Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Diesel exhaust fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) is an aqueous urea solution made with 32.5% urea and 67.5% deionized water. It is standardised as AUS 32 (aqueous urea solution) in ISO 22241. DEF is a consumable in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) that lowers NOₓ concentration in the diesel exhaust emissions from diesel engines.
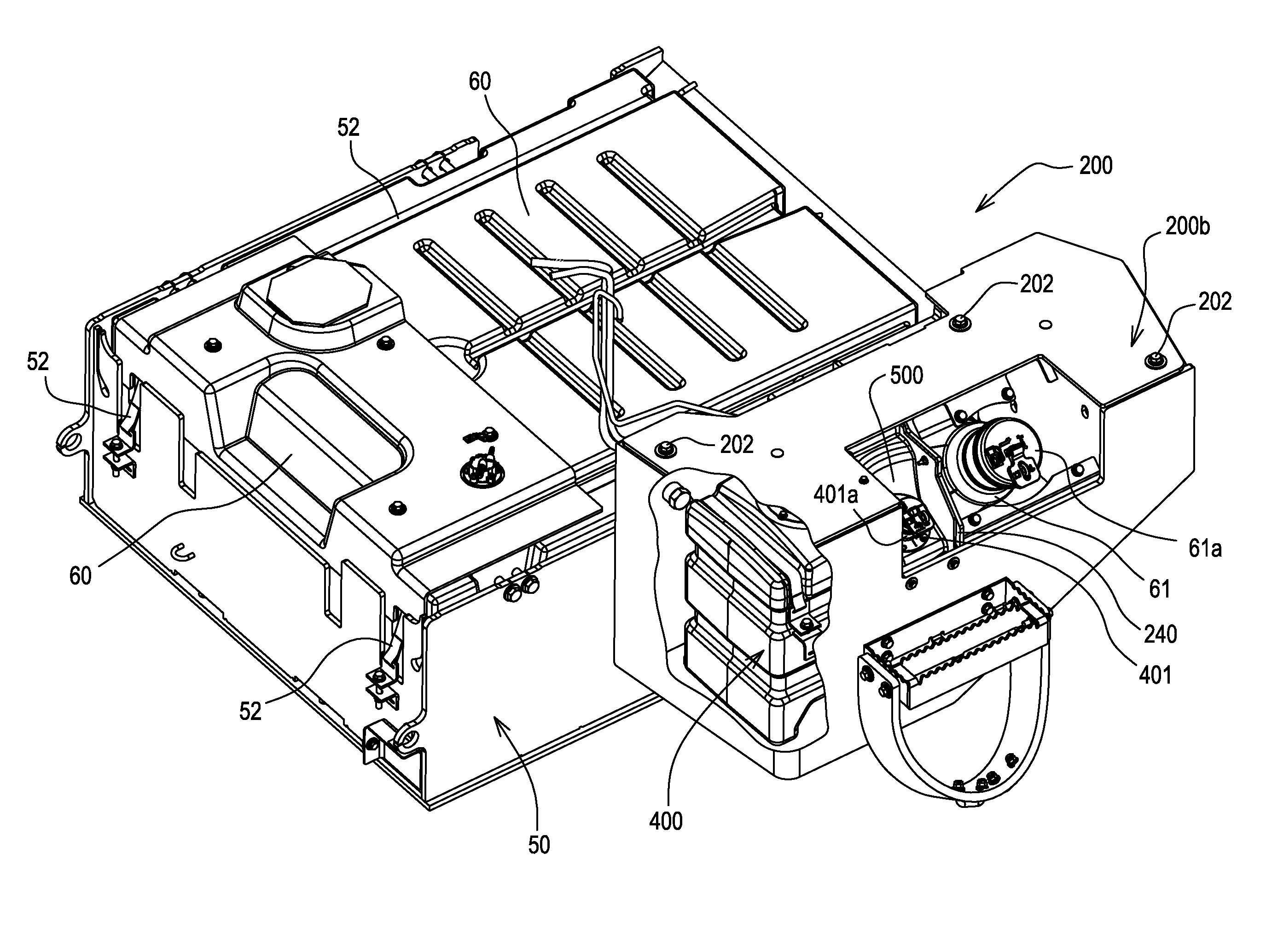
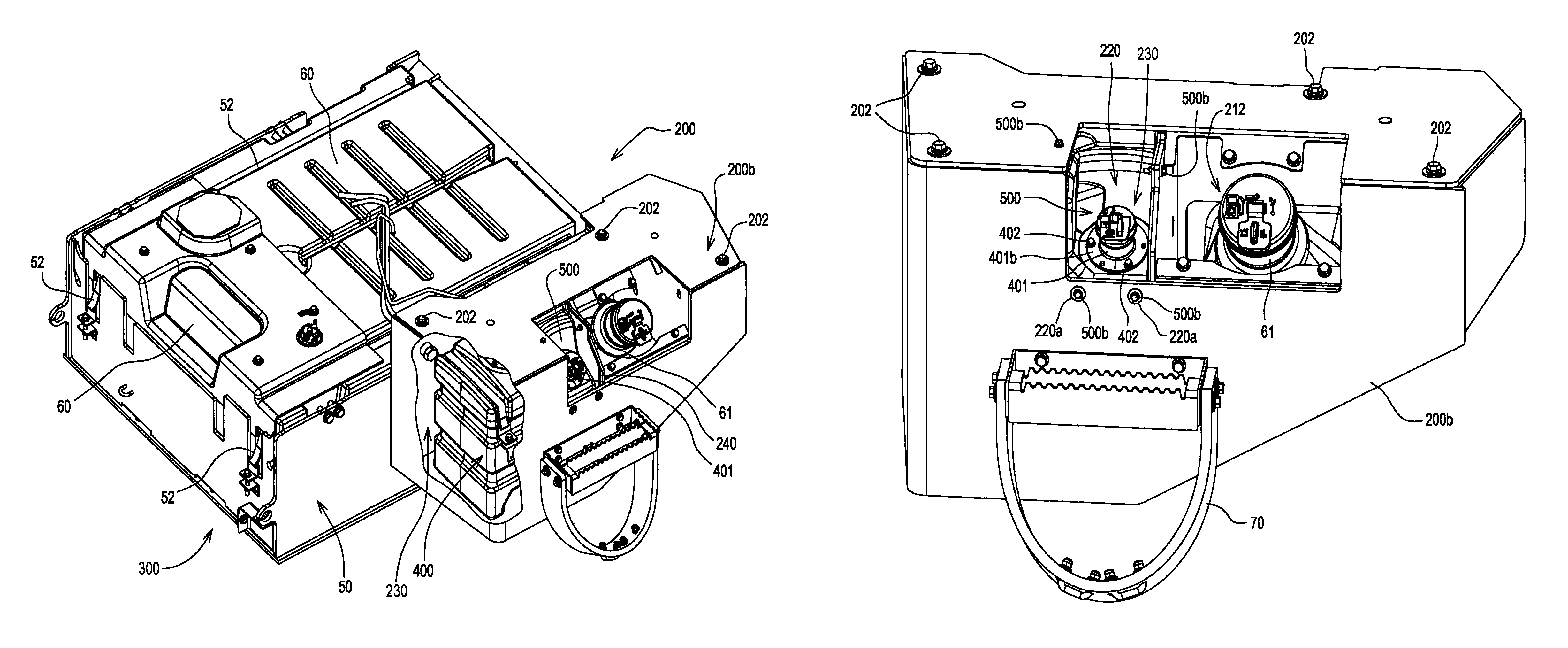
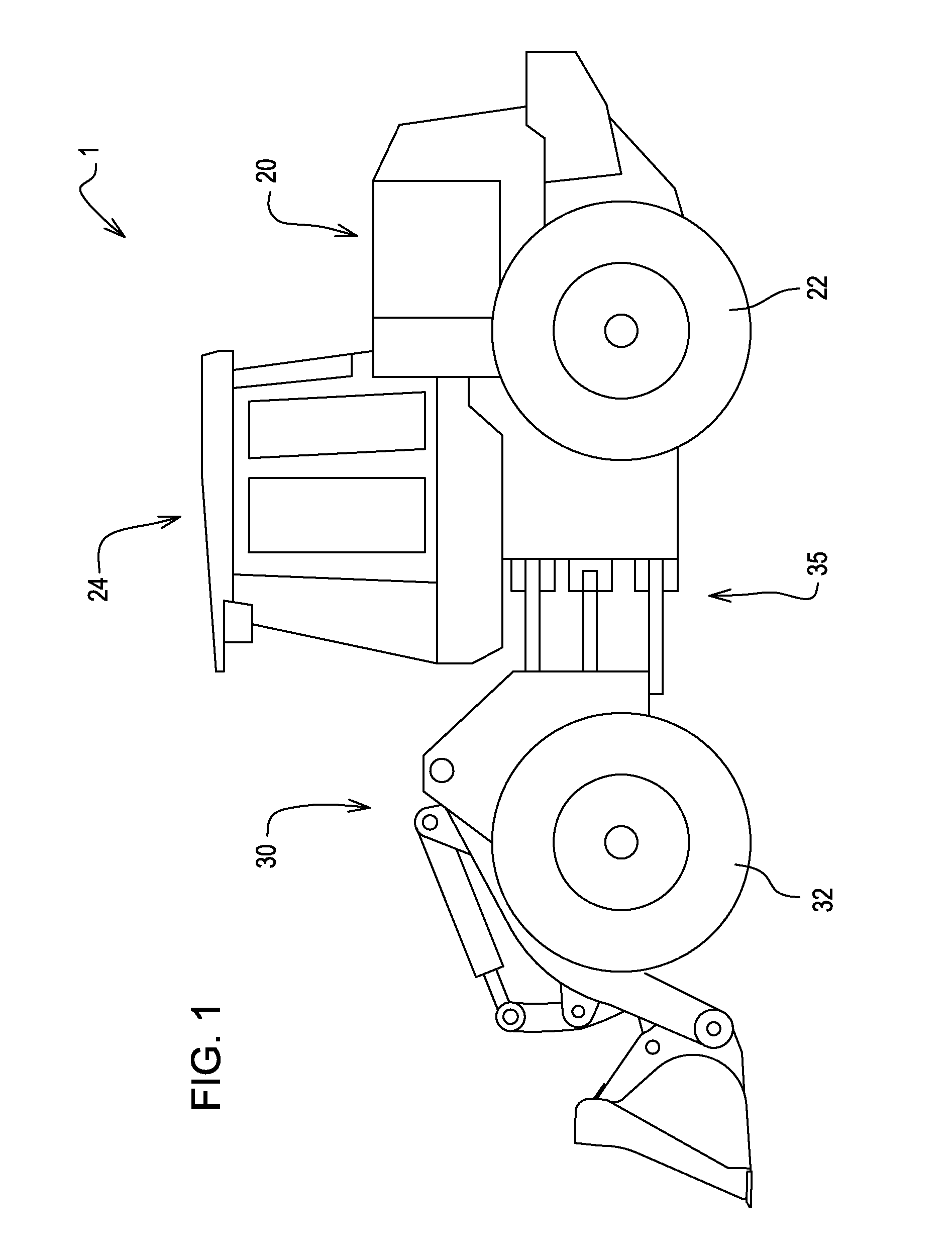
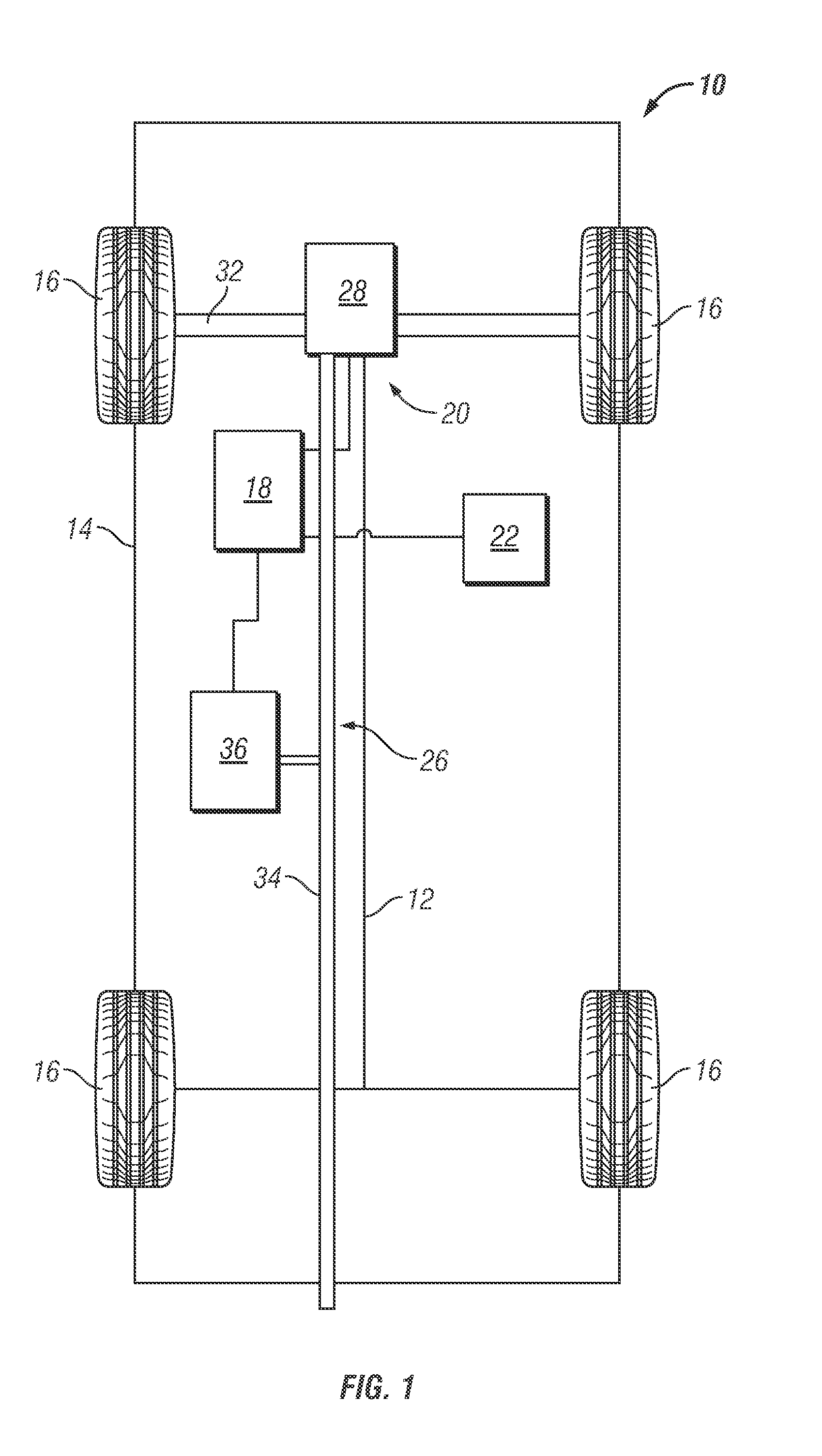
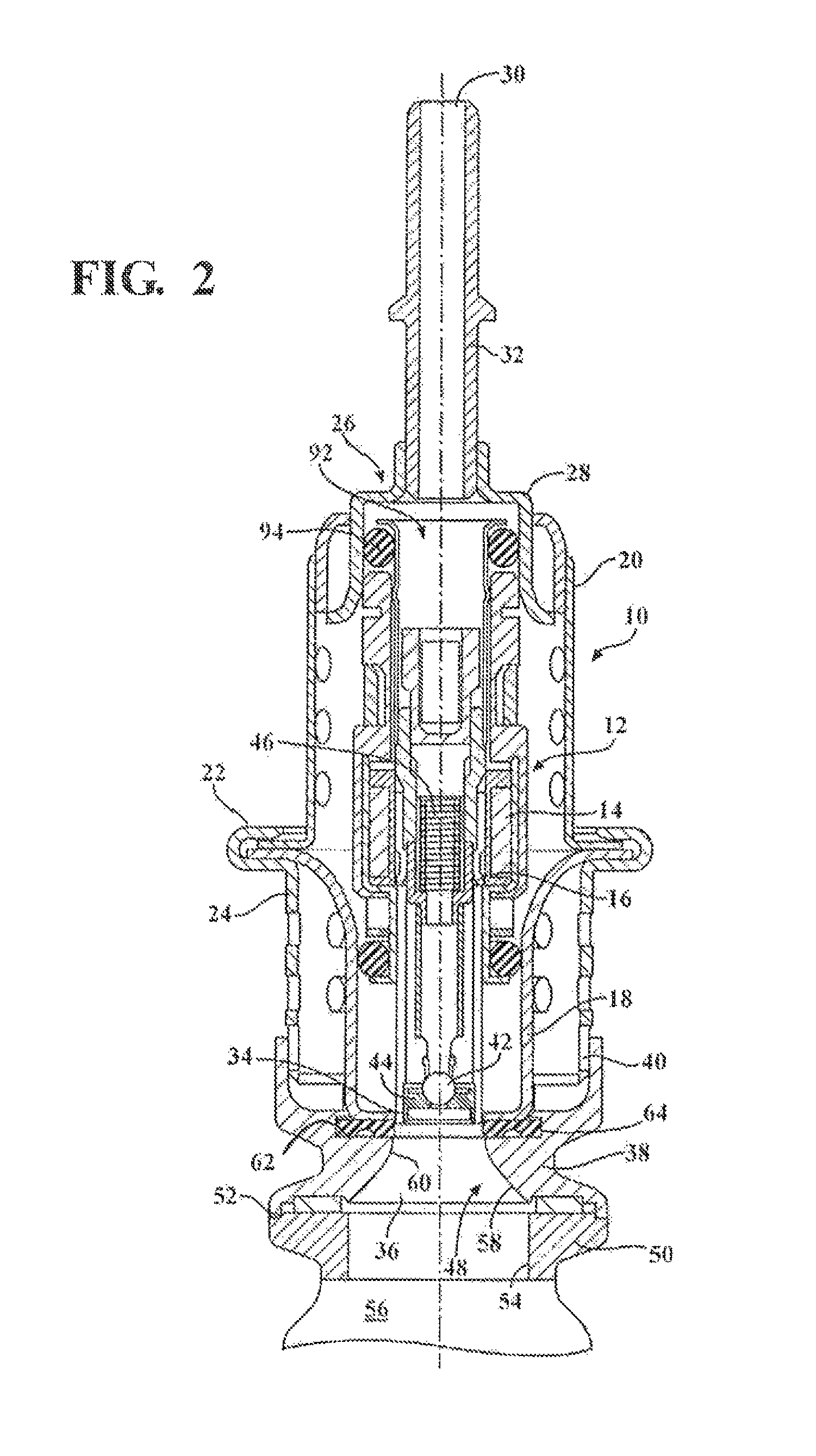
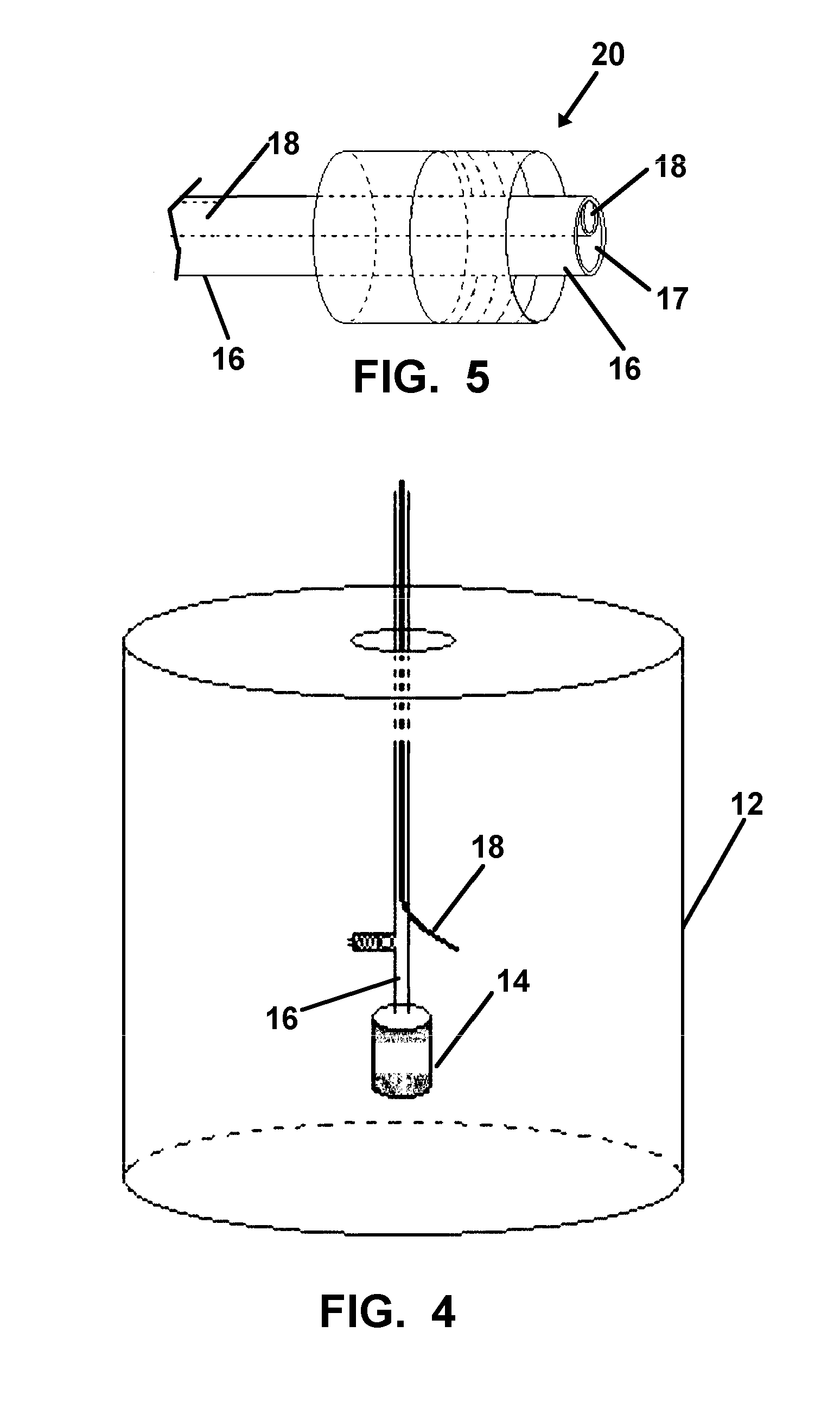
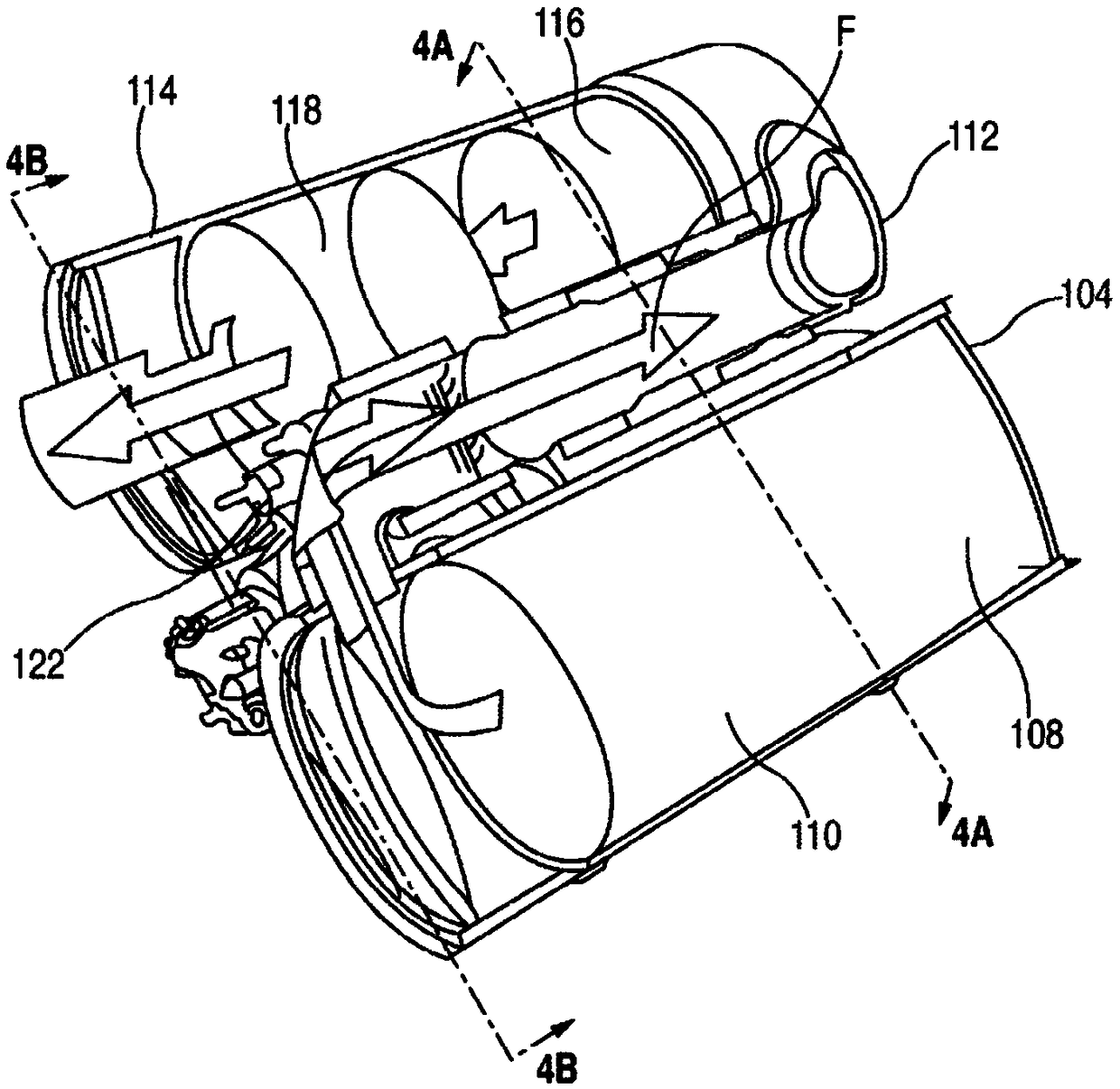
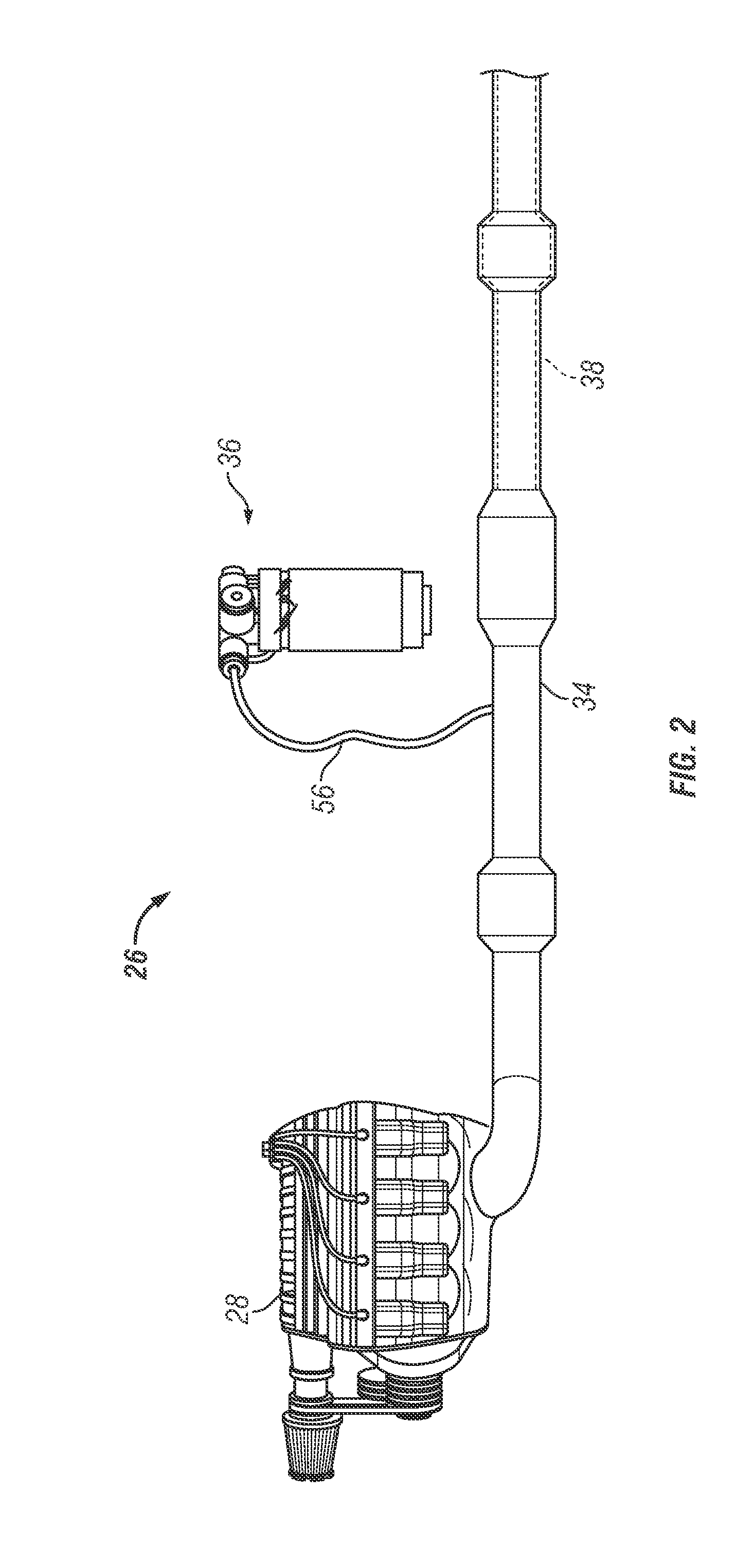
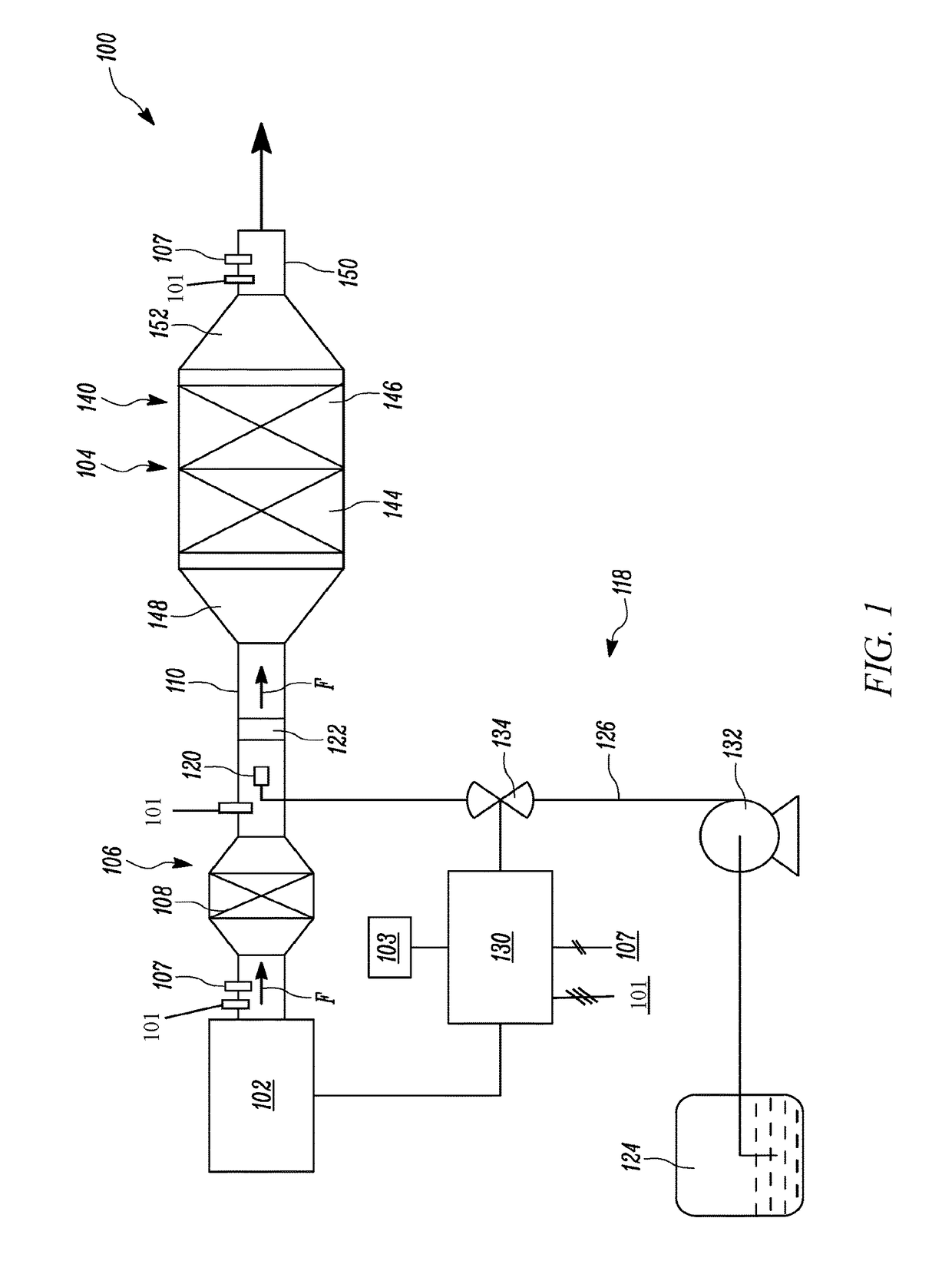
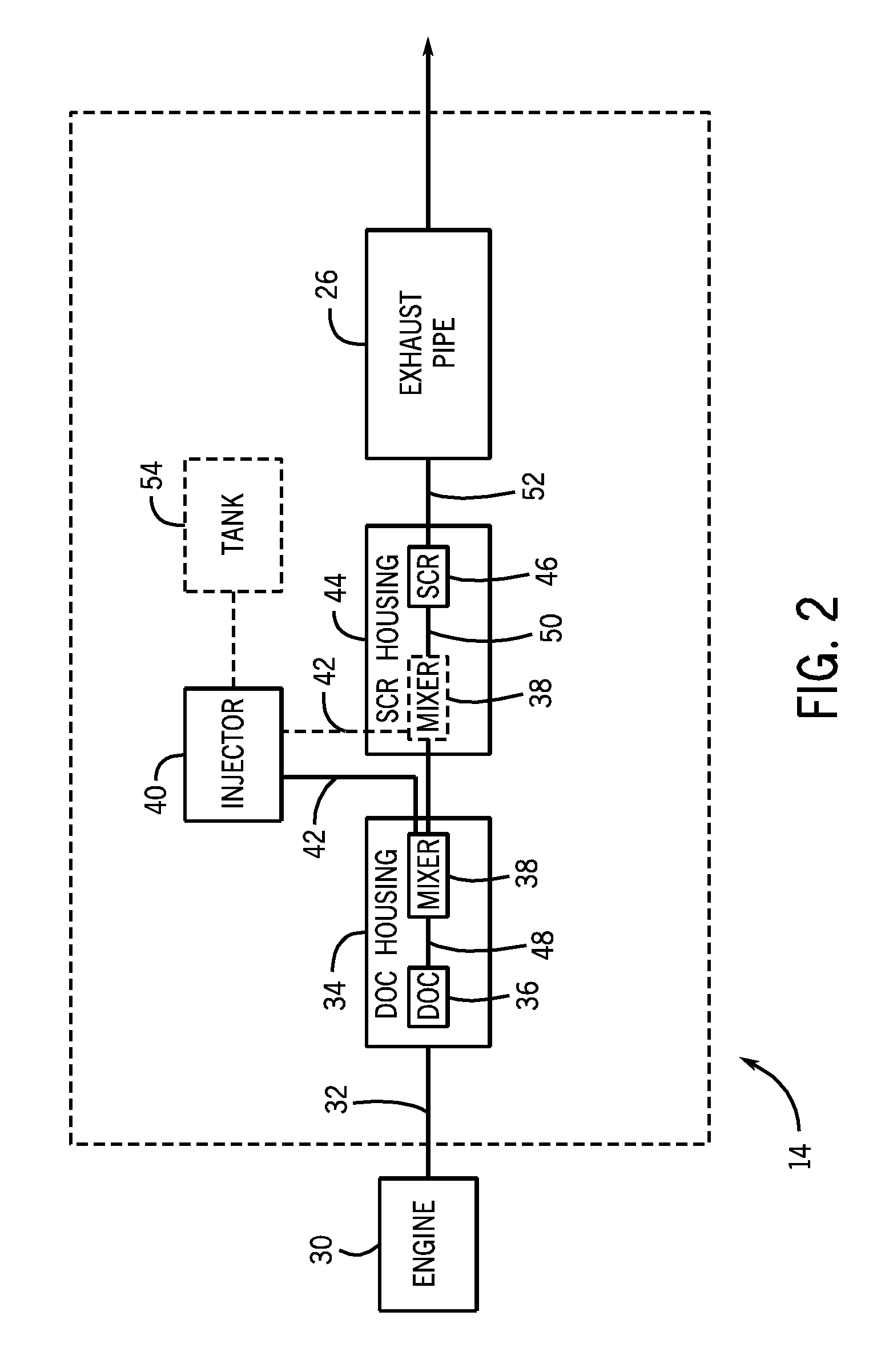
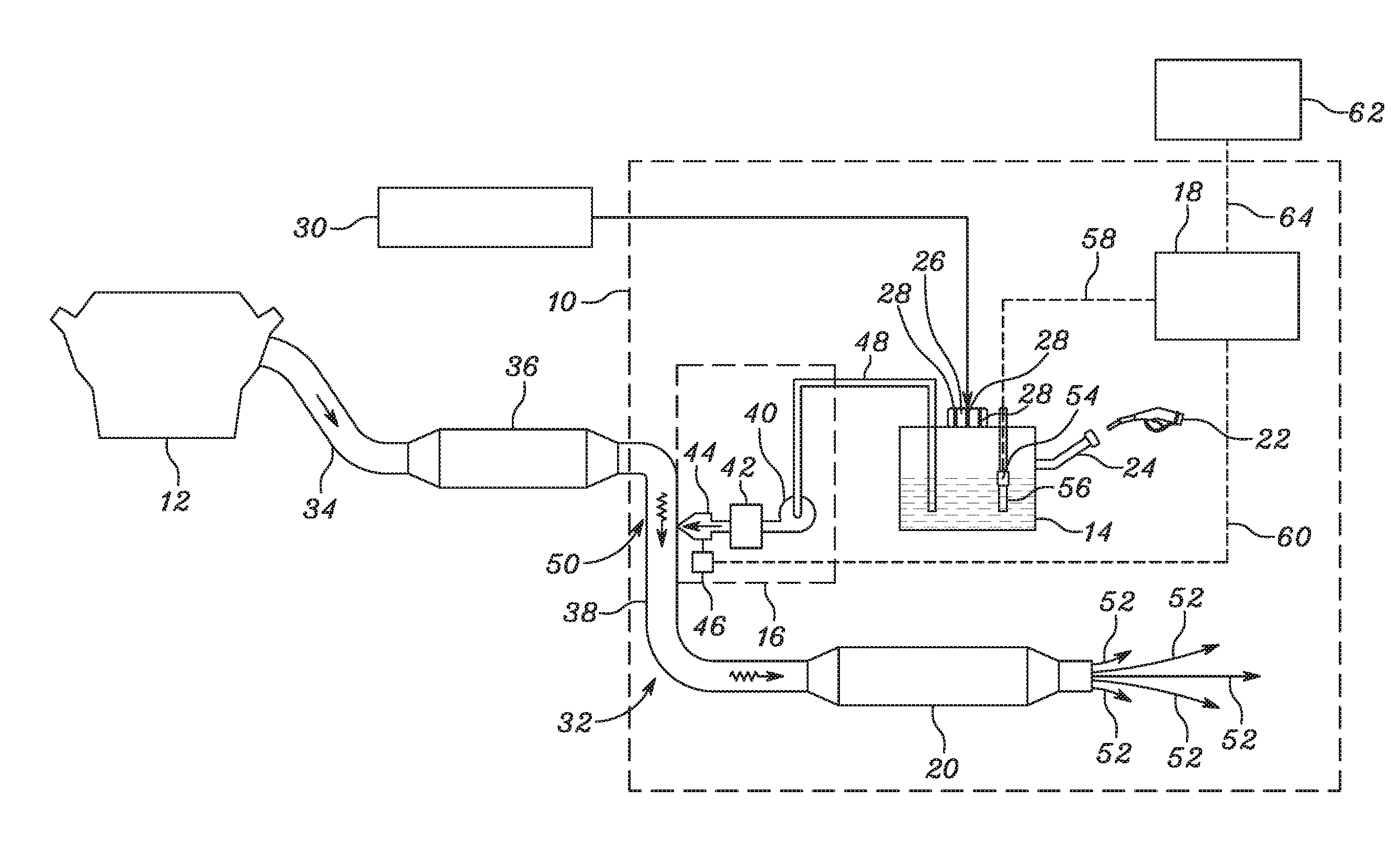
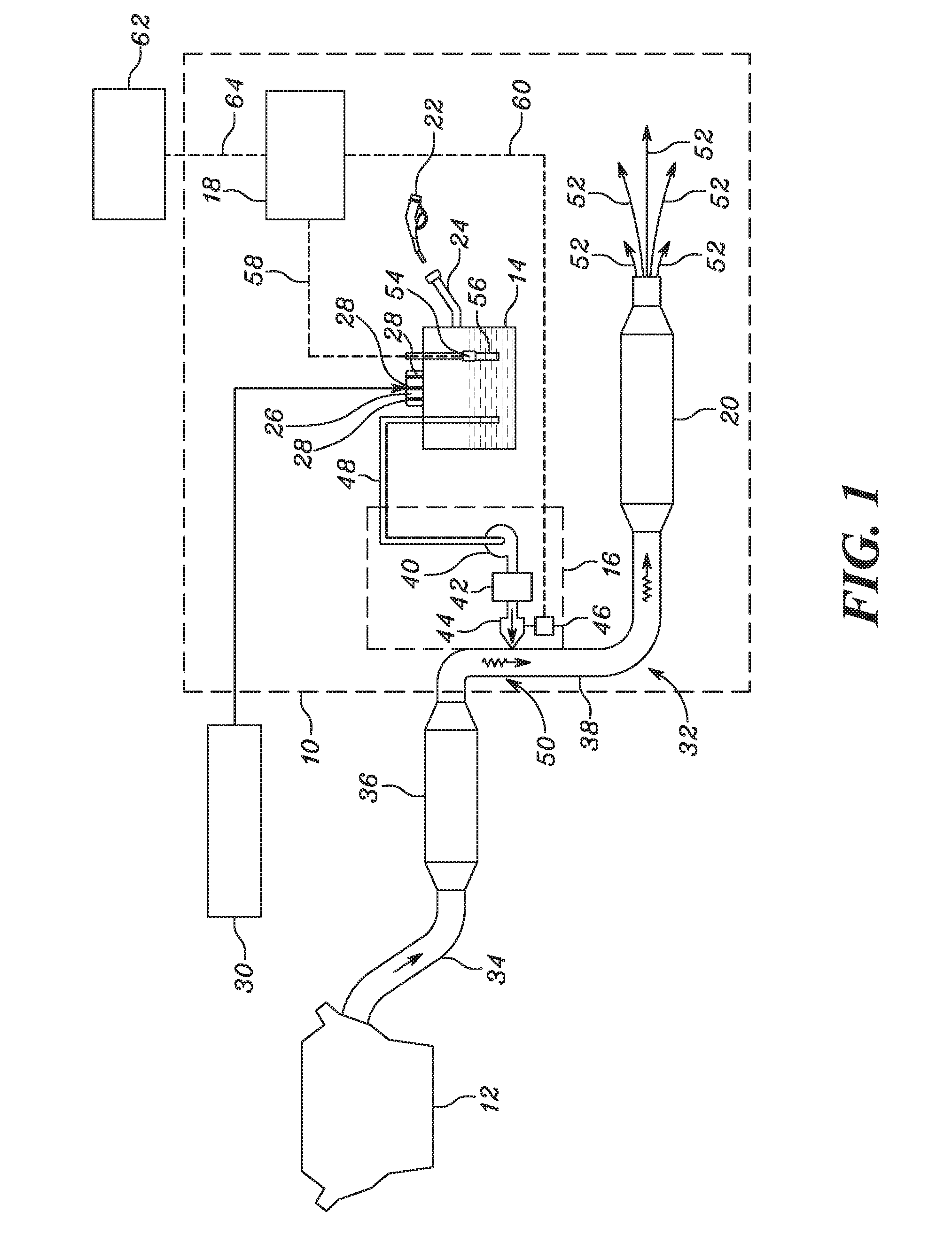
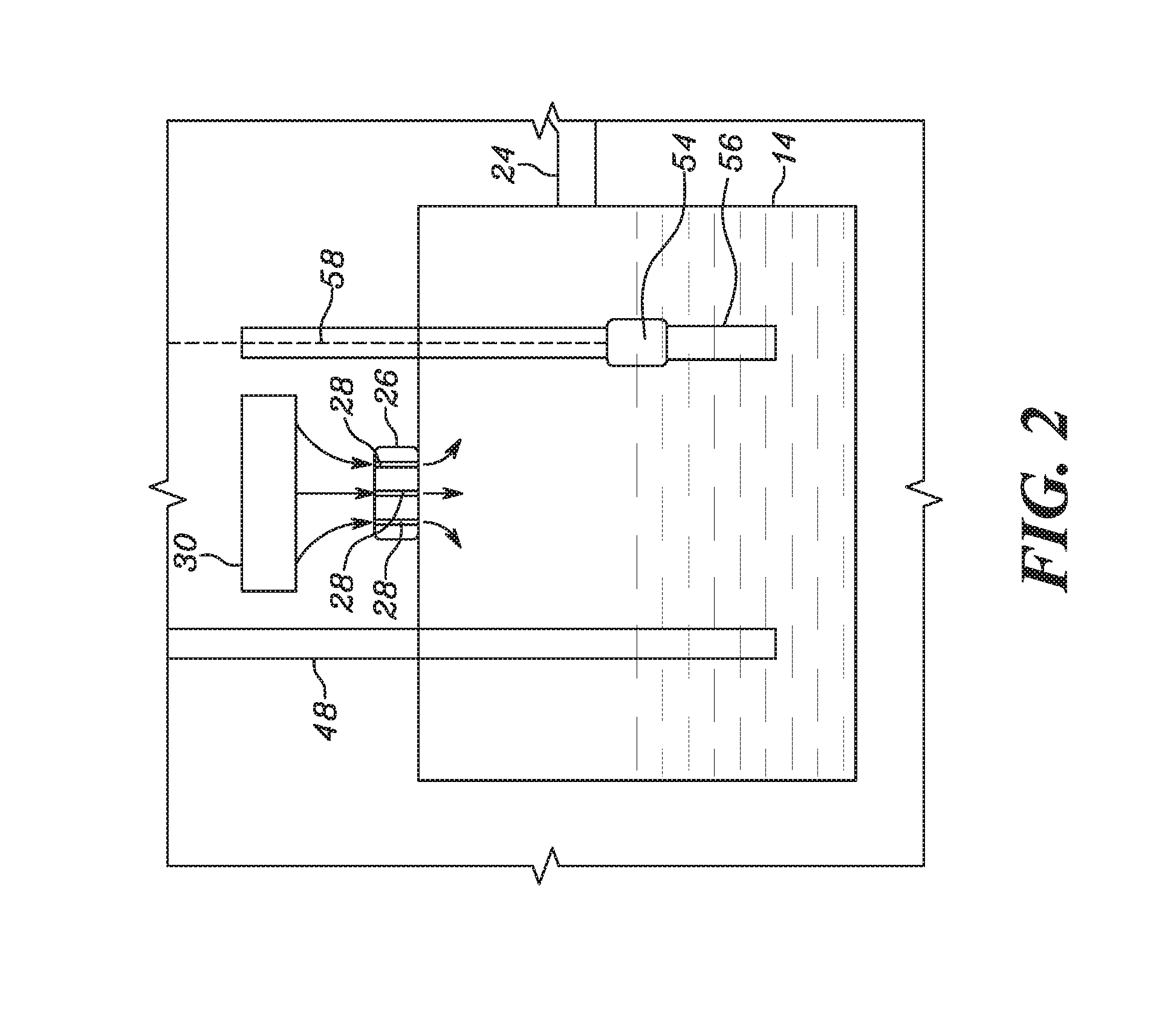
Diesel exhaust fluid and fuel fill system
ActiveUS20130292386A1Easy accessIncrease the use of spaceExhaust apparatusInternal framesFuel tankDiesel exhaust fluid
Owner:DEERE & CO
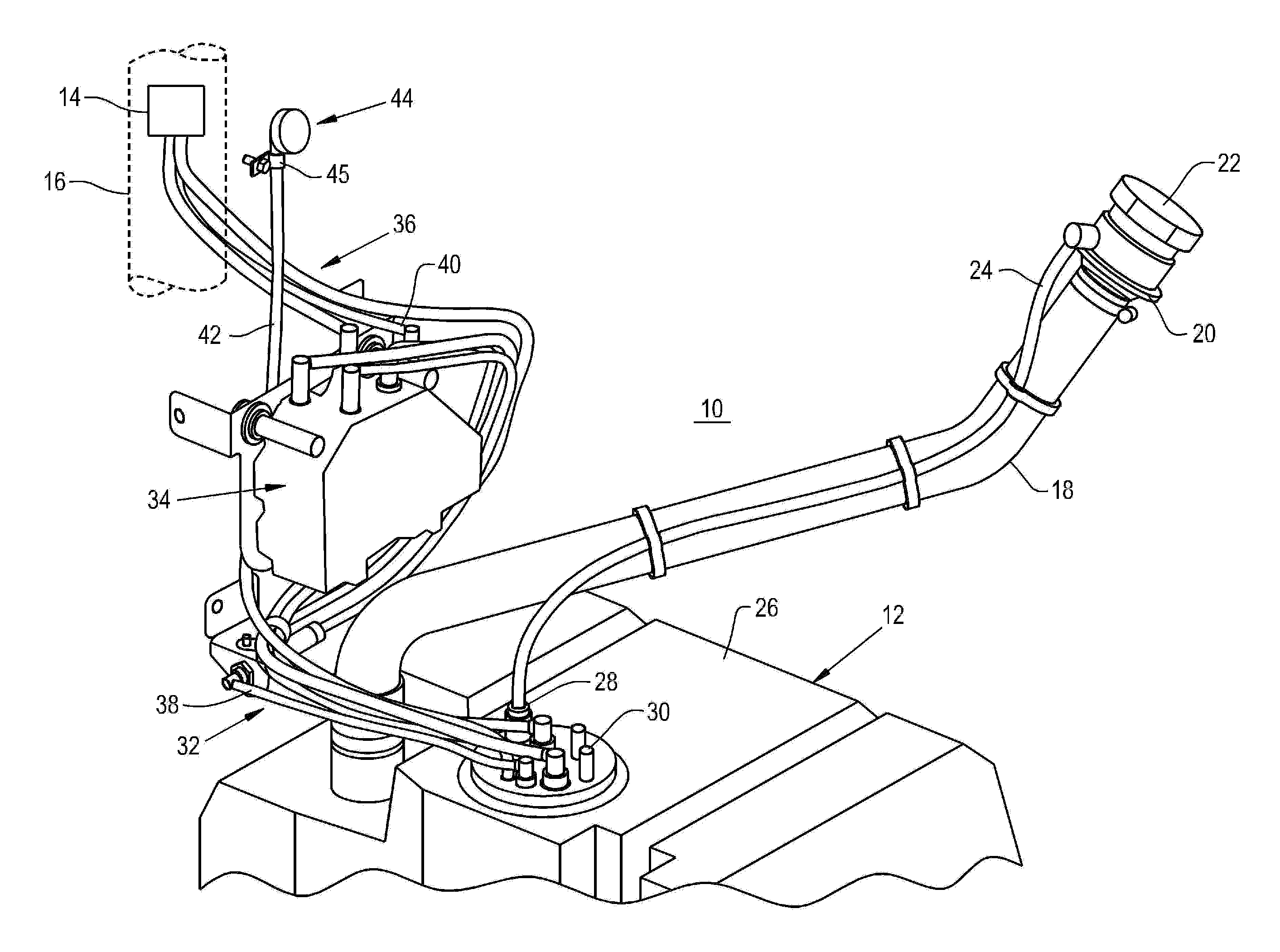
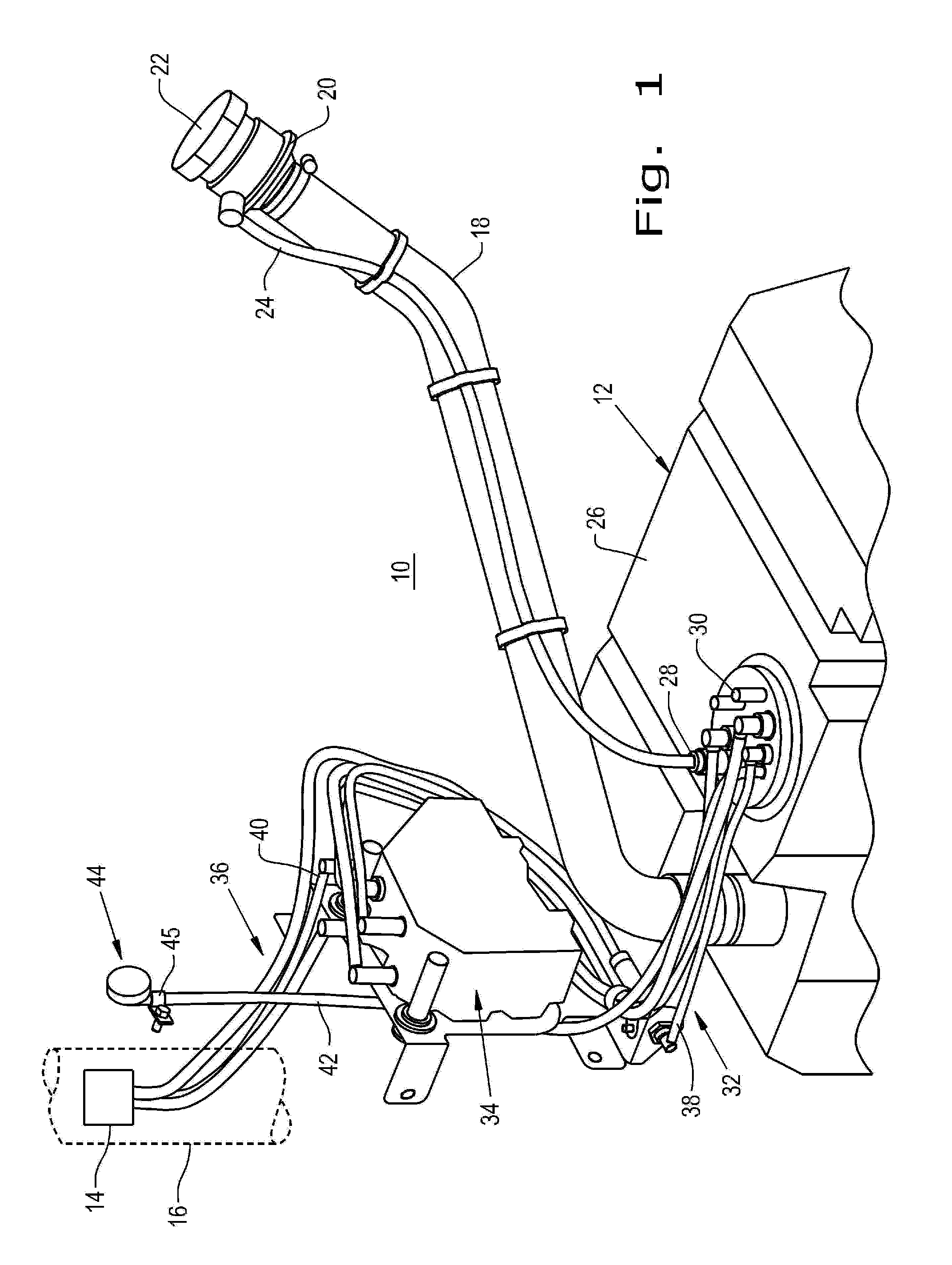
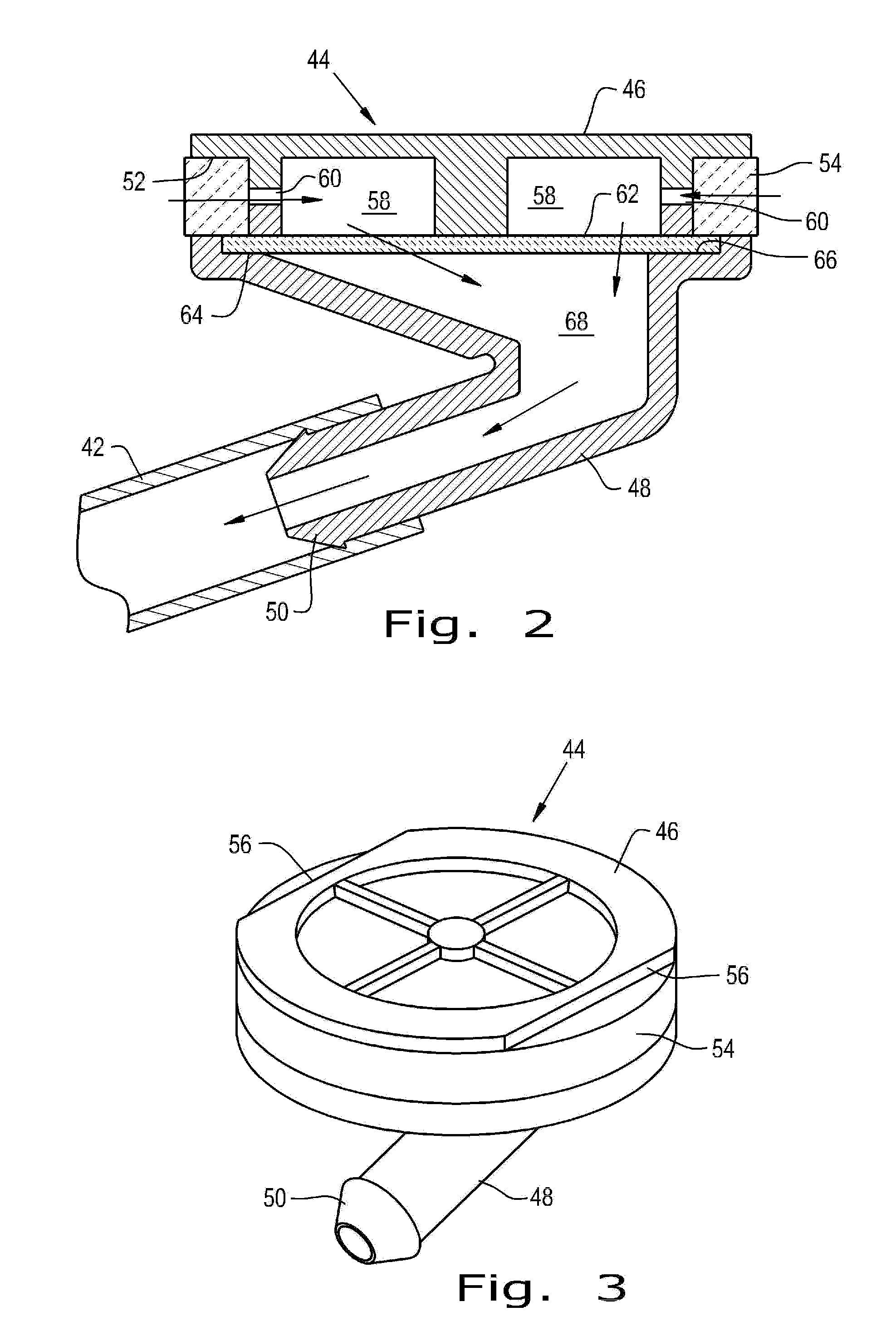
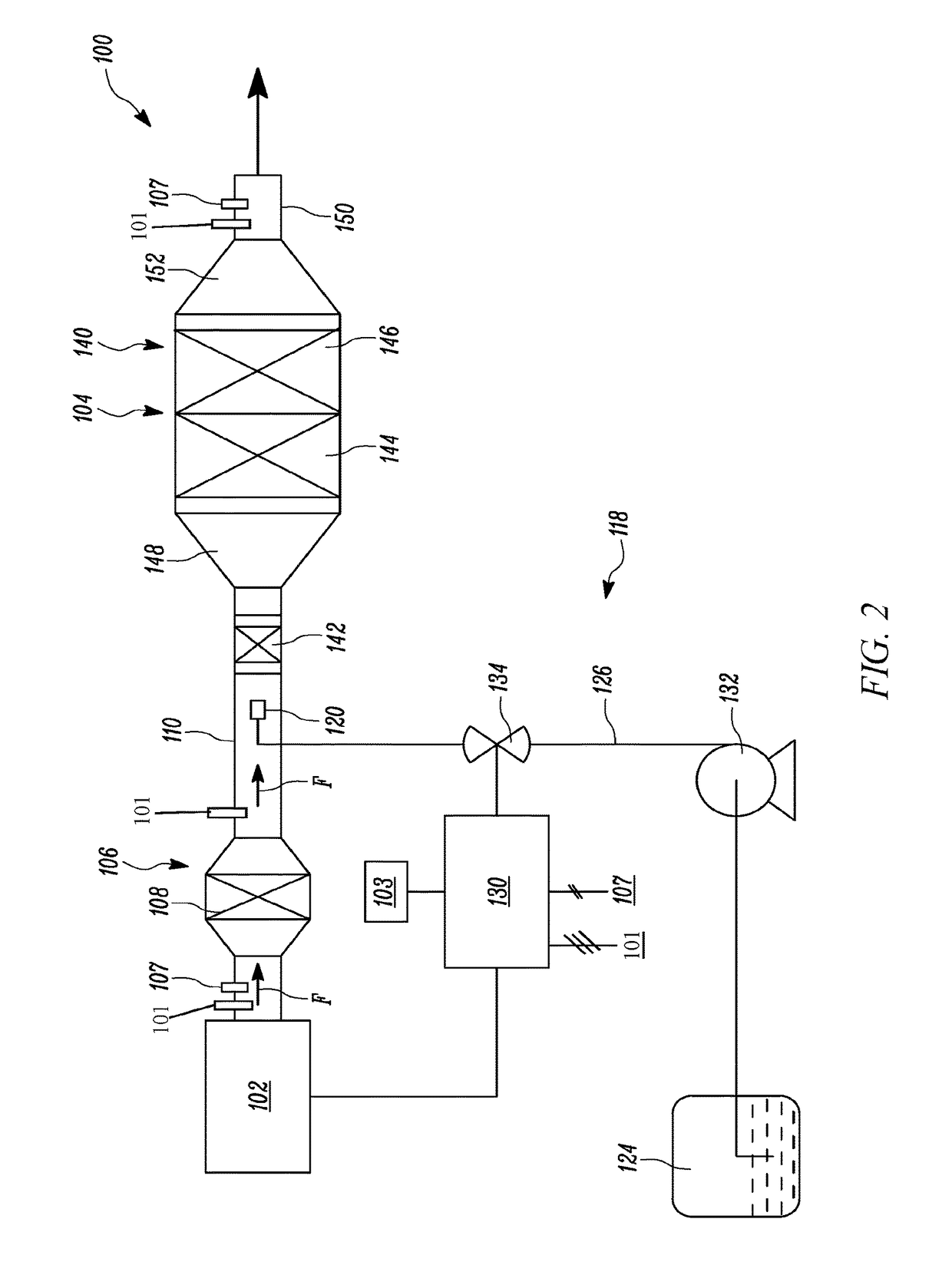
Diesel exhaust fluid and fuel fill system
ActiveUS8695827B2Easy accessEasy to useExhaust apparatusUnderstructuresFuel tankDiesel exhaust fluid
Owner:DEERE & CO
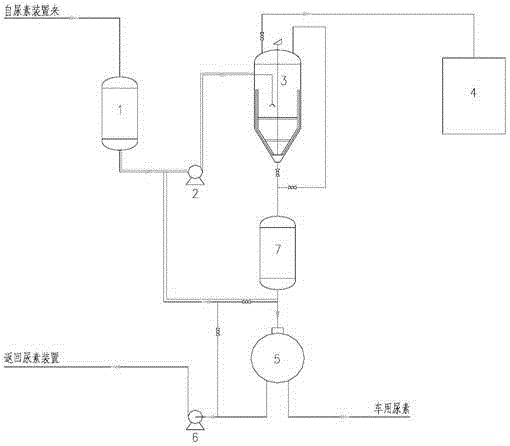
Diesel exhaust fluid production method
ActiveCN104557617AHigh riskIncrease costUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCooling effectCrystallization temperature
The invention provides a diesel exhaust fluid production method. The method comprises the following steps: sending an ammonia-and-carbon dioxide removed urea synthesis reaction liquid from the synthesis workshop section of a urea production device to a crystallization kettle, carrying out vacuum flash evaporation crystallization, centrifuging the obtained crystallization kettle material after the vacuum flash evaporation crystallization to obtain separated crystals as a diesel exhaust fluid product, and returning the obtained liquid phase material to the urea production device. The method uses a flash evaporation cooling effect to make a urea solution supersaturated and crystallized in order to obtain the high quality diesel exhaust fluid product, so the energy utilization efficiency is increased, and the diesel exhaust fluid yield is obviously higher than that in the prior art at a same crystallization temperature.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
