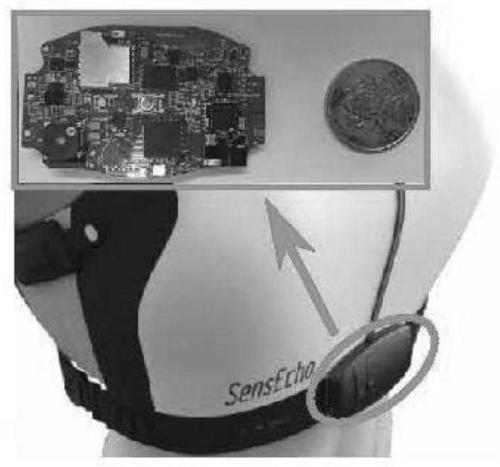
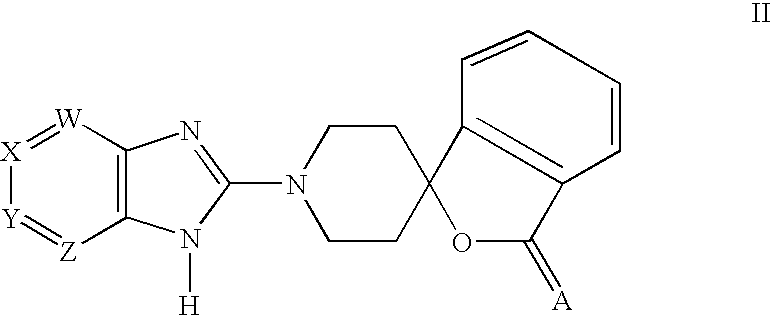
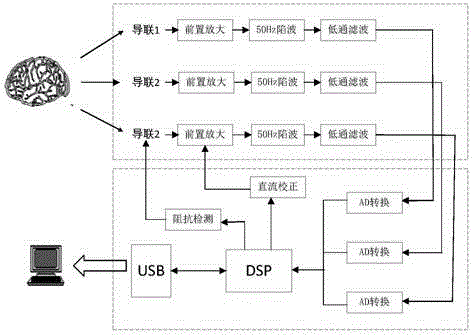
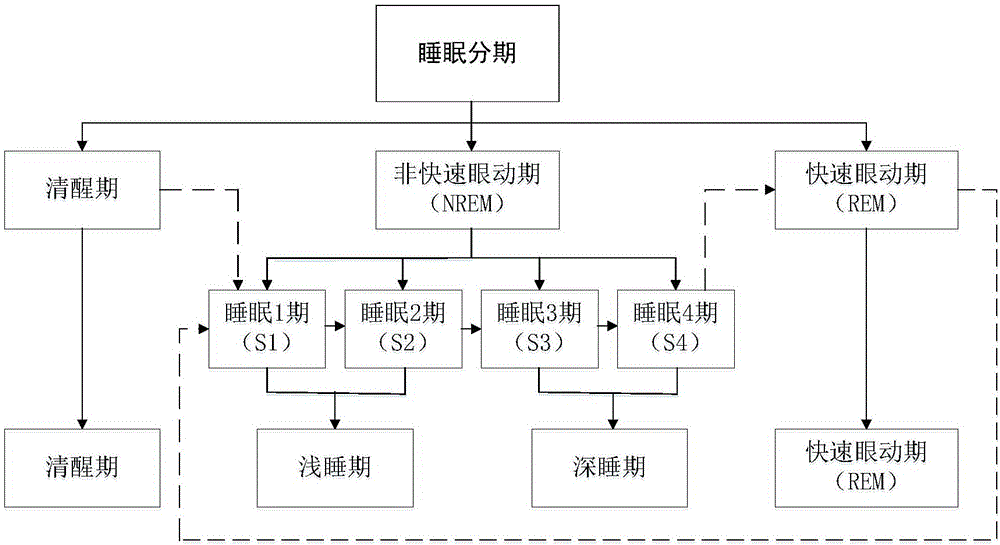
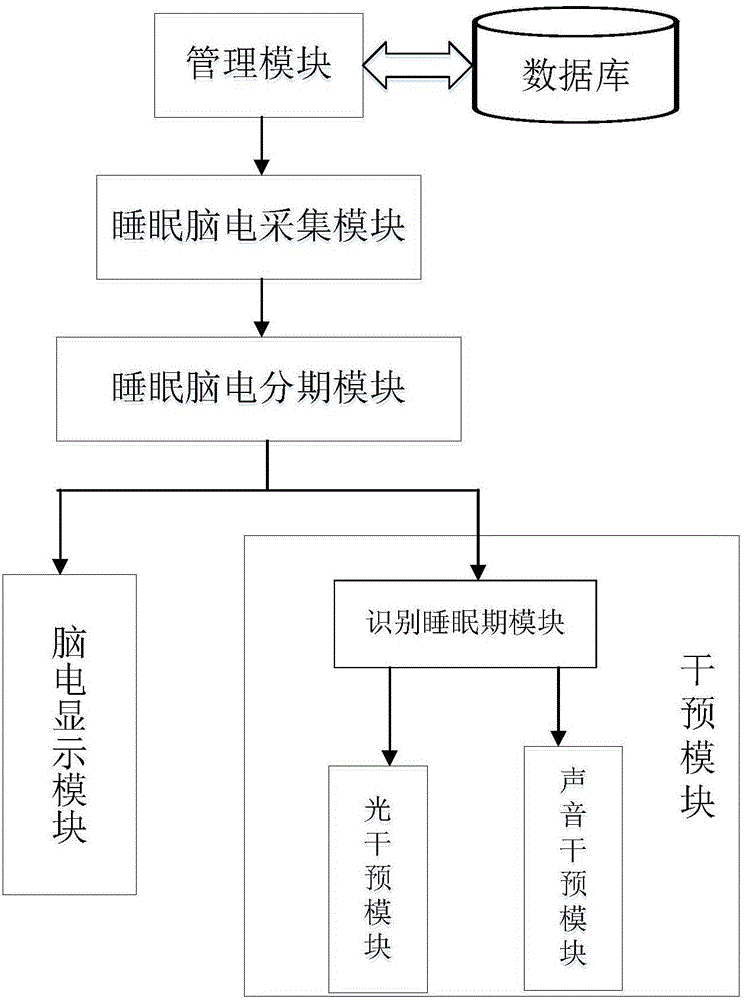
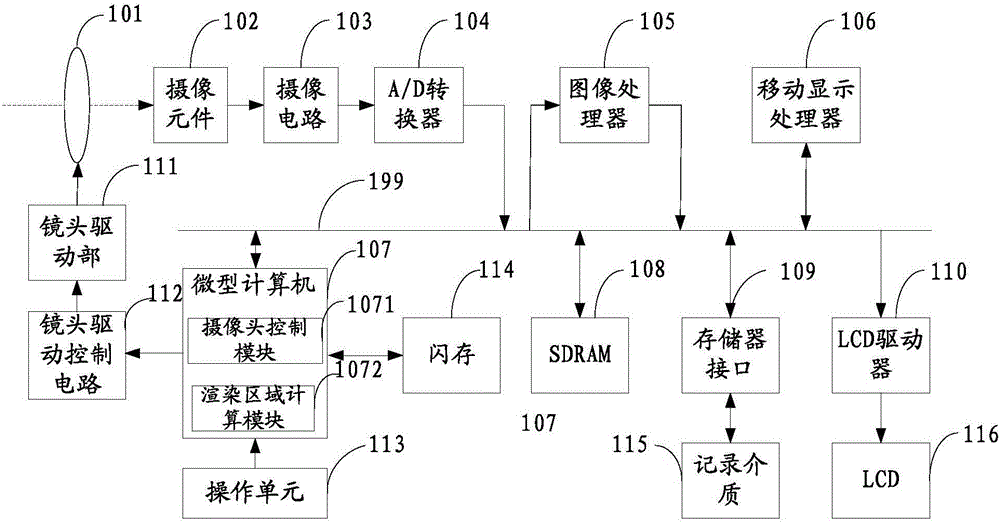
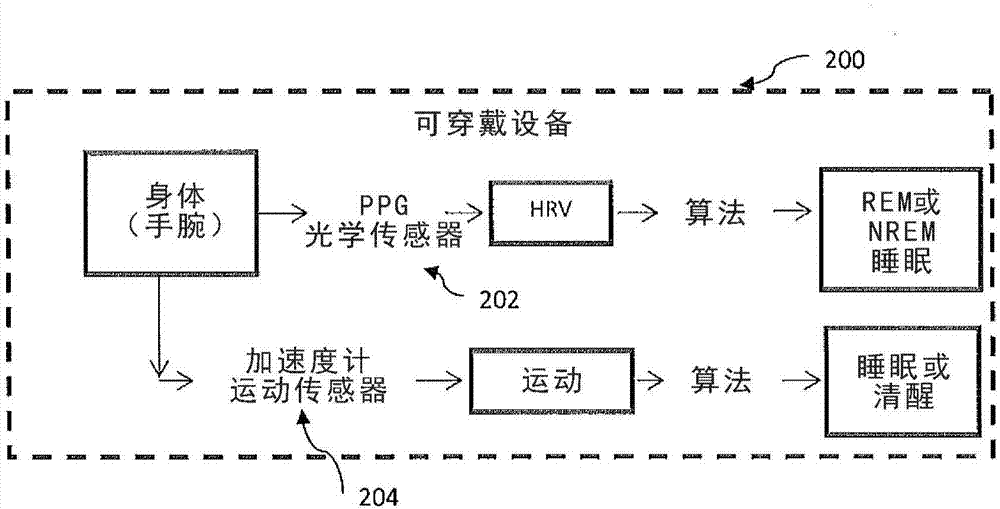
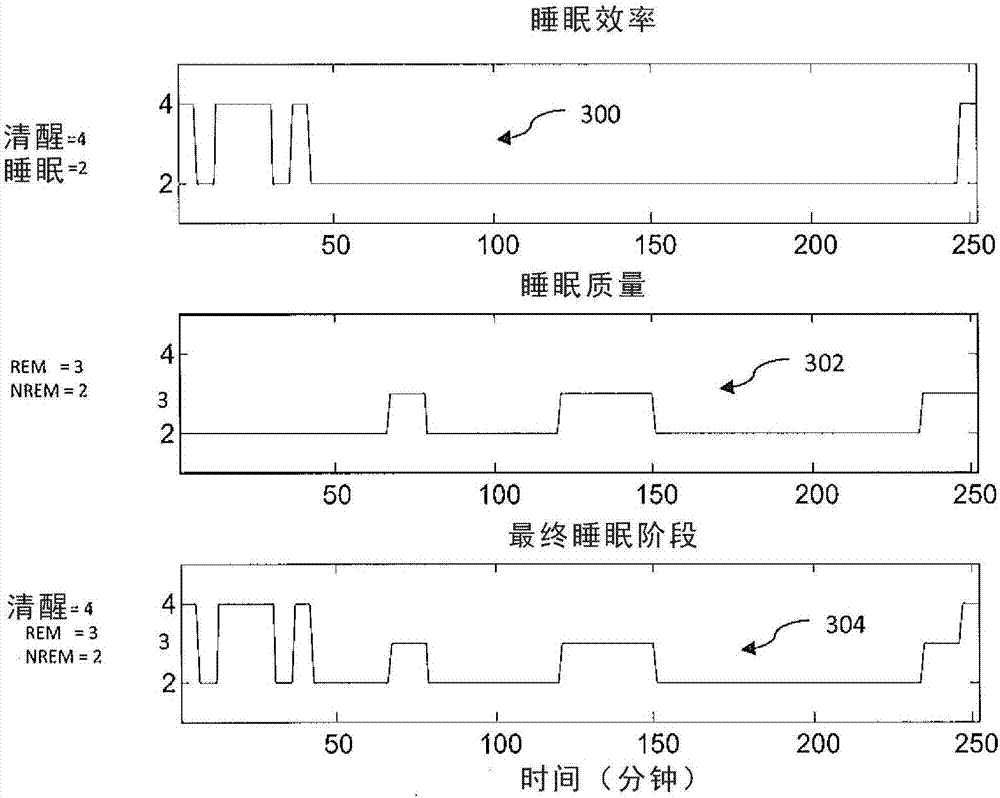
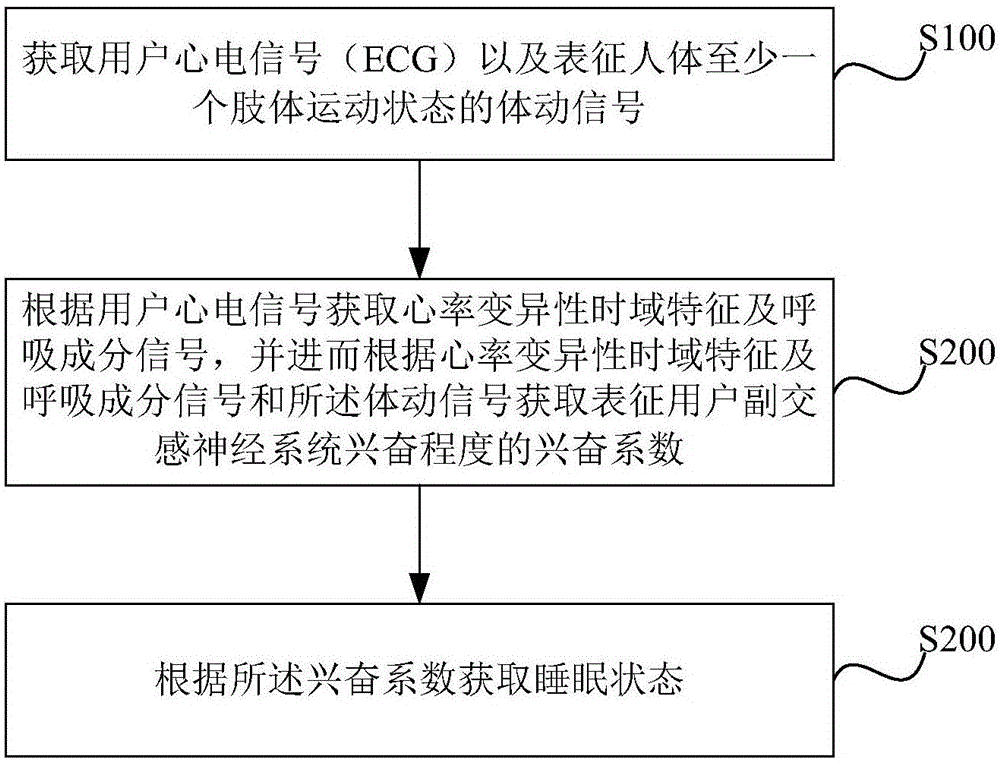
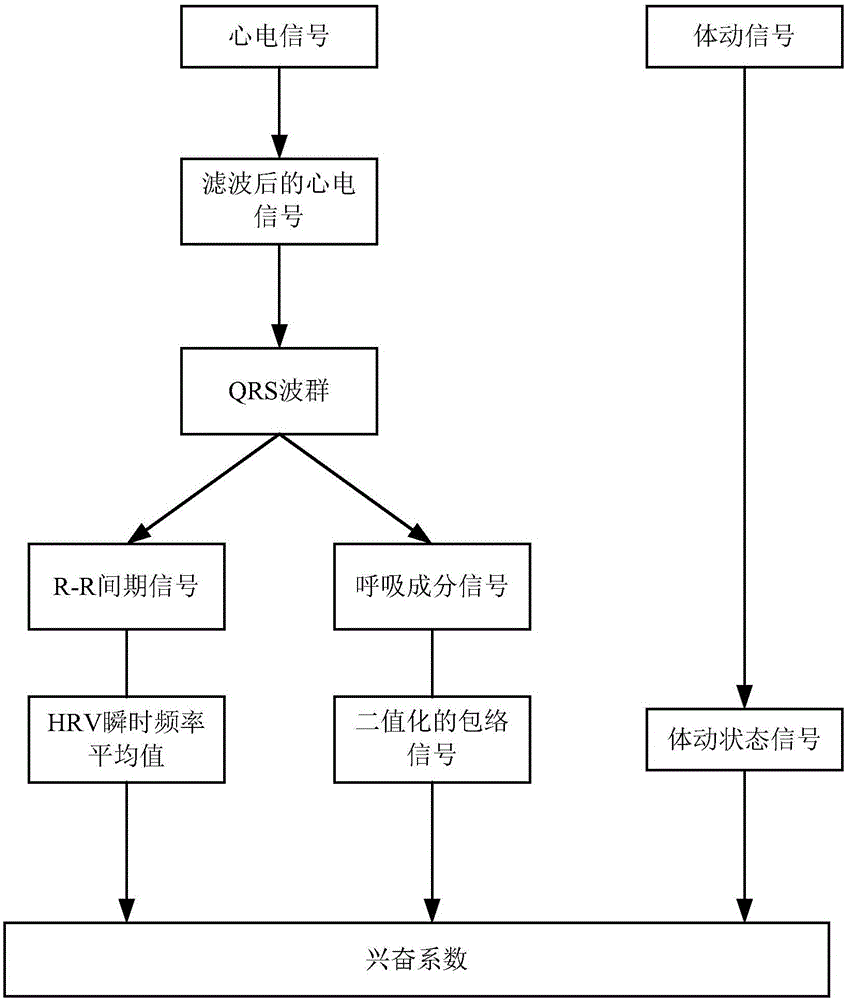
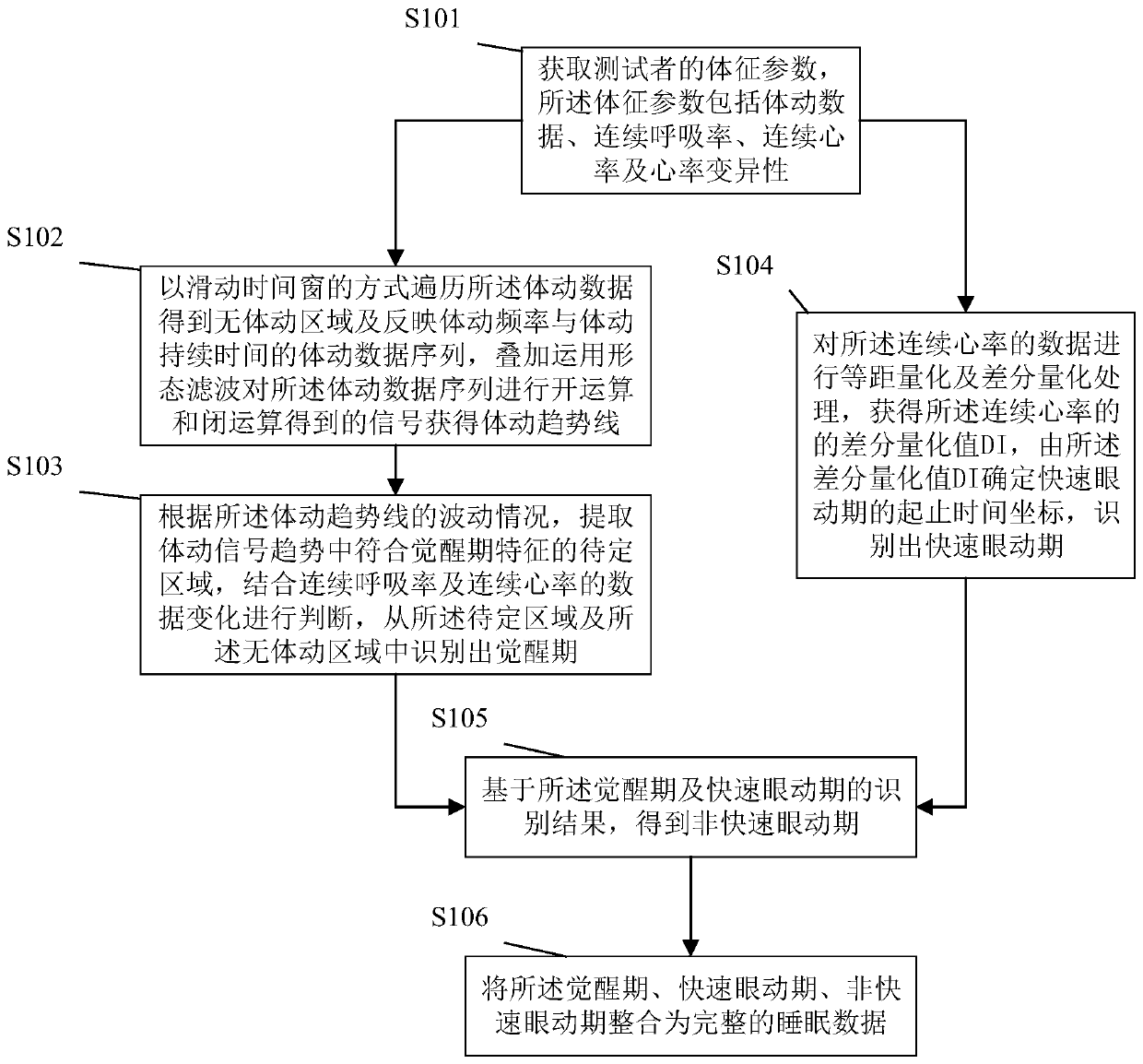
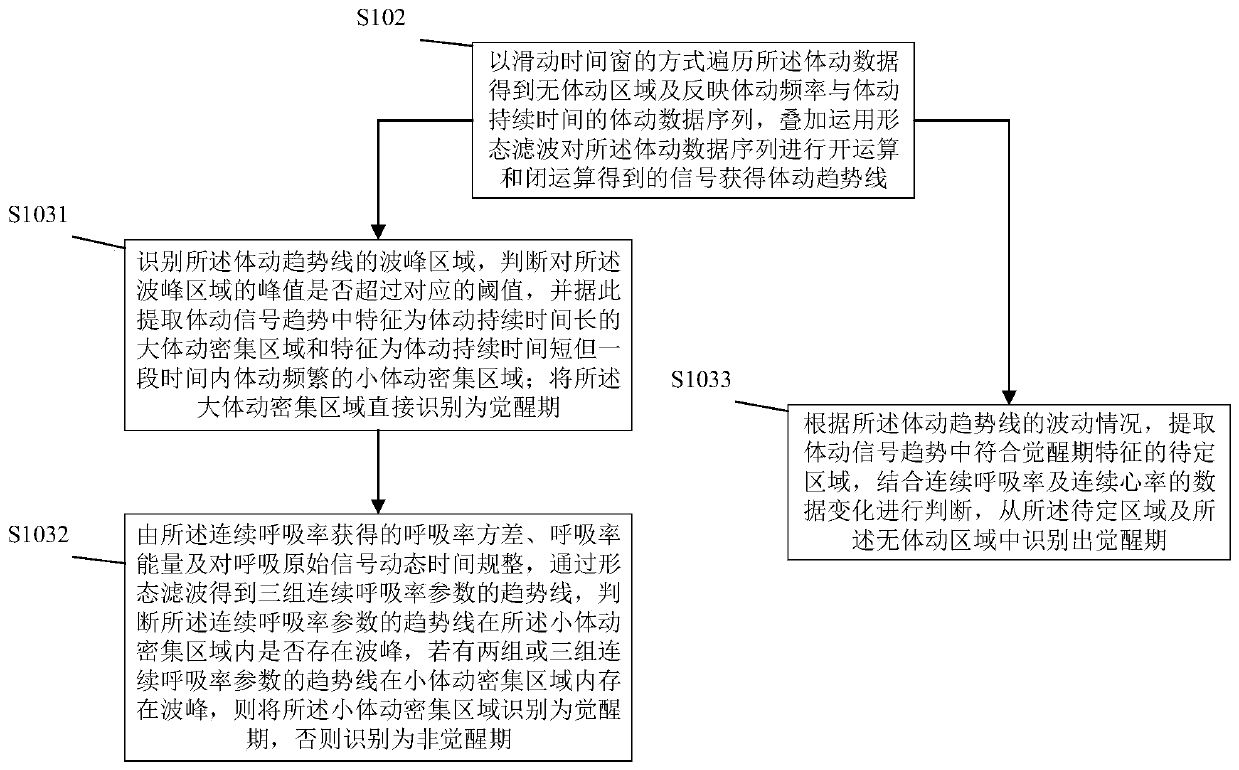
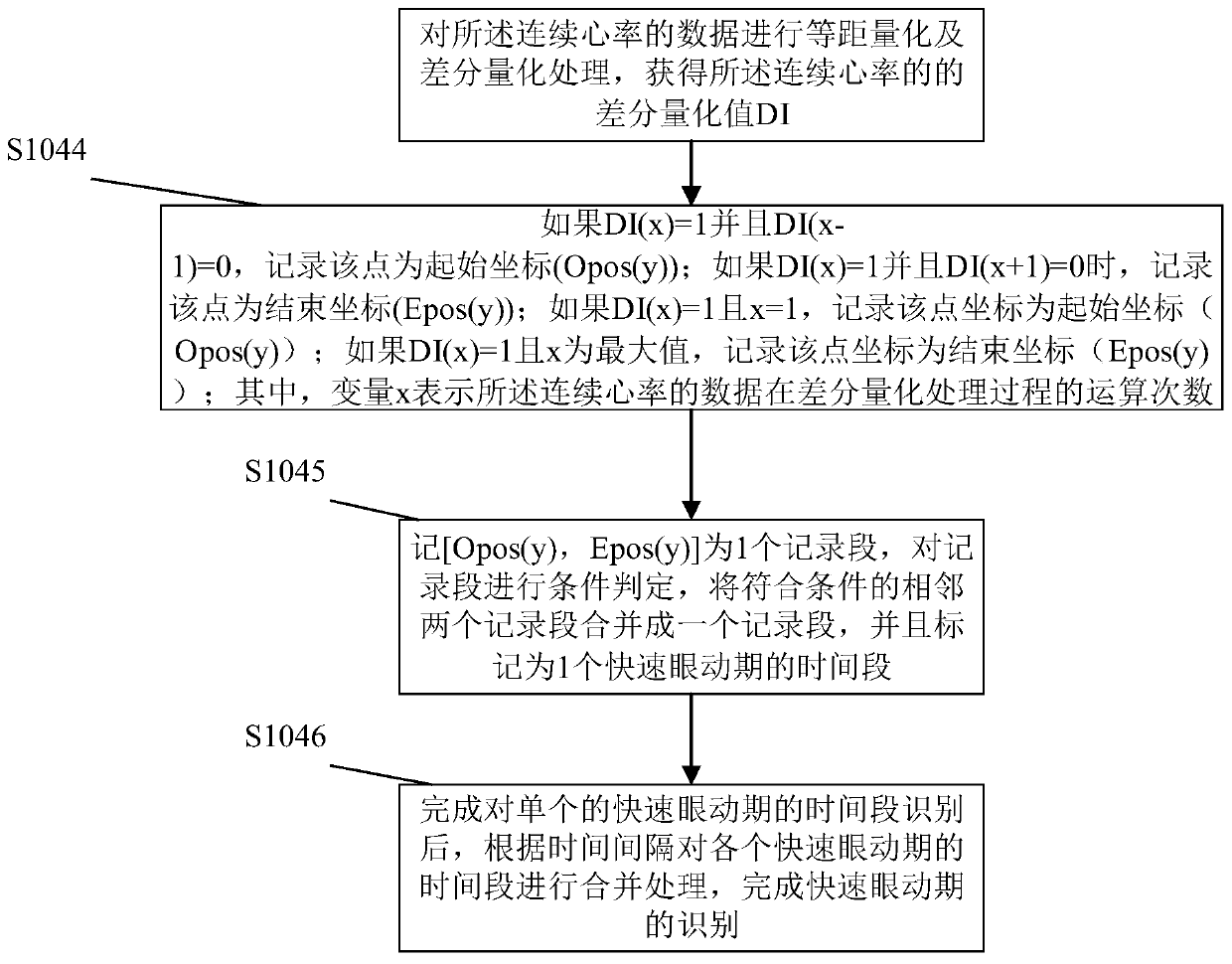
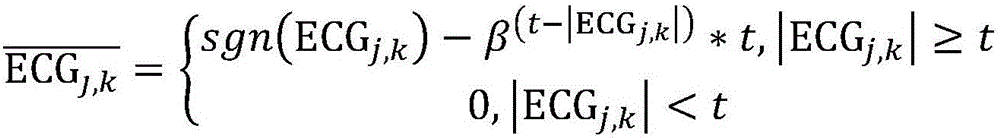Patents
Literature
52 results about "Rapid Eye Movements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
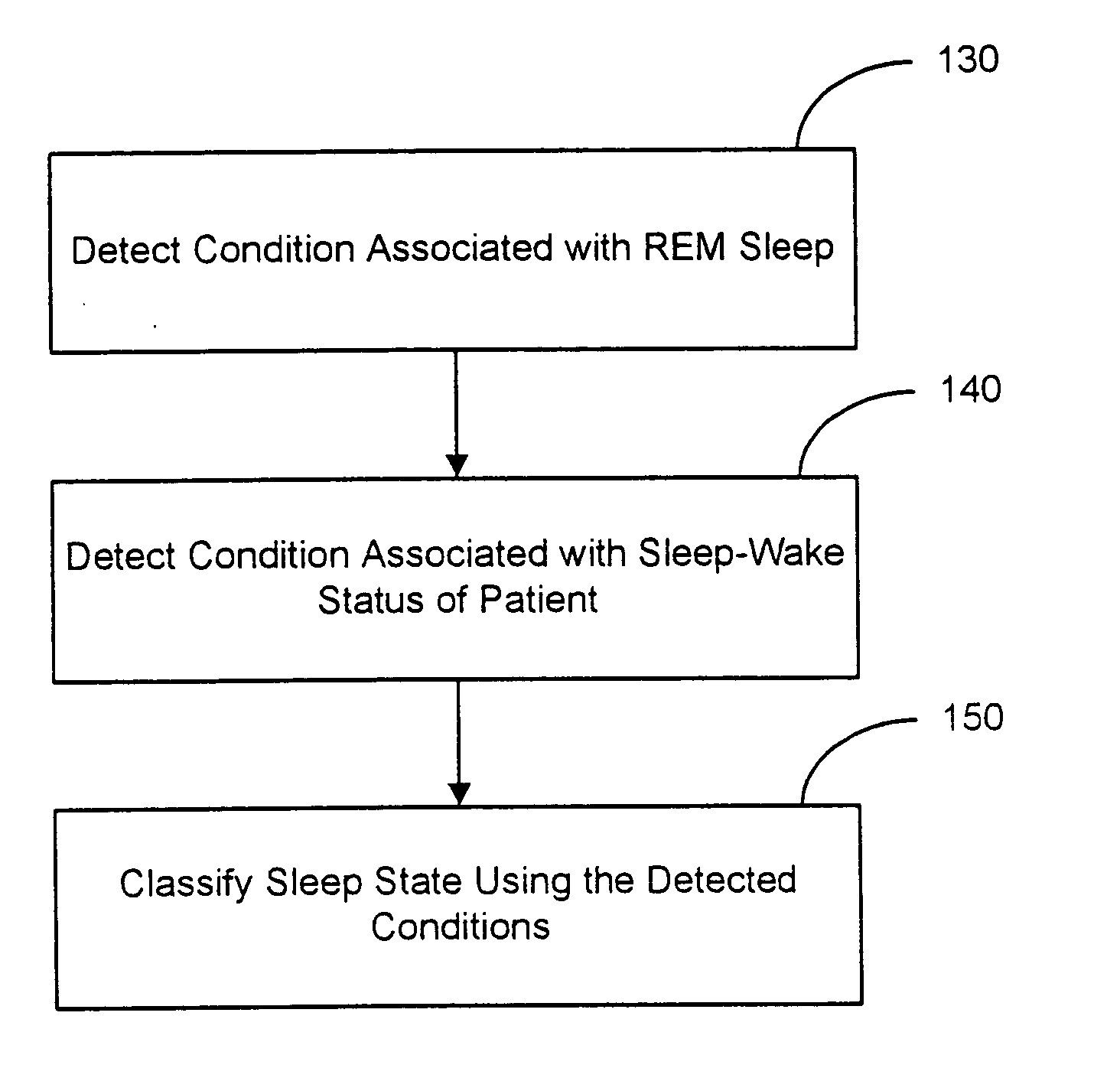
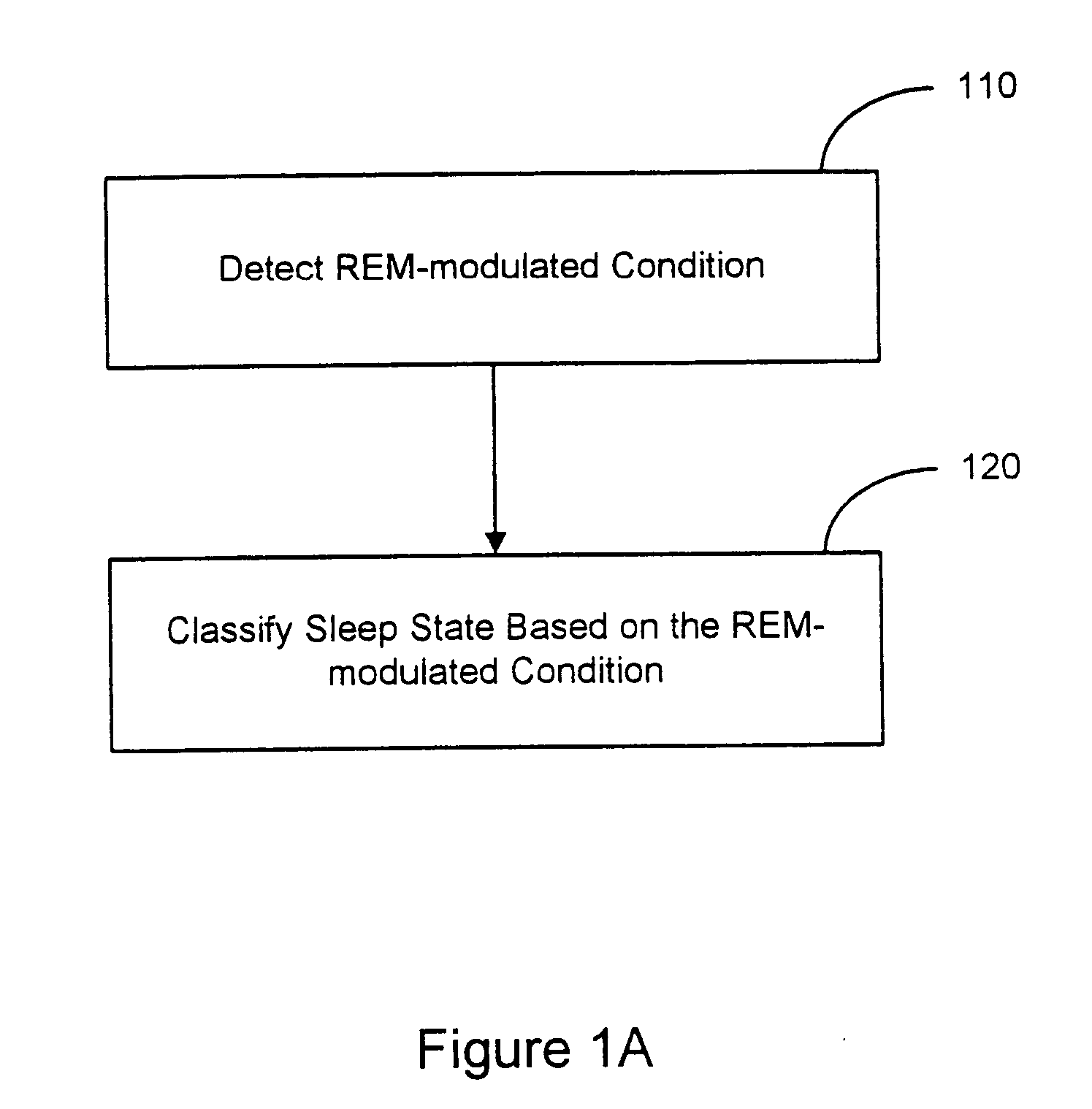
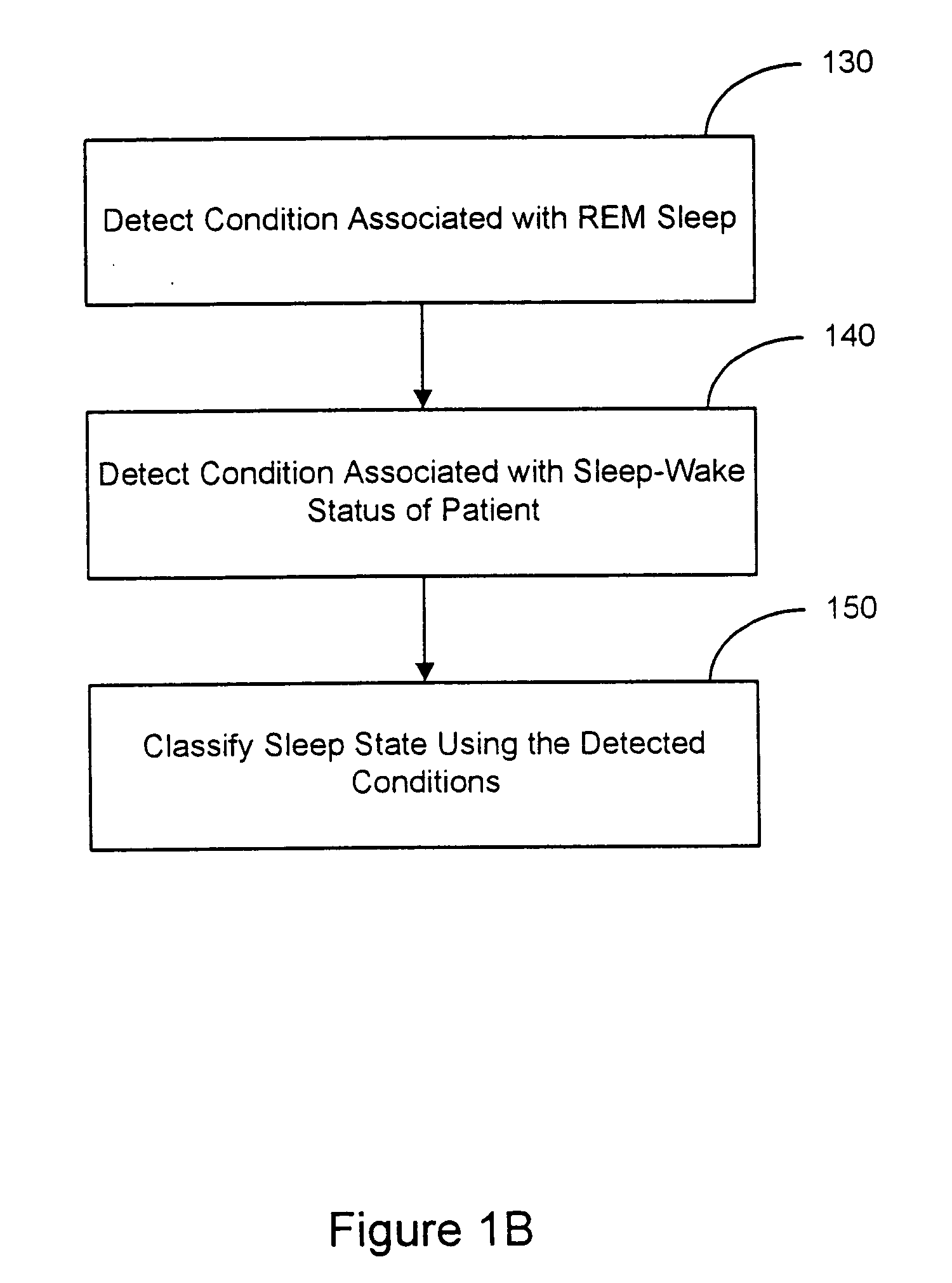
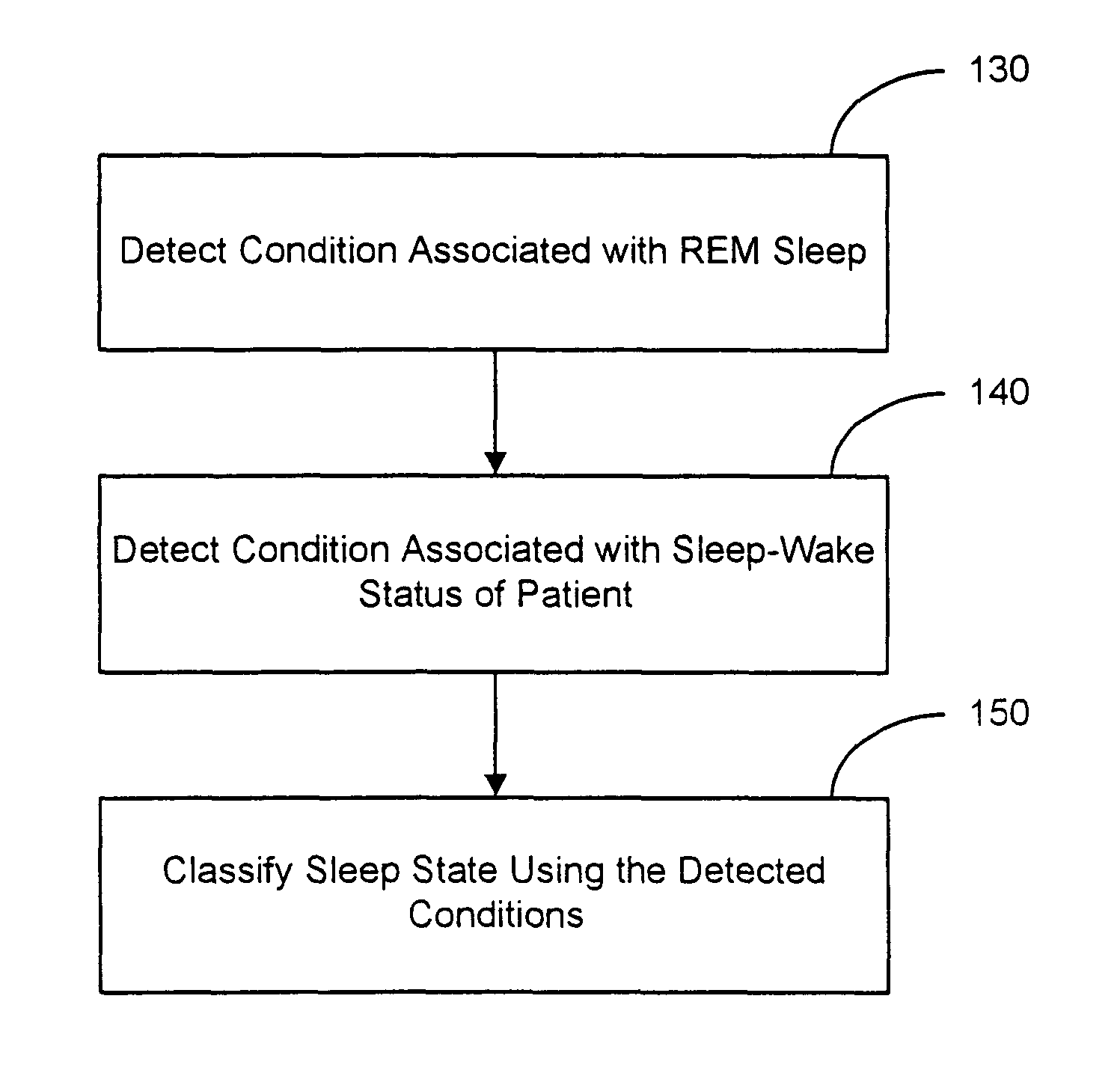
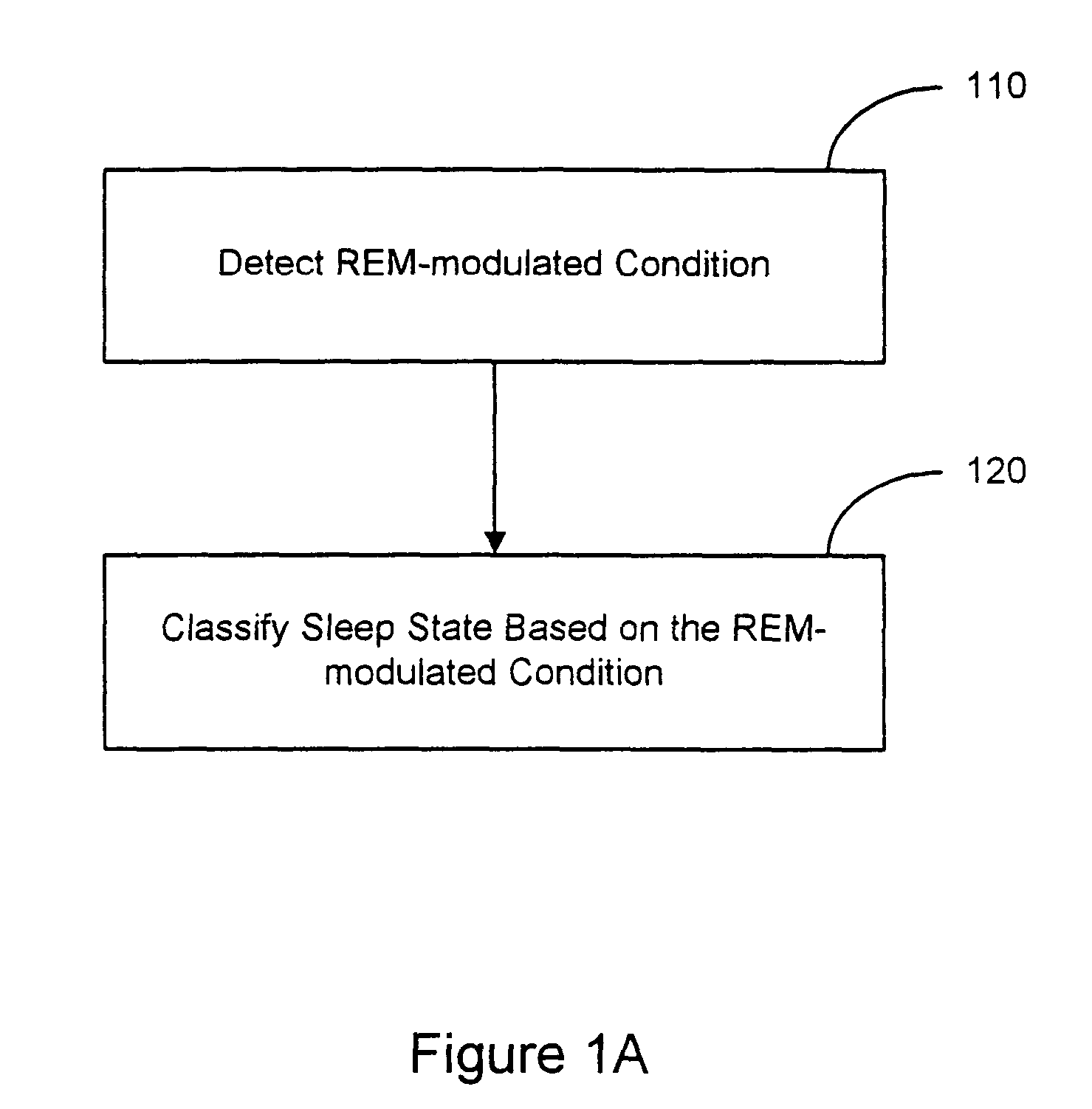
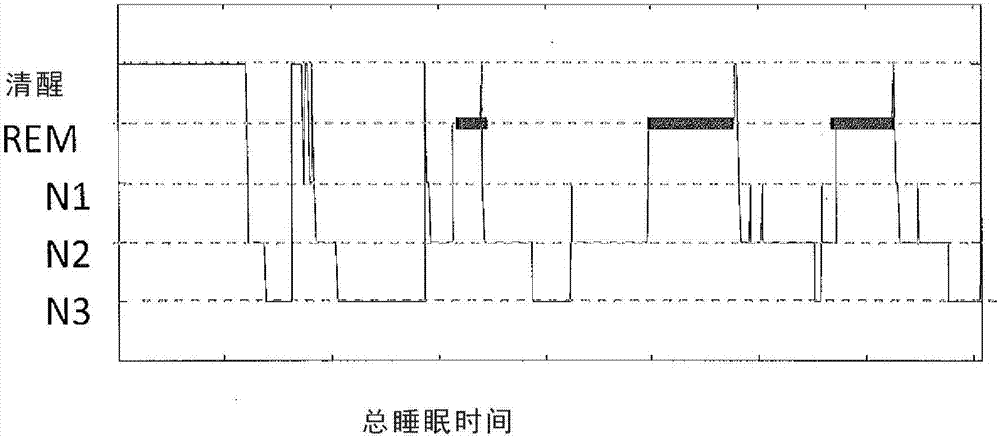
