Patents
Literature
40 results about "Fault mitigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
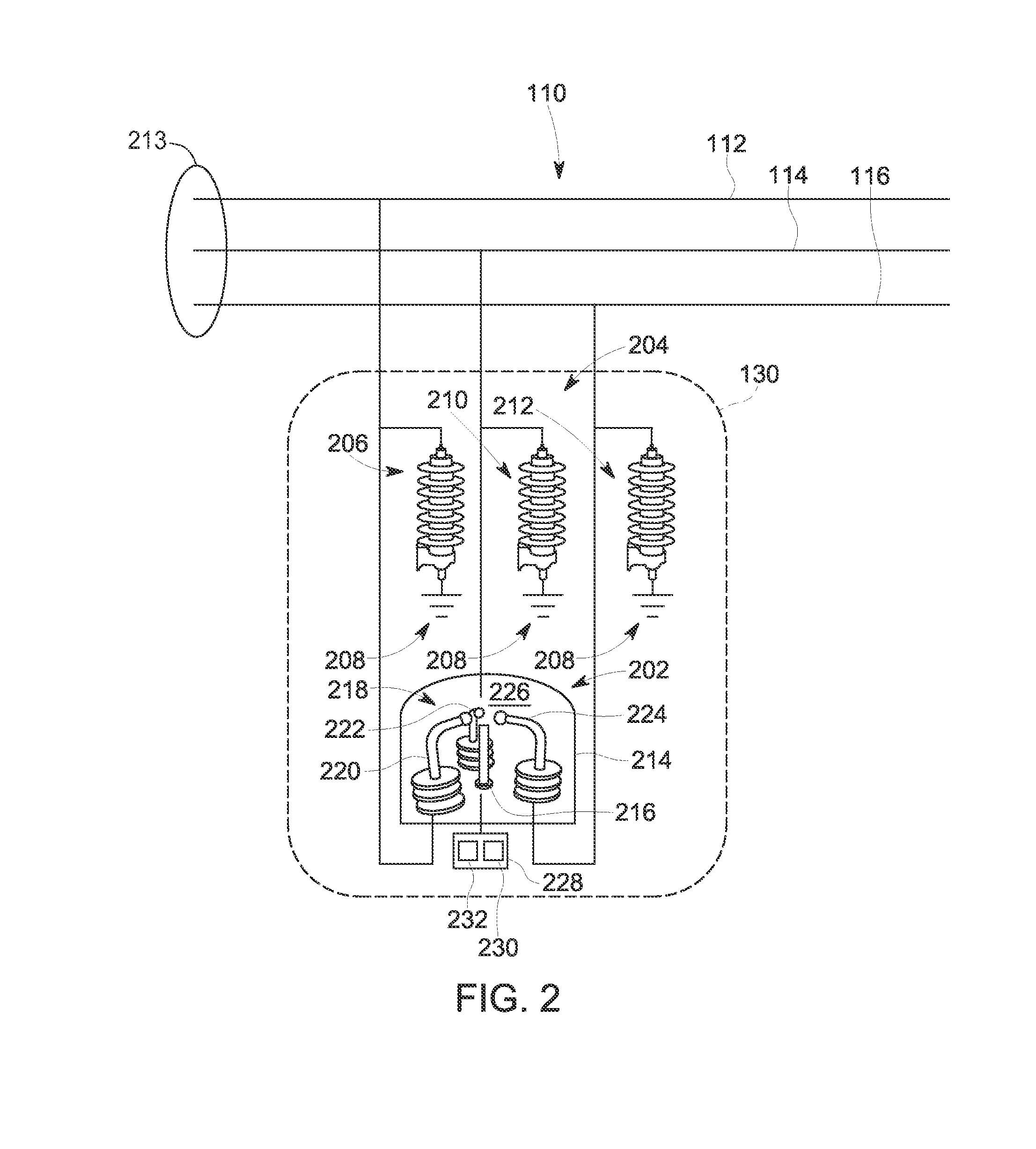
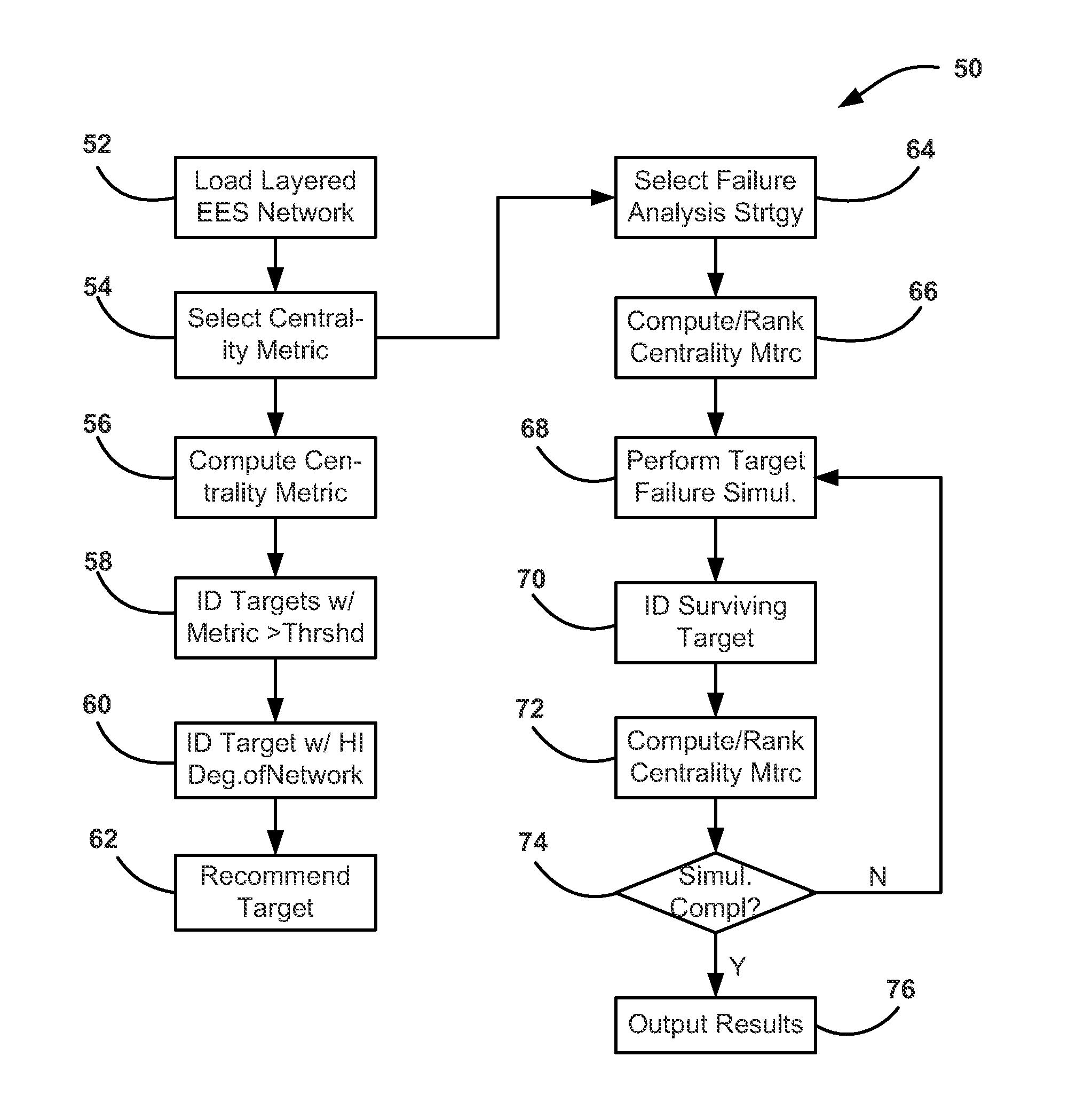
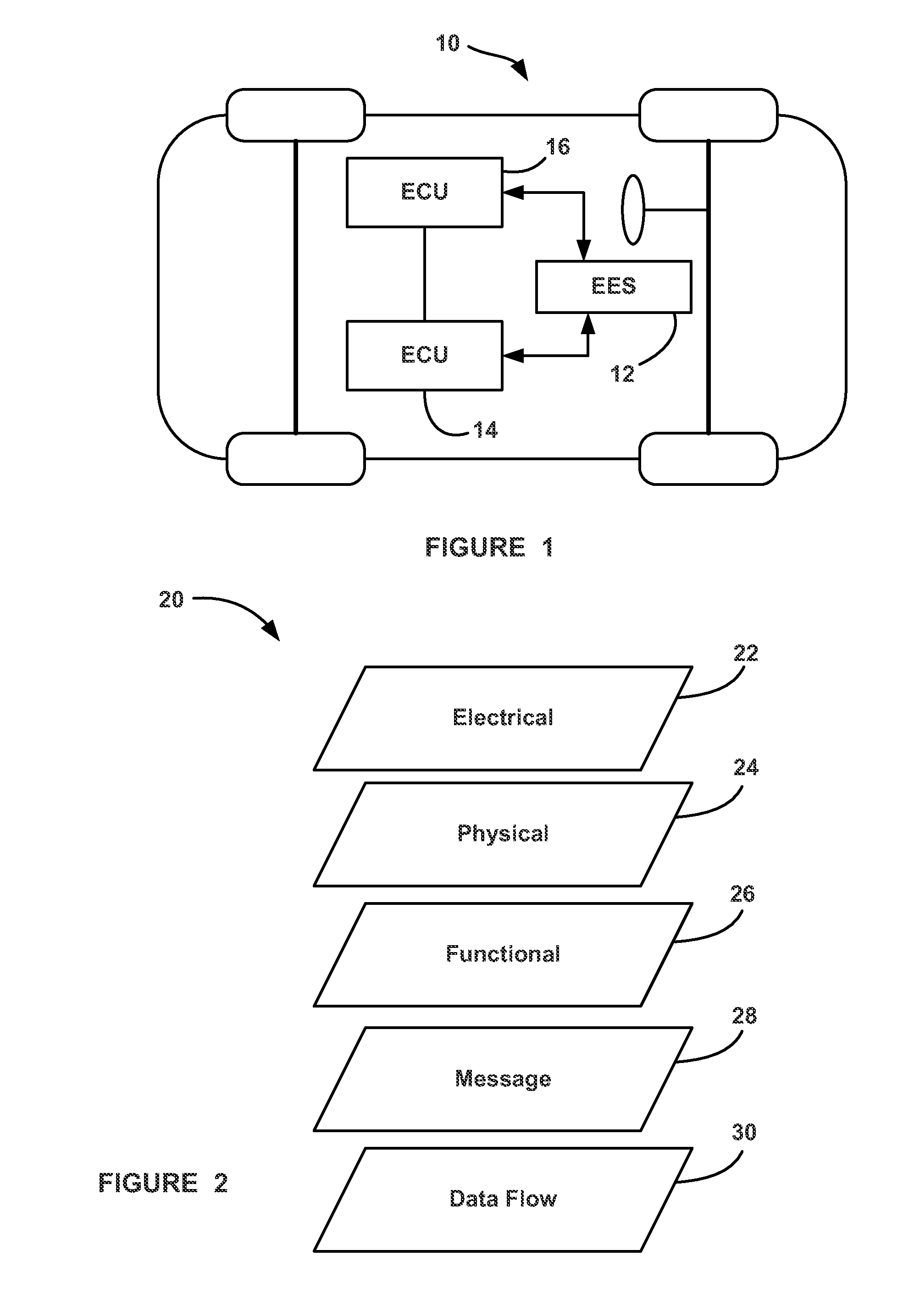
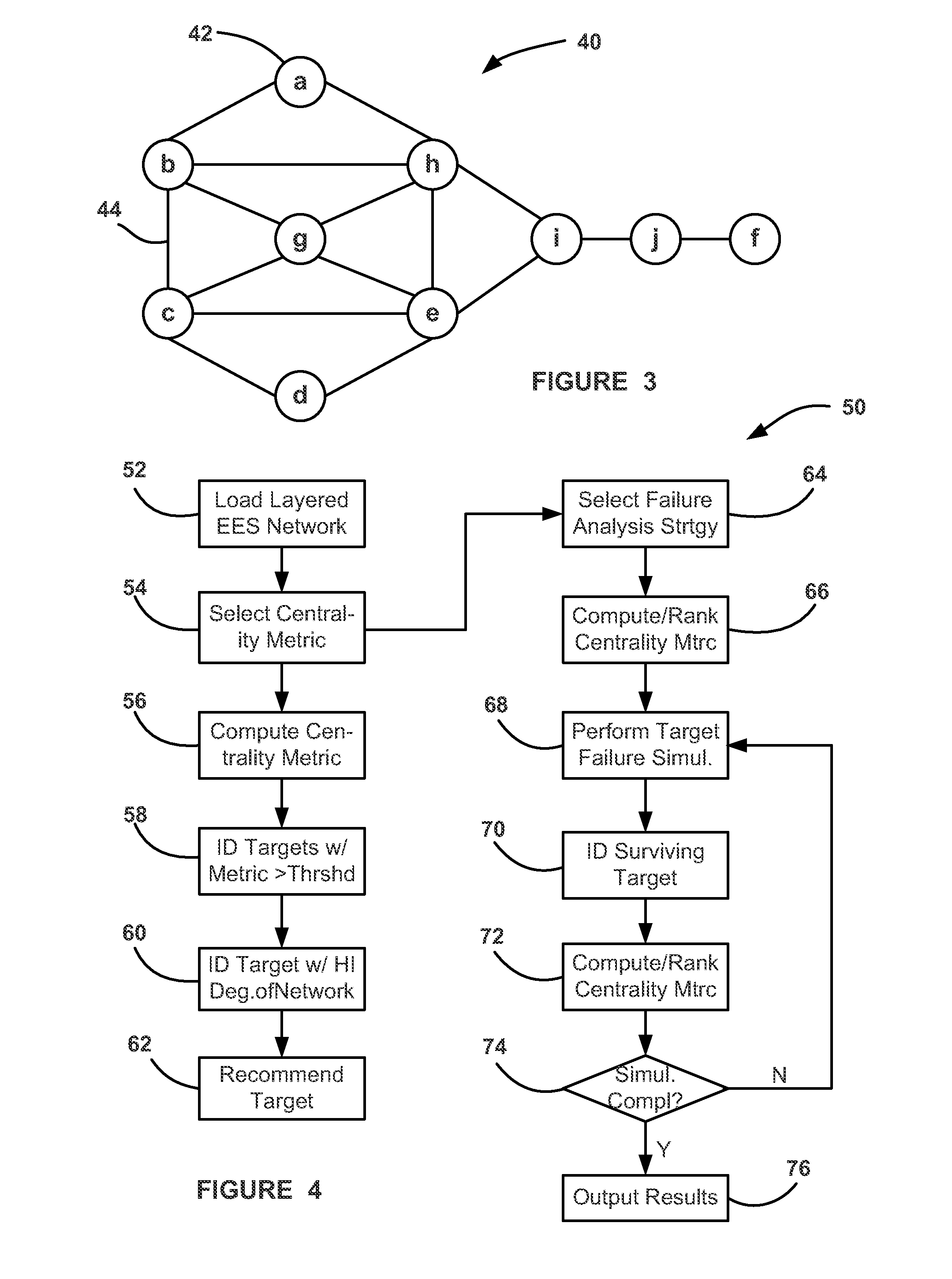
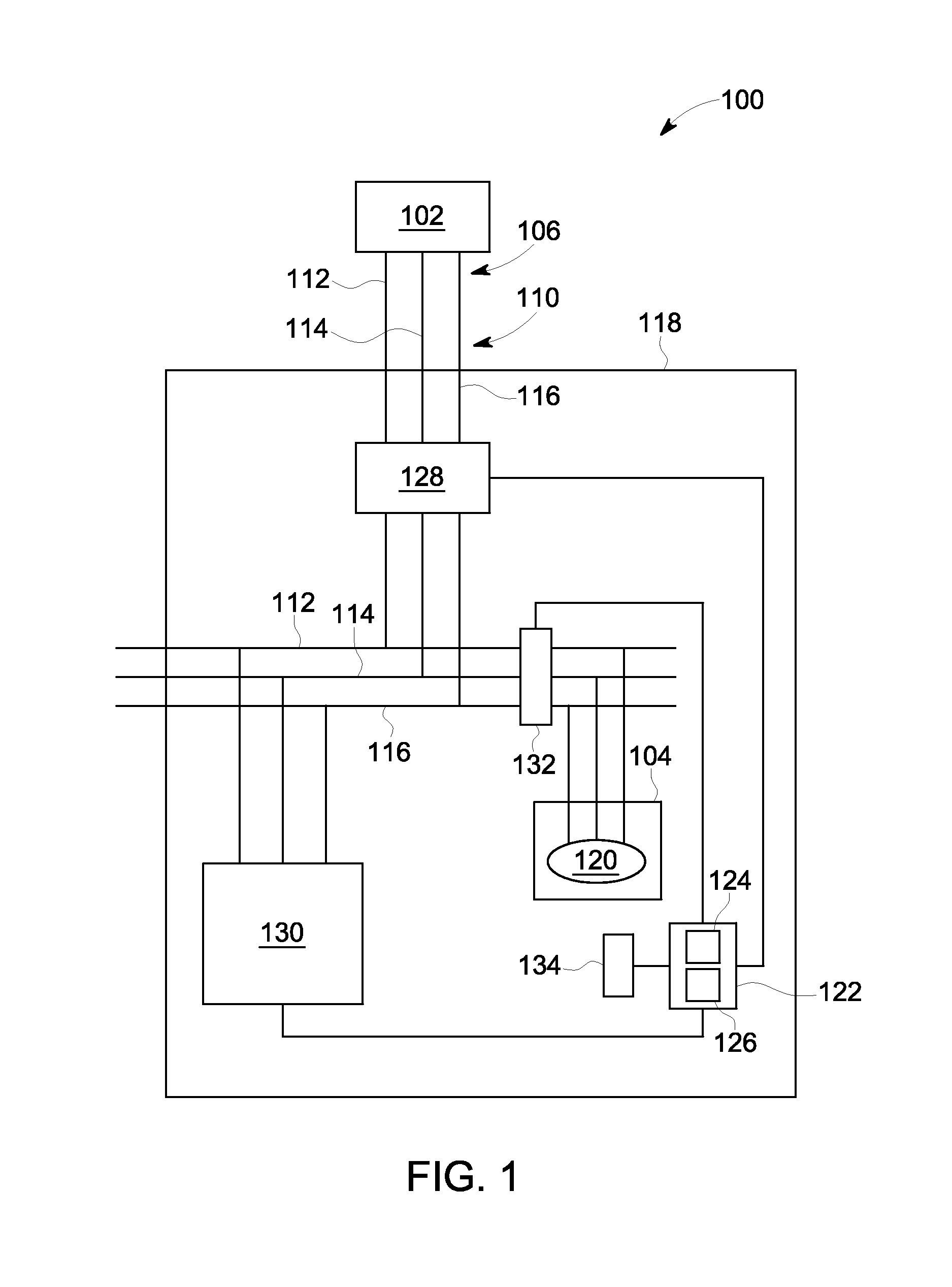
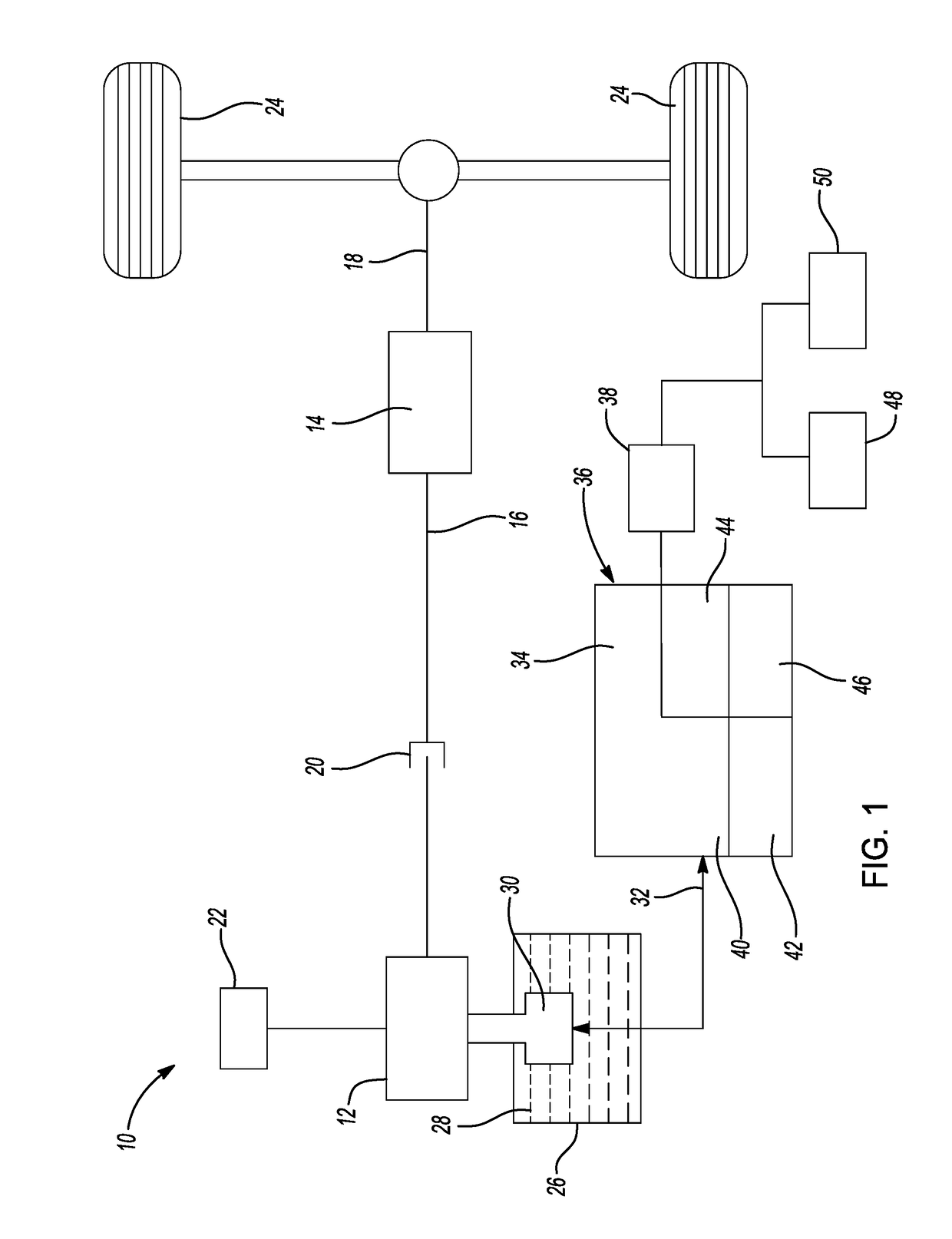
System and methods for fault-isolation and fault-mitigation based on network modeling
ActiveUS20120303348A1Error detection/correctionTesting/monitoring control systemsElectronic systemsNetwork model
A system and method for identifying a monitoring point in an electrical and electronic system (EES) in a vehicle. The method includes defining a network model of the EES where potential monitoring point locations in the model are identified as targets, such as nodes. The method then computes a betweenness centrality metric for each target in the model as a summation of a ratio of a total number of shortest paths between each pair of targets and a number of shortest paths that pass through the target whose betweenness centrality metric is being determined. The method identifies which of the betweenness centrality metrics are greater than a threshold that defines a minimum acceptable metric and determines which of those targets meets a predetermined model coverage. The monitoring point is selected as the target that best satisfies the minimum metric and the desired coverage.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
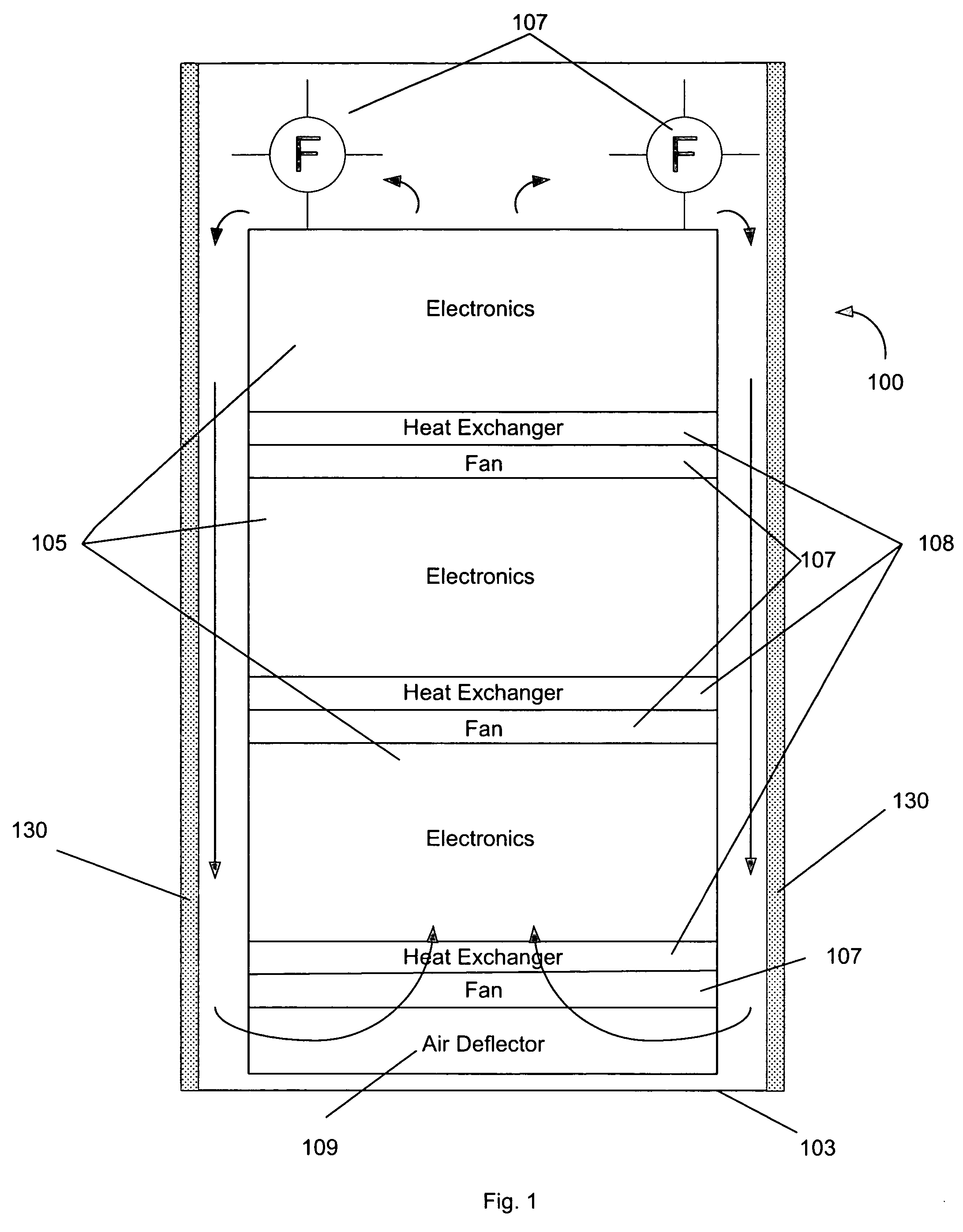
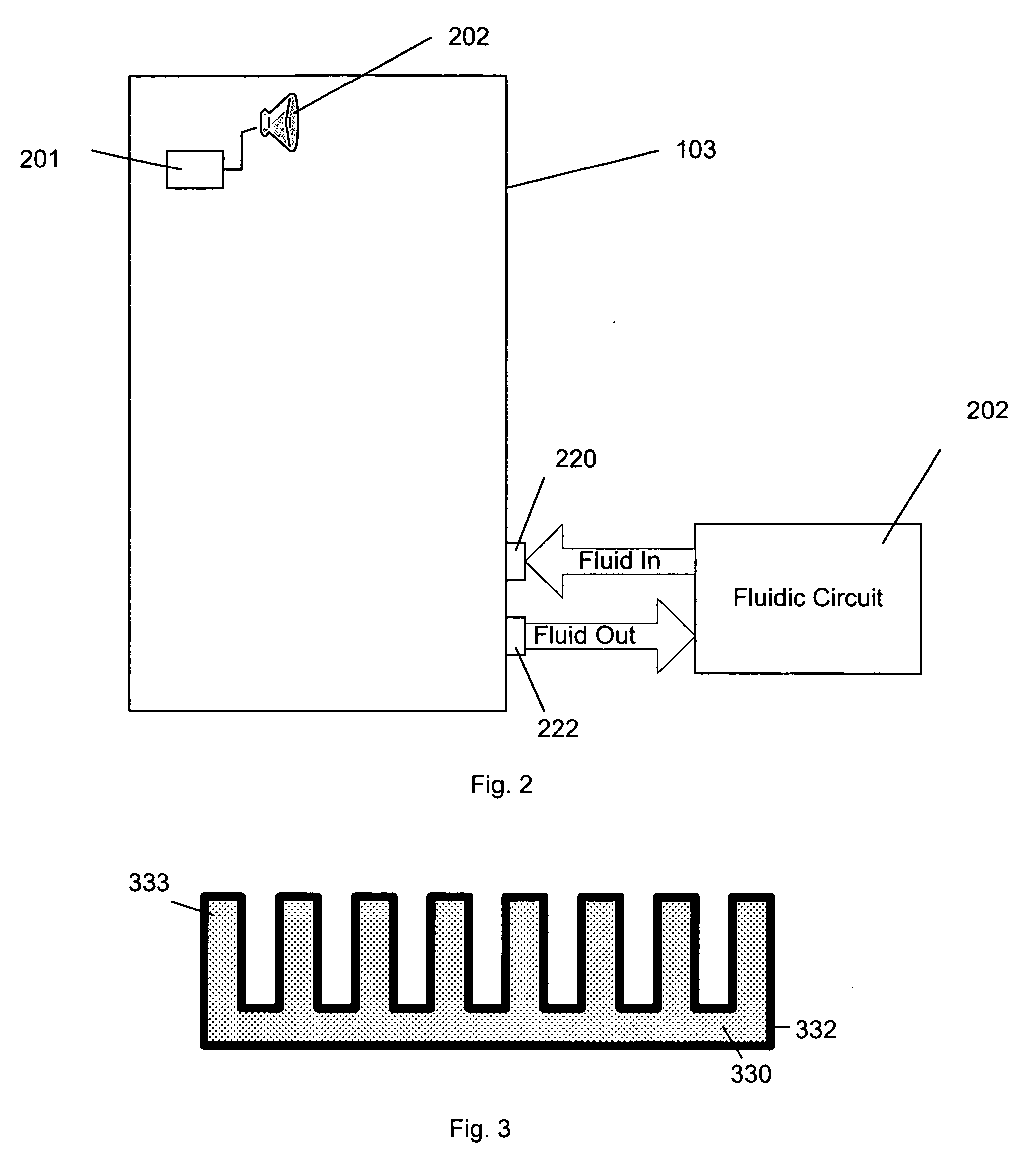
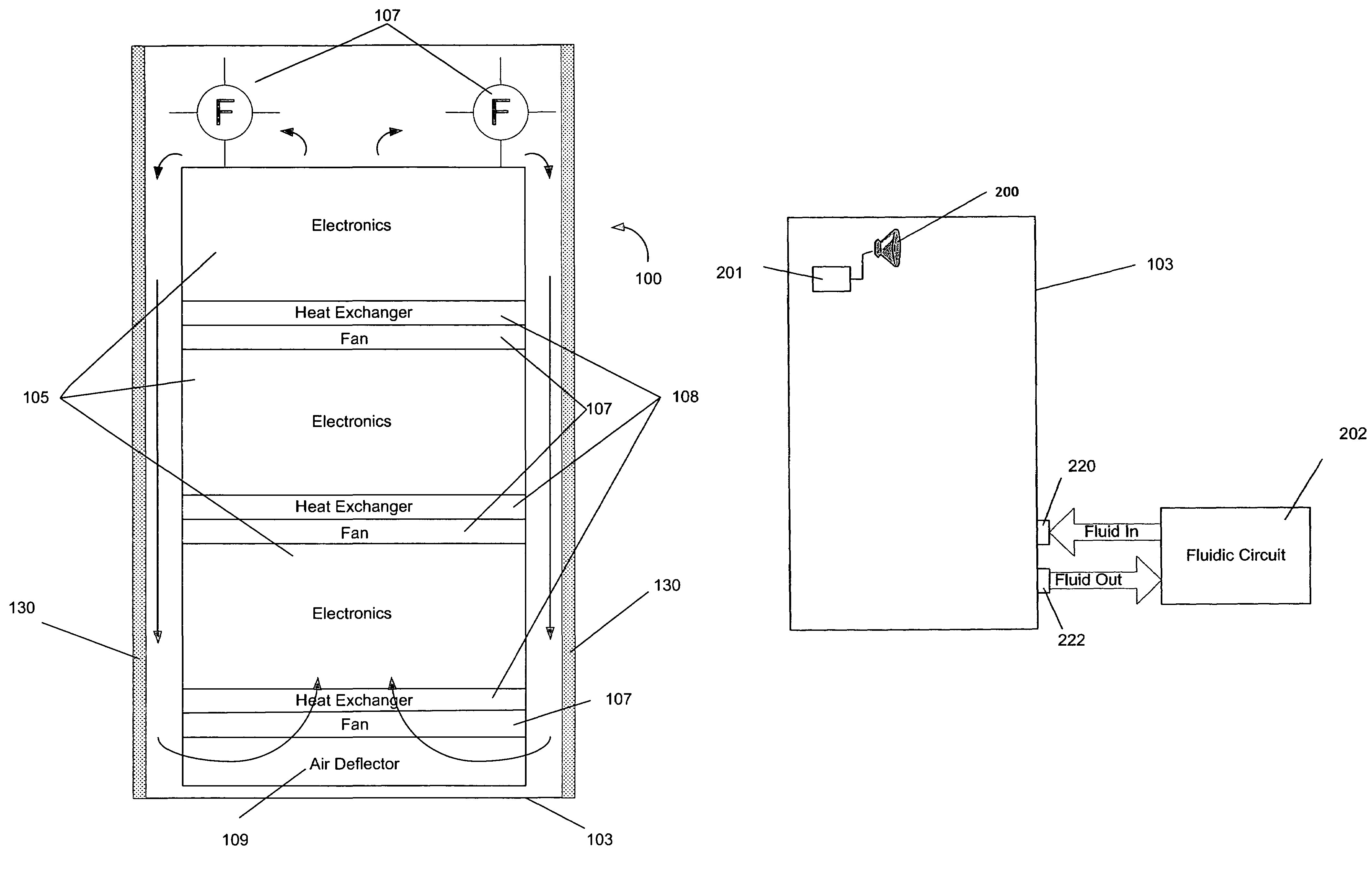
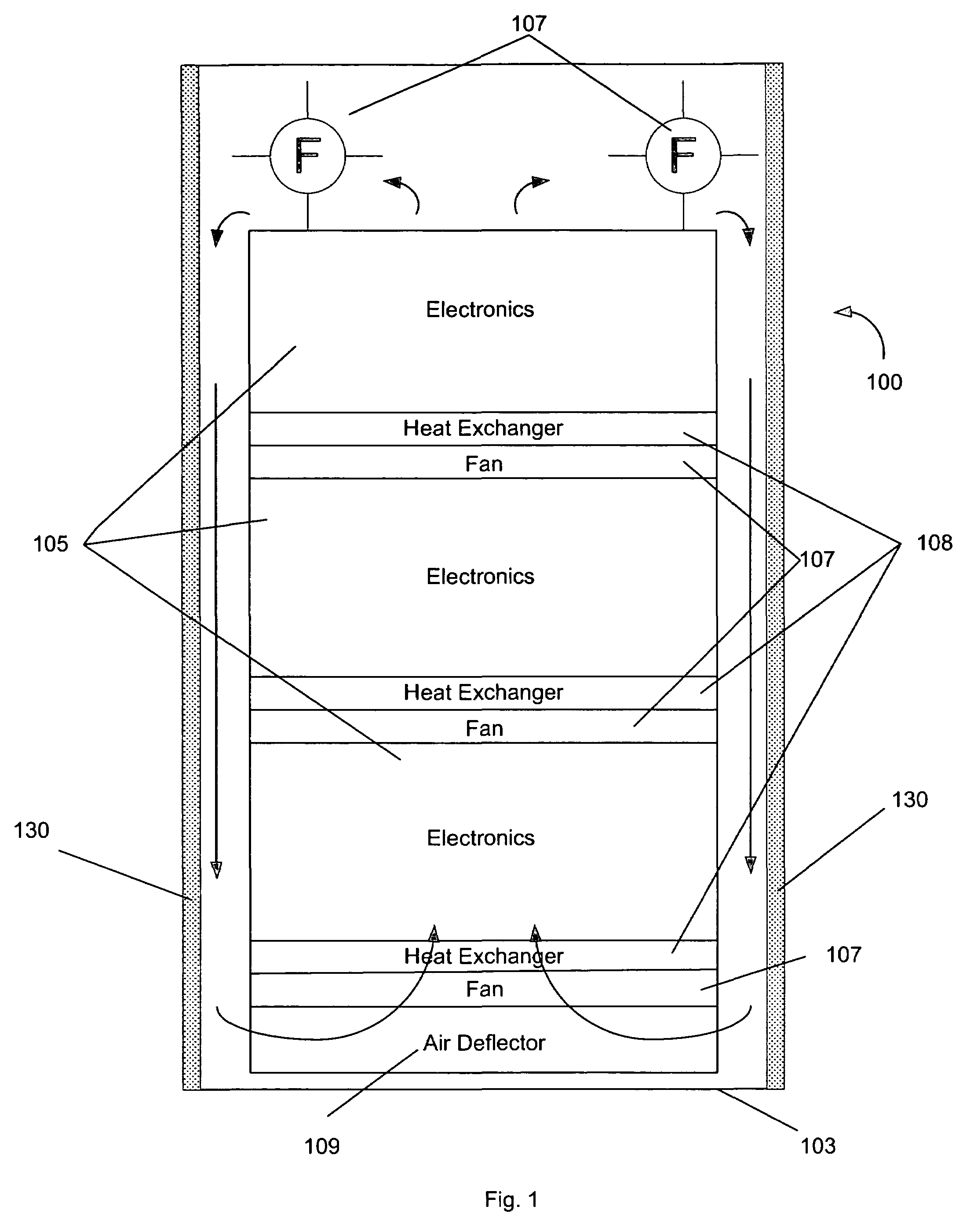
Cooling failure mitigation for an electronics enclosure
ActiveUS20050174733A1Digital data processing detailsIndirect heat exchangersElectronic componentPhase-change material
A system for permitting orderly shutdown of electronic components. The system includes an enclosure populated with one or more electronic components. A fan positioned within the enclosure generates an airflow across the one or more electronic components, the airflow being cooled by a heat exchanger. A phase change material is positioned within the enclosure to absorb heat from the airflow in the event of a failure associated with the heat exchanger.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
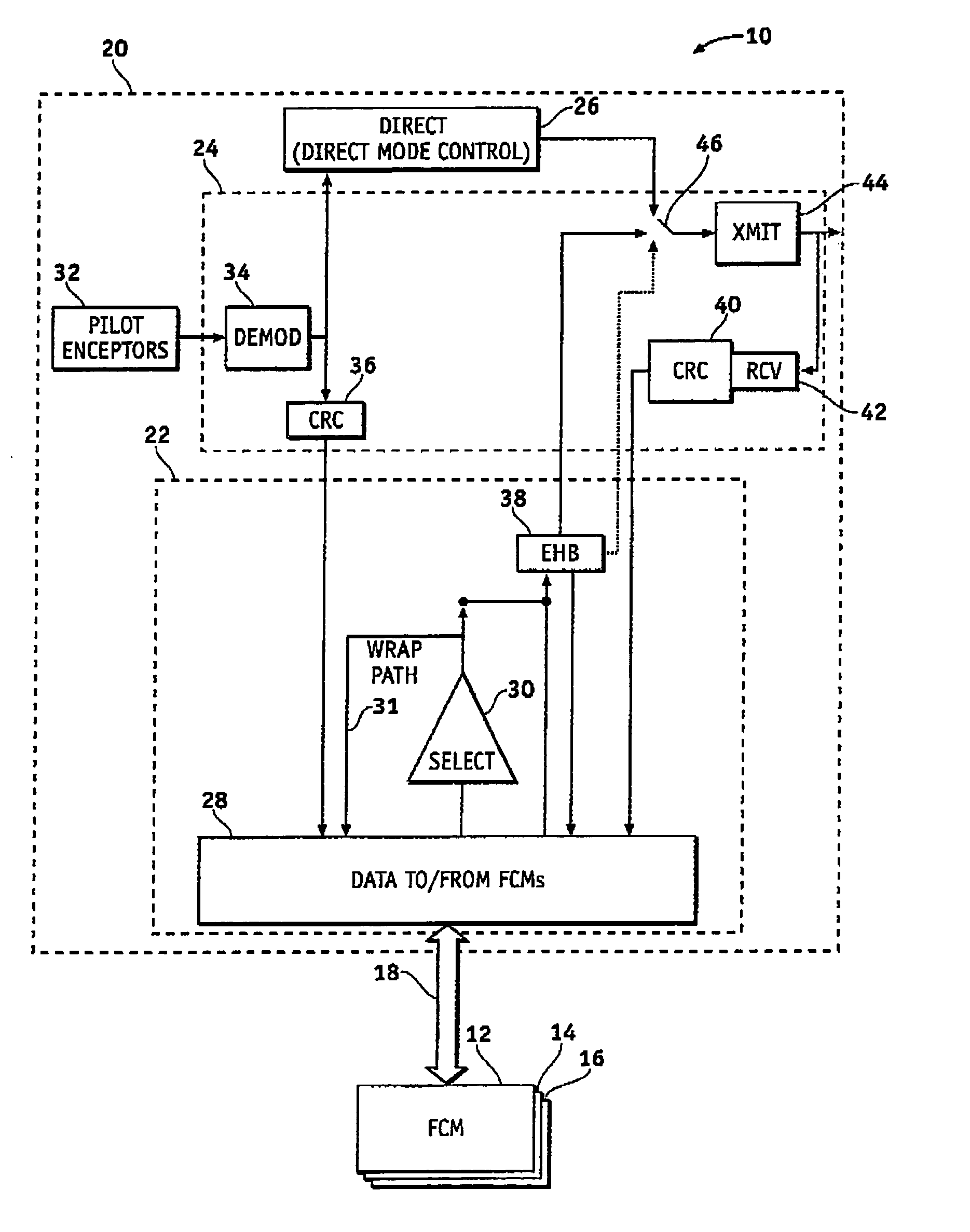
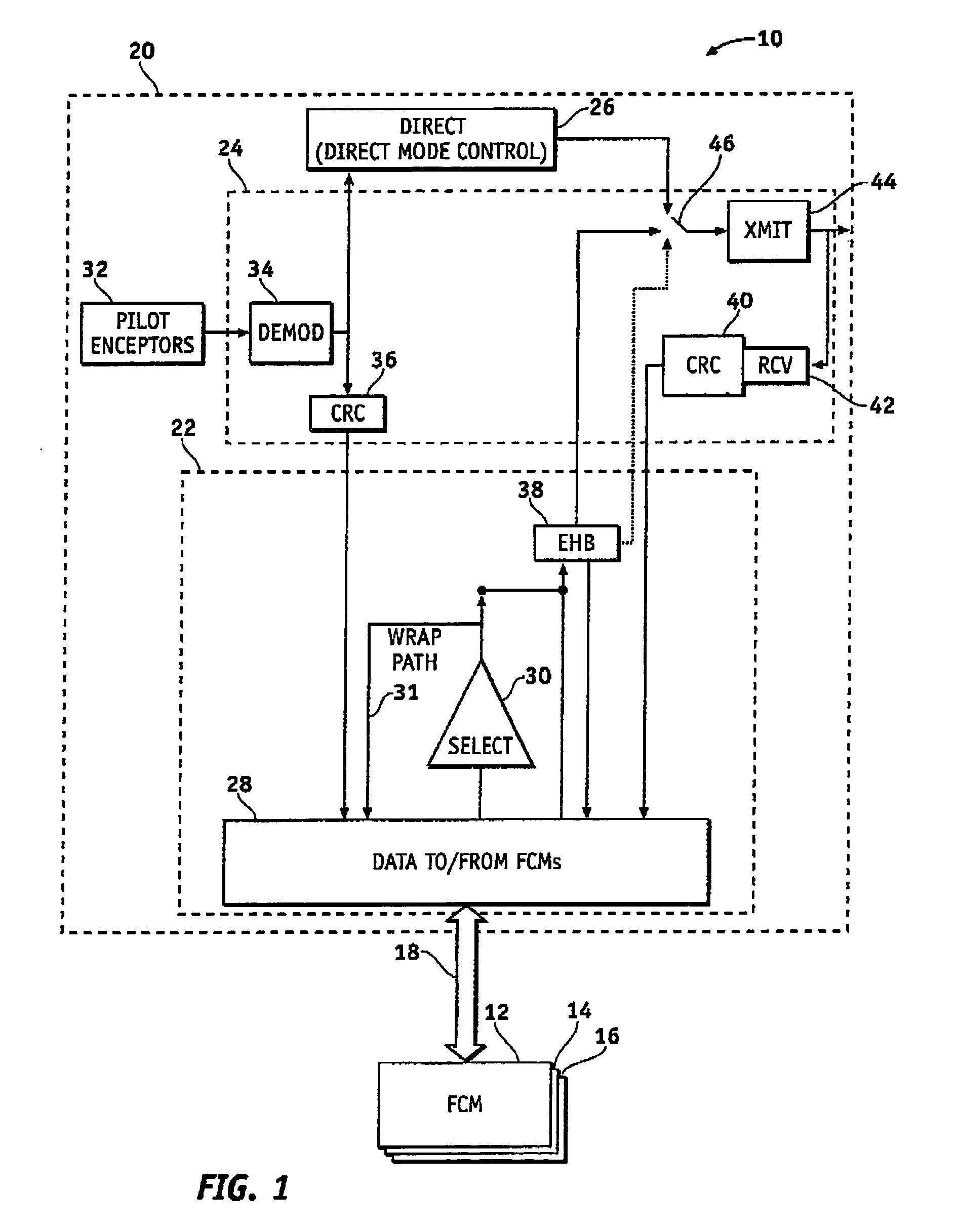
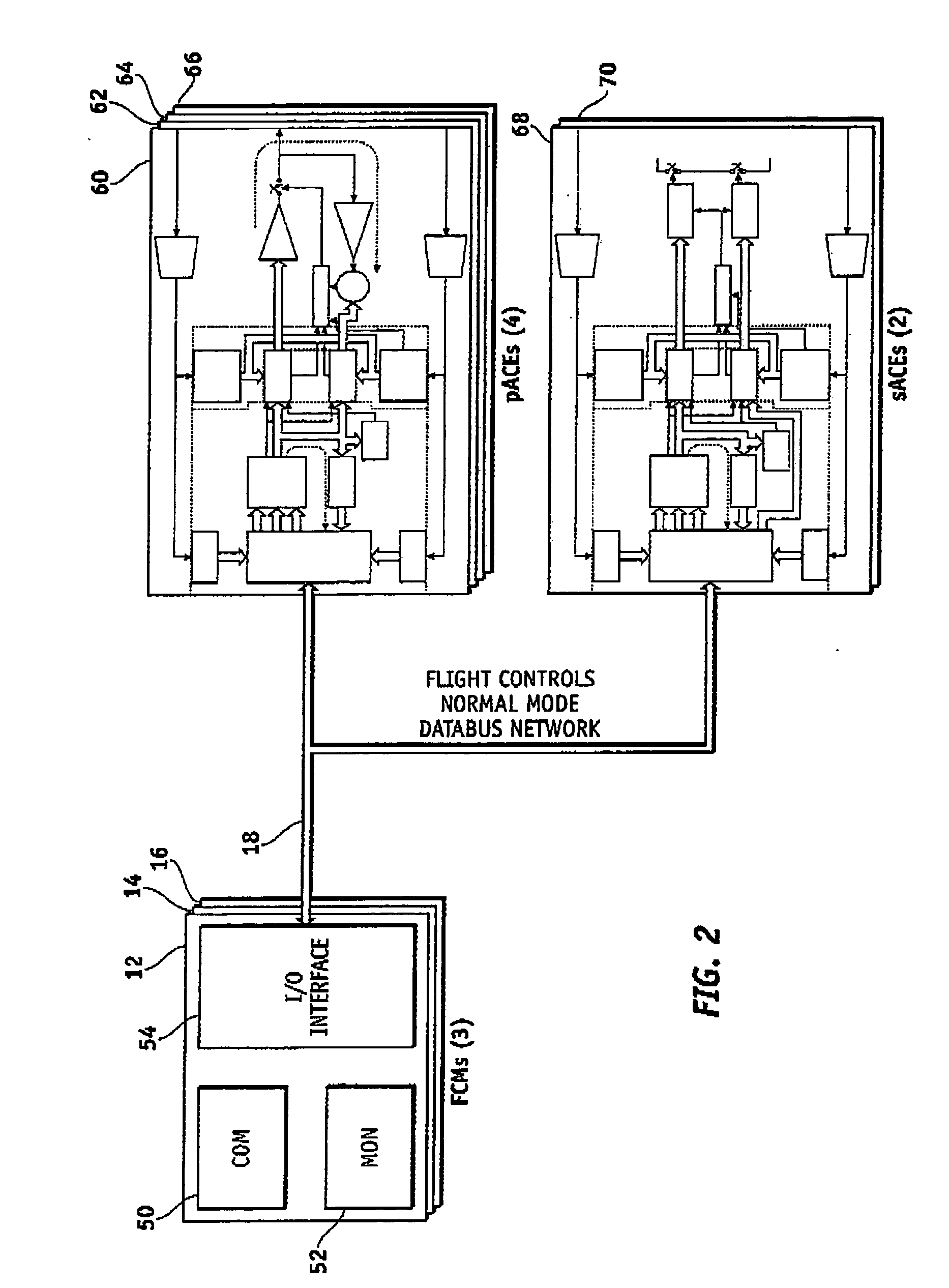
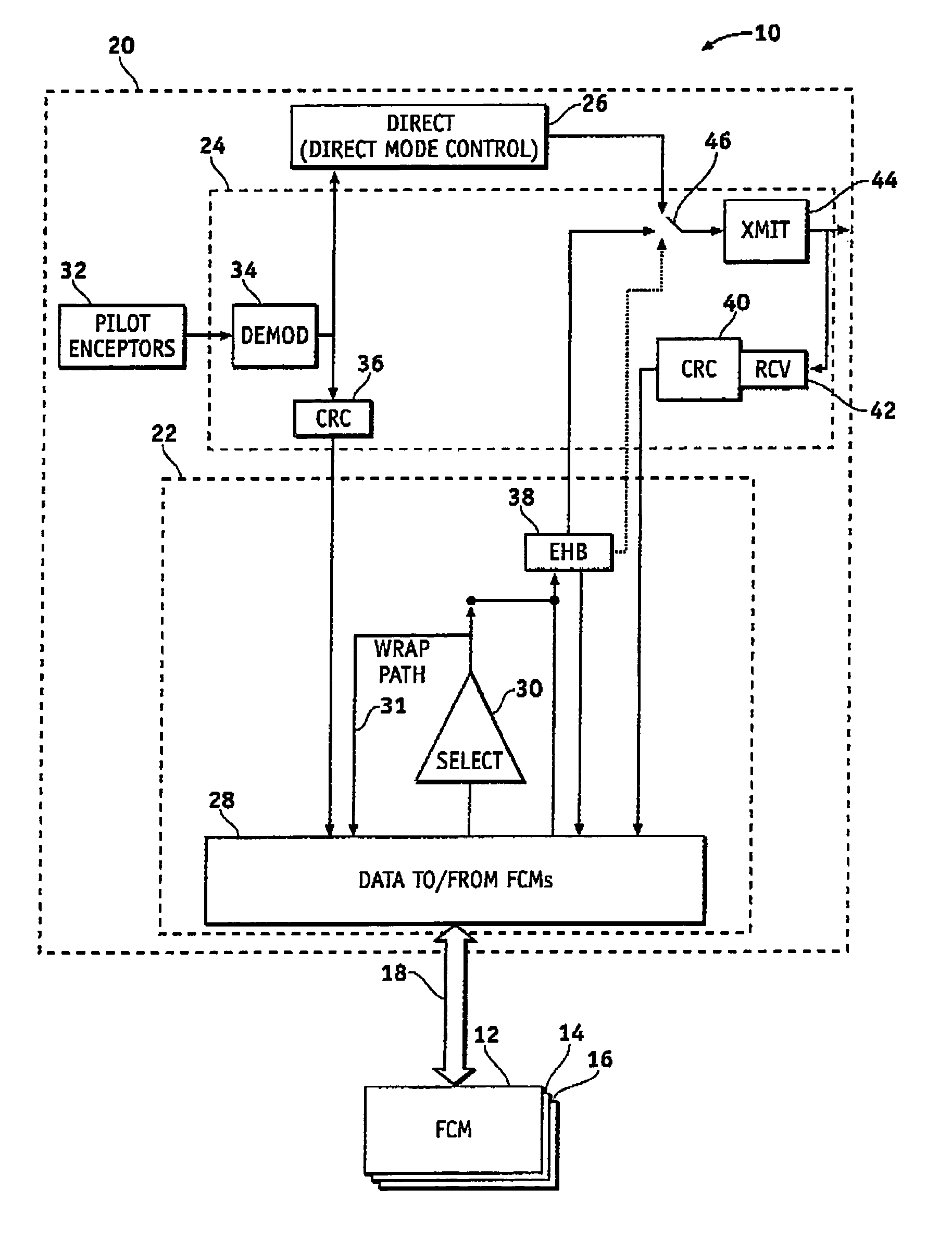
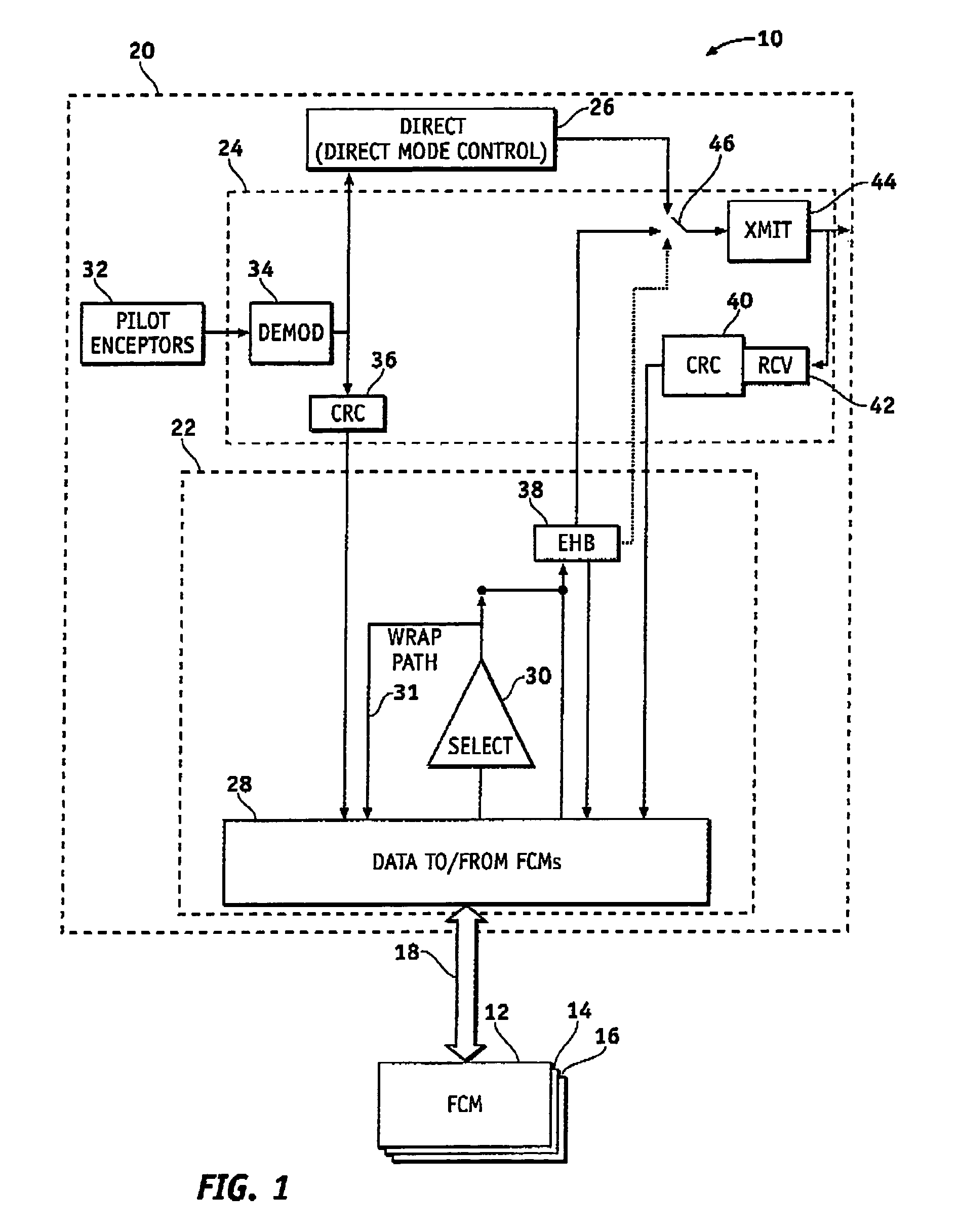
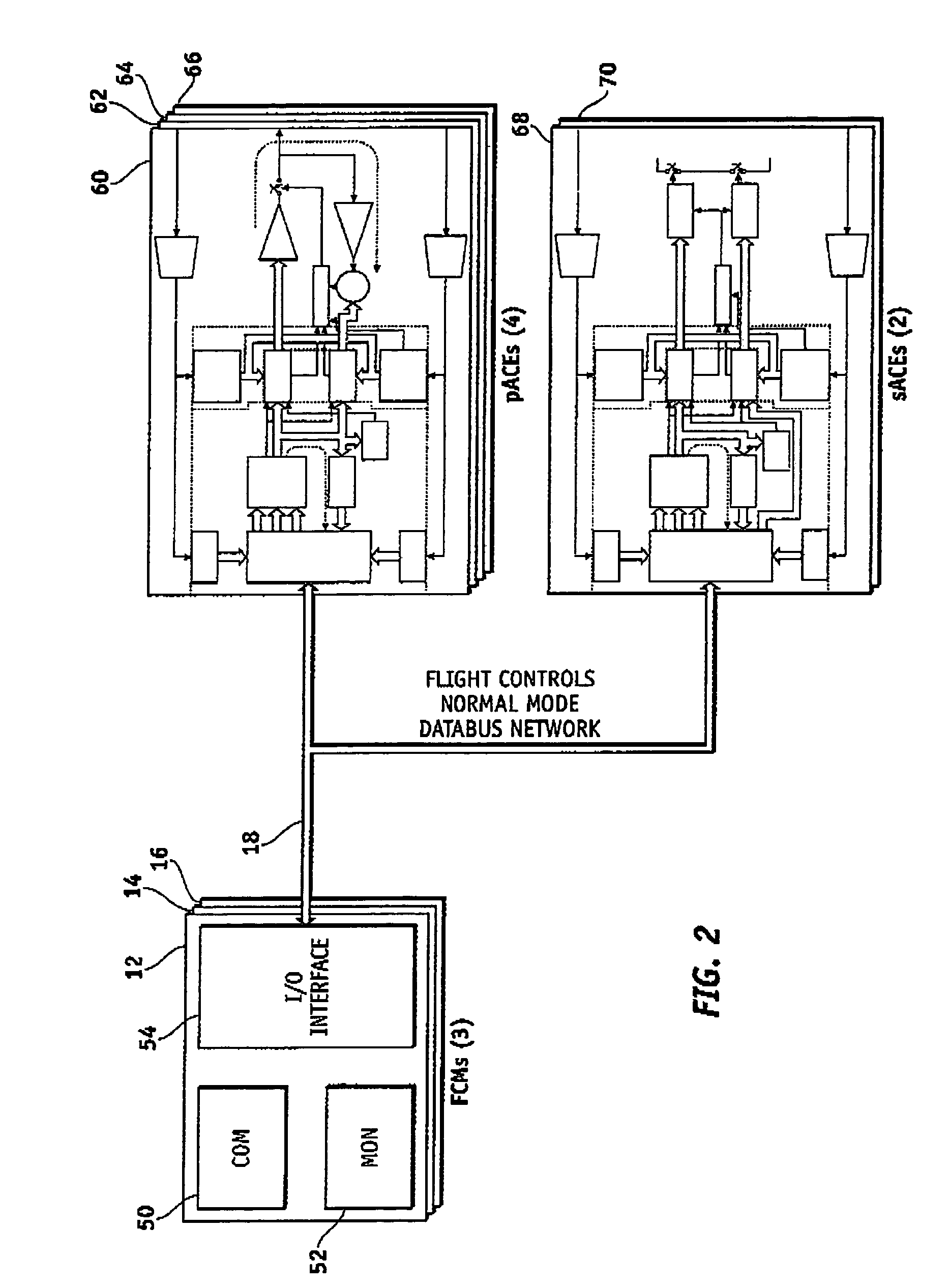
System and method of redundancy management for fault effect mitigation
Methods and systems are provided for redundancy management of a fly-by-wire avionics system. A control module for producing a control signal is provided comprising a common processing partition for receiving a flight input signal and at least one first mode input signal, a first processing partition coupled to the common processing partition and configured to receive the first mode input signals and flight input signal from the common processing partition, and a second processing partition coupled to the common processing partition. The first processing partition produces a first mode output signal in response to one of the first mode input signals and flight input signal. The second processing partition generates a second mode signal in response to the flight input signal when the first processing partition fails. The common processing partition produces the control signal in response to one of the first mode output signal and second mode signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Cooling failure mitigation for an electronics enclosure