System And Method For Controlling Transmission Of A Machine
InactiveUS20150240939A1Low costReduce operating conditionsAnalogue computers for trafficGearing controlWork cycleProcess engineering
A method of operating a machine having an engine and a transmission drivably coupled to the engine is provided. The method includes determining a power usage value of a work cycle of the machine based at least on a plurality of machine parameters and determining an operating cost map based at least on a fuel price and a Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) price. The method includes determining a current operating cost based on the operating cost map and a current operating condition that is based on at least one of the machine parameters. The method includes determining a low cost operating condition corresponding to an operating cost less than the current operating cost. The low cost operating condition corresponds to a power of the machine that is greater than or equal to the power usage value. The method includes regulating the transmission to obtain the low cost operating condition.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Bag in box dispensing container
A bag-in-box dispensing system includes a box with a facing. A bag having a spout is placed with the box. A removable extension hose and a connector having snap wings for securing the extension hose to the spout is also provided. A bag-in-box dispensing system is also provided that includes a box with a facing configured with a removable flap. A bag with a spout containing a liquid inside said box is positioned within the box and a spout retracted under the removable flap. A removable extension hose is placed in the interior of the box for direct coupling to the spout or via a connector. A process of filling a vehicle DEF tank with diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) from the box is also provided.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
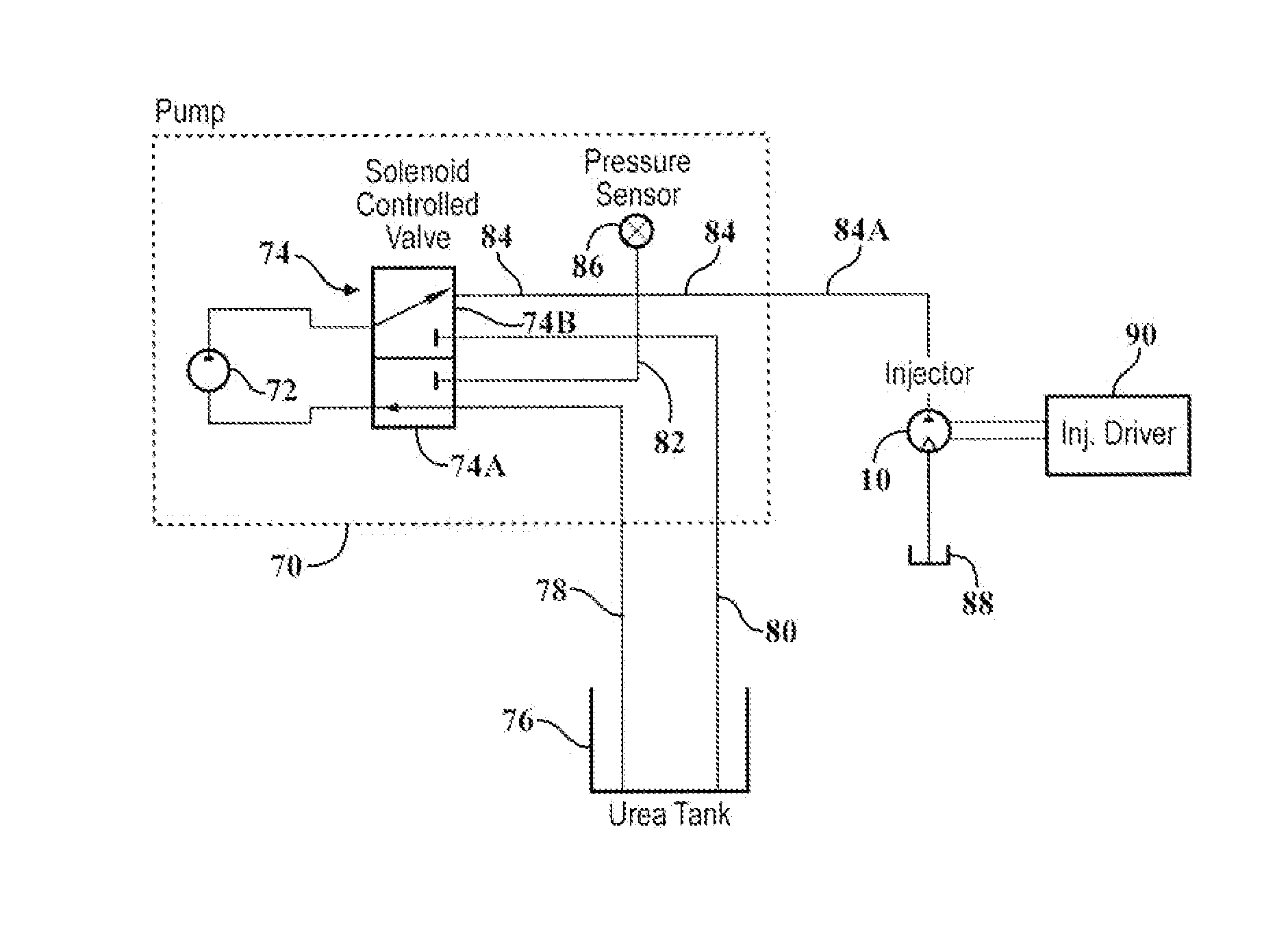
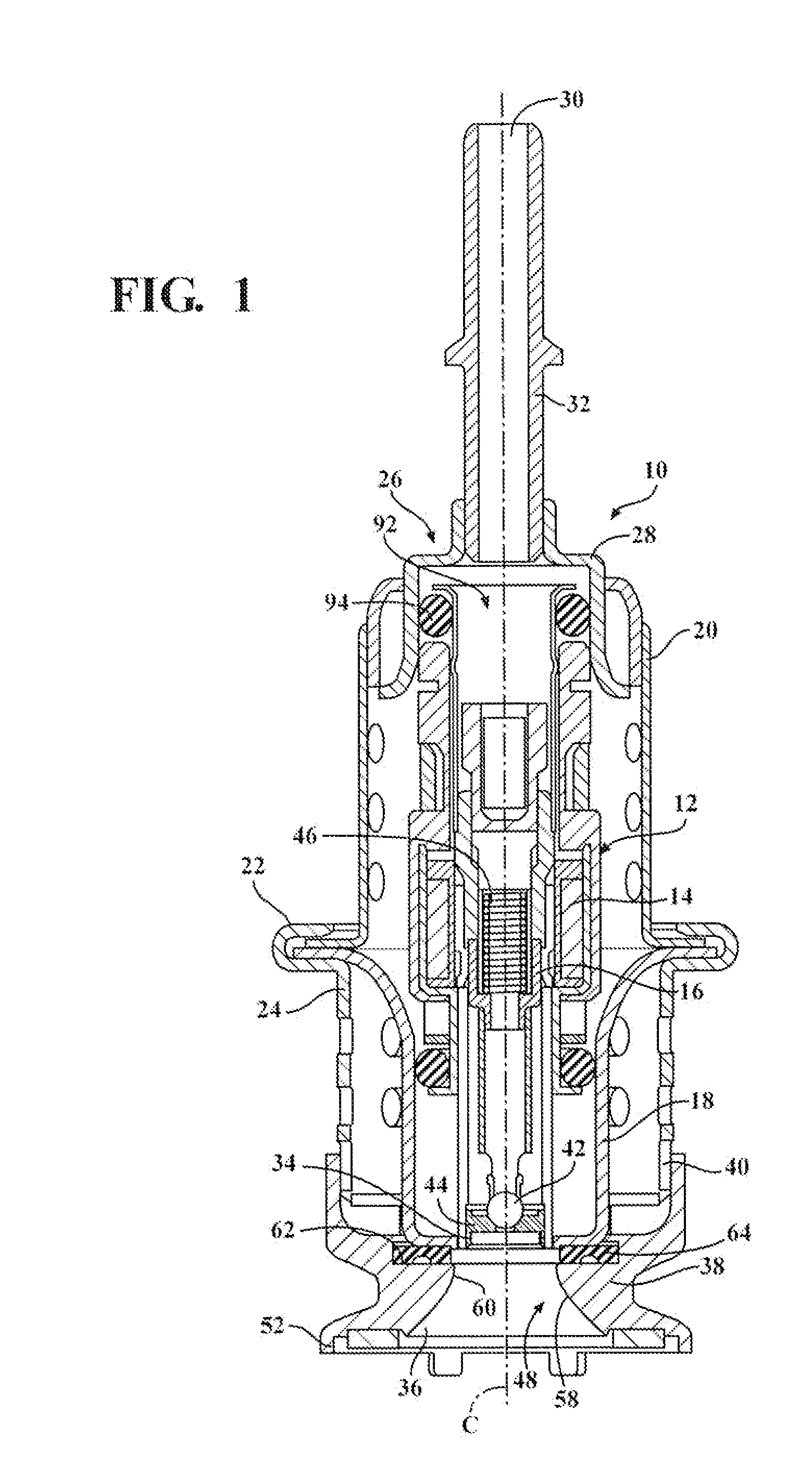
