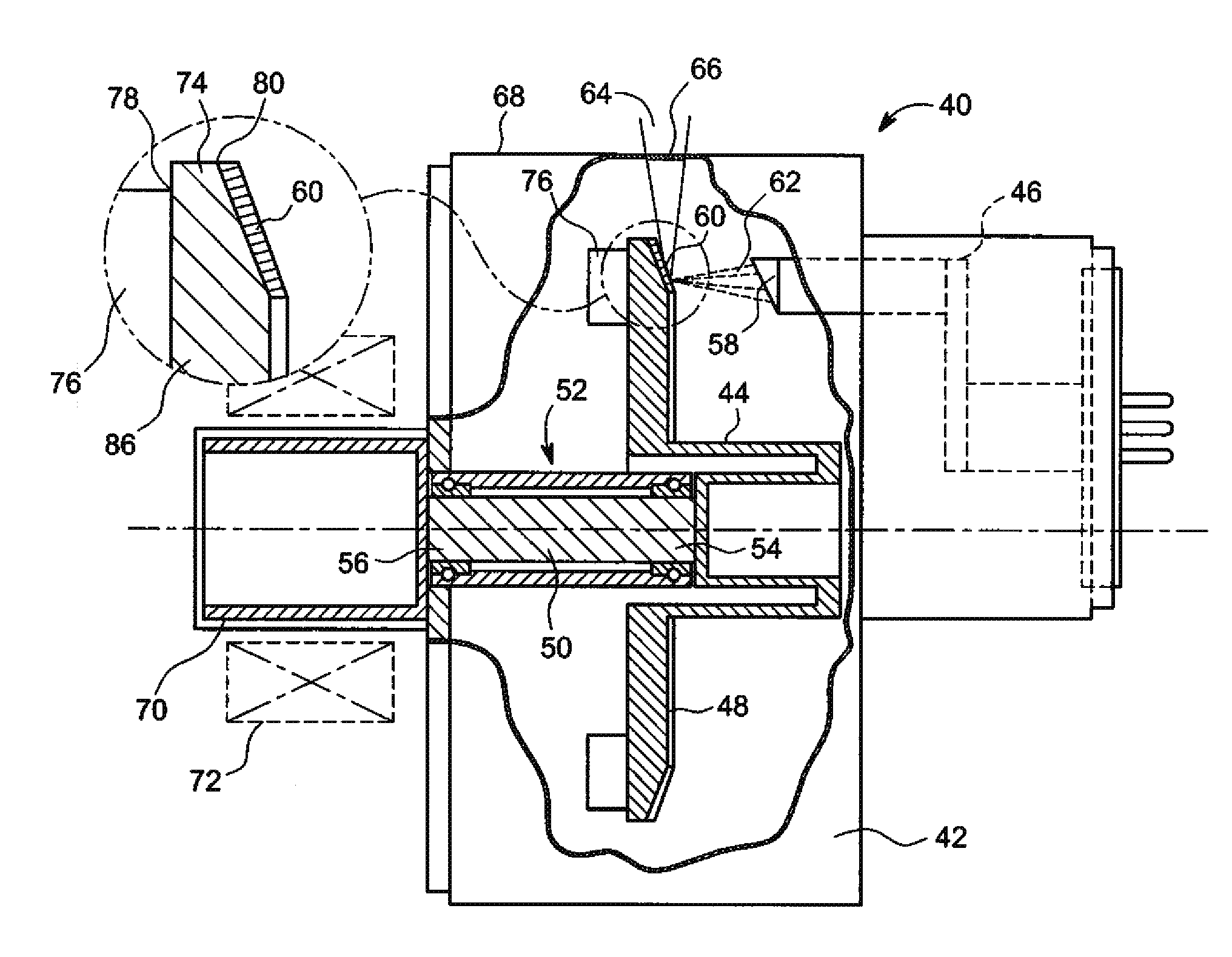
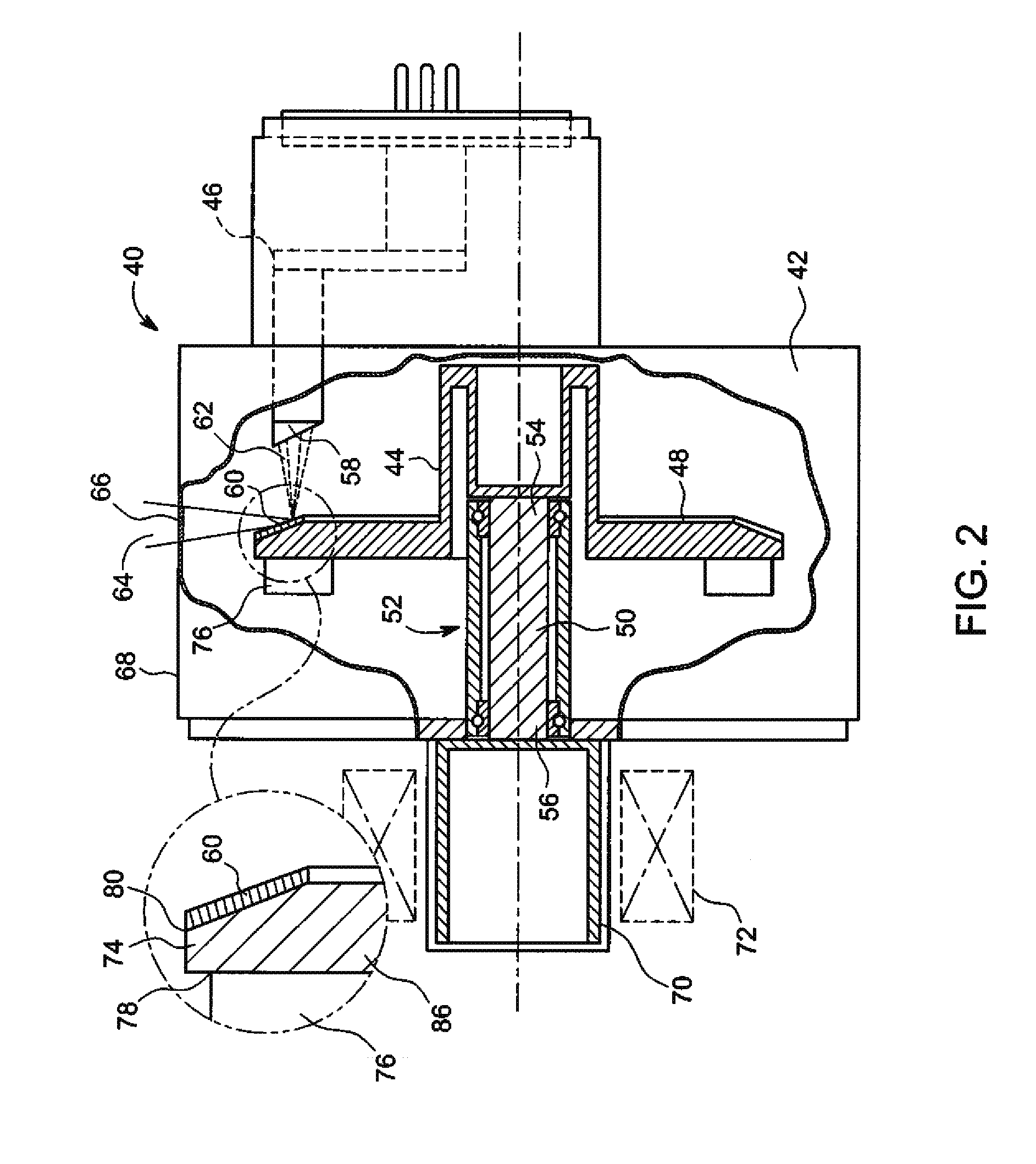
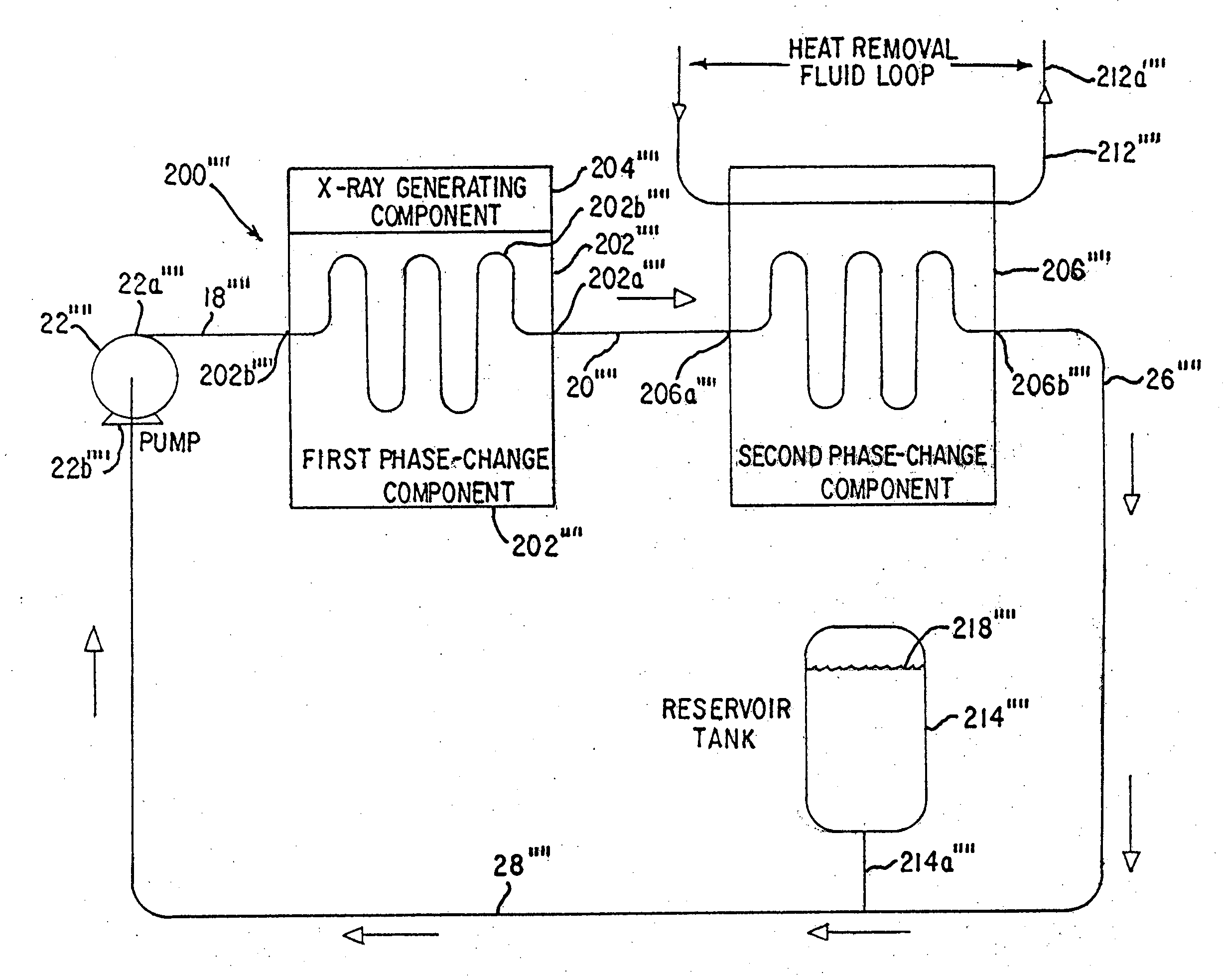
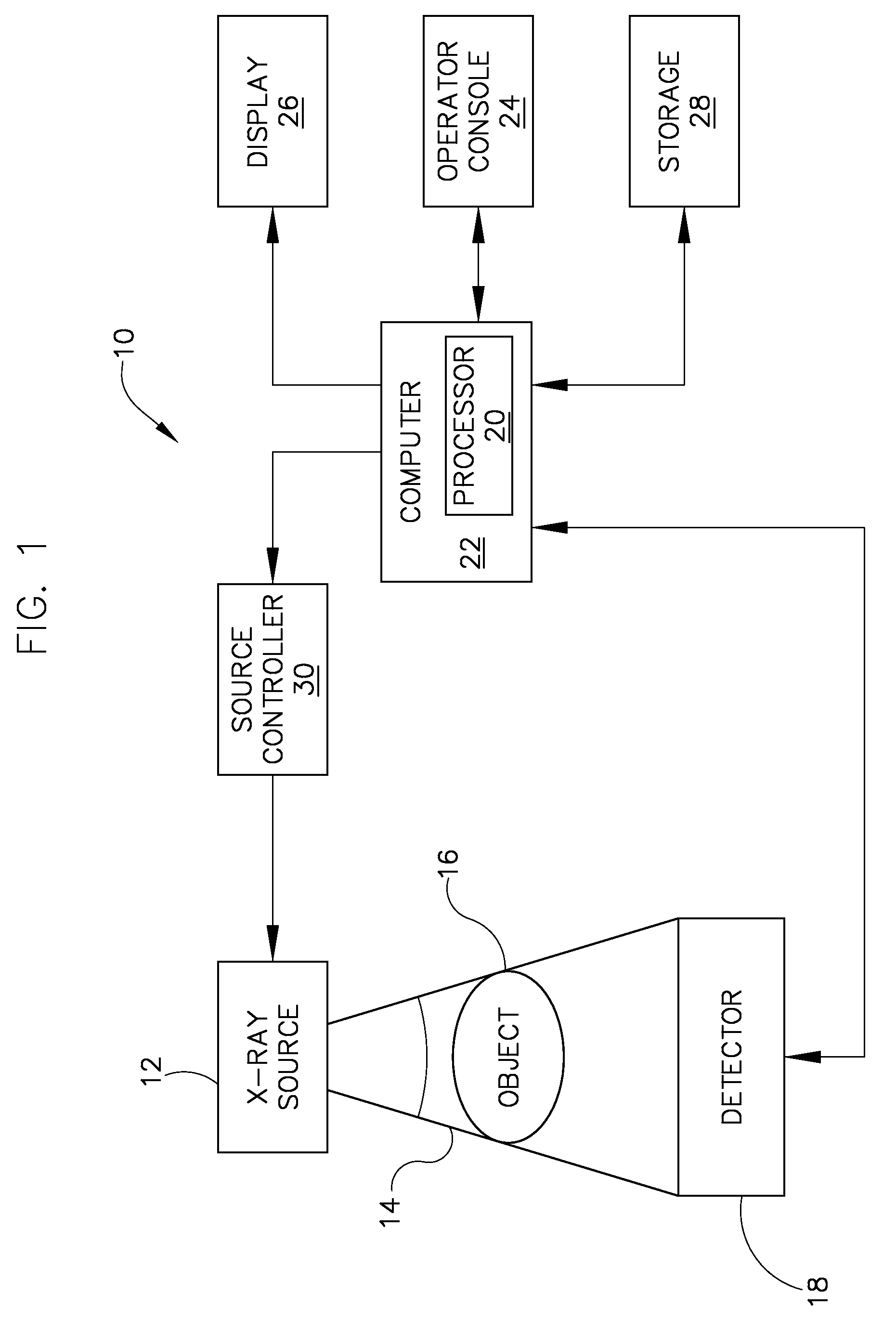
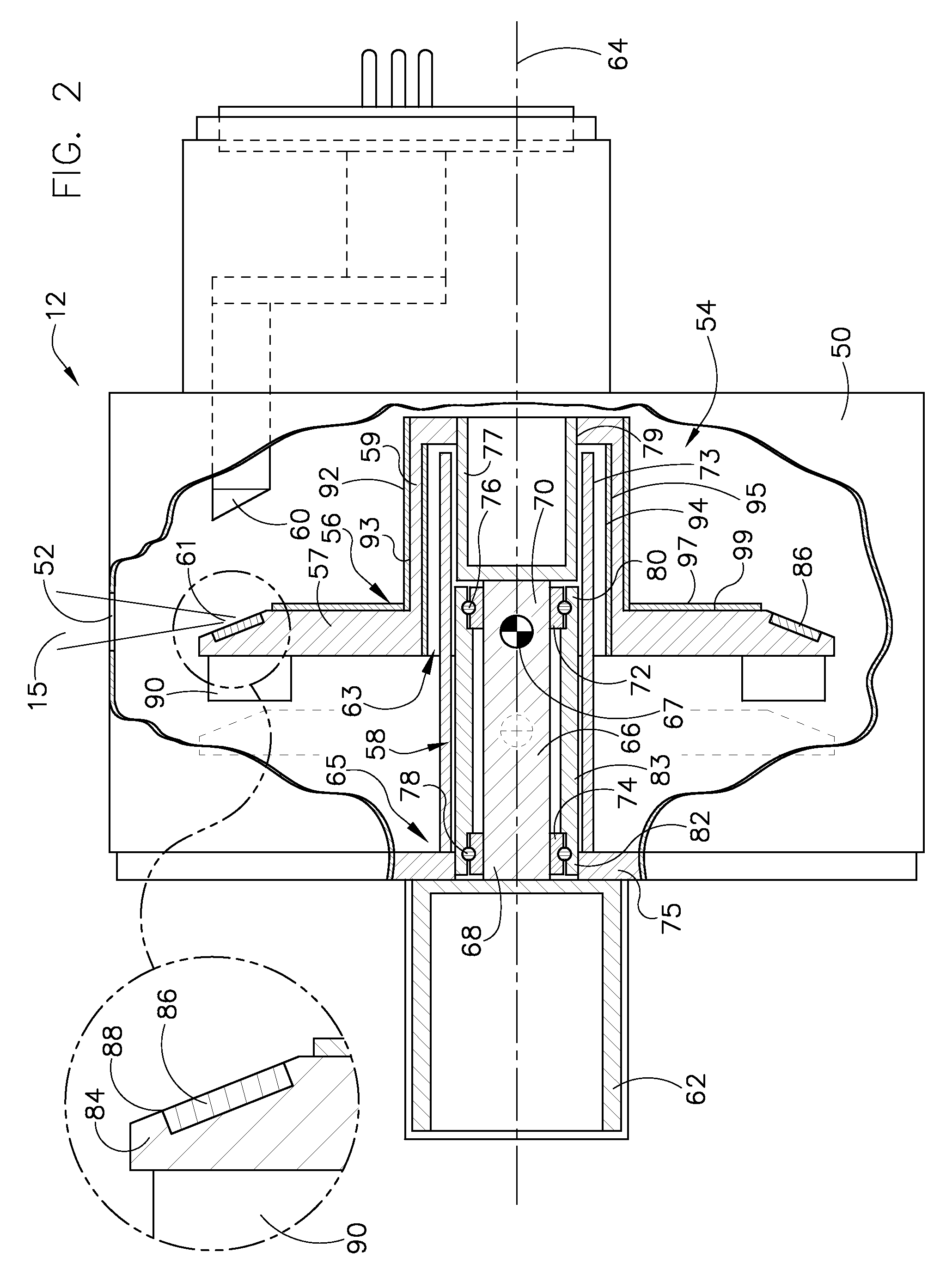
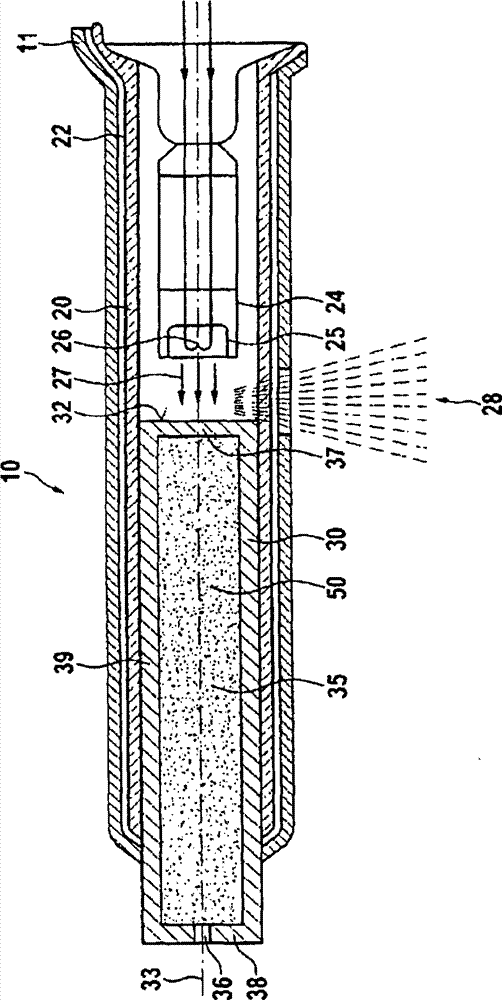
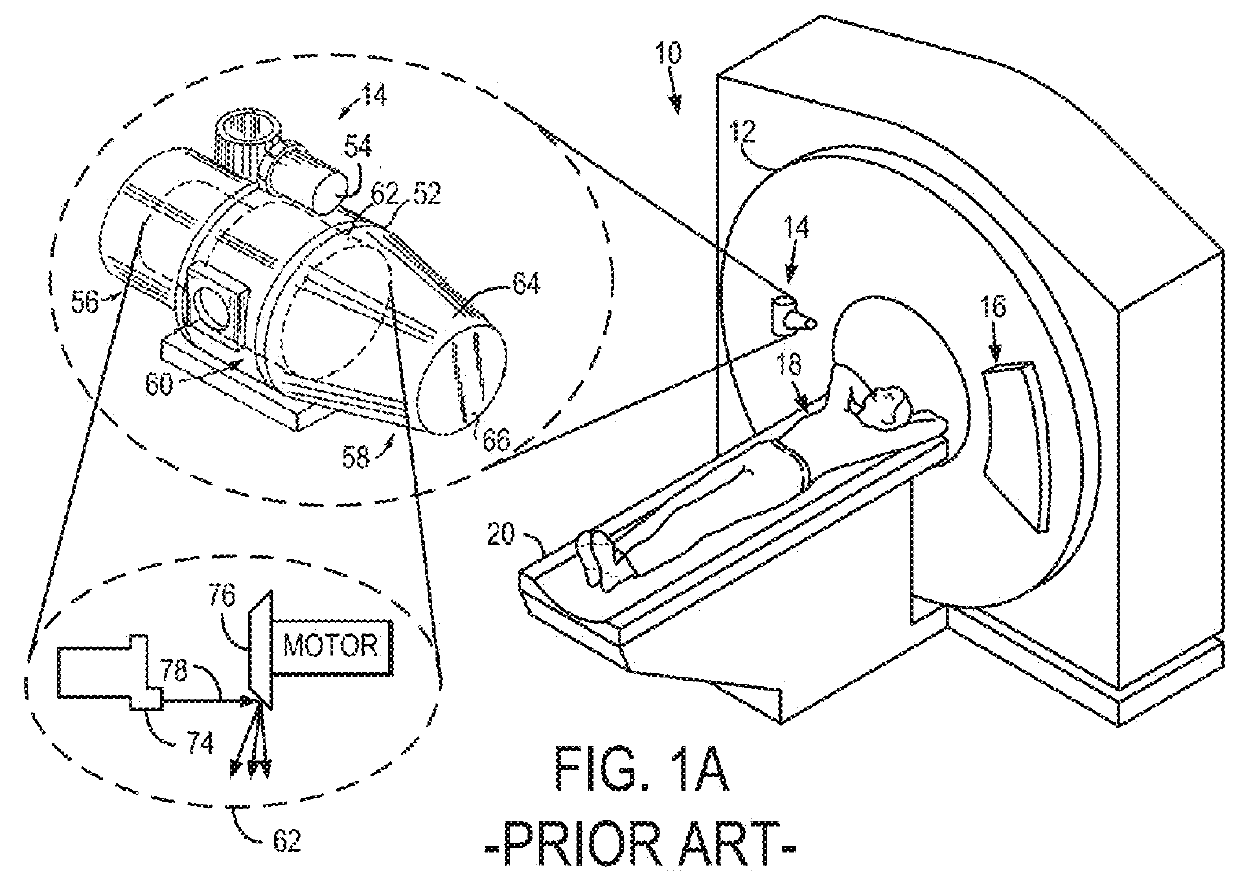
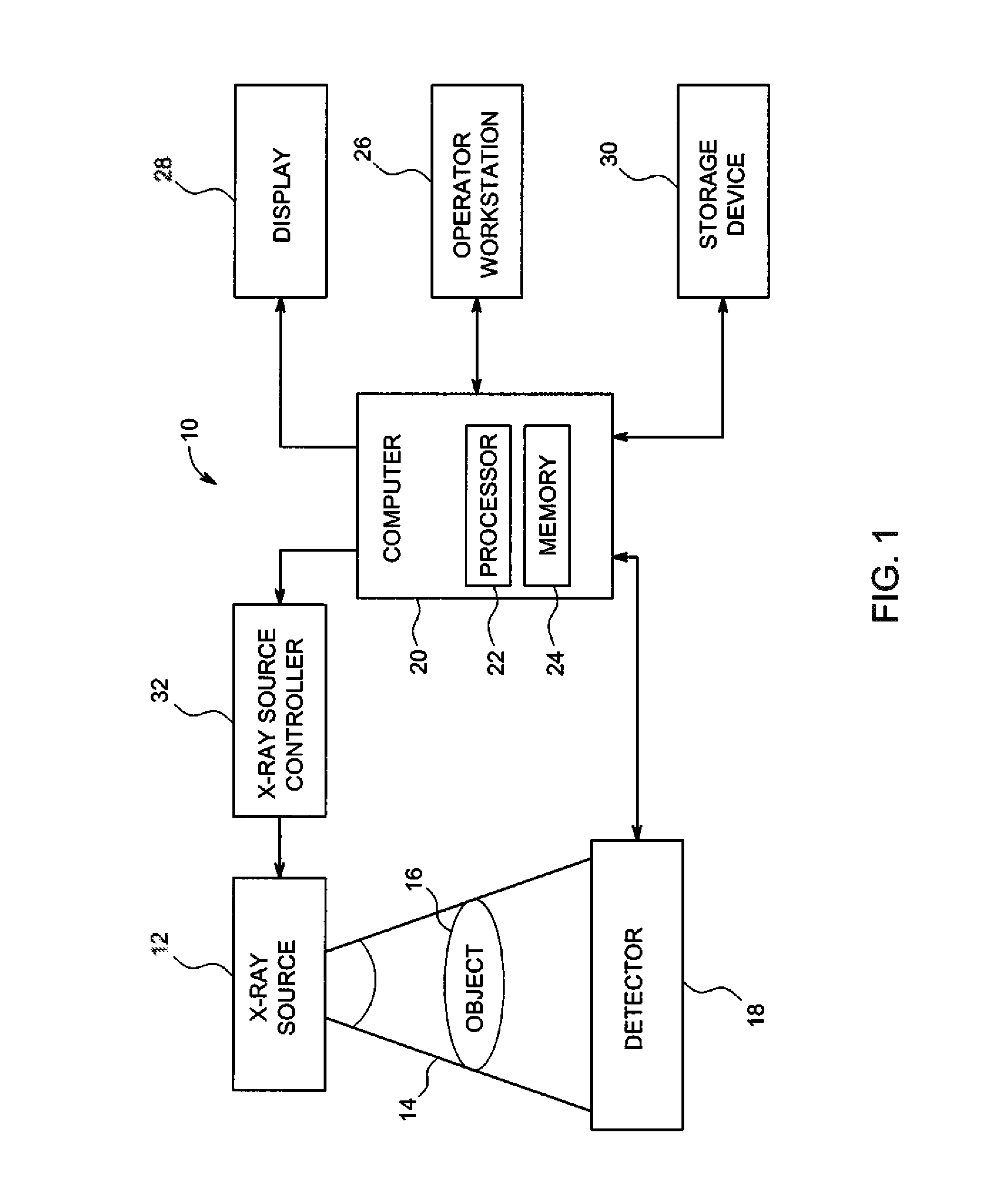
Patents
Literature
57results about "X-ray tube cooling method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
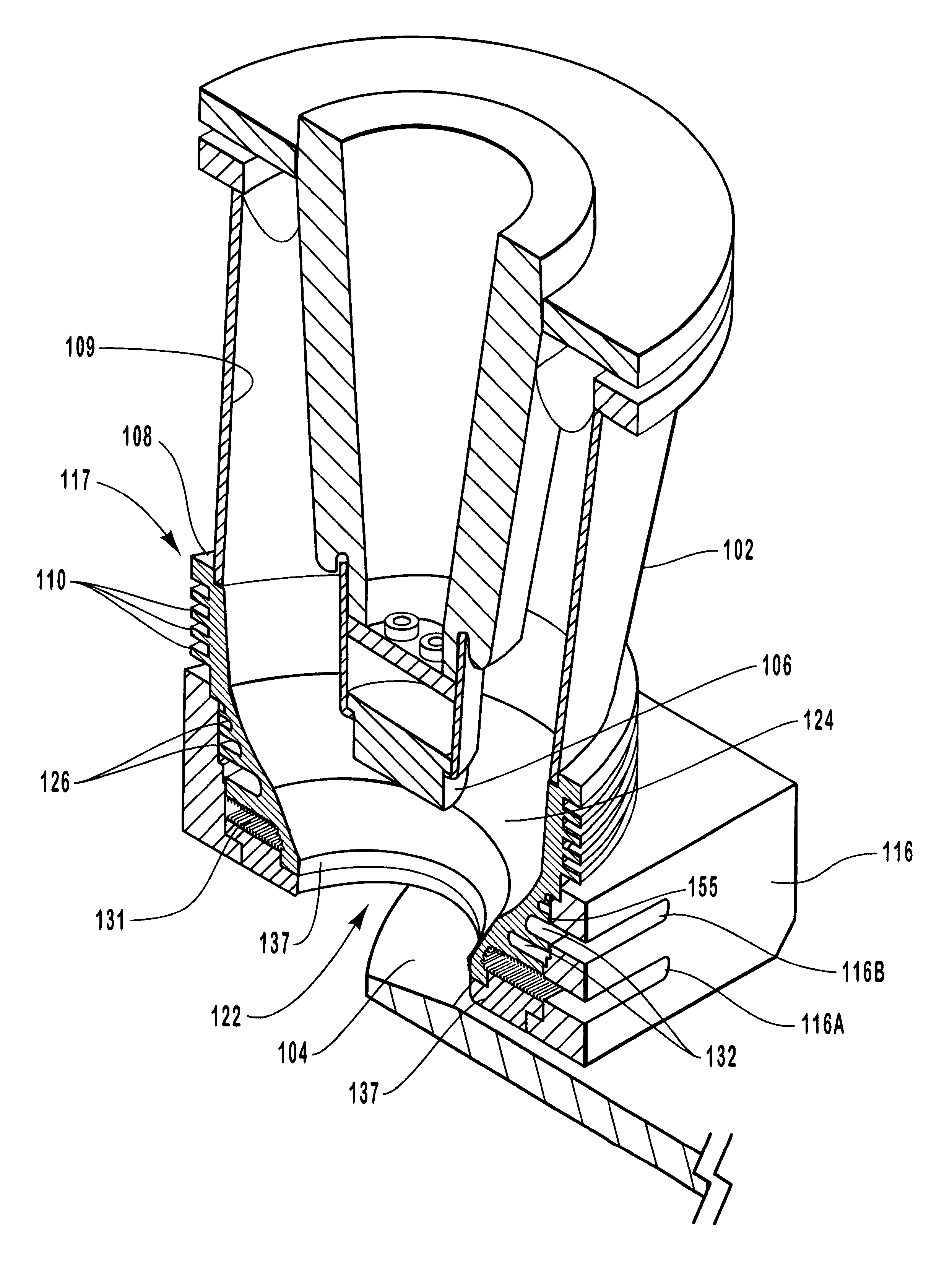
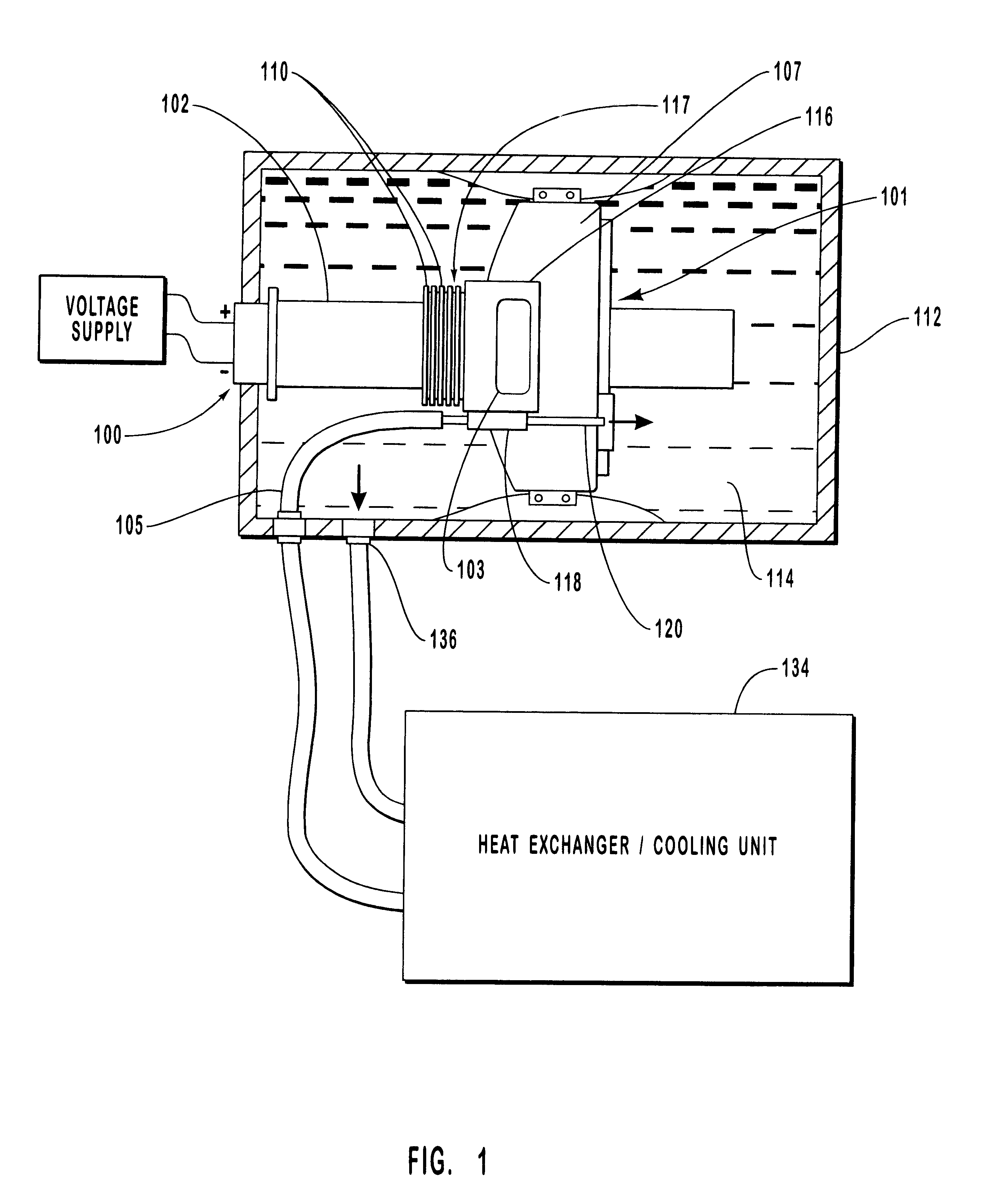
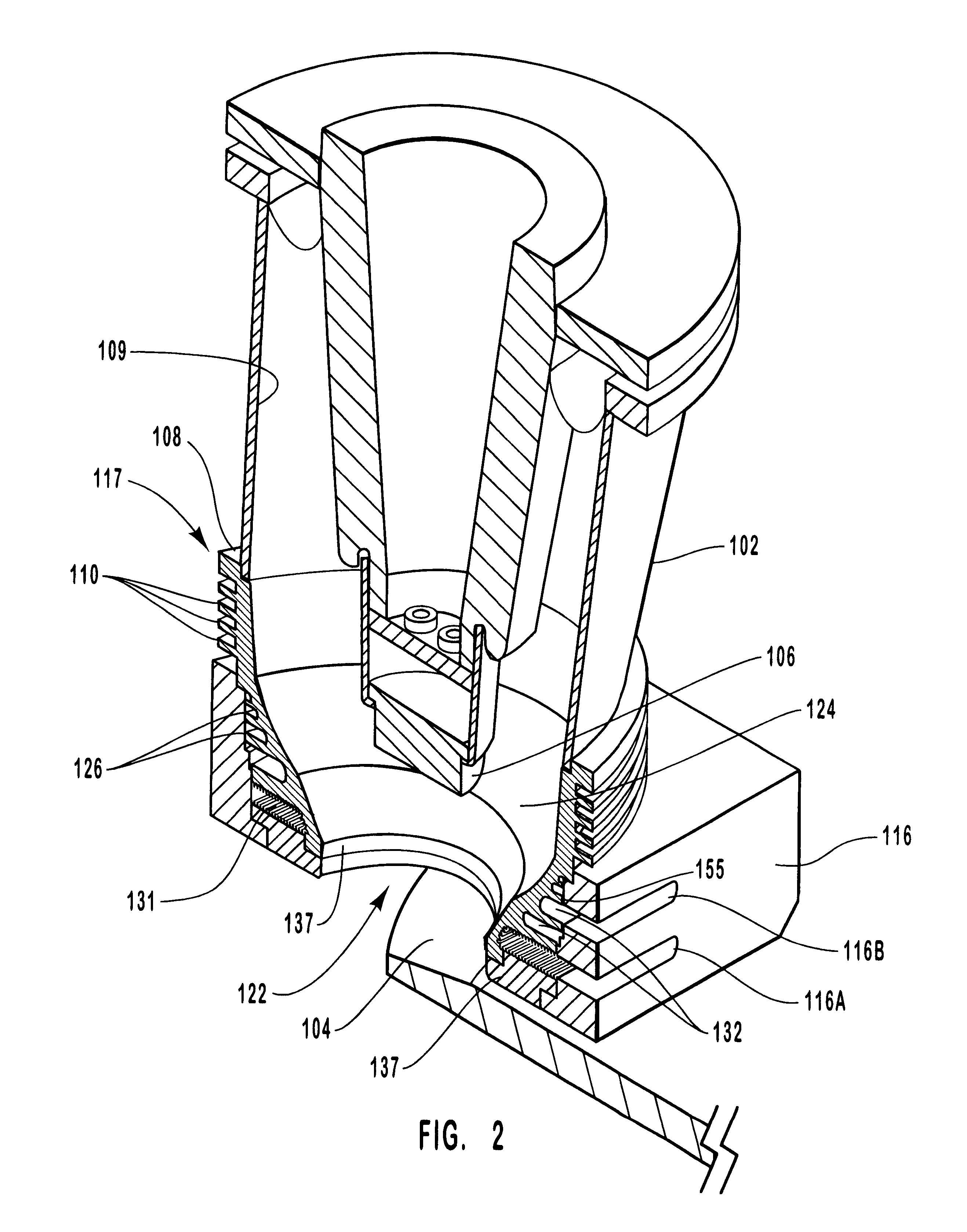
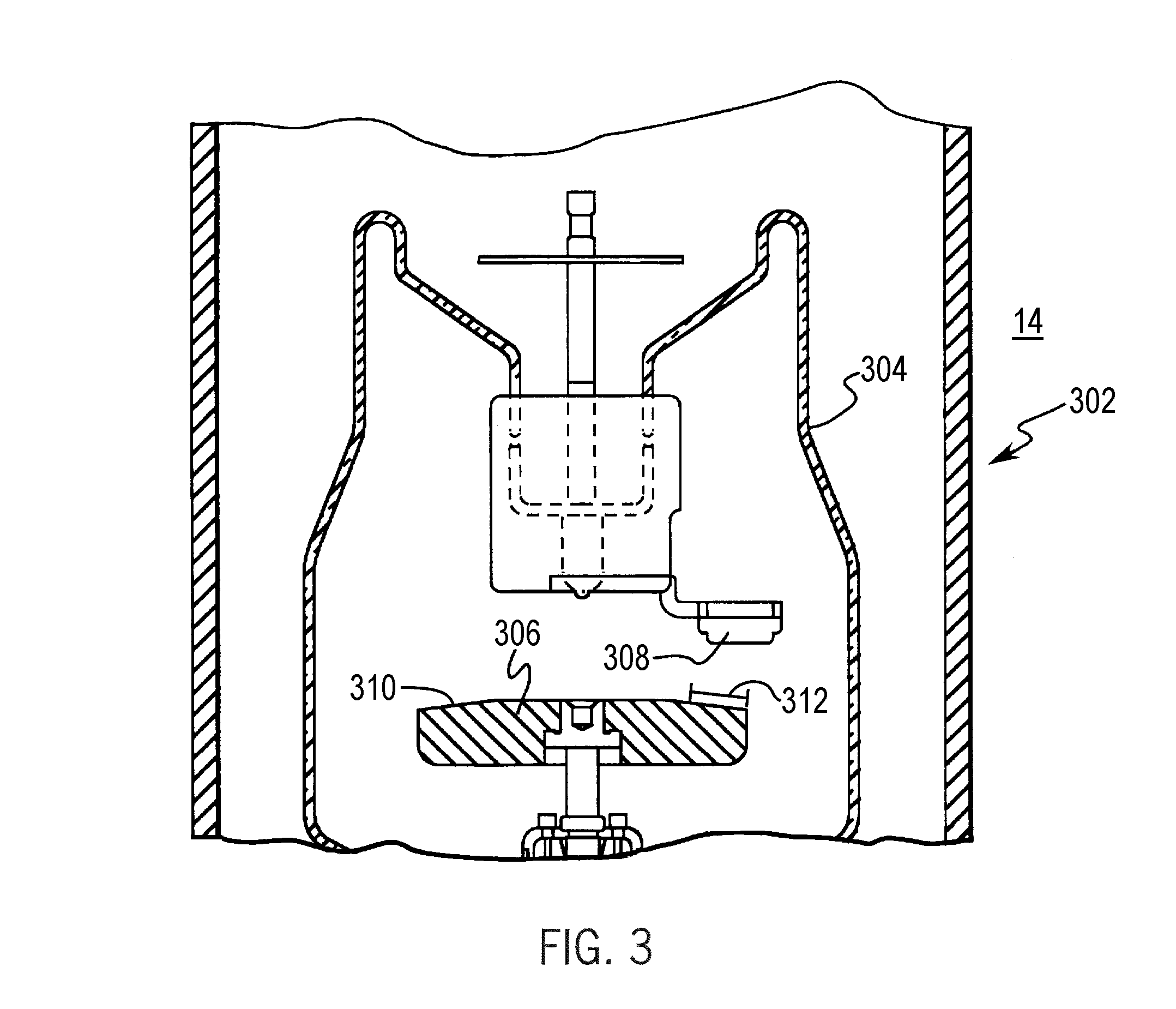
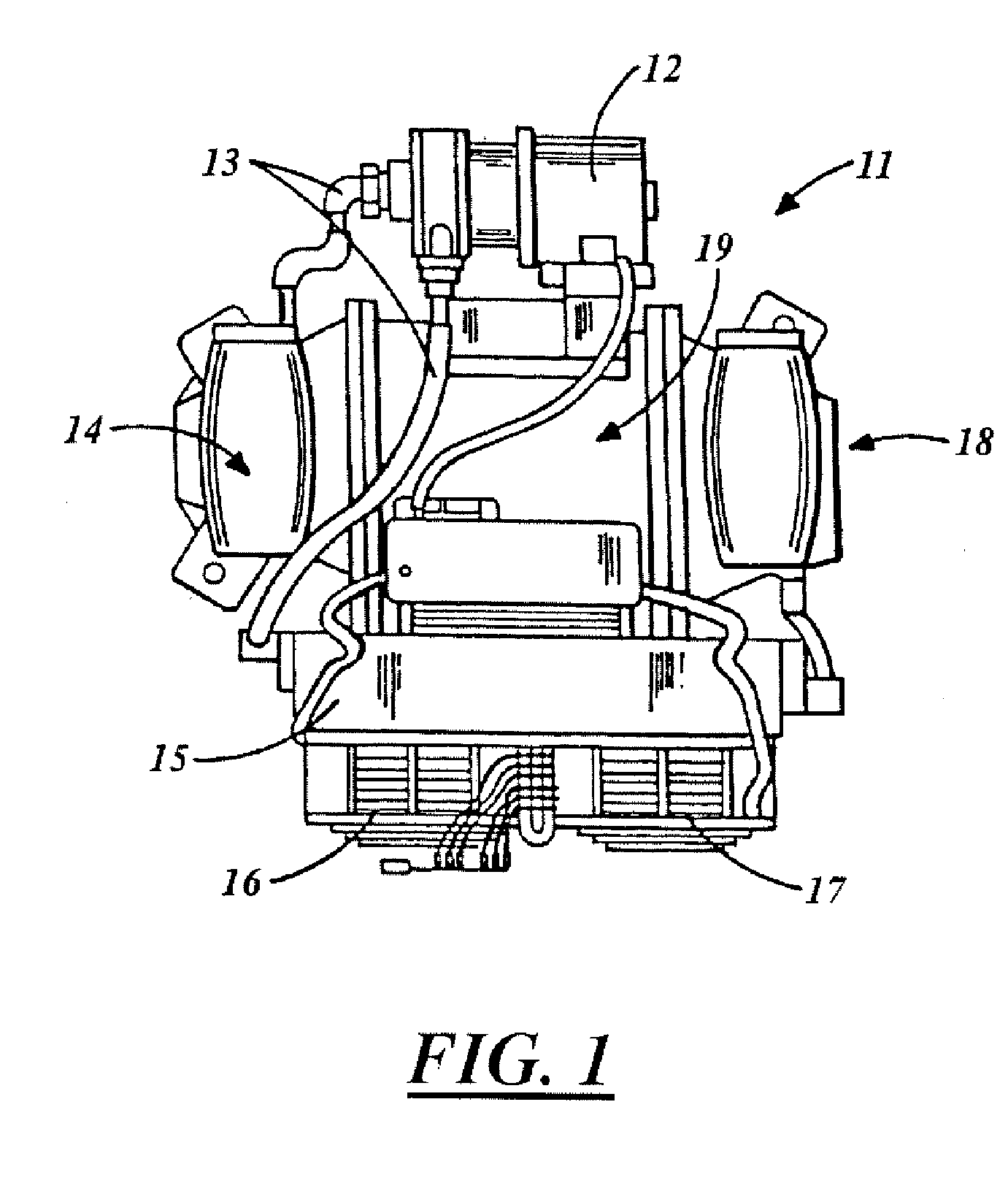
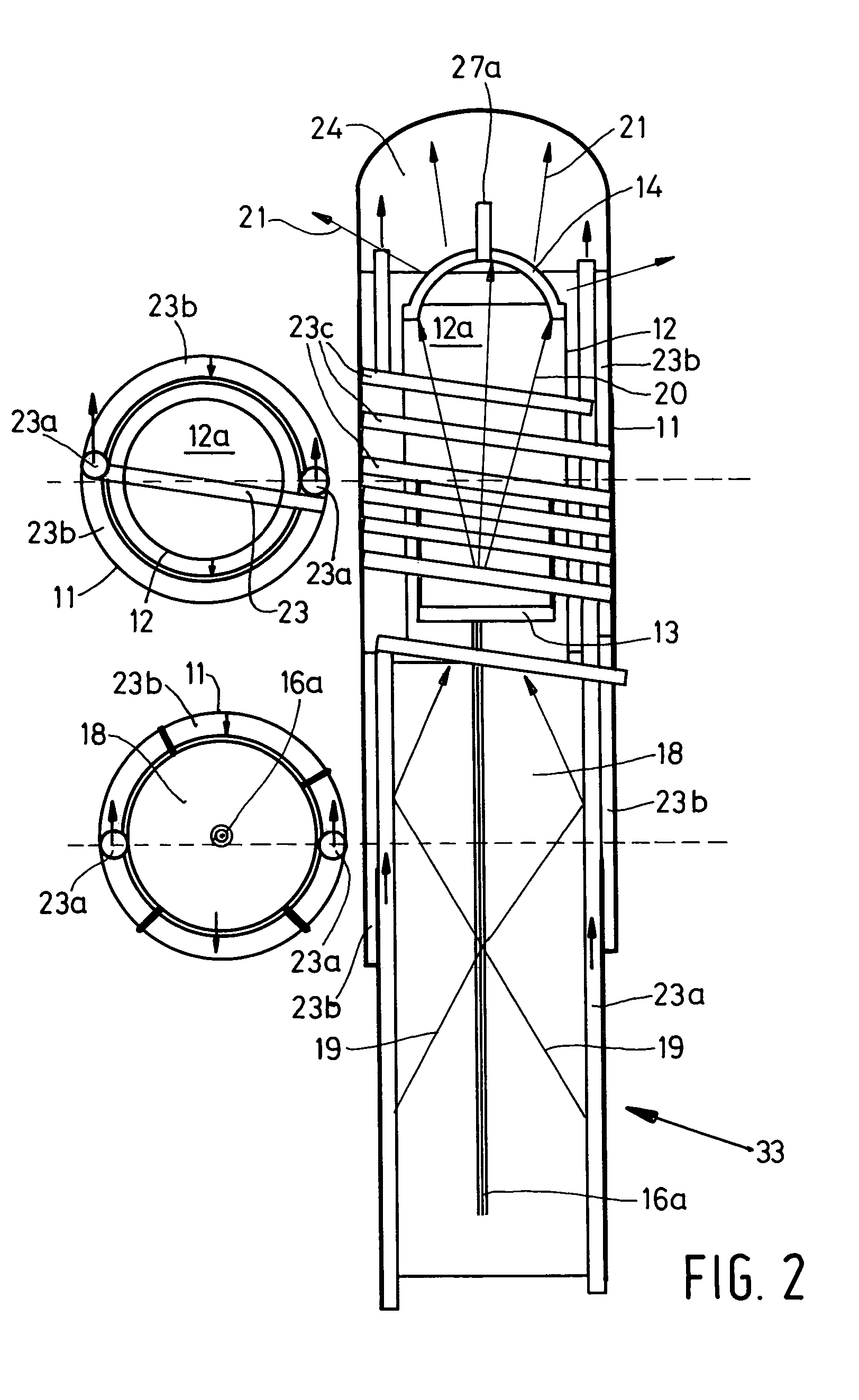
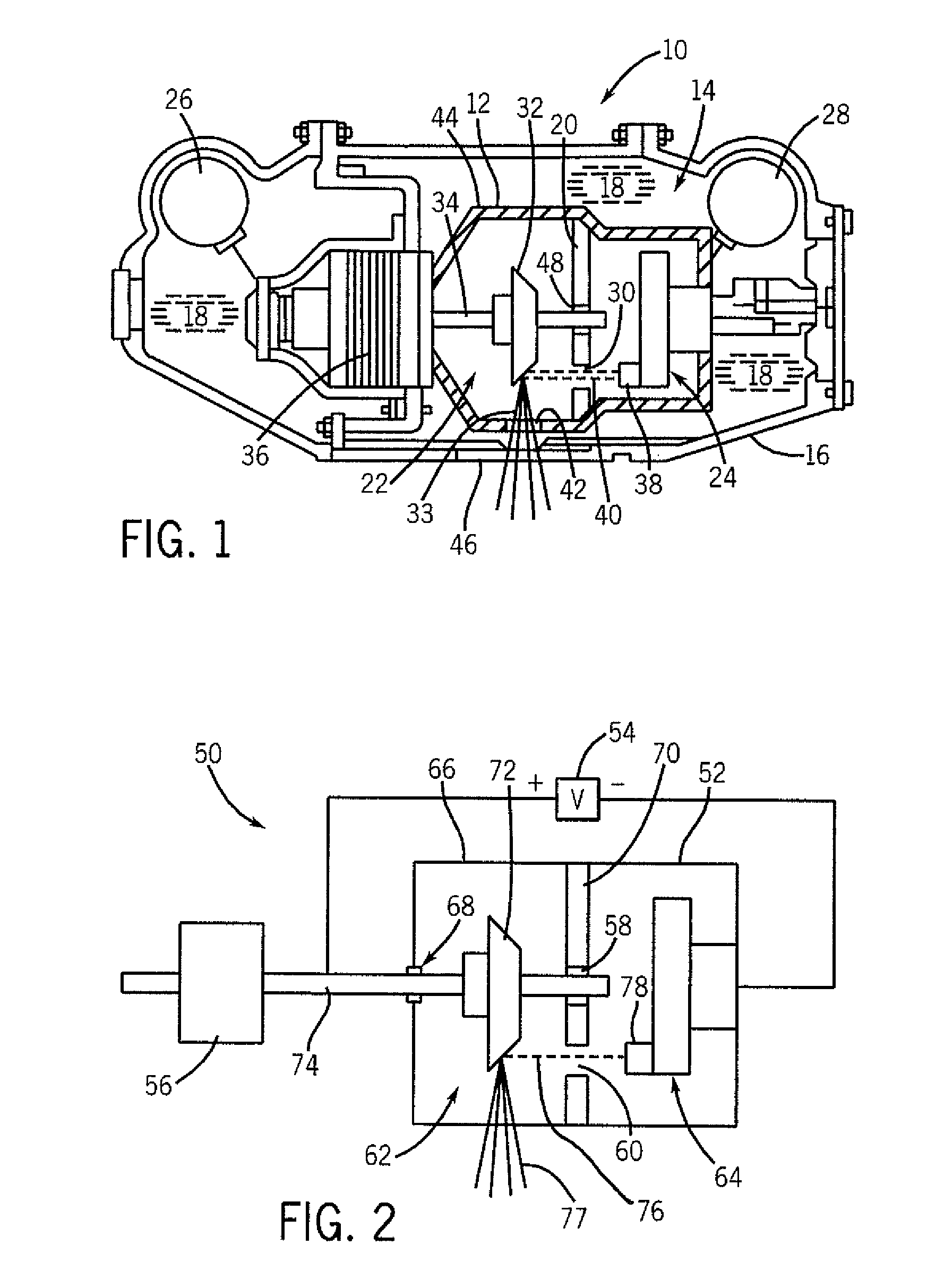
Large surface area x-ray tube shield structure
InactiveUS6519318B1Effective coolingImprove heat transfer performanceX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerElectron sourceCooling effect
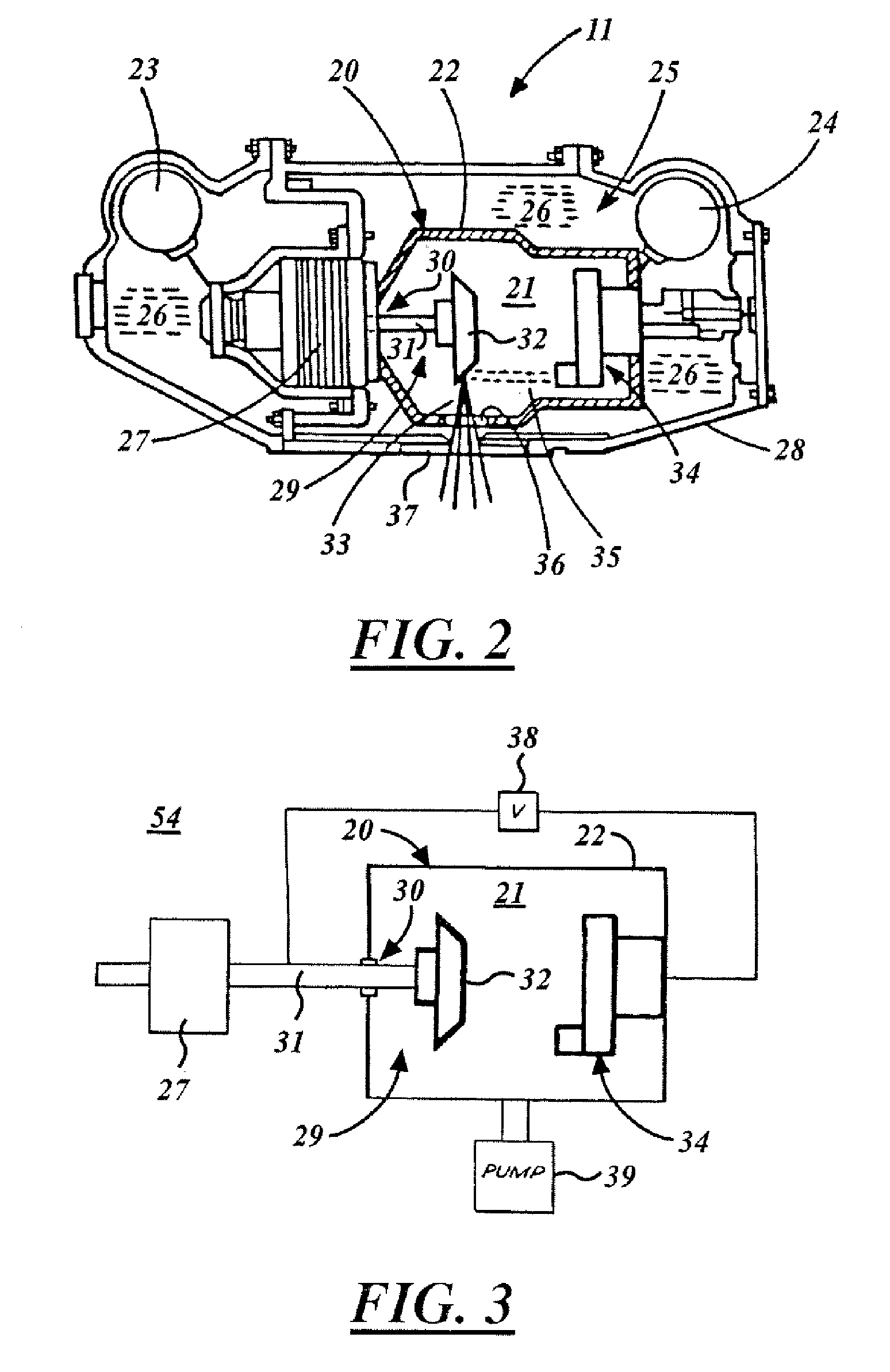
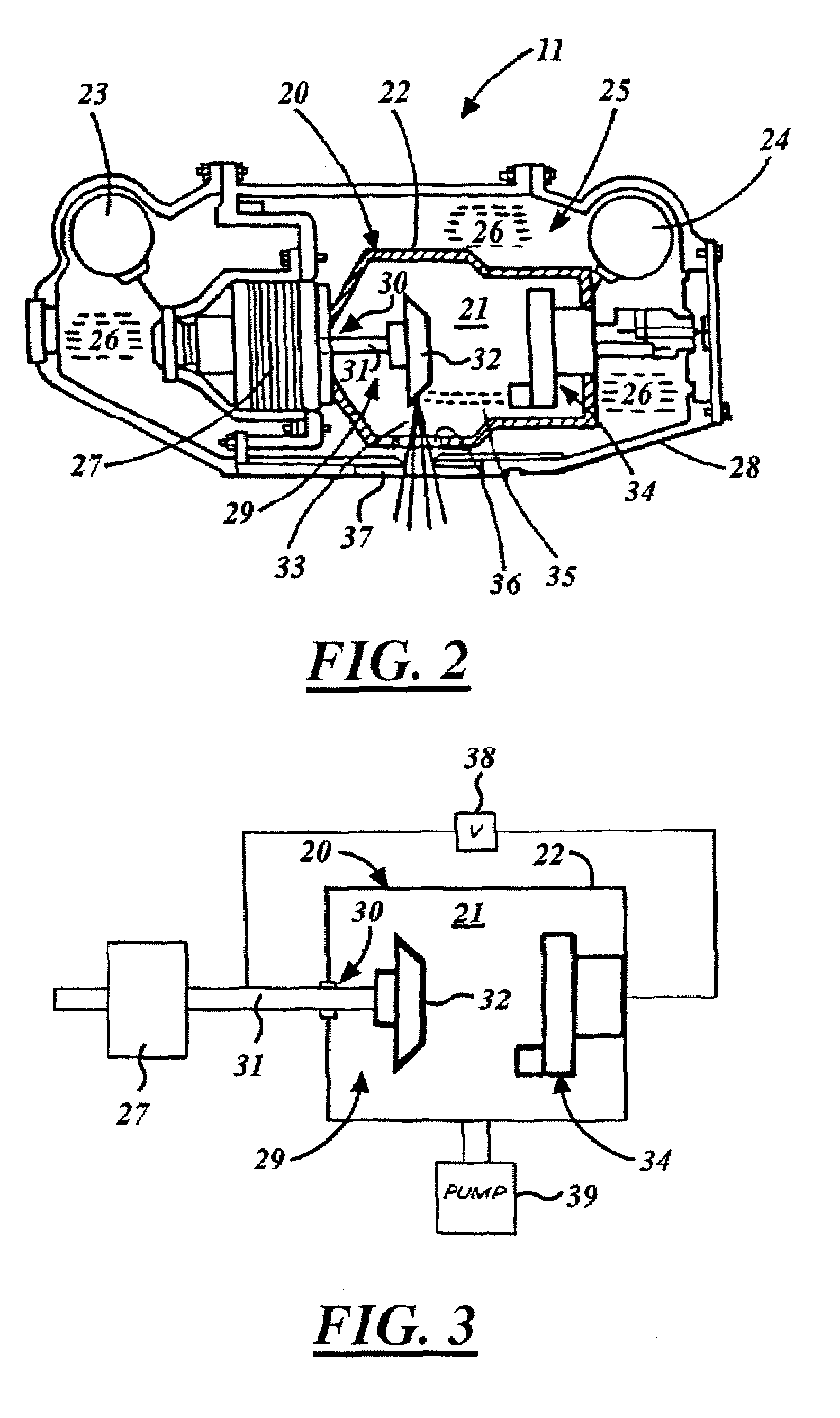
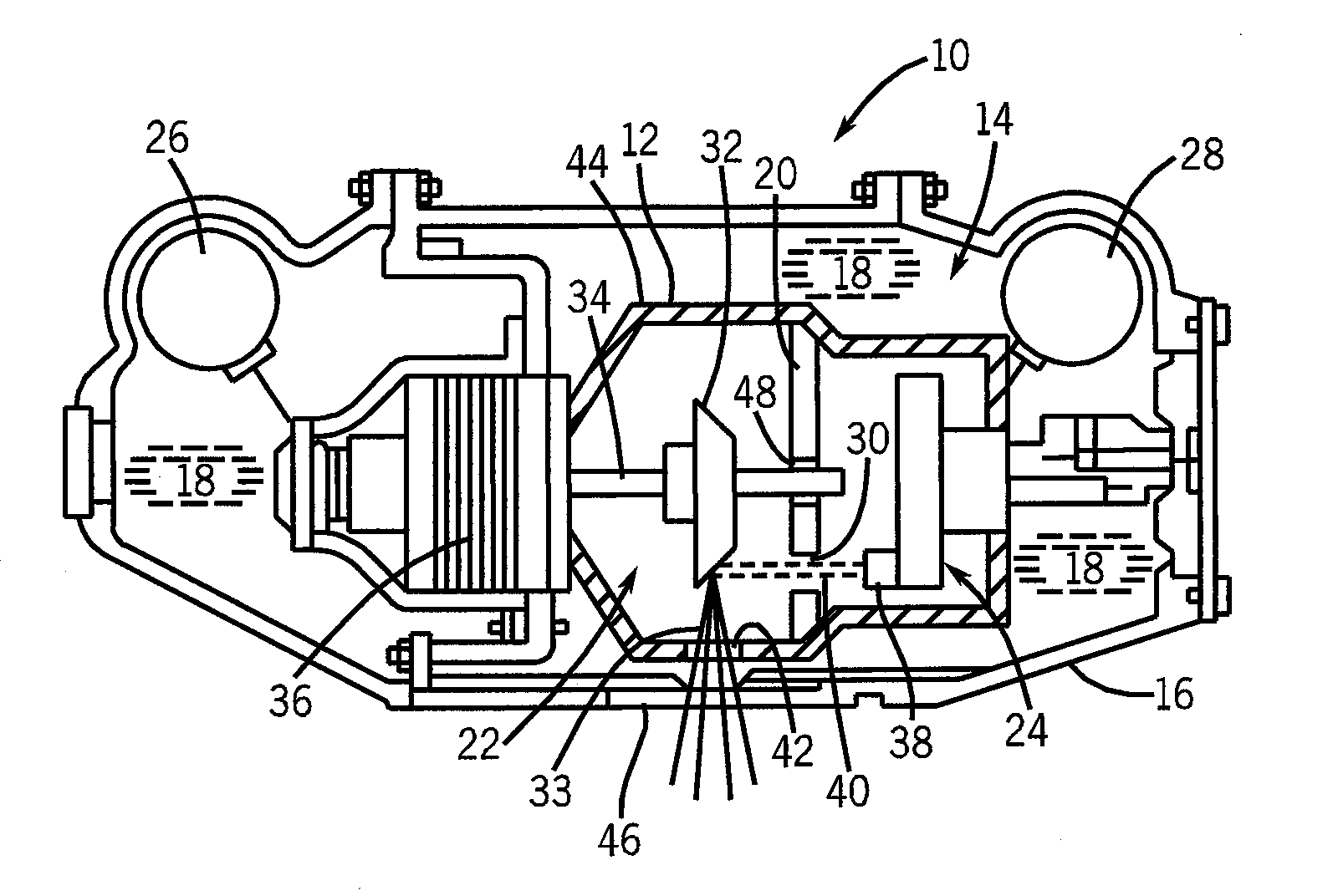
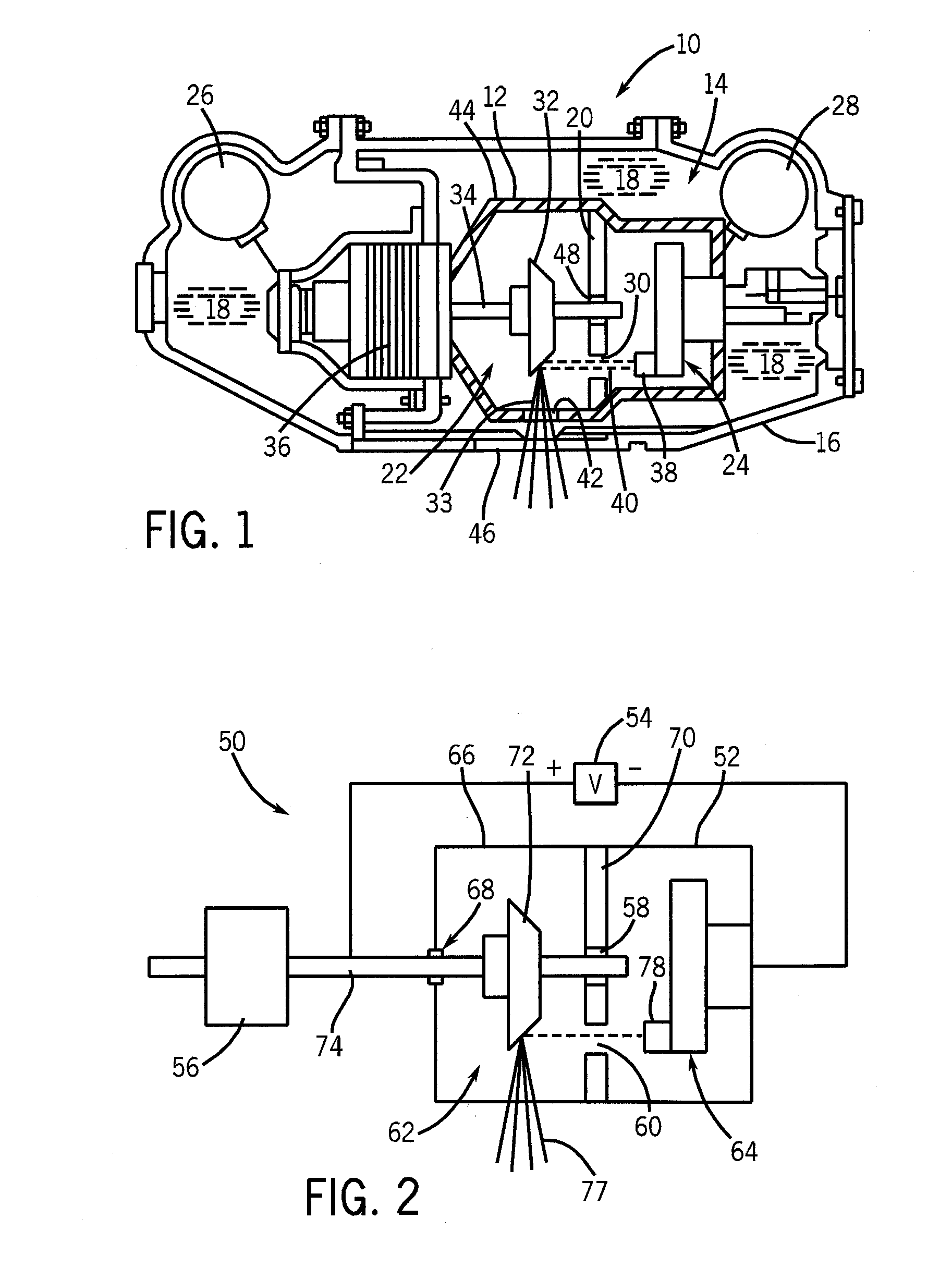
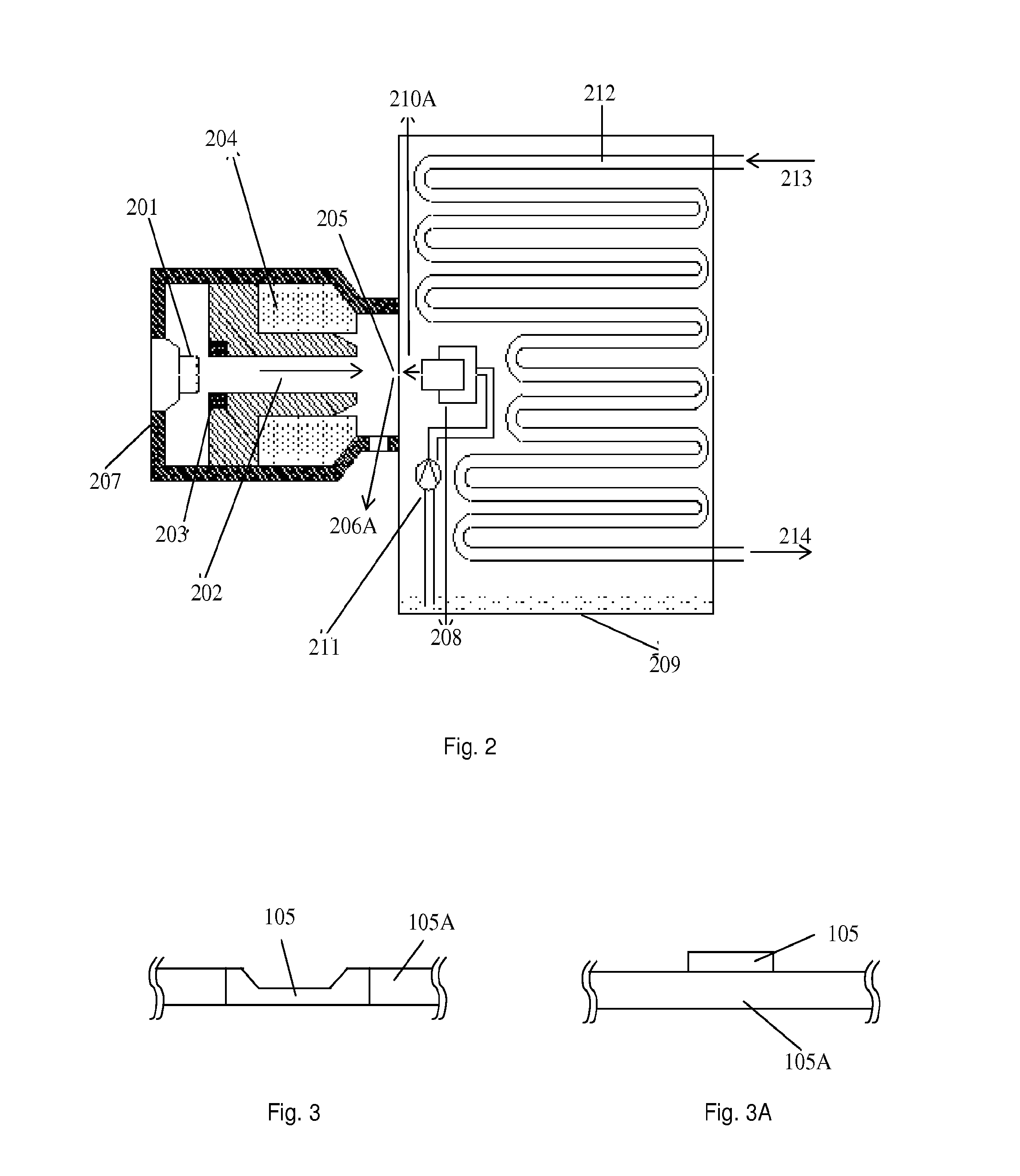
An improved x-ray tube cooling system is disclosed. The system utilizes a shield structure that is connected between a cathode cylinder and an x-ray tube housing and is disposed between the electron source and the target anode. The shield includes a plurality of cooling fins to improve overall cooling of the x-ray tube and the shield so as to extend the life of the x-ray tube and related components. When