Patents
Literature
94results about How to "Reliable mating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus improving item transactions with real-time controls and navigation
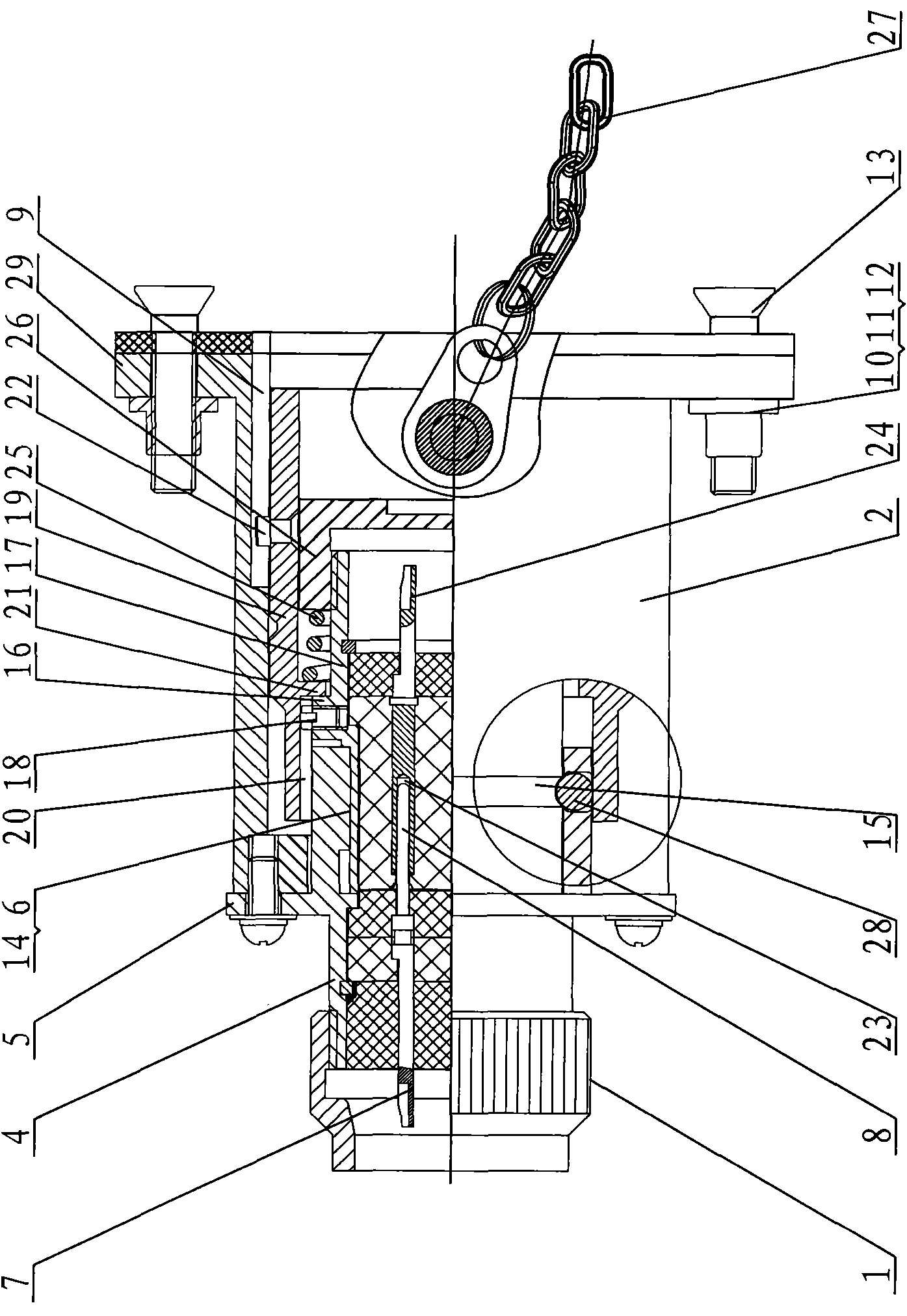
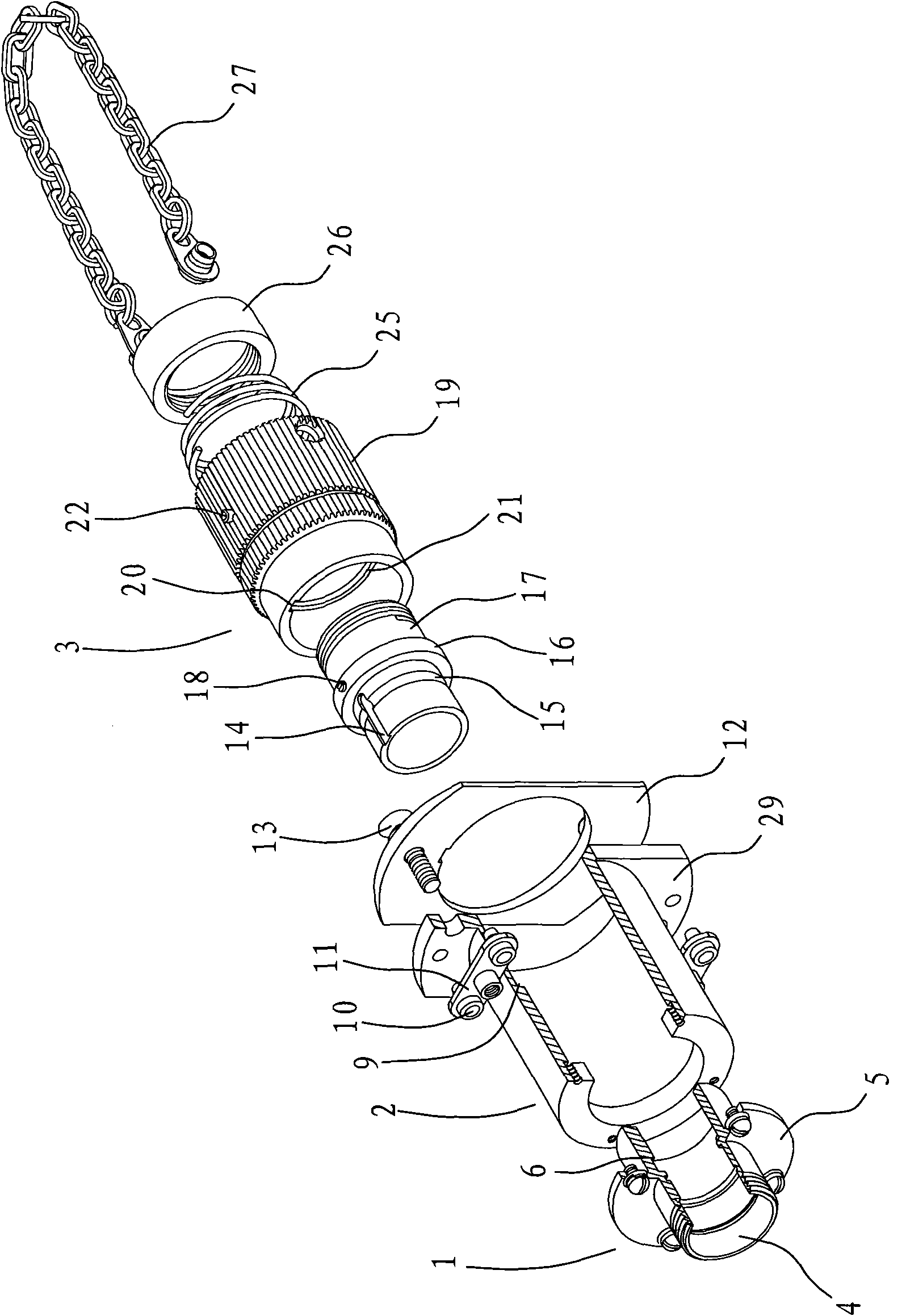
InactiveUS20120080517A1Reliable matingReliable engagementComplete banking machinesFinanceReal-time Control SystemPayment
Invention describes real-time control system increasing shopping efficiency, maintaining item quality, inventory, and directing customer transactions, requiring handling and processing of items only once. Invention controls access to items inside modules via card with unique embedded identification features. Invention stores customer transactions and entered shopping lists. Invention per customer selected shopping list and items availability, will in real-time navigate customer to complete required transactions within customer selected criteria. Invention controls card identification features and modules containing items. Invention based on card identification and item identification such as barcode information will store customer executed transactions, and will require customer to pay for completed transactions before leaving the store. Invention in real-time maintains inventory of items, controls environment surrounding items, and reports items exceeding shelf life limit preventing their transaction. Invention analyzes transactions executed by the card, correlates transactions to customer at payment module, stores behavior patterns for future optimizations of transactions.