ActiveUS7327578B2Digital data processing detailsIndirect heat exchangersElectronic componentPhase-change material
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
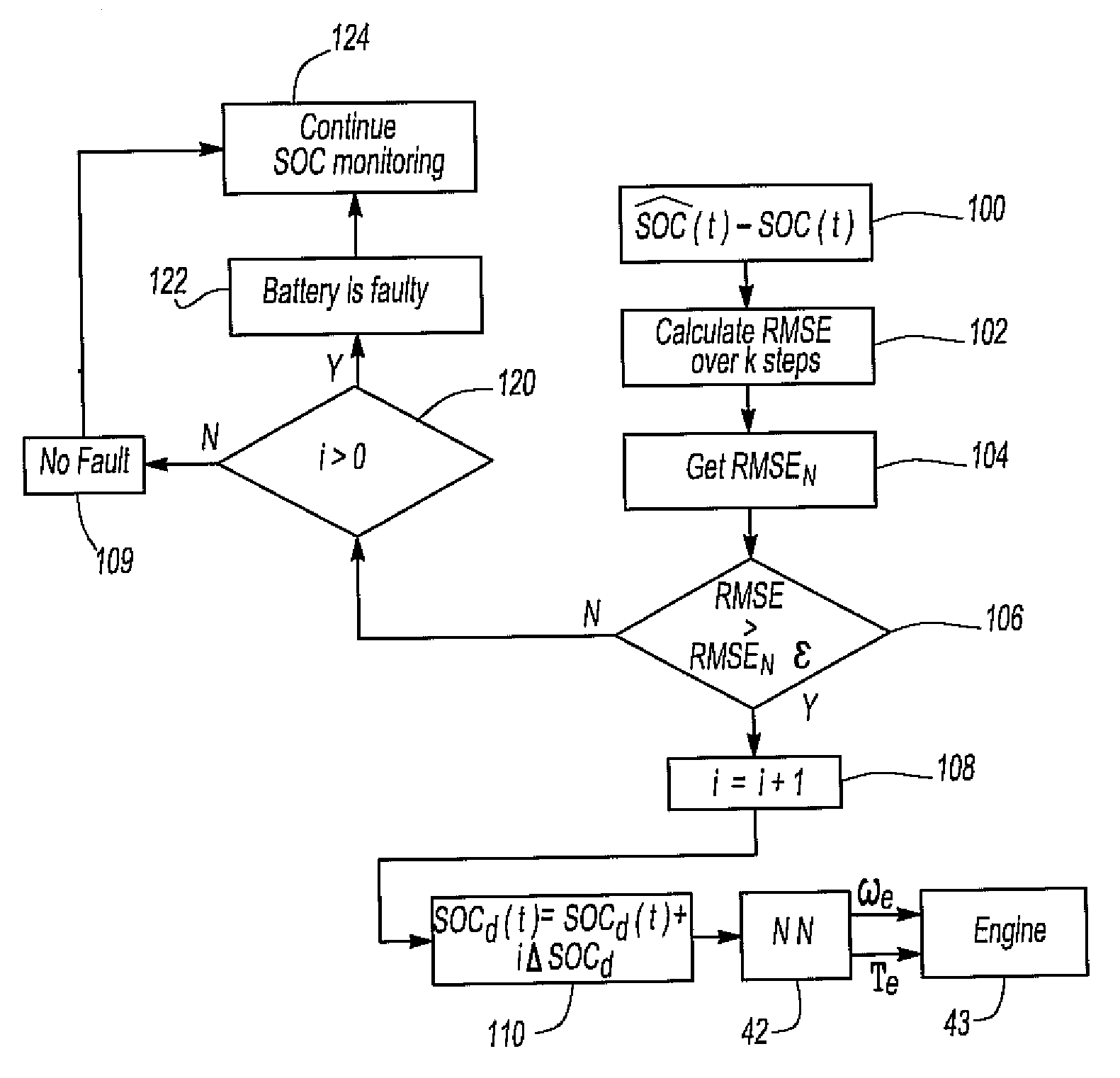
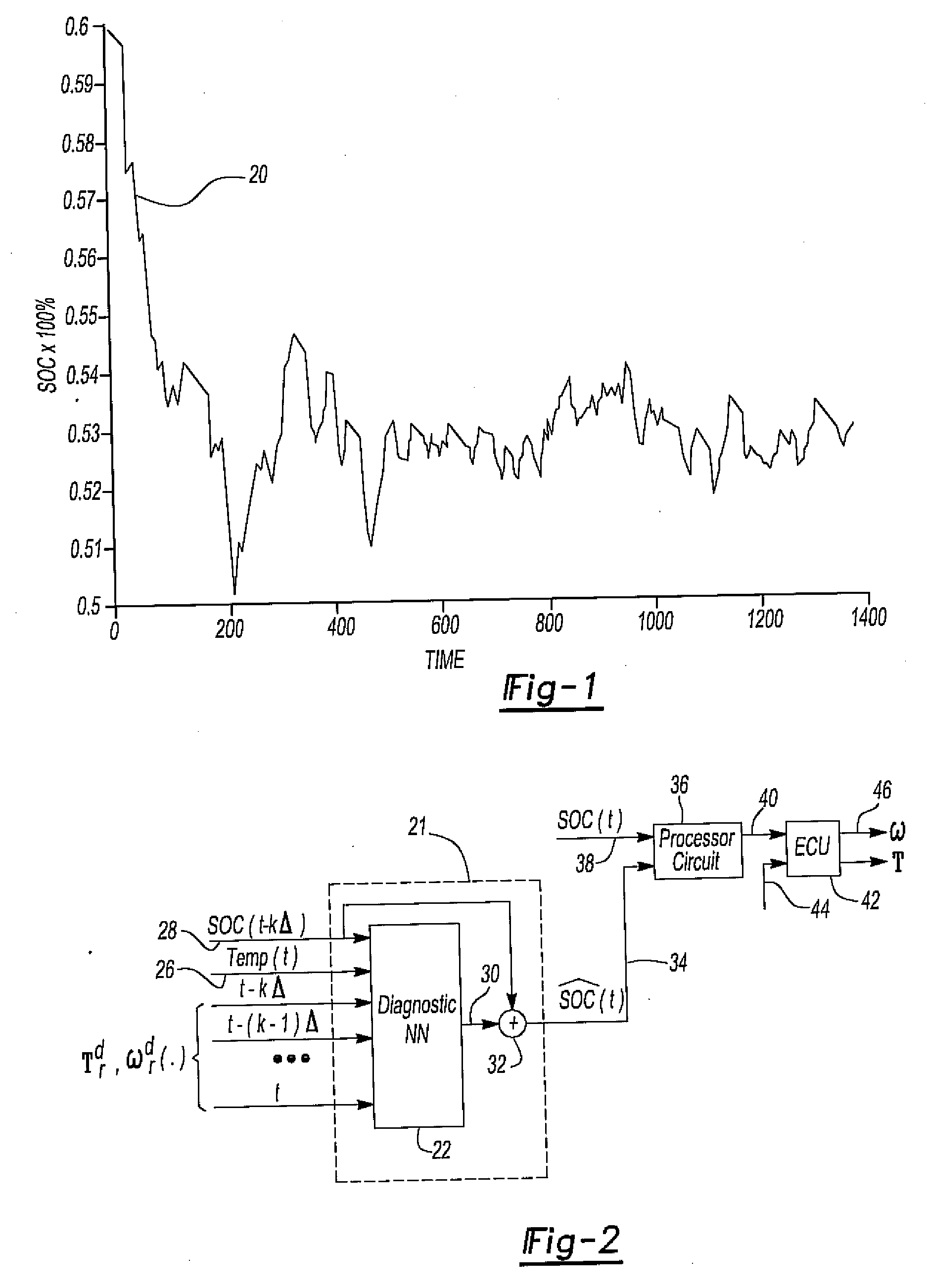
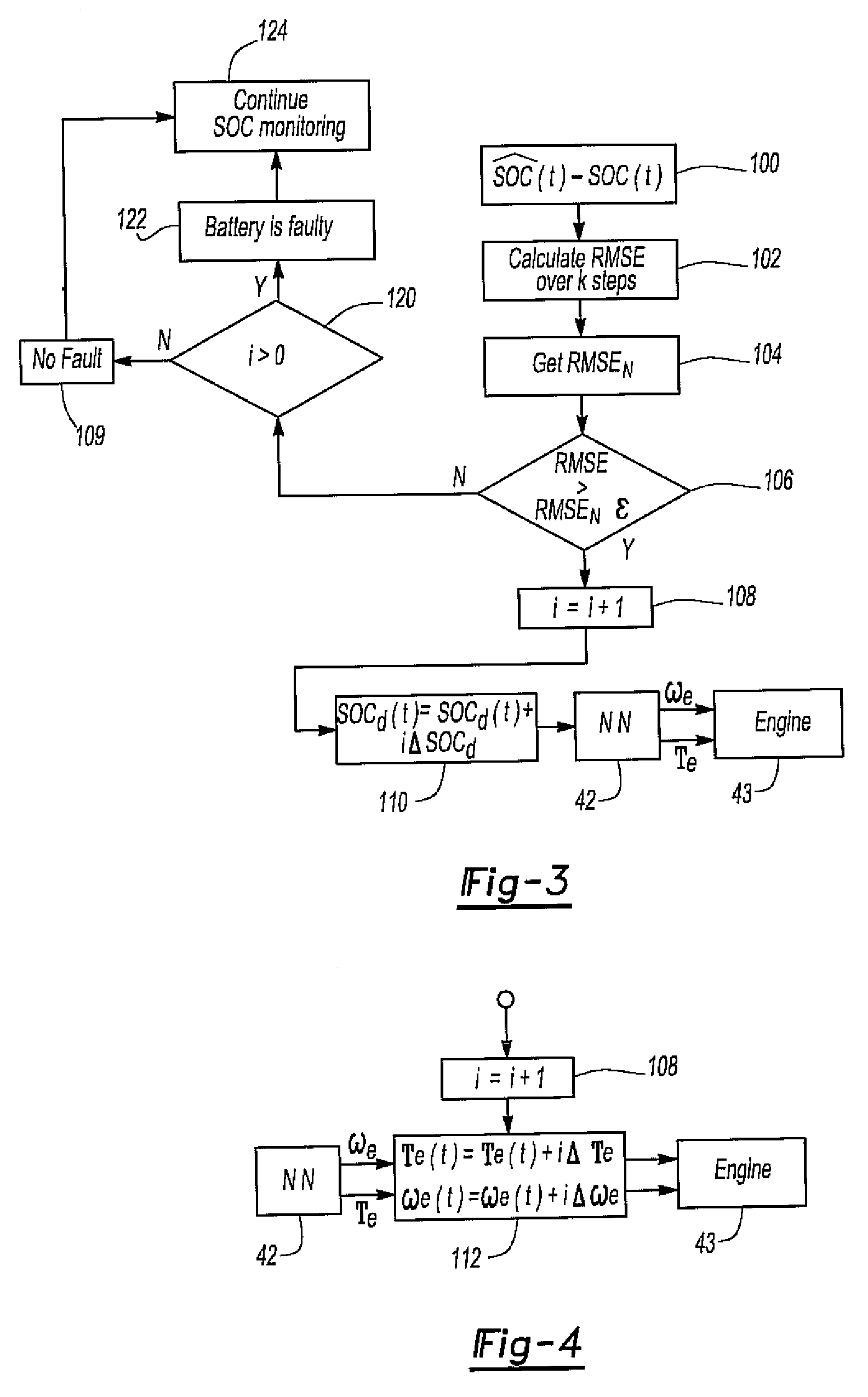
System for detecting a battery malfunction and performing battery mitigation for an hev
InactiveUS20090112395A1Reduce chargeConvenient charging statusVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingState of chargeElectric vehicle
A system for detecting malfunction of a battery in a hybrid electric vehicle and optionally mitigating the battery fault. A neural network forms a diagnostic circuit which receives signals representative of the required driveshaft torque and speed over a diagnostic period and a prior state of charge of the battery at the beginning of the diagnostic period as input signals. The diagnostic circuit generates an output signal representing a difference between an estimated state of charge of the battery at the end of the diagnostic period and the actual state of charge of the battery. In the event that the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, a battery fault signal is generated. The battery fault signal may be employed to vary the engine speed and / or torque to perform battery fault mitigation by increasing the state of charge of the battery.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA
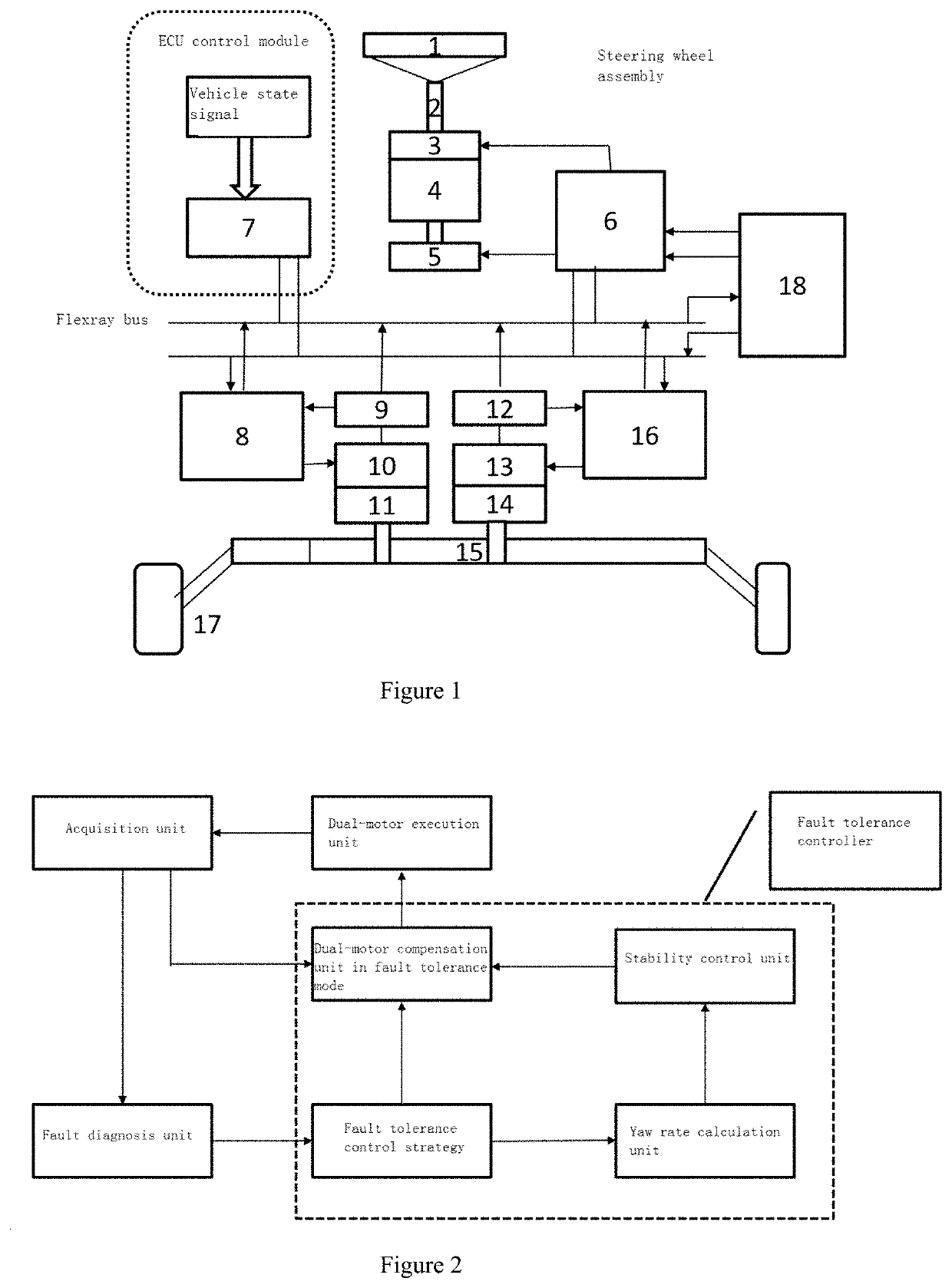
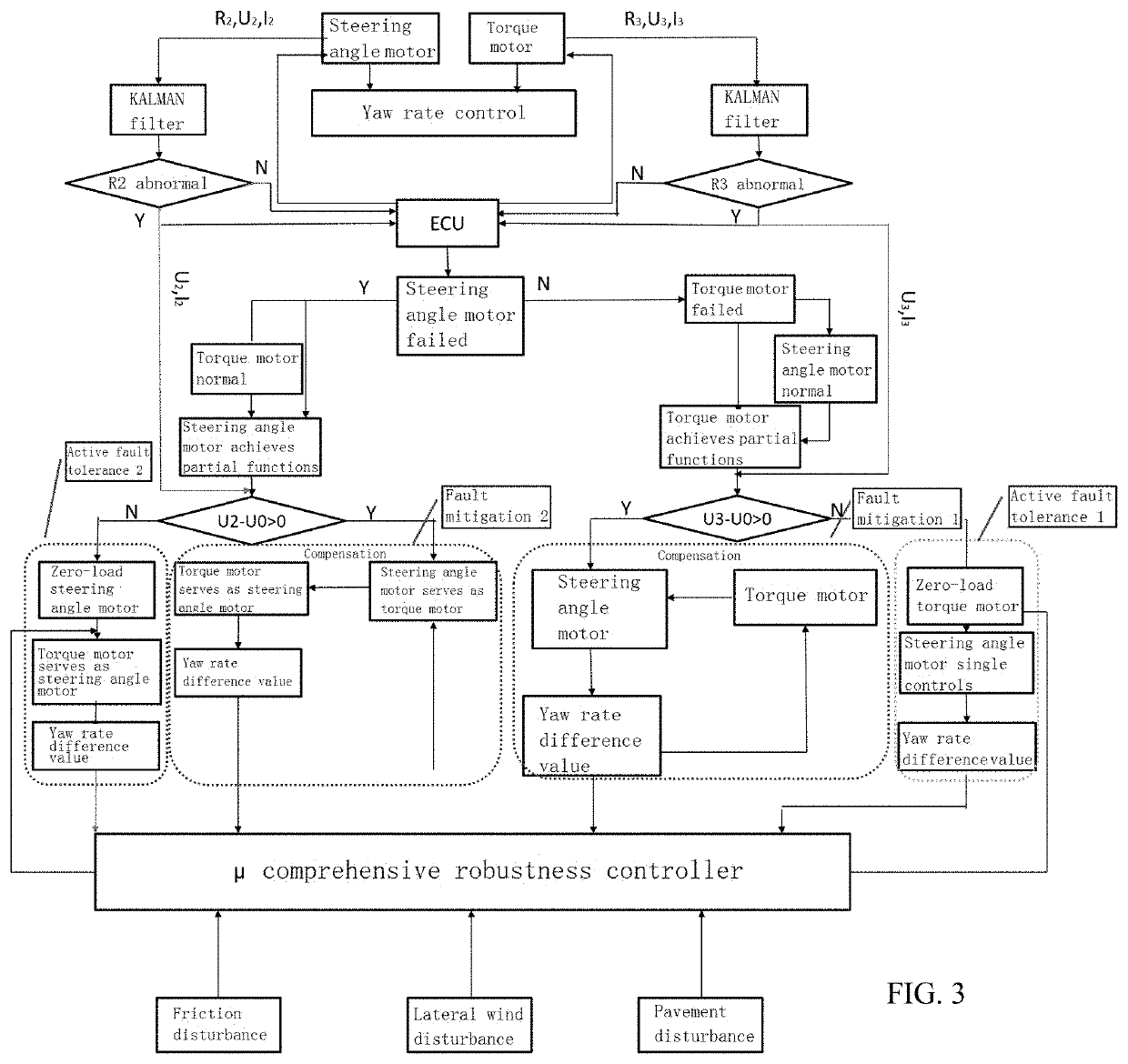
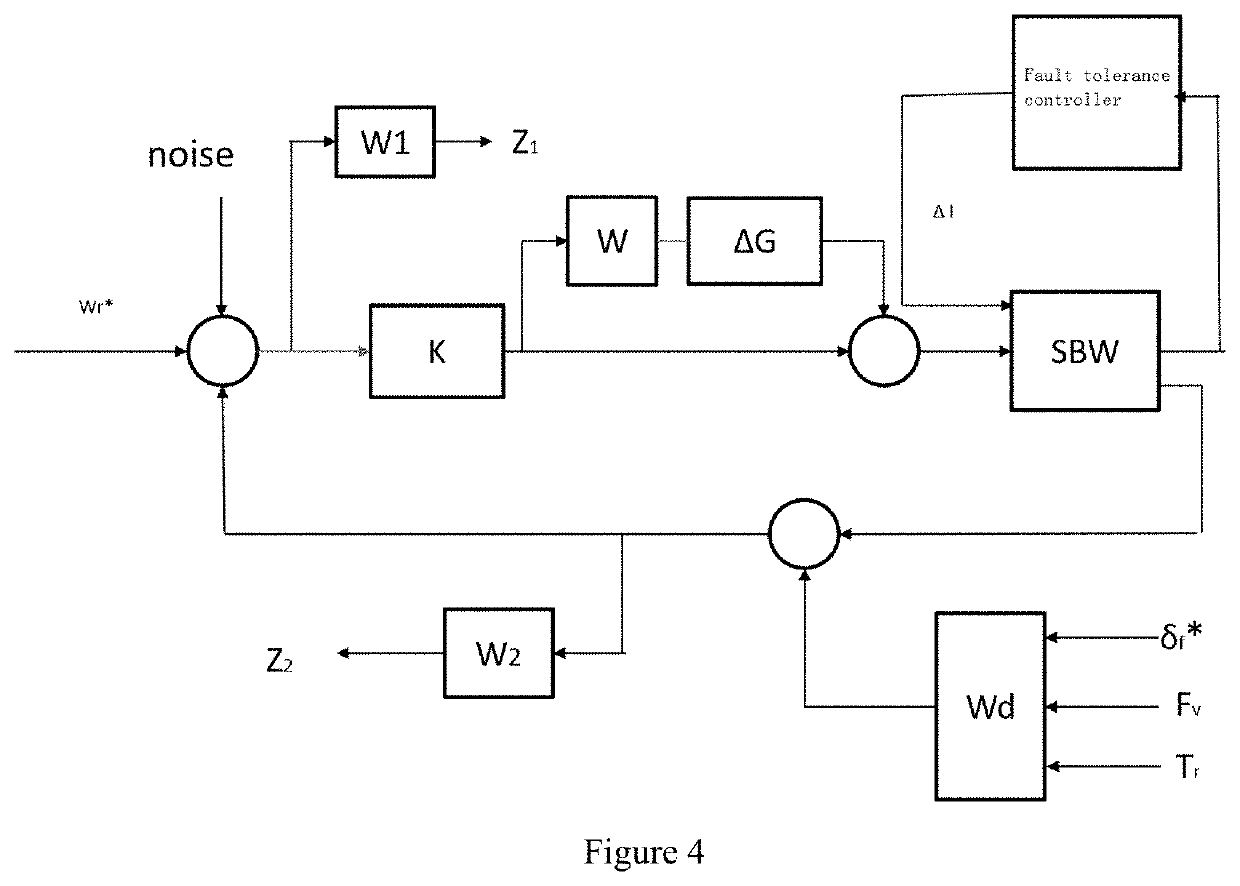
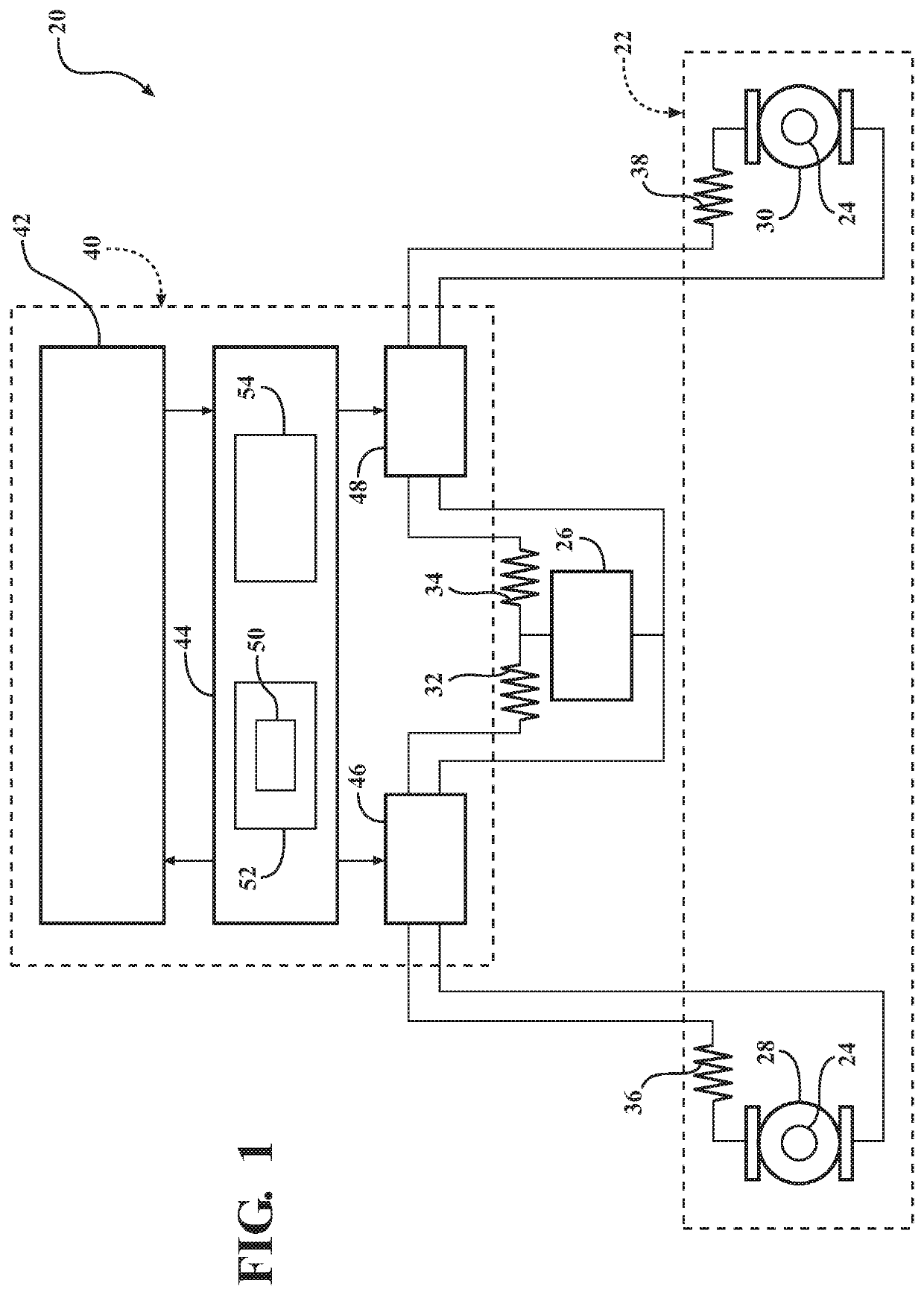
Active Fault Tolerance and Fault Mitigation System Based on Steer-by-wire with Dual Motors and Control Method Therefor
PendingUS20210269087A1Enhanced advantageImprove reliabilitySteering linkagesMechanical steering gearsSteering wheelGear wheel
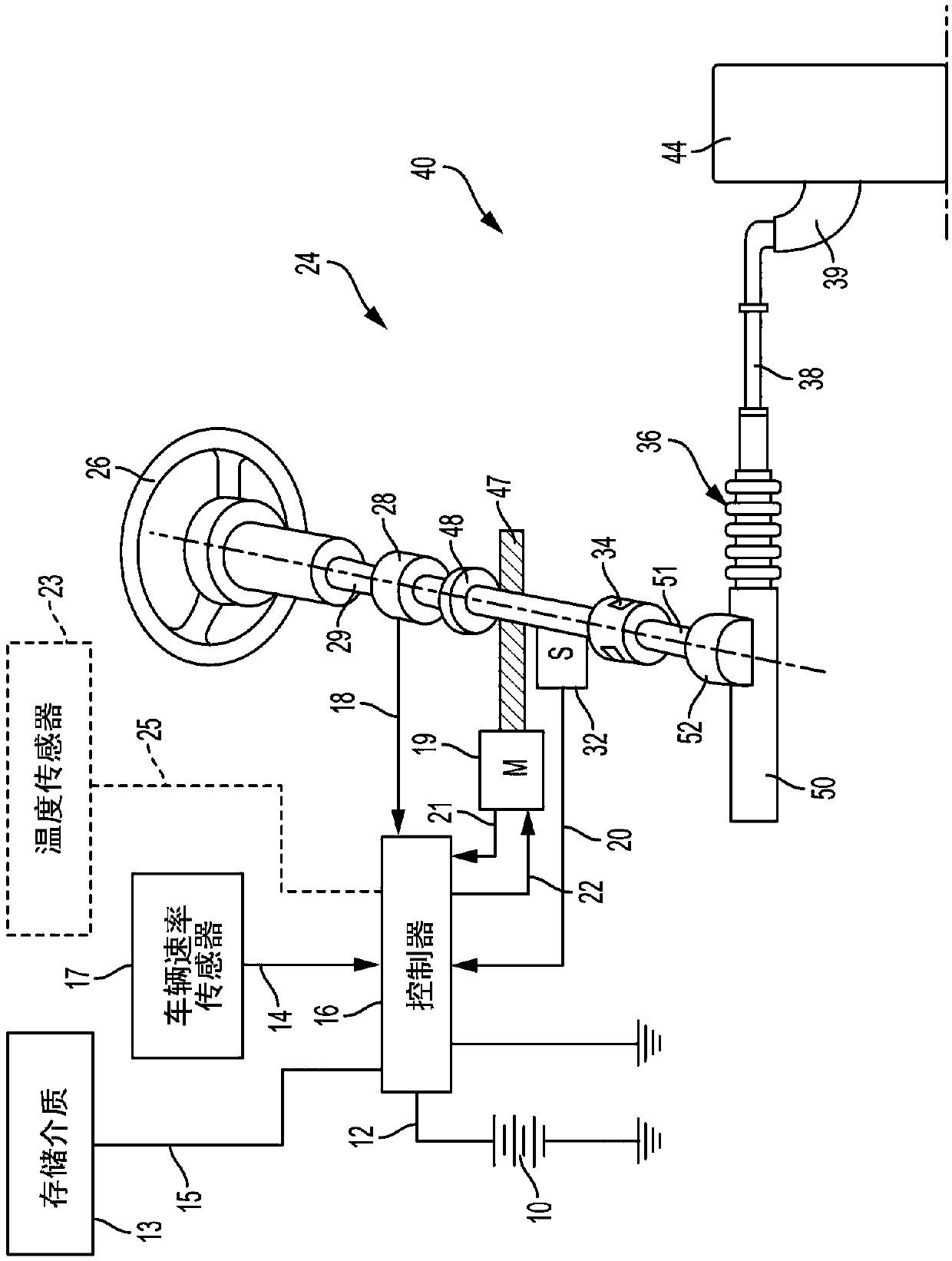
An active fault tolerance and fault mitigation system based on steer-by-wire dual motors and a mode switching control method thereof are provided. The system includes an acquisition unit, a steering wheel assembly, an ECU control module, a front wheel steering assembly, and a fault tolerance controller (18) which are sequentially connected. The acquisition unit transmits an acquired vehicle signal to the ECU control module, and then a corresponding compensation strategy is selected by means of a fault tolerance control strategy unit, a yaw rate calculation unit, a stability control unit, and a dual-motor compensation unit to act on a rack and pinion mechanism (15). The system and method can perform switching in an active fault tolerance and fault mitigation mode to achieve optimal control of the real-time performance of a vehicle, thereby ensuring the driving performance and higher performance of the vehicle in a field fault condition.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
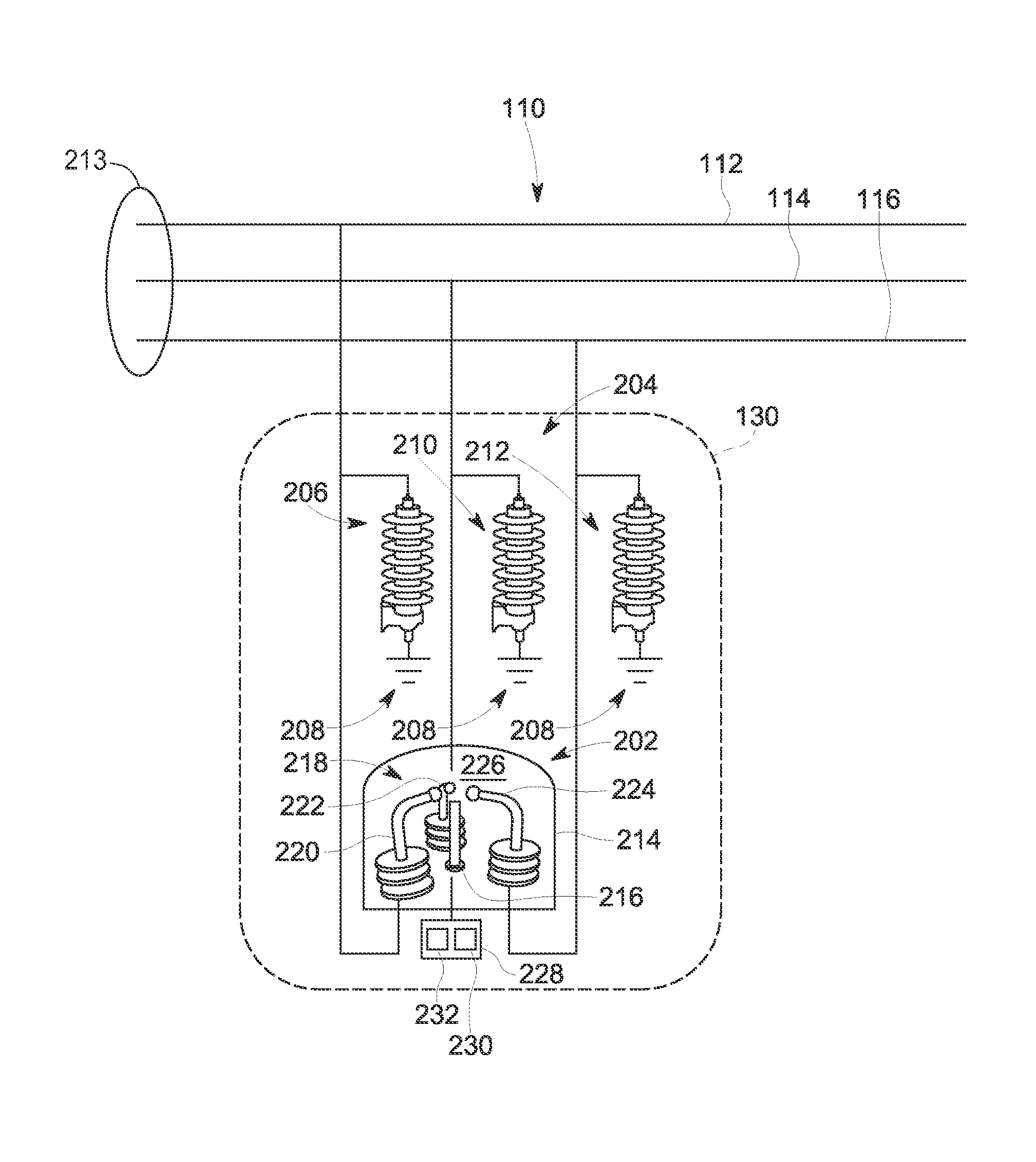
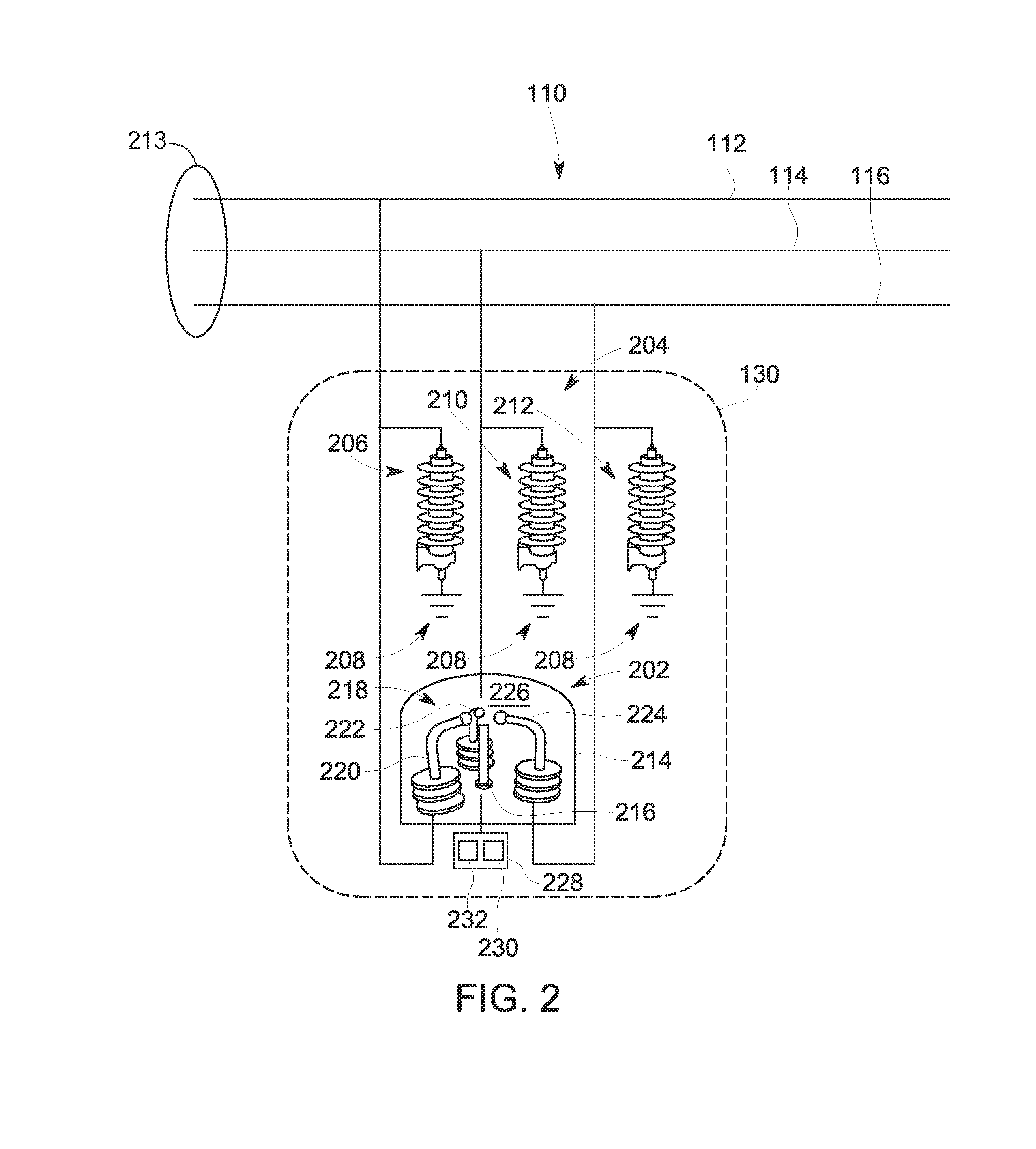
