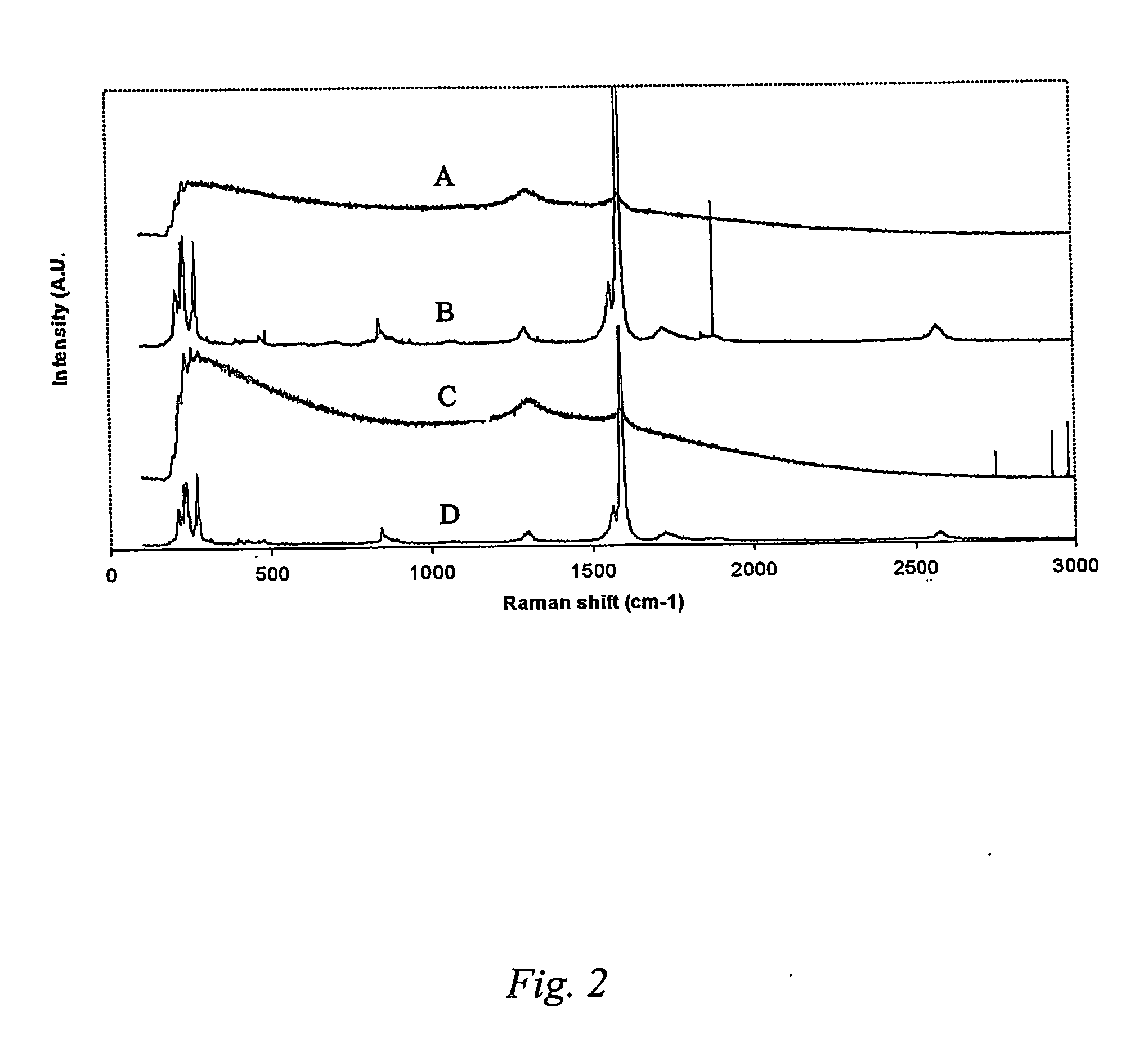
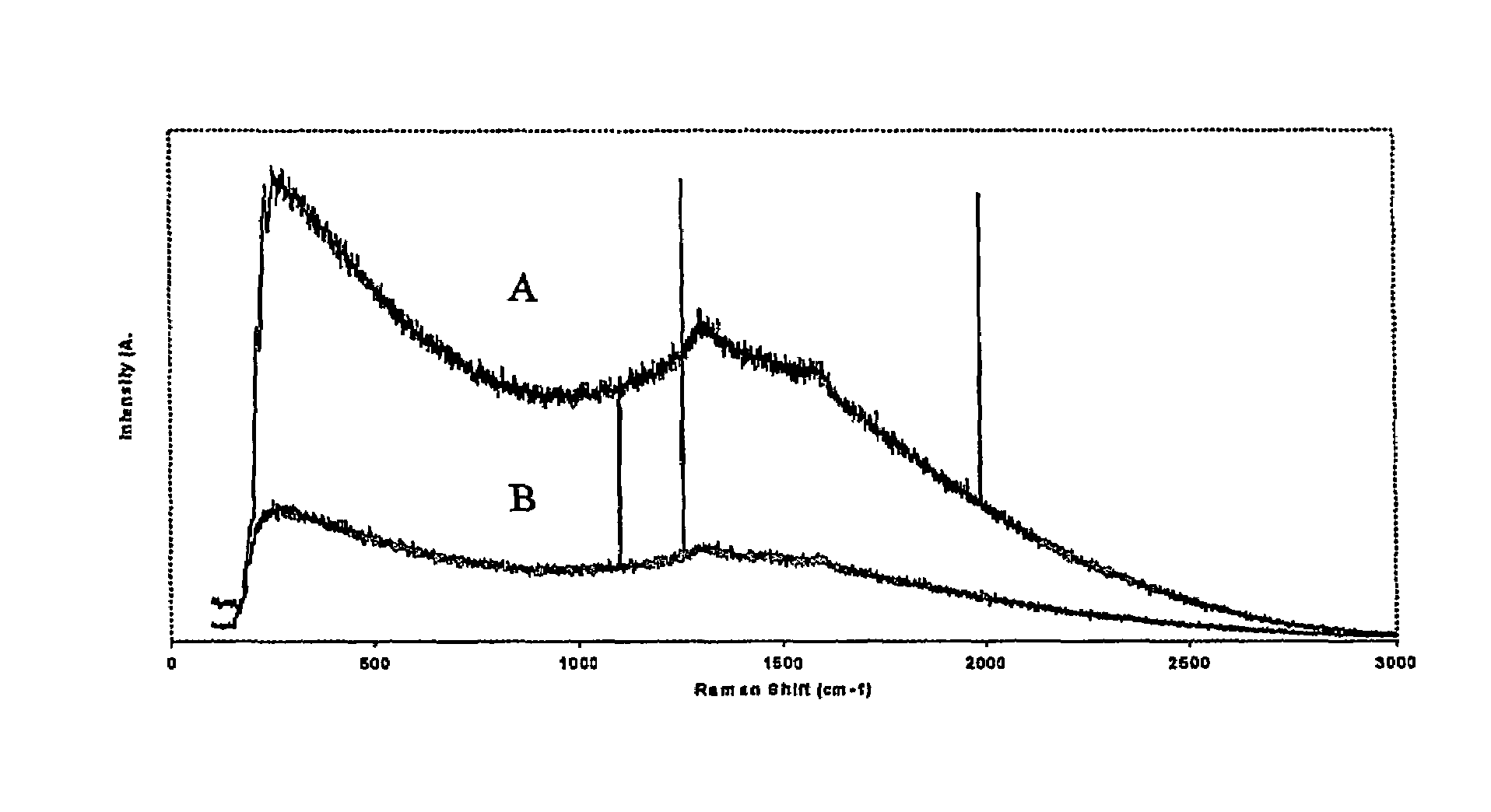
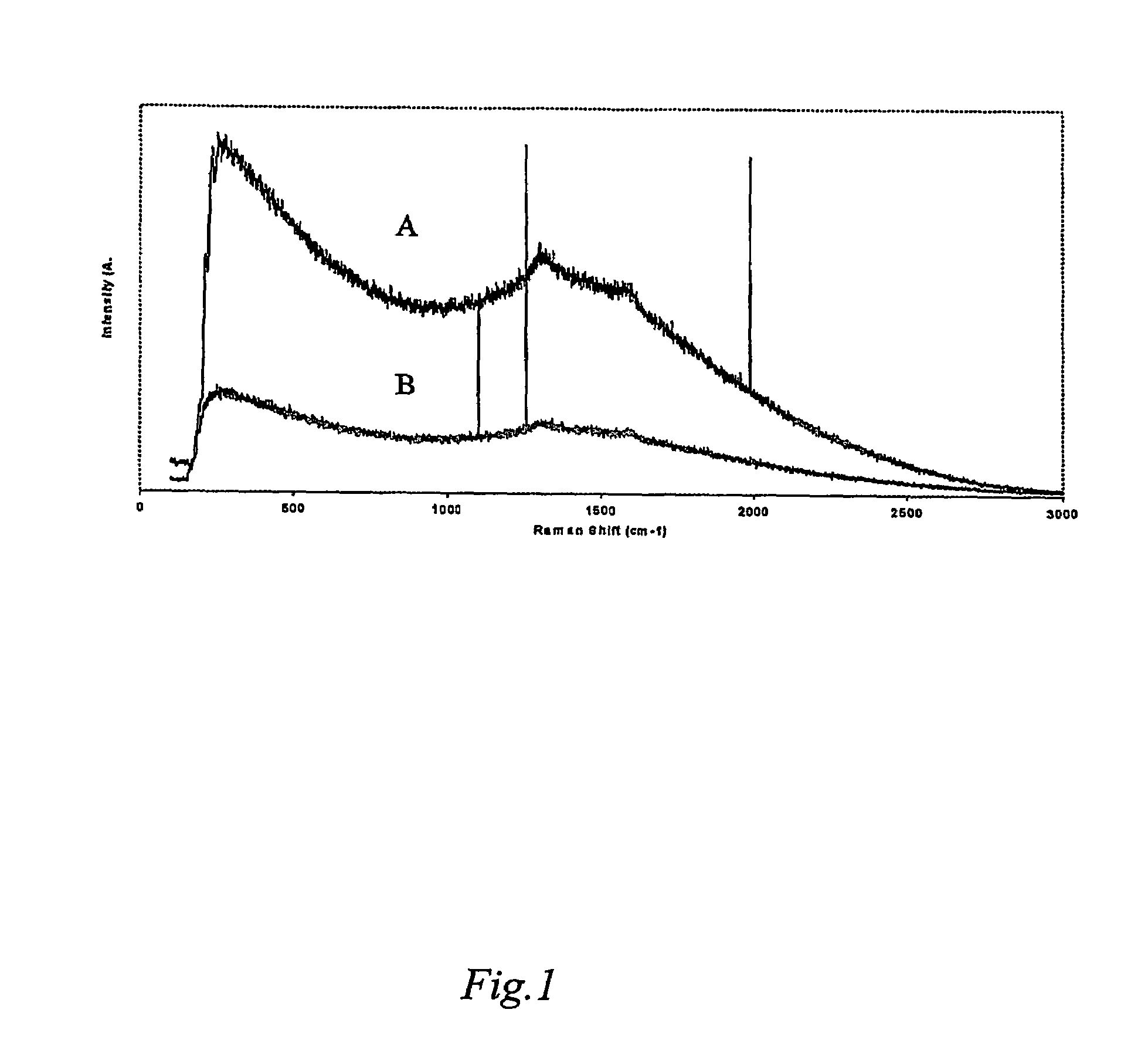
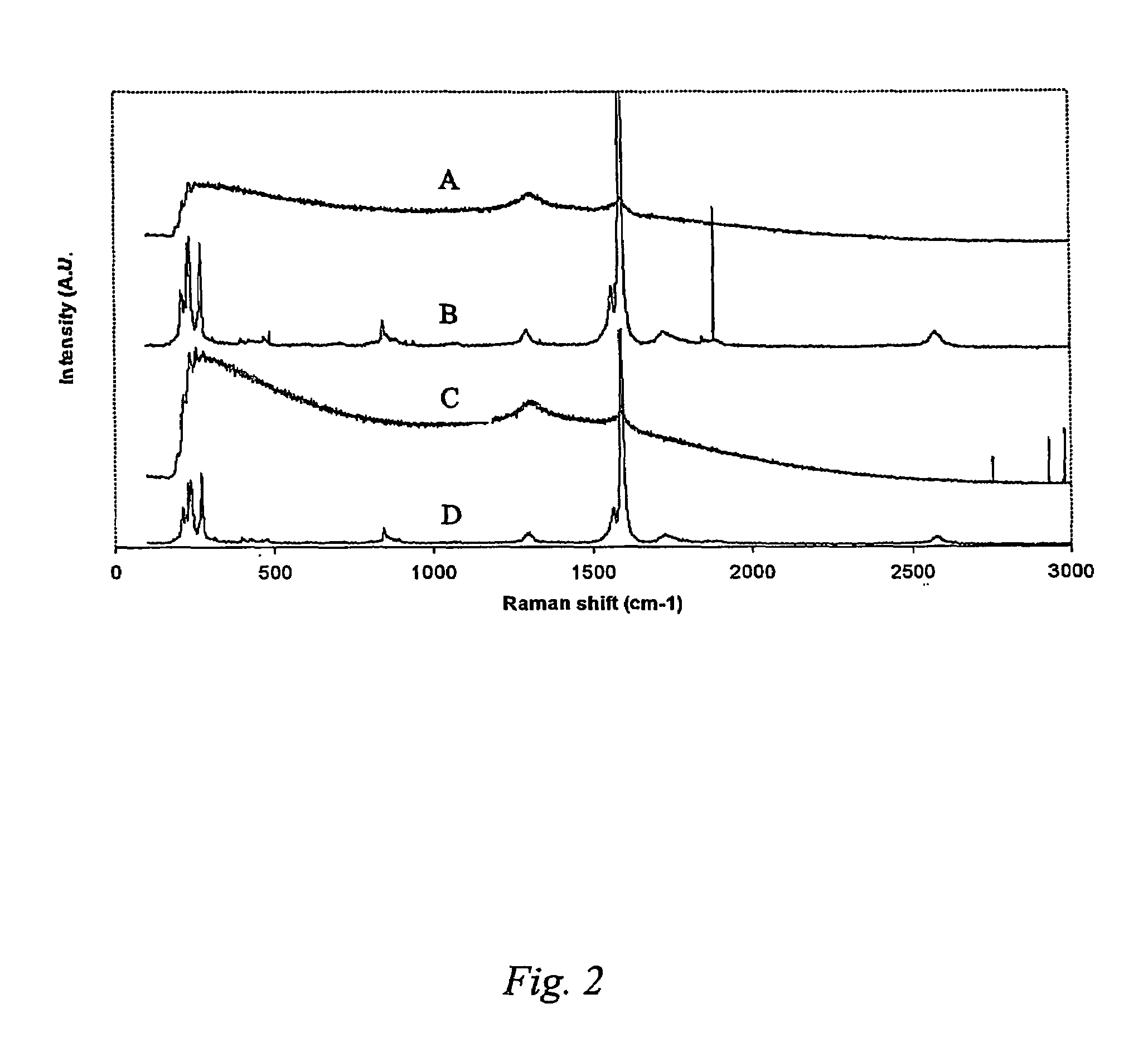
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Radiation Interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiation Interaction involves the interaction of a stream of subatomic particles or transmitted energy waves (such as electromagnetic radiation) with a biological component.
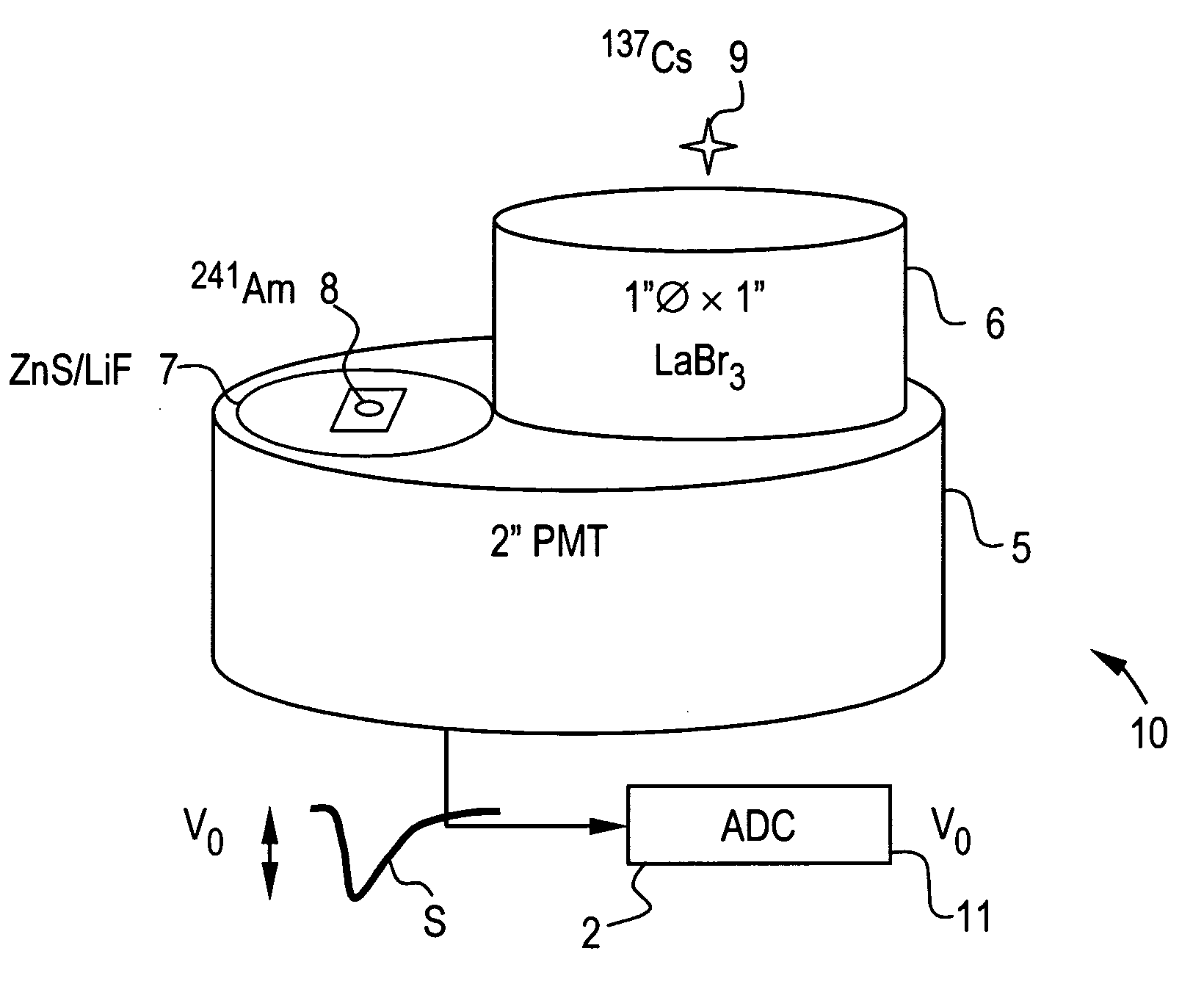
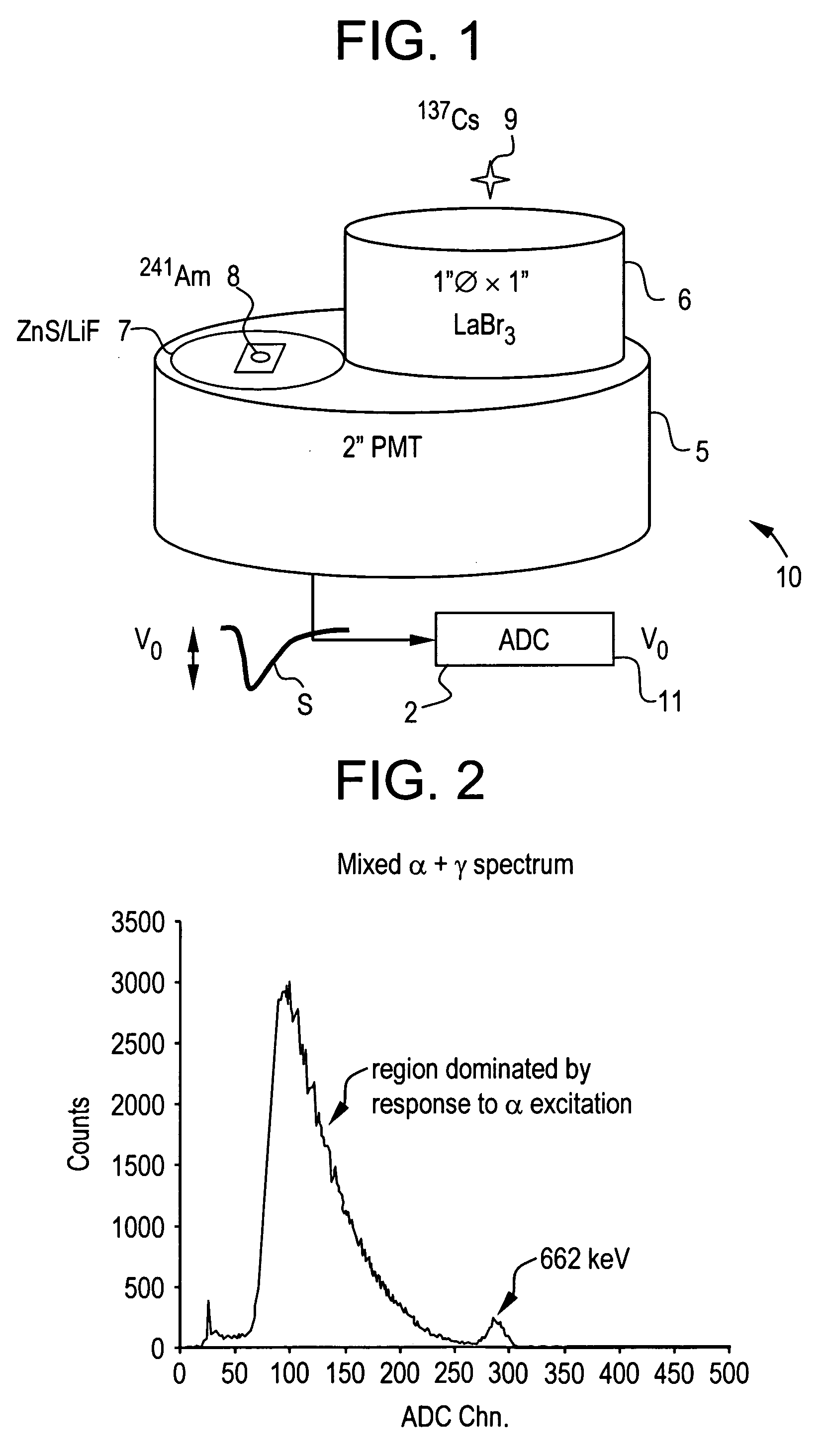
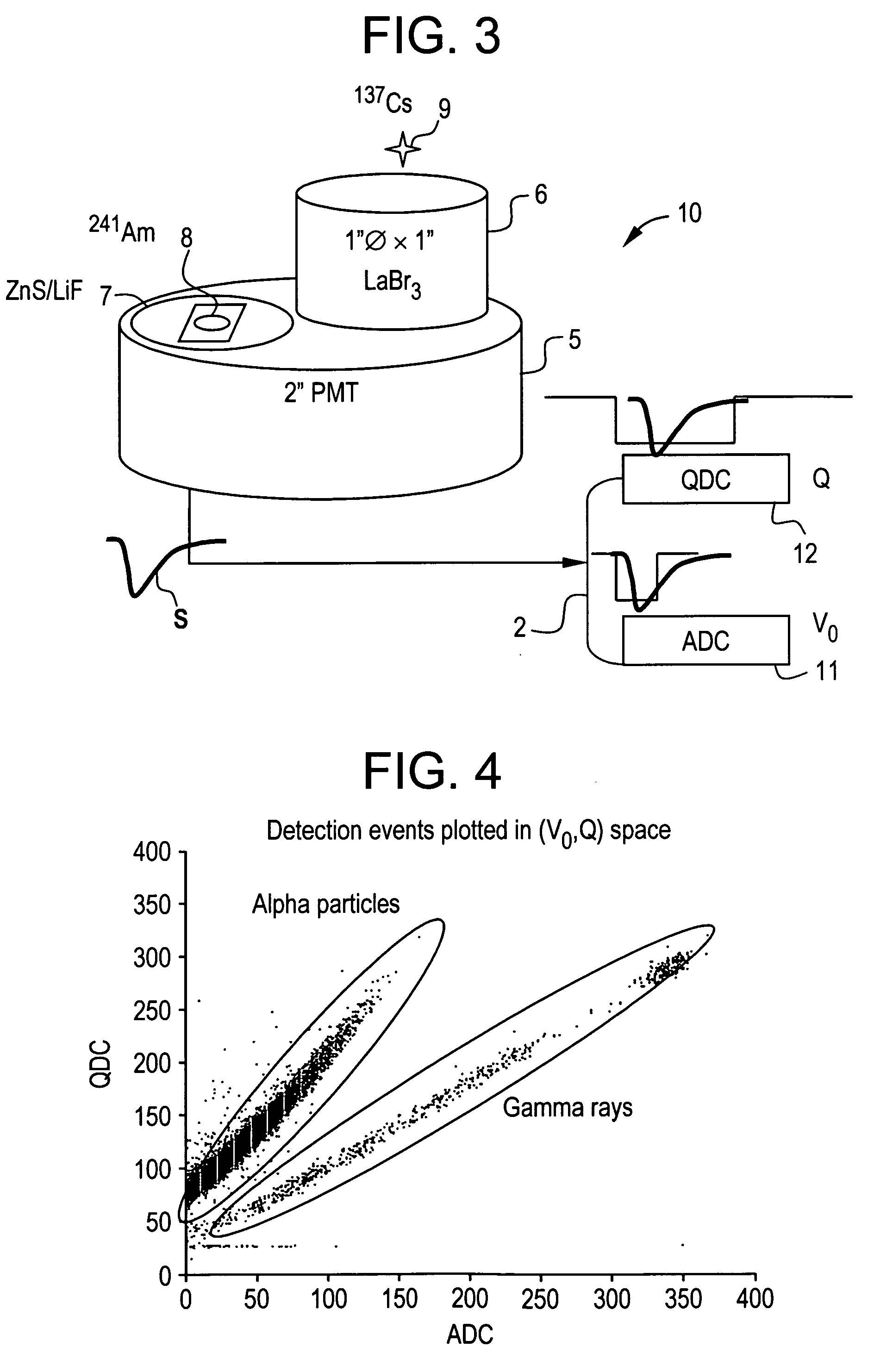
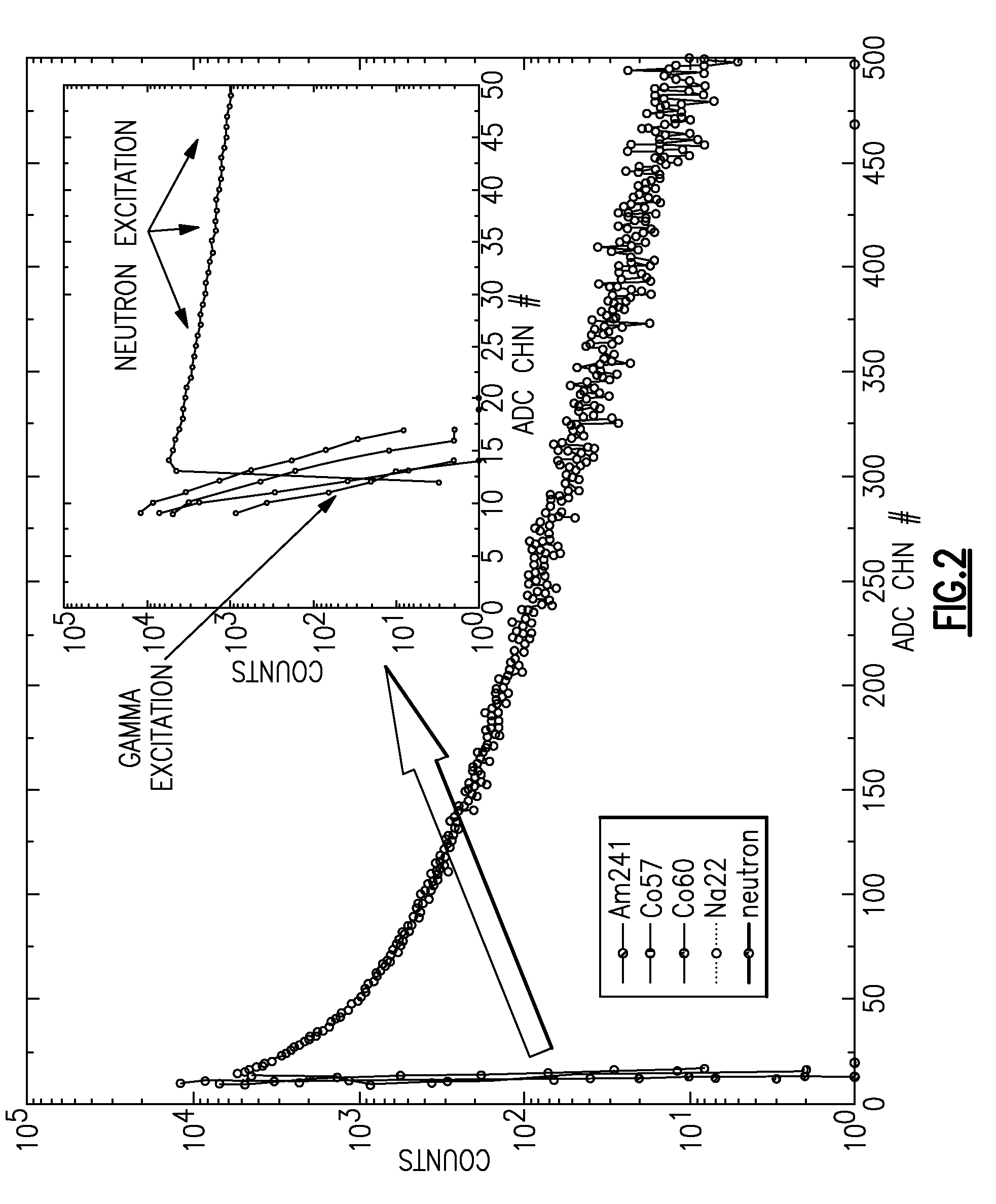
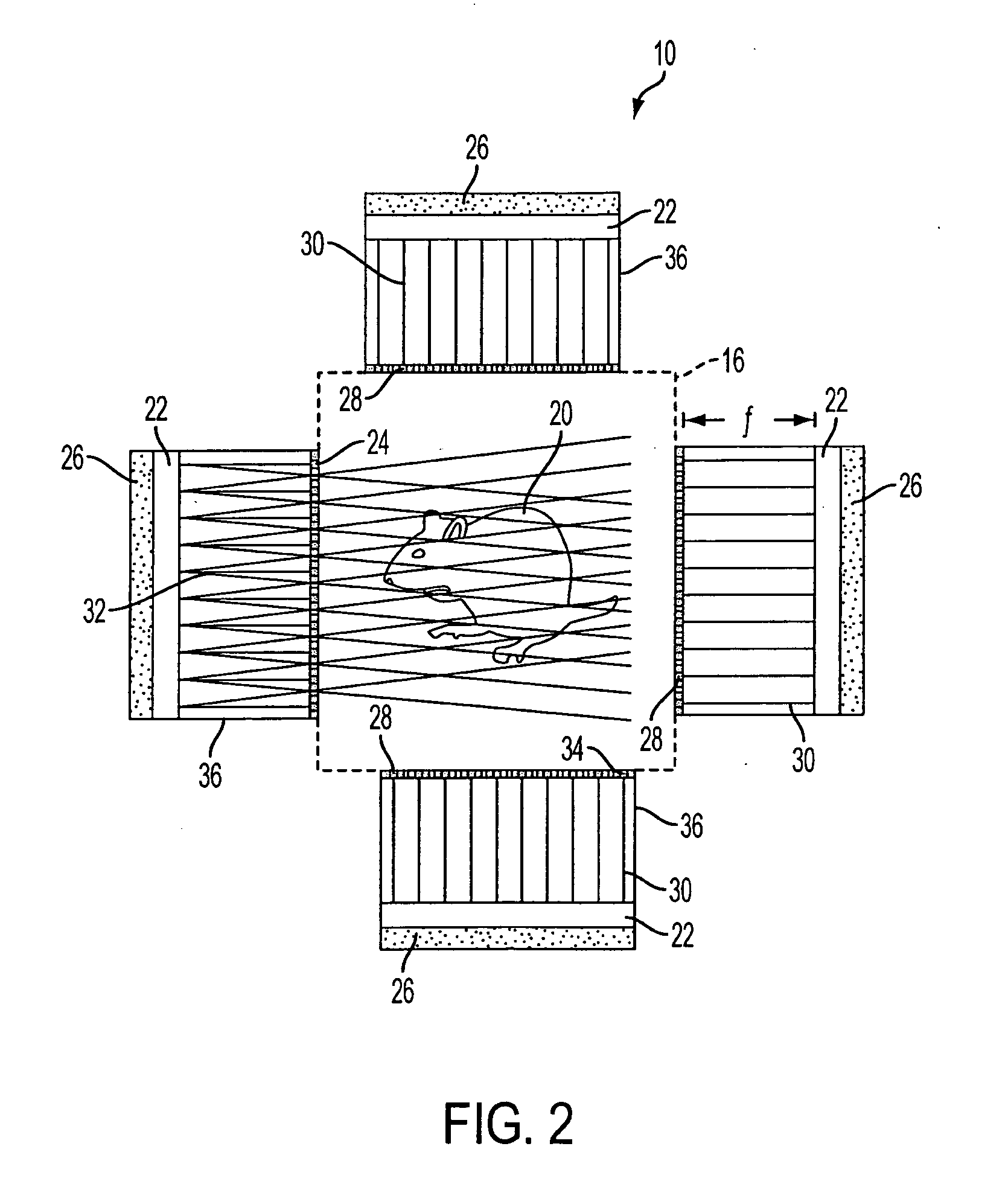
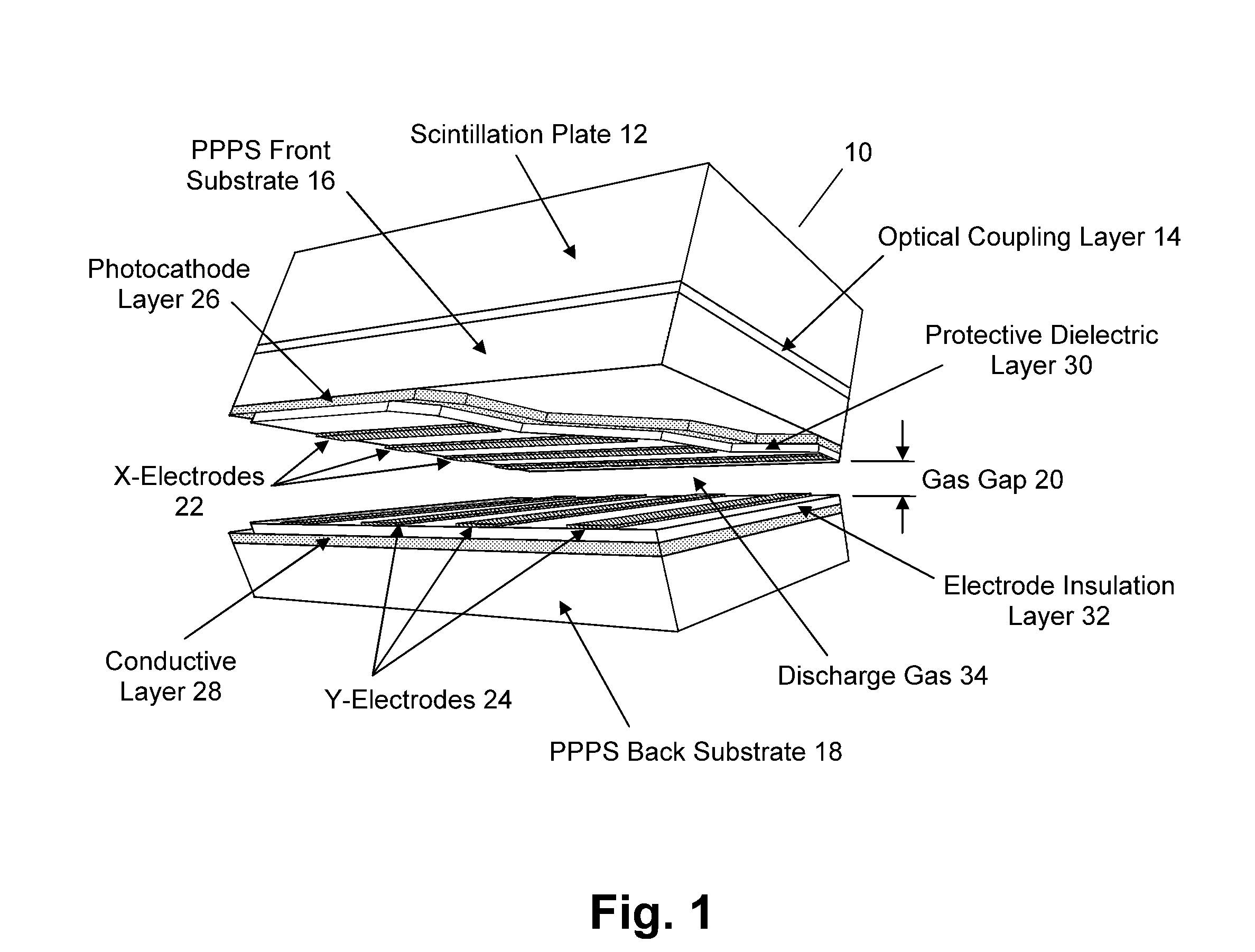
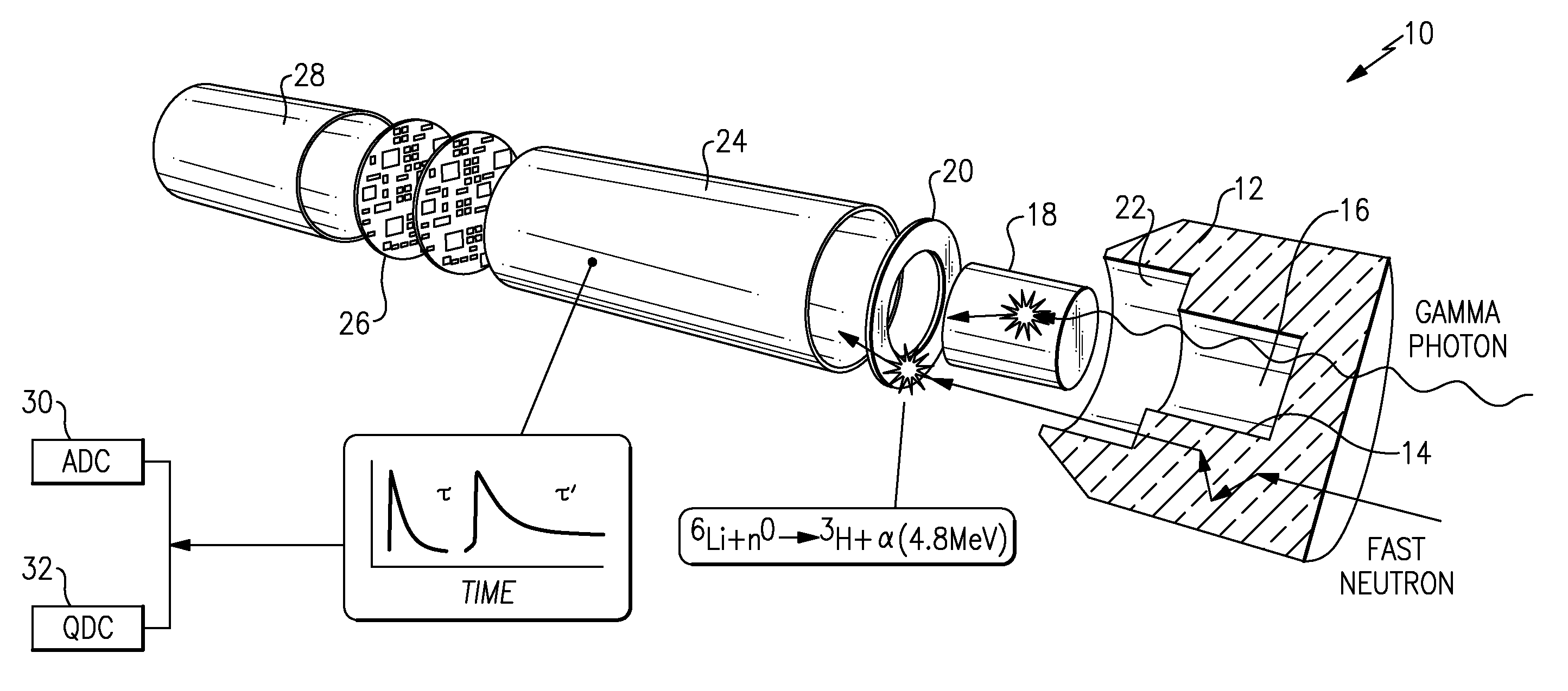
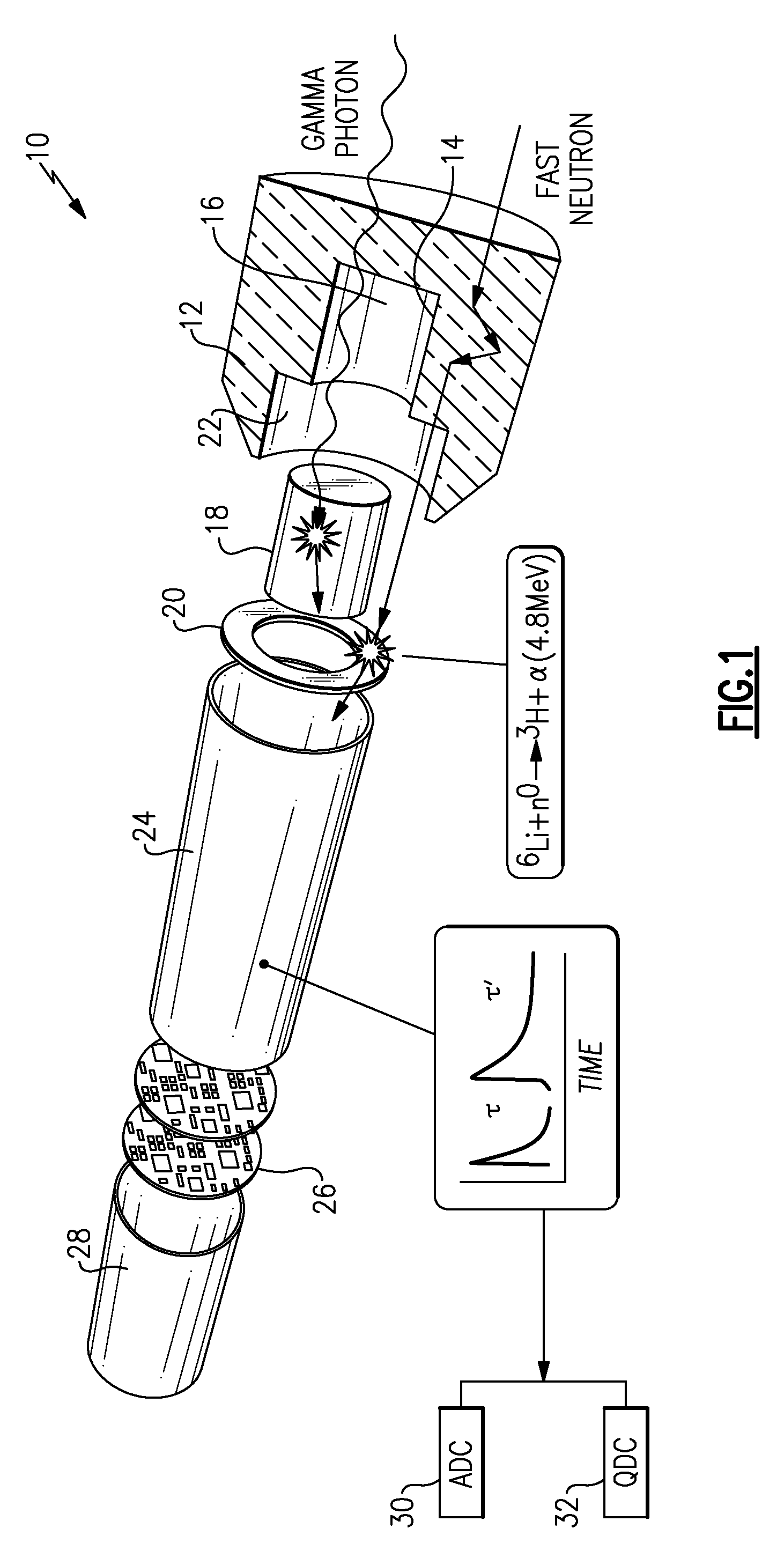
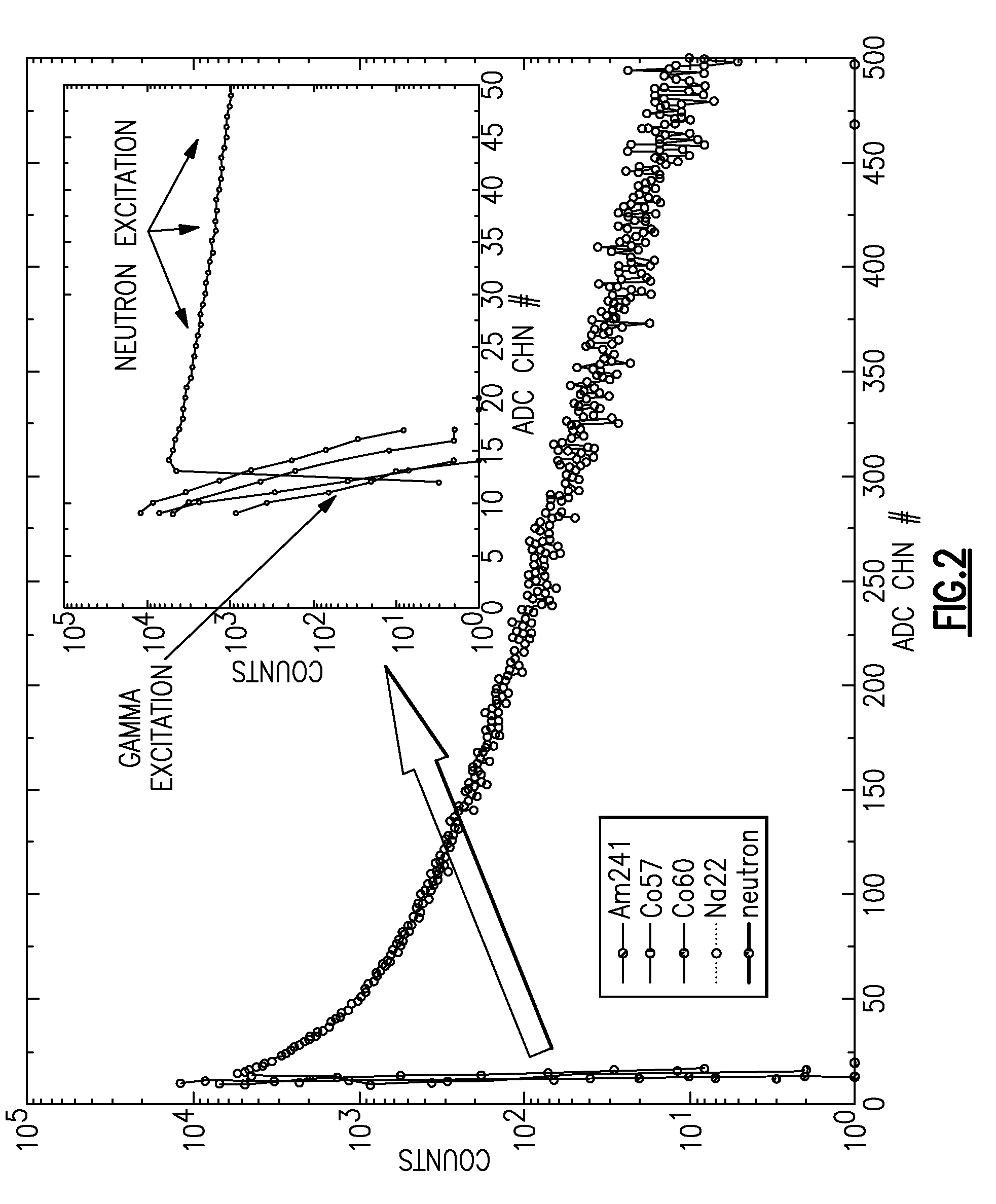
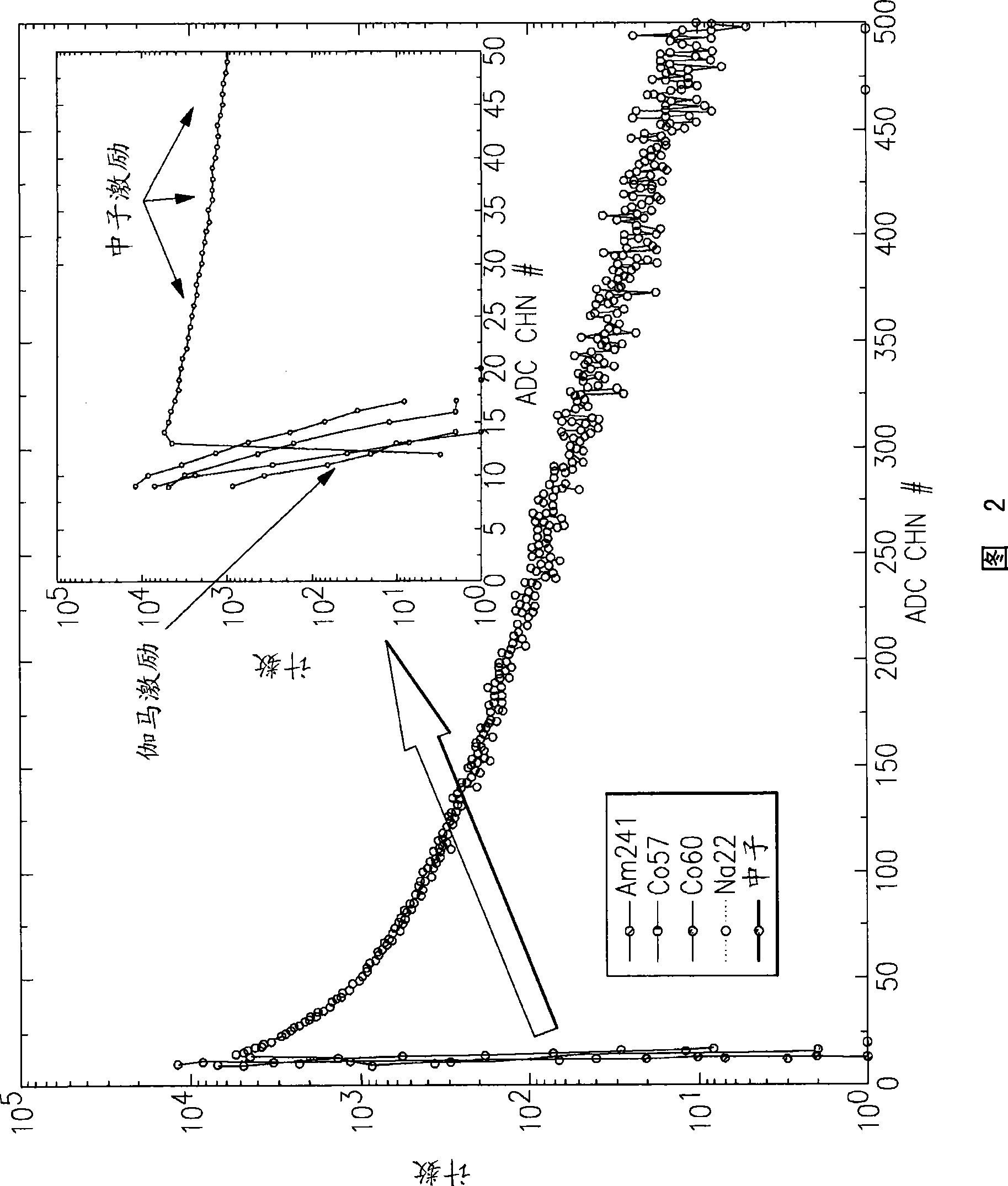
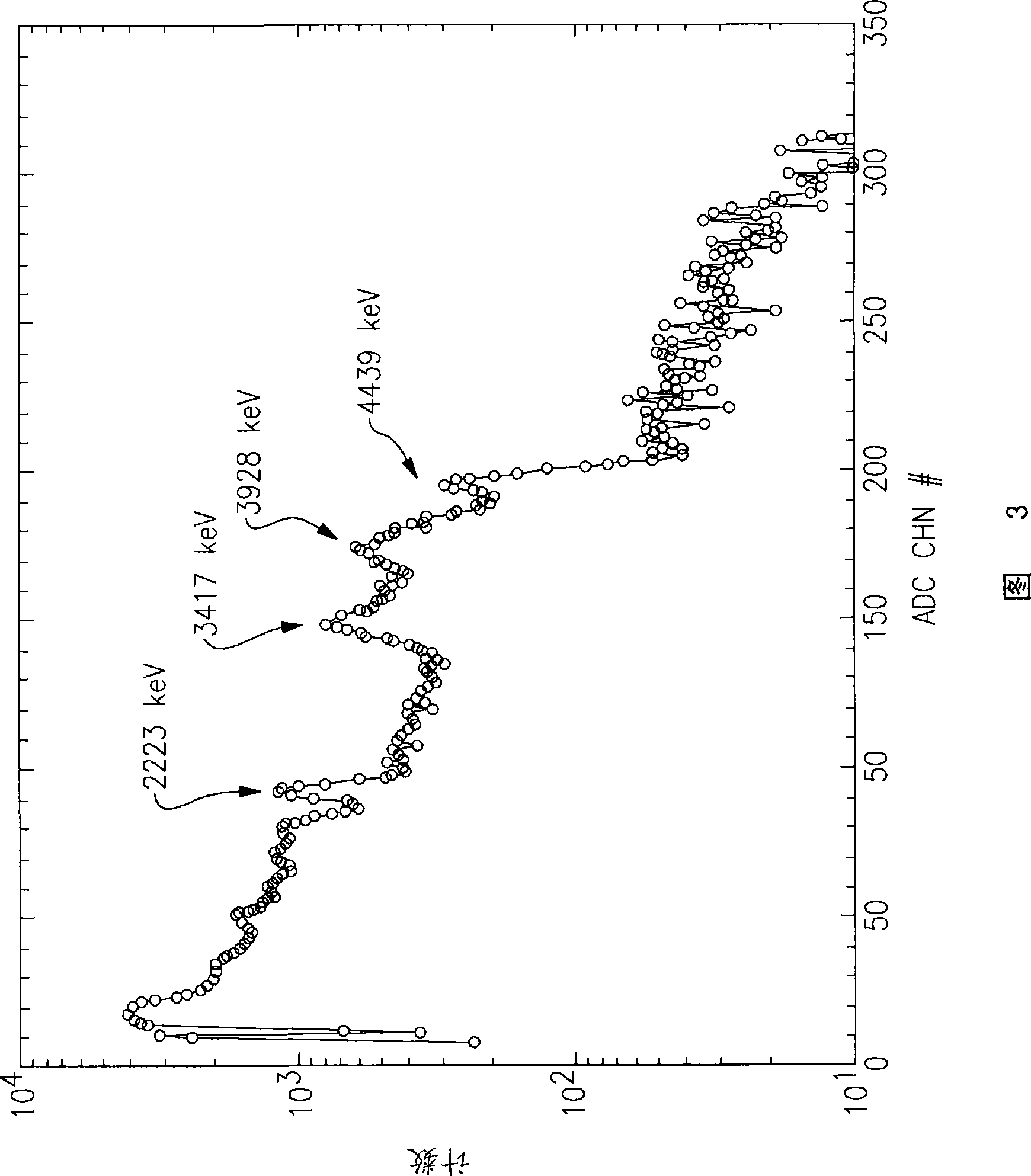
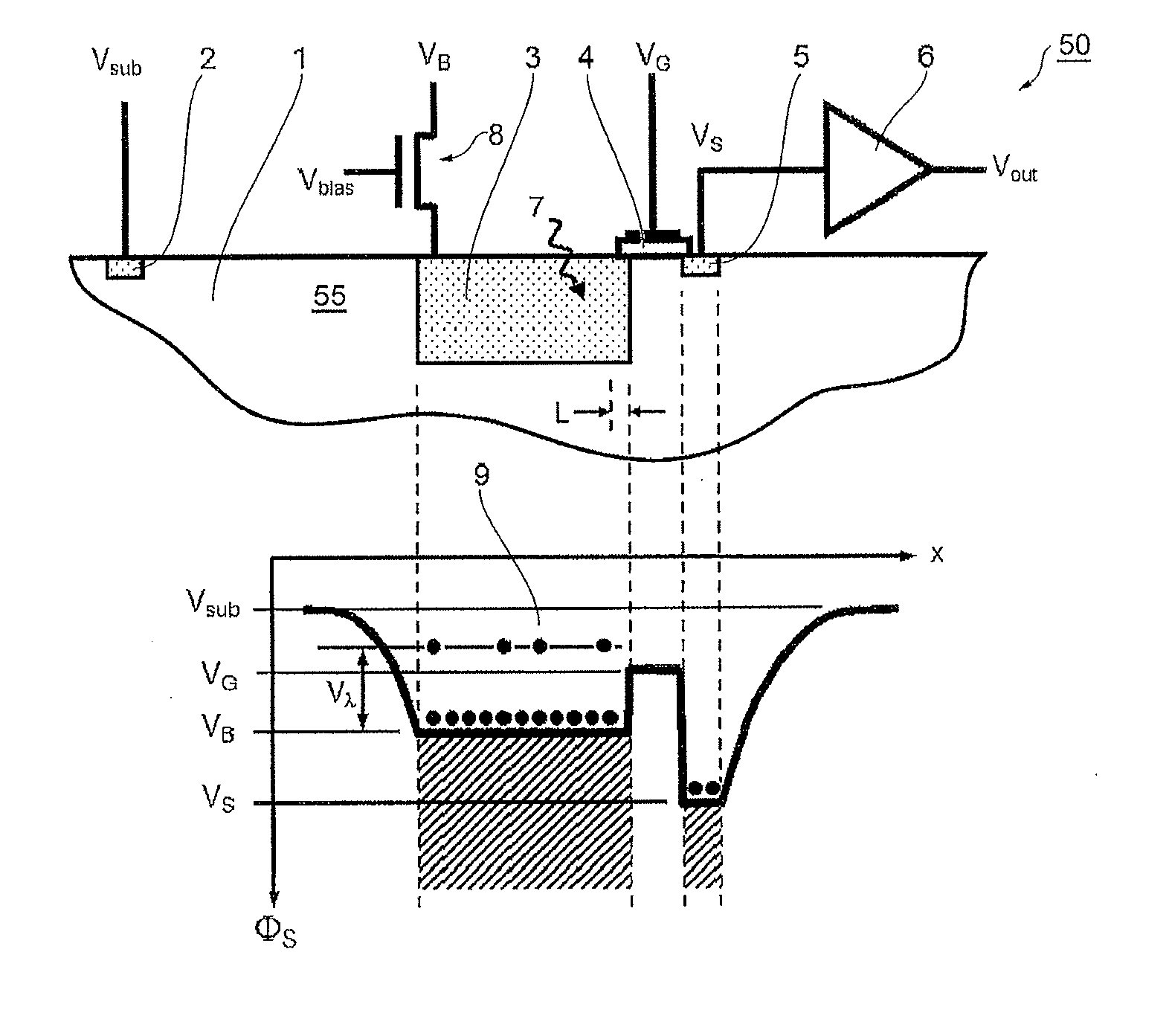
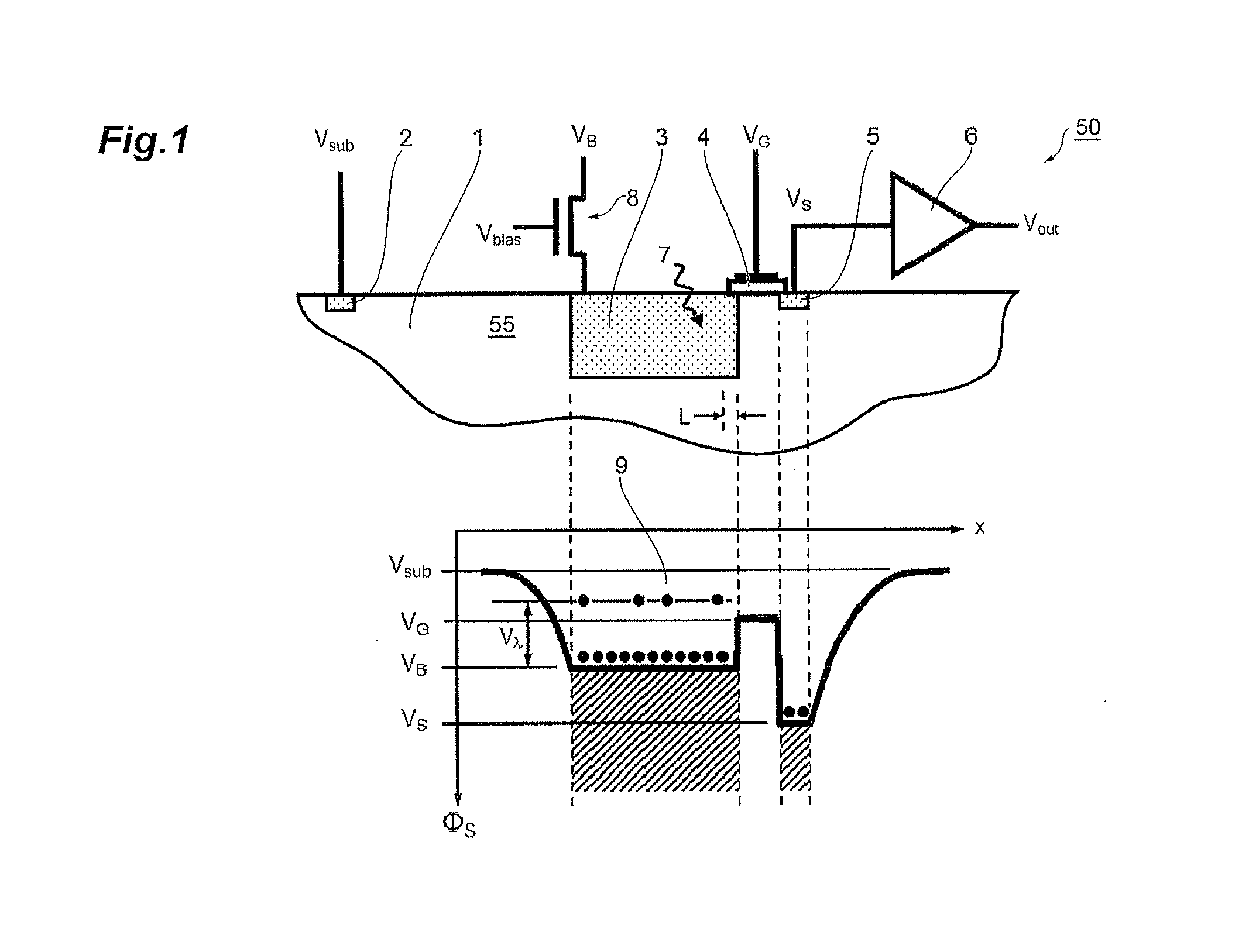
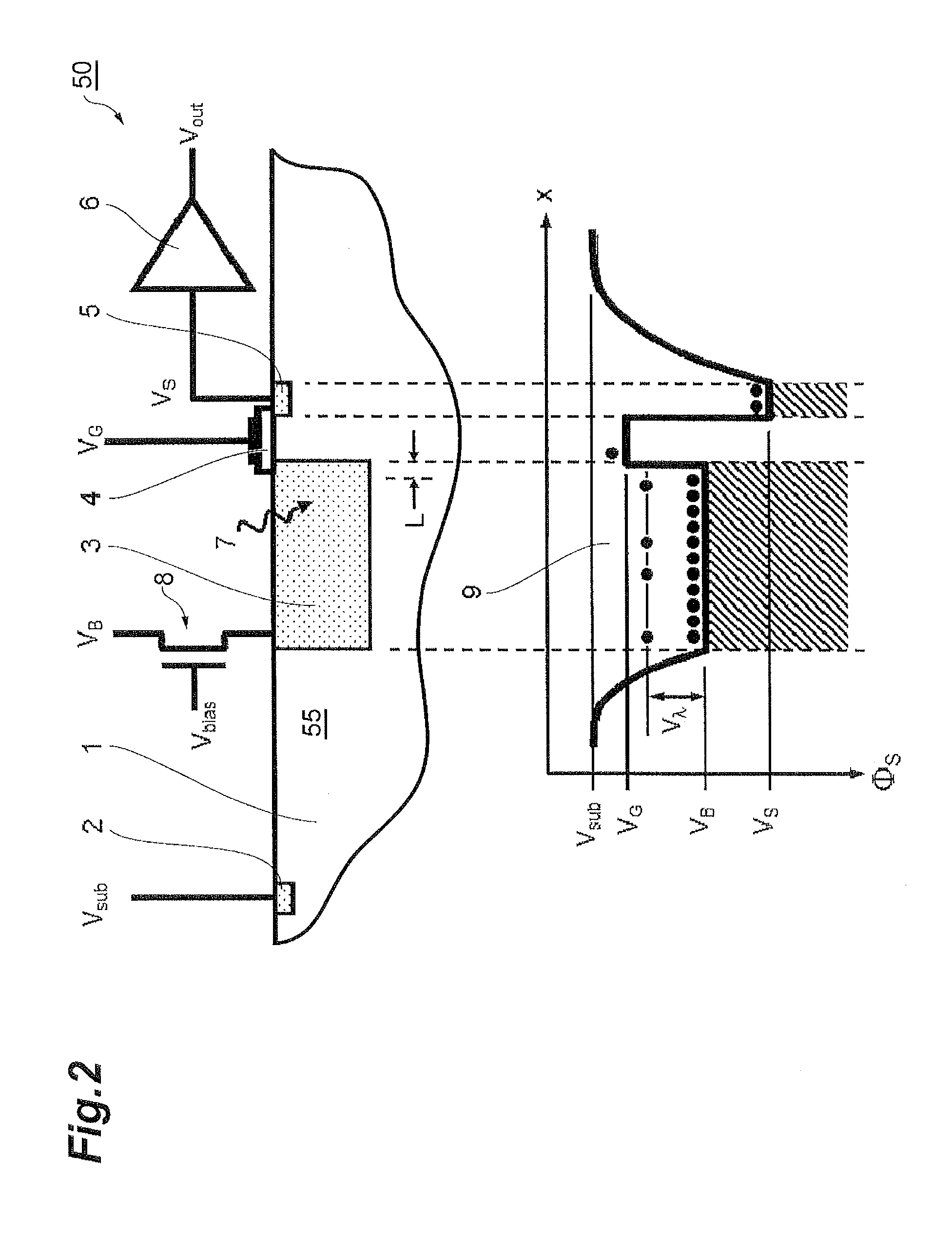
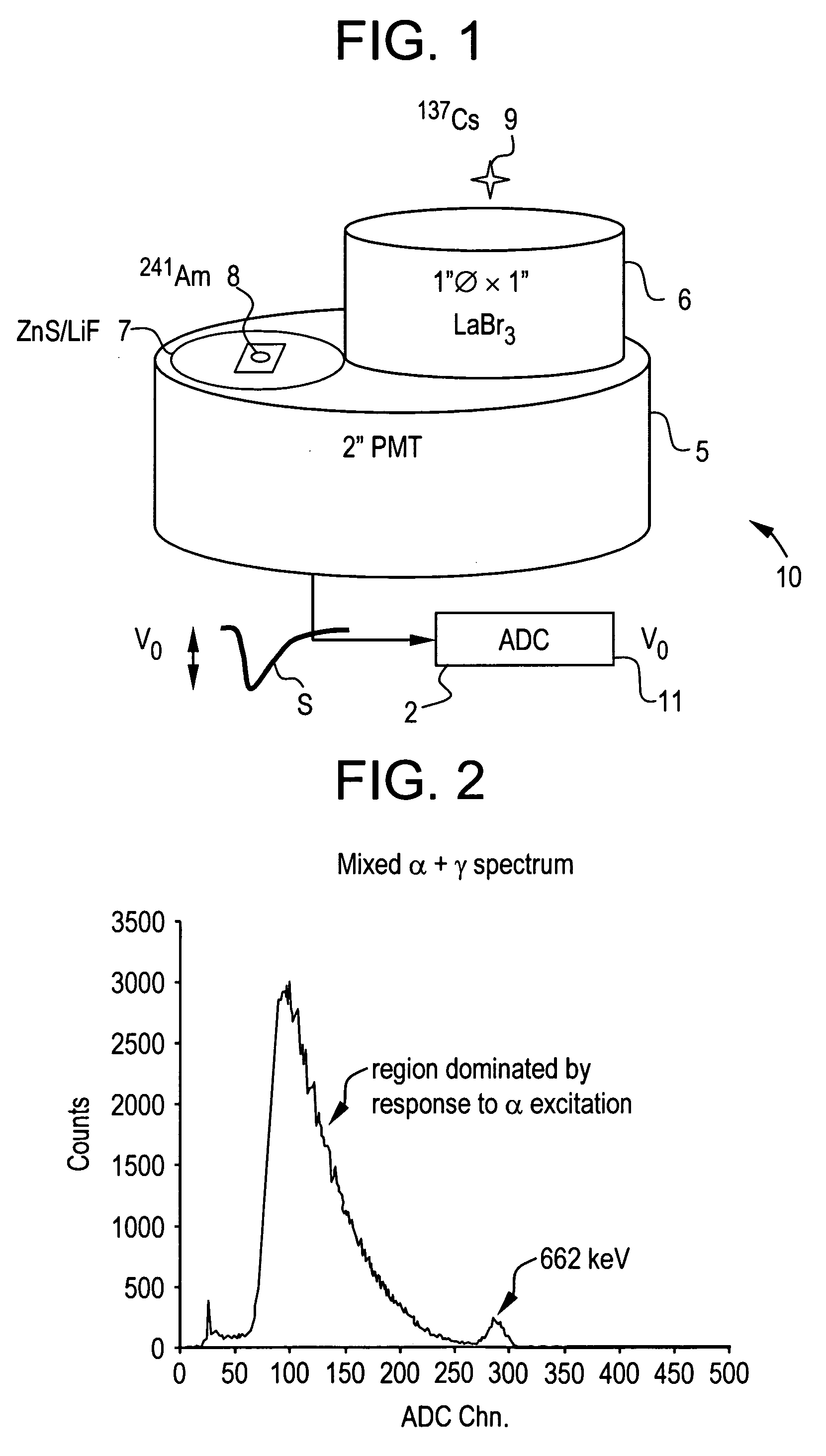
Pulse shape discrimination method and apparatus for high-sensitivity radioisotope identification with an integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector
InactiveUS20070290136A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacteristic energyGamma energy
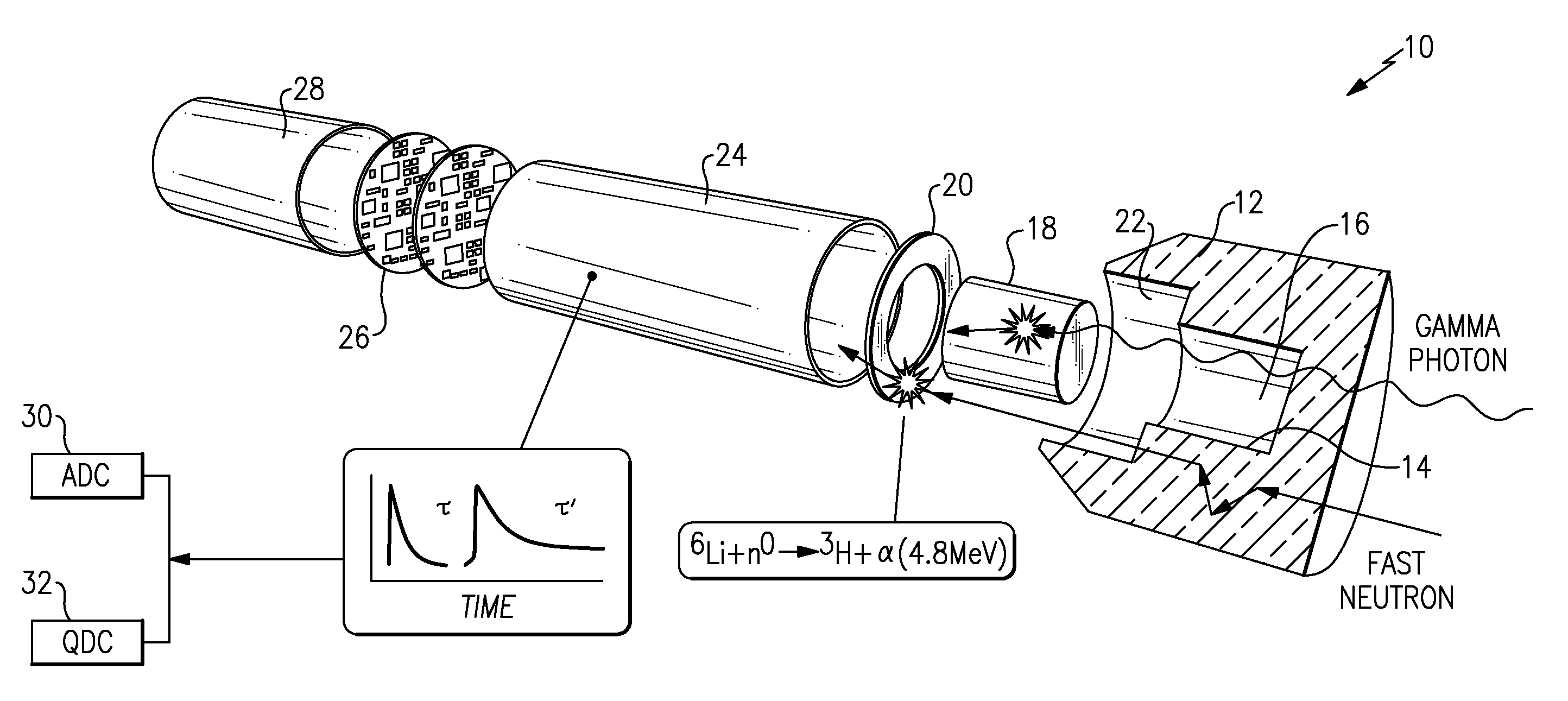
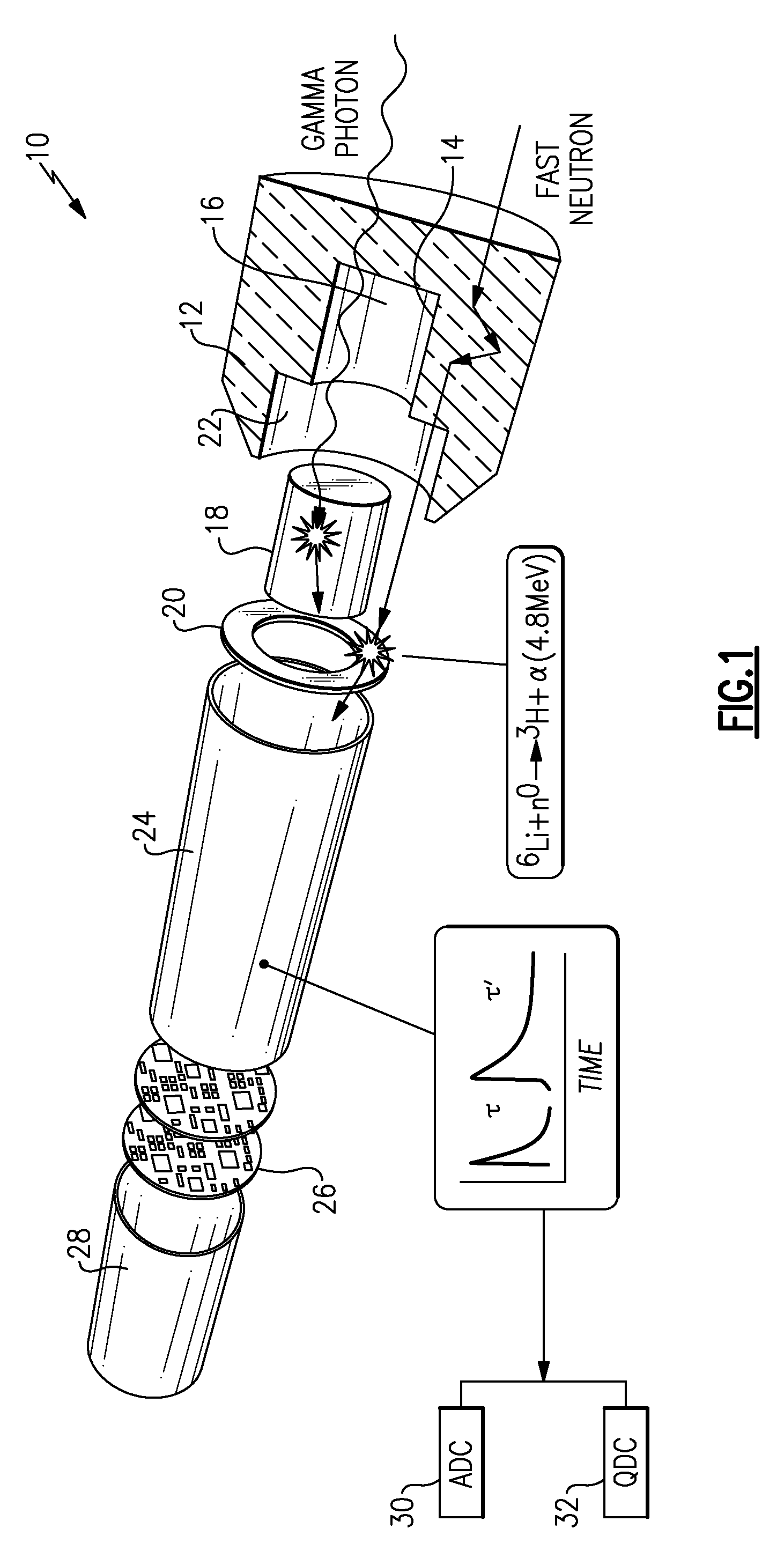
A method and apparatus for discriminating the types of radiation interacting with an integrated radiation detector having of a pulse-mode operating photosensor which is optically coupled to a gamma-ray scintillator sensor and a neutron scintillator sensor and uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse processing provides for, among other things, faithful representation of the true energy spectrum of the gamma radiation field and allows for radioisotope identification by searching for the presence of characteristic energy lines in the gamma energy spectrum. The pulse shape discrimination method ensures that the high sensitivity and resolution of the isotope identification function is not affected during operation in mixed neutron-gamma fields.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Radiation Detector Assembly, Radiation Detector, and Method for Radiation Detection
ActiveUS20090179155A1Easy to detectMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesCharge carrierField strength
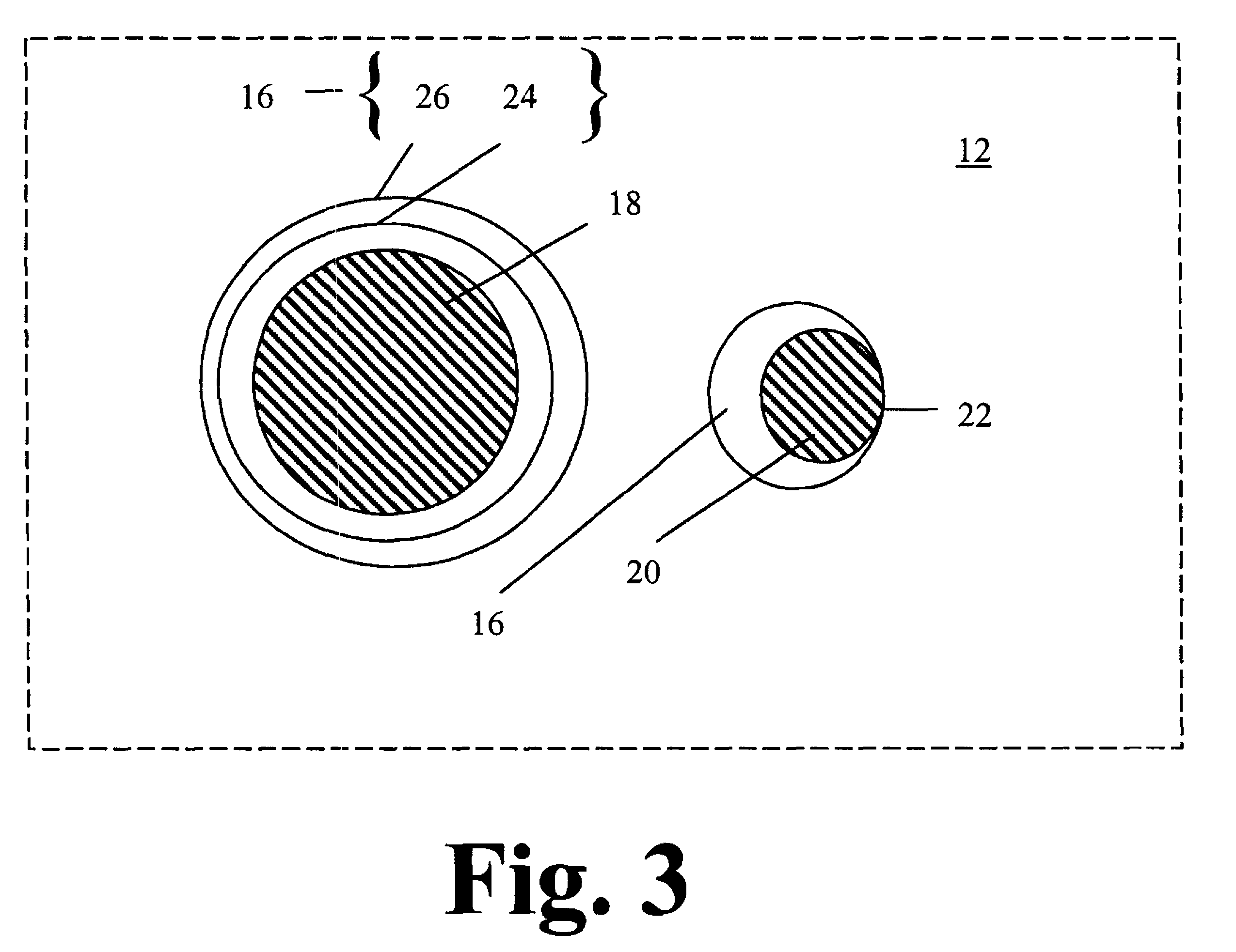
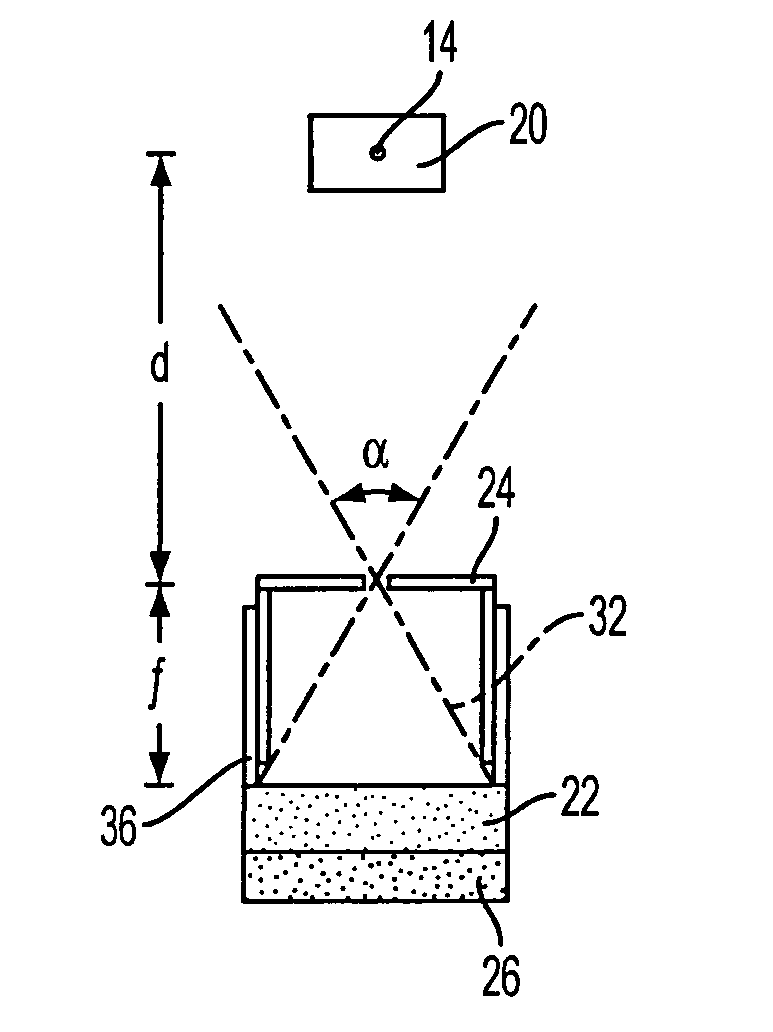
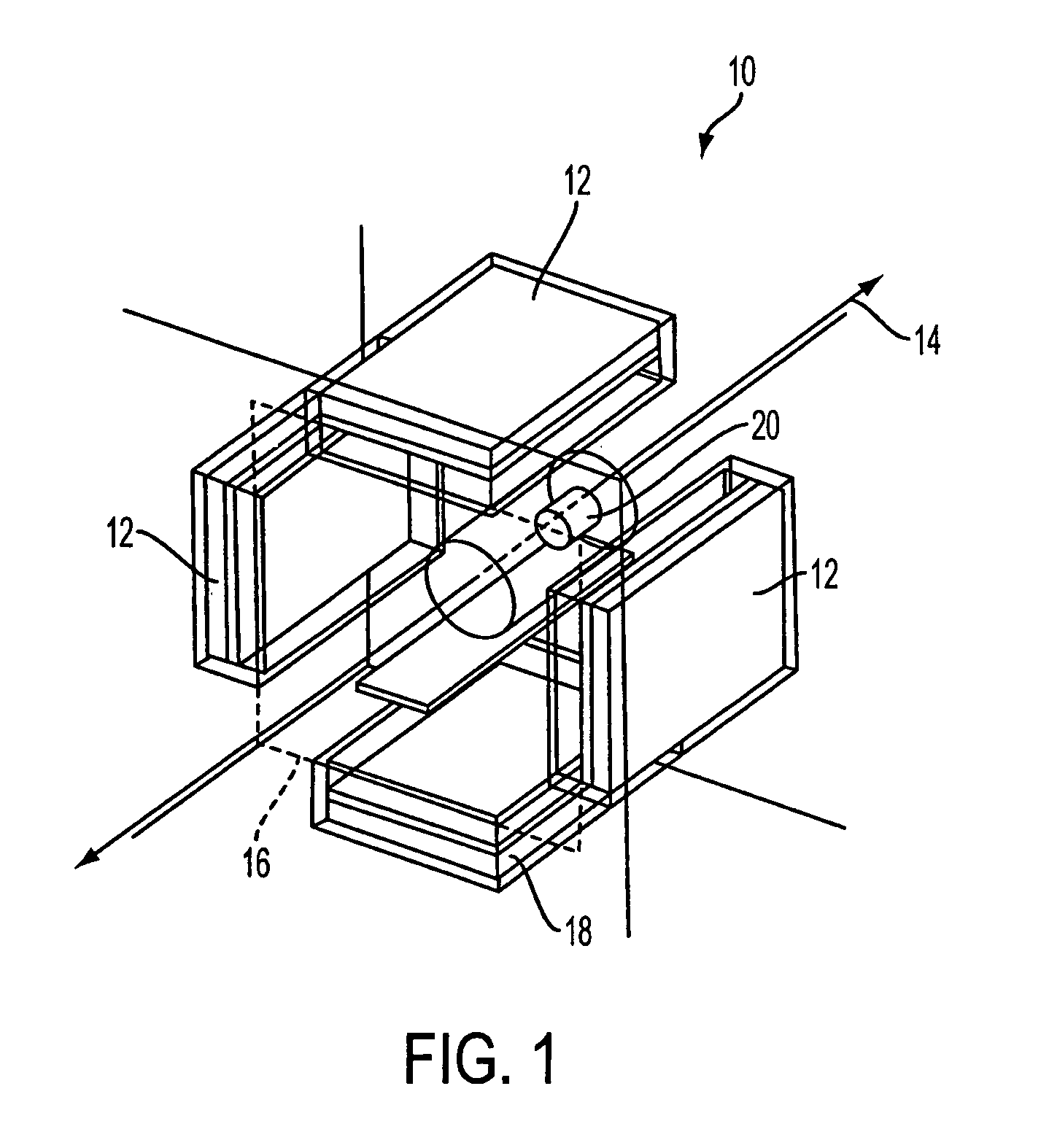