Owner:BRAUNSTEIN ZACHARY L
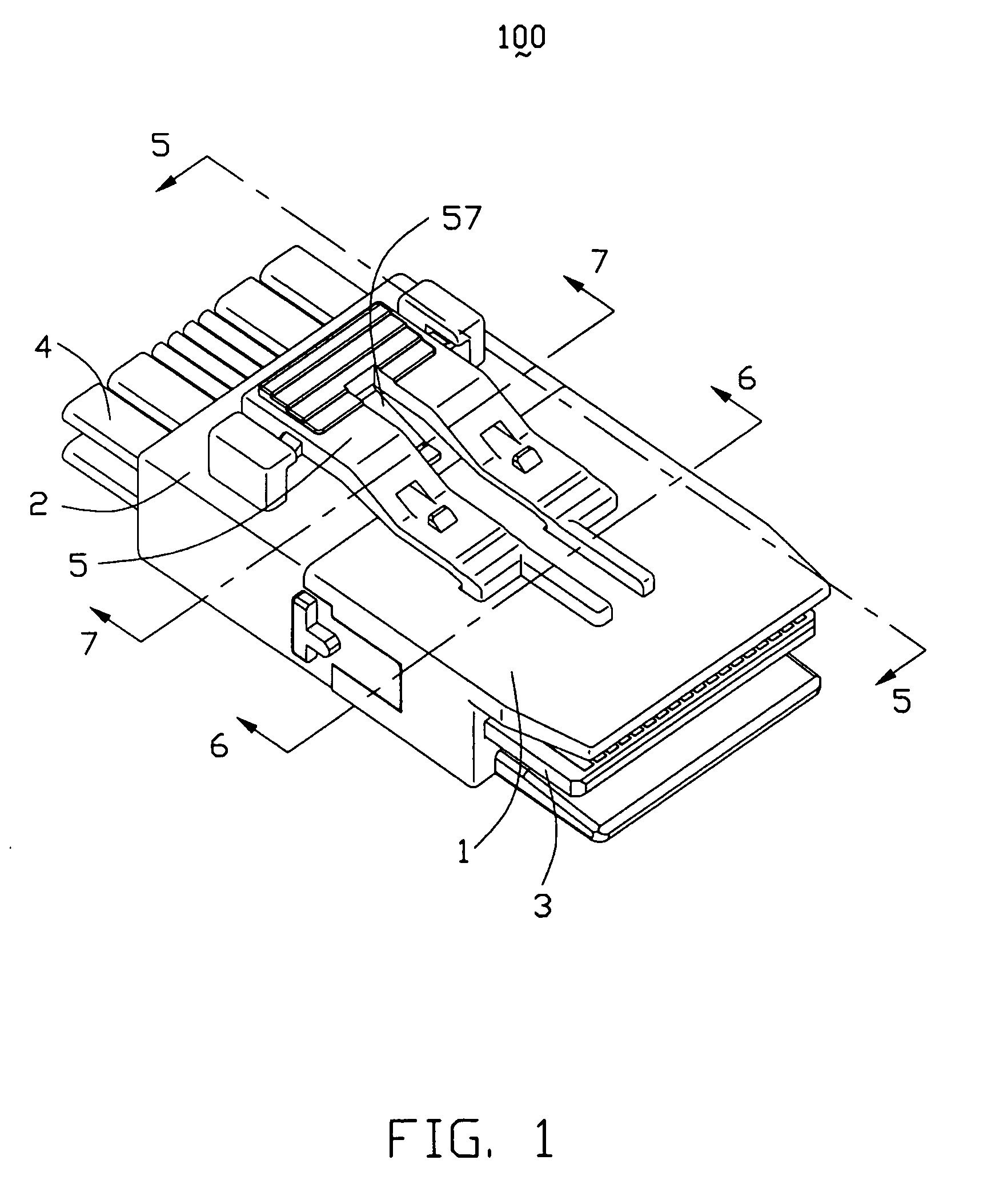
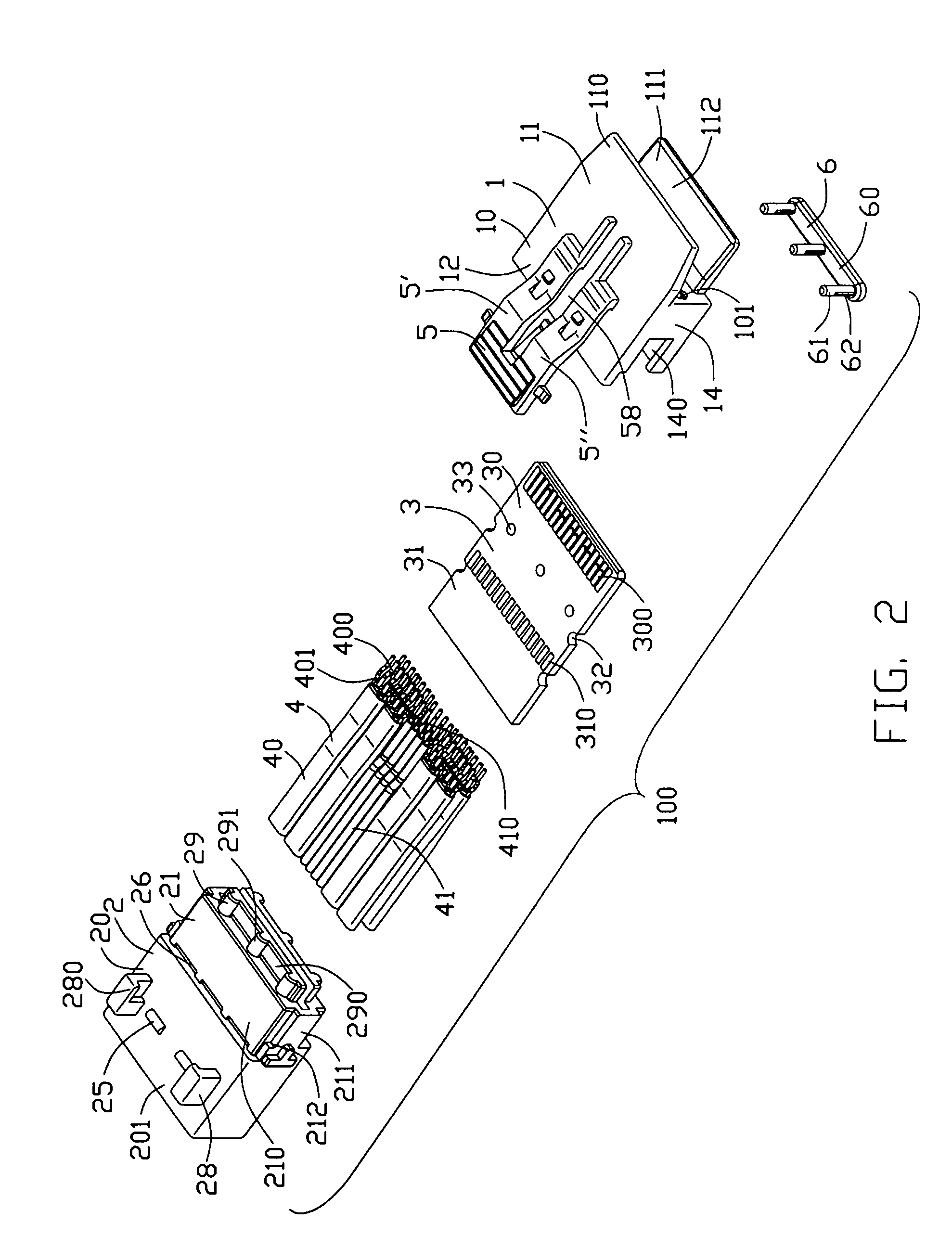
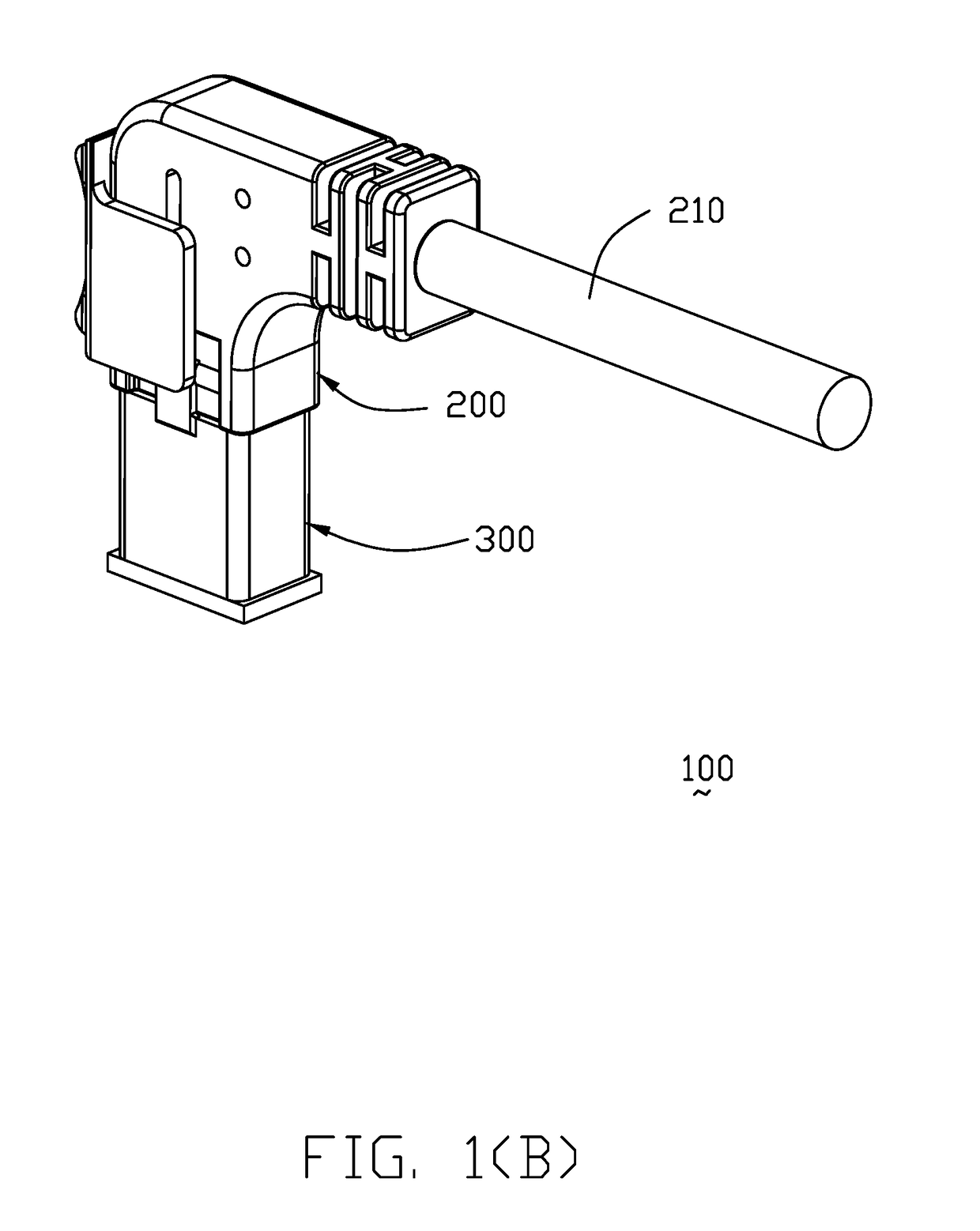
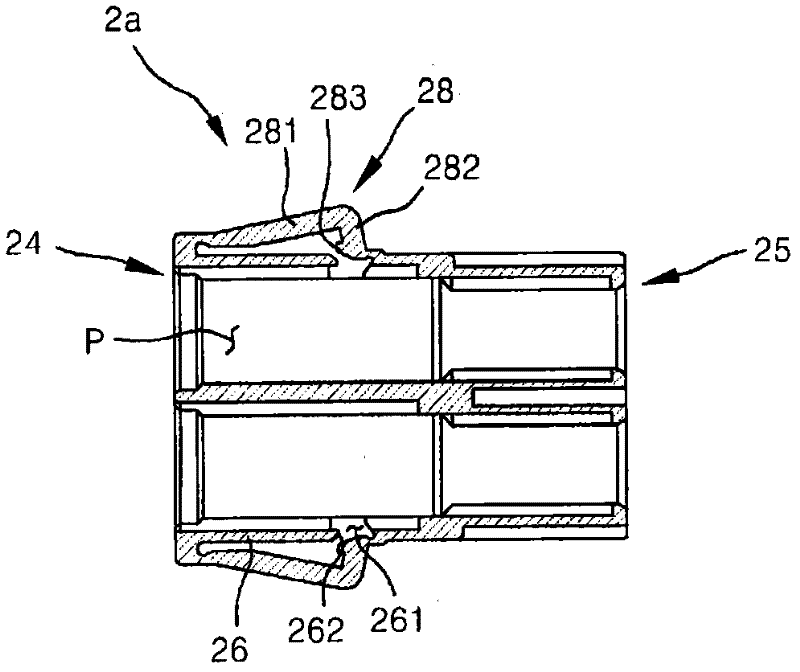
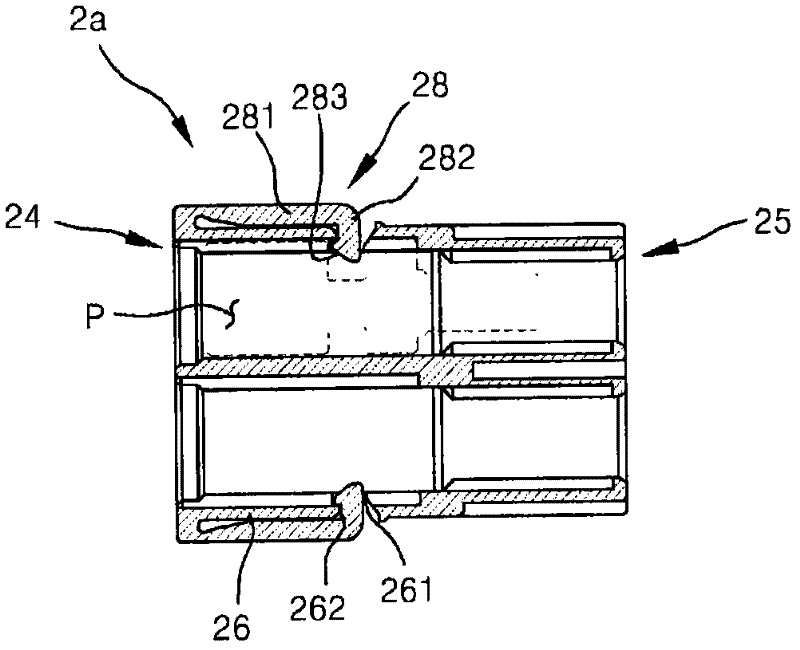
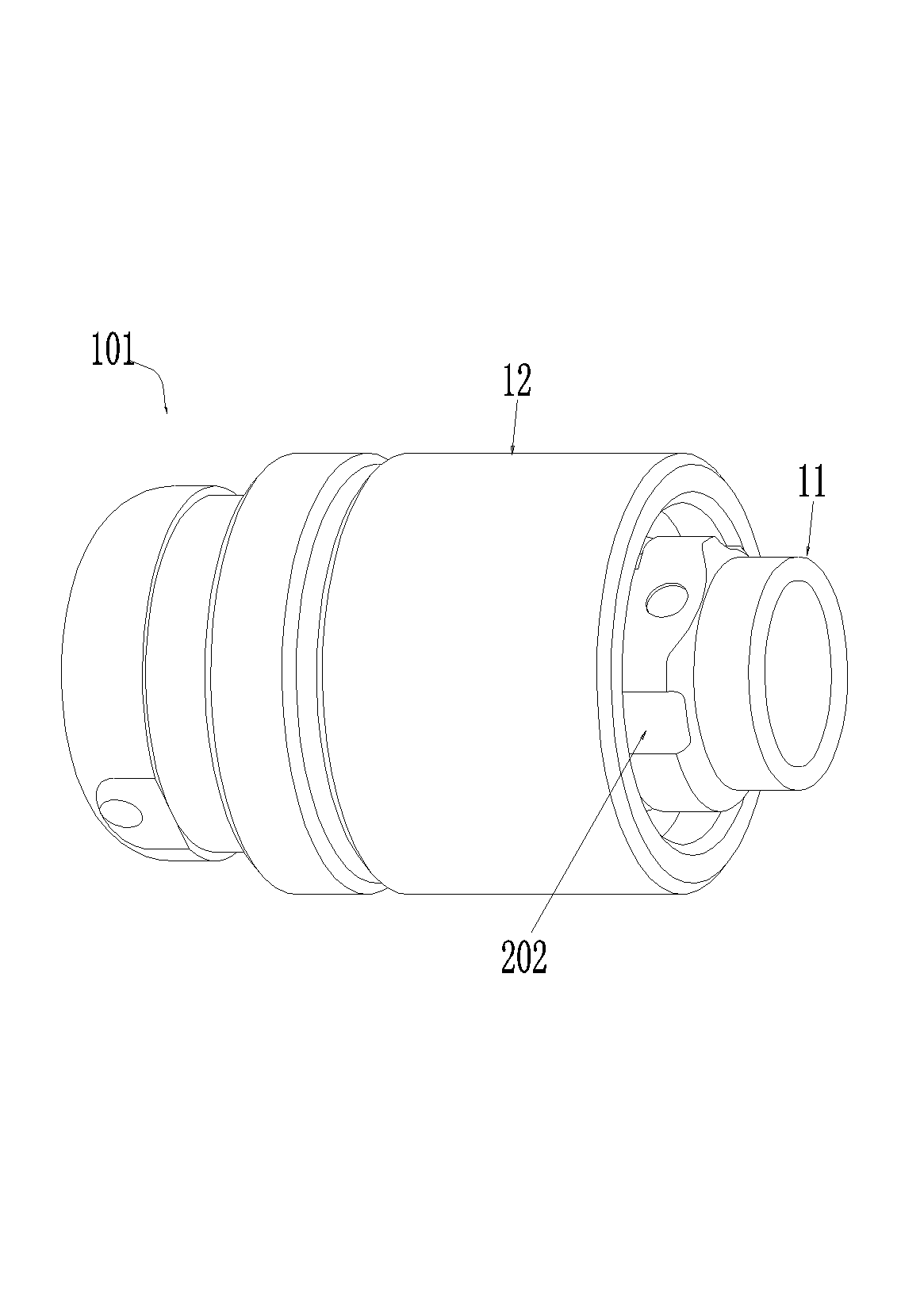
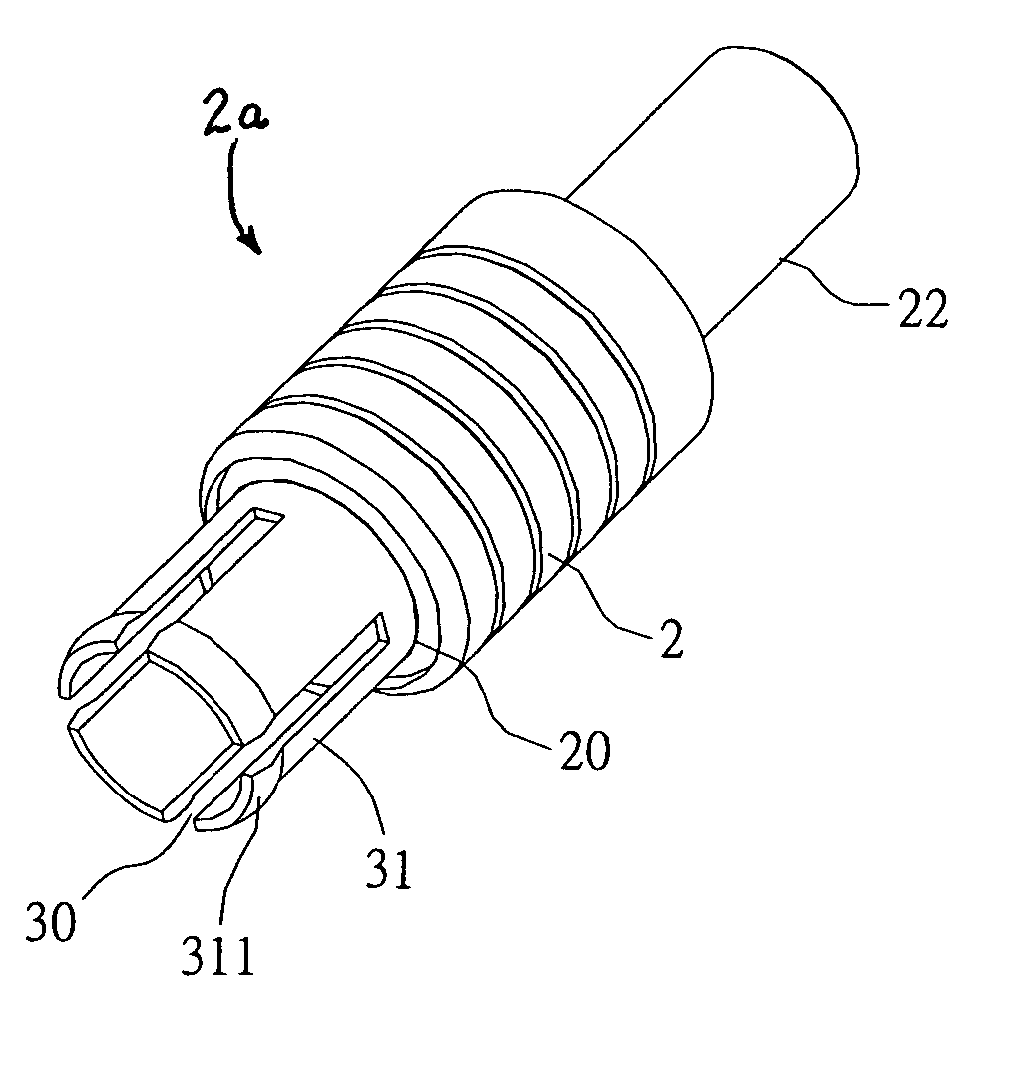
Cable connector assembly with unitary latch
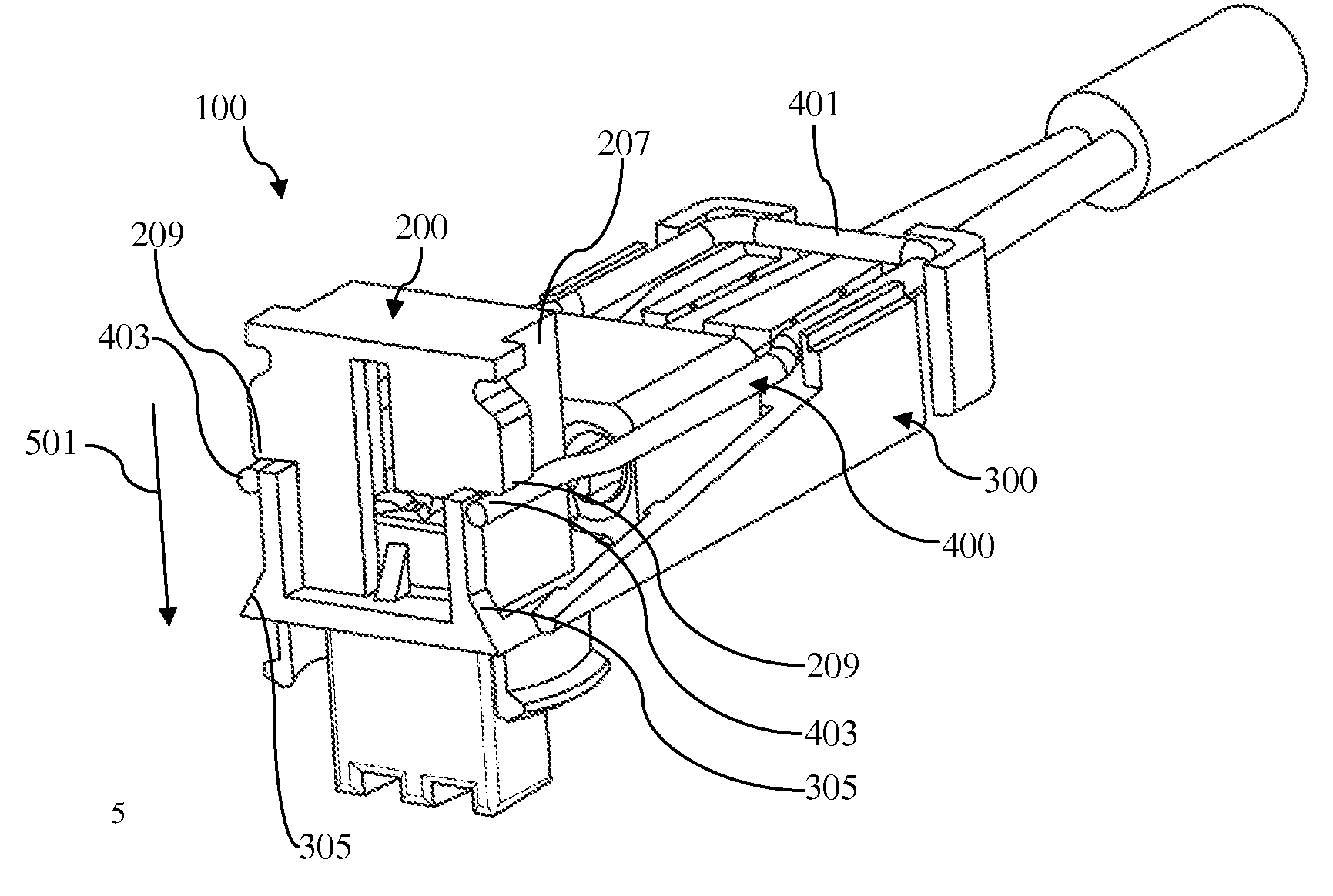
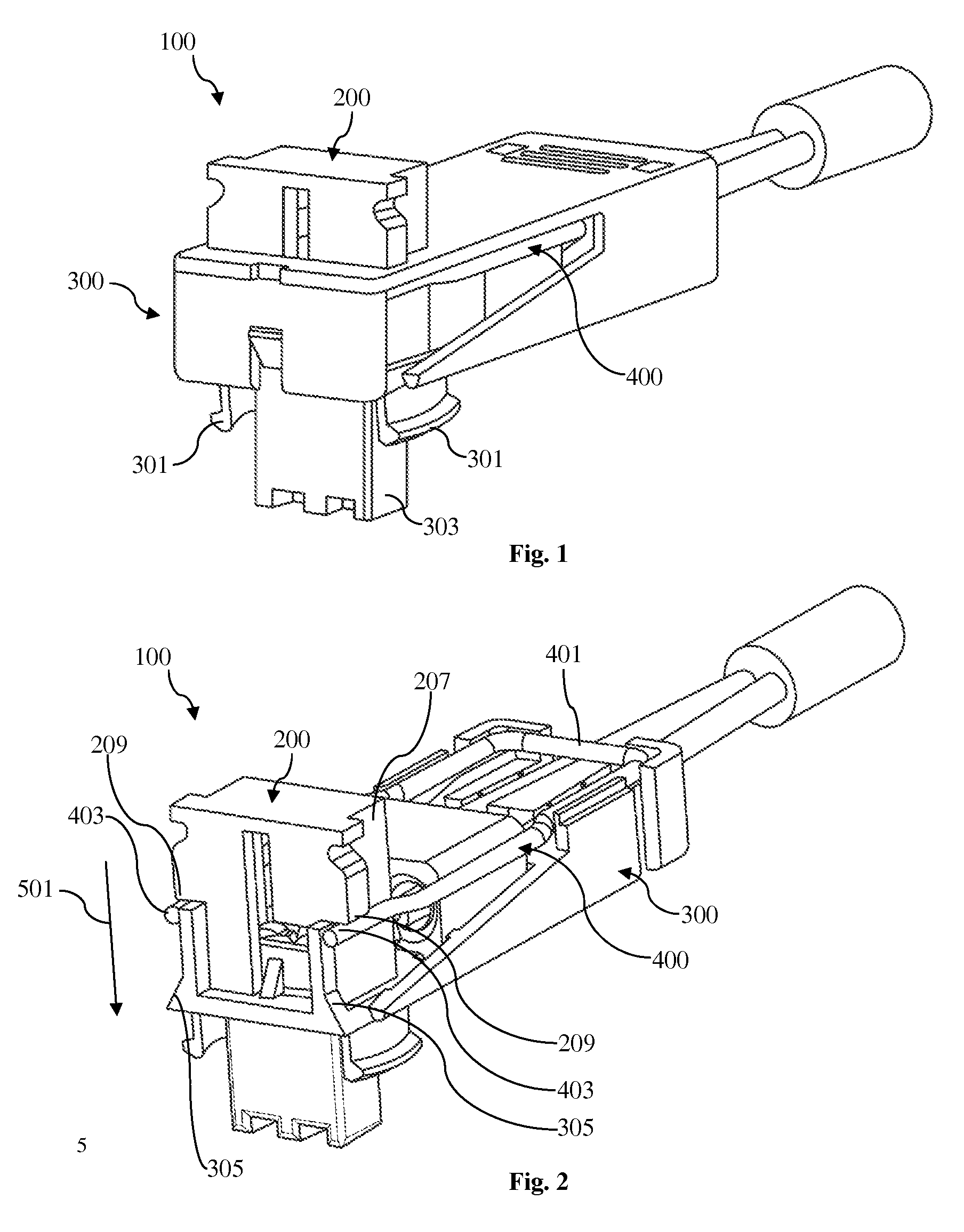
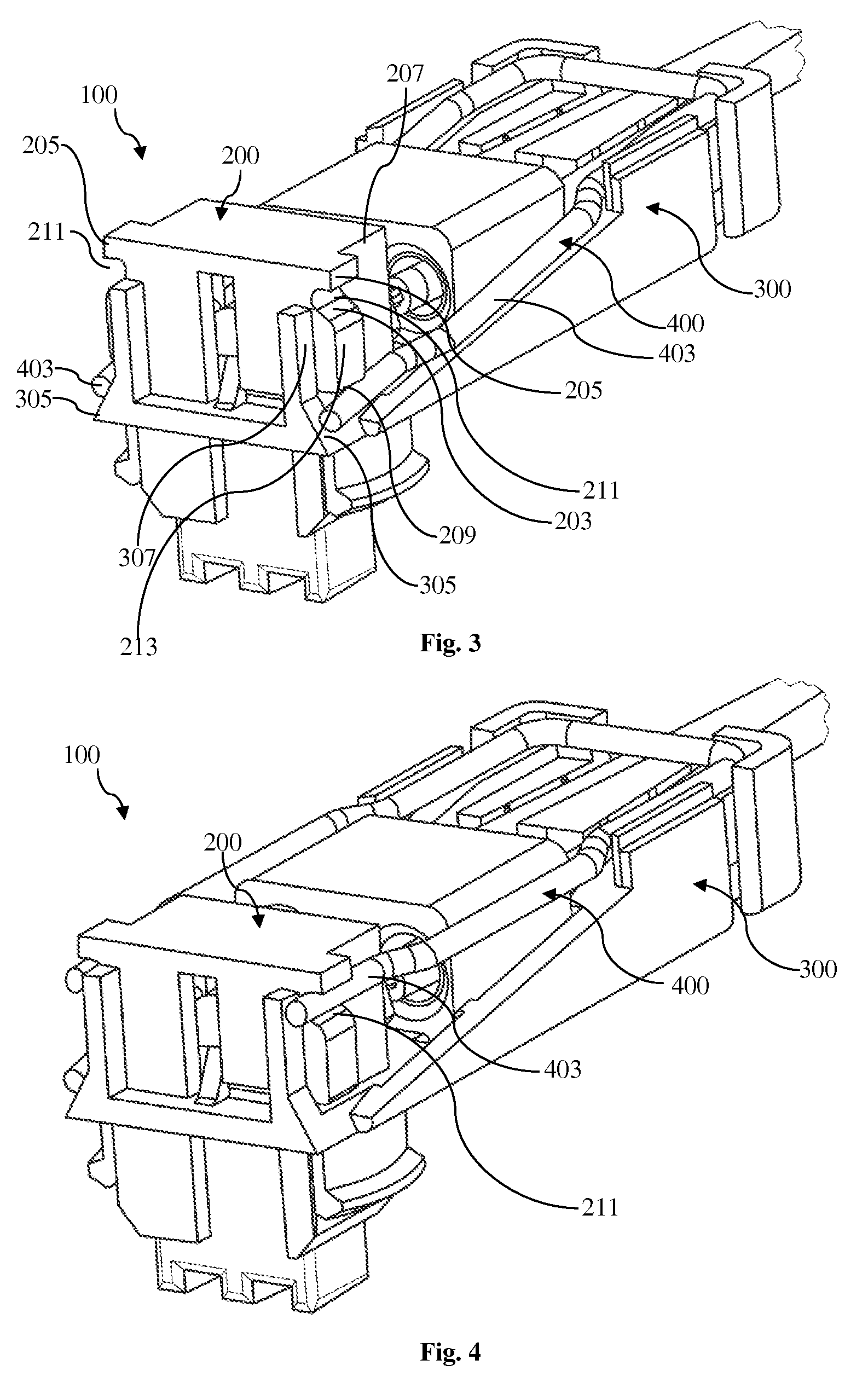
InactiveUS7232329B1Improved latchReliable matingCoupling device detailsFixed connectionsElectrical conductorEngineering
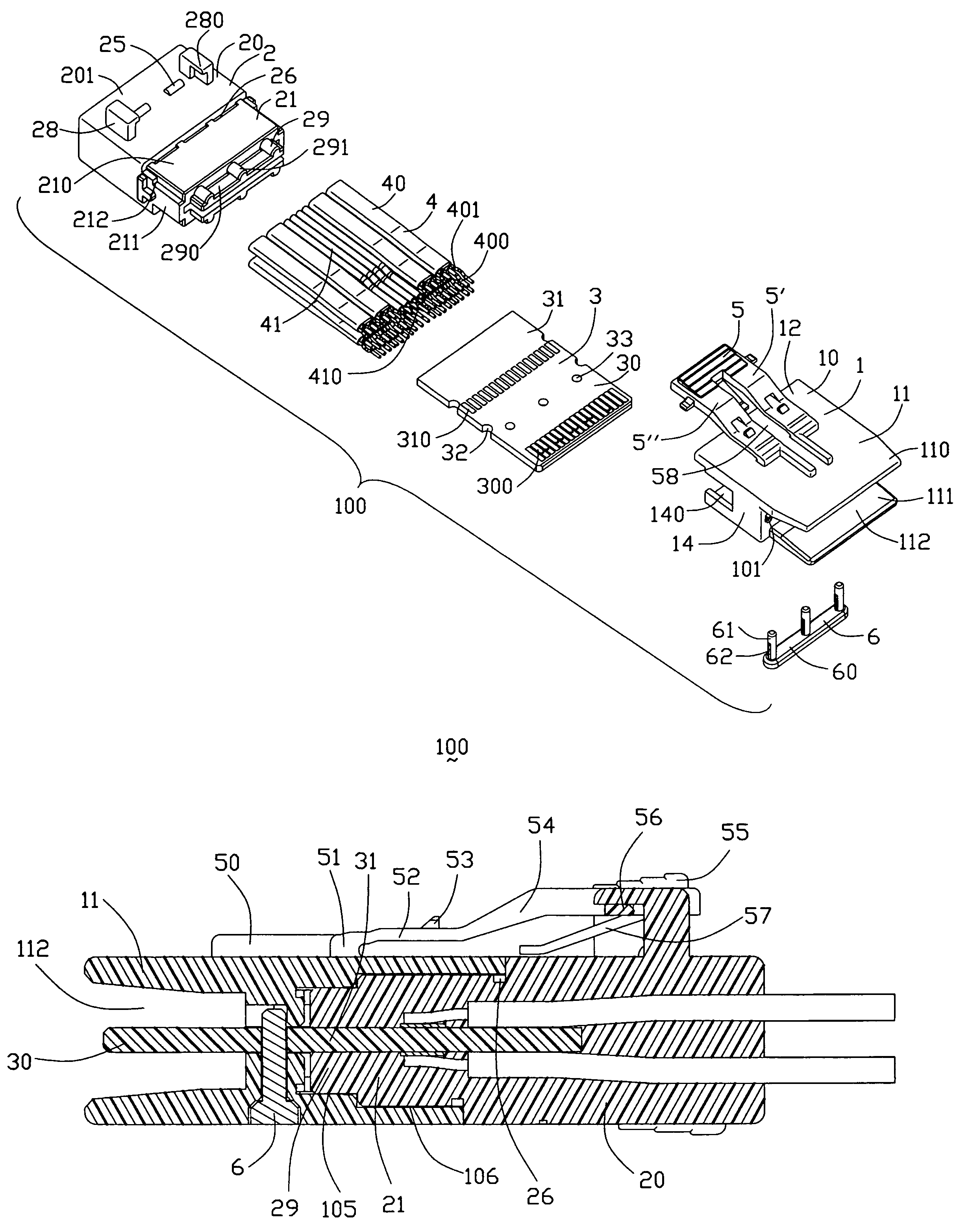
A cable connector assembly (100) includes a housing defining a mating interface, a printed circuit board (3) received in the housing, and defining a mating portion (30) accessible from the mating interface (11), a cable (4) with a number of conductors electrically attached to the printed circuit board and a latch (5) unitarily molded with the connector housing.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
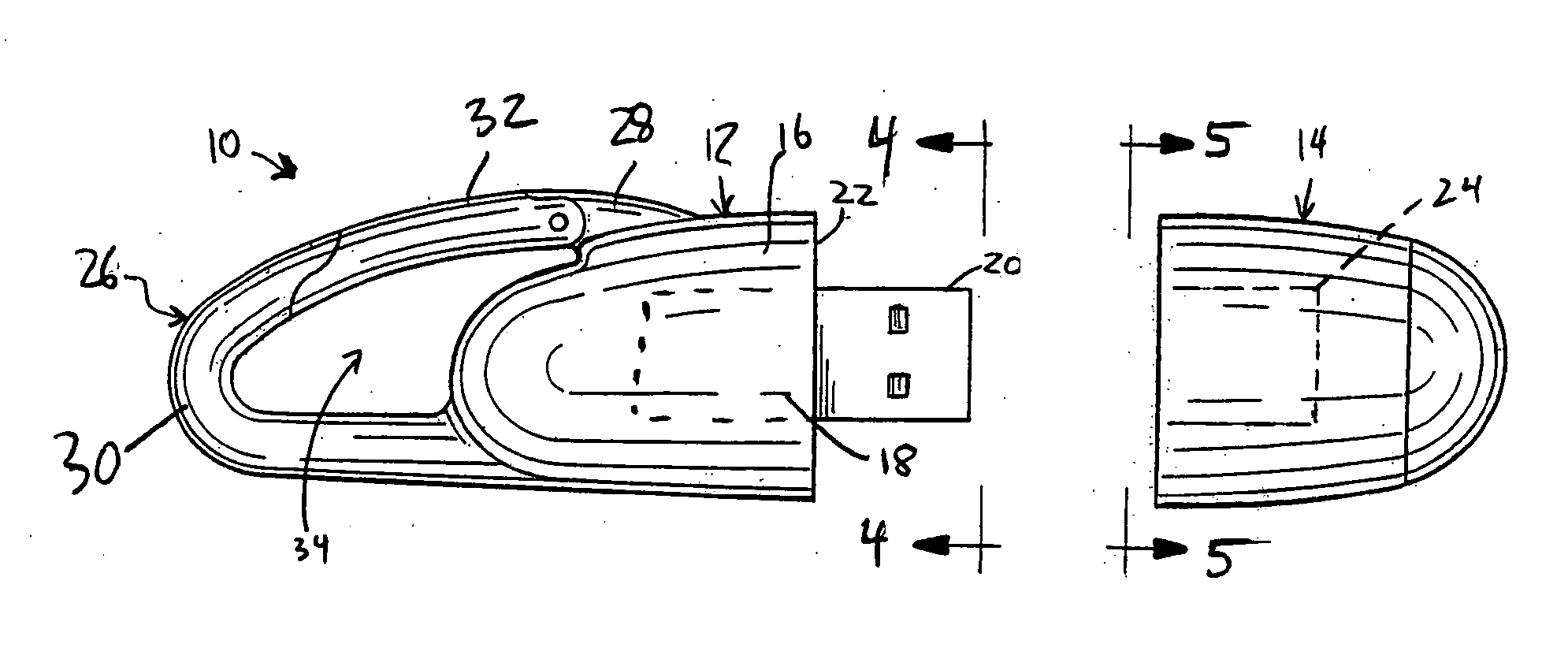
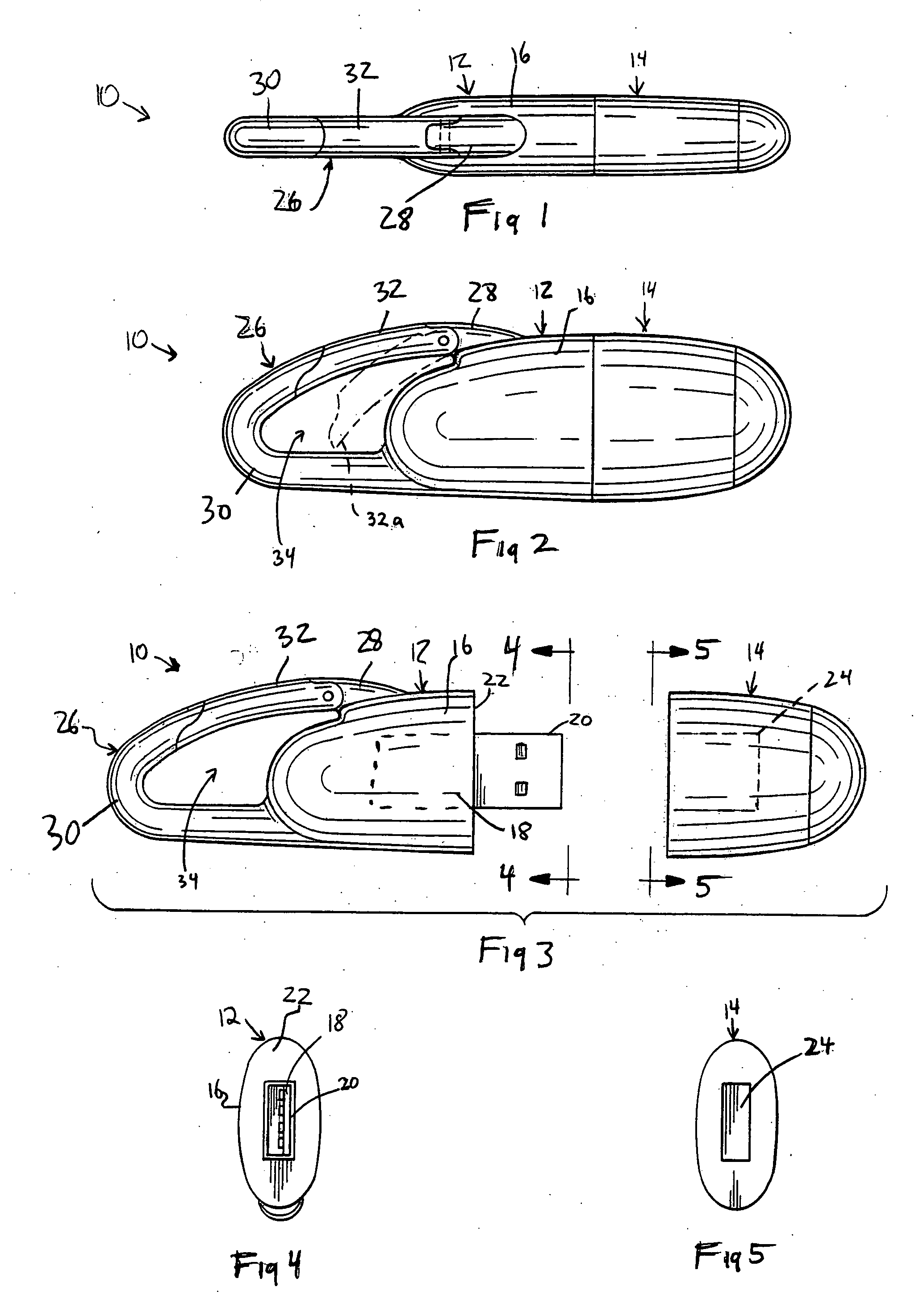
Portable memory device having a carabiner
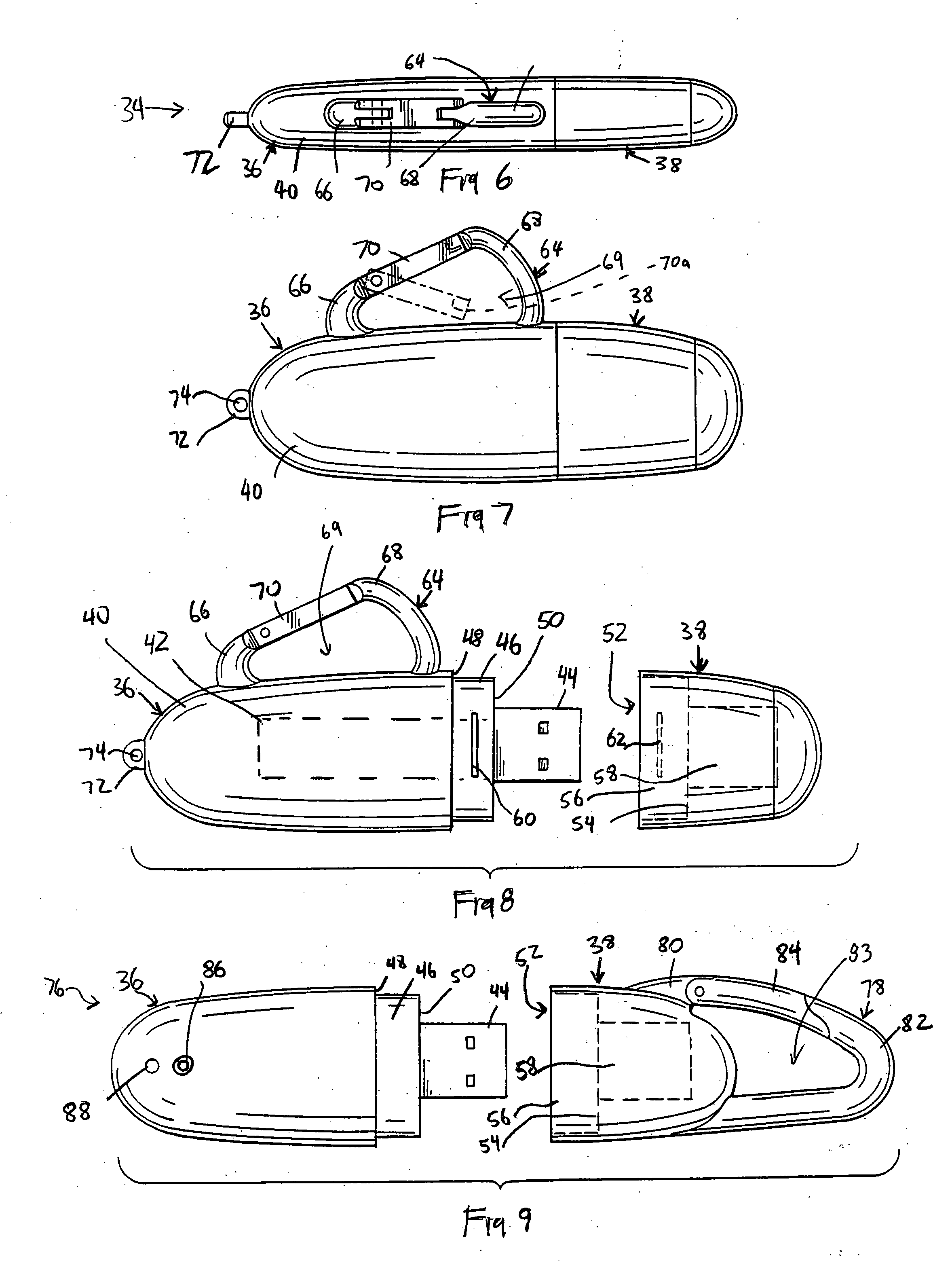
InactiveUS20050277316A1Easy to useSecure attachmentComputer periphery connectorsLive contact access preventionInternal memoryEmbedded system