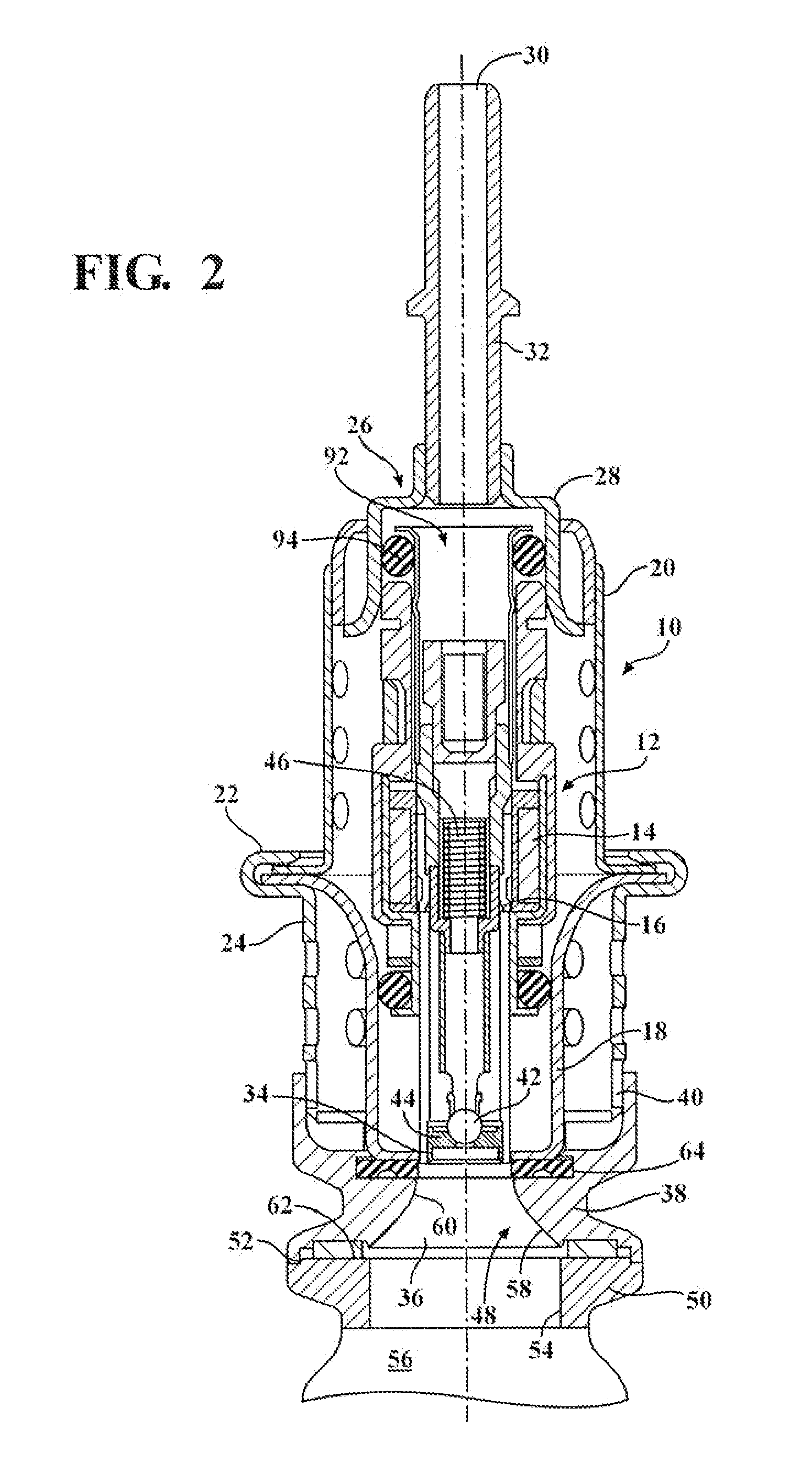
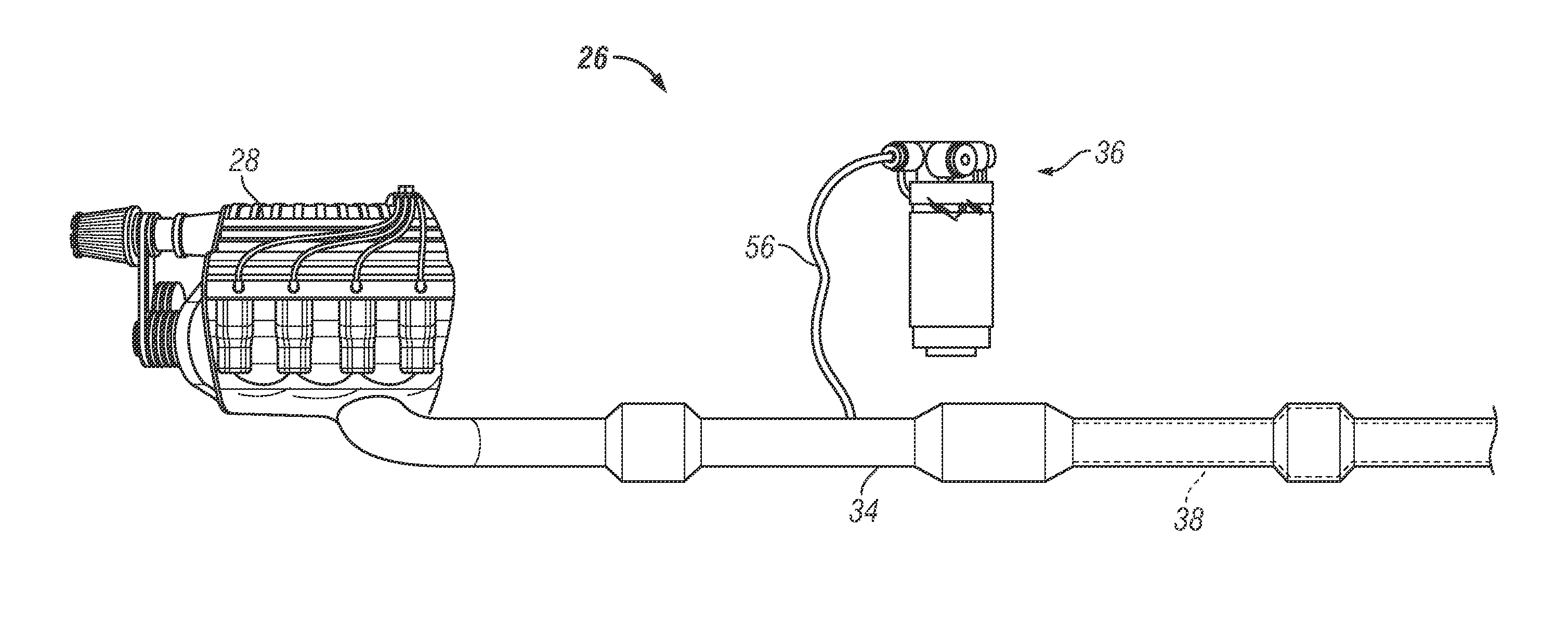
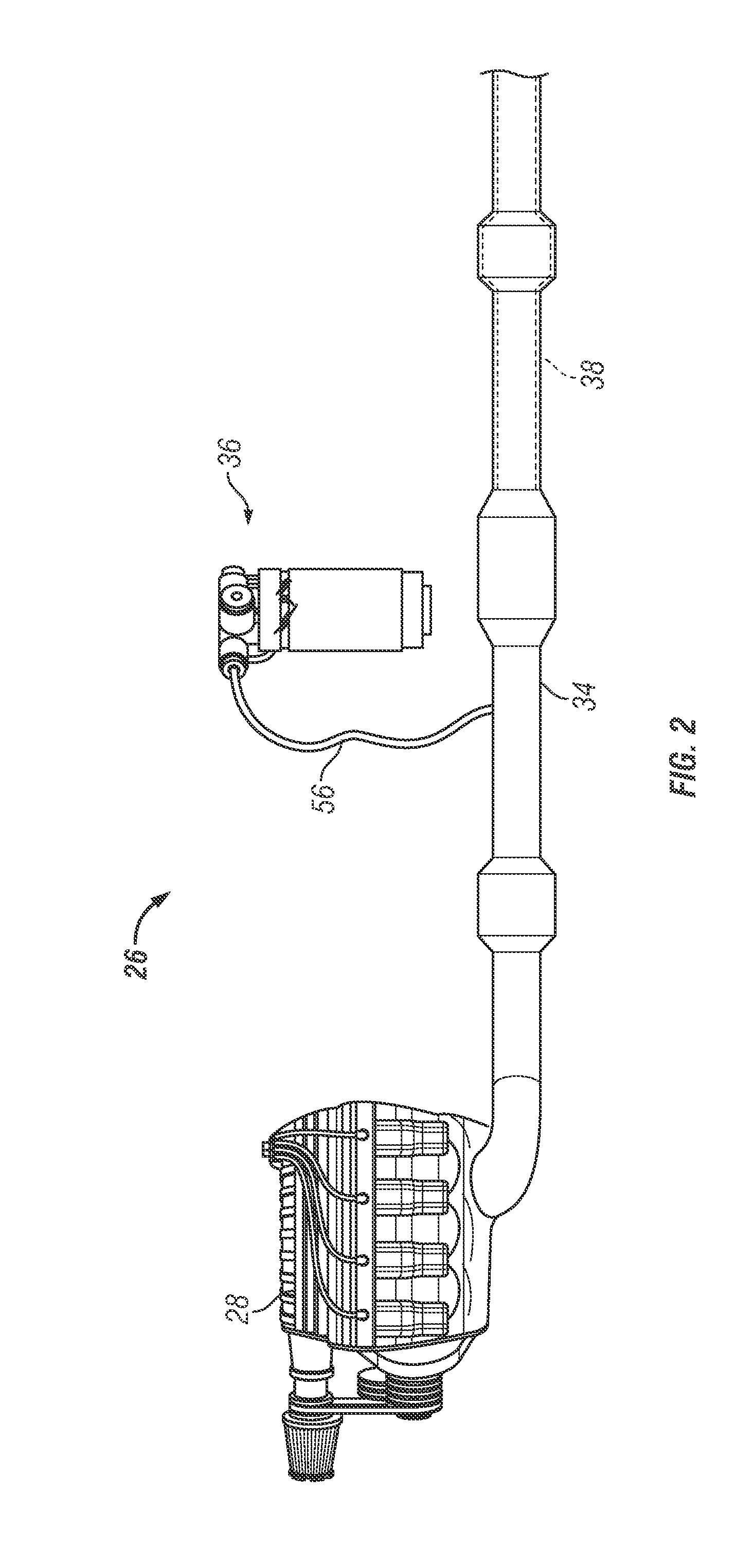
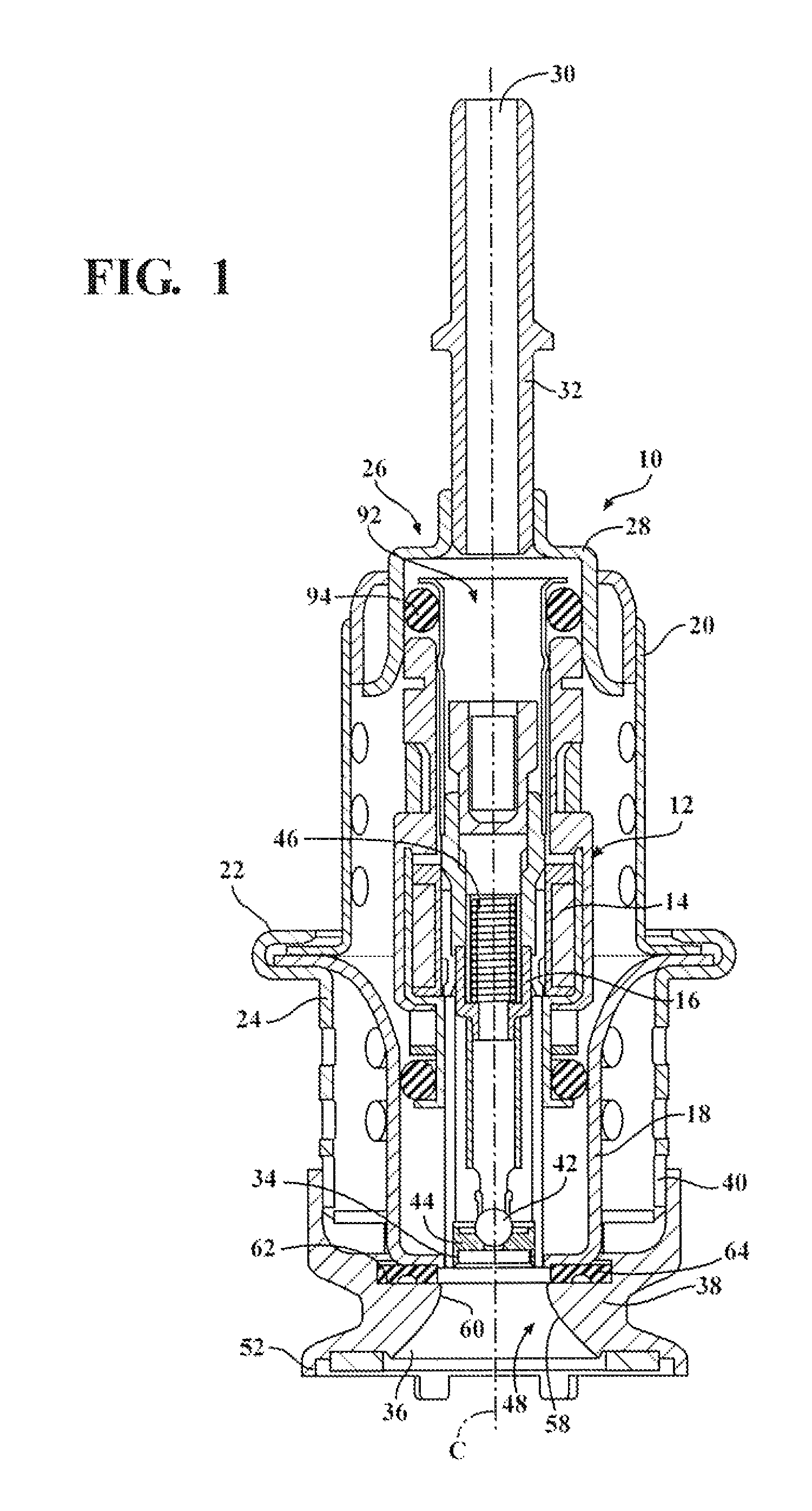
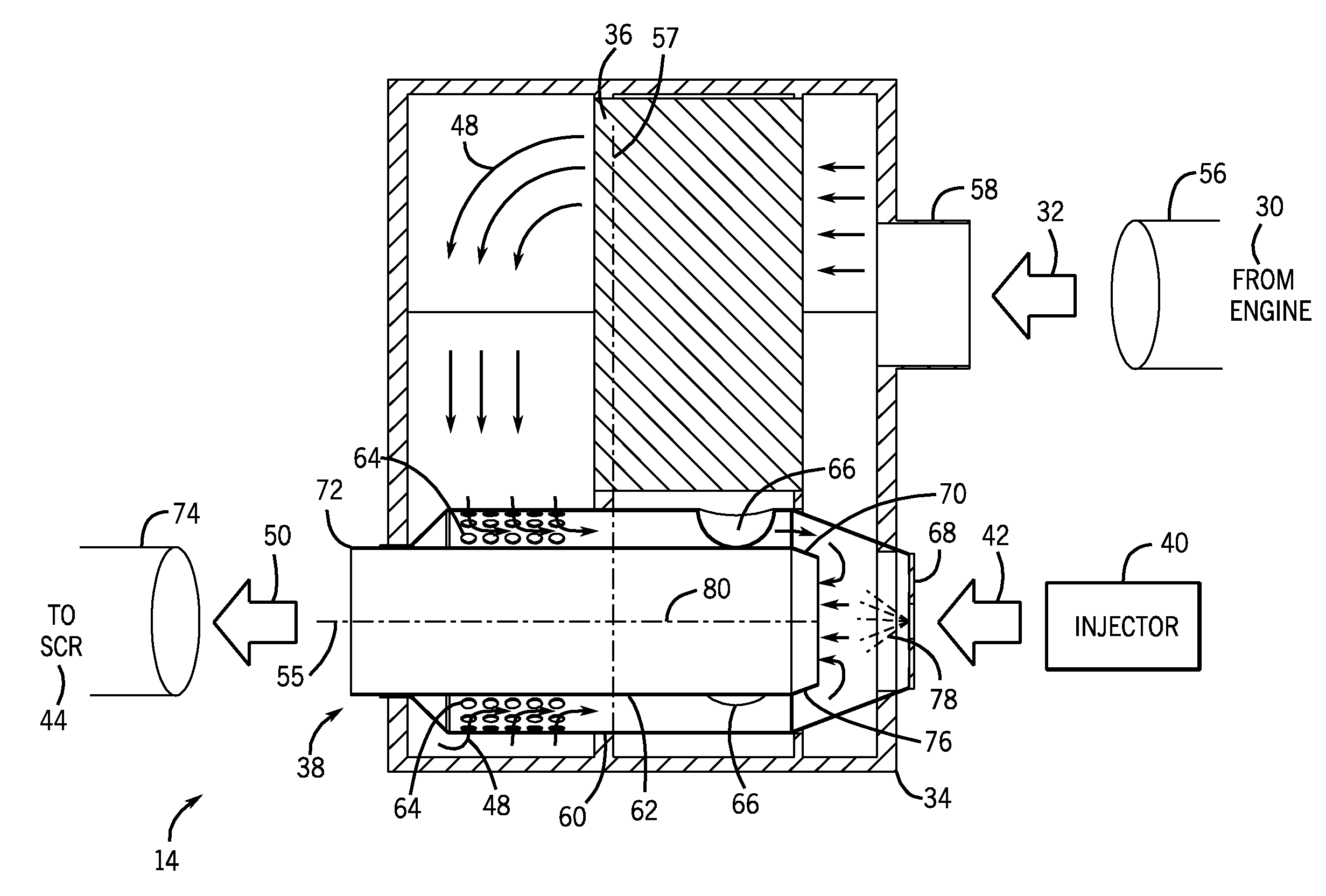
Purge system for reductant delivery unit for a selective catalytic reduction system
ActiveUS20150115051A1Maximize fluid volumeReduce sealing load of sealingInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesAmbient pressure
A purge procedure which is part of an injector, that may be used as part of a reductant delivery unit (RDU), where the RDU is part of a selective catalytic reduction system for injecting diesel exhaust fluid into an exhaust system, to control exhaust emissions. The RDU delivers a reductant carrier to the engine exhaust system. The purge process includes a control strategy to improve the quality of the purge cycle (i.e., increase the amount of fluid evacuated). The sequence of the purge event is adjusted in order to generate a strong vacuum in the fluid supply line and the injector—this enhances the efficiency of the purge by increasing the initial flow rates through the injector. However, upon opening the injector, the pressure inside the fluid path increases to a level just below the ambient pressure outside the injector, therefore the gas flow rate is substantially reduced.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
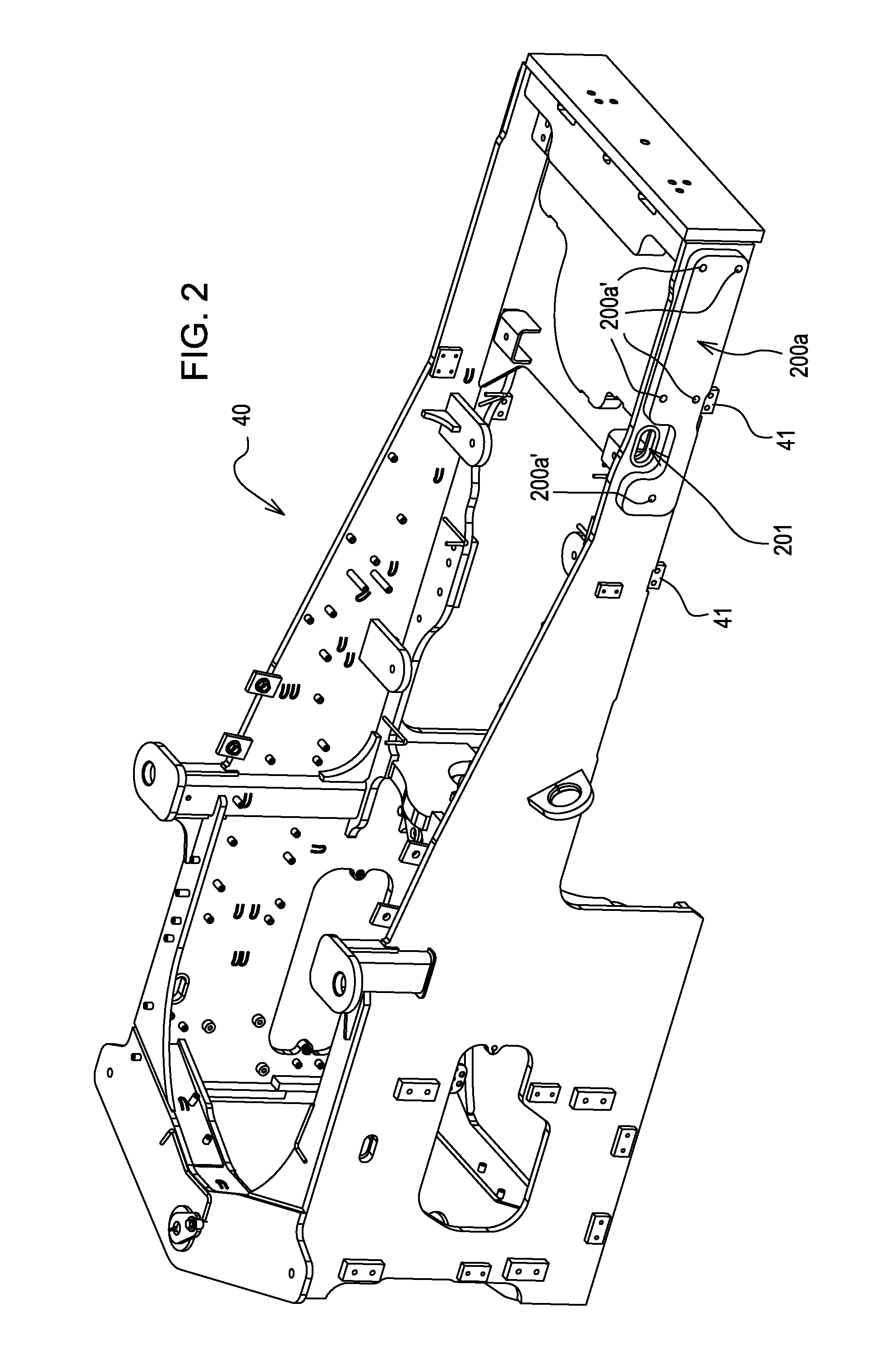
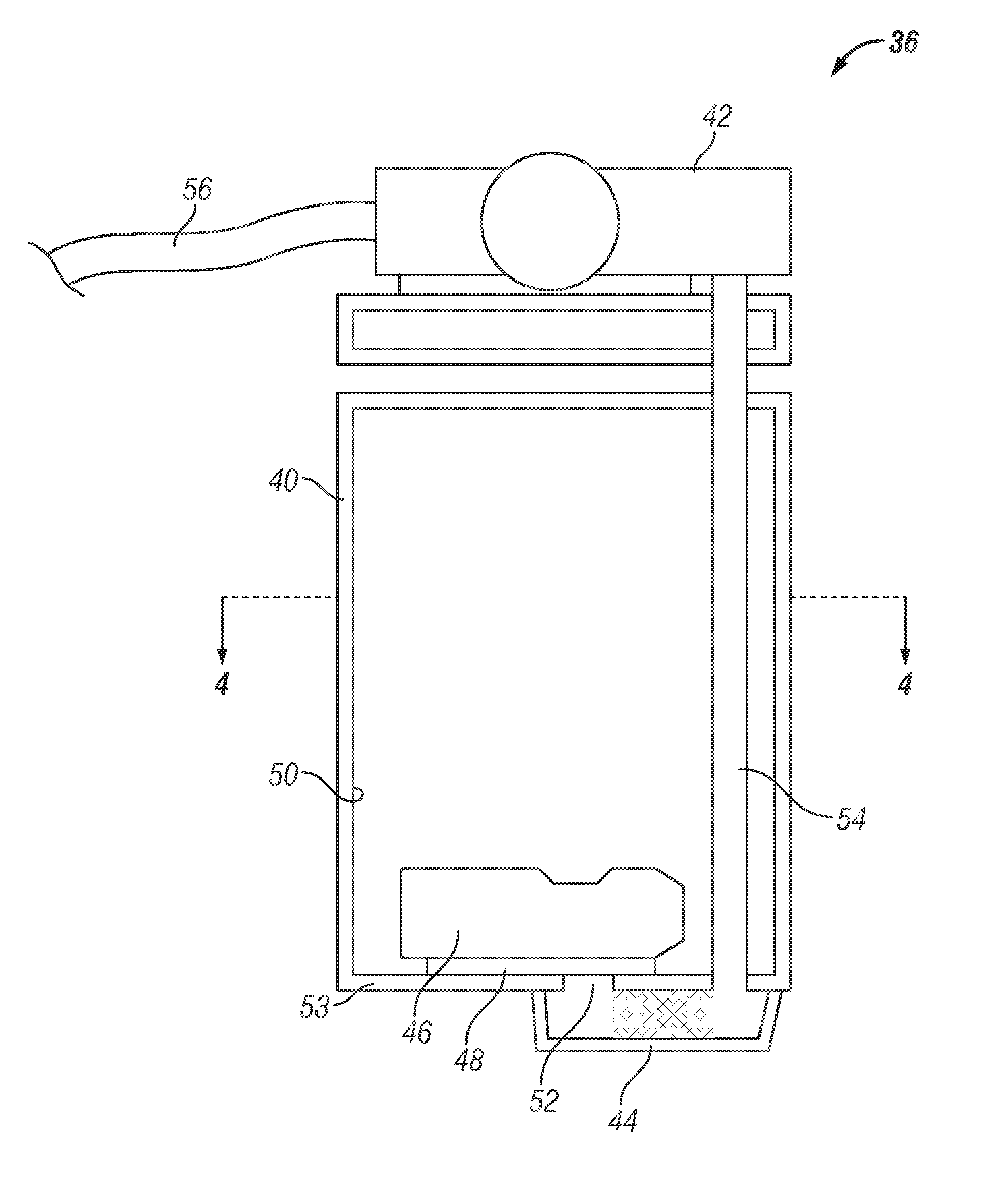
Diesel exhaust fluid system having a reservoir spacer
InactiveUS20110283689A1Internal combustion piston enginesDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringDiesel exhaust fluid
Diesel exhaust fluid systems are provided. The diesel exhaust fluid systems include a fluid reservoir having an inner surface and an opening therethrough, a fluid reservoir heating device positioned within the fluid reservoir, and a fluid reservoir spacer positioned within the fluid reservoir and between the inner surface of the fluid reservoir and the fluid reservoir heating device. The fluid reservoir spacer includes first and second portions on opposing sides of the opening through the fluid reservoir
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Purge system for reductant delivery unit for a selective catalytic reduction system