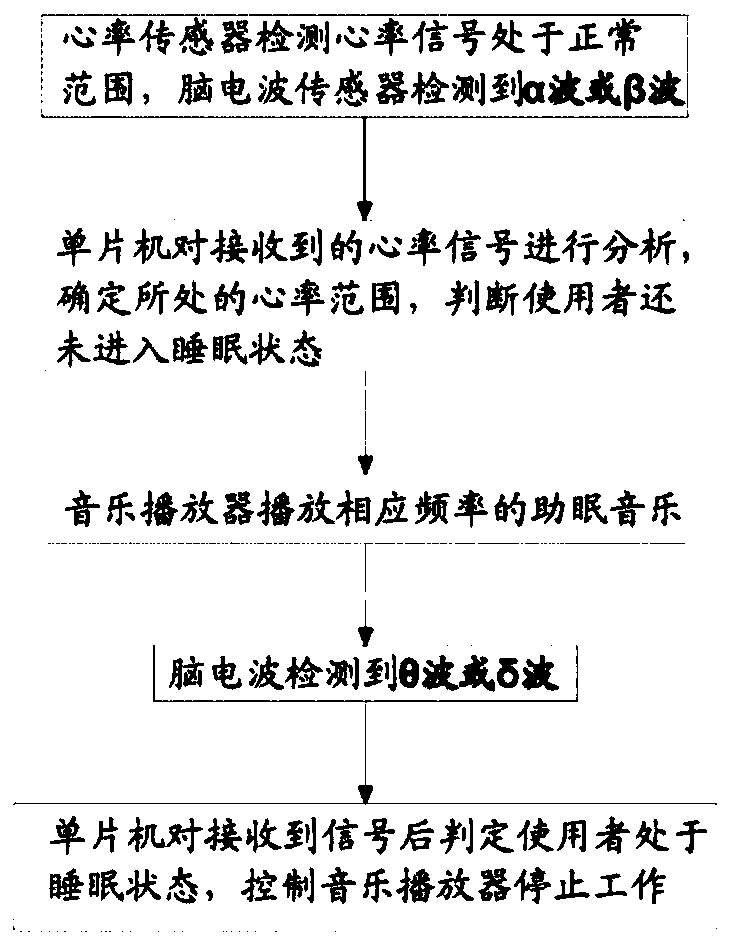
Sleep state classification
Systems and methods for sleep state classification involve detecting conditions related to sleep, including at least one condition associated with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Additionally, a condition modulated by the sleep-wake status of the patient may be detected. A medical system that is partially or fully implantable incorporates sensors and circuitry for detecting and processing the sleep-related signals. A sleep state processor classifies the patient's sleep state based on the sleep-related signals. Sleep state classification may be used in connection with the delivery of sleep state appropriate therapy, diagnostic testing, or patient monitoring.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
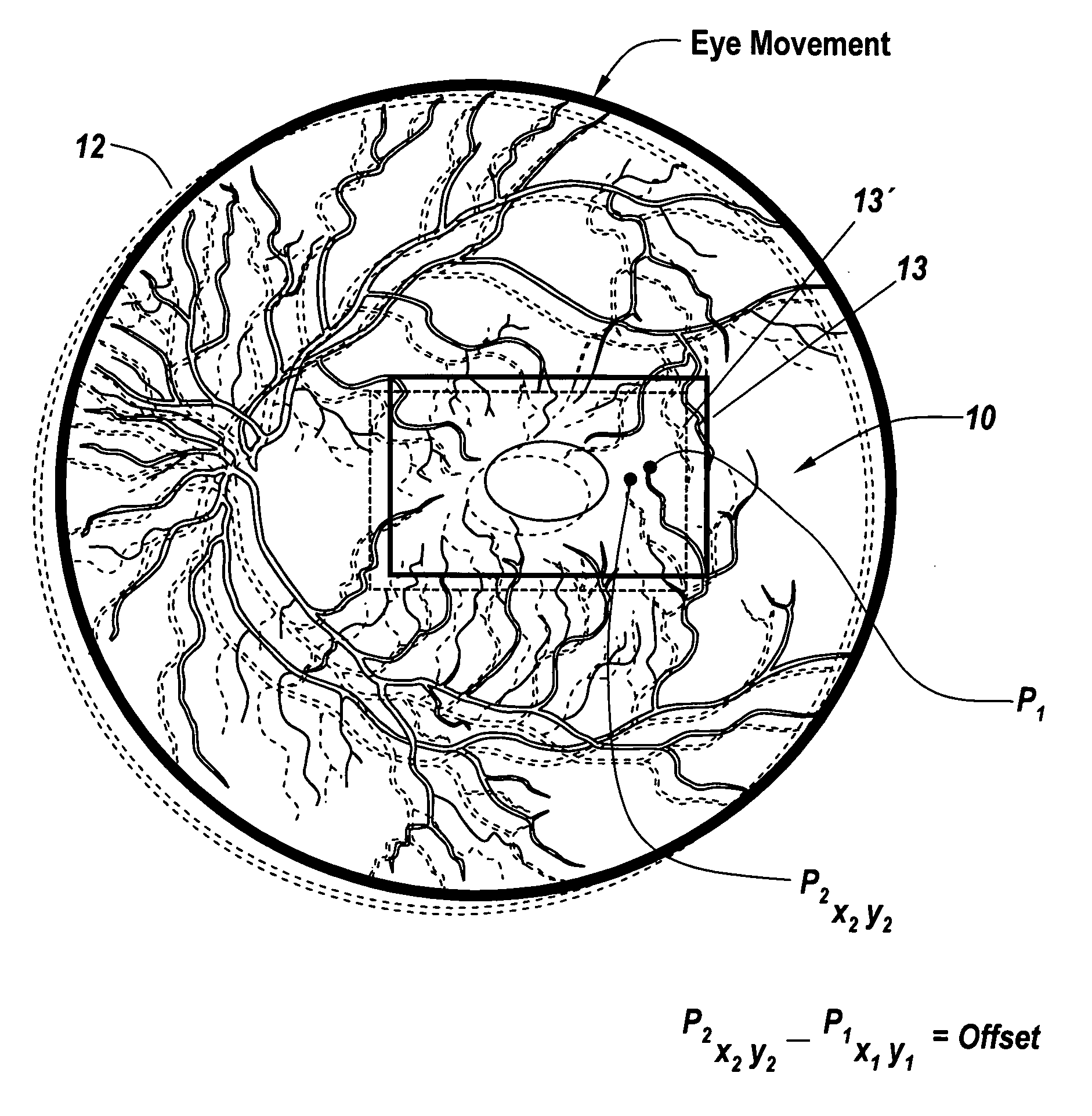
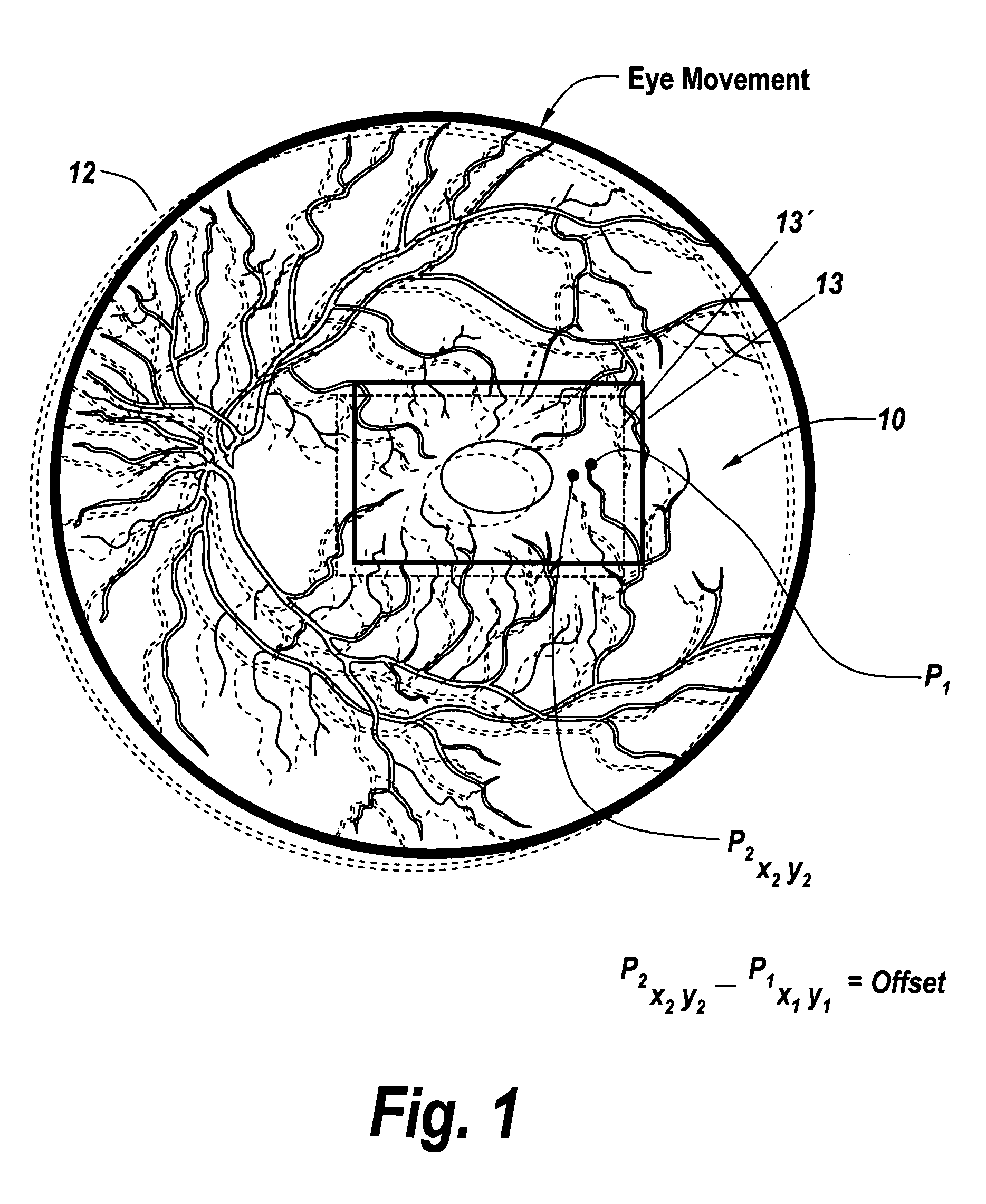