Method and systems for discharging energy from an electrical fault
ActiveUS20130329325A1Spark gaps with auxillary triggeringSwitchgear arrangementsElectrical FailureElectrical conductor
An electrical fault mitigation system includes a mitigation device including a containment chamber defining a cavity, a first electrode positioned within the cavity and coupled to a first conductor, and a second electrode positioned within the cavity and coupled to a second conductor. The mitigation device also includes a first voltage source, and a plasma gun positioned within the cavity and configured to emit ablative plasma using the first voltage source to discharge energy from an electrical fault. The system also includes a first voltage limiter device configured to limit a voltage of the first conductor from increasing above a predetermined threshold to prevent a second voltage source from generating a second electrical arc between the first electrode and the second electrode when the second voltage source applies a voltage across the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:ABB SPA
System and methods for fault-isolation and fault-mitigation based on network modeling
ActiveUS8577663B2Error detection/correctionTesting/monitoring control systemsElectronic systemsNetwork model
A system and method for identifying a monitoring point in an electrical and electronic system (EES) in a vehicle. The method includes defining a network model of the EES where potential monitoring point locations in the model are identified as targets, such as nodes. The method then computes a betweenness centrality metric for each target in the model as a summation of a ratio of a number of shortest paths between each pair of targets in the model that pass through the target whose betweenness centrality metric is being determined to a total number of shortest paths between each pair of targets. The method identifies which of the betweenness centrality metrics are greater than a threshold that defines a minimum acceptable metric and determines which of those targets meets a predetermined model coverage. The monitoring point is selected as the target that best satisfies the minimum metric and the desired coverage.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus, system, and method for mitigating diesel exhaust fluid deposits and associated conditions
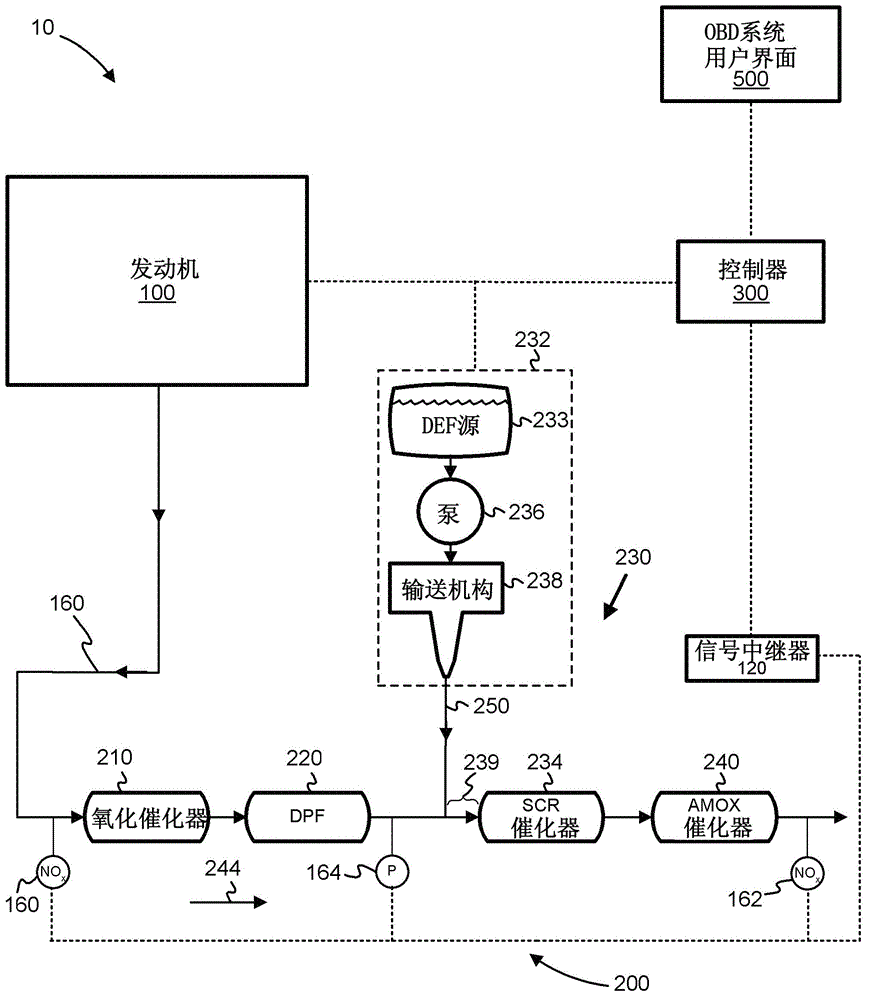
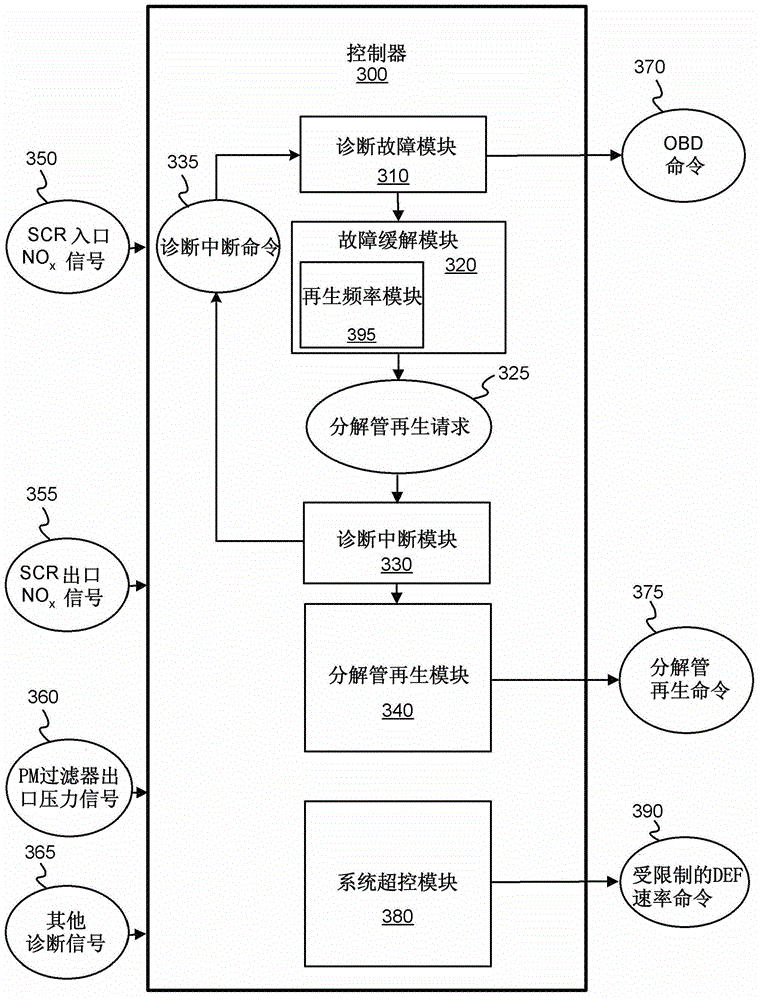
According to one embodiment, described herein is an apparatus for mitigating on-board diagnostic (OBD) faults generated by an OBD system of an internal combustion engine (ICE) system (10) having a selective catalytic reduction system (230) with a diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) decomposition tube (239). The apparatus includes a fault mitigation module (320) that is configured to monitor at least one OBD signal of the OBD system and issue a request (325) for regenerating the DEF decomposition tube when a value of the at least one OBD signal reaches a predetermined regeneration threshold corresponding with the at least one OBD signal. The regeneration threshold is reachable prior to an OBD fault threshold corresponding with the at least one OBD signal. The apparatus also includes a regeneration module (340) that is configured to regenerate the DEF decomposition tube according to the issued request.
