Patents
Literature
111 results about "Radio signal strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
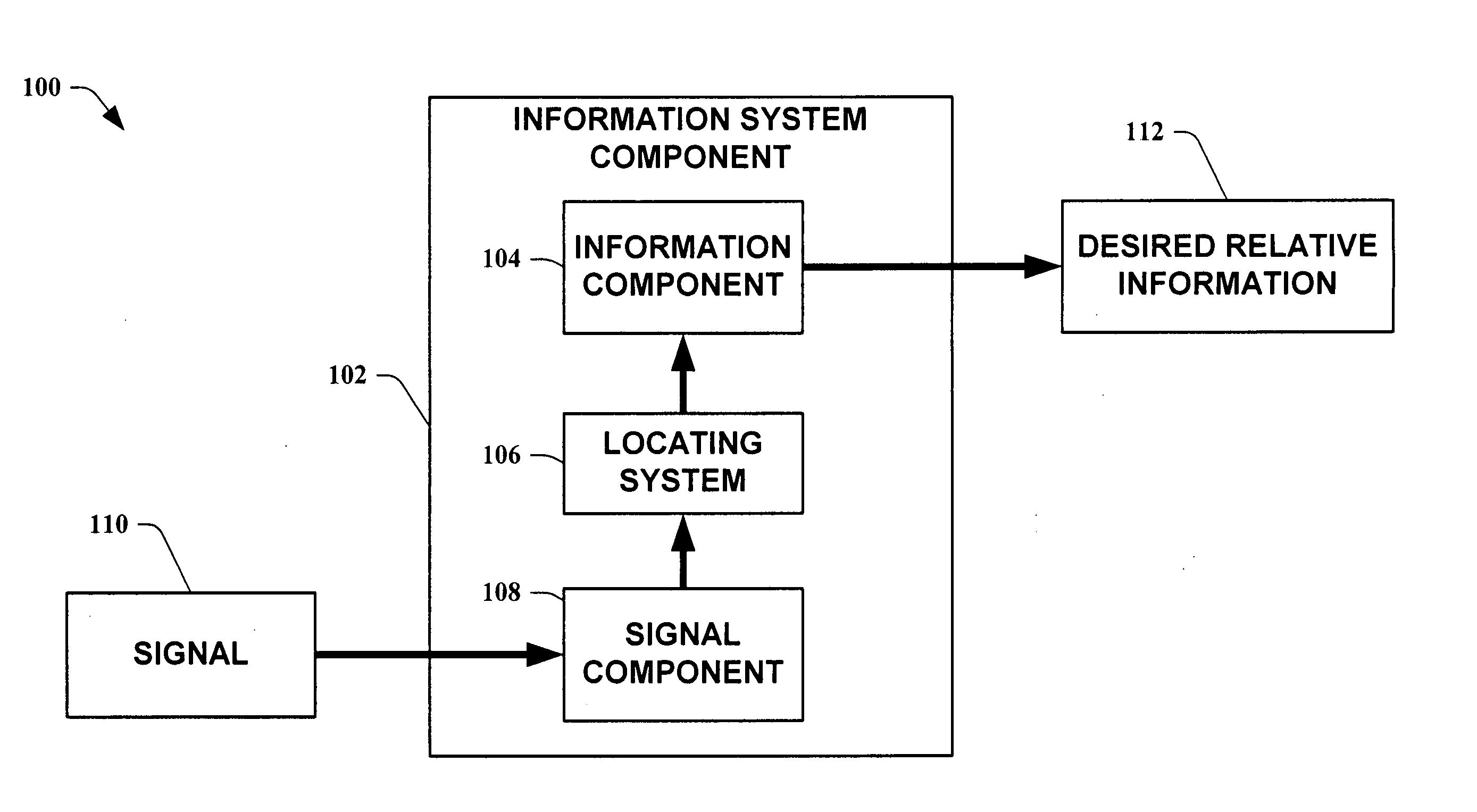
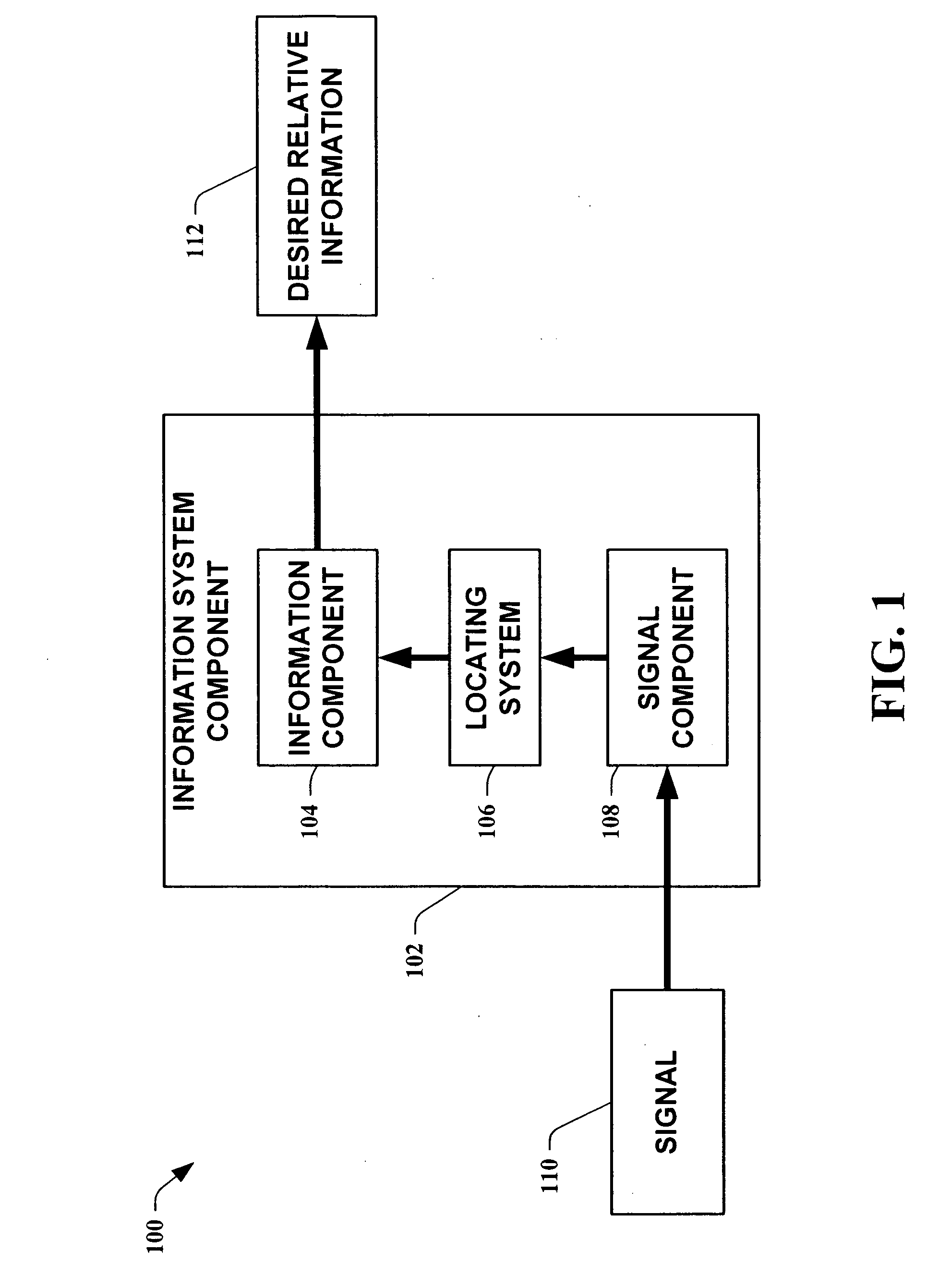
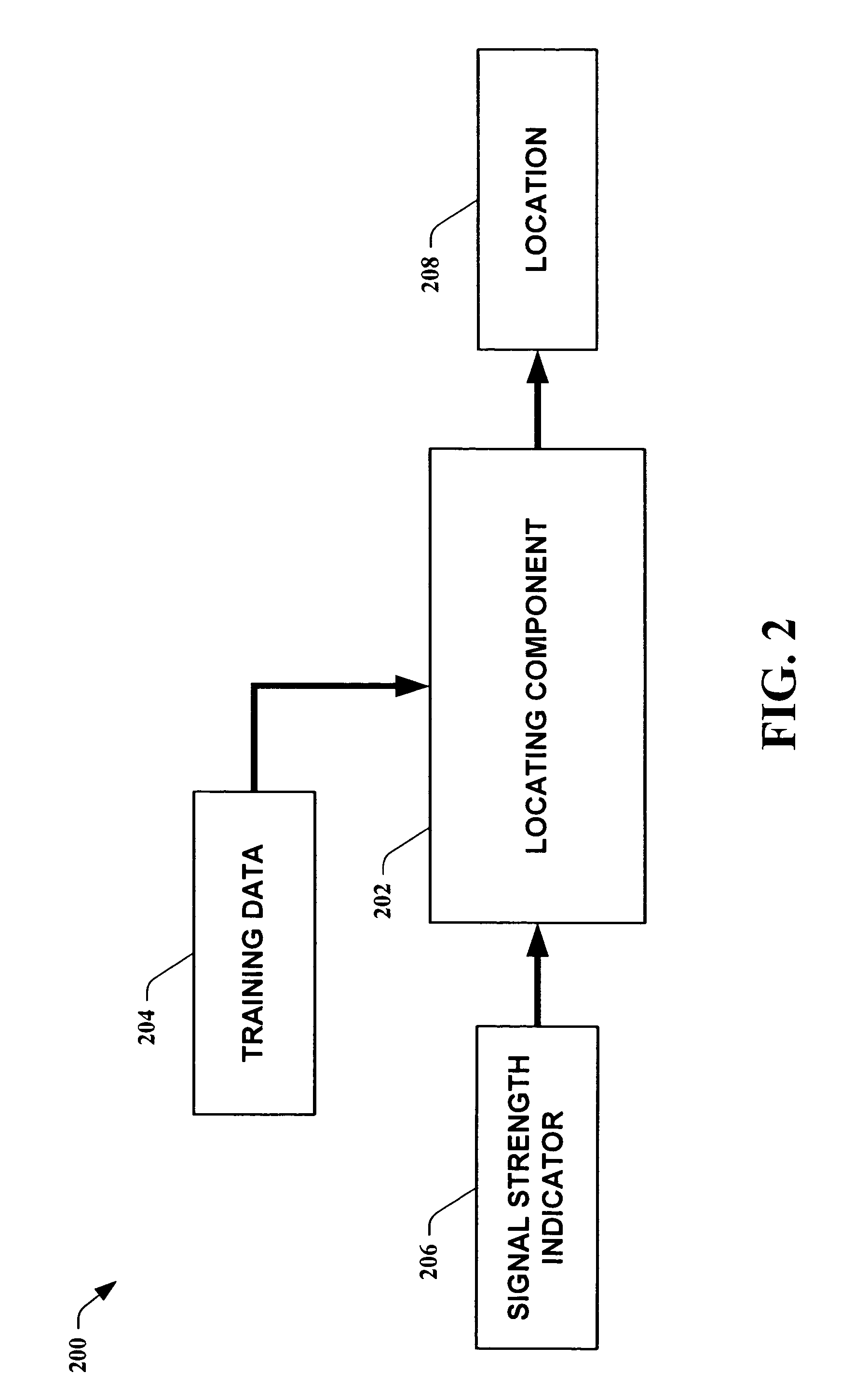
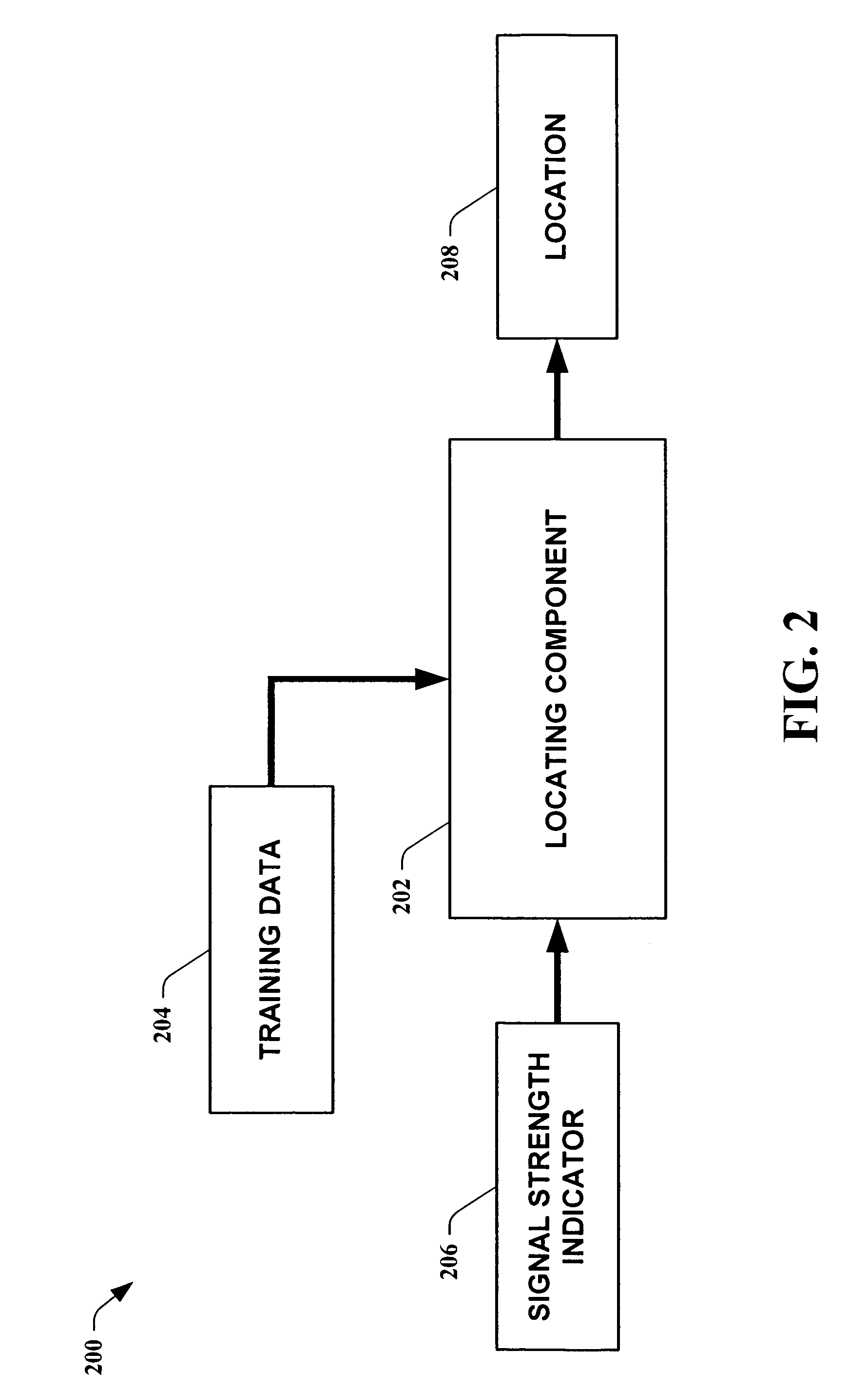
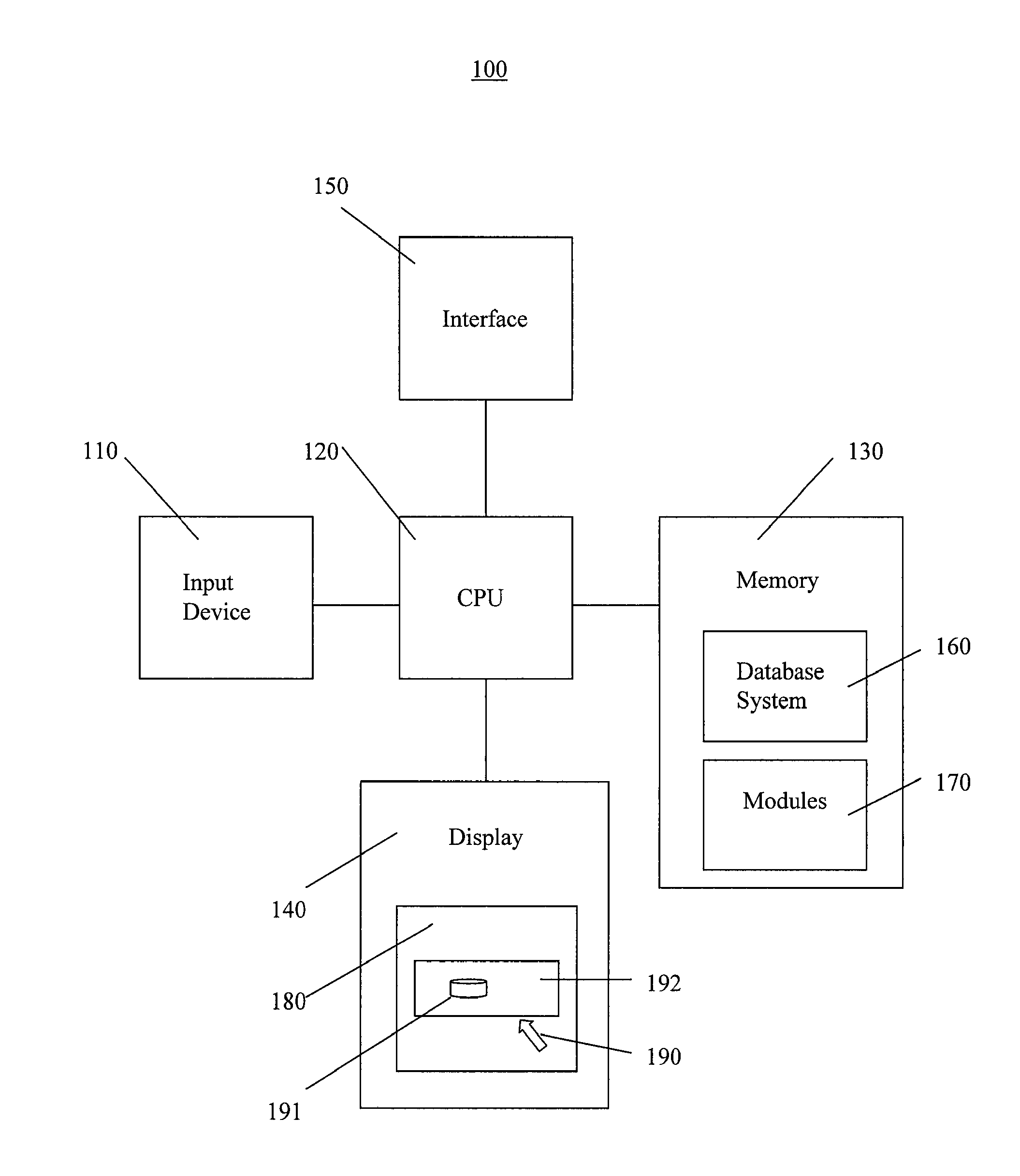
Methods for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS20050020278A1Facilitates approximationSubstantial accuracy in determining locationRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationAlgorithmLocation Equipment
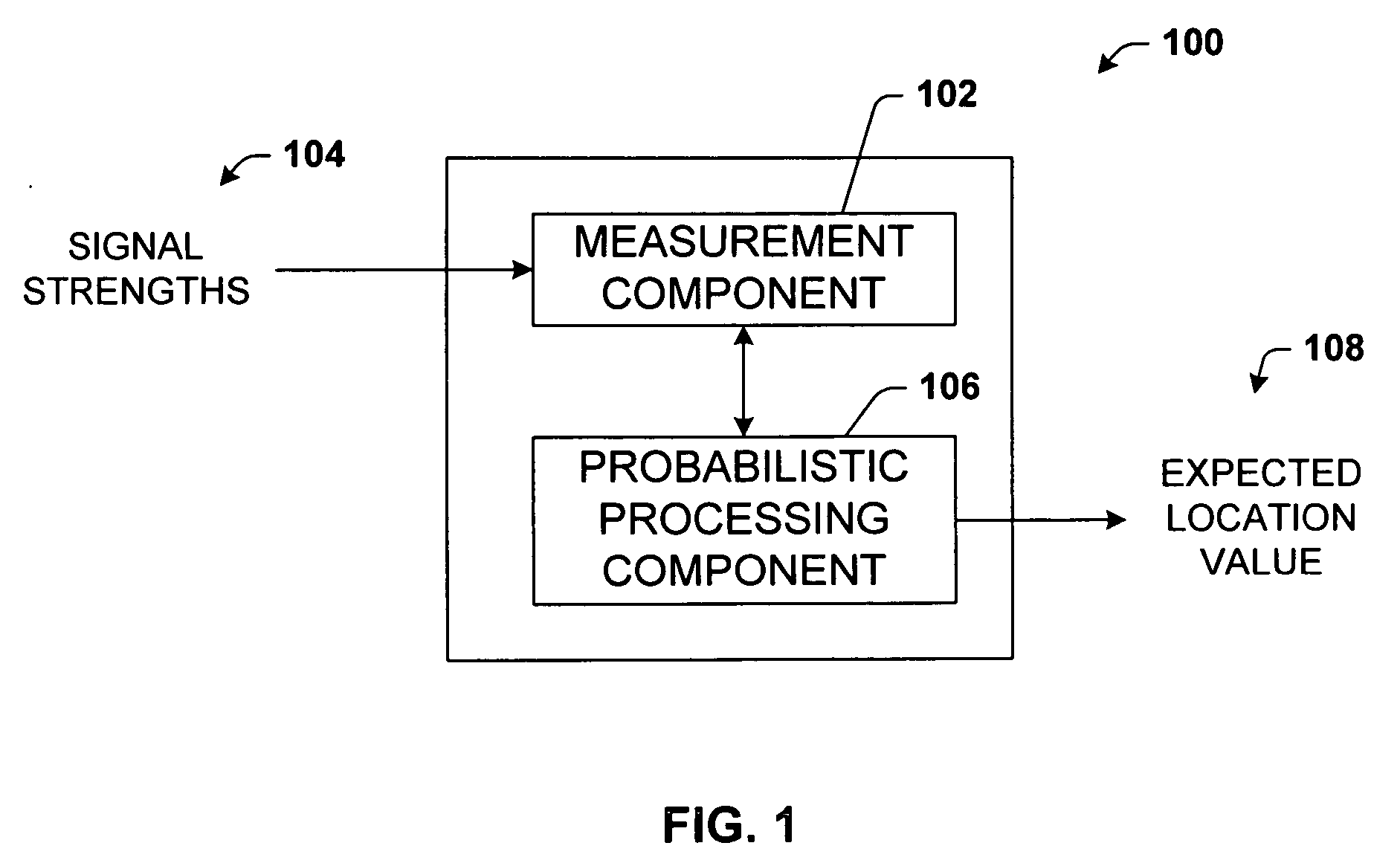
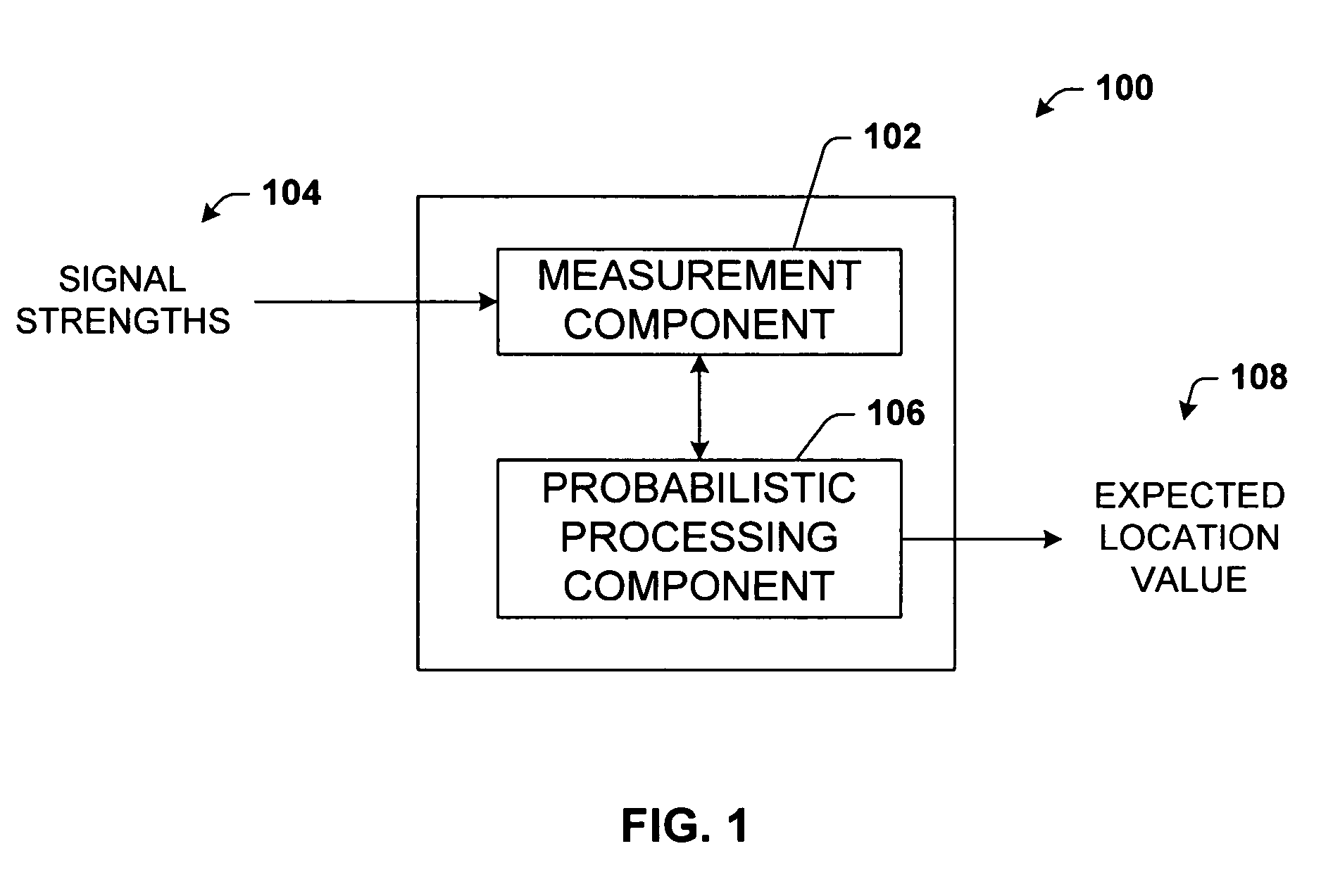
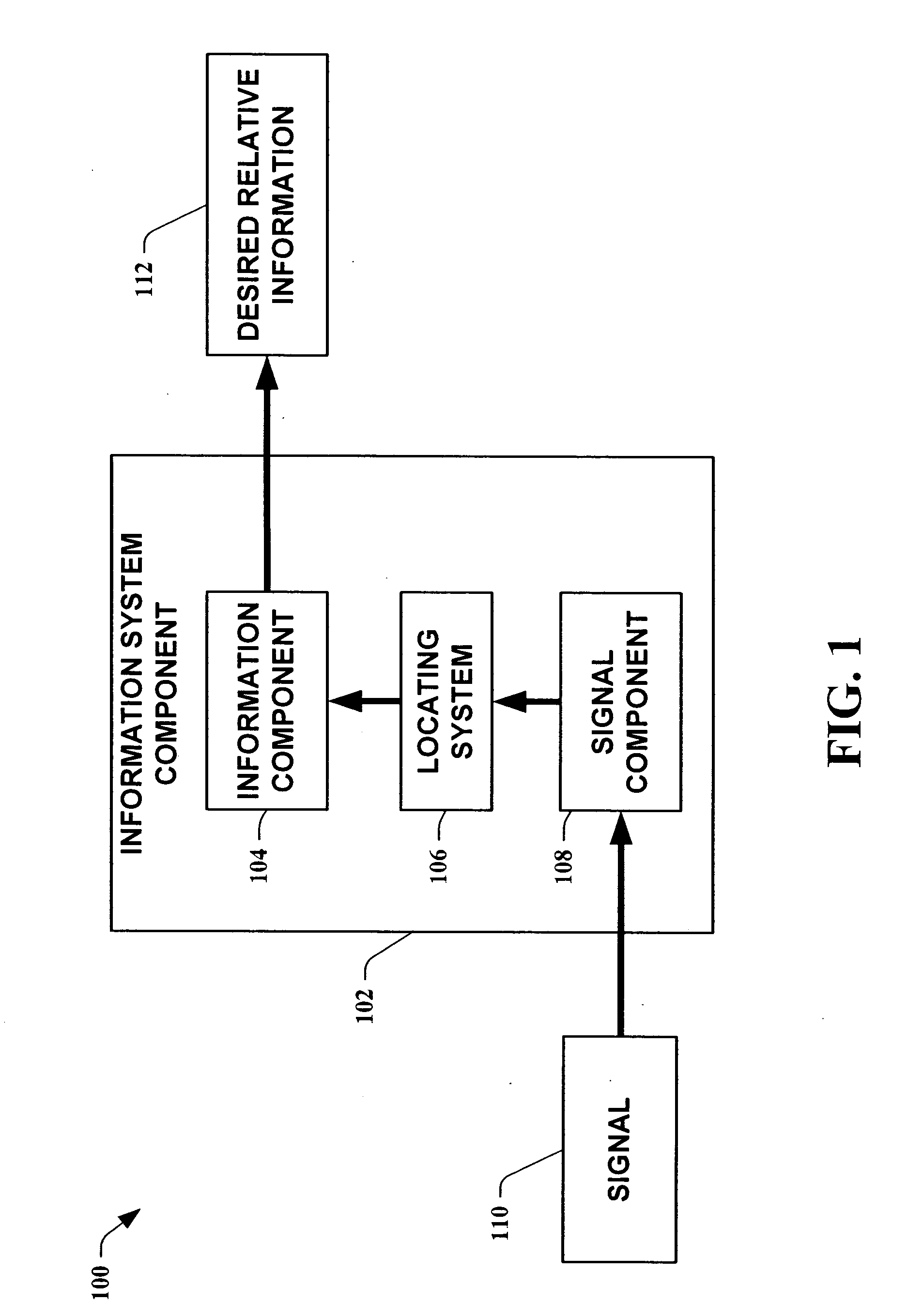
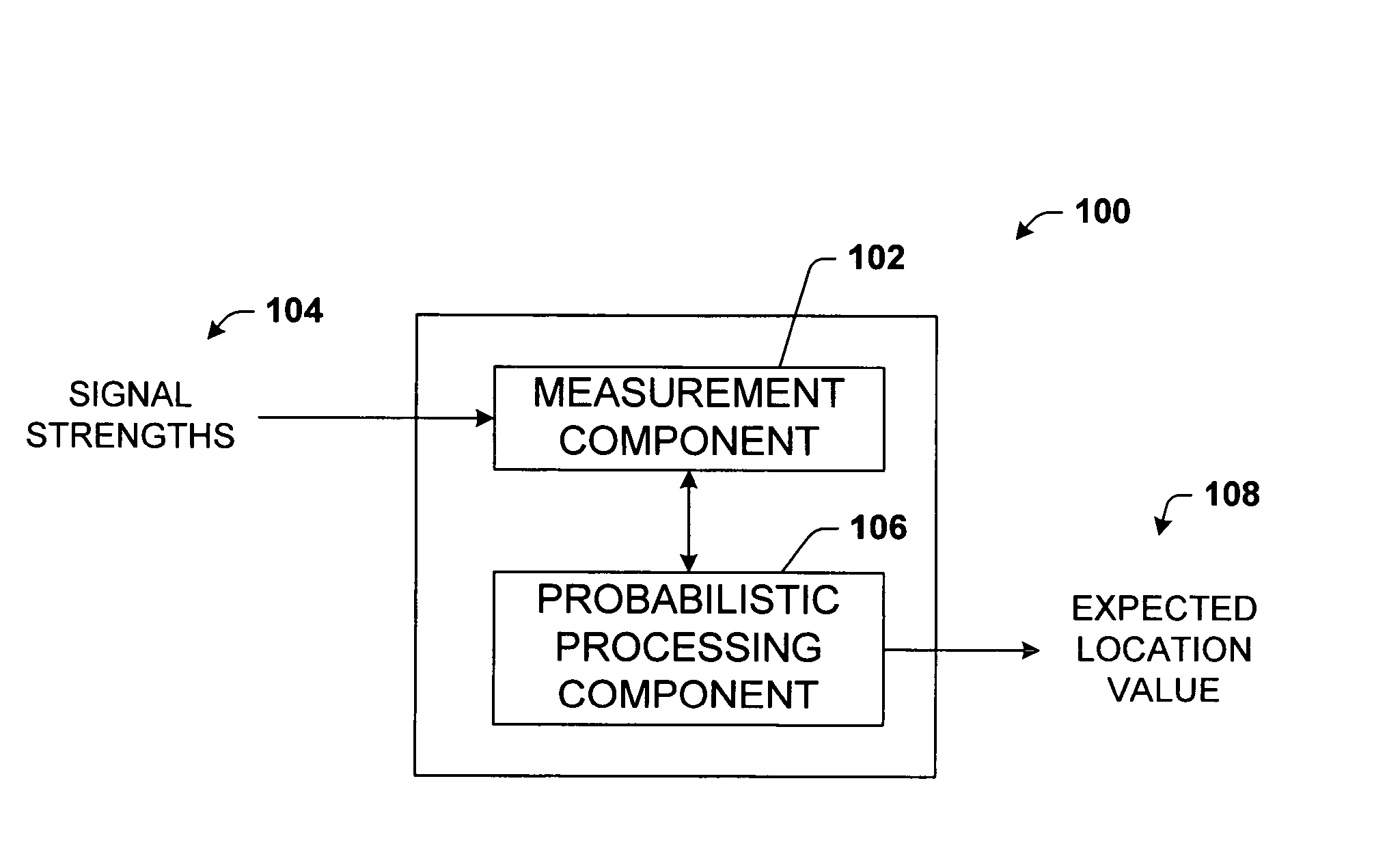
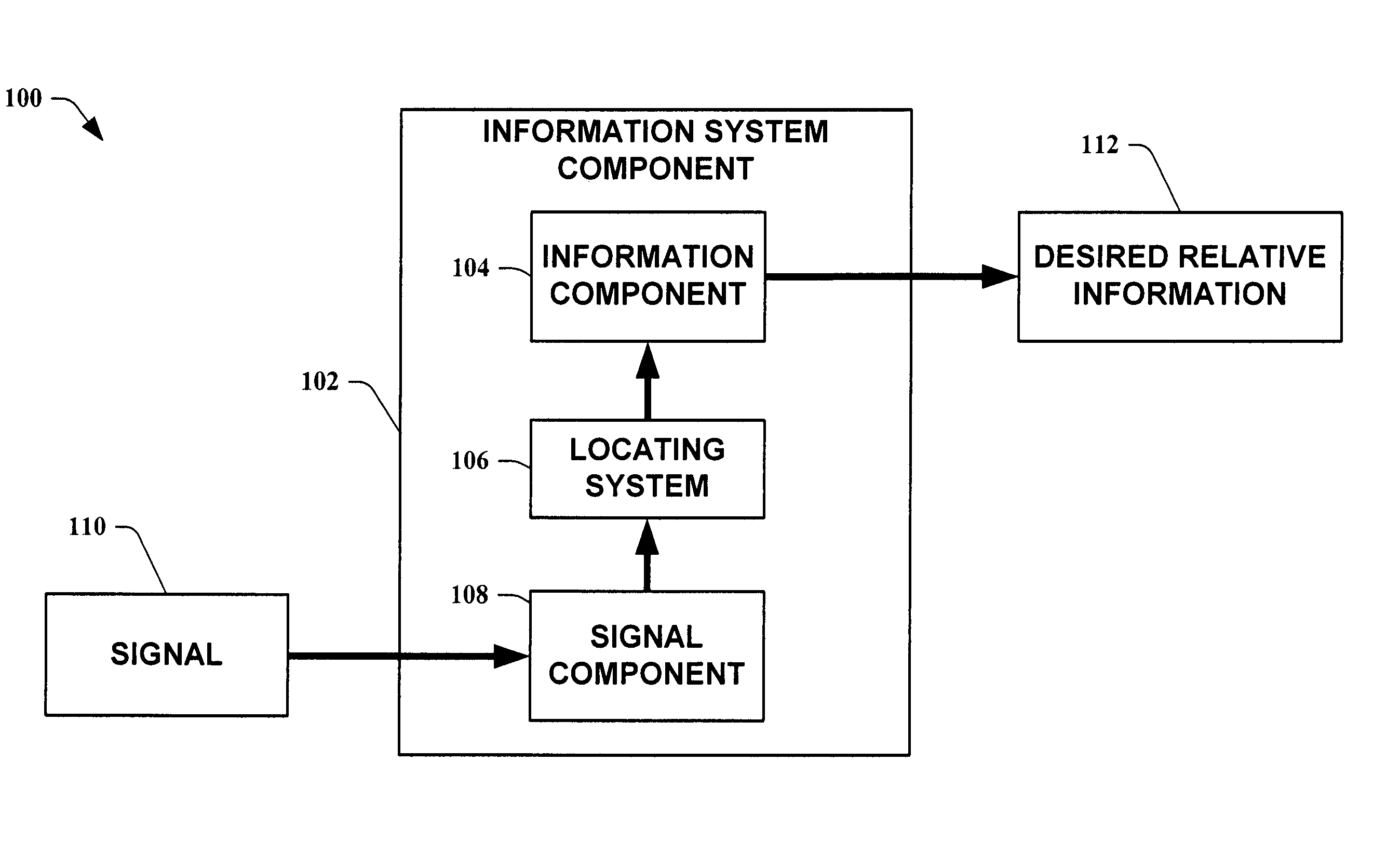
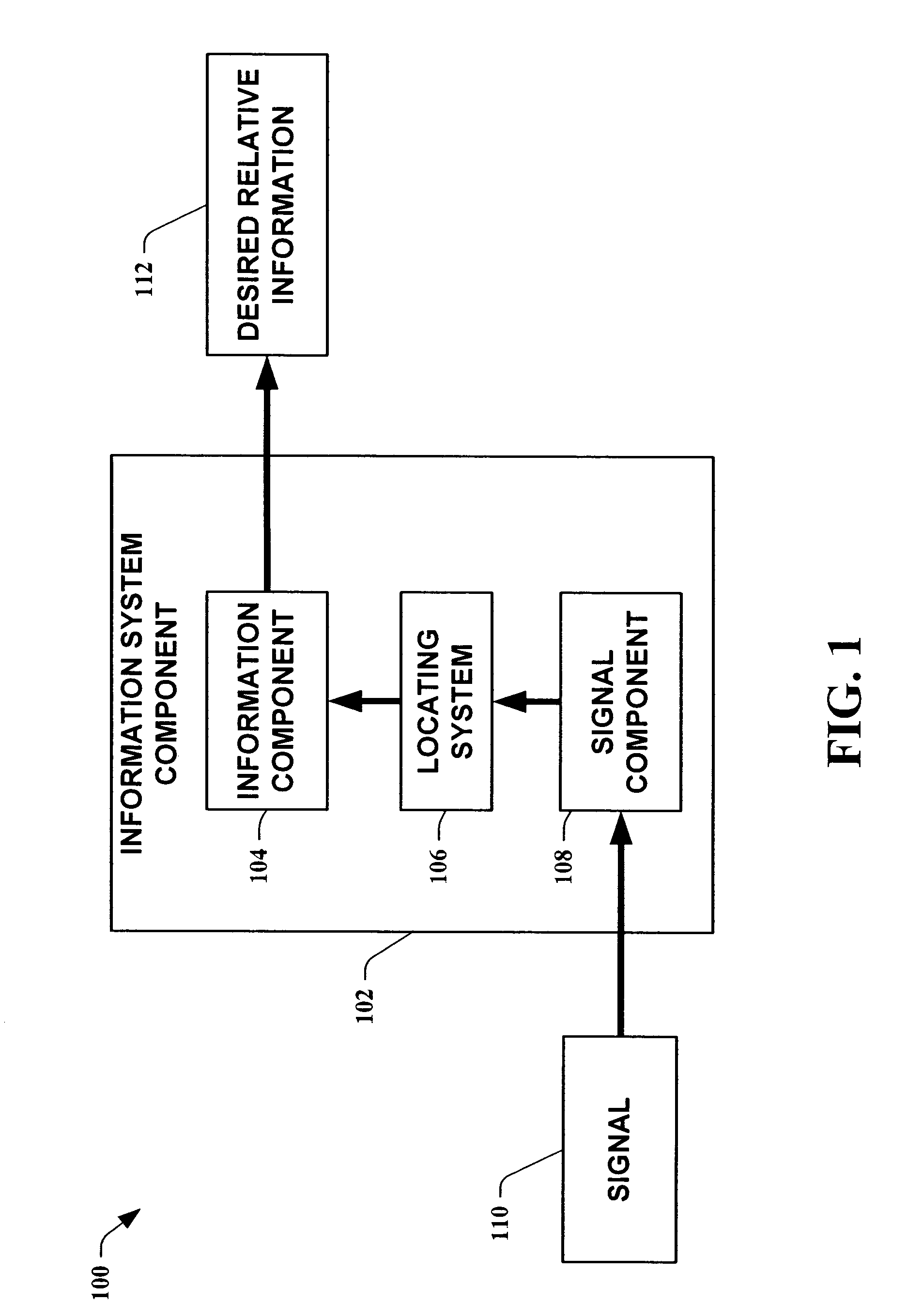
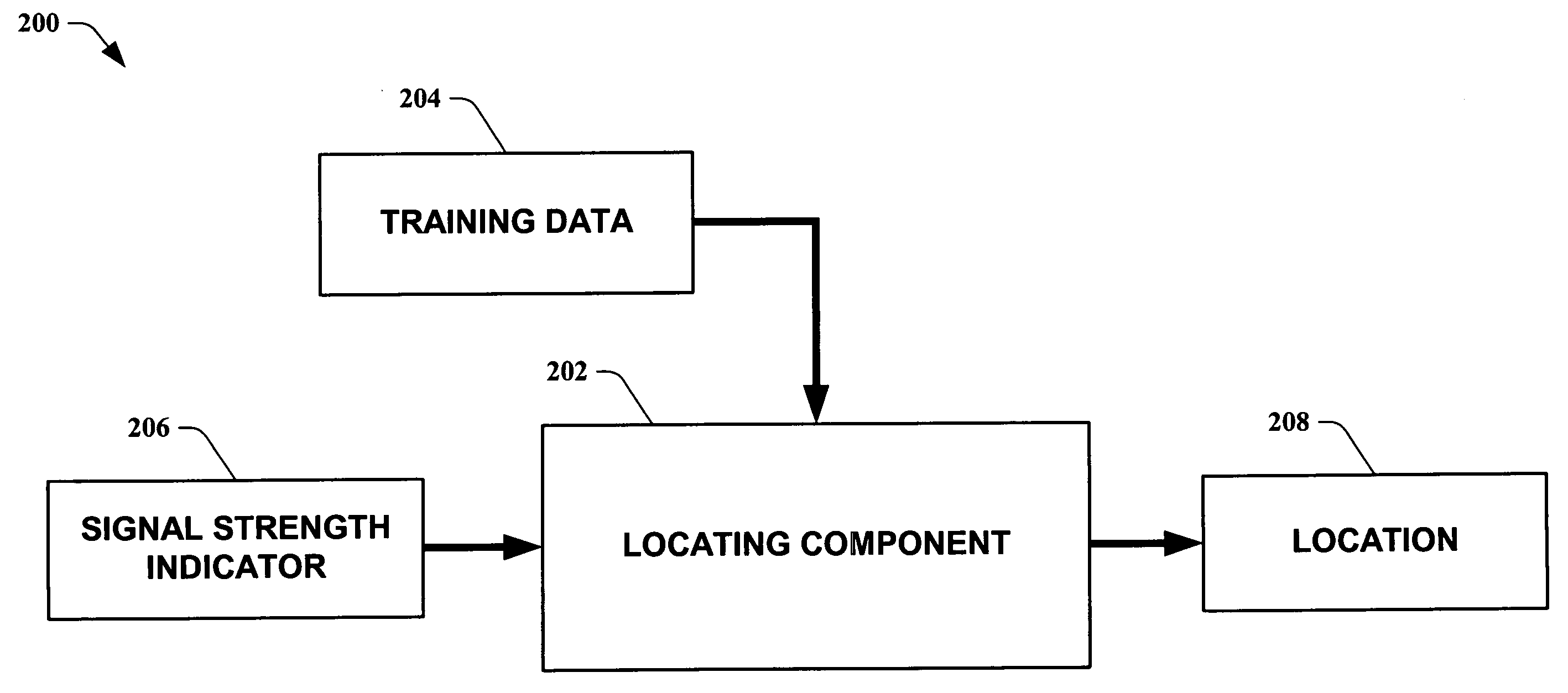
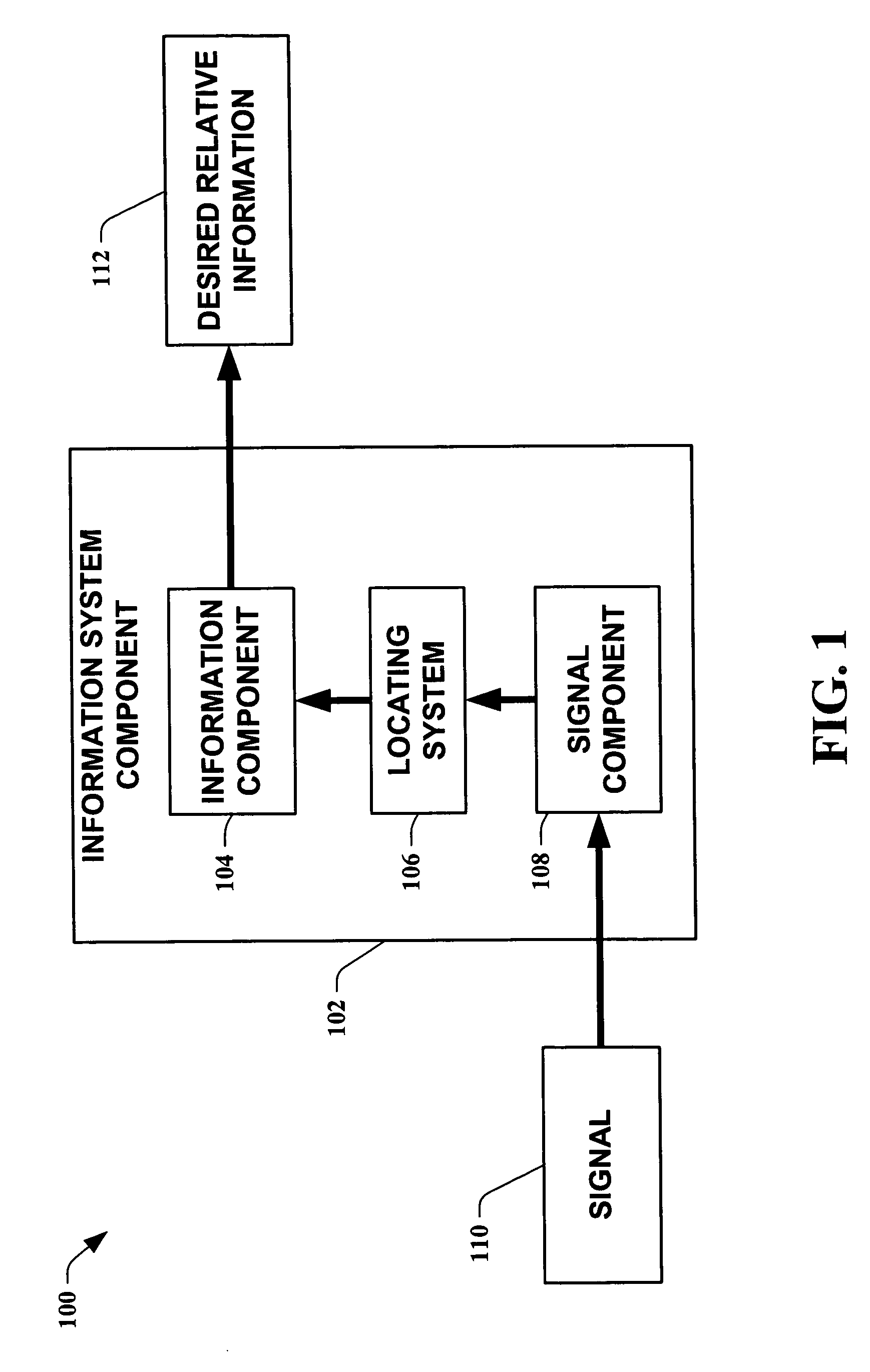
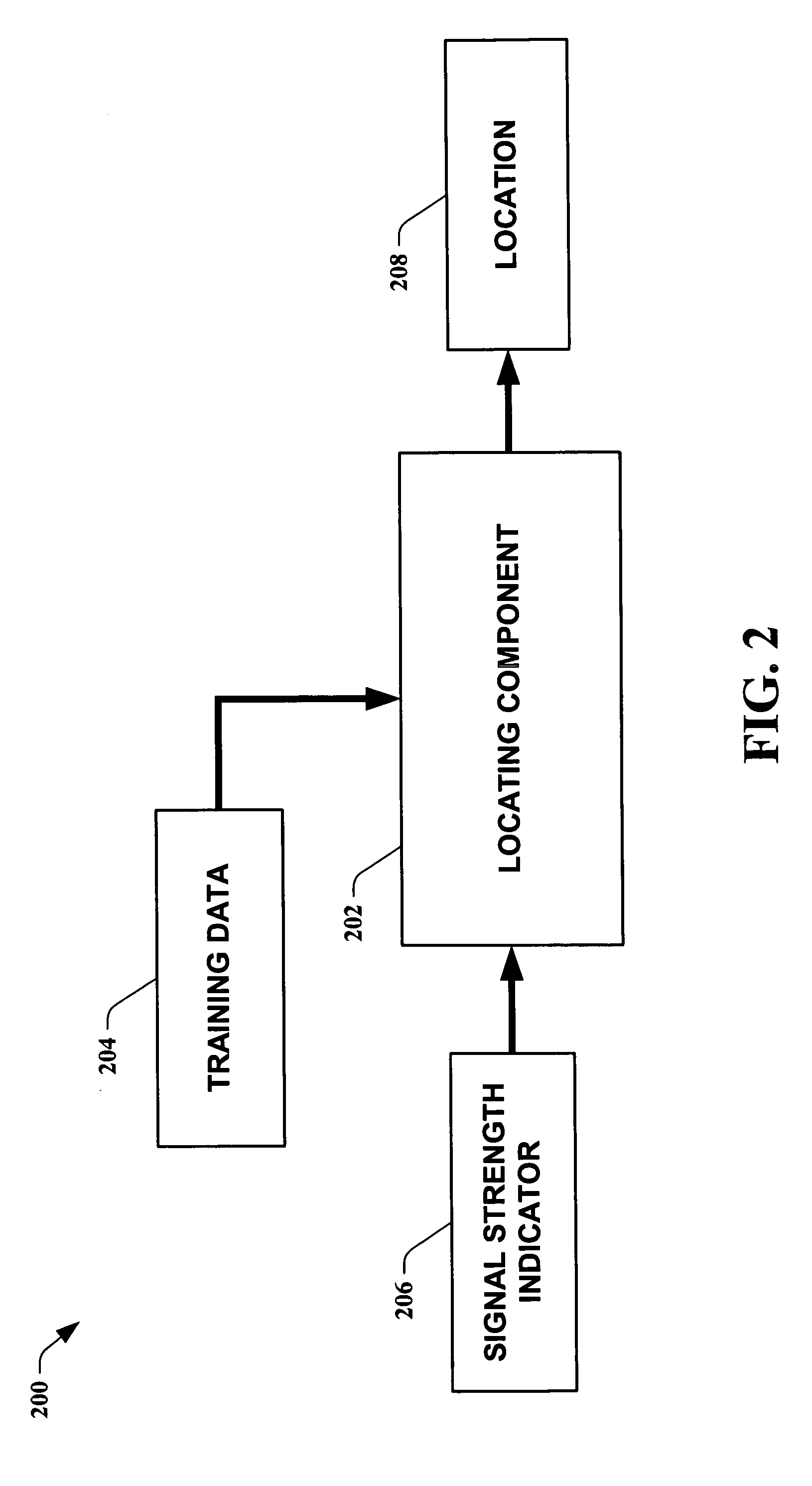
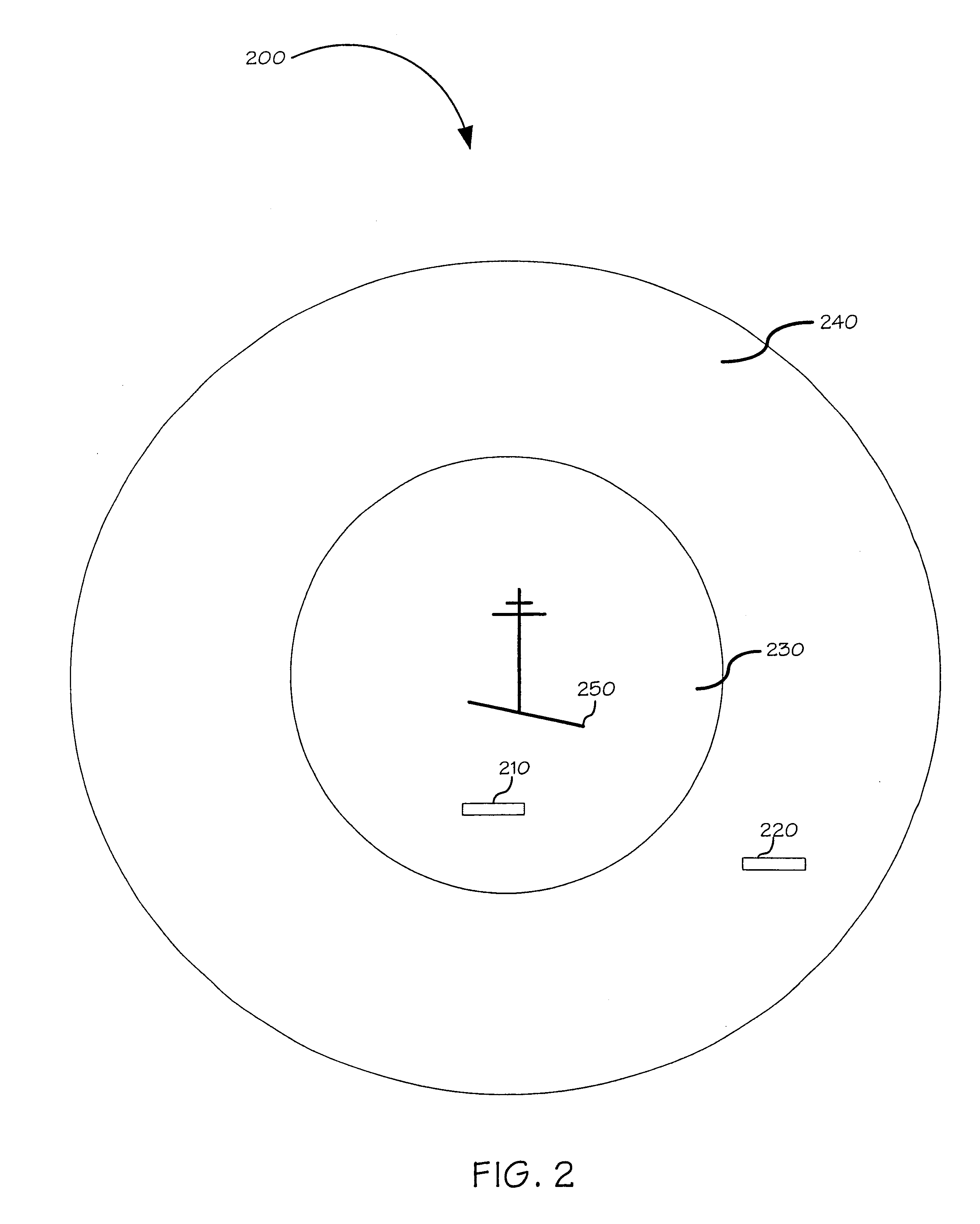
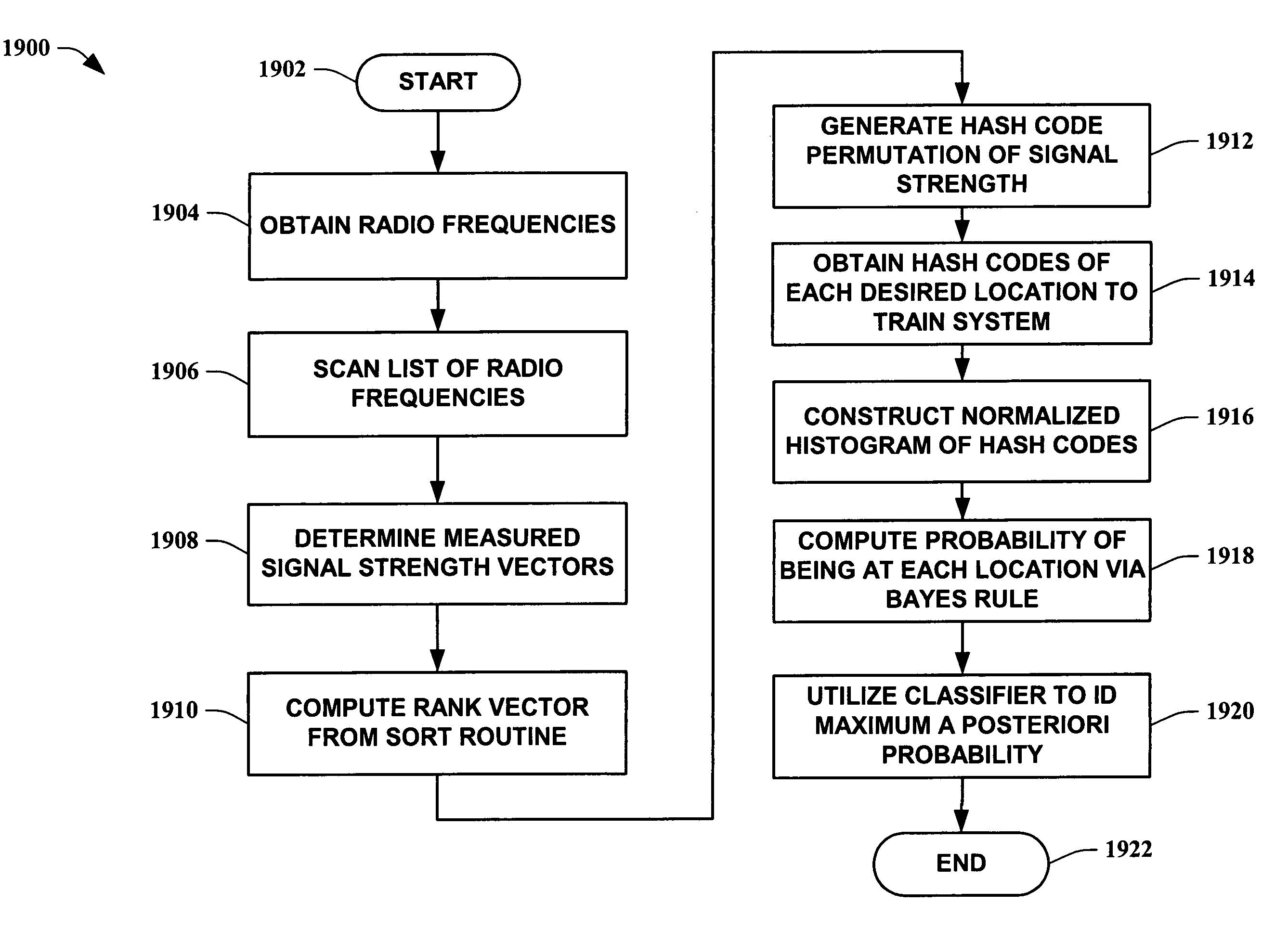
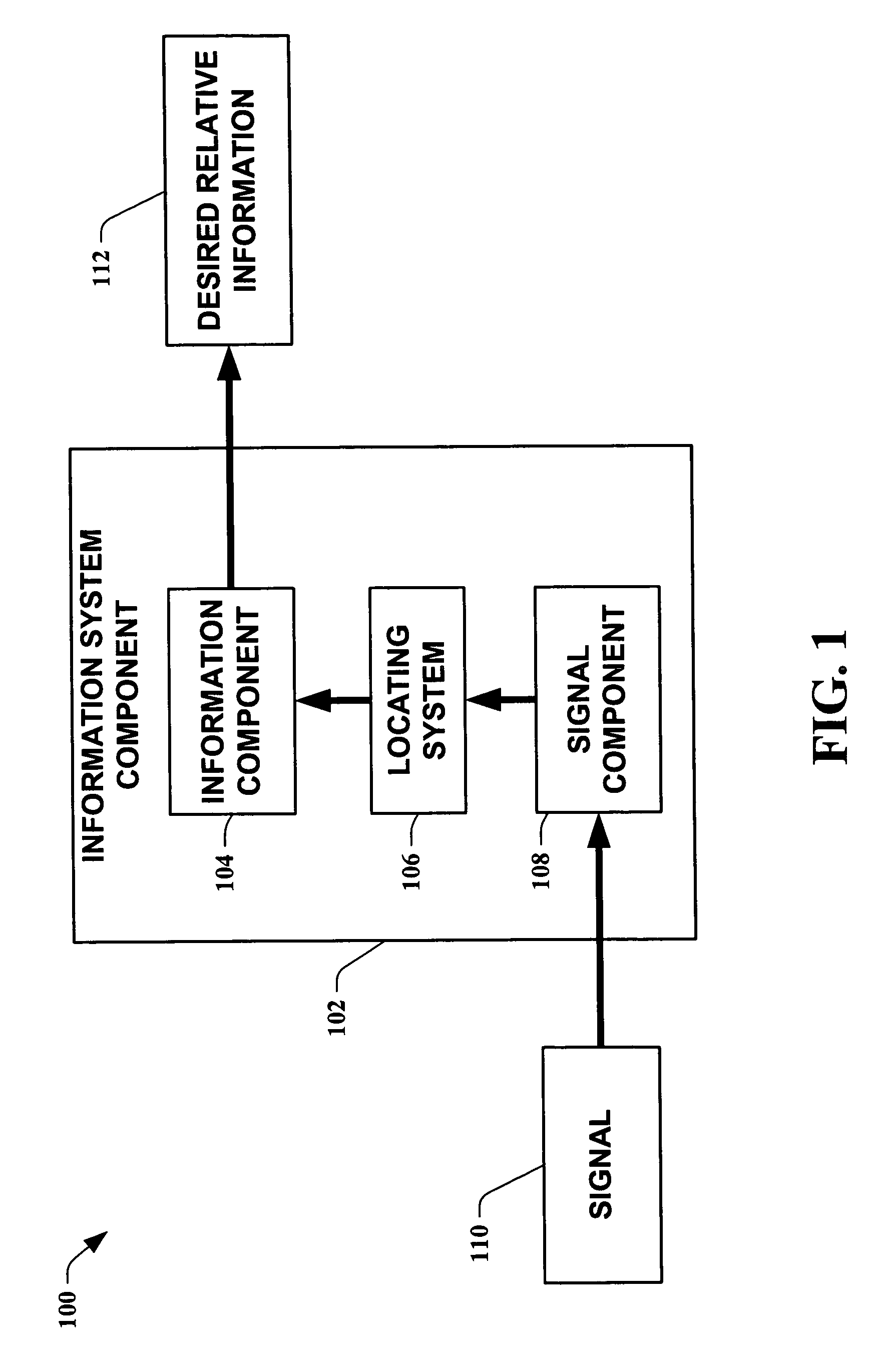
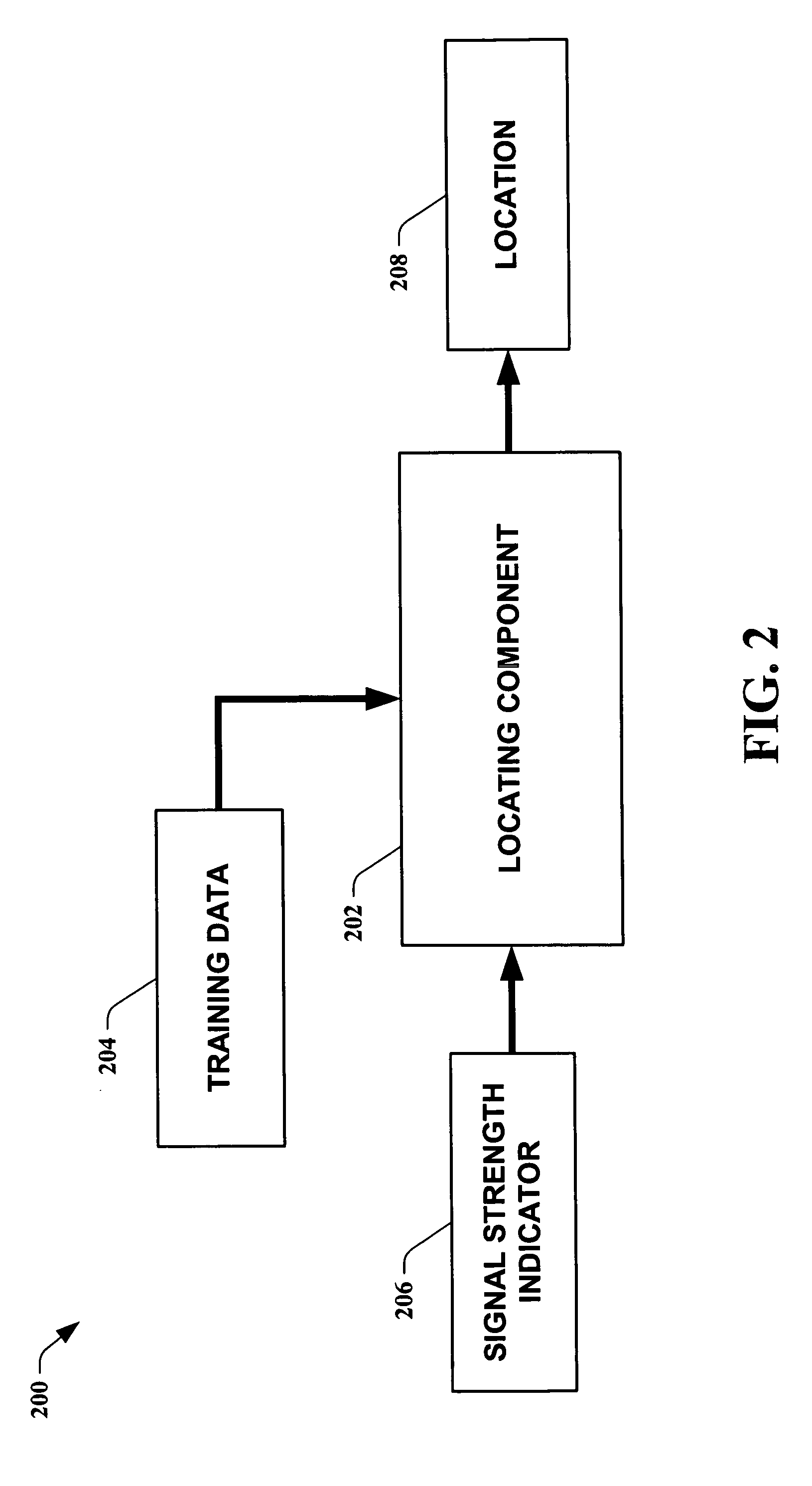
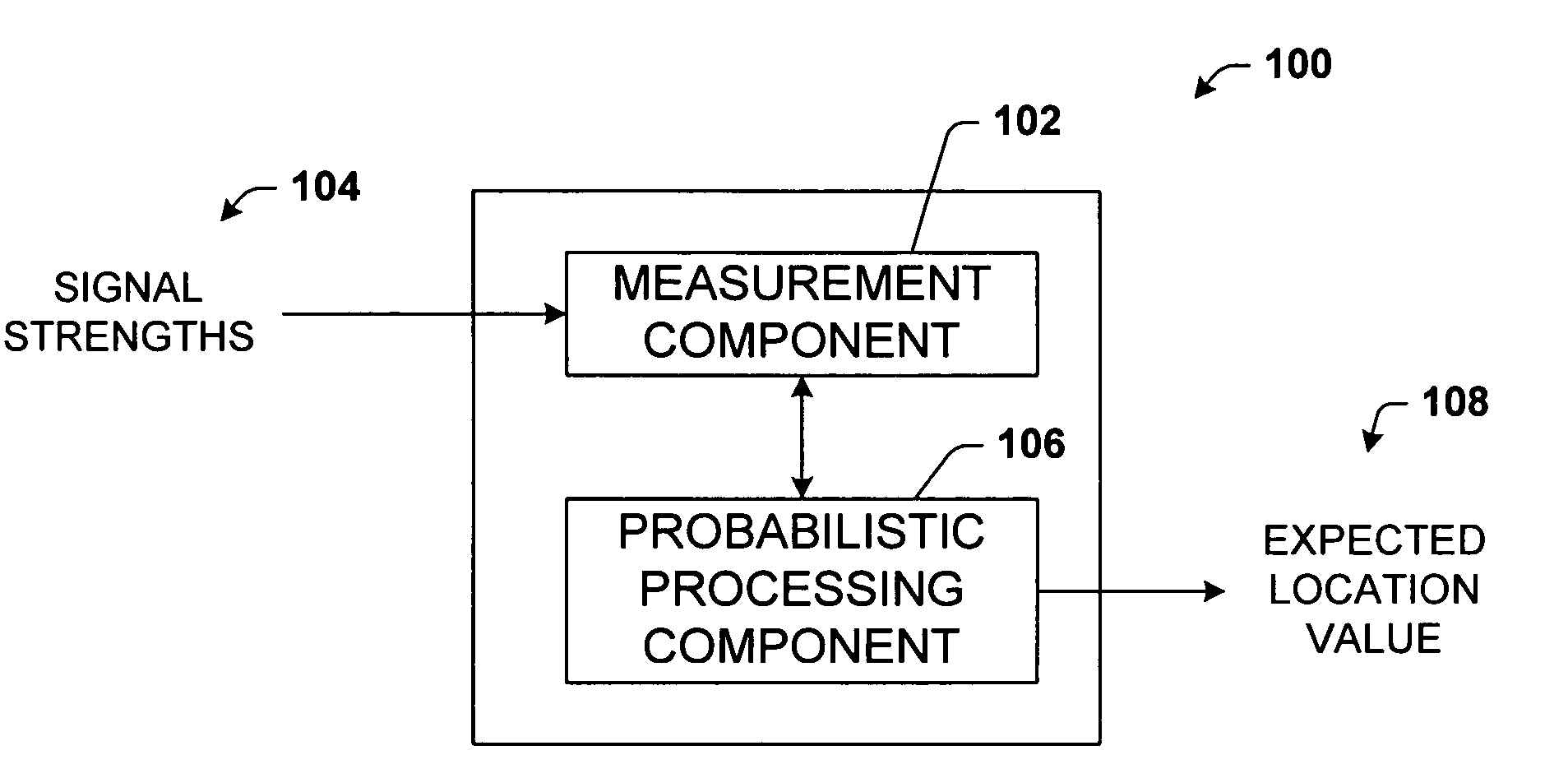
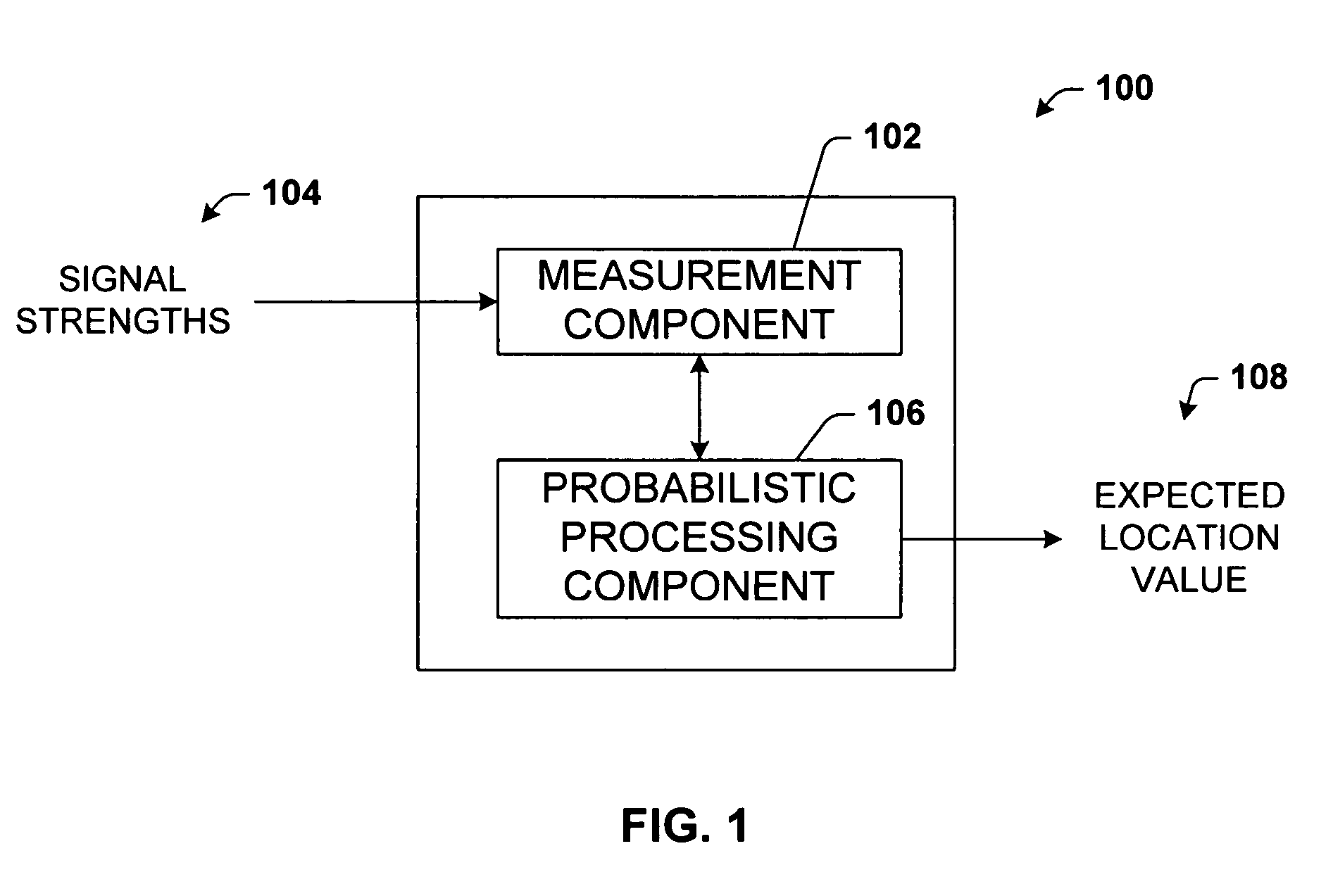
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In an instance of the invention, learning and inference methods are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and methods for determining the location dynamics of a portable computing device
InactiveUS20050270236A1Easy to trackFacilitate communicationData processing applicationsDirection finders using radio wavesProgram planningFloor plan
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and methods for determining the location dynamics of a portable computing device
InactiveUS7053830B2Easy to trackFacilitate communicationData processing applicationsDirection finders using radio wavesSimulationPositioning system
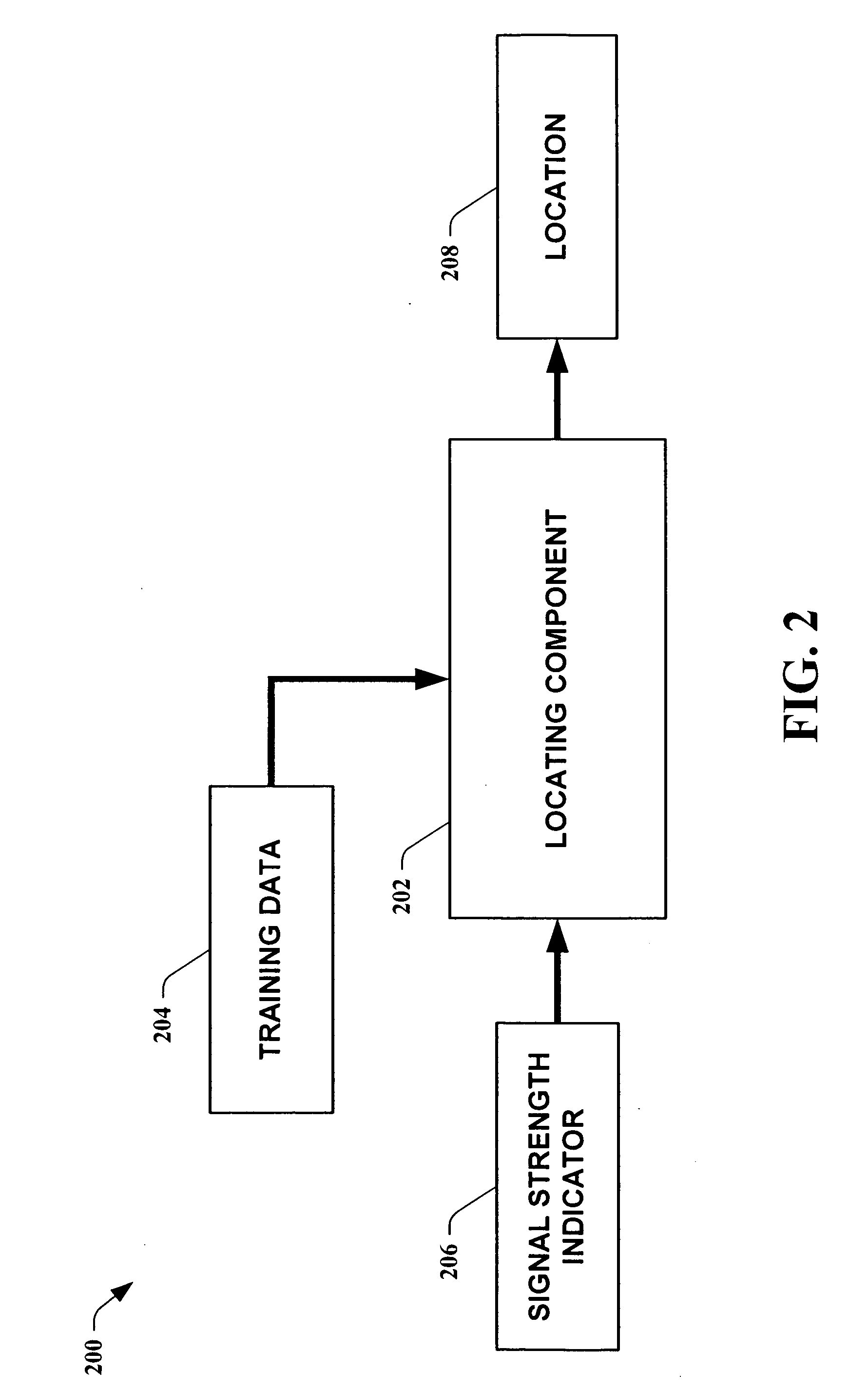
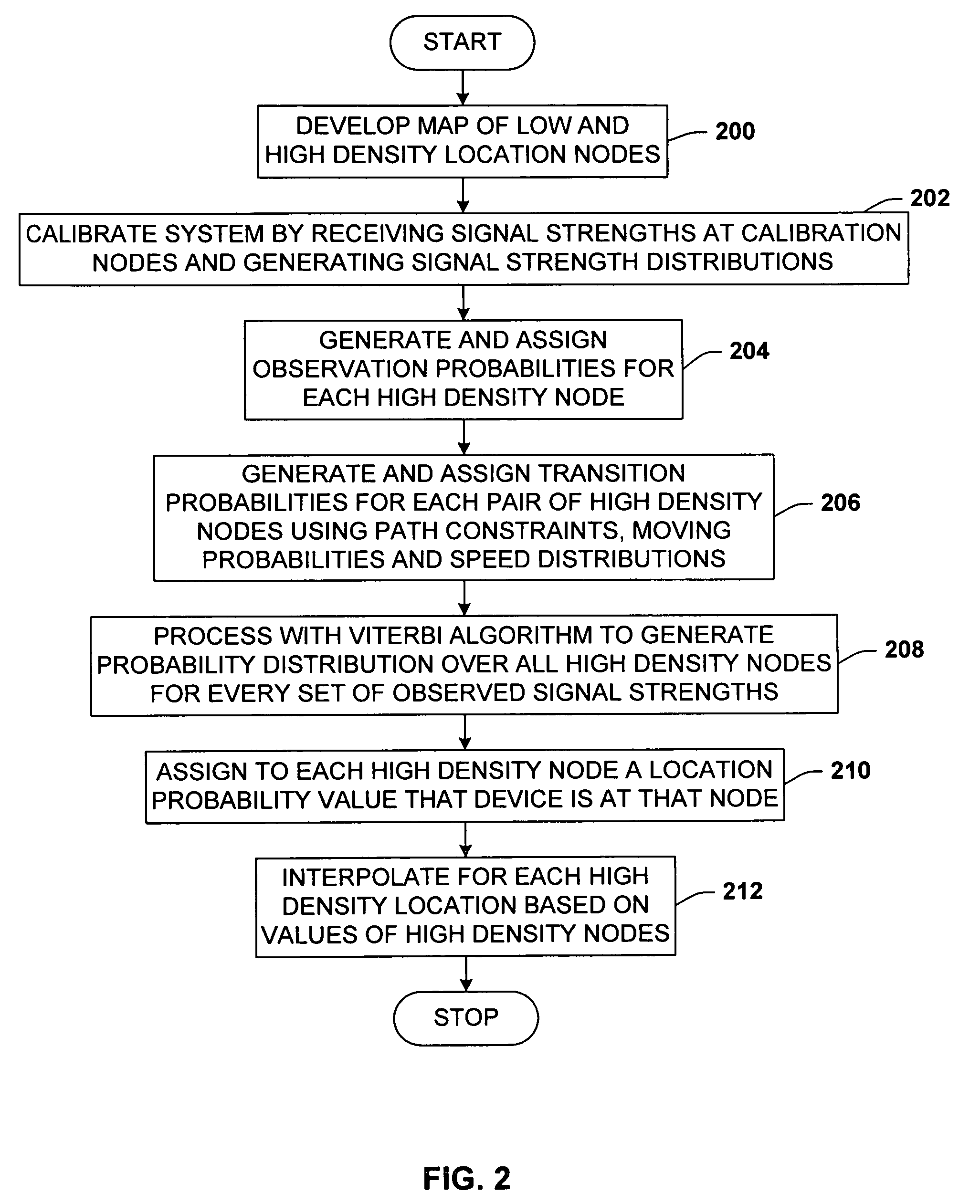
