Patents
Literature
33results about "Trigometric functions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
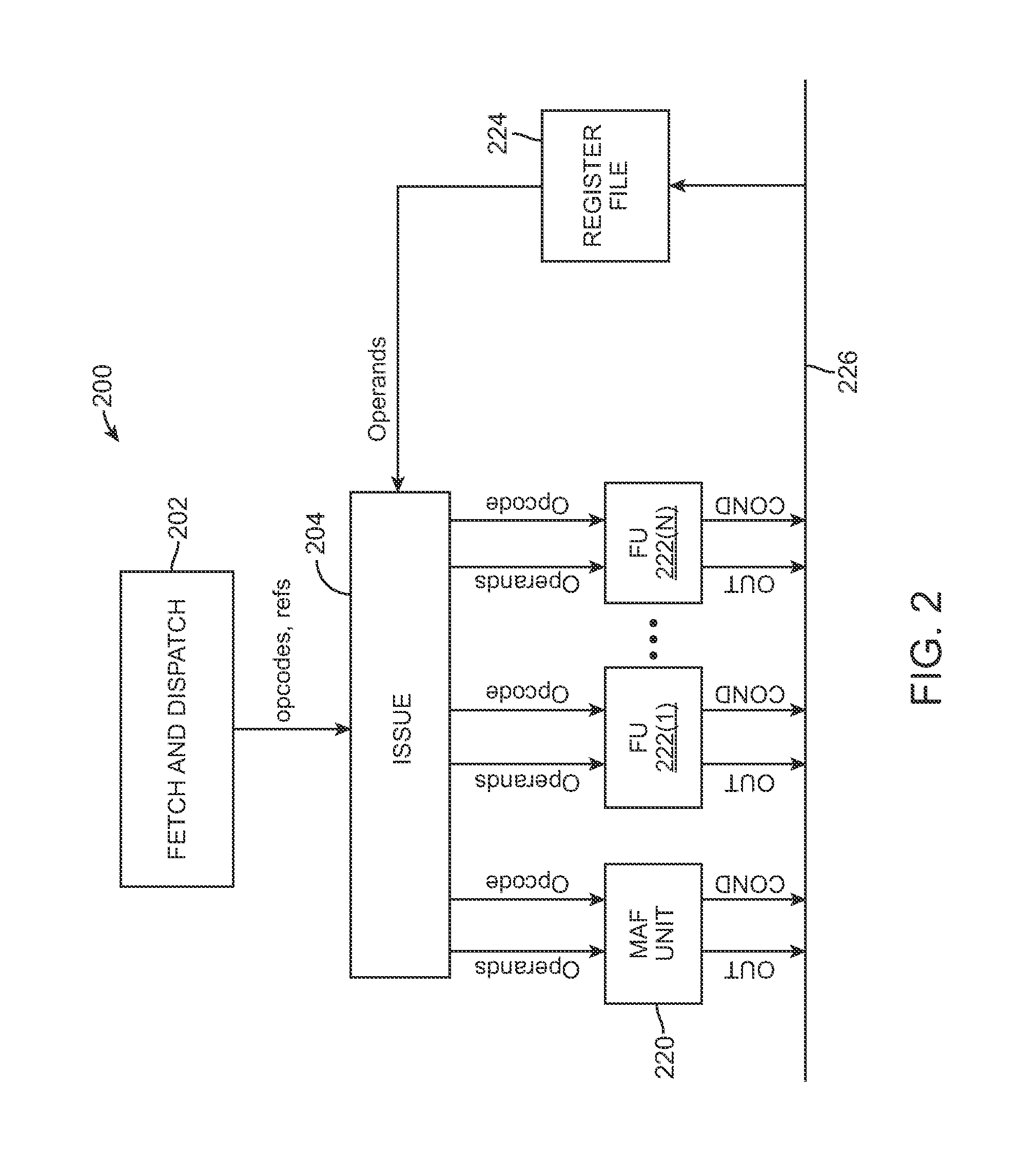
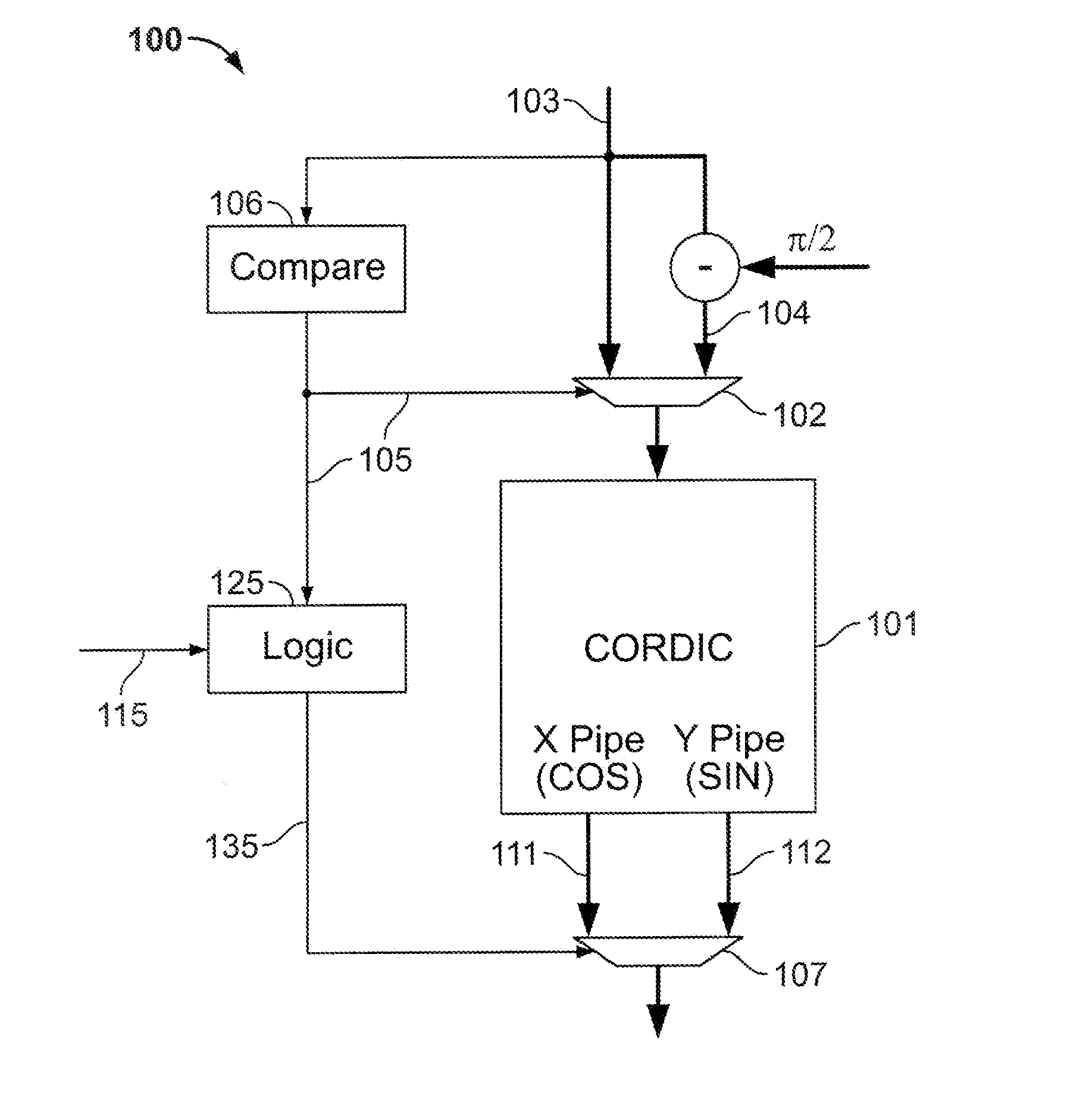
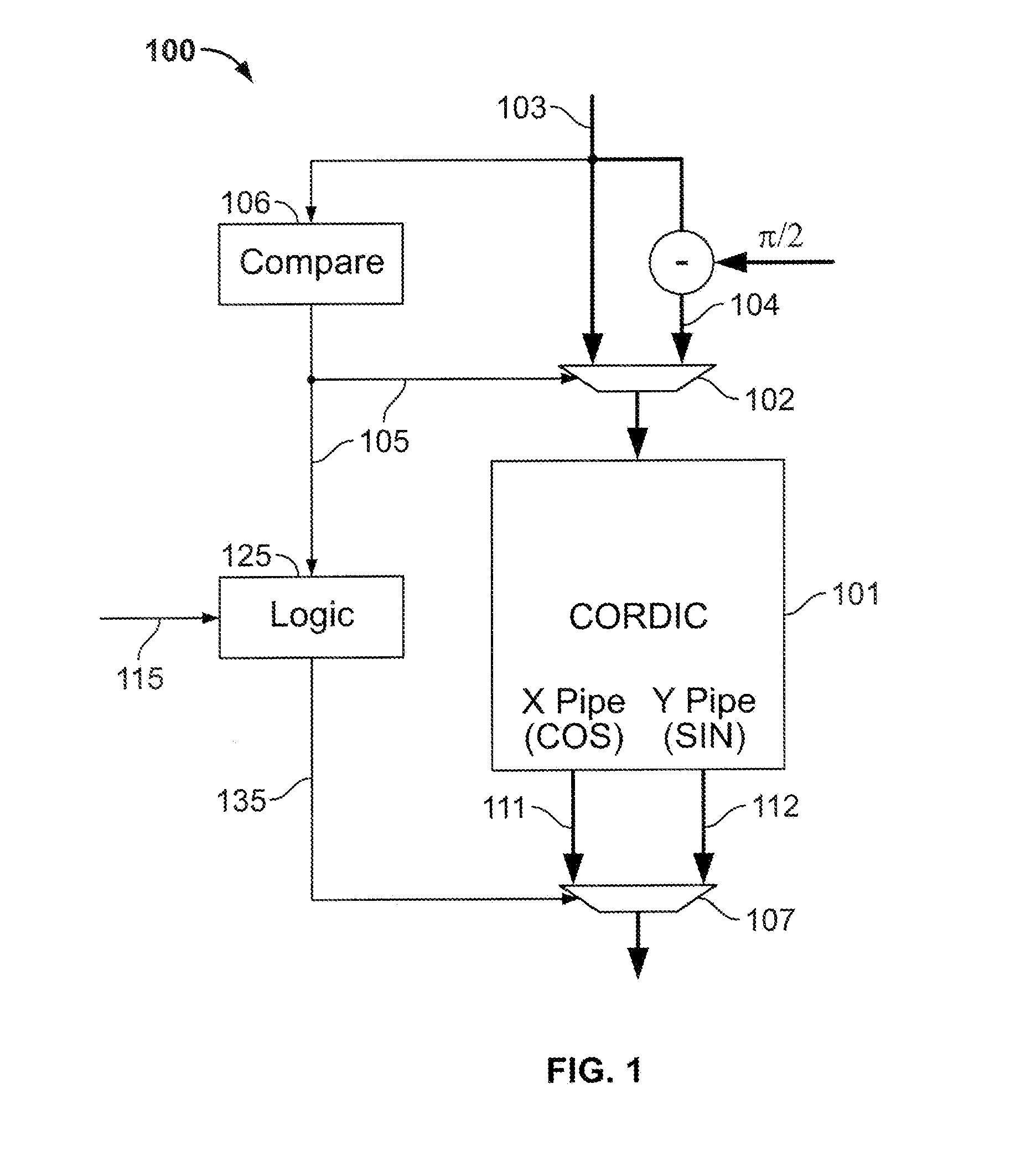
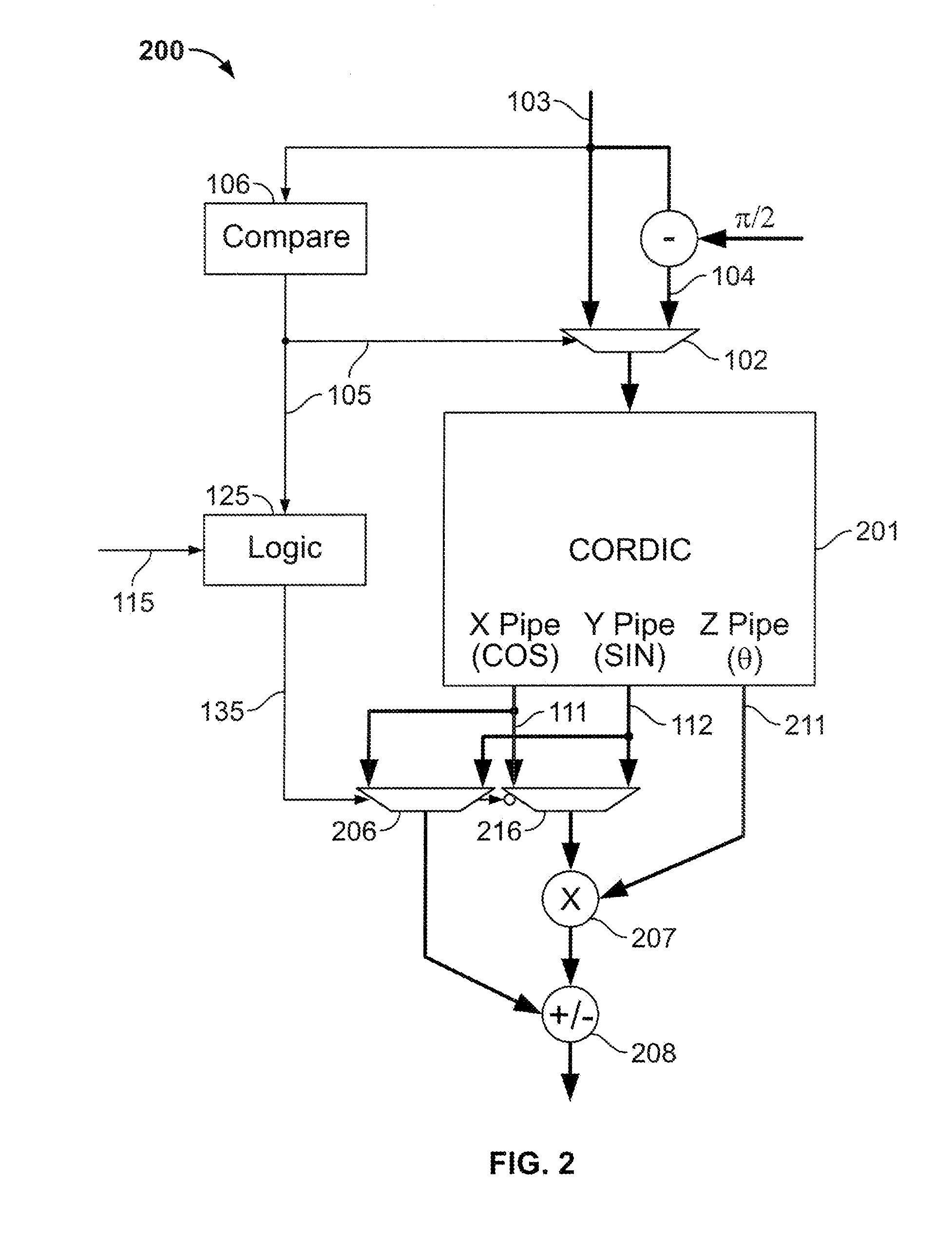
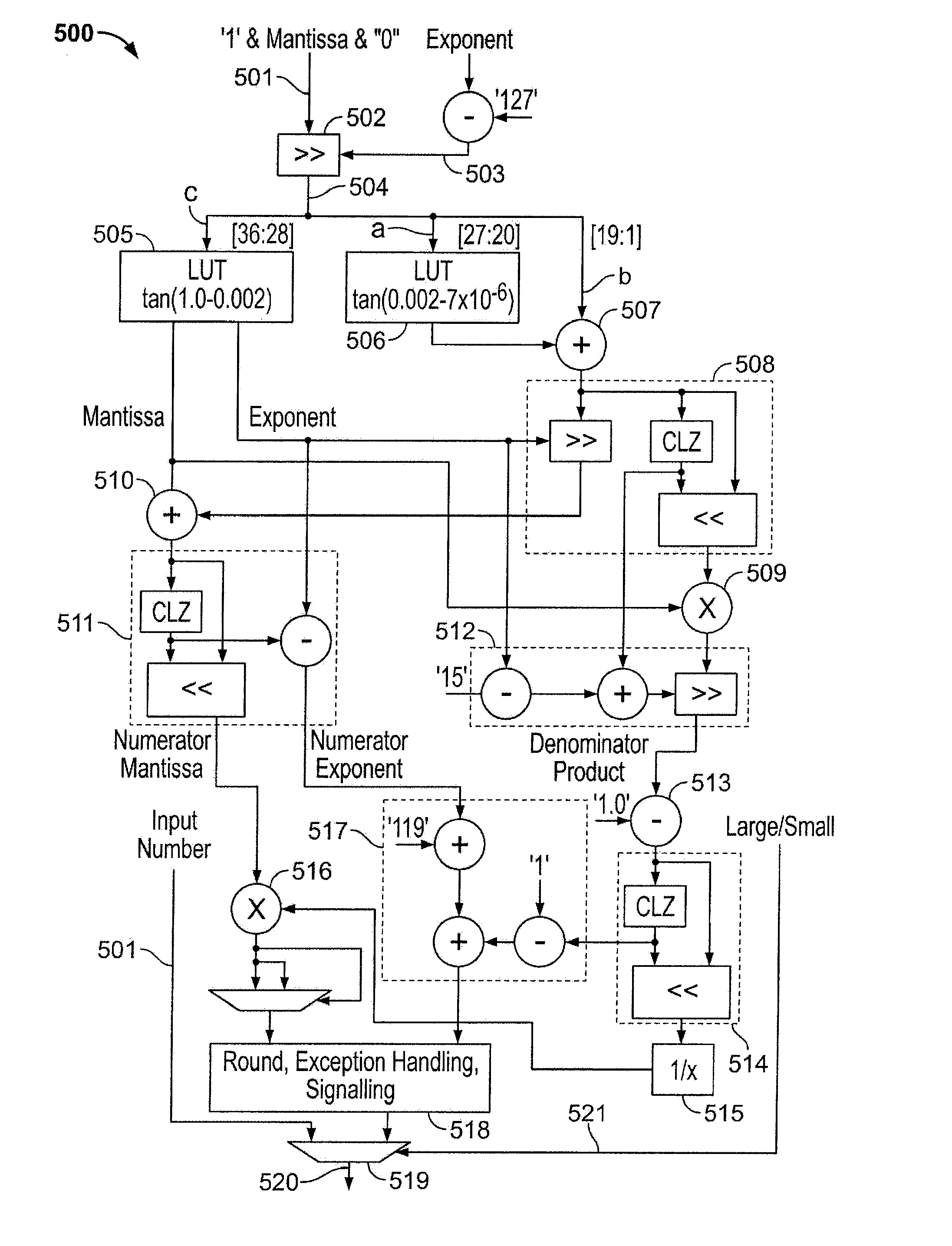
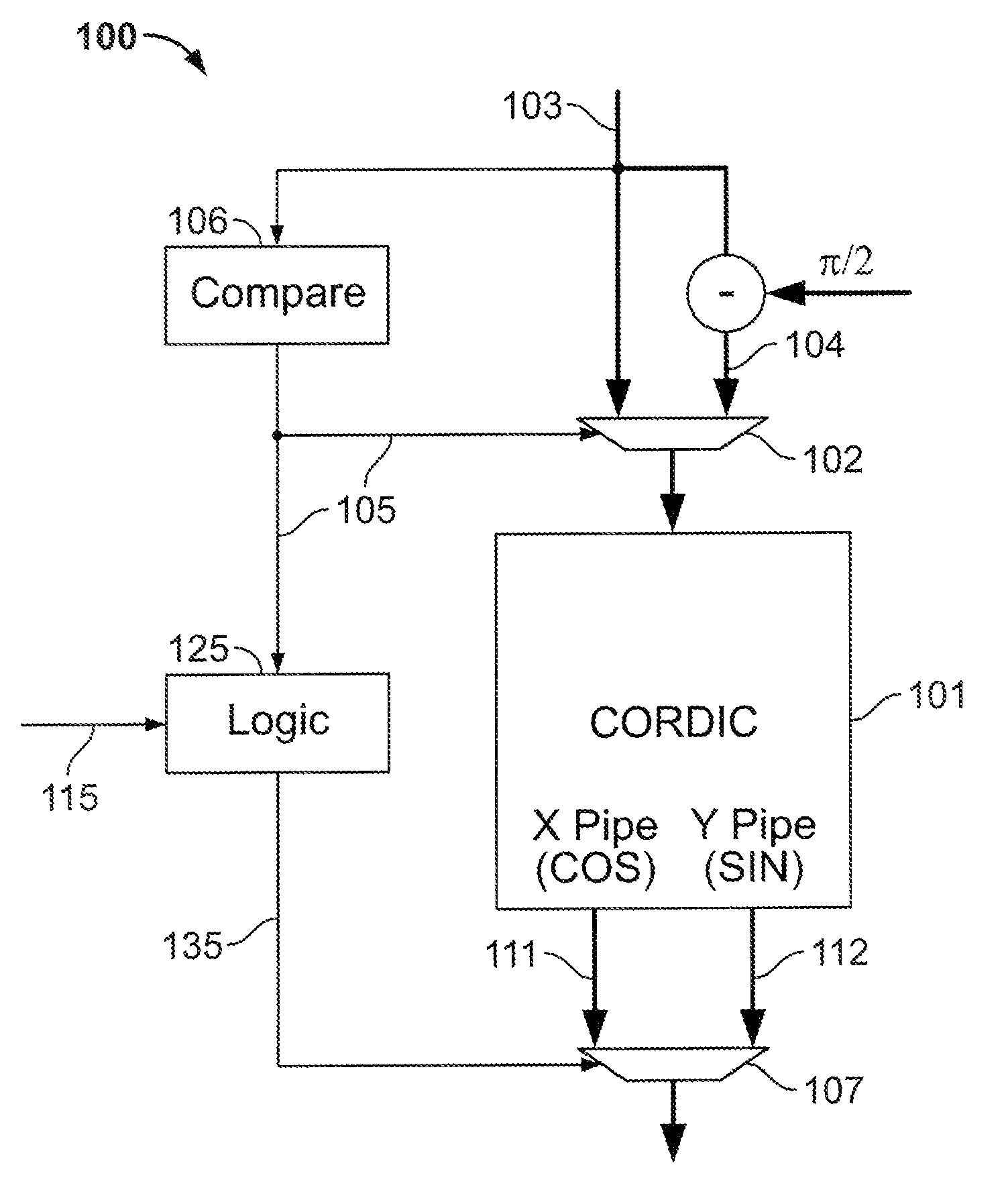
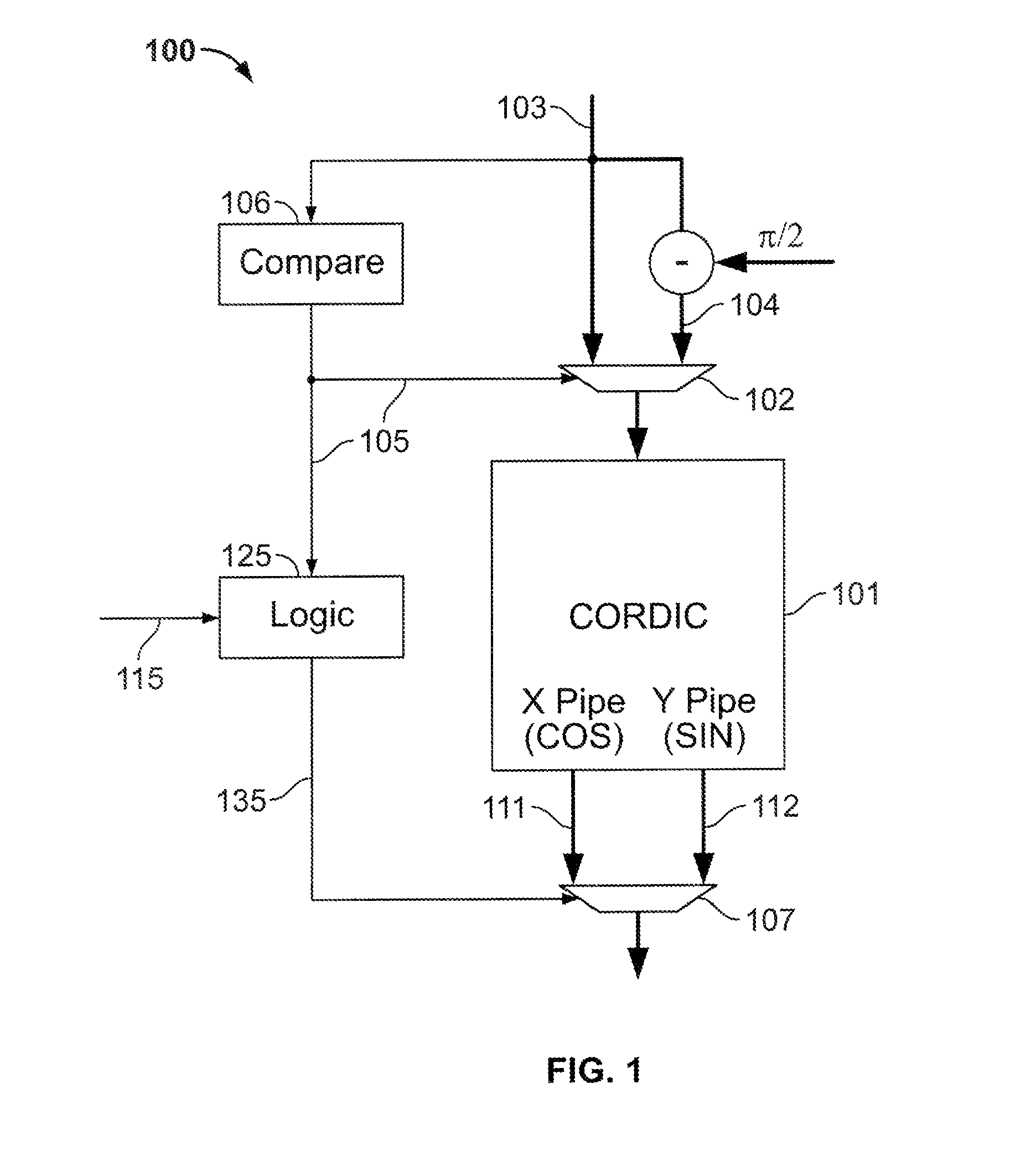
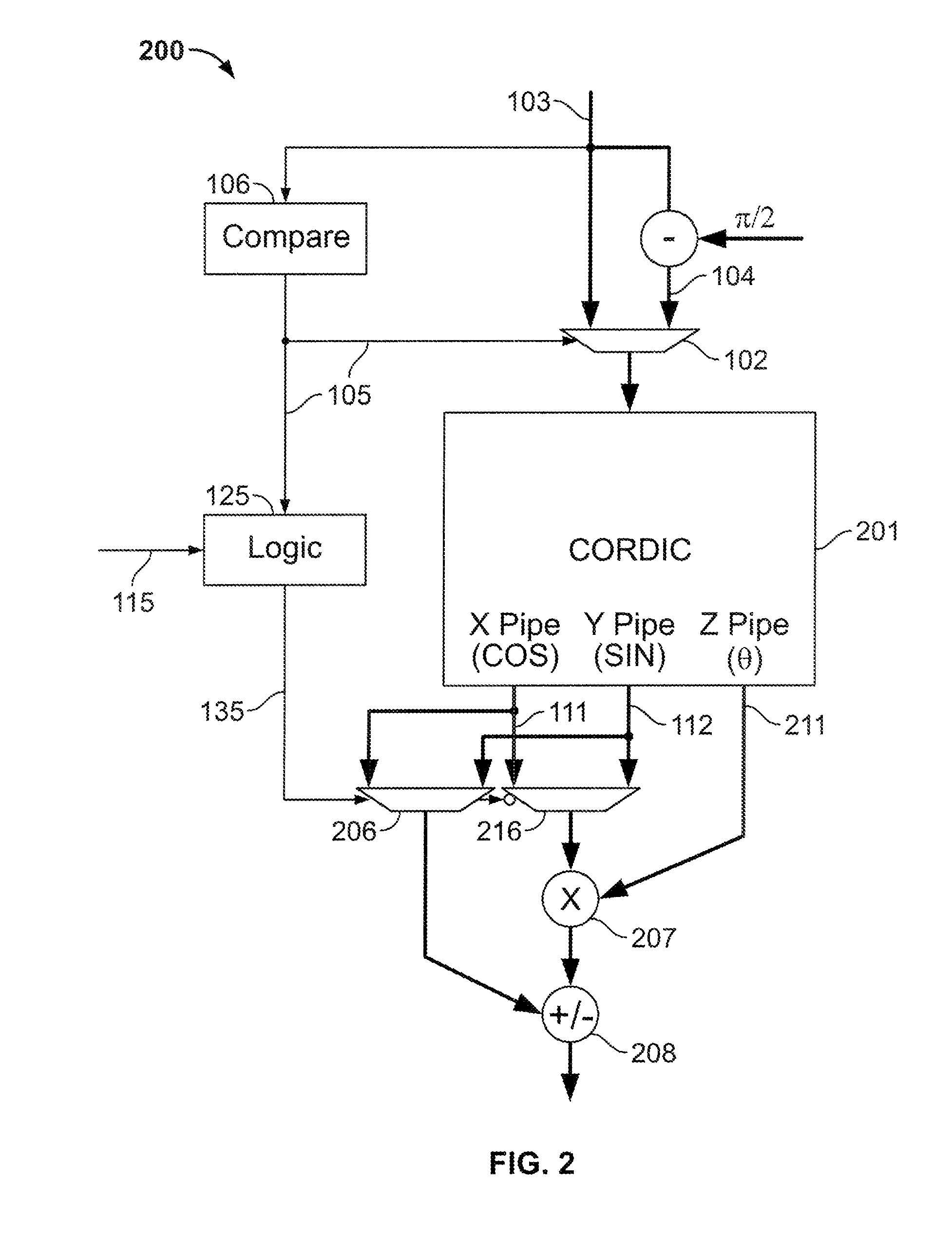
Calculation of trigonometric functions in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20120054256A1The result is accurateTrigometric functionsDigital function generatorsComputer scienceIntegrated circuit design
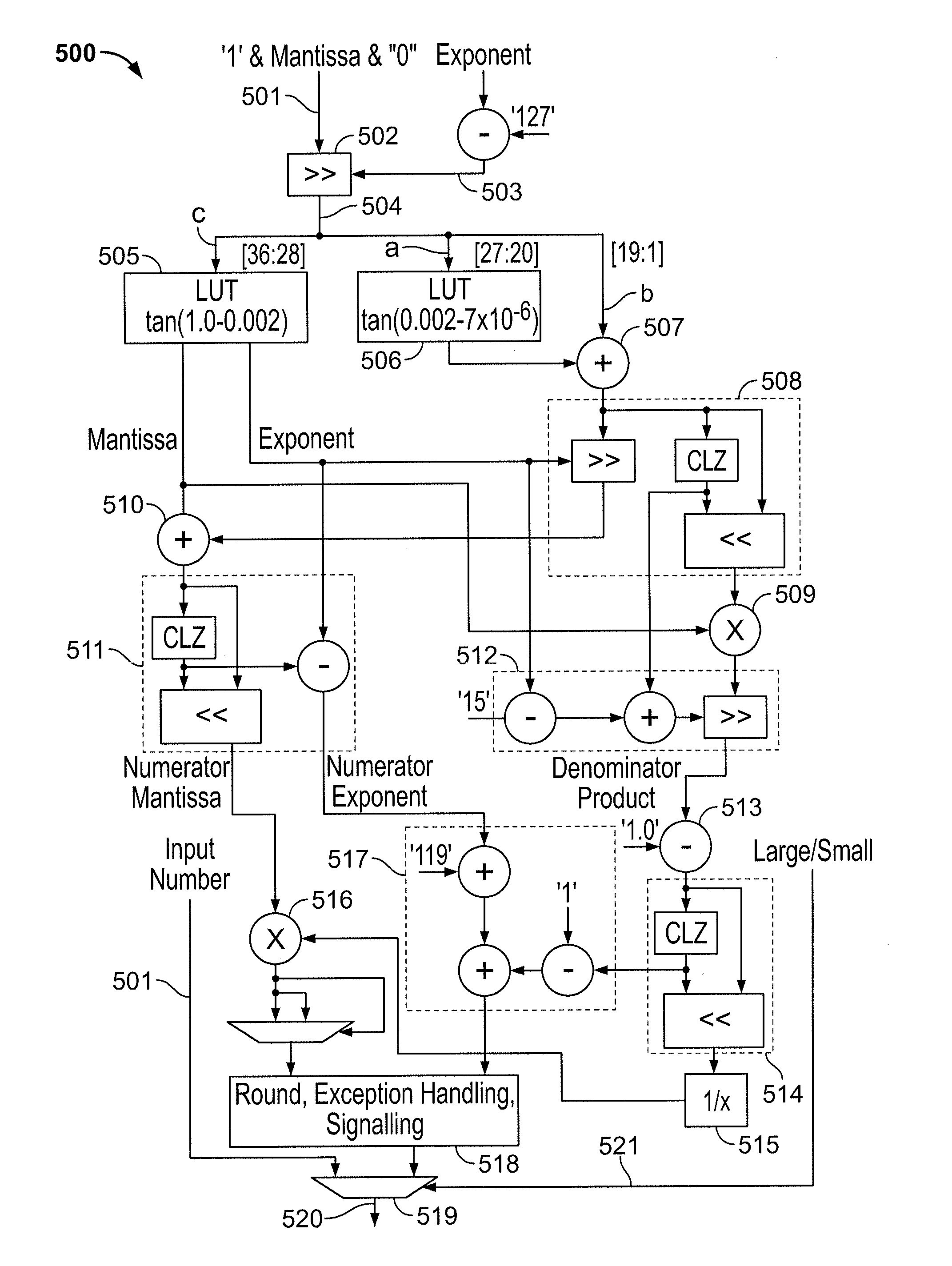
Circuitry for computing a tangent function of an input value includes first look-up table circuitry that stores pre-calculated tangent values of a limited number of sample values, circuitry for inputting bits of the input value of most significance as inputs to the first look-up table circuitry to look up one of the pre-calculated tangent values as a first intermediate tangent value, circuitry for calculating a second intermediate tangent value from one or more ranges of remaining bits of the input value, and circuitry for combining the first intermediate tangent value and the second intermediate tangent value to yield the tangent function of the input value.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
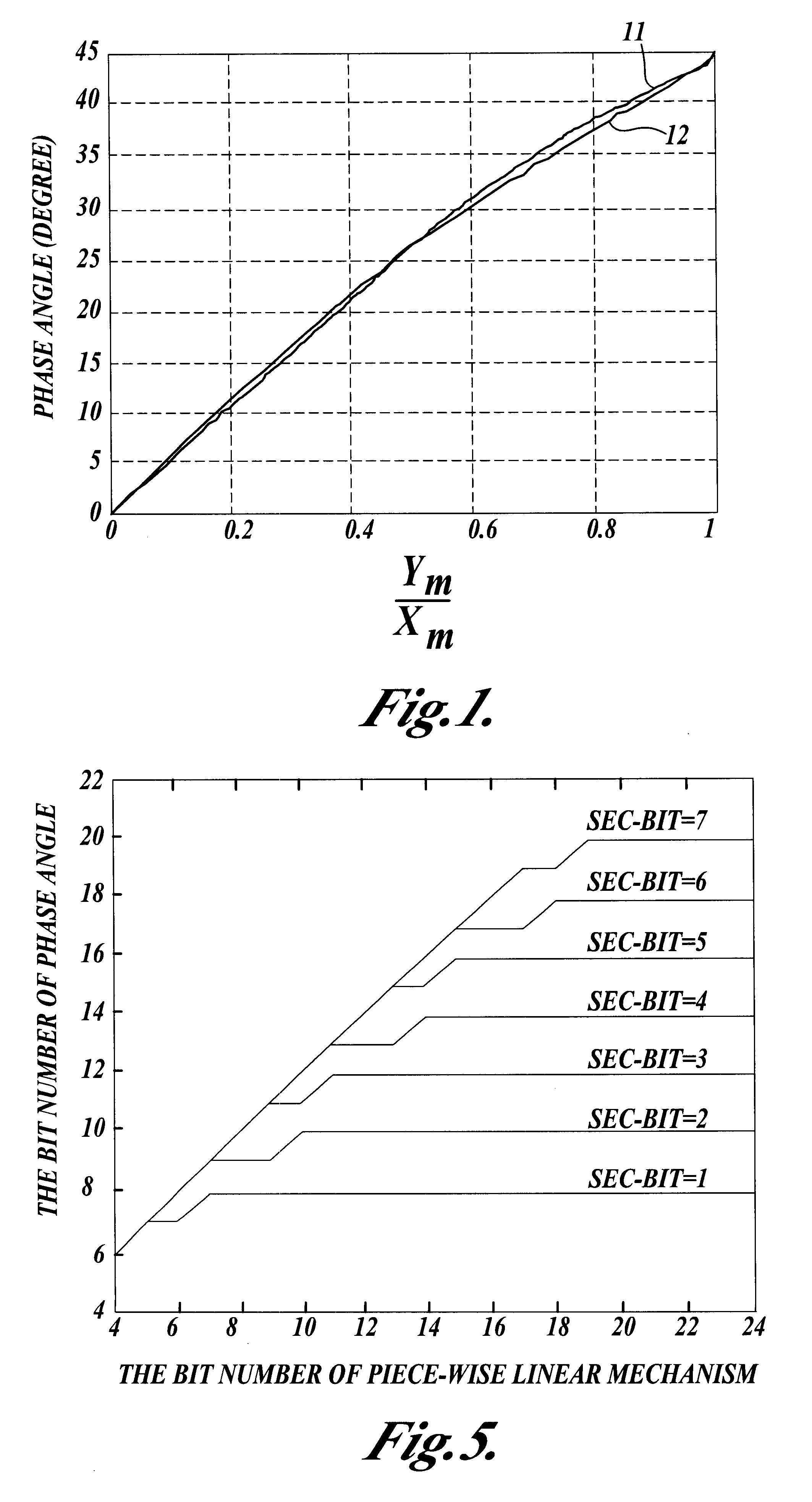
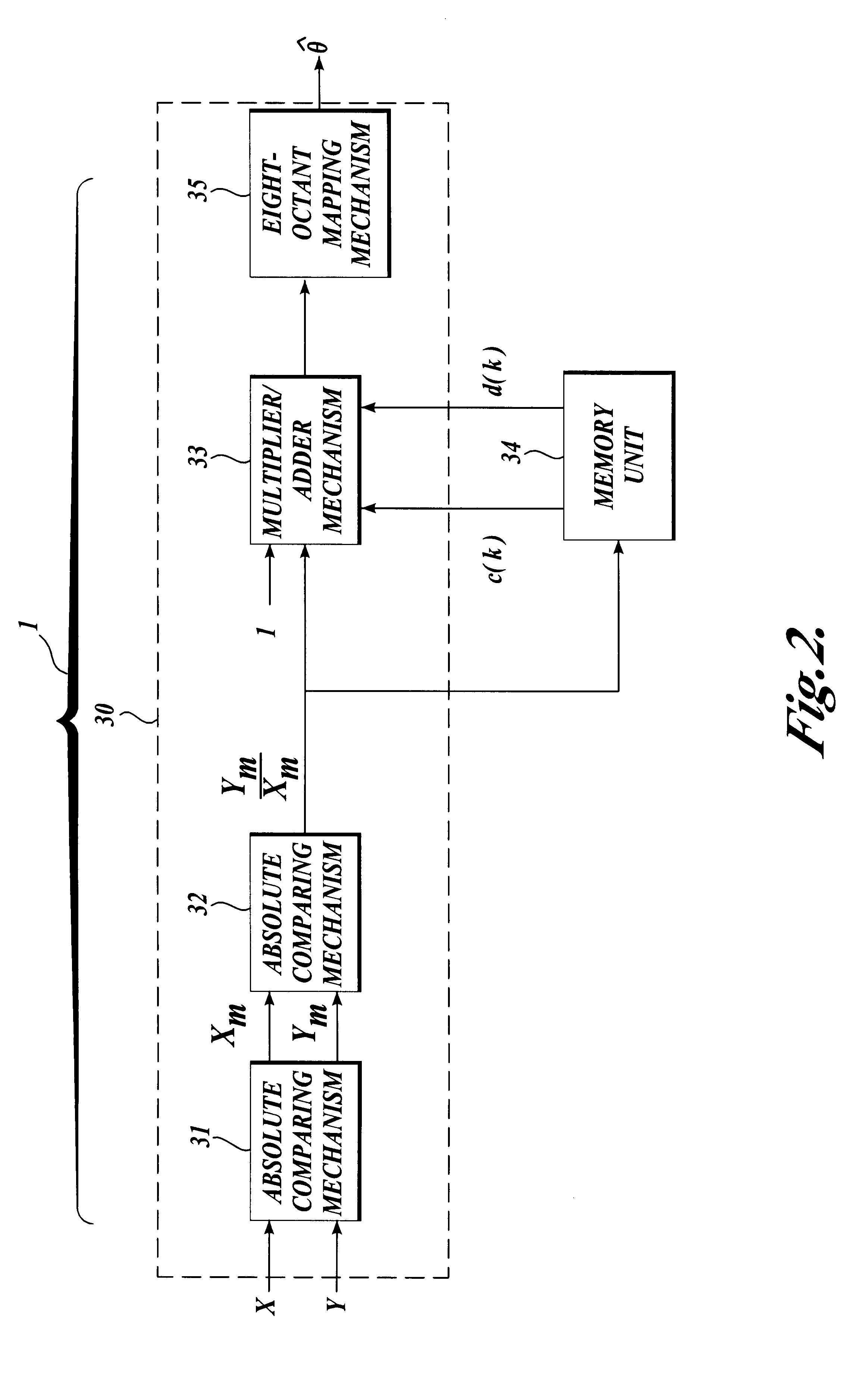
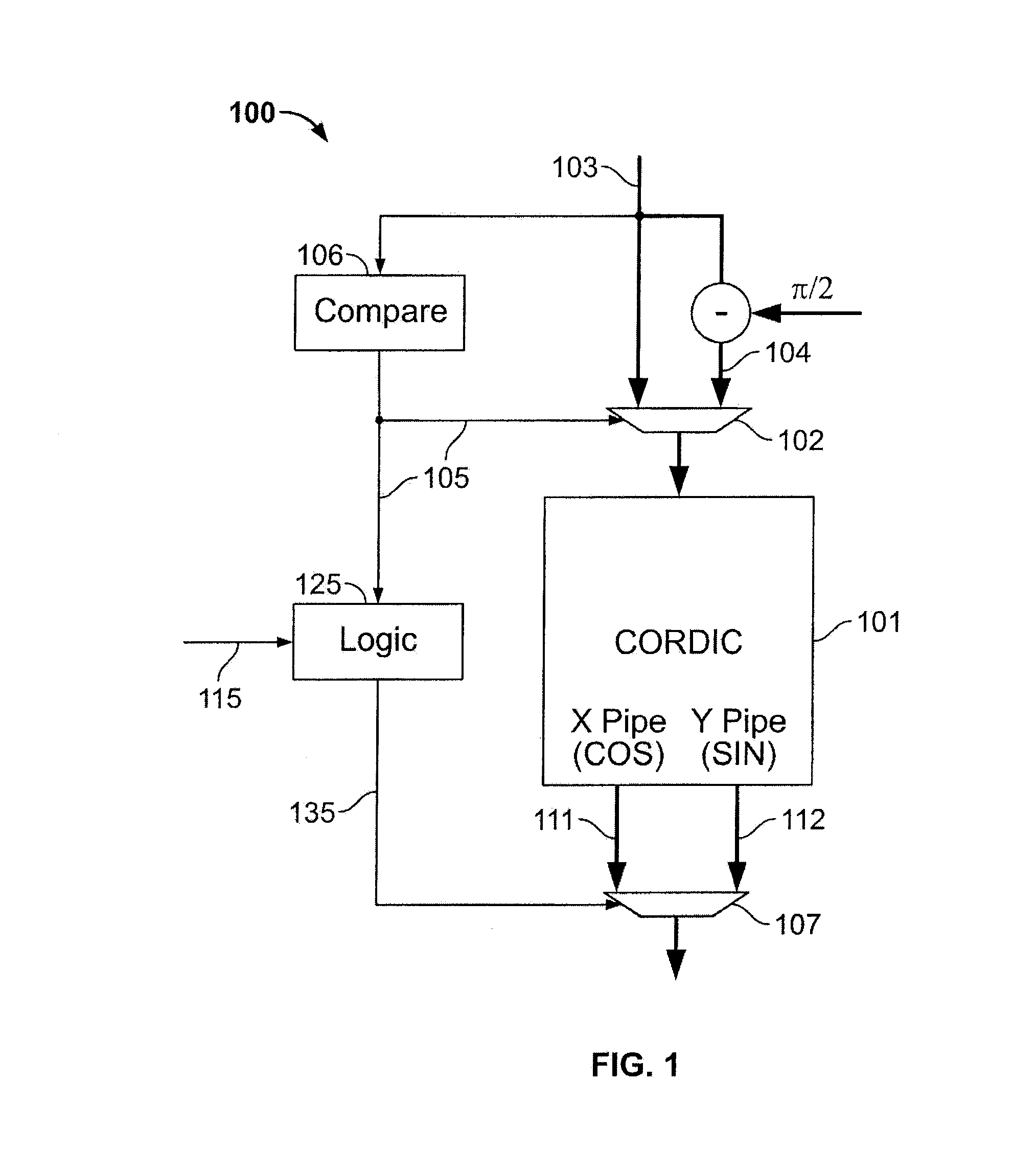
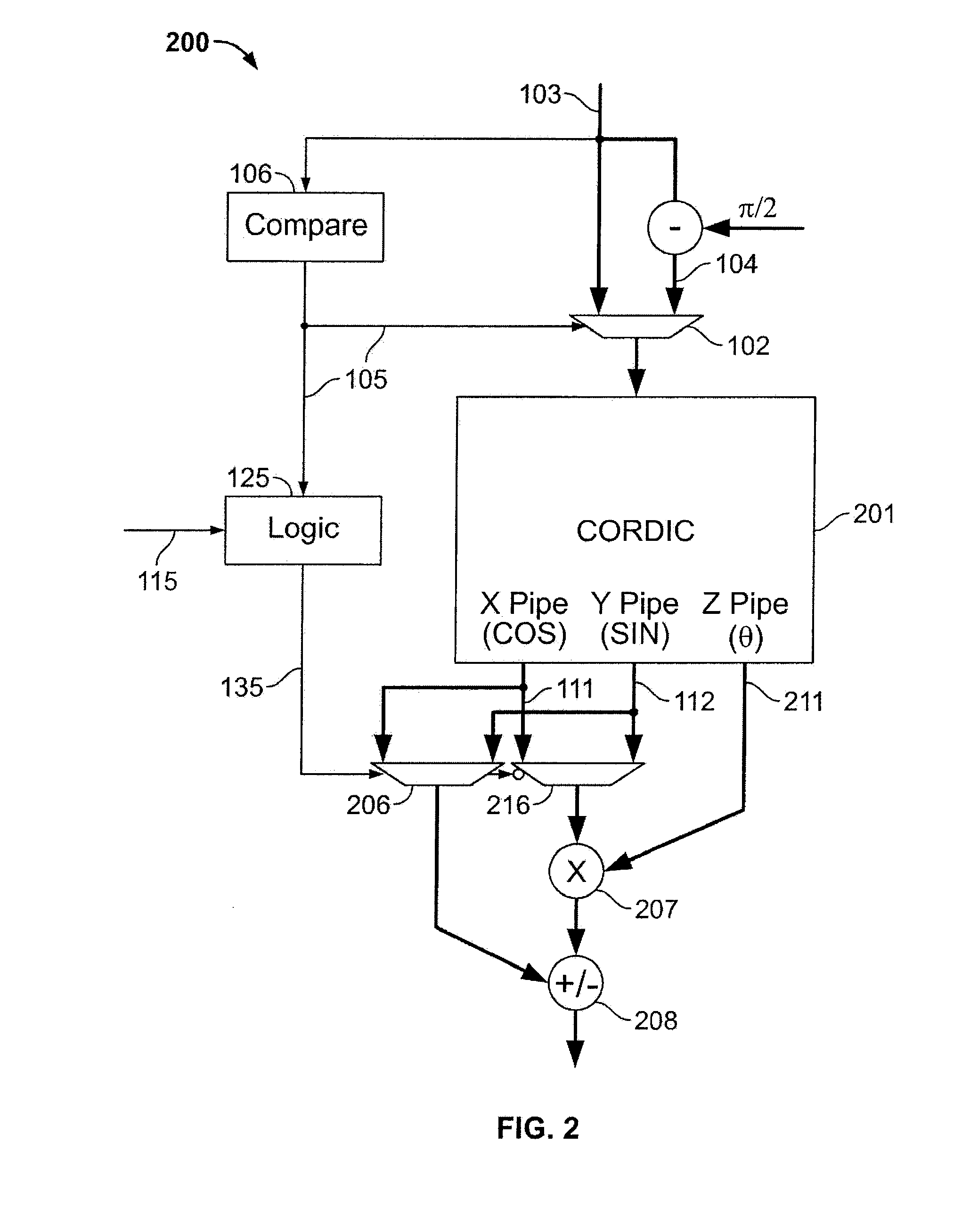
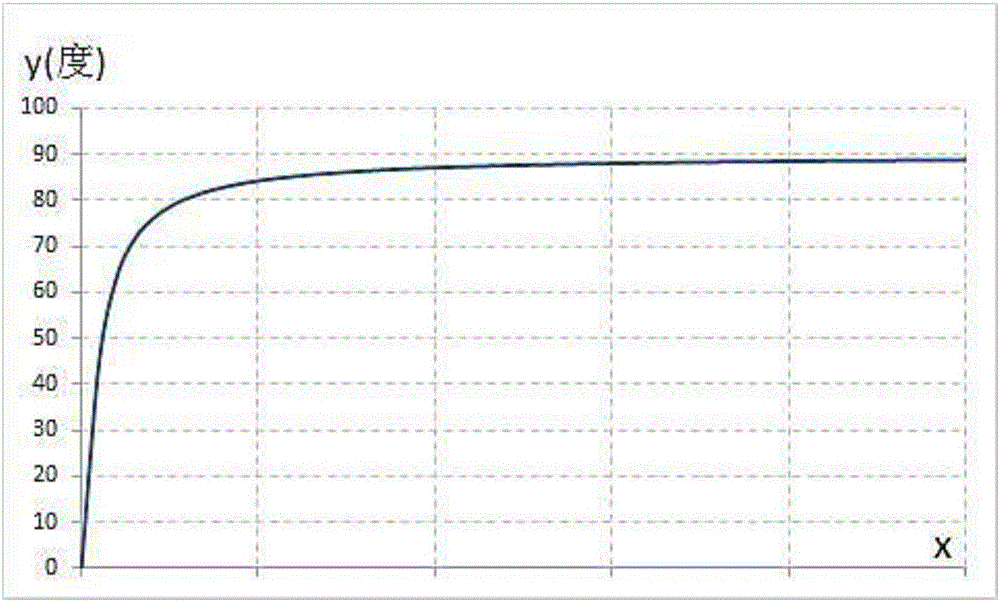
Apparatus and method for implementing an inverse arctangent function using piecewise linear theorem to simplify
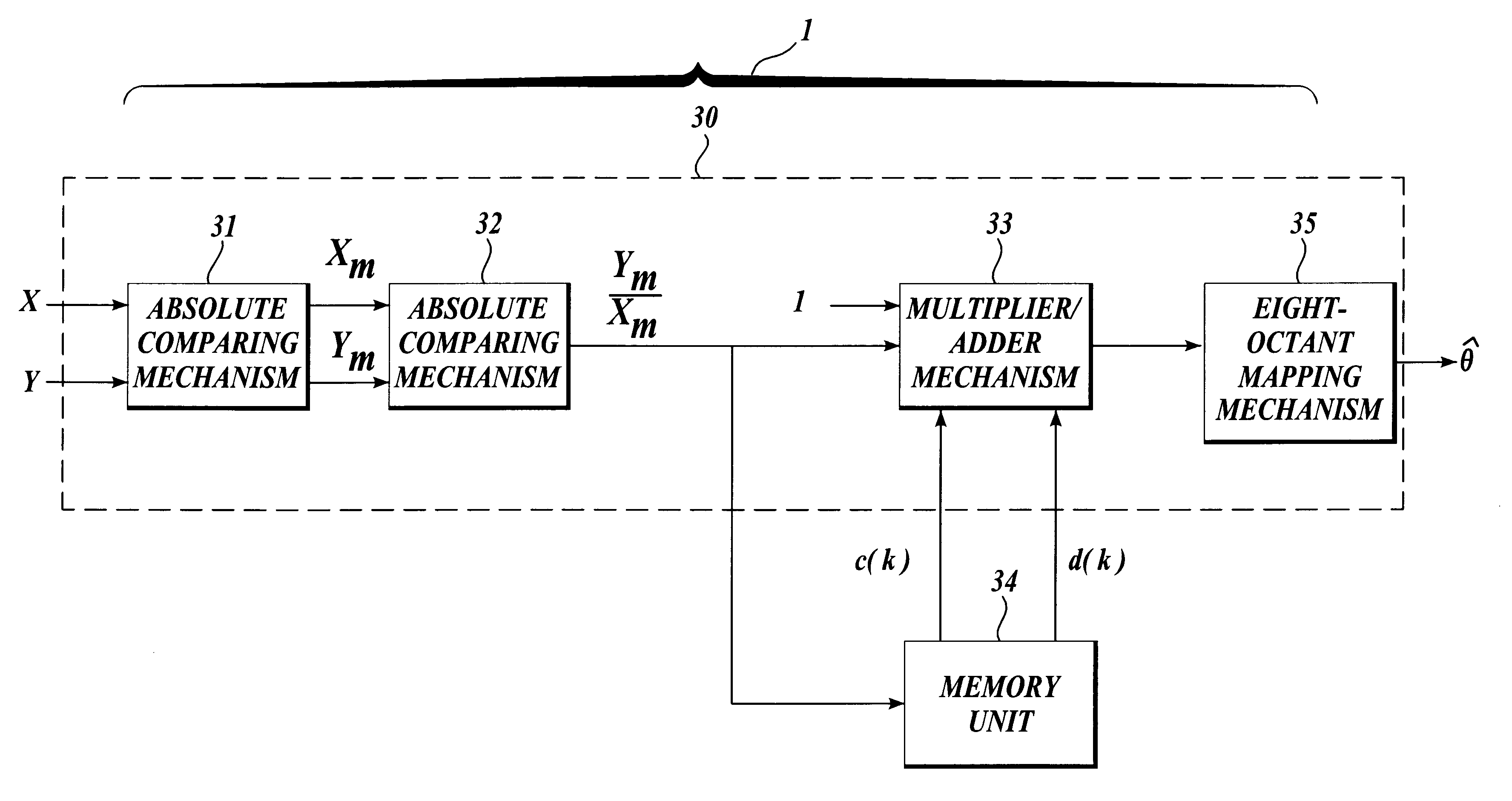
The present invention discloses an apparatus and method for implementing an inverse arctangent function using piecewise linear theorem to simplify and used to transform a right-angled coordinate point X and Y to a phase angle theta of an inverse arctangent function. The present invention uses T-line combination to approach an inverse arctangent function between 0 degree to 45 degree, and determines which piecewise linear region the right-angled coordinate point is located at. A coefficient table stored in a memory is used to compute {circumflex over (theta)} which is the approximate value of the phase angle theta. The phase angle {circumflex over (theta)} between 45 degree to 360 degree can be mapped to the approximate phase angle {circumflex over (theta)} between 0 degree to 45 degree using linear combination.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
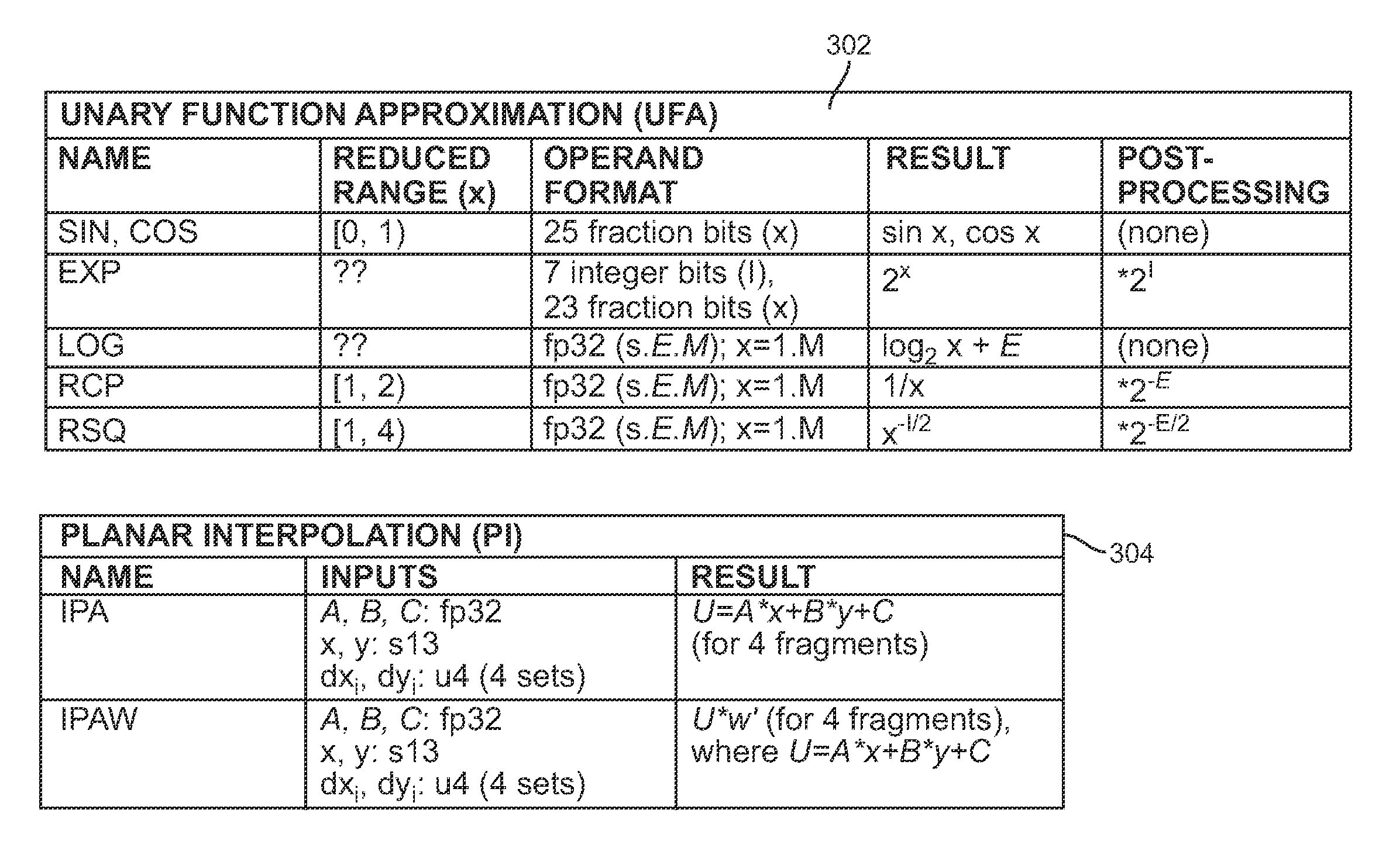
Multipurpose arithmetic functional unit
ActiveUS8190669B1Trigometric functionsComputations using contact-making devicesOperandUnary function
