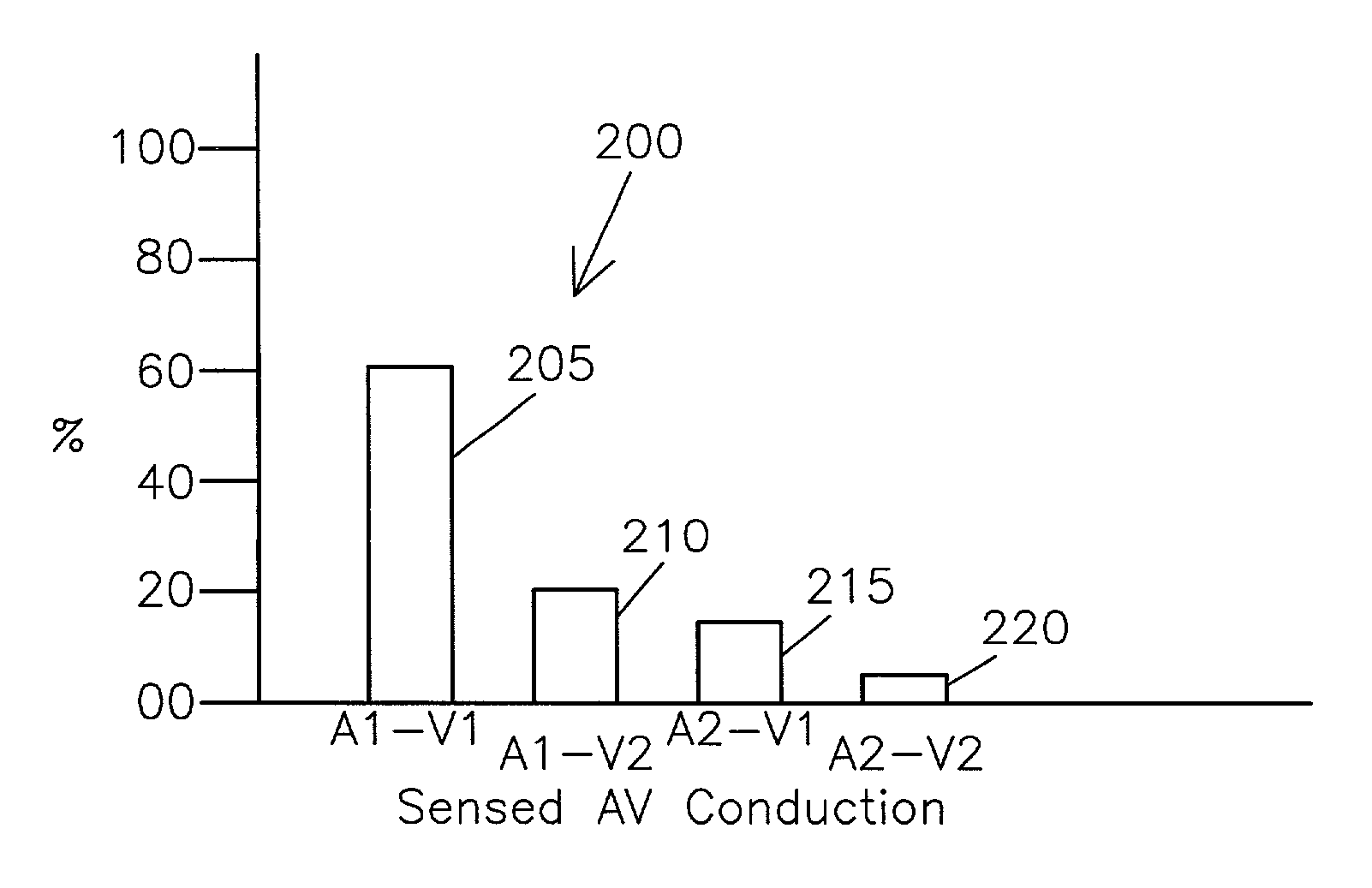
Cardiac resynchronization with adaptive A1-A2 and/or V1-V2 intervals
InactiveUS6839592B2Improve heart functionIncrease cardiac outputHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationPulse ratePace rate
In a system that provides bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular pacing, the system adjusts an interval between paces delivered to the atria, and / or an interval between paces delivered to the ventricles, as a function of heart rate. By adjusting the interval between paces as a function of heart rate, the atria and / or ventricles may be activated in a more synchronous and more hemodynamically efficient fashion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bi-atrial and/or bi-ventricular patient safety cable and methods regarding same
InactiveUS20020183819A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsElectrical conductorY connector
A bi-atrial and / or bi-ventricular patient safety cable includes a multi-conductor insulated external cable having a Y-connector portion, an external lead connector assembly, and two or more lead adaptors. The patient safety cable is used to electrically connect one or more implantable leads "in parallel" to an external medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Diagnostic features in biatrial and biventricular pacing systems
InactiveUS7058443B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac pacemaker electrodeVentricular pacing
A biatrial and / or biventricular pacing system is used in a diagnostic context. By placing a pacing / sensing lead in three or four chambers of the heart, various conduction sequences can be determined and the originating chamber of various arrhythmias can be identified. This information is stored temporarily in the pacemaker until it is extracted for analysis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods of energy efficient, atrial-based Bi-ventricular fusion-pacing