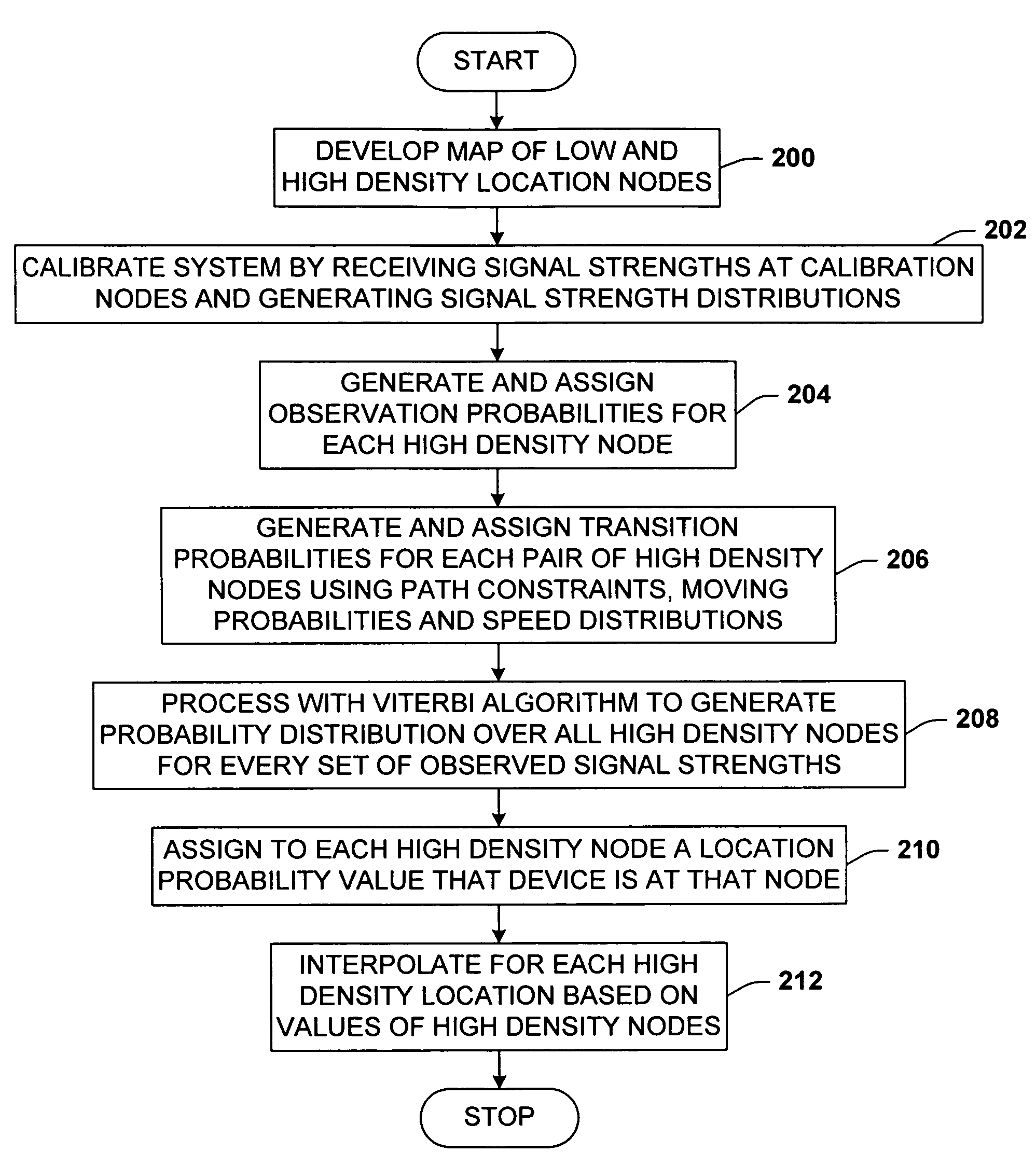
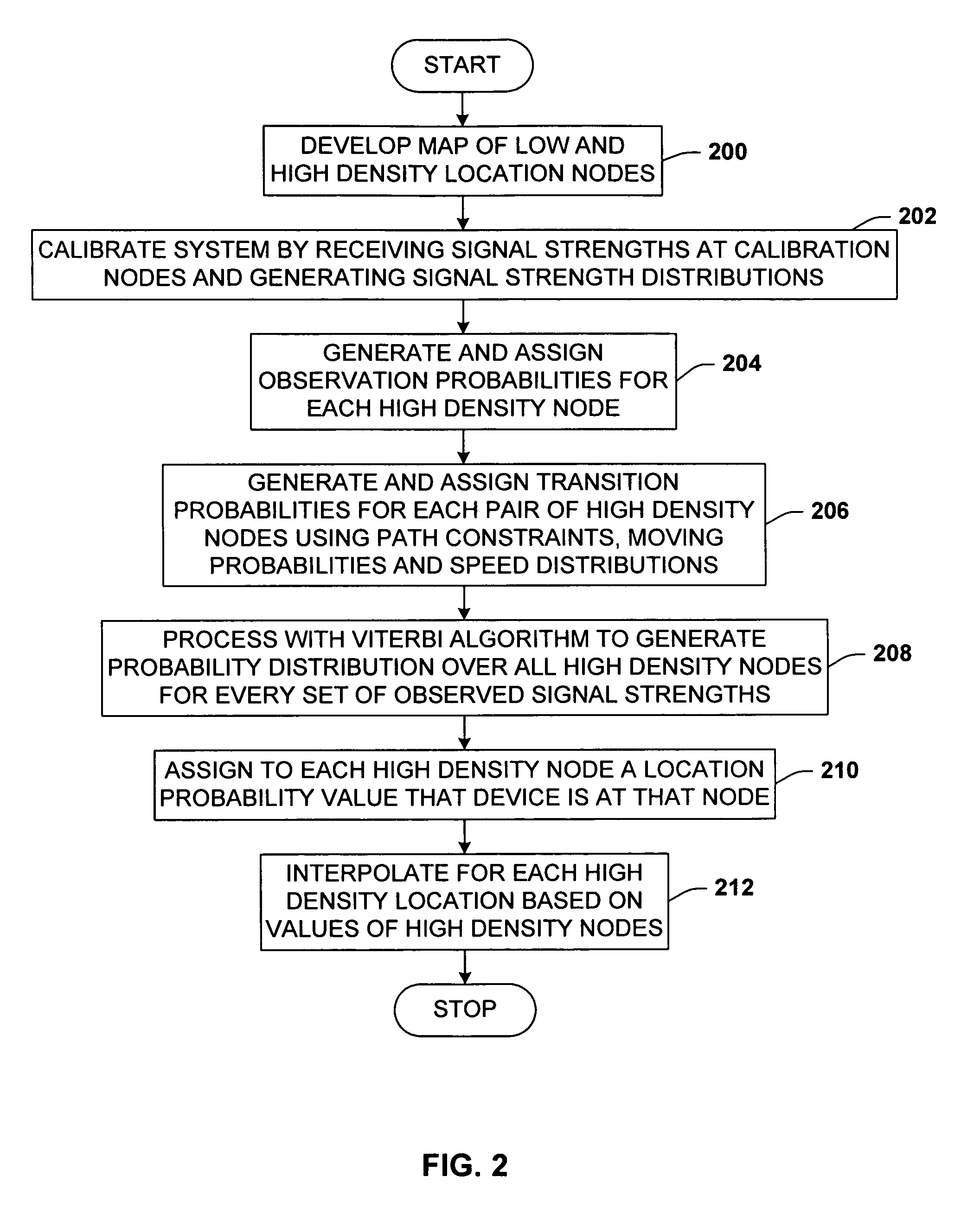
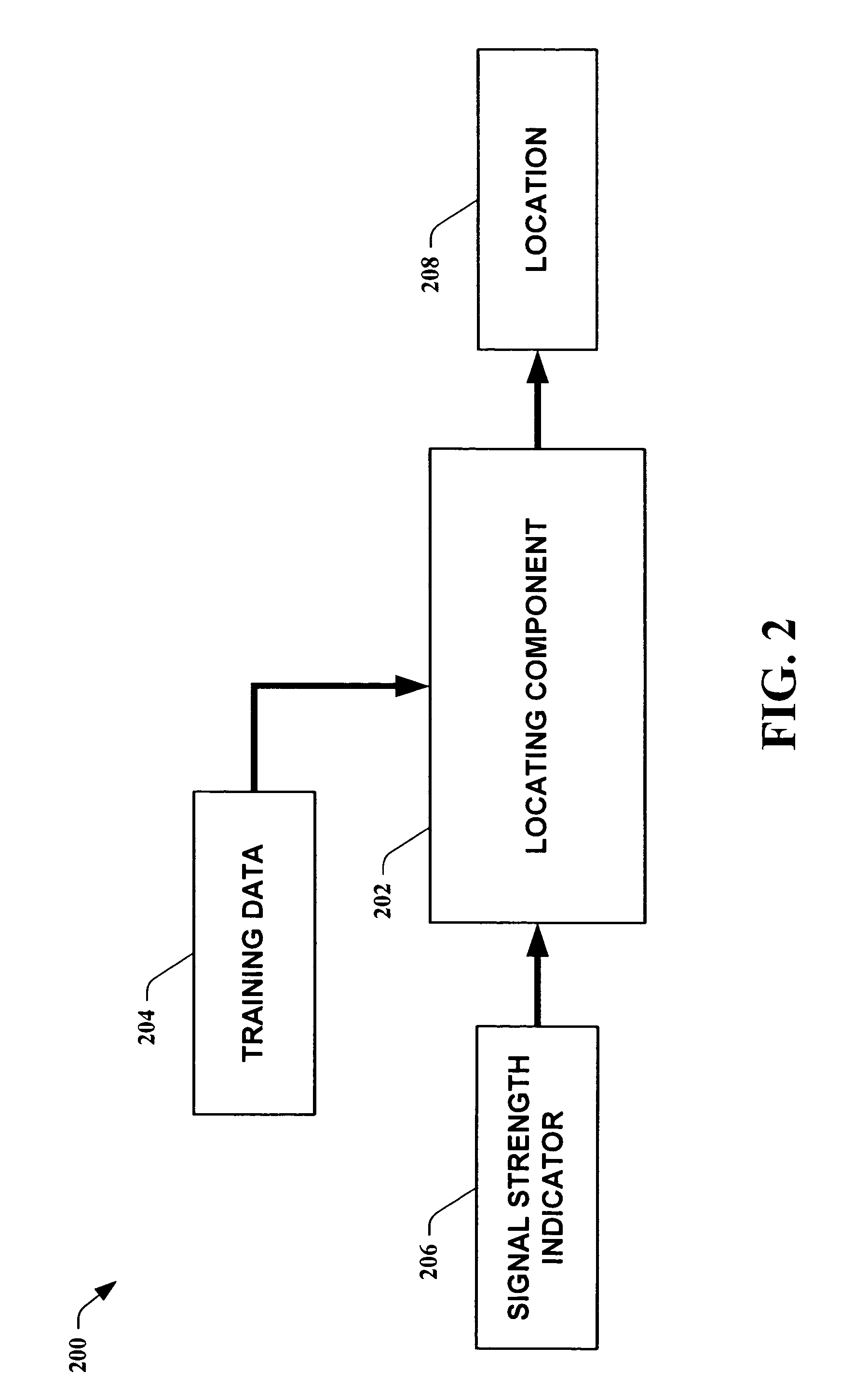
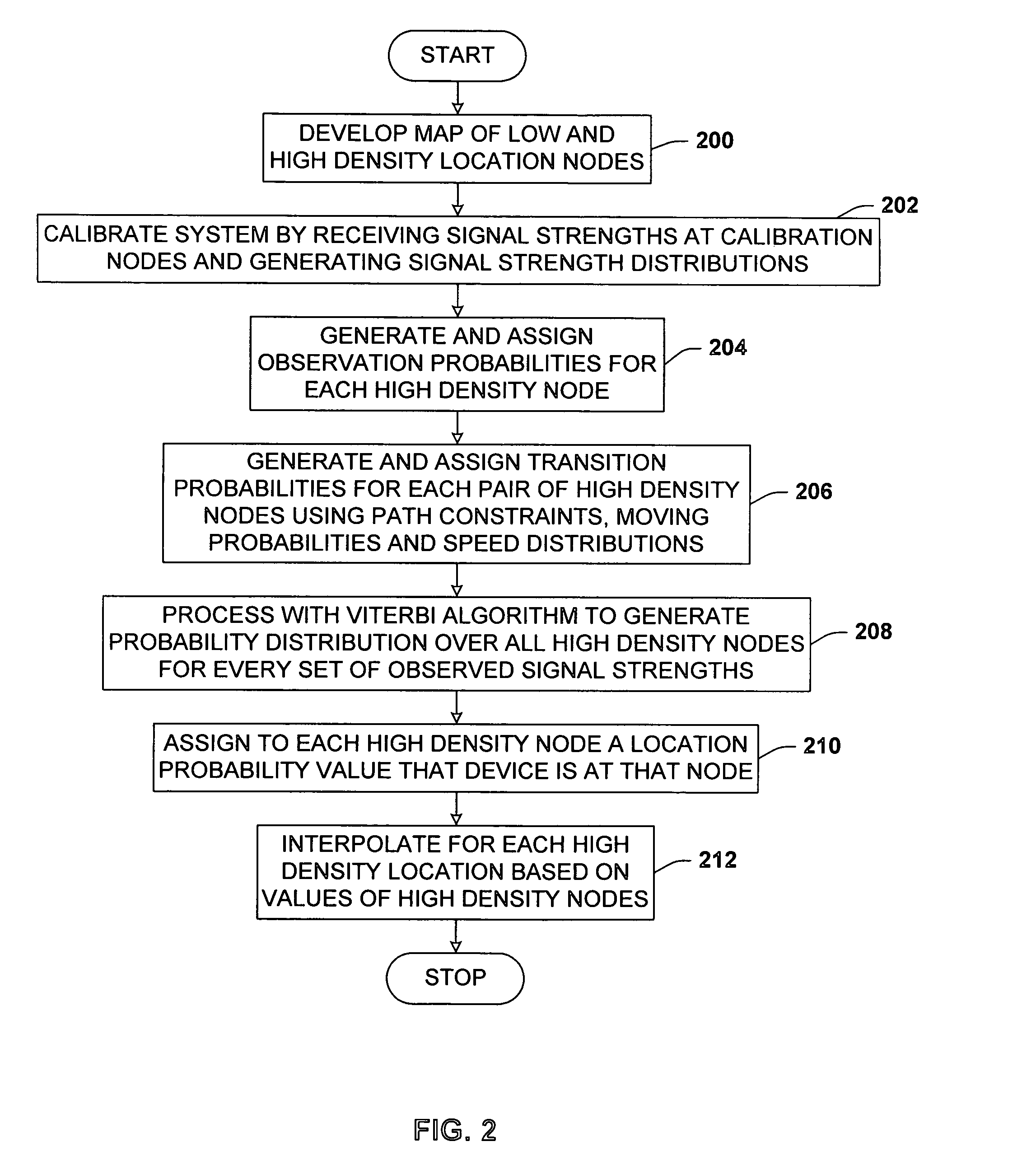
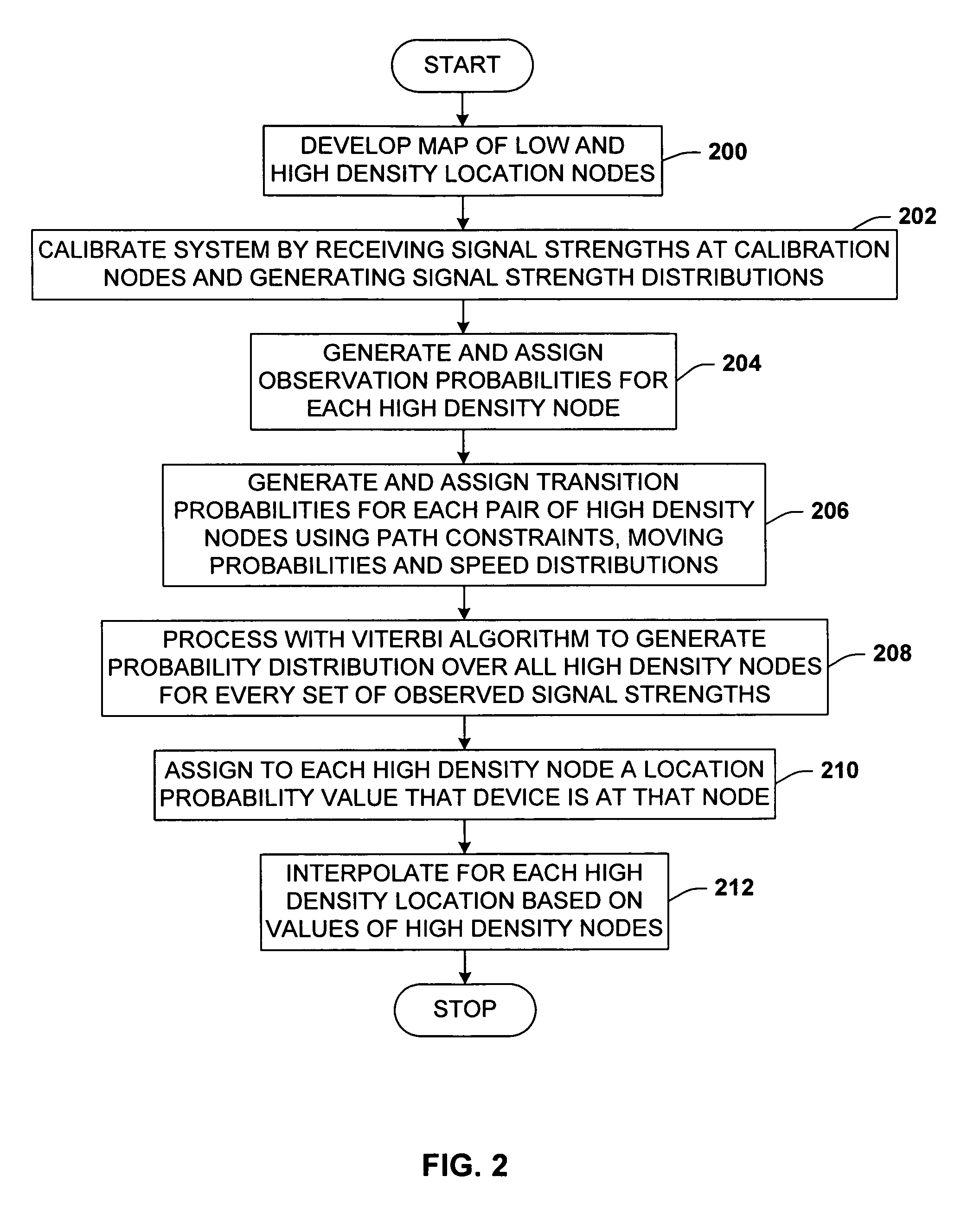
A location system for locating and determining the motion and velocity of a wireless device. The methods include direct inferences about whether a device is in motion versus static based on a statistical analysis of the variation of radio signal strengths over time. The system is trained according to a sparse set of identified locations from which signal strengths are measured. The system uses the signal properties of the identified locations to interpolate for a new location of the wireless device. The system uses a probabilistic graph where the identified locations of the floor plan, expected walking speeds of pedestrians, and independent inference of whether or not the device is in motion are used to determine the new location of the device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Intrusion detection system and method
ActiveCN101436336ALow installation costLow maintenance costBurglar alarm electric actuationInterference resistanceNetwork addressing
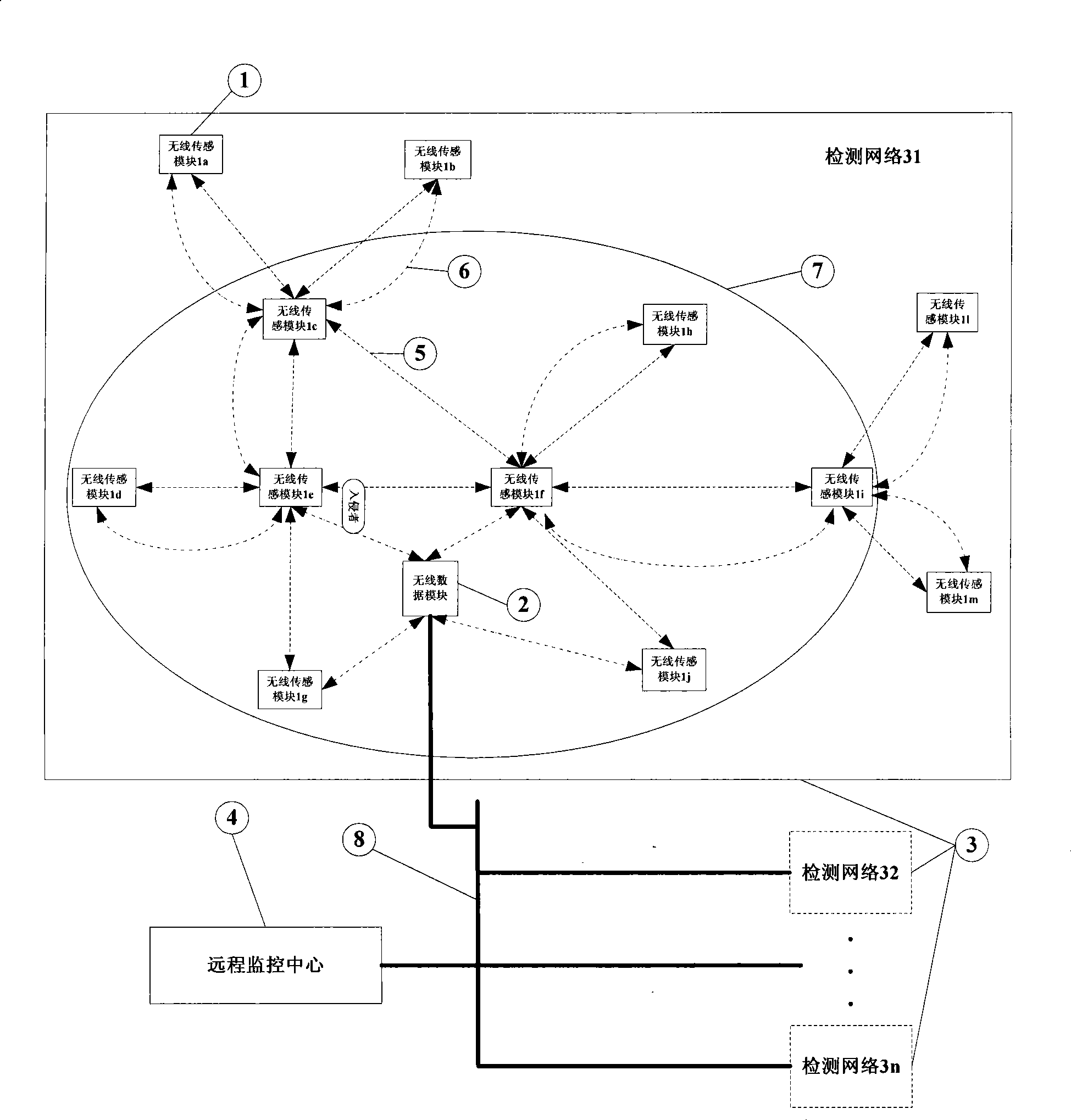
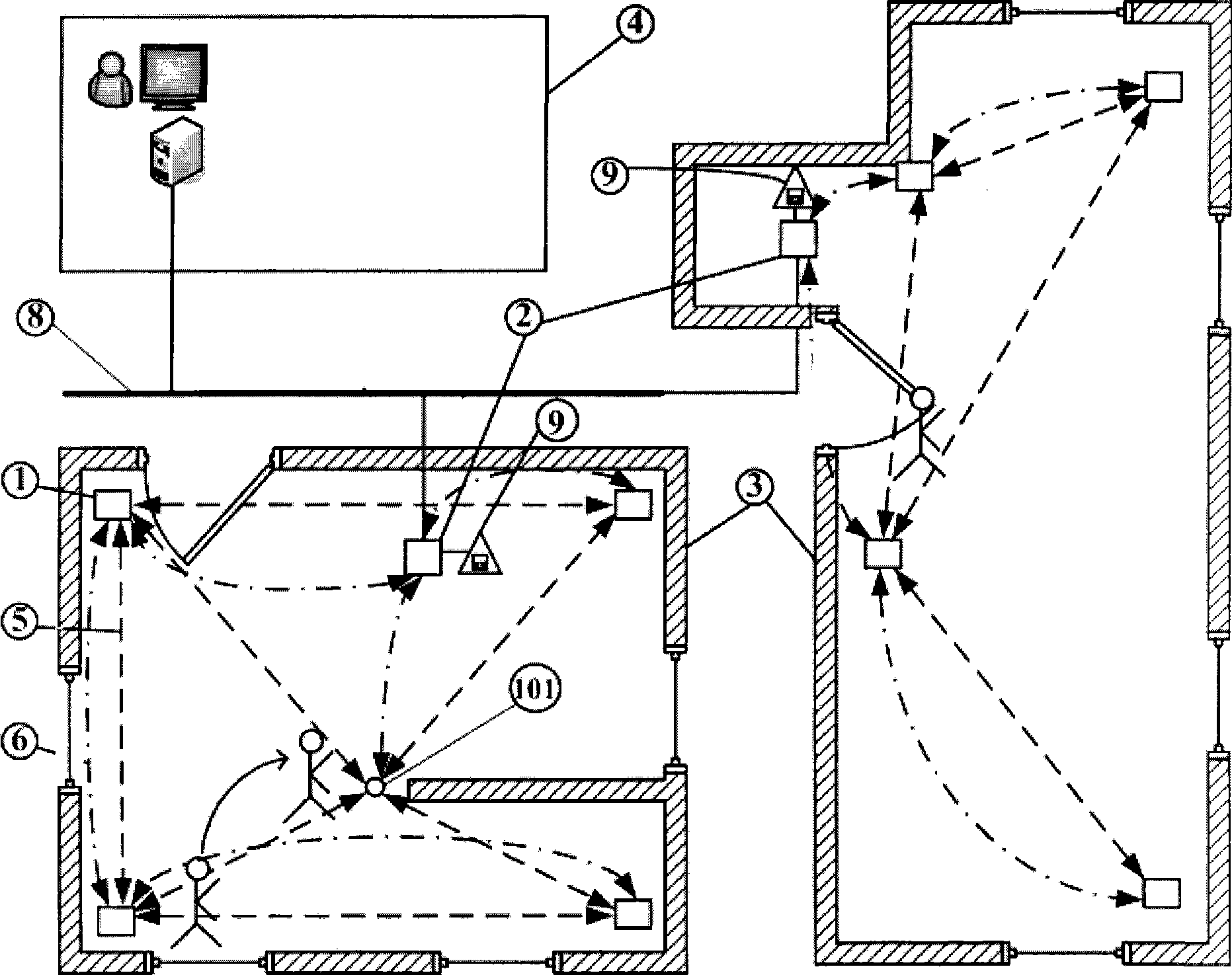
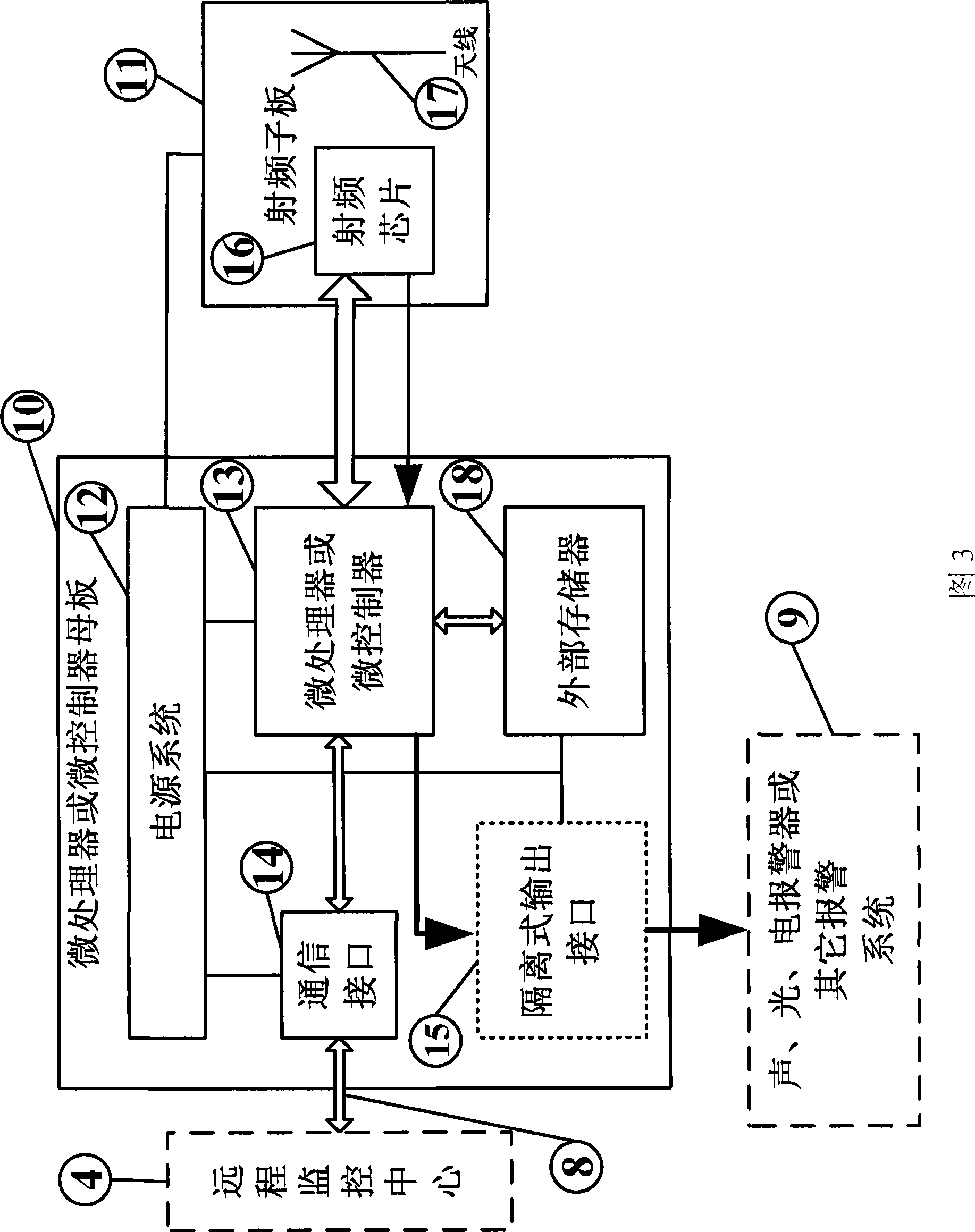
The invention discloses an intrusion detection system and a method thereof. The system has a plurality of detection networks arranged on a guarding site; and a bus is used to connect the detection networks to a remote monitoring center. The method comprises the following steps: a wireless sensing module is added into a network established by a wireless data module and uploads a neighbor sheet after receiving a network address distributed by the wireless data module; a network topological graph is formed at the remote monitoring center end; broadcast is transmitted and received after the work parameters