Patents
Literature
67 results about "Native resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
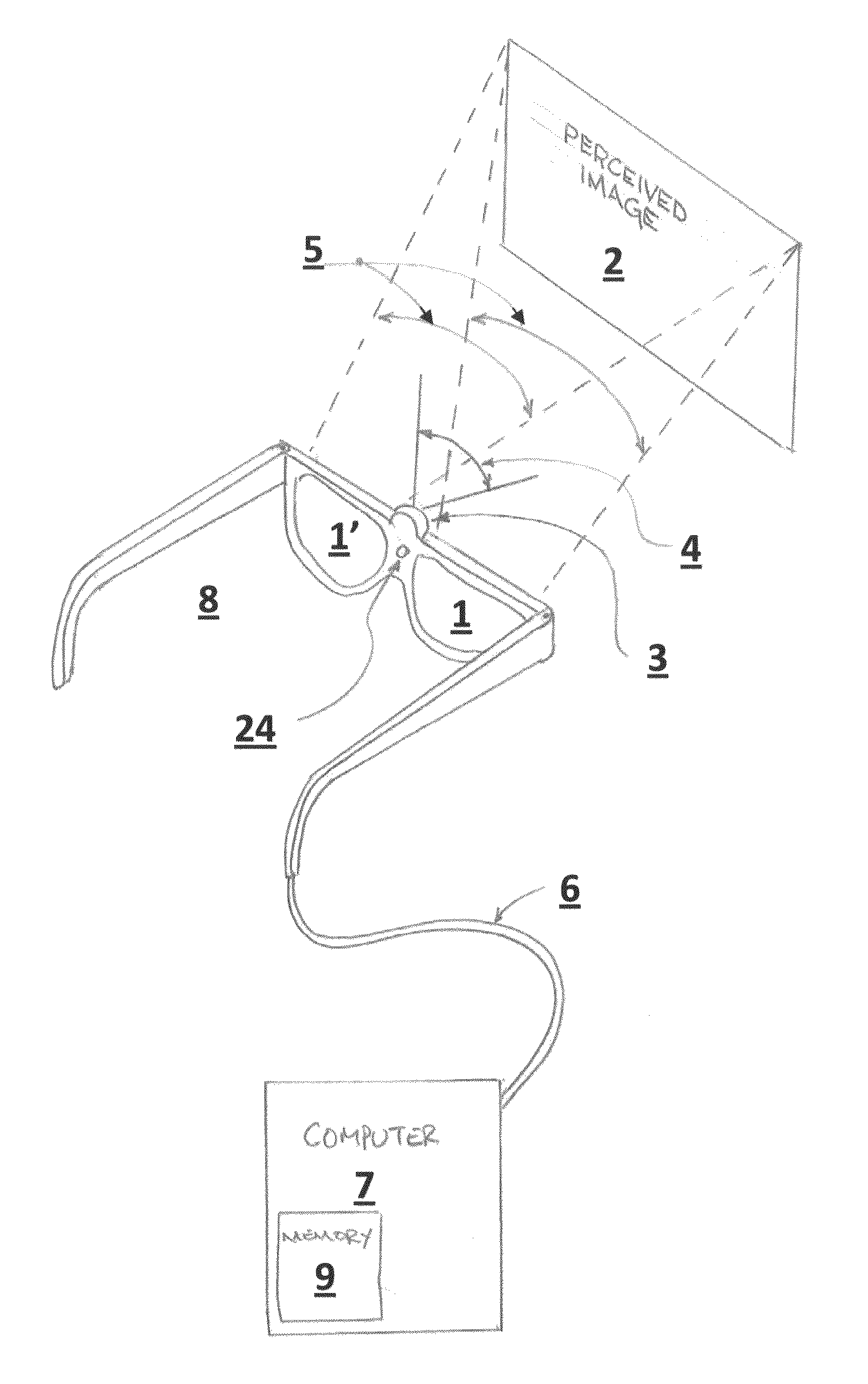
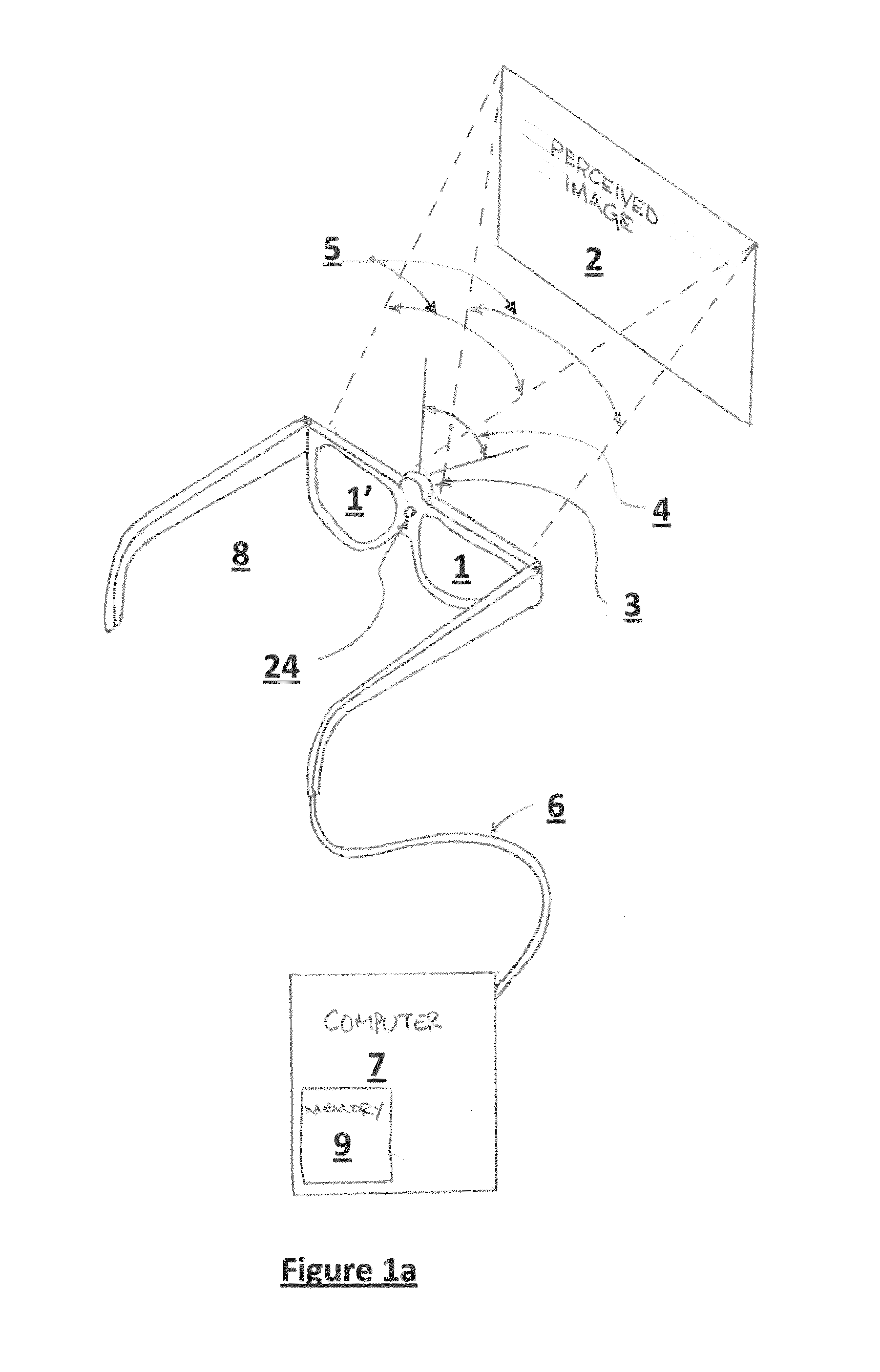
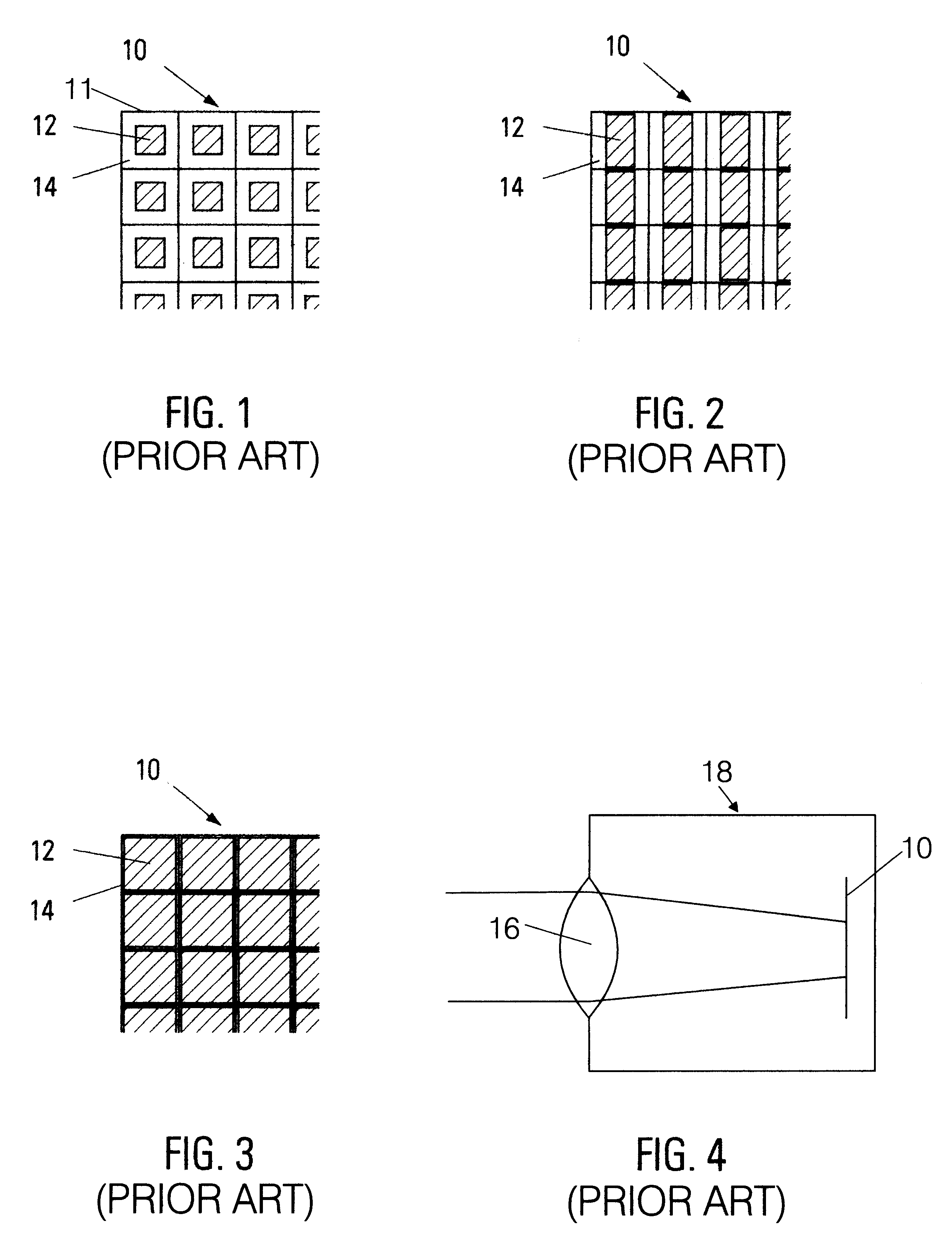
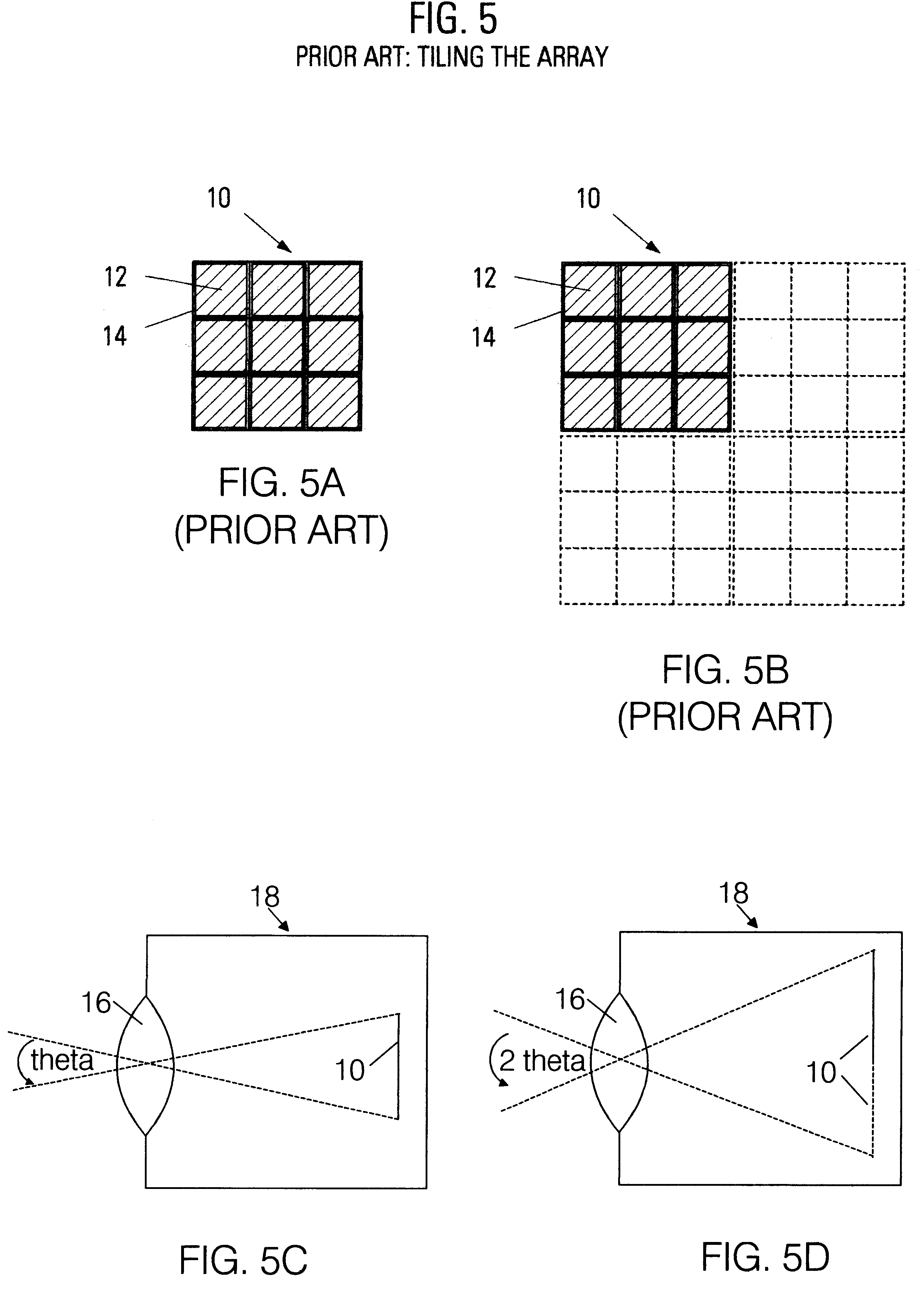
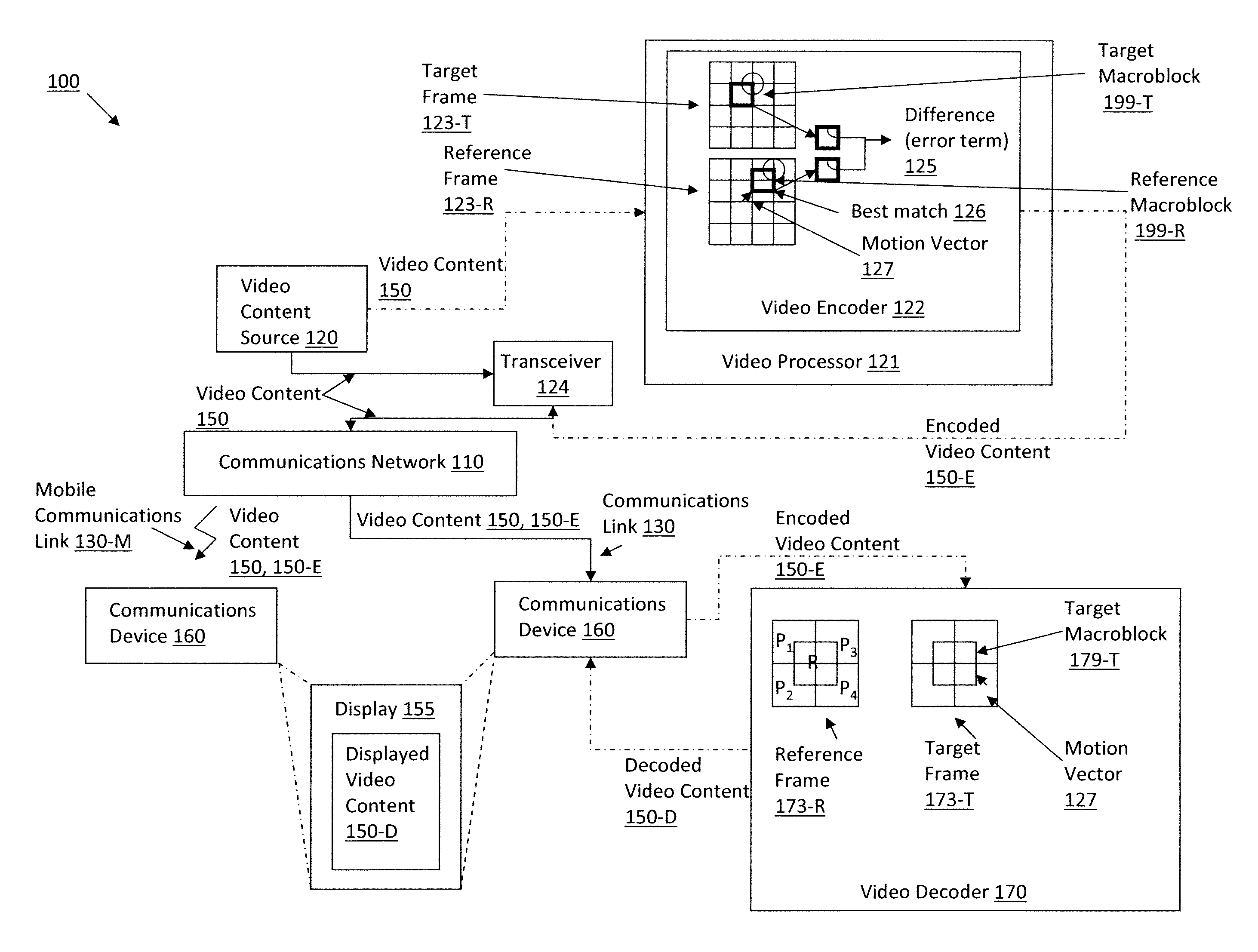
The native resolution of a LCD, LCoS or other flat panel display refers to its single fixed resolution. As an LCD consists of a fixed raster, it cannot change resolution to match the signal being displayed as a CRT monitor can, meaning that optimal display quality can be reached only when the signal input matches the native resolution. An image where the number of pixels is the same as in the image source and where the pixels are perfectly aligned to the pixels in the source is said to be pixel perfect.
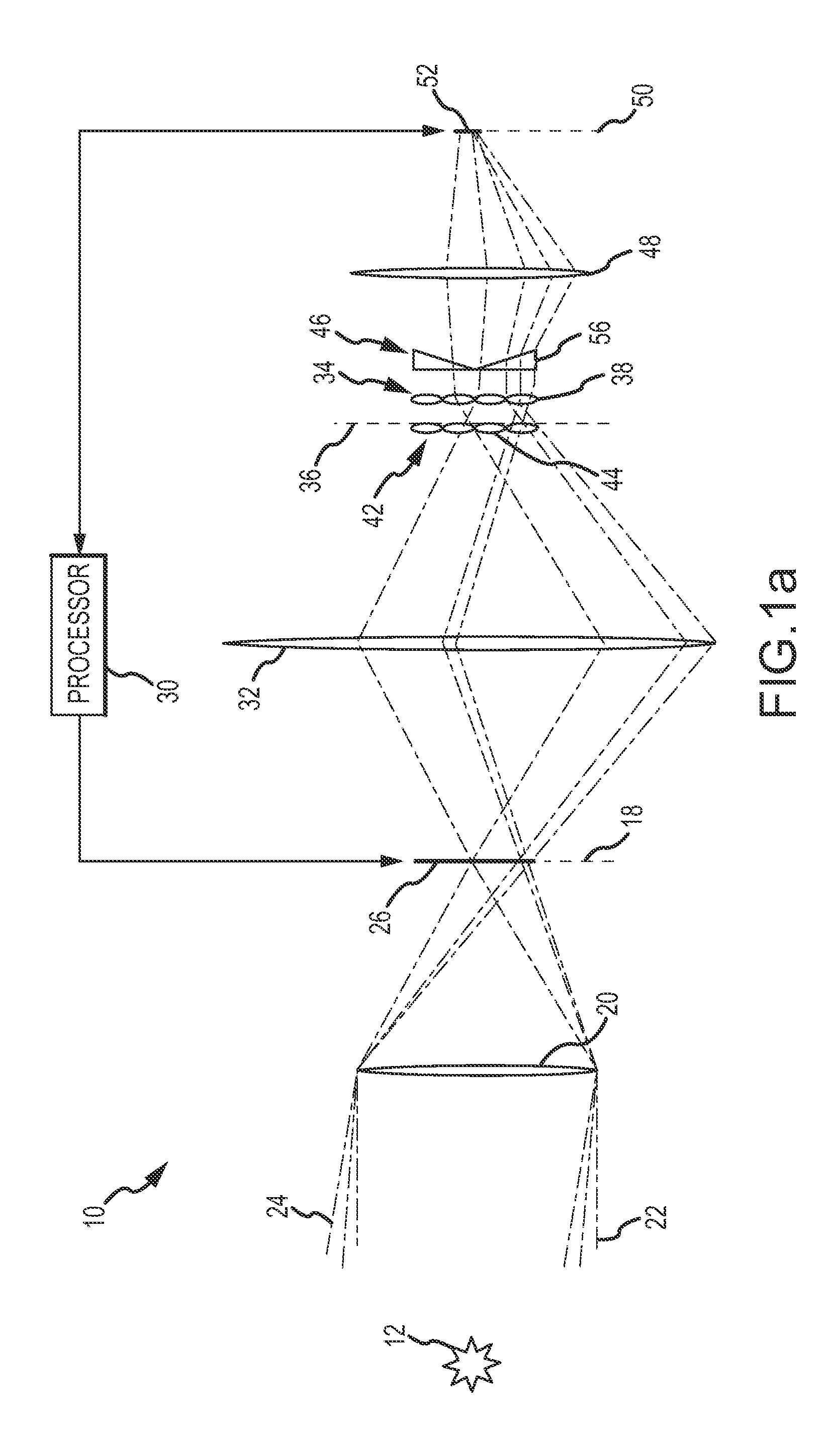
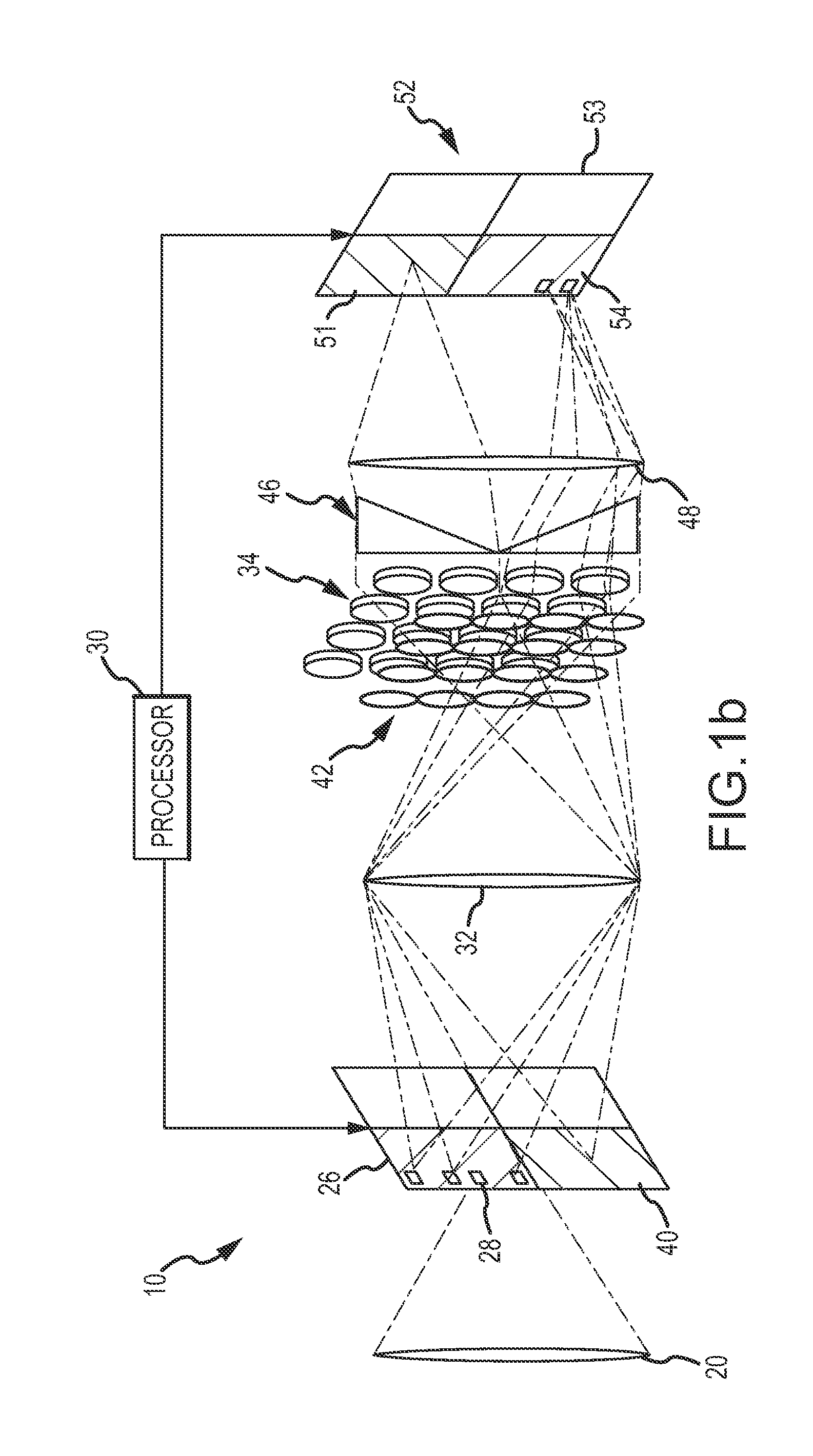
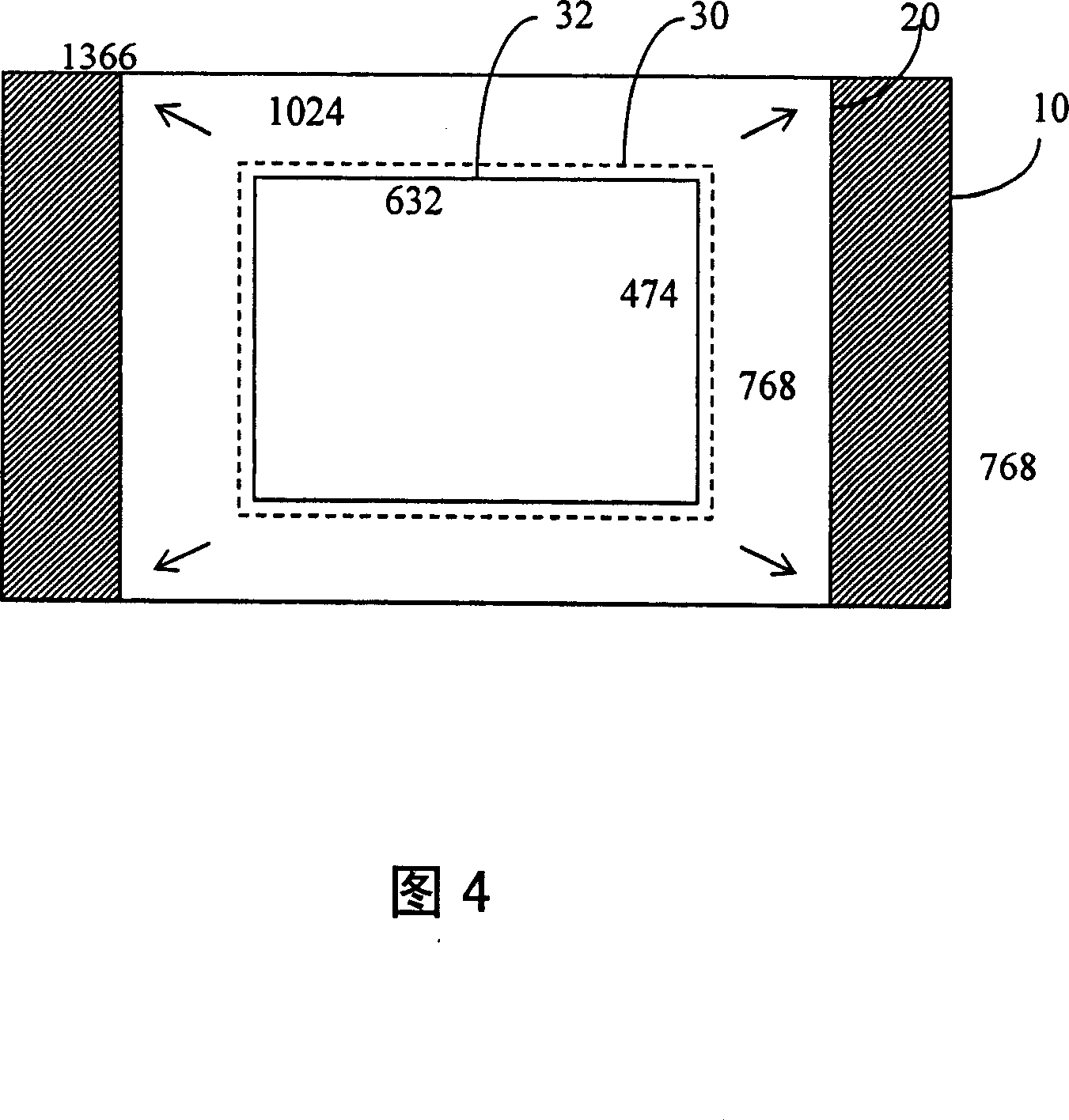
Apparatus and Method for a Dynamic "Region of Interest" in a Display System
ActiveUS20110043644A1Improve usabilityLower latencyTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage resolutionNative resolution
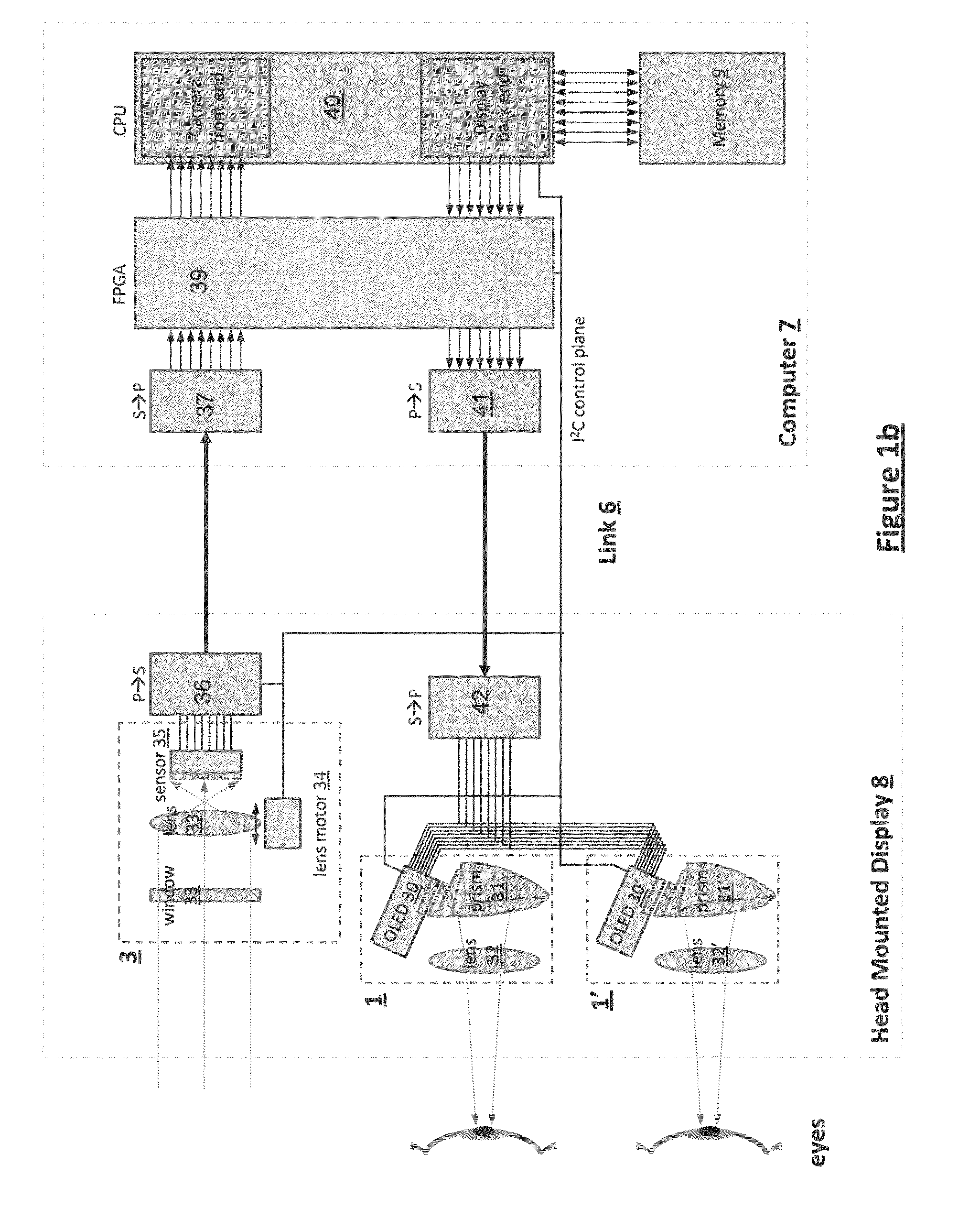
A method and apparatus of displaying a magnified image comprising obtaining an image of a scene using a camera with greater resolution than the display, and capturing the image in the native resolution of the display by either grouping pixels together, or by capturing a smaller region of interest whose pixel resolution matches that of the display. The invention also relates to a method whereby the location of the captured region of interest may be determined by external inputs such as the location of a person's gaze in the displayed unmagnified image, or coordinates from a computer mouse. The invention further relates to a method whereby a modified image can be superimposed on an unmodified image, in order to maintain the peripheral information or context from which the modified region of interest has been captured.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Resolution-enhancement method for digital imaging
InactiveUS6570613B1High resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital imagingImage resolution
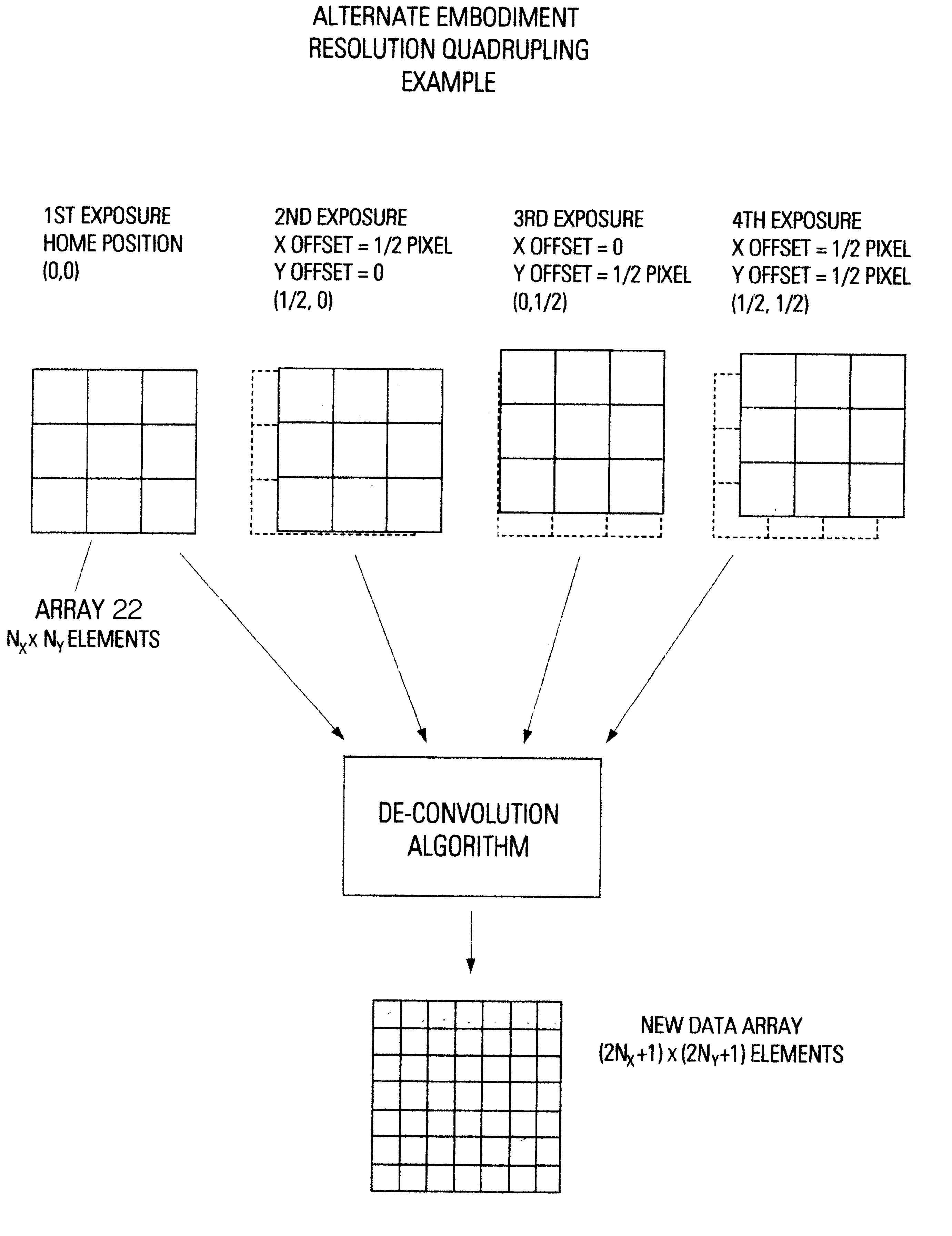
A method for resolution enhancement of a still-image made by a digital imaging device. The method allows the use of high-aperture-ratio sensing arrays that produce resolution-enhancement, independent of the angle of view. Resolution-enhancement is achieved using a multiple-exposure technique of a sub-pixel overtap in conjunction with a whole-pixel shift. The method suppresses color-aliasing in a multiple-exposure native-resolution mode and enables the use of a single camera for single-exposure and multiple-exposure modes.
Owner:HOWELL
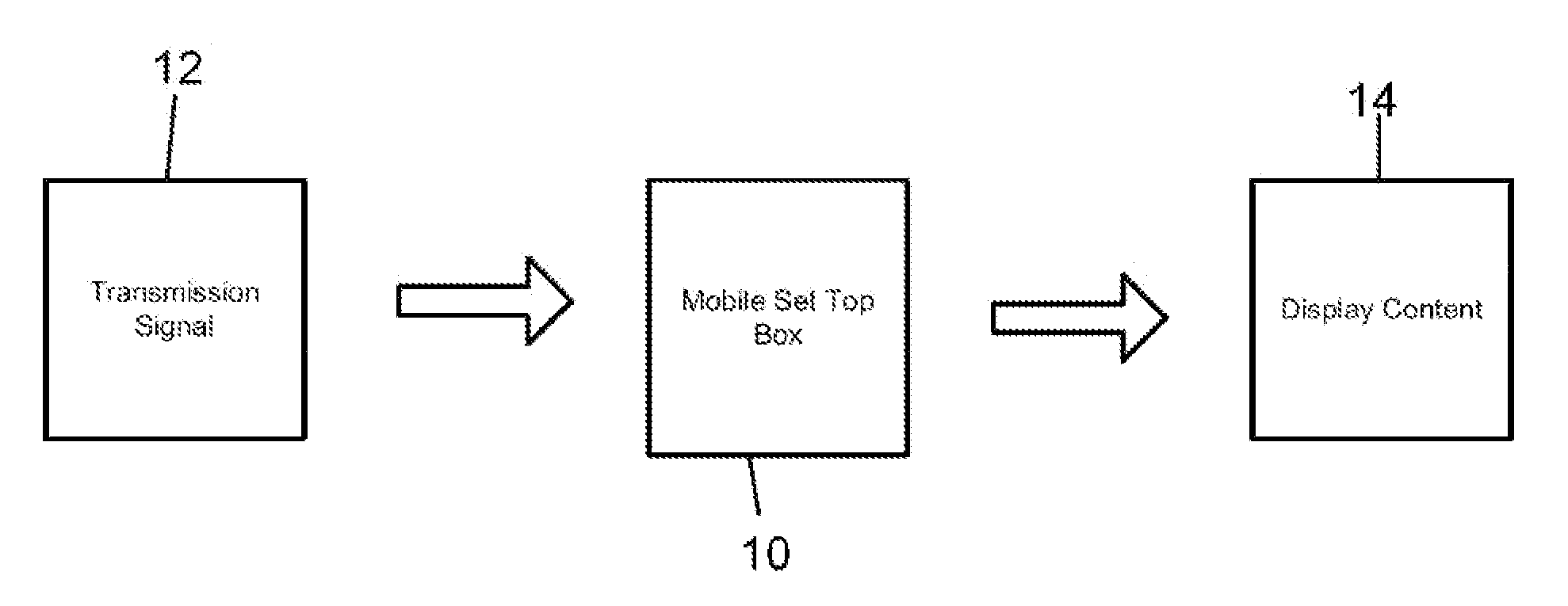
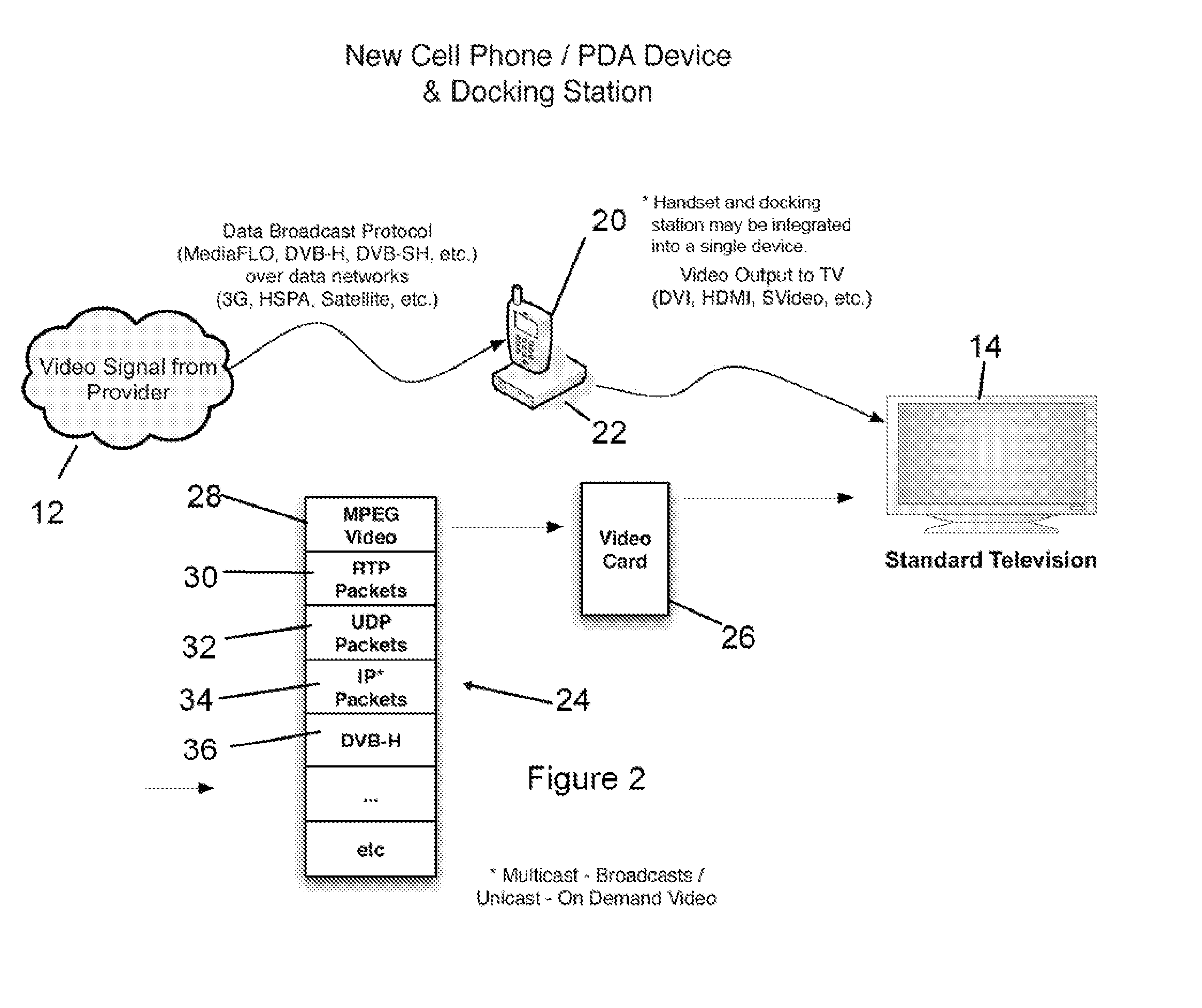
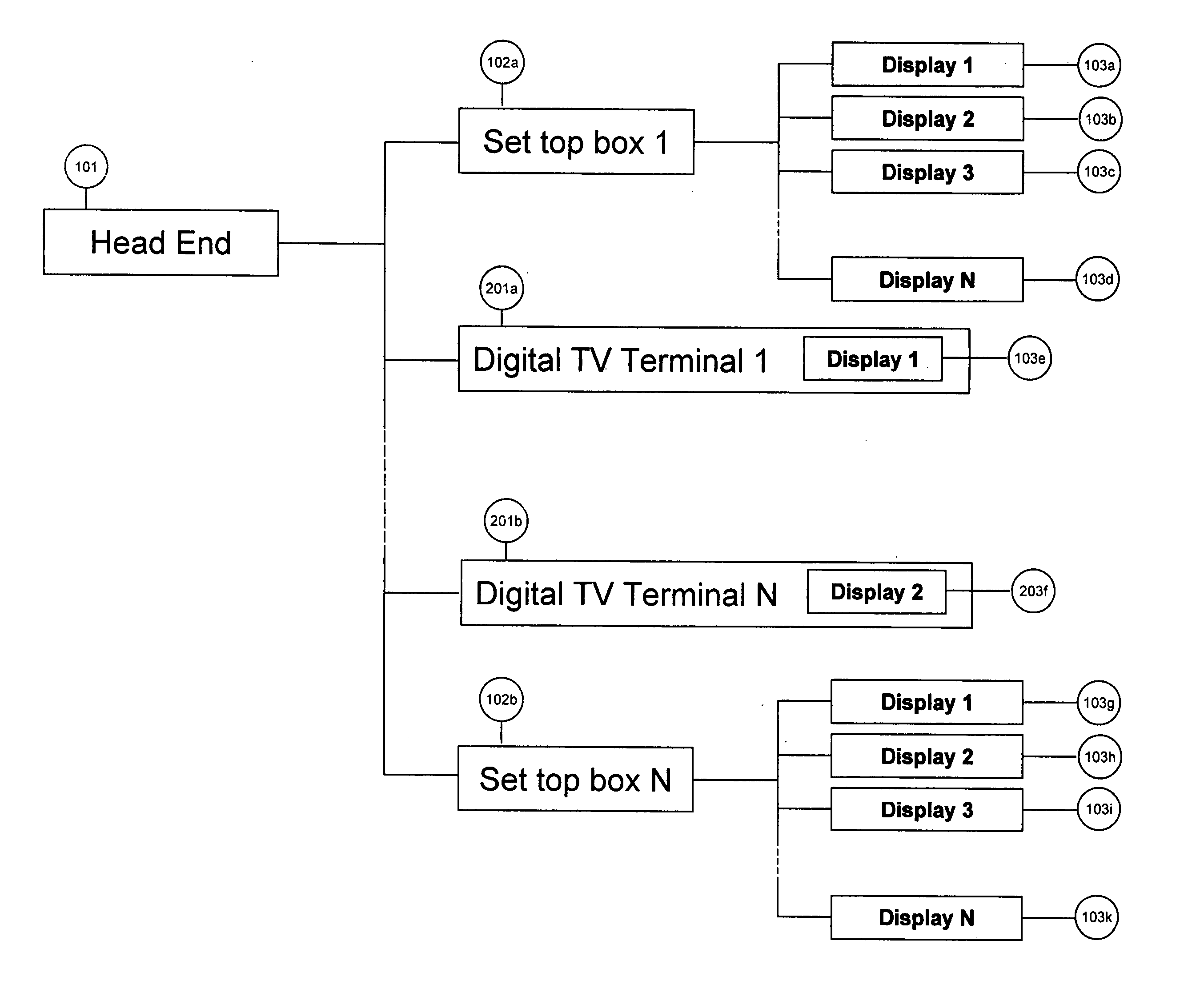
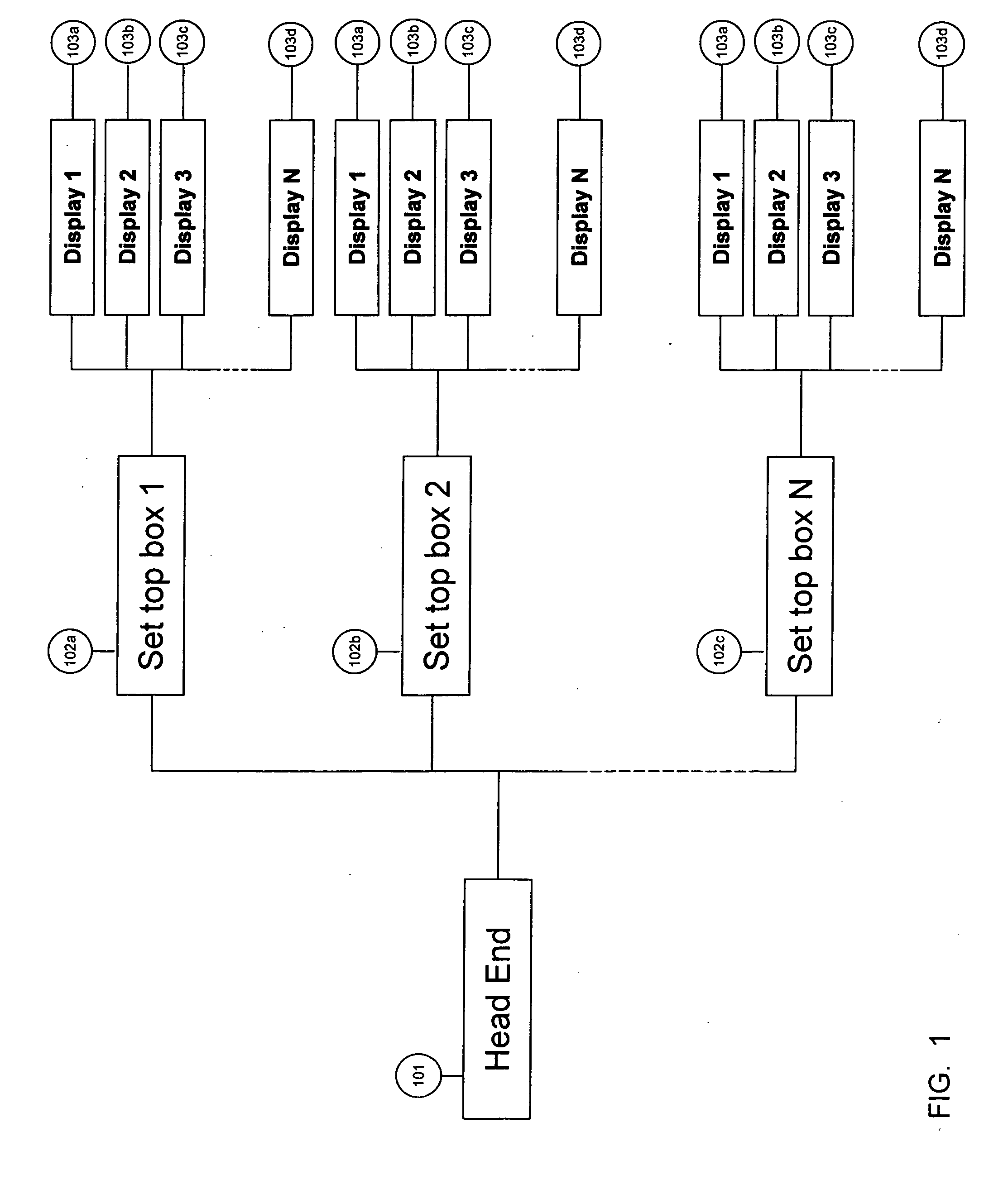
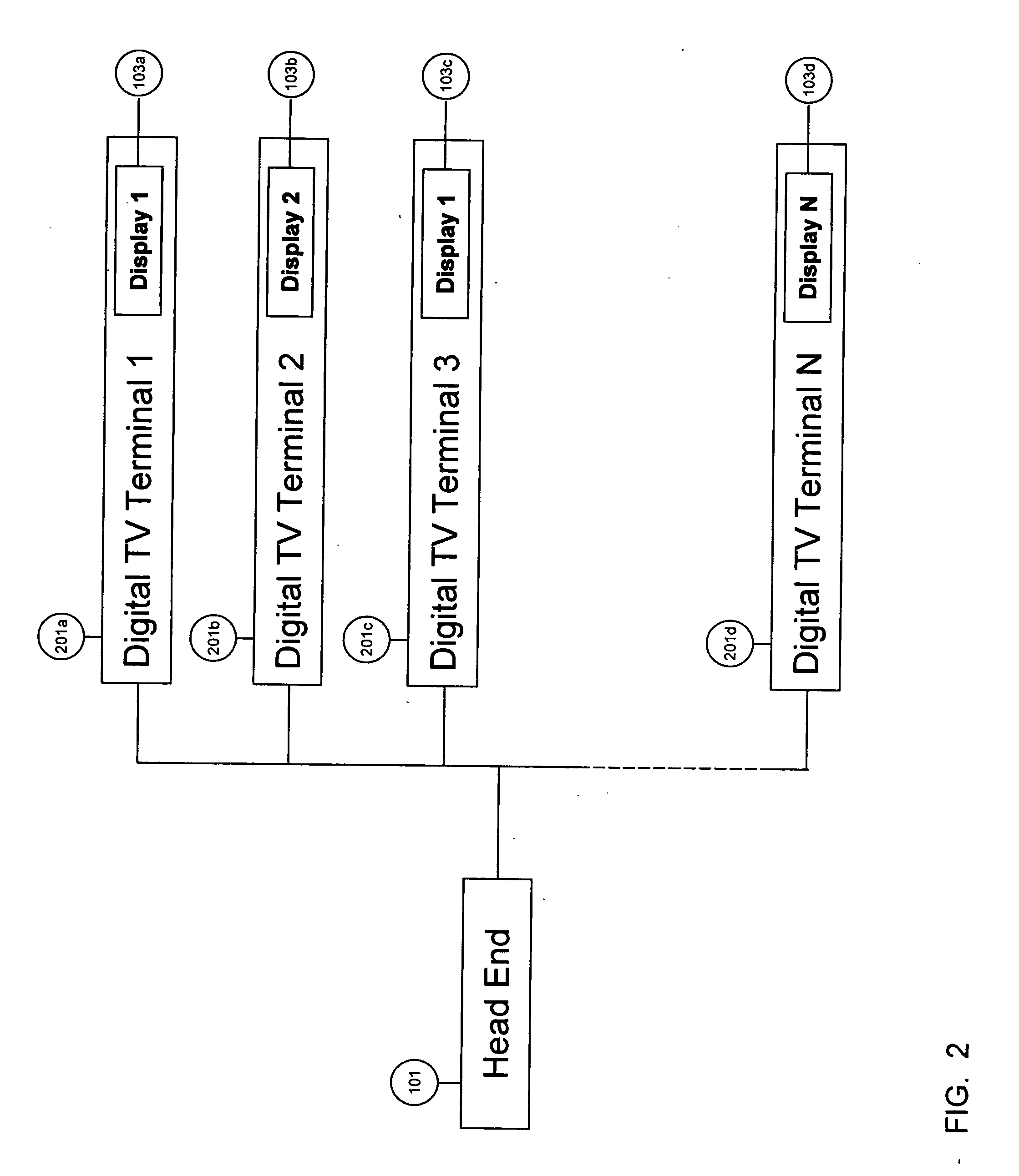
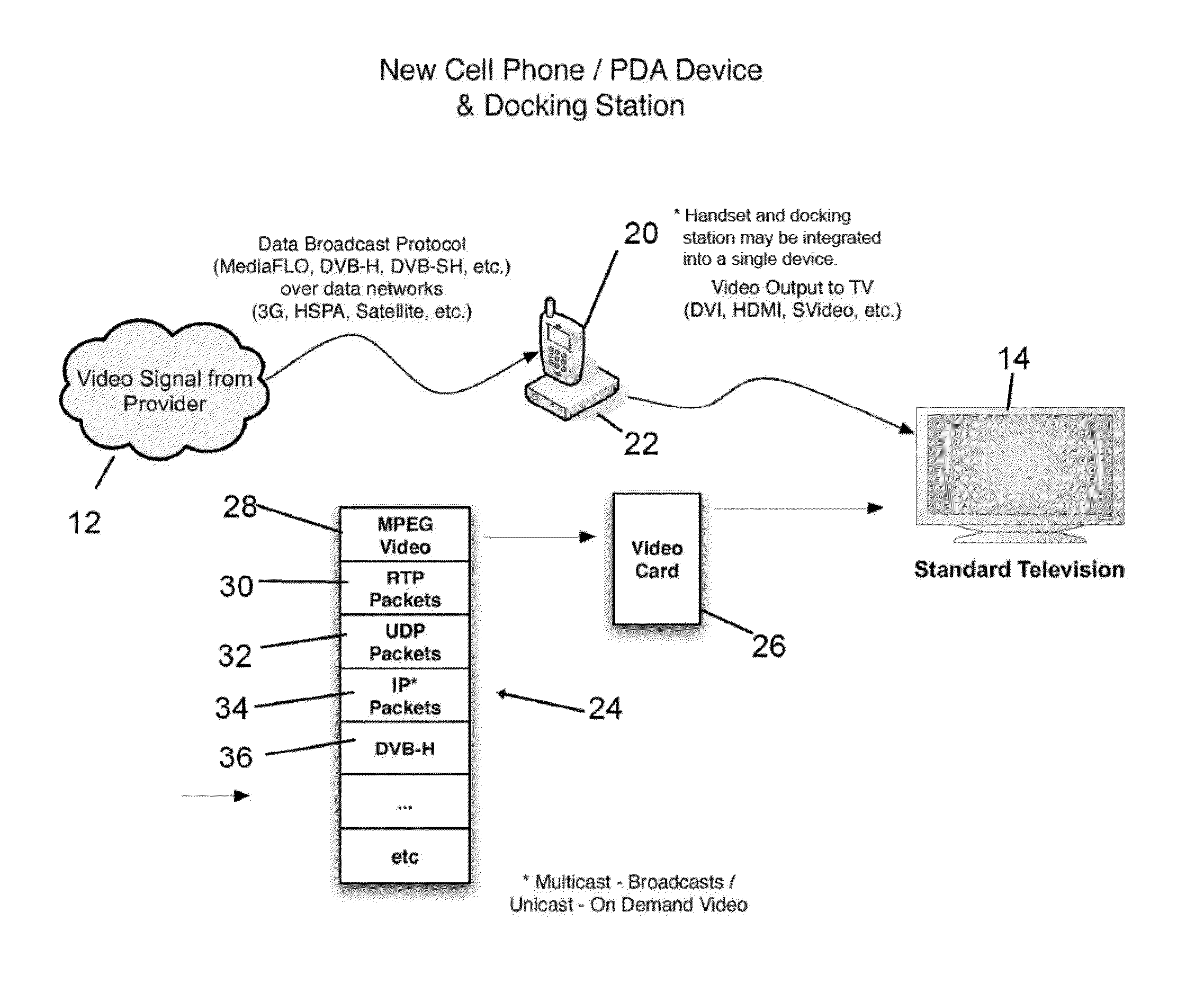
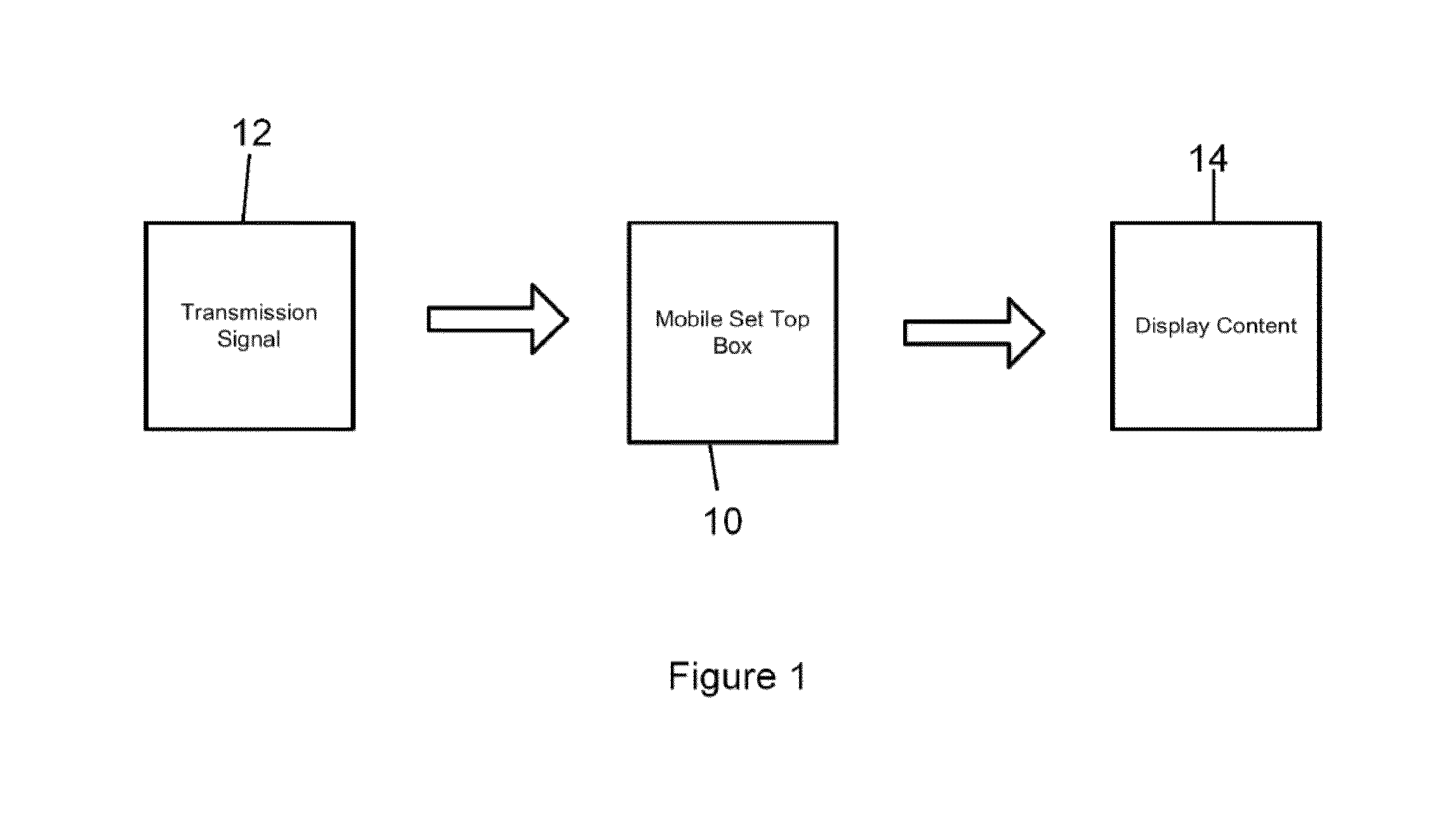
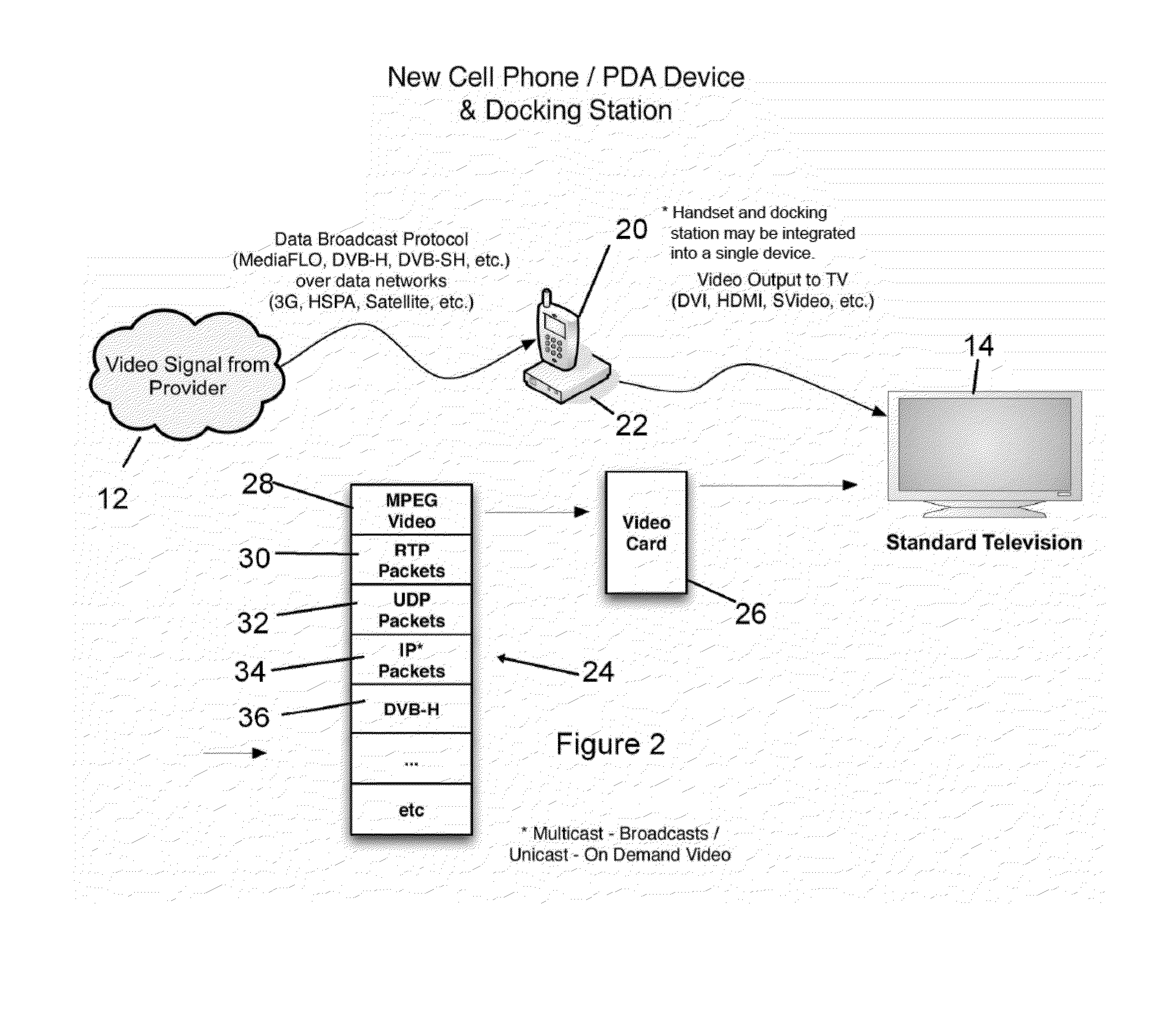
Mobile Set Top Box
ActiveUS20100169935A1Alignment for track following on tapesAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsImage resolutionNative resolution
A system is provided in which IP or media content residing on or being streamed to a mobile phone is forwarded to a display. The media content supports a native resolution of the mobile phone that is significantly smaller than a native resolution of said display. The system has media content processing circuitry, which up-scales the media content to the display native resolution. The system forwards the up-scaled media content to the display, whereby the display provides the up-scaled media content to a viewer.
Image capturing device for high-resolution images and extended field-of-view images
InactiveUS20100134641A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera lensMaximum level