The present invention enables hemodynamic efficiencies for patients suffering from intraventricular conduction delays or conduction blockage. The invention effectively overcomes such conduction delay or block (e.g., left bundle branch block, “LBBB,” or right bundle branch block, “RBBB”) by delivering a novel form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Specifically, a single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is triggered from an atrial event (e.g., intrinsic or evoked depolarization). The triggering event may emanate from the right atrium (RA) or the left atrium (LA). A single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is delivered prior to the intrinsic depolarization of the other ventricle and thus promotes intraventricular electromechanical synchrony during CRT delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
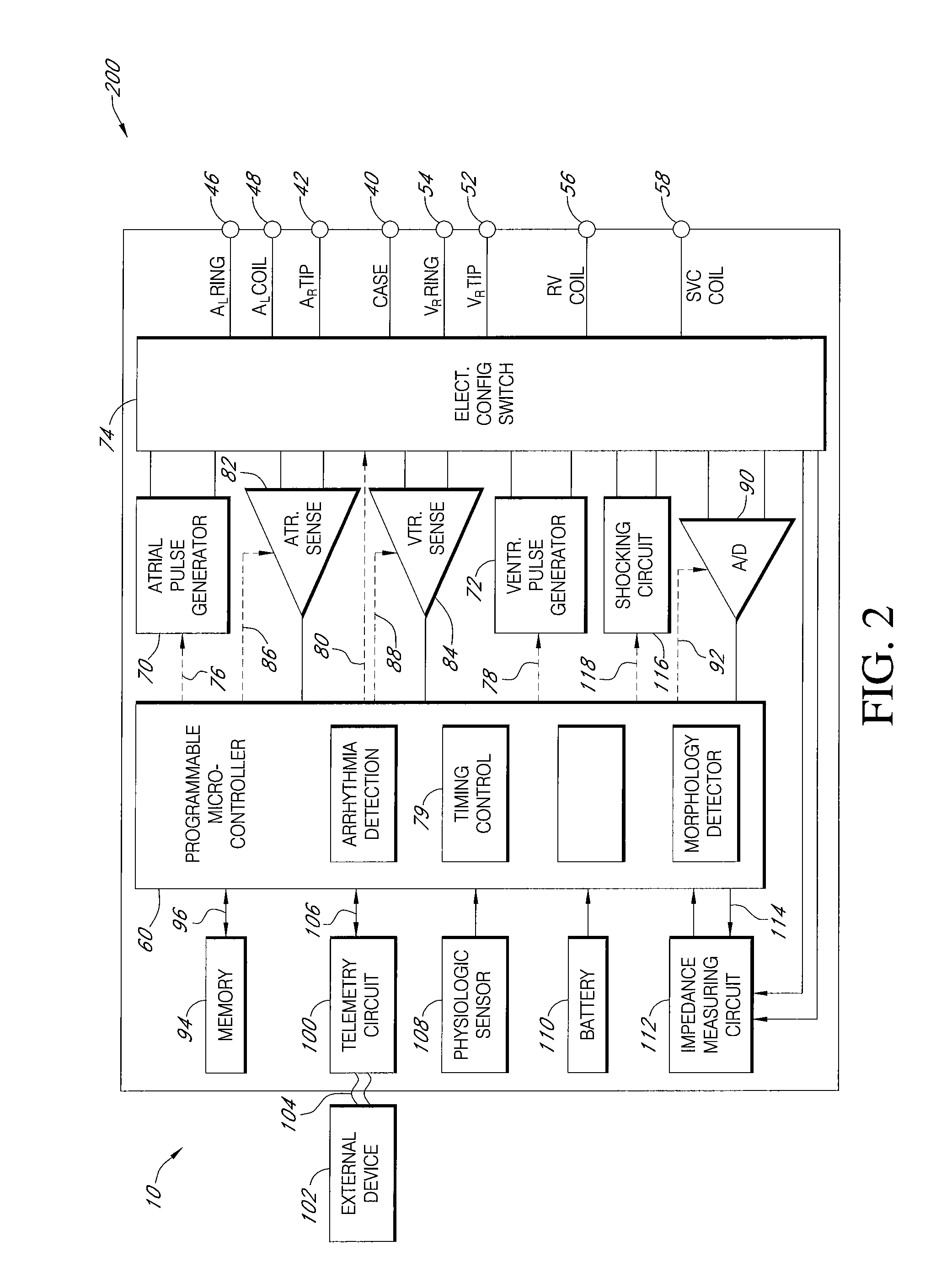
Implantable bi-ventricular stimulation device and system, and bi-ventricular stimulation and sensing method
InactiveUS6961613B2Overcome problemsEasy to implementHeart stimulatorsControl circuitBiventricular stimulation
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device has a control circuit that within a time cycle, delivers pacing pulses with both first and second pacing circuits with a time gap between a pacing pulse delivered by these pacing circuits. The time gap can be such that a pacing pulse delivered by the second pacing circuits falls substantially within a first time interval in which an evoked response can be expected to a pacing pulse delivered by the first pacing circuit. The control circuit performs a temporary modification of the operation of the device such that during at least one time cycle no pacing pulse is delivered by the second pacing circuit during the first time interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
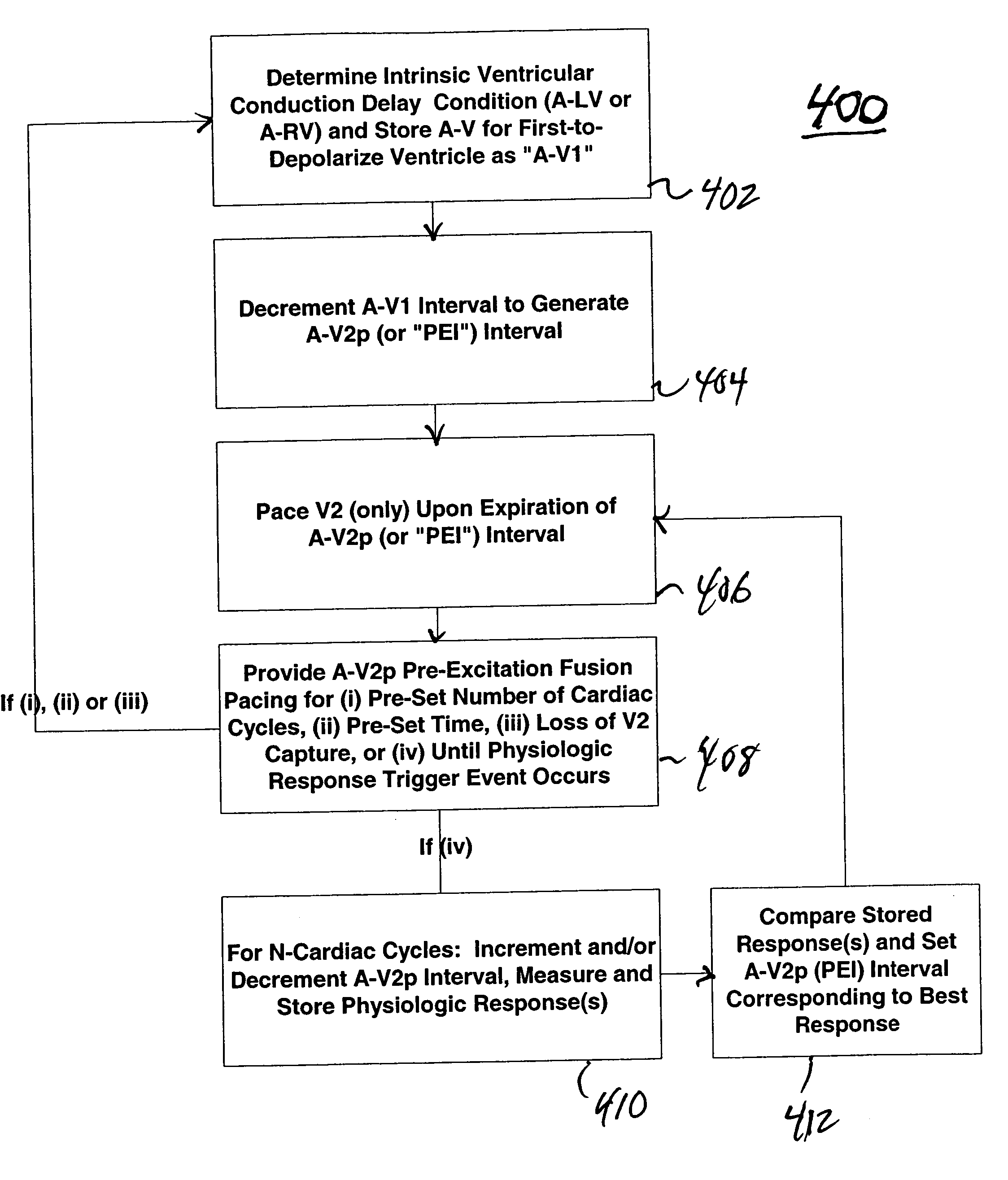
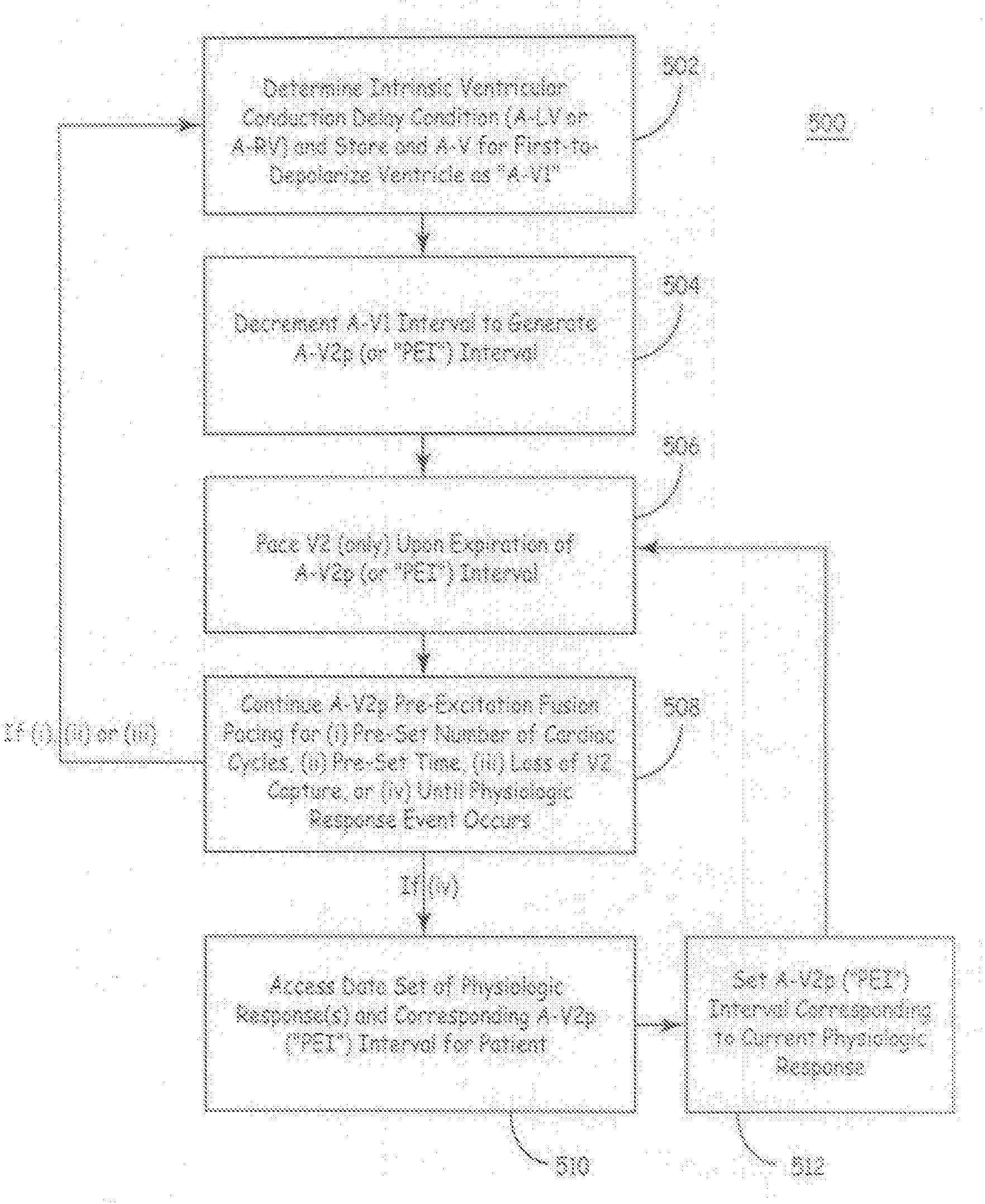
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Real-time optimization of right to left ventricular timing sequence in bi-ventricular pacing of heart failure patients