Multipurpose arithmetic functional units can perform planar attribute interpolation and unary function approximation operations. In one embodiment, planar interpolation operations for coordinates (x, y) are executed by computing A*x+B*y+C, and unary function approximation operations for operand x are executed by computing F2(xb)*xh2+F1(xb)*xh+F0(xb), where xh=x−xb. Shared multiplier and adder circuits are advantageously used to implement the product and sum operations for both classes of operations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Calculation of trigonometric functions in an integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20110320513A1The result is accurateTrigometric functionsDigital function generatorsComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Calculation of trigonometric functions in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20120054254A1Trigometric functionsDigital function generatorsComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
Owner:ALTERA CORP
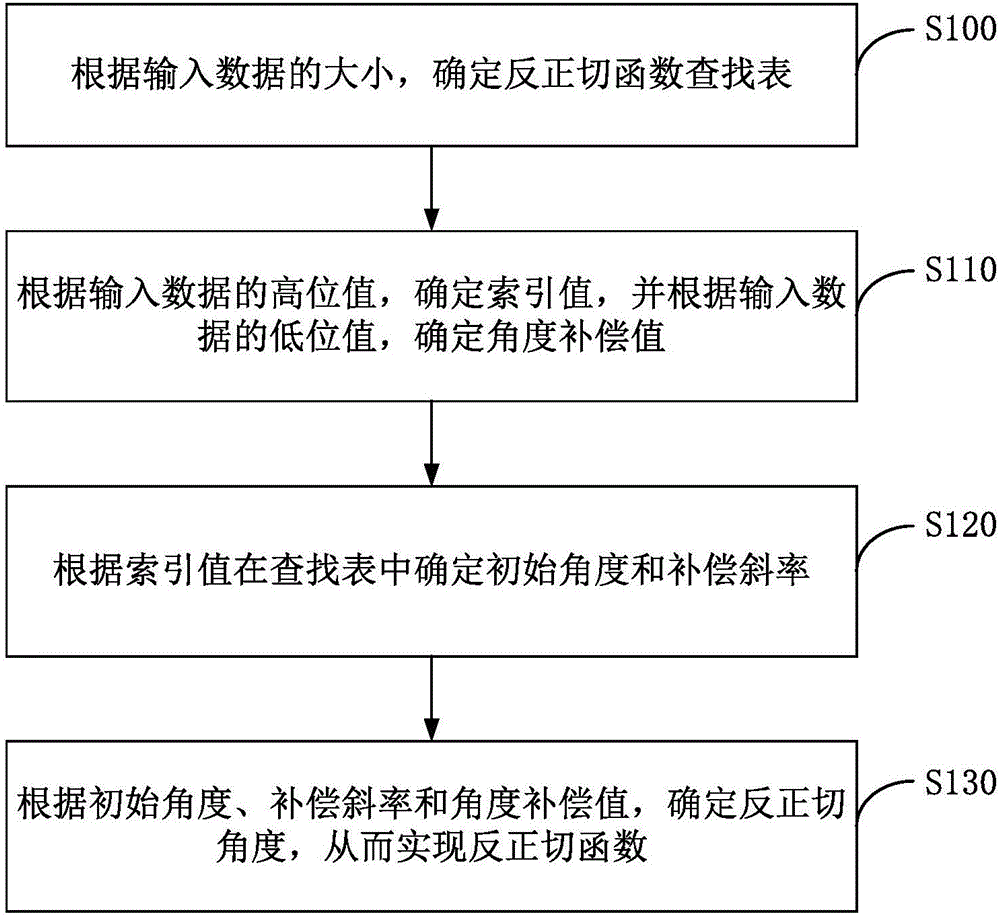
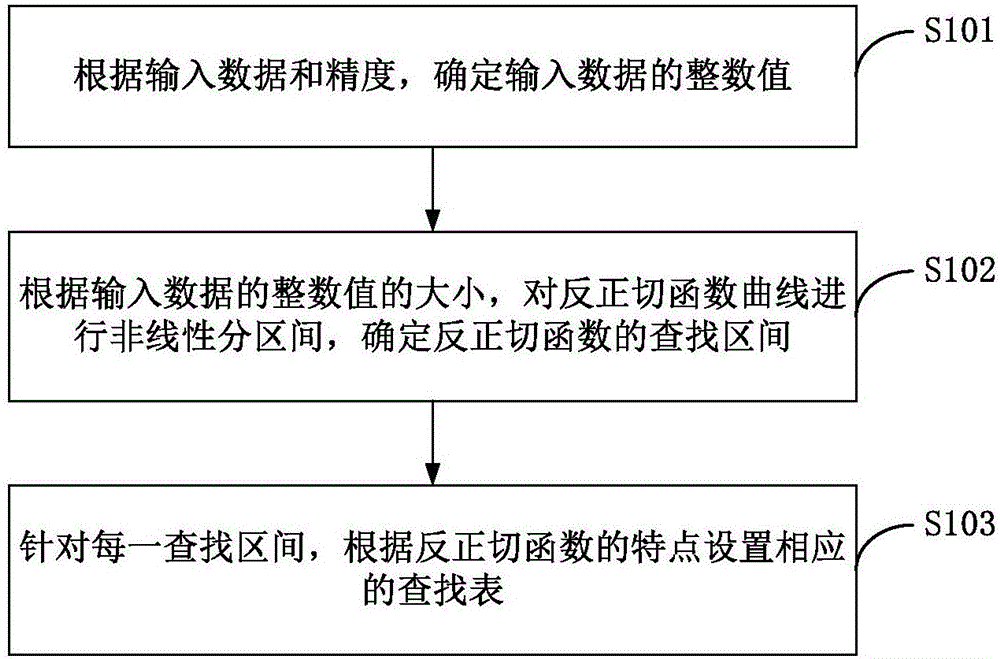
Sectional table look-up based arc-tangent function realization method and device
InactiveCN106227291AReduce computationReduce computational costTrigometric functionsDigital function generatorsLookup tableTangent function
The invention discloses a sectional table look-up based arc-tangent function realization method and device. The realization method includes: determining an arc-tangent function lookup table according to the size of inputted data; determining an index value according to a high value of the inputted data, determining an angle compensation value according to a low value of the inputted data, and determining initial angle and compensation slope in the lookup table according to the index value; determining arc-tangent angle according to the initial angle, compensation slope and angle compensation value so as to realize the arc-tangent function. Through the realization method and device, the technical problem about how to realize the arc-tangent function of infinite interval is solved, calculation in the angle solving process of the arc-tangent function is reduced, calculation cost is reduced under the condition that data accuracy is assured, and limited storage space is saved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
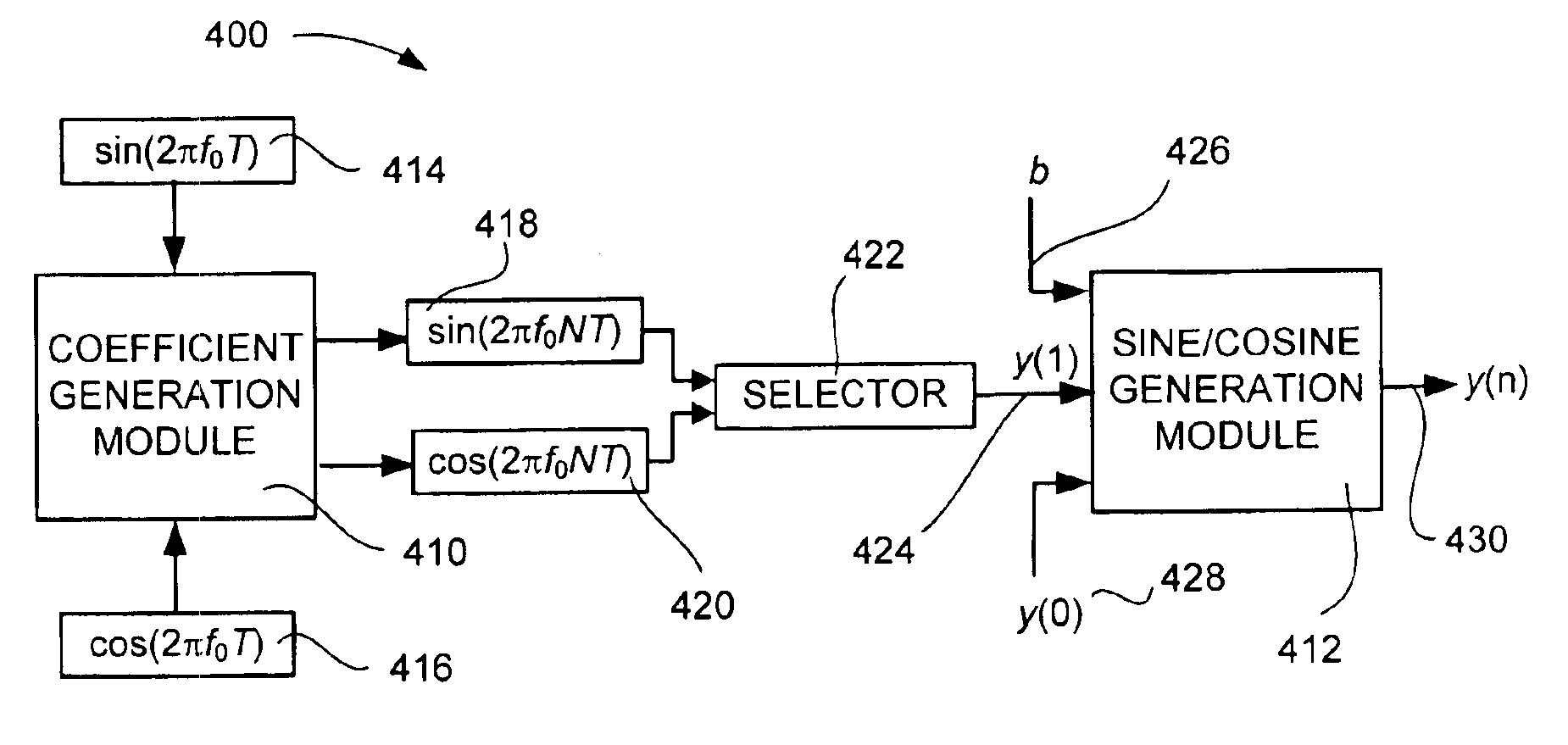
Digital sine/cosine wave generator
A digital sine / cosine wave generator generates discrete values representative of either a sine wave or a cosine wave. The digital sine / cosine wave generator generates sine and / or cosine waves by implementing a difference equation of the form y(n)=b*y(n−2)−y(n−1). One of the initial conditions of the difference equation is selected from a series of values generated by a coefficient generator. The frequency of the sine and / or cosine wave generated by the sine / cosine wave generator is dependent on, and may be selected according to, which of the series of values generated by a coefficient generator is chosen as an initial condition of the difference equation.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
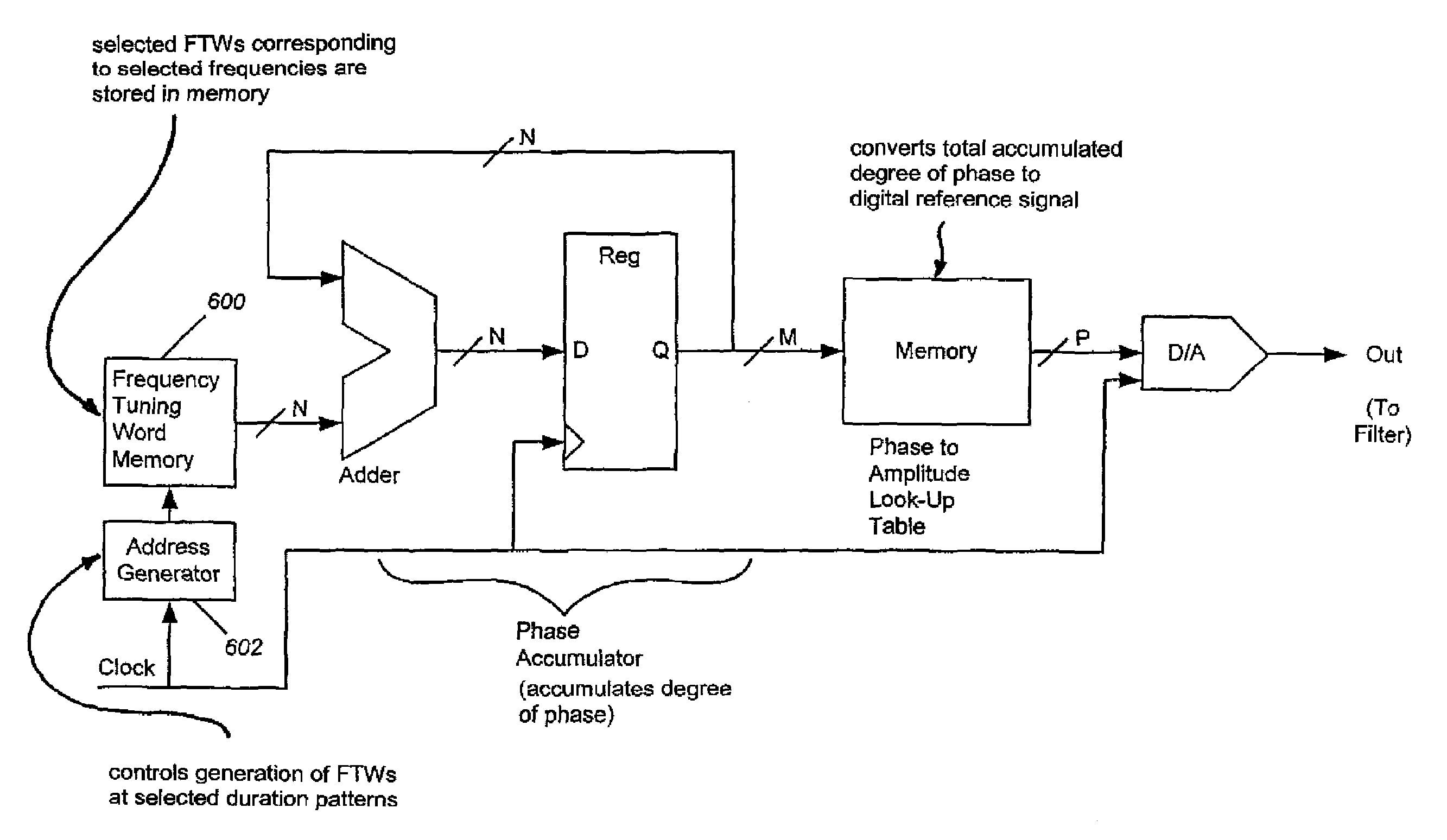
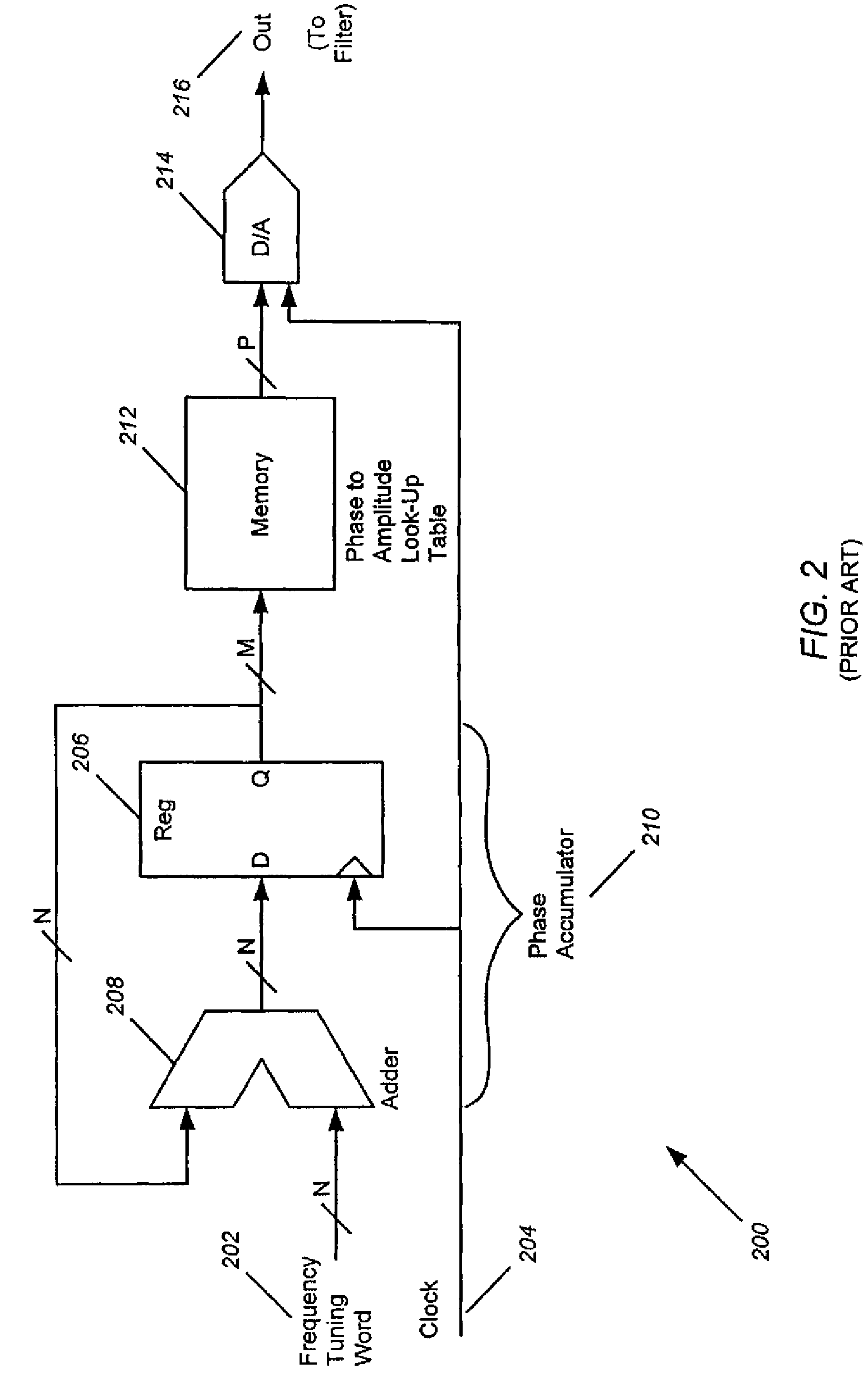