An image capturing device, such as a digital camera, is able to take photos having a resolution higher than the native resolution capabilities of the device determined by the imager. The device can also take photos having a field-of-view (FOV) that is greater than the normal capabilities of the device. The photos taken have a higher vertical and horizontal FOV (or only an increased horizontal FOV creating a panoramic photo) than the lens of the imager allows natively. The imager of the device may be positioned to point in different directions using an actuator, that is, the actuator can pan and tilt the imager. The imager can also zoom in or out at various levels and has a maximum zoom level. To create either type of photo, an array of cells is used as a tool to capture a series of subimages where the imager is pointed in different directions for each subimage. To create the high-resolution photo, the imager is zoomed into its maximum level and captures each of the subimages based on the array of cells. To create the extended FOV photo, the imager is panned and tilted as much as possible using the actuator and captures each of the subimages based on the array of cells. In both cases the subimages are then stitched together to form a final image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for a dynamic "region of interest" in a display system
ActiveUS20160282624A1Lower latencyProvide benefitsInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsImage resolutionNative resolution
A method and apparatus of displaying a magnified image comprising obtaining an image of a scene using a camera with greater resolution than the display, and capturing the image in the native resolution of the display by either grouping pixels together, or by capturing a smaller region of interest whose pixel resolution matches that of the display. The invention also relates to a method whereby the location of the captured region of interest may be determined by external inputs such as the location of a person's gaze in the displayed unmagnified image, or coordinates from a computer mouse. The invention further relates to a method whereby a modified image can be superimposed on an unmodified image, in order to maintain the peripheral information or context from which the modified region of interest has been captured.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
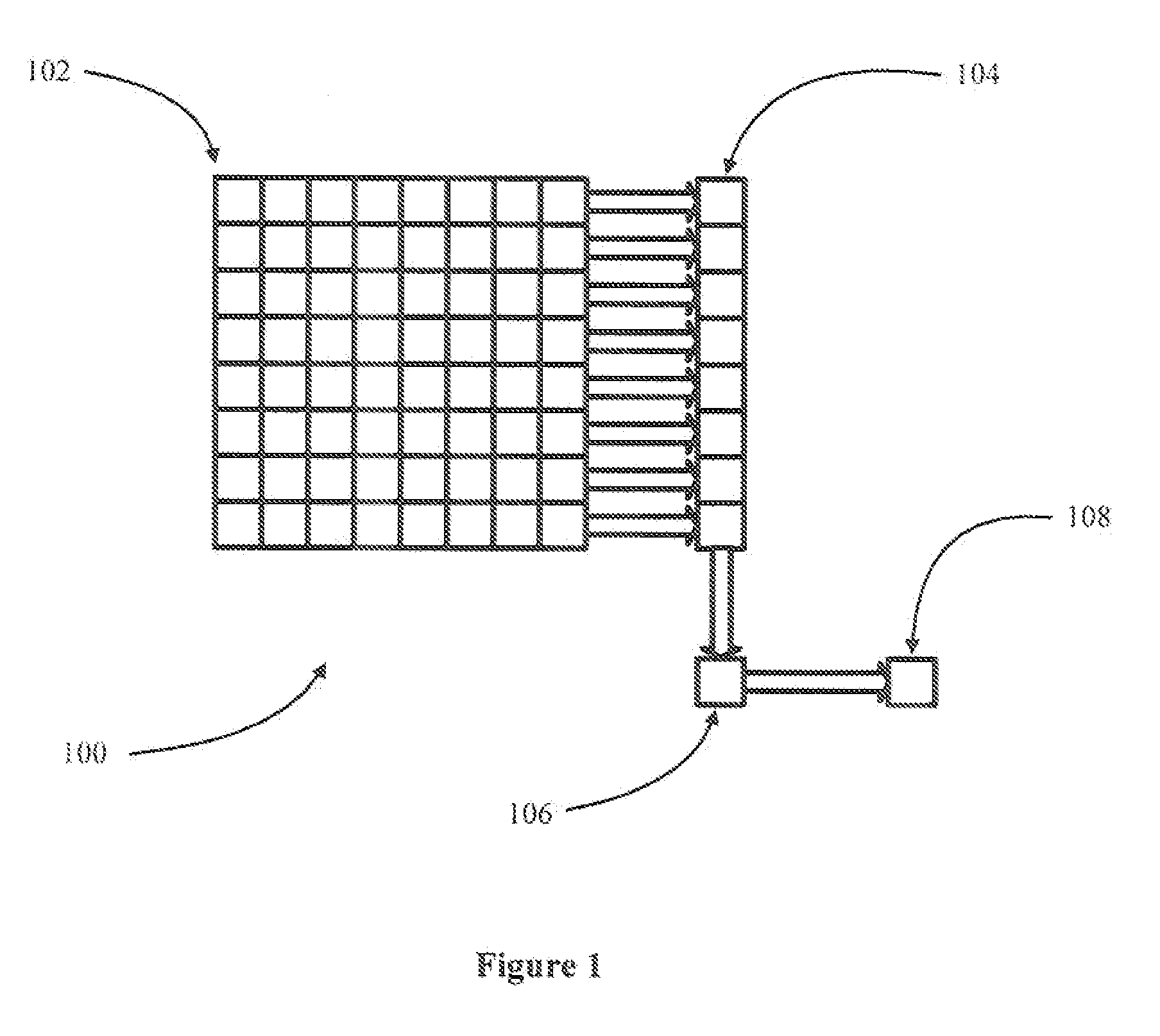
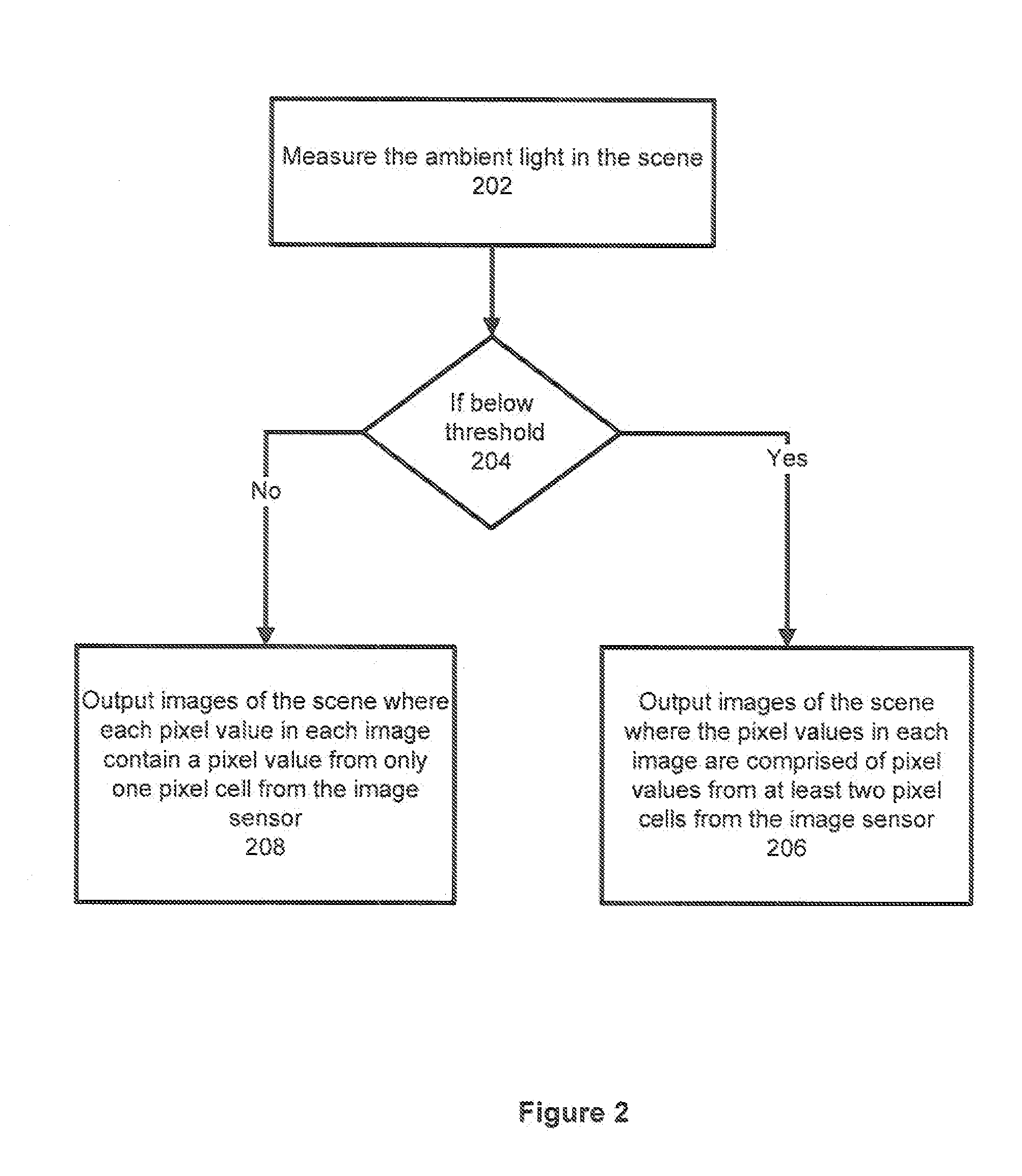
Automatic Pixel Binning
InactiveUS20110267495A1Television system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
In accordance with at least some embodiments, a method for outputting video images is disclosed. The method starts by measuring the ambient light in a scene. When the ambient light in the scene is lower than a threshold, images of the scene are created in the analog domain by combining multiple pixel values from imaging cells in an image sensor. The analog image will have a lower resolution than the native resolution of the image sensor. The images of the scene are converted into the digital domain and up-sampled to match the native resolution of the image sensor. The up-sampled images are used as the outputted video images. When the ambient light in the scene is not lower than a threshold, images of the scene are outputted where each pixel value in the image is created from the pixel value from only one pixel cell in the image sensor.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Hybrid text and image based encoding
A configuration for encoding and decoding the data is disclosed herein. A server retrieves webpage content to filter and extract text and image data. The text data is encoded using a lossless encoder, whereas the image data is downsampled to a lower resolution and encoded using a lossy encoder. The encoded text and image data is transmitted over a network. Once the encoded data is received on the client device, the text and image data is decoded using an inverse encoding algorithm and resized at a resolution appropriate to the native resolution of the display device.
Owner:OTELLO CORP ASA
Method of adjusting bandwidth usage of remote display devices based upon user proximity