A portable electronic storage device with an internal memory device includes a base, a memory device arranged in connection with the base, an adapter connected to the memory device, a cover detachably connected to the base and a clip arranged on the base or cover for enabling the base or cover to be removably clipped to an object. The adapter is arranged on the base such that when the cover is detached from the base, the adapter is exposed and can be coupled to an I / O port of a computer and when the cover is connected to the base, the adapter is covered by the cover thereby preventing damage to the adapter and memory device.
Owner:PENCOA CORP
Foldable support leg and pallet assembly formed therefrom
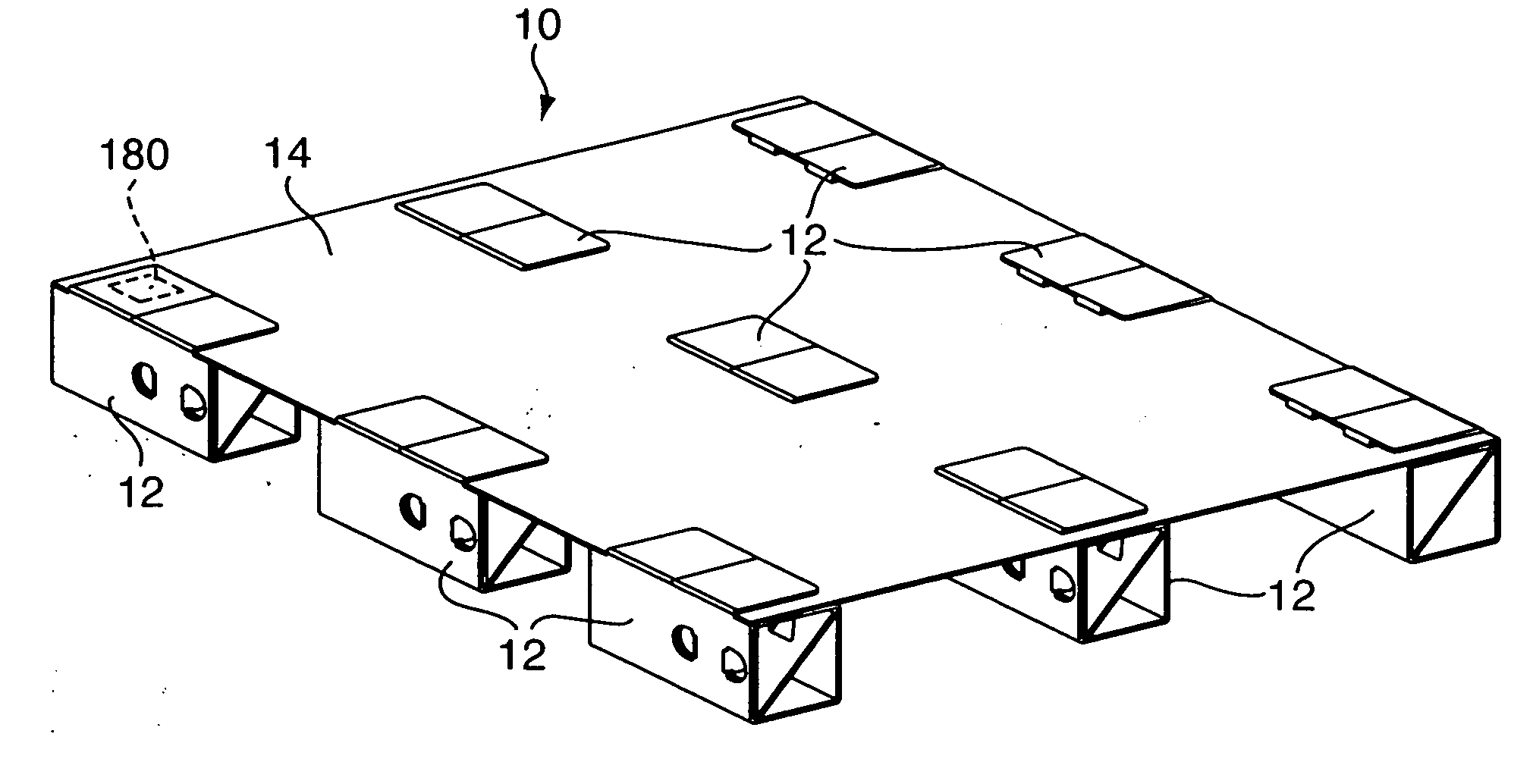
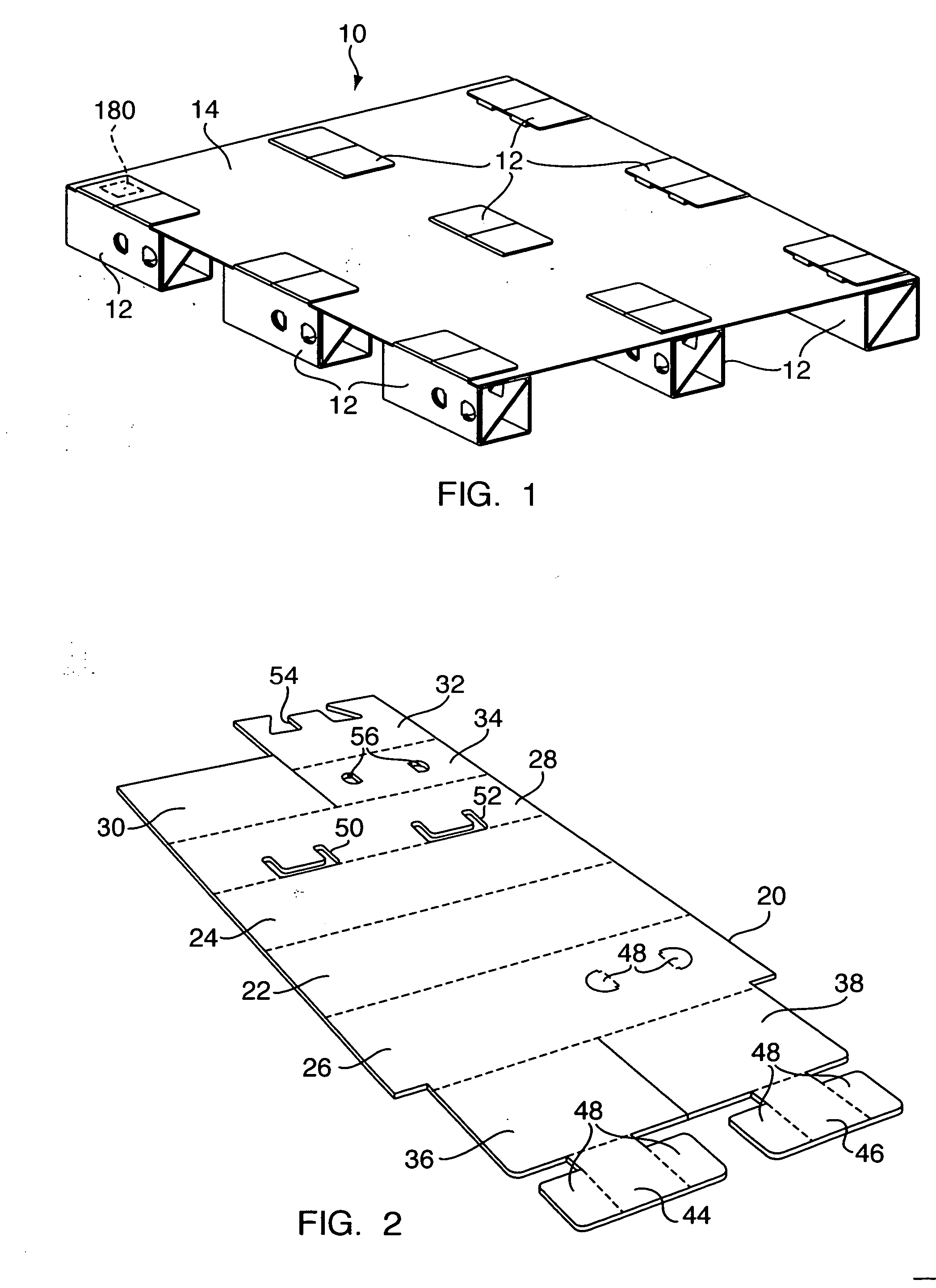
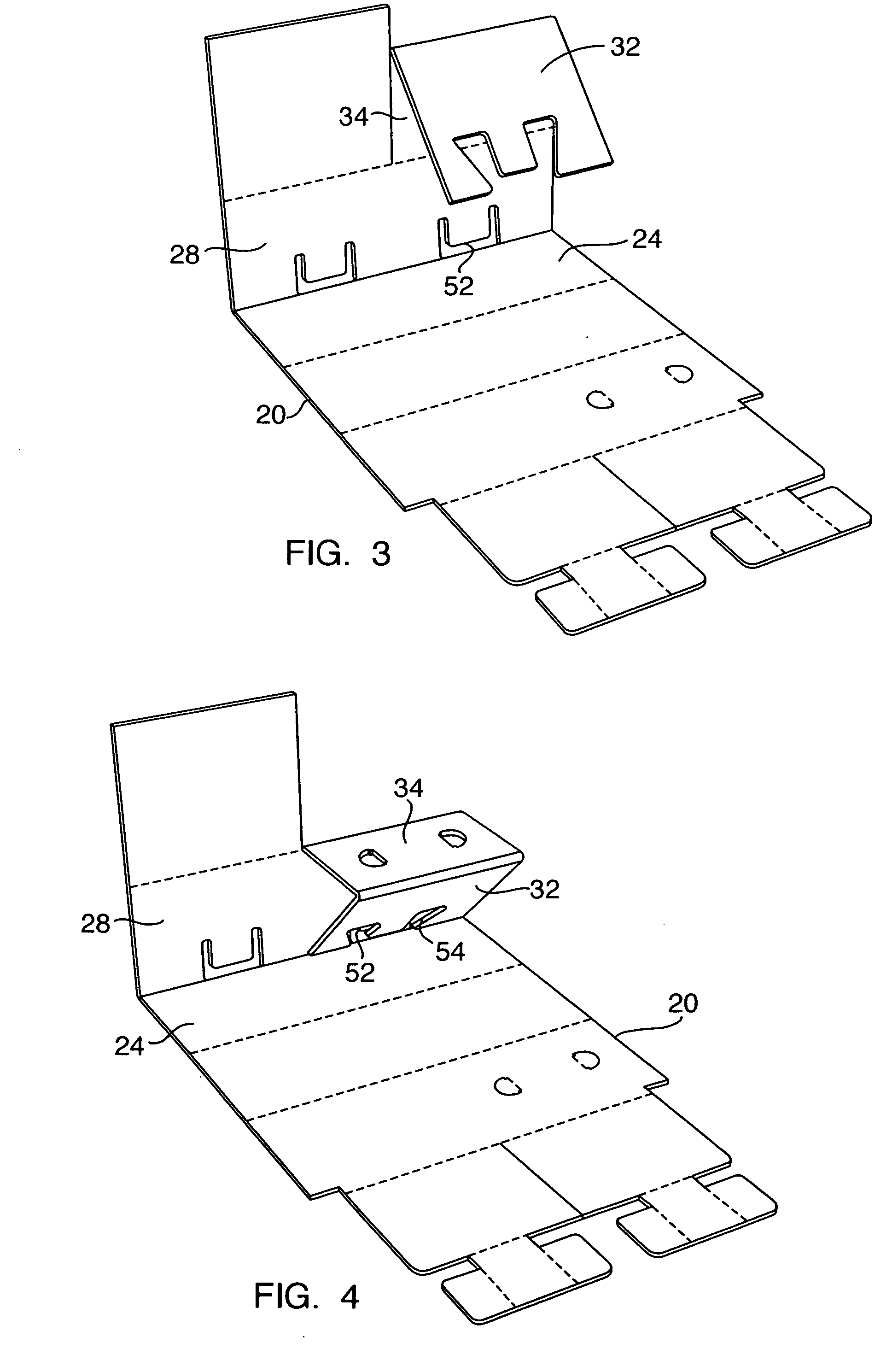
InactiveUS20070068426A1Enhancing structural conformityStrong load bearing capacityRigid containersPalletSheet material
A support leg includes a sheet of material configured into a sequence of adjacent panels and including a first tab, a first cutout configured to receive the first tab being formed within one of the panels, wherein the sheet is foldable into a nested panel structure defining an interior cavity. A pallet deck includes a sheet of material having a plurality of first cutouts and second cutouts defined therein, wherein each first cutout is dimensioned to allow insertion of the at least one tab and at least one panel of the foldable support leg and each second cutout is dimensioned to allow insertion of the at least one tab, each second cutout being spaced apart from each first cutout such that the at least one panel is able to substantially extend therebetween. A pallet assembly is formed by mating a plurality of support legs to a pallet deck.
