Patents
Literature
34 results about "Whole slide image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
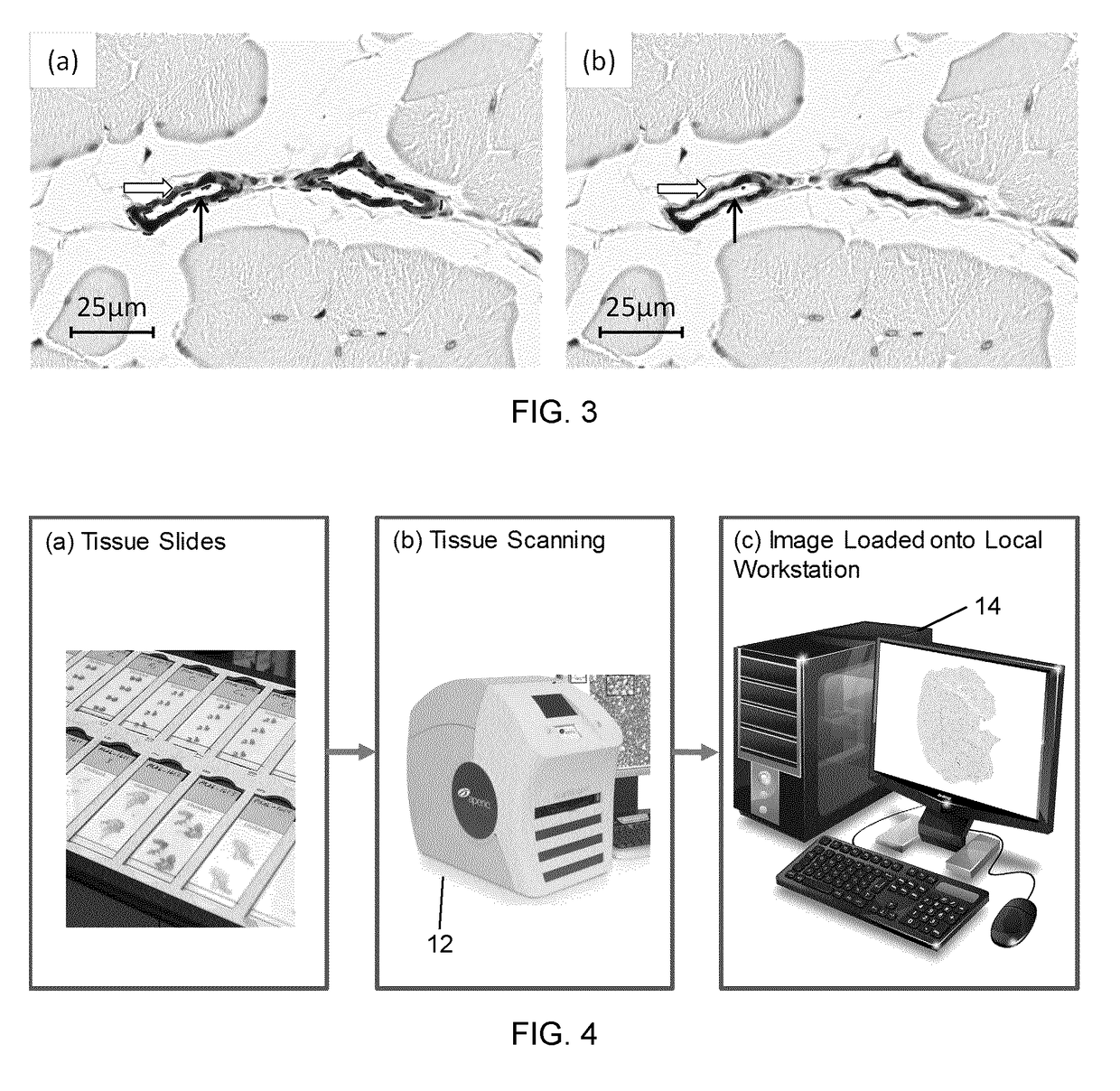
Whole slide imaging is the software manipulation of digital images of tissue sections that have been scanned at various magnifications. This enables the viewer to zoom in on areas of interest, thereby simulating the examination of glass slides under a traditional microscope.
Few-shot learning based image recognition of whole slide image at tissue level
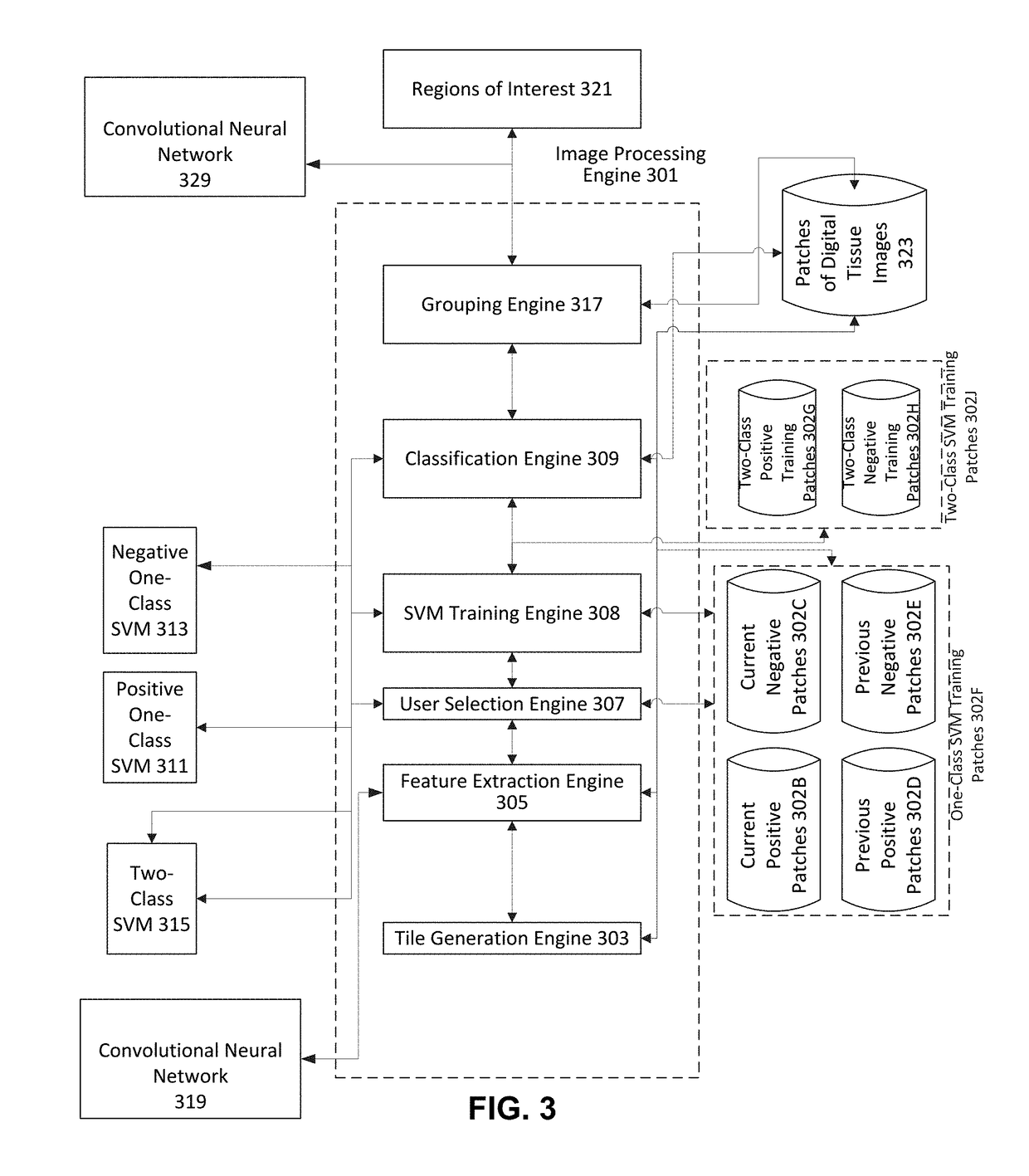
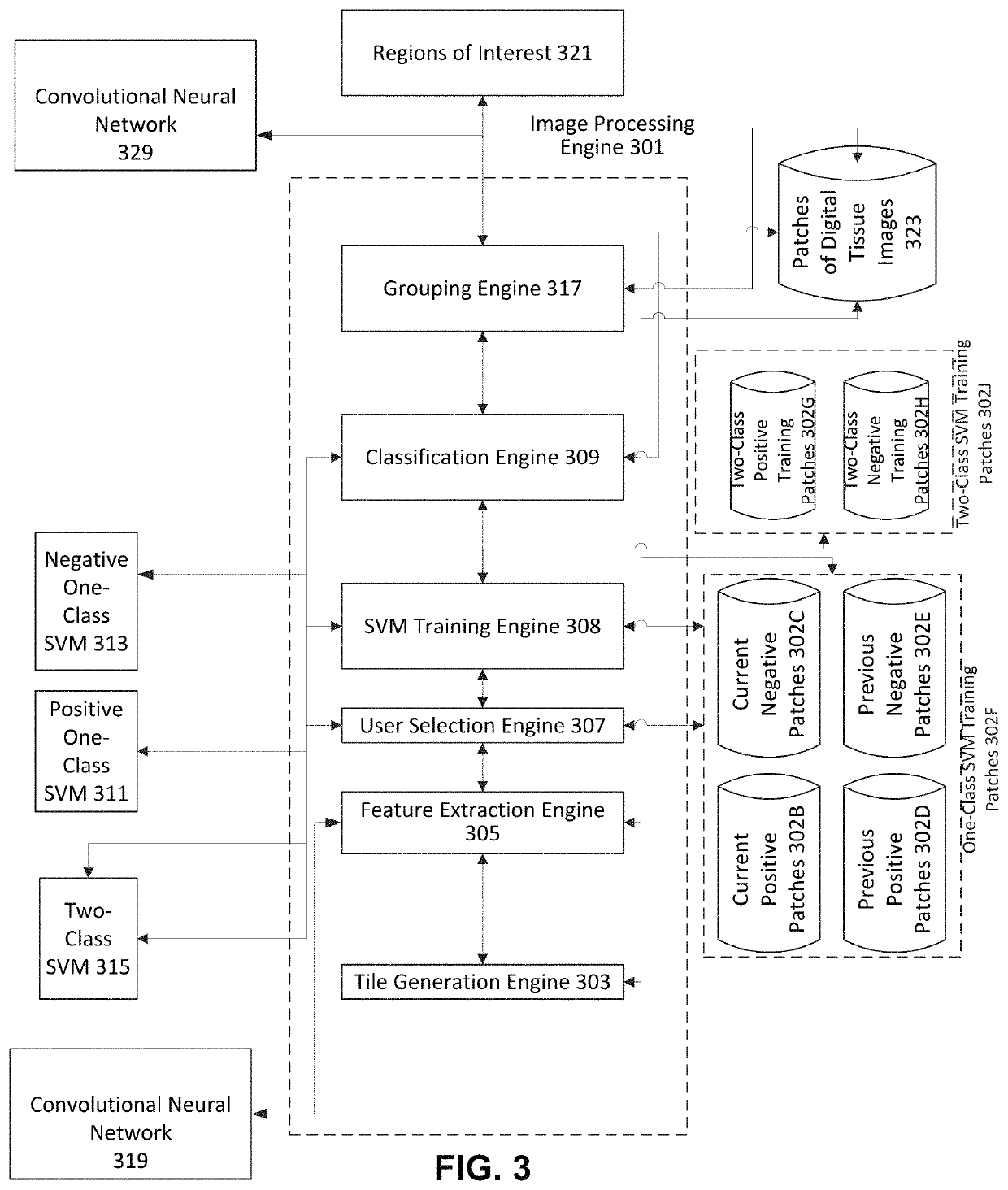
A computer implemented method of generating at least one shape of a region of interest in a digital image is provided. The method includes obtaining, by an image processing engine, access to a digital tissue image of a biological sample; tiling, by the image processing engine, the digital tissue image into a collection of image patches; obtaining, by the image processing engine, a plurality of features from each patch in the collection of image patches, the plurality of features defining a patch feature vector in a multidimensional feature space including the plurality of features as dimensions; determining, by the image processing engine, a user selection of a user selected subset of patches in the collection of image patches; classifying, by applying a trained classifier to patch vectors of other patches in the collection of patches, the other patches as belonging or not belonging to a same class of interest as the user selected subset of patches; and identifying one or more regions of interest based at least in part on the results of the classifying.
Owner:NANTOMICS LLC
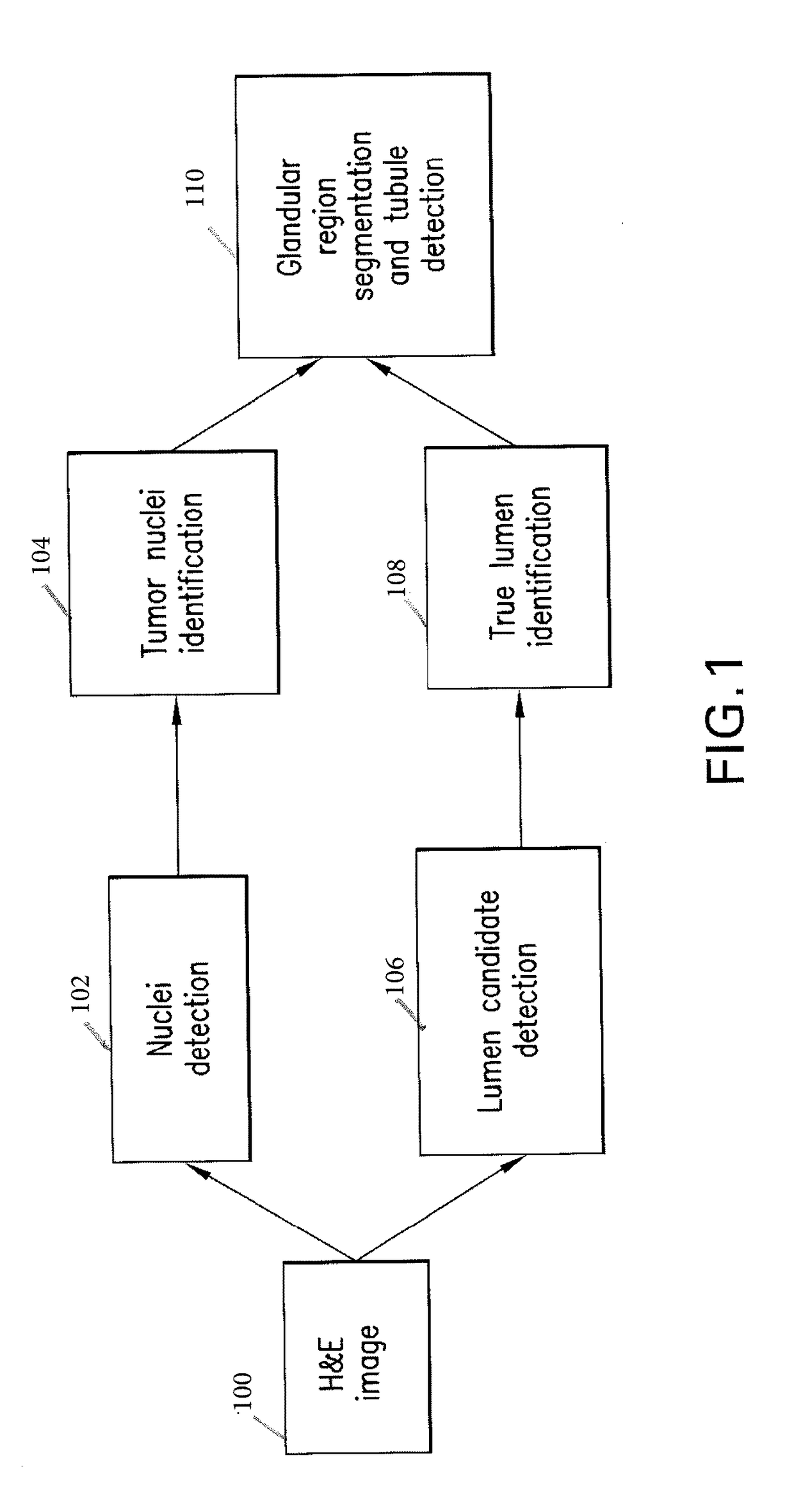
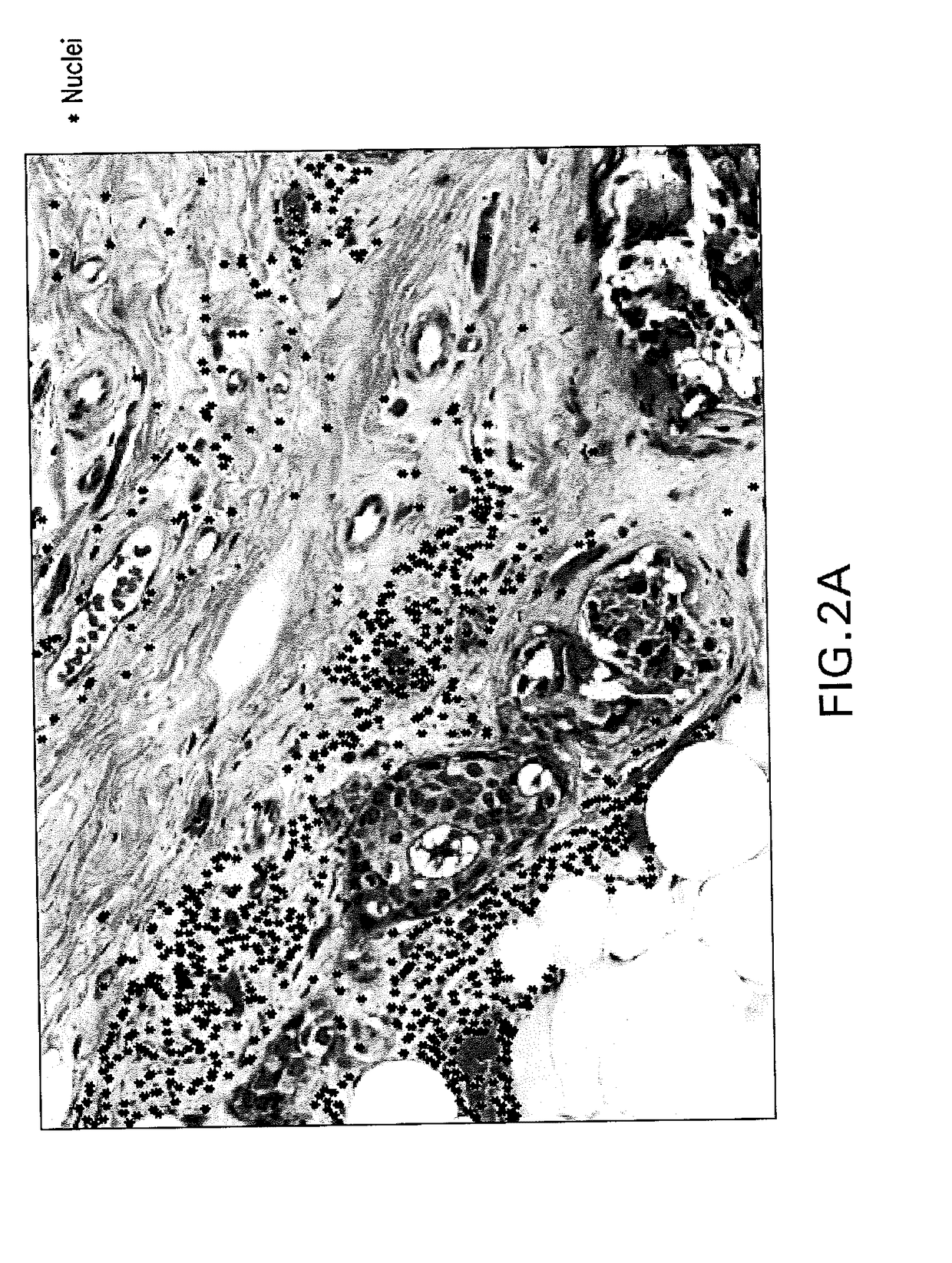
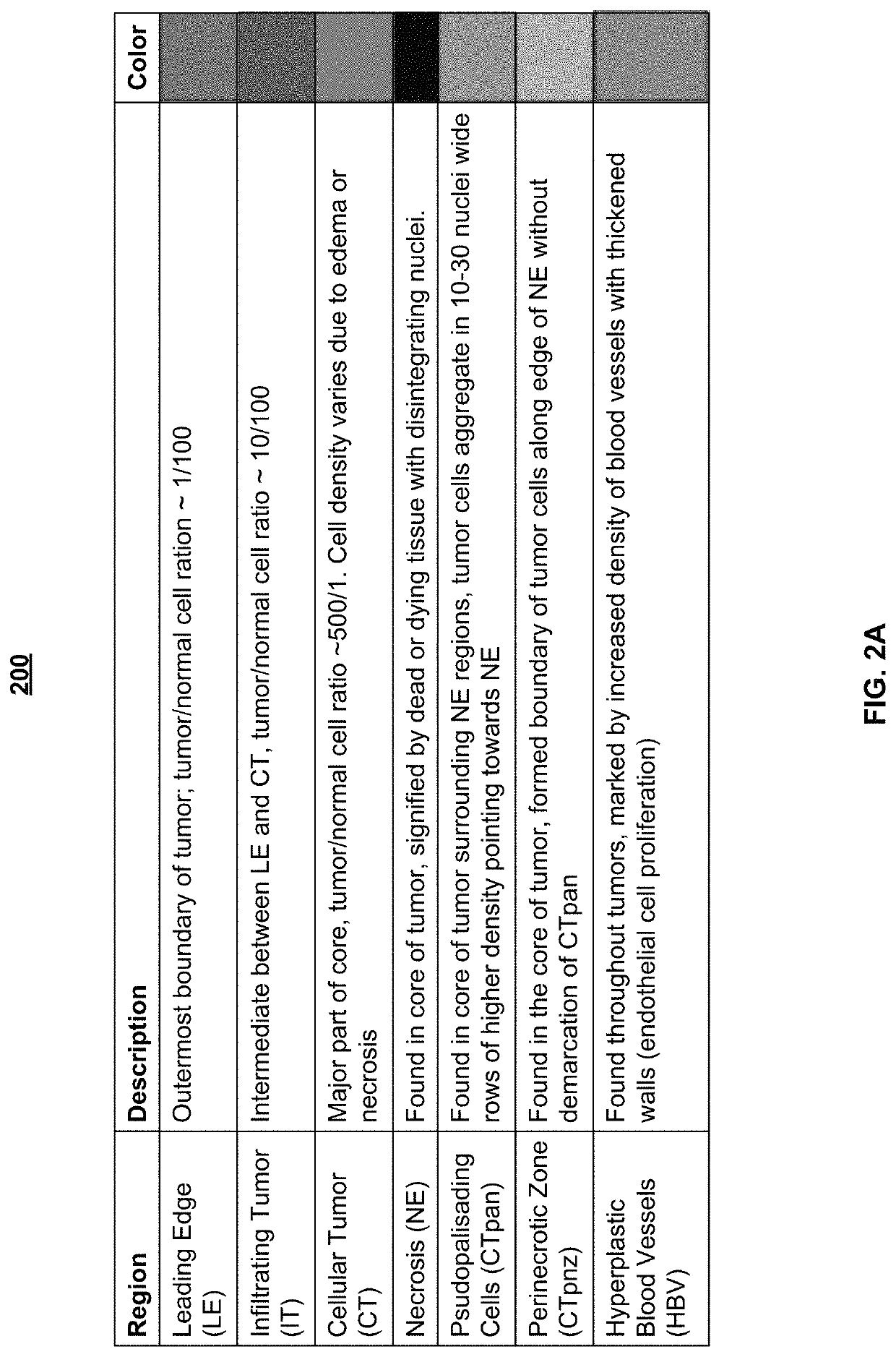
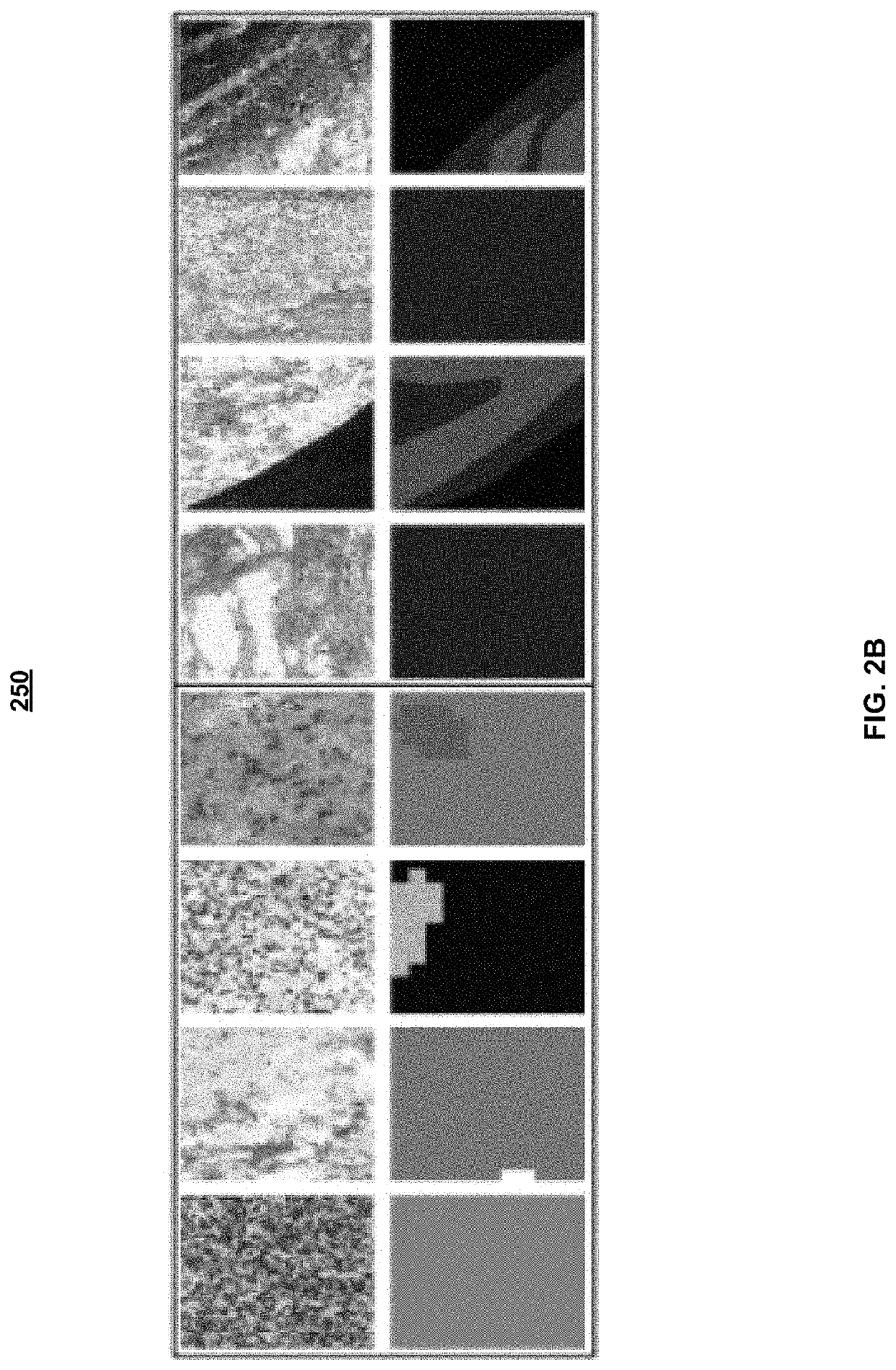
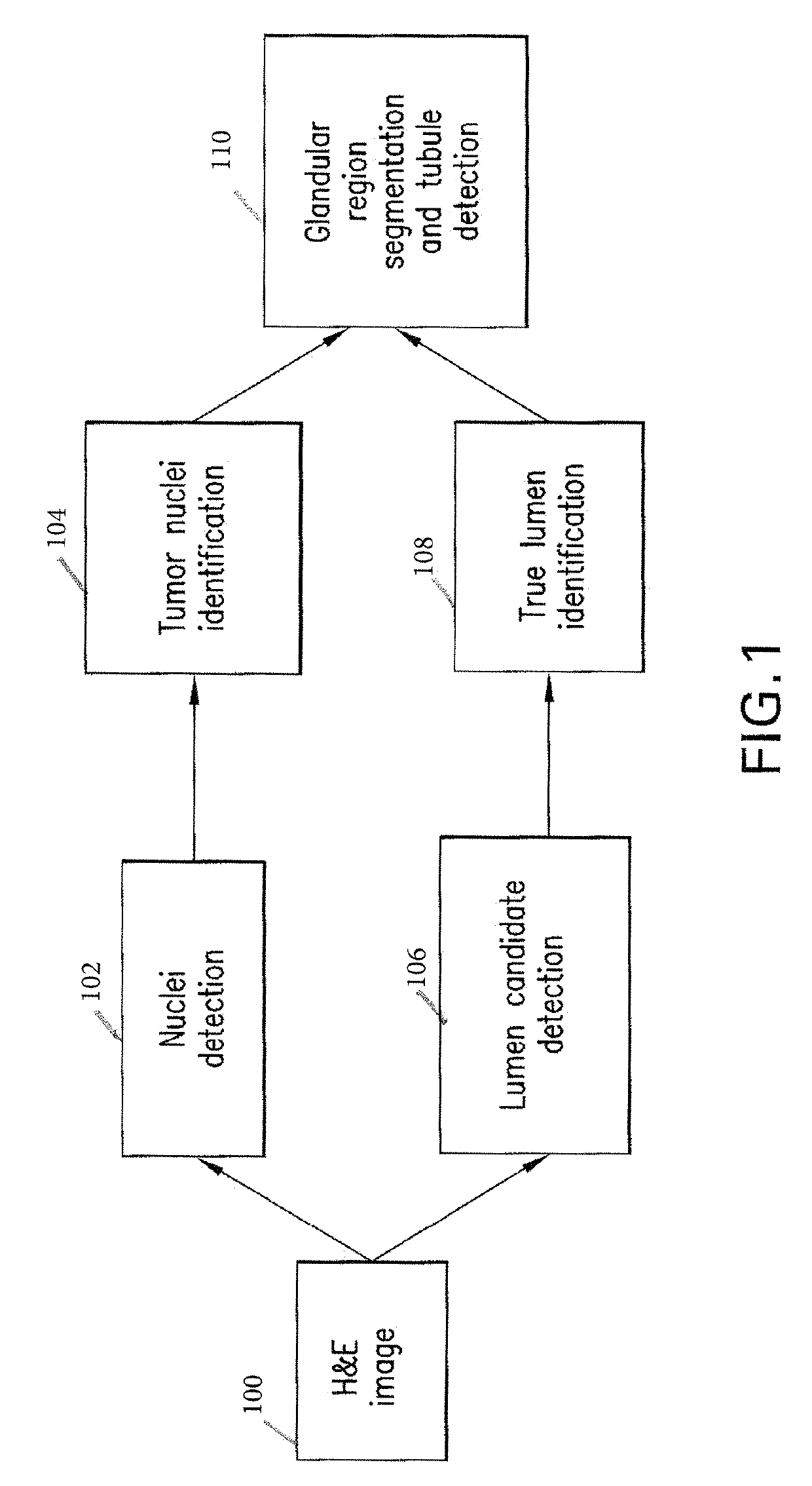
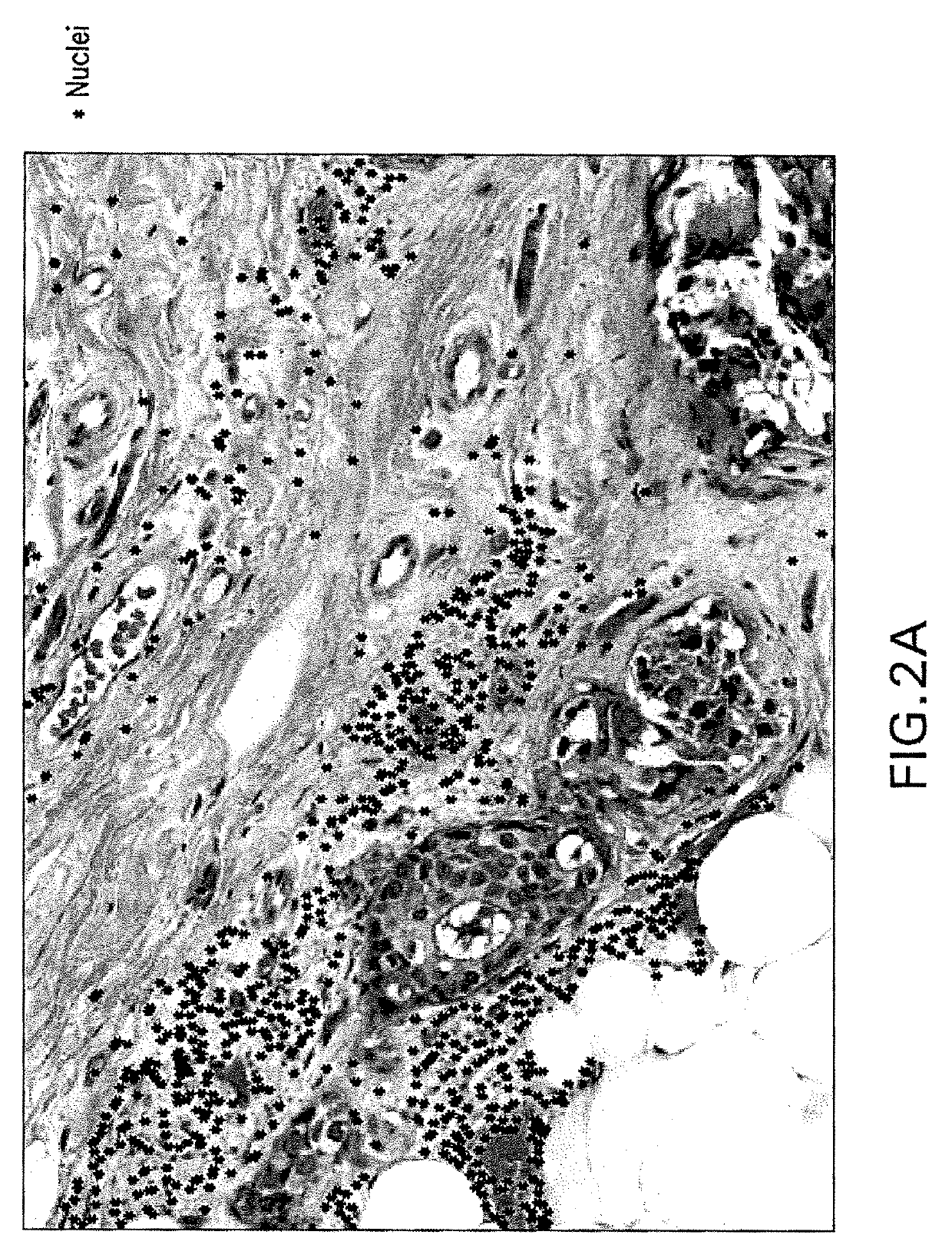
Automatic glandular and tubule detection in histological grading of breast cancer
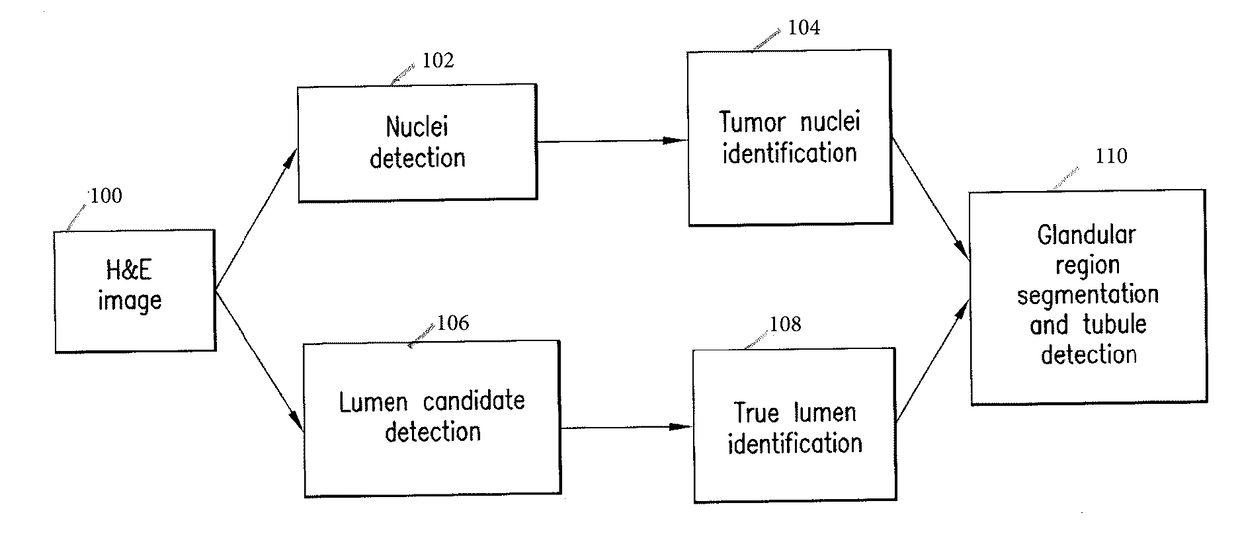
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for automatically identifying glandular regions and tubule regions in a breast tissue sample are provided. An image of breast tissue is analyzed to detect nuclei and lumen candidates, identify tumor nuclei and true lumen from the candidates, and group tumor nuclei with neighboring tumor nuclei and lumina to define tubule glandular regions and non-tubule glandular regions of the image. Learnt supervised classifiers, such as random forest classifiers, can be applied to identify and classify the tumor nuclei and true lumina. Graph-cut methods can be applied to group the tumor nuclei and lumina and to define the tubule glandular regions and non-tubule glandular regions. The analysis can be applied to whole slide images and can resolve tubule areas with multiple layers of nuclei.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