InactiveUS20110211114A1Compressed digital format may be very largeBandwidth of a typical home media server environment may be exceededPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
An exemplary method of processing video content is provided which allows for adjusting the resolution, bitrate, or other target display characteristic of the video content based on information collected from an electronic device, such as a display device or intermediary electronic component. The exemplary method includes the steps of collecting information from an electronic device, determining a target display characteristic based on the collected information, adjusting the video content based on the target display characteristic, and transmitting the adjusted video content to the electronic device. The collected information may include the viewing distance of a user from a display device, the display area or native resolution of the display device, values from a menu option on the display device, and so forth.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
Interactive TV application display method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070016925A1Save interactive application developmentReduce maintenance costsTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsDigital interface
A system and method for accurately rendering an interactive TV application is accomplished by adjusting the contents of an on-screen buffer (OSD) to match the native physical characteristics of a target display device, preferably using fonts specific to the display device. Typically the character data is merged with graphics data and still or moving video background information and passed to the display using an analog or digital interface. Since the native resolution of the display is ideally identical to the resolution of the OSD buffer, the display device will not need to enlarge or reduce the rendering of the application. As a result, the character and graphics data will not be distorted by the display rasterizing process.
Owner:VAYSMAN ARTHUR +1
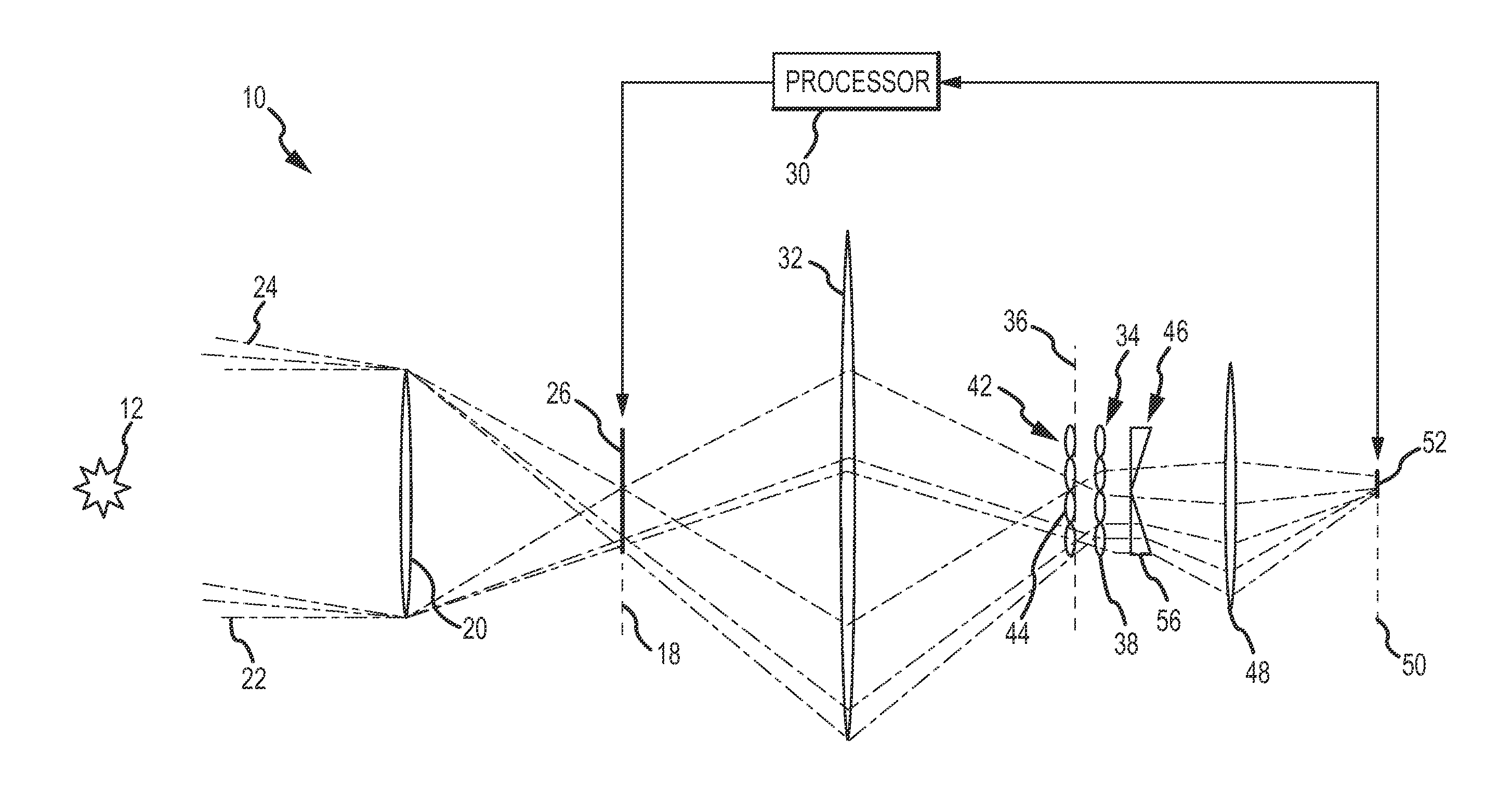
Digitally scanned multi-cell electro-optic sensor
ActiveUS20140231650A1Increase signal strengthIntegration periodTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryOptical radiationSpatial light modulator
A digitally scanned multi-cell EO sensor comprises a low-resolution multi-cell imaging detector. An array of optical focusing elements decomposes the sensor's FOV into at least four sub-fields. A sub-field directing array and focusing optic direct the optical radiation onto the imaging detector. In a first tilt mode, the optical radiation from the sub-fields is directed into at least four spatially separated sub-regions that each map to a different detector cell. A high-resolution spatial light modulator (SLM) digitally scans the FOV to select different portions of the FOV to map onto the different detector cells to time demultiplex spatially overlapping portions of the FOV onto each detector cell to stitch together a sub-image of a selected area of the FOV up to the native resolution of the SLM.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for scaling and cropping images for television display
InactiveCN101068333ACathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo signal spatial resolution conversionImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
The present invention provides a method for scaling and cropping an image for display on a television screen of native resolution. Unlike conventional method which over-expands the image, the method described herein crops the image (optionally) and scales it to fit the native resolution of the display screen without over-expanding the image. The method includes the steps of receiving a source television image having a native image resolution, scaling the source television image using a scaling ratio to produce a scaled television image having a resolution equal to or less than the native screen resolution in both a vertical and a horizontal direction, and displaying the scaled television image on the television screen. The scaling ratio may be the same or different in the vertical and horizontal directions.