ActiveUS7203541B2Improve performanceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerWall motion
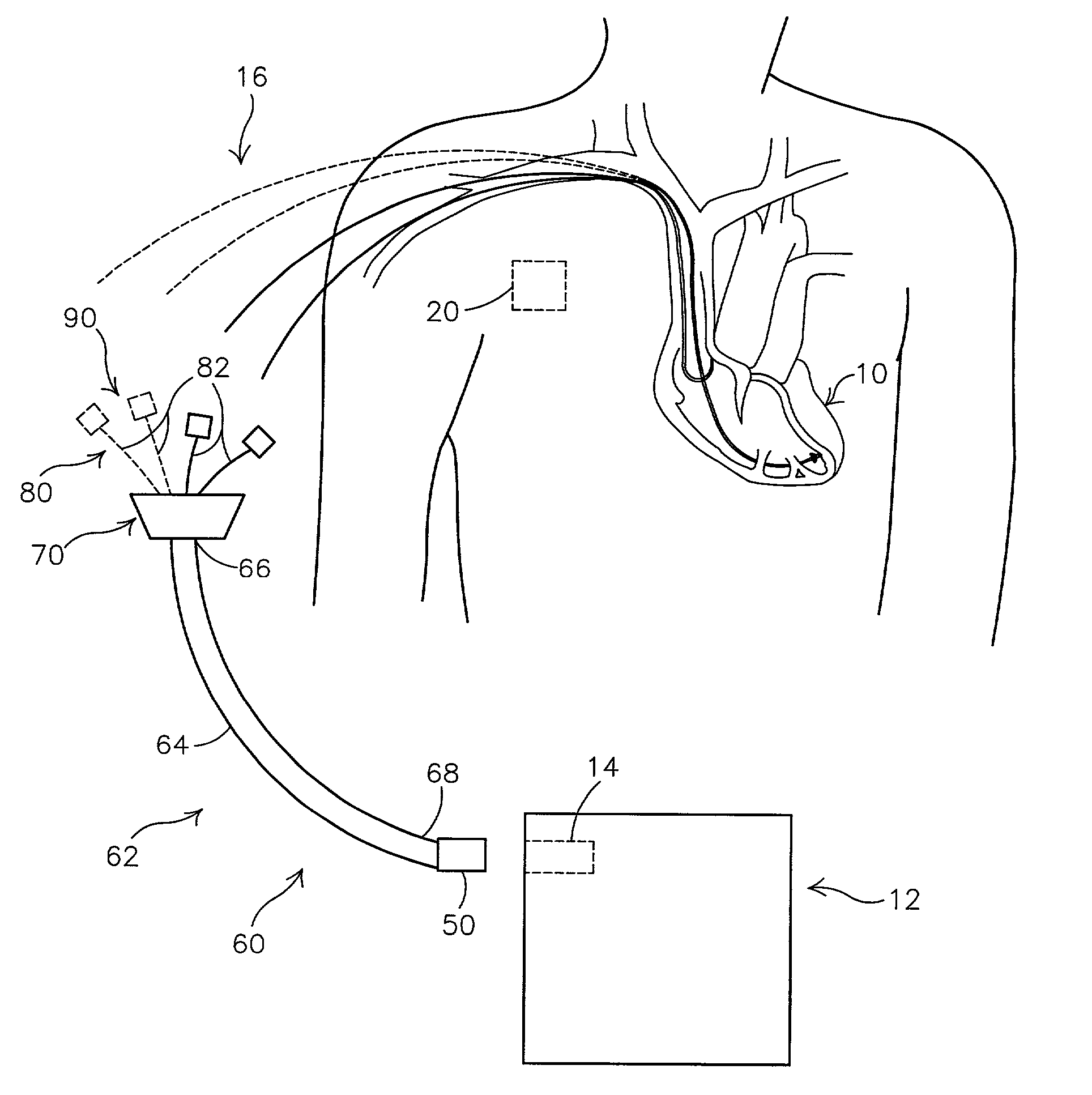
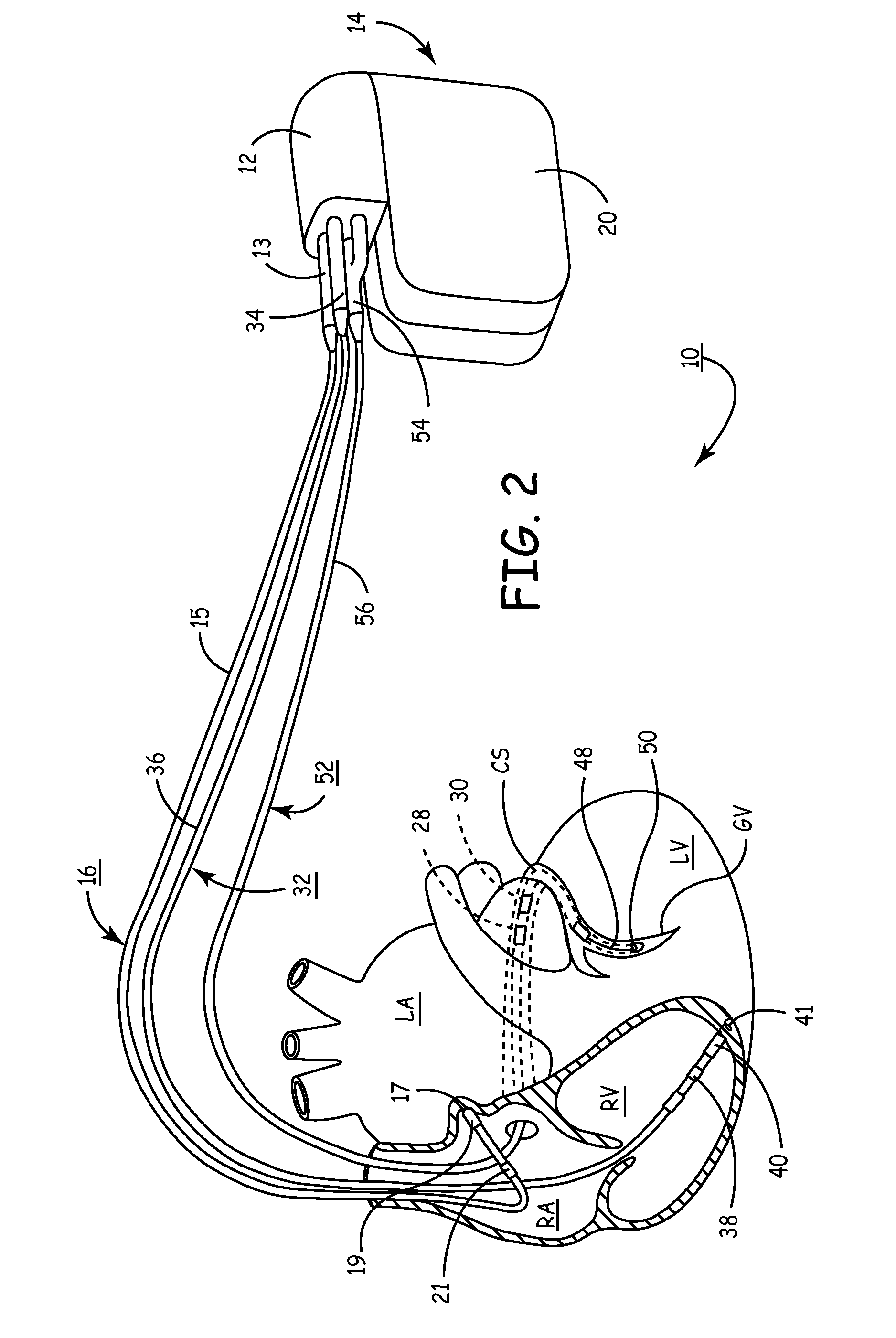
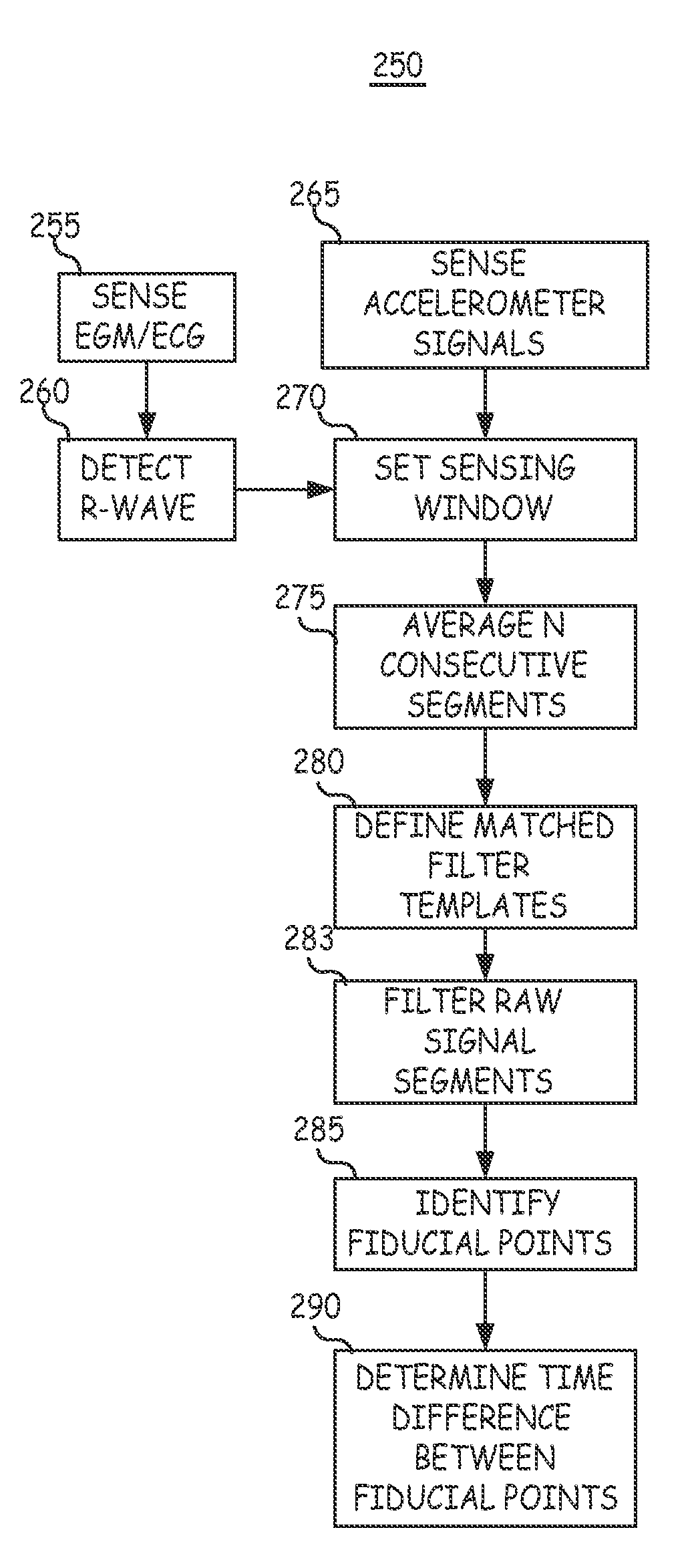
A system and automated method for assessing ventricular synchrony in ambulatory patients is provided including at least one mechanical sensor (e.g., accelerometer, tensiometric sensor, force transducer, and the like) operatively coupled to a first myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a first chamber, and a second mechanical sensor operatively coupled to a second myocardial location in order to measure a wall motion signal of a second chamber. The wall motion signals are processed in order to identify the time at which a fiducial (e.g., an inflection point, a threshold crossing, a maximum amplitude, etc.) occurs for each respective signal. The temporal separation between the fiducial points on each respective signal is measured as a metric of ventricular synchrony and can be optionally utilized to adjust pacing therapy timing to improve synchrony.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Admittance measurement for tuning bi-ventricular pacemakers
ActiveUS20120150252A1Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerCardiac pacemaker electrode
An apparatus for treating a heart of a patient includes a first lead and at least a second lead for pacing the heart adapted to be in electrical communication with the heart. The apparatus includes a microcontroller in communication with the first and second leads which triggers the first lead at either different times or the same time from when the microcontroller triggers the second lead. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a microcontroller in communication with the first and second leads that determines heart volume, including stroke volume, end-systolic volume, and calculated values including ejection fraction, from admittance from signals from the first and second leads