ActiveUS9273581B2Improve purge efficiencyPrevent component damage during freezing conditionsInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesAmbient pressure
A purge procedure which is part of an injector, that may be used as part of a reductant delivery unit (RDU), where the RDU is part of a selective catalytic reduction system for injecting diesel exhaust fluid into an exhaust system, to control exhaust emissions. The RDU delivers a reductant carrier to the engine exhaust system. The purge process includes a control strategy to improve the quality of the purge cycle (i.e., increase the amount of fluid evacuated). The sequence of the purge event is adjusted in order to generate a strong vacuum in the fluid supply line and the injector—this enhances the efficiency of the purge by increasing the initial flow rates through the injector. However, upon opening the injector, the pressure inside the fluid path increases to a level just below the ambient pressure outside the injector, therefore the gas flow rate is substantially reduced.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Venting system for a diesel exhaust fluid filler pipe
ActiveUS20140060699A1Reduce spit backIncrease nozzle functionalityLarge containersSolid materialDiesel exhaust fluidExhaust gas
A venting system for a filler pipe coupled to a diesel exhaust fluid tank in a vehicle is provided. In one example approach the venting system comprises a plurality of cut-outs in an interior surface of the filler pipe along the interior diameter of the filler pipe in a top surface of the filler pipe.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
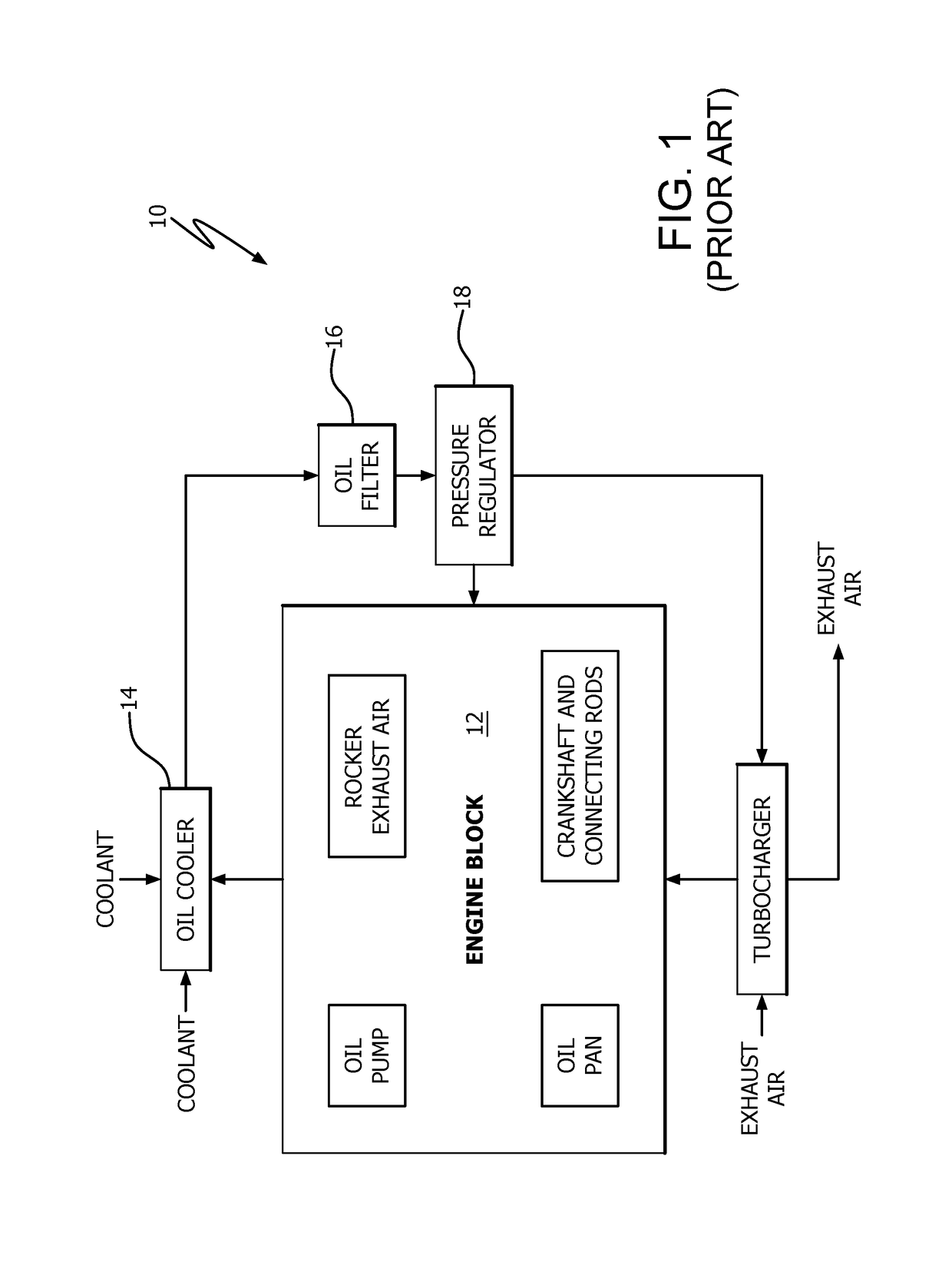
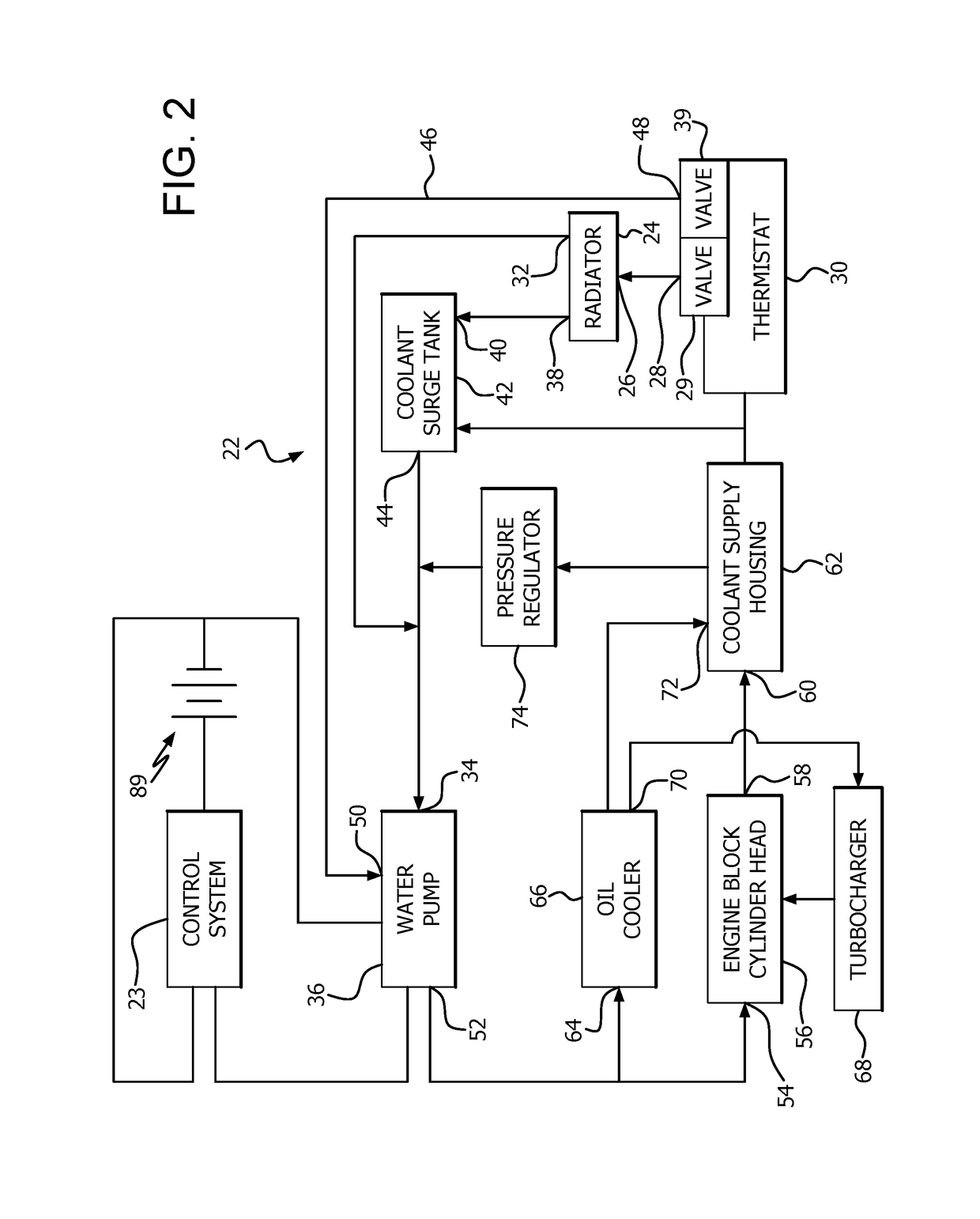
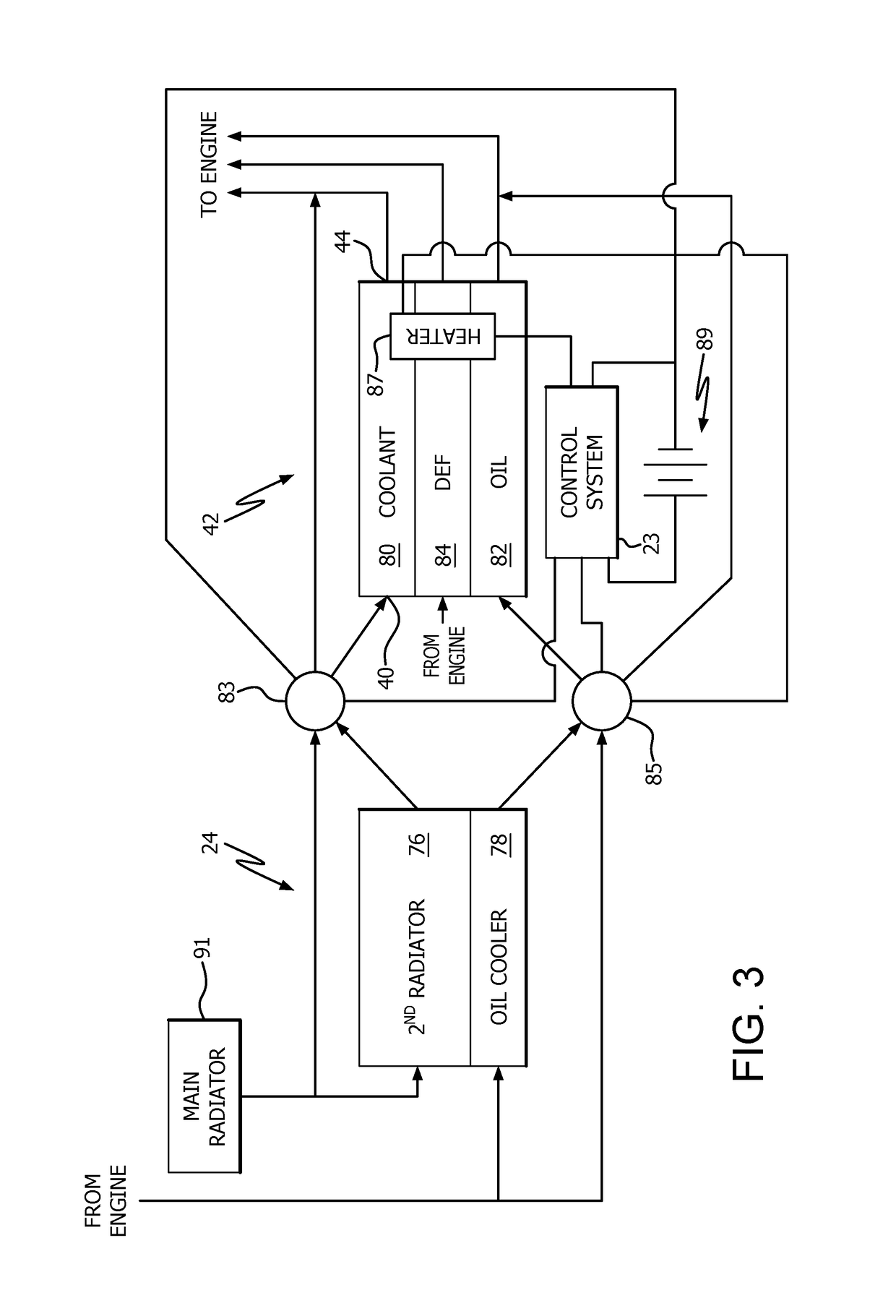
Engine temperature control system
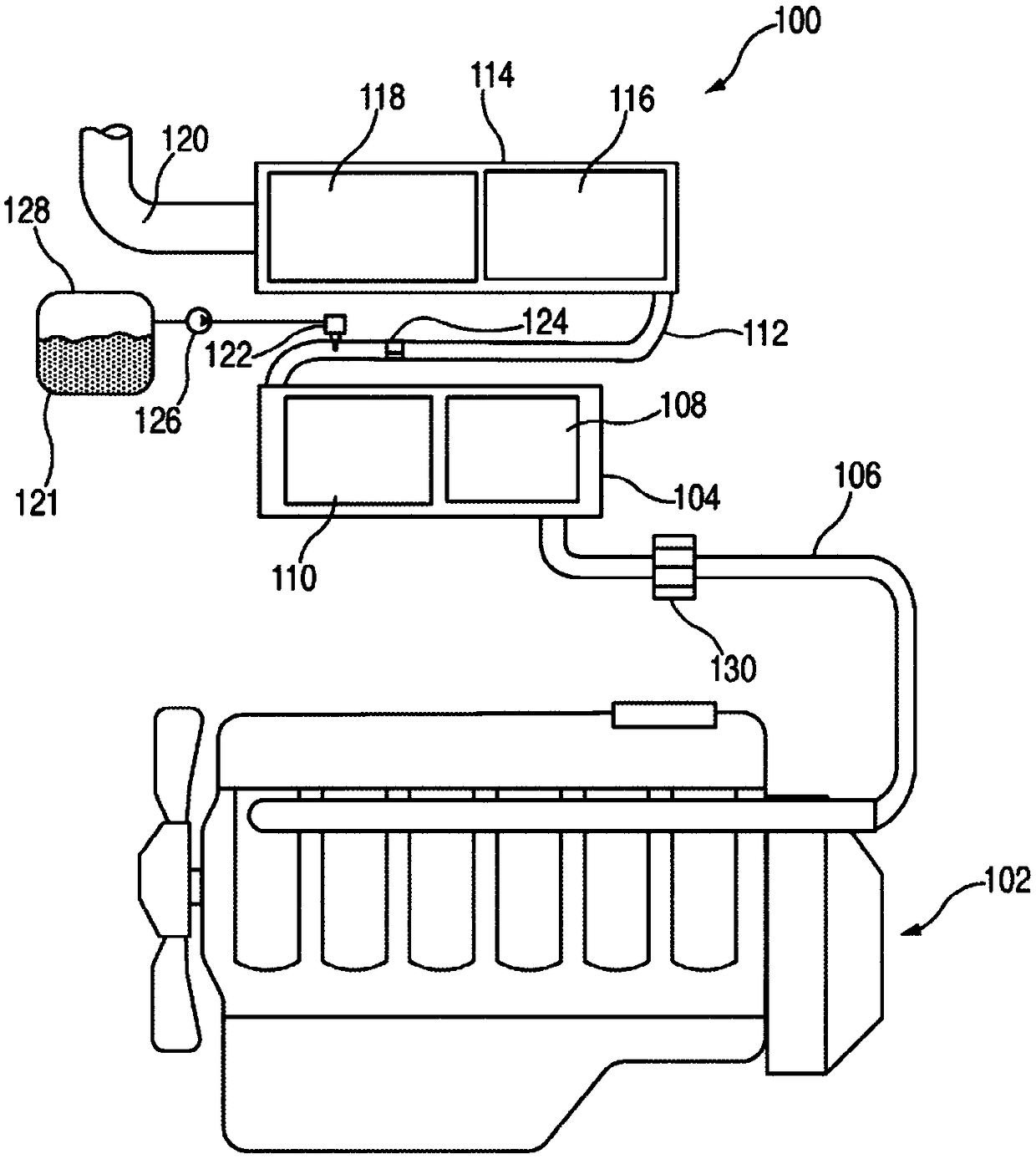
An engine temperature control system is provided for heating and / or cooling engine fluids to resist deviation of the temperature of these fluids from a temperature range wherein optimal fluid performance is achieved. Some examples of the temperature control system provide for preheating fluids such as coolant, lubricant, or diesel exhaust fluid prior to starting the engine. Other examples of the temperature control system provide for improved cooling of lubricants utilized for high heat generating components such as turbochargers, continuing cooling of these fluids after the engine is stopped.