Owner:新泰辉煌公司
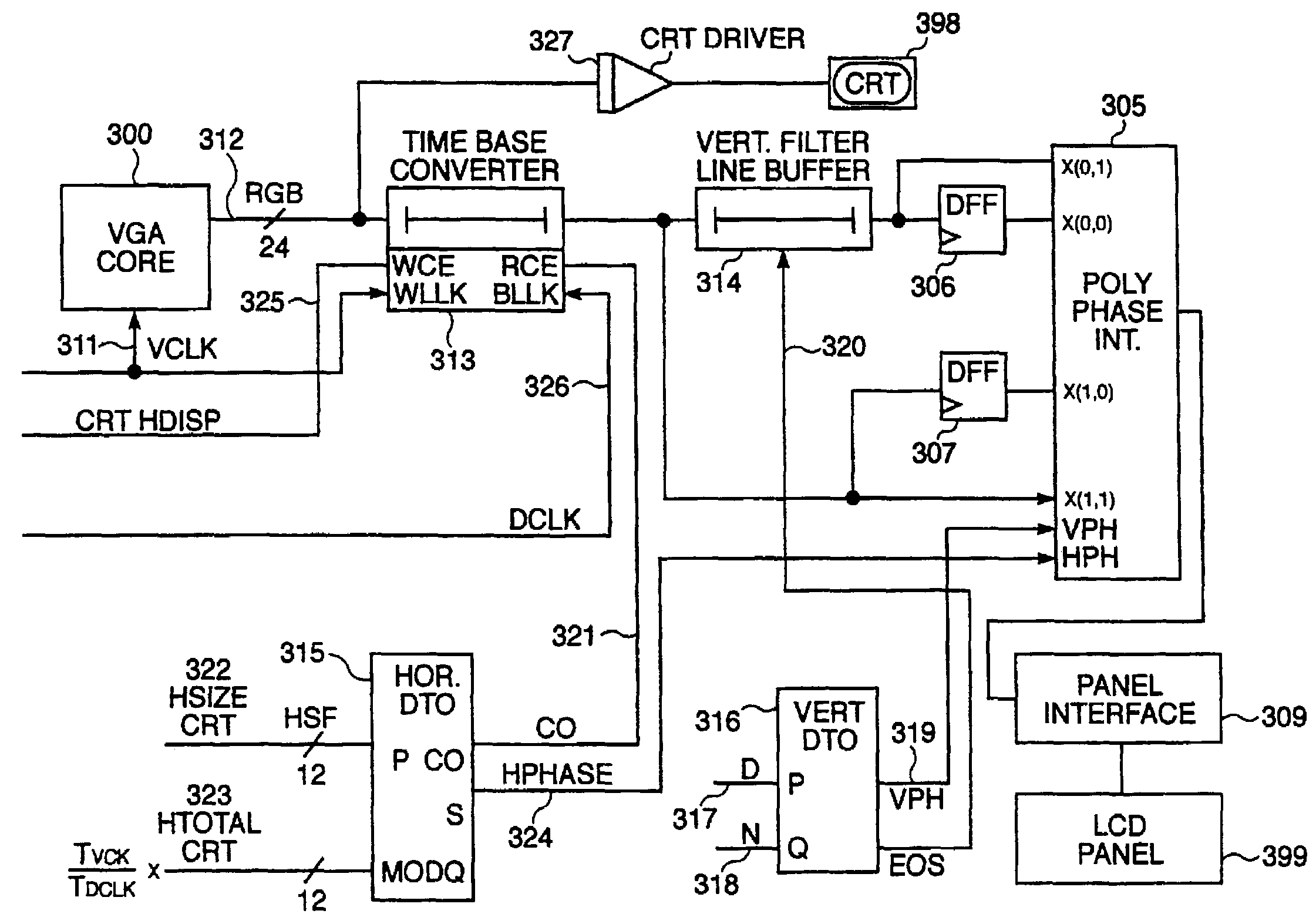
Method and apparatus for asynchronous display of graphic images
InactiveUS7209133B2Reduce resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsImage resolution
A display controller in a computer system controls the asynchronous output of graphics display data in a computer system having at least one fixed resolution flat panel display. Fixed panel displays may have problems displaying non-native resolutions particularly at lower resolutions. The controller of the present invention uses a time base converter, horizontal and vertical Discrete Time Oscillators (DTO), and polyphase interpolator, which may be Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)-based to expand graphics display data asynchronously from native resolution to at least one resolution suitable for display on a fixed resolution panel. Graphics data may also be output asynchronously to a CRT. Time base converter receives frequency related input parameters and generates at least one asynchronous output at the desired output resolution.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
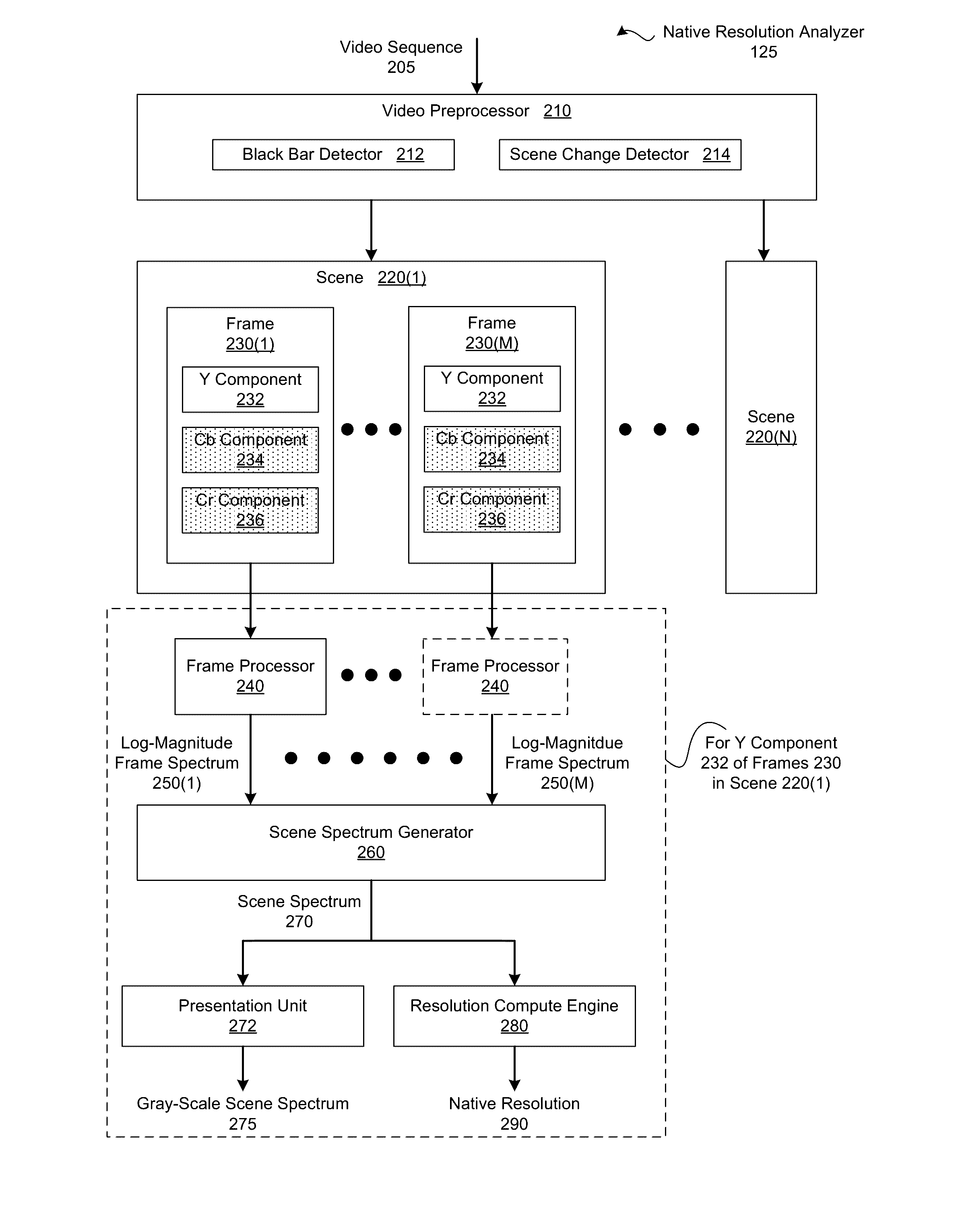
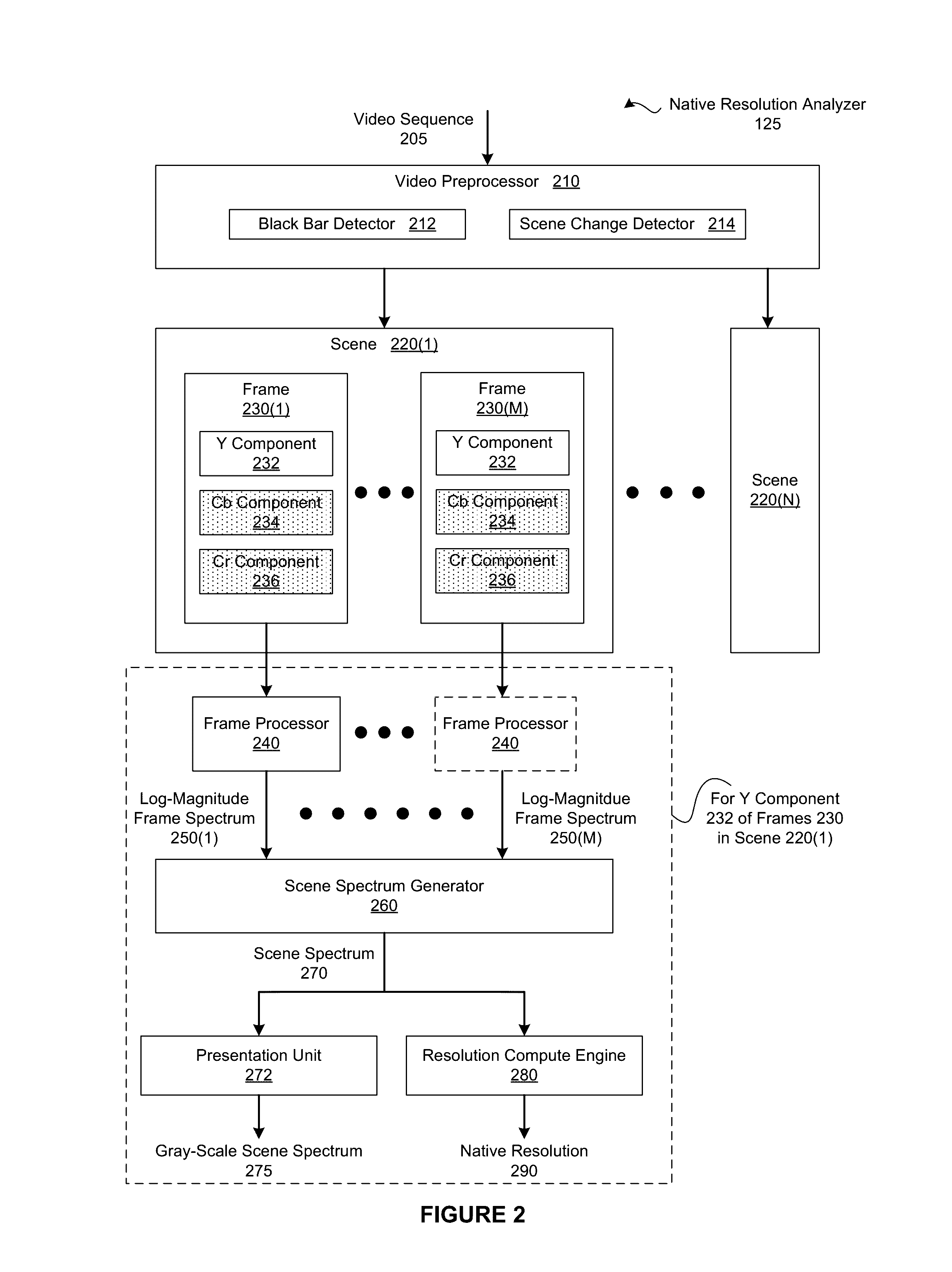
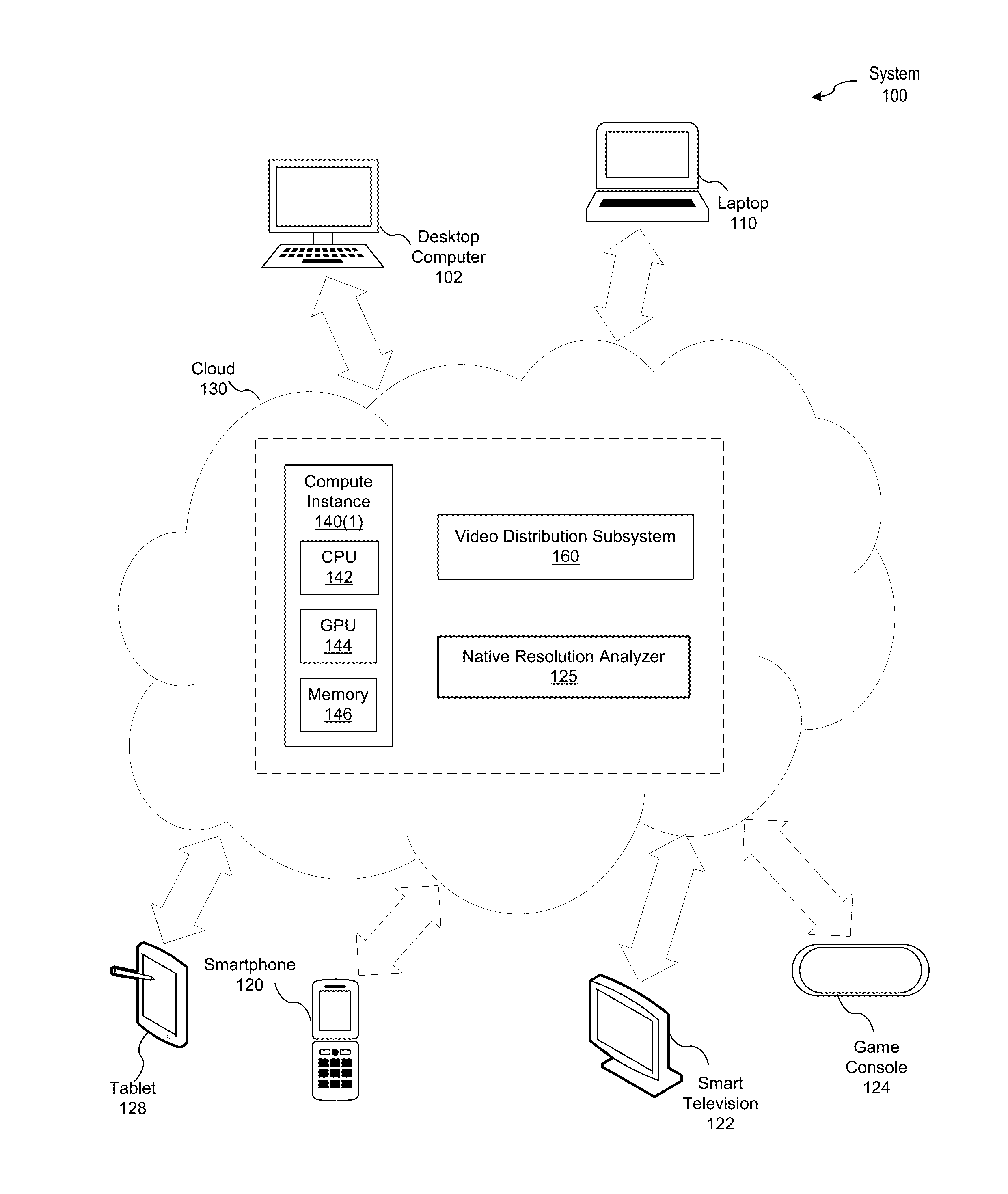
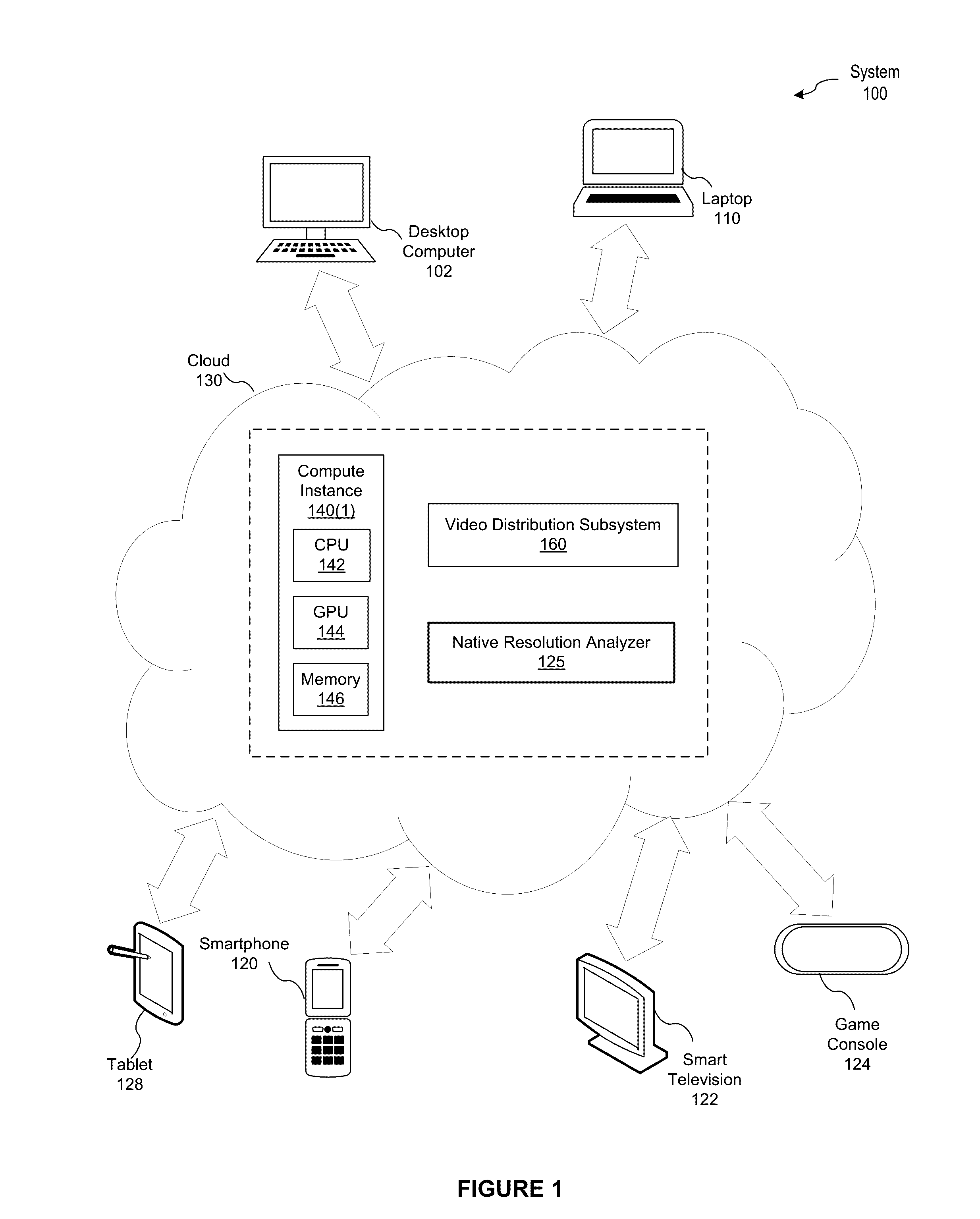
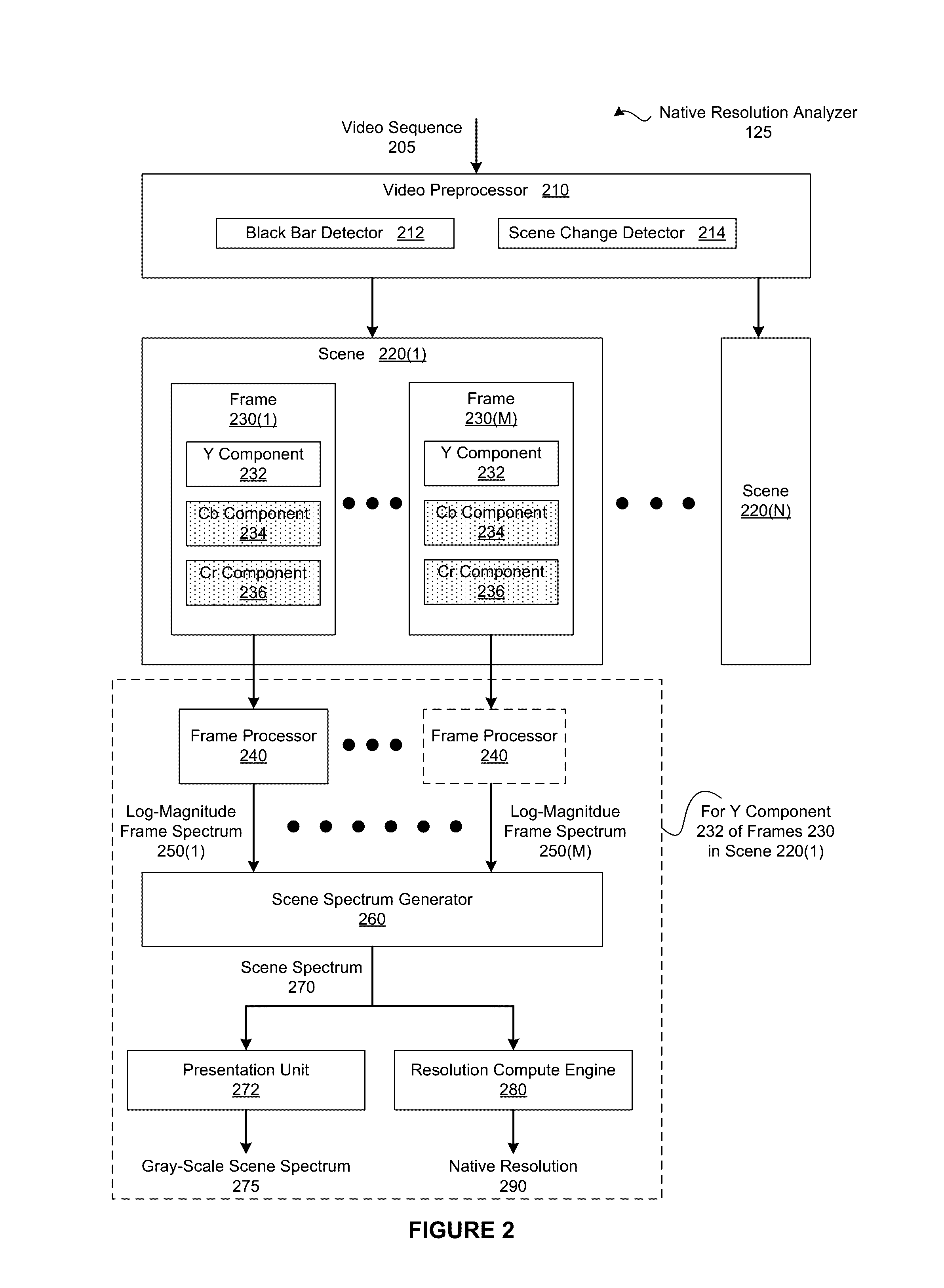
Determining native resolutions of video sequences
ActiveUS20160379057A1Reduce resource consumptionReduce resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionVideo sequence
In one embodiment of the present invention, a native resolution analyzer generates a log-magnitude spectrum that elucidates sampling operations that have been performed on a scene. In operation, the native resolution analyzer performs a transform operation of a color component associated with a frame included in the scene to generate a frame spectrum. The native resolution analyzer then normalizes the magnitudes associated with the frame spectrum and logarithmically scales the normalized magnitudes to create a log-magnitude frame spectrum. This two dimensional log-magnitude frame spectrum serves as a frequency signature for the frame. More specifically, patterns in the log-magnitude spectrum reflect re-sampling operations, such as a down-sampling and subsequent up-sampling, that may have been performed on the frame. By analyzing the log-magnitude spectrum, discrepancies between the display resolution of the scene and the lowest resolution with which the scene has been processed may be detected in an automated fashion.