of the remote monitoring center are received; the radio signal strength of the broadcasting signal is acquired and is routed and uploaded to the wireless data module; the wireless data module carries out a decision algorithm according to the information so as to determine whether the intrusion behavior brings about the abnormality of the radio signal strength; in case of abnormity, the wireless data module gives off an alarm and determines the position of an intruder through the positioning algorithm in a sensitive area; and the position of the intruder and the alarm information are sent to the remote monitoring center. The intrusion detection system can identify the intrusion behavior, give off the alarm and determine the position of the intruder without being easily affected by environmental factors, as well as has a high interference killing capability and low cost.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
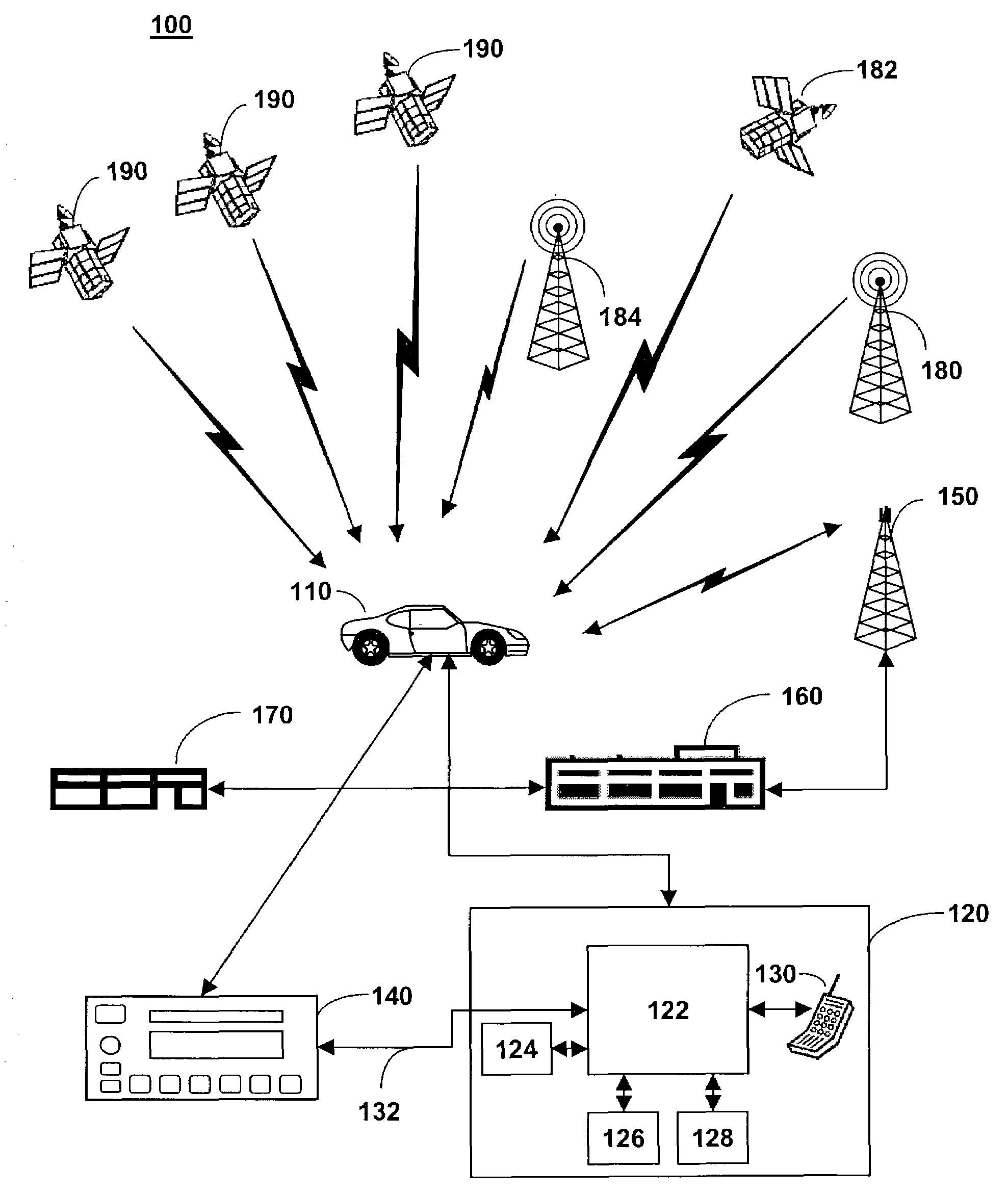
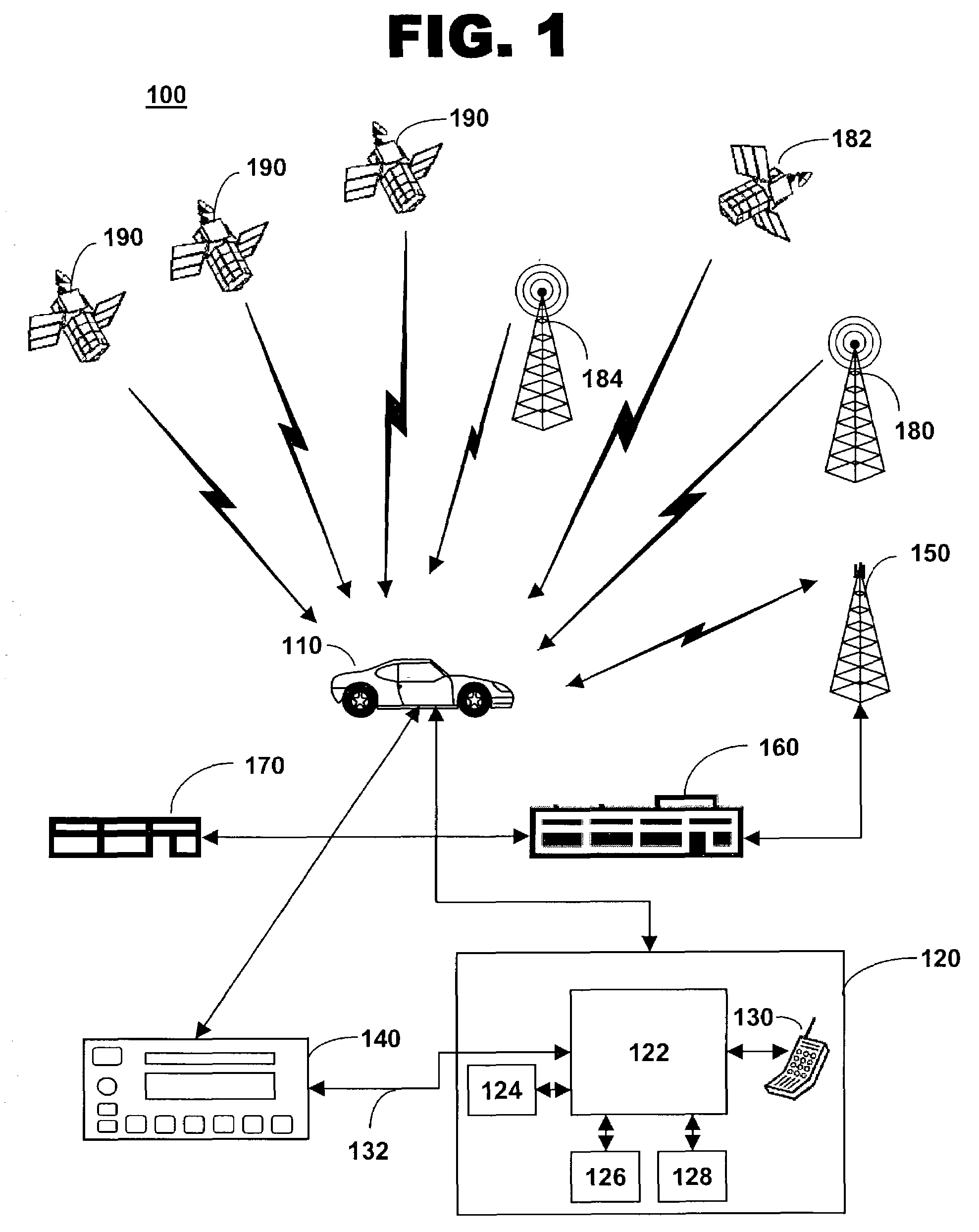
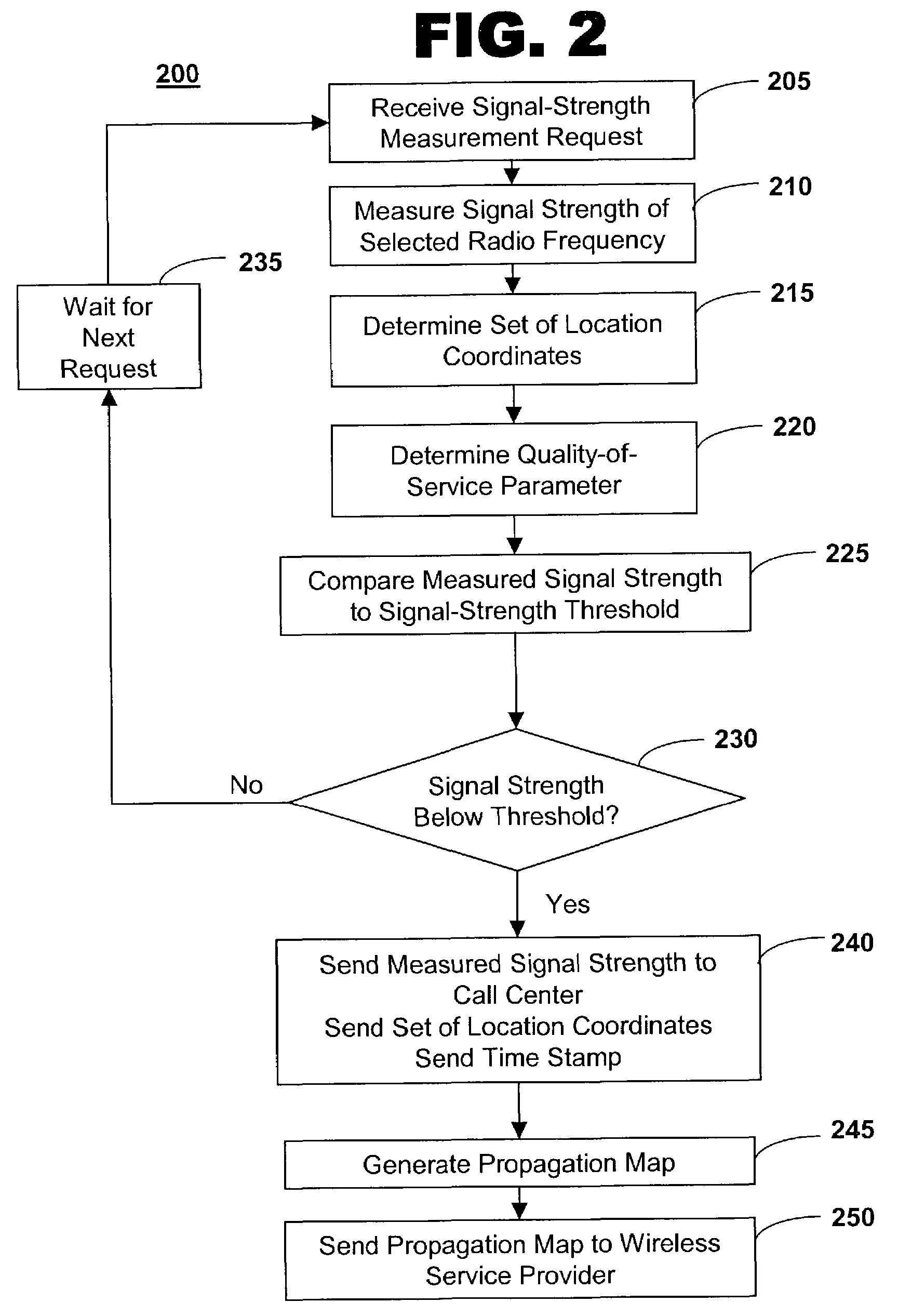
Radio signal strength mapping through a telematics system
ActiveUS7373152B2Receivers monitoringTelephonic communicationRadio signal strengthInformation handling system
The invention provides a method of and system for determining a radio-frequency signal strength at a mobile vehicle. A signal strength measurement request is received from a call center for a selected radio frequency, a signal strength of the selected radio frequency is measured at the mobile vehicle, and the measured signal strength is sent to the call center.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
Systems for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS20050020277A1Facilitates approximationSubstantial accuracy in determining locationInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesAlgorithmLocation Equipment