Method and apparatus for improving the frequency resolution of a direct digital synthesizer
InactiveUS7606849B2High purityHigh frequency resolutionTrigometric functionsDigital circuit testingImage resolutionSwitching frequency
The present invention is directed to the use of a DDS to generate a high purity reference signal with high frequency resolution by switching a frequency tuning word (FTW) between particular values for particular time durations to produce two or more closely spaced frequencies that appear at the DDS output as a single frequency. Given a DDS switching between F1 and F2 such that F1 is present for time T1 and F2 is present for time T2, with the total period of the repeating pattern being T=T1+T2, in order for the output of the DDS to produce a single high-purity frequency that is the time-weighted average of the alternating frequencies, the condition |F1−F2|<<π / T must be satisfied. The time-weighted average frequency Favg=(T1·F1+T2·F2) / (T+T2). By an appropriate choice of T1 and T2, Favg can be set to any frequency between these two frequencies.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
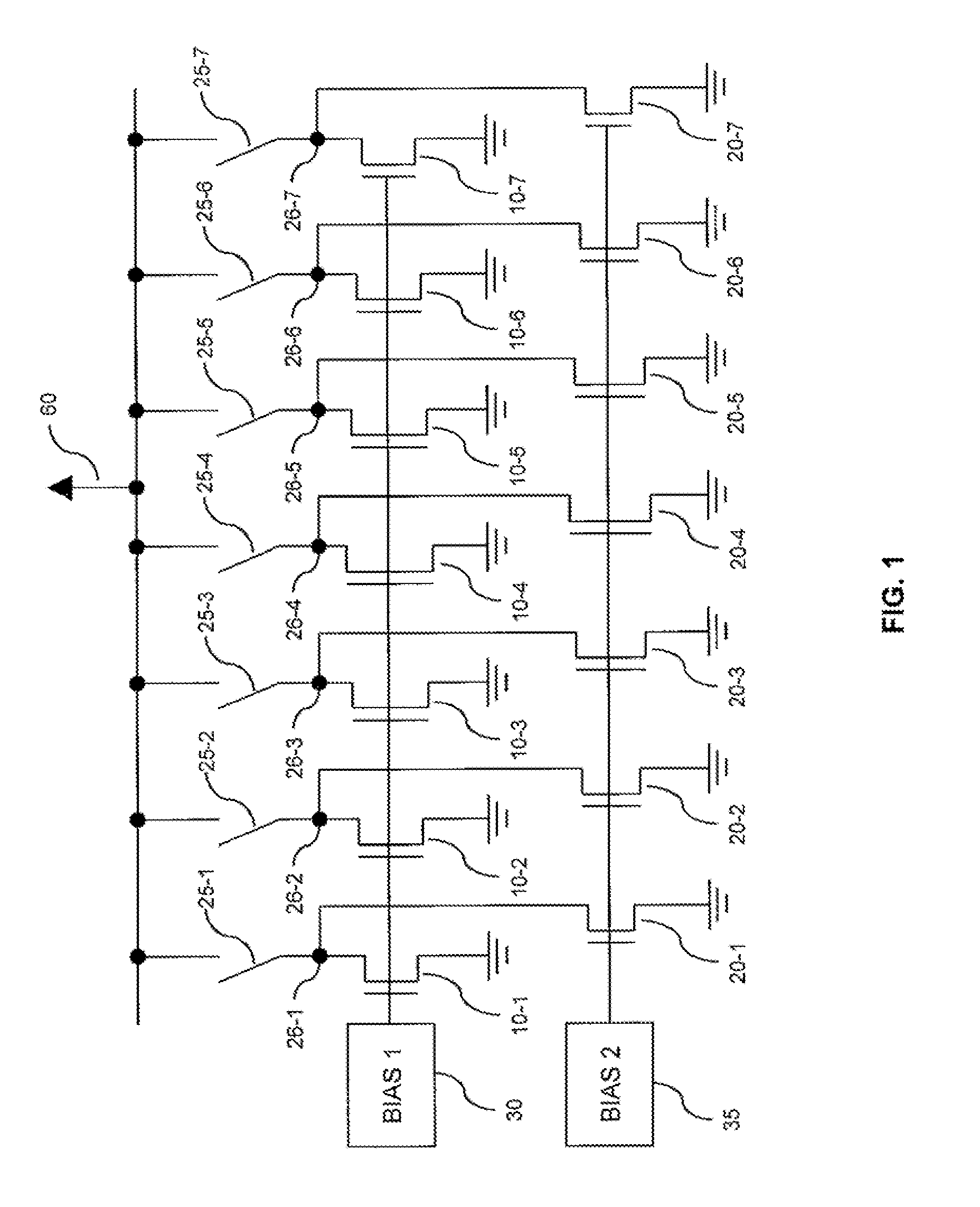
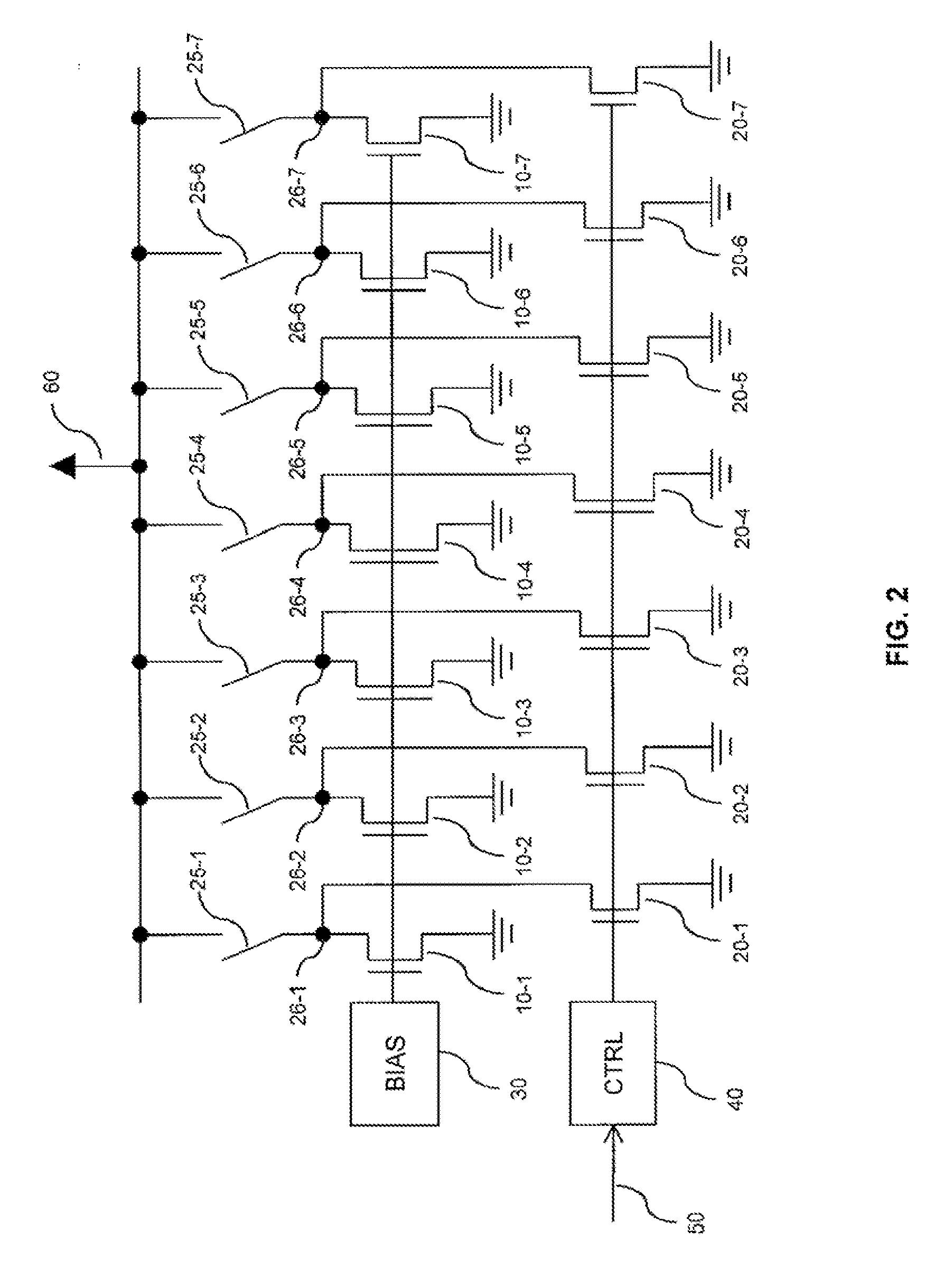
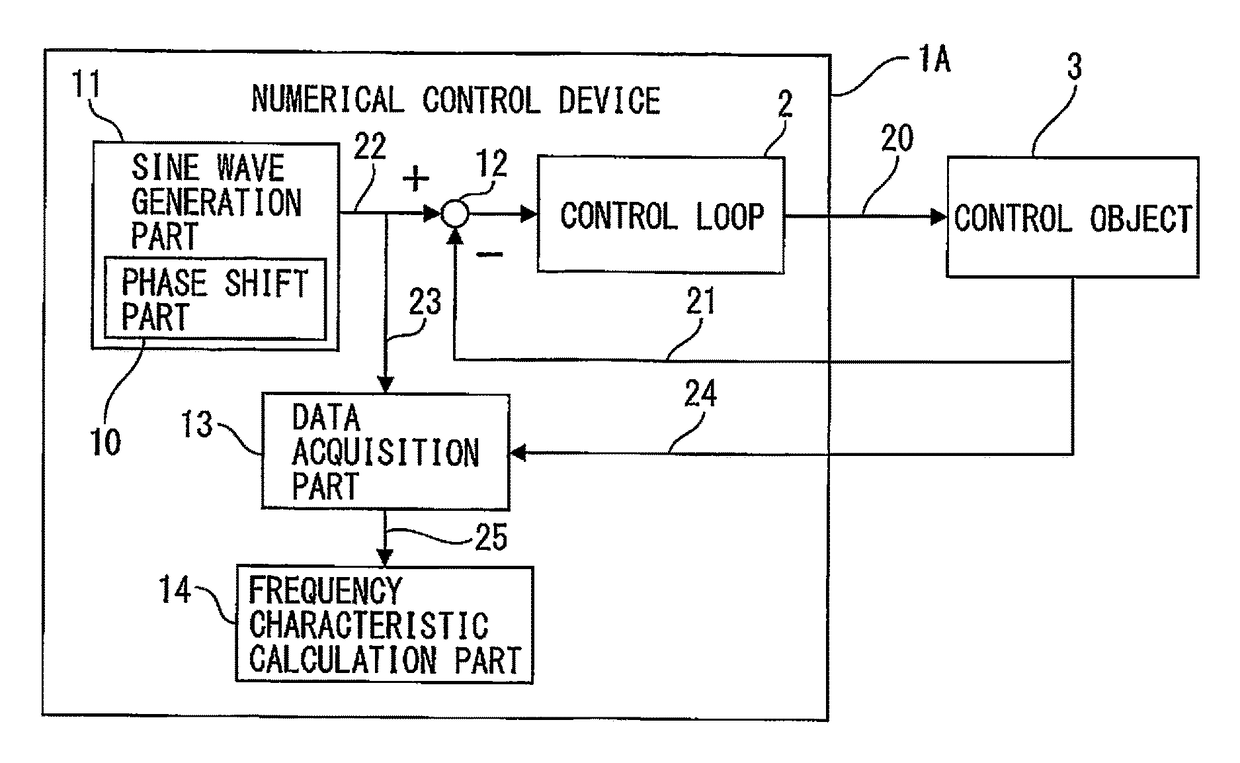
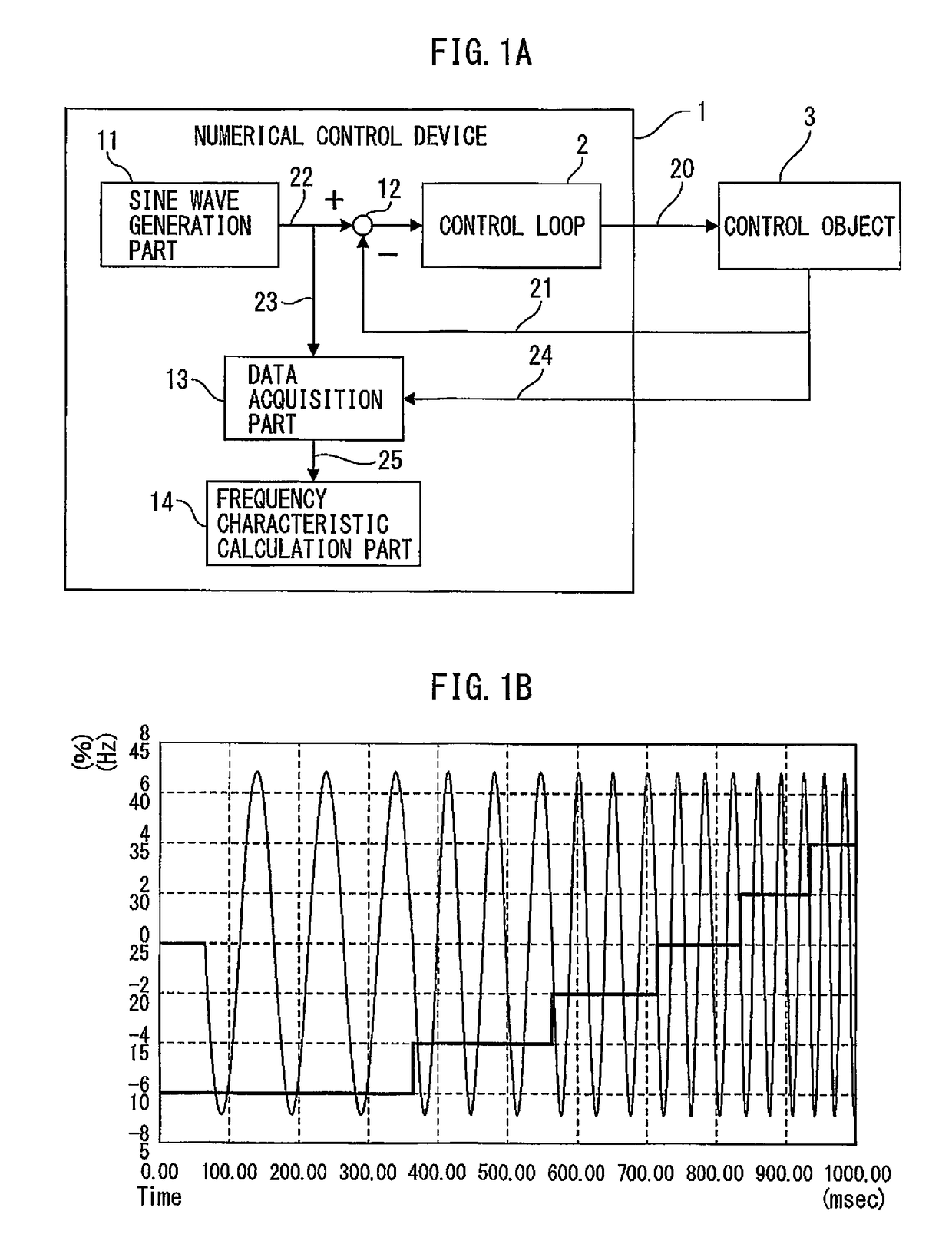
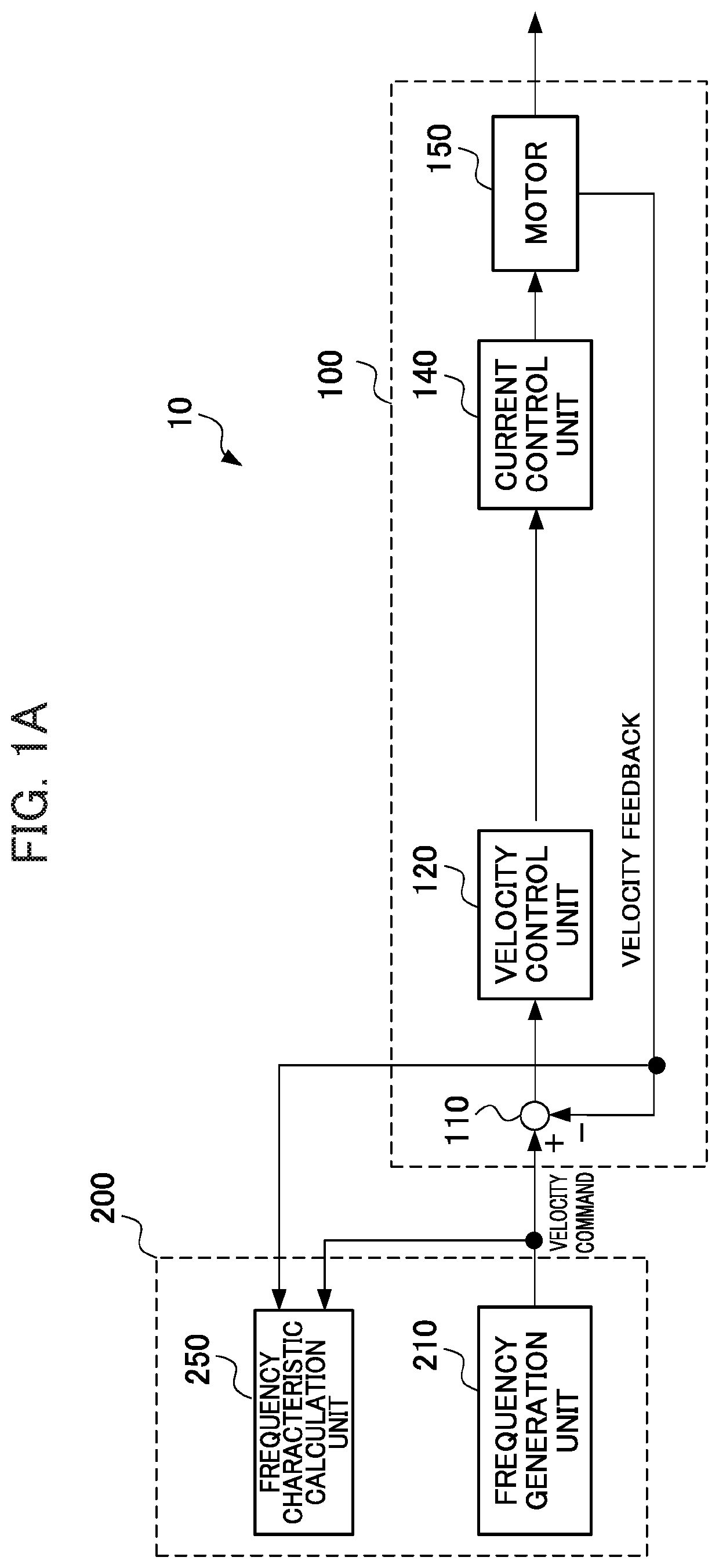
Numerical control device having function of calculating frequency characteristic of control loop
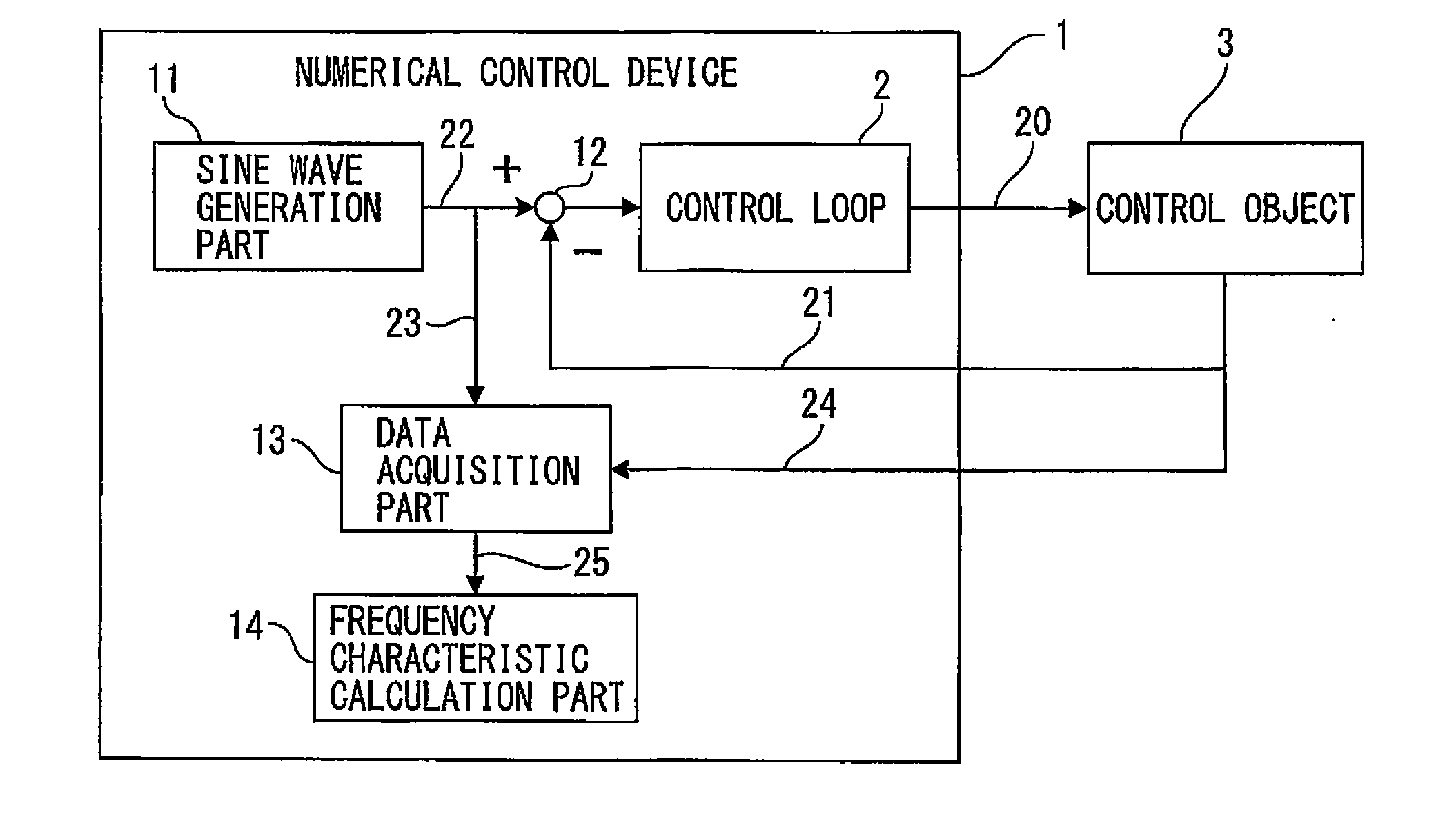
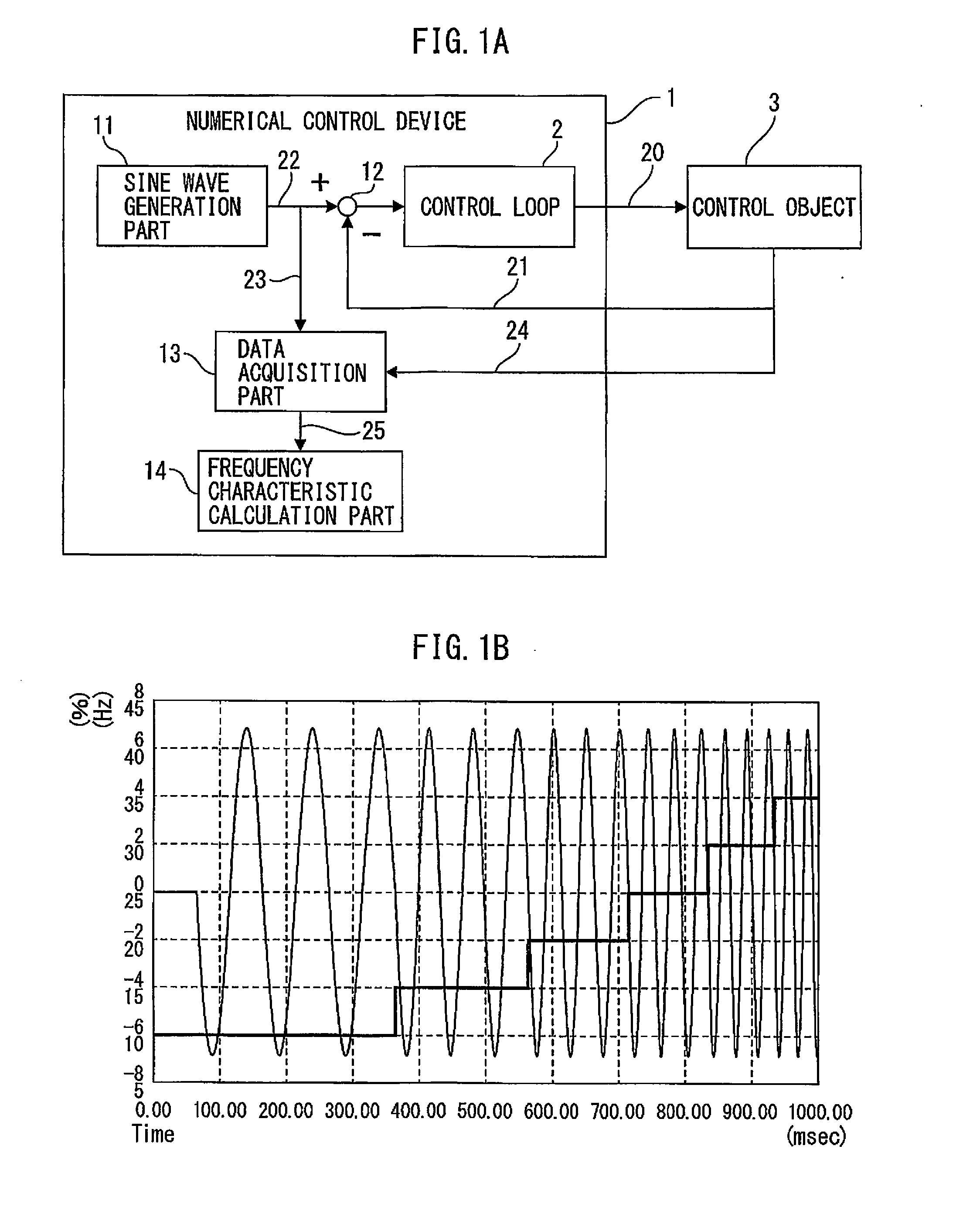
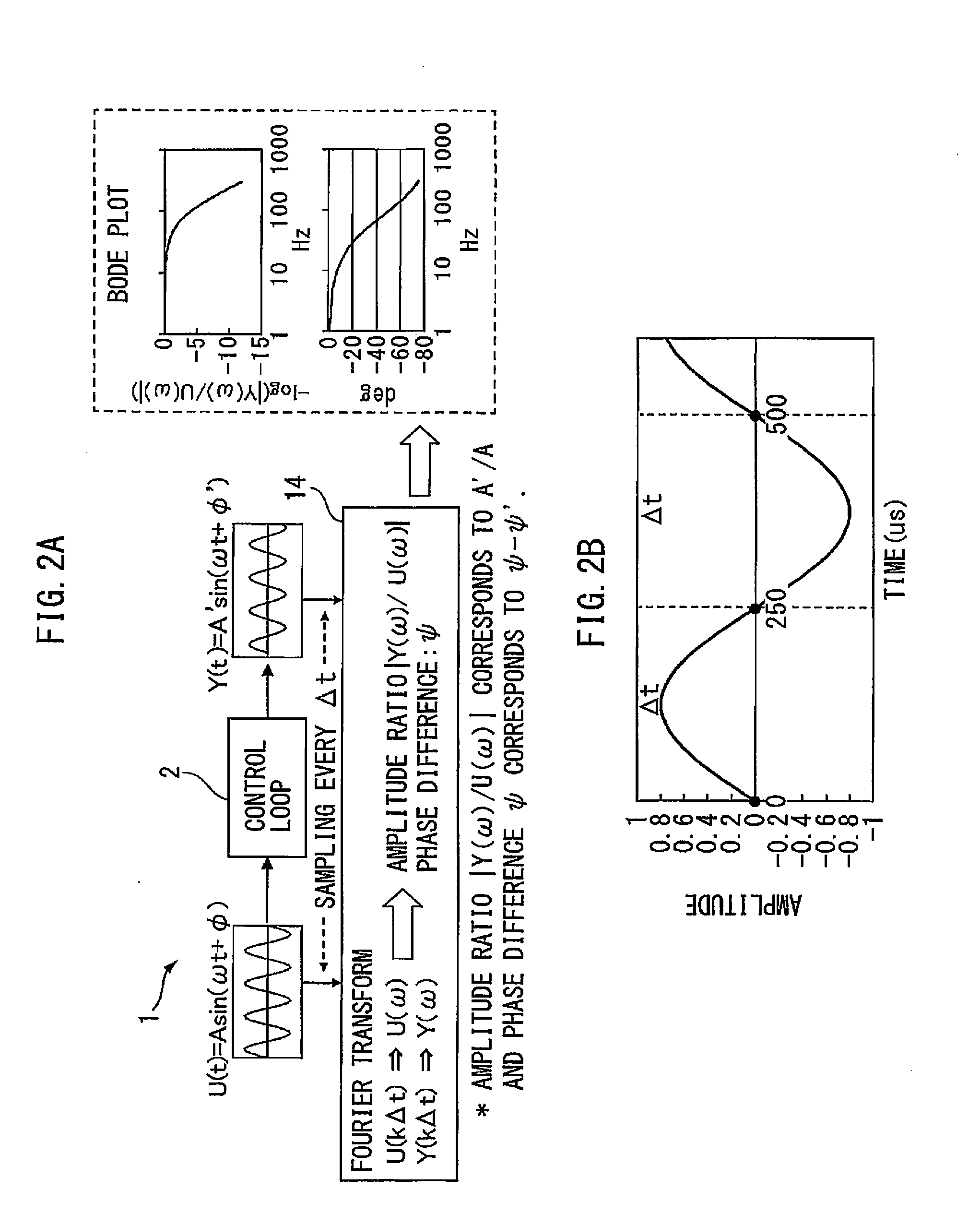
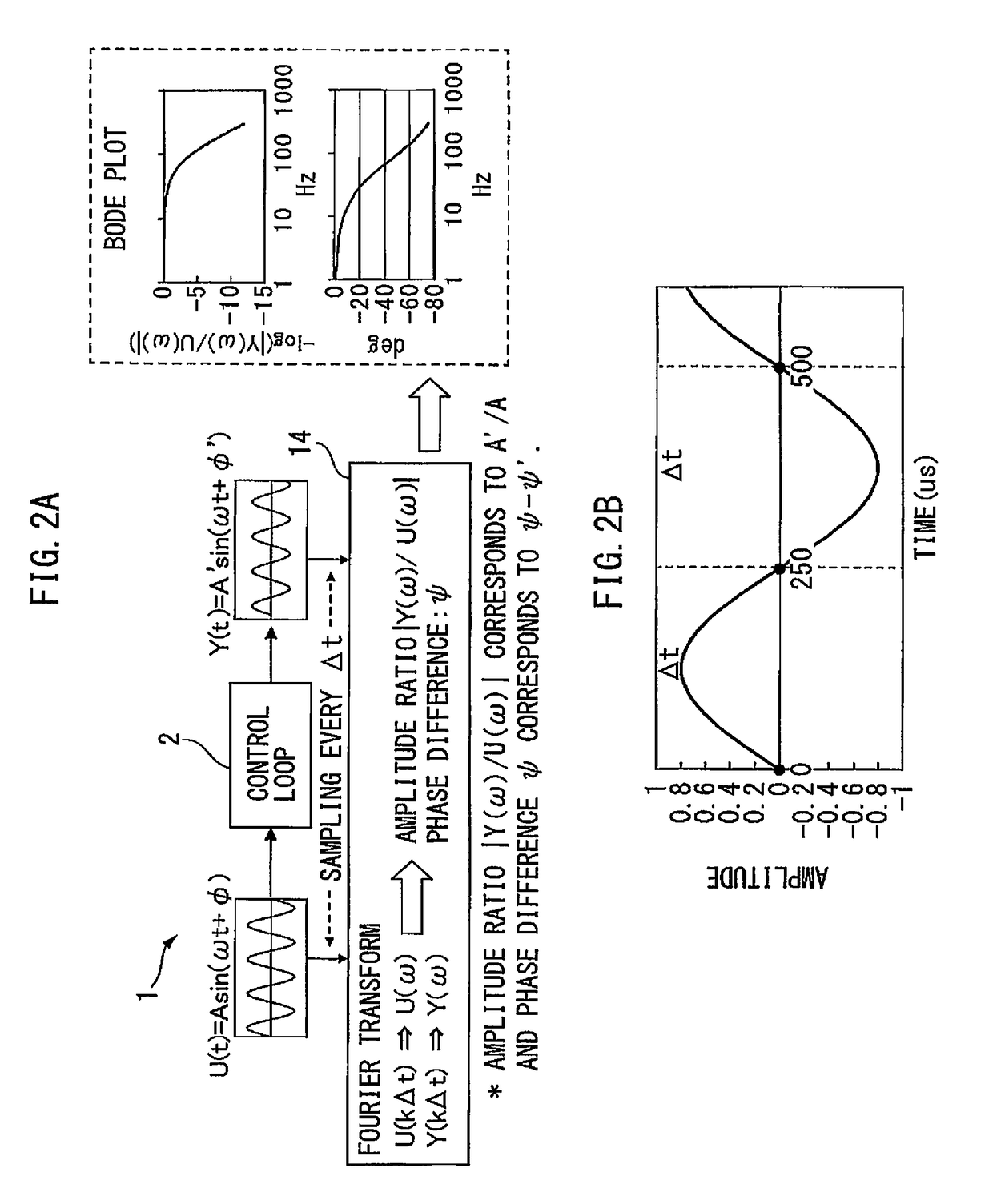
ActiveUS20150241869A1Easy to measureHigh measurement accuracyTrigometric functionsSampled-variable control systemsNumerical controlPhase shifted
A numerical control device wherein a sinusoidal signal generated by a sine wave generation part is input by a control loop excitation part to a control loop of the control object, the input signal input to the control loop and the output signal from the control object are sampled by the data acquisition part periodically, and the sampling data is used by the frequency characteristic calculation part to calculate the frequency characteristic of the control loop to control the control object, wherein the frequency characteristic calculation part uses data obtained by inputting a sinusoidal signal obtained by shifting an initial phase of the sinusoidal signal by a phase shift part provided at a sine wave generation part by exactly a certain amount to the control loop a plurality of times to calculate the frequency characteristic of the control loop to thereby improve the measurement precision regardless of the sampling frequency.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Digital Waveform Synthesis
A circuit is provided with a plurality current cells. The current cells each comprise a main current source and an auxiliary current source coupled in parallel. The main current source supplies a main current to a current output of the current cell, and the auxiliary current source supplies an auxiliary current to the current output of the current cell. The main current sources are weighted according to a first predefined waveform, and the auxiliary current sources are weighted according to a second predefined waveform which is different from the first predefined waveform.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