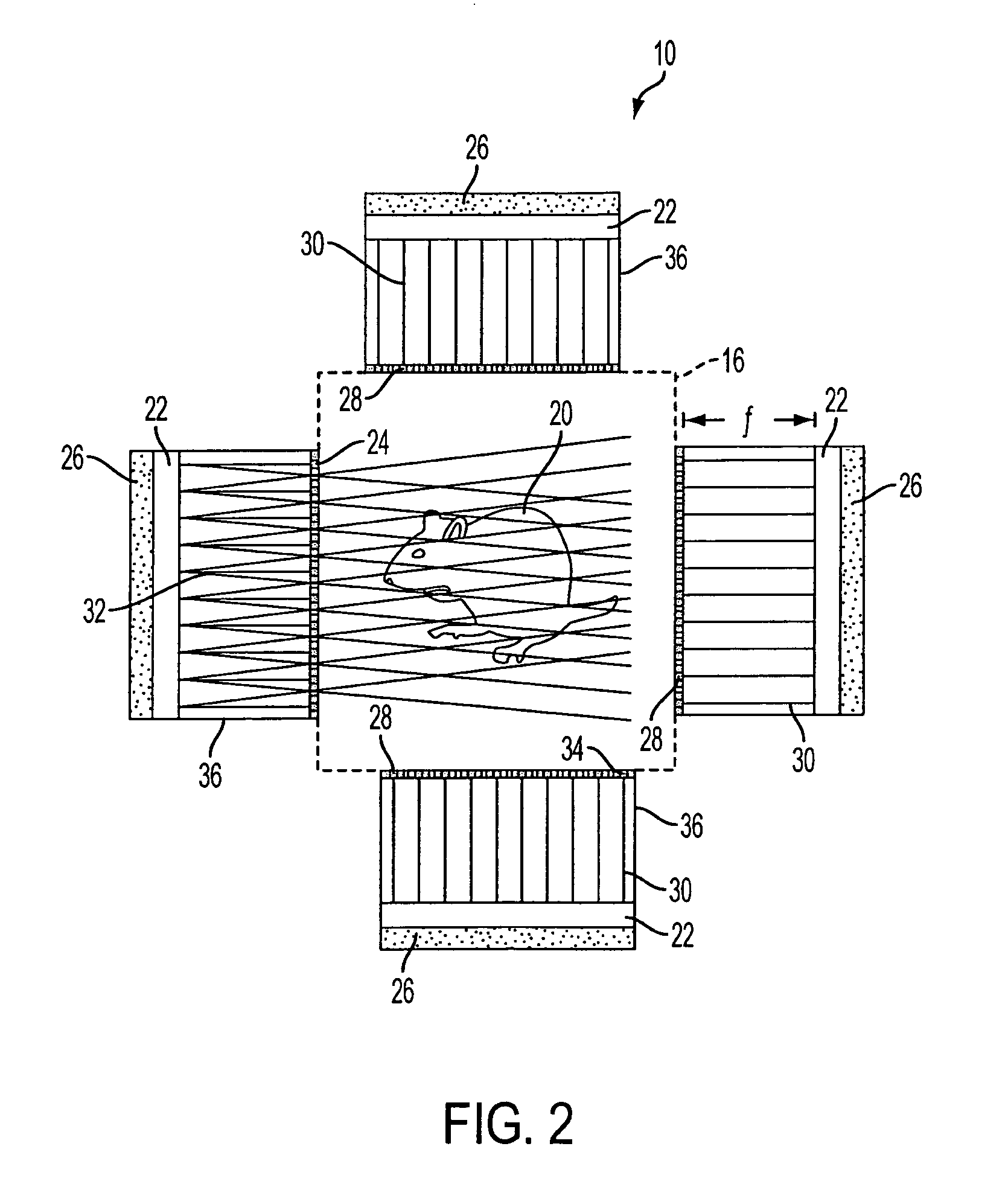
An assembly for detecting radiation is described. The assembly includes a host matrix with particles suspended within the host matrix. The particles are capable of generating a charge carrier upon interaction with the radiation. A first electrode is disposed adjacent to a first surface of the host matrix, and a second electrode disposed adjacent to a second surface of the host matrix. A power source operatively connects to one of the first or second electrodes. The power source establishes an electric field between the first and second electrodes such that a ratio of a mobility-lifetime-field strength product of the charge carrier to the thickness of the host matrix is greater than or equal to 0.1. A radiation detector and a method for detecting radiation are also described.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Functionalized carbon nanotube-polymer composites and interactions with radiation
The present invention involves the interaction of radiation with functionalized carbon nanotubes that have been incorporated into various host materials, particularly polymeric ones. The present invention is directed to chemistries, methods, and apparatuses which exploit this type of radiation interaction, and to the materials which result from such interactions. The present invention is also directed toward the time dependent behavior of functionalized carbon nanotubes in such composite systems.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Functionalized carbon nanotube-polymer composites and interactions with radiation
The present invention involves the interaction of radiation with functionalized carbon nanotubes that have been incorporated into various host materials, particularly polymeric ones. The present invention is directed to chemistries, methods, and apparatuses which exploit this type of radiation interaction, and to the materials which result from such interactions. The present invention is also directed toward the time dependent behavior of functionalized carbon nanotubes in such composite systems.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
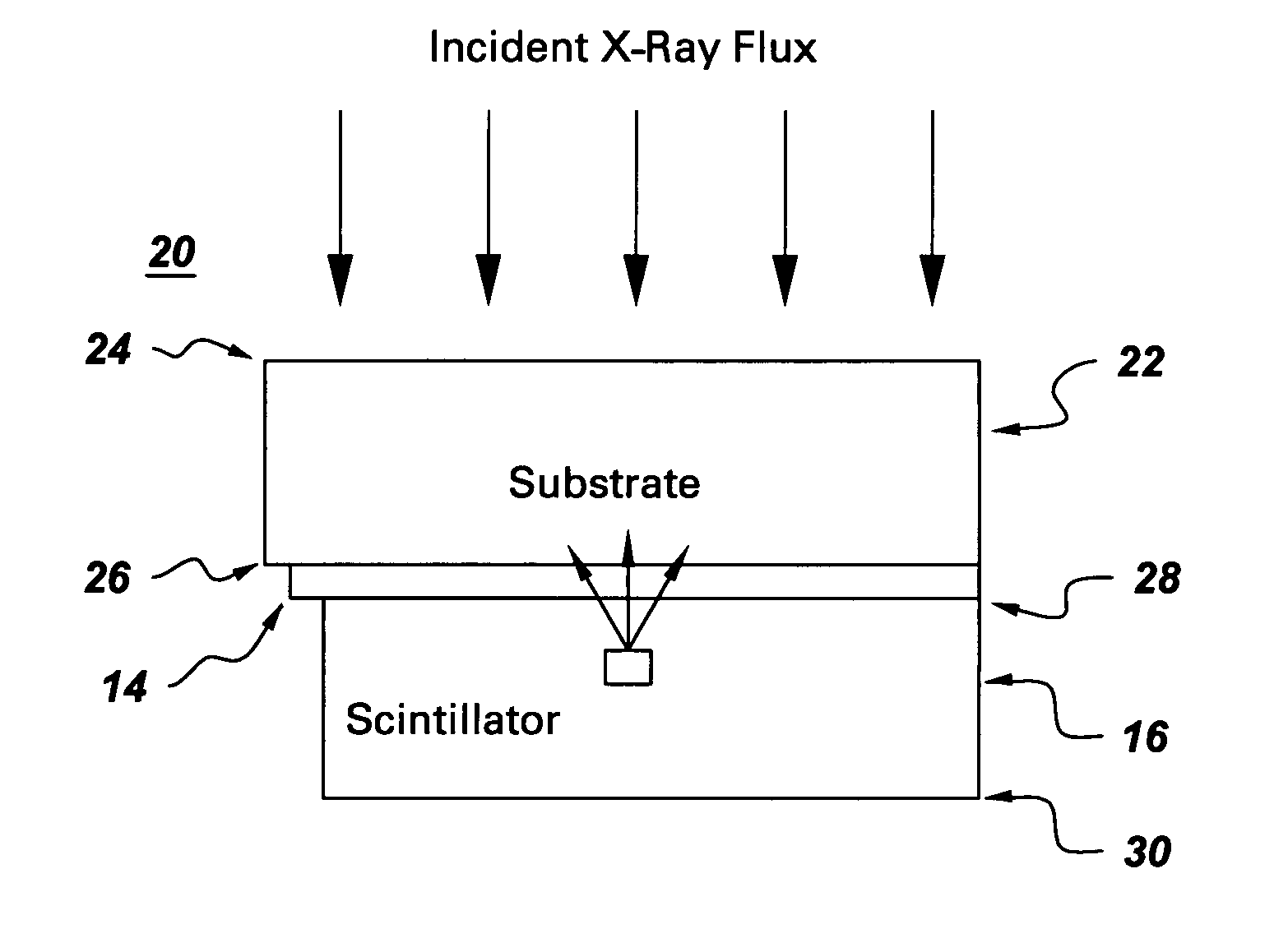
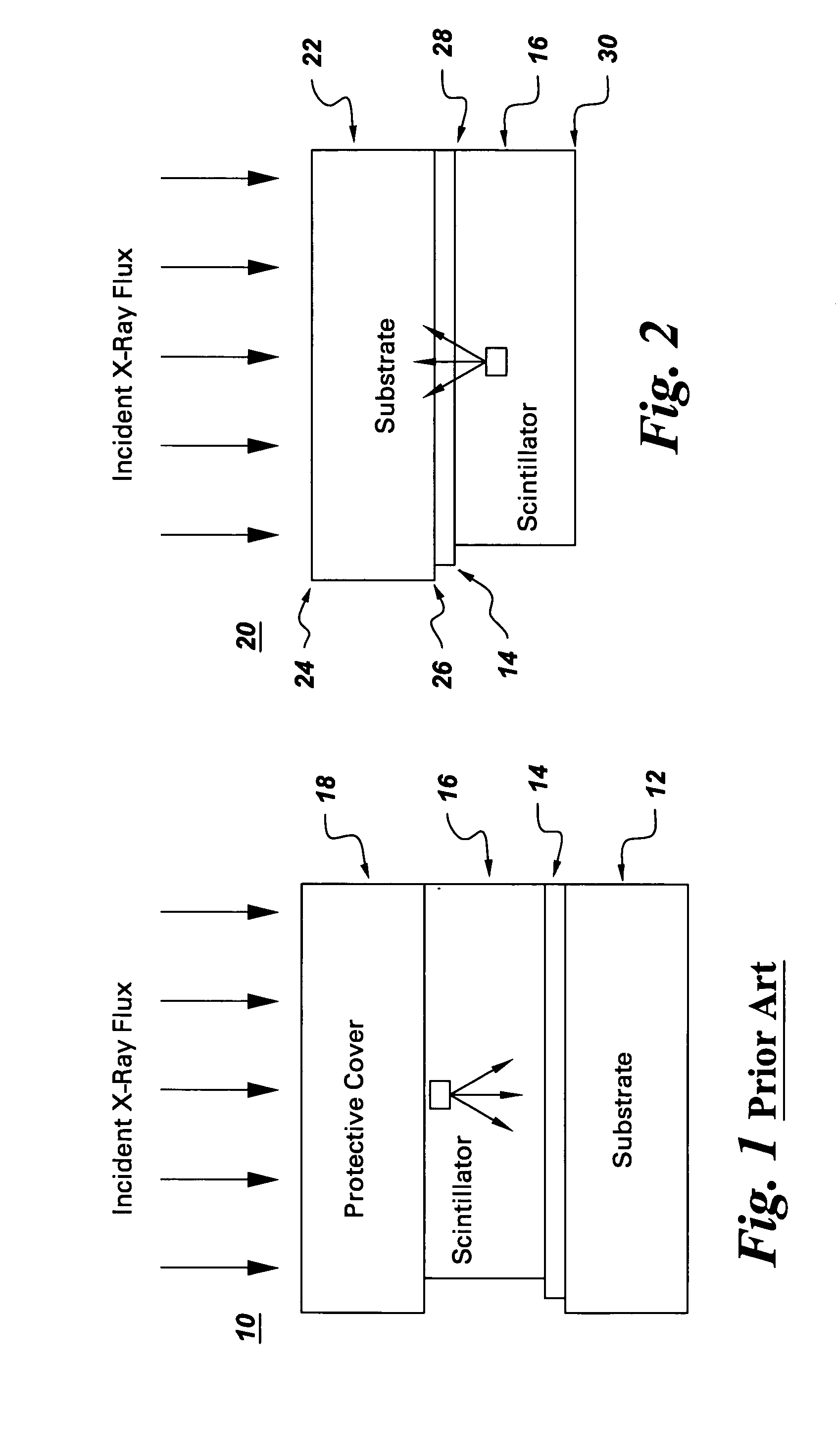
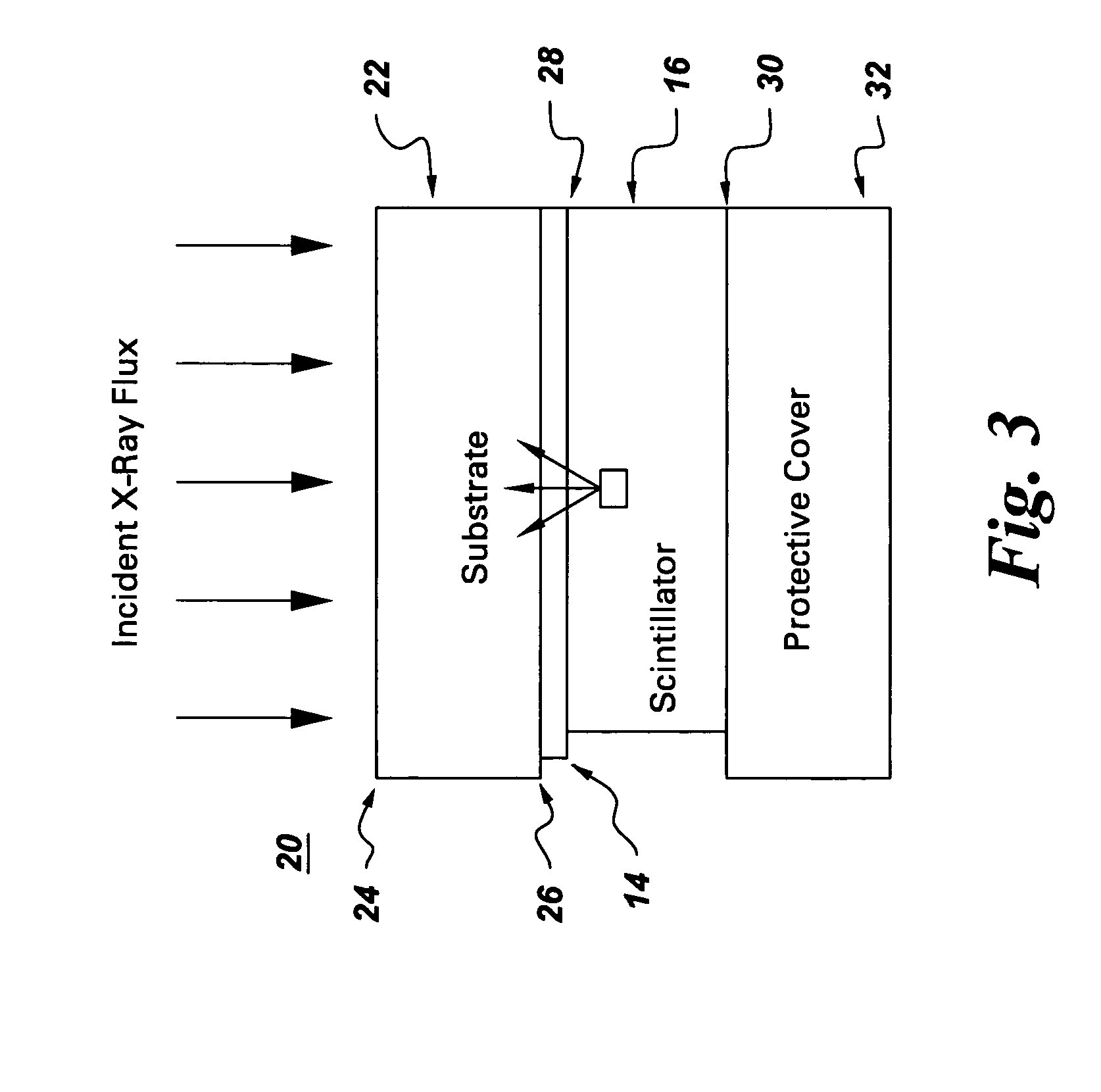
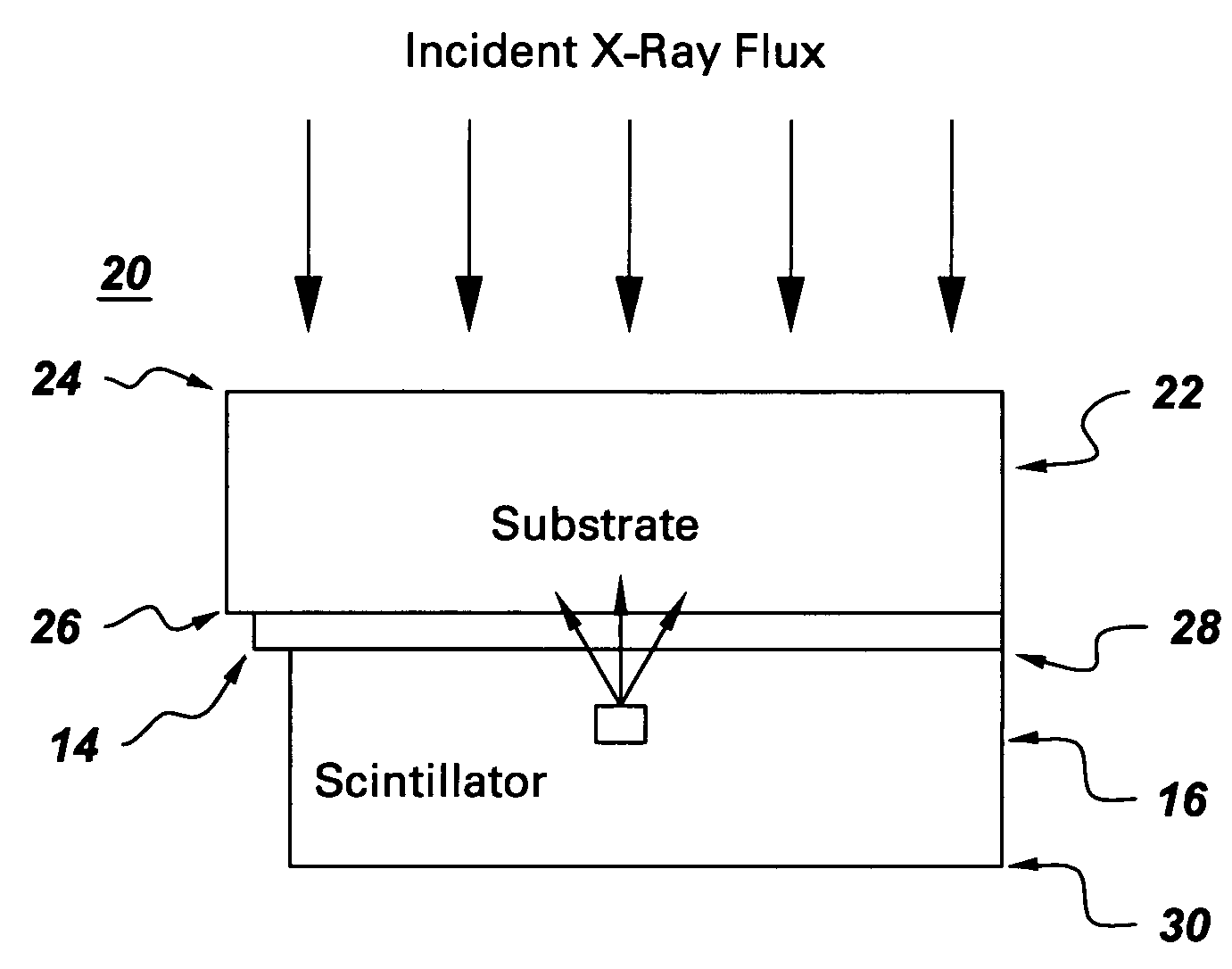
Solid-state radiation imager with back-side irradiation