Owner:PROD LOGIX
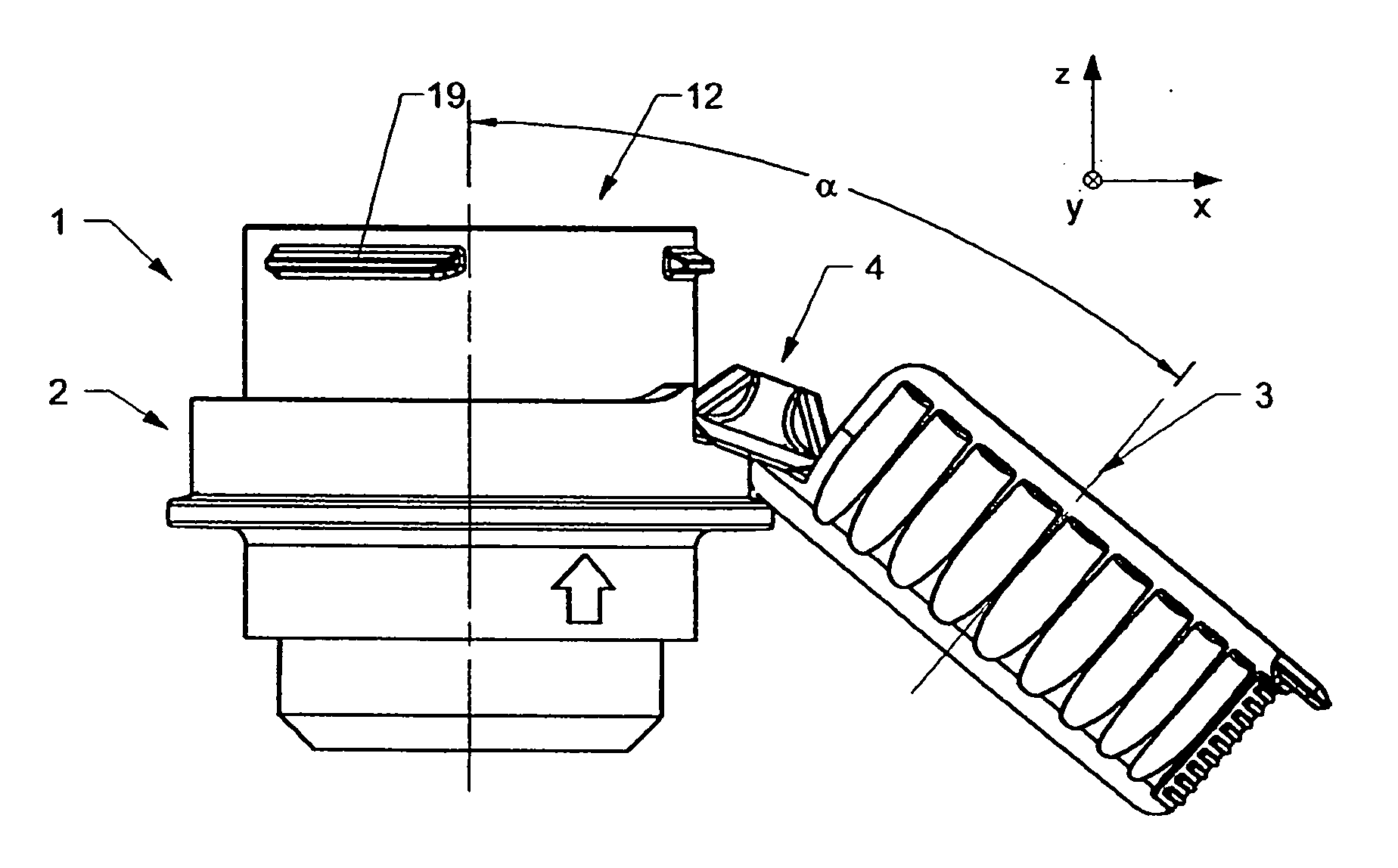
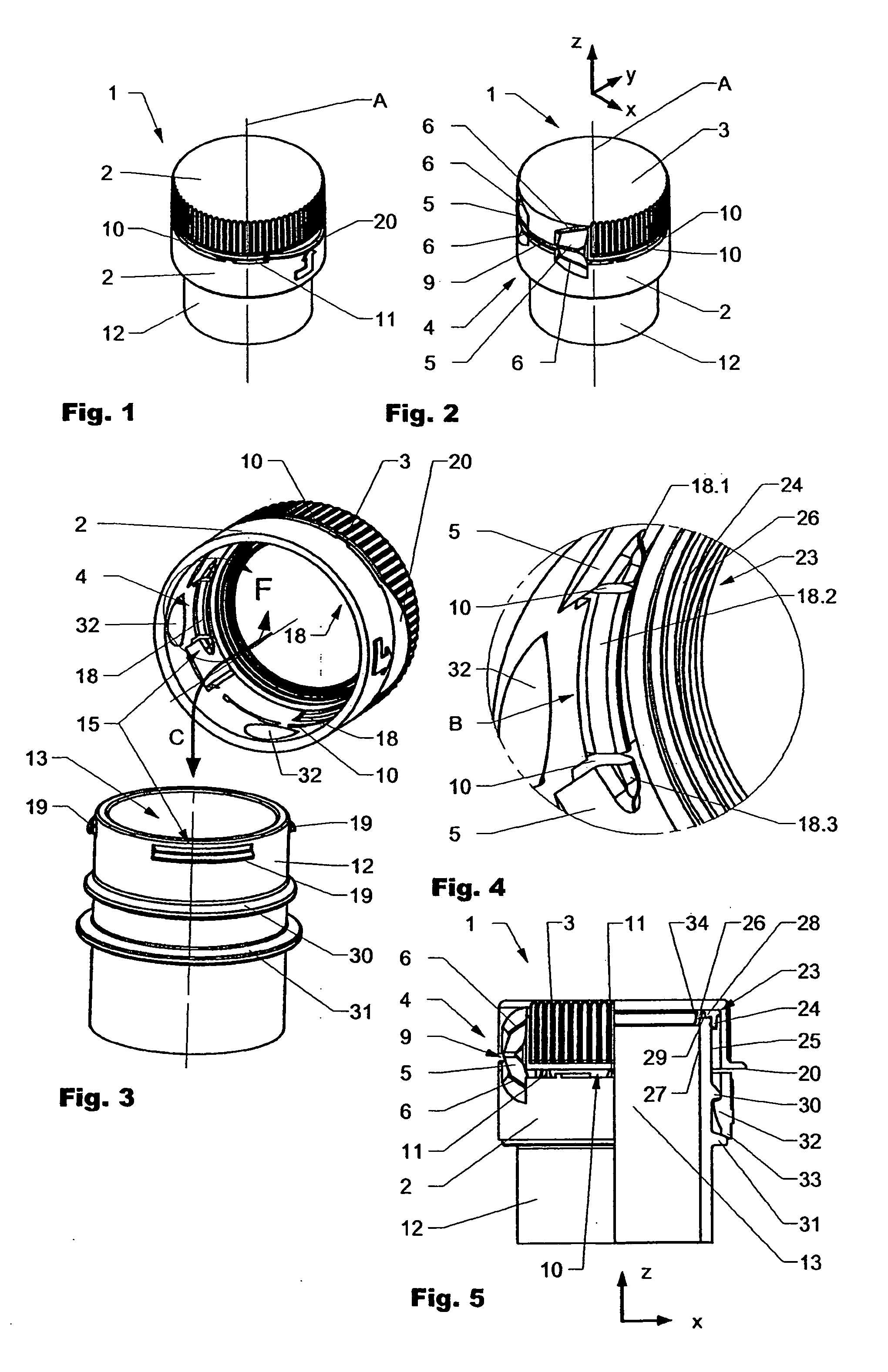
Hinged Closure
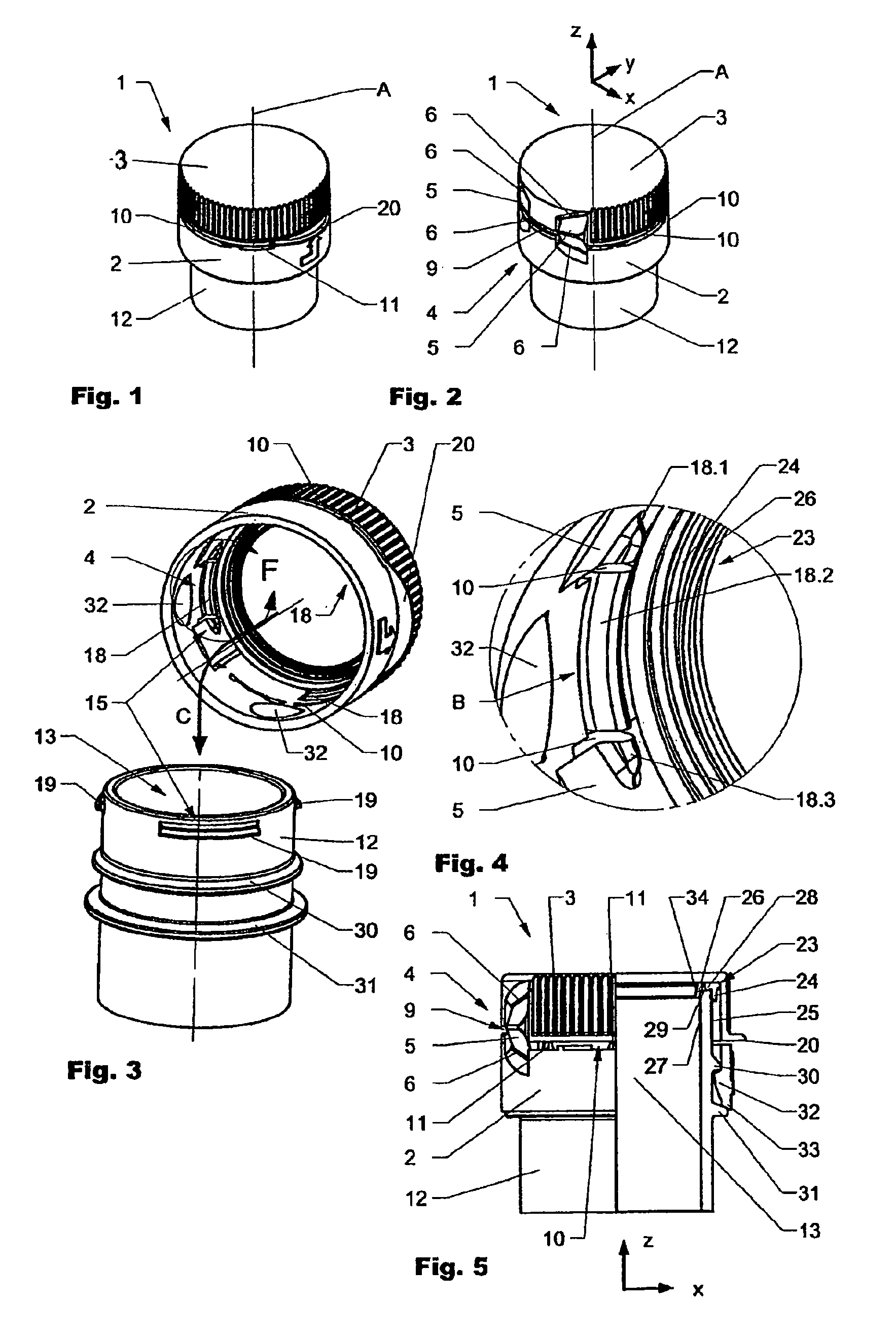
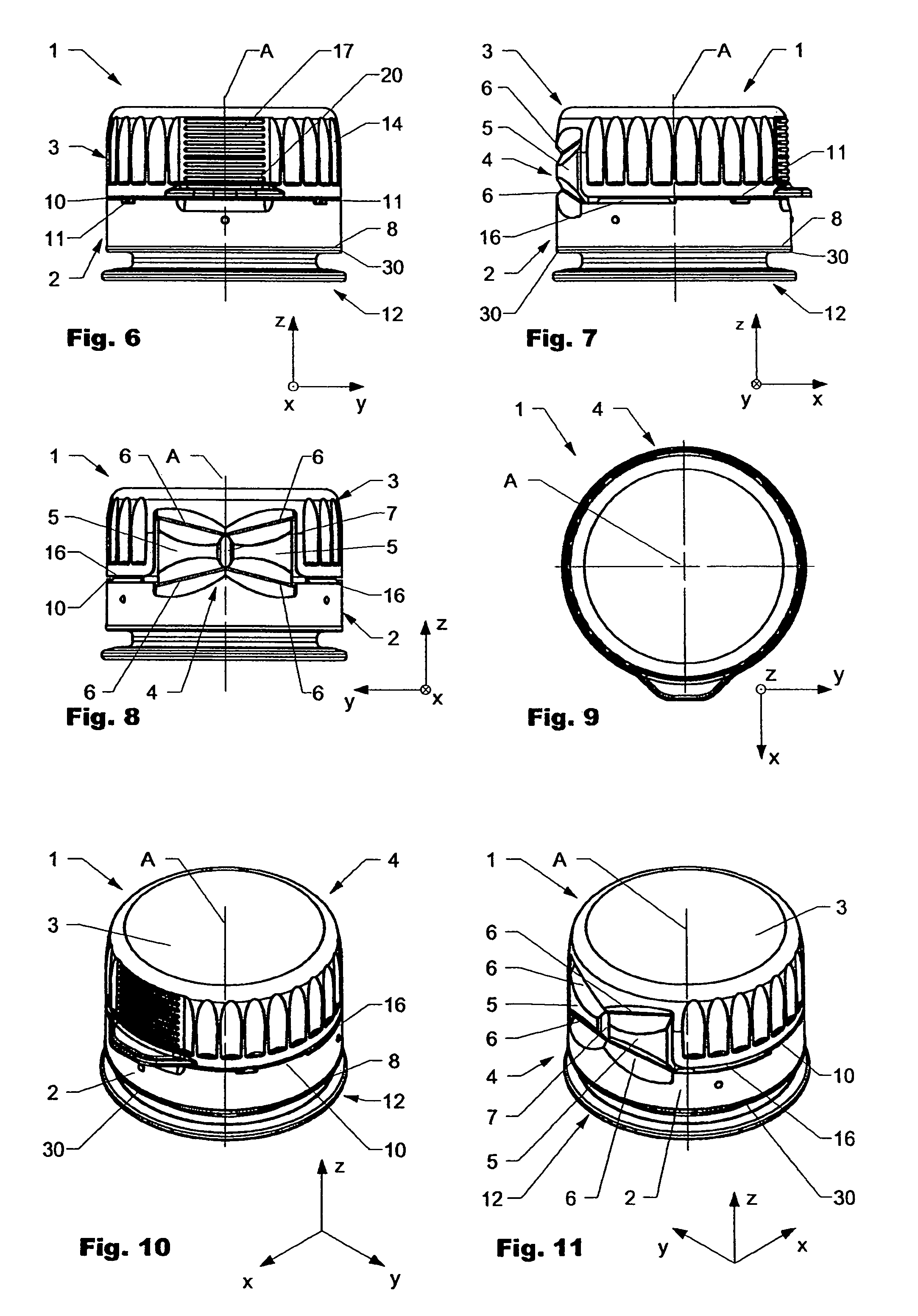
ActiveUS20100005641A1Easy to disinfectReduce selection requirementsCapsClosure using stoppersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CREANOVA UNIVERSAL CLOSURES
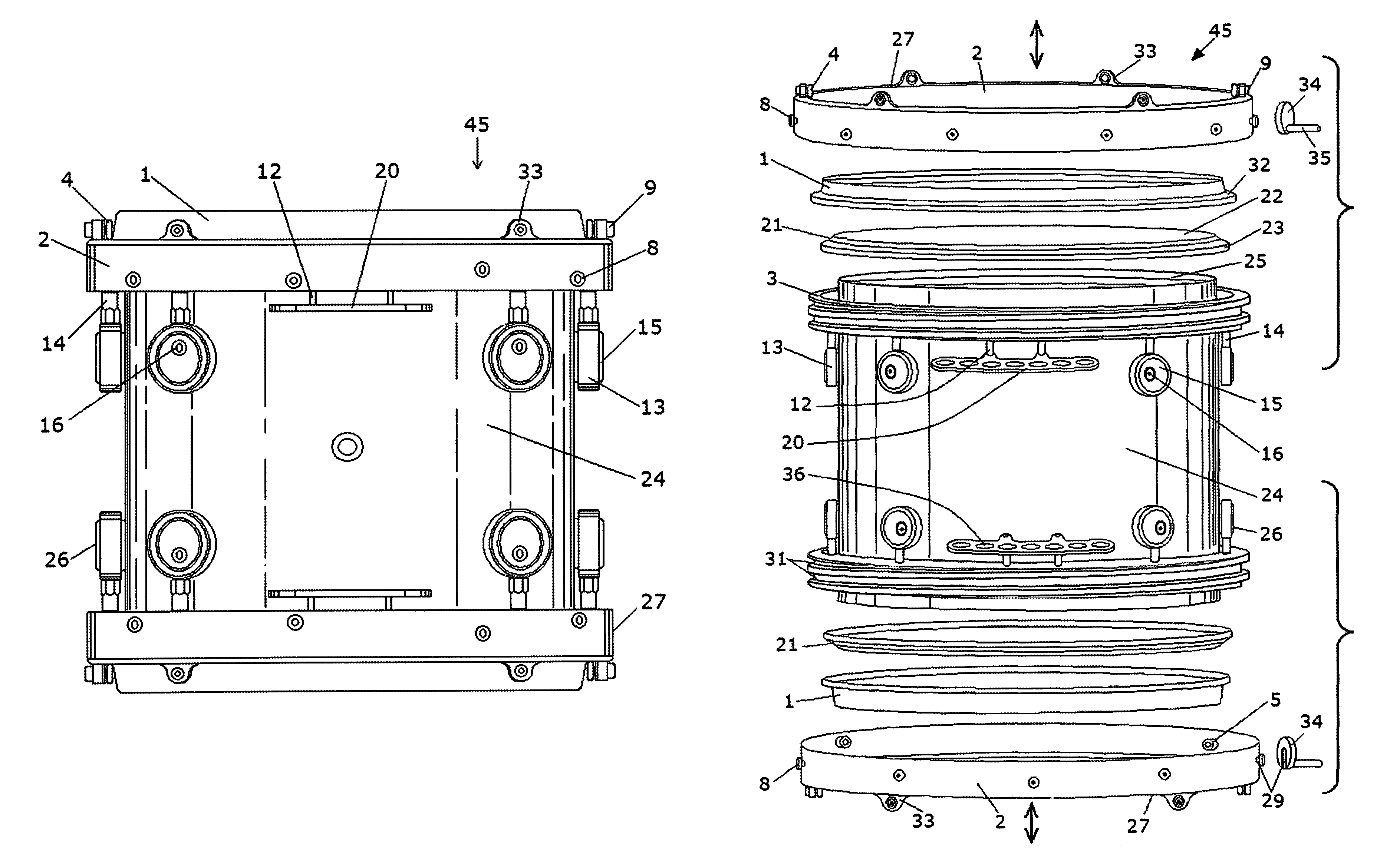
Rotation activated drum tuning system
ActiveUS7501567B1Increased mechanical advantageMinimized contact areaPercussion musical instrumentsBearing downEngineering
A drum tuning system which rotates clockwise or counterclockwise to adjust the tension of a drum head fitted over the open end of a drum body. It utilizes a rotating ring having numerous opposing equally spaced vertically projecting tabs along the top of the body's diameter, each with inward facing wheels that ride on the horizontal surface of a separate inner hoop bearing down on the drum head. The rotating actuator ring is fitted with multiple radial cleats projecting from its outside diameter for grasping it. A radius plate having horizontal holes extends from the drum body, and a tool engages the radial cleats on the rotating actuator ring to facilitate rotation. Multiple adjustable eccentric lugs are used to raise and lower the drum camming mechanism in relation to the open end of the drum body where attached. Horizontal projecting links support the drum attached to suspension mounting systems.