Owner:NETFLIX
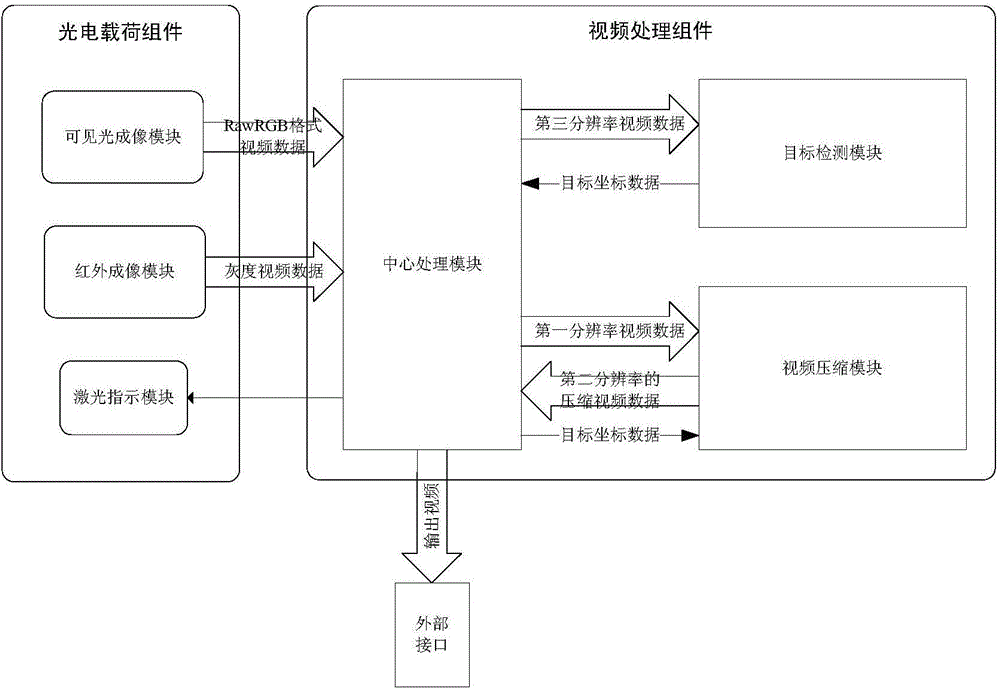
Multi-source imaging load for unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN104580858AMaintain Interface ConsistencyMeet the needs of useTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a multi-source imaging load for an unmanned aerial vehicle. The multi-source imaging load comprises a visible light imaging module, an infrared imaging module, a laser indication module, a central processing module, a target detection module and a video compression module, wherein the central processing module directly controls the laser indication module, acquires video data from the visible light imaging module and the infrared imaging module, sends the video data with the native resolution to the video compression module after converting the video data into data in the same data format, sends down-sampled video data to the target detection module, and outputs compressed video data returned by the video compression module and target coordinate data returned by the target detection module to an external interface. The load has the advantages of small size, low weight, strong function and the like and can fully meet requirements of day-and-night photoelectric detection at middle and close distances, and convenience can be brought to usage under different environment and application conditions through matched usage of multiple loads.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Multiple resolution optical imager using single size image elements
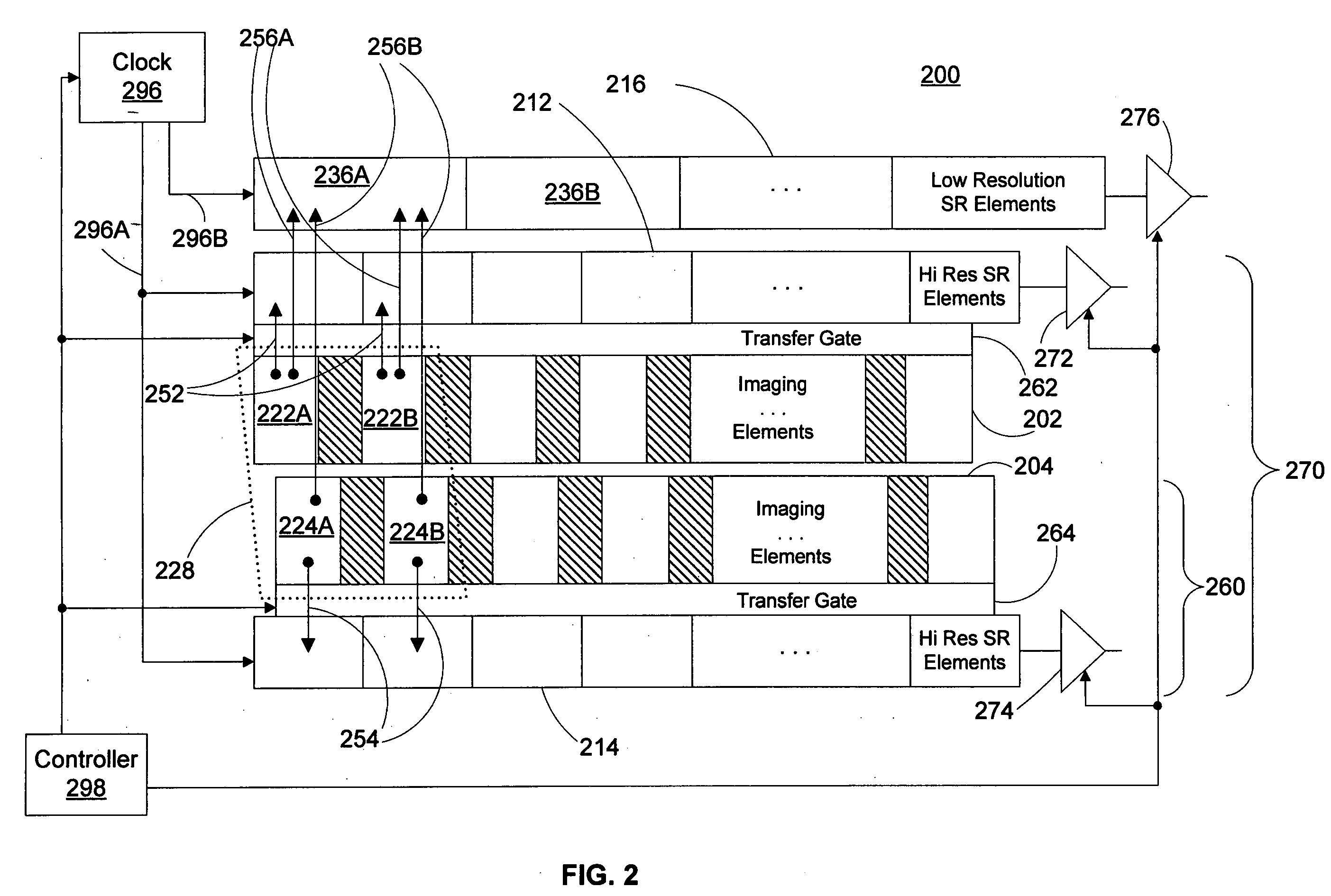
InactiveUS20060146154A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsShift registerImage resolution
An image sensor has two or three rows of imaging elements, all the imaging elements being of the same size. This provides the rows with a native resolution. The image sensor is also provided with three shift registers. First and second shift register elements receive information from respective corresponding imaging element in a first and second row of imagining elements while shift register elements of the third shift register receive information from four imaging elements. The four imaging elements form a super-pixel, allowing the sensor to output information in a low resolution mode, as well a native and a high resolution mode.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
Molecular light valve display having sequenced color illumination
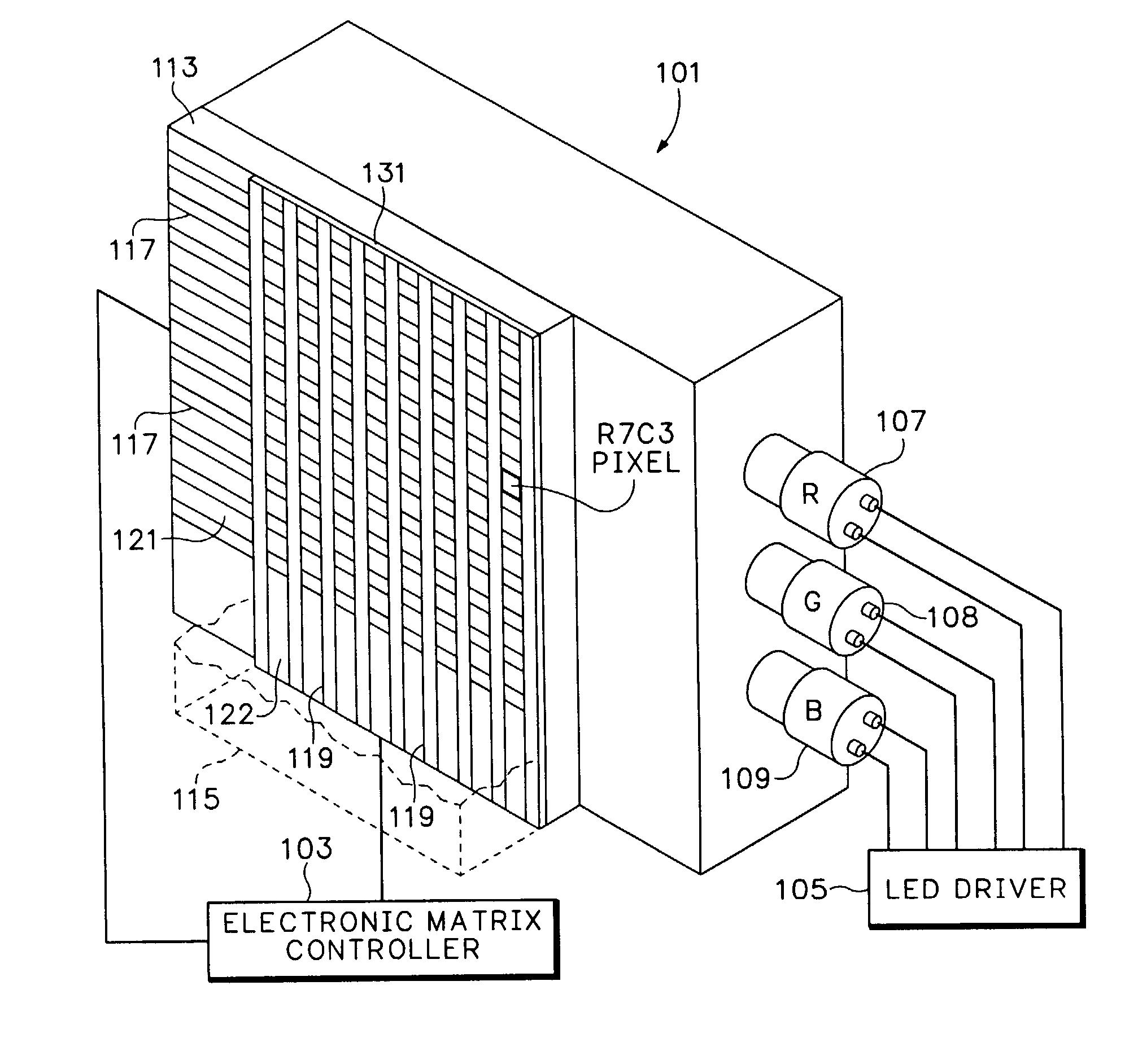
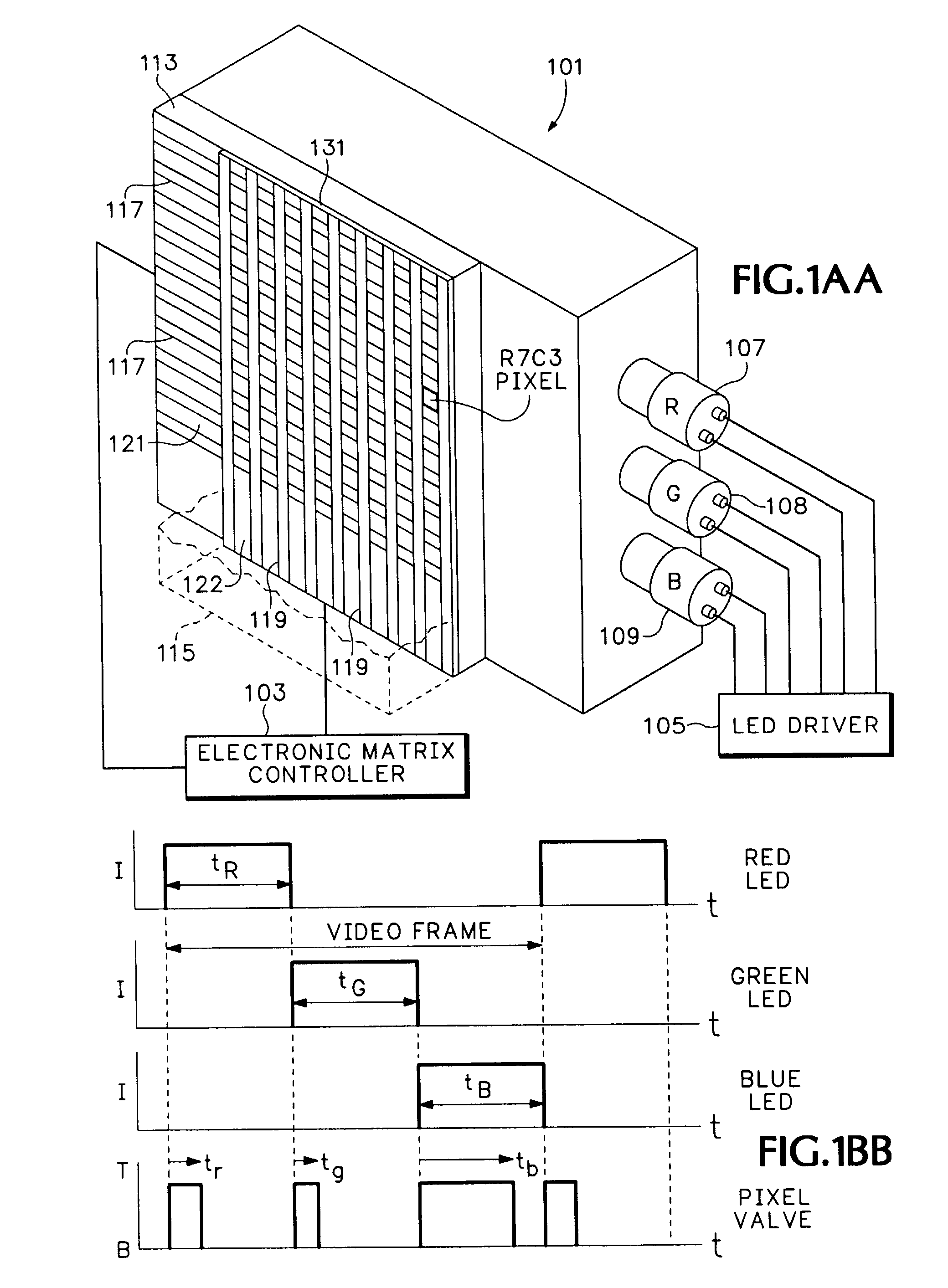
InactiveUS7113165B2Easy to understandStatic indicating devicesCoupling light guidesGamutImage resolution
A molecular light valve controlled color display. The display is formed through a layer of such molecules between a crossbar array of transparent electrodes, the crossbar intersections forming addressable pixels. A rapid sequencing of primary colors is controlled by molecular light valves congruent with display pixels. Native display resolution for a full gamut of colors is maintained for each pixel via a temporally distributed color pixel scheme. Both still and motion images can be displayed. Molecular valves, or switches, transition between two optically distinct states, e.g., transparent and black.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Low power DVD playback in a portable computing system
InactiveUS7643731B2Reduce power consumptionExtend battery lifeTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Data translation
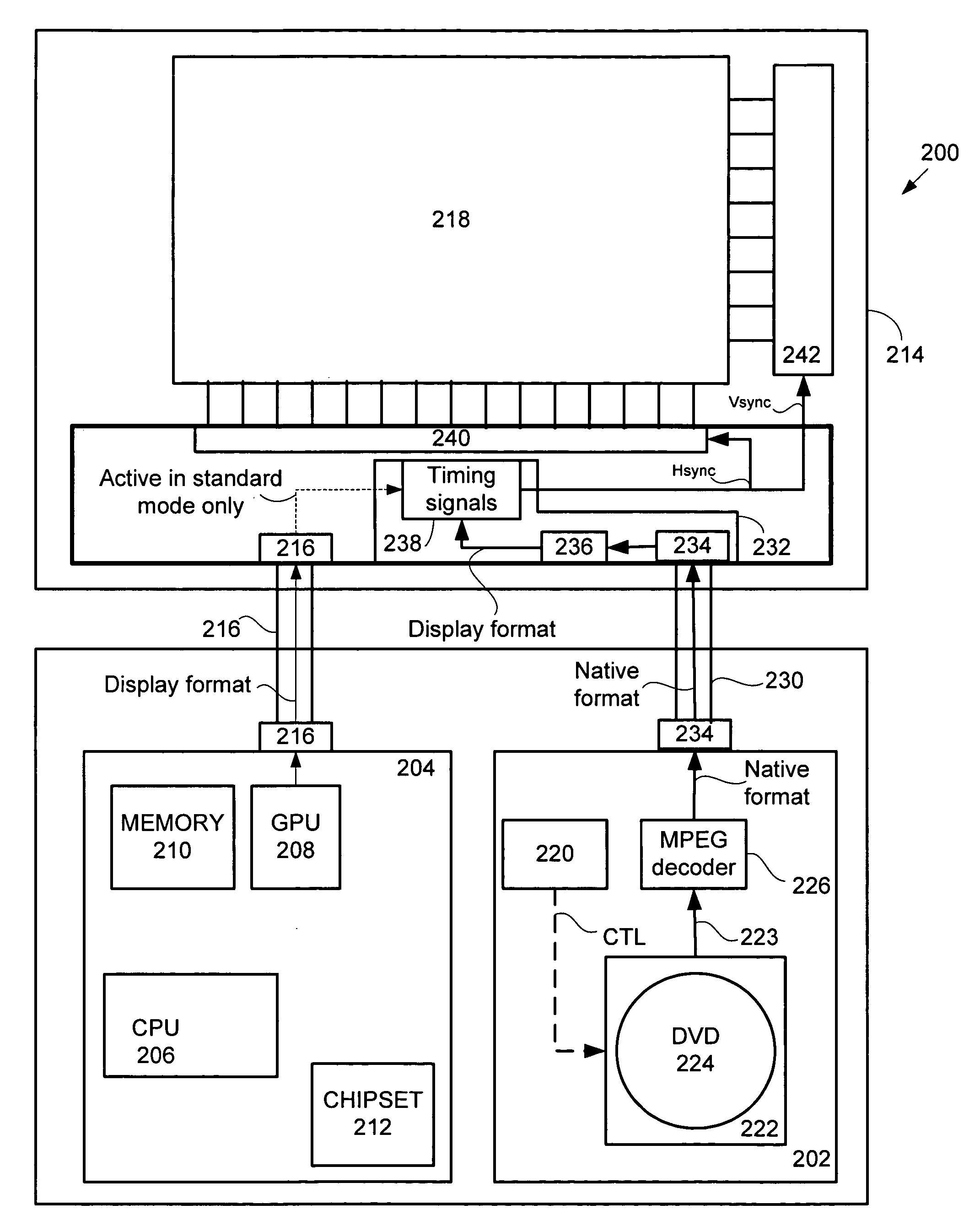
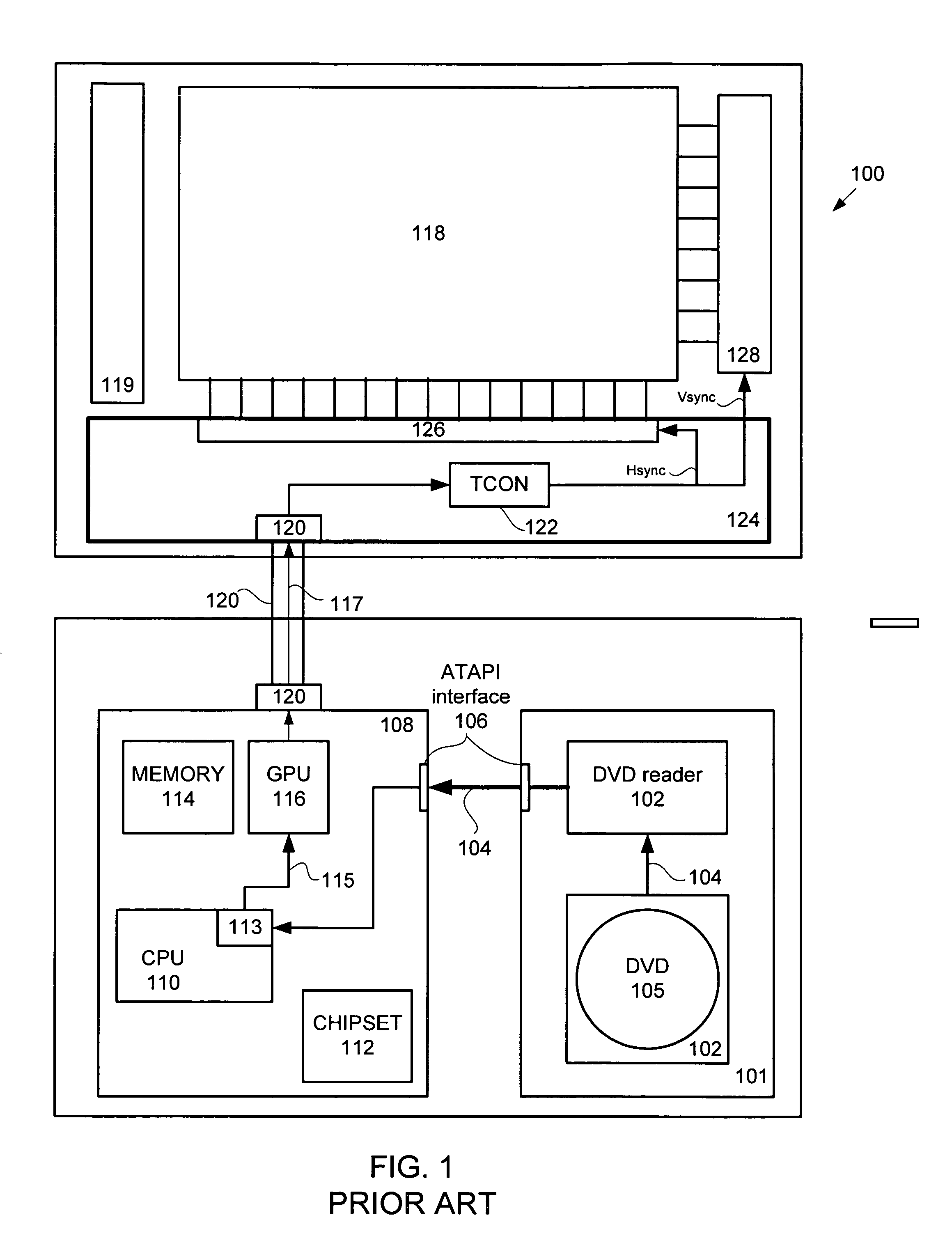
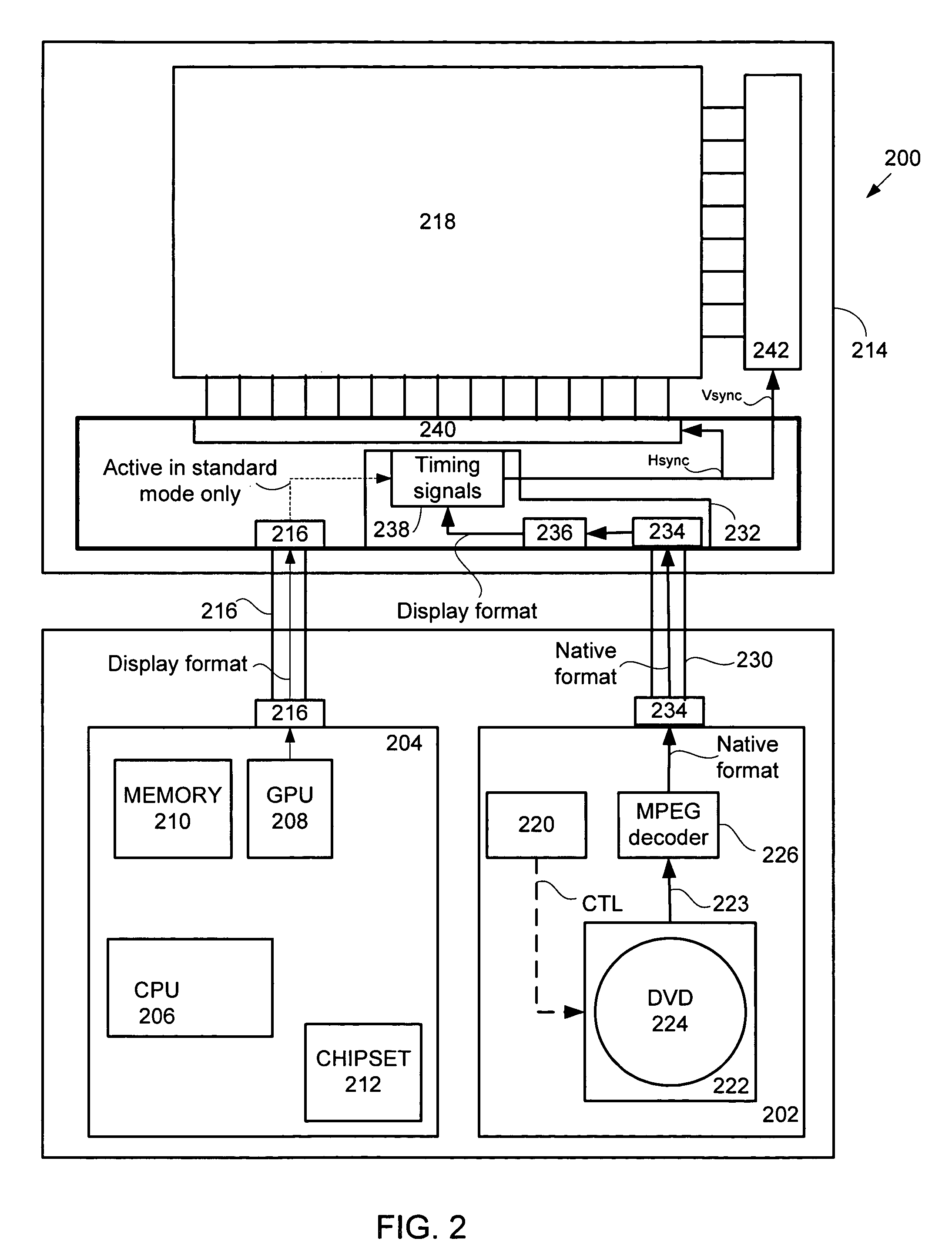
In a DVD playback mode only, the first type interface is disabled and a DVD driver unit having a hardware DVD decoder connected to a DVD reader unit arranged to read video data from a DVD inserted therein is powered on. In the described embodiment, the DVD decoder unit is also connected to the display screen by way of a second type interface is powered on. The video data is read from the DVD by the DVD reader unit and sent by the DVD reader unit to the hardware DVD decoder unit which then decodes the video data before passing it directly to a timing controller unit coupled to the display screen by way of the second type interface. The timing controller unit converts the video data at a native resolution to a display screen resolution that is then displayed on the display screen.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Method for scaling and cropping images for television display
InactiveUS20070258012A1Image distortionColor signal processing circuitsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method of processing an image for display on a television screen is described. Unlike conventional method which over-expands the image, the method described herein crops the image (optionally) and scales it to fit the native resolution of the display screen without over-expanding the image. The method includes the steps of receiving a source television image having a native image resolution, scaling the source television image using a scaling ratio to produce a scaled television image having a resolution equal to or less than the native screen resolution in both a vertical and a horizontal direction, and displaying the scaled television image on the television screen. The scaling ratio may be the same or different in the vertical and horizontal directions.
Owner:EMERSON RADIO CORP
Method for 3D visual mapping using 3D stereoscopic video content
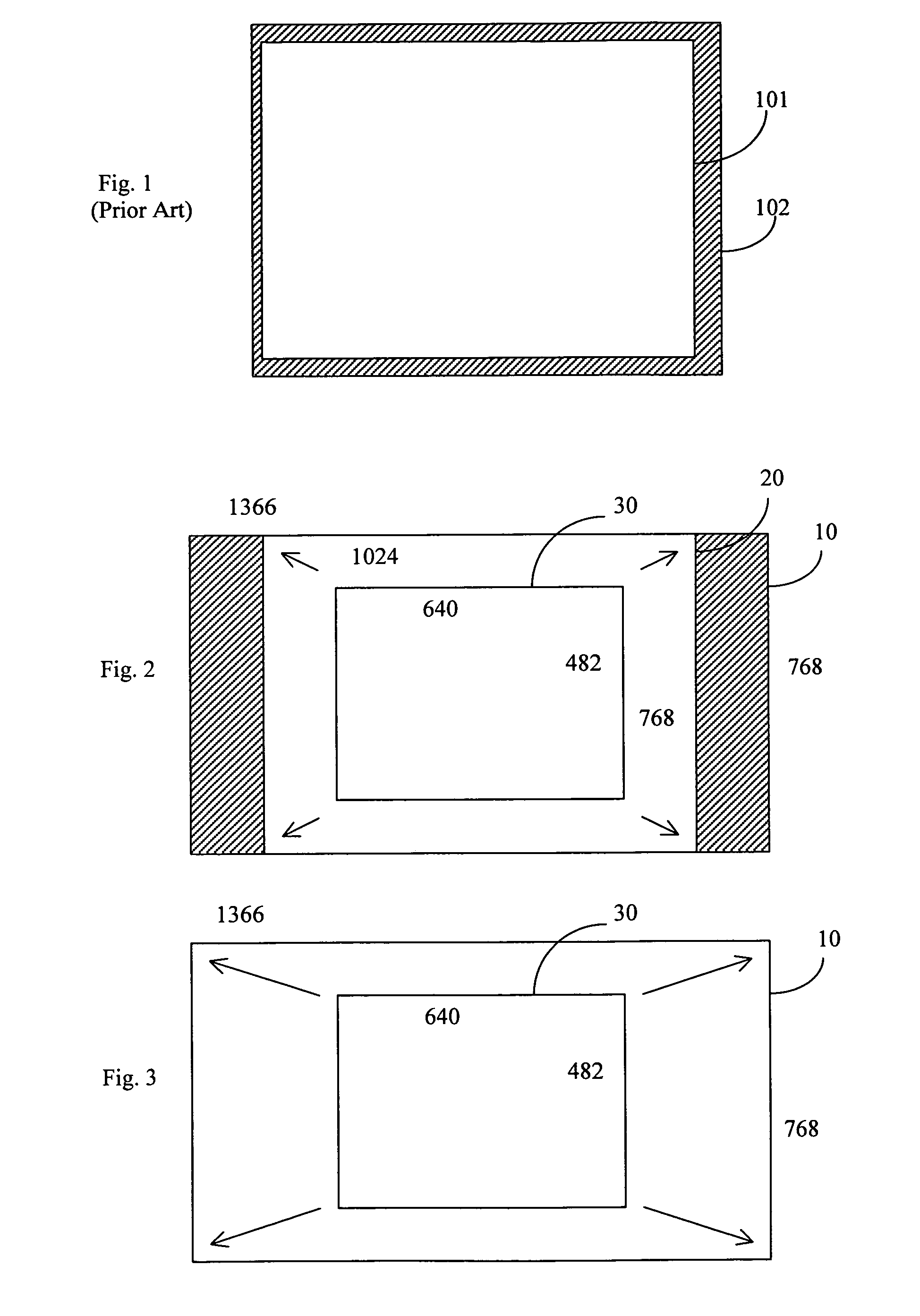
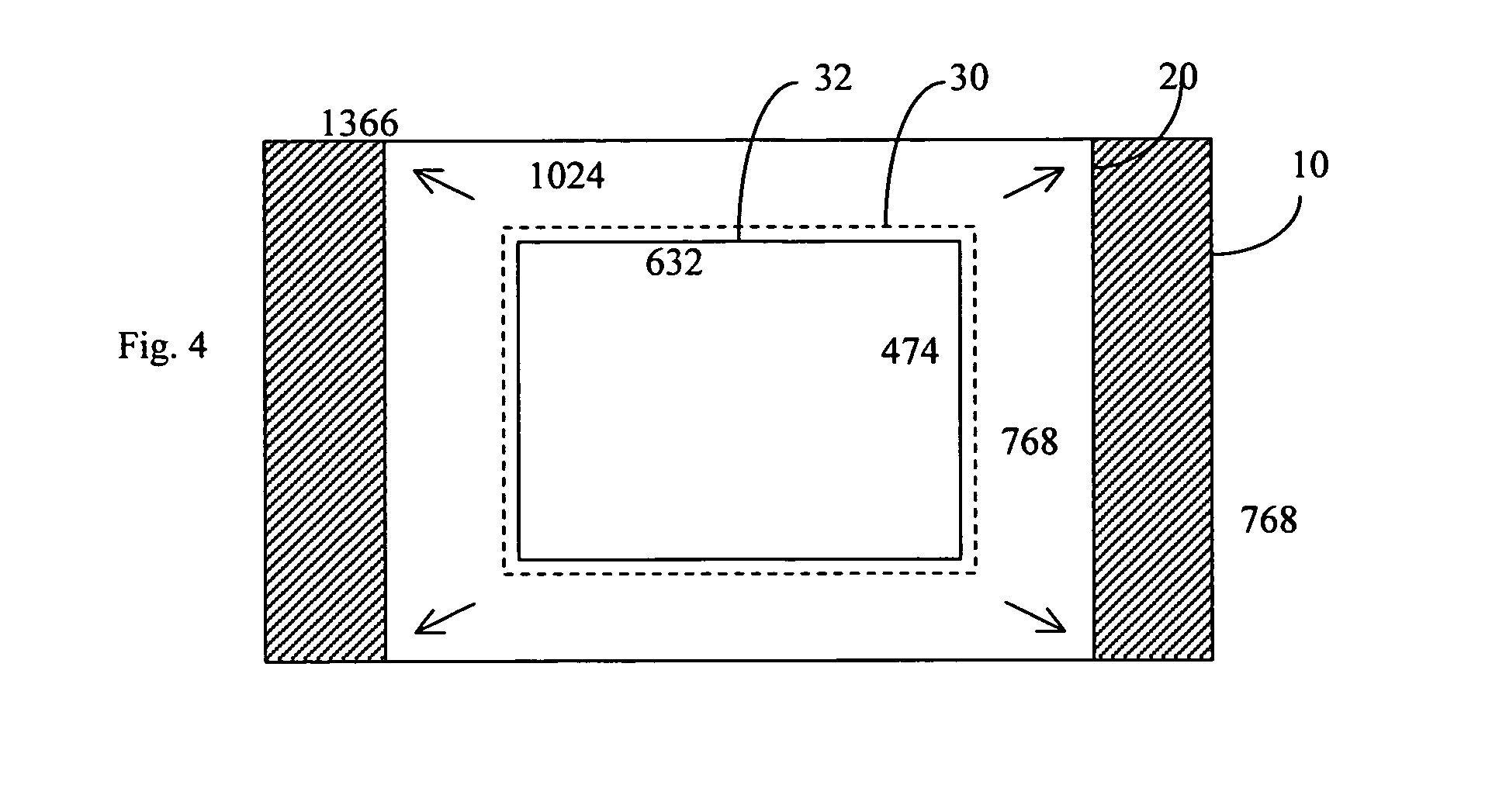
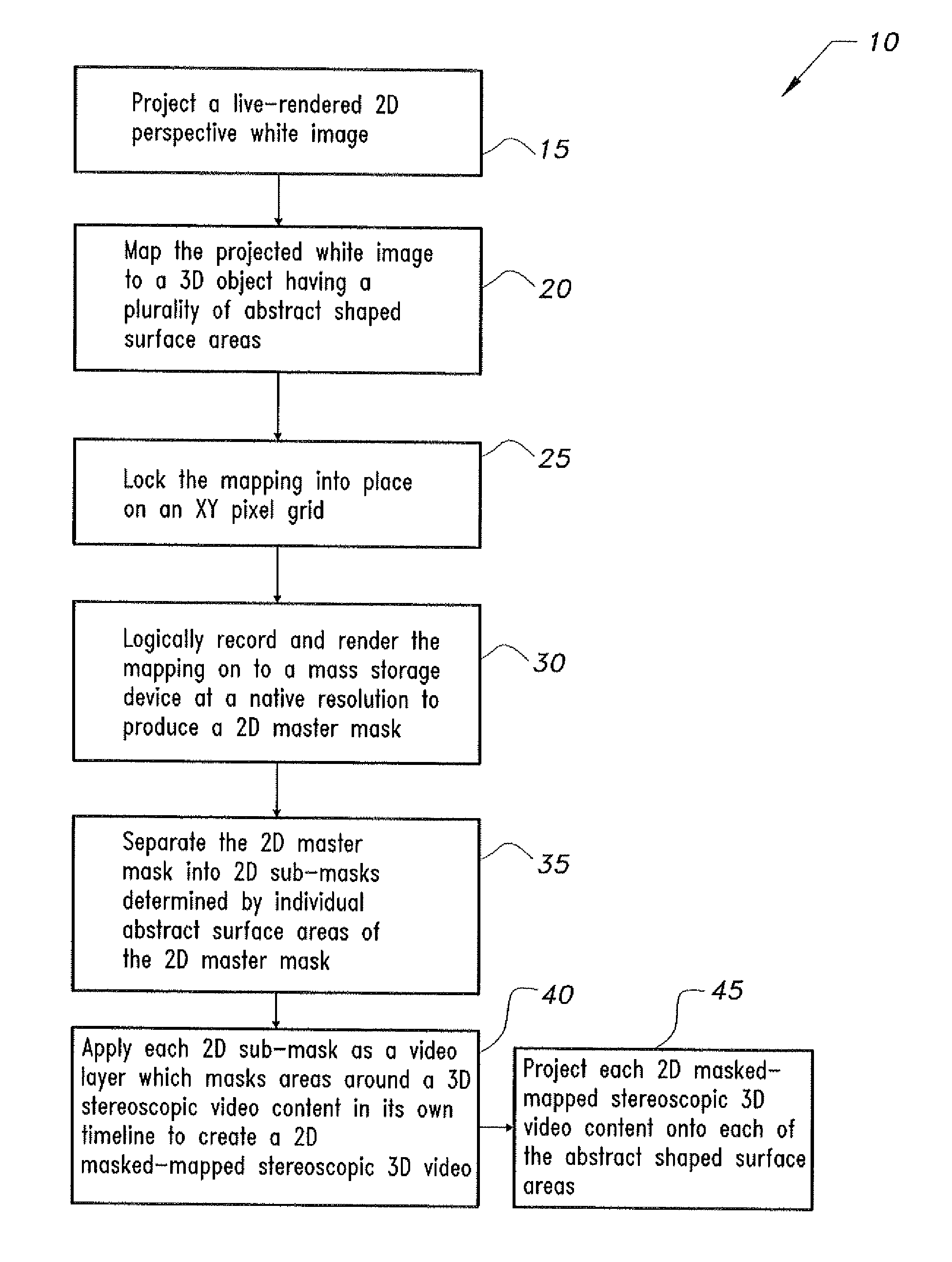
InactiveUS20130044184A1Readily apparentColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsHard disc driveStereoscopic video
The method for 3D visual mapping using 3D stereoscopic video content records live 2D perspective white images mapped to architectural or other 3D objects having abstract shaped surfaces to create 2D perspective masks fitting the surface shapes. Each abstract surface area is covered by a dedicated projector and controller. The mapping is locked into place on a pixel grid, the project being logically recorded-rendered onto a hard drive at native resolution to produce a 2D master mask, which is separated into sub-masks determined by the individual areas of the 2D master mask. Each 2D sub-mask is applied as a video layer and used to mask areas around 3D stereoscopic video content in its timeline. The 2D masked-mapped stereoscopic 3D video can be played on 3D stereoscopic projectors. A common clock synchronizes the processors for playback of the 3D content on the 3D surface areas.