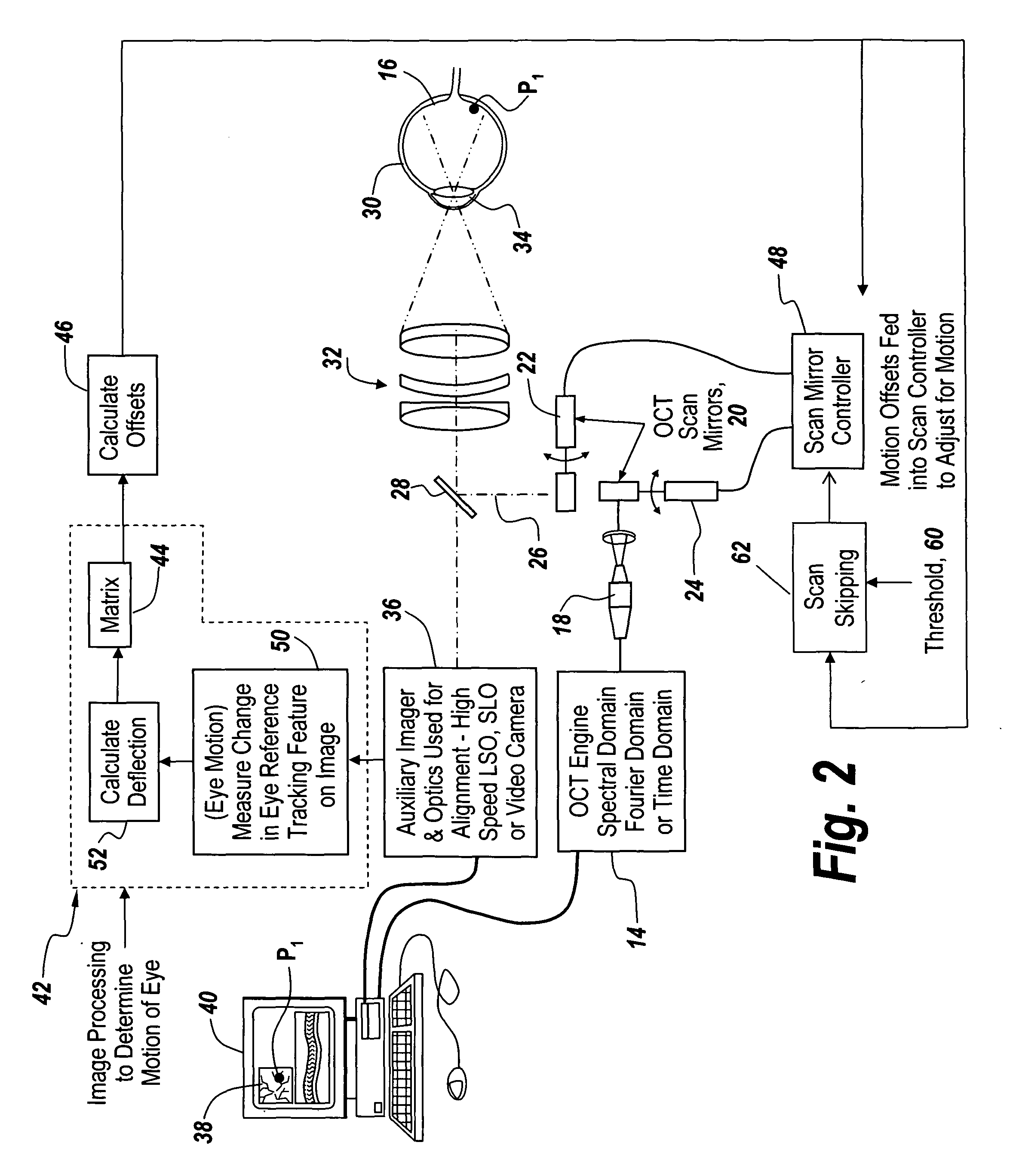
Region based vision tracking system for imaging of the eye for use in optical coherence tomography
InactiveUS20130010259A1Improve accuracyGood repeatabilityEye diagnosticsReference RegionRapid Eye Movements
For optical coherence tomography engines a method for eliminating the effects of the movement of the eye on the optical coherence tomography scan calculates the motion of the eye from an image from an auxiliary scanning system and compares a reference region to a corresponding region in the image associated with the next frame, with the change in position sensing the motion of the eye. This is followed by utilizing this sensed motion to generate accurate offsets for the scanning mirror patterns of the OCT engine. Additionally, scan skipping is utilized to obviate the effects of rapid eye movement that occur at rates faster than the image acquisition rate.