Owner:SPINAZZOLA DAVID MICHAEL
Ultraviolet lamp for use in water purifiers
Owner:LIGHT SOURCES INC
Hinged closure for a container neck
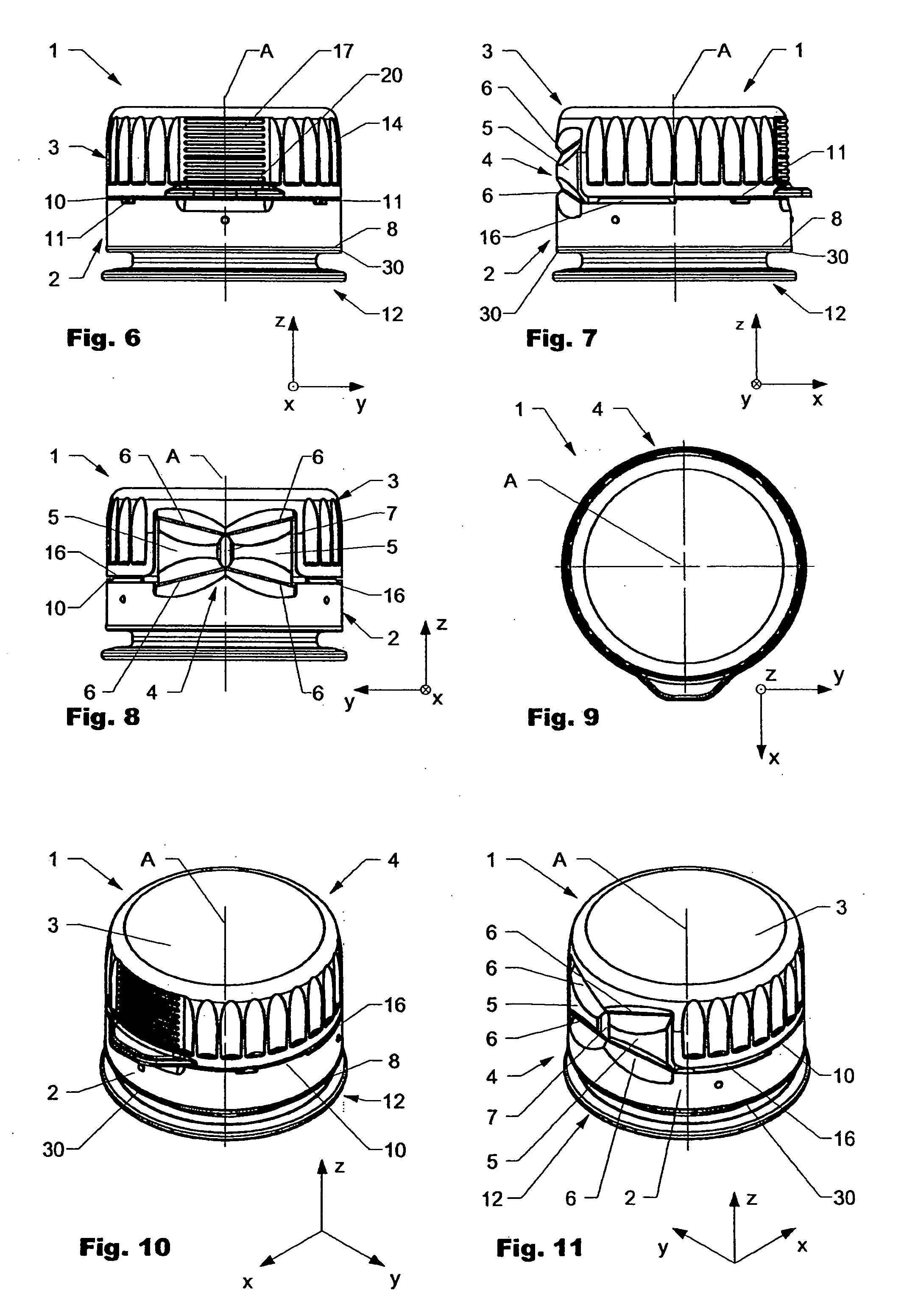
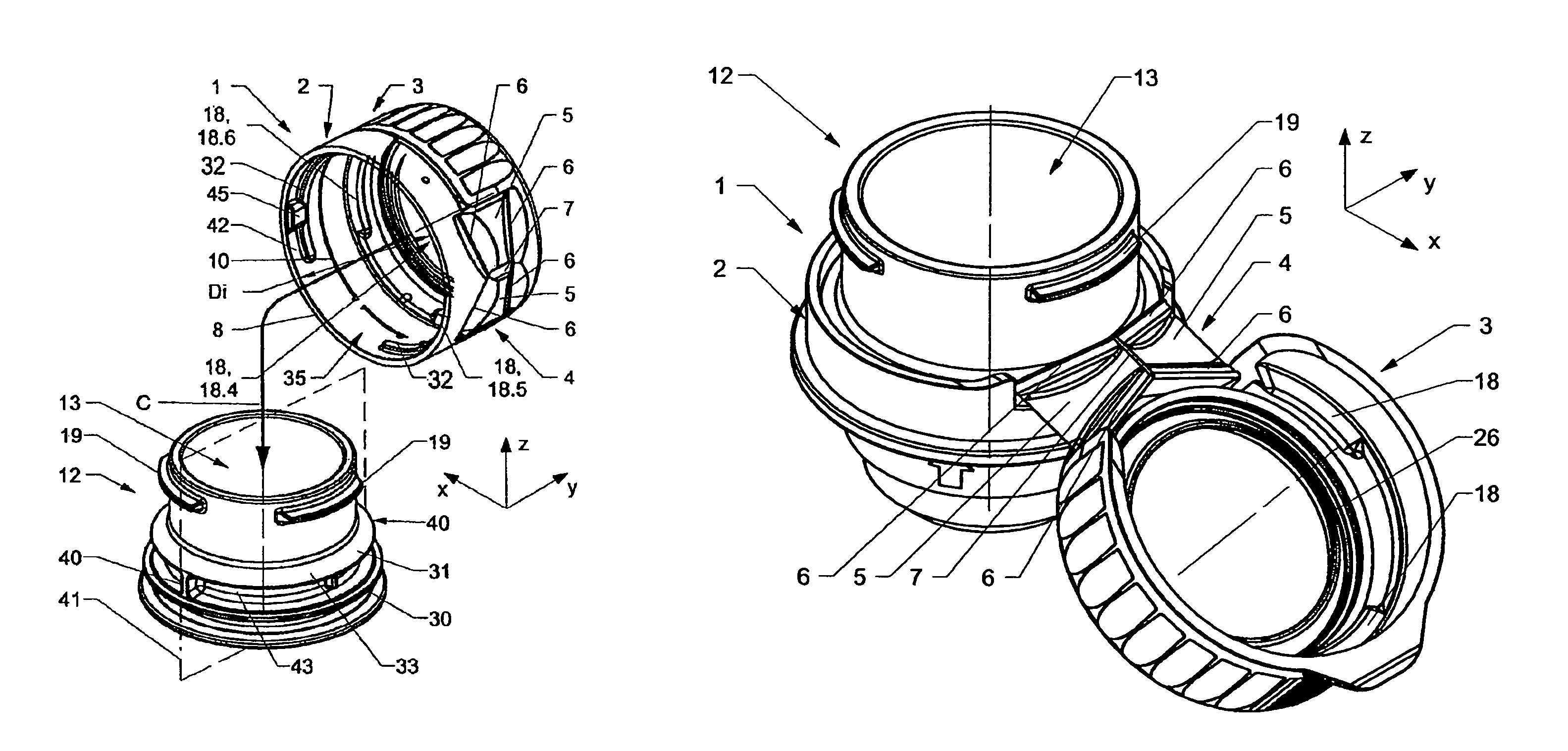
ActiveUS8794460B2Neck finish is more simpleAvoid disadvantagesCapsClosure using stoppersEngineeringStructural engineering
Owner:CREANOVA UNIVERSAL CLOSURES
Crown spring cage tyep pin and jack component and jack thereof
InactiveCN102005663AImprove insertion forcePlug firmlyCoupling contact membersBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a crown spring cage tyep pin and jack component and a jack thereof. the crown spring cage tyep jack comprises an inner sleeve, wherein an outer sleeve is sleeved outside the inner sleeve, a crown spring penetrates through the inner bore of the inner sleeve; two parallel elastic clamping strips are symmetrically arranged on the port part of the inner bore of the outer sleeve; and the distance between the two elastic clamping strips is less than the minimum internal diameter of the crown spring. The crown spring cage tyep pin and jack component comprises a pin and a jack, wherein the jack contains the inner sleeve; the outer sleeve is sleeved outside the inner sleeve, the crown spring penetrates through the inner bore of the inner sleeve; the two parallel elastic clamping strips are symmetrically arranged on the port part of the inner bore of the outer sleeve, the distance between the two elastic clamping strips is less than the internal diameter of the crown spring; and the pin contains a needle-like connection-peg, and the circumference surface of the needle-like connection-peg is provided with a clamping structure which fits with the two elastic clamping strips in a clamping manner. The elastic clamping strips are arranged on the port part of the jack; and during plugging, the clamping structure on the pin fits with the elastic clamping strips in the clamping manner, thus the reliable plugging of the pin and the jack can be realized and the pin is difficult to separate from the jack.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION OPTICAL-ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Tamper-Resistant Storage Container
The present invention is directed to a tamper-resistant storage container. The storage container includes a container and lid portion having formed channels and surfaces along their perimeters configured to interlock securely to each other to attach the lid to the container. The lid includes at least one open area spanned by a breakaway stringer defining an area of weakness along a perimeter of the lid such that removing or attempting to remove the lid from the container breaks the stringer to provide a visible indication that the container has been opened or tampered with.
Owner:D& W FINE PACK
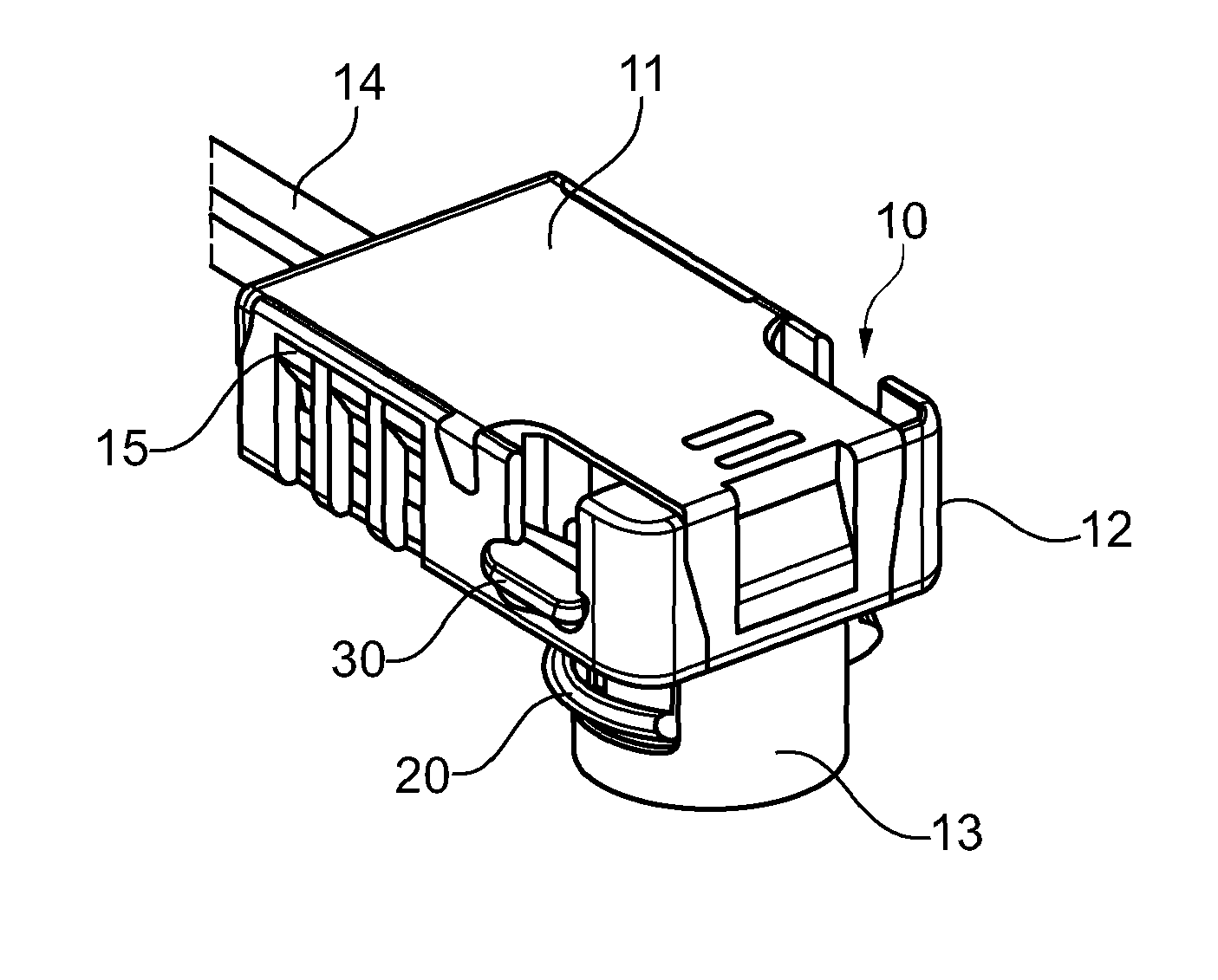
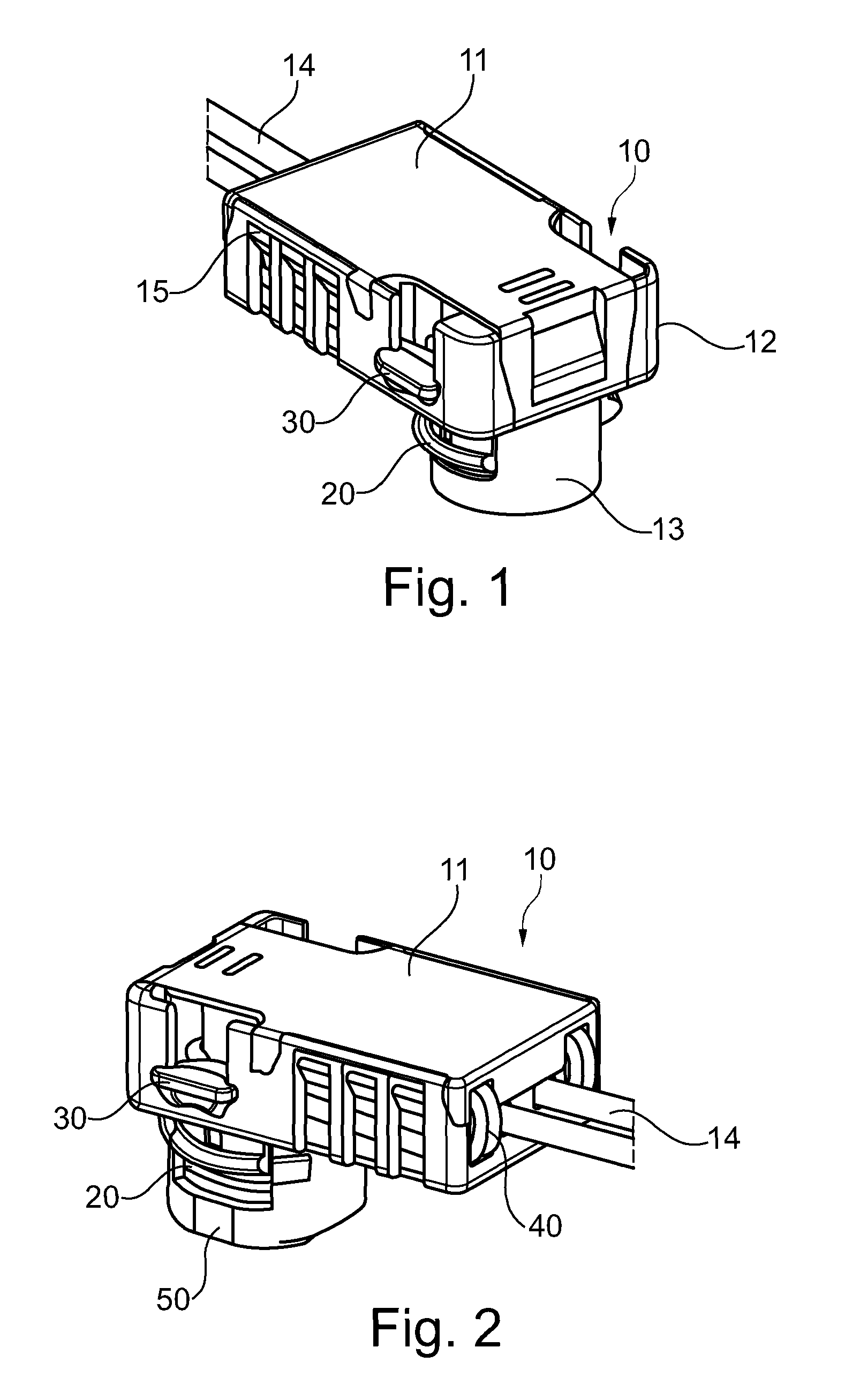
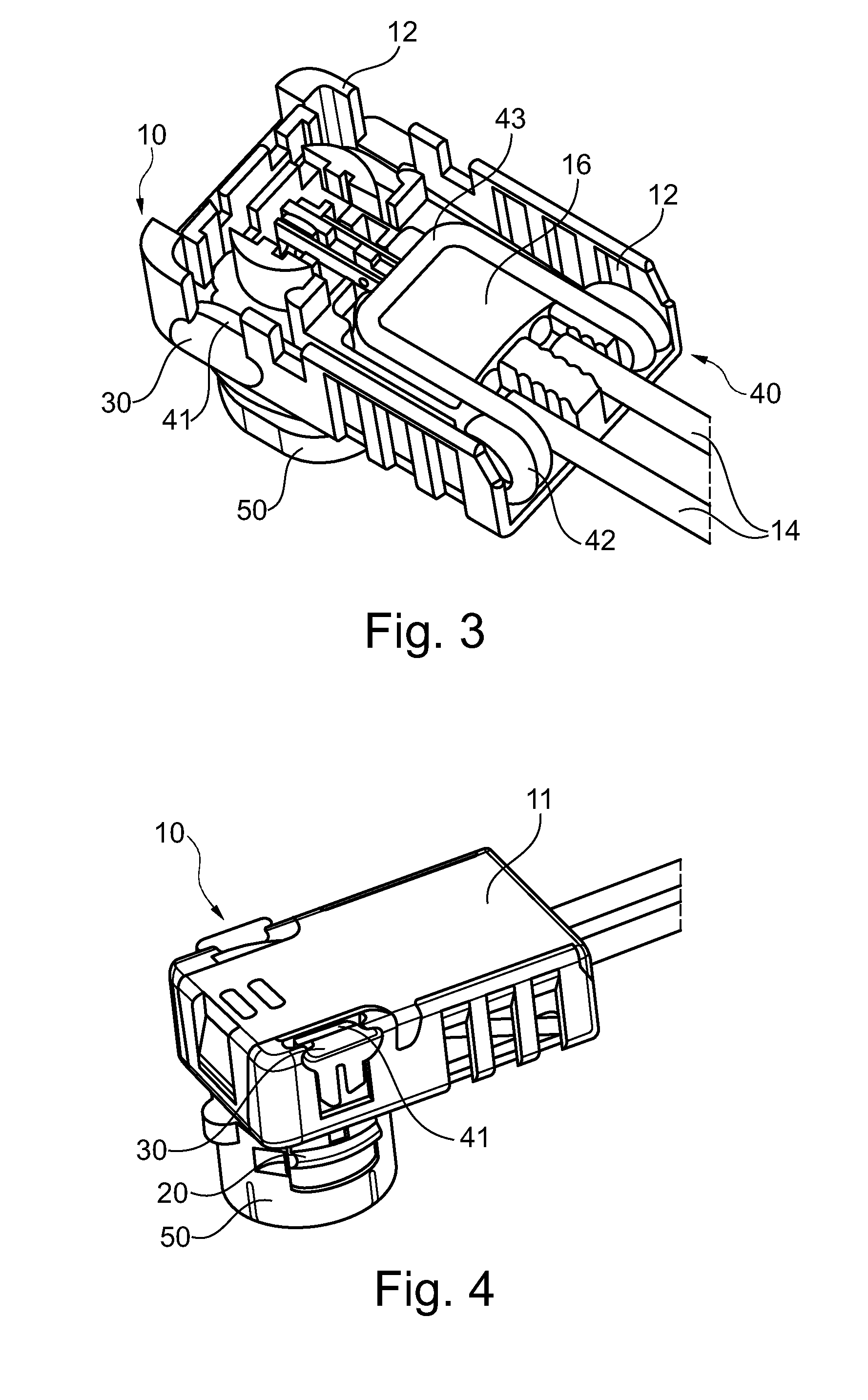
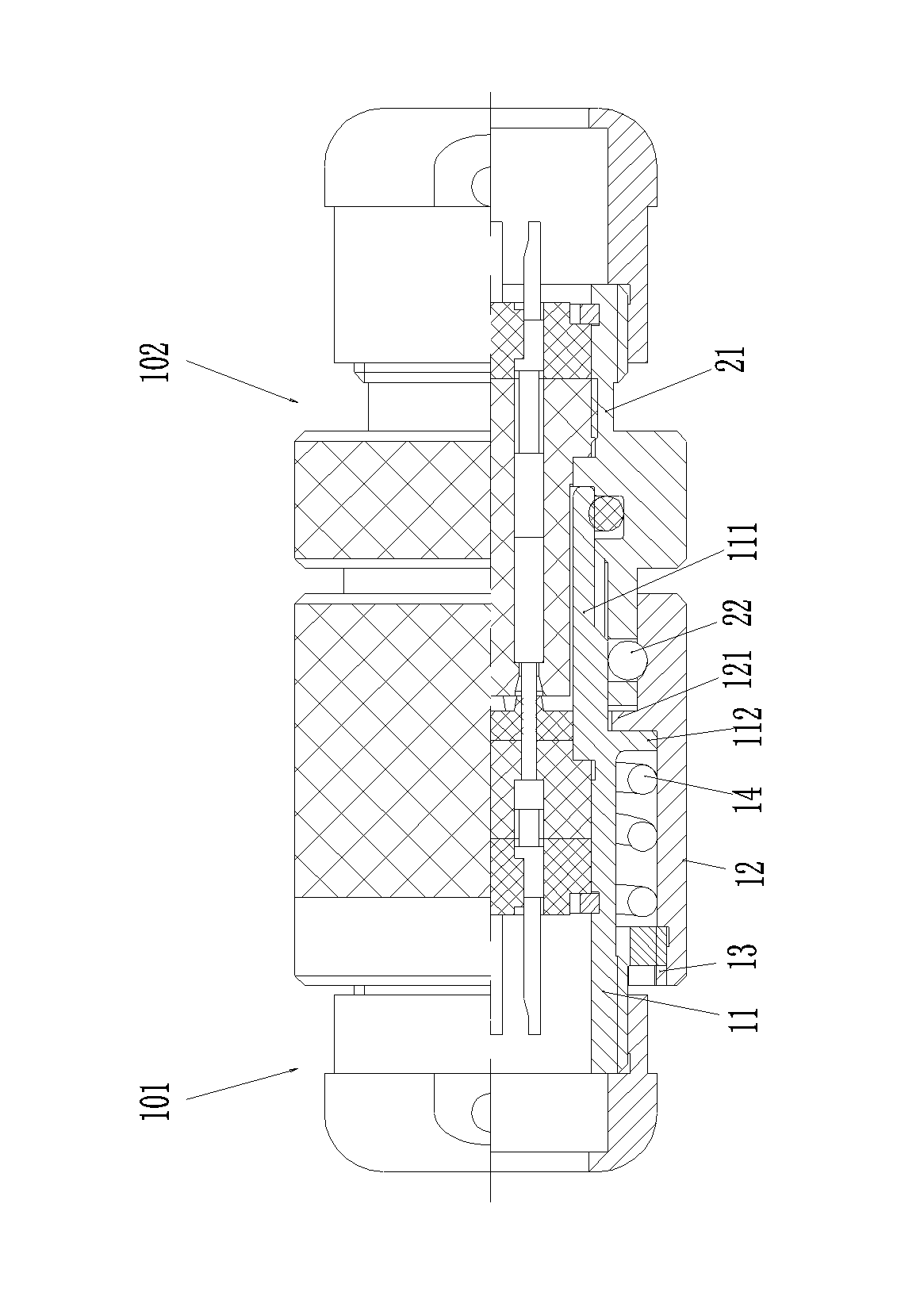
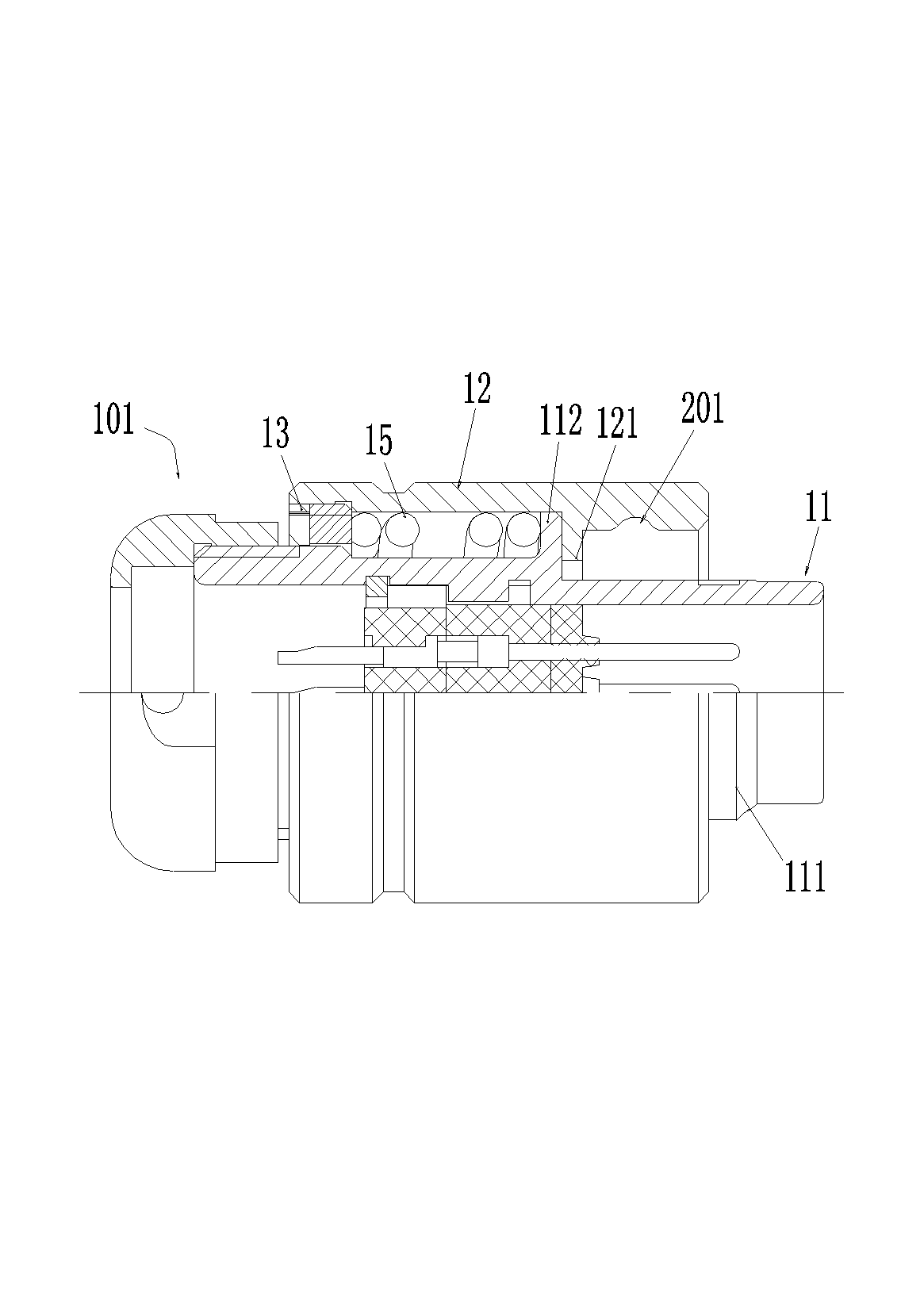
Electrical connector assembly with locking structures thereof
ActiveUS20180241154A1Reliable matingLarge mating forceTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsEngineeringElectrical connector
A receptacle connector includes an insulative housing equipped with a plurality of receptacle contacts and enclosed by a capsular metallic shield sub-assembly. An insulative holder encloses the shield sub-assembly with a deflectable latching structure thereon. The plug connector includes an insulative body equipped with a plurality of plug contacts. An internal PCB is located behind the housing and soldered with the corresponding contacts. A capsular metallic shell encloses the insulative body and adapted to be received within the metallic shield during mating. A cable is connected to the PCB. An insulative cover encloses the internal PCB, the rear portion of the insulative body and the front portion of the cable with a retaining structure to be coupled with the latching structure, and a sliding assurance structure ensuring the latching structure and the retaining structure to be securely engaged with each other for maintaining the reliable mating.
Owner:FOXCONN INTERCONNECT TECHNOLOGY LIMITED
Connector assembly with automatic secondary lock
ActiveUS9409536B2Reliable matingVehicle connectorsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSpring forceEngineering
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Connector assembly