Owner:酷敏斯IP公司
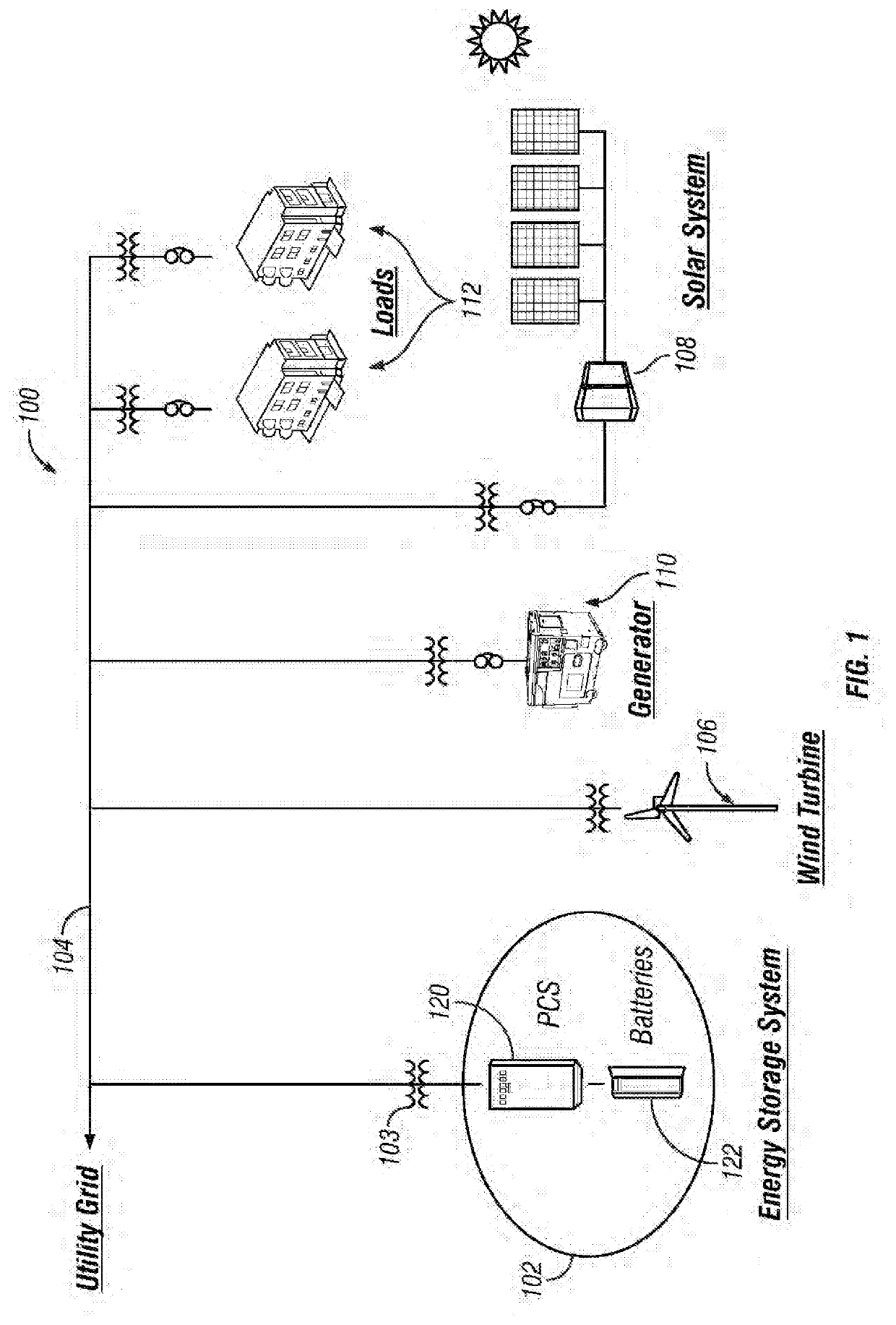
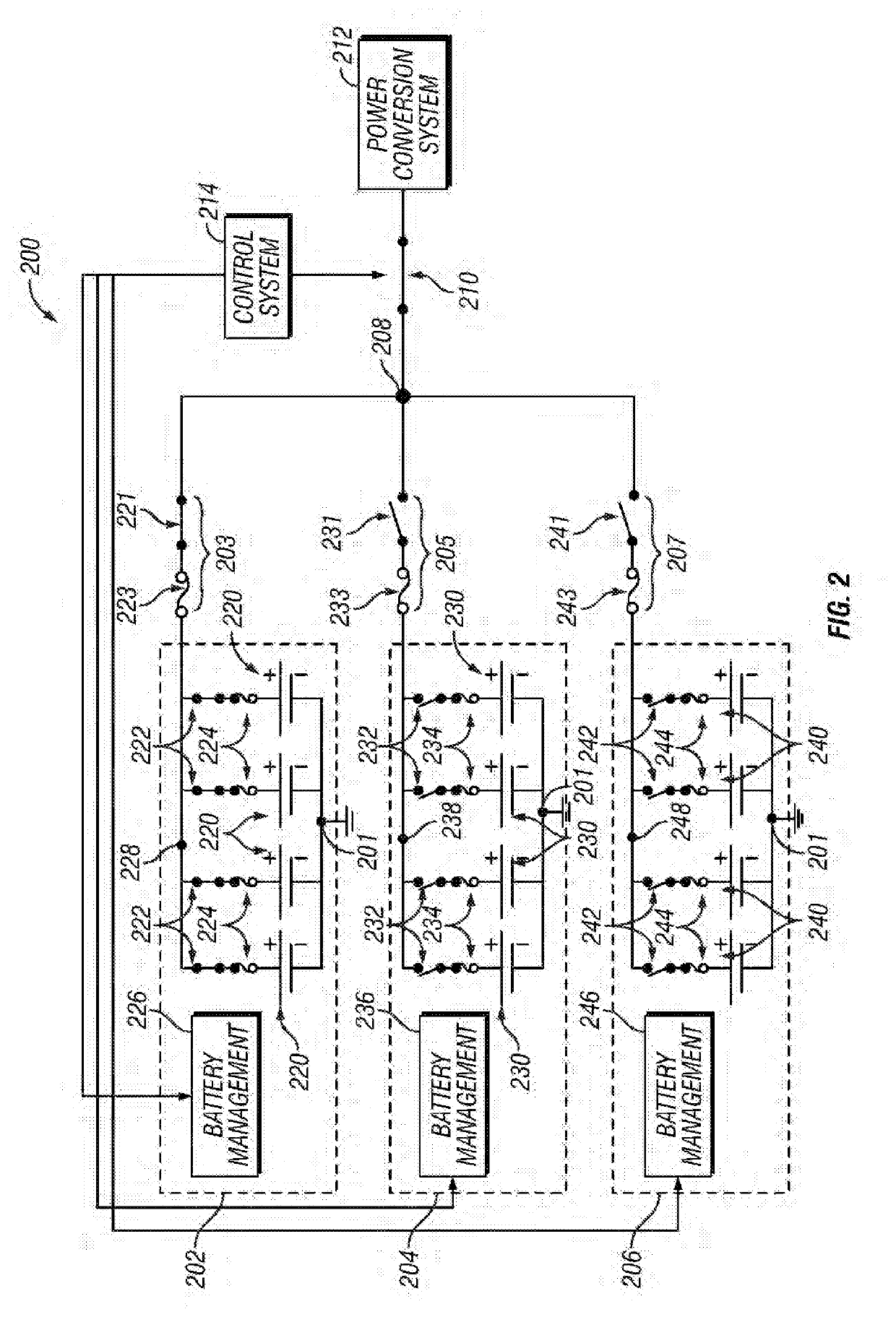
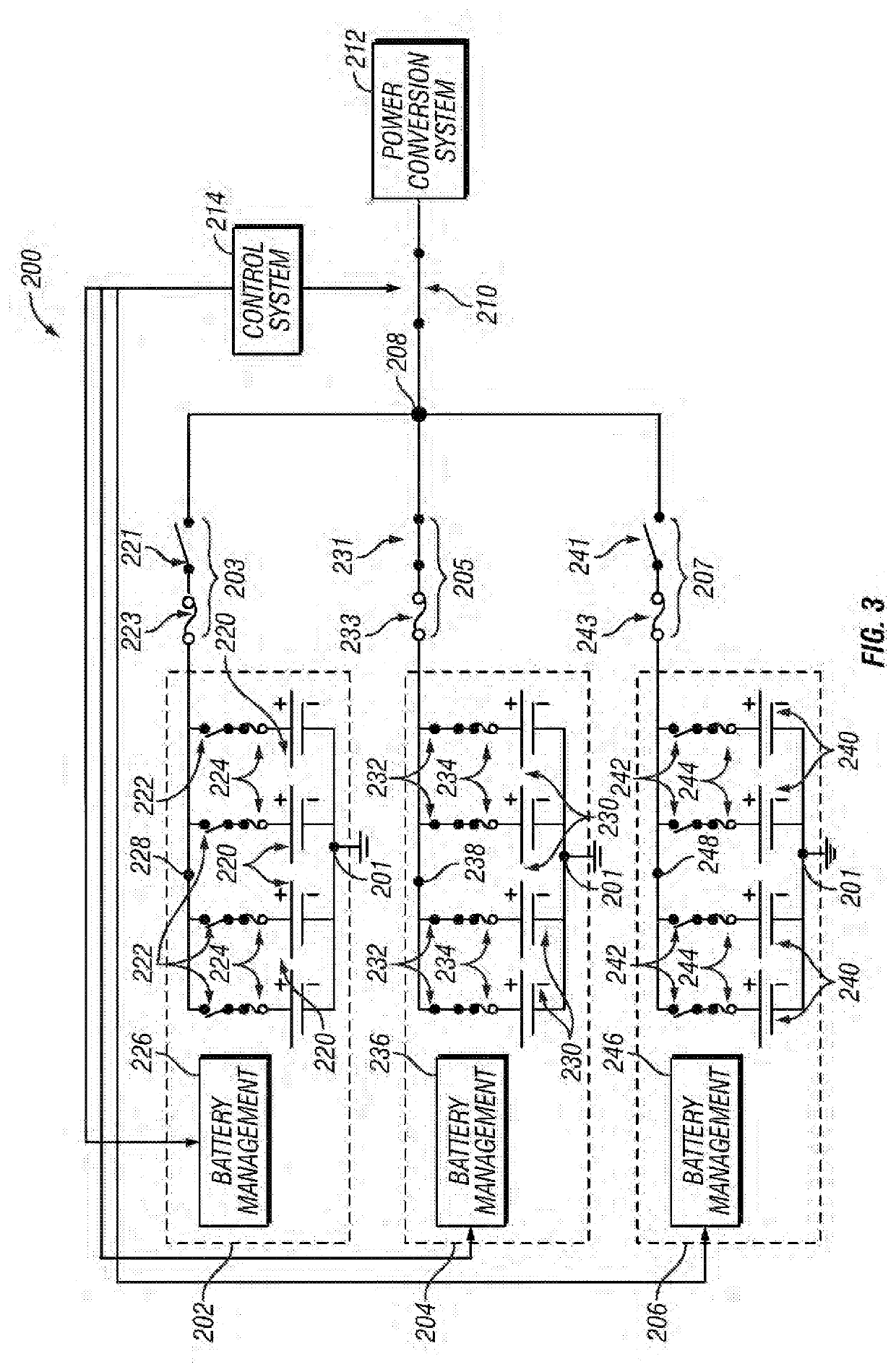
Energy storage systems and methods for fault mitigation
InactiveUS20200144845A1Circuit monitoring/indicationCharging stationsControl systemElectrical connection
Electrical systems and related operating methods are provided. One exemplary electrical system includes a power conversion system, a plurality of battery strings, a plurality of switching arrangements configured electrically in series between the respective battery strings and an interface to the power conversion system, and a control system coupled to the plurality of switching arrangements. The switching arrangements are operated to electrically connect a selected one of the battery strings to the power conversion system while concurrently isolating remaining battery strings from the power conversion system and the selected battery string.
Owner:S&C ELECTRIC
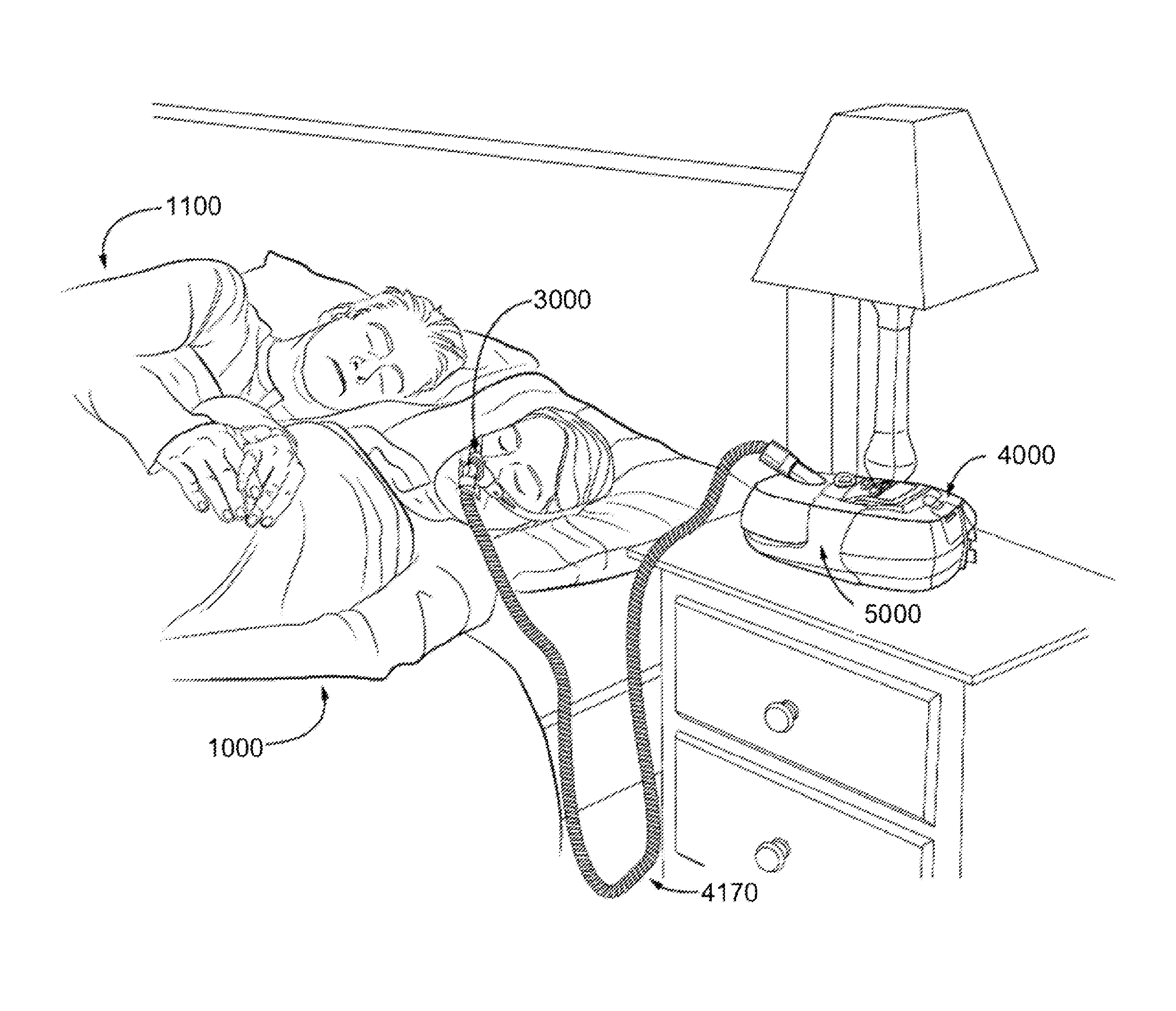
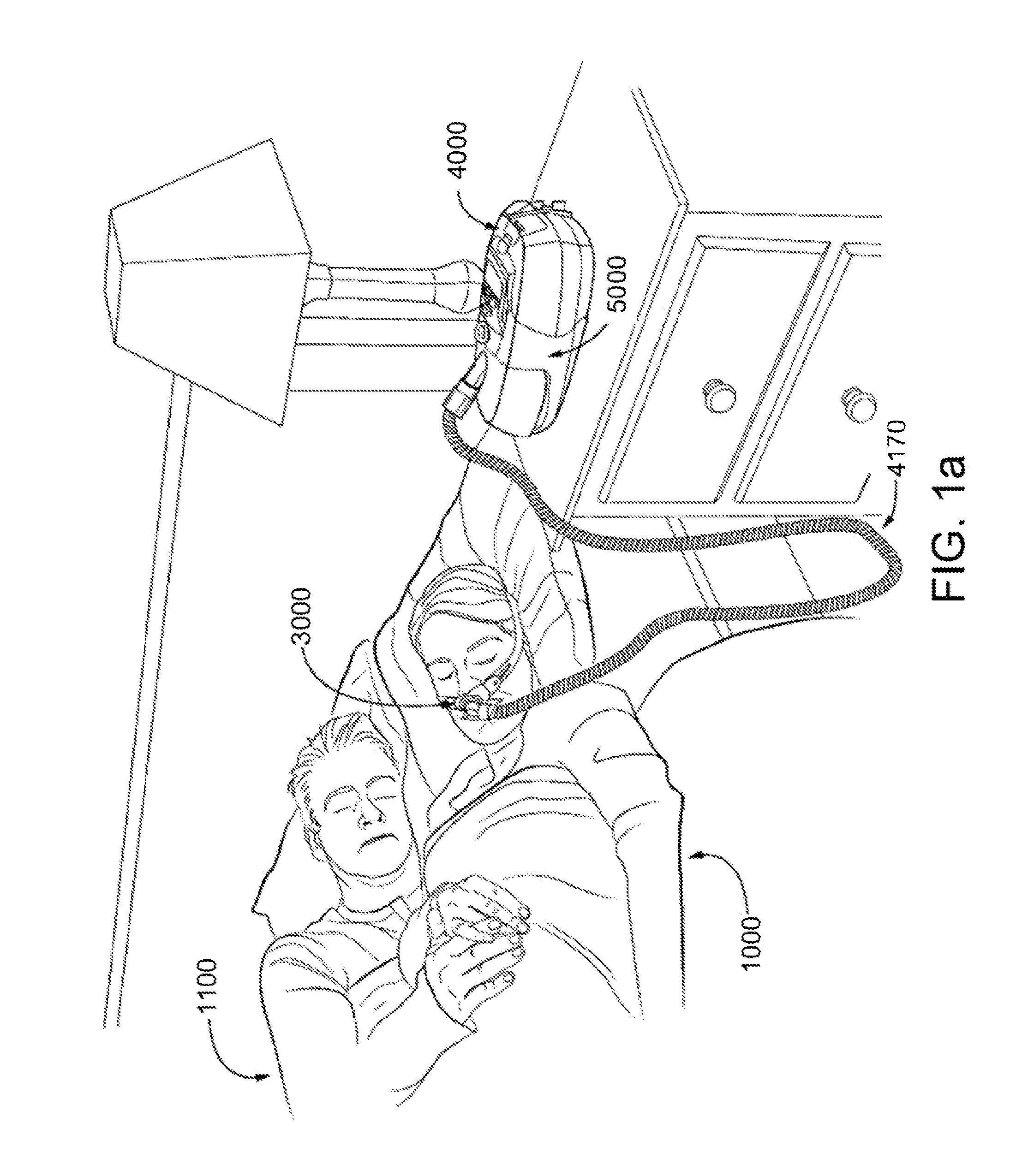
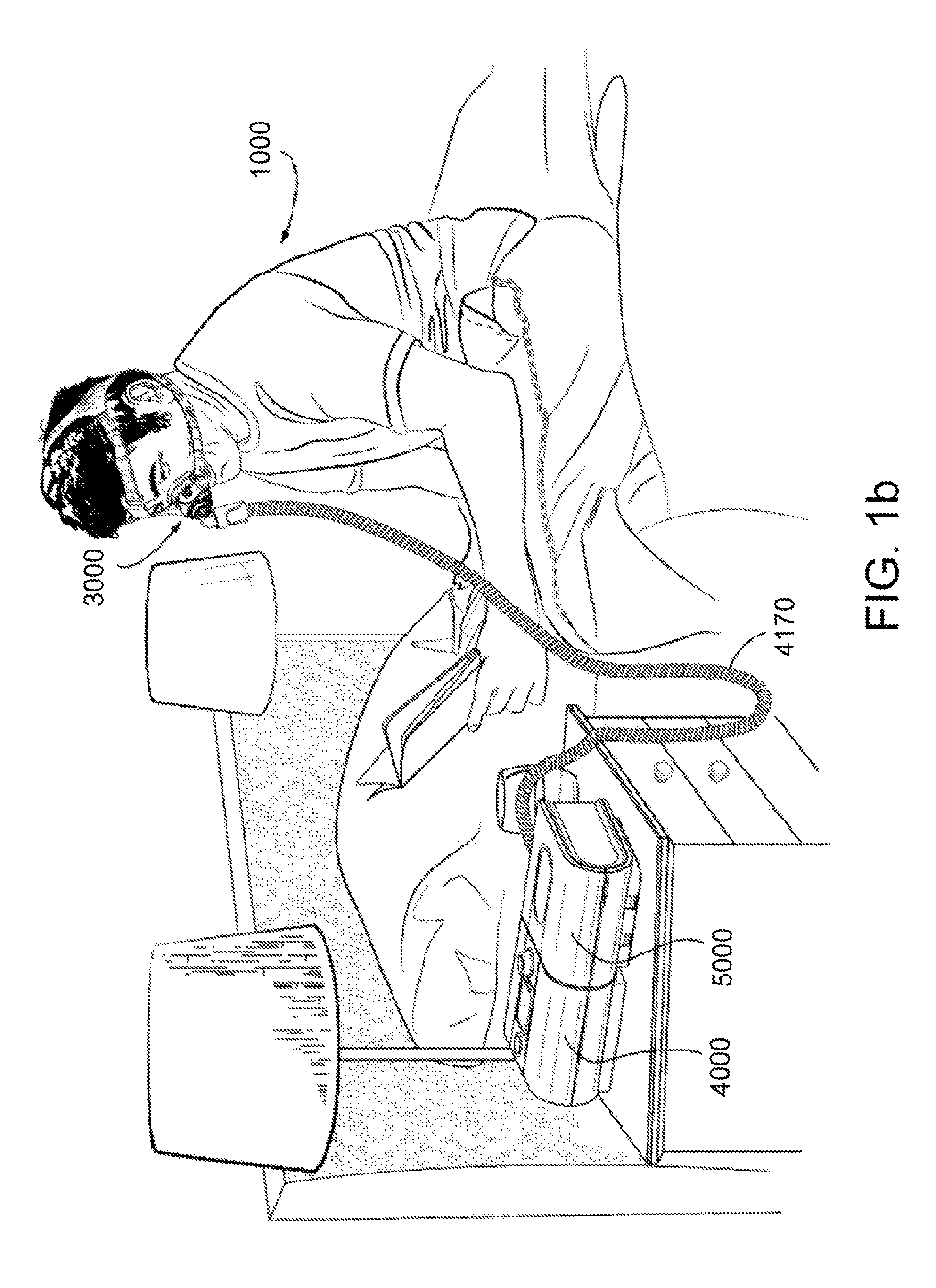
Motor drive system for respiratory apparatus
ActiveUS20160375209A1Simple and safe solutionImprove efficacyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAC motor controlControl engineeringElectric machinery
A respiratory apparatus includes components to protect operations of the apparatus. For example, in some versions, the apparatus may include a power supply, a motor powered by the power supply, and a transient absorption diode circuit between the motor and the power supply. The transient absorption diode circuit may be configured to absorb energy generated by the motor from rotational kinetic energy. Such absorption may serve to protect the components of the apparatus. In some examples, the apparatus may include a fault mitigation integrated circuit (IC). The IC circuit may be included in the respiratory apparatus to detect one or more faults based on physical and system parameters of the apparatus. The fault mitigation integrated circuit may generate a signal to stop the motor based on the detected fault, and may digitally communicate with a processor information about the detected fault.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and systems for discharging energy from an electrical fault
ActiveUS8922958B2Spark gaps with auxillary triggeringSwitchgear arrangementsElectrical conductorVoltage source
An electrical fault mitigation system includes a mitigation device including a containment chamber defining a cavity, a first electrode positioned within the cavity and coupled to a first conductor, and a second electrode positioned within the cavity and coupled to a second conductor. The mitigation device also includes a first voltage source, and a plasma gun positioned within the cavity and configured to emit ablative plasma using the first voltage source to discharge energy from an electrical fault. The system also includes a first voltage limiter device configured to limit a voltage of the first conductor from increasing above a predetermined threshold to prevent a second voltage source from generating a second electrical arc between the first electrode and the second electrode when the second voltage source applies a voltage across the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:ABB SPA
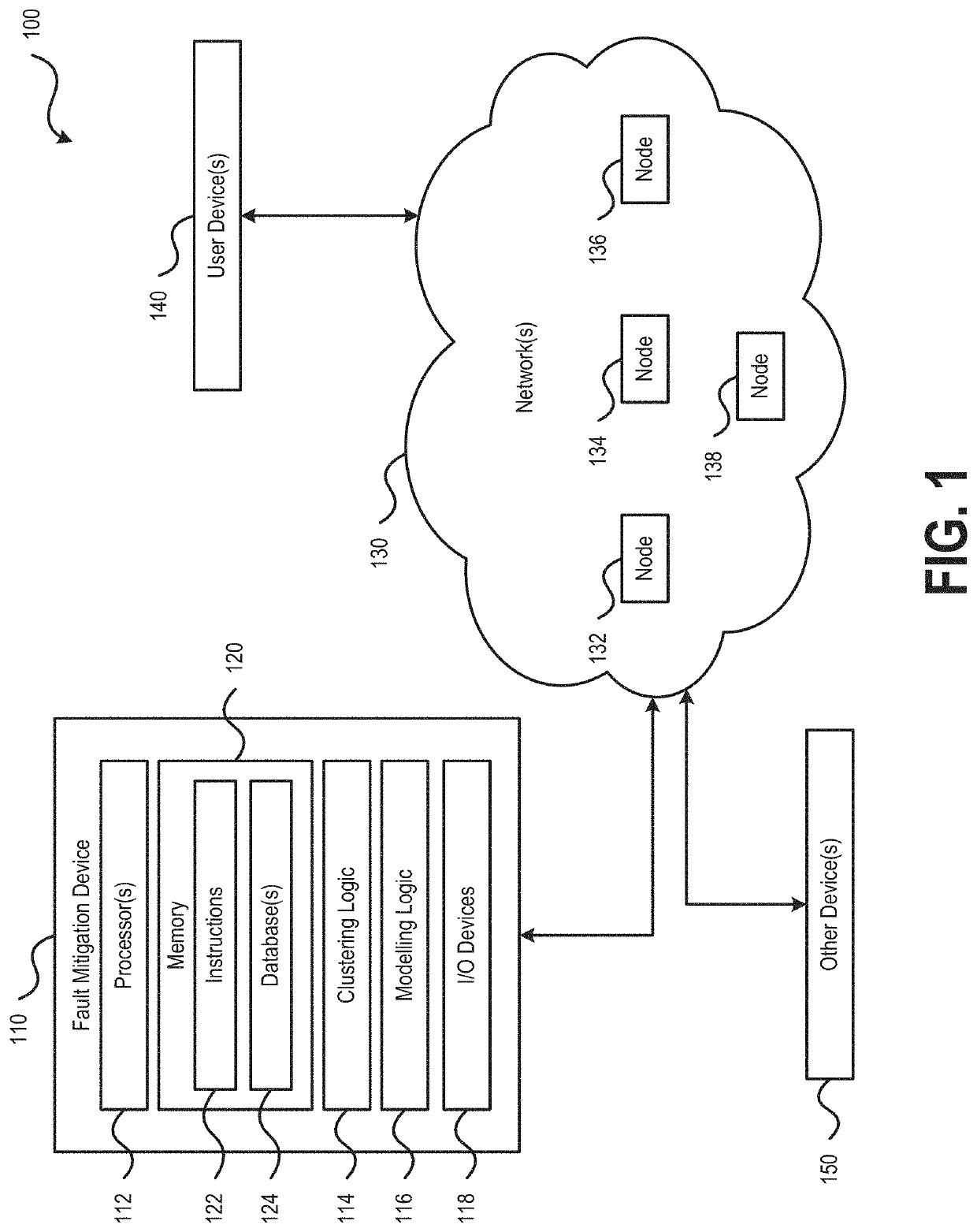
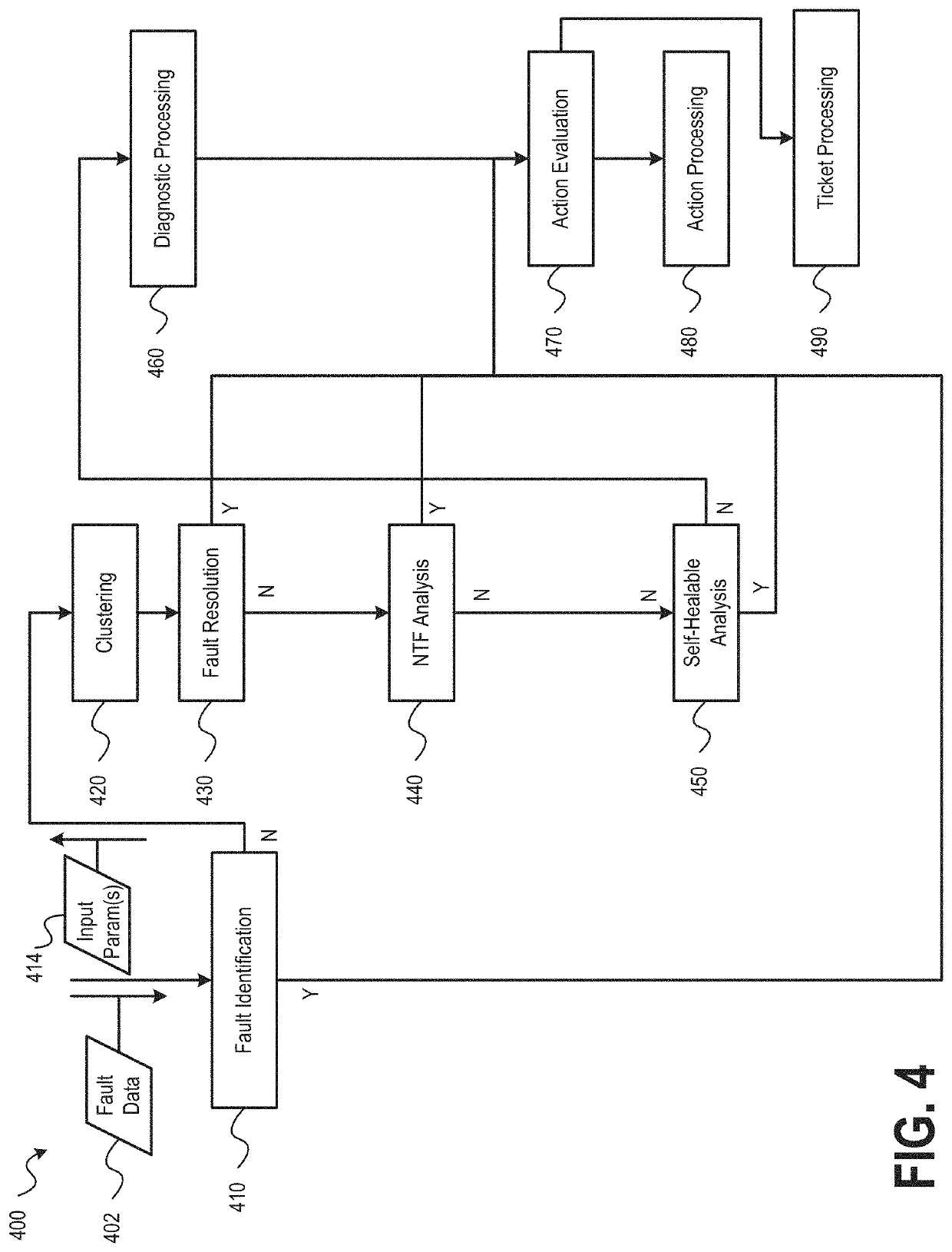
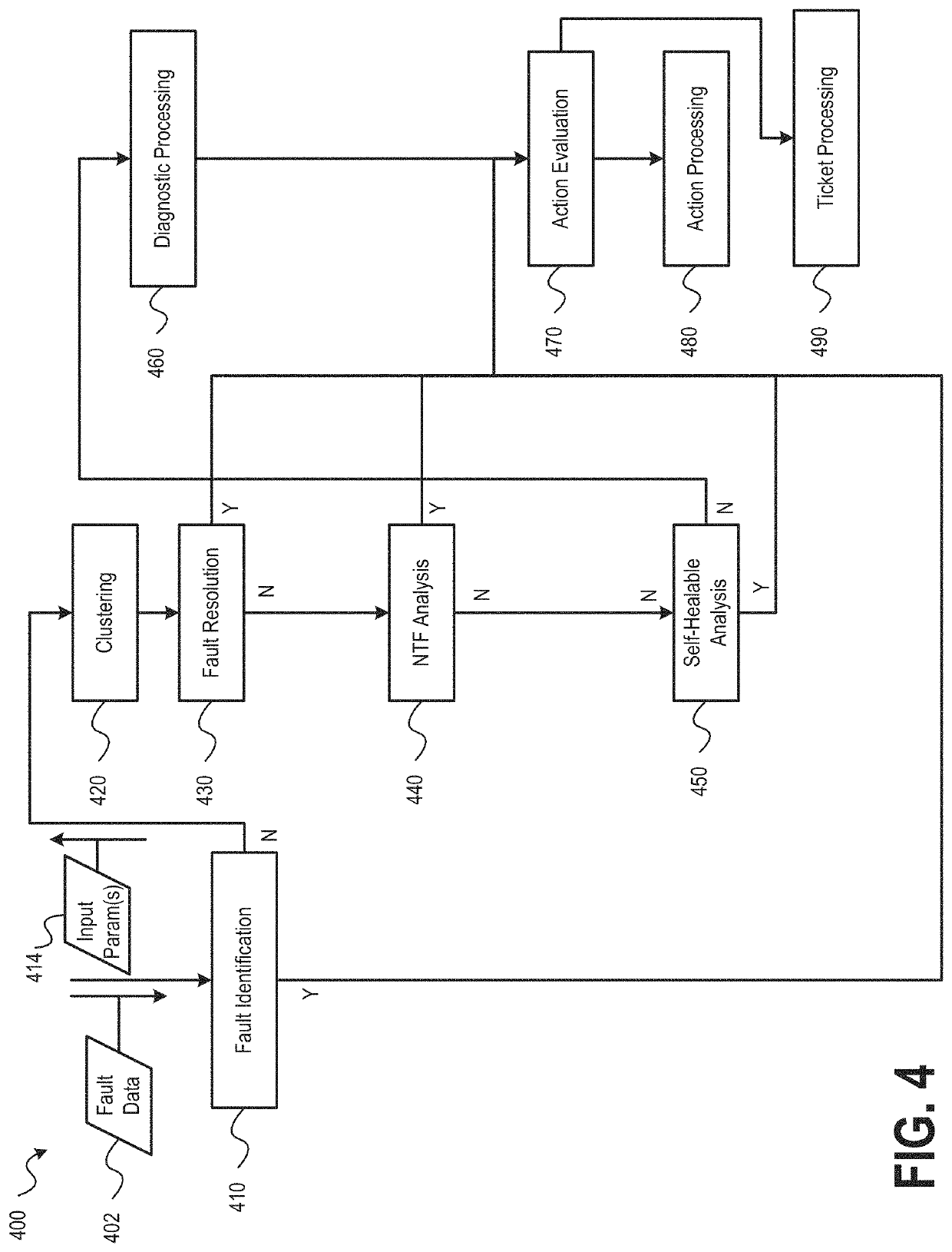
Intelligent network operation platform for network fault mitigation
ActiveUS20210397497A1Rapid diagnosisQuick resolutionNon-redundant fault processingMachine learningIntelligent NetworkCluster algorithm
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SOLUTIONS LTD
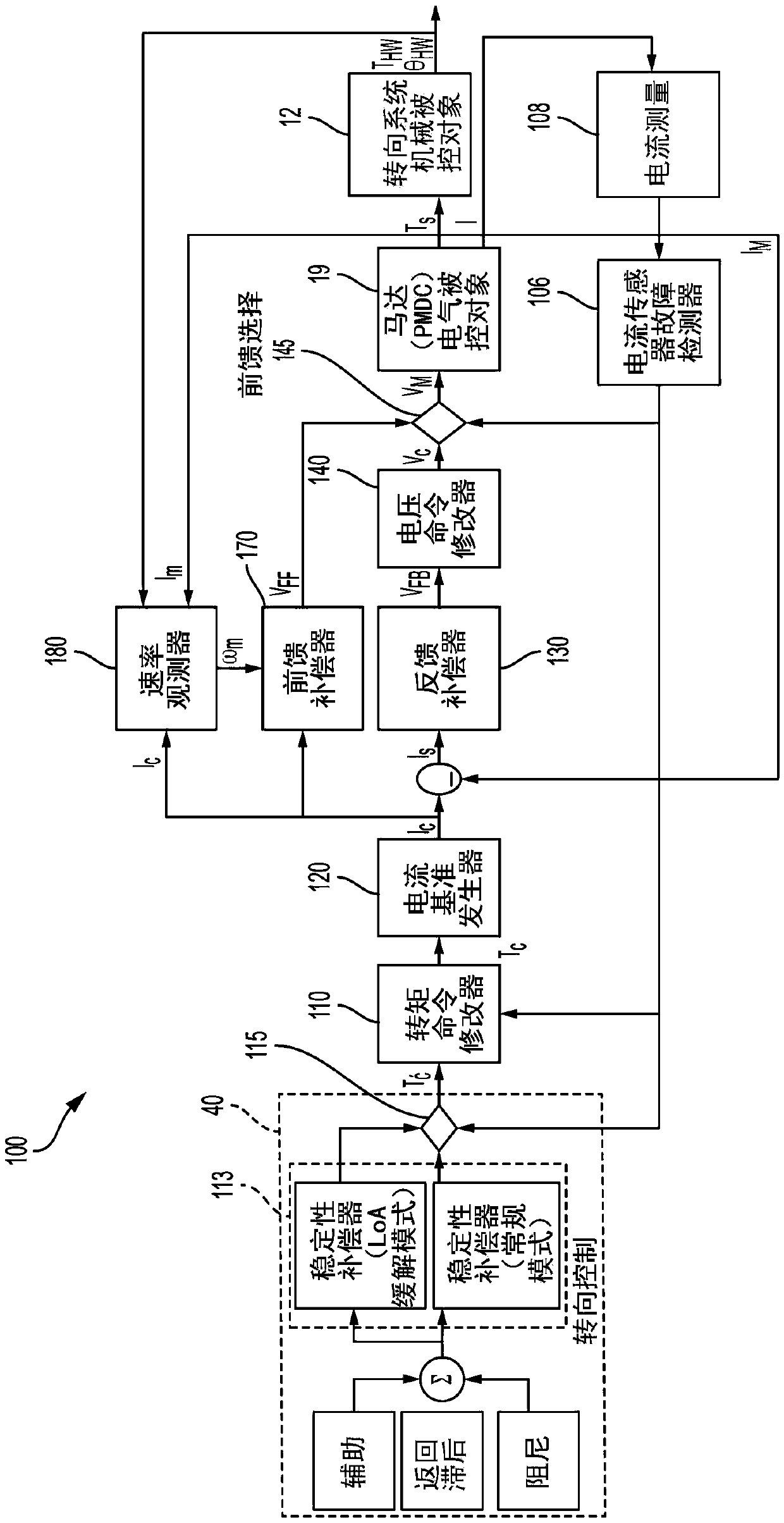
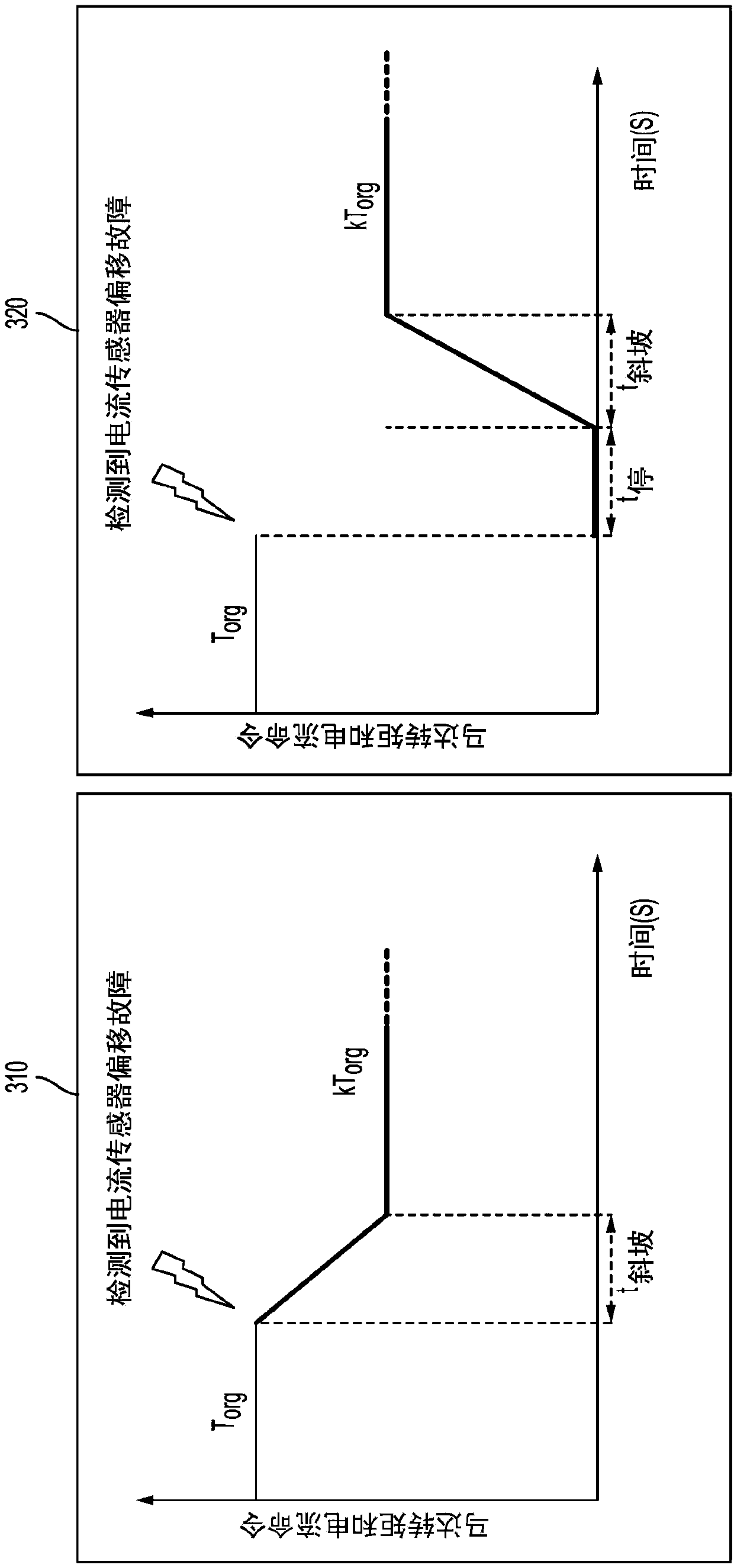
Current sensor fault mitigation for steering systems with permanent magnet DC drives
ActiveCN109756169AElectronic commutation motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlControl systemCurrent sensor
Technical solutions are described for current sensor fault mitigation for systems with permanent magnet DC drives. An example power steering system includes a brush motor, and a motor control system that generates an amount of torque using the brush motor, the amount of torque corresponding to a torque command. The motor control system includes a current sensor fault detector that detects a current sensor fault associated with a current sensor used to measure a current across the brush motor. The motor control system further includes a velocity observer that computes an estimated motor velocity in response to the current sensor fault. The motor control system further includes a feed forward controller that generates a current command for generating the amount of torque using the brush motor, the current command generated using the estimated motor velocity. The described technical solution solves the technical problem of current sensor fault mitigation of a EPS system based on PMDC drive.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG
Intelligent network operation platform for network fault mitigation
ActiveUS20220114041A1Rapid diagnosisQuick resolutionNon-redundant fault processingMachine learningIntelligent NetworkCluster algorithm
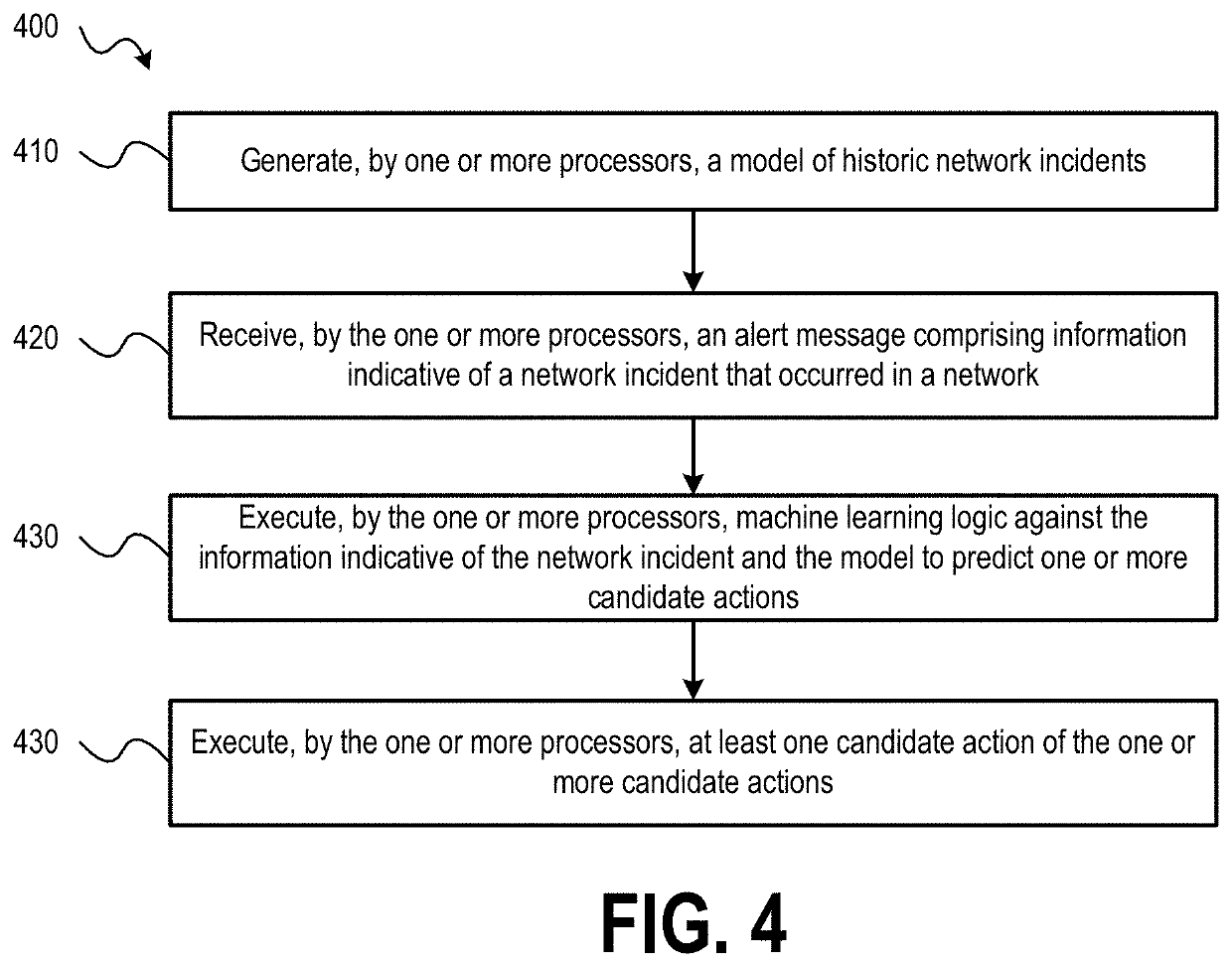