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the present invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In another instance of the present invention, a system utilizes learning and inference methods that are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to systems that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The present invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a system that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Mobile radio communication apparatus
InactiveUS20070026893A1Maintain compatibilityCo-operative working arrangementsNear-field systems using receiversMobile radioComputer science
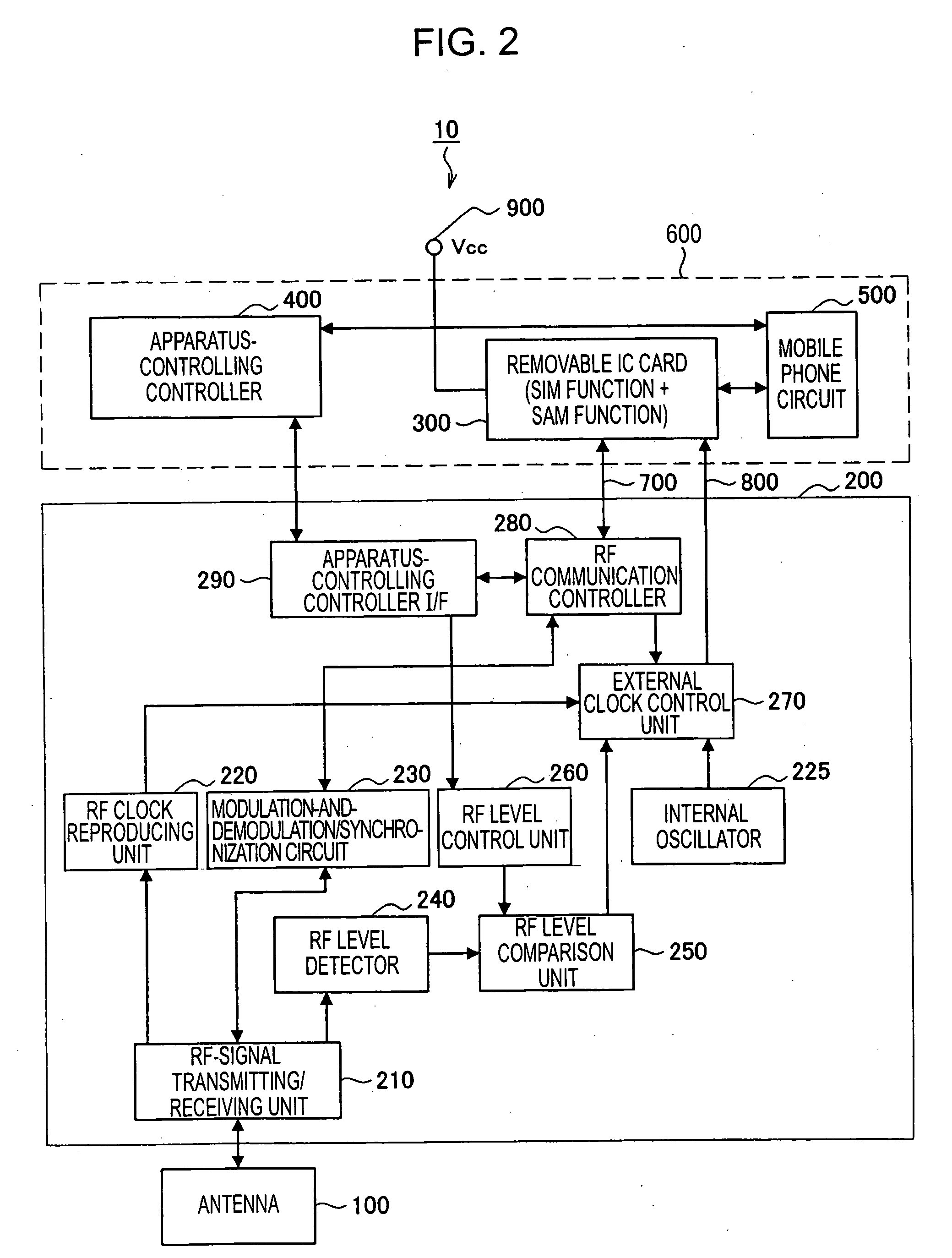
A mobile radio communication device can automatically initialize the mode of a SAM card (or the SAM function area of an IC card) after executing radio communication with an external radio communication apparatus. The mobile radio communication device transmits / receives data to / from an external radio communication apparatus located in an area that allows radio communication. In the mobile radio communication device, an IC card that receives power supply from a mobile radio communication device main-unit, that manages data transmitted / received to / from the external radio communication apparatus, and that manages a communication mode state of the mobile radio communication device is detachably connected to the mobile radio communication device main-unit. The mobile radio communication device further includes radio-signal strength determining means for determining whether or not a strength of radio signals received from the external radio communication apparatus is less than or equal to a preset threshold value, and IC-card-mode initializing means for resetting a mode of the IC card to an initial state when the radio-signal strength determining means determines that the strength of the radio signals is less than or equal to the threshold value.