Owner:SOPHRIN JOSHUA
System and method for obtaining images with offset utilized for enhanced edge resolution
A method in a machine vision inspection system for obtaining two images of a workpiece with a desired sub-pixel offset between the images. The images are acquired using a fast multiple image acquisition mode of operation of a camera in the machine vision inspection system. In various implementations, the method includes removing the offset between the images such that the workpiece is congruent in the images and combining the congruent image data. The combined image data has a resolution better than that allowed by the native resolution of a camera that acquires images in the machine vision inspection system. The method may be implemented in an edge feature video tool for measuring edge features on the workpiece. The motion direction utilized for obtaining the two images may be made to be transverse to the edge direction of an edge that is being measured.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Determining native resolutions of video sequences
ActiveUS20160381401A1Reduce resource consumptionReduce resolutionColor signal processing circuitsUsing detectable carrier informationImage resolutionVideo sequence
In one embodiment of the present invention, a native resolution analyzer generates a log-magnitude spectrum that elucidates sampling operations that have been performed on a scene. In operation, the native resolution analyzer performs a transform operation of a color component associated with a frame included in the scene to generate a frame spectrum. The native resolution analyzer then normalizes the magnitudes associated with the frame spectrum and logarithmically scales the normalized magnitudes to create a log-magnitude frame spectrum. This two dimensional log-magnitude frame spectrum serves as a frequency signature for the frame. More specifically, patterns in the log-magnitude spectrum reflect re-sampling operations, such as a down-sampling and subsequent up-sampling, that may have been performed on the frame. By analyzing the log-magnitude spectrum, discrepancies between the display resolution of the scene and the lowest resolution with which the scene has been processed may be detected in an automated fashion.
Owner:NETFLIX
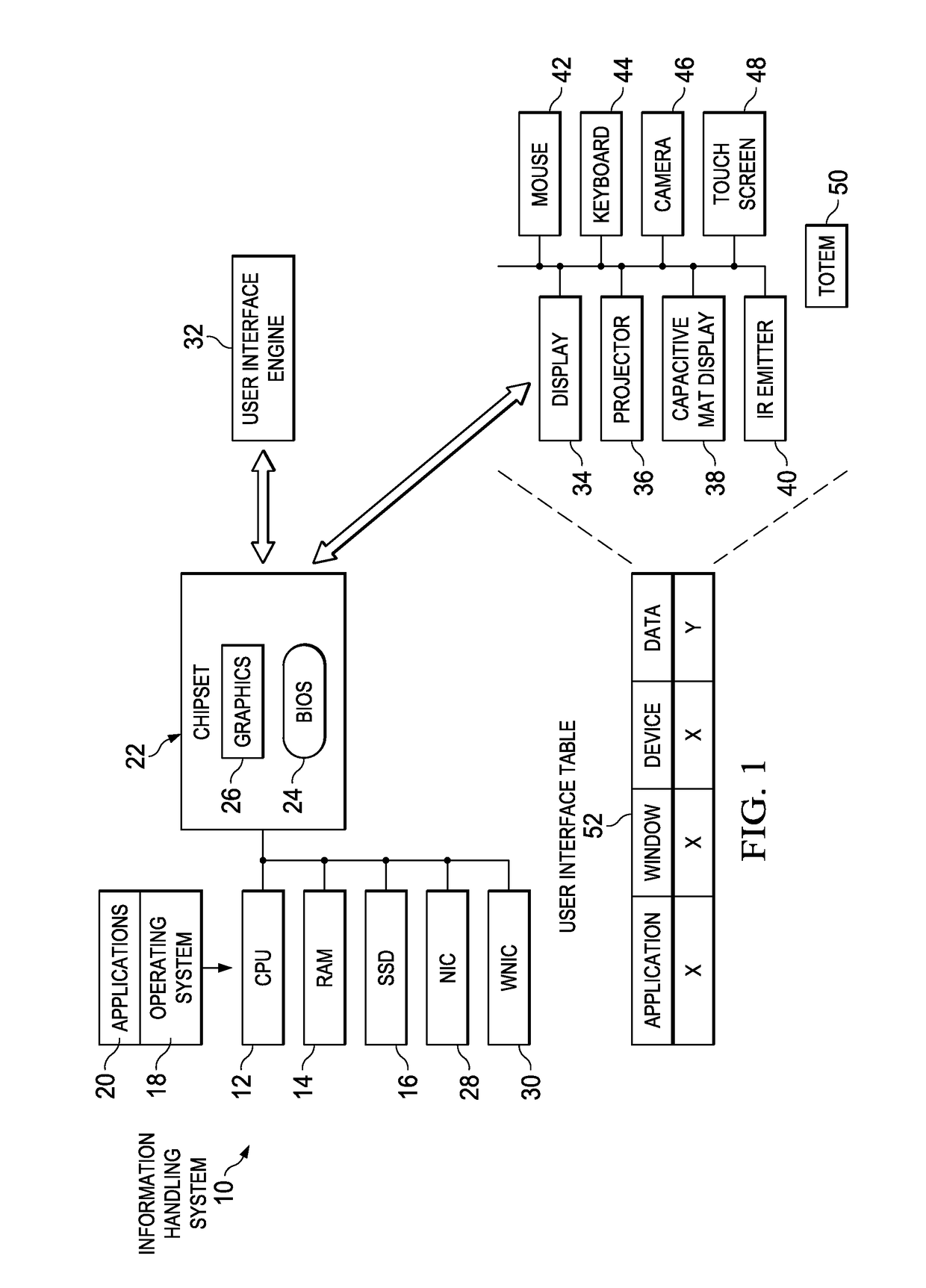
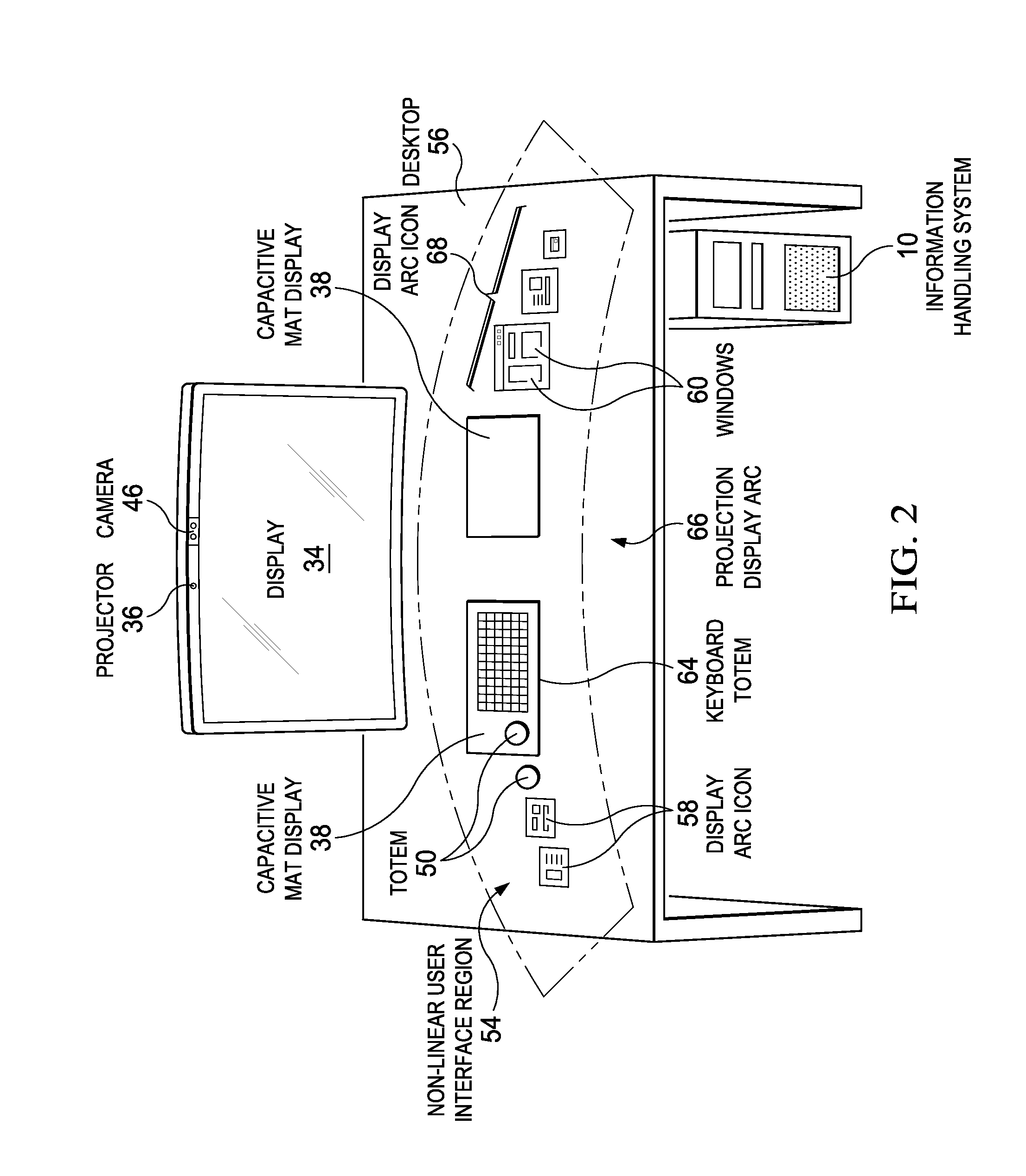
Dynamic display resolution management for an immersed information handling system environment
ActiveUS10139854B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsInput/output for user-computer interactionPower supply for data processingGraphicsImage resolution
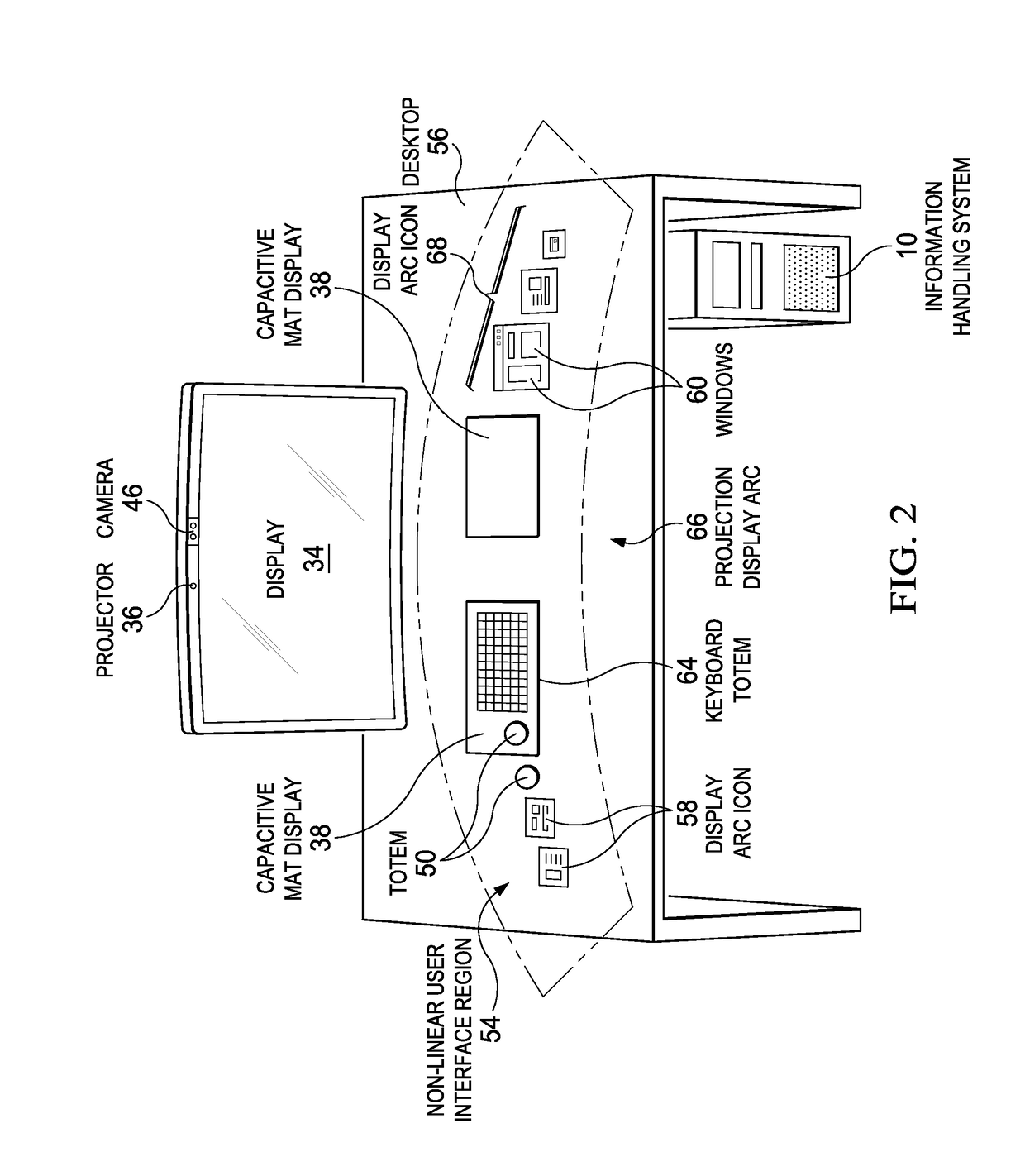
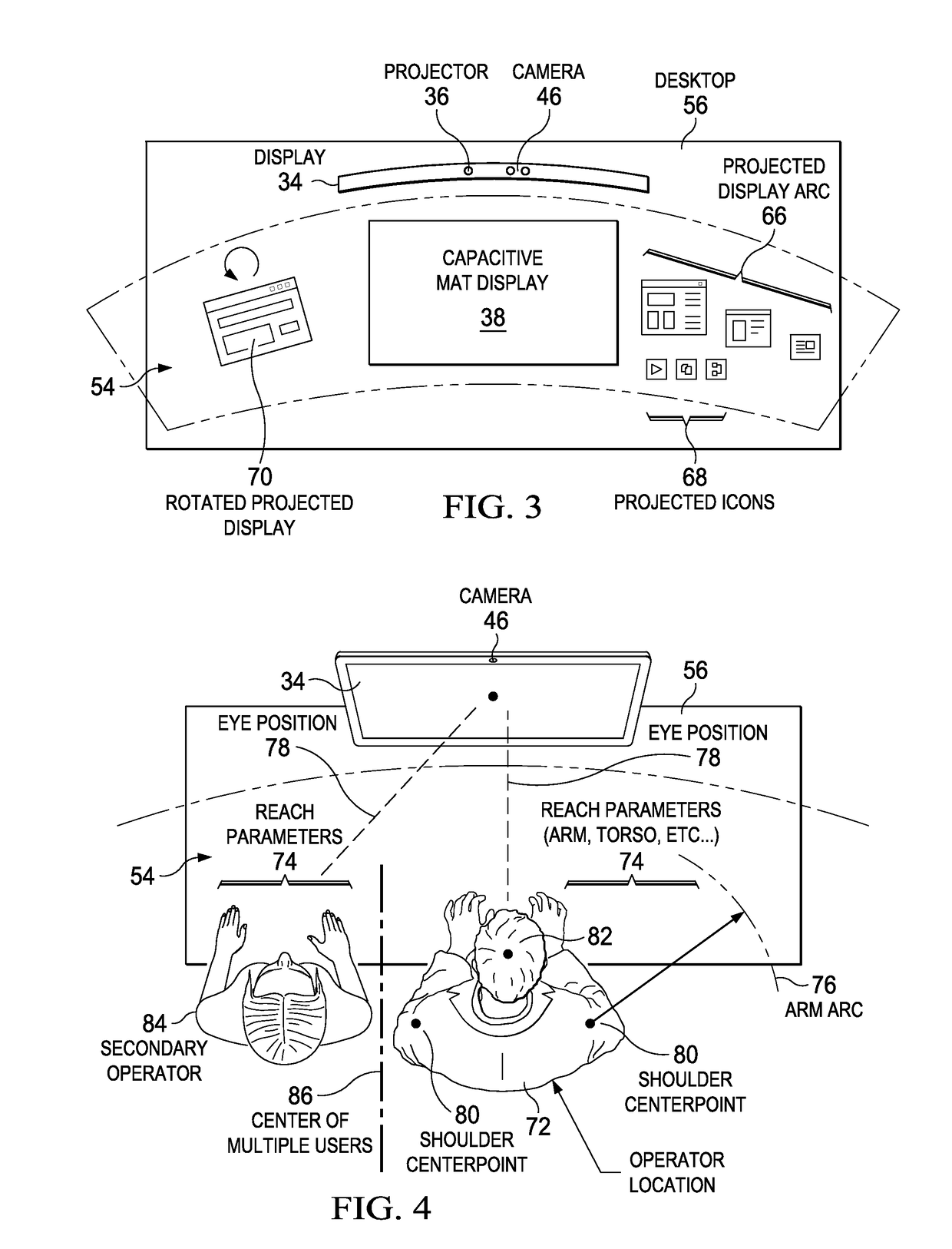
A display device presents visual information with native and non-native resolutions stored in EDID and provided to a graphics controller. Non-native resolutions are generated in response to an object detected that interferes with the presenting of the visual information, such as an object between a projector and projection surface or an object placed on a capacitive mat display. The non-native resolutions present the visual information to avoid the object and are stored in EDID in association with object characteristics to allow re-use of the non-native resolutions when visual information at the display is blocked by an object with similar characteristics.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
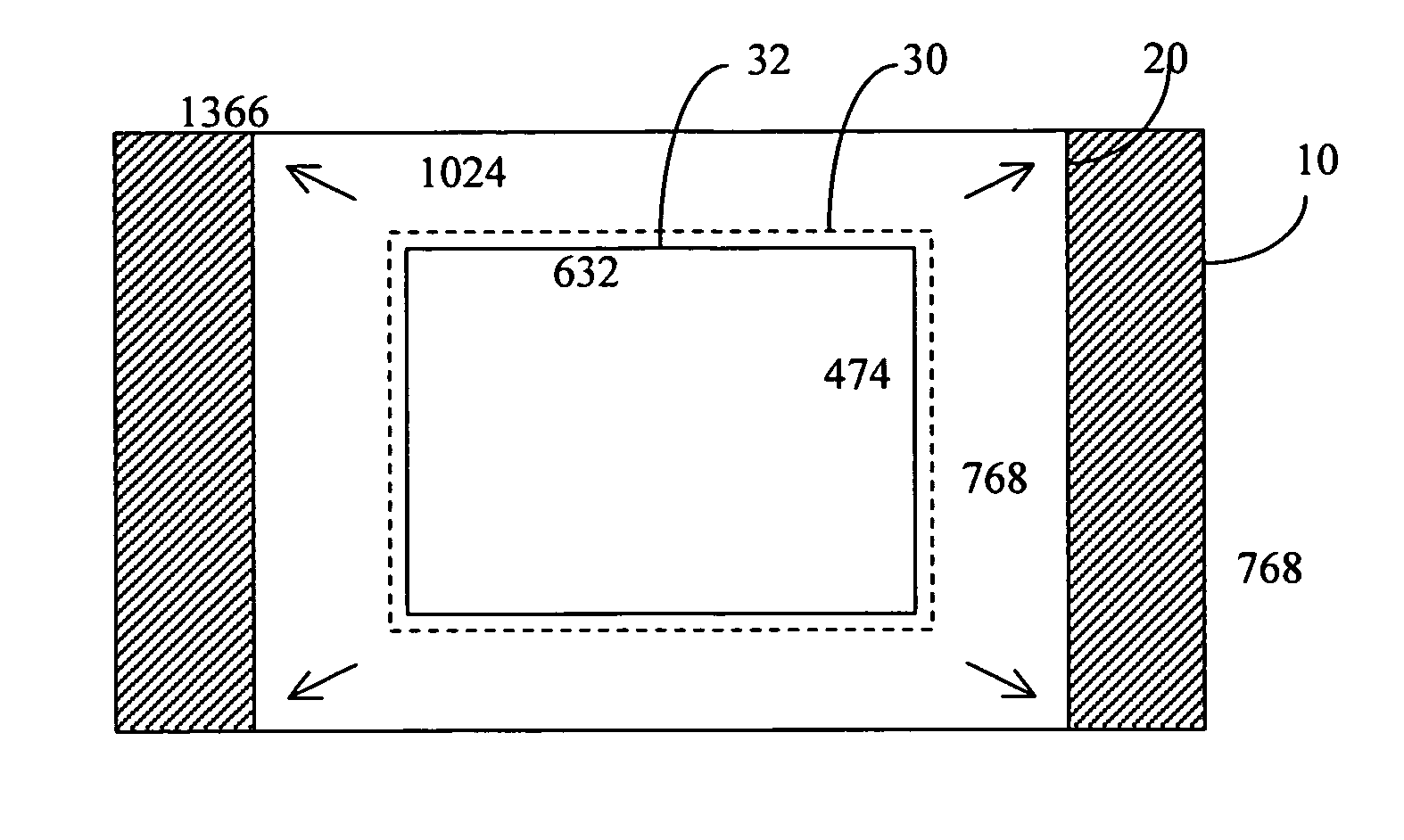
Method to improve usability of high pixel density displays
InactiveUS20140184603A1Improve experienceGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsPixel densityComputer graphics (images)
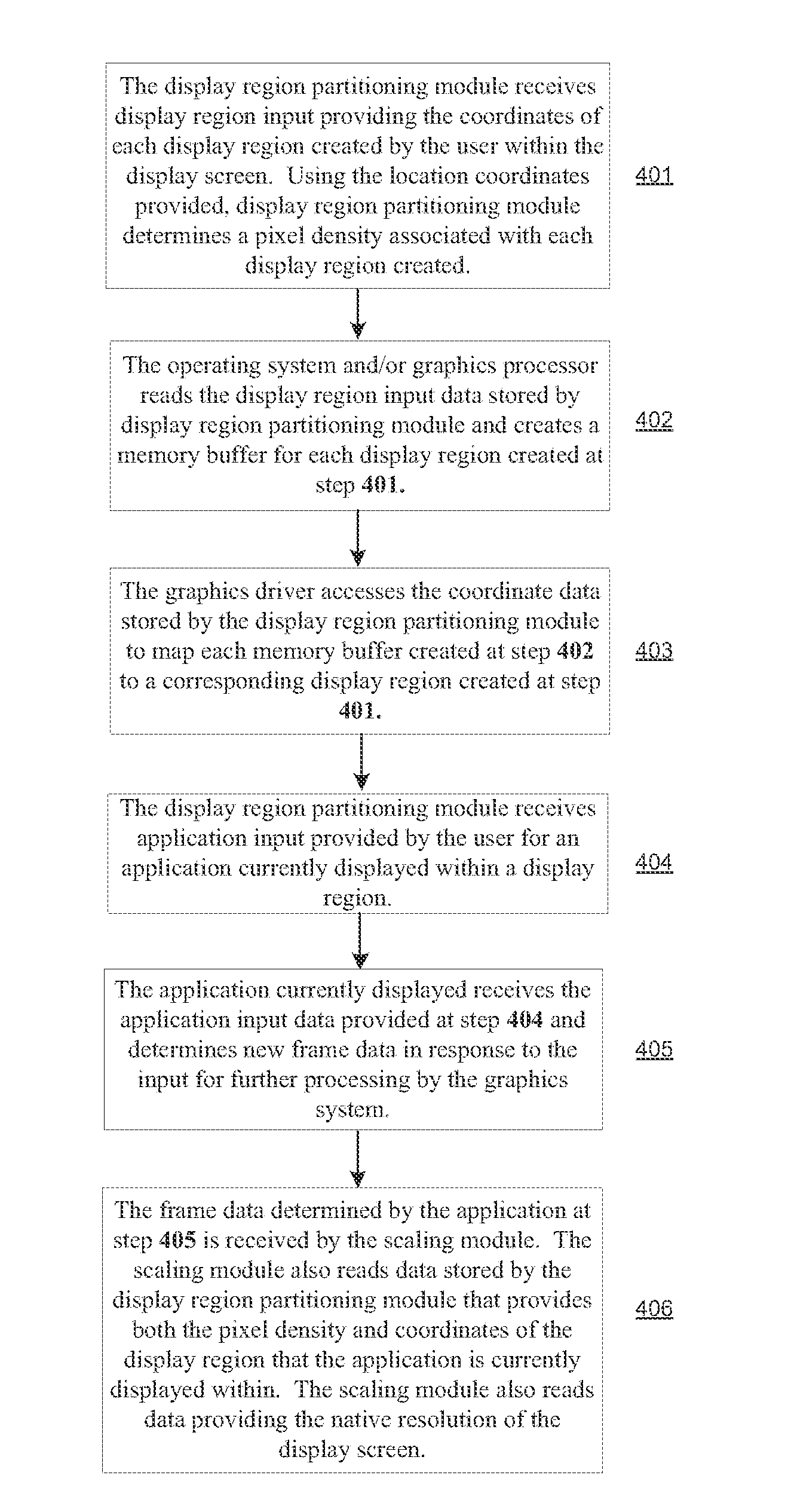
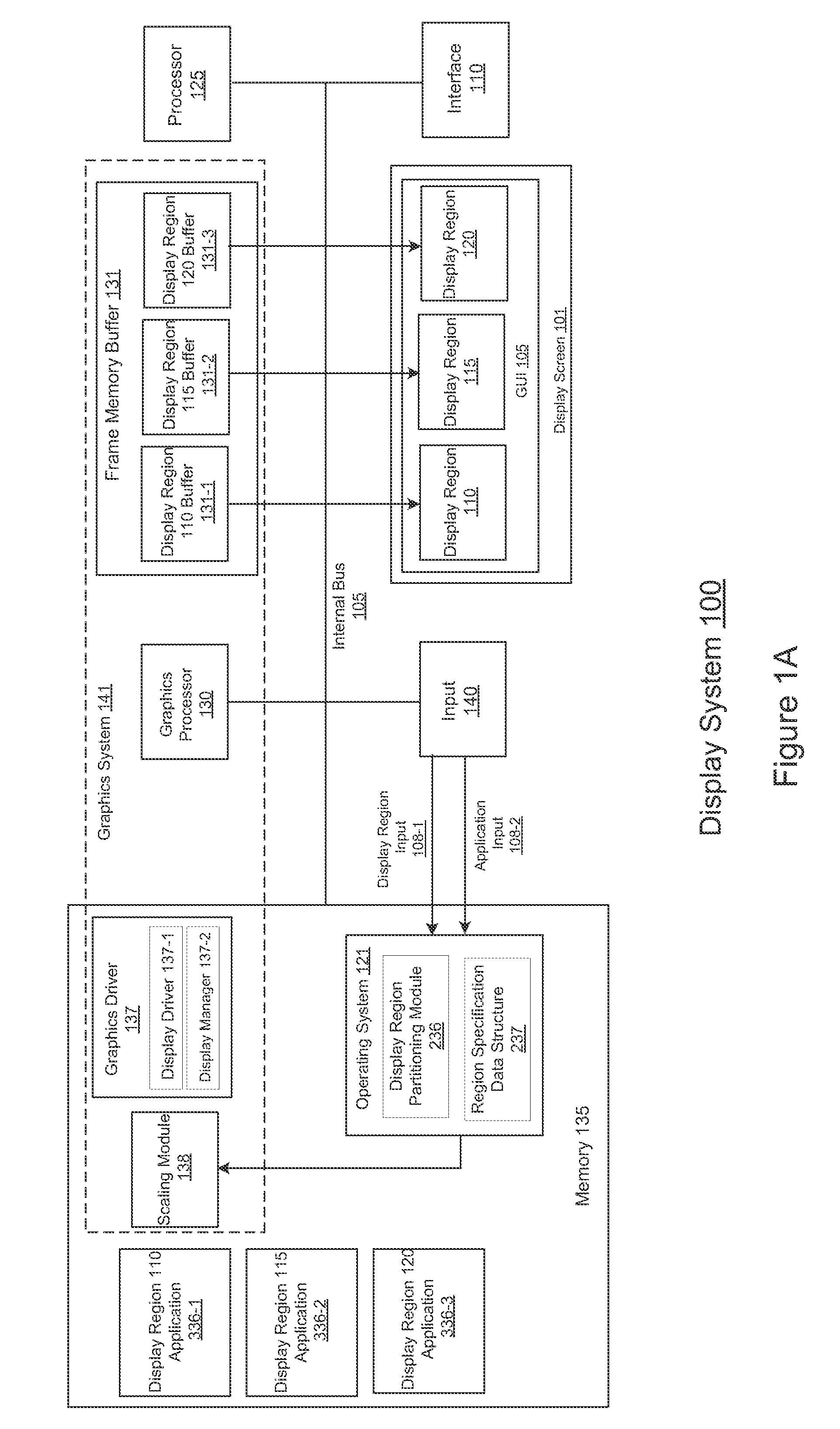