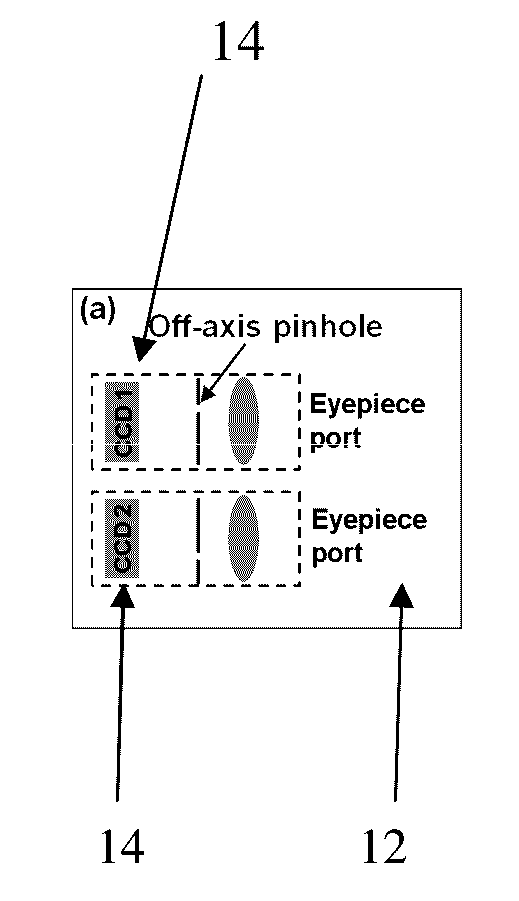
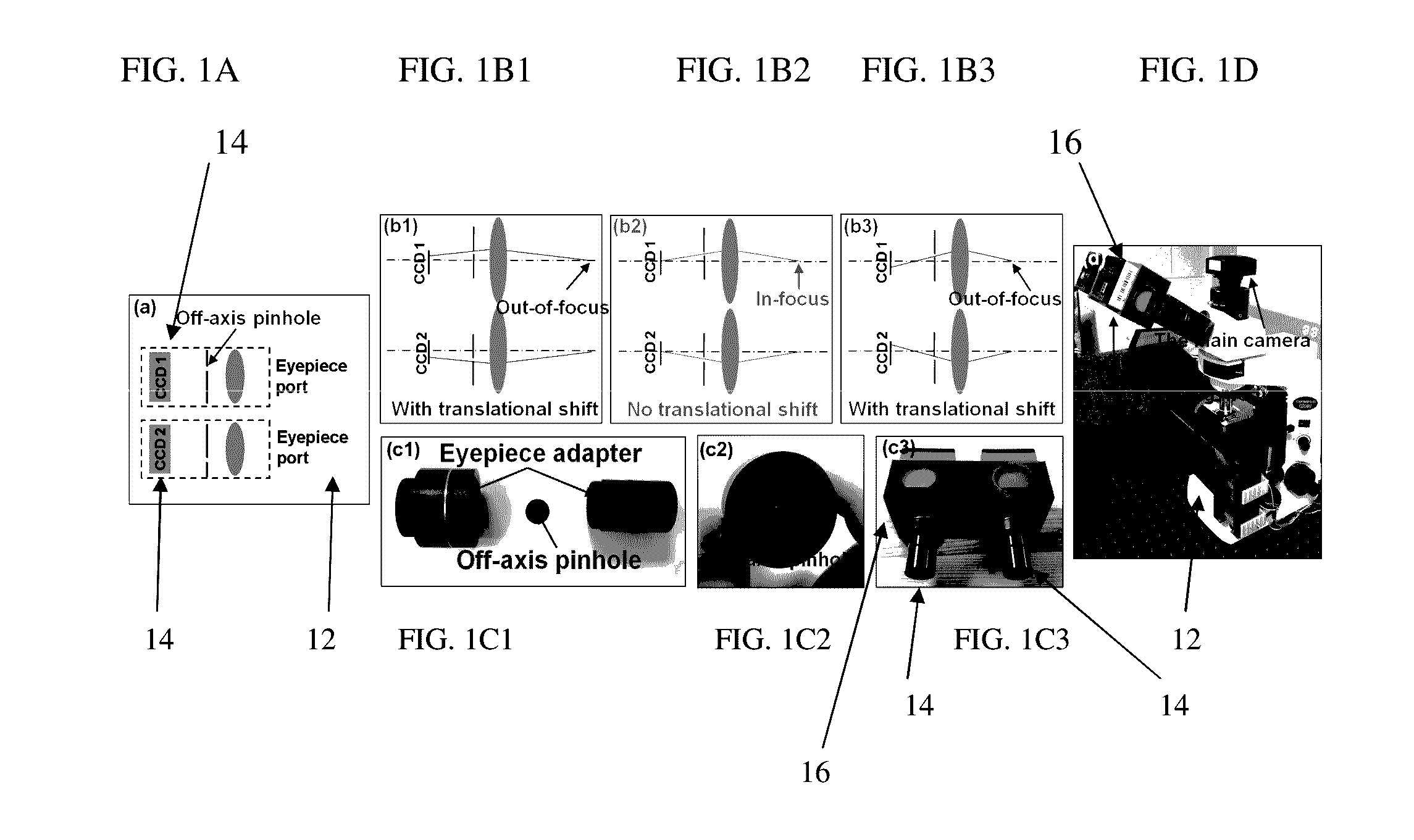
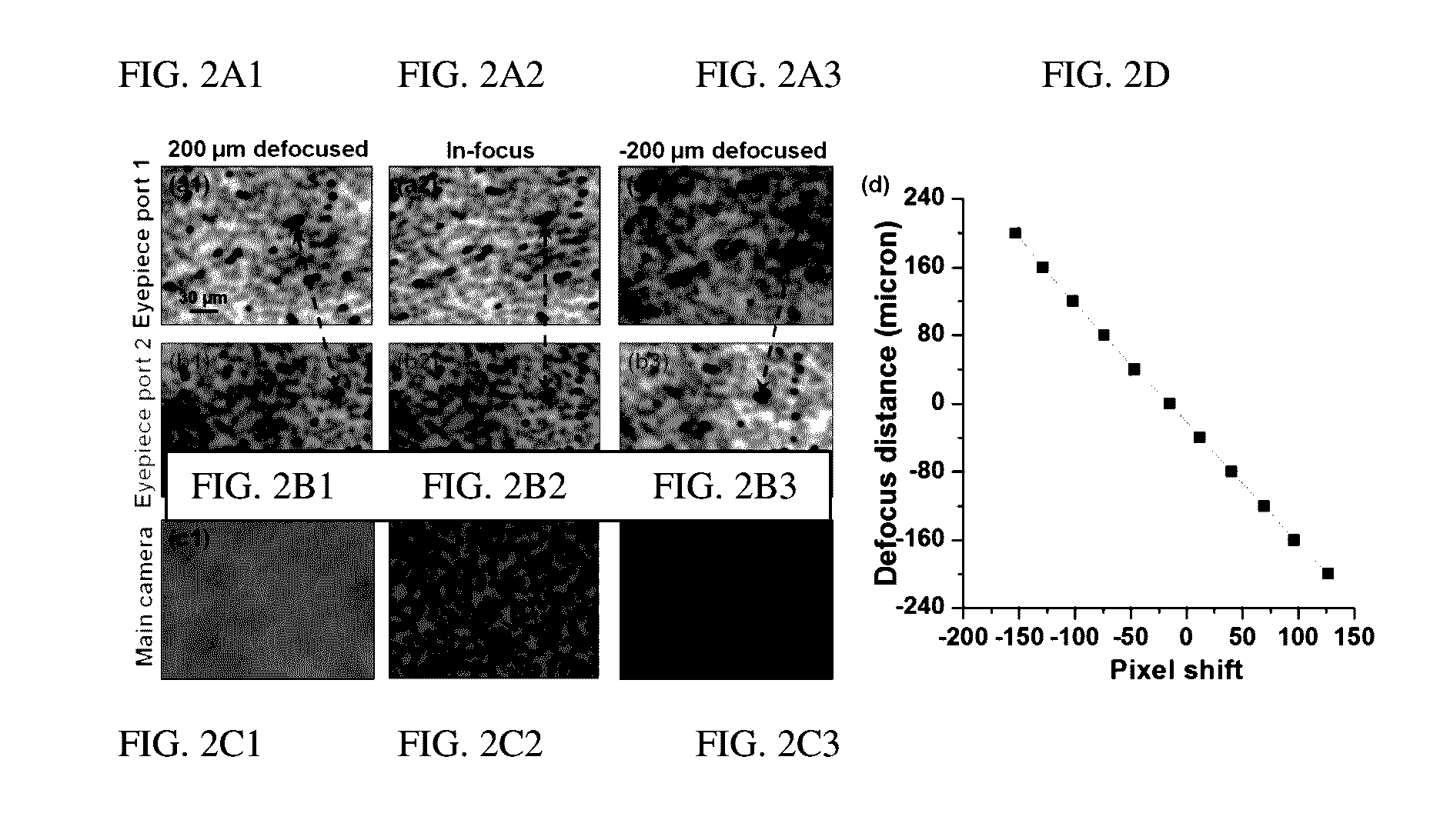
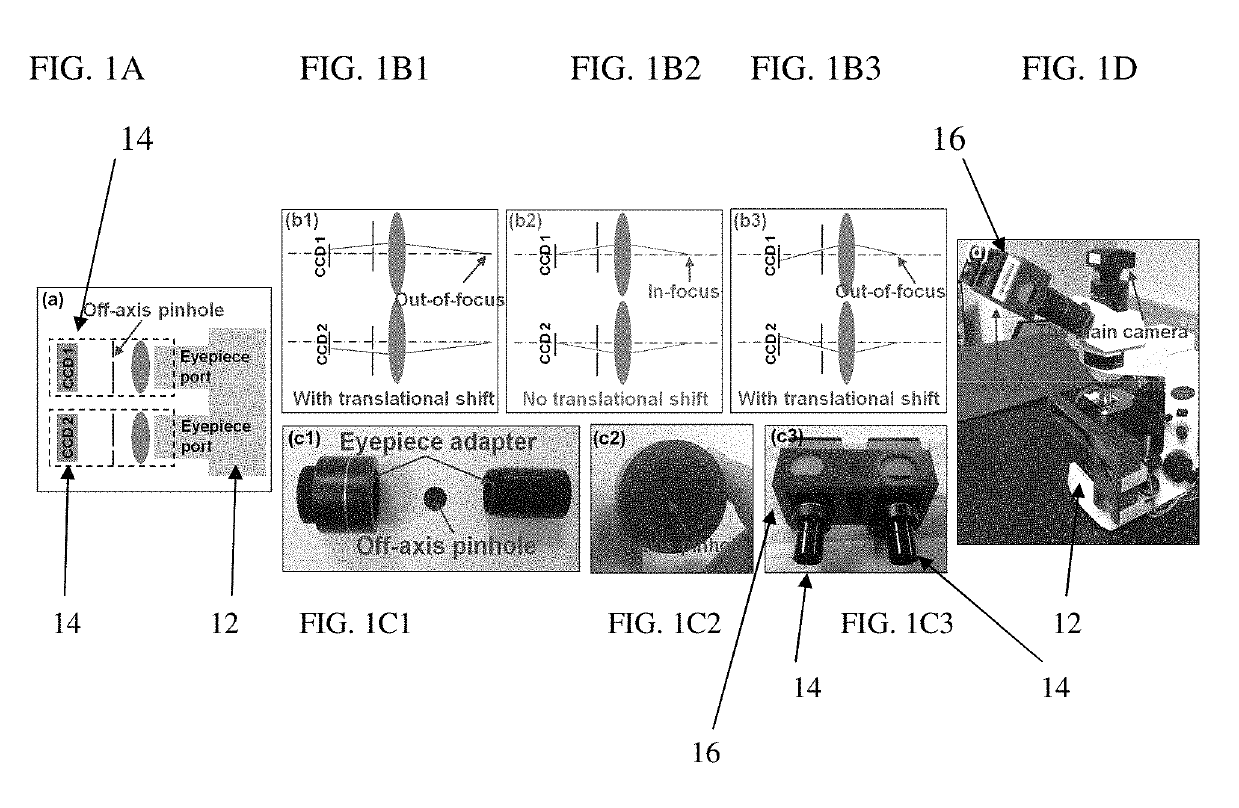
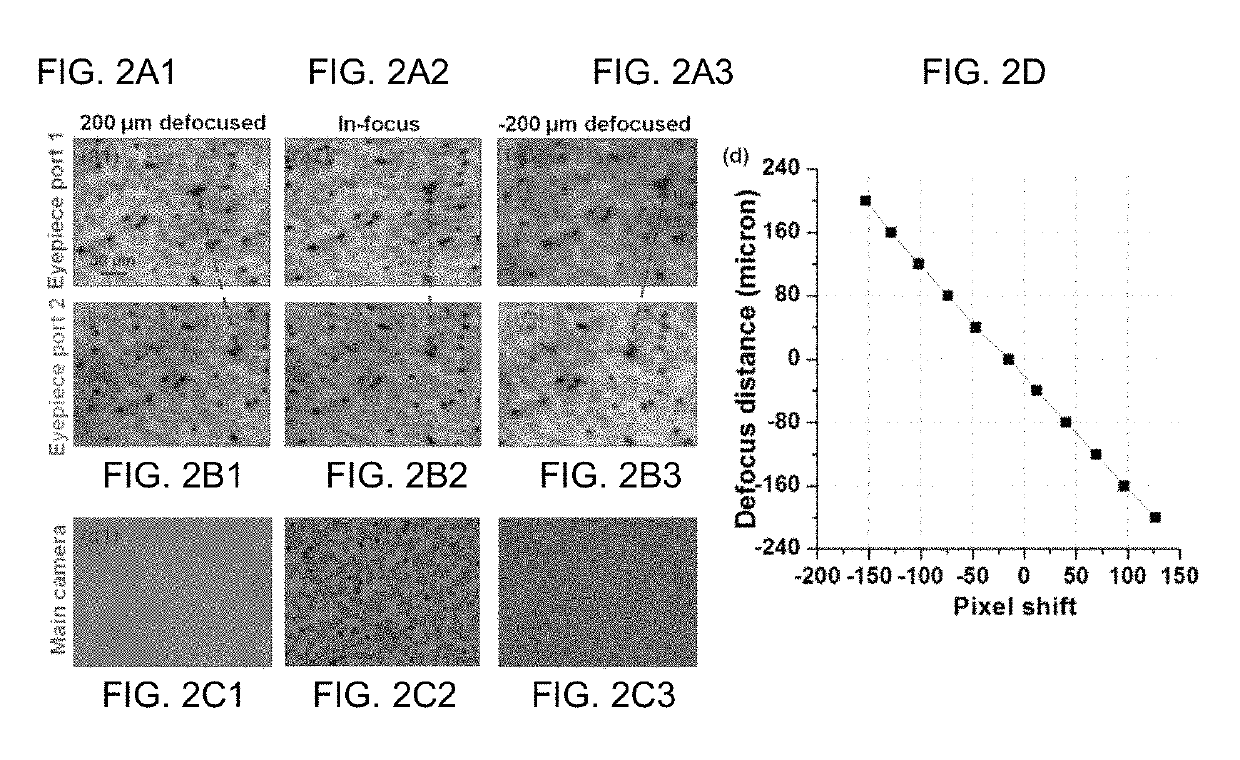
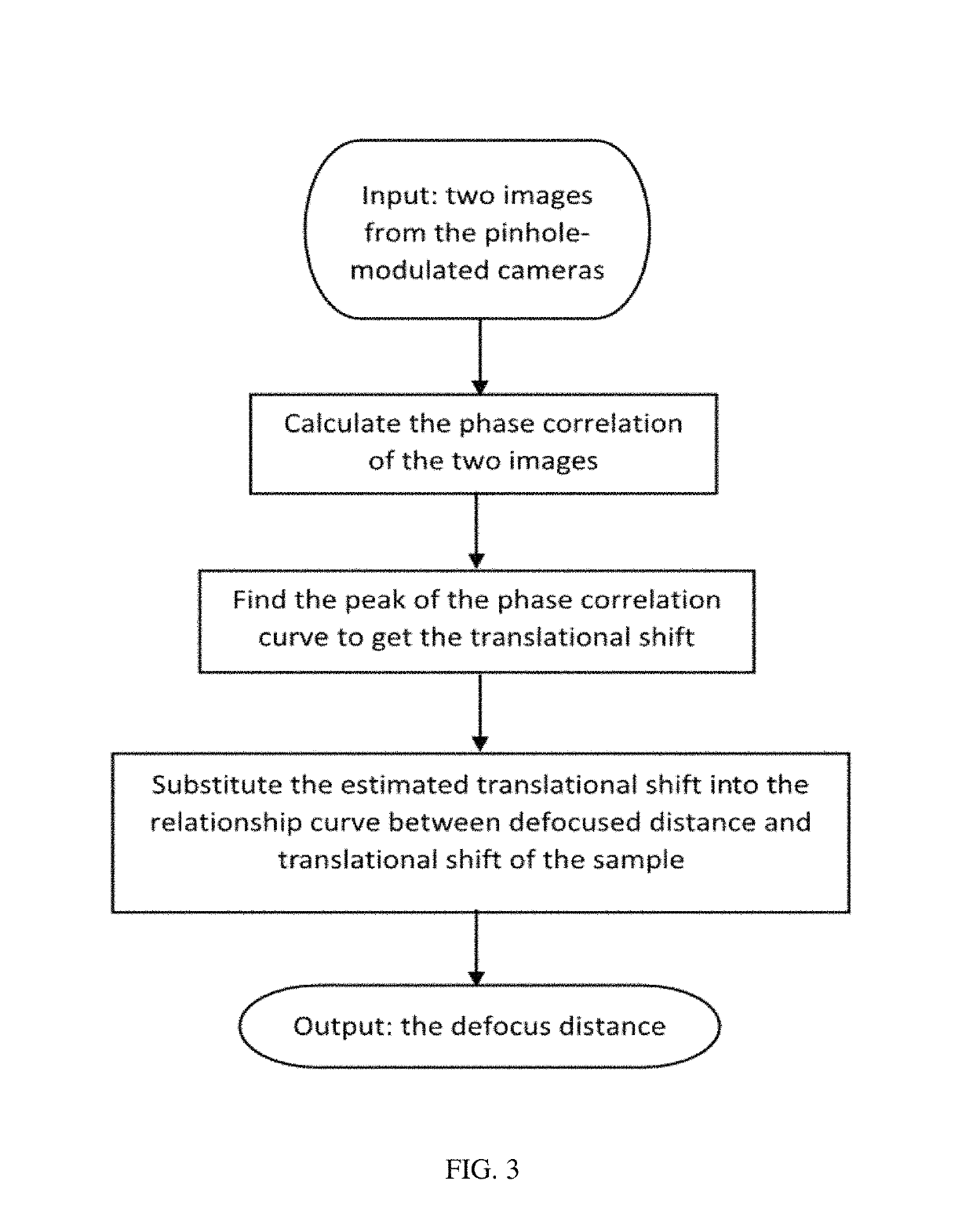
Imaging Assemblies With Rapid Sample Auto-Focusing
ActiveUS20170031146A1Improved and faster and cheap diagnosis/prognosisHigh-throughput imagingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDiseaseEyepiece
Advantageous instruments, assemblies and methods are provided for undertaking imaging techniques (e.g., microscopic imaging techniques). The present disclosure provides improved imaging techniques, equipment and systems. More particularly, the present disclosure provides advantageous microscopy / imaging assemblies with rapid sample auto-focusing (e.g., microscopy / imaging assemblies having instant focusing for rapid sample imaging with auto-focusing). The present disclosure provides for high-throughput whole slide imaging with instant focal plane detection. A whole slide imaging platform / assembly that uses instant focusing systems / methods for high-speed sample autofocusing is provided. Such exemplary platforms / assemblies can be used for digital pathology or the like, and can provide improved, faster and cheaper diagnosis / prognosis of ailments / diseases. At least two exemplary rapid-focus systems for whole slide imaging are provided, a first system including two pinhole-modulated cameras mounted on the eyepiece ports of a microscope platform / assembly, and a second system including one pinhole-modulated camera mounted on the epi-illumination arm for auto-focusing.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
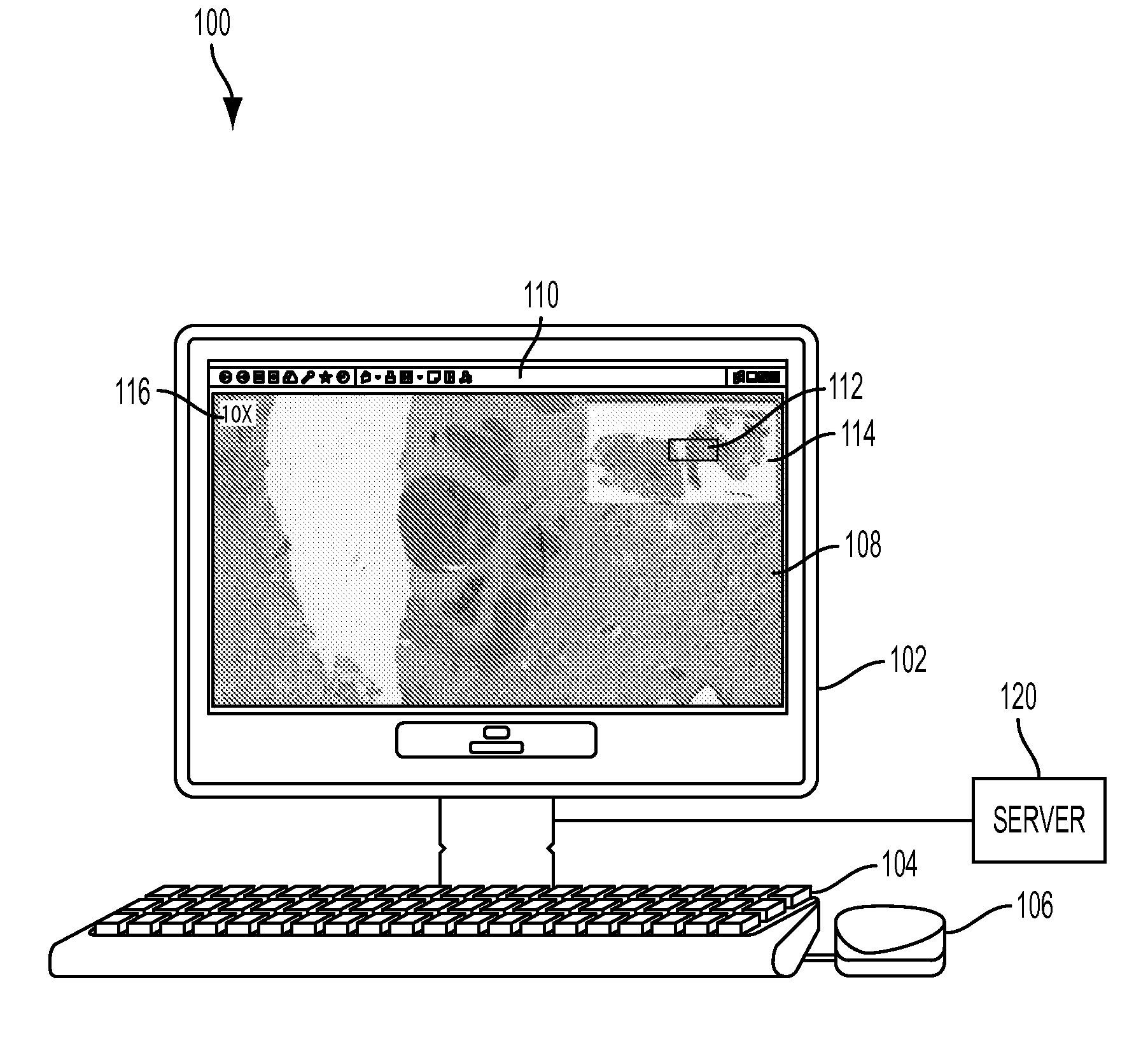
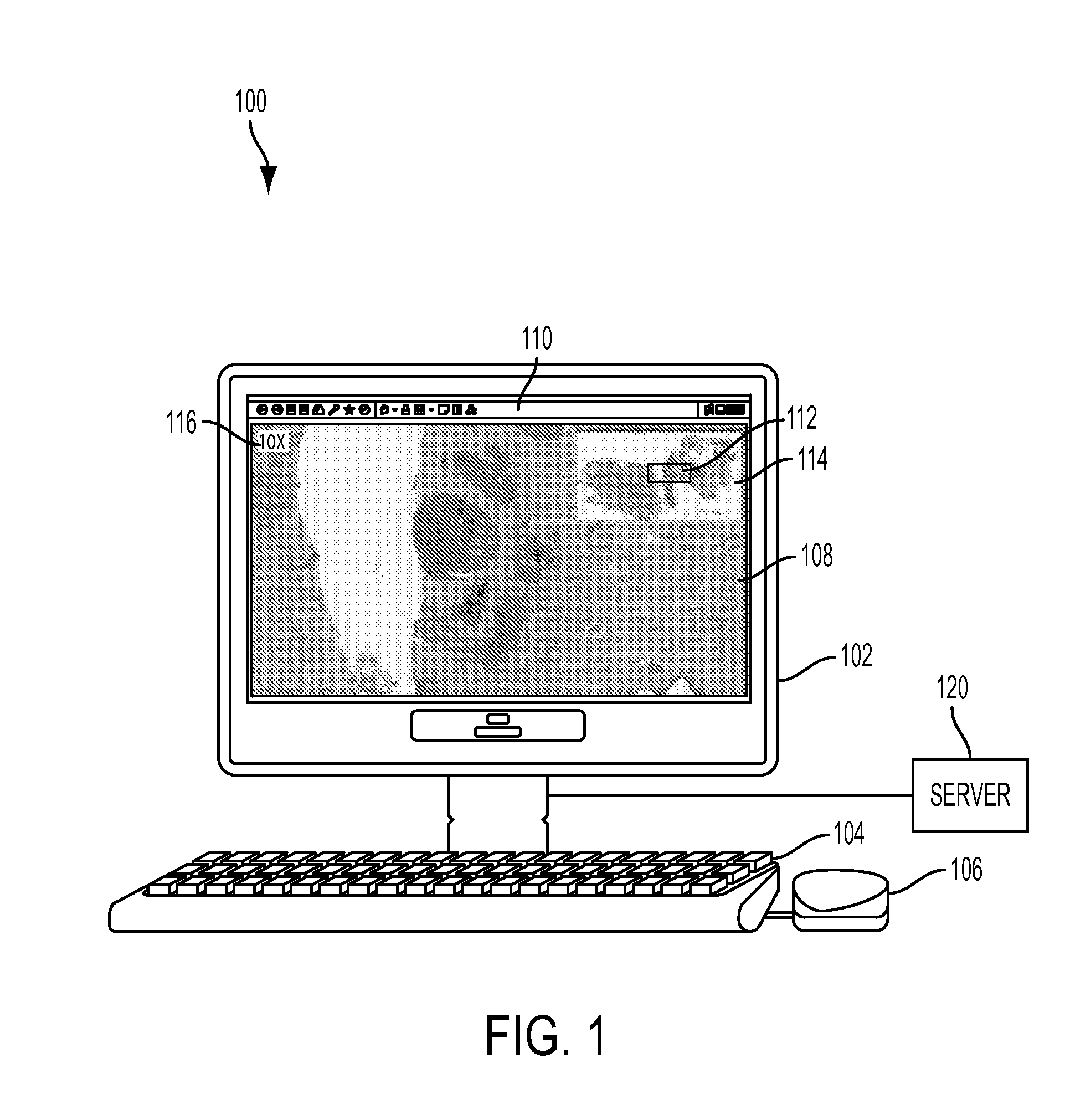
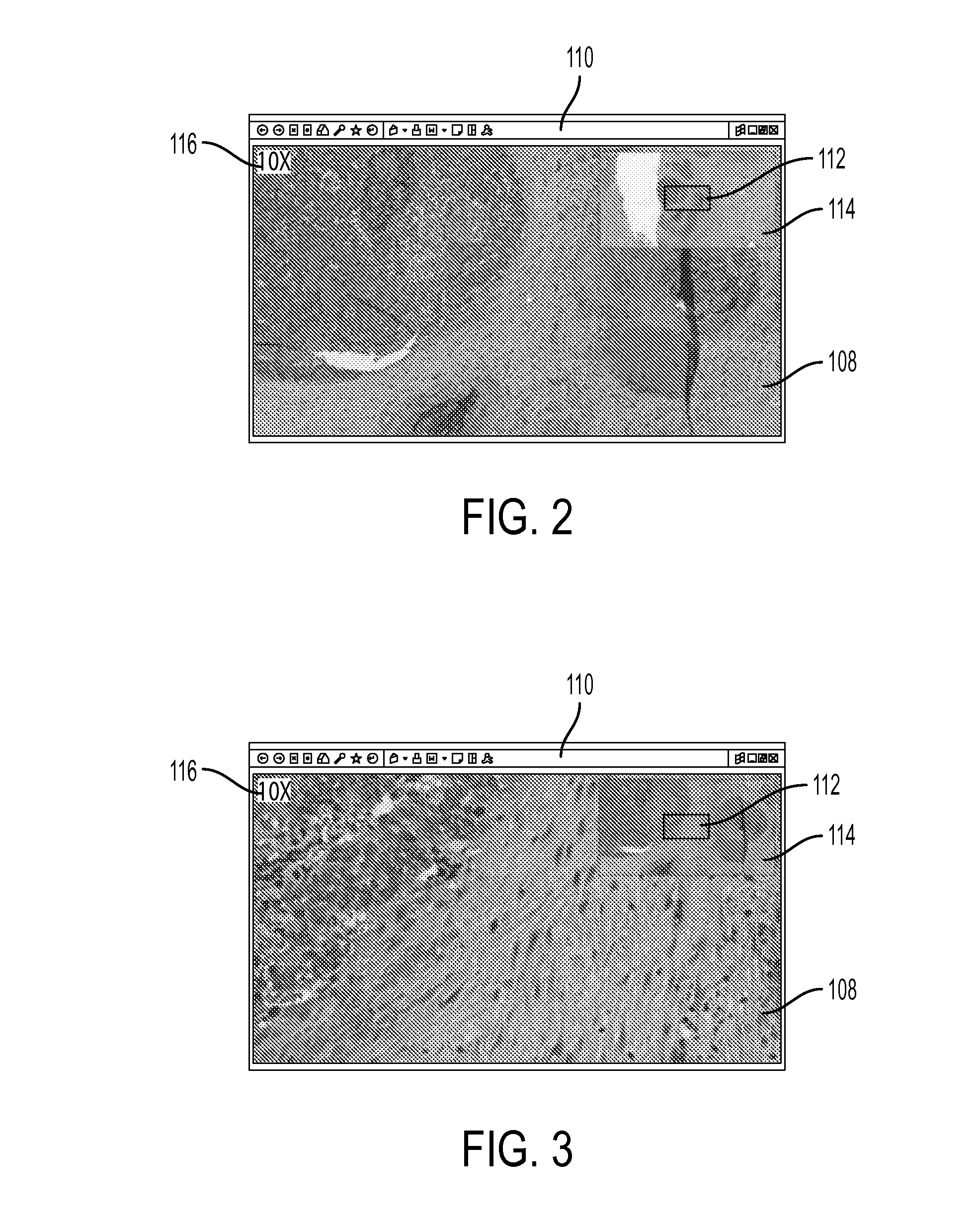
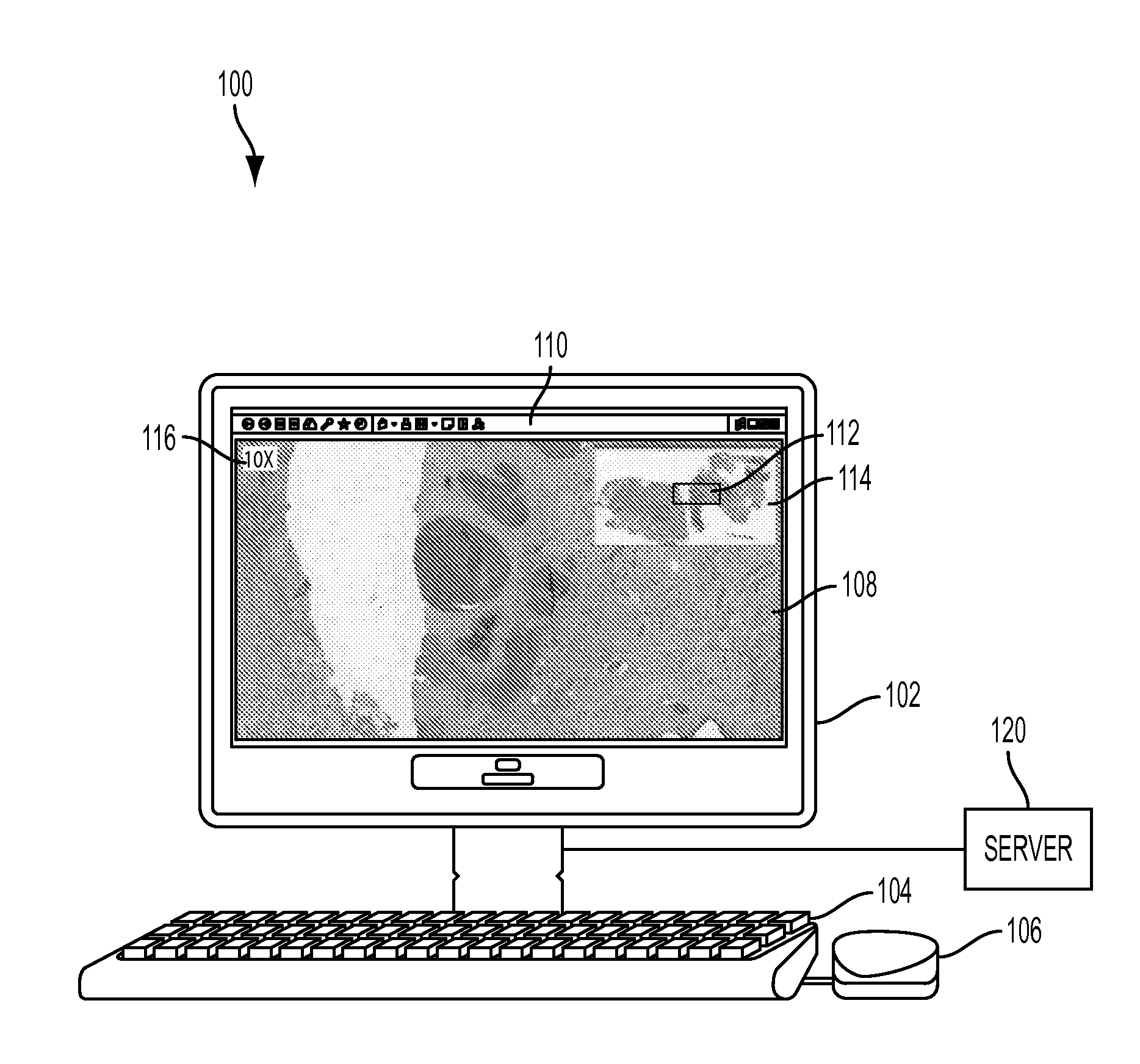
System and Method for Improved Viewing and Navigation of Digital Images
InactiveUS20080123916A1Color television signals processingCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital imageField of view
A system and method for improved viewing and navigation of large digital images, such as whole slide images used in microscopy. The system and method displays the digital image along with movable navigation and field of view boxes that enable a viewer to pan the digital image in an accurate manner, and also performs automatic absolute reorientation of the digital image and automatic relative reorientation of subsequent digital images in relation to the first digital image.