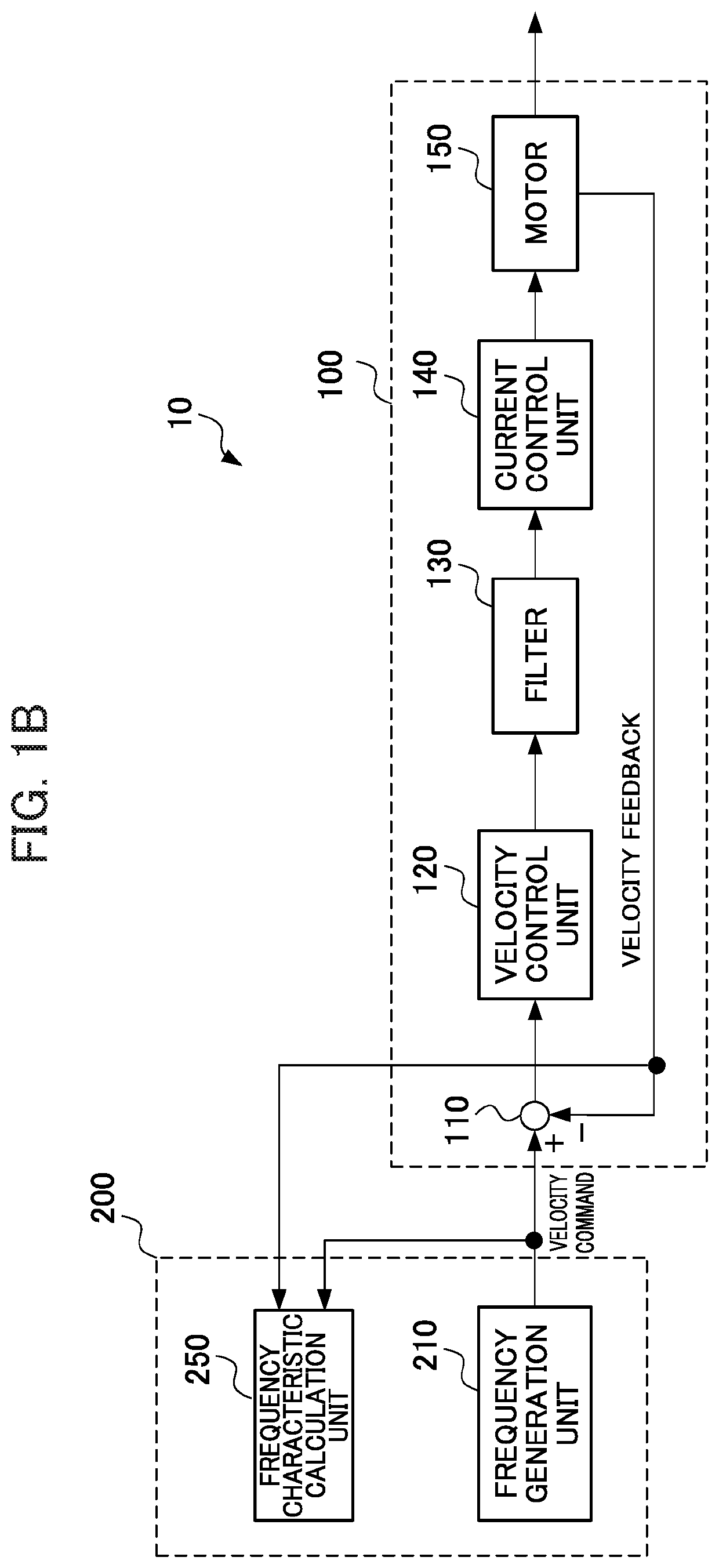
Numerical control device having function of calculating frequency characteristic of control loop
ActiveUS9887865B2High measurement accuracyEasy to measureTrigometric functionsModulated-carrier systemsNumerical controlPhase shifted
A numerical control device wherein a sinusoidal signal generated by a sine wave generation part is input by a control loop excitation part to a control loop of the control object, the input signal input to the control loop and the output signal from the control object are sampled by the data acquisition part periodically, and the sampling data is used by the frequency characteristic calculation part to calculate the frequency characteristic of the control loop to control the control object, wherein the frequency characteristic calculation part uses data obtained by inputting a sinusoidal signal obtained by shifting an initial phase of the sinusoidal signal by a phase shift part provided at a sine wave generation part by exactly a certain amount to the control loop a plurality of times to calculate the frequency characteristic of the control loop to thereby improve the measurement precision regardless of the sampling frequency.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Calculation of trigonometric functions in an integrated circuit device
InactiveUS8589463B2Trigometric functionsDigital function generatorsComputer scienceIntegrated circuit
Owner:ALTERA CORP
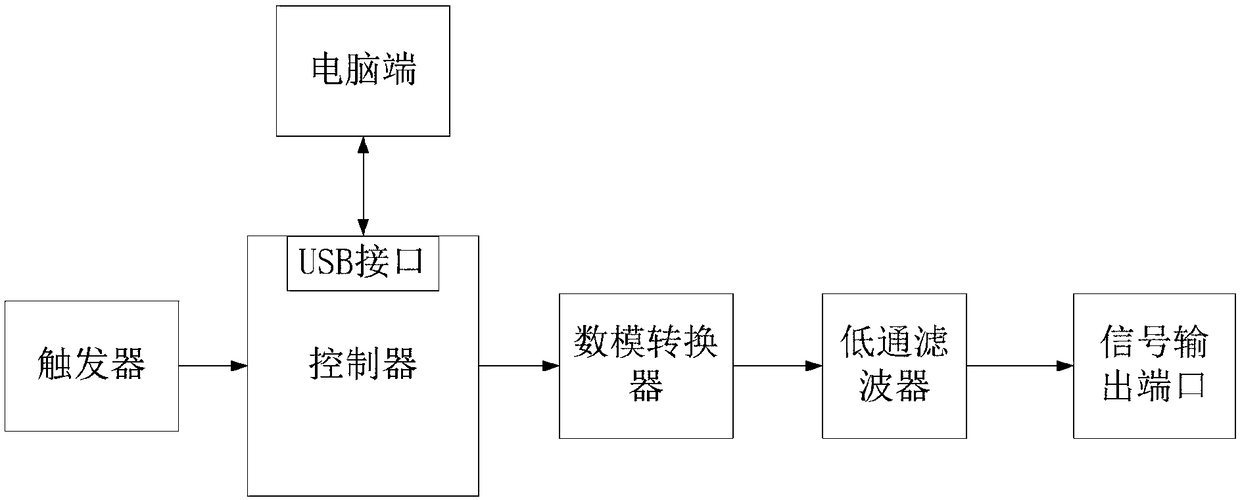
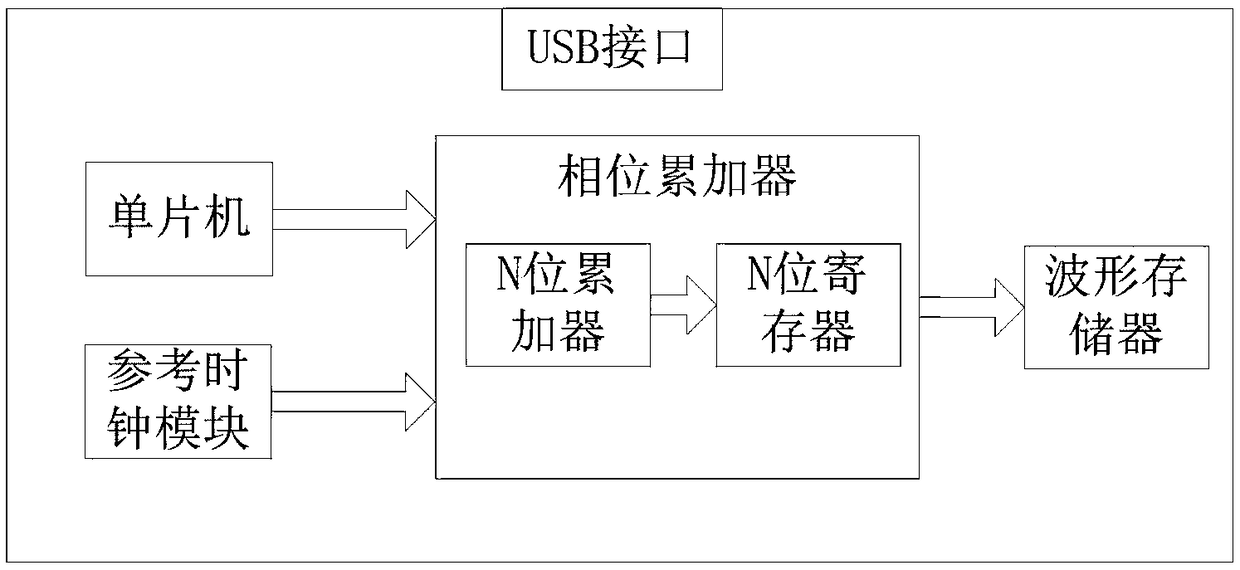
Program-controlled triangular wave generation system
PendingCN108646851AImprove stabilityLow costTrigometric functionsDigital function generatorsMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
The invention relates to a program-controlled triangular wave generation system, comprising a trigger, a controller, a digital-to-analog converter and a low-pass filter with a signal output port sequentially connected through signal ports, wherein the controller is connected with a computer terminal through signals; the controller comprises a phase accumulator, a single chip microcomputer, a reference clock module and a waveform memory all connected with the phase accumulator through signals. As the single chip microcomputer is adopted as the control part, the problem of high cost caused by the red programmable digital device of the prior art is avoided, the low cost of the system is realized, and the frequency and the amplitude of the triangular wave are controlled by a trigger, so that the triangular wave generation system can be debugged more conveniently; at the same time, by setting the reference clock module and the phase accumulator, the waveform is accumulated and the stabilityof waveform is improved.