A system and method of scalable resolution display are presented. Embodiments of the present invention are operable to partition the native resolution (e.g., available pixel density) of a high pixel density display screen into multiple display regions (windows) in a manner such that each partitioned display region is capable of independently displaying scaled output with respect to its allotted native resolution. As such, both high pixel count images and “low” pixel count images may be displayed simultaneously within the same high pixel density display screen in a manner that enhances the user's visual experience.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Resolution-tunable pixel arrangement algorithm suitable for cylindrical mirror type stereoscopic display
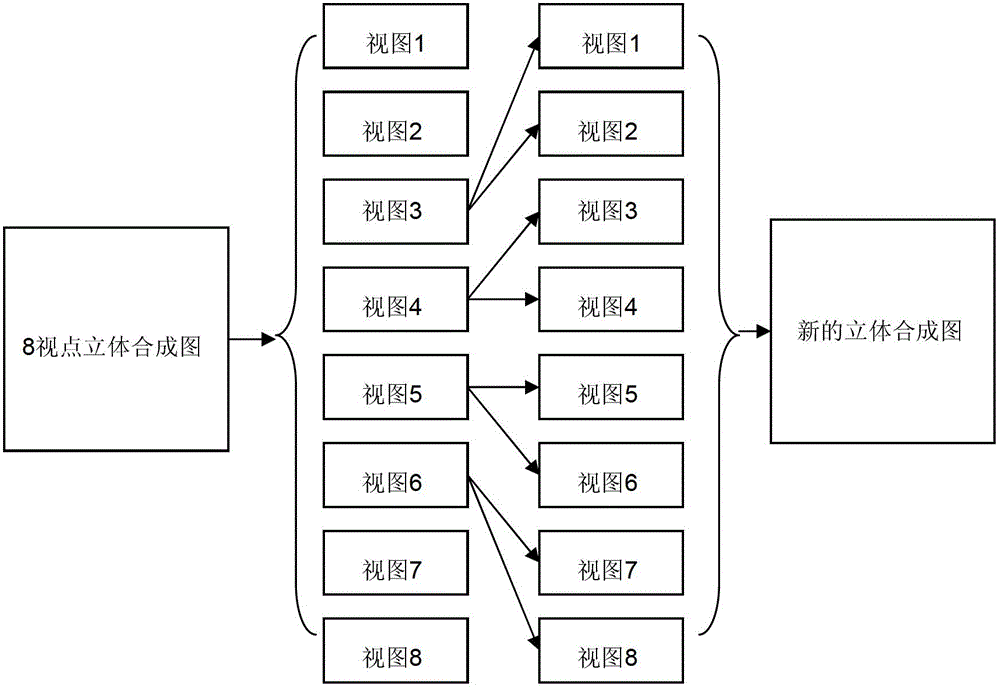
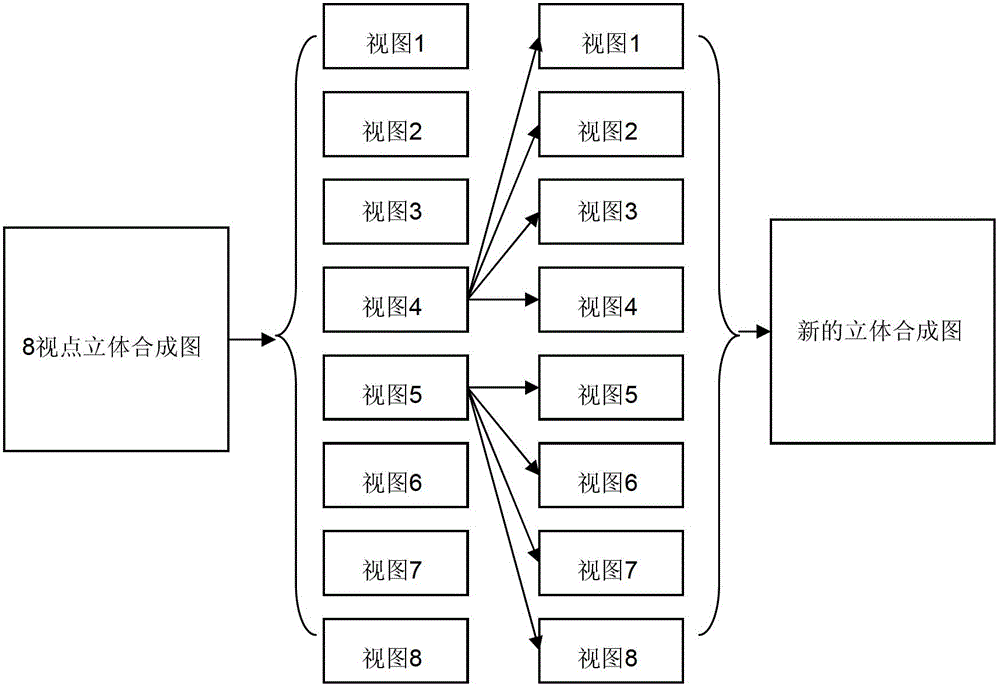
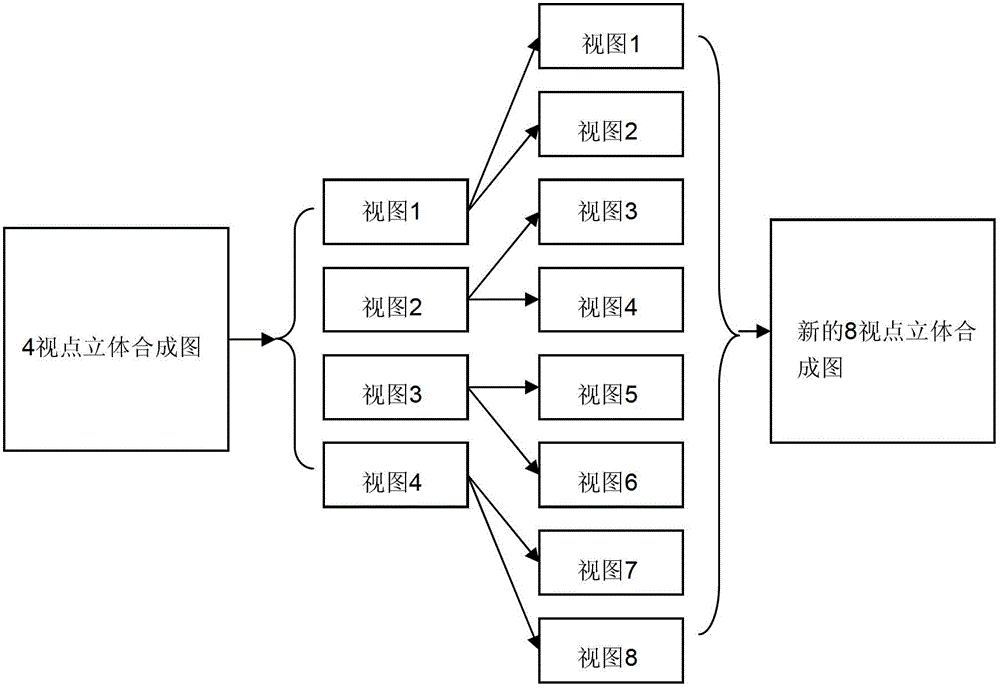
The invention discloses a resolution-tunable pixel arrangement algorithm suitable for cylindrical mirror type stereoscopic display, which comprises the following steps: firstly converting stereoscopic images with tunable resolution and then carrying out non-integer error pixel compensation on the converted stereoscopic images. The resolution-tunable pixel arrangement algorithm has the advantages that the display of the same stereoscopic image with different resolutions on the same cylindrical mirror type stereoscopic display can be realized, and further, the proposes of combining the display resolution and displaying the stereoscopic images with 8, 4 and 2 viewpoints in a combined manner are achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
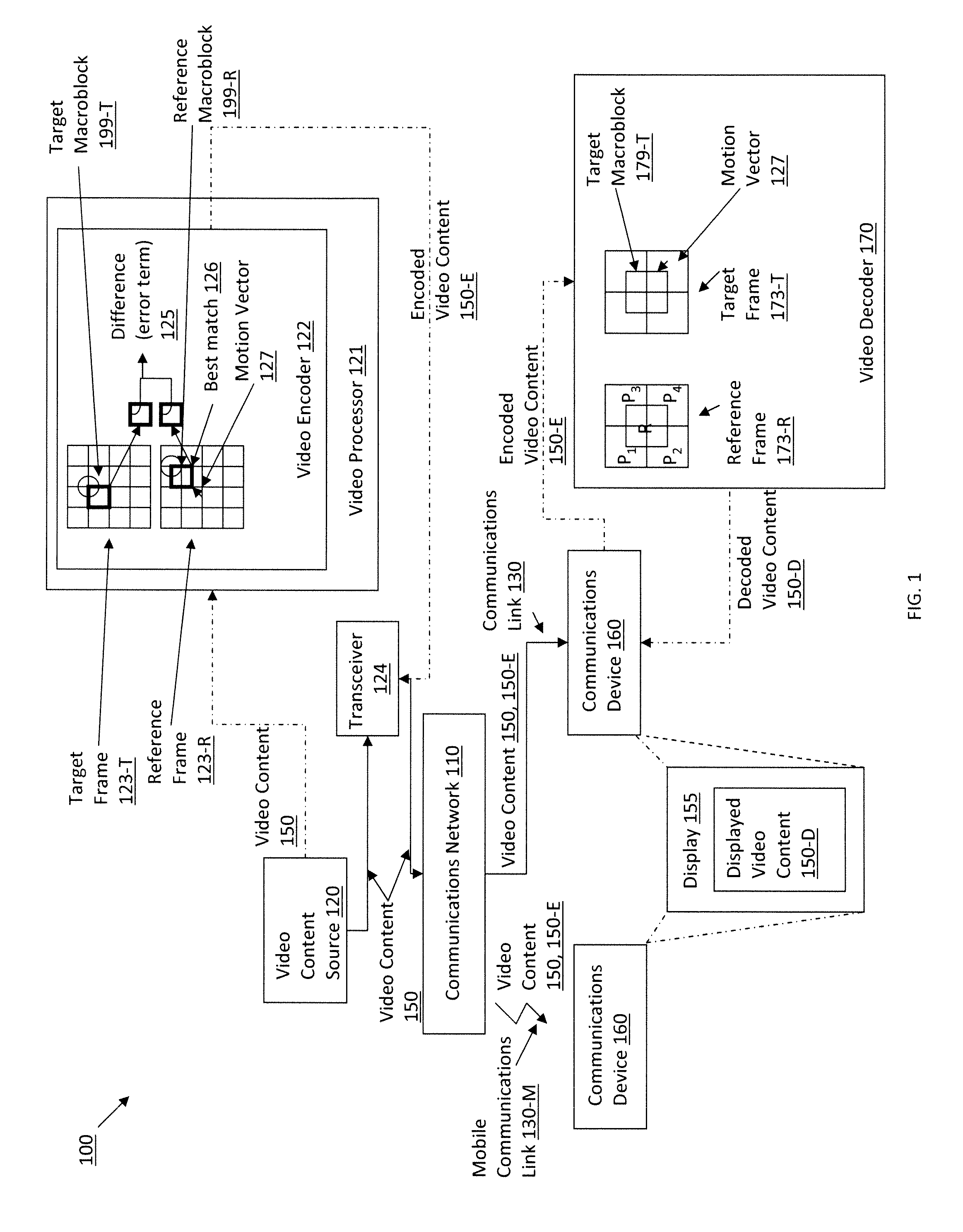
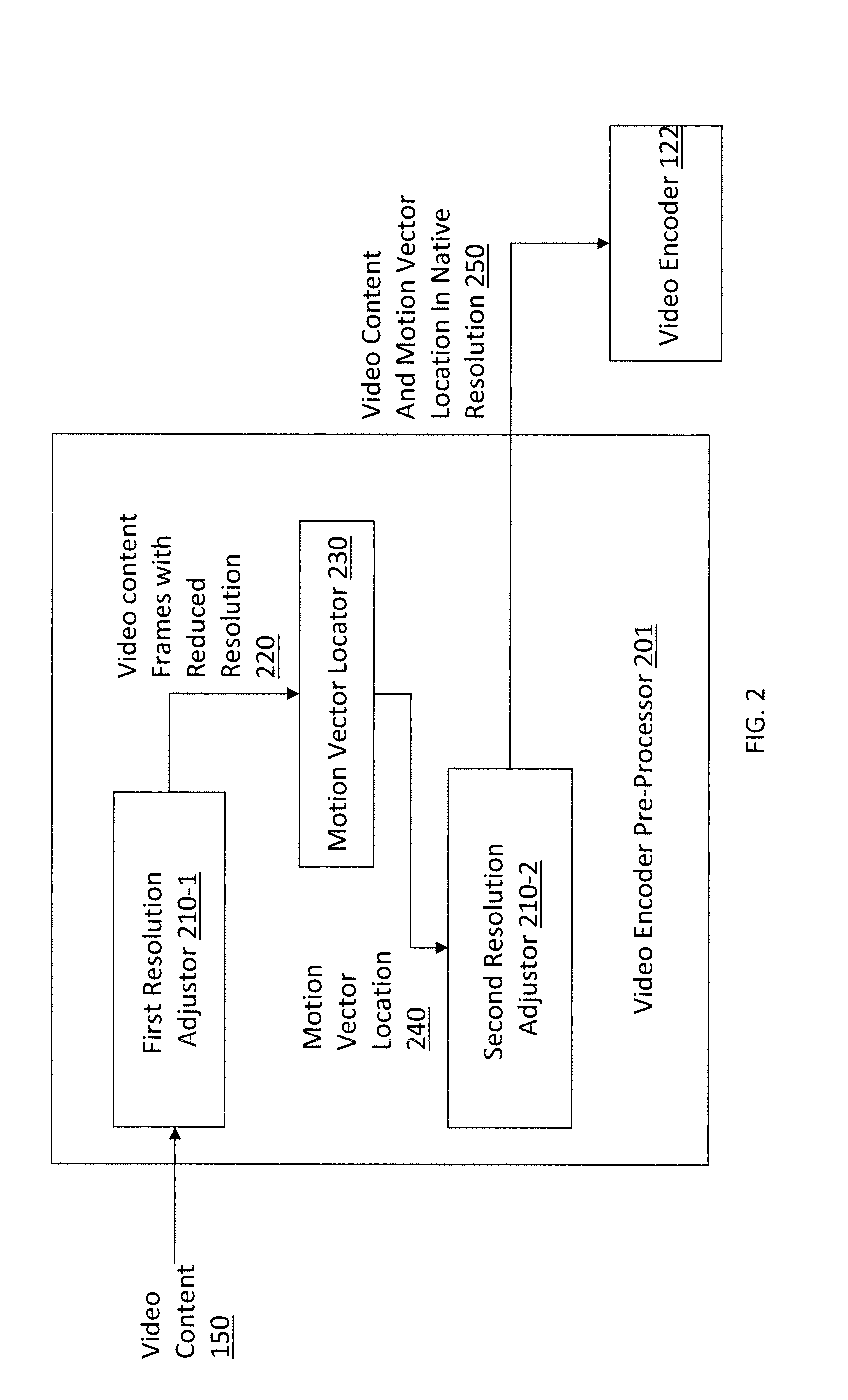
Method and apparatus for finding a motion vector
ActiveUS20130294516A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorSlide window
Methods and related systems for encoding video streams are described. Reference and target frames of a video stream are scaled to reduce their resolution. A sliding window is used to compare the reduced resolution reference and target frames and identify blocks, outlined by a sliding window, that include similar content. A motion vector indicating the motion of the identified similar content is determined. Once the motion vector is determined, the reference and target frames are restored to their native resolution and a translated location for the motion vector is identified in the restored frames. The translated location of the motion vector may be used in encoding the frames of the video stream.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
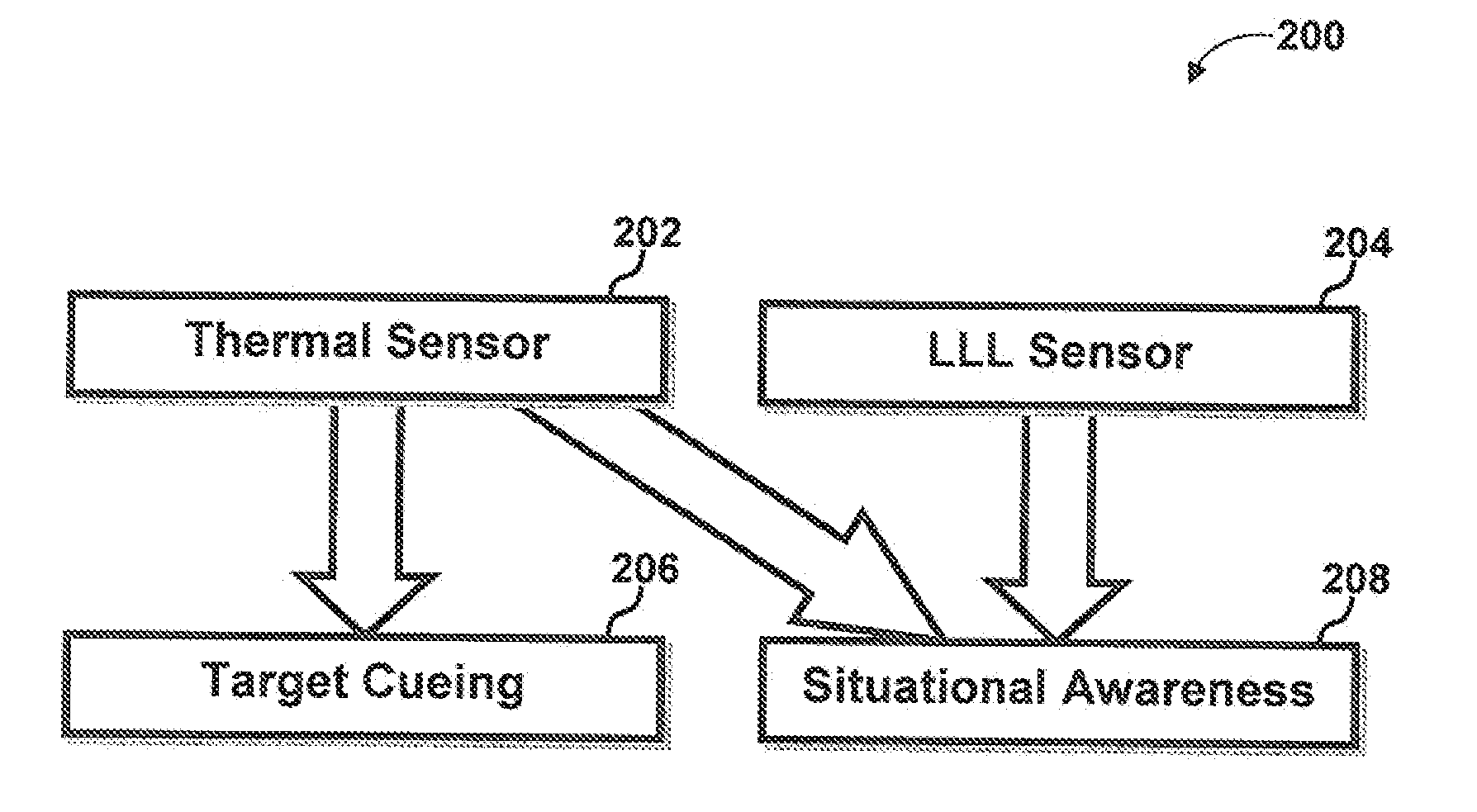
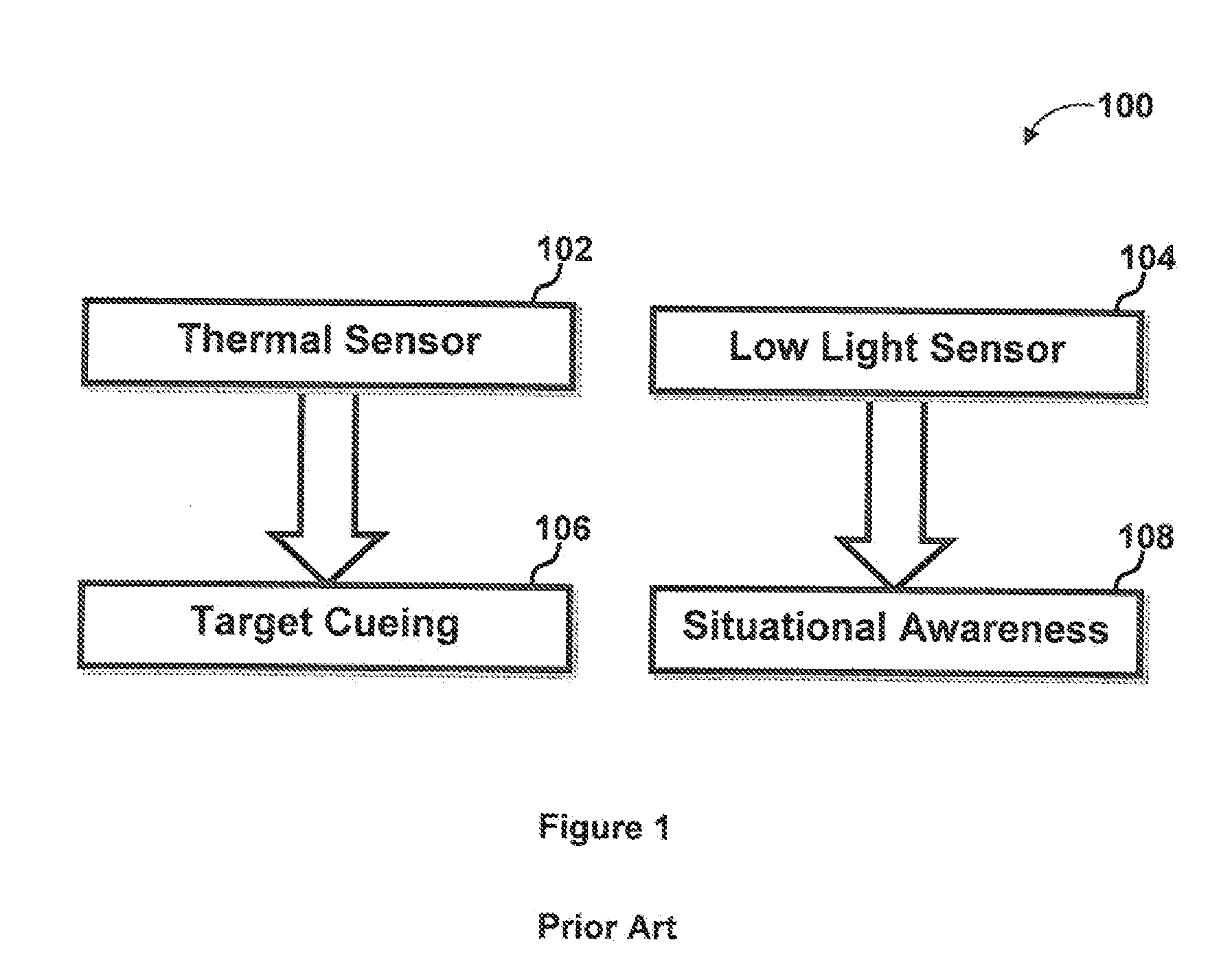
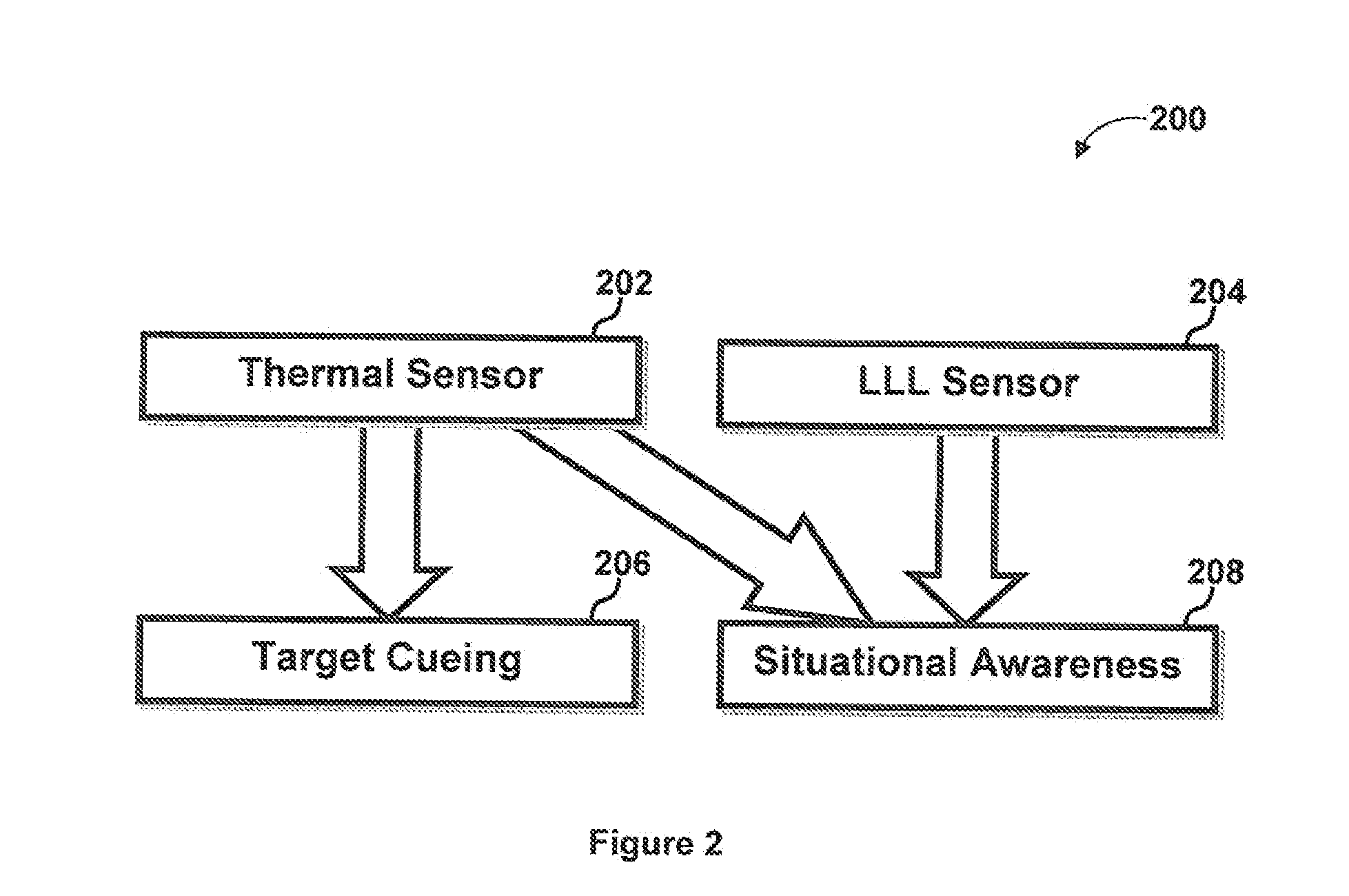
System and method for situational awareness and target cueing
ActiveUS20130057698A1Reduce contributionImprove rendering capabilitiesTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryImage resolutionNative resolution
A system and method for situational awareness and target cueing for use in military applications is disclosed. In extreme low light situations where the LLL sensor cannot provide SA information, the system allocates thermal information to the green SA channel to maintain the supply of contextual information to the user and thus situational awareness (SA) never drops below the native resolution of the thermal sensor. This improved SA capability, surpasses any existing LLL sensor technology in a single channel (stand-alone) application in overcast star light and below conditions.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Dynamic Display Resolution Management for an Immersed Information Handling System Environment
ActiveUS20160313789A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsInput/output for user-computer interactionHousing of computer displaysGraphicsImage resolution