InactiveUS20130252455A1Reliable matingEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsVehicle connectorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A connector assembly comprising a connector housing, a secondary locking member and a safety spring bar, whereby the secondary locking member and the safety spring bar are assigned to the connector housing. The secondary locking member is movable between a first and a second position, whereby the safety spring bar is adapted to lock the secondary locking member in its second position. The secondary locking member comprises a deflection surface adapted to engage the safety spring bar when the secondary locking member is moved in an insertion direction. Thereby, upon movement of the secondary locking member, the safety spring bar is deflected essentially in the insertion direction, urging the secondary locking member towards its first position. When the secondary locking member is placed in the second position, the safety spring bar is adapted to snap into a safety position, to lock the secondary locking member in its second position
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Coaxial cable connector
ActiveCN102204019AAvoid accidental separationImprove reliabilityEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElectrically conductive connectionsCoaxial cableEngineering
A coaxial cable connector to enhance coupling between internal components of coaxial cables is disclosed. The coaxial cable connector includes a male connector in which a male terminal assembly is fixed and a female connector in which a female terminal assembly connected to the male terminal assembly during coupling between the connectors is fixed. Each of the terminal assemblies has a catching protrusion. Each of the connectors has an elastic plate. The elastic plate has a catching hole in which the corresponding catching protrusion is caught. Each of the terminal assemblies has a groove. Each of the connectors has a fixing piece. The fixing piece is fitted in the corresponding groove.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS AMP KOREA
Insertion and extraction force controllable electric connector component and plug thereof
ActiveCN103259134ALow positioning accuracy requirementsReliable matingIncorrect coupling preventionElectricitySteel ball
The invention relates to the field of electric connectors, in particular to an insertion and extraction force controllable electric connector component and a plug thereof. The insertion and extraction force controllable electric connector component comprises the plug and a socket, wherein the front end of the plug is used as a pluggable end, and the front end of the socket is used as a pluggable end. A pluggable segment is arranged on the front portion of a plug shell, and a pluggable channel for the pluggable segment to insert is arranged on the front portion of the socket shell. A steel ball is further arranged on the socket shell, and a locking cap capable of moving back and forth is arranged on the plug shell. Locking grooves for the steel ball to be clamped in are formed in the inner wall face of the locking cap, and a push spring is arranged between the plug shell and the locking cap in an ejecting mode. The push spring pushes the locking cap backwards, and a sliding groove corresponding to the steel ball is formed in the outer peripheral face of the pluggable segment of the plug shell. The front end of the sliding groove penetrates through the front end face of the pluggable segment, and a step face is formed on the rear end wall of the sliding groove. The step face is used for blocking the steel ball when the steel ball and the corresponding locking grooves are staggered front-back, and the steel ball can cross the step face backwards when the steel ball is clamped into the corresponding locking grooves. By means of the insertion and extraction force controllable electric connector component and the plug thereof, the problem that insertion and extraction force of an existing direct-plugging type electric connector component is uncontrollable is solved.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION OPTICAL-ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Fork cartridge driver
A fork cartridge driver having an outer ring and an inner driver which is reversible to engage both a fork cap and a fork cartridge. Also a second embodiment of a fork cartridge driver having an enclosed slot. Also a third embodiment of a fork cartridge driver having an engagement feature mate. Also a method for disassembling a fork cartridge assembly, which includes a fork cap having an octagonal outline portion and a fork cartridge having a ridge using a fork cartridge driver which is reversible.
Owner:MOTION PRO
Retractable Animal Tether
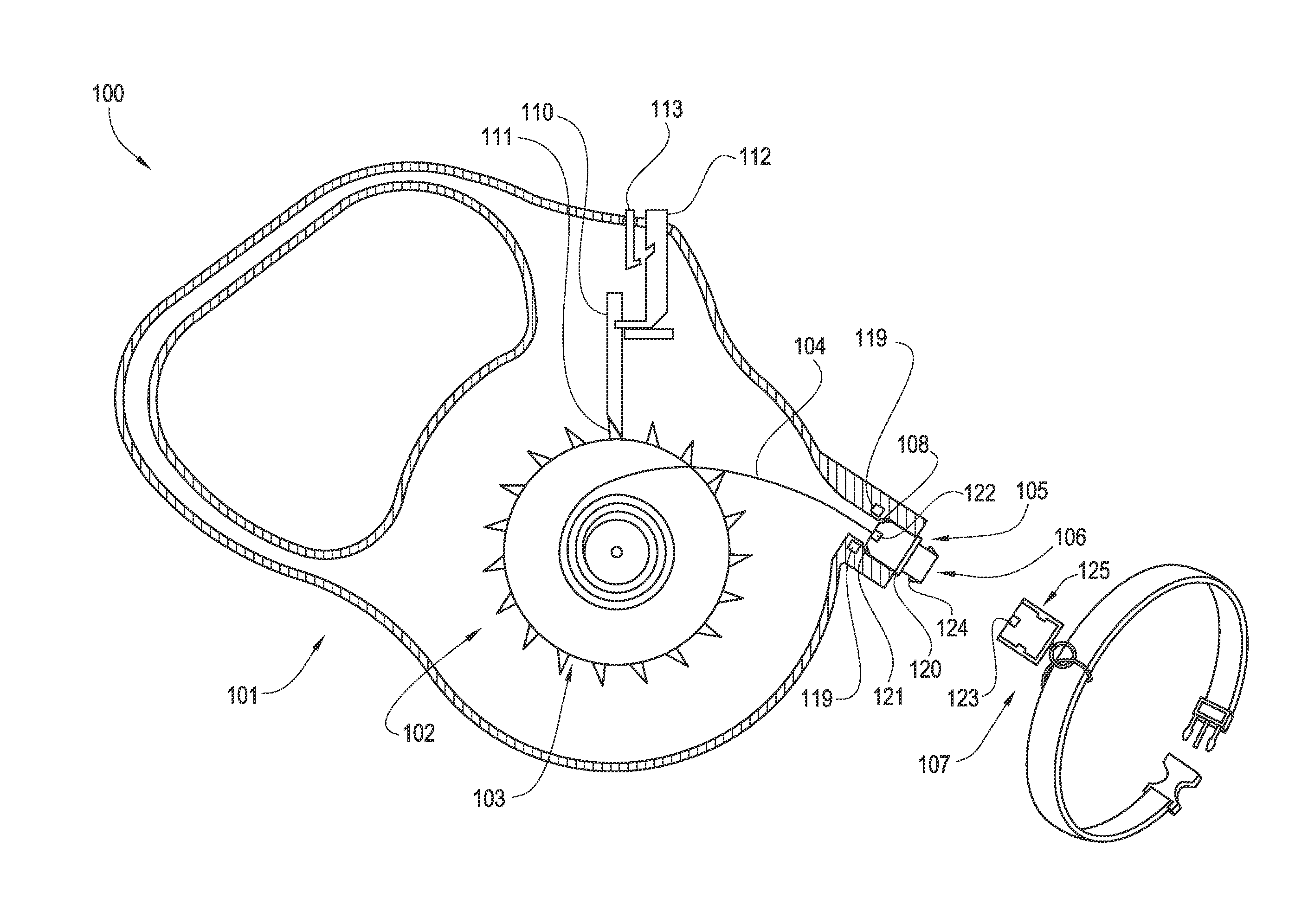
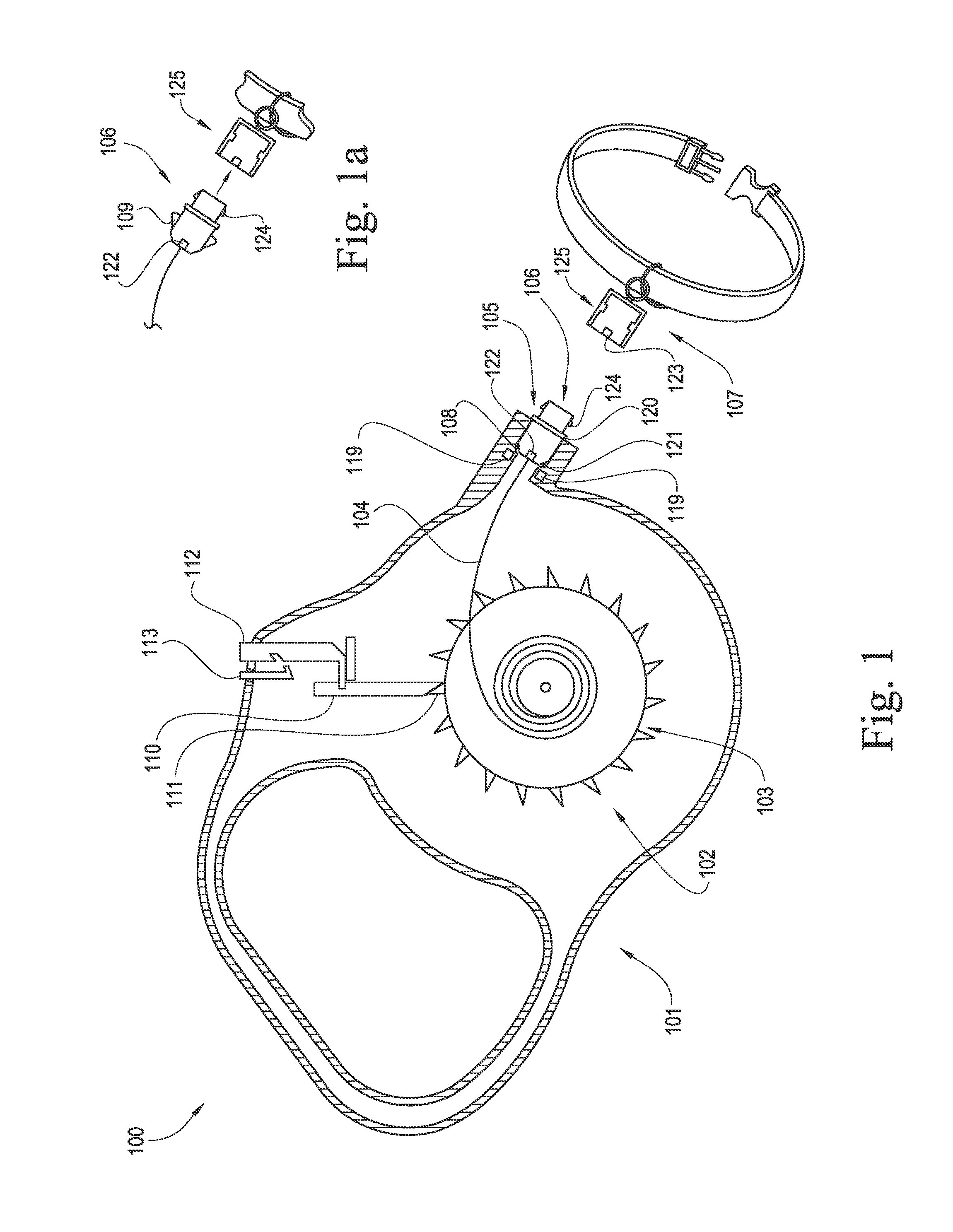
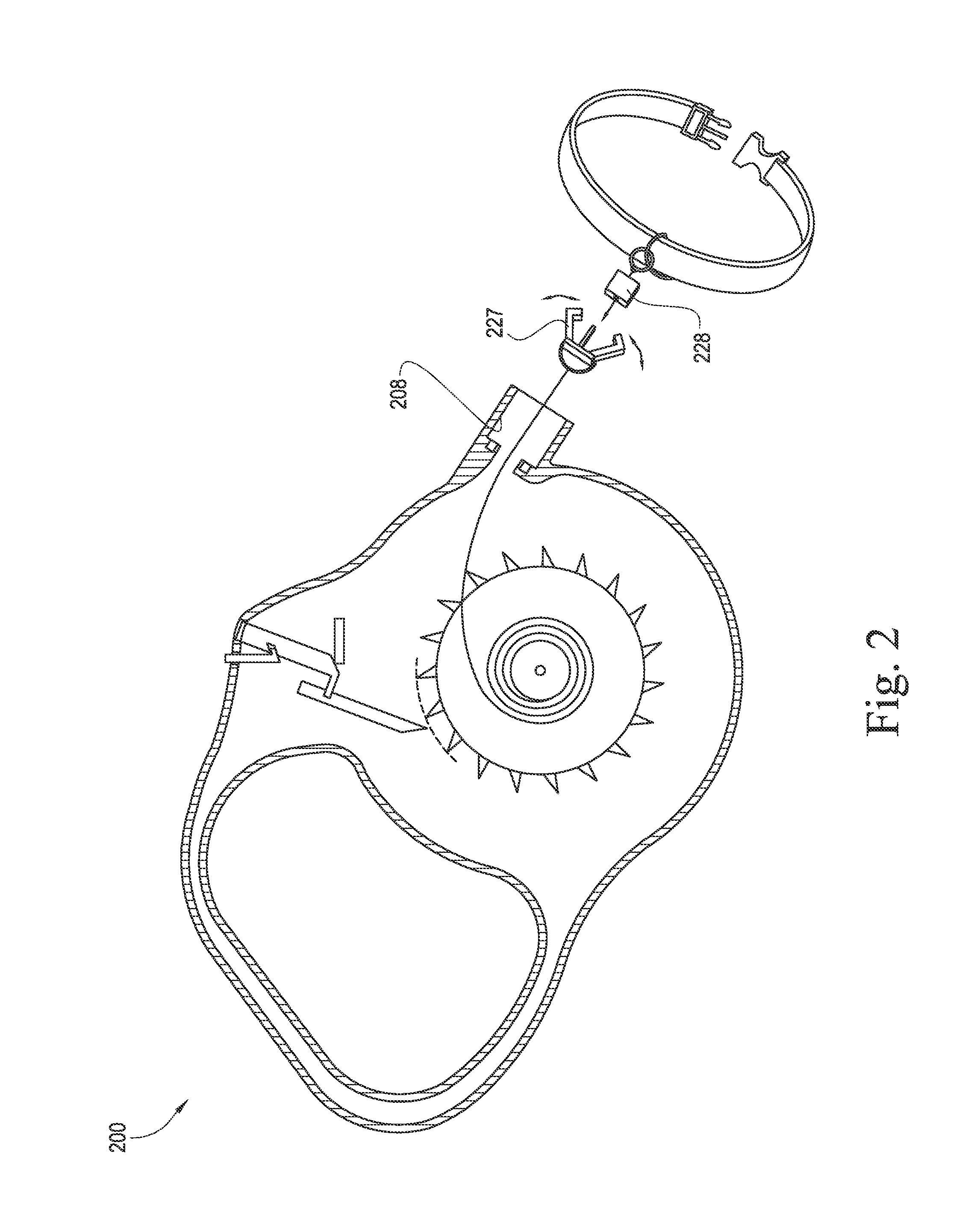
ActiveUS20160066545A1Avoid couplingReliable matingTaming and training devicesCavity wallMechanical engineering
An apparatus for tethering an animal is disclosed. The apparatus has a leash housing, a retractor assembly contained within the leash housing, a tether with a first end connected to the retractor assembly and a second end extensible through a leash connector cavity opening disposed in the leash housing and connected to a leash connector, and at least one leash connector release that is capable of being depressed by a leash connector cavity wall when the leash connector is retracted into the leash connector cavity.