Owner:TESLOVICH DARIUS
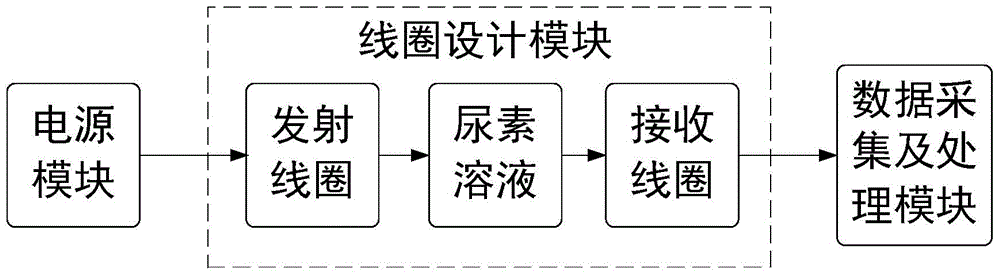
Online diesel exhaust fluid solution concentration monitoring system and monitoring method for automobile SCR system
InactiveCN104792828AAvoid contactIncreased sensitivityMaterial impedanceProcess moduleData acquisition
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Purging and sealing-reductant delivery unit for selective catalytic reduction systems
ActiveUS9777859B2Improve purge efficiencyImprove sealingInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusExhaust fumesEngineering
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
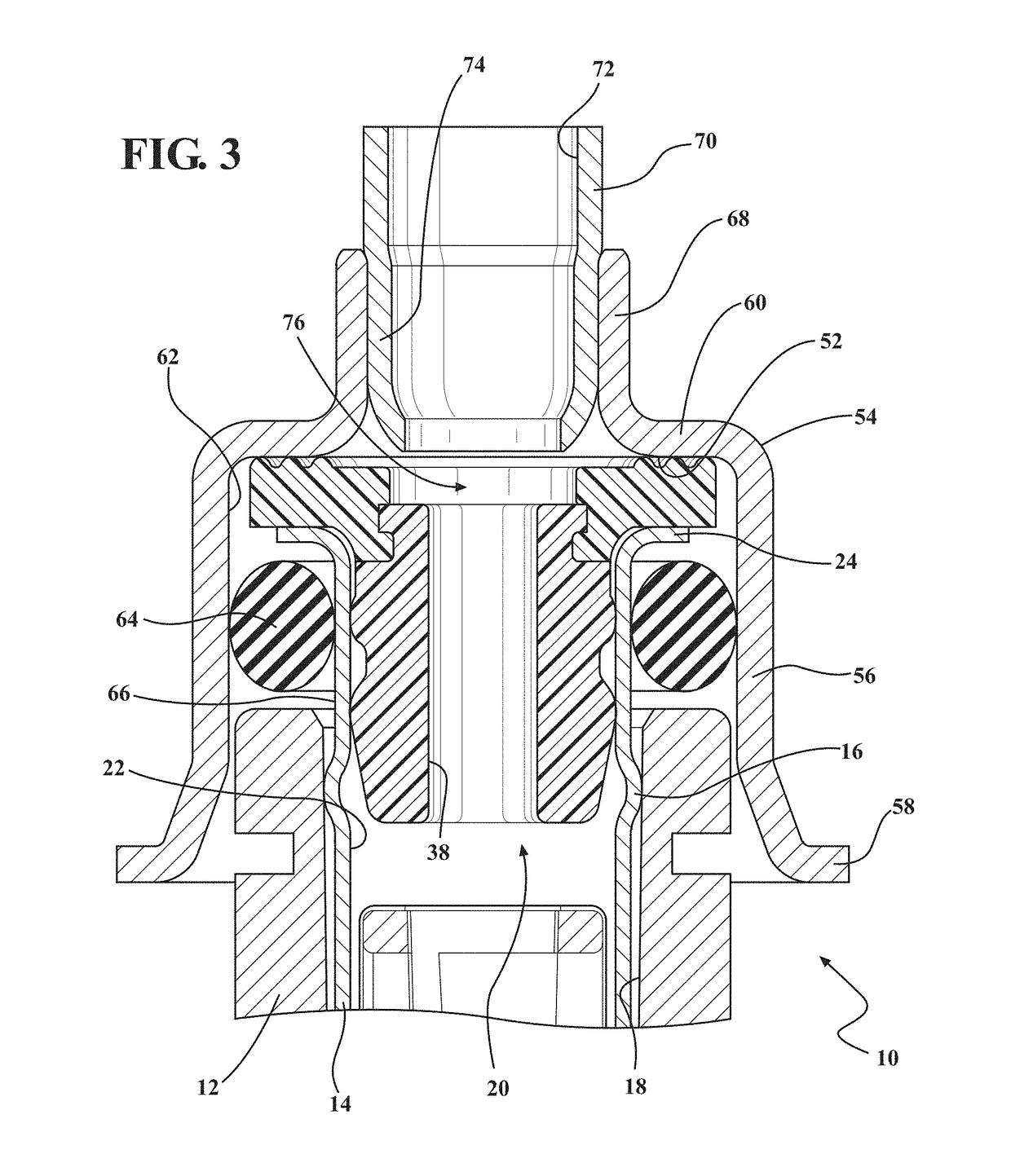
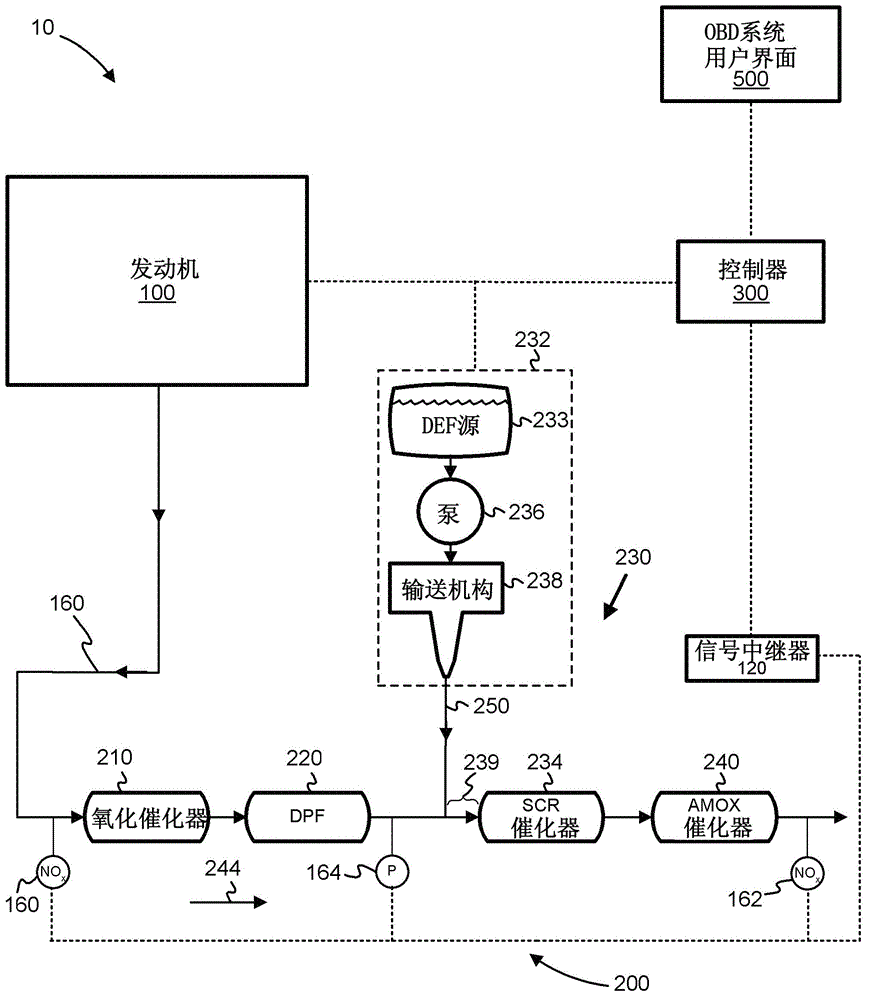
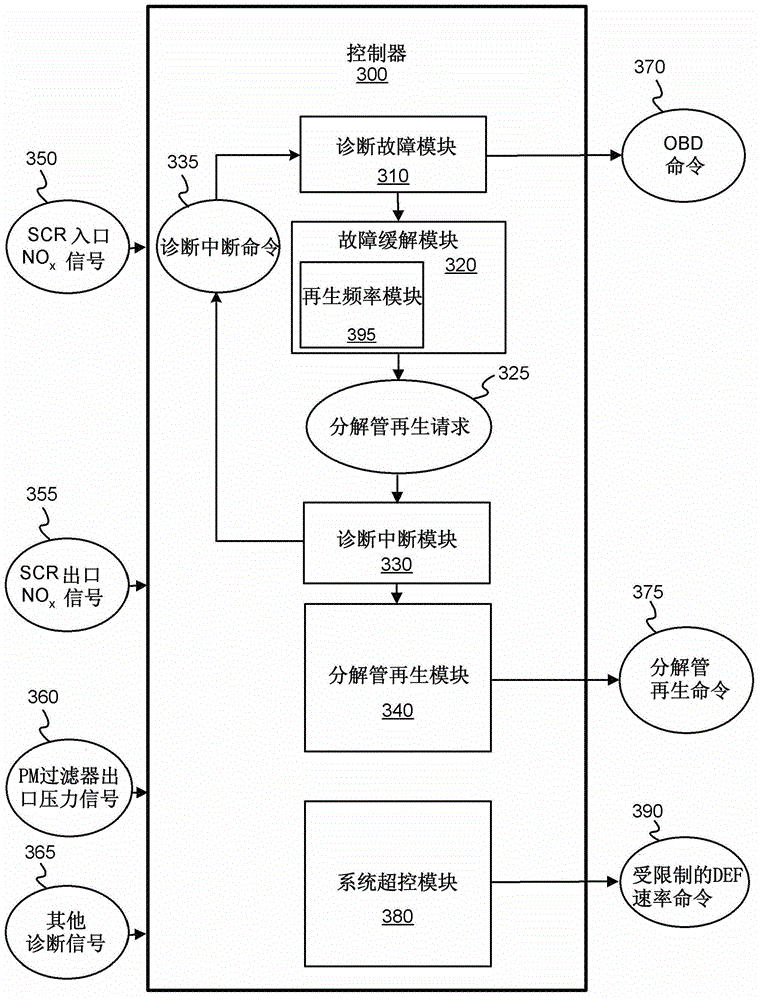
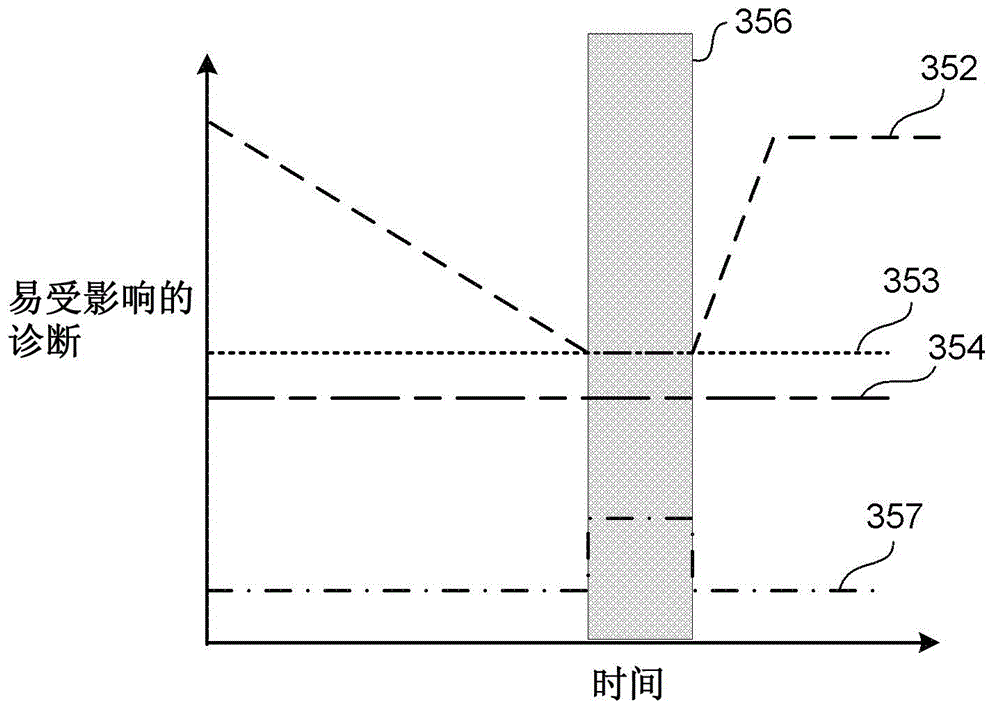
Apparatus, system, and method for mitigating diesel exhaust fluid deposits and associated conditions
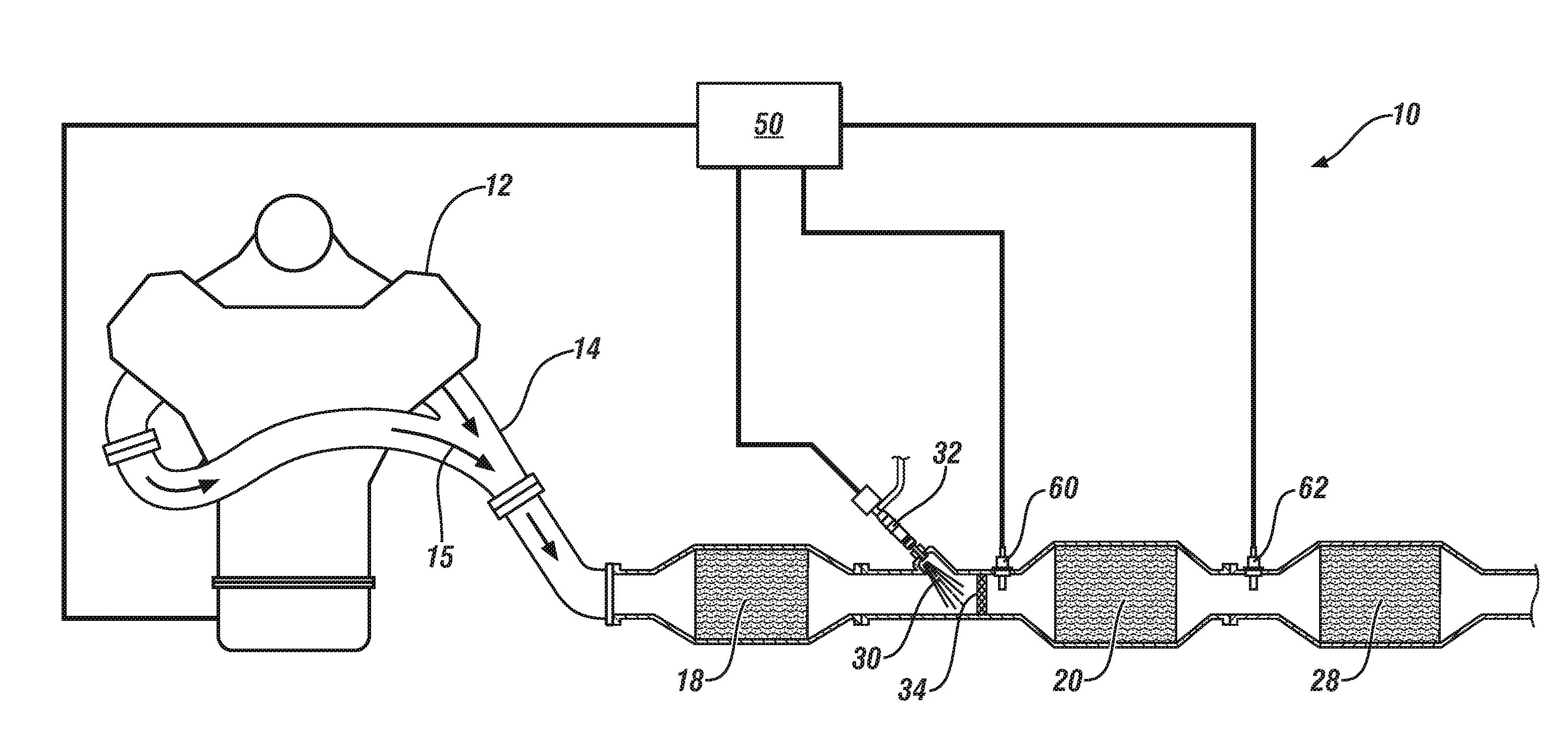
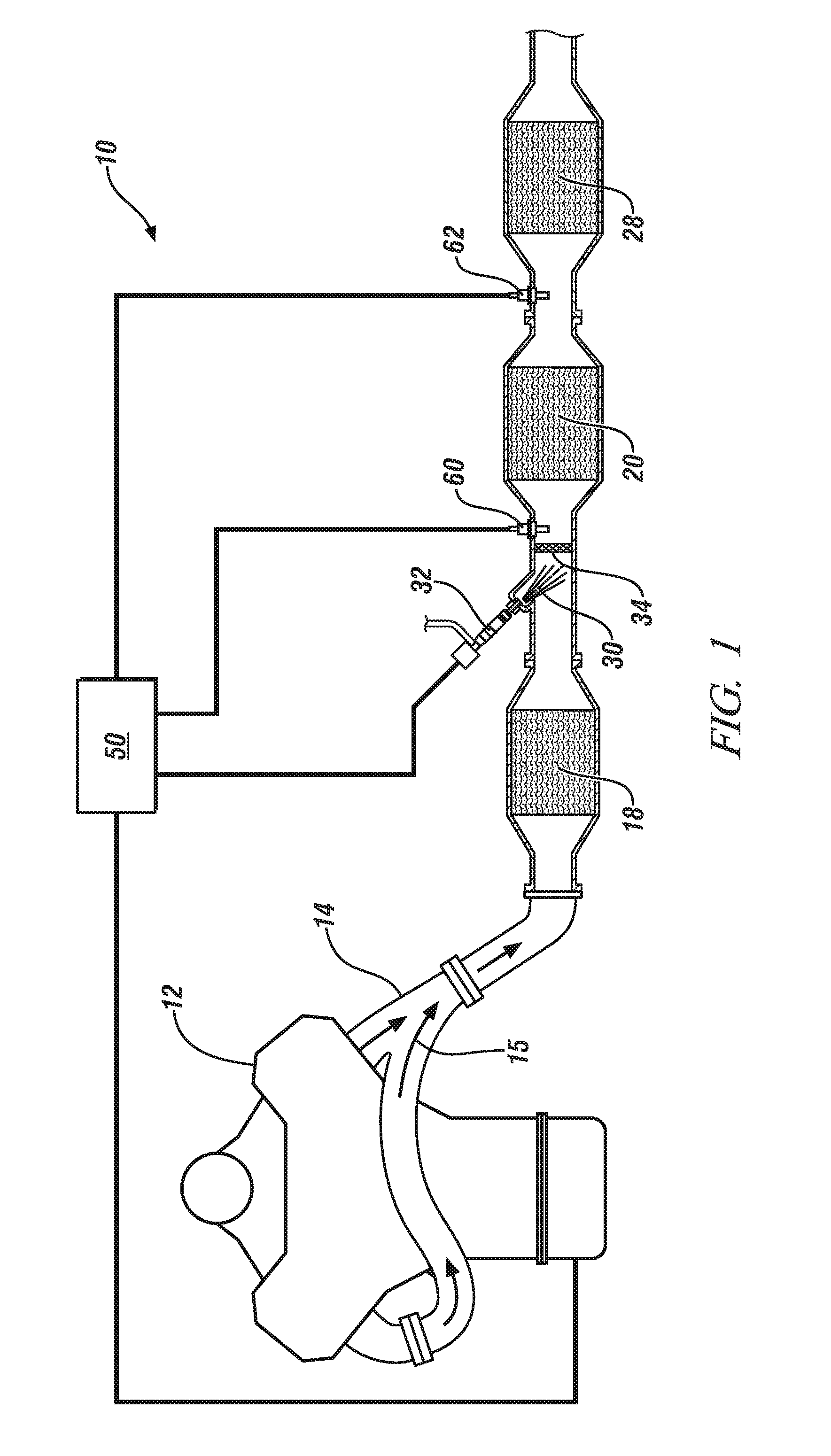
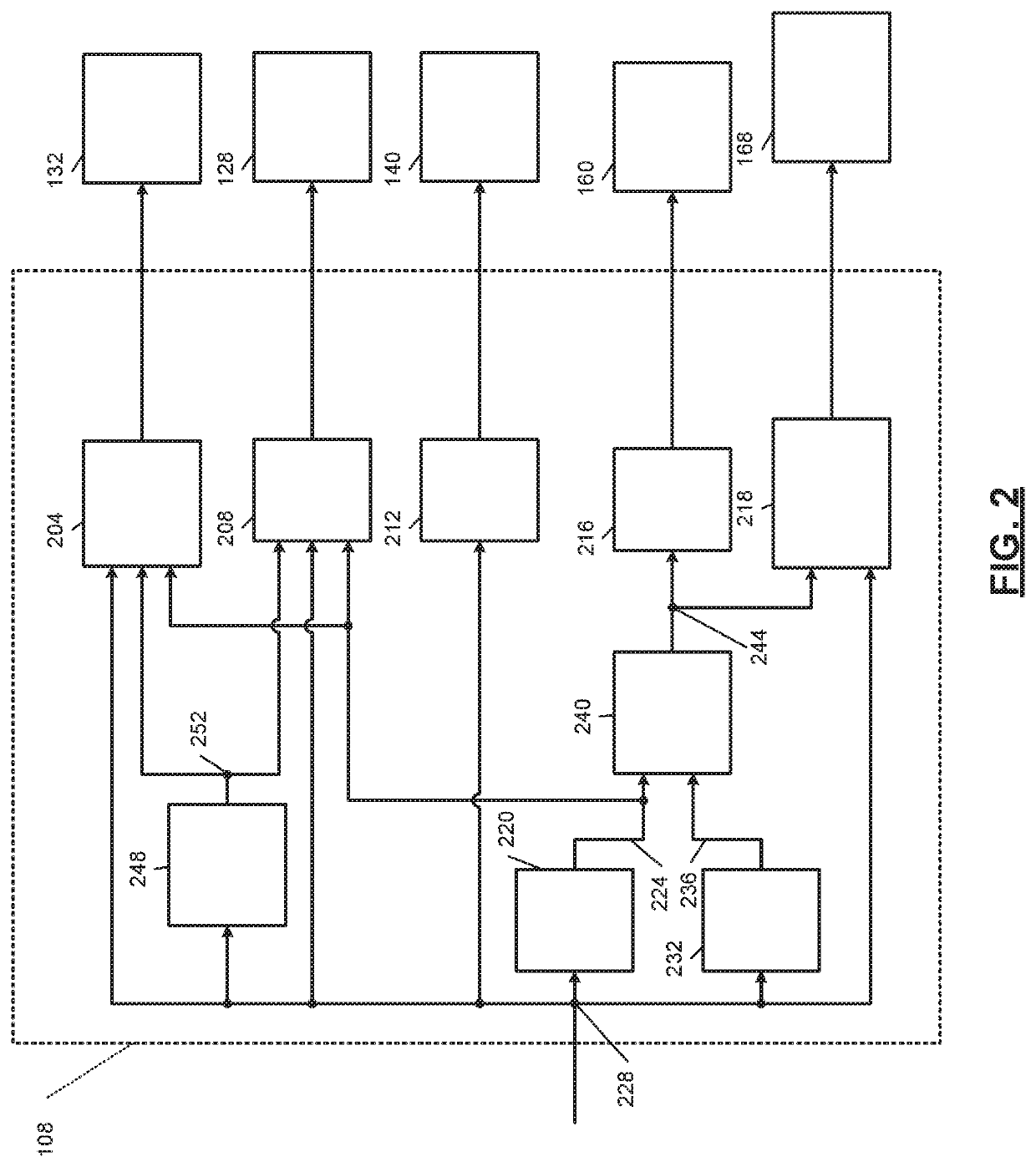
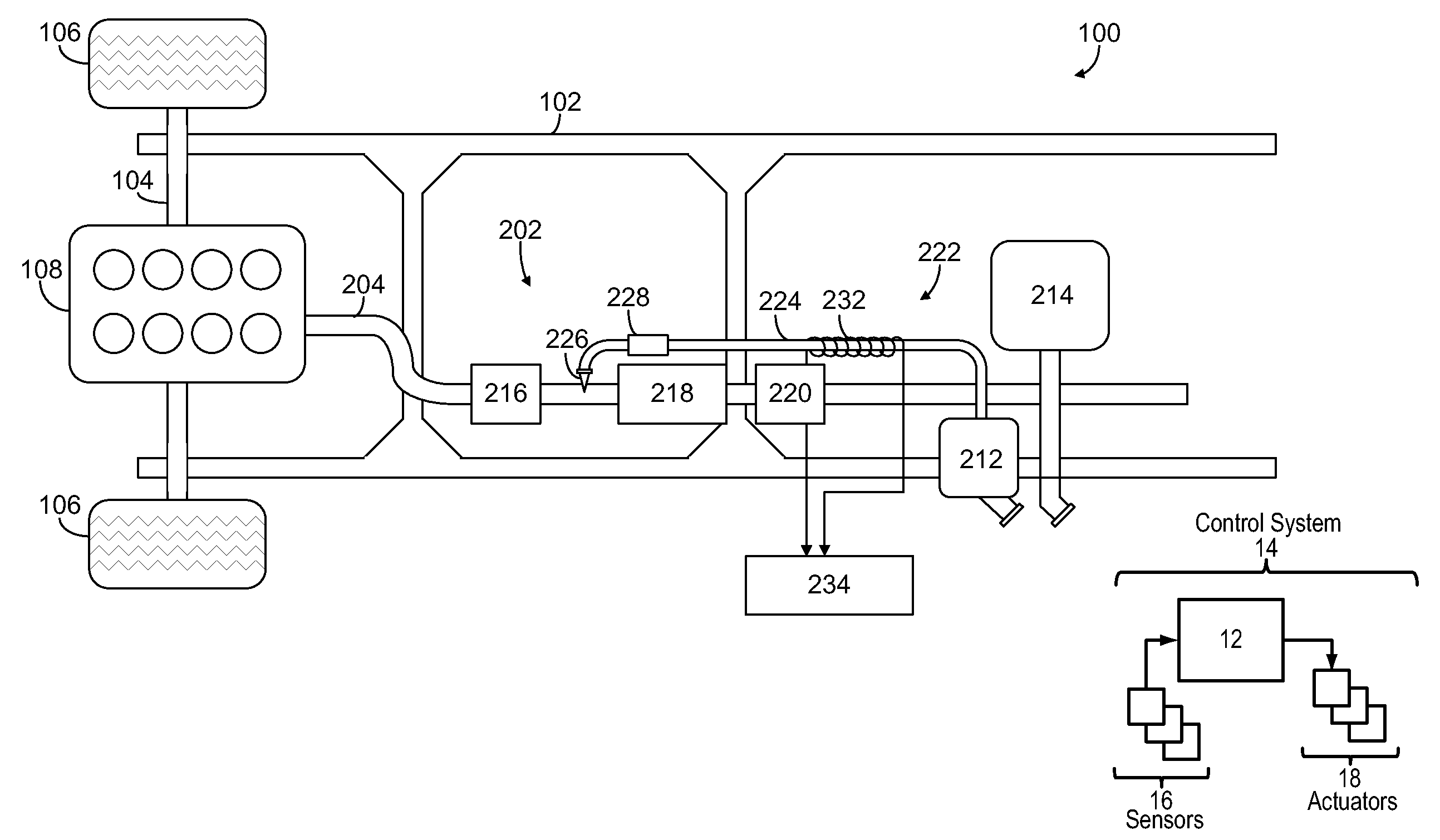
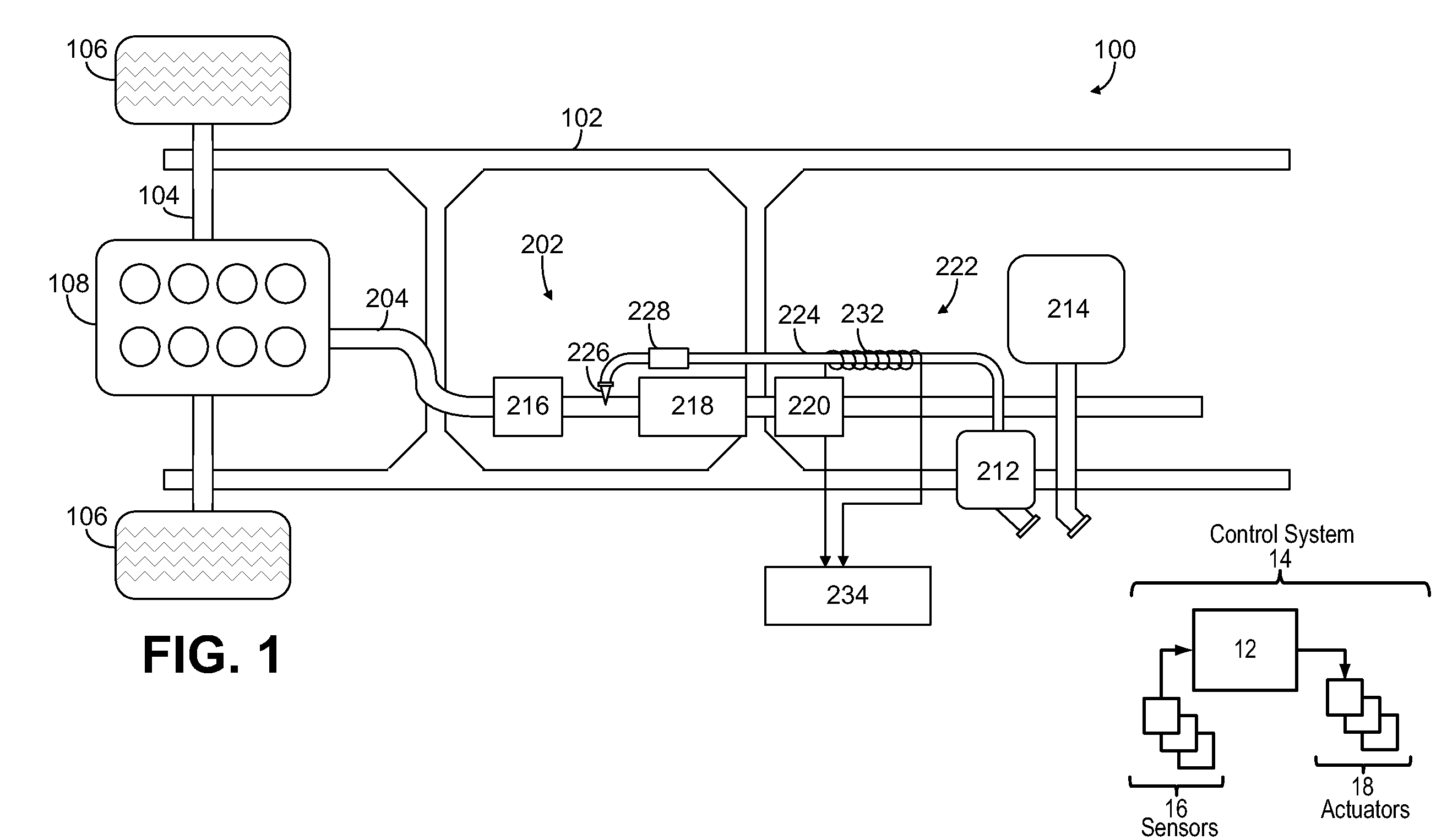
According to one embodiment, described herein is an apparatus for mitigating on-board diagnostic (OBD) faults generated by an OBD system of an internal combustion engine (ICE) system (10) having a selective catalytic reduction system (230) with a diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) decomposition tube (239). The apparatus includes a fault mitigation module (320) that is configured to monitor at least one OBD signal of the OBD system and issue a request (325) for regenerating the DEF decomposition tube when a value of the at least one OBD signal reaches a predetermined regeneration threshold corresponding with the at least one OBD signal. The regeneration threshold is reachable prior to an OBD fault threshold corresponding with the at least one OBD signal. The apparatus also includes a regeneration module (340) that is configured to regenerate the DEF decomposition tube according to the issued request.