immersed in a reservoir of coolant fluid, the fins facilitate improved heat transfer by convection from the shield to the to the coolant fluid. The cooling effect achieved with the cooling fins is further augmented by a convective cooling system provided by a plurality of fluid passageways formed within the shield, which are used to provide a fluid path to the coolant. In particular, a cooling unit takes fluid from the reservoir, cools the fluid, then circulates the cooled fluid through the fluid passageways. One or more depressions of "V" shaped cross section defined on the surfaces of the fluid passageways serve to facilitate nucleate boiling of the coolant in the passageway, and thereby materially increase the heat flux through the passageway to the coolant. Additionally, one or more extended surfaces disposed on the surfaces of the fluid passageways also facilitate a relative increase in the rate of heat transfer from the shield structure to the coolant. After flowing through the fluid passageway, the coolant is then discharged from the fluid passageways and directed over the cooling fins. In some embodiments, the fluid passageways are oriented so as to provide a greater heat transfer rate in certain sections of the shield than in other sections. Also disclosed is an improved braze joint for connecting the shield to the x-ray tube housing.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Apparatus for increasing radiative heat transfer in an x-ray tube and method of making same
InactiveUS7672433B2Improve thermal efficiencyX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-rayCarbide
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
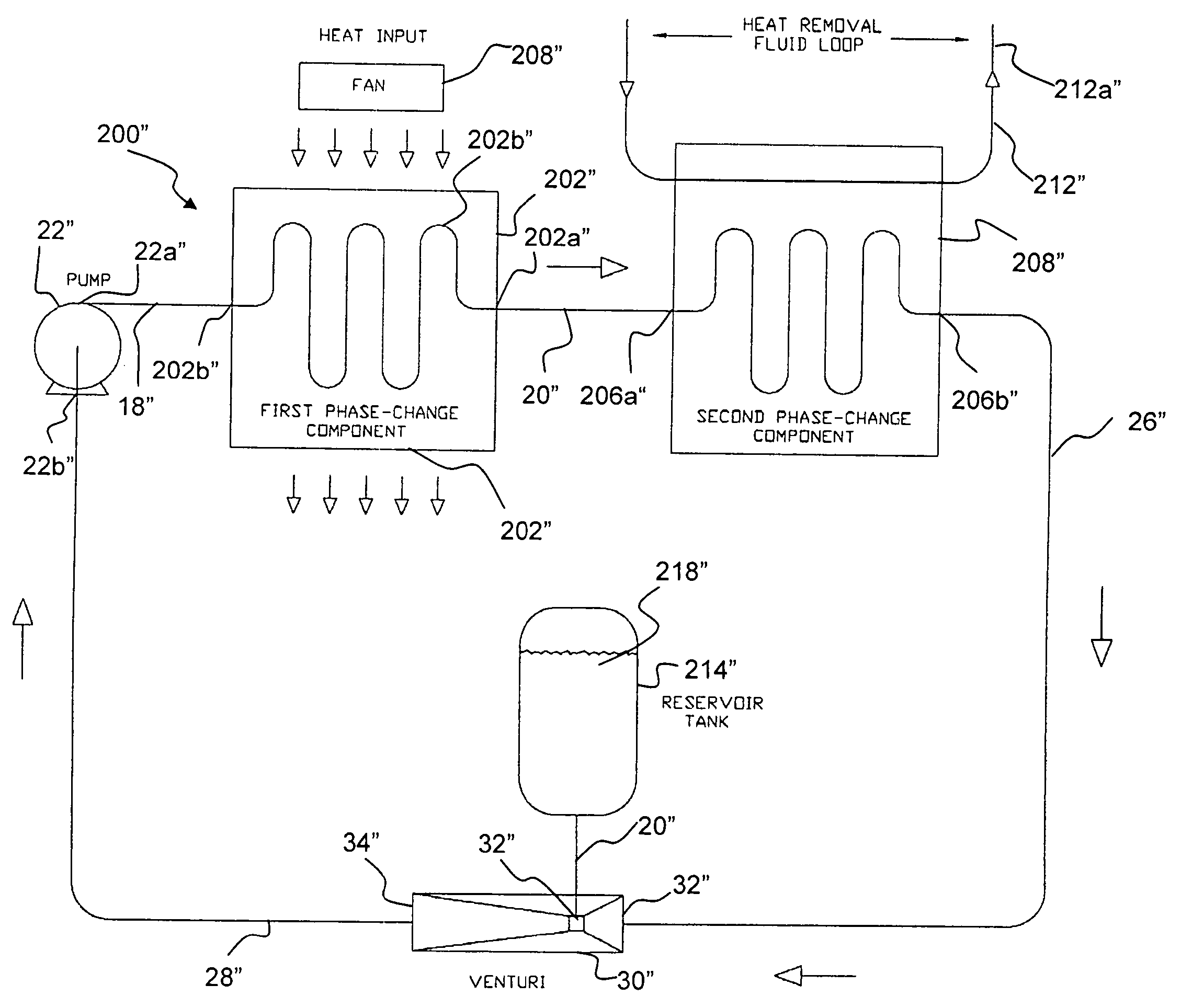
Method and system for cooling heat-generating component in a closed-loop system
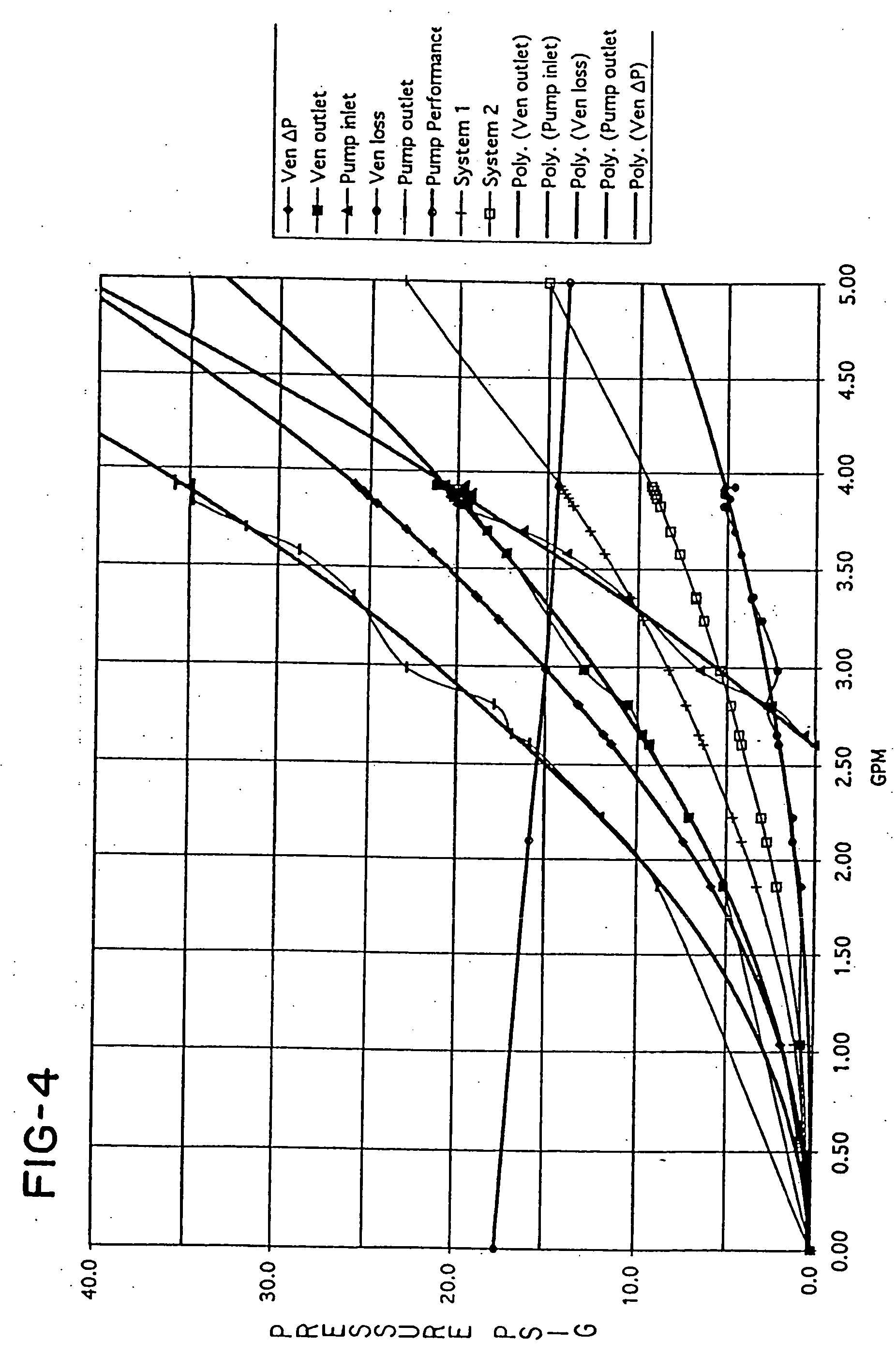
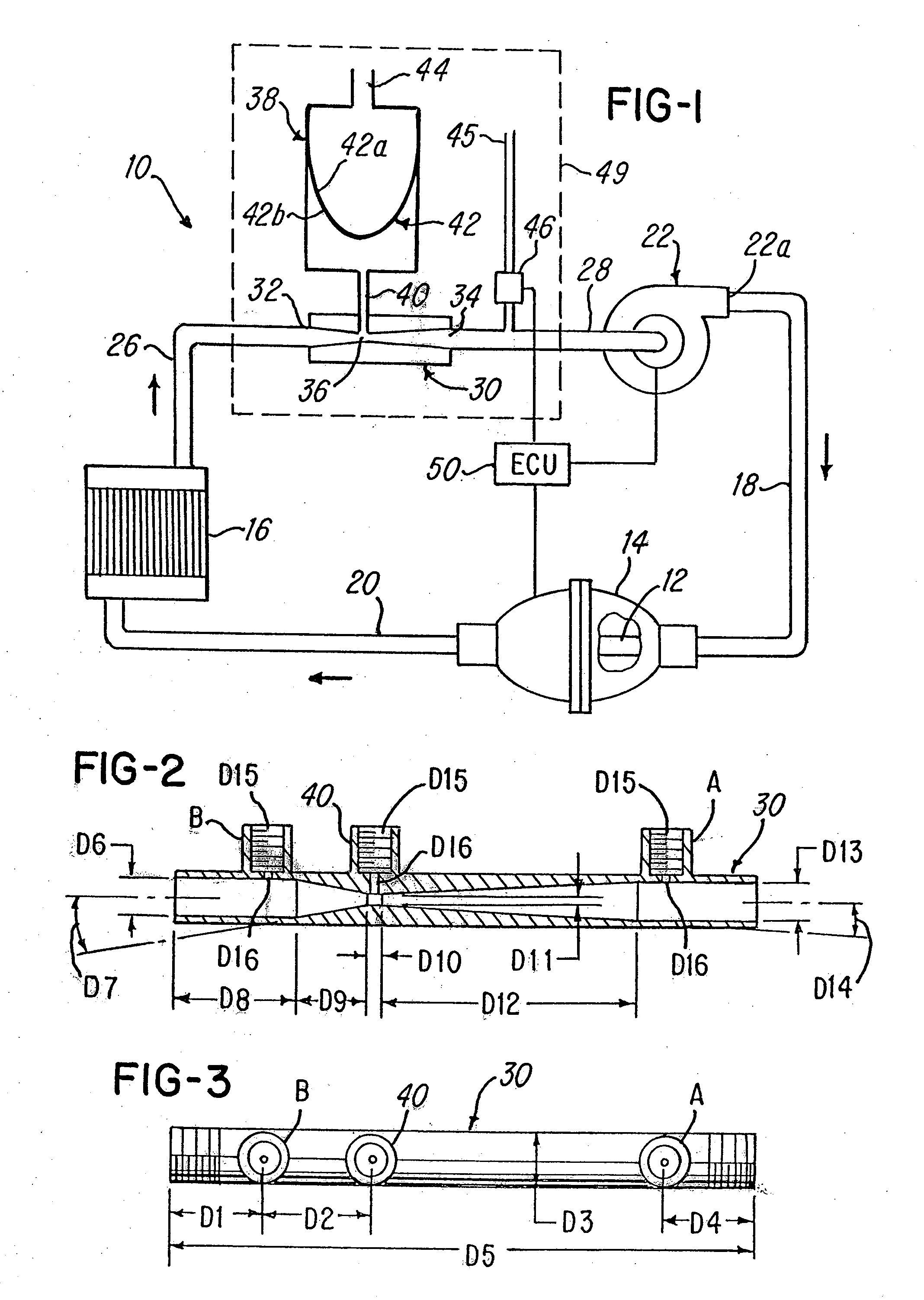
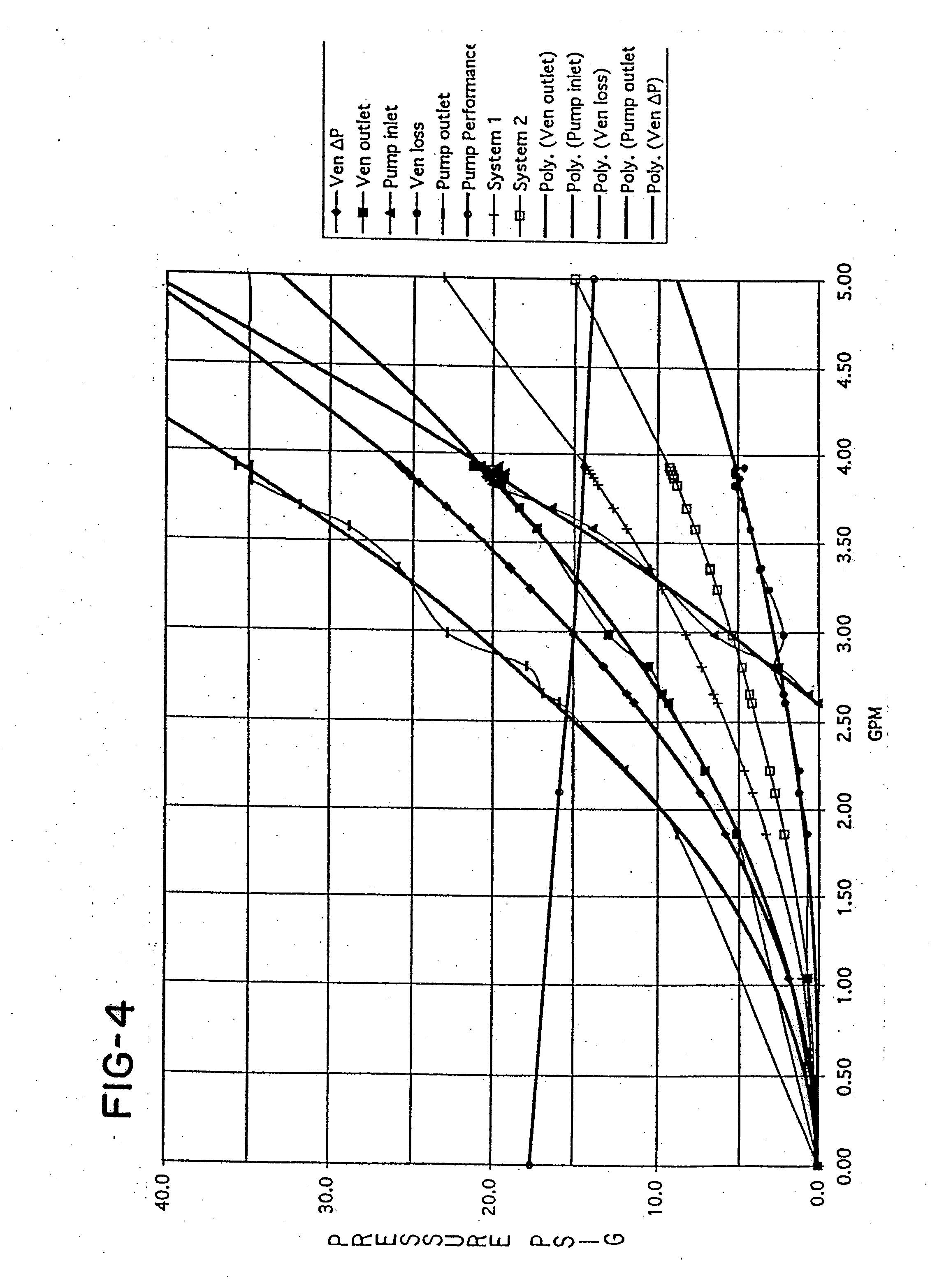
InactiveUS20060140346A1Promote useIncrease pressureDomestic cooling apparatusX-ray tube electrodesCavitationFluid phase
A system and method for reducing or eliminating pump cavitation in a closed system having at least one or a plurality of fluid phase changes. The system comprises a venturi having a throat which is coupled to a reservoir tank.
Owner:TARK
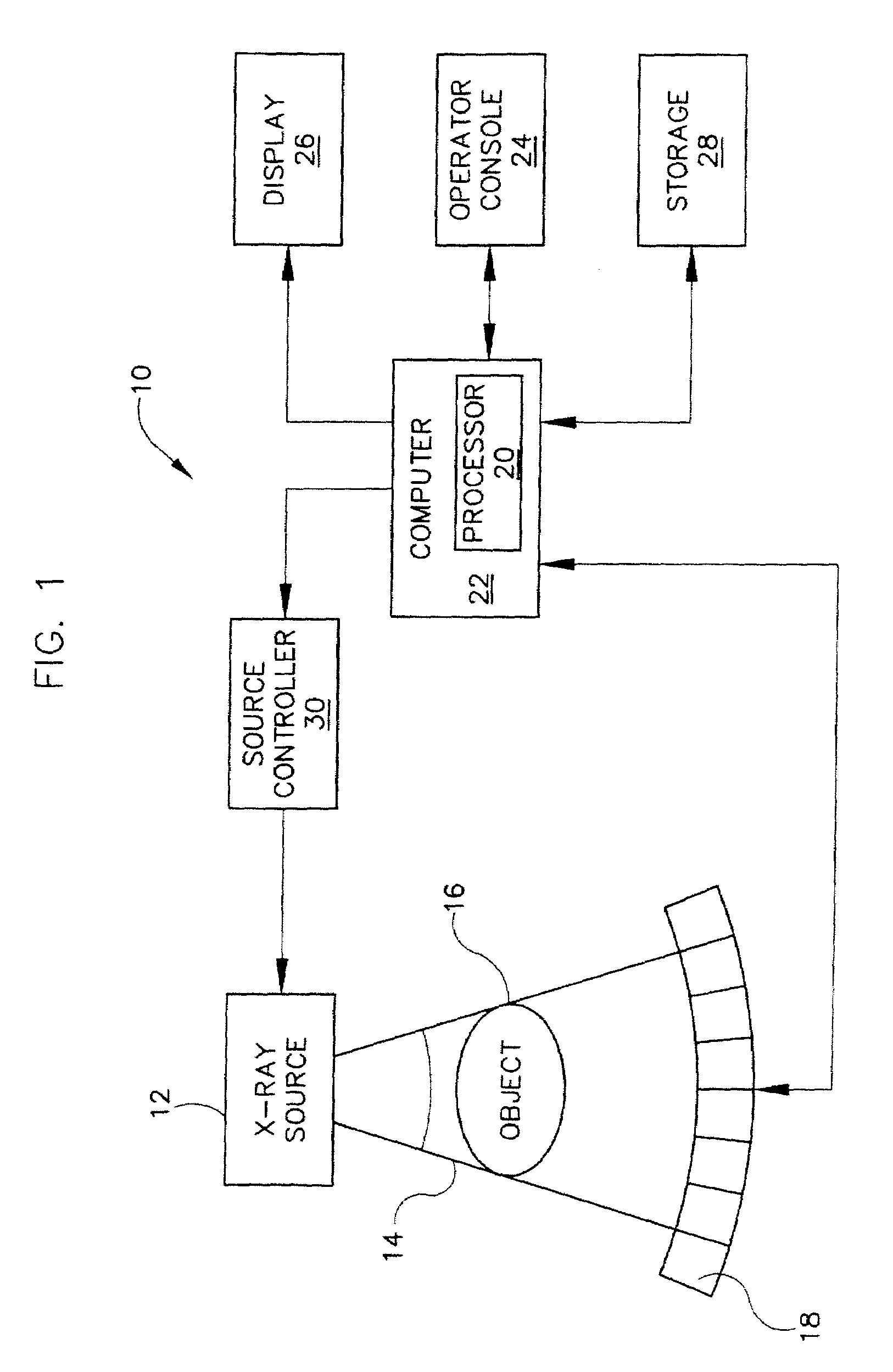
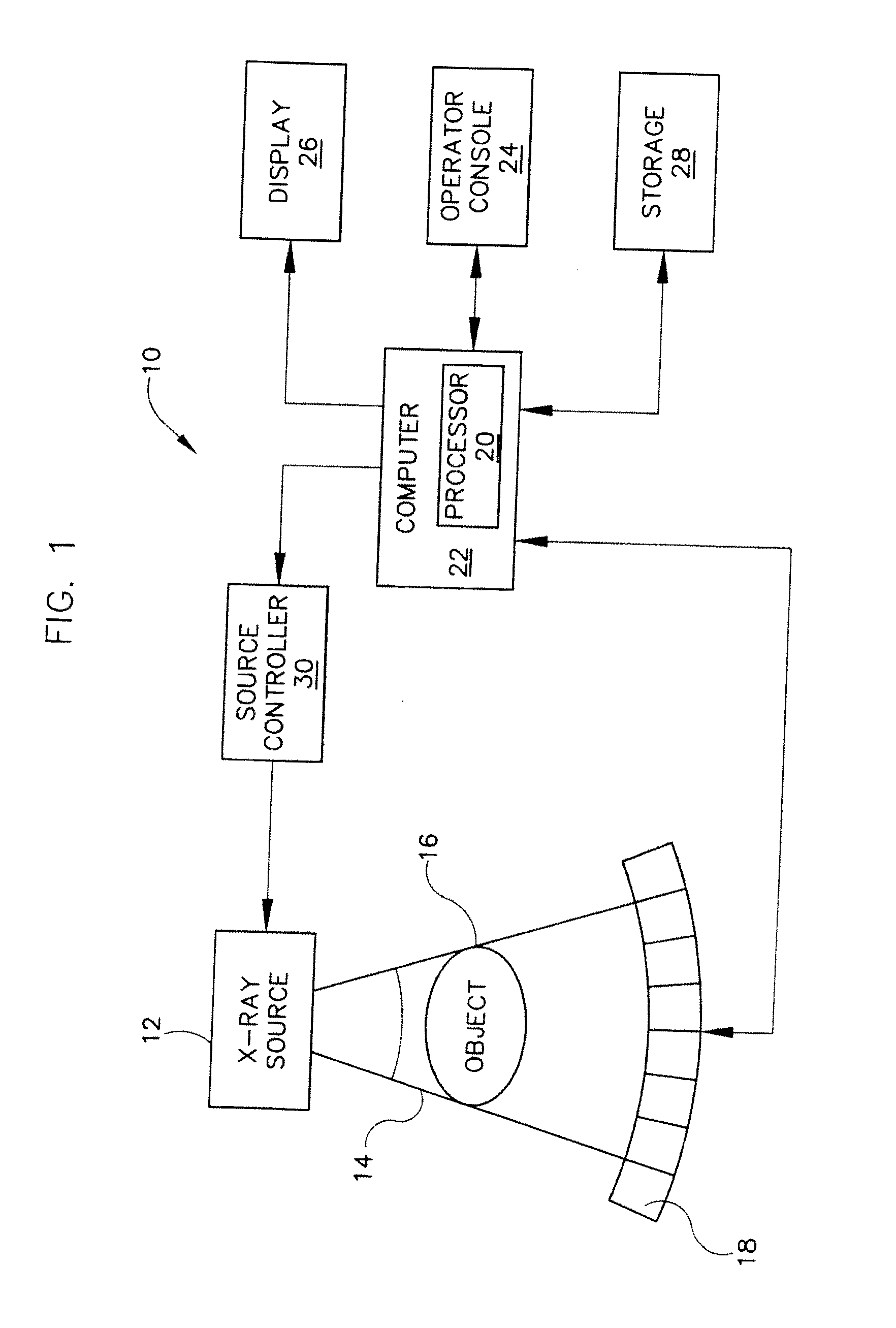
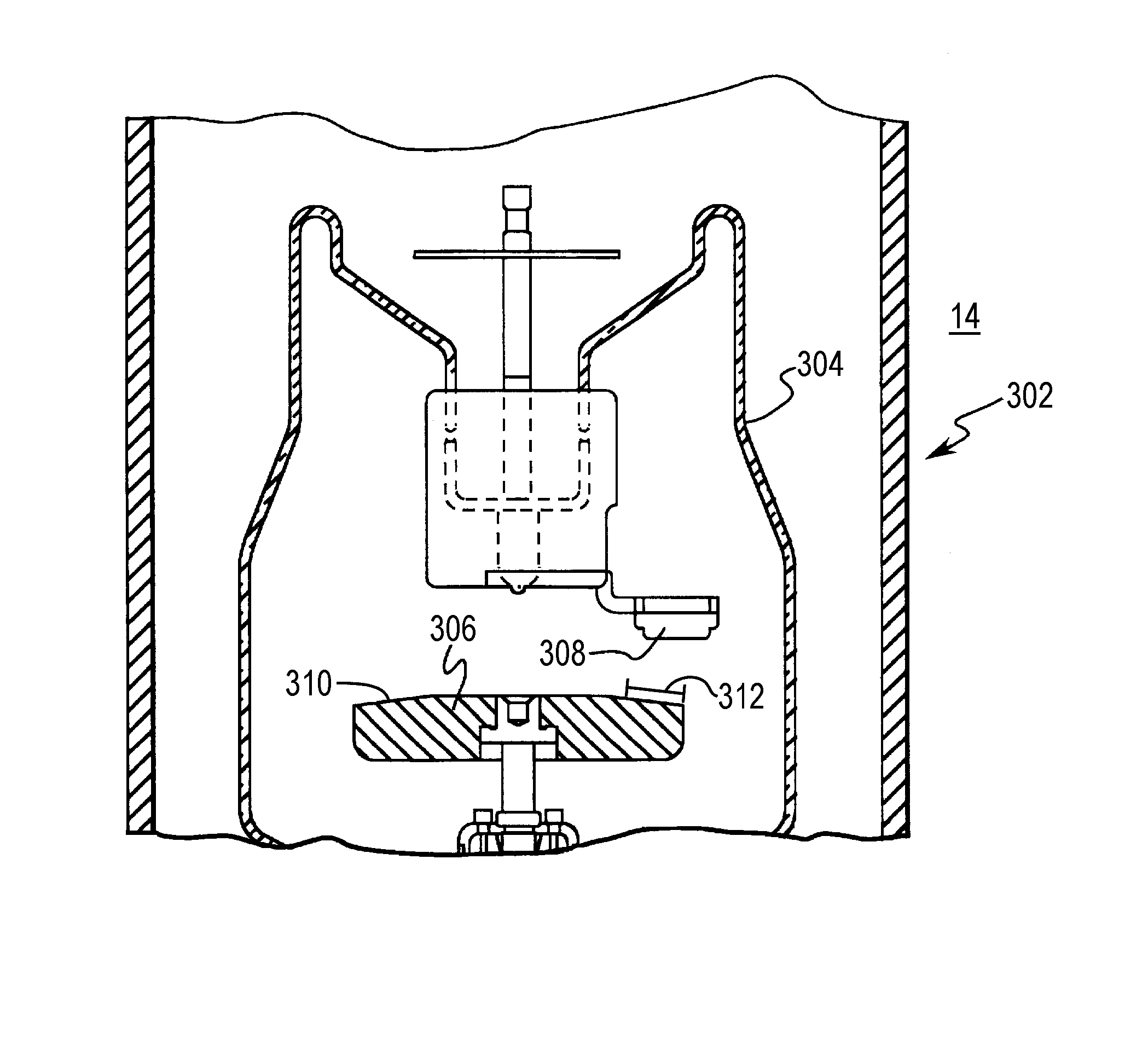
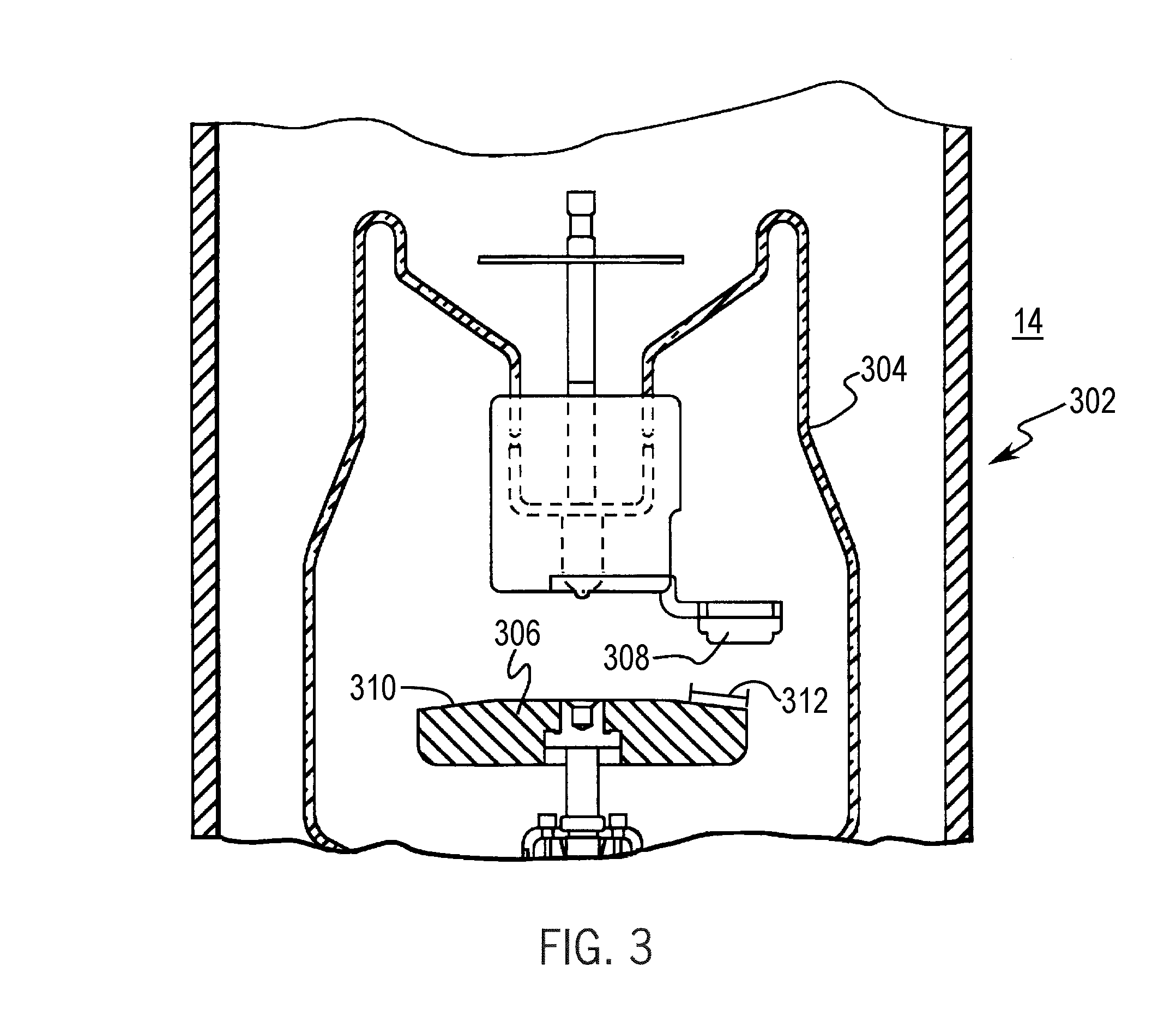
Computerized tomography (CT) imaging system with monoblock X-ray tube assembly
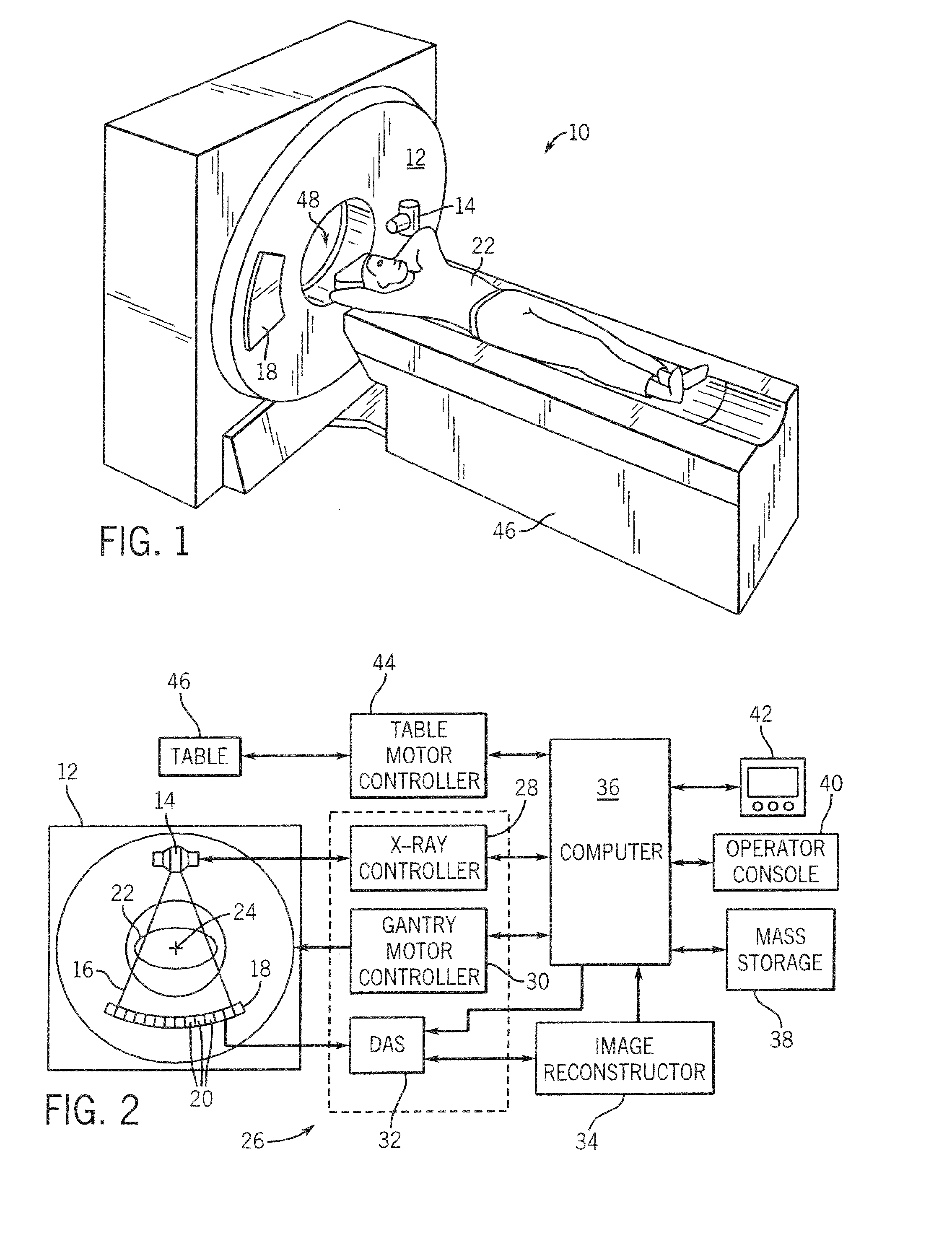
ActiveUS7396160B2Small sizeReduce weightMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayX-ray
A system for cooling an X-ray tube in a CT machine comprising a heat sink for drawing heat away from the X-ray tube and a collimator connected to the heat sink and adapted to collimate the X-rays emitted by the X-ray tube and “focus” those X-rays on an X-ray detector, the heat sink body being formed out of the same material as the emitter of the X-ray tube, such that the emitter opening of the X-ray tube will remain aligned with both the heat sink window and the collimator opening even when the emitter of the X-ray tube undergoes thermal expansion.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
X-ray tube target and method of repairing a damaged x-ray tube target
ActiveUS20110007872A1Low costHuge savingsX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesX-rayTime-Consuming
An x-ray tube target and method of repairing a damaged x-ray tube target. The x-ray tube target includes an original substrate and a portion of the original substrate that includes a new portion of a substrate and a new target track that is attached to a void in the original substrate. The method includes removal and replacement of damaged materials on used anode targets of x-ray tubes, thereby enabling recovery of used anode targets without the use of expensive and time consuming layer deposition methods. The method also avoids the high costs and long development cycles associated with known repair and refabrication methods for anode targets of x-ray tubes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for cooling heat-generating component in a closed-loop system
InactiveUS20060280292A1Promote useIncrease pressureX-ray tube electrodesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleCavitationFluid phase
A system and method for reducing or eliminating pump cavitation in a closed system having at least one or a plurality of fluid phase changes. The system comprises a venturi having a throat which is coupled to a reservoir tank.