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods, and computer-readable storage media that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify, diagnose, and mitigate occurrences of network faults or incidents within a network. Historical network incidents may be used to generate a model that may be used to evaluate real-time occurring network incidents, such as to identify a cause of the network incident. Clustering algorithms may be used to identify portions of the model that share similarities with a network incident and then actions taken to resolve similar network incidents in the past may be identified and proposed as candidate actions that may be executed to resolve the cause of the network incident. Execution of the candidate actions may be performed under control of a user or automatically based on execution criteria and the configuration of the fault mitigation system.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SOLUTIONS LTD
System and method of redundancy management for fault effect mitigation
ActiveUS7693616B2Navigation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlFly-by-wireControl signal
Methods and systems are provided for redundancy management of a fly-by-wire avionics system. A control module for producing a control signal is provided comprising a common processing partition for receiving a flight input signal and at least one first mode input signal, a first processing partition coupled to the common processing partition and configured to receive the first mode input signals and flight input signal from the common processing partition, and a second processing partition coupled to the common processing partition. The first processing partition produces a first mode output signal in response to one of the first mode input signals and flight input signal. The second processing partition generates a second mode signal in response to the flight input signal when the first processing partition fails. The common processing partition produces the control signal in response to one of the first mode output signal and second mode signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fault mitigation for electrical actuator using regulated voltage control
ActiveUS20190036321A1RemissionDecrease duty cycleElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringControl theory
A method for mitigating an electrical actuator fault in a system containing multiple actuators includes: applying multiple predetermined conditions to each of multiple actuators in a vehicle system to identify when at least one of the multiple actuators is in a faulted condition; and increasing an input voltage to all of the actuators to increase an output of the at least one of the multiple actuators in the faulted condition to mitigate the faulted condition.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Intelligent network operation platform for network fault mitigation
ActiveUS11204824B1Rapid diagnosisQuick resolutionNon-redundant fault processingMachine learningIntelligent NetworkCluster algorithm
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods, and computer-readable storage media that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify, diagnose, and mitigate occurrences of network faults or incidents within a network. Historical network incidents may be used to generate a model that may be used to evaluate real-time occurring network incidents, such as to identify a cause of the network incident. Clustering algorithms may be used to identify portions of the model that share similarities with a network incident and then actions taken to resolve similar network incidents in the past may be identified and proposed as candidate actions that may be executed to resolve the cause of the network incident. Execution of the candidate actions may be performed under control of a user or automatically based on execution criteria and the configuration of the fault mitigation system.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SOLUTIONS LTD
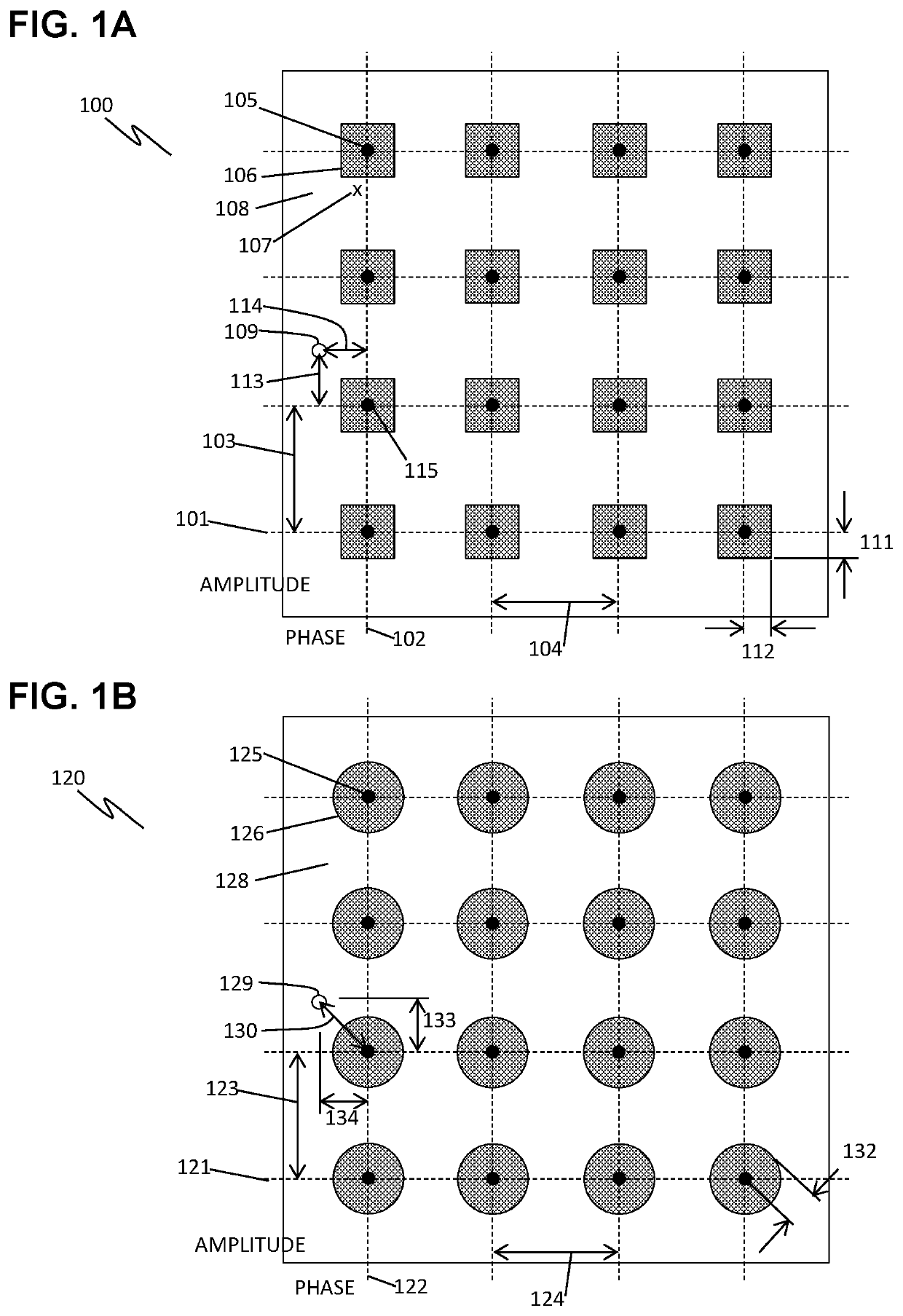
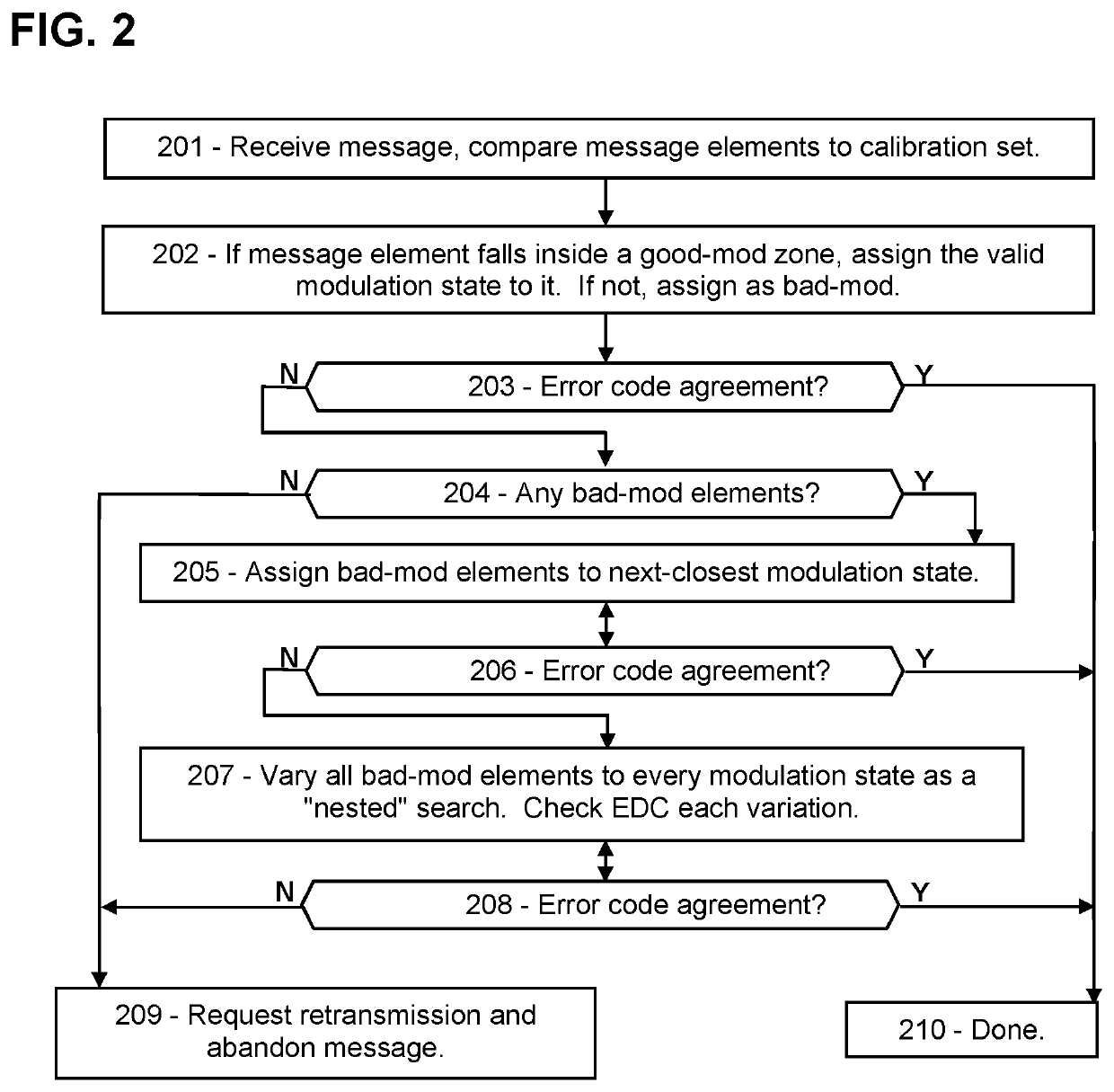
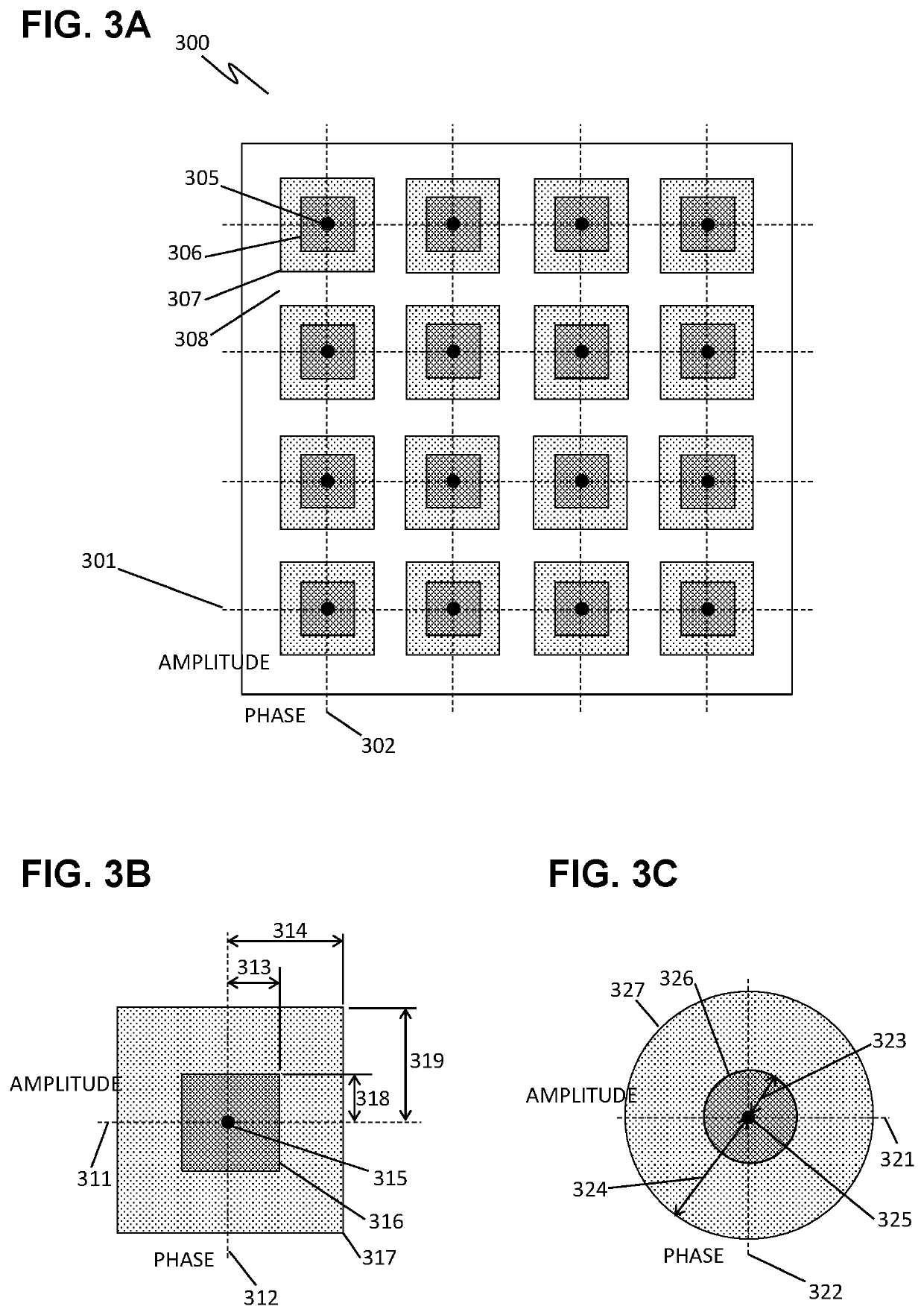
Error Correction by Merging Copies of 5G/6G Messages
ActiveUS20220140938A1Transmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringResource elementDistributed computing
Disclosed are procedures for measuring the modulation quality of each message resource element in a failed 5G or 6G communication, thereby revealing the most likely fault locations in the message. The types of modulation deviations in the low-quality message elements can provide further guidance as to the correct demodulation. In addition, after receiving a second copy, the copies can be merged by selecting the highest quality message elements from each version, where the quality is related to how far each message element's modulation deviates from the calibrated “states” of the modulation scheme. The receiver may also determine directional information based on the modulation of each message element, and may compare versions to determine the most likely correct state of each message element. Such strategies may directly recover the original message, or may greatly reduce the number of variations that need to be tested. When implemented, fault mitigation as disclosed herein can resolve message failures, improve communication reliability, reduce latency, and improve network operations overall, according to some embodiments.