Owner:酷敏斯IP公司
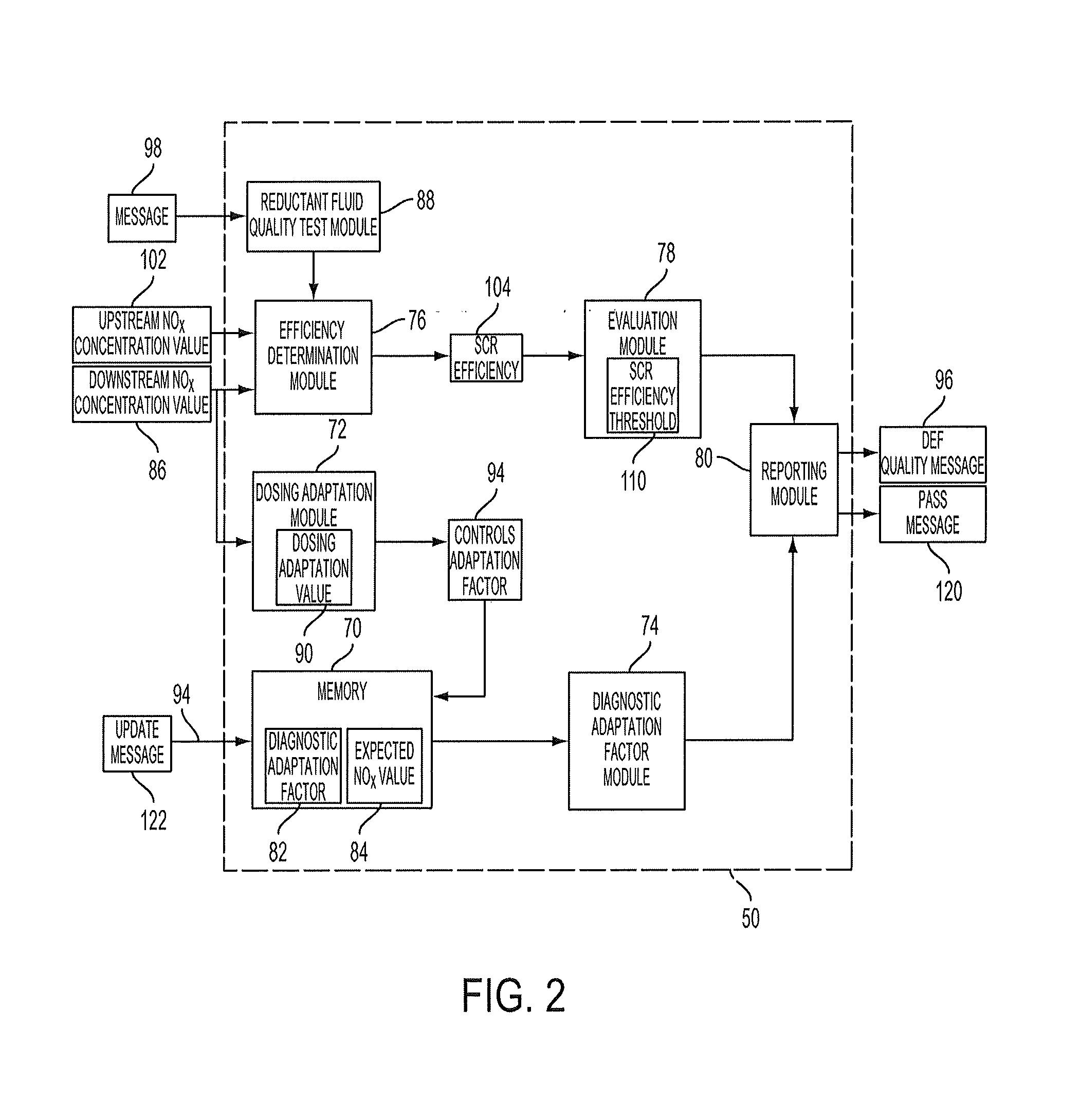
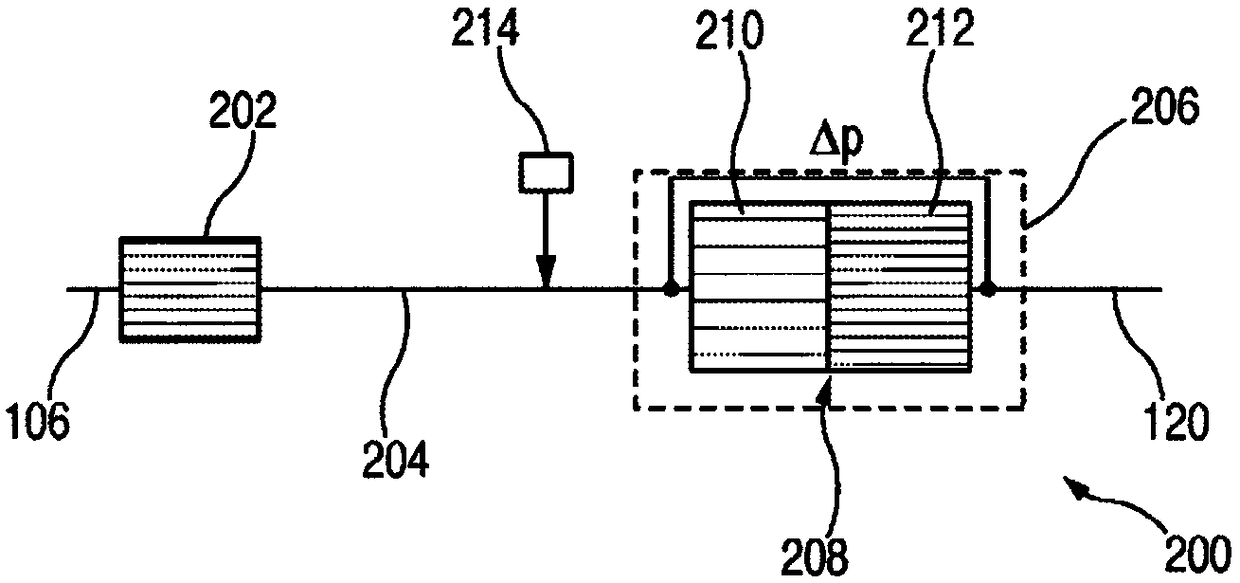
System for Indicating Quality of a Diesel Exhaust Fluid ("DEF")
ActiveUS20130298533A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDiesel exhaust fluidTreatment system
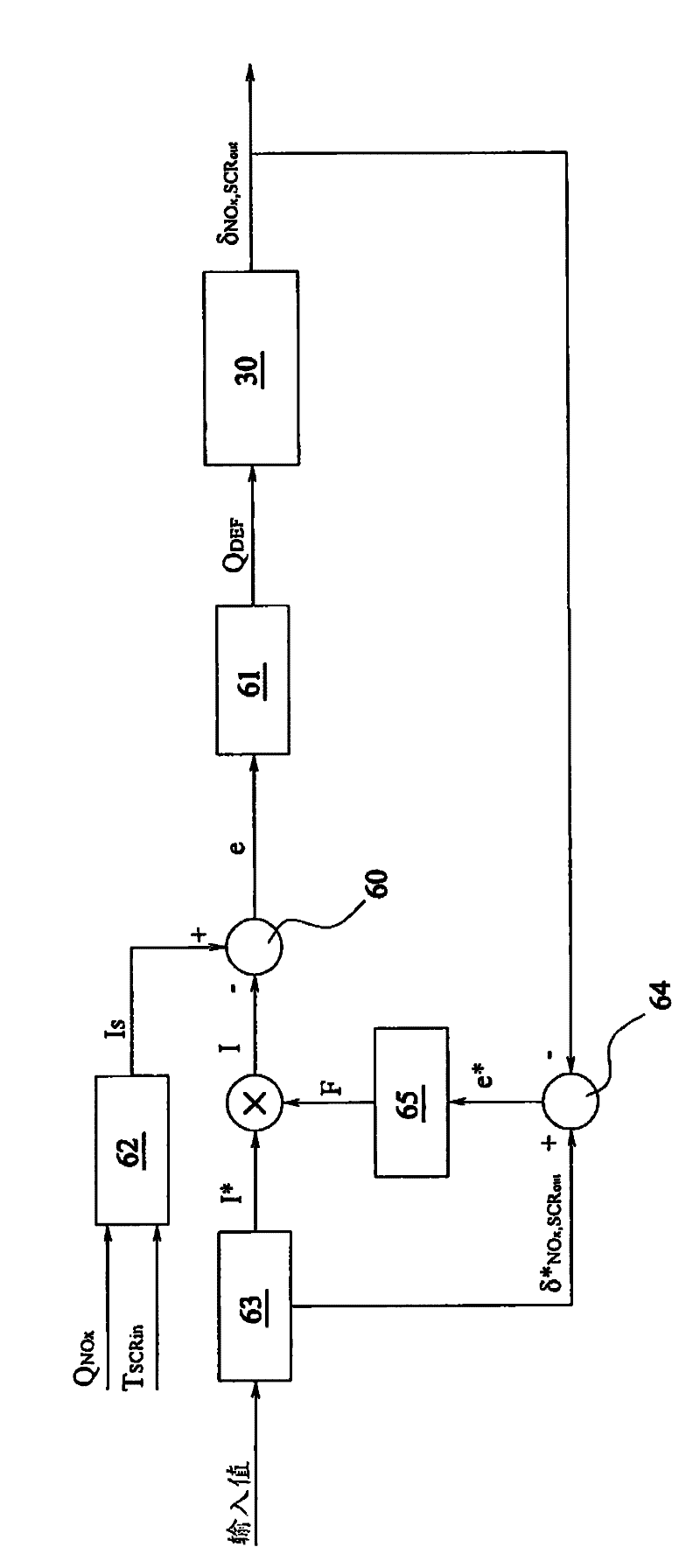
An exhaust gas treatment system for an internal combustion engine is provided having an exhaust gas conduit, a diesel exhaust fluid (“DEF”) source, a selective catalytic reduction (“SCR”) device, a NOx sensor, and a control module. The DEF source supplies a DEF having a quality factor. The NOx sensor is in fluid communication with the exhaust gas conduit. The NOx sensor is located downstream of the SCR device and is configured for detecting a NOx concentration value. The control module is in communication with the DEF source and the NOx sensor. The control module stores a diagnostic adaptation factor and an expected NOx value. The control module includes a dosing module for determining a controls adaptation factor that is based on a deviation between the NOx concentration value and the expected NOx value. The diagnostic adaptation factor is selectively updated with the controls adaptation factor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
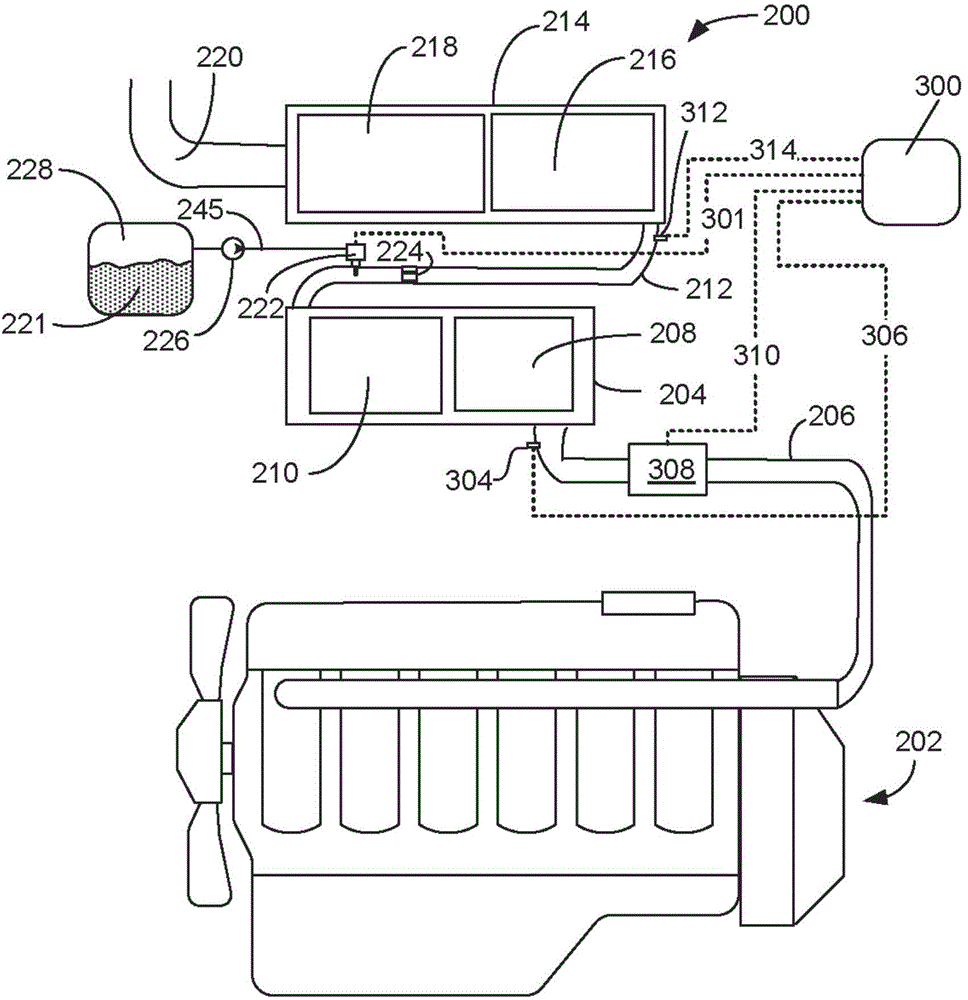
Engine and coolant system control systems and methods
ActiveUS20190383187A1Reduce componentsLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlControl systemComputer module
A coolant control system of a vehicle includes a coolant pump that pumps coolant to a second radiator that is different than a first radiator that receives coolant from an engine of the vehicle. A diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) injector injects a DEF into an exhaust system and receives coolant output from the second radiator. A fuel heat exchanger transfers heat between coolant and fuel flowing therethrough. An engine control module is configured to determine a temperature of the DEF injector, control a duty cycle of the coolant pump, determine a vaporized condition of the coolant based on a DEF injector temperature, optionally further, in response to determining a vaporized condition of the coolant, implement a vapor purge by oscillating the duty cycle of the coolant pump, and optionally further identify a low-coolant condition of the coolant control system based on the vapor purges implemented during a time period.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System for indicating quality of a diesel exhaust fluid (“DEF”)
An exhaust gas treatment system for an internal combustion engine is provided having an exhaust gas conduit, a diesel exhaust fluid (“DEF”) source, a selective catalytic reduction (“SCR”) device, a NOx sensor, and a control module. The DEF source supplies a DEF having a quality factor. The NOx sensor is in fluid communication with the exhaust gas conduit. The NOx sensor is located downstream of the SCR device and is configured for detecting a NOx concentration value. The control module is in communication with the DEF source and the NOx sensor. The control module stores a diagnostic adaptation factor and an expected NOx value. The control module includes a dosing module for determining a controls adaptation factor that is based on a deviation between the NOx concentration value and the expected NOx value. The diagnostic adaptation factor is selectively updated with the controls adaptation factor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Secondary containment system for DEF storage container
InactiveUS20110024432A1Maintain temperatureDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusCentral layerDiesel exhaust fluid
A secondary containment system used to transport and store a tank containing diesel exhaust fluid. The secondary containment system having a containment body comprising an end wall, a back wall, two side walls, a bottom, and a top, wherein the walls are integral to the bottom, and wherein the top can be displaced from the containment body. The containment body is constructed of a three-layer configuration comprising an inner layer, an outer layer, and a central layer sandwiched therebetween. The inner layer defines a chamber in which the tank containing diesel exhaust fluid is stored. The chamber is sized and shaped so that the tank is positioned in the chamber and defines a void between walls of the inner layer and the tank containing diesel exhaust fluid. The inner layer and outer layer are preferably constructed of a UV protected polyethylene, and the central layer is constructed of a 2″-2 lb. density polyurethane insulation material having an R17 value.
Owner:JORGENSEN ROY W
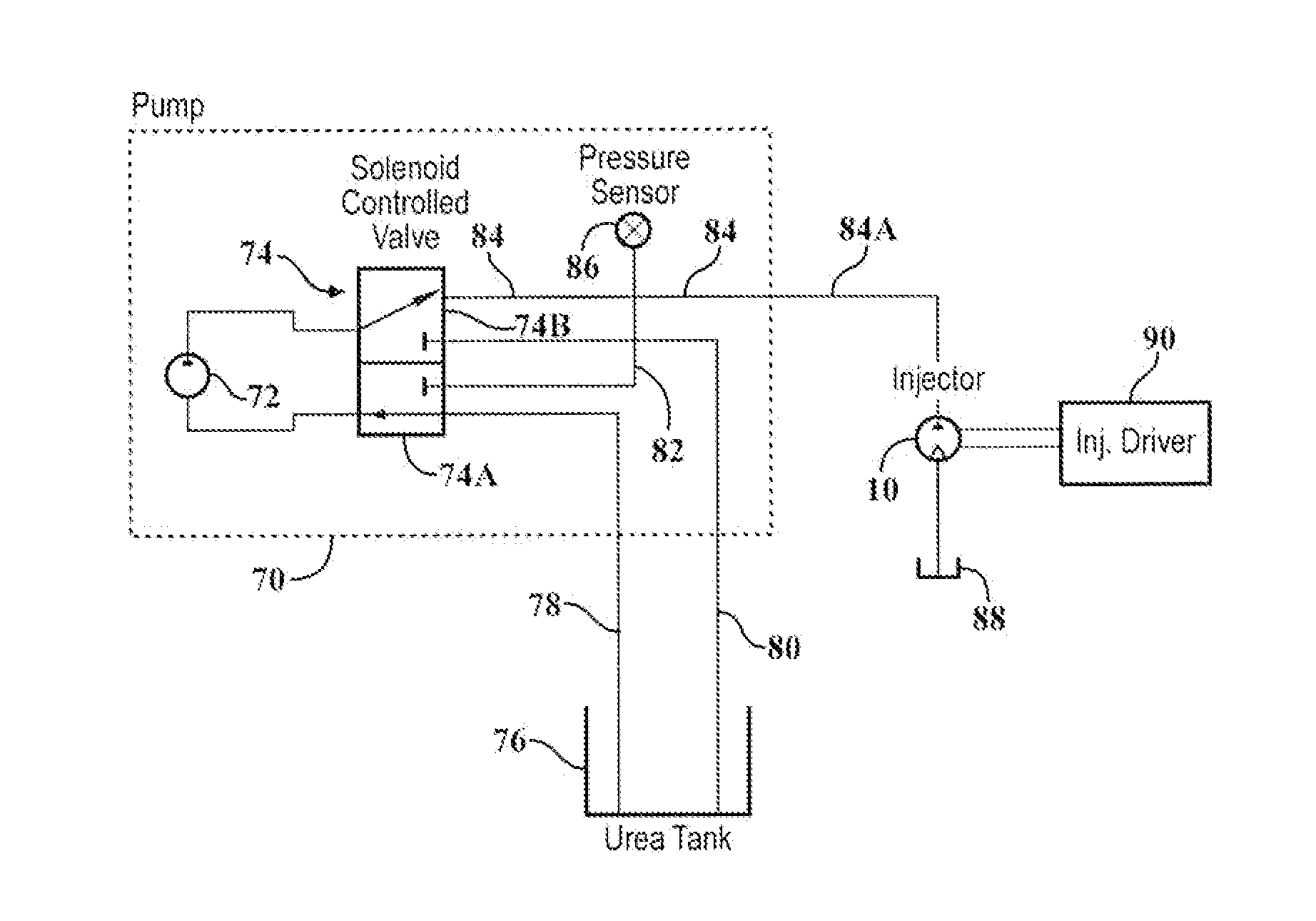
Ejection metering module for SCR (selective catalytic reduction) and controlling method of ejection metering module
ActiveCN104948271ALow costInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusPulser pumpWorking fluid
The invention discloses an ejection metering module for SCR (selective catalytic reduction) and a controlling method of the ejection metering module. The ejection metering module comprises a support, a pulse pump mounted at one end of the support, an upper end cover fixed at the other end of the support, an ejection nozzle and a controller, and is characterized in that the support extends from the upper portion of a DEF (diesel exhaust fluid) storage tank deeply to the bottom of the DEF storage tank and is fixed on the diesel exhaust fluid storage tank via the upper end cover, the controller controls the pulse pump to work, the pulse pump comprises a solenoid driver, a plunger pump and an internal flow passage which penetrates through the pulse pump axially, working fluid (DEF) enters an inlet of the internal flow passage via a first filter arranged at the inlet at the lower end of the internal flow passage, an outlet of the internal flow passage is higher than the inlet of the same in arrangement, part of the working fluid in the internal flow passage is pumped to the ejection nozzle through the plunger pump, and the other part of the working fluid is drained from the pulse pump via the outlet of the internal flow passage. Characteristic parameters of the pulse pump are prestored in the controller, so that the ejection metering module is capable of working in a slave mode or an intelligent (master) mode.