and uses the admittance as feedback to control heart volume ejected, as measured by stroke volume, calculated values such as ejection fraction, and control end-systolic volume, with respect to the first and second leads. A method for treating the heart of a patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Fusion Pacing Enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
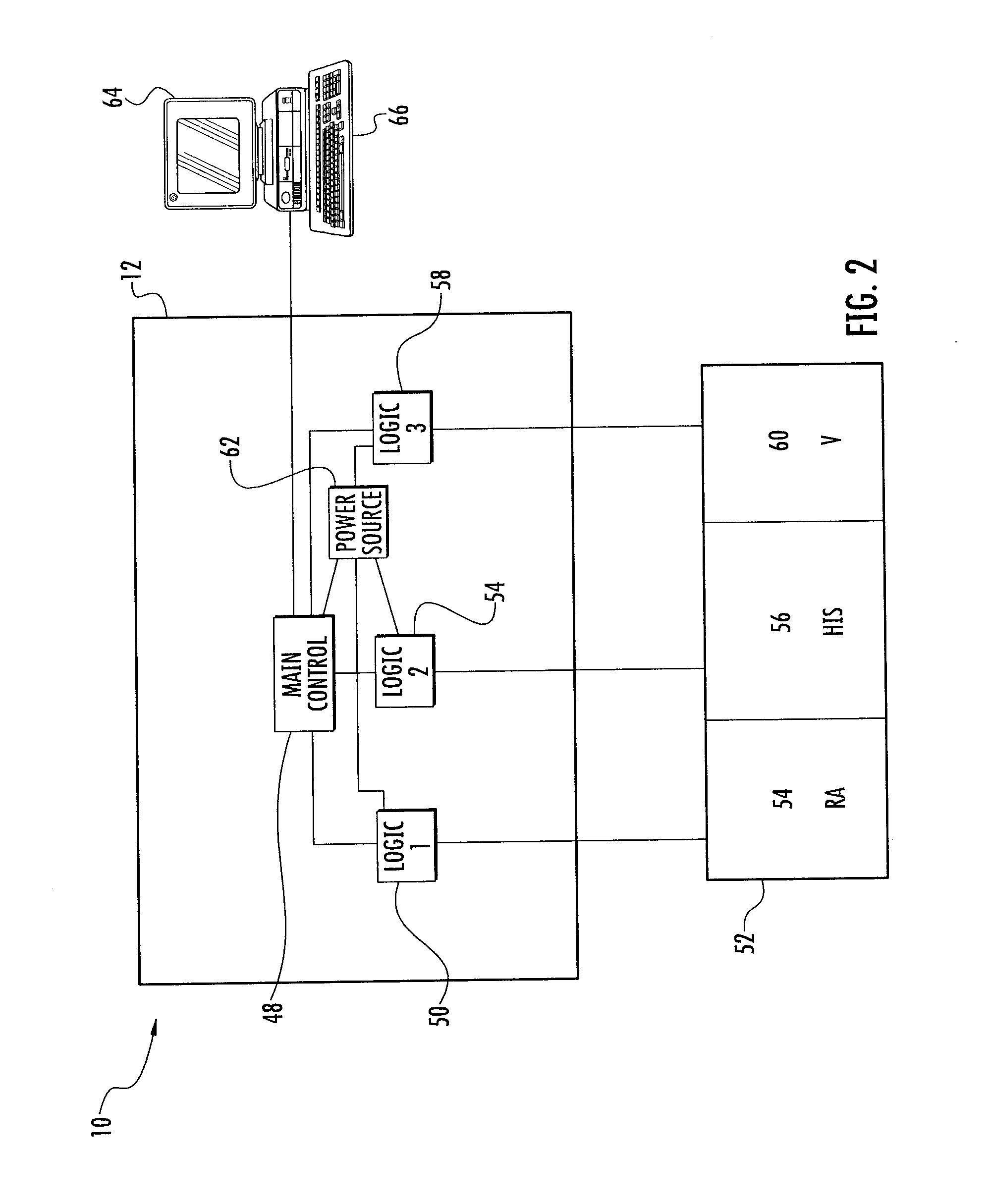
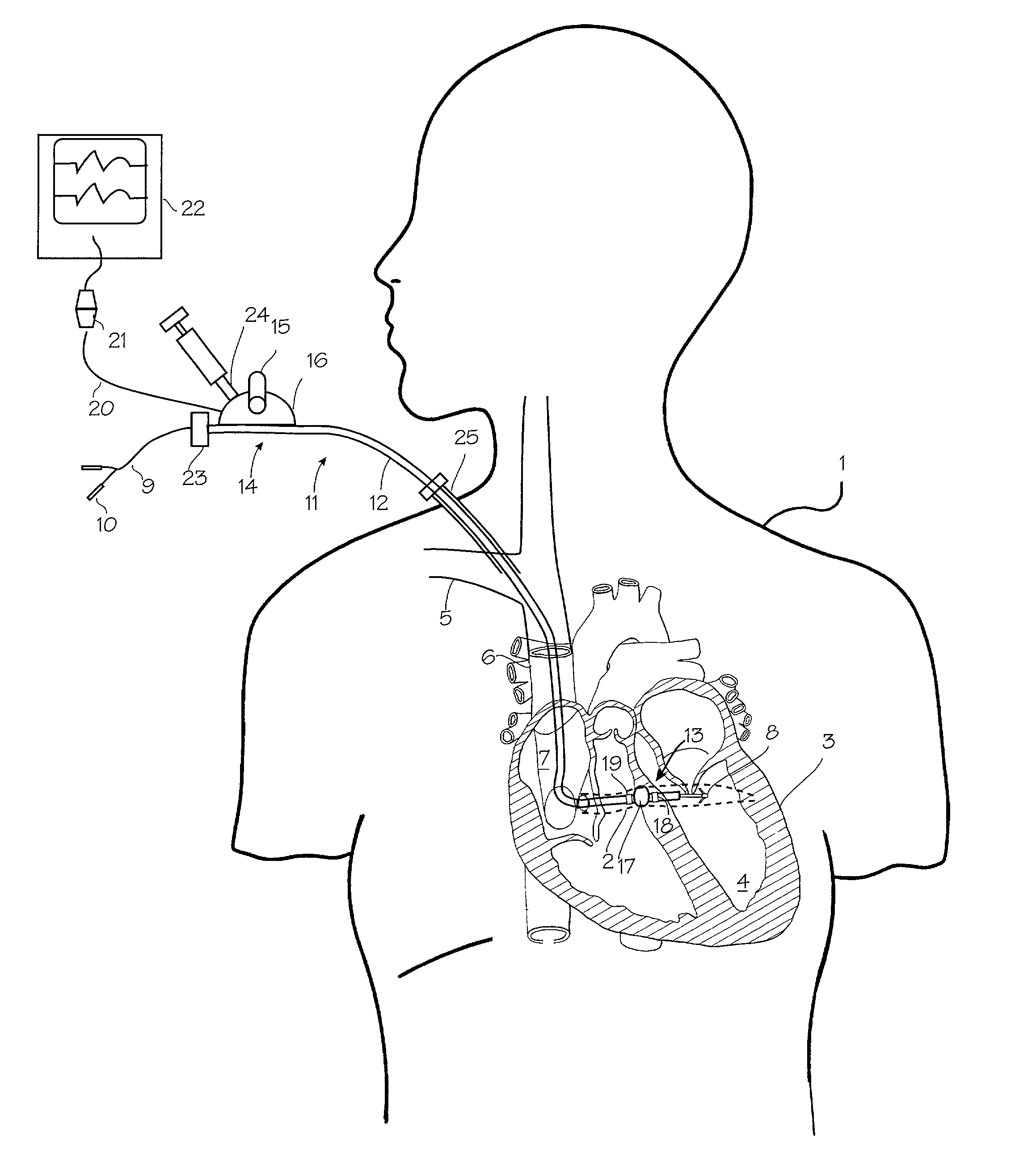
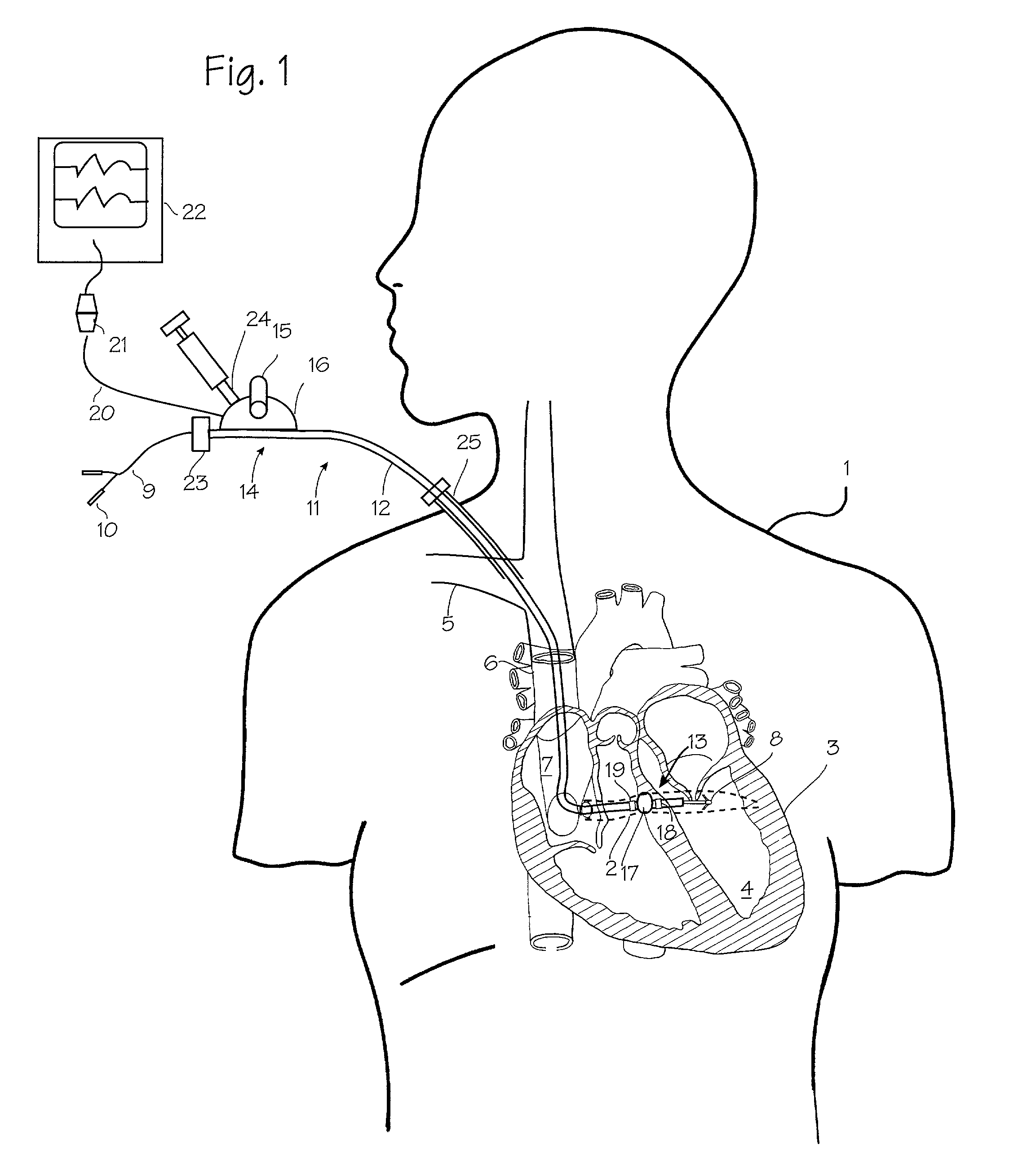
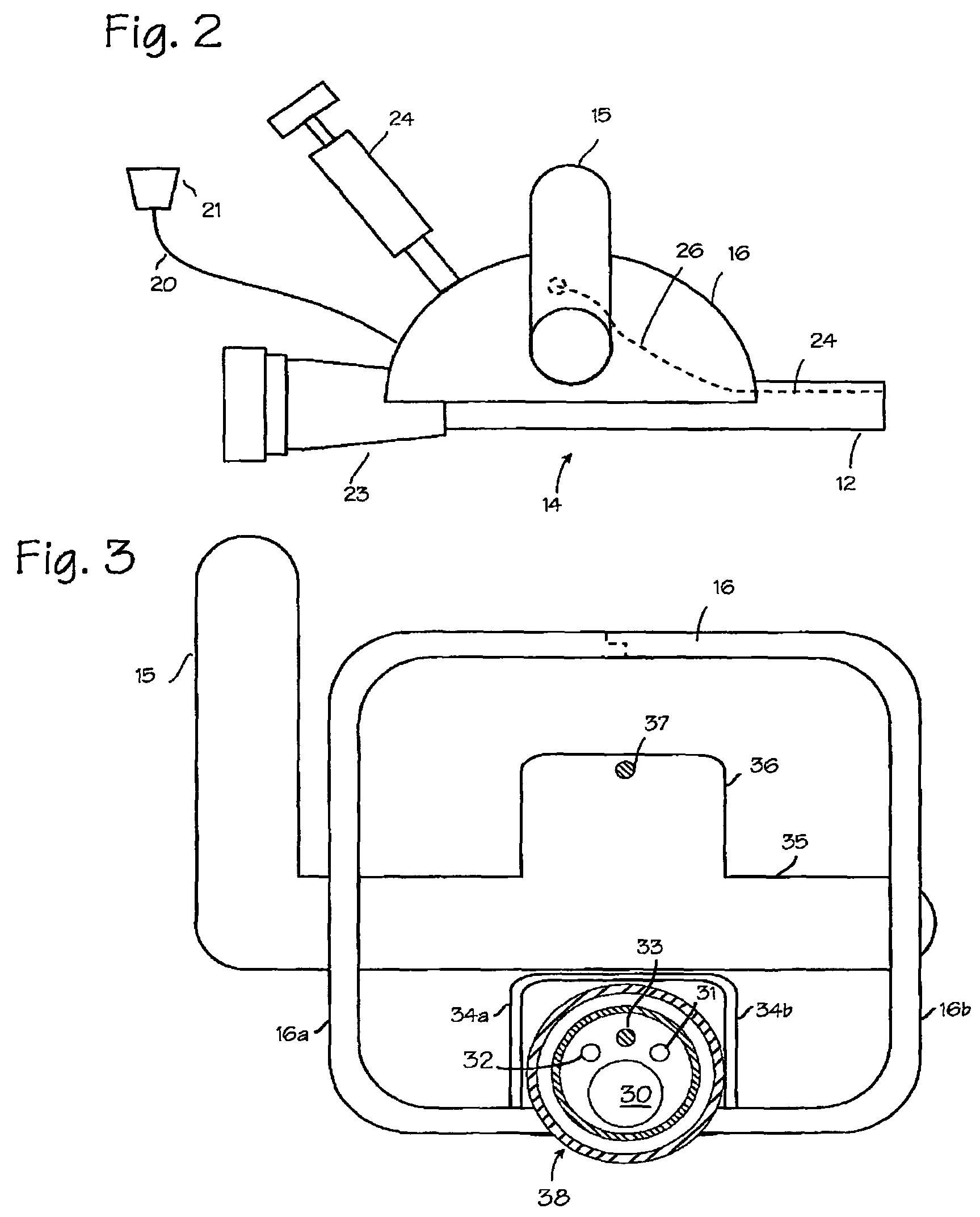
Device And Method For Peri-Hisian Pacing And/Or Simultaneous Bi-Ventricular or Tri-Ventricular Pacing For Cardiac Resynchronization
InactiveUS20110230922A1Maximize cardiac outputRapid depolarizationHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaSudden death
The present invention provides a pacing device and method that allows for preferential right atrial, at or near the His bundle, and ventricular pacing, either individually or in combination, including tri-ventricular pacing. The pacing device includes a power source and one or more logic circuits allowing for programmable delivery of pacing to any combination of the right atria, the para-Hisian region, and the right and / or the left ventricles. The pacing device allows the user to select which site(s) to pace as well at the appropriate relative timing of pacing impulse delivery to any of these three previously mentioned sites. The device is constructed and arranged to be combined with an atrial sensing / pacing electrode to allow for atrio-ventricular sequential tri-ventricular pacing or variants of such. Also, a defibrillator lead can be incorporated into the device to allow for protection from ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death.
Owner:FISHEL ROBERT S
Catheter systems and methods for placing bi-ventricular pacing leads
ActiveUS7840261B2Minimizes proximal forceEasy to cutTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesCardiac pacemaker electrodeImplanted pacemaker
Owner:BIOCARDIA