Owner:ULTRALOGIC 6G LLC
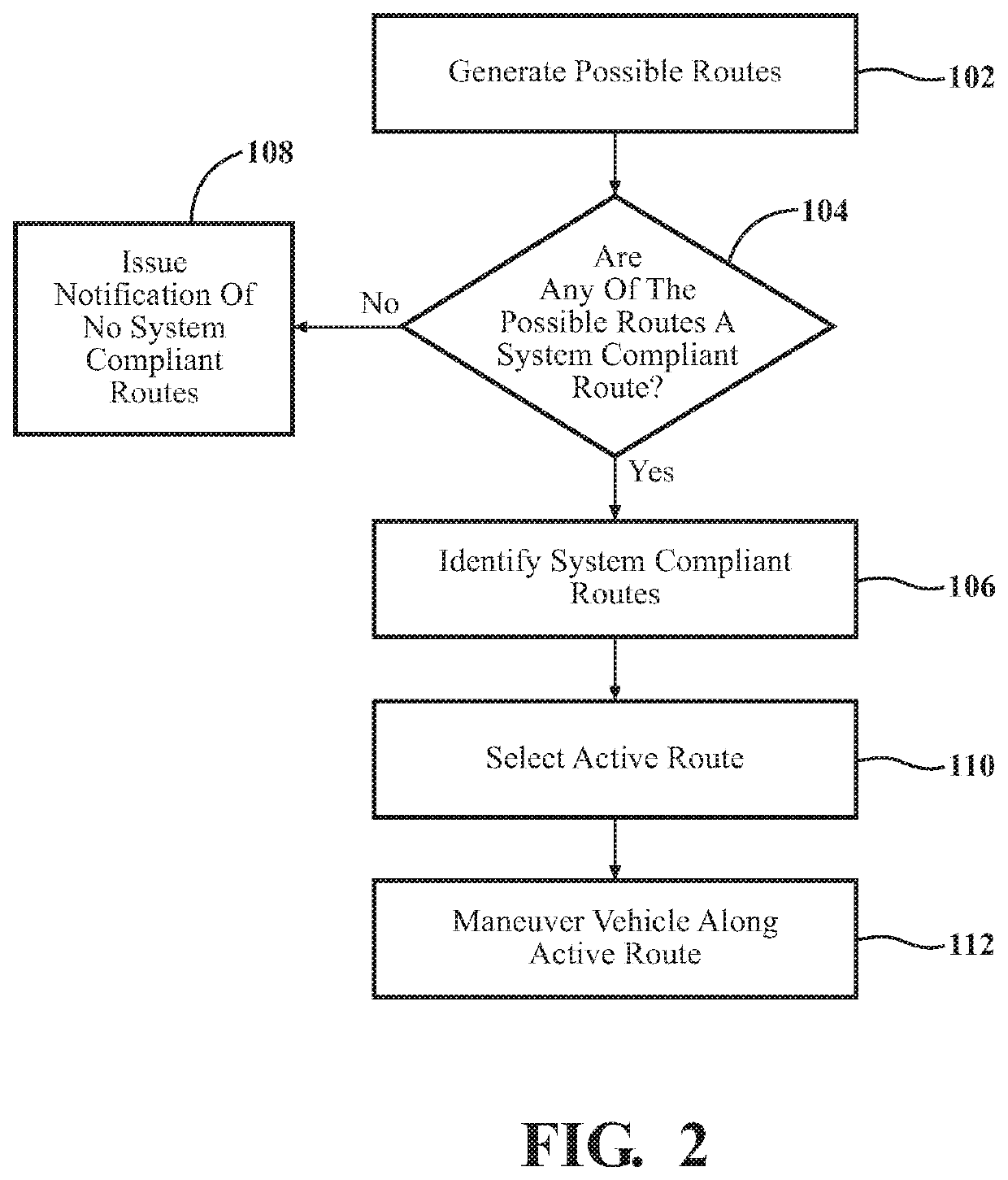
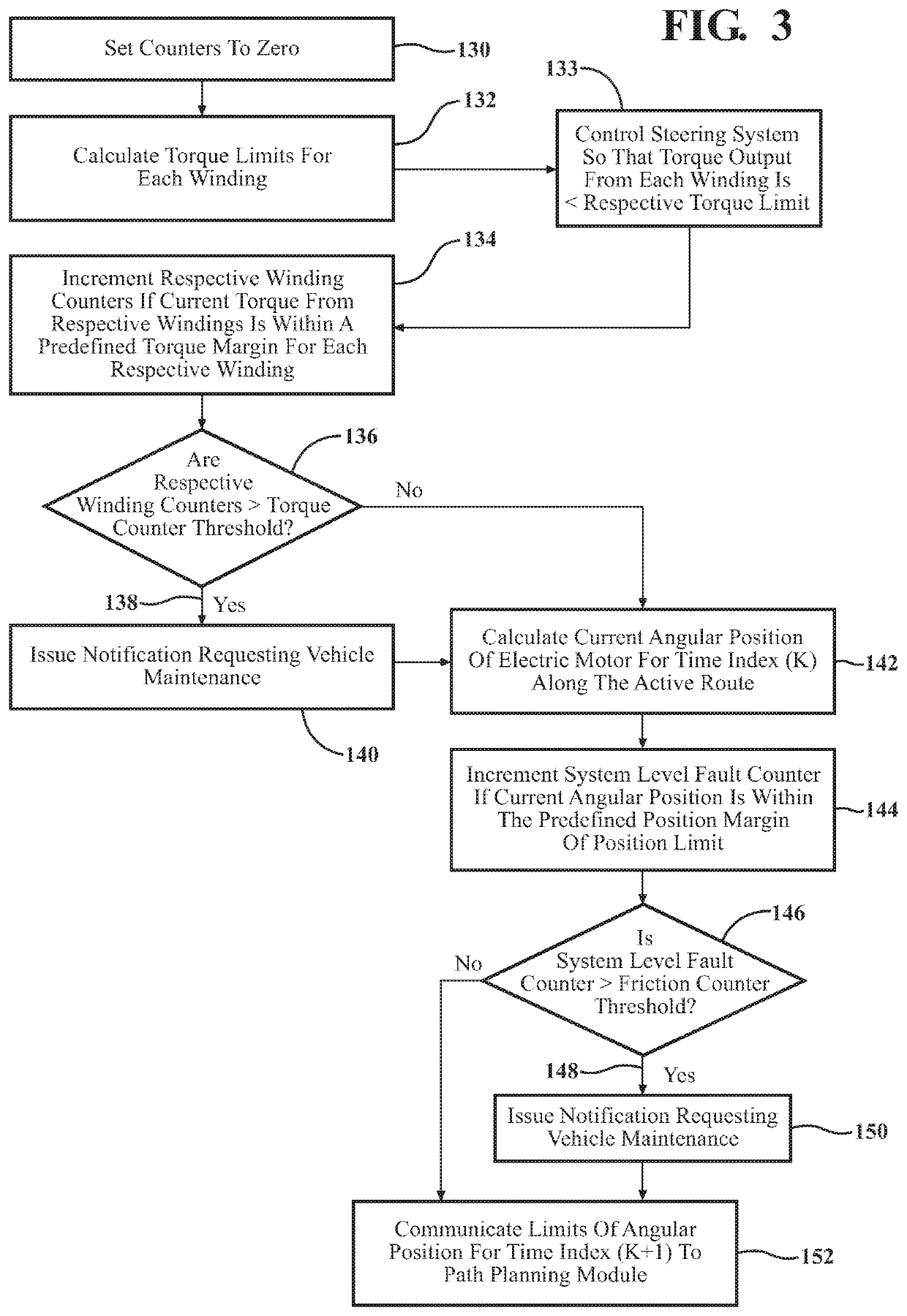
System and method of predictive fault mitigation for electric power steering system in a vehicle
InactiveUS20200023891A1Reduce functionReduce restrictionsAutonomous decision making processRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectric power steeringControl engineering
A method of controlling a vehicle having an electric power steering system includes generating a plurality of possible routes. Each of the plurality of possible routes that require a steering torque that is within an available torque range is identified as a system compliant route. Each of the plurality of possible routes that require an angular position of an electric motor of the electric power steering system at all time indices throughout that route that are within an available motor position range are also identified as a system compliant route. One of the identified system compliant routes is selected based on at least one selection criteria, and designated as an active route. The electric power steering system is then controlled to maneuver the vehicle along the active route. The electric power steering system is monitored as the vehicle moves along the active route to identify degradation of its capabilities.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
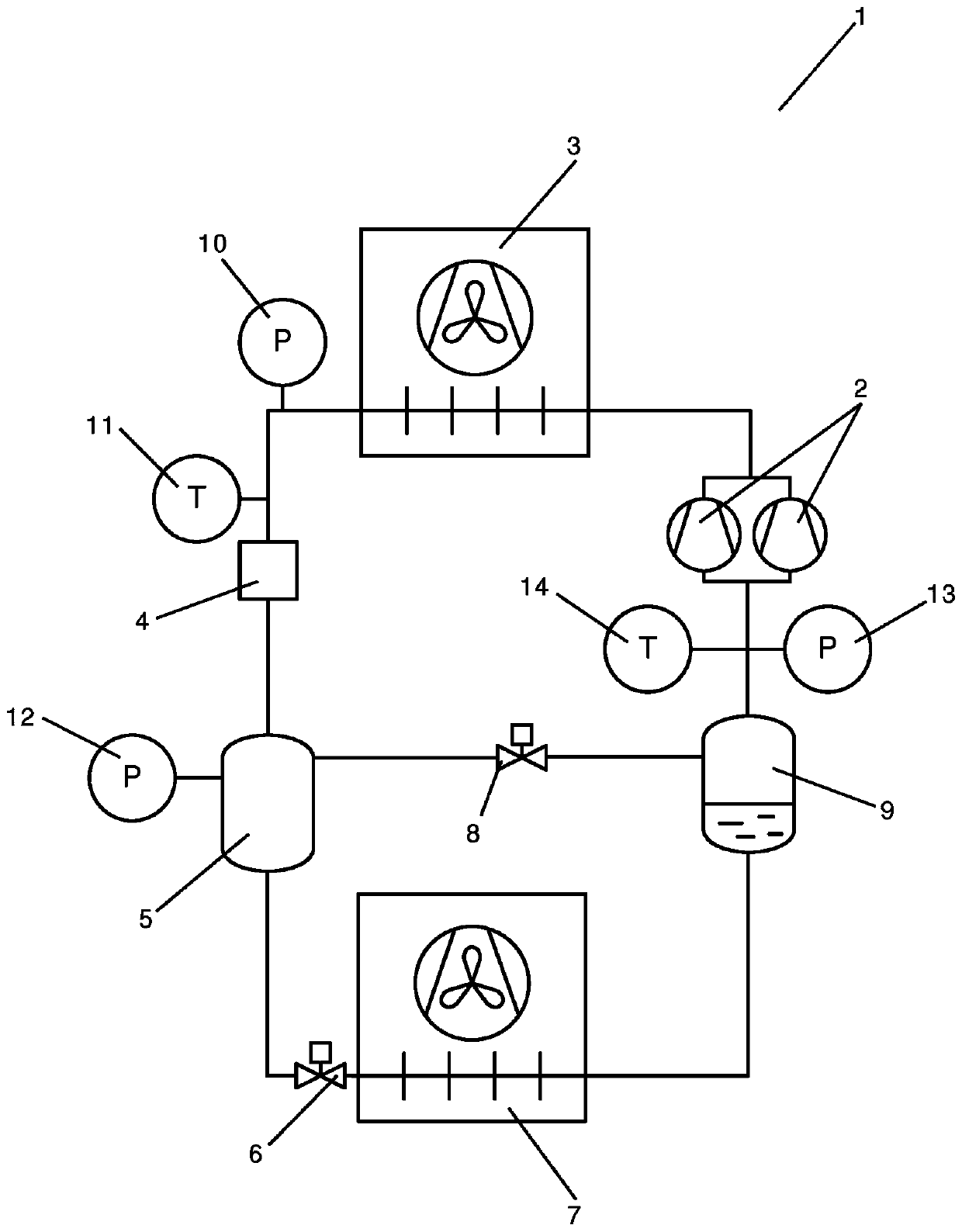
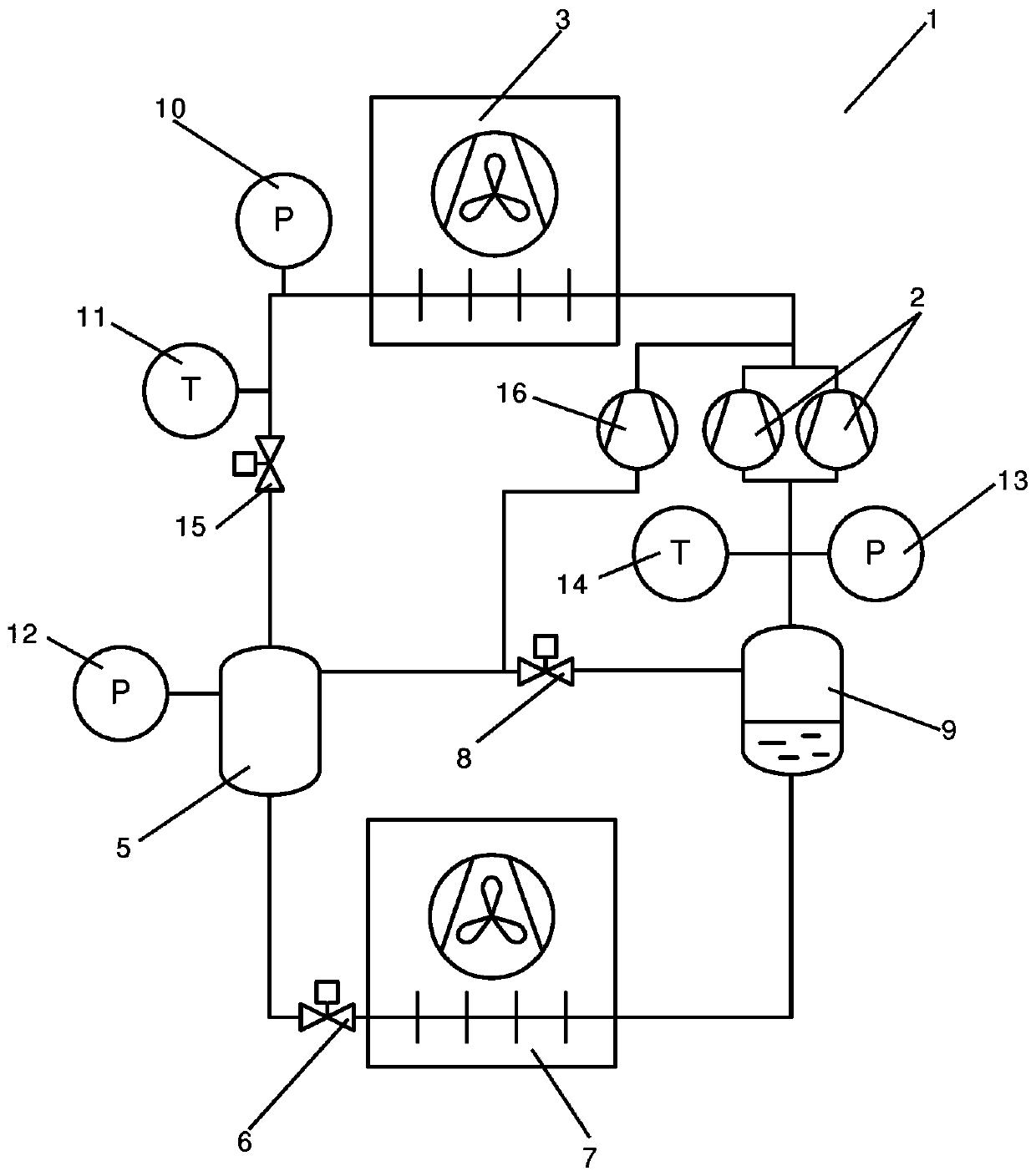
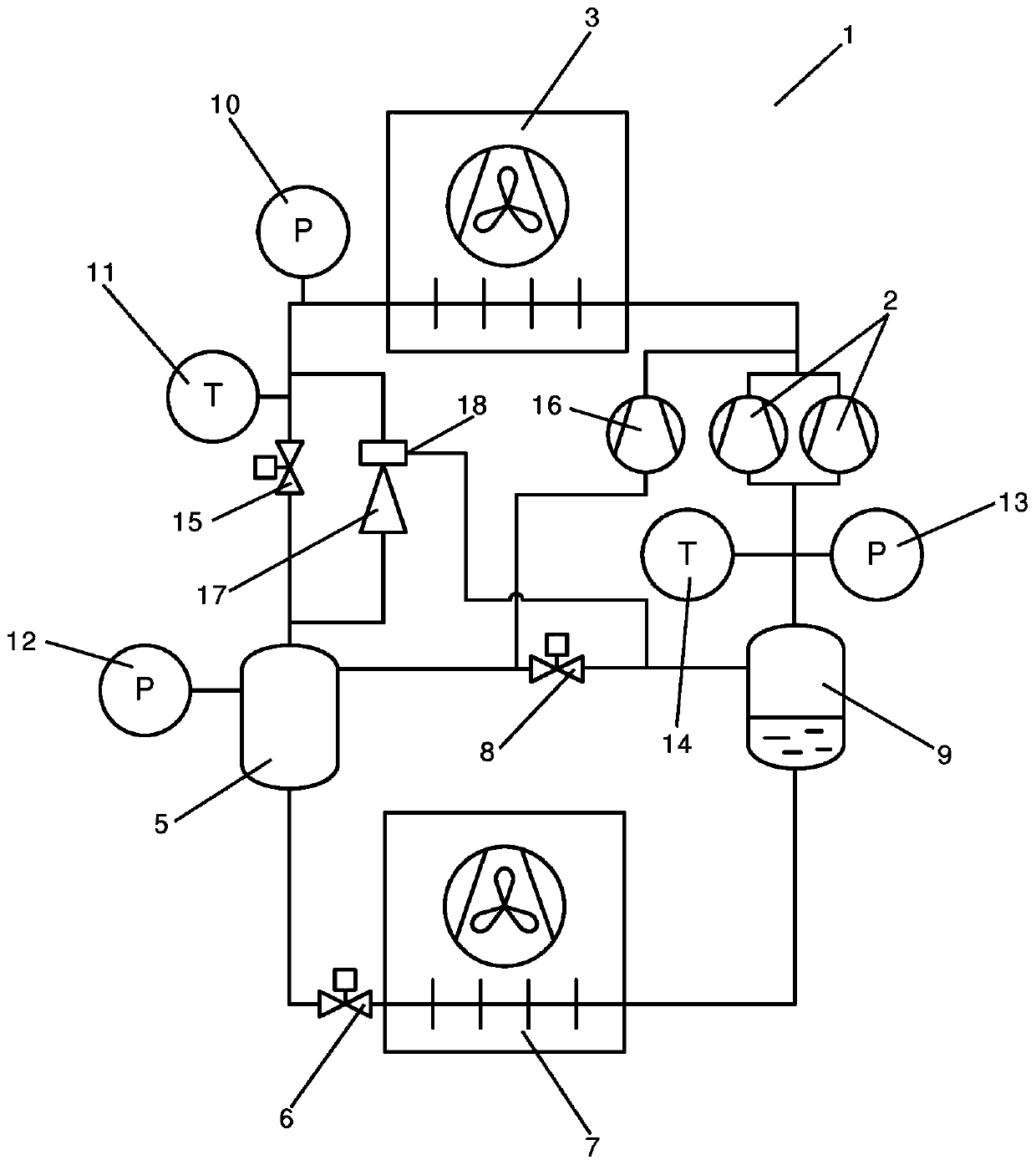
A method for handling fault mitigation in a vapour compression system
A method for controlling a vapour compression system (1) is disclosed. A mass flow of refrigerant along a part of the refrigerant path is estimated, based on measurements performed by one or more pressure sensors (10, 12, 13) for measuring a refrigerant pressure at selected positions along the refrigerant path and one or more temperature sensors (11, 4) for measuring a refrigerant temperature at selected positions along the refrigerant path. A refrigerant pressure or a refrigerant temperature at a selected position a pressure sensor (10, 12, 13) or temperature sensor (11, 14) along the refrigerant path is derived, based on the estimated mass flow. The vapour compression system (1) is allowed to continue operating, even if a sensor (10, 11, 12, 13, 14) is malfunctioning or unreliable.
Owner:DANFOSS AS
Fault mitigation for electrical actuator using regulated voltage control
ActiveUS10615585B2Decrease duty cycleIncrease productionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl theoryVoltage control
A method for mitigating an electrical actuator fault in a system containing multiple actuators includes: applying multiple predetermined conditions to each of multiple actuators in a vehicle system to identify when at least one of the multiple actuators is in a faulted condition; and increasing an input voltage to all of the actuators to increase an output of the at least one of the multiple actuators in the faulted condition to mitigate the faulted condition.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
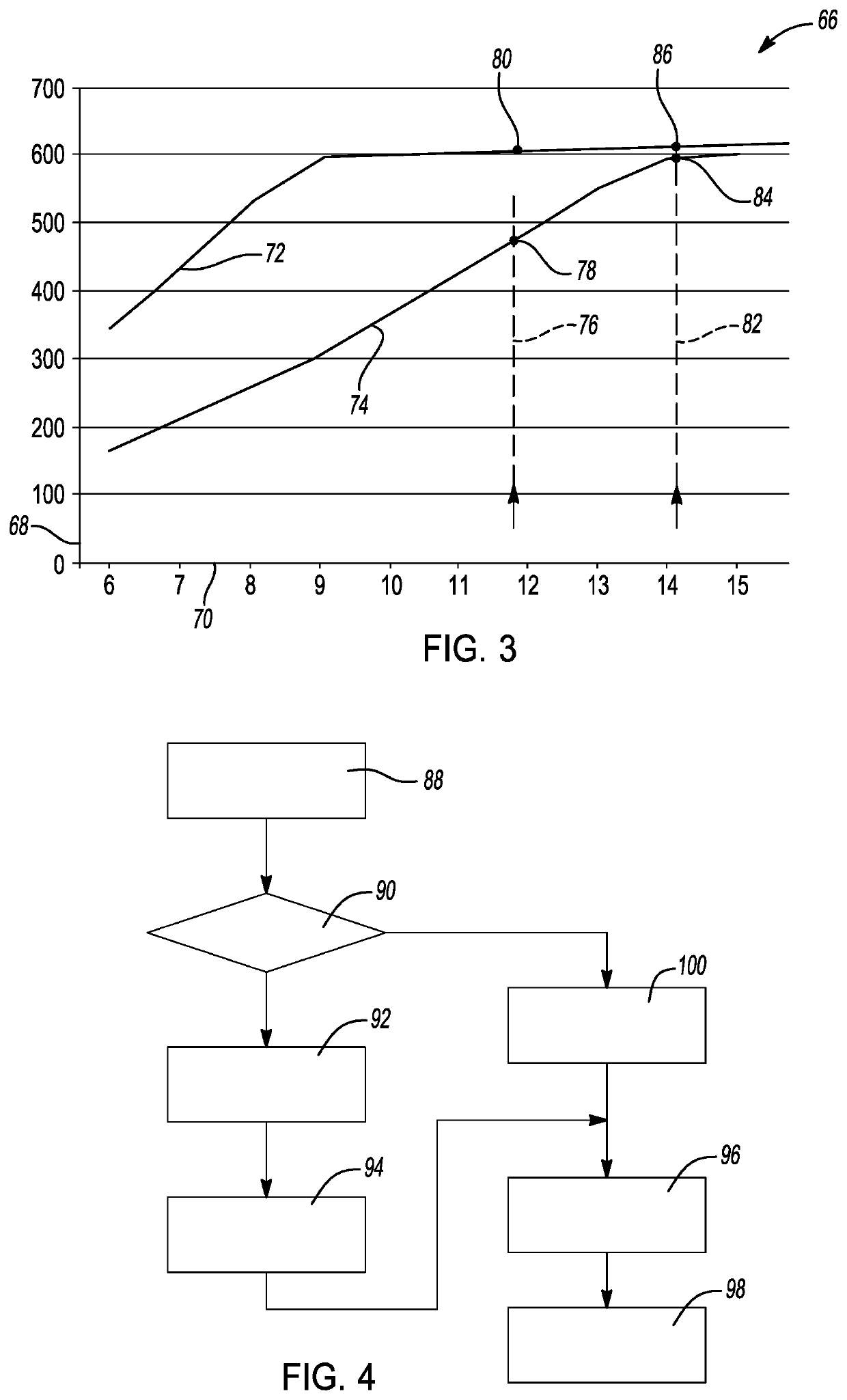
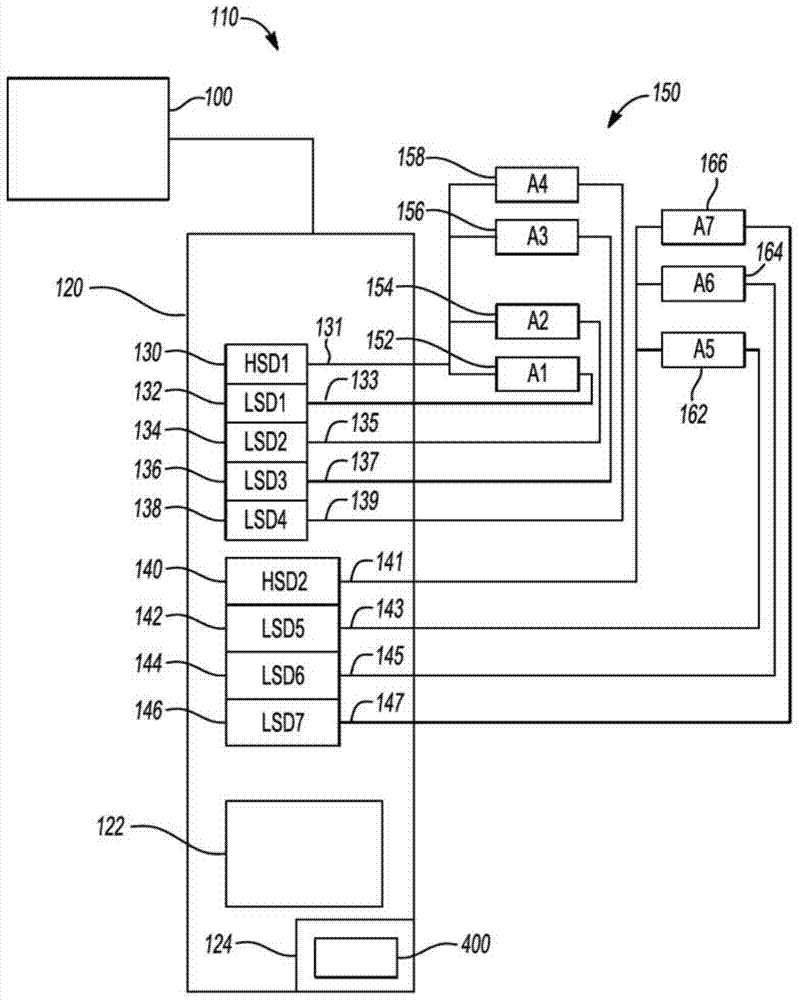
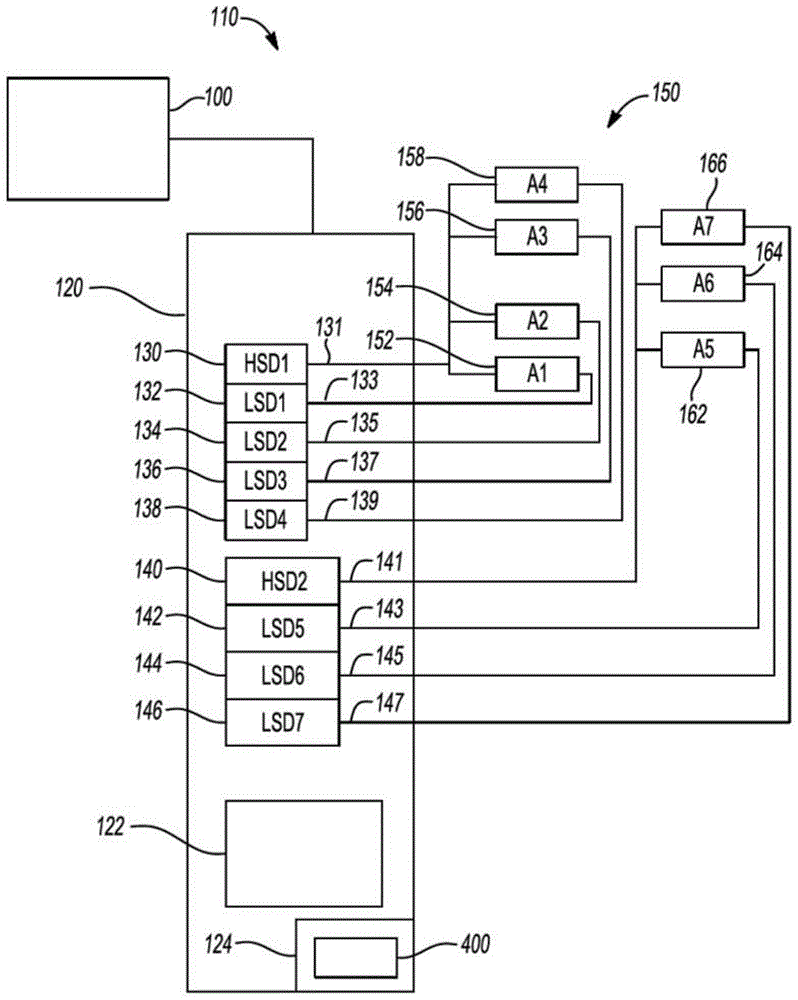
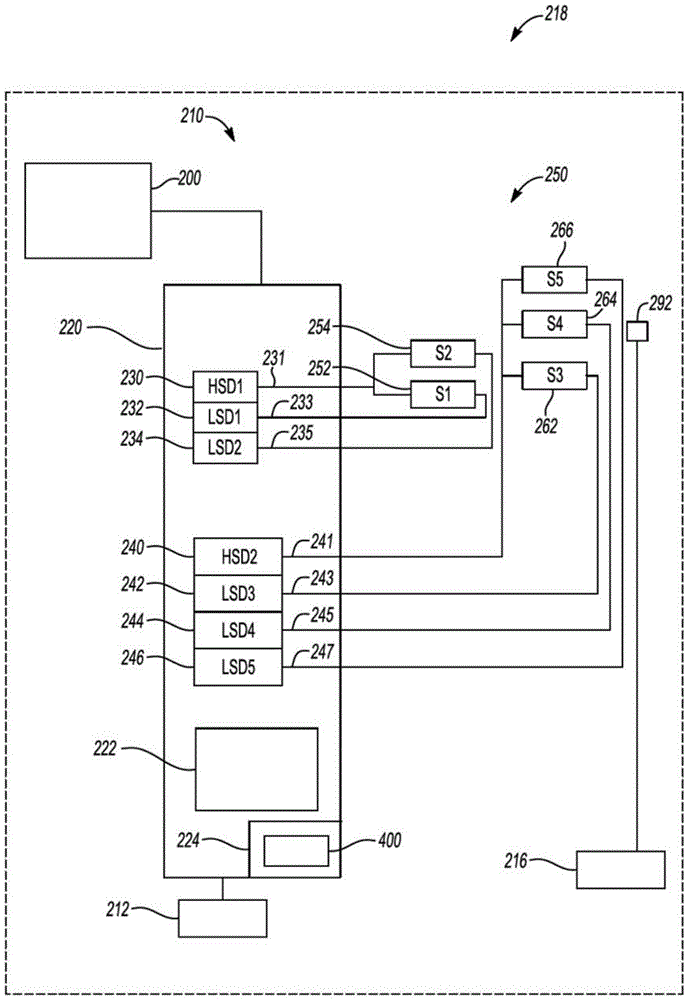
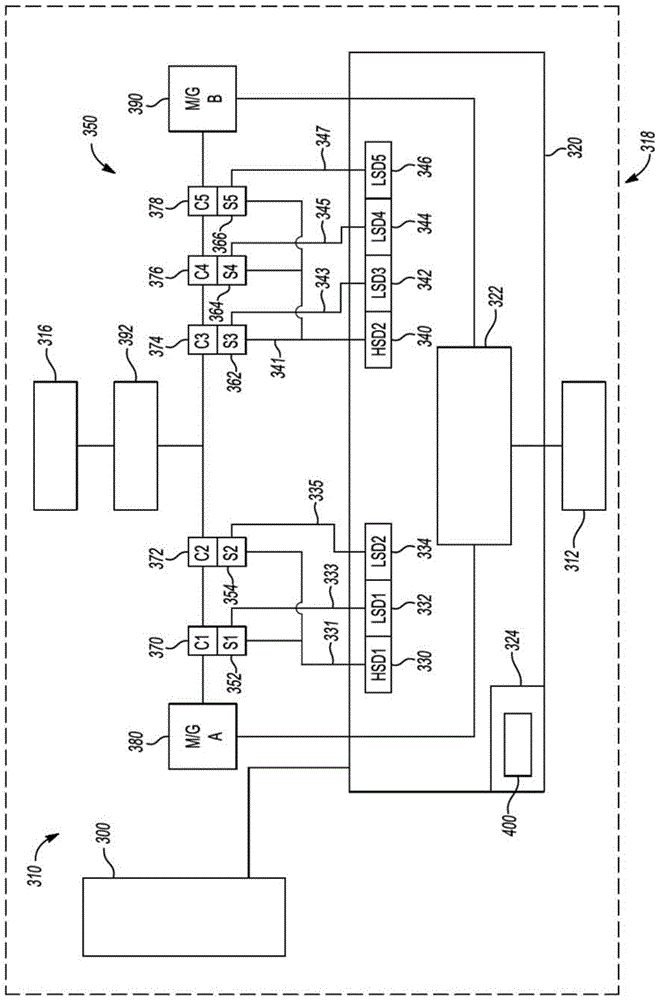
System and method for providing fault mitigation for vehicle system
A system and method for providing fault mitigation in a vehicle system are provided. The vehicle system has high side drivers (HSDs) and low side drivers (LSDs) are provided. The system includes a first HSD and a plurality of first LSDs. The system also includes a selected first plurality of actuators, with each actuator connected to the first HSD and connected to a respective one of the first LSDs to operate in a first operational mode. The system further includes a second HSD and a plurality of second LSDs. The system also includes a selected second plurality of actuators, with each actuator connected to the second HSD and connected to a respective one of the second LSDs to operate in a second operational mode. When a failed component sets a fault, the corresponding HSD is turned off and the other HSD is turned on, enabling the vehicle system to operate in the non-faulted operational mode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