A solid-state imager with back-side irradiation. The present invention provides a solid-state imager that includes a substantially radiation transparent substrate adapted to receive incident radiation. The radiation travels through the substrate and a pixelated array of photosensitive elements to a scintillator material, which absorbs the radiation. The pixelated array of photosensitive elements receives light photons and measures the amount of light generated by radiation interactions with the scintillator material. With this imager, there is less spreading and blurring and thus a better quality image. In another embodiment, there is a substantially transparent material disposed between the pixelated array of photosensitive elements and the scintillator material. The substantially transparent material absorbs and substantially blocks electrons from entering the active regions of the pixelated array of photosensitive elements. This enables the imager to perform for a longer period of time according to its specifications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
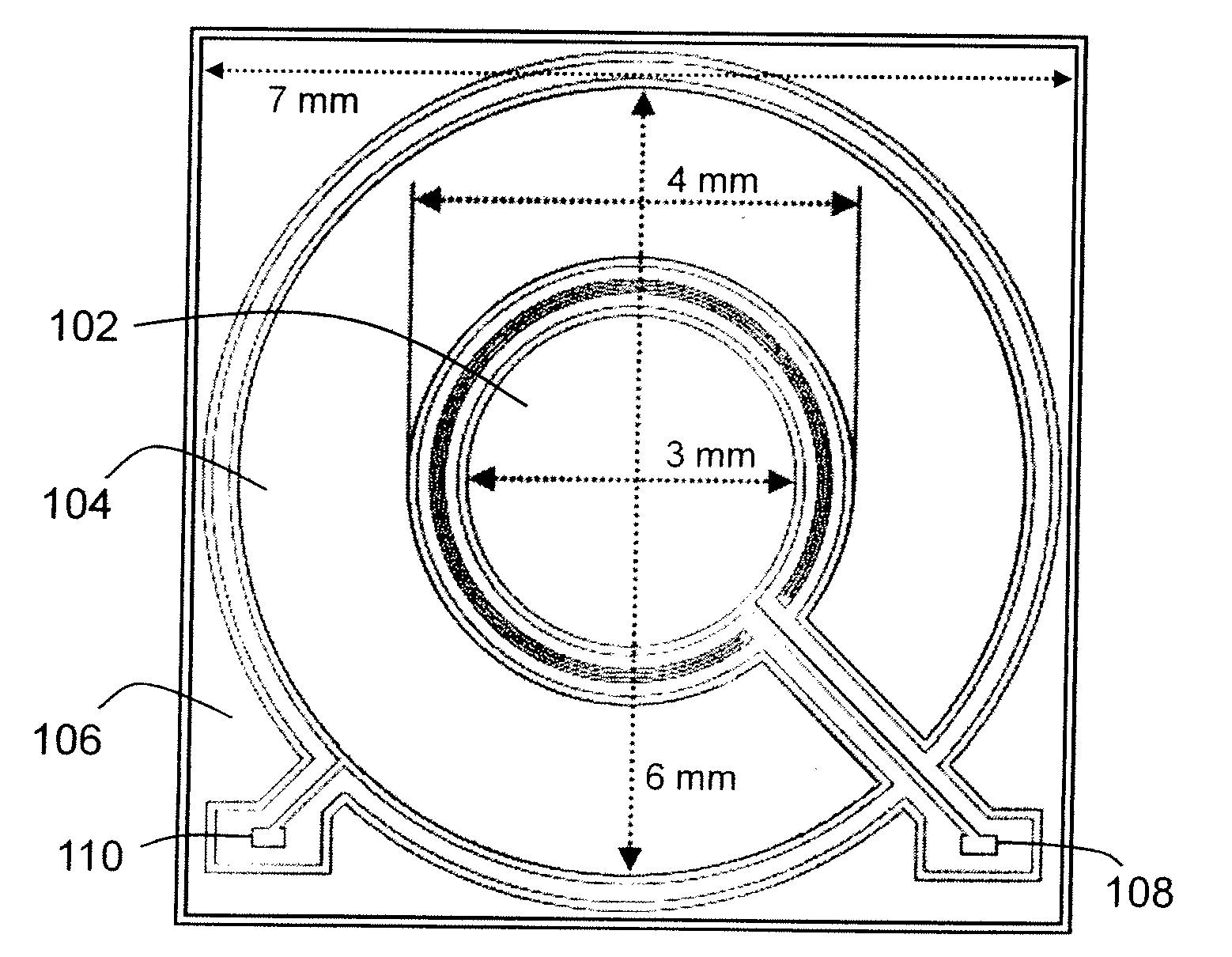
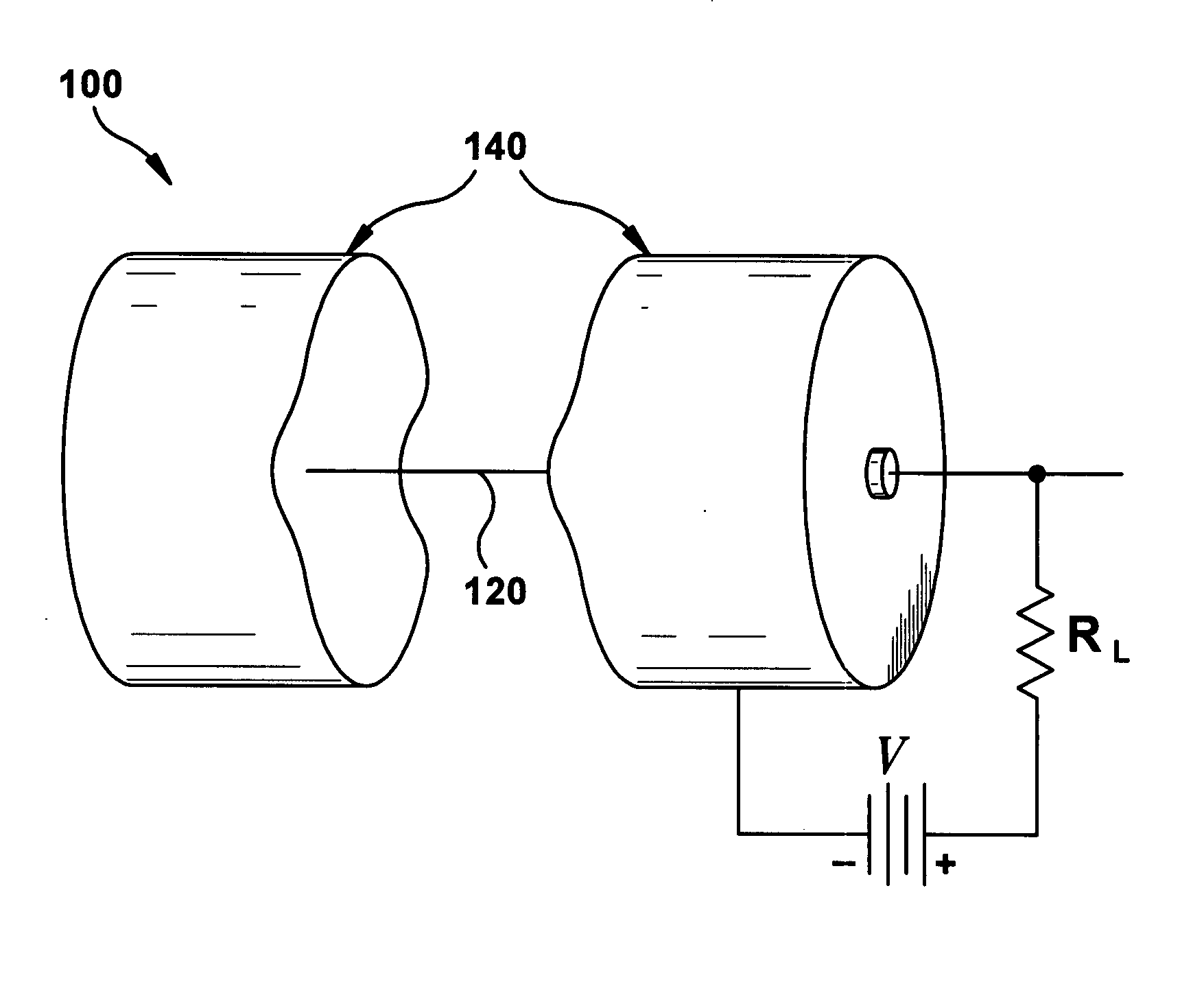
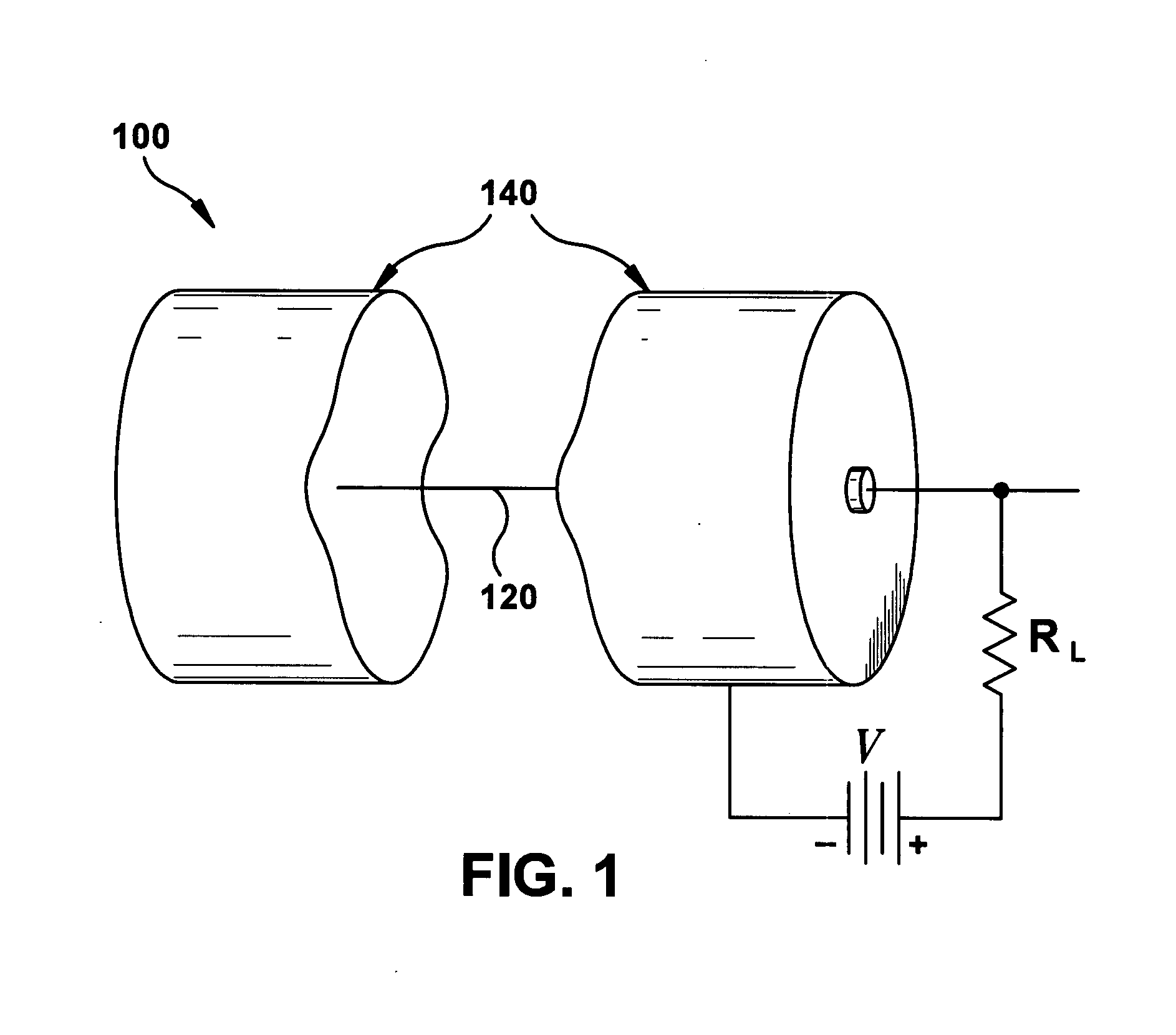
Dual radiation detector
ActiveUS20100090115A1Improve detection efficiencyMade particularly compact and efficientMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation diagnosticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A radiation detection apparatus and method, the apparatus (100) comprising a first scintillator (112) for interacting with radiation and outputting light in response thereto, a first photodetector (102) adjacent to the first scintillator (112) for receiving and detecting light from the first scintillator (112) and outputting (108) a first output signal in response thereto, a second scintillator (114) located around the first scintillator (112), for interacting with radiation and outputting light in response thereto, and a second photodetector (104) adjacent to the second scintillator (114) for receiving and detecting light from the second scintillator (114) and outputting (110) a second output signal in response thereto.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
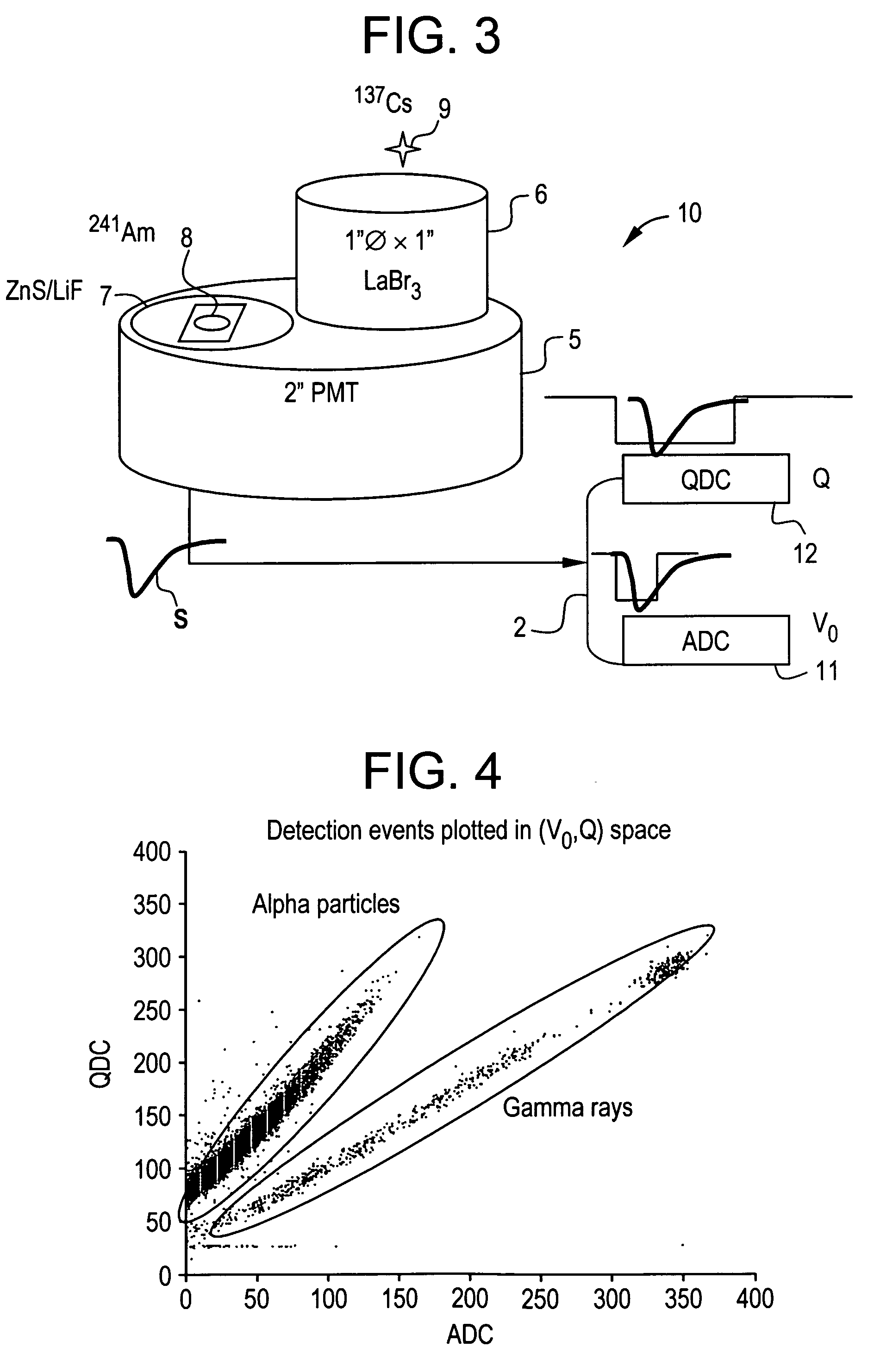
Integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector with adaptively selected gamma threshold
InactiveUS20090140150A1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma energyAnalog-to-digital converter