Owner:UPMC
Whole slide image registration and cross-image annotation devices, systems and methods
The disclosure relates to devices, systems and methods for image registration and annotation. The devices include computer software products for aligning whole slide digital images on a common grid and transferring annotations from one aligned image to another aligned image on the basis of matching tissue structure. The systems include computer-implemented systems such as work stations and networked computers for accomplishing the tissue-structure based image registration and cross-image annotation. The methods include processes for aligning digital images corresponding to adjacent tissue sections on a common grid based on tissue structure, and transferring annotations from one of the adjacent tissue images to another of the adjacent tissue images.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
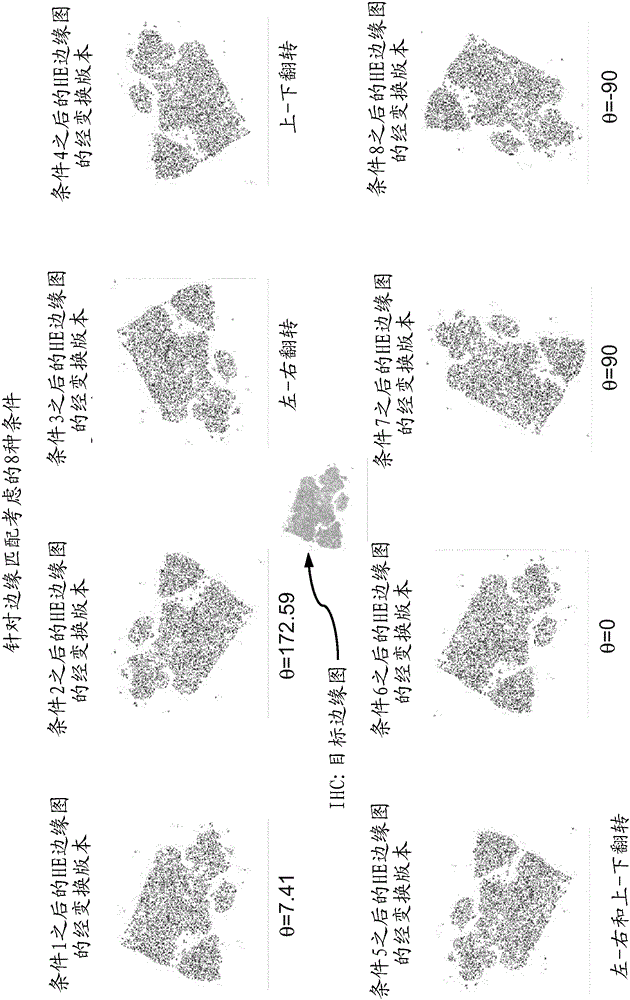
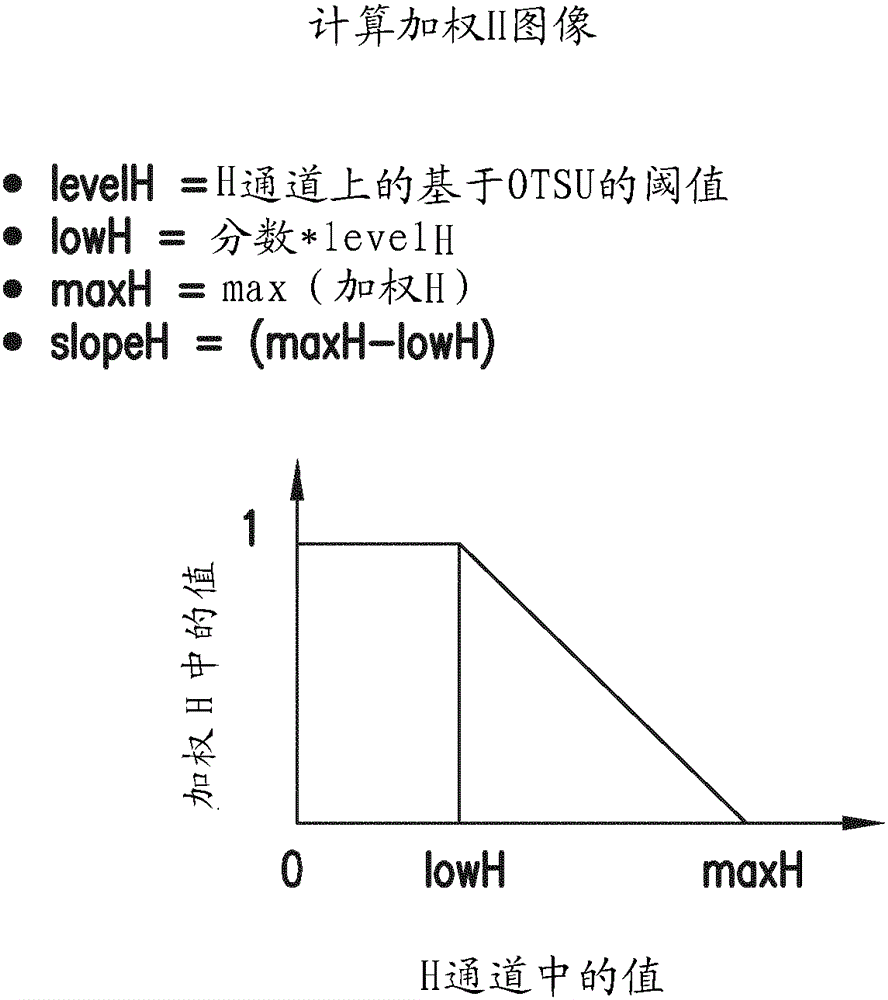
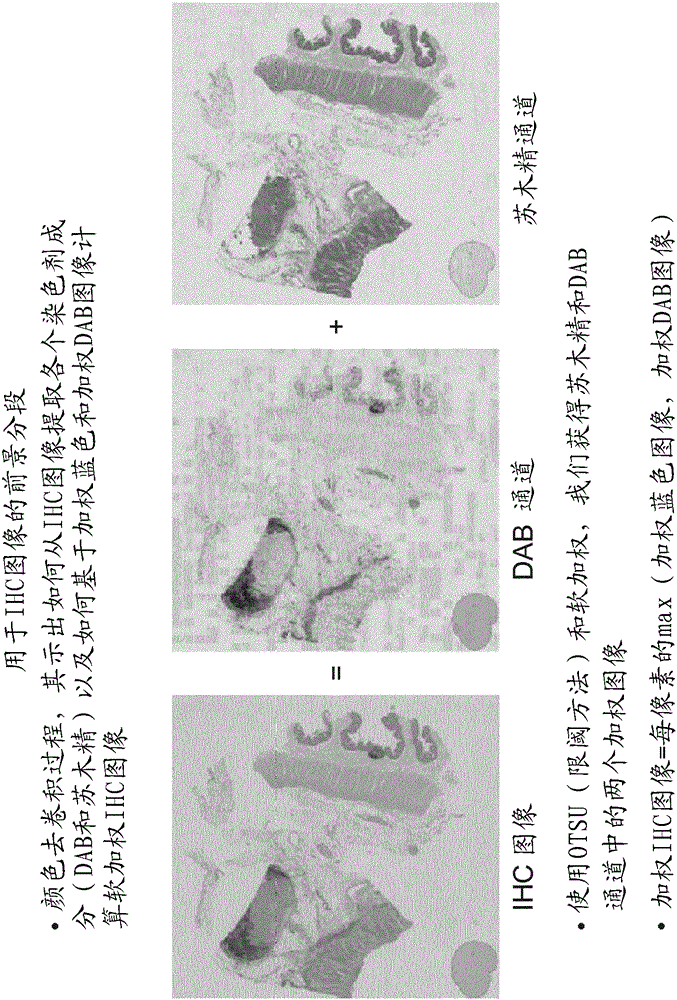
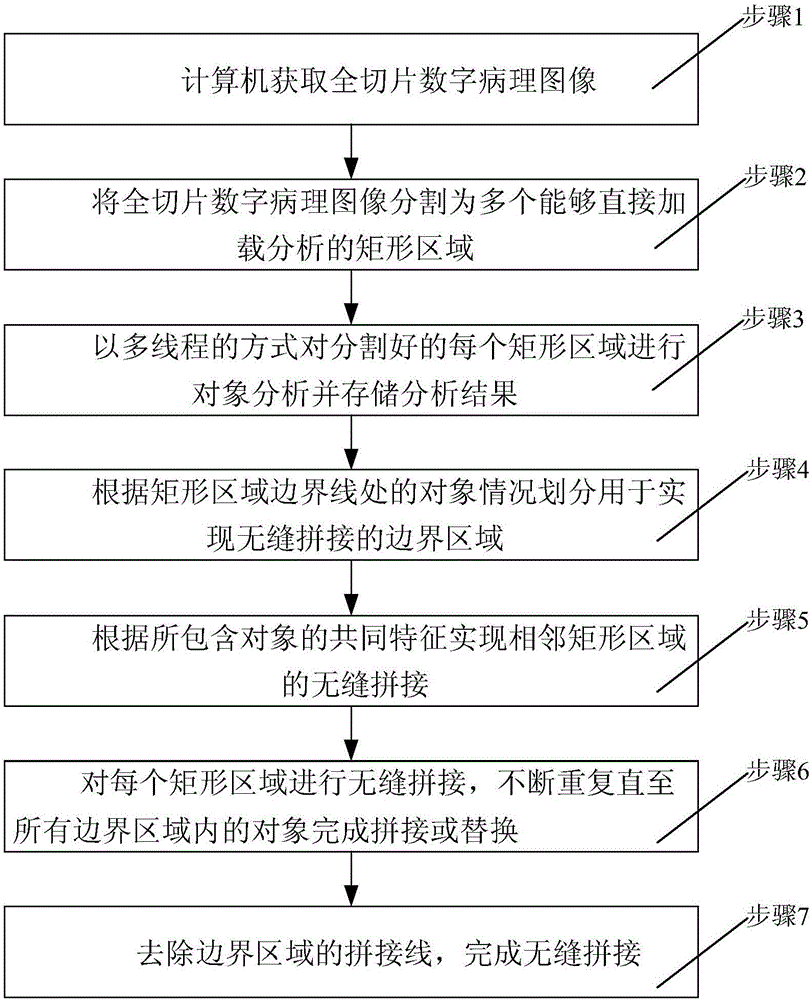
Whole slide digital pathological image processing and analysis method
InactiveCN106408573AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingImaging analysis
The invention discloses a whole slide digital pathological image processing and analysis method, and belongs to the field of the whole slide digital pathological image processing and analysis optimization method. The method comprises the steps that step one, a whole slide image (WSI) is segmented into multiple areas, and each area is analyzed; and step two, objects near the boundary of the areas are spliced. The disadvantages of the existing histopathological analysis software can only browse the whole slide digital image and cannot realize analysis or seamless splicing of the whole slide image and is low in efficiency, long in time consumption and blurred in image can be overcome. The main purpose of the method is to process whole slide digital pathological image analysis, segment the whole slide image into multiple areas with the help of the computer and the fine algorithm and automatically perform high-precision multi-vision seamless splicing and processing so that the analysis time can be shortened and the analysis precision can be enhanced, and the high-quality visual data can be acquired to be applied to various fields of pathological histology.