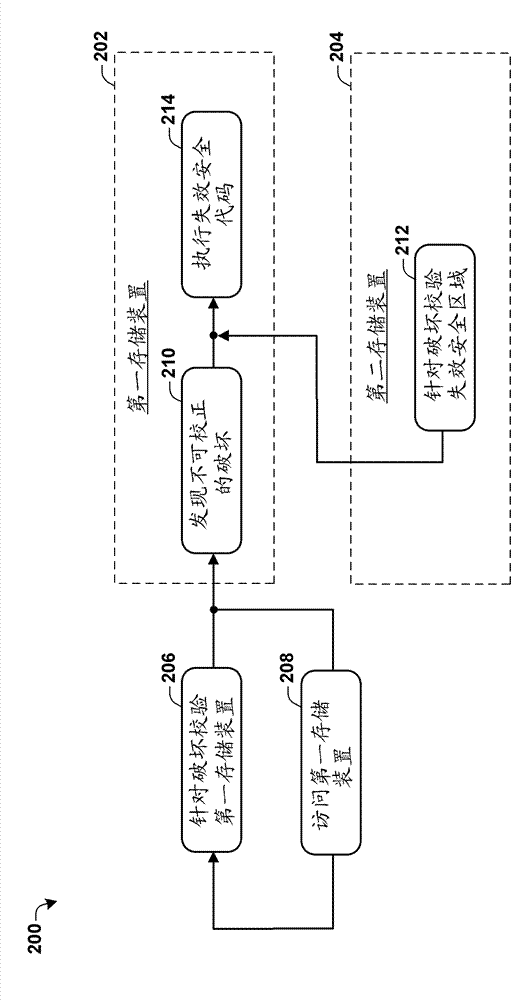
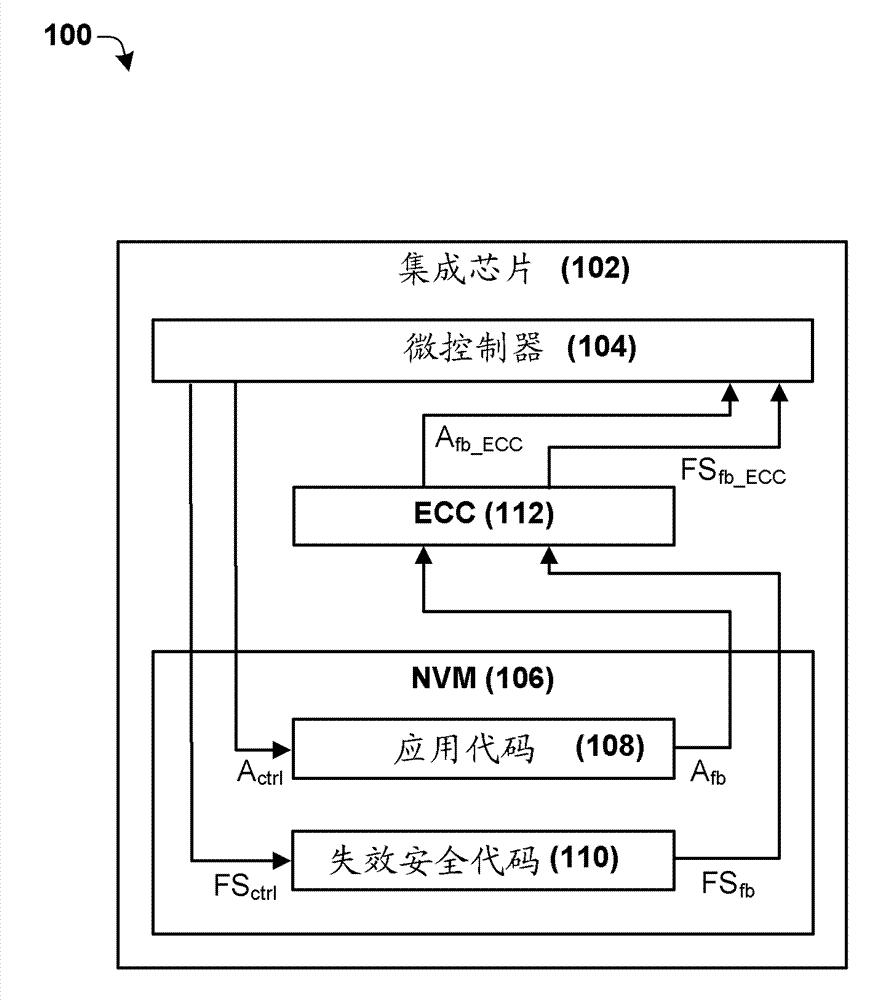
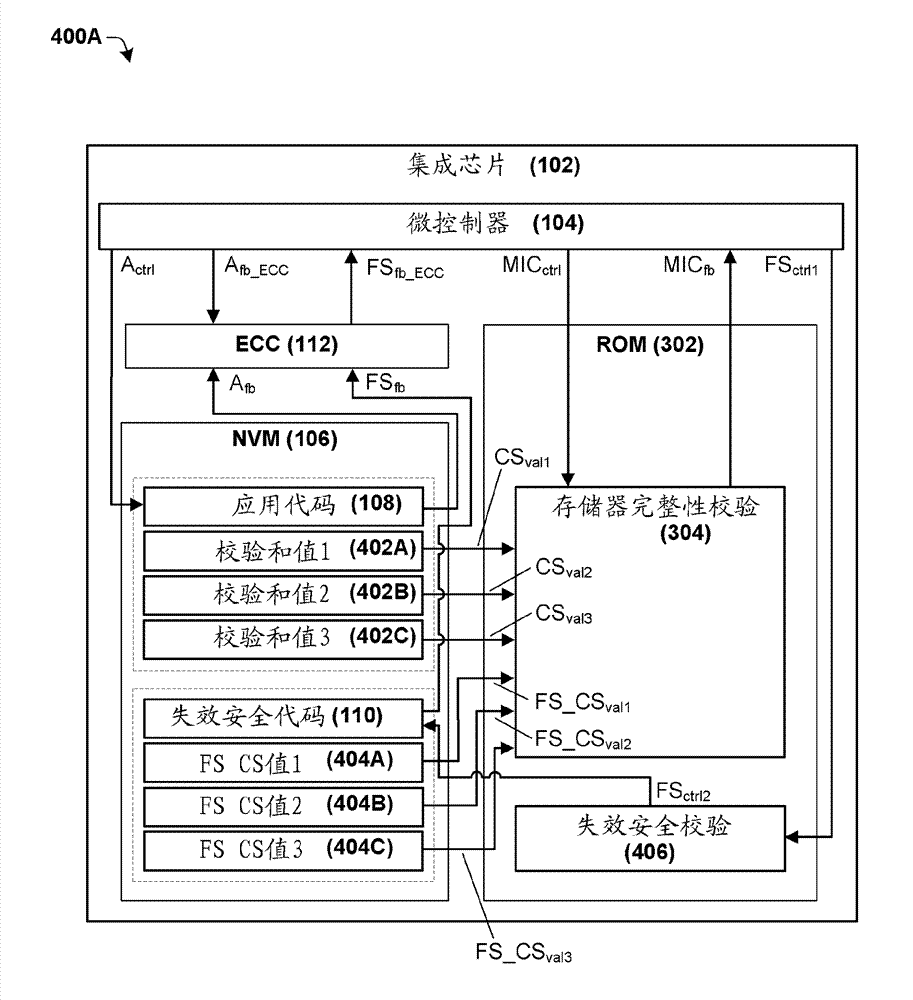
Fail safe code functionality
Some aspects of the present disclosure provide for a system and method for fault mitigation of a non-volatile memory (NVM) store subject to error correction code (ECC) checking. A simple and robust means to test the integrity of failsafe code stored within the non-volatile memory prior to execution are disclosed. In some embodiments, the failsafe code comprises program elements to communicate the memory failure to other parts of the system, or to execute an orderly shutdown. In the event that an ECC error occurs, the failsafe code can be verified, and upon successful verification, executed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
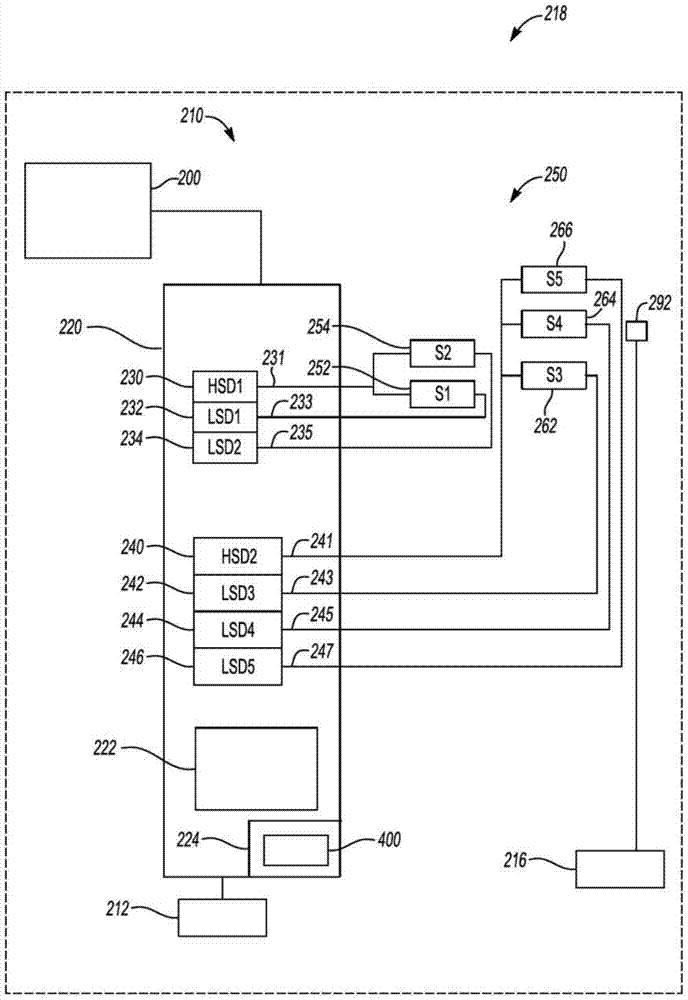
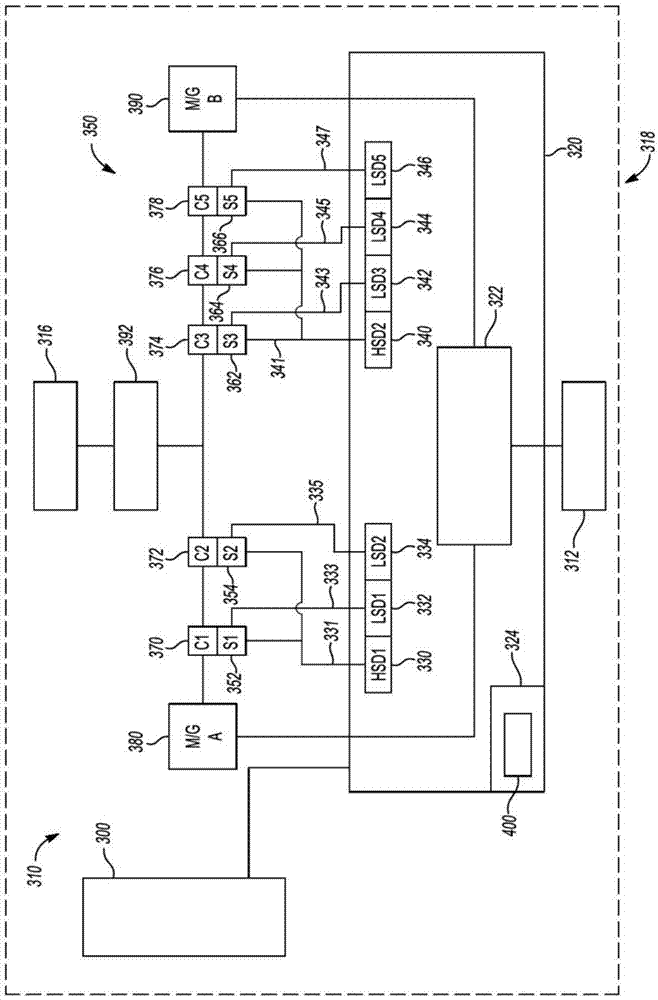
System and method for providing fault mitigation for vehicle systems
Systems and methods are provided for providing fault mitigation in a vehicle system having a high side driver (HSD) and a low side driver (LSD). The system includes a first HSD and multiple first LSDs. The system also includes a selected plurality of first actuators, wherein each actuator is connected to the first HSD and to a corresponding one of the first LSDs to operate in the first mode of operation. The system further includes a second HSD and a plurality of second LSDs. The system also includes a selected plurality of second actuators, wherein each actuator is connected to the second HSD and to a corresponding one of the second LSDs to operate in the second mode of operation. When a failed component sets a fault, the corresponding HSD is switched off and the other HSDs are switched on, enabling the vehicle system to operate in a fault-free operating mode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
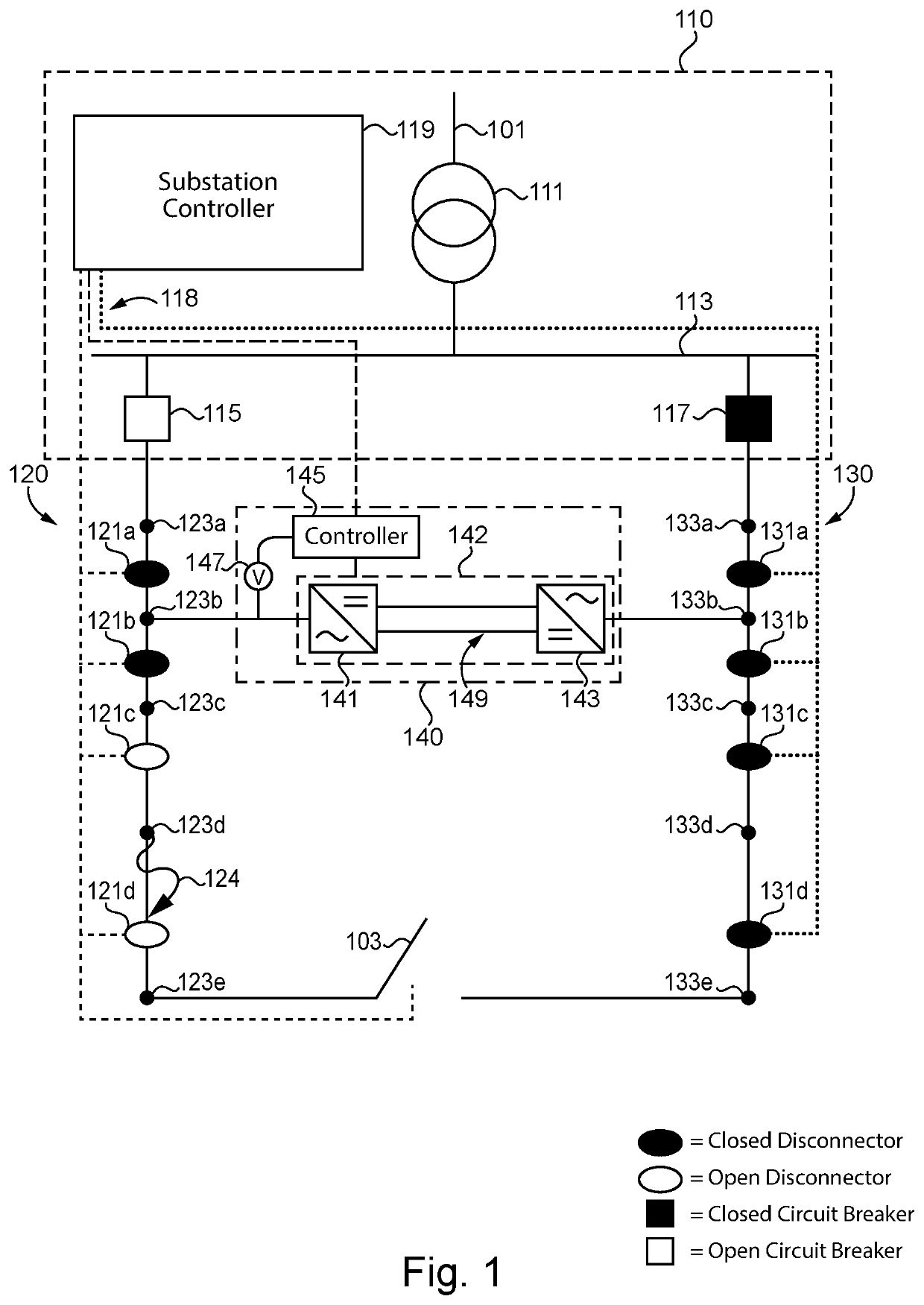
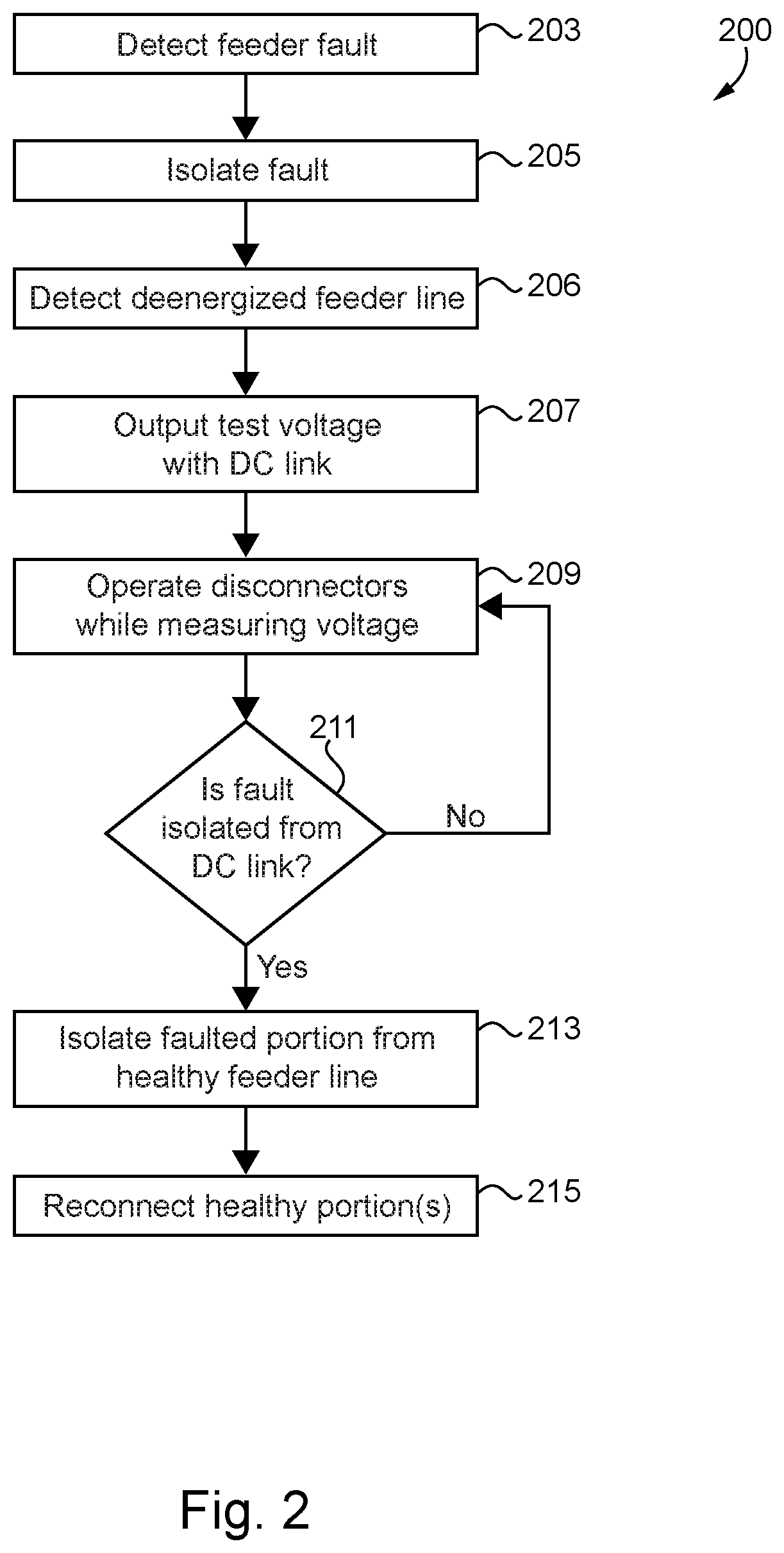
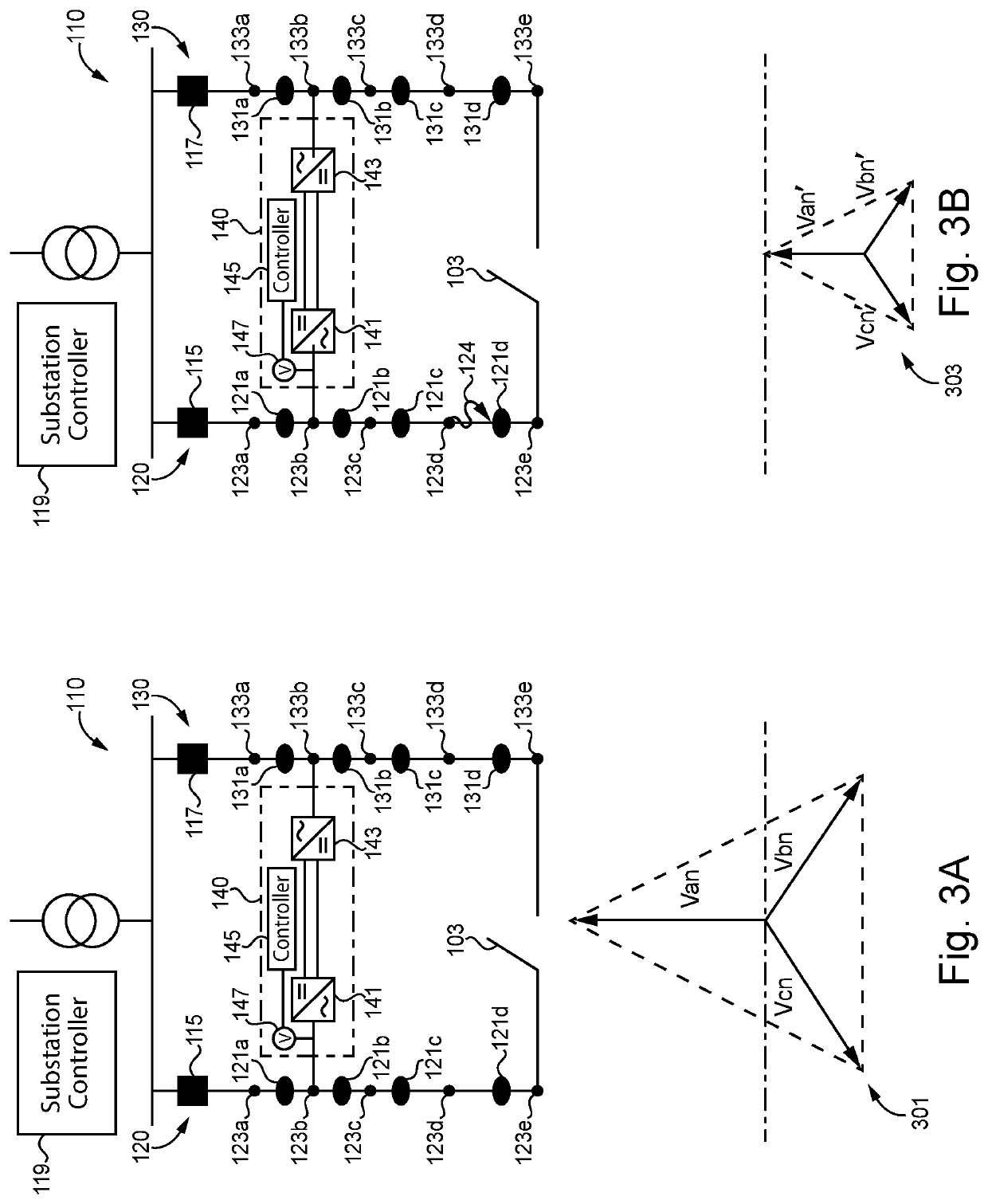
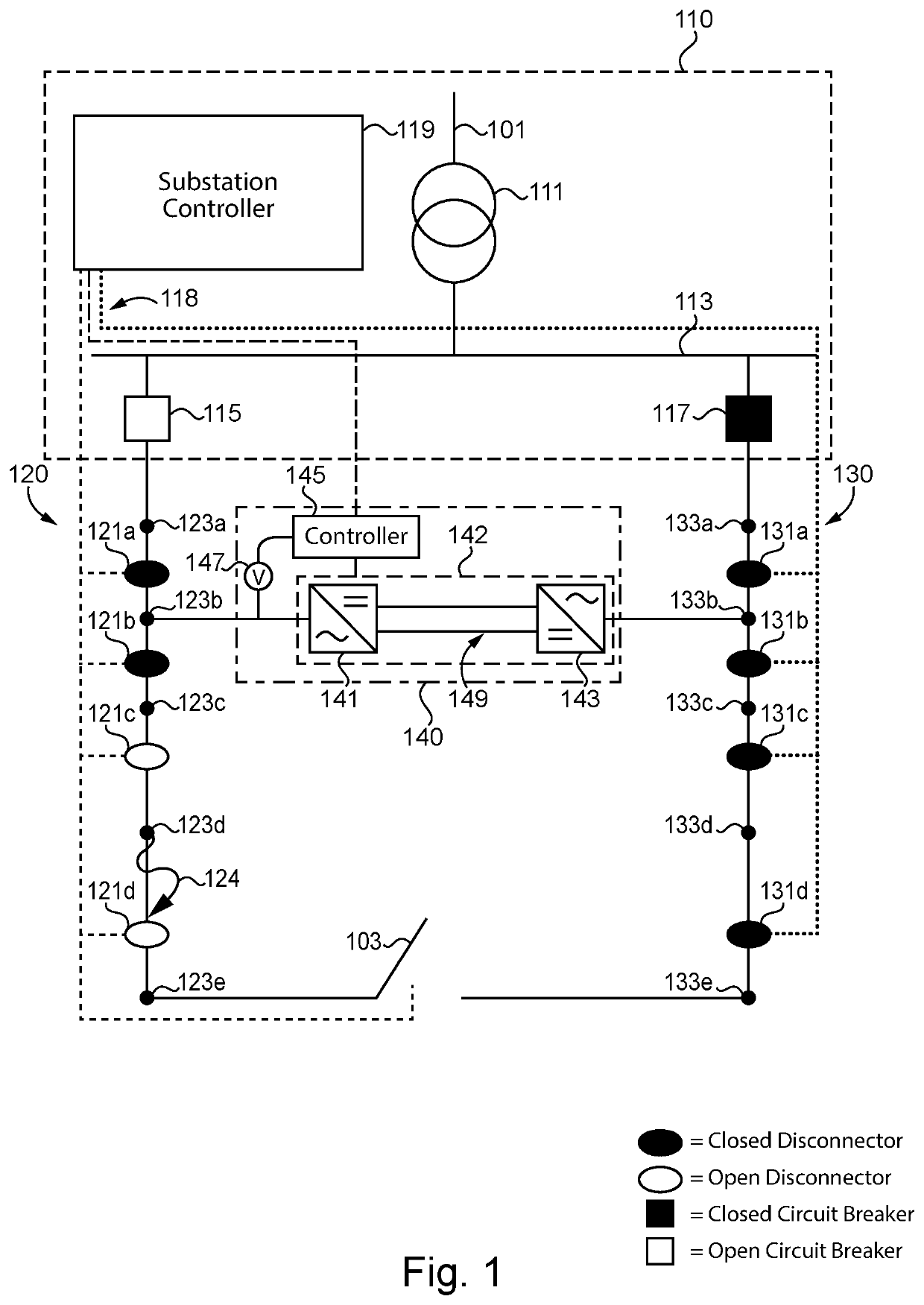
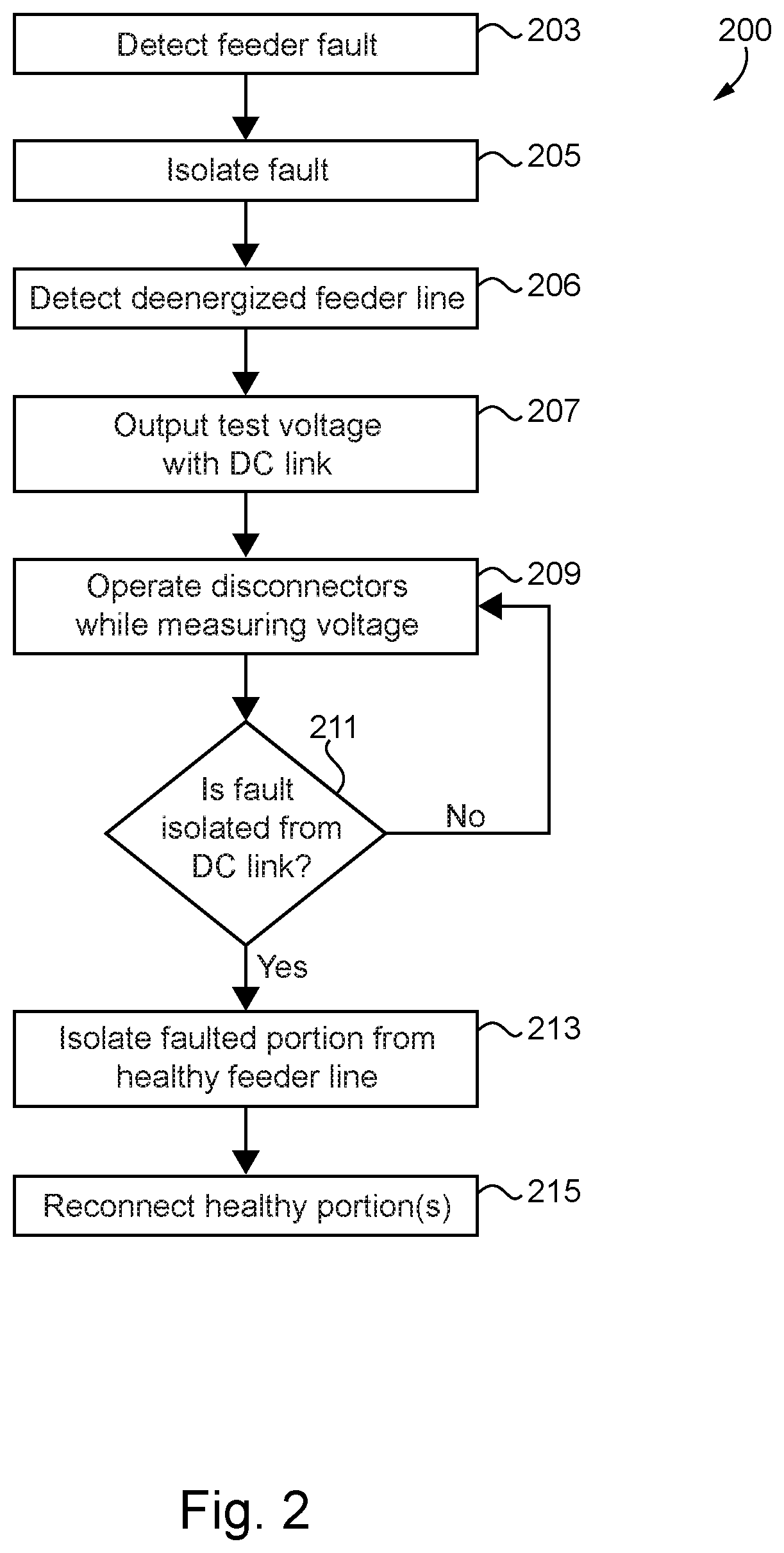
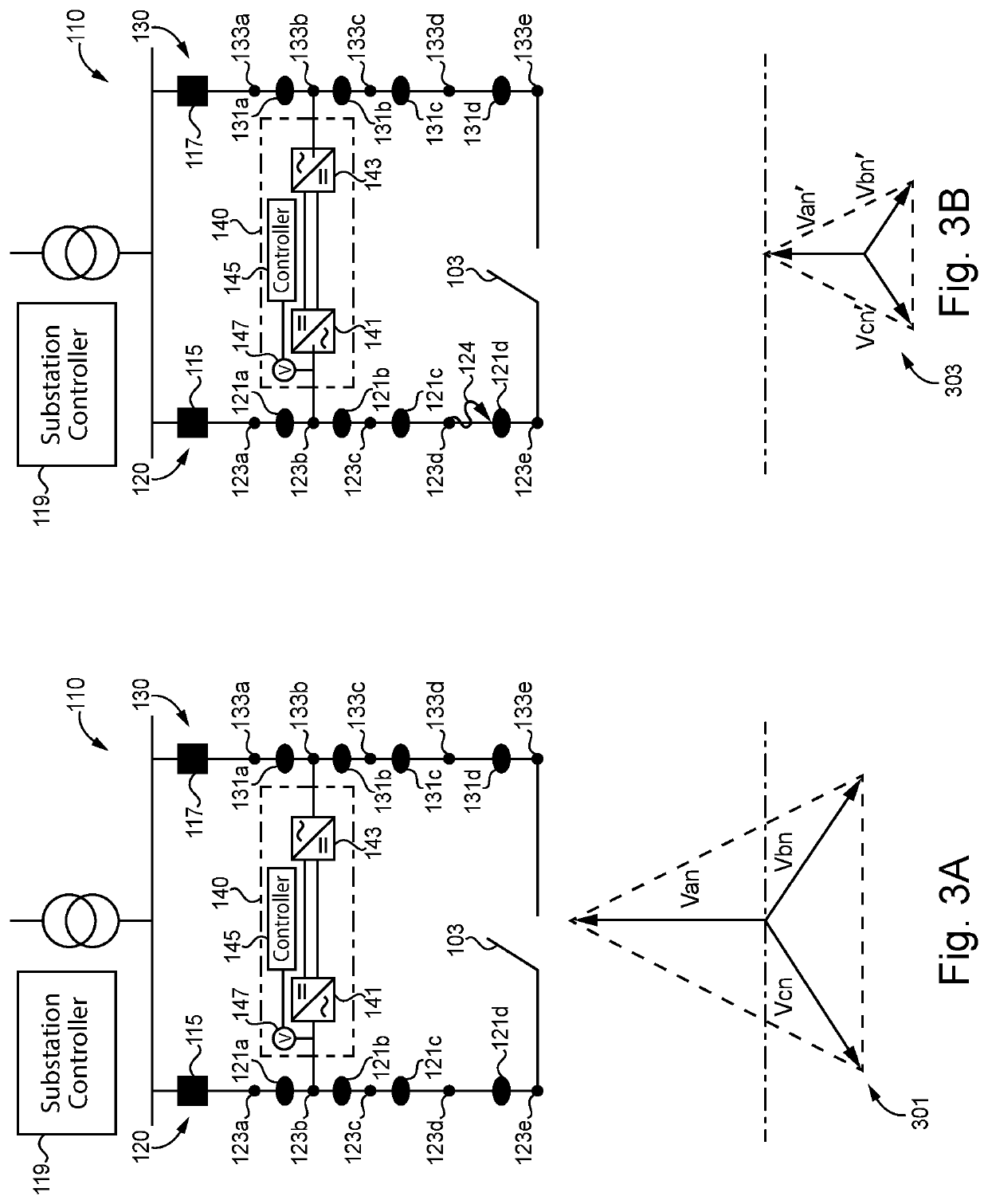
Fault mitigation in medium voltage distribution networks
ActiveUS11121543B2Electric power transfer ac networkEmergency protection detectionLow voltageControl system
Unique systems, methods, techniques and apparatuses of fault mitigation are disclosed. One exemplary embodiment is a fault mitigation system for a medium voltage alternating current (MVAC) distribution network including a direct current (DC) link and a control system. The DC link is coupled to a first feeder line and a second feeder line. The control system is structured to determine a first feeder line is deenergized, operate the DC link so as to receive MVAC from a second feeder line and output low voltage alternating current (LVAC) to the first feeder line, operate a plurality of isolation devices, measure the LVAC in response to operating the plurality of isolation devices, determine a fault is isolated from a healthy portion of the first feeder line using the received LVAC measurements, and reenergize the healthy portion of the first feeder line.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Fault mitigation in medium voltage distribution networks
ActiveUS20200212668A1Electric power transfer ac networkEmergency protection detectionLow voltageControl system