Owner:SONY CORP
System and methods for determining the location dynamics of a portable computing device
InactiveUS20050258957A1Easy to trackFacilitate communicationData processing applicationsNetwork topologiesProgram planningSimulation
A location system for locating and determining the motion and velocity of a wireless device. The methods include direct inferences about whether a device is in motion versus static based on a statistical analysis of the variation of radio signal strengths over time. The system is trained according to a sparse set of identified locations from which signal strengths are measured. The system uses the signal properties of the identified locations to interpolate for a new location of the wireless device. The system uses a probabilistic graph where the identified locations of the floor plan, expected walking speeds of pedestrians, and independent inference of whether or not the device is in motion are used to determine the new location of the device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Ultra wide band device and detect-and-avoid method thereof
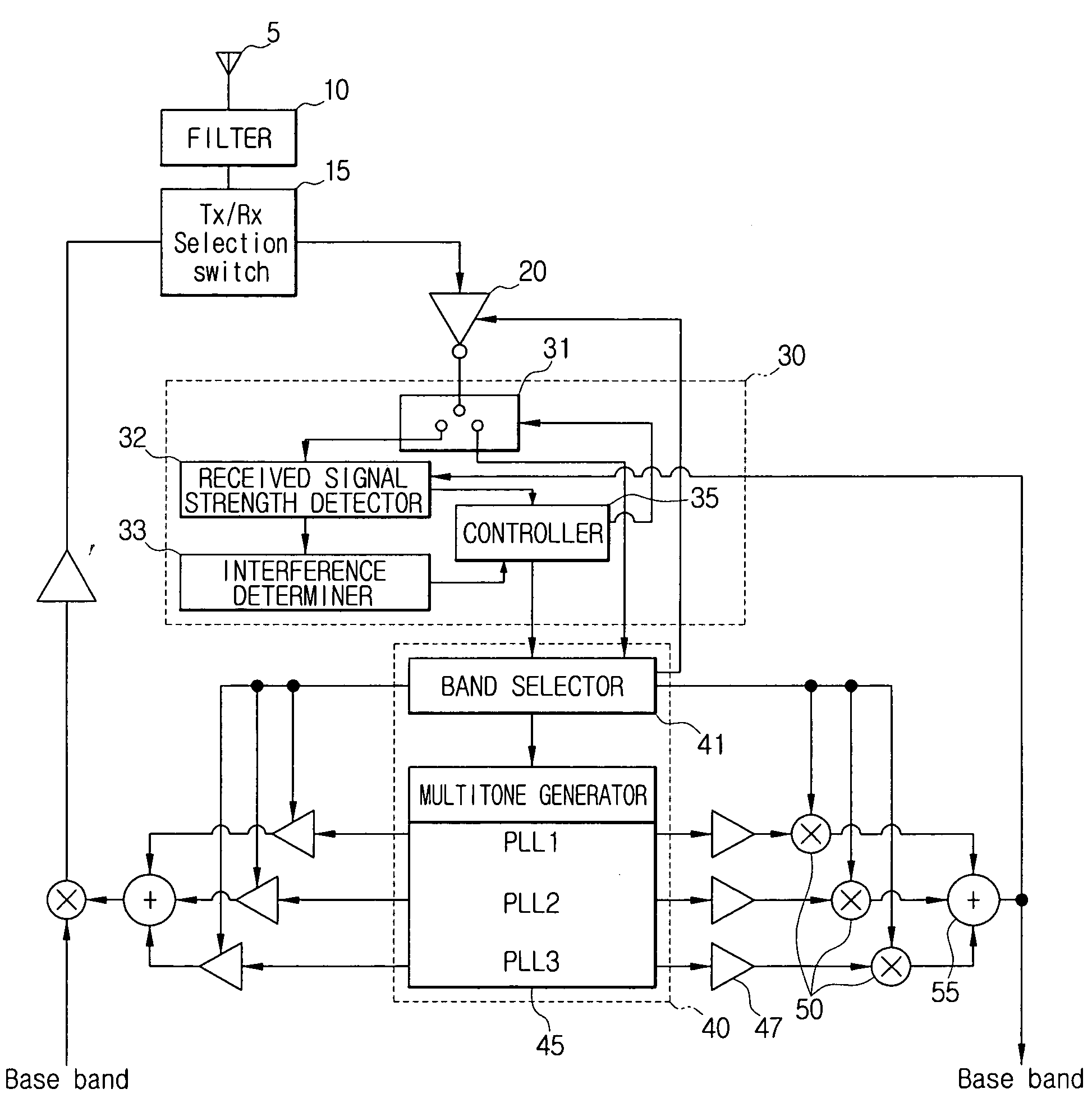
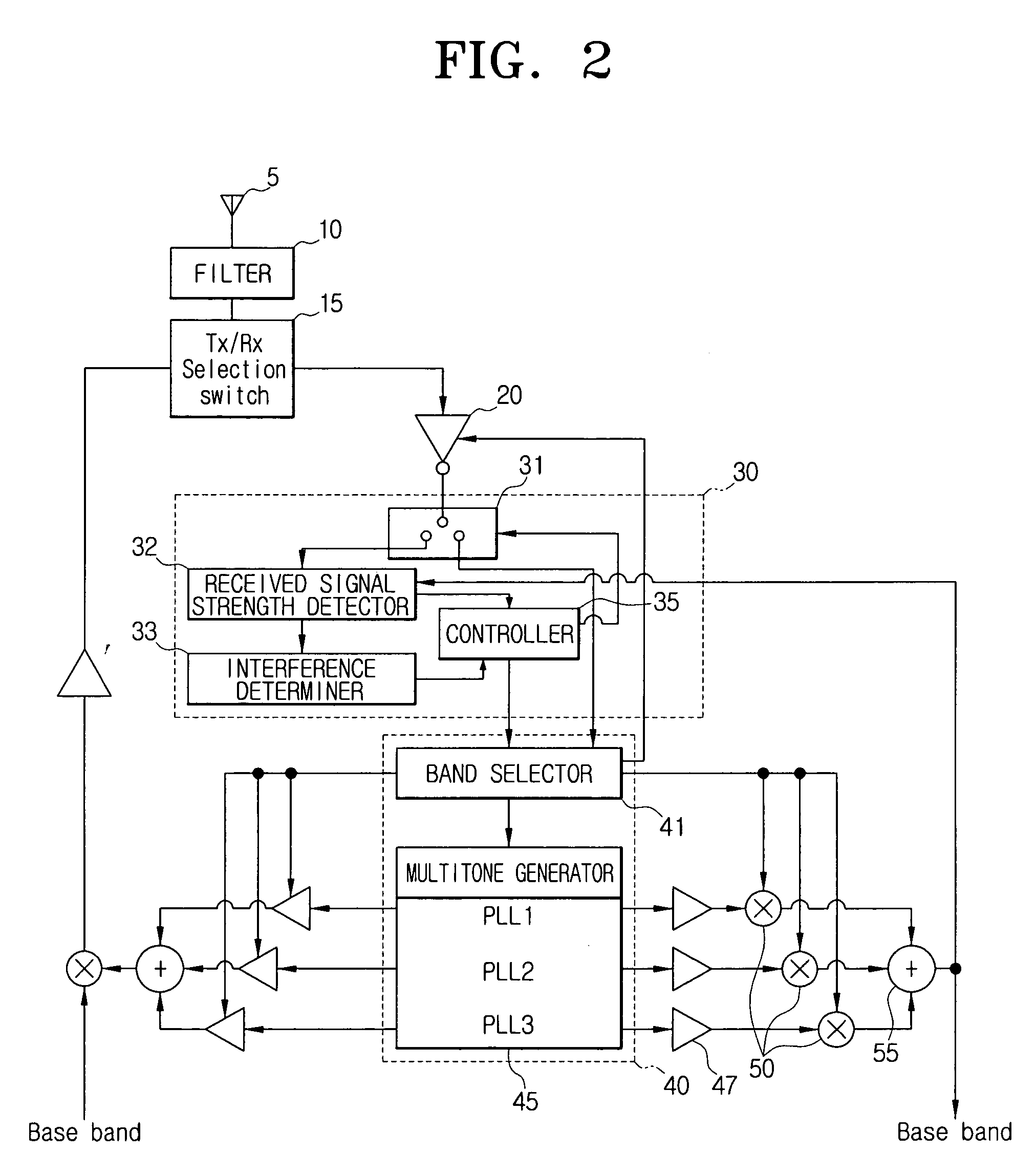
ActiveUS20080045175A1Spectral gaps assessmentData switching by path configurationDetect and avoidWide band
An ultra wide band (UWB) device and a detect and avoid (DAA) method thereof are provided. The UWB device includes a detect and avoid (DAA) module block which detects a strength of radio signals received in a plurality of channels and determines communicability of the channels; a multitone generation block which generates a plurality of frequencies corresponding to the plurality of the channels and outputs one of the plurality of frequencies; and a controller which controls the multitone generation block to generate frequencies of an available channel which is determined to be communicable by the DAA module block. The method includes detecting a strength of radio signals received in a plurality of channels; determining communicability of the channels according to the detected strength of the radio signals; generating frequencies corresponding to a channel which is determined to be communicable; and transmitting or receiving a signal using the generated frequencies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for detecting and identifying device utilization
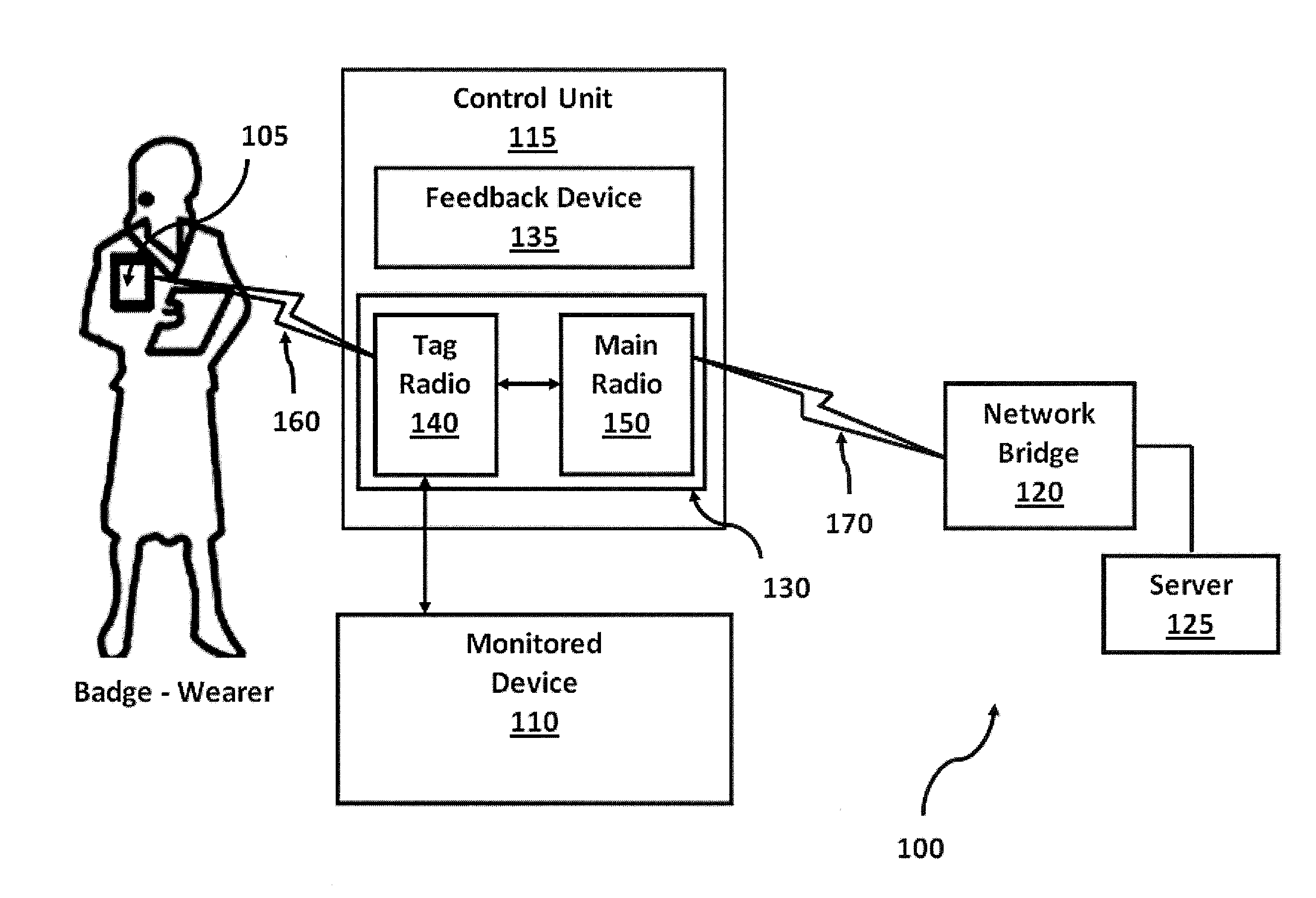
InactiveUS20140218173A1Amount of timeImprove accuracyWireless architecture usageCo-operative working arrangementsRadio equipmentEngineering
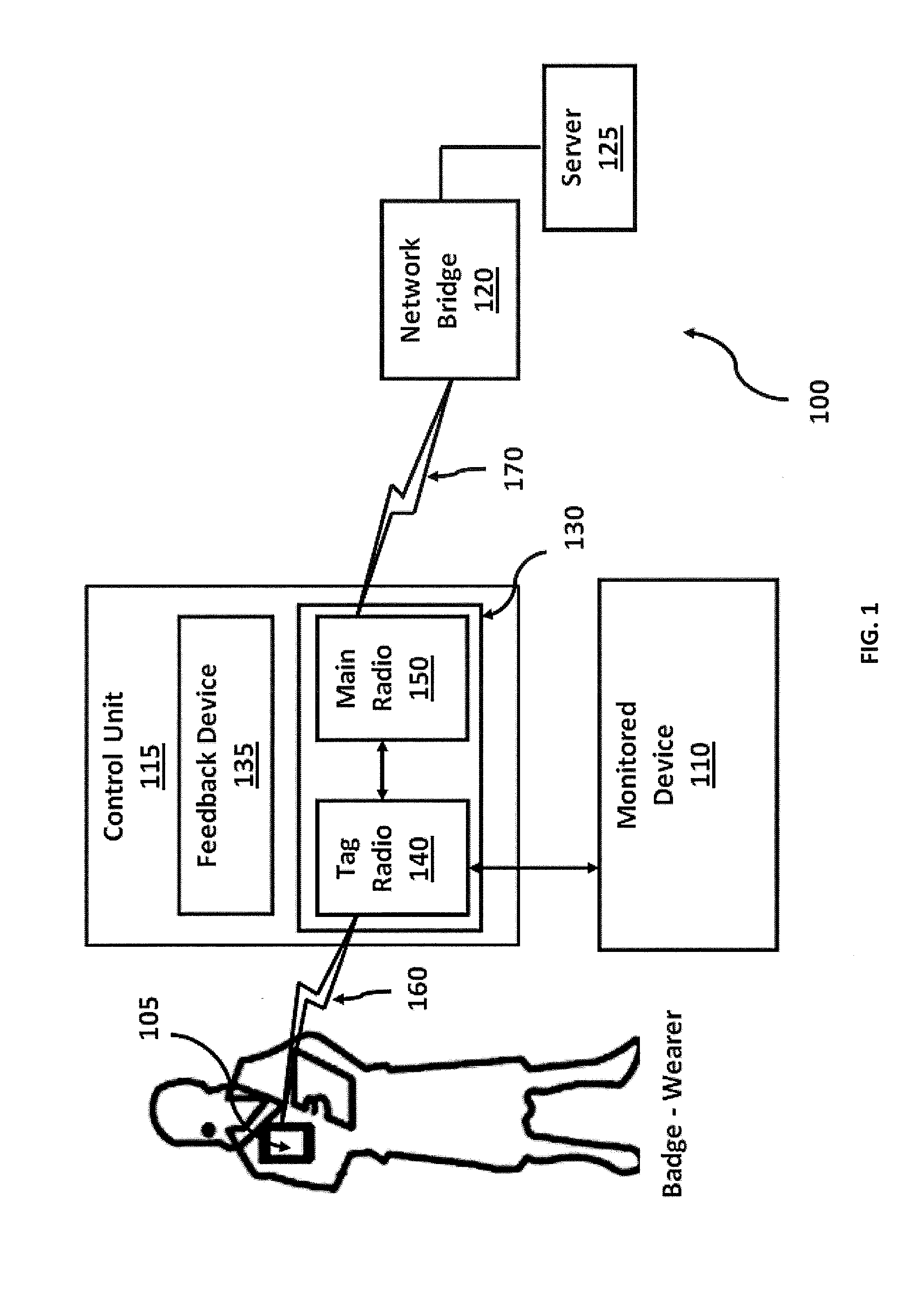
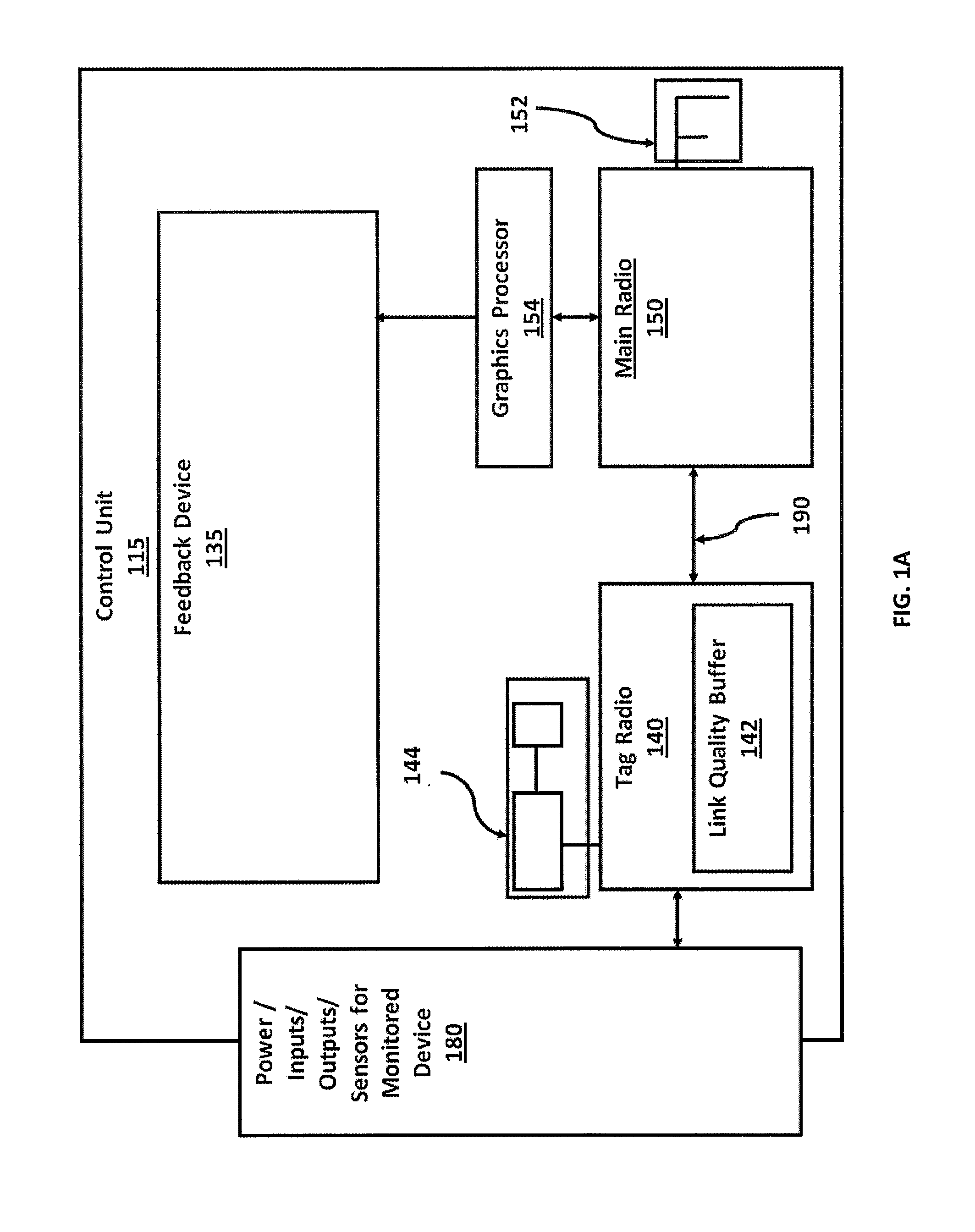
A control unit associated with a monitored device, wherein the control unit has a tag radio and a main radio. The tag radio has a first antenna operable to detect and communicate with a wearable tag associated with an asset, such as a person, a piece of equipment, or a supply, over a first communications channel. The main radio has a second antenna operable to communicate data over a second communications channel. In a preferred embodiment, the control unit is operable to communicate simultaneously with a wearable tag and with a communications network using the tag radio and the main radio, respectively. Further, the tag radio is operable to determine actions of a person associated with a wearable tag based upon Radio Signal Strength Identification (RSSI) values detected in short-range communications from the wearable tag.