An integrated radiation detector having a pulse-mode operating photosensor optically coupled to a gamma sensing element and a neutron sensing element is disclosed. The detector includes pulse shape and processing electronics package that uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse shape and processing electronics package determines a maximum gamma energy from the spectrum associated with gamma rays detected by the gamma sensing element to adaptively select a gamma threshold for the neutron sensing element. A light pulse attributed to the neutron sensing element is a valid neutron event when the amplitude of the light pulse is above the gamma threshold.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Temperature sensing apparatus
InactiveUS6527441B1Easy temperatureHigh sensitivityThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryMonitors radiationElectromagnetic radiation
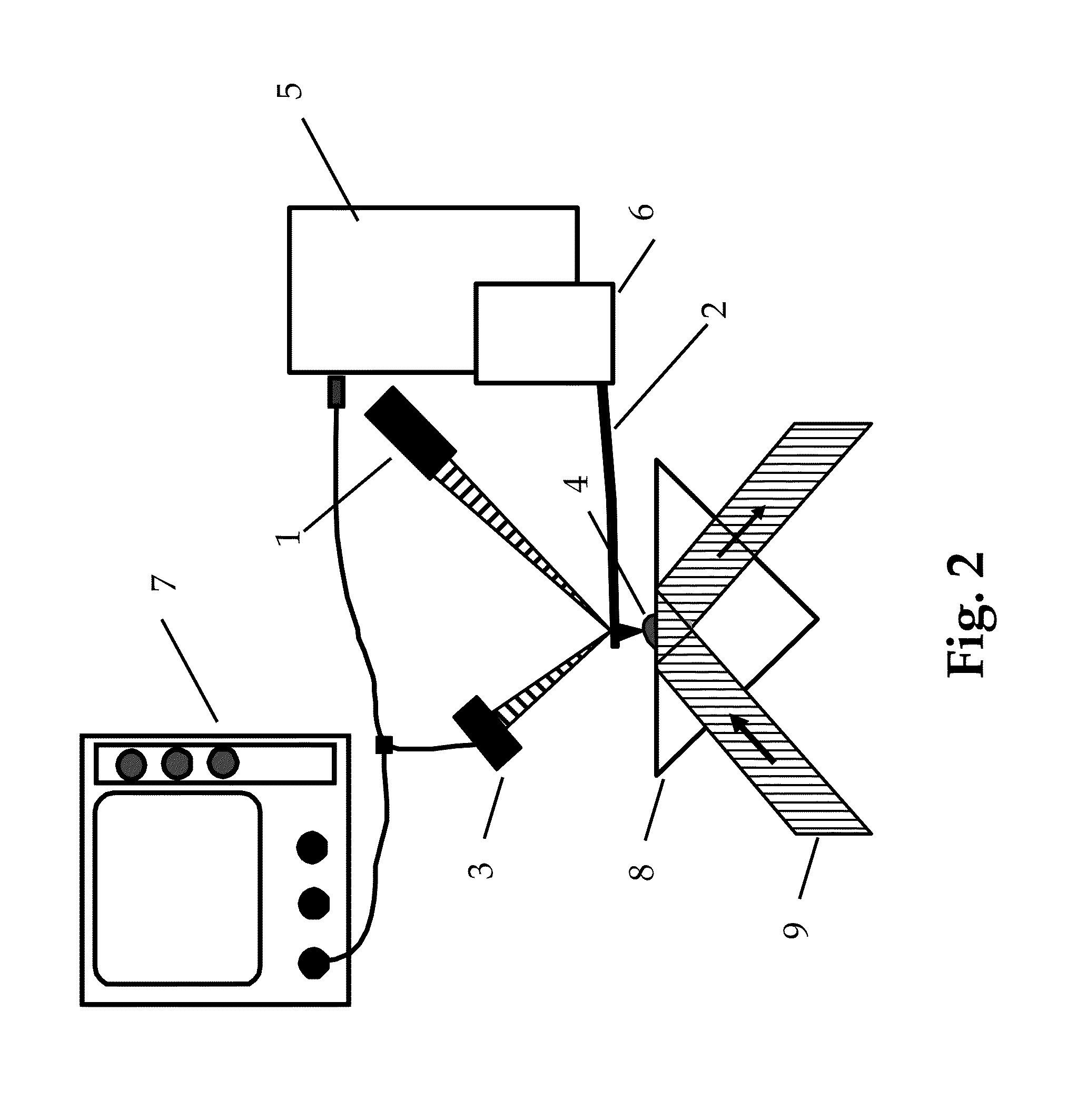
Temperature sensing apparatus comprises a source of electromagnetic radiation (1), a wavelength-selective element (3) which interacts with radiation emitted from the source (1) and a detection system (6) which monitors radiation from the wavelength-selective element (3). The wavelength-selective element (3) is fixedly mounted on a substantially rigid substrate (not shown). The apparatus can be used for temperature sensing in aquatic environments.
Owner:OPTASENSE HLDG LTD
Reading method and apparatus for a three-dimensional information carrier
InactiveUS6992965B1Increase the number ofReduce crosstalkMechanical record carriersRecord information storageDirected UnitLight beam
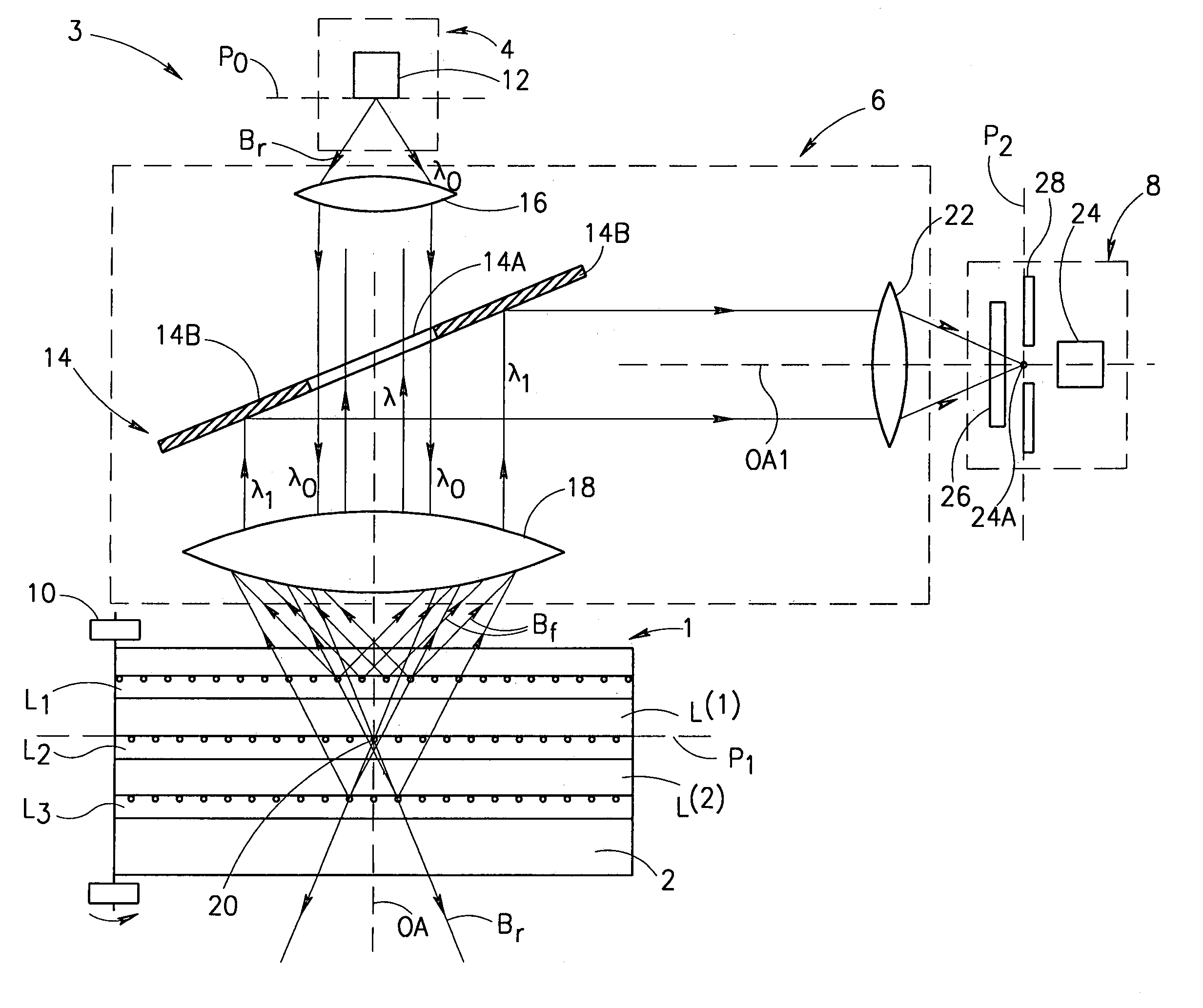
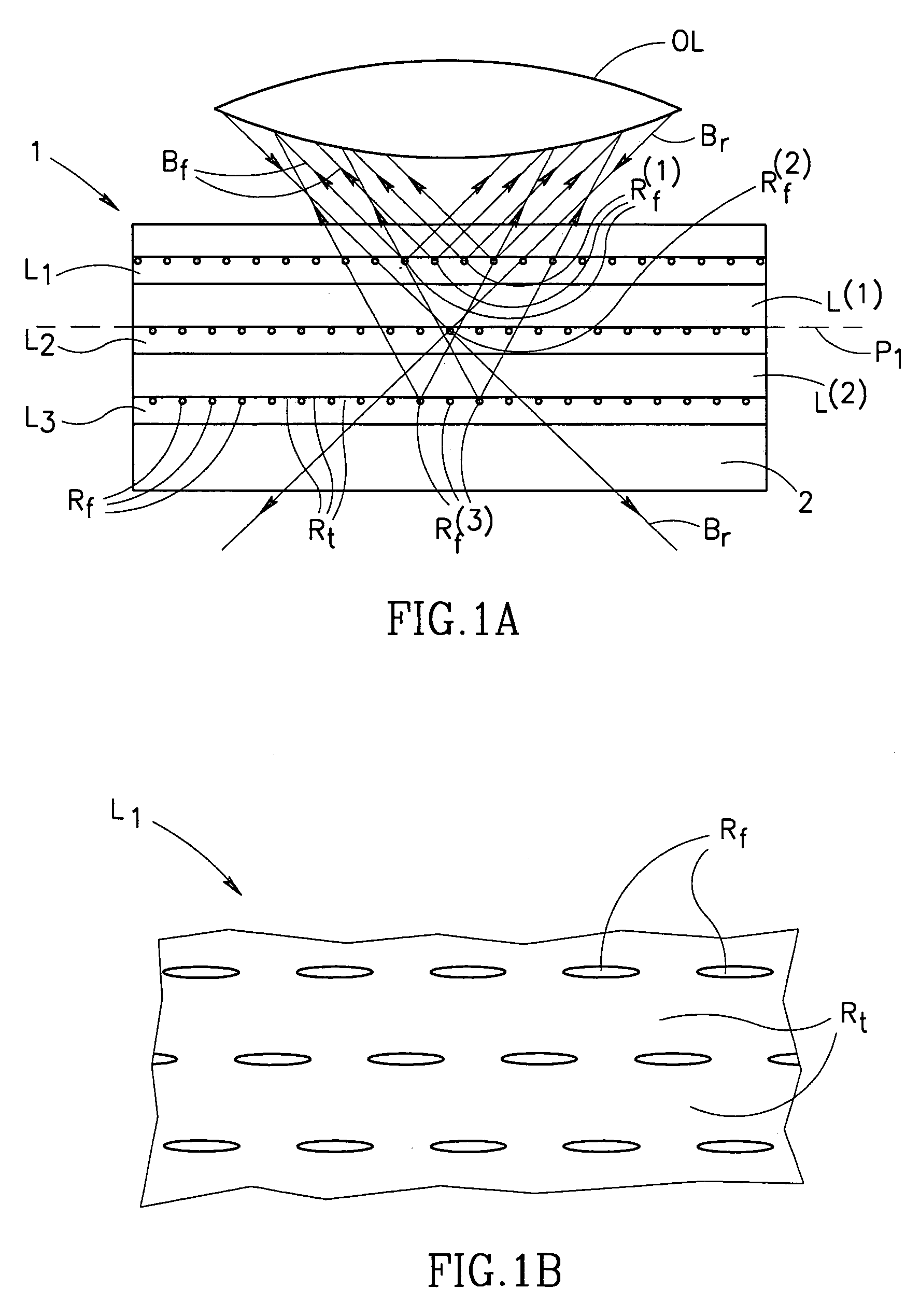
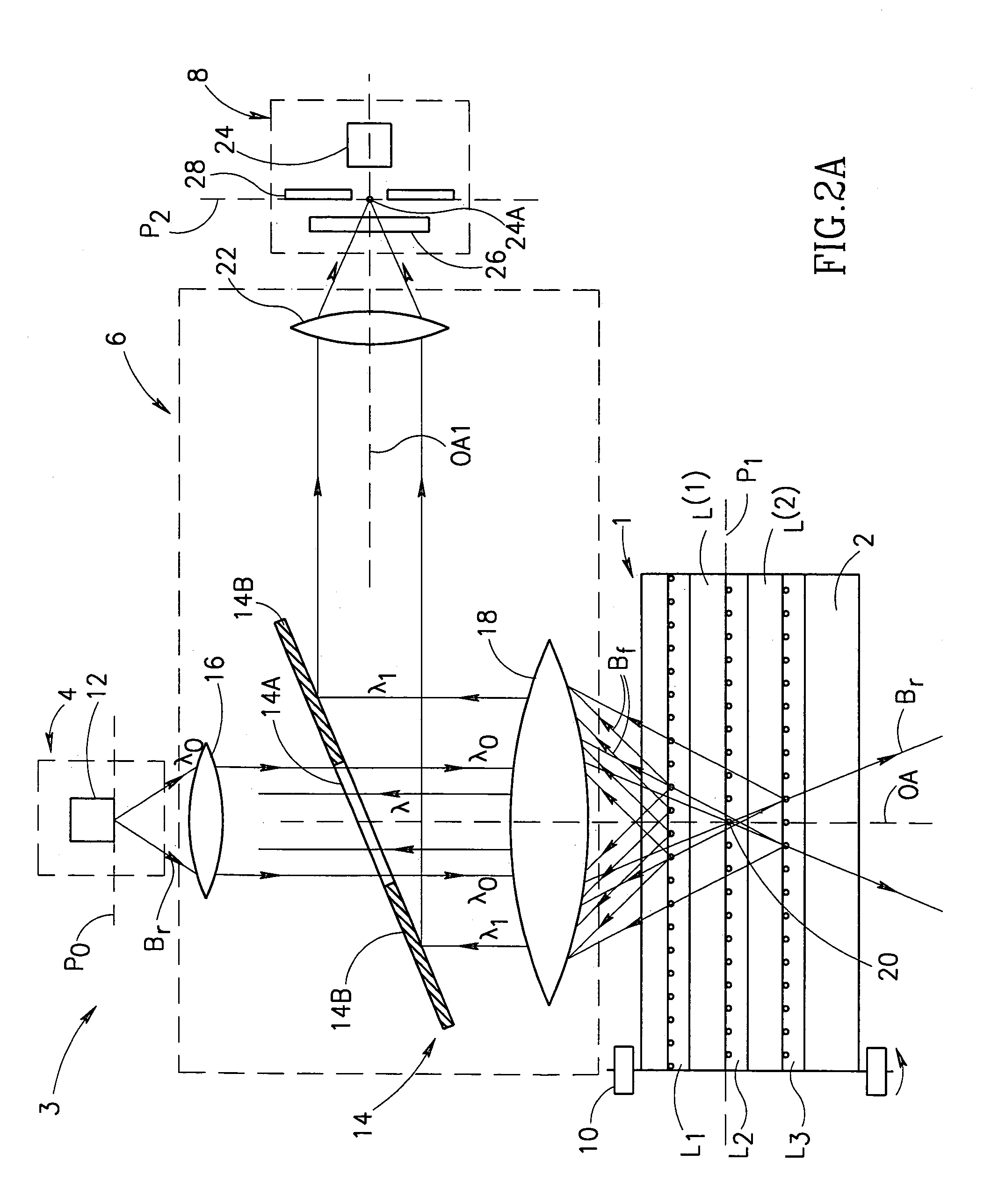
A method and apparatus for reading in a three-dimensional information carrier are presented. The three-dimensional information carrier is formed with a plurality of spaced-apart data regions, each surrounded by surrounding-regions. The data regions are made of a material capable of generating an output excited radiation, when interacting with a predetermined incident exciting radiation, while the surrounding regions are substantially optically transparent. The apparatus comprises an illumination unit, a light directing unit and a detector unit. The illumination unit produces a scanning beam of the incident radiation. The light directing unit projects the incident radiation onto a scan region located in an addressed plane inside the carrier and collects the output radiation. The light directing unit is capable of picking up a predetermined portion of the collected output radiation, so as to provide spatial separation of the output radiation components produced by the data regions located in the addressed plane and the output radiation components produced by the data regions located at any other location inside the carrier.