Owner:成都意科科技有限责任公司
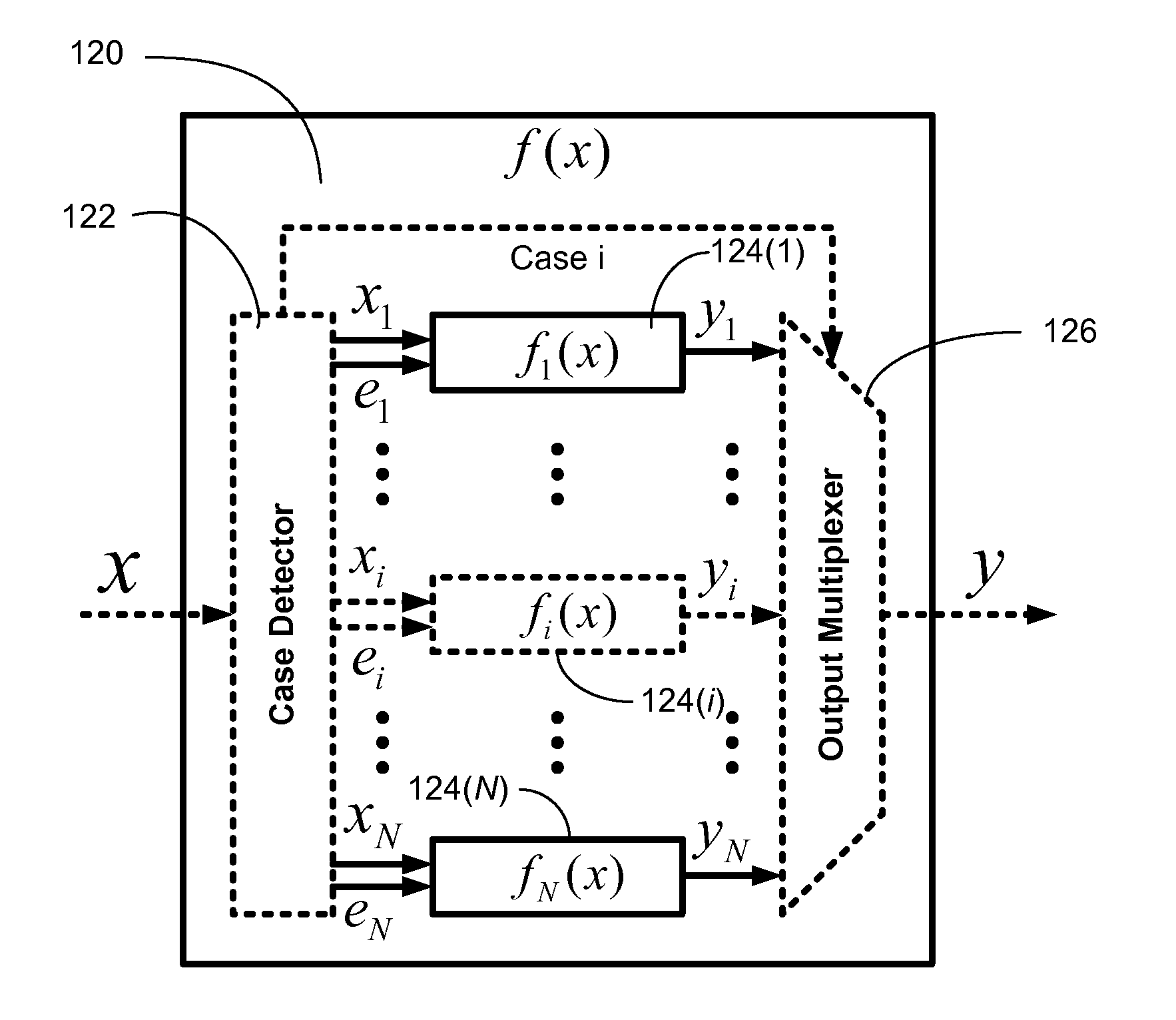
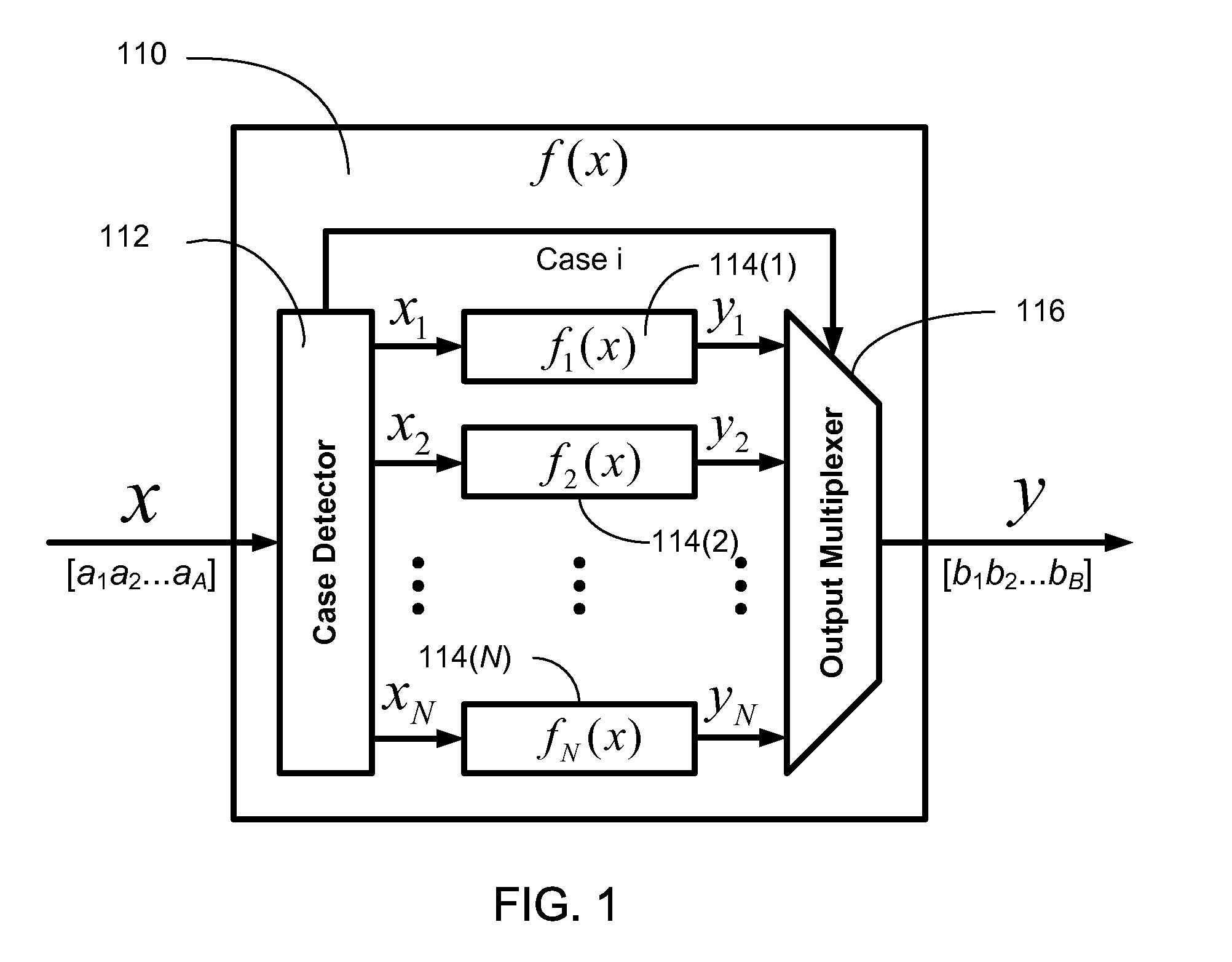
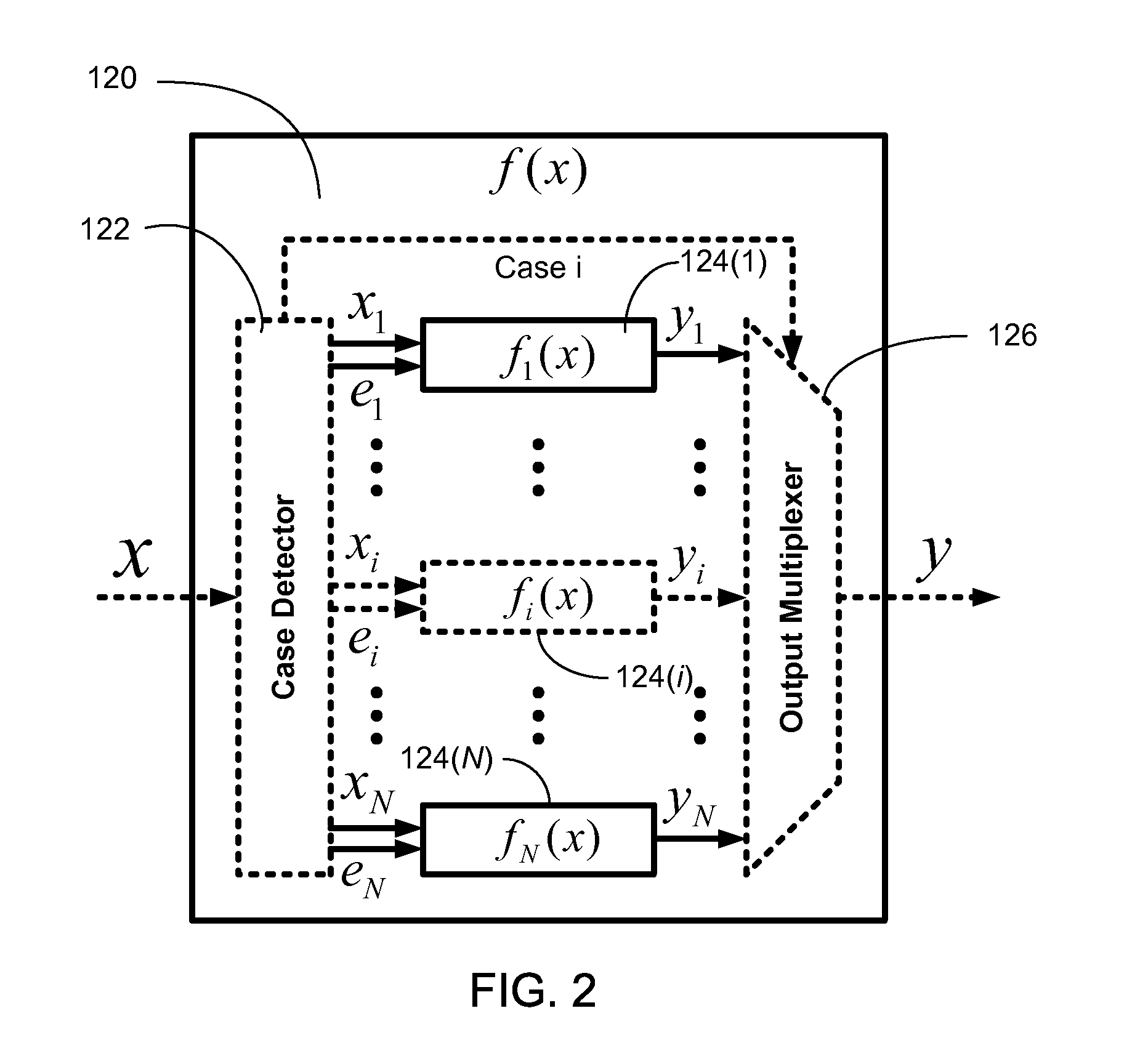
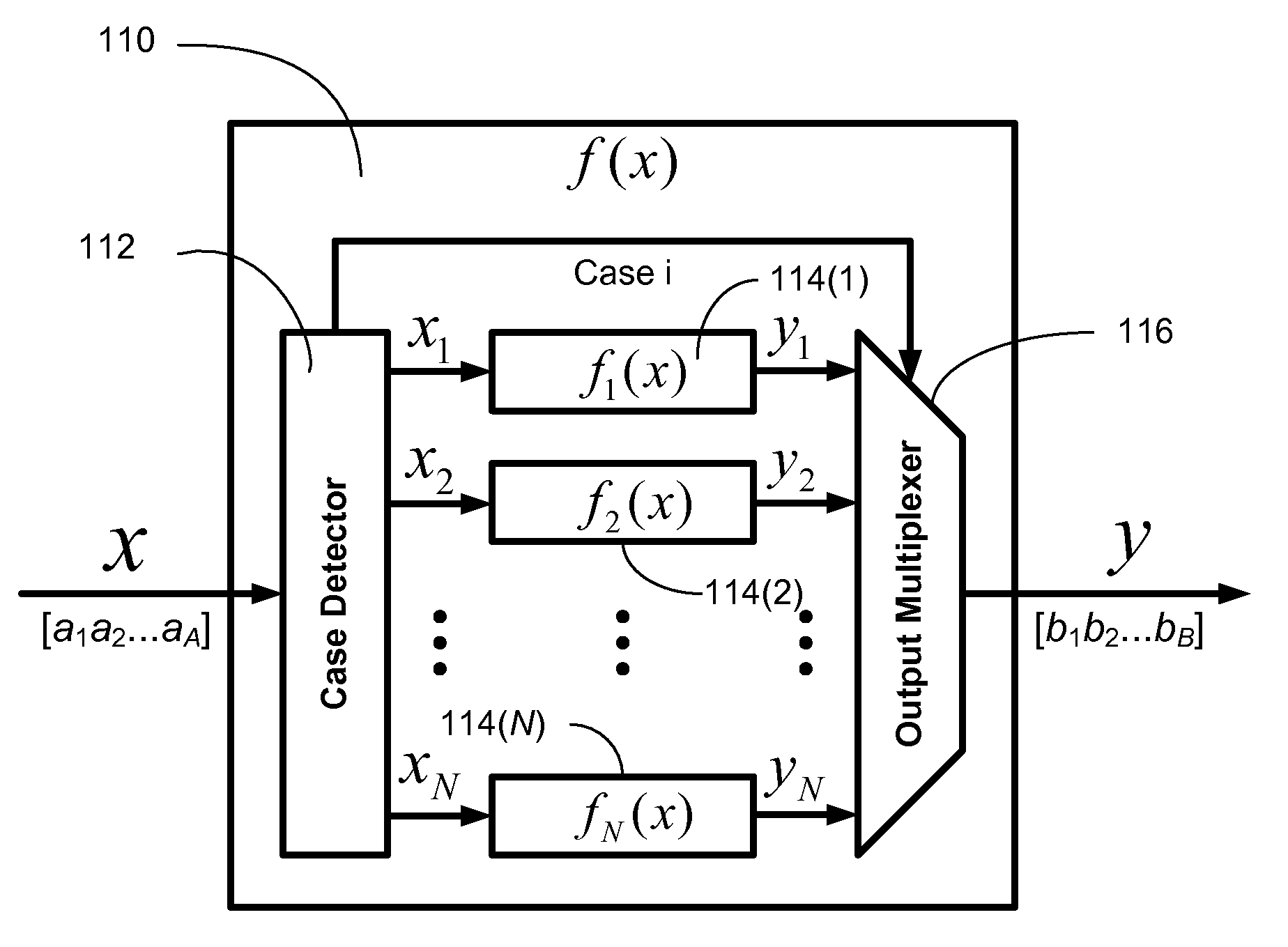
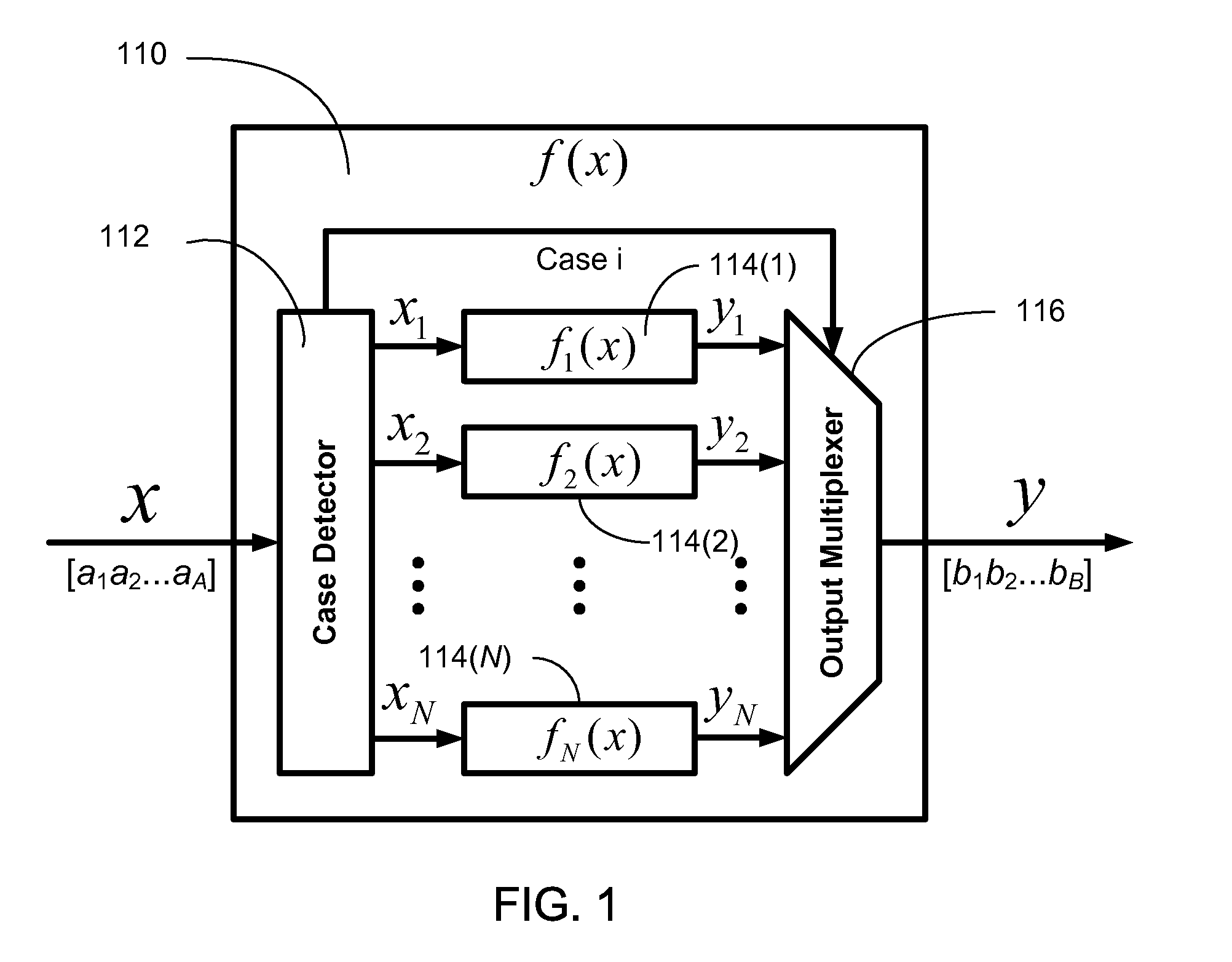
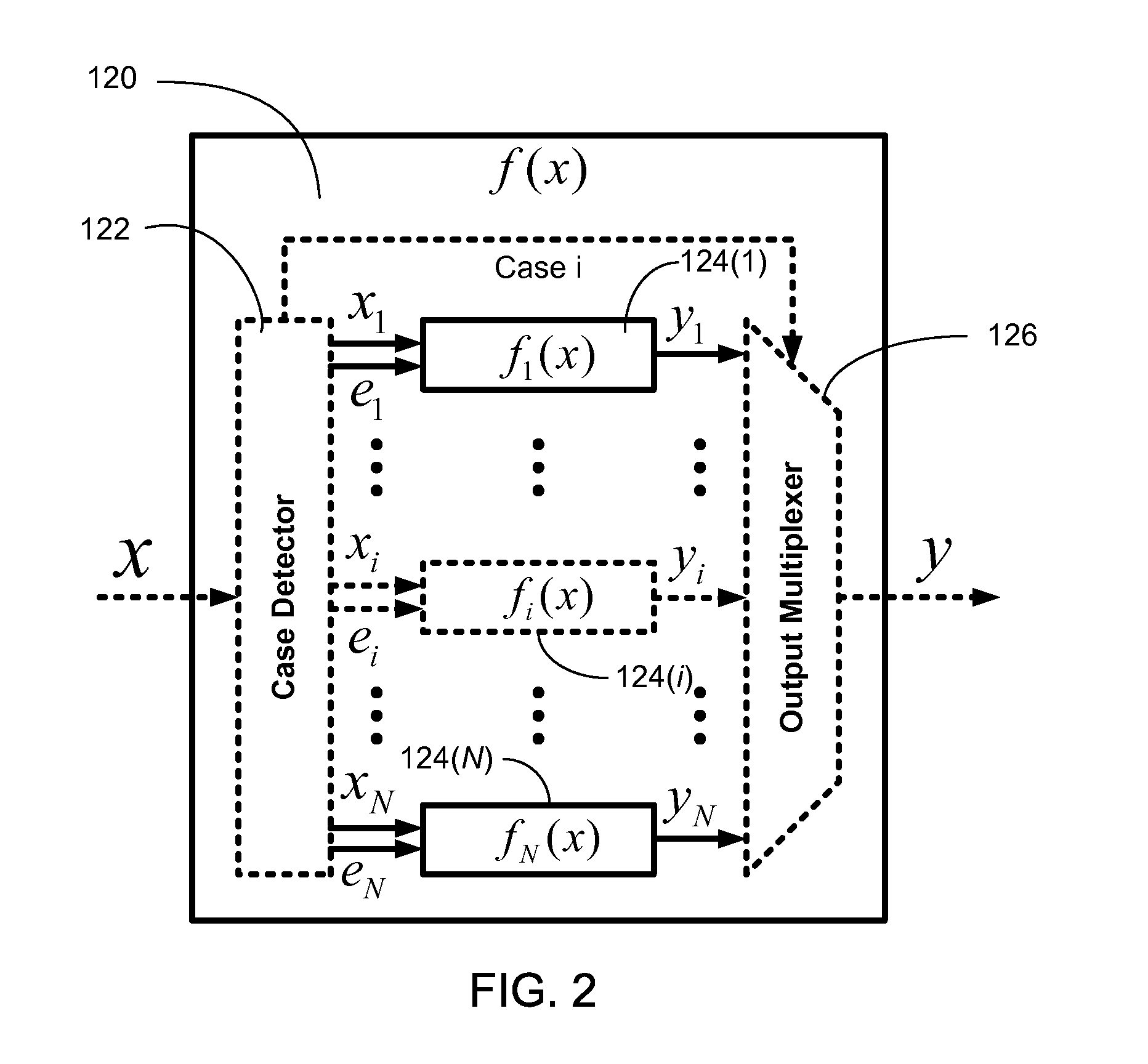
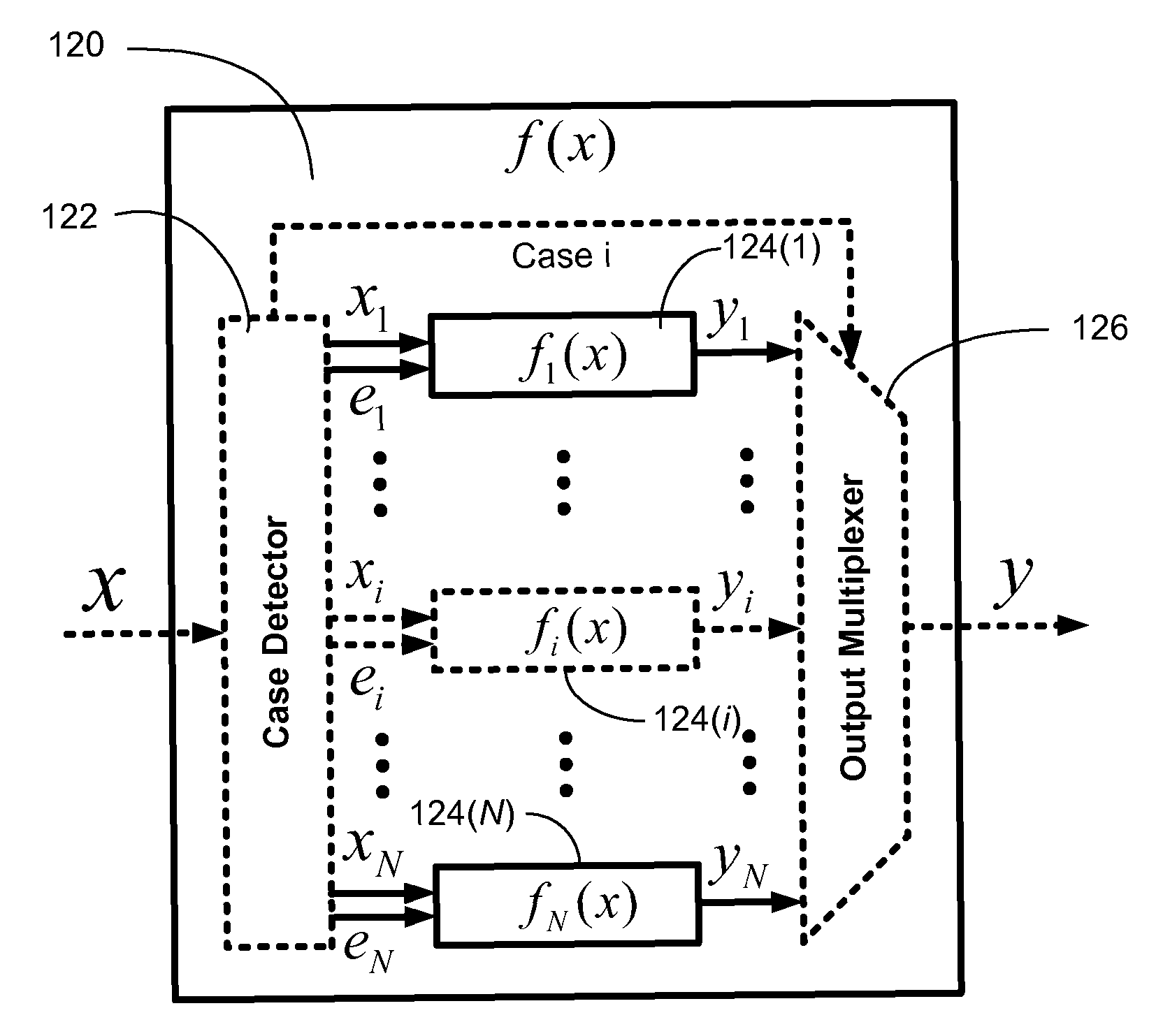
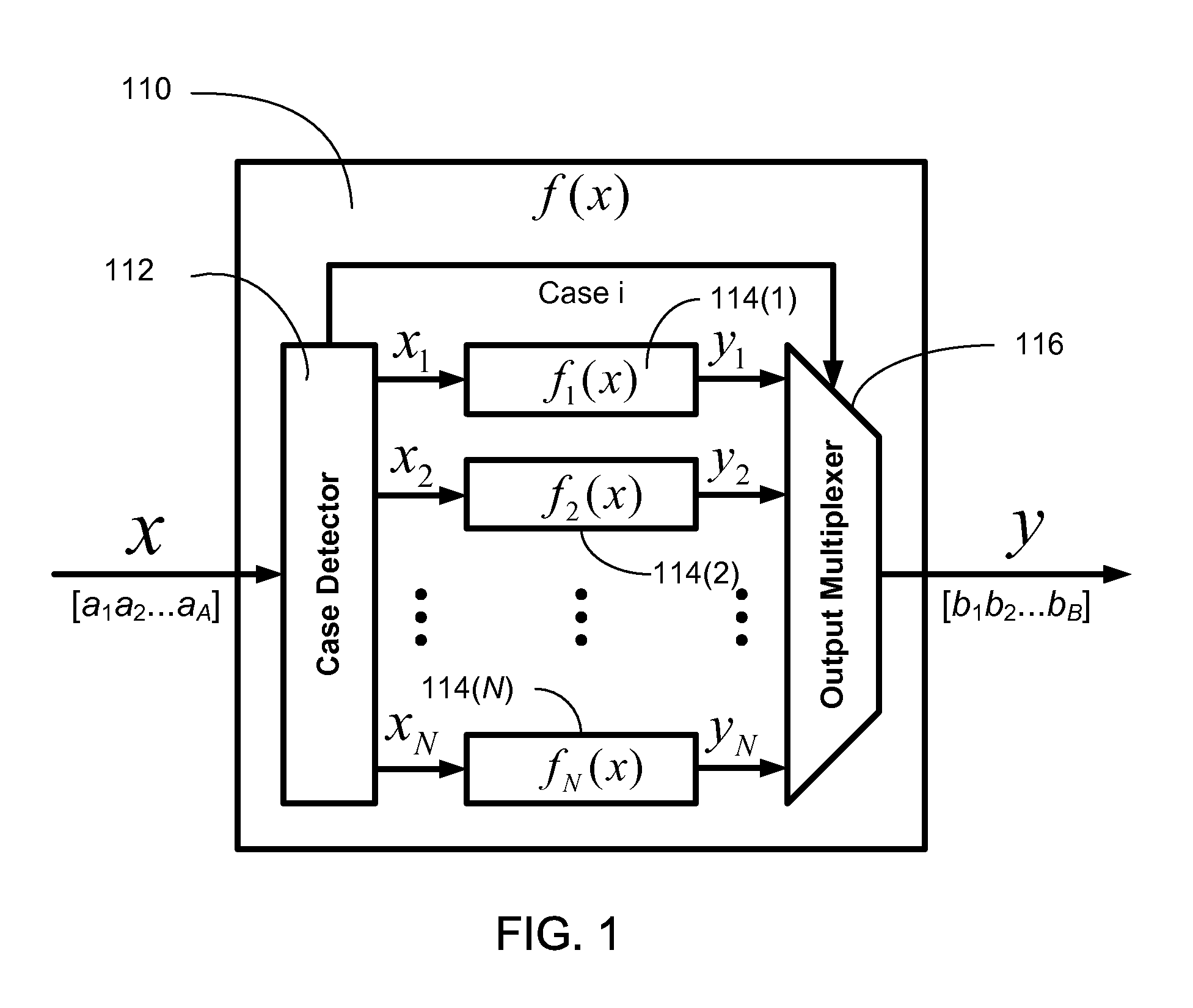
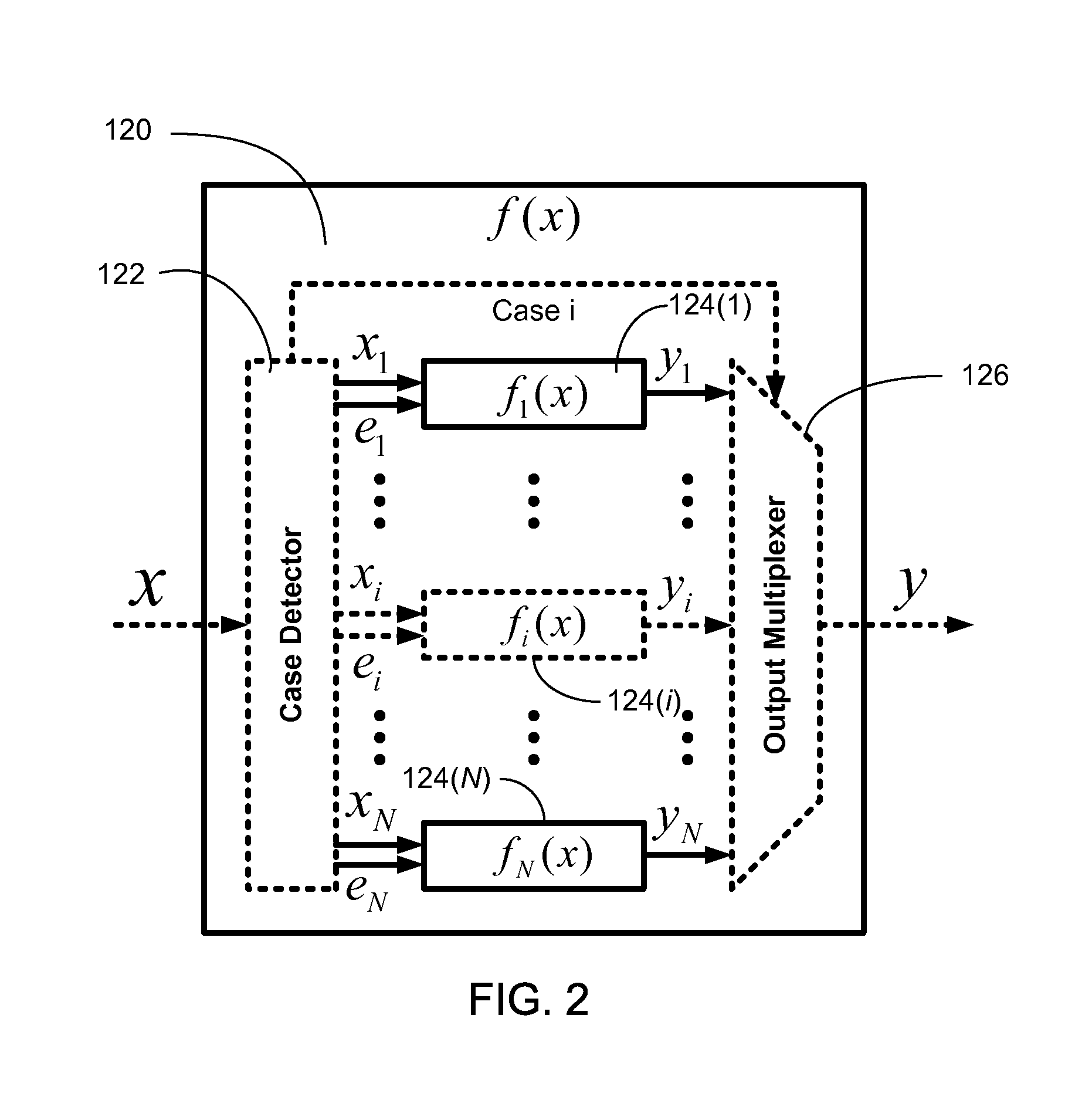
Efficient function generator using case detection and output selection
ActiveUS8650235B2Maximize rateMaximize throughputTrigometric functionsPower supply for data processingControl engineeringCase detection
A function generator for a digital system includes a plurality of sub-function generators. Each sub-function generator has an input that receives a respective input value and has an output that provides a respective output value responsive to the respective input value. A case detector receives a system input value and selectively routes at least a first portion of the system input value to the input of at least one selected sub-function generator. The case detector selects the selected sub-function generator in response to at least a second portion of the system input value. The case detector further suppresses transitions of data on the input of at least one non-selected sub-function generator. The case detector further selects the respective output value provided by the at least one selected sub-function generator and provides the selected respective output value as a function generator output value.