Owner:无锡恒和环保科技有限公司
Method for controlling injection of diesel exhaust fluid into exhaust pipe of internal combustion engine
InactiveCN102251836AReduce consumptionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusControl parametersDiesel exhaust fluid
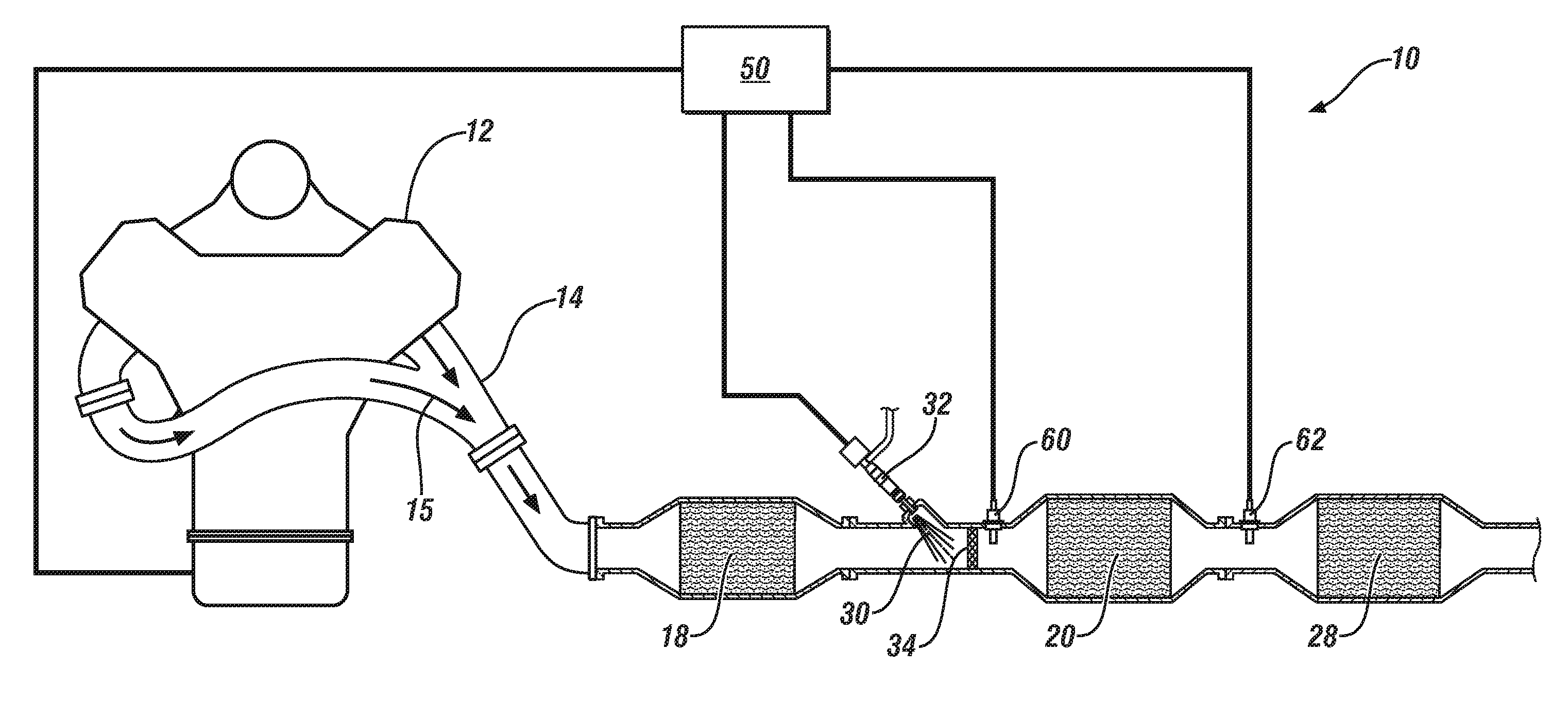
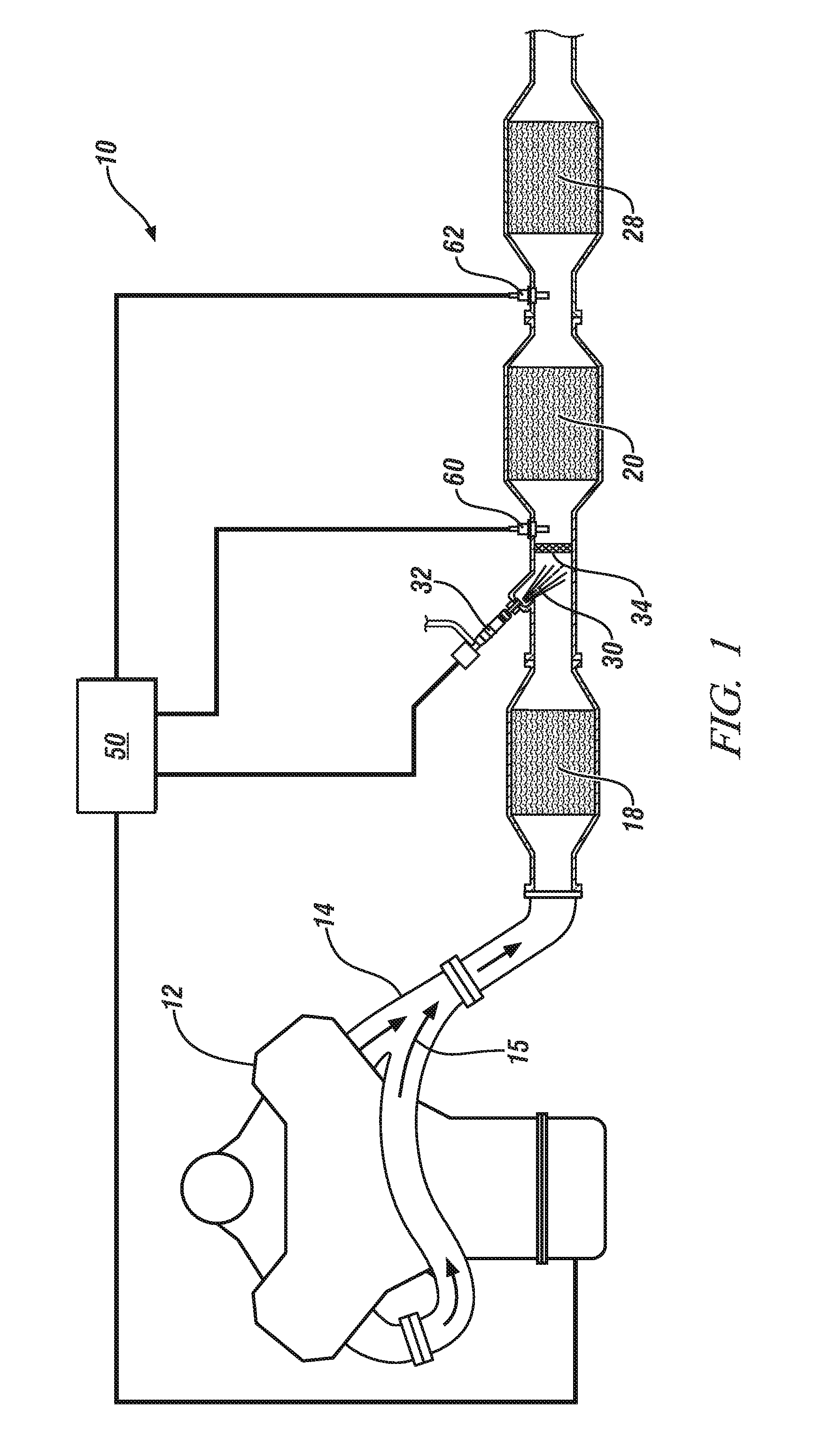
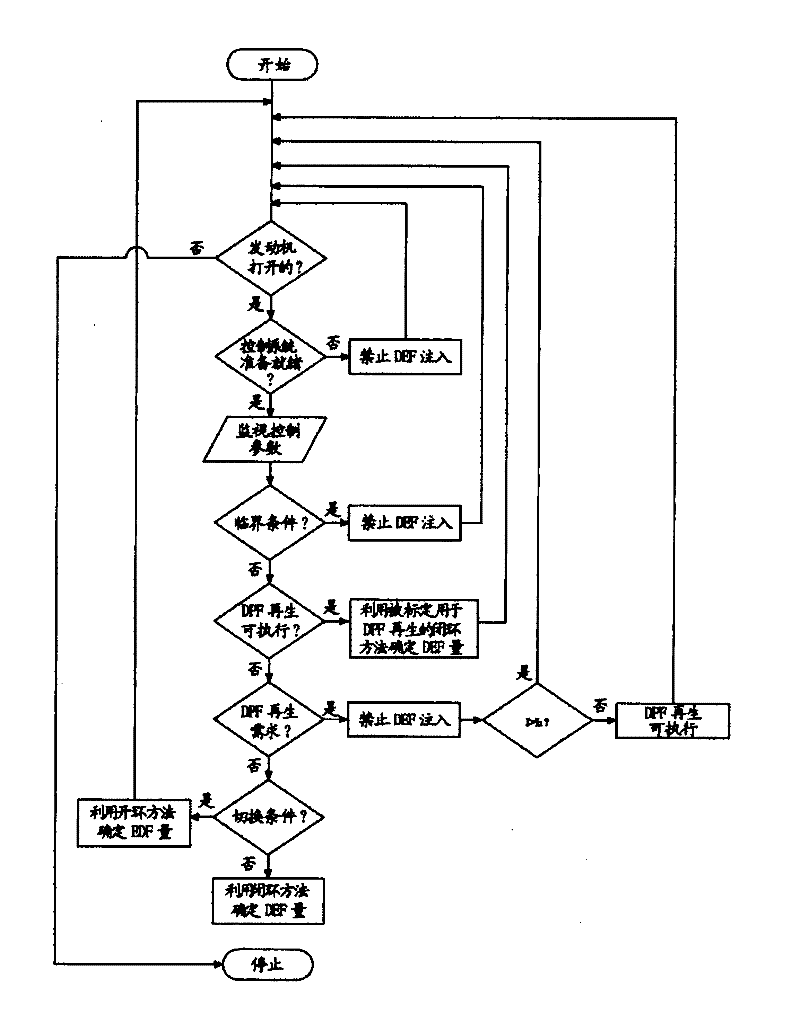
A method is provided for controlling injection of Diesel Exhaust Fluid into an exhaust pipe (30) of an internal combustion engine (10) equipped with a Selective Reduction Catalyst. The method includes, but is not limited to monitoring a value of a control parameter influencing an operation of the Selective Reduction Catalyst (33), injecting a quantity of Diesel Exhaust Fluid, controlling the quantity of Diesel Exhaust Fluid (QDEF) to be injected employing a closed loop procedure or an open loop procedure, switching between the closed loop procedure and the open loop procedure, when value of the control parameter crosses a first threshold value of the control parameter.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus and Method for DEF Tank Filling
InactiveUS20160167940A1Shorten the timeSpillage is eliminated or significantly decreasedExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusEngineeringDiesel exhaust fluid
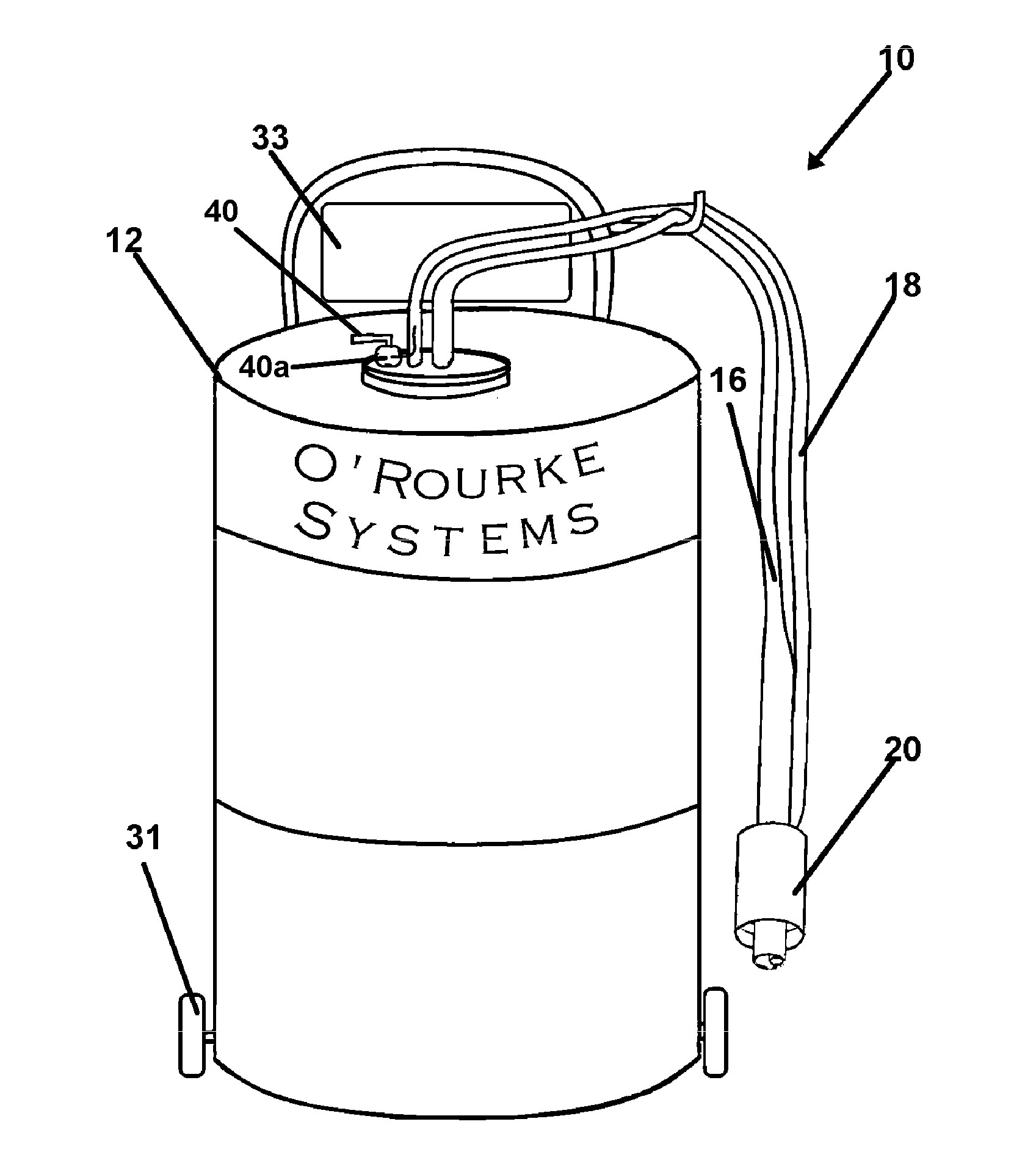
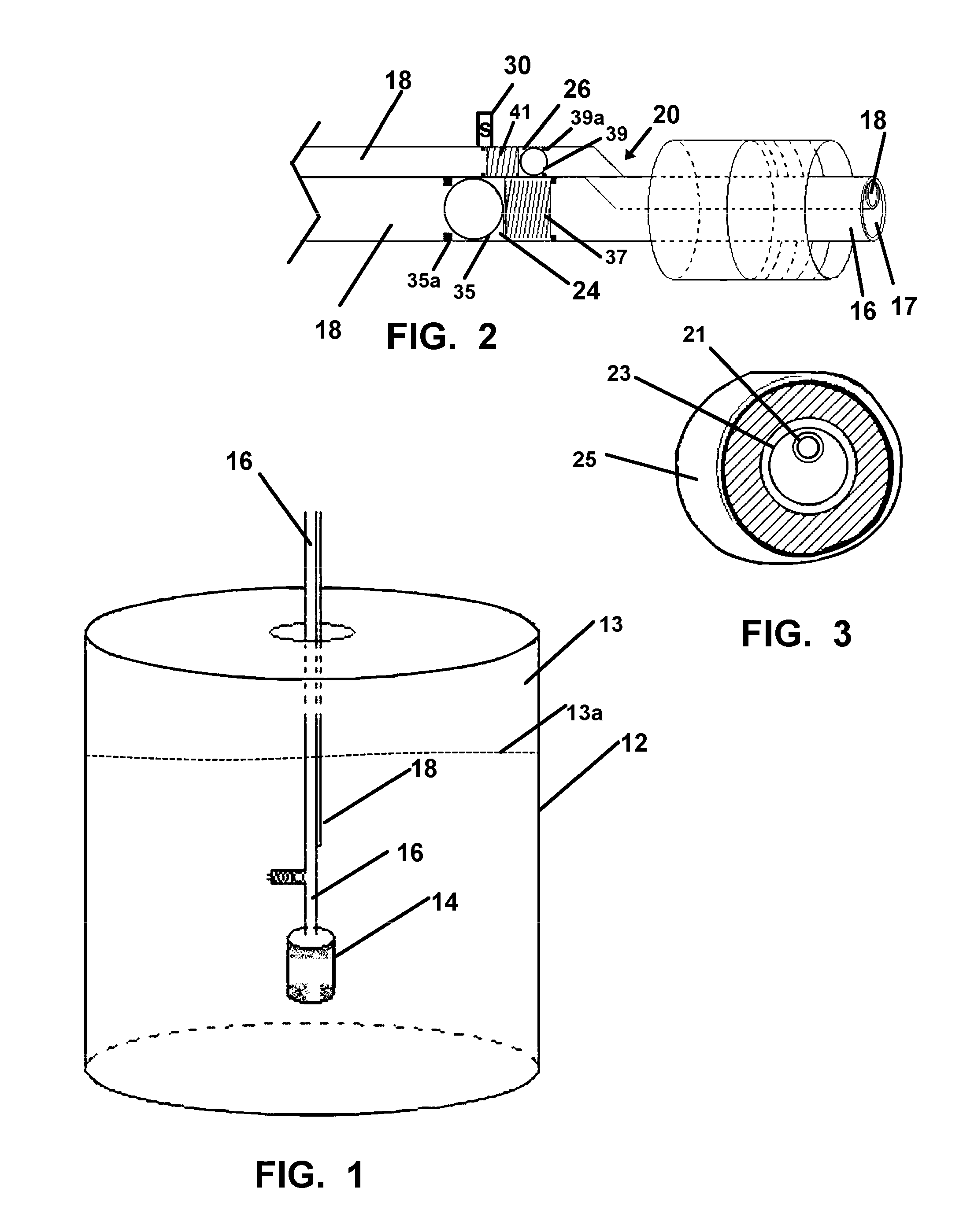
A refill device for a diesel exhaust fluid tank is provided which employs a nozzle connection to the fluid tank to provide replenishment of the exhaust fluid from a reservoir. Fluid from the reservoir is communicated to the fluid tank using a pump providing a pressurized fluid supply through a first hose. A second hose engaged with the nozzle vents air from the fluid tank for the duration of filling by the first hose.
Owner:OROURKE SEAN J
Diesel exhaust fluid tank breather assembly
ActiveUS20150159529A1Simplified and reliableAvoid passingSemi-permeable membranesMembranesBreatherExhaust fumes
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P
Vehicle relocatable exhaust system components
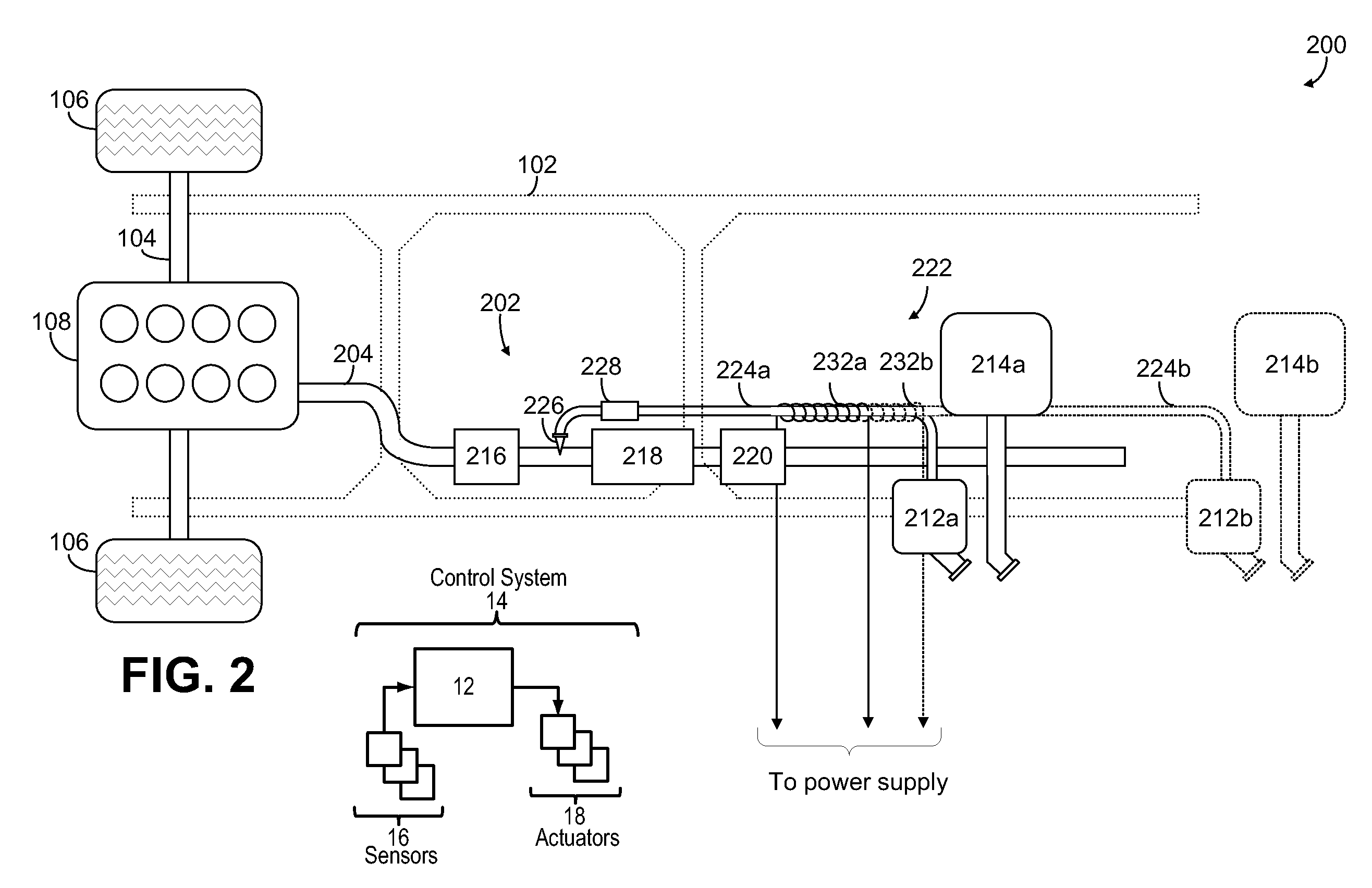
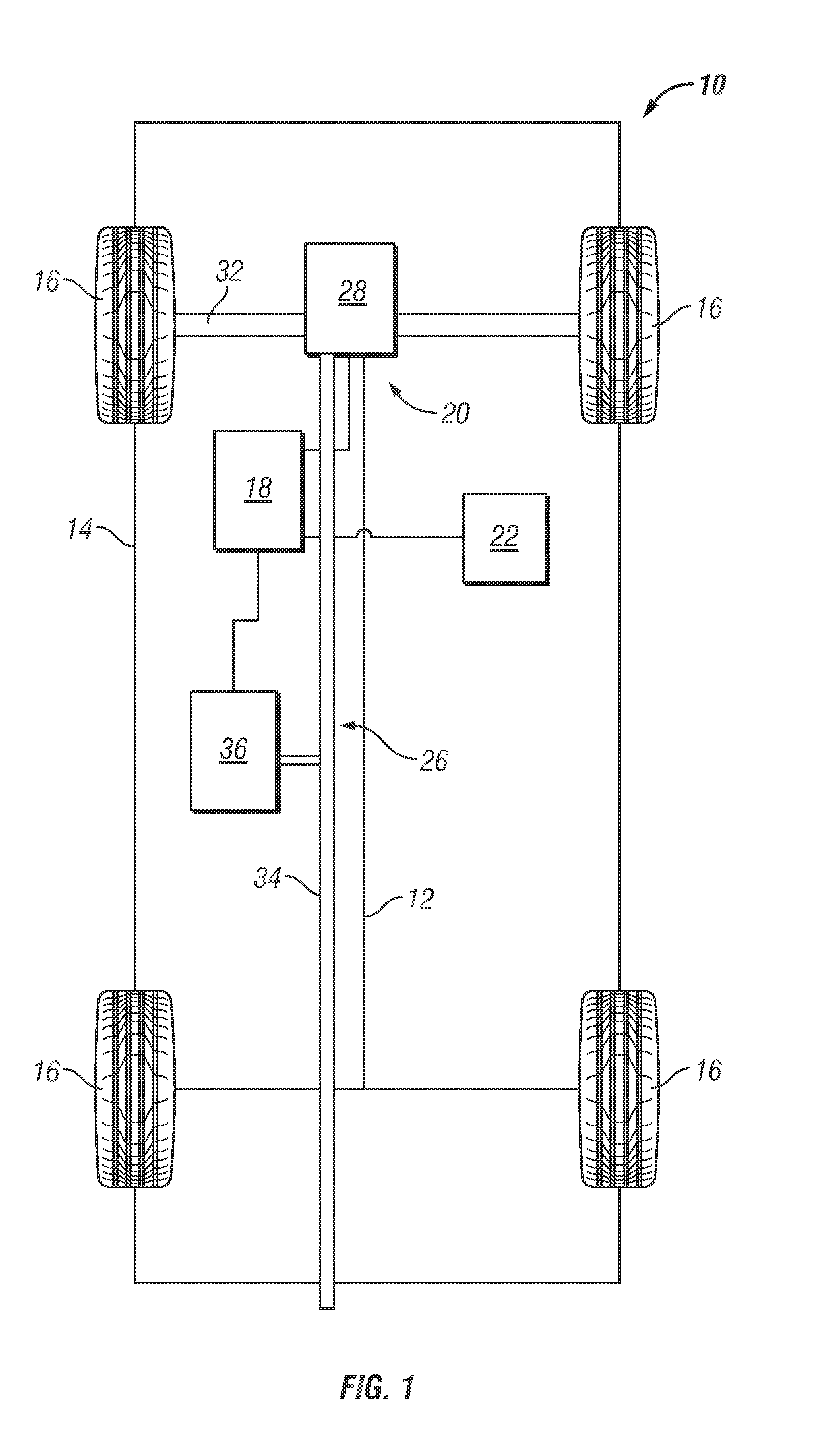
ActiveUS20110061373A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusControl systemDiesel exhaust fluid
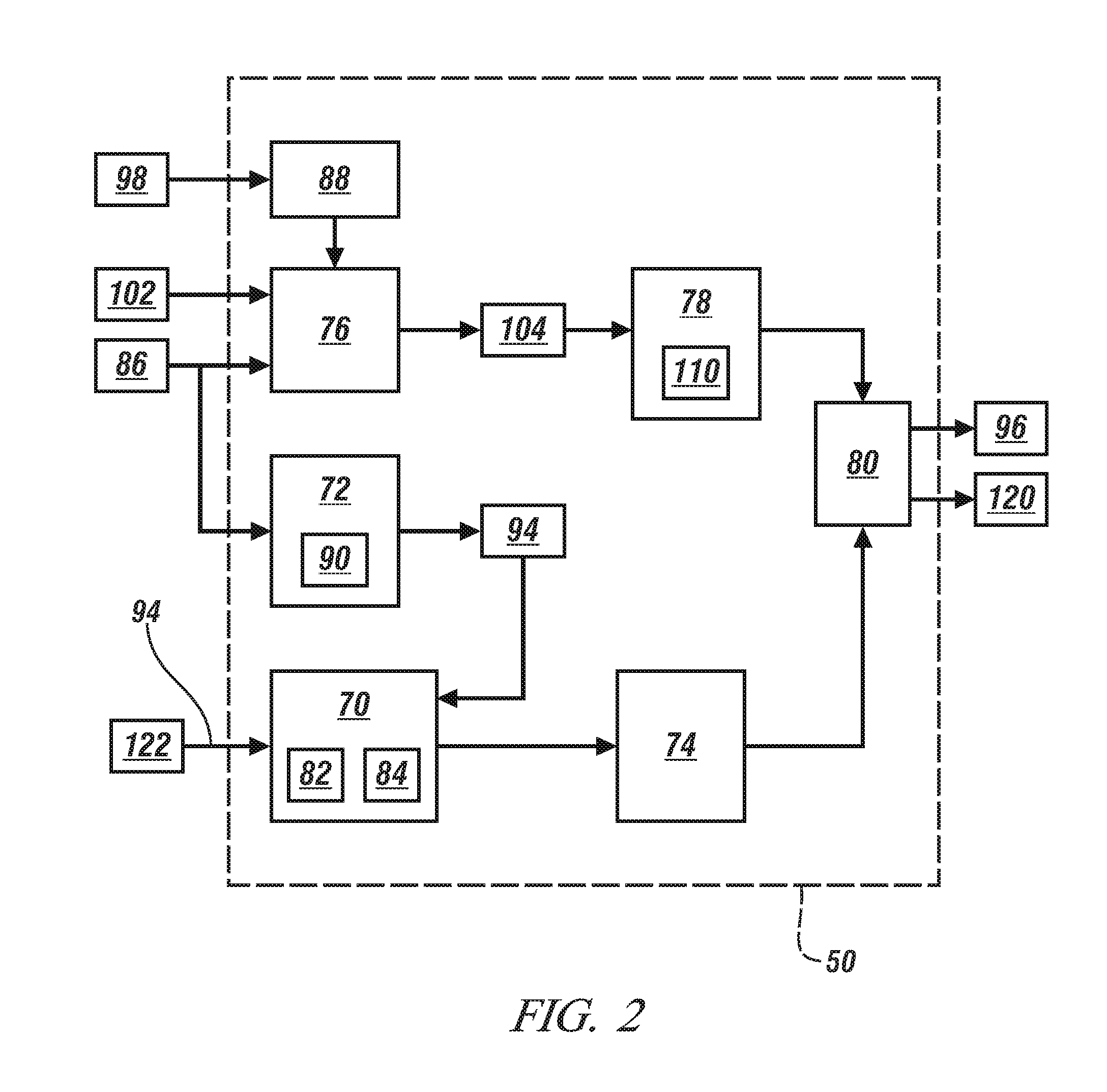
Modification of reductant (e.g., diesel exhaust fluid, DEF) tank location, for example during vehicle up-fitting may result in less than optimal operation of the DEF system due to inaccurate DEF system calibration. In one example approach, the above issue can be at least partially addressed by adjusting control system parameters for system control and diagnostics based on an input indicative of, or any modification to, the DEF tank location. In this way, DEF tank location flexibility is maintained, while also maintaining emission control and diagnostic accuracy.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust after-treatment system
PendingCN108779694AReduce gasInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle separationDieselingProcess engineering
An after-treatment system (200) includes, in series along an exhaust gas flow direction through the after-treatment system (200): a diesel oxidation catalyst (108)), a diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) delivery device, a soot- reducing device and a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Diesel exhaust fluid system having a reservoir spacer
InactiveUS8523018B2Internal combustion piston enginesDomestic cooling apparatusEngineeringDiesel exhaust fluid
Diesel exhaust fluid systems are provided. The diesel exhaust fluid systems include a fluid reservoir having an inner surface and an opening therethrough, a fluid reservoir heating device positioned within the fluid reservoir, and a fluid reservoir spacer positioned within the fluid reservoir and between the inner surface of the fluid reservoir and the fluid reservoir heating device. The fluid reservoir spacer includes first and second portions on opposing sides of the opening through the fluid reservoir.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
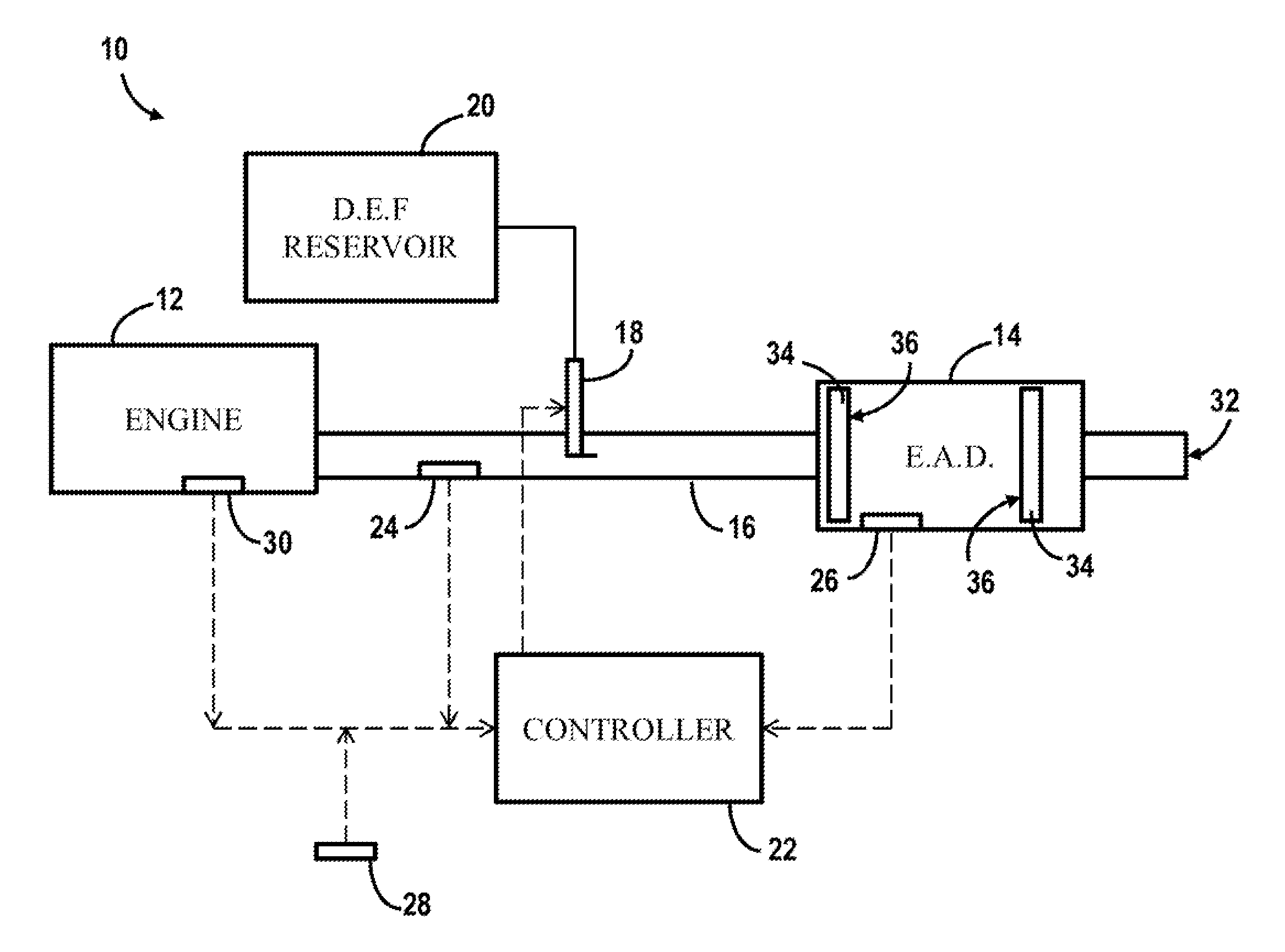
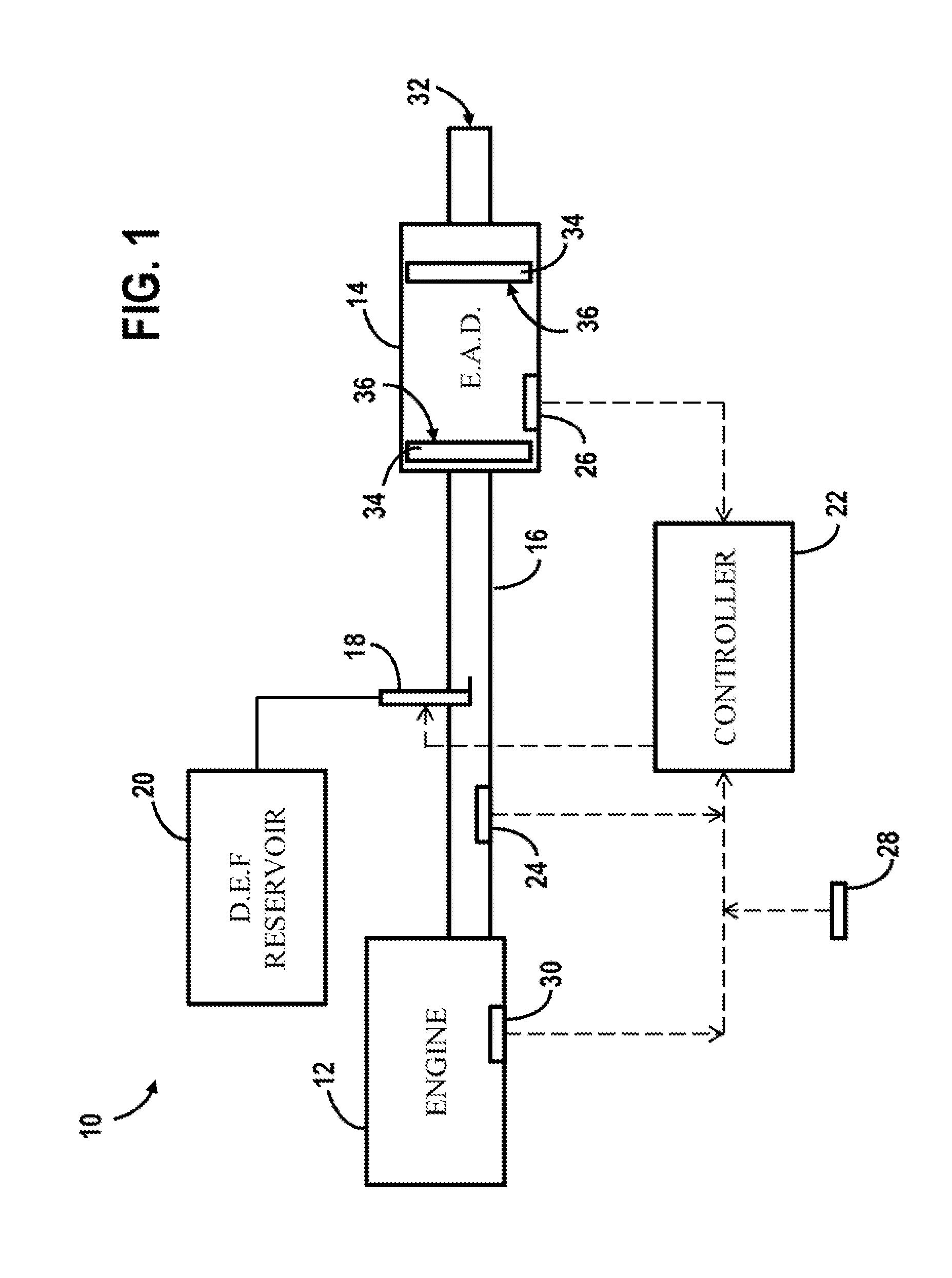
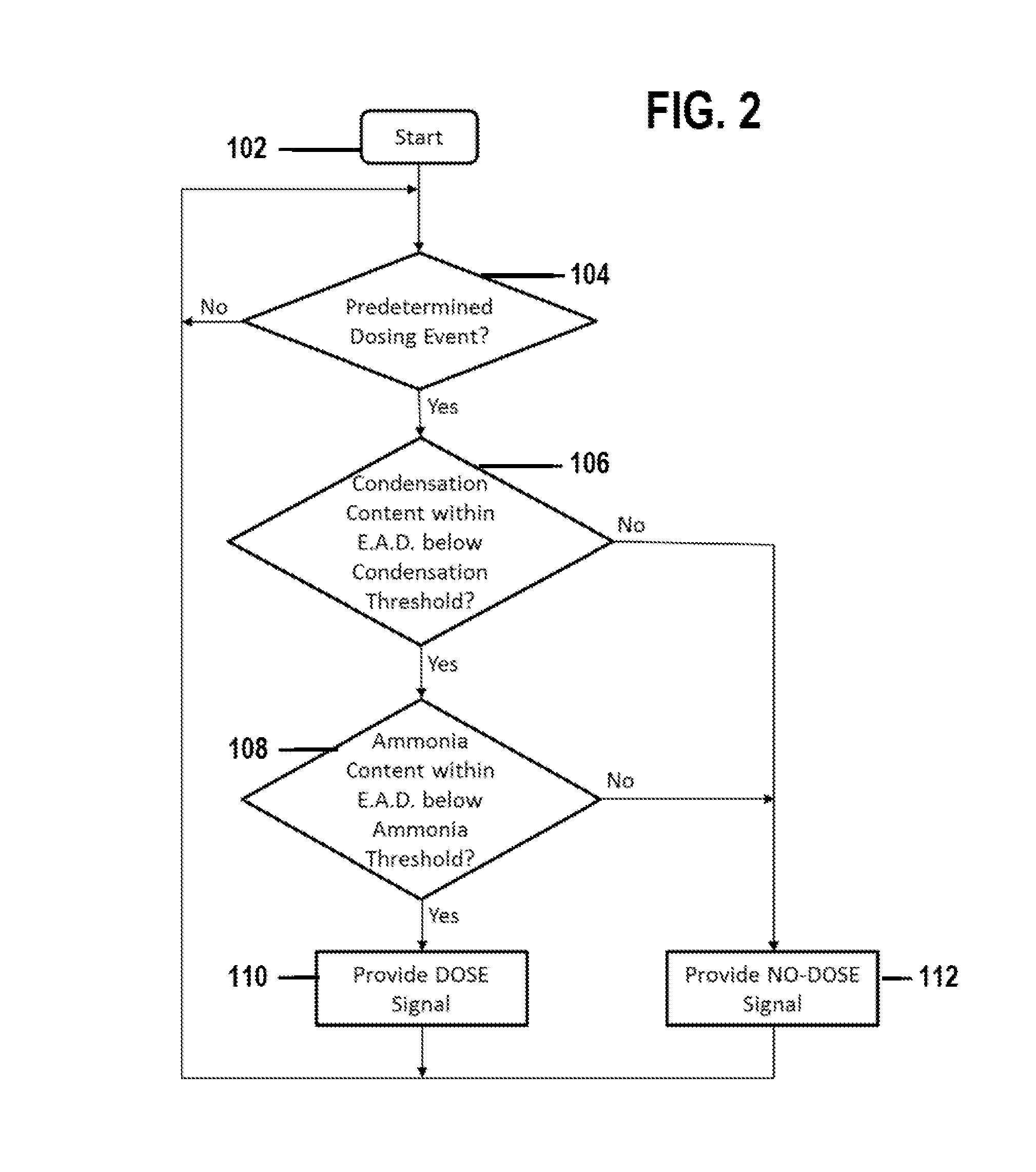
Diesel exhaust system and method for controlling exhaust fluid dosing
ActiveUS20160194996A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusWater coolingDiesel exhaust fluid