Owner:D DATA
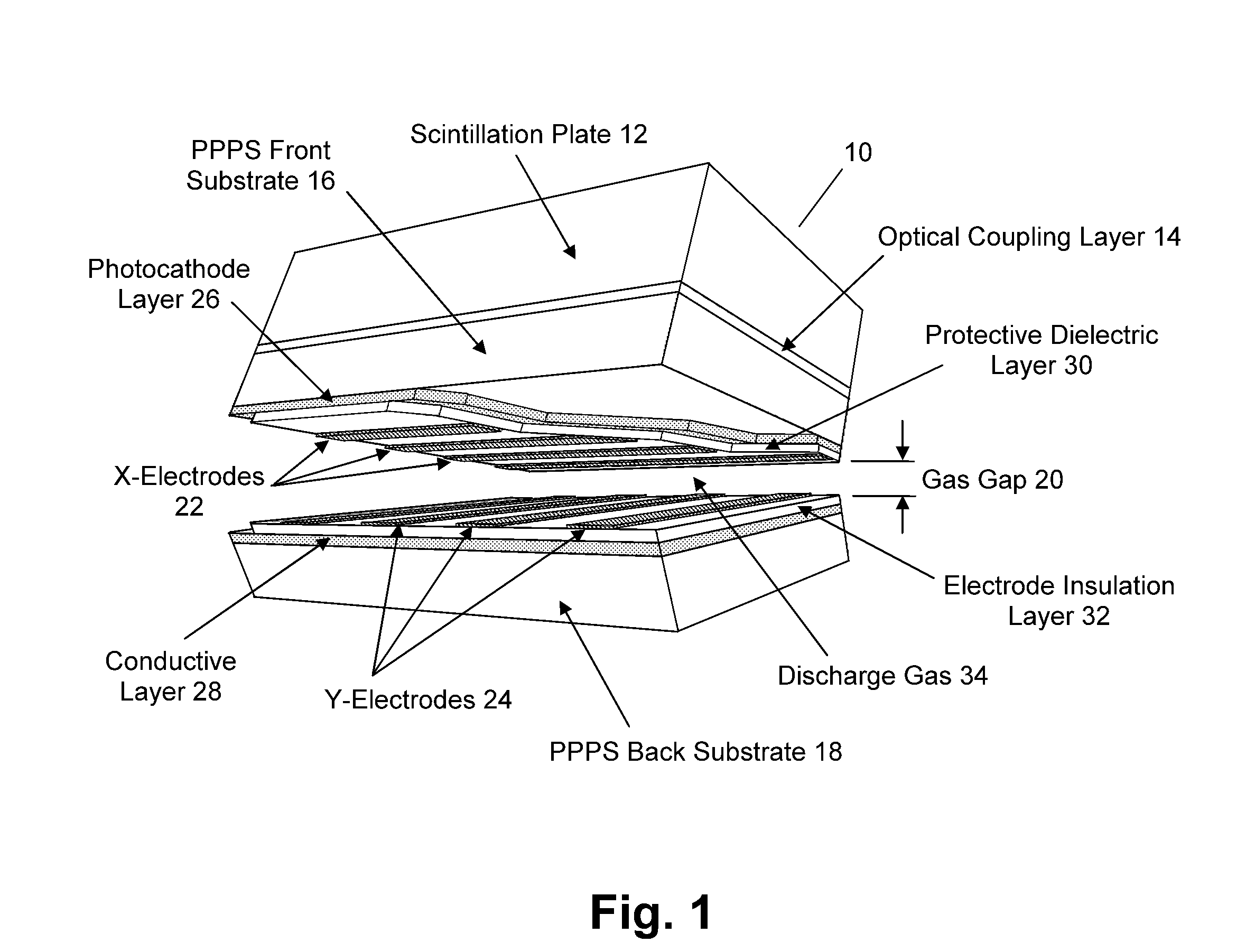
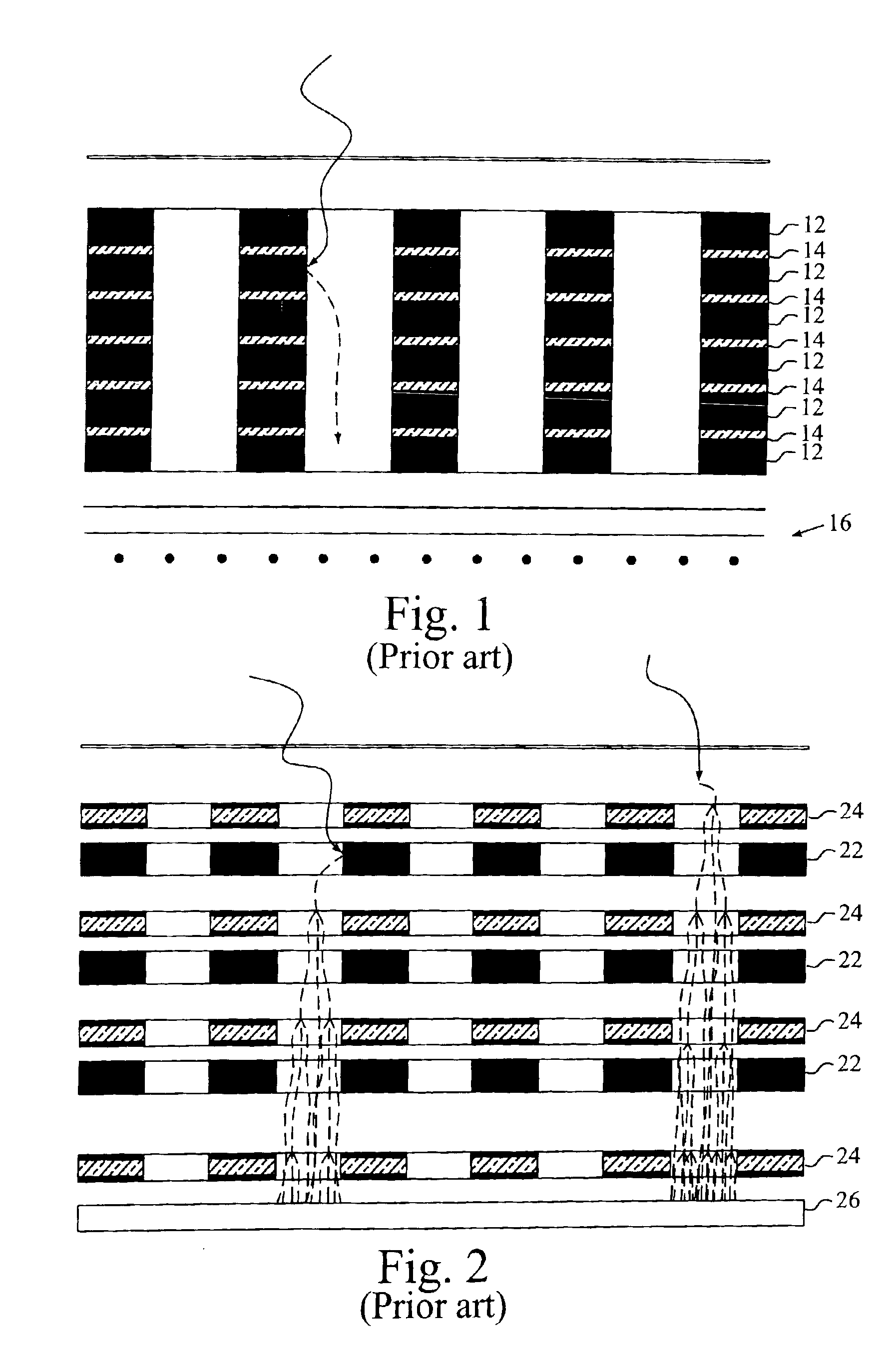
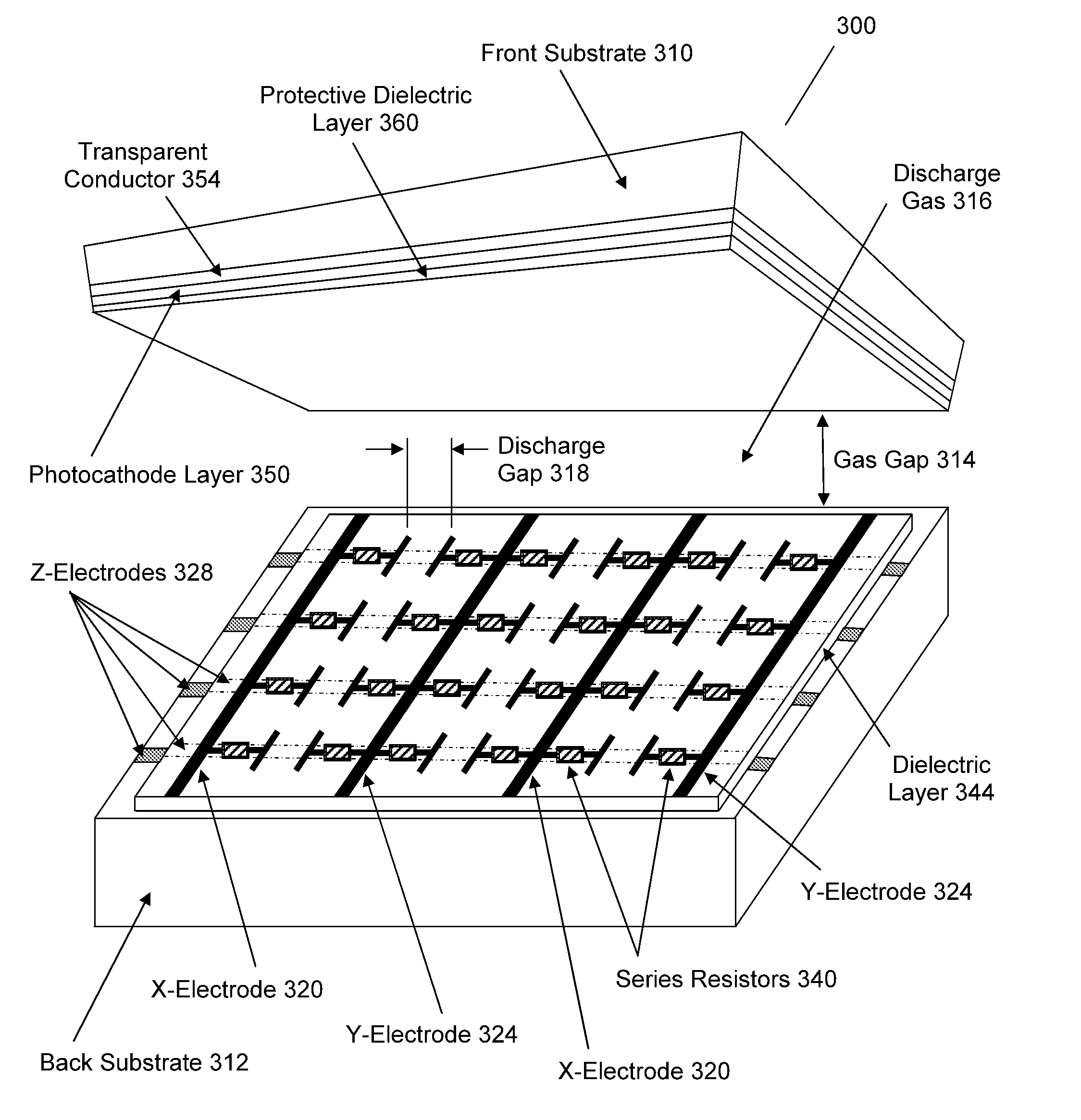
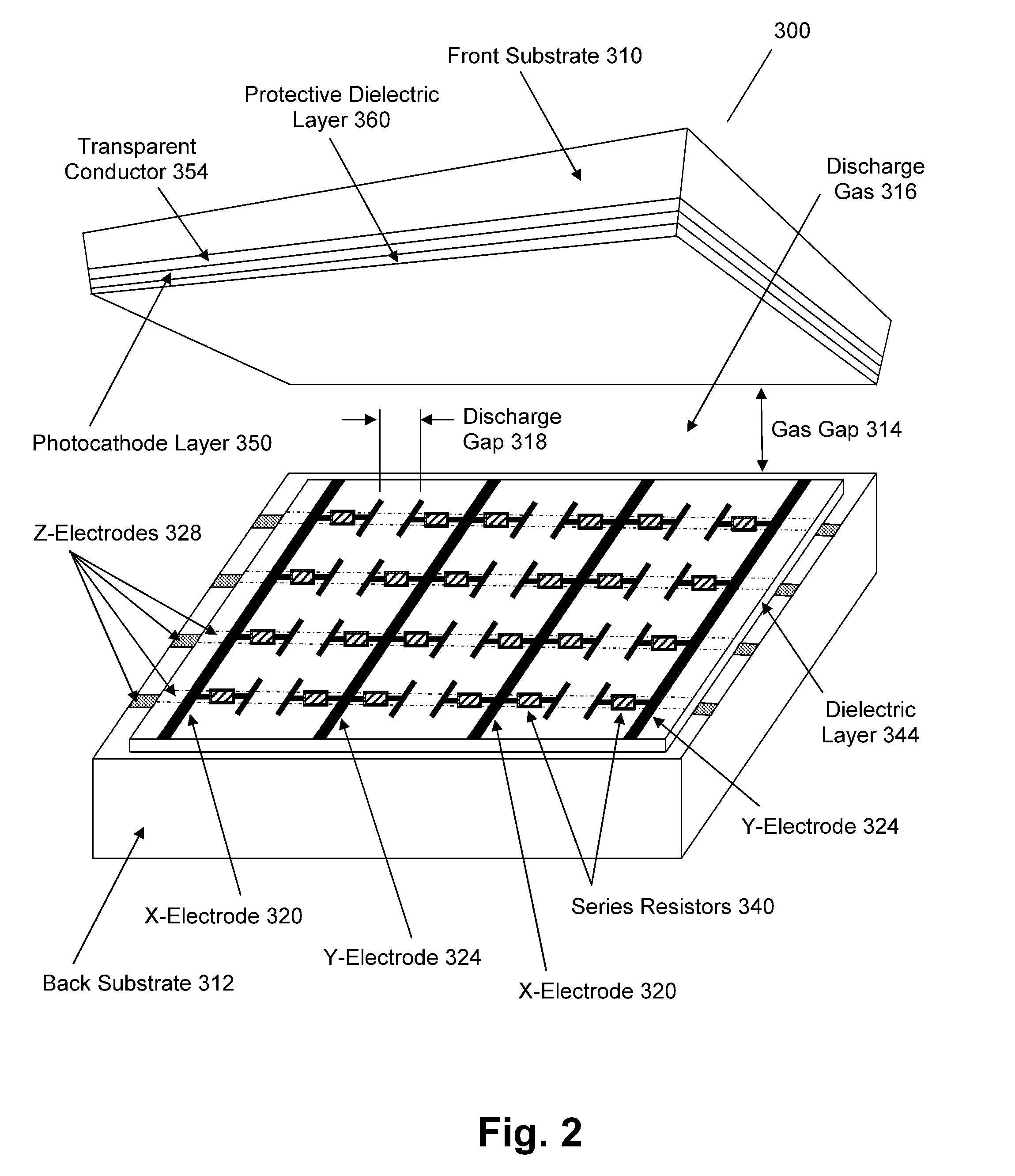
Plasma Panel Based Radiation Detector
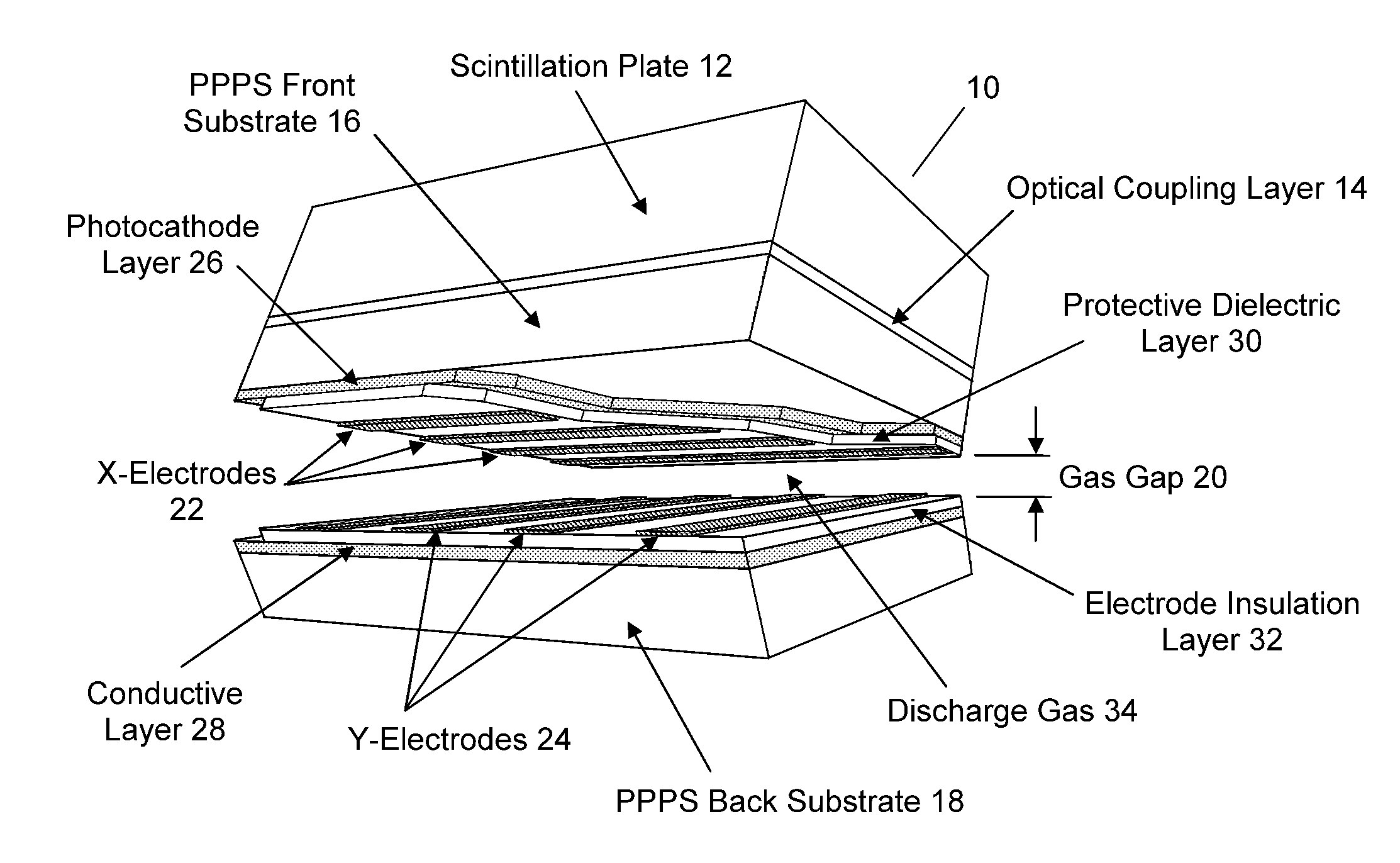
InactiveUS20080210878A1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityPhotocathode
A radiation counting detector includes a first substrate and a second substrate that is generally parallel to first substrate and forms a gap with the first substrate. A gas is contained within the gap. A photocathode layer is coupled to one side of the first substrate and faces the second substrate. A first electrode is coupled to the second substrate and a second electrode is electrically coupled to the first electrode. A first impedance is coupled to the first electrode and a second impedance is coupled to the second electrode. A power supply is coupled to at least one of the electrodes. A first discharge event detector is coupled to the first impedance and a second discharge event detector is coupled to the second impedance. The radiation counting detector further includes a plurality of pixels, each capable of outputting a gas discharge pulse upon interaction with radiation received from the photocathode. Each gas discharge pulse is counted as having an approximately equal value. The radiation counting detector further includes circuitry for detecting if a gas discharge pulse is output from the pixels, and for counting each gas discharge pulse as an individual event.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSORS
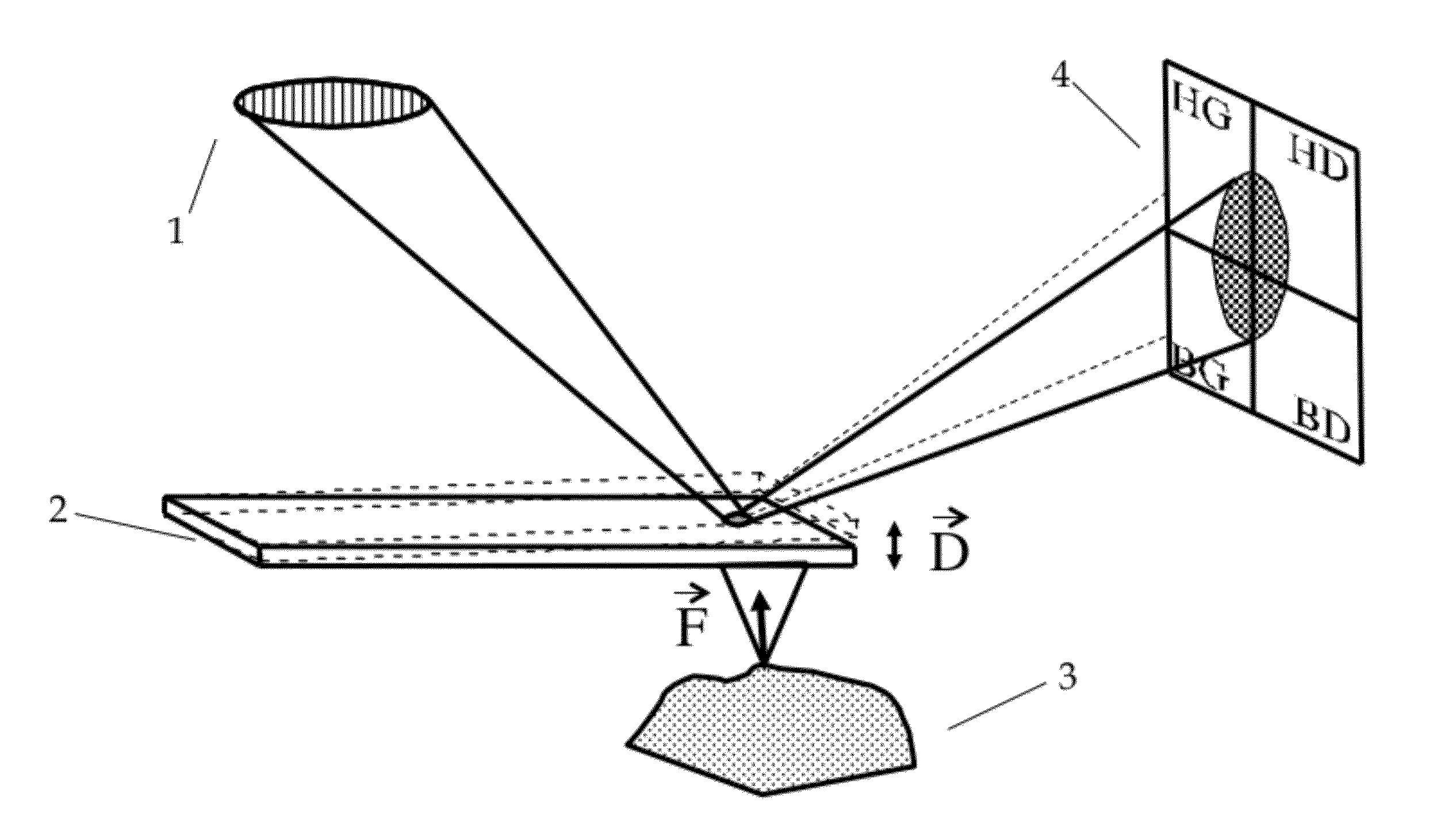
High frequency deflection measurement of IR absorption
ActiveUS8869602B2Reduce impactEnhanced electric fieldNanotechnologyColor/spectral properties measurementsImage resolutionIr absorption
An AFM based technique has been demonstrated for performing highly localized IR spectroscopy on a sample surface by using the AFM probe to detect wavelength dependent IR radiation interaction, typically absorption with the sample in the region of the tip. The tip may be configured to produce electric field enhancement when illuminated by a radiation source. This enhancement allows for significantly reduced illumination power levels resulting in improved spatial resolution by confining the sample-radiation interaction to the region of field enhancement which is highly localized to the tip.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Ruggedized high temperature compatible radiation detector
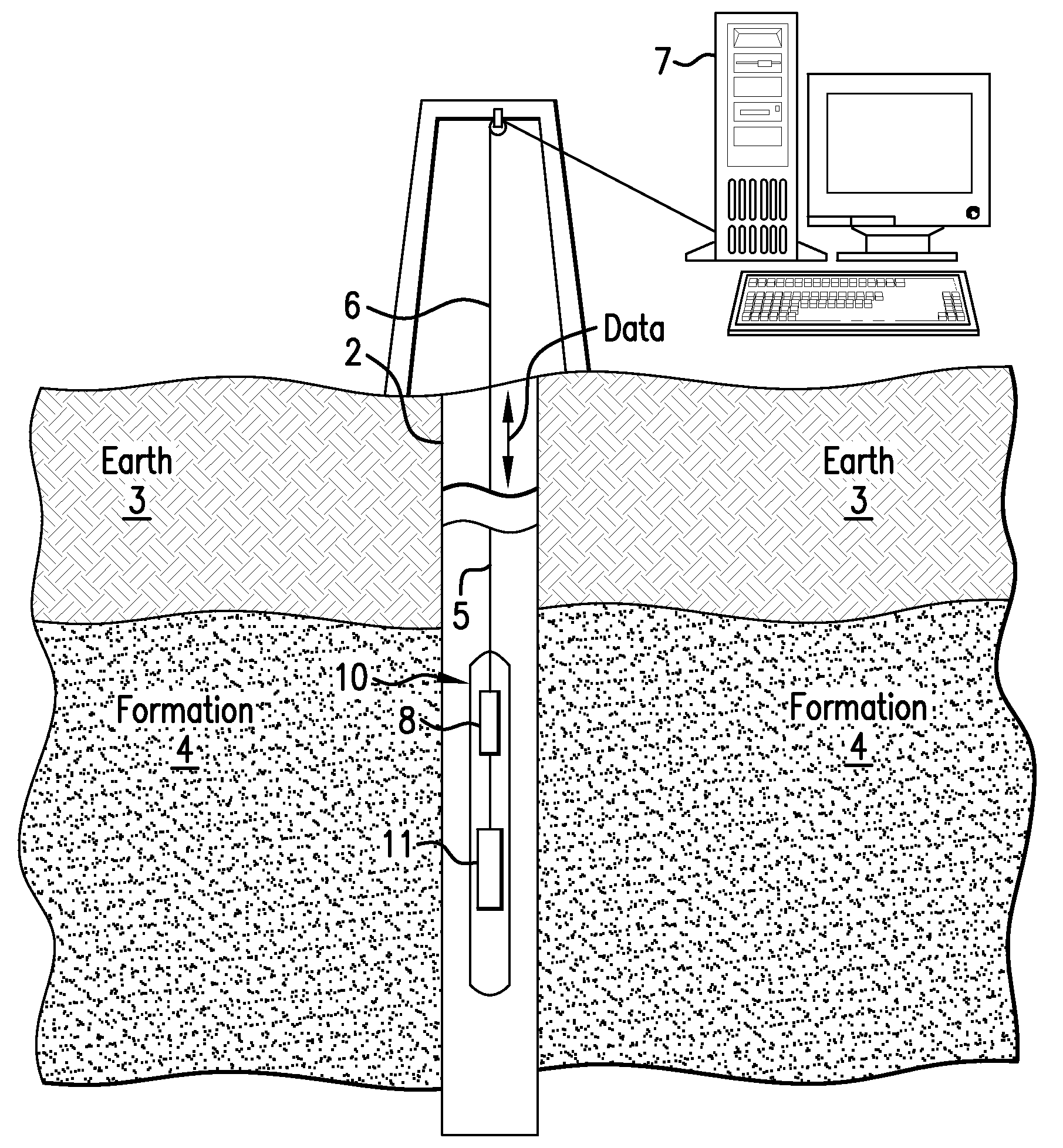
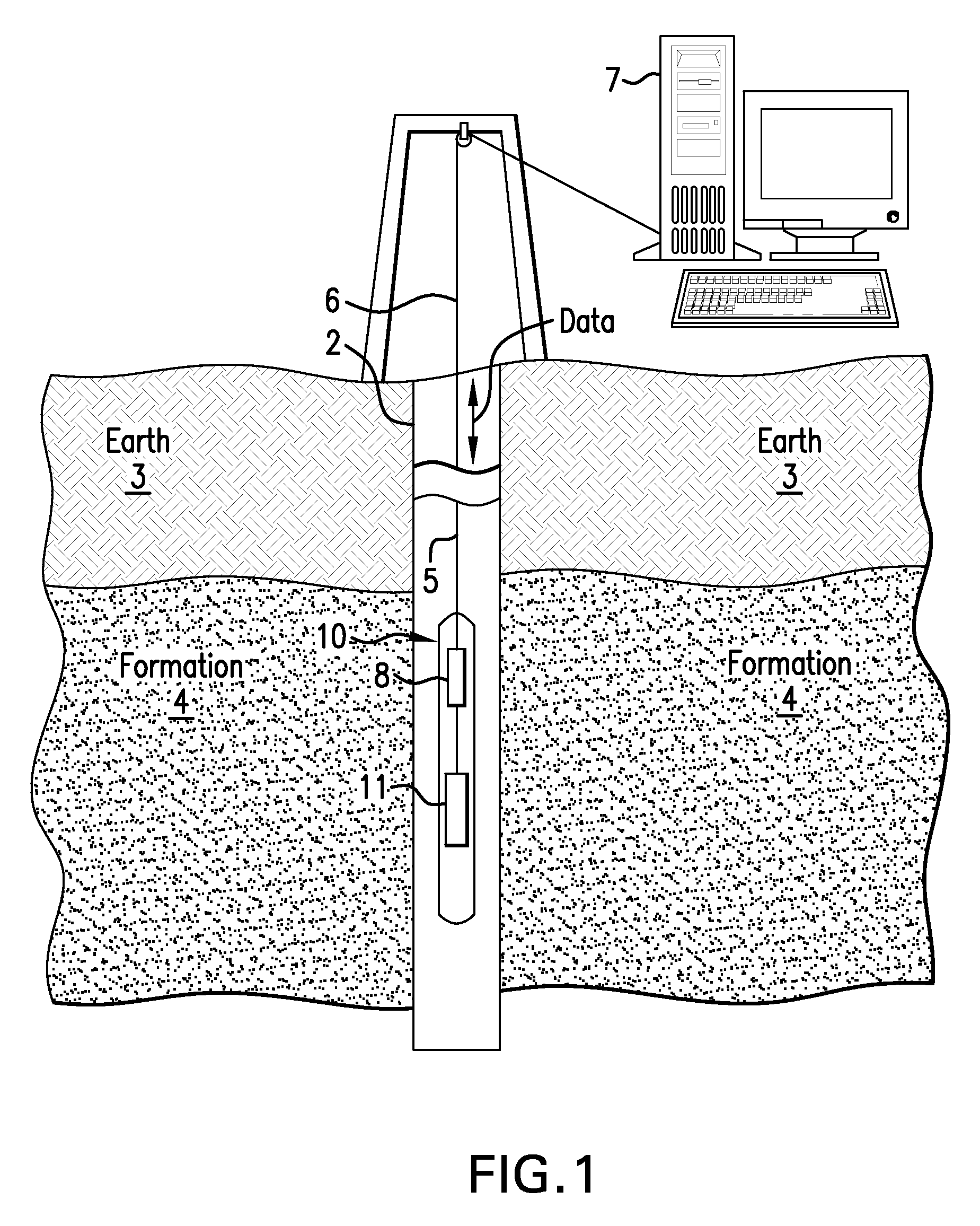
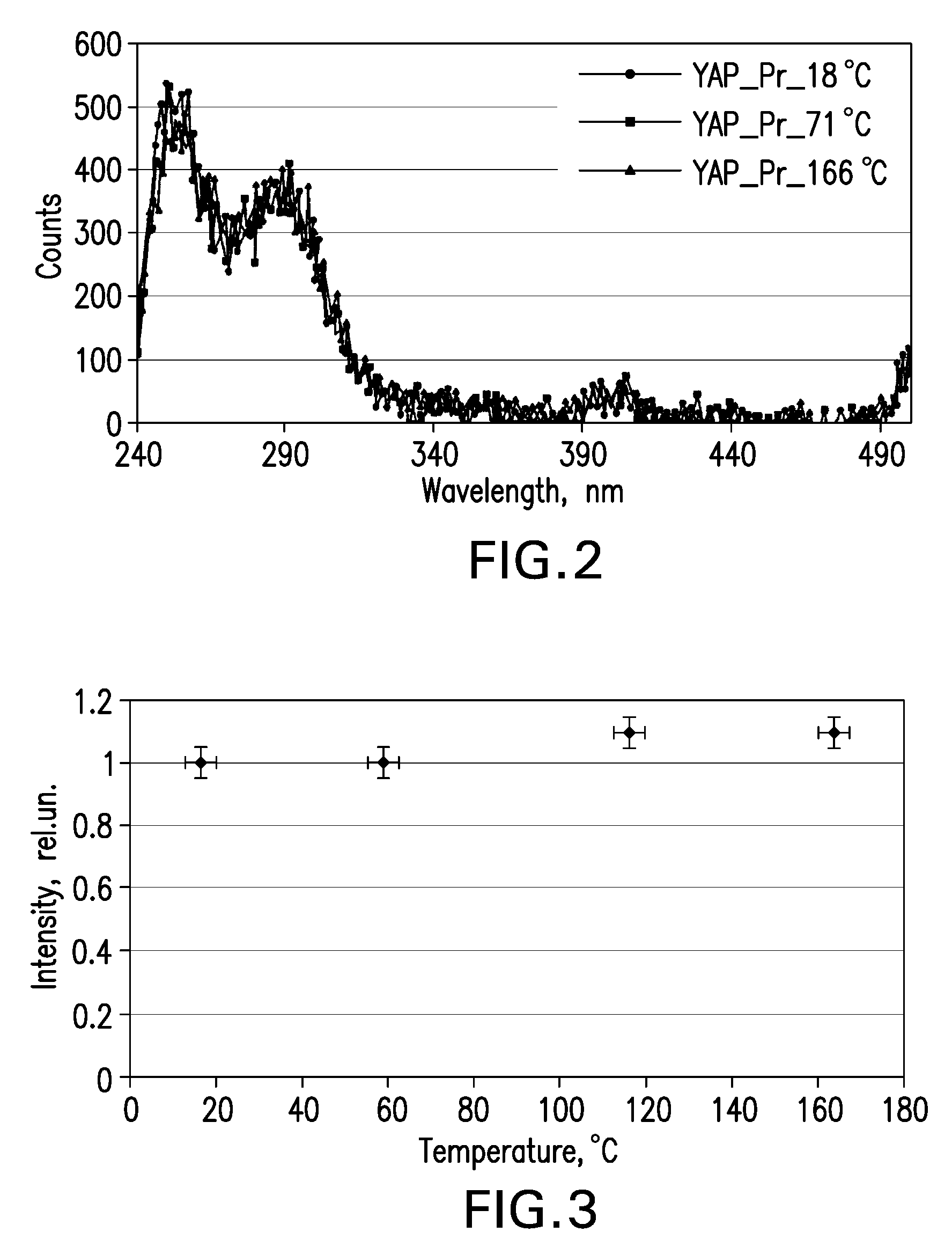
Disclosed is an apparatus configured to detect radiation at high temperatures in a borehole penetrating the earth. The apparatus includes a scintillation material that interacts with the radiation to generate photons, at least one solid-state photodetector optically coupled to the scintillation material and configured to detect the radiation by detecting the generated photons, and at least one optical element disposed between the scintillation material and the at least one solid-state photodetector and configured to concentrate the photons generated in the scintillation material onto the at least one solid-state photodetector.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
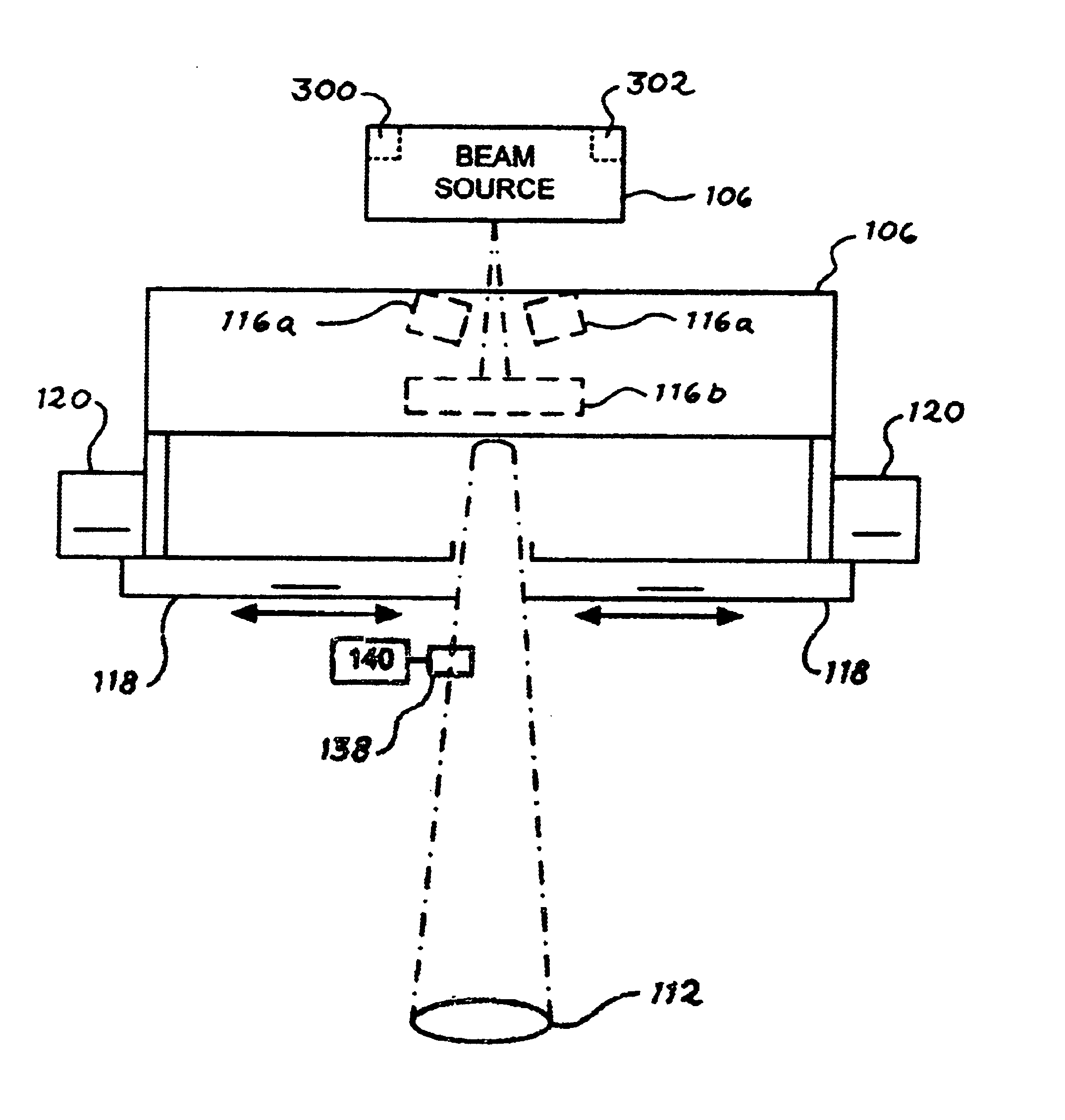
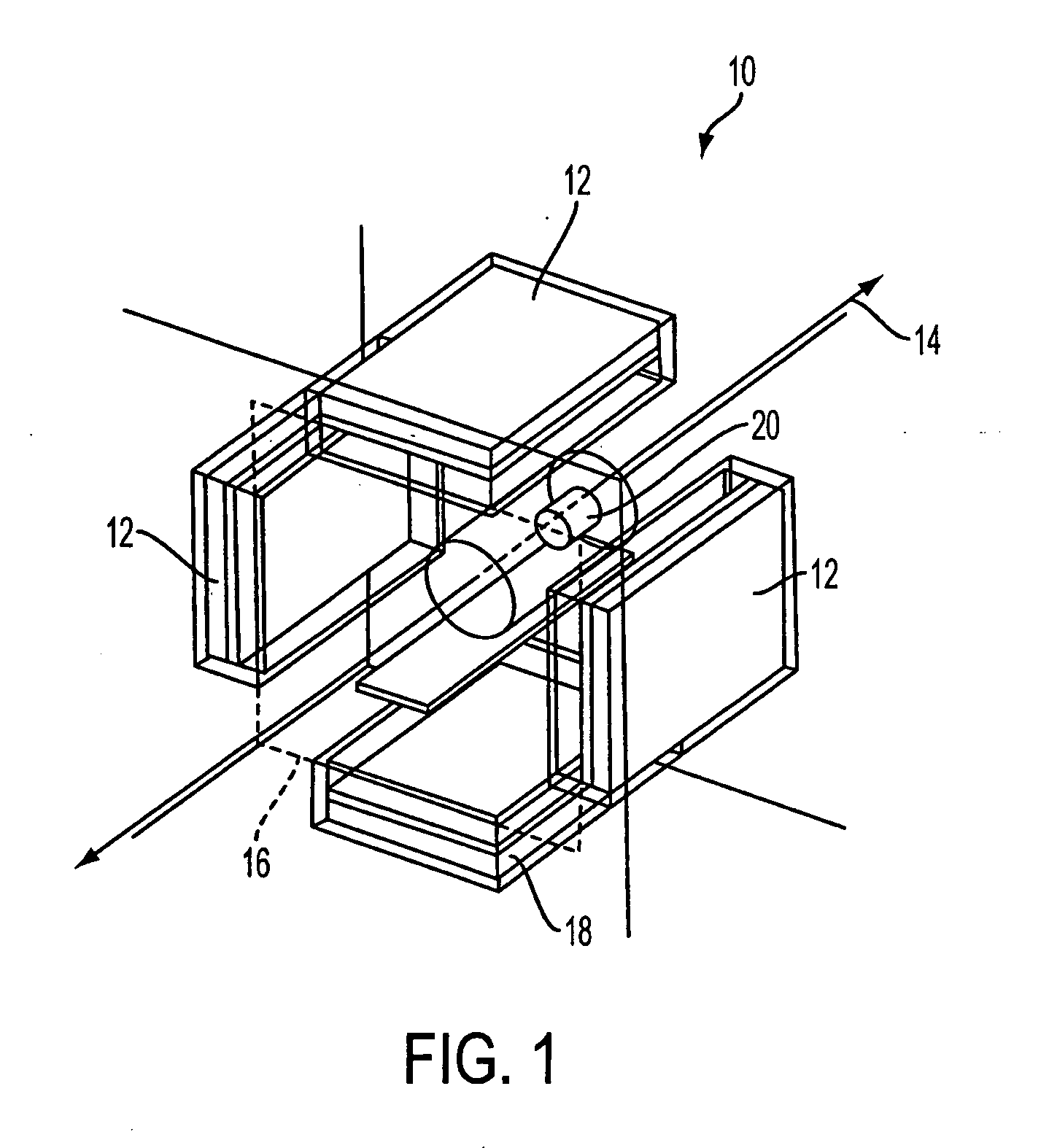
