Process and device for smelting ferronickel and nickel-containing molten iron by using lower-nickel materials
A technology of molten nickel iron and materials, applied in the field of equipment to realize this process, can solve the problems of high sulfur content, high process cost, high energy consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
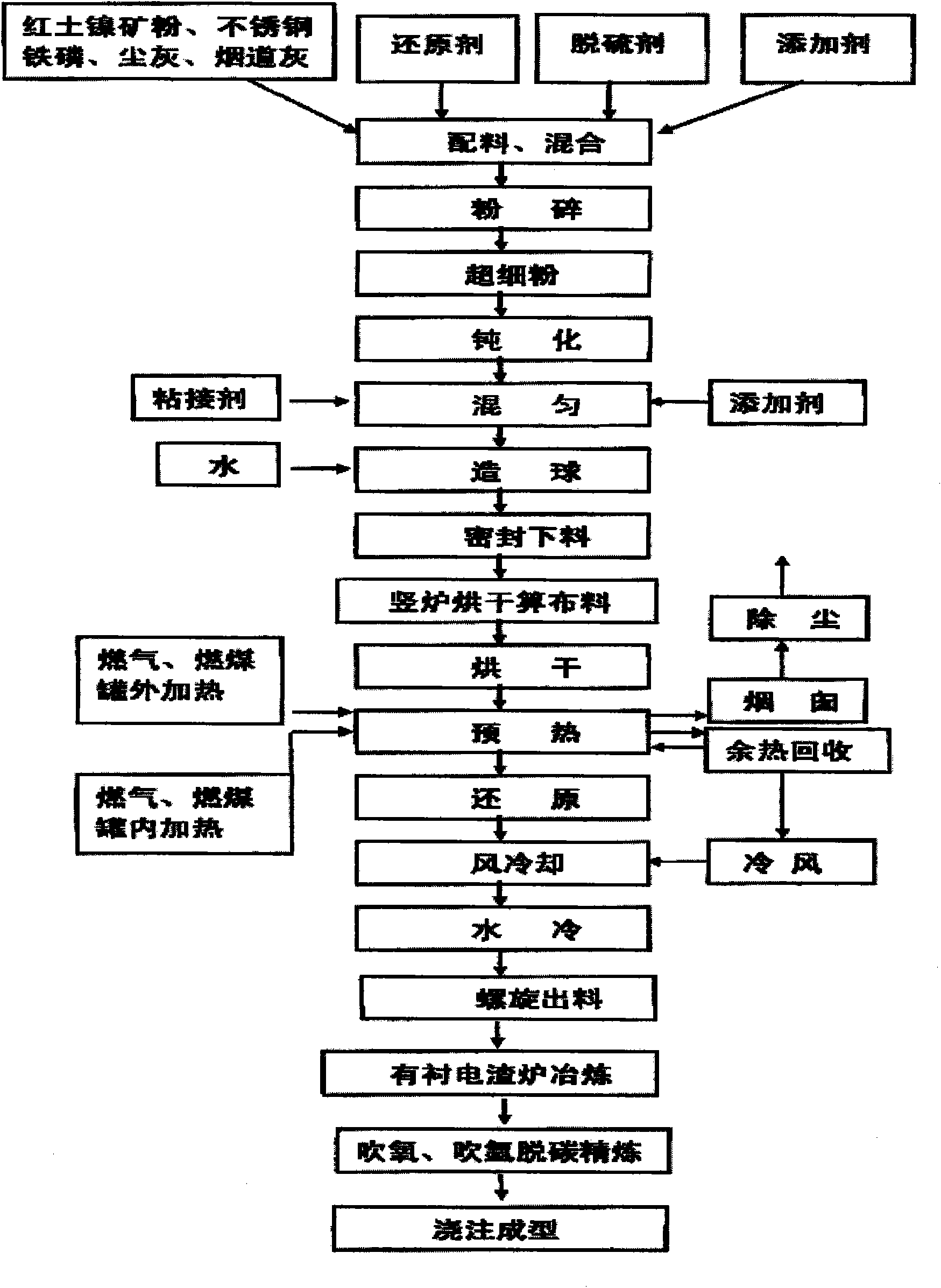
[0083] Example 1: figure 1 For the process flow diagram of the present invention, in figure 1 Among them, the process scheme to solve its technical problems is:
[0084] Mix ferronickel-containing raw materials with reducing agent, flux, and catalytic additives, and after mixing, crush them to below 200 meshes to make a mixture; then put the mixture into a ball mill for ball milling to prepare superfine powder. Carry out passivation; add water to dissolve in the catalytic additive to obtain an aqueous solution, mix the superfine powder, aqueous solution and binder together, and form a pellet after mixing evenly: ignite the fuel in the internal and external heaters in the vertical reduction furnace, and put The prepared pellets are sent into the reduction furnace through the screw feeder, and are evenly and loosely arranged on the grate of the drying bed to dry the pellets, and then roast the pellets after drying. CO, H in the roasting area and in the gas 2 React with the hy...