Unique systems, methods, techniques and apparatuses of fault mitigation are disclosed. One exemplary embodiment is a fault mitigation system for a medium voltage alternating current (MVAC) distribution network including a direct current (DC) link and a control system. The DC link is coupled to a first feeder line and a second feeder line. The control system is structured to determine a first feeder line is deenergized, operate the DC link so as to receive MVAC from a second feeder line and output low voltage alternating current (LVAC) to the first feeder line, operate a plurality of isolation devices, measure the LVAC in response to operating the plurality of isolation devices, determine a fault is isolated from a healthy portion of the first feeder line using the received LVAC measurements, and reenergize the healthy portion of the first feeder line.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Systems and methods for current limiting
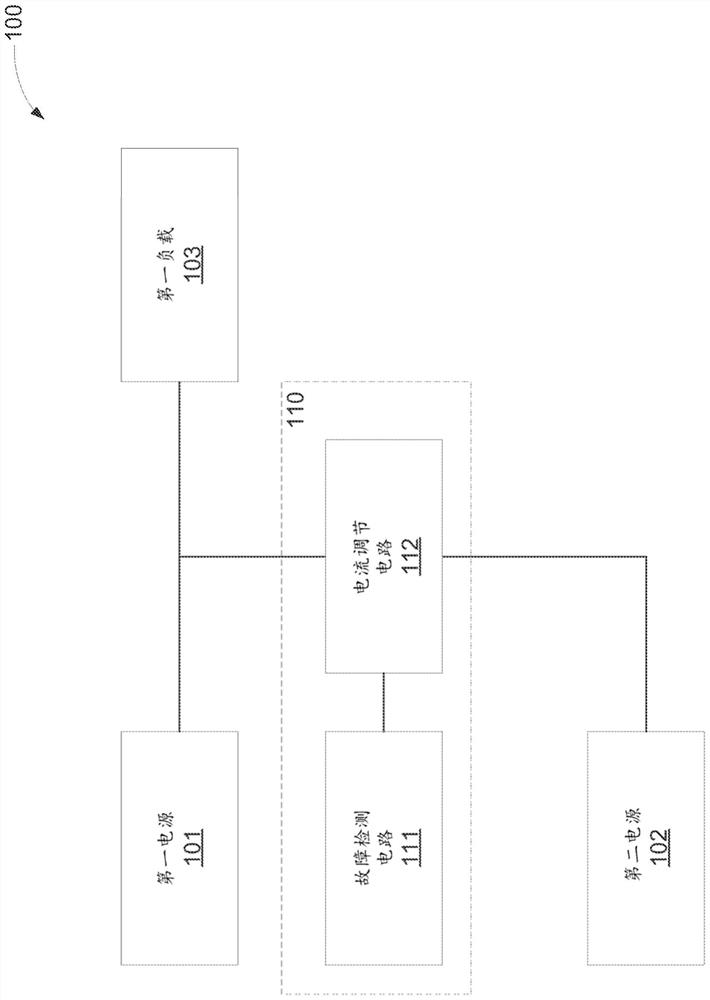
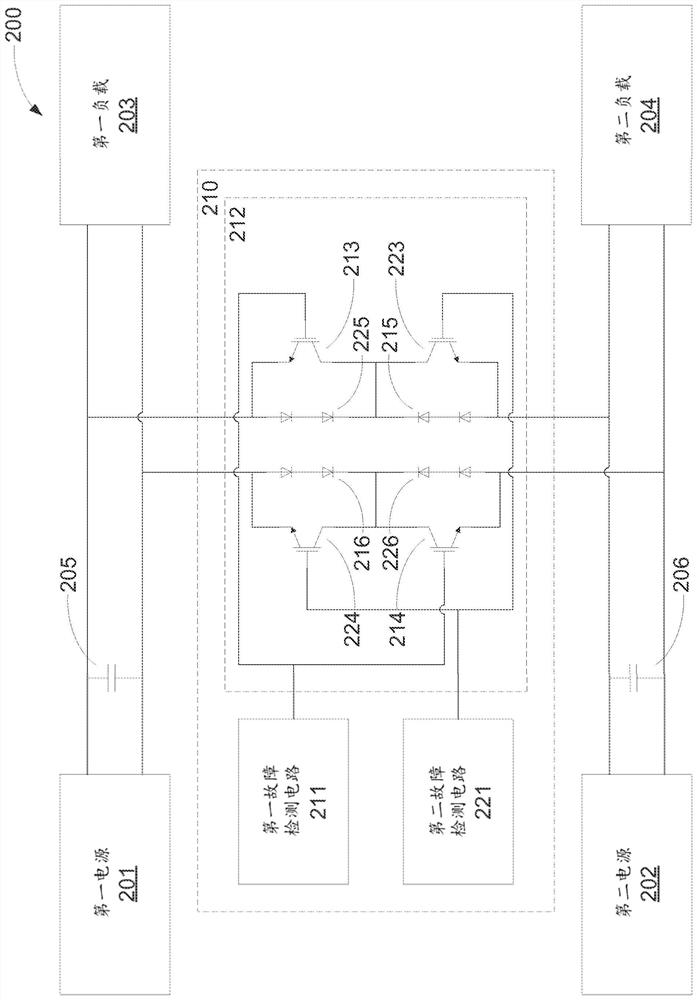
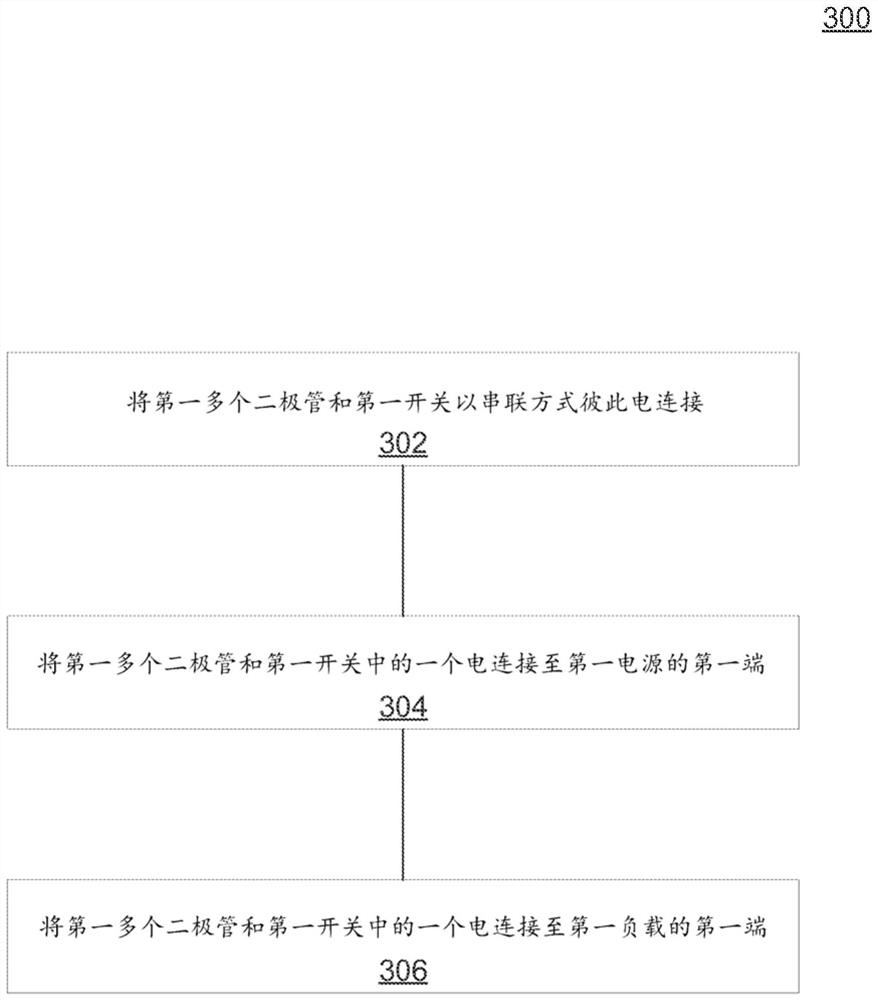
ActiveCN107534314BDc source parallel operationPower oscillations reduction/preventionCurrent limitingElectrical connection
An example system includes a first power source. The system also includes a first load electrically connected to the first power source. The system also includes a second power source. The system further includes fault mitigation circuitry. A fault mitigation circuit is used to detect a fault of the first power supply. A fault mitigation circuit is for electrically connecting the second power source to the first load in response to detecting a fault. The fault mitigation circuit is for limiting current flow from the second power source through the fault mitigation circuit.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
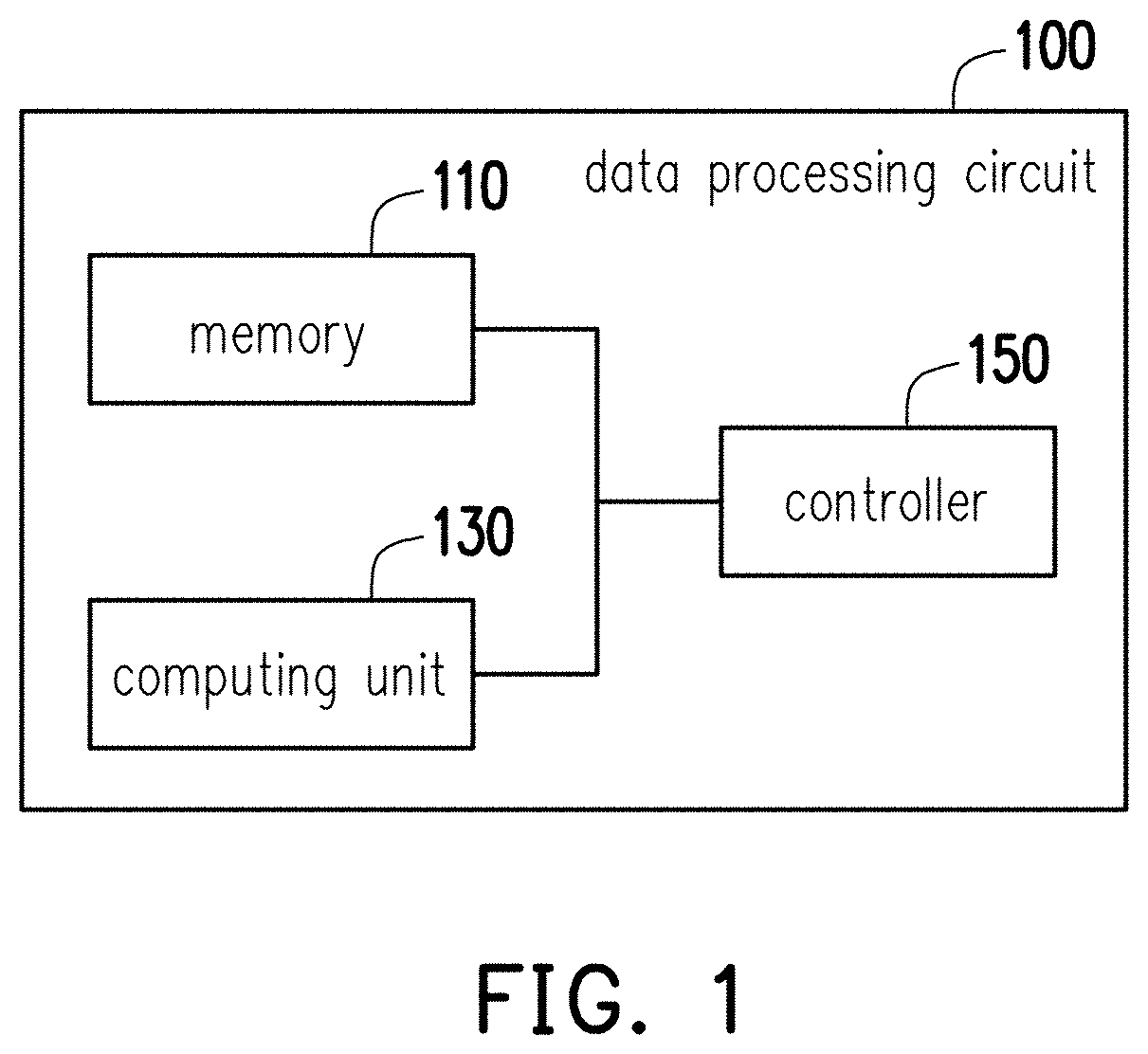
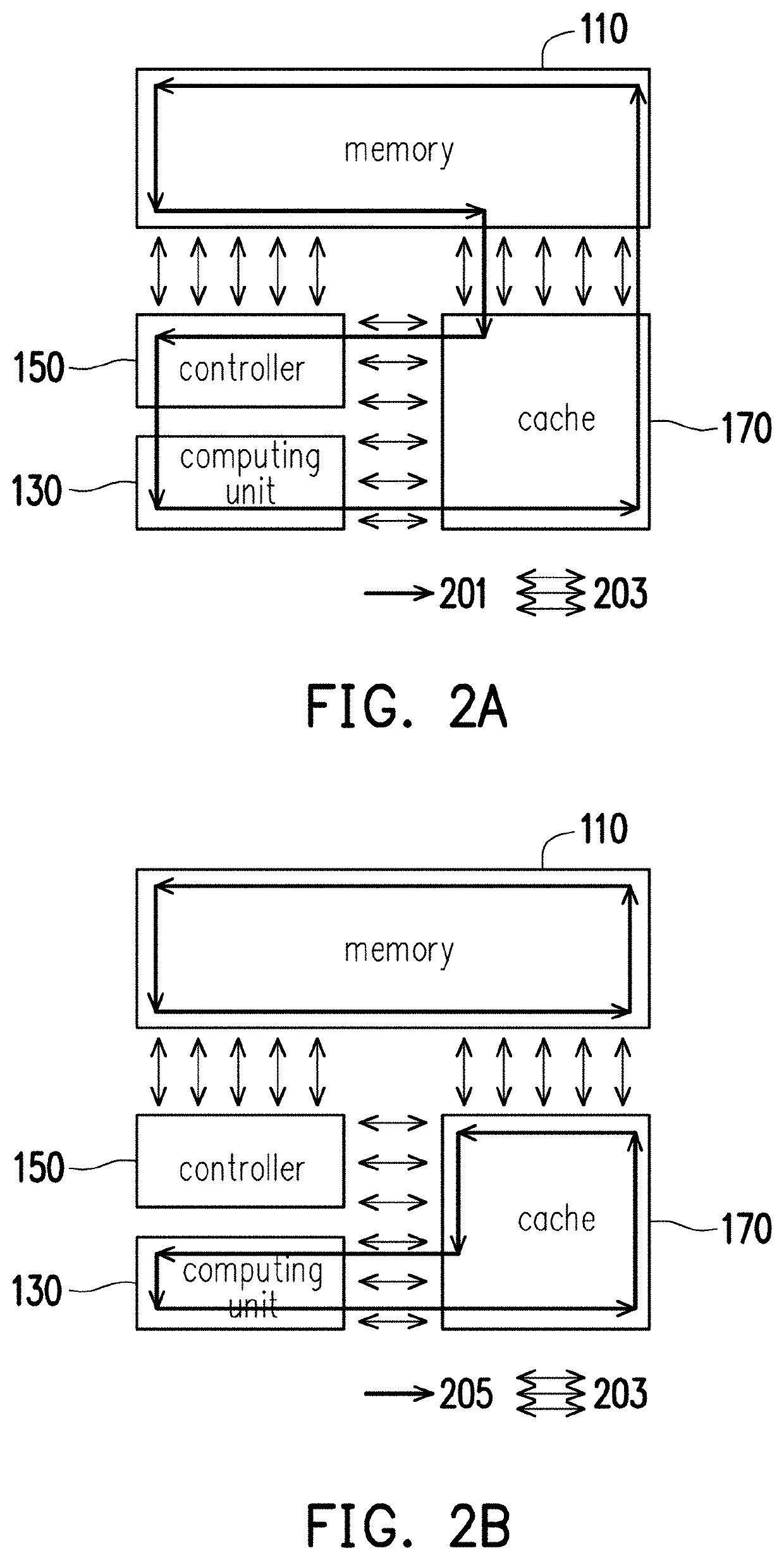
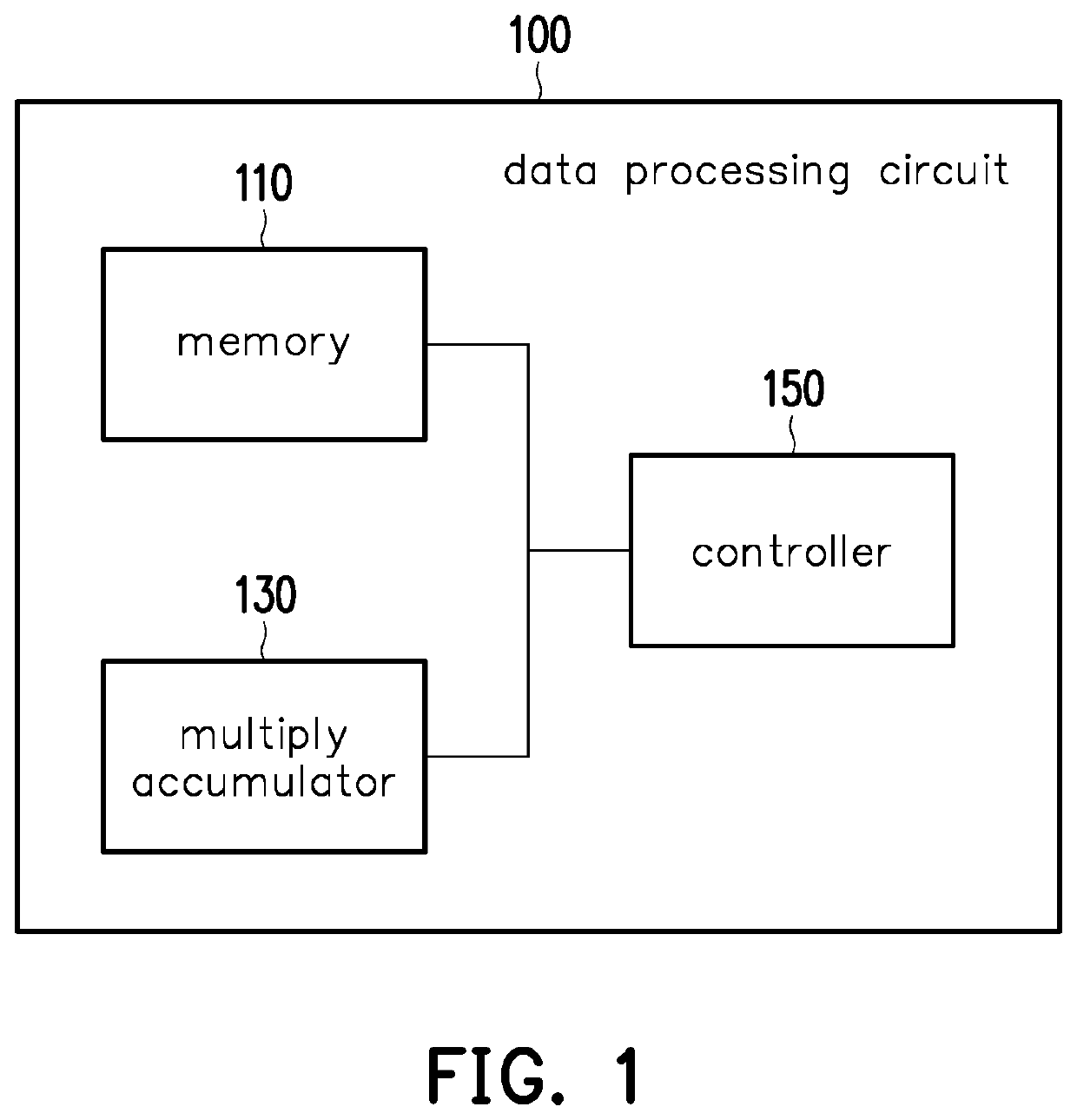
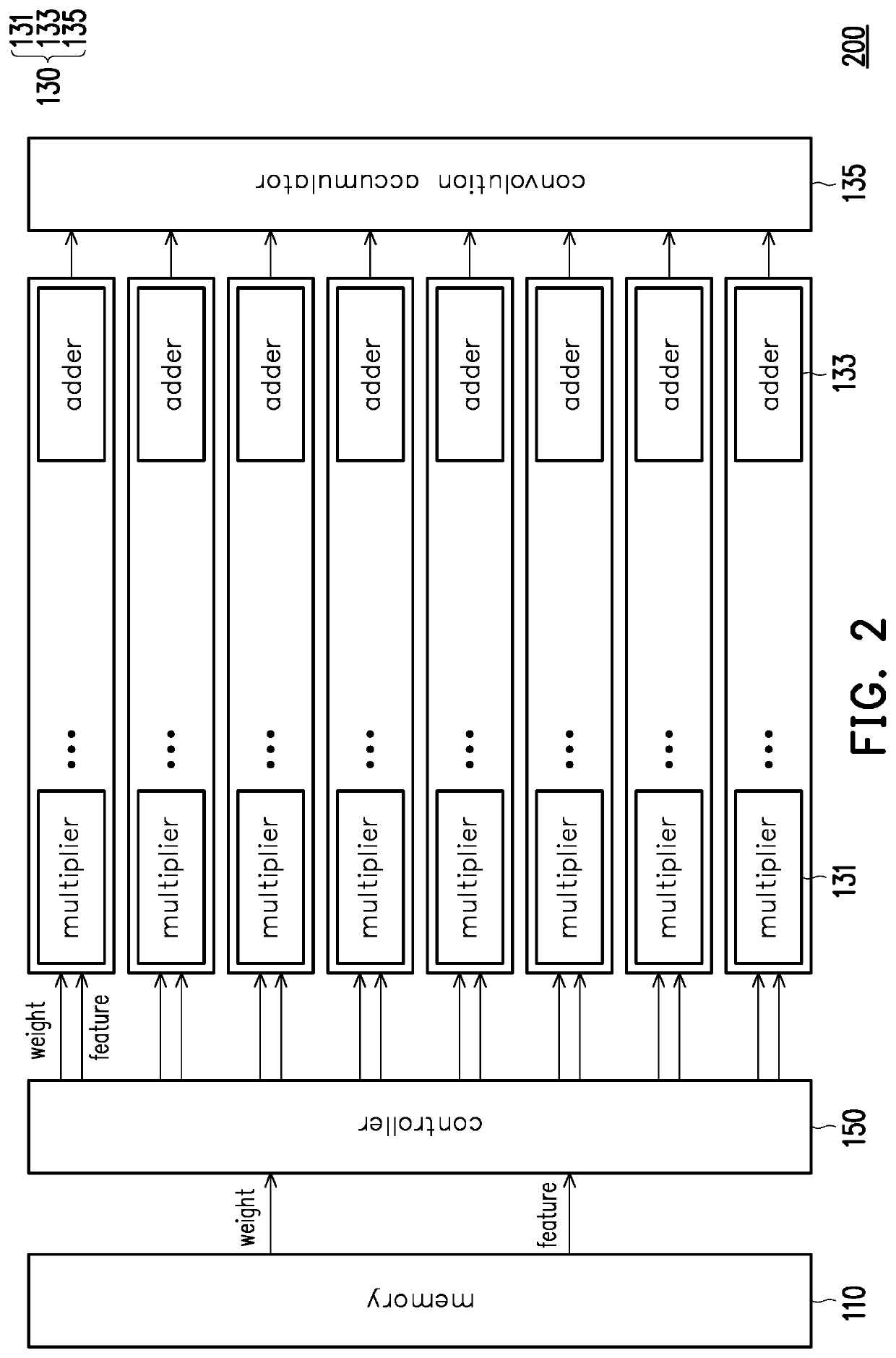
Data processing circuit and fault-mitigating method
PendingUS20220342736A1High error rateComputation using non-contact making devicesError avoidanceFault mitigationSequencing data
A data processing circuit and a fault-mitigating method are provided. In the method, multiple sub-sequences are divided from sequence data. A first sub-sequence of the sub-sequences is accessed from a memory for a multiply-accumulate (MAC) operation to obtain a first computed result. The MAC operation is performed on a second sub-sequence of the sub-sequences in the memory to obtain a second computed result. The first and the second computed results are combined, where the combined result of the first and the second computed results is related to the result of the MAC operation on the sequence data directly. Accordingly, the error rate could be reduced, so as to mitigate fault.
Owner:SKYMIZER TAIWAN INC
Data processing circuit and fault-mitigating method
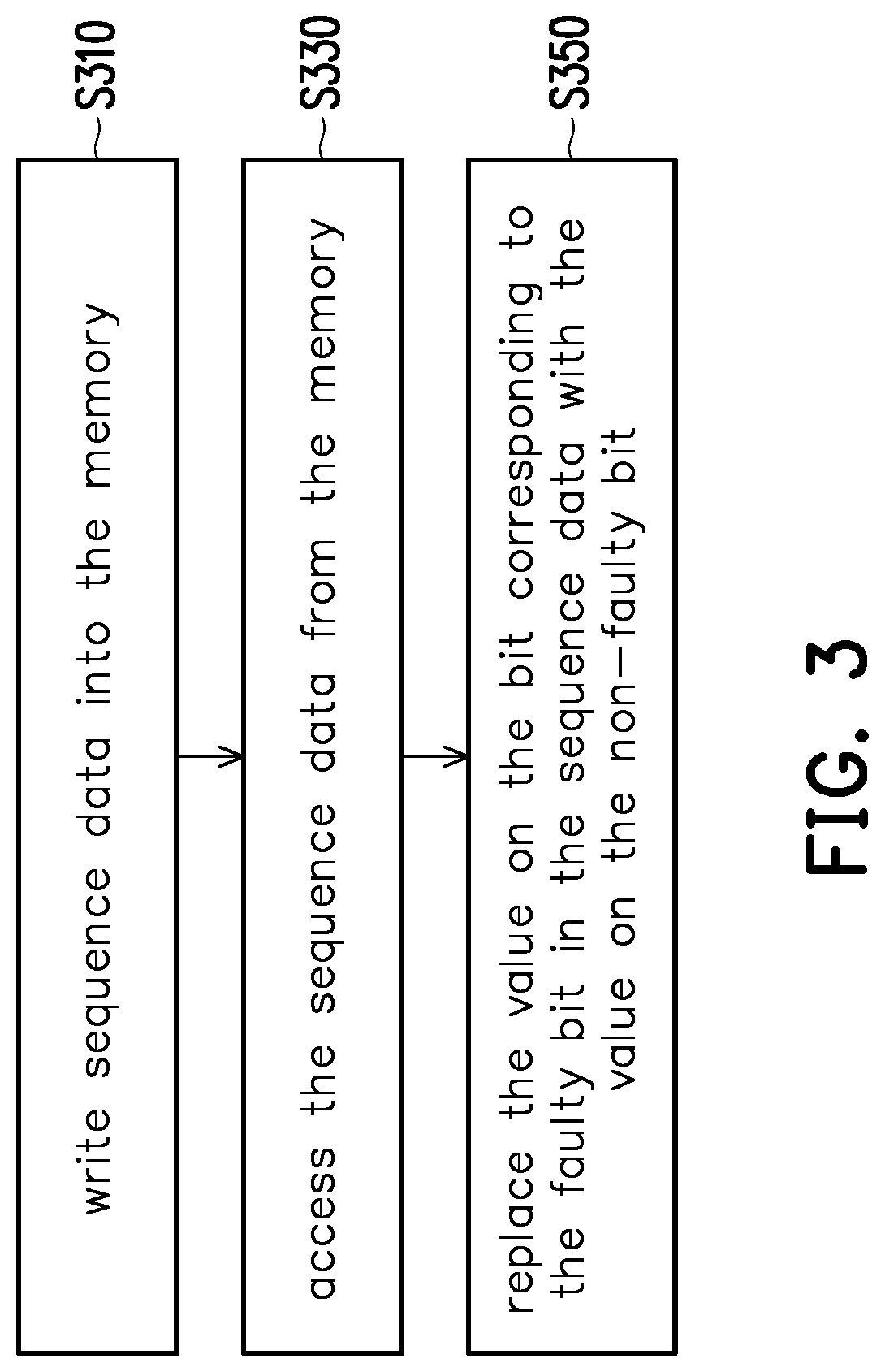
ActiveUS20220138064A1Improve accuracyHigh similarityDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionTerm memory
A data processing circuit and a fault-mitigating method, which are adapted for a memory having a faulty bit, are provided. The memory is configured to store data related to an image, a weight for a multiply-accumulate (MAC) operation of image feature extraction, and / or a value for an activation operation. Sequence data is written into the memory. The bit number of the sequence data equals to the bit number used for storing data in a sequence block of the memory. The sequence data is accessed from the memory, wherein the access of the faulty bit in the memory is ignored. The value of the faulty bit is replaced by the value of a non-faulty bit in the memory to form new sequence data. The new sequence data is used for MAC. Accordingly, the accuracy of image recognition can be improved for the faulty memory.
Owner:SKYMIZER TAIWAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com