Owner:诸暨微因生物科技有限公司
Method and system for digital staining of label-free fluorescence images using deep learning
PendingCN112106061AShorten the timeLow costImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageGenerative adversarial network
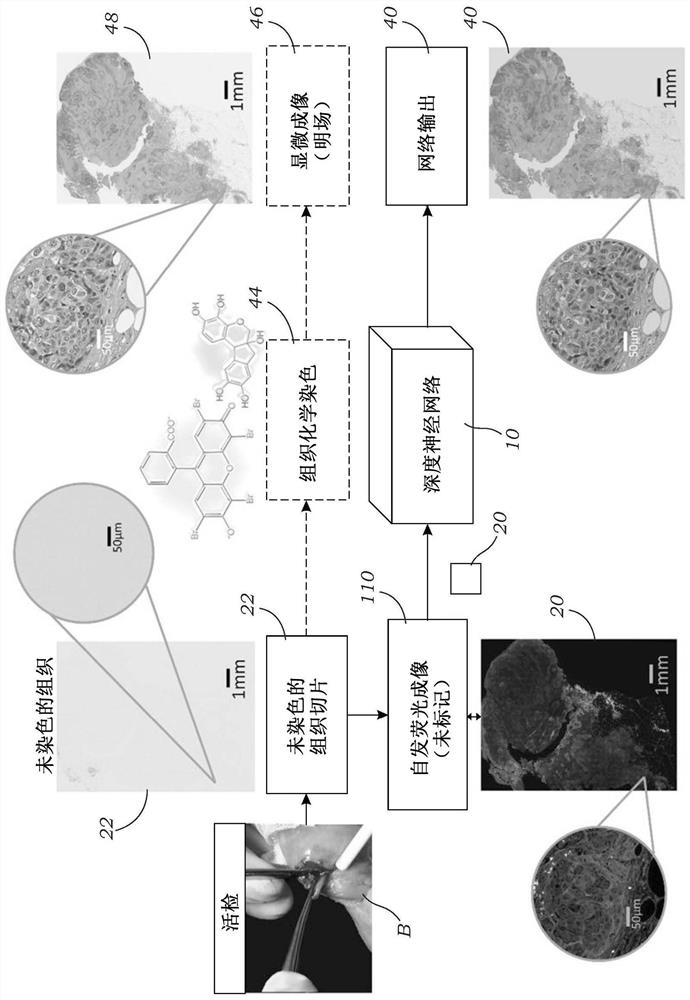
A deep learning-based digital staining method and system are disclosed that enables the creation of digitally / virtually-stained microscopic images from label or stain-free samples based on autofluorescence images acquired using a fluorescent microscope. The system and method have particular applicability for the creation of digitally / virtually-stained whole slide images (WSIs) of unlabeled / unstained tissue samples that are analyzes by a histopathologist. The methods bypass the standard histochemical staining process, saving time and cost. This method is based on deep learning, and uses, in oneembodiment, a convolutional neural network trained using a generative adversarial network model to transform fluorescence images of an unlabeled sample into an image that is equivalent to the brightfield image of the chemically stained-version of the same sample. This label-free digital staining method eliminates cumbersome and costly histochemical staining procedures and significantly simplifiestissue preparation in pathology and histology fields.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
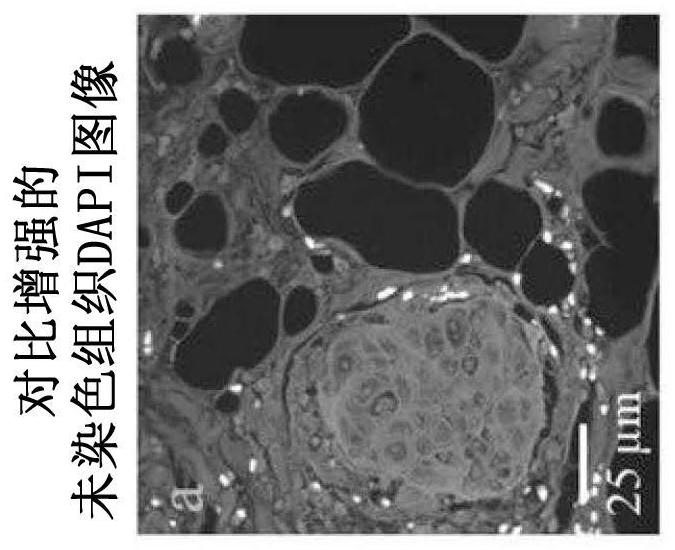
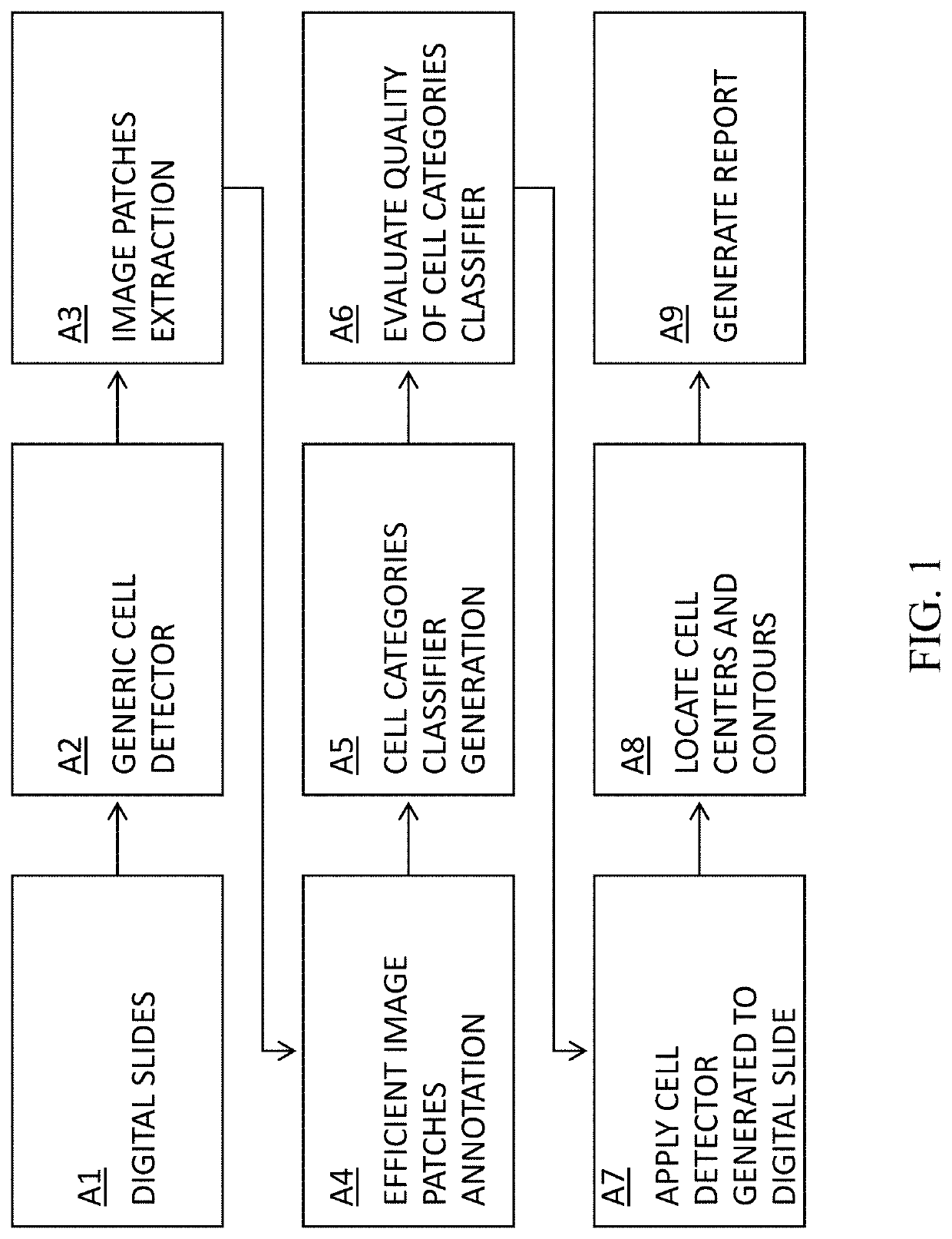
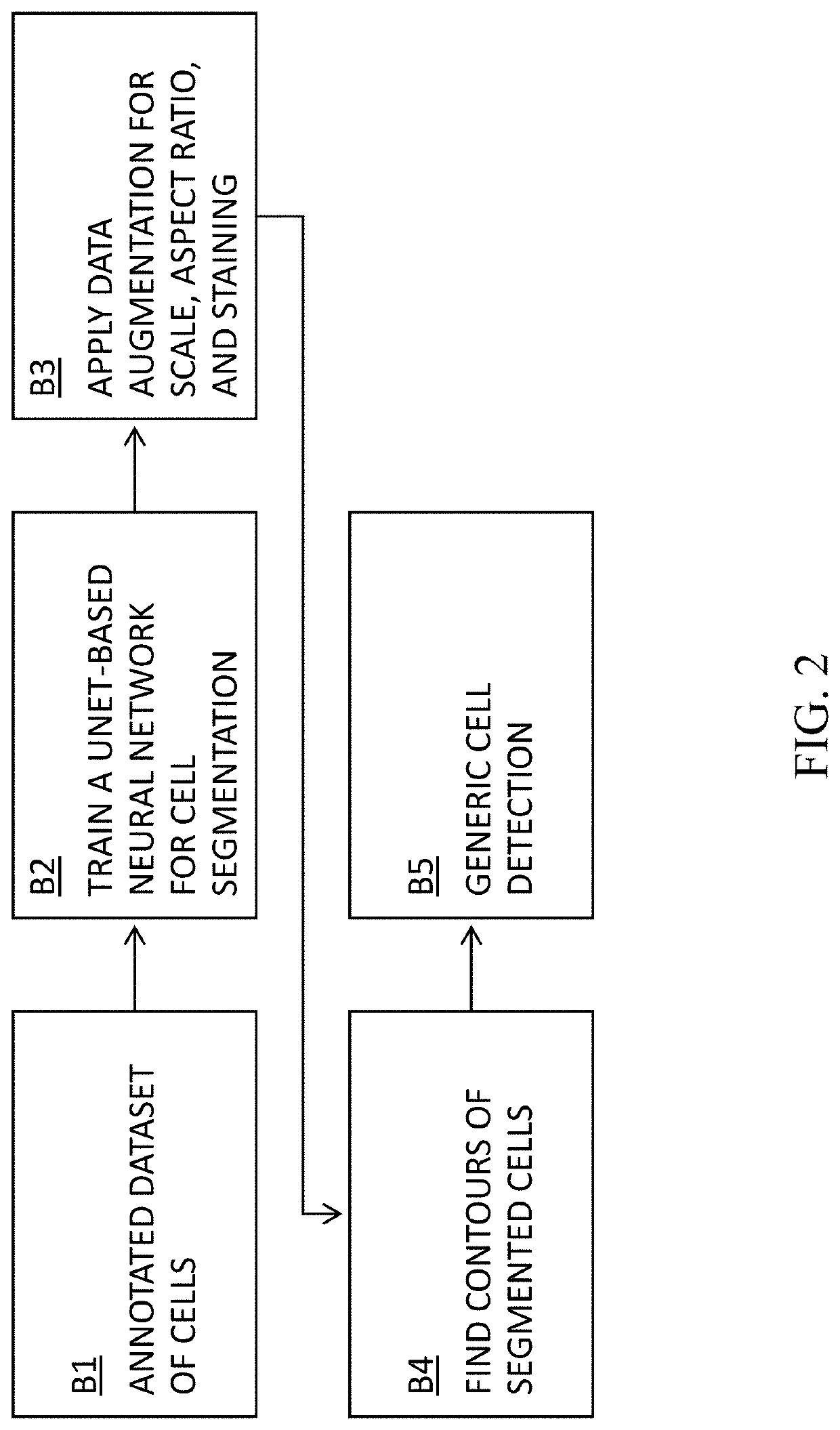
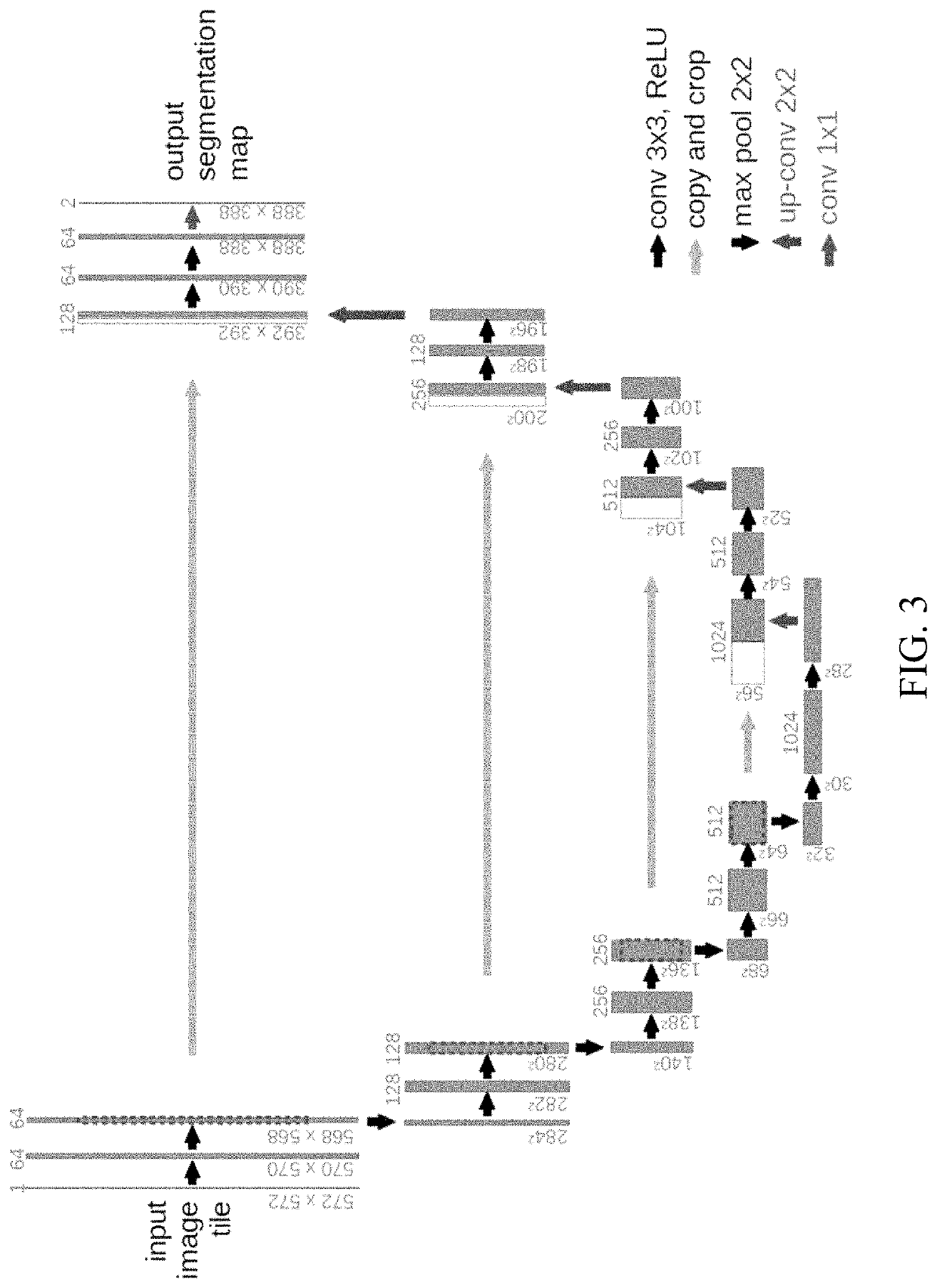
Cell Detection Studio: a system for the development of Deep Learning Neural Networks Algorithms for cell detection and quantification from Whole Slide Images
The invention is made out of methods for the development of Deep Neural Networks for cell detection and quantification in Whole Slide Images (WSI):1. Method to create generic cell detector that detects the centers and contours of all cells in a WSI.2. Method to create algorithms to detect cells of specific categories and that can classify between various types of cells of different categories.3. Method for efficient cell annotation with online learning.4. Method for efficient cell annotation with active learning.5. Method for efficient cell annotation with online learning and data balancing.6. Method for auto annotation of cells7. Cell Detection Studio: a method to create an AI based system that provides pathologists with a semi-automatic tool to create new algorithms aiming to find cells of specific categories in WSI digitally scanned from histological specimen
Owner:DEEPATHOLOGY LTD
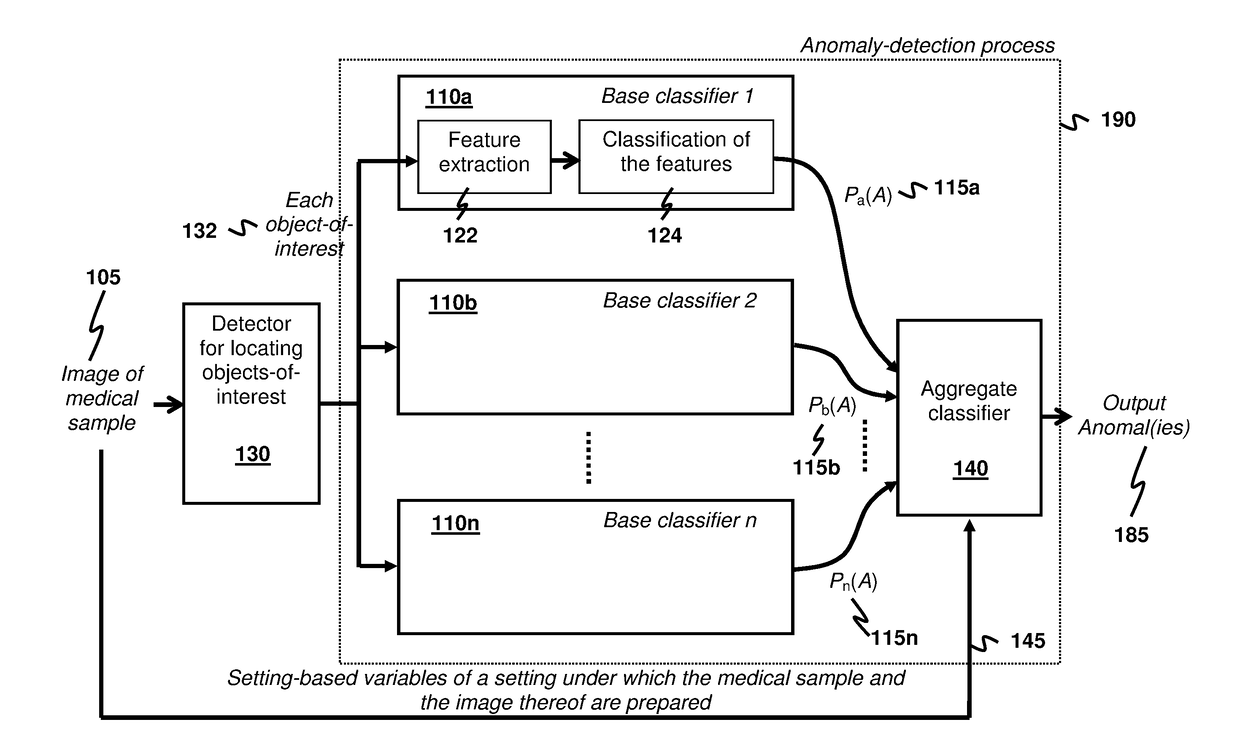
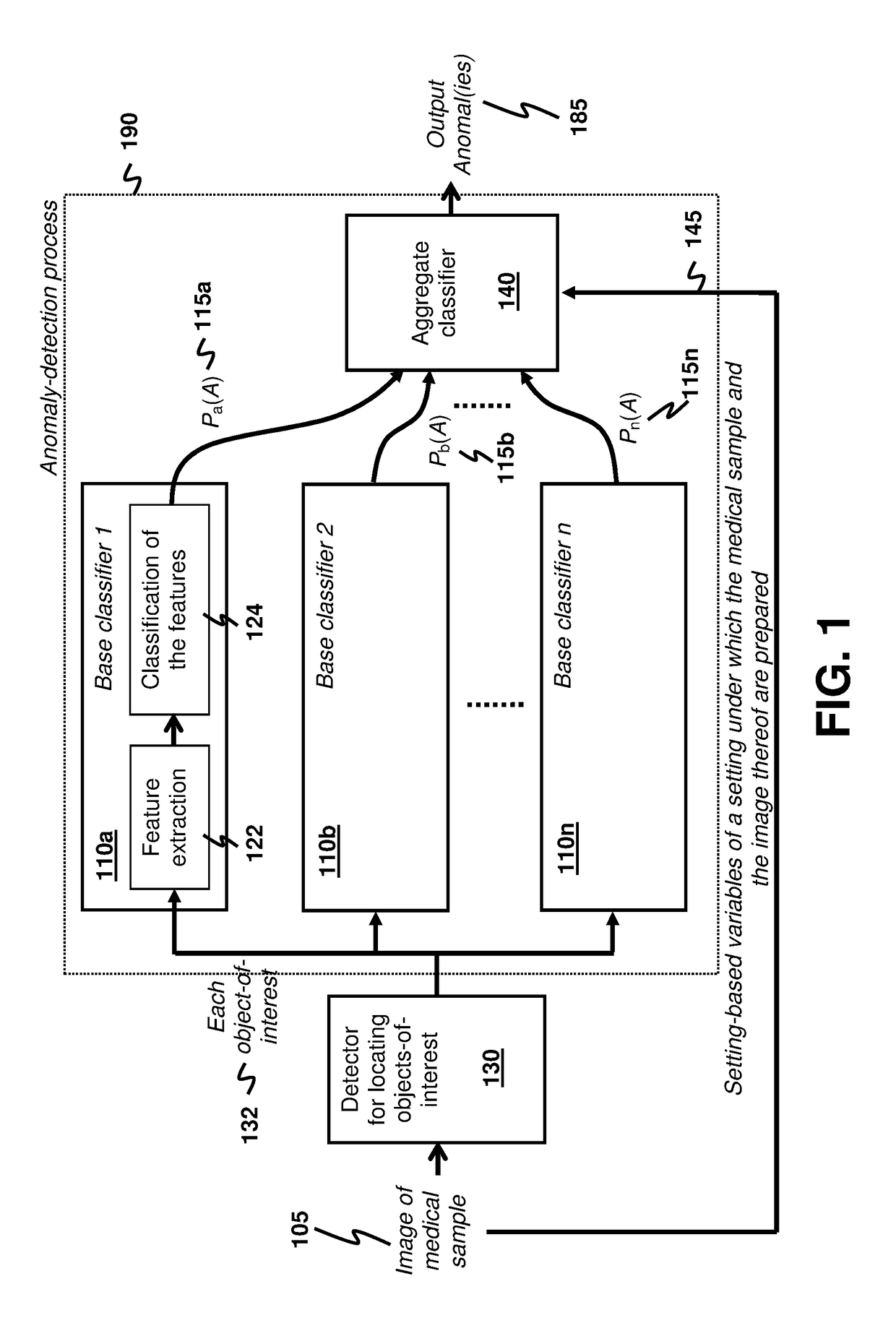
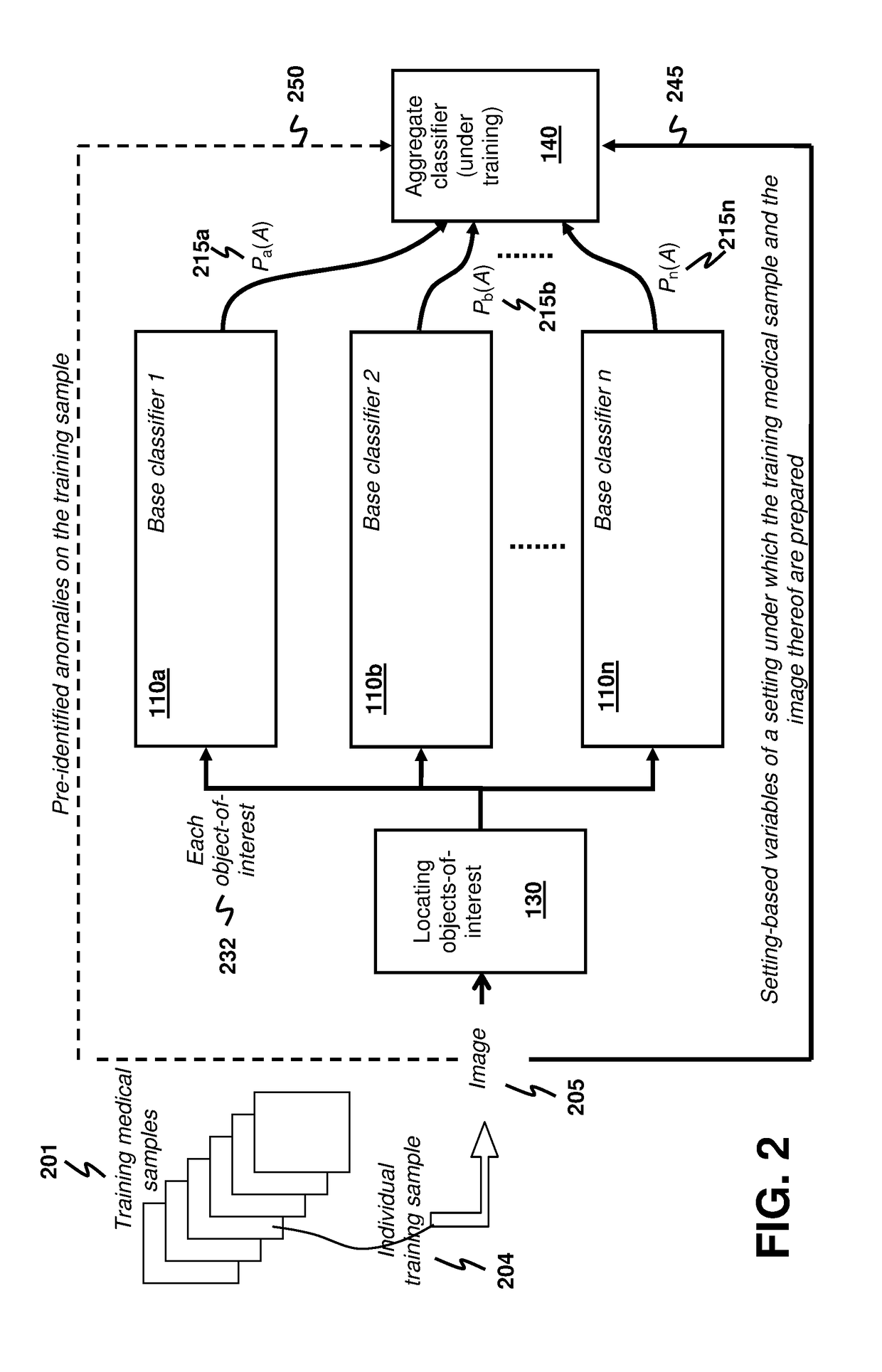
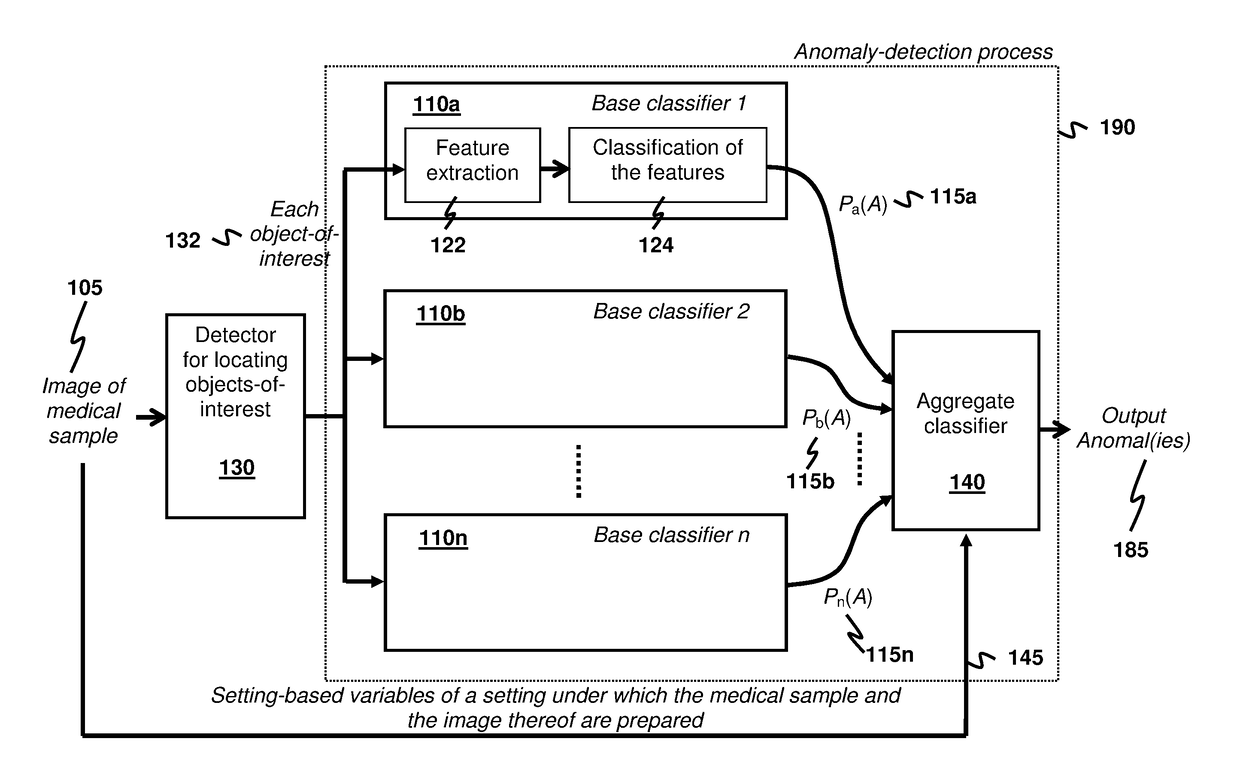
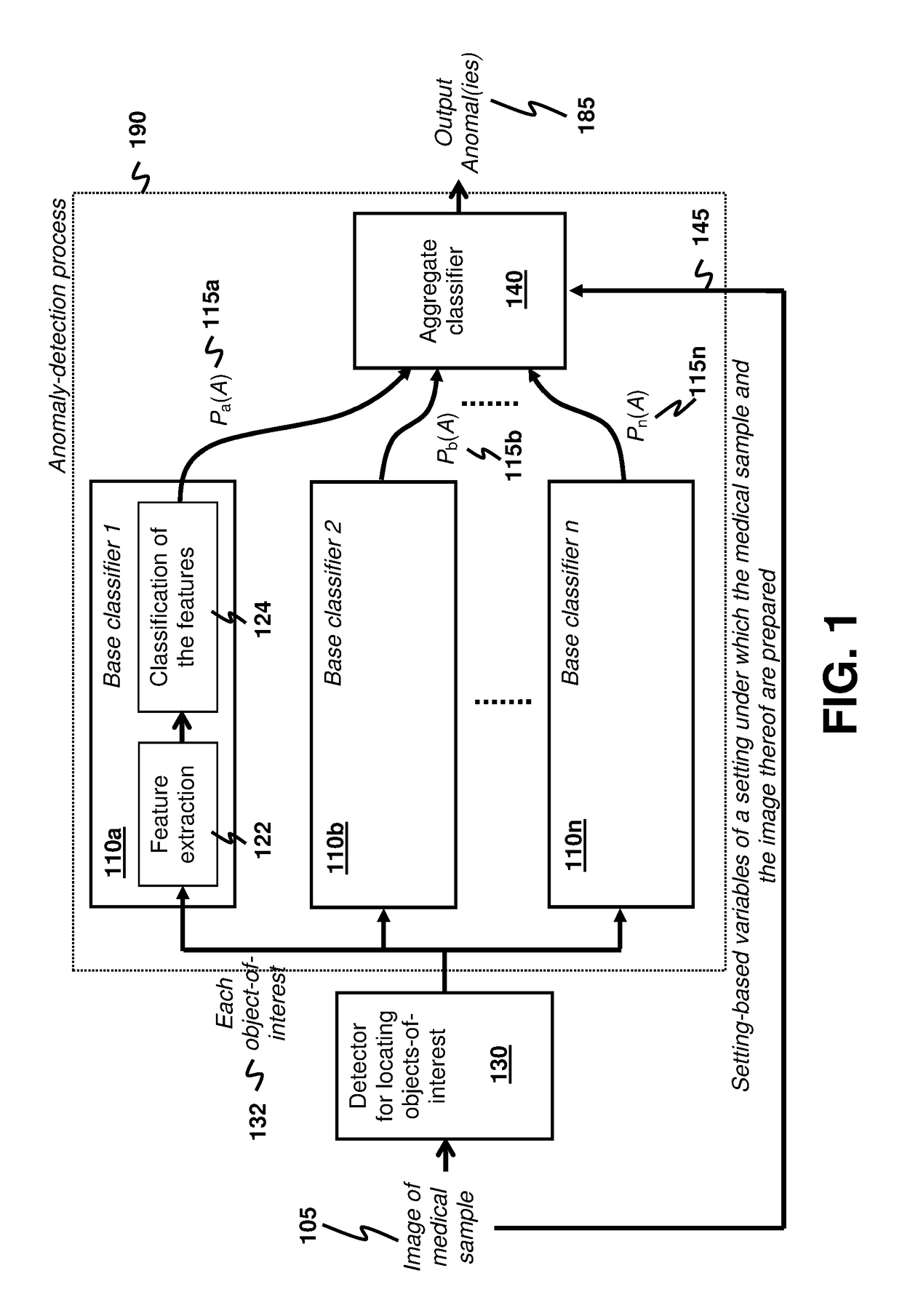
Anomaly Detection for Medical Samples under Multiple Settings
Using multiple imaging modes in whole slide image screening is potentially useful to reduce false positives. To use multiple imaging modes, a method for locating anomalies on a medical sample from an image thereof uses an anomaly-detection process that comprises using plural base classifiers individually to classify an object-of-interest suspected to be an anomaly. Each base classifier respectively extracts features of the object-of-interest and generates, according to the extracted features, a score indicating a likelihood of the object-of-interest being anomalous. The anomaly-detection process further comprises using an aggregate classifier to combine the scores generated by the base classifiers to determine whether the object-of-interest is the anomaly. The aggregate classifier determines a dependability measure for each base classifier according to setting-based variables of a setting under which the sample and the image are obtained, and then selectively combines the scores of the base classifiers according to the dependability measures.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