Owner:TOROSYAN ARTHUR
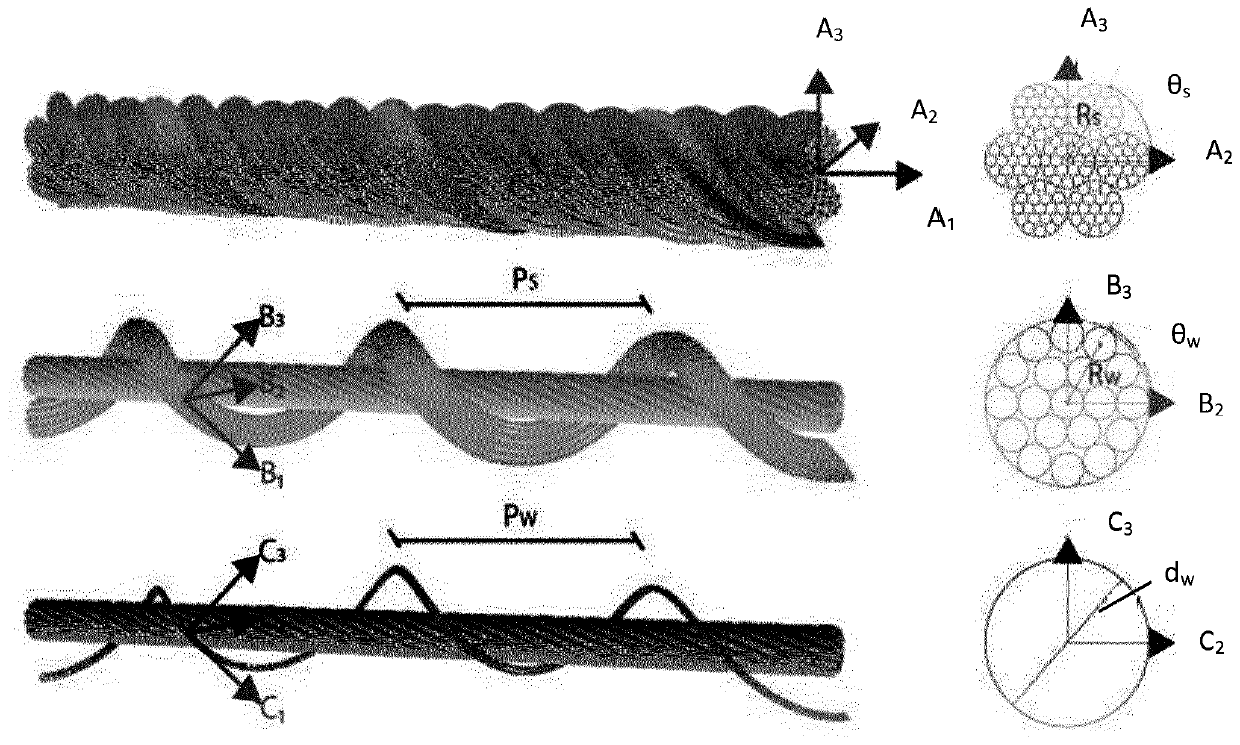
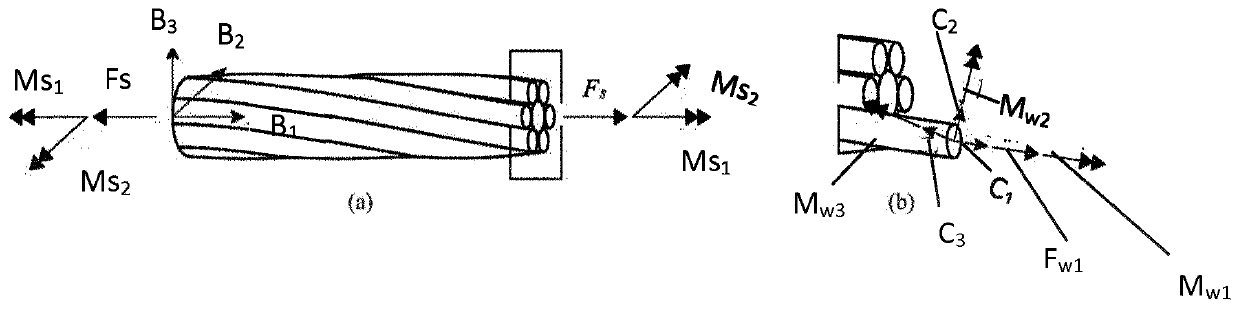
Method for evaluating temperatures in active heave compensation ropes
The invention relates to a method for evaluating temperatures in active heave compensation ropes, comprising the following steps: describing the geometry of ropes as composite structures obtained through assemblies of helical components in hierarchical levels: wires, strands and the rope itself; using a mechanical model of the strand that represents the material properties of each wire, under the assumption of linear elastic behavior; using a mechanical model of the rope that represents the combined action of tensile loads and imposed bending curvature; using a thermal model for the evaluation of the rope temperature increase (Ts) with respect to the ambient temperature, the thermal model comprising two main dissipation sources: the friction between strands or rope and a sheave and the friction between wires or between strands and compare rope temperature increase (Ts) obtained by the thermal model with a value of a predetermined temperature threshold.
Owner:REDAELLI TECNA
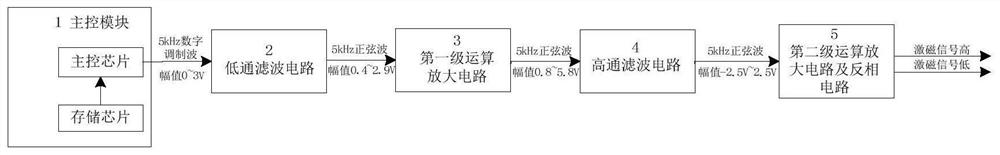
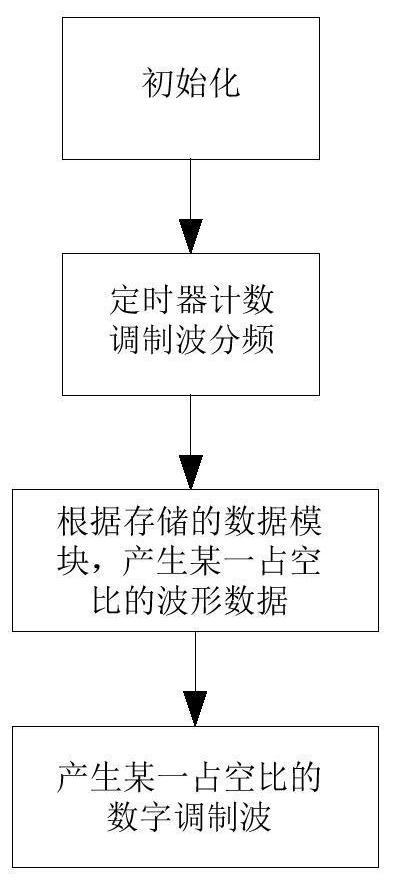
System and method for generating rotary transformer excitation signal
PendingCN113900475ALow costReduce volumeTrigometric functionsAngle modulation detailsLow-pass filterHemt circuits
The invention discloses a rotary transformer excitation signal generation system and method, and the system comprises a main control module which is used for generating a digital modulation wave which changes according to a sine rule; a low-pass filter which is used for converting the digital modulation wave into a sine wave; a first-stage operation amplification circuit which is used for carrying out the first-stage amplification of the sine wave; a high-pass filter circuit which is used for blocking sine waves; a second-stage operational amplification circuit which is used for carrying out second-stage amplification on the sine waves; and a phase inverting circuit which is used for inverting the sine waves to generate rotary transformer excitation signals. The problems of large weight, large size, high cost and difficulty in integration of the existing rotary transformer excitation signal generation method are solved, and the rotary transformer excitation signal generation method has the advantages of low cost, small size, light weight, easiness in integration and the like.
Owner:HEBEI HANGUANG HEAVY IND
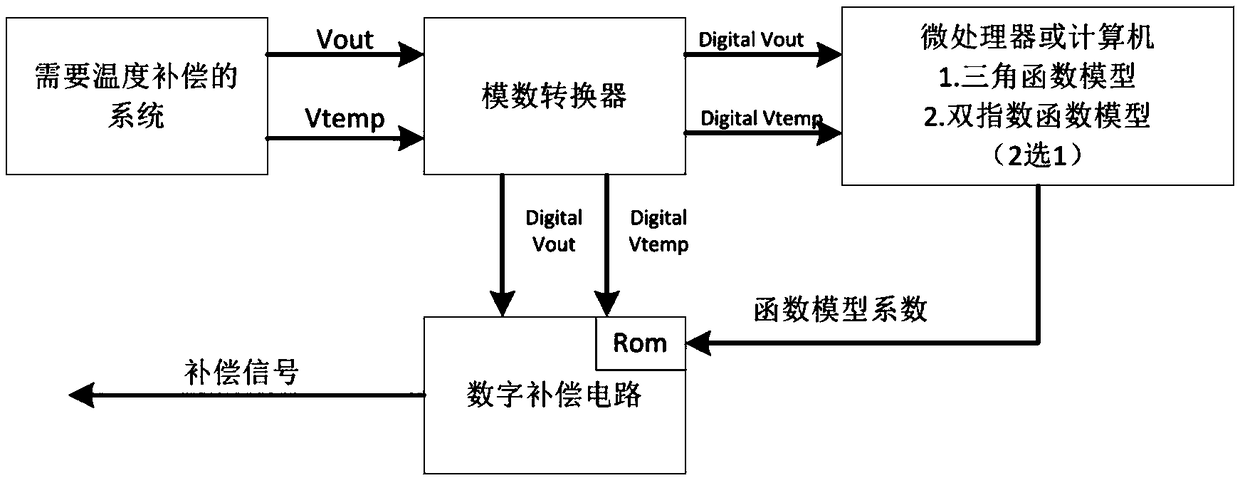
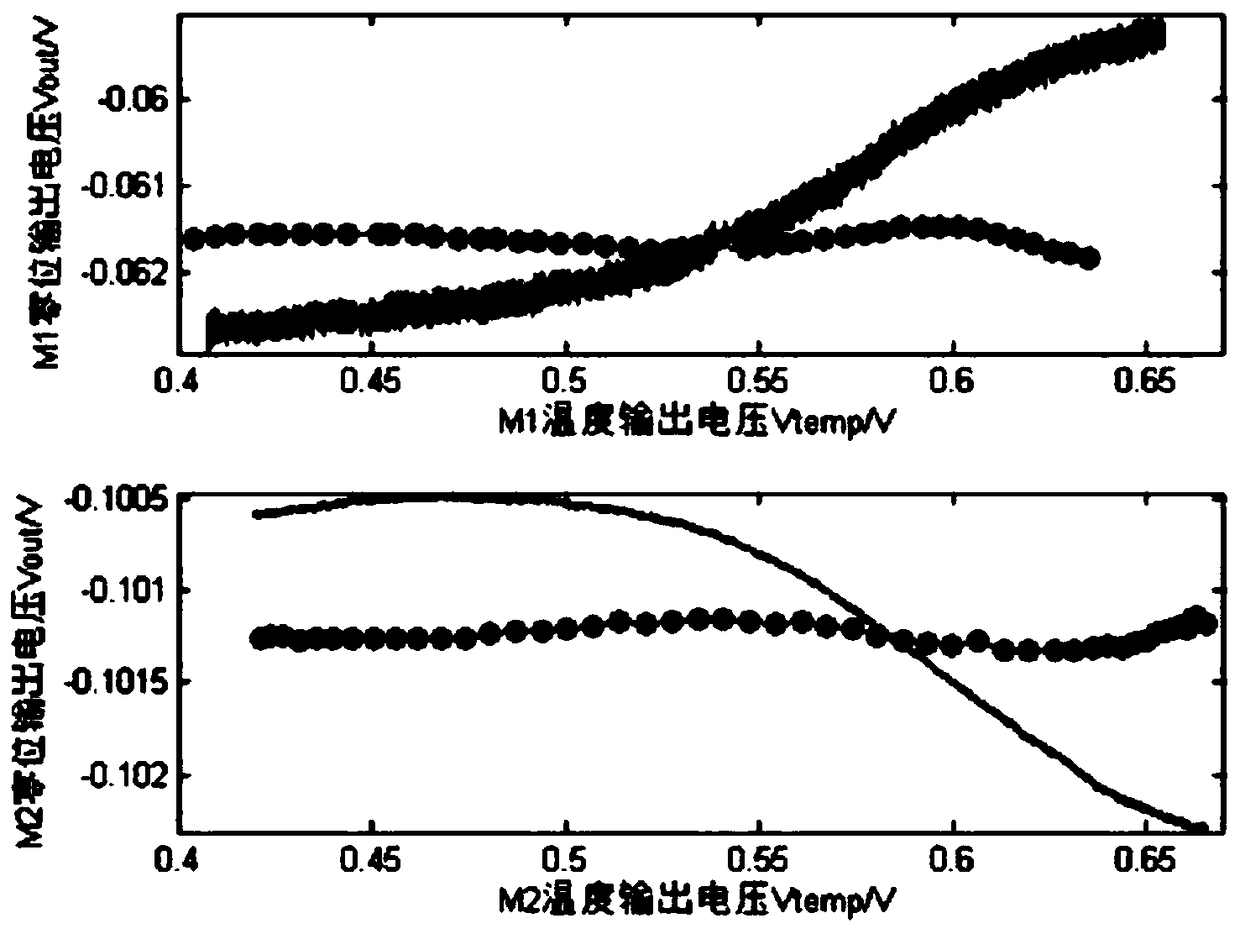
Infinite order temperature compensation system easy to implement
InactiveCN108875142ATo achieve the fitting effectLess coefficientTrigometric functionsSpecial data processing applicationsLookup tableDigital-to-analog converter
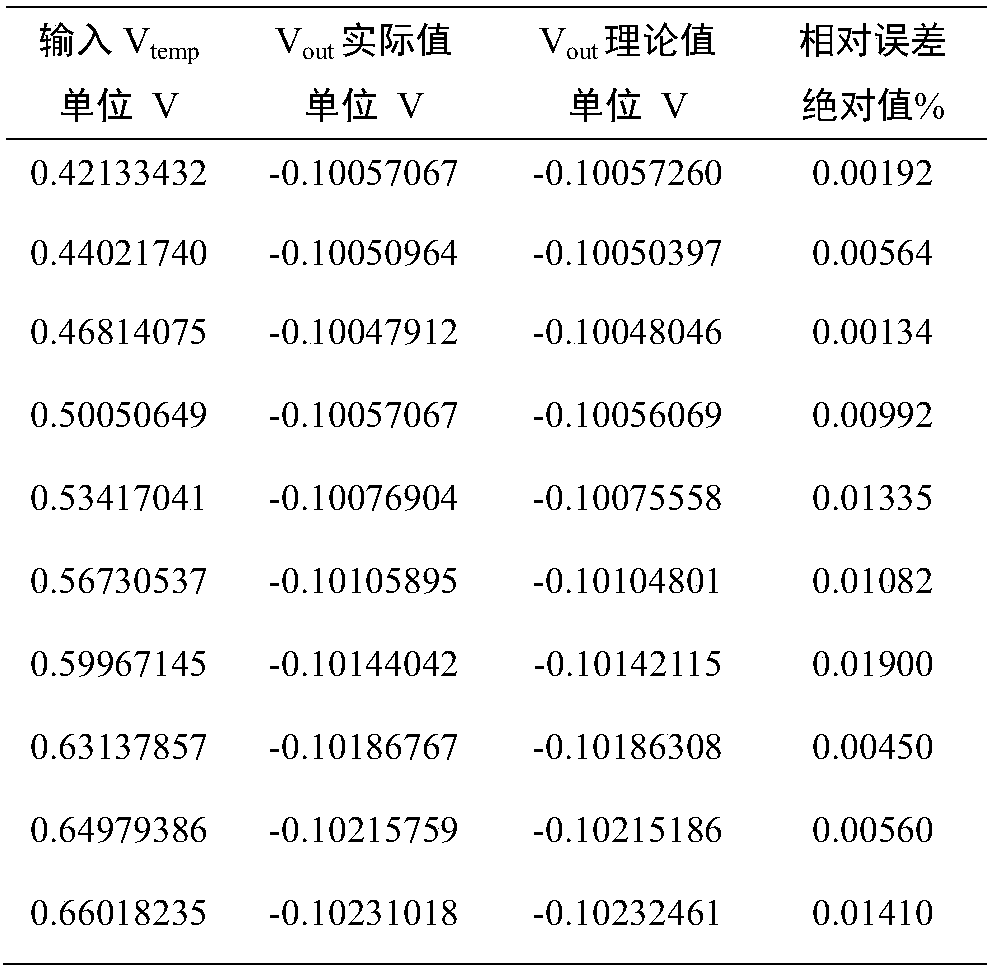
The invention discloses an infinite order temperature compensation system easy to implement. Signals output by a system which needs to be subjected to temperature compensation include a temperature simulation value Vtemp and a voltage simulation value Vout, and two signals are transmitted to a digital-to-analog converter; the digital-to-analog converter converts the simulation temperature value Vtemp and the simulation voltage value Vout into a digital temperature value Digital Vtemp and a digital voltage value Digital Vout by ADC, and outputs the digital temperature value Digital Vtemp and the digital voltage value Digital Vout to a microprocessor; a function model is selected at the microprocessor, the function models include a triangle function model and a double-exponential function model, and the digital temperature value Digital Vtemp and the digital voltage value Digital Vout are fit to obtain a function model coefficient to transmit to a storage module Rom of a digital compensated circuit; the digital compensated circuit carries out compensation on the input digital temperature value Digital Vtemp and digital voltage value Digital Vout and the function model coefficient read by the ROM by adopting a CORDIC algorithm or a lookup table method, and finally outputs a compensation signal; and the infinite order temperature compensation system easy to implement achieves the technical effects that a fitting effect of a higher order polynomial can be reached, and the infinite order temperature compensation system adopts few coefficients, and is simple to calculate and easyto implement.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High accuracy sin-cos wave and frequency generators, and related systems and methods
InactiveUS8659331B2Improve accuracyLow hardware costTrigometric functionsOscillations generatorsPhase correlationLookup table
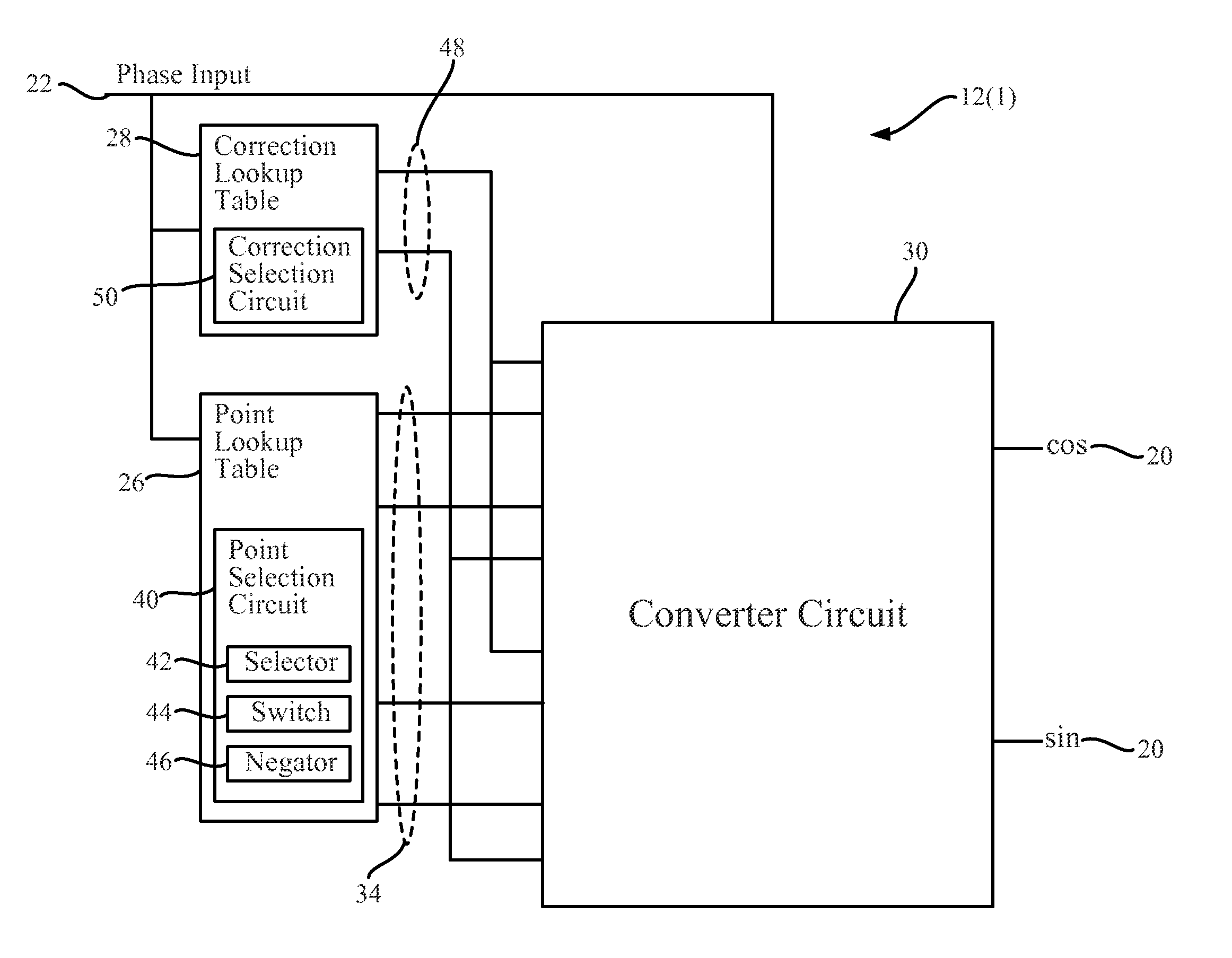
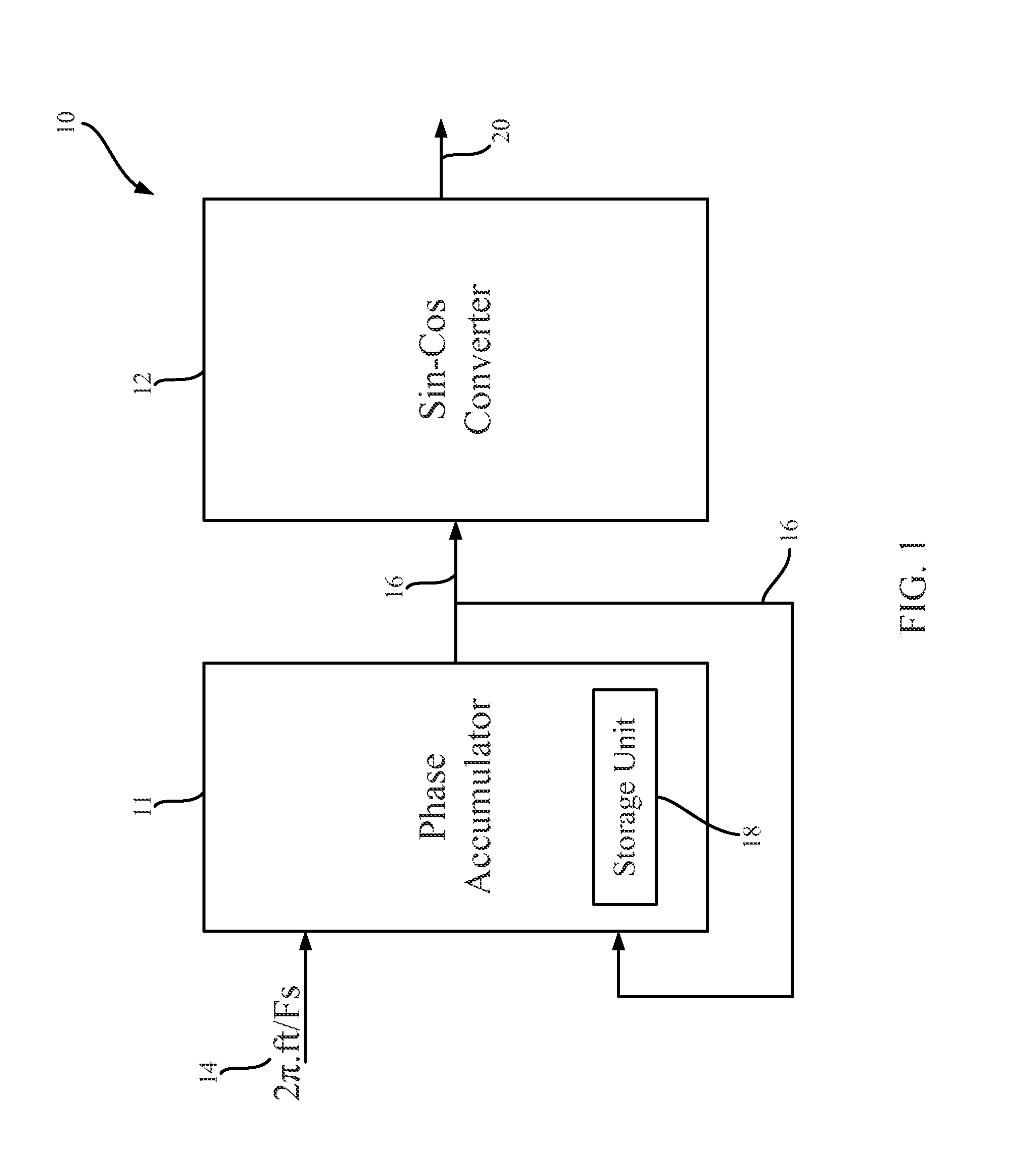
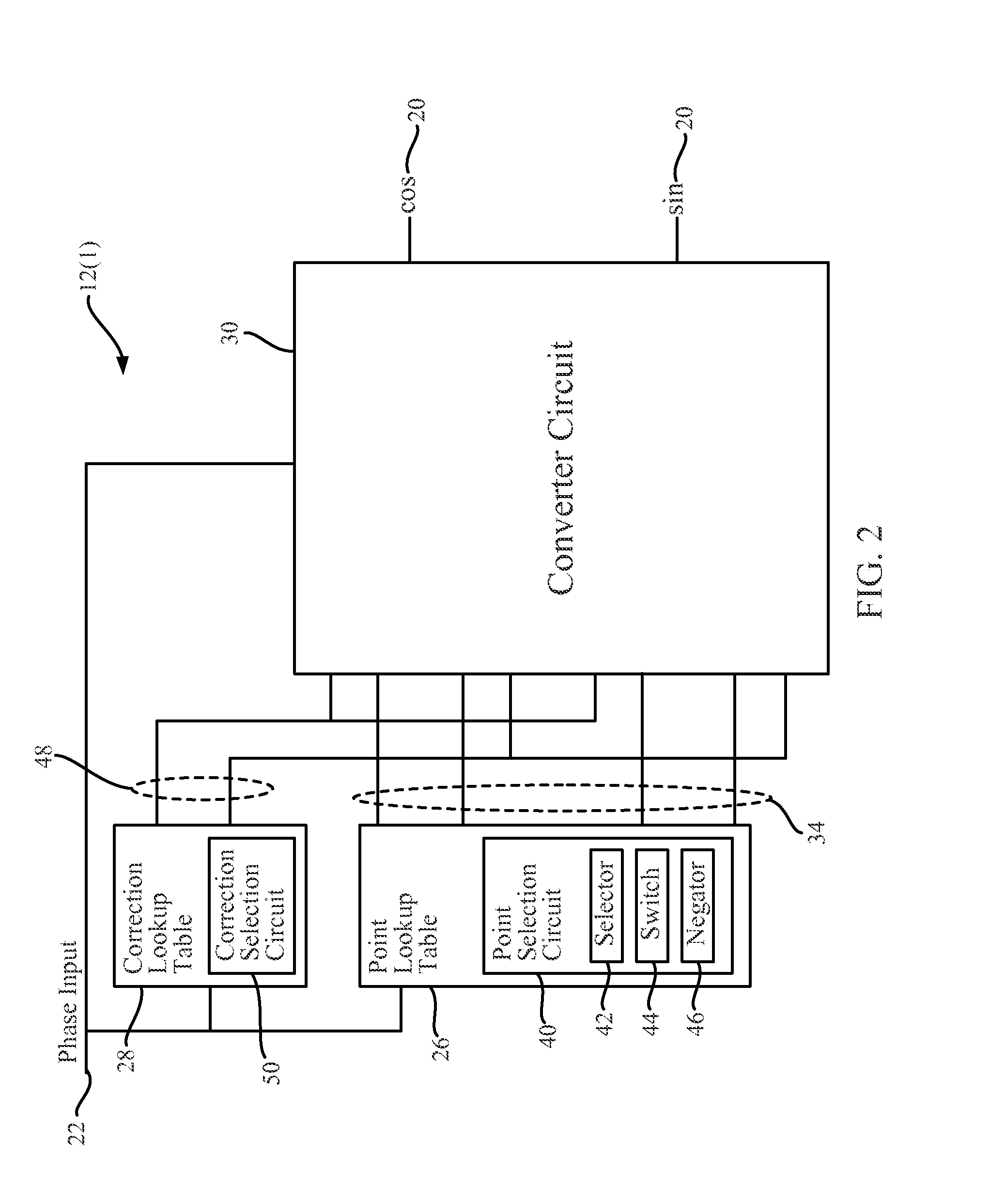
High accuracy sin-cos wave and frequency generators, and related systems and methods. In non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein, the sin-cos wave generators can provide highly accurate sin-cos values for sin-cos wave generation with low hardware costs and small lookup table requirements. The embodiments disclosed herein may include a circuit to conduct an arithmetic approximation of a sin-cos curve based on a phase input. The circuit may be in communication with a point lookup table and a correction lookup table. The tables may receive the phase input and match the phase input to main sin-cos endpoints associated with the phase, and to a correction value for the phase. These values which are selected based on the phase input, may be communicated to a converter circuit where the arithmetic functions are applied to the values resulting in a sin-cos curve value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Efficient Function Generator Using Case Detection and Output Selection
ActiveUS20110276613A1Maximize rateMaximize throughputTrigometric functionsPower supply for data processingControl engineeringCase detection
A function generator for a digital system includes a plurality of sub-function generators. Each sub-function generator has an input that receives a respective input value and has an output that provides a respective output value responsive to the respective input value. A case detector receives a system input value and selectively routes at least a first portion of the system input value to the input of at least one selected sub-function generator. The case detector selects the selected sub-function generator in response to at least a second portion of the system input value. The case detector further suppresses transitions of data on the input of at least one non-selected sub-function generator. The case detector further selects the respective output value provided by the at least one selected sub-function generator and provides the selected respective output value as a function generator output value.