Owner:SWIFTIPET
Connector assembly with a hook-in-place feel
ActiveCN102280758AReliable matingEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsIncorrect coupling preventionEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a connector assembly with hand feeling of connection in place. An inner connecting nut is rotationally sleeved at the front part of a plug shell of the connector assembly and is axially arranged on the plug shell in a limiting manner. An outer connecting cap is axially slidingly sleeved on the periphery of the inner connecting nut and is arranged on the inner connecting nut in an anti-dropping manner. Driving keys are circumferentially arranged on an inner circumferential surface of the outer connecting cap and axially extend. Matching keys are arranged circumferentially on a peripheral surface of the inner connecting nut and are meshed with the driving keys to drive when the inner connecting nut is screwed in a socket shell. A jacking step structure is arranged at the front part of the periphery of the socket shell and is jacked with the front end part of the outer connecting cap to ensure that the inner connecting nut moves forwards relative to the outer connecting cap before the inner connecting nut and the socket shell are screwed in place. Annular accommodating slots are arranged on the inner circumferential surface of the outer connecting cap, and each annular accommodating slot divides each driving key into a front part and a back part and contains each matching key when the outer connecting cap and the jacking step structure are jacked after the inner connecting nut and the socket shell are screwed in place.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION OPTICAL-ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Junction box
InactiveUS20120024558A1Achieve effectAvoid enteringCoupling device detailsGaseous cathodesFlangeHollow cylinder
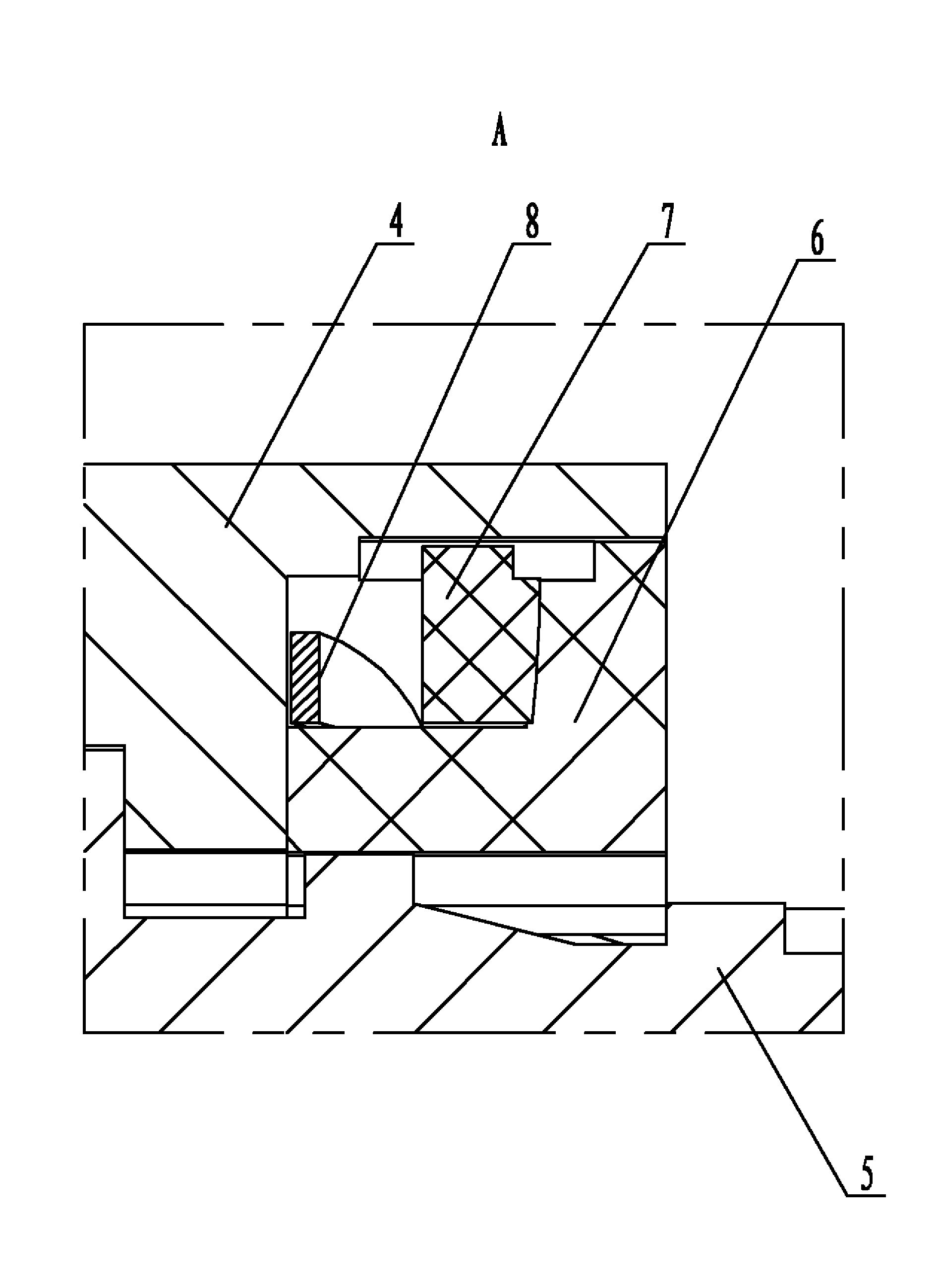
A junction box includes a base, a cover snap-fitted into the base and a ventilation valve on the cover. The ventilation valve includes a first hollow cylinder that has a first inner bore having a first thread and a bottom having an open area that includes an annular flange; a second hollow cylinder; and a waterproof air-permeable membrane. The second hollow cylinder has a second thread on an outer surface thereof, a first end, a second end and a second inner bore. The first end has an annular groove. The waterproof air-permeable membrane is disposed between the first end of the second hollow cylinder and the bottom of the first hollow cylinder. A specific distance, smaller than an axial feeding amount of the first thread when being threaded by one turn, is formed between the top of the annular flange and the top of the annular groove.
Owner:KS TERMINALS INC
Ultraviolet lamp for use in water purifiers
ActiveUS20080182454A1PolarizationReduce chanceElectric discharge tubesCouplings bases/casesEngineering
Owner:LIGHT SOURCES INC
Separation-type switching control electric connector
ActiveCN101820127AReliable matingSimple designEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCouplings bases/casesSeparated stateEngineering
The invention relates to a separation-type switching control electric connector which is composed of an adapter plug, a socket and a fixed sleeve, wherein the socket is fixedly connected with one end of the fixed sleeve by a flange disk on a base case of the socket; the adapter plug is arranged in the inner chamber of the mounting end of the fixed sleeve and is in plug-in or separation state with the socket in the inner chamber of the fixed sleeve; one end of the socket is connected with a signal input end and a signal output end, and the other end of the socket is connected with the adapter plug which is a test plug or an actual combat plug; and the test plug or the actual combat plug is respectively plugged with the socket to ensure that the signal input end and the signal output end of a socket signal are communicated with and outputs the test signal or the actual combat signal. The signal of the electric connector is input and output from the socket, is respectively connected with the socket by a plurality of adapter plugs to realize multifunctional switching without providing respective electric passages for each function, satisfies the installation requirements of high precision and small space of the internal devices of special equipment, and has compact structure and convenient and quick switch of plugging and unplugging.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND GRP HANGLIAN TECH CO LTD
Junction box
InactiveUS8273985B2Moisture is preventedAchieve effectCoupling device detailsGaseous cathodesEngineeringFlange
A junction box includes a base, a cover snap-fitted into the base and a ventilation valve on the cover. The ventilation valve includes a first hollow cylinder that has a first inner bore having a first thread and a bottom having an open area that includes an annular flange; a second hollow cylinder; and a waterproof air-permeable membrane. The second hollow cylinder has a second thread on an outer surface thereof, a first end, a second end and a second inner bore. The first end has an annular groove. The waterproof air-permeable membrane is disposed between the first end of the second hollow cylinder and the bottom of the first hollow cylinder. A specific distance, smaller than an axial feeding amount of the first thread when being threaded by one turn, is formed between the top of the annular flange and the top of the annular groove.
Owner:KS TERMINALS INC
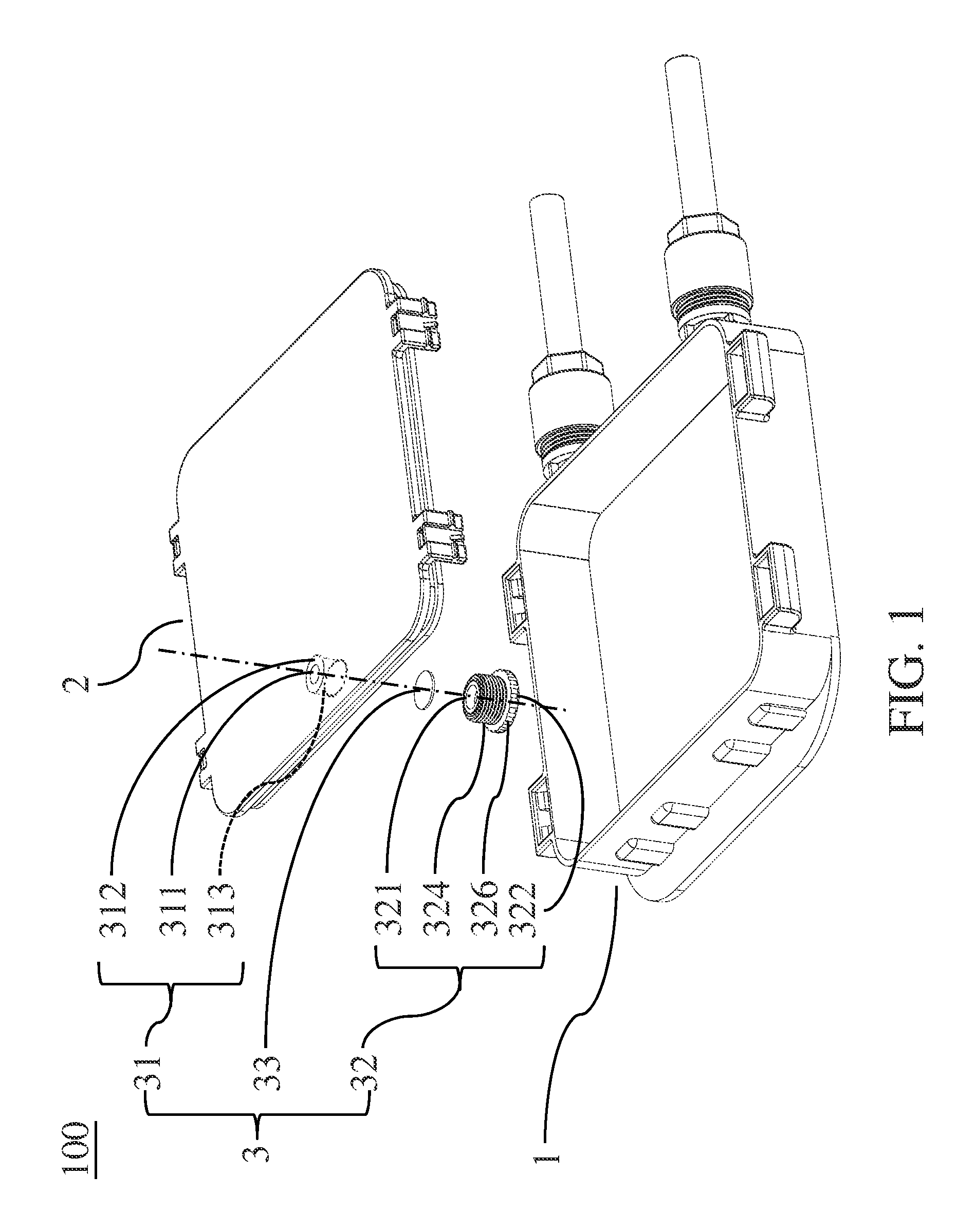
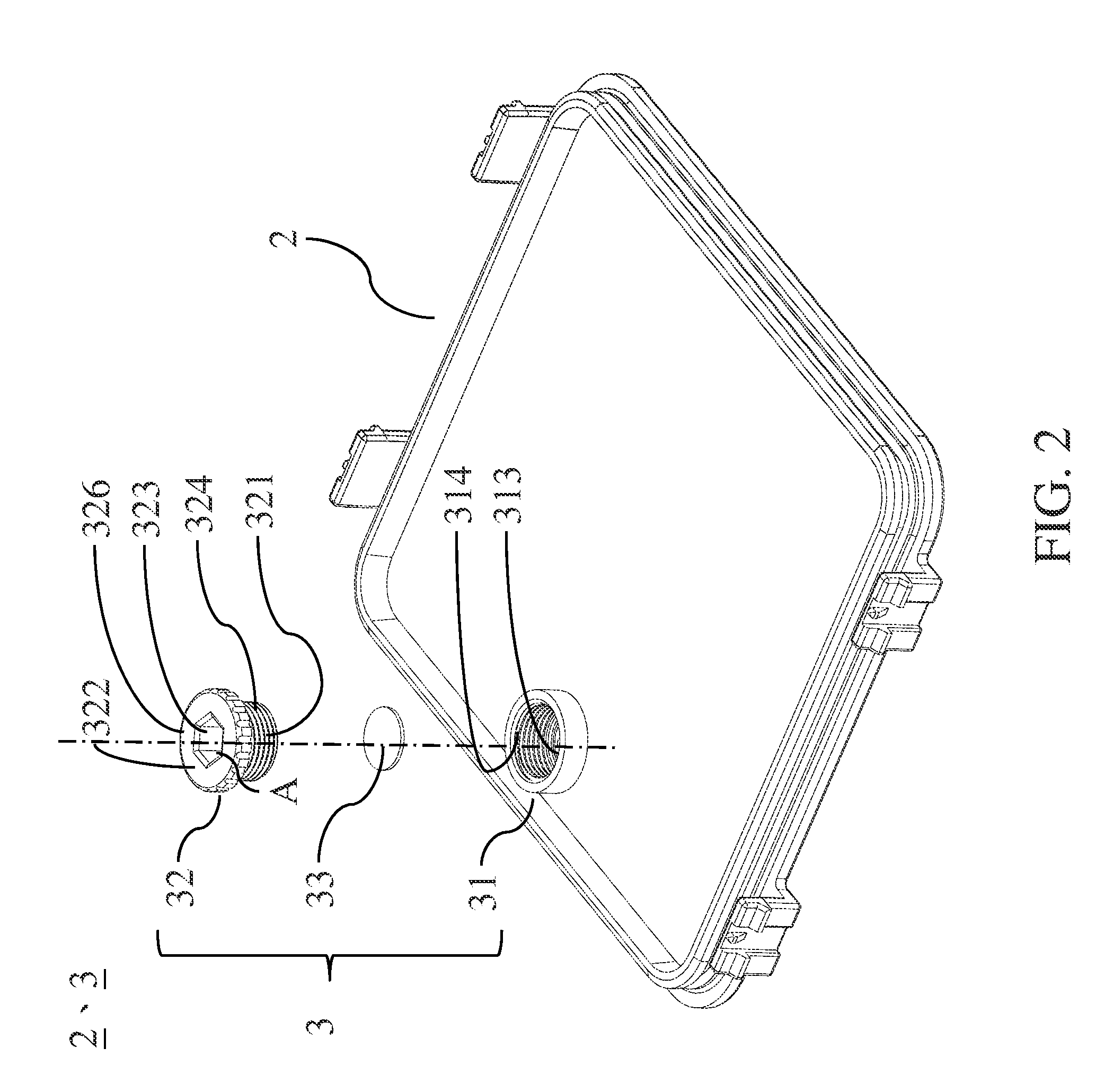
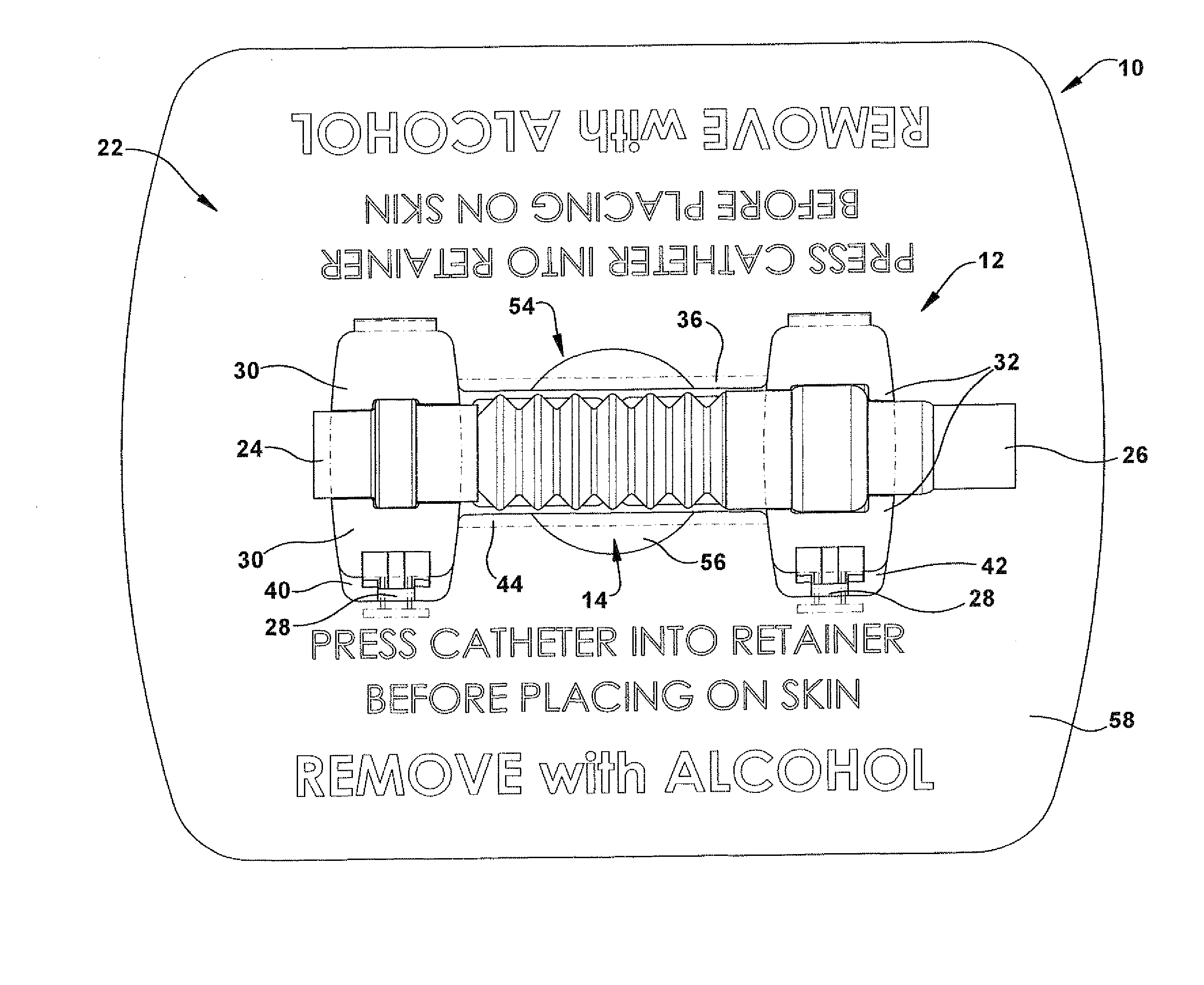
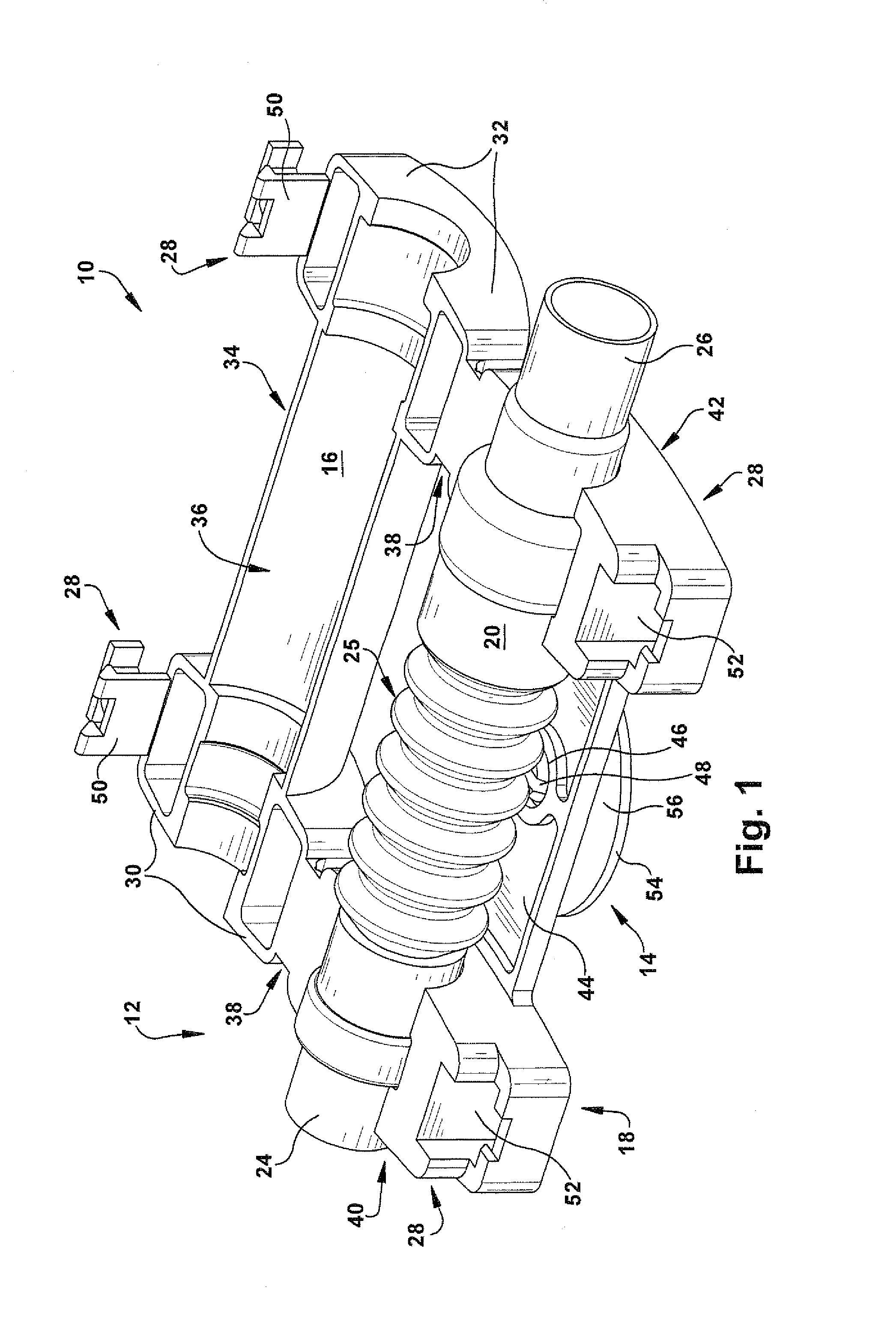
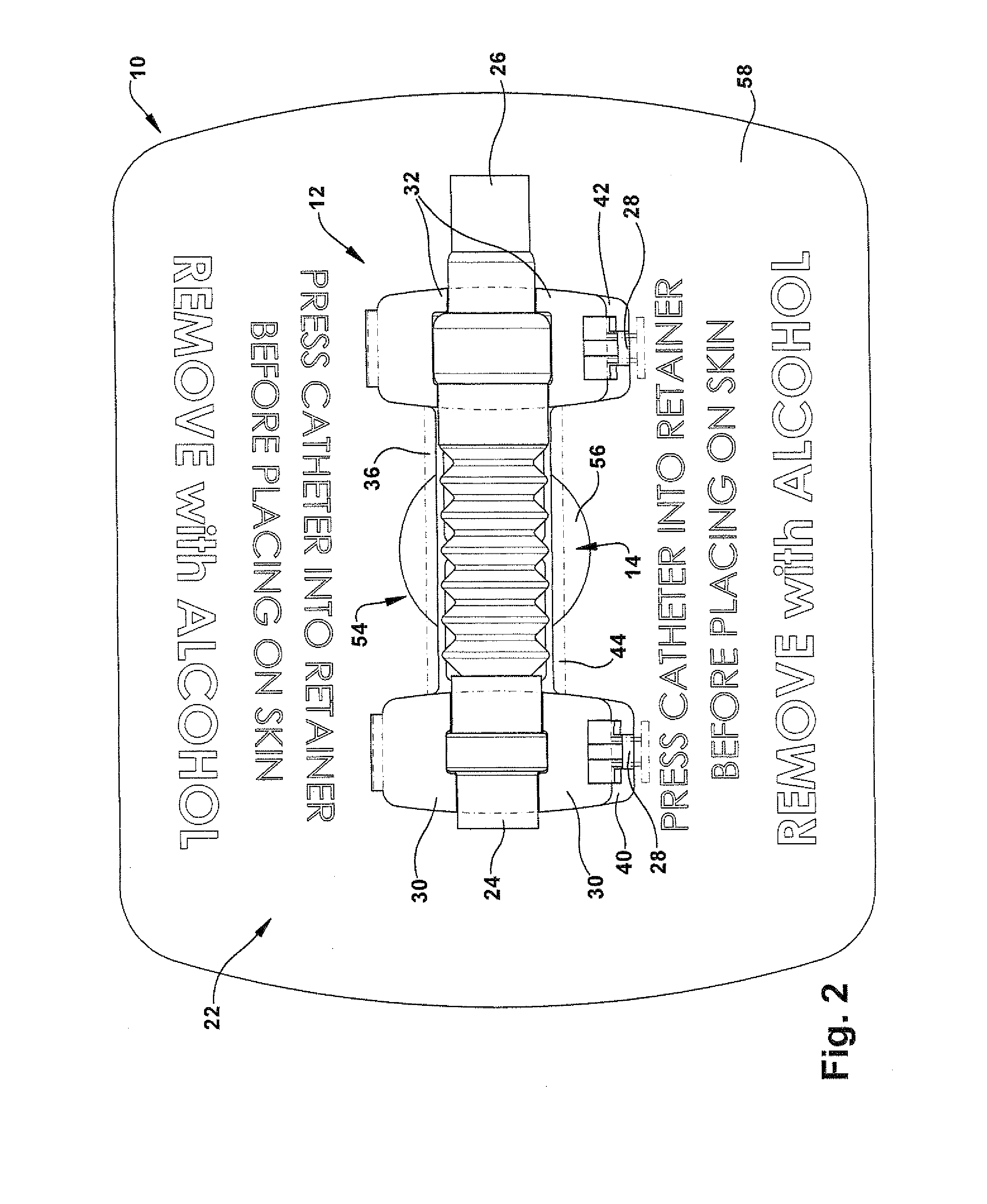
Urinary catheter stabilizer and method of use
InactiveUS20120116357A1Prevent and mitigate constrictionReliable matingWound drainsCatheterUrinary catheterStent
A urinary catheter stabilizer comprises a body member, a rotatable adhesion member, and an adhesive laminar membrane. The body member includes an upper cradle member that is hingedly attached to a lower cradle member. Each of the upper and lower cradle members is adapted to receive a bellows of a urinary catheter. The bellows includes oppositely disposed proximal and distal ends and a ribbed portion extending therebetween. Each of the upper and lower cradle members includes a proximal end portion, a distal end portion, and a main body portion extending between the proximal and distal end portions. The rotatable adhesion member is securely connected to the lower cradle member. The rotatable adhesion member includes a base portion having oppositely disposed first and second surfaces. The adhesive laminar membrane includes oppositely disposed first and second major surfaces. A portion of the first major surface is securely attached to the first surface of the base portion of the rotatable adhesion member.