Fusion pacing enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
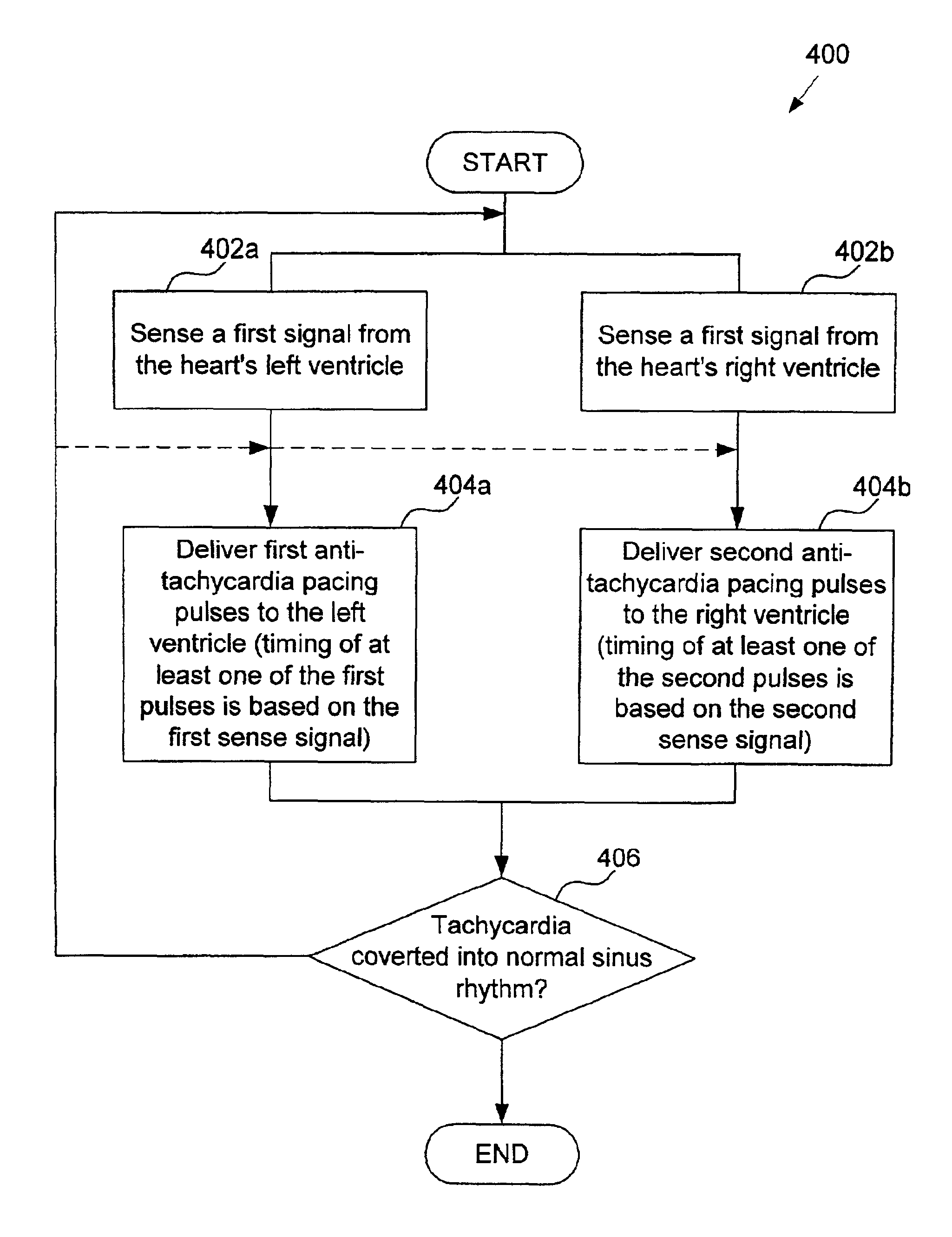
Anti-tachycardia pacing methods and devices
Improved methods and devices perform anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a ventricular tachycardia (VT) to normal sinus rhythm. In one embodiment of the invention bi-ventricular (BV) ATP is employed. In this embodiment the right ventricle and left ventricle of a patient's heart are independently paced based on signals sensed in each chamber.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable bi-ventricular stimulation device and system, and bi-ventricular stimulation and sensing method
ActiveUS20040116971A1Shorten the time intervalImprove reliabilityHeart stimulatorsControl circuitBiventricular stimulation
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device has a control circuit that within a time cycle, delivers pacing pulses with both first and second pacing circuits with a time gap between a pacing pulse delivered by these pacing circuits. The time gap can be such that a pacing pulse delivered by the second pacing circuits falls substantially within a first time interval in which an evoked response can be expected to a pacing pulse delivered by the first pacing circuit. The control circuit performs a temporary modification of the operation of the device such that during at least one time cycle no pacing pulse is delivered by the second pacing circuit during the first time interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Bi-ventricular ventricular capture management in cardiac resynchroniziation therapy delivery devices
ActiveUS20130090702A1Great likelihoodSignificant comprehensive benefitsHeart stimulatorsVentricular conductionCRTS