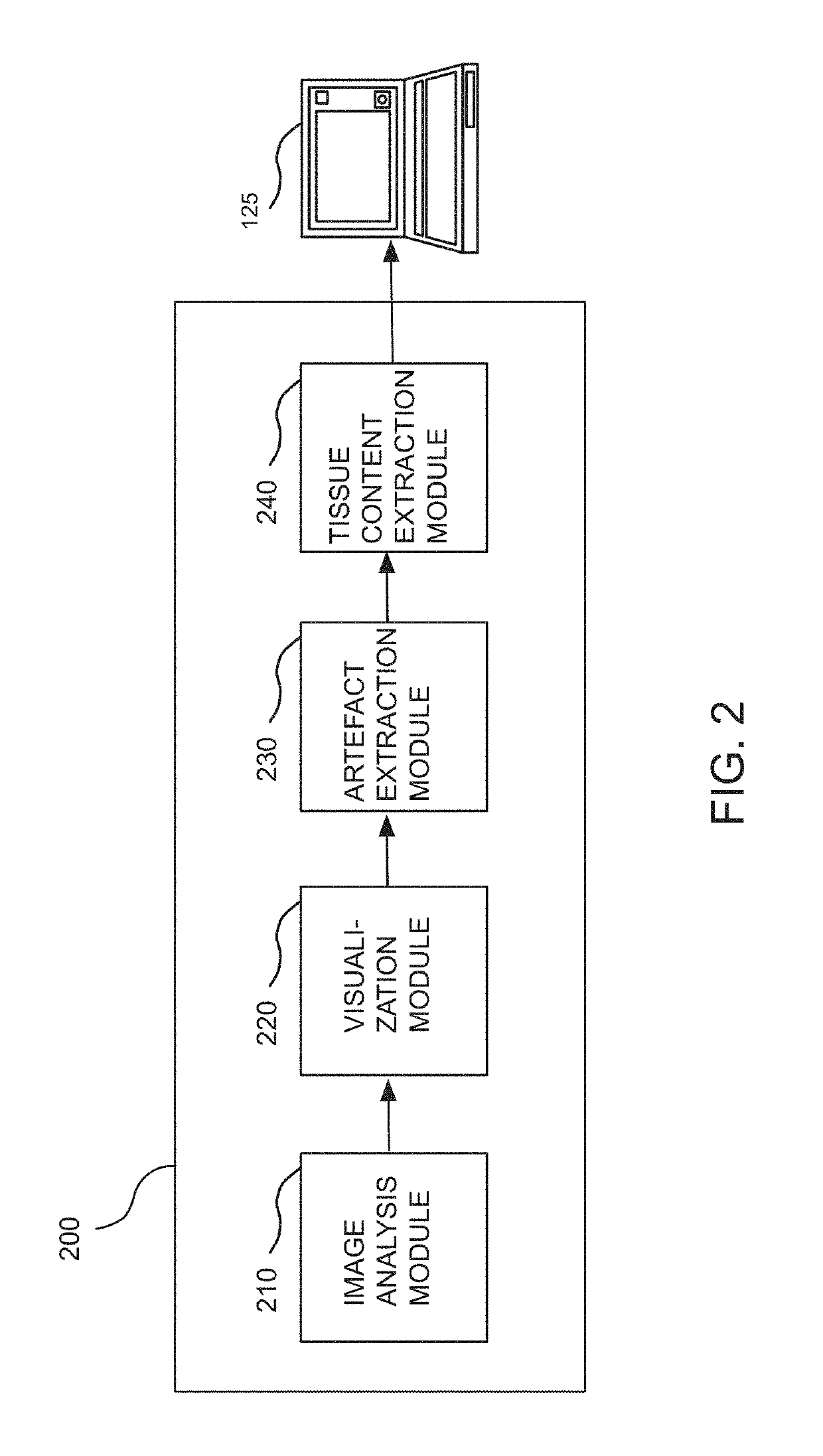
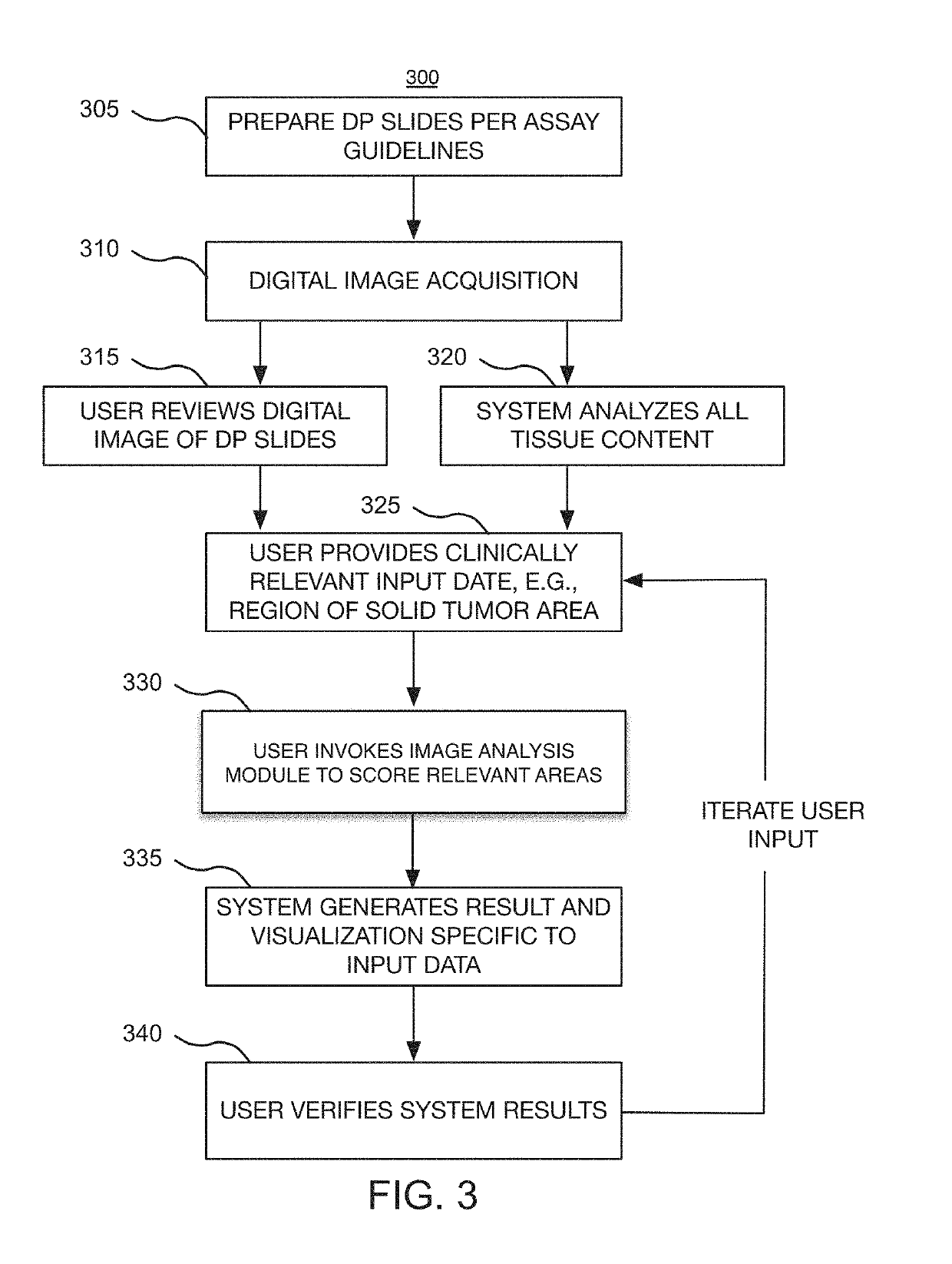
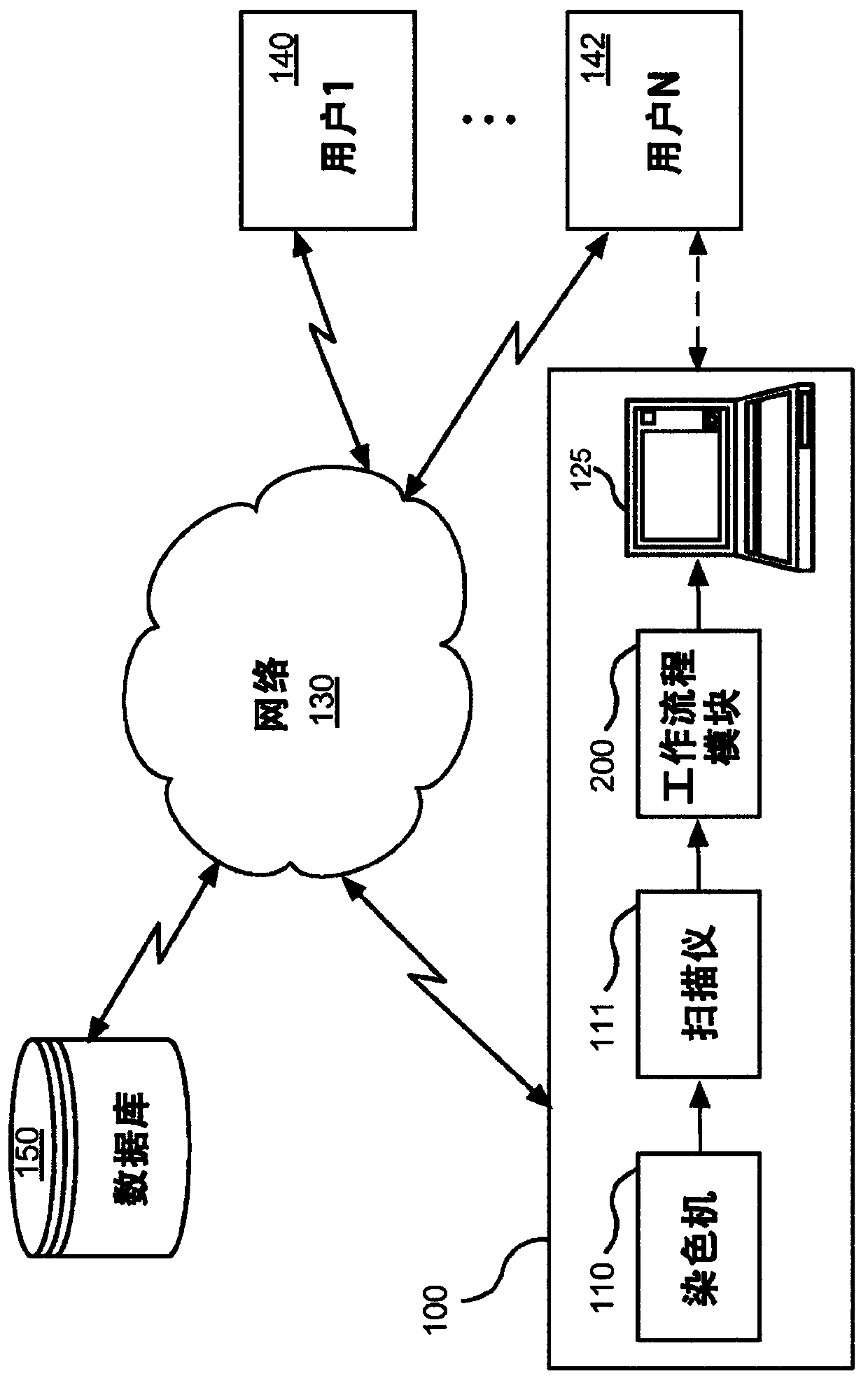
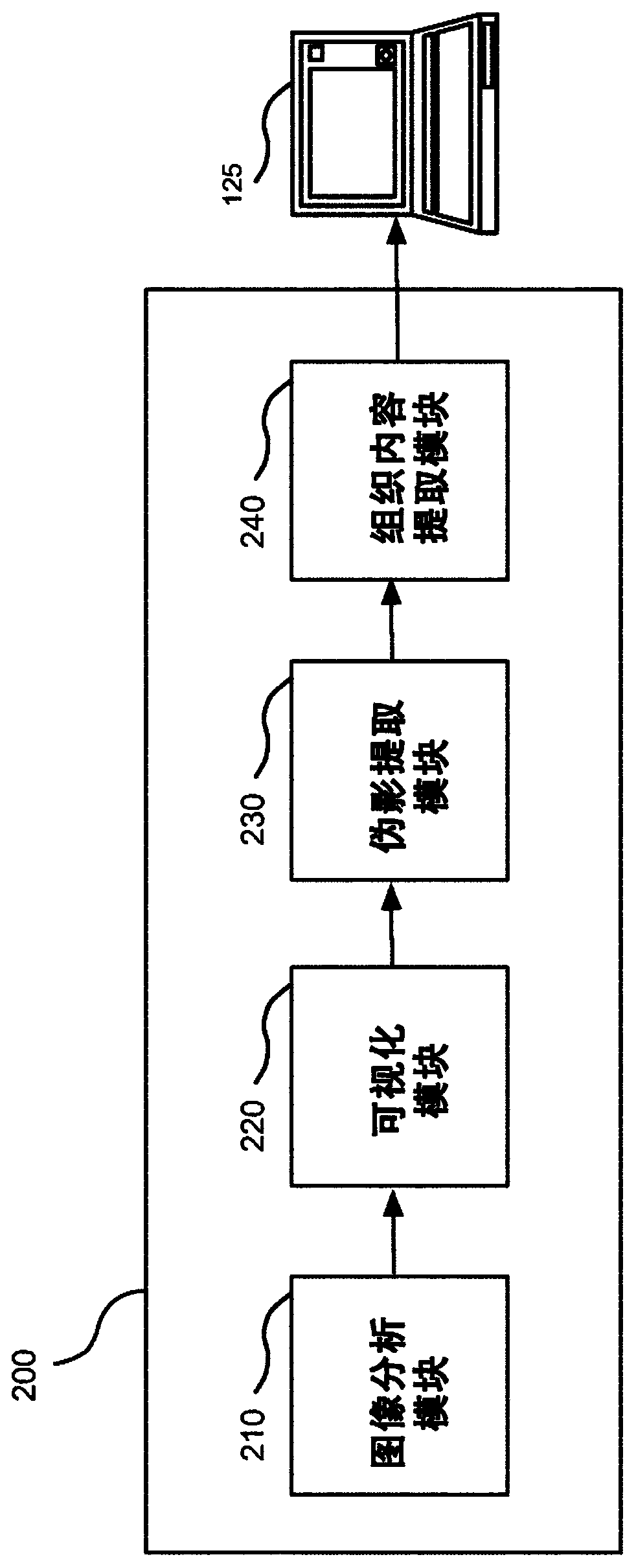
Digital pathology system and associated workflow for providing visualized whole-slide image analysis
ActiveUS20190236780A1Adapt to a wide rangeIntuitive visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisComputer science
A digital pathology system and associated method and computer program product provide a quantitative analysis of entire tissue slides as well as intuitive, effective, fast, and precise quantification of biomarker expressions across relevant areas of the entire tissue slides. The digital pathology system enables a novel workflow that allows the user to efficiently outline clinically relevant morphology in its entirety, including solid tumor areas. Quantitative analysis results are then efficiently and intuitively provided to the user for all tissue content (i.e., millions of cells) within seconds. This efficiency is made possible by a pre-computation step that computes and stores image analysis results for later retrieval. Visualizing vast amount of data effectively is another component of the system that provides information and confidence to the user about the biomarker expression levels.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Digital pathology system and associated workflow for providing visualized whole-slide image analysis
A digital pathology system and an associated method and computer program product provide a quantitative analysis of entire tissue slides as well as intuitive, effective, fast, and precise quantification of biomarker expressions across relevant areas of the entire tissue slides. The digital pathology system enables a novel workflow that allows the user to efficiently outline clinically relevant morphology in its entirety, including solid tumor areas. Quantitative analysis results are then efficiently and intuitively provided to the user for all tissue content (i.e., millions of cells) within seconds. This efficiency is made possible by a pre-computation step that computes and stores image analysis results for later retrieval. Visualizing vast amount of data effectively is another componentof the system that provides information and confidence to the user about the biomarker expression levels.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
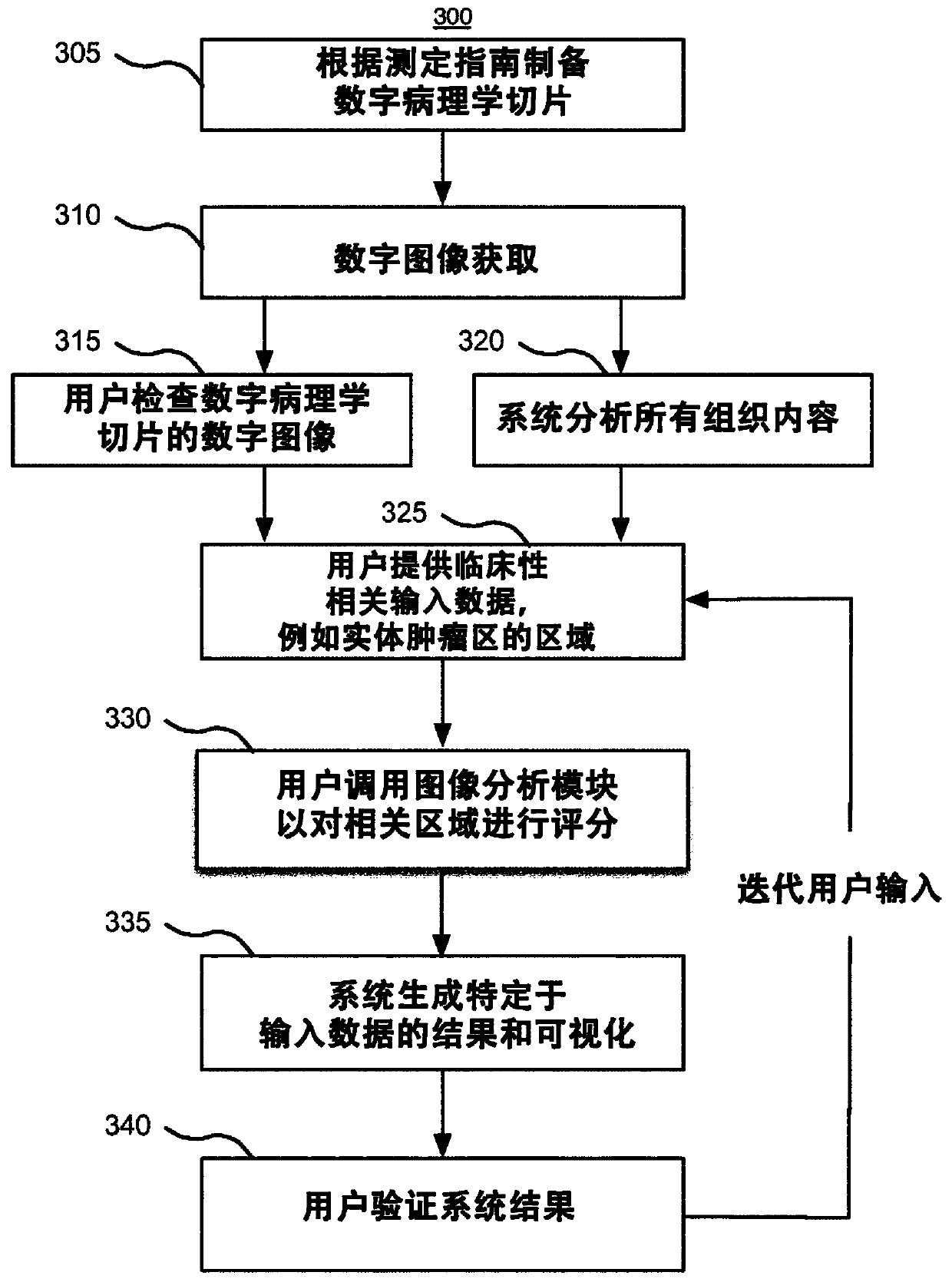
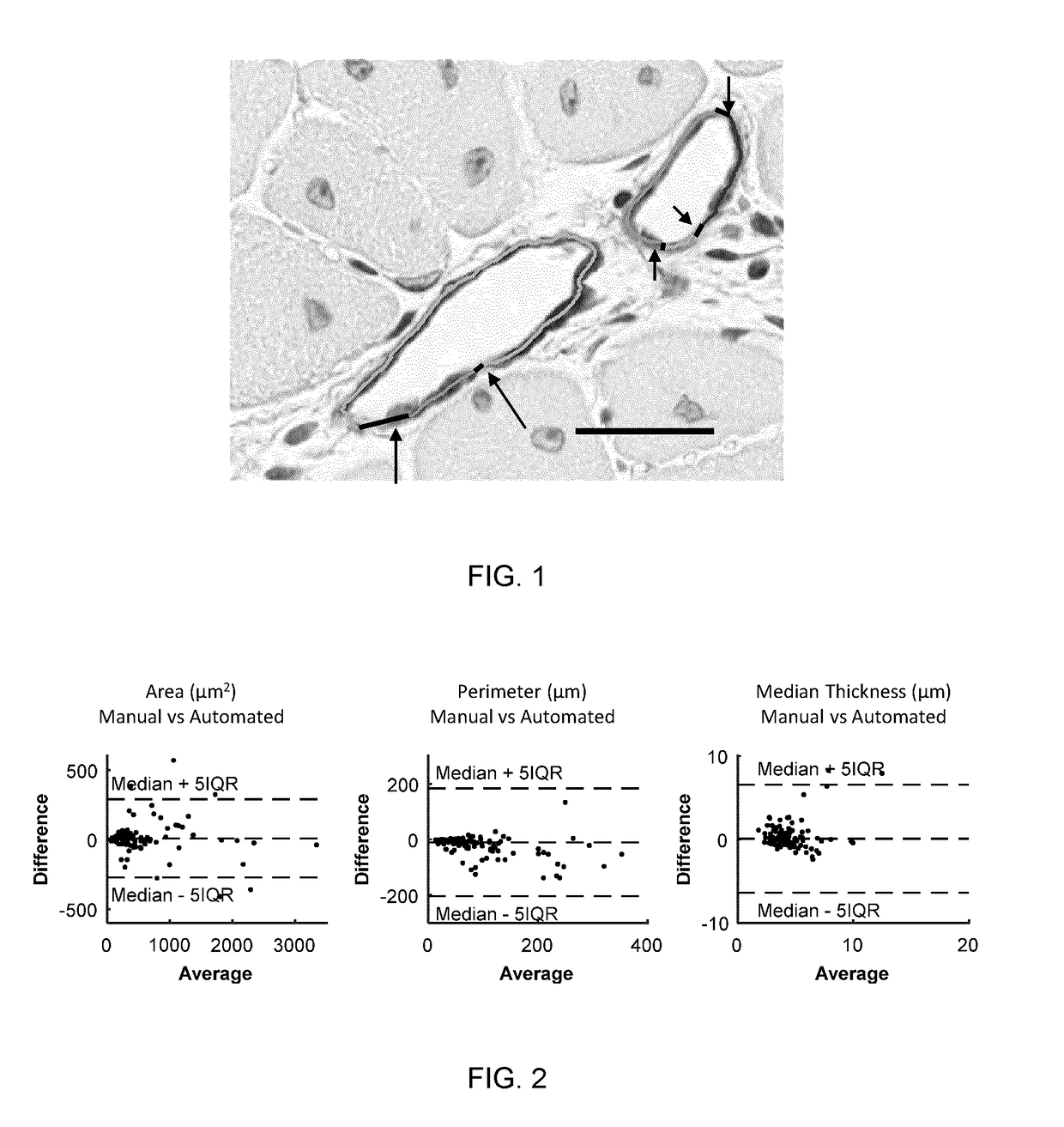
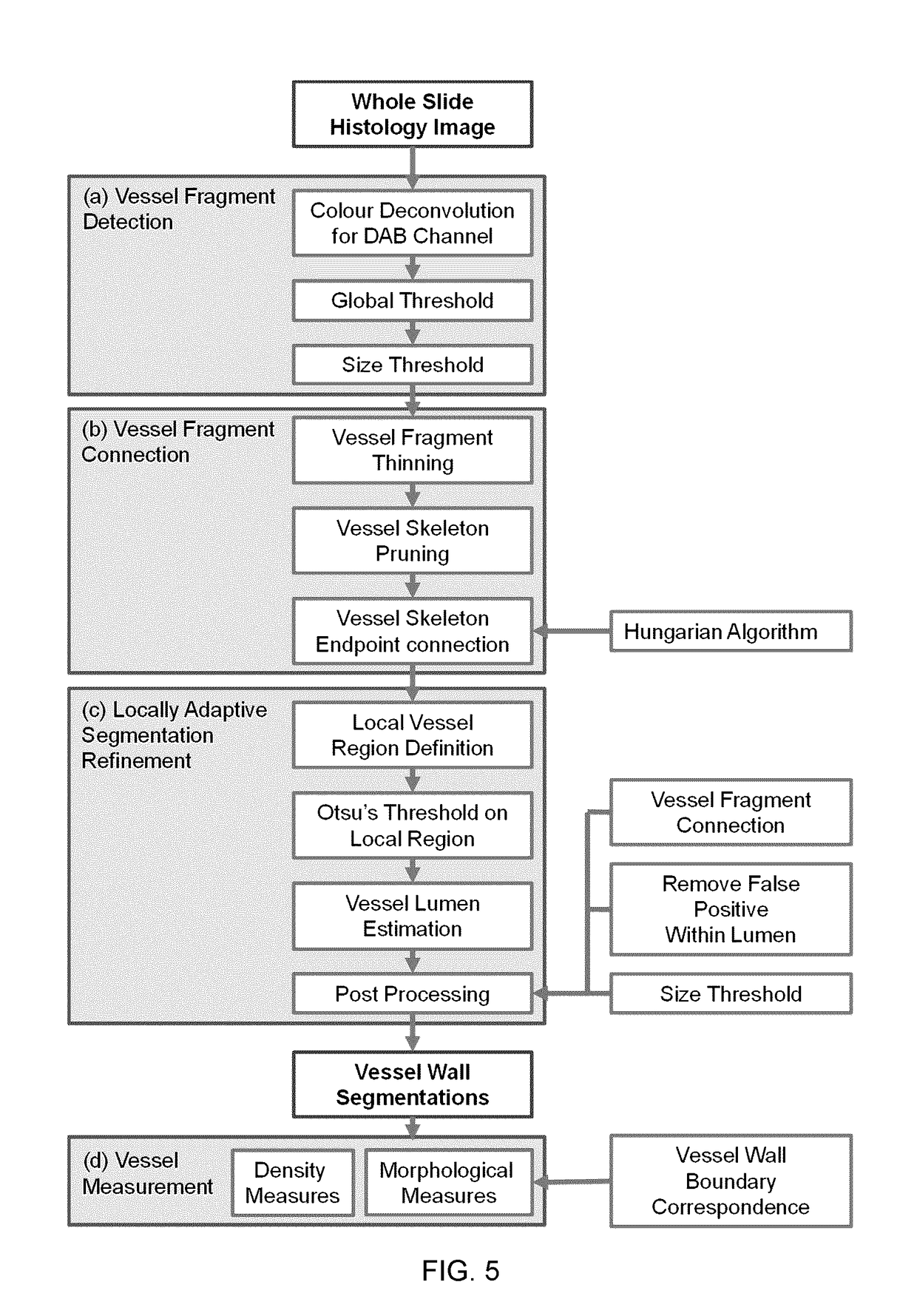
Automated segmentation of histological sections for vasculature quantification
A fully automated method for detecting and measuring a target of interest such as vasculature, capable of processing whole slide images and extracting large number of targets of interest per slide. The method includes the steps of: (a) obtaining a digital image of a tissue specimen; (b) using a first set of mathematical algorithms based on objectively-defined criteria to isolate the one or more targets of interest from the slide, thereby detecting the one or more targets of interest; and (c) using a second set of mathematical algorithms based on objectively-defined criteria to construct boundaries around the detected targets of interest and obtain quantitative attributes of these one or more targets throughout the slide, thereby measuring the one or more targets.