Owner:TOROSYAN ARTHUR
Digital waveform synthesis
A circuit is provided with a plurality current cells. The current cells each comprise a main current source and an auxiliary current source coupled in parallel. The main current source supplies a main current to a current output of the current cell, and the auxiliary current source supplies an auxiliary current to the current output of the current cell. The main current sources are weighted according to a first predefined waveform, and the auxiliary current sources are weighted according to a second predefined waveform which is different from the first predefined waveform.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Tanh and sigmoid function execution
PendingUS20220066737A1Trigometric functionsComputations using contact-making devicesParallel computingTheoretical computer science
Examples described herein relate to instructions to request performance of tanh and sigmoid instructions. For example, a compiler can generate native tanh instructions to perform tanh. In some examples, a tanh function can be compiled into instructions that include an instruction to perform either tanh(input) or tanh(input) / input depending on a value of the input to generate an intermediate output; an instruction to cause a performance of generation of scale factor based on the input; and an instruction to cause performance of a multiplication operation on the intermediate result with the scale factor. For example, a sigmoid function can be compiled to cause a math pipeline to perform a range check and performs operations based on a range.
Owner:INTEL CORP
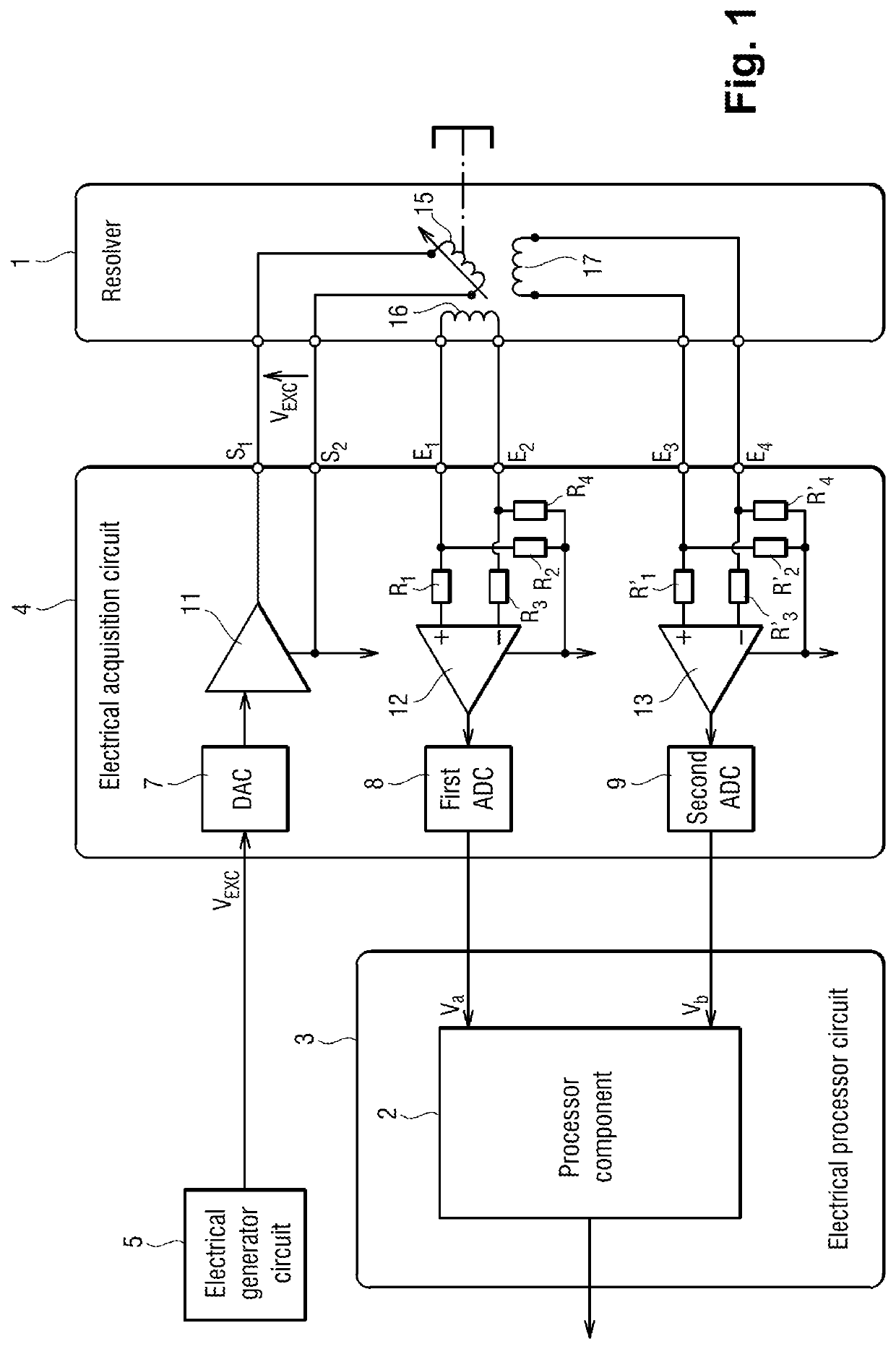
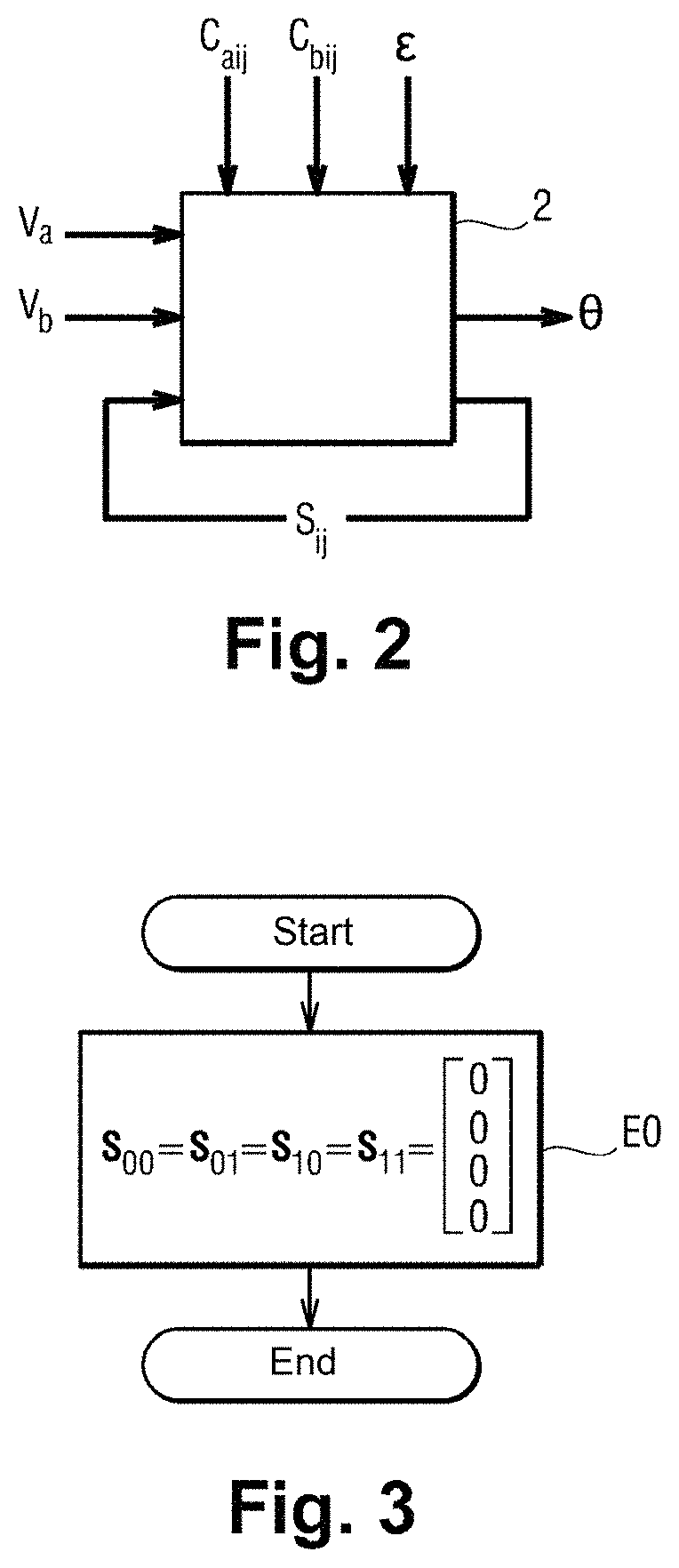
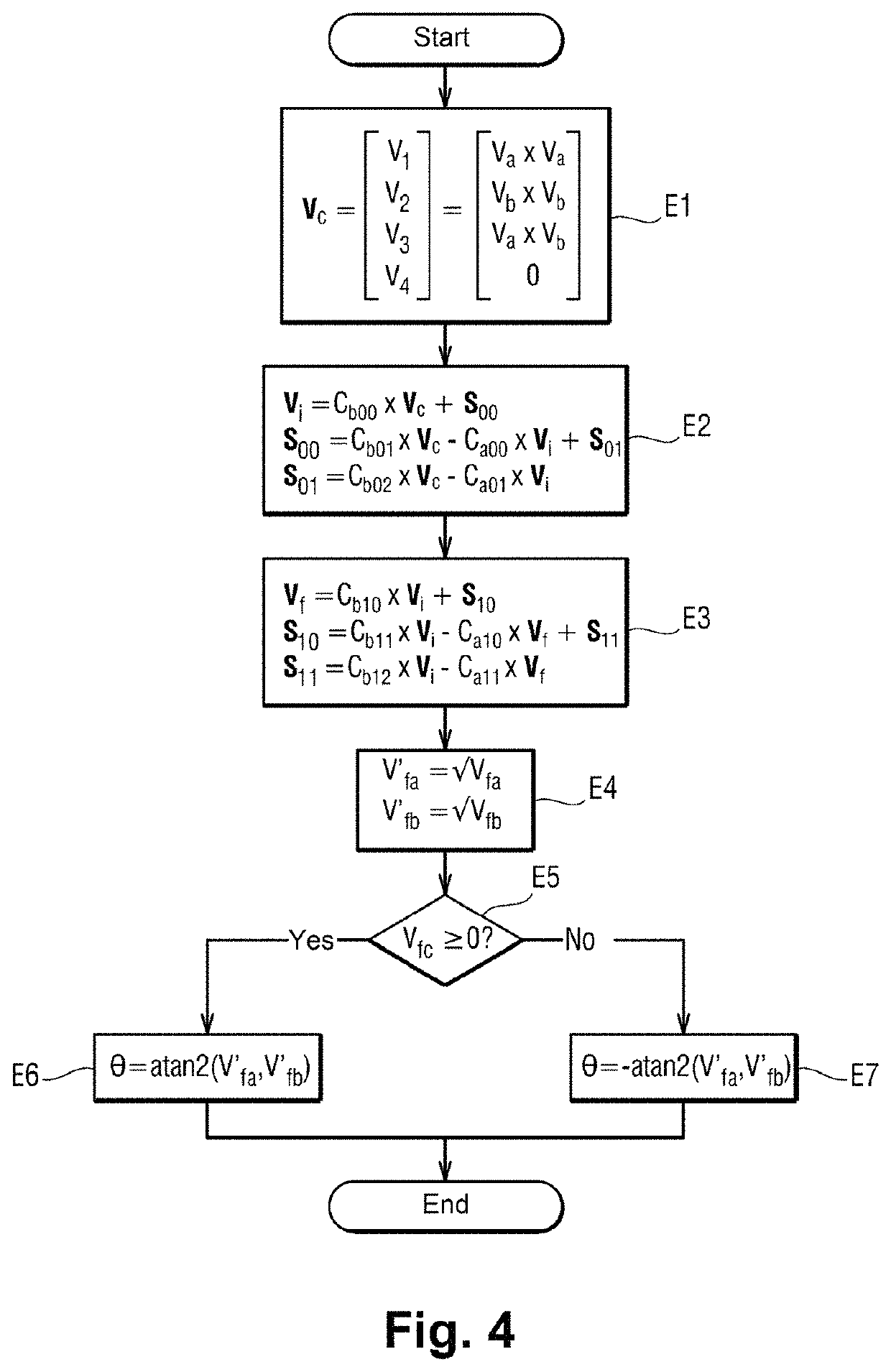
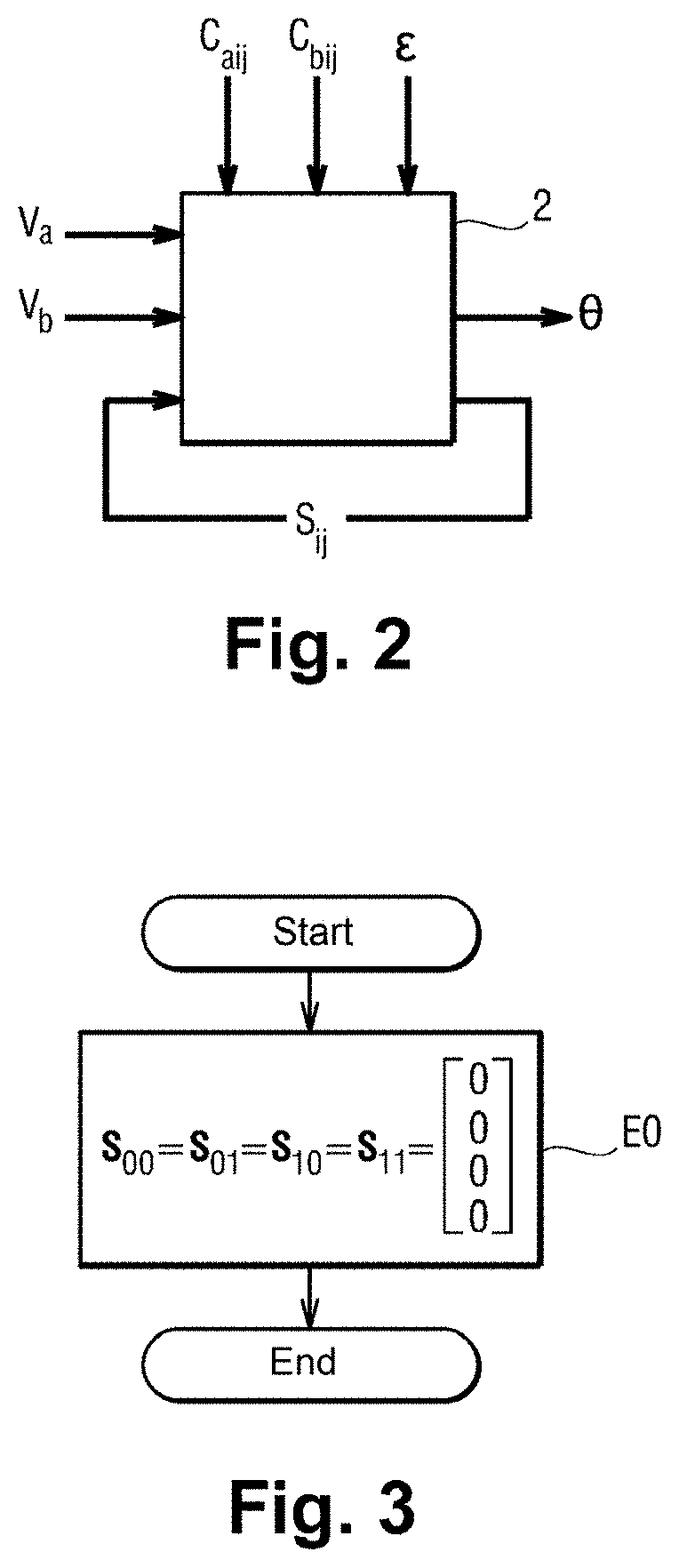
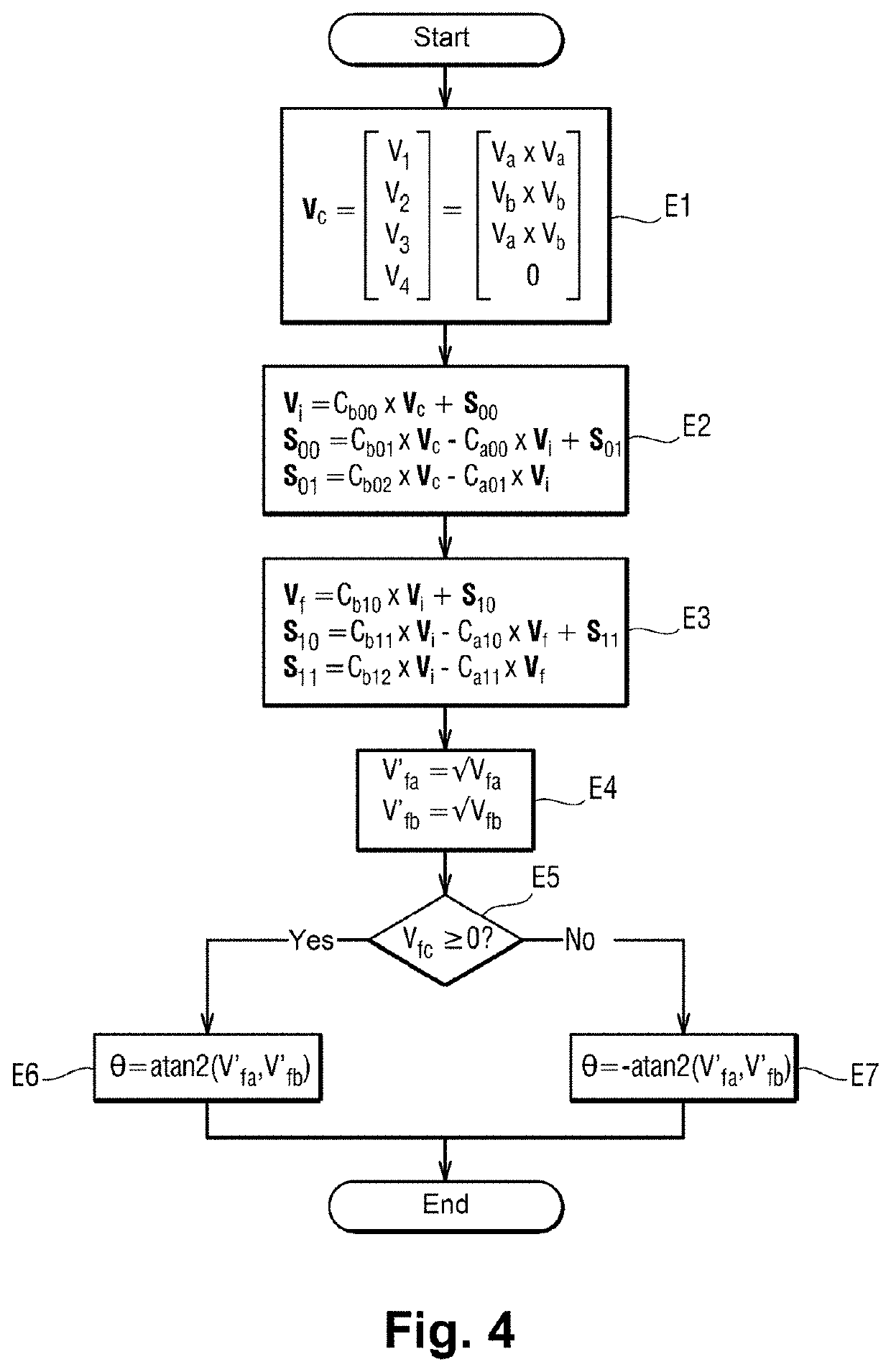
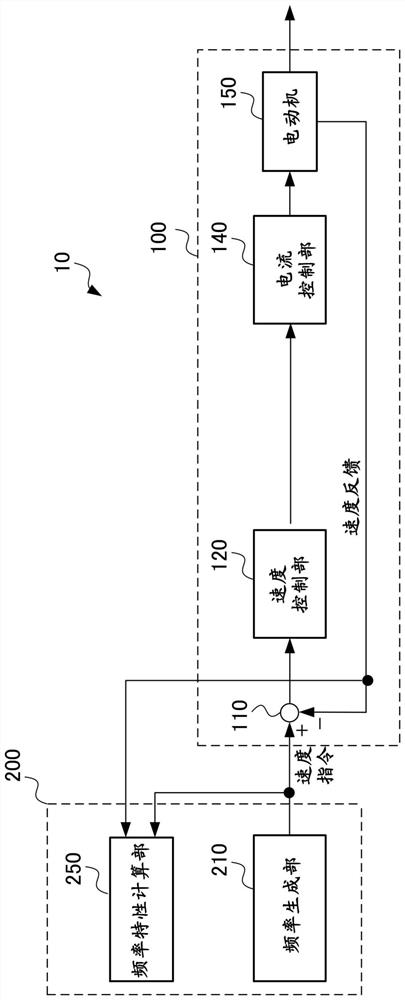
Method for measuring a displacement
ActiveUS10962387B2Reduce weightImprove reliabilityTrigometric functionsFrequency analysisLow-pass filterClassical mechanics
A method of measuring a movement, the method comprising the steps of: acquiring and digitizing both a first measurement voltage across the terminals of a first secondary winding and also a second measurement voltage across the terminals of a second secondary winding of an inductive movement sensor; multiplying the first measurement voltage by itself in order to obtain a first component of a crossed vector, multiplying the second measurement voltage by itself in order to obtain a second component of the crossed vector, and multiplying together the first measurement voltage and the second measurement voltage in order to obtain a third component of the crossed vector; applying the crossed vector as input to a lowpass filter in order to obtain a filtered vector, and estimating the movement from the components of the filtered vector.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRONICS & DEFENSE
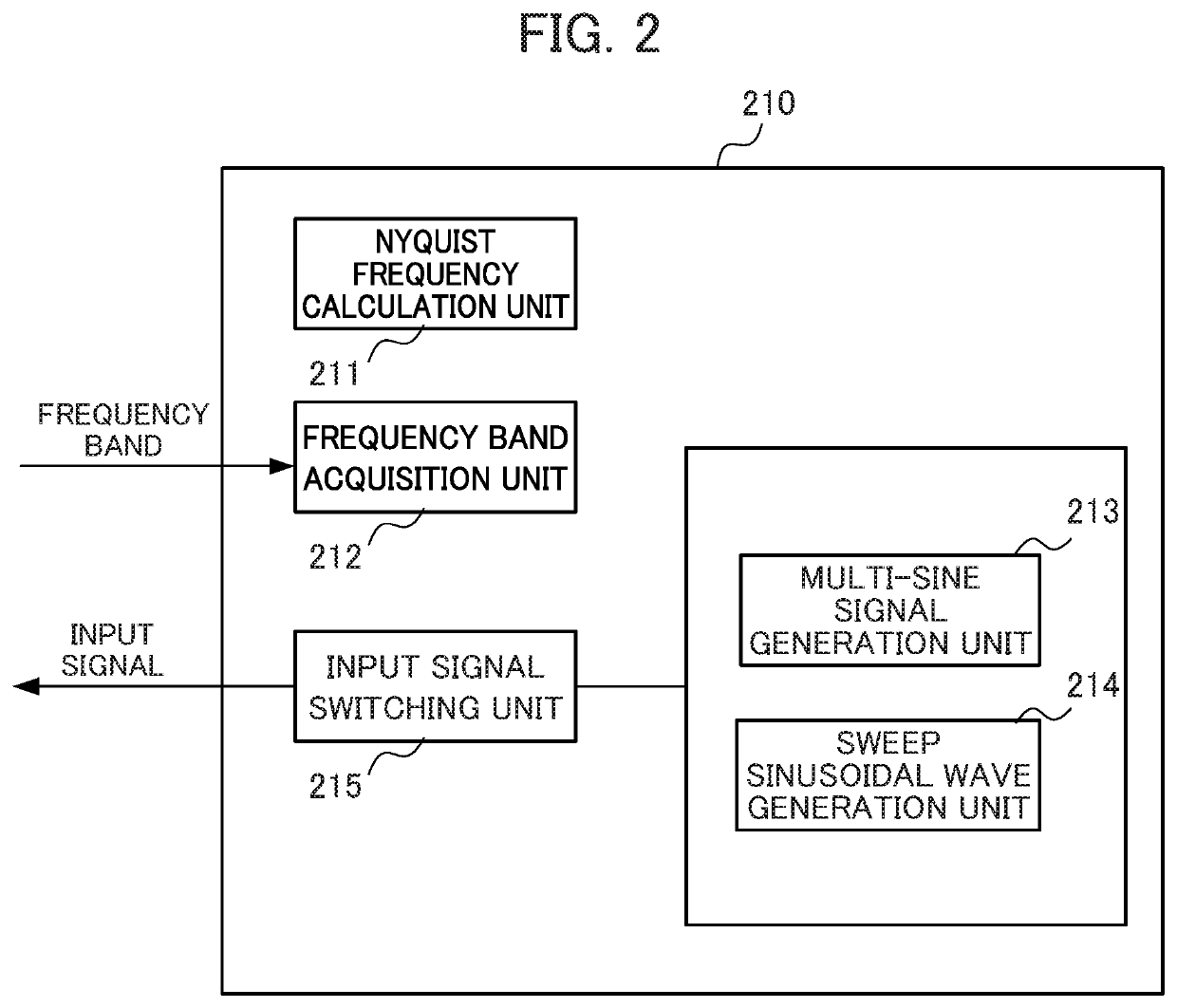
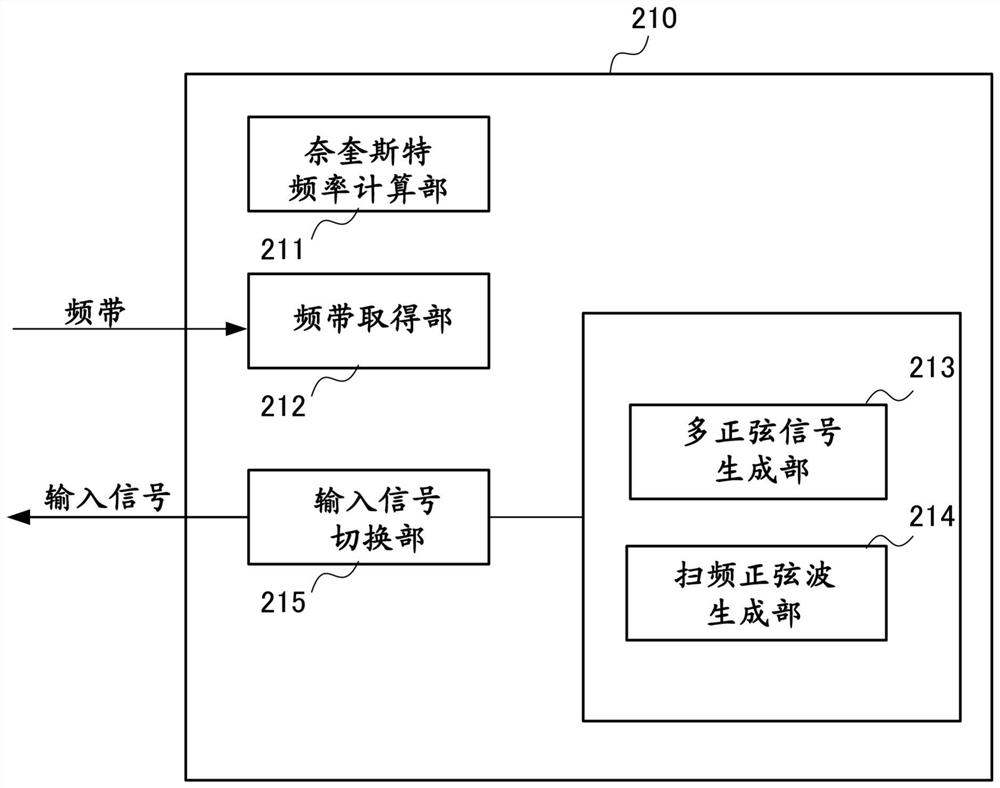
Frequency characteristic measurement device, controller and frequency characteristic measurement method
ActiveUS20200310485A1High measurement accuracyReduced measurement timeTrigometric functionsResistance/reactance/impedenceControl theoryFrequency characteristic
A frequency characteristic measurement device that measures the frequency characteristic of a measurement target includes: a multi-sine signal generation unit that generates a multi-sine signal; a sweep sinusoidal wave generation unit that generates a plurality of sweep sinusoidal waves; an input signal switching unit that selects any one of the multi-sine signal and the sweep sinusoidal waves so as to input the selected one to the measurement target; a data acquisition unit that acquires, at a predetermined sampling frequency, sampling data of an input signal which is input to the measurement target and sampling data of an output signal which is output from the measurement target; and a characteristic calculation unit that calculates a frequency characteristic including the gain and the phase of the input and output signals in the measurement target from the sampling data of the input and output acquired.