Owner:SONOMED IP HLDG
Treatment of neurological disorders related to rapid eye movement (REM) sleep disturbances with NPY Y5 receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20050119285A1Reducing REM sleepTreating and preventing neurological disordersBiocideNervous disorderRapid Eye MovementsNeurological disorder
This invention relates to a method for treating and preventing neurological disorders related to rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep disturbances in a mammal comprising administering to the mammal an amount of an NPY Y5 receptor antagonist which effectively reduces REM sleep.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Acousto-optic sleep intervention system and method based on electroencephalogram signals
ActiveCN106725462AEasy accessImprove sleep qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSleep stagingIntervention program
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
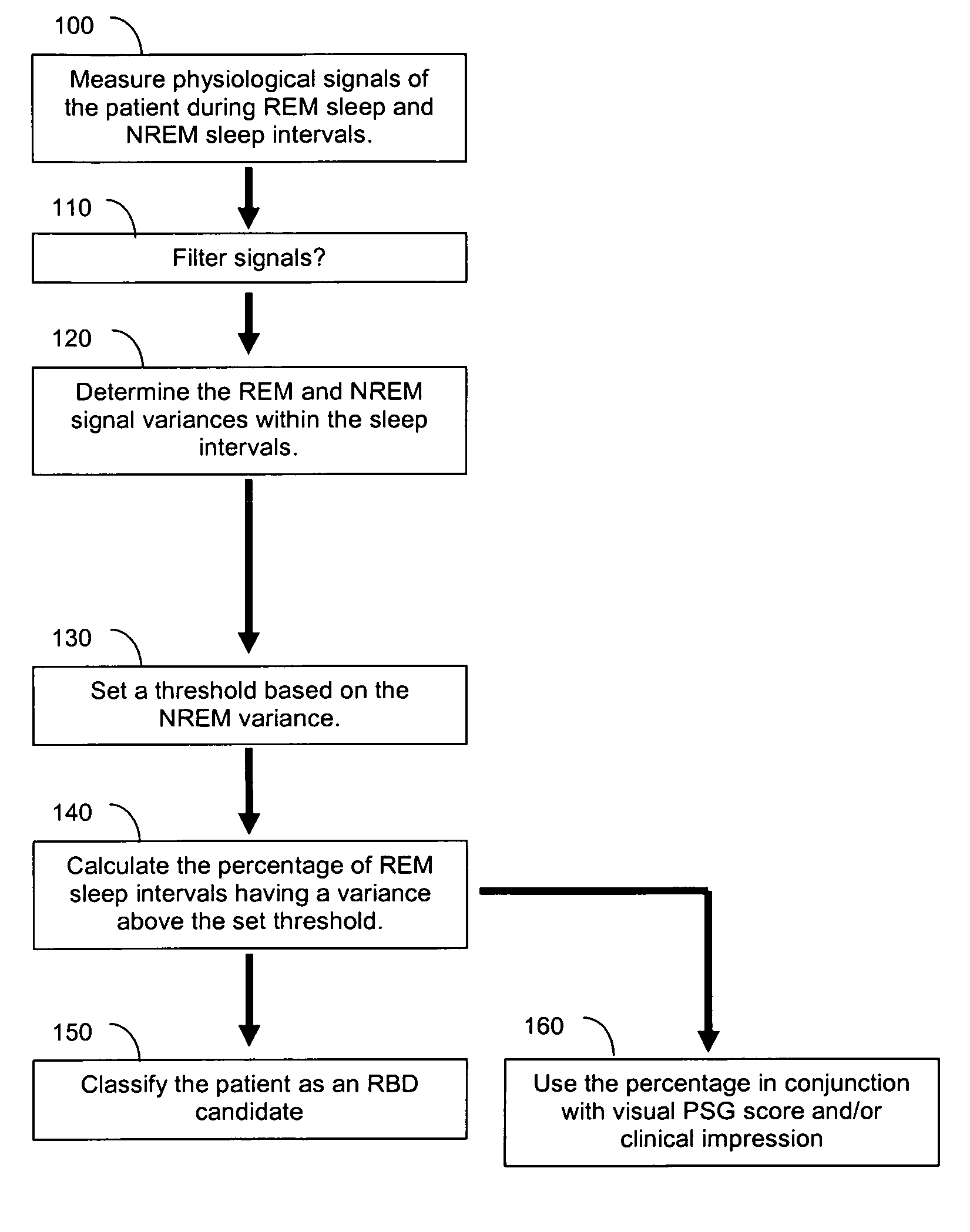
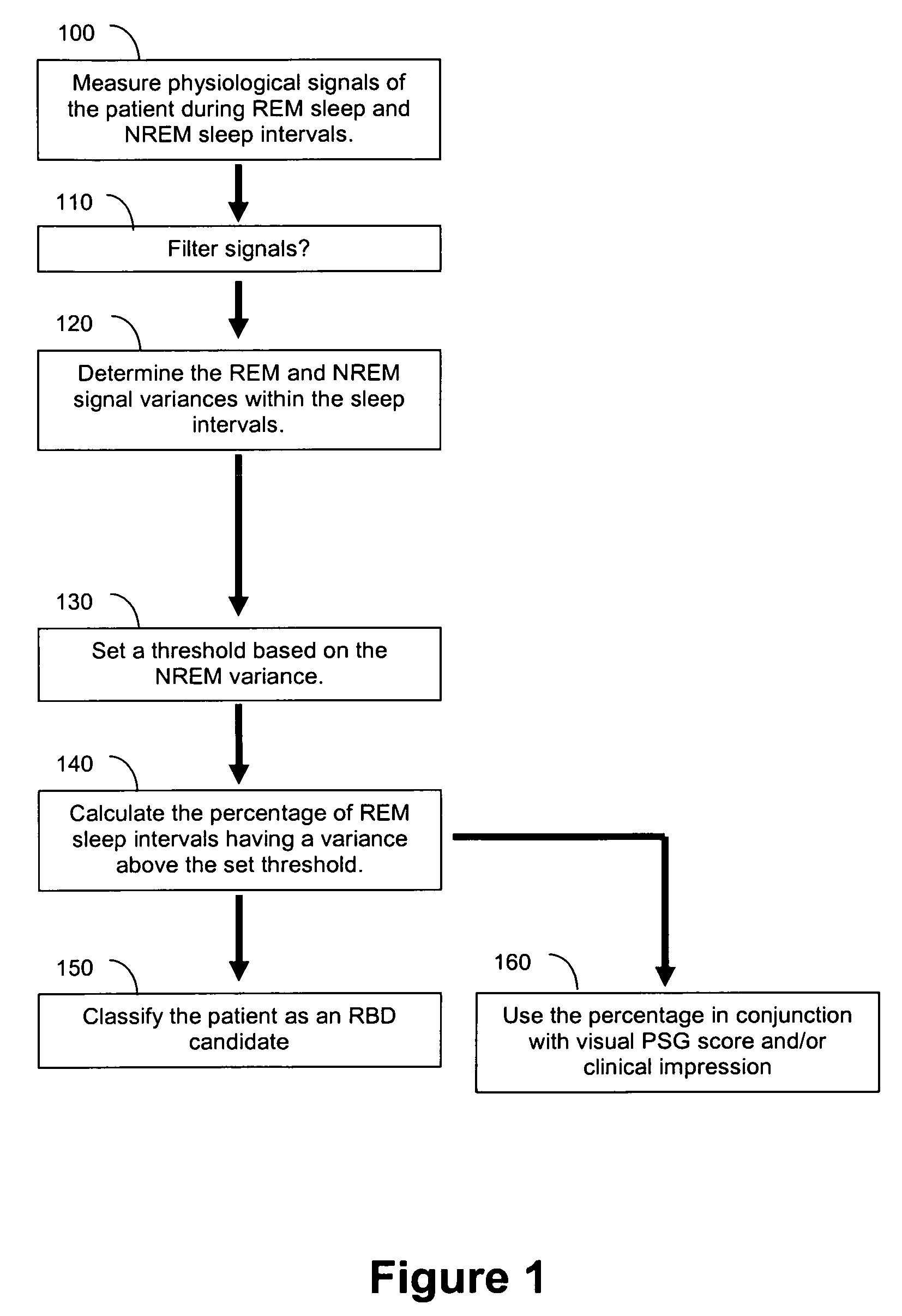
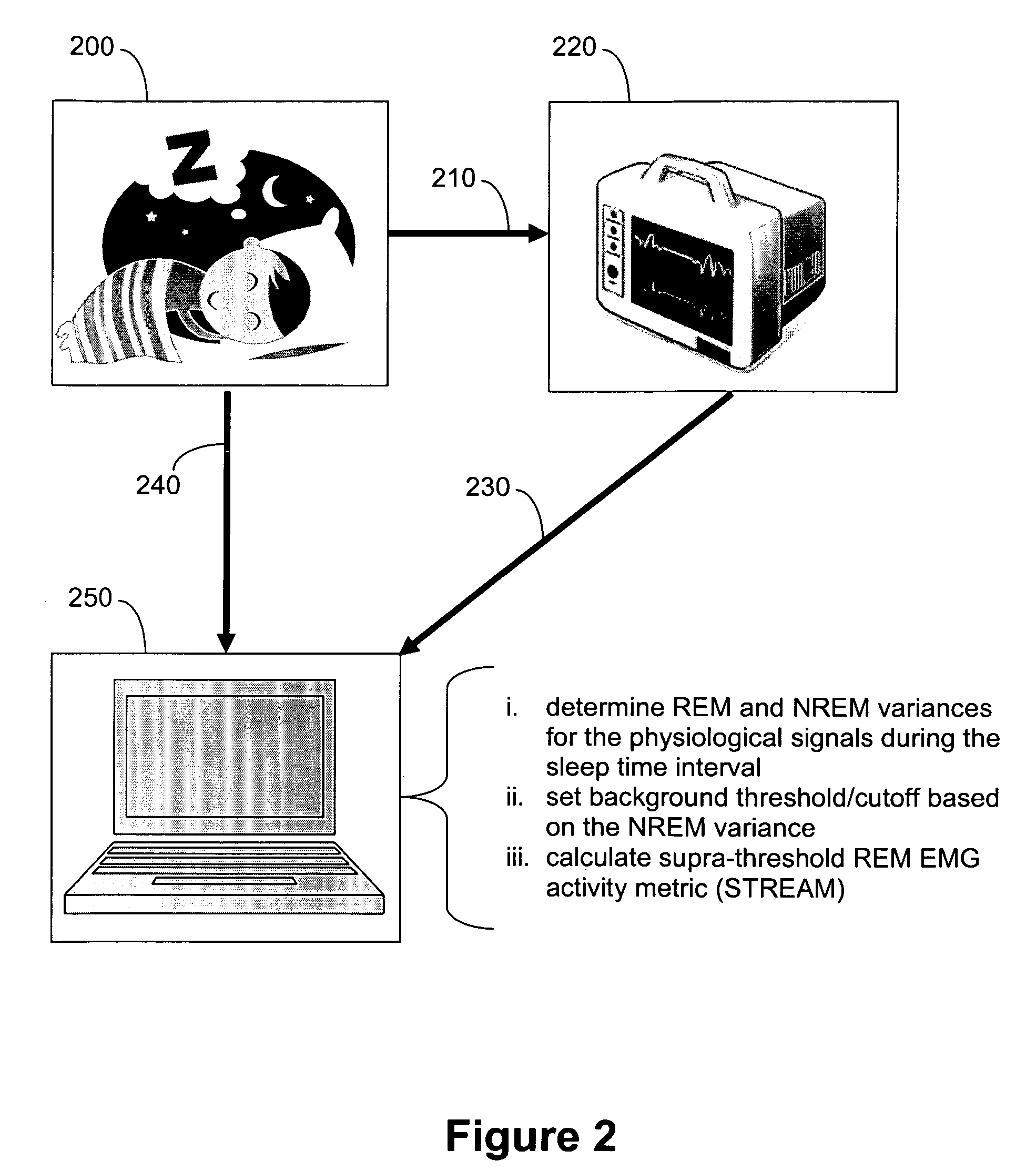
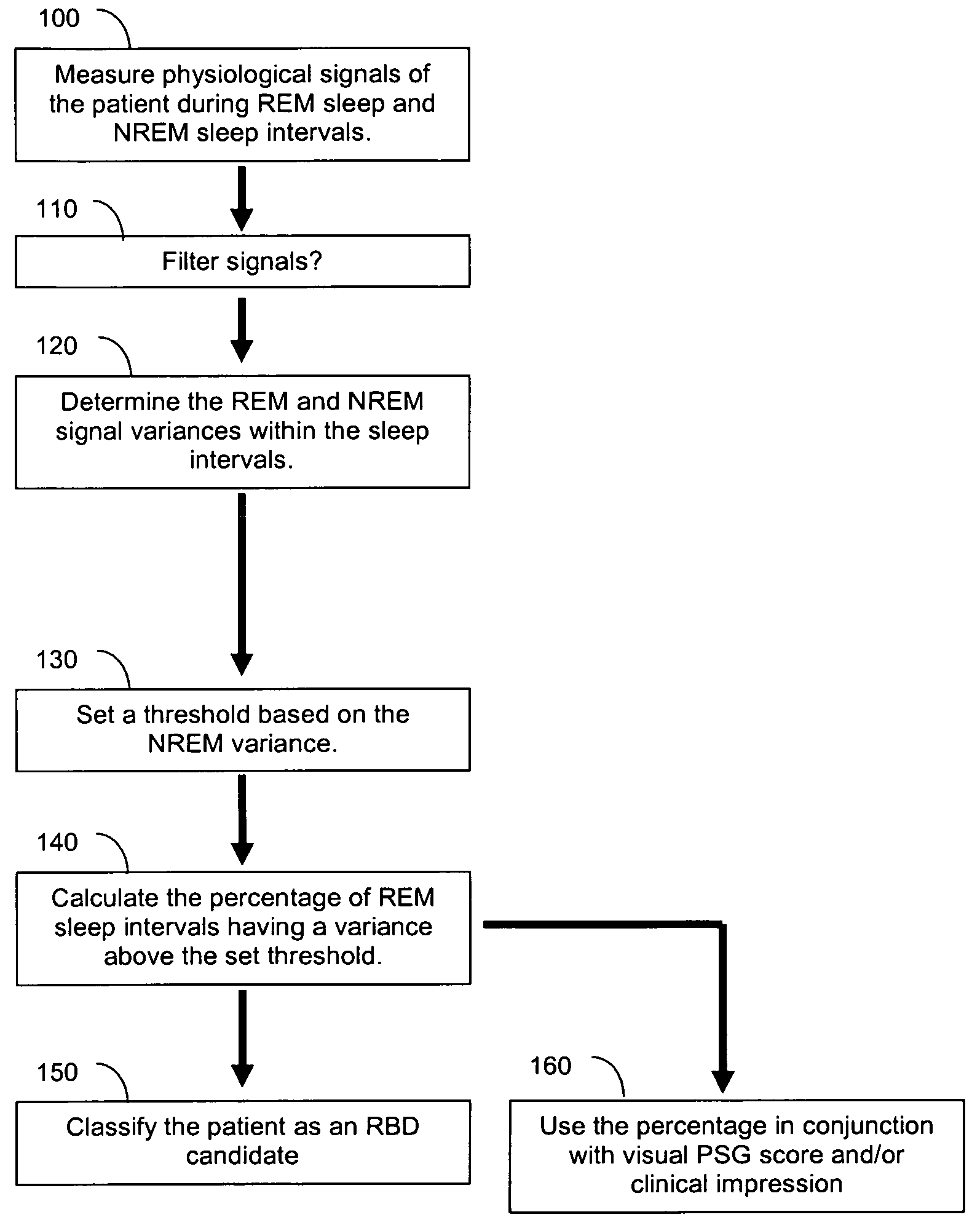
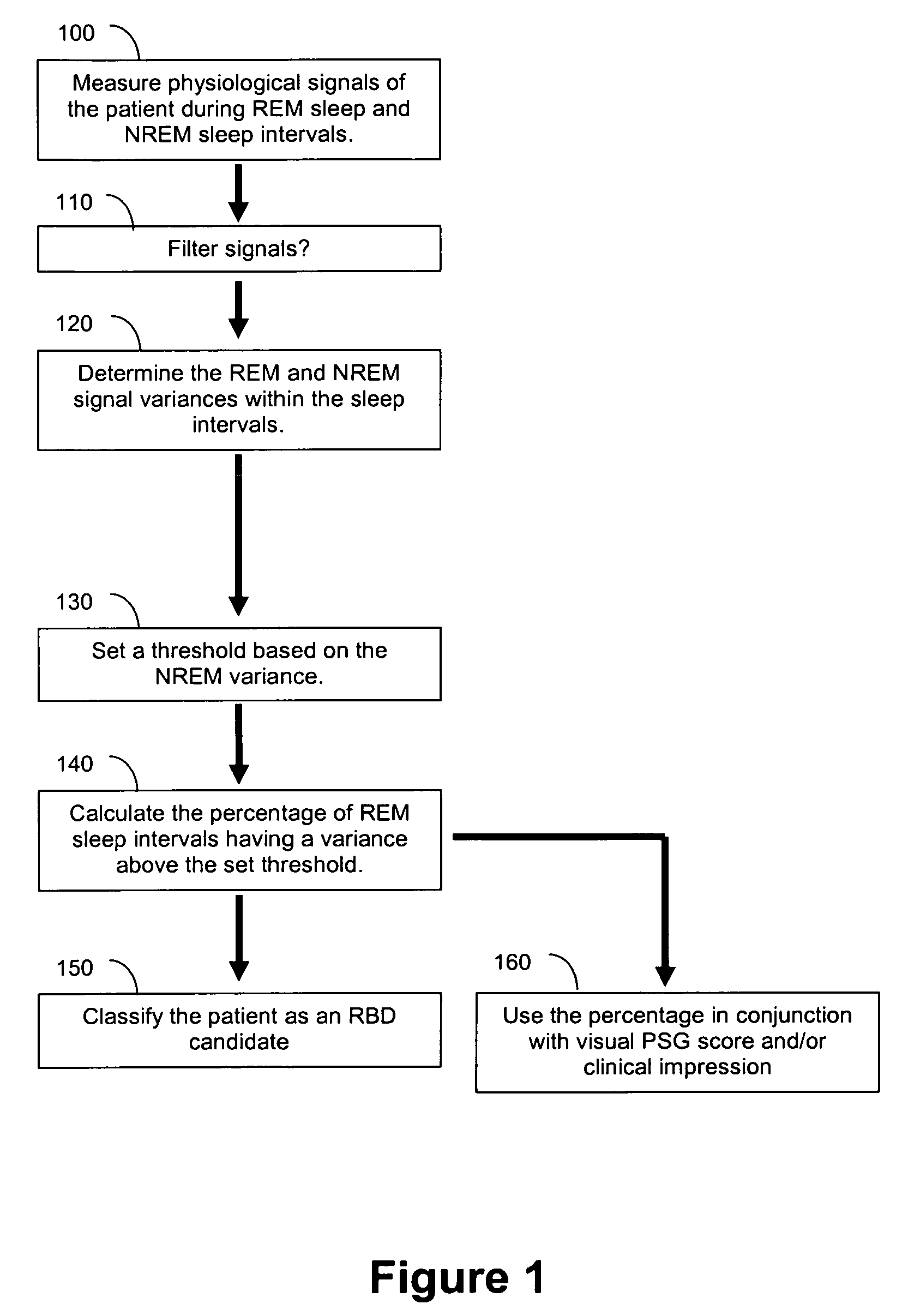
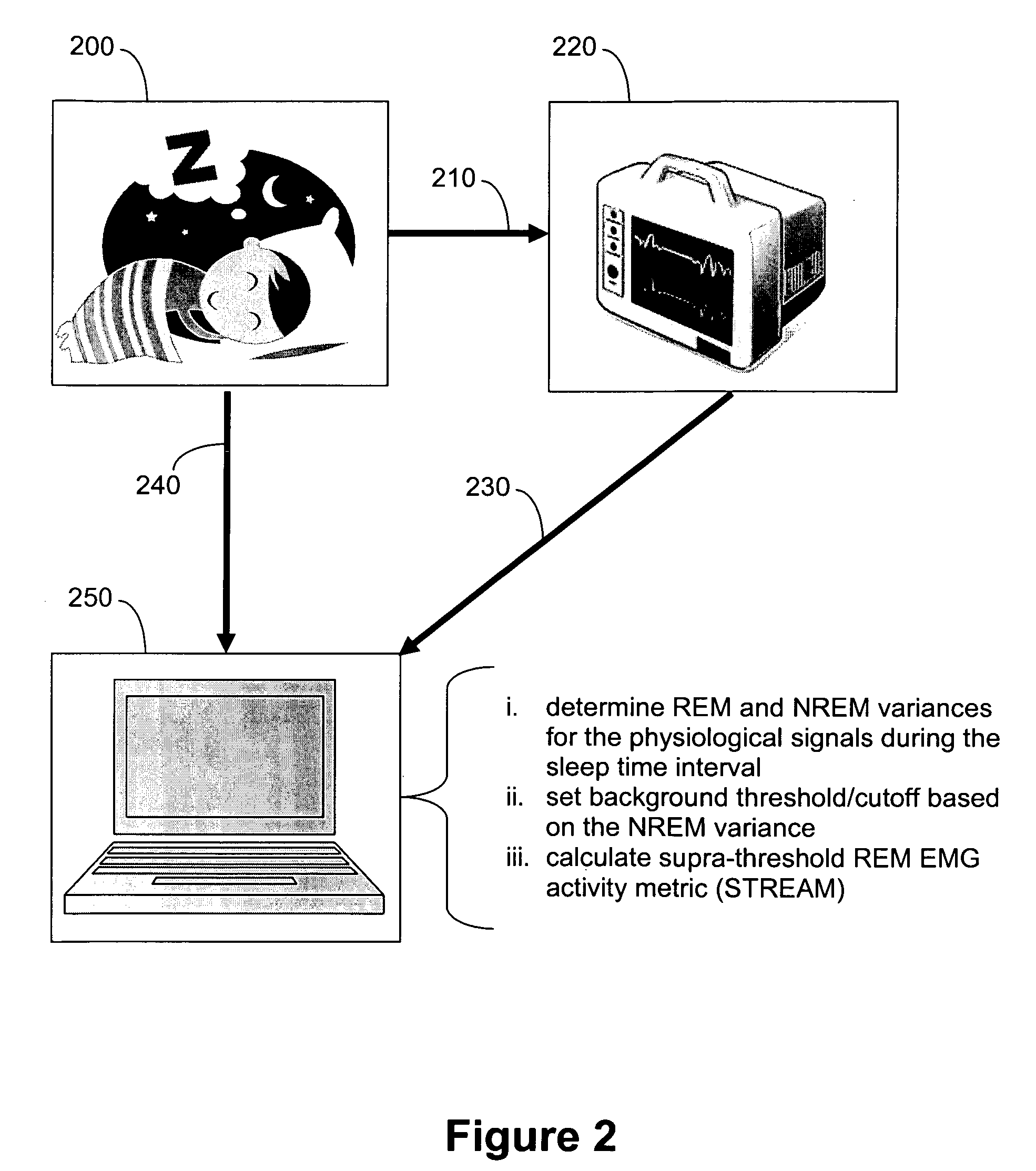
Automated polysomnographic assessment for rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder
Methods and systems for diagnosing or assessing rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD). Muscle tone or activity variance during rapid eye movement (REM) and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep intervals of a polysomnogram are compared. A threshold based on the NREM data is used to identify a subject-specific threshold for abnormality in the REM variance. A metric that includes the percentage of REM variance exceeding the threshold relates to RBD.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +1
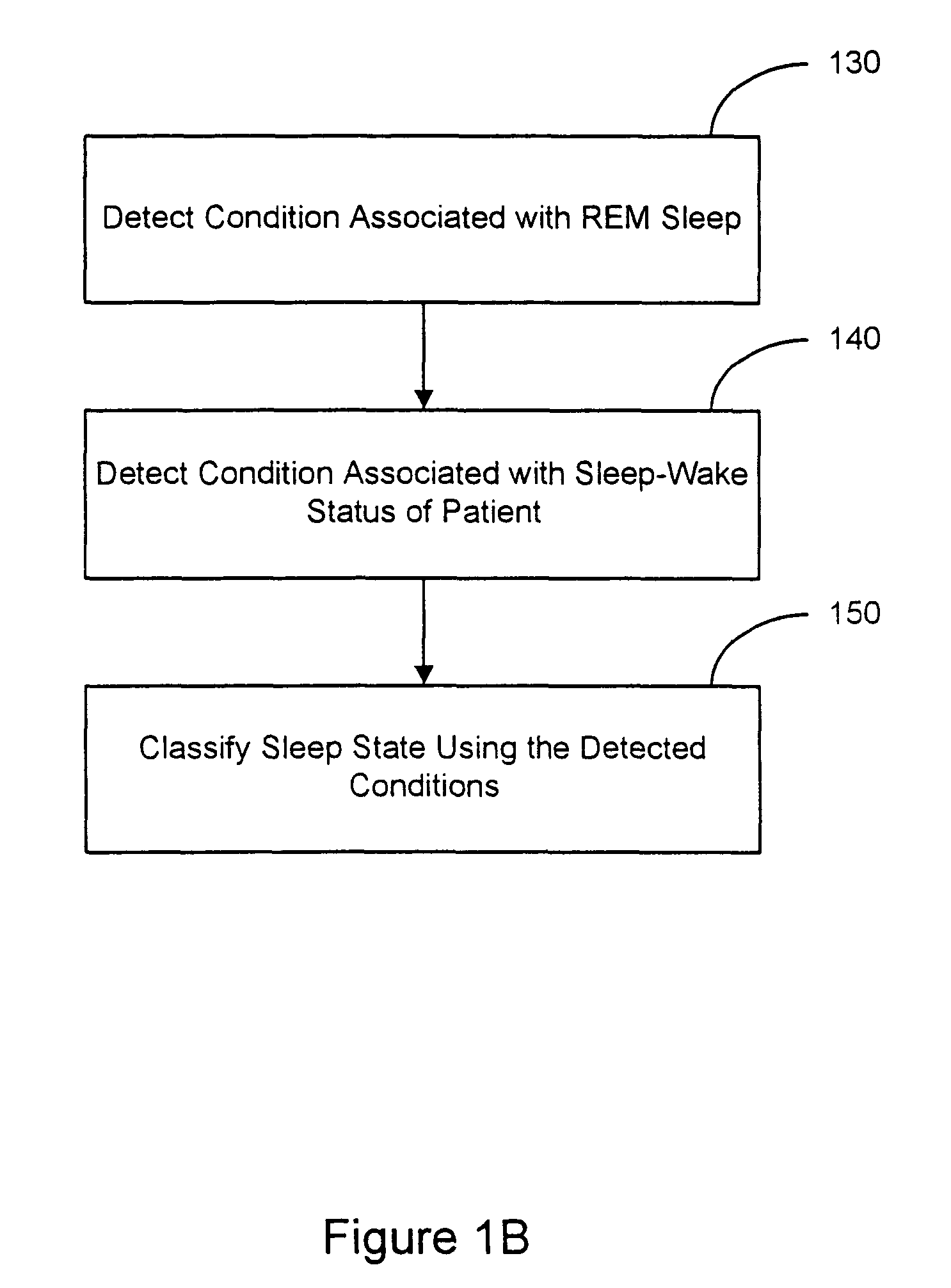
Sleep state classification
Systems and methods for sleep state classification involve detecting conditions related to sleep, including at least one condition associated with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Additionally, a condition modulated by the sleep-wake status of the patient may be detected. A medical system that is partially or fully implantable incorporates sensors and circuitry for detecting and processing the sleep-related signals. A sleep state processor classifies the patient's sleep state based on the sleep-related signals. Sleep state classification may be used in connection with the delivery of sleep state appropriate therapy, diagnostic testing, or patient monitoring.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
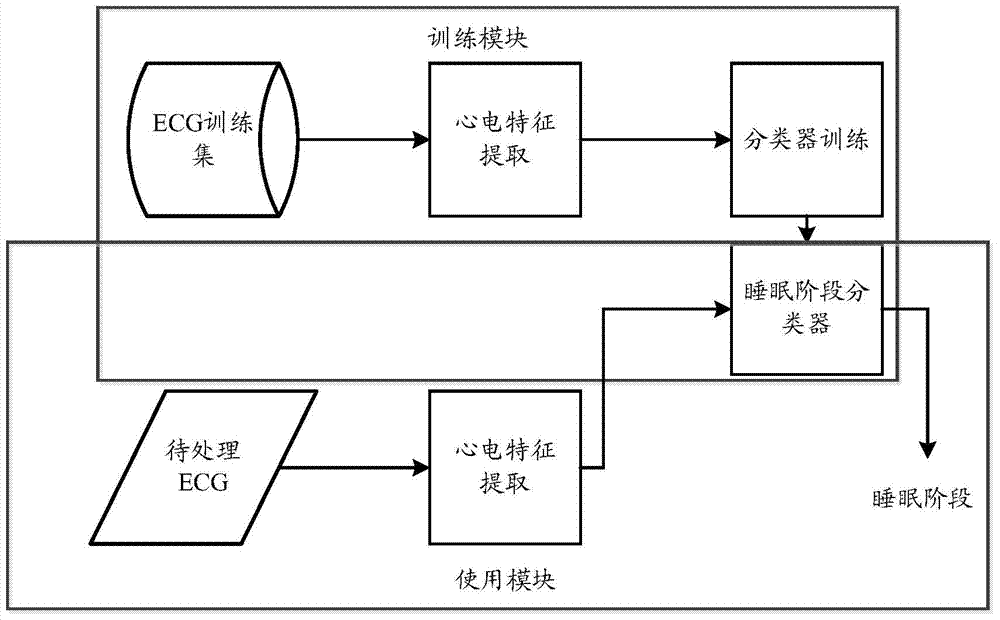
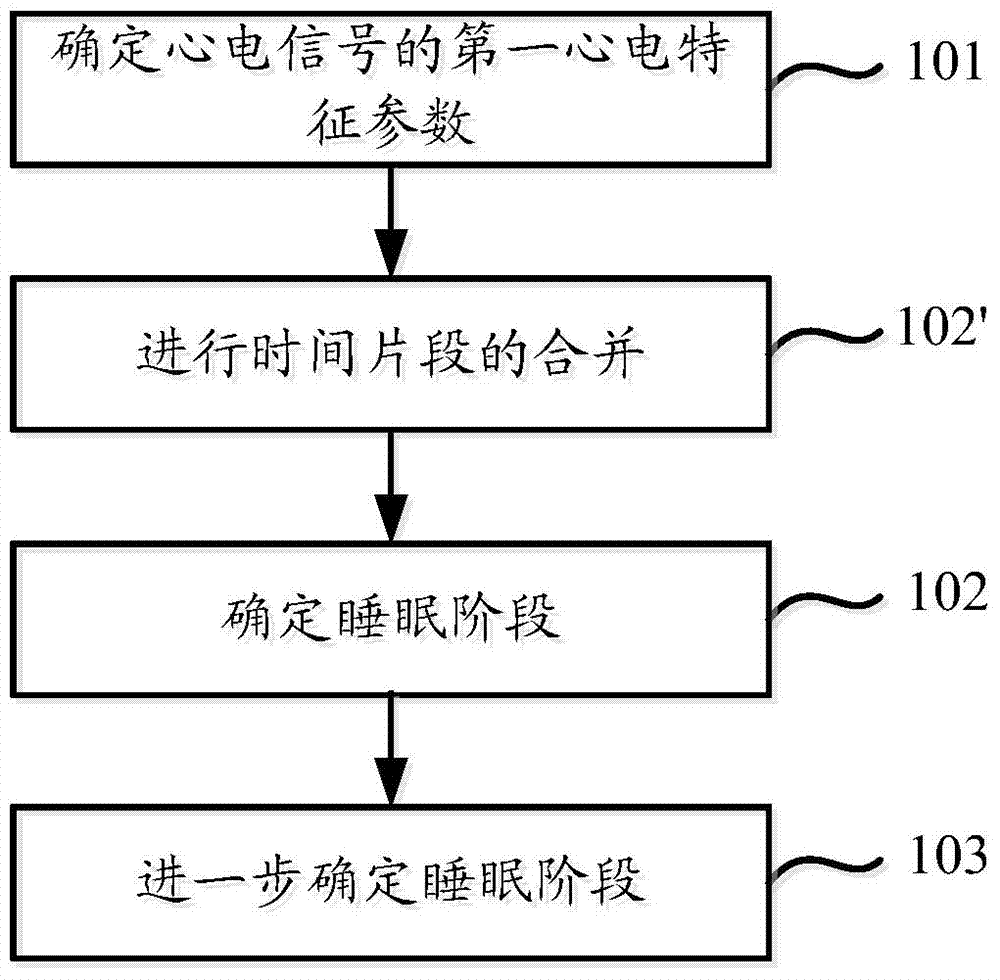
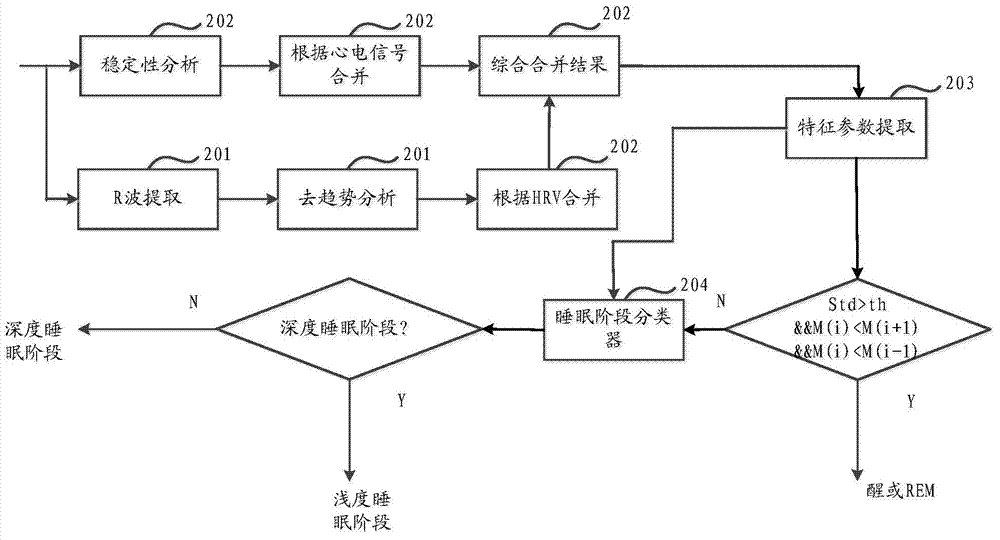
Sleep stage determining method and sleep stage determining system
ActiveCN104720748ARealize OKGuaranteed accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalLight sleep
An embodiment of the invention provides a sleep stage determining method and a sleep stage determining system. The sleep stage determining method includes: determining a first electrocardio characteristic parameter of an electrocardio signal, and determining whether a sleeper is in a waking stage or an REM (rapid eye movements) sleep stage or not within a time segment by means of judging whether the first electrocardio characteristic parameter satisfies a characteristic of the waking stage or the REM sleep stage or not within the time