Owner:LONG AVERY DALLAS +2
Systems for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS7738881B2Facilitates approximationMaximum accuracyInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesAlgorithmLocation Equipment
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods for determining the approximate location of a device from ambient signals
InactiveUS7319877B2Facilitates approximationMaximum accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationAlgorithmLocation Equipment
The present invention leverages changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations to determine a device's location. In one instance of the invention, inference procedures are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In an instance of the invention, learning and inference methods are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention facilitates approximations for locating a device by providing a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
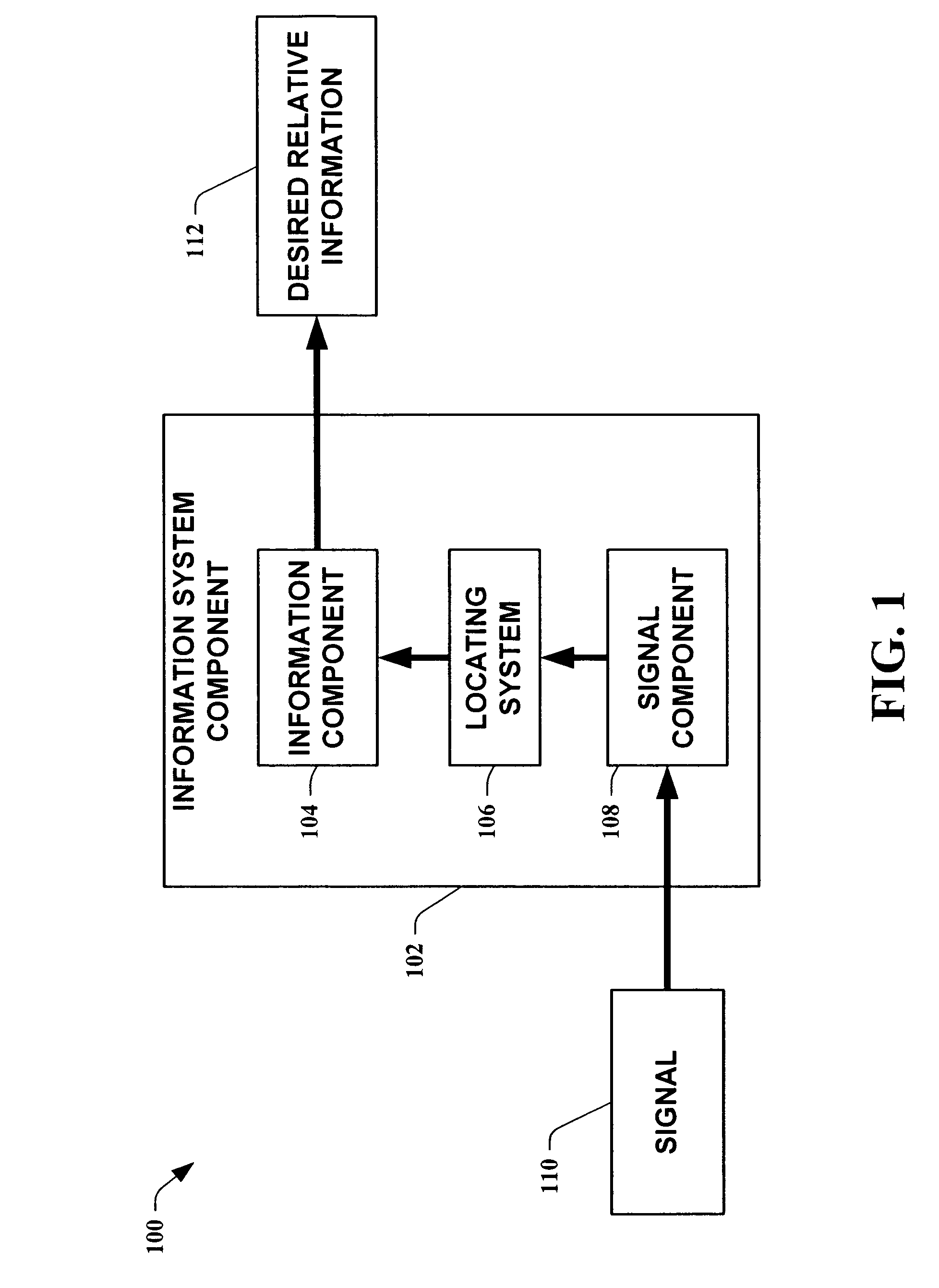
Utilization of the approximate location of a device determined from ambient signals
InactiveUS20050020210A1Wide coverageLow resource utilizationRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationService provisionAlgorithm
The present invention employs approximate device locations determined from changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations. In one instance of the invention, the approximate device locations are based on inference procedures that are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In another instance of the invention, approximate device locations derived from learning and inference methods that are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors are utilized. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention utilizes approximations for a device location that is based on a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations. Several location-centric services are supported, including receipt of location-specific information such as traffic reports, emergency information, transmission about device location, and time-sensitive promotions such as discounts offered by businesses for load balancing the provision of services.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
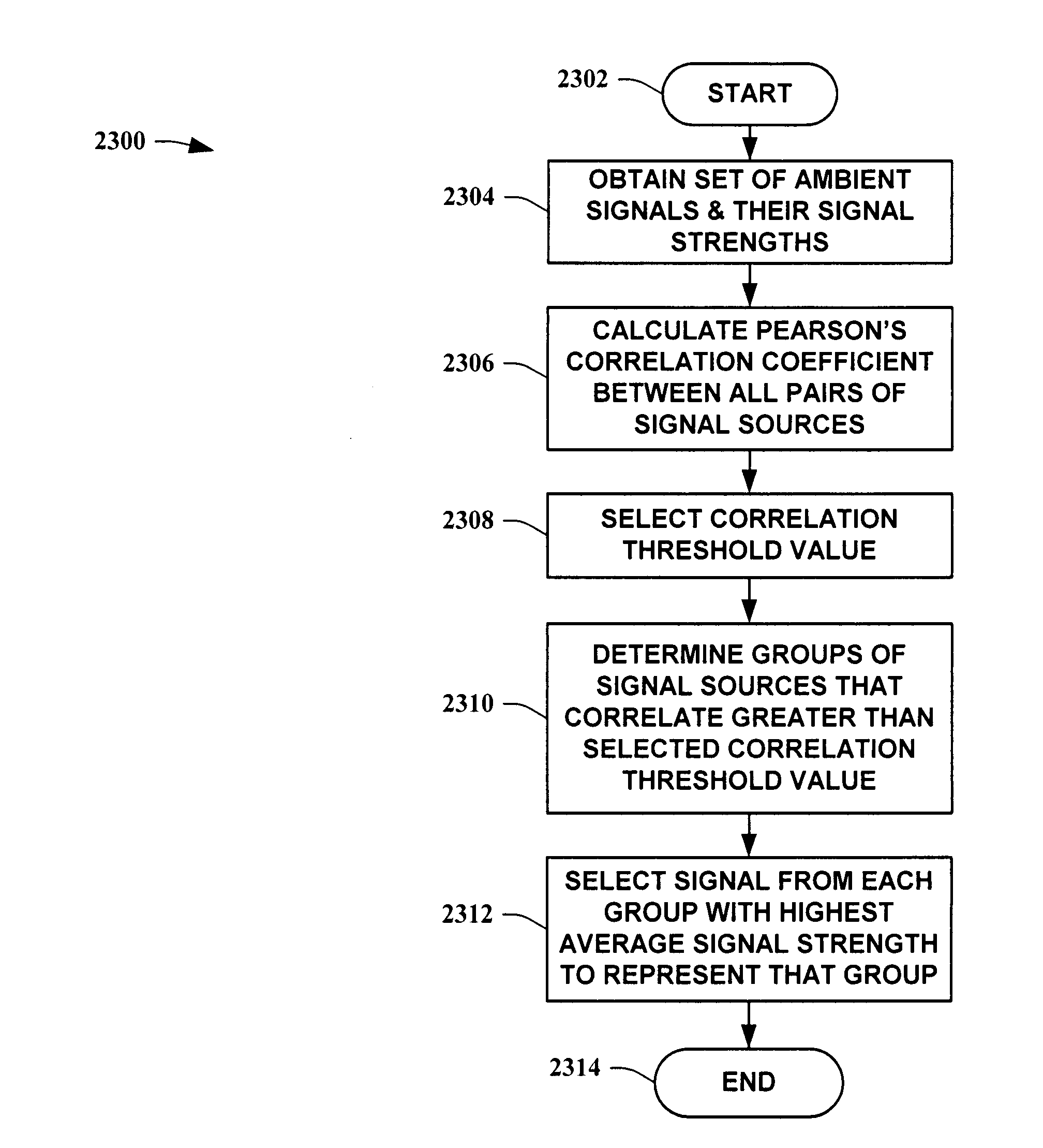
Similarity based wireless sensor network mobile node positioning method
InactiveCN103118333AHigh positioning accuracyStrong anti-interferenceNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesComputation complexityRound complexity
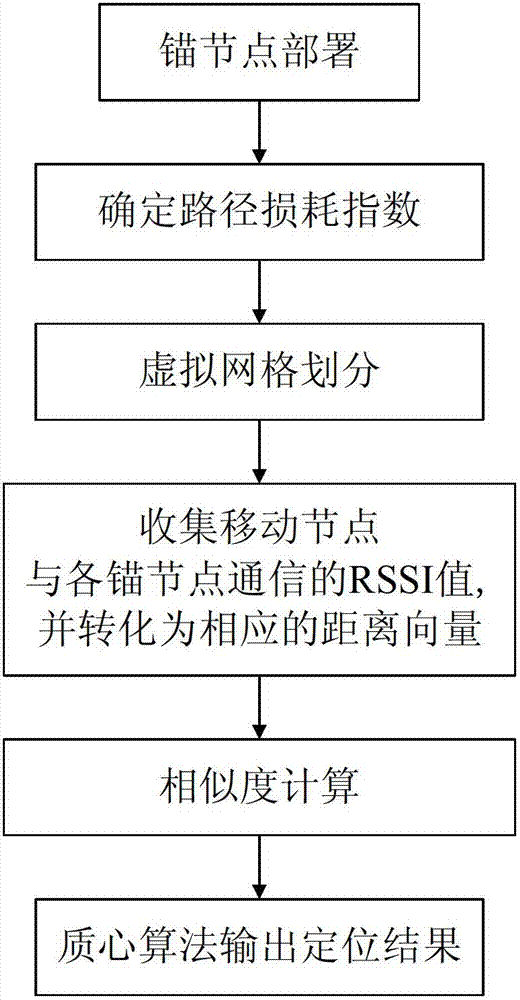
The invention relates to a similarity based wireless sensor network mobile node positioning method. The method includes the steps: after anchor node deployment is finished, each anchor node uploads a data package including self node ID (identity) and position to a sink node, and the sink node collects the data packages of the anchor nodes to establish a digital link list; according to anchor distribution information in the digital link list, the sink node performs virtual grid division for a greenhouse and returns to a coordinate of grid vertexes except for those outside a zone boundary; the sink node collects a group of RSSI (radio signal strength indication) values of communication of mobile nodes with the anchor nodes and coverts the values into distance vector by the aid of a simplified lognormal shadow model; similarity among the distance values corresponding to the mobile nodes and the grid vertexes except for those outside the zone boundary is computed through a similarity function; and a centroid of a zone enclosed by a grid vertex set with the highest similarity serves as an estimated coordinate of the mobile nodes. The method is accurate in estimation of mobile node coordinates, low in computation complexity, perfect, and excellent in positioning performance.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three-dimensional accurate positioning method based on wireless sensor network
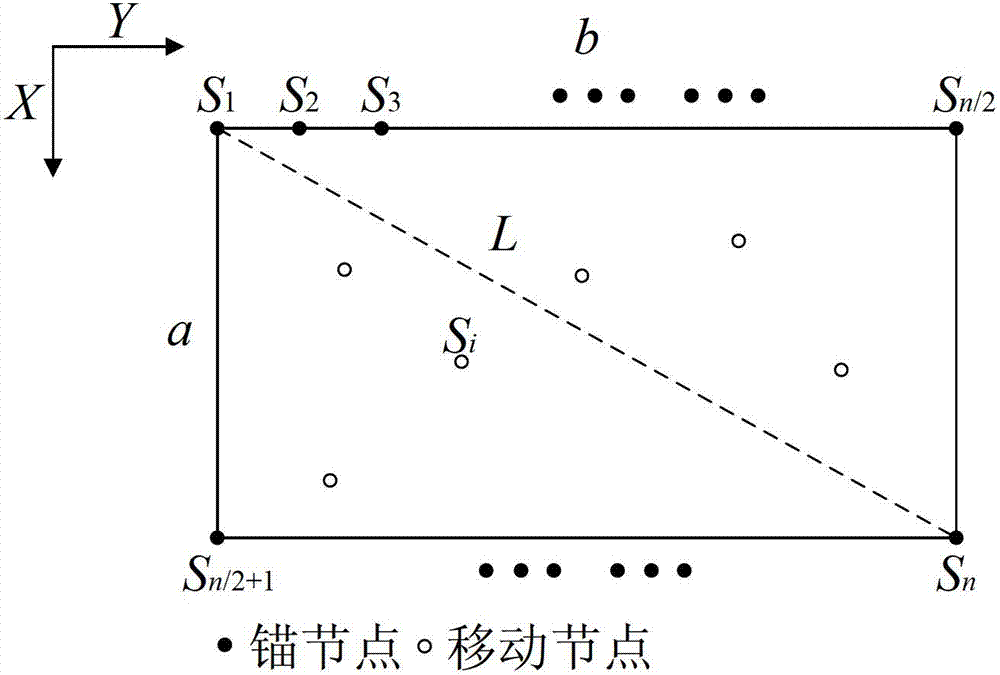
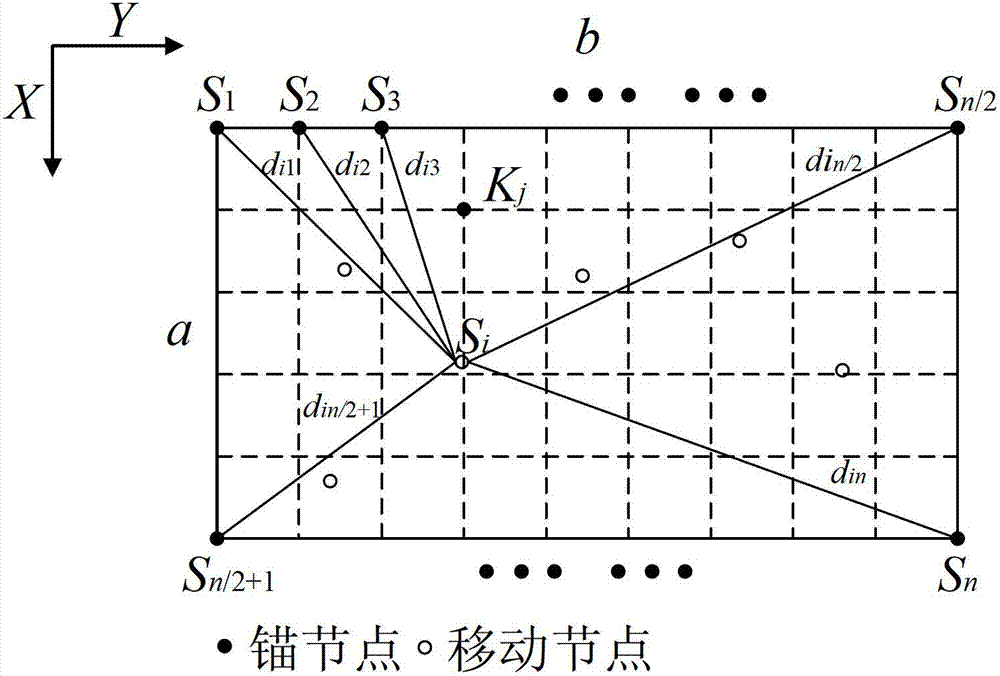
InactiveCN101635880AHigh positioning accuracyLower requirementNetwork topologiesLocation information based serviceHand heldSelf-organizing network
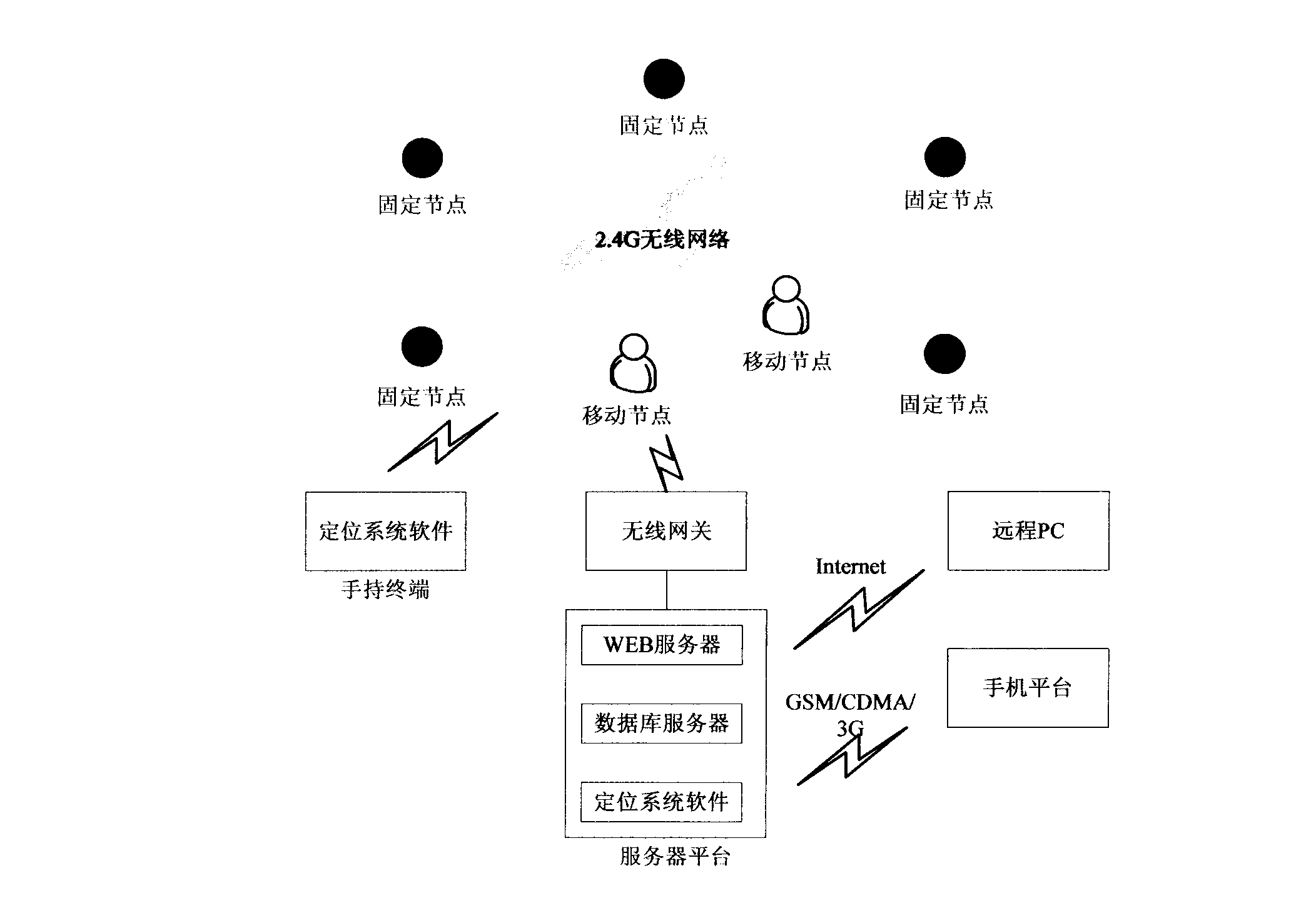
The invention relates to a three-dimensional accurate positioning method based on wireless sensor network. The method includes that a certain amount of fixed nodes are preset at places required to be positioned and coordinates X, Y and Z of each point are configured by positioning system software. Personnel or device required to be positioned is allocated with a mobile node, each mobile node is required to communicate with at least four nearby fixed nodes, the fixed node transmits radio signal strength received from the mobile node to the positioning system software by each node and gateway while the real-time coordinate of the mobile node is calculated by three-dimensional accurate positioning algorithm, then a three-dimensional building or cartographical model is imported, and a user can look up the position of the personnel or device by a remote PC, mobile phone or hand-held terminal. The invention realizes ad hoc network supported ground wireless three-dimensional accurate positioning system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Mobile device positioning system
InactiveCN103220777ADetermine 2D positionNetwork topologiesPosition fixationNetwork connectionMobile device
The invention discloses a mobile device positioning system. The mobile device positioning system comprises access points (APs), a positioning server, a network adapter and a positioning computing engine (PCE). The access points (APs) are wireless local area network (WLAN) access points, and the number of the access points is one or more than one. The positioning server comprises a radio signal strength (RSS) characteristic database, and the RSS characteristic database provides an RSS distribution diagram of the access points (APs) based on a set of disperse locations in a target area. The network adapter is used for providing network connection service of a mobile device and the access points (APs). The positioning computing engine (PCE) is used for determining positions of the mobile device based on the RSS characteristic database and receiving signals from one or more than one access point. According to the mobile device positioning system and method, RSS of neighboring multiple access points (APs) received by the mobile device like WIFI labels and an intelligent cell phone with RSS characteristic data of the disperse locations in the target area in the database are compared, and therefore two-dimensional locations of the plane where the mobile devices are positioned can be determined.
Owner:佛山市络研科技有限公司
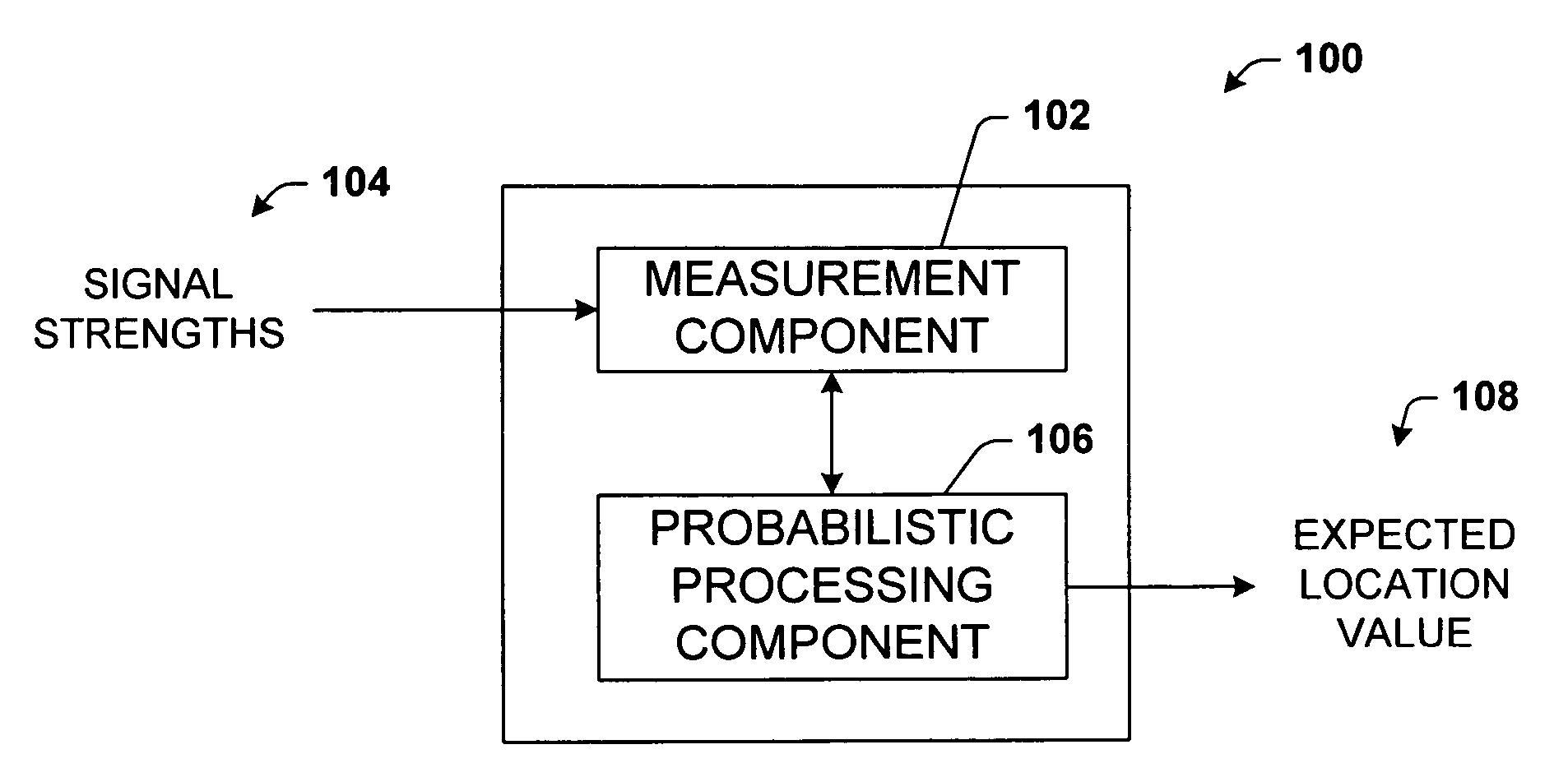
Location estimation system, method and program
InactiveUS20090109095A1Improve estimation accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationAlgorithmEstimation methods
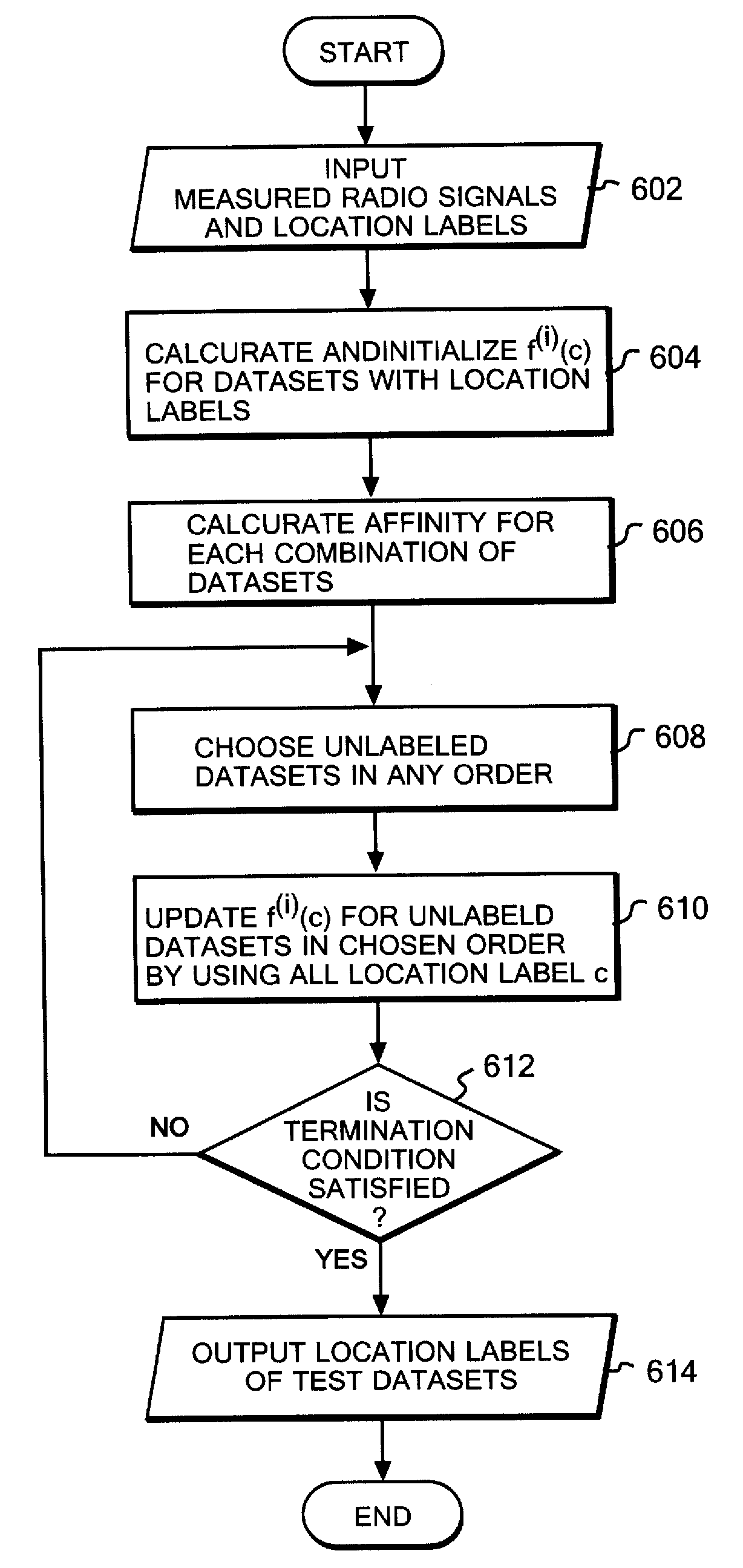
A location estimation method using label propagation. The achieved location estimation method is robust to variations in radio signal strengths and is highly accurate by using the q-norm (0<q<1), especially, for calculating the similarities among radio signal strength vectors. The accuracy in location estimation is further improved by putting more importance on the time-series similarities. Specifically, the time-series similarity is calculated by using time-series values indicating the temporal order of radio signal strengths during the measurement. If the time-series similarity is larger than the similarity between the radio signal strength vectors, the time-series similarity is preferentially used. The exponential attenuation function can also be used for calculating the similarities, instead of the q norm (0<q<1).
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for the prediction of coverage areas of a cellular network
InactiveUS20130281100A1Easy to useHigh precisionNetwork planningUltrasound attenuationComputer terminal
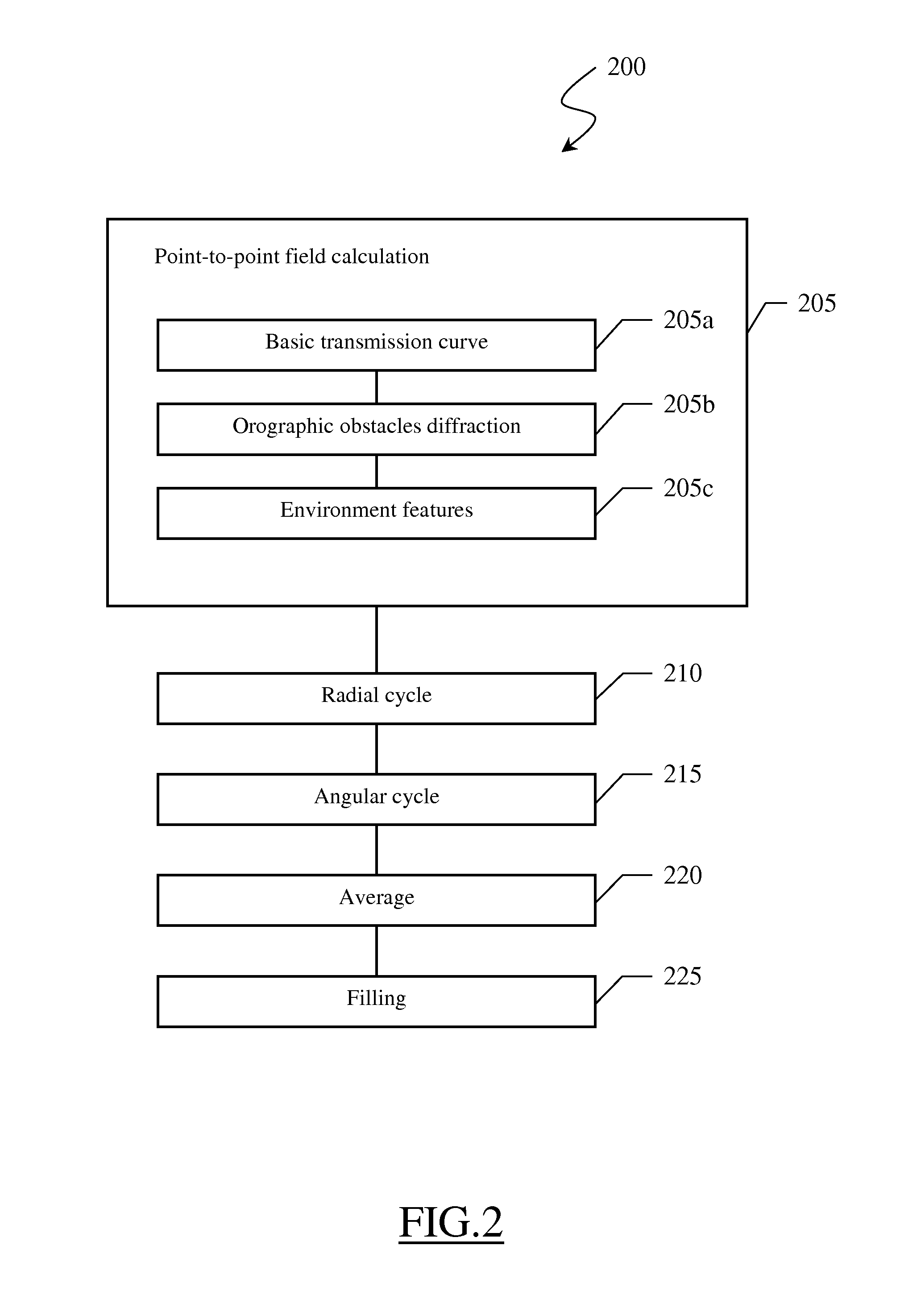
A method predicting coverage area of a radiocommunications network including plural network cells distributed over a geographic area. The method includes calculating by simulation an irradiated electromagnetic field irradiated by a radio base station of the network in plural measure locations within the geographic area corresponding to respective expected positions of a user terminal. The calculating includes, for each measure location, calculating a basic transmission curve indicative of a basic attenuation of a radioelectric signal strength in the measure location, and associating to the basic transmission curve at least one correction factor for refining the radioelectric signal strength basic attenuation by taking account of shielding effects on the radioelectric signal strength due to obstacles to the propagation of the radioelectric signal.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Automatic radio button mute
A system and method of eliminating static while utilizing pre-programmed tuner buttons on a radio is disclosed. The system of the present invention mutes a pre-programmed tuner button frequency when the radio signal for the pre-programmed frequency is below a threshold value. Further the system of the present invention may automatically tune to an alternate frequency when radio signal strength of the pre-programmed tuner button frequency is below a threshold value.