A method for controlling dosing of a diesel exhaust fluid includes providing a diesel engine and an exhaust system. The exhaust system includes an exhaust aftertreatment device and is coupled to the diesel engine. An injection device is provided in the exhaust system for dosing the diesel exhaust fluid into the exhaust system according to a predetermined routine. A water condensation content of the exhaust aftertreatment device is determined. A dosing event, directed by the predetermined routine, is precluded so that the injection device is not operated to provide diesel exhaust fluid to the exhaust aftertreatment device when the water condensation content of the exhaust aftertreatment device is determined to be above a specified threshold value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP +1
System, apparatus, and method to address unwanted def-based deposits in diesel exhaust system
ActiveUS20170292430A1Increase heightImprove heat transfer performanceGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesEvaporationDiesel exhaust fluid
An exhaust system for a diesel engine is provided. The exhaust system includes a component body with a surface, and a surface treatment disposed on some of the surface or all of the surface. The surface treatment is disposed so as to receive Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injected into the exhaust system during operation of the diesel engine. The surface treatment facilitates increased heat transfer to the received DEF to promote water evaporation and urea thermolysis of the received DEF.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
System, apparatus, and method to address unwanted DEF-based deposits in diesel exhaust system
ActiveUS9890682B2Improve heat transfer performanceSimple structureGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesEvaporationDiesel exhaust fluid
An exhaust system for a diesel engine is provided. The exhaust system includes a component body with a surface, and a surface treatment disposed on some of the surface or all of the surface. The surface treatment is disposed so as to receive Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injected into the exhaust system during operation of the diesel engine. The surface treatment facilitates increased heat transfer to the received DEF to promote water evaporation and urea thermolysis of the received DEF.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
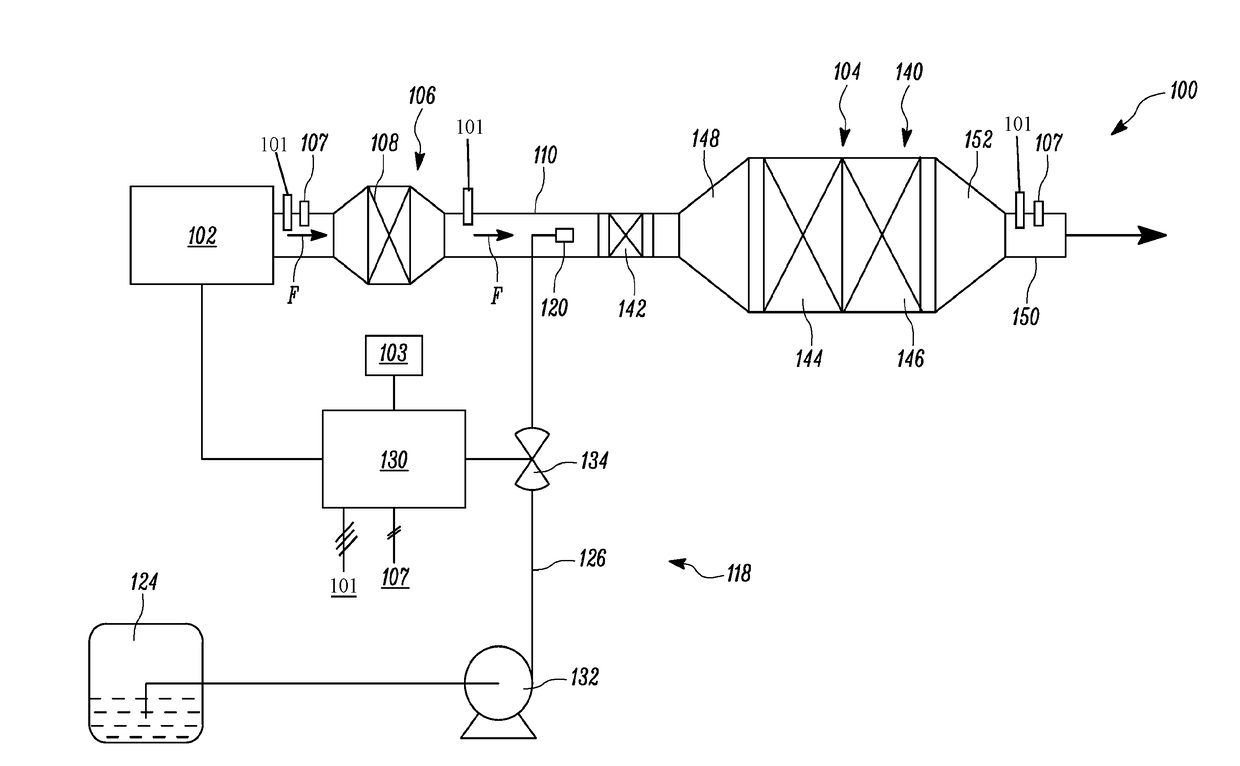
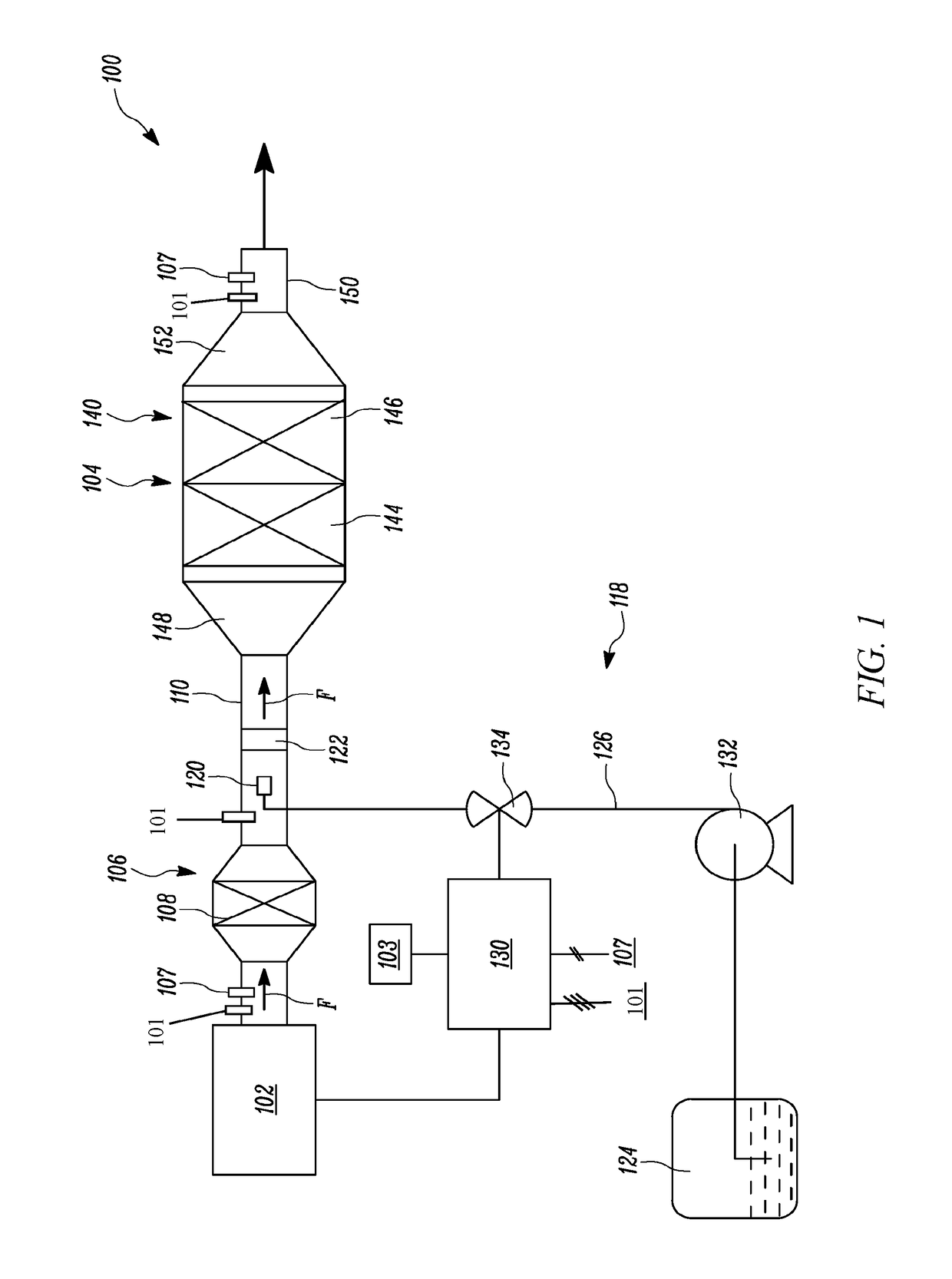
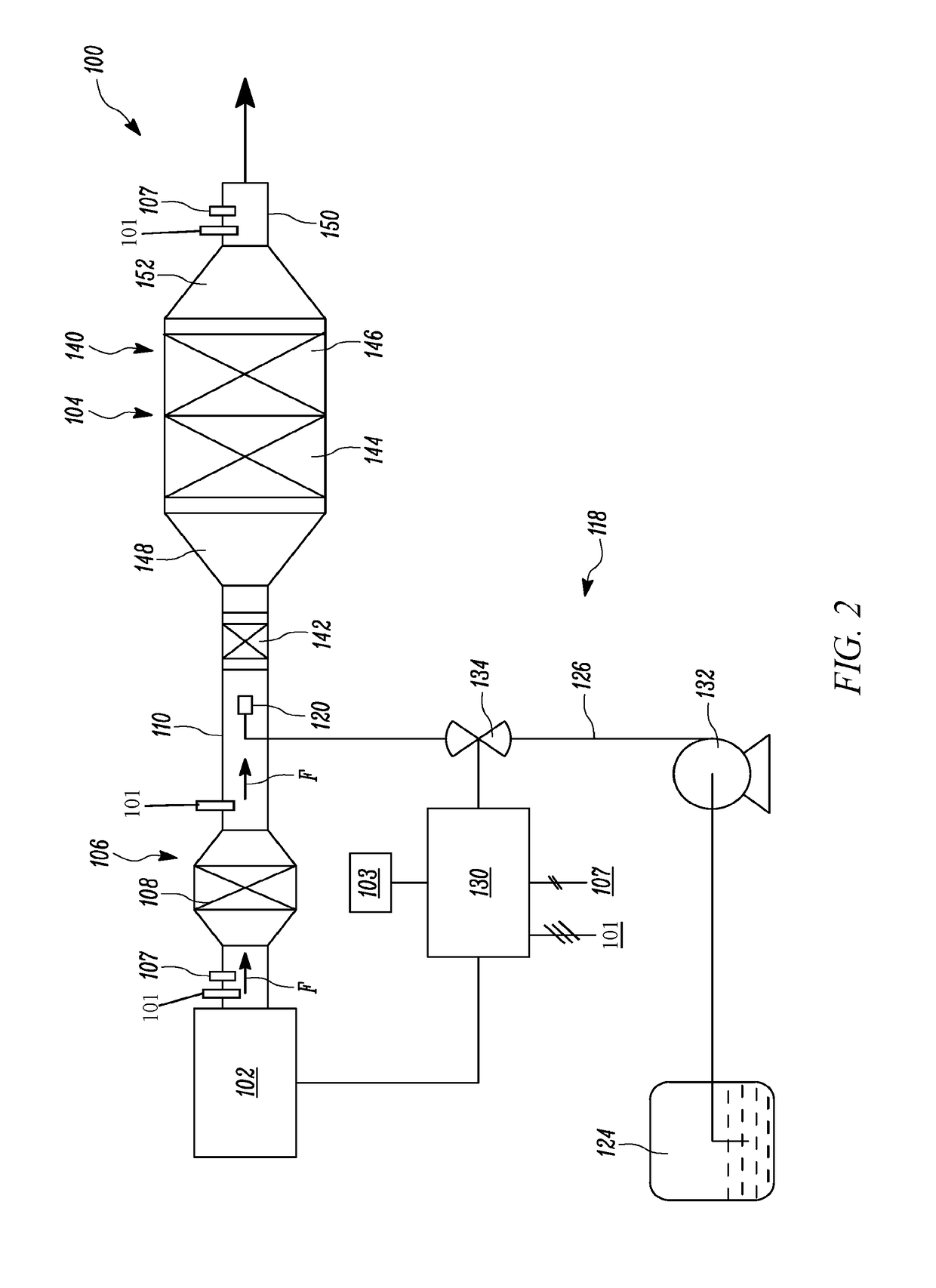
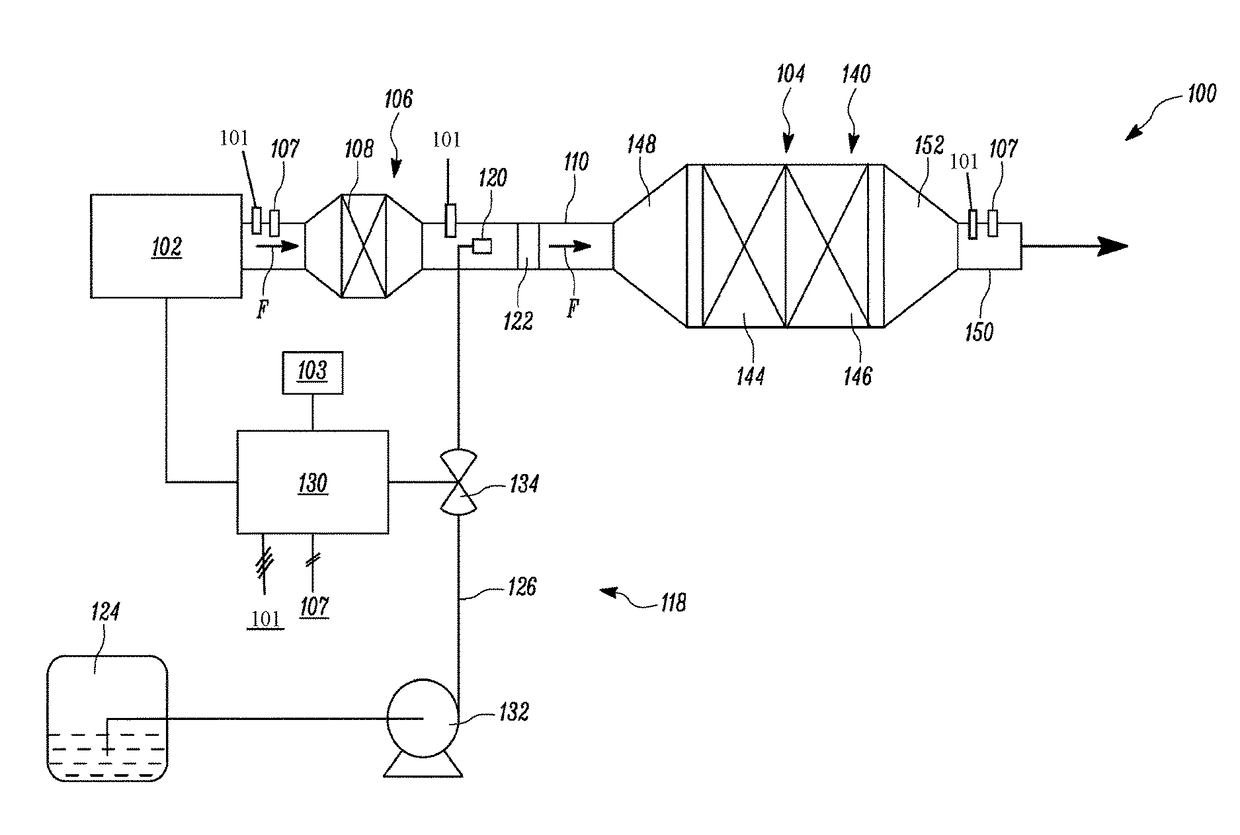
System and Method for Injector Fault Remediation
A machine includes an engine having an exhaust system. A diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) injector provides metered amounts of DEF and includes a valve adapted to selectively open in response to a command. A controller associated with the engine and the DEF injector monitors operation of the DEF injector to detect a fault and activates a failure remediation cycle when the fault has been detected. The remediation cycle includes heating the exhaust gas to heat the DEF injector and melt any urea crystals that may be causing the fault, and activating the valve of the DEF injector to evacuate molten urea from within the DEF injector.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
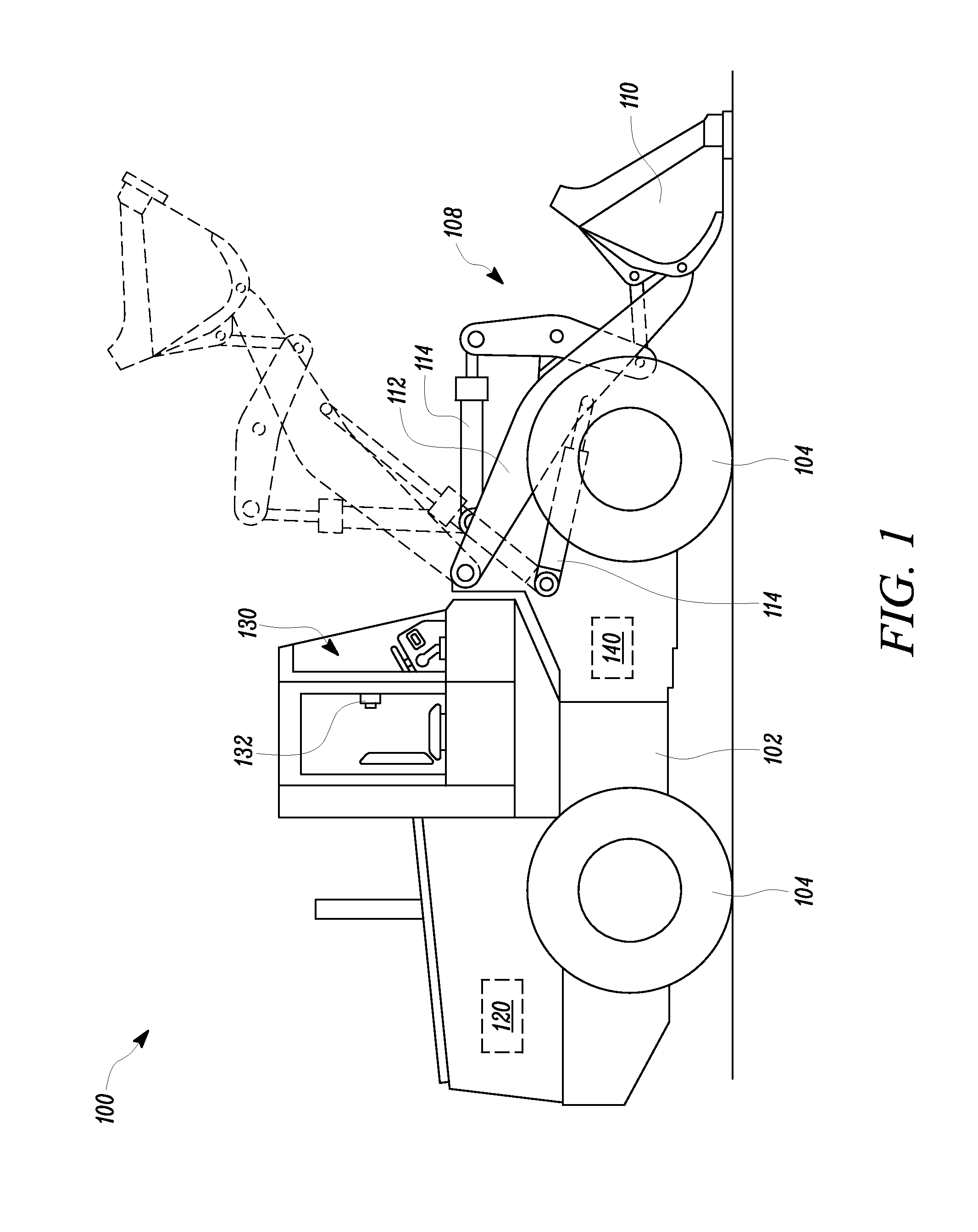
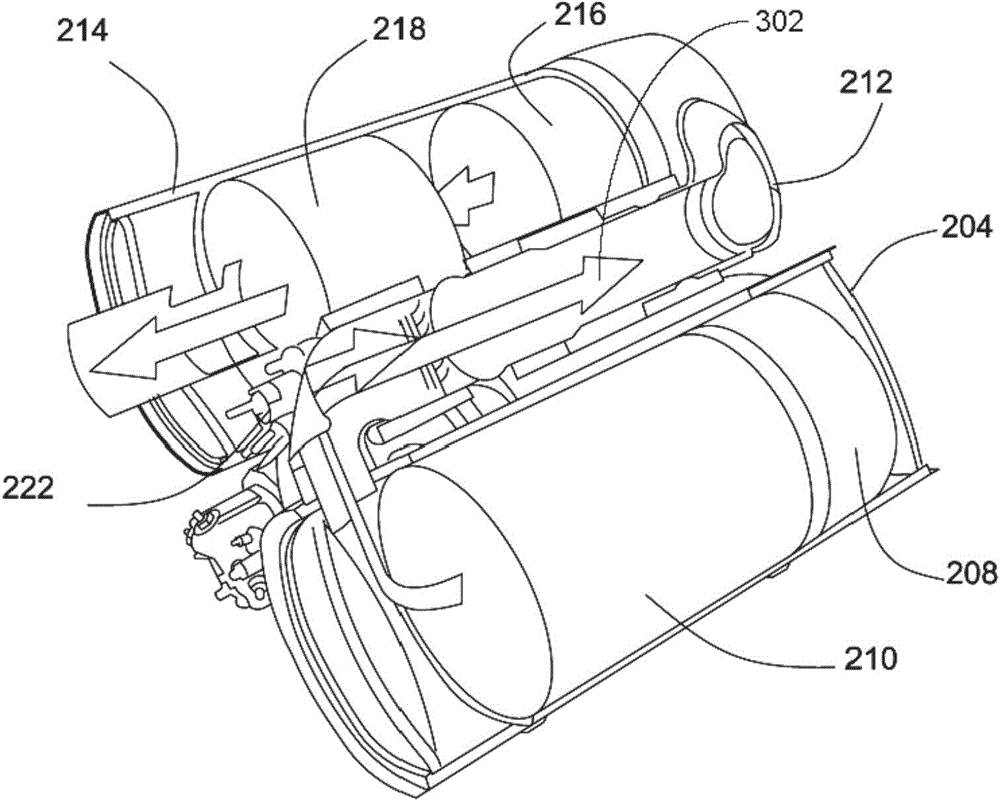
Exhaust system for an agricultural vehicle
An exhaust system for an agricultural vehicle is provided that includes a mixer configured to receive a spray of diesel exhaust fluid along a longitudinal axis of the mixer and an exhaust flow along a direction cross-wise to the longitudinal axis of the mixer. Additionally, the mixer is configured to mix the diesel exhaust fluid with the exhaust gas. Furthermore, the mixer is configured to discharge the exhaust gas along the longitudinal axis of the mixer.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP +2
Method and system for detecting malfunctioning of fluid tank of machine
A method is disclosed for detecting a malfunctioning of a tank containing fluid, using a processor and a level sensor. The processor calculates a rate of consumption of the fluid in the tank. The processor further calculates an estimated change in level of the fluid in the tank based on the rate of consumption of the fluid. The level sensor determines a measured change in level of the fluid in the tank. The processor compares the estimated change in level of the fluid with the measured change in level of the fluid. The processor further determines the malfunctioning of the tank if a difference between the estimated change in level of the fluid and the measured change in level of the fluid exceeds a predetermined value. The fluid contained in the tank is a diesel exhaust fluid.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com