Owner:LONDON HEALTH SCI CENT RES
Explainable ai (XAI) platform for computational pathology
PendingCN113892148AImprove accuracyImprove quality of careImage enhancementImage analysisComputational pathologyPathology diagnosis
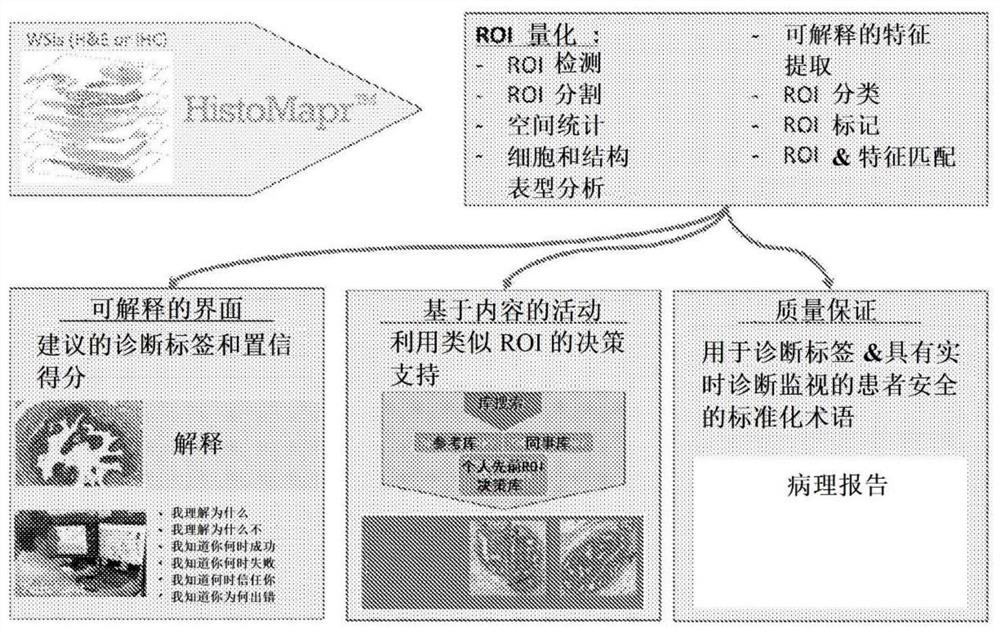
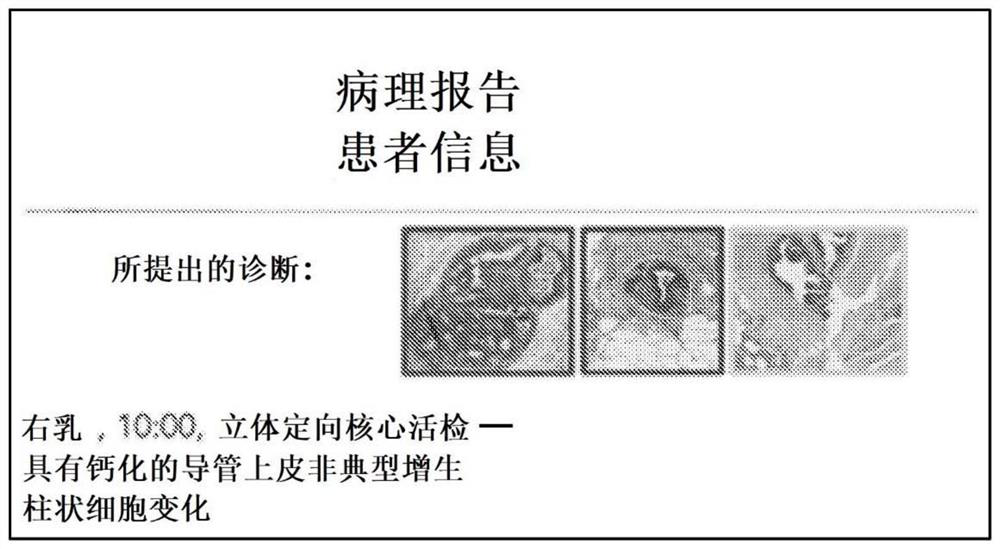
Pathologists are adopting digital pathology for diagnosis, by using whole slide images (WSIs). Explainable Al (xAI) is a new approach to Al that can reveal underlying reasons for its results. As such, xAI can promote the safety, reliability, and accountability of machine learning for critical tasks such as pathology diagnosis. HistoMapr provides intelligent xAI guides for pathologists to improve the efficiency and accuracy of pathological diagnoses. HistoMapr can previews entire pathology cases' WSIs, identifies key diagnostic regions of interest (ROIs), determines one or more conditions associated with each ROI, provisionally labels each ROI with the identified conditions, and can triages them. The ROIs are presented to the pathologist in an interactive, explainable fashion for rapid interpretation. The pathologist can be in control and can access xAI analysis via a why interface. HistoMapr can track the pathologist's decisions and assemble a pathology report by using suggested, standardized terminology.
Owner:SPINTELLX INC
Few-shot learning based image recognition of whole slide image at tissue level
A computer implemented method of generating at least one shape of a region of interest in a digital image is provided. The method includes obtaining, by an image processing engine, access to a digital tissue image of a biological sample; tiling, by the image processing engine, the digital tissue image into a collection of image patches; obtaining, by the image processing engine, a plurality of features from each patch in the collection of image patches, the plurality of features defining a patch feature vector in a multidimensional feature space including the plurality of features as dimensions; determining, by the image processing engine, a user selection of a user selected subset of patches in the collection of image patches; classifying, by applying a trained classifier to patch vectors of other patches in the collection of patches, the other patches as belonging or not belonging to a same class of interest as the user selected subset of patches; and identifying one or more regions of interest based at least in part on the results of the classifying.
Owner:NANTOMICS LLC
Method and apparatus for analysis of tissue microarrays
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
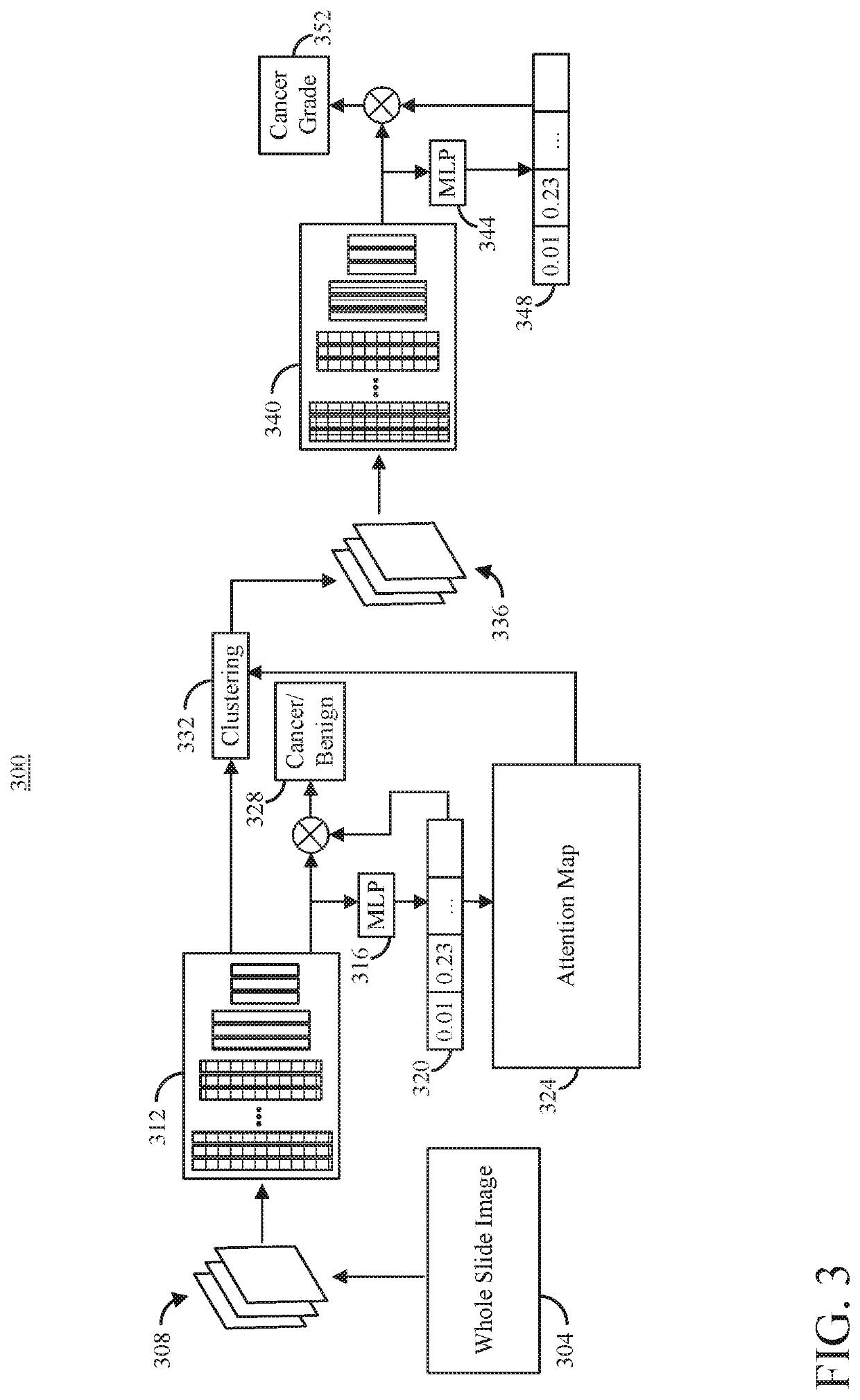
Systems and Methods for Automated Image Analysis
In accordance with one aspect of the disclosure, an image analysis system is provided. The image analysis system includes at least one processor configured to access image tiles associated with a patient, each tile comprising a portion of a whole slide image, individually provide a first group of image tiles to a first trained model, receive a first set of feature objects from the first trained model, cluster feature objects from the first set of feature objects to form a number of clusters, calculate a number of attention scores based on the first set of feature objects, select a second group of tiles, individually provide the second group of image tiles to a second trained model, receive a second set of feature objects from the second trained model, generate a cancer grade indicator, and cause the cancer grade indicator to be output.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
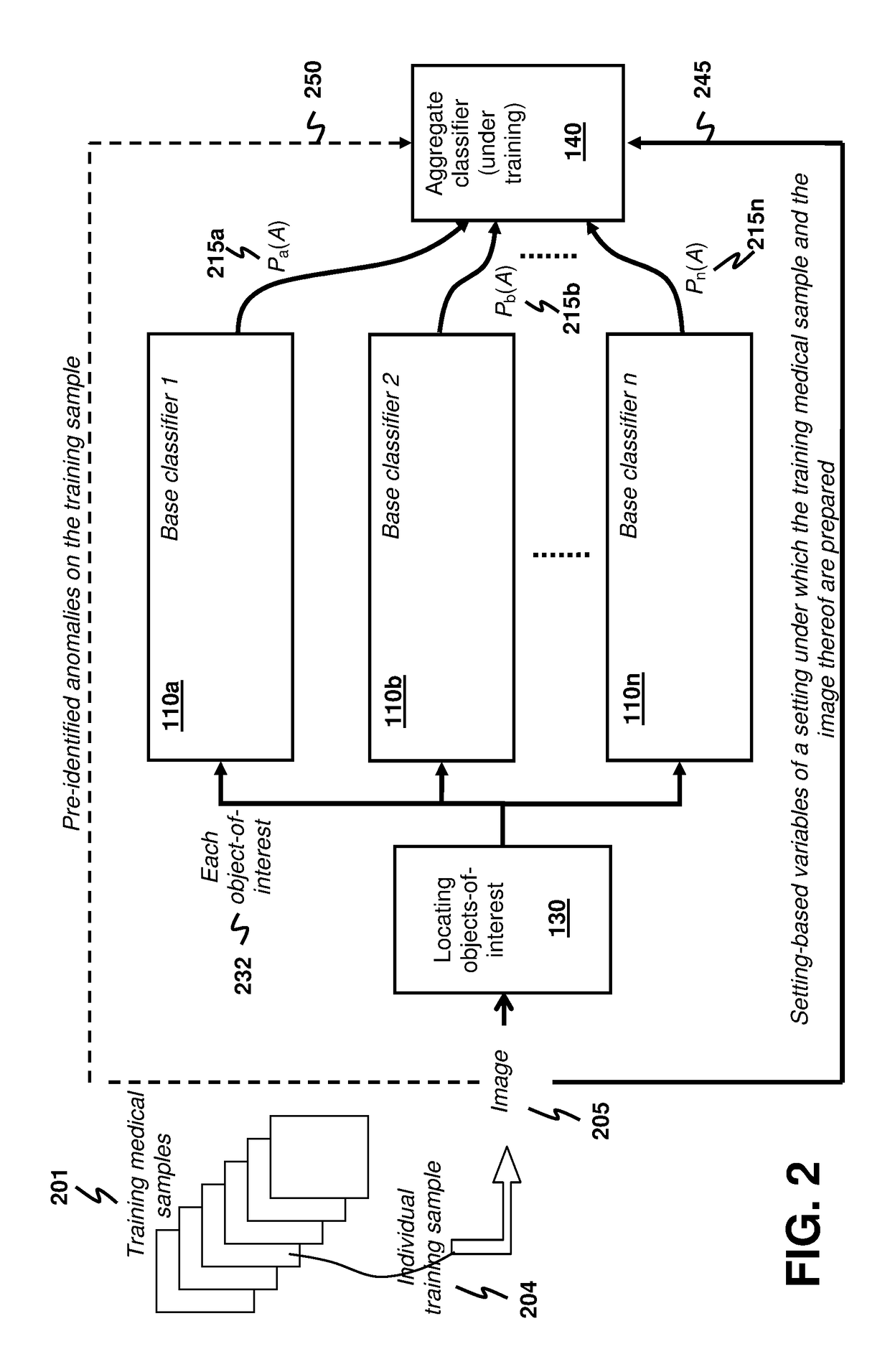
Anomaly detection for medical samples under multiple settings
Using multiple imaging modes in whole slide image screening is potentially useful to reduce false positives. To use multiple imaging modes, a method for locating anomalies on a medical sample from an image thereof uses an anomaly-detection process that comprises using plural base classifiers individually to classify an object-of-interest suspected to be an anomaly. Each base classifier respectively extracts features of the object-of-interest and generates, according to the extracted features, a score indicating a likelihood of the object-of-interest being anomalous. The anomaly-detection process further comprises using an aggregate classifier to combine the scores generated by the base classifiers to determine whether the object-of-interest is the anomaly. The aggregate classifier determines a dependability measure for each base classifier according to setting-based variables of a setting under which the sample and the image are obtained, and then selectively combines the scores of the base classifiers according to the dependability measures.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
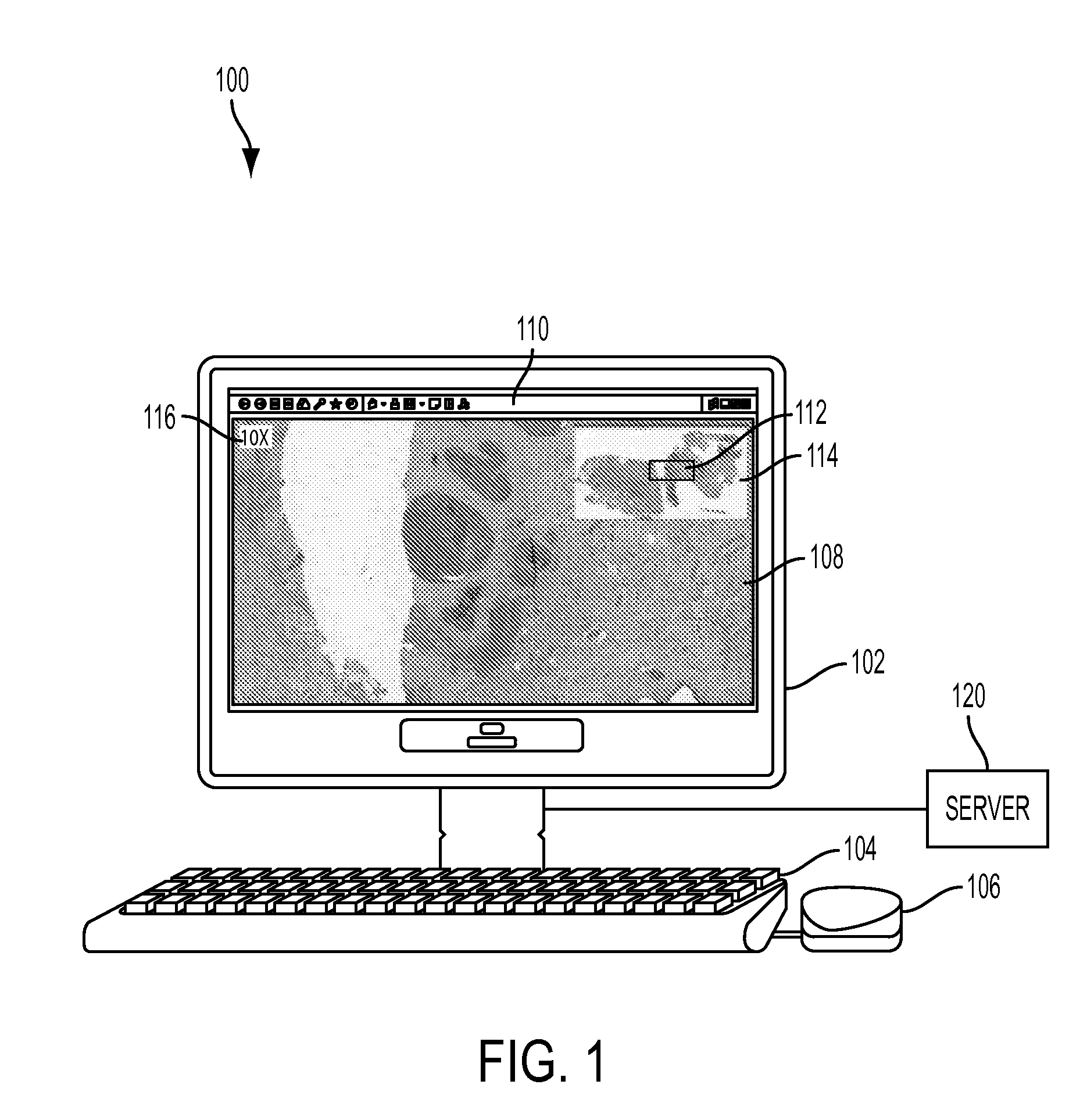
System and method for improved viewing and navigation of digital images
InactiveUS8249315B2Television system detailsColor television signals processingDigital imageField of view
A system and method for improved viewing and navigation of large digital images, such as whole slide images used in microscopy. The system and method displays the digital image along with movable navigation and field of view boxes that enable a viewer to pan the digital image in an accurate manner, and also performs automatic absolute reorientation of the digital image and automatic relative reorientation of subsequent digital images in relation to the first digital image.