segment. Determination of a macro sleep structure is achieved by means of distinguishing the waking stage, the REM sleep stage or other similar sleep stages. Sleep stage determination is achieved by means of rule judgment, and accordingly, accuracy of sleep stage determination is guaranteed. Moreover, a sleep stage classifier can be used cooperatively to achieve comprehensive judgment on the sleep stages and can be used for classifying other kinds of sleep stages into a light sleep stage and a deep sleep stage so as to achieve a micro sleep structure, and accordingly, accuracy of sleep stage judgment is further improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
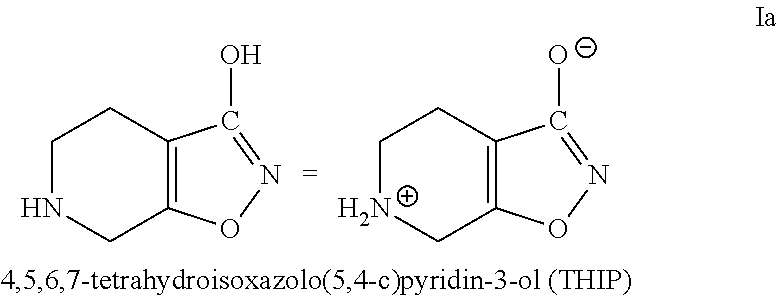
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition and treating secondary insomnia
InactiveUS20150352085A1Increasing tonic inhibitionNormalize sleep architectureBiocideNervous disorderSleep architectureDisease
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition in a subject in need thereof, for example a subject with Fragile X syndrome or Angelman syndrome are disclosed. Methods of treating secondary insomnia in a subject with a neurodegenerative disease or disorder are also disclosed. The methods can include administering the subject an effective amount of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo(5,4-c)pyridin-3-ol (THIP) or a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, increase tonic inhibition in neurons of the subject; to increase slow wave sleep (SWS) and / or slow wave activity (SWA), normalize sleep architecture, reduce secondary insomnia, increase non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, increase sleep continuity, enhance delta activity within NREM, increase or improve total sleep time (TST), increase or improve sleep efficiency, reduce total time awake (TAA), reduce number of awakenings (NWA), reduce latency to persistent sleep (LPS), or to reduce wake after sleep onset (WASO), in the subject, or any combination thereof.
Owner:OVID THERAPEUTICS
Automated polysomnographic assessment for rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder
Methods and systems for diagnosing or assessing rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD). Muscle tone or activity variance during rapid eye movement (REM) and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep intervals of a polysomnogram are compared. A threshold based on the NREM data is used to identify a subject-specific threshold for abnormality in the REM variance. A metric that includes the percentage of REM variance exceeding the threshold relates to RBD.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY +1
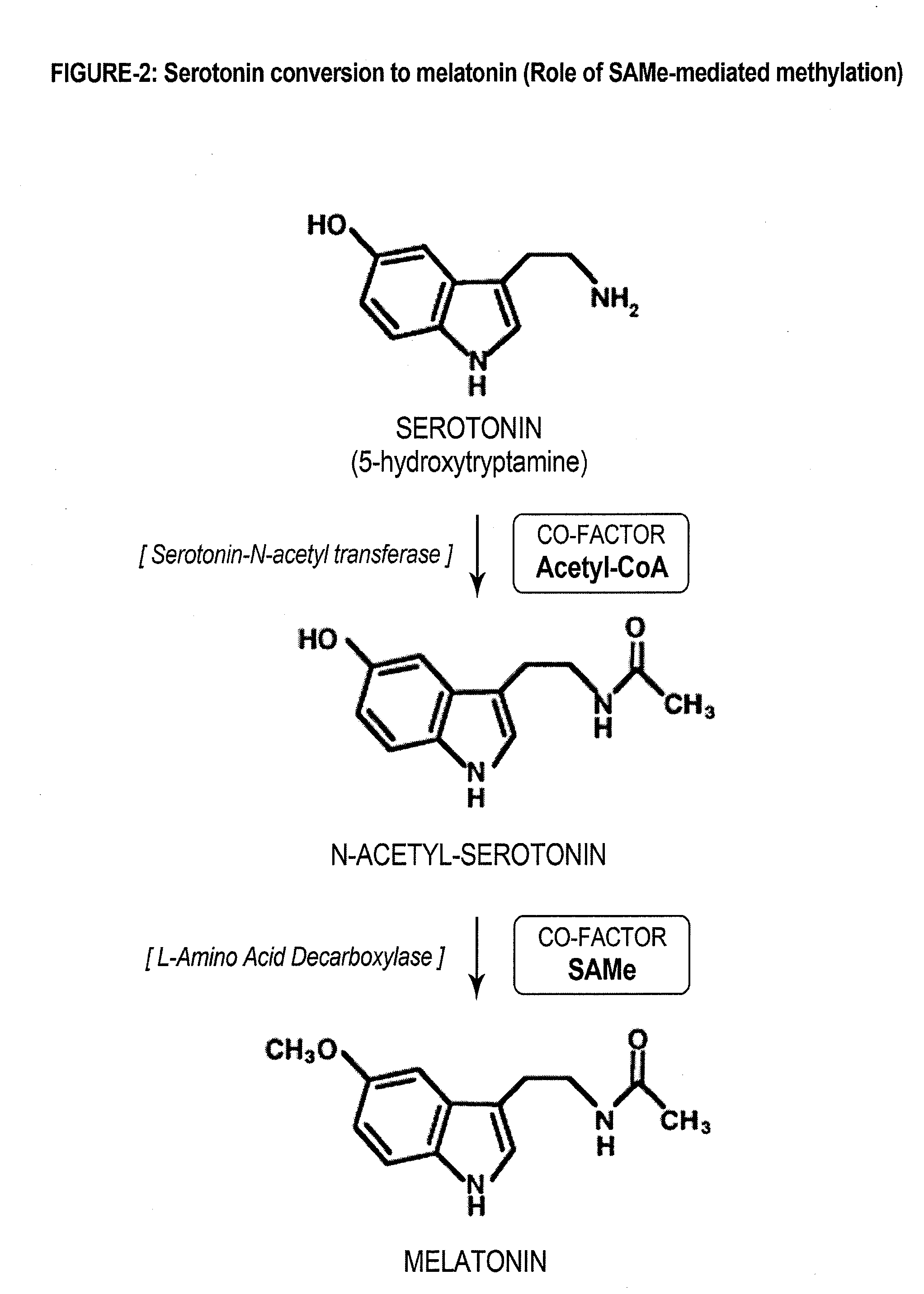
BIO-REPLENISHMENT (BioRep) FOR IMPROVING SLEEP ARCHITECTURE
InactiveUS20130064804A1Easy to pumpGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSleep architectureS-Adenosyl methionine
Methods to prepare a bio-replenishment (BioRep) with specific combinations of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), lactoferrin (LF) and ribonuclease (RNAse) to restore regular sleep pattern are described. Additionally, compositions of functional delivery systems that recreate both alternate phases of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep cycles are disclosed. These methods and compositions have implications in the clinical management of various sleep disorders including insomnia, circadian rhythm disorders and obstructive sleep apnea.