Optimal configuration of photon and electron multileaf collimators in mixed beam radiotherapy
ActiveUS6937693B2Reduce dosageSmall penumbraX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMixed beamLight beam
A radiation therapy method that includes directing a beam along a beam path toward a treatment area. Performing a correction process on the beam, the process includes selectively collimating the beam based on a dose that takes into account bremsstrahlung interactions caused by the beam.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
High Frequency Deflection Measurement of IR Absorption
ActiveUS20120167261A1Reduce impactEnhanced electric fieldNanotechnologyColor/spectral properties measurementsImage resolutionIr absorption
An AFM based technique has been demonstrated for performing highly localized IR spectroscopy on a sample surface by using the AFM probe to detect wavelength dependent IR radiation interaction, typically absorption with the sample in the region of the tip. The tip may be configured to produce electric field enhancement when illuminated by a radiation source. This enhancement allows for significantly reduced illumination power levels resulting in improved spatial resolution by confining the sample-radiation interaction to the region of field enhancement which is highly localized to the tip.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
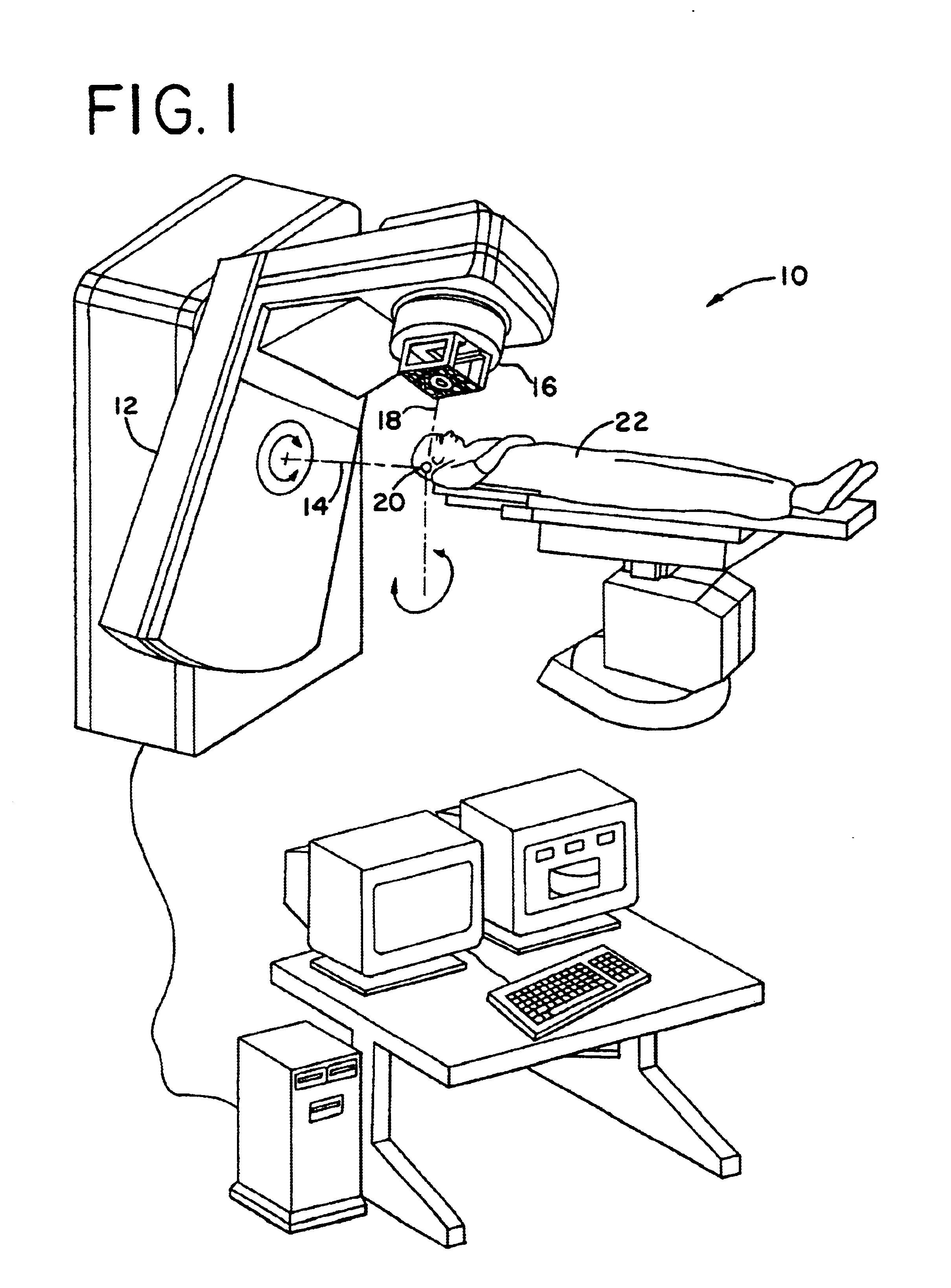
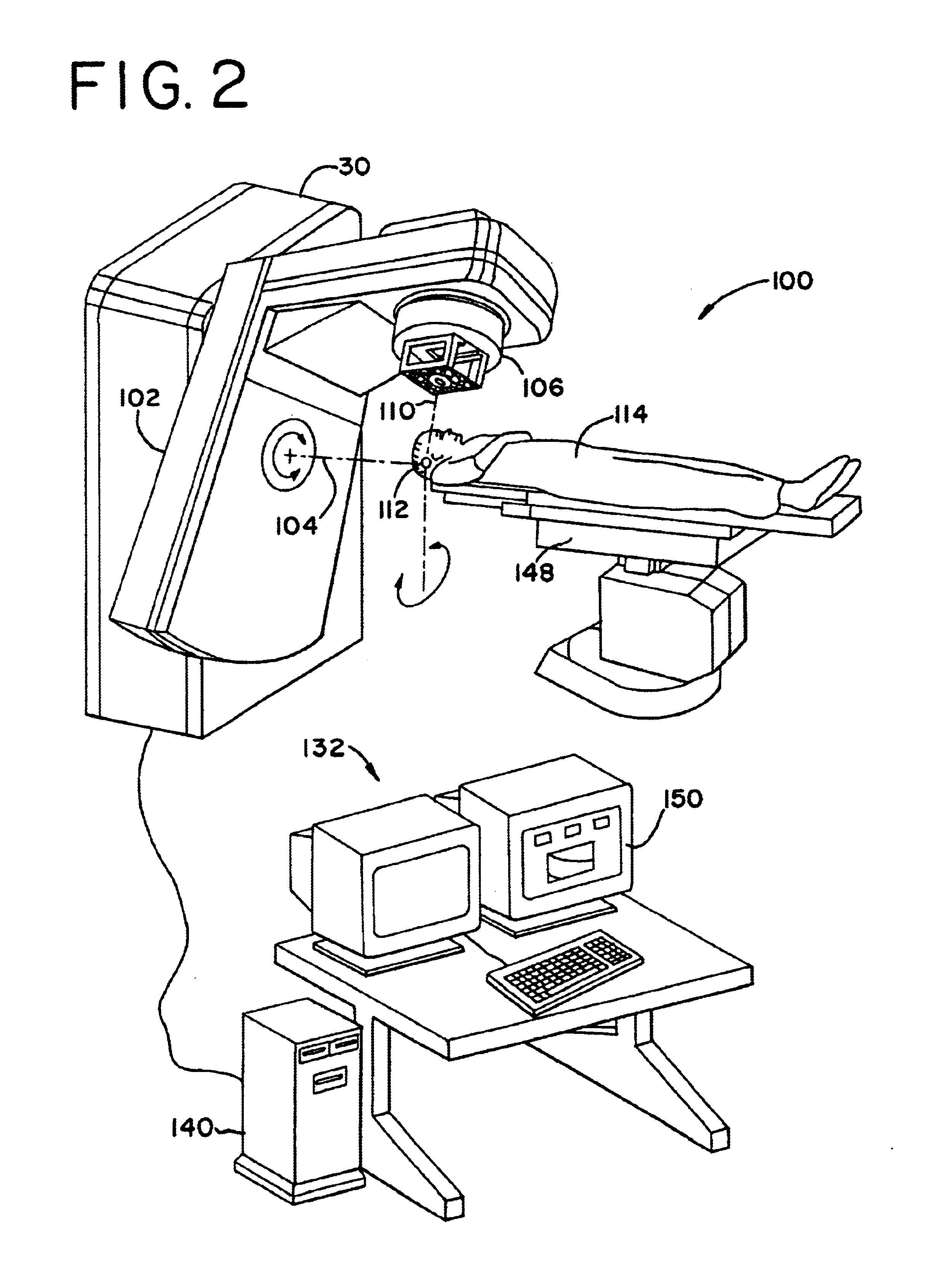
Preclinical SPECT system using multi-pinhole collimation
InactiveUS20080001088A1Handling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionTest object
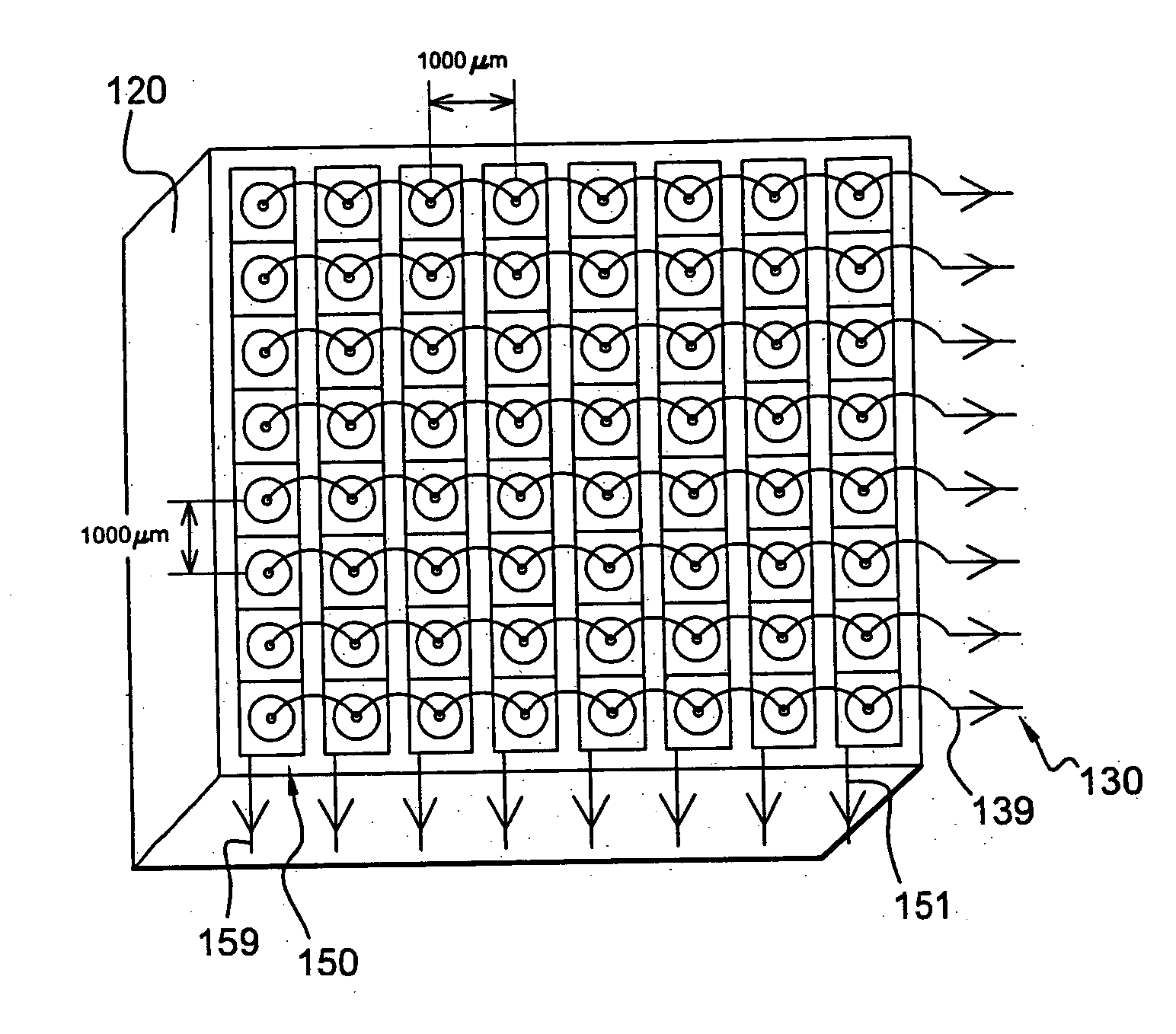
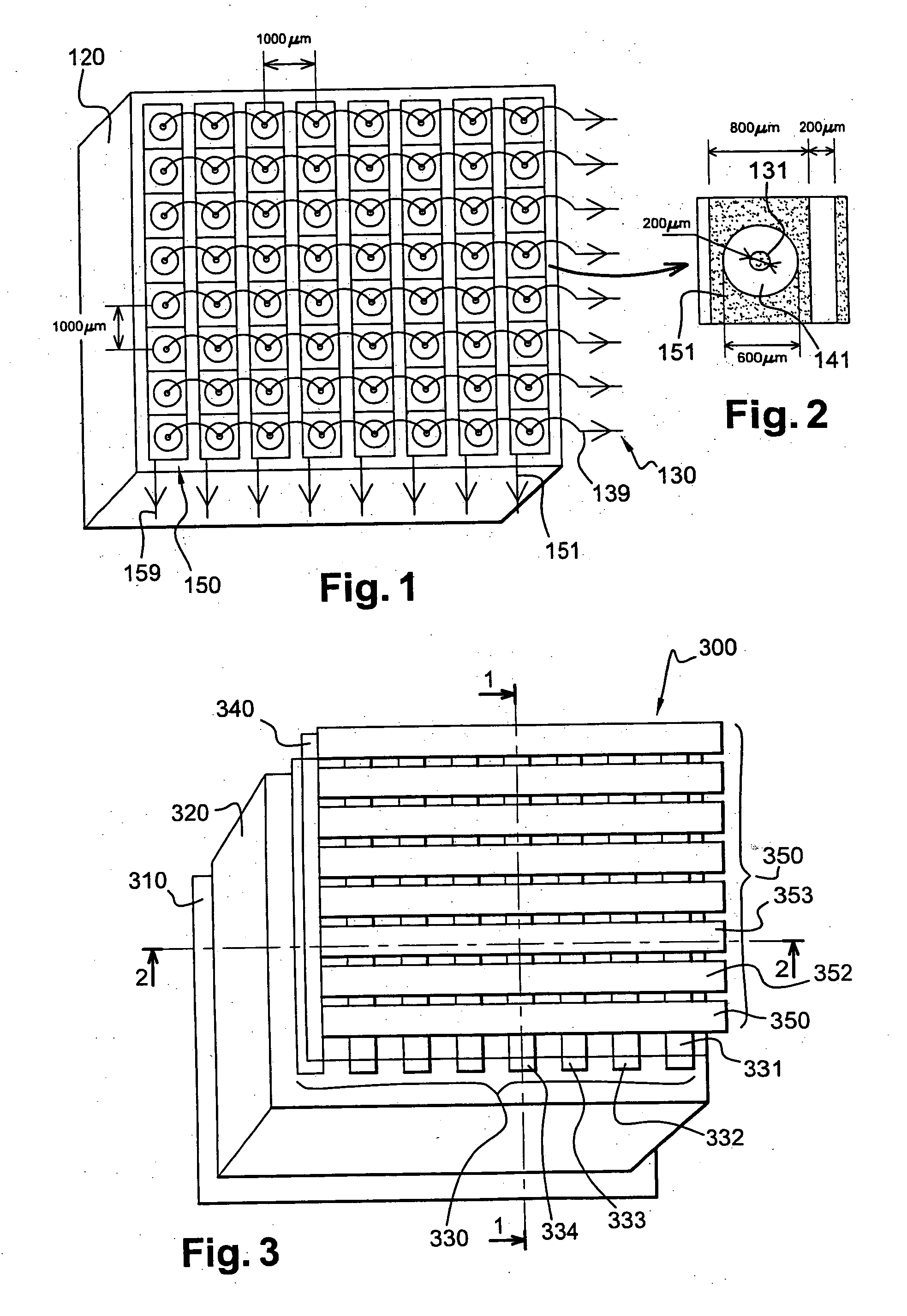
A preclinical nuclear imaging detector system, including a gantry and one or more detector assemblies, each including a scintillator configured to interact with radiation emanating from a target test object being imaged and at least one pinhole collimator, having one or more pinhole apertures formed therein. The pinhole collimator is disposed between the target object and the scintillator, wherein a distance between the pinhole aperture and the scintillator is selected as a function of the number of pinhole apertures provided in the collimator and to optimize one of sensitivity or spatial resolution, such that the one or more pinhole apertures collectively project a unitary minified radiation image of the target object onto the scintillator. Further, one or more photosensors are optically coupled to the scintillator to receive interaction events from the scintillator.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
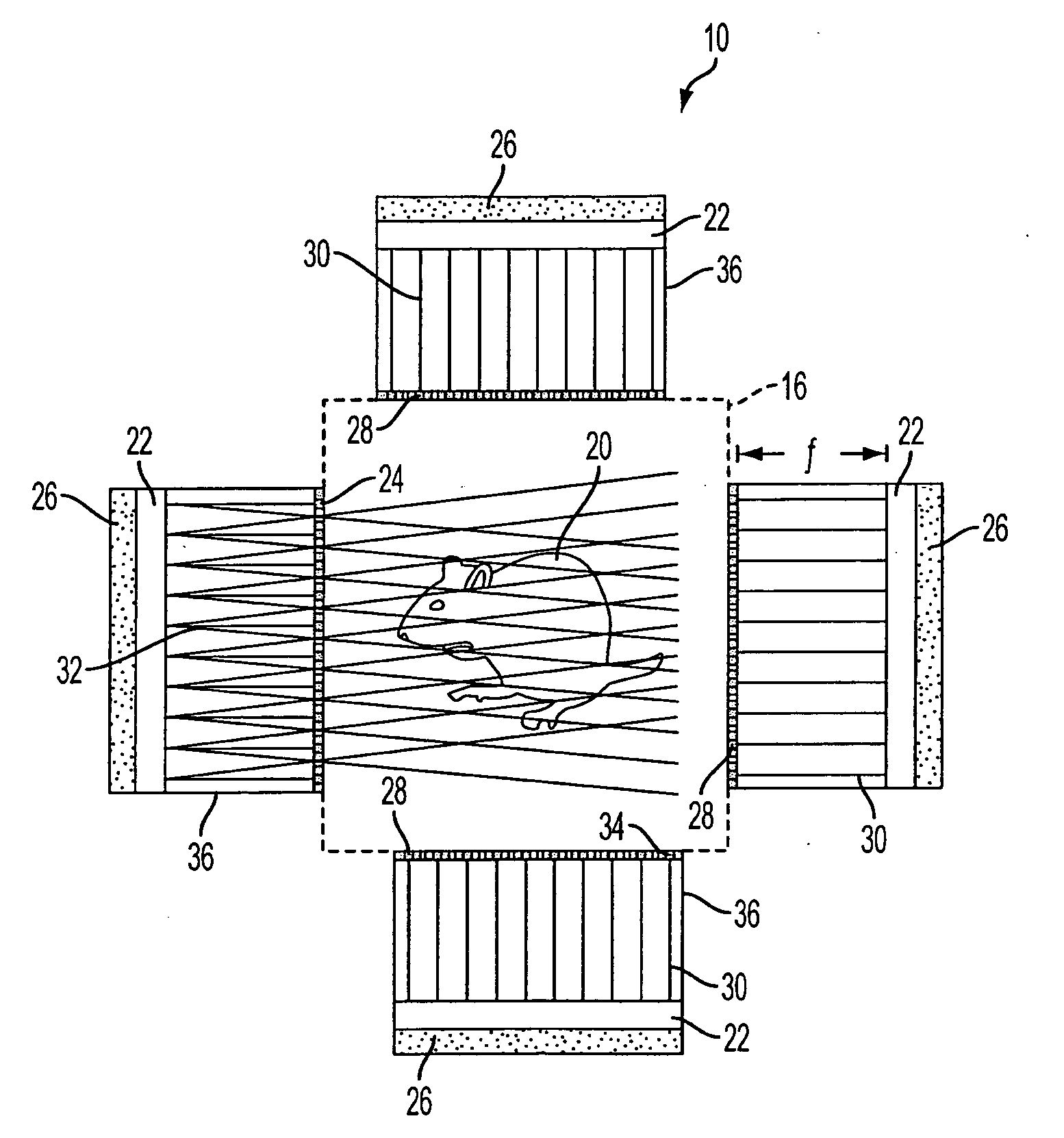
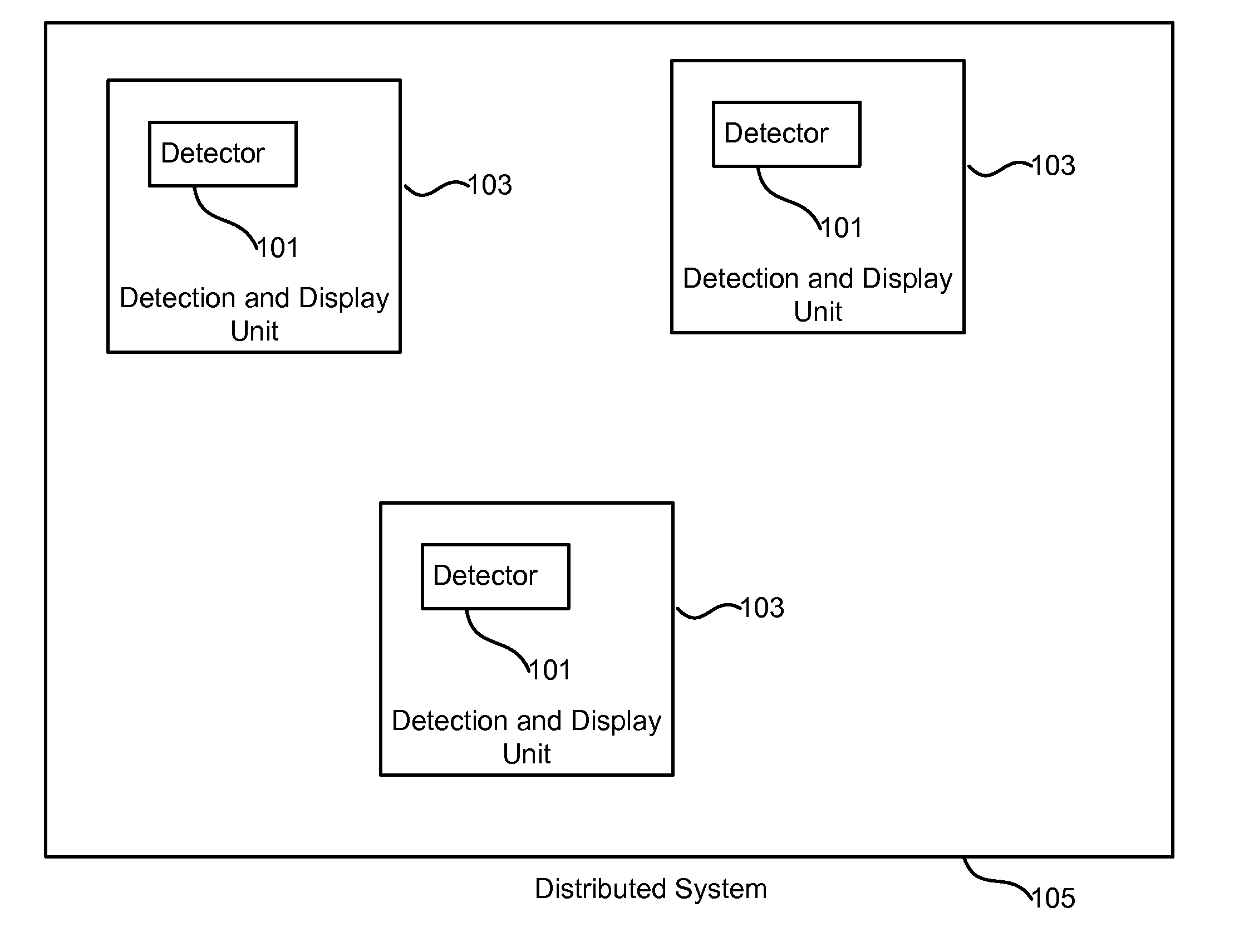
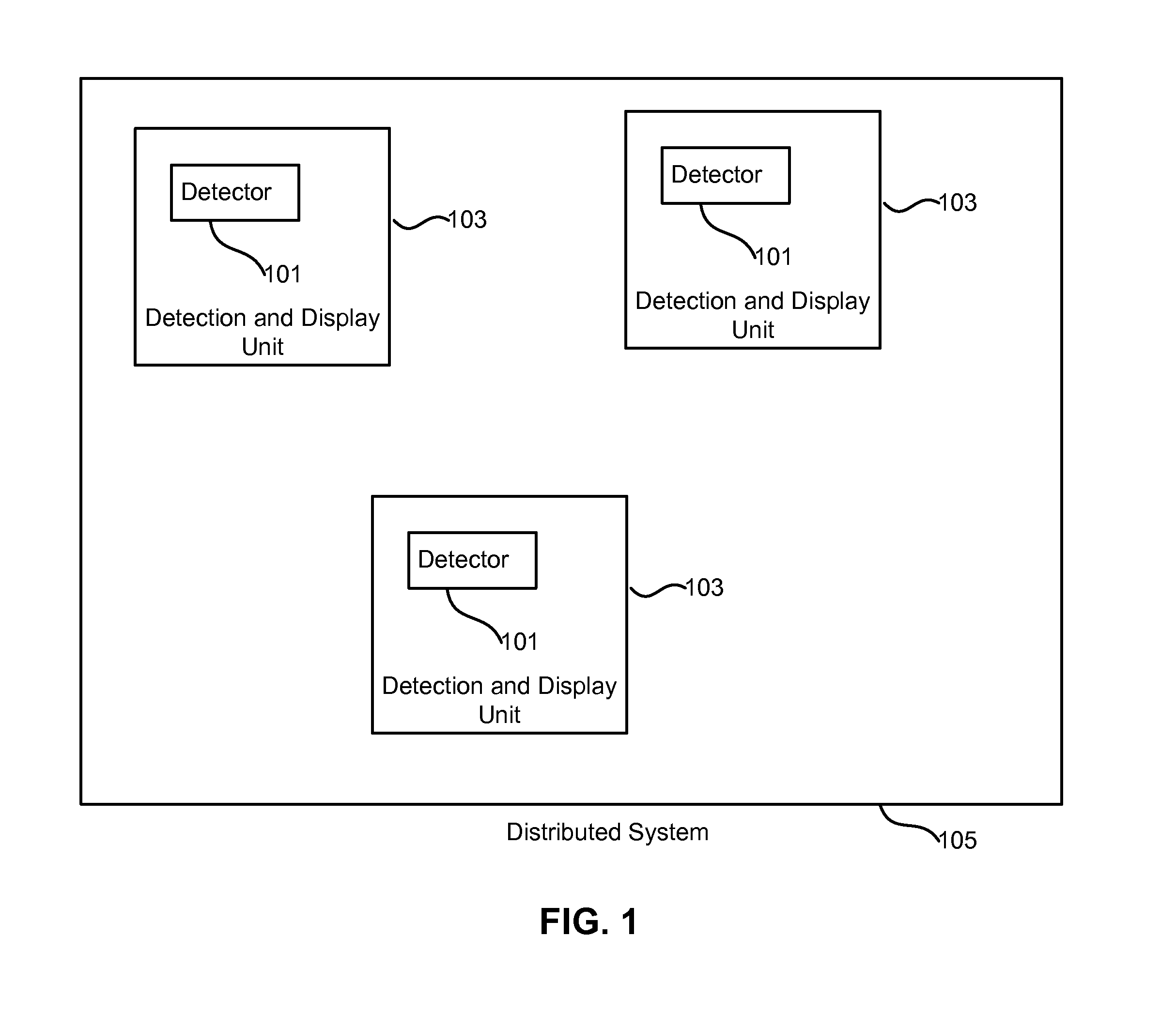
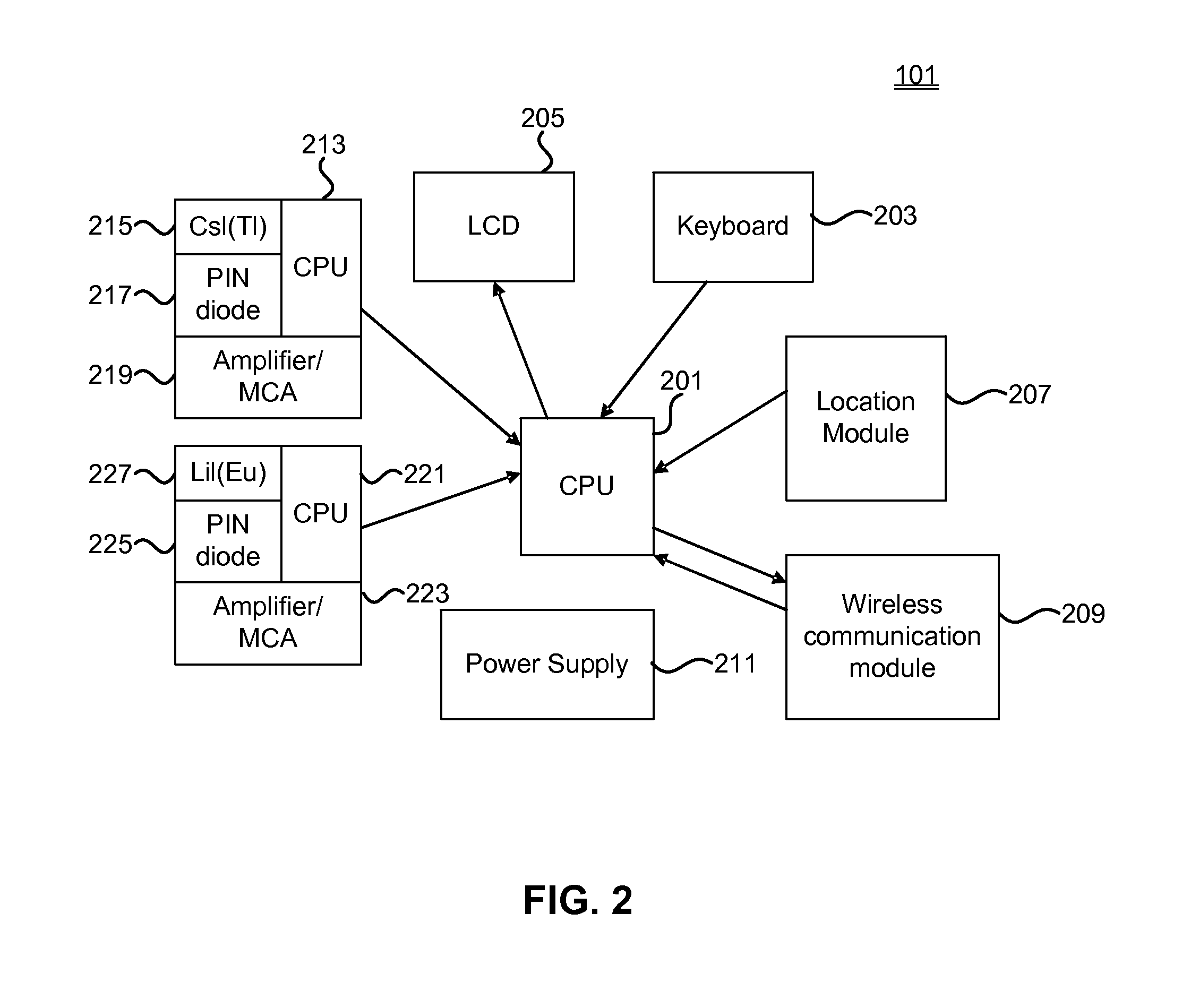
Distributed system for radiation detection utilizing multiple clustered detectors
ActiveUS8502158B1Intuitive imageEasy to understandMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsComputer scienceData integration
Owner:POLIMASTER IP SOLUTIONS
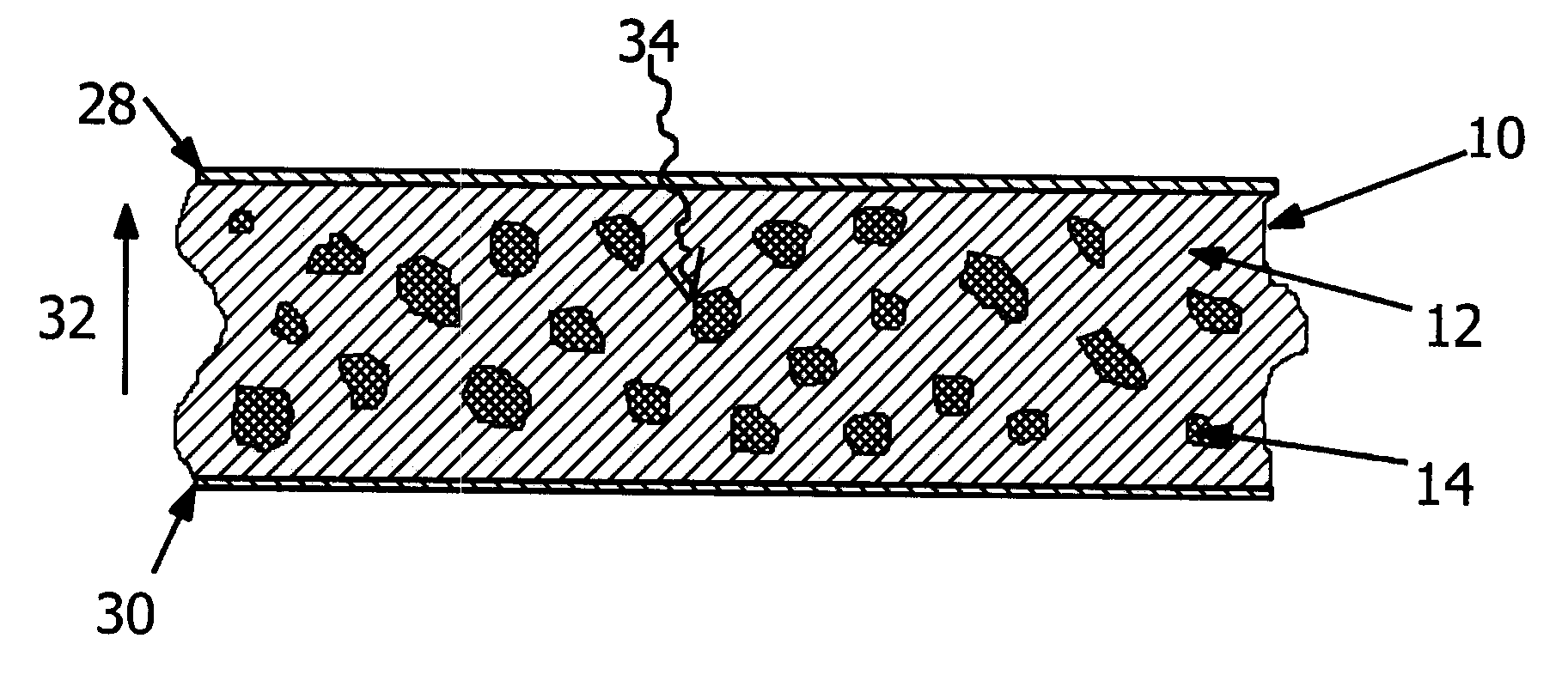
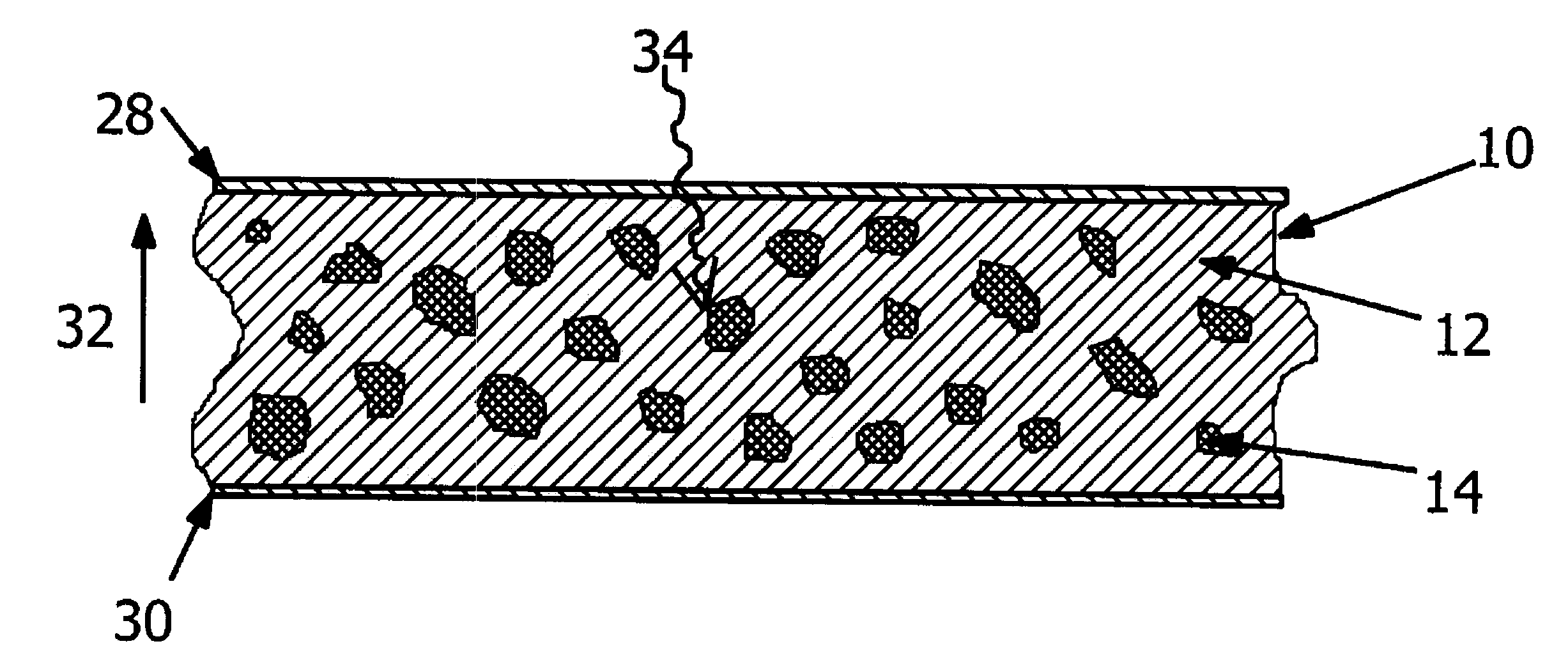
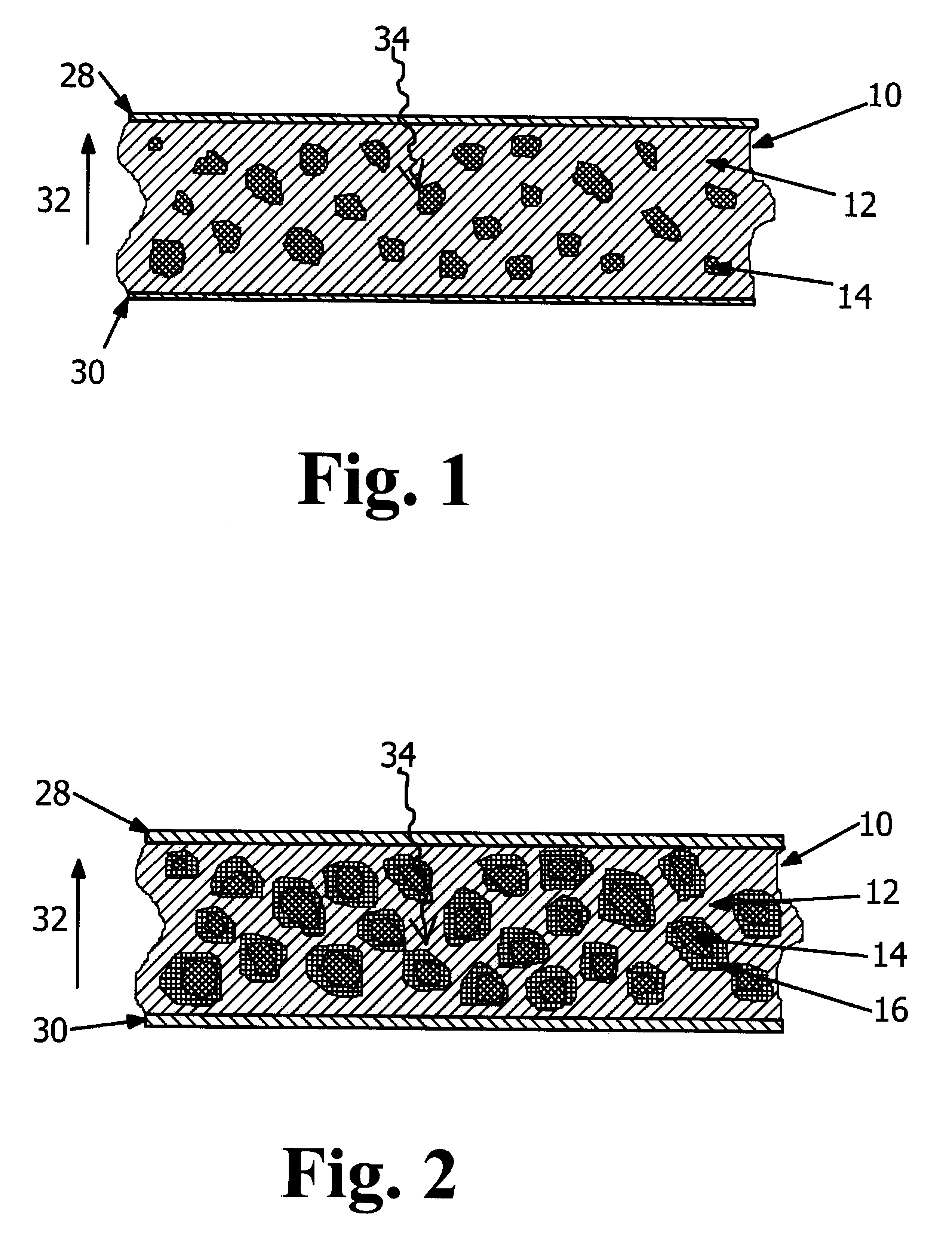
Radiation detector using a composite material and process for manufacturing this detector
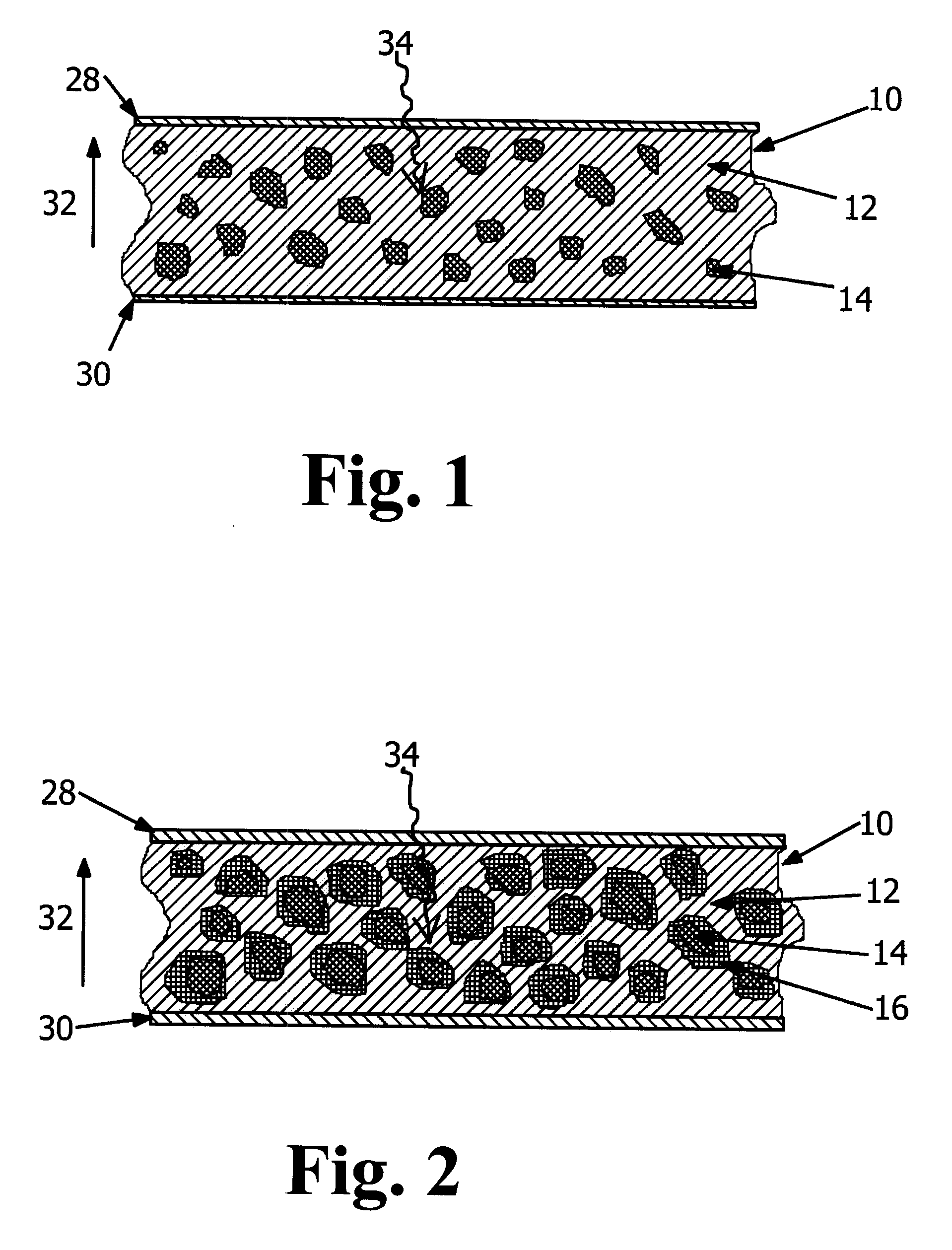
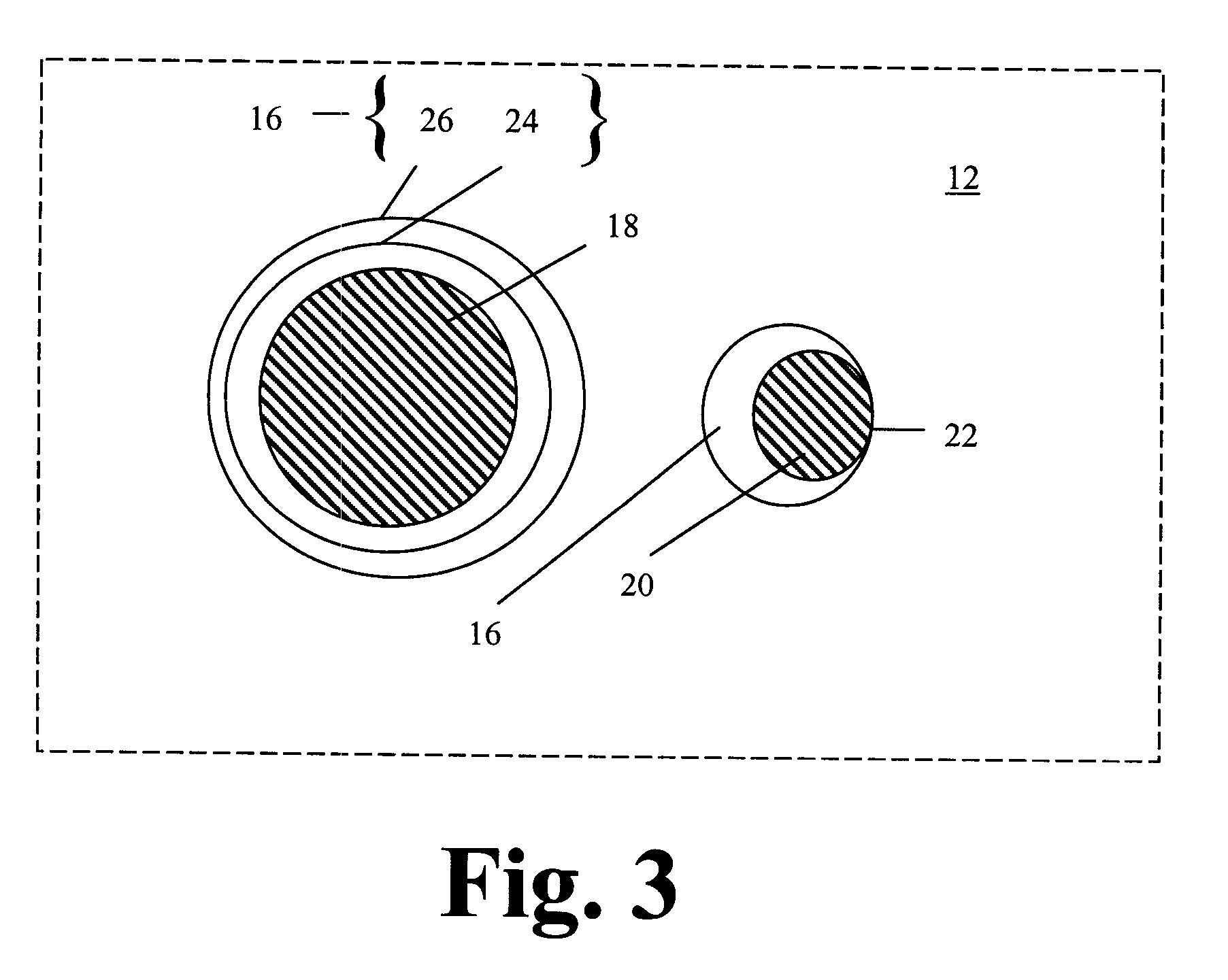
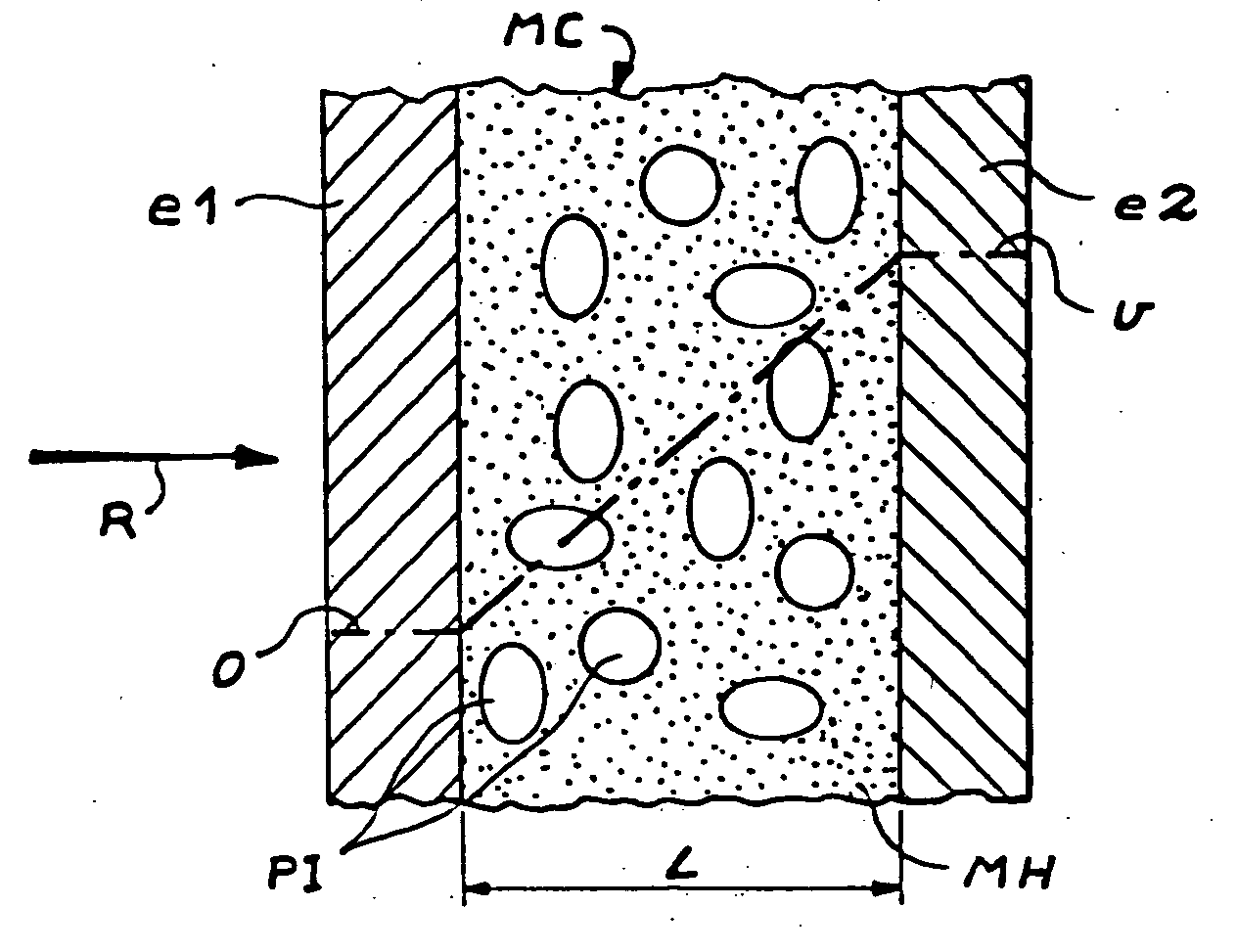