Owner:TARK
X-ray anode focal track region
A focal track region of an x-ray anode in an example is electrochemically etched. In a further example, an x-ray anode comprises a thermally-compliant focal track region for impingement of electrons from an x-ray cathode to create an x-ray source. The thermally-compliant focal track region comprises a pattern of discrete relative expanses and gaps.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tube, x-ray system, and method for generating x-rays
InactiveUS7835501B2Increase power intensityReduced stabilityX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayX-ray
According to an exemplary embodiment an x-ray tube comprises a cathode, rotable disc anode, and a focal spot modulating unit, wherein the cathode is adapted to emit an electron beam, and wherein the focal spot modulating unit is adapted to modulate the electron beam in such a way that an intensity distribution of the electron beam on a focal spot on the anode is asymmetric such that the intensity of the electron beam on the focal spot is higher at the front of the focal spot with respect to the rotation direction.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
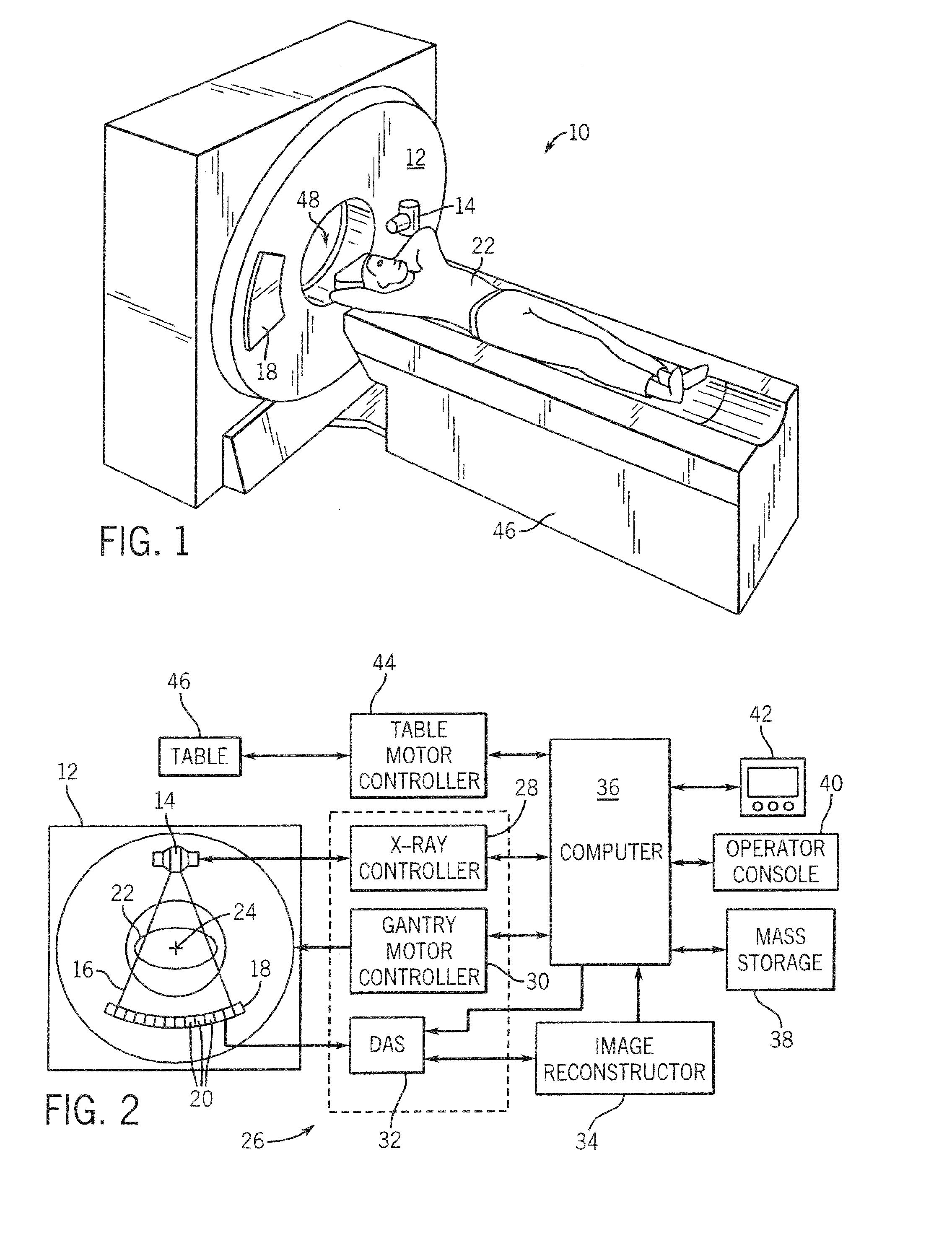
Computed tomography system having cooling system
ActiveUS20160235378A1X-ray tube bearing assembly coolingPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputed tomographyOperational system
A cooling system of a computed tomography (CT) system provides for a more efficient operation than known heretofore. The cooling system of the CT system includes a gantry and a table that moves an object into a bore of the gantry. The gantry includes part boxes mounted therein, and blade elements are formed in regions of the part boxes. The cooling system of the CT system includes a cooling method that includes a multiple cooling method including a stand-by mode and an operating mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for increasing radiative heat transfer in an x-ray tube and method of making same
InactiveUS20090285363A1Improve thermal efficiencyX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesCarbideX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
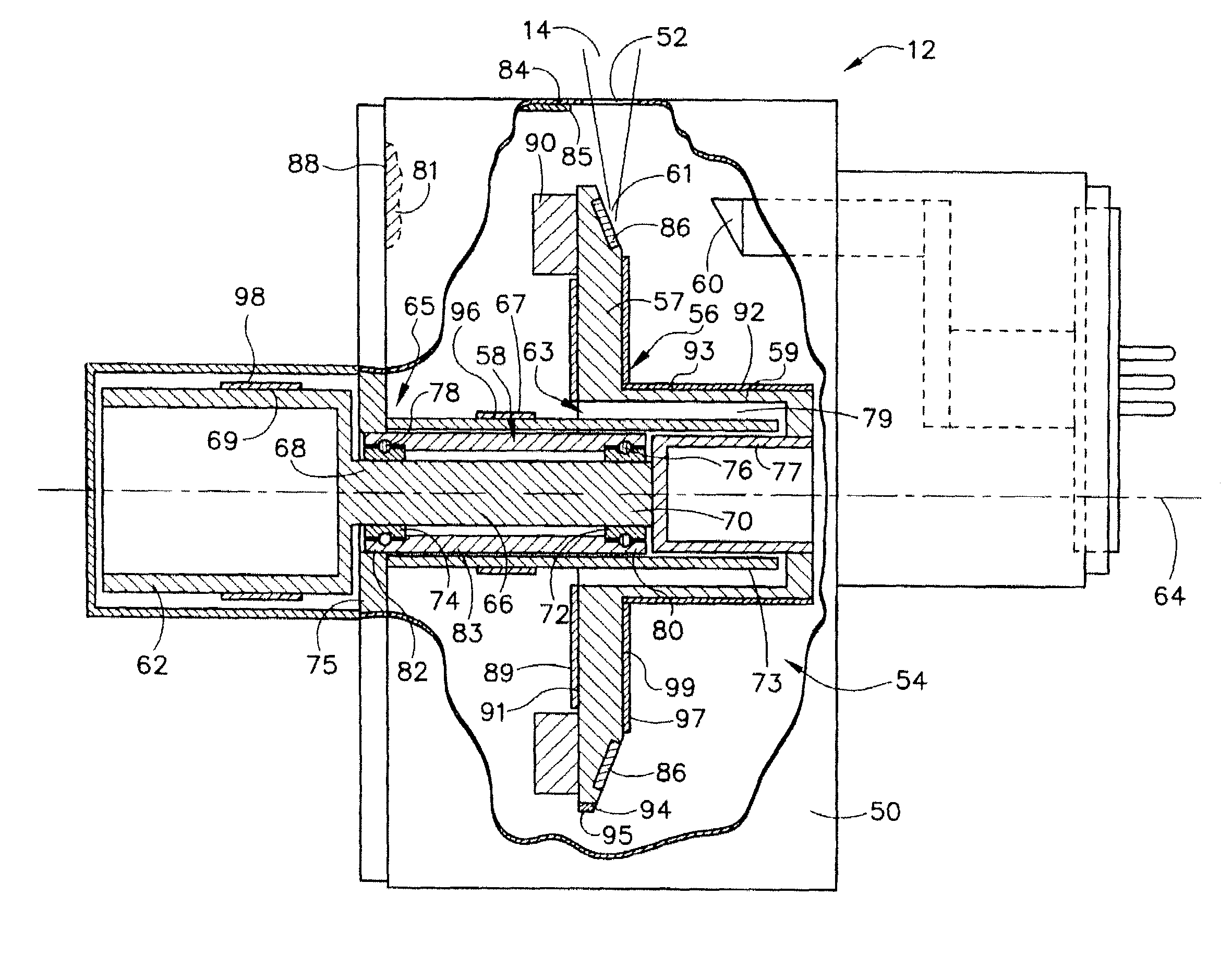
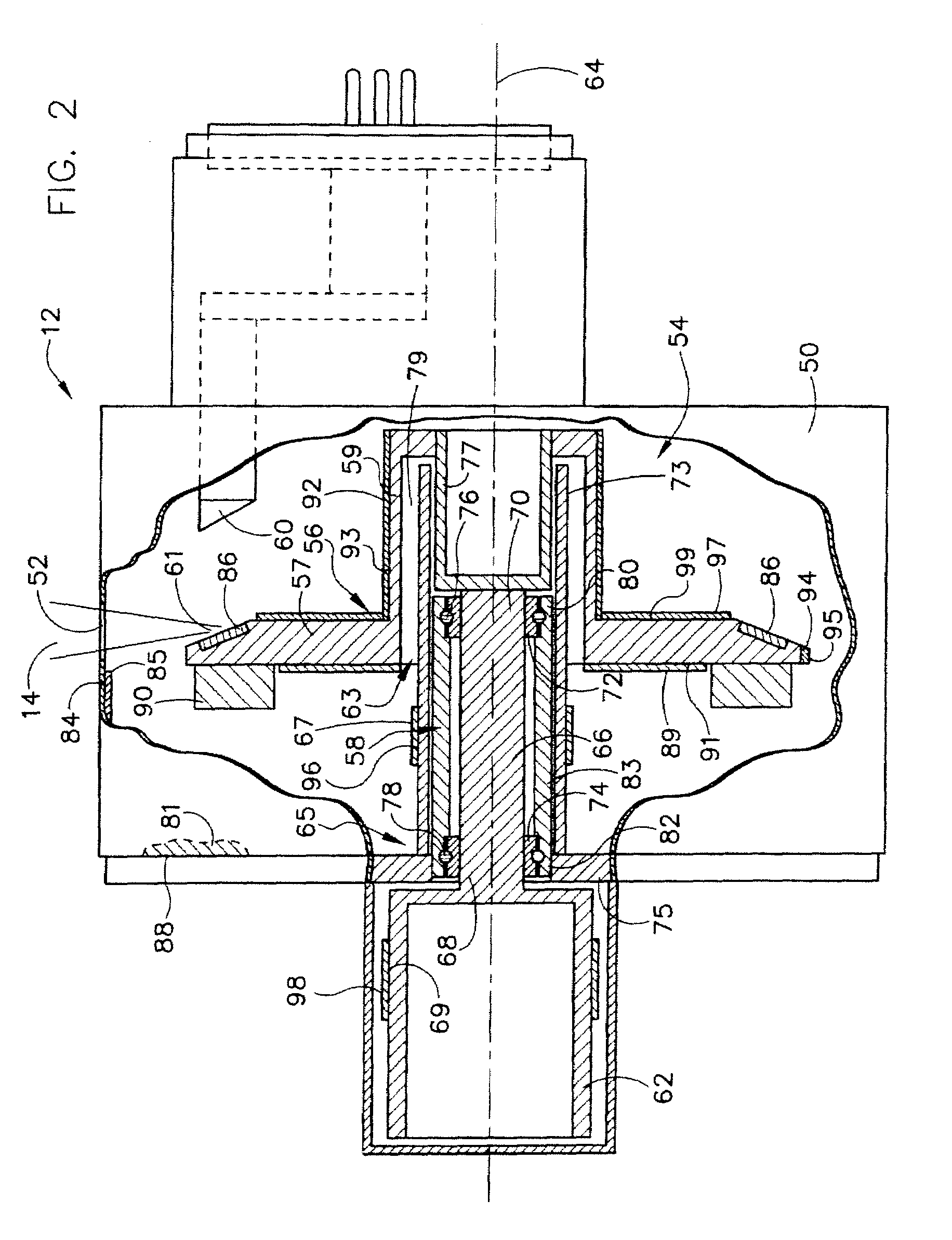
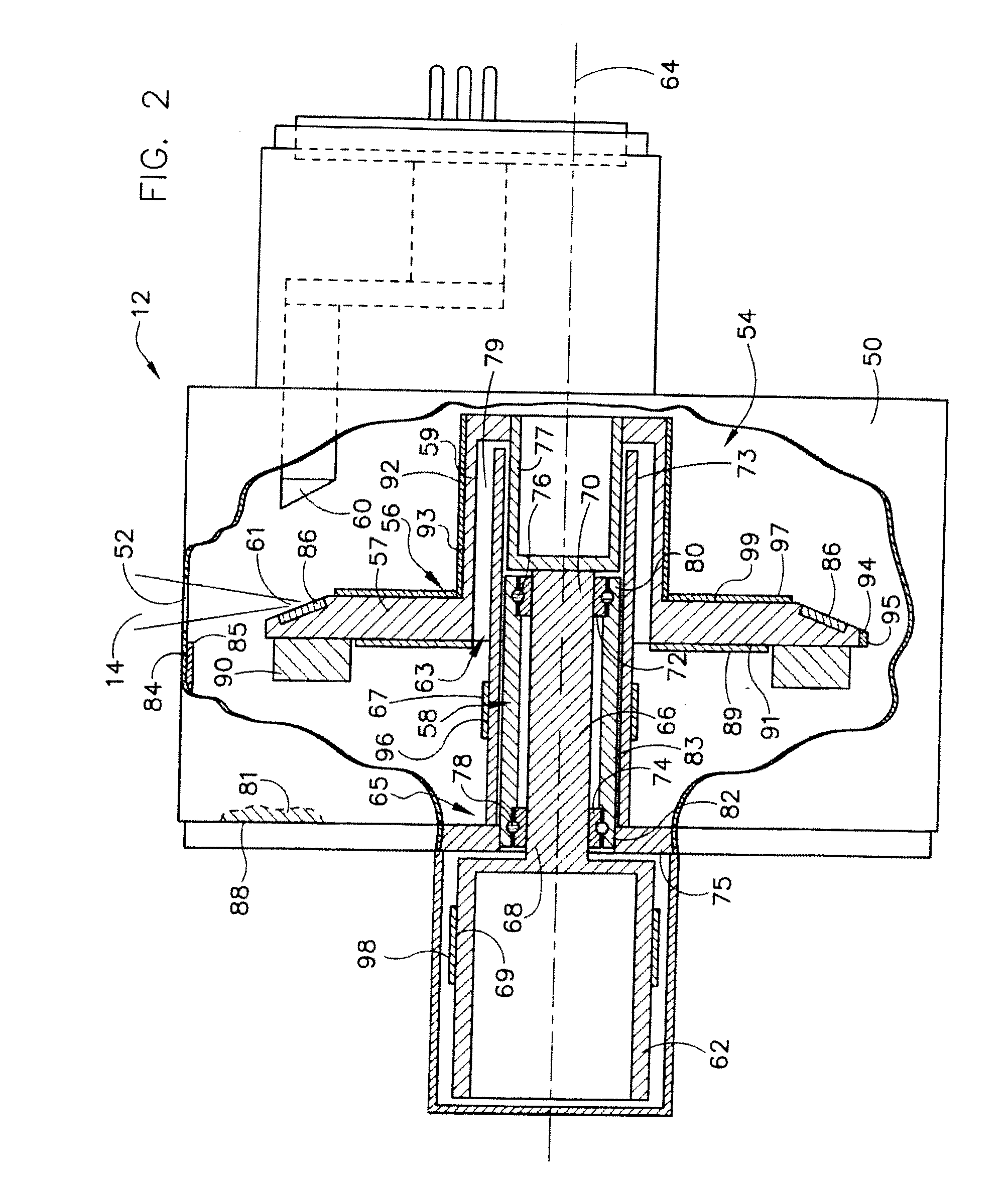
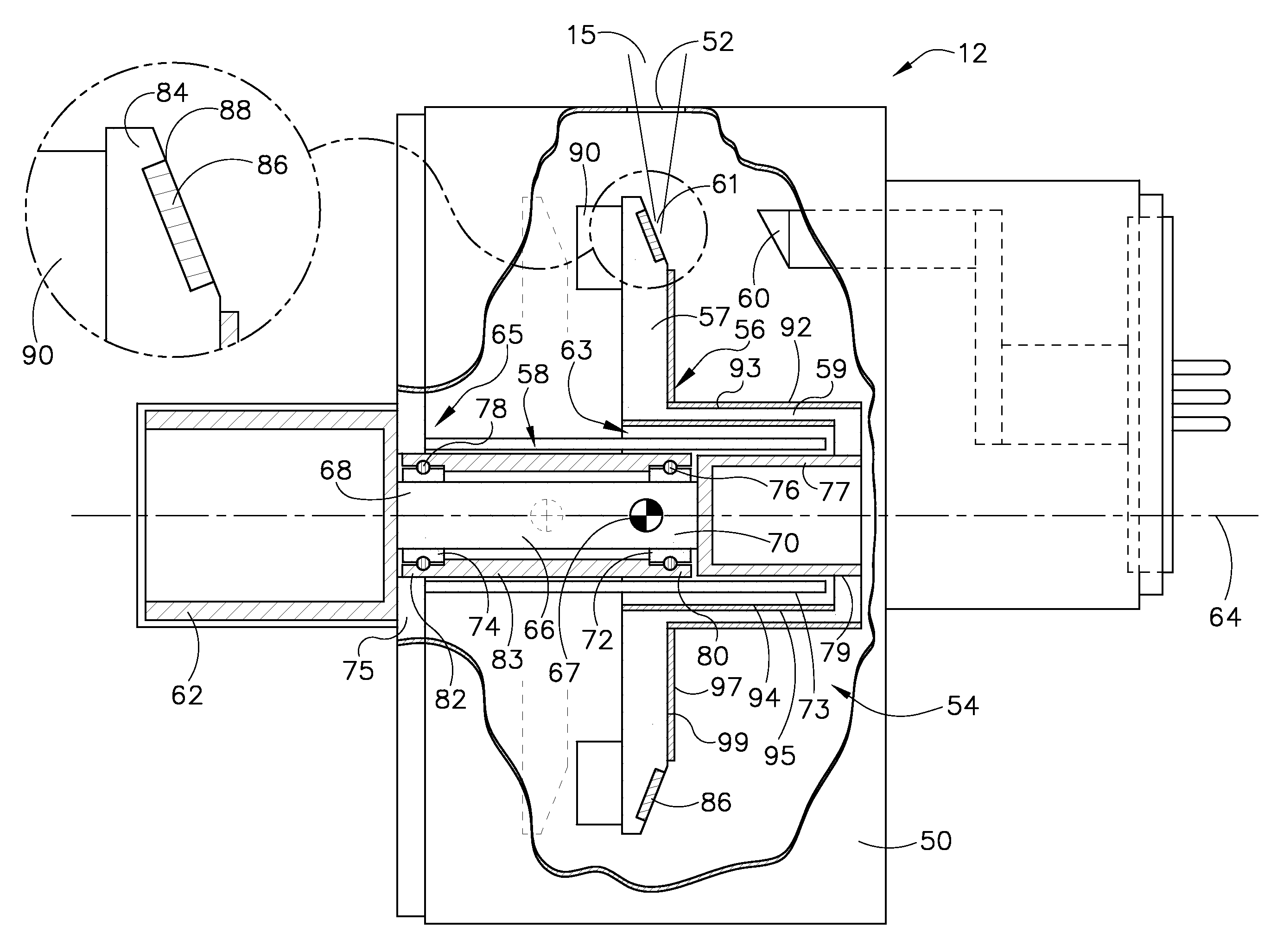
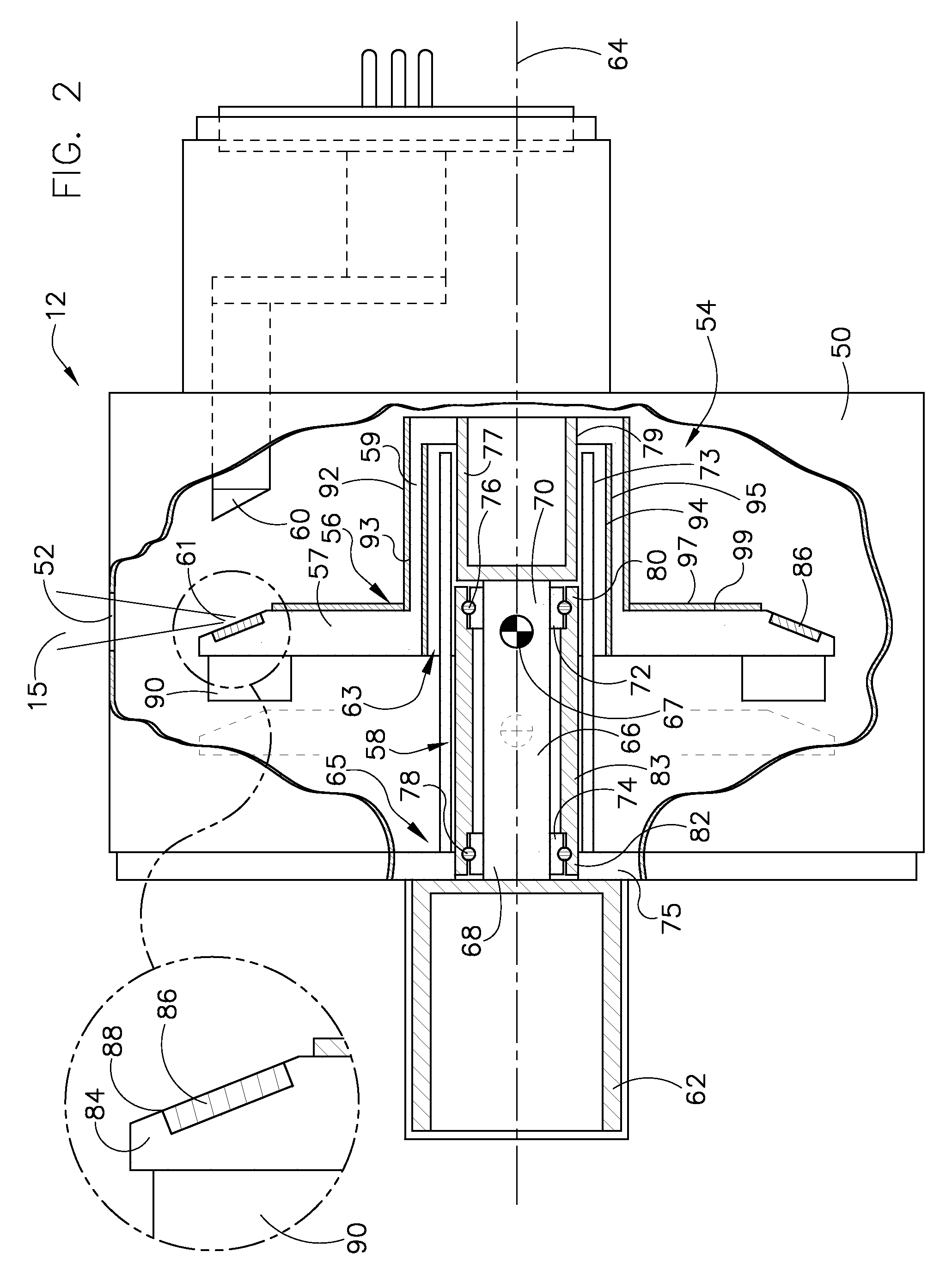
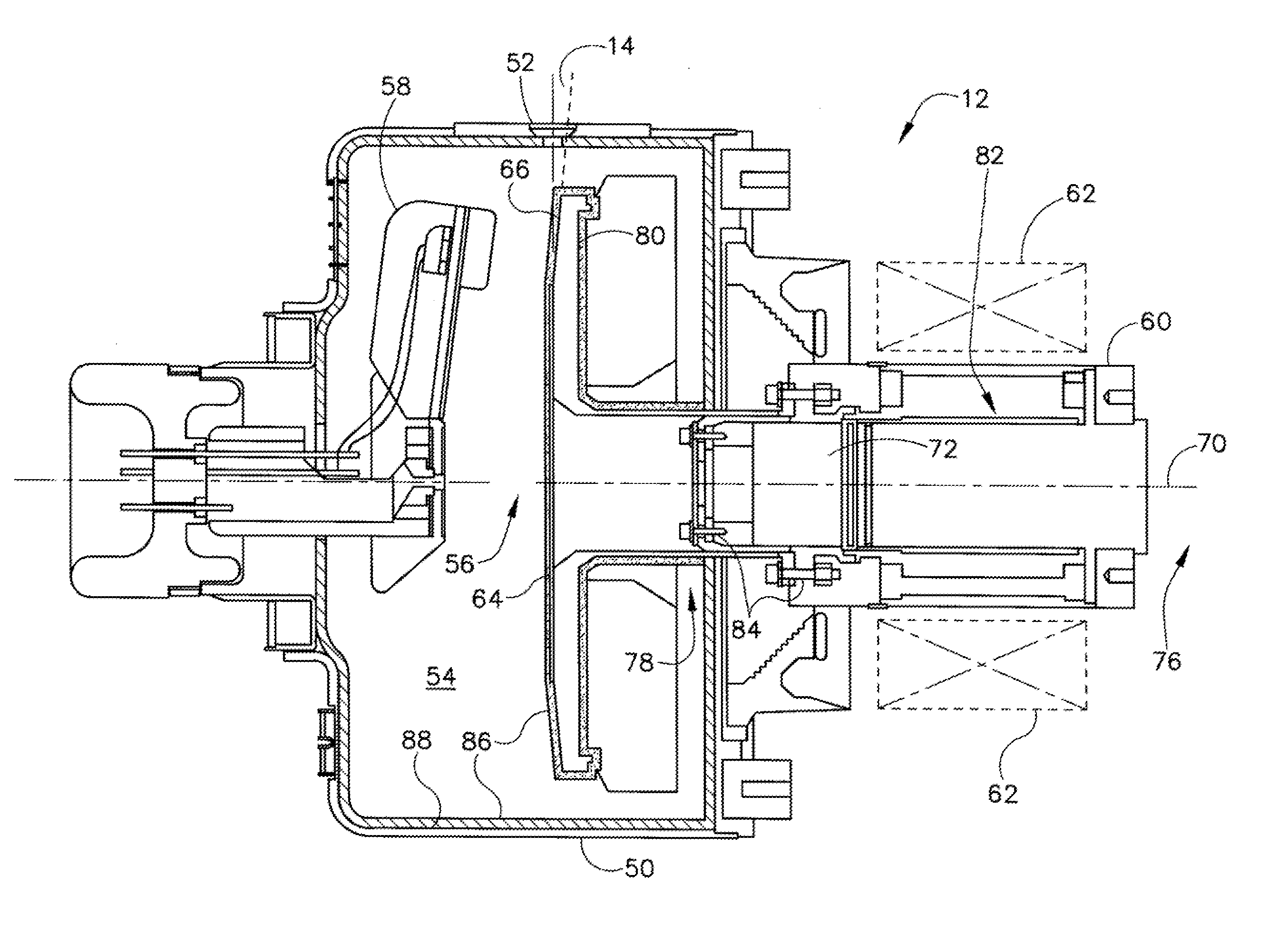
Structure for collecting scattered electrons
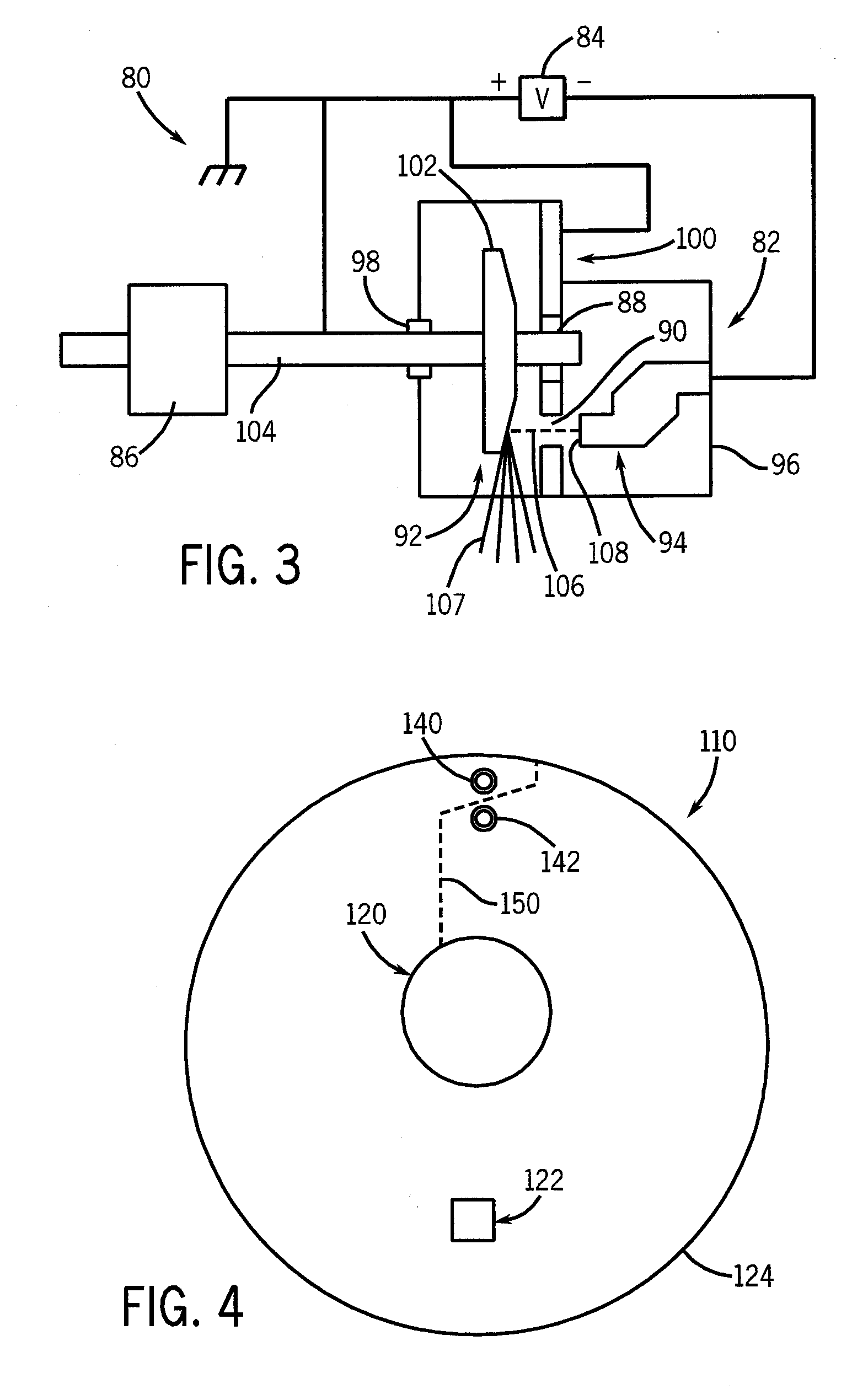
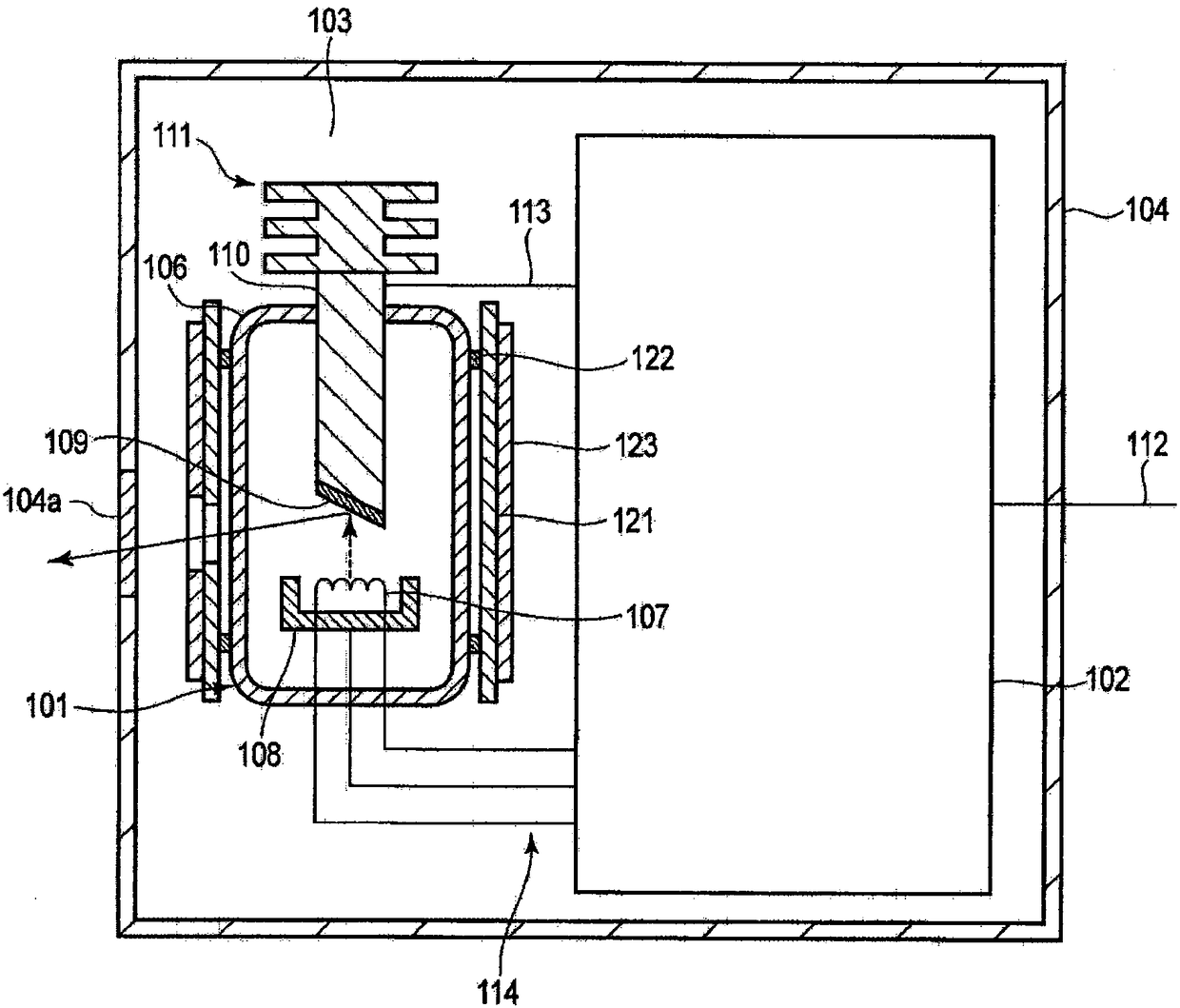
A structure for collecting scattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode and an electron-attracting anode is disclosed herein. The electron-collecting structure includes a two-sided first plate, a two-sided second plate, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is both electrically conductive and thermally emissive and is mountable within the vessel so that its first side at least partially faces the anode. The second plate is also thermally emissive and has a first side that is substantially conterminous with the second side of the first plate. Furthermore, the second plate additionally has an internal conduit for conveying a heat-absorbing fluid within. Both the fluid inlet and the fluid outlet are in fluid communication with the conduit in the second plate. During operation, the structure is able to attract scattered electrons and transfer thermal energy attributable to the electrons away from the structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Structure for collecting scattered electrons
InactiveUS7359486B2X-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerThermal energyThermionic emission