Owner:NAIDU LP
REM-sleep directed visual alarm system and method
ActiveUS7956756B2Convenient timeMinimize pitfallDiagnostics using lightPerson identificationSommeil paradoxalRapid Eye Movements
The present apparatus and method for using the same detects Rapid Eye Movement (REM) in a sleeping mammal and awakens the mammal after the cessation of a specific episode of REM. The system comprises an alarm setting unit for setting a predetermined wakeup time, a data collection unit for collecting physiological data from the mammal over time, a processing unit for determining the occurrence and cessation of REM and for providing a stimulation signal for awakening the mammal within a prescribed window of time before the predetermined wakeup time and after the cessation of REM and after the mammal's nadir in body temperature with respect to time.
Owner:KUBEY ALAN +1
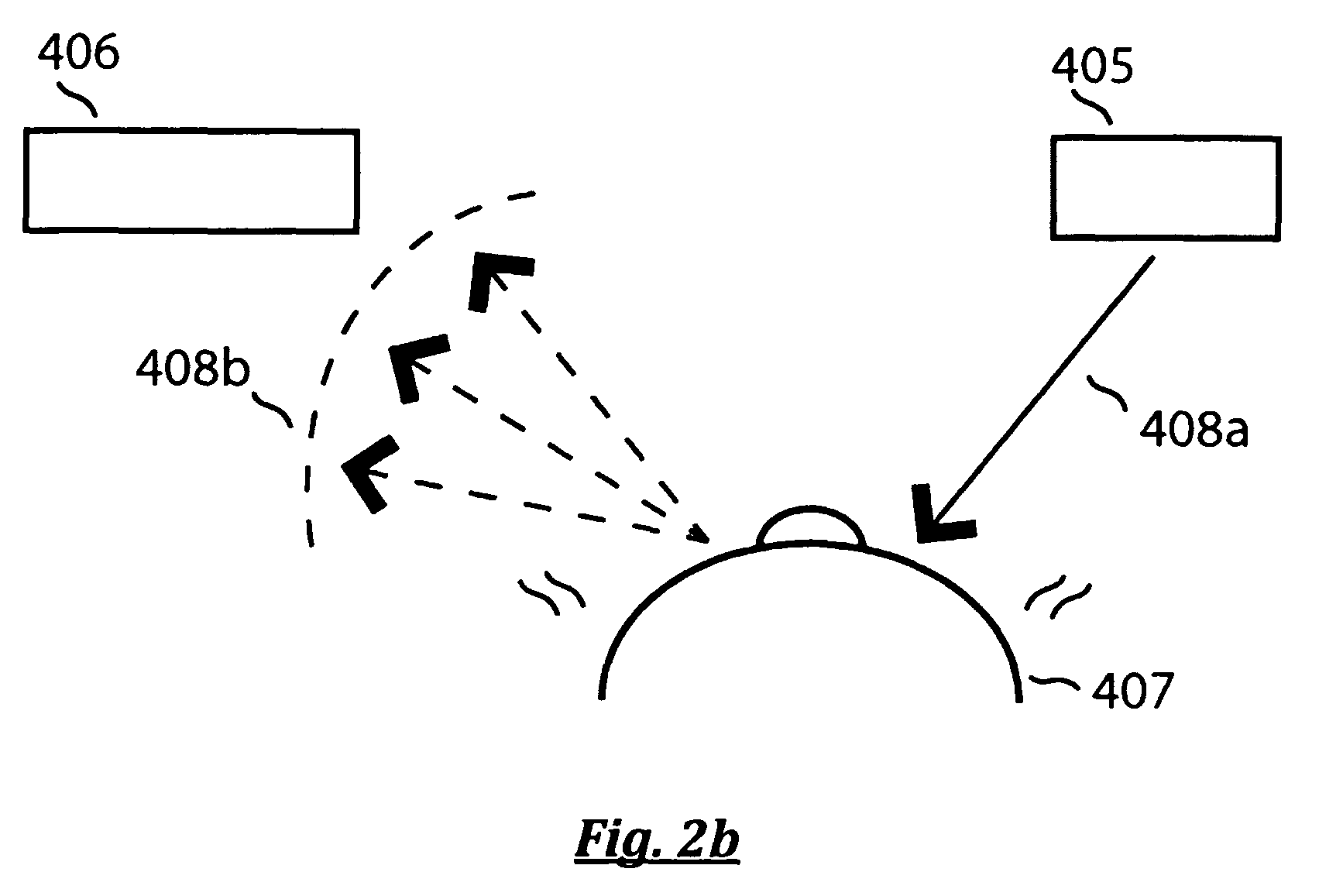
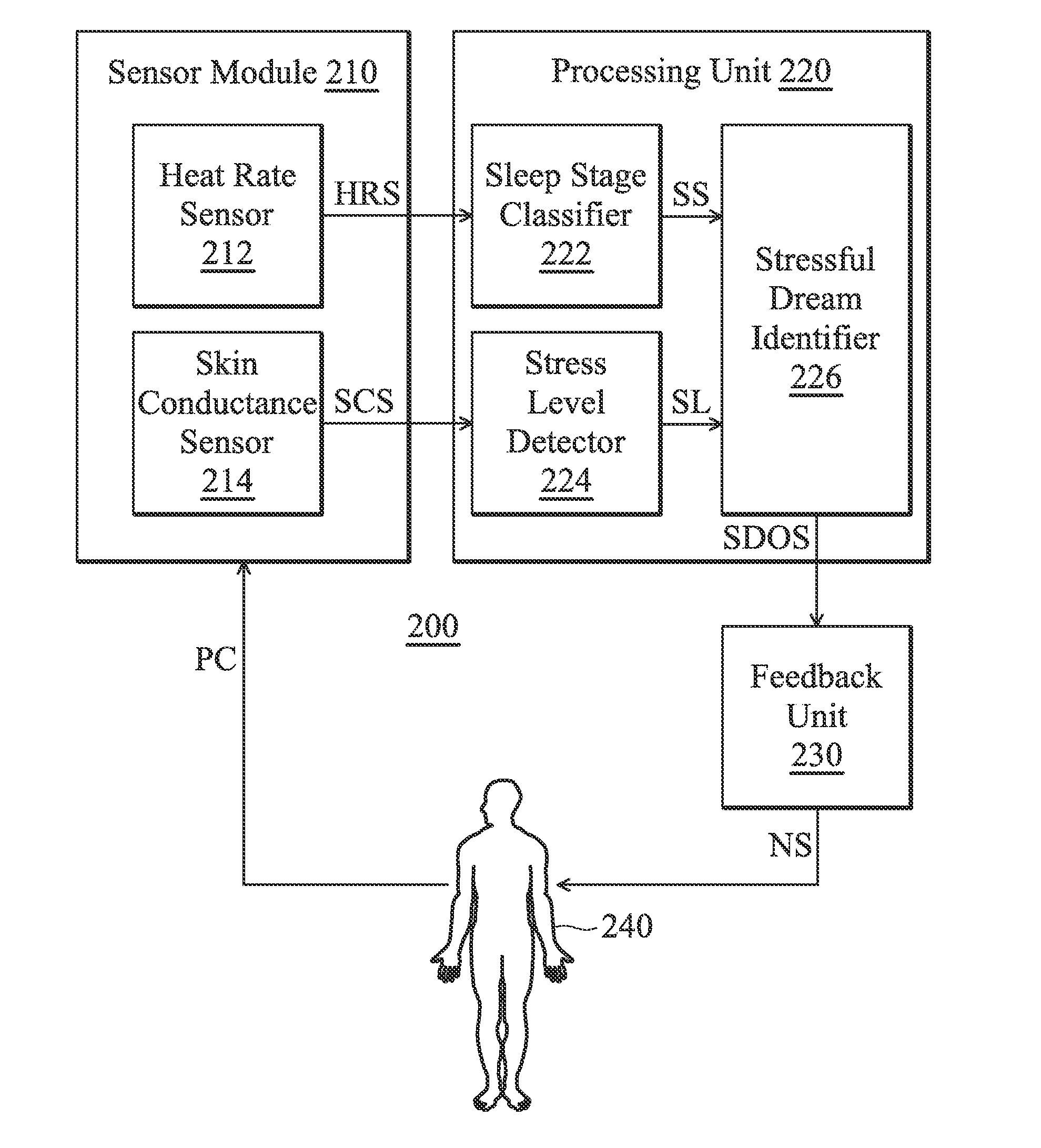
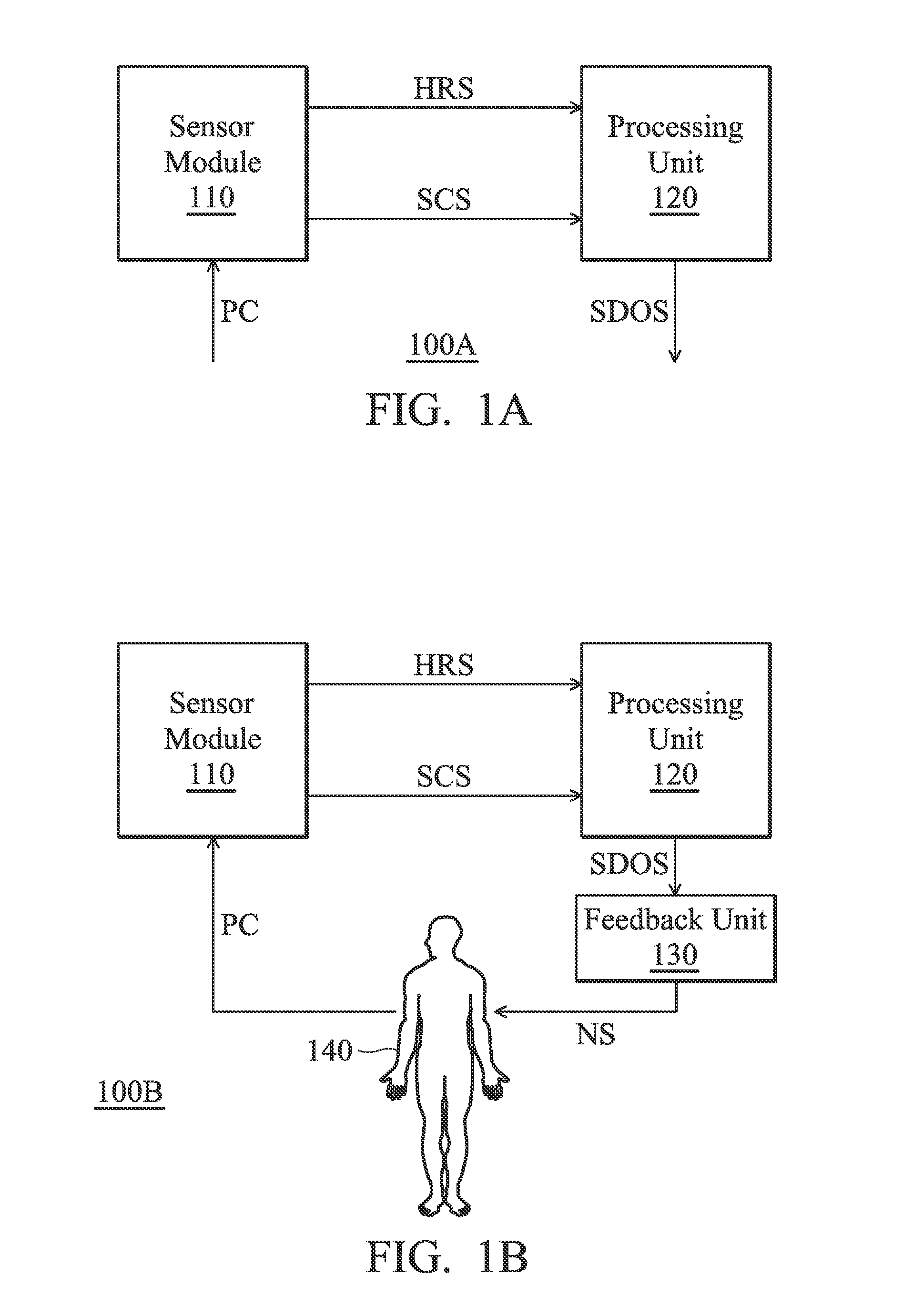
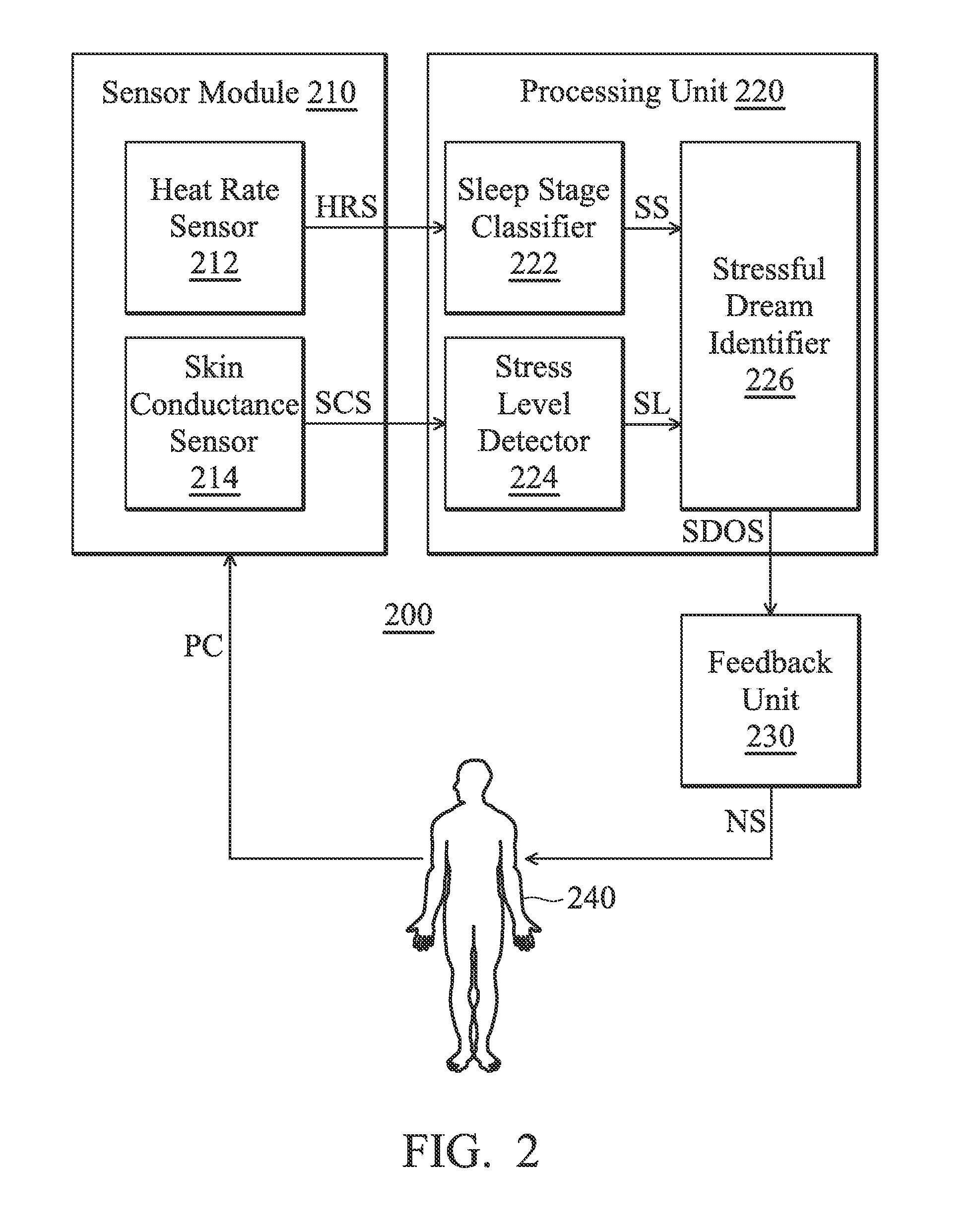
Method for managing sleep quality and apparatus utilizing the same
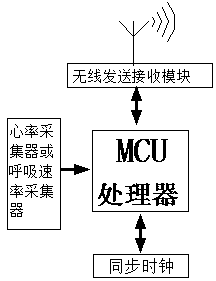
A sleep quality management apparatus includes a sensor module and a processing unit. The sensor module is configured to provide a heart rate signal and a skin conductance signal. The processing unit is coupled to the sensor module. The processing unit is configured to determine a sleep stage and a stress level according to the heart rate signal and the skin conductance signal so as to identify a stressful dream occurrence. The stressful dream occurrence is identified when the sleep stage corresponds to a rapid eye movement (REM) stage and the stress level corresponds to a stressful state.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Rendering control method, rendering control device and mobile terminal
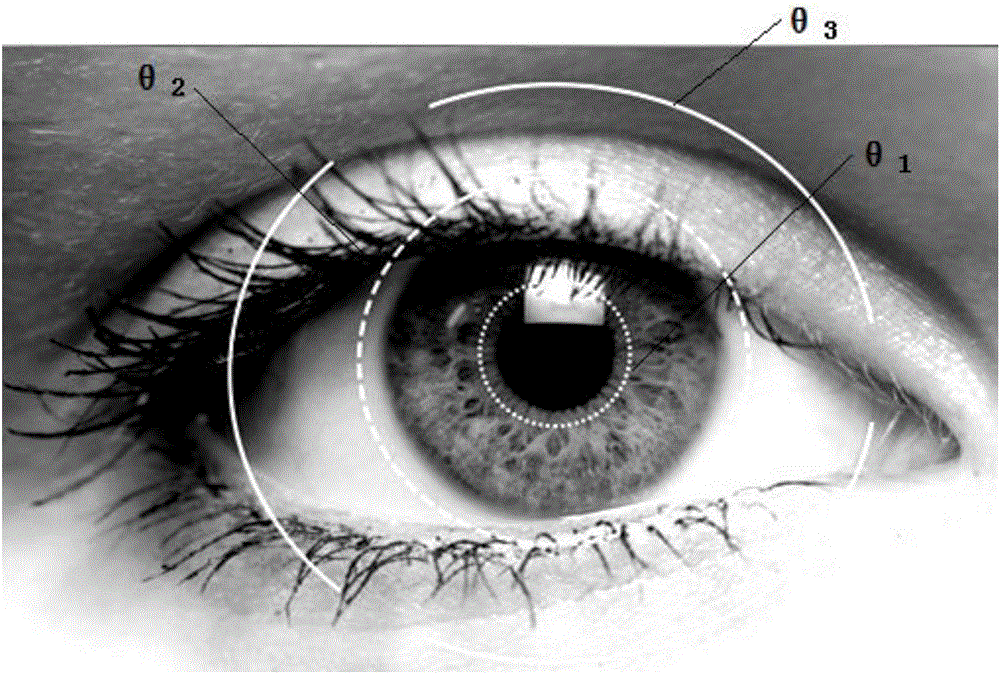
ActiveCN106101533AEasy to coverPrevent detectionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCurrent pointRapid Eye Movements
The invention discloses a rendering control method, a rendering control device and a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of promoting a refresh rate value of a front camera to a preset target refresh rate value from a default refresh rate value when the mobile terminal opens a virtual reliability application; figuring out a fine rendering region according to the target refresh rate value obtained after promotion and the current point of regard of a user on a screen of the mobile terminal in order to carry out fine rendering on pixel points in the fine rendering region; carrying out normal rendering processing on other regions outside the fine rendering region; and lastly, presenting a rendered picture to the user on the screen. The invention has the following beneficial effects that the precise rendering region is determined by the target refresh rate value which can be better adaptive to the rapid eye movement than the existing fixed refresh rate value, the obtained precise rendering region can better cover the visual range of the user, the user is prevented from perceiving a rough rendering picture outside the fine rendering region during the rapid eye movement, and the visual perception and the satisfaction of the user are improved.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
System and method for assessment of sleep
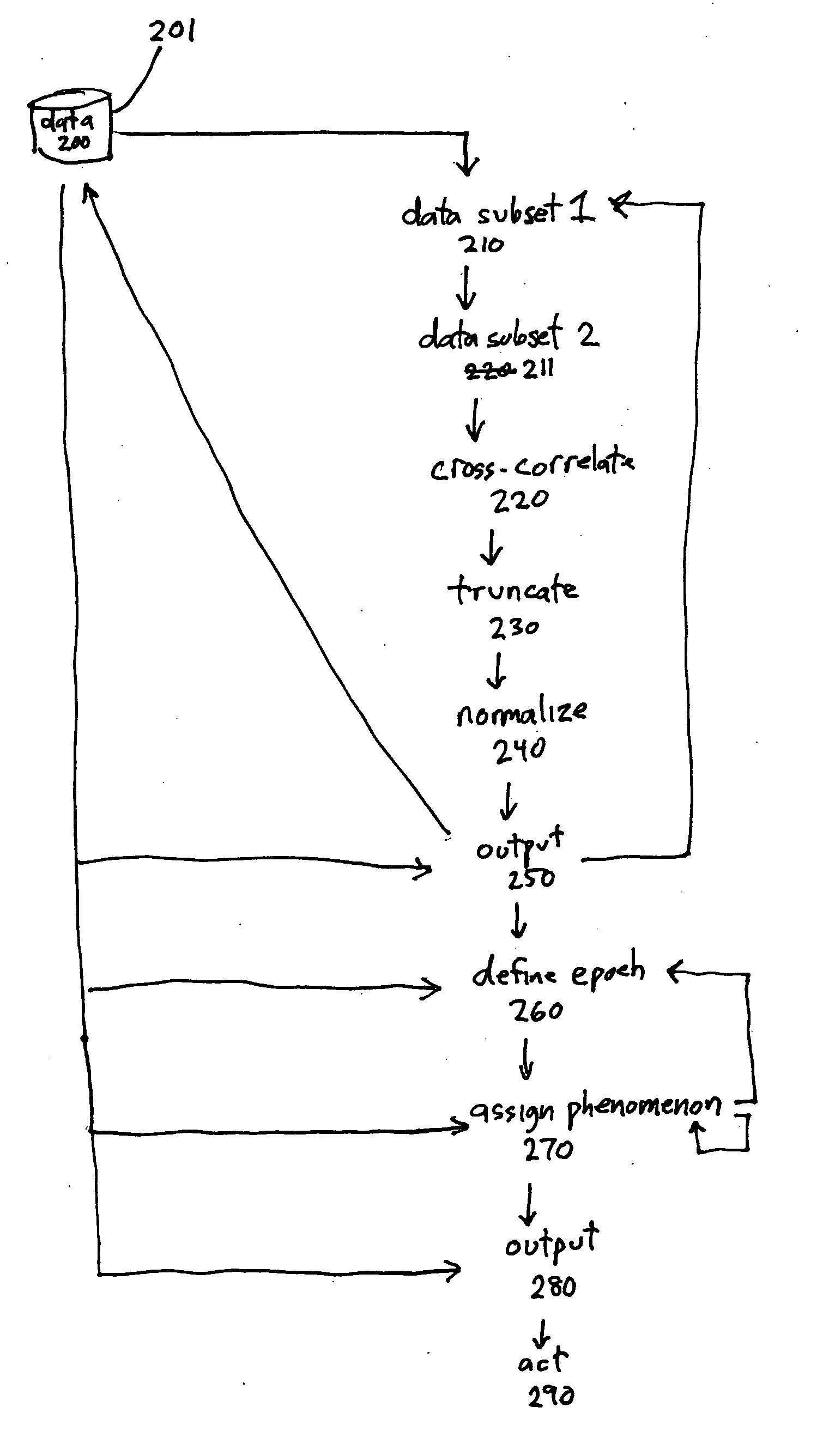
InactiveUS20070179395A1Eliminate lag timeAuscultation instrumentsRespiratory organ evaluationBiological bodyRapid Eye Movements
A method and system for characterizing breathing in an organism are disclosed. The method acquires data values indicative of periodic respiratory function, for example, tracheal sound envelope data acquired during a period of time associated with a sleep period of the organism. The method defines a first subset of data values among the data values and a second subset of data values among the data values. Cross-correlating the first and second subsets of data values yields a first result vector which is truncated, normalized, and output. These steps are optionally repeated for other subsets of data. From the resulting output, the organism's average respiratory rate may be determined. In addition, periods of time corresponding to sleep, wakefulness, rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep, and non-REM sleep may be identified. The time it takes the organism to fall asleep may also be determined.