Embodiment 2
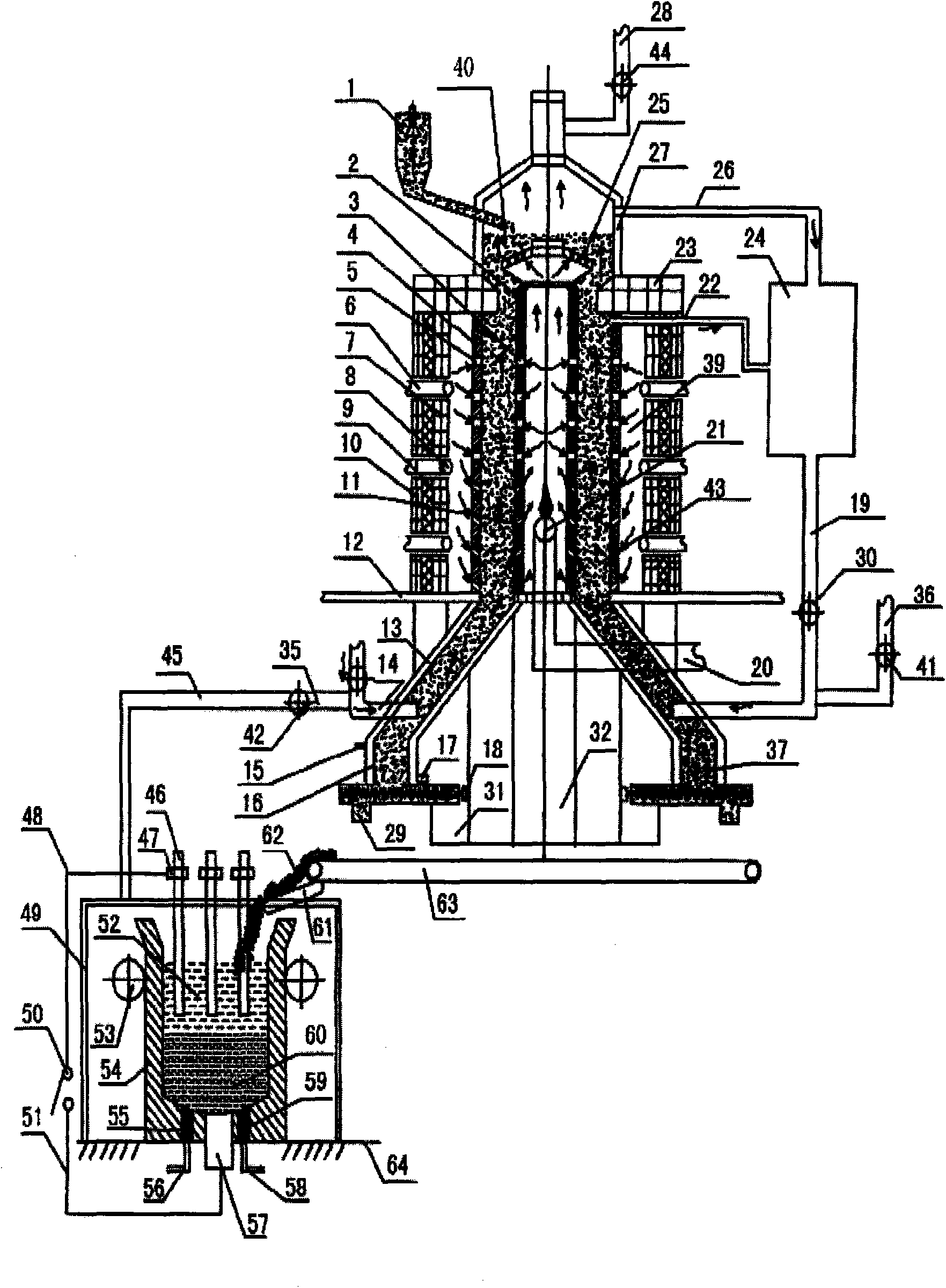
[0105] Example 2: figure 2 It is the first equipment structure diagram of the present invention, in figure 2 Among them, the equipment scheme that the present invention solves its technical problem is:
[0106] This equipment is composed of two systems of reduction equipment and smelting equipment. Wherein the reduction equipment adopts the shaft furnace body structure, and the reduction equipment includes a furnace base (12), an upper furnace body, a lower furnace body, an upper furnace cover, a drying bed furnace grate (25), a sealed feeding device (1), Purification device and waste heat circulation device, the upper furnace body is connected above the furnace base, the lower furnace body is connected below the furnace base, the upper furnace cover is connected to the upper end of the upper furnace body, and the drying bed furnace grate is located on the upper At the upper end of the furnace body, the purification device is connected with the upper furnace body and the l...