The present invention provides a technique for verifying pacing capture of a ventricular chamber, particularly to ensure desired delivery of a ventricular pacing regime (e.g., “CRT”). The invention also provides ventricular capture management by delivering a single ventricular pacing stimulus and checking inter-ventricular conduction during a temporal window to determine if the stimulus captured. If a loss-of-capture LOC) signal results from the capture management testing, then the applied pacing pulses are modified and the conduction test repeated. If LOC, an alert message can issue. Other aspects include: use of a trend of A-RV / LV and LV-RV timing intervals to monitor changes in the patient's heart conduction properties; bi-ventricular verification test and search—while still pacing BiV by detecting latent sense; single-V pacing threshold search, use of timing of sense in other V chamber to establish capture and LOC windows; (iv) use of a premature V pace rather than short AV interval if VV cannot be discriminated from AV; (v) option to run a threshold search only if the Bi-ventricular verification test fails.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Epicardial heart rhythm management devices, systems and methods
InactiveUS9597514B2Solution to short lifeIncrease heart stimulation rateEpicardial electrodesCannulasPericardial spaceBi ventricular
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to epicardial heart rhythm management. In some embodiments a method is provided for managing heart rhythm by implanting a pa device within the pericardial space of a patient. In some embodiments, an implantable device is provided for pacing the epicardial surface of a patient. The device may include a first module coupled to a second module by a tether. The first and second modules may be selectively placed for bi-ventricular pacing or for dual chamber pacing in some embodiments. Optionally the modules may be separate and may wirelessly communicate with one another and may also communicate with a heart stimulation device programmer. Optionally, a plurality of devices may be implanted in the pericardial space. A delivery device for delivering the implantable device to the pericardial space is also provided. Further embodiments provide implant retrieval devices and methods.