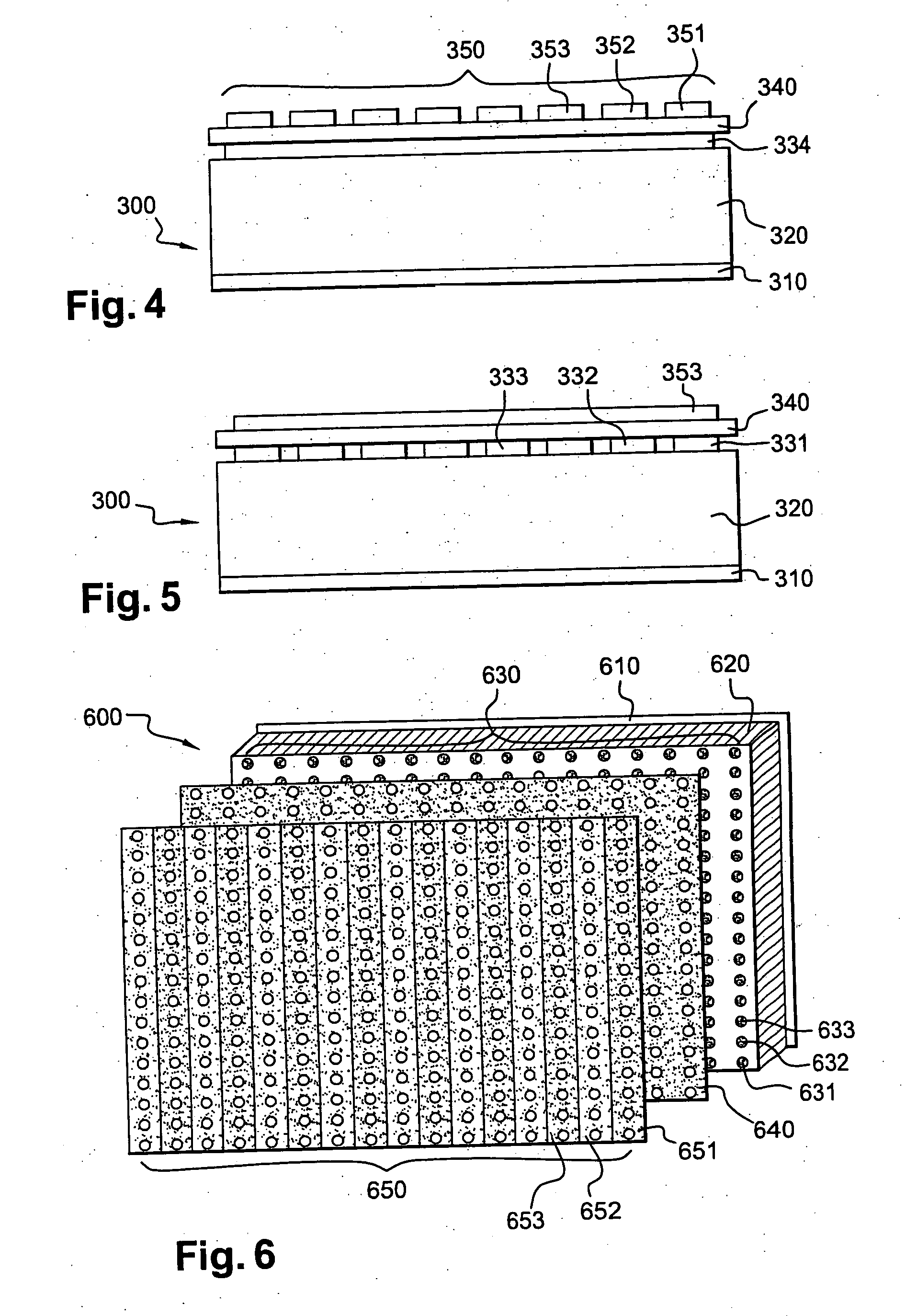
Detector of radiation using a composite material and process for manufacturing this detector. This detector comprises layers (6) of a semiconducting composite material comprising a host matrix made of a polymer and semiconducting-type guest particles dispersed through the host matrix, means (22-26) for creating an electric field in these layers and a stack of sheets (4) of a first material emitting particles by interaction with the radiation, the layers alternating with the sheets, each of the layers being associated with one of the sheets, the stack having opposite faces, each containing the edges of the sheets and layers, the means of creation of the field, comprising, for each layer, a group of parallel and conductive tracks (22) which extend from one face to the other, parallel to this layer, and which are in contact with it.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
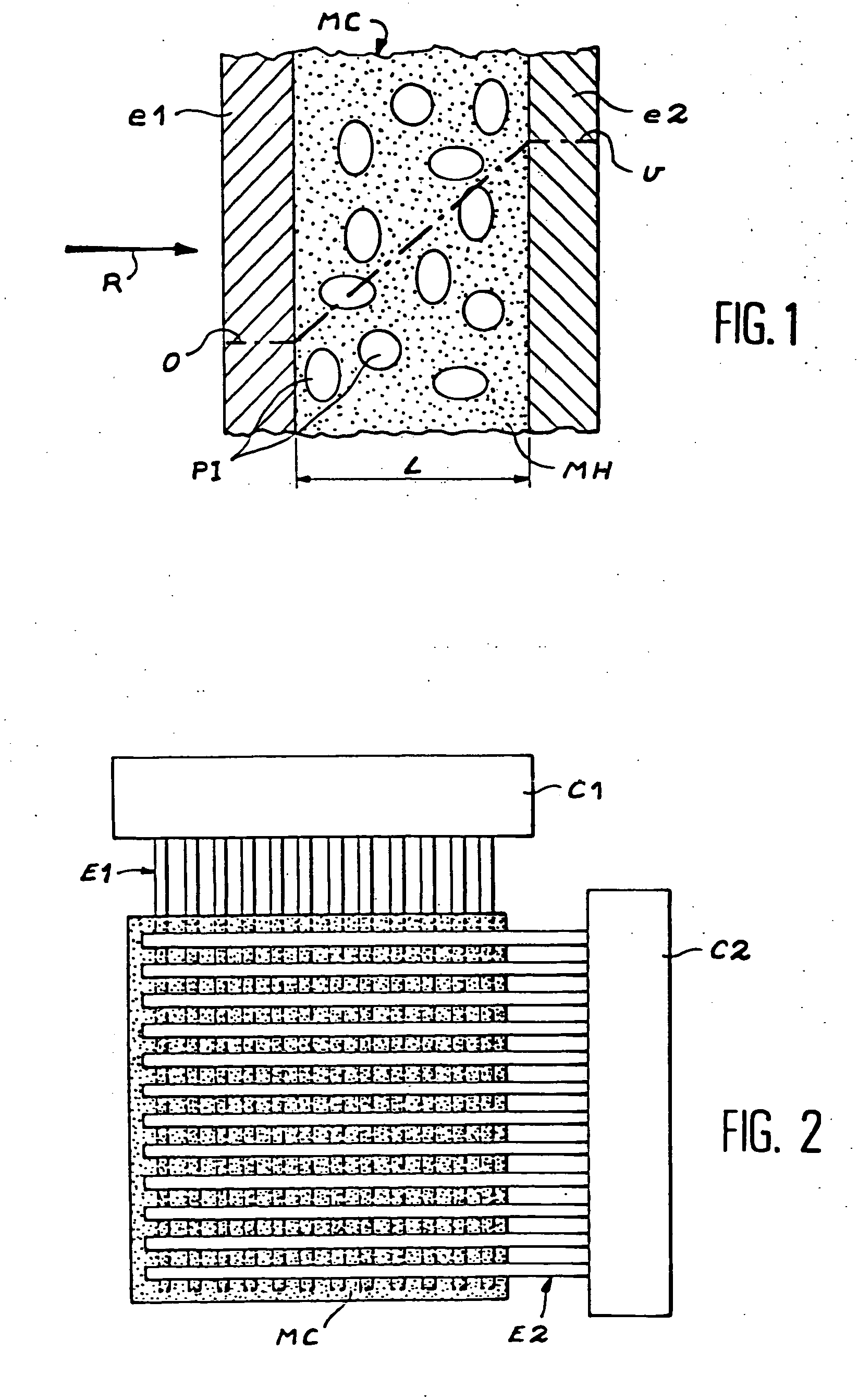
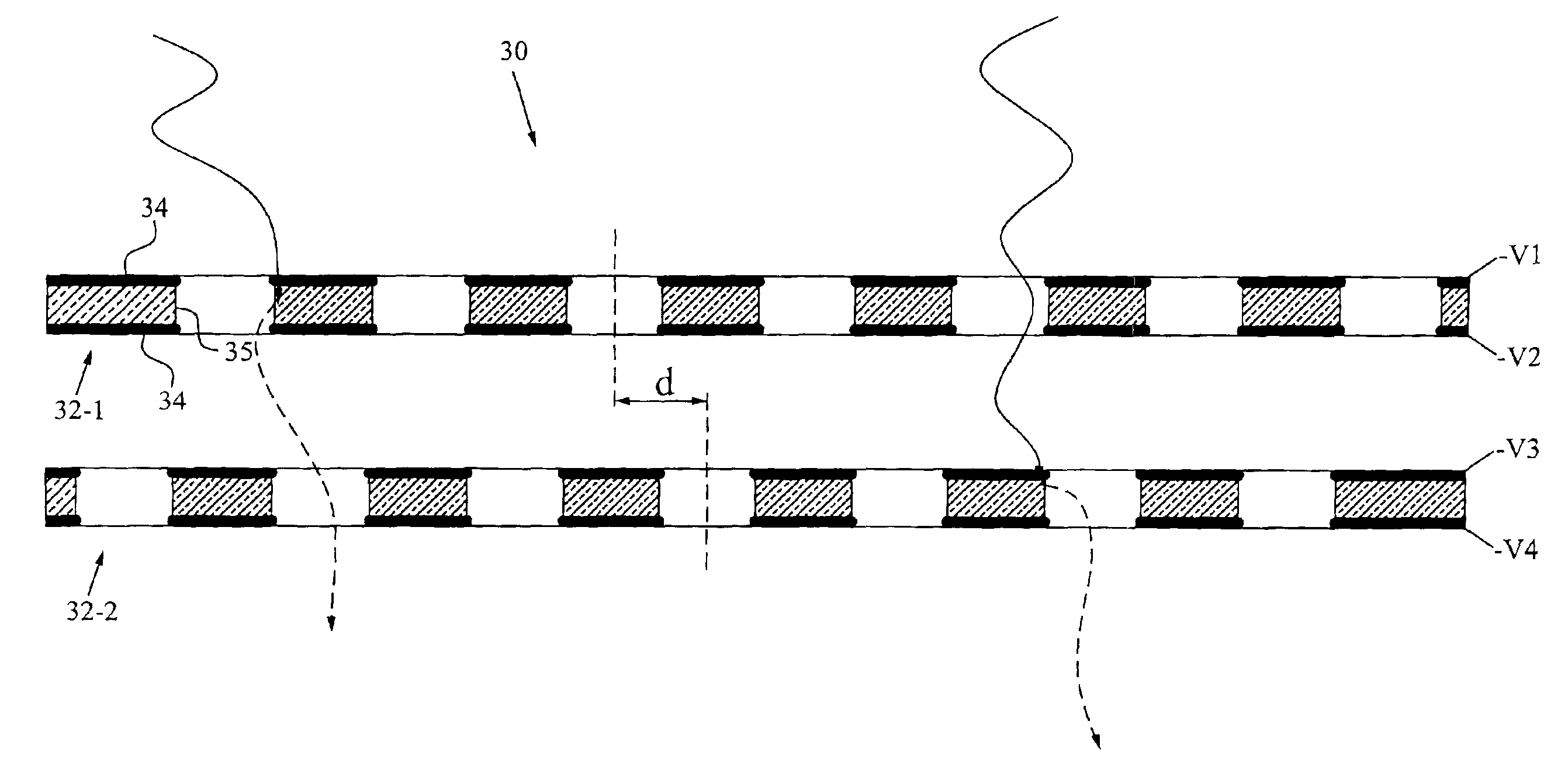
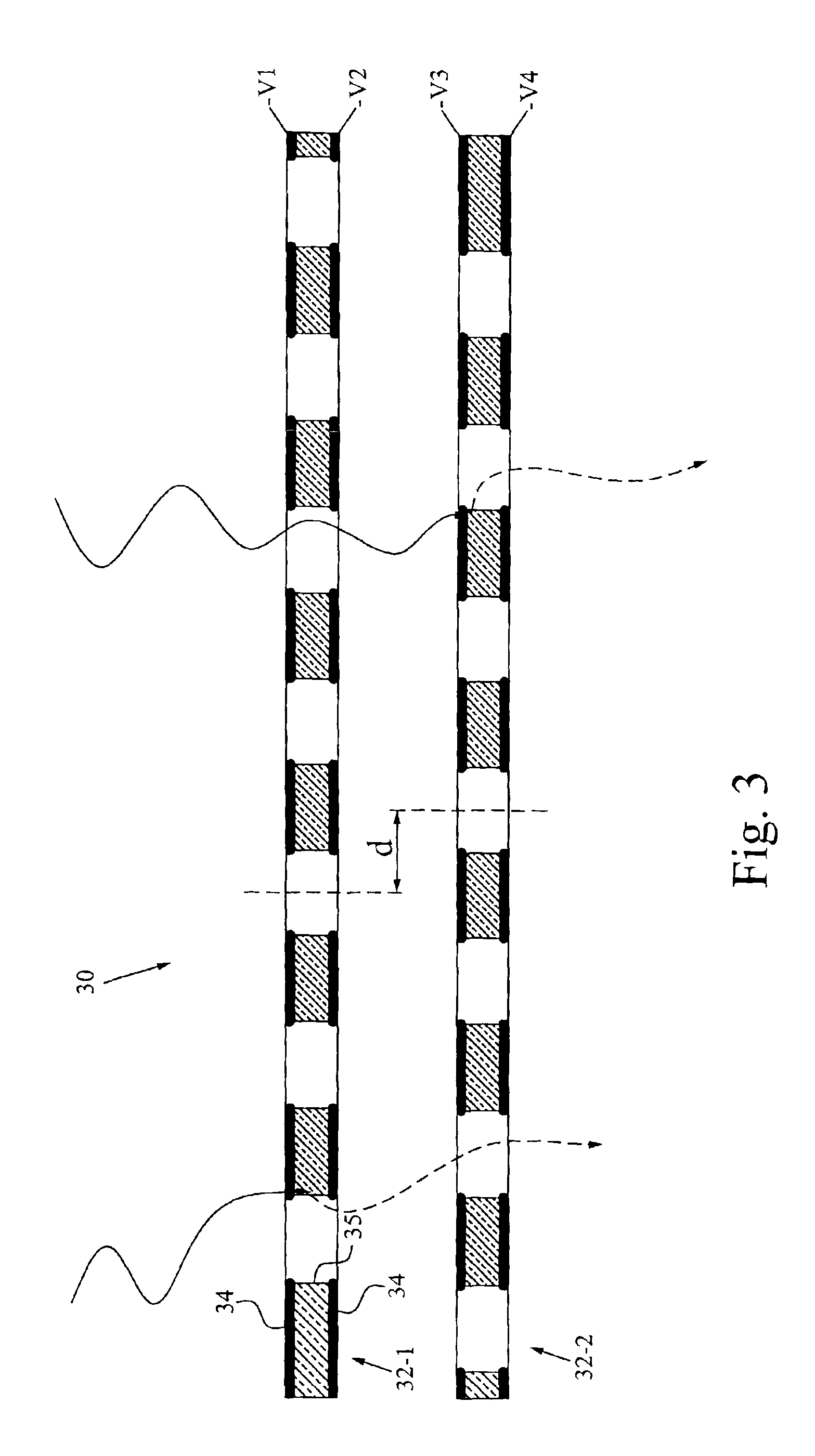
Multi-layered radiation converter
InactiveUS6891166B2Quality improvementImprove efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesHigh absorptionElectron
The invention relates to a multi-layered radiation converter, a radiation detector comprising such a converter as well as a radiation-based imaging system using such a detector. Each converter layer (32) in the radiation converter is adapted for interaction with incident radiation to cause the emission of electrons into drift holes defined in the converter layer. The drift holes of one converter layer (32-1) are staggered with respect to the drift holes of another converter layer (32-2). By mutually shifting the converter layers such that the drift holes of two different layers are no longer well-aligned, but rather staggered with respect to each other, the effective conversion area will be increased, and the probability of incoming radiation passing through the stack without interaction with the converter layers will be significantly reduced. In this way, high absorption efficiency for incident radiation inside the multi-layered converter structure is ensured, while still maintaining transparency for emitted electrons through the drift holes.
Owner:C-RAD IMAGING AB
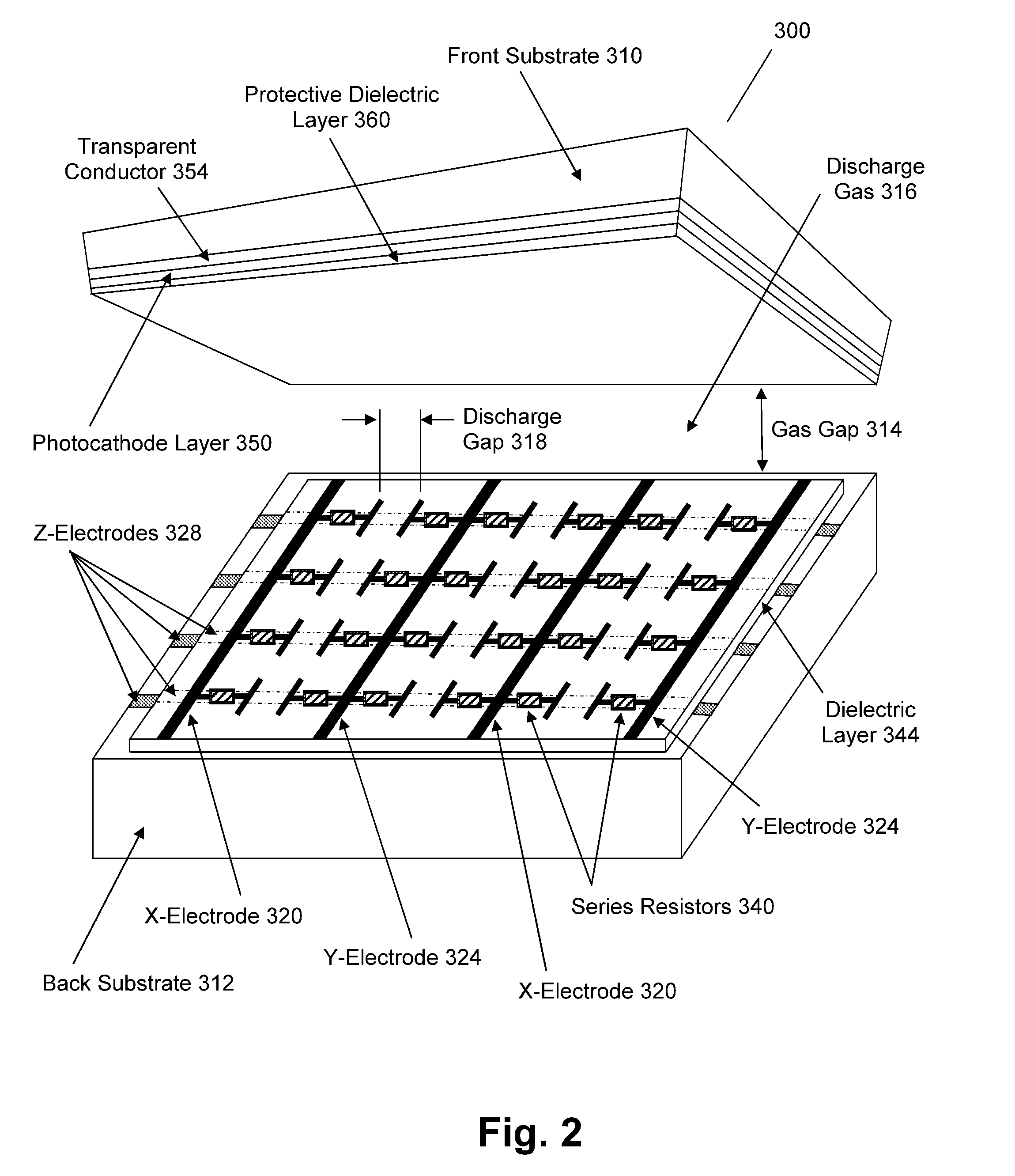
Plasma panel based radiation detector
InactiveUS7683340B2Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityPhotocathode
A radiation counting detector includes a first and a second substrate. A gas is contained within the gap between the substrates. A photocathode layer is coupled to one side of the first substrate and faces the second substrate. A first electrode is coupled to the second substrate and a second electrode is electrically coupled to the first electrode. A first impedance is coupled to the first electrode and a second impedance is coupled to the second electrode. A power supply is coupled to at least one electrode. A first discharge event detector is coupled to the first impedance and a second discharge event detector is coupled to the second impedance. The radiation counting detector further includes a plurality of pixels, each capable of outputting a gas discharge pulse upon interaction with radiation received from the photocathode. Each gas discharge pulse is counted as an individual event having an approximately equal value.