Owner:GATEWAY
Utilization of the approximate location of a device determined from ambient signals
InactiveUS7202816B2Direction finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlLoad SheddingAlgorithm
The present invention employs approximate device locations determined from changes in the sensed strength of radio signals at different locations. In one instance of the invention, the approximate device locations are based on inference procedures that are used to process ambient commercial radio signals, to estimate a location or a probability distribution over the locations of a device. In another instance of the invention, approximate device locations derived from learning and inference methods that are applied to rank vector of signal strength vectors are utilized. Moving to such rank orderings leads to methods that bypass consideration of absolute signal strengths in location calculations. The invention utilizes approximations for a device location that is based on a method that does not require a substantial number of available ambient signal strengths while still providing useful location inferences in determining locations. Several location-centric services are supported, including receipt of location-specific information such as traffic reports, emergency information, transmission about device location, and time-sensitive promotions such as discounts offered by businesses for load balancing the provision of services.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for deregistering out-of-coverage range devices in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20080299969A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesLocal area networkRadio signal strength
A method for deregistering wireless devices from a registration server for a wireless local area network, comprising: sending an initial registration request message from a wireless device to the registration server, the initial registration request message including an initial expiration interval; measuring radio signal strength at the wireless device; and, determining whether the radio signal strength has decreased to below a predetermined level and, if so, sending an updated registration request message from the wireless device to the registration server, the updated registration request message including an updated expiration interval less than the initial expiration interval thereby allowing timely deregistering of the wireless device by the registration server.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
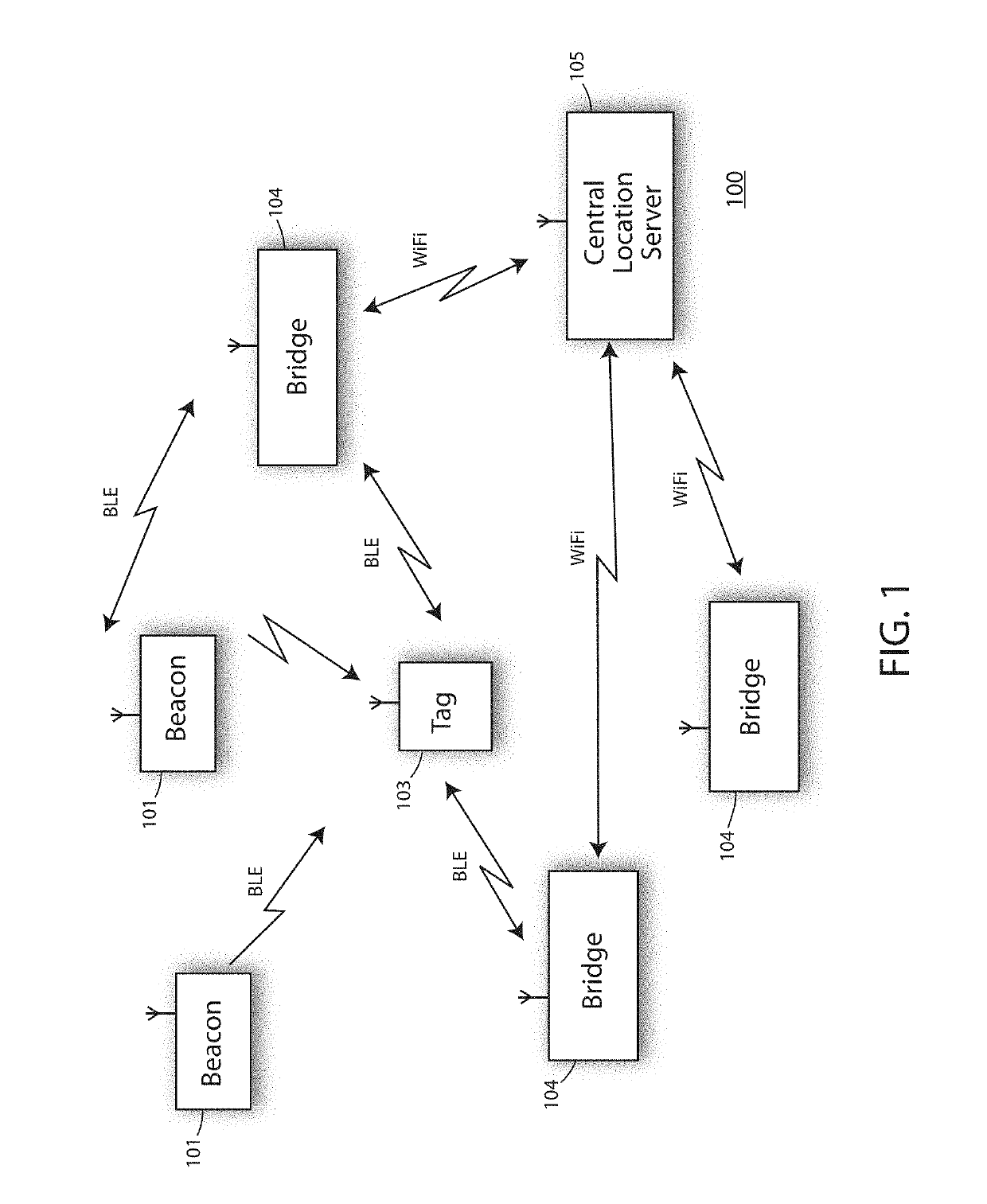
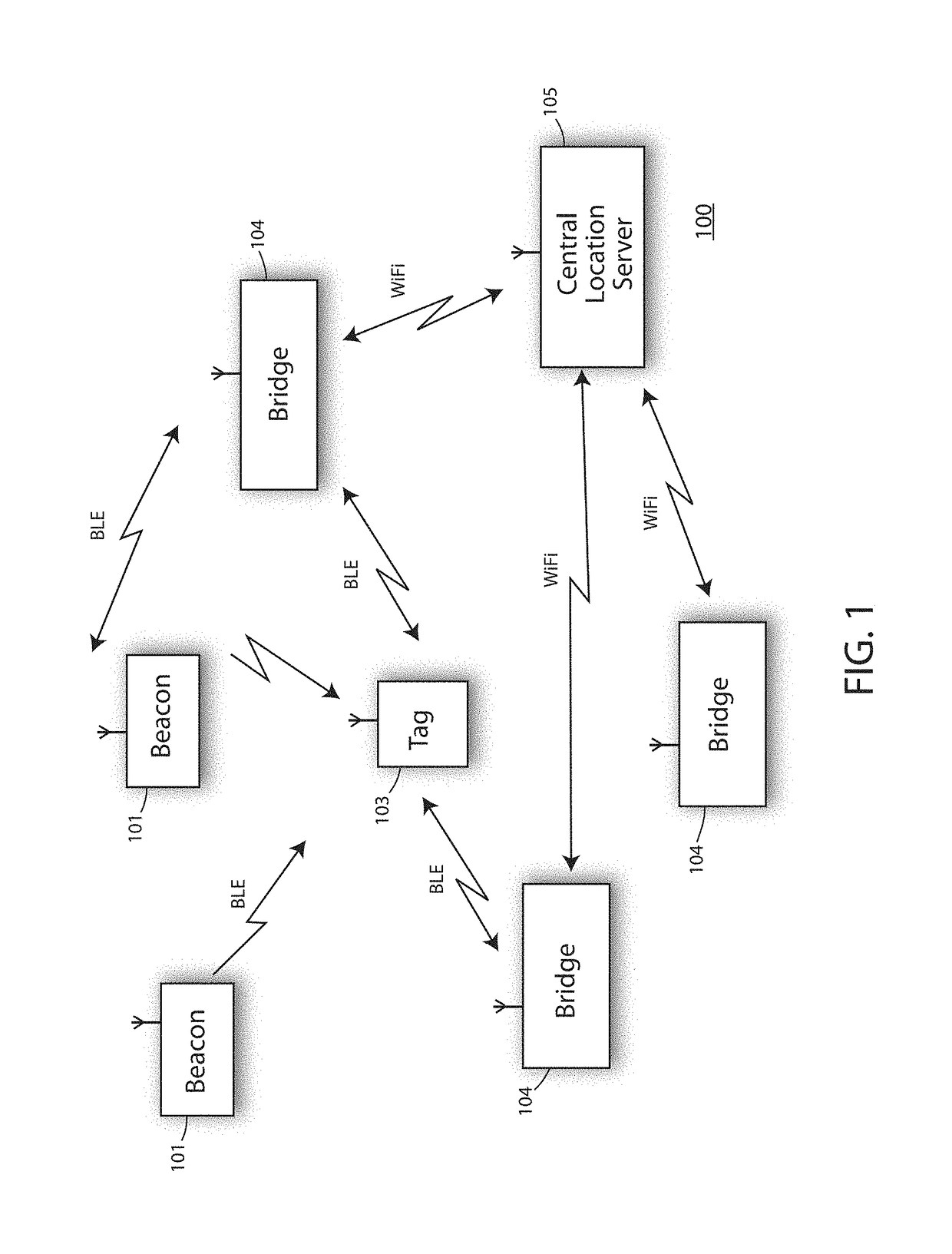
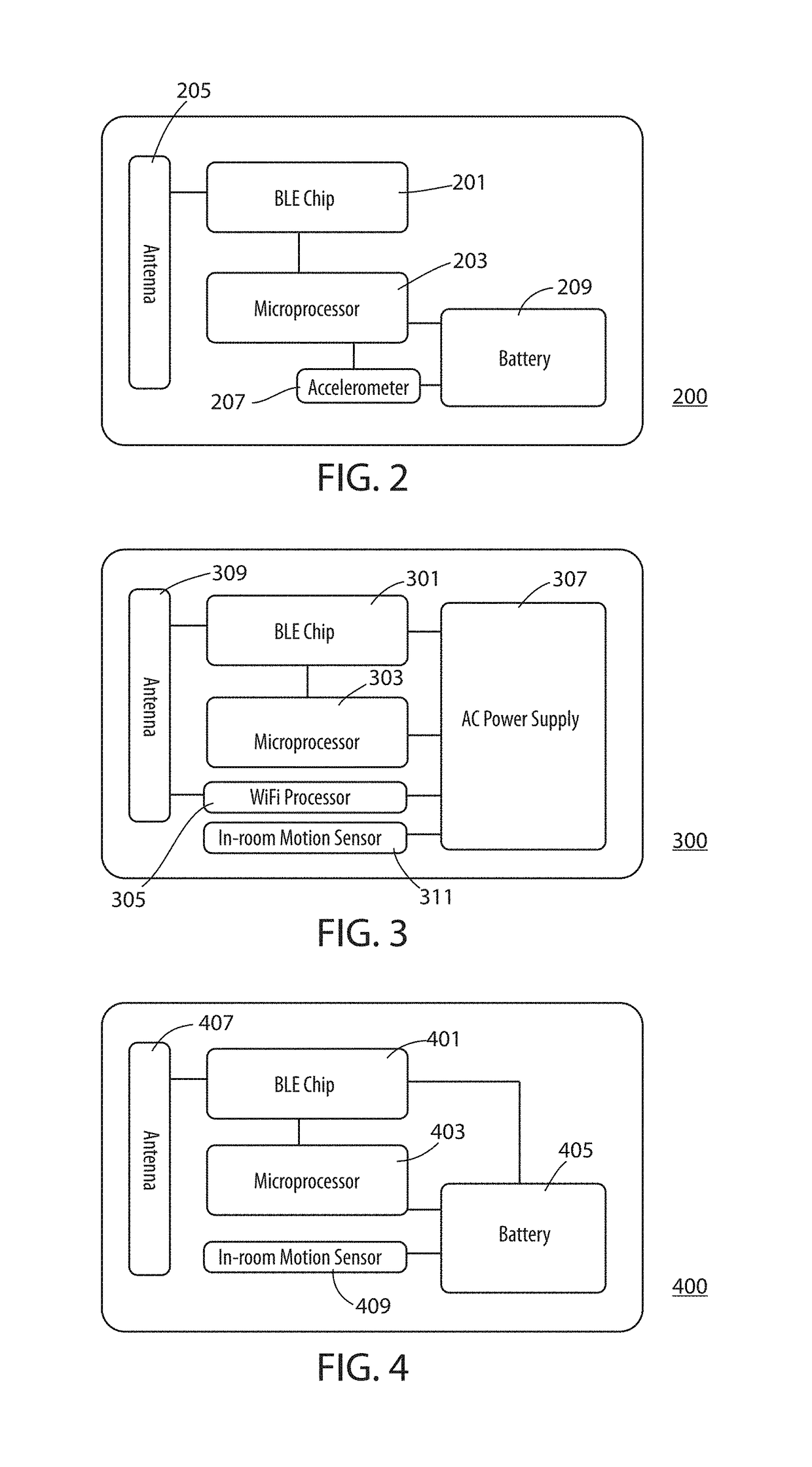
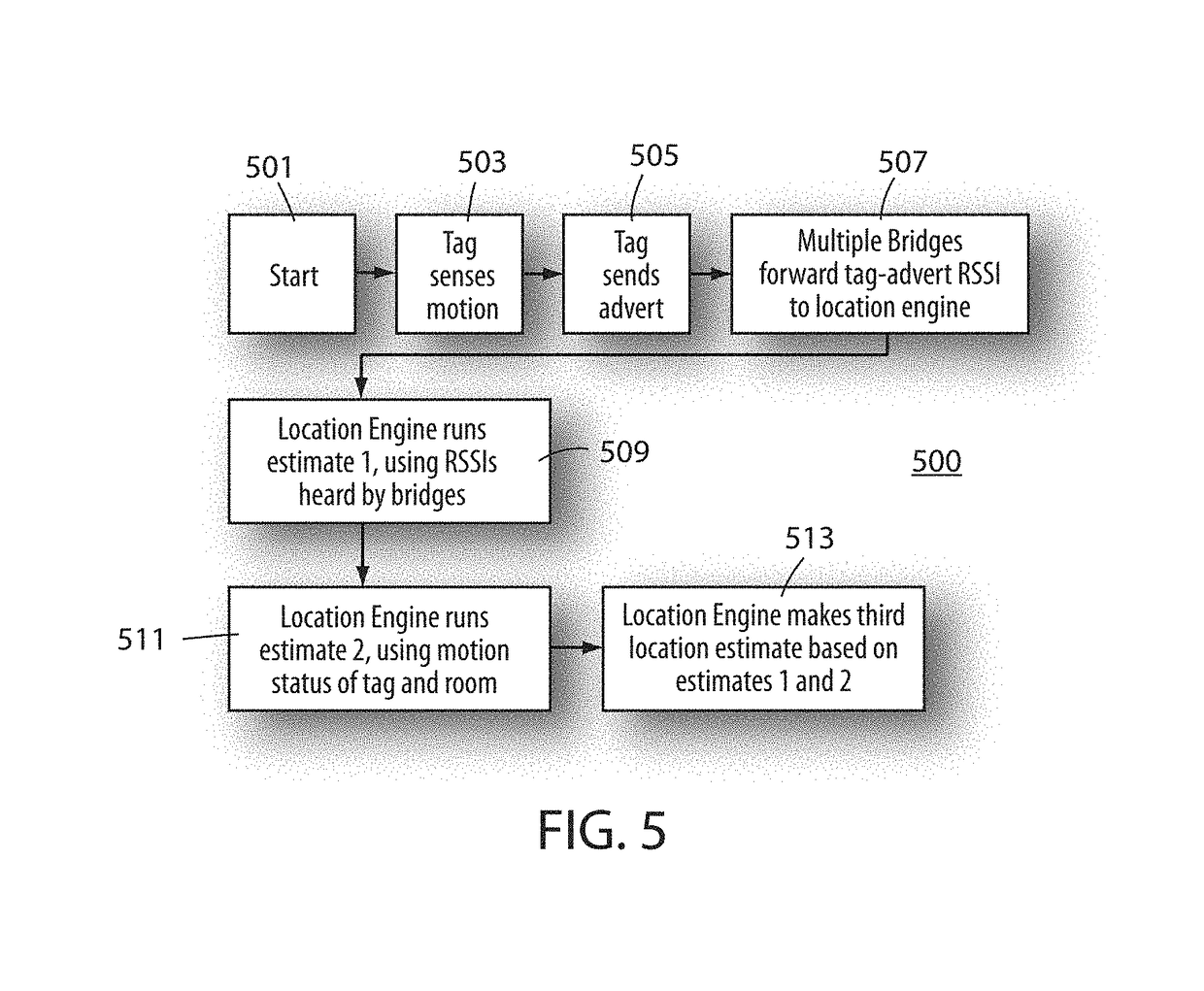
Real-time location system (RTLS) having tags, beacons and bridges, that uses a combination of motion detection and RSSI measurements to determine room-location of the tags
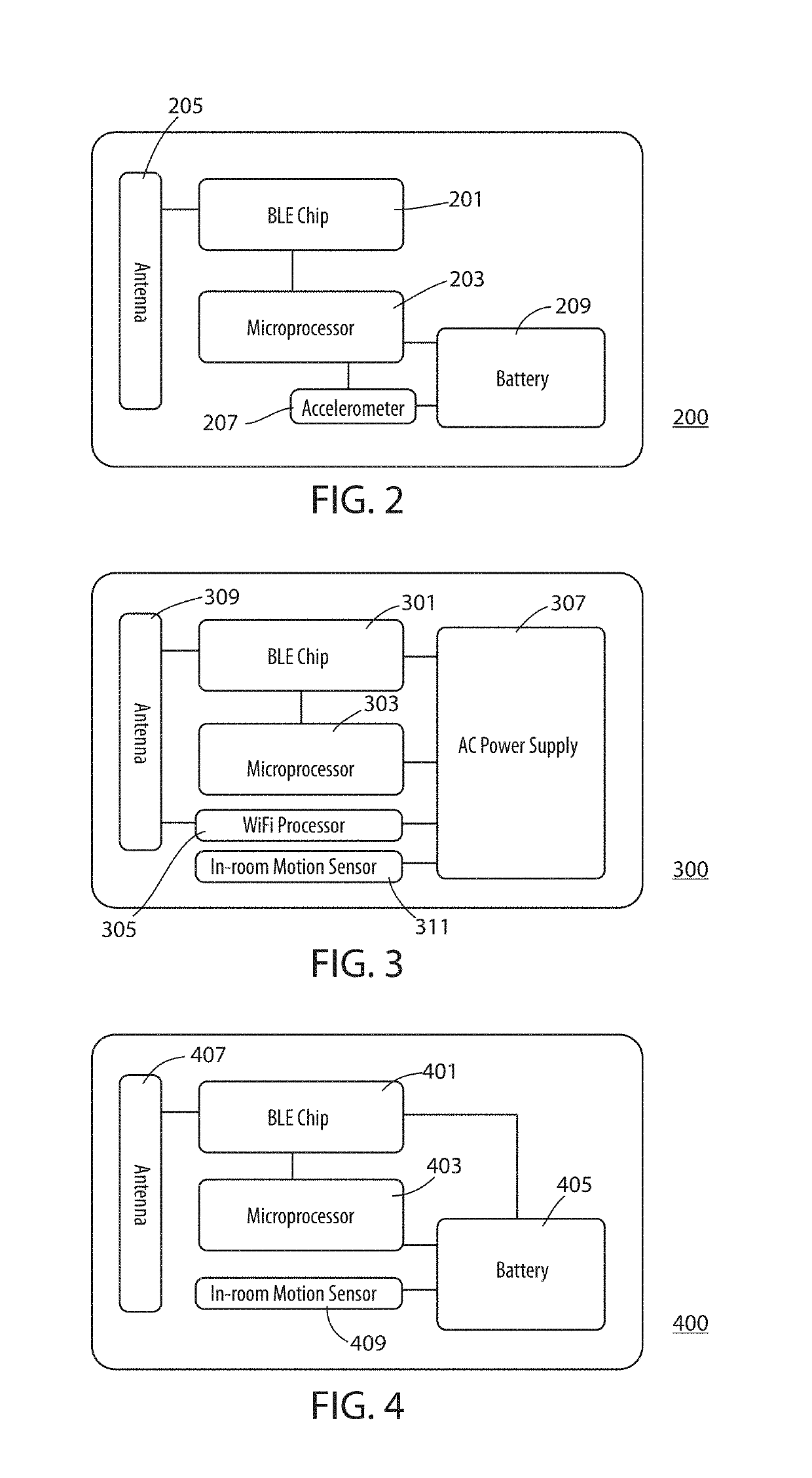
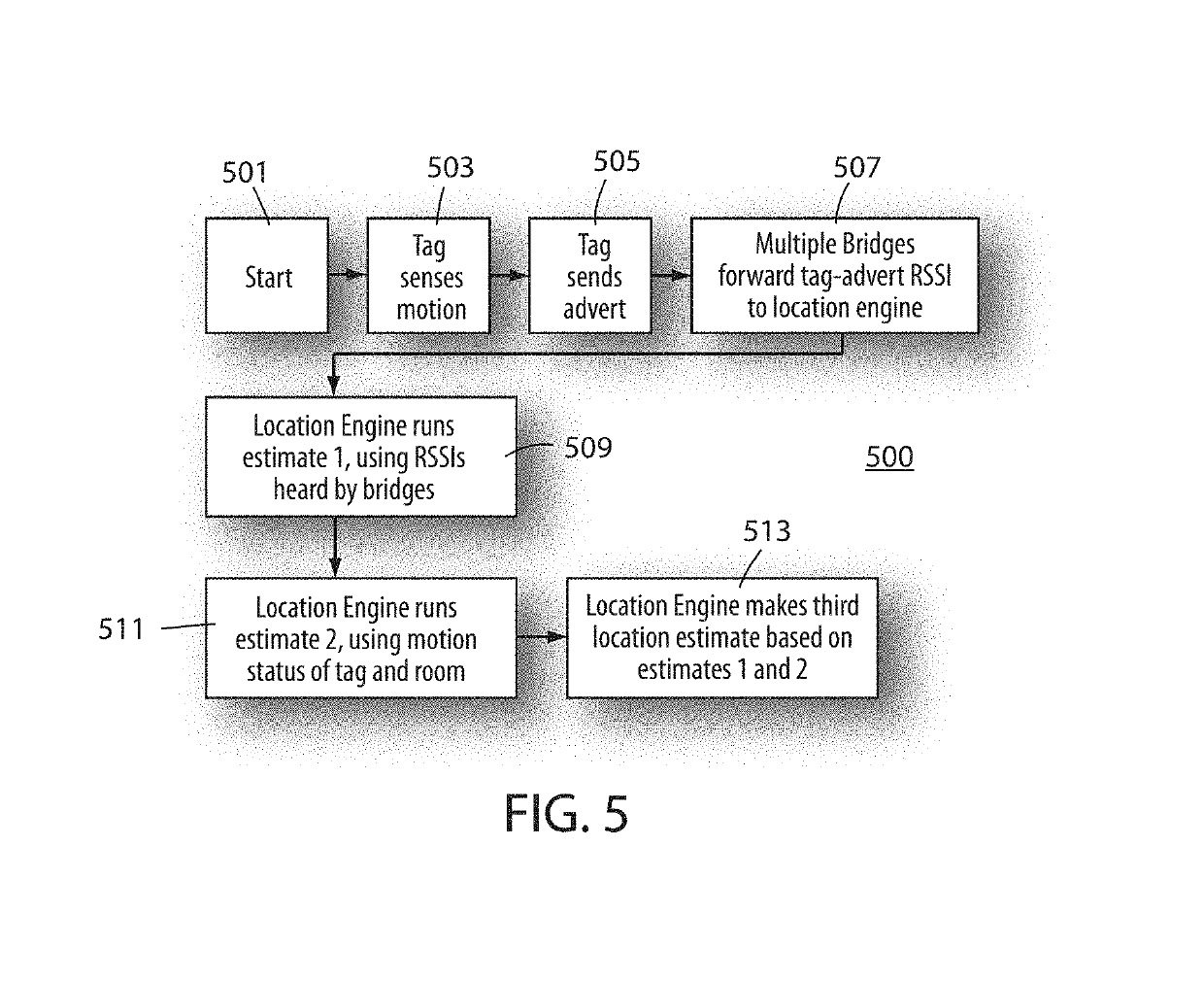
A real-time location system (RTLS) uses transmitting and listening tags, bridges, and beacons. The fixed beacons broadcast BLE advertisements containing motion-status information about recent history of perceived motion in. a room as determined from a motion sensor in the beacon. The bridges forward the beacon's received advertisements to a location engine, which records timestamps of motion events seen by each beacon in each room. One or more tags then report their own motion status based on a tag-based accelerometer. The system utilizes a series of location-engine steps, to estimate the room-location of the tags based on a specific combination of RSSI analysis, and a comparison of tag-motion history to the perceived arid recorded motion-status in a room. This analysis of tag-motion history and motion-in-room status produces a better estimate of room-level location of the tag than can be estimated by simple proximity or multi-lateration using radio signal strengths.
Owner:INFINITE LEAP
Anti-collision method for identifying multiple radio frequency identification (RFID) tabs
InactiveCN102622564AImprove efficiencyImprove communication stabilitySensing record carriersTime rangeReceived signal strength indication
The invention discloses an anti-collision method for identifying multiple radio frequency identification (RFID) tabs, which is characterized in that according to the index of a radio signal strength indicator (RSSI) communicating between the RFID tabs and a reader, regional division is performed on the induction range of the reader to form a plurality of different induction areas; the RFID tabs covered by each induction area form a corresponding tab group; and moreover, data are transmitted by the RFID tabs in different tab groups at different time ranges, whereas data transmission is realized between the RFID tabs in the same one group and the reader by adopting a conventional anti-collision algorithm. The problem that normal communication cannot be realized because signal collision is generated in the communication process of a great number of tabs and the reader can be effectively solved, the identification efficiency under such the condition is greatly increased, and the misreading rate can be effectively reduced. The reader is higher in reading efficiency and communication stability when reading the information of a great amount of tabs.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Radio frequency warning system for ferromagnetic threats
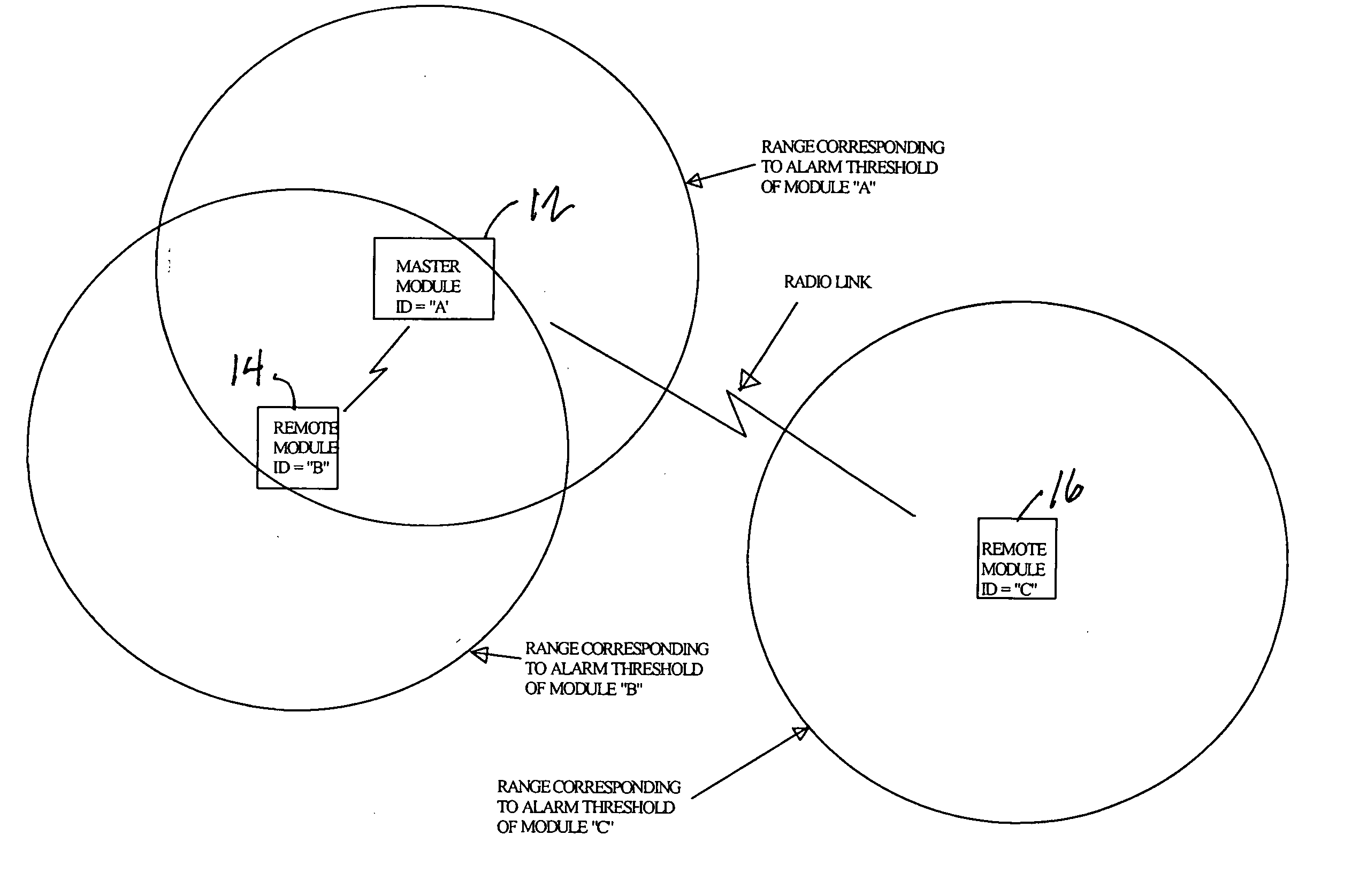
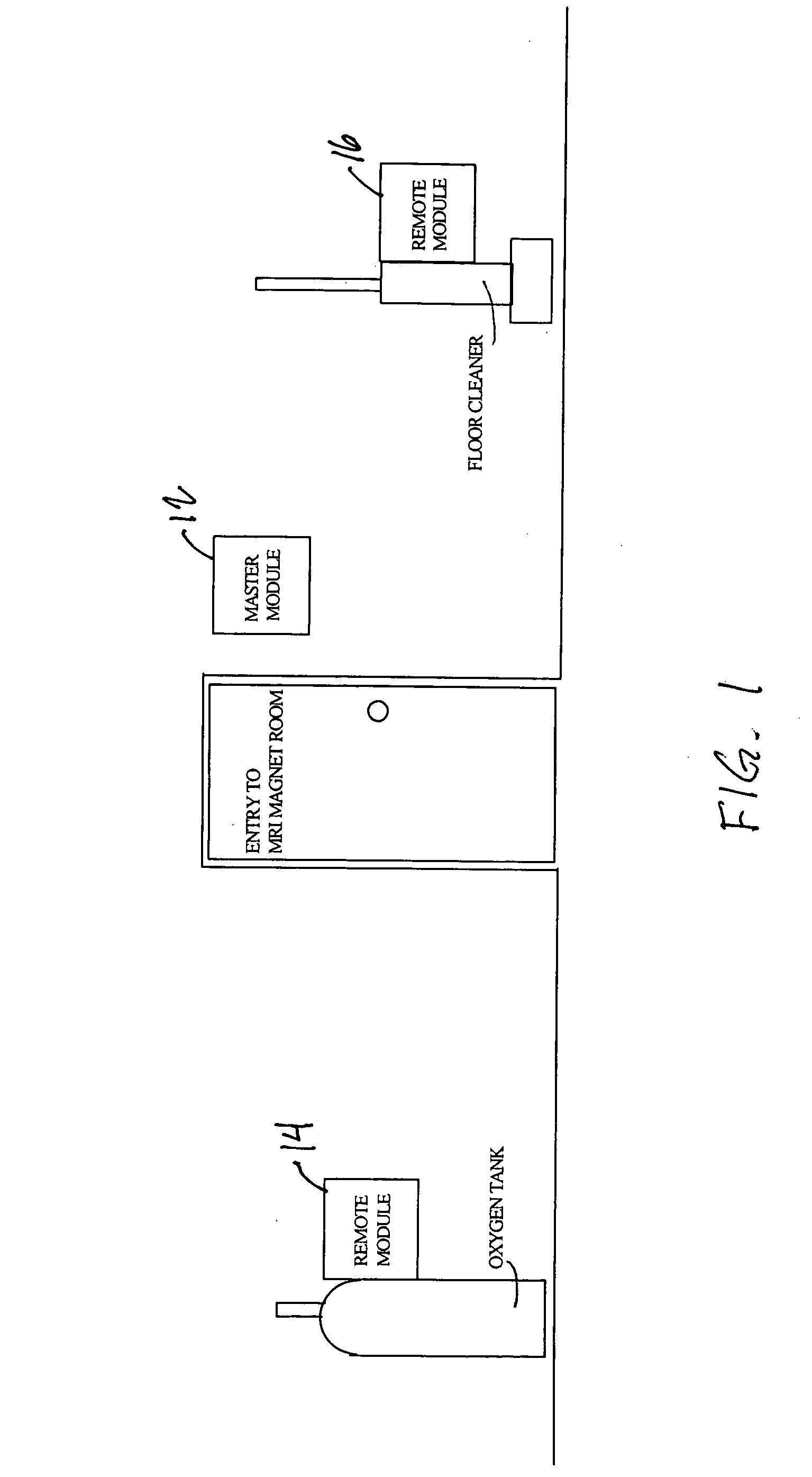
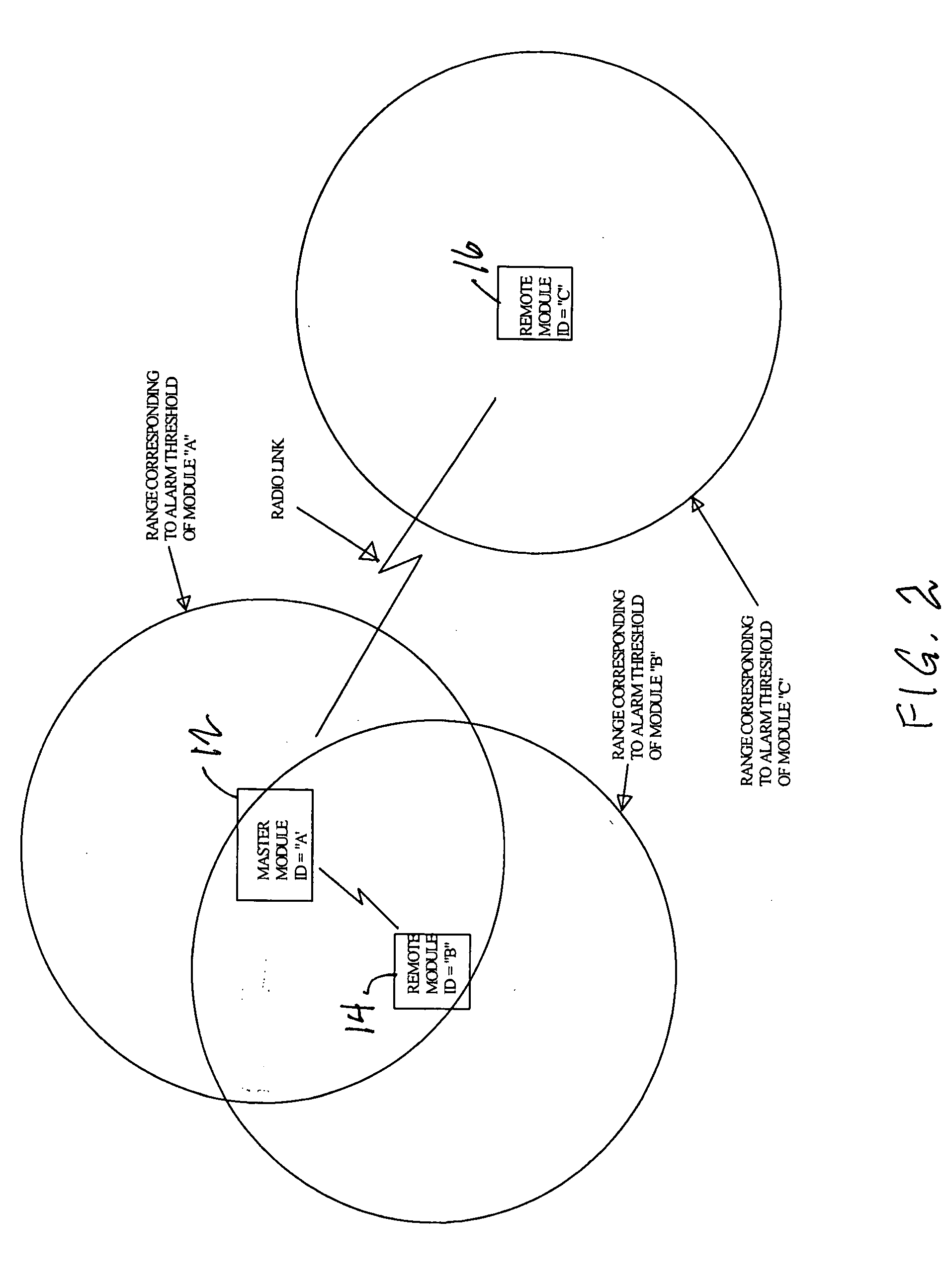
InactiveUS20070296576A1Avoid interferenceOptical signallingAlarmsTransceiverUltimate tensile strength
A ferromagnetic threat warning system utilizing two or more radio frequency transmitters or transceivers. A remote transmitter or transceiver is attached to each ferromagnetic threat that may enter the area to be protected. A master receiver or transceiver is mounted at each door controlling entry into the area to be protected. Communication between any master unit and one or more remote units generates an alarm when one or more threat objects approaches within a preselected distance of any master unit. Approach of a threat object within the preselected distance from a door can be detected when the strength of a radio signal between the remote unit associated with the threat object and the master unit near the door reaches a predetermined level. Generation of an alarm can be initiated at either the affected remote unit or the affected master unit. Generation of an alarm at either the affected remote unit or the affected master unit can also result in generation of an alarm at the other of the two units.