Owner:SOTOS JOHN G +1
Device for the treatment of sleep-related conditions
InactiveUS20120212345A1Well formedUser/patient communication for diagnosticsAuscultation instrumentsRapid Eye MovementsSleep apnea
A device and related methods are provided. The device may be for the treatment and detection of various medical and non-medical conditions, including for detecting and treating snoring and sleep apnea, for detecting rapid eye movement of a sleeping person, and for detecting drowsiness or sleepiness of a person. The device may include an alert indicator for providing alerts to the person and a sensor configured for sensing one or more conditions of the person and communicating the condition to the alert indicator.
Owner:PURSUIT ENTERPRISES
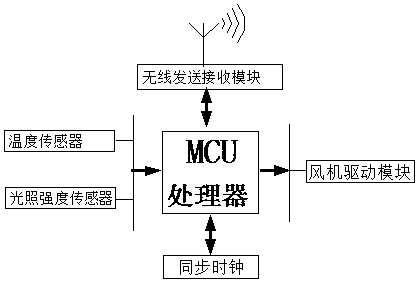
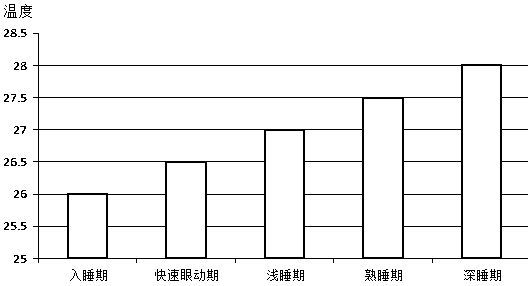
Automatic temperature adjusting air conditioner based on user deep sleep, air conditioner system and control method
InactiveCN107606754AMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsOlder peopleRapid Eye Movements
The invention provides an automatic temperature adjusting air conditioner based on user deep sleep, an air conditioner system and a control method. Different sleep periods where a human body stays areobtained by collecting and processing the heart rates or respiration rates of a plurality of people; the output refrigerating capacity can be adjusted timely according to the different sleep periodswhere the human body stays; the refrigerating capacity is decreased step by step by adjusting the refrigerating capacity output in the falling asleep period, the rapid eye movement period, a light sleeping period, a sound sleeping period and a sleep sleeping period, and accordingly the indoor temperature is maintained to be in an optimal temperature interval. When there are the multiple people ina room, the control priority of the system is transferred to the person who falls asleep firstly and enters in the deep level sleep firstly, when other people enters in the deeper level sleeping period, and then the control right of the system can be transferred. The heart rate or the respiration rate of the person who possesses the control right of the system joins to adjust the output refrigerating capacity exclusively, and the heart rate or the respiration rate of other people cannot join to adjust the output refrigerating capacity. When there are old people and children in a room, the control priority of the system is transferred to the old people and the children, therefore protection to the human body is enhanced, and the automatic temperature adjusting air conditioner benefits the health of the human body.
Owner:宋彦震
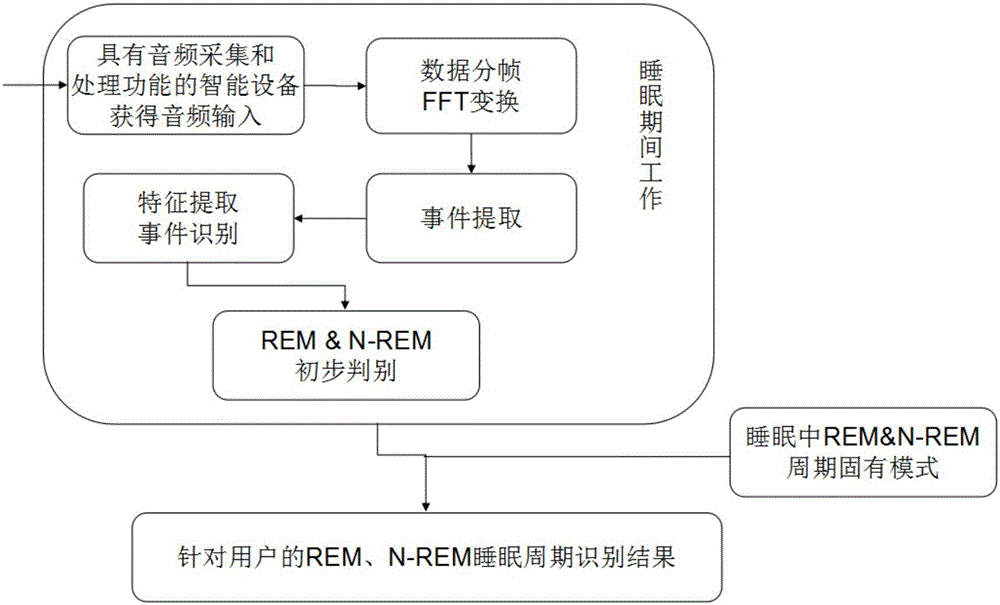
Sleep stage recognition method based on audio processing
The invention discloses a sleep stage recognition method based on audio processing. According to the method, intelligent equipment with functions of audio acquisition and processing is used and comprises a smartphone and a smartwatch, wherein an audio module is used as an audio acquisition device; numerical characteristics of acquired audio frequency are extracted, sleep related events (including snoring, trunk movement, coughing and odontoprisis) occurring during sleeping are recognized with a mode recognition method, external expression differences of people in the REM (rapid eyes movement) sleep stage and the N-REM (non-rapid-eyes movement) sleep stage are taken as entry points, and the sleep stage is recognized for sleep of people in combination with the external expression differences of people in the medical REM sleep stage and the medical N-REM sleep stage. The method has the advantages that the equipment is simple and easy to obtain, an equipment room and a server room for communication are not required, the method is non-invasive and the like, and the method can be widely applied to multiple application fields of daily sleeping monitoring, sleeping quality evaluation, living habit evaluation and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition and treating secondary insomnia
Owner:OVID THERAPEUTICS
Device and method for sleep monitoring
A device and method for sleep monitoring, in particular to a device and method for determining time-to-sleep and wake periods during sleep and to a device and method for determining rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non REM (NREM) sleep. The method for determining time-to-sleep and wake periods during sleep comprising the steps of obtaining motion data representative of motion of a user; detecting the time-to-sleep from the motion data based on a first time-above-threshold (TAT) threshold and a first proportional integration method (PIM) threshold; and detecting the wake periods during sleep from the motion data based on a second TAT threshold and a second PIM threshold.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Sleep state analysis method
ActiveCN106333652ASleep quality impactImprove accuracyRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSleep stateRem sleep deprivation
The invention discloses a sleep state analysis method. REM (Rapid Eyes Movement) sleep can be recognized via body movement information in combination with vegetative nerve balance analysis. Thus, the objective sleep quality of a patient is further evaluated more accurately via awakening, stable or instable sleep and REM sleep conditions.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
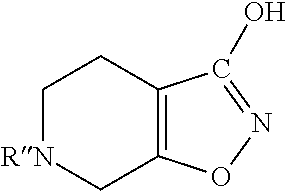
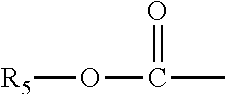
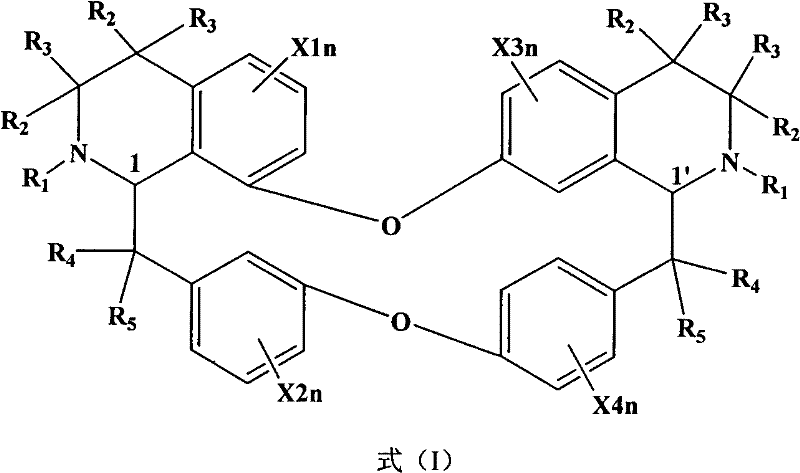
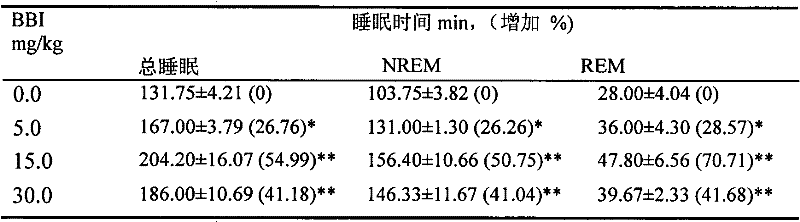
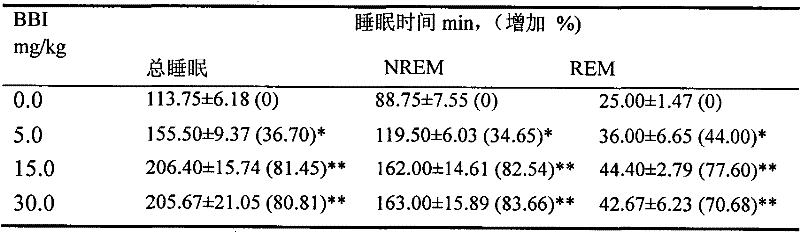
Application of bisbenzylisoquinoline compound or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparing medicine or healthcare product for improving sleep
The invention discloses a new use of bisbenzylisoquinoline compound shown in formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof except for tetrandrine and fangchinoline. The use is application of the bisbenzylisoquinoline compound shown in formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparing a medicine or healthcare product for treating insomnia and improving sleep. The bisbenzylisoquinoline compound shown in formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be used as an effective component and made into any dosage form. The result of animal experiment indicates that: the bisbenzylisoquinoline compound shown in formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can obviously prolong the total sleep time of normal rats and mouse, including REM (rapid eye movement) sleep time and NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep time. The application disclosed by the invention is suitable for various types of insomnia or sleep disorders.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Sleep staging monitoring method
ActiveCN110236491AAccurate identificationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSleep stagingRapid Eye Movements
The invention relates to a sleep staging monitoring method. The method carries out sleep staging monitoring by taking multi-dimensional vital sign parameters such as continuous heart rate, respiration rate and body movement as identification basis, and realizes accurate identification of an awakening period, a rapid eye movement period and a non-rapid eye movement period.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Computer architecture for identifying sleep stages
A computing machine receives sensor data representing airflow or air pressure. The computing machine determines, using an artificial neural network, a current sleep stage corresponding to the sensor data. The current sleep stage is one of: wake, rapid eye movement (REM), light sleep, and deep sleep. The artificial neural network comprises a convolutional neural network (CNN), a recurrent neural network (RNN), and a conditional random field (CRF). The computing machine provides an output representing the current sleep stage.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +2
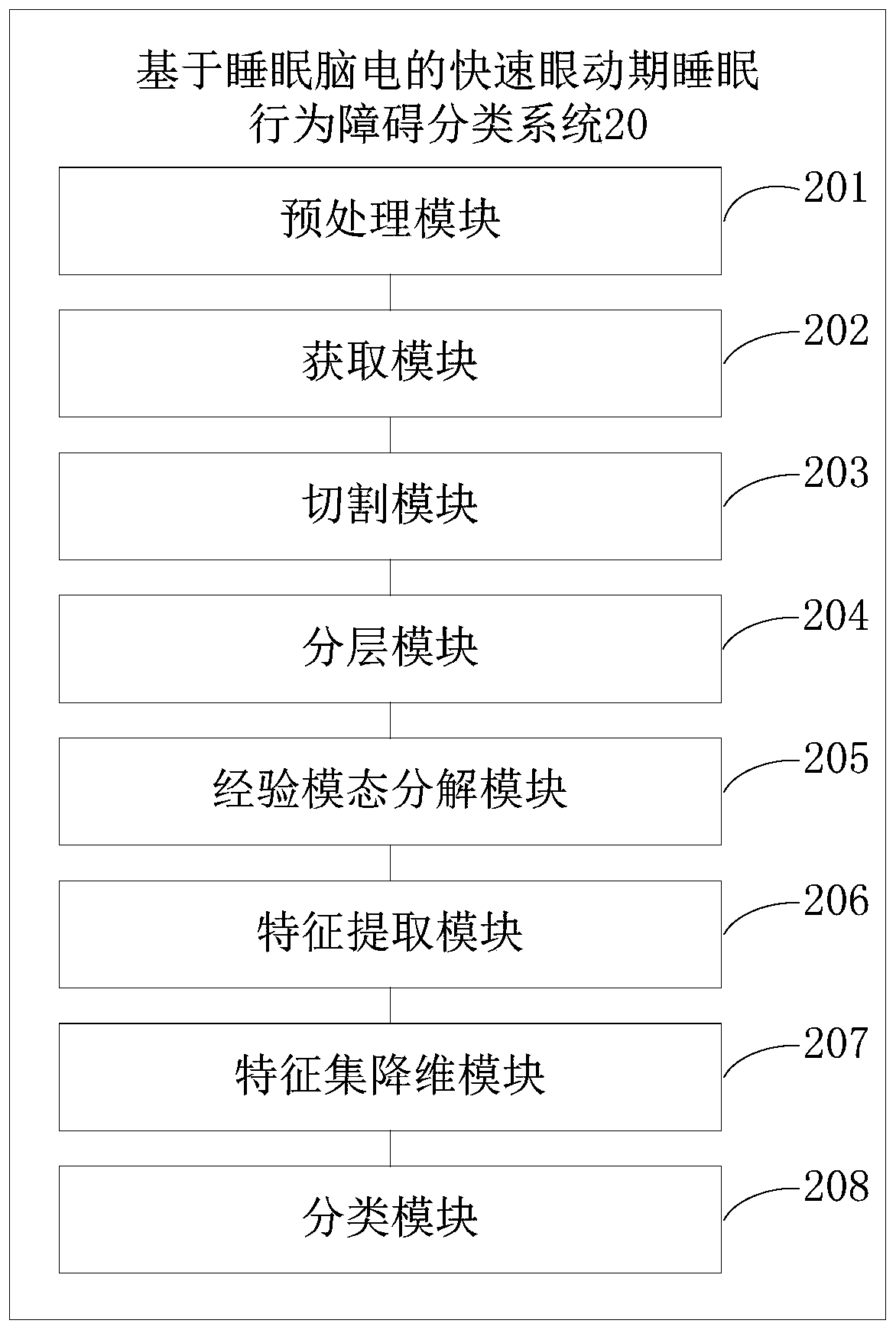
Rapid eye movement period sleep behavior disorder classification method based on sleep electroencephalogram
The invention discloses a rapid eye movement period sleep behavior disorder classification method based on sleep electroencephalogram. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing an acquired sleep electroencephalogram signal of a patient, acquiring an electroencephalogram signal of an electroencephalogram interval in a sleep R period, cutting according to a preset signal length to acquire a plurality of sub-signal segments, layering an original electroencephalogram signal of each sub-signal segment, and enabling a frequency domain component after wavelet transform to approximatelycorrespond to different wave bands of original electroencephalogram according to the frequency of the electroencephalogram; carrying out empirical mode decomposition (EMD) to obtain a multilayer intrinsic mode function (IMF); performing feature extraction on the electroencephalogram signals of different wave bands and the multilayer intrinsic mode function, and performing dimensionality reductionon the feature set PCA to obtain a low-dimensional feature set; and carrying out classification and identification by using the feature set after dimension reduction, and classifying patients suffering from Parkinson's disease accompanied by rapid eye movement sleep disorder, Parkinson's disease not accompanied by rapid eye movement sleep disorder and idiopathic rapid eye movement period sleep behavior disorder. Complex PSG detection is simplified into electroencephalogram detection, a whole night does not need to be consumed, the number of times of measurement is reduced, an accurate recognition result is obtained, and then a very good auxiliary effect can be achieved on treatment of the illness state of a patient.