Owner:UPMC
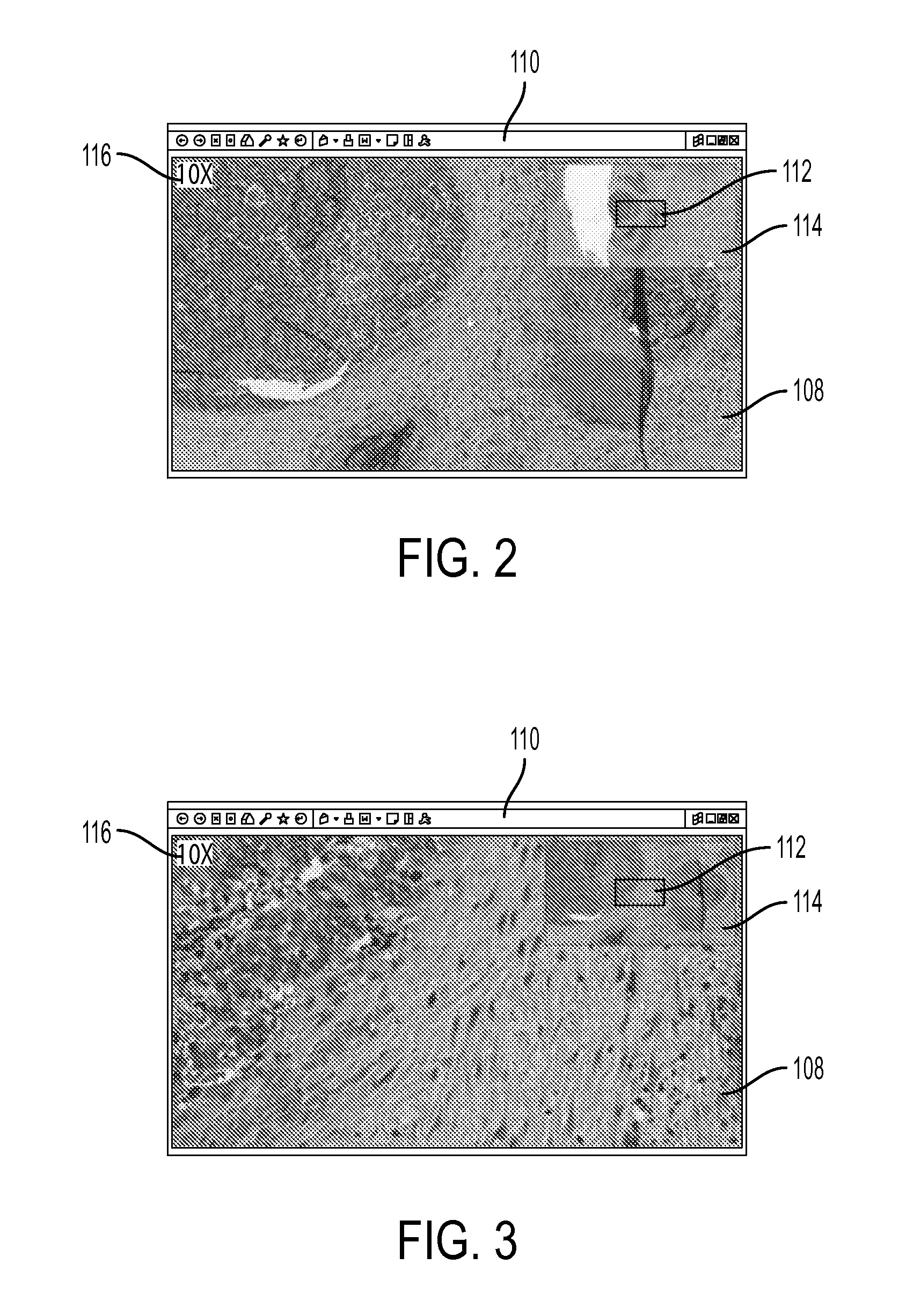
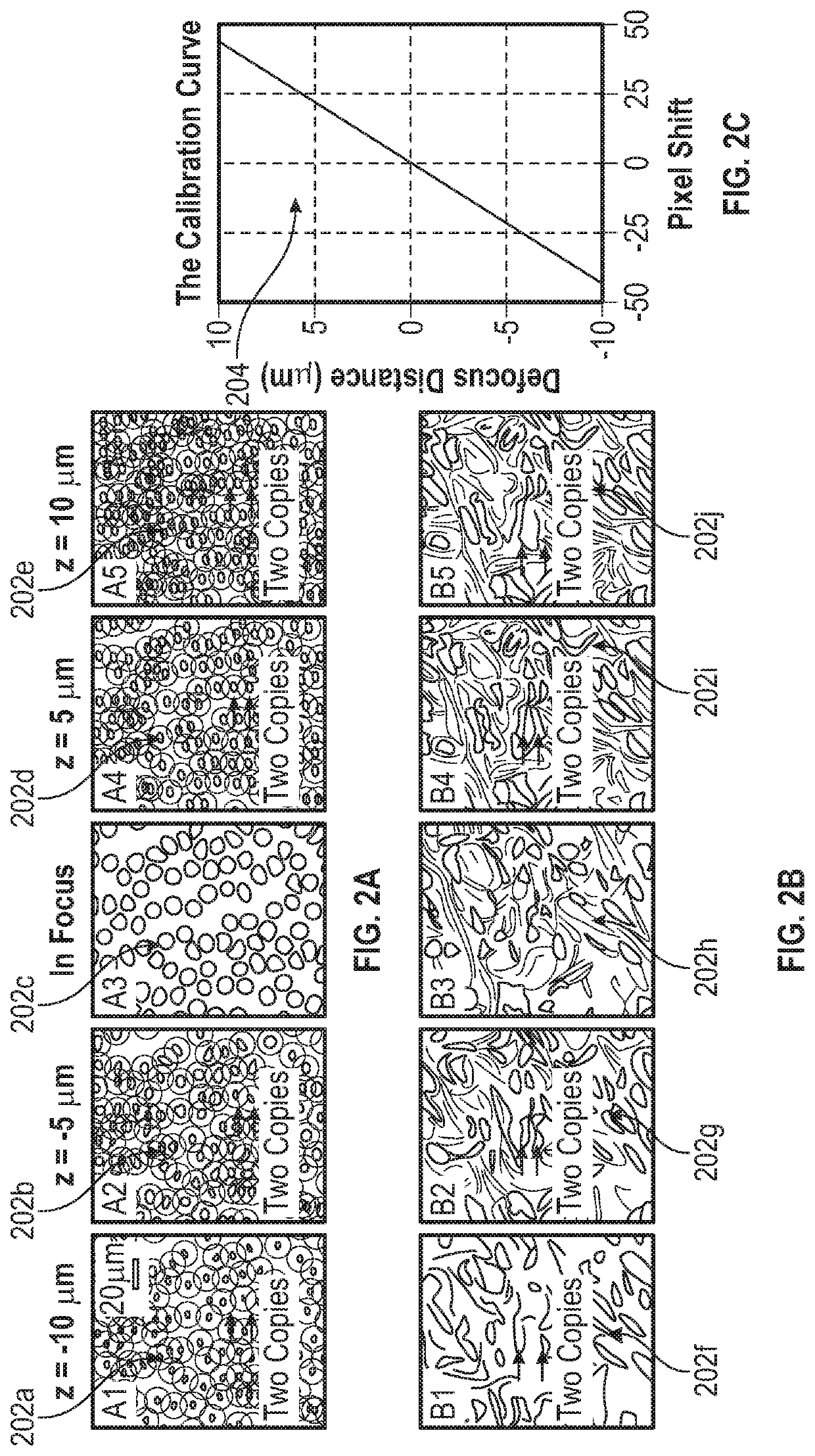
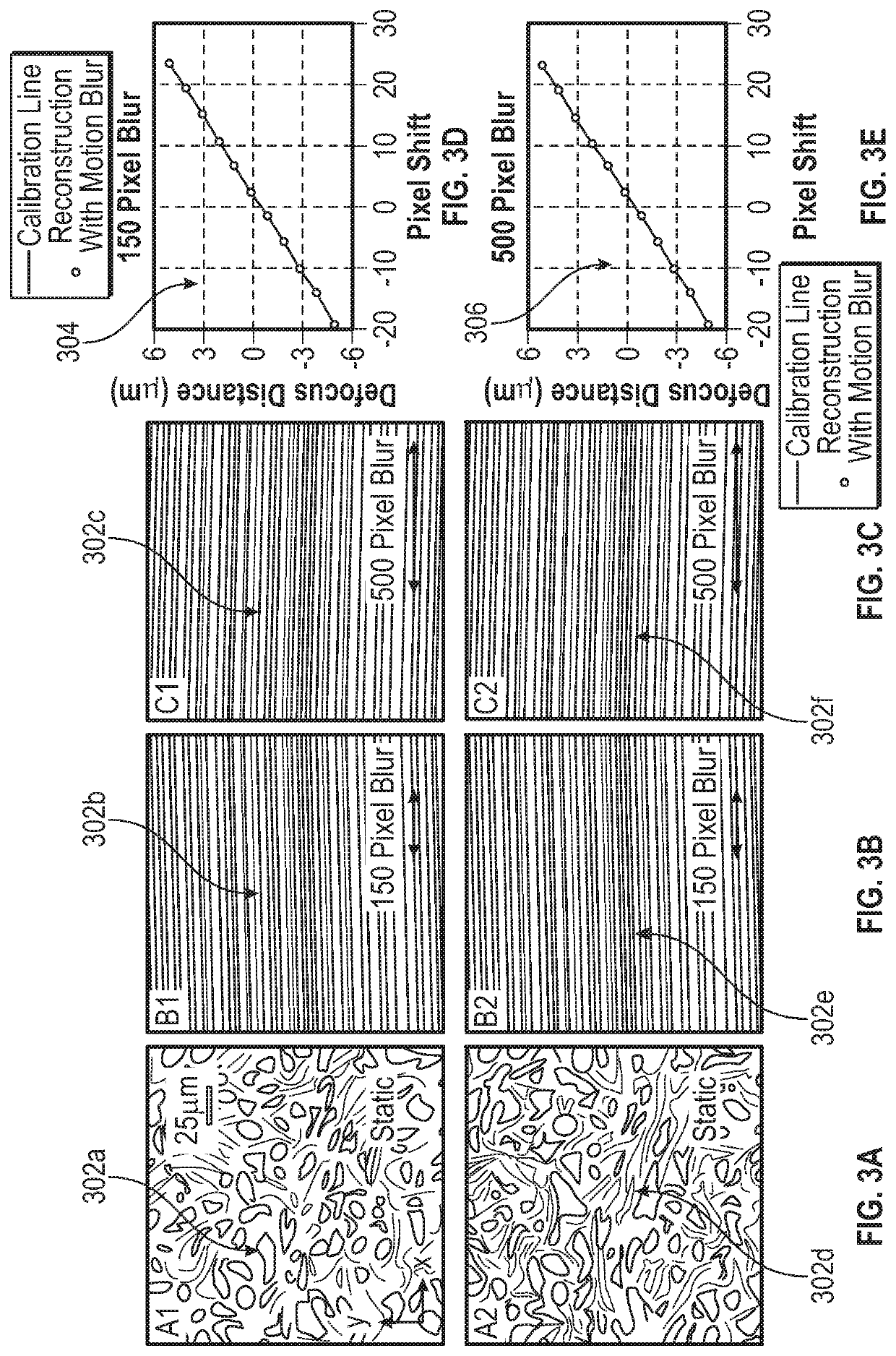
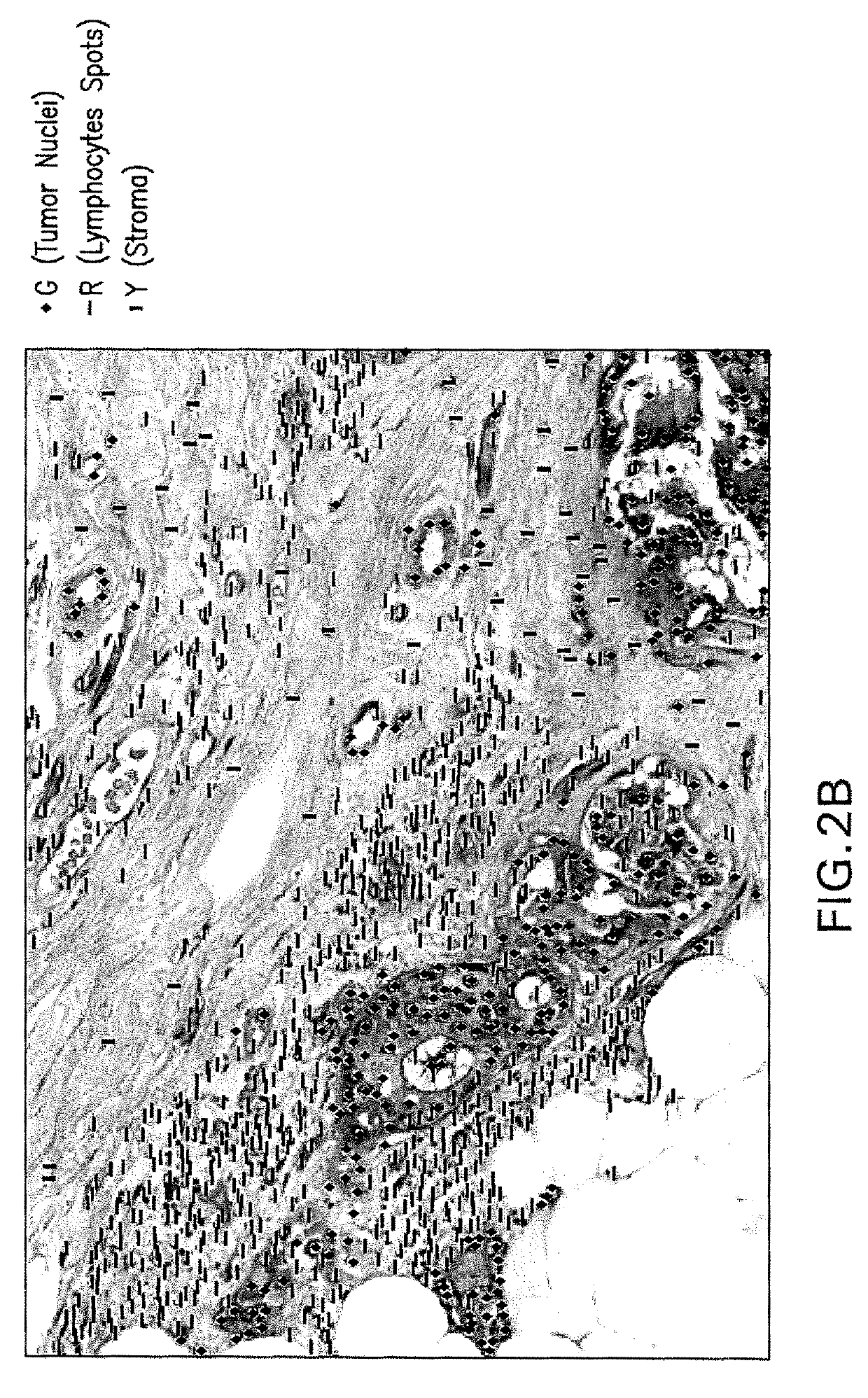
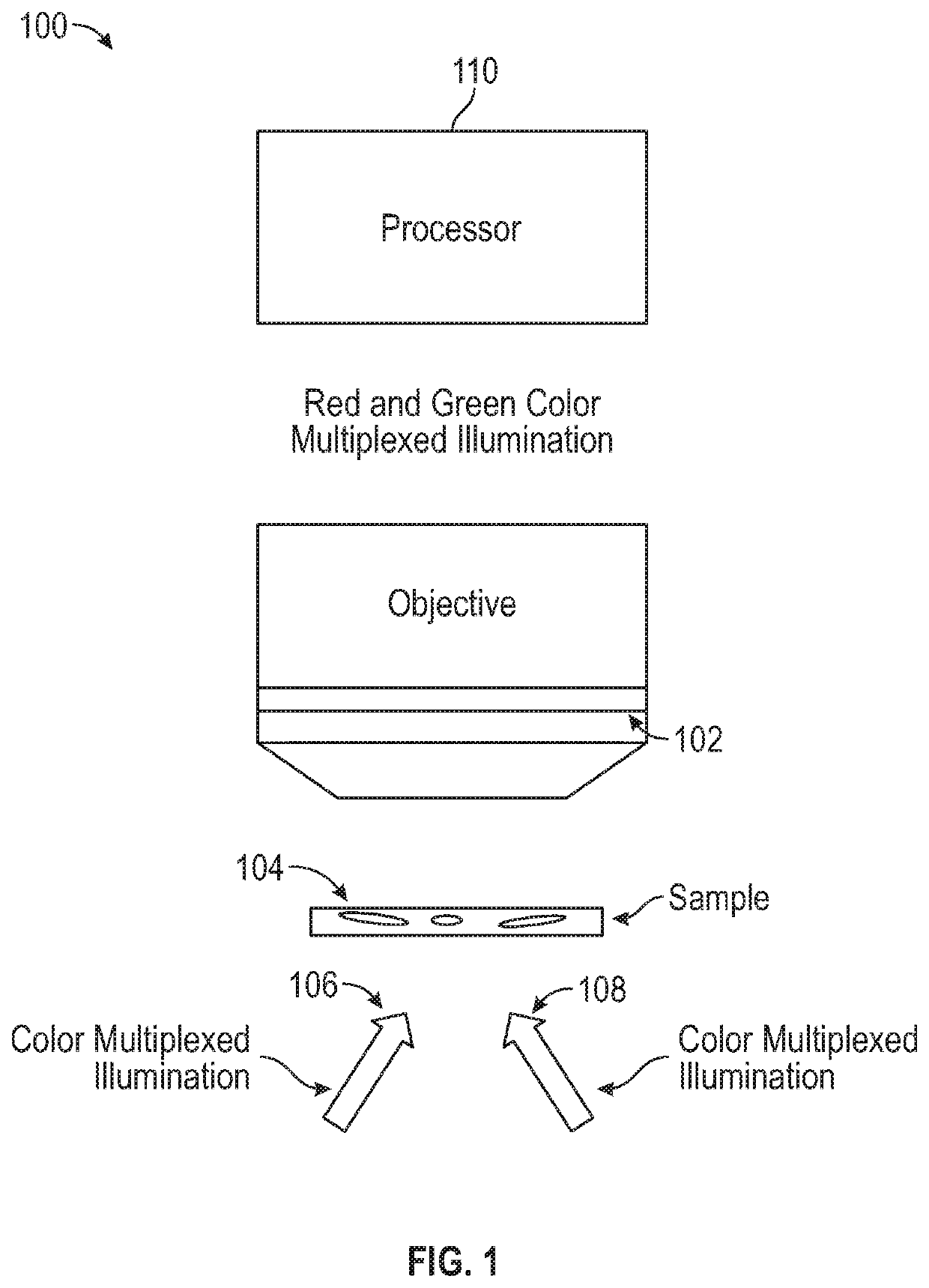
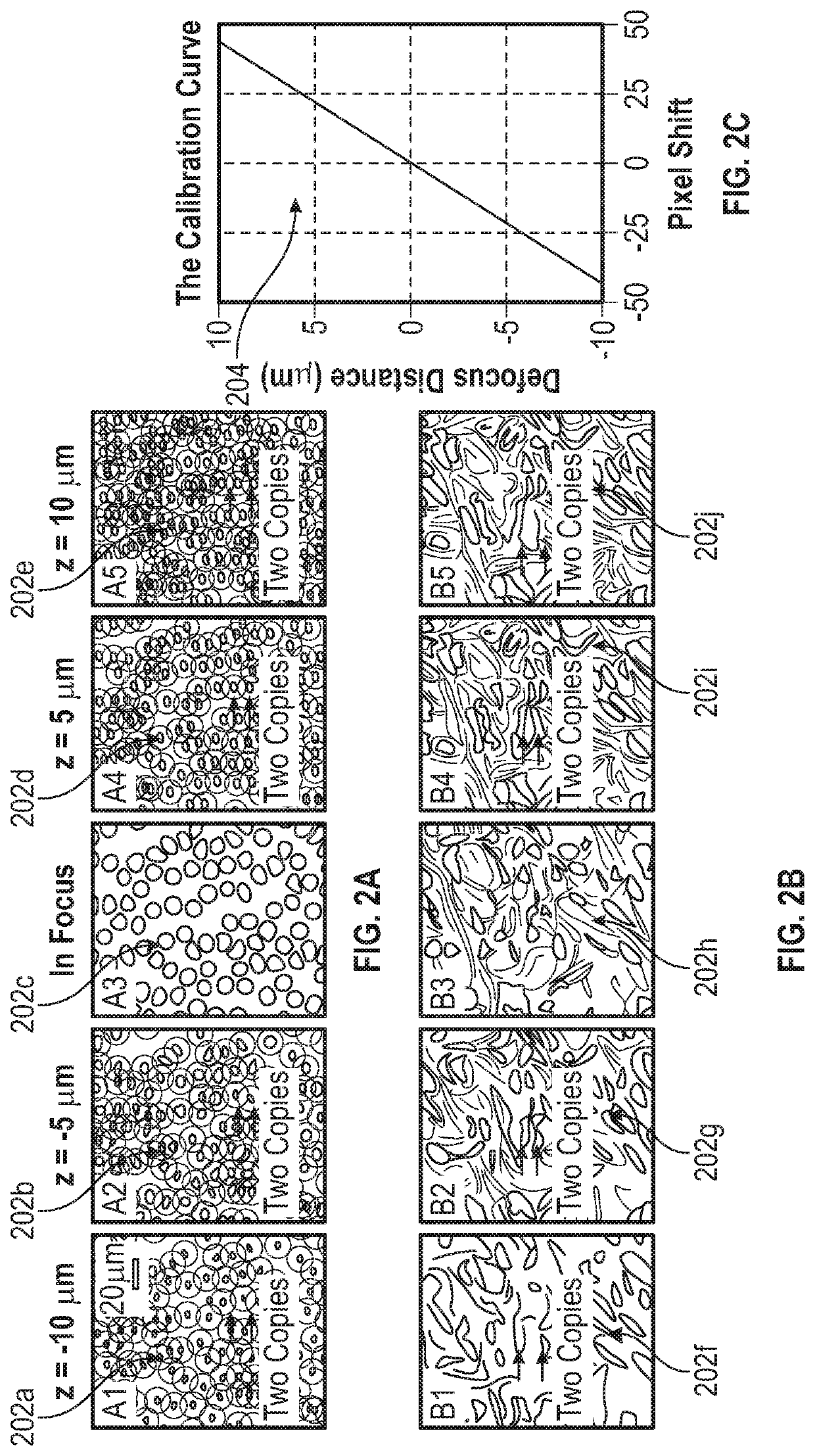
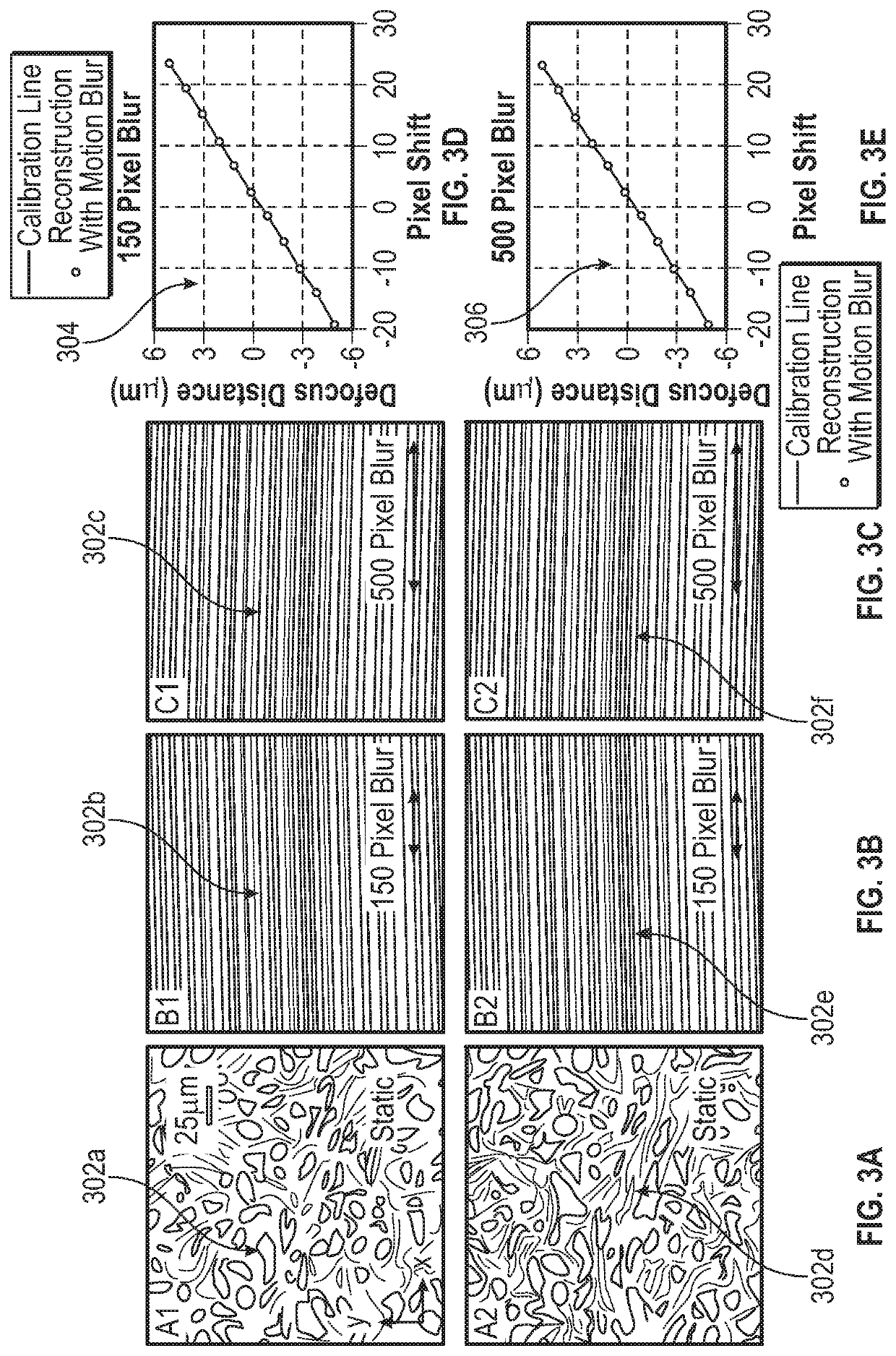
Methods and Systems for Single Frame Autofocusing Based on Color-Multiplexed Illumination
ActiveUS20200358946A1Maximizing mutual informationTelevision system detailsImage analysisAngle of incidenceOphthalmology
The present disclosure includes systems and methods for capture a whole slide image of a sample. In exemplary embodiments, a camera is configured to capture a digital image of a sample. The system captures a bright field image of the sample, and captures a digital image of the sample illuminated from a first incident angle at a first wavelength and a second incident angle at a second wavelength. The system can determine whether the sample is defocused based on the transitional shift between a first wavelength channel and a second wavelength channel of the captured digital image. The system can determine the defocus distance based on the transitional shift and autofocus using the defocus distance such the bright field image is in focus.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Systems and Methods for Digital Pathology
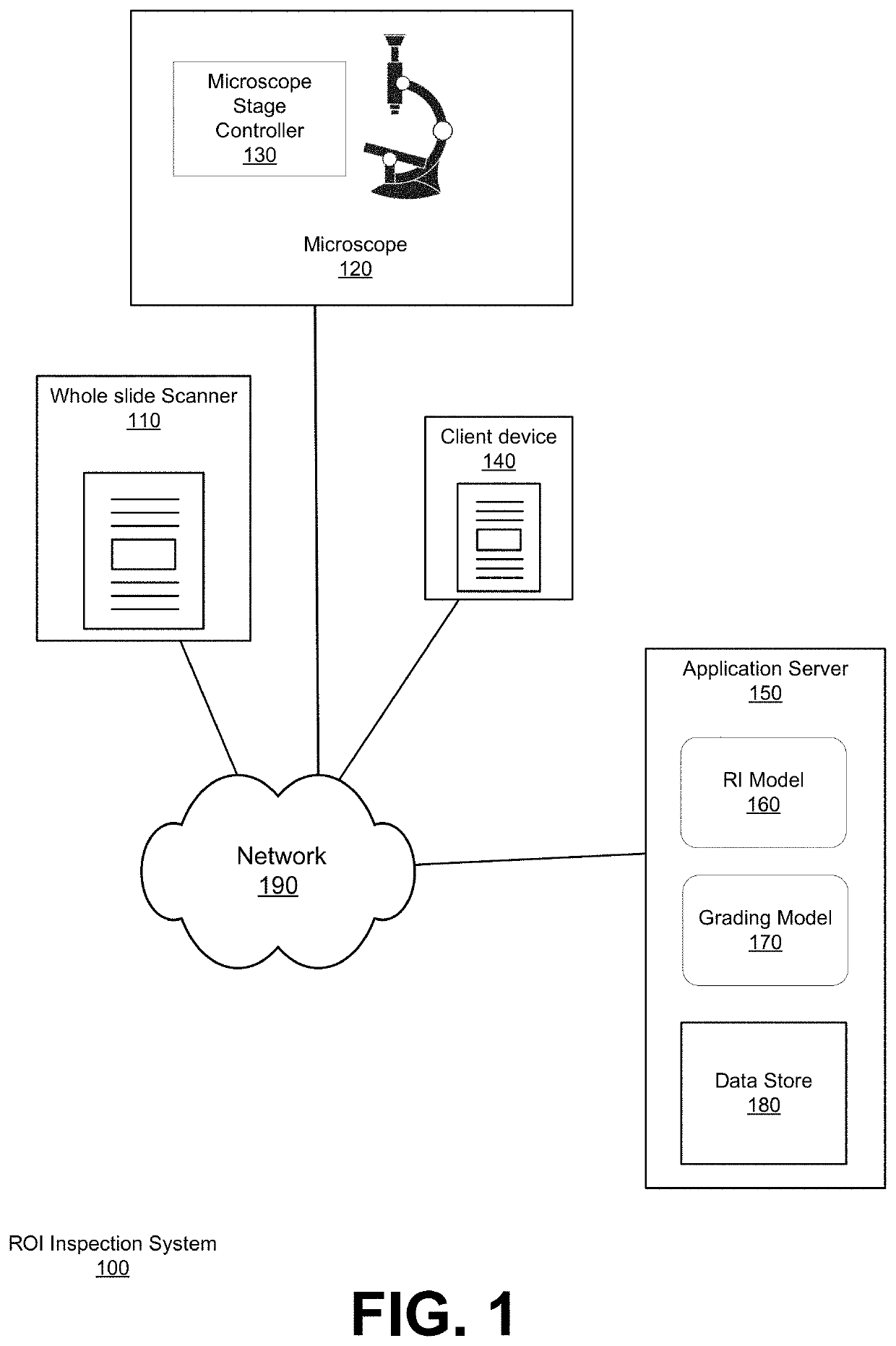
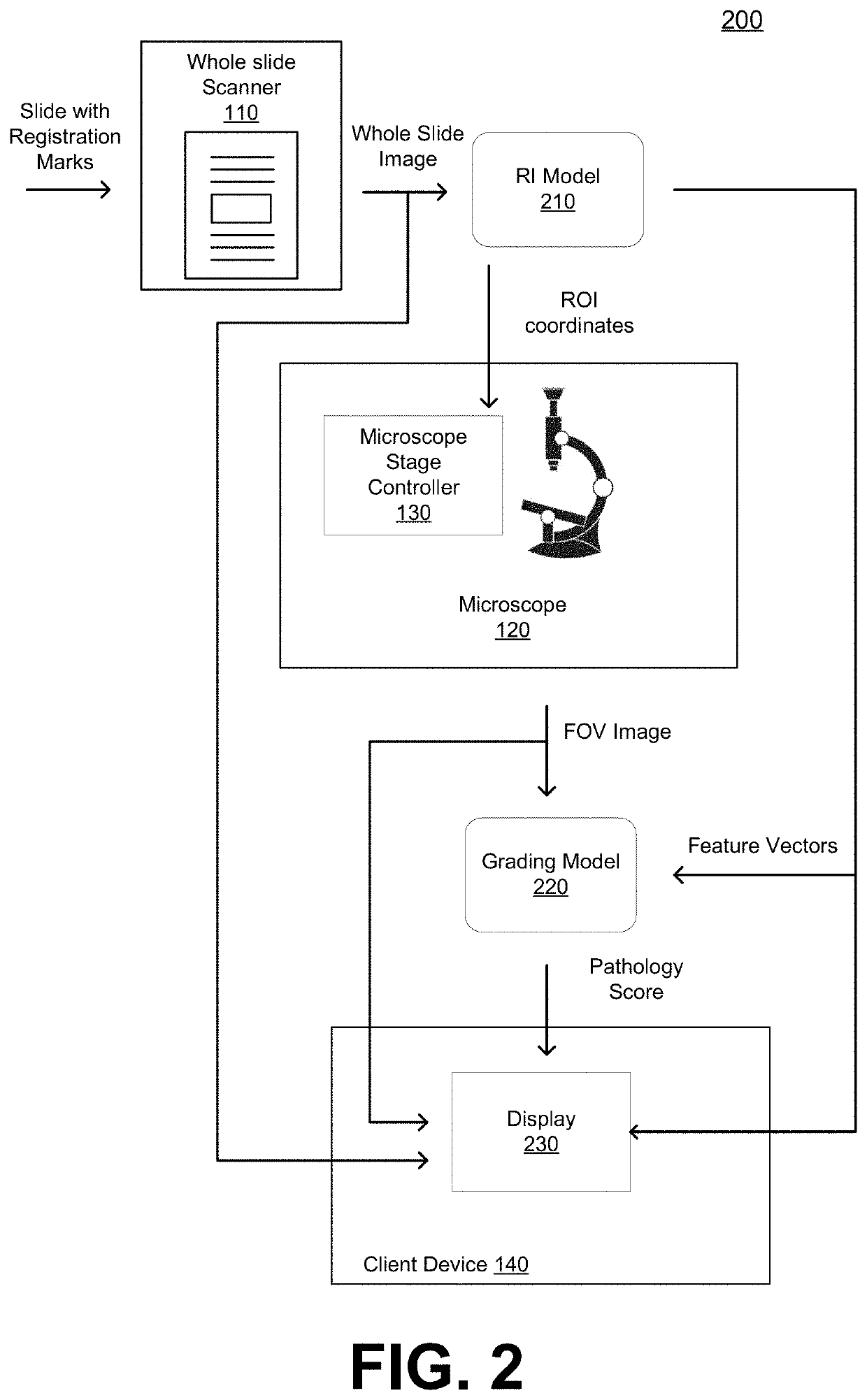
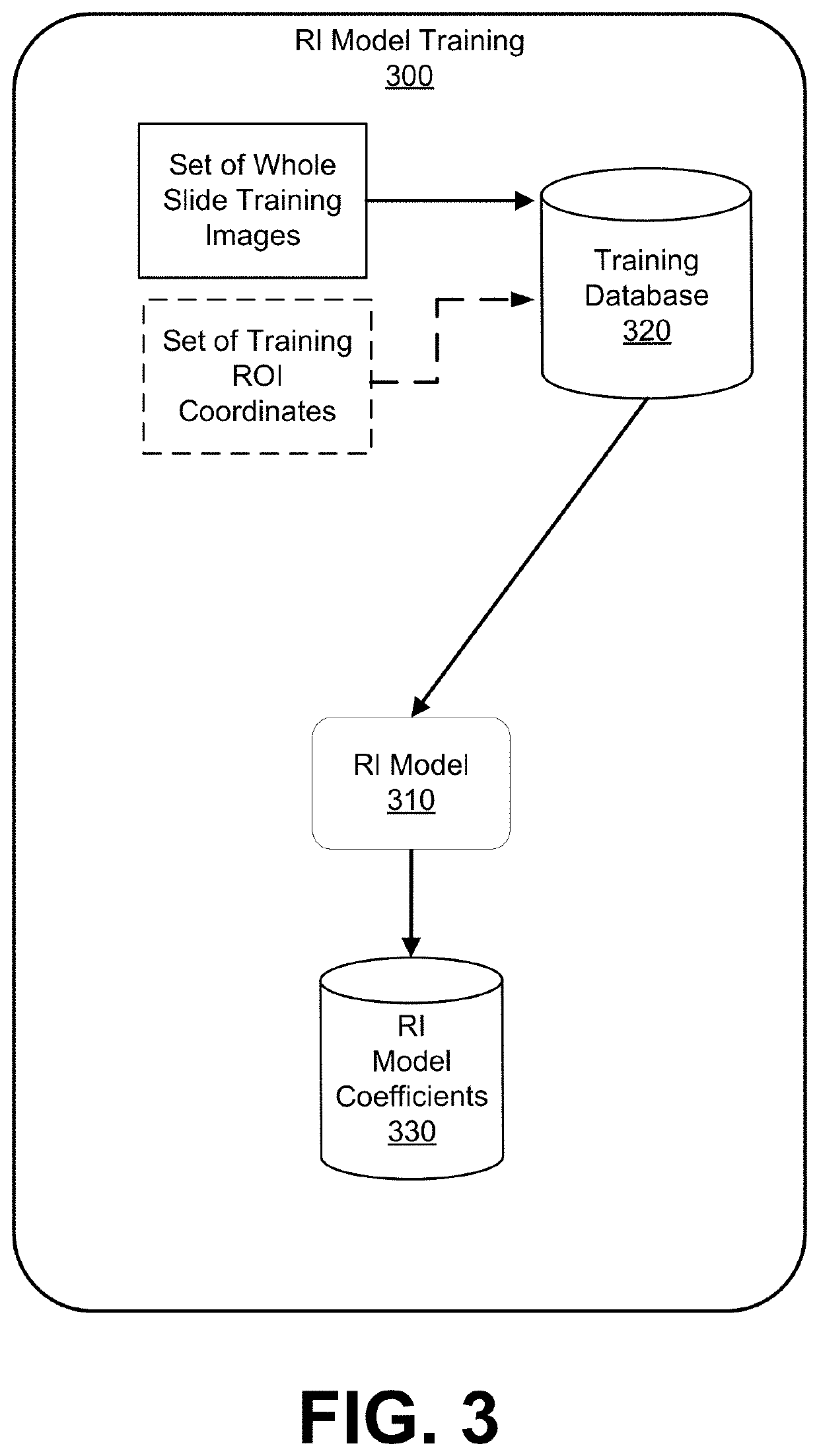
PendingUS20220138939A1Improve easeIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscope slideDisease
Systems and methods for digital pathology in accordance with embodiments of the invention obtain a whole slide image of a microscope slide that includes a registration mark, wherein the registration mark is associated with a coordinate system. The method inputs the whole slide image into a region identification (RI) model to extract features of the whole slide image and generate feature vectors for the extracted features, detects a presence of a region of interest (ROI) based on the feature vectors, determines a set of coordinates of the ROI in the coordinate system, and translates a microscope stage of a microscope holding the microscope slide to a position corresponding to the coordinates of the ROI. The method captures a field of view (FOV) image with the microscope and inputs the FOV image into a grading model to determine a pathology score that indicates a likelihood of a presence of a disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for automatic assessment of cancer
ActiveUS20200349399A1Reduce workloadImage enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesAggressive diseaseNeutral network
Cancer can be an aggressive disease. It is critical to determine the most effective patient-specific treatment quickly. Exemplary embodiments use a data-driven approach to extracting tumor information from data obtain from Whole Slide Image that is uploaded through an interface. Exemplary embodiments generate the following information about a tumor from a biopsy slide using neural networks: annotated areas of relevant tissues, molecular subtype, and expression status of an important gene and include three steps: the segmentation of tumor features; prediction of molecular subtype; and prediction of gene methylation status from a WSI.
Owner:KOPPARAPU KAVYA VENKATA KOTA SAI
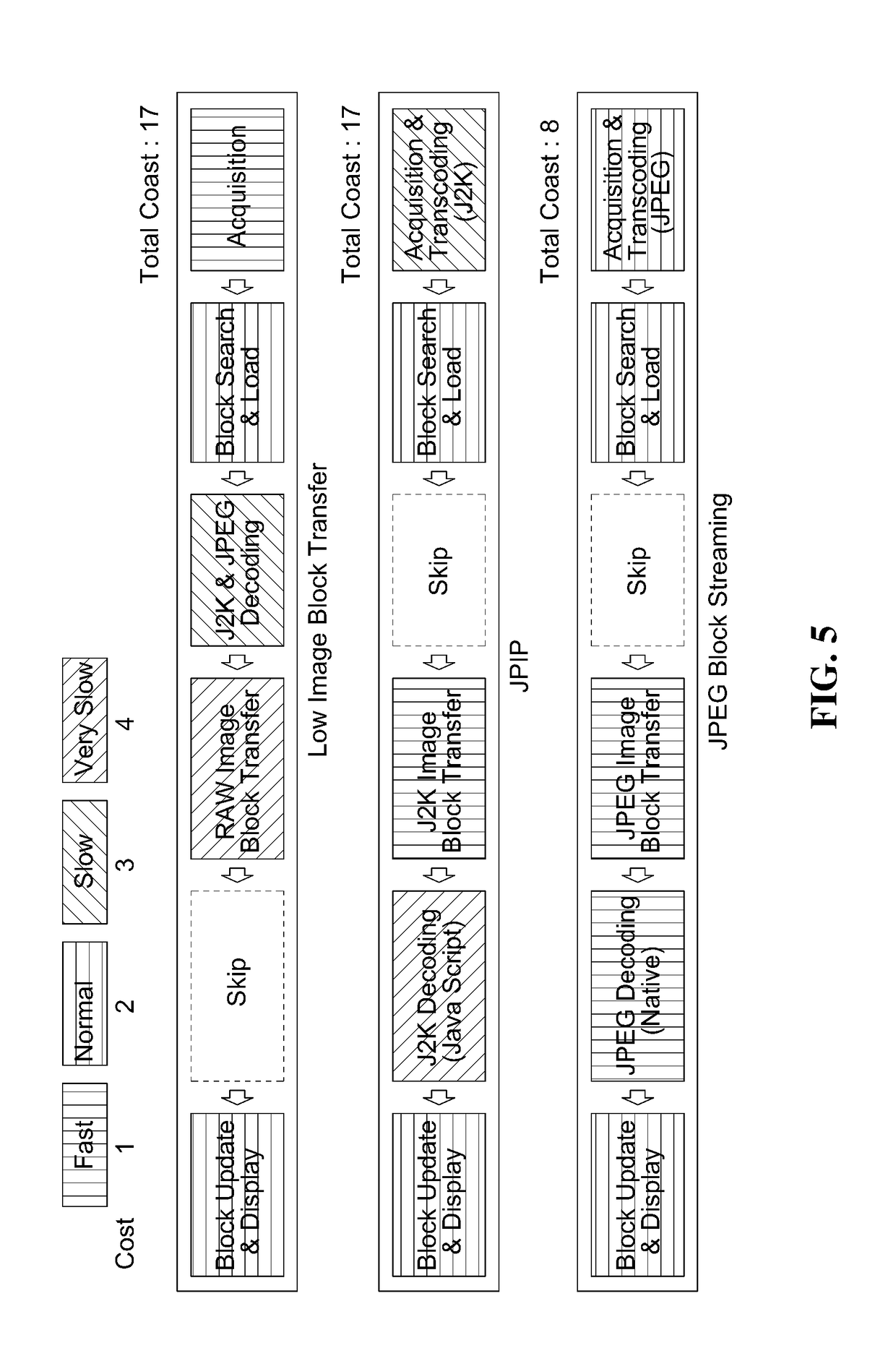
Wsi streaming method
ActiveUS20190051018A1Reduce performance degradationReduce time costImage codingBiological testingImage compressionComputer vision
Provided is a method in which a web client receives a whole slide image (WSI) having an image compression format and a tile size different depending on a digital pathology vendor from a digital pathology server in a streaming manner. The method includes a WSI acquisition operation of acquiring the WSI from the digital pathology server. The WSI acquisition operation includes a normalized tile definition operation of defining a normalized tile having a minimized time cost, a determination operation of comparing a tile with the normalized tile, and a conversion operation of optimizing the tile with the normalized tile.
Owner:INFINITT HEALTHCARE CO LTD
A method to determine a degree of abnormality, a respective computer readable medium and a distributed cancer analysis system
PendingCN112543934AProcessing speedEasy to implement global applicationImage enhancementImage analysisCancer cellRadiology