Owner:MEDNOVUS
Mobile robot and charging system and charging control method thereof
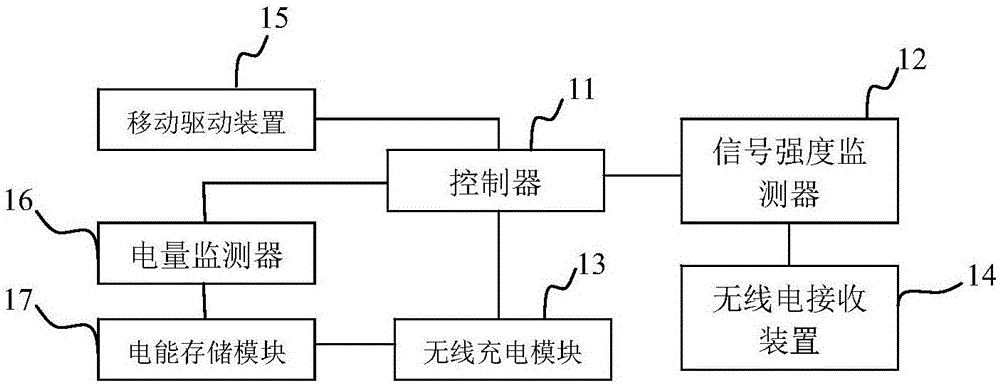
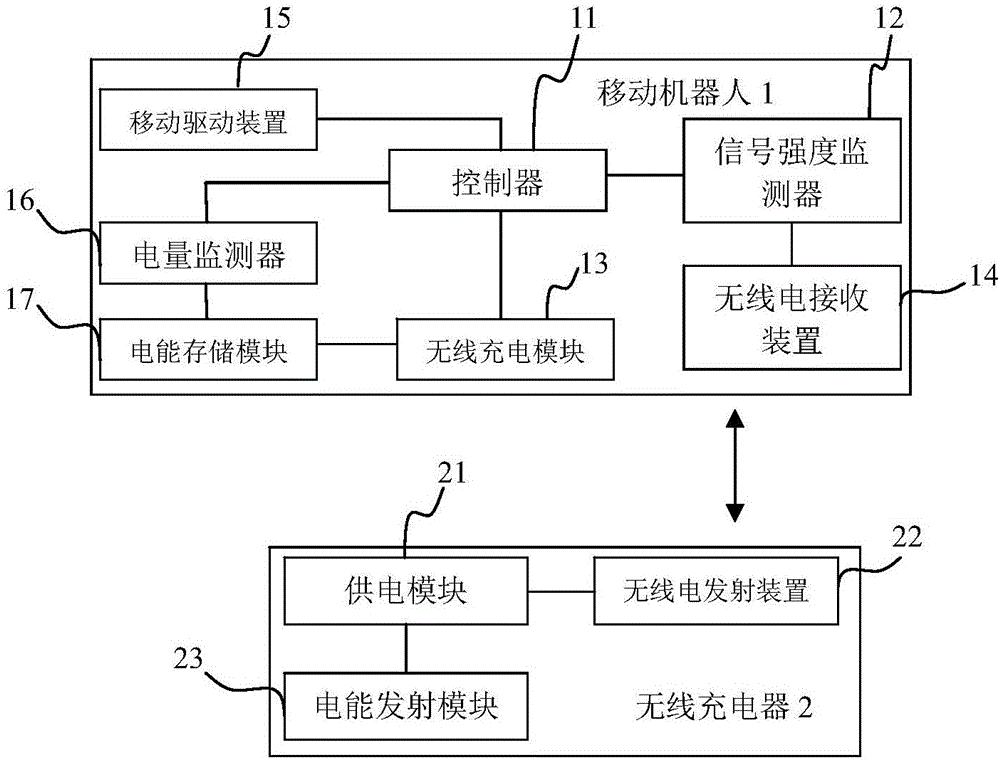
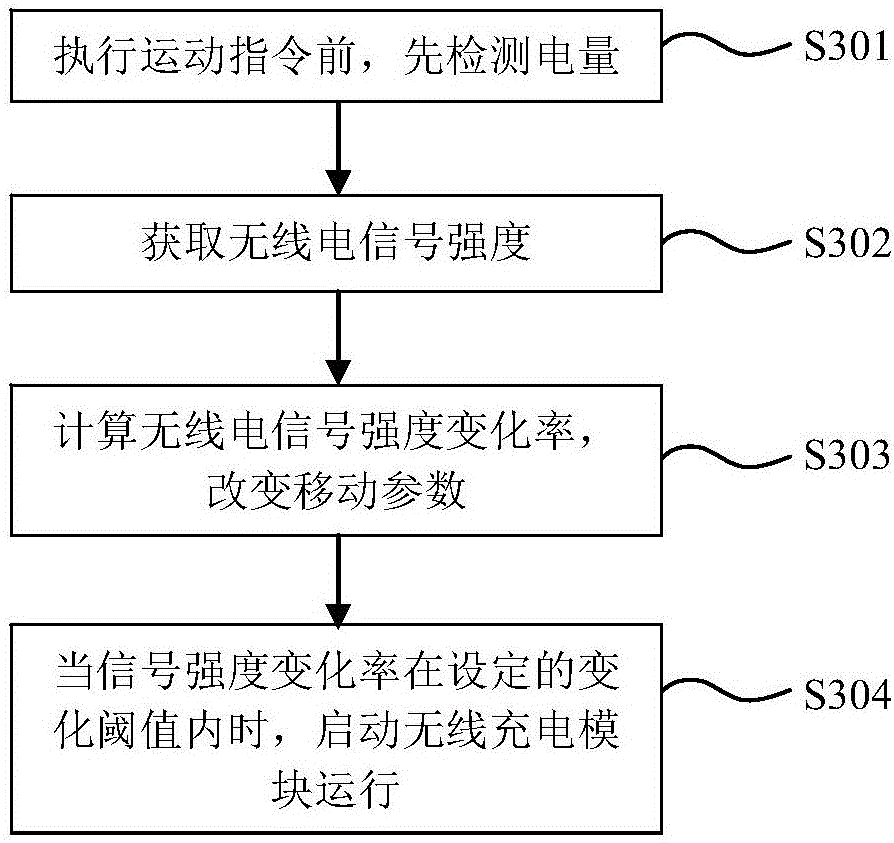
PendingCN106671138AAvoid wear and tearExtended service lifeProgramme-controlled manipulatorBatteries circuit arrangementsOperating instructionRadio reception
The invention provides a mobile robot and a charging system and charging method thereof. The mobile robot comprises a controller, and also comprises an electrical quantity monitoring device, a mobile drive device, a signal strength monitoring device, a radio receiving device, a wireless charging module and an electric energy storage module which are all connected with the controller. The charging control method comprises the steps that the controller sends a remnant electrical quantity acquisition instruction to the electrical quantity monitoring device when receiving a motion instruction from a user; when the electrical quantity is small, the controller sends a current position radio signal strength acquisition instruction to the signal strength monitoring device, the radio signal strength variation rate is calculated, and the moving parameters of the mobile drive device are set according to the obtained radio signal strength variation rate; and when the obtained radio signal strength variation rate meets the set variation threshold value, an operating instruction is sent to the radio charging module. By adoption of the wireless charging mode, precise positioning and charging port inserting are not needed, abrasion of charging equipment can be avoided, the service lives of a charger and the charging port of the mobile robot are prolonged.
Owner:北京创想智控科技有限公司
Communication device and method for reminding the user of information processing status with the display part
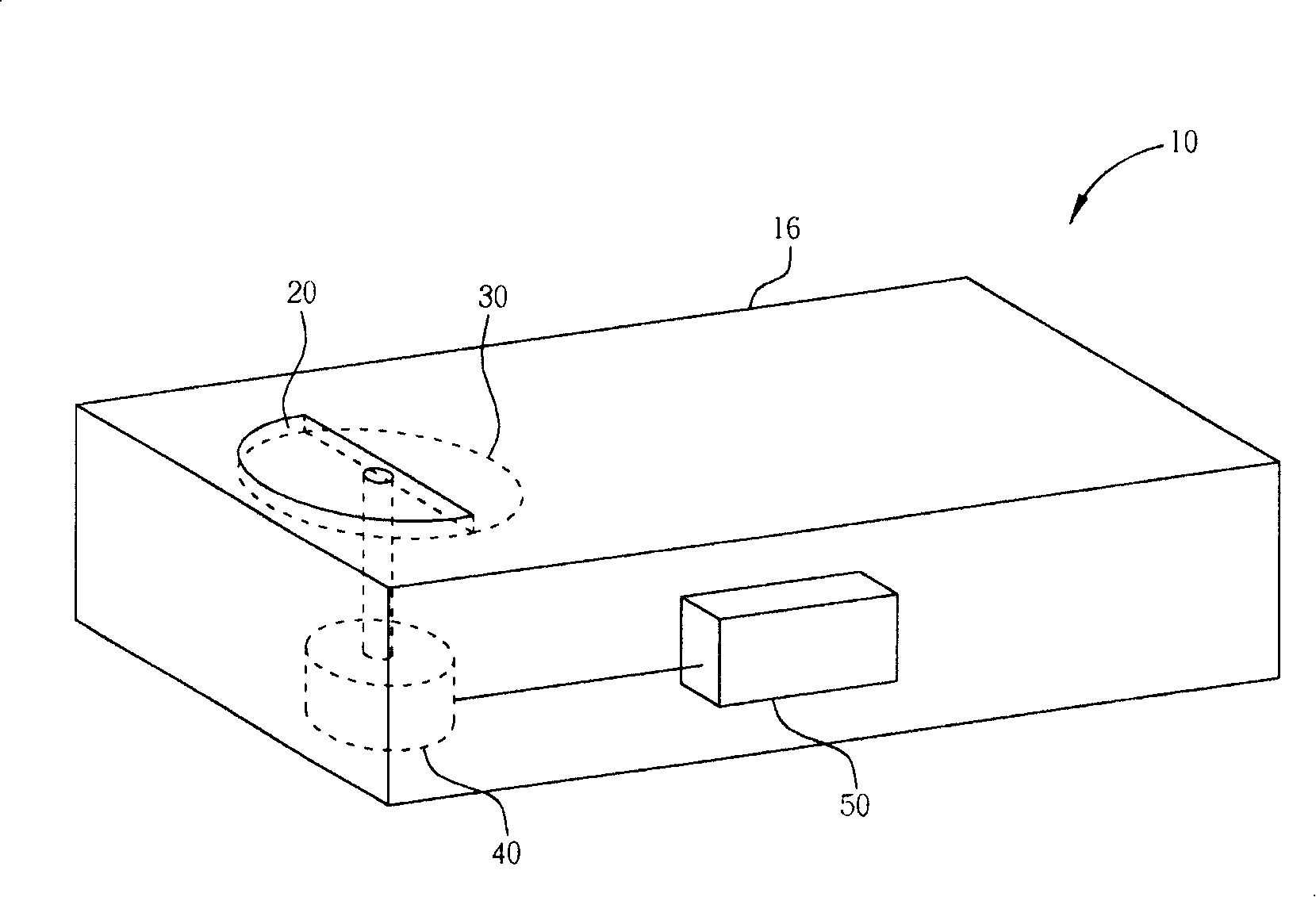
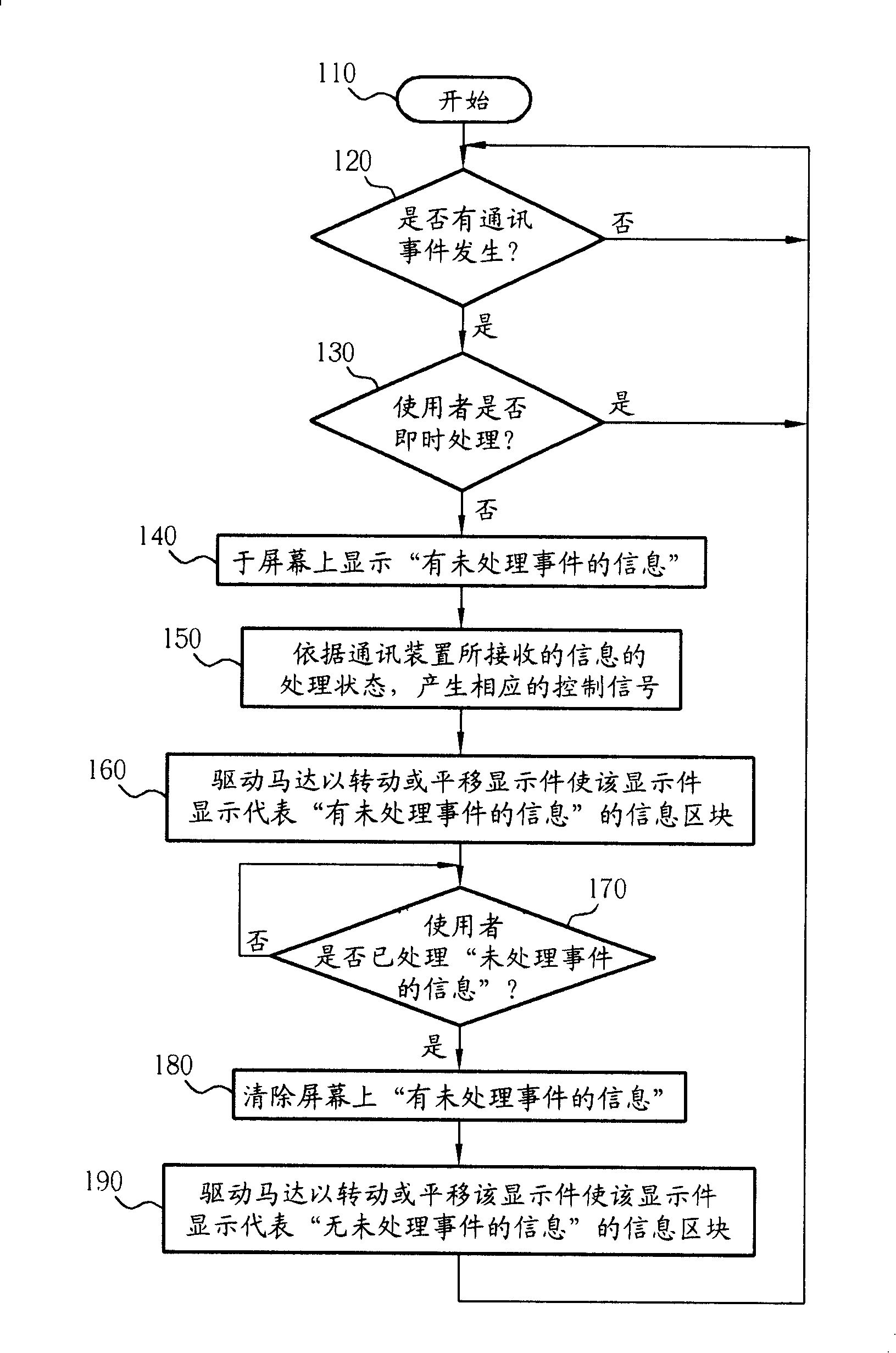
InactiveCN101188824ATo overcome the problem of having to consume power all the time to remind the user of specific informationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelephone set constructionsInformation processingCommunication device
The invention relates to a method by setting a display component on the conspicuous part of a communication device which can display different information pieces, and an information piece can be displayed in the normal power-on state. When specific information is produced (such as untreated events like a missed call or a new short message, or indication events like battery state information or radio signal strength information), a motor which can control the display component is driven to change the information piece displayed by the display component in the conspicuous part of the communication device, and the information piece displayed by the display component in the conspicuous part can be maintained without continuous extra power supply.
Owner:BENQ CORP
System and methods for determining the location dynamics of a portable computing device
InactiveUS20050270235A1Easy to trackFacilitate communicationData processing applicationsDirection finders using radio wavesSimulationPositioning system
A location system for locating and determining the motion and velocity of a wireless device. The methods include direct inferences about whether a device is in motion versus static based on a statistical analysis of the variation of radio signal strengths over time. The system is trained according to a sparse set of identified locations from which signal strengths are measured. The system uses the signal properties of the identified locations to interpolate for a new location of the wireless device. The system uses a probabilistic graph where the identified locations of the floor plan, expected walking speeds of pedestrians, and independent inference of whether or not the device is in motion are used to determine the new location of the device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for the relative navigation of aircraft and spacecraft using a phased array antenna
InactiveUS20060232470A1Beacon systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringNavigation system
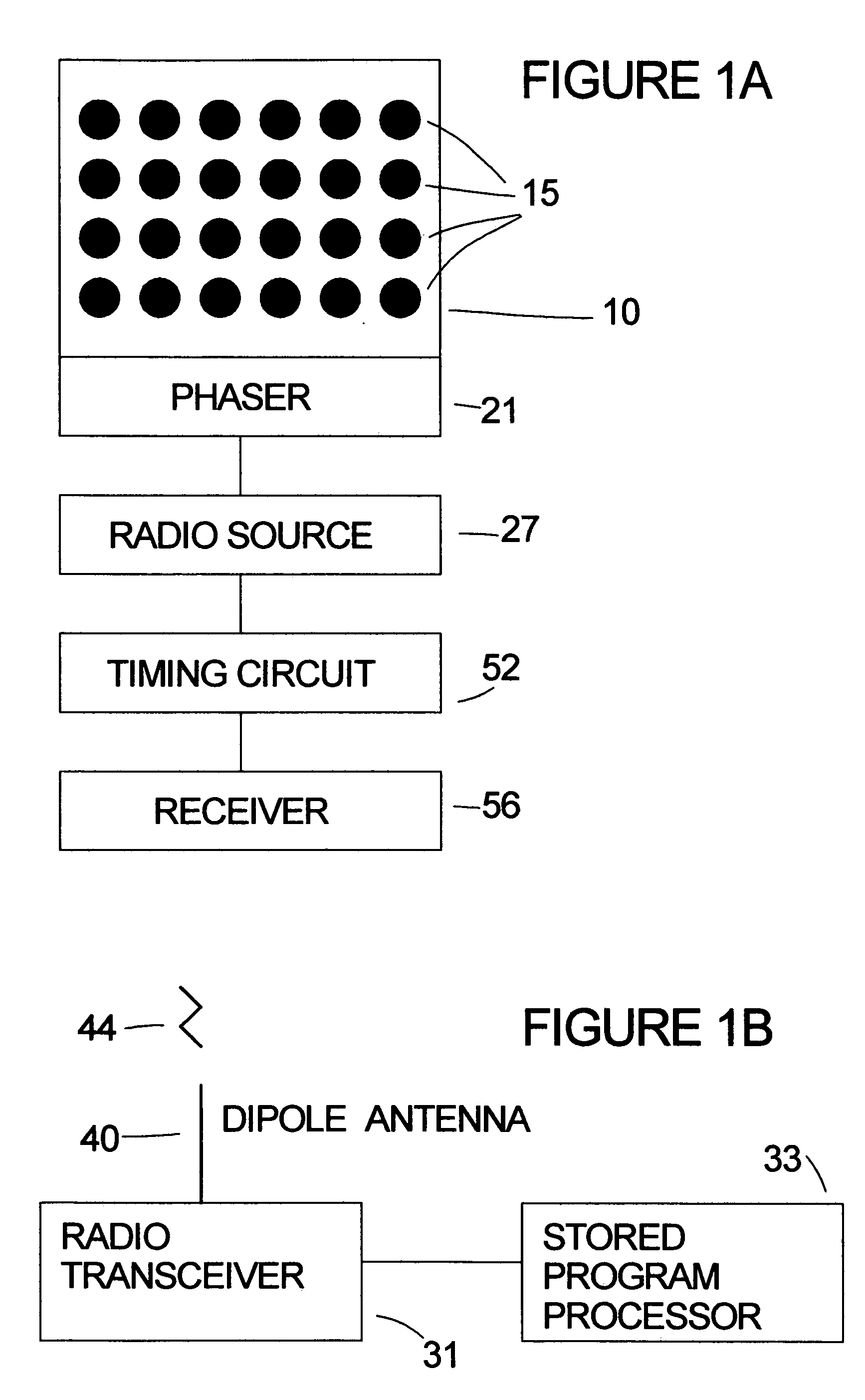
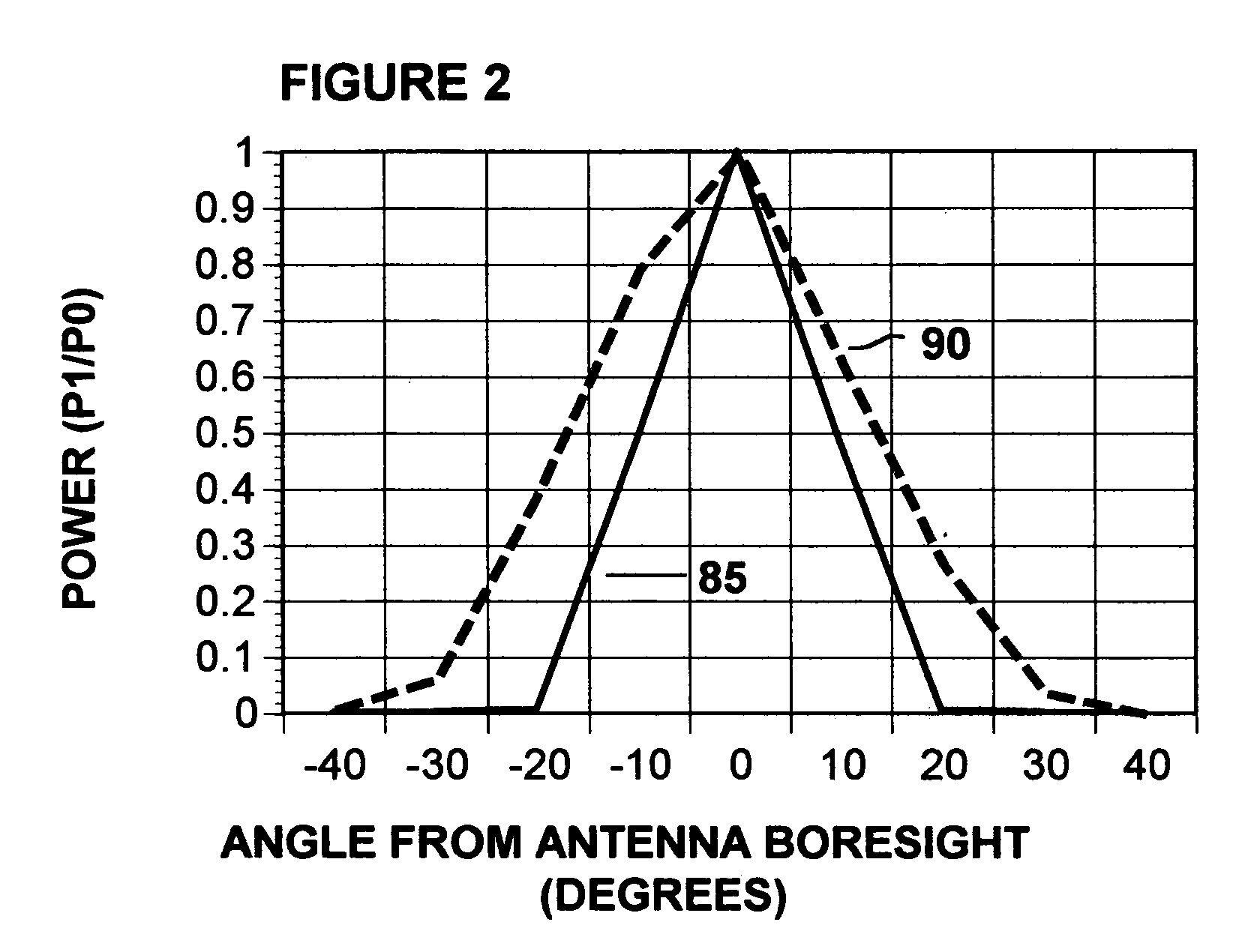
A system for the relative navigation of aircraft and spacecraft is disclosed which uses a series of short duration, unmodulated radio pulses transmitted from a phased array antenna. The aircraft or spacecraft whose position is to be determined from another is called as the local station, whereas the other craft with the phased array antenna system is called as the transmitting station. The local station transmits a radio query pulse to the transmitting station. In response to the radio query pulse, the transmitting station transmits a series of unmodulated radio pulses, where each radio pulse is transmitted with a three dimensional radiation pattern that is different than the three dimensional radiation patterns of the other radio pulses transmitted by the transmitting station. A receiver attached to the local station aircraft or spacecraft receives each radio pulse, generates a signal that describes the radio signal strength of the received signal and sends that signal strength number to a stored program processor which stores that signal strength number into memory. After a series of radio signals are received at the local station and at least two radio signal strength measurements are stored in memory, the stored program processor calculates the power ratio or ratios of each received radio signal strength from each radio pulse transmitted by the transmitting location. Bearing is then determined by comparing the calculated radio signal power ratios with a library of angles that correspond to specific power ratios for all radio radiation patterns transmitted. The local station also records the time elapsed from when the first radio pulse is received from the transmitting station after the radio query pulse is sent. Range is determined by dividing that elapsed time by two and multiplying that time with the speed of light.
Owner:MALLICK BRIAN
Method of offload selection inheterogeneous wireless communication networks
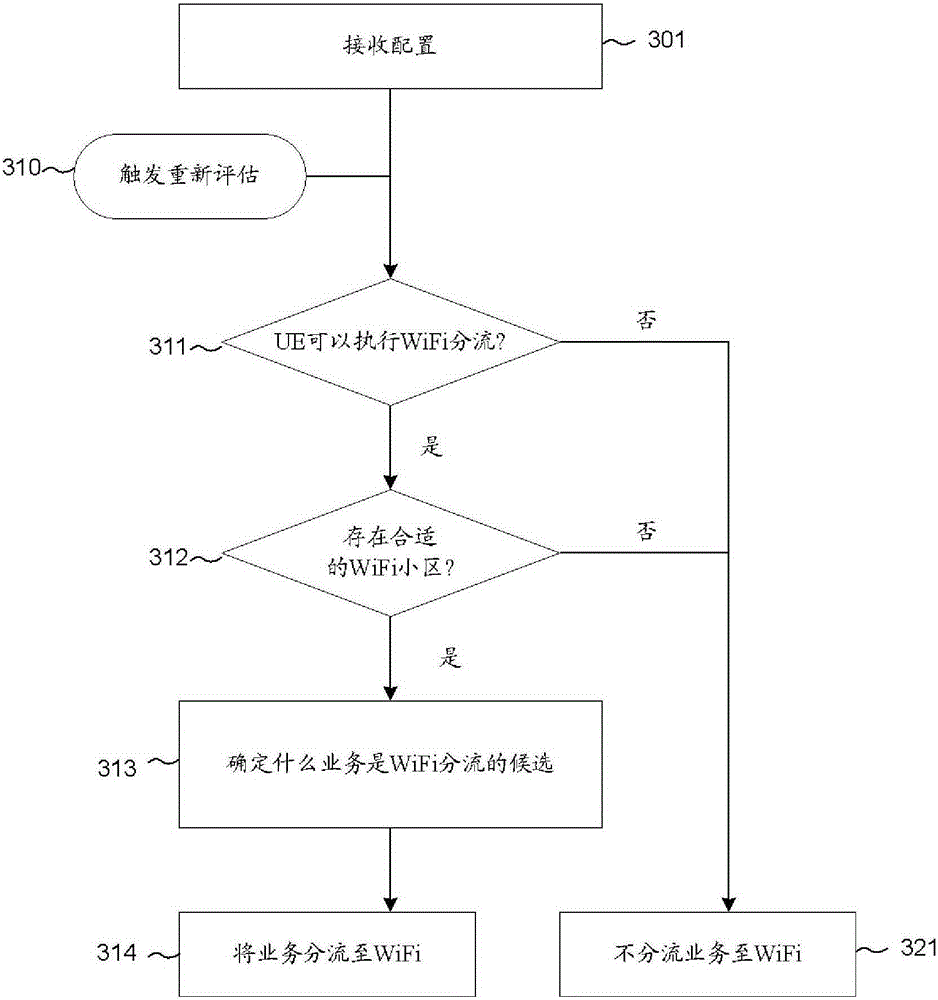
ActiveCN105191398ANetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesRadio access technologyTelecommunications
A method of offload selection for a UE to select between 3GPP RAT and WLAN cell is provided. The UE receives configuration information that applies to selecting WLAN or 3GPP radio access technology (RAT). The UE determines if the UE may perform WLAN offload by evaluating 3GPP radio access network (RAN) conditions where at least one RAN condition is related to a radio signal strength or a radio signal quality in 3GPP RAT. The UE then determines if there is at least one suitable WLAN cell by evaluating WLAN conditions. The UE also determines if there is candidate traffic for WLAN offload. Finally, the UE steers the determined traffic to WLAN if the UE may perform WLAN offload and if there is at least one suitable WLAN cell. Otherwise, the UE steers the determined traffic to 3GPP RAT.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Bluetooth low energy (BLE) real-time location system (RTLS) having simple transmitting tags, beacons and bridges, that use a combination of motion detection and RSSI measurements to determine room-location of the tags
A real-time location system (RTLS) uses Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) transmitting tags, bridges, and beacons. The fixed beacons broadcast BLE advertisements containing motion-status information about recent history of perceived motion in a room as determined from a motion sensor in the beacon. The bridges forward the beacon's received advertisements to a location engine, which records timestamps of motion events seen by each beacon in each room. One or more simple transmitting tags then report their own motion status based on a tag-based accelerometer. The system utilizes a series of location-engine steps, to estimate the room-location of the tags based on a specific combination of RSSI analysis, and a comparison of tag-motion history to the perceived and recorded motion-status in a room. This analysis of tag-motion history and motion-in-room status produces a better estimate of room-level location of the tag than can be estimated by simple proximity or multi-lateration using radio signal strengths.
Owner:INFINITE LEAP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com