Owner:FANUC LTD
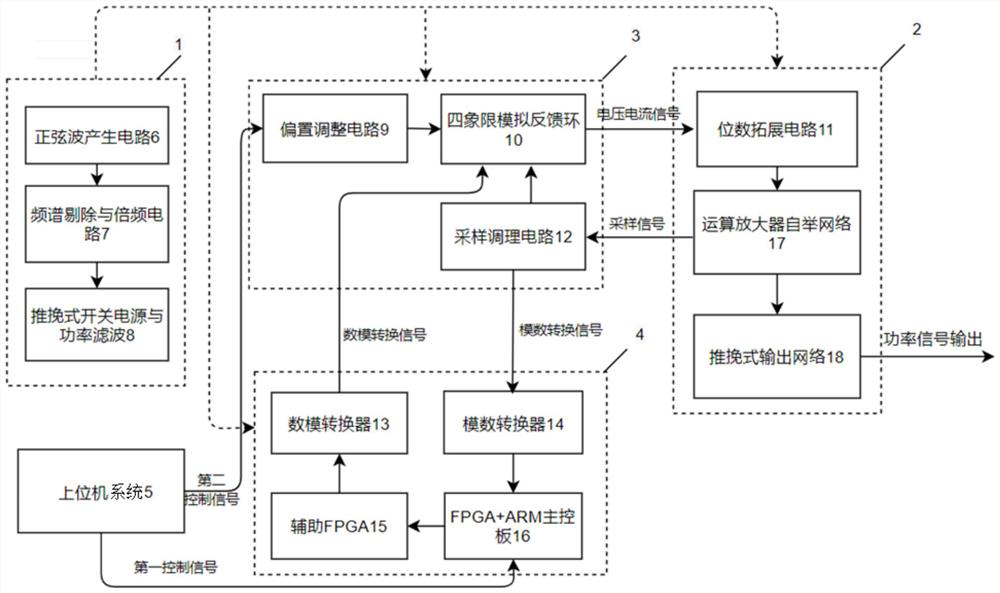
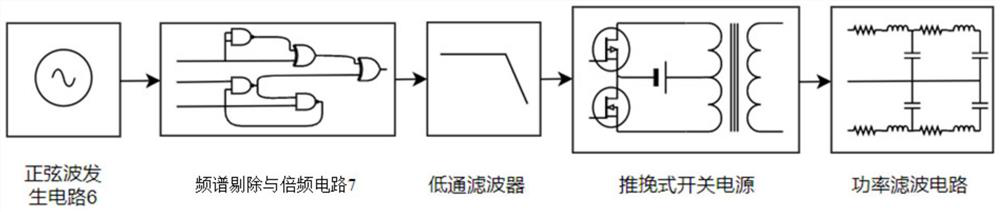
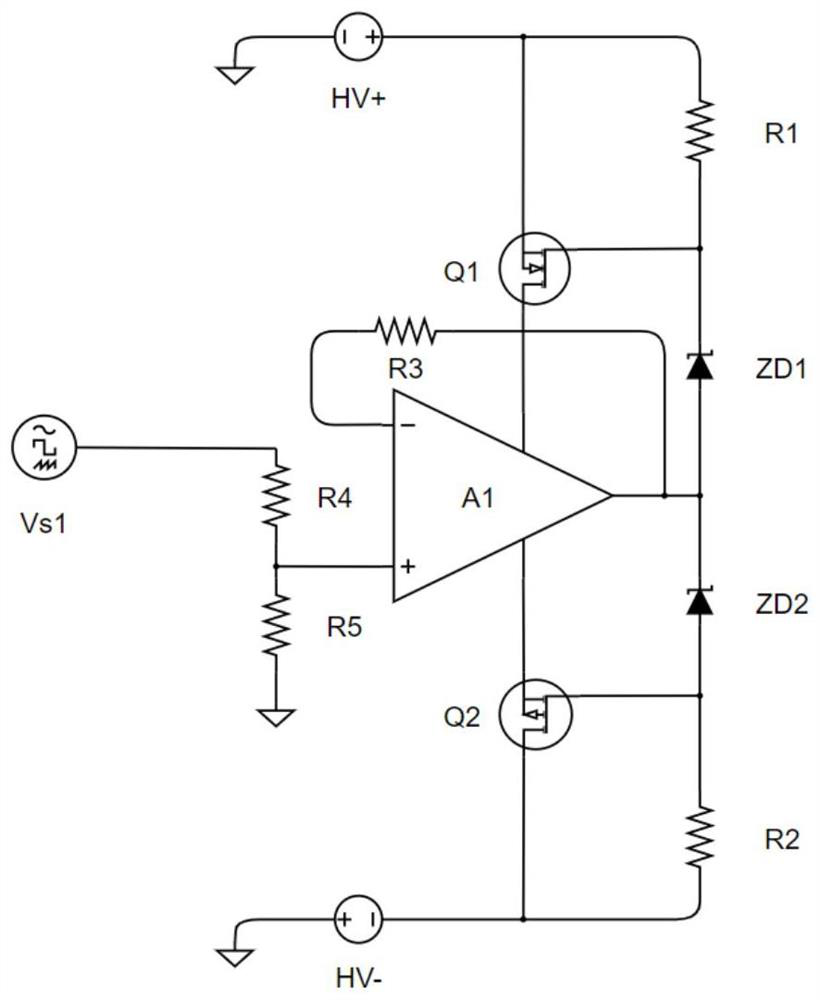
Power waveform generator with four-quadrant feedback loop and control method thereof
PendingCN114094991ASolve the lack of functionalityTrigometric functionsDigital function generatorsAnalog feedbackControl signal
The invention provides a power waveform generator with a four-quadrant feedback loop and a control method thereof, the generator is controlled by a user to respectively output a first control signal and a second control signal through an upper computer and a graphical interface, the first control signal is input into an FPGA + ARM main control board, an instruction is analyzed into a secondary instruction and sent to an auxiliary FPGA, the digital-to-analog converter is controlled to generate a signal after digital-to-analog conversion, and the signal is output to the four-quadrant analog feedback ring to generate an arbitrary waveform signal; the second control signal directly controls the bias adjustment circuit and outputs a proper bias signal to the four-quadrant analog feedback ring; the four-quadrant analog feedback loop superposes the received signals and then outputs voltage and current signals to the digit expansion circuit, further pushes the bootstrap network of the operational amplifier to generate voltage driving waveforms, and further generates power waveforms in any shapes through the push-pull output network.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for evaluating temperatures in active heave compensation ropes
InactiveUS20200104543A1Fast deterioration of ductilityTrigometric functionsSurveyWire rodMechanical models
Method for evaluating temperatures in active heave compensation ropes comprising the following steps: describe the geometry of ropes as composite structures obtained through assemblies of helical components in hierarchical levels: wires, strands and the rope itself; use a mechanical model of the strand that represents the material properties of each wire, under the assumption of linear elastic behavior; use a mechanical model of the rope that represents the combined action of tensile loads and imposed bending curvature; use a thermal model for the evaluation of the rope temperature increase (Ts) with respect to the ambient temperature, the thermal model comprising two main dissipation sources: the friction between strands or rope and a sheave and the friction between wires or between strands and compare rope temperature increase (Ts) obtained by the thermal model with a value of a predetermined temperature threshold.
Owner:REDAELLI TECNA
Efficient function generator using case detection and output selection
InactiveUS7984090B1The result is validMaximize rateTrigometric functionsPower supply for data processingControl engineeringCase detection
A function generator for a digital system includes a plurality of sub-function generators. Each sub-function generator has an input that receives a respective input value and has an output that provides a respective output value responsive to the respective input value. A case detector receives a system input value and selectively routes at least a first portion of the system input value to the input of at least one selected sub-function generator. The case detector selects the selected sub-function generator in response to at least a second portion of the system input value. The case detector further suppresses transitions of data on the input of at least one non-selected sub-function generator. The case detector further selects the respective output value provided by the at least one selected sub-function generator and provides the selected respective output value as a function generator output value.
Owner:TOROSYAN ARTHUR
Method for measuring a displacement
ActiveUS20200284618A1Reduce weightImprove reliabilityTrigometric functionsFrequency analysisLow-pass filterClassical mechanics
A method of measuring a movement, the method comprising the steps of: acquiring and digitizing both a first measurement voltage across the terminals of a first secondary winding and also a second measurement voltage across the terminals of a second secondary winding of an inductive movement sensor; multiplying the first measurement voltage by itself in order to obtain a first component of a crossed vector, multiplying the second measurement voltage by itself in order to obtain a second component of the crossed vector, and multiplying together the first measurement voltage and the second measurement voltage in order to obtain a third component of the crossed vector; applying the crossed vector as input to a lowpass filter in order to obtain a filtered vector; and estimating the movement from the components of the filtered vector.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRONICS & DEFENSE
Frequency characteristic measurement device, controller and frequency characteristic measurement method
PendingCN111751616AHigh measurement accuracyReduced measurement timeProgramme controlTrigometric functionsControl theoryFrequency characteristic
The invention provides a frequency characteristic measurement device, a controller and a frequency characteristic measurement method. The frequency characteristic measurement device that measures thefrequency characteristic of a measurement target includes: a multi-sine signal generation unit that generates a multi-sine signal; a sweep sinusoidal wave generation unit that generates a plurality ofsweep sinusoidal waves; an input signal switching unit that selects any one of the multi-sine signal and the sweep sinusoidal waves so as to input the selected one to the measurement target; a data acquisition unit that acquires, at a predetermined sampling frequency, sampling data of an input signal which is input to the measurement target and sampling data of an output signal which is output from the measurement target; and a characteristic calculation unit that calculates a frequency characteristic including the gain and the phase of the input and output signals in the measurement target from the sampling data of the input and output acquired.
Owner:FANUC LTD
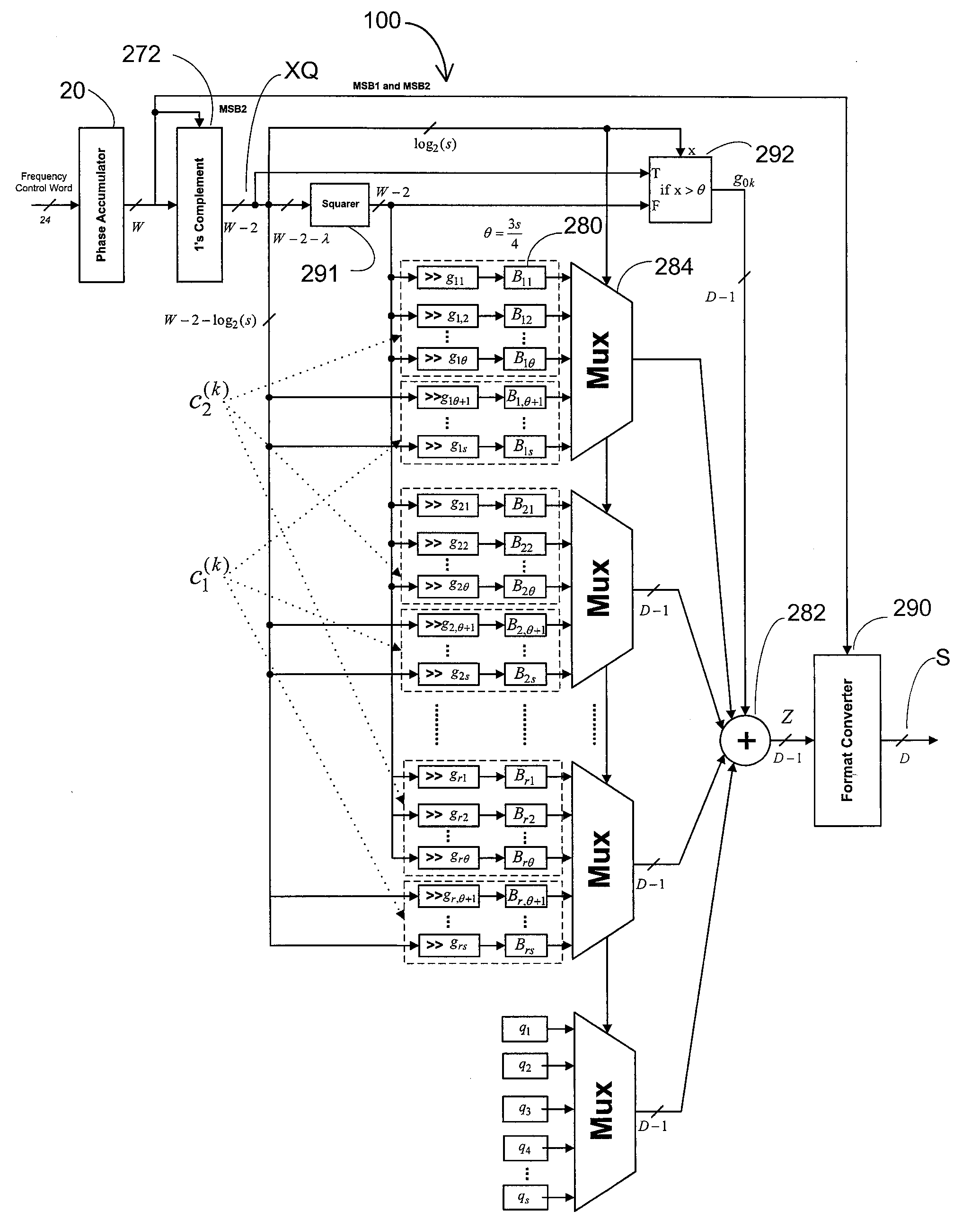
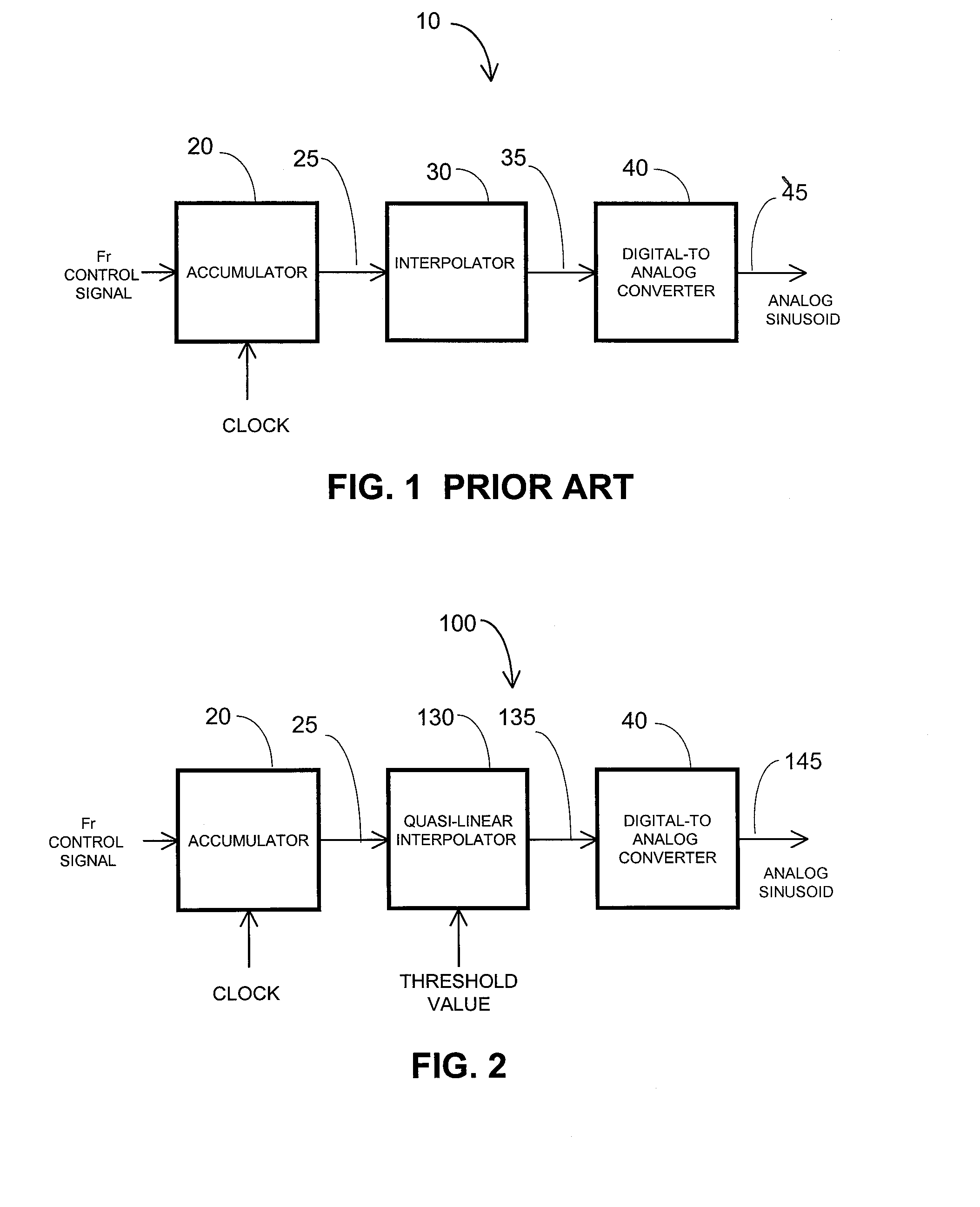
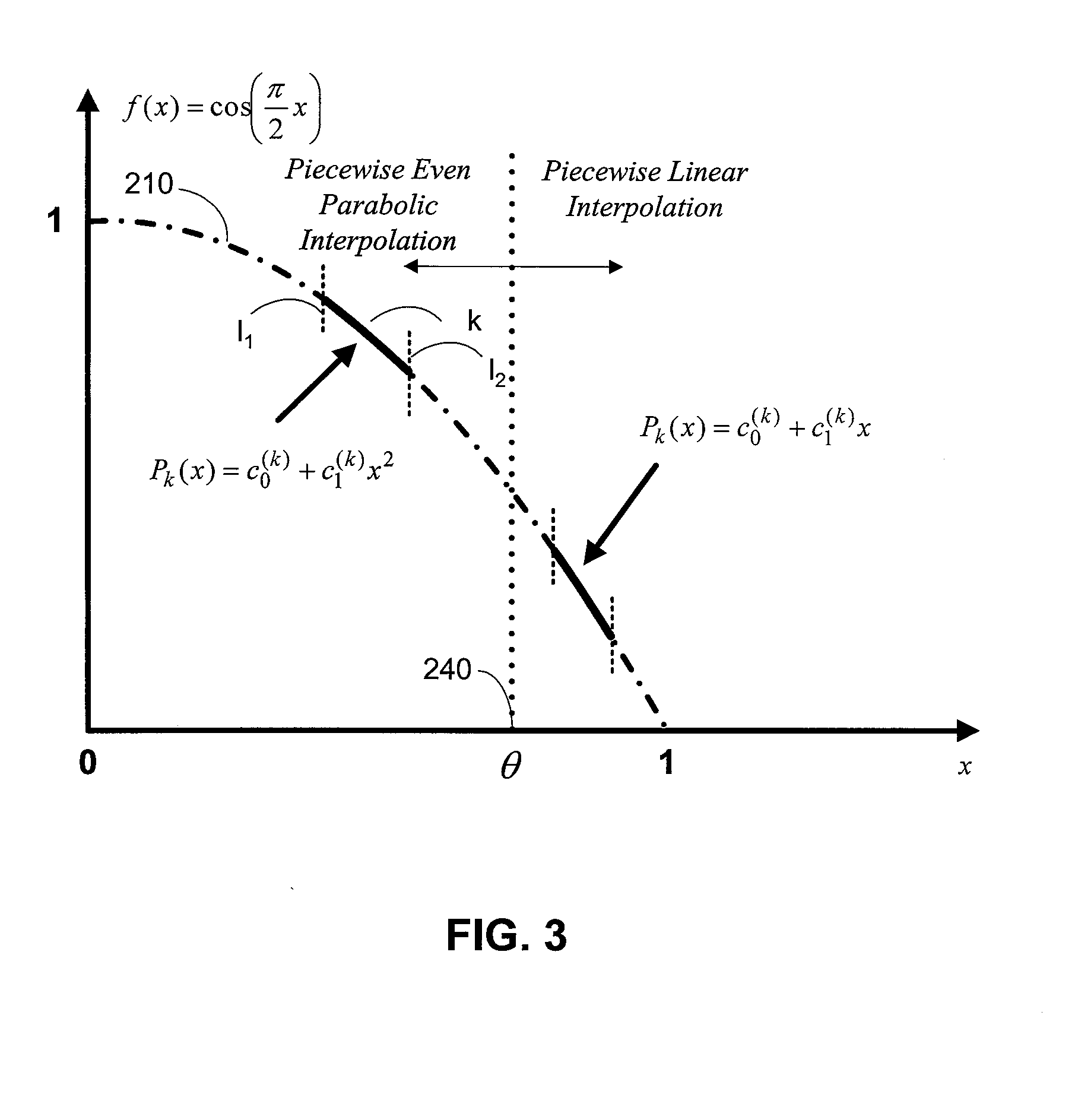
Direct digital frequency synthesizer with phase selectable interpolator
InactiveUS20080298527A1Trigometric functionsDigital data processing detailsFrequency synthesizerLow complexity
The disclosure relates to improved direct digital frequency synthesizers. A synthesizer in one embodiment is comprised of an accumulator that provides a phase signal and an interpolator having two or more interpolation polynomials. The polynomial that processes the phase signal is selected by comparing the phase signal to a threshold value. A reduced complexity digital circuit is provided for implementing the improved synthesizer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
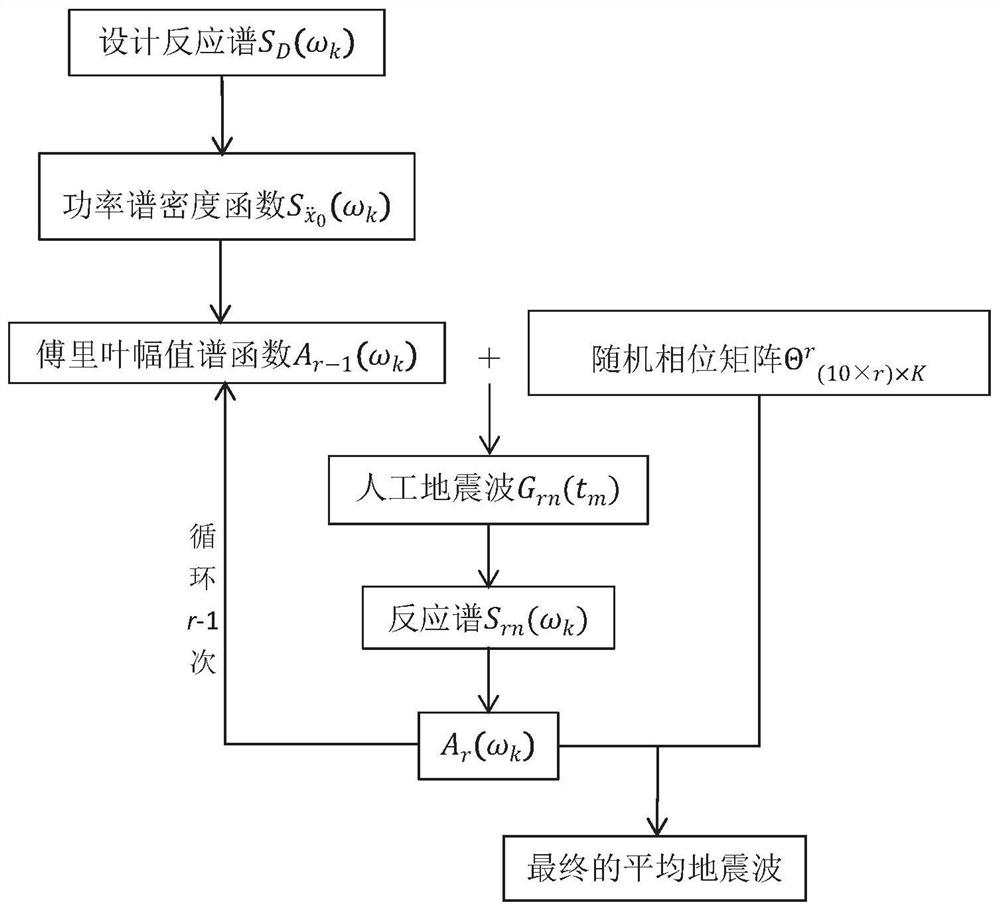
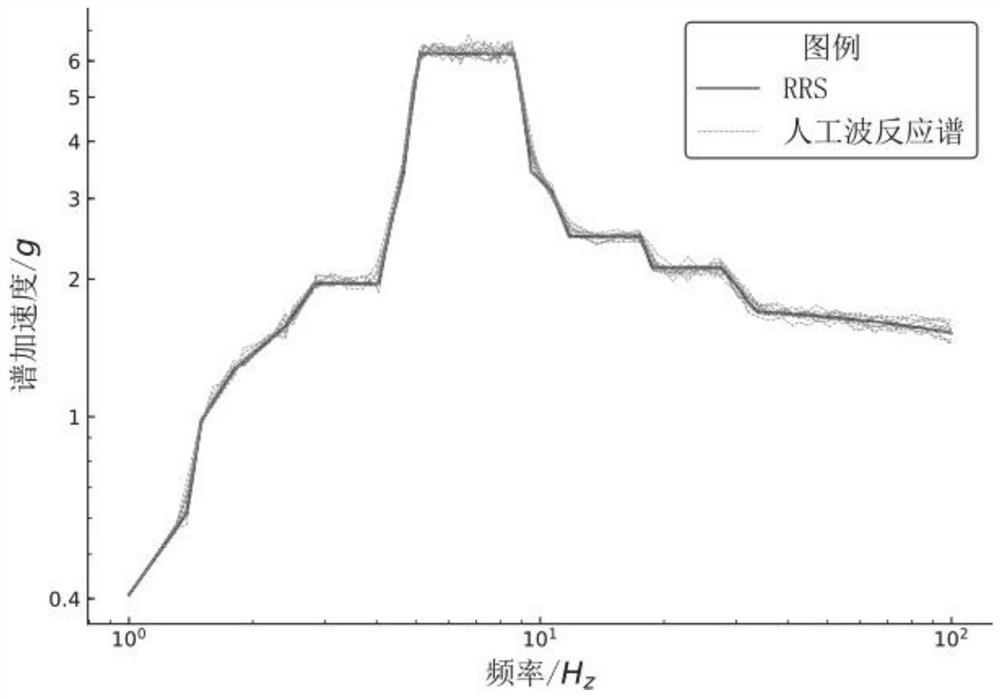
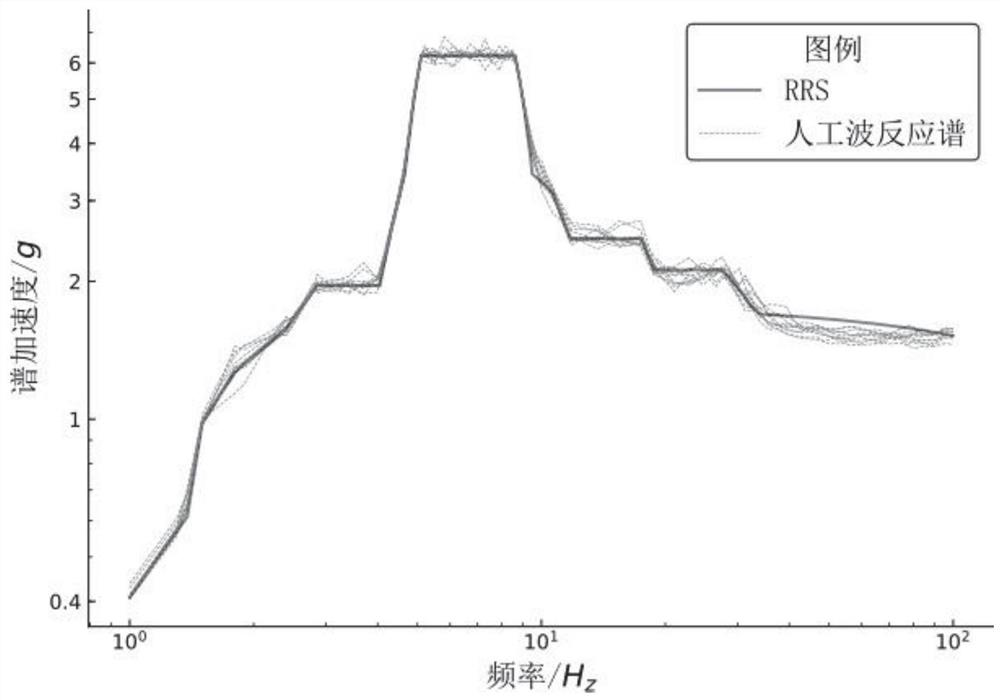
Artificial wave response spectrum fitting calculation method based on multi-phase spectrum iteration
ActiveCN112287291AEffects of reduced convergence accuracyTrigometric functionsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational physicsResponse spectrum
The invention provides an artificial wave response spectrum fitting calculation method based on multi-phase spectrum iteration, and aims at solving the problems existing in artificial seismic waves ofa traditional frequency domain method fitting envelope design response spectrum, when Fourier amplitude spectrum iteration is carried out, R * 10 groups of random phase spectrums are generated and R* 10 artificial waves are generated in the R-th iteration, and the R * 10 groups of random phase spectrums are calculated. Iteration is carried out by using an error between the average value of the reaction spectrums corresponding to the artificial waves and the designed reaction spectrum, so that the condition that the final fitting result of the random phase spectrum cannot be converged is avoided. In the process of designing the reaction spectrum through frequency domain method fitting, a multi-phase spectrum matrix is mainly used, a single and invariant phase spectrum is not used any more, a complex Fourier phase spectrum is used for each iteration, and the influence of the random phase spectrum of the artificial wave on the convergence precision of a final fitting result is also reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com