Owner:济南国科医工科技发展有限公司
Method and device for improving sleep quality, and intelligent wearable equipment
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for improving the sleep quality, and intelligent wearable equipment. After a user falls asleep, the sleep stages of the user are monitored, the exercise intensity of the user in the non-sleep time period is acquired after it is monitored that the user enters a deep sleep period, and if the exercise intensity of the user is greater thanor equal to a preset exercise intensity threshold, audio playing equipment is notified to play deep sleep brain wave audio so as to trigger brain wave resonance of the user and prolong deep sleep duration in order to make the body of the user have a full rest; and after the user is monitored to enter the rapid eye movement period, the mental pressure of the user in the non-sleep time period is acquired, and if the mental pressure of the user is greater than or equal to a preset mental pressure value, the audio playing equipment is notified to play the brain wave audio for stimulating the rapid eye movement period so as to prolong the rapid eye movement period of the user in order to relieve the mental pressure of the user.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
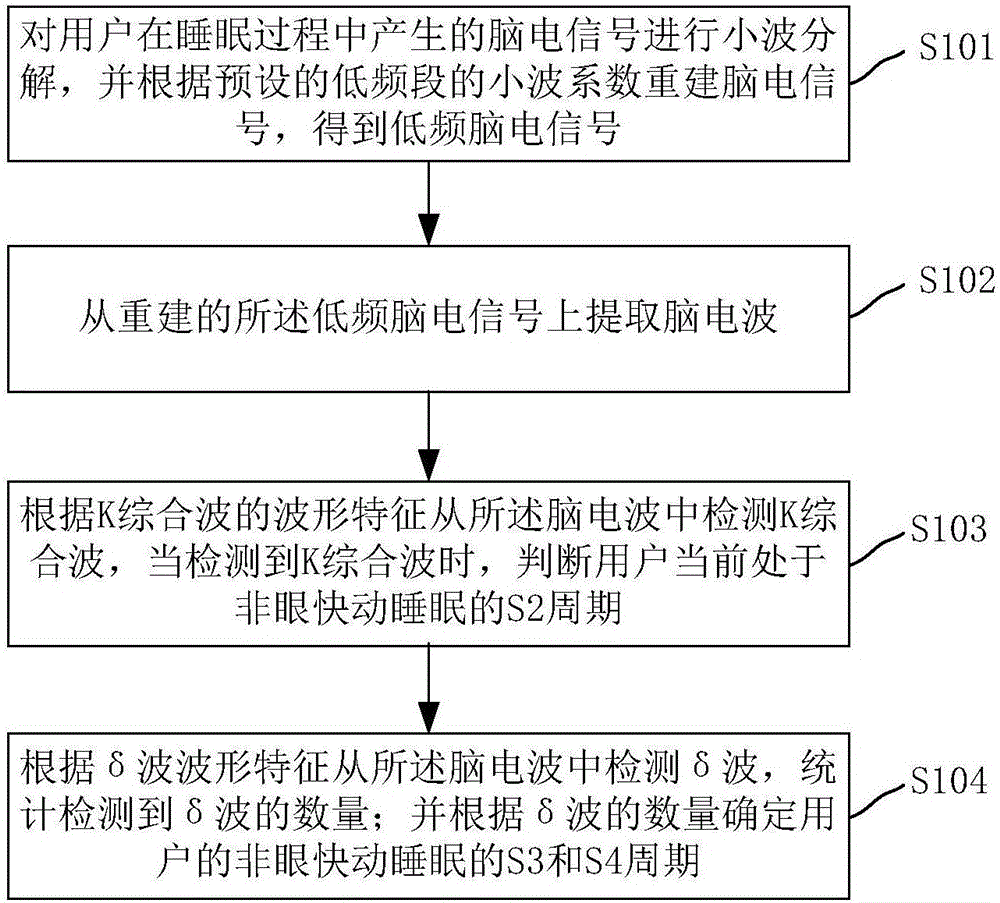
Sleep cycle detection method and sleep cycle detection system in sleep state analysis
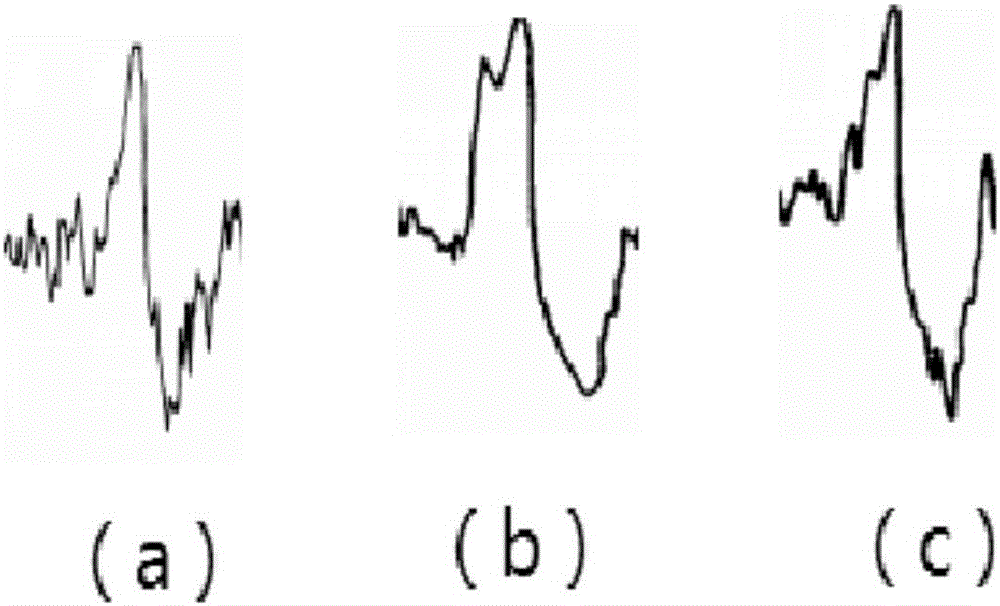
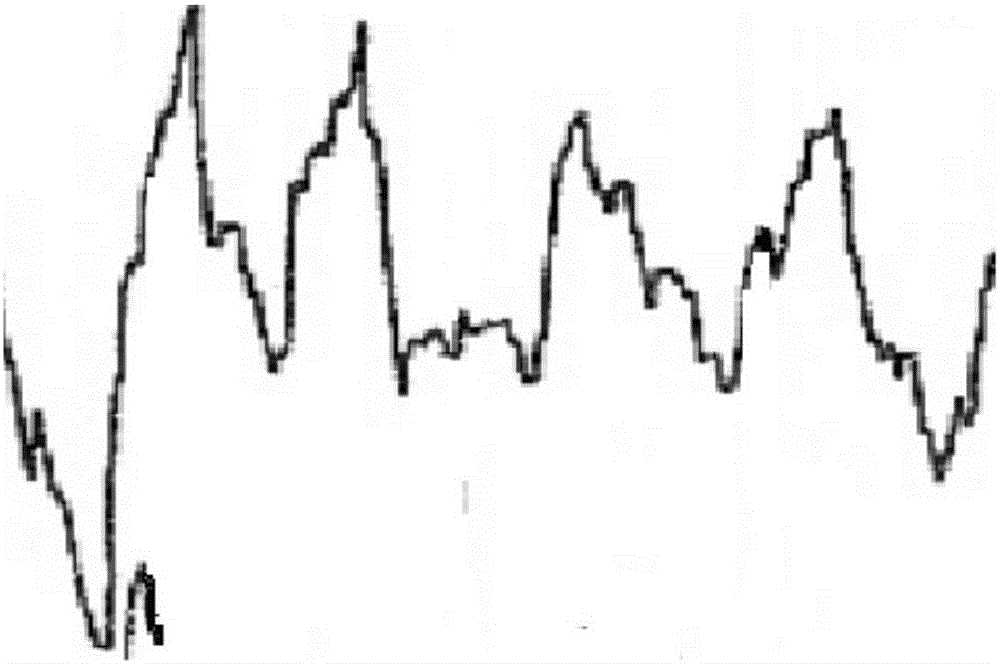
ActiveCN106333674AAvoid disturbing influenceAccurate detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSleep stateWavelet decomposition
The invention relates to a sleep cycle detection method and a sleep cycle detection system in sleep state analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: performing wavelet decomposition for electroencephalogram generated during the sleep process of a user, rebuilding electroencephalogram according to a preset wavelet coefficient of a low frequency band, and obtaining low-frequency electroencephalogram; extracting a brain wave from the rebuilt low-frequency electroencephalogram; detecting a K comprehensive wave in the brain wave according to a waveform characteristic of the K comprehensive wave, and when the K comprehensive wave is detected, determining that the user currently stays at a cycle S2 of non-rapid eye movement sleep; detecting a delta wave from the brain wave according to the waveform characteristic of the delta wave, and counting the number of the detected delta waves; and determining cycles S3 and S4 of non-rapid eye movement sleep of the user according to the number of the delta waves. By adopting the technical scheme, the electroencephalogram can be prevented from being interfered, whether the user currently stays at a cycle S2 to S4 of the non-rapid eye movement of the user can be accurately detected, and the accuracy is higher.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
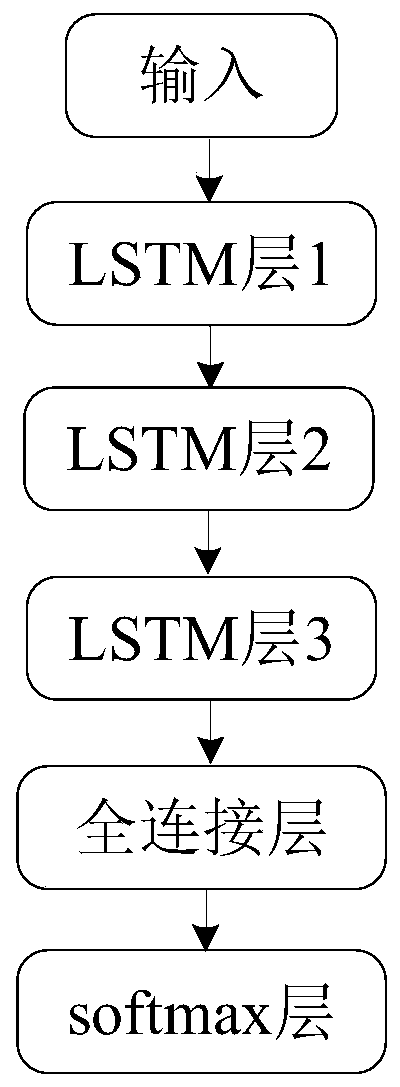
Sleep staging method based on BLSTM and sleep staging device based on BLSTM
PendingCN111407262AVerify robustnessResolving RR interval mutationsRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSleep stagingPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides a sleep staging method based on BLSTM and a sleep staging device on the BLSTM. The BLSTM comprises two training layers and one output layer, wherein each training layer comprises 16 units, the output layer comprises 4 units, and the four units correspond to an awakening stage, a light sleep stage, a deep sleep stage and a rapid eye movement stage of sleep respectively; and input characteristics of the BLSTM comprise a characteristic extracted from an RR interphase signal, a characteristic extracted from a breathing signal and a characteristic extracted from cardiopulmonary coupling. The method and device acquire cardiopulmonary signals of a testee using a low-cost wearable multi-sensor system, conduct four-classification sleep staging by a bidirectional recursive neural network model which has an LSTM function and realize accurate staging of sleep.
Owner:北京海思瑞格科技有限公司
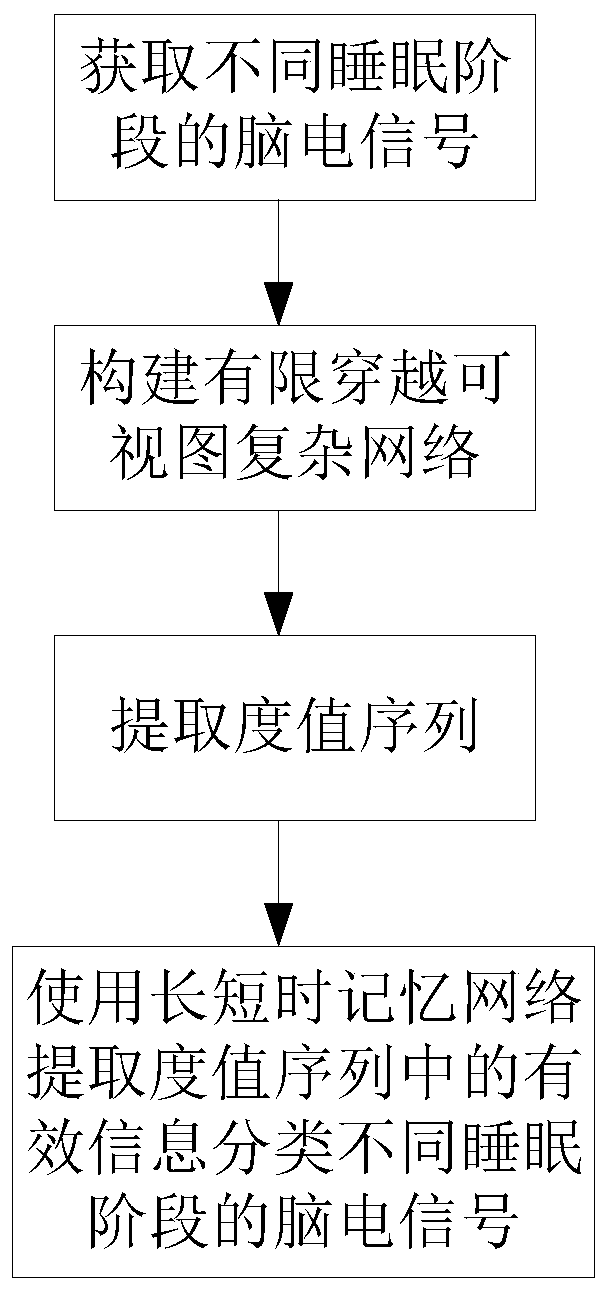
Sleep stage classification method based on complex networks and deep learning and application thereof
InactiveCN110367933AAchieve understandingBrain state understandingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNODALAlgorithm
A sleep stage classification method based on complex networks and deep learning and application thereof are provided. The sleep stage classification method comprises: acquiring characteristic indexesof a finite passage visibility graph complex network, to be specific, establishing the finite passage visibility graph complex network to extract node degrees, acquiring a node degree sequence according to the node degrees, and applying the node degree sequence as a characteristic index of the finite passage visibility graph complex network; establishing finite passage visibility graph complex networks having a finite passage visual range of 1 for sleep stage electroencephalography fragments; classifying the sleep stage electroencephalogram fragments into four classes according to awake stage,light sleep stage, deep sleep stage and rapid eye movement stage by means of 10-fold cross validation and a long short term memory model. The method of the invention is applicable to head-set intelligent wearable devices; by analyzing sleep electroencephalogram measured by the intelligent wearable devices, it is possible to understand the brain state of a user and provide necessary early warnings.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and device for controlling intelligent household electrical appliance to assist sleep, and intelligent household electrical appliance
ActiveCN113819617AMeet the needs of different sleep stagesImprove experienceMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAromatherapyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER AIR CONDITIONER GENERAL CORP LTD +2
Sleep monitoring method, device and equipment
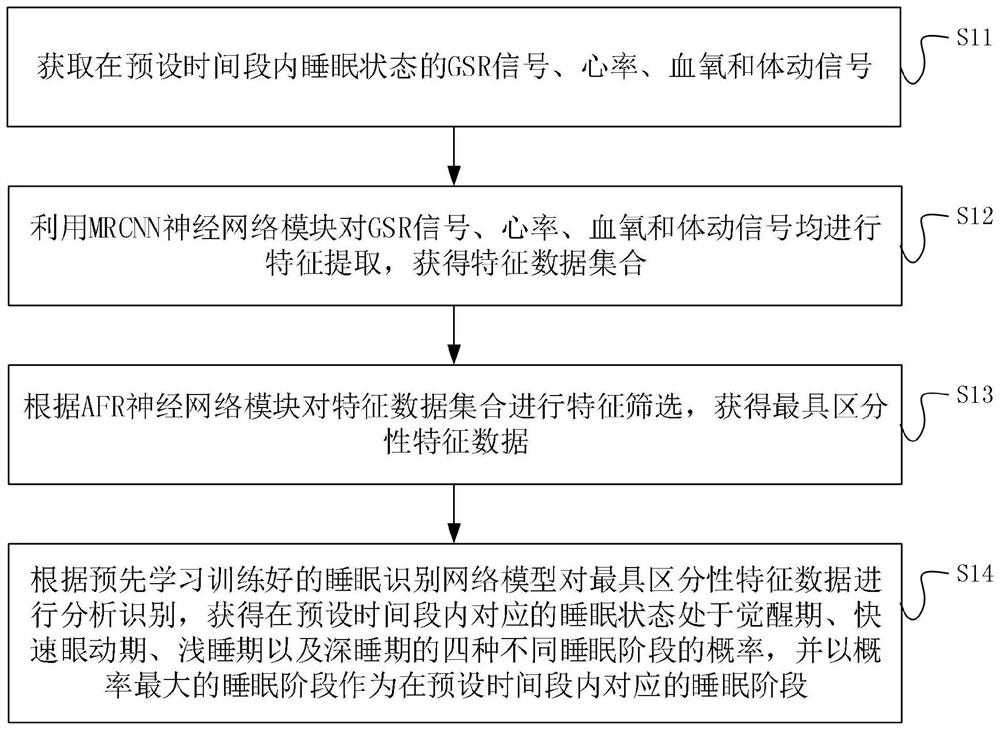
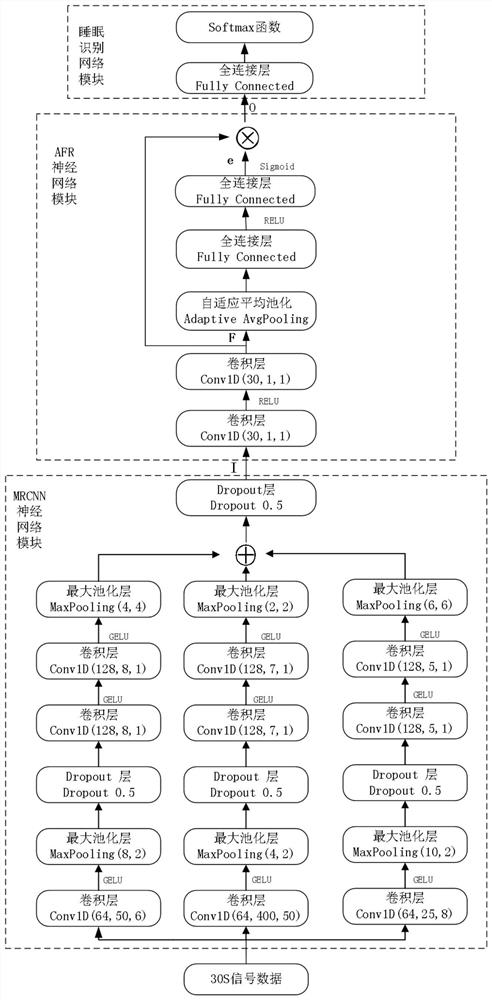
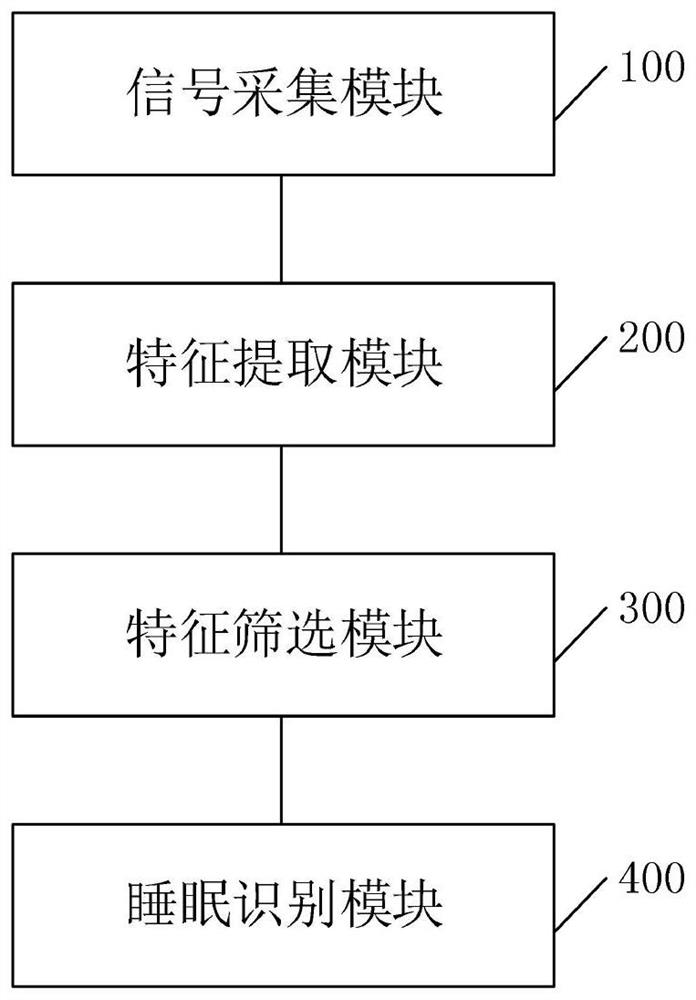
PendingCN114587288AAccurate analysisImprove effectivenessSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateRapid Eye MovementsBody movement
The invention discloses a sleep monitoring method, device and equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a GSR signal, a heart rate, blood oxygen and a body movement signal of a sleep state in a preset time period; performing feature extraction on the signal data by using an MRCNN neural network module and an AFR neural network module to obtain data with most distinctive features; analyzing and identifying the most distinctive feature data according to a sleep identification network model learned and trained in advance to obtain the probability that the corresponding sleep state is in four different sleep stages of an awakening stage, a rapid eye movement stage, a light sleep stage and a deep sleep stage in a preset time period; the sleep stage with the maximum probability is used as the corresponding sleep stage in the preset time period. According to the application, the GSR signal, the heart rate, the blood oxygen and the body movement signal of the testee are extracted through the MRCNN neural network module and the AFR neural network module to obtain the data with the most distinctive features, and accurate and effective monitoring of the sleep stage of the testee is realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com