A structure for collecting scattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode and an electron-attracting anode is disclosed herein. The electron-collecting structure includes a two-sided first plate, a two-sided second plate, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is both electrically conductive and thermally emissive and is mountable within the vessel so that its first side at least partially faces the anode. The second plate is also thermally emissive and has a first side that is substantially conterminous with the second side of the first plate. Furthermore, the second plate additionally has an internal conduit for conveying a heat-absorbing fluid within. Both the fluid inlet and the fluid outlet are in fluid communication with the conduit in the second plate. During operation, the structure is able to attract scattered electrons and transfer thermal energy attributable to the electrons away from the structure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for increasing heat radiation from an x-ray tube target shaft
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
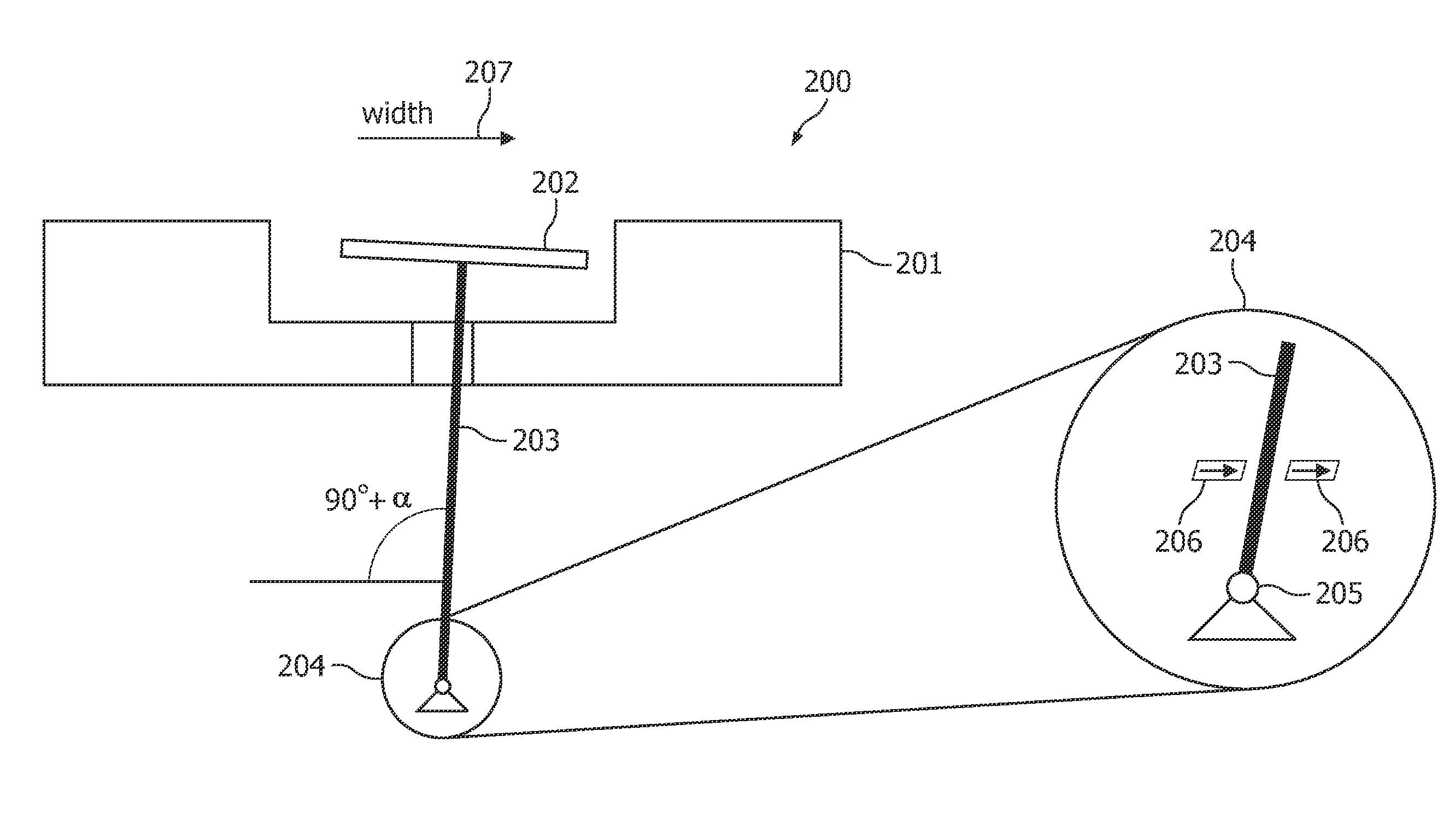
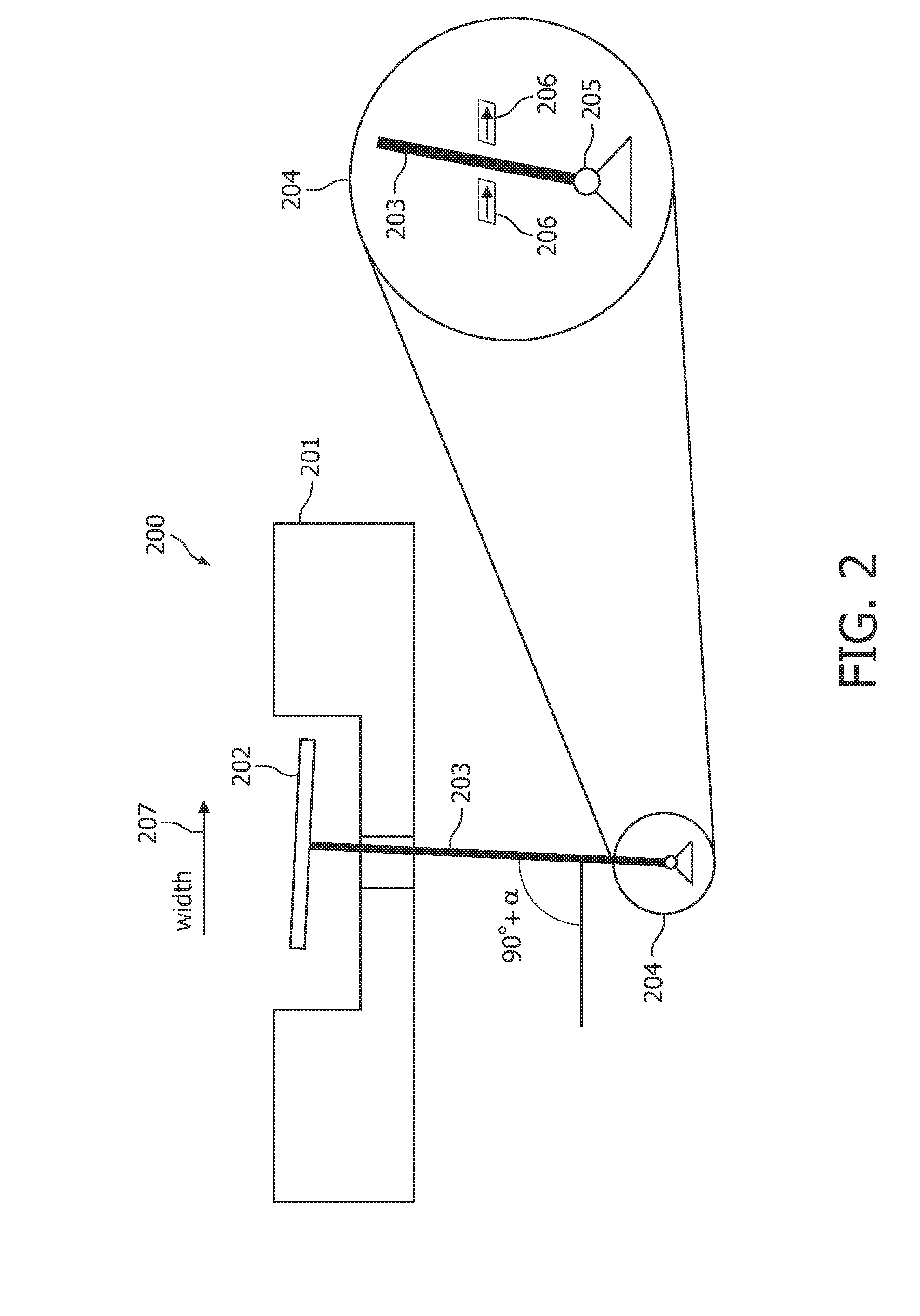
Tungsten oxide coated x-ray tube frame and anode assembly
ActiveUS20120189104A1High emissivityImprove heat transfer performanceX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesTarget surfaceX-ray
An x-ray tube having a coated x-ray tube frame inner surface and a coated anode assembly is provided. The x-ray tube includes an x-ray tube frame in which an anode assembly is disposed therein. A cathode assembly is also disposed within the x-ray tube frame that emits an electron beam to strike a target surface of the anode assembly and form x-rays. A plasma-sprayed tungsten oxide coating is formed on an inner surface of the x-ray tube frame and on the anode assembly to dissipate heat created by the electron beam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cryogenic x-ray source device
ActiveUS7027560B2Easy to controlControl DimensionsX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesWorking temperatureX-ray
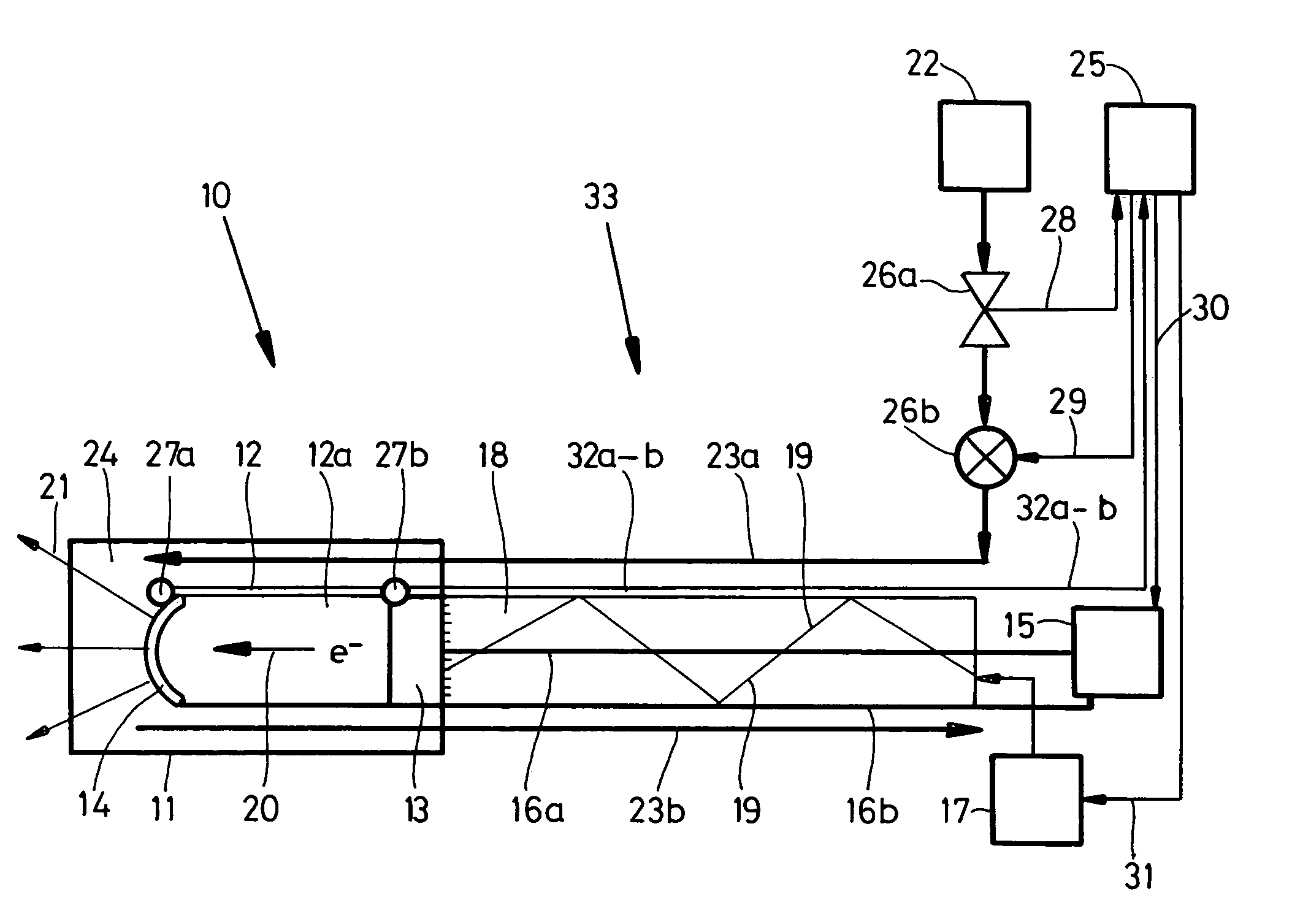
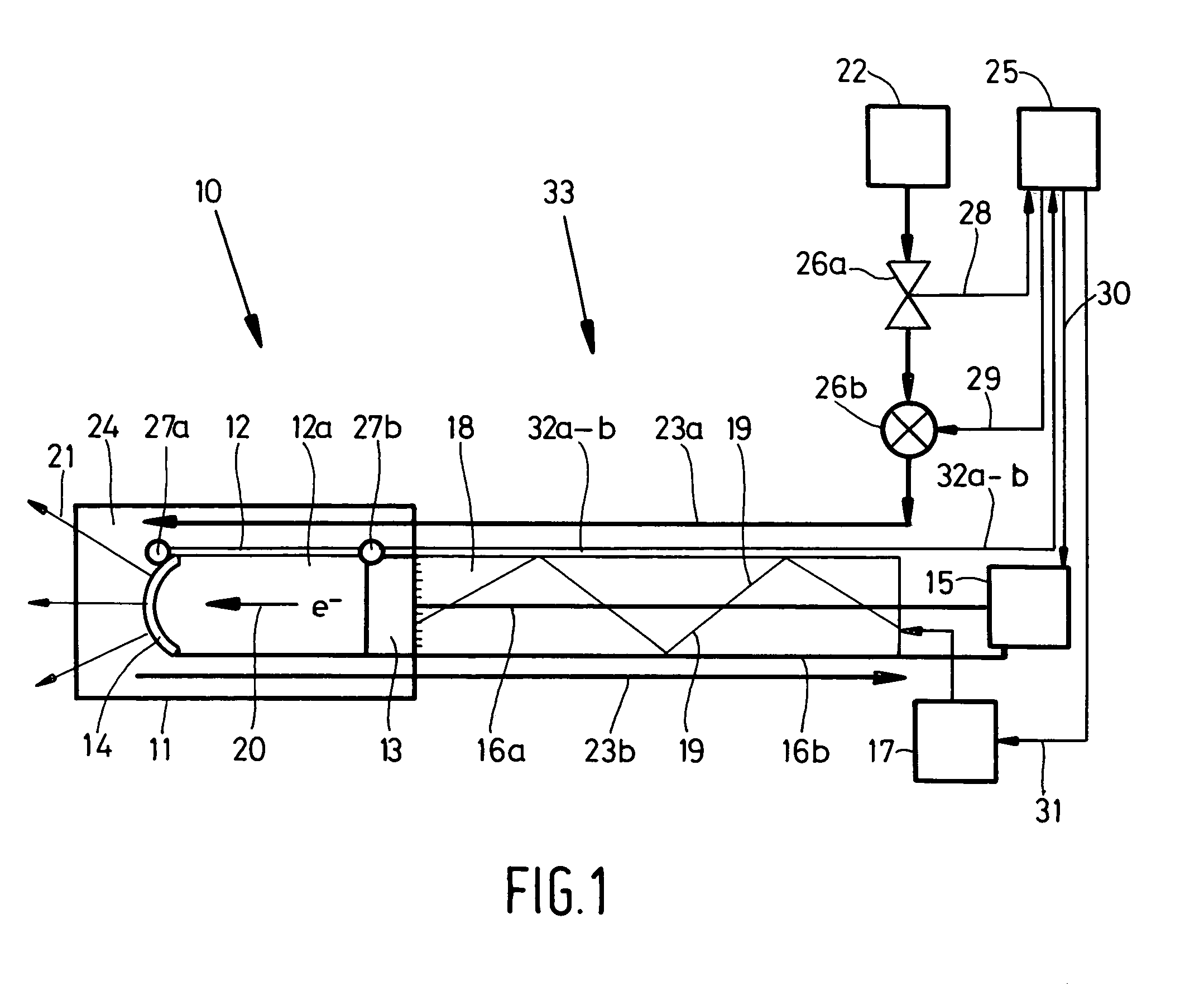
The invention relates to a miniature X-ray source device connected to a distal end of a guiding wire for insertion towards a desired location within an animal body for effecting radiation therapy, said X-ray source device at least comprising a vacuum tube accommodated in said housing containing a cathode and an anode spaced apart at some distance from each other; electron freeing means for freeing electrons from the cathode; electric field means for applying during use a high-voltage electric field between said cathode and said anode for accelerating said free electrons; said vacuum tube being at least partly transparent to X-ray radiation emitted by said anode, as well as cooling means for cooling at least said anode.It is an object to provide a miniature X-ray source device having further limited constructional dimensions and an improved control of the working temperature of at least the anode and hence the working conditions of the miniature X-ray source device.According to the invention the miniature X-ray source device is hereto characterised in that said cooling means are cryogenic cooling means. More in particular in a specific embodiment of said miniature X-ray source device said cooling means comprise at least one supply passageway for supplying pressurized gas towards said anode and at least one exhaust passageway for exhausting said pressurized gas from said anode, said supply passageway and said exhaust passageway being interconnected by means of an expansion chamber surrounding at least partly said anode.