Owner:HAKKY SAID I +2
Spacing aligning device based on micro rectangular floating blind-mating connector
ActiveCN107039845AGuaranteed radial centering functionGuaranteed flexibilityCoupling device detailsCircular discAxial compression
The invention relates to the technical field of a blind-mating connector, and specifically relates to a spacing aligning device based on a micro rectangular floating blind-mating connector. The spacing aligning device based on a micro rectangular floating blind-mating connector mainly includes an automatic aligning mechanism and a rectangular floating plug, wherein the rectangular floating plug is arranged at the upper end of the automatic aligning mechanism, and is fixedly connected with the automatic aligning mechanism; the automatic aligning mechanism mainly includes a slide disc, a disc spring, a cladding disc and axial compression springs; the disc spring is arranged on the upper end surface of the slide disc, and is fixedly connected with the slide disc; the cladding disc is arranged on the disc spring in a back-off manner; and the axial compression springs are arranged at the lower end surface of the slide disc. The spacing aligning device based on a micro rectangular floating blind-mating connector has the advantages that through limitation on the connector by means of spacing frames, an axial floating spring, the automatic aligning mechanism and a mounting support, the floating plug can automatically return to the axial and radial central positions and cannot move randomly, thus guaranteeing that guide pillars of the connector are aligned with and smoothly plugged in guide sleeves.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Coaxial connector
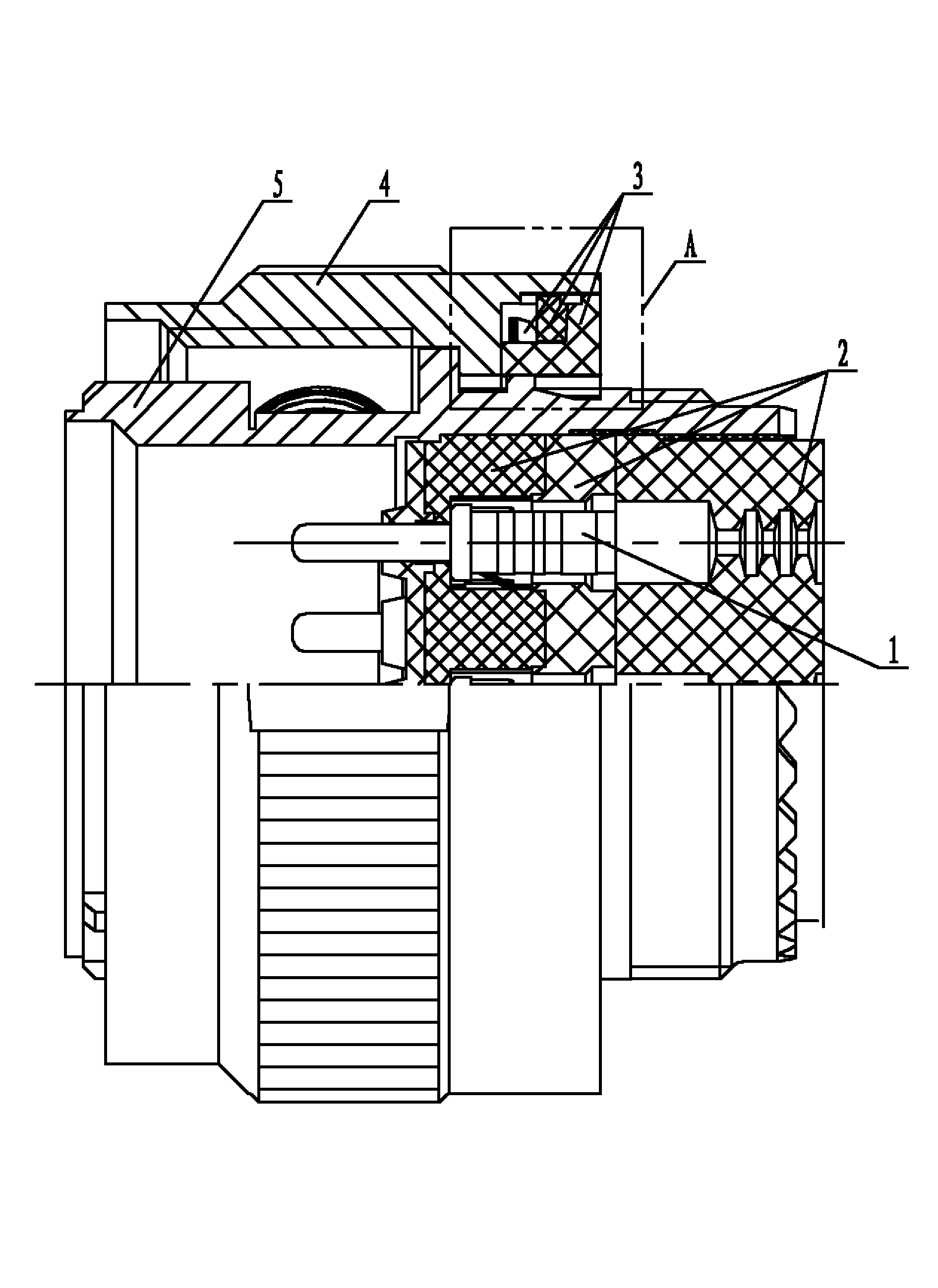
InactiveUS20050272310A1Improve electrical performanceWide applicationLine/current collector detailsSoldered/welded conductive connectionsSolderingEngineering
A coaxial connector for connection with a coaxial cable has an insulative sleeve, a connection member, and a conductive terminal. The connection member is a tubular conductive structure. The insulative sleeve is positioned in the connection member. The connection member has an inscribed surface formed at a rear end thereof. The conductive terminal has a positioning recess formed at a rear end thereof for soldering with a core of the coaxial cable. A conductive layer of the coaxial cable is penetrated into the rear end of the connection member and is adjacent to the inscribed surface for soldering with the connection member. Therefore, the connection between the coaxial cable and the coaxial connector is easy, and the position of the coaxial cable is accurate. Moreover, because it is not necessary to spread the conductive layer of the coaxial cable, it maintains a better electrical property, so as to have a broad application, a wide range of frequency, and a high stability and small loss of signals thereof.
Owner:MOLEX INC
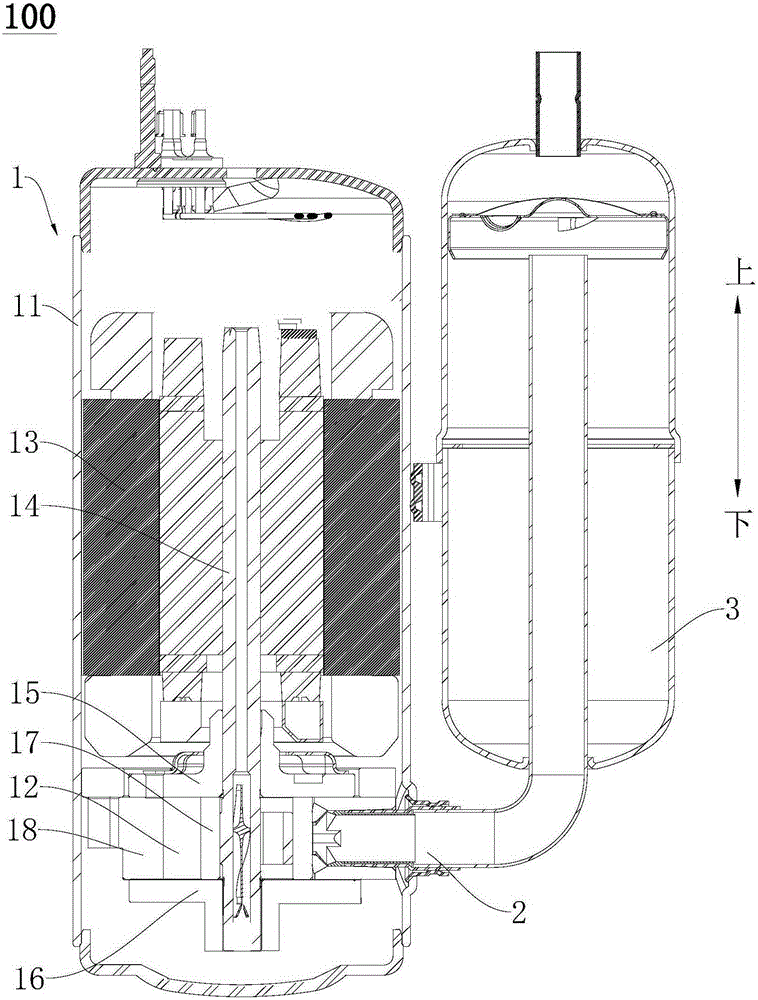
Compressor assembly
ActiveCN105221435AImprove reliabilitySmooth matingRotary/oscillating piston pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsEngineeringWelding
The invention discloses a compressor assembly which comprises a compressor and an air sucking pipe assembly. The compressor comprises a shell and a compression mechanism. The compression mechanism is provided with a compression cavity. The air sucking pipe assembly is used for guiding refrigerants into the compression cavity. The air sucking pipe assembly comprises a connecting pipe, an air guiding pipe and an air sucking pipe. The part, located outside the shell, of the connecting pipe is provided with a first welding pipe section. The first welding pipe section and the outer end of the connecting pipe are spaced. The inner end of the air guiding pipe penetrates in the connecting pipe and is communicated with the compression cavity. The air guiding pipe is provided with a second welding pipe section. The second welding pipe section and the first welding pipe section are connected in a laser welding manner, and the inner end of the air sucking pipe penetrates in the air guiding pipe and is communicated with the air guiding pipe. According to the compressor assembly, due to the fact that the non-exterior end of the air guiding pipe and the non-exterior end of the air sucking pipe are connected in a laser welding manner so that welding sealing can be formed between the connecting pipe and the air guiding pipe, and the reliability of the compressor assembly can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIZHI COMPRESSOR +1
Locking strap holder-seamer
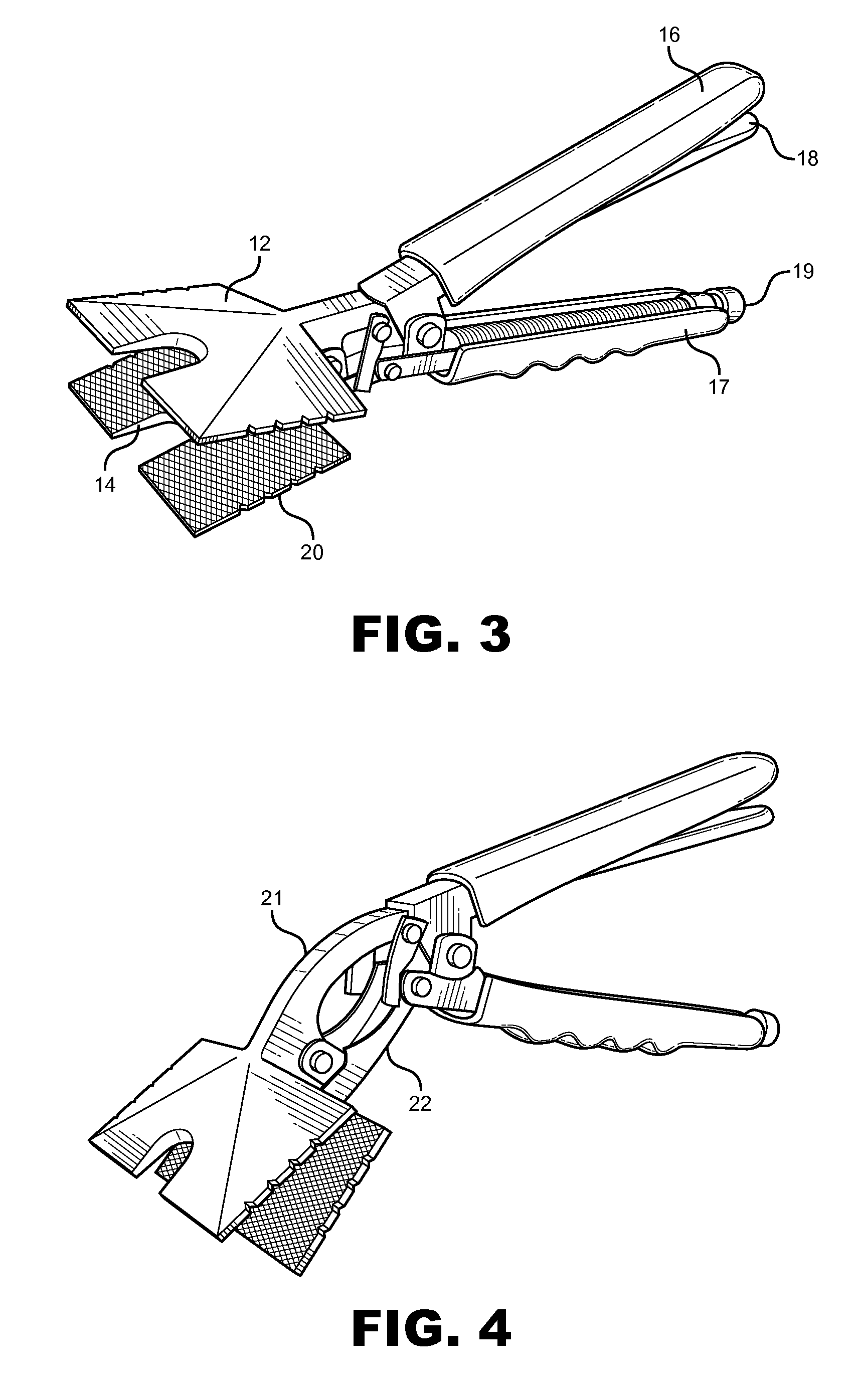
A lockable pipe support holding device of the plier type is provided, having large flat jaws for gripping pipe straps, shoes, hangers and materials. The jaws have a textured inner surface and notched grooves along the lateral edges to promote firm grip on metal and bending of the same. A “U” shaped recess along the front edge of the jaws allows fasteners to be inserted into a strap or similar object being securely held by the tool. A user may adjust the gap between jaws by means of an adjustment screw in a handle. In addition the jaws may be locked in place and then unlocked by means of a lever housed in a handle. Consequently, a user may insert fasteners into a working area of an object without having to hold onto the tool while doing so.
Owner:FACHORN MARK
Reinforced bolt
InactiveCN103291152AReasonable designEasy to useConstruction fastening devicesBiomedical engineering
Owner:KUNSHAN ZHIKE HARDWARE PROD
Floating connector
ActiveCN103606784AAddress blind-mating installation requirementsReliable matingCoupling device detailsSpherical angleEngineering
The invention relates to a floating connector. A structure of the floating connector comprises an outer connector casing, an inner floating casing, an arc sleeve and a connection member, wherein an outer side of a tail portion of the inner floating casing is a spherical structure, an end face of the tail portion of the inner floating casing is provided with symmetrical straight slots in a radial direction, an inner side of the arc sleeve is a spherical inner wall which is in matching with an outer spherical structure of the tail portion of the inner floating casing, mutual rotation can be realized, the connection member penetrates through the outer connector casing and is plugged in the straight slots of the inner floating casing, elastic members with different heights at two ends are arranged between the outer connector casing and the inner floating casing, and an axial line of the inner floating casing and an axial line of the outer connector casing have a deflection angle and are superposed when rotation to a certain angle is realized. According to the floating connector, a spherical angle rotation structure is utilized, blind plugging requirements for two angle-rotation abut panels are effectively satisfied, when the panels are mounted and dimension deviation occurs in a product, position correction of one floating end can be carried out automatically, and thereby smooth plugging of a fixedly-mounted plug or socket can be realized.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 23 RES INST
Slip fit quick disconnect pipe coupler
ActiveUS20060279079A1Easy to disassembleReliable matingPump componentsJoints with sealing surfacesCouplingEngineering
A slip fit quick disconnect pipe coupler having an insertion portion and a housing portion which mate to form a sealed coupling between pipes. The coupler uniquely provides positive pipe coupling with extreme ease of disassembly or dis-connection of two pipes. The coupler utilizes a uniquely designed L-shaped tool which allows quick decoupling and easy removal of the separated insertion portion and attached pipes without the need for a plumbing technician to lean or crawl into the space occupied by the coupler.
Owner:WEBER PATENT HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com