Owner:VQUAD MEDICAL
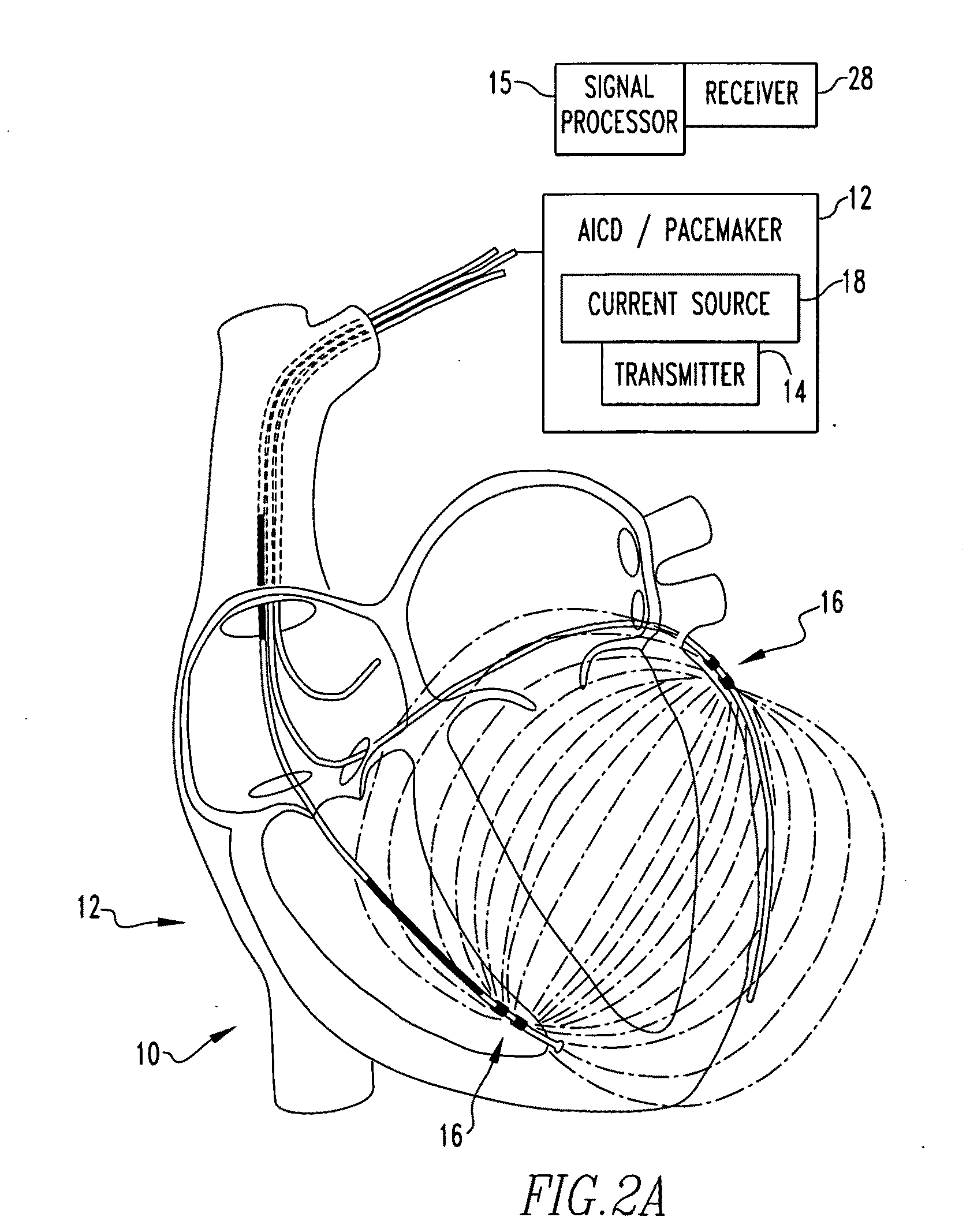
Method and Apparatus for Determining Cardiac Performance in a Patient
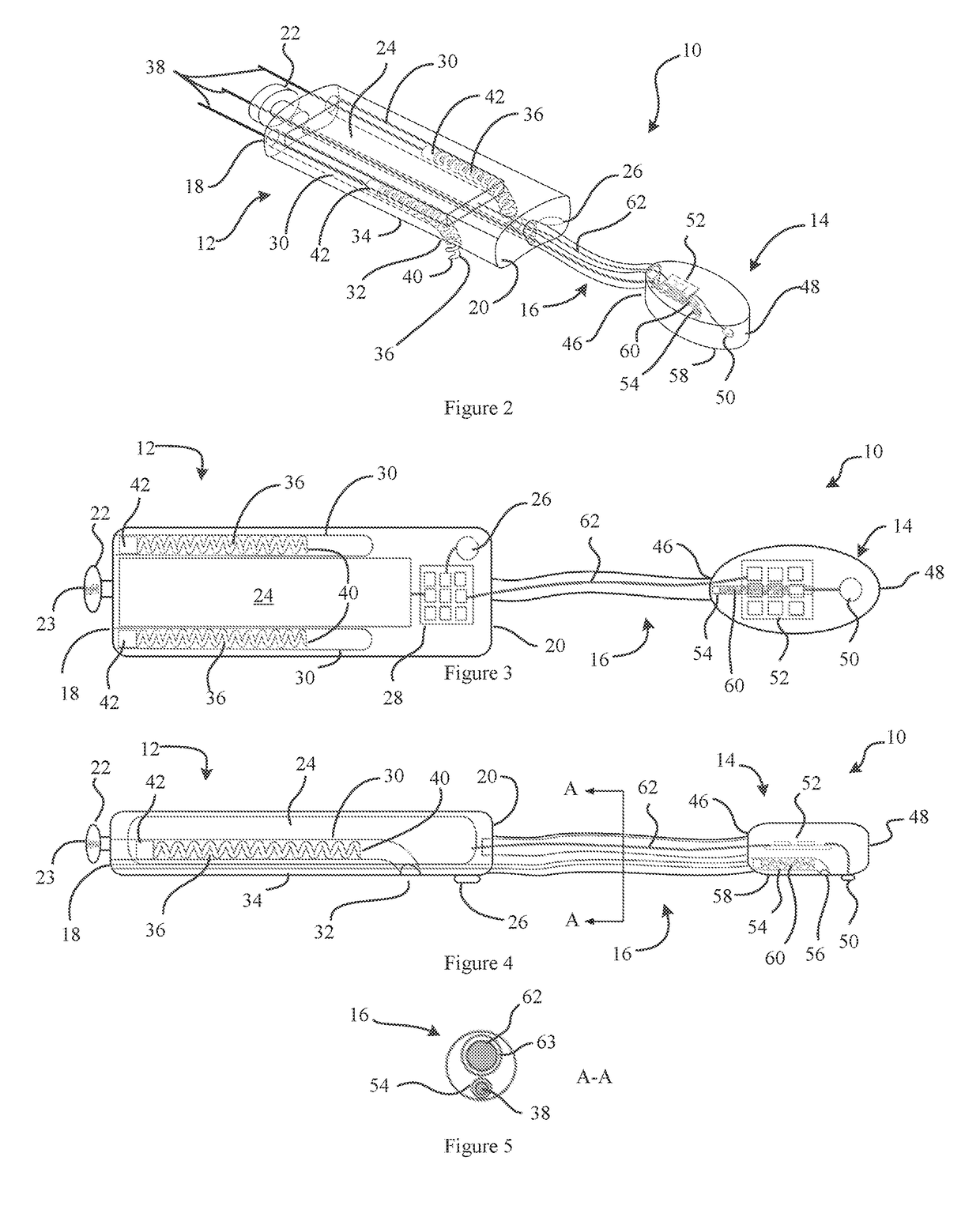
PendingUS20090210020A1Determining performanceDetermining volumeHeart defibrillatorsCatheterVoltage generatorCardiac pacemaker electrode
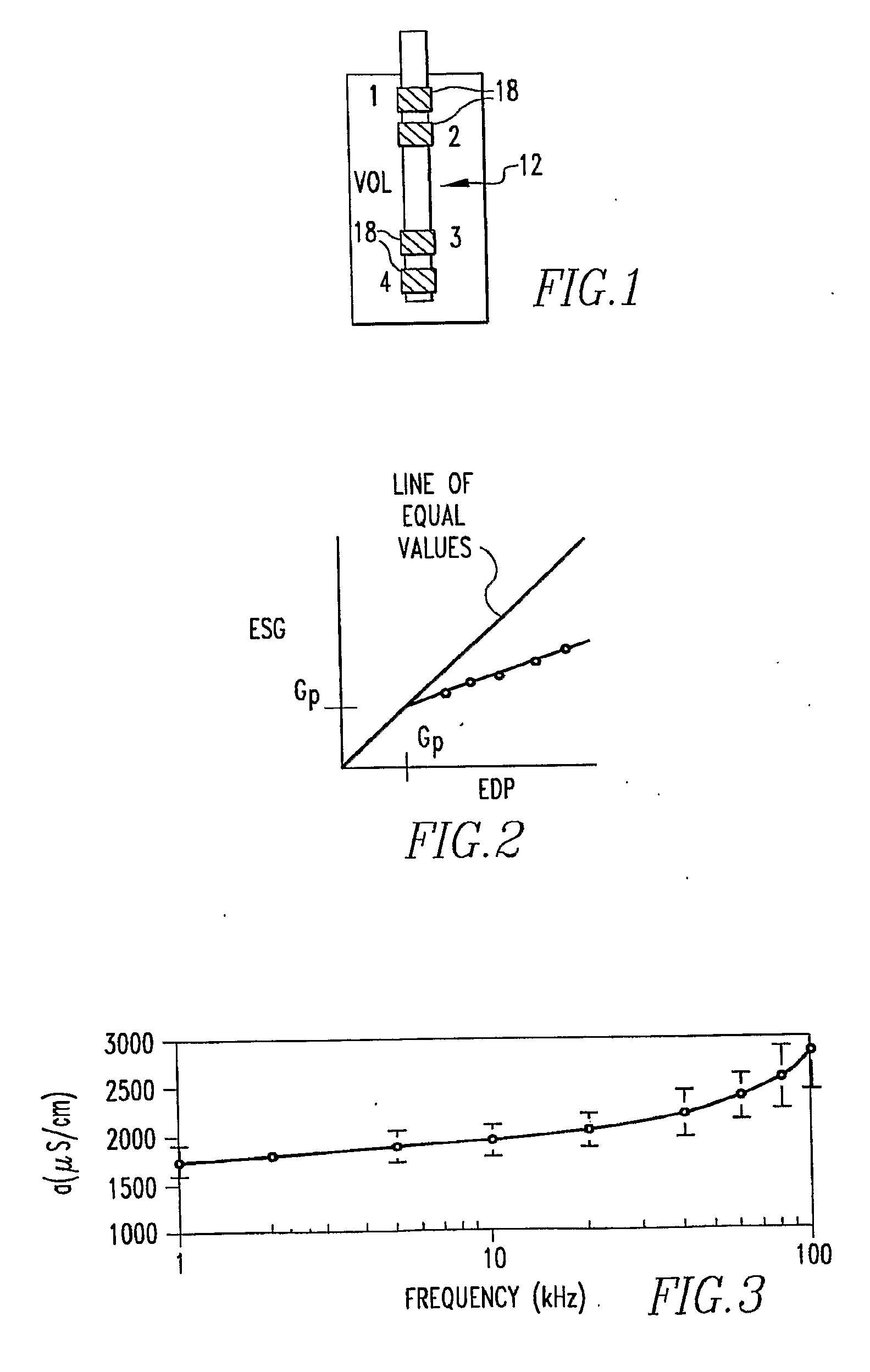
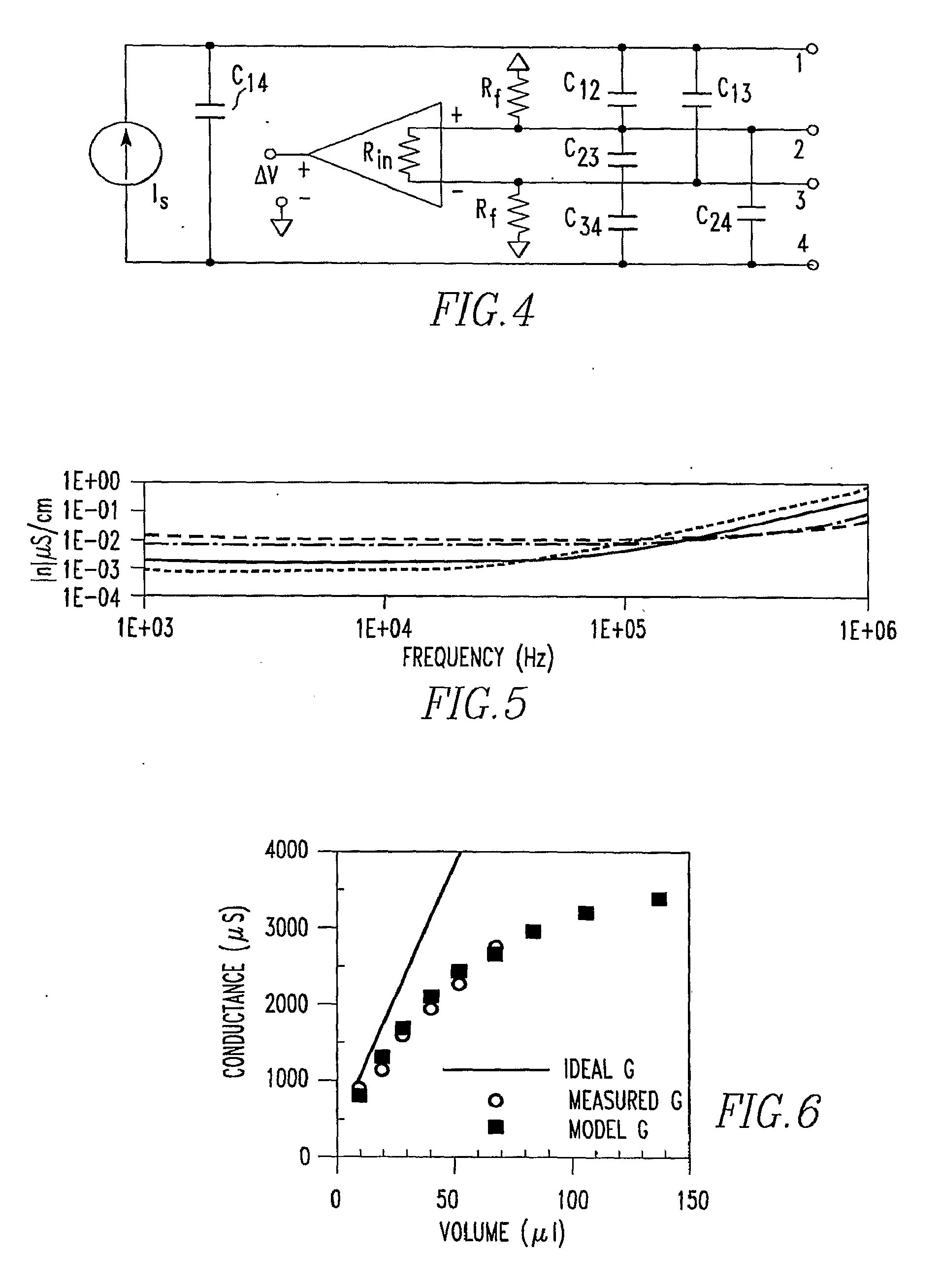
An apparatus for determining heart transplant rejection of a heart in a patient includes at least two electrodes adapted to be sewn into the heart that span the left ventricle. The apparatus includes a voltage generator adapted to be inserted in the patient which generates a voltage to the two electrodes and senses the resulting voltage from the two electrodes. A method for determining heart transplant rejection of a heart in a patient. A pacemaker for a patient (including bi-ventricular pacing and AICDs). The pacemaker includes an RV lead having four electrodes adapted to be inserted into the RV apex. The pacemaker includes a voltage generator which generates a voltage signal to the electrodes and senses the instantaneous voltage along the length of the RV and determines the real and imaginary components to remove the myocardial components of the septum and RV free wall to determine absolute RV blood volume. The pacemaker includes a battery connected to the voltage generator. The pacemaker includes a defibrillator connected to the battery. The pacemaker can also be a bi-ventricular pacemaker to restore RV and LV synchrony during contraction. A method for assisting a heart of a patient.
Owner:FELDMAN MARC D +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com