Owner:INTEGRATED SENSORS
Solid-state radiation imager with back-side irradiation
A solid-state imager with back-side irradiation. The present invention provides a solid-state imager that includes a substantially radiation transparent substrate adapted to receive incident radiation. The radiation travels through the substrate and a pixelated array of photosensitive elements to a scintillator material, which absorbs the radiation. The pixelated array of photosensitive elements receives light photons and measures the amount of light generated by radiation interactions with the scintillator material. With this imager, there is less spreading and blurring and thus a better quality image. In another embodiment, there is a substantially transparent material disposed between the pixelated array of photosensitive elements and the scintillator material. The substantially transparent material absorbs and substantially blocks electrons from entering the active regions of the pixelated array of photosensitive elements. This enables the imager to perform for a longer period of time according to its specifications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector with adaptively selected gamma threshold
InactiveUS7626178B2Measurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsGamma energyAnalog-to-digital converter
An integrated radiation detector having a pulse-mode operating photosensor optically coupled to a gamma sensing element and a neutron sensing element is disclosed. The detector includes pulse shape and processing electronics package that uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse shape and processing electronics package determines a maximum gamma energy from the spectrum associated with gamma rays detected by the gamma sensing element to adaptively select a gamma threshold for the neutron sensing element. A light pulse attributed to the neutron sensing element is a valid neutron event when the amplitude of the light pulse is above the gamma threshold.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector with adaptively selected gamma threshold
InactiveCN101452080AMeasurement with scintillation detectorsRadiation intensity measurementGamma energyDigital converter
The invention relates to an integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector with adaptively selected gamma threshold. The integrated radiation detector (10) having a pulse-mode operating photosensor (24) optically coupled to a gamma sensing element (18) and a neutron sensing element (20) is disclosed. The detector (10) includes a pulse shape and processing electronics package (26) that uses an analogto digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse shape and processing electronics package (26) determines a maximum gamma energy from the spectrum associated with gamma rays detected by the gamma sensing element (18) to adaptively select a gamma threshold for the neutron sensing element (20). A light pulse attributed to the neutron sensing element (20) is a valid neutron event when the amplitude of the light pulse is above the gamma threshold.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Radiation detector assembly, radiation detector, and method for radiation detection
ActiveUS7977643B2Easy to detectMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesCharge carrierField strength
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
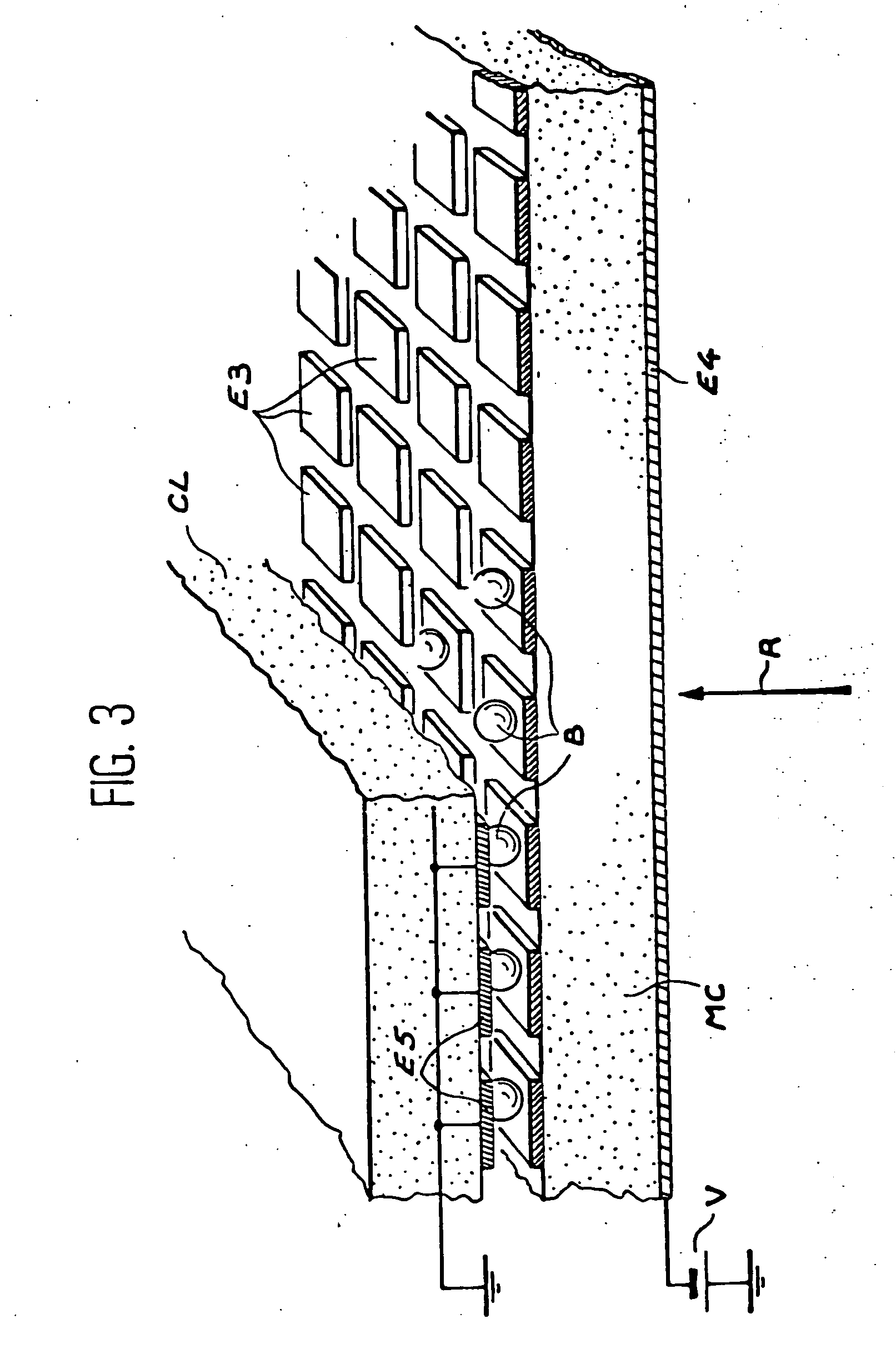
Device with stacked electrodes for detecting radiation and method of detecting ionizing radiation that uses such a device
InactiveUS20070001122A1Enhance the imageEasy to produceSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectron holeCapacitance
This device for detecting ionizing radiation has a stacked structure comprising a first set of electrodes, a sensing element capable of interacting with the incident radiation to be detected by releasing mobile charges (electron-hole pairs) and a second set of electrodes, said first and second sets being intended to collect the mobile charges thus released. This stack also comprises a third set of electrodes intended to measure the charges induced by movement of the mobile charges, the electrodes in said third set being separated from those that constitute said second set by an electrically insulating layer defined so as to enable capacitive connection between the electrodes of said second set and the electrodes of said third set.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Semiconductor photosensor for infrared radiation
ActiveUS20150280047A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMobile chargeParticle physics
A photosensor for the detection of infrared radiation in the wavelength range of 1 to 1000 micrometers consists of a semiconductor substrate with a highly doped interaction volume for the incoming radiation. At the edge of this highly doped region, an extended gate electrode is placed consisting of a conducting material on top of an insulating layer. On the other side of the gate electrode, another highly doped semiconductor region is placed, acting as a charge collector. Through free carrier absorption in the interaction volume, incoming photons impart their energy on mobile charge carriers. In the case of free electrons, the gate electrode is biased slightly below the reset voltage of the interaction volume, so that the electrons carrying the additional energy of the absorbed photons can predominantly make the transition from the interaction volume across the gate electrode area to the charge collector volume.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Pulse shape discrimination method and apparatus for high-sensitivity radioisotope identification with an integrated neutron-gamma radiation detector
InactiveUS7388206B2Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacteristic energyGamma energy
A method and apparatus for discriminating the types of radiation interacting with an integrated radiation detector having of a pulse-mode operating photosensor which is optically coupled to a gamma-ray scintillator sensor and a neutron scintillator sensor and uses an analog to digital converter (ADC) and a charge to digital converter (QDC) to determine scintillation decay times and classify radiation interactions by radiation type. The pulse processing provides for, among other things, faithful representation of the true energy spectrum of the gamma radiation field and allows for radioisotope identification by searching for the presence of characteristic energy lines in the gamma energy spectrum. The pulse shape discrimination method ensures that the high sensitivity and resolution of the isotope identification function is not affected during operation in mixed neutron-gamma fields.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Radiation detector employing amorphous material
InactiveUS20080283762A1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmorphous metalMetal
A radiation detector is provided having an anode wire formed of an amorphous metal alloy. In one embodiment the radiation detector comprises a cathode assembly. The cathode assembly includes a main portion, a first end and a second end, where the first end opposes the second end. The cathode assembly also includes a radiation interacting material. An anode extends within the cathode assembly from the first end to the second end, and the anode is comprised of an amorphous metal alloy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High resolution gamma measurements and imaging
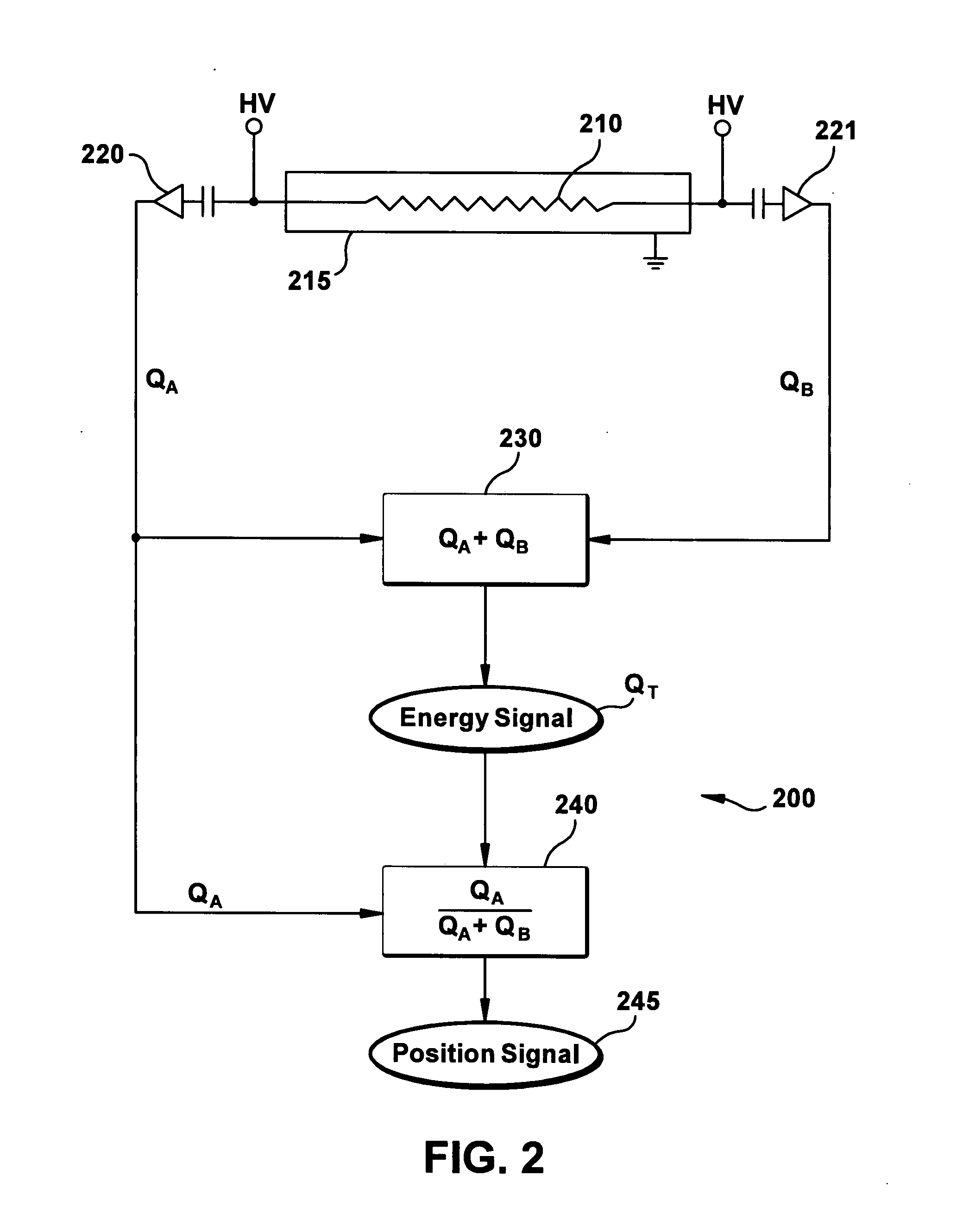
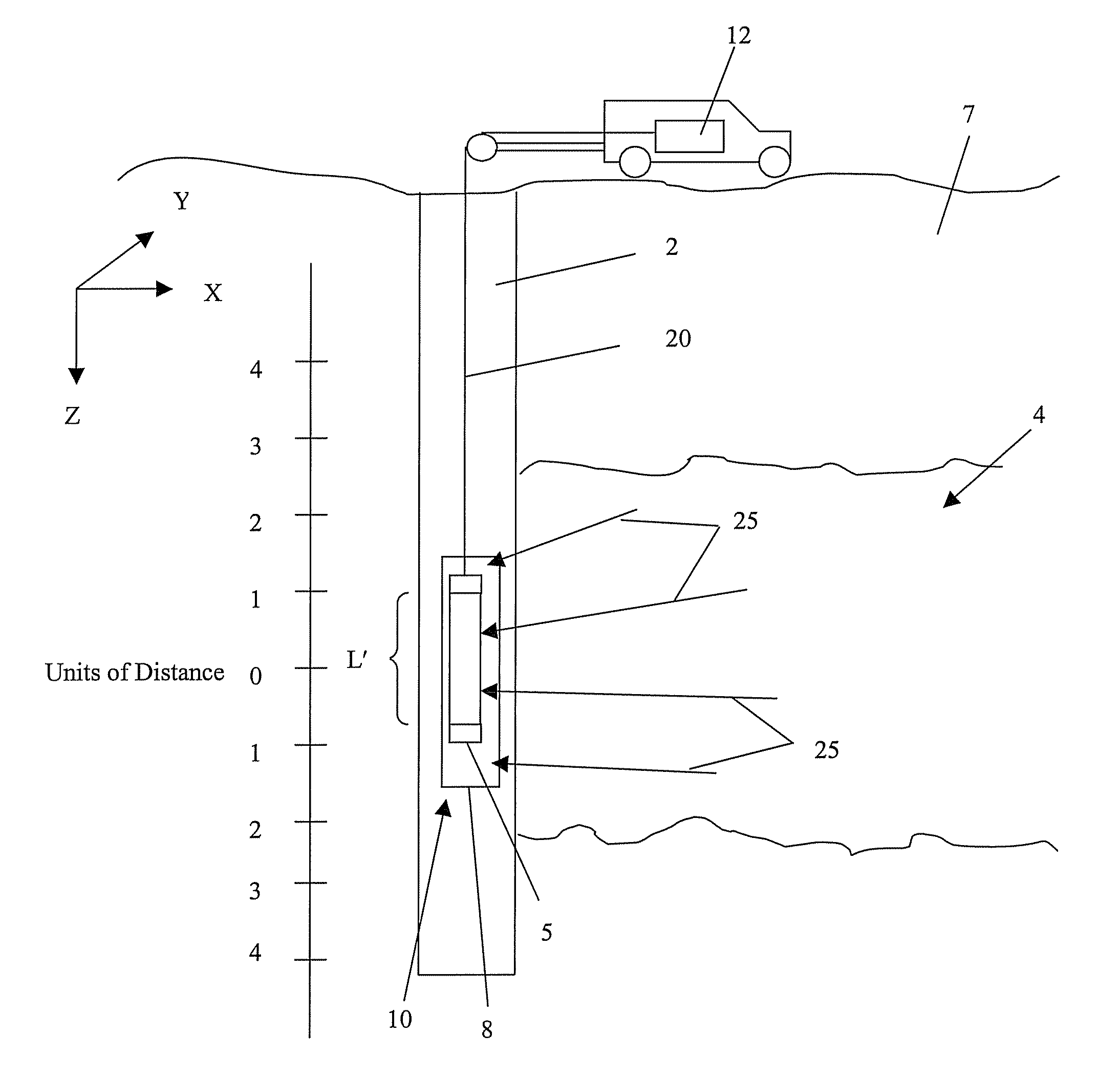
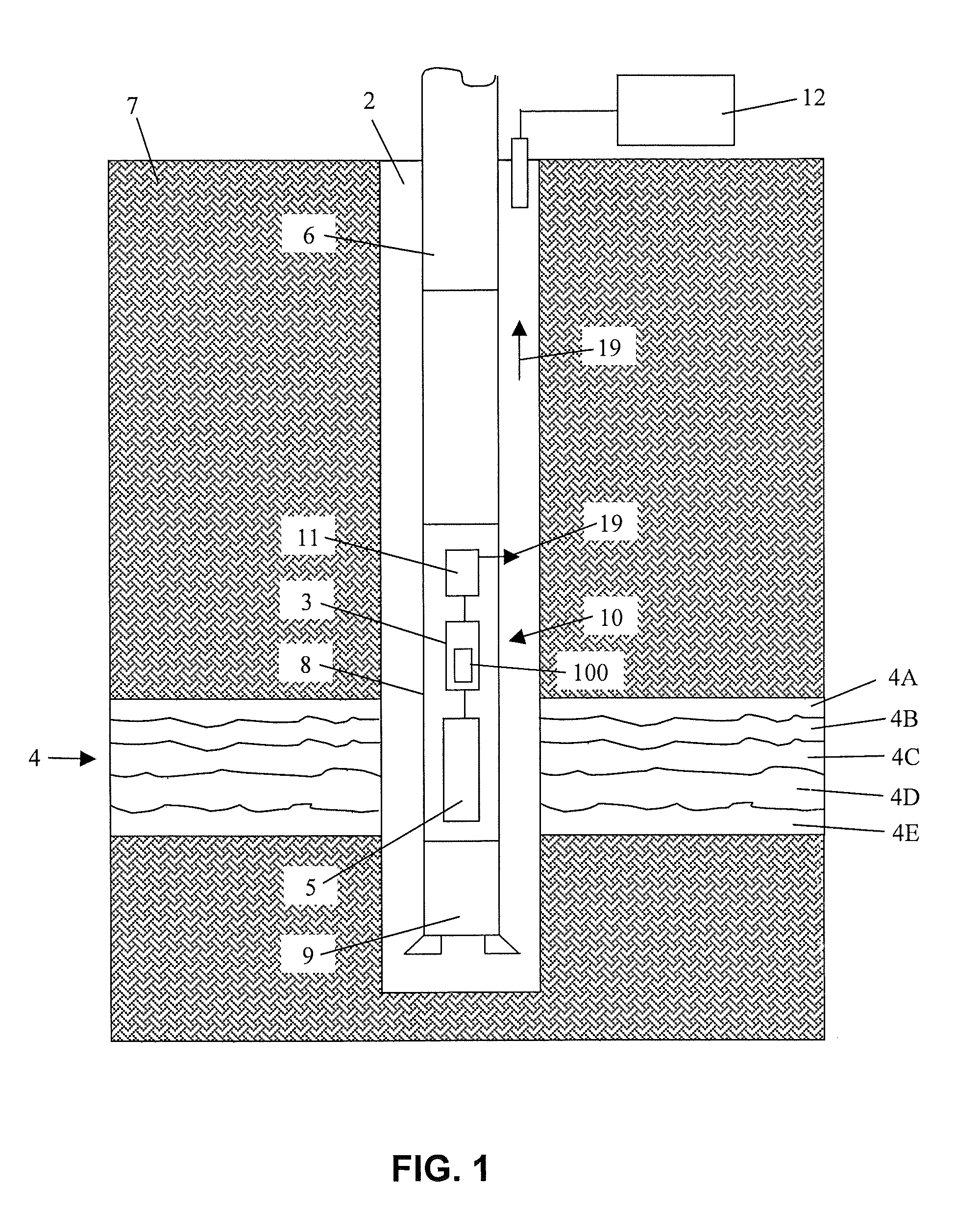
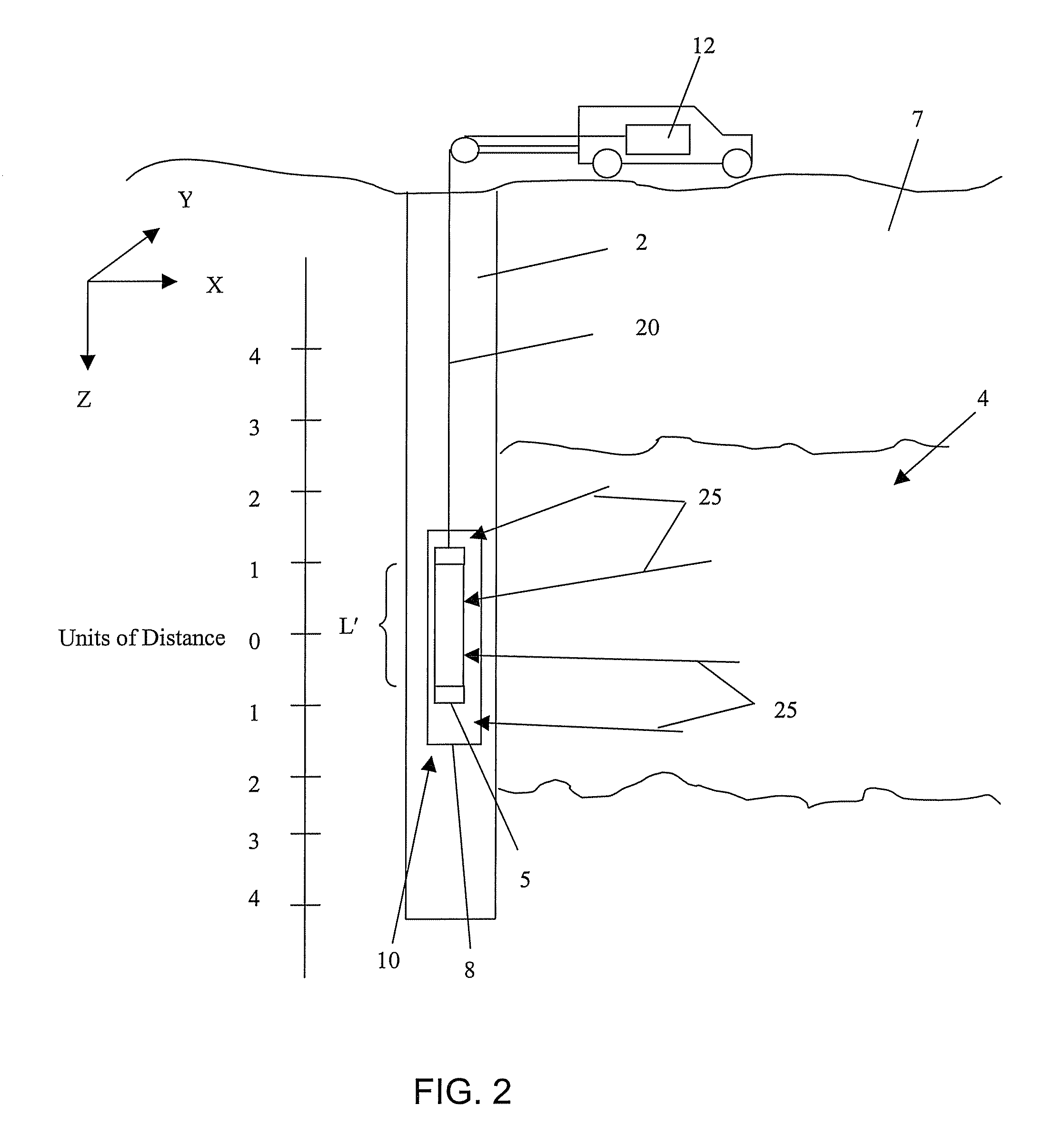
A method for measuring radiation in a borehole, the method including placing a detector comprising a scintillator and a plurality of photodetectors in the borehole; detecting a radiation interaction with a first photodetector; detecting the radiation interaction with at least a second photodetector; and determining a location of the interaction from the detecting; wherein the location provides information regarding formations surrounding the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Preclinical SPECT system using multi-pinhole collimation
InactiveUS7579600B2Material analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImage resolutionScintillator
A preclinical nuclear imaging detector system, including a gantry and one or more detector assemblies, each including a scintillator configured to interact with radiation emanating from a target test object being imaged and at least one pinhole collimator, having one or more pinhole apertures formed therein. The pinhole collimator is disposed between the target object and the scintillator, wherein a distance between the pinhole aperture and the scintillator is selected as a function of the number of pinhole apertures provided in the collimator and to optimize one of sensitivity or spatial resolution, such that the one or more pinhole apertures collectively project a unitary minified radiation image of the target object onto the scintillator. Further, one or more photosensors are optically coupled to the scintillator to receive interaction events from the scintillator.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
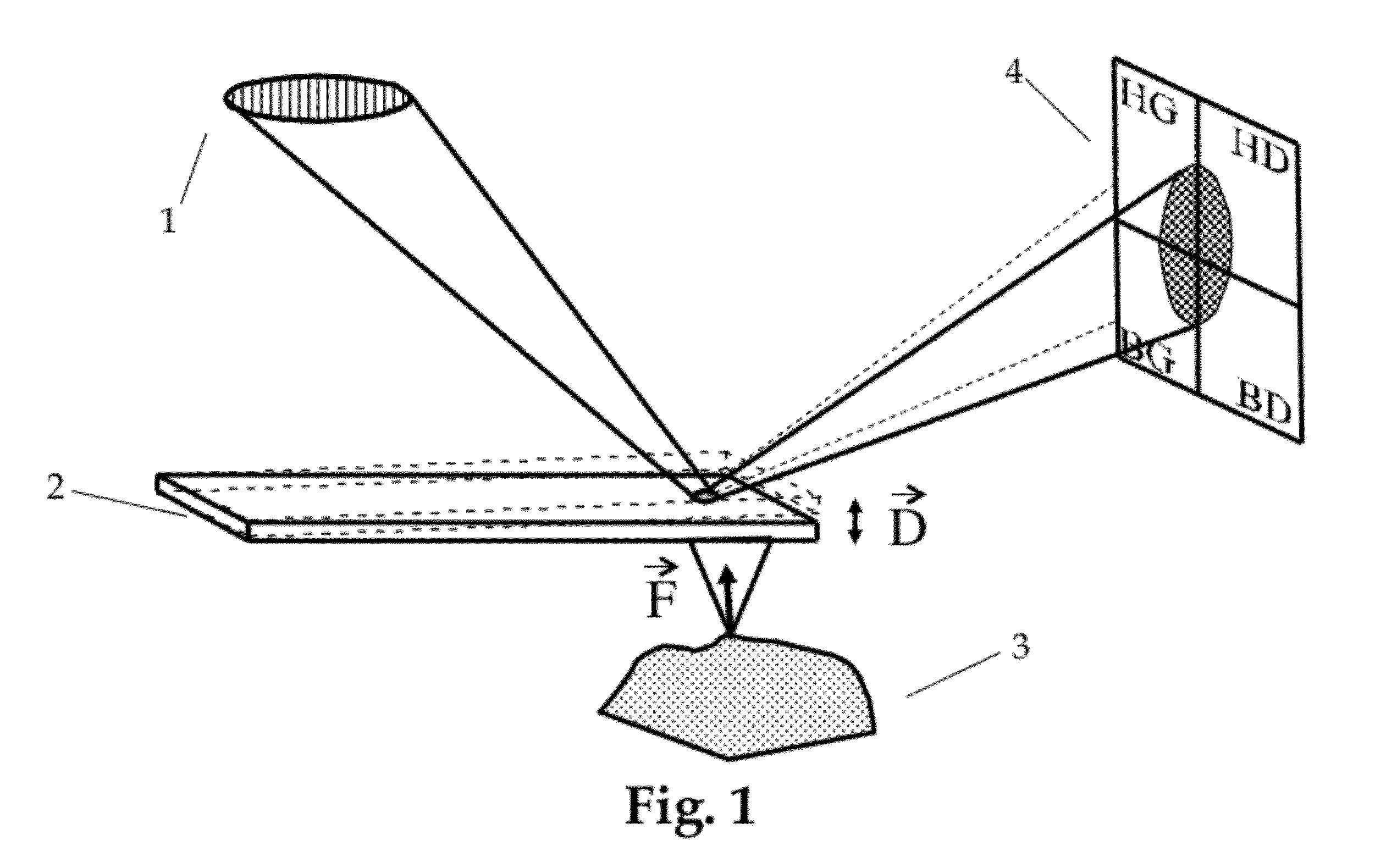
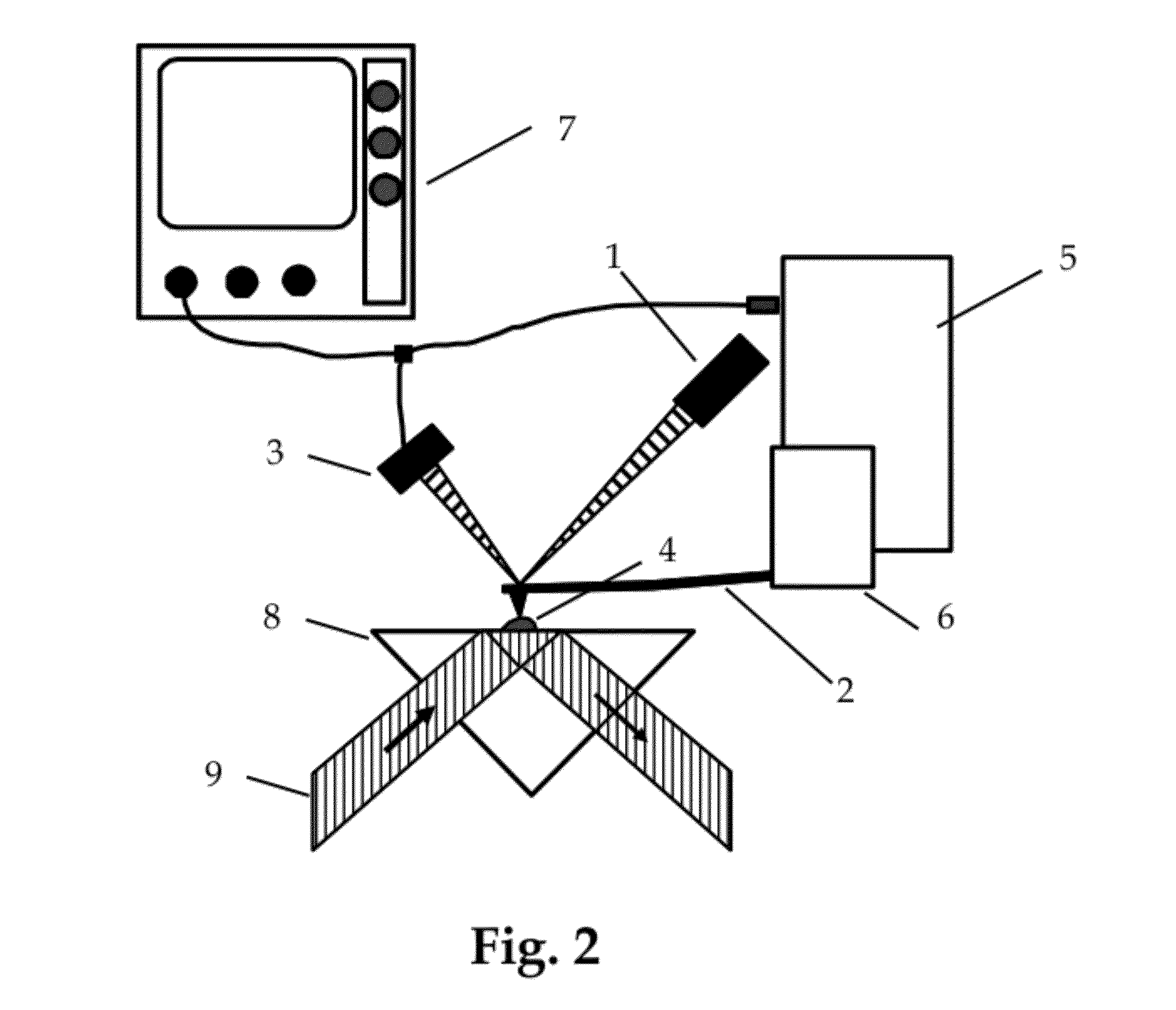
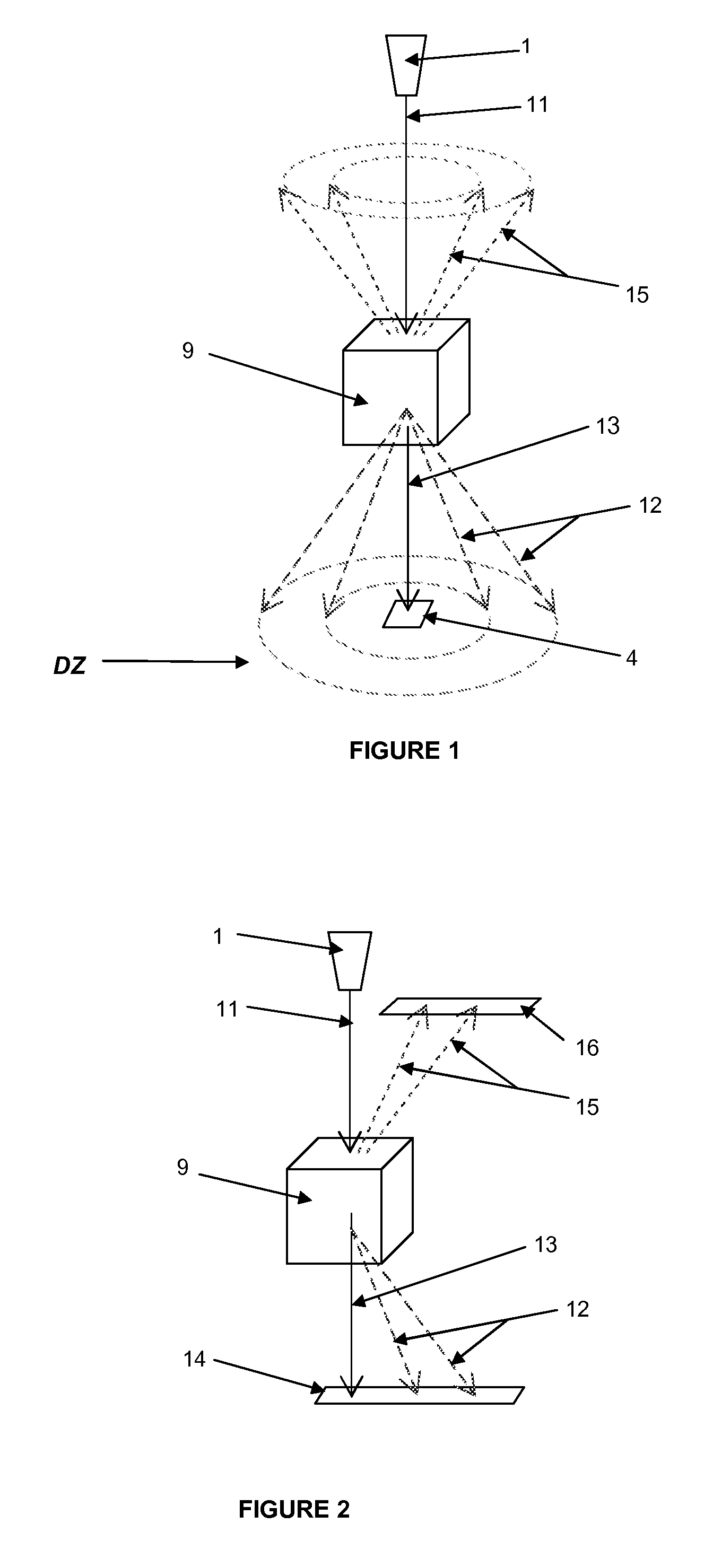
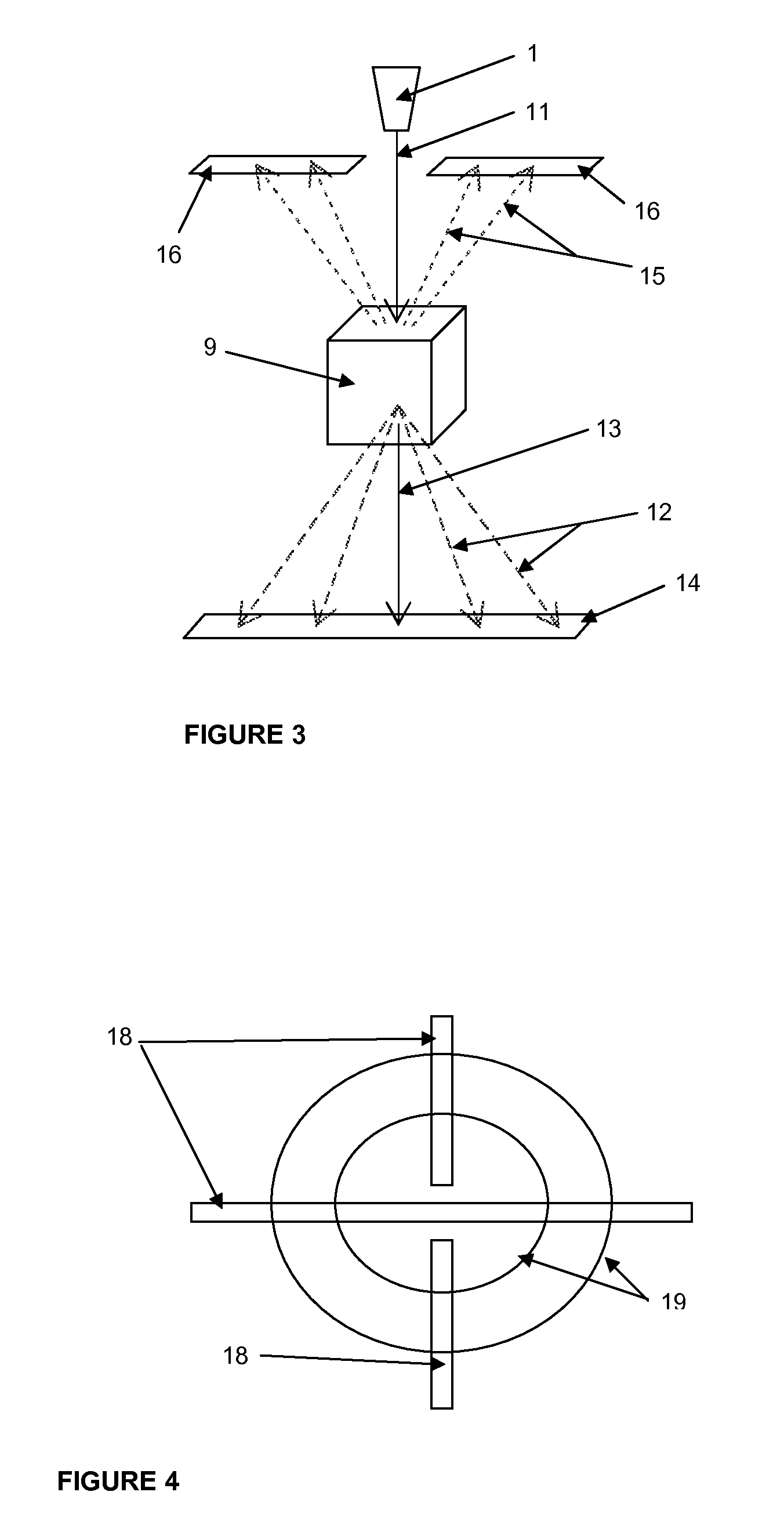
Apparatus and method for characterisation of materials
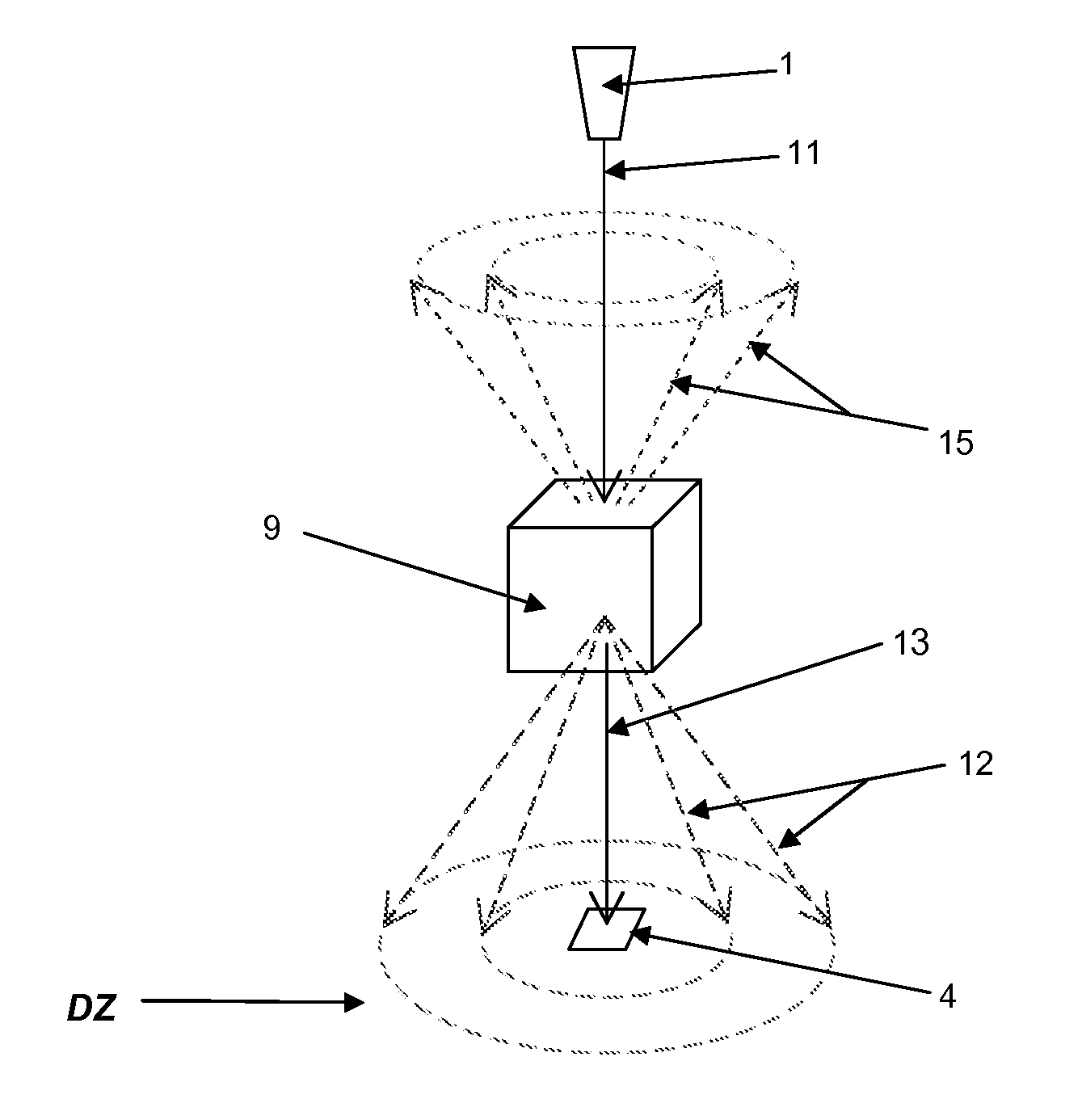
ActiveUS8781072B2Simple materialThe recognition effect is accurateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNuclear radiation detectionForward scatterUltimate tensile strength
An apparatus and method are described for obtaining radiation interaction data from an object to enable better determination of the composition of the object. A radiation source and a radiation detector system are used to collect both transmitted and scattered radiation, preferably including radiation from at least one forward scatter mode. The detector system is capable of detecting and collecting spectroscopically resolvable information about incident radiation. Each intensity dataset is resolved across at least three of energy bands within the spectrum of the source, and this data may then be processed numerically to enable better determination of the composition of the object.
Owner:KROMEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com