Current cancer screening methods are not suitable to be applied on a broad scale and are not transparent to the patient. The problem is solved by a method to determine a degree of abnormality, the method comprising the following steps: a) receiving a whole slide image (11, w, 722), the whole slide image (11, w, 733) depicting at least a portion of a cell; b) classifying at least one image tile (13, 601, 721, 721', 721'') of the whole slide image (11, w, 722) using a neural network (600) to determine a local abnormality degree value (15, a_j, 519, 719, 719', 719'') associated with the at leastone image tile (13, 601, 721, 721', 721''), the local abnormality degree value (15, a_j, 519, 719, 719', 719'') indicating a likelihood that the associated at least one segment depicts at least a partof a cancerous cell; and c) determining a degree of abnormality (17) for the whole slide image (11, w, 722) based on the local abnormality degree value (15, a_j, 519, 719, 719', 719'') for the at least one image tile (13, 601, 721, 721', 721'').
Owner:H LABS股份有限公司
Imaging assemblies with rapid sample auto-focusing
ActiveUS10330906B2Improved and faster and cheap diagnosis/prognosisIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDiseaseEyepiece
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
System and method for automatic assessment of cancer
ActiveUS10748040B2Accurate data-drivenShorten diagnostic timeImage enhancementImage analysisBlastomaBrain biopsy
Owner:KOPPARAPU KAVYA VENKATA KOTA SAI
Automatic glandular and tubule detection in histological grading of breast cancer
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods and systems for single frame autofocusing based on color- multiplexed illumination
ActiveUS11356593B2Maximizing mutual informationTelevision system detailsImage analysisAngle of incidenceOphthalmology
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Computer implemented method and module for accessing a dicom whole slide image database
Owner:SERVICIO ANDALUZ DE SALUD (SAS)
A method for auxiliary diagnosis of cervical histopathology based on attention mechanism
ActiveCN113724842BImprove diagnostic efficiencyImprove diagnostic accuracyImage analysisMedical imagesPattern recognitionCervical tissue
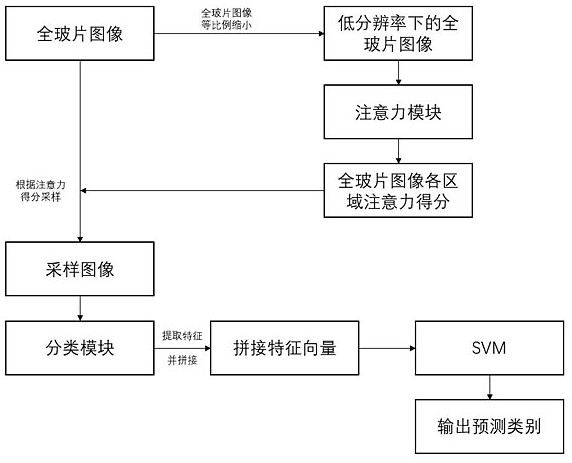
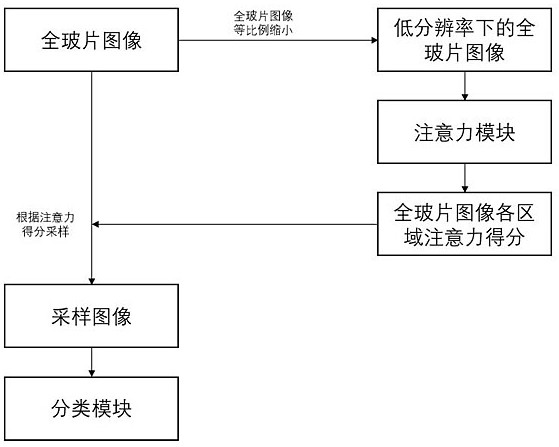
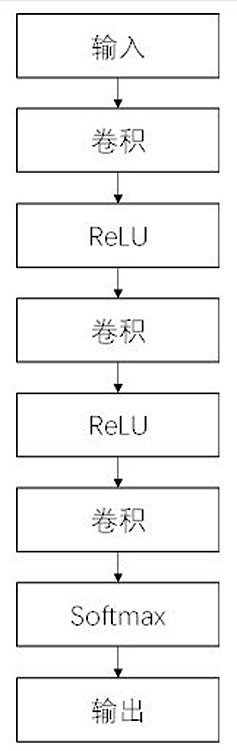
The invention provides an auxiliary diagnosis method for cervical histopathology based on an attention mechanism, which comprises reducing the whole glass slide image of cervical histopathology according to the proportion r to obtain a low-resolution image; building and initializing an attention module and a classification module; The rate image is input into the attention module, and the attention score is calculated; the position of the pixel with high attention score in the image is obtained, and the set size k blocks are intercepted; the small block is input into the training classification module, and the features of the small block with high score are extracted , get the feature vector, train the support vector machine classifier, input the trained support vector machine classifier, and realize the classification. The diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of the original method were improved. The lesion area in the positive cervical histopathological full-slide image is located to avoid the interference of the negative part in the positive cervical histopathological full-slide image to the classification model. Using attention mechanism to detect suspicious lesions in cervical histopathological whole slide images.
Owner:WUHAN LANDING INTELLIGENCE MEDICAL CO LTD
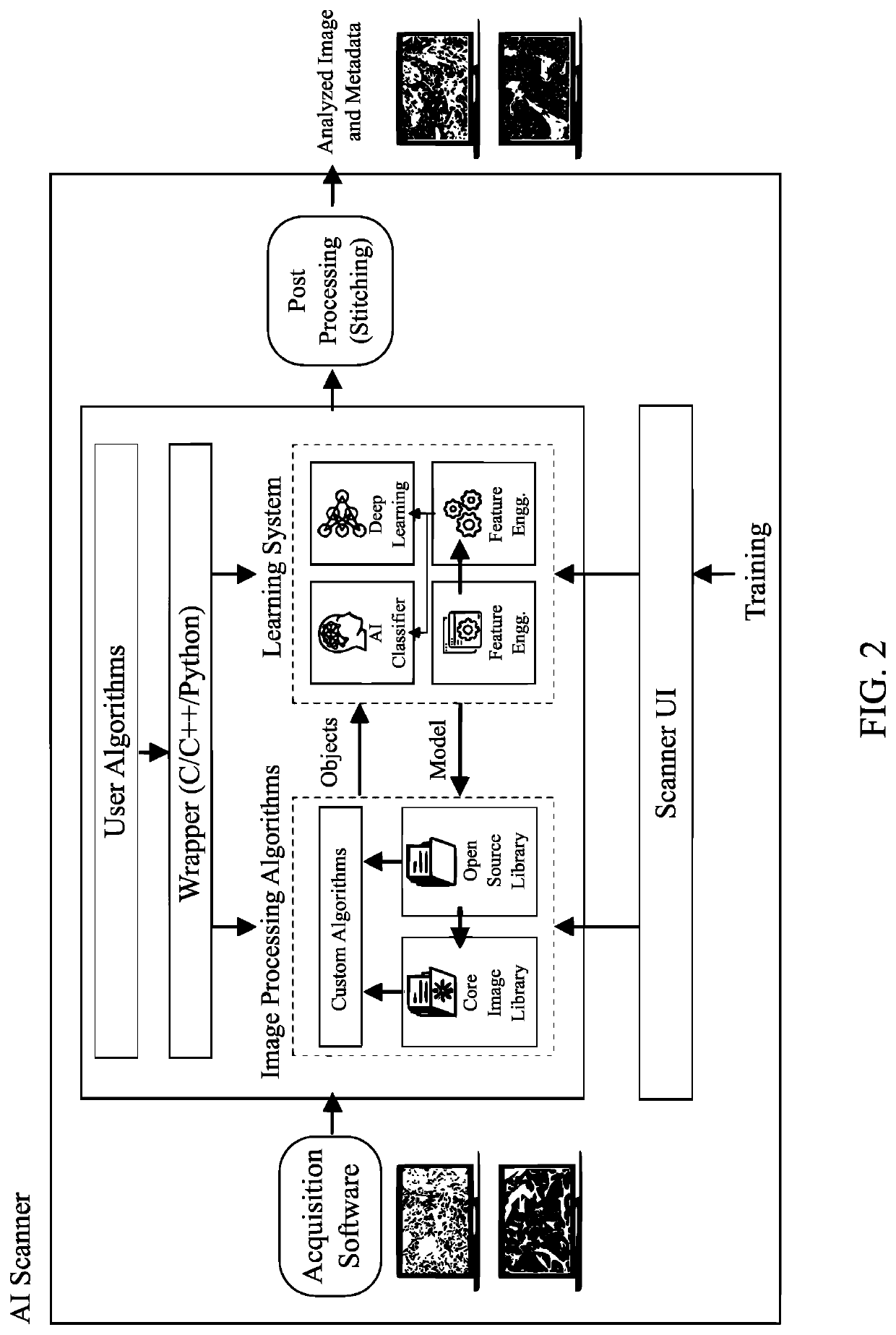
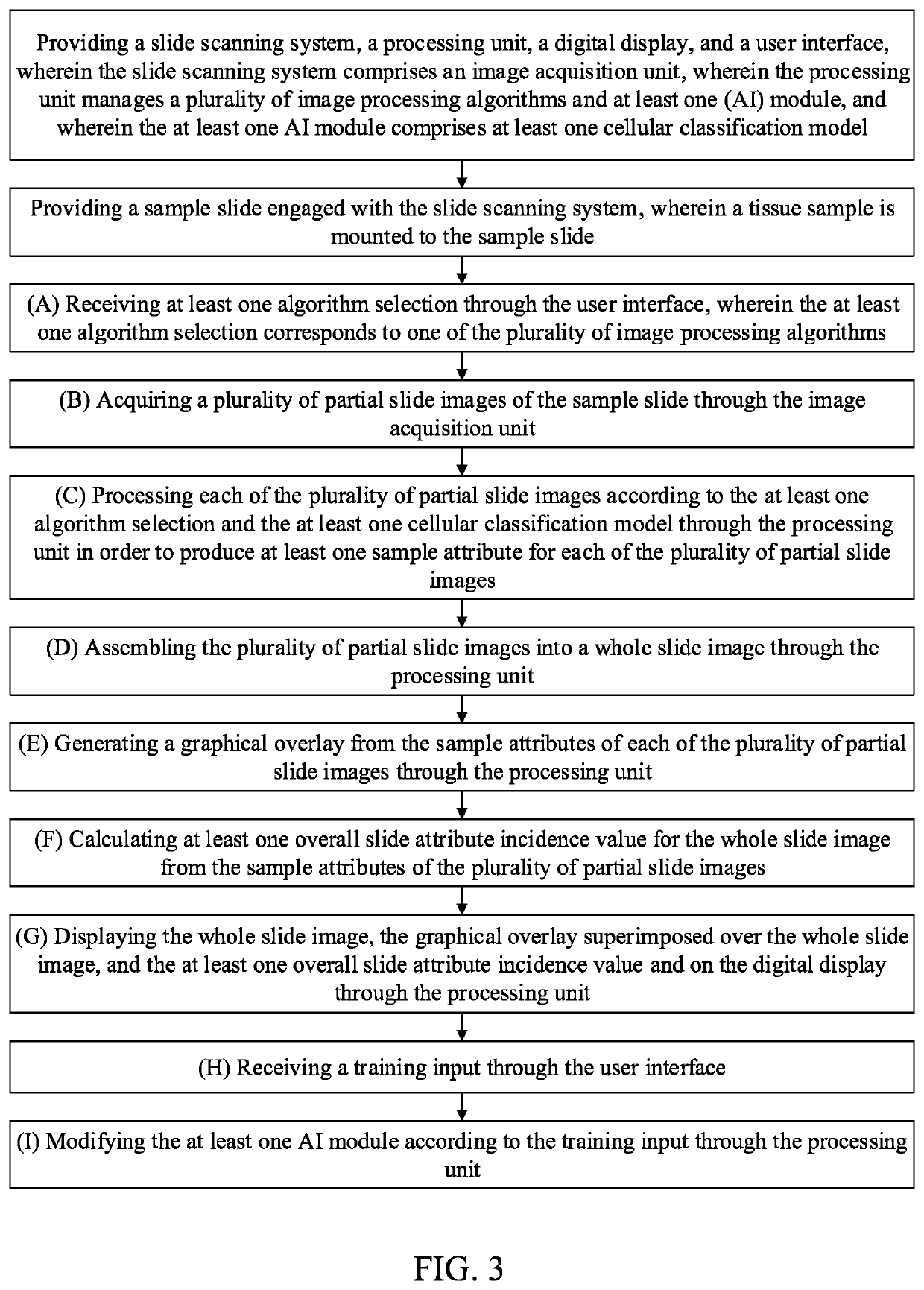
Method of Operation of An Artificial Intelligence-Equipped Specimen Scanning and Analysis Unit to Digitally Scan and Analyze Pathological Specimen Slides
In a method of operation of an artificial intelligence-equipped specimen scanning and analysis unit to digitally scan and analyze pathological specimen slides, a sample slide with a mounted tissue sample is scanned and analyzed according to one or more user-selected algorithms in order to generate a heatmap visually depicting the presence of one or more user-selected sample attributes of the tissue sample. One or more artificial intelligence modules, including a deep learning computation module, is provided and can be trained by the user for future analysis of new samples. One or more regions of interest may be selected from the heatmap to include in the results of the analysis. A focus window may be used to closely inspect any given region of the whole slide image, and a trail map is generated from the movement of the focus window.
Owner:OPTRASCAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com