A display device presents visual information with native and non-native resolutions stored in EDID and provided to a graphics controller. Non-native resolutions are generated in response to an object detected that interferes with the presenting of the visual information, such as an object between a projector and projection surface or an object placed on a capacitive mat display. The non-native resolutions present the visual information to avoid the object and are stored in EDID in association with object characteristics to allow re-use of the non-native resolutions when visual information at the display is blocked by an object with similar characteristics.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
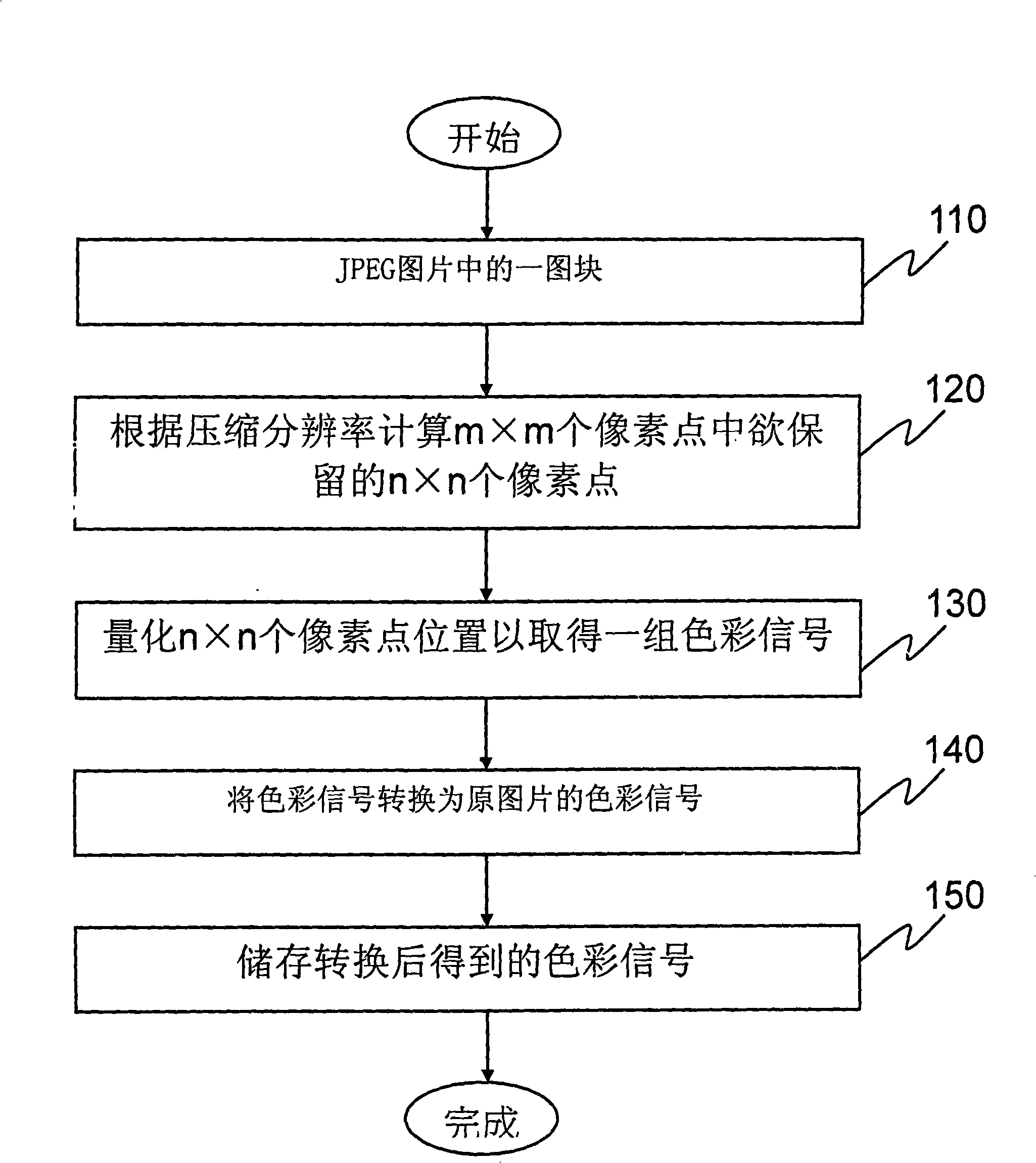
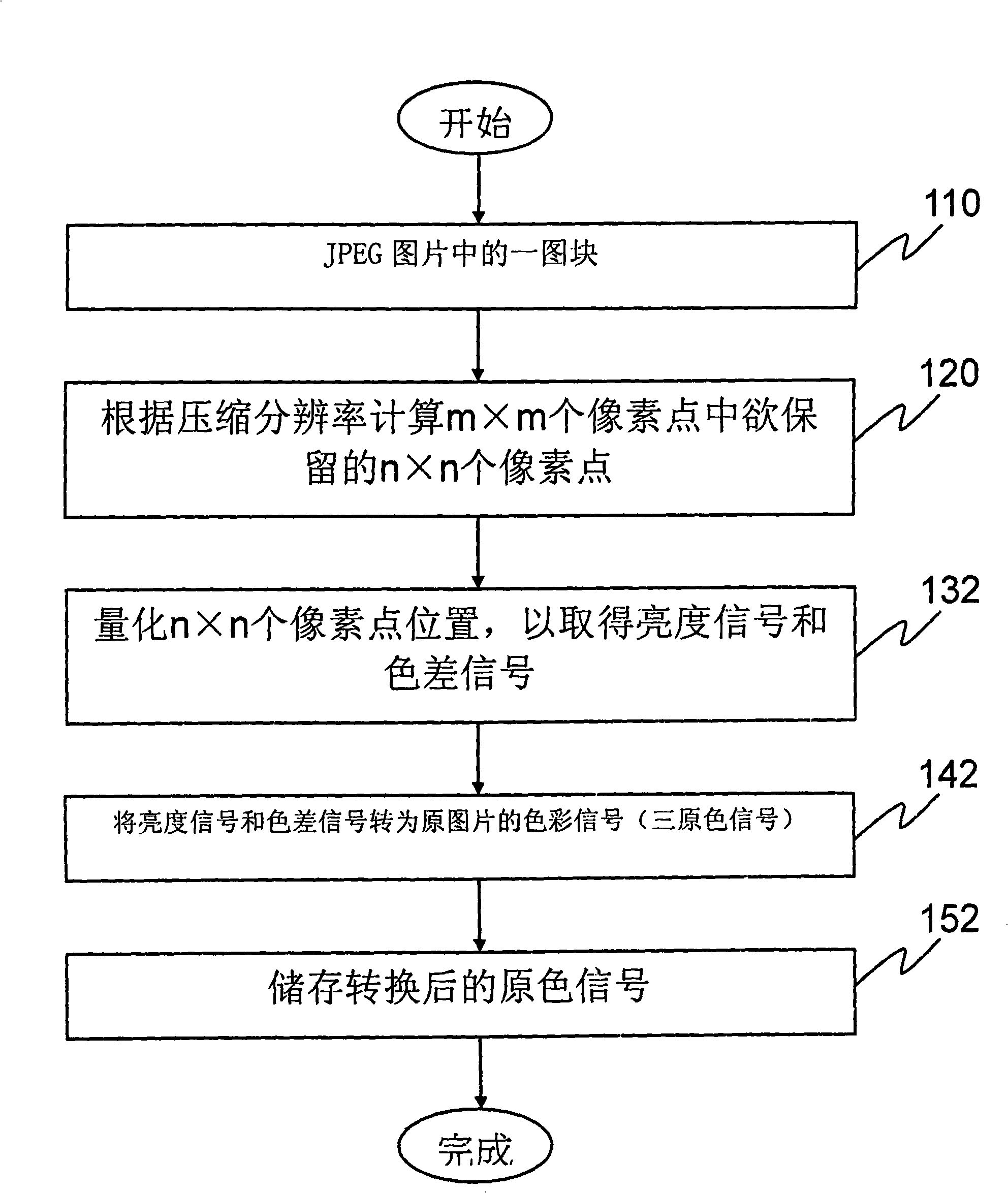
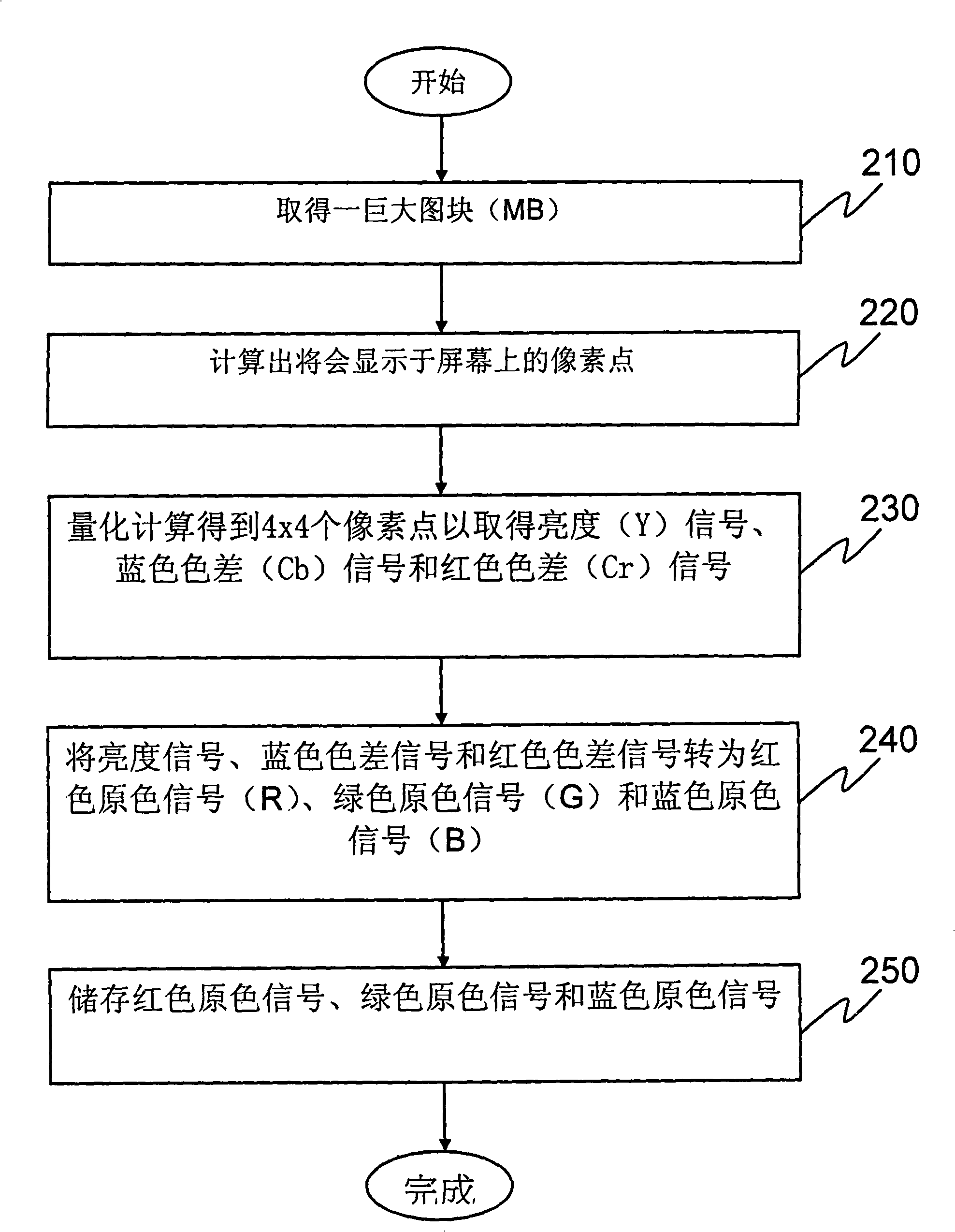
Buffer saving image decompressing storing method and module thereof
InactiveCN101287057ASave memoryCode conversionPictoral communicationImage resolutionNative resolution
The invention discloses a picture decompression and storage method and a module thereof for saving scratch-pad memory, wherein, the picture decompression and storage method comprises the following steps: acquiring a picture block which has 'm' multiplying 'm' pixel dots and native resolution, calculating 'n' multiplying 'n' pixel dots to be reserved among the 'm' multiplying 'm' pixel dots according to compression resolution; quantifying the location of the 'n' multiplying 'n' pixel dots so as to acquire a group of color signals; converting the color signals into the color signals of the original picture and storing the color signals. As display resolution of the screen is smaller than the resolution of the original picture in certain condensed proportion, the whole JPEG picture block does not need to be conserved. The method of the invention and the picture storage module thereof can achieve the technical effect of saving the memory.
Owner:WUDI SCI & TECH (XIAN) CO LTD
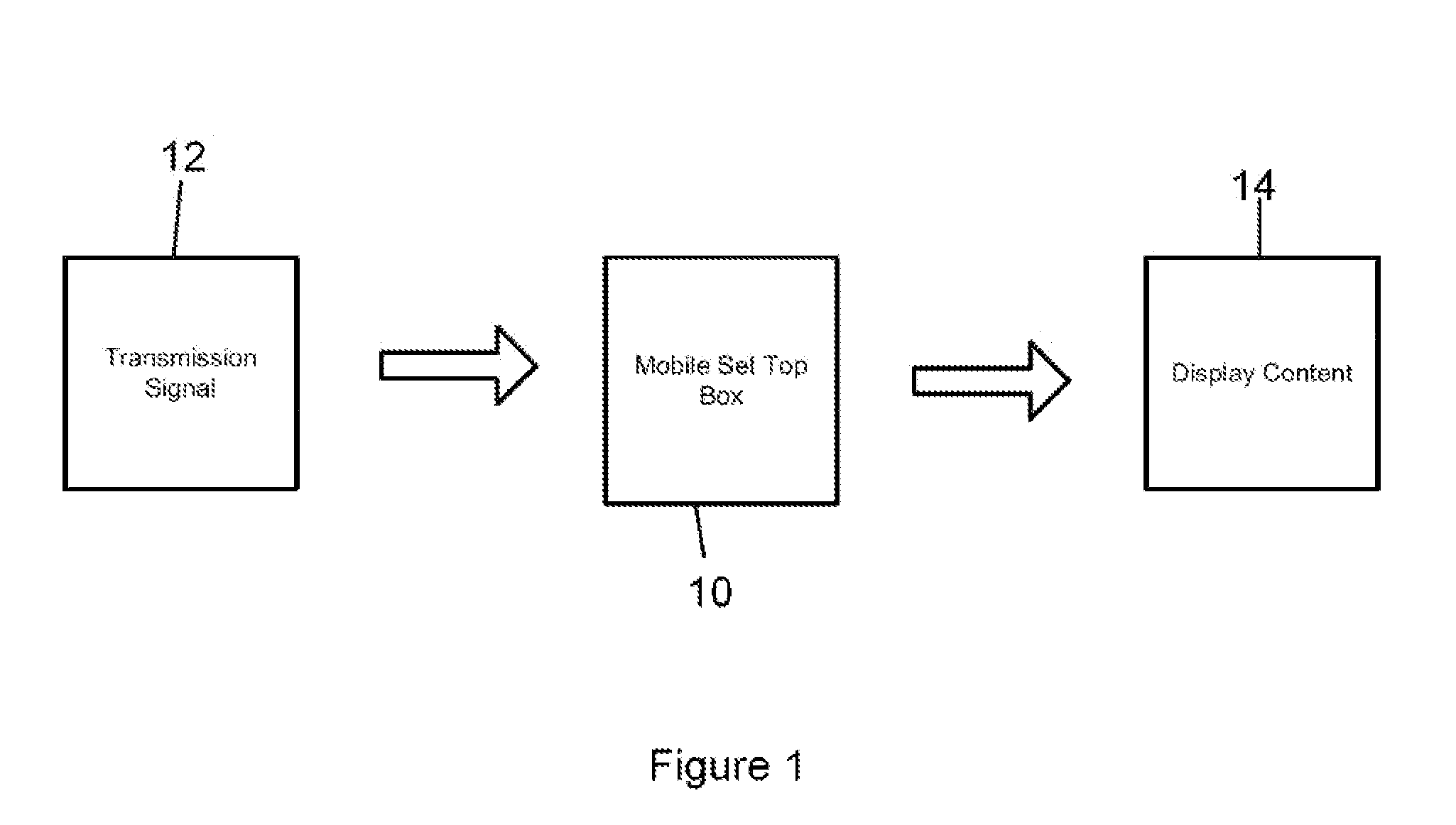
Mobile set top box
ActiveUS8863223B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAlignment for track following on tapesImage resolutionNative resolution
A system is provided in which IP or media content residing on or being streamed to a mobile phone is forwarded to a display. The media content supports a native resolution of the mobile phone that is significantly smaller than a native resolution of said display. The system has media content processing circuitry, which up-scales the media content to the display native resolution. The system forwards the up-scaled media content to the display, whereby the display provides the up-scaled media content to a viewer.
Owner:MV3 PARTNERS
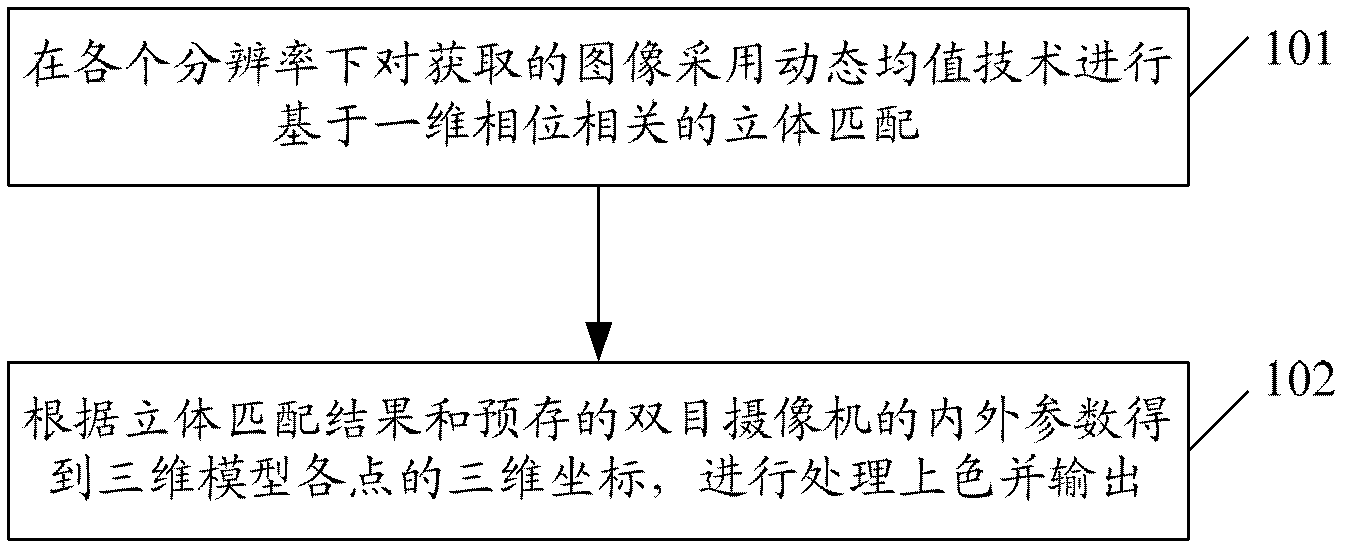
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and system
ActiveCN103325140AAchieve reconstructionShorten operation timeImage analysis3D modellingPhase correlationStereo matching
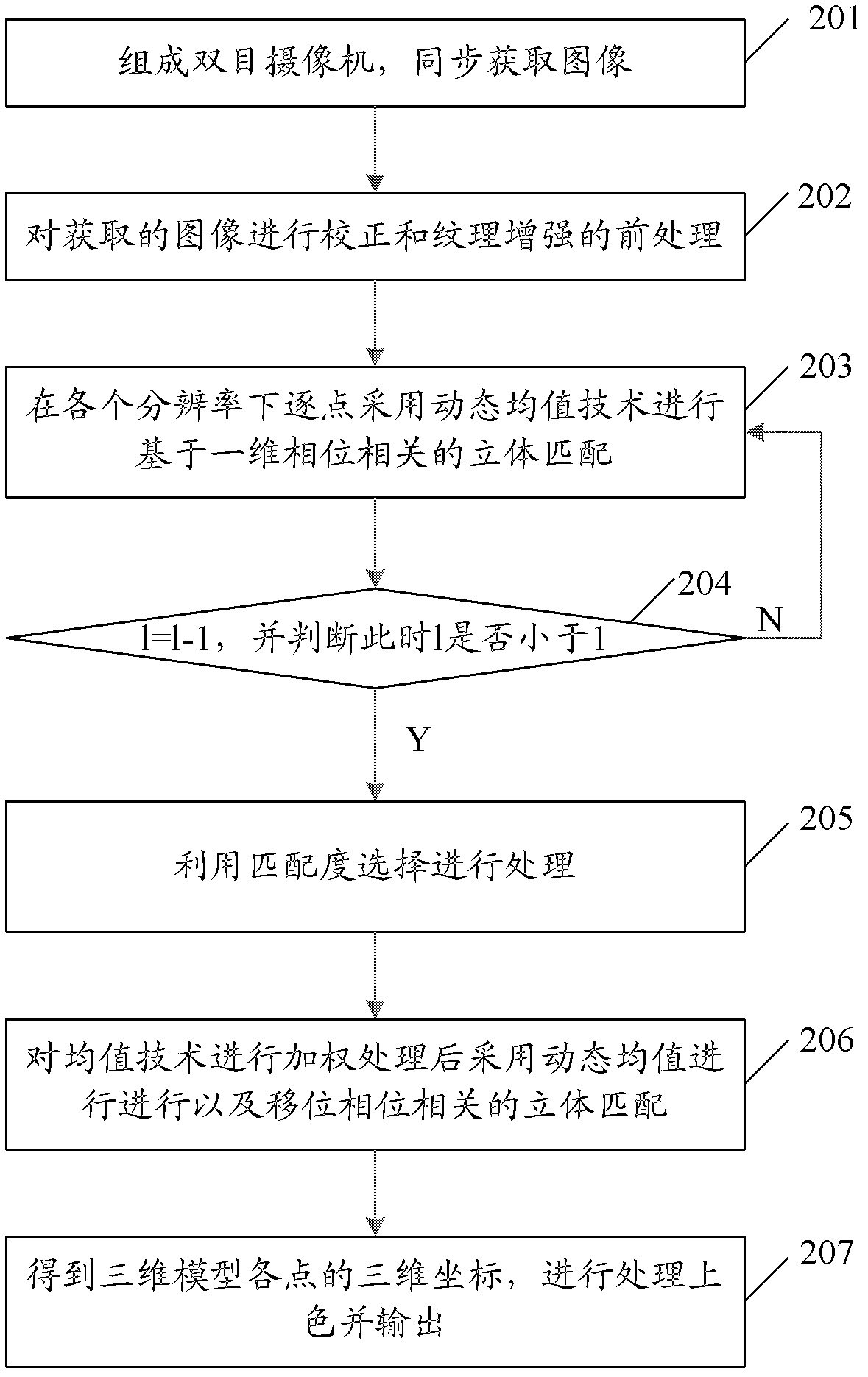
The invention provides a three-dimensional reconstruction method and a system. The three-dimensional reconstruction method comprises steps of adopting dynamic averaging techniques to captured images under any resolution to perform three-dimensional matching based on one-dimensional phase correlation; and obtaining three-dimensional coordinates of each point of a three-dimensional model according to three-dimensional matching results and prestored internal and external parameters of a binocular video camera, and performing a coloring process for output. Three-dimensional matching is performed by using one-dimensional phase related algorithm under different resolution in combination with the dynamic averaging techniques, matching precision is provided through a small amount of calculation, and matching degree is further utilized for matching selectively before images of native resolution are matched. The dynamic averaging techniques are subjected to weighting processing during the matching process, thereby greatly reducing calculation time of outputting high-precision three-dimensional models, improving matching efficiency, and enabling rapid achievement of three-dimensional model reconstruction.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com