Embodiment 3
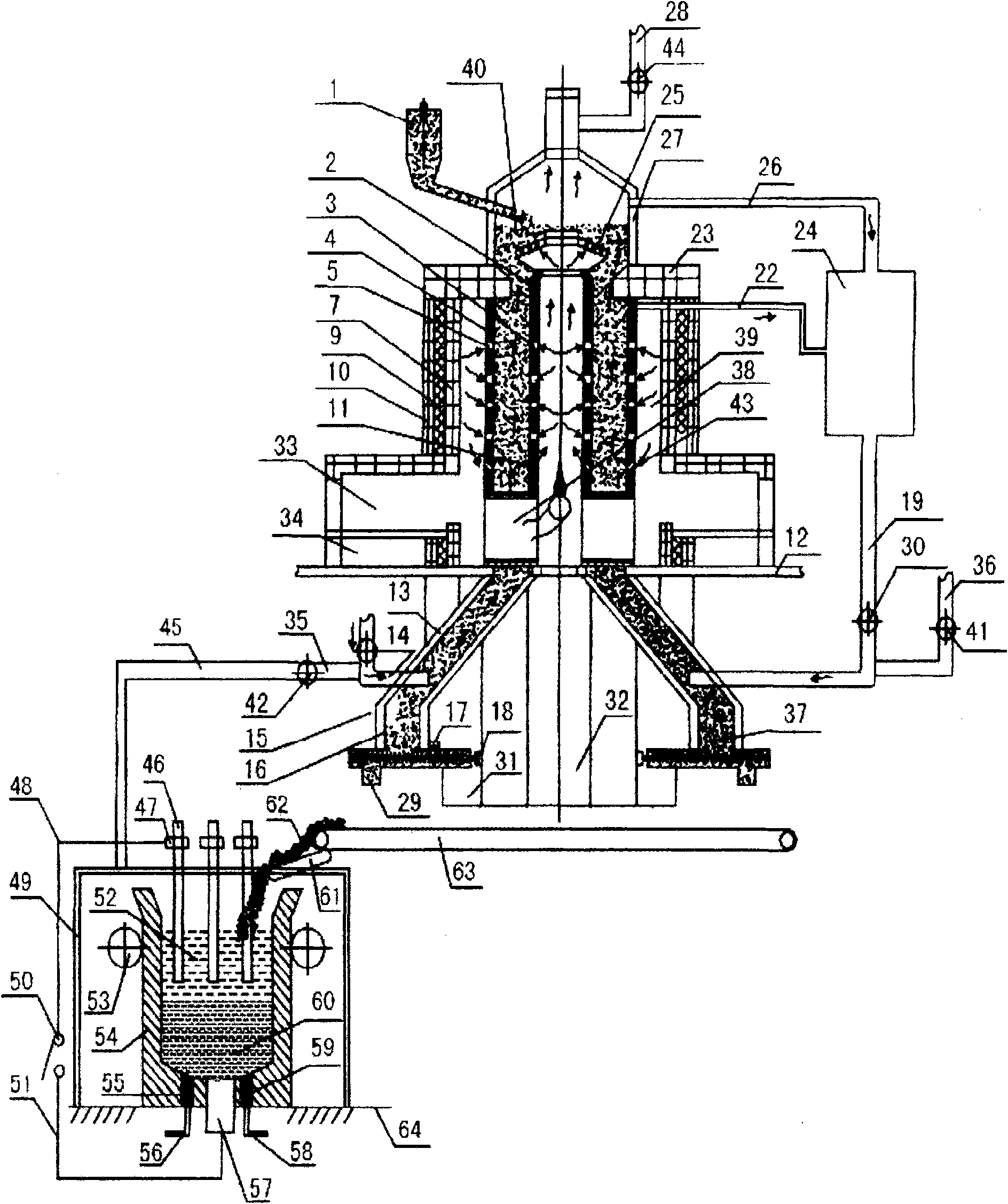
[0123] Example 3: image 3 It is the second equipment structure diagram of the present invention, in image 3 Among them, the upper furnace body in the reduction equipment includes an inner heating tank 2, a reducing gas outlet 3, an outer heating reduction tank 4, a heating air inlet 5, a refractory brick 7, a refractory fiber 9, a reduction furnace shell 10, and internal and external heating Tank air inlet 11, coal-fired combustion chamber 33, slag discharge chamber 34, internal heating channel 38, heating chamber 39, roasting reduction zone 43, reduction furnace shell, refractory brick layer, external heating reduction tank and internal heating tank are set in sequence , the reduction furnace shell is located at the outermost layer, the inner heating tank is located at the innermost layer, the coal-fired combustion chamber 33 and the slag discharge chamber 34 are located at the lower end of the upper furnace body, and the internal heating channel 38 is located at the inner ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com