Owner:NUCLETRON OPERATIONS
X-ray anode focal track region
A focal track region of an x-ray anode in an example is electrochemically etched. In a further example, an x-ray anode comprises a thermally-compliant focal track region for impingement of electrons from an x-ray cathode to create an x-ray source. The thermally-compliant focal track region comprises a pattern of discrete relative expanses and gaps.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computerized tomography (CT) imaging system with monoblock X-ray tube assembly
ActiveUS20060251218A1Small sizeReduce weightMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesX-rayEngineering
A system for cooling an X-ray tube in a CT machine, wherein the X-ray tube is of the type comprising a rear cylindrical portion, a front cylindrical portion, an annular face formed at the intersection of the rear cylindrical portion and the front cylindrical portion, and an emitter opening formed in the front cylindrical portion for emitting X-rays from the X-ray tube, the system comprising: a heat sink for drawing heat away from the X-ray tube, the heat sink comprising an annular body having an axial opening, and a window extending radially through the annular body, the heat sink being configured to receive the front cylindrical portion of the X-ray tube within the axial opening of the heat sink, with the emitter opening of the X-ray tube being aligned with the heat sink window; and a collimator connected to the heat sink and adapted to collimate the X-rays emitted by the X-ray tube and “focus” those X-rays on an X-ray detector, the collimator comprising a collimator opening, with the collimator being connected to the heat sink such that the collimator opening is aligned with the heat sink window and the emitter opening of the X-ray tube; the heat sink body being formed out of the same material as the emitter of the X-ray tube, such that the emitter opening of the X-ray tube will remain aligned with both the heat sink window and the collimator opening even when the emitter of the X-ray tube undergoes thermal expansion.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
X-ray tube, x-ray system, and method for generating x-rays
InactiveUS20100008470A1Increase power intensityReduced stabilityX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingSoft x rayX-ray
According to an exemplary embodiment an x-ray tube comprises a cathode, rotable disc anode, and a focal spot modulating unit, wherein the cathode is adapted to emit an electron beam, and wherein the focal spot modulating unit is adapted to modulate the electron beam in such a way that an intensity distribution of the electron beam on a focal spot on the anode is asymmetric such that the intensity of the electron beam on the focal spot is higher at the front of the focal spot with respect to the rotation direction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
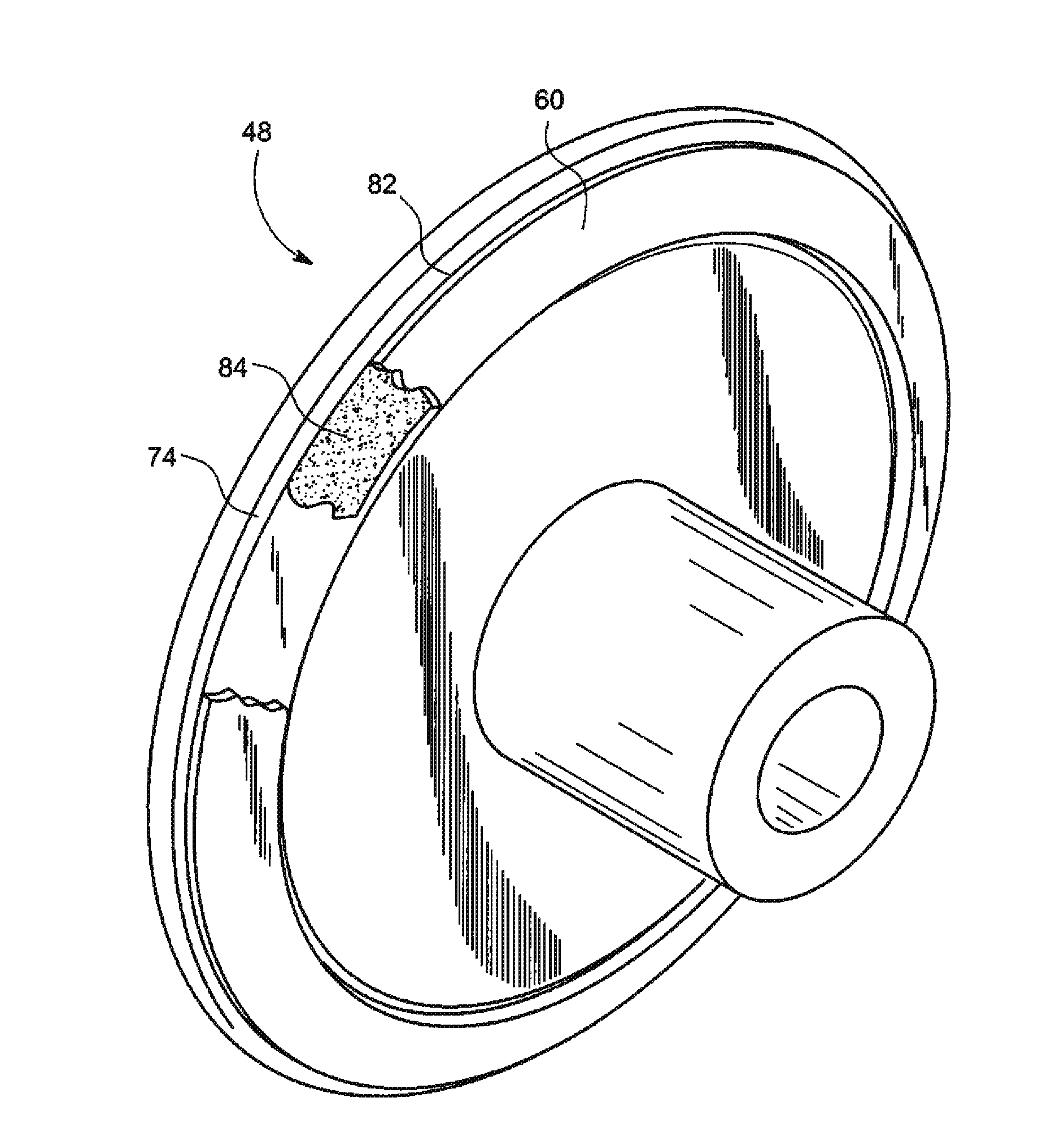
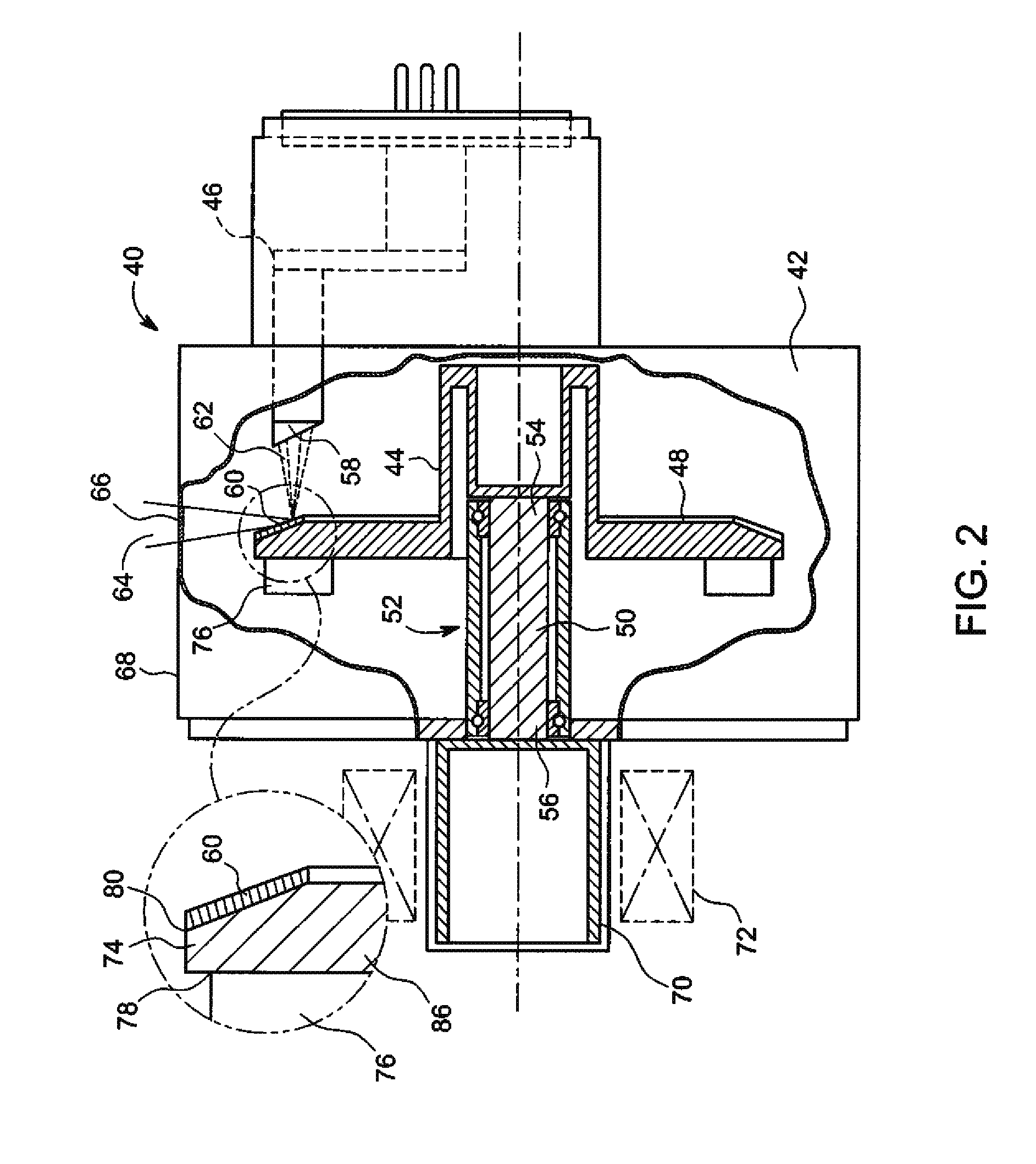
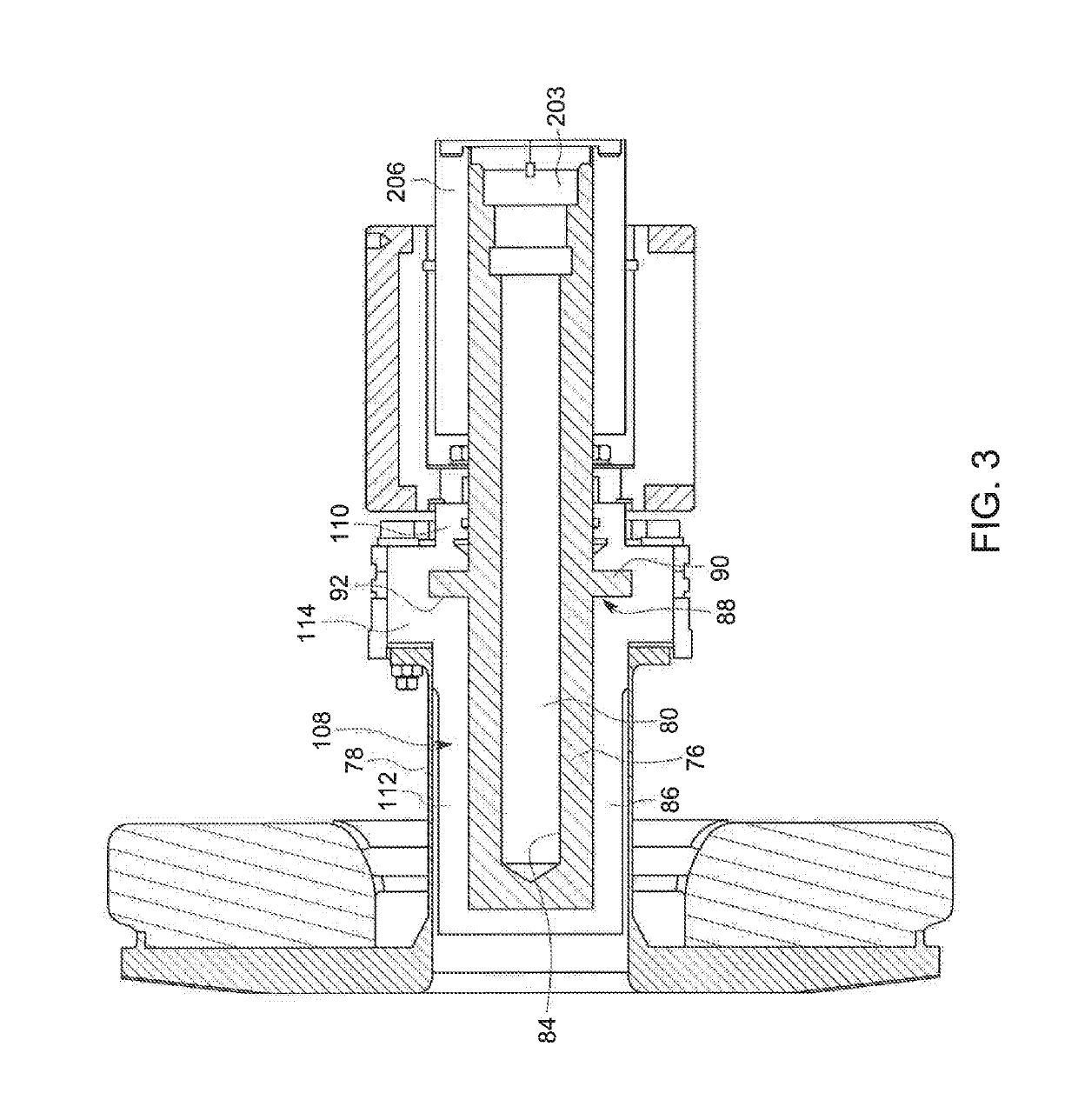
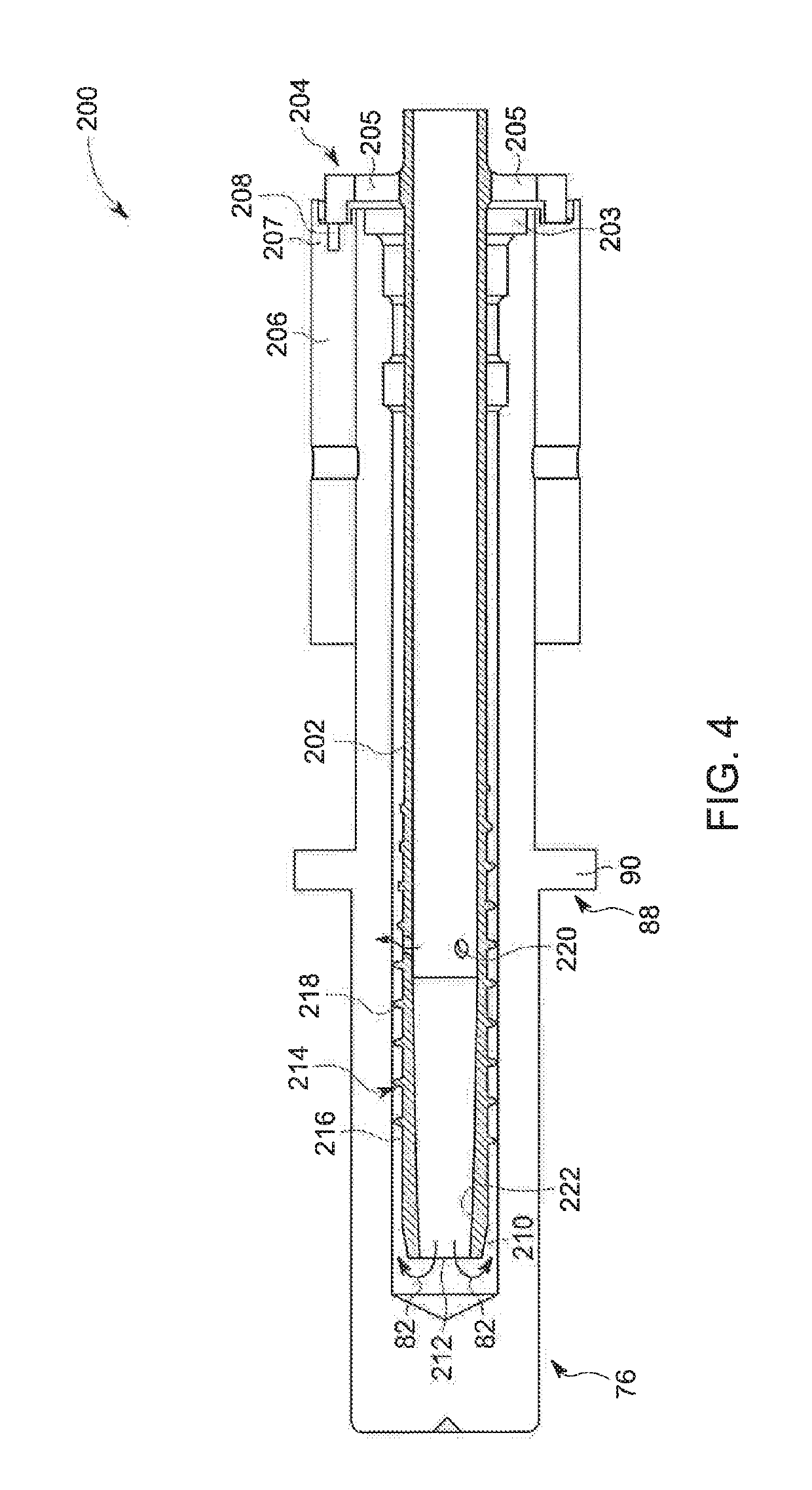
Rotating union for a liquid cooled rotating X-ray target
A rotating union for an X-ray target is provided. The rotating union for the X-ray target comprises a housing, a coolant-slinging device comprising a rotating shaft having an inner diameter and an outer diameter, a proximal end and a distal end, and a bore therein, one or more slingers coupled to a proximal end of the rotating shaft; a drain annulus coupled to the one or more slingers, wherein the one or more slingers are configured to direct a coolant to the drain annulus and the drain annulus is configured to direct the coolant through a primary coolant outlet; and a stationary tube having a first end and a second end, wherein at least a portion of the stationary tube is disposed within the bore of the rotating shaft.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
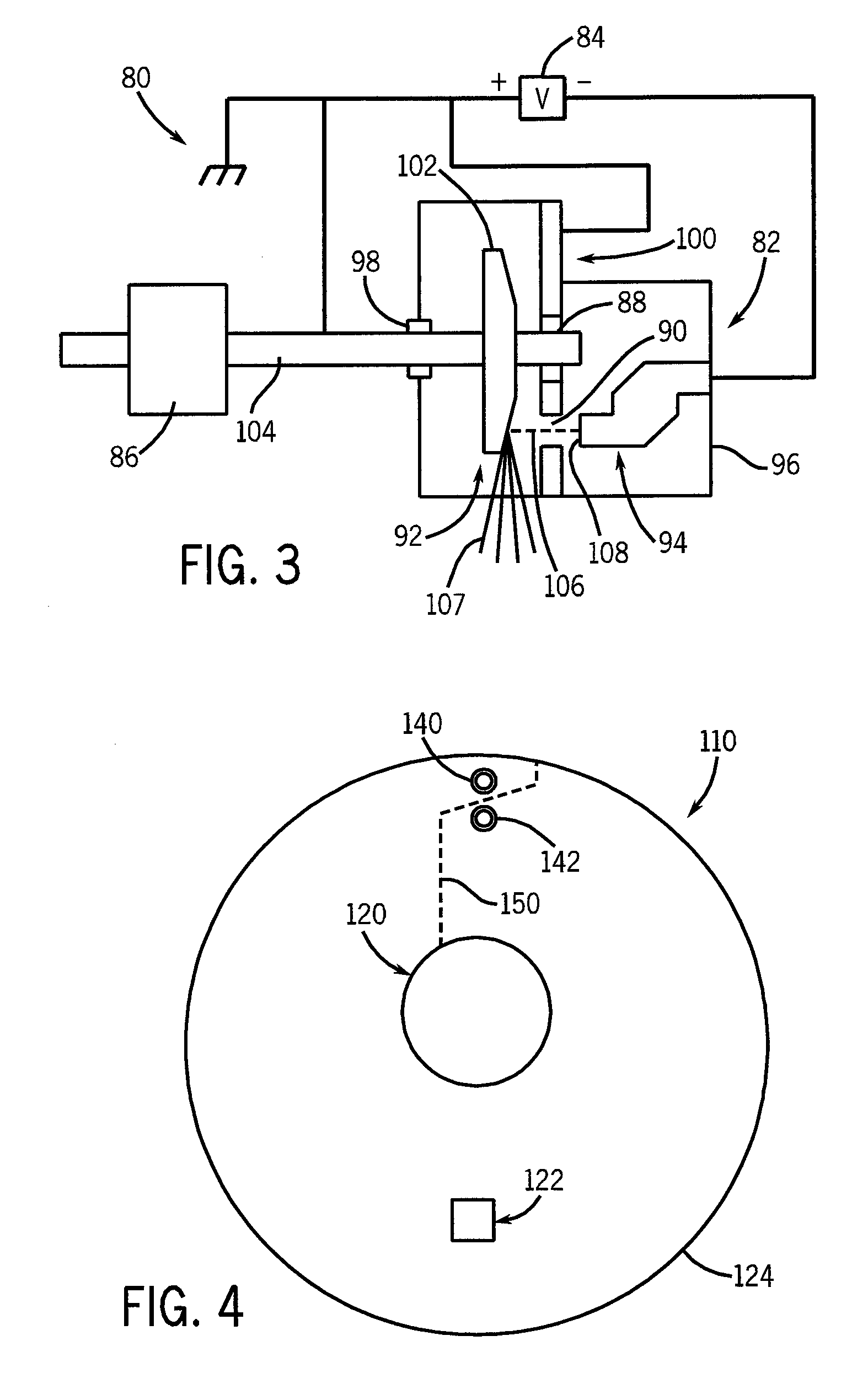
System and method for collecting backscattered electrons in an x-ray tube
A system and method for collecting backscattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode assembly and an electron-attracting anode assembly. The system and method comprises an electron collector assembly including a first plate, a second plate, an internal member, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is mounted within the vessel closest to the anode assembly. The second plate is mounted within the vessel closest to the cathode assembly. The internal member is positioned between the first plate and the second plate, and includes an internal conduit for conveying a heat absorbing cooling fluid therethrough.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for increasing heat radiation from an x-ray tube target shaft
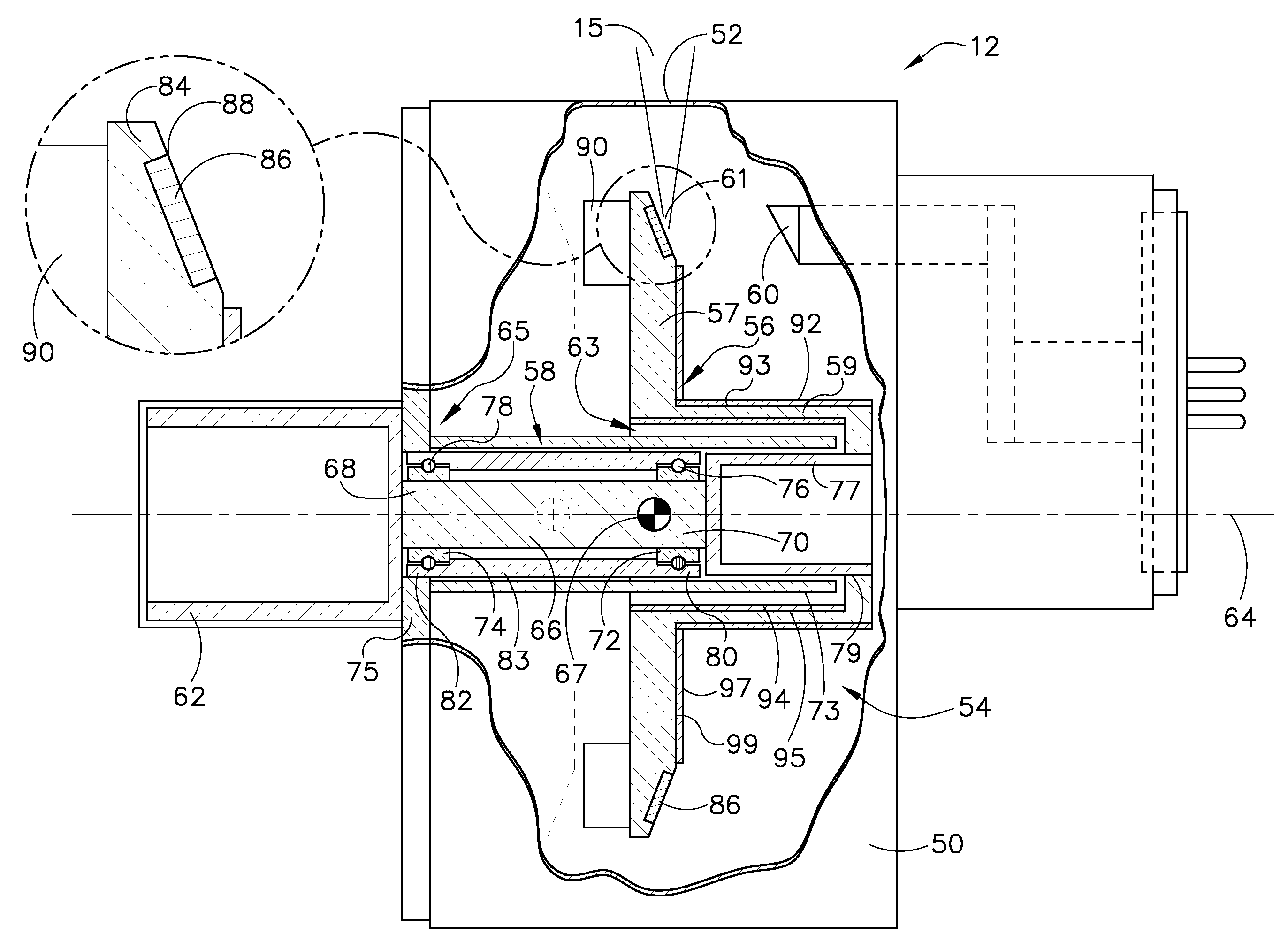
A target for generating x-rays includes a target substrate, a target shaft attached to the target substrate, and a radiation emissive coating applied to at least one of the target substrate and the target shaft, wherein a center-of-gravity of the target is positioned between a front bearing assembly and a rear bearing assembly of an x-ray tube.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
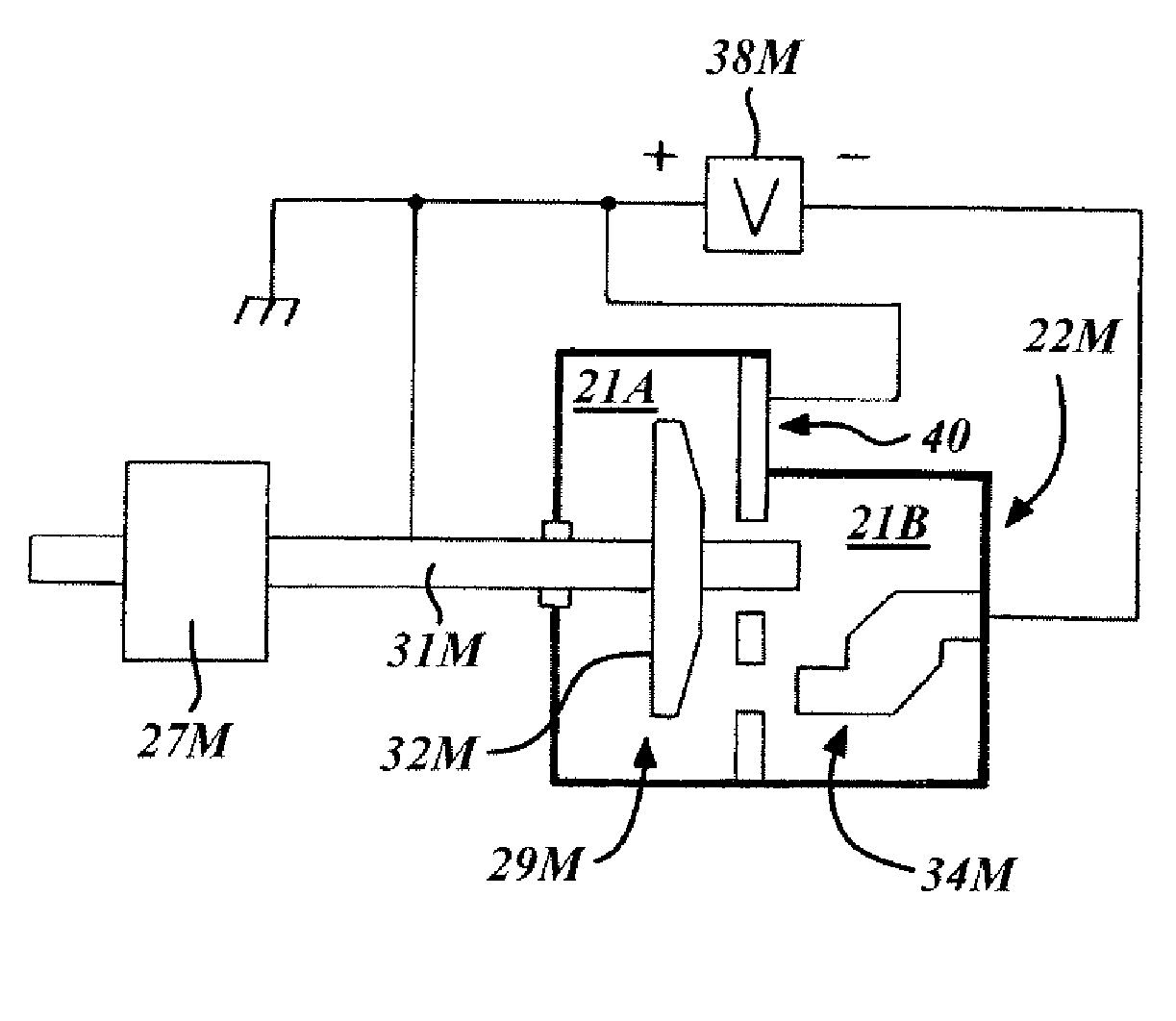
Cooled stationary anode for an x-ray tube
InactiveCN104520962ACycle optimizationImprove cooling effectX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesInorganic saltsHigh intensity
An X-ray tube 10 with an anode 30 comprising at least a rod shaped body with a front wall having target area 32 as target for an electron beam 27 on its frontal side provides a high intensity of X-ray radiation if the anode 30 has at least one cavity extending to the front wall, the cavity having a coating 50 of at least one inorganic salt.
Owner:QUANTUM TECH DEUT
System And Method For Multi-Source X-Ray-Based Imaging
ActiveUS20160056008A1Overcomes drawbackHigh currentX-ray tube anode coolingComputerised tomographsX-rayVacuum chamber
An imaging module includes a plurality of cathodes and respective gates, each cathode configured to generate a separate beam of electrons directed across a vacuum chamber and each gate matched to at least one respective cathode to enable and disable each separate beam of electrons from being directed across the vacuum chamber. A target anode is fixed within the vacuum chamber and arranged to receive the separate beam of electrons from each of the plurality of cathodes and, therefrom, generate a beam of x-rays. A deflection system is arranged between the plurality of cathodes and the target anode to generate a variable magnetic field to control a path followed by each of the separate beams of electrons to the target anode.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cooling mechanism for high-brightness x-ray tube using phase change heat exchange
ActiveUS20160064176A1Increase brightnessExtended service lifeX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesGas phaseX-ray
A mechanism for cooling the anode of an x-ray tube using a phase change material to transfer heat away from the anode. The x-ray tube is joined to a sealed heat exchange chamber which contains a liquid metal as a liquid to vapor phase change material (L-V PCM). The back side of the anode is exposed to an interior of the heat exchange chamber, and a jet sprayer inside the heat exchange chamber sprays a liquid of the metal onto the back side of the heated anode. The L-C PCM evaporates on that surface to carry away the heat, and the vapor then condenses back into the liquid on the cool surfaces of the heat exchange chamber. The surfaces of the heat exchange chamber may be cooled by convection cooling. Optionally, pipes containing a circulating cooling fluid may be provide inside the heat exchange chamber.
Combined head and ray imaging device
ActiveCN108257837AUniform distribution of temperature gradientReduce temperature differenceX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesTemperature differenceEngineering
The invention discloses a combined head and a ray imaging device. The combined head comprises a casing, a ray tube, a pump and a tube, wherein the casing is provided with a sealed cavity, the ray tubeis arranged in the sealed cavity, the pump and the tube are arranged in the sealed cavity, the pump is arranged at one side away from the positive pole of the ray tube, one end of the tube is connected with an outlet of the pump while the other end thereof extends to the position near the positive pole of the ray tube, or, the pump is arranged near the positive pole of the ray tube, one end of the tube is connected with an inlet of the pump while the other end thereof extends to the side way from the positive pole of the ray tube. An insulating medium at the position away from the positive pole can be pumped to the position near the positive pole, the insulating medium in the sealed cavity can be driven to form a cycle, and thus, temperature difference between the position of the positivepole and other positions can be reduced greatly, and temperature graded distribution of the insulating medium in the sealed cavity can be more uniform.
Owner:SUZHOU POWERSITE ELECTRIC CO LTD
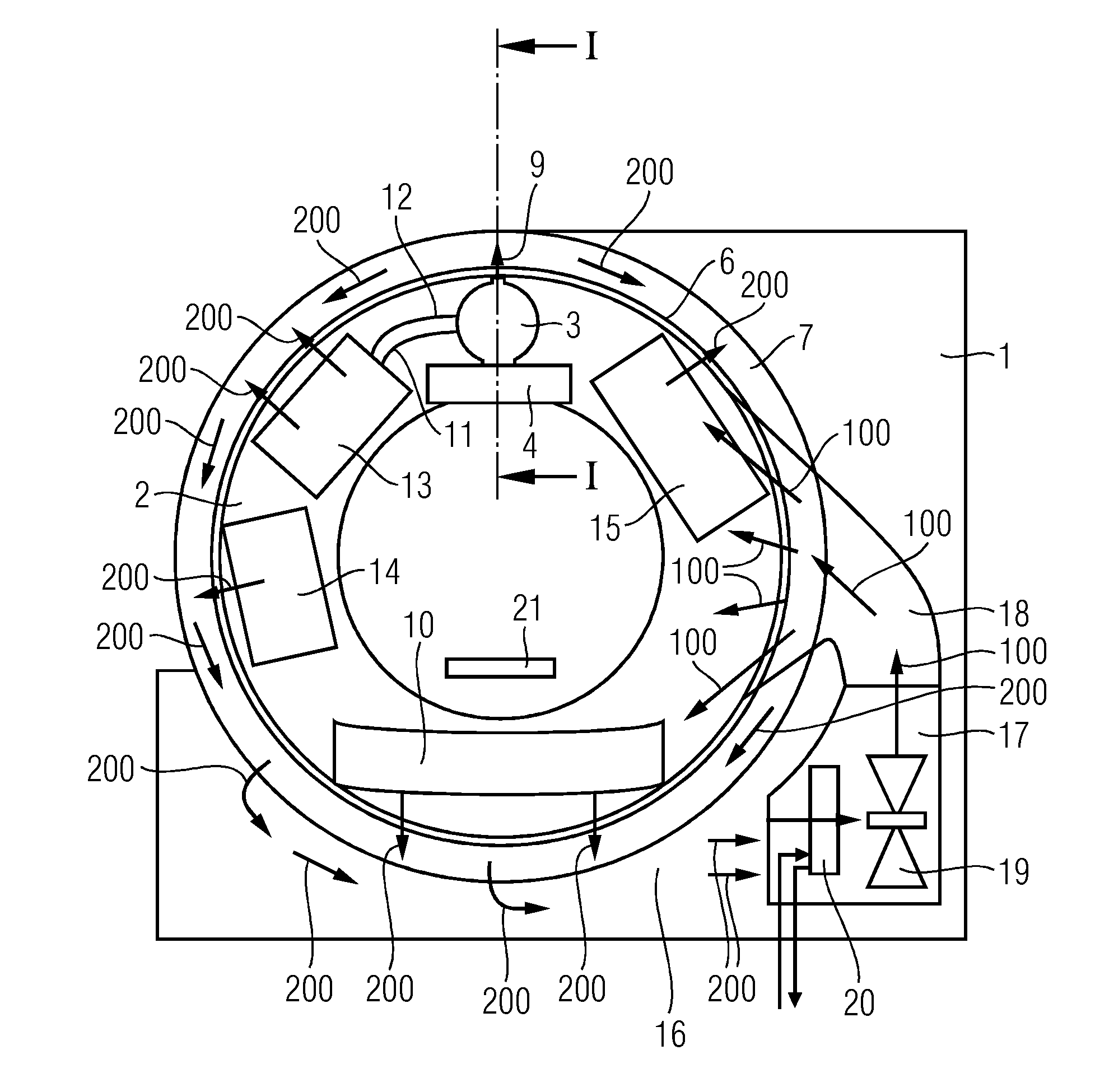
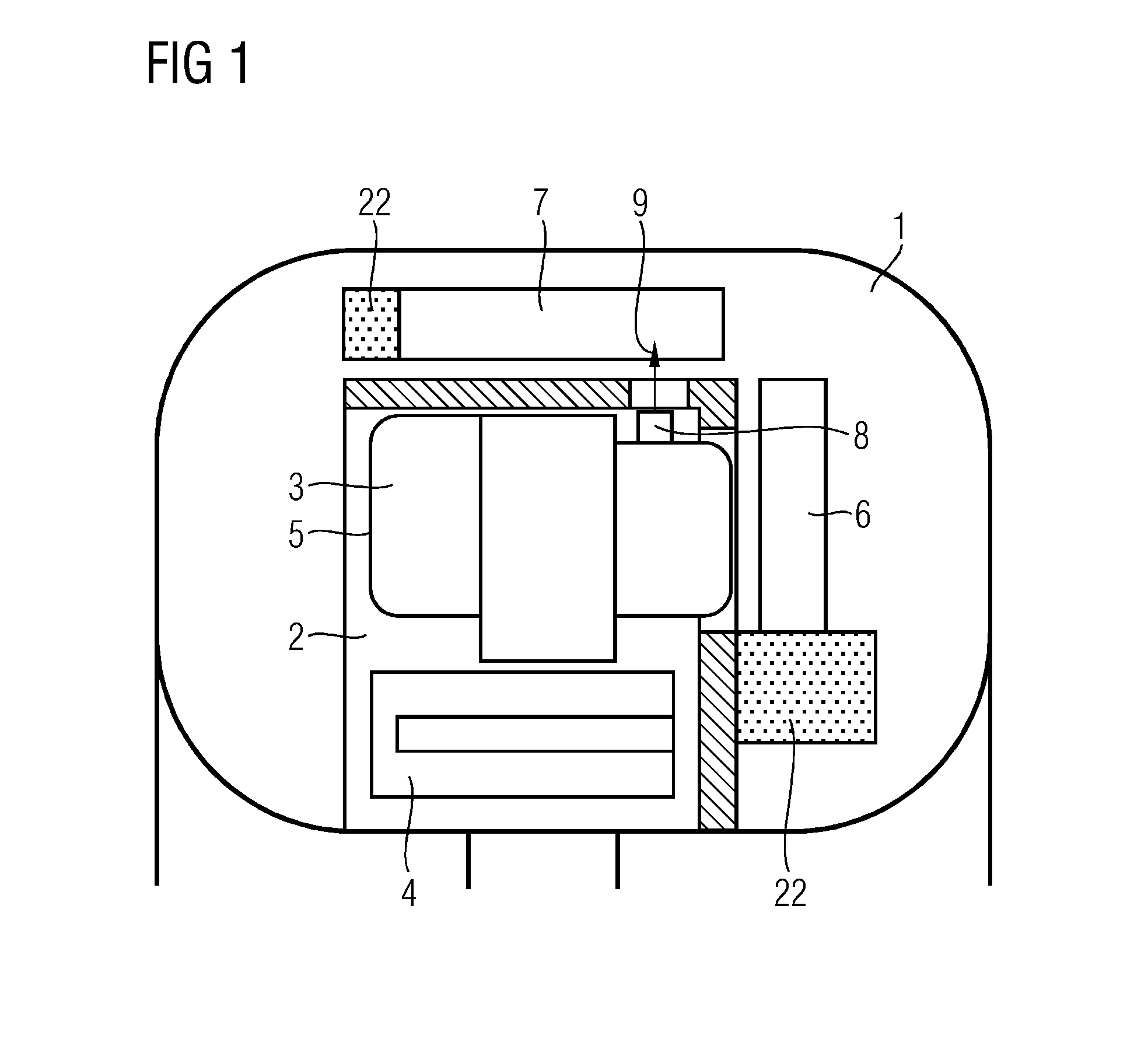
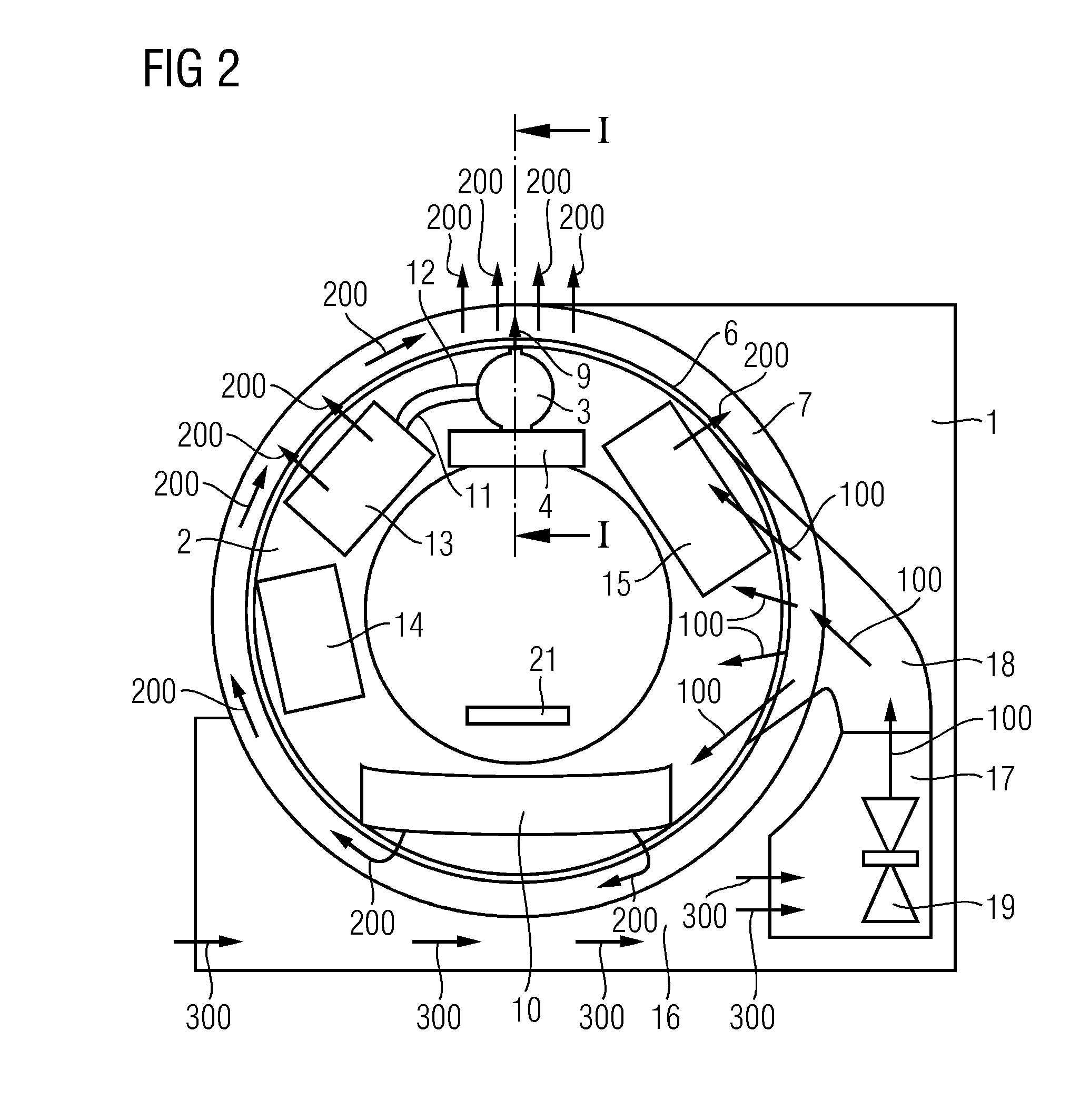
CT system
ActiveCN104939855AWill not be damagedSimple designMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesEngineeringCooling fluid
The embodiments relate to a CT system with a stationary part and a rotatable part, which is supported rotatably in the stationary part. At least one x-ray tube unit cooled by a cooling fluid, an x-ray detector lying opposite the x-ray tube unit, and a cooling device coupled in terms of fluid technology to the x-ray tube unit via a coolant circuit are disposed in the rotatable part. A cooling air channel, through which cooling air is able to be fed into the rotatable part, and an exhaust air channel, through which heated exhaust air is able to be taken away from the rotatable part, are disposed in the stationary part. In accordance with the embodiments, at least one overpressure relief valve is disposed in the coolant circuit, through which the cooling fluid is able to be conveyed away in the exhaust air channel.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for collecting backscattered electrons in an x-ray tube
A system and method for collecting backscattered electrons within a substantially evacuated vessel containing both an electron-emitting cathode assembly and an electron-attracting anode assembly. The system and method comprises an electron collector assembly including a first plate, a second plate, an internal member, a fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet. The first plate is mounted within the vessel closest to the anode assembly. The second plate is mounted within the vessel closest to the cathode assembly. The internal member is positioned between the first plate and the second plate, and includes an internal conduit for conveying a heat absorbing cooling fluid therethrough.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray tube target and method of repairing a damaged x-ray tube target
An x-ray tube target and method of repairing a damaged x-ray tube target. The x-ray tube target includes an original substrate and a portion of the original substrate that includes a new portion of a substrate and a new target track that is attached to a void in the original substrate. The method includes removal and replacement of damaged materials on used anode targets of x-ray tubes, thereby enabling recovery of used anode targets without the use of expensive and time consuming layer deposition methods. The method also avoids the high costs and long development cycles associated with known repair and refabrication methods for anode targets of x-ray tubes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cooling Spiral Groove Bearing Assembly
ActiveUS20190103244A1Increased turbulenceSpeed up heat exchangeX-ray tube anode coolingX-ray tube electrodesSpiral groove bearingEngineering
A liquid metal or spiral groove bearing structure for an x-ray tube and associated process for manufacturing the bearing structure is provided that includes a bearing shaft rotatably disposed in a bearing housing or shell. The shell includes a thrust seal engaged with a sleeve to maintain co-axiality for the rotating liquid metal seal formed in the shell about the shaft. The shaft has a bore for the introduction of a cooling fluid into the bearing assembly in which is disposed a cooling tube. The cooling tube includes turbulence-inducing features to increase the turbulence of the cooling fluid flowing through the cooling tube, consequently enhancing the heat exchange between the cooling fluid and the shaft. This maximizes the heat transfer from the shaft to the oil, allowing materials with lower thermal conductivities, such as non-refractory materials, to be used to form the bearing shaft and shell.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CT System
The embodiments relate to a CT system with a stationary part and a rotatable part, which is supported rotatably in the stationary part. At least one x-ray tube unit cooled by a cooling fluid, an x-ray detector lying opposite the x-ray tube unit, and a cooling device coupled in terms of fluid technology to the x-ray tube unit via a coolant circuit are disposed in the rotatable part. A cooling air channel, through which cooling air is able to be fed into the rotatable part, and an exhaust air channel, through which heated exhaust air is able to be taken away from the rotatable part, are disposed in the stationary part. In accordance with the embodiments, at least one overpressure relief valve is disposed in the coolant circuit, through which the cooling fluid is able to be conveyed